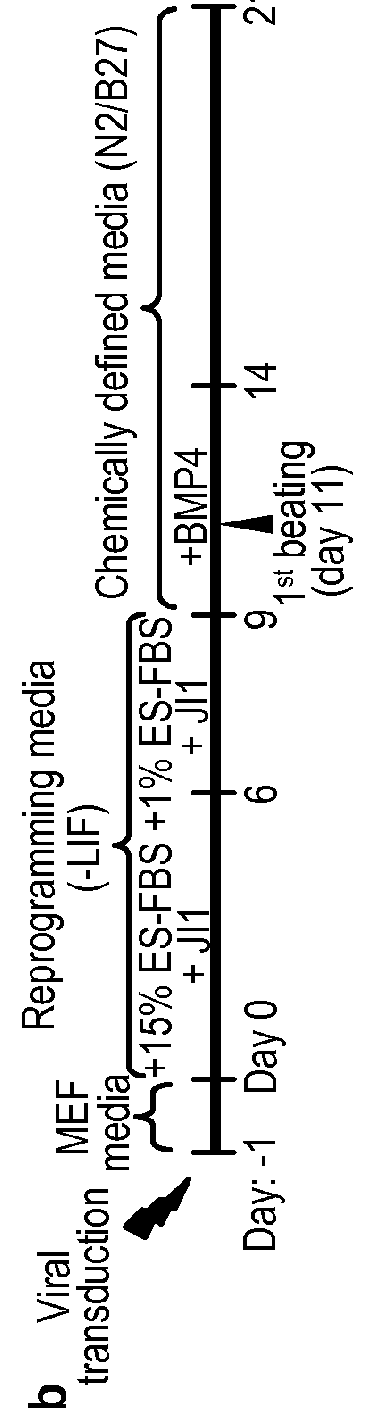
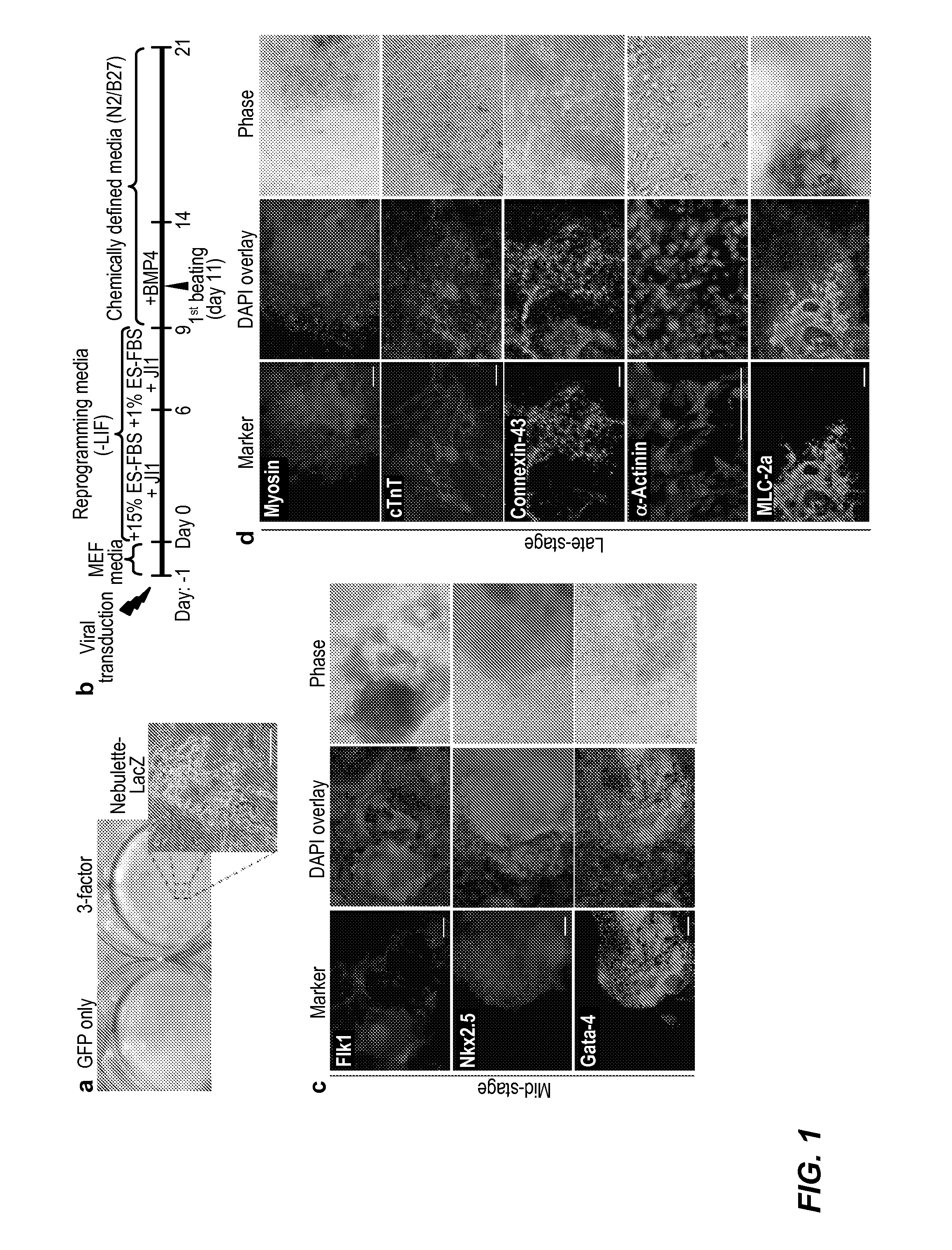
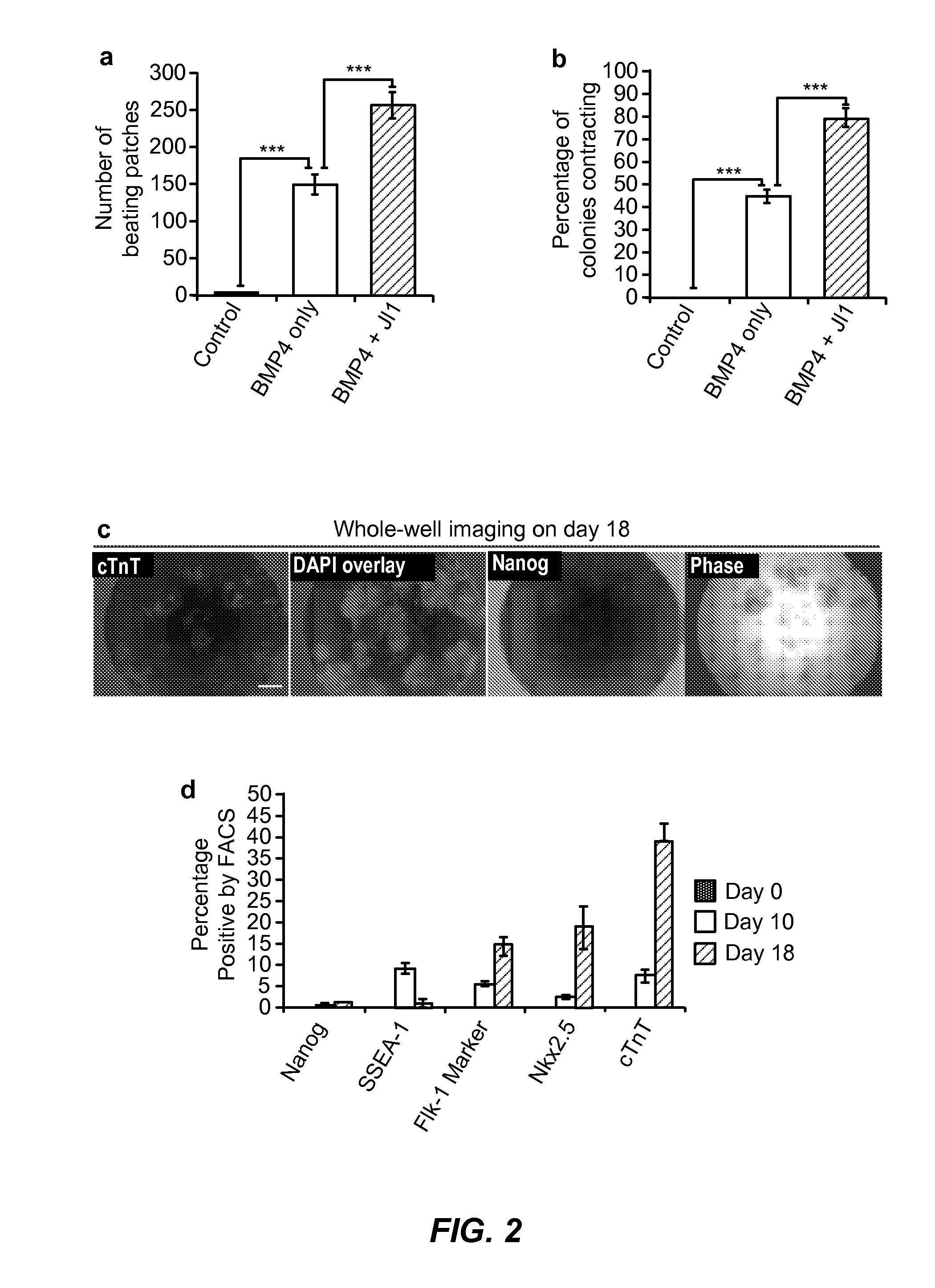
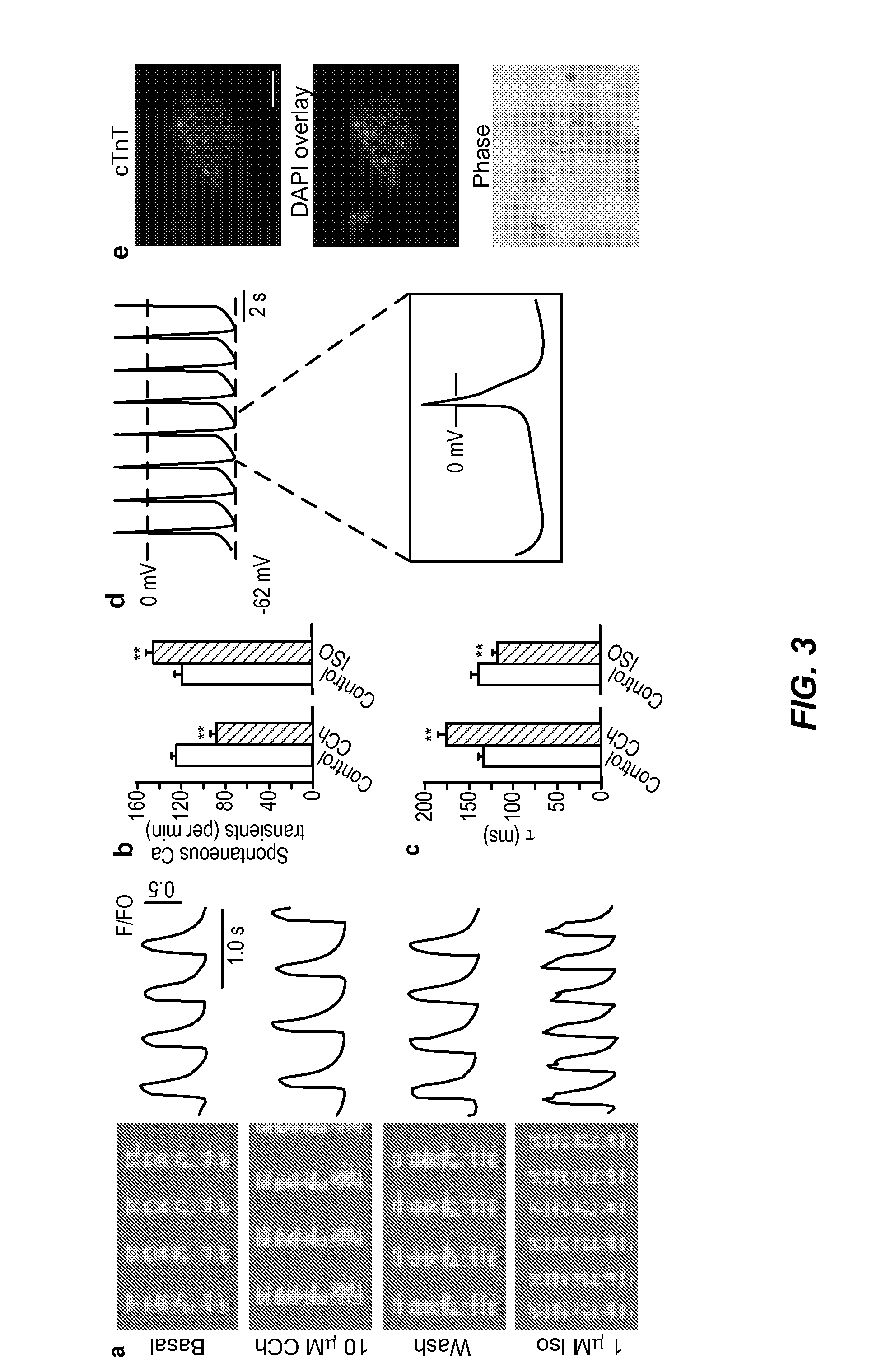
Patents
Literature
152 results about "Transdifferentiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Transdifferentiation, also known as lineage reprogramming, is a process in which one mature somatic cell transforms into another mature somatic cell without undergoing an intermediate pluripotent state or progenitor cell type. It is a type of metaplasia, which includes all cell fate switches, including the interconversion of stem cells. Current uses of transdifferentiation include disease modeling and drug discovery and in the future may include gene therapy and regenerative medicine. The term 'transdifferentiation' was originally coined by Selman and Kafatos in 1974 to describe a change in cell properties as cuticle producing cells became salt-secreting cells in silk moths undergoing metamorphosis.
Autogenic living scaffolds and living tissue matrices: methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050226856A1Preventing host rejectionThicker and strongBiocideSkin implantsTransdifferentiationOrganism
A 3-dimensional structure comprising suitable cells (or entities) and the ECM (or matrix) that has been completely produced and arranged by these cells (or entities) that promotes the differentiation, dedifferentiation and / or transdifferentiation of cells and / or formation of tissue in vitro and in vivo, while at the same time promoting cell growth, proliferation, migration, acquisition of in vivo-like morphology, or combinations thereof, and that 1. provides structural and / or nutritional support to cells, tissue, organs, or combinations thereof, termed an “Autogenic Living Scaffold” (ALS); or 2. is capable of being transformed into a more complex tissue (or matrix) or a completely different type of tissue (or matrix), termed a “Living Tissue Matrix” (LTM). Autogenic means it is self-produced. The living cells that produce the LTM or ALS, or are added to Autogenic Living Scaffolds, may be genetically engineered or otherwise modified. The matrix component of the ALS or LTM provides a structural framework for cells that guide their direction of growth, enables them to be correctly spaced, prevents overcrowding, enables cells to communicate between each other, transmit subtle biological signals, receive signals from their environment, form bonds and contacts that are required for proper functioning of all cells within a unit such as a tissue, or combinations thereof. The ALS or LTM may thus provide proper or supporting mechanical and chemical environments, signals, or stimuli to other cells, to the cells that produce the ALS, to surrounding tissue at an implantation site, to a wound, for in vitro and ex vivo generation and regeneration of cells, tissue and organs, or combinations thereof. They may also provide other cells with nutrients, growth factors, and / or other necessary or useful components. They may also take in or serve as buffers for certain substances in the environment, and have also some potential at adapting to new environments.
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
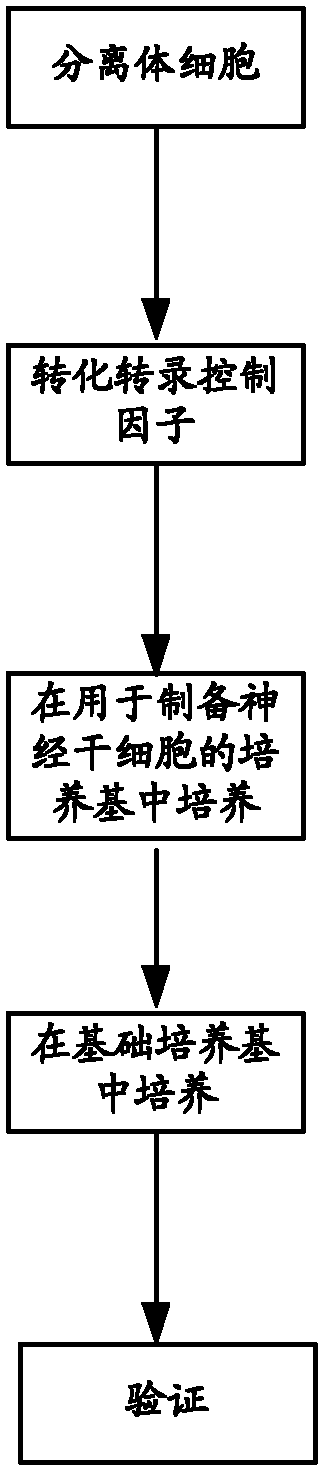
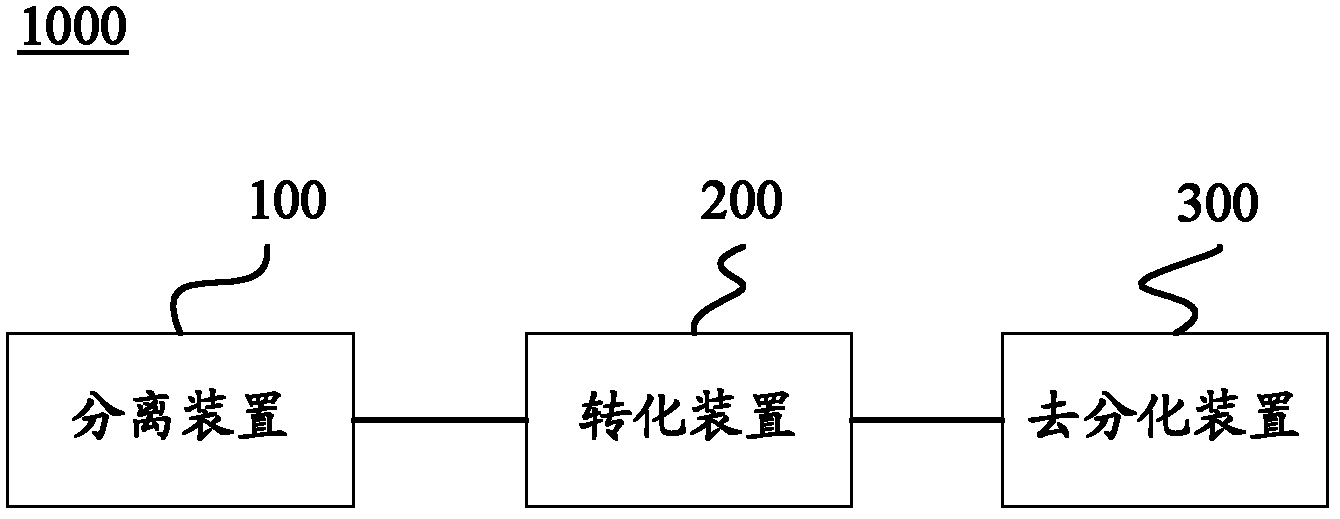
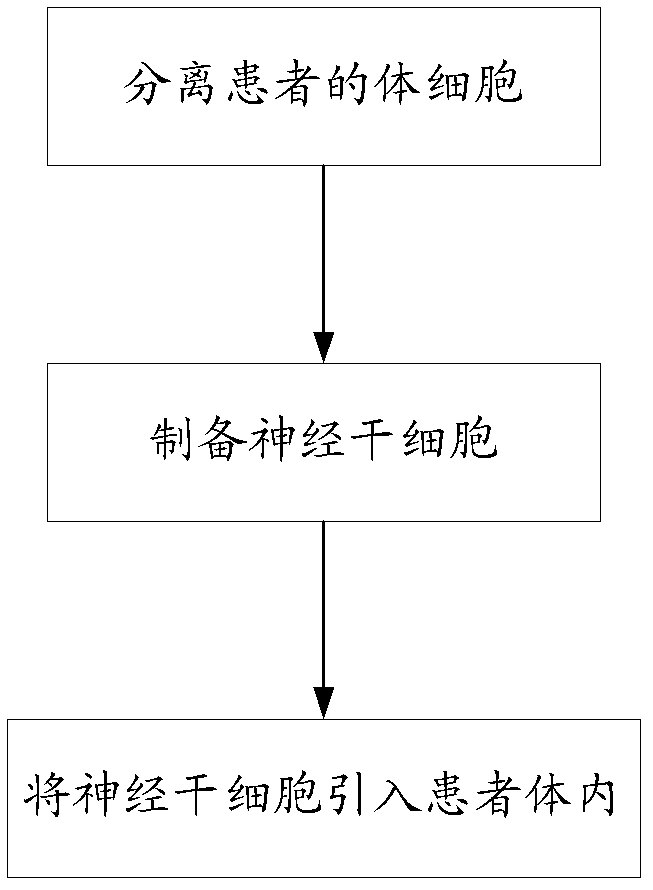
Method for inducing transdifferentiation of somatic cells into neural stem cells and application thereof
ActiveCN104894060AGood pluripotent differentiation performanceNervous disorderNervous system cellsDiseaseTransdifferentiation
Provided are a method for inducing the transdifferentiation of somatic cells into neural stem cells and application for same. Using a combination of a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, a glycogen synthase kinase (GSK-3) inhibitor, and a transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) signal pathway inhibitor, in a low-oxygen normal physiological environment, induce somatic cells such as fibroblasts and epithelial cells to form into neural stem cells having good pluripotency and passage stability.
Owner:CENT FOR EXCELLENCE IN MOLECULAR CELL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Culture medium for preparing neural stem cells and application thereof
ActiveCN102604894ABioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderTransdifferentiationTranscription regulator
The invention relates to a culture medium for preparing neural stem cells and an application of the culture medium. The culture medium for preparing the neural stem cells comprises a culture medium suitable for the growth of stem cells, and a cell signal pathway inhibitor which is selected from at least one of the following agents: a GSK (Glaxo Smith Klein) inhibitor, an MEK (Methyl Ethyl Ketone) inhibitor, a TGF (Transforming Growth Factor)-beta inhibitor, a ROCK inhibitor and a BMP inhibitor. The somatic cells are cultured by using the culture medium, especially the somatic cells for expressing the transcription regulator are cultured, so as to effectively transdifferentiate the somatic cells into neutral stem cells and the transdifferentiation time is greatly shortened.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Autogenic living scaffolds and living tissue matrices: methods and uses thereof
InactiveUS8043614B2More utilityPromote growthBiocideSkin implantsTransdifferentiationCell-Extracellular Matrix
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
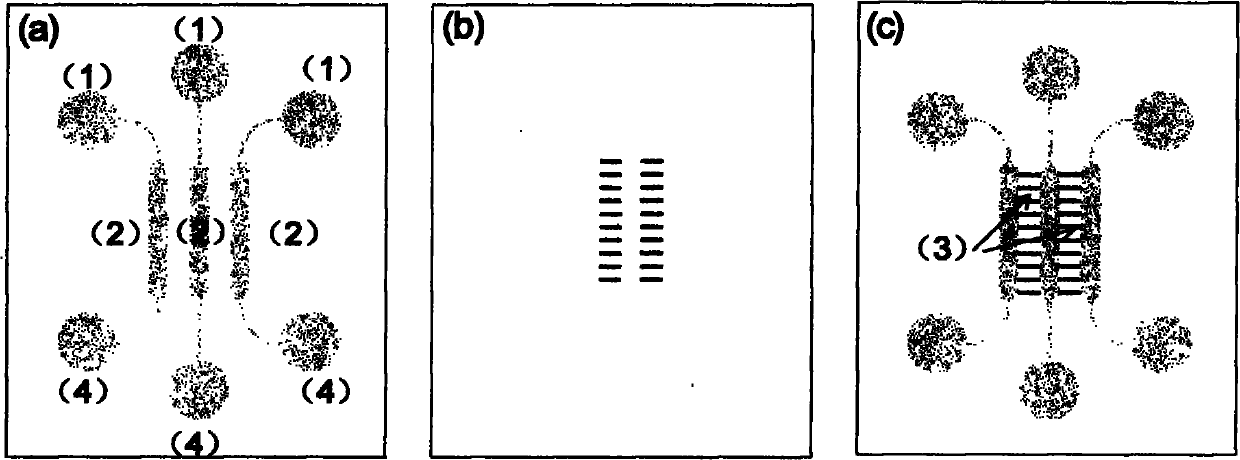
Microfluidic chip and method for studying non-contact type cell co-cultivation by using the same
InactiveCN102021116AReduce dosageImprove microenvironmentMicrobiological testing/measurementTissue/virus culture apparatusTransdifferentiationContact type
The present invention provides a microfluidic chip and a method for studying non-contact type cell co-cultivation by using the same. The microfluidic chip comprises a sample inlet, a cell cultivation room, a cell migration region and a waste pool. The upper end of the cell cultivation room is connected to the sample inlet and the lower end of the cell cultivation room is connected to the waste pool. Three parallel cell cultivation rooms are joined by cell migration region. The microfluidic chip provides good microenvironment for non-contact type cell co-cultivation, enables to form a concentration gradient in the cell migration region and facilitates observation of cell migration process in real time and research of transdifferentiation. The invention is advantageous in easy operation, simple manufacturing and small dosage of samples.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Therapeutic uses of microvesicles and related micrornas
InactiveUS20130143314A1Predictable and effective therapeutic resultThe result is validNervous disorderMicroencapsulation basedDiseaseTransdifferentiation
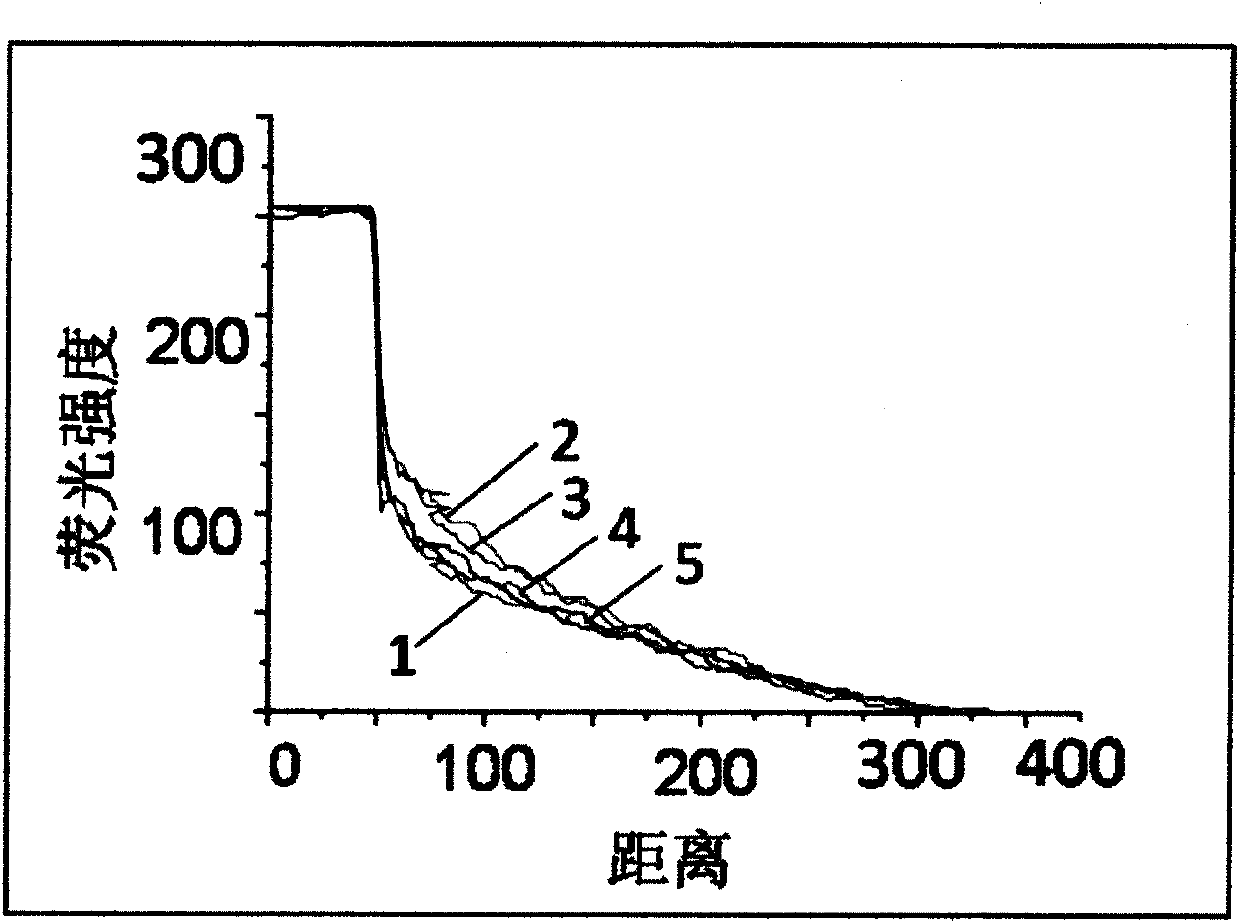
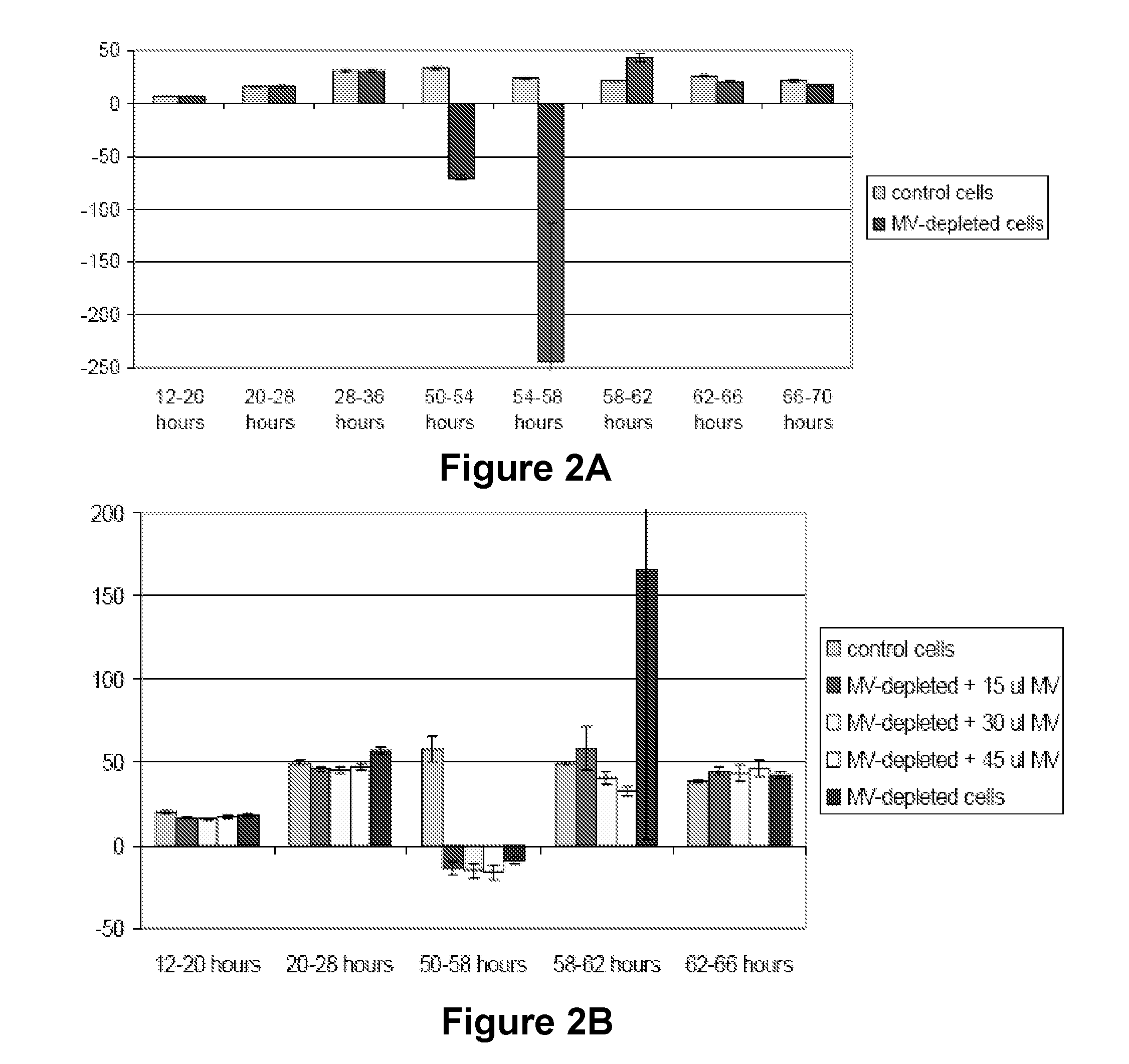
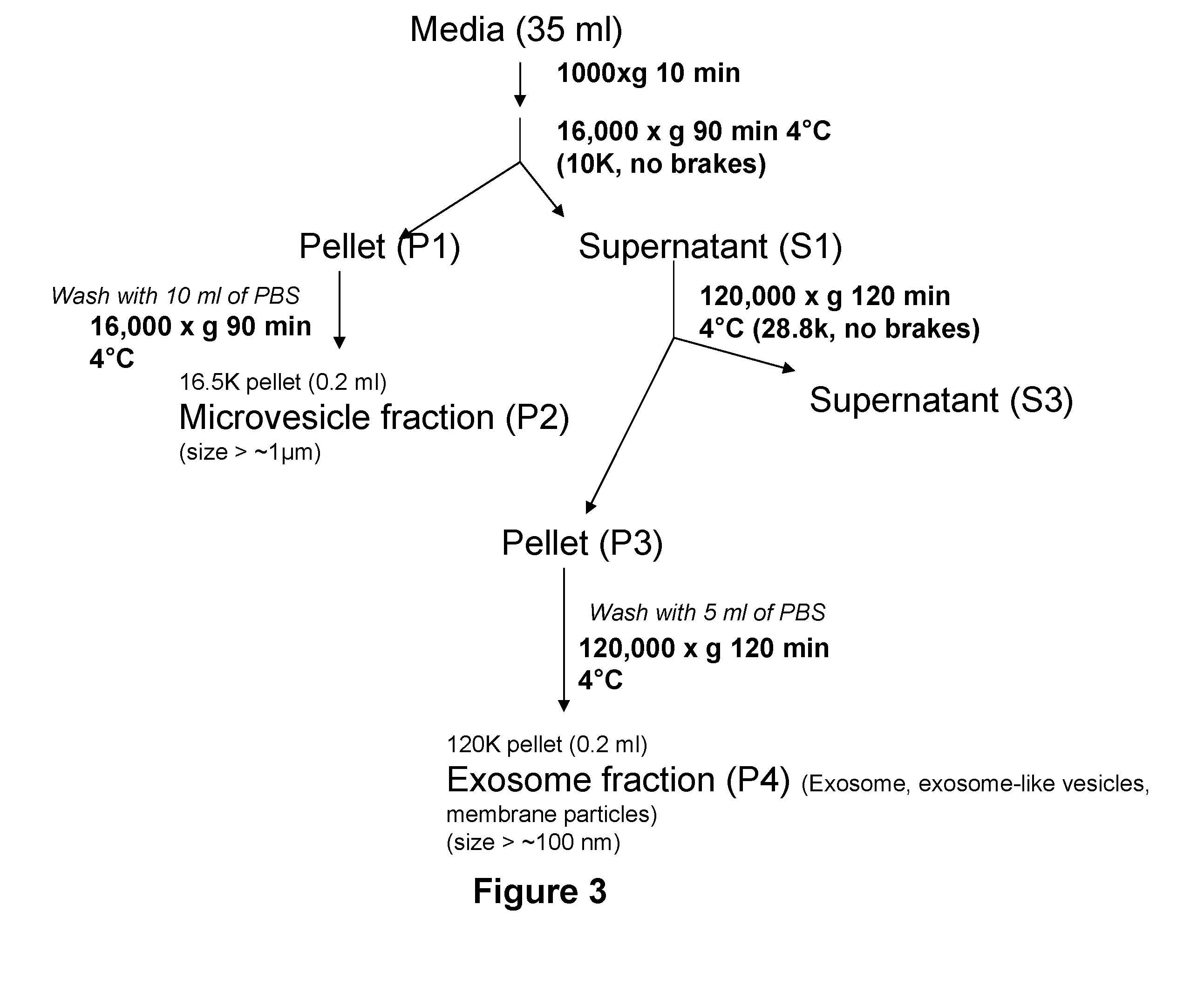
The present invention provides improved methods and compositions based on microvesicles for the treatment of various diseases, disorders and conditions. In particular, the present invention encompasses the recognition that microvesicles contain specific microRNAs which may function as intercellular regulators involved in cell or tissue regeneration, remodeling, reconstruction, reprogramming or transdifferentiation. Thus, among other things, the present invention provides methods and compositions based on microvesicles and / or associated microRNAs that provide more predictable and effective therapeutic results.
Owner:THE UNIV COURT OF THE UNIV OF GLASGOW
Reprogramming of cells to a new fate
Methods and compositions for transdifferentiation of an animal cell from (i) a first pluripotent cell fate to a second nonpluripotent cell fate or (ii) from a non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate to a different non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Cells exhibiting neuronal cell progenitor characteristics and methods of making them
Disclosed are cells exhibiting neuronal progenitor cell characteristics, and methods of making them from marrow adherent stem cells by regulating cellular pathways in the marrow adherent stem cells that are associated with glial transdifferentiation of the marrow adherent stem cells.
Owner:SANBIO
Reprogramming of cells to a new fate
Methods and compositions for transdifferentiation of an animal cell from (i) a first pluripotent cell fate to a second nonpluripotent cell fate or (ii) from a non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate to a different non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
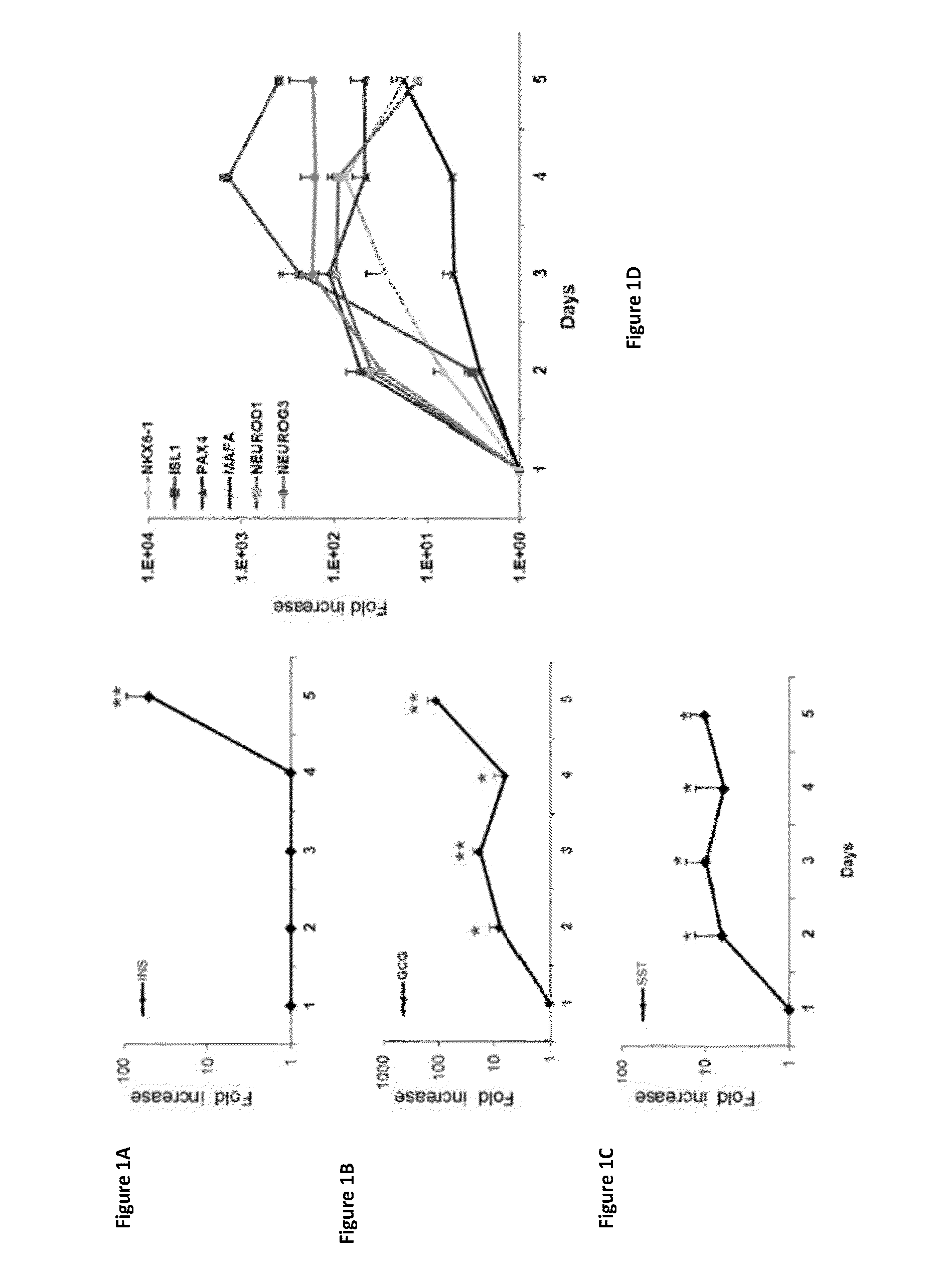
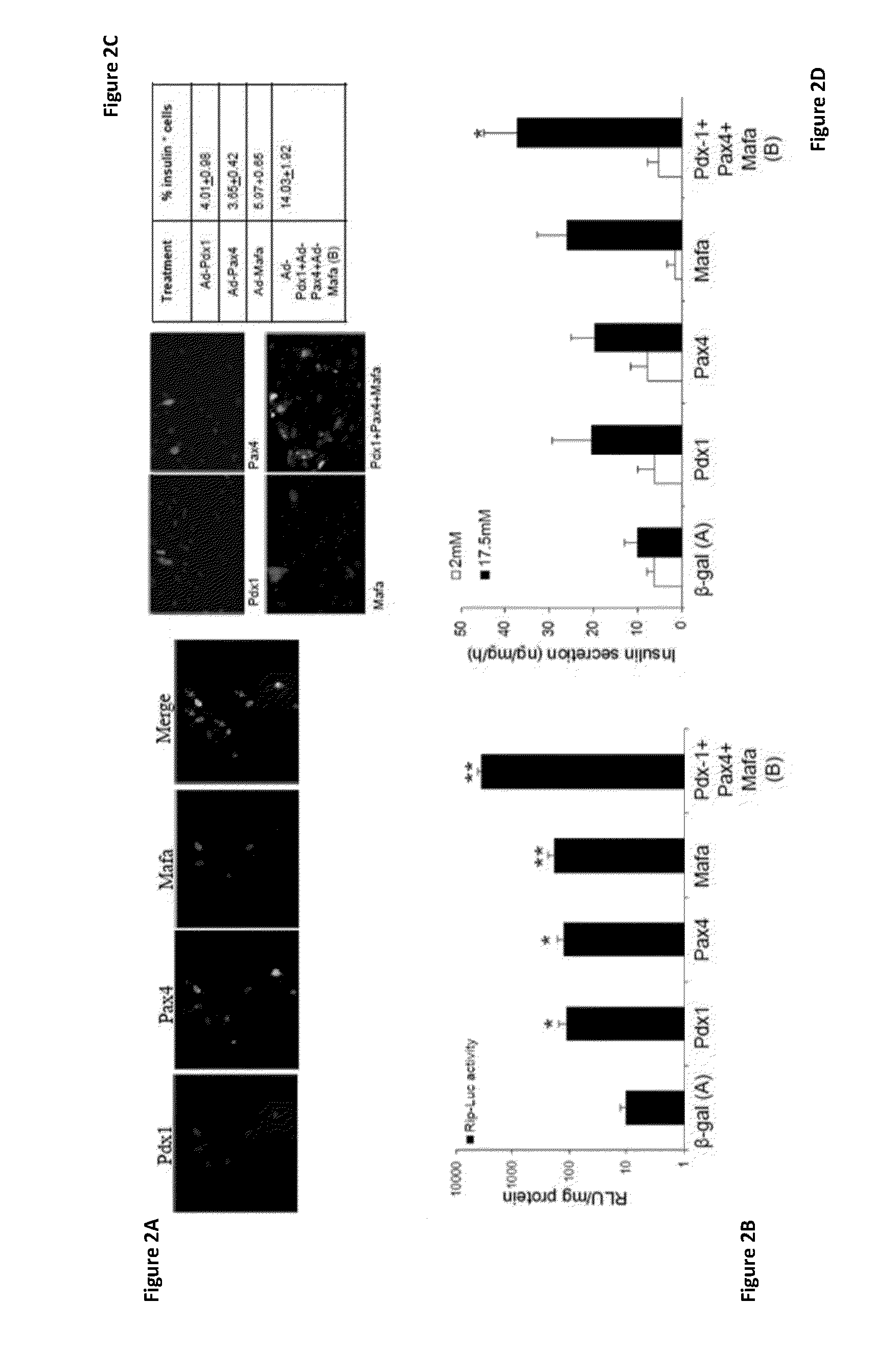
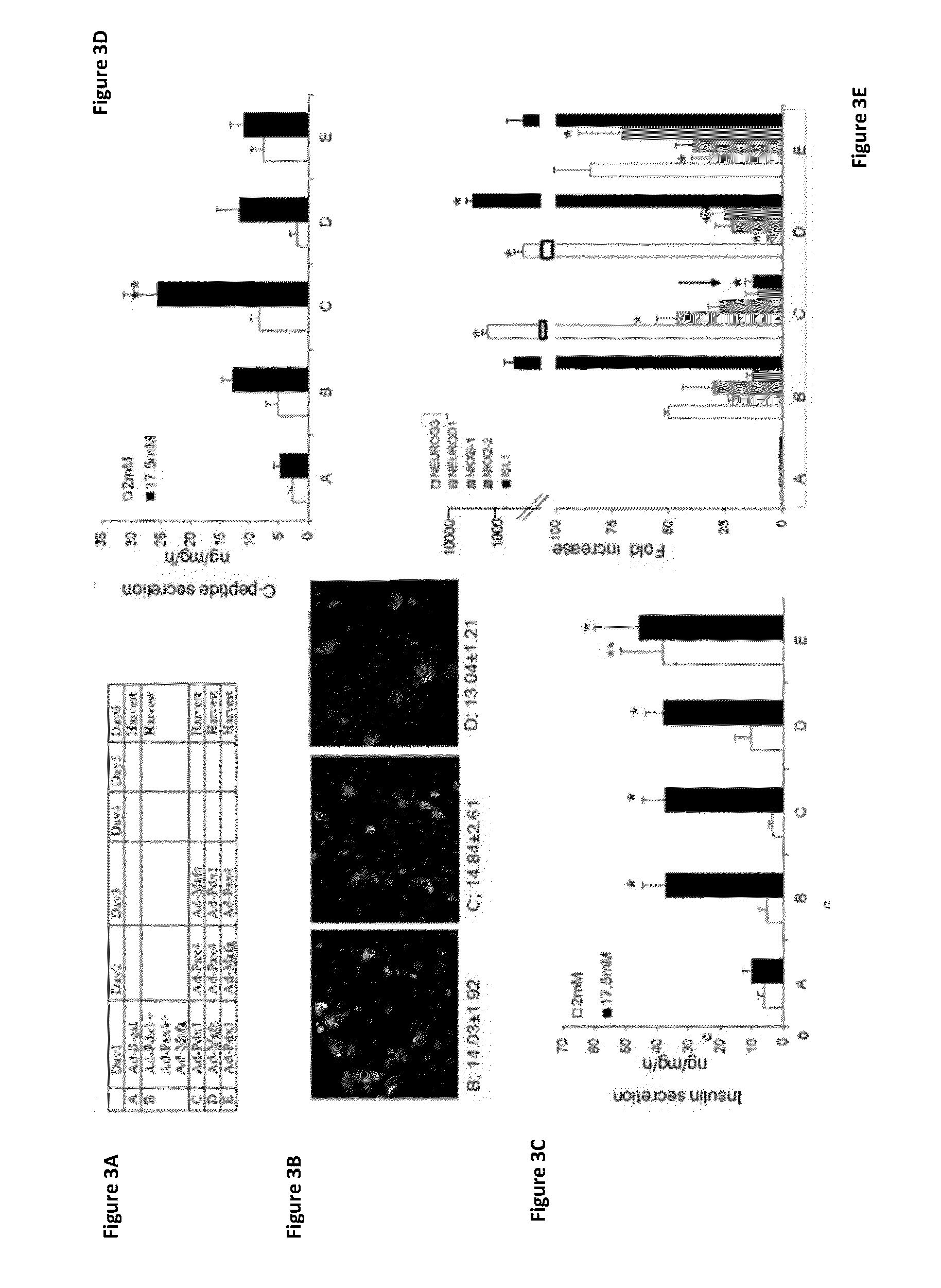
Methods for in vitro expansion and transdifferentiation of human pancreatic acinar cells into insulin-producing cells
InactiveUS20060122104A1Easy to makeEasy to testPeptide/protein ingredientsPancreatic cellsTransdifferentiationCell phenotype
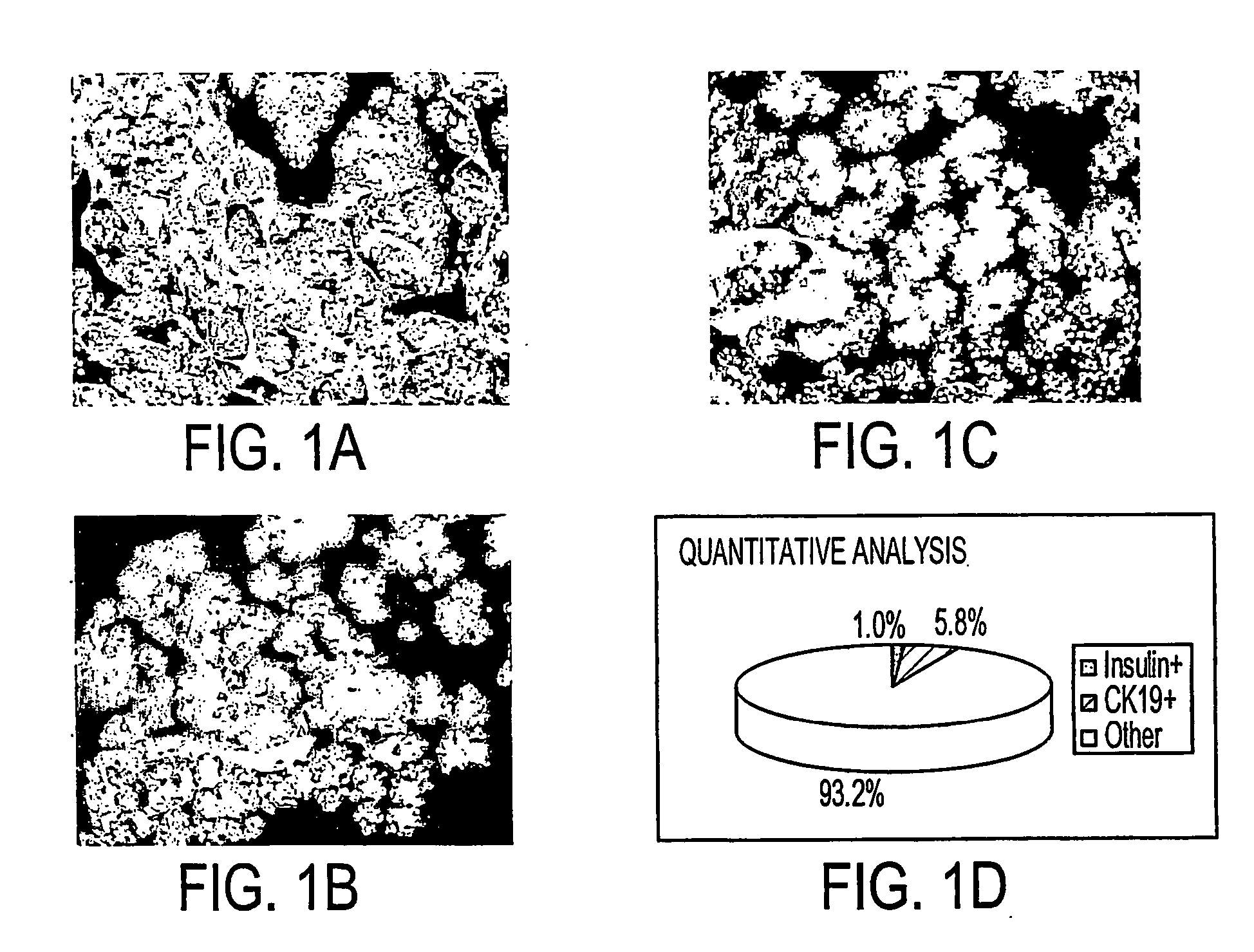
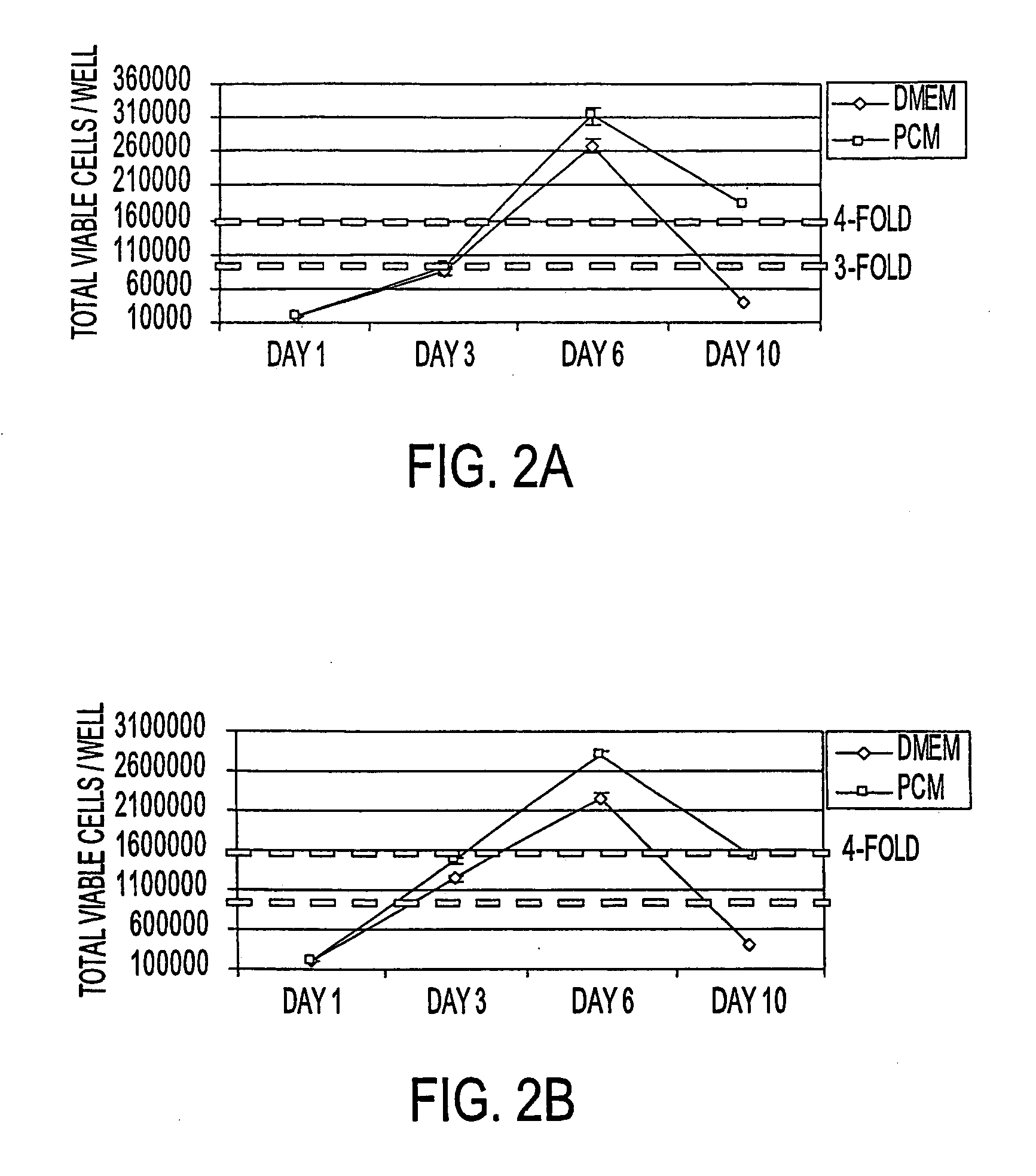
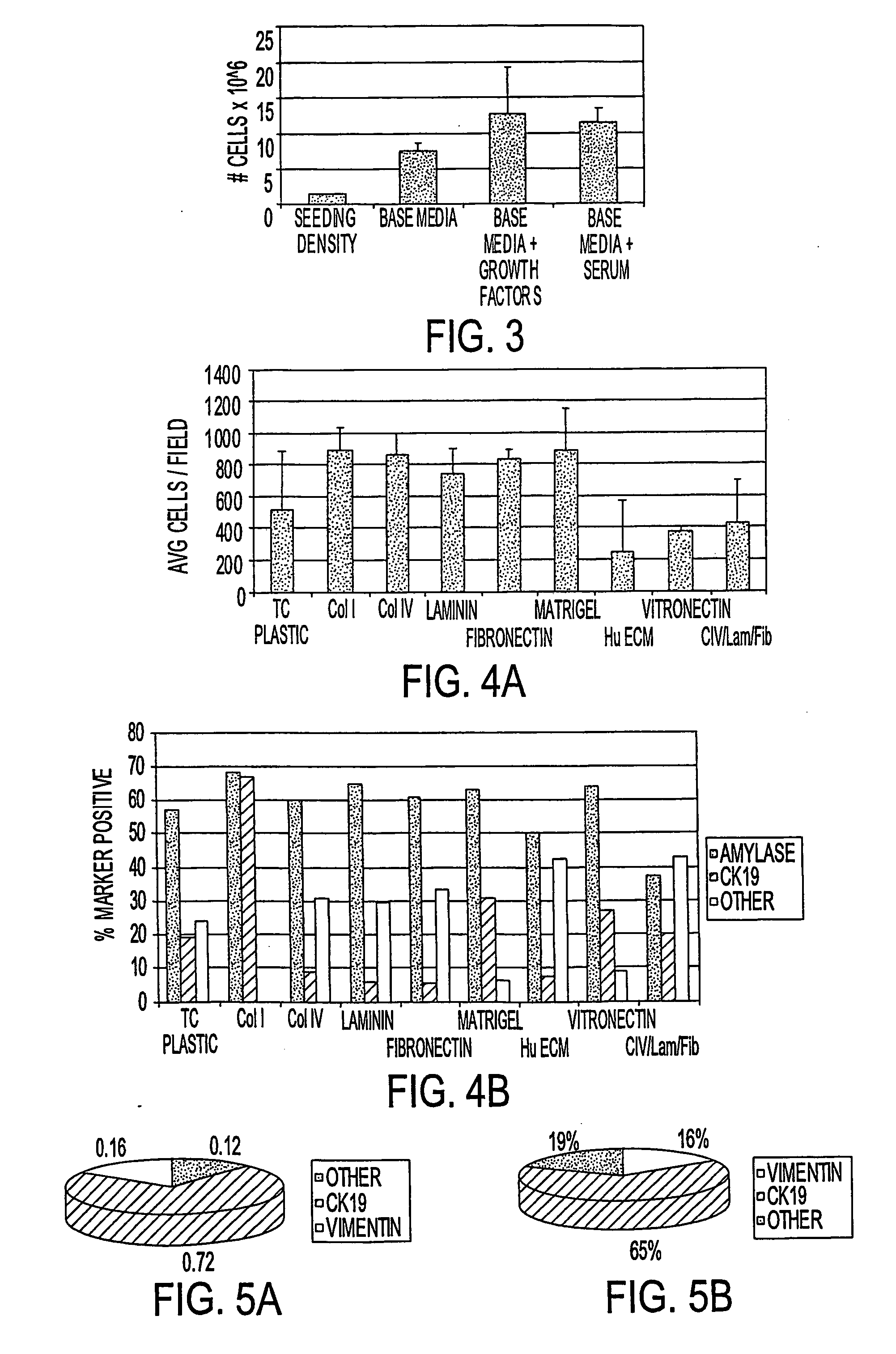
This invention relates, e.g., to a method for expanding mammalian acinar cells, comprising culturing the cells in a cell culture system comprising a cell culture medium and a cell attachment surface, under conditions wherein the acinar cells undergo a 3-4 fold expansion together with transdifferentiation into a modified cell phenotype (IP cells) showing characteristics of acinar cells and liver cells. The invention also relates to a method for transforming these IP cells to insulin-producing cells in vitro, comprising culturing the cells in a novel, defined medium. Also disclosed are suitable culture media for performing these methods, isolated cells having the phenotype of IP cells and / or produced by these methods, and kits for performing the methods.
Owner:BECTON DICKINSON & CO
Stem Cells and Signals Developed for Use in Tissue and Organ Repair and Replacement
Methods and compositions for repairing tissue. Certain embodiments of the invention involve transdifferentiation of cells in a manner not heretofore provided for. One embodiment of the invention features methods for producing stem cells. These methods can involve exposing cells (e.g., human fibroblasts) to a processed or activated egg extract (e.g., activated egg extract); and culturing the cells for a period of time to become stem cells. A cell culture can be performed in two or three dimensions, so that organ tissue or whole organs may be produced, e.g., for transplantation. Another embodiment of the invention features methods for promoting wound healing by using signaling complexes.
Owner:TEI BIOSCI
Surface-mediated gene therapy type artificial lens and preparation method for same
ActiveCN104825249APrevent proliferationReduce incidenceIntraocular lensTransdifferentiationViral Genes
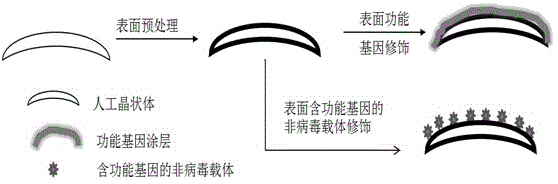
The invention discloses a surface-mediated gene therapy type artificial lens and a preparation method for the same. A plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) containing a functional gene or a non-viral gene vector loaded with the plasmid DNA containing the functional gene is fixedly arranged on the surface of the artificial lens. The artificial lens and the preparation method for the same have the advantages that a surface-deviated gene therapy vector is obtained by a surface gene modification method, so that the epithelial cell proliferation and transdifferentiation of the lens are suppressed by a surface-mediated gene therapy method, and the artificial lens capable of effectively suppressing after cataract is obtained.
Owner:WENZHOU MEDICAL UNIV
Reprogramming of Cells to a New Fate
The present invention generally provides methods and compositions for transdifferentiation of an animal cell from a first non-pluripotent cell fate to a second non-pluripotent cell fate. Also provided are methods and compositions for the transdifferentiation of an animal cell from a non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate to a different non-pluripotent mesodermal, endodermal, or ectodermal cell fate.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
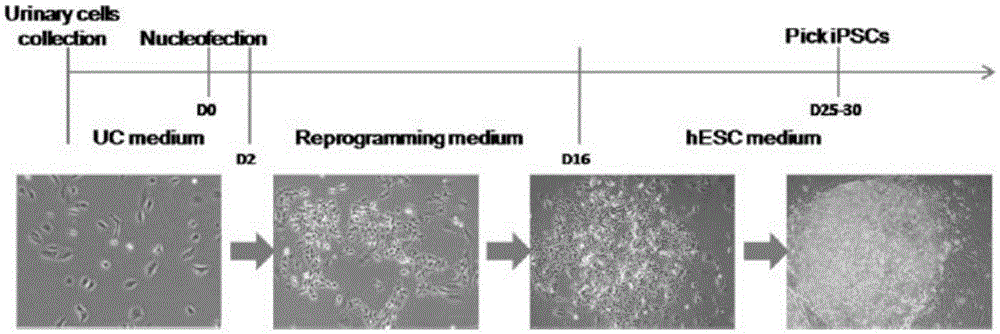
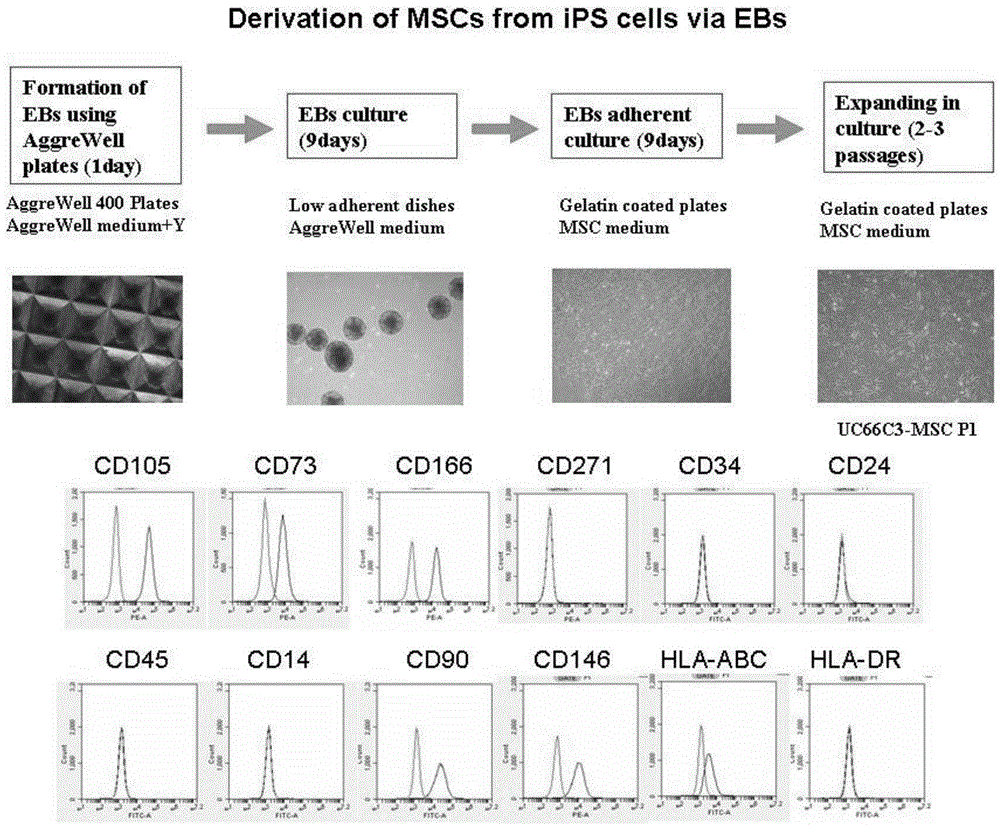
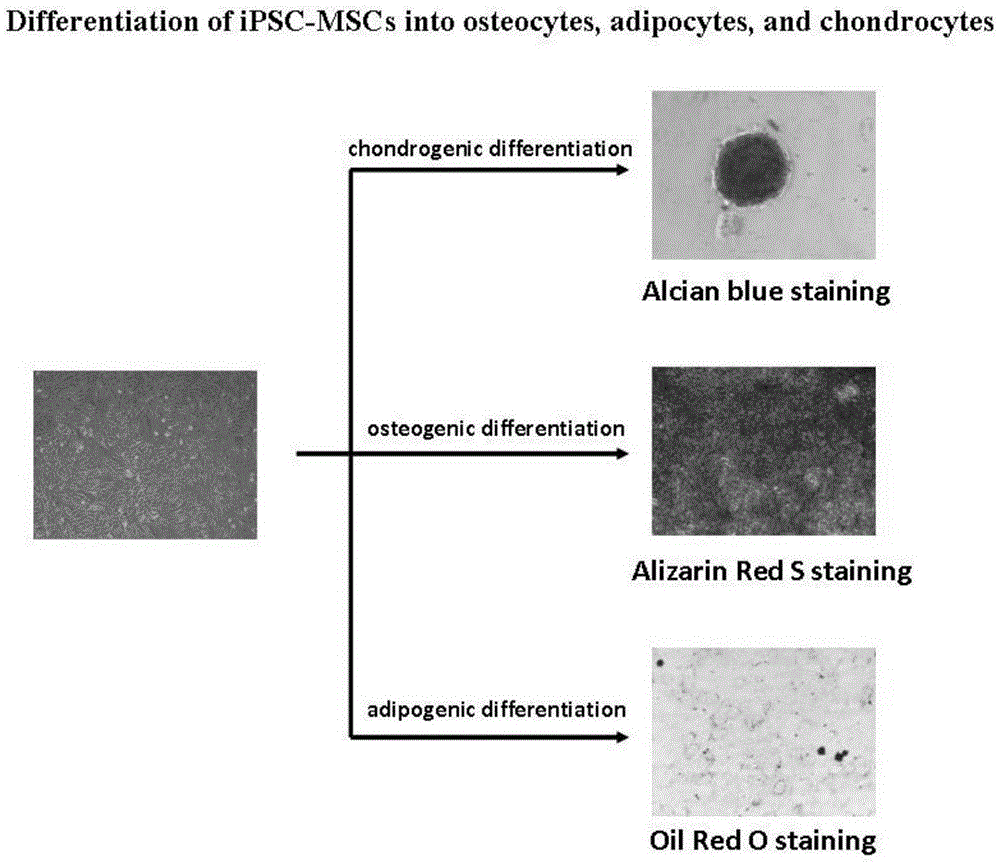
Method for constructing cartilage tissues by aid of human urine cells
The invention provides a method for preparing cartilage tissues from artificial in-vitro sources by the aid of human urine cells in an in-vitro manner. The method includes steps of (1), a), reprogramming the human urine cells to generate induced pluripotent stem cells and directionally differentiating the induced pluripotent stem cells to obtain mesenchymal stem cells, or b), carrying out transdifferentiation to generate the mesenchymal stem cells; (2), cultivating the mesenchymal stem cells obtained at the step (1) in cartilage induced differentiation media to obtain the cartilage tissues from the artificial in-vitro sources. The method has the advantages that the cartilage tissues are constructed in the in-vitro manner and can be used for replacing damaged or lesion tissue cells, so that the purpose of repairing cartilage can be achieved, and the effective method is provided for constructing the cartilage tissues in the in-vitro manner and has huge application value.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
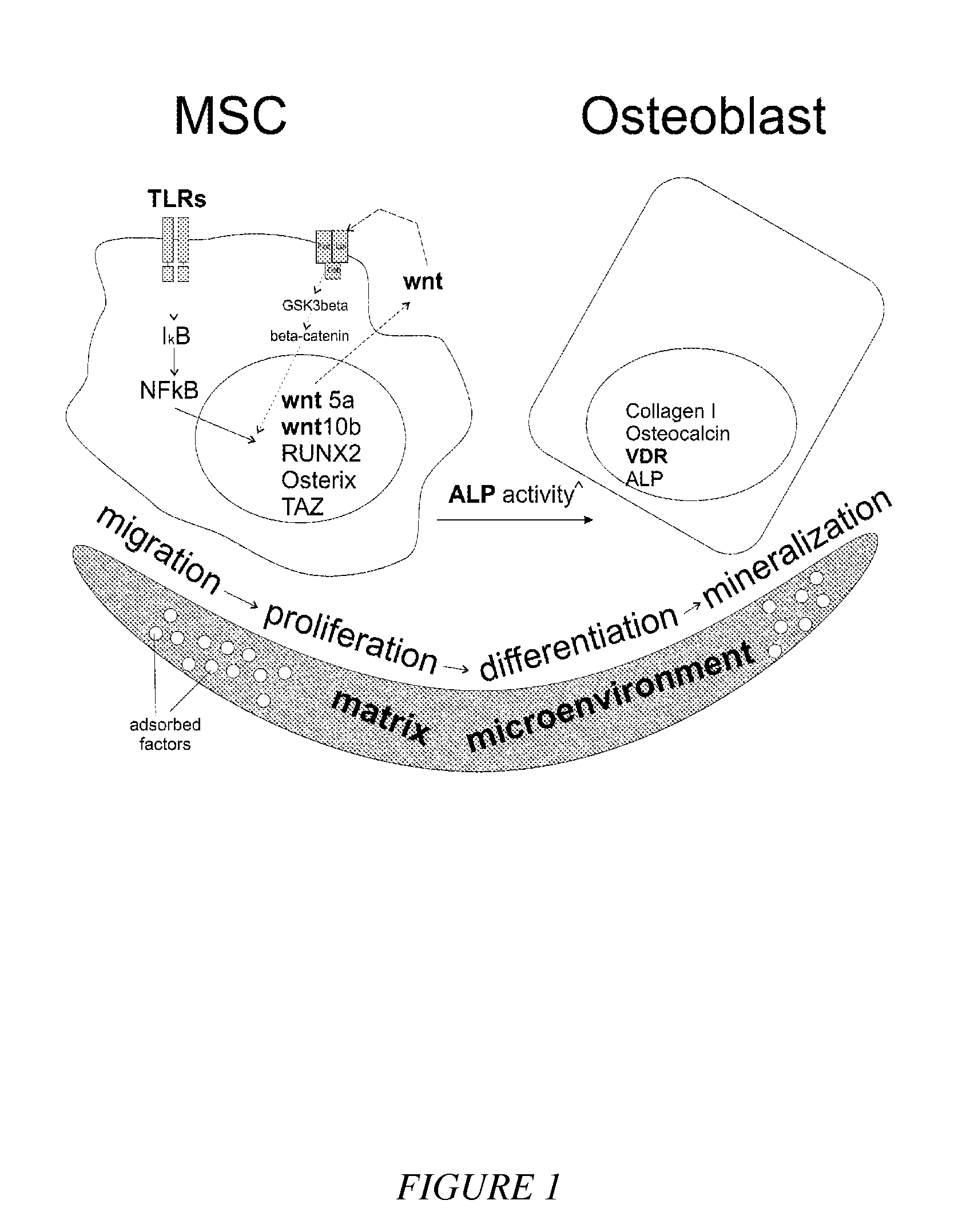
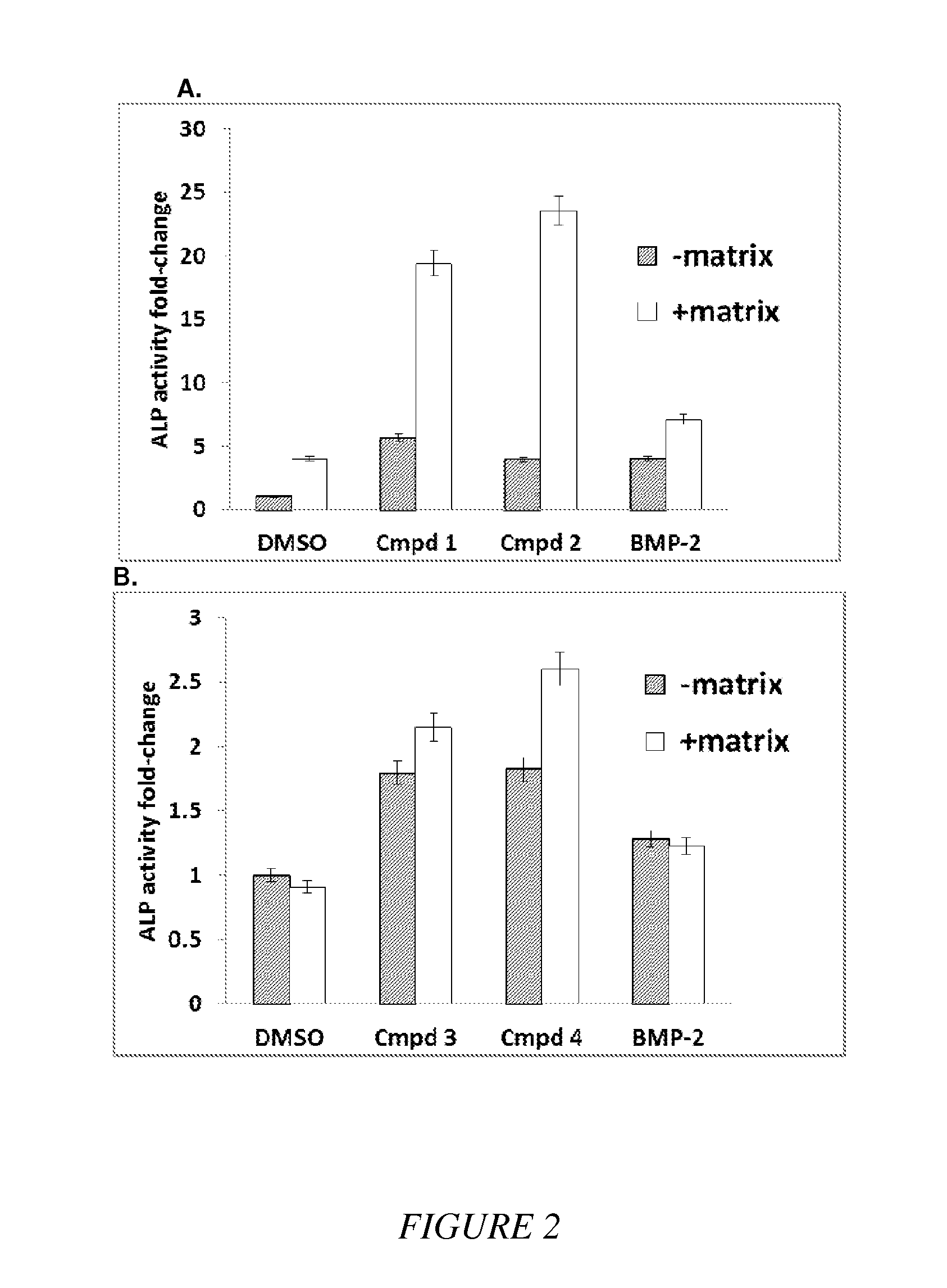
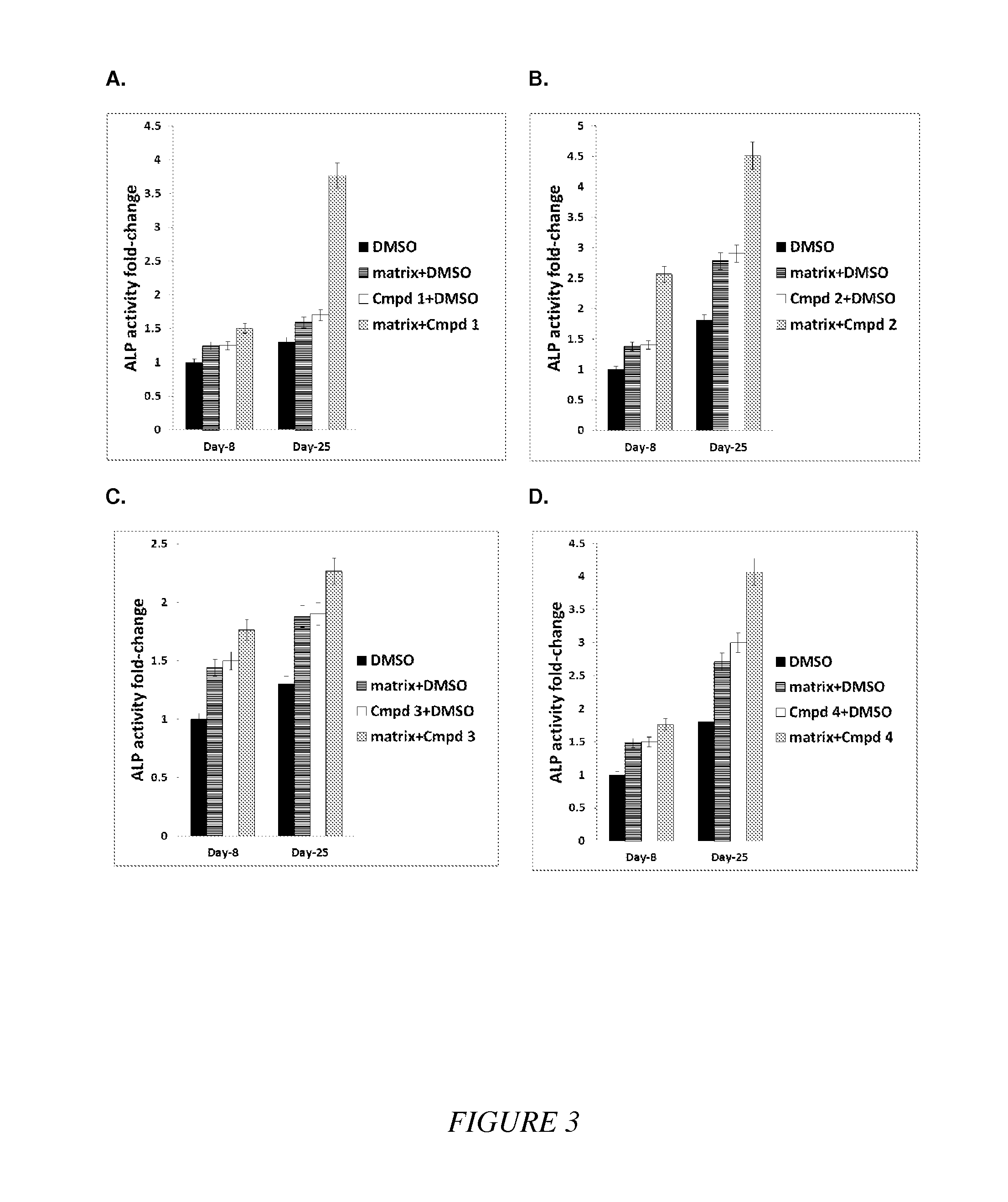
Compounds and matrices for use in bone growth and repair
Compositions of small molecules, matrices, and isolated cells including methods of preparation, and methods for differentiation, transdifferentiation, and proliferation of animal cells into the osteoblast blast cell lineage were described. Examples of osteogenic materials that were administered to cells or co-cultured with cells are represented by compounds of Formula II, IV, and VI independently or preferably in combination with a matrix to afford bone cells. Small molecule-stimulated cells were also combined with a matrix, placed with a cellular adhesive or material carrier and implanted to a site in an animal for bone repair. Matrix pretreated with compounds of Formula II, IV, and VI were also used to cause cells to migrate to the matrix that is of use for therapeutic purposes.
Owner:HUMAN BIOMOLECULAR RES INST
Medicinal composition for inducing direct conversion of fibroblasts into nerve cells, and use of medicinal composition
InactiveCN106337037AAchieve transdifferentiationEasy transitionCulture processNervous system cellsTransdifferentiationFibroblast
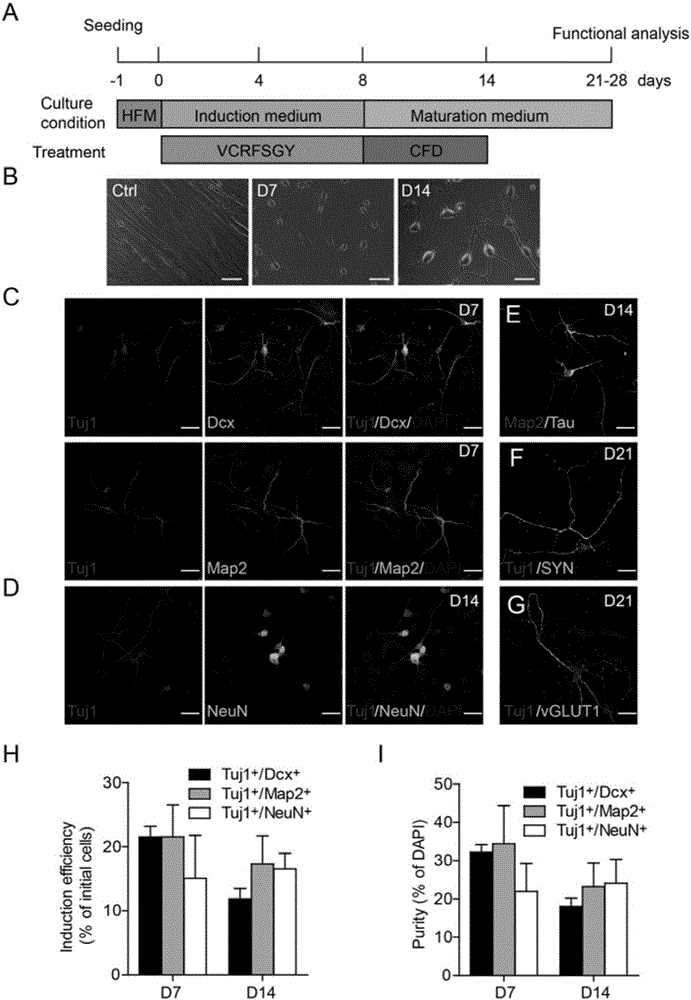
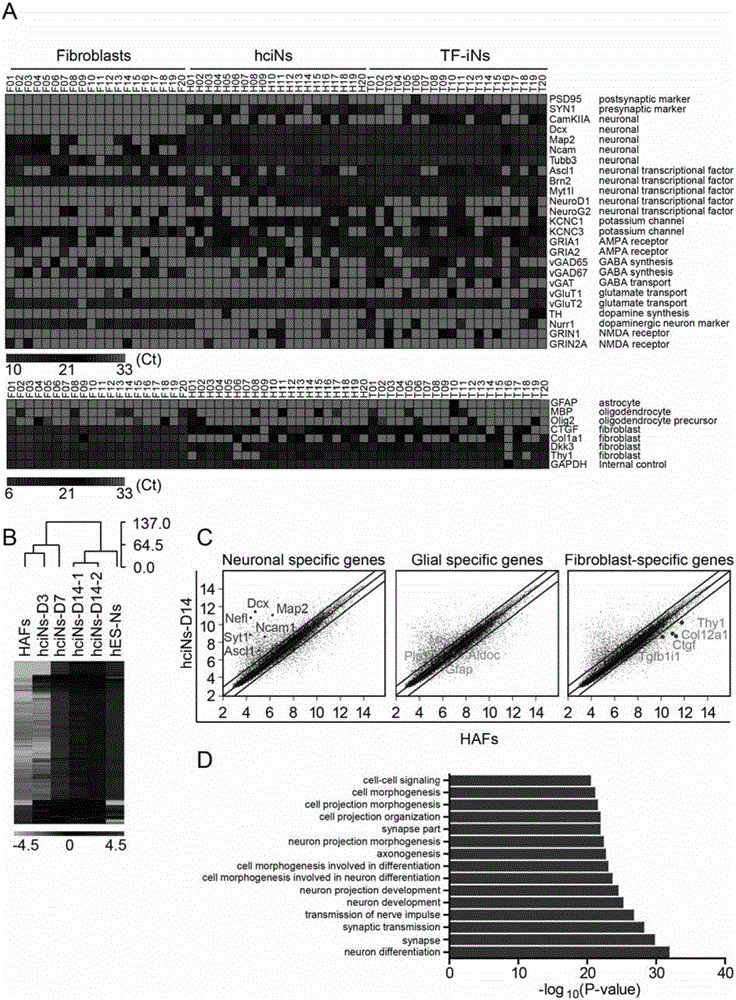
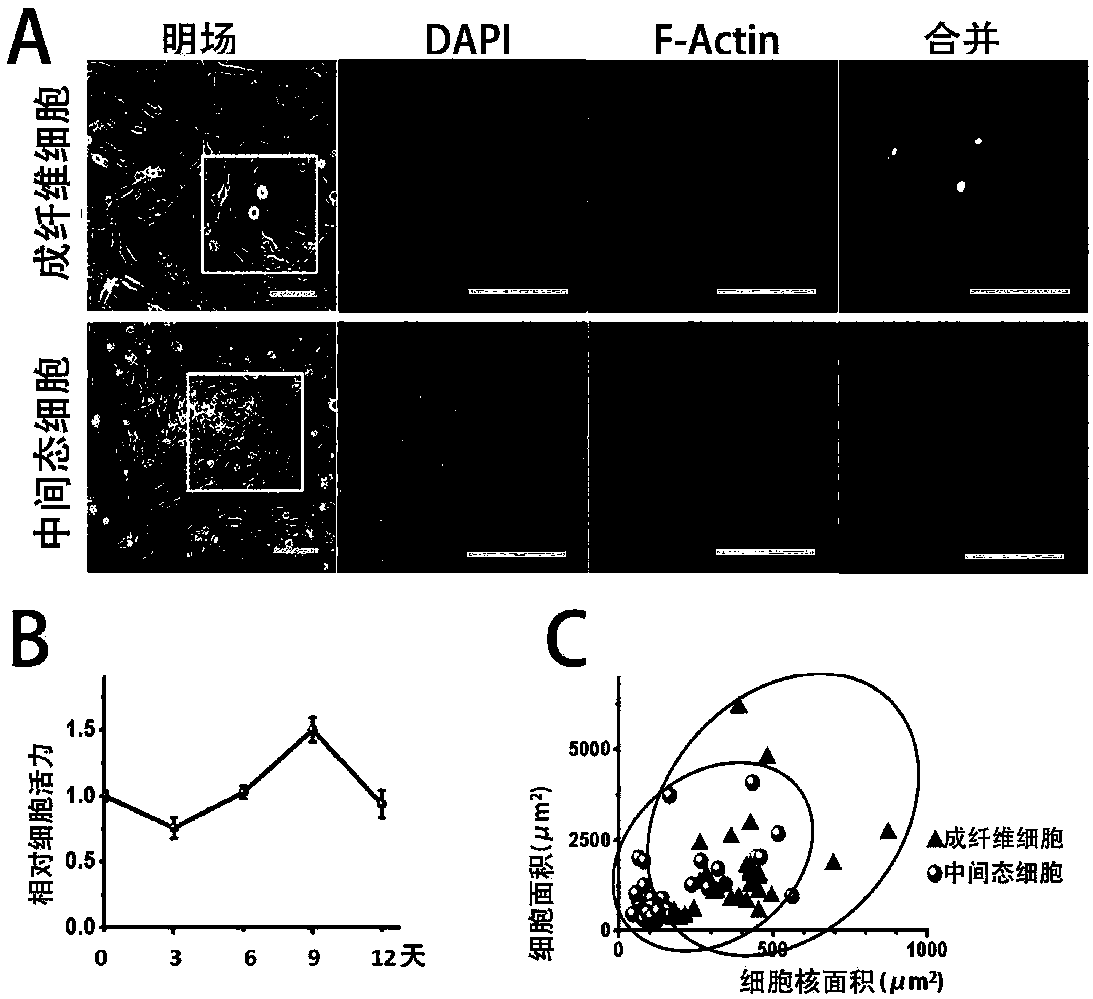
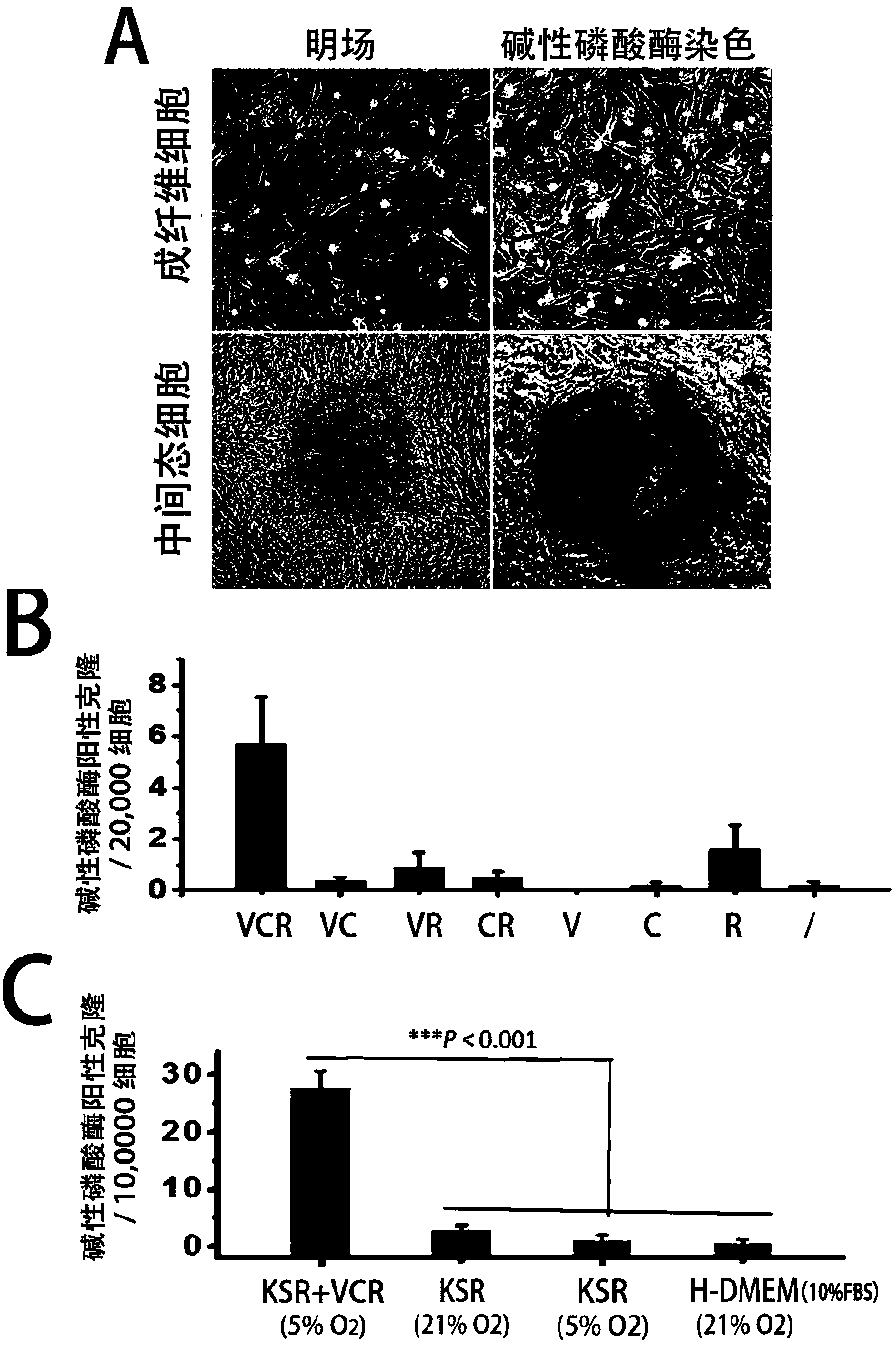
The invention relates to the biotechnical field, and concretely relates to a medicinal composition for inducing direct conversion of fibroblasts into nerve cells, and a use of the medicinal composition. Transdifferentiation between nerve cell non-genealogies is realized through micro-molecular compound combination without exogenous gene. VCRFSGY treated fibroblasts rapidly leave the cell cycle at the third day is found for the first time, which hints that neuron cells formed by chemical induction of human fibroblasts may bypass the proliferation intermediate state, so the medicinal composition has extremely high clinic and market values. Additionally, a situation that Retinoic acid or Parnate can be respectively added on the basis of a VCRFSGY compound combination in order to well promote the induction efficiency is further found.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Induction medium for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into adipocyte and application thereof
The invention discloses an induction medium inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into adipocyte, an induction method and application thereof. The induction medium contains a basal culture medium and an induction micromolecule combination, wherein the induction micromolecule combination is SG or 6TF, S is SB431542, G is GSK126, 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, and F is forskolin. The induction medium can induce and trans-differentiate the fibrolast into the adipocyte, the obtained adipocyte contains a normal adipocyte specificity molecular tag and has a normal fat adipogenesis function, and a new approach is provided for solving the cellular source problem of regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods of transdifferentiation and methods of use thereof
Disclosed herein is a method for manufacturing a population of human insulin producing cells from non-pancreatic β-cells, wherein the resulting insulin producing cells have increased insulin content, or increased glucose regulated secretion of insulin, or a combination of both.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES +1
Method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into neuronal cells and application thereof
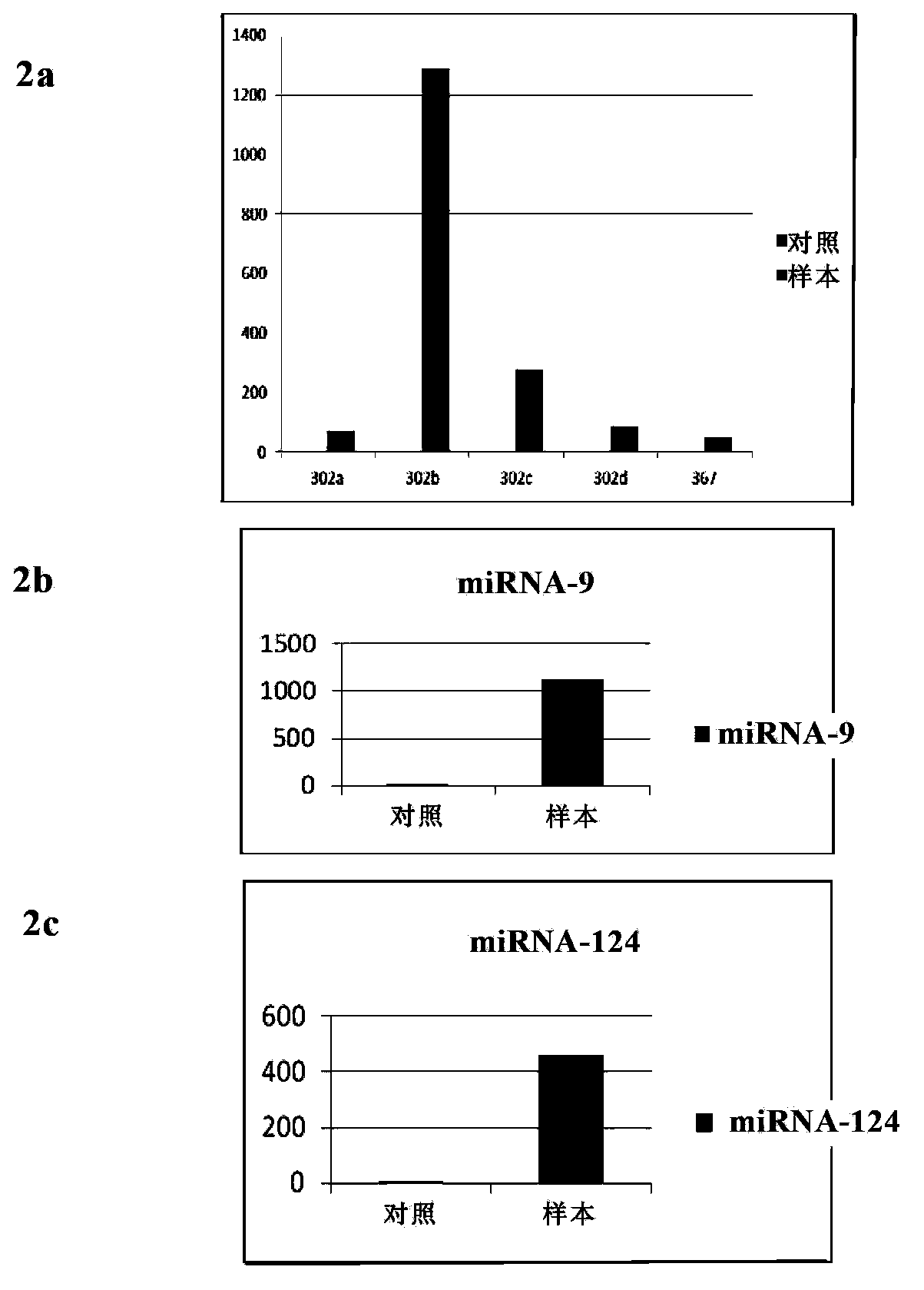
The invention relates to a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts into neuronal cells and application thereof. Specifically, miRNA-302 / 367 clusters, miRNA-9 and miRNA-124 are indispensable for the transdifferentiation of the fibroblasts into the neuronal cells; no obvious stem cell cloning stage takes place in the transformation process, and a retrovirus system is adopted to stably and efficiently express the miRNA-302 / 367 clusters, the miRNA-9 and the miRNA-124 in human fibroblasts, and therefore, a series of biochemical reactions of cells are adjusted and the fibroblasts are trans-differentiated into the neuronal cells. The invention also provides application of a miRNA combination (the miRNA-302 / 367 clusters, the miRNA-9 and the miRNA-124).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL PROD CO LTD
Antisense composition and method for treating cancer
InactiveUS20050261249A1Confirm specificity of bindingLimited to nonOrganic active ingredientsBiocideTransdifferentiationHeteroduplex
A method and composition for of treating cancer, and in particular, for arresting the progression of a solid or primary cancer to a more invasive, metastatic state, are disclosed. The composition includes a substantially uncharged antisense compound (i) having a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) capable of uptake by target cancer cells in the subject, (iii) containing between 10-40 nucleotide bases, and (iv) having a base sequence effective to hybridize to a region of processed or preprocessed human SNAIL RNA transcript. The compound, when administered to the subject, is effective to form within target cancer cells in the subject, a base-paired heteroduplex structure composed of human SNAIL RNA transcript and the oligonucleotide compound, where this structure is characterized by a Tm of dissociation of at least 45° C. The compound is administered in an amount sufficient to inhibit SNAIL expression in target cancer cells, thereby to inhibit the progression of the patient's cancer to a more invasive, metastatic state. Also disclosed are methods for preventing the transdifferentiation of peritoneal mesothelial cells and failure of ultrafiltration in a patient undergoing peritoneal dialysis, by including the compound in the patient dialysis fluid.
Owner:AVI BIOPHARMA
Method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into similar testicular interstitial cells by combination of transcription factors
ActiveCN106636210AReduce riskShort timeGenetically modified cellsMammal material medical ingredientsTransdifferentiationTesticular Interstitial Cells
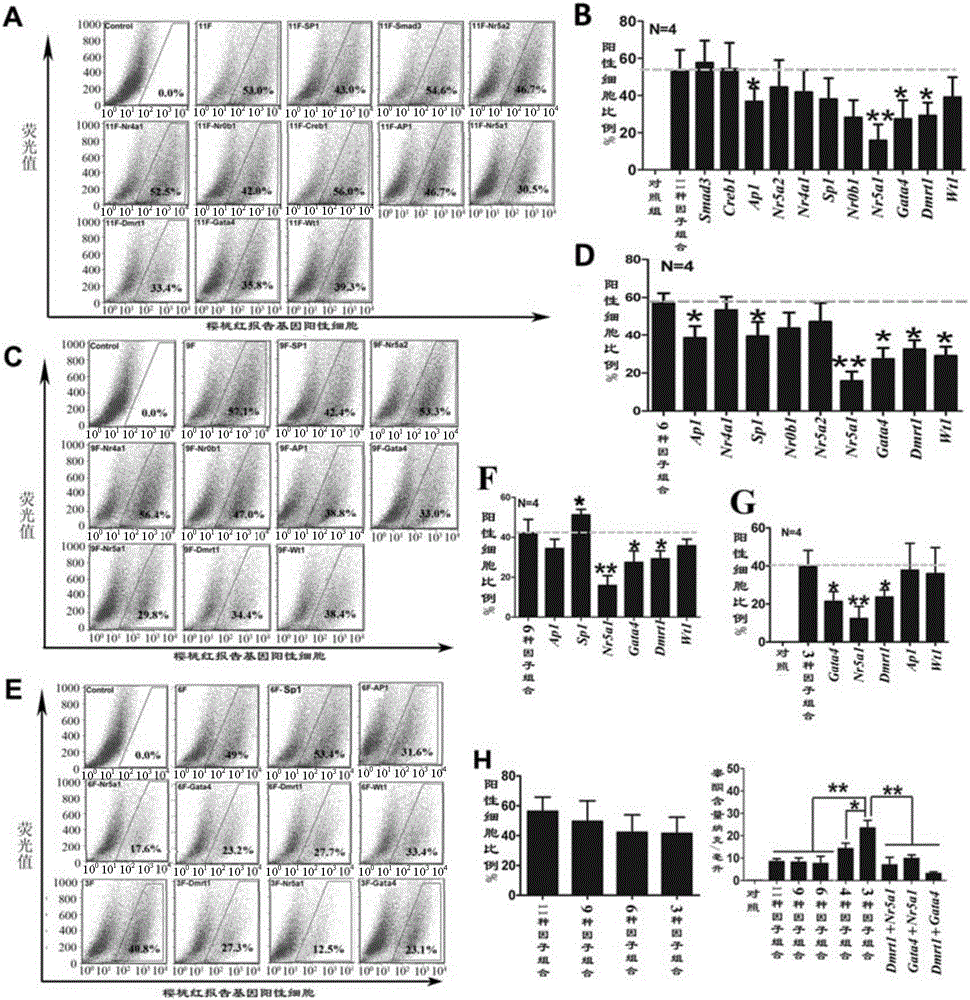
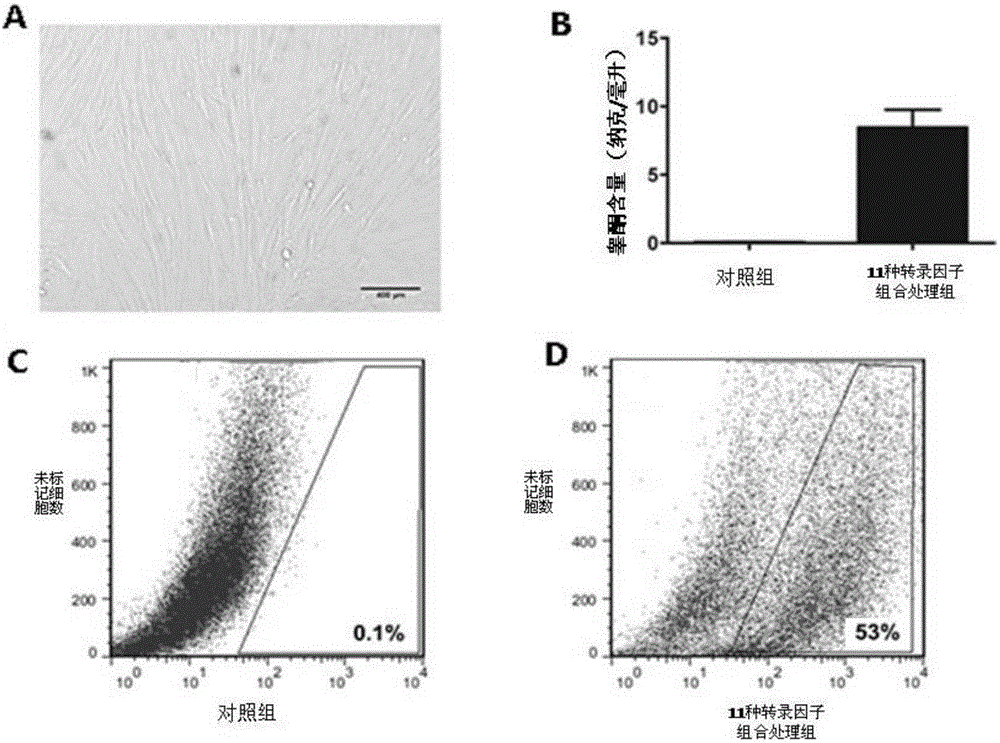
The invention relates to a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblast into similar testicular interstitial cells. The method is characterized in that required transcription factors are respectively cloned to lentiviral vectors, and packaged to be virus particles for transfection to fibroblast; by utilizing an overexpression transcription factor method, inducing transdifferentiation of the fibroblast into inducible testicular interstitial cells, wherein the transcription factors are sourced from human beings, mice or rats, and the transcription factors are a part selected from a group of Dmrt1, Nr0b1, Sp1, Wt1, Nr4a1, Nr5a2, AP1, Creb1, Smad3, Nr5a1 and Gata4,or a combination of all transcription factors. The cells after transdifferentiation have the androgen synthesis related gene expression profile similar to that of mature testicular interstitial cells, and can synthesize and secrete testosterone. The similar testicular interstitial cells prepared with the method can be used for treating male hypogonadism syndrome.
Owner:BIOPHARM RES & DEV CENT JINAN
Method for inducing mouse fibroblasts into cartilage by adopting small-molecule composition
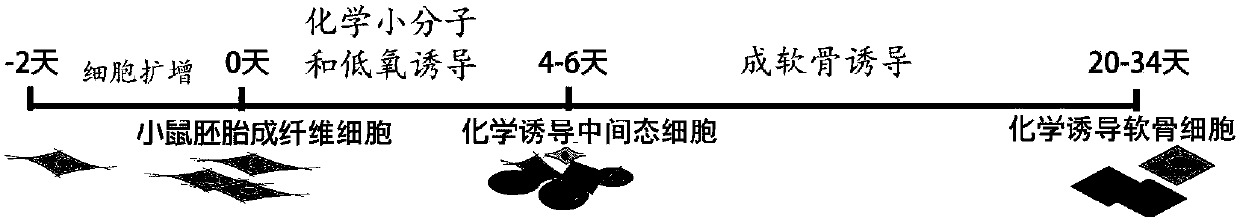
ActiveCN107674859AAvoid missingImprove induction efficiencyCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCartilage cellsTransdifferentiation
The invention discloses a method for inducing mouse fibroblasts into cartilage by adopting a small-molecule composition. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out adherent culture on mouse embryo fibroblasts, removing a culture medium, slowly adding a chemical induction culture medium containing the small-molecule composition, carrying out culturing in the environment having the temperature of 37 DEG C and containing 3-8% of oxygen, 3-8 % of carbon dioxide and the balance of nitrogen, wherein the chemical induction culture medium containing the small-molecule composition is replaced every 2-3 days; carrying out continuous culturing for 4-12 days, thus obtaining intermediate state cells, wherein the small-molecule composition comprises an HDAC inhibitor, a GSK-3 inhibitor and aTGF-beta signal channel inhibitor; and transferring the intermediate state cells to a cartilage inducing medium, carrying out culturing in the environment having the temperature of 37 DEG C and containing 15-25% of oxygen, 3-8 % of carbon dioxide and the balance of nitrogen, wherein the cartilage inducing medium is replaced by the fresh cartilage inducing medium once every 3-4 days, and carryingout culturing for 14-28 days, thus obtaining a cartilage cell cluster. With the method provided by the invention, the problem that in the traditional methods, the fibroblasts can be induced to form cartilage cells through transdifferentiation only after an exogenous gene is introduced is solved, and the method provided by the invention is expected to be used for further solving the problem that seed cells of cartilage cells are in shortage or in-situ focus fibrosis exists.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Methods for regeneration of a mammalian lens
The invention relates to methods for transdifferentiation of body tissues which can be used to generate specific cell types needed for regenerating a lens in the mammalian eye, following loss or removal of the original lens.
Owner:BARANOWITZ STEVEN
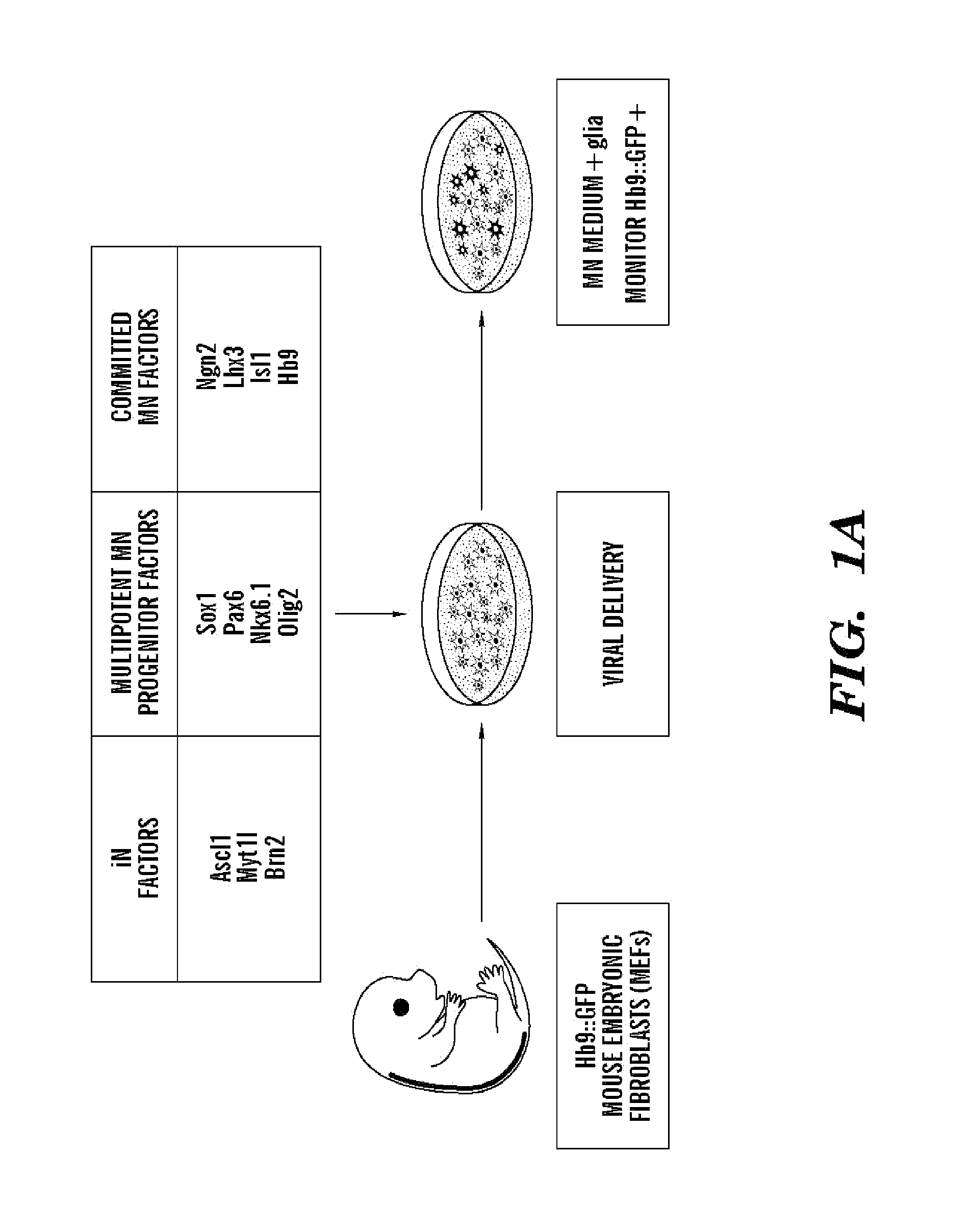
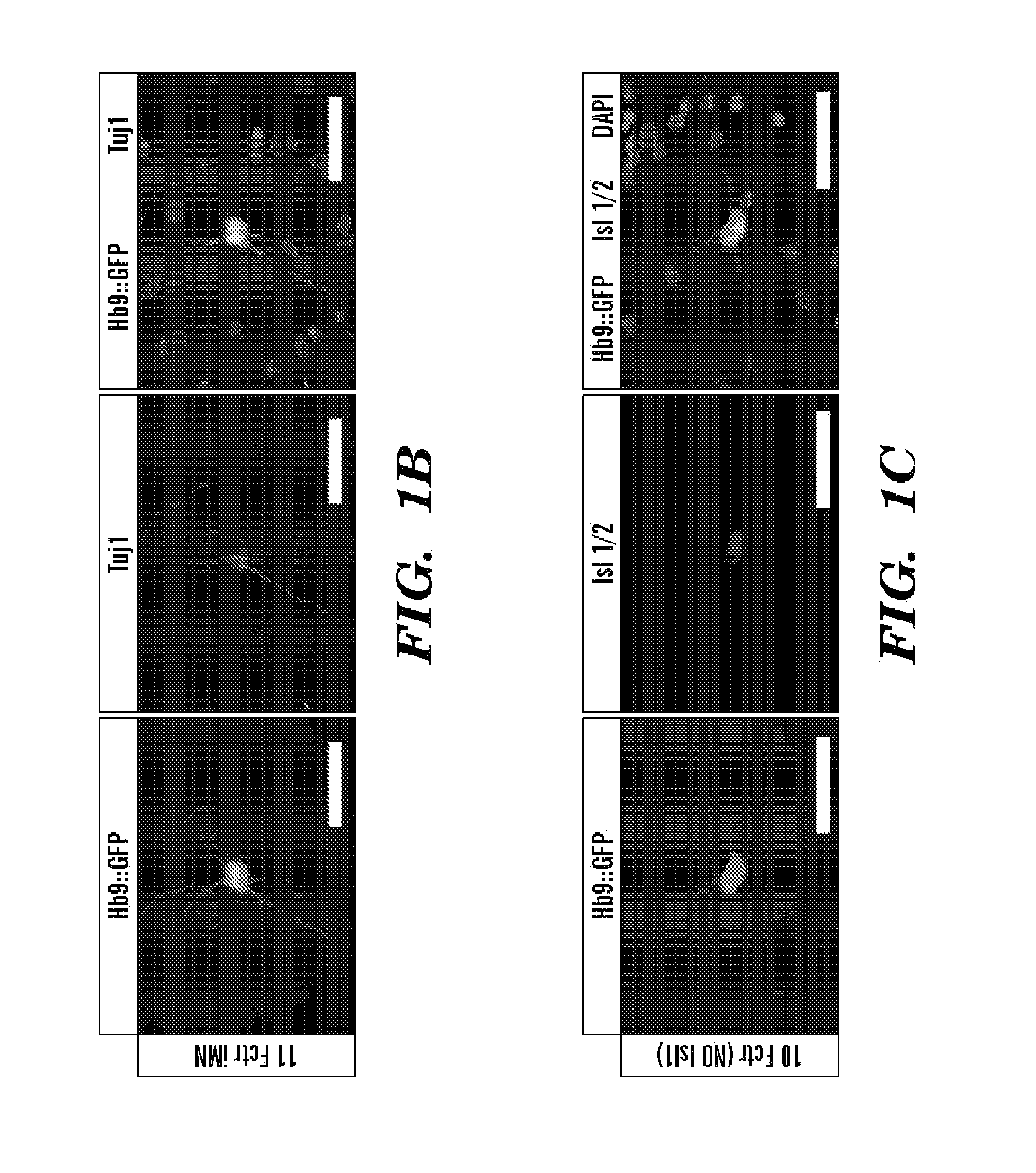
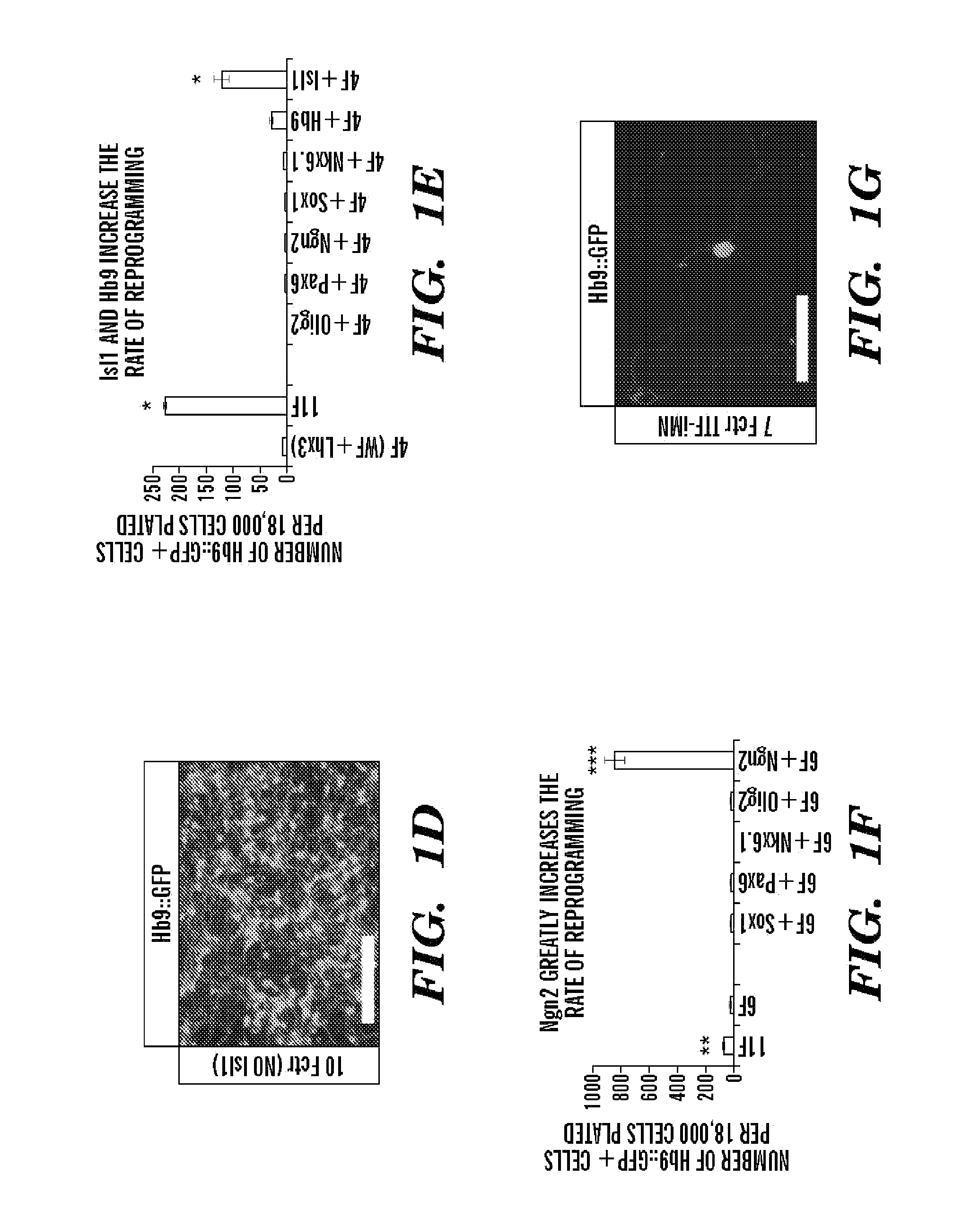
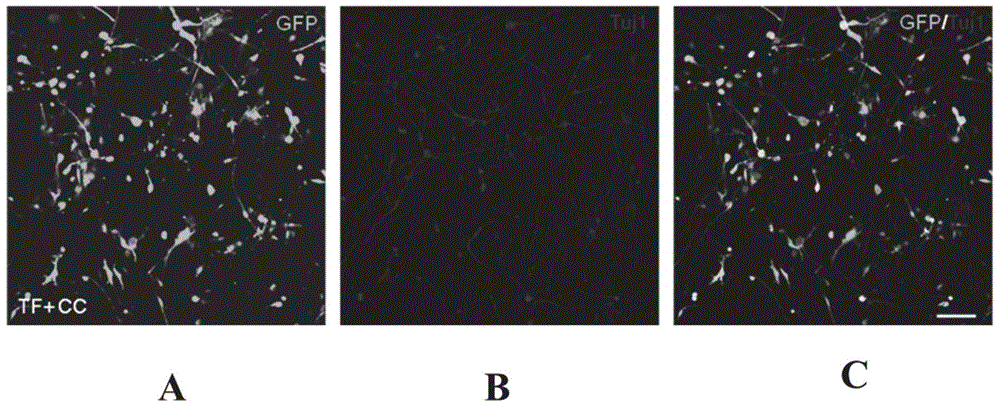
Conversion of somatic cells into functional spinal motor neurons, and methods and uses thereof
The present invention provides methods of transdifferentiation of somatic cells, for example, directly converting a somatic cell of a first cell type, e.g., a fibroblast into a somatic cell of a second cell type, are described herein. In particular, the present invention generally relates to methods for converting a somatic cell, e.g., a fibroblast into a motor neuron, e.g., an induced motor neuron (iMN) with characteristics of a typical motor neuron. The present invention also relates to an isolated population comprising induced motor neurons (iMNs), compositions and their use in the treatment of motor neuron diseases such as ALS and SMA. In particular, the present invention relates to direct conversion of a somatic cell to an induced motor neuron (iMN) having motor neuron characteristics by increasing the protein expression of at least three motor-neuron inducing (MN-inducing) factors selected from Lhx3, Ascl1, Brn2, Myt1l, Isl1, Hb9, Ngn2 or NeuroD1 in a somatic cell, e.g., a fibroblast to convert the fibroblast to an induced motor neuron (iMN) which exhibits at least two characteristics of an endogenous motor neuron.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP +1
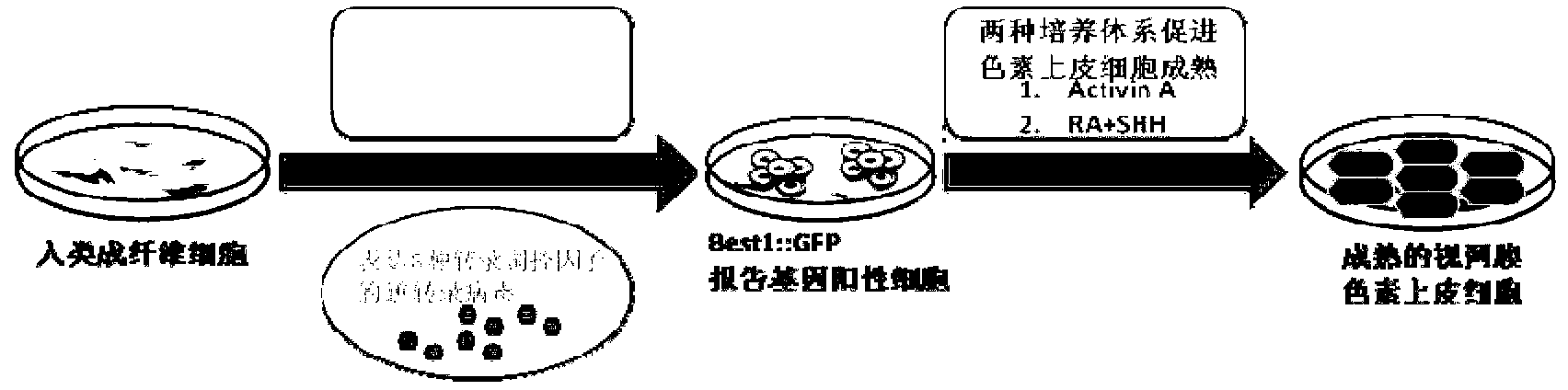
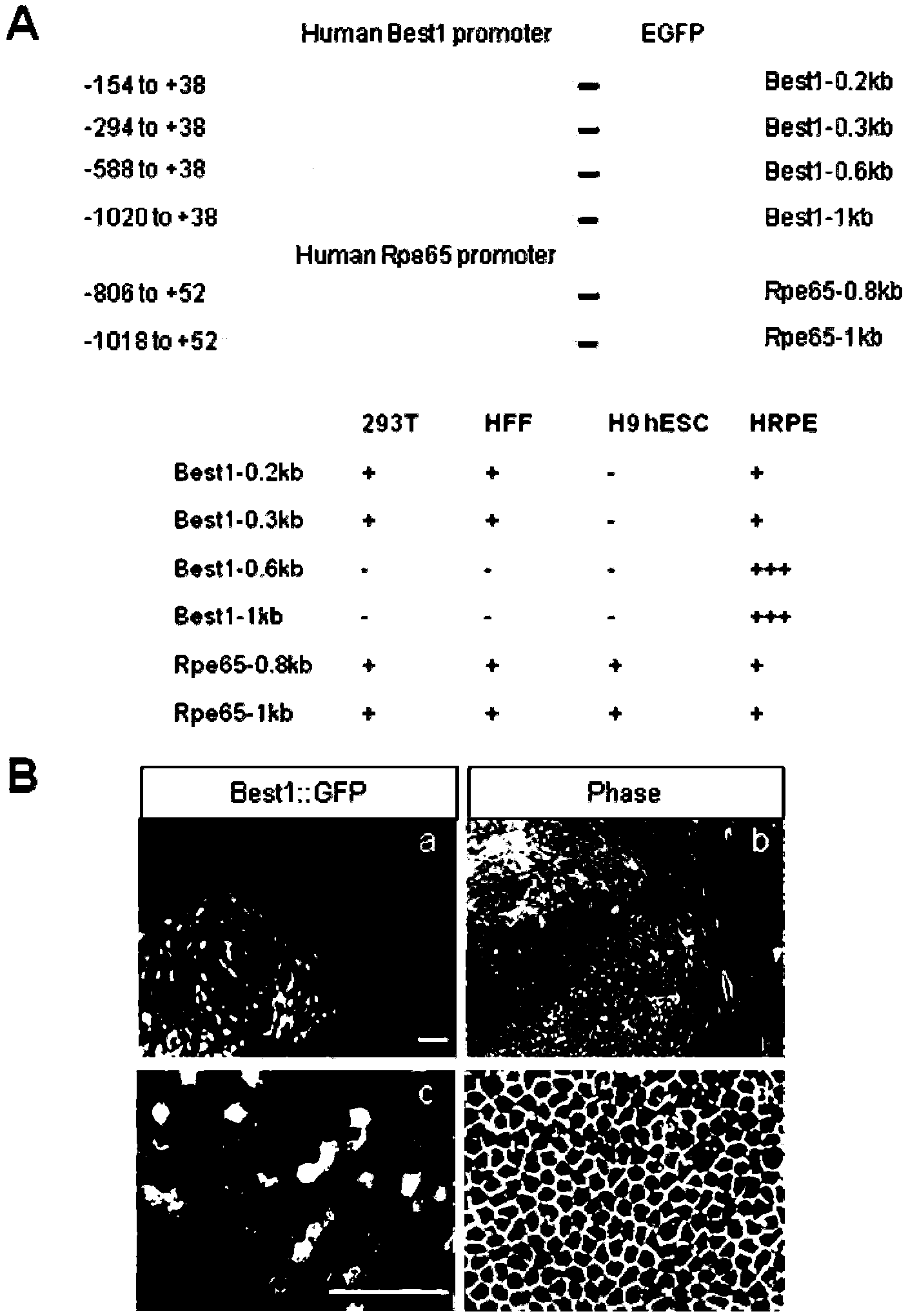
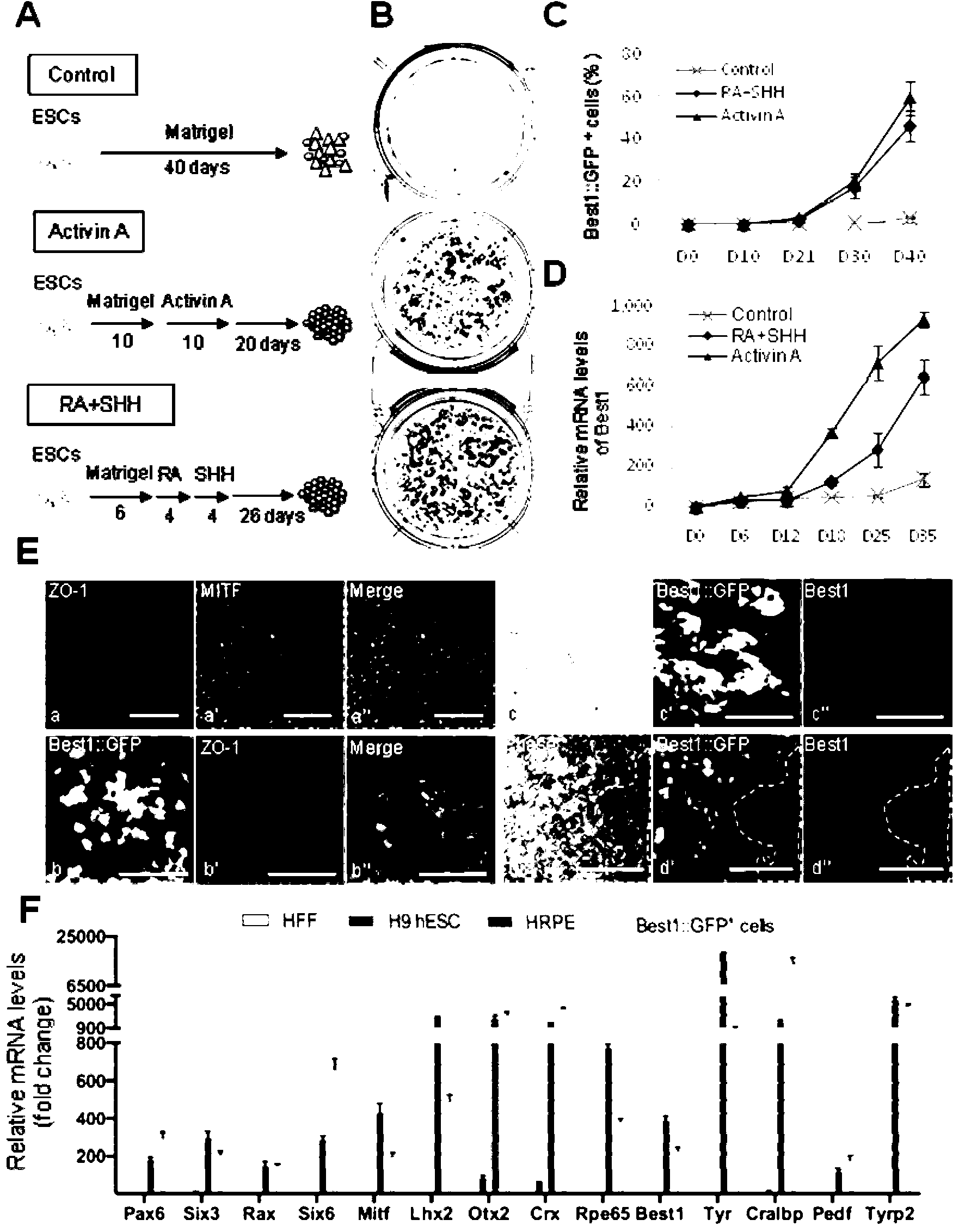
Method for transdifferentiation of human fibroblast to retinal pigment epithelium
ActiveCN103290051AVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsTransdifferentiationFibroblast
The invention relates to a method for transdifferentiation of human fibroblast to retinal pigment epithelium. The method comprises the steps of transferring various transcriptional regulation factors and reporter genes into mammal fibroblast, and then, culturing the fibroblast with various culturing mediums to obtain the retinal pigment epithelium.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
Method for inducing fibroblasts into neuronal cells by transdifferentiation and application of fibroblasts
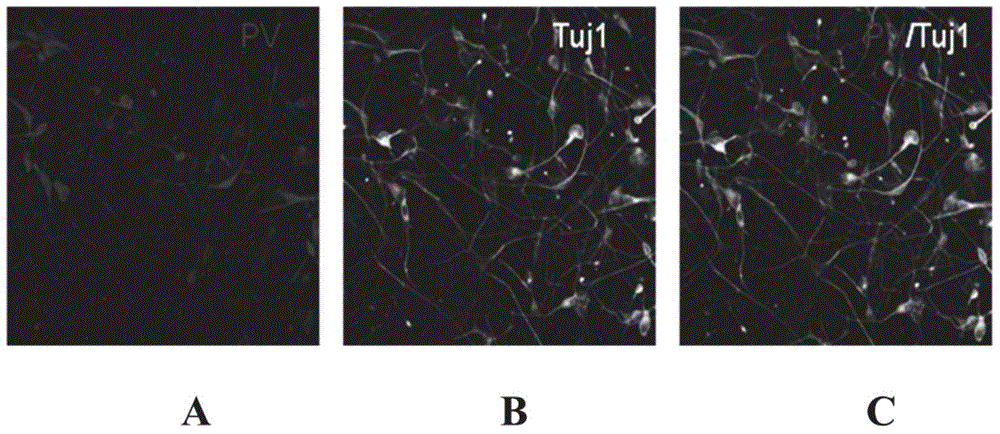
ActiveCN105331634AEfficiently obtainedConvenient treatmentNervous disorderNervous system cellsTransdifferentiationDisease injury
The invention provides a composition used for transforming fibroblasts into PV (parvalbumin) neurons, also provides a method for transforming the fibroblasts into neuronal cells and further provides the neuronal cells prepared according to the method. The composition contains one or more of Ascl1 gene and FSK (forskolin). The invention further provides application of the composition and the neuronal cells to preparation of medicines for treating nervous system diseases. According to experiments, the PV neuronal cells can be efficiently obtained by means of transdifferentiation to treat epilepsy after transplantation, memory improvement can be realized by reducing frequency of epileptic seizures, and accordingly a new approach is created for treatment of epilepsy and related diseases.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Cell reprogramming
PendingCN109072200ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsBlood/immune system cellsTransdifferentiationBiochemistry
The invention relates to methods and compositions for converting one cell type to another cell type. Specifically, the invention relates to transdifferentiation of a cell to a different cell type. Theinvention relates to a method for determining the transcription factors required for conversion of a source cell to a cell exhibiting at least one characteristic of a target cell type. The inventionalso relates to method of reprogramming or forward programming a source cell.
Owner:重组生物科技有限公司
Method for reprogramming spinal marrow astrocytes into motor neurons through induction
ActiveCN110283788ANervous system cellsCell culture active agentsTransdifferentiationStatistical analysis
The invention provides a method for reprogramming spinal marrow astrocytes into motor neurons through induction. The method comprises steps as follows: (1) primary rat astrocytes are subjected to pure culture; (2) 7 small molecule drugs including SB431542, LDN-193189, RA, bFGF, Purmorphamine, Forskolin and VPA are selected according to substances required in the stages of neuron induction and motor neuron formation and development, and the astrocytes are induced and reprogrammed in vitro through the small molecule drugs; (3) the reprogramming and differentiation conditions of the astrocytes to the motor neurons are analyzed through observation of morphologic change of cells and methods of chemical technology analysis of immunofluorescent cells, real-time fluorescent quantitative PCR analysis and statistical analysis. The rat astrocytes can be successfully induced and reprogrammed into the motor neutrons in vitro through small molecular drug composition, and the transdifferentiation exceeds 75%; in-situ direct reprogramming of the astrocytes to the neurons is a possibly comparatively feasible thought in SCI (spinal cord injury) repairing and functional reconstruction treatment.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
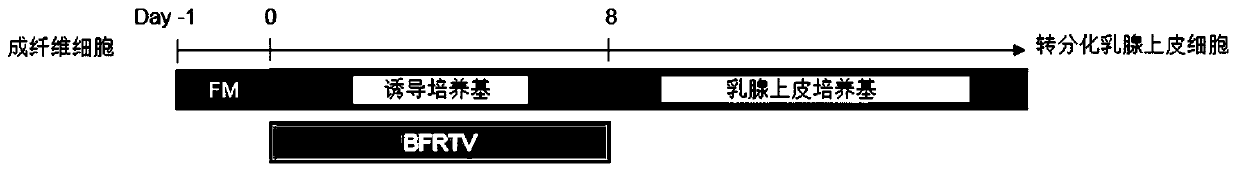
Method for transdifferentiation of somatic cells into mammary epithelial cells by using small-molecule compound through in-vitro induction
ActiveCN110951673AShort timeAvoid limited proliferative capacity in vitroEpidermal cells/skin cellsCulture processTransdifferentiationFibroblastic cell
The invention provides a method for transdifferentiation of somatic cells into mammary epithelial cells by using a small-molecule compound through in-vitro induction. Expression of TGFbeta R1 and related loci thereof is inhibited, and transdifferentiation of somatic cells into mammary epithelial cells through in-vitro induction is achieved. By adopting the method, the blank of a technique for transdifferentiation of fibroblast into mammary epithelial cells through induction of the small-molecule compound is made up, and a research platform for research of in-vitro research on mammary gland bioreactors, mammary development and differentiation, breast cancer and ransdifferentiation of fibroblast into other types of functional cells is provided.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV +1
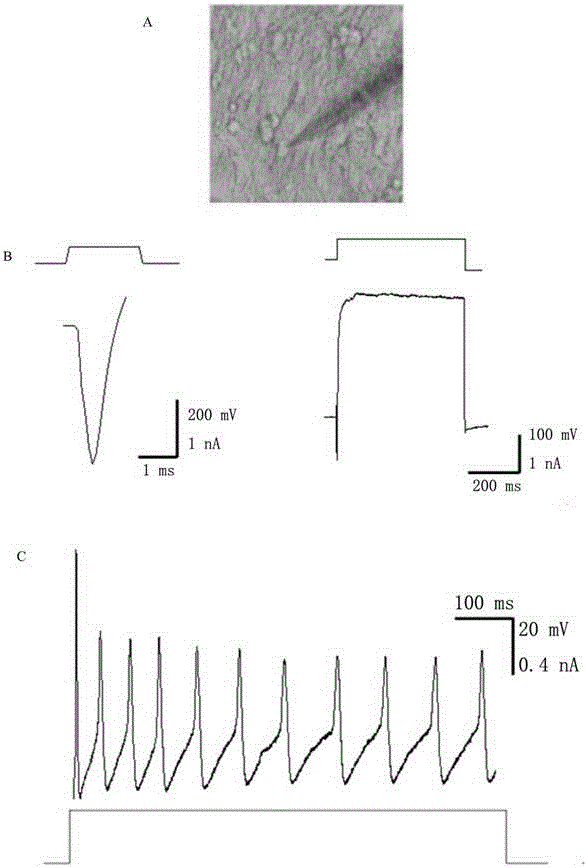
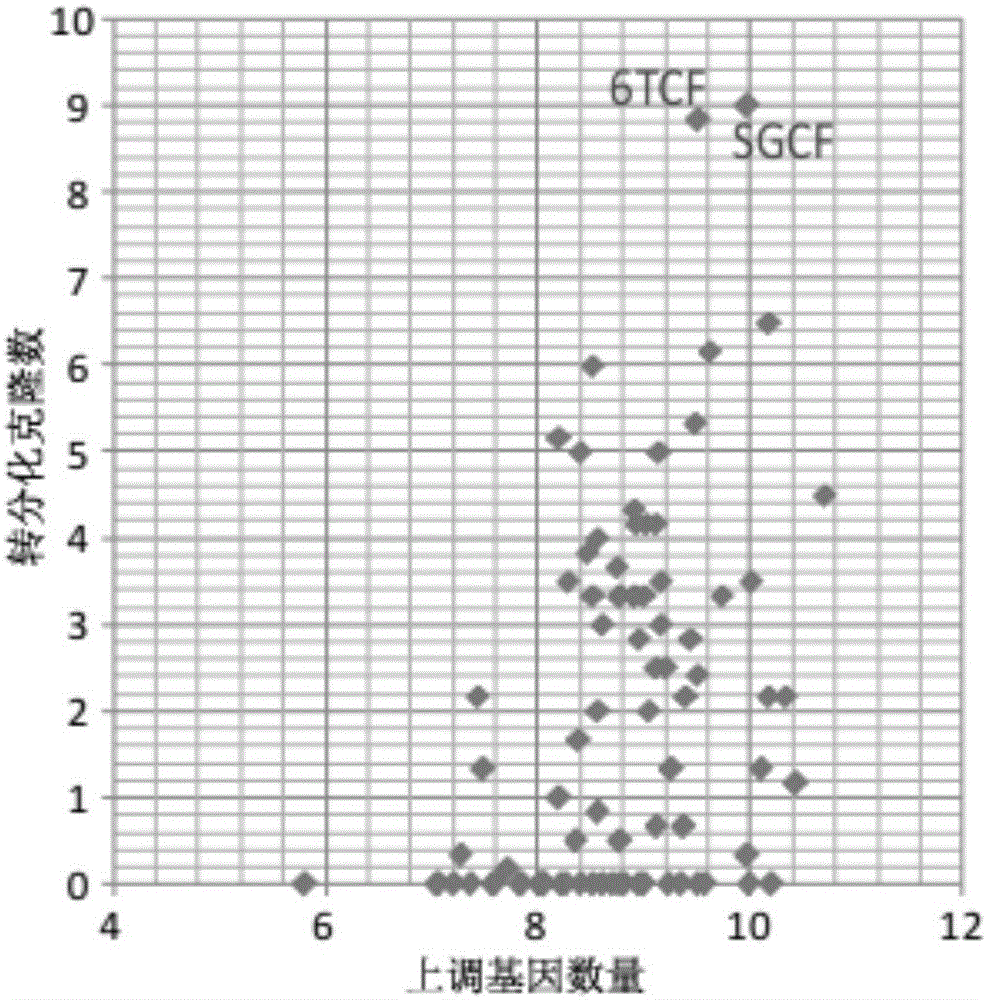
Method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts to nerve cells
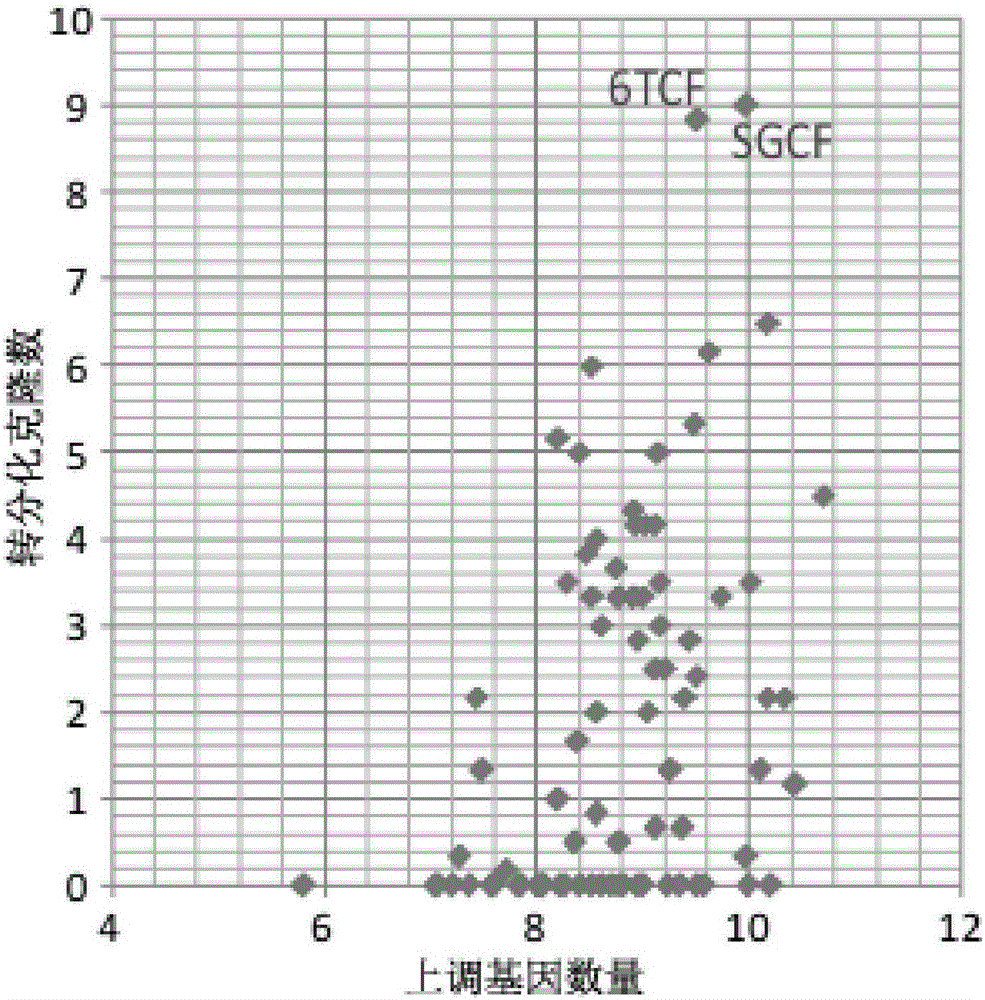
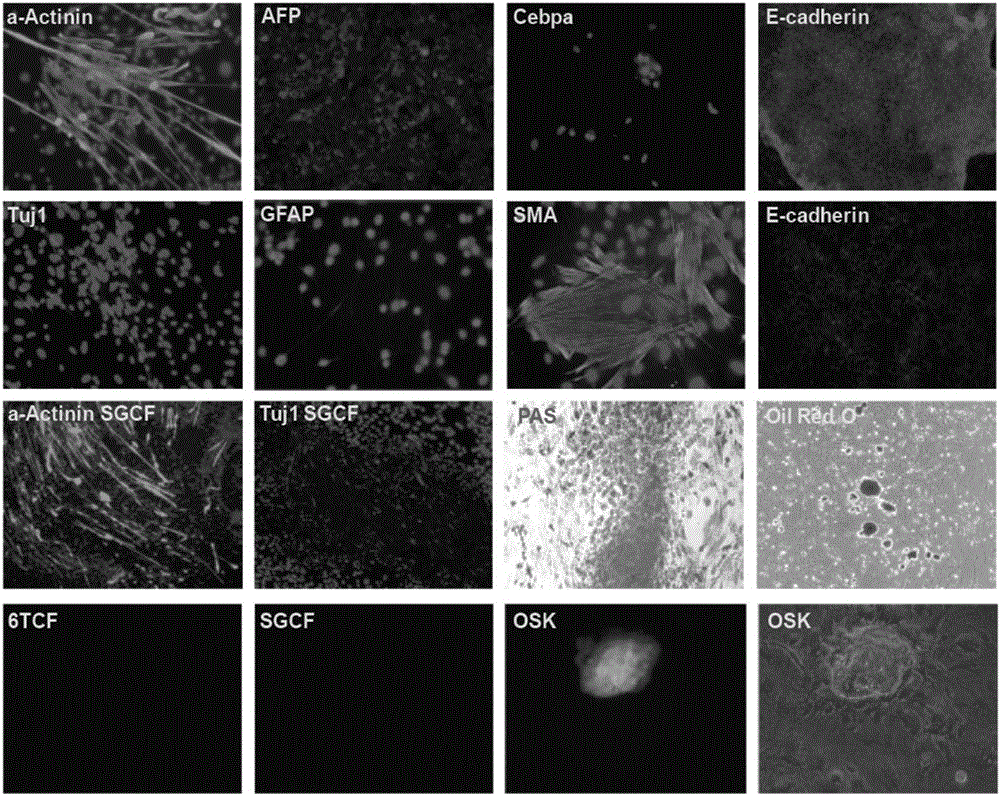
The invention discloses a method for inducing transdifferentiation of fibroblasts to nerve cells. The method comprises the following steps: (1) culturing the fibroblasts for 20 to 30 hours; (2) transferring the fibroblasts into a culture medium containing an inducing micromolecular combination 6TCF, continuing to carry out culturing for 6 to 8 days, and replacing the culture medium once every 2 to 4 days during the culturing; (3) then, transferring the fibroblasts into a culture medium containing inducing micromolecular combinations 6TCF and 8CFV, continuing to carry out culturing for 7 to 16 days, and replacing the culture medium once every 2 to 4 days during the culturing, thereby obtaining the nerve cells, wherein 6 means E61541, T means tranylcypromine, C means CHIR99021, F means forskolin, 8 means A-83-01 and V means valproic acid. According to the method, through adding the inducing micromolecular combinations into the culture media, the fibroblasts can be trans-differentiated into the nerve cells through inducing, and the obtained nerve cells have specific molecular tags of normal nerve cells and have functions of the normal nerve cells, so that a new way is provided for solving the problem in cell sources of regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com