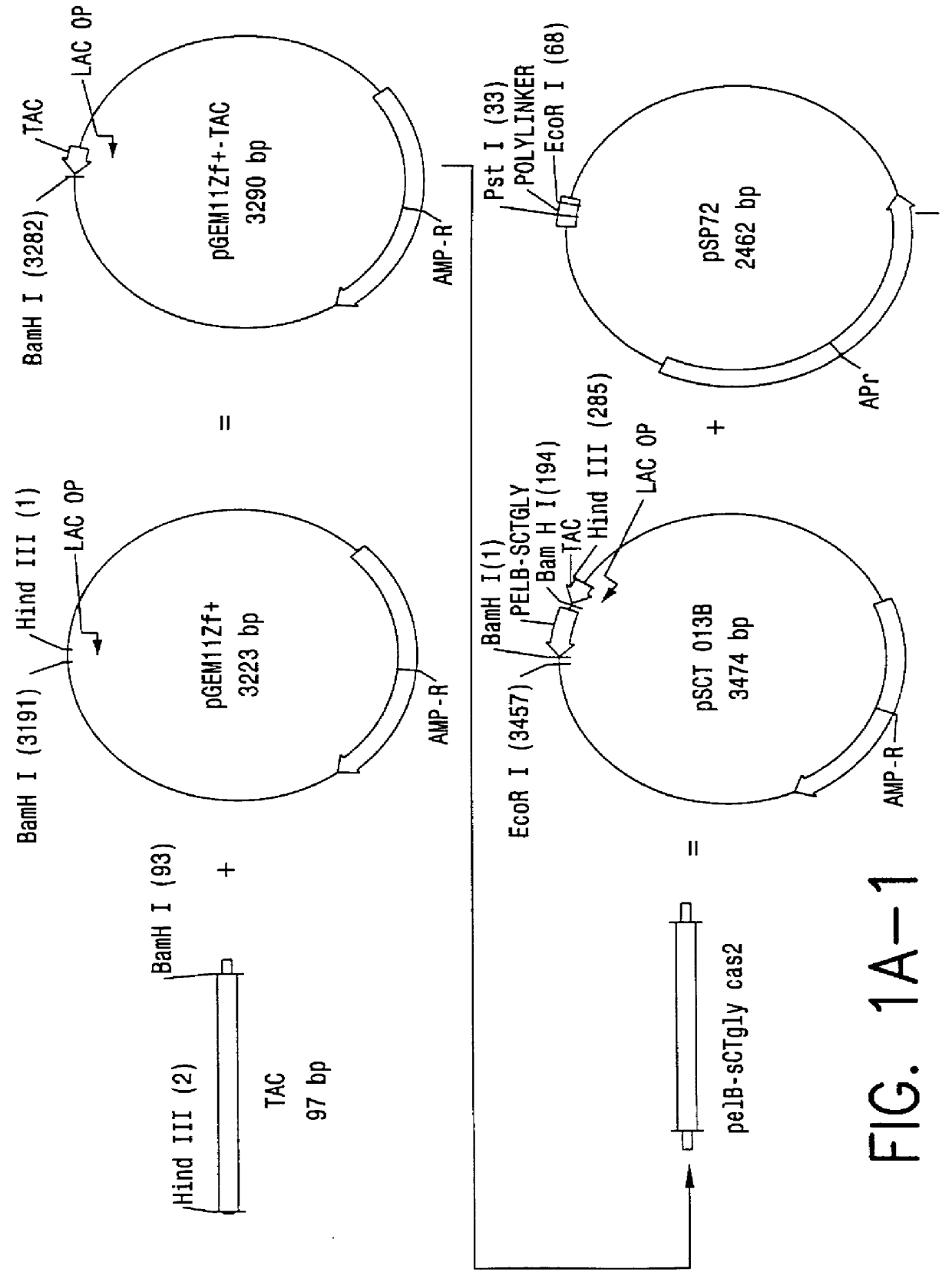
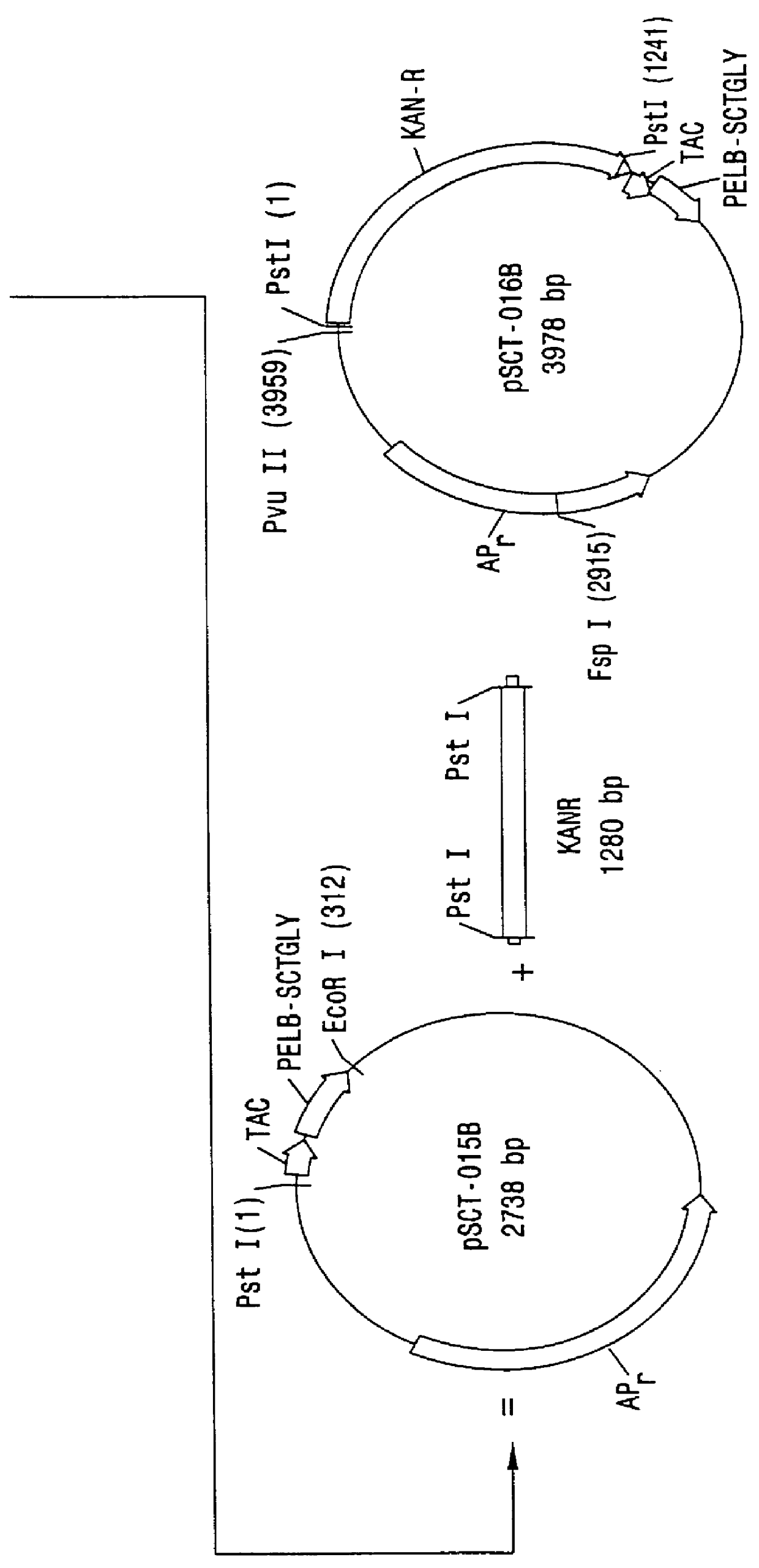
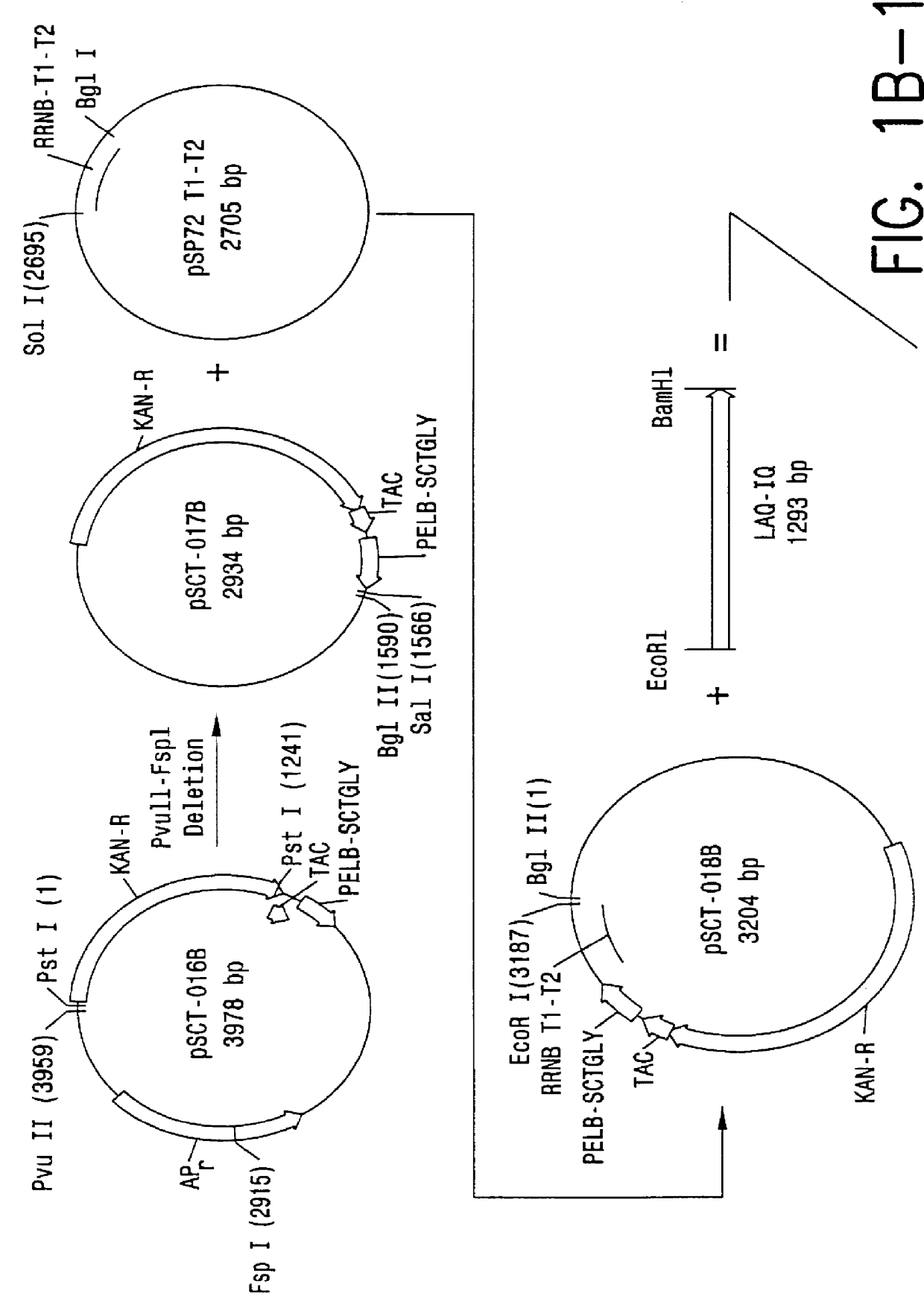
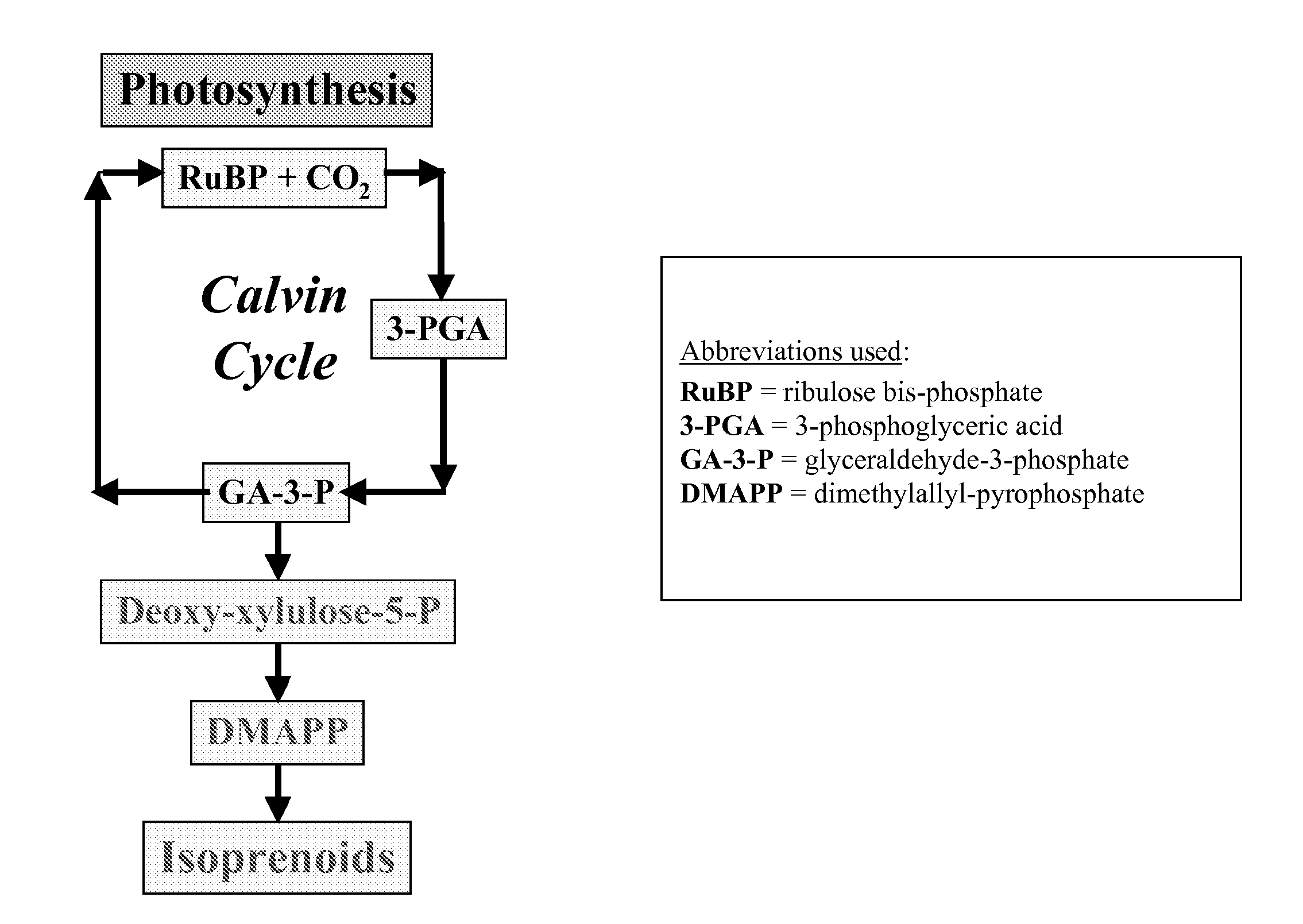
Patents
Literature
2159 results about "Genetically engineered" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Genetically engineered food, also known as genetically modified (GM) food, comes from plants or animals that have had genes from other plants or animals inserted into them. Although humans have modified food plants and animals for many centuries by breeding,...
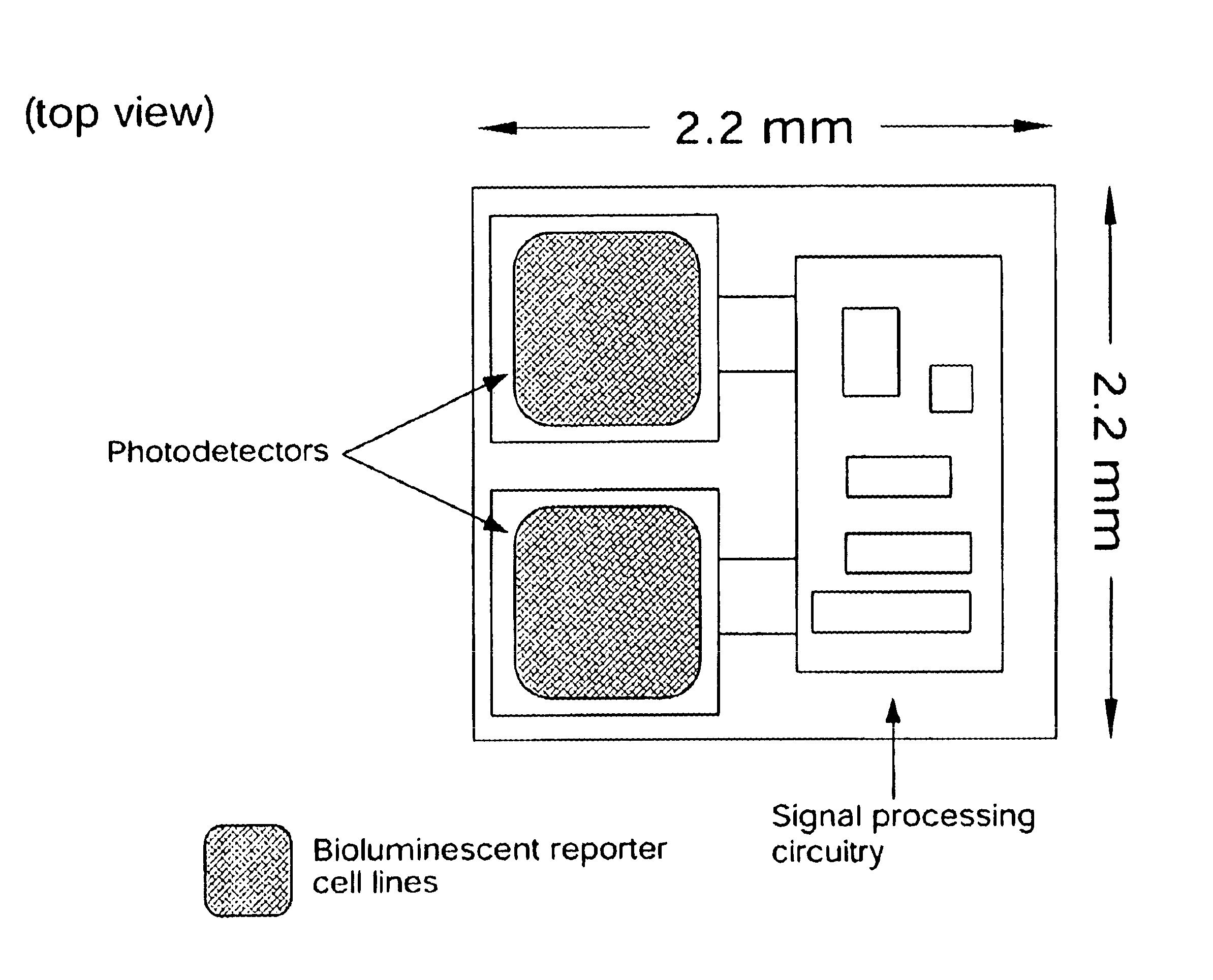
In vivo biosensor apparatus and method of use
InactiveUS6673596B1Less can be administeredCost-effective administration of drugBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIn vivoGenetically engineered
Disclosed are bioluminescent bioreporter integrated circuit devices that detect selected analytes in fluids when implanted in the body of an animal. The device comprises a bioreporter that has been genetically engineered to contain a nucleic acid segment that comprises a cis-activating response element that is responsive to the selected substance operably linked to a gene encoding a bioluminescent reporter polypeptide. In preferred embodiments, the target analyte is glucose, glucagons, or insulin. Exposure of the bioreporter to the target substance causes the response element to up-regulate the nucleic acid sequence encoding the reporter polypeptide to produce a luminescent response that is detected and quantitated. In illustrative embodiments, the bioreporter device is encapsulated on an integrated circuit that is capable of detecting the emitted light, processing the resultant signal, and then remotely reporting the results. Also disclosed are controlled drug delivery systems capable of being directly or indirectly controlled by the detection device that provide drugs such as insulin to the animal in reponse to the amount of target analyte present in the body fluids.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND +1
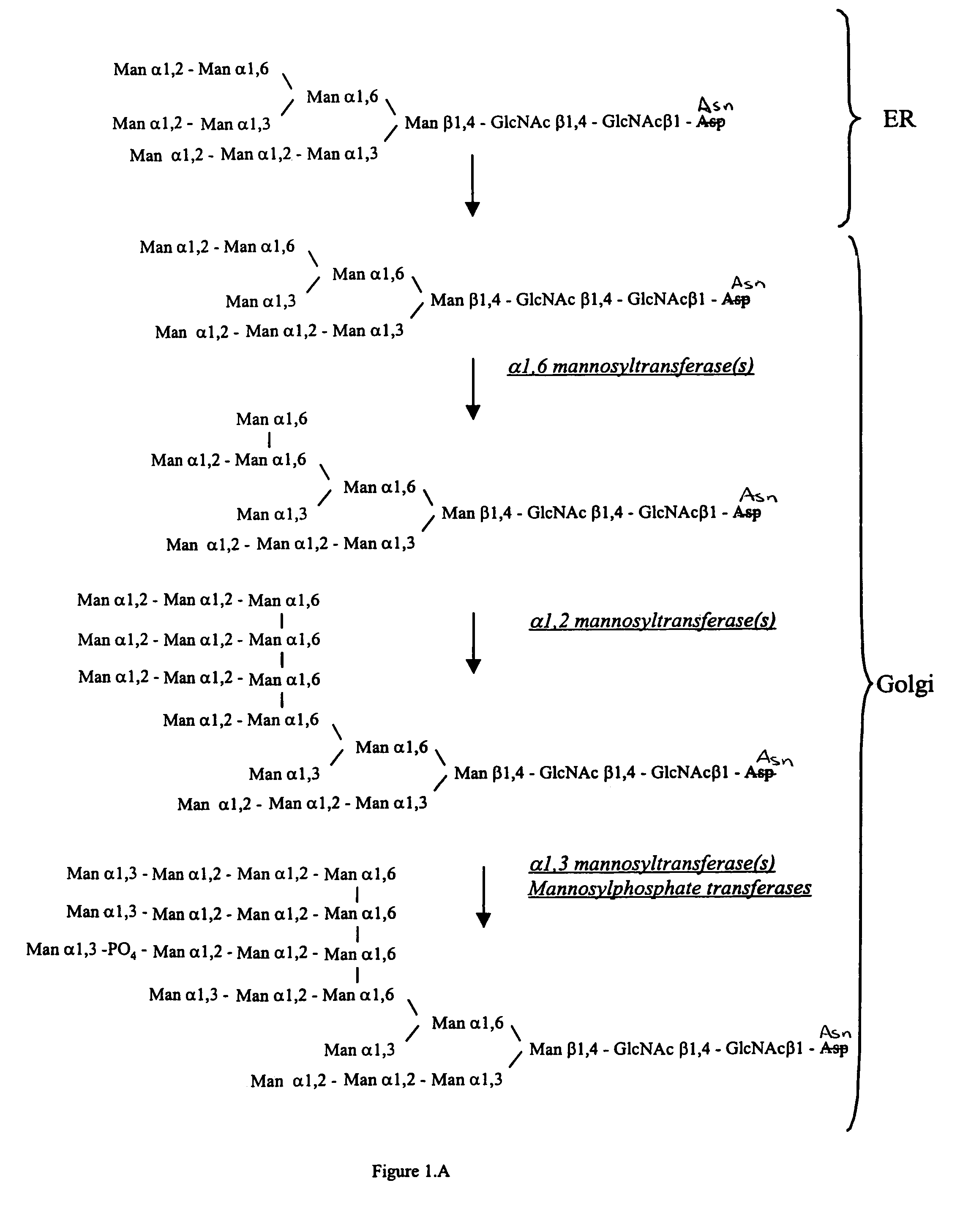
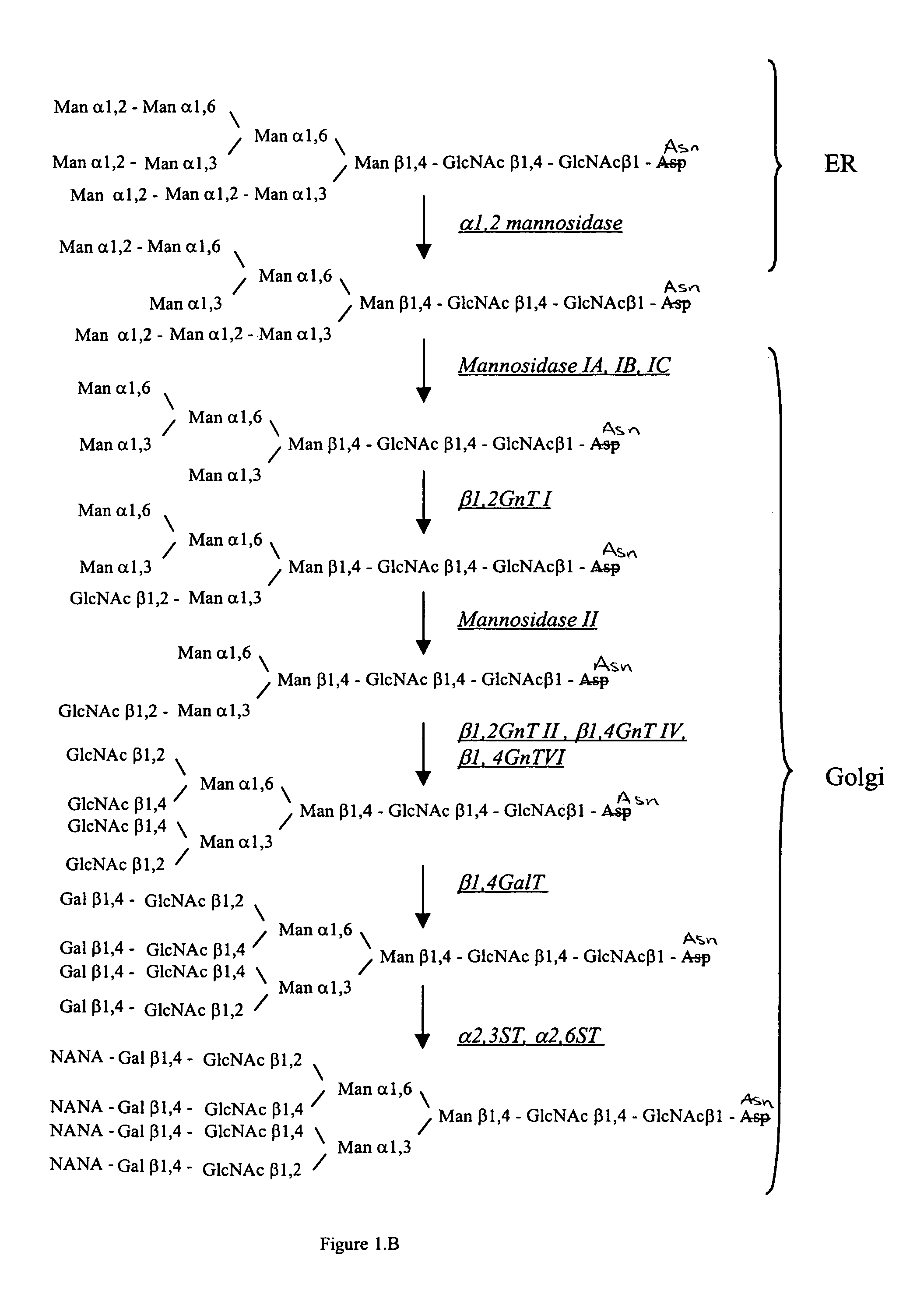
Methods for producing modified glycoproteins
Cell lines having genetically modified glycosylation pathways that allow them to carry out a sequence of enzymatic reactions, which mimic the processing of glycoproteins in humans, have been developed. Recombinant proteins expressed in these engineered hosts yield glycoproteins more similar, if not substantially identical, to their human counterparts. Thelower eukaryotes, which ordinarily produce high-mannose containing N-glycans, including unicellular and multicellular fungi are modified to produce N-glycans such as Man5GlcNAc2 or other structures along human glycosylation pathways. This is achieved using a combination of engineering and / or selection of strains which: do not express certain enzymes which create the undesirable complex structures characteristic of the fungal glycoproteins, which express exogenous enzymes selected either to have optimal activity under the conditions present in the fungi where activity is desired, or which are targeted to an organelle where optimal activity is achieved, and combinations thereof wherein the genetically engineered eukaryote expresses multiple exogenous enzymes required to produce “human-like” glycoproteins.
Owner:GLYCOFI
CE7-specific redirected immune cells
Genetically engineered, CE7-specific redirected immune cells expressing a cell surface protein having an extracellular domain comprising a receptor which is specific for CE7, an intracellular signaling domain, and a transmembrane domain, and methods of use for such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CE7+ neuroblastoma are disclosed. In one embodiment, the immune cell is a T cell and the cell surface protein is a single chain FvFc:ζ receptor where Fv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CE7 linked by peptide, Fc represents a hinge —CH2—CH3 region of a human IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. DNA constructs encoding a chimeric T-cell receptor and a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor are also disclosed.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor
InactiveUS7446179B2Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsIntracellular signallingTransmembrane domain
The present invention relates to a genetically engineered, CD19-specific chimeric T cell receptor and to immune cells expressing the chimeric receptor The present invention also relates to the use of such cells for cellular immunotherapy of CD9+ malignancies and for abrogating any untoward B cell function. The chimeric receptor is a single chain scFvFc:ζ receptor where scFvFc designates the extracellular domain, scFv designates the VH and VL chains of a single chain monoclonal antibody to CD19, Fc represents at least part of a constant region of an IgG1, and ζ represents the intracellular signaling domain of the zeta chain of human CD3. The extracellular domain scFvFc and the intracellular domain ζ are linked by a transmembrane domain such as the transmembrane domain of CD4. In one aspect, the chimeric receptor comprises amino acids 23-634 of SEQ I DNO:2. The present invention further relates to a method of making a redirected T cell expressing a chimeric T cell receptor by electroporation using naked DNA encoding the receptor.
Owner:CITY OF HOPE
Virus vectors and methods of making and administering the same
The present invention provides genetically-engineered parvovirus capsids and viruses designed to introduce a heterologous gene into a target cell. The parvoviruses of the invention provide a repertoire of vectors with altered antigenic properties, packaging capabilities, and / or cellular tropisms as compared with current AAV vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
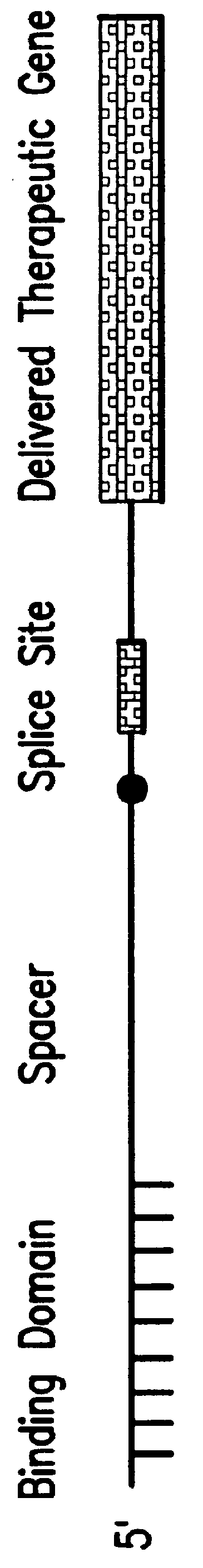
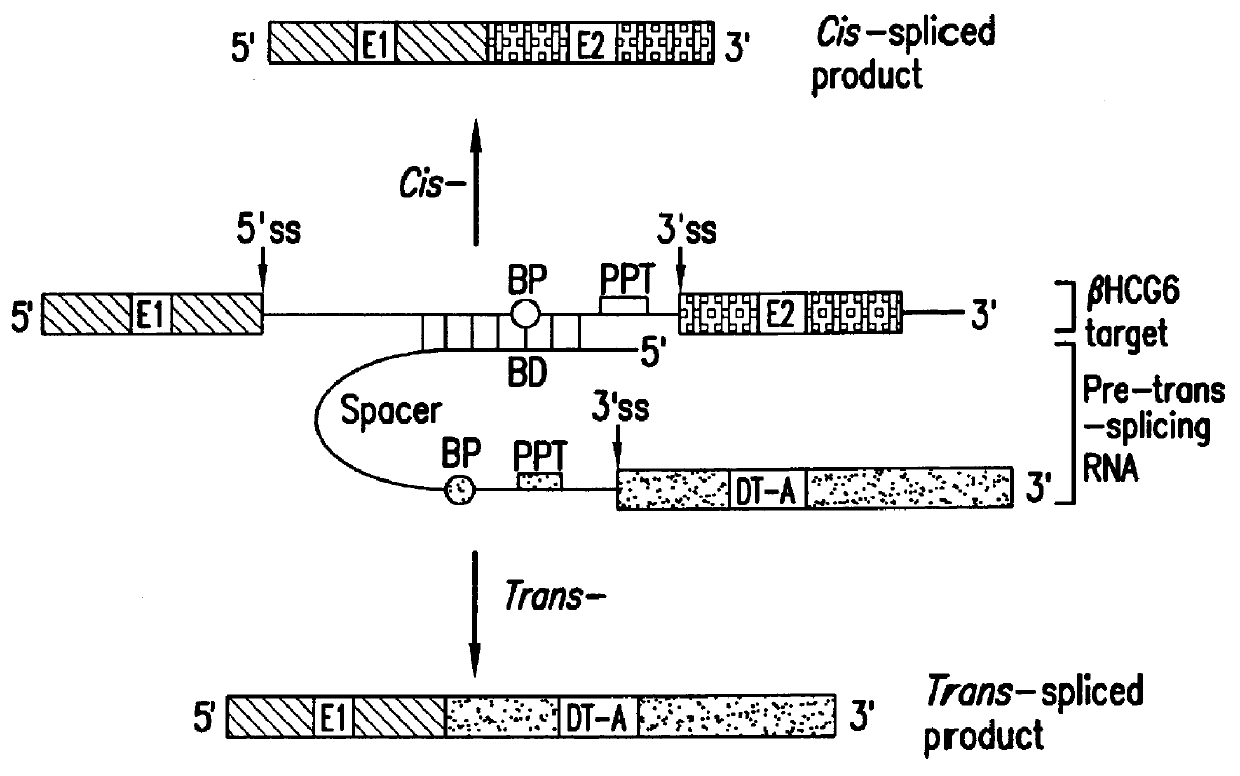
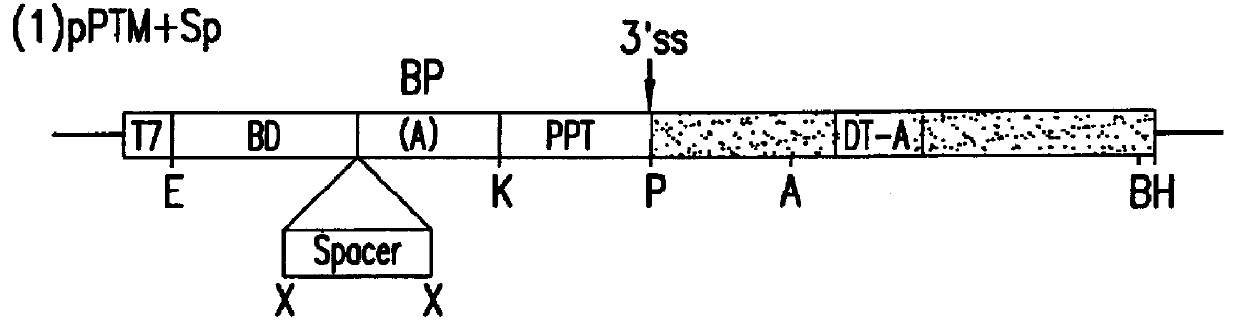
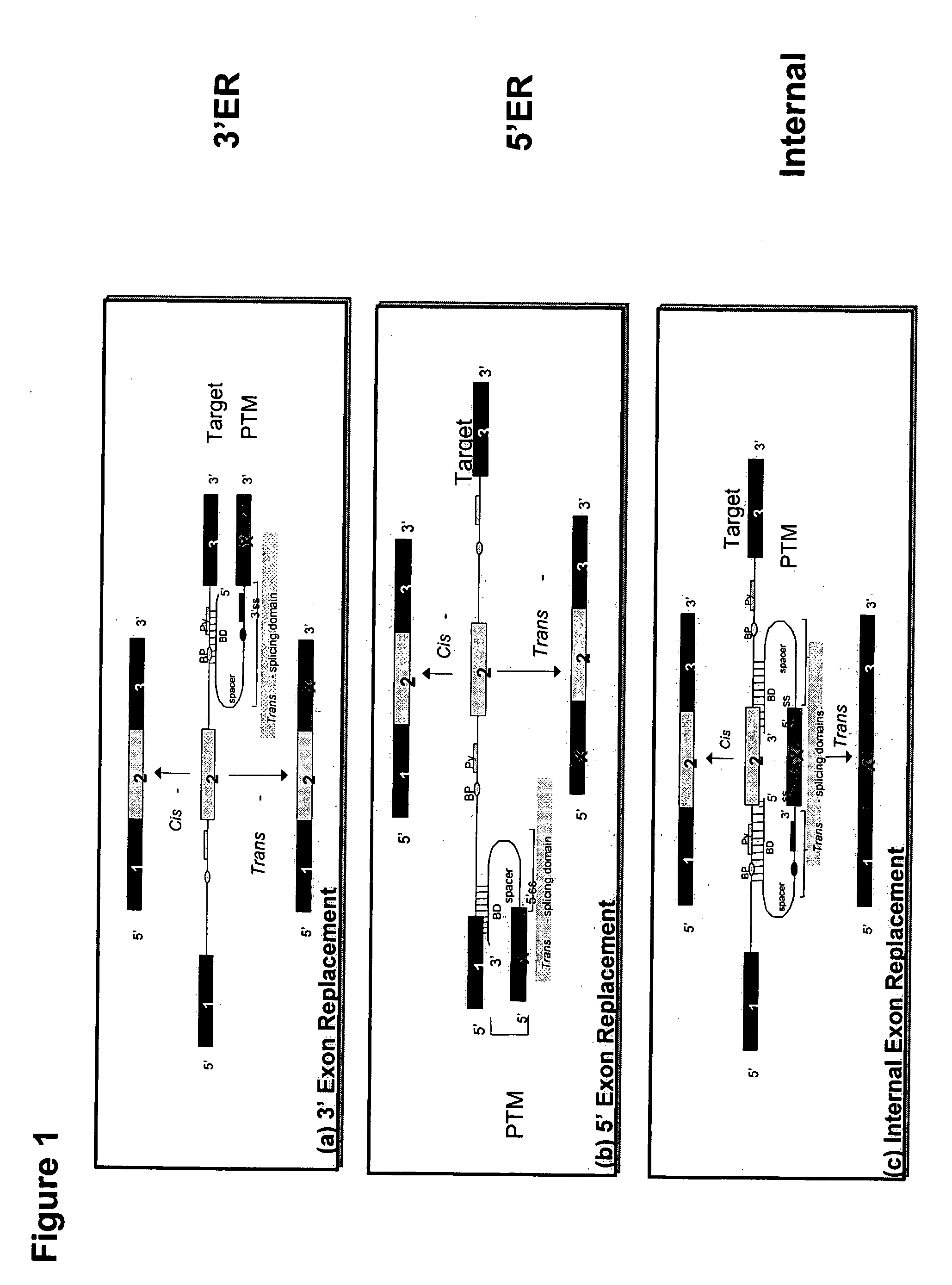
Methods and compositions for use in spliceosome mediated RNA trans-splicing
The molecules and methods of the present invention provide a means for in vivo production of a trans-spliced molecule in a selected subset of cells. The pre-trans-splicing molecules of the invention are substrates for a trans-splicing reaction between the pre-trans-splicing molecules and a pre-mRNA which is uniquely expressed in the specific target cells. The in vivo trans-splicing reaction provides a novel mRNA which is functional as mRNA or encodes a protein to be expressed in the target cells. The expression product of the mRNA is a protein of therapeutic value to the cell or host organism a toxin which causes killing of the specific cells or a novel protein not normally present in such cells. The invention further provides PTMs that have been genetically engineered for the identification of exon / intron boundaries of pre-mRNA molecules using an exon tagging method. The PTMs of the invention can also be designed to result in the production of chimeric RNA encoding for peptide affinity purification tags which can be used to purify and identify proteins expressed in a specific cell type.
Owner:INTRONN HLDG +1
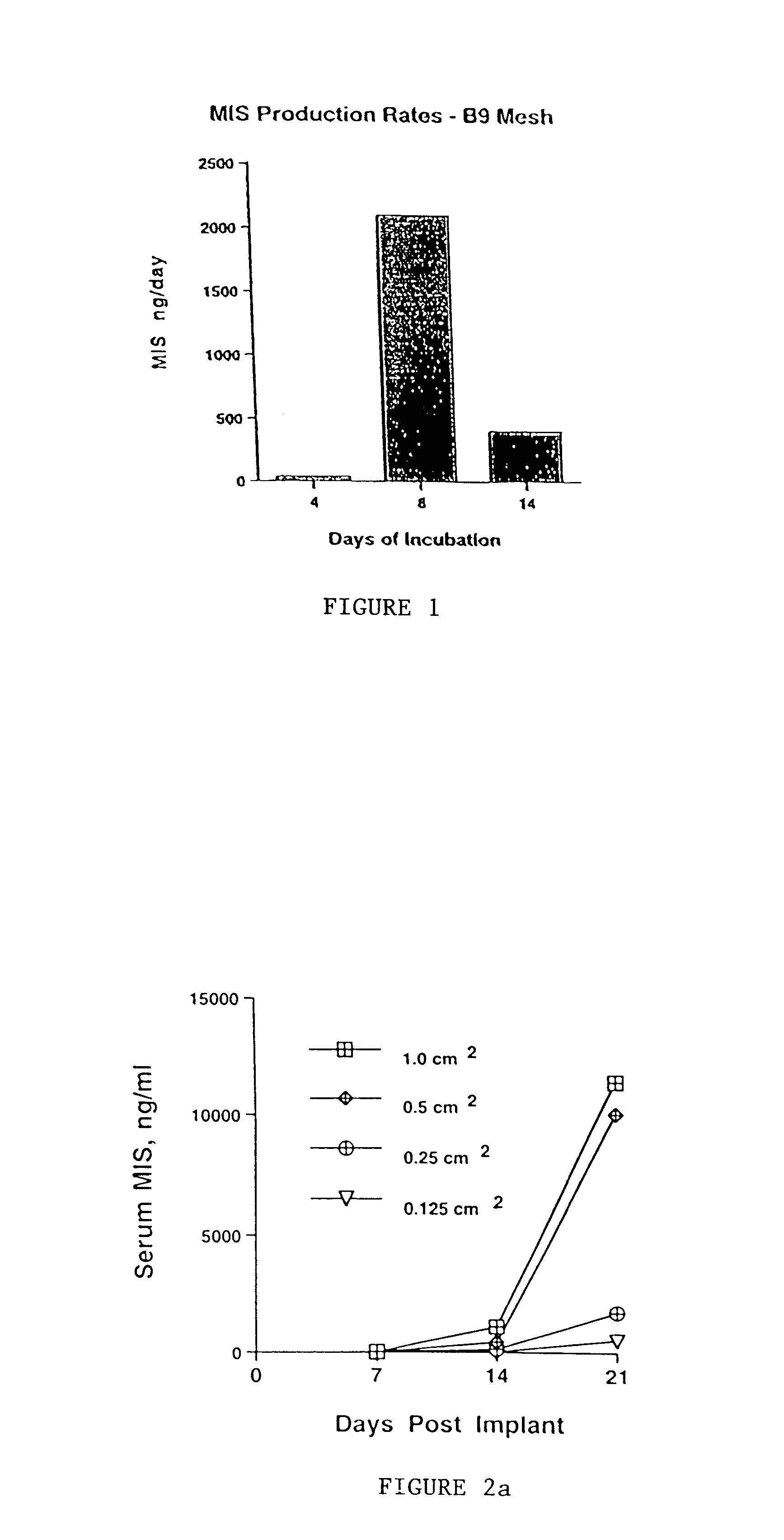
Delivery of therapeutic biologicals from implantable tissue matrices
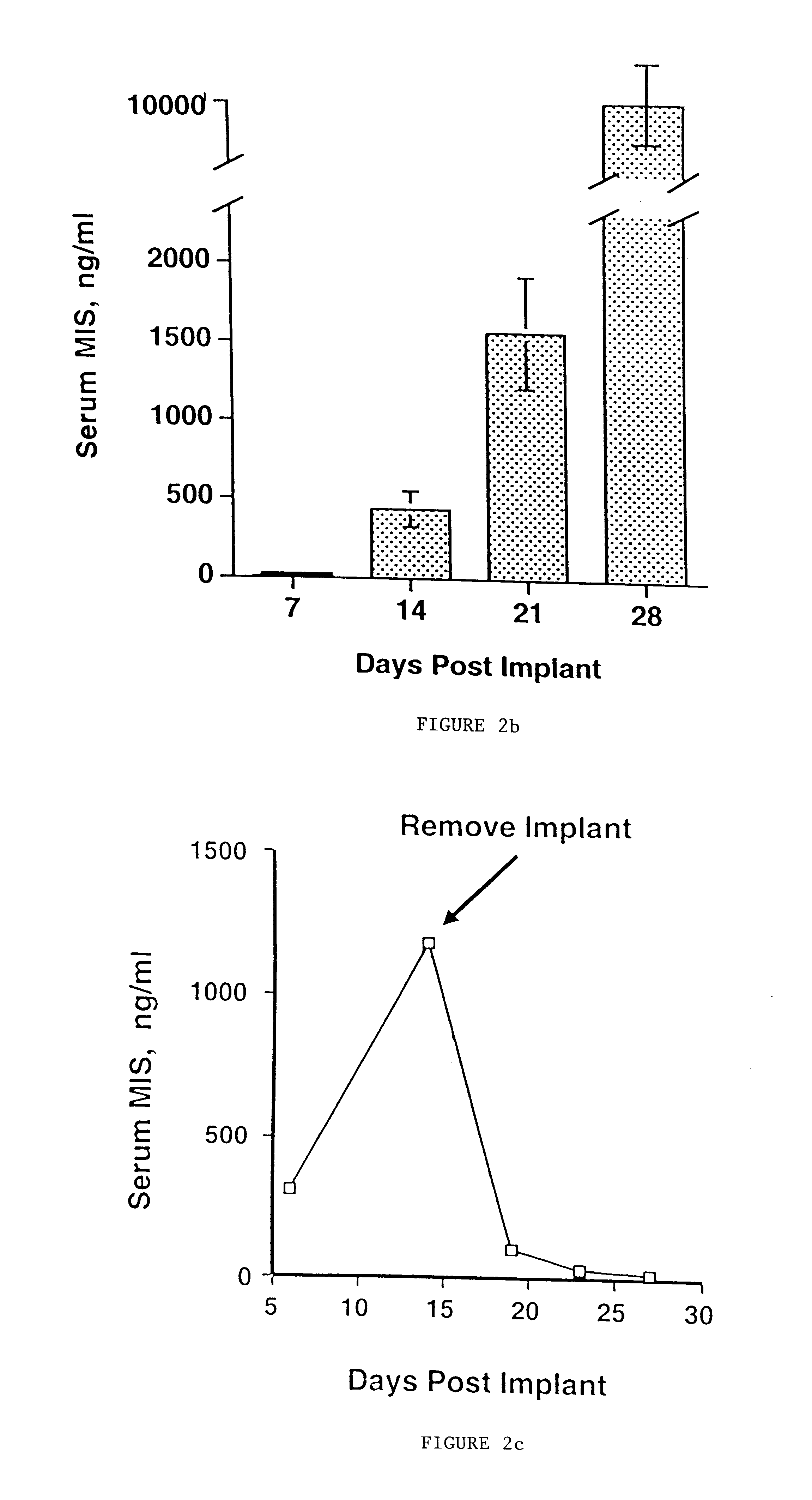
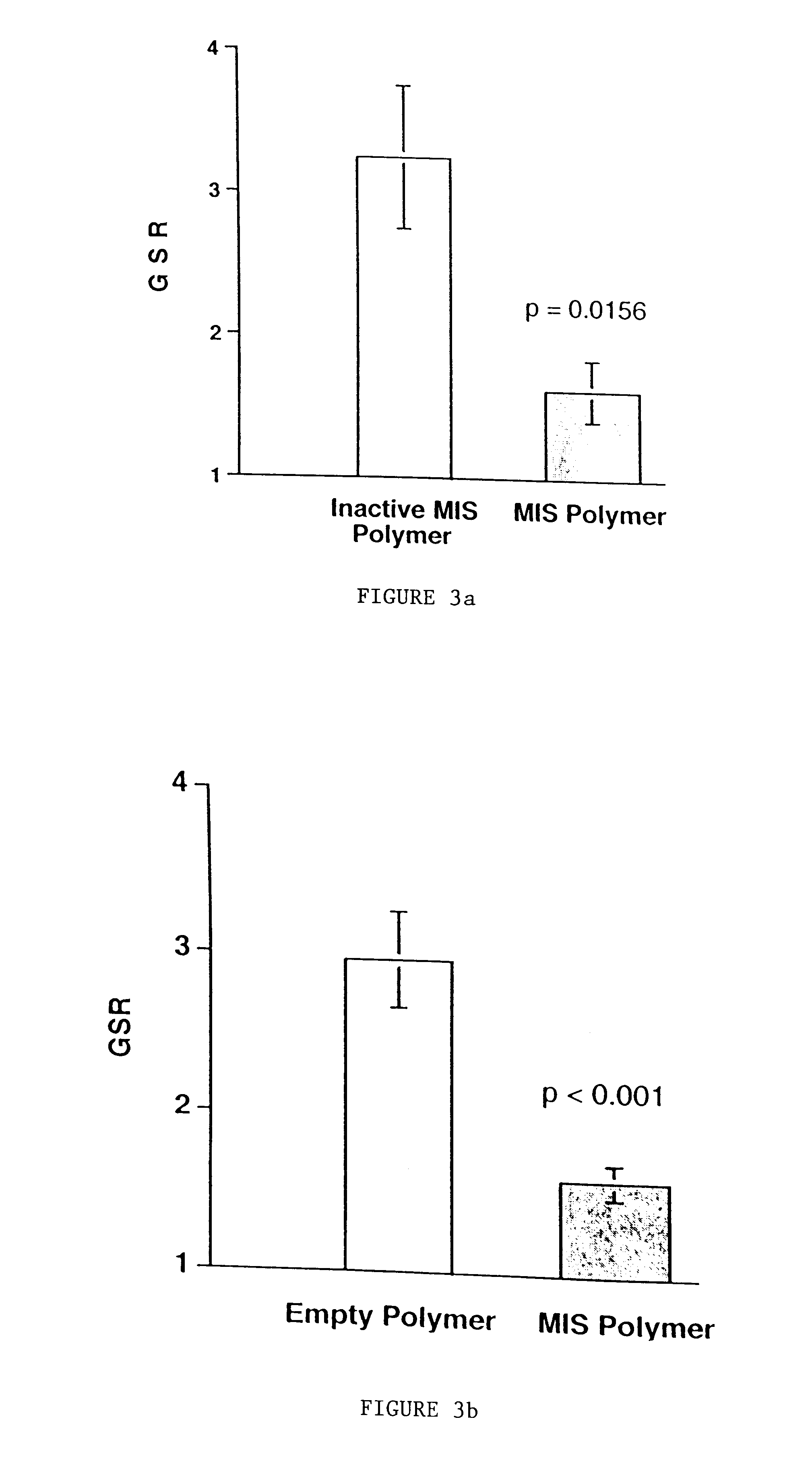
Normal cells, such as fibroblasts or other tissue or organ cell types, are genetically engineered to express biologically active, therapeutic agents, such as proteins that are normally produced in small amounts, for example, MIS, or other members of the TGF-beta family Herceptin(TM), interferons, andanti-angiogenic factors. These cells are seeded into a matrix for implantation into the patient to be treated. Cells may also be engineered to include a lethal gene, so that implanted cells can be destroyed once treatment is completed. Cells can be implanted in a variety of different matrices. In a preferred embodiment, these matrices are implantable and biodegradable over a period of time equal to or less than the expected period of treatment, when cells engraft to form a functional tissue producing the desired biologically active agent. Implantation may be ectopic or in some cases orthotopic. Representative cell types include tissue specific cells, progenitor cells, and stem cells. Matrices can be formed of synthetic or natural materials, by chemical coupling at the time of implantation, using standard techniques for formation of fibrous matrices from polymeric fibers, and using micromachining or microfabrication techniques. These devices and strategies are used as delivery systems via standard or minimally invasive implantation techniques for any number of parenterally deliverable recombinant proteins, particularly those that are difficult to produce in large amounts and / or active forms using conventional methods of purification, for the treatment of a variety of conditions that produce abnormal growth, including treatment of malignant and benign neoplasias, vascular malformations (hemangiomas), inflammatory conditions, keloid formation, abdominal or plural adhesions, endometriosis, congenital or endocrine abnormalities, and other conditions that can produce abnormal growth such as infection. Efficacy of treatment with the therapeutic biologicals is detected by determining specific criteria, for example, cessation of cell proliferation, regression of abnormal tissue, or cell death, or expression of genes or proteins reflecting the above.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Polyhydroxyalkanoate biopolymer compositions
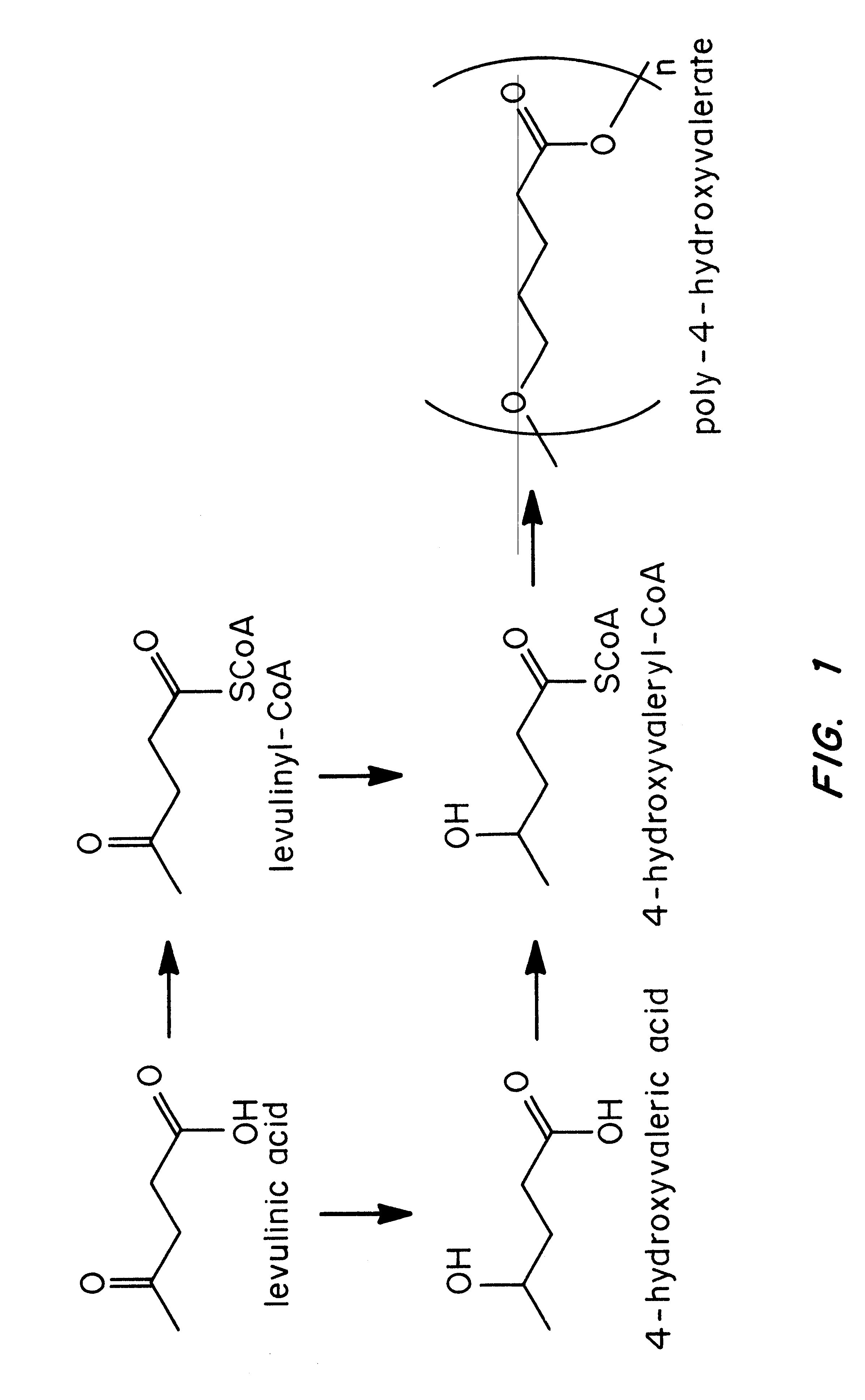
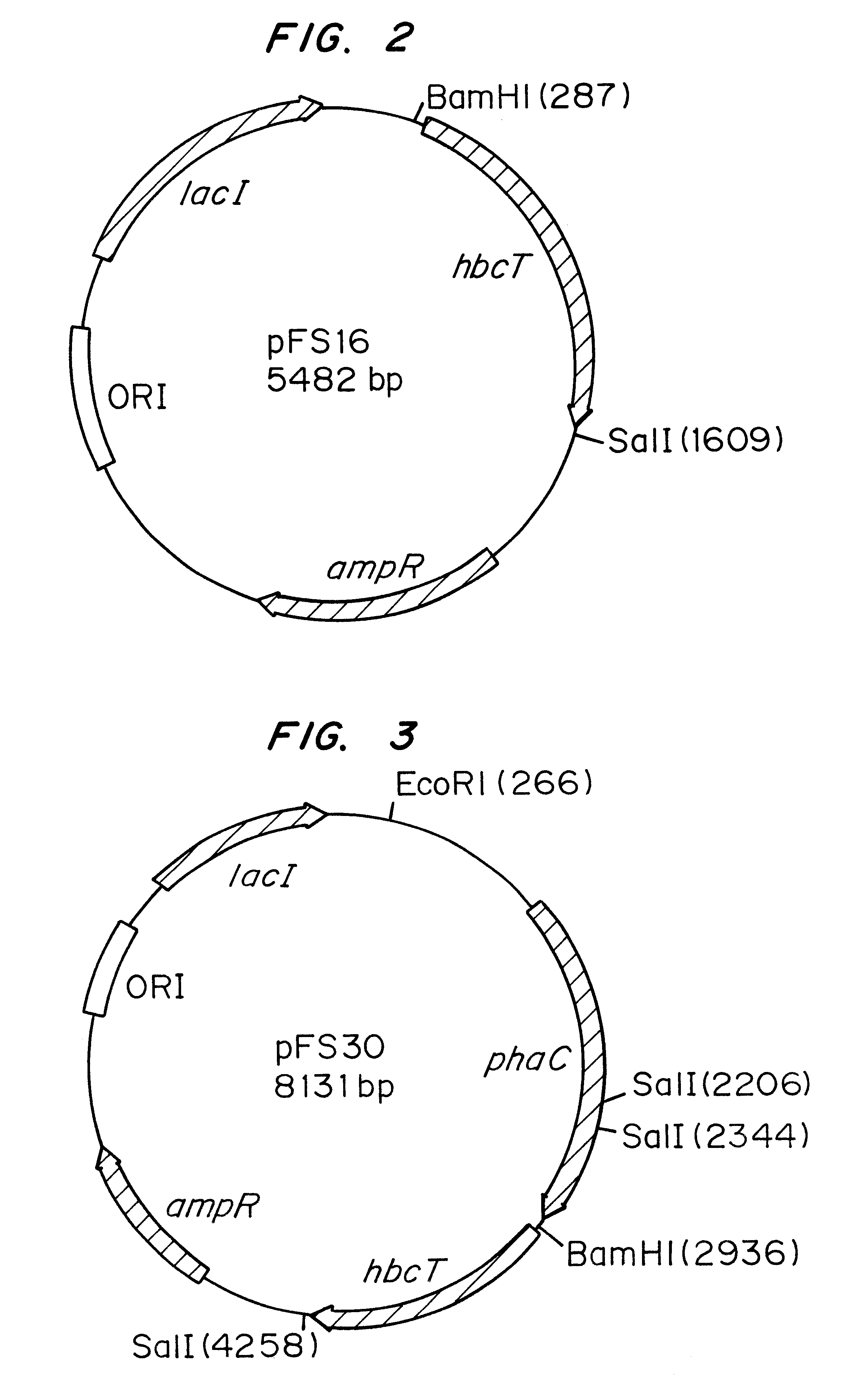
Several novel PHA polymer compositions produced using biological systems include monomers such as 3-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxypropionate, 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxyvalerate, 4-hydroxybutyrate, 4-hydroxyvalerate and 5-hydroxyvalerate. These PHA compositions can readily be extended to incorporate additional monomers including, for example, 3-hydroxyhexanoate, 4-hydroxyhexanoate, 6-hydroxyhexanoate or other longer chain 3-hydroxyacids containing seven or more carbons. This can be accomplished by taking natural PHA producers and mutating through chemical or transposon mutagenesis to delete or inactivate genes encoding undesirable activities. Alternatively, the strains can be genetically engineered to express only those enzymes required for the production of the desired polymer composition. Methods for genetically engineering PHA producing microbes are widely known in the art (Huisman and Madison, 1998, Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews, 63: 21-53). These polymers have a variety of uses in medical, industrial and other commercial areas.
Owner:METABOLIX
Preparation of recombinant factor VIII in a protein free medium
InactiveUS6171825B1Eliminate and at least greatly reduce riskImprove productivityFactor VIICulture processFactor iiManganese
Recombinant Factor VIII can be produced in relatively large quantities on a continuous basis from mammalian cells in the absence of any animal-derived proteins such as albumin by culturing the cells in a protein free medium supplemented with polyol copolymers, preferably in the presence of trace metals such as copper. In very preferred embodiments, the medium includes a polyglycol known as Pluronic F-68, copper sulfate, ferrous sulfate / EDTA complex, and salts of trace metals such as manganese, molybdenum, silicon, lithium and chromium. With an alternative medium which included trace copper ions alone (without polyol copolymers) we were also able to enhance the productivity of Factor VIII in recombinant cells such as BHK cells that are genetically engineered to express Factor VIII.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC +1
Autogenic living scaffolds and living tissue matrices: methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050226856A1Preventing host rejectionThicker and strongBiocideSkin implantsTransdifferentiationOrganism
A 3-dimensional structure comprising suitable cells (or entities) and the ECM (or matrix) that has been completely produced and arranged by these cells (or entities) that promotes the differentiation, dedifferentiation and / or transdifferentiation of cells and / or formation of tissue in vitro and in vivo, while at the same time promoting cell growth, proliferation, migration, acquisition of in vivo-like morphology, or combinations thereof, and that 1. provides structural and / or nutritional support to cells, tissue, organs, or combinations thereof, termed an “Autogenic Living Scaffold” (ALS); or 2. is capable of being transformed into a more complex tissue (or matrix) or a completely different type of tissue (or matrix), termed a “Living Tissue Matrix” (LTM). Autogenic means it is self-produced. The living cells that produce the LTM or ALS, or are added to Autogenic Living Scaffolds, may be genetically engineered or otherwise modified. The matrix component of the ALS or LTM provides a structural framework for cells that guide their direction of growth, enables them to be correctly spaced, prevents overcrowding, enables cells to communicate between each other, transmit subtle biological signals, receive signals from their environment, form bonds and contacts that are required for proper functioning of all cells within a unit such as a tissue, or combinations thereof. The ALS or LTM may thus provide proper or supporting mechanical and chemical environments, signals, or stimuli to other cells, to the cells that produce the ALS, to surrounding tissue at an implantation site, to a wound, for in vitro and ex vivo generation and regeneration of cells, tissue and organs, or combinations thereof. They may also provide other cells with nutrients, growth factors, and / or other necessary or useful components. They may also take in or serve as buffers for certain substances in the environment, and have also some potential at adapting to new environments.
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
Production of humanized antibodies in transgenic animals
InactiveUS7129084B2Low immunogenicityUseful in therapyImmunoglobulins against bacteriaImmunoglobulins against virusesHuman animalGene conversion
This invention relates to humanized antibodies and antibody preparations produced from transgenic non-human animals. The non-human animals are genetically engineered to contain one or more humanized immunoglobulin loci which are capable of undergoing gene rearrangement and gene conversion in the transgenic non-human animals to produce diversified humanized immunoglobulins. The present invention further relates to novel sequences, recombination vectors and transgenic vectors useful for making these transgenic animals. The humanized antibodies of the present invention have minimal immunogenicity to humans and are appropriate for use in the therapeutic treatment of human subjects.
Owner:THERAPEUTIC HUMAN POLYCLONALS
Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASC) as delivery tool for treatment of cancer
InactiveUS20110027239A1Efficient killingSystemic non-specific responses will be minimalBiocideSpecial deliveryAnticarcinogenStromal cell
The present invention generally relates to use of adult Adipose-derived stromal cells (ASC) and genetically engineered ASC for the treatment of cancer. In particular, the present invention generally relates, in part to a method for treating a subject with cancer comprising administering to the subject a composition comprising engineered ASCs which have been modified to express a gene encoding at least one anti-cancer agent. In some embodiments, an anti-cancer agent is a pro-apoptotic agent. In some embodiments an anti-cancer agent is an agent which inhibits the expression of an oncogene.
Owner:TISSUE GENESIS
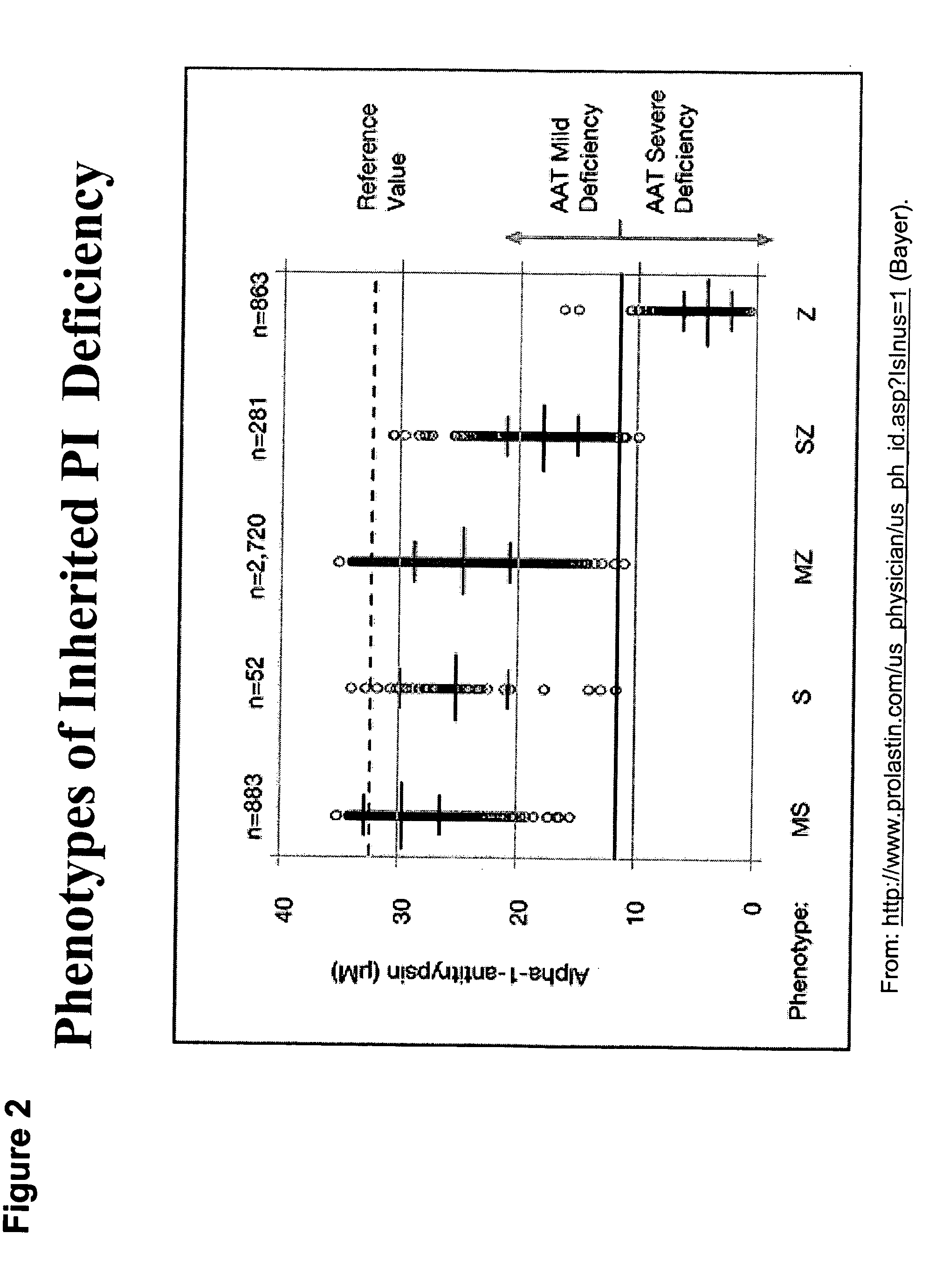
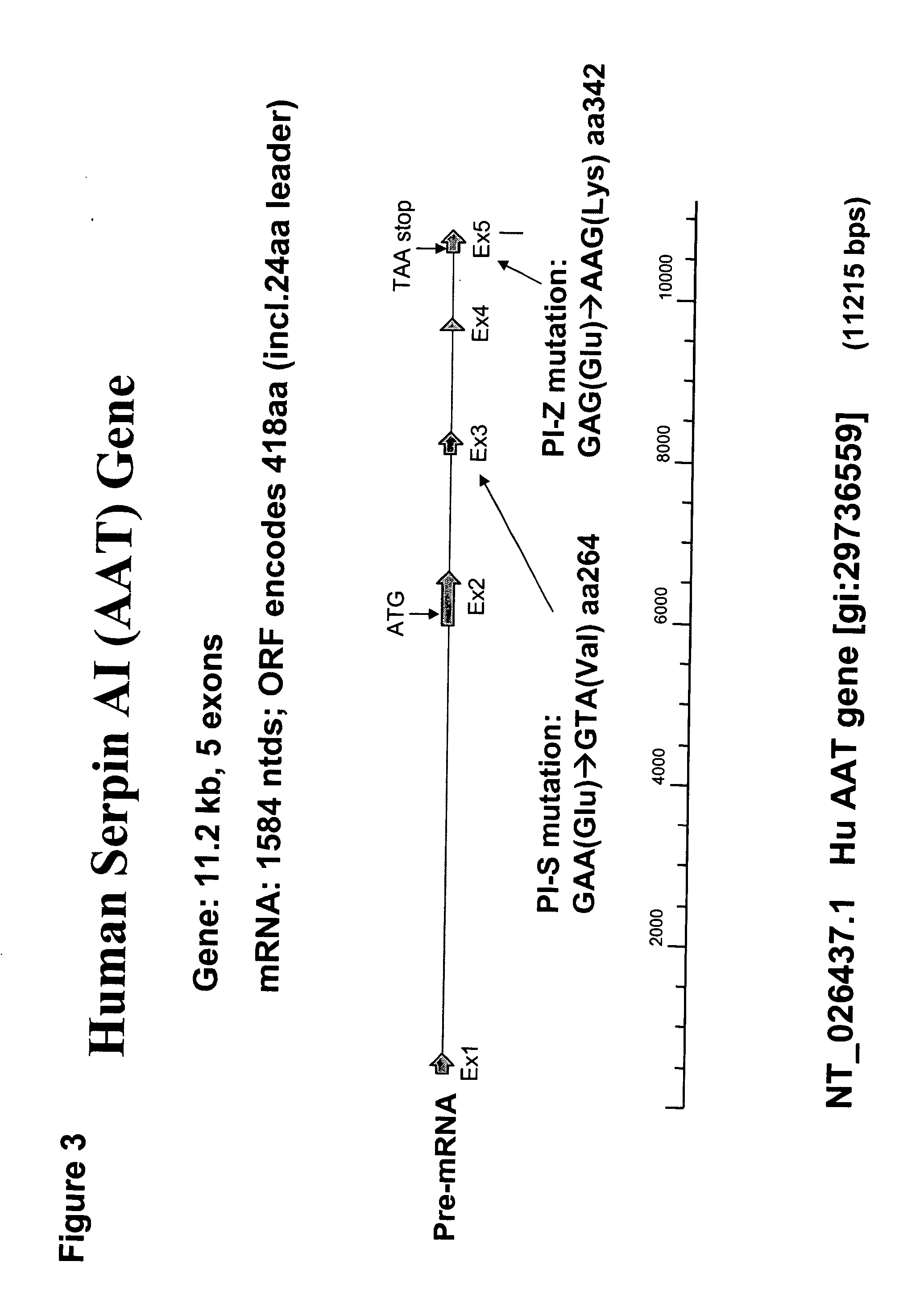
Correction of alpha-1-antitrypsin genetic defects using spliceosome mediated RNA trans splicing
InactiveUS20060234247A1Reduce lungReduce liver pathologySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseRNA Trans-Splicing
The present invention provides methods and compositions for generating novel nucleic acid molecules through targeted spliceosomal mediated RNA trans-splicing. The compositions of the invention include pre-trans-splicing molecules (PTMs) designed to interact with a SERPINA1 target precursor messenger RNA molecule (target pre-mRNA) and mediate a trans-splicing reaction resulting in the generation of a novel chimeric RNA molecule (chimeric RNA). In particular, the PTMs of the present invention include those genetically engineered to interact with SERPINA1 target pre-mRNA so as to result in correction of SERPINA1 genetic defects responsible for AAT deficiency. The PTMs of the invention may also comprise sequences that are processed out of the PTM to yield duplex siRNA molecules directed specifically to mutant SERPIN A1 mRNAs. Such duplexed siRNAs are designed to reduce the accumulation of toxic AAT protein in liver cells. The methods and compositions of the present invention can be used in gene therapy for correction of SERPINA1 disorders such as AAT deficiency.
Owner:VIRXSYS
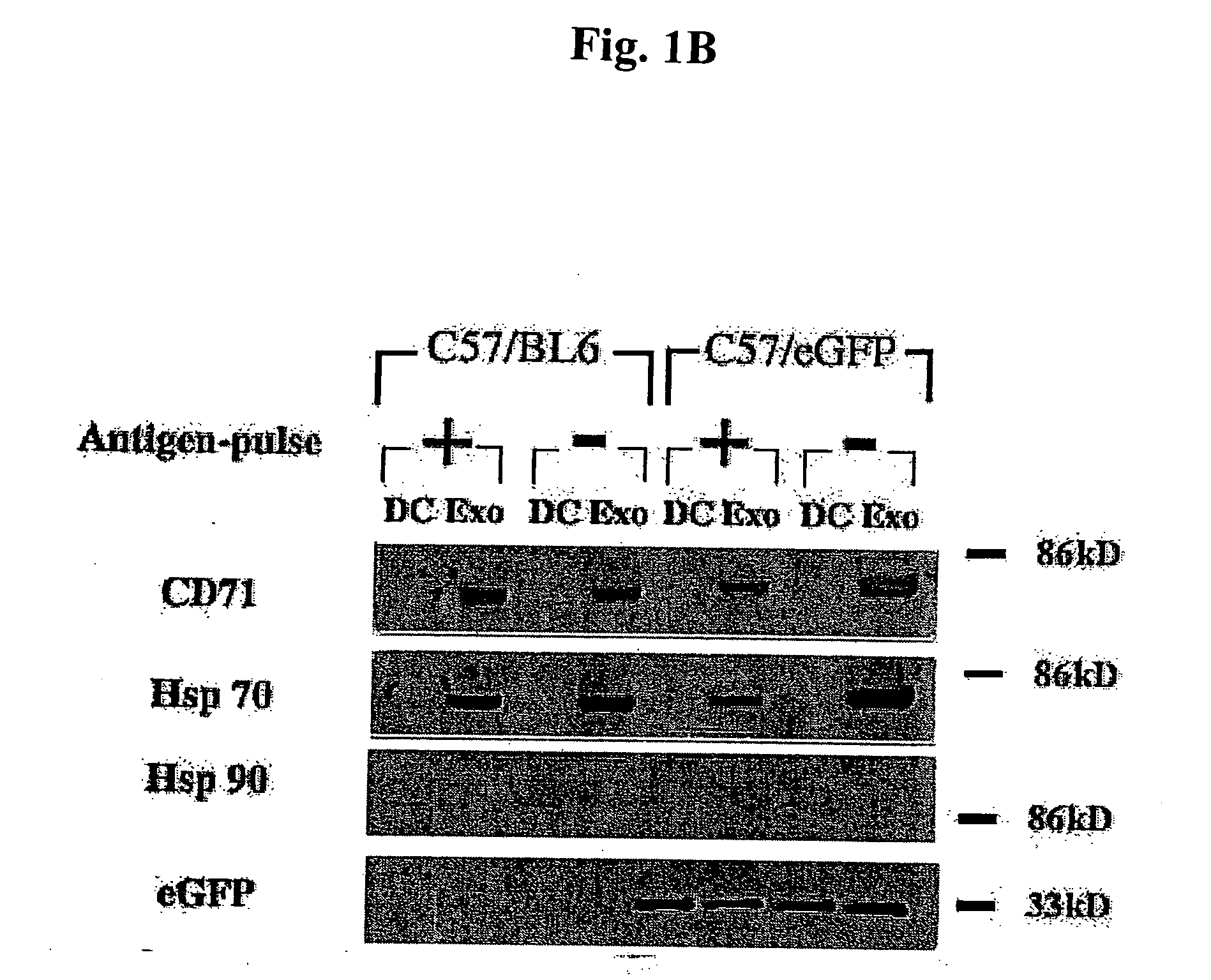
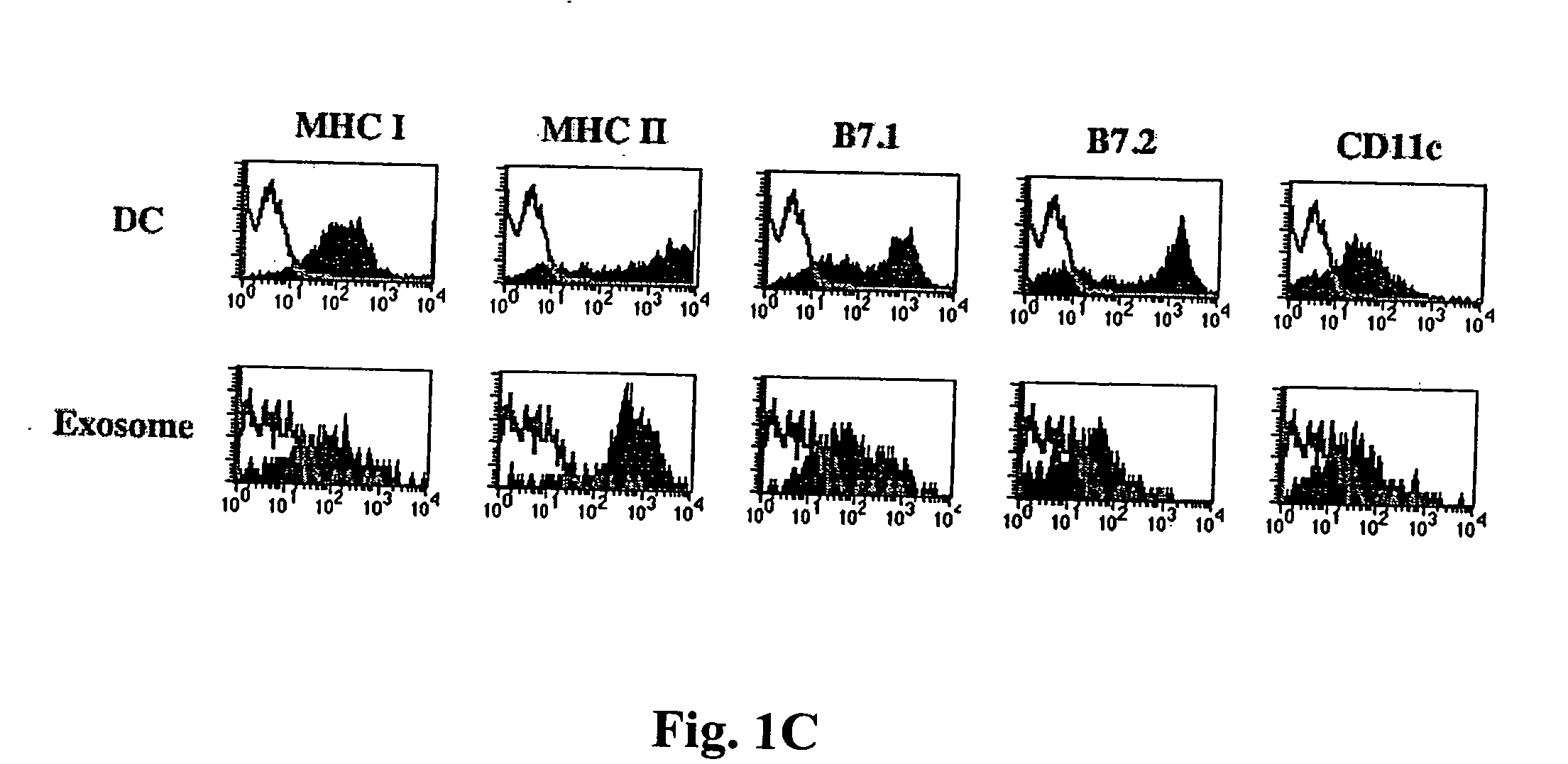
Immunosuppressive exosomes
InactiveUS20060116321A1Suppress undesirable immune responseStimulate immune responseNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCytokine SuppressionDendritic cell
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for use in mediating an immunosuppressive reaction. The compositions of the invention comprise exosomes having immunosuppressive activity. Such exosomes may be derived from a variety of different cell types, including antigen presenting cells such as dendritic cells and macrophages. Prior to isolation of exosomes, the cells may be genetically engineered to express molecules capable of enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of said exosomes and / or may be exposed to one or more agents, such as cytokines or cytokine inhibitors, which are also capable of enhancing the immunosuppressive activity of exosomes. The present invention also relates to the use of such exosomes for the treatment of diseases and disorders associated with undesirable activation of the immune system. The present invention also includes exosomes isolated directly from serum that have been shown to be immunosuppressive.
Owner:PITTSBURGH UNIV OF THE +1
Direct expression of peptides into culture media
InactiveUS6103495AReduced viabilityImprove breathabilityBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth phaseBiotechnology
Expression systems are disclosed for the direct expression of peptide products into the culture media where genetically engineered host cells are grown. High yield was achieved with novel vectors, a special selection of hosts, and / or fermentation processes which include careful control of cell growth rate, and use of an inducer during growth phase. Special vectors are provided which include control regions having multiple promoters linked operably with coding regions encoding a signal peptide upstream from a coding region encoding the peptide of interest. Multiple transcription cassettes are also used to increase yield. The production of amidated peptides using the expression systems is also disclosed.
Owner:ENTERIS BIOPHARMA
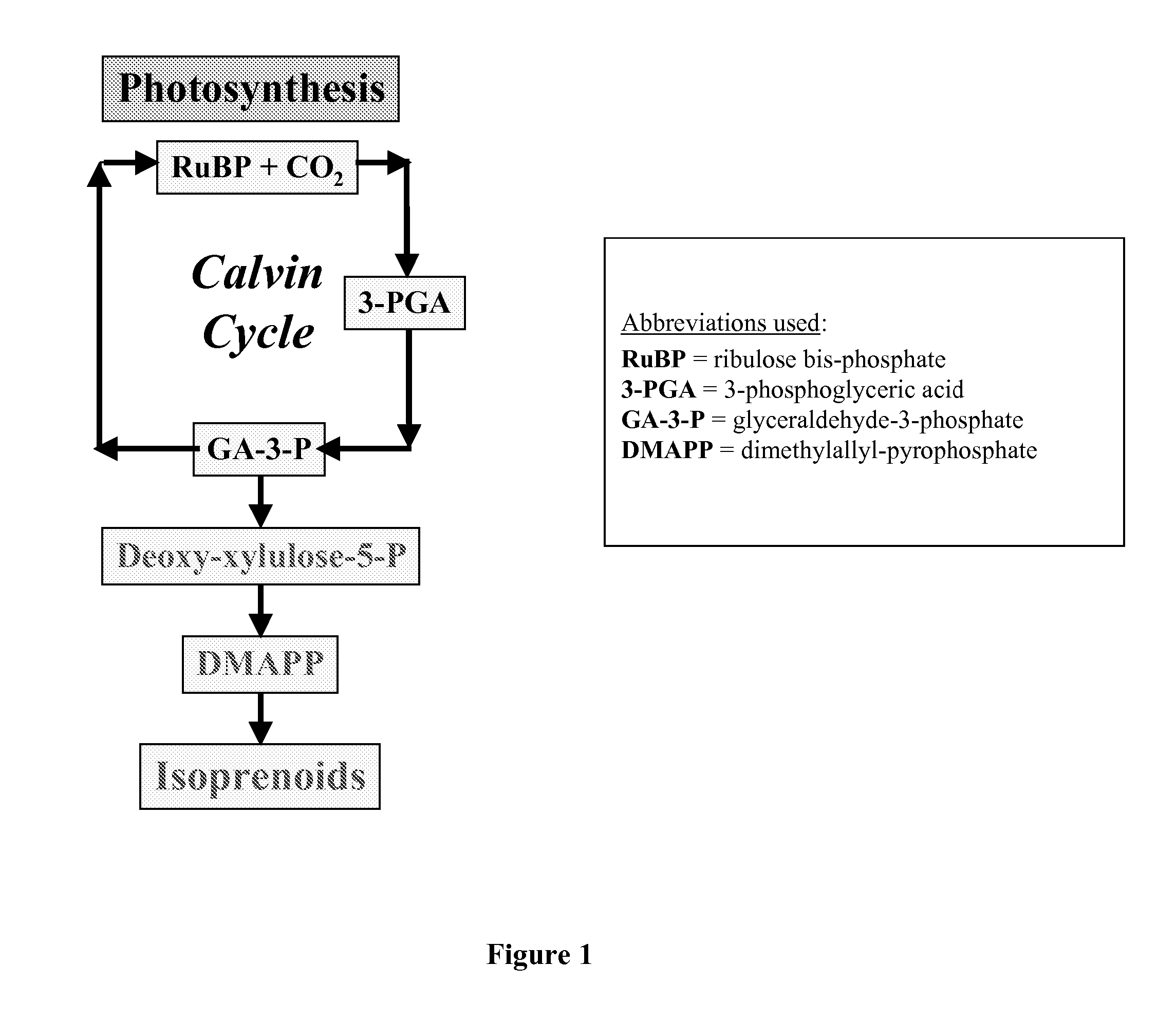
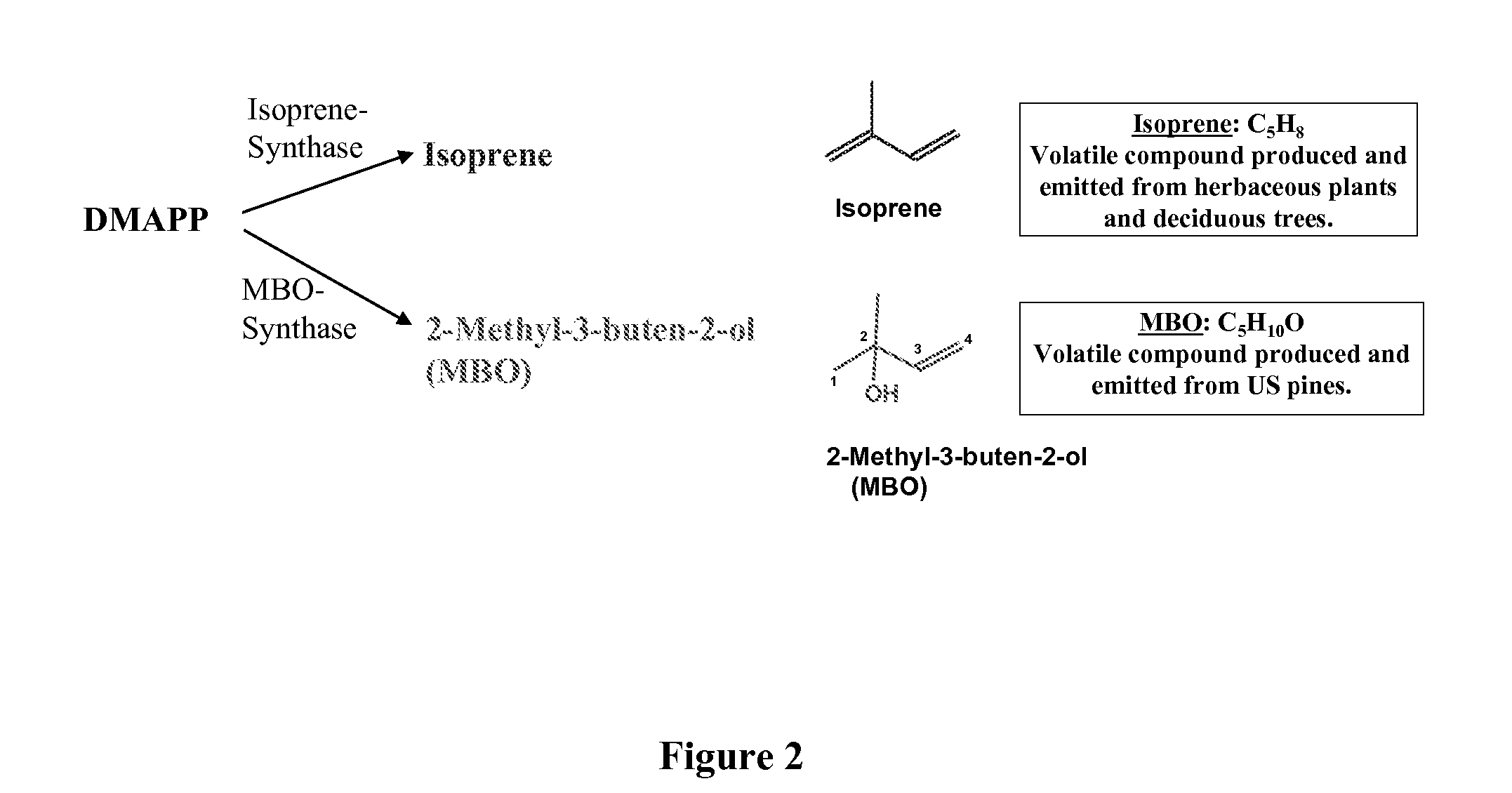
Short chain volatile hydrocarbon production using genetically engineered microalgae, cyanobacteria or bacteria
ActiveUS20080038805A1Promote reproductionLow costBacteriaUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaCyanobacteria
The present invention provides methods and compositions for producing isoprene hydrocarbons from microalgae, cyanobacteria, and photosynthetic and non-photosynthetic bacteria.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
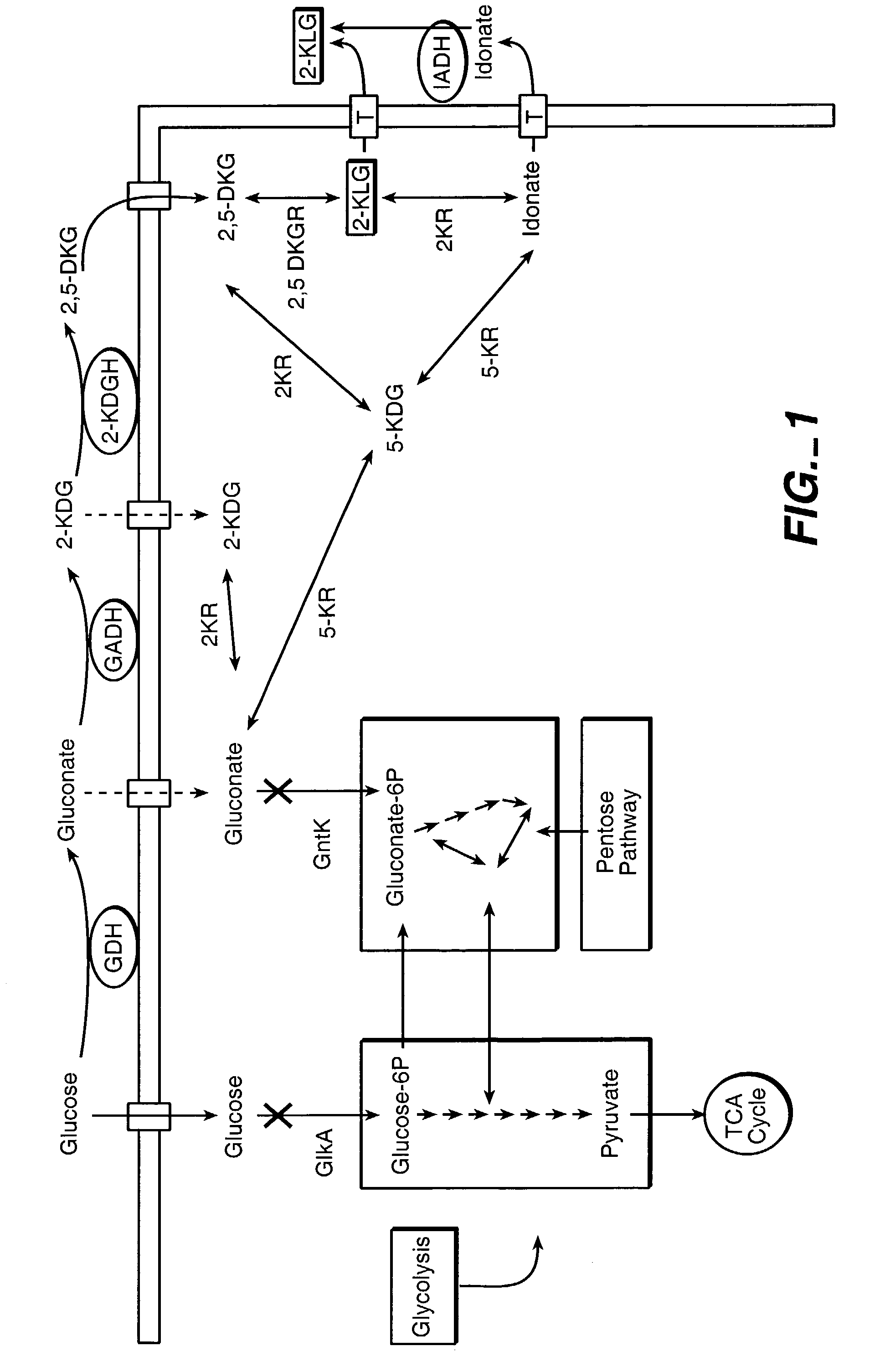
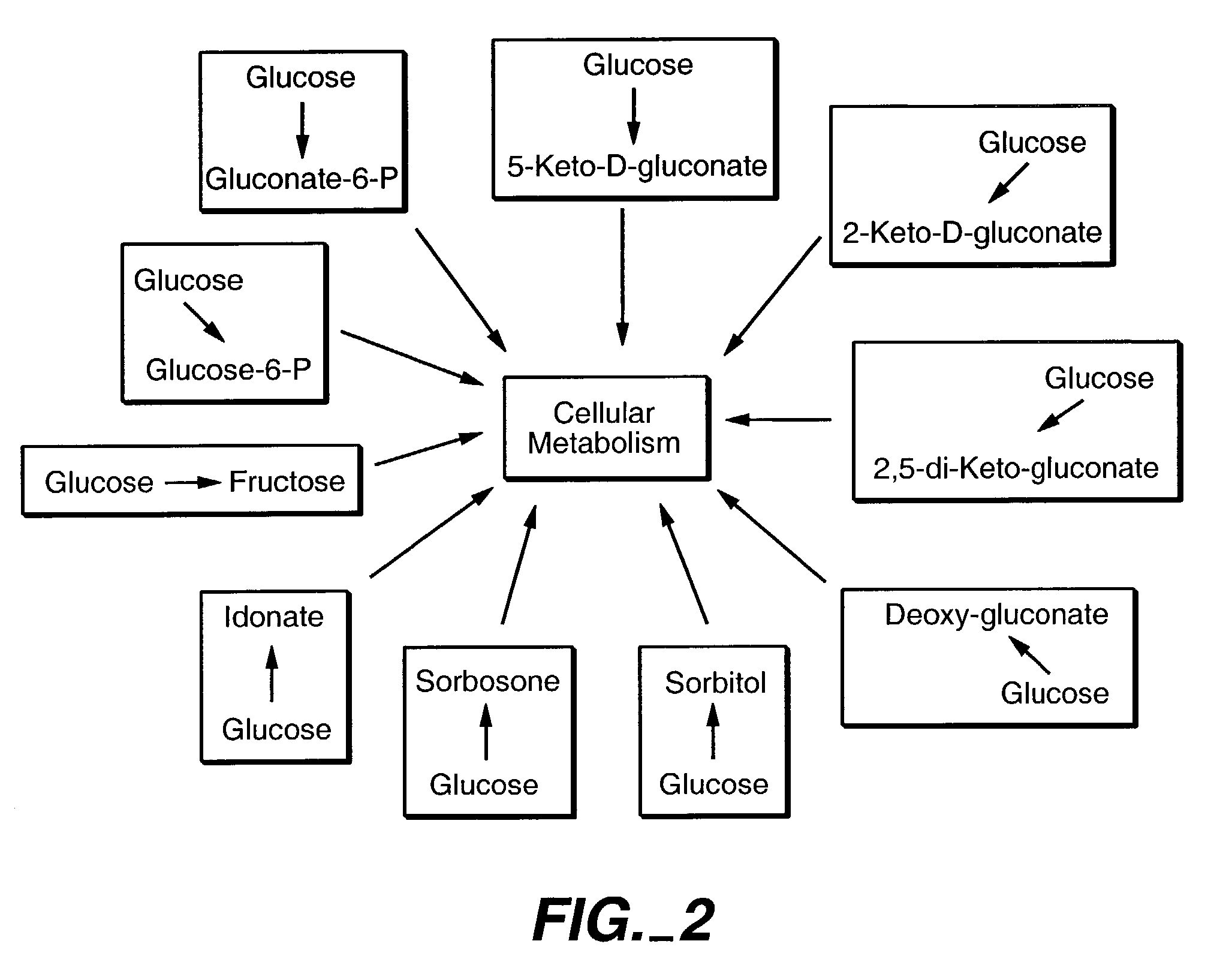
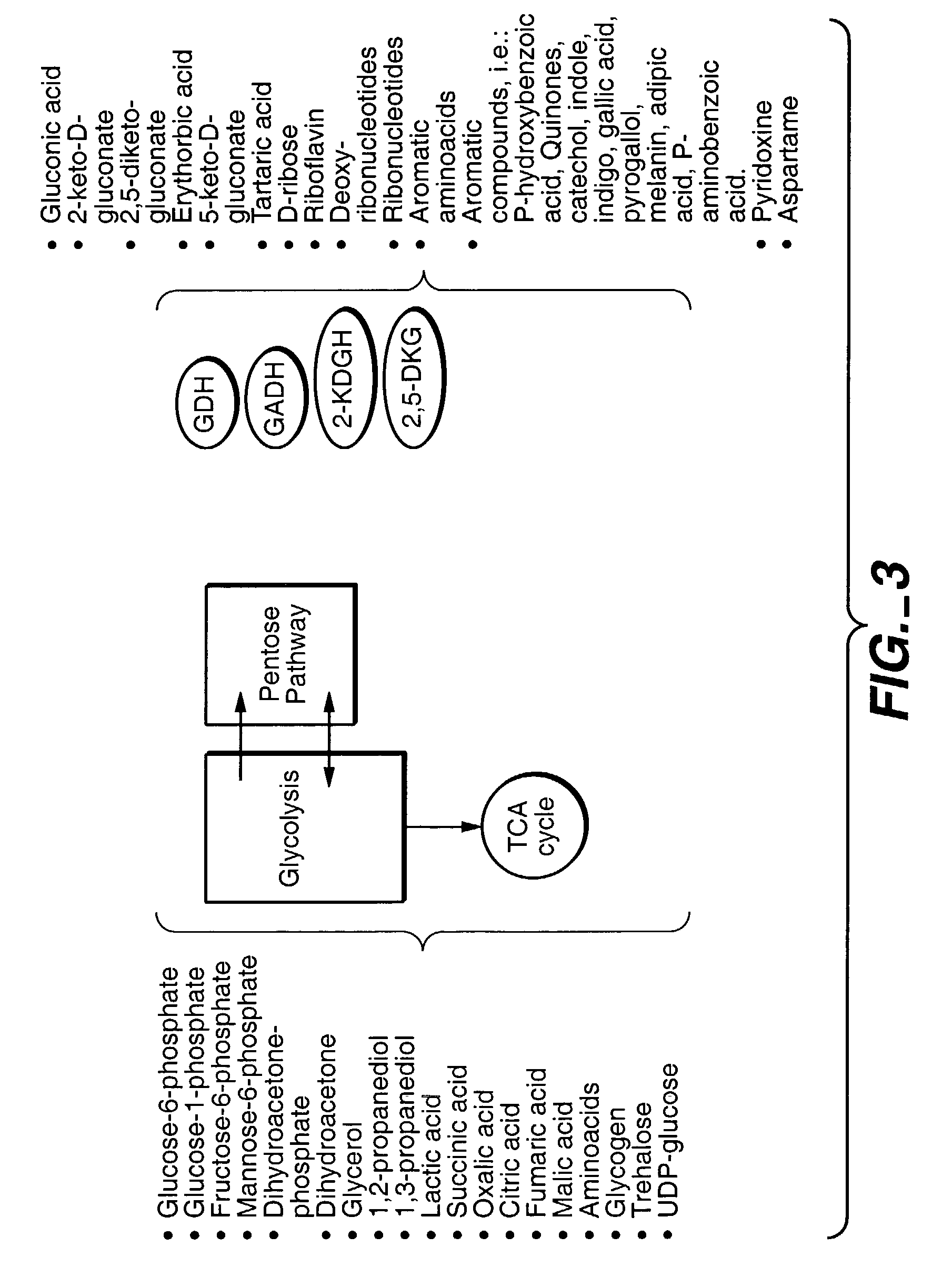
Method of uncoupling the catabolic pathway of glycolysis from the oxidative membrane bound pathway of glucose conversion
InactiveUS7241587B2Increase volumeMeet actual needsBacteriaSugar derivativesPhosphorylationGluconic acid
The invention provides methods for producing products comprising improved host cells genetically engineered to have uncoupled productive and catabolic pathways. In particular, the present invention provides host cells having a modification in nucleic acid encoding an endogenous enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-glucose at its 6th carbon and / or a modification of nucleic acid encoding an enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-gluconate at its 6th carbon. Such improved host cells are used for the production of products, such as, ascorbic acid intermediates. Methods for making and using the improved host cells are provided. Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for glucokinase and gluconokinase are provided.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
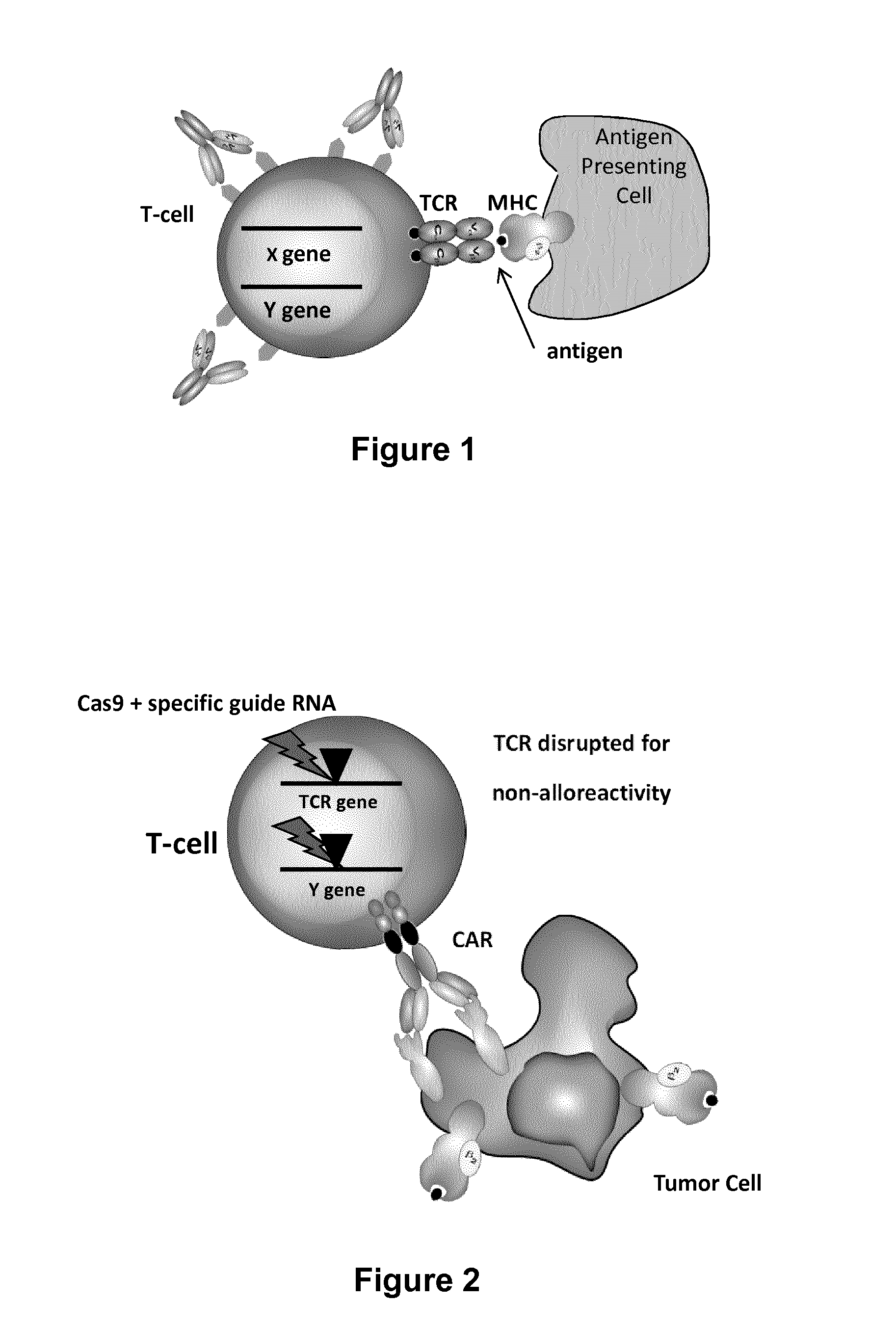
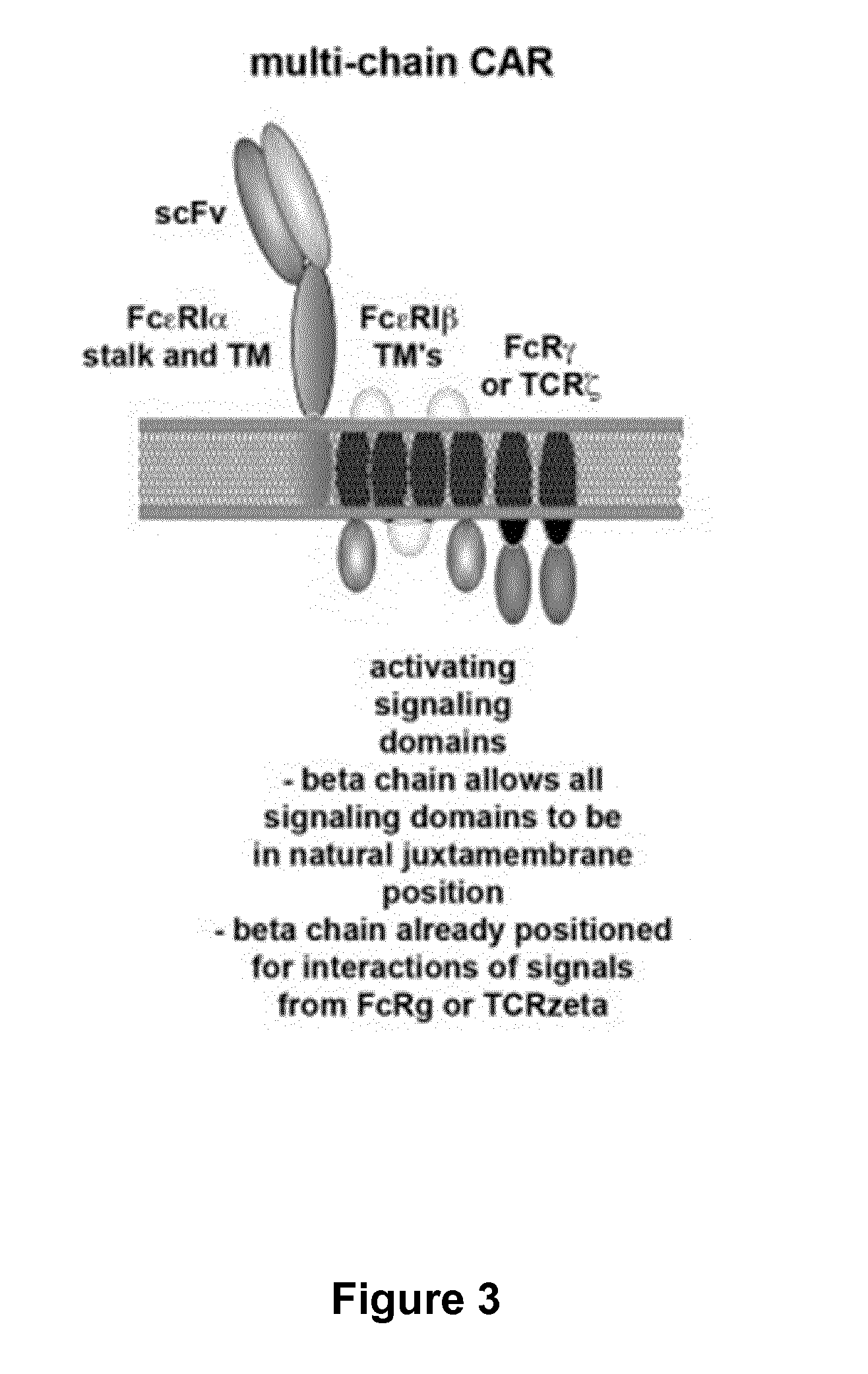
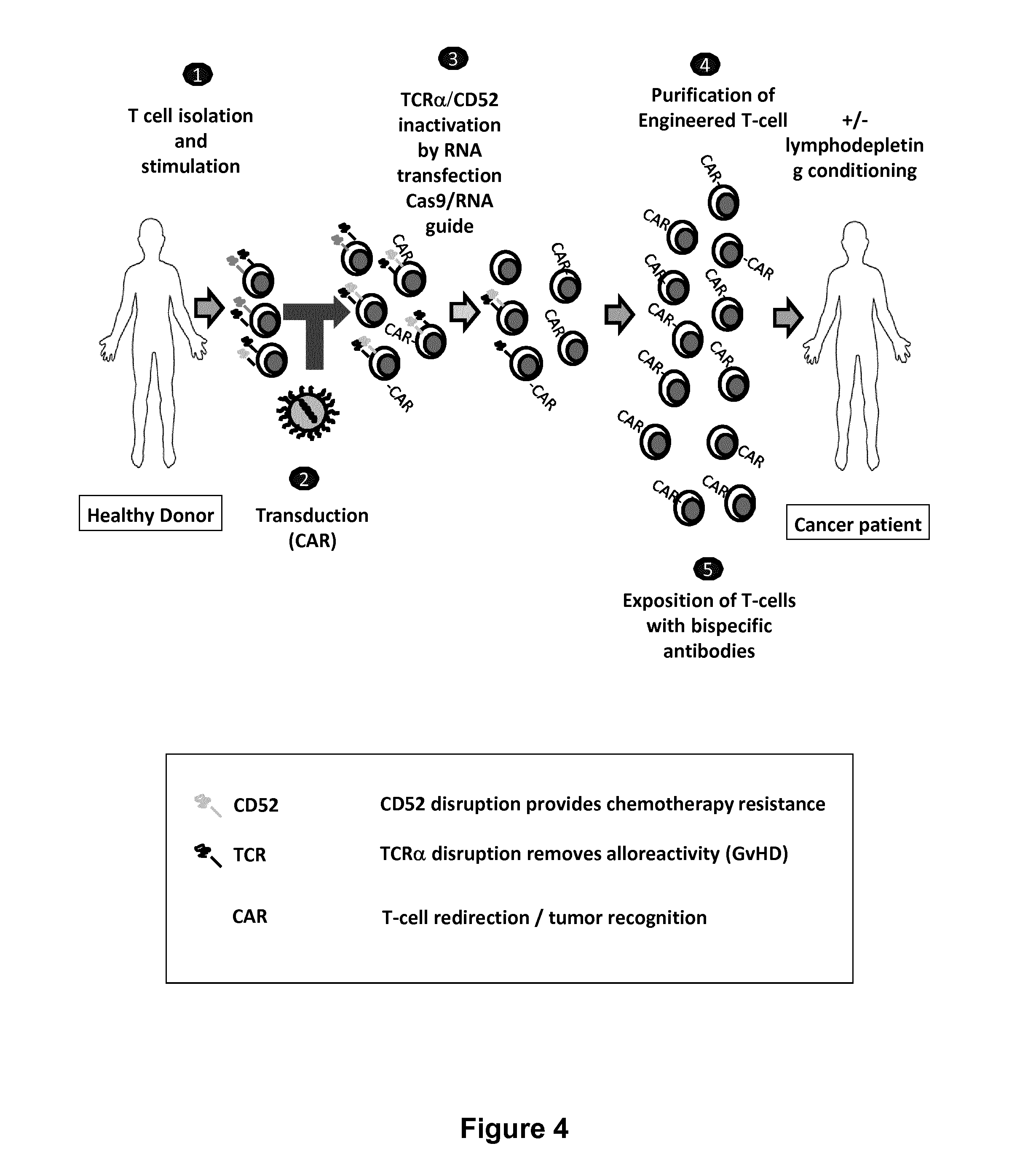
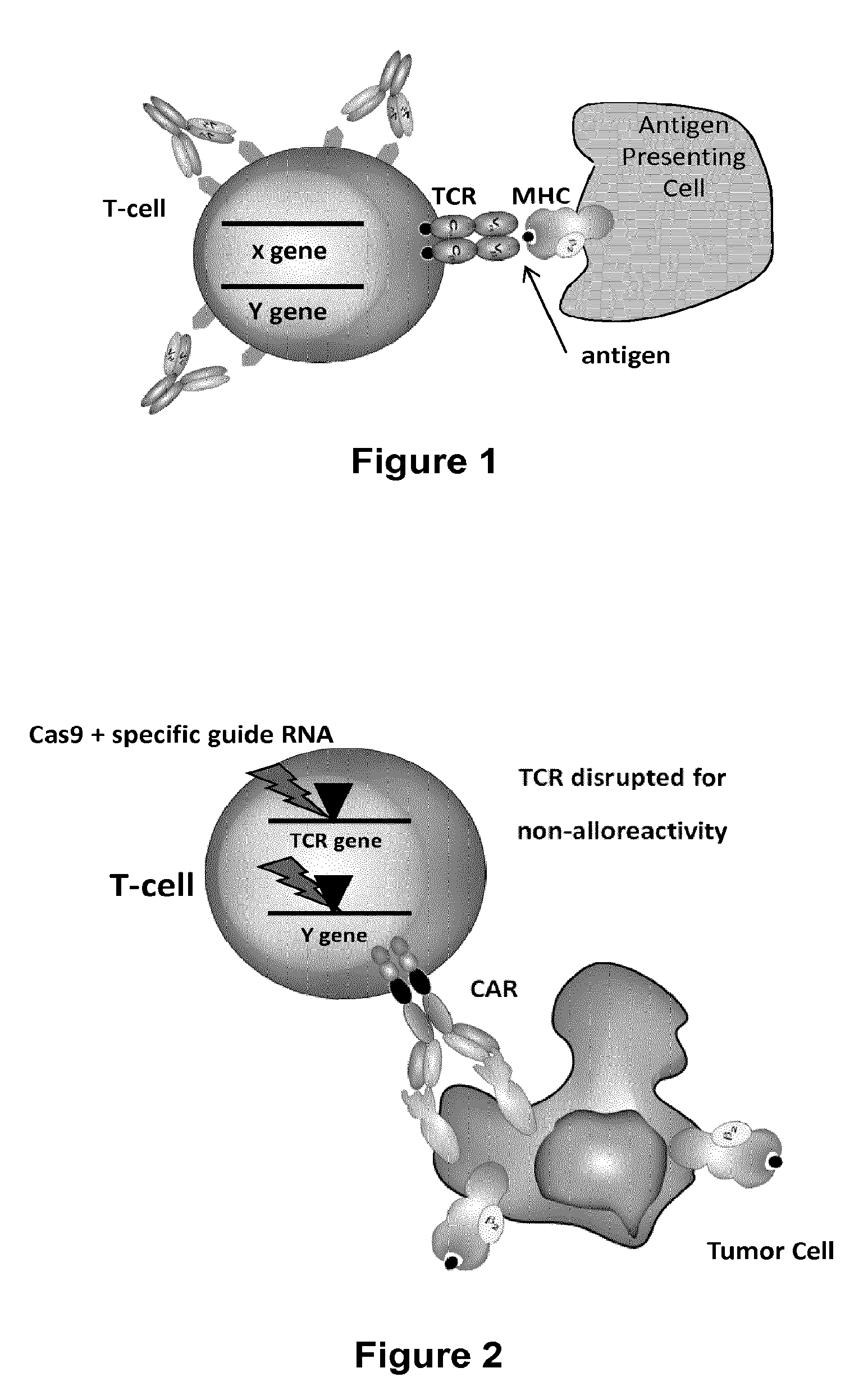
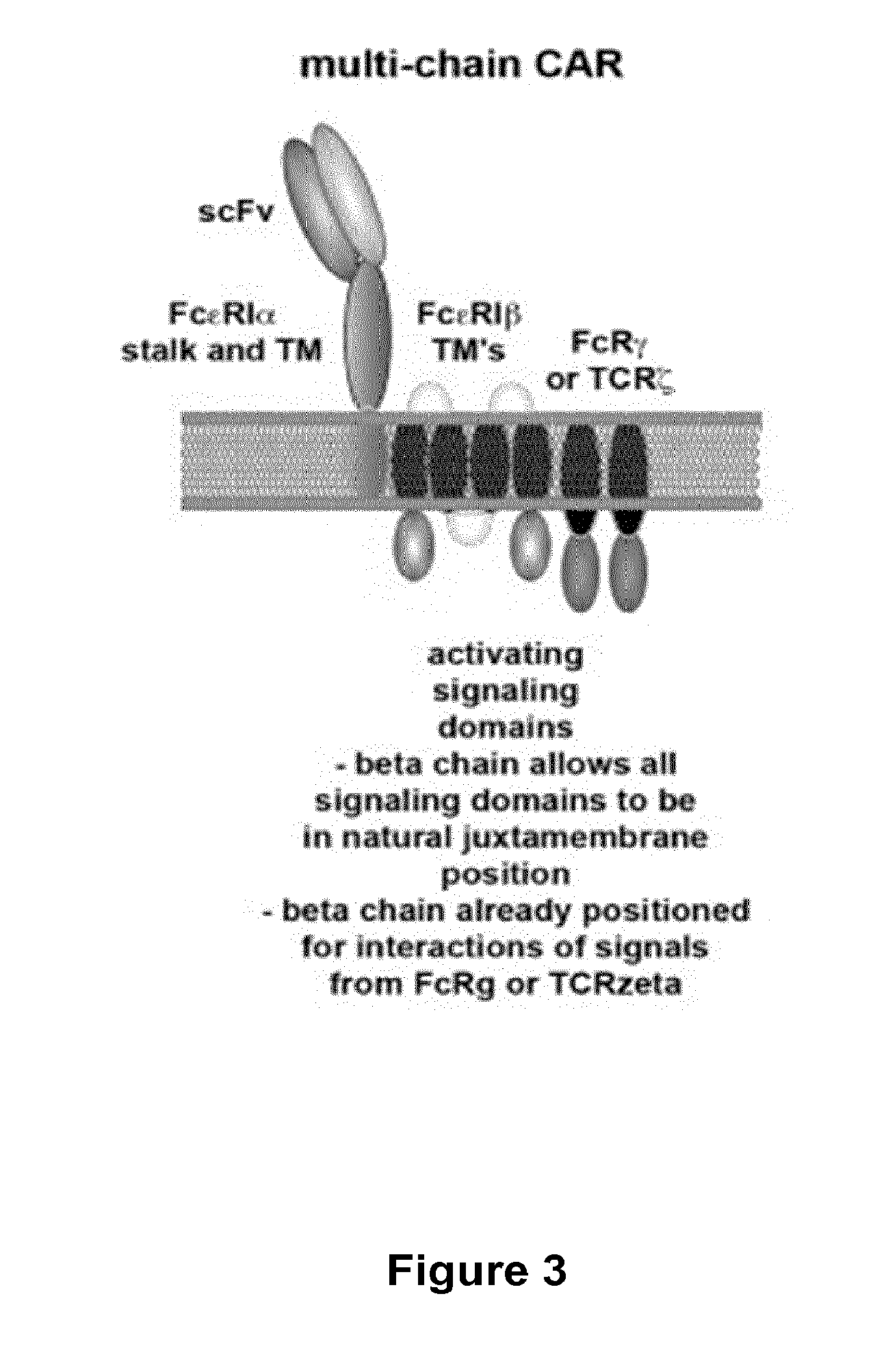
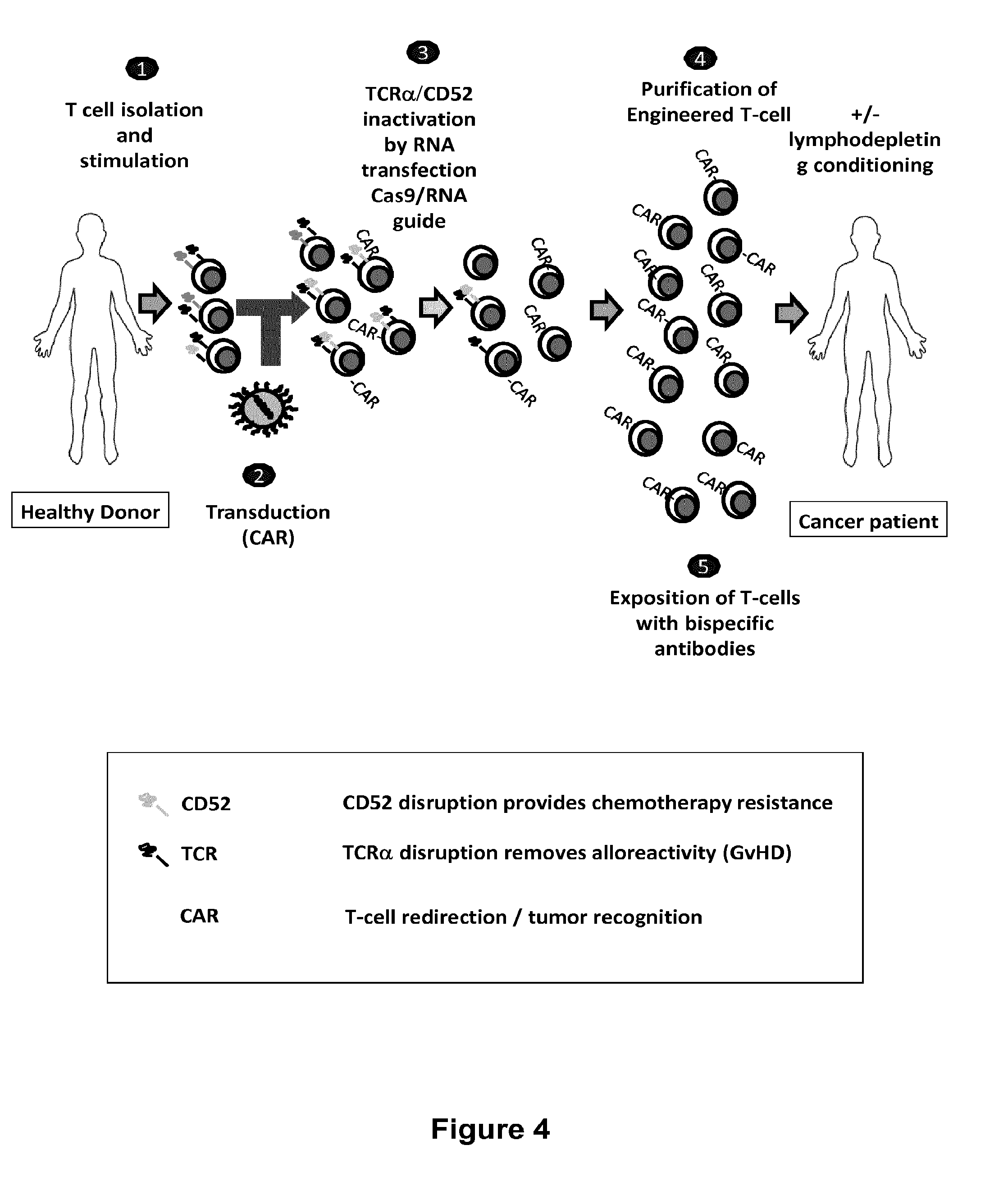
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160272999A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
Methods for engineering t cells for immunotherapy by using rna-guided cas nuclease system
ActiveUS20160184362A1Accurate modificationHydrolasesGenetically modified cellsInfected cellAntigen receptors
The present invention relates to methods of developing genetically engineered, preferably non-alloreactive T-cells for immunotherapy. This method involves the use of RNA-guided endonucleases, in particular Cas9 / CRISPR system, to specifically target a selection of key genes in T-cells. The engineered T-cells are also intended to express chimeric antigen receptors (CAR) to redirect their immune activity towards malignant or infected cells. The invention opens the way to standard and affordable adoptive immunotherapy strategies using T-Cells for treating cancer and viral infections.
Owner:CELLECTIS SA
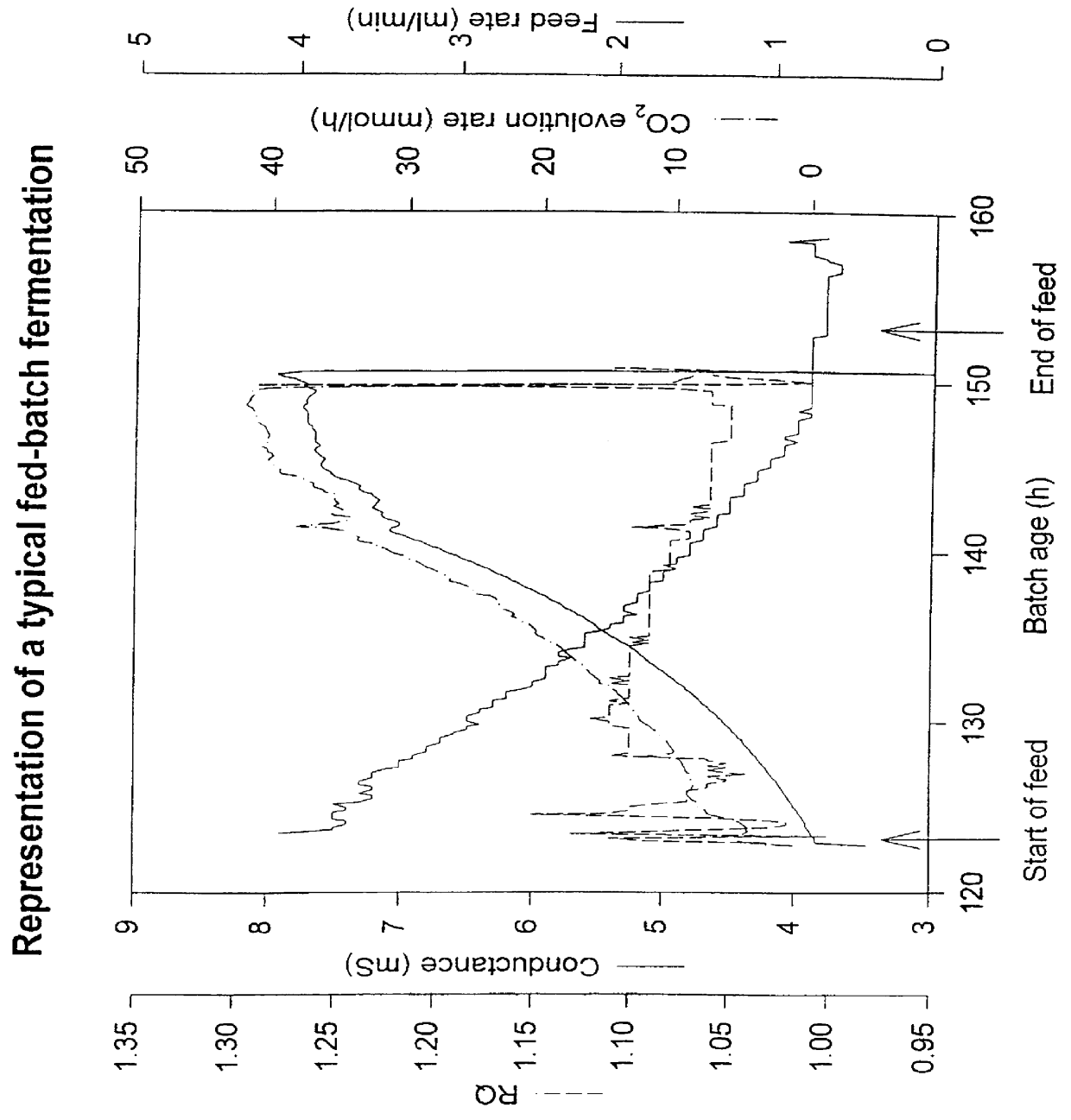
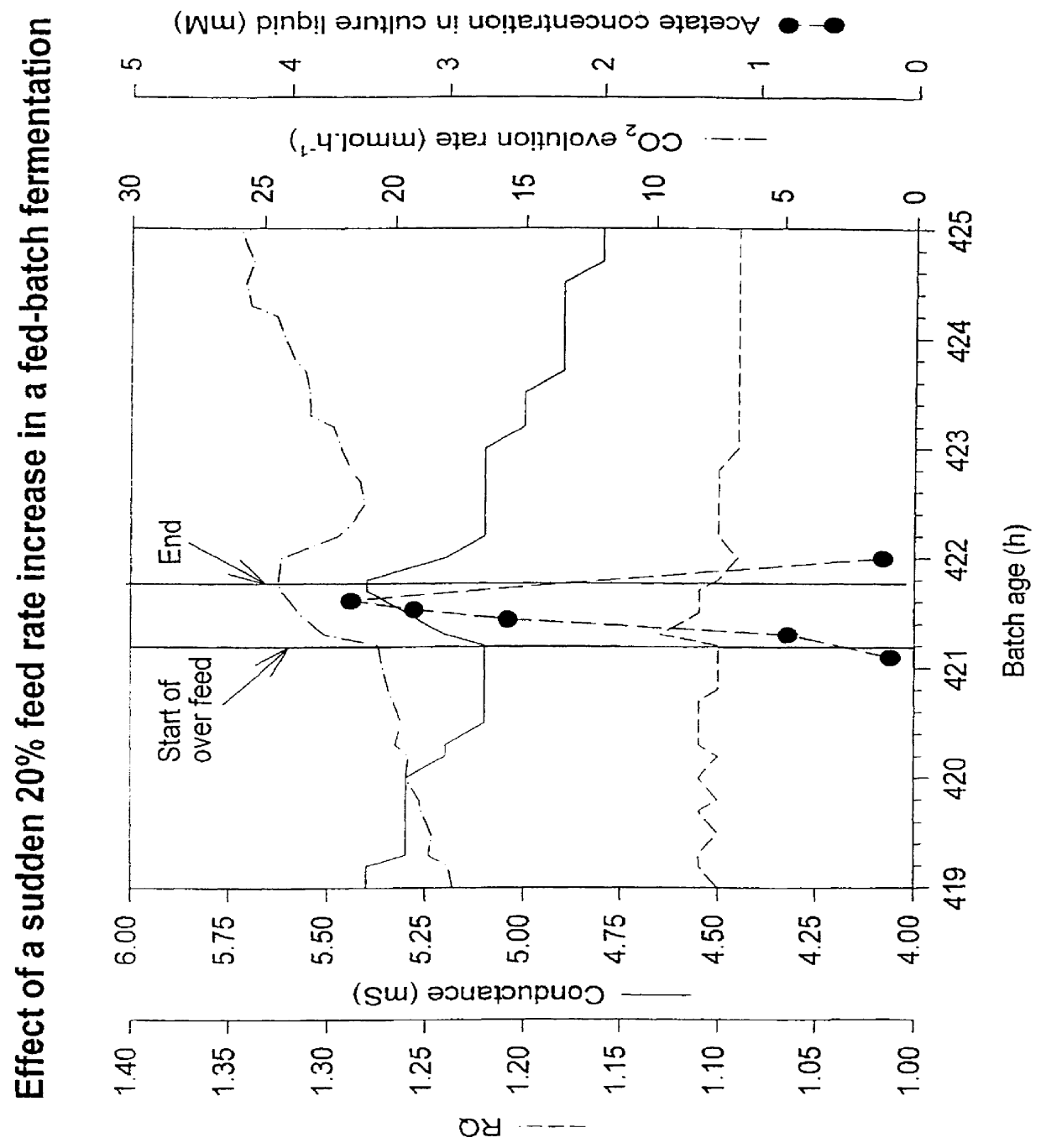
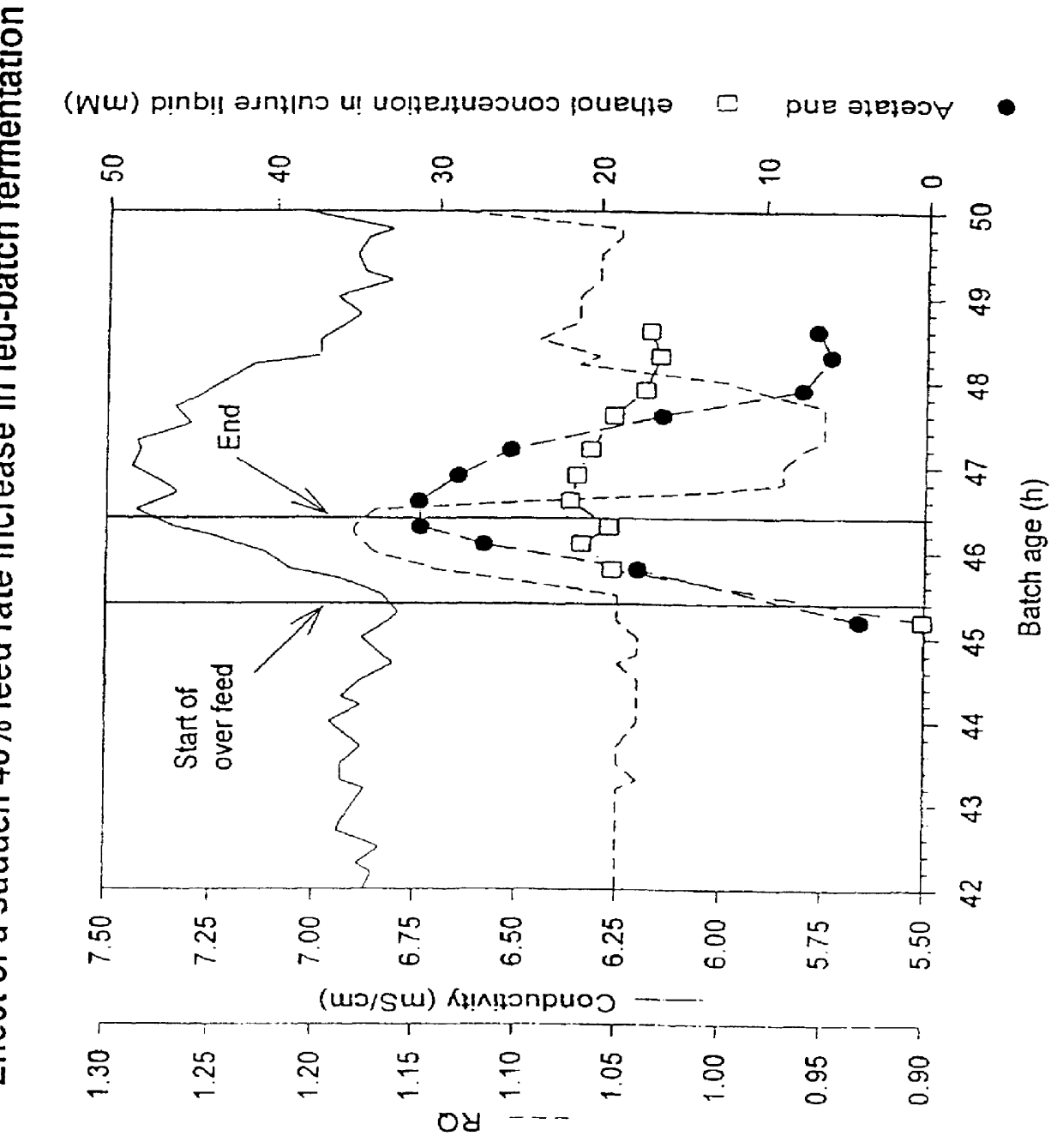
Fermentation control
PCT No. PCT / GB97 / 00669 Sec. 371 Date Sep. 11, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Sep. 11, 1998 PCT Filed Mar. 12, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 33973 PCT Pub. Date Sep. 18, 1997A process of culturing a microorganism in a culture medium in which process the addition of feed medium is controlled by using the production of a by-product as a measure of the culture conditions, characterized in that the by-product is an electrically charged metabolite produced by the microorganism, and in that the production of the metabolite is monitored by measuring the conductance of the culture medium. The metabolite may be acetate and the microorganism may be yeast which is genetically engineered to produce a desired polypeptide.
Owner:ALBUMEDIX AS
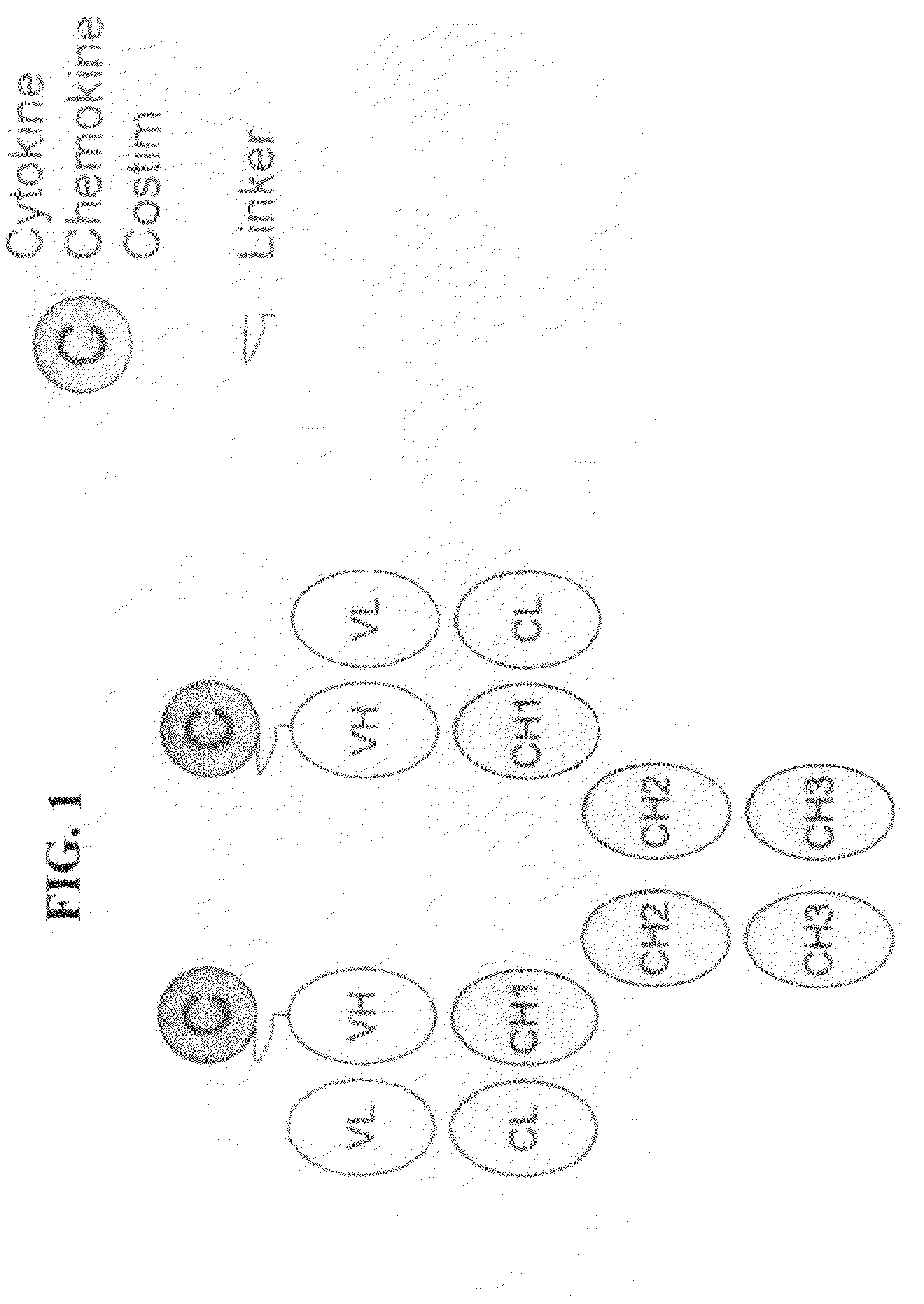
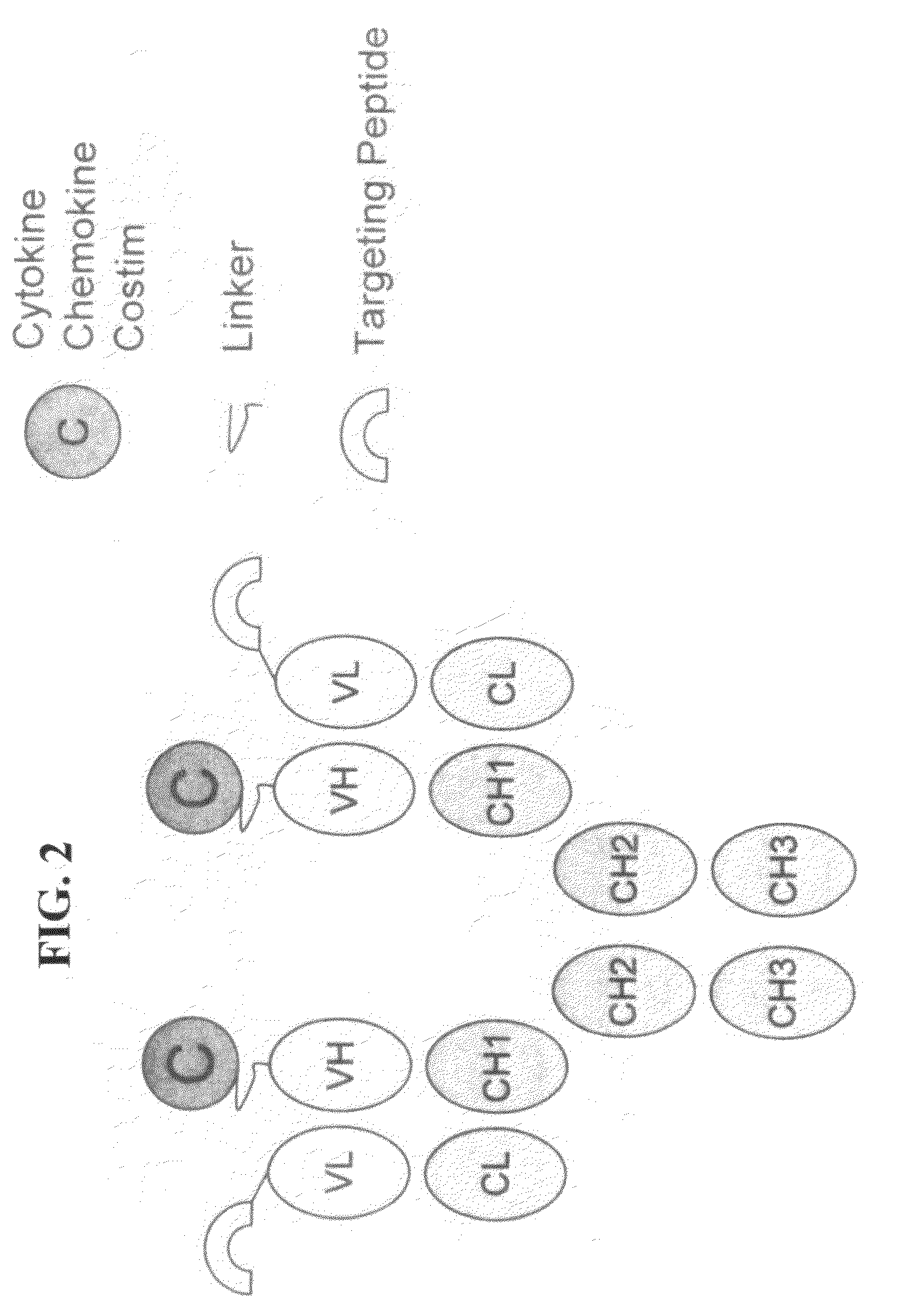
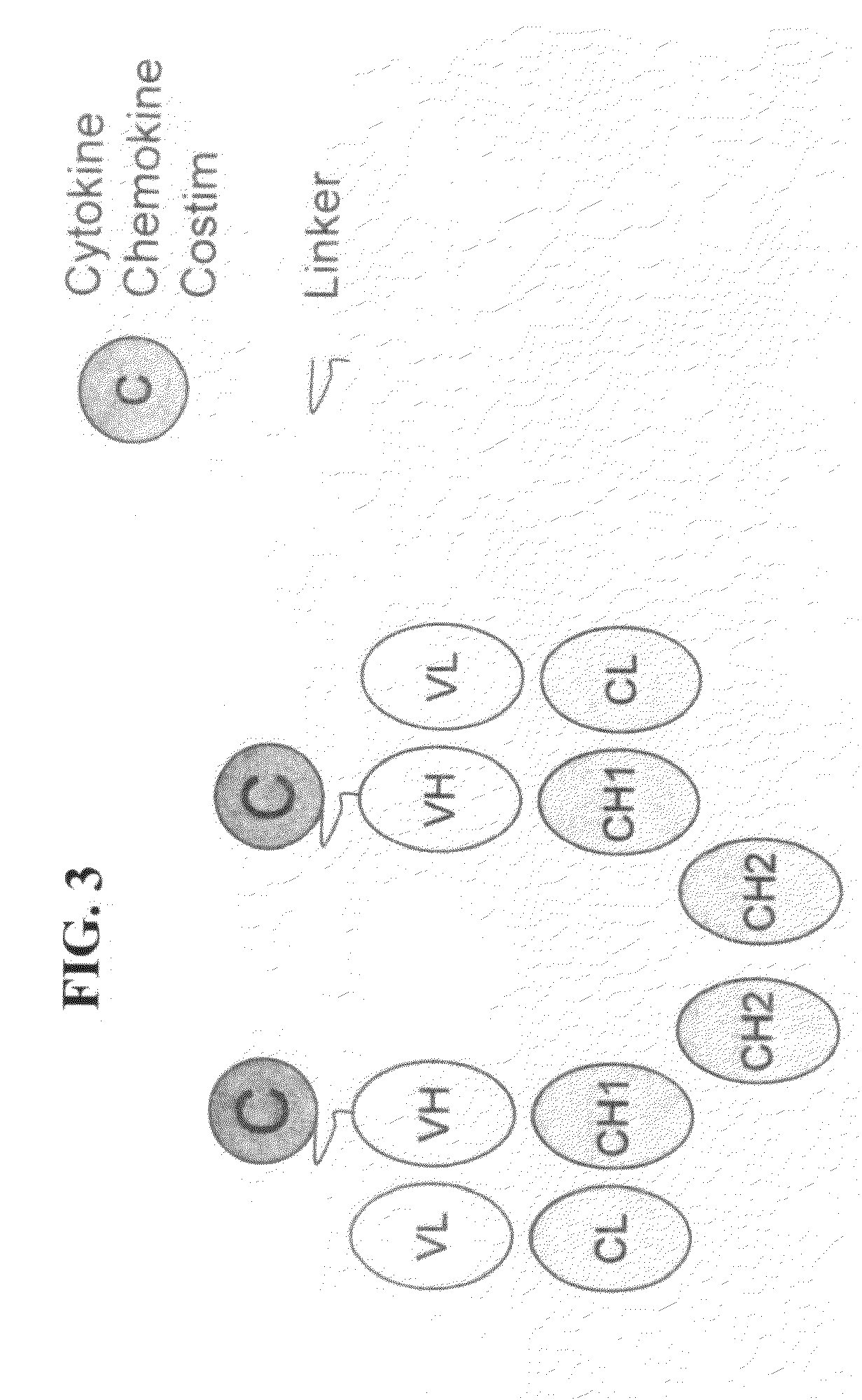
Engineered fusion molecules immunotherapy in cancer and inflammatory diseases
InactiveUS20090226435A1Promote optimal activation of T cellConvenient treatmentChemokinesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsTumor targetAbnormal tissue growth
The field of the present invention relates to genetically engineered fusion molecules, methods of making said fusion molecules, and uses thereof in anti-tumor immunotherapies. More specifically, the present invention relates to engineered fusion molecules consisting of a tumor targeting moiety fused with one or more costimulatory molecules / chemokines / cytokines.
Owner:KHARE SANJAY
Method for establishing humanized rat drug evaluation animal model
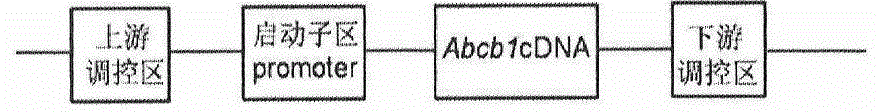
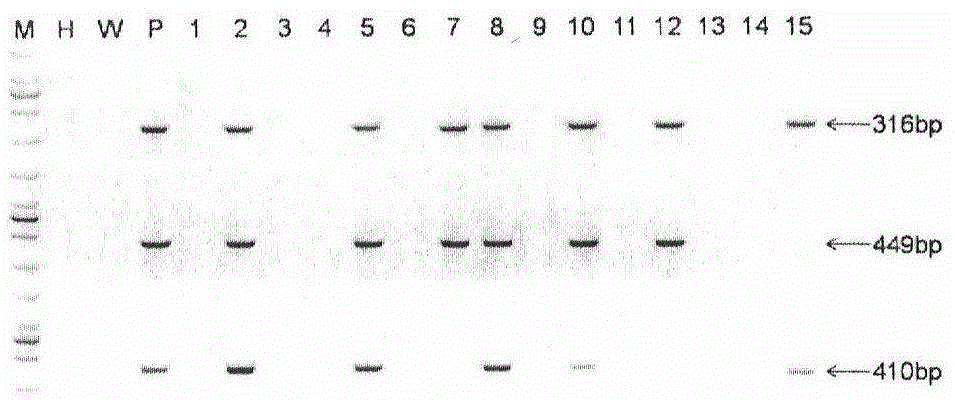
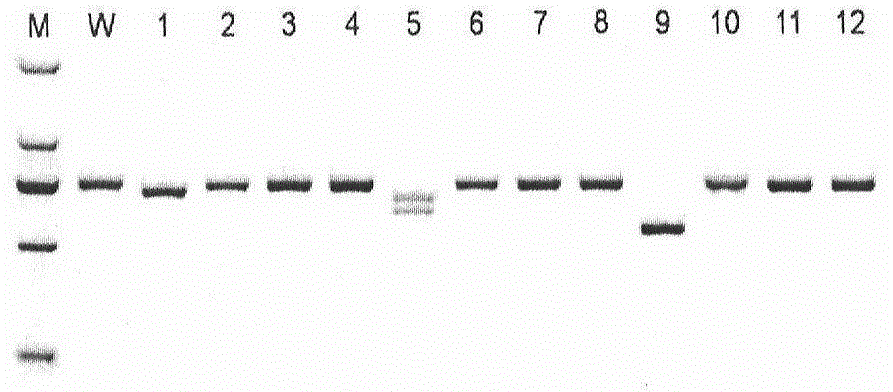
InactiveCN104593418AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryLarge fragmentEngineered genetic
The invention provides a method for establishing a humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. According to the method, a multidrug resistance gene 1 (Abcb1)-knocked-out genetically engineered rat is obtained through a microinjection method by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout technology and 153kb bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) fragments containing a humanized Abcb1 promoter and cDNA is simultaneously inoculated into the rat genome through the microinjection method by virtue of a large fragment transgenic technology to obtain a transgenic rat capable of stably expressing human Abcb1 and the genetically engineered rat and the transgenic rat are hybridized to establish the humanized rat drug evaluation animal model. RT-PCR analysis shows that Abcb1 expression profiles of humanized Abcb1 rat are significantly different from those of the rat endogenous Abcb1. The method has the beneficial effects that the humanized rat capable of expressing human Abcb1 is obtained and the rat is used for expressing human Abcb1 genes and has closer expression profiles to those of human so that the model can be well used for the efficacy evaluation of newly developed drugs.
Owner:INST OF LAB ANIMAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
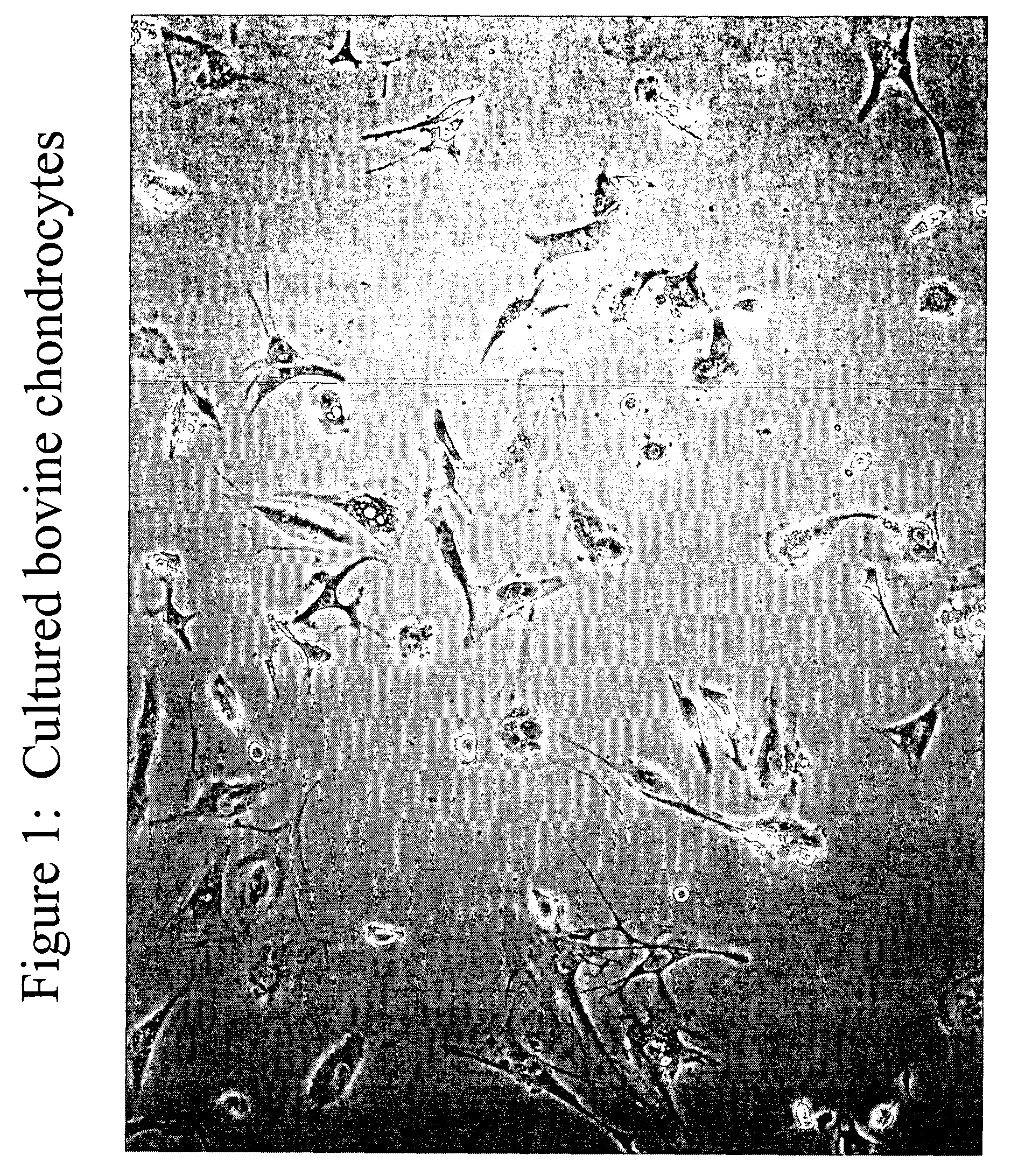
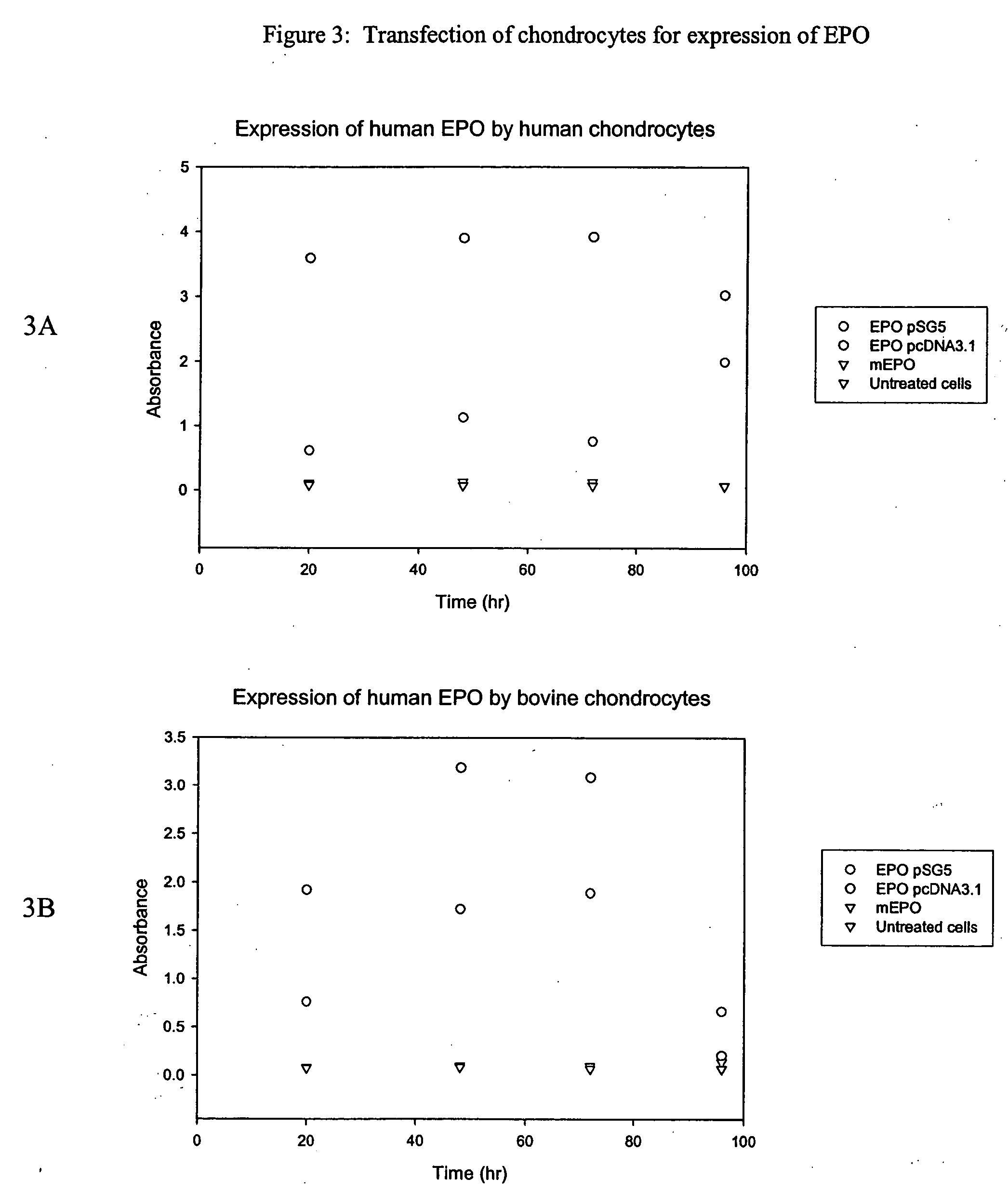
Chondrocyte therapeutic delivery system
ActiveUS20050054595A1Easy to optimizeAmeliorate disorderSenses disorderNervous disorderGenetically engineeredDelivery system
Methods and compositions for producing therapeutic agents using chondrocytes are provided. The genetically engineered chondrocytes can be used to express the therapeutic agent in a subject, including in an environment typically associated with chondrocytes and in an environment not typically associated with chondrocytes.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
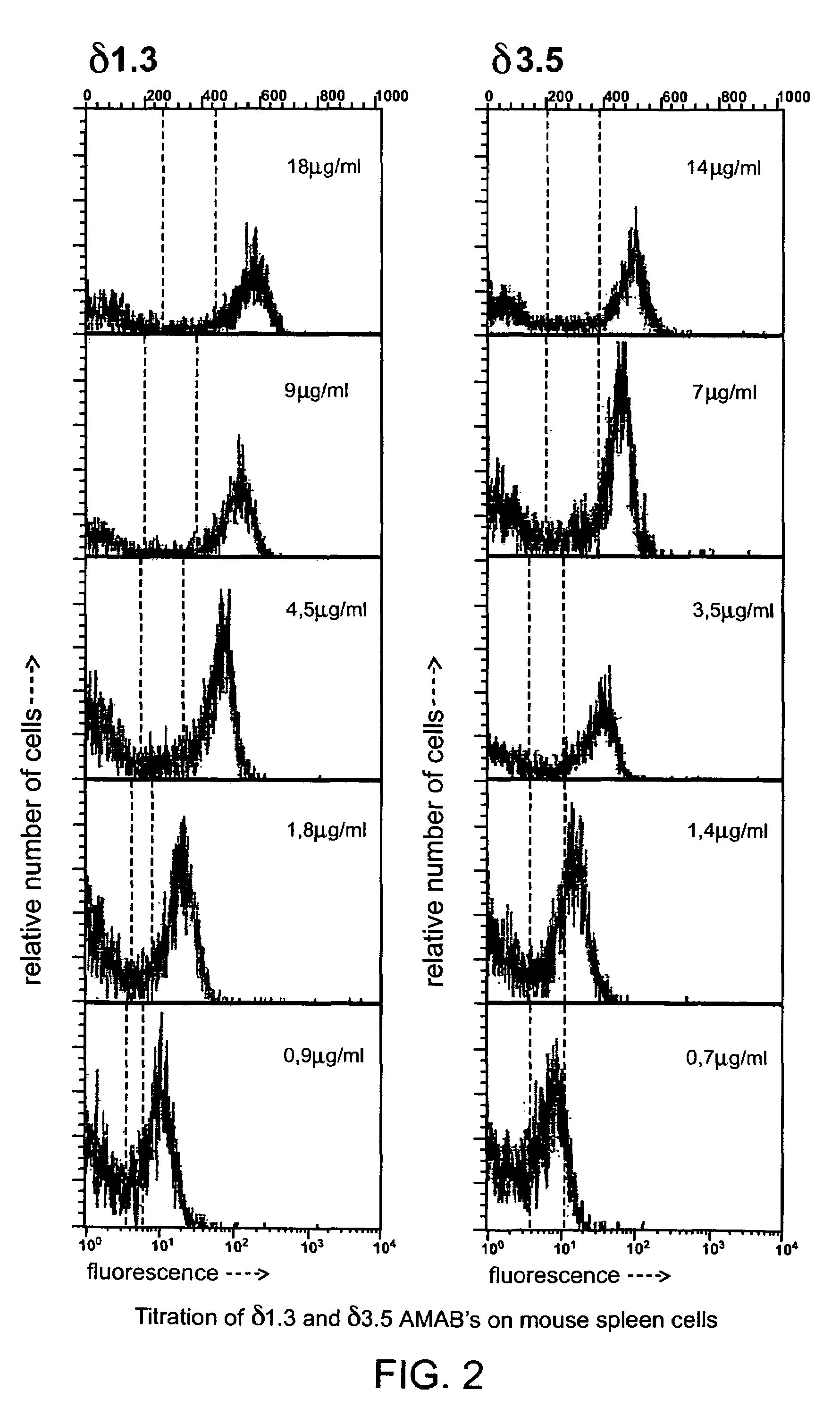
Antibodies against epitopes with homology to self antigens, methods of preparation and applications thereof
This invention provides novel methods of obtaining autologous monoclonal antibodies (AMABs) to self-antigens or homologs thereof. The method involves obtaining a genetically engineered host animal that does not biosynthesize at least one epitope of the antigen and utilizes the lack of self-tolerance of the host to the epitope to produce antibodies specific to the antigen. The invention also encompasses the AMABs produced by the methods. The invention further encompasses methods of isolating cells comprising the use of such AMABs that have specificity for a cell surface antigen.
Owner:MILTENYI BIOTEC
Redirected, genetically-engineered t regulatory cells and their use in suppression of autoimmune and inflammatory disease
InactiveUS20100135974A1Effective quantityOvercome scarcityBiocideAntipyreticIntracellular signallingInflammatory Bowel Diseases
A redirected Treg cell is endowed with specificity toward a selected target antigen or ligand. The cell contains a chimeric receptor polypeptide that is expressed in a single, continuous chain, with an extracellular recognition region displayed on the surface of the cell, a transmembrane region and an intracellular signaling region. The extracellular recognition region is specific for the selected target antigen or ligand. The intracellular signaling region includes a combination of T-cell signaling polypeptide moieties, which combination, upon binding of the extracellular recognition region to the selected target antigen or ligand, triggers activation of the redirected Treg cells to cause suppression of T-cell mediated immunity. Such redirected Treg cells may be used to suppress undesired activity of T effector cells thereby mediating an immune or inflammatory response. They are particularly useful in treating T effector cell-mediated diseases, such as inflammatory bowel disease, transplant rejection and GVH disease.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Products and methods for in vivo secretion of monatin
InactiveUS20070099277A1Increase amino acid transportEasy to transportBacteriaTransferasesMicroorganismIn vivo
Products and methods for the in vivo production of monatin sweetener are provided. The products include microorganisms that are genetically modified to secrete or to improve secretion of monatin; microorganisms that are genetically modified to produce monatin; and microorganisms that are genetically modified to both secrete or improve secretion of monatin and produce monatin. The methods include producing monatin in such genetically engineered microorganisms.
Owner:CARGILL INC
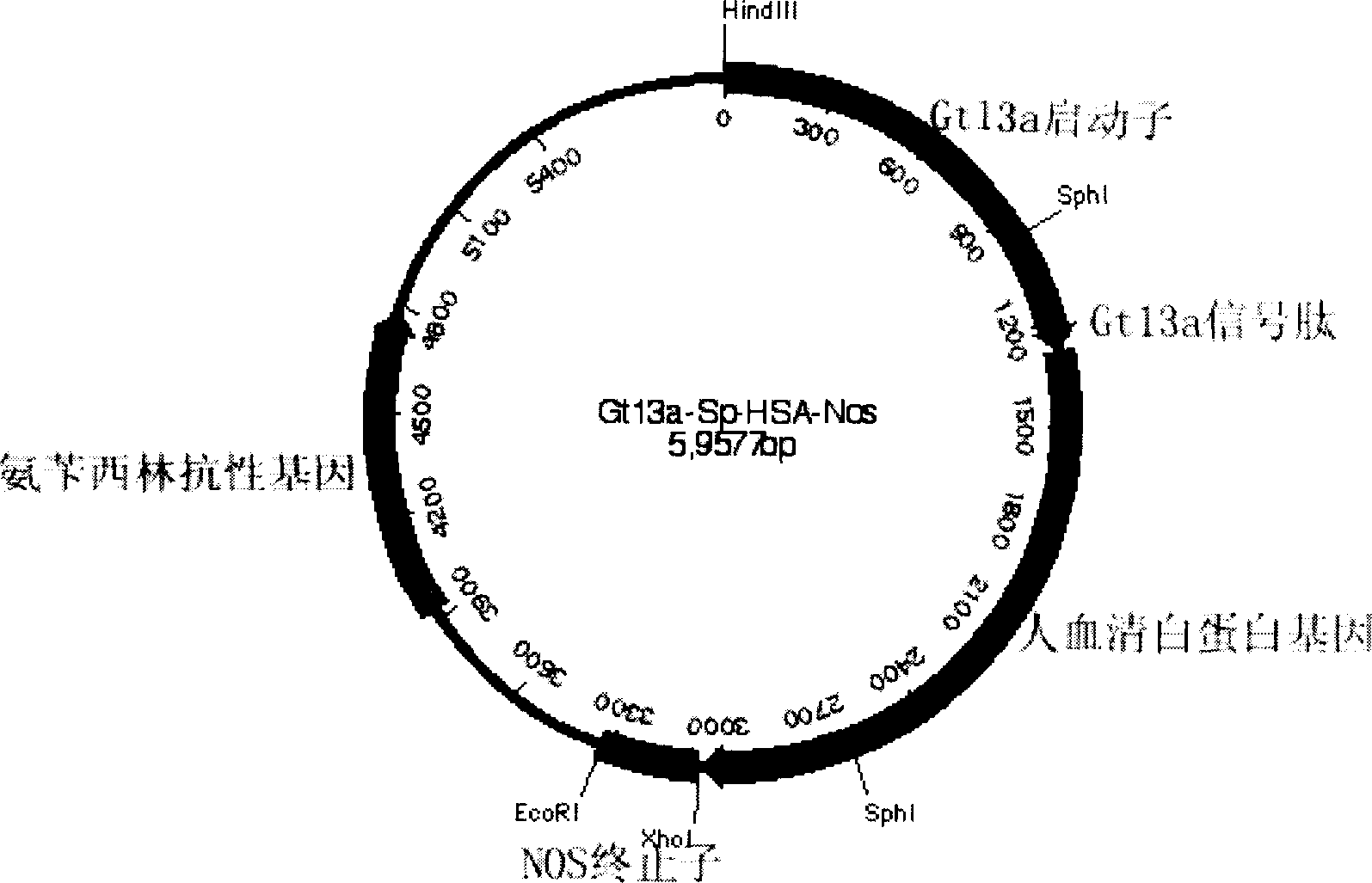
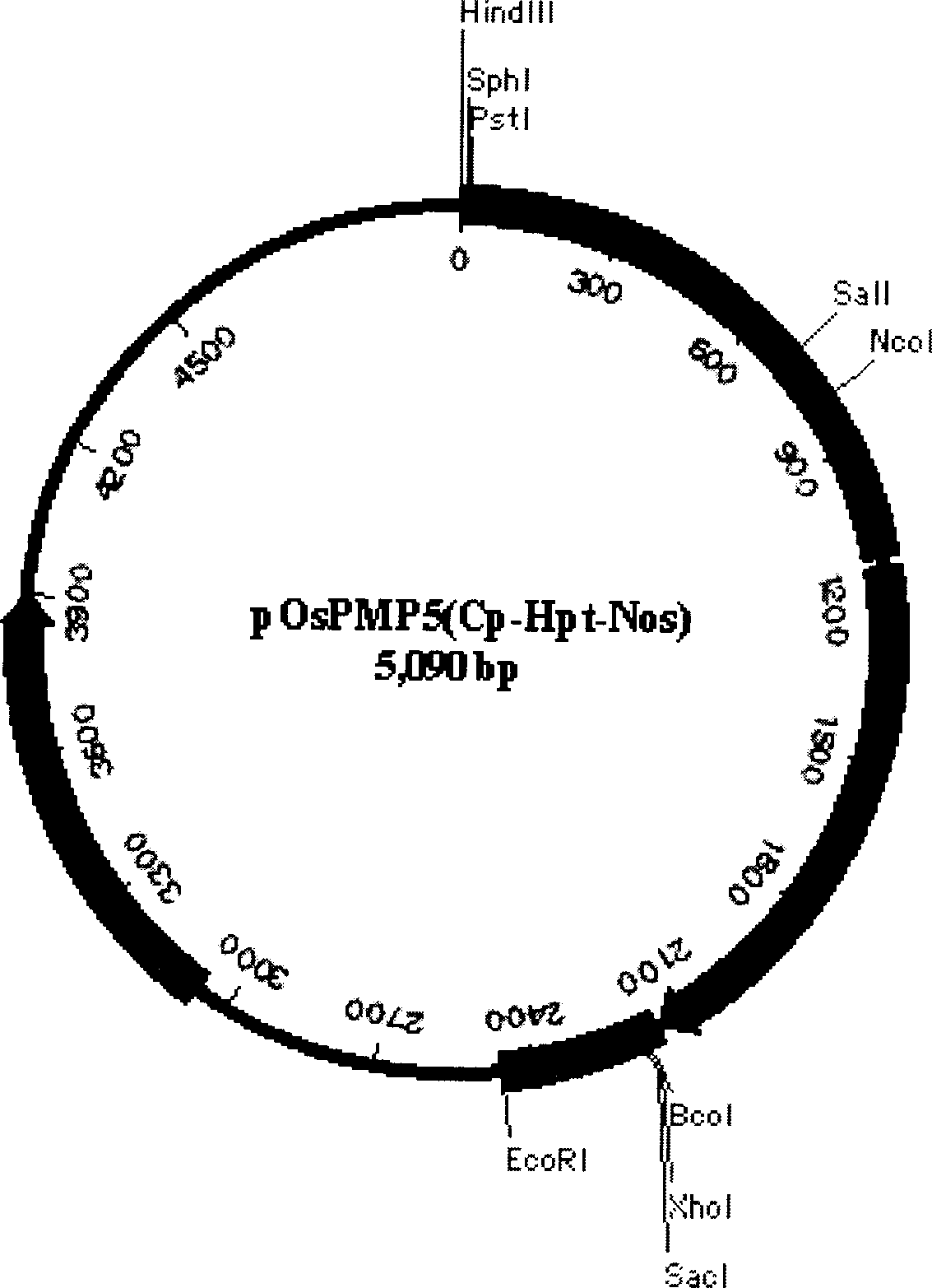
Production of recombinant human serum albumin with rice-embryo milk cell as biological reactor
ActiveCN1896239ANo pollution in the processEfficient expressionSerum albuminFermentationSerum protein albuminEmbryo
Production of recombinant human serum albumin with rice albuminous cell as biological reactor is carried out by taking rice albuminous cell protein as storage site for recombinant protein, taking rice albuminous specific expression starter and signal peptide, entering inductive recombinant human serum albumin into inner-film system of rice serum albumin cell and storing it in rice albuminous protein. It is cheap, has more yield and higher expression.
Owner:WUHAN HEALTHGEN BIOTECHNOLOGY CORP
Products and Methods for In Vivo Secretion of Monatin
Products and methods for the in vivo production of monatin sweetener are provided. The products include microorganisms that are genetically modified to secrete or to improve secretion of monatin; microorganisms that are genetically modified to produce monatin; and microorganisms that are genetically modified to both secrete or improve secretion of monatin and produce monatin. The methods include producing monatin in such genetically engineered microorganisms.
Owner:CARGILL INC
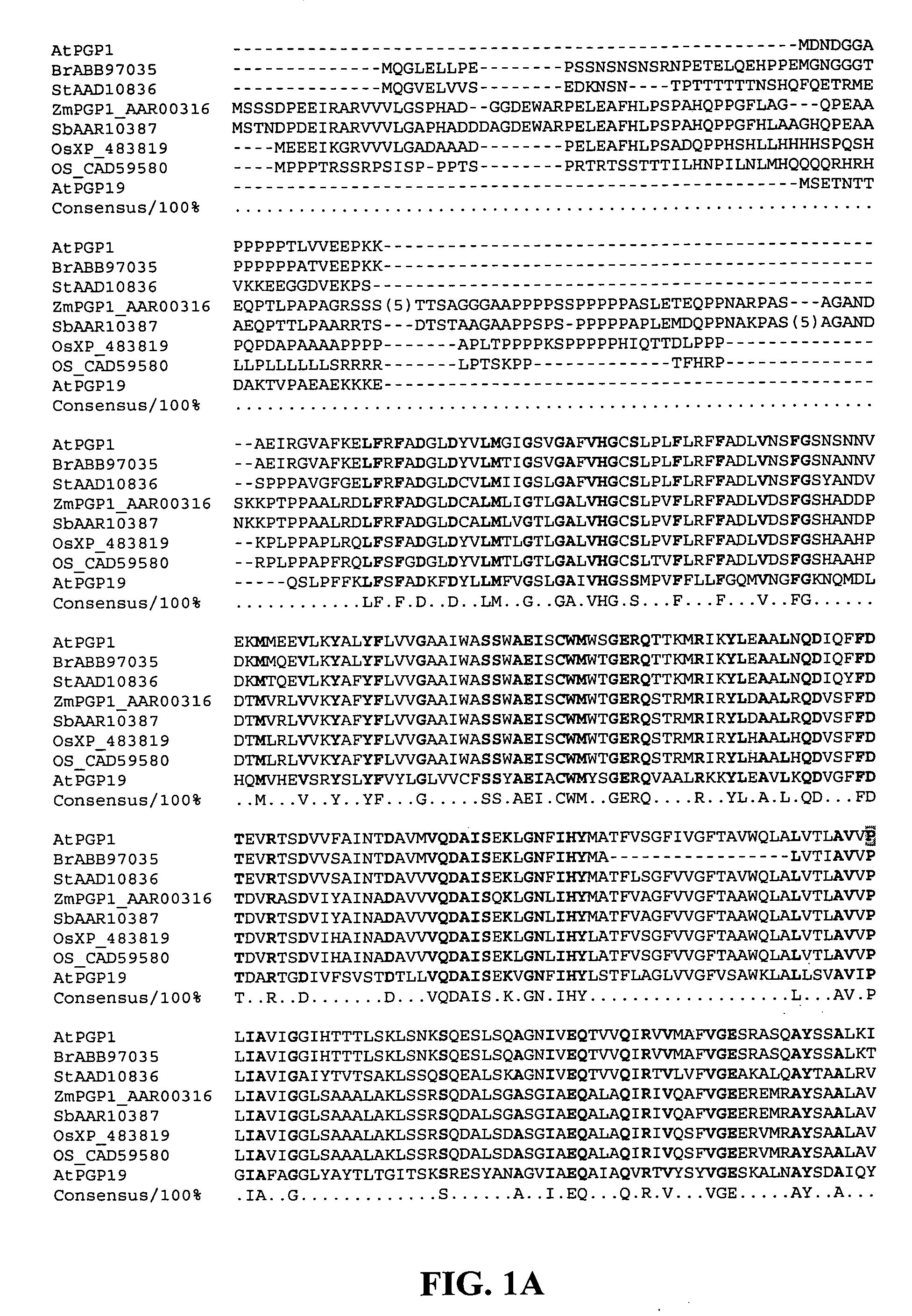
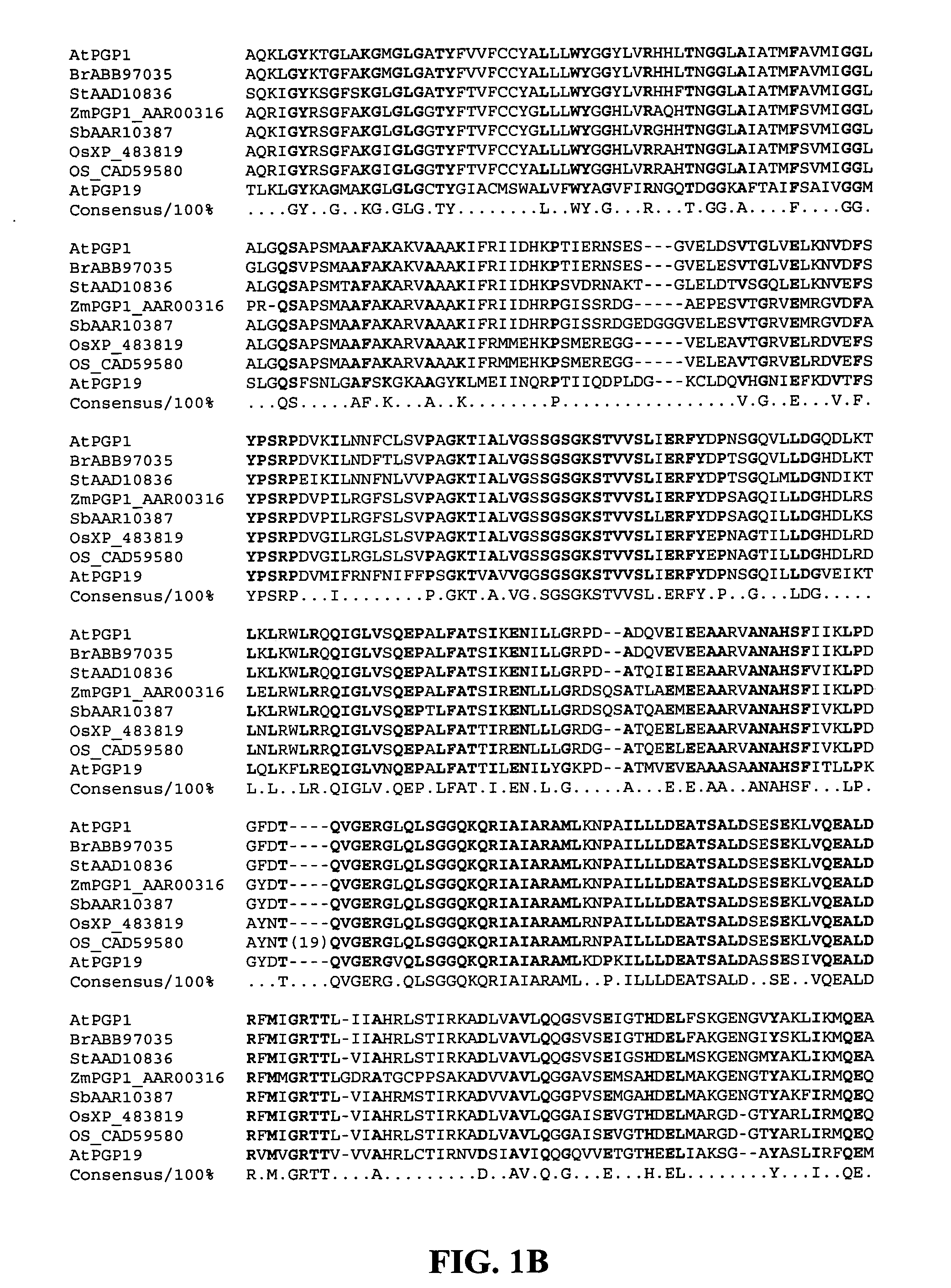
Gene encoding resistance to acetolactate synthase-inhibiting herbicides
InactiveUS20060130172A1Inhibit growthInhibition of reproductionTransferasesOther foreign material introduction processesAcetolactate synthaseSulfonylurea
A mutant acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme that confers cross-resistance to all sulfonylurea, imidazolinone, pyrimidinyloxybenzoate, triazolopyrimidine and sulfonylamino-carbonyl-triazolinone herbicides is provided. The mutant enzyme contains an aspartic acid to glutamic acid substitution mutation at a newly identified conserved region of the ALS enzyme. A gene encoding the enzyme is also provided, as are transgenic plants that have been genetically engineered to contain and express the gene. The transgenic plants are cross-resistant to sulfonylurea, imidazolinone, pyrimidinyloxybenzoate, triazolopyrimidine and sulfonylamino-carbonyl-triazolinone herbicides.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
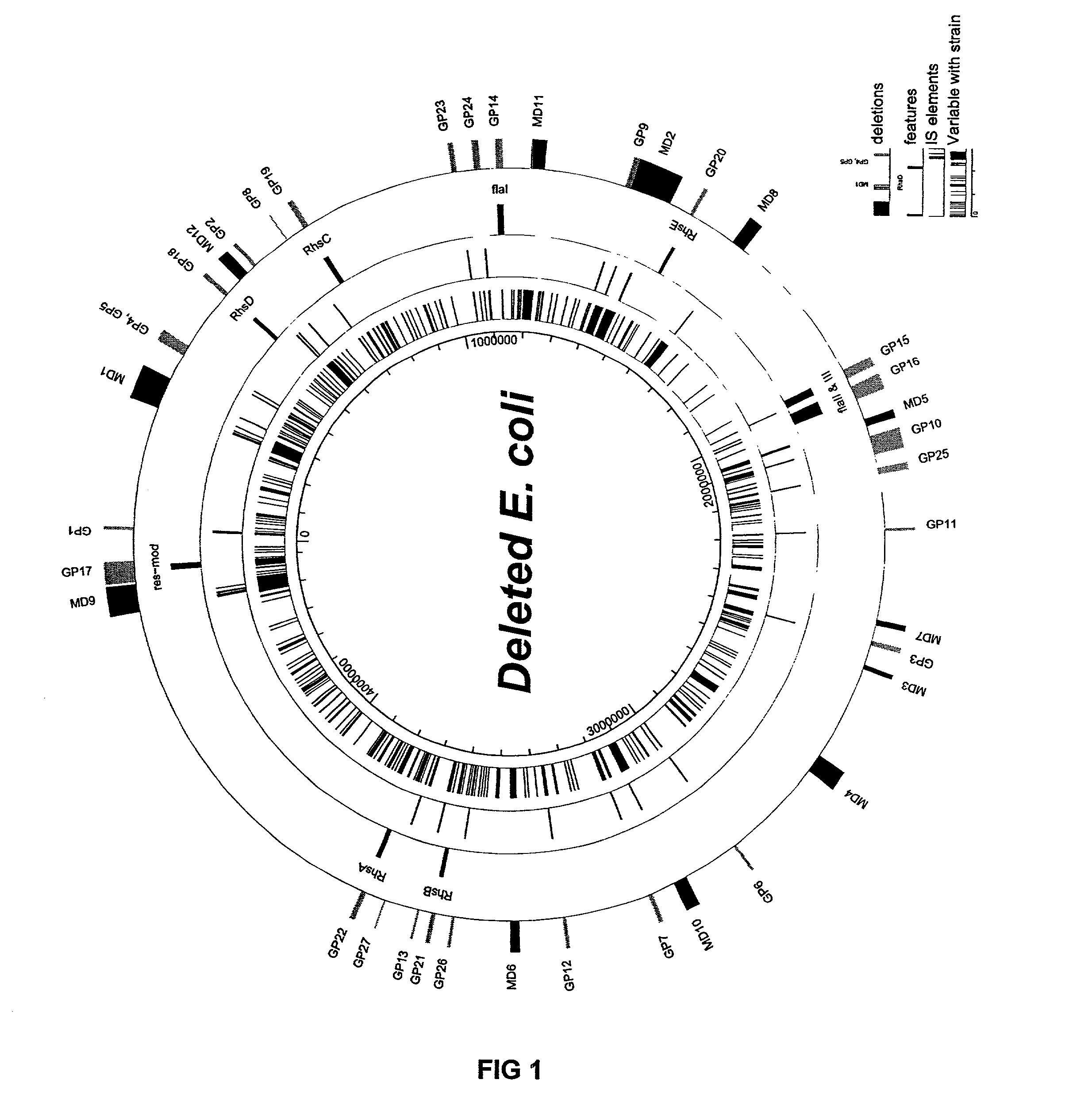
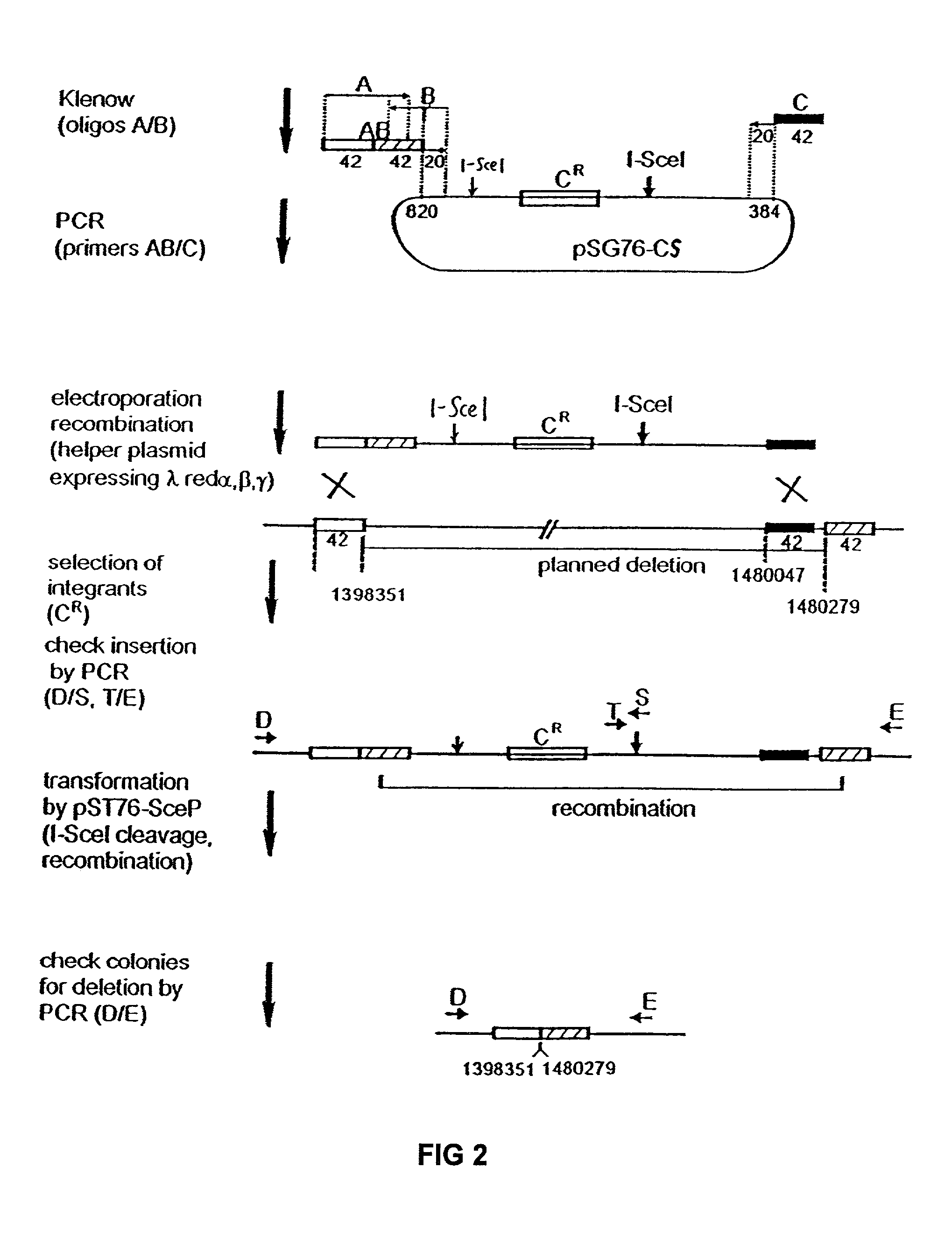
Bacteria with reduced genome
InactiveUS6989265B2Efficient processingEasy to purifyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomic DNAGenetically engineered
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be at least 2 to 14% smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com