Patents
Literature
4355 results about "Drug release" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
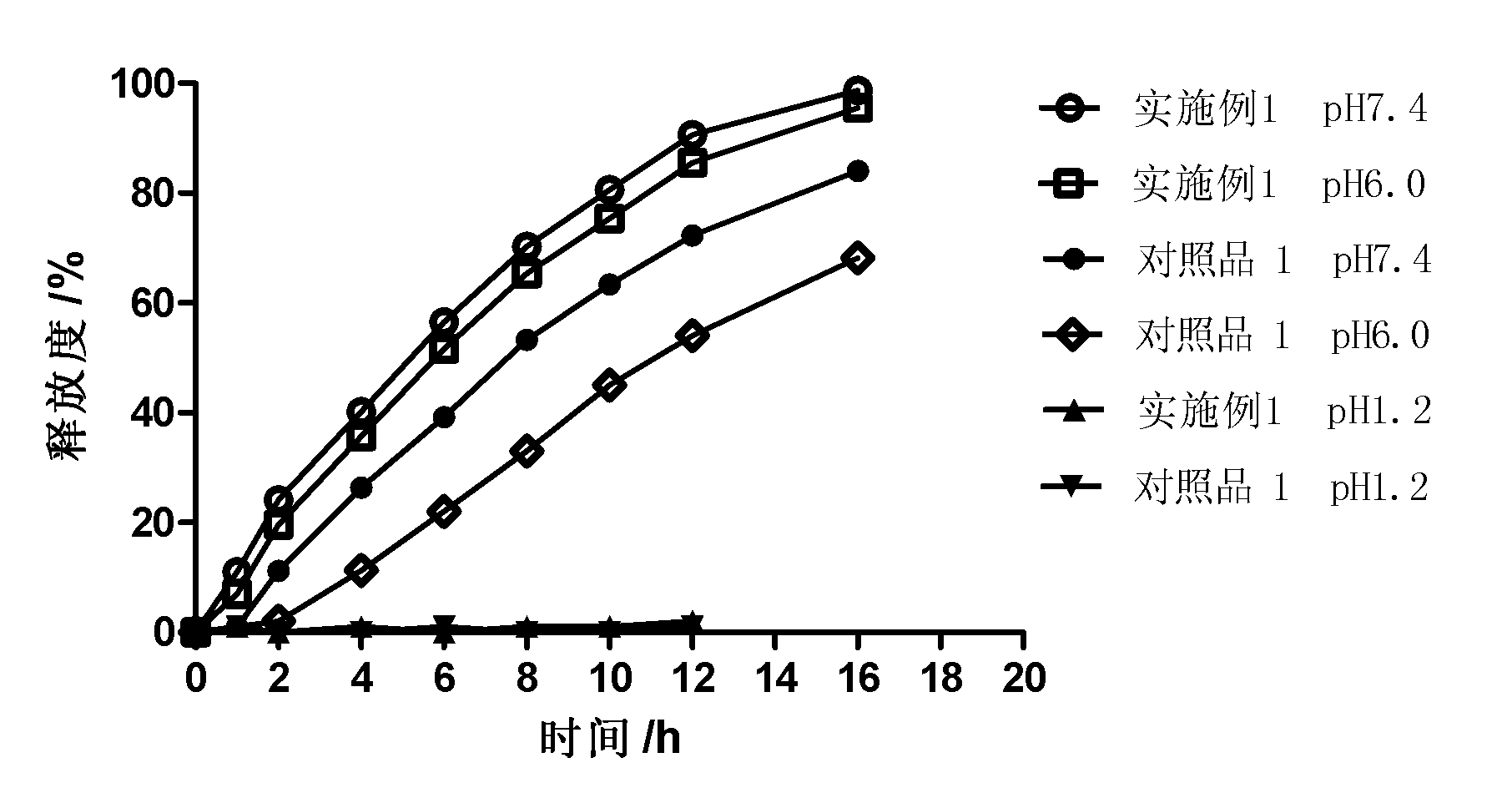
Drug Release. Drug release is an important property of a therapeutic system, constituting a prerequisite to absorption of the therapeutic agent and one that contributes to the rate and extent of active availability to the body.
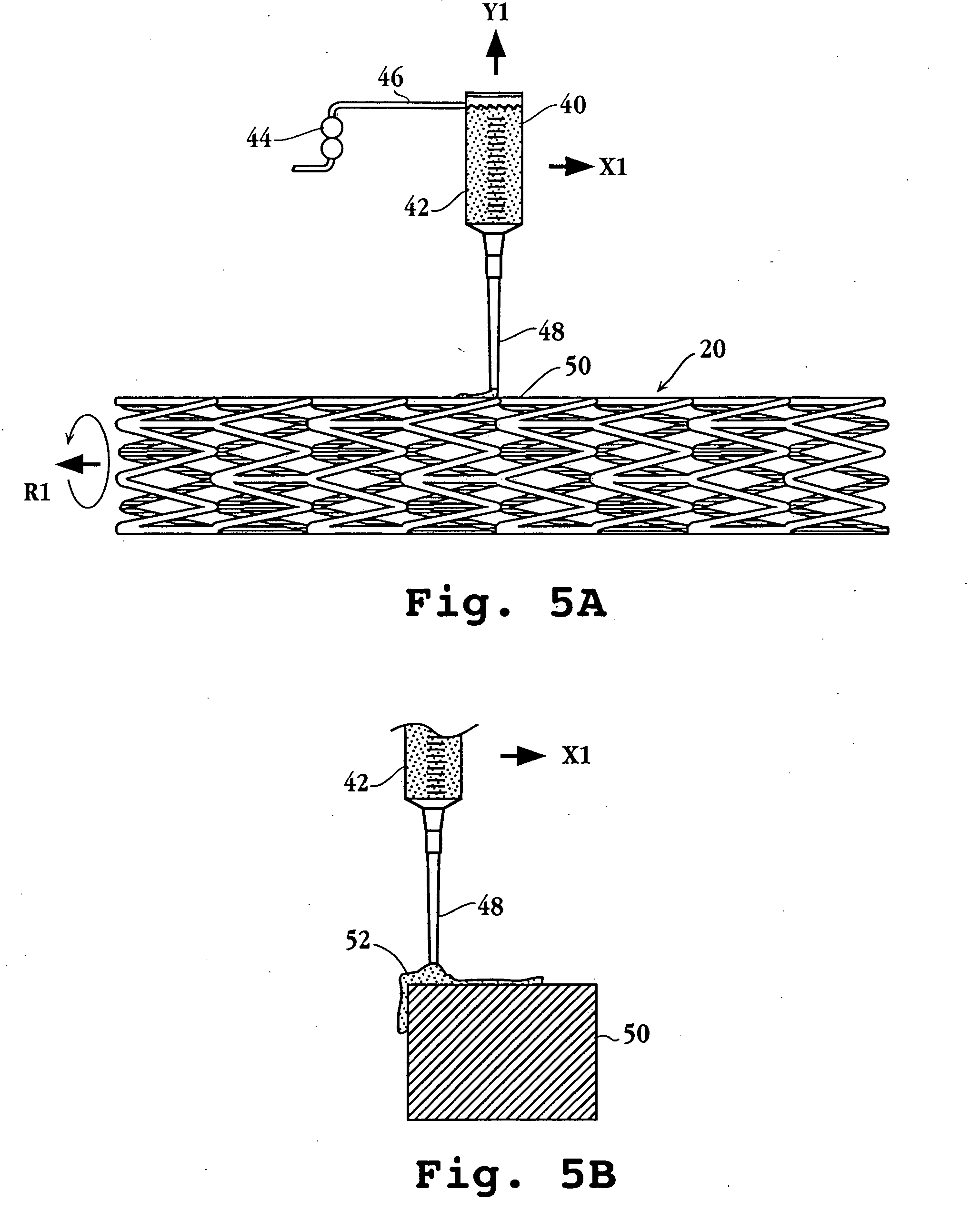
Drug releasing anastomosis devices and methods for treating anastomotic sites
ActiveUS7108701B2Reduce drug toxicityGood curative effectSuture equipmentsSurgical needlesBiological bodyReady to use
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The medical devices may be coated with any number of biocompatible materials. Therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may be mixed with the biocompatible materials and affixed to at least a portion of the medical device. These therapeutic drugs, agents or compounds may also further reduce a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. Various materials and coating methodologies may be utilized to maintain the drugs, agents or compounds on the medical device until delivered and positioned.
Owner:WYETH
Devices and methods for treating pain associated with tonsillectomies
Described here are devices and methods for treating one or more conditions or symptoms associated with a tonsil procedure. In some variations, a drug-releasing device may be at least partially delivered to one or more tonsillar tissues before, during, or after a tonsil procedure. In some variations, the drug-releasing device may be configured to be biodegradable. In other variations, the drug-releasing device may comprise one or more hemostatic materials or one or more adhesives. The drug-releasing device may be configured to release one or more drugs or agents, such as, for example, one or more analgesics, local anesthetics, vasoconstrictors, antibiotics, combinations thereof and the like.
Owner:INTERSECT ENT INC
Drug releasing coatings for medical devices
ActiveUS20080118544A1Avoid dependenceAvoid disadvantagesOrganic active ingredientsBiocideControlled releaseDrug release
The invention relates to a medical device for delivering a therapeutic agent to a tissue. The medical device has a layer overlying the exterior surface of the medical device. The layer contains a therapeutic agent and an additive. The additive has a hydrophilic part and a hydrophobic part and the therapeutic agent is not enclosed in micelles or encapsulated in particles or controlled release carriers.
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Drug-delivery endovascular stent and method for treating restenosis
InactiveUS6939376B2Efficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryRestenosisPoly dl lactide
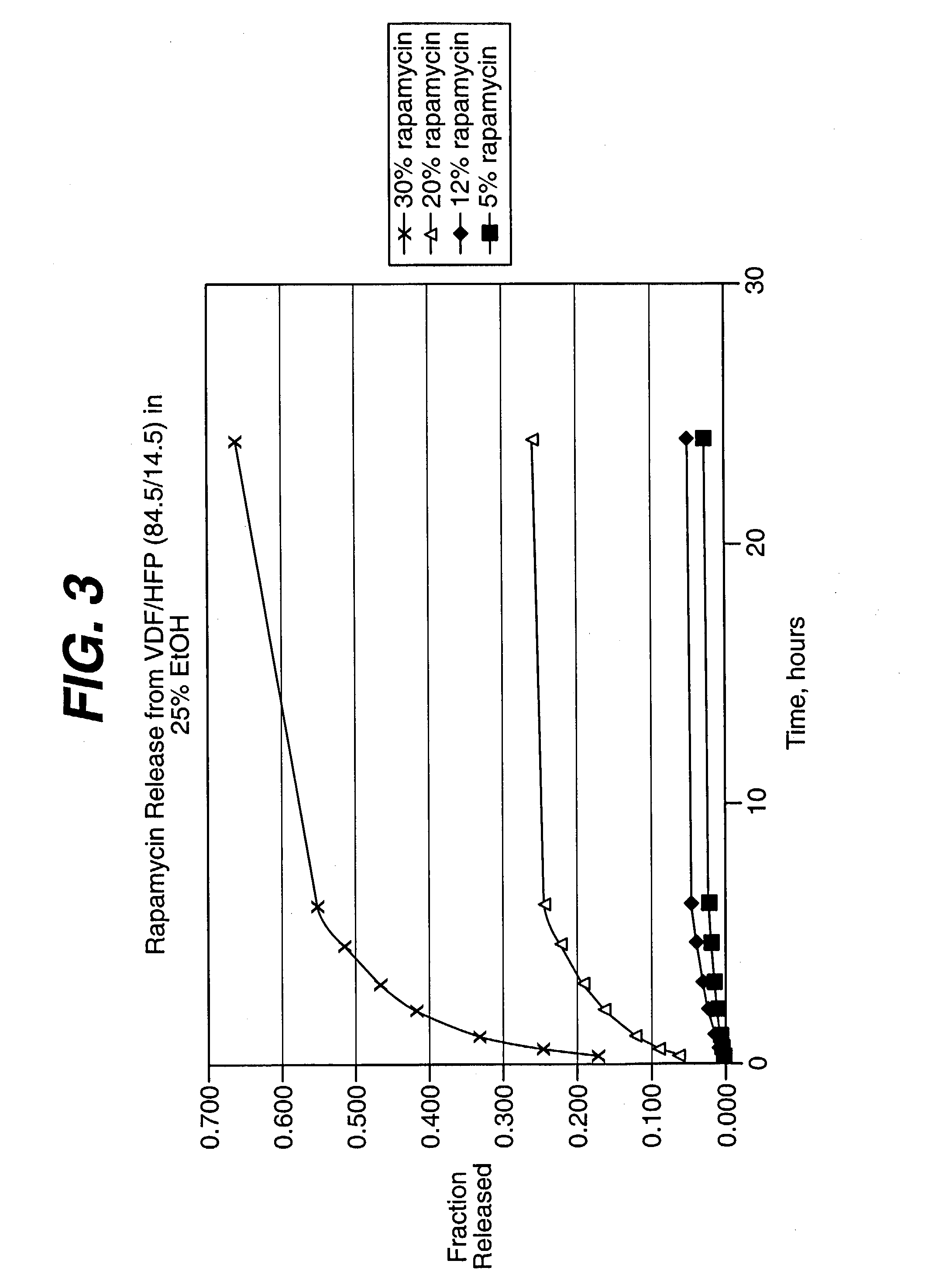
An intravascular stent and method for inhibiting restenosis, following vascular injury, is disclosed. The stent has an expandable, linked-filament body and a drug-release coating formed on the stent-body filaments, for contacting the vessel injury site when the stent is placed in-situ in an expanded condition. The coating releases, for a period of at least 4 weeks, a restenosis-inhibiting amount of a monocyclic triene immunosuppressive compound having an alkyl group substituent at carbon position 40 in the compound. The stent, when used to treat a vascular injury, gives good protection against clinical restenosis, even when the extent of vascular injury involves vessel overstretching by more than 30% diameter. Also disclosed is a stent having a drug-release coating composed of (i) 10 and 60 weight percent poly-dl-lactide polymer substrate and (ii) 40-90 weight percent of an anti-restenosis compound, and a polymer undercoat having a thickness of between 1-5 microns.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
Sustained release opioid formulations and method of use
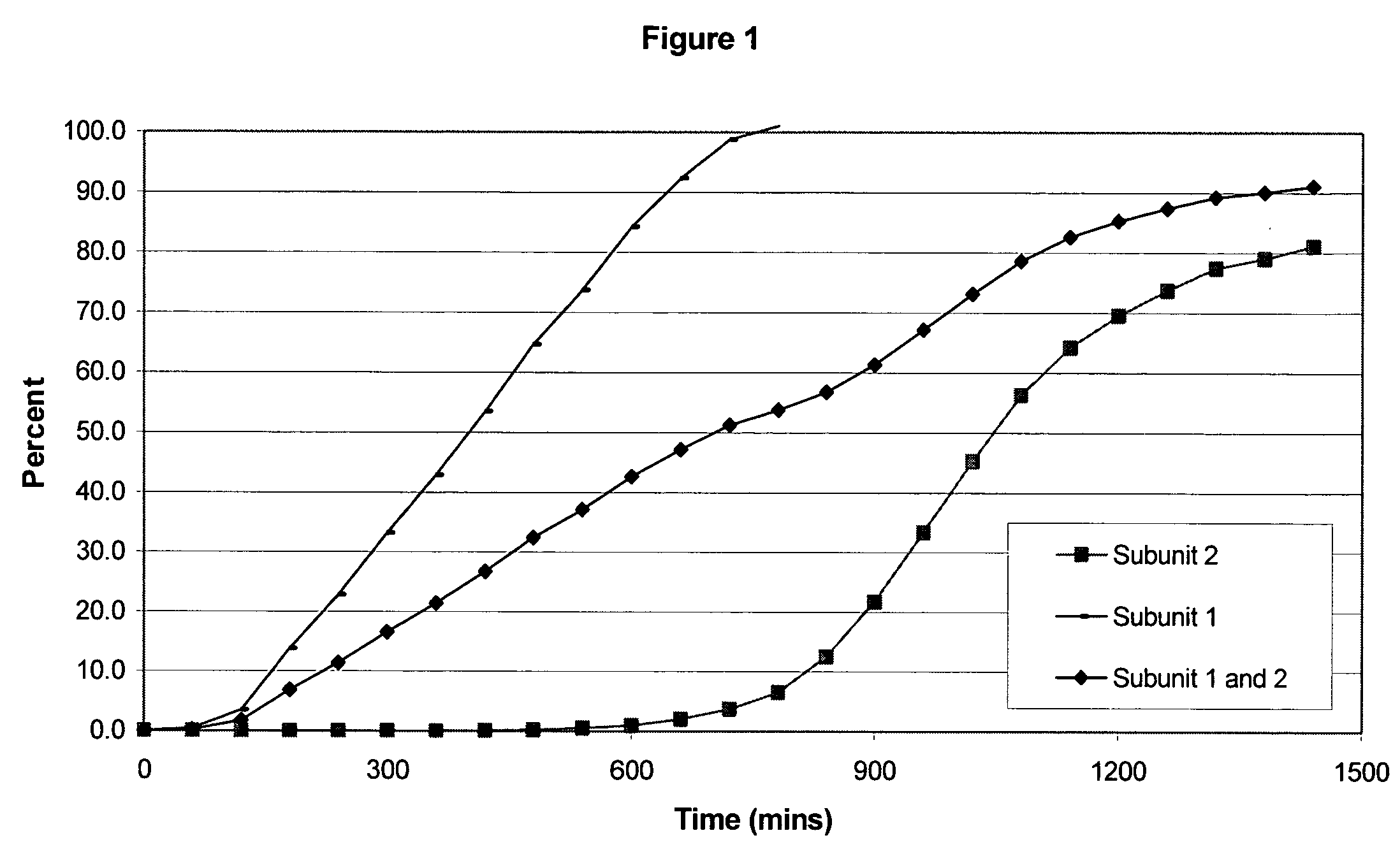
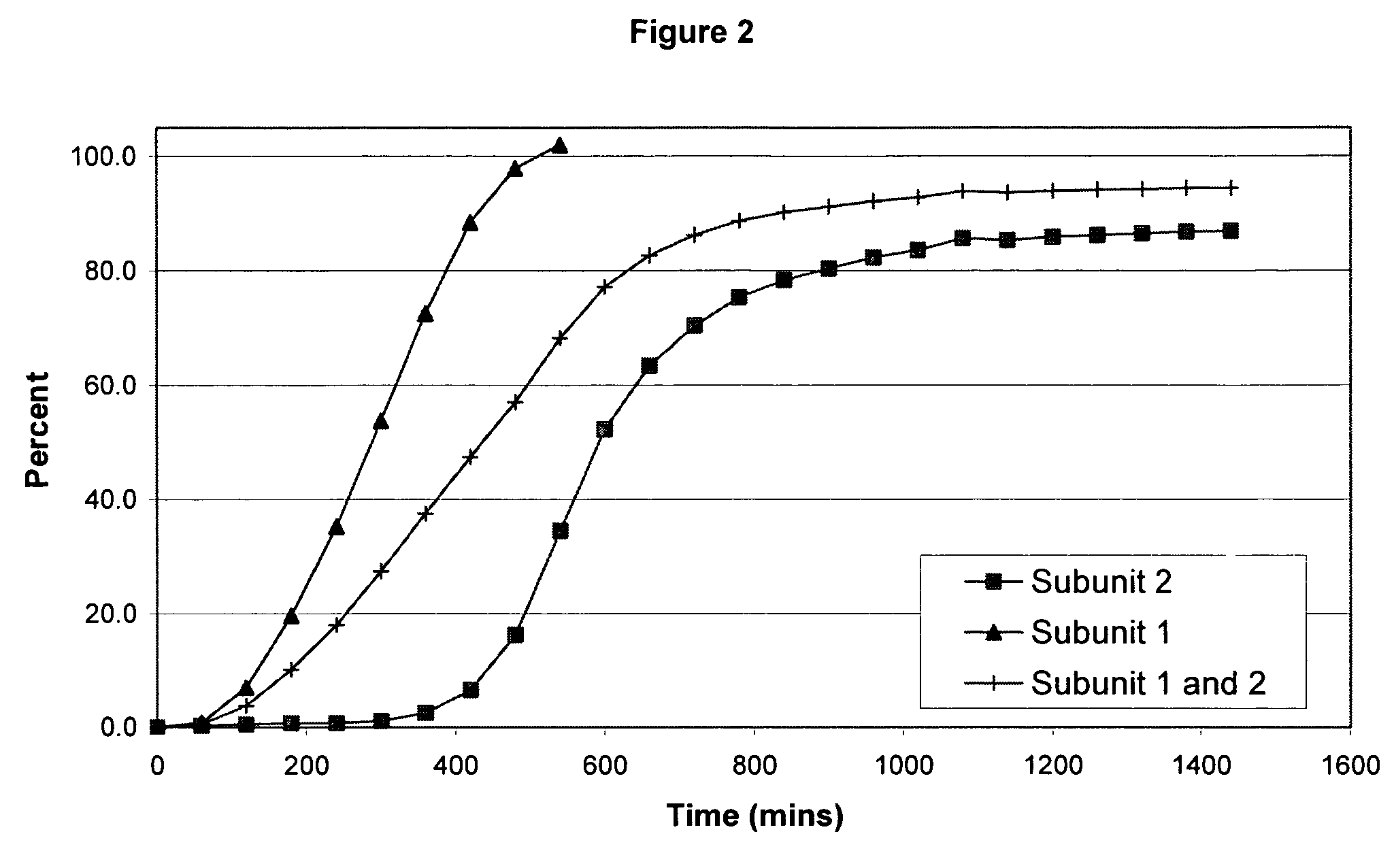
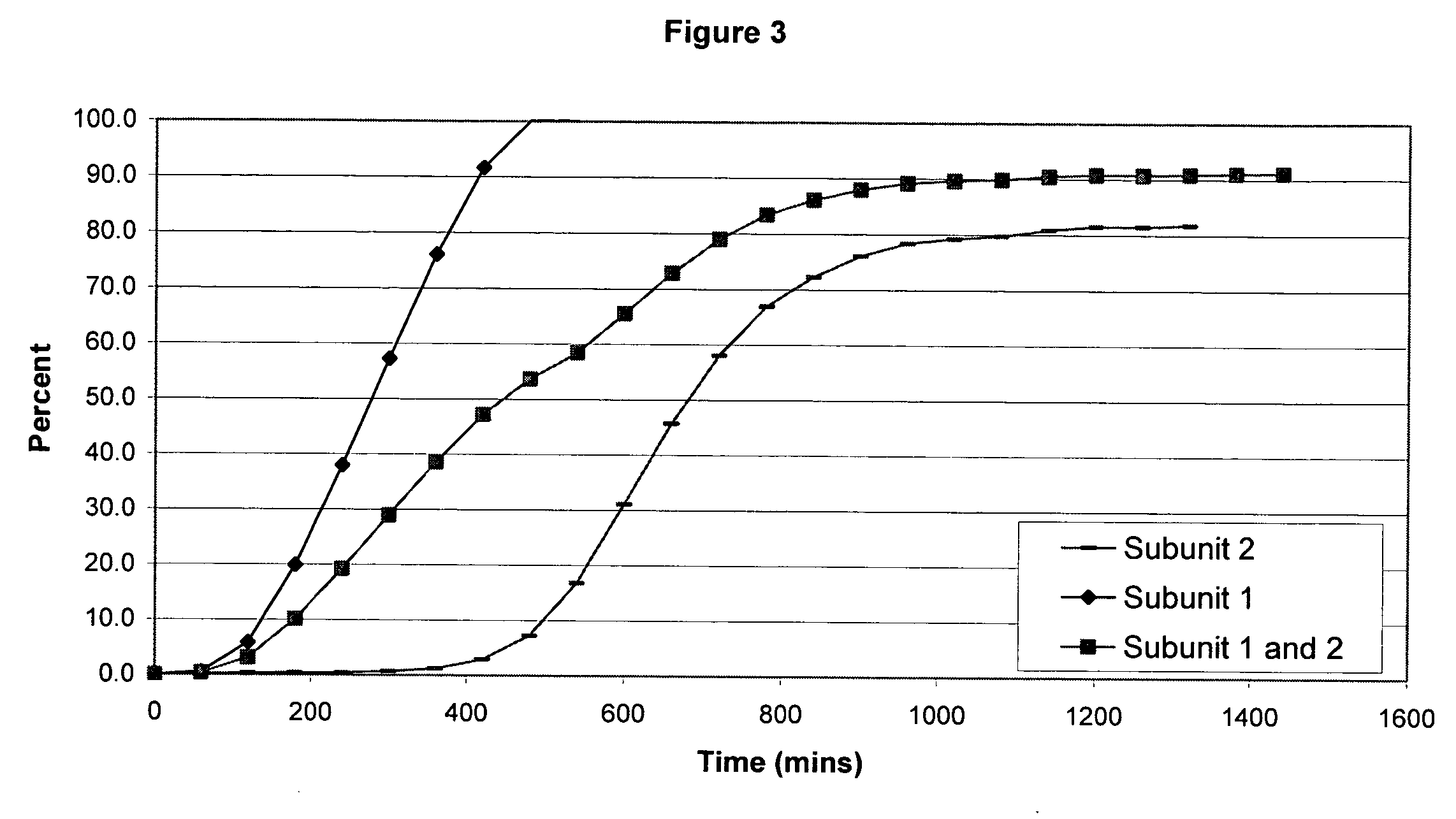
The invention combines two different subunits with different release profiles in novel sustained-release oral dosage forms. In particular, the oral dosage forms include a subunit that comprises an opioid analgesic and a sustained-release material, wherein the dissolution rate in-vitro of the subunit, when measured by the standard USP Drug Release test of U.S. Pharmacopeia XXVI (2003) <724>, is less than about 10% within about 6 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; less than about 10% within about 8 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; less than about 10% within about 10 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; or less than about 10% within about 12 hours and at least about 60% within about 24 hours; the dosage form providing a duration of therapeutic effect of about 24 hours.
Owner:ALPHARMA PHARMA
Oral devices and methods for controlled drug release
Drug dosage forms, which are housed in oral devices, and methods for controlled drug release are provided. The oral devices are permanently or removably inserted in the oral cavity and refilled or replaced as needed. The controlled drug release may be passive, based on the dosage form, or electronically controlled, for a high-precision, intelligent, drug delivery. Additionally, the controlled release may be any one of the following: release in accordance with a preprogrammed schedule, release at a controlled rate, delayed release, pulsatile release, chronotherapeutic release, closed-loop release, responsive to a sensor's input, release on demand from a personal extracorporeal system, release in accordance with a schedule specified by a personal extracorporeal system, release on demand from a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system, and release in accordance with a schedule specified by a monitoring center, via a personal extracorporeal system. Drug absorption in the oral cavity may be assisted by an electrotransport mechanism. The oral devices require refilling or replacement at relatively long intervals of weeks or months, maintain a desired dosage level in the oral cavity, hence in the gastrointestinal tract, for extended periods, address situations of narrow drug therapeutic indices, and by being automatic, ensure adherence to a prescribed medication regimen.
Owner:WOLFAF ANDY +1
Rapid Diffusion of Large Polymeric Nanoparticles in the Mammalian Brain
ActiveUS20130183244A1Reduce deliveryHigher drug payloadPowder deliveryNervous disorderGene deliveryHydrophilic coating
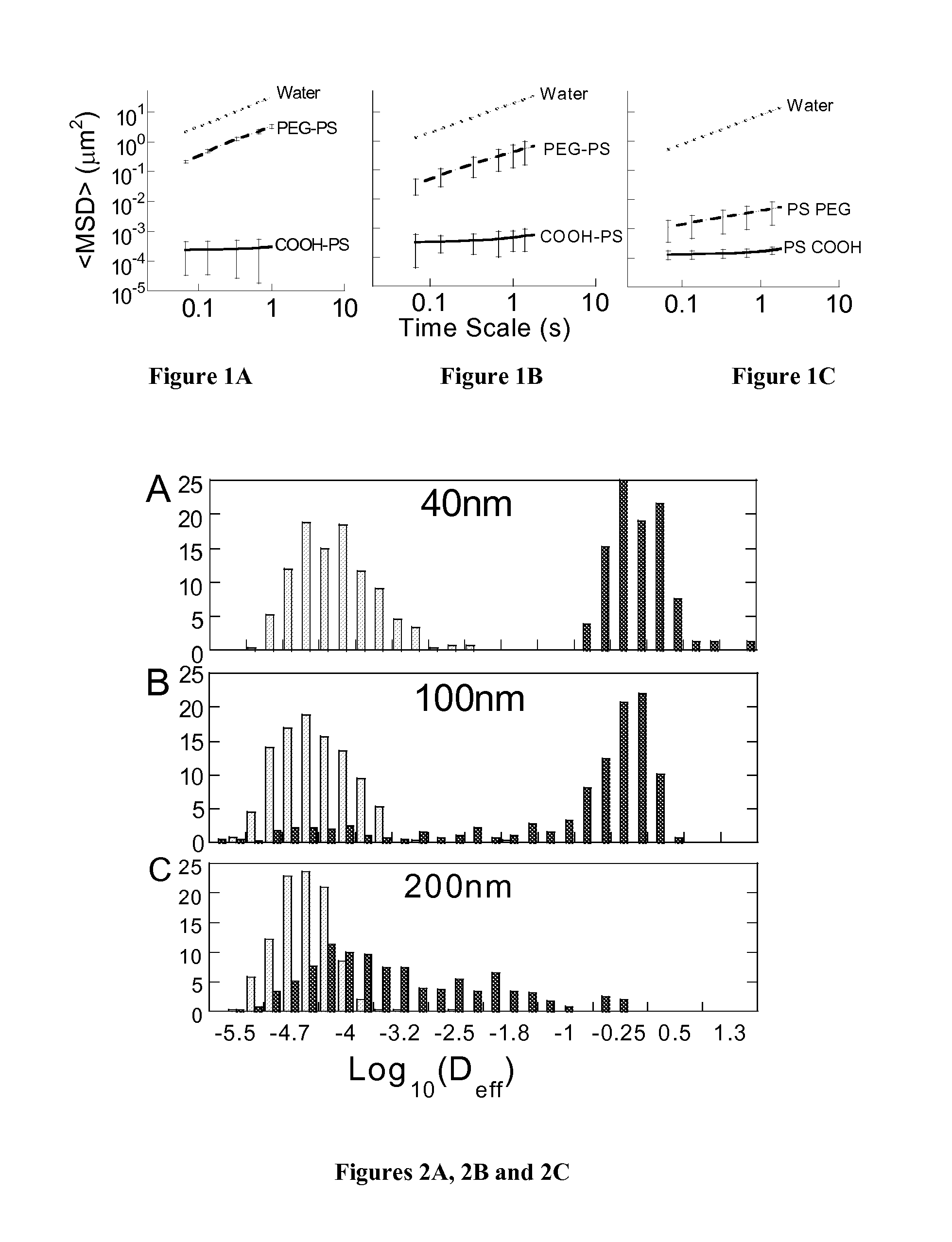
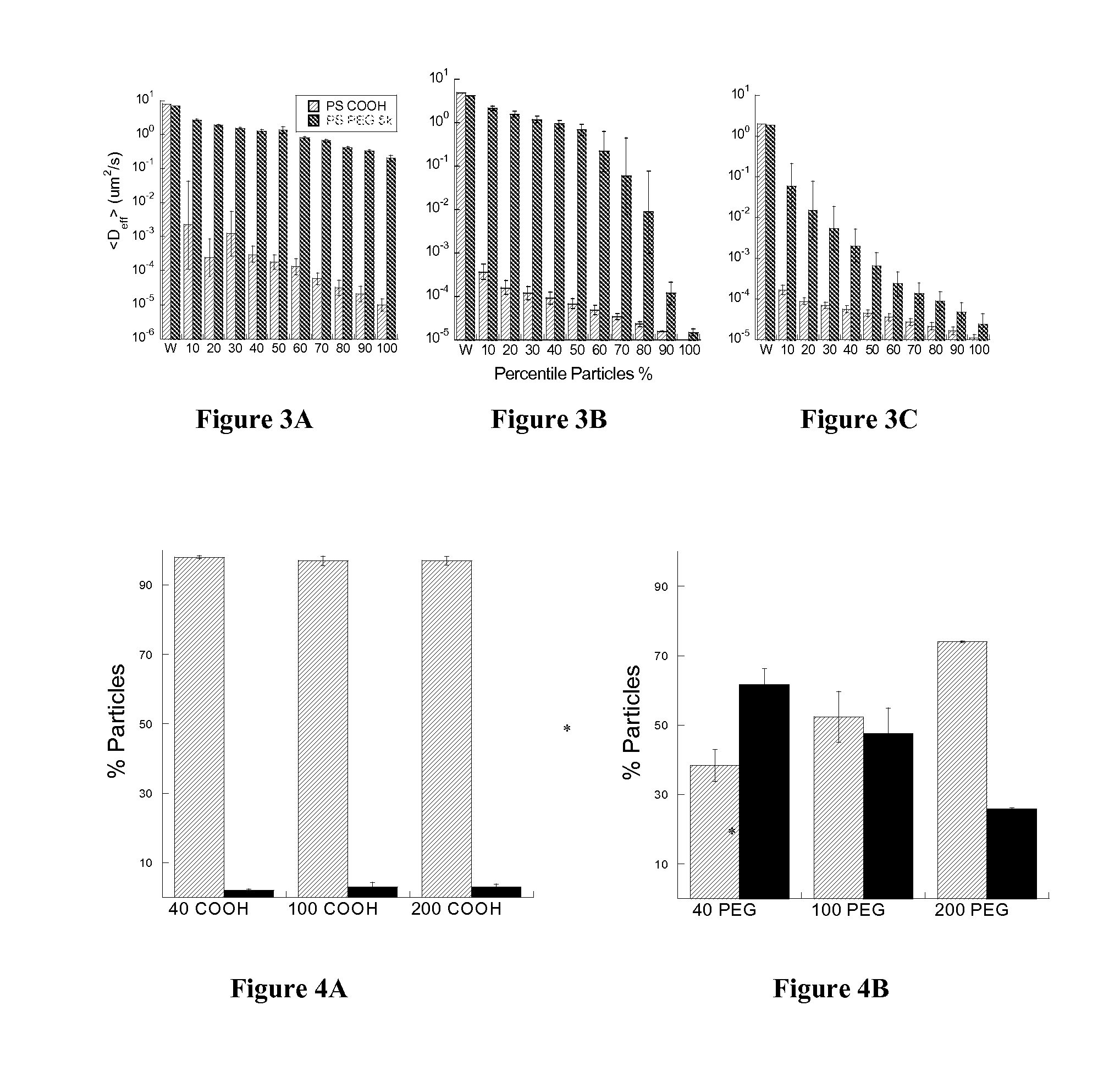
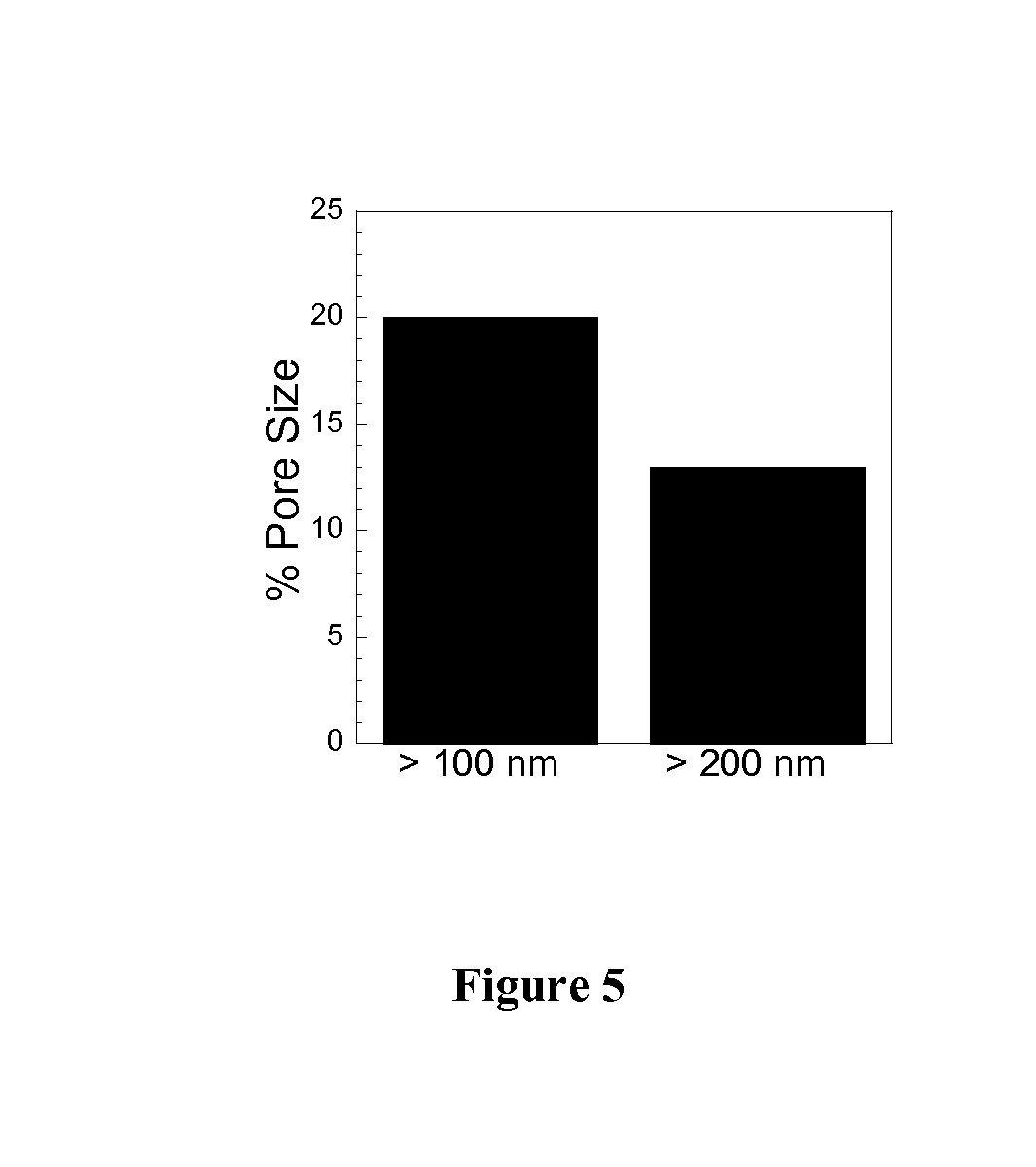
Non-adhesive particles as large as 110 nm can diffuse rapidly in the brain ECS, if coated with hydrophilic coatings such as PEG coatings and preferably having neutral surface charge. The ability to achieve brain penetration with larger particles will significantly improve drug and gene delivery within the CNS since larger particles offer higher drug payload, improved drug loading efficiency, and significantly longer drug release durations.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Medical device rapid drug releasing coatings comprising a therapeutic agent and a contrast agent
ActiveUS20080255510A1Improve the immunityReduction tendencyBiocideMedical devicesTherapeutic effectDrug release
The invention relates to a coated medical device for rapid delivery of a therapeutic agent to a tissue in seconds to minutes. The medical device has a layer overlying the exterior surface of the medical device. The layer contains a therapeutic agent, a contrast agent, and an additive.
Owner:LUTONIX INC
Medical articles having regions with polyelectrolyte multilayer coatings for regulating drug release
The medical articles which comprise the following: (a) a ceramic or metallic region whose surface comprises a plurality of depressions, (b) a multilayer coating region comprising multiple polyelectrolyte layers deposited over the surface of the ceramic or metallic region; and (c) a therapeutic agent disposed beneath or within the multilayer coating region. According to another aspect of the present invention, medical articles are provided, which comprise: (a) a ceramic or metallic region, (b) a multilayer coating region comprising multiple polyelectrolyte layers deposited over a surface of the ceramic or metallic region, the multilayer coating region comprising a plurality of protuberances; and (c) a therapeutic agent disposed within regions beneath the protuberances. Also described herein are methods of making such medical articles, and methods of administering a therapeutic agent to a patent using such medical articles.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Drug-delivery endovascular stent and method of forming the same
ActiveUS20050038505A1Prevent restenosisEfficient releaseOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPolymer substrateInsertion stent
An intravascular stent and method for inhibiting restenosis, following vascular injury, is disclosed. The stent has an expandable, linked-filament body and a drug-release coating formed on the stent-body filaments, for contacting the vessel injury site when the stent is placed in-situ in an expanded condition. The coating releases, for a period of at least 4 weeks, a restenosis-inhibiting amount of a monocyclic triene immunosuppressive compound having an alkyl group substituent at carbon position 40 in the compound. The stent, when used to treat a vascular injury, gives good protection against clinical restenosis, even when the extent of vascular injury involves vessel overstretching by more than 30% diameter. Also disclosed is a stent having a drug-release coating composed of (i) 10 and 60 weight percent poly-d / -lactide polymer substrate and (ii) 40-90 weight percent of an anti-restenosis compound, and a polymer undercoat having a thickness of between 1-5 microns.
Owner:BIOSENSORS INT GROUP
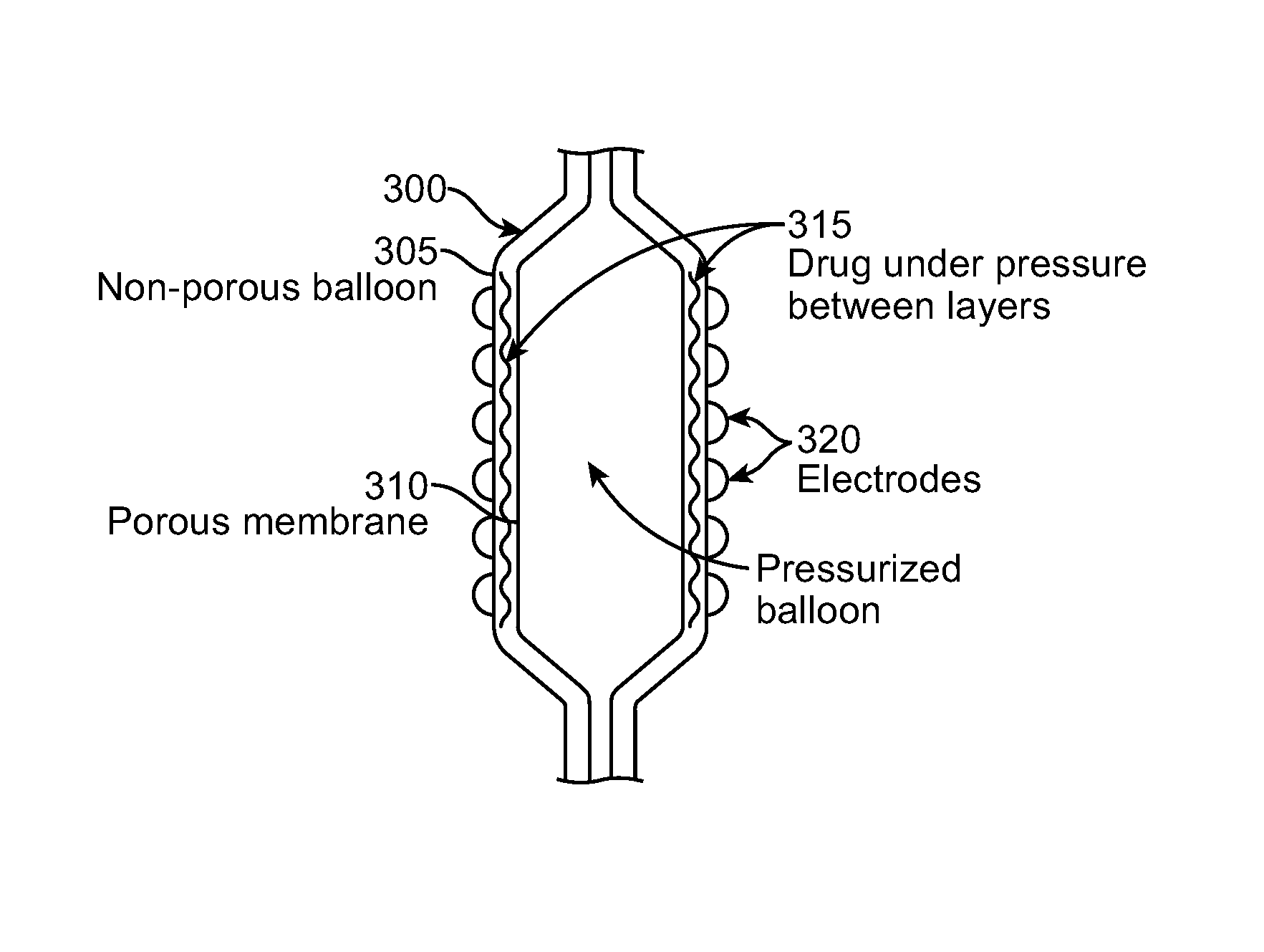
Selective drug delivery in a lumen
Methods and systems are disclosed for selective drug or fluid delivery in a lumen through a coating or fluid delivery channels. One system includes an elongate catheter having a proximal end and a distal end with an axis therebetween, the catheter having a radially expandable balloon near the distal end and an energy delivery portion proximate the balloon for transmission of energy, a thermally changeable coating having a releasable drug coupled to the balloon, the thermally changeable coating being oriented to be urged against the body tissue when the expandable balloon expands and an energy source operatively coupled to the energy delivery portion configured to energize the energy delivery portion to heat and liquefy the thermally changeable coating to release the drug to the body tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
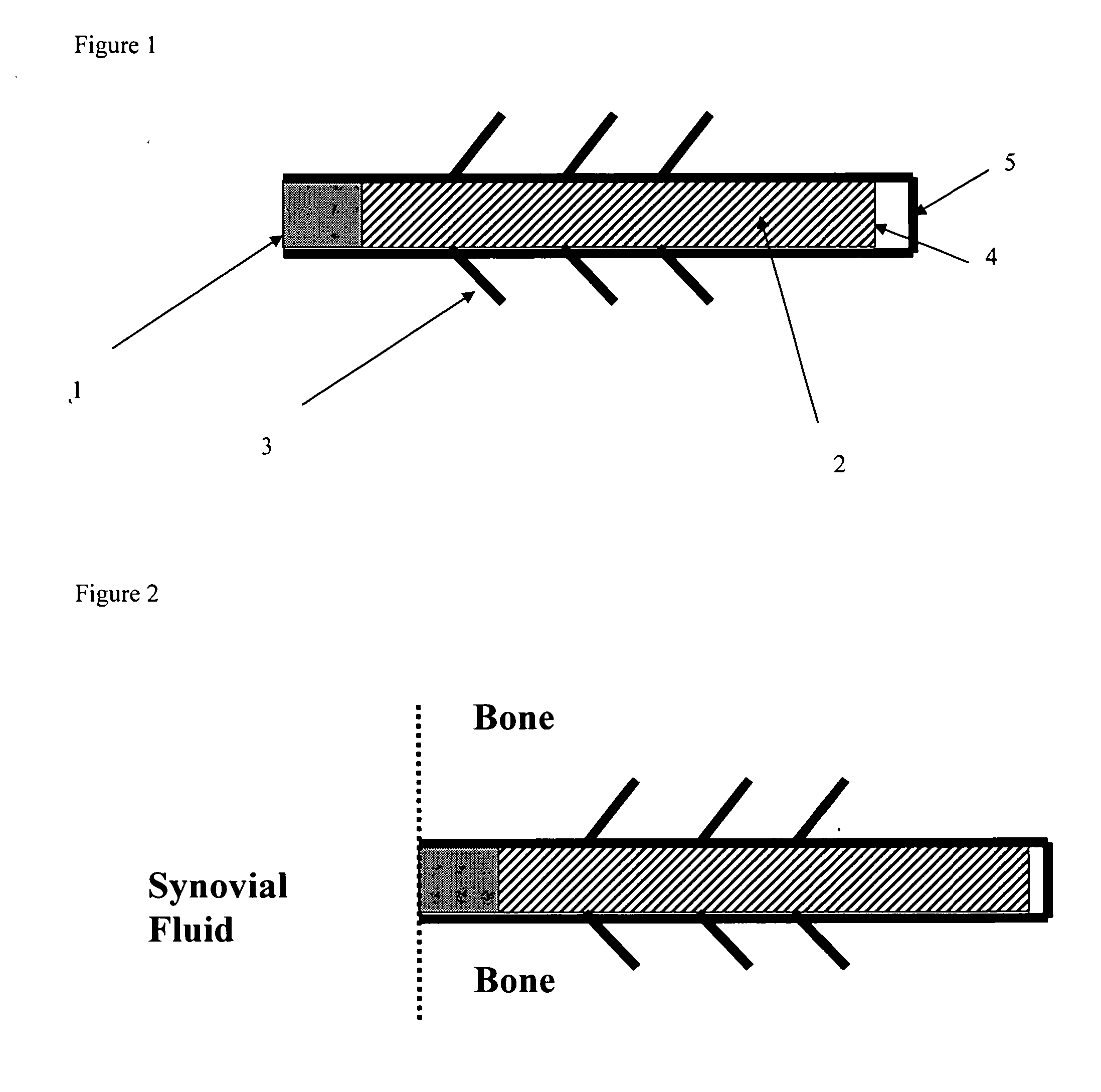
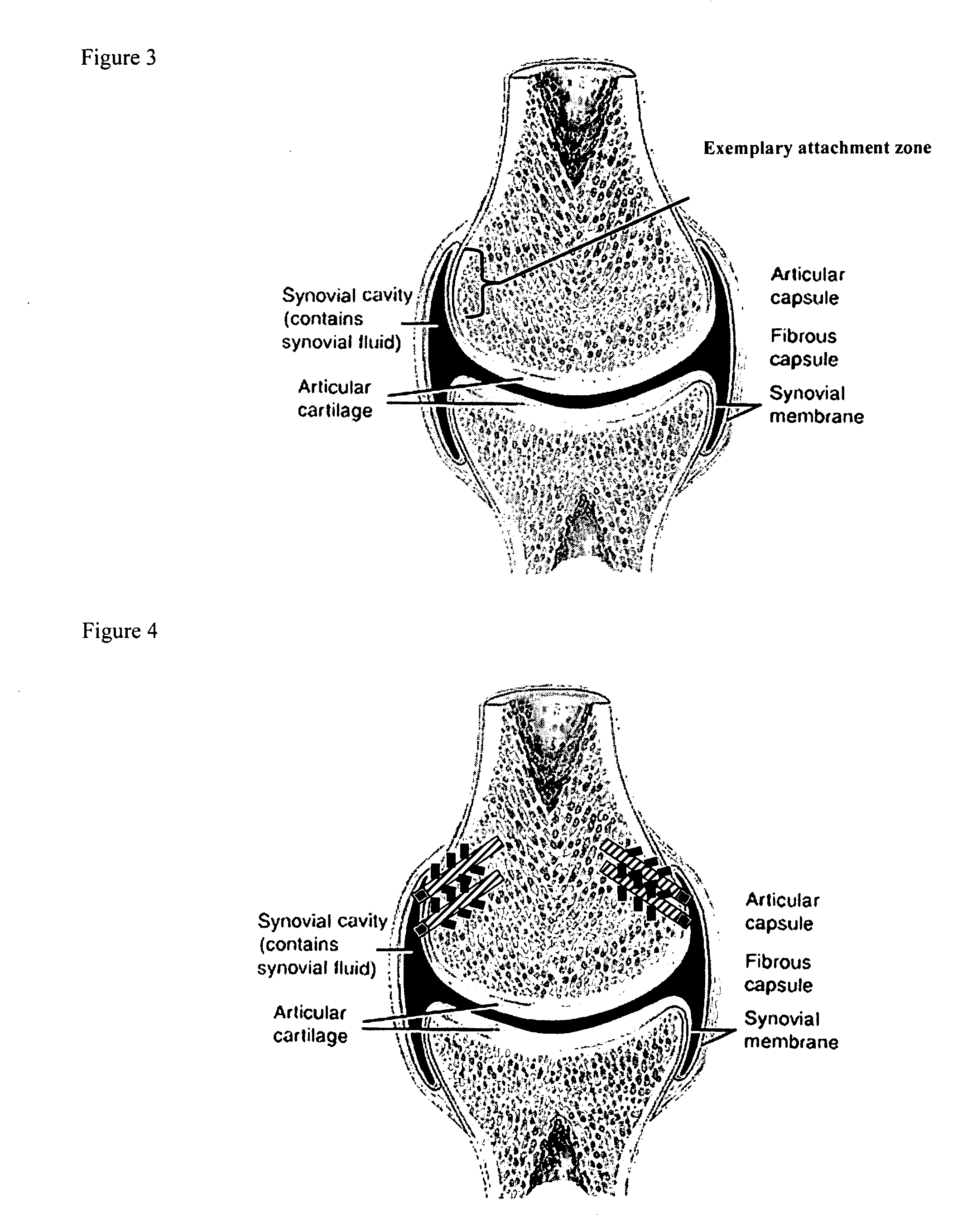
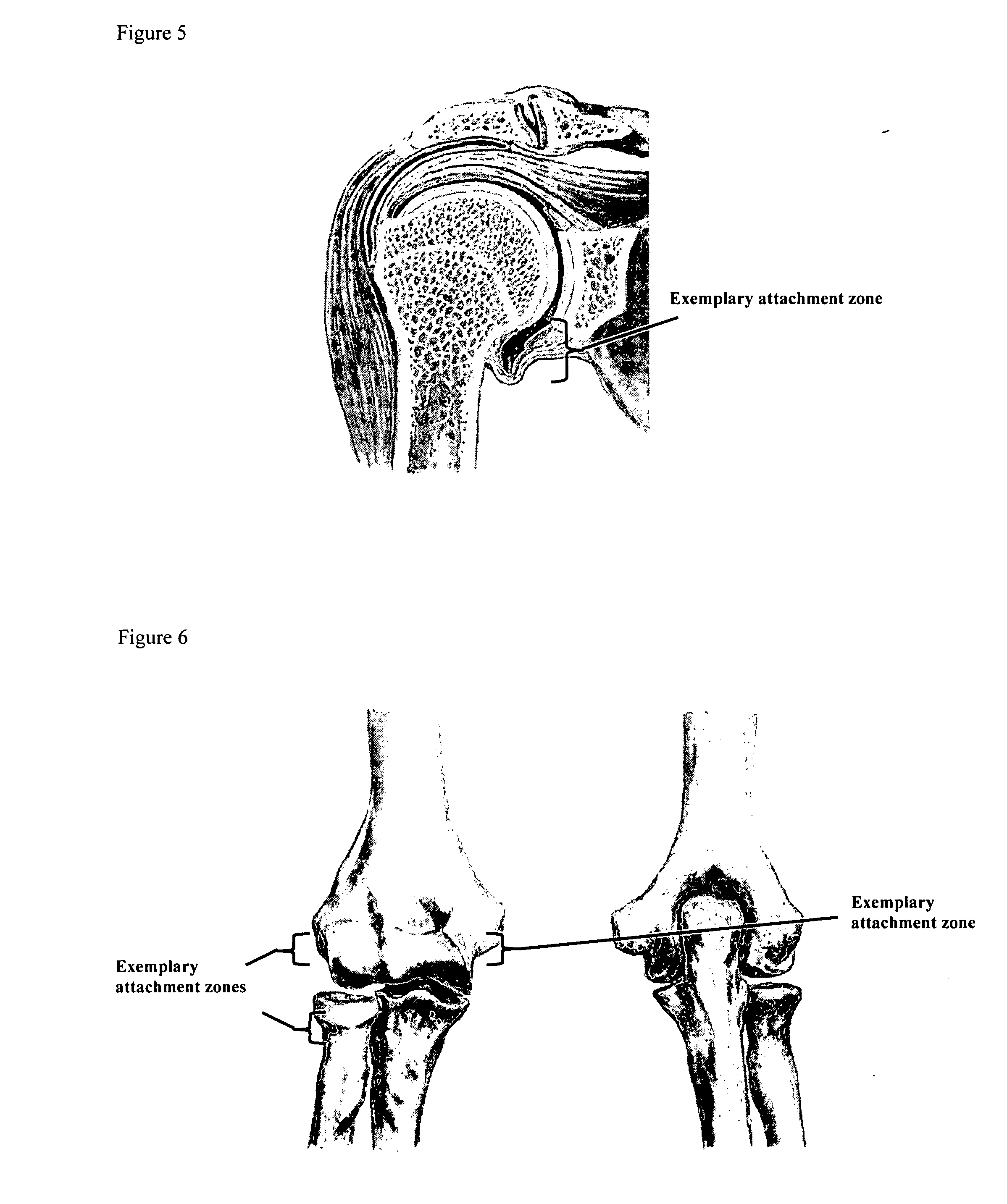
Drug delivery to a joint
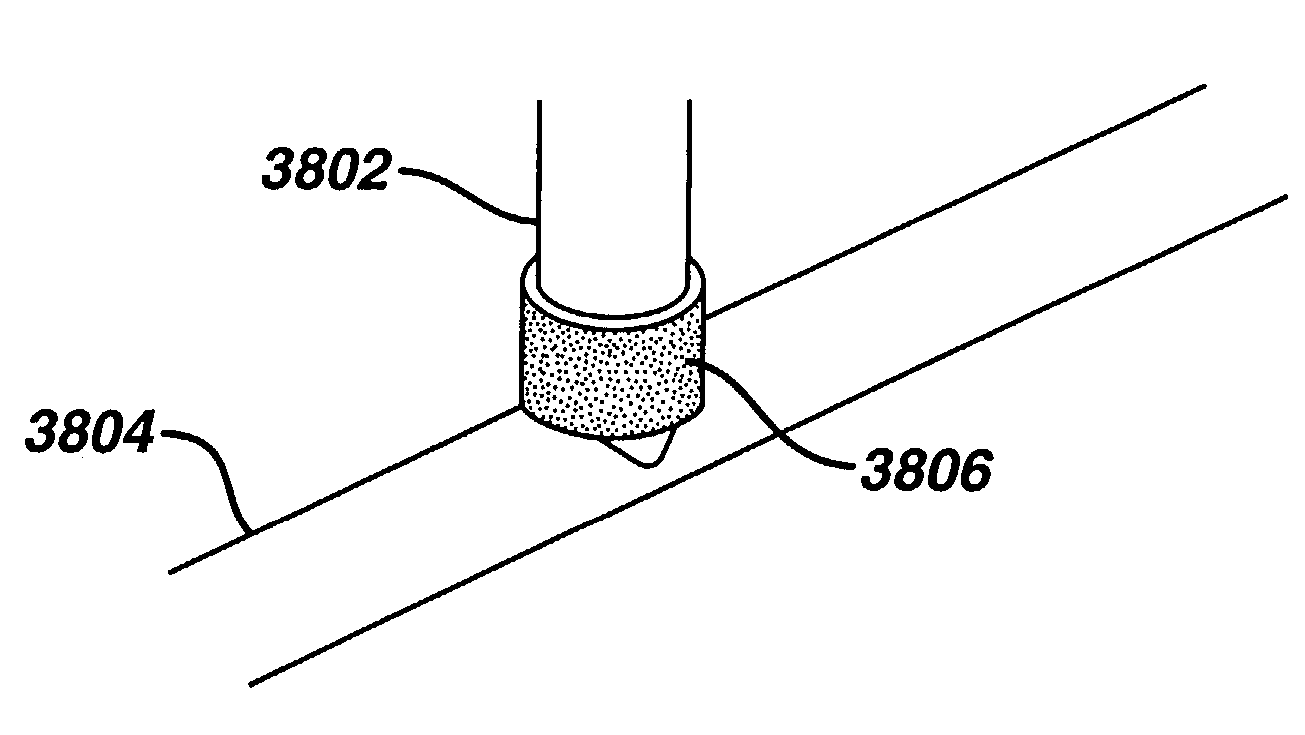
A method of intra-articular drug delivery may include selecting an attachment zone in a synovial joint; affixing a drug release device in the attachment zone, the drug release device comprising a base affixable in the attachment zone, a sustained-release drug carrier, and a drug, the device positioned so that the device releases the drug into the synovial fluid of the synovial joint, and so that agitation of the synovial fluid facilitates elution of the drug from the drug release device.
Owner:NEW YORK SOC FOR THE RUPTURED & CRIPPLED MAINTAINING THE HOSPITAL FOR SPECIAL SURGERY
Controlled release preparation
InactiveCN101987081AImprove stabilityRelease impact mitigationInorganic non-active ingredientsSuppositories deliveryParticulatesChemical reaction
The invention discloses a controlled release preparation with improved performance. The controlled release preparation comprises a core containing medicament and a controlled release film covering the outside of the core and being almost insoluble in water as well as stomach and intestines digestive juice. The controlled release film comprises particulate matters of a water soluble medicinal additive, the water-soluble medicinal additive is covered by a polymer film which can be soluble in the stomach and / or intestines digestive juice but almost insoluble in water, the polymer and the medicinal additive can not produce chemical reaction or can produce chemical reaction but do not produce water-insoluble non-gaseous products and the pharmaceutically unacceptable products, and the amount of the polymer is no more 700% of that of the medicinal additive. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the controlled release preparation. The controlled release preparation has the advantages of improved medicament release reproducibility, reduced medicament release lag time, accelerated medicament release and improved bioavailability, can realize located controlled release, delayed controlled release and interval type or pulse type controlled release of the medicament in the gastrointestinal tract, and the like.
Owner:钟术光
Porous coatings for drug release from medical devices
InactiveUS20050079199A1Increase ratingsIncrease load capacityWound drainsSurgeryPorous coatingSurface layer
Extravascular implantable medical devices are described. The devices include a polymeric layer comprising a polymeric matrix and pores. Therapeutic agent is loaded in the matrix, in the pores, or in the matrix and the pores. The devices include a structural surface layer. Additional therapeutic agent may be loaded in or on the surface layer. The devices may also include one or more intermediate layer, into or onto which additional therapeutic agent may be loaded.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Selective Drug Delivery In a Lumen
InactiveUS20100125239A1Lower impedanceAvoid treatmentUltrasound therapyStentsDrug releaseBody tissue
Methods and systems are disclosed for selective drug or fluid delivery in a lumen through a coating or fluid delivery channels. One system includes an elongate catheter having a proximal end and a distal end with an axis therebetween, the catheter having a radially expandable balloon near the distal end and an energy delivery portion proximate the balloon for transmission of energy, a thermally changeable coating having a releasable drug coupled to the balloon, the thermally changeable coating being oriented to be urged against the body tissue when the expandable balloon expands and an energy source operatively coupled to the energy delivery portion configured to energize the energy delivery portion to heat and liquefy the thermally changeable coating to release the drug to the body tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
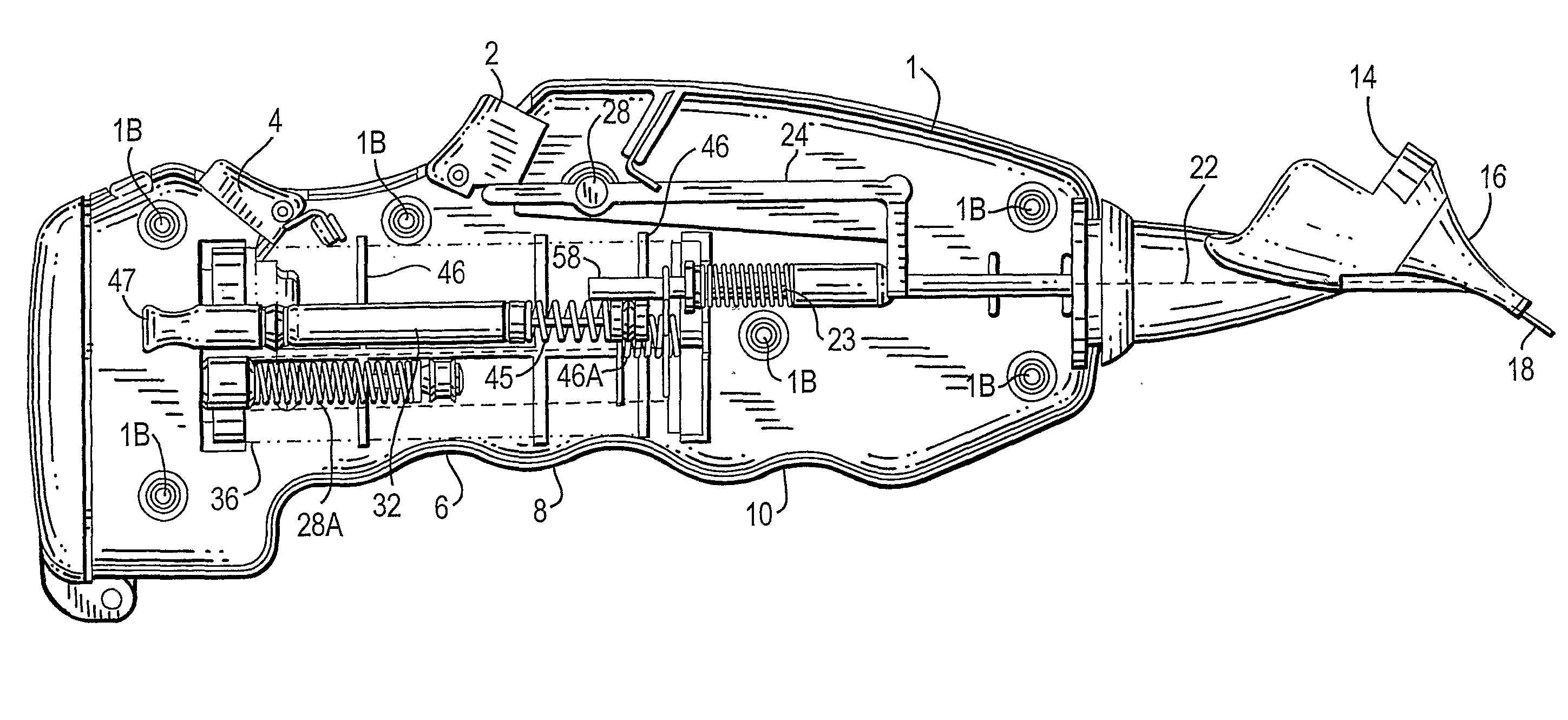
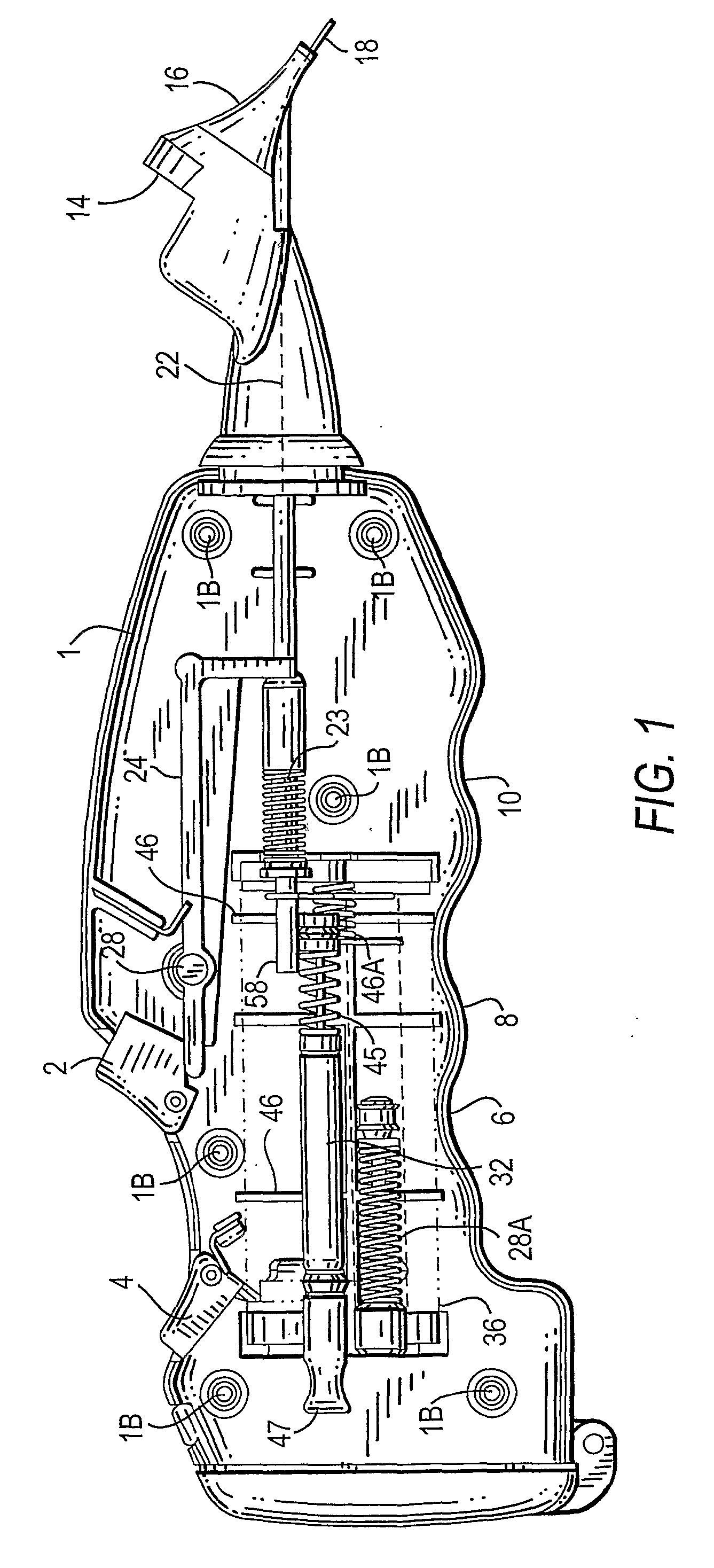
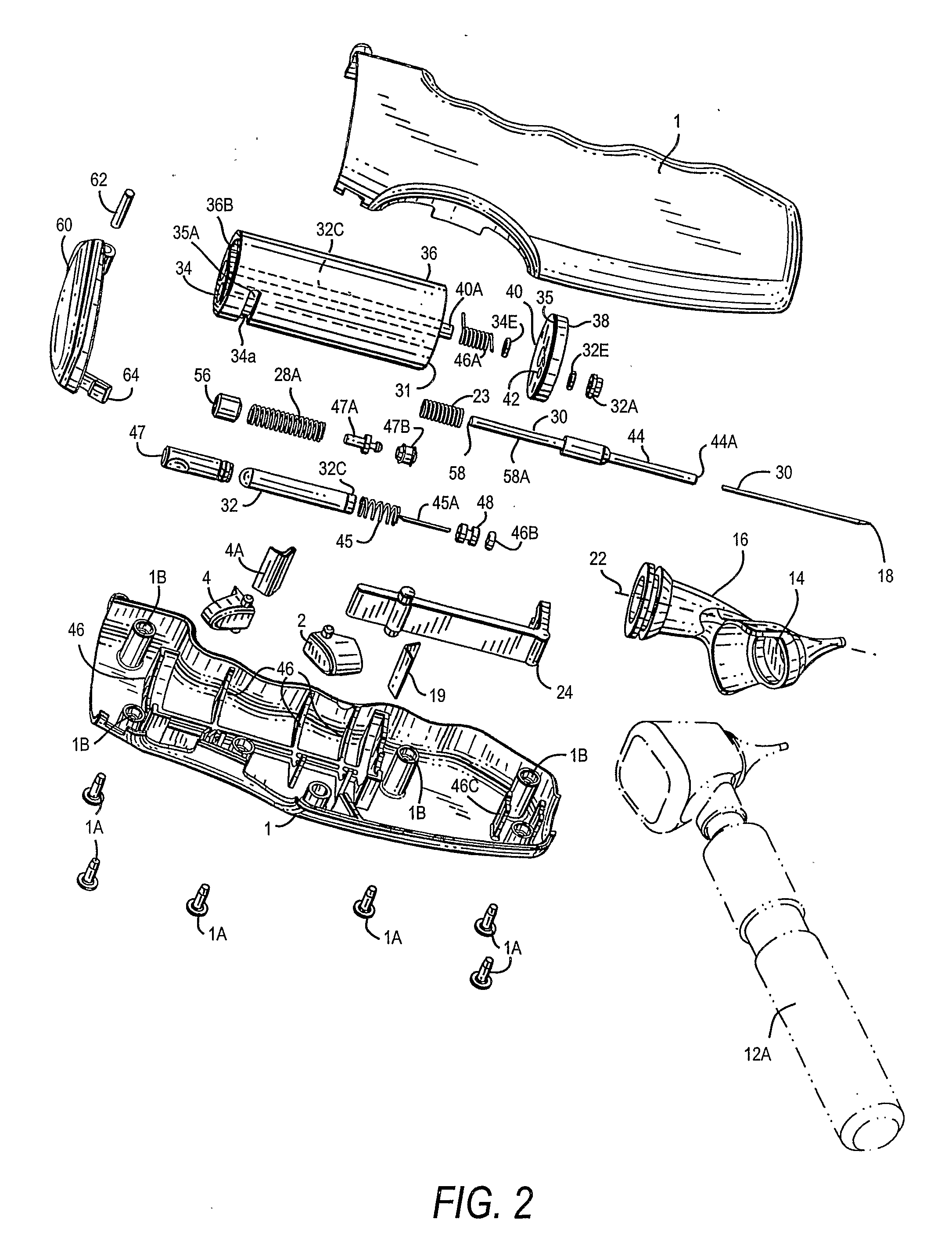
Combined otic aspirator and medication dispenser
A device for making an incision in the tympanic membrane, withdrawing fluid from the tympanic cavity and administering a medicament to the space behind the tympanic membrane is provided. The device has a barrel-shaped casing (1) having a rotatable end turret (38). A first trigger (2) allows a shaft (18) to pierce the tympanic membrane and a tubular vacuum cartridge (32). The cartridge allows aspiration of fluid. A second trigger (4) causes medicament (34) to be released into the space behind the tympanic membrane.
Owner:AURIS MEDICAL LLC
Methods of manufacturing medical devices for controlled drug release
The present invention is a medical device for controlling the release of an active agent. The medical device has a supporting structure having a porous body disposed therein. At least one elution rate controlling matrix containing an effective amount of at least one active agent is disposed within the pores of the porous body in a manner that protects the matrix from mechanical damage. The medical device may therefore be used for controlled drug release applications. Additionally, the present invention discloses a method for using the medical device for the treatment and prevention of diseases in mammals. This invention further relates to a method for using the medical device for treating and preventing vascular diseases.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC
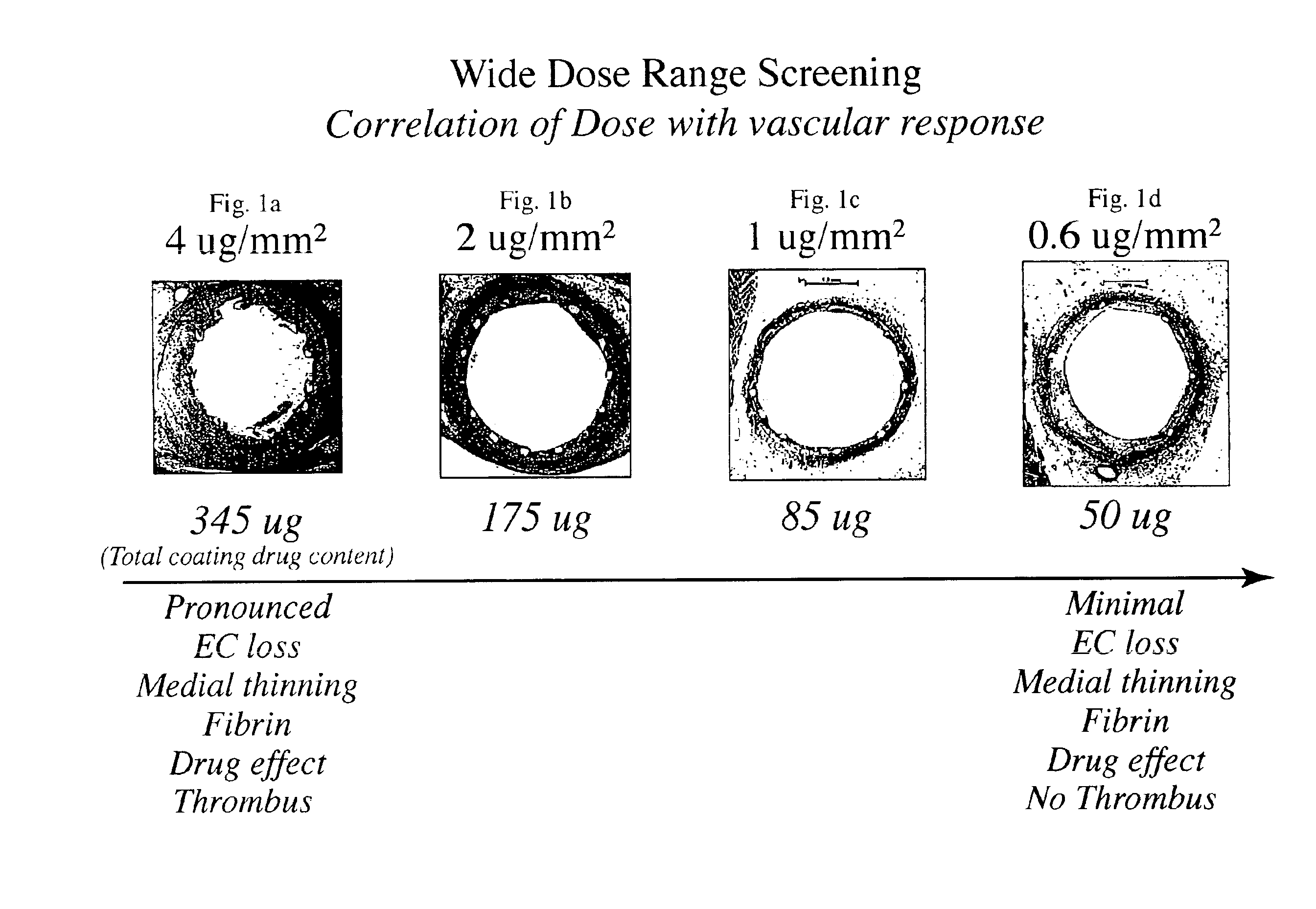
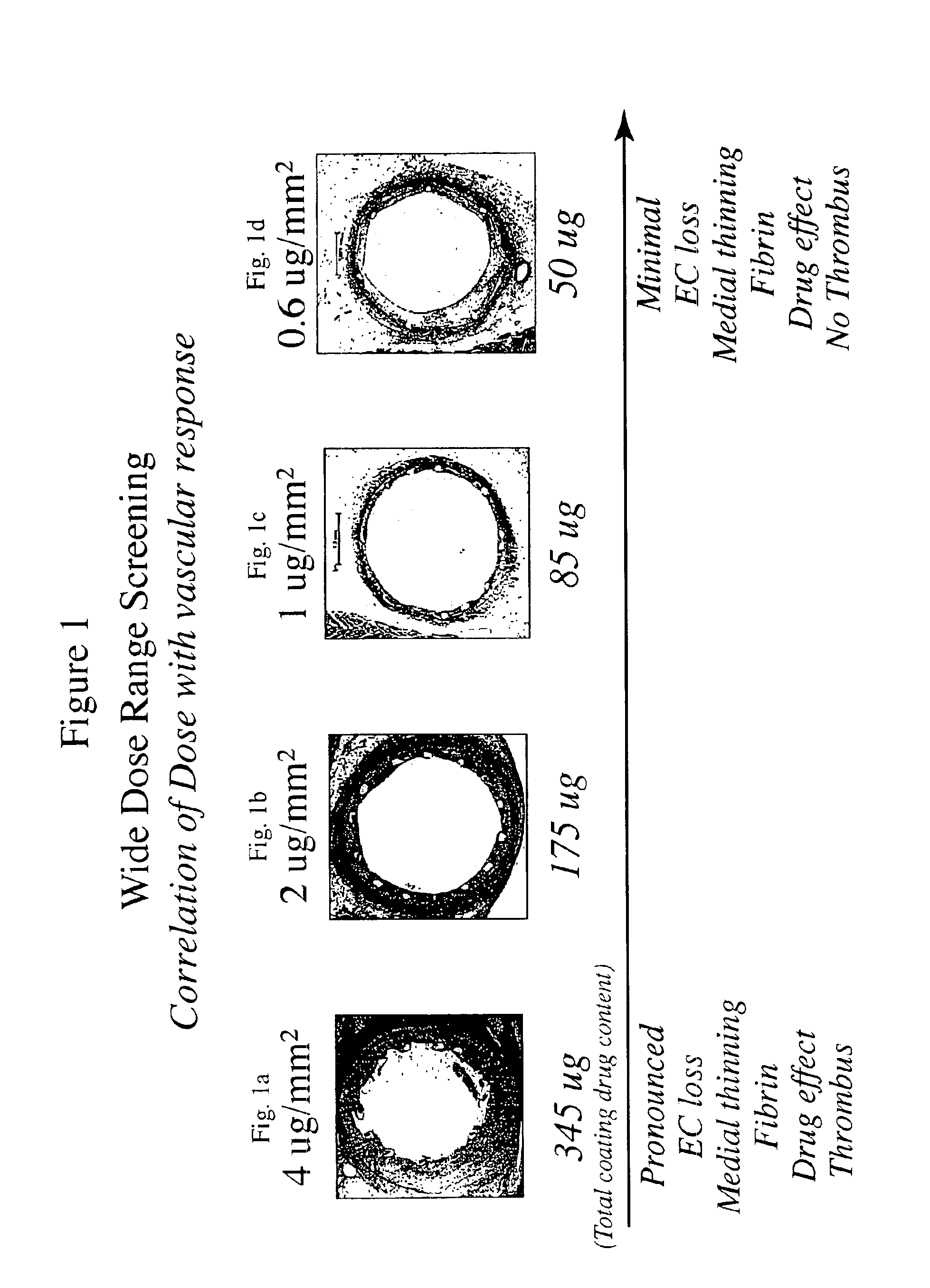
Optimized dosing for drug coated stents
The inventors have found that both the drug dose and drug release profiles are significant factors for the safety and efficacy of drug coated stents. The inventors have identified optimum dosing and release kinetics for drug coated stents. In particular, the inventors have determined dosing and release kinetics that permit the delivery of the lowest effective drug dosage, thus enhancing patient safety and minimizing any side effects from the drug.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
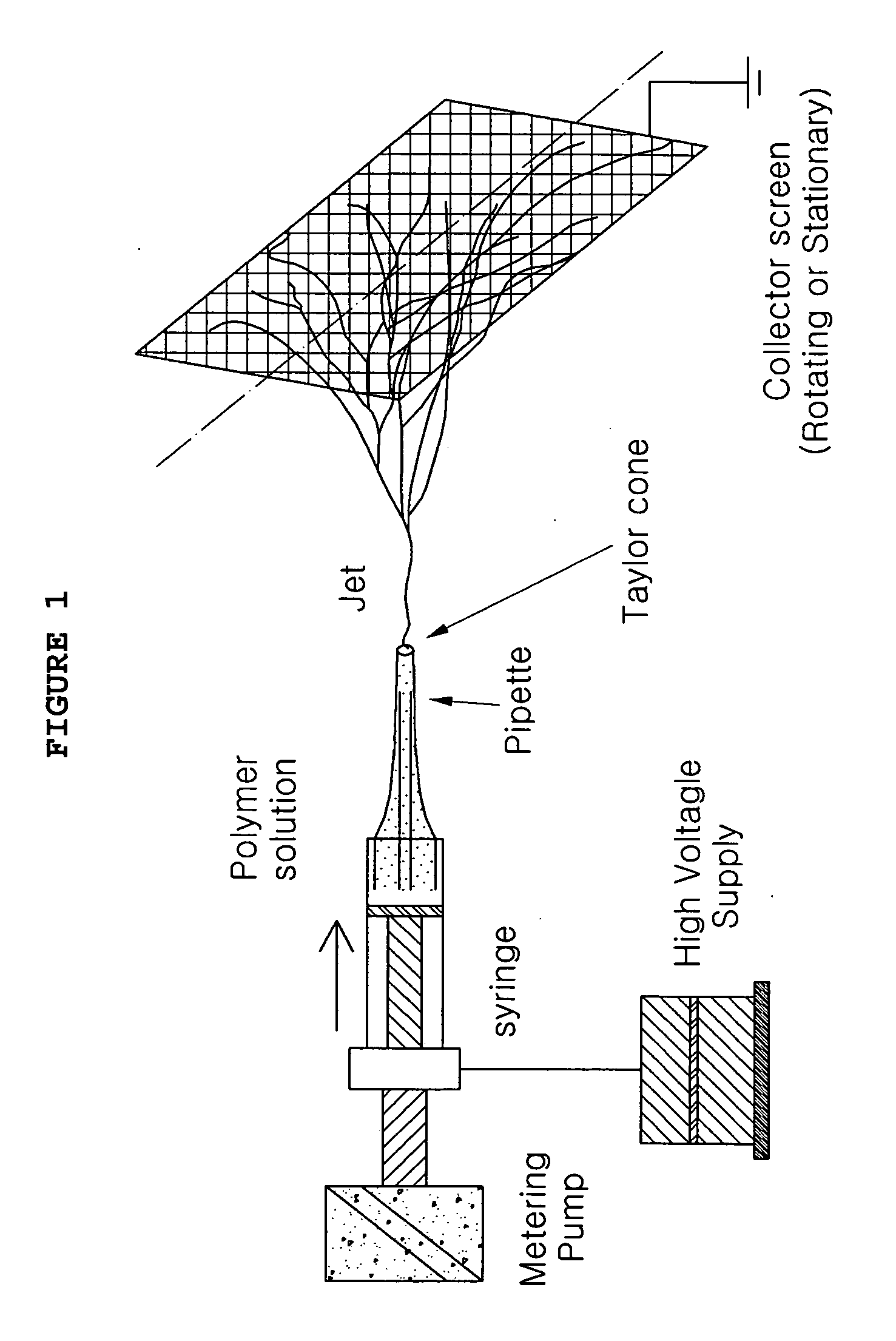
Nanofibrous nonwoven membrane of silk fibroin for guided bone tissue regeneration and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060095137A1Easy to controlSimple processMaterial nanotechnologyElectric discharge heatingBone tissueBiocompatibility Testing
The present invention relates to a membrane for guided bone tissue regeneration and, more particularly, to a membrane for guided bone tissue regeneration having a structure that silk fibroin nanofibers obtained by removing sericin from silk fibers are formed as a nonwoven, and a manufacturing method thereof. A membrane for guided bone tissue regeneration according to the present invention has a predetermined strength, biocompatibility, and biodegradability, and may maintain a sustained drug release system, when drugs are added in the manufacturing process. Additionally, a membrane for guided bone tissue regeneration according to the present invention may be modified corresponding to the condition of usage, because a thickness of the membrane may be adjusted by controlling fineness of nanofibers, compactness of nanofibers, and pore size of a multiporous structure may be adjusted, in a nonwoven manufacturing process. A nanofibrous membrane for guided bone tissue regeneration according to the present invention is manufactured by freezing rapidly, drying a silk fibroin solution obtained by removing sericin from silk fibers, and by electrospinning after dissolving the dried silk fibroin in an electrospinning solvent. The membrane according to the present invention has excellent adhesion and air permeability, and is thereby effective in regeneration of damaged periodontal tissues.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Drug eluting medical device with an expandable portion for drug release
The present invention relates to a medical device and a method of delivering a drug to a target circulation or tissue. The medical device has an expandable portion which is fabricated from a porous elastomeric material with a plurality of voids therein. The voids are loaded with drugs in various formulations. Upon inflation of the expandable portion, the overall diameter increases, the wall thickness decreases and, consequently, the voids are stretched to cause the drug to be expelled from the voids and into the bodily lumen or tissue adjacent to the medical device. The voids include any open volume within the expandable portion capable of containing the drug.
Owner:ZULI HLDG LTD
Systems for releasing active ingredients, based on biodegradable or biocompatible polymers with a shape memory effect
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT GEESTHACHT ZENT FUER MATERIAL UND KUESTENFORSCHUNG
Method and articles for remote magnetically induced treatment of cancer and other diseases, and method for operating such article
InactiveUS20070196281A1Avoid damagePowder deliveryHeart defibrillatorsAbnormal tissue growthCancer cell
This invention describes unique treatment methods and innovative articles that can be placed in a human or animal body to enable controlled destruction of diseased tissue. The methods include destruction of diseased cells and tissues by magnetically controlled motion and an externally controllable drug delivery process with a capability to start and stop the drug delivery at any time, for any duration. This invention provides two approaches to diseased cell destruction, (1) magneto-mechanical disturbance of cell structure (e.g. cancer cells) for cell lysis and (2) magnetically activated drug release at local regions (e.g. tumors) from a magnetic-particle-containing drug reservoir. The invention also provides combinations of both the above treatments for dual therapy. It further combines one or both of the treatments with magnetic hyperthermia for multifunctional cell destruction therapy. The approaches can be combined with magnetic MRI for monitoring the accuracy of placement as well as for following up the cancer destruction progress and appropriate reprogramming of the magneto-mechanical therapy and remote-controlled drug release.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Mixtures of various triblock polyester polyethylene glycol copolymers having improved gel properties
InactiveUS7018645B1Good curative effectMinimize side effectsPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsPolymer scienceErosion rate
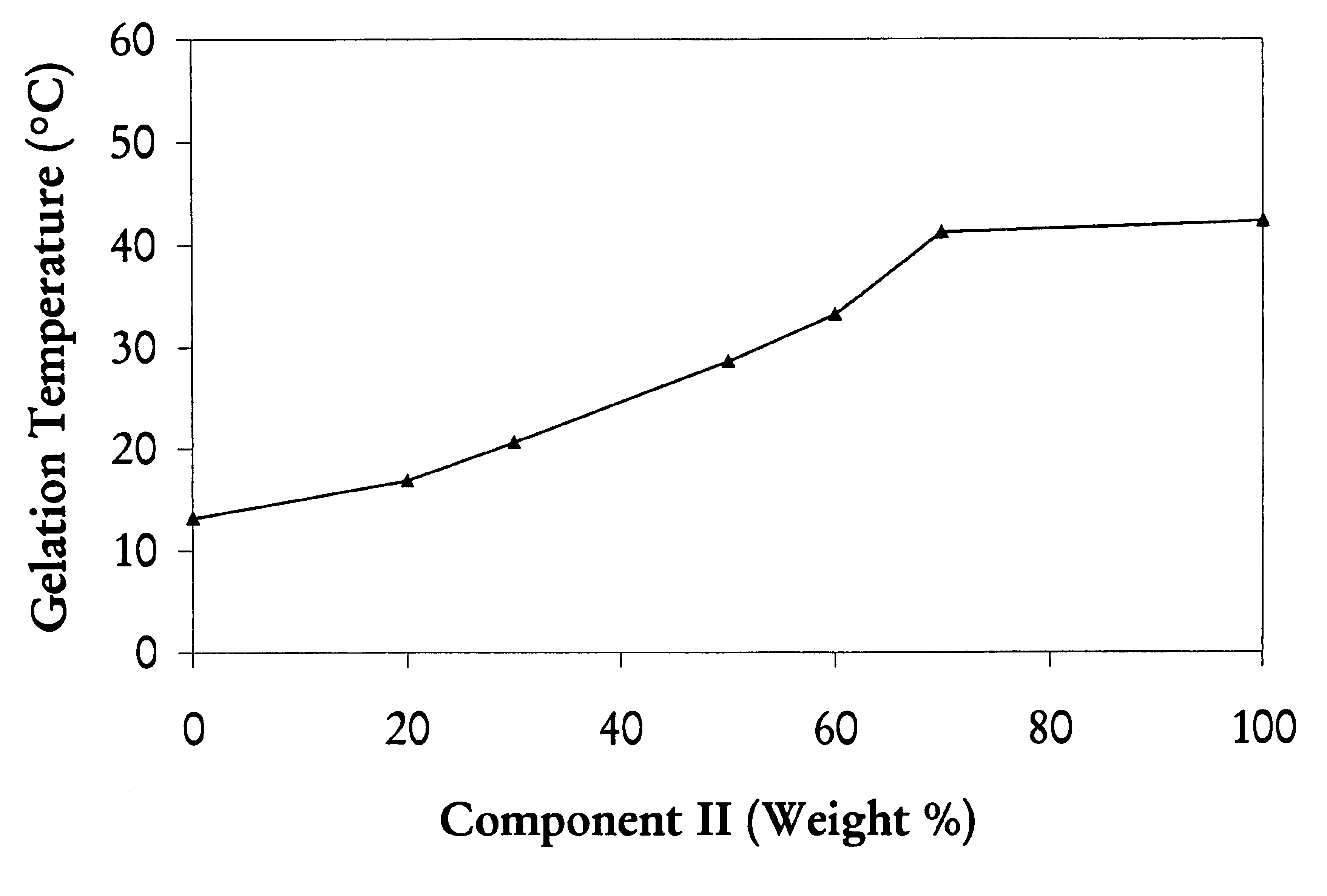
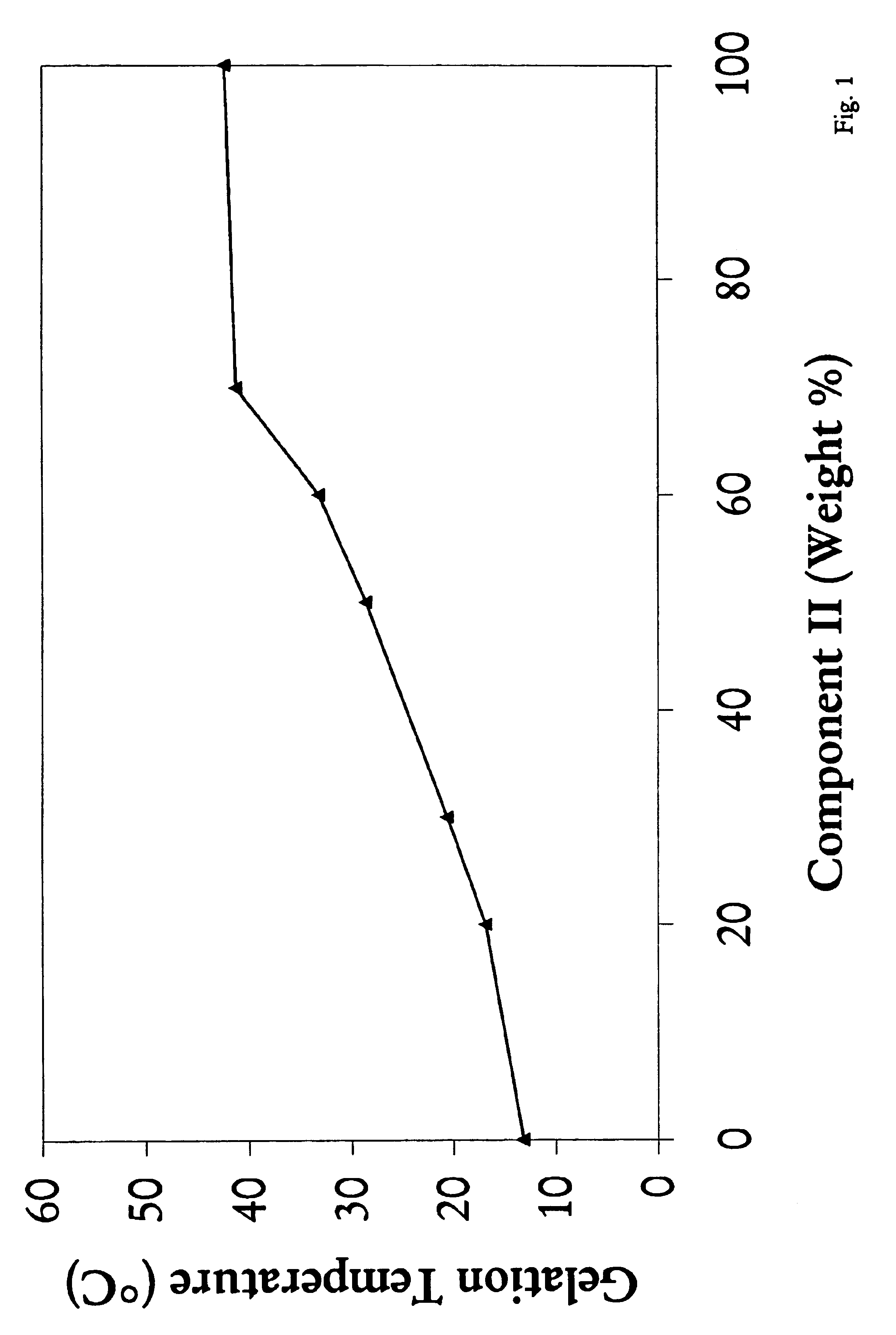
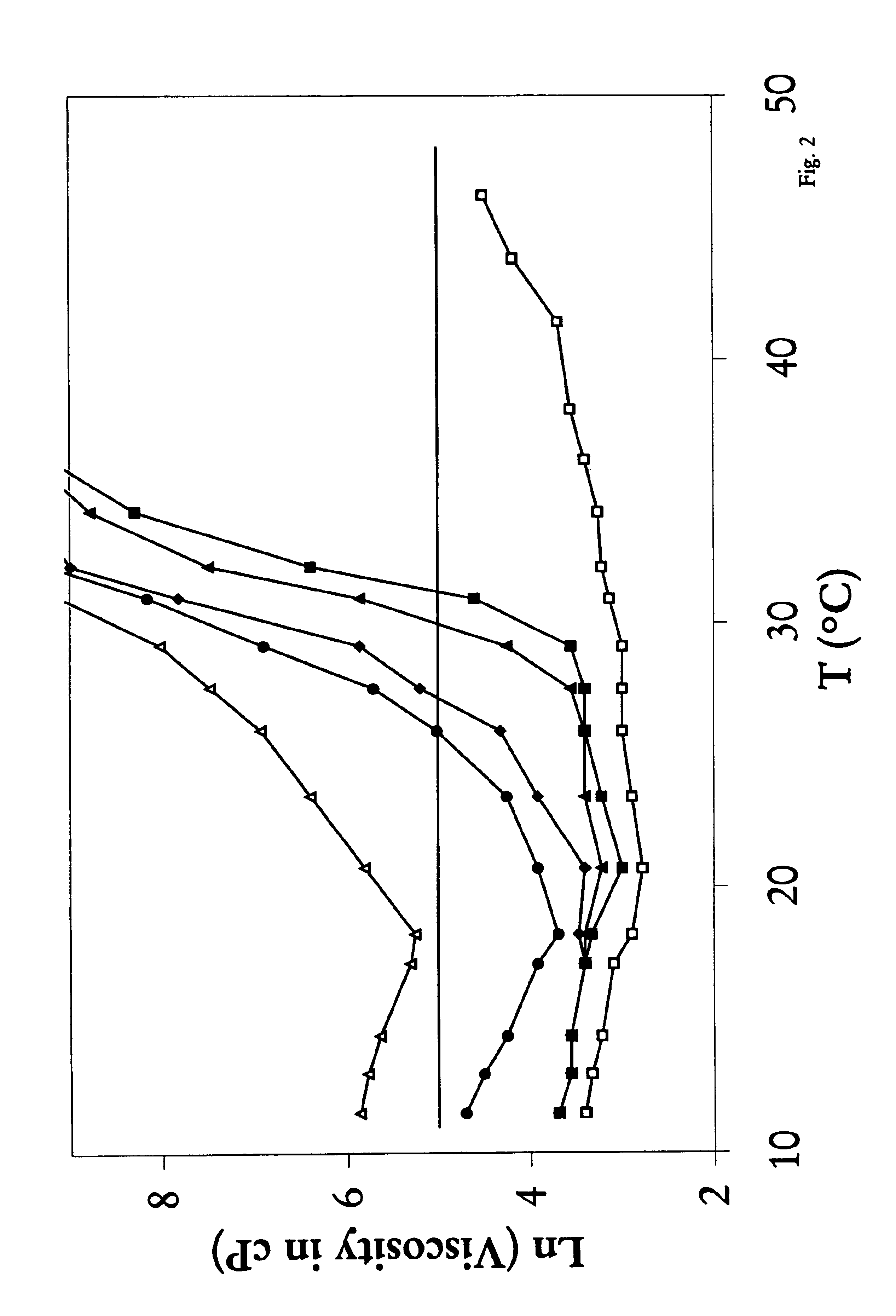
A water soluble, biodegradable reverse thermal gelation system comprising a mixture of at least two types of tri-block copolymer components is disclosed. The tri-block copolymer components are made of a hydrophobic biodegradable polyester A-polymer block and a hydrophilic polyethylene glycol B-polymer block. The drug release and gel matrix erosion rates of the biodegradable reverse thermal gelation system may be modulated by various parameters such as the hydrophobic / hydrophilic component contents, polymer block concentrations, molecular weights and gelation temperatures, and weight ratios of the tri-block copolymer components in the mixture.
Owner:BTG INT LTD
Timed pulsatile drug delivery systems
A pharmaceutical dosage form such as a capsule capable of delivering therapeutic agents into the body in a time-controlled or position-controlled pulsatile release fashion, is composed of a multitude of multicoated particulates (beads, pellets, granules, etc.) made of one or more populations of beads. Each of these beads except an immediate release bead has at least two coated membrane barriers. One of the membrane barriers is composed of an enteric polymer while the second membrane barrier is composed of a mixture of water insoluble polymer and an enteric polymer. The composition and the thickness of the polymeric membrane barriers determine the lag time and duration of drug release from each of the bead populations. Optionally, an organic acid containing intermediate membrane may be applied for further modifying the lag time and / or the duration of drug release. The pulsatile delivery may comprise one or more pulses to provide a plasma concentration-time profile for a therapeutic agent, predicted based on both its pharmaco-kinetic and pharmaco-dynamic considerations and in vitro / in vivo correlations.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
Method for producing a microparticle
InactiveUS6022564AQuality improvementEfficient productionBiocidePowder deliveryHydrogen atomCarboxylic acid
This invention provides a method for producing a microparticle which comprises pulverizing a solid preparation comprising a compound represented by the formula: wherein ring A is an optionally substituted benzene ring; R is a hydrogen atom or an optionally substituted hydrocarbon group; B is an optionally esterified or amidated carboxyl group; X is -CH(OH)- or -CO-; k is 0 or 1; and n is 0, 1 or 2 or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof and a biodegradable polymer of alpha -hydroxycarboxylic acid in the presence of a pulverizing auxiliary, which can provide microparticles which are less adhesive and involve less aggregation and are thus excellent in drug entrapment ratio and control of drug-release in a desired particle size.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Use of a Partially Neutralized, Anionic (Meth)Acrylate Copolymer as a Coating for the Production of a Medicament Releasing Active Substance at Reduced Ph Values
(EN) The invention relates to the use of a partially neutralized, anionic (meth)acrylate copolymer comprising radically polymerized units of 25 to 95 percent by weight of C1 to C4 alkyl esters of acrylic or methacrylic acid and 5 to 75 percent by weight of (meth)acrylate monomers with an anionic group, at least 4 percent of which are neutralized by means of a base, for producing a medicament that is provided with an active substance-containing core and is coated with the partially neutralized, anionic (meth)acrylate copolymer. Said medicament releases at least 30 percent of the active substance contained therein in 30 minutes at a pH at which the active substance is sufficiently soluble and stable and at which the corresponding medicament that is coated with the non-neutralized anionic (meth)acrylate polymer releases less than 10 percent of the active substance contained therein.
Owner:EVONIK OPERATIONS GMBH
Tamper-resistant tablet providing immediate drug release
InactiveUS20130028970A1High weight ratioImproved release profileOrganic active ingredientsBiocideParticulatesImmediate release
The invention relates to a tamper-resistant tablet comprising(i) a matrix material in an amount of more than one third of the total weight of the tablet; and(ii) a plurality of coated particulates in an amount of less than two thirds of the total weight of the tablet; wherein said particulates comprise a pharmacologically active compound and a physiologically acceptable polymer, preferably a polyalkylene oxide; and form a discontinuous phase within the matrix material;which preferably provides under in vitro conditions immediate release of the pharmacologically active compound in accordance with Ph. Eur.;and method of using said tablet to treat pain and other conditions.
Owner:GRUNENTHAL GMBH
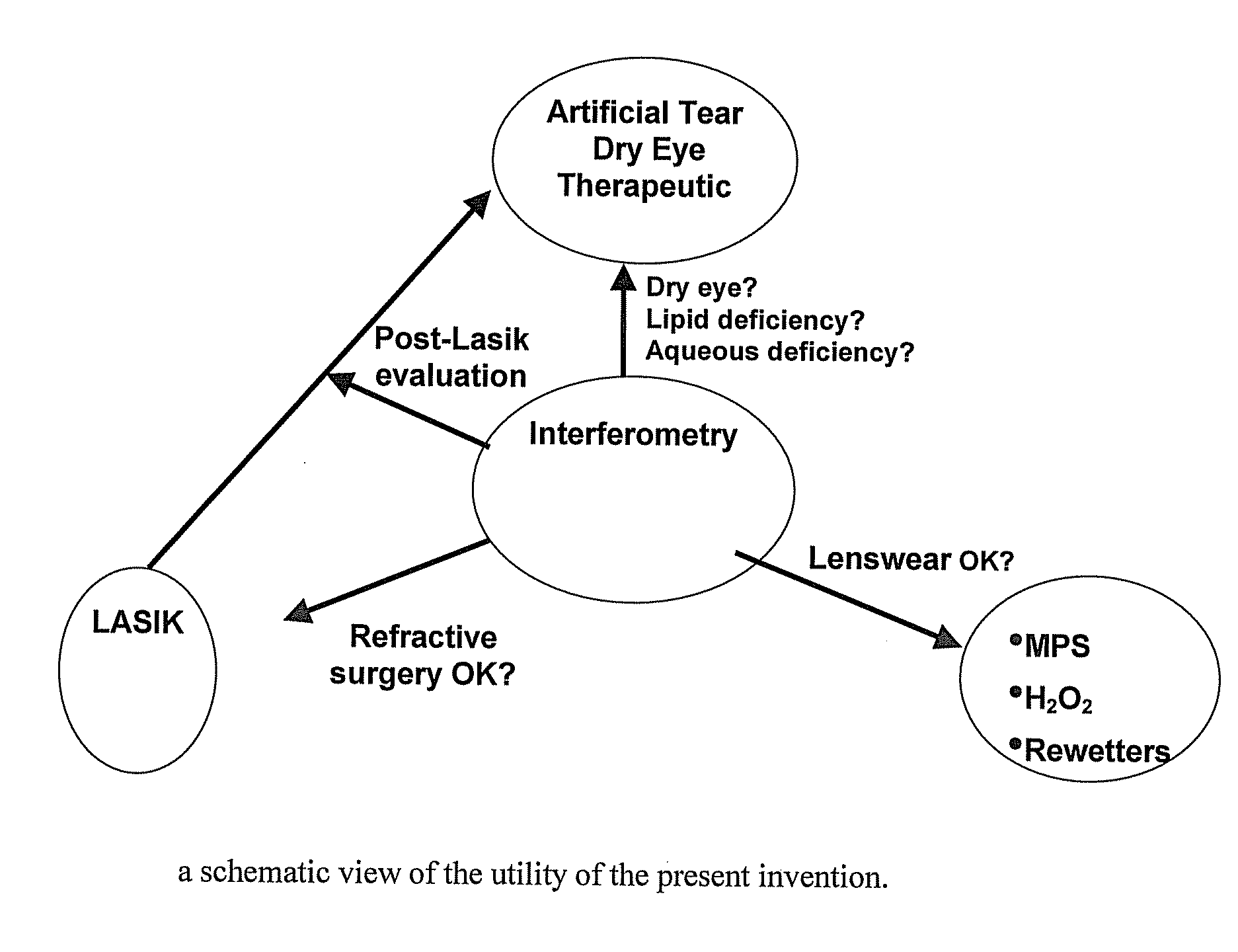
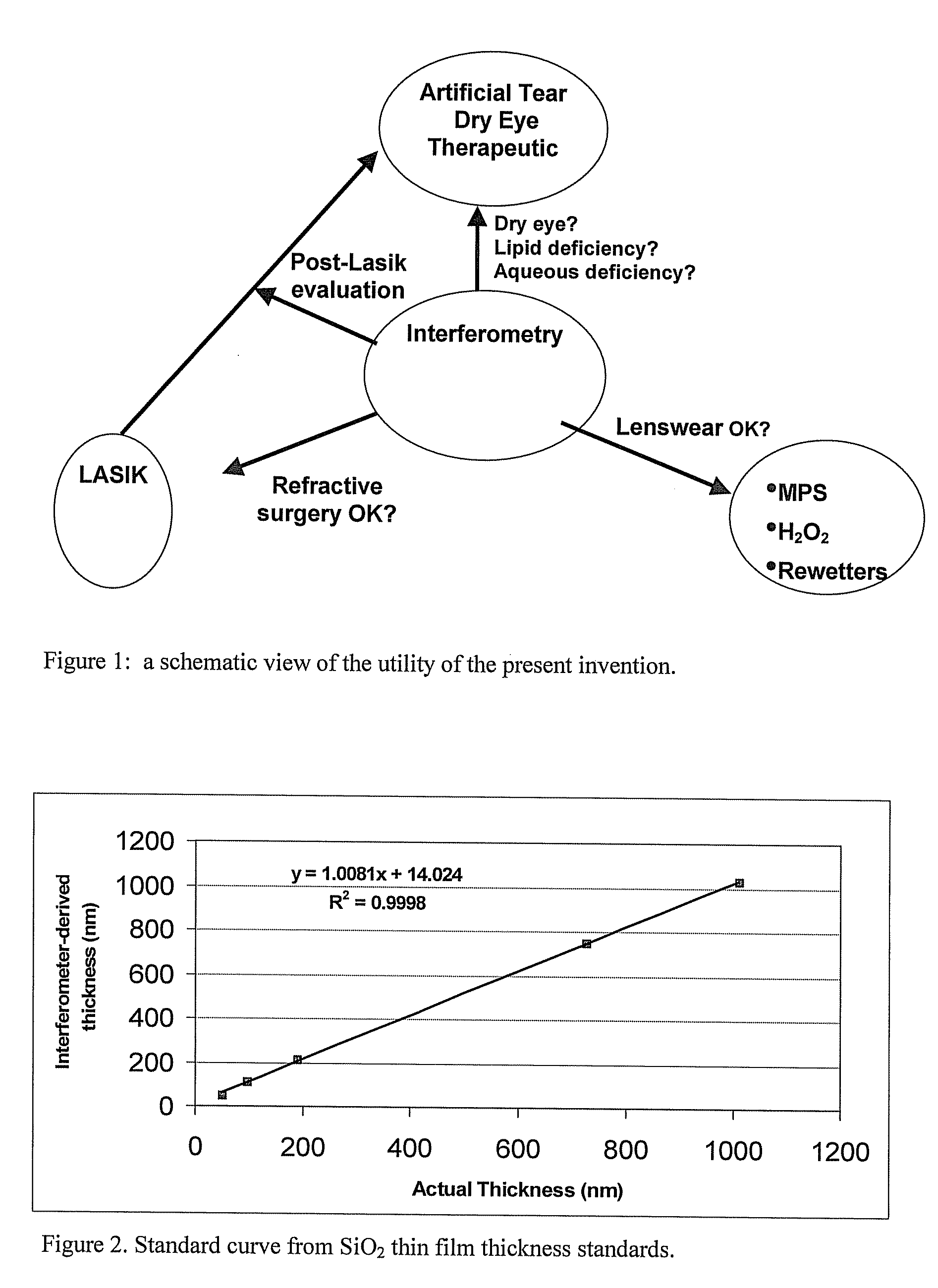
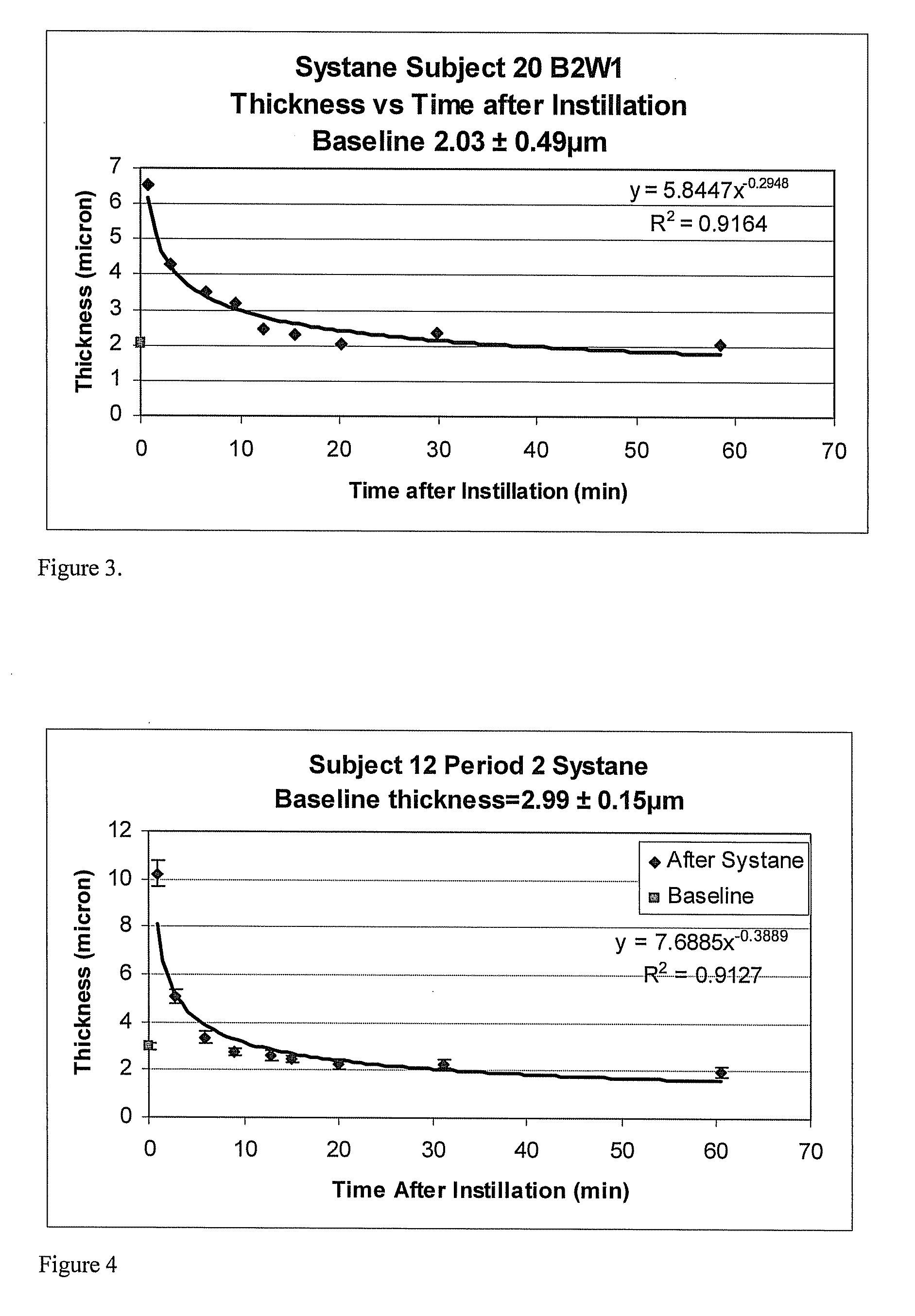
Methods and devices for measuring tear film and diagnosing tear disorders
Methods and devices measure eye blinks and tear film lipid and aqueous layer thickness before and following ophthalmic formula application onto the ocular surface, especially wherein the ophthalmic formula is an artificial tear. The methods and devices are suitable for dry eye diagnosis. The methods and devices are suitable for use to evaluate ophthalmic formula effects on the tear film and to use such information to diagnose ophthalmic formula treatment of ocular disease conditions such as dry eye in the absence of contact lens wear or post-surgical eye drop treatment and diagnosis. The methods and devices are also suitable for use in the optimization of ophthalmic drug dosage forms and sustained drug release.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
Medical devices having nanoporous coatings for controlled therapeutic agent delivery
According to an aspect of the present invention, implantable or insertable medical devices are provided which contain (a) one or more depressions that contain at least one therapeutic agent, and (b) a nanoporous coating, disposed over the therapeutic-agent-containing depressions, which regulate transport of species between the therapeutic-agent-containing depressions and the exterior of the device. The implantable or insertable devices are configured to preform a role beyond mere drug delivery, for example, providing mechanical and / or electrical functions within the body, among other functions. An advantage of the present invention is that medical devices may be provided, which release therapeutic agents in quantities far exceeding the void volume within the nanoporous coating, while at the same time providing functionality that extends beyond drug delivery. Such release may further approach or achieve a zero order kinetic drug release profile.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
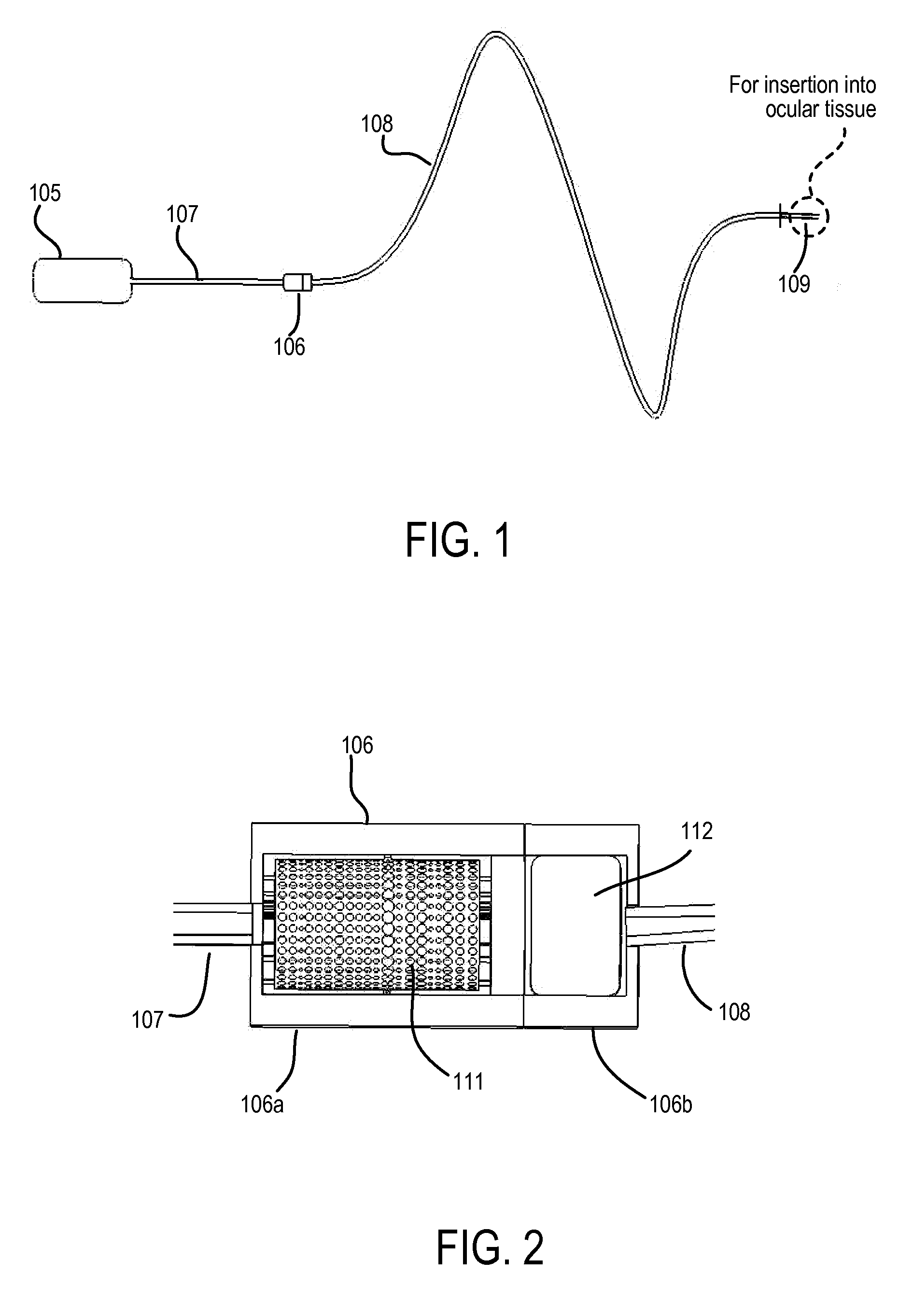
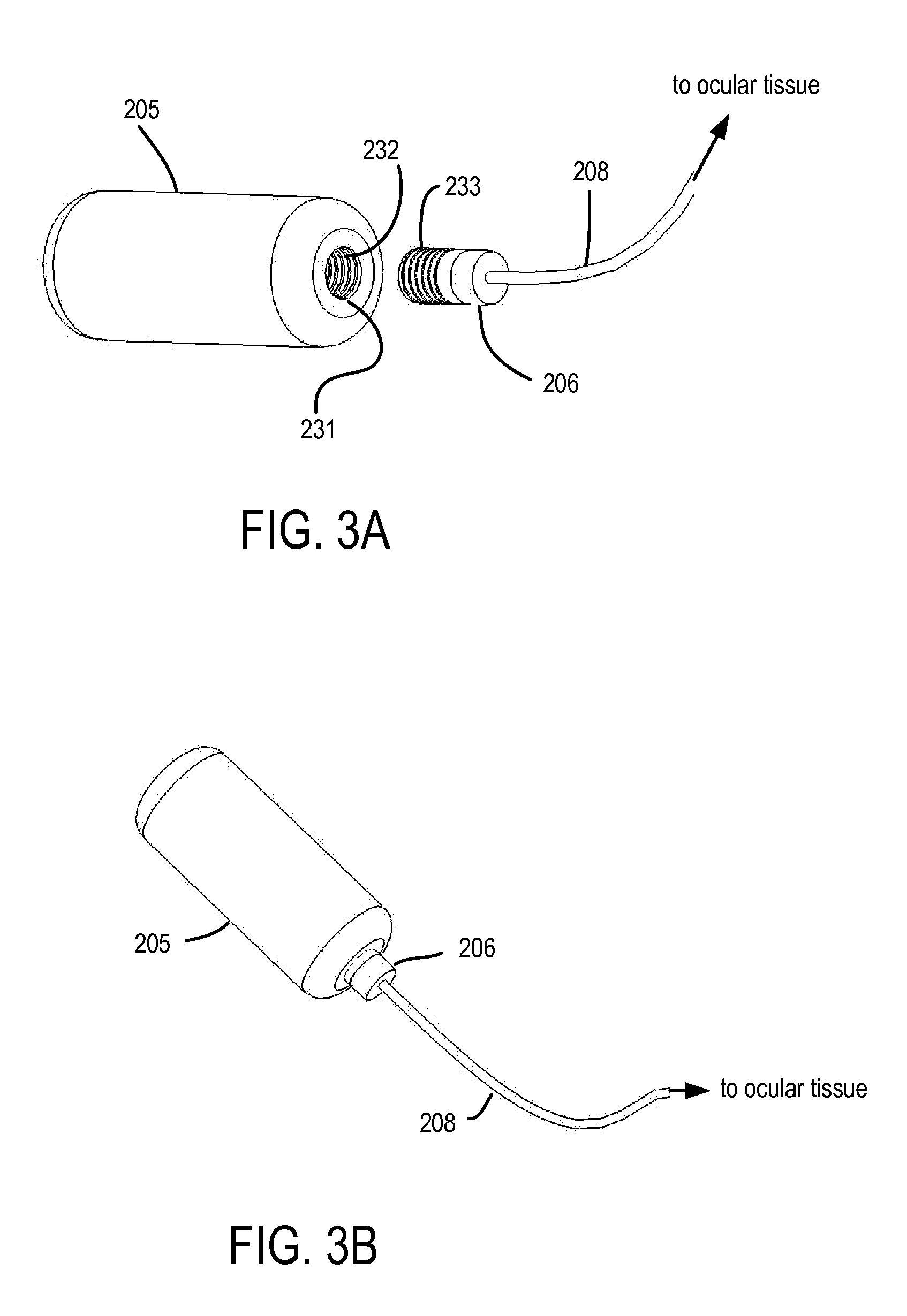
Devices, Systems and Methods for Ophthalmic Drug Delivery
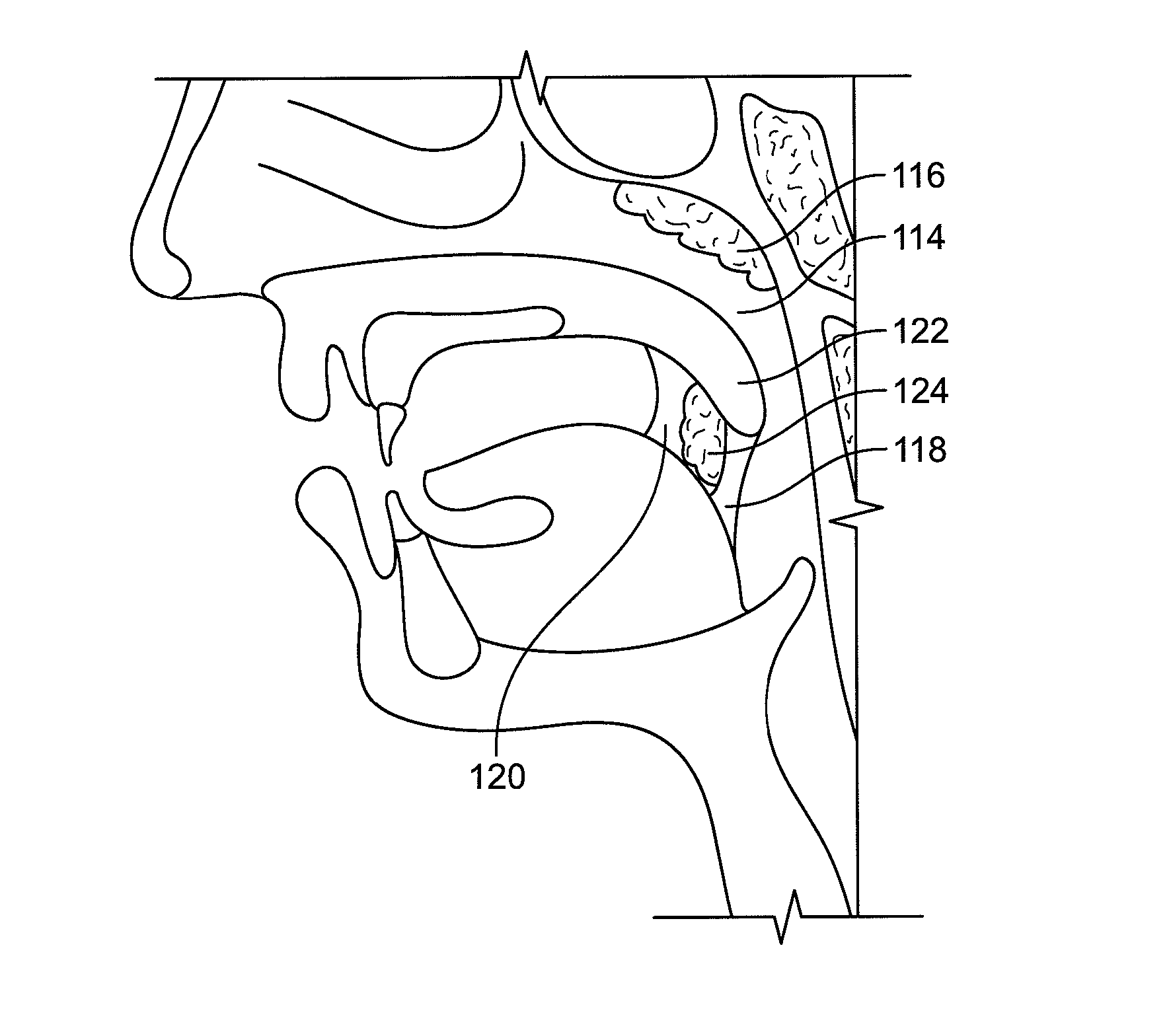
Devices, systems and techniques for delivering drugs to an ocular tissue are described. In at least some embodiments, a terminal component (e.g., a needle or open end of a catheter) is implanted in an ocular tissue and used to deliver one or more drugs. The delivered drugs may come from a source which is also implanted, or may be introduced from an external source (e.g., via a port). Both solid and liquid drug formulations can be used. Ocular implants can alternatively include a thin film coating that releases a drug into an ocular tissue.
Owner:NEUROSYSTEC CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com