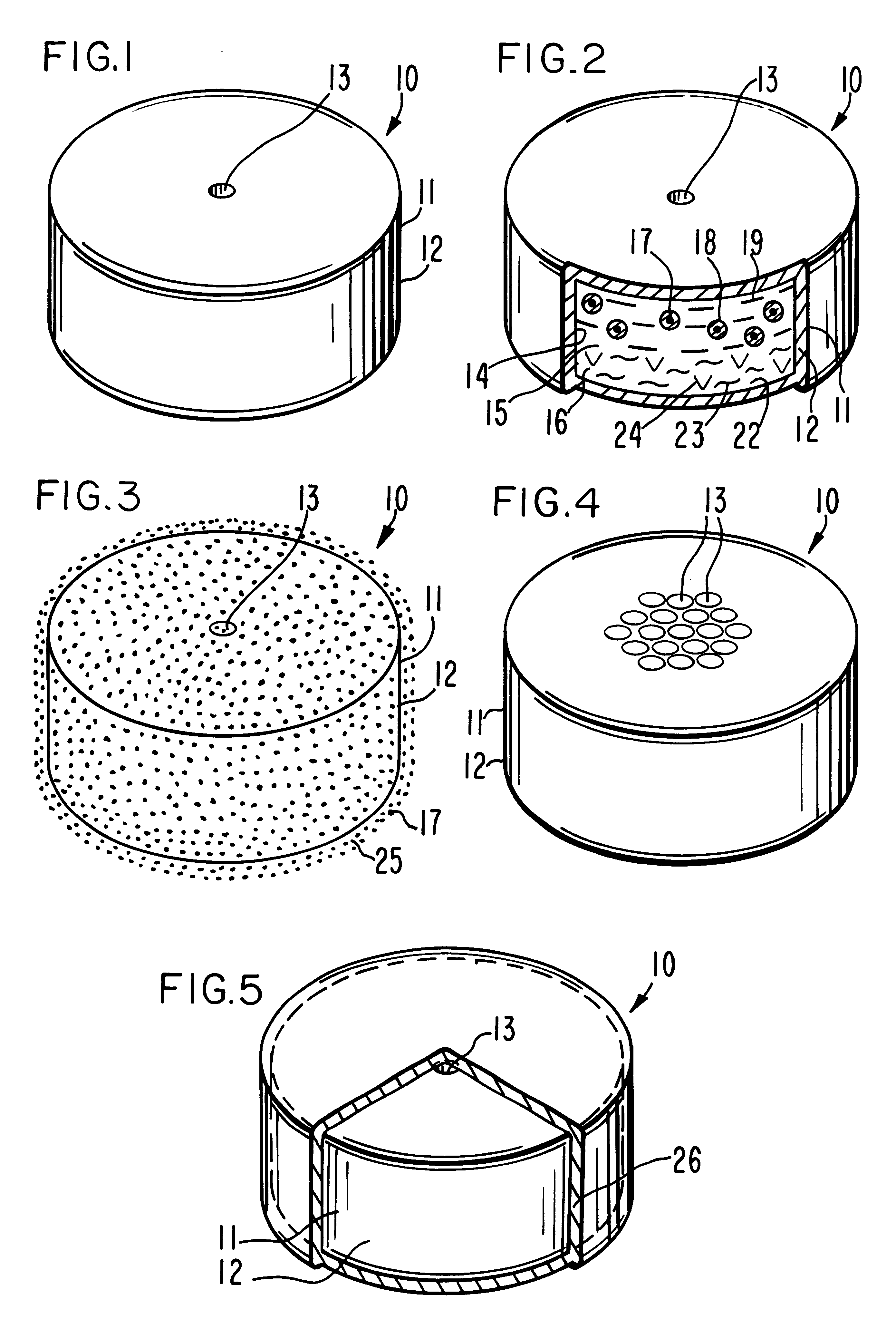
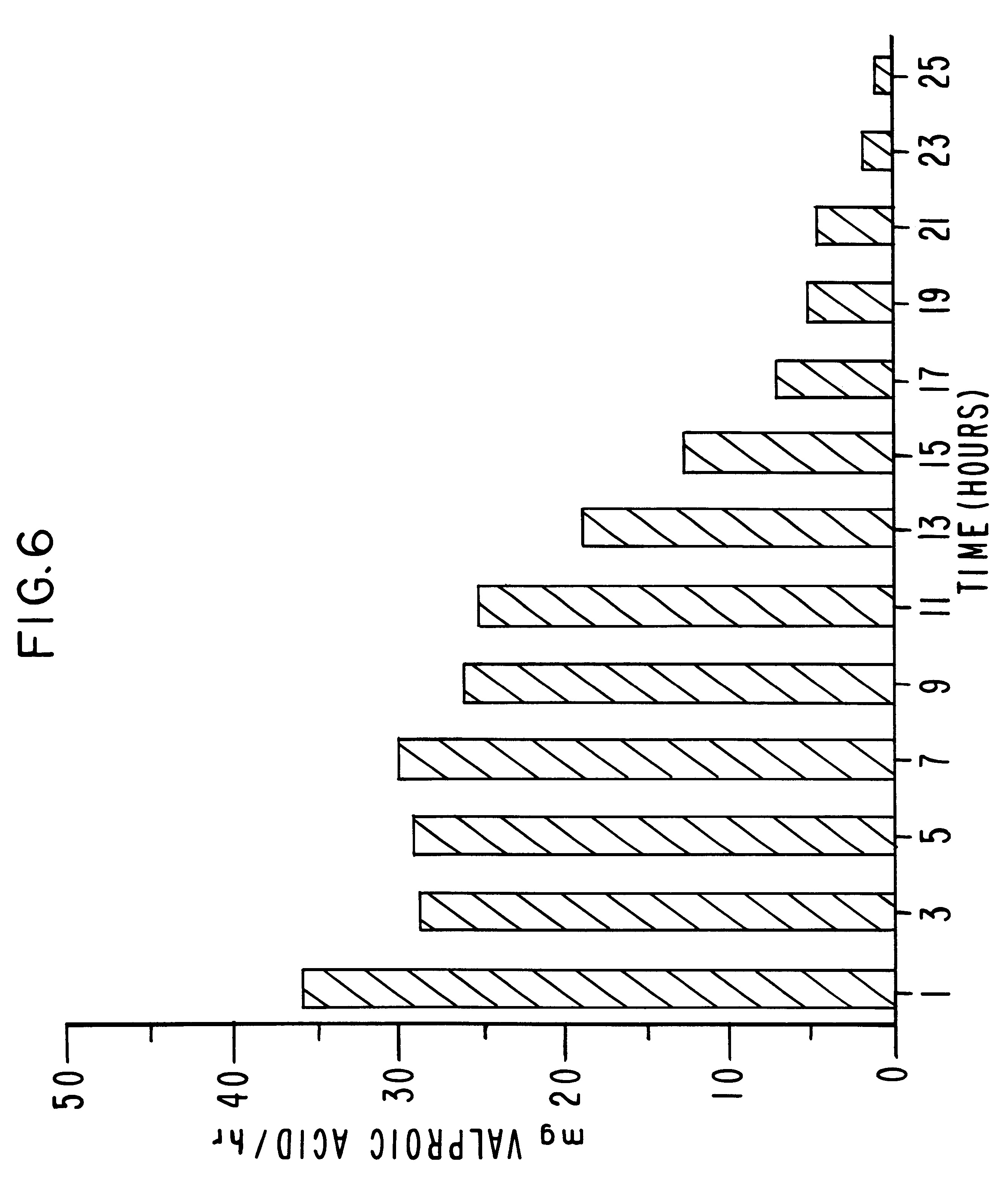
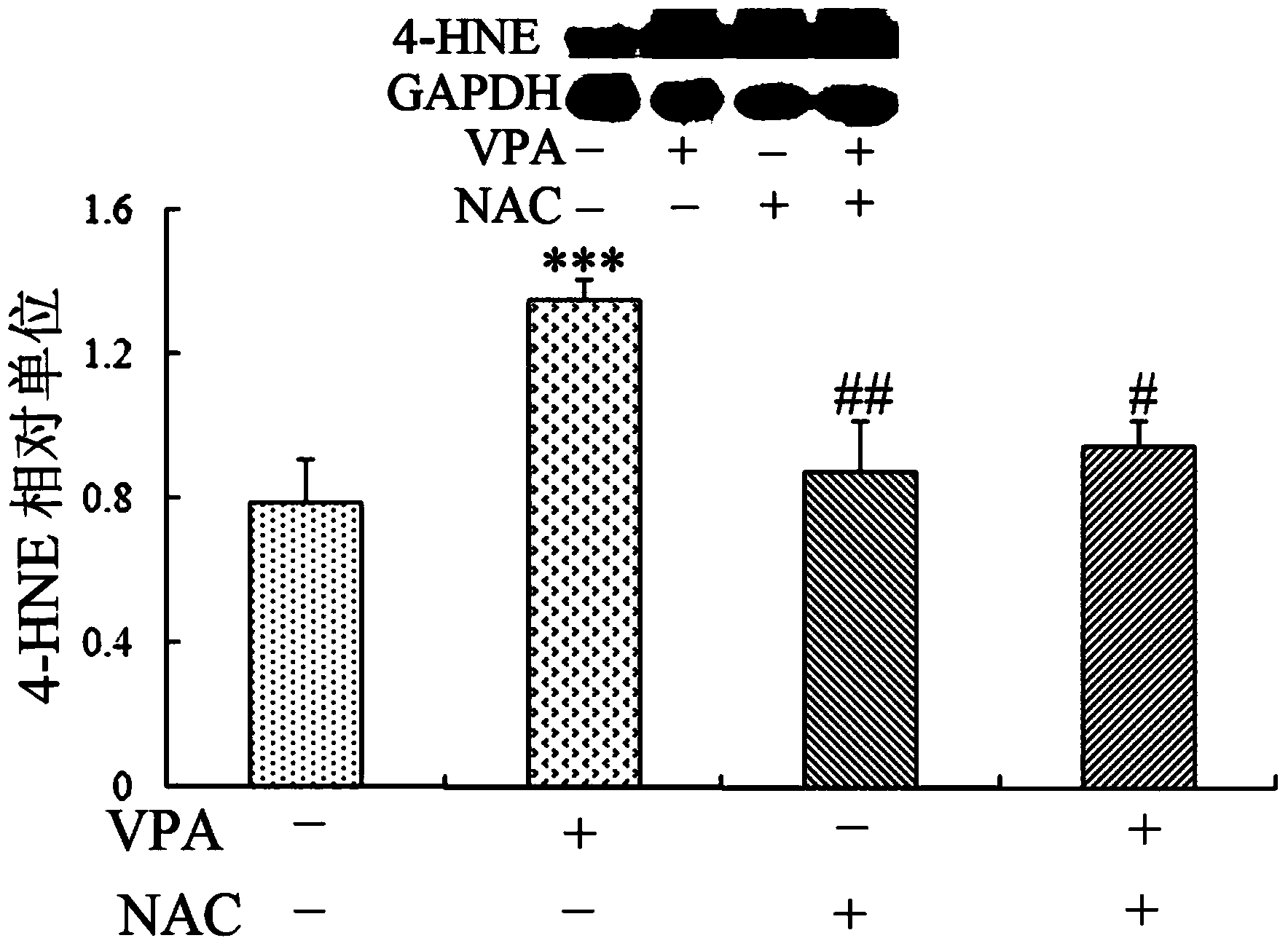
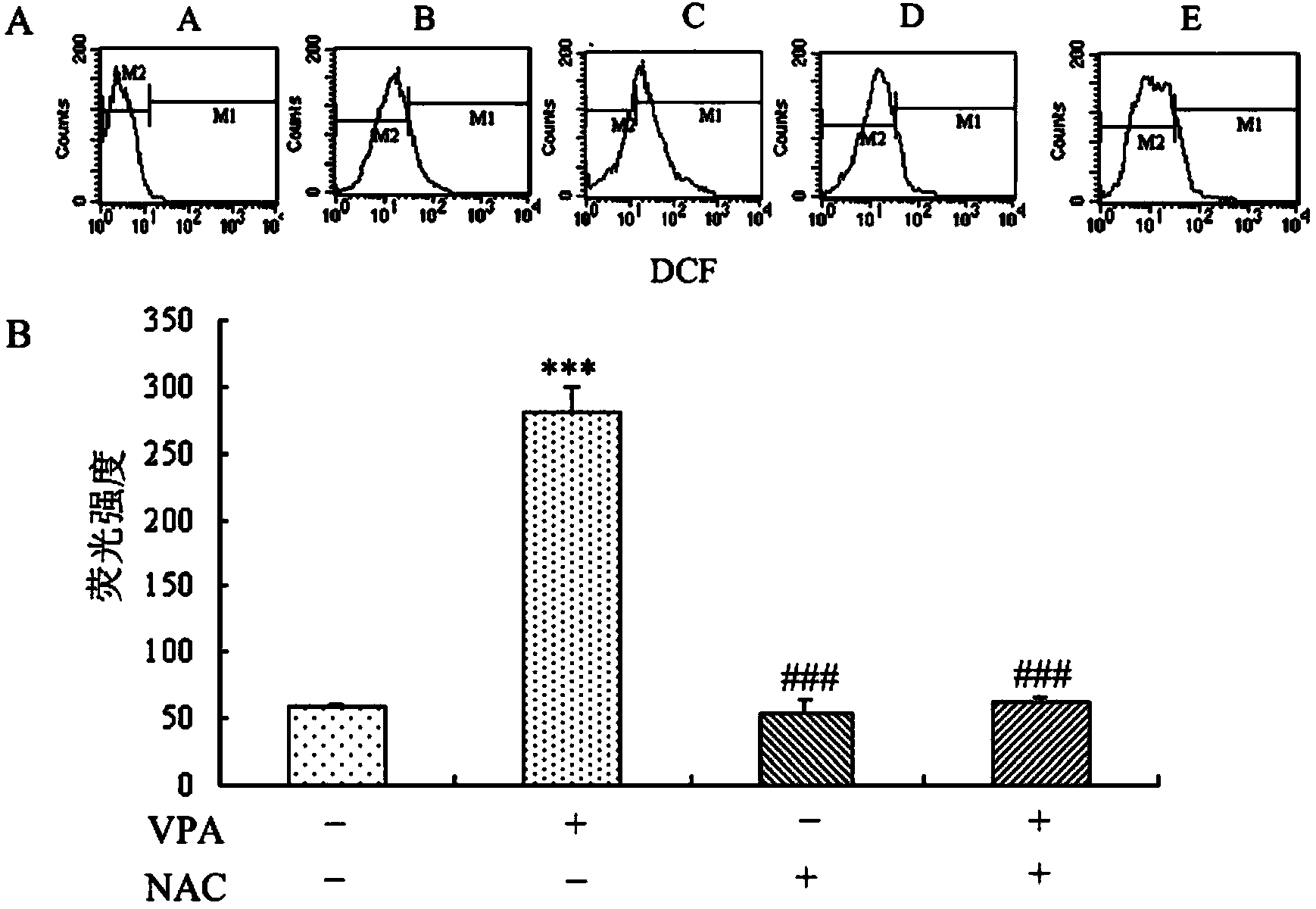
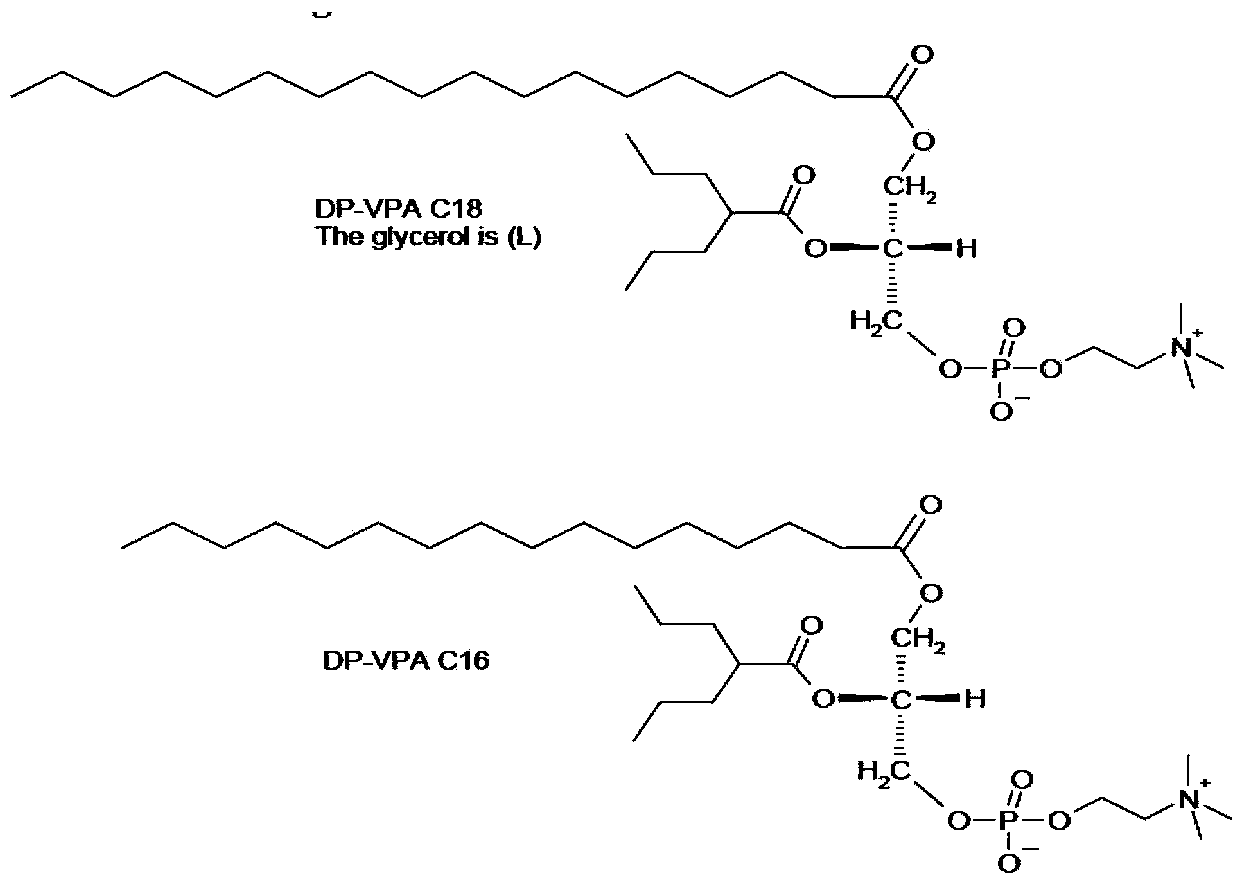
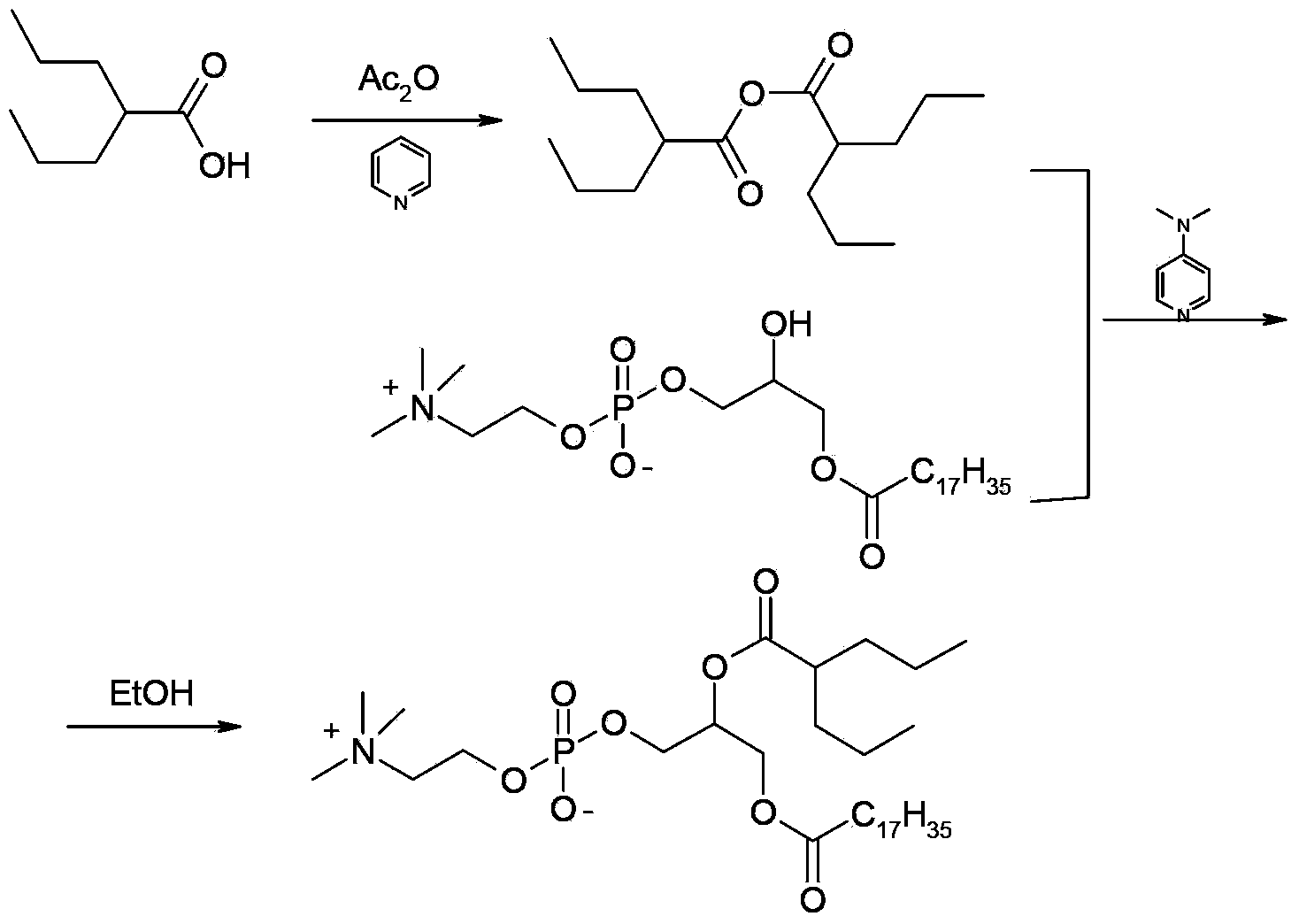
Patents
Literature
205 results about "Valproic Acid" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
This medication is used to treat seizure disorders, mental/mood conditions (such as manic phase of bipolar disorder), and to prevent migraine headaches.
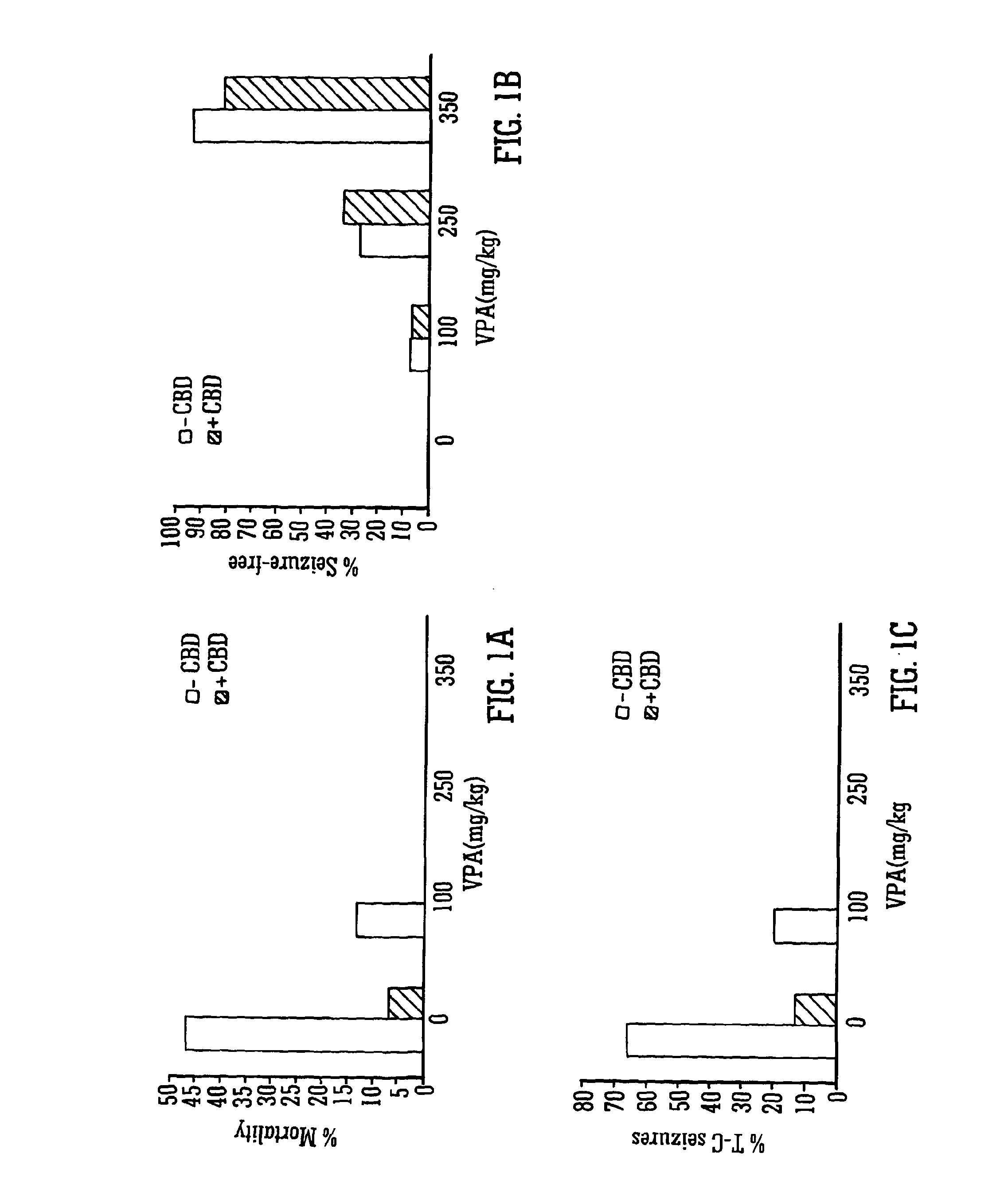
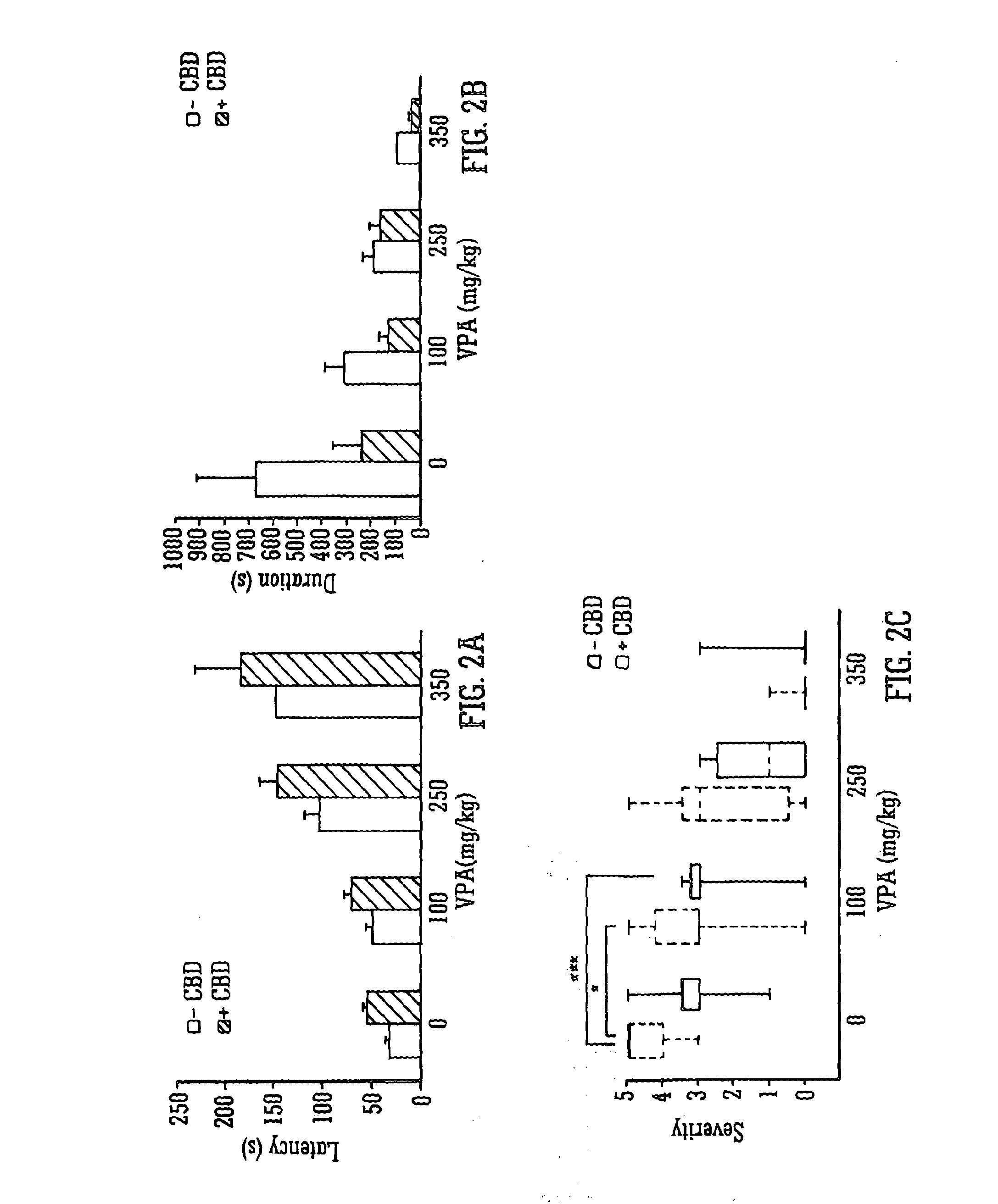
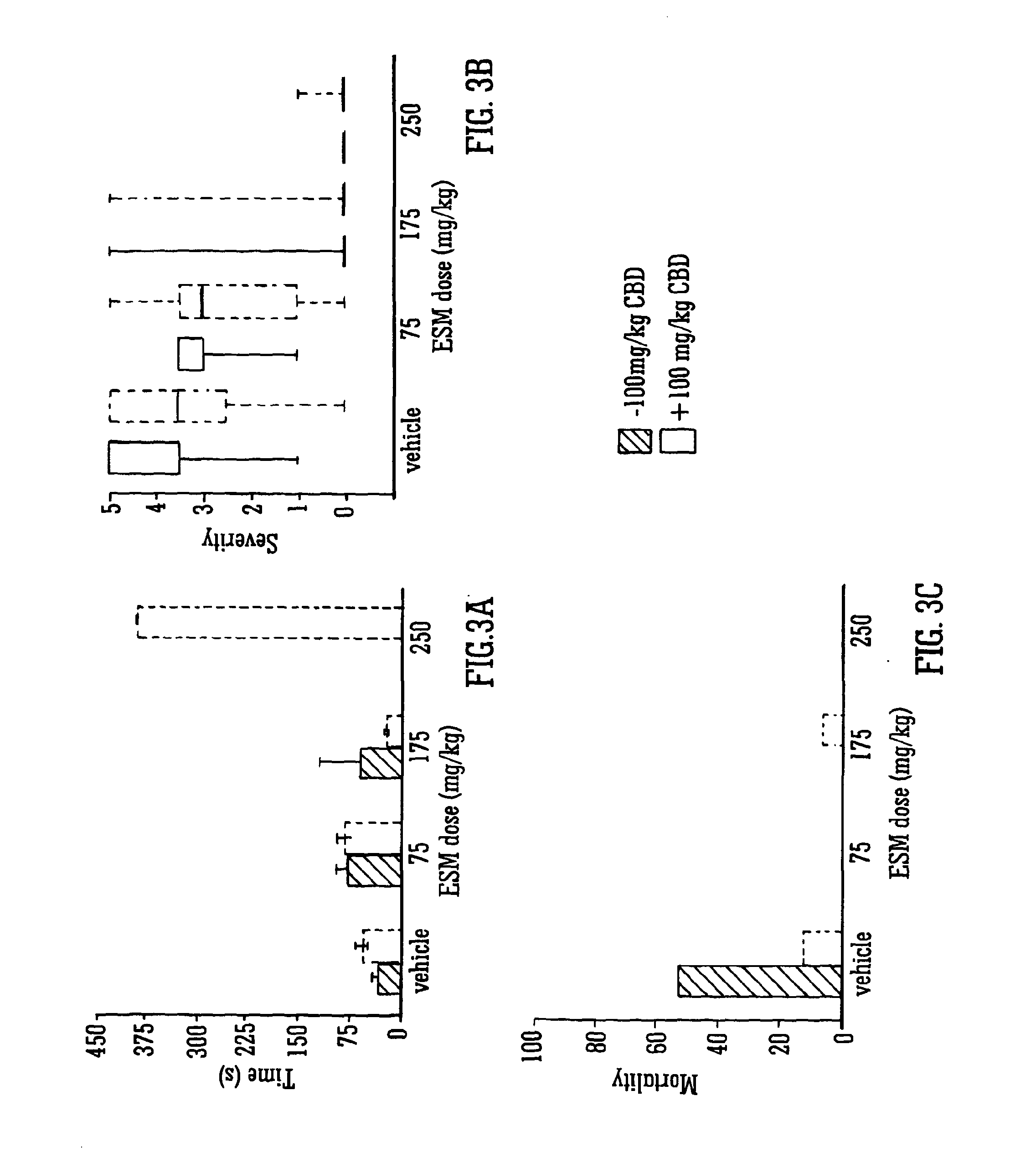
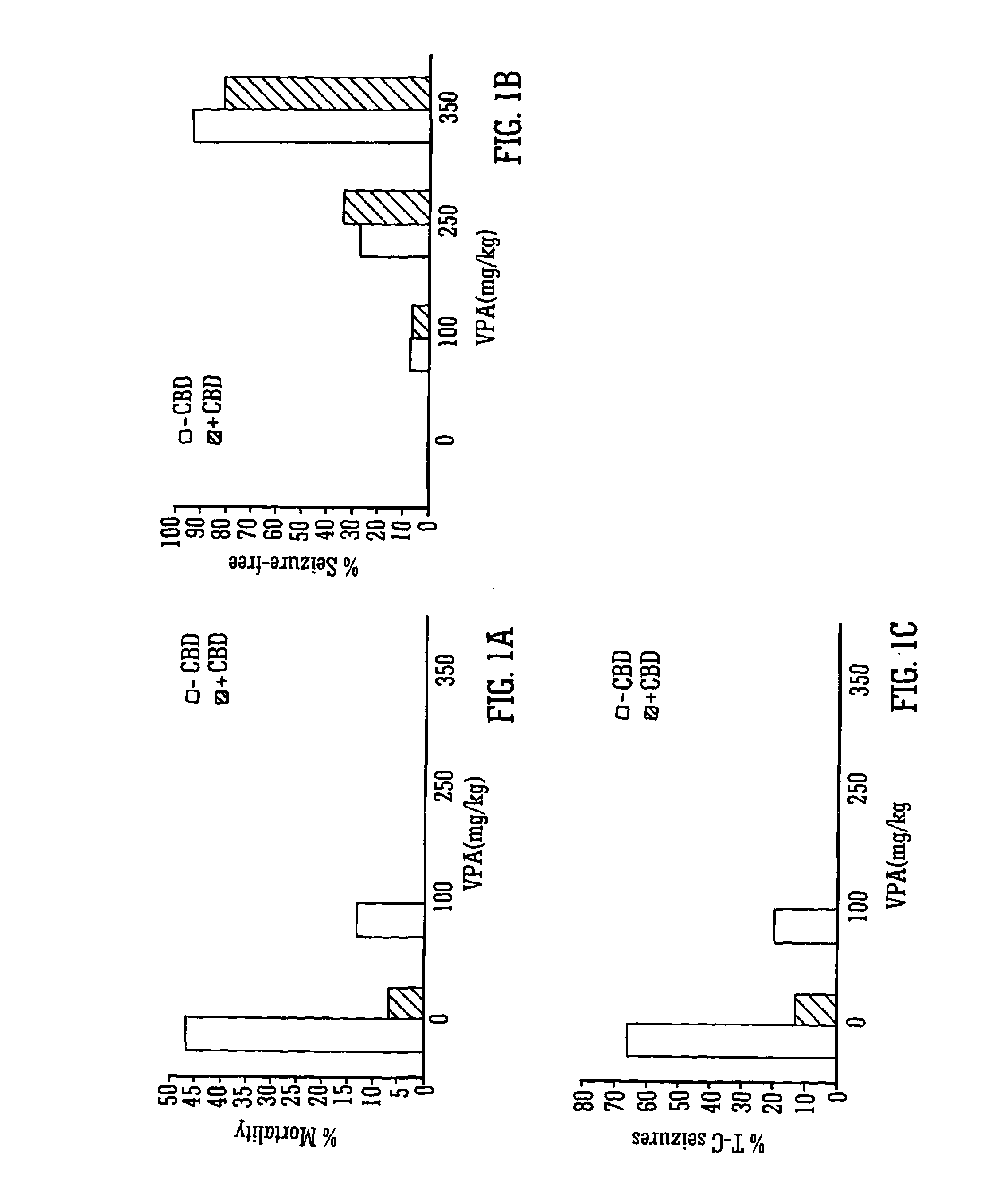
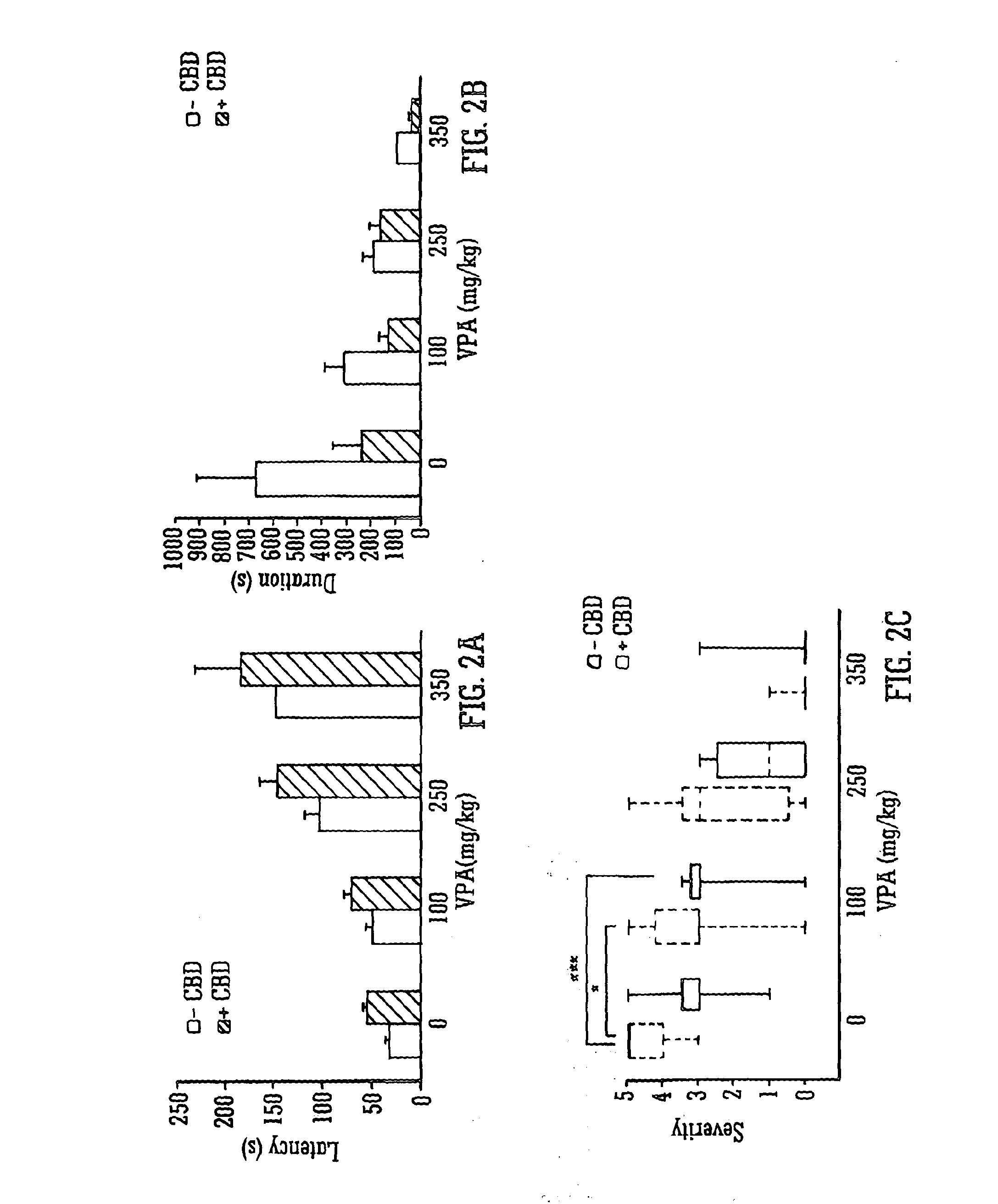
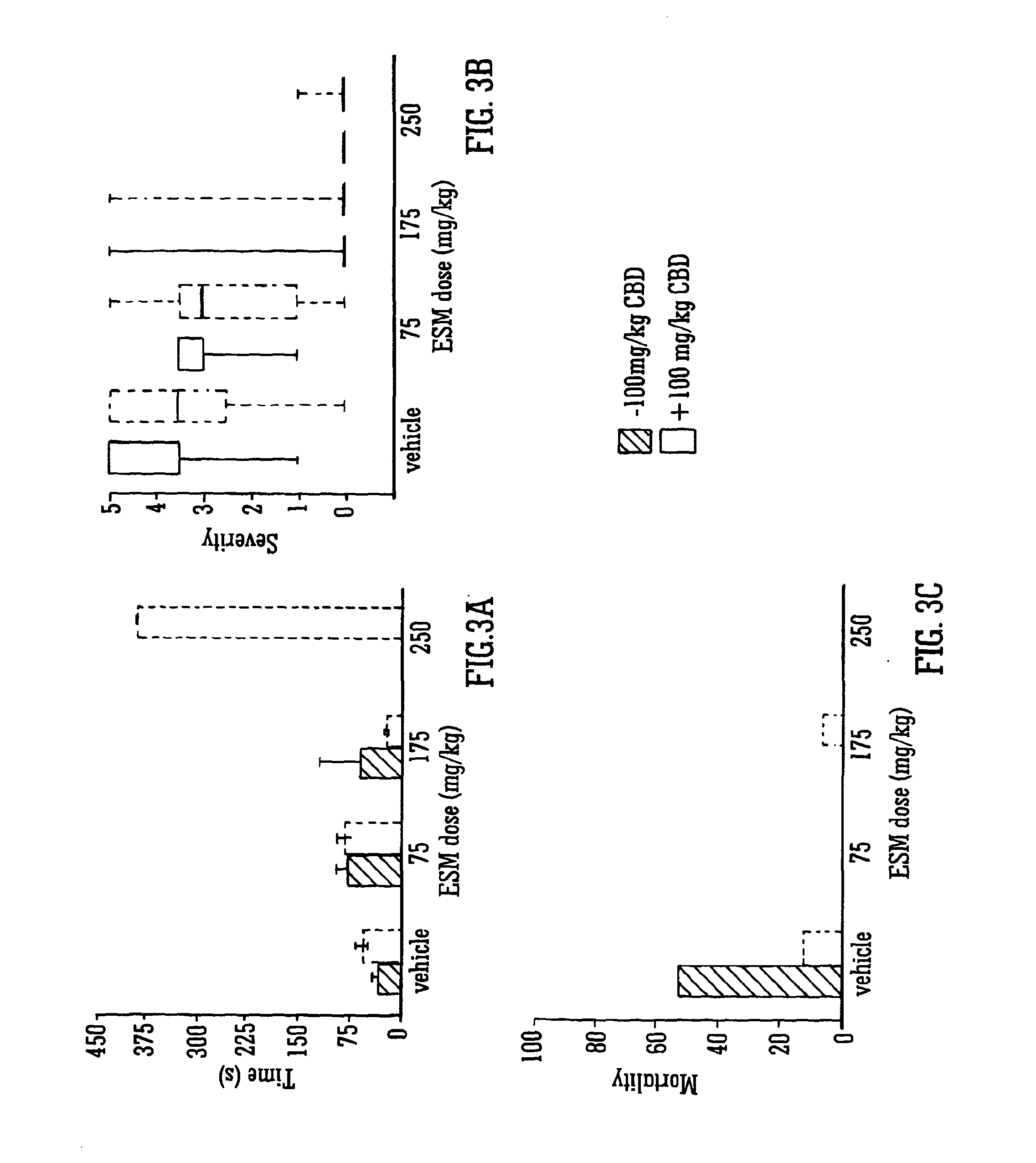
Use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) in combination with a standard Anti-epileptic drug (SAED) in the treatment of epilepsy
InactiveUS20130296398A1Reduce severityReduce mortalityBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidCannabidiol
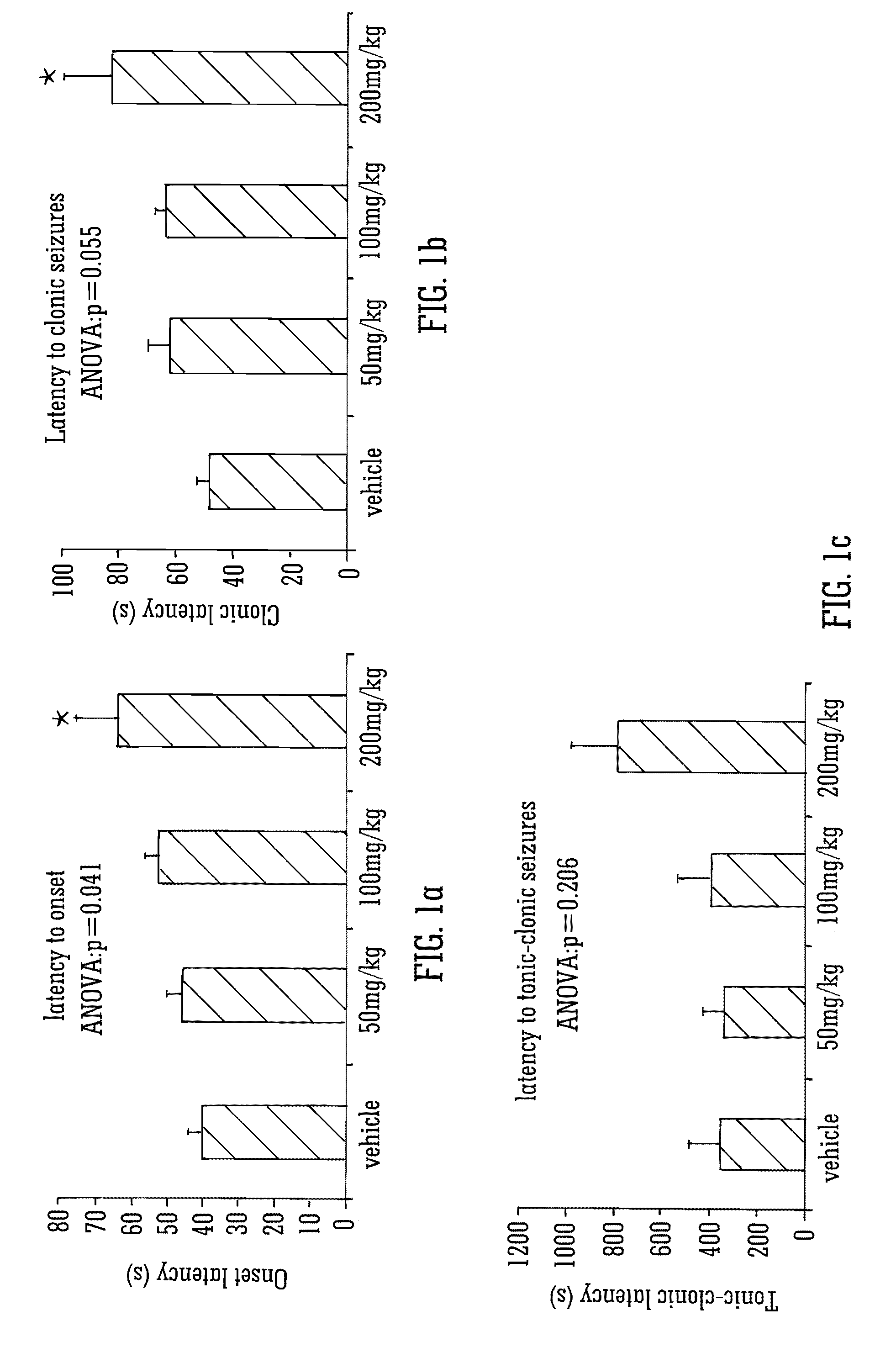
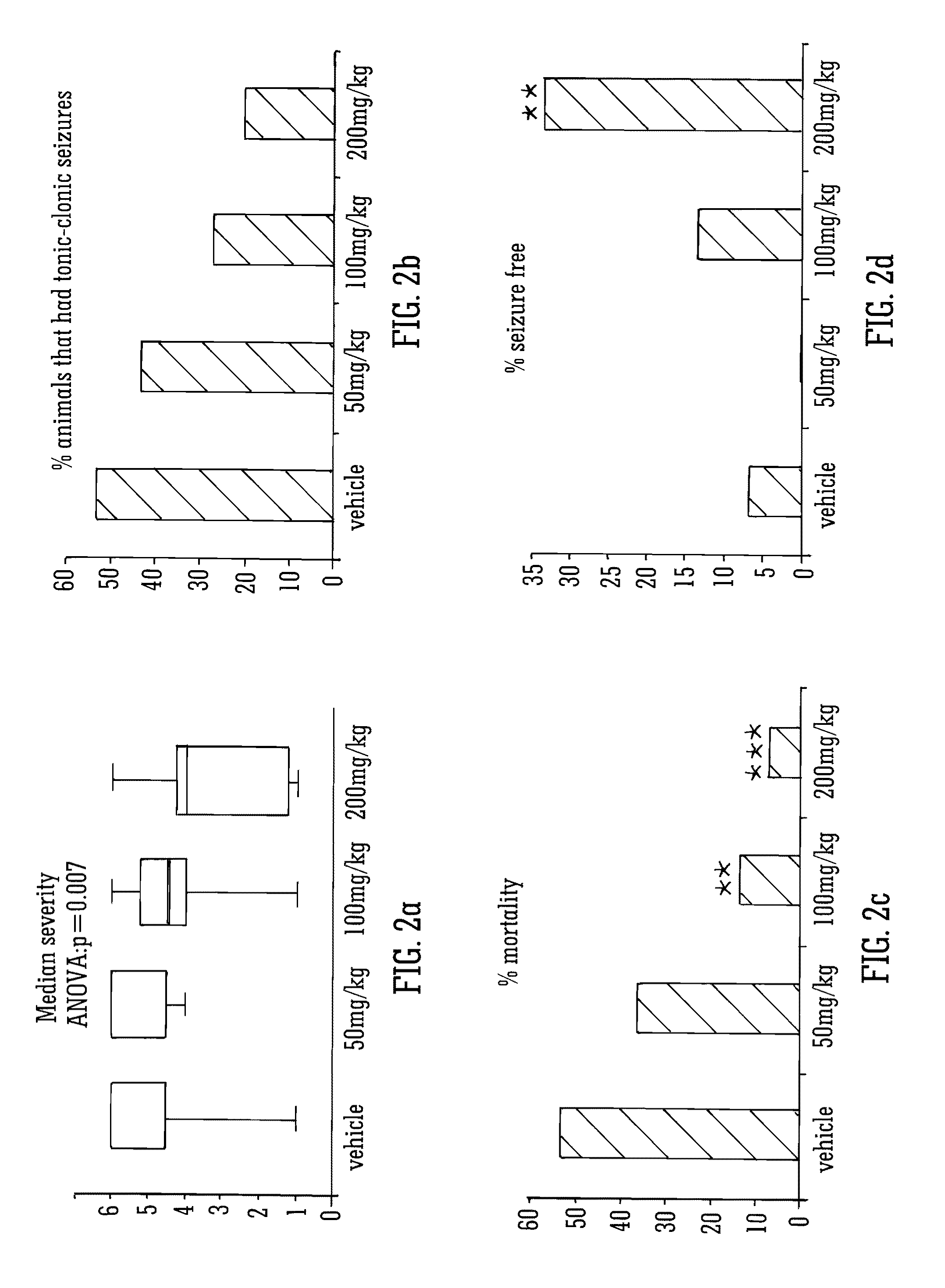
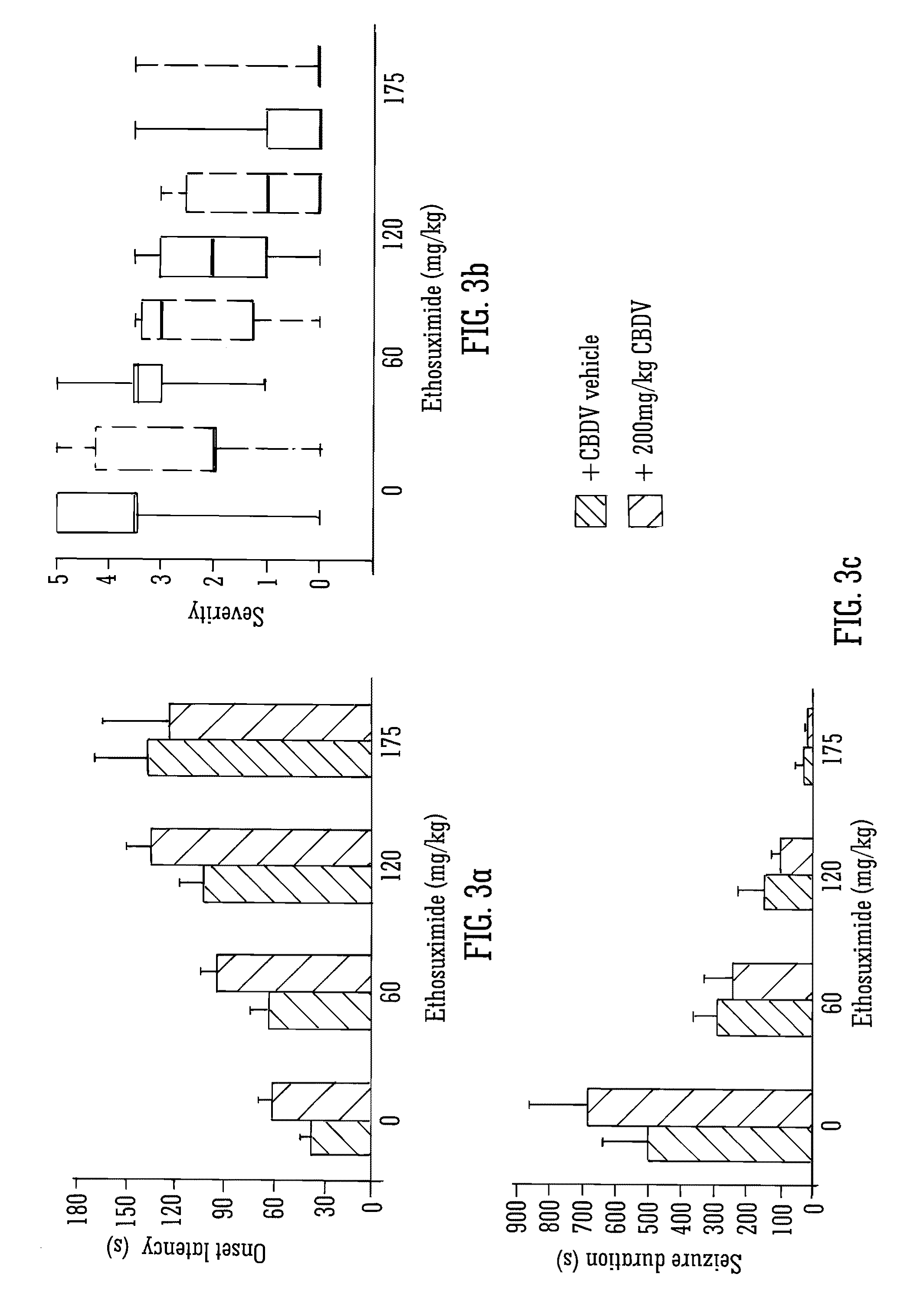
The invention relates to the use of cannabidiol (CBD), at a dose of greater than 300 mg / day, in combination with a standard anti-epileptic drug (SAED) which acts via sodium or calcium channels, for use in the treatment of epilepsy. The SAED is preferably one which•modifies low-threshold or transient neuronal calcium currents,or•reduces high-frequency neuronal firing and sodium-dependent action potentials and enhances GABA effects. Preferred SAEDs are ethosuximide and valproate.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD +1
Use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidiol (CBD) in combination with a standard Anti-epileptic drug (SAED) in the treatment of epilepsy
InactiveUS20140155456A9Reduces high-frequency neuronal firingGood effectBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidCannabidiol
The invention relates to the use of cannabidiol (CBD), at a dose of greater than 300 mg / day, in combination with a standard anti-epileptic drug (SAED) which acts via sodium or calcium channels, for use in the treatment of epilepsy. The SAED is preferably one which•modifies low-threshold or transient neuronal calcium currents,or•reduces high-frequency neuronal firing and sodium-dependent action potentials and enhances GABA effects. Preferred SAEDs are ethosuximide and valproate.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD +1
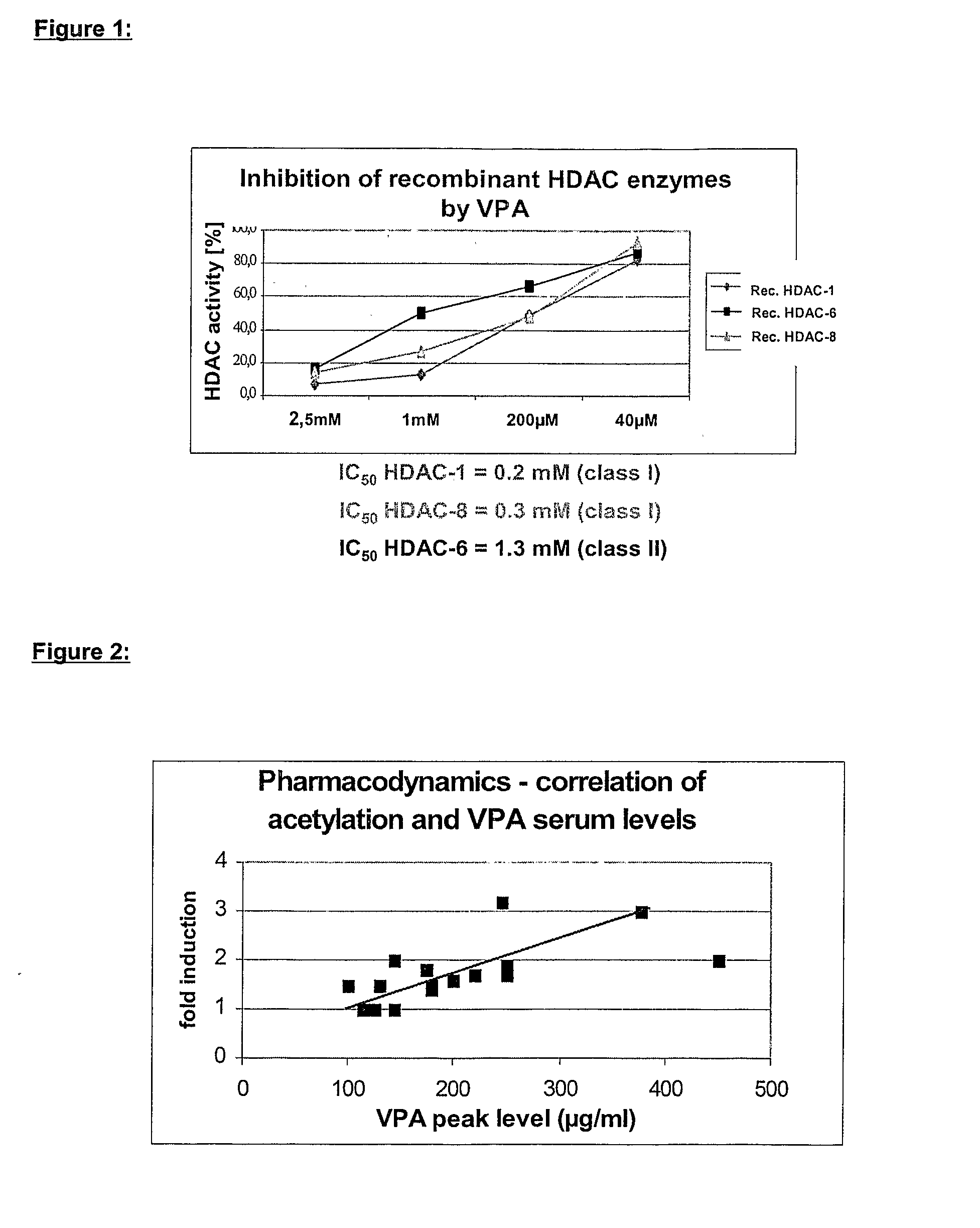
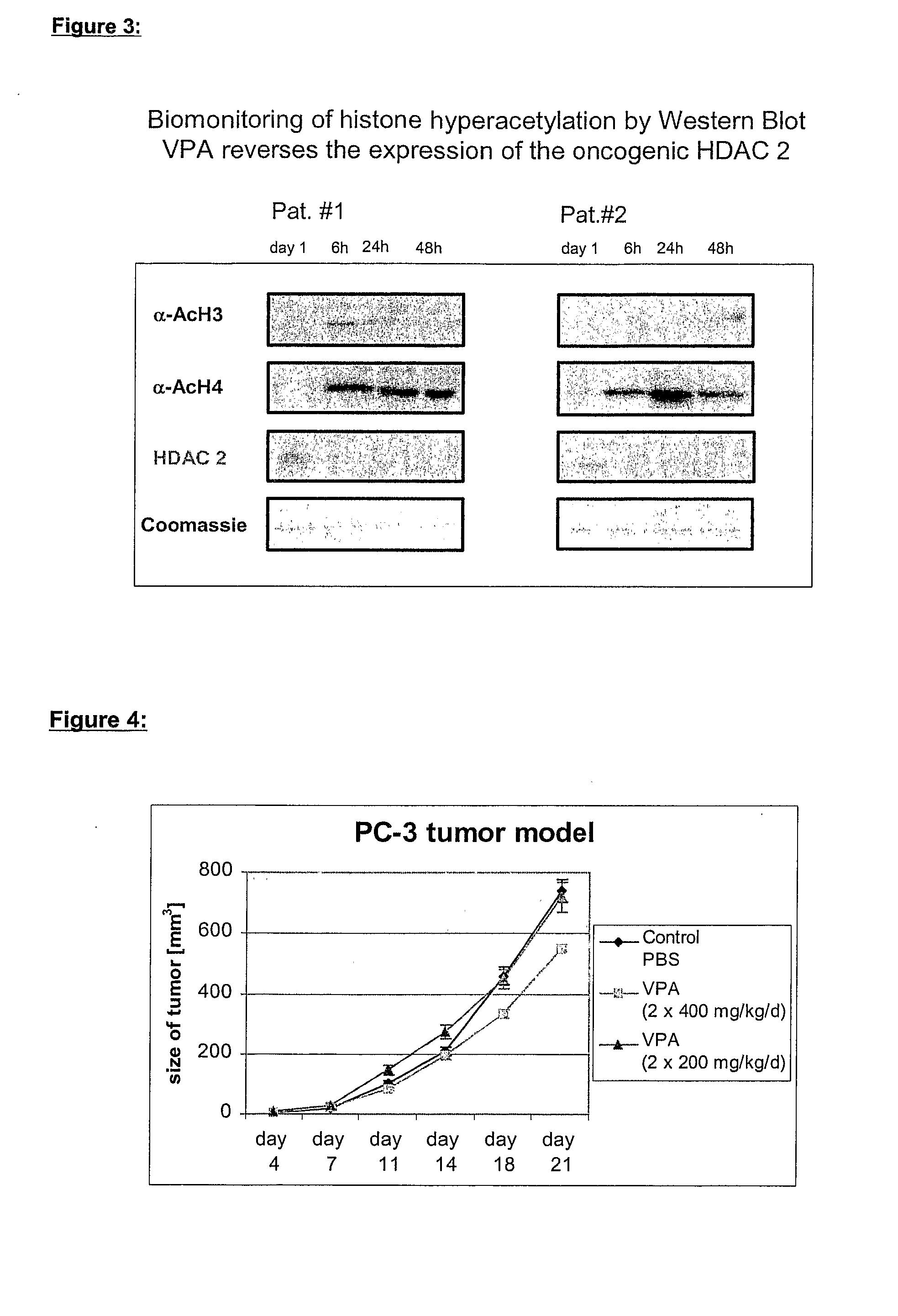
Formulation comprising histone deacetylase inhibitors
InactiveUS20070232528A1Inhibition becomes largerInhibit HDAC target enzymesBiocideSenses disorderValproic AcidApoptosis
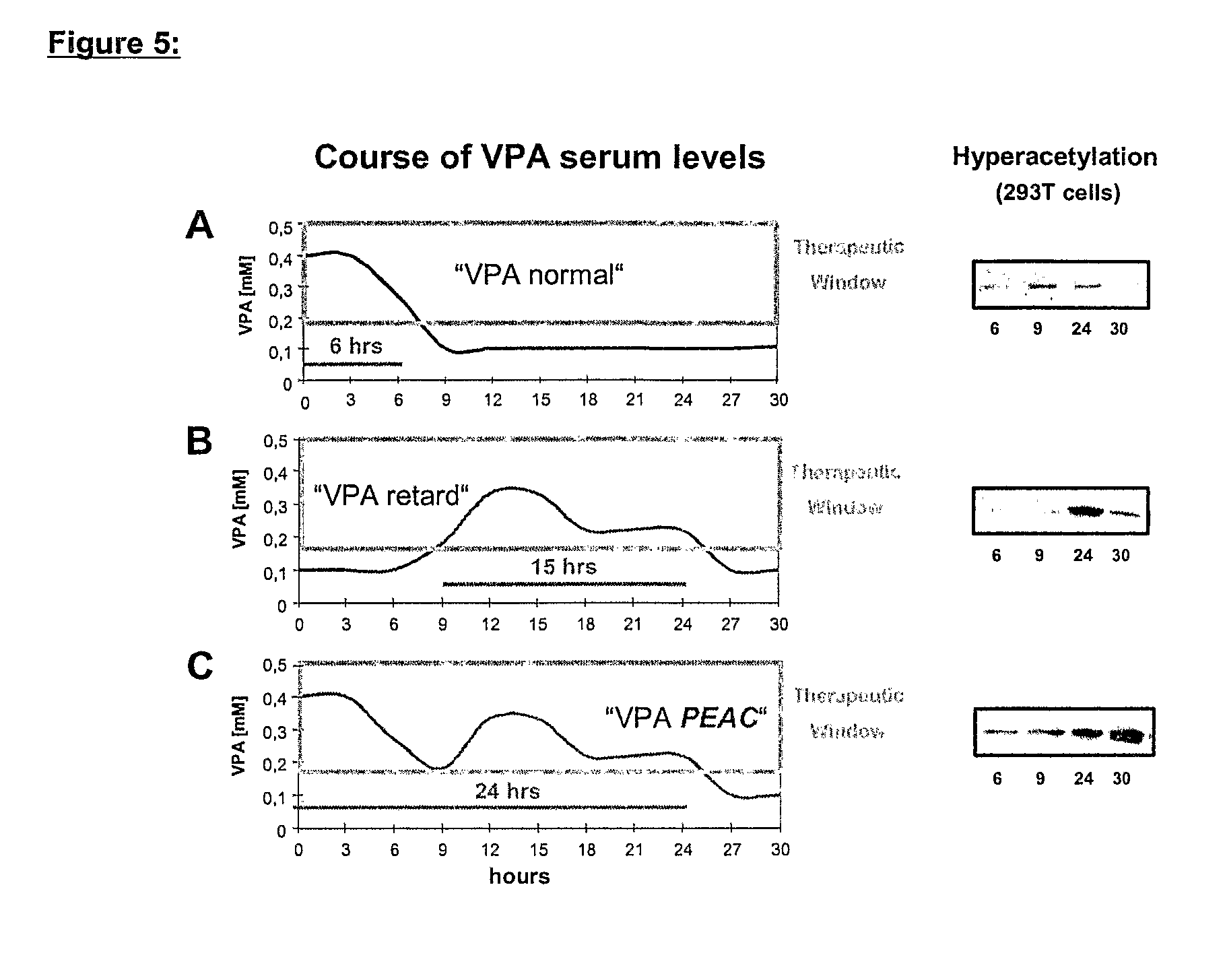
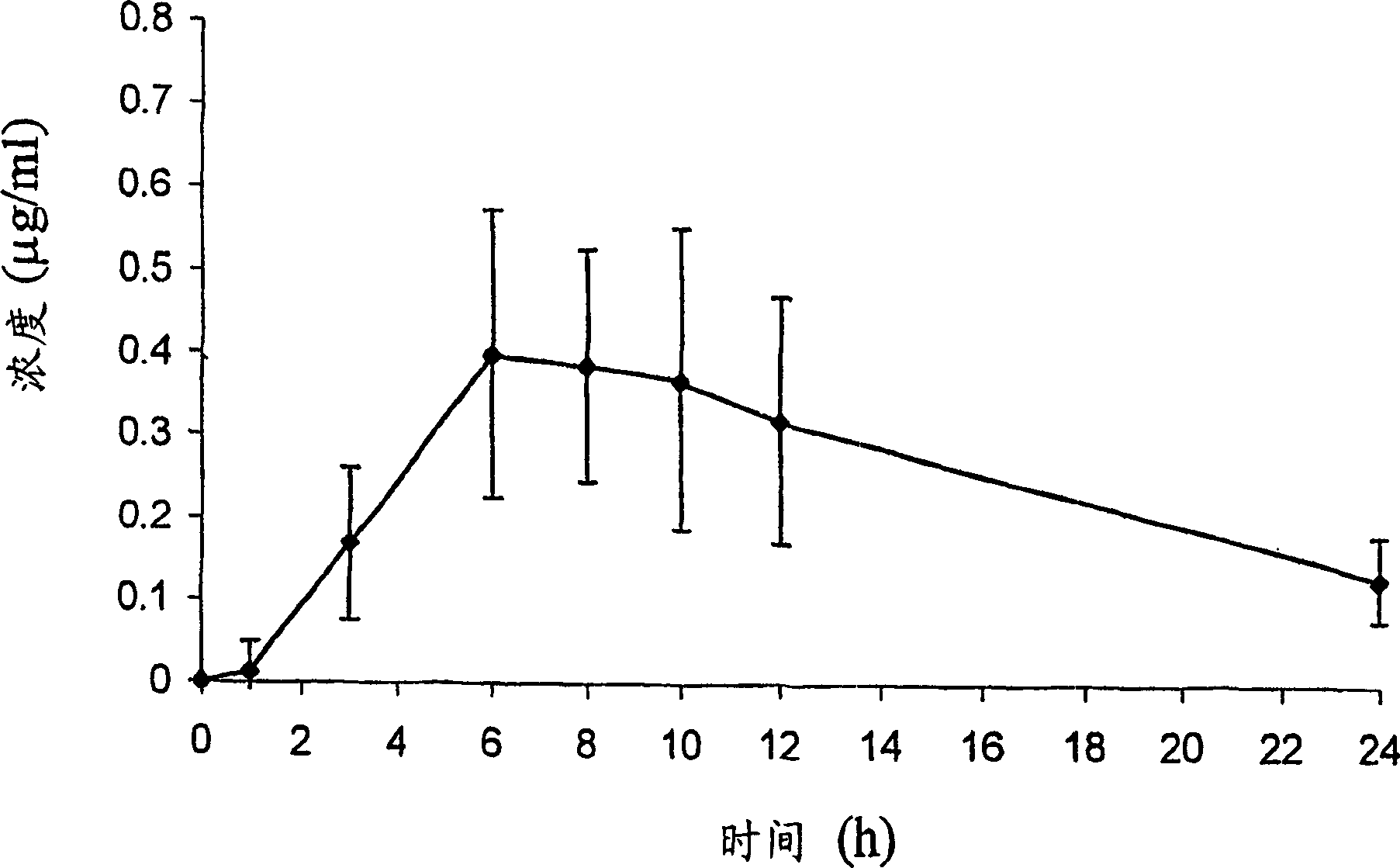
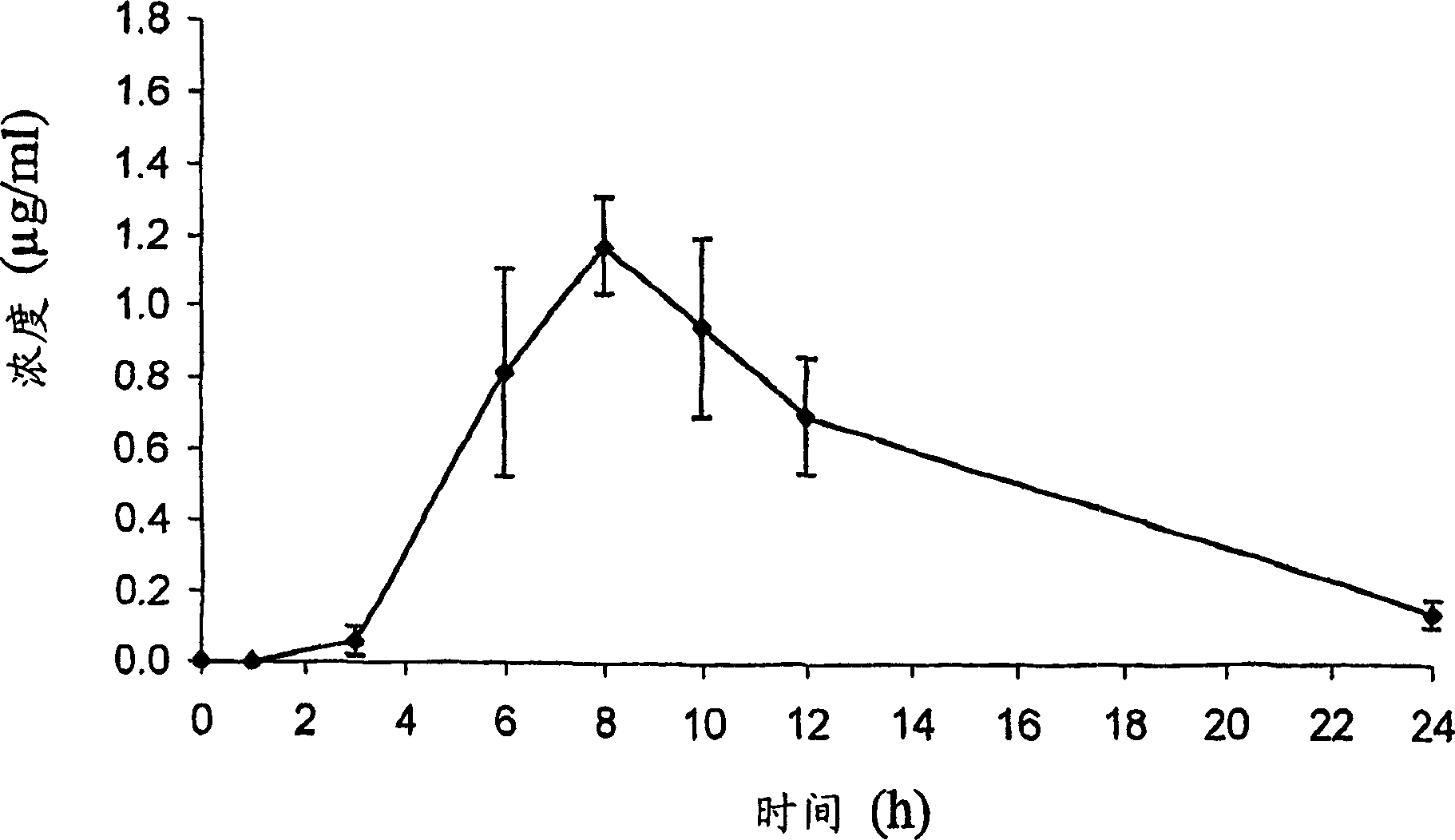
The present invention relates to an orally available galenics formulation of Valproic Acid or derivatives thereof exhibiting a specific bi-phasic pharmacokinetic profile optimized for maximum inhibition of histone deacetylases in a therapeutic setting. This specific galenics formulation is designed for the treatment of malignant diseases and diseases associated with hypoacetylation of histones or in which induction of hyperacetylation has a beneficial effect, e.g., by induction of differentiation and / or apoptosis. Due to the bi-phasic release pattern the resulting pharmacokinetic profile is able to inhibit HDAC target enzymes most efficiently and to subsequently induce histone hyperacetylation in a rapid as well as a long-lasting fashion. This profile secures the efficient modulation of a desired target gene expression profile which contributes to the therapeutic benefit.
Owner:TOPOTARGET GERMANY AG +1
Use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin (CBDV) in the treatment of epilepsy
ActiveUS9125859B2Growth inhibitionReduces high-frequency neuronal firingBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidPhenobarbital
This invention relates to the use of the phytocannabinoid cannabidivarin (CBDV) and combinations of the phytocannabinoid CBDV with tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) and cannabidiol (CBD) in the treatment of epilepsy. The invention further relates to the use of the phytocannabinoid CBDV in combination with standard anti-epileptic drugs (SAEDs). Preferably the SAED is one of ethosuximide, valproate or phenobarbital.
Owner:GW PHARMA LTD
Topical Use of Valproic Acid for the Prevention or Treatment of Skin Disorders
The present invention relates to a topically applicable formulation containing Valproic Acid or a derivative thereof which can be used alone or in combination with topically applicable formulations of retinoids or of nuclear receptor ligands, or of chemotherapeutic agents (e.g. 5-Fluorouracil). The formulation is useful for the topical treatment of cancerous skin disorders, such as Basal Cell Carcinoma, Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Keratoakantoma, Bowen Disease, cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma and also for the topical treatment of pre-malignant lesions, and of inflammations of the skin and / or mucosa. The invention also relates to the use of this topically applicable formulation for the protection from UV light and for the treatment of sun burn. The invention includes the use of VPA for the manufacture of a clinically used medicament for the topical treatment of the human diseases listed above.
Owner:TOPOTARGET GERMANY AG
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
InactiveUS20060074451A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateSpinal electrodesHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Combination therapy comprising the use of protein kinase C modulators and Histone Deacetylase inhibitors for treating HIV-1 latency
InactiveUS20100166806A1Adverse propertyPrevent HIV-1-induced cytotoxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptaseHydroxamic acid
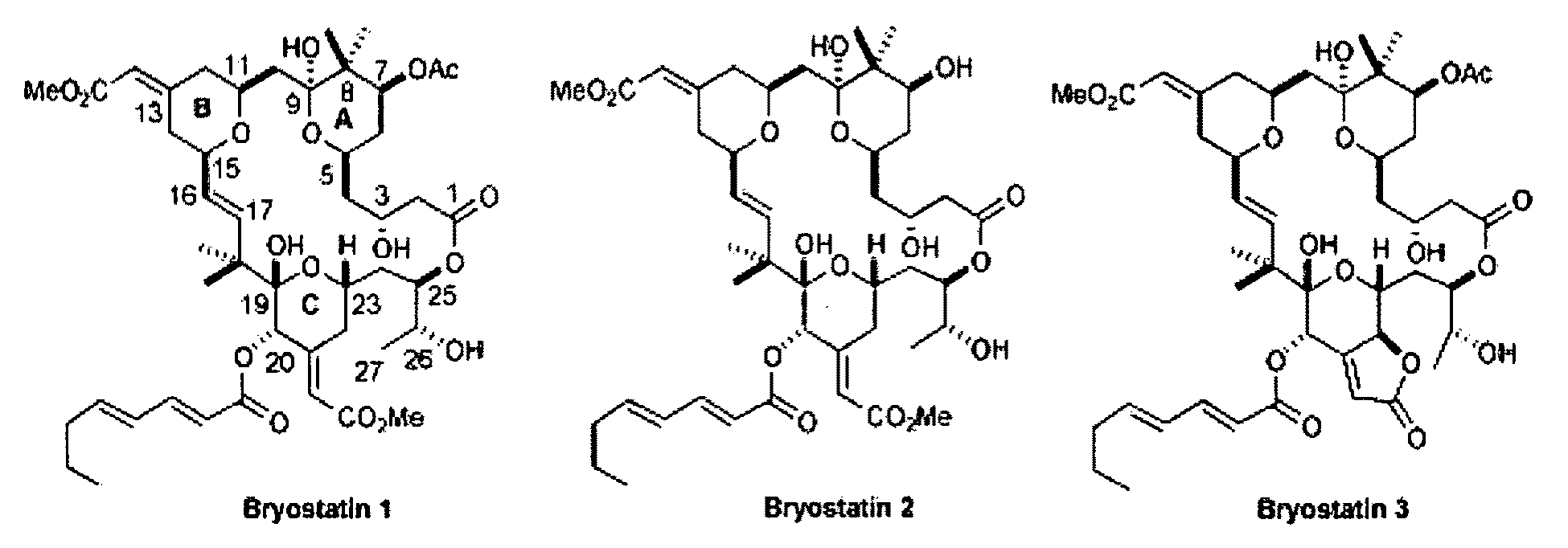
The invention relates to a combination of treatments, more particularly a combination treatment for HIV-1 infection. The present invention is directed to the use of bryostatin-1 and their natural and synthetic derivatives for AIDS therapy, in particular to the use of bryostatins in combination with other active drugs such as Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors and anti-retrovirals, for the treatment of HIV-1 latency. According to the present invention, we provide a combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 latency which employs bryostatin-1 (and analogues) and one of the following HDAC inhibitors; valproic acid, butyrate derivatives, hydroxamic acids and benzamides. While HDACi can be used in continuous dosing protocol, bryostatins can be used following a cyclical dosing protocol. Bryostatins can be formulated in pharmaceutical acceptable carriers including nanoparticles, phospholipids nanosomes and / or biodegradable polymer nanospheres. This combination therapy needs to be used in patients treated with antiretroviral therapy (HIV-1 protease inhibitors, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor inhibitors and fusion inhibitors).
Owner:APHIOS
Solid Pharmaceutical Dosage Form
InactiveUS20110028456A1High drug loadingEasy to manufacturePowder deliveryBiocideValsartanTrenbolone
A pharmaceutical composition comprising a solid unit dosage form comprising: one or more of pharmaceutically active ingredients selected from valacyclovir, olanzapine, voriconazole, topotecan, artesunate, amodiaquine, guggulosterone, ramipril, telmisartan, tibolone, atorvastatin, simvastatin, amlodipine, ezetimibe, fenofibrate, tacrolimus, valgancyclovir, valsartan, clopidrogel, estradiol, trenbolone, efavirenz, metformin, pseudoephedrine, verapamil, felodipine, valproic acid / sodium valproate, mesalamine, hydrochlorothiazide, levosulpiride, nelfinavir, cefixime and cefpodoxime proxetil in combination with a water insoluble polymer and / or a water soluble polymer. Methods for making the pharmaceutical composition are also disclosed.
Owner:CIPLA LTD
Method for providing sustained antiepileptic therapy
InactiveUS6287598B1Patient compliance is goodGood for healthBiocidePill deliveryValproic AcidExtended time
This invention pertains to a dosage form for the management of epilepsies wherein the dosage form comprises administering valproic acid or a valproic acid derivative at a continuous rate over an extended time.
Owner:ENCINAL PHARMA INVESTMENTS
Methods and compositions for expansion of stem cells and other cells
Presented herein are methods of generating a multipotent or immature cell from a mature somatic cell, involving contacting a mature somatic cell with one or more small molecule compounds selected from: a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor; a glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) inhibitor; one or more transforming growth factor-beta receptor (TGF-βR) inhibitors; one or more lysine-specific demethylase 1 (LSD1) inhibitors; a cAMP agonist; a histone lysine methyltransferase (EZH2) inhibitor; and a histone methyltransferase (HMTase) G9a inhibitor; valproic acid. Also provided are methods of generating a multipotent or immature cell from a somatic cell, by driving expression of OCT4, or an OCT4 functional homolog or derivative, under the control of a high expressing promoter. Presented herein are also methods of stem cell expansion, stem cell regeneration and differentiation, which comprise contacting stem cells with one or more small chemical compounds.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells and application of inducing culture medium
ActiveCN105861428ASkeletal/connective tissue cellsCell culture active agentsFibroblastCells fibroblast
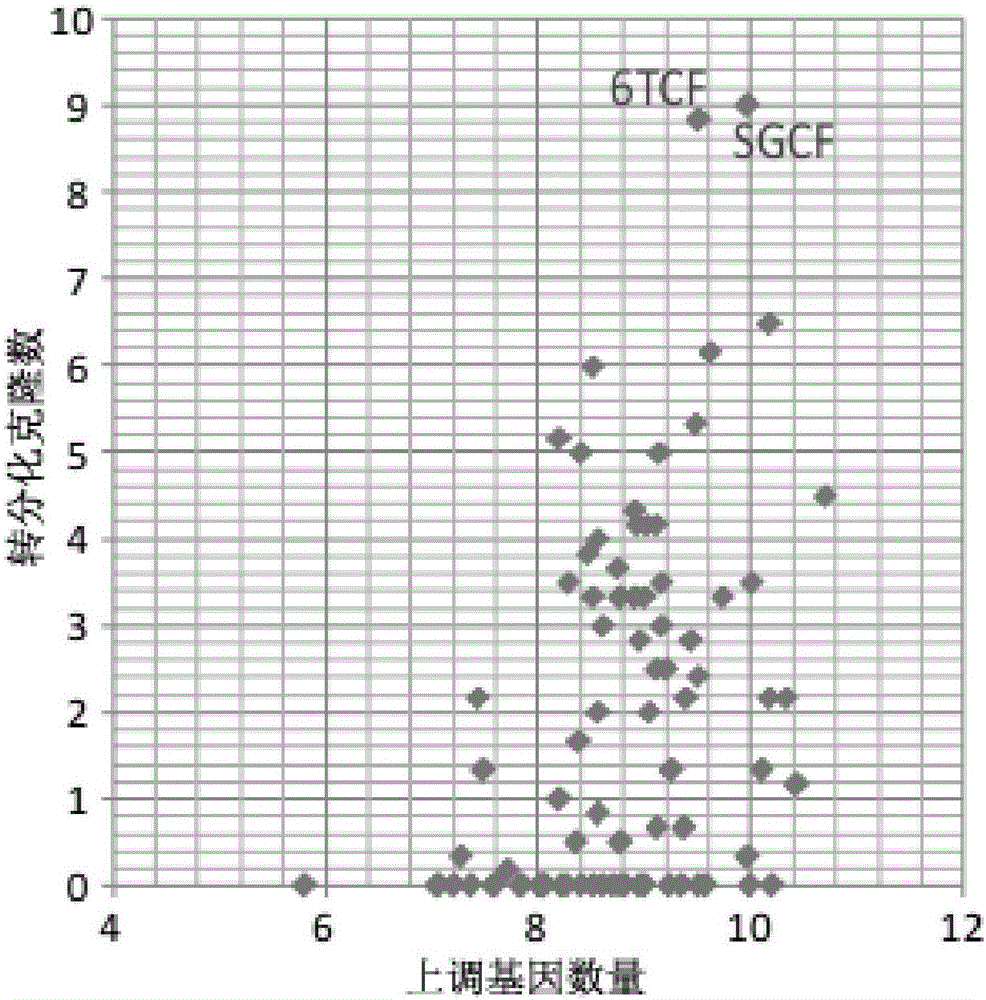
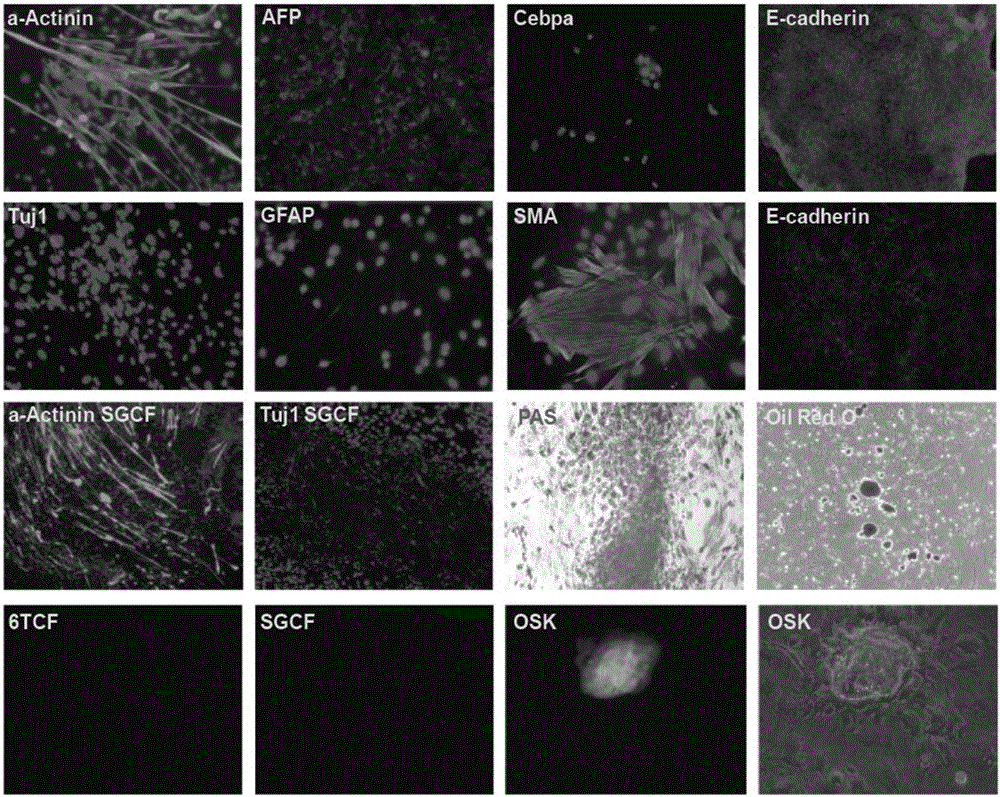
The invention discloses an inducing culture medium for inducing fibroblast to trans-differentiate into cardiac muscle cells, a method and an application of the inducing culture medium. The inducing culture medium comprises a basic culture medium and an inducing small molecular assembly which is 6TCFOW or SCFOV, wherein 6 is E61541, T is tranylcypromine, C is CHIR99021, F is forskolin, O is Dorsomorphin, W is IWR-I, S is SB431542, and V is valproic acid. The inducing culture medium can trans-differentiate the fibroblast into the cardiac muscle cells which have normal cardiac muscle cell specific molecular tags and a normal cardiac muscle function, so that a new way is provided for solving the cell source problem of the regenerative medicine.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
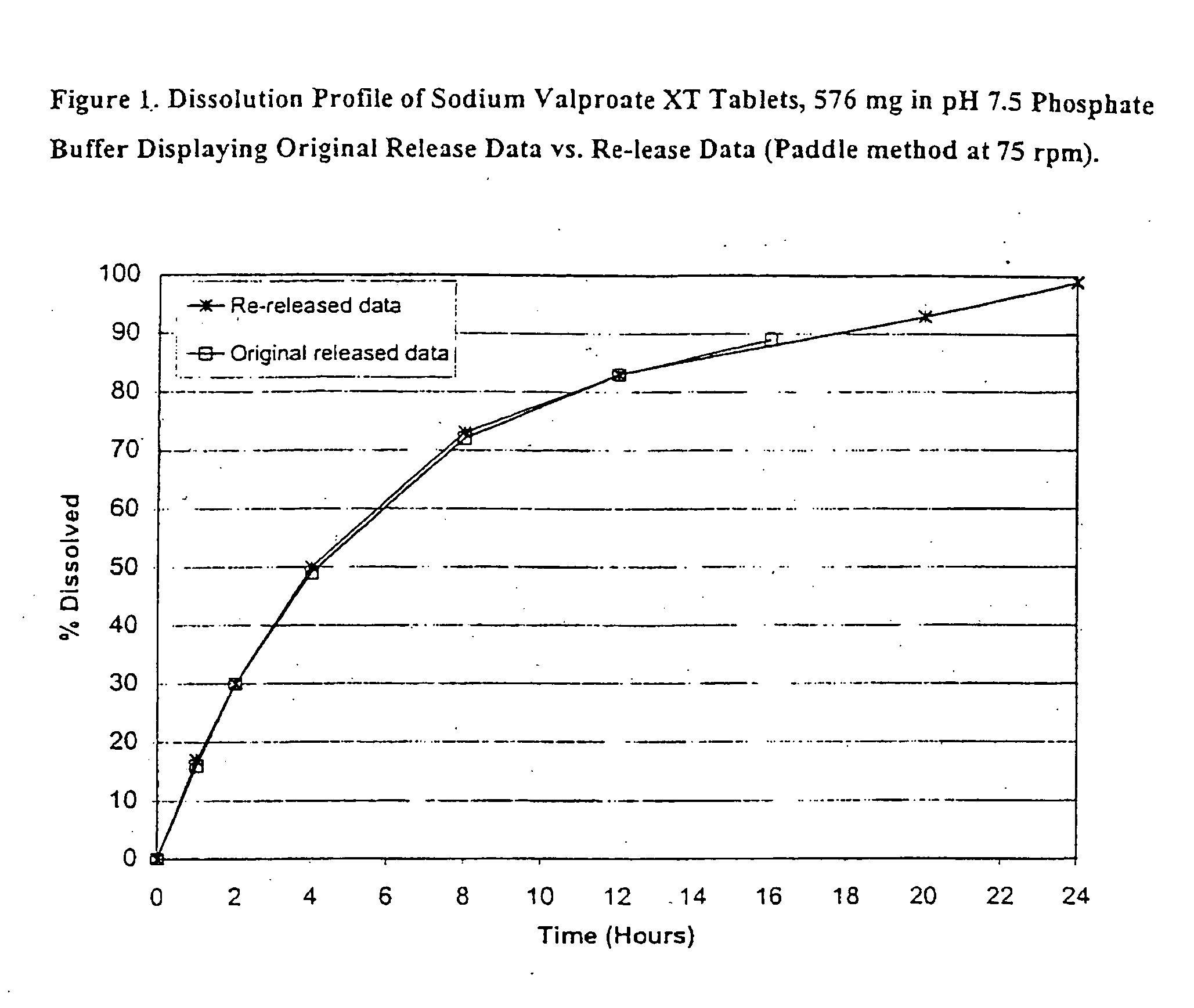
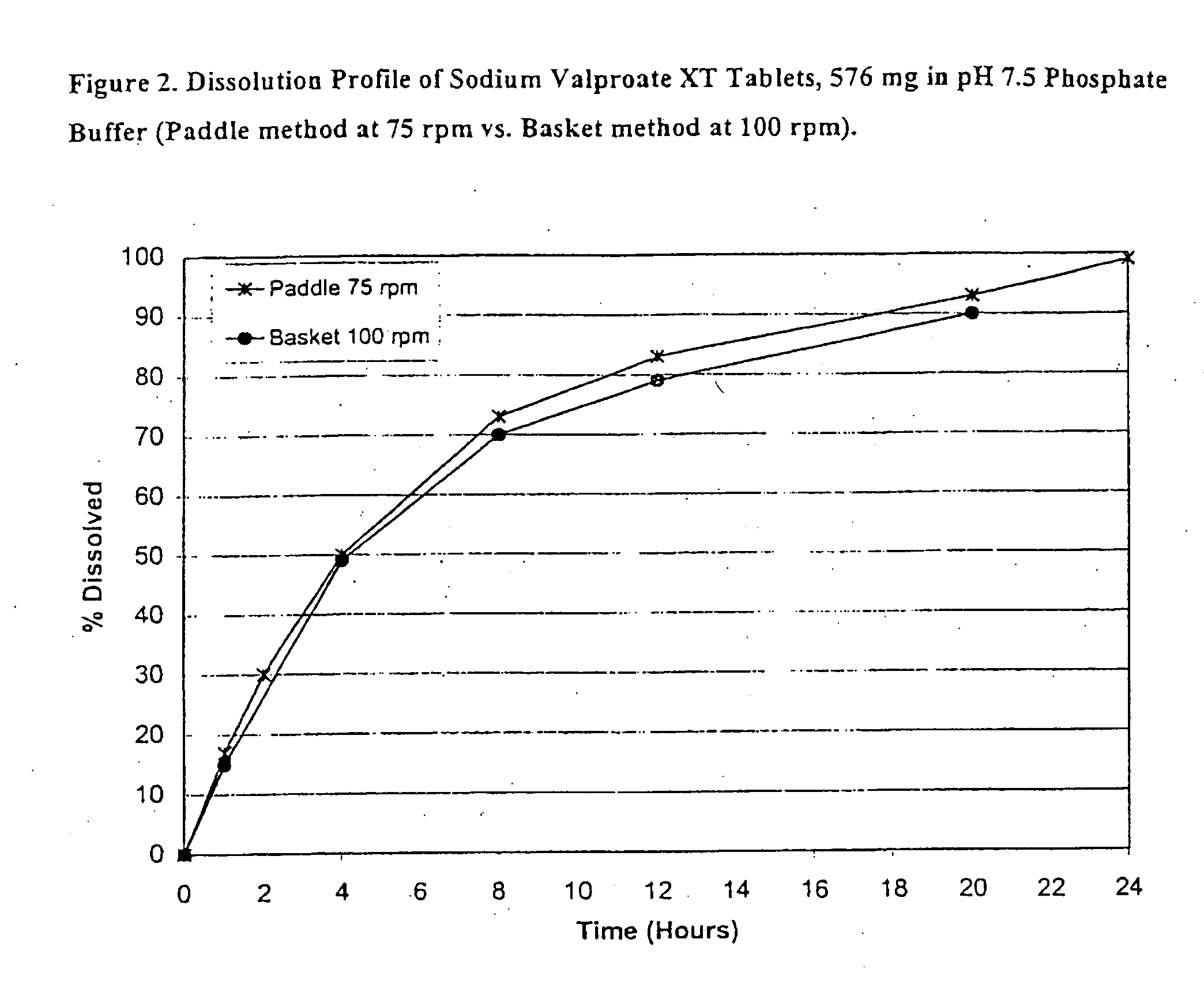
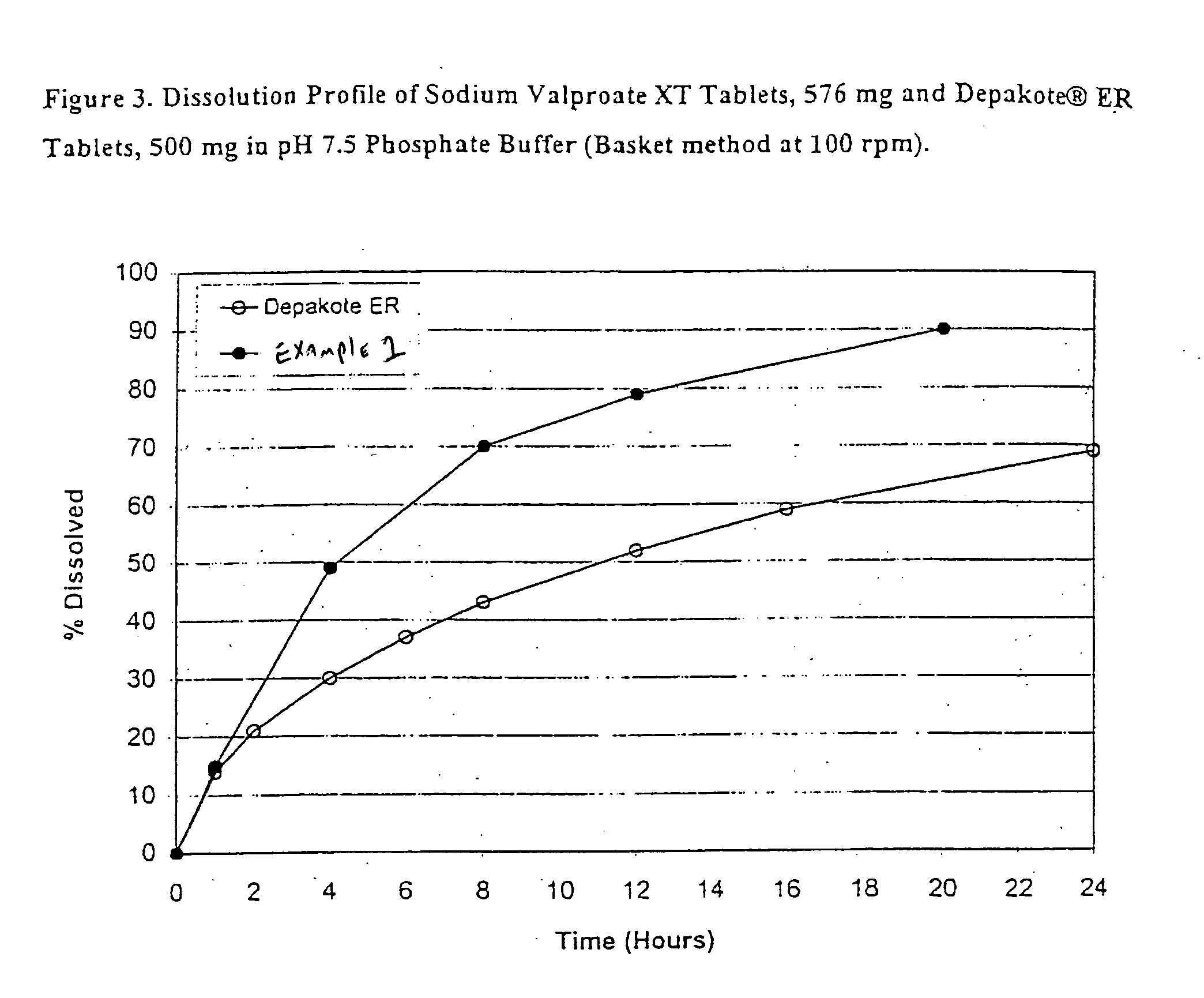
Controlled release sodium valproate formulation
InactiveUS20050276850A1Increase release rateBiocideGranular deliveryValproic AcidControlled-Release Formulations
Disclosed is a controlled release formulation comprising valproic acid, pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, amide thereof, or derivative thereof.
Owner:ANDRX
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
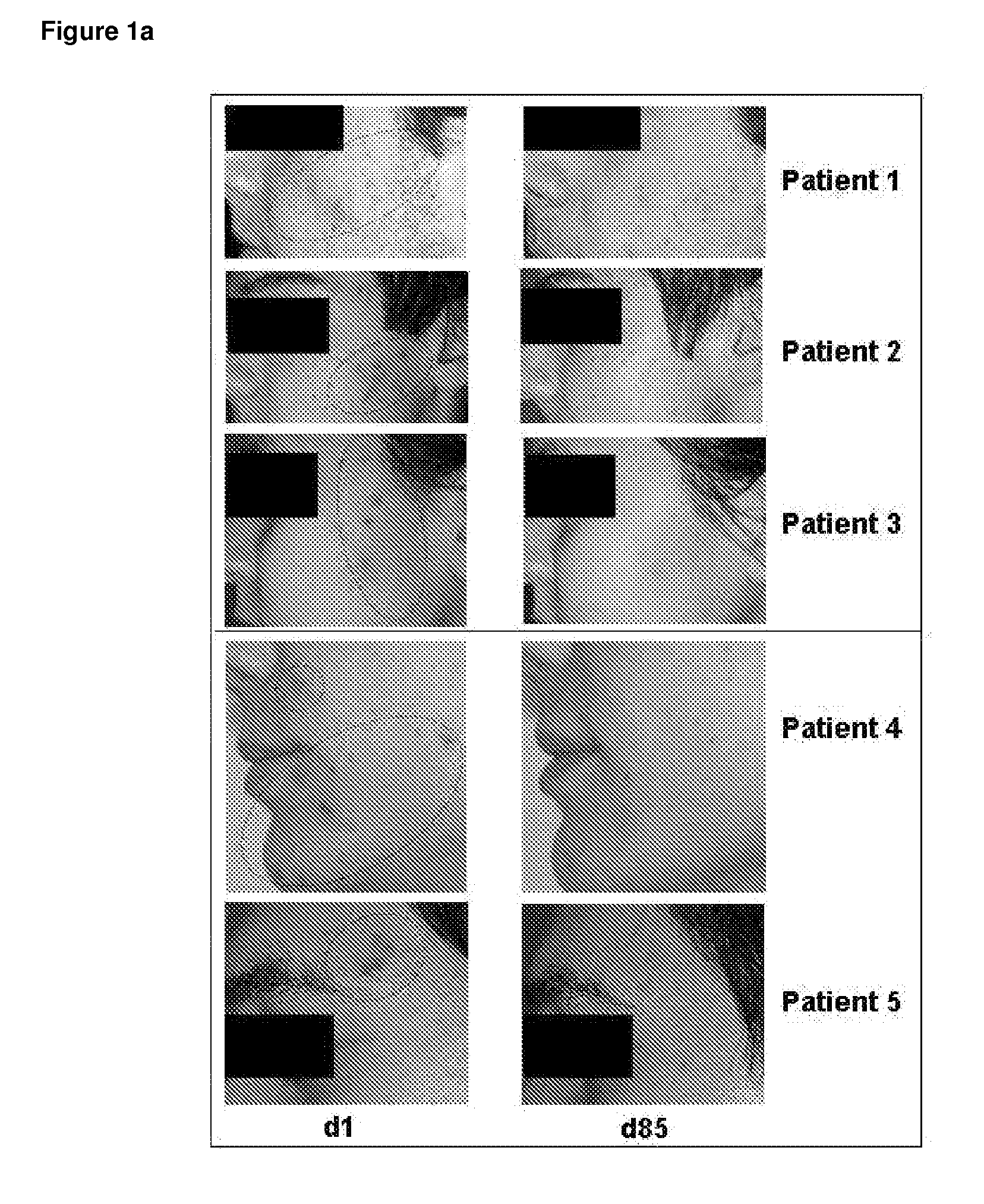
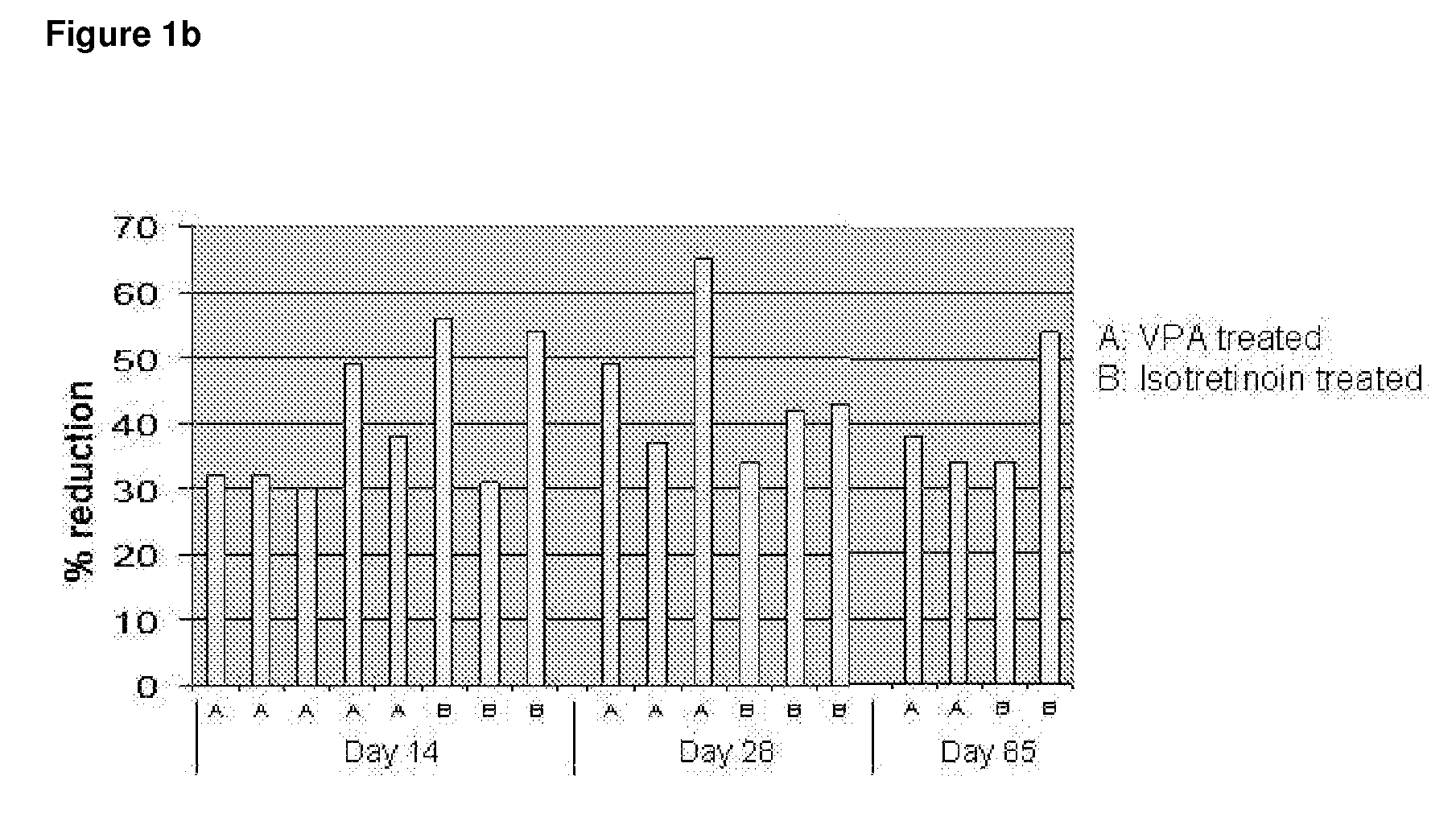
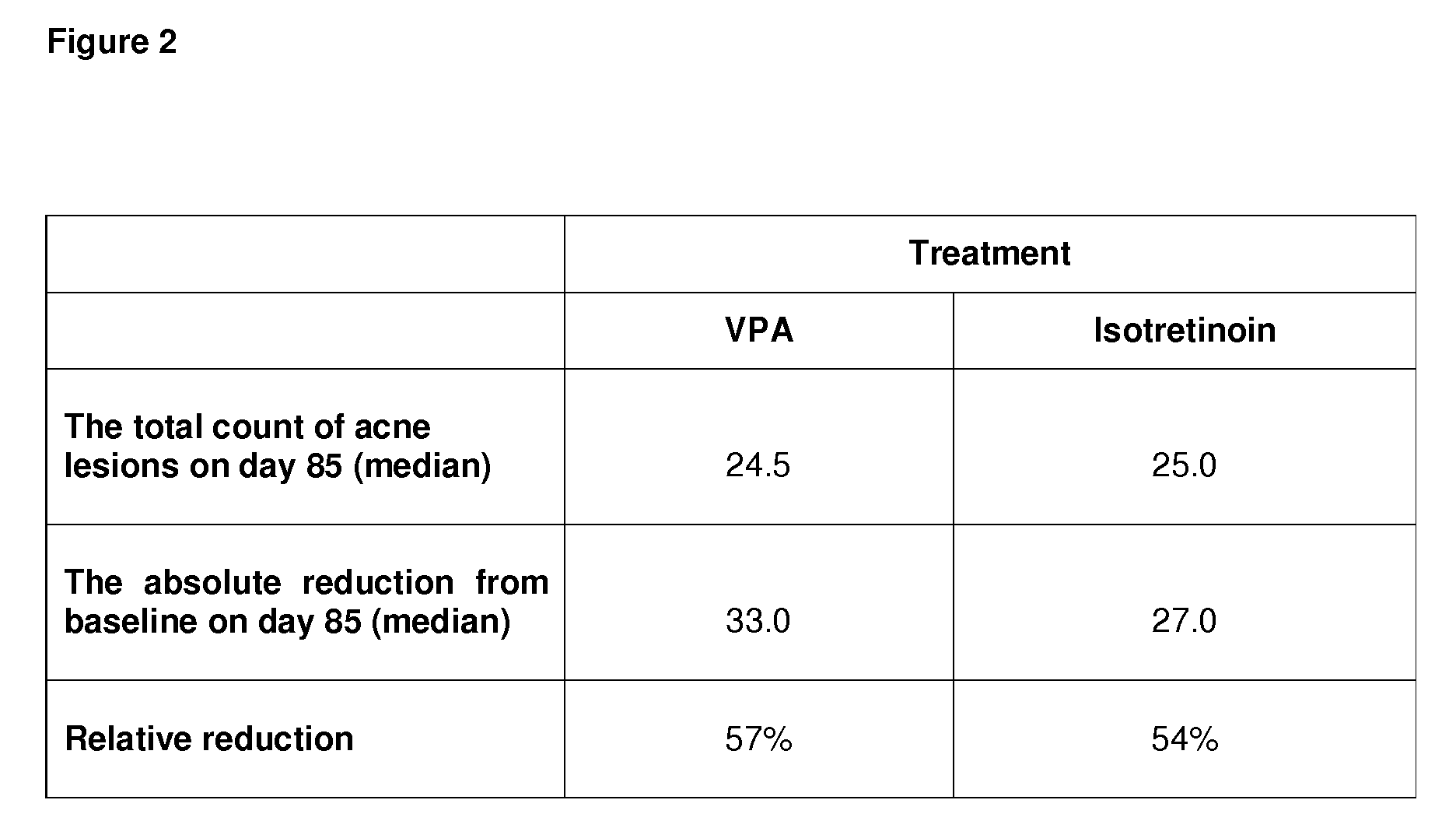
Use of valproic acid for the topical treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris
InactiveUS20090186809A1Improve toleranceGood local tolerabilityAntibacterial agentsBiocideClinical efficacyValproic Acid
The present invention provides a surprising therapeutic beneficial use for the topical application of valproic acid as a single agent therapy for patients suffering from mild to moderate acne vulgaris. Topically applied VPA has a clinical efficacy comparable to that of the marketed standard medication for this indication, isotretinoin. Furthermore, topically applied VPA is on average well to very well tolerated. The invention relates to the topical medical use of VPA for the treatment of acne vulgaris and comprises the topical application of VPA or of a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof.
Owner:TOPOTARGET GERMANY AG
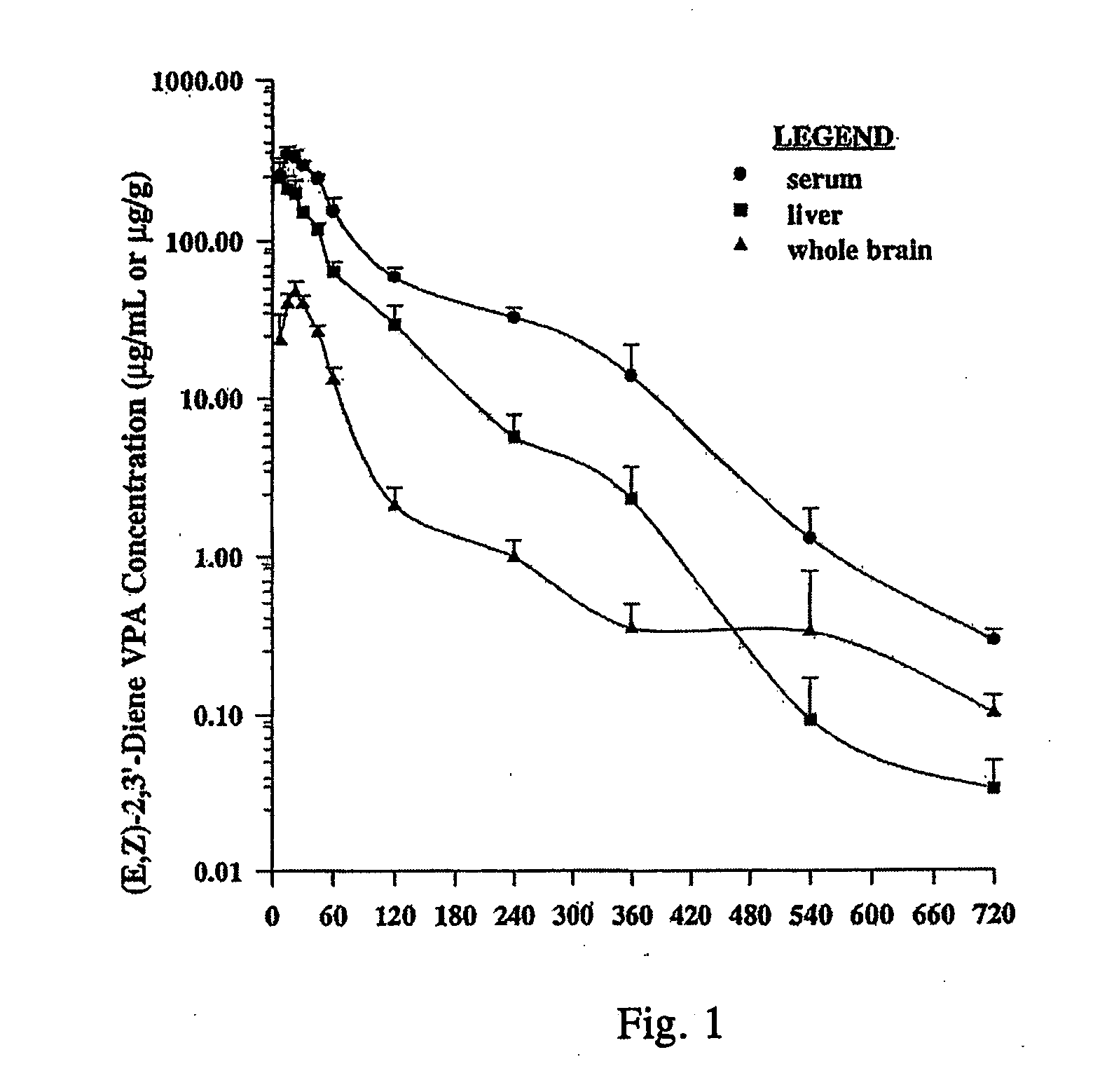
Valproic acid analogues and pharmaceutical composition thereof
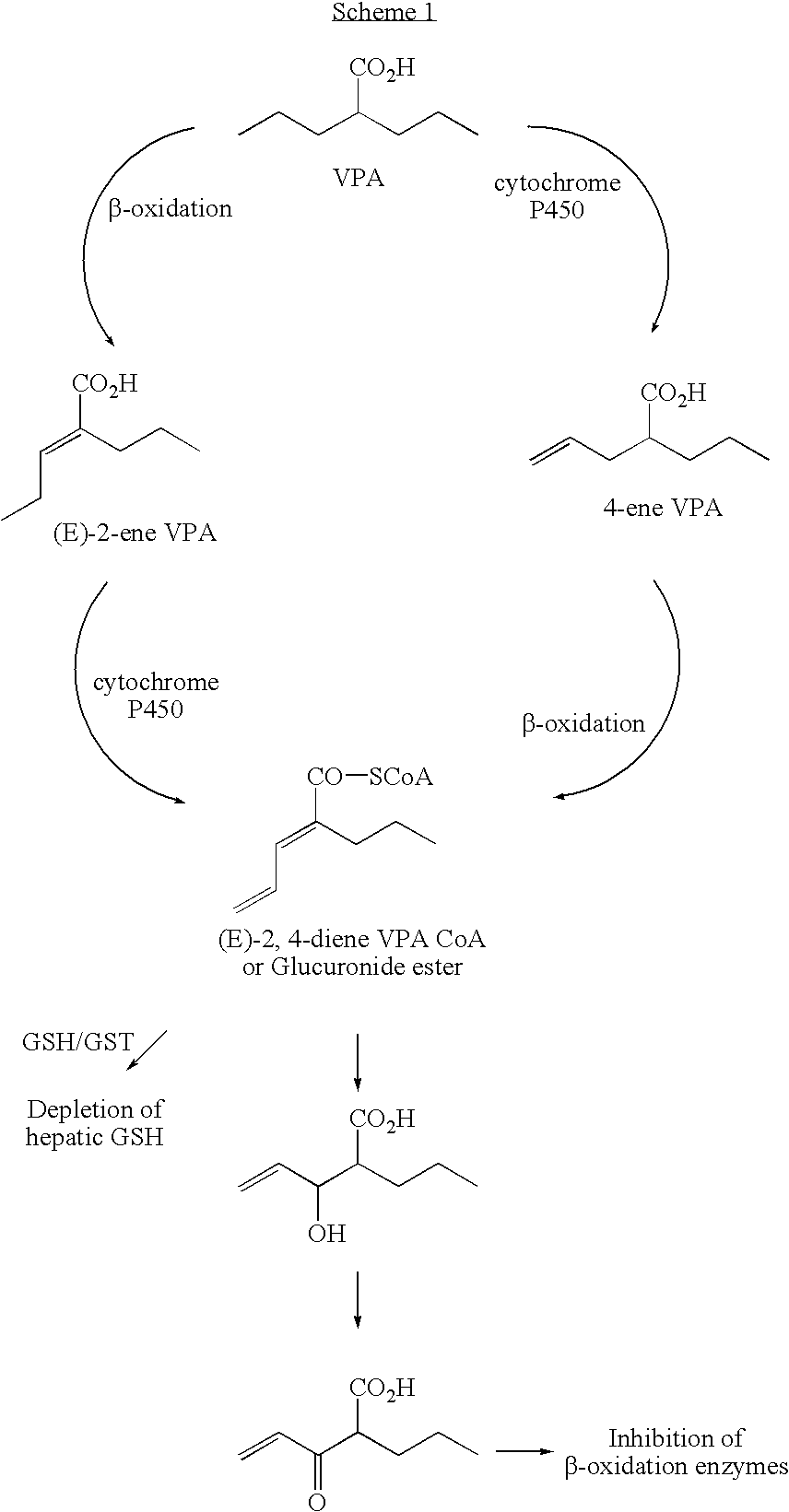
Analogues of valproic acid useful in treating neuroaffective disorders including convulsions, bipolar disorder, and migraine headache are disclosed. The analogues are halide liver substituted analogues, cyclic analogues, and conjugated diene analogues of valproic acid. Pharmaceutical compositions or prodrugs containing the analogues or pharmaceutically acceptable salts thereof are disclosed. Methods of malting the compounds and treating mammals with neuroaffective disorders are also disclosed.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Use of valproic acid for enhancing production of recombinant proteins in mammalian cells
InactiveUS20090023186A1Increasing batch yieldLow production costImmunoglobulinsFermentationBiotechnologyValproic Acid
Culturing cells for the commercial production of proteins for diagnosis and therapy is a costly and time consuming process. The equipment required is expensive, and production cost are high. In order to provide commercially viable processes it is desirable to use cell lines which produce large quantities of product with each production run. However, most cells do not produce large quantities of desired product per se either because they do not produce a large quantity of product per unit of time (specific productivity) or because they do not survive long enough in the culture medium (time). Here, we identified that addition of a valproic acid compound to the culture medium increases overall (batch) yield and titer. More importantly, compared to the widely used sodium butyrate, batch yields using a valproic acid compound as a medium additive are significantly higher.
Owner:HILDINGER MARKUS
Medicament for prophylactic and/or therapeutic treatment of alzheimer-type dementia
InactiveUS20100035927A1Prolonged therapeutic periodAvoid symptomsBiocideNervous disorderValproic AcidTherapeutic treatment
A medicament for prophylactic and / or therapeutic treatment of Alzheimer-type dementia, which comprises donepezil hydrochloride and valproic acid or a salt thereof in combination.
Owner:NAGOYA CITY UNIVERSITY +1
Heavy-load valproic acid drug sustained release tablet and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104146976AReduce volumeEasy to swallowNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCarrageenanValproic Acid
The invention relates to a heavy-load valproic acid drug sustained release tablet and a preparation method of a heavy-load valproic acid drug sustained release tablet and belongs to the field of pharmaceutical preparations. The heavy-load valproic acid drug sustained release tablet is mainly used for treating clinically primary generalized epilepsy. A valproic acid drug comprises valproic acid and pharmaceutically acceptable salt, ester or amide. According to the invention, a novel hydrophilic gel skeleton controlled release system is applied; in polymer matrix selection, a novel controlled release matrix material with good biocompatibility is selected; and the controlled release matrix is a composition of chitosan and one or more of, but not limited to, sodium alginate, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, carrageenan, xanthan gum, hyaluronic acid, polyacrylic resin and an acrylic polymer. Synergic control of slow release of a drug composite is achieved through joint application of different polymers and the chitosan and by employing property difference of the different polymers and intelligent interaction with the chitosan, a combined action of different drug release mechanisms is realized, and a slow release effect of the drug composite up to 24h can be achieved.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Valproic acid homogeneous-phase enzyme immunity rapid detection kit
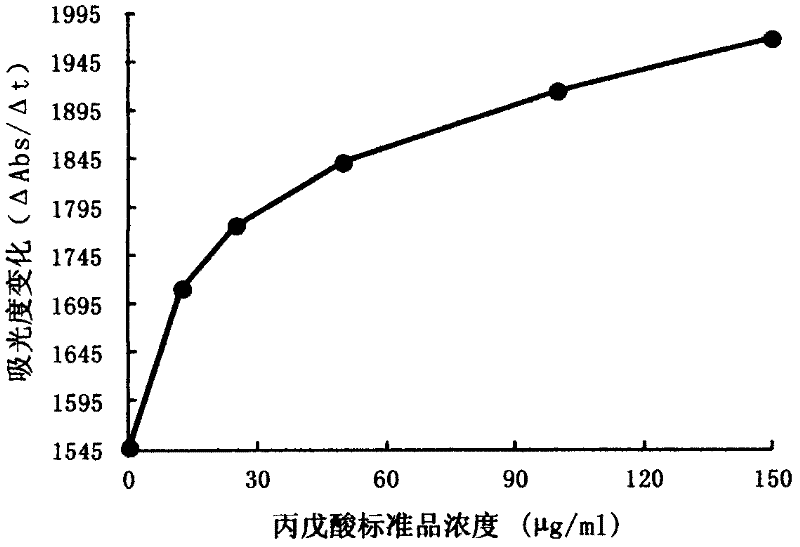
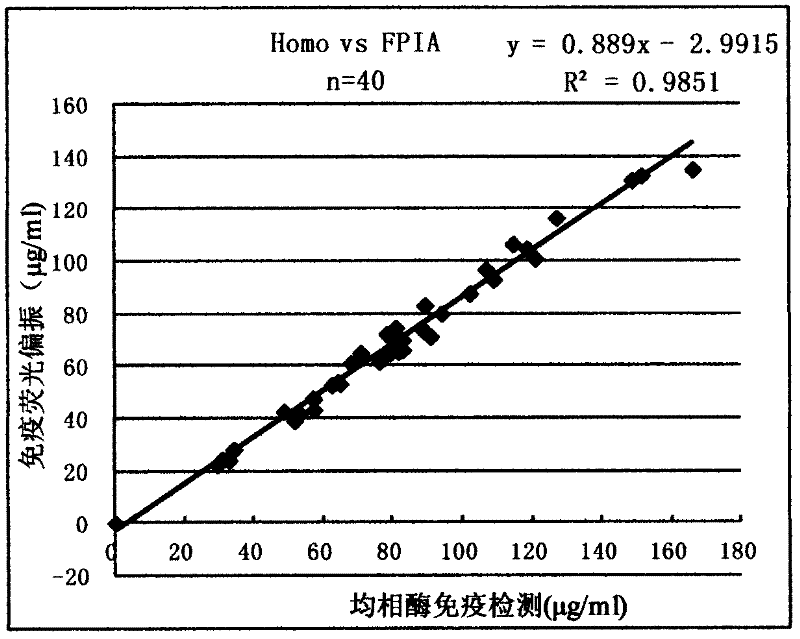
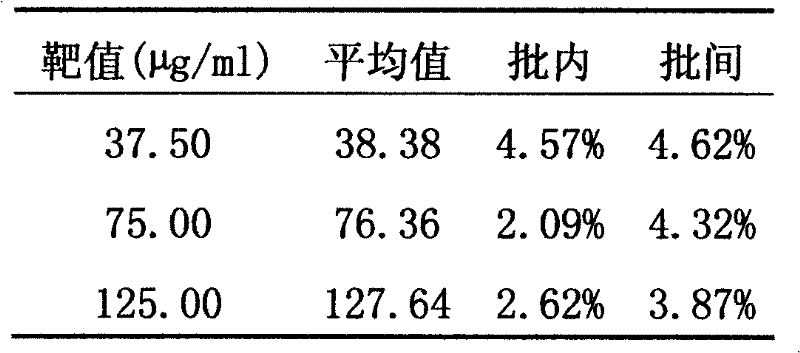
InactiveCN102507917AMeet the needs of concentration detectionHigh sensitivityBiological testingSide effectValproic Acid
The invention relates to the technical field of valproic acid blood drug level monitoring, and specifically discloses a valproic acid homogeneous-phase enzyme immunity rapid detection kit. With derivative synthesis, valproic acid is connected onto bovine serum albumin (BSA), such that an immunizing antigen is obtained. An obtained polyclonal antibody has valproic acid specificity. Experiment data shows that when the reagent is used for detecting valproic acid, no cross reaction occurs between the reagent and other commonly used medicines; an analysis sensitivity is better than 25ng / ml; within-run precision and within-run precision coefficient of variability (CV) are both smaller than 4.7%; and compared with a fluorescence polarization immunoassay (EPIA) method, an R2 value reaches 0.98. The kit can be used in various routine analysis instruments. Because of characteristics of simple operation, high speed, low cost, and high sensitivity, with the kit, automatic detection can easily be realized. The kit assists in guiding clinical customized medication. With the kit, toxic or side effect of medicines is reduced, and curative effect optimization is realized.
Owner:SICHUAN KINGMED DIAGNOSTICS CENT
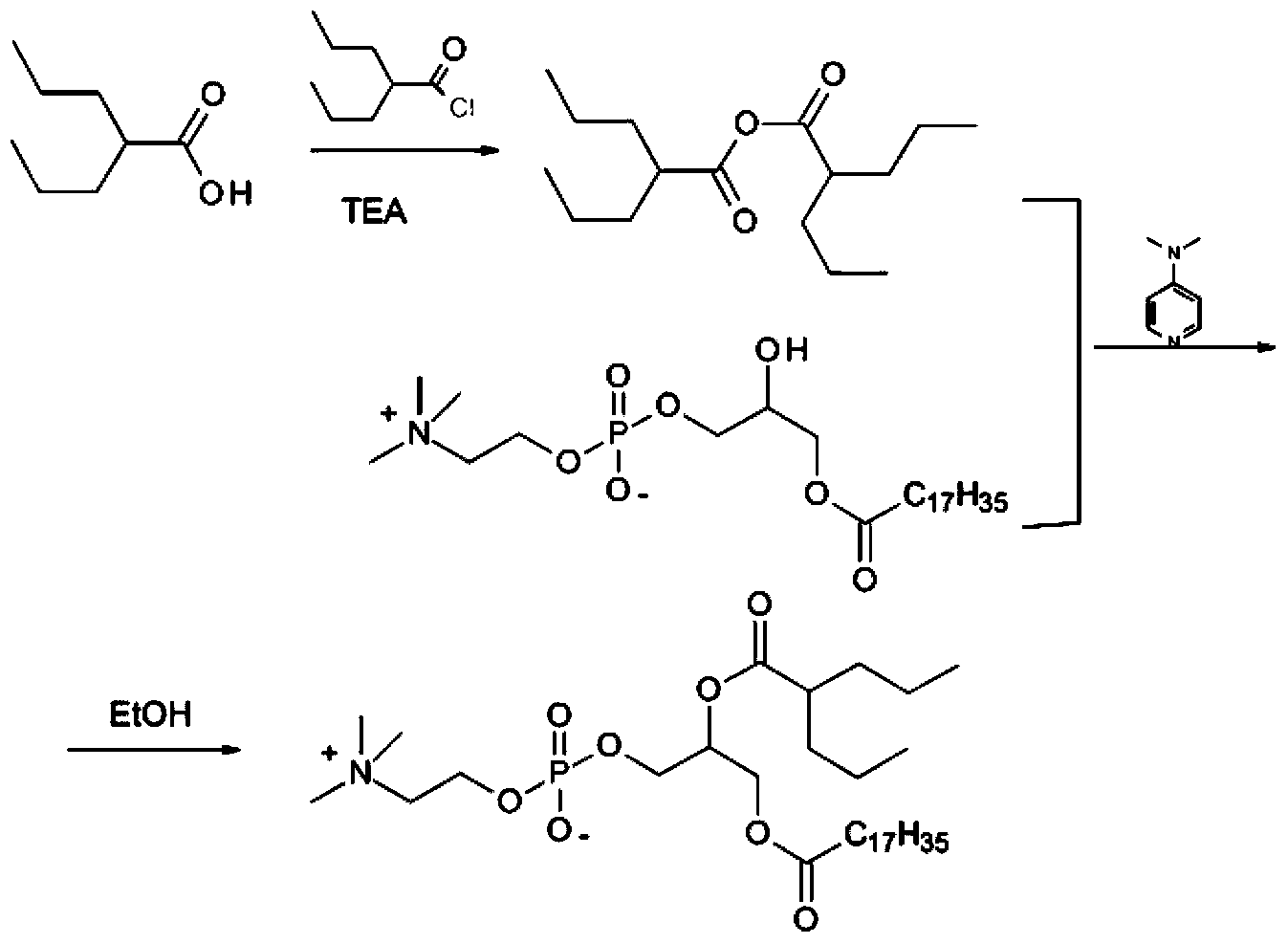
Phospholipid derivatives of valproic acid and mixtures thereof
The present invention relates to a compound, namely a phospholipid derivative of valproic acid, compositions comprising said compound and their use for the treatment of epilepsy, migraine, bipolar disorders and pain.
Owner:迪-药品有限公司
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
InactiveUS20060004414A1Raise the possibilityIncrease heart rateCatheterHeart stimulatorsDiseaseAntiarrhythmic effect
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Technique for preparing disodium valproate
InactiveCN101003476AShort cycleLow costCarboxylic acid salt preparationValproic AcidSodium divalproex
This invention discloses a process for preparing sodium divalproate. The process comprises: dissolving valproic acid and sodium valproate at a mol ratio of 1:1 in an appropriate solvent, and vacuum-distilling the solvent at 55-90 deg.C to obtain sodium divalproate. The process has such advantages as easy control, no byproducts, high product yield, high product quality, and low cost. The process can be used for mass production of sodium divalproate.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods Related to the Treatment of Neurodegenerative and Inflammatory Conditions
The invention includes methods of neuroprotection, inducing release of neurotrophic factors, inhibiting the over-activation of innate immune cells, attenuating the toxin-induced death and / or damage of tissues, reducing inflammation, treating an inflammation-related condition, and inhibiting NADPH oxidase, that includes contacting or administering an effective amount of at least one compound of the invention that include: valproic acid, sodium butyrate, and salts thereof; opioid peptides; a peptide comprising the tripeptide GGF; and morphinans, such as naloxone, naltrexone, 3-hydroxy-morphinan and dextromethorphan.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
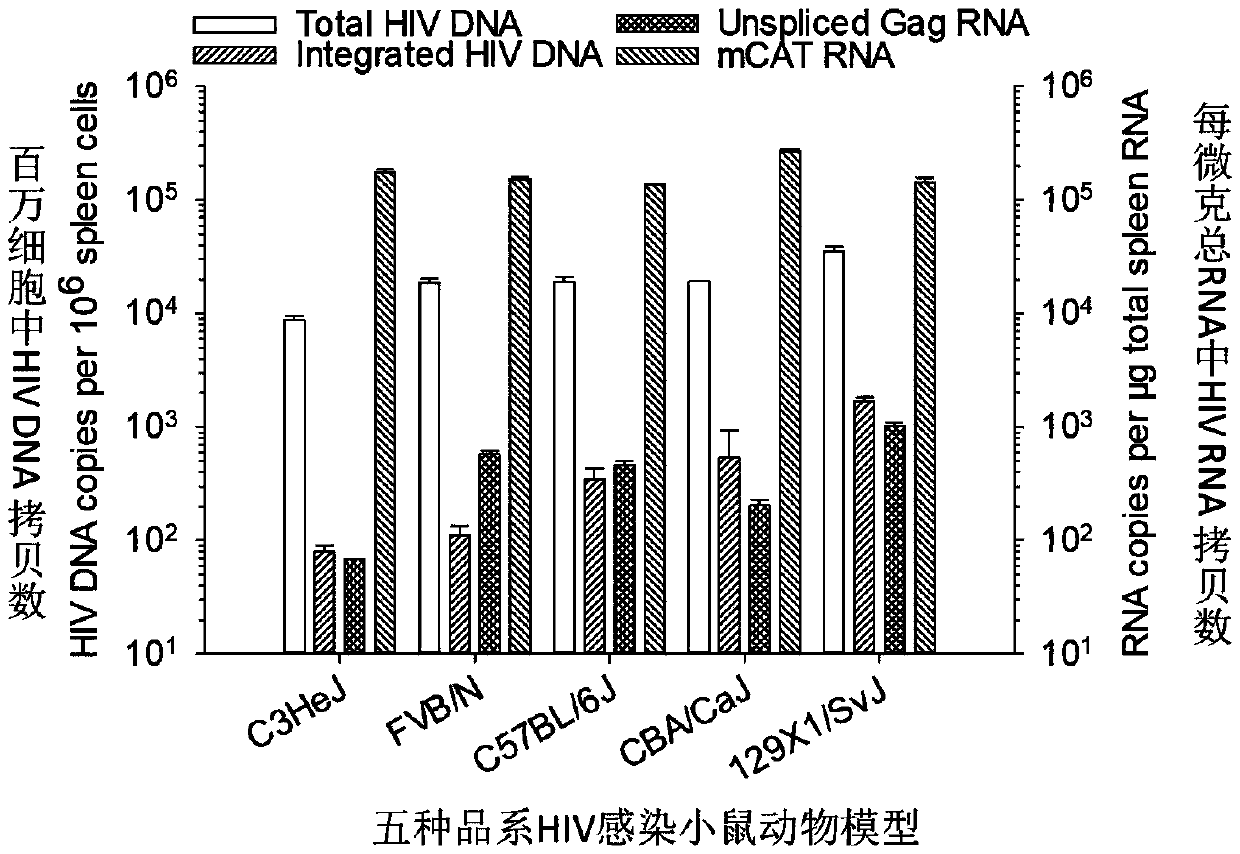
Composition for activating latent HIV virus and application thereof
ActiveCN109620954AFully activatedHigh induction activationAntiviralsAntibody ingredientsSide effectValproic Acid
The invention relates to the field of medicine, in particular to a composition for activating an HIV latent virus and application thereof. The composition consists of a monoclonal antibody drug, a histone deacetylase inhibitor and a PKC activator, wherein the monoclonal antibody drug is selected from an anti-human CD3 monoclonal antibody and an anti-human CD28 monoclonal antibody, the histone deacetylase inhibitor is selected from at least one of vorinostat and valproic acid, and a PKC activator is 12-deoxyphorbol-13-acetic acid (Prostratin). The main obstacle to cure the HIV is that the HIV establishes a hidden 'reservoir' of viruses in the body at the very early stage of infection. The composition has the effect of significantly activating latent HIV-infected CD4+ T cells, can activate the HIV latent virus simultaneously at the cellular level, the chromatin level and the HIV-specific transcription factor level, can fully activate the HIV pre-virus in the resting CD4+ T cells withoutsignificant cytotoxic side effects and is a necessary way to HIV functional healing.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
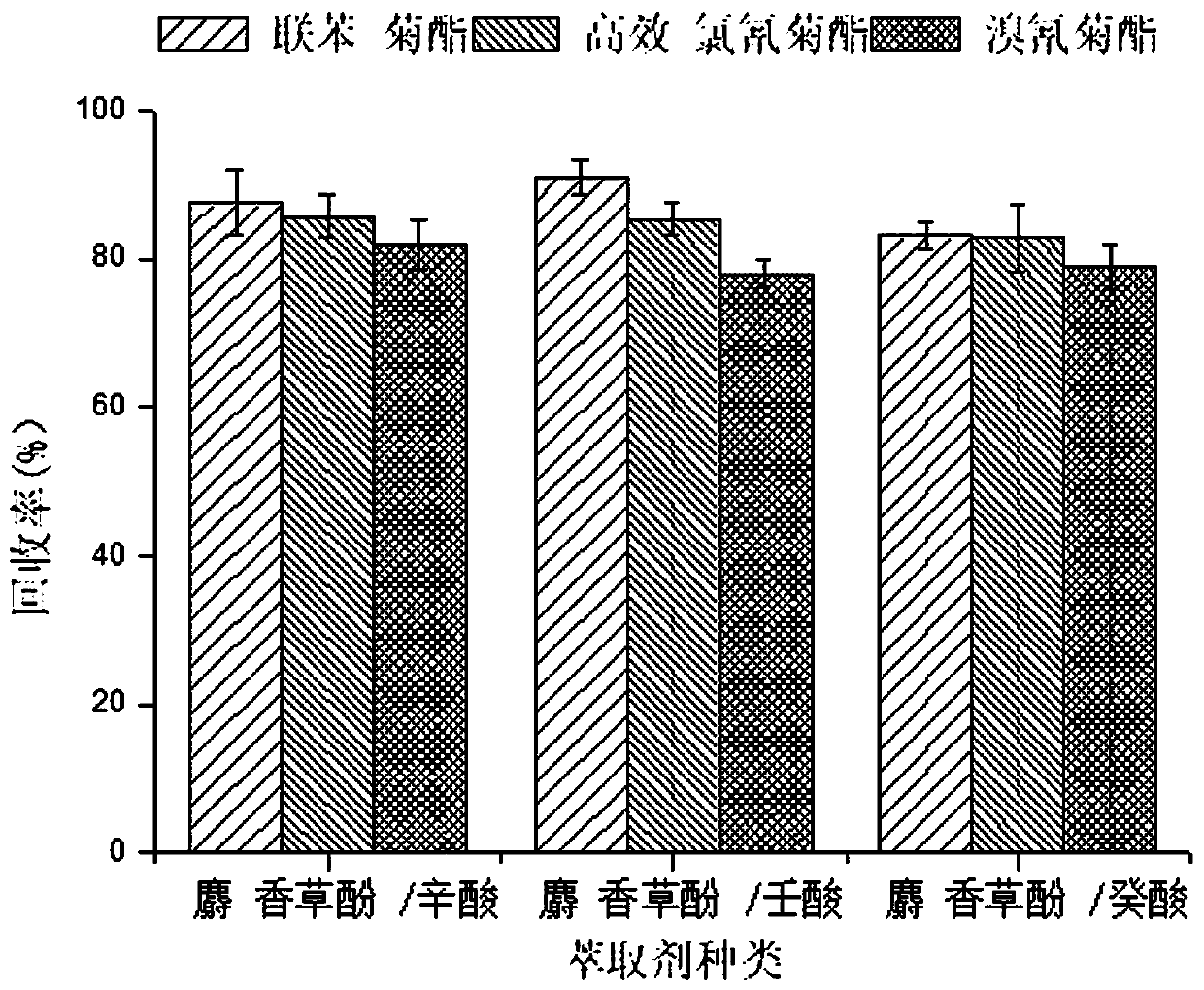
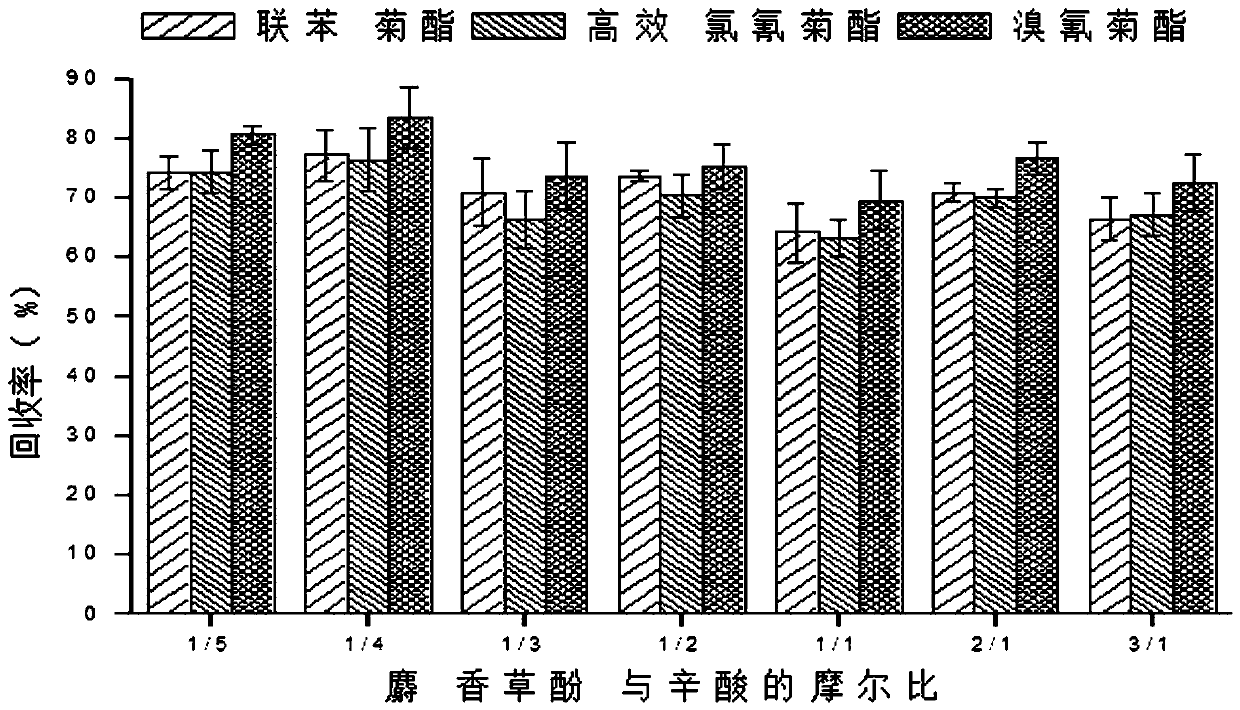
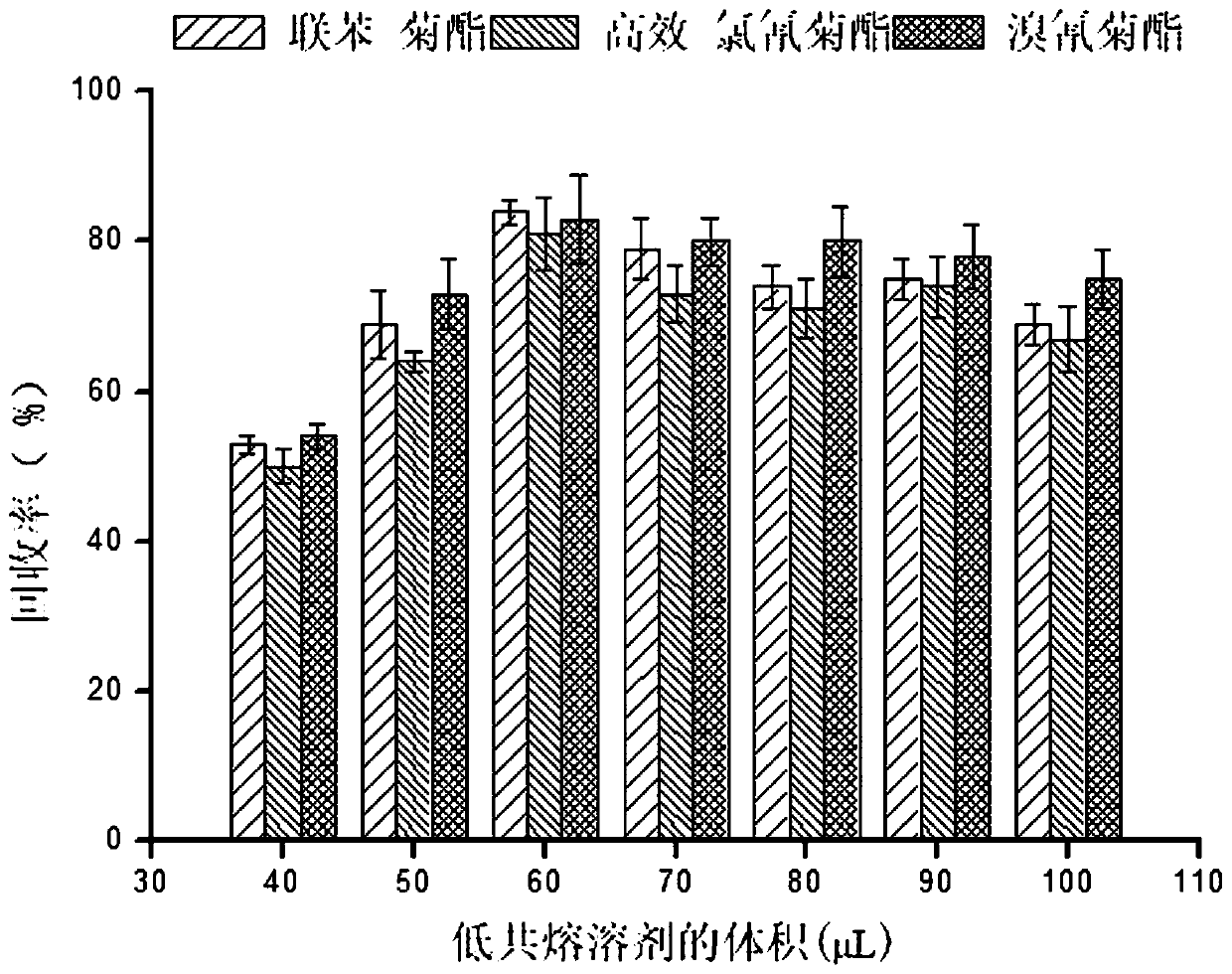
Method for measuring pyrethroid pesticides in grain by dispersion liquid micro-extraction-high performance liquid chromatography
The invention belongs to the technical field of food chemistry, and provides a method for measuring pyrethroid pesticides in grain by dispersion liquid micro-extraction-high performance liquid chromatography. Thymol or choline chloride is used as a hydrogen-bond acceptor, valproic acid, hexylic acid, heptanoic acid, caprylic acid, n-nonanoic acid or capric acid is used as a hydrogen-bond donor, the mole ratio of the hydrogen-bond acceptor to the hydrogen-bond donor is 1 / 5, 1 / 4, 1 / 3, 1 / 2, 1 / 1, 2 / 1, 3 / 1 or 4 / 1; a hydrophobic eutectic solvent formed by mixing the hydrogen-bond acceptor and the hydrogen-bond donor is used as an extraction agent, liquid micro-extraction is performed, and the pyrethroid pesticides in grain are measured by high performance liquid chromatography. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of being simple to operate, quick, sensitive, less usage of extraction agent, easy to collect, green and environment-friendly, can be used for detecting pyrethroid pesticides in a number of grain samples. The usage of harmful organic solvent can be avoided, and less extraction agent is used; and the method has the significant advantages of being simple and quick to operate, easy to collect, green and environment-friendly, and good in reproducibility.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Method and system for the prediction of cardiac arrhythmias, myocardial ischemia, and other diseased condition of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges
Methods and systems are provided for determining an increased likelihood of the occurrence of a cardiac arrhythmia, myocardial ischemia, congestive heart failure and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges in a patient. The methods and systems comprise monitoring the sympathetic neural discharges of a patient from the stellate ganglia, the thoracic ganglia, or both, and detecting increases in the sympathetic neural discharges. The methods and systems may further comprise delivering therapy to the patient in response to a detected increase in the sympathetic neural discharge, such as delivering one or more pharmacological agents; stimulating myocardial hyperinnervation in the sinus node and right ventricle of the heart of the patient; and applying cardiac pacing, cardioversion or defibrillation shocks. Pharmacologic agents which may be used in connection with the delivery of include those which are known to exert anti-arrhythmic effect and anti-convulsant agents, such as phenytoin, carbamazepine, valproate, and phenobarbitone. Other pharmacologic agents may be used to treat impending myocardial ischemia and other diseased conditions of the heart associated with elevated sympathetic neural discharges.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Application of sulindac in preparation of medicine for treating autism
InactiveCN103622941AHas antioxidant propertiesReduce generationOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderValproic AcidSulindac
The invention discloses application of sulindac in preparation of a medicine for treating autism. The application of sulindac in preparation of the medicine for treating autism is characterized in that a VPA (Valproic Acid) autism animal model shows that sulindac is able to reduce abnormal behavior of an autistic, such as repeated mechanical behavior deficiency and human communication disorders; the primary culture neuron and VPA autism animal model verify the occurrence mechanism of autism as well as the functional mechanism of sulindac in treating autistic, and also prove that sulindac has oxidation resistance, and the oxidation resistance is related to down-regulating of the activity of a canonical Wnt signal channel. Therefore, sulindac is able to reduce the repeated mechanical behavior, abnormal behavior and human communication disorders of the autistic and can be used for preparing the medicine for treating autism.
Owner:XINXIANG MEDICAL UNIV
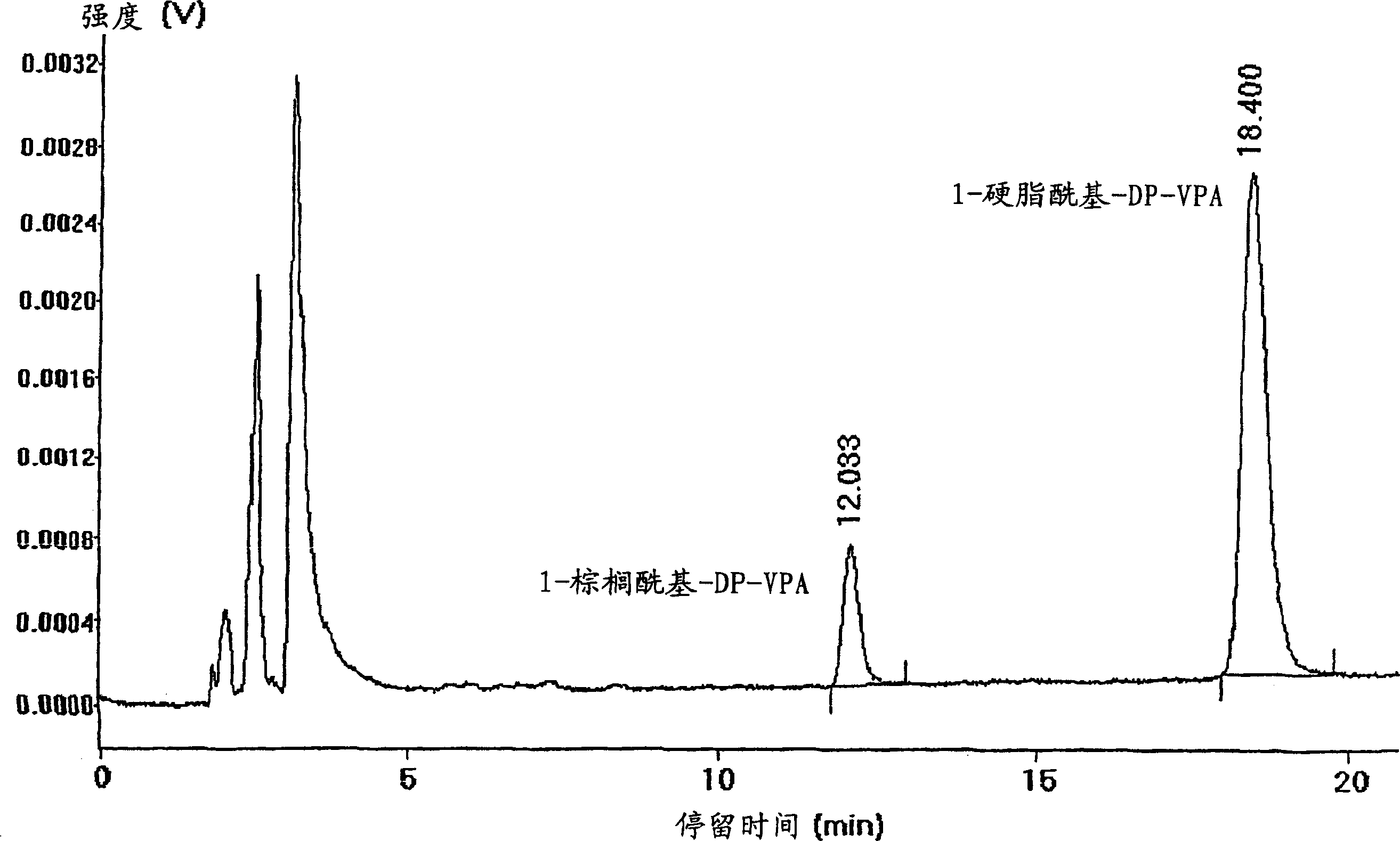
Preparation method of valproic acid phospholipid derivative
ActiveCN104230981AEasy to purifyHigh purityPhosphatide foodstuff compositionsAcetic anhydrideValproic Acid
The invention belongs to the field of organic compound preparation, and discloses a preparation method of a valproic acid phospholipid derivative. The method comprises the following steps: by using tetrahydrofuran as a solvent and triethylamine as an acid-binding agent, reacting propyl valeric chloride and equal mole of valproic acid at 10-50 DEG C, filtering, distilling to obtain valproic acid anhydride, adding lysophosphatidyl choline into the valproic acid anhydride solution, reacting at 60-85 DEG C under the catalytic action of 4-dimethylaminopyridine for 2-6 hours, adding acetone to precipitate the product, and refining with ethanol / acetone to obtain the valproic acid phospholipid derivative. By reacting the valproic acid and propyl valeric chloride to prepare the valproic acid anhydride, no influence of the acetic anhydride exists, and the valproic acid anhydride can be easily purified to obtain the high-purity valproic acid anhydride, thereby preparing the high-purity valproic acid phospholipid derivative.
Owner:NHWA PHARMA CORPORATION
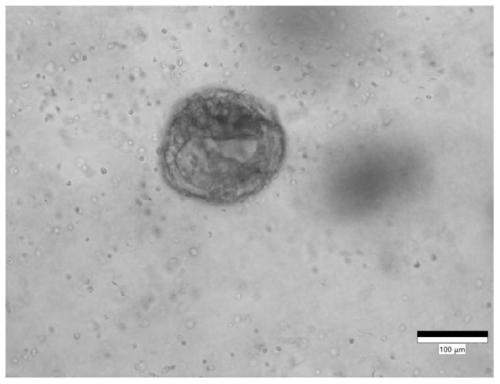
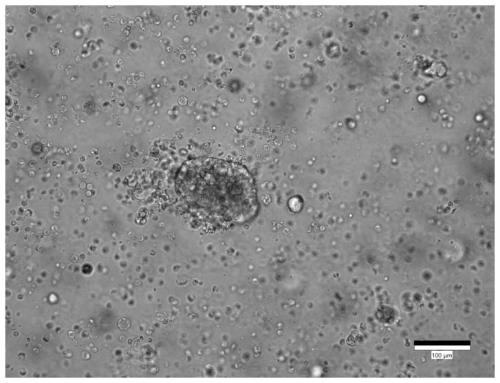
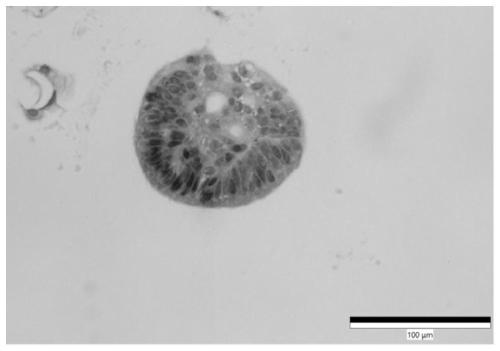
Culture medium for stomach cancer organs and culture method
ActiveCN111411083ALow costReduce the risk of contaminationCell dissociation methodsCulture processPenicillinValproic Acid
The invention provides a culture medium for stomach cancer organs and a culture method. The culture medium comprises a basic culture medium 1640, specific addition factors and sterile water, wherein the mass ratio of the basic culture medium 1640 to the sterile water is 99:1; and the specific addition factors comprise B27 without vitamin A, N-acetylcysteine, EGFs (epidermal growth factors), Noggin, R-spondin 1, Wnt3a, CHIR99021, thiazovivin, Gastrin I, valproic acid, a penicillin and streptomycin mixed liquid, amphotericin B and Primocin. The culture medium can be adopted to culture the stomach cancer organs, morphology structures and gene characteristics of primary tissue can be maintained, the risk of microorganism pollution in stomach cancer culture can be effectively reduced, and the success rate and the survival rate of stomach cancer organ culture can be increased.
Owner:ACCURATE INT BIOTECHNOLOGY (GUANGZHOU) CO LTD
Methods related to the treatment of neurodegenerative and inflammatory conditions
The invention includes methods of neuroprotection, inducing release of neurotrophic factors, inhibiting the over-activation of innate immune cells, attenuating the toxin-induced death and / or damage of tissues, reducing inflammation, treating an inflammation-related condition, and inhibiting NADPH oxidase, that includes contacting or administering an effective amount of at least one compound of the invention that include: valproic acid, sodium butyrate, and salts thereof; opioid peptides; a peptide comprising the tripeptide GGF; and morphinans, such as naloxone, naltrexone, 3-hydroxy-morphinan and dextromethorphan.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com