Genetically engineered bacterium for producing L-valine with high yield and establishment method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and valine, applied in the field of microorganisms and molecular biology, can solve the problems of low L-valine yield, insufficient supply of pyruvate, weak metabolic flow, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
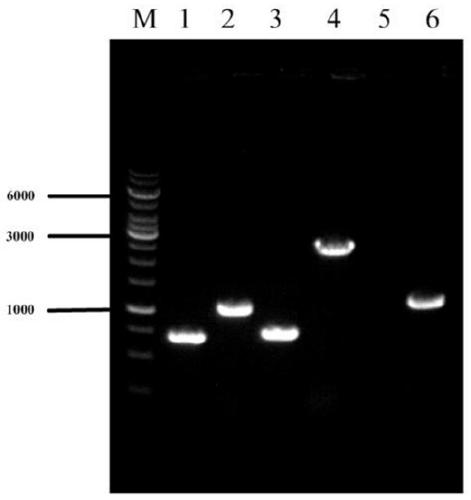
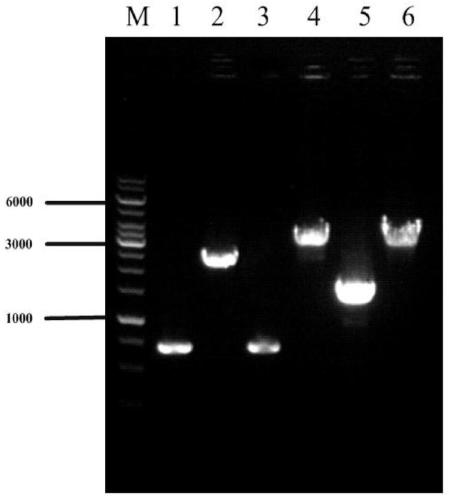
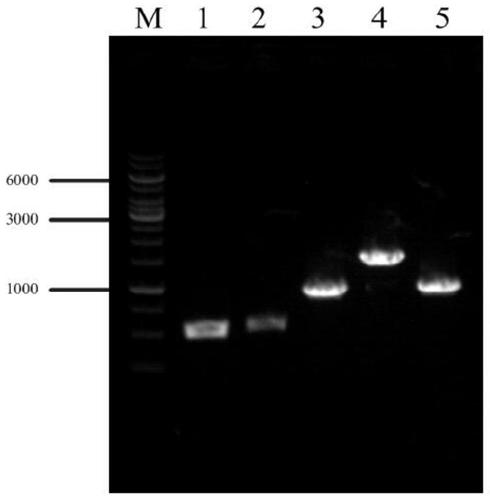
[0026] The efficient production of L-valine strains VHY01, VHY02, and VHY03 were constructed, and the gene editing method used was referred to the literature (Li Y, Lin Z, Huang C, et al. Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli using CRISPR–Cas9 mediated genome editing. Metabolic engineering, 2015,31:13-21.), the specific method is as follows:
[0027] 1 The acetolactate synthase coding gene alsS was integrated into the pseudogene site ydeU to construct strain VHY01
[0028] 1.1 Preparation of recombinant DNA fragments
[0029] The alsS gene was integrated into the ydeU pseudogene locus. Using the genome of Bacillus subtilis B.subtilis 168 as a template, the gene alsS (SEQ ID NO: 1) was amplified by PCR; using the genome of E. S, UP-ydeU-A, DN-ydeU-S, DN-ydeU-A); promoter P trc Designed in the downstream primer of the upstream homology arm and the upstream primer of the alsS gene. The integrated fragment P was obtained by overlapping PCR with the upper and lower homology...
Embodiment 2
[0071] The method for producing L-valine by fermentation of genetically engineered bacteria VHY01, VHY02, and VHY03 is as follows:
[0072] (1) Shake flask fermentation of strains VHY01, VHY02, and VHY03:
[0073] Slant culture: Streak inoculation of -80°C preserved strains on the activated slant, culture at 37°C for 12 hours, and subculture twice;
[0074] Shake flask seed culture: use the inoculation loop to scrape two rings of slant seeds and inoculate them into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing 30mL of seed medium, culture at 37°C and 200rpm for 8-10h;
[0075] Shake flask fermentation culture: Inoculate 10-15% inoculum into a 500mL Erlenmeyer flask containing fermentation medium (final volume is 30mL), 37°C, 200r / min shaking culture, during the fermentation process, maintain the pH at 6.7-7.0; add 60% (m / v) glucose solution to maintain fermentation;
[0076] The composition of the slant medium is: glucose 5g / L, peptone 10g / L, beef extract 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaC...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com