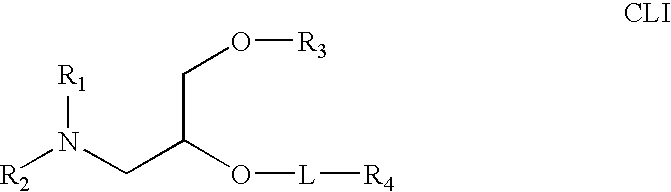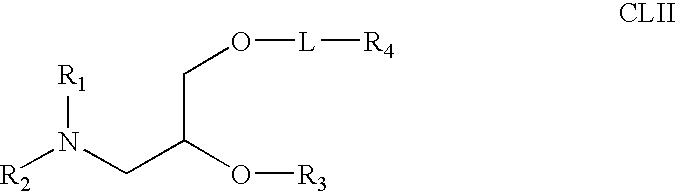Patents
Literature
9159 results about "Microparticle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
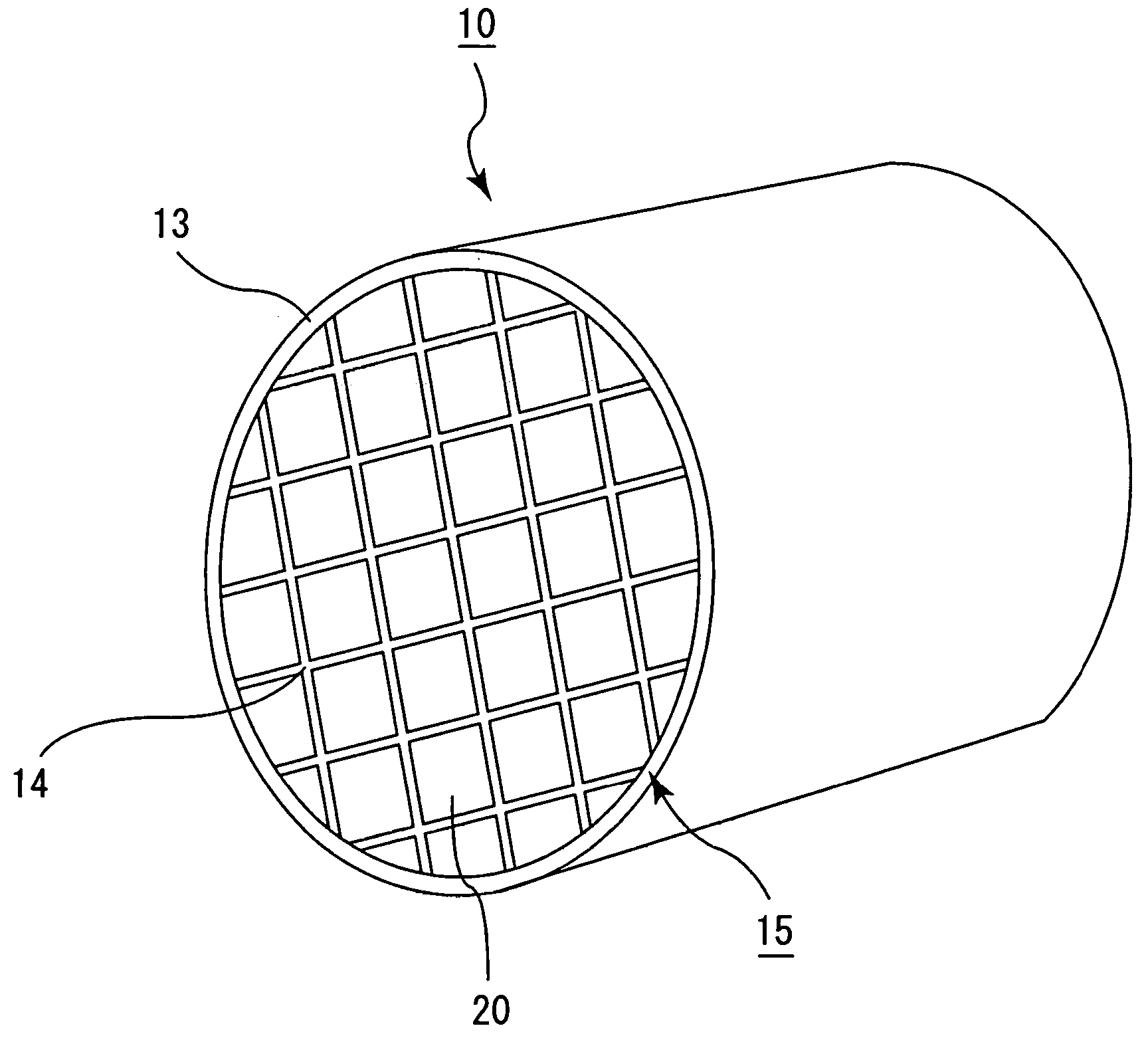
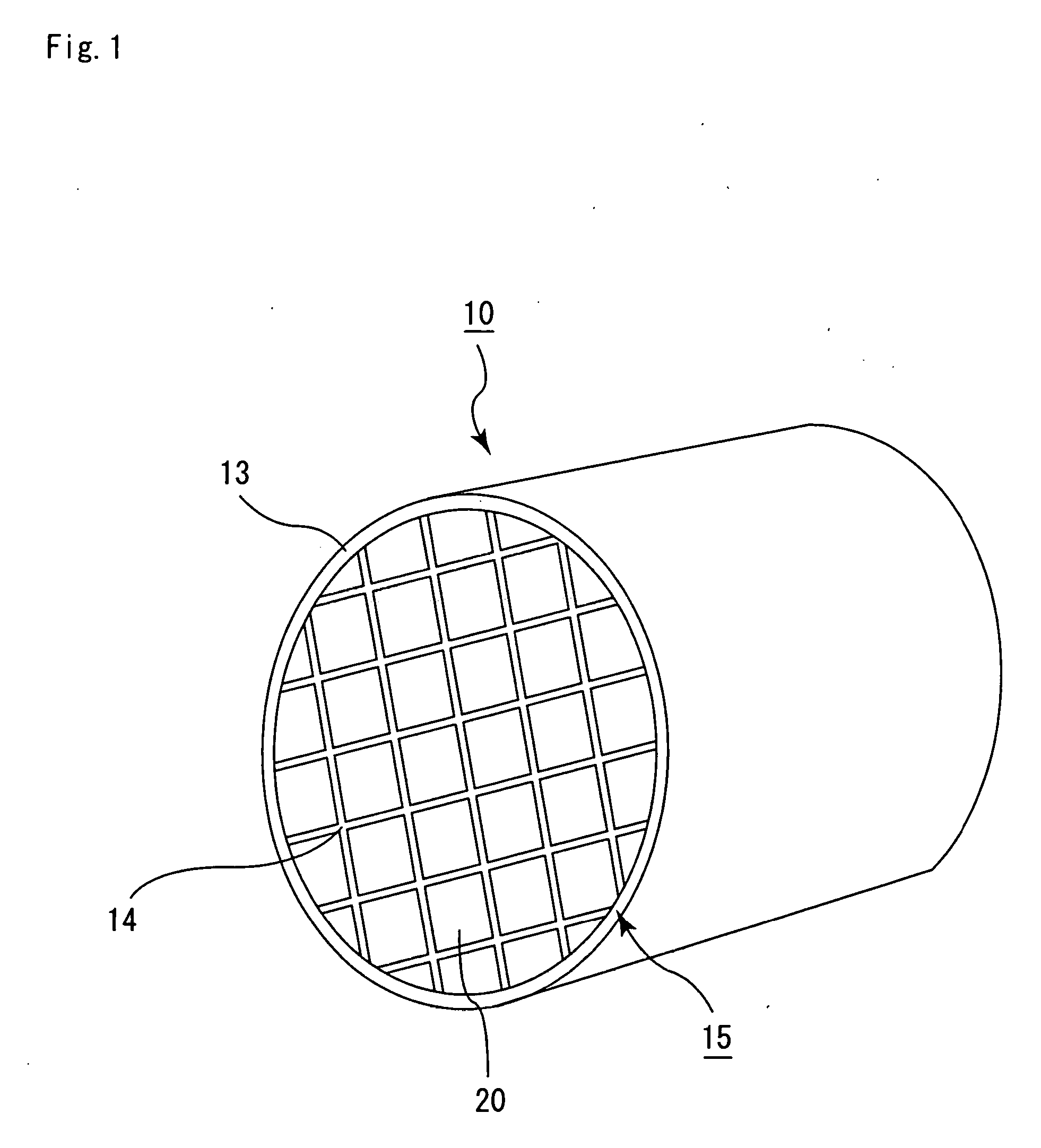
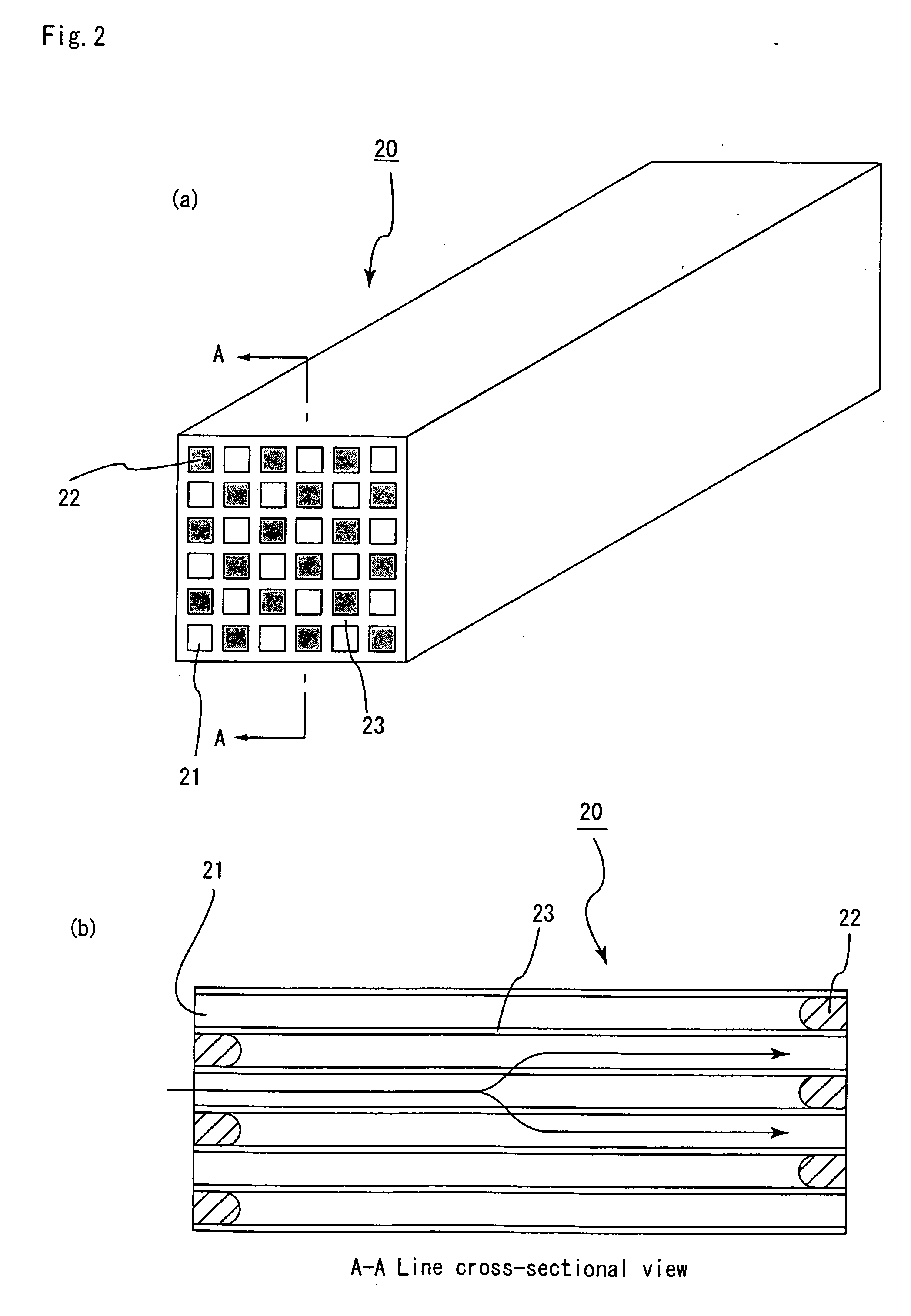
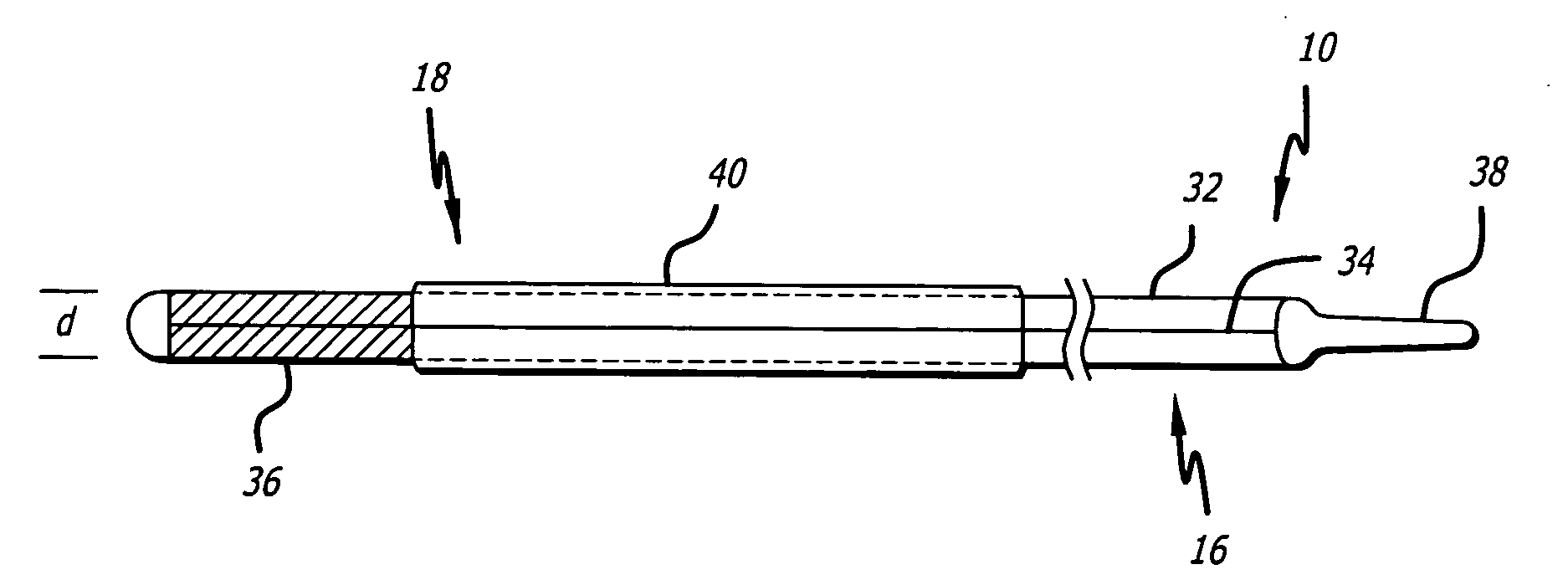
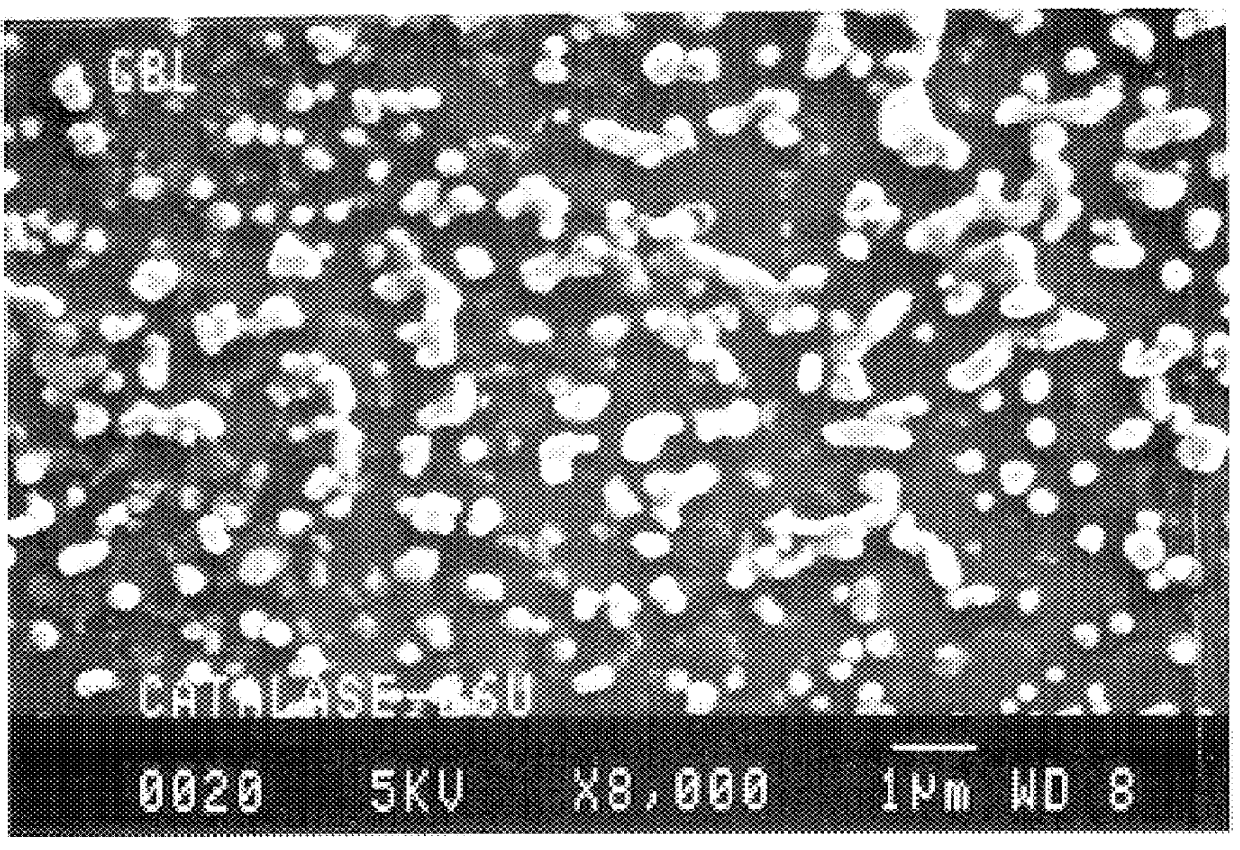
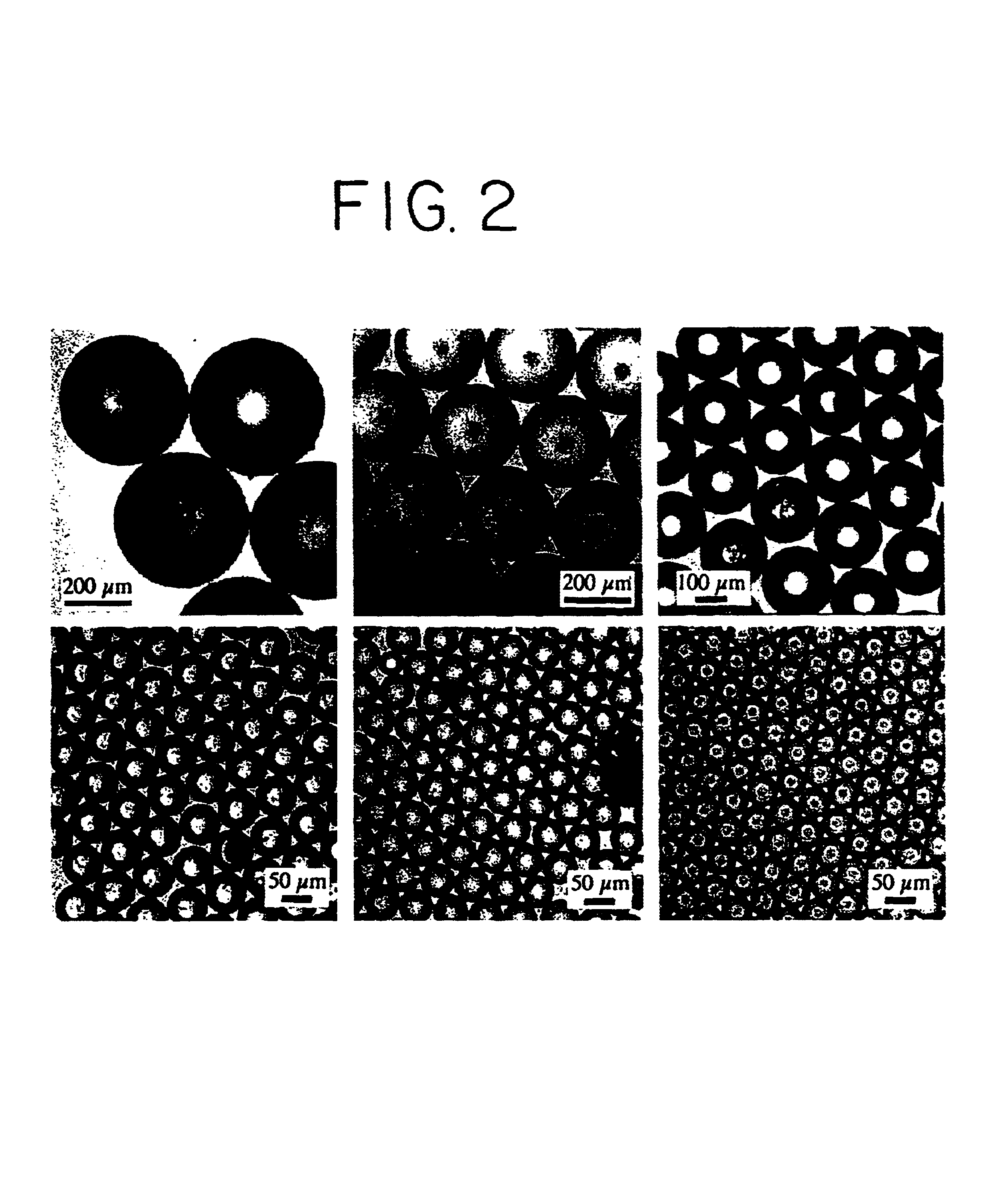
Microparticles are particles between 1 and 1000 μm in size. Commercially available microparticles are available in a wide variety of materials, including ceramics, glass, polymers, and metals. Microparticles encountered in daily life include pollen, sand, dust, flour, and powdered sugar.
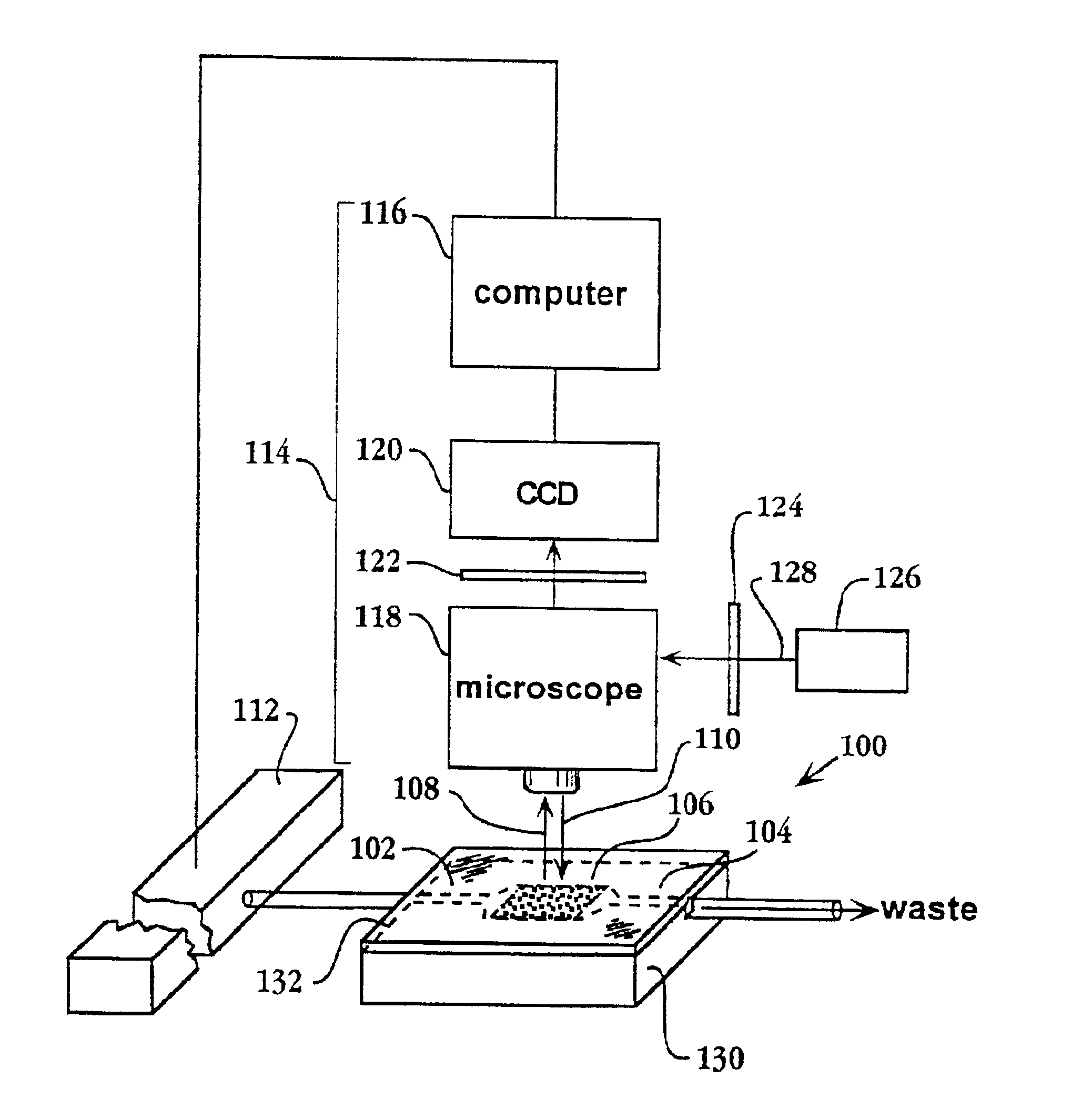
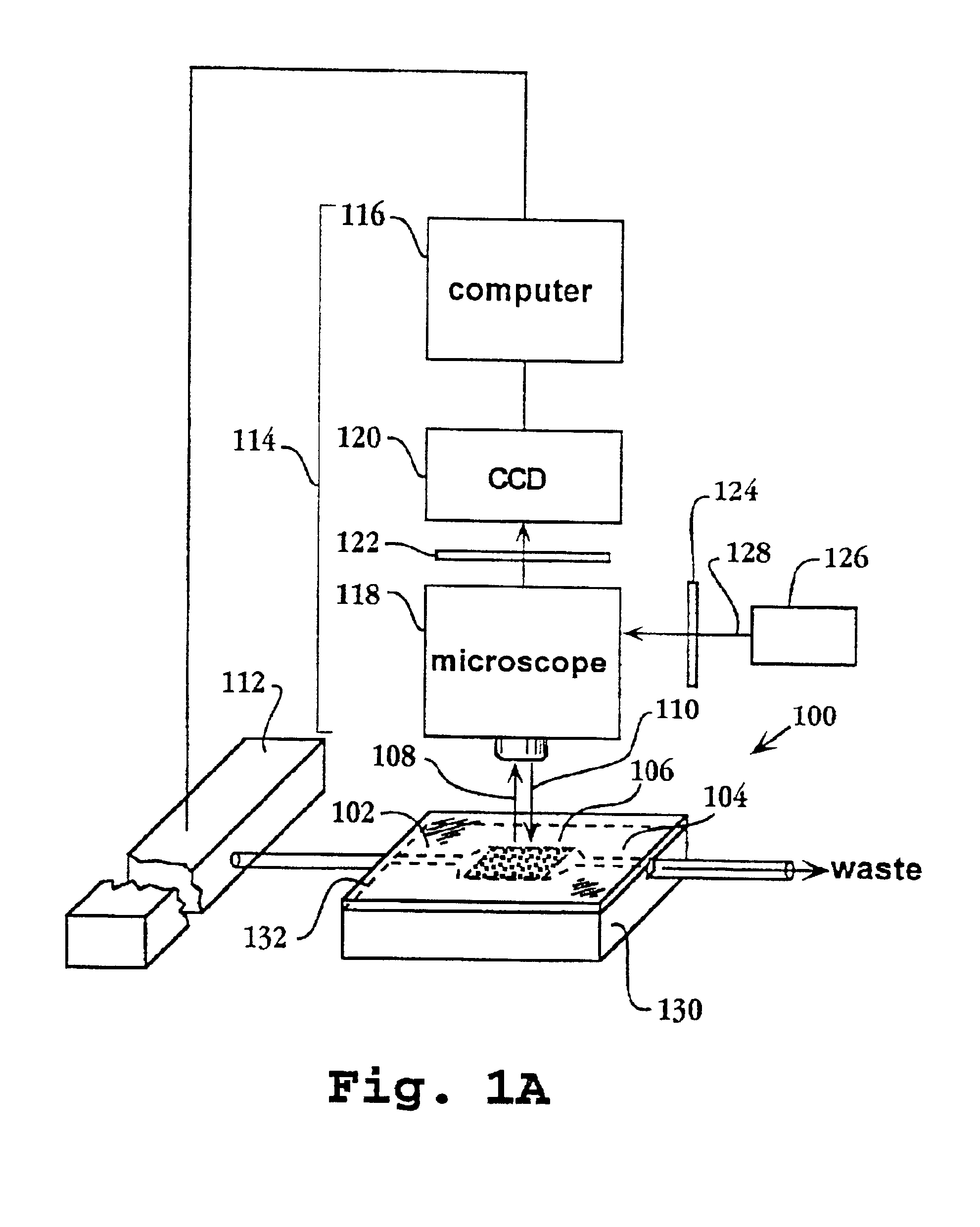
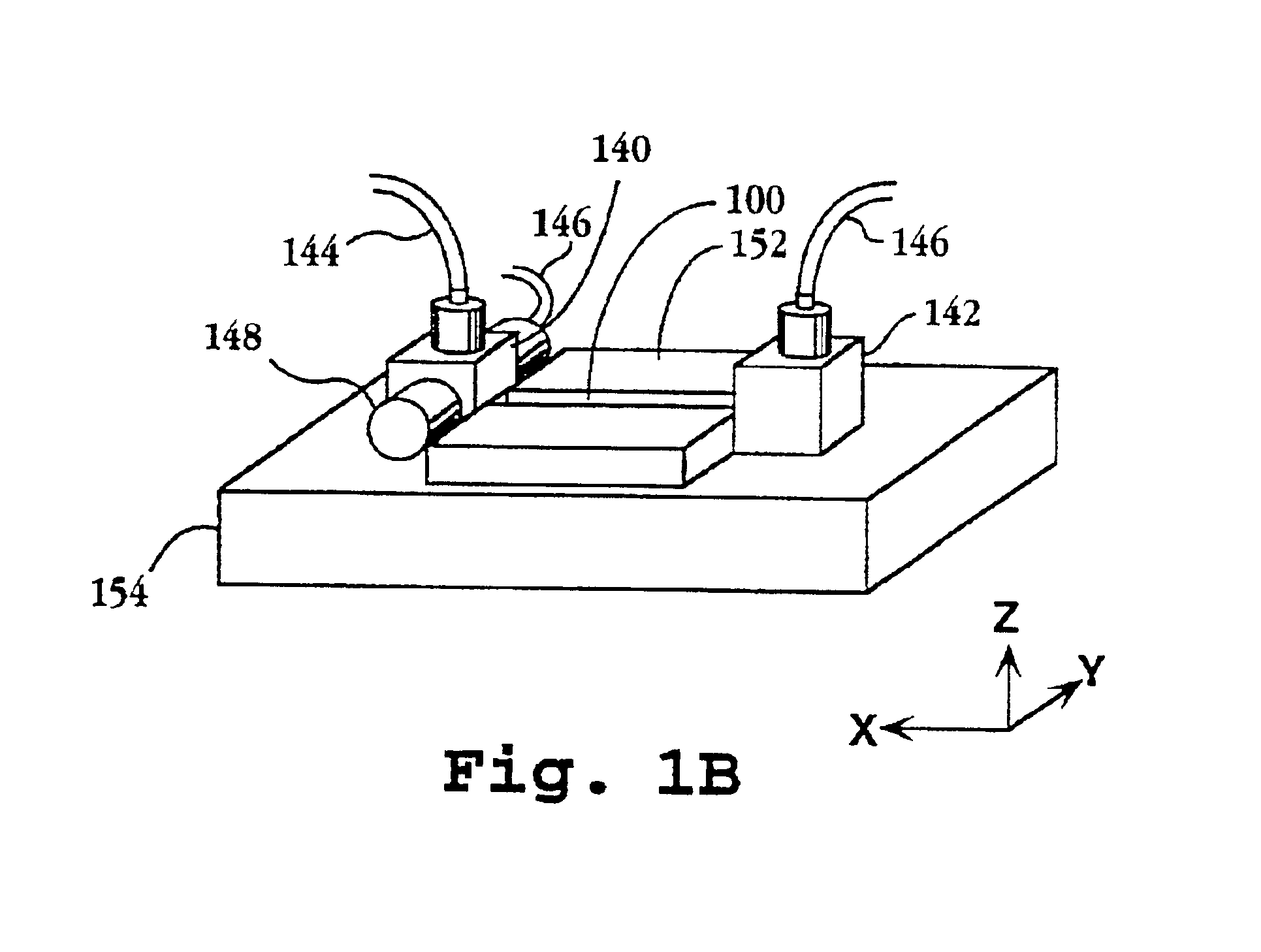
System and apparatus for sequential processing of analytes
InactiveUS6969488B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteMicroparticle
An apparatus and system are provided for simultaneously analyzing a plurality of analytes anchored to microparticles. Microparticles each having a uniform population of a single kind of analyte attached are disposed as a substantially immobilized planar array inside of a flow chamber where steps of an analytical process are carried out by delivering a sequence of processing reagents to the microparticles by a fluidic system under microprocessor control. In response to such process steps, an optical signal is generated at the surface of each microparticle which is characteristic of the interaction between the analyte carried by the microparticle and the delivered processing reagent. The plurality of analytes are simultaneously analyzed by collecting and recording images of the optical signals generated by all the microparticles in the planar array. A key feature of the invention is the correlation of the sequence of optical signals generated by each microparticle in the planar array during the analytical process.
Owner:SOLEXA
Sutures and surgical staples for anastamoses, wound closures, and surgical closures
InactiveUS8016881B2Improve featuresControlled release rateSuture equipmentsStentsSurgical stapleMicroparticle
The invention relates to sutures and surgical staples useful in anastomoses. Various aspects of the invention include wound closure devices that use amphiphilic copolymer or parylene coatings to control the release rate of an agent, such as a drug or a biological material, polymerizing a solution containing monomers and the agent to form a coating, using multiple cycles of swelling a polymer with a solvent-agent solution to increase loading, microparticles carrying the agent, biodegradable surgical articles with amphiphilic copolymer coatings, and sutures or surgical staples the deliver a drug selected from the group consisting of triazolopyrimidine, paclitaxol, sirolimus, derivatives thereof, and analogs thereof to a wound site.
Owner:MIRUS LLC
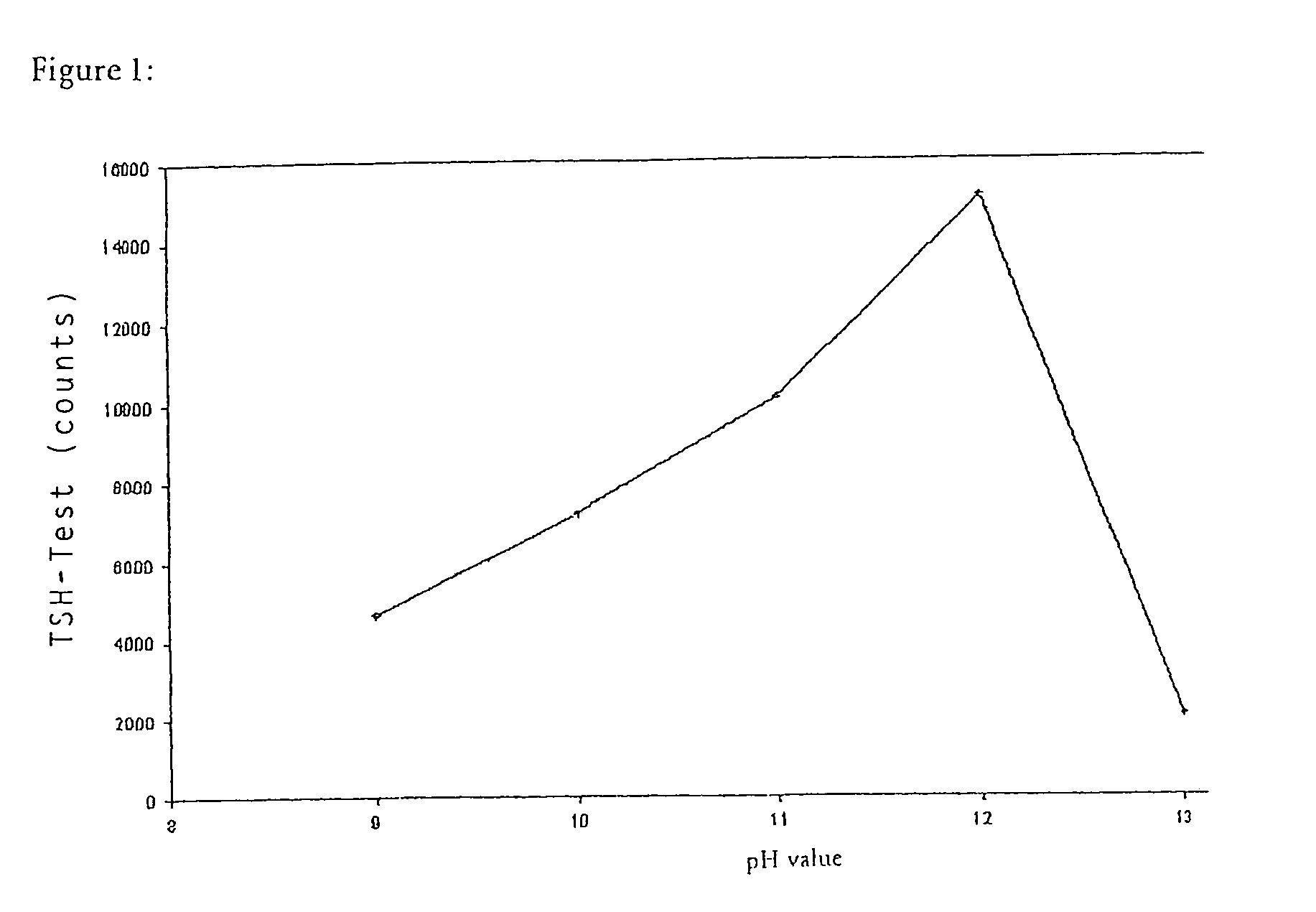
Method for producing microparticles loaded with proteins
InactiveUS7335401B2Improve bindingLow degreePowder deliveryLiquid surface applicatorsMicroparticleChemistry
The present invention concerns a method for producing microparticles loaded with proteins which is characterized in that the microparticles are loaded in suspension under strongly alkaline conditions. The invention also concerns microparticles which can be produced using this method and their use in a binding test e.g. in an immunoassay.
Owner:ROCHE DIAGNOSTICS OPERATIONS INC
Porous drug matrices and methods of manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6932983B1Lower the volumePrevent precipitationPowder deliveryNanotechDrugs solutionWater soluble drug
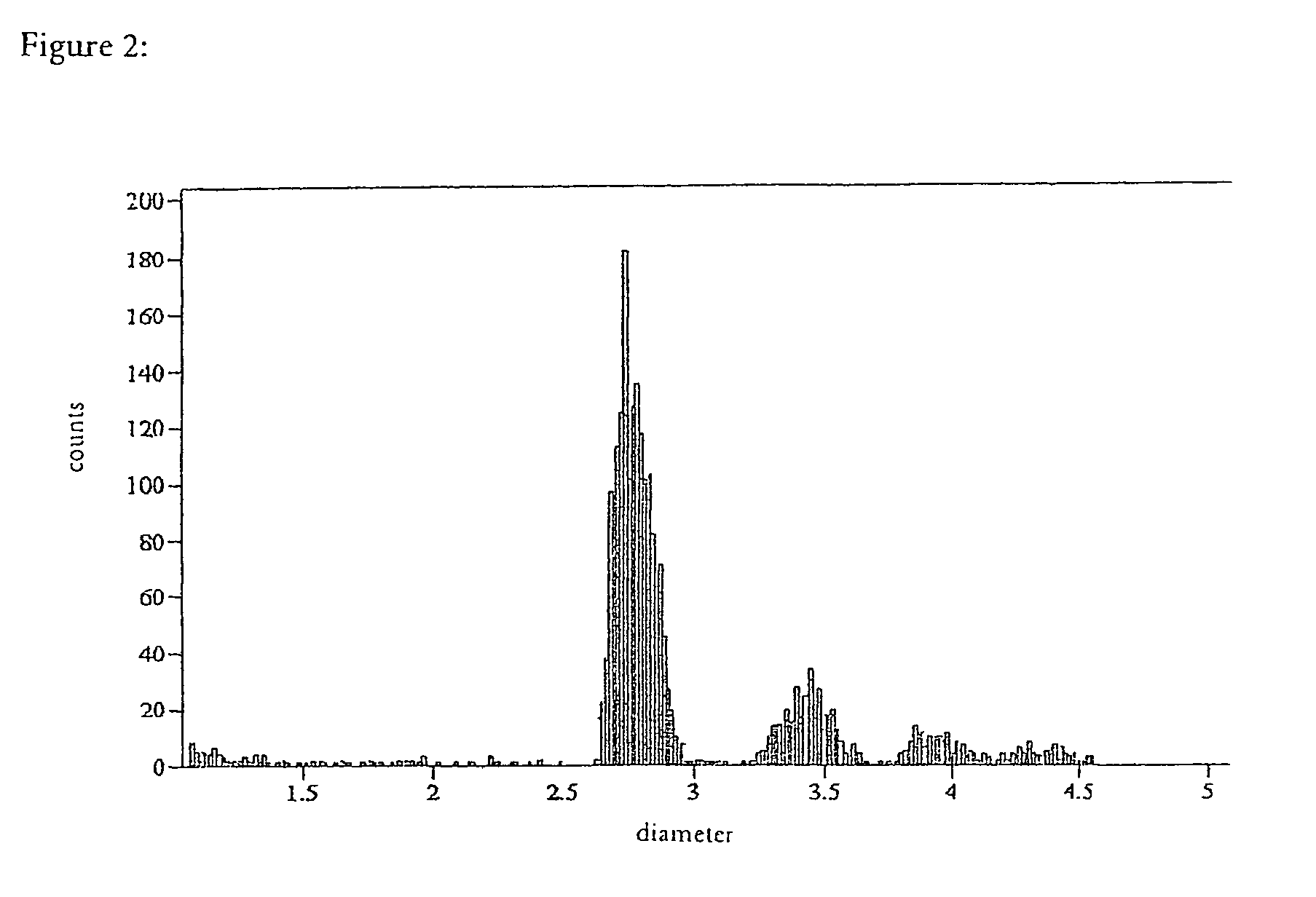
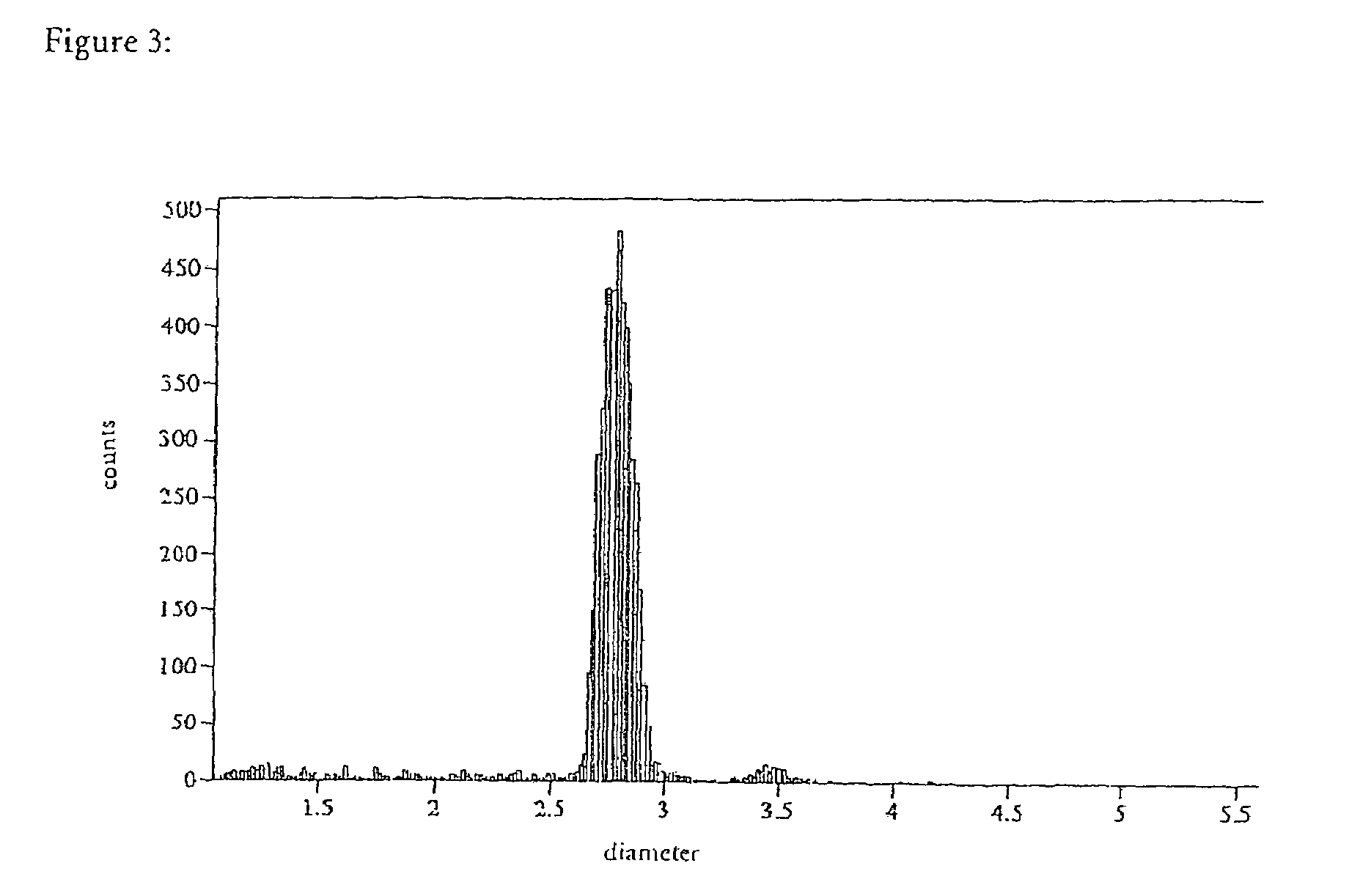
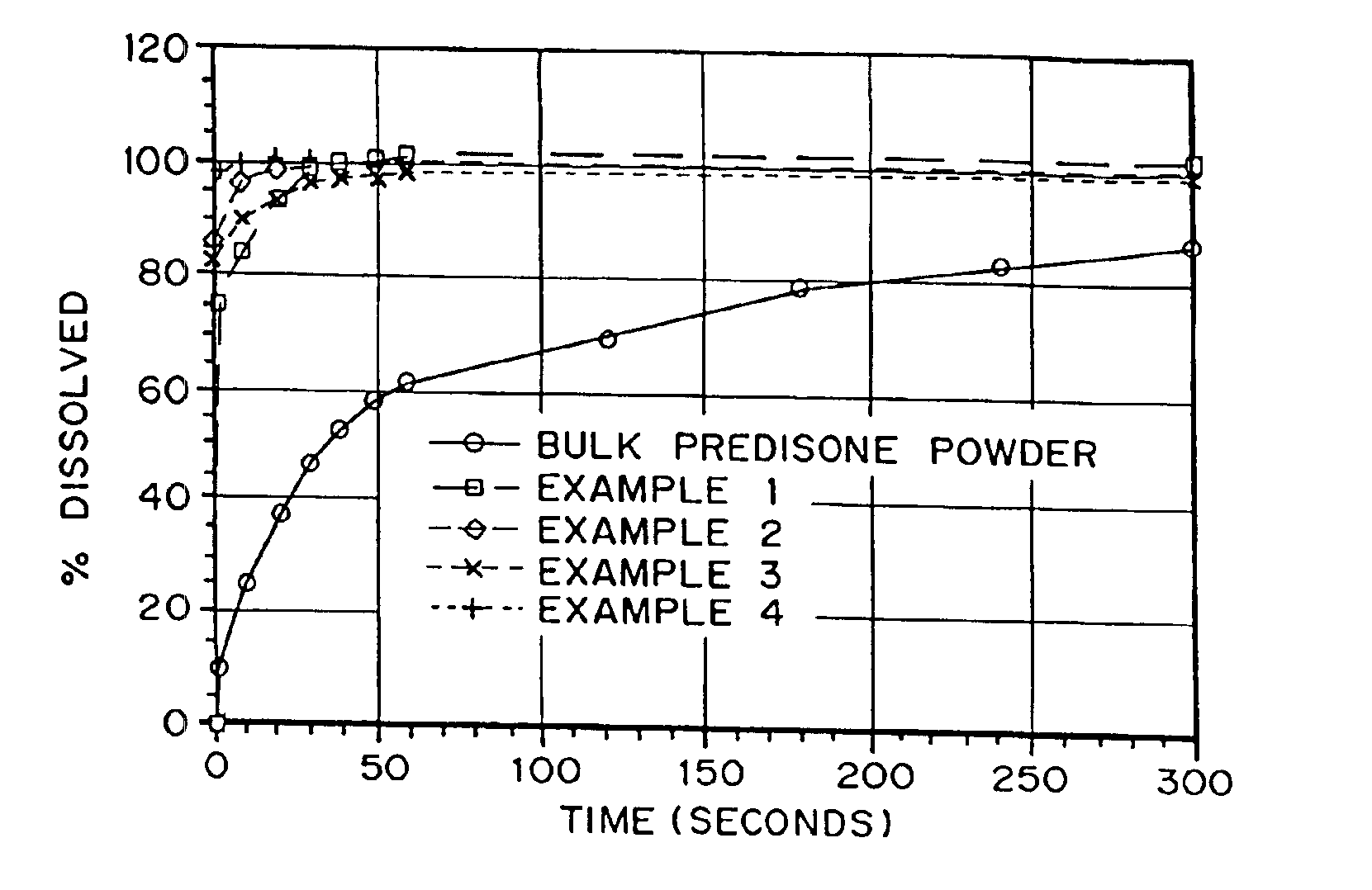
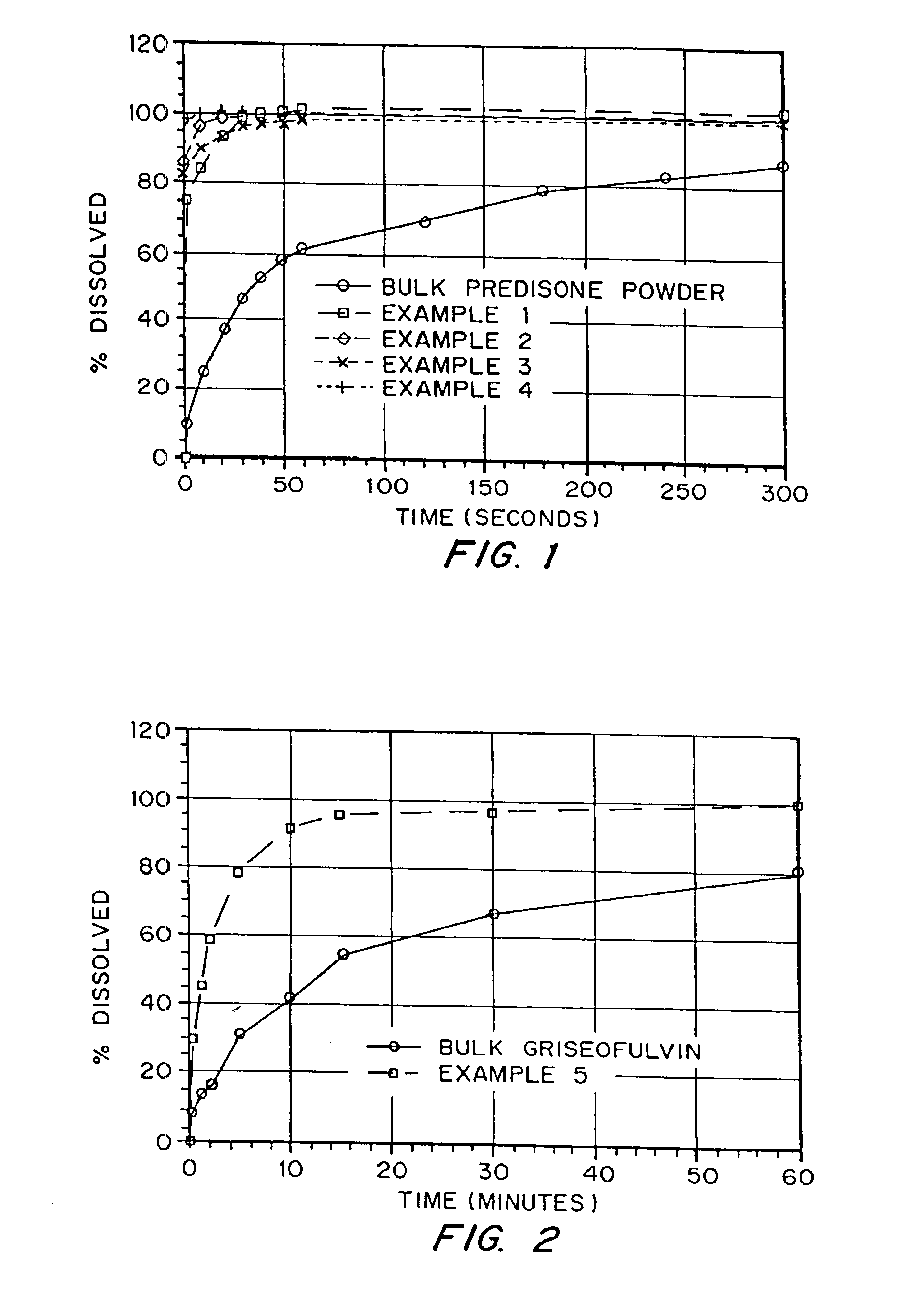
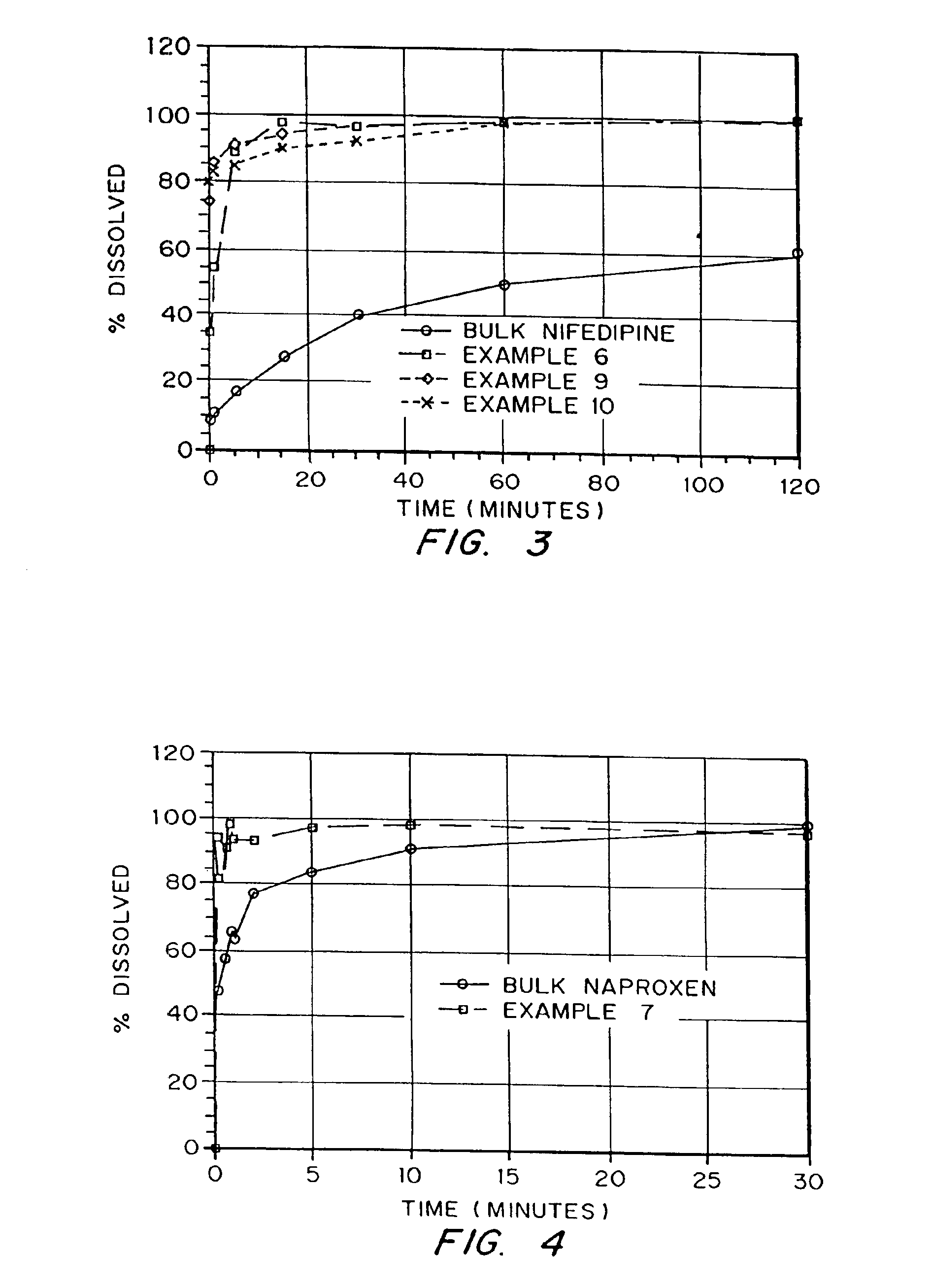
Drugs, especially low aqueous solubility drugs, are provided in a porous matrix form, preferably microparticles, which enhances dissolution of the drug in aqueous media. The drug matrices preferably are made using a process that includes (i) dissolving a drug, preferably a drug having low aqueous solubility, in a volatile solvent to form a drug solution, (ii) combining at least one pore forming agent with the drug solution to form an emulsion, suspension, or second solution, and (iii) removing the volatile solvent and pore forming agent from the emulsion, suspension, or second solution to yield the porous matrix of drug. The pore forming agent can be either a volatile liquid that is immiscible with the drug solvent or a volatile solid compound, preferably a volatile salt. In a preferred embodiment, spray drying is used to remove the solvents and the pore forming agent. The resulting porous matrix has a faster rate of dissolution following administration to a patient, as compared to non-porous matrix forms of the drug. In a preferred embodiment, microparticles of the porous drug matrix are reconstituted with an aqueous medium and administered parenterally, or processed using standard techniques into tablets or capsules for oral administration.
Owner:ACUSPHERE INC
Targeted and high density drug loaded polymeric materials
ActiveUS20060002852A1Increase molecular densityHigh densityPowder deliveryBiocideAntigenWound dressing
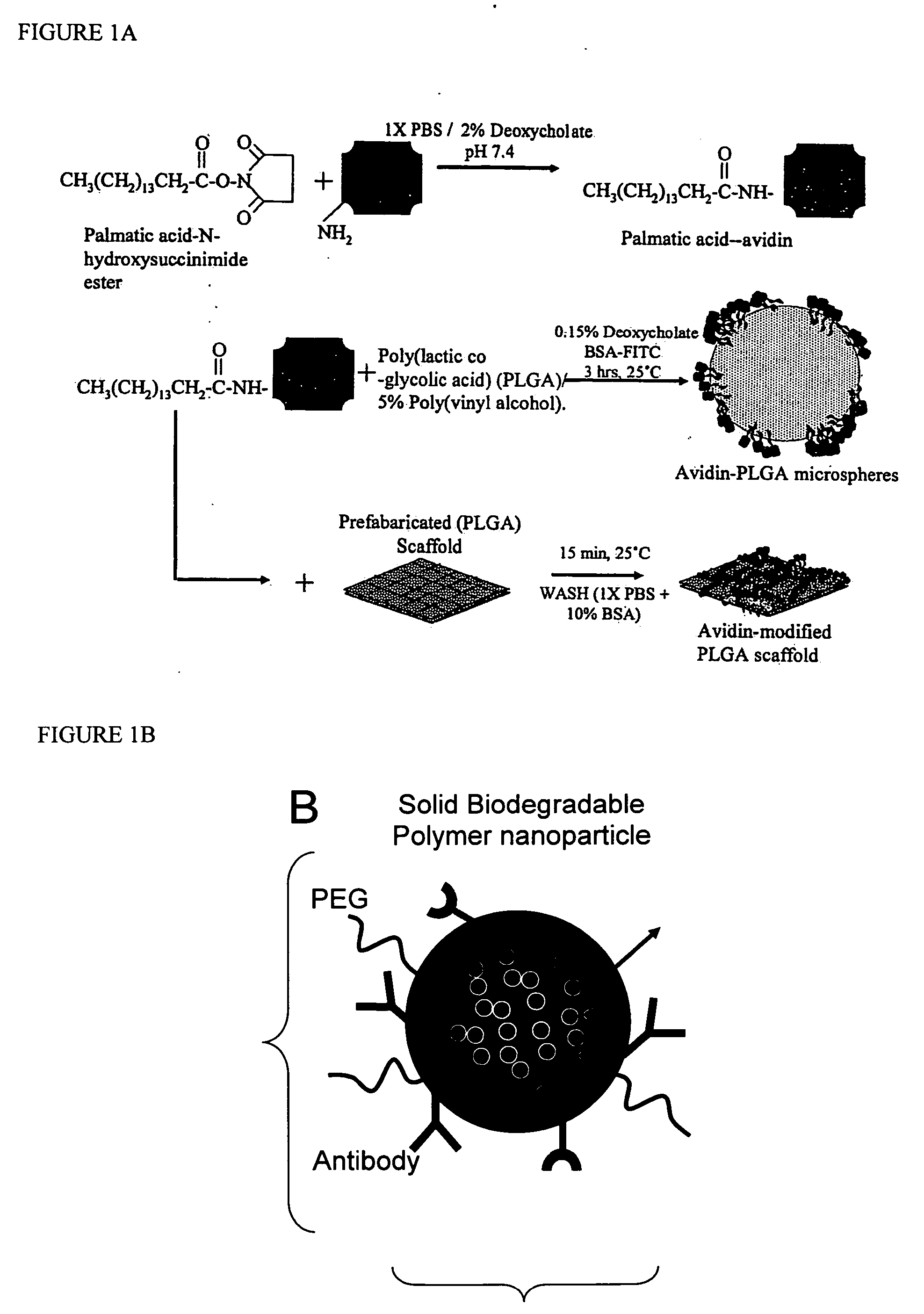
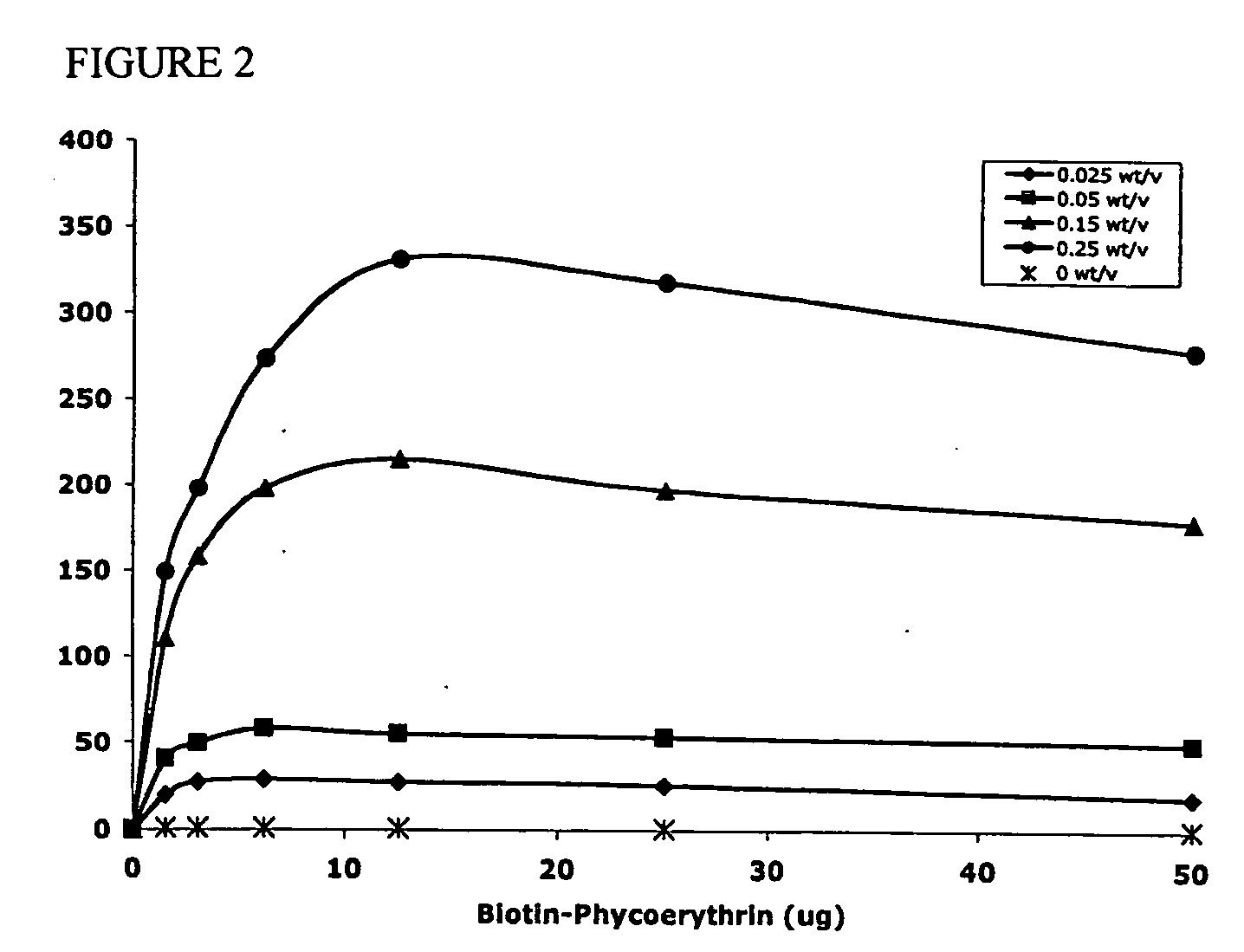
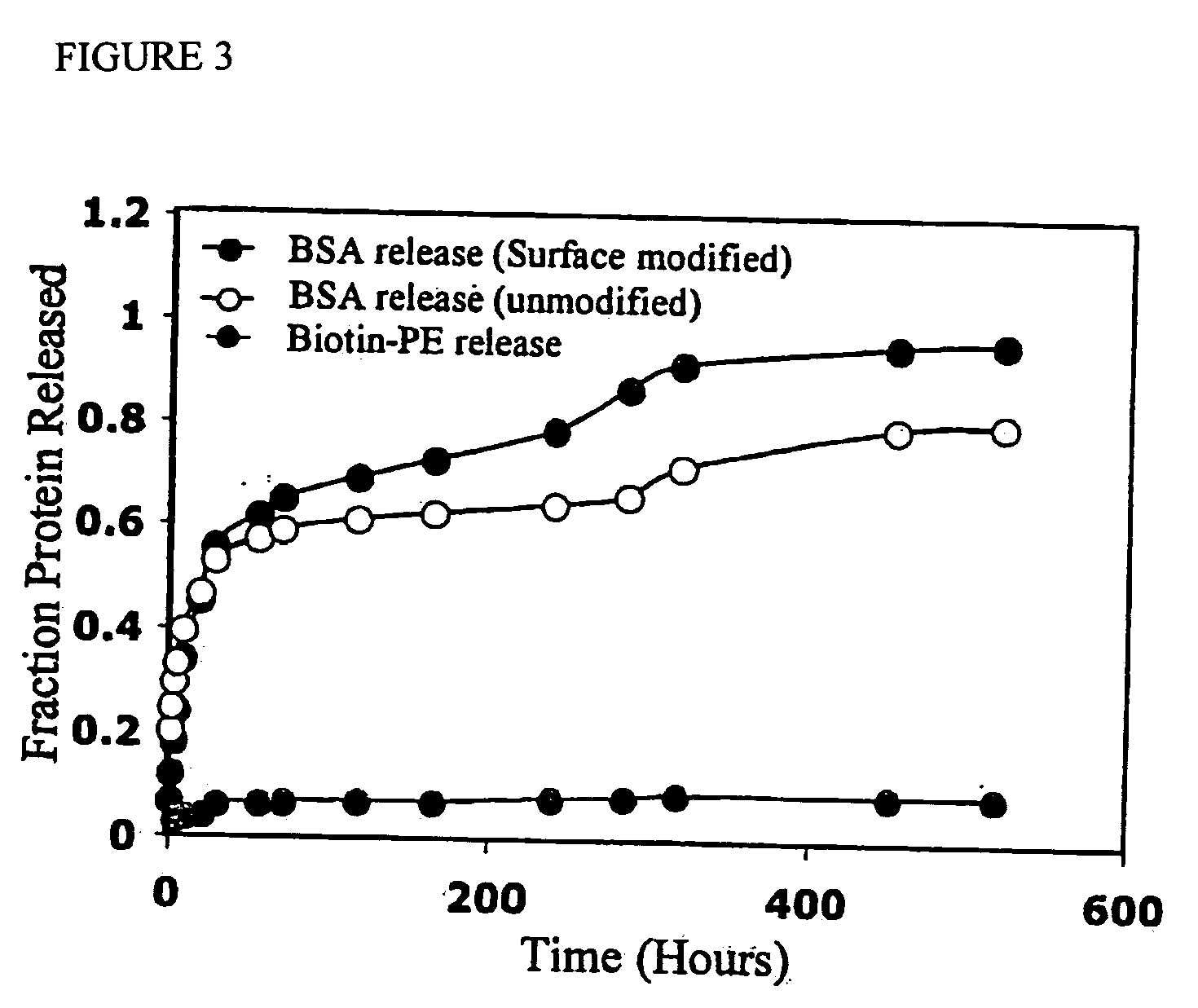
Polymeric delivery devices have been developed which combine high loading / high density of molecules to be delivered with the option of targeting. As used herein, “high density” refers to microparticles having a high density of ligands or coupling agents, which is in the range of 1000-10,000,000, more preferably between 10,000 and 1,000,000 ligands per square micron of microparticle surface area. A general method for incorporating molecules into the surface of biocompatible polymers using materials with an HLB of less than 10, more preferably less than 5, such as fatty acids, has been developed. Because of its ease, generality and flexibility, this method has widespread utility in modifying the surface of polymeric materials for applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering, as well other other fields. Targeted polymeric microparticles have also been developed which encapsulate therapeutic compounds such as drugs, cellular materials or components, and antigens, and have targeting ligands directly bound to the microparticle surface. Preferred applications include use in tissue engineering matrices, wound dressings, bone repair or regeneration materials, and other applications where the microparticles are retained at the site of application or implantation. Another preferred application is in the use of microparticles to deliver anti-proliferative agents to the lining of blood vessels following angioplasty, transplantation or bypass surgery to prevent or decrease restenosis, and in cancer therapy. In still another application, the microparticles are used to treat or prevent macular degeneration when administered to the eye, where agents such as complement inhibitors are administered.
Owner:YALE UNIV
Targeted delivery of active/bioactive and perfuming compositions
Described are controlled, time-release microparticulate active and bioactive compositions (including perfuming compositions) for targeted delivery to surfaces such as skin, hair and fabric and the environment proximate thereto, where the active and bioactive materials have a calculated log10P values of between 1 and 8 (P being the n-octanol-water partition coefficient). Such compositions include the active or bioactive material in single phase, solid solution in a wax or polymer matrix also having coated thereon and / or containing a compatible surfactant. Also described are processes and apparatus for preparing such compositions and processes for using same. Furthermore, certain component(s) of the aforementioned compositions in combination with one another are novel, and other components have novel uses in increasing fragrance substantivity, particularly in hair care preparations such as hair gels and shampoos.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS7404969B2Reduce deliveryAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationMolecular composition
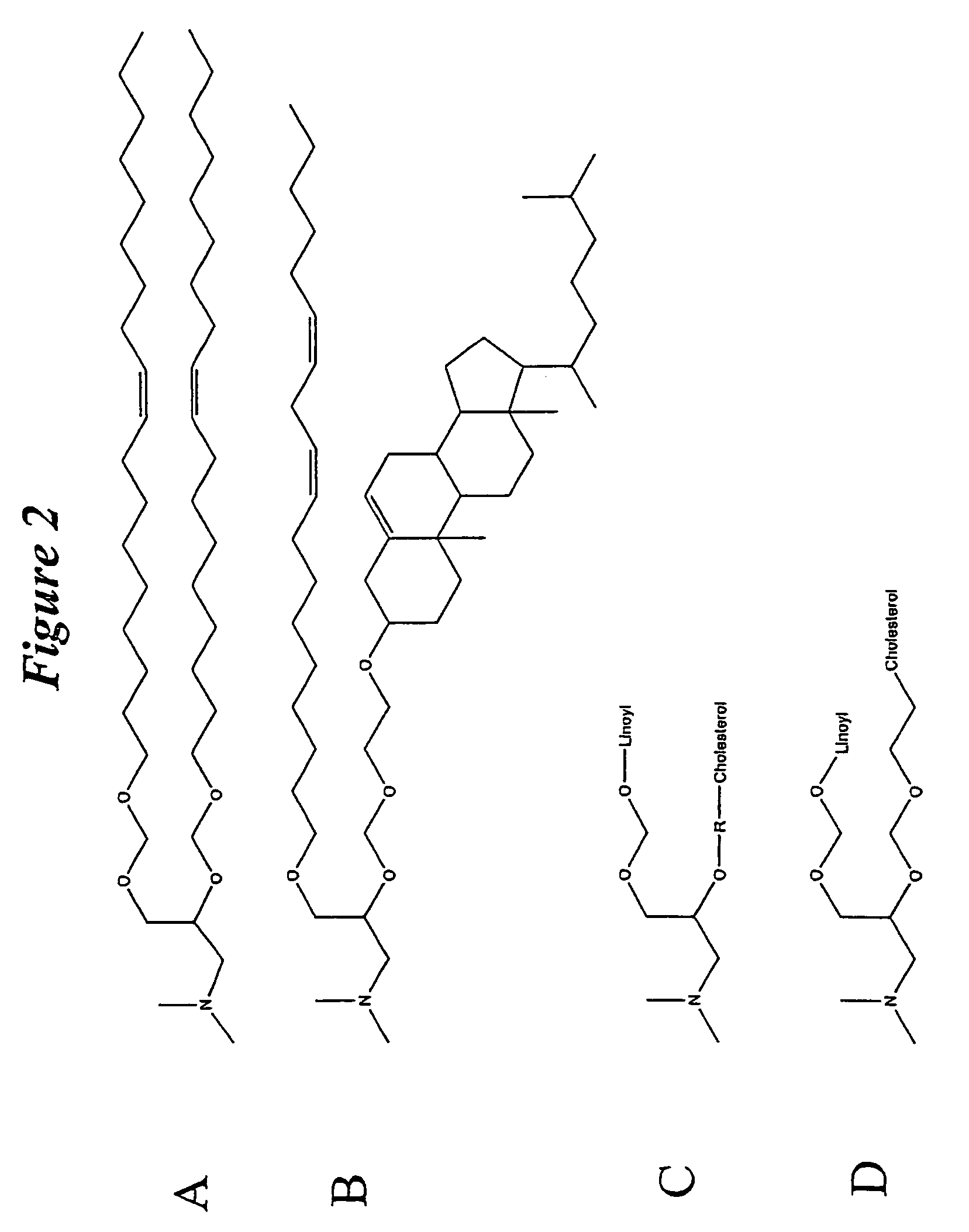
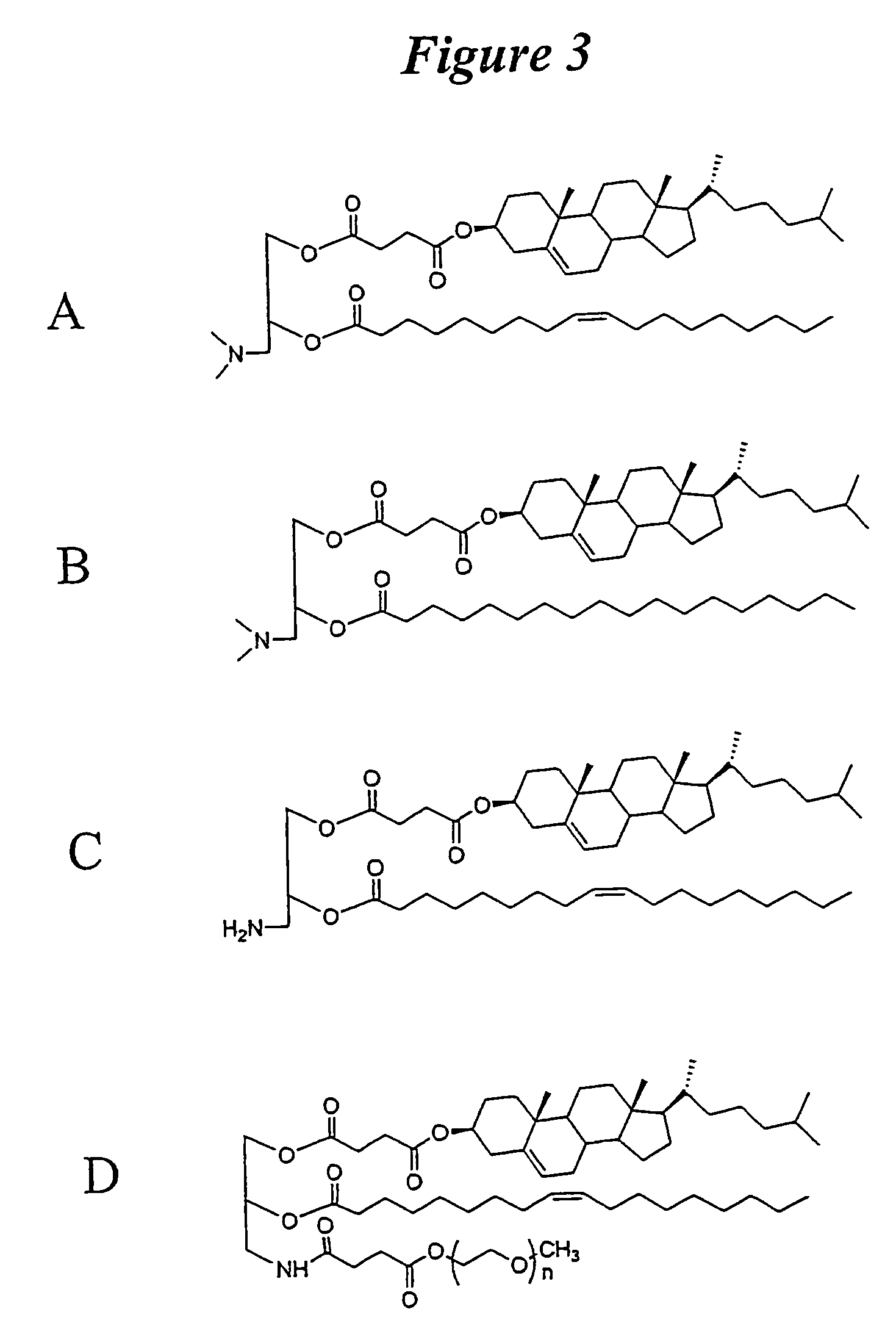
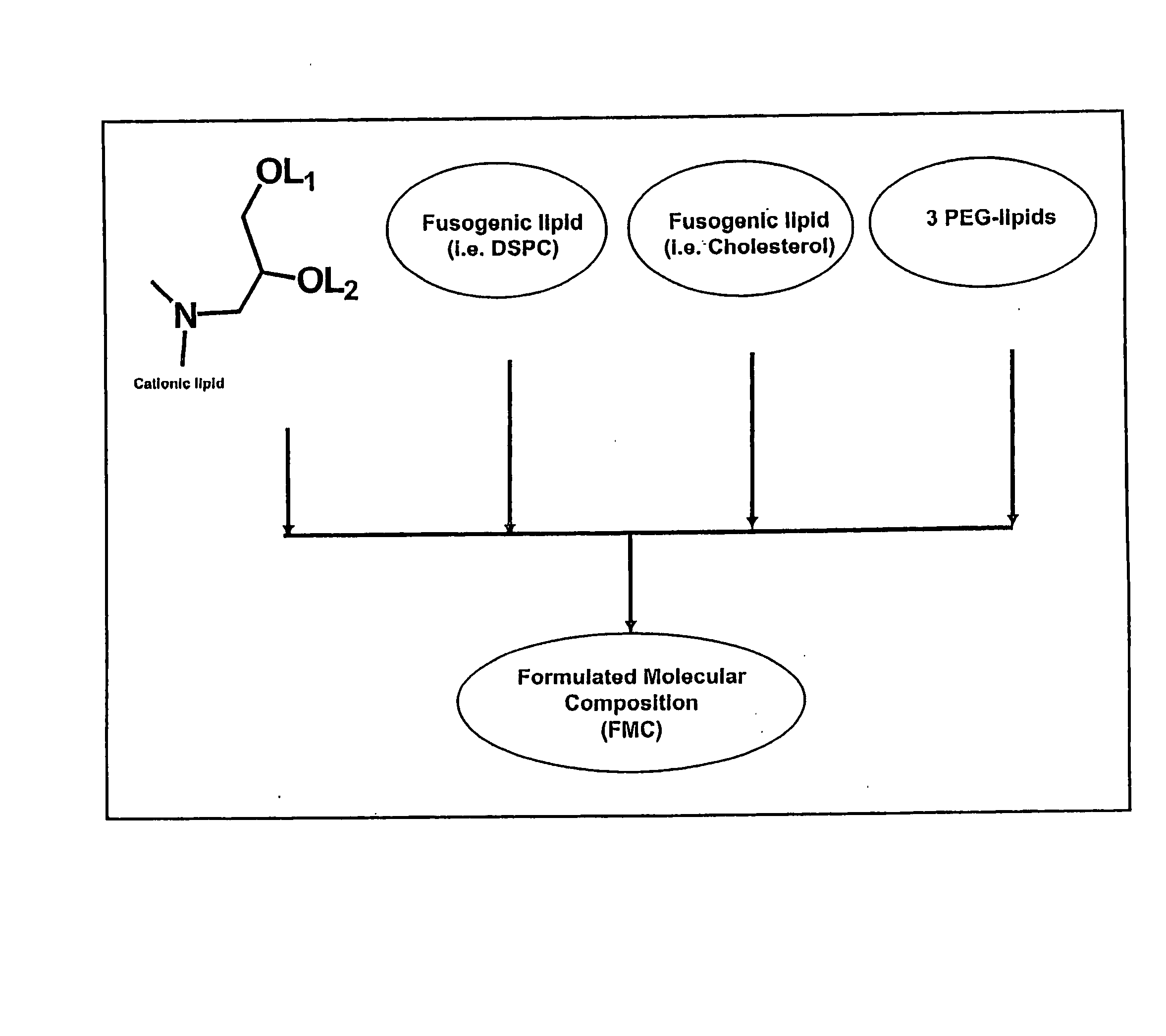
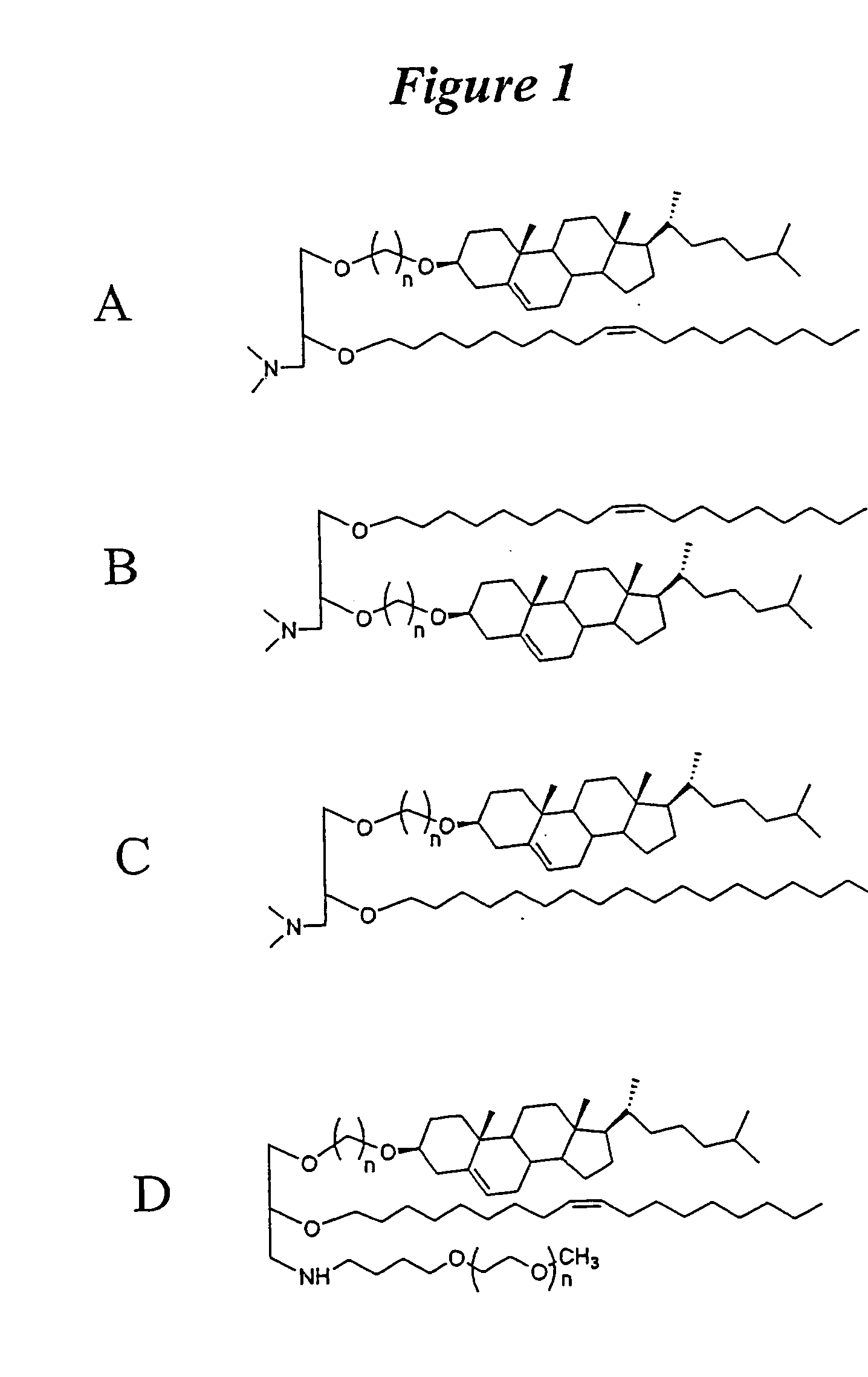
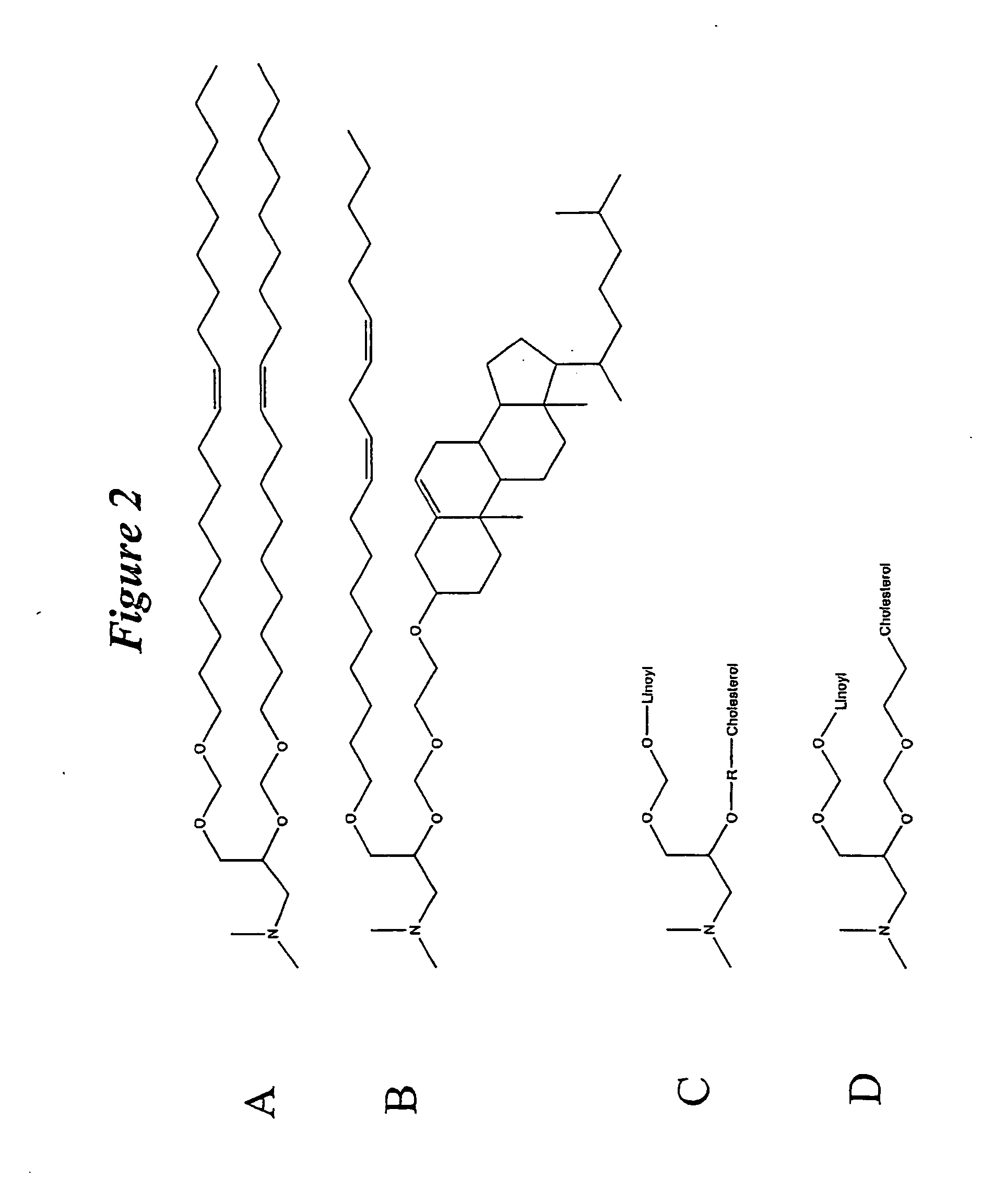
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver short interfering nucleic acid (siNA). The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods for the reduction and elimination of particulate contamination with CVD of amorphous carbon
InactiveUS20060014397A1Minimal defect formationReduce particle pollutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial surfacesVariable thicknessMicroparticle
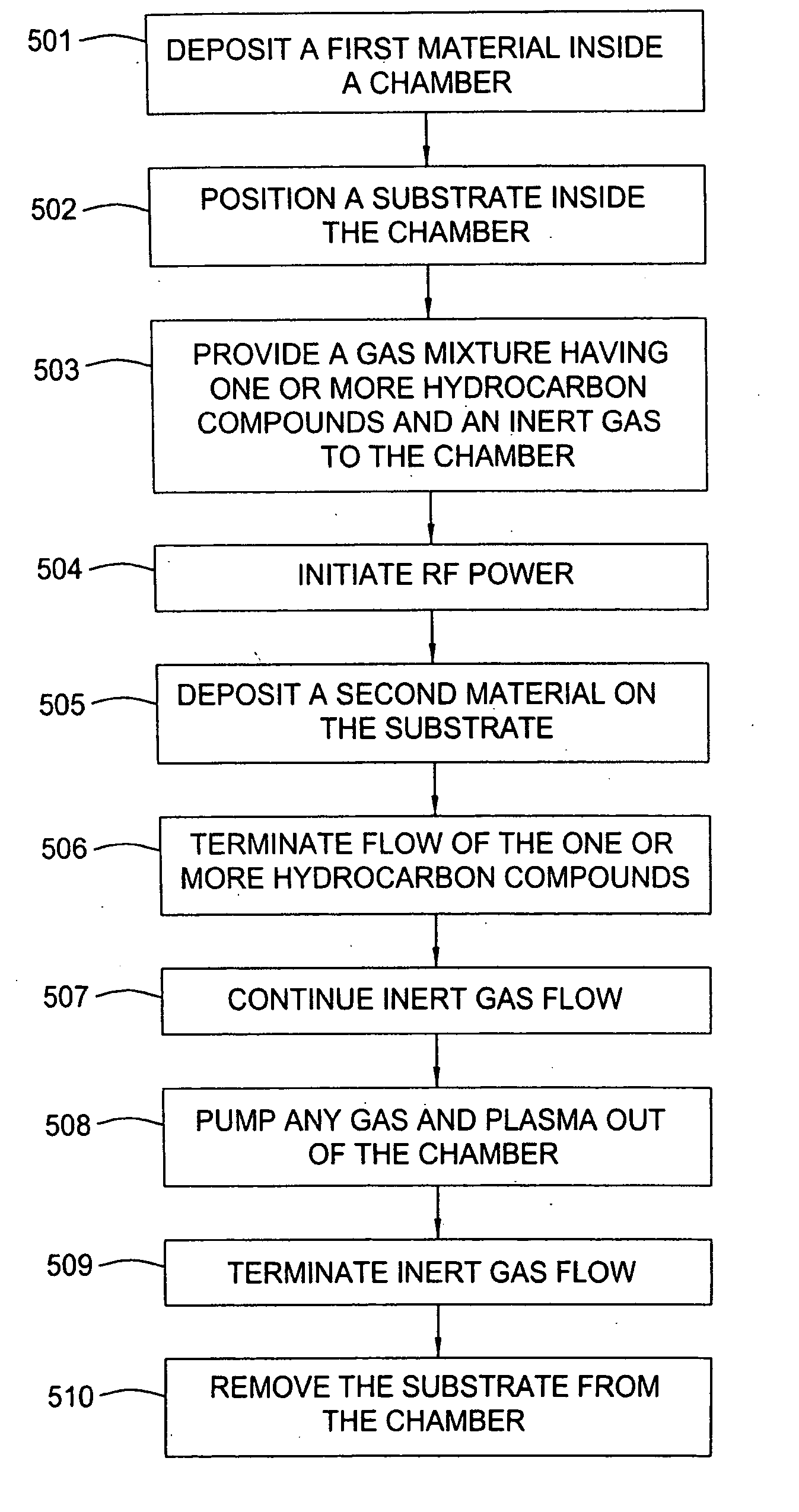
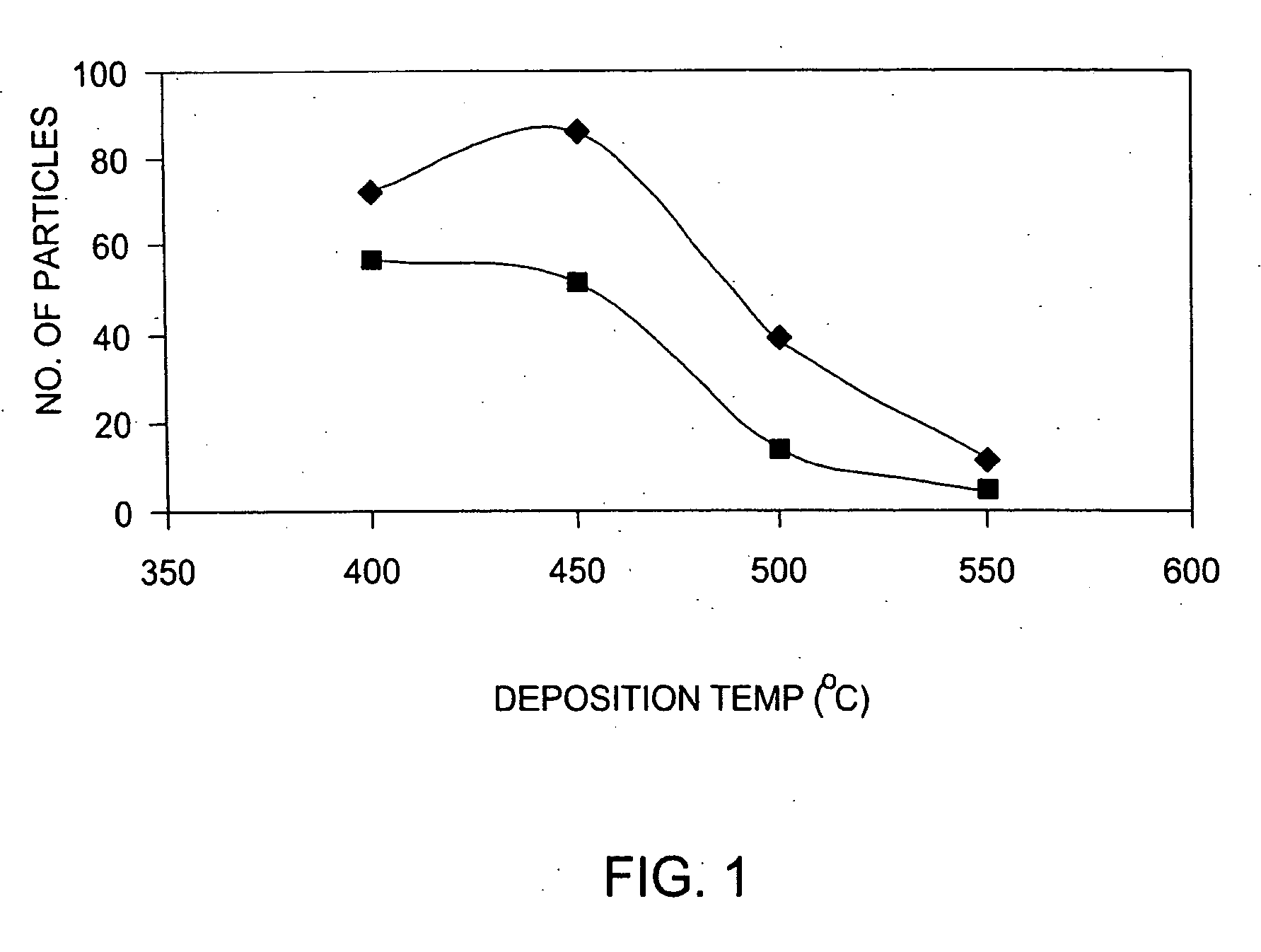
A method is provided for forming an amorphous carbon layer, deposited on a dielectric material such as oxide, nitride, silicon carbide, carbon doped oxide, etc., or a metal layer such as tungsten, aluminum or poly-silicon. The method includes the use of chamber seasoning, variable thickness of seasoning film, wider spacing, variable process gas flows, post-deposition purge with inert gas, and post-deposition plasma purge, among others, to make the deposition of an amorphous carbon film at low deposition temperatures possible without any defects or particle contamination.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC +1
Apparatus for preparing a solid phase microparticulate composition
InactiveUS6042792ALow costImproved substantivityCosmetic preparationsComponent separationWaxMicroparticle
Described are controlled, time-release microparticulate active and bioactive compositions (including perfuming compositions) for targeted delivery to services such as skin, hair and fabric and the environment proximate thereto, where the active and bioactive materials have a calculated log10P values of between 1 and 8 (P being the n-octanol-water partition coefficient). Such compositions include the active or bioactive material in single phase, solid solution in a wax or polymer matrix also having coated thereon and / or containing a compatible surfactant. Also described are processes and apparatus for preparing such compositions and processes for using same. Furthermore, certain component(s) of the aforementioned compositions in combination with one another are novel, and other components have novel uses in increasing fragrance substantivity.
Owner:INTERNATIONAL FLAVORS & FRAGRANCES
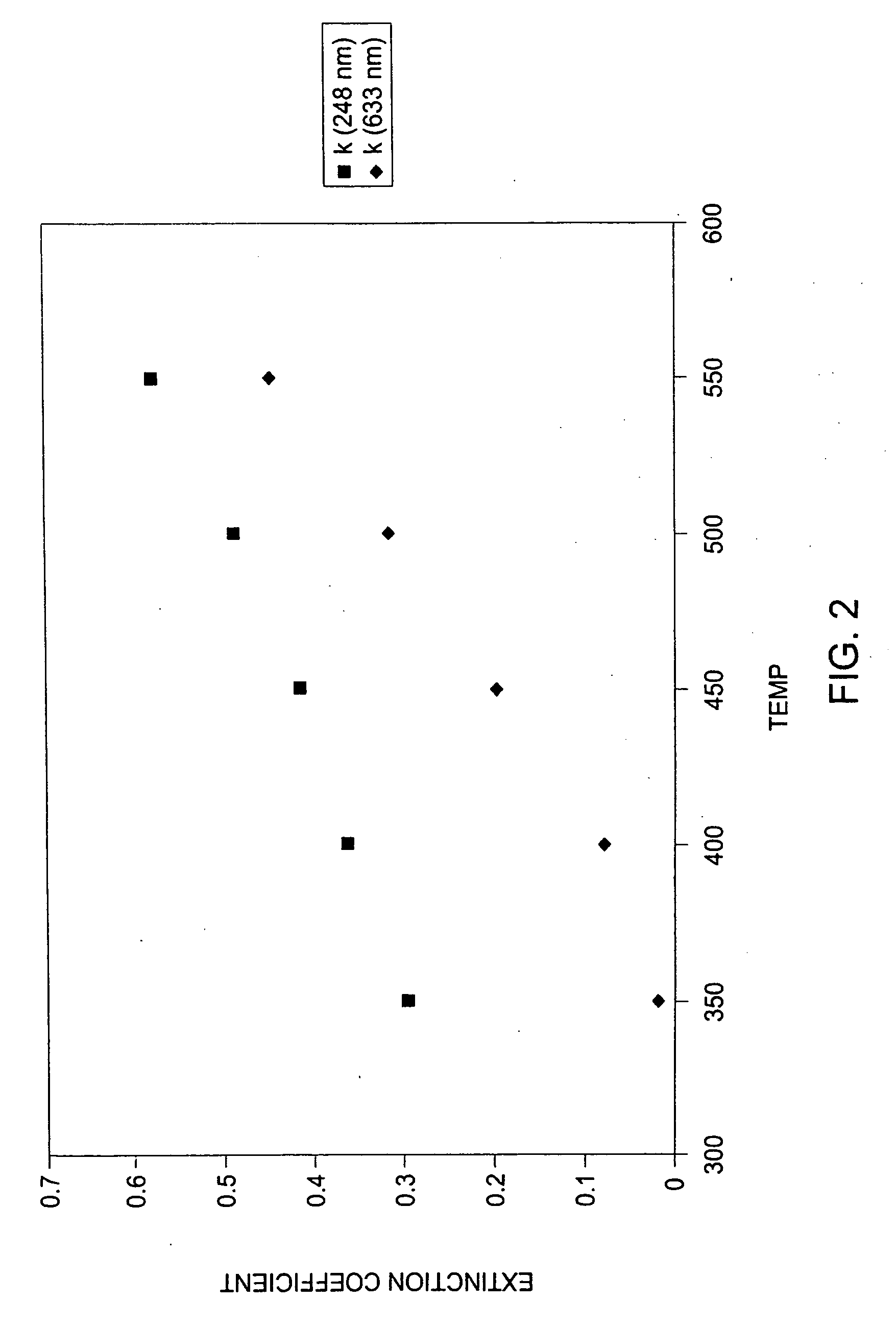
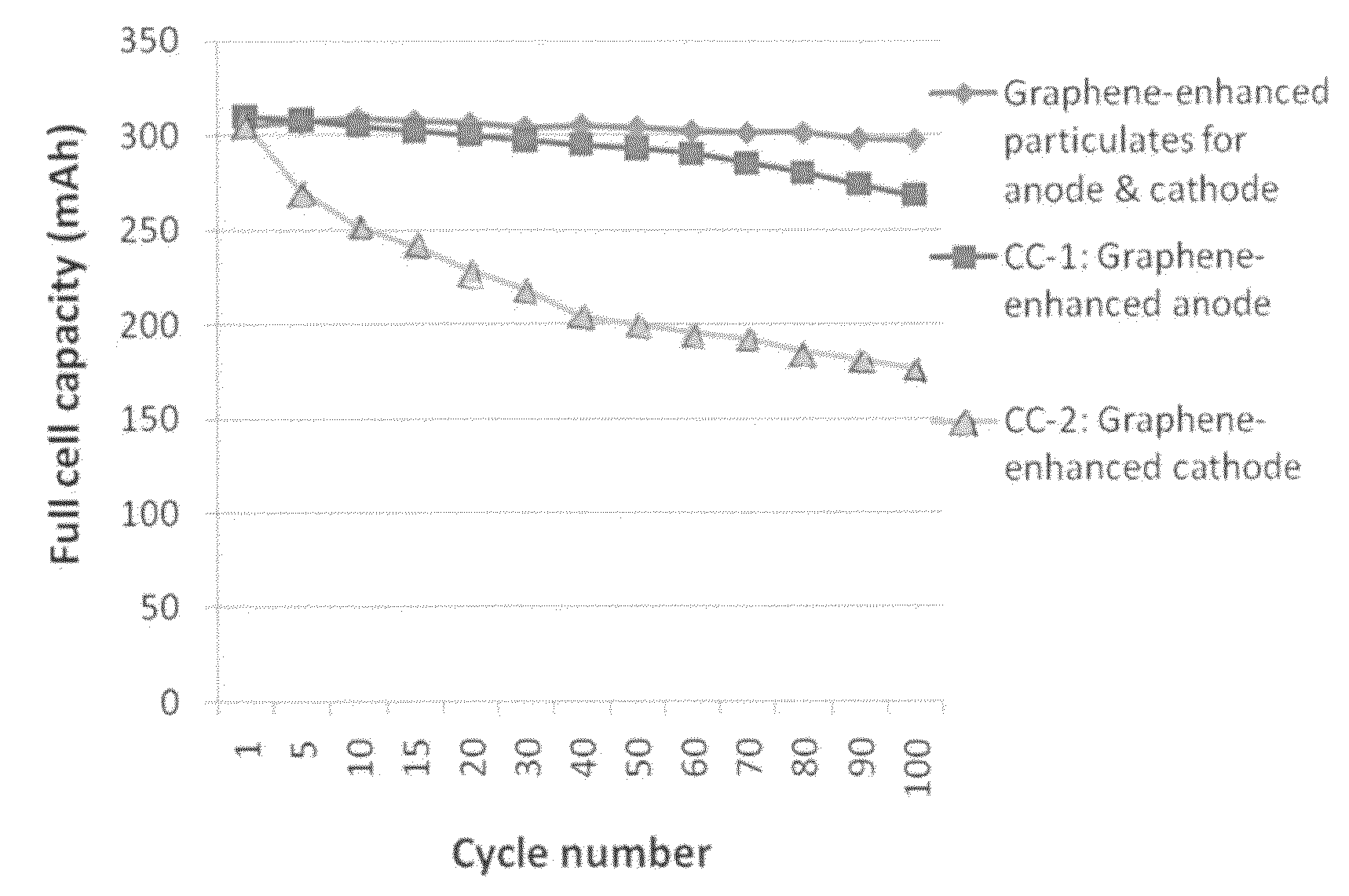
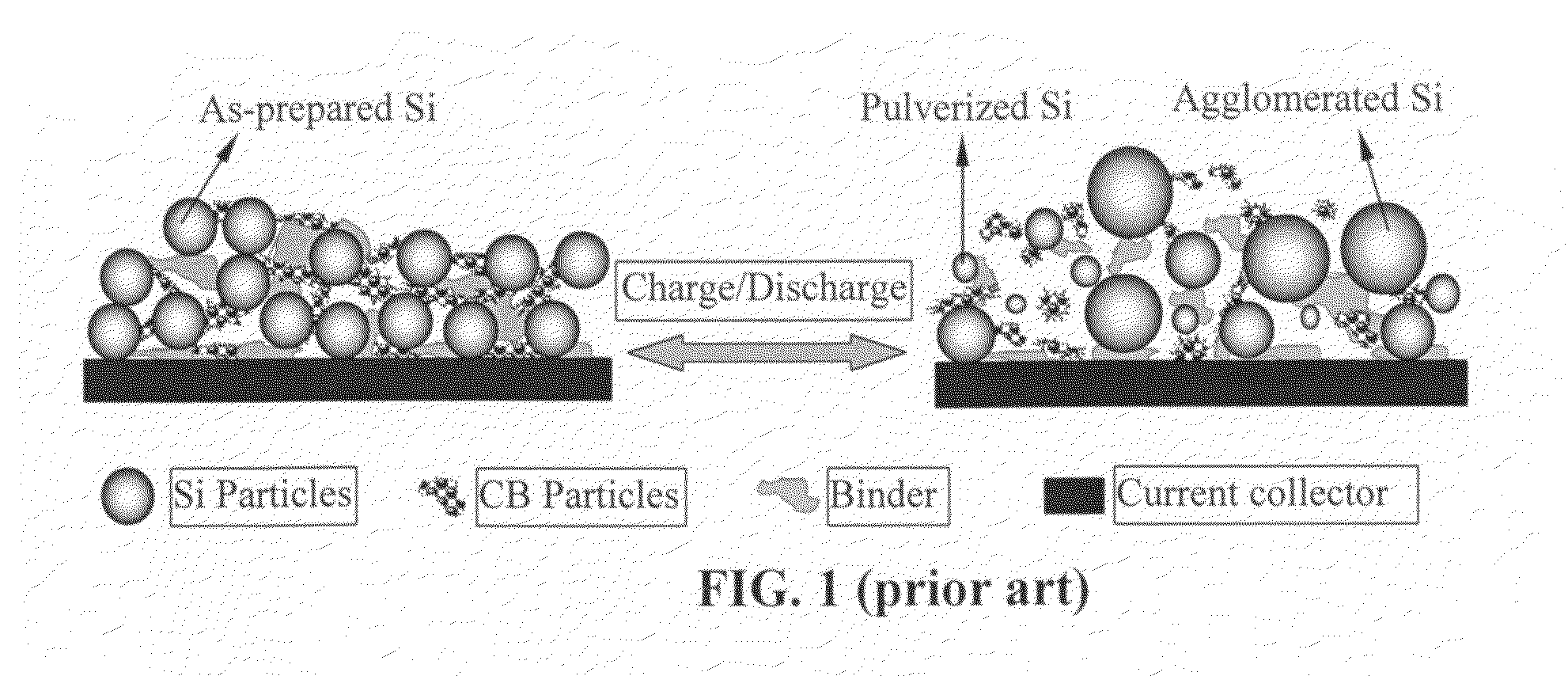
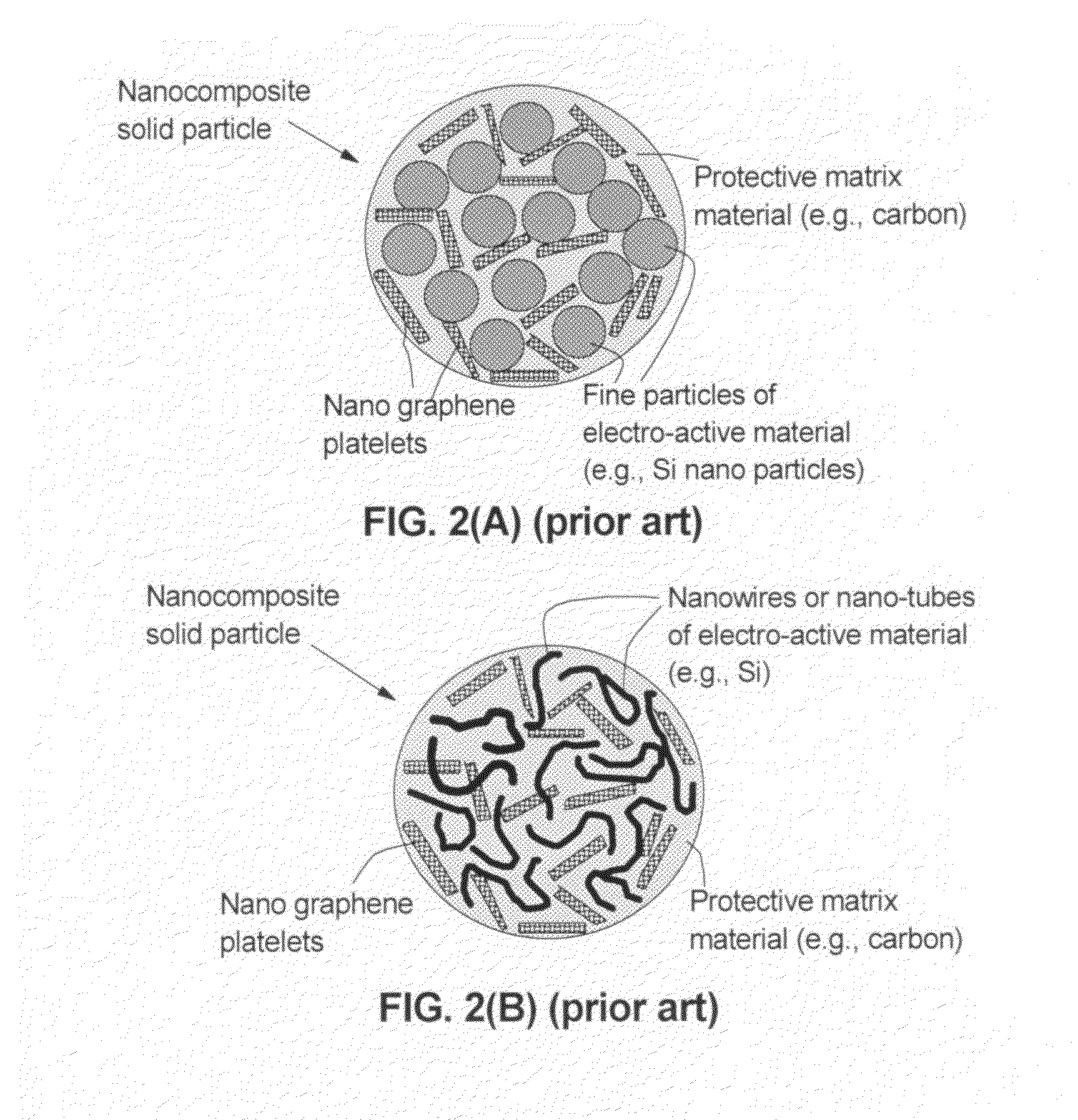
Graphene-enhanced anode particulates for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20120064409A1Enhanced Li-ion insertionIncrease capacityNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesMicroparticle
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium-ion battery anode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single sheet of graphene or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine anode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm. The graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into the particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the anode active material particles. The amount of graphene is at least 0.01% by weight and the amount of the anode active material is at least 0.1% by weight, all based on the total weight of the particulate. A lithium-ion battery having an anode containing these graphene-enhanced particulates exhibits a stable charge and discharge cycling response, a high specific capacity per unit mass, a high first-cycle efficiency, a high capacity per electrode volume, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Disposable vacuum filtration apparatus capable of detecting microorganisms and particulates in liquid samples
InactiveUS6913152B2Increase valueEasy to disassemblePreparing sample for investigationUltrafiltrationMicroorganismWrinkle skin
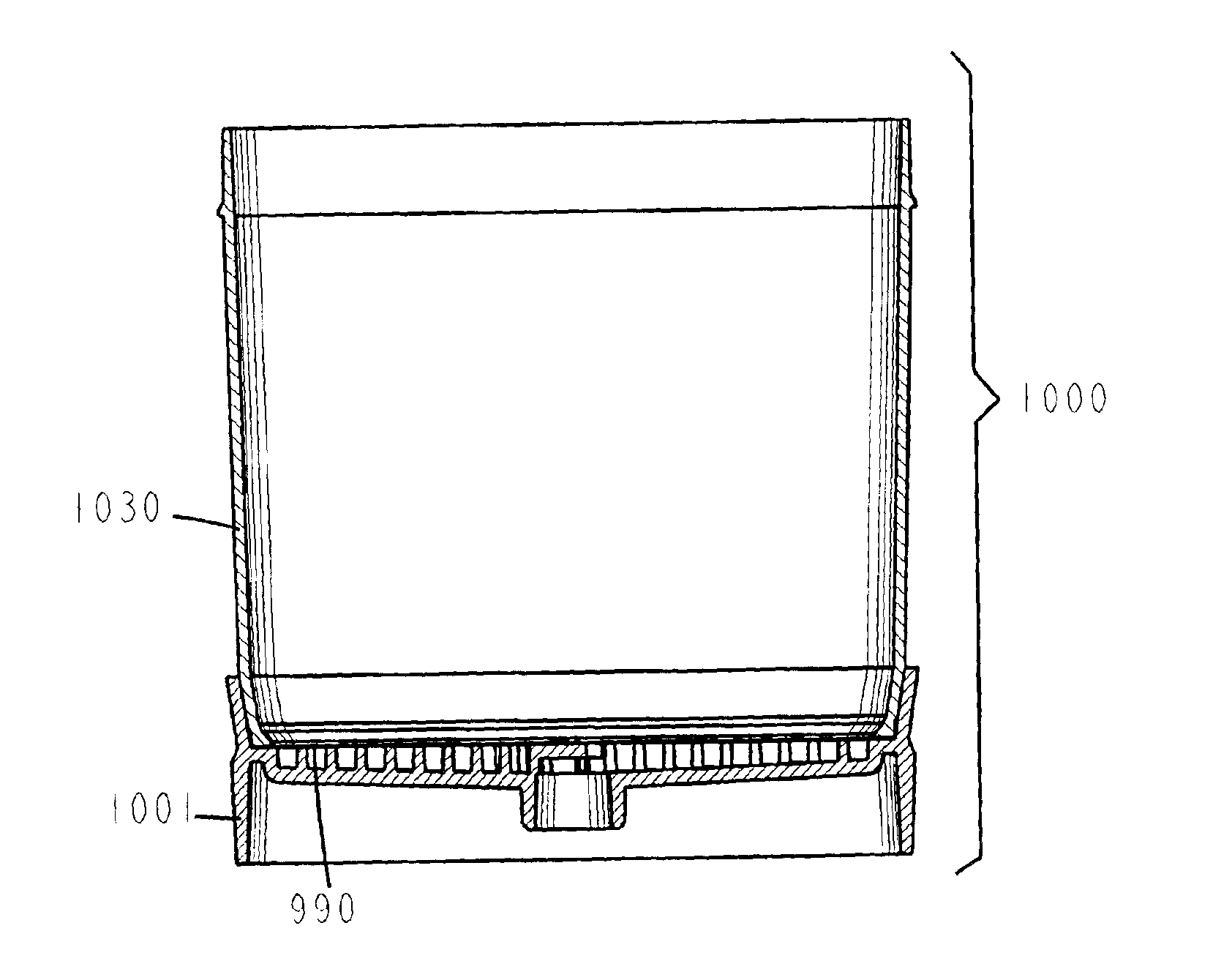
A vacuum filtration apparatus (900) for detecting microorganisms and particulates in liquid samples. The apparatus includes a base (901), an absorbent pad (991), a filter (990), a funnel (930), and a lid (960). The funnel is releasably attached to the base, and may contain an integral flexible seal for releasably sealing the filter to the base. The outer wall of the lid may be segmented to make it flexible, this flexibility allows it to be releasably attached to the funnel or the base. The apparatus is designed so that any funnel will fit any base, and any lid will fit any base or any funnel when all parts are manufactured to normal tolerances. The apparatus may be configured to to keep the filter wrinkle free in both the dry and wet states.
Owner:FOXX LIFE SCI
Particulate acellular tissue matrix
A method of processing an acellular tissue matrix to give a particulate acellular tissue matrix includes: cutting sheets of dry acellular tissue matrix into strips; cryofracturing the dry acellular tissue matrix strips at cryogenic temperatures; separating the resulting particles by size at cryogenic temperatures; and freeze drying the fraction of particles desired size to remove any moisture that may have been absorbed to give a dry particulate acellular tissue matrix. Rehydration of the dry particulate acellular tissue matrix may take place just prior to use. The particulate acellular tissue may be applied to a recipient site, by way of injection, spraying, layering, packing, in-casing or combinations thereof. The particulate acellular tissue may further include growth and stimulating agents selected from epidermal growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, nerve growth factor, keratinocyte growth factor, platelet derived growth factor, vasoactive intestinal peptide, stem cell factor, bone morphogetic proteins, chondrocyte growth factor and combinations thereof. Other pharmaceutically active compounds may be combined with the rehydrated particulate material including: analgesic drugs; hemostatic drugs; antibiotic drugs; local anesthetics and the like to enhance the acceptance of the implanted particulate material. The particulate material product may also be combined with stem cells selected from mesenchymal stem cells, epidermal stem cells, cartilage stem cells, hematopoietic stem cells and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
Photobleach speckle and laundry detergent compositions containing it
InactiveUS20030087790A1Little and no stainingLittle or no stainingOrganic detergent compounding agentsDetergent dyesParticulatesBleach
A speckle composition for use in particulate laundry detergent compositions comprising a porous granular carrier, and at least 0.01 wt % photobleach, preferably at least 0.05 wt %, more preferably at least 0.1 wt %, based on the active ingredient the composition being layered with a finely divided high carrying capacity particulate material and / or a water-soluble material. The most preferred photobleach is a blend of Zn and Al sulphonated phthalocyanine.
Owner:HENKEL IP & HOLDING GMBH
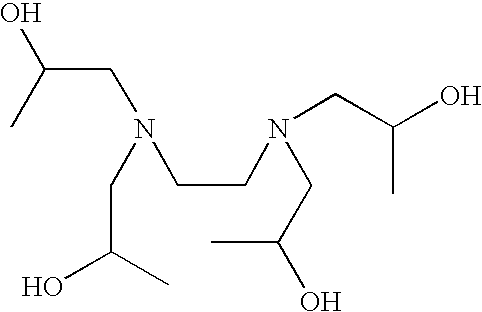
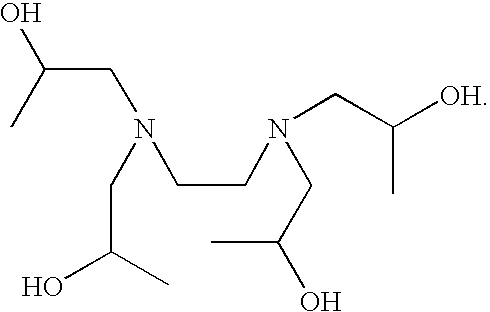
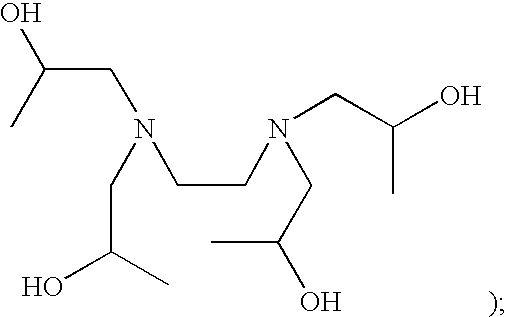
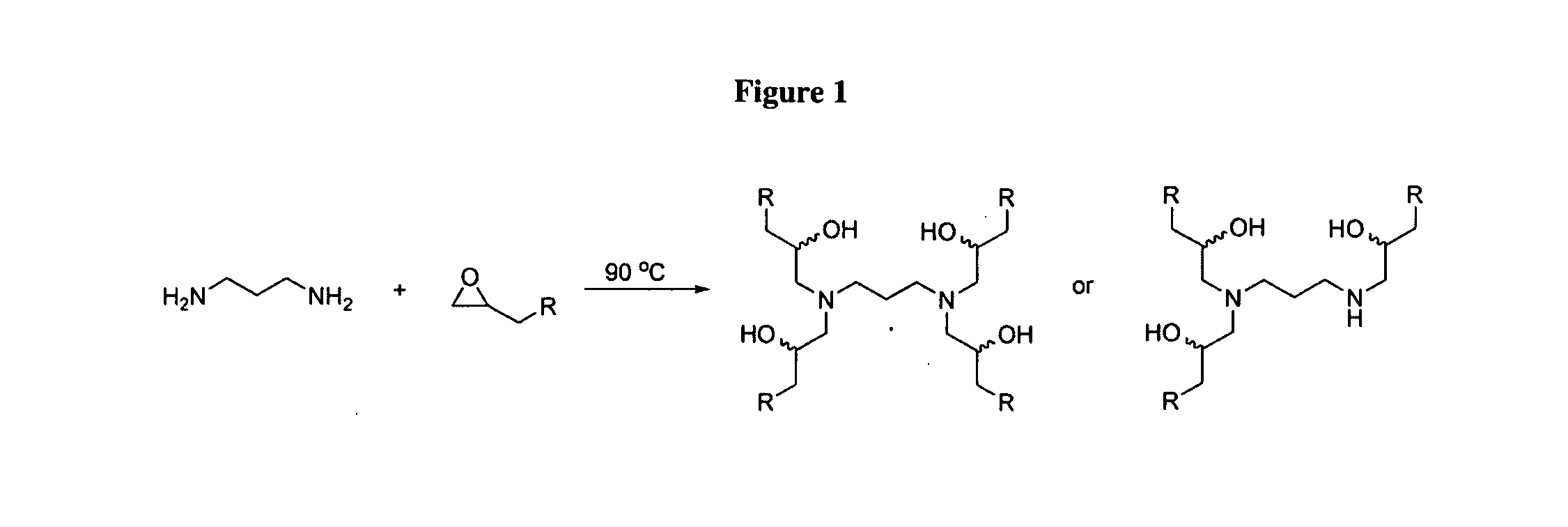
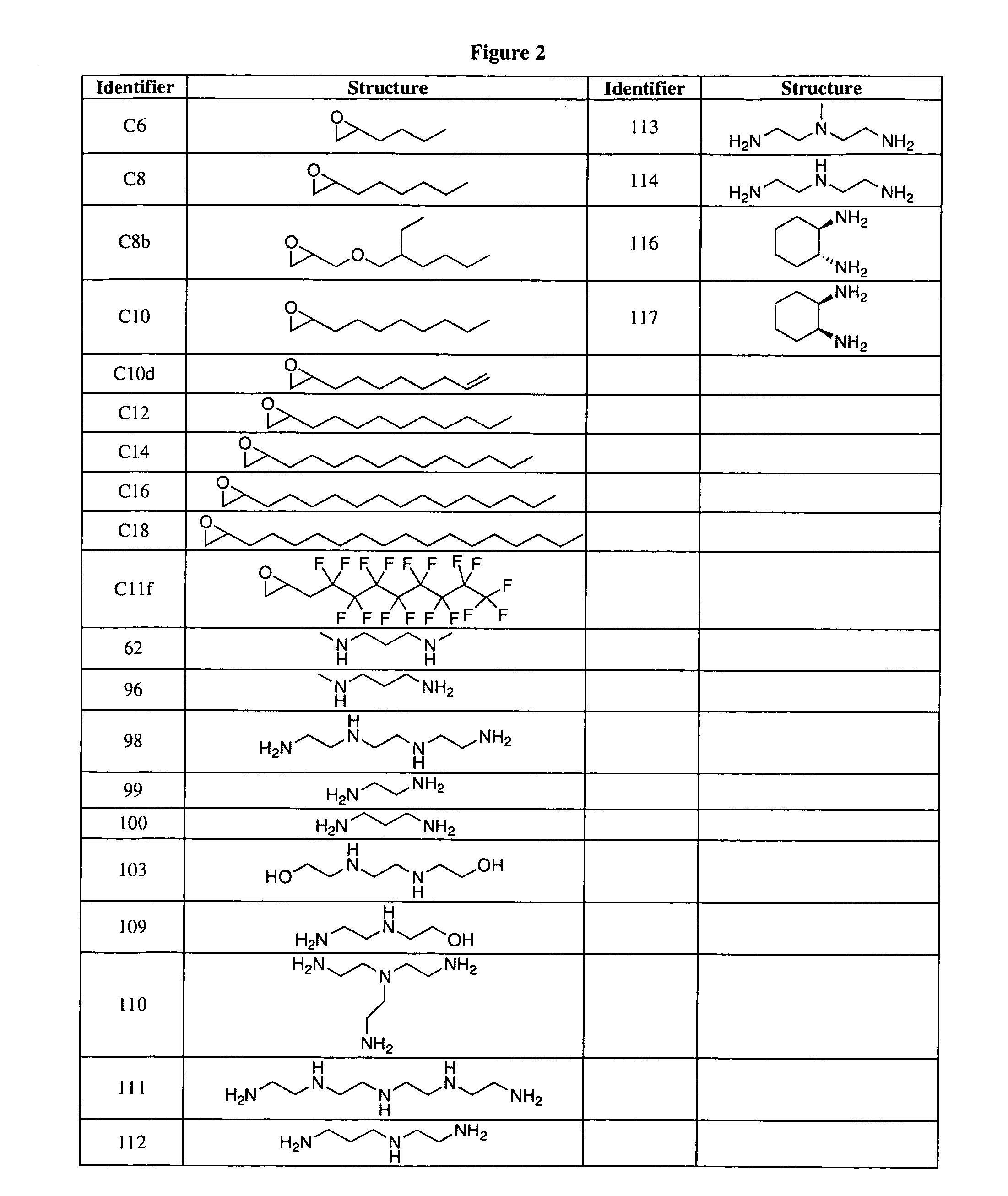
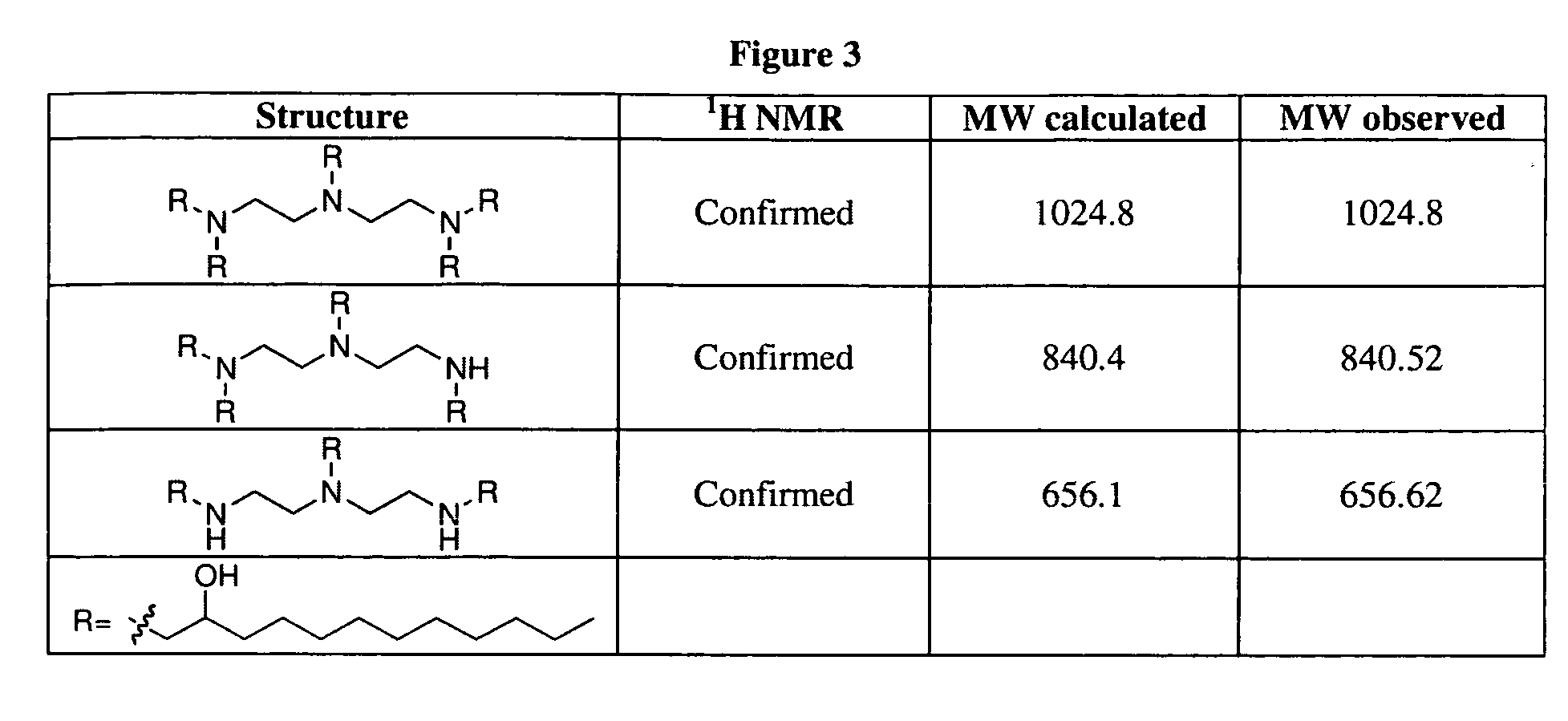
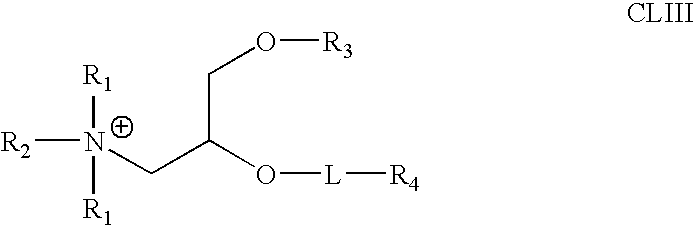
Aminoalcohol lipidoids and uses thereof
Aminoalcohol lipidoids are prepared by reacting an amine with an epoxide-terminated compound are described. Methods of preparing aminoalcohol lipidoids from commercially available starting materials are also provided. Aminoalcohol lipidoids may be prepared from racemic or stereochemically pure epoxides. Aminoalcohol lipidoids or salts forms thereof are preferably biodegradable and biocompatible and may be used in a variety of drug delivery systems. Given the amino moiety of these aminoalcohol lipidoid compounds, they are particularly suited for the delivery of polynucleotides. Complexes, micelles, liposomes or particles containing the inventive lipidoids and polynucleotide have been prepared. The inventive lipidoids may also be used in preparing microparticles for drug delivery. They are particularly useful in delivering labile agents given their ability to buffer the pH of their surroundings.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination, adhesive, coating material and process for producing honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination
ActiveUS20050109023A1Reduce thermal stressAlleviating generated thermal stressCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesAdhesive
An object of the present invention is to provide a honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases which makes it possible to alleviate a thermal stress generated due to occurrence of a local temperature change and which is less likely to generate cracks and superior in strength and durability, an adhesive that has a low thermal capacity and is capable of alleviating the thermal stress, a coating material that has a low thermal capacity with a superior heat insulating property and is capable of alleviating the thermal stress, and a manufacturing method of the honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases that can improve precision in the outside dimension, and reduce damages in the manufacturing processes. The present invention relates to a honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases, having a structure in that a plurality of column-shaped porous ceramic members, each having a number of through holes that are placed side by side in the length direction with partition wall interposed therebetween, are combined with one another through adhesive layers so that the partition wall that separate the through holes are allowed to function as a filter for collecting particulates, and in this structure, the thermal expansion coefficient αL of the adhesive layer and the thermal expansion coefficient αF of the porous ceramic member are designed to have the following relationship: 0.01<|αL−αF| / αF<1.0.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Drug eluting implants to prevent cardiac apoptosis
Implantable devices are configured to be positioned in or near the heart and to carry and deliver an anti-apoptotic drug to a treatment site in or near the heart. The implantable devices include, but are not limited to, leads, stents, heart valves, atrial septal defect devices, cardiac patches and ventricular restraint devices. Depending on the composition of the device, the drug may be carried by the device through a coating applied to the device, or may be included in the device during the device manufacturing process. The drug may also be included in microparticles, such a microspheres, that are delivered locally through a conduit, such as a catheter.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Microparticle coated medical device
A drug-loaded microparticle is applied to a medical device for subsequent application to biological tissues. A method of formulating a drug-loaded microparticle and applying it to the surface of a medical device, such as a stent, is disclosed. The drug-loaded microparticle is formulated by combining a drug with various chemical solutions. Specified sizes of the microparticles and amounts of drug(s) contained within the microparticles may be varied by altering the proportions of the chemicals / solutions. In addition to various drugs, therapeutic substances and radioactive isotopes may also be loaded into the microparticles. The drug-loaded microparticle are suspended in a polymer solution forming a polymer matrix. The polymer matrix may be applied to the entire surface or only selected portions of the medical device via dipping, spraying or combinations thereof.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Poly(beta-amino alcohols), their preparation, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130302401A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsChemical structureFibrosis
A new class of poly(beta-amino alcohols) (PBAAs) has been prepared using combinatorial polymerization. The inventive PBAAs may be used in biotechnology and biomedical applications as coatings (such as coatings of films or multilayer films for medical devices or implants), additives, materials, excipients, non-biofouling agents, micropatterning agents, and cellular encapsulation agents. When used as surface coatings, these PBAAs elicited different levels of inflammation, both in vitro and in vivo, depending on their chemical structures. The large chemical diversity of this class of materials allowed us to identify polymer coatings that inhibit macrophage activation in vitro. Furthermore, these coatings reduce the recruitment of inflammatory cells, and reduce fibrosis, following the subcutaneous implantation of carboxylated polystyrene microparticles. These polymers may be used to form polyelectrolyte complex capsules for cell encapsulation. The invention may also have many other biological applications such as antimicrobial coatings, DNA or siRNA delivery, and stem cell tissue engineering.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
ActiveUS20080020058A1Improves various propertyImprove the immunityAntibacterial agentsPowder deliveryLipid formationCholesterol
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), short hairpin RNA (shRNA), and RNAi inhibitor molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Lipid nanoparticle based compositions and methods for the delivery of biologically active molecules
The present invention relates to novel cationic lipids, transfection agents, microparticles, nanoparticles, and short interfering nucleic acid (siNA) molecules. The invention also features compositions, and methods of use for the study, diagnosis, and treatment of traits, diseases and conditions that respond to the modulation of gene expression and / or activity in a subject or organism. Specifically, the invention relates to novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents that effectively transfect or deliver biologically active molecules, such as antibodies (e.g., monoclonal, chimeric, humanized etc.), cholesterol, hormones, antivirals, peptides, proteins, chemotherapeutics, small molecules, vitamins, co-factors, nucleosides, nucleotides, oligonucleotides, enzymatic nucleic acids, antisense nucleic acids, triplex forming oligonucleotides, 2,5-A chimeras, dsRNA, allozymes, aptamers, decoys and analogs thereof, and small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules, to relevant cells and / or tissues, such as in a subject or organism. Such novel cationic lipids, microparticles, nanoparticles and transfection agents are useful, for example, in providing compositions to prevent, inhibit, or treat diseases, conditions, or traits in a cell, subject or organism. The compositions described herein are generally referred to as formulated molecular compositions (FMC) or lipid nanoparticles (LNP).
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Preparation of protein microparticles by supercritical fluid precipitation
InactiveUS6063910AUniform and fine particle sizePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsMicroparticleSolvent
The present invention comprises passing a solution of a soluble material, preferably a protein, in a solvent through a continuum of supercritical antisolvent fluid and precipitating the soluble material. This can be conducted by passing the solution through the continuum of supercrital fluid in the form of droplets, which can be sprayed through the supercritical fluid. The plurality of droplets can be passed cocurrently or countercurrently with respect to a stream of antisolvent fluid. Alternatively, the solution can be passed through the continuum of supercritical antisolvent fluid in the form of a thin film or a plurality of fine streams.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Printable electronic display
InactiveUS6980196B1Easy to manufactureLow costElectromagnetic wave systemStatic indicating devicesMicroparticleNonlinear element
A display system includes a substrate upon which the display system is fabricated; a printable electrooptic display material, such as a microencapsulated electrophoretic suspension; electrodes (typically based on a transparent, conductive ink) arranged in an intersecting pattern to allow specific elements or regions of the display material to be addressed; insulating layers, as necessary, deposited by printing; and an array of nonlinear elements that facilitate matrix addressing. The nonlinear devices may include printed, particulate Schottky diodes, particulate PN diodes, particulate varistor material, silicon films formed by chemical reduction, or polymer semiconductor films. All elements of the display system may be deposited using a printing process.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Compositions and methods for controlling the release of chemicals placed on particulates
InactiveUS20050028976A1Simple methodSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsParticulatesCompound (substance)
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for creating and using particulate materials having treating agents absorbed thereon and coated with a degradable coating material. One embodiment of a method of the present invention provides a method treating to a subterranean formation comprising placing a coated, treated particulate into a subterranean formation wherein the coated, treated particulate comprises a particulate material having a treating agent placed thereon and a substantially complete layer of a degradable coating material coated placed thereon over the treating agent.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Microparticles with adsorbent surfaces, methods of making same, and uses thereof
InactiveUS6884435B1Stimulate immune responseEasy to usePowder deliverySsRNA viruses positive-senseAntigenDisease
The present invention is directed to microparticles, to microparticle compositions containing the same, to methods of forming the same, and to uses for the same, including use for a vaccine, for raising an immune response, for treatment of a disease and for diagnosis of a disease. The microparticles comprise a biodegradable polymer, such as a poly(α-hydroxy acid), a polyhydroxy butyric acid, a polycaprolactone, a polyorthoester, a polyanhydride, or a polycyanoacrylate, and a detergent selected from a cationic detergent and an anionic detergent. The microparticles further comprise an antigen adsorbed on the surface of the microparticle.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
Lipid-nucleic acid particles prepared via a hydrophobic lipid-nucleic acid complex intermediate and use for gene transfer
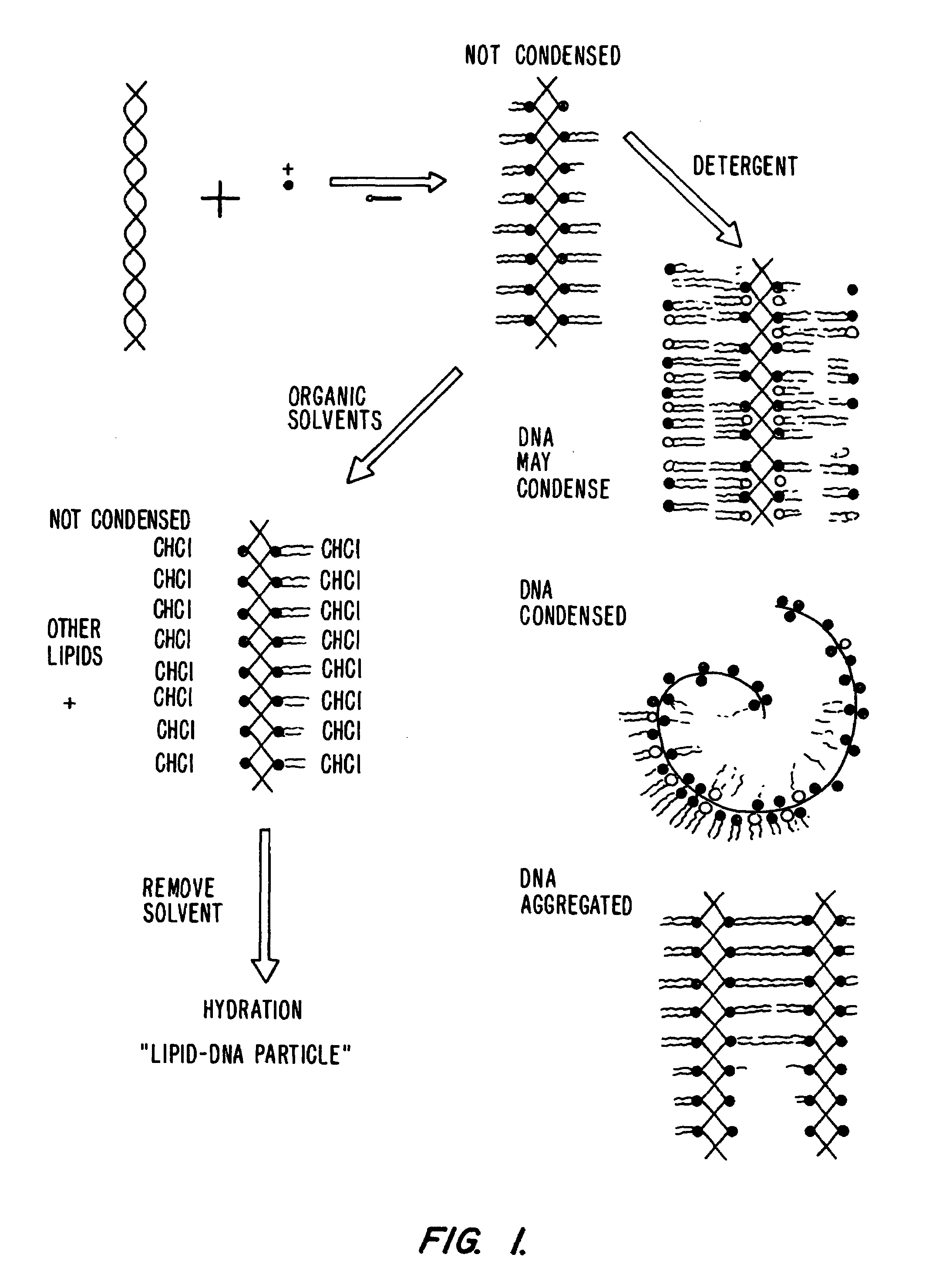
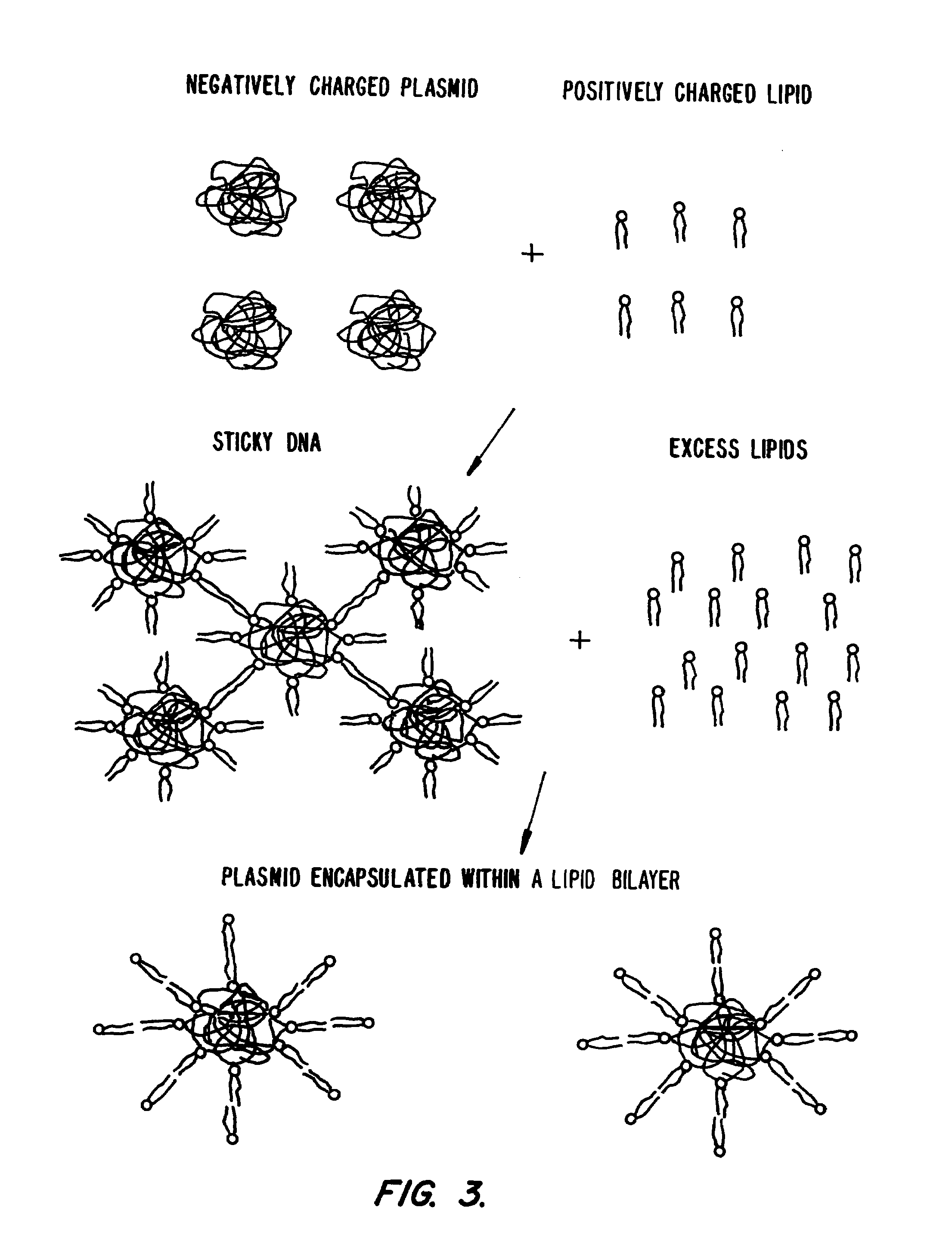
Novel lipid-nucleic acid particulate complexes which are useful for in vitro or in vivo gene transfer are described. The particles can be formed using either detergent dialysis methods or methods which utilize organic solvents. Upon removal of a solubilizing component (i.e., detergent or an organic solvent) the lipid-nucleic acid complexes form particles wherein the nucleic acid is serum-stable and is protected from degradation. The particles thus formed have access to extravascular sites and target cell populations and are suitable for the therapeutic delivery of nucleic acids.
Owner:TEKMIRA PHARMA CORP +1
Abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical compositions of opioids and other drugs
ActiveUS7399488B2Good treatment effectSmall dosePowder deliveryNervous disorderAdditive ingredientWater insoluble
An abuse-deterrent pharmaceutical composition has been developed to reduce the likelihood of improper administration of drugs, especially drugs such as opiods. In the preferred embodiment, a drug is modified to increase its lipophilicity. In preferred embodiments the modified drug is homogeneously dispersed within microparticles composed of a material that is either slowly soluble or not soluble in water. In some embodiments the drug containing microparticles or drug particles are coated with one or more coating layers, where at least one coating is water insoluble and preferably organic solvent insoluble, but enzymatically degradable by enzymes present in the human gastrointestinal tract. The abuse-deterrent composition retards the release of drug, even if the physical integrity of the formulation is compromised (for example, by chopping with a blade or crushing) and the resulting material is placed in water, snorted, or swallowed. However, when administered as directed, the drug is slowly released from the composition as the composition is broken down or dissolved gradually within the GI tract by a combination of enzymatic degradation, surfactant action of bile acids, and mechanical erosion.
Owner:COLLEGIUM PHARMA INC
Microparticles
InactiveUS6669961B2Minimal deformationHardening of the spheresPowder deliveryNanostructure manufactureMicroparticleNanometre
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
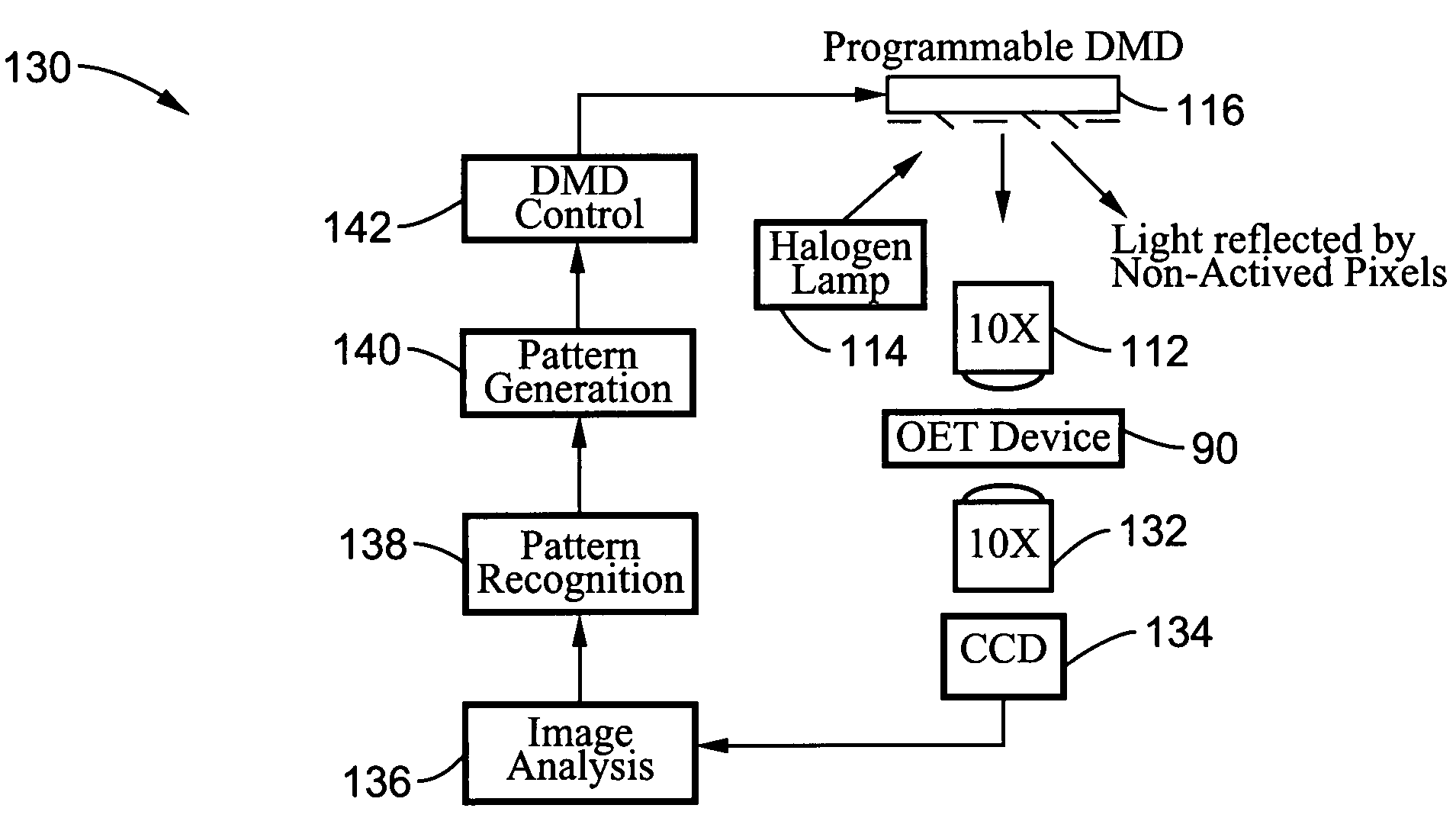
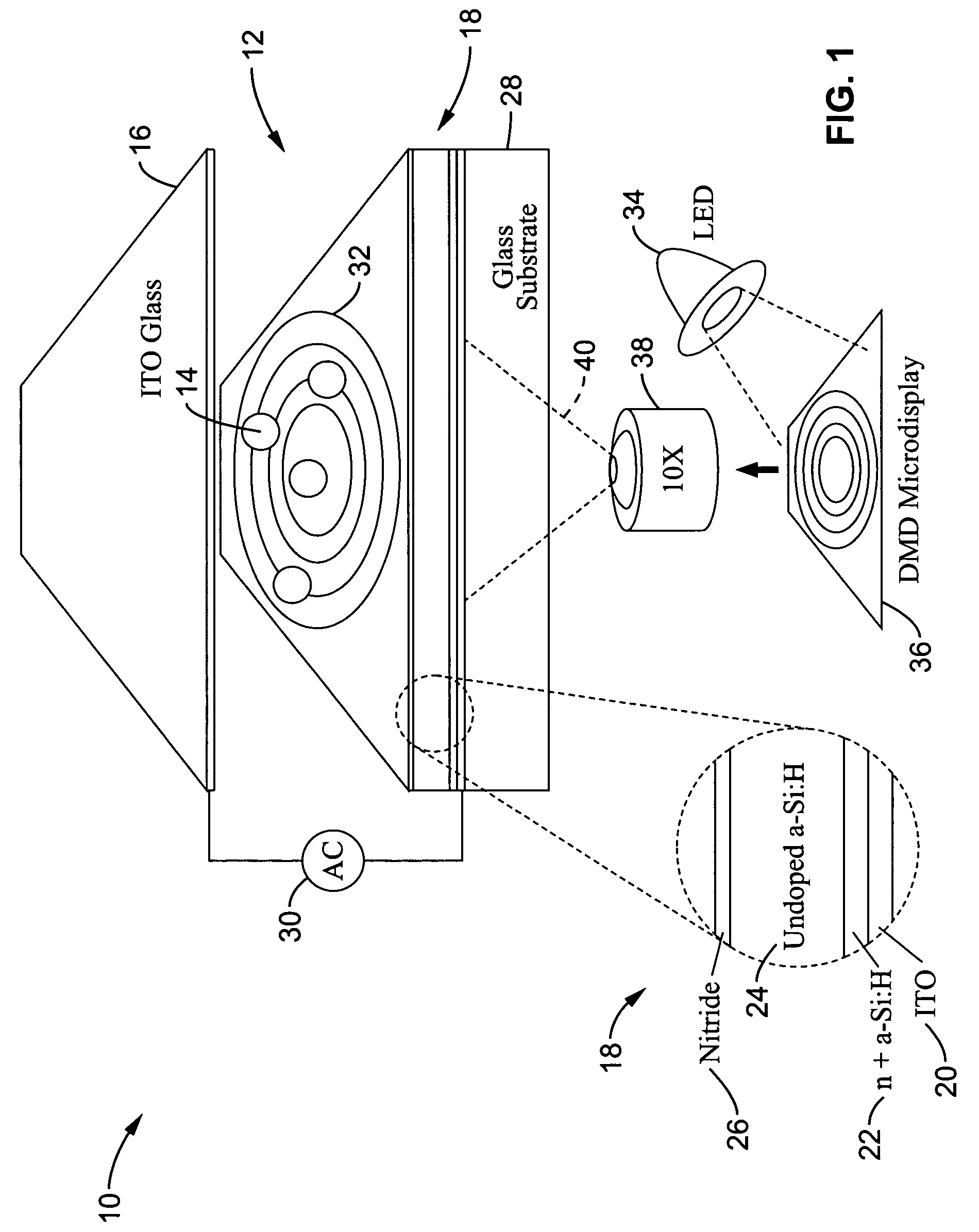
Optoelectronic tweezers for microparticle and cell manipulation
ActiveUS7612355B2Easy to operateEasy to createElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMicroparticleOpto electronic
An optical image-driven light induced dielectrophoresis (DEP) apparatus and method are described which provide for the manipulation of particles or cells with a diameter on the order of 100 μm or less. The apparatus is referred to as optoelectric tweezers (OET) and provides a number of advantages over conventional optical tweezers, in particular the ability to perform operations in parallel and over a large area without damage to living cells. The OET device generally comprises a planar liquid-filled structure having one or more portions which are photoconductive to convert incoming light to a change in the electric field pattern. The light patterns are dynamically generated to provide a number of manipulation structures that can manipulate single particles and cells or groups of particles / cells. The OET preferably includes a microscopic imaging means to provide feedback for the optical manipulation, such as detecting position and characteristics wherein the light patterns are modulated accordingly.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Golf ball with vapor barrier layer and method of making same
A golf ball comprising a core, a barrier layer enveloping the core, and a cover enveloping the barrier layer, wherein the barrier layer has a moisture vapor transmission rate less than that of the cover, and the barrier layer comprises a thermoplastic or thermoset composition of microparticles dispersed in a binder.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
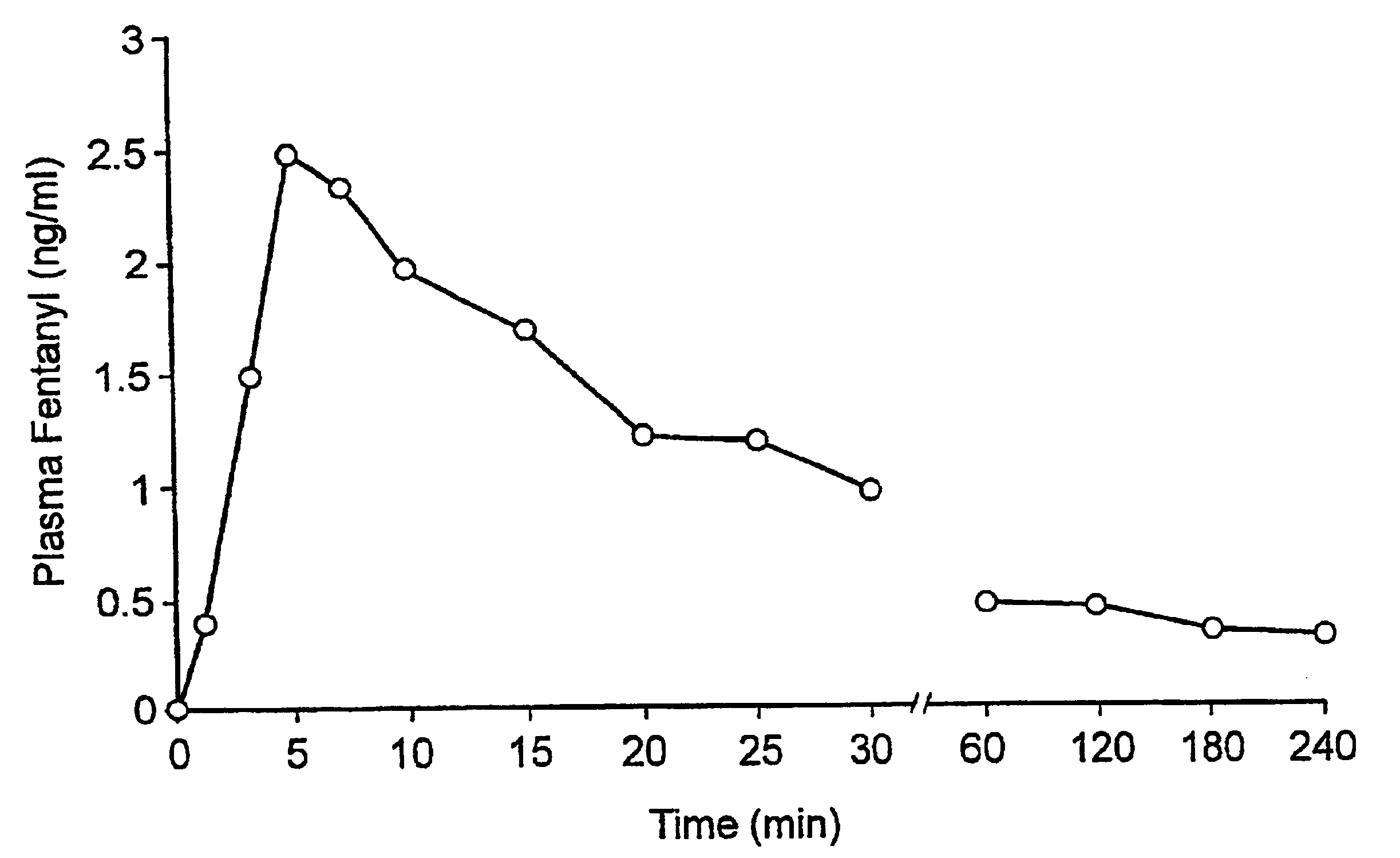
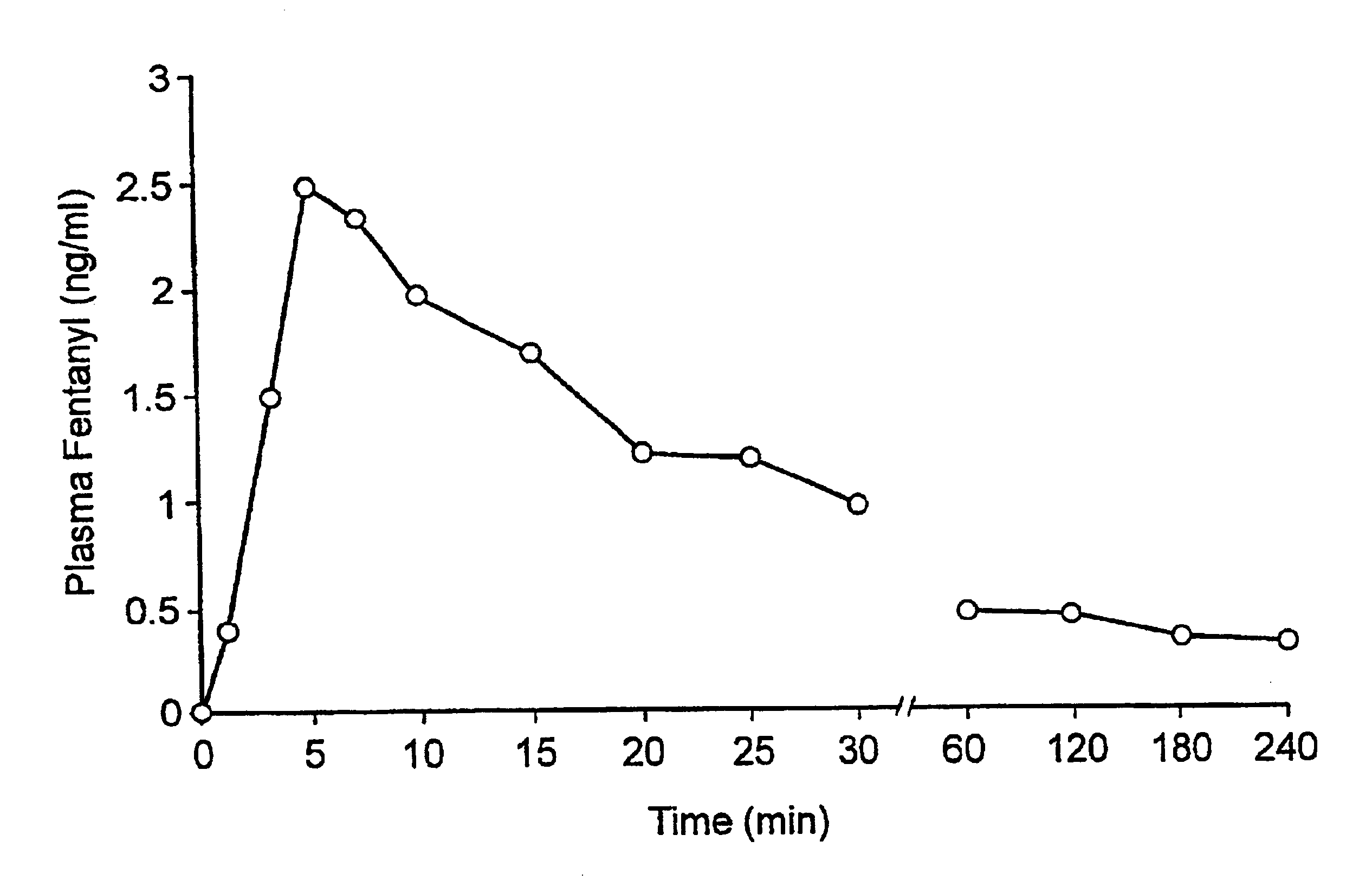
Fentanyl composition for the treatment of acute pain
A pharmaceutical composition for the treatment of acute pain by sublingual administration is described. The composition comprises an essentially water-free, ordered mixture of fentanyl or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in the form of microparticles which are adhered to the surface of carrier particles which are substantially larger than the particles of fentanyl, and are essentially water-soluble. In a preferred embodiment, the composition also contains a bioadhesion and / or mucoadhesion promoting agent. The invention also relates to the preparation of the composition, and to the use of the composition for the treatment of acute pain.
Owner:DIABAKT AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com