Patents
Literature
3214results about How to "Reduce thermal stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
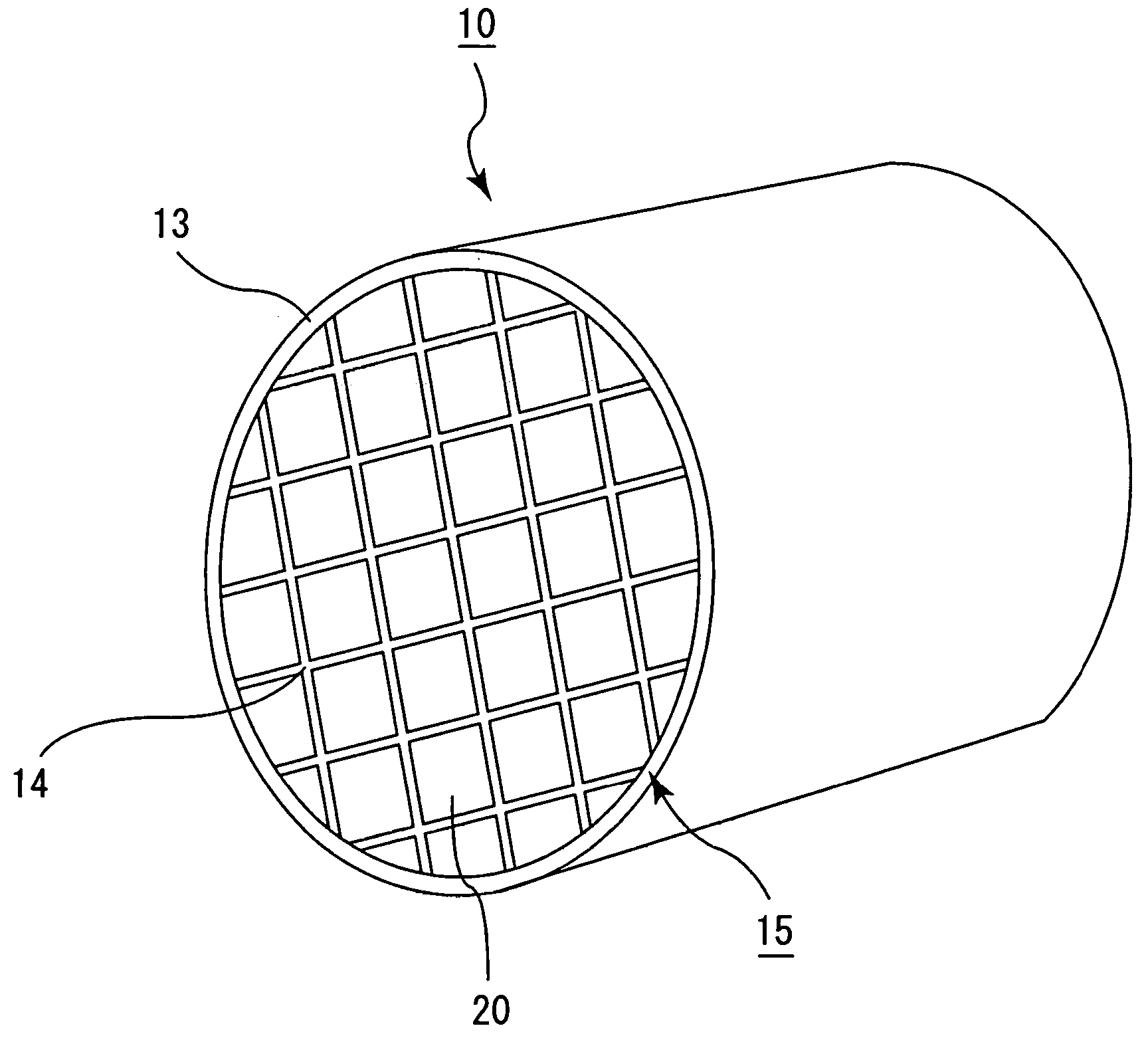
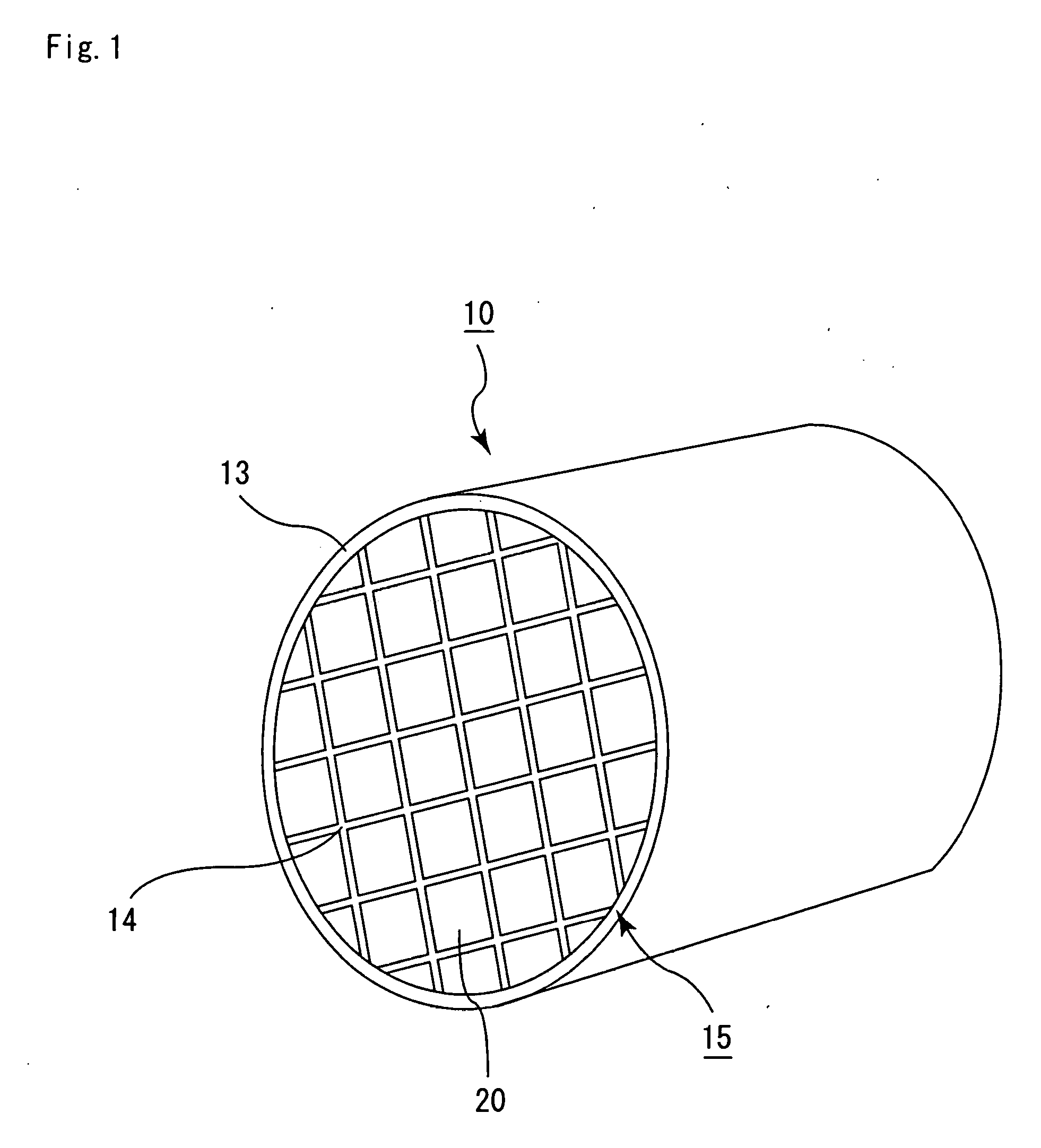
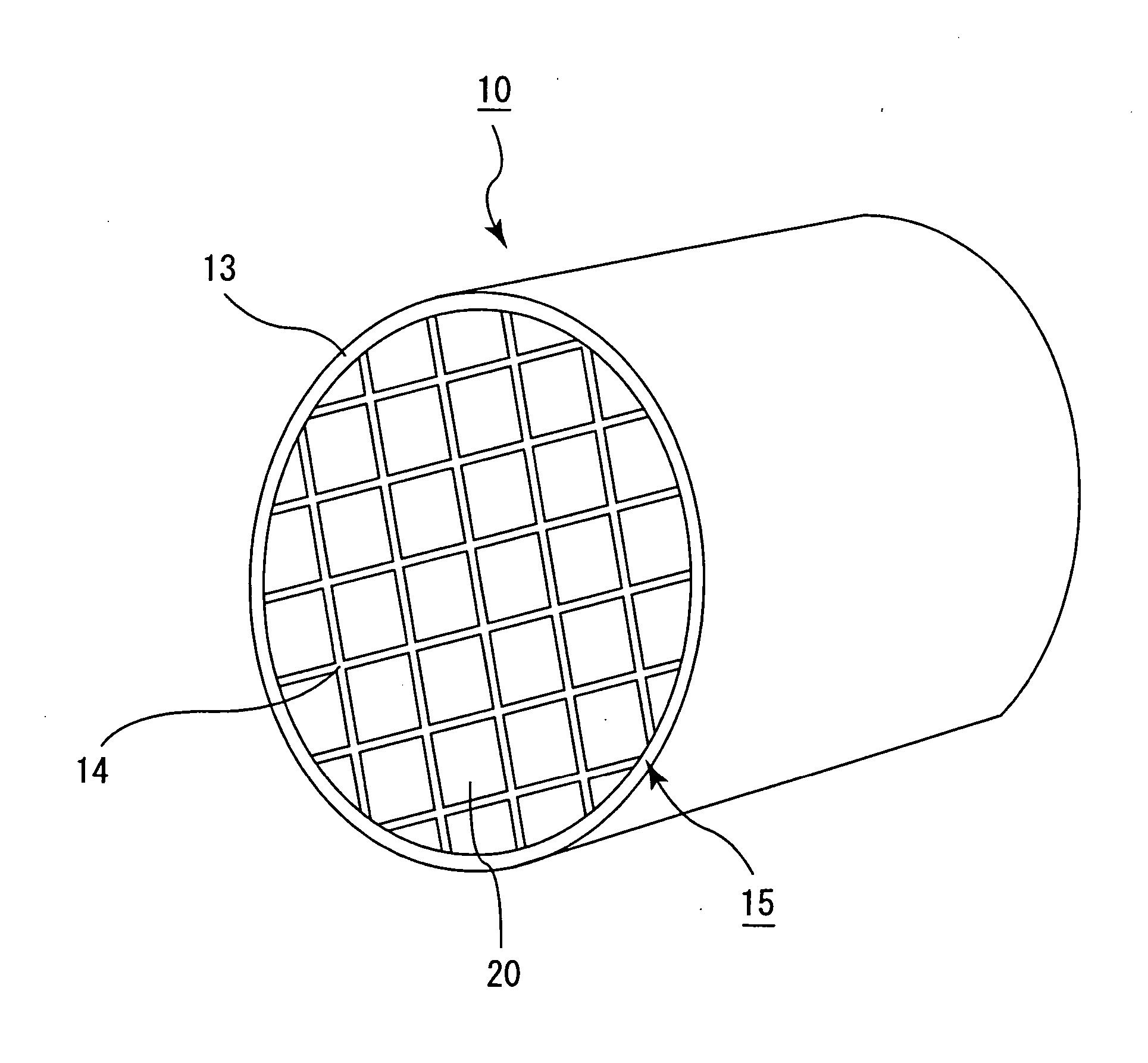
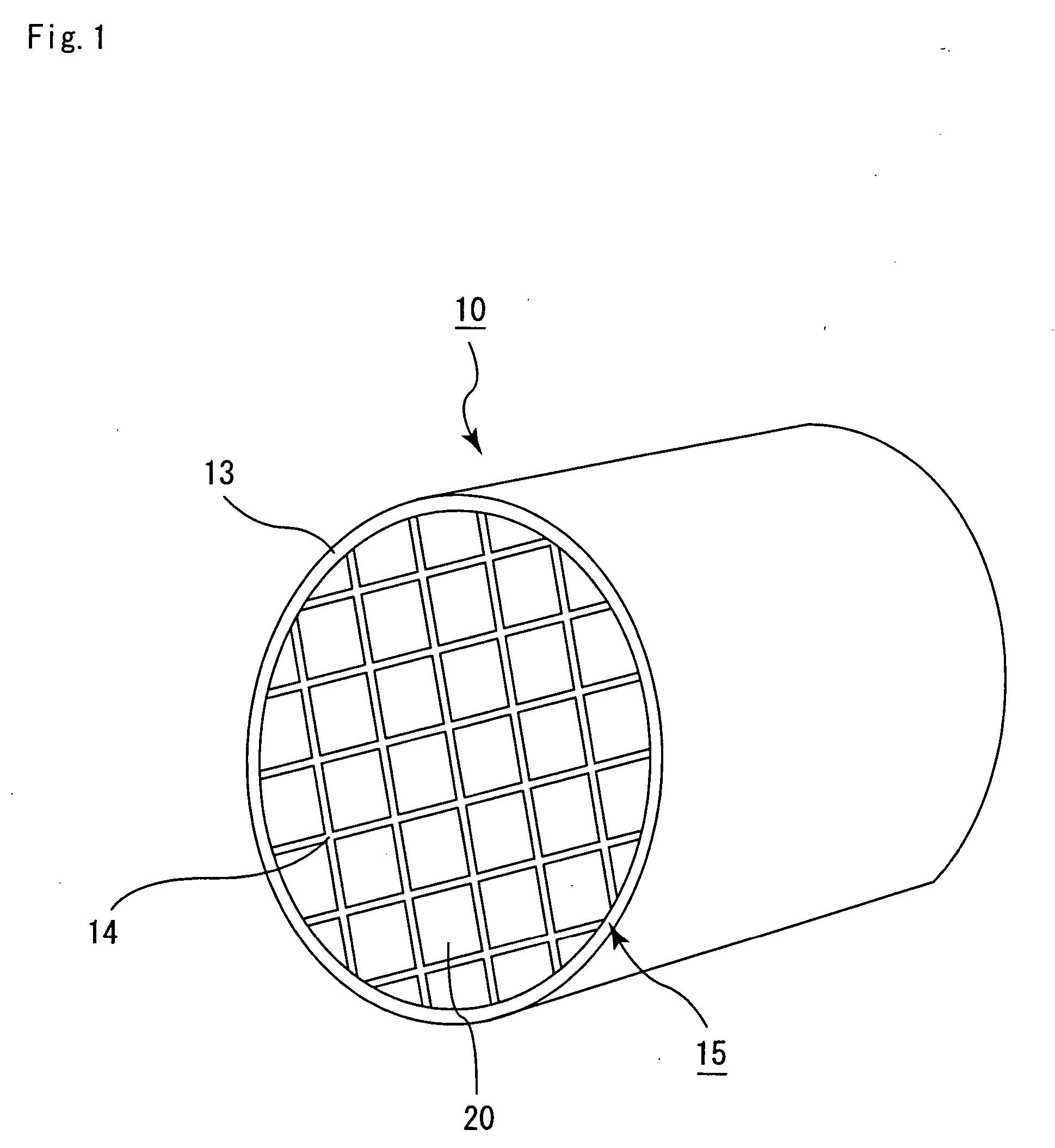
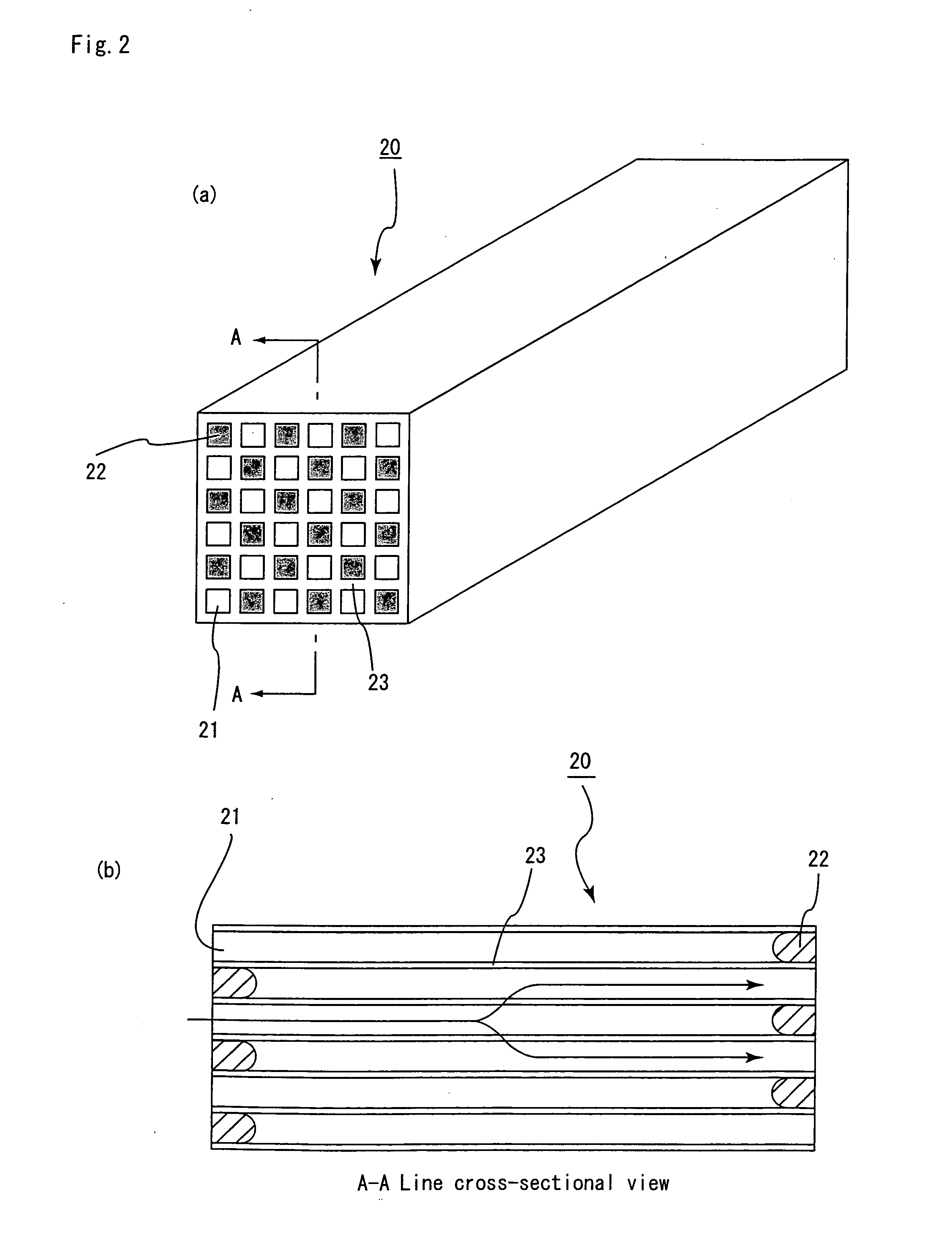
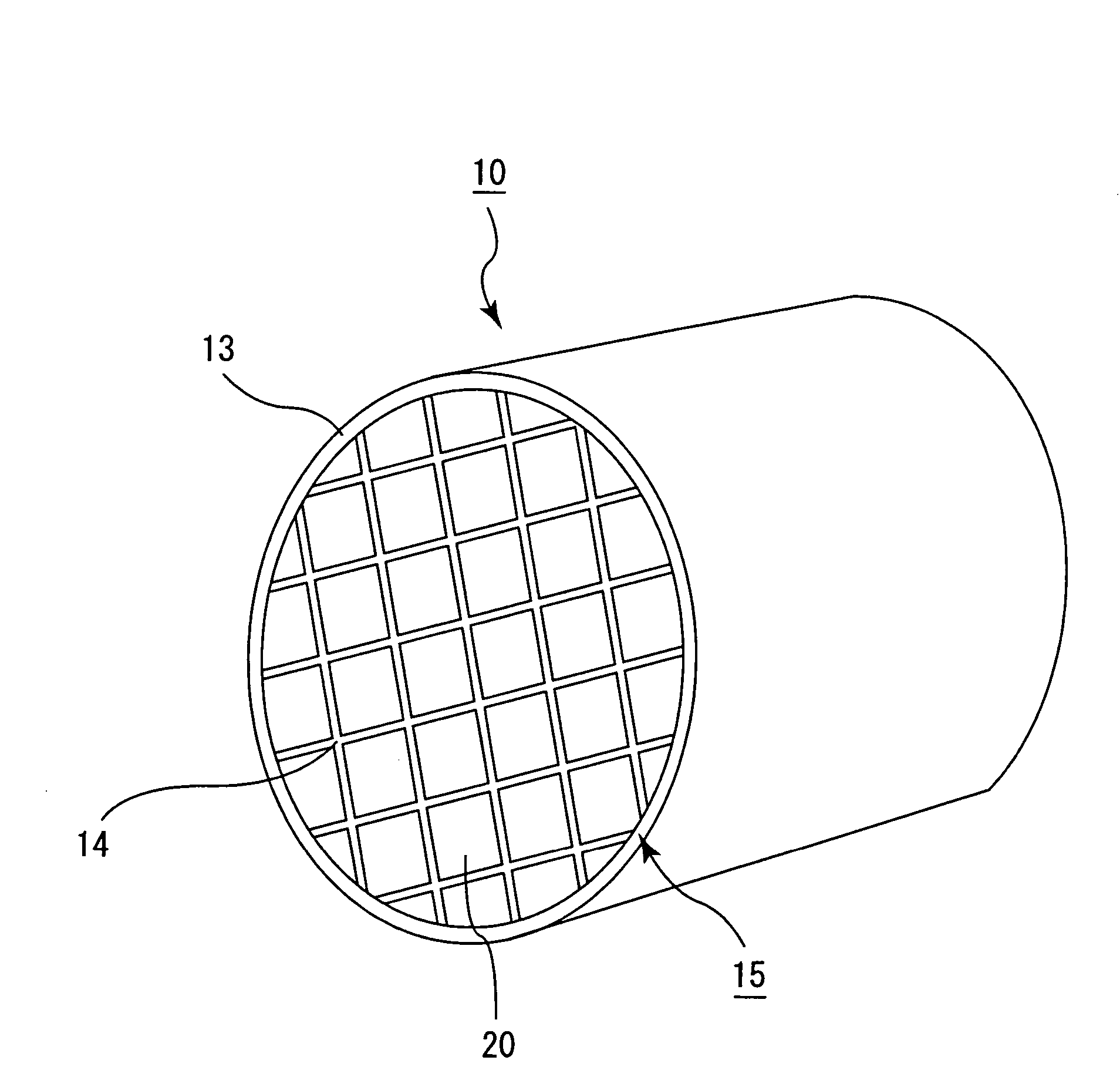
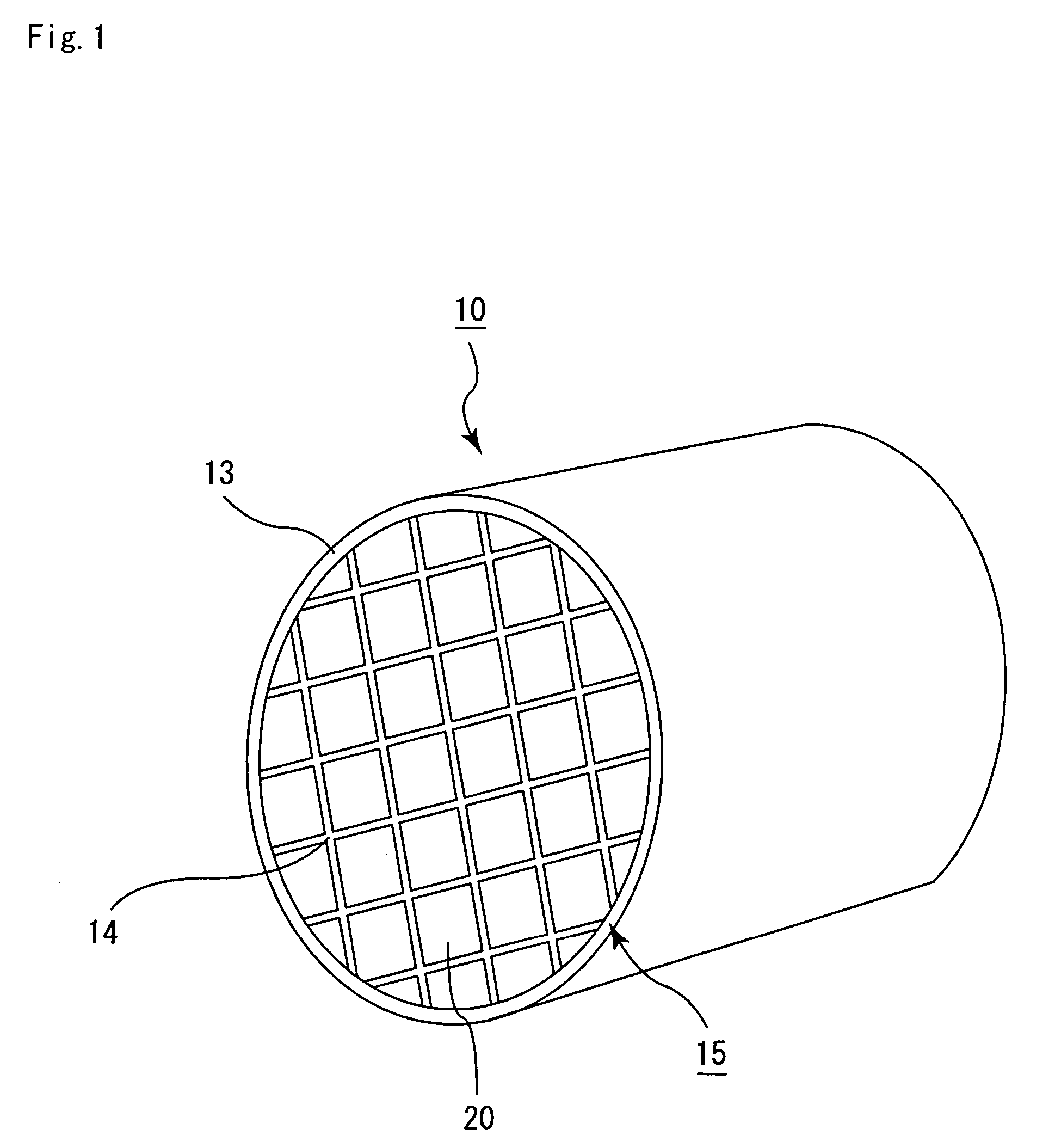
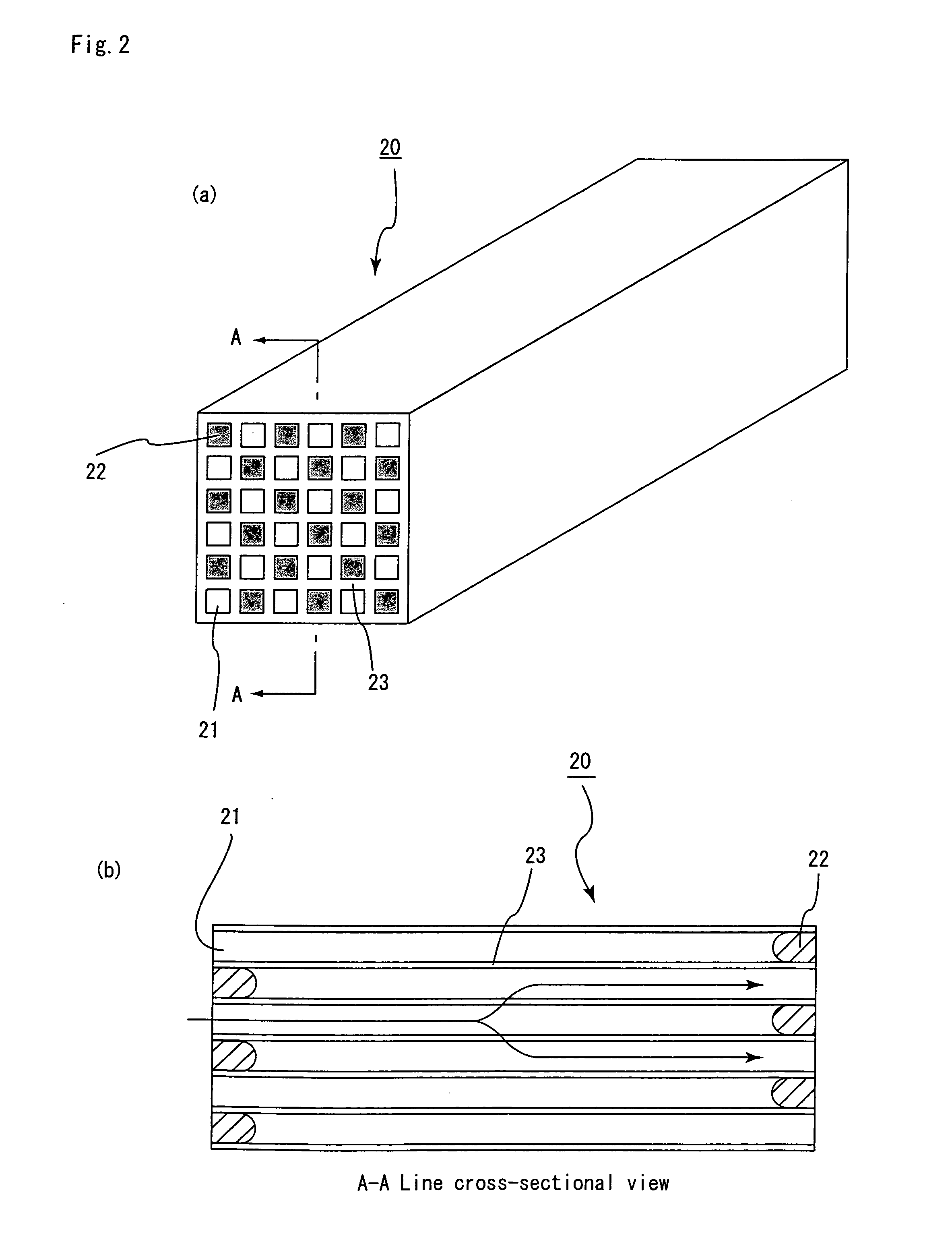
Honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination, adhesive, coating material and process for producing honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination
ActiveUS20050109023A1Reduce thermal stressAlleviating generated thermal stressCombination devicesDispersed particle filtrationParticulatesAdhesive
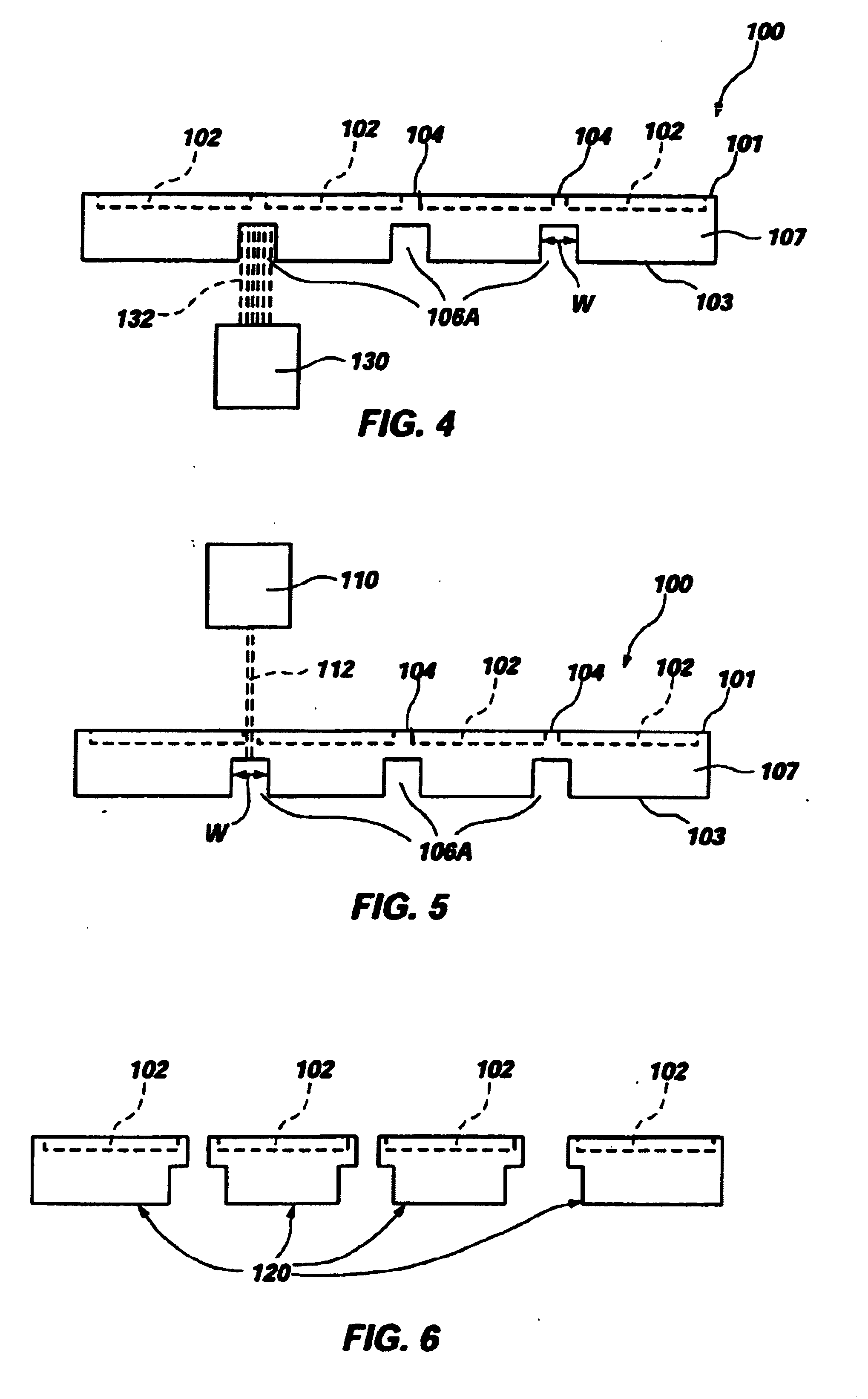
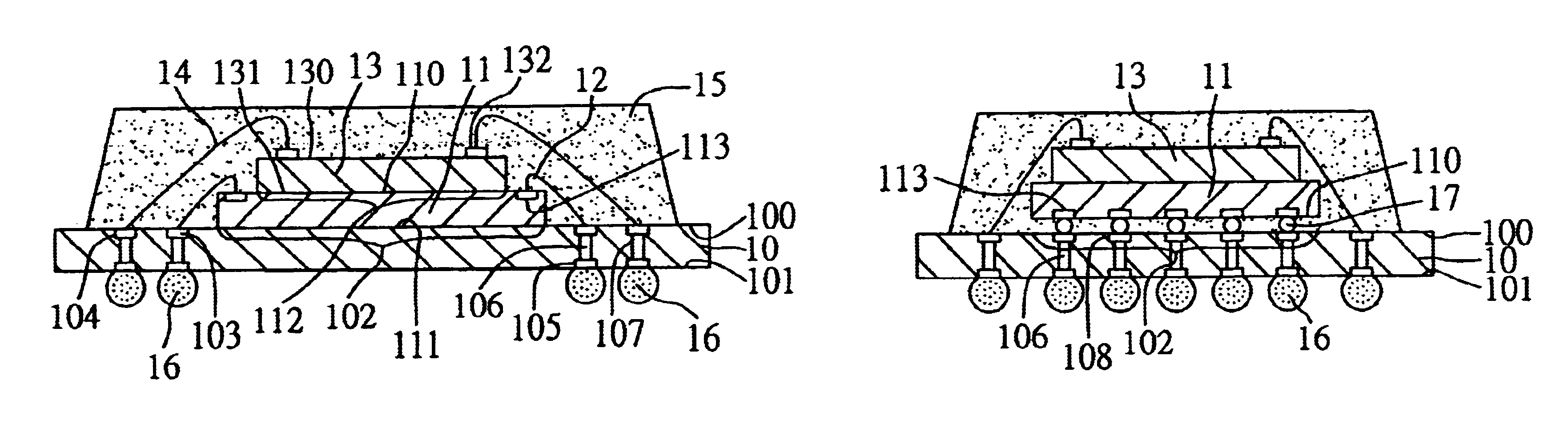
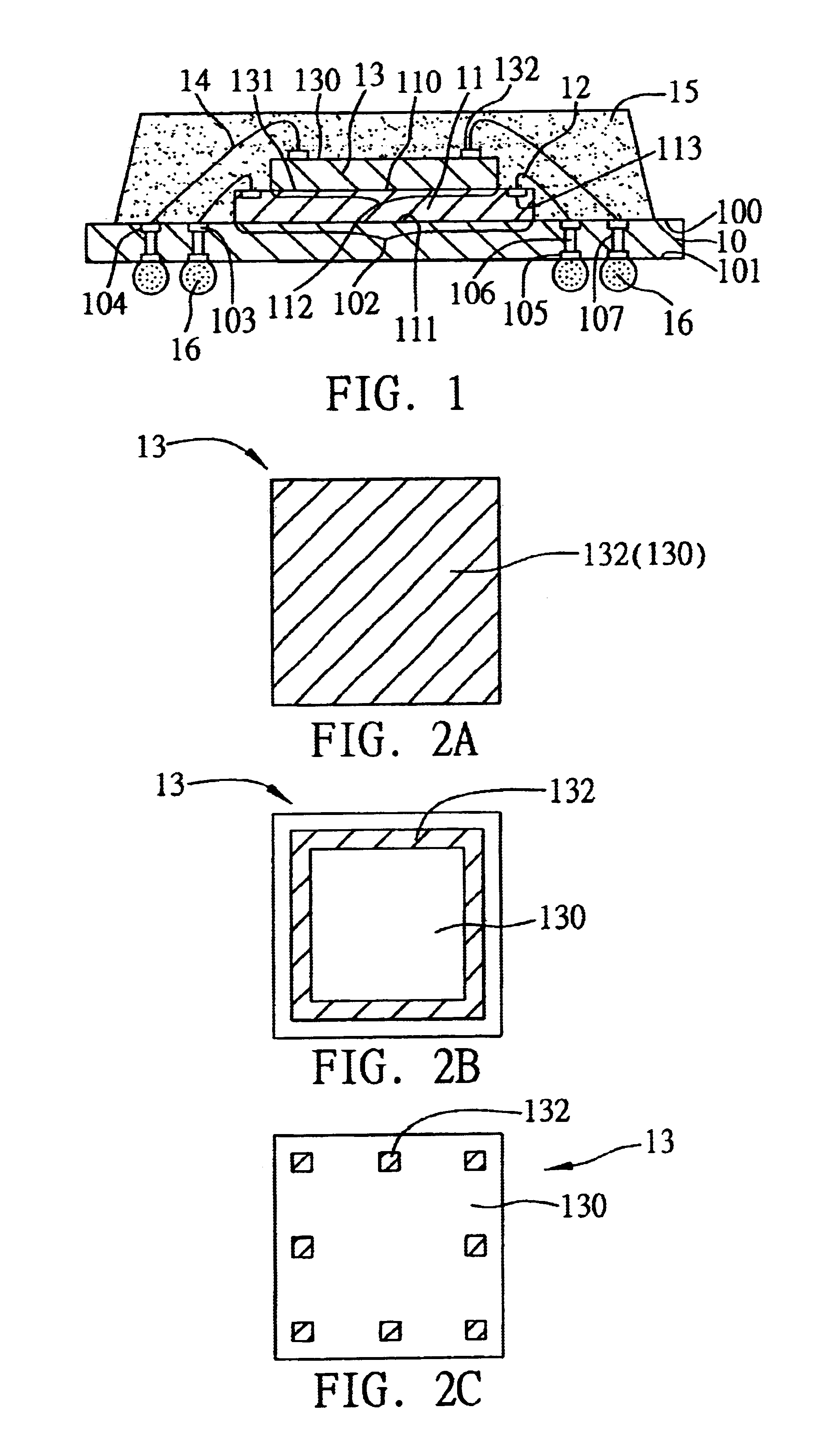
An object of the present invention is to provide a honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases which makes it possible to alleviate a thermal stress generated due to occurrence of a local temperature change and which is less likely to generate cracks and superior in strength and durability, an adhesive that has a low thermal capacity and is capable of alleviating the thermal stress, a coating material that has a low thermal capacity with a superior heat insulating property and is capable of alleviating the thermal stress, and a manufacturing method of the honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases that can improve precision in the outside dimension, and reduce damages in the manufacturing processes. The present invention relates to a honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases, having a structure in that a plurality of column-shaped porous ceramic members, each having a number of through holes that are placed side by side in the length direction with partition wall interposed therebetween, are combined with one another through adhesive layers so that the partition wall that separate the through holes are allowed to function as a filter for collecting particulates, and in this structure, the thermal expansion coefficient αL of the adhesive layer and the thermal expansion coefficient αF of the porous ceramic member are designed to have the following relationship: 0.01<|αL−αF| / αF<1.0.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
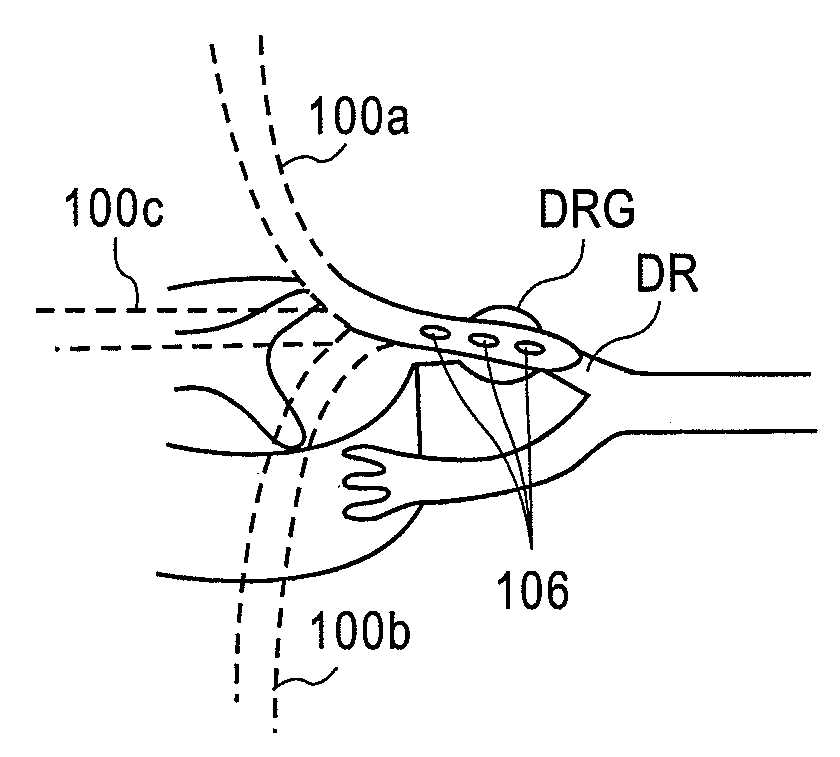
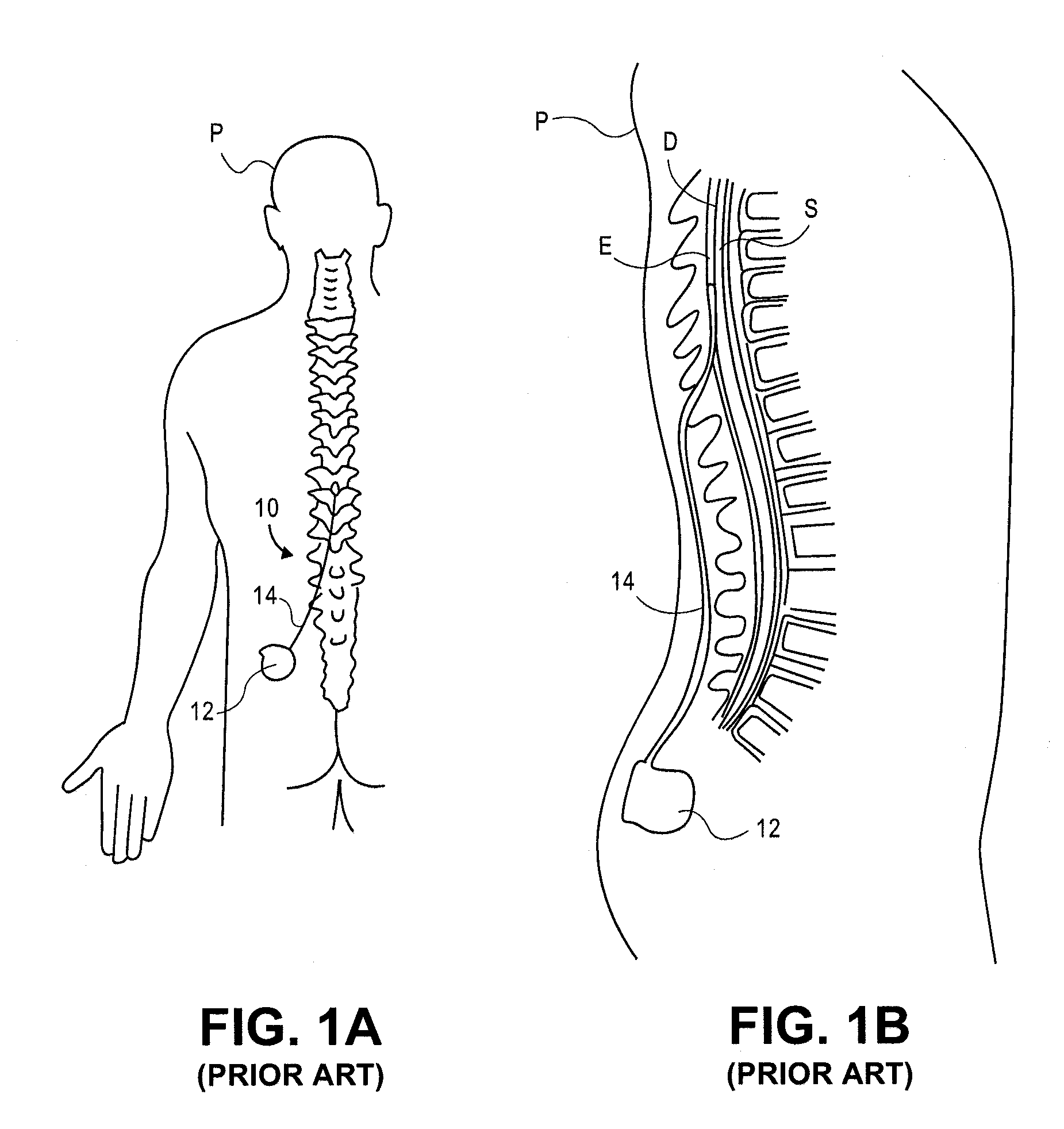
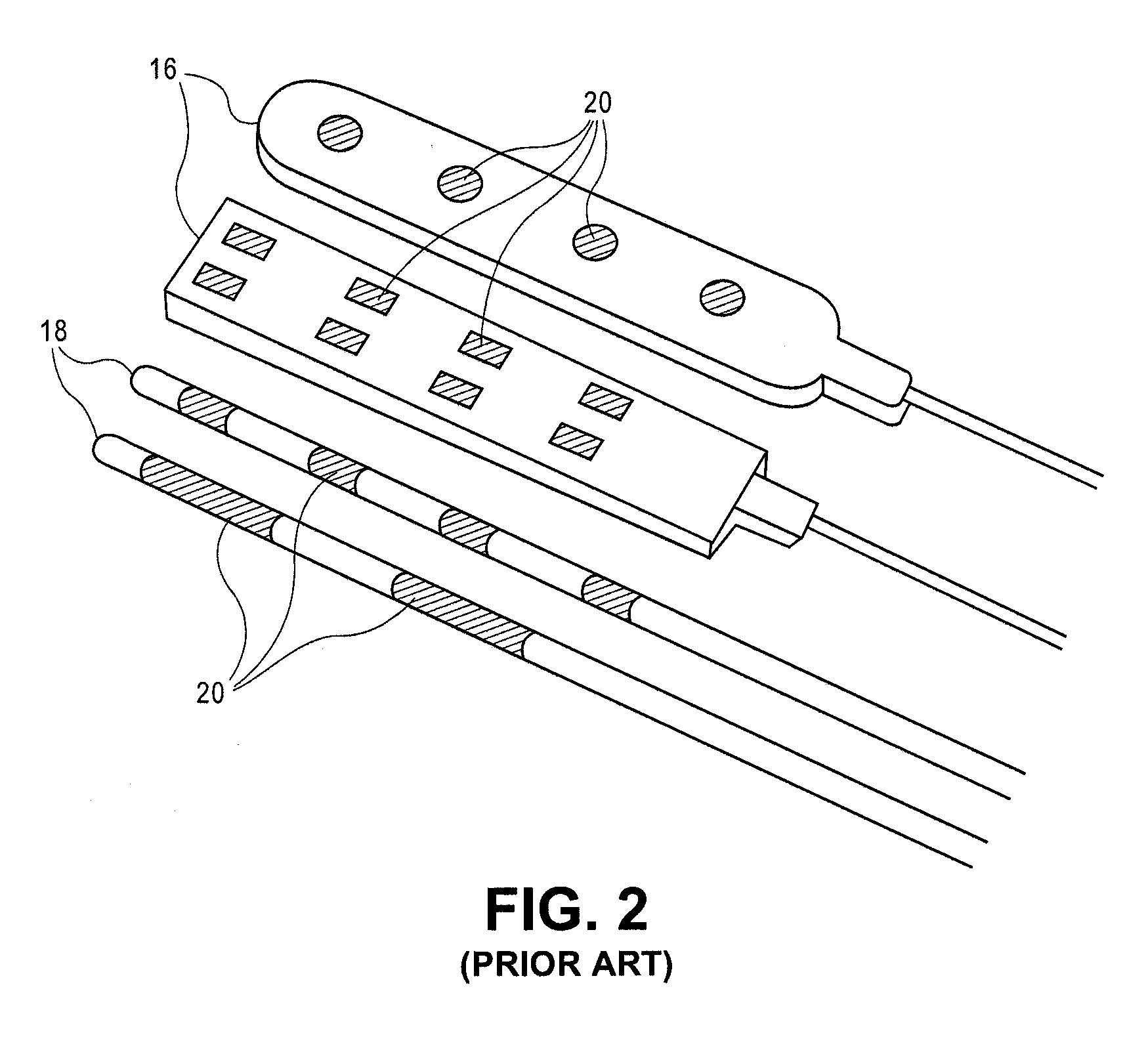
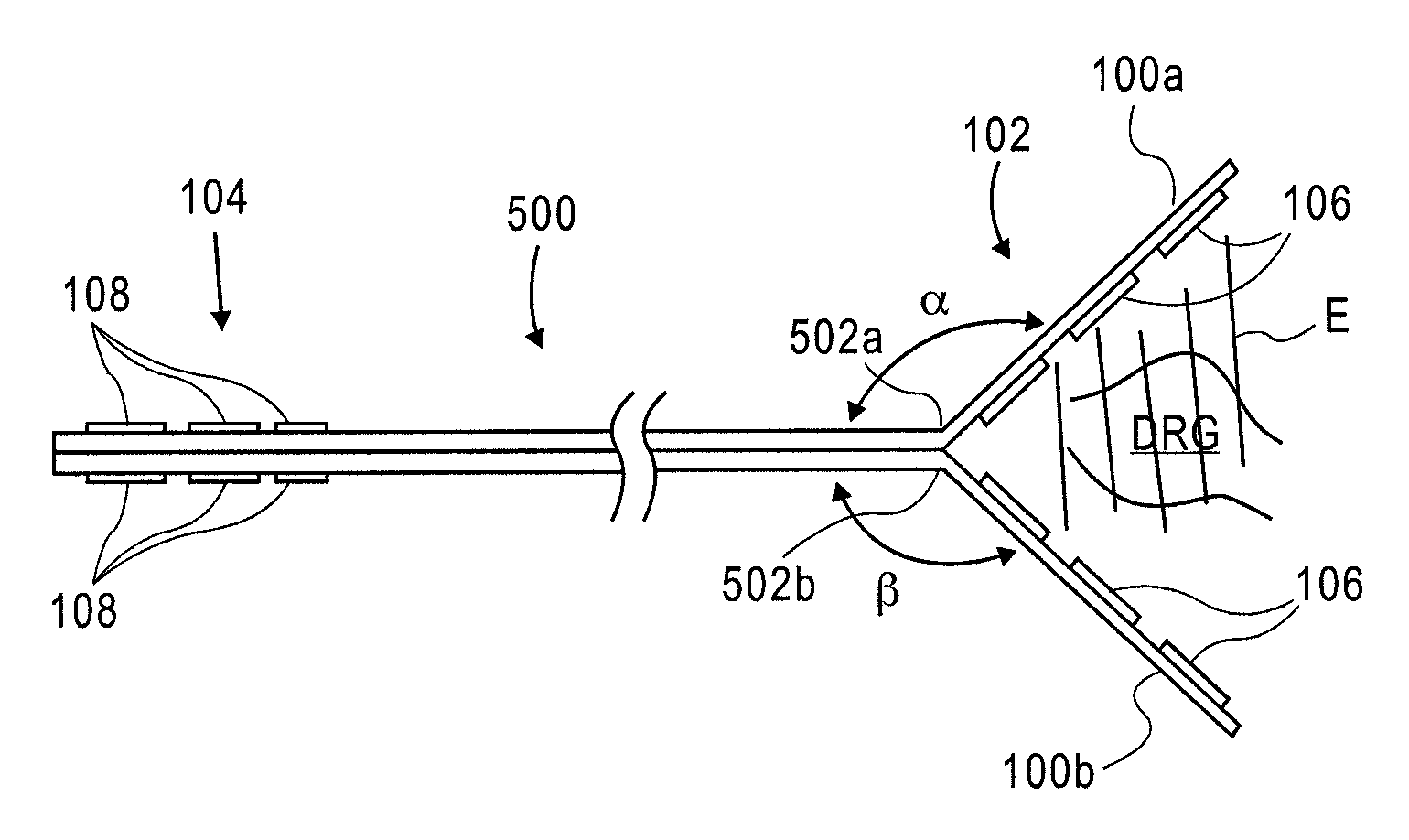
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
InactiveUS20080140152A1Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesExternal electrodesDielectricFlexible circuits
Devices, systems and methods are provided for stimulation of tissues and structures within a body of a patient. In particular, implantable leads are provided which are comprised of a flexible circuit. Typically, the flexible circuit includes an array of conductors bonded to a thin dielectric film. Example dielectric films include polyimide, polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) or other biocompatible materials to name a few. Such leads are particularly suitable for stimulation of the spinal anatomy, more particularly suitable for stimulation of specific nerve anatomies, such as the dorsal root (optionally including the dorsal root ganglion).
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Sintered ceramic compact and ceramic filter
InactiveUS20060051556A1Shock mitigationAvoid micro cracksDispersed particle filtrationExhaust apparatusCeramic sinteringMetallurgy
The present invention provides for a ceramic sintered body and a ceramic filter having a long-term stability which can prevent cracks from occurring due to the breakage of ceramic particles when thermal stress is applied in regeneration process and the like, and can prevent catalyst carried from deteriorating when regeneration treatment is conducted repeatedly. The invention is a ceramic sintered body comprising ceramic coarse particles and porous bonding layers existing between the ceramic coarse particles to connect the particles and comprising ceramic fine particles having an average particle size smaller than that of the ceramic coarse particles and / or the aggregates thereof, and a ceramic filter prepared by using the ceramic sintered body.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Pillar-to-pillar flip-chip assembly
ActiveUS7569935B1Reduce thermal stressPrevent peelingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder maskSolder ball
A pillar-to-pillar flip-chip assembly primarily comprises a substrate, a chip disposed on the substrate, a plurality of first copper pillars on the bonding pads of the chip, a plurality of second copper pillars on the bump pads of the substrate, and a soldering material. A first height of the first copper pillars protruding from the active surface of the chip is the same as a second height of the second copper pillars from the solder mask on the substrate. When the soldering material electrically and mechanically connects the first copper pillars to the second copper pillars, a plurality of central points of the soldering material are formed on an equal-dividing plane between the chip and the substrate to reduce the direct stresses exerted at the soldering material to avoid peeling or breaks from the bump pads. Moreover, each of conventional solder balls is replaced with two soldered copper pillars to meet the lead-free requirements with higher reliability and lower costs.
Owner:POWERTECH TECHNOLOGY
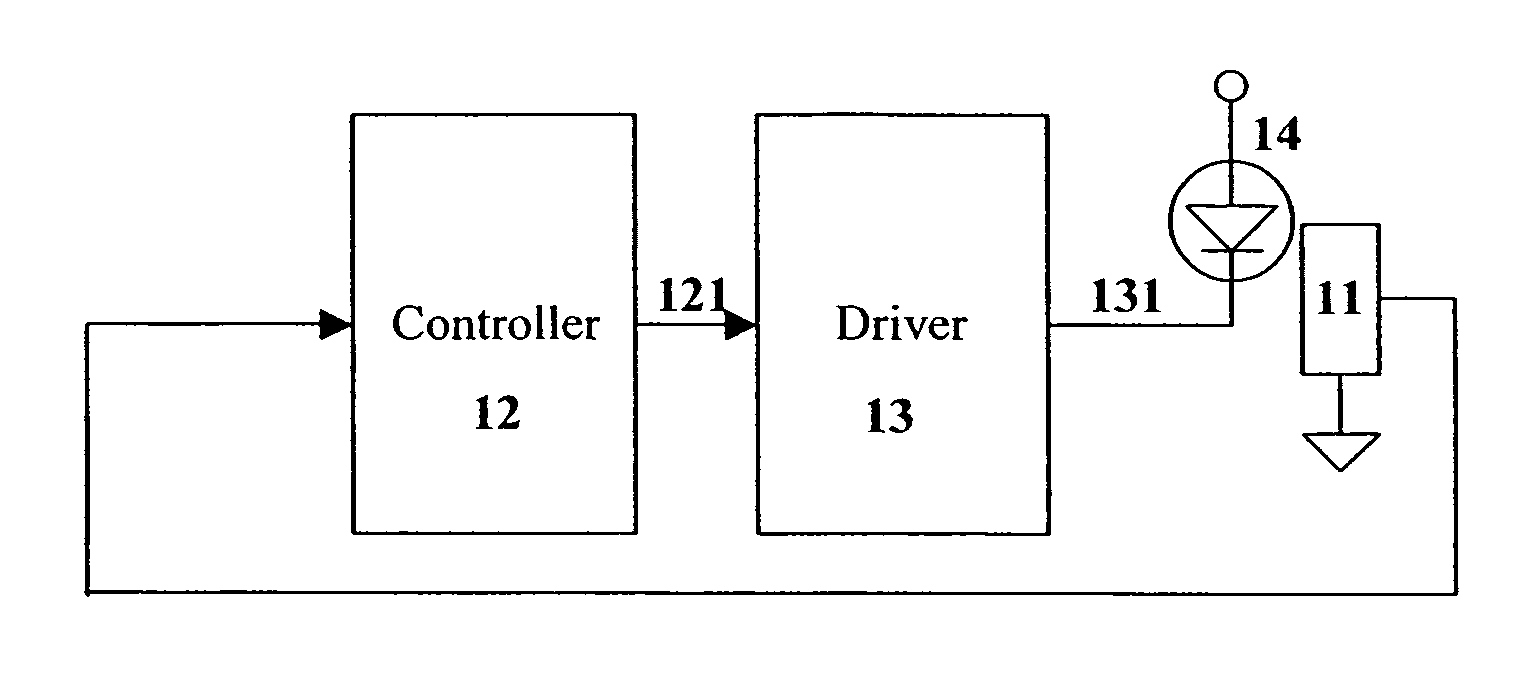
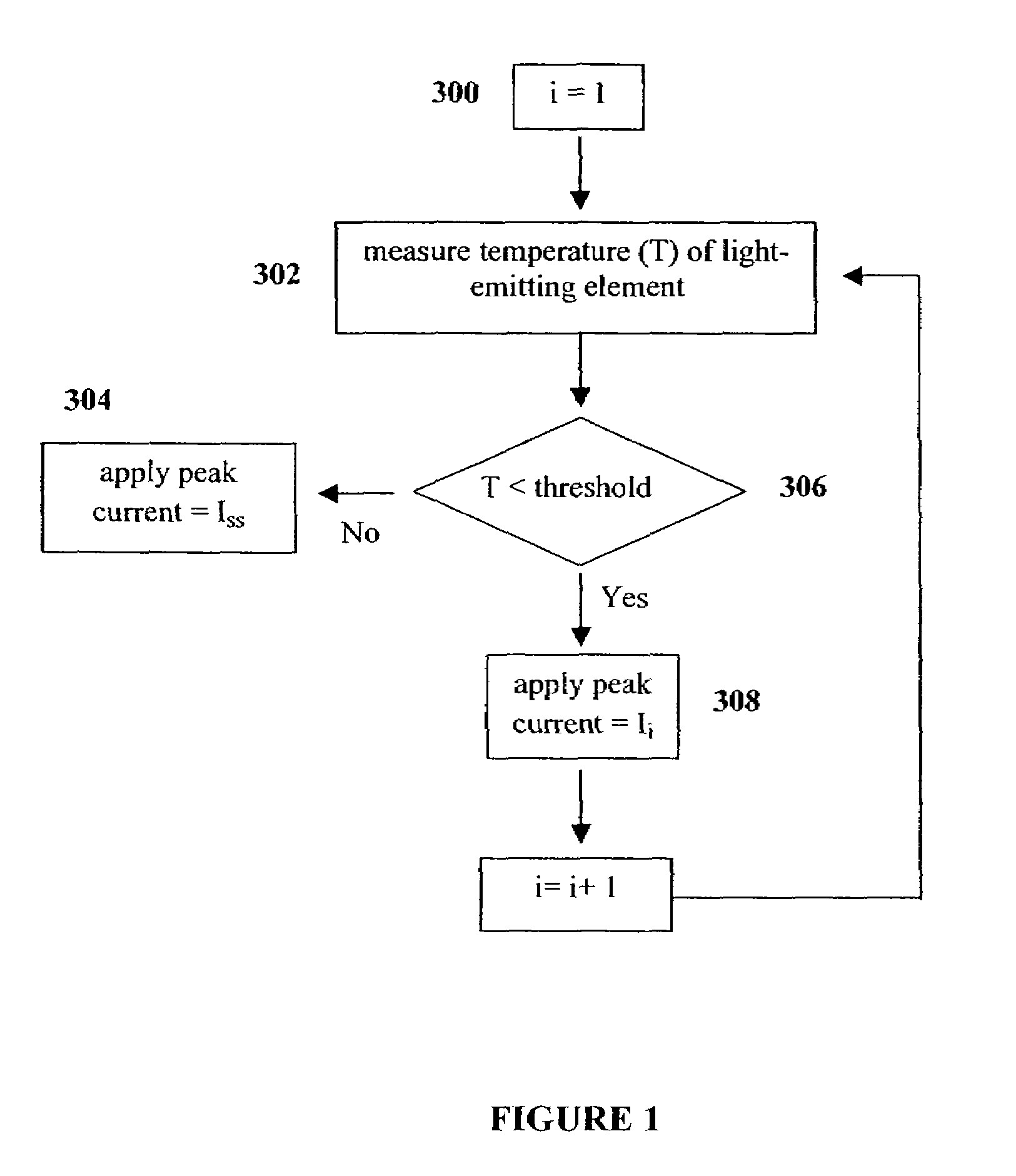
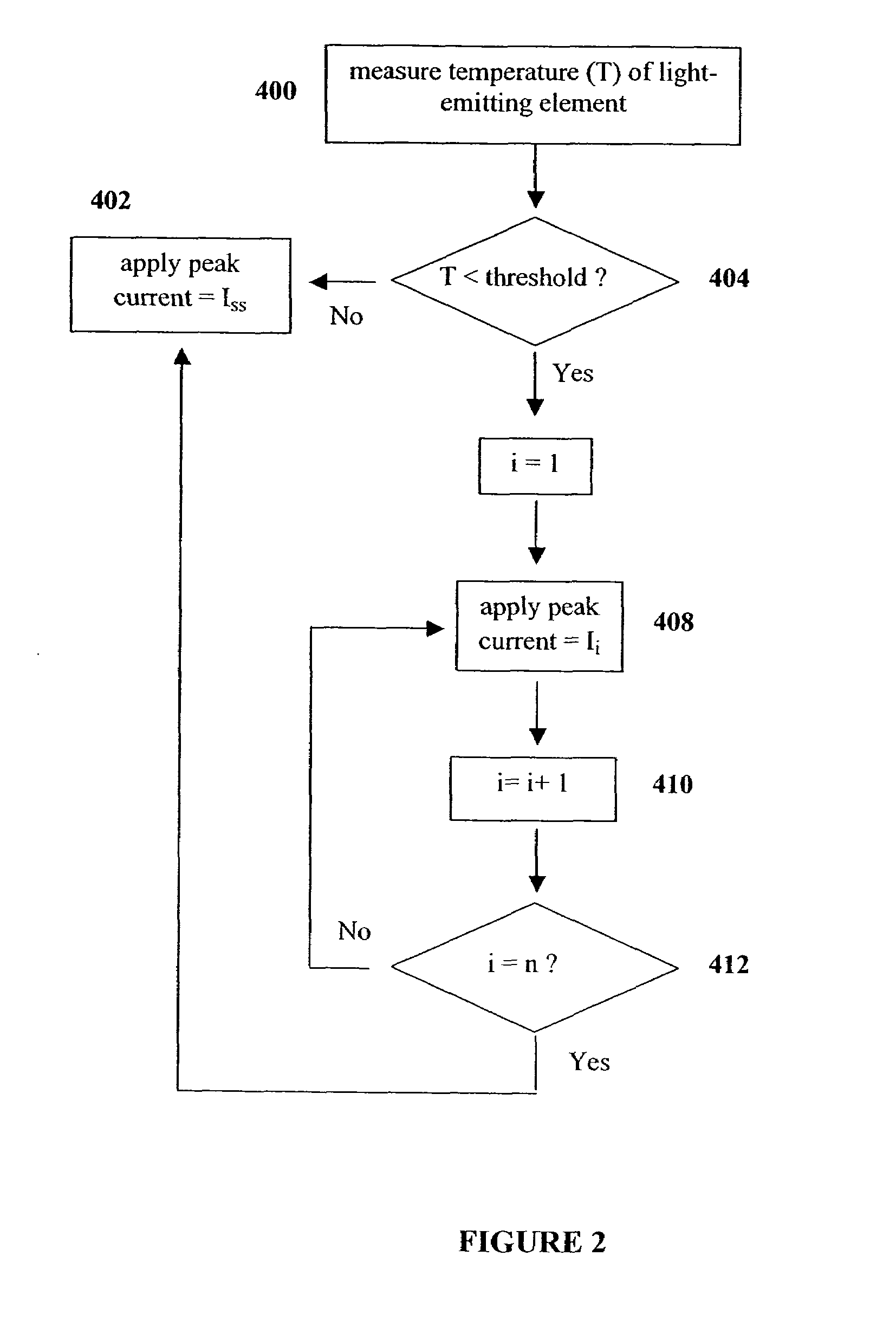
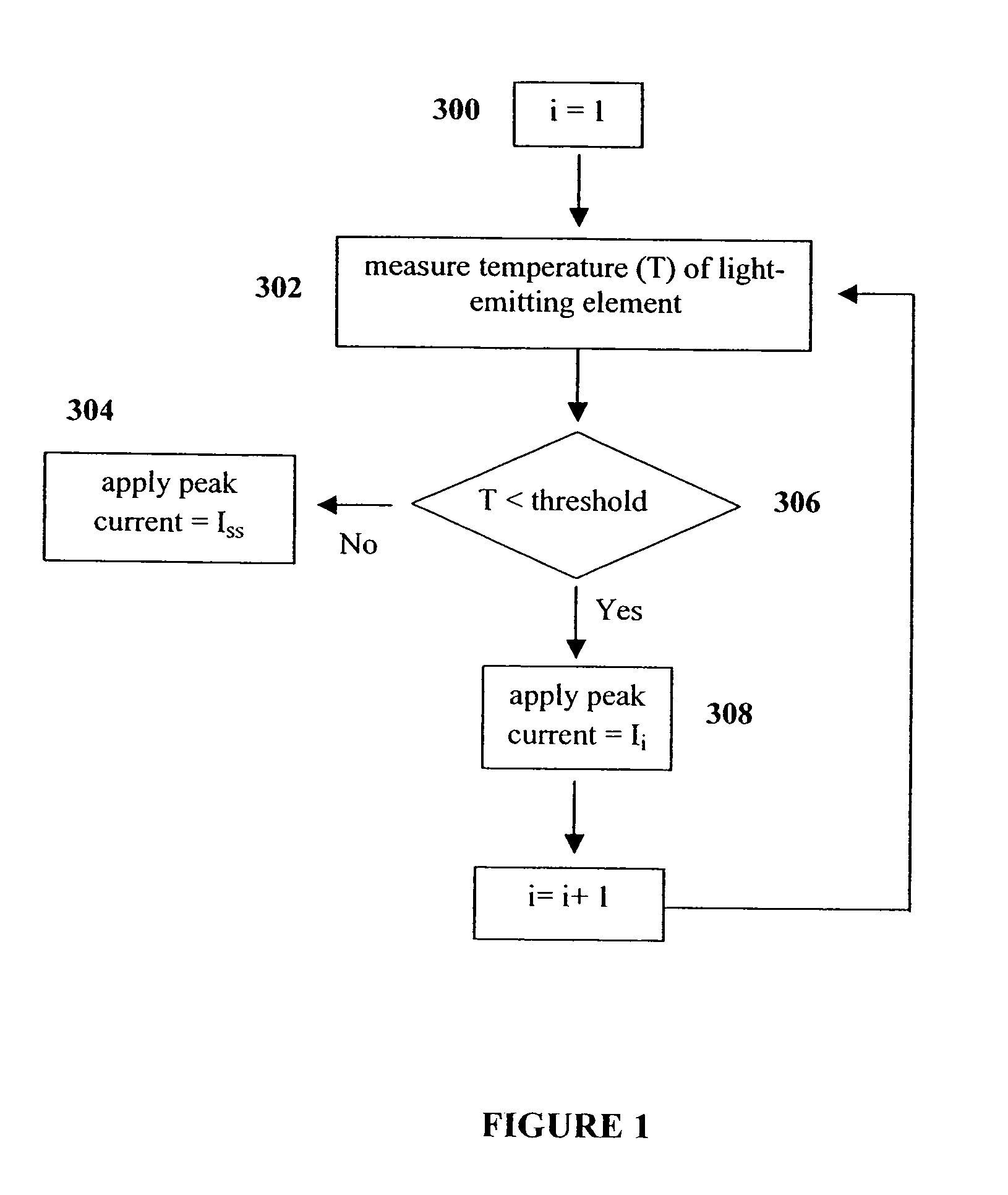
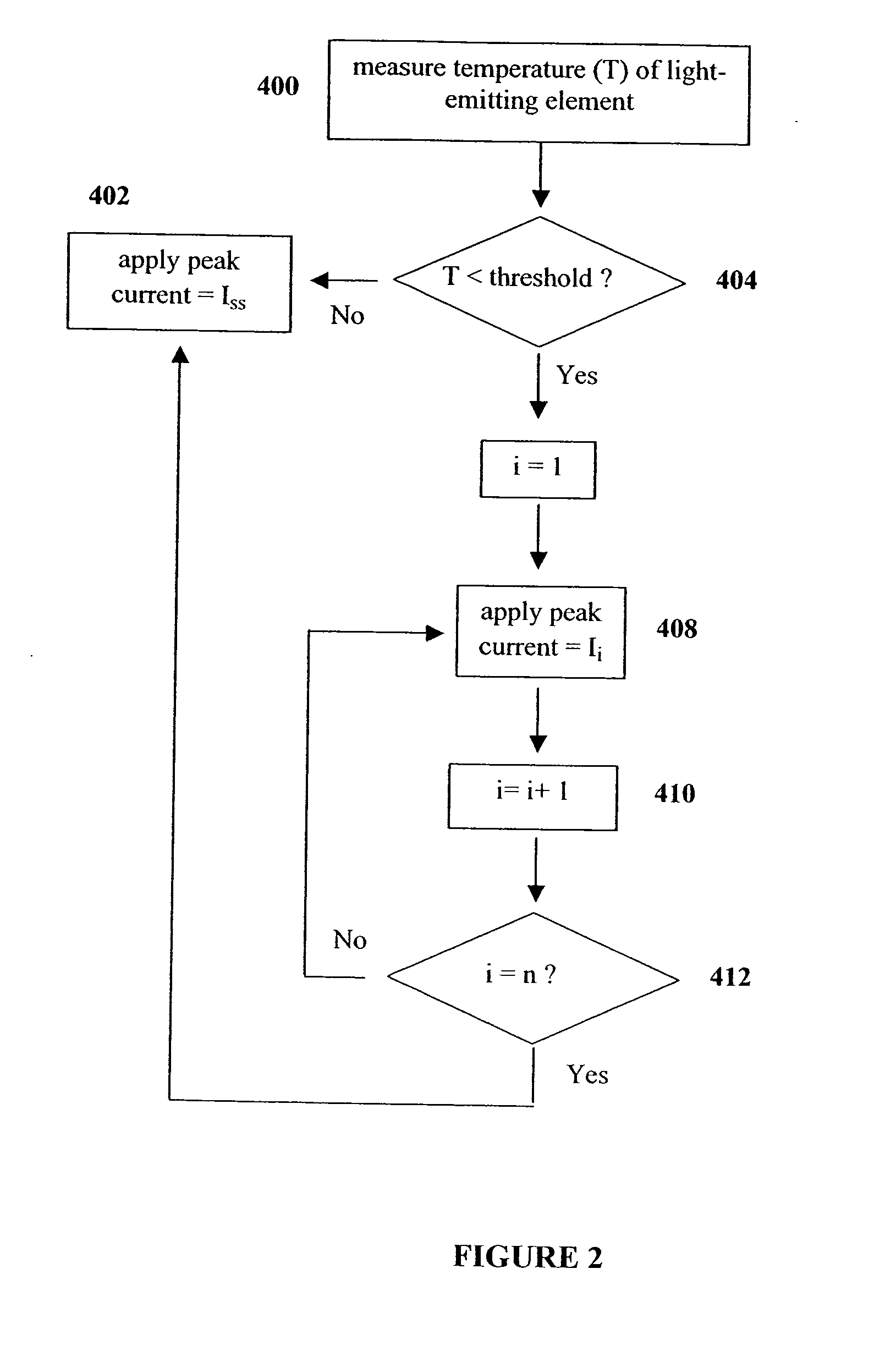
Method and apparatus for controlling thermal stress in lighting devices
ActiveUS7538499B2Reduce thermal stressStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentLight equipment
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the thermal stress in lighting devices, for example light-emitting elements, that are exposed to large thermal gradients typically upon start-up, for example light-emitting elements operating in relatively cold ambient environments. The present invention provides an apparatus that can reduce this thermal stress, wherein the apparatus comprises a temperature determination mechanism for evaluating the temperature of the light-emitting elements prior to activation, and a control system to control the drive current such that it is gradually ramped up to the desired steady state peak current value, wherein the ramping of the drive current is dependent on the evaluated temperature of the light-emitting element.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Selective laser melting rapid prototyping equipment for direct manufacturing of large parts
ActiveCN102266942AMeet the process requirementsReduce construction costsIncreasing energy efficiencySelective laser meltingLaser array
The invention discloses a selective laser melting rapid forming device for directly manufacturing large-size compact parts, which mainly comprises a laser array, an optical system array, a forming cylinder, a forming cylinder vertical sectional heating thermal-insulation structure, a forming cylinder weight balancing system, a substrate leveling device, a double-recovering cylinder, a double powder storing box, a double quantitative powder sending and discharging device, a powder paving device, a protective atmosphere cover, a gas purifying system and a control system, wherein an adopted optical system is composed of a plurality of optical system units and a mechanical moving platform, and the coverage area of the optical system can be randomly expanded or reduced. The size of the parts manufactured by using the selective laser melting rapid forming device provided by the invention is more than the size of the parts manufactured by using the existing national and foreign selective laser melting processes. The forming efficiency is multiplied while the forming precision, the parts complexity and the mechanical property are not changed.
Owner:TECH LASER TECH SHANGHAI CO LTD
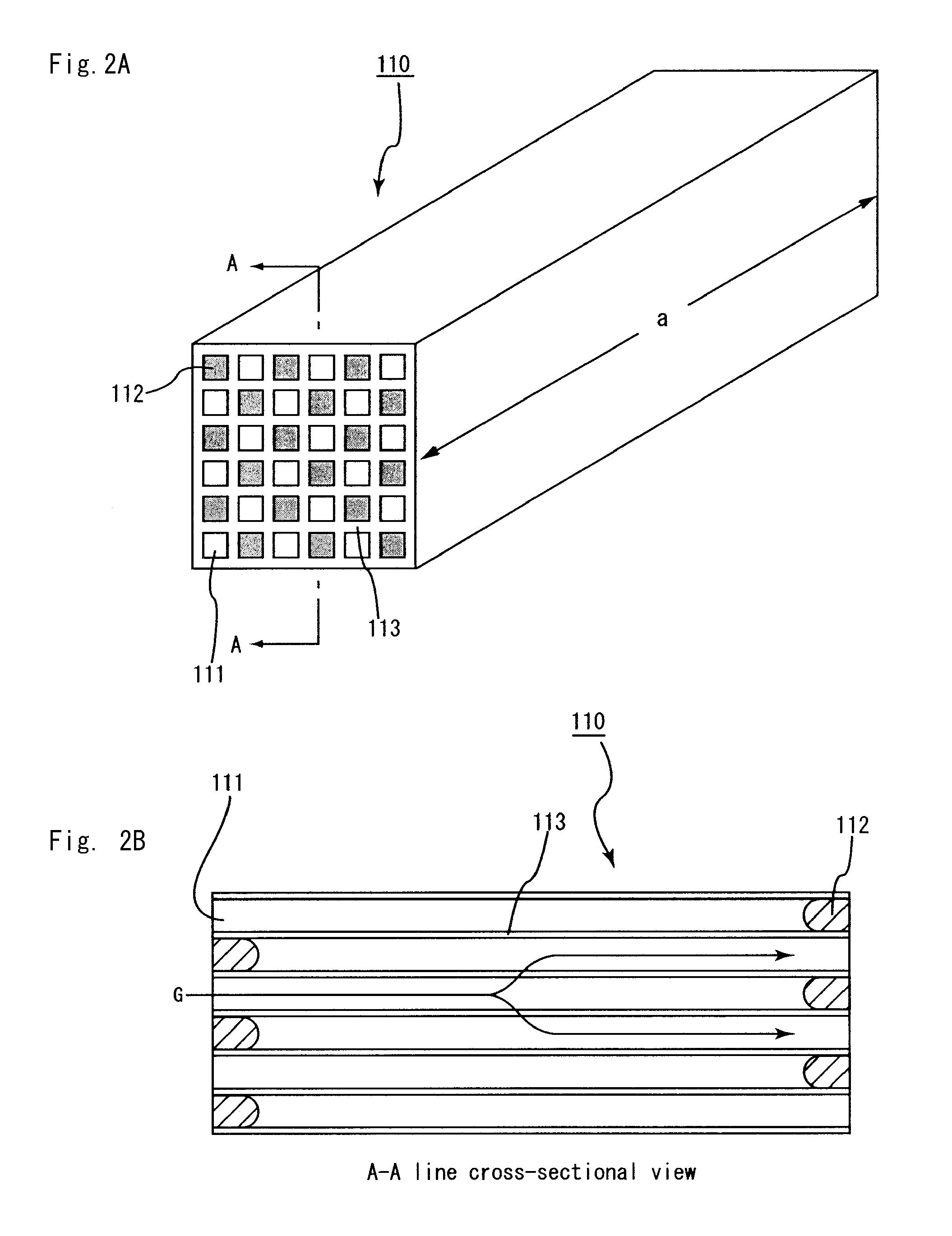
Methods and apparatus relating to singulating semiconductor wafers and wafer scale assemblies
ActiveUS20050202651A1Increase distanceAvoid excessive widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSemiconductor
Methods relating to the singulation of dice from semiconductor wafers. Trenches or channels are formed in the bottom surface of a semiconductor wafer, corresponding in location to the wafer streets. The trenches may be formed by etching or through an initial laser cut. The wafer is then singulated along the streets with a laser preferably having a beam narrower than the trenches. Multiple, laterally spaced lasers may be used in combination during a single pass to perform simultaneous singulating cuts. Additional edge protection for integrated circuitry on the active surface of the semiconductor dice may be provided by forming trenches or channels along the streets in the active surface instead of the bottom surface, disposing protective material along the streets and within the trenches prior to singulation and cutting through the wafer, leaving protective material on the sidewalls of the channels.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases, adhesive, coating material, and manufacturing method of honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases
InactiveUS20080241015A1Increased durabilityHigh strengthCombination devicesPhysical/chemical process catalystsParticulatesAdhesive
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Thermally enhanced semiconductor package with EMI shielding
InactiveUS6865084B2Reduce thermal stressSimple structureMagnetic/electric field screeningSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolder ballElectromagnetic interference
A thermally enhanced semiconductor package with EMI (electric and magnetic interference) shielding is provided in which a chip is mounted on and electrically connected to a surface of a substrate, and a thermally conductive member is stacked on the chip and electrically coupled to the surface of the substrate by bonding wires. An encapsulant is formed and encapsulates the chip, thermally conductive member, and bonding wires. A plurality of solder balls are implanted on an opposite surface of the substrate. The thermally conductive member is grounded via the bonding wires, substrate, and solder balls, and provides an EMI shielding effect for the chip to protect the chip against external electric and magnetic interference. The thermally conductive member has a coefficient of thermal expansion similar to that of the chip, and reduces thermal stress exerted on the chip and enhances mechanical strength of the chip to thereby prevent chip cracks.
Owner:SILICONWARE PRECISION IND CO LTD
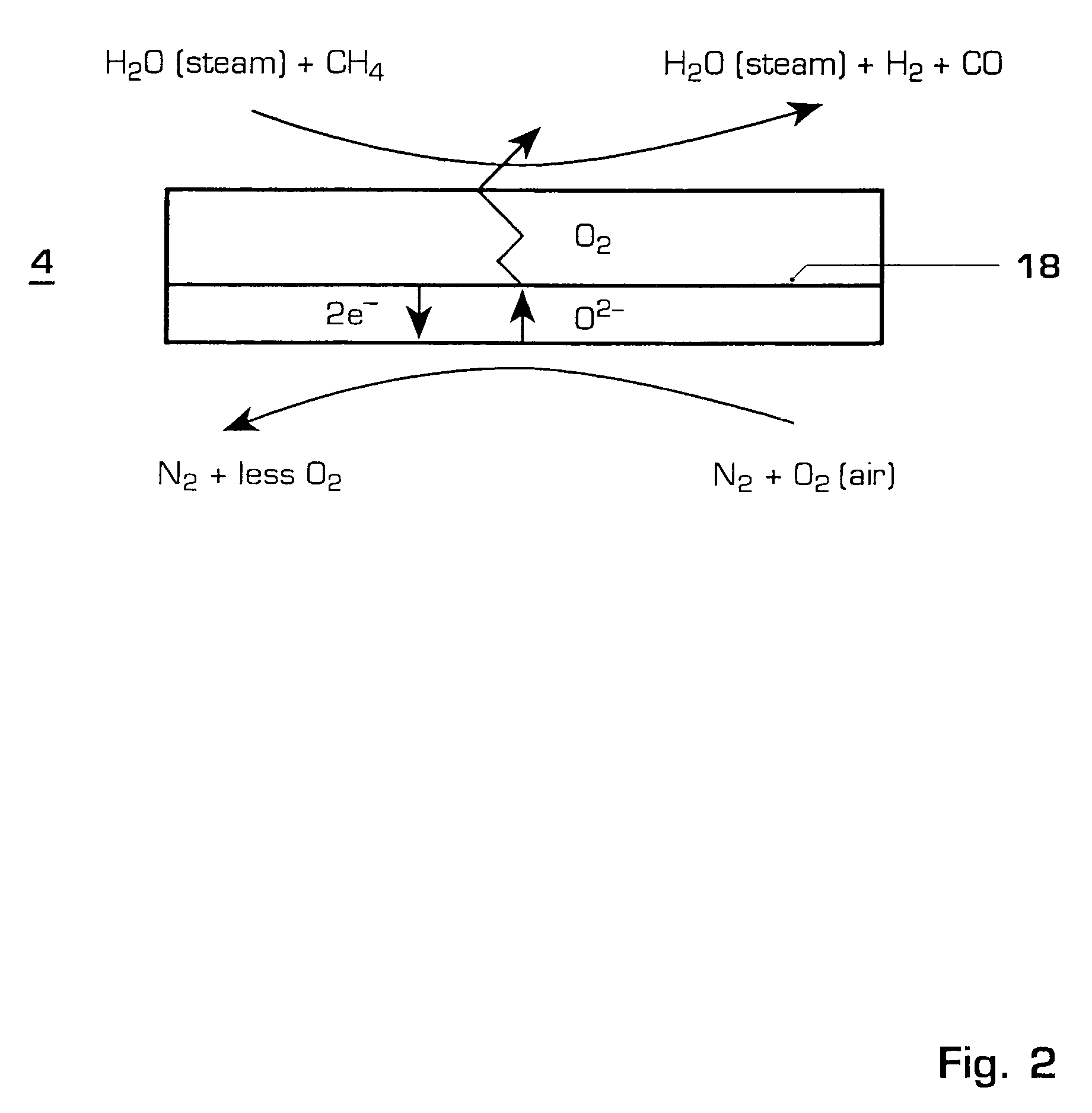
Gas turbine power plant and method of operating the same
InactiveUS7363764B2Improve efficiencyAvoid disadvantagesHydrogenOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideSyngasPartial oxidation
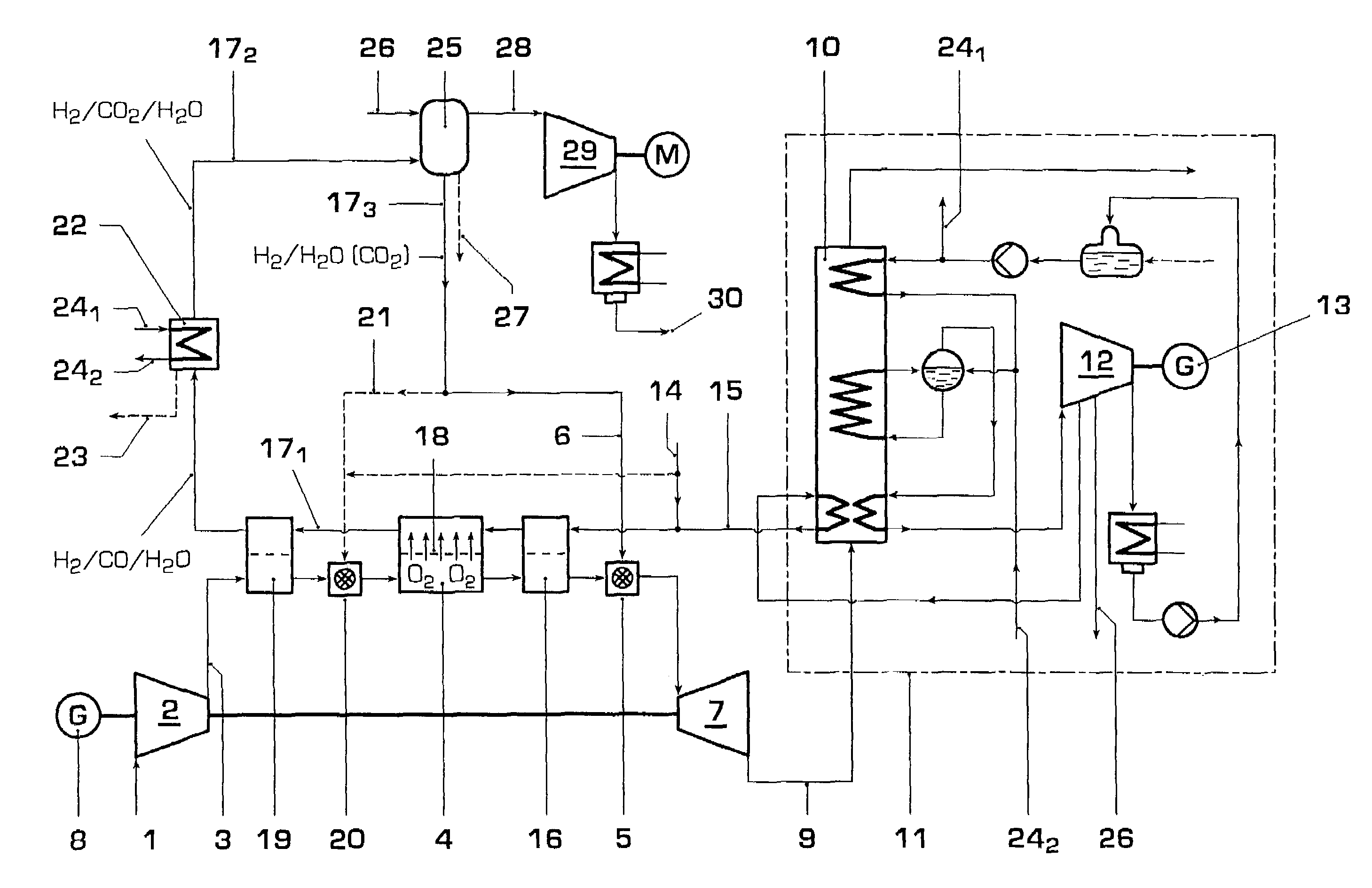
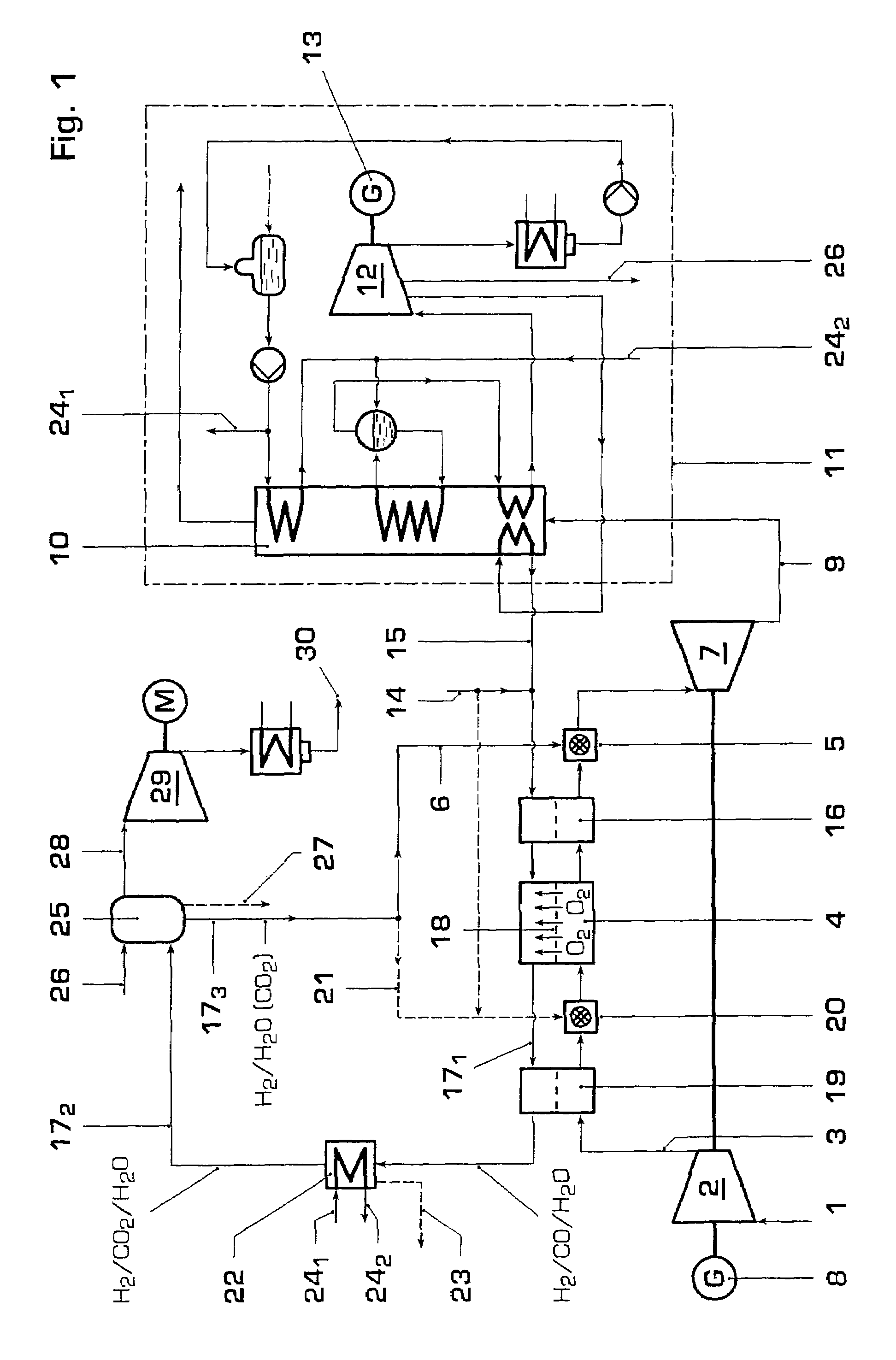
A method of operating a gas turbine power plant and gas turbine power plant are disclosed wherein hydrogen for the combusting process is produced by feeding natural gas mixed with steam through a membrane / partial oxidation reactor and converting the natural gas at least to H2 and CO. Thereby oxygen is transferred from the compressed air through the membrane of the membrane / partial oxidation reactor and the oxygen is used for the partial oxidation process of the natural gas. The process is followed by converting the syngas in a CO shift reactor and a CO shift reactor to a CO2 removal equipment to mainly hydrogen.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
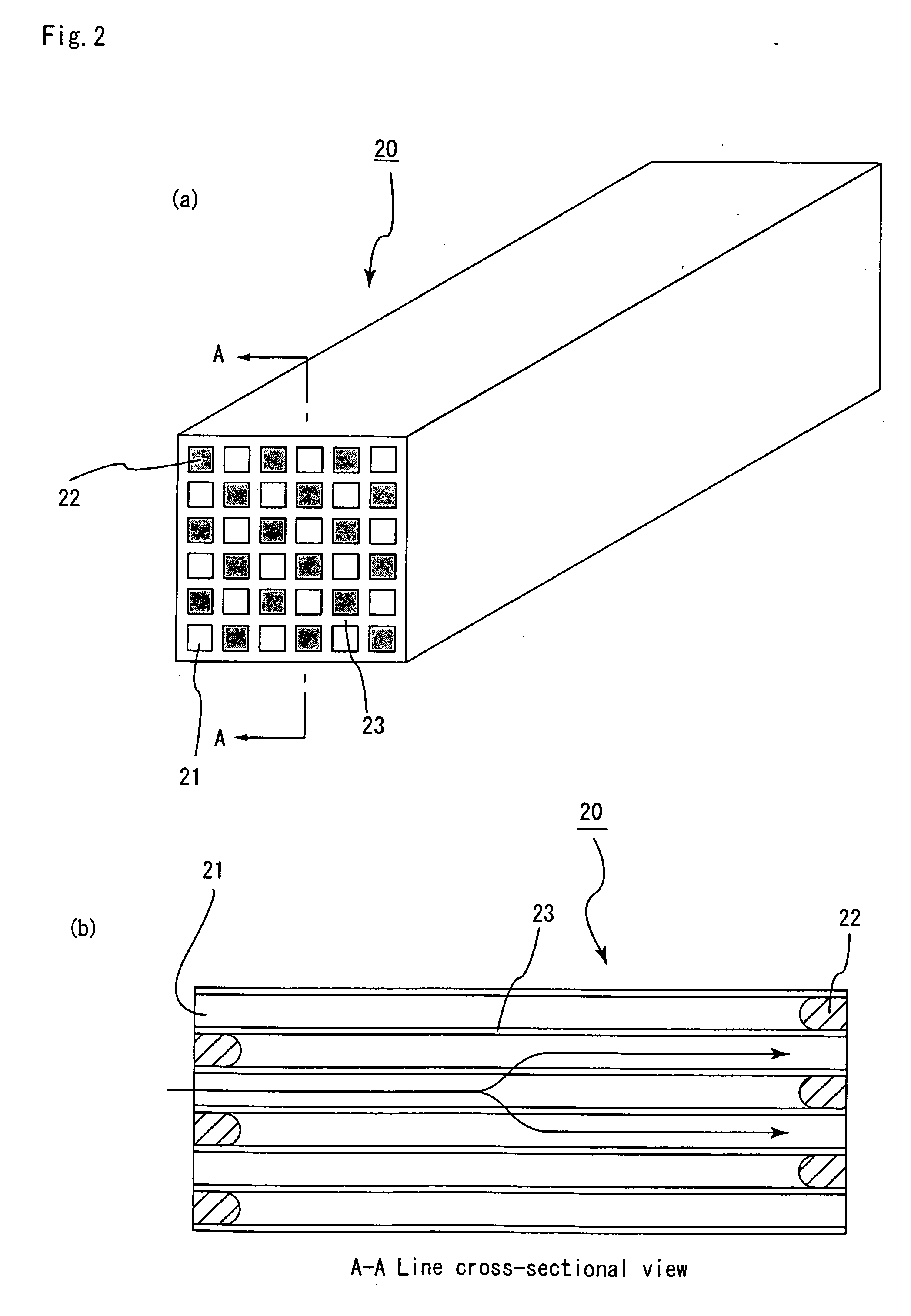
Honeycomb structure and method for manufacturing honeycomb structure
ActiveUS20080318001A1Improve heat resistanceAvoid loopholesDispersed particle filtrationSolid waste managementYoung's modulusCell wall
A honeycomb structure includes a ceramic block and a sealing material layer. The ceramic block includes a plurality of honeycomb fired bodies each having a large number of cells longitudinally disposed substantially in parallel with one another with a cell wall between the cells, an adhesive layer for bonding side faces of the honeycomb fired bodies, and a cavity-holding member placed between the side faces of the honeycomb fired bodies. The sealing material layer is formed on a peripheral face of the ceramic block. The cavity-holding member includes a nonflammable material having Young's modulus of at least about 0.001 GPa and at most about 0.07 GPa.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
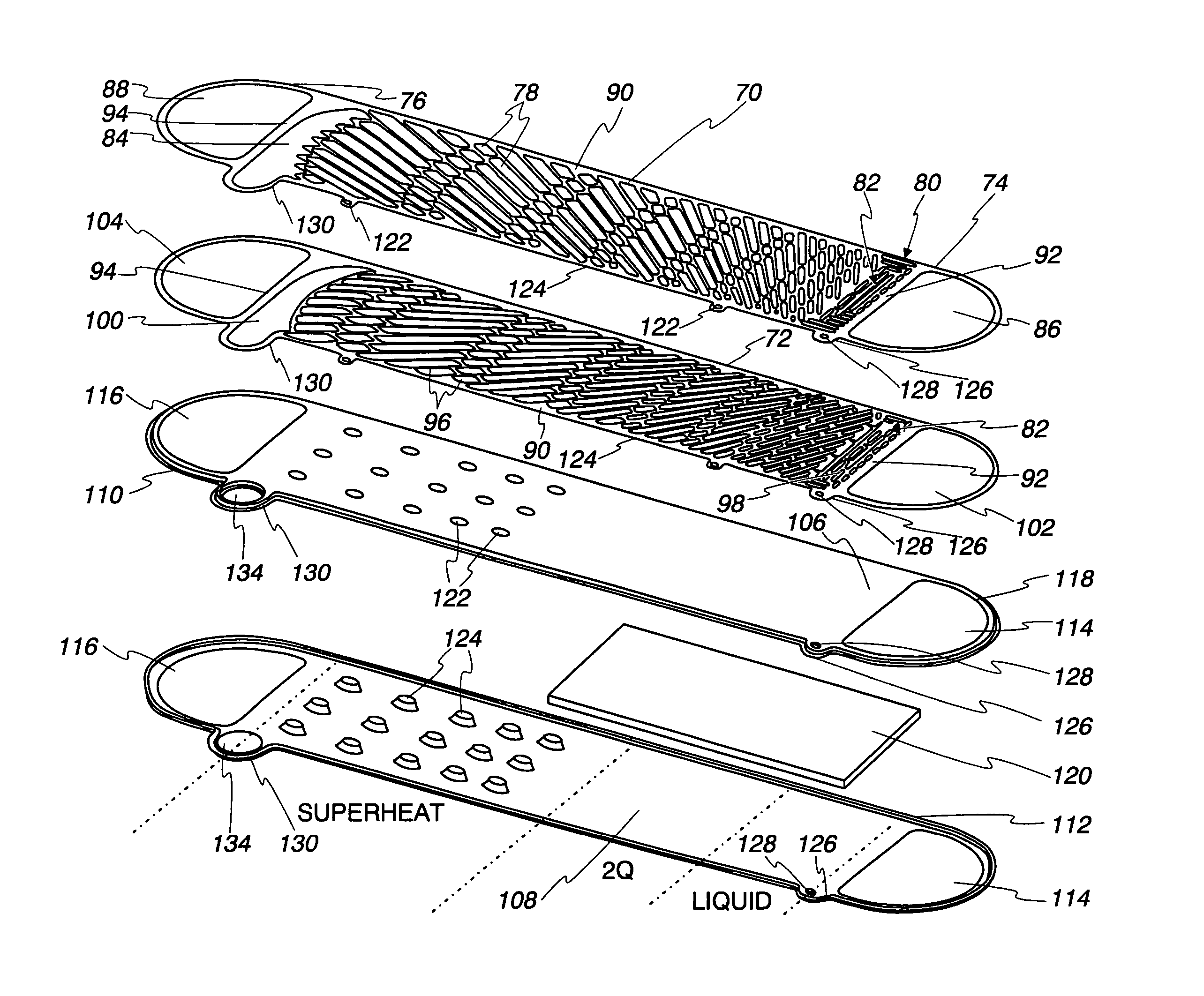
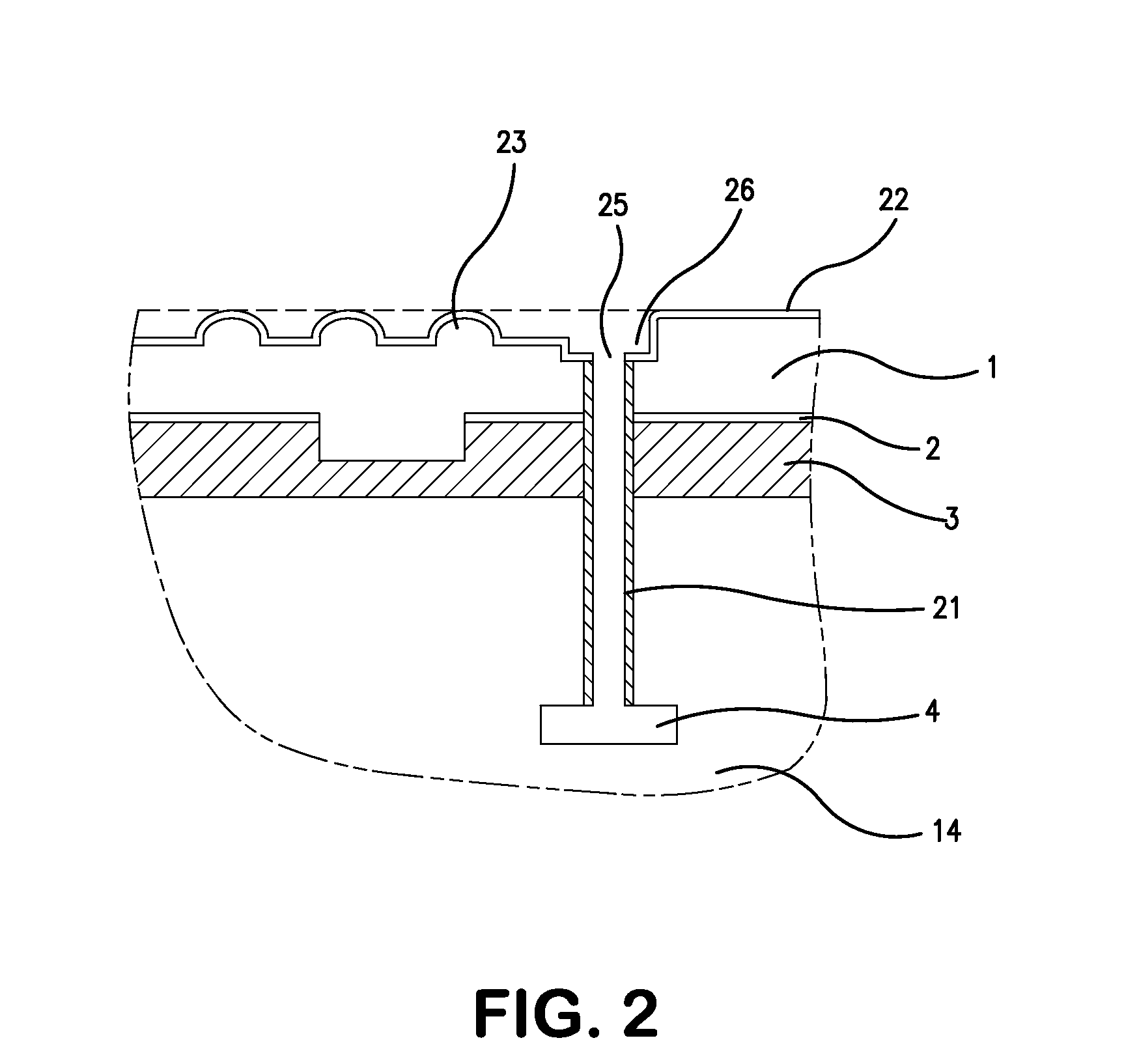
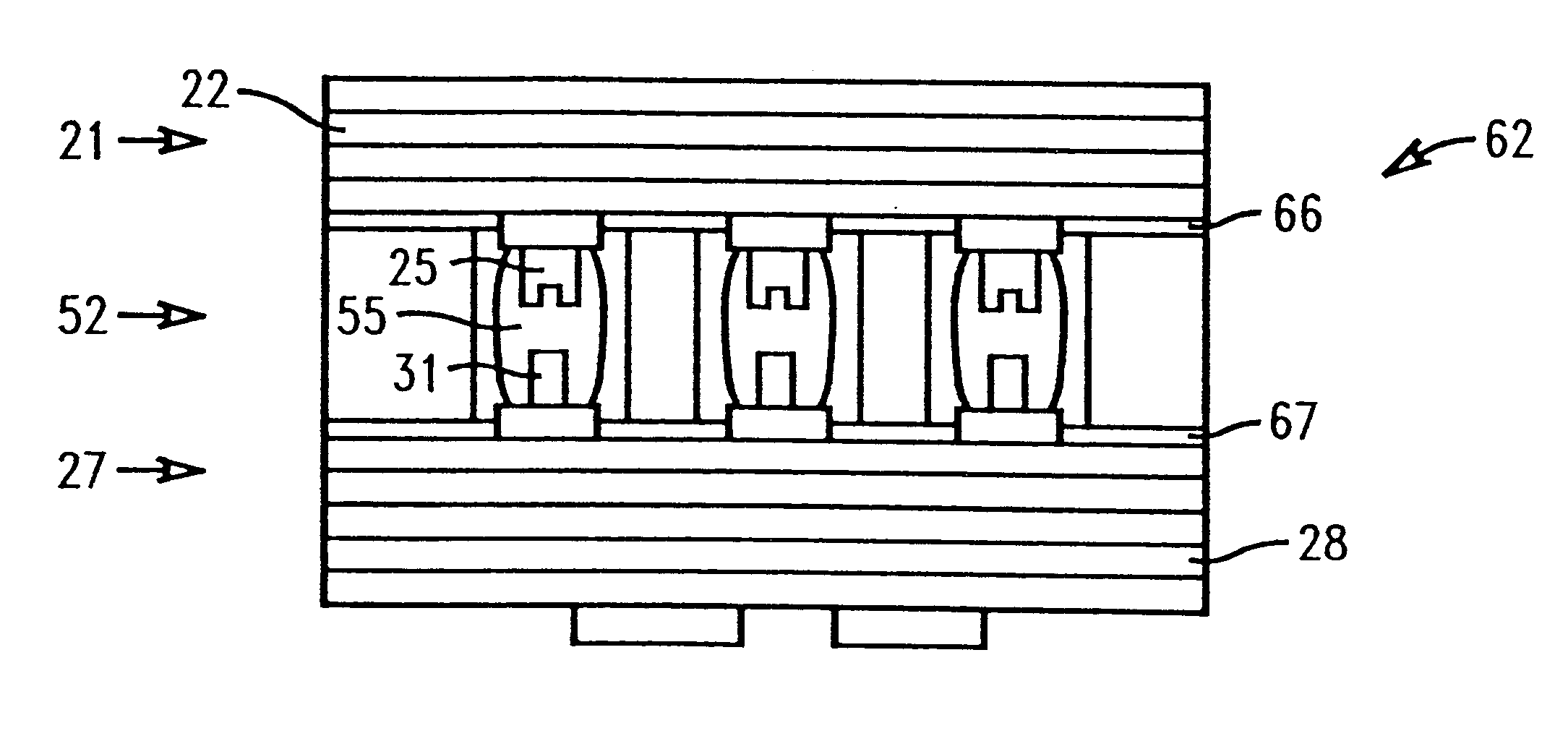
Honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination
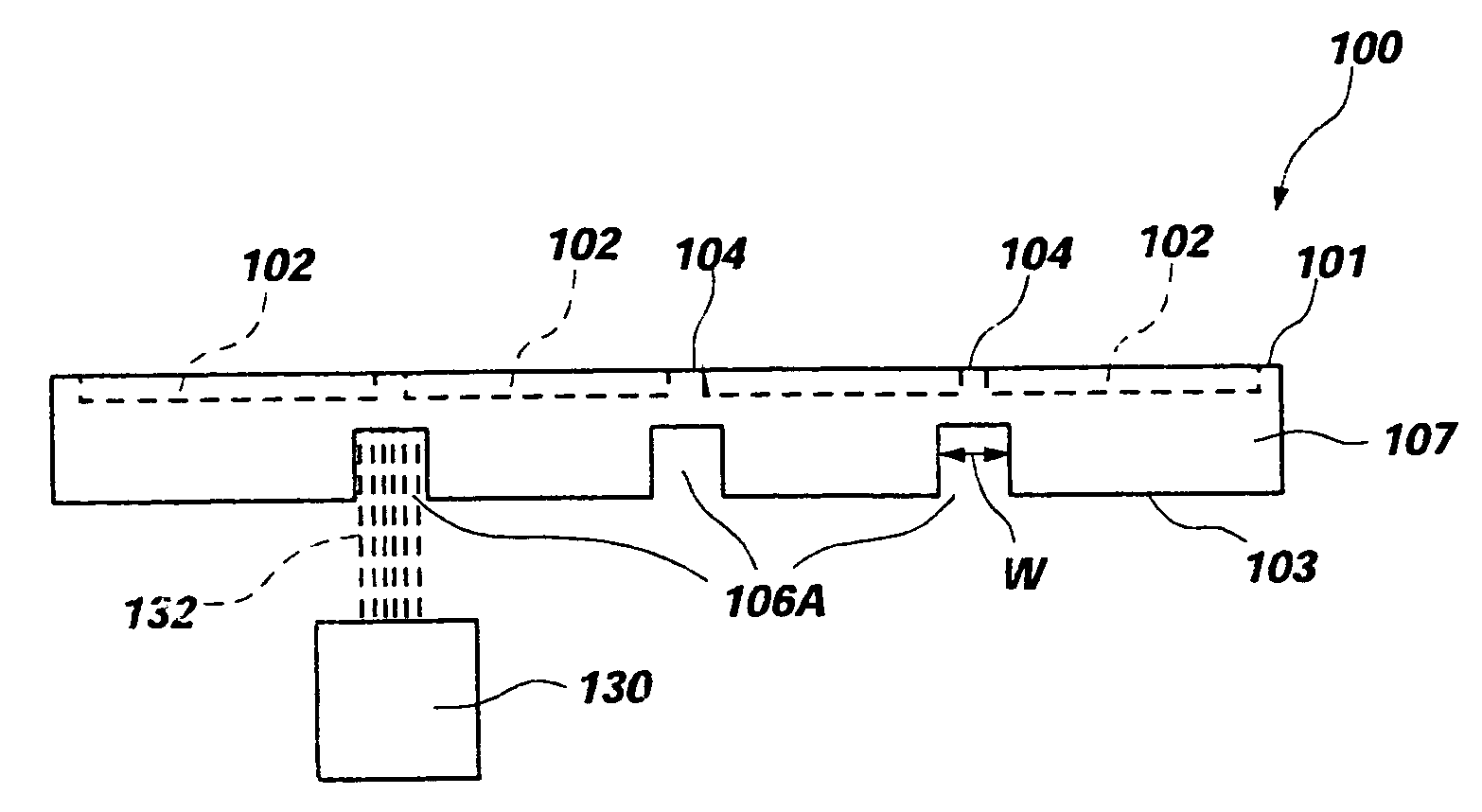
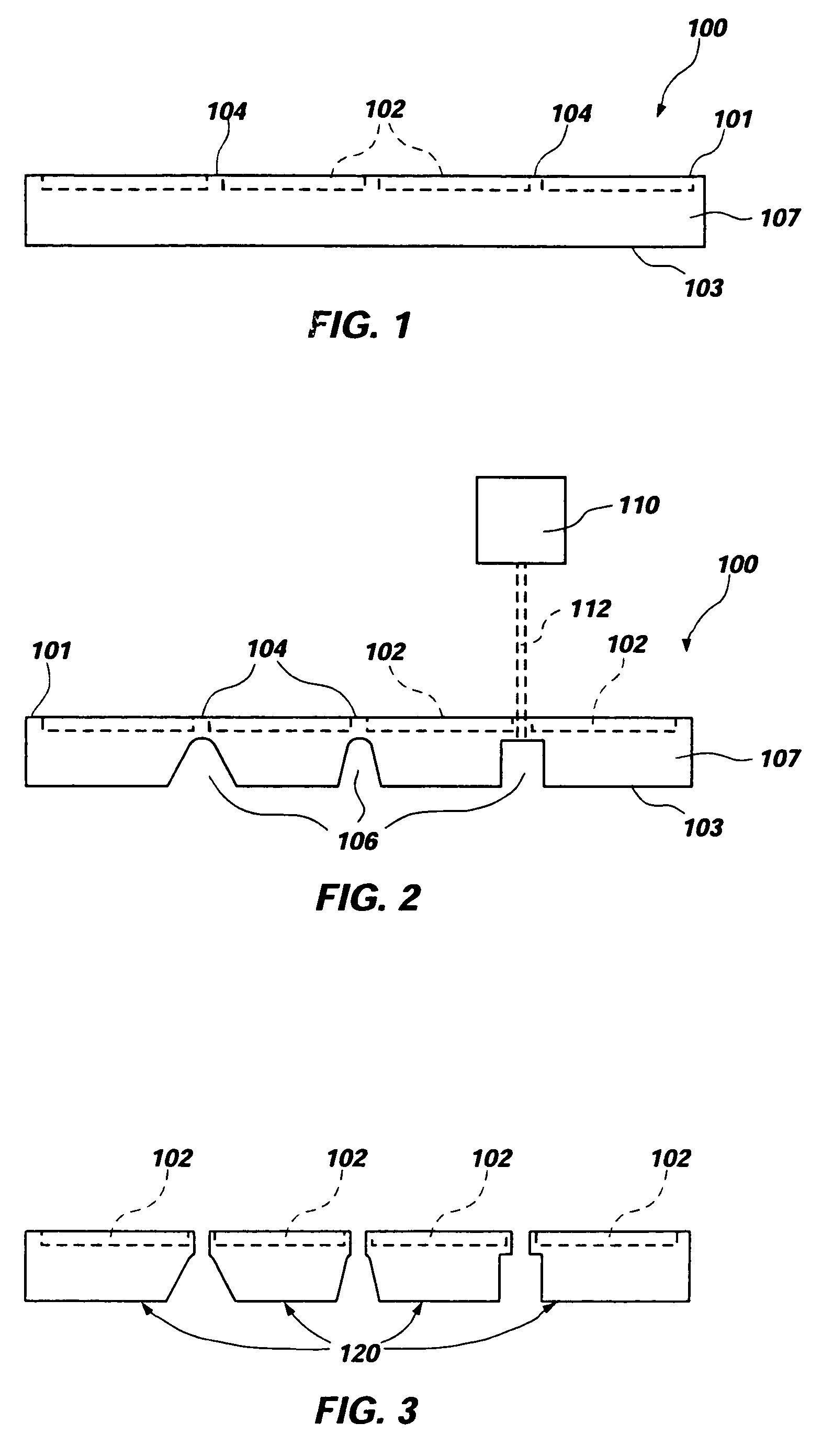
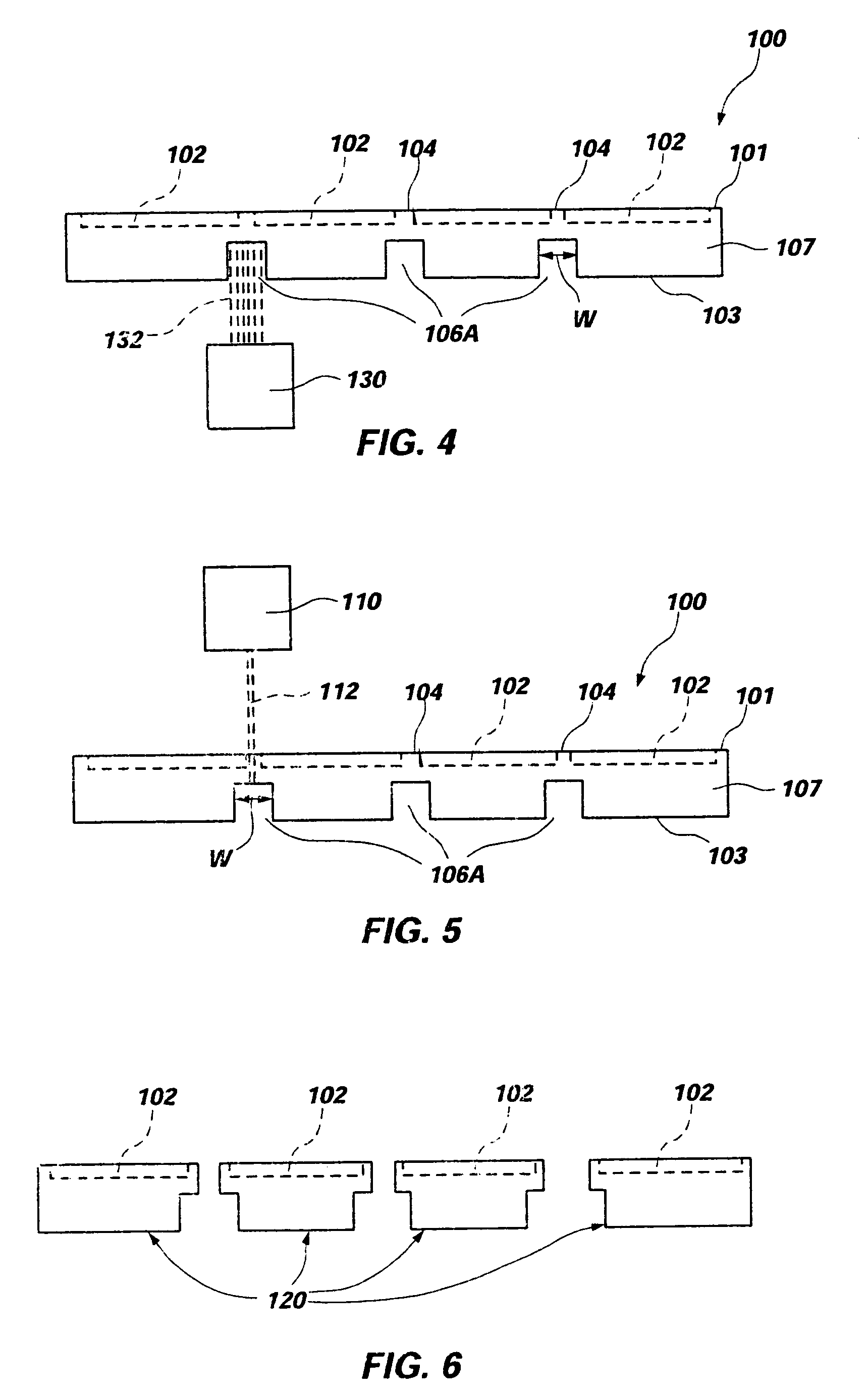
ActiveUS20050076626A1Reduce thermal stressHigh strengthCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesHoneycomb
A honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases, which makes it possible to alleviate a thermal stress generated due to occurrence of a local temperature change, is less likely to generate cracks, and is excellent in strength and durability. The honeycomb filter has a structure in which a plurality of column-shaped porous ceramic members, each having a number of through holes that are placed side by side in the length direction with a partition wall interposed therebetween, are combined with one another through adhesive layers so that the partition wall that separates the through holes are allowed to function as a filter for collecting particulates. A thermal expansion coefficient αL of the adhesive layer and a thermal expansion coefficient αF of the porous ceramic member is as follows: 0.01<|αL−αF| / αF<1.0.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Honeycomb filter for exhaust gas decontamination
ActiveUS7309370B2High strengthIncreased durabilityCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentParticulatesHoneycomb
A honeycomb filter for purifying exhaust gases, which makes it possible to alleviate a thermal stress generated due to occurrence of a local temperature change, is less likely to generate cracks, and is excellent in strength and durability. The honeycomb filter has a structure in which a plurality of column-shaped porous ceramic members, each having a number of through holes that are placed side by side in the length direction with a partition wall interposed therebetween, are combined with one another through adhesive layers so that the partition wall that separates the through holes are allowed to function as a filter for collecting particulates. A thermal expansion coefficient αL of the adhesive layer and a thermal expansion coefficient αF of the porous ceramic member is as follows:0.01<|αL−αF| / αF<1.0.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD
Compressed air energy storage system having a standby warm keeping system including an electric air heater
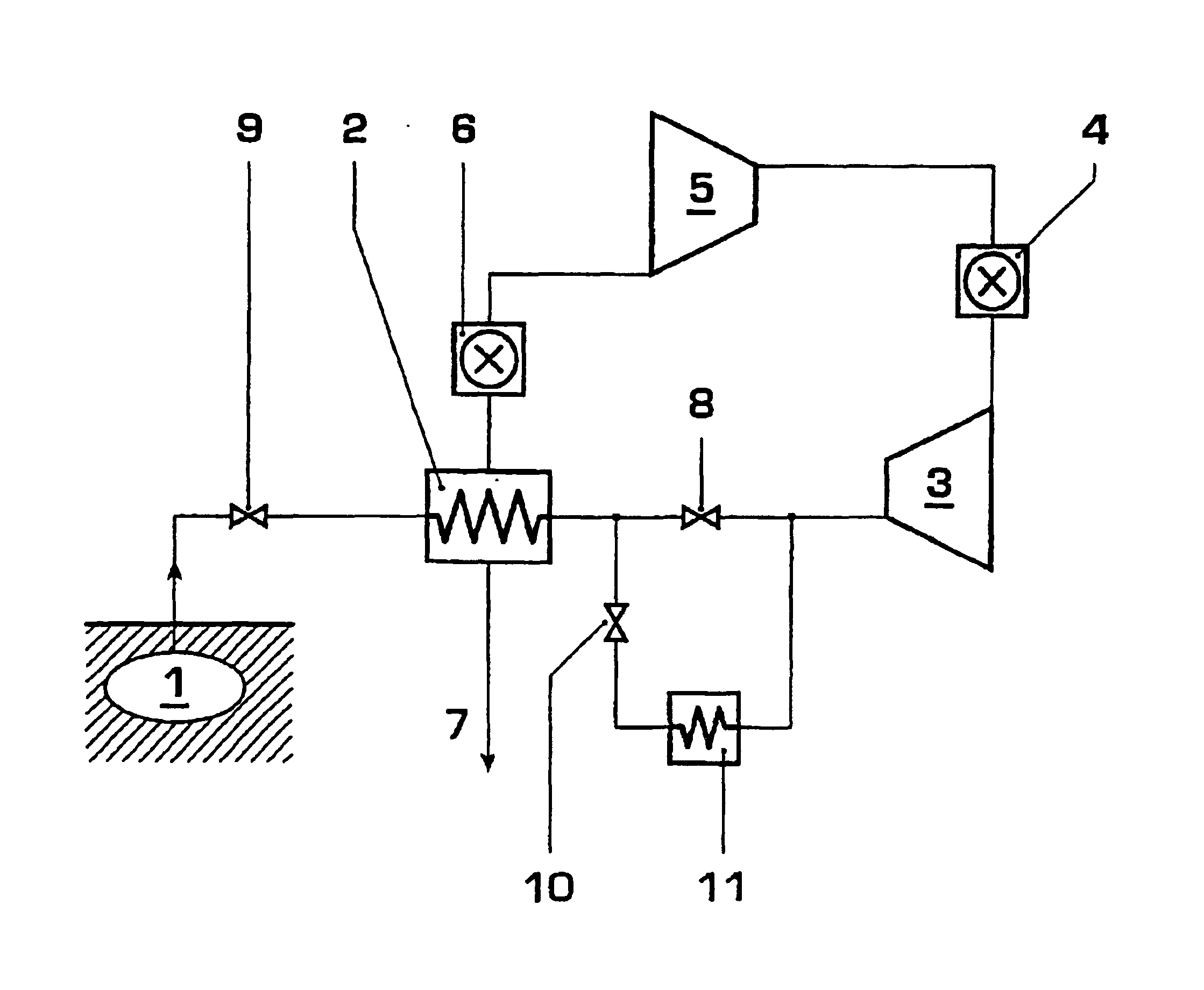
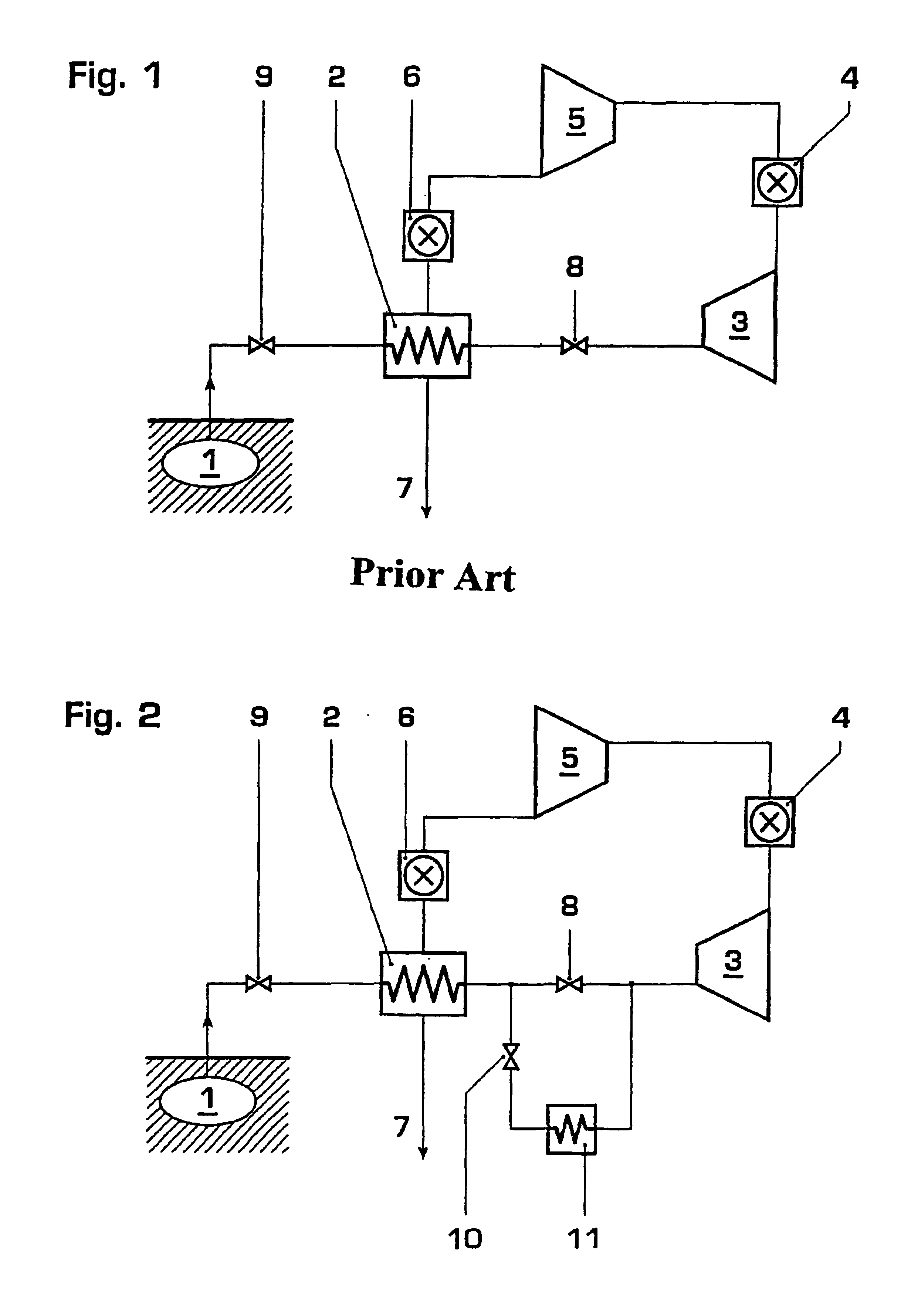
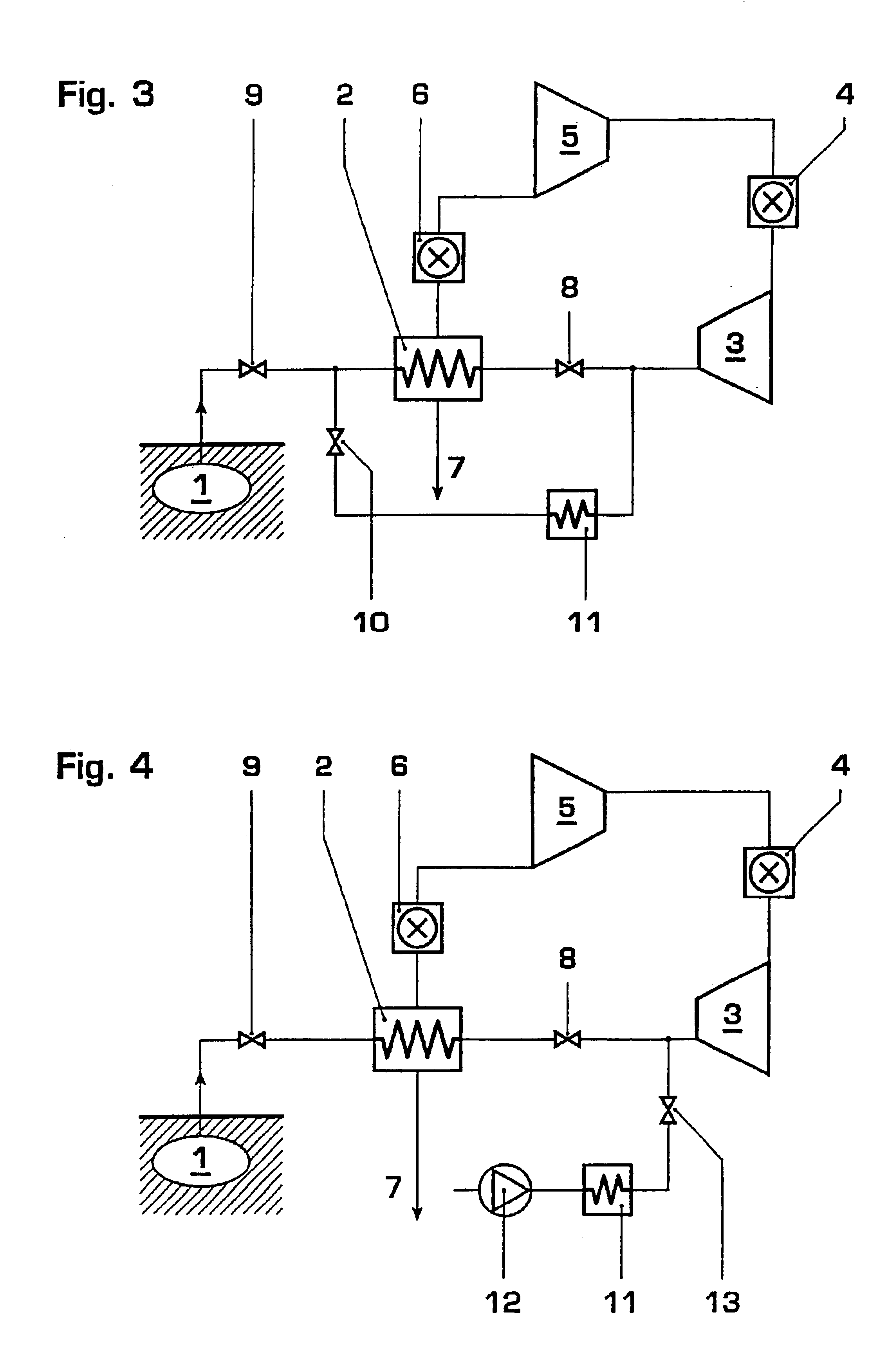
InactiveUS6848259B2Reduce thermal stressEasy temperature controlGas turbine plantsJet propulsion plantsTemperature controlCombustor
A compressed air energy storage system comprises a cavern (1) for stored compressed air and a system for providing the compressed air to a power train (3, 5), this system including a recuperator (7) and a first valve arrangement (8) that controls the flow of the compressed air from the recuperator and to the power train (3, 5). A system for warm-keeping of the power train (3, 5) during stand-by operation of the compressed air energy storage system comprises the recuperator (2) and / or an auxiliary electrical air heater (11) and a second valve arrangement (10, 13) for controlling the airflow for warm-keeping. The system for warm-keeping of the power train allows improved temperature control and avoids disadvantages associated with a warm-keeping system having a combustor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Synchronous sintering process for electronic beam selection zone and three dimension layered producing device
ActiveCN1648802AHigh speedHigh precisionComputer controlElectron beam welding apparatusRapid scanHeat stress
The present invention relates to technology and apparatus with high energy beam to sinter or melt and deposit material successively to realize laminated solid manufacture. The present invention features that the electronic beam scan controller controls the electronic beam to scan fast in pattern projection mode for heating powder homogeneously. Each scanning of the electronic beam has short time in the selected area, so that the scan initiating point has no great temperature change generated during the whole scanning course. Through one or several frames of scanning, the material in the forming area has temperature synchronously raised to reach the sintering or re-melting temperature for deposition onto the forming area before synchronous cooling. The present invention has greatly reduced heat stress and raised forming precision and quality.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Implantable flexible circuit leads and methods of use
InactiveUS9314618B2Easy to manufactureStrong specificitySpinal electrodesDiagnostic recording/measuringDielectricAnatomical structures
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL LUXEMBOURG HLDG SMI S A R L SJM LUX SMI
Method and apparatus for controlling thermal stress in lighting devices
ActiveUS20060202914A1Reduce thermal stressStatic indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesDriving currentLight equipment
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for controlling the thermal stress in lighting devices, for example light-emitting elements, that are exposed to large thermal gradients typically upon start-up, for example light-emitting elements operating in relatively cold ambient environments. The present invention provides an apparatus that can reduce this thermal stress, wherein the apparatus comprises a temperature determination mechanism for evaluating the temperature of the light-emitting elements prior to activation, and a control system to control the drive current such that it is gradually ramped up to the desired steady state peak current value, wherein the ramping of the drive current is dependent on the evaluated temperature of the light-emitting element.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
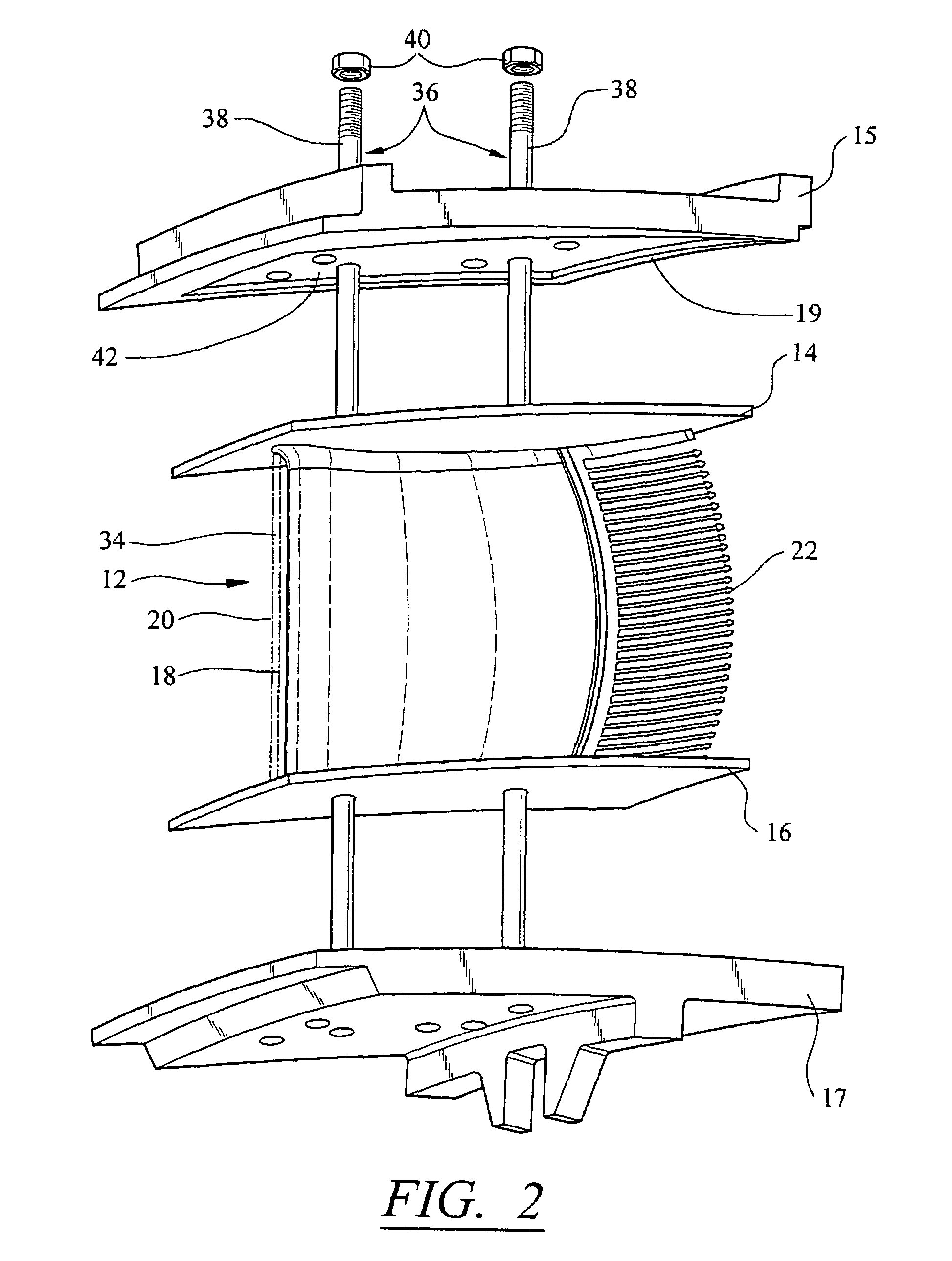
Support system for a composite airfoil in a turbine engine
ActiveUS7326030B2Improve abilitiesLess likely can be damagedPropellersPump componentsSupporting systemTurbine
A turbine airfoil support system for coupling together a turbine airfoil formed from two or more components, wherein the support system is particularly suited for use with a composite airfoil. In at least one embodiment, the turbine airfoil support system may be configured to attach shrouds to both ends of an airfoil and to maintain a compressive load on those shrouds while the airfoil is positioned in a turbine engine. Application of the compressive load to the airfoil increases the airfoil's ability to withstand tensile forces encountered during turbine engine operation.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Pressure wave generator and process for manufacturing the same
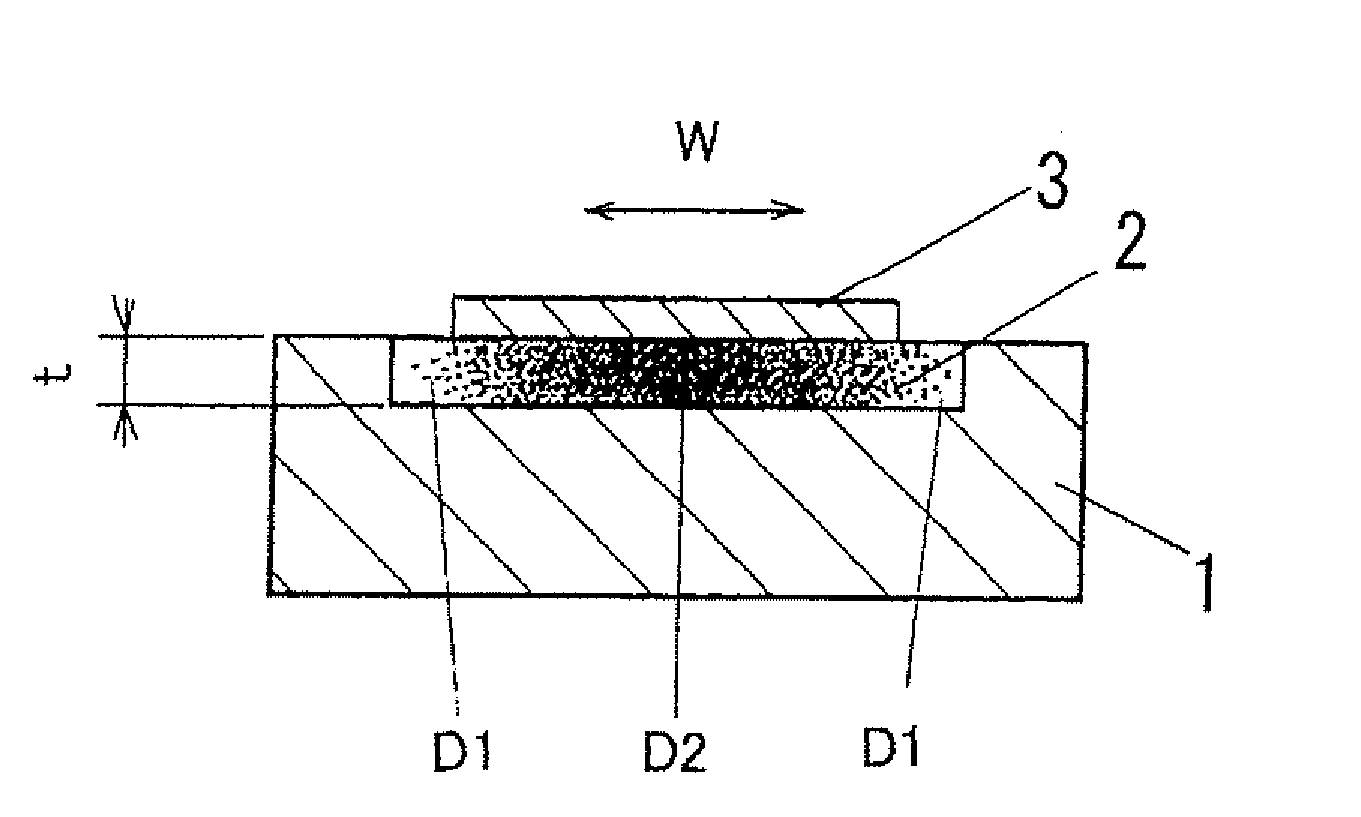
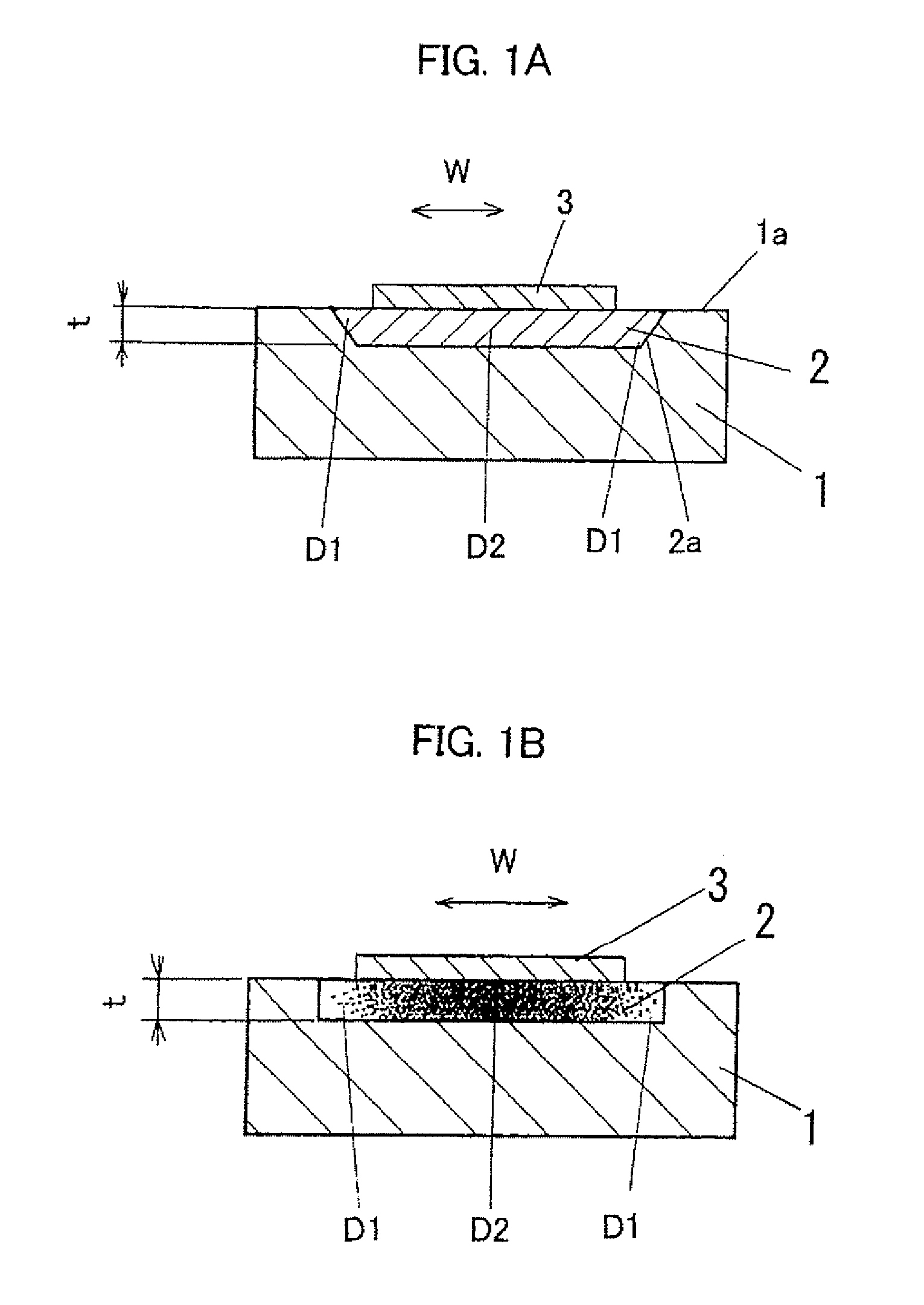
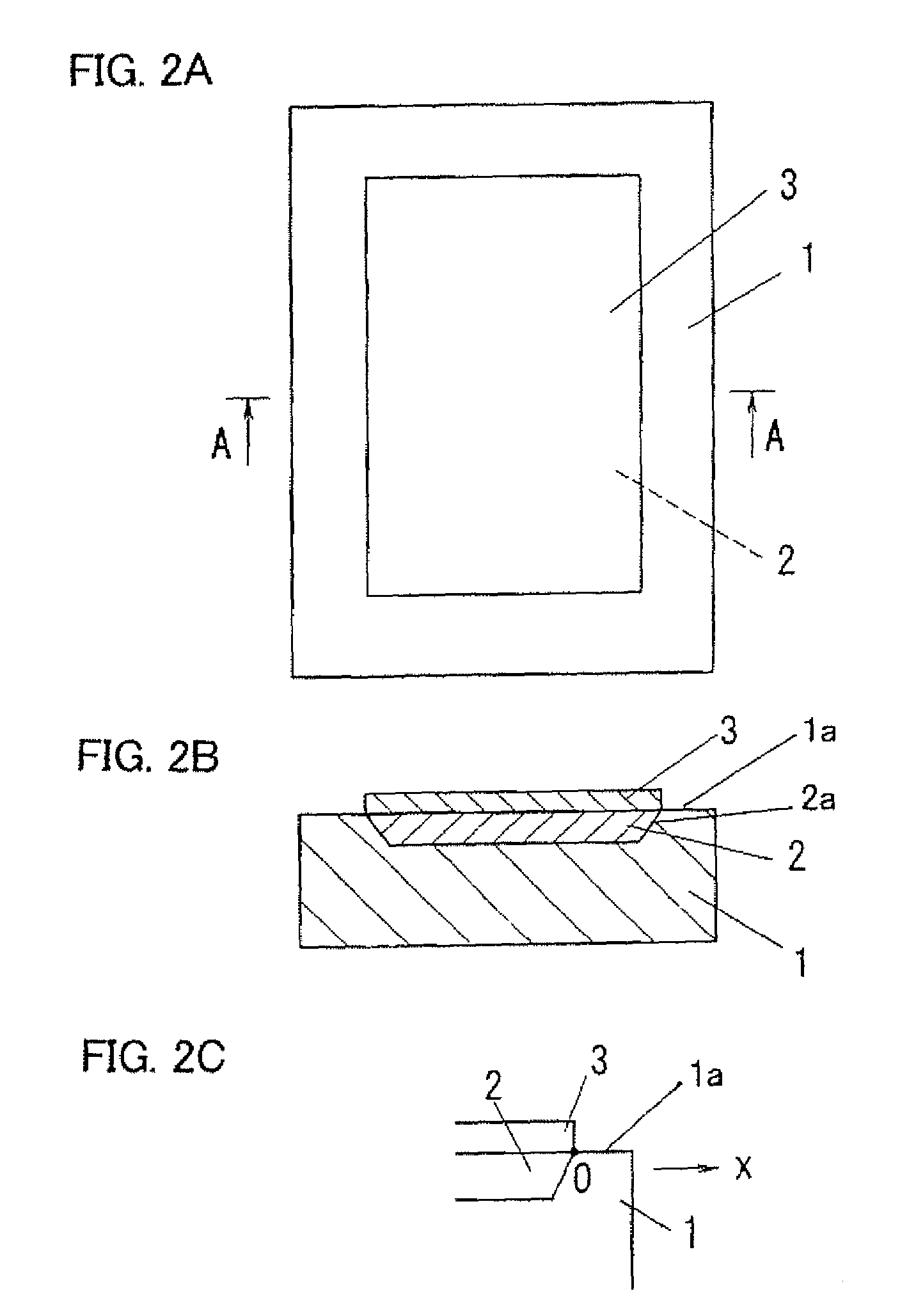
InactiveUS7474590B2Reduce the likelihood of occurrenceMade smallMicrophonesElectrothermic-effect transistorPorosityElectrical conductor
Even when compression stress is generated because a volume of a thermal insulation layer 2 is expanded due to oxidized by oxygen in the air, occurrence of cracks and fractures of the thermal insulation layer and a heating conductor 3 caused by the cracks are prevented by dispersing the compression stress. A pressure wave generator comprises a substrate 1, the thermal insulation layer 2 of porous material which is formed on a surface of the substrate 1 in thickness direction, and the heating conductor 3 of thin film formed on the thermal insulation layer 2, and generates pressure waves by heat exchange between the heating conductor 3 and a medium. When a thickness at the center of the thermal insulation layer 2 in width direction W is used as a reference thickness, and it is assumed that distribution of thickness of thermal insulation layer in the width direction is averaged with the reference thickness, porosity in an outer peripheral portion of the thermal insulation layer is made smaller than porosity in the center portion. By making the porosity in the outer peripheral portion of the thermal insulation layer 2 smaller, a number of immovable points on the outer periphery of the thermal insulation layer 2 restricted by the substrate 1 is increased and the positions of them are dispersed, so that the compression stress compressed in the outer peripheral portion of the thermal insulation layer 2 can be dispersed.
Owner:MATSUSHITA ELECTRIC WORKS LTD
Methods relating to singulating semiconductor wafers and wafer scale assemblies
ActiveUS20060079024A1Increase distanceAvoid excessive widthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWaferingEngineering
Methods relating to the singulation of dice from semiconductor wafers. Trenches or channels are formed in the bottom surface of a semiconductor wafer, corresponding in location to the wafer streets. The trenches may be formed by etching or through an initial laser cut. The wafer is then singulated along the streets with a laser preferably having a beam narrower than the trenches. Multiple, laterally spaced lasers may be used in combination during a single pass to perform simultaneous singulating cuts. Additional edge protection for integrated circuitry on the active surface of the semiconductor dice may be provided by forming trenches or channels along the streets in the active surface instead of the bottom surface, disposing protective material along the streets and within the trenches prior to singulation and cutting through the wafer, leaving protective material on the sidewalls of the channels.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
System for utilizing solar step developing heat
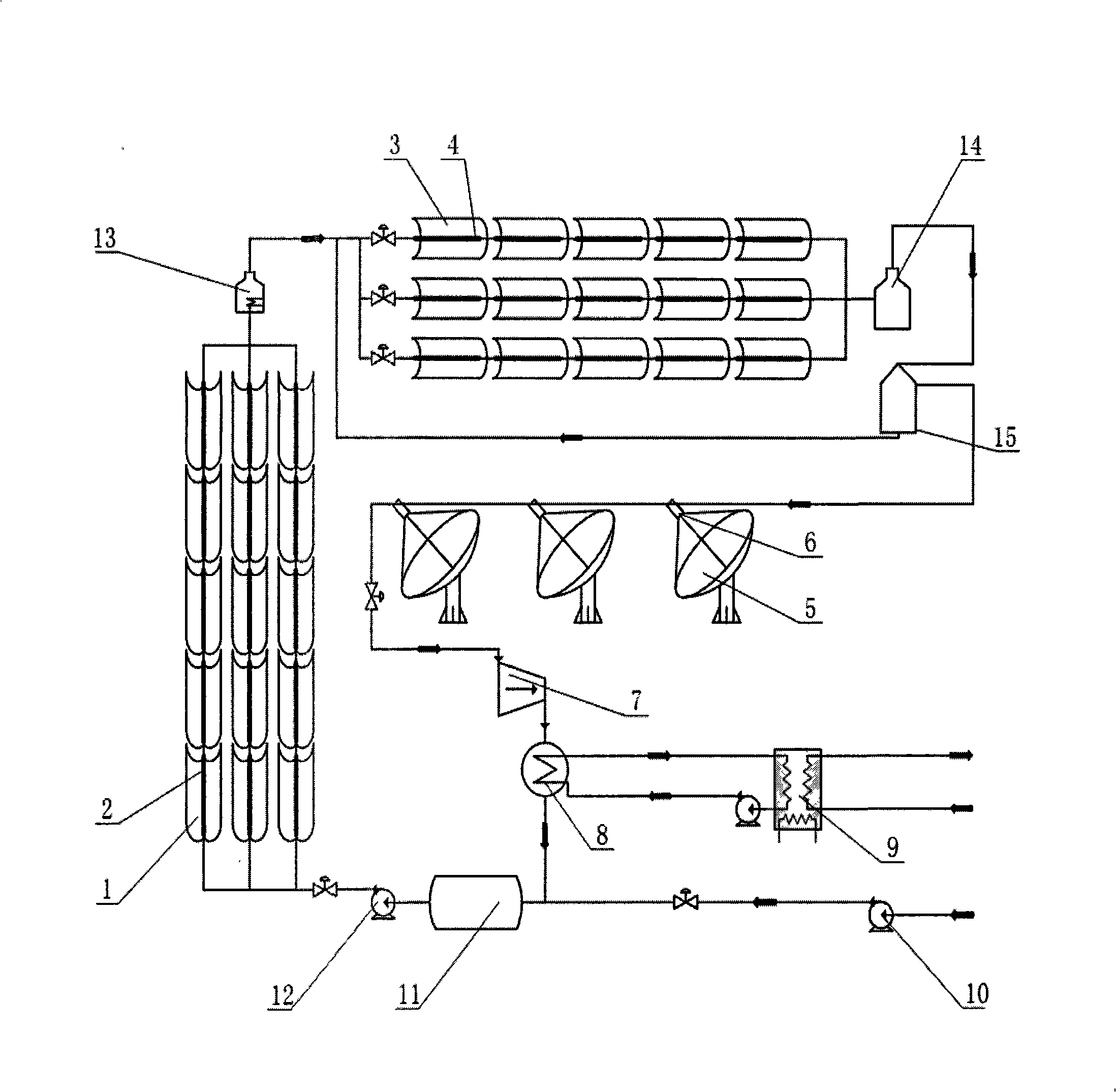
InactiveCN101354191AImprove reliabilityReduce thermal stressSolar heating energyFrom solar energyEngineeringSteam turbine
The invention relates to a cascade-developed heat utilization system of solar energy, which adopts that: in a low temperature section, a complex parabolic condenser is matched with a normal temperature receiver and the normal temperature receiver is output to an intermediate temperature section; in the intermediate temperature section, a parabolic trench-typed condenser is matched with an intermediate temperature receiver which is output to a high temperature section through a gas-water separator; in the high temperature section, a disk-typed condenser is matched with a high-temperature receiver which is output to a steam turbine. The cascade-developed heat utilization system of solar energy of the invention solves the defects that disk type is too expensive in manufacturing, and the trench type incurs the conflict between the reliability and the efficiency at high temperature, and the like. The effects of the cascade-developed heat utilization system of solar energy of the invention lie in that: the low temperature section adopts the complex parabolic condenser, the intermediate temperature section adopts the parabolic trench-typed condenser and the high temperature section adopts the parabolic disk-typed condenser; the three heat collecting sections are connected in series and respective advantages thereof are utilized while respective defects thereof are avoided; the three heat collecting sections are led to be combined dynamically to produce synergistic effects.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Semiconductor device
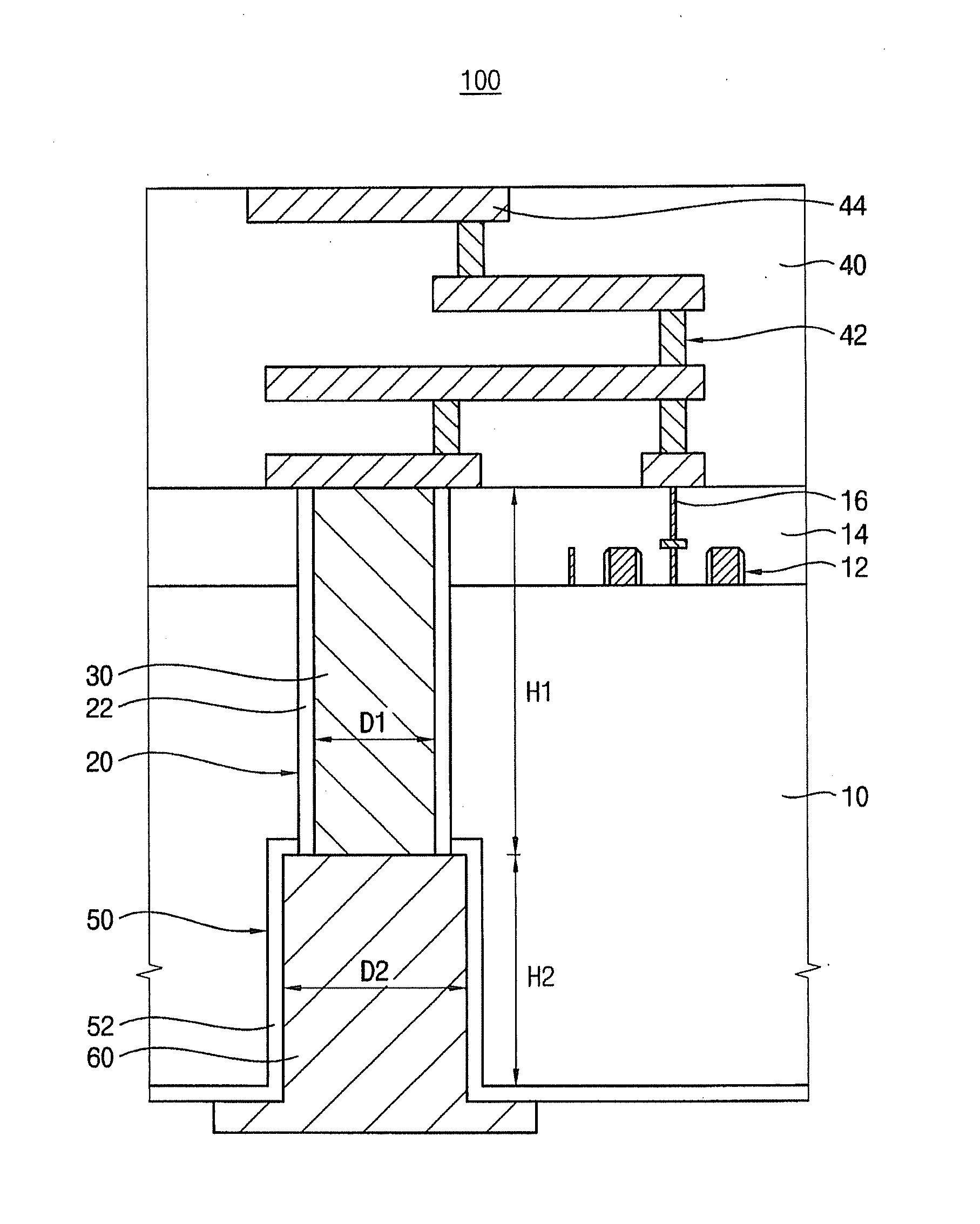
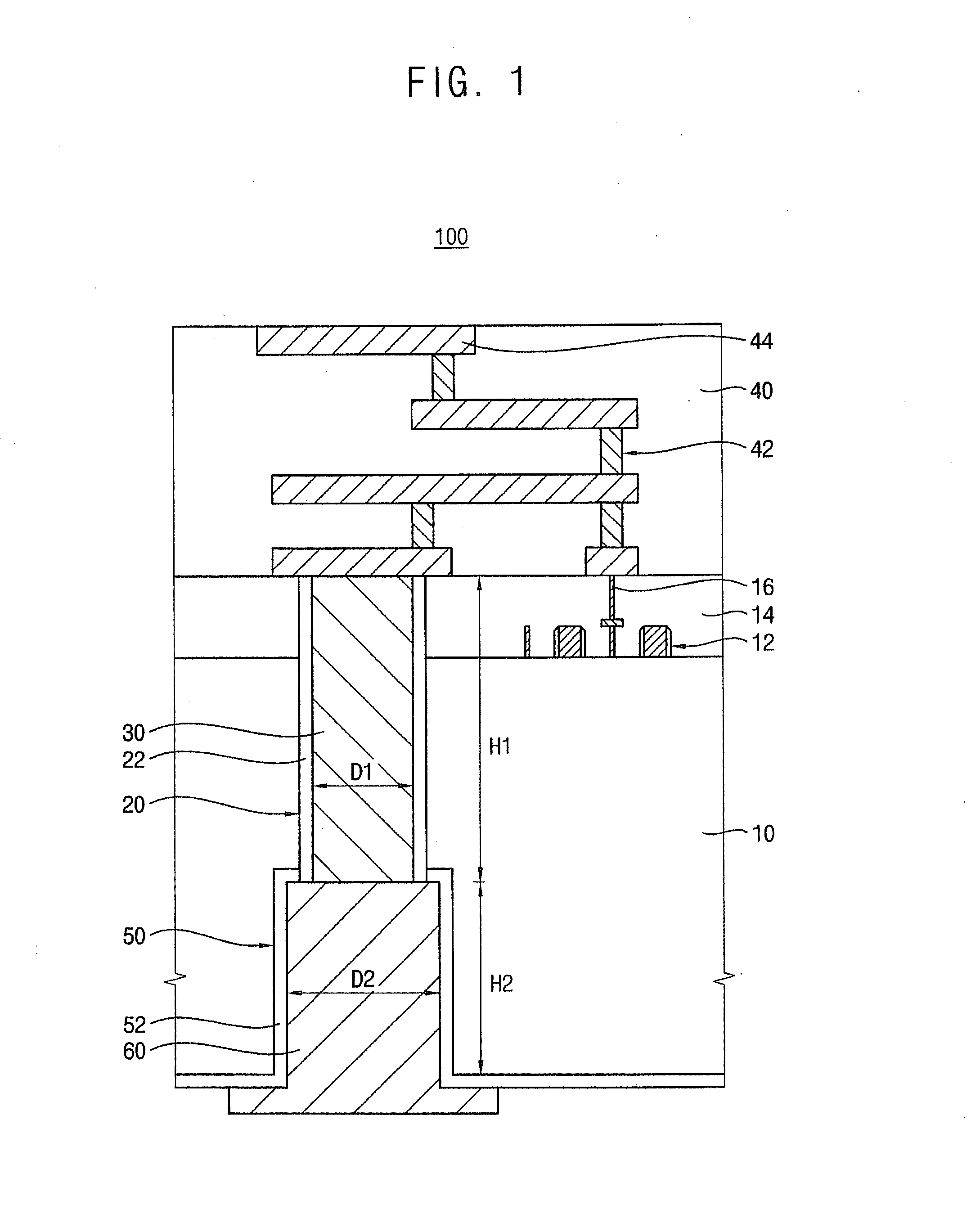
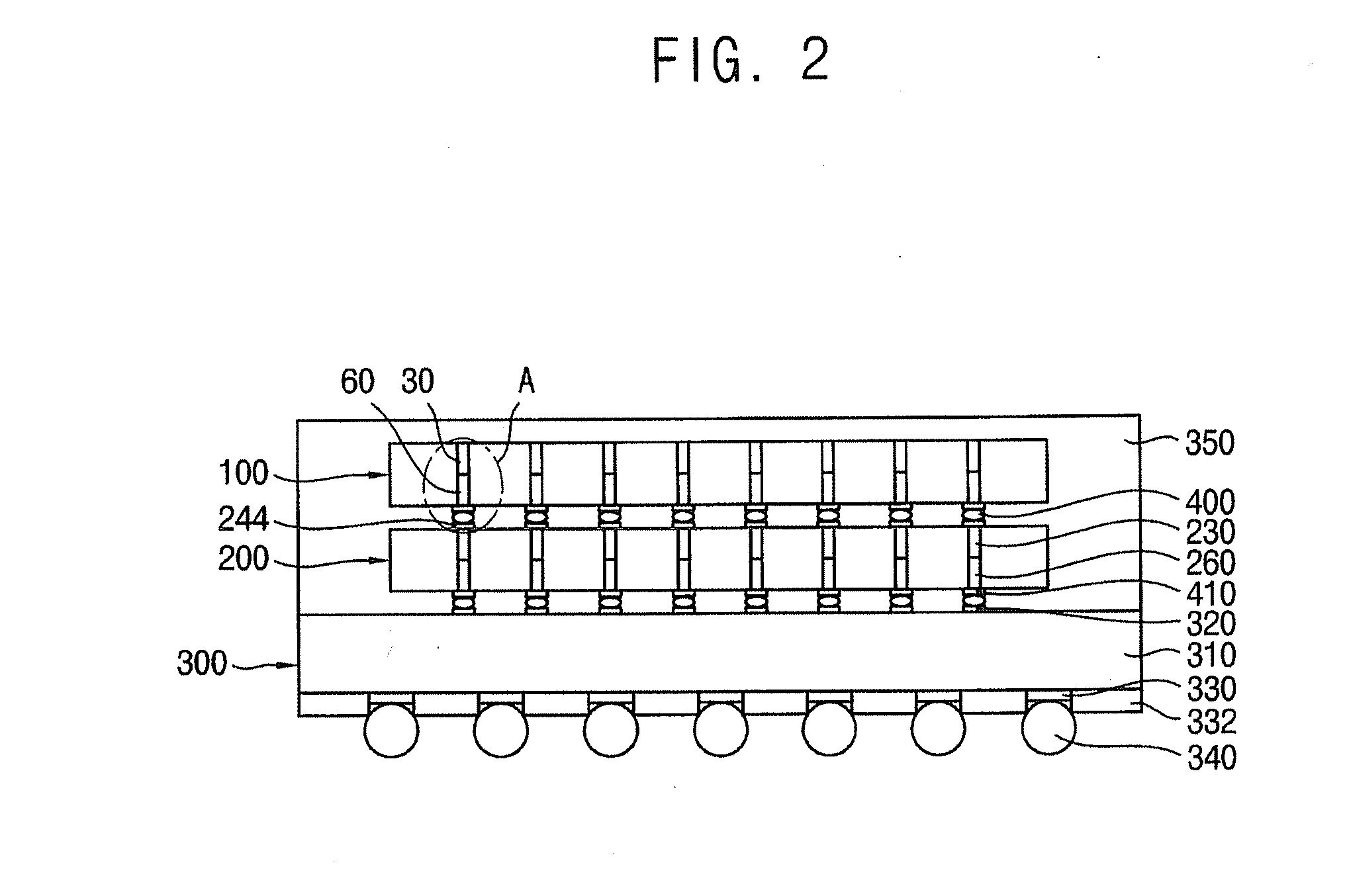
ActiveUS20120056330A1Reduce thermal stressLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialSemiconductor
A semiconductor device may include a substrate and a through electrode. The substrate may have a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface, the substrate including circuit patterns formed on the first surface. The through electrode penetrates the substrate and may be electrically connected to the circuit pattern, the through electrode including a first plug that extends from the first surface in a thickness direction of the substrate and a second plug that extends from the second surface in the thickness direction of the substrate so as to be connected to the first plug.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
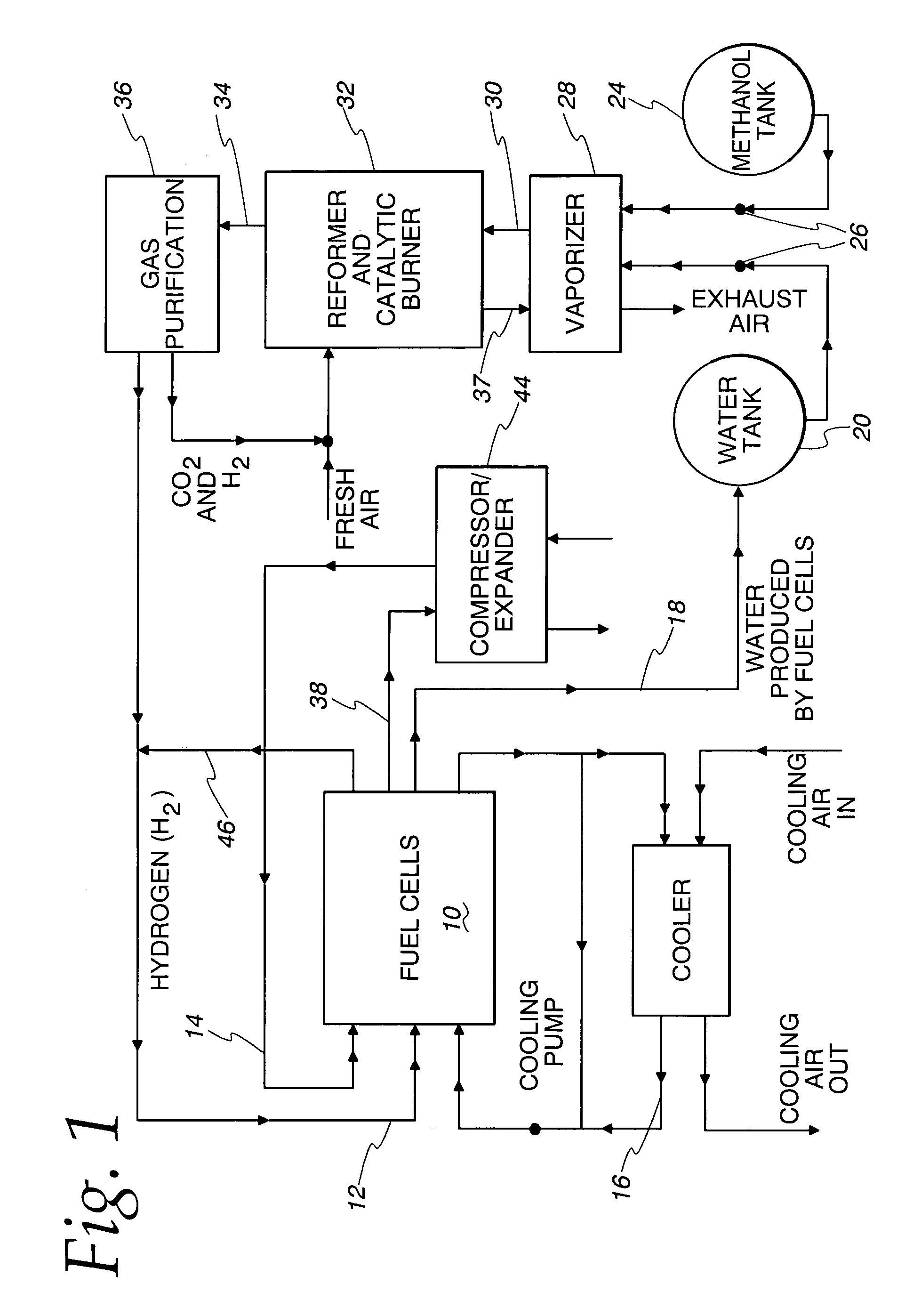
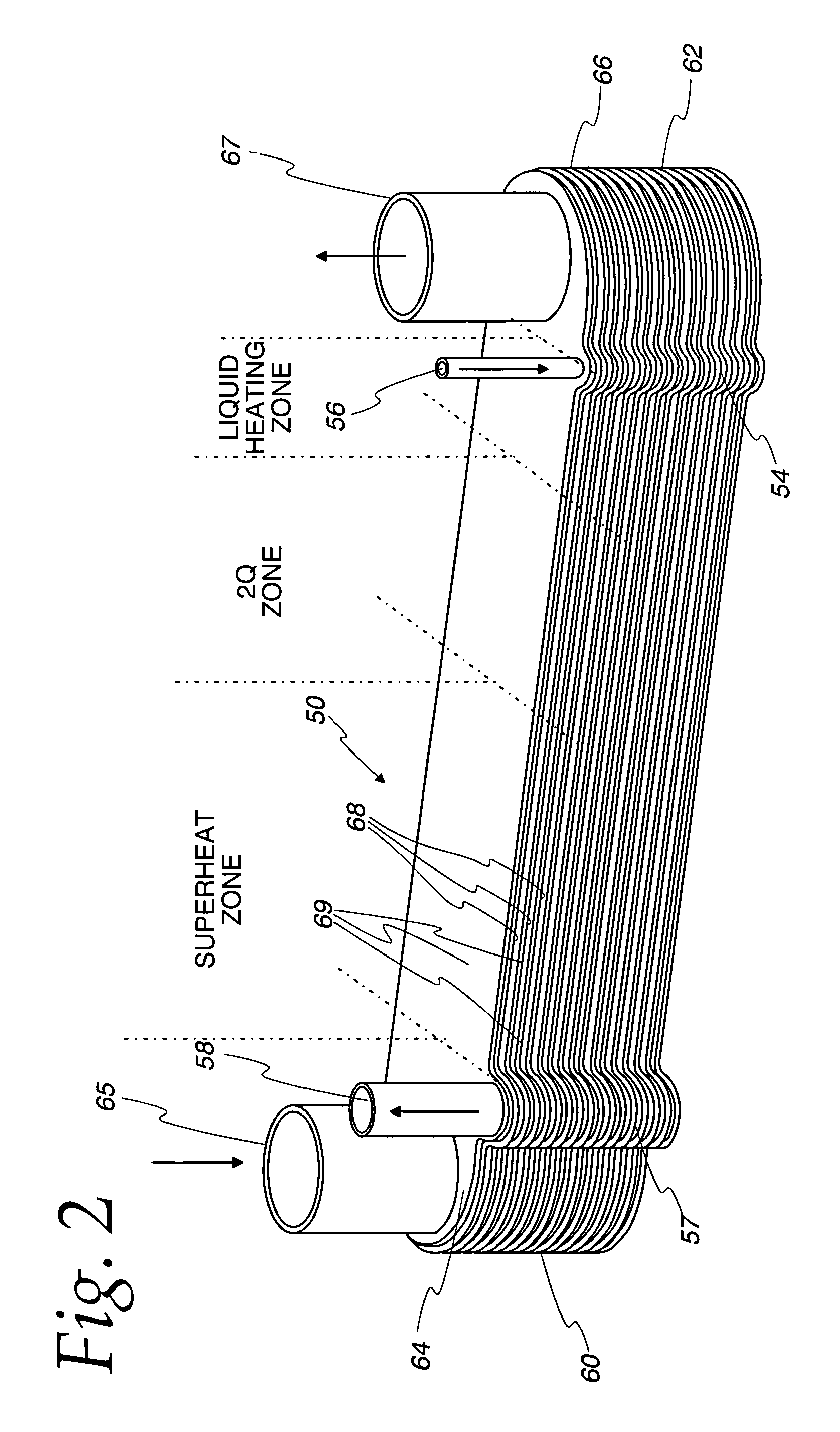
Fuel vaporizer for a reformer type fuel cell system
InactiveUS7063047B2Short response timeReduced effectivenessFuel cell heat exchangeHeat transfer modificationFuel cellsWater flow
Large thermal stresses are avoided and the fuel charge reduced in a vaporizer particularly suited for use in a reformer type fuel cell system and having a construction that includes alternating fuel / water flow path defining cells (68) and hot gas flow path cells (69) by providing heat transfer augmentation, such as a lanced and offset fin (120), only in that part of the gas flow path structure (69) adjacent the regions in the fuel / water flow path cells (68) where heating of the liquid fuel / water and vaporizing of the fuel / water where the mixture exists is a two phase material occurs and not in the area adjacent those parts of the fuel / water flow path structure (68) in which superheating of the vaporized fuel / water mixture is occurring.
Owner:MODINE MFG CO
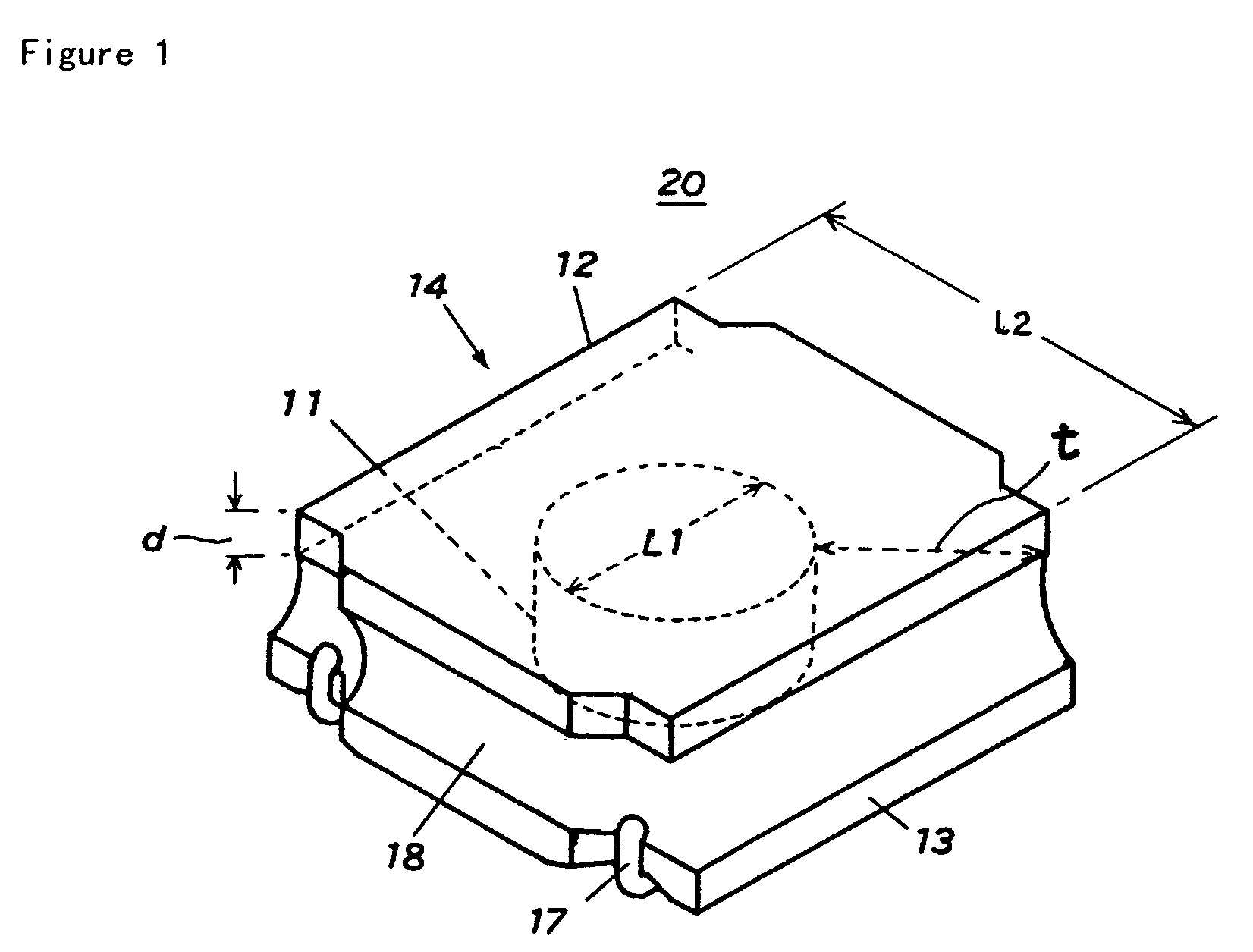
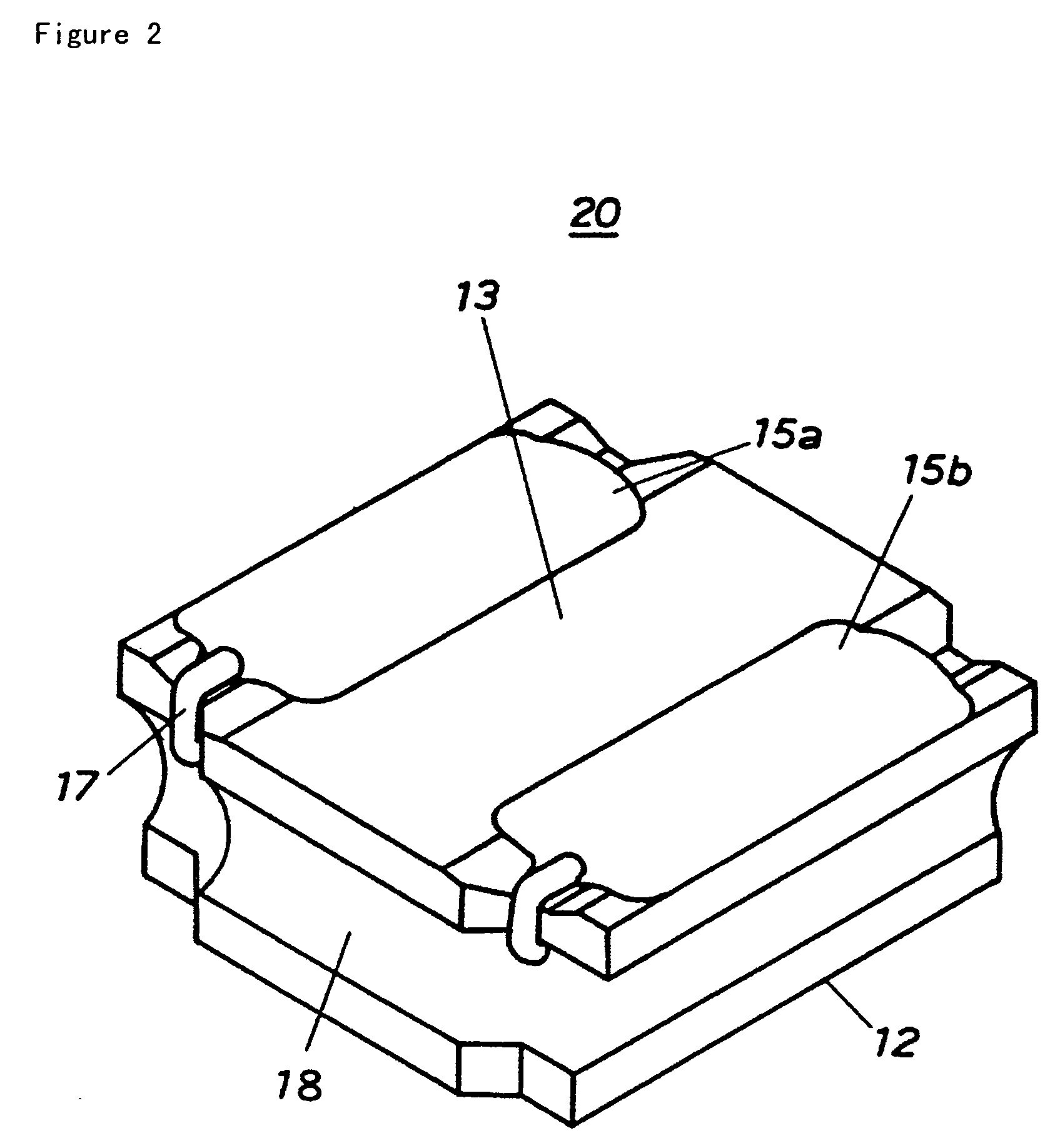
Surface-mounting coil component and method of producing the same
ActiveUS7209022B2Low costReduced durabilityTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsShear modulusSurface mounting
A surface-mounting choke coil has a resin coating material with magnetic powder which is filled a space between the upper flange and the lower flange of a drum-type ferrite core, while covering the circumferential of the winding. The resin coating material with magnetic powder has a glass transition temperature Tg of about −20° C. or lower, more preferably about −50° C. or lower in a course of transferring from a glass state to a rubber state during changing of shear modulus with respect to temperature as a physical property when hardening, and the thickness of the upper flange of the drum-type ferrite core is about 0.35 mm or less, and a value of a ratio L2 / L1 of an outer diameter L2 of the upper flange to a diameter L1 of the winding core of the drum-type ferrite core is about 1.9 or more.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
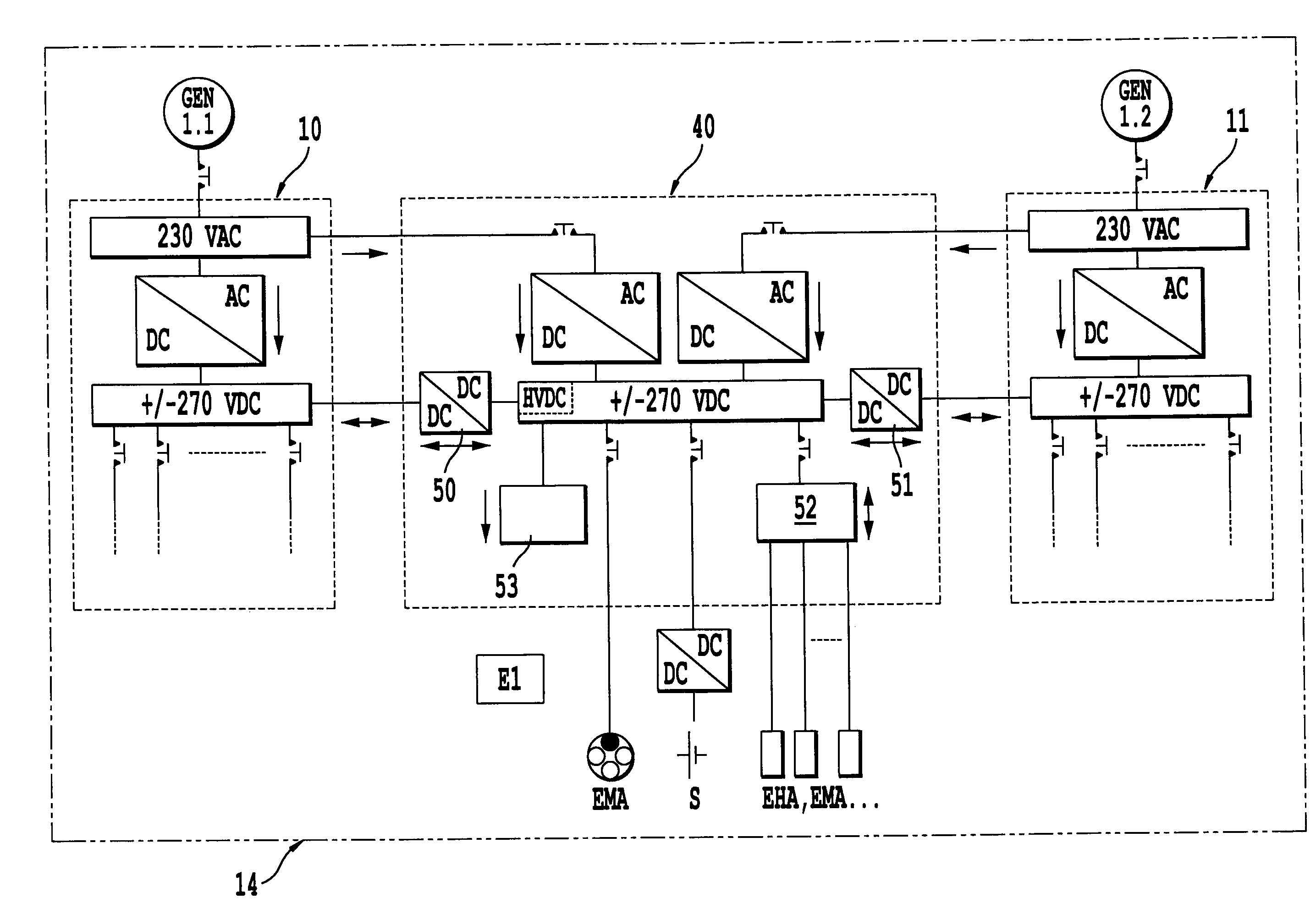
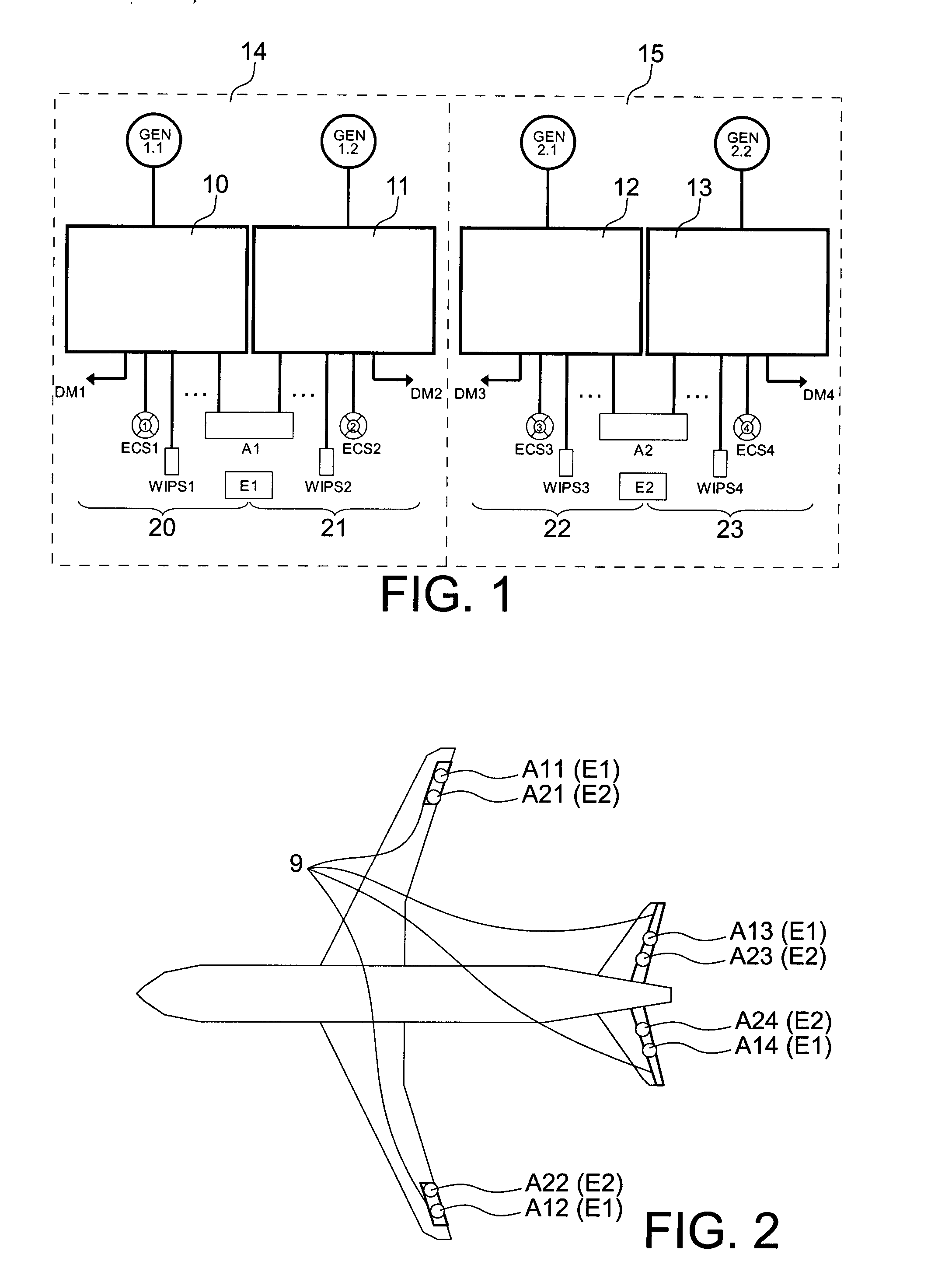
System and method for supplying power for actuators on board an aircraft
InactiveUS20080174177A1Consume energyReduce thermal stressBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric power distributionOn boardAlternating current
The invention relates to a system and a method for supplying power to an aircraft comprising several generators supplying alternating current to several different primary electrical master boxes (10, 11, 12 and 13), the various aircraft loads being connected to each of these master boxes. This system comprises conventional master boxes (10, 11, 12 and 13) which supply power loads and at least one master box (40, 41) devoted to actuator loads, this at least one devoted master box being connected to conventional master boxes.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
High-average power active mirror solid-state laser with multiple subapertures
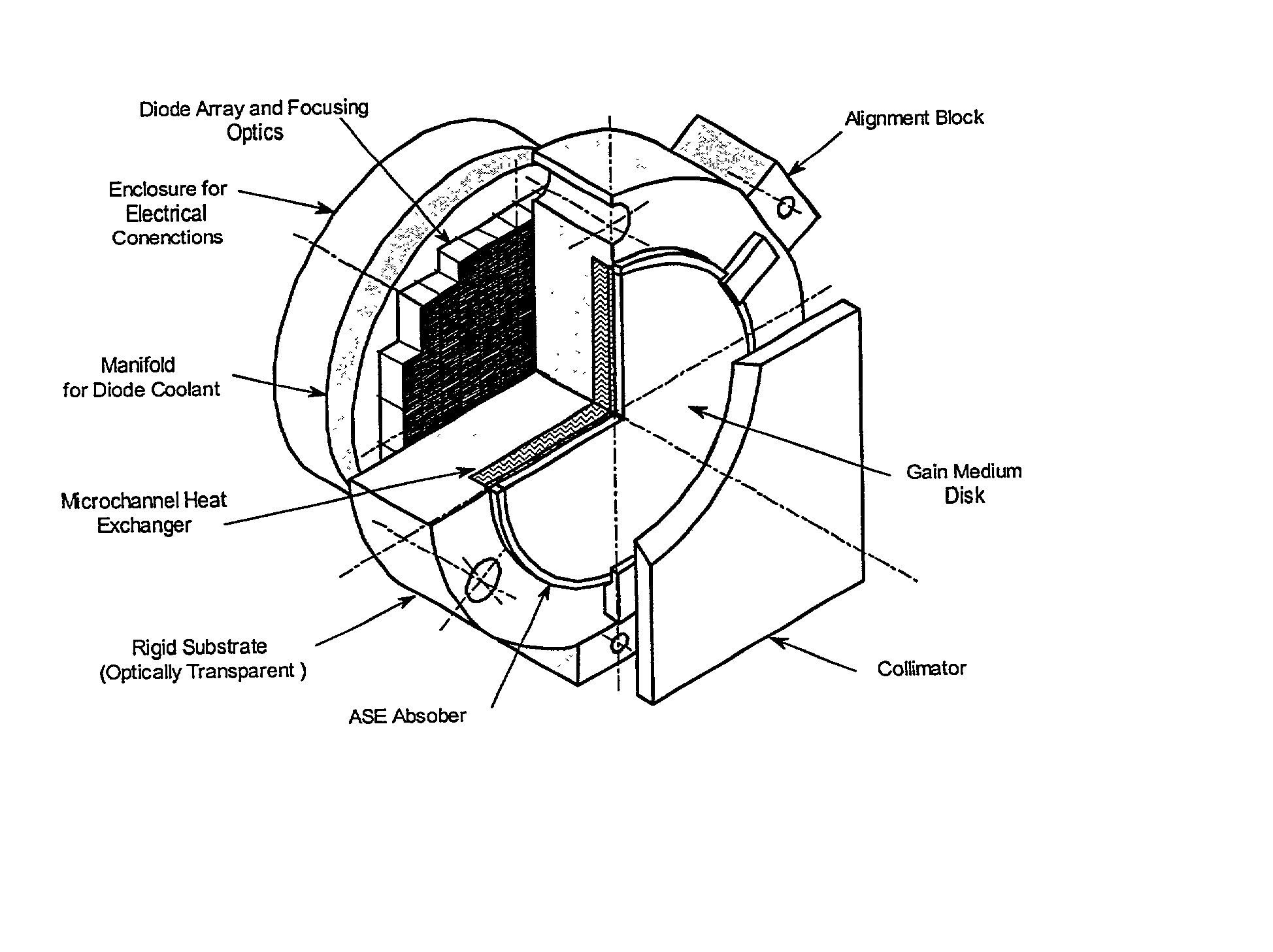
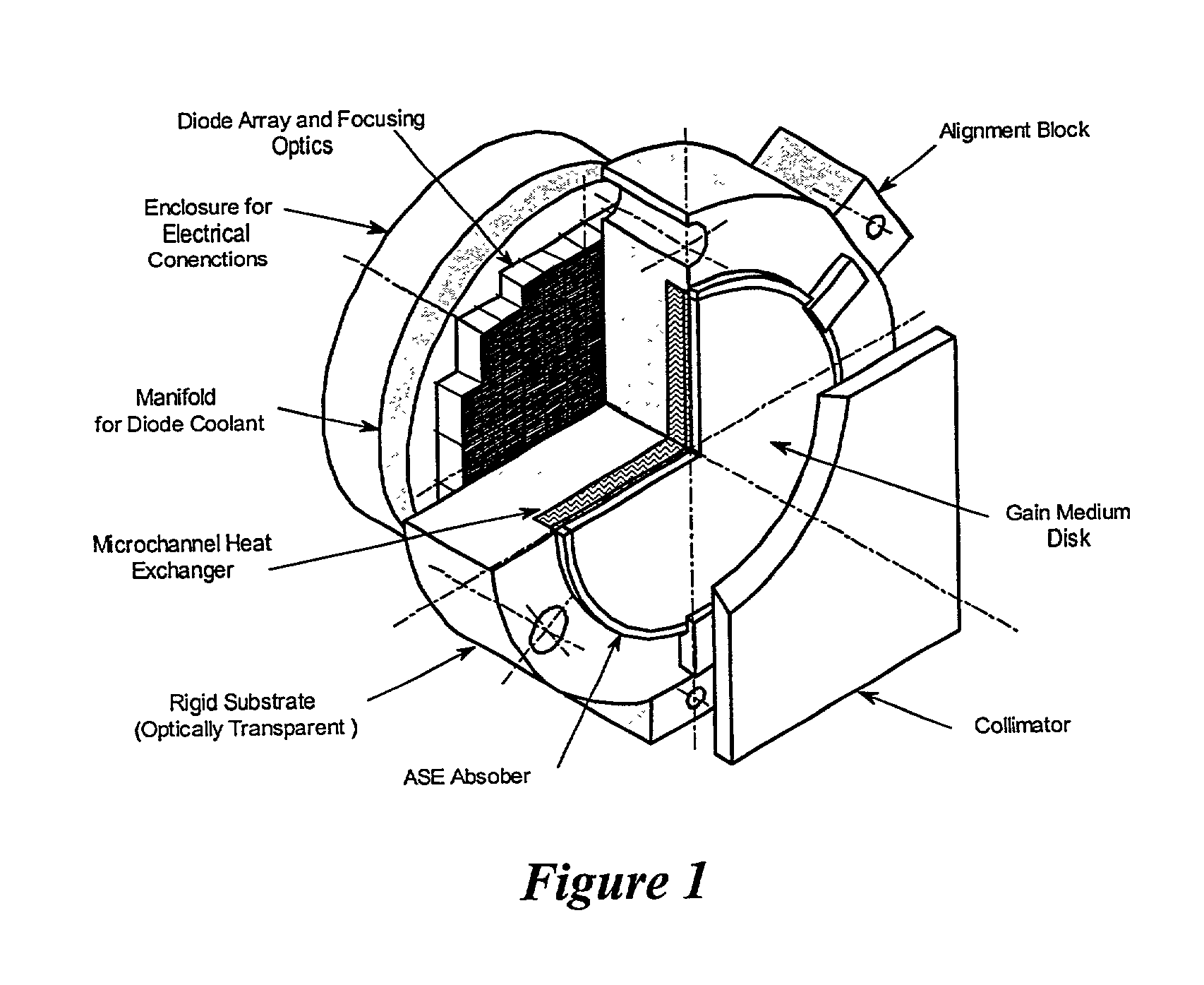
InactiveUS20020110164A1Precise positioningRelieve pressureActive medium materialActive medium shape and constructionOptical coatingHydrostatic pressure
An apparatus and method for achieving ultrahigh-power output from a solid-state laser. The solid-state laser of the subject invention uses multiple disk-shaped laser gain media (subapertures) placed adjacent to each other to fill an optical aperture of an AMA module. In one preferred embodiment each of the laser gain media is provided with optical coatings for operation in the active mirror configuration. Furthermore, each of the laser gain media is hydrostatic pressure-clamped to a rigid, cooled substrate, which allows it to maintain a prescribed shape even when experiencing significant thermal load. A cooling medium can be provided to a heat exchanger internal to the substrate and / or flowed through the passages on the substrate surface, thereby directly cooling the laser gain medium.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Fuse breakdown method adapted to semiconductor device
InactiveUS20070007621A1Increase distanceInhibit degassingTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsDevice materialEvaporation
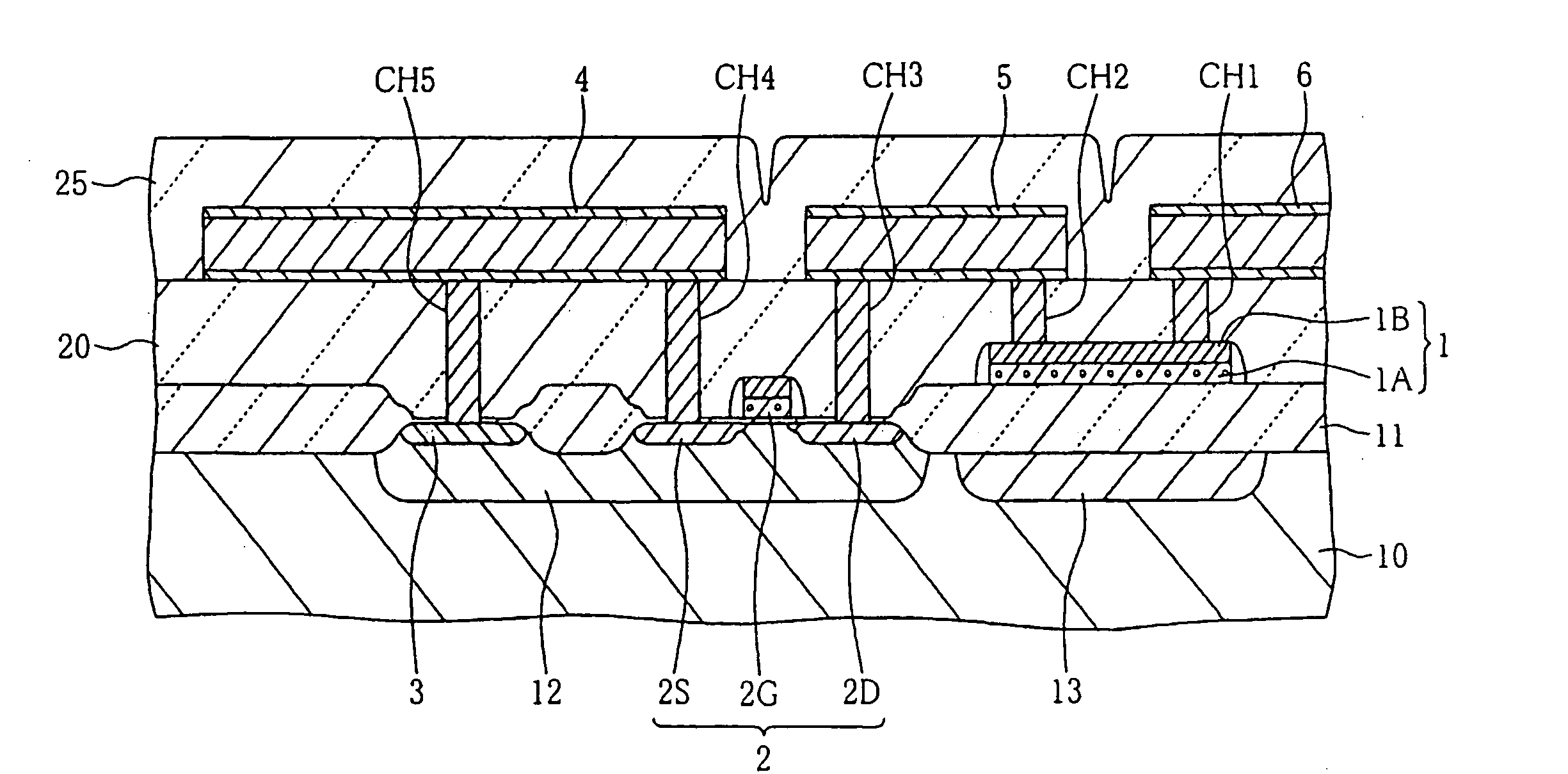
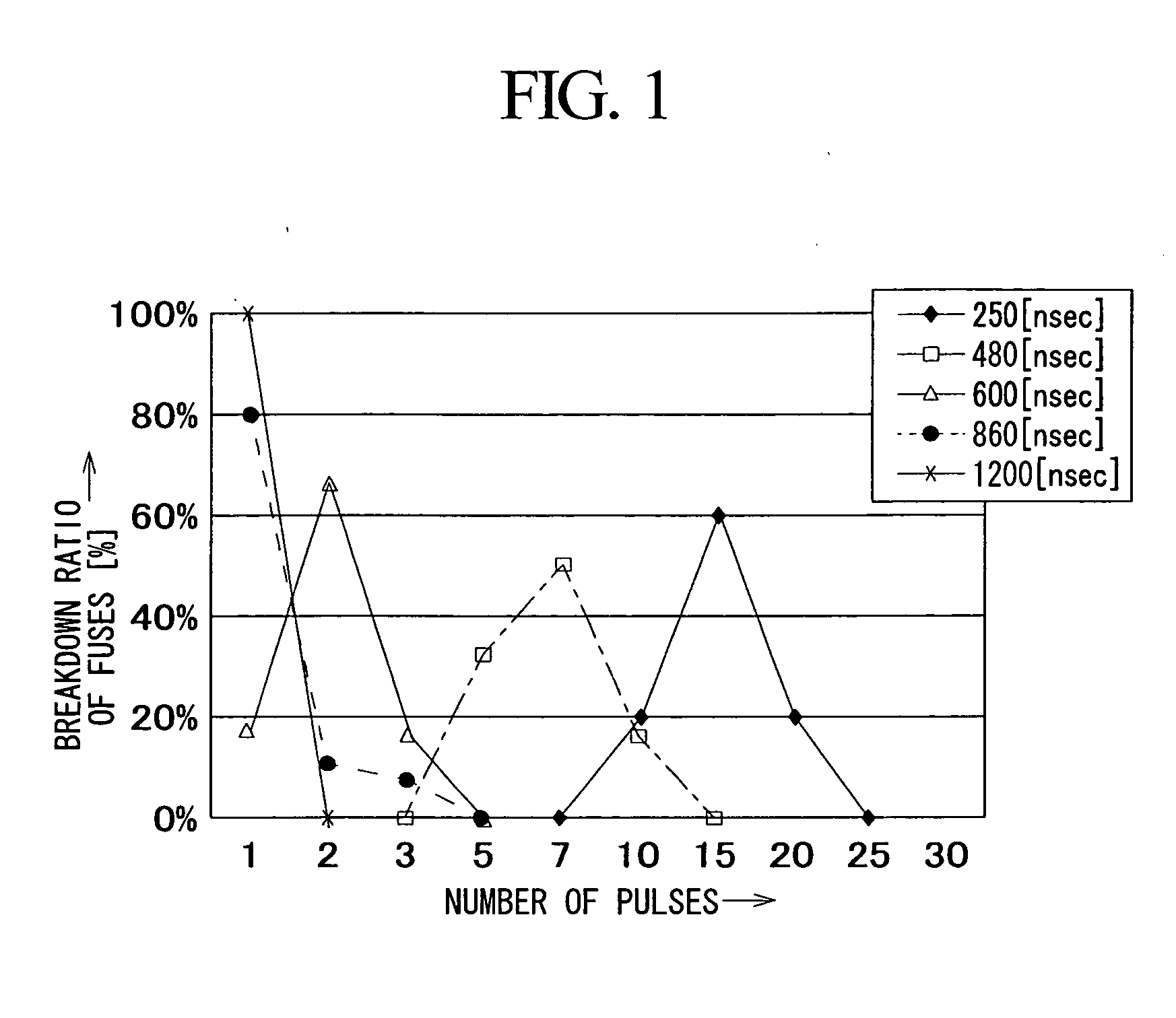
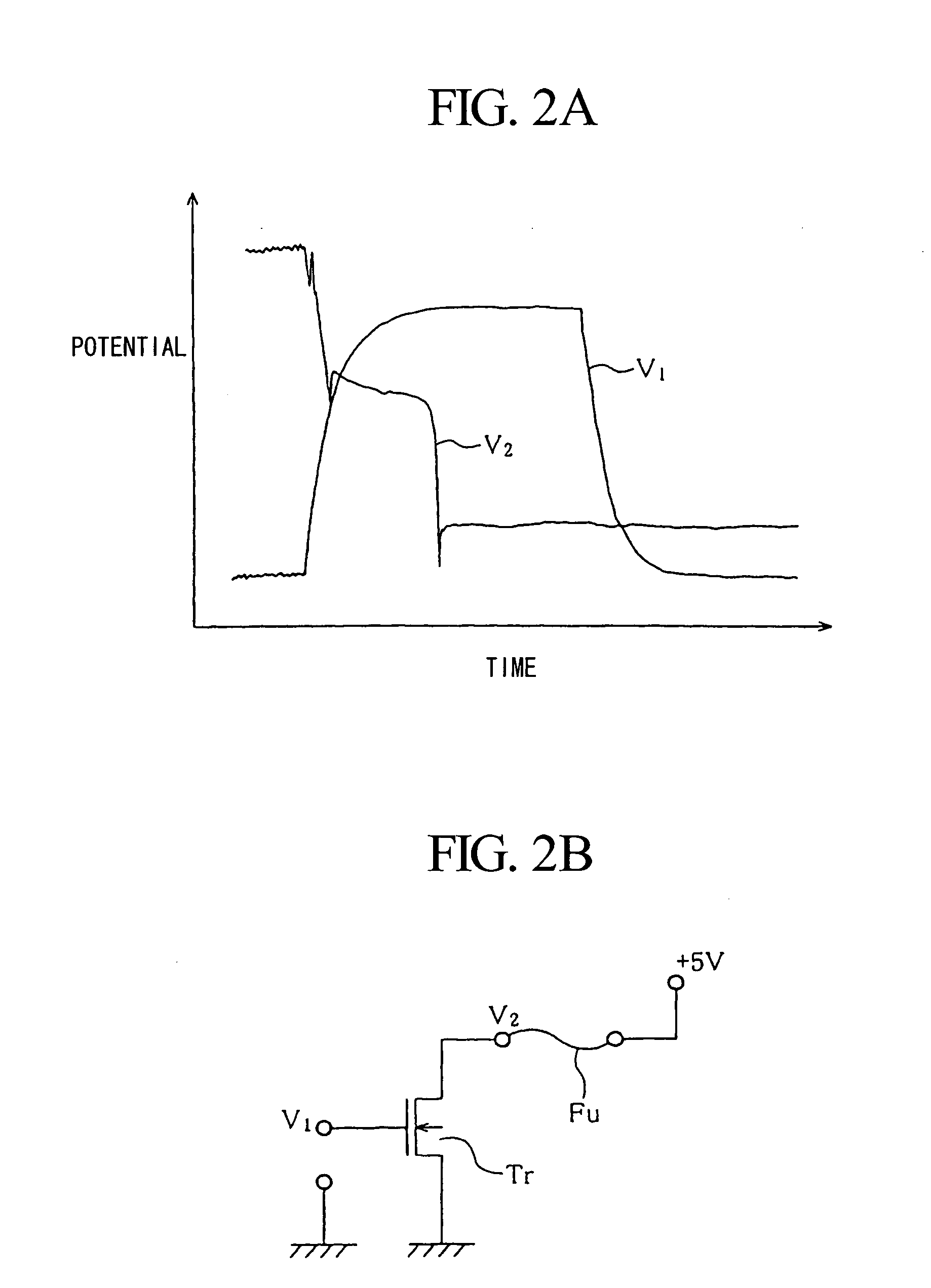
A plurality of pulses each having relatively low energy are consecutively applied to a subject fuse to cause breakdown, wherein the total energy of pulses is set in light of a prescribed breakdown threshold, which is calculated in advance. The subject fuse has a pair of terminals and an interconnection portion that is narrowly constricted in the middle so as to realize fuse breakdown with ease. A pulse generator generates pulses, which are repeatedly applied to the subject fuse by way of a transistor; then, it stops generating pulses upon detection of fuse breakdown. Side wall spacers are formed on side walls of fuses, which are processed in a tapered shape so as to reduce thermal stress applied to coating insulating films. In addition, pulse energy is appropriately determined so as to cause electro-migration in the subject fuse, which is thus increased in resistance without causing instantaneous meltdown or evaporation.
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
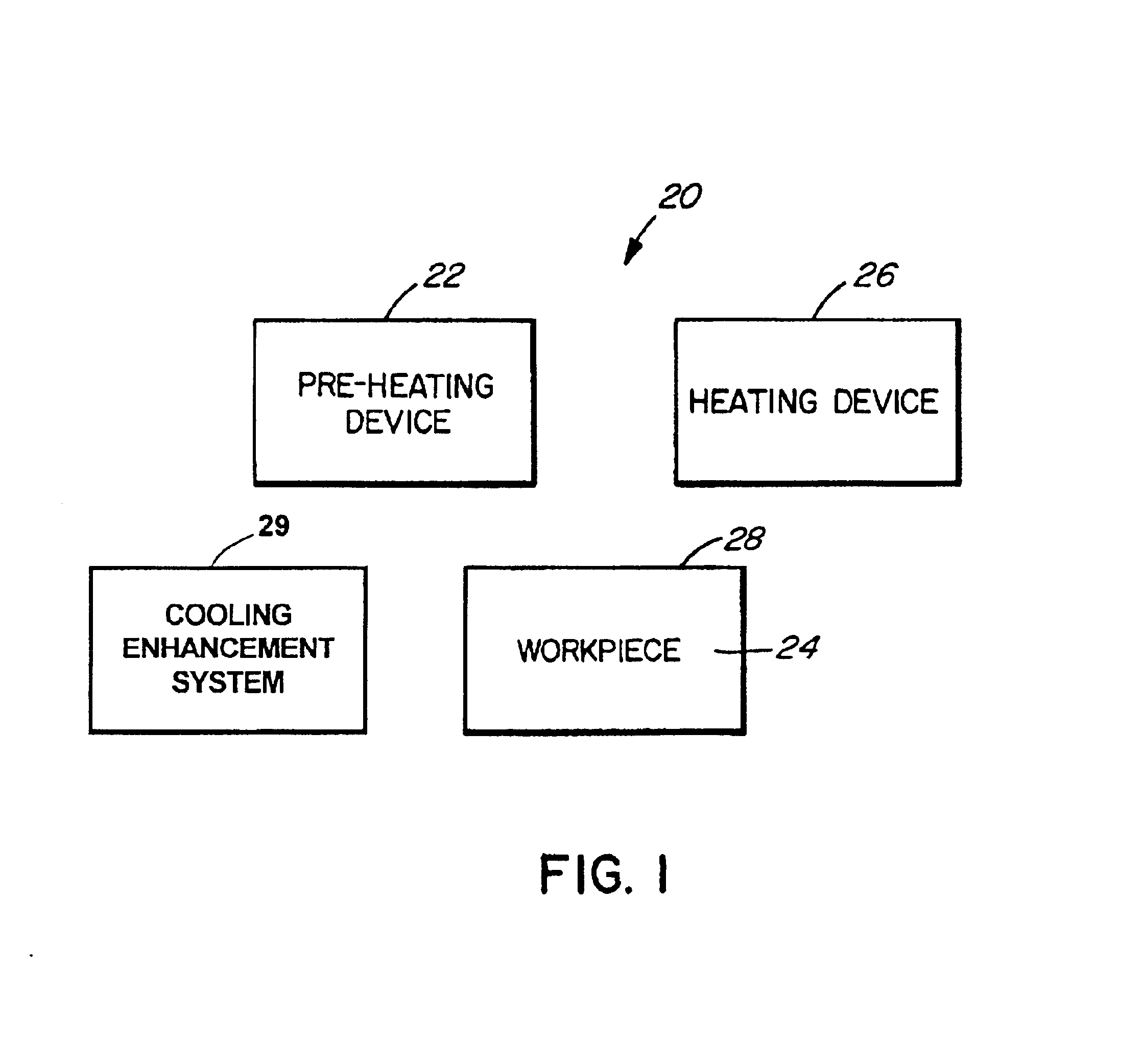
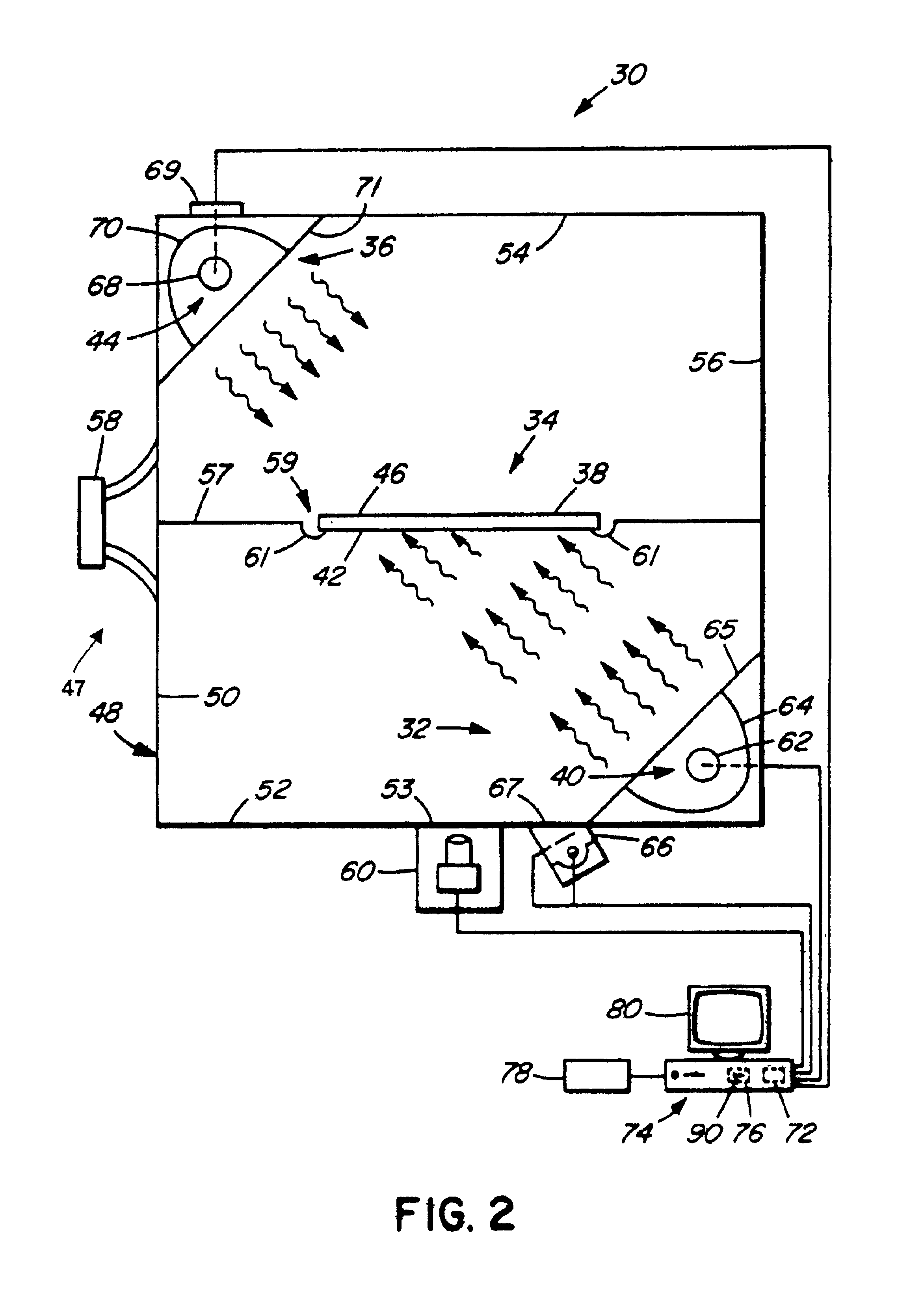
Heat-treating methods and systems
InactiveUS6941063B2Improve cooling effectWeakening rangeMechanical apparatusDrying solid materials with heatThermal radiationSemiconductor
A method involves pre-heating a workpiece to an intermediate temperature, heating a surface of the workpiece to a desired temperature greater than the intermediate temperature, and enhancing cooling of the workpiece. Enhancing cooling may involve absorbing radiation thermally emitted by the workpiece. An apparatus includes a first heating source for heating a first surface of a semiconductor wafer, a second heating source for heating a second surface of the semiconductor wafer, and a first cooled window disposed between the first heating source and the semiconductor wafer.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
Polyceramic e-chuck
ActiveUS20090002913A1Reduce thermal stressEasy to controlSleeve/socket jointsElectric discharge tubesCapacitanceDielectric layer
The present invention discloses an electrostatic chuck for clamping work substrates, said chuck comprising three layers, where the dielectric constant of included non-conductive layers is selected to provide overall lower capacitance to the chuck. In the chuck assembly of the present invention, the top dielectric layer that is in contact with a substrate, such as, for example, a wafer, has a dielectric constant that is preferably greater than about 5, with a resistivity that is preferably greater than about 1E6 ohm.m, whereas the bottom dielectric layer has a dielectric constant that is preferably less than about 5 and a resistivity that is preferably greater than about 1E10 ohm.m. The intermediate layer preferably has a conductive layer where the resistivity is less than about 1 ohm.m. The electrostatic chuck may be bonded to heat sinks coated with anti-arc dielectrics. The heat sink can also be used as an RF electrode. The heat sink may have provisions for coolants and gas channels to feed a cooling gas to the backside of a wafer. The heat sink may have feed thrus to power the segmented electrodes in the electrostatic chuck. The passages for the feed thrus, gas feed holes and lift pins may be lined with ceramics or polymers to prevent any discharge to the heat sink. The electrostatic chuck is for clamping work substrates like Si, GaAs, SiO2, etc. used in semiconductor tools.
Owner:FM INDS
Method and structure to prevent distortion and expansion of organic spacer layer for thin film transfer-join technology
InactiveUS6329609B1Cost-effective and reliableReduces distortion of and damage to and surface topographyPrinted circuit assemblingElectrically conductive connectionsContact padAdhesive
An electronic component structure assembly comprising a thin film structure bonded to a multilayer ceramic substrate (MLC) using solder connections and wherein a non-conductive, compliant spacer preferably with a layer of thermoplastic adhesive on each surface thereof is interposed between the underlying MLC carrier and overlying thin film structure. The spacer includes a pattern of through-holes which corresponds to opposing contact pads of the thin film structure and MLC. The contact pads of at least one of the thin film structure or MLC have posts (e.g., metallic) thereon and the posts extend partly into the spacer through-holes whereby the height of the posts are greater than the thickness of the adhesive. The posts of the MLC have solder bumps thereon. After reflow under pressure the thin film structure is electrically and mechanically connected to the MLC and the join method has been found to provide a reliable and cost-effective process. The joined components also have enhanced operating life.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com