Patents
Literature
11895 results about "Steam turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
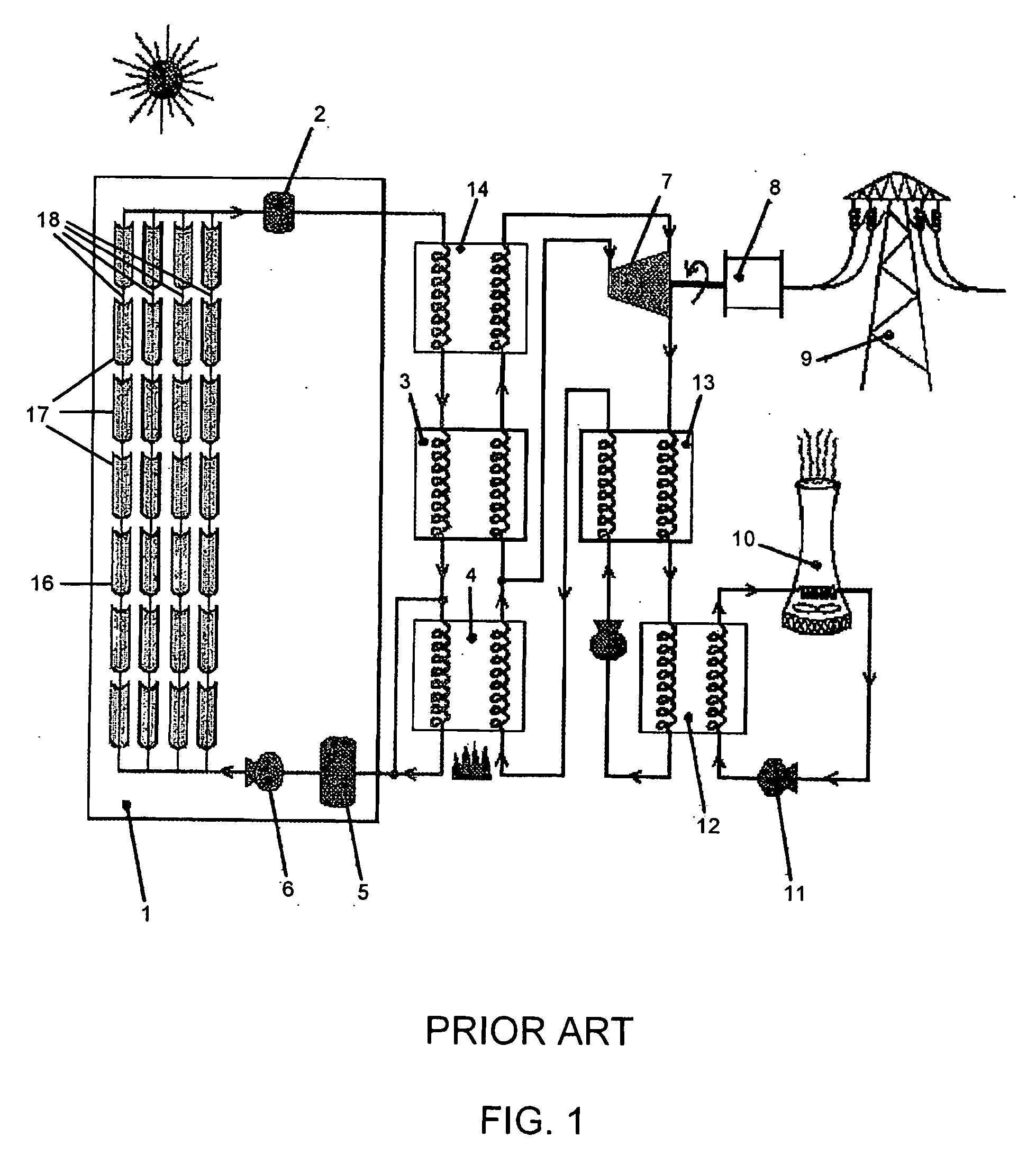
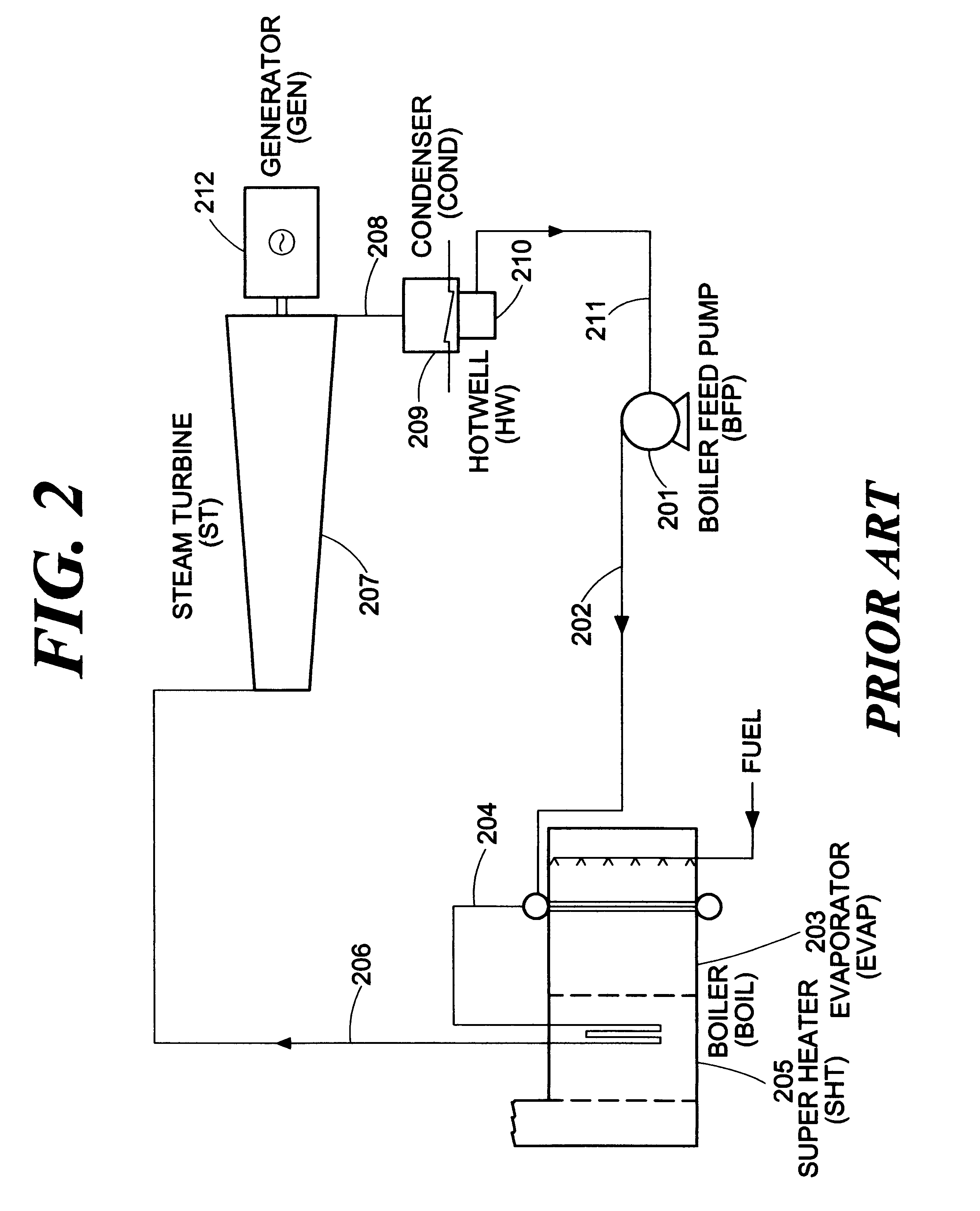
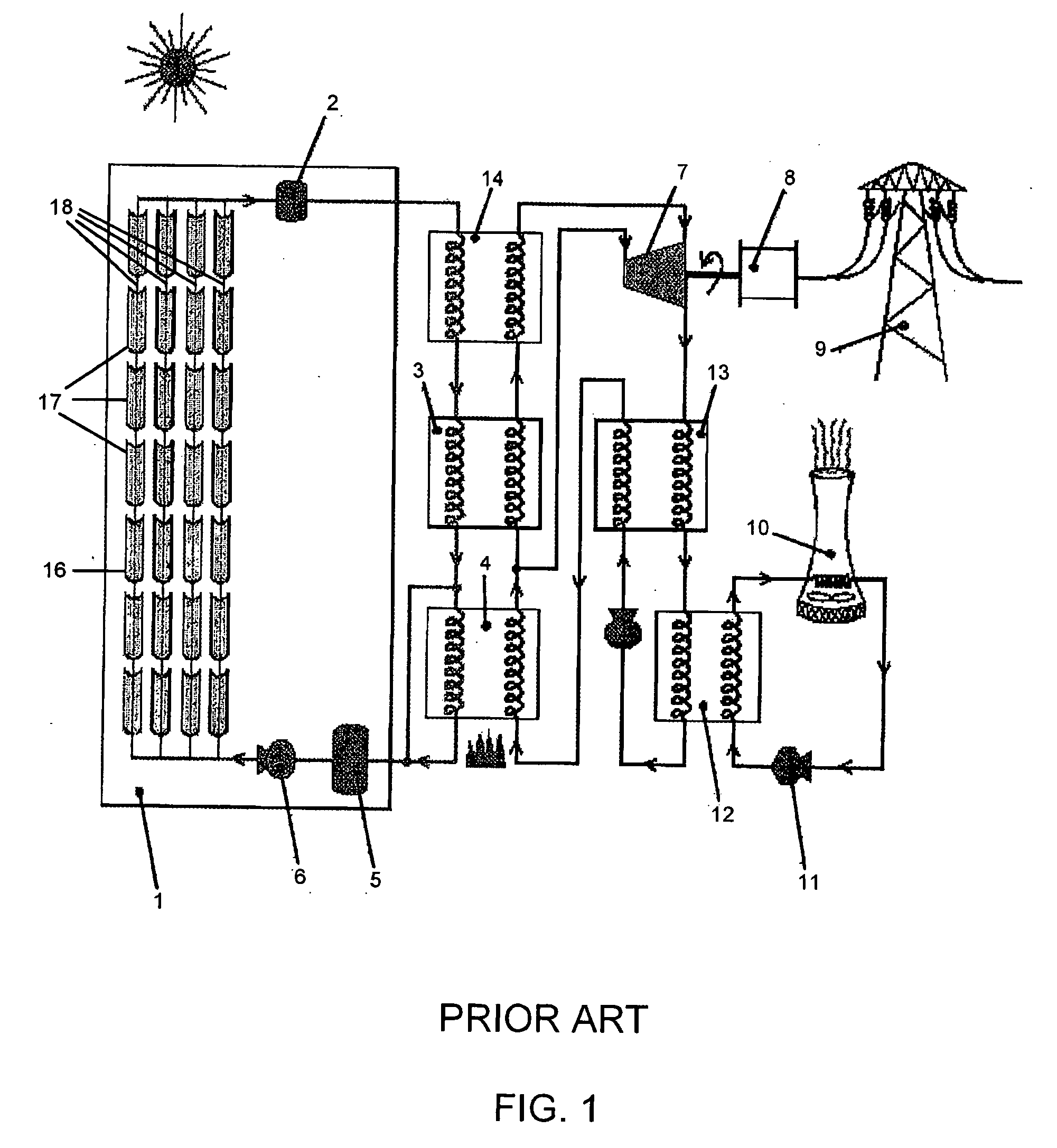
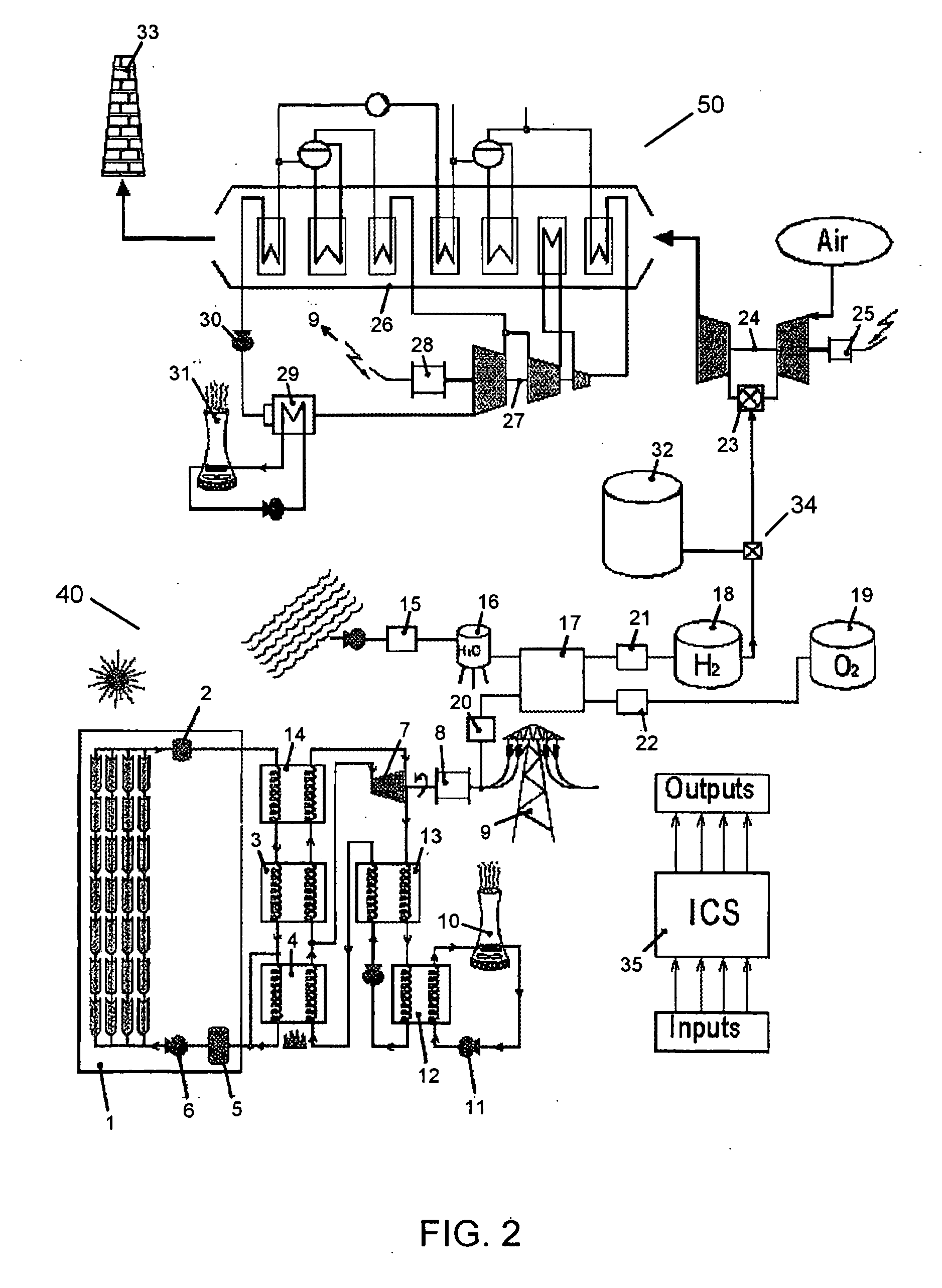
A steam turbine is a device that extracts thermal energy from pressurized steam and uses it to do mechanical work on a rotating output shaft. Its modern manifestation was invented by Charles Parsons in 1884.
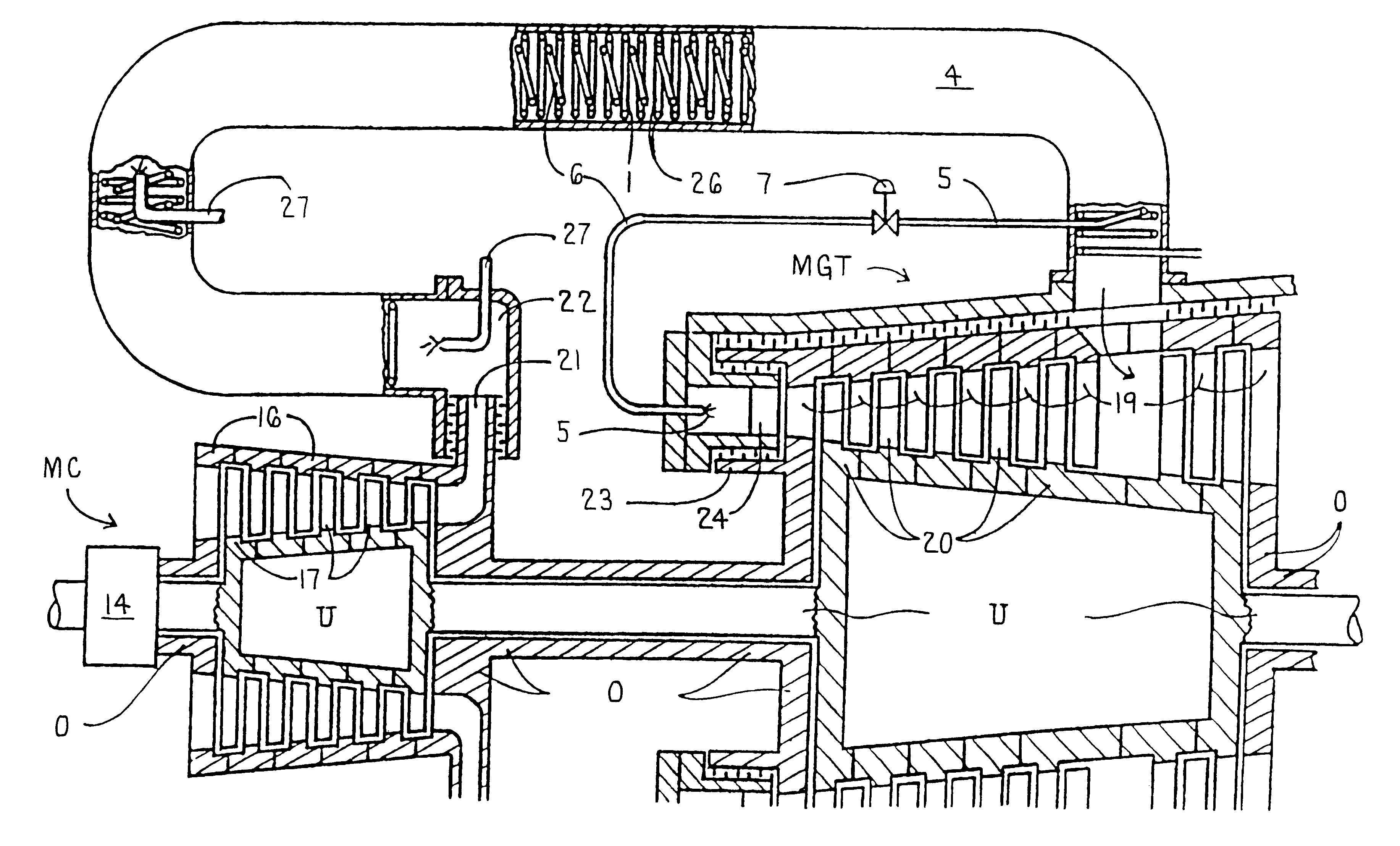
Combined steam and gas turbine engine with magnetic transmission
InactiveUS6263664B1Wide areaImprove system efficiencyContinuous combustion chamberGearingThermal energyCombustion chamber
In a combined steam and gas turbine engine cycle, a combustion chamber is made durable against high pressure and enlarged in length to increase the operation pressure ratio, without exceeding the heat durability temperature of the system while increasing the fuel combustion gas mass flow four times as much as the conventional turbine system and simultaneously for greatly raising the thermal efficiency of the system and specific power of the combined steam and gas turbine engine.Water pipes and steam pipes are arranged inside the combustion chamber so that the combustion chamber can function as a heat exchanger and thereby convert most of the combustion thermal energy into super-critical steam energy for driving a steam turbine and subsequently raising the operation pressure ratio and the thermal efficiencies of the steam turbine cycle and gas turbine cycle. The combustion gas mass flow can be also increased by four times as much as the conventional turbine system (up to the theoretical air to fuel ratio) and the thermal efficiency and the specific power of the gas turbine cycle are considerably increased.Further, the thermal efficiency of the combined system is improved by installing a magnetic friction power transmission system to transmit the power of the system to outer loads.
Owner:TANIGAWA HIROYASU +1
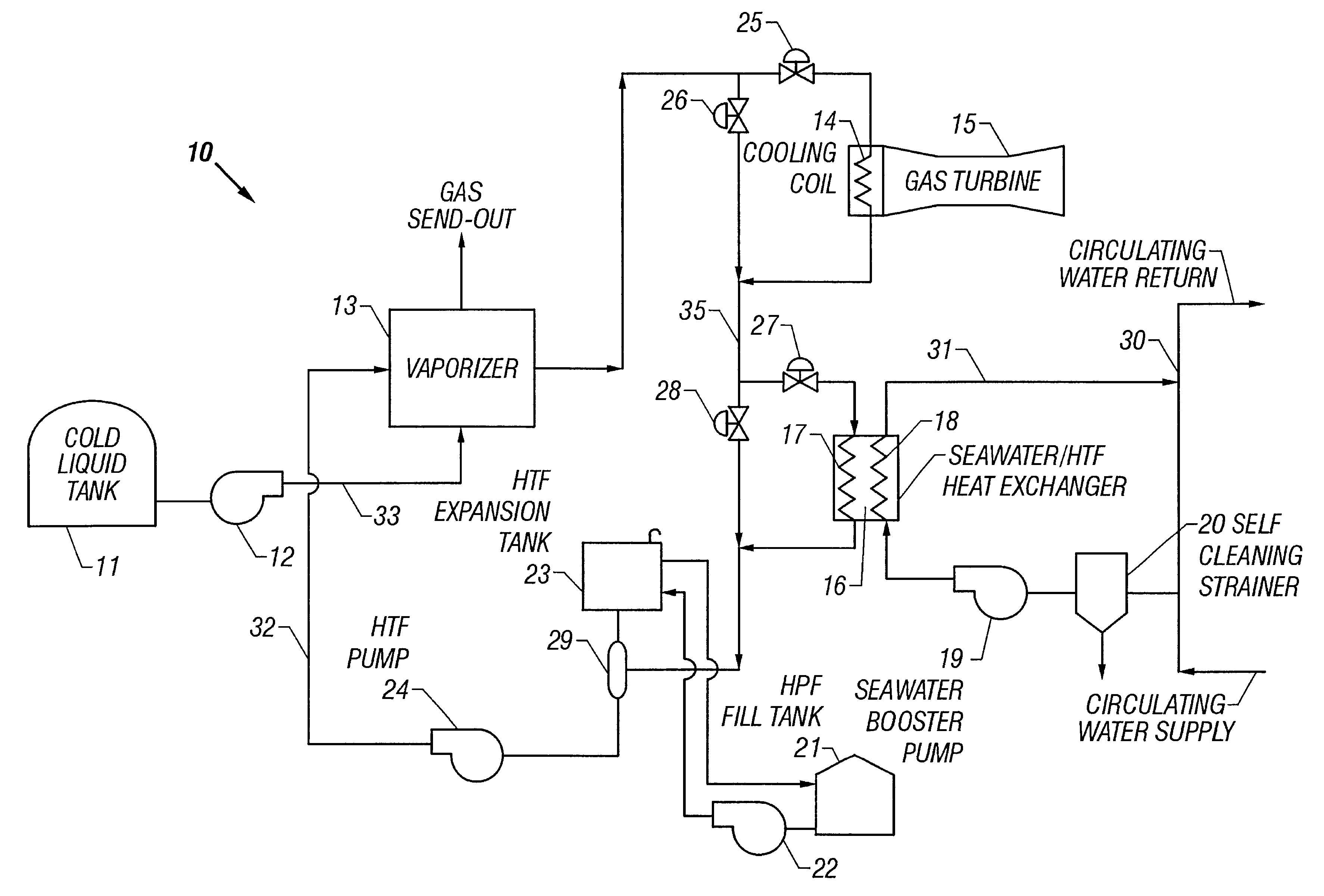
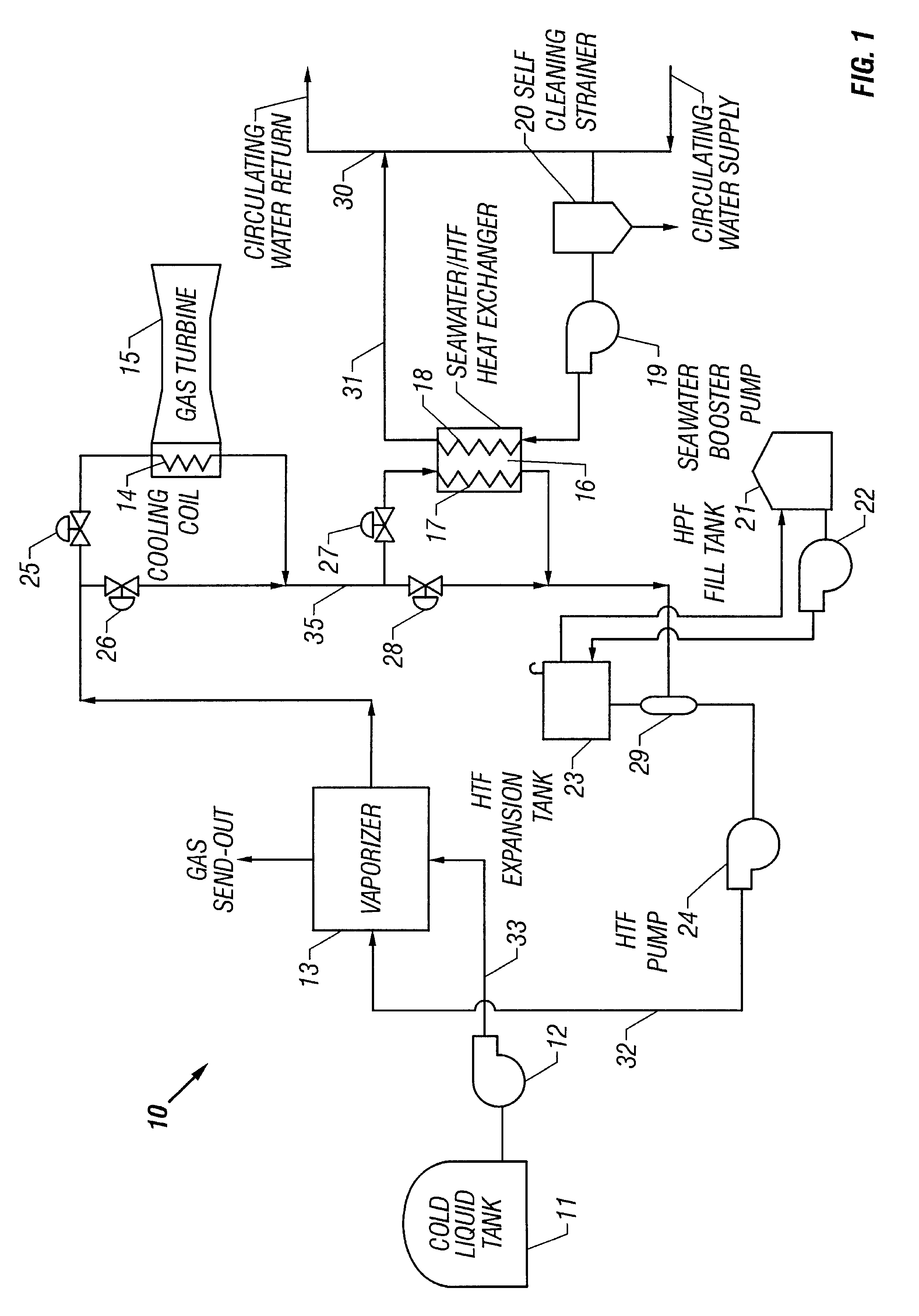
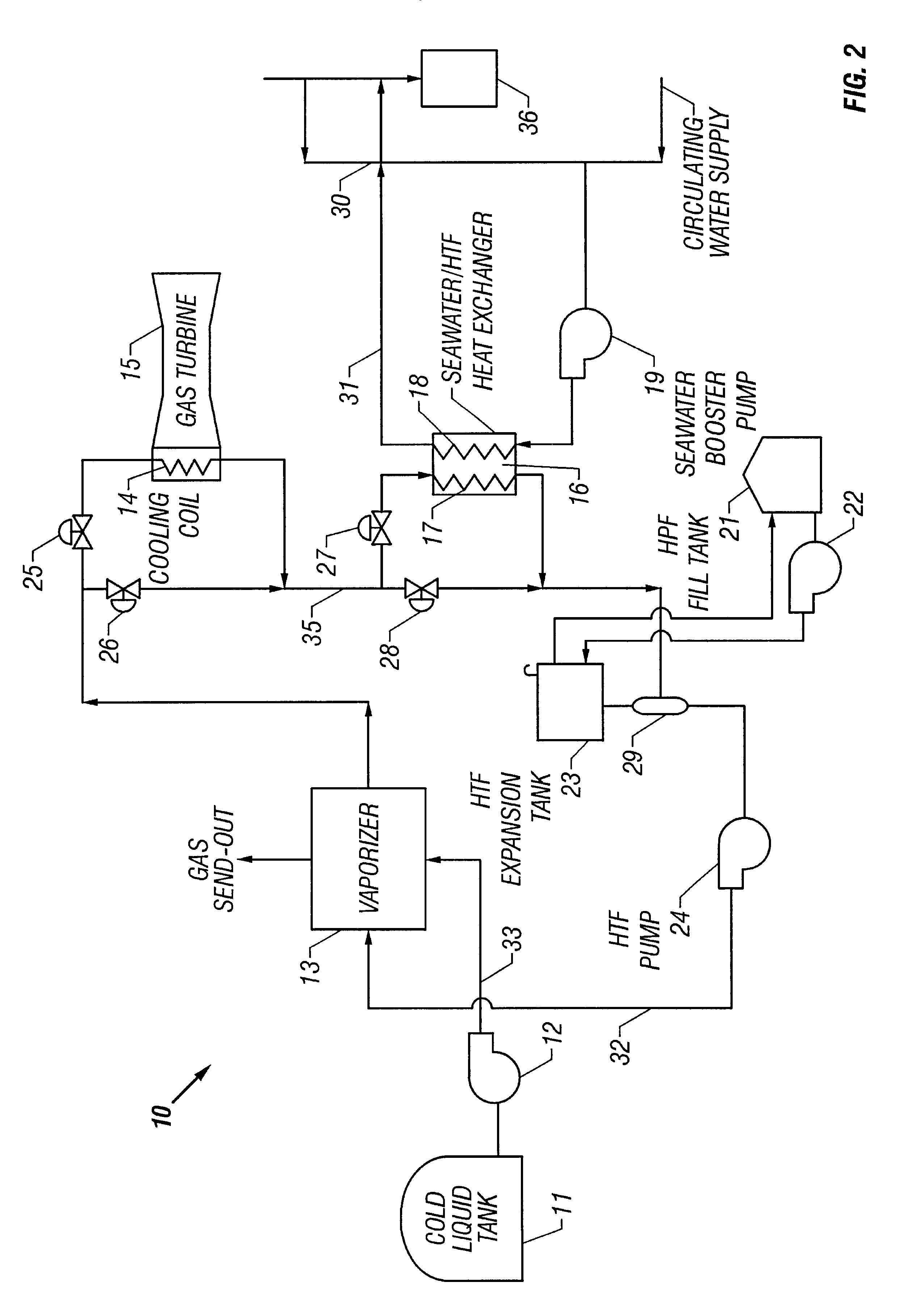
Method and apparatus for vaporizing liquid natural gas in a combined cycle power plant
InactiveUS6367258B1Turbine/propulsion engine coolingTurbine/propulsion fuel heatingPower stationProcess engineering
A method and apparatus for increasing the efficiency of a combined cycle generation plant by assisting the vaporization of cold liquid including liquefied natural gas ("LNG") or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) in a combined cycle power plant. Cold liquid vaporization is assisted by circulating a warm heat transfer fluid to transfer heat to a LNG / LPG vaporizer. The heat transfer fluid is chilled by LNG / LPG cold liquid vaporization and warmed by heat from a gas turbine. The heat transfer fluid absorbs heat from the air intake of a gas turbine and from a secondary heat transfer fluid circulating in a combined cycle power plant. Chilling the gas turbine air intake densifies the air and increases the gas turbine output. Chilling the steam condenser cooling water increases steam turbine output. The effects of chill recovery is higher output and better efficiency of the combined cycle plant.
Owner:BECHTEL CORP
Reforming system for combined cycle plant with partial CO2 capture
A combined cycle system includes, a pre-steam-methane-reformer operating at a temperature of less than about 800 degrees Celsius to reform a mixed fuel stream to generate a first reformate stream, a water-gas-shift reactor to convert carbon monoxide in the first reformate stream to carbon dioxide and form a second reformate stream, a carbon dioxide removal unit for removing carbon dioxide from the second reformate stream and form a carbon dioxide stream and a third reformate stream; wherein less than about 50 percent of the carbon contained in the mixed fuel stream is recovered as carbon dioxide by the removal unit, a gas turbine unit for generating power and an exhaust stream, and a steam generator unit configured to receive the exhaust stream, wherein the heat of the exhaust stream is transferred to a water stream to generate the steam for the mixed fuel stream and for a steam turbine.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
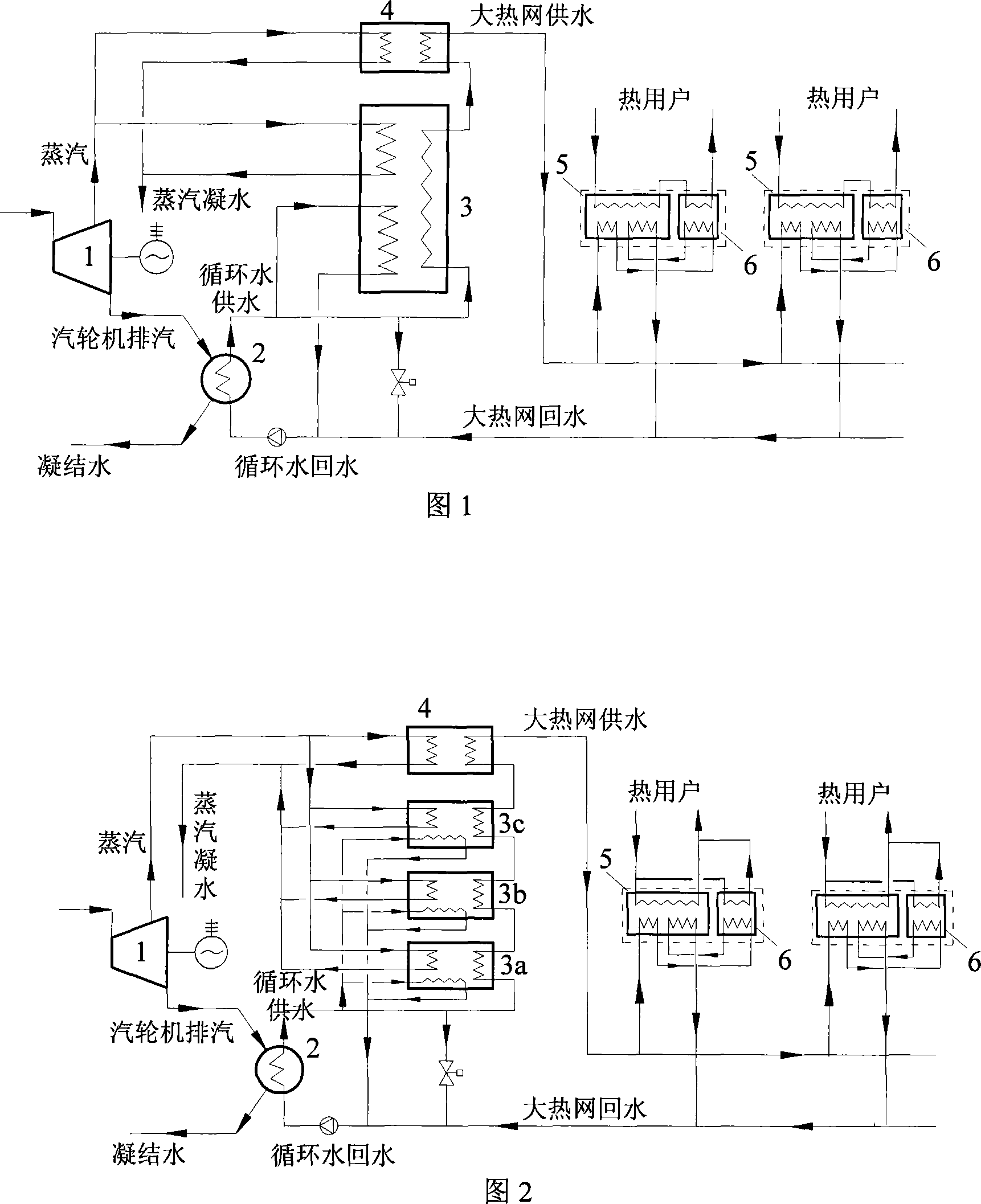
Method for recovering waste heat of thermal power plant and heating and supplying heat to hot water in a stepping way
ActiveCN101619662AImprove utilization efficiencyReduce exergy lossSteam useCombined combustion mitigationCooling towerSteam condensation
The invention discloses a method for recovering the waste heat of a thermal power plant and heating and supplying heat to hot water in a stepping way. In the method, low-temperature heat-net return water is firstly mixed with circulating cooling water positioned on an outlet of a cooling condenser or exchanges heat with the circulating cooling water positioned on the outlet of the cooling condenser to be increased in temperature and then sequentially delivered into an each-step vapour absorption type heat pump and a vapor-water heat exchanger in a series connection way to be gradually heated to be increased in temperature to heat supplying temperature and finally discharged through a water supplying pipeline; the circulating cooling water absorbs the waste steam condensation heat of a steam turbine in the cooling condenser, then one path of the circulating cooling water is directly mixed with the low-temperature heat-net return water or heats the low-temperature heat-net return water through the heat changer, the other path of the circulating cooling water is delivered into an each-step absorption type heat pump unit to be used as a low-order heat source of the absorption type heat pump unit, and the redundant heat of the circulating cooling water is discharged to the environment through a cooling tower. The invention uses the steam extraction of the steam turbine as a driving heat source of the absorption type heat pump so that the low-temperature heat-net return water is heated in a stepping way, thereby reducing the effective energy loss; the waste heat of the discharged steam of the steam turbine is sufficiently recovered in a direct heating way and an absorption type heat pump temperature increasing heating way, therefore, the comprehensive energy usage efficiency of the thermal power plant is enhanced.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Hybrid Generation with Alternative Fuel Sources
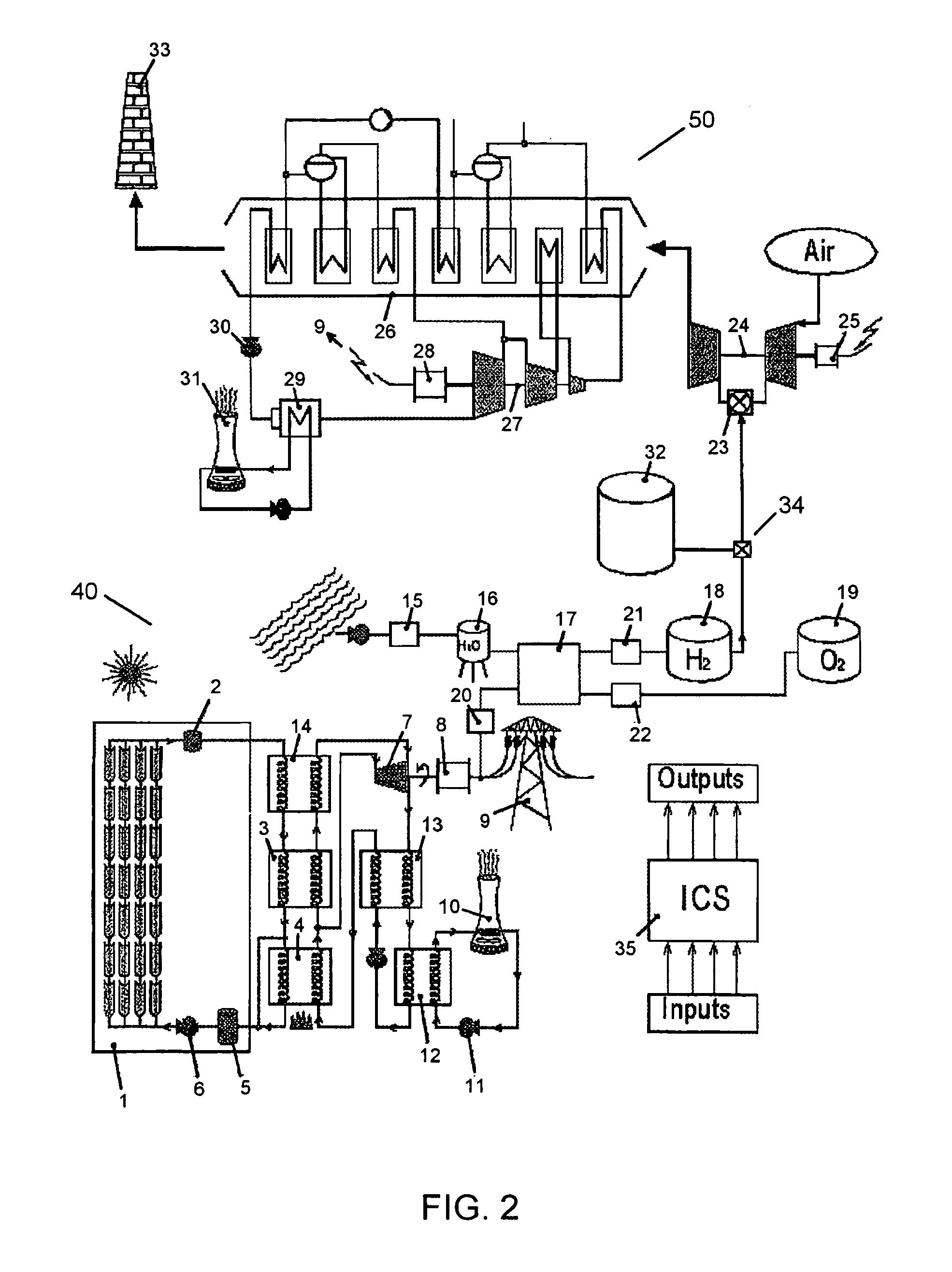
InactiveUS20070157614A1Increase rangeIncreasing total rated powerSolar heating energyAuxillary drivesElectricityAlternative fuels
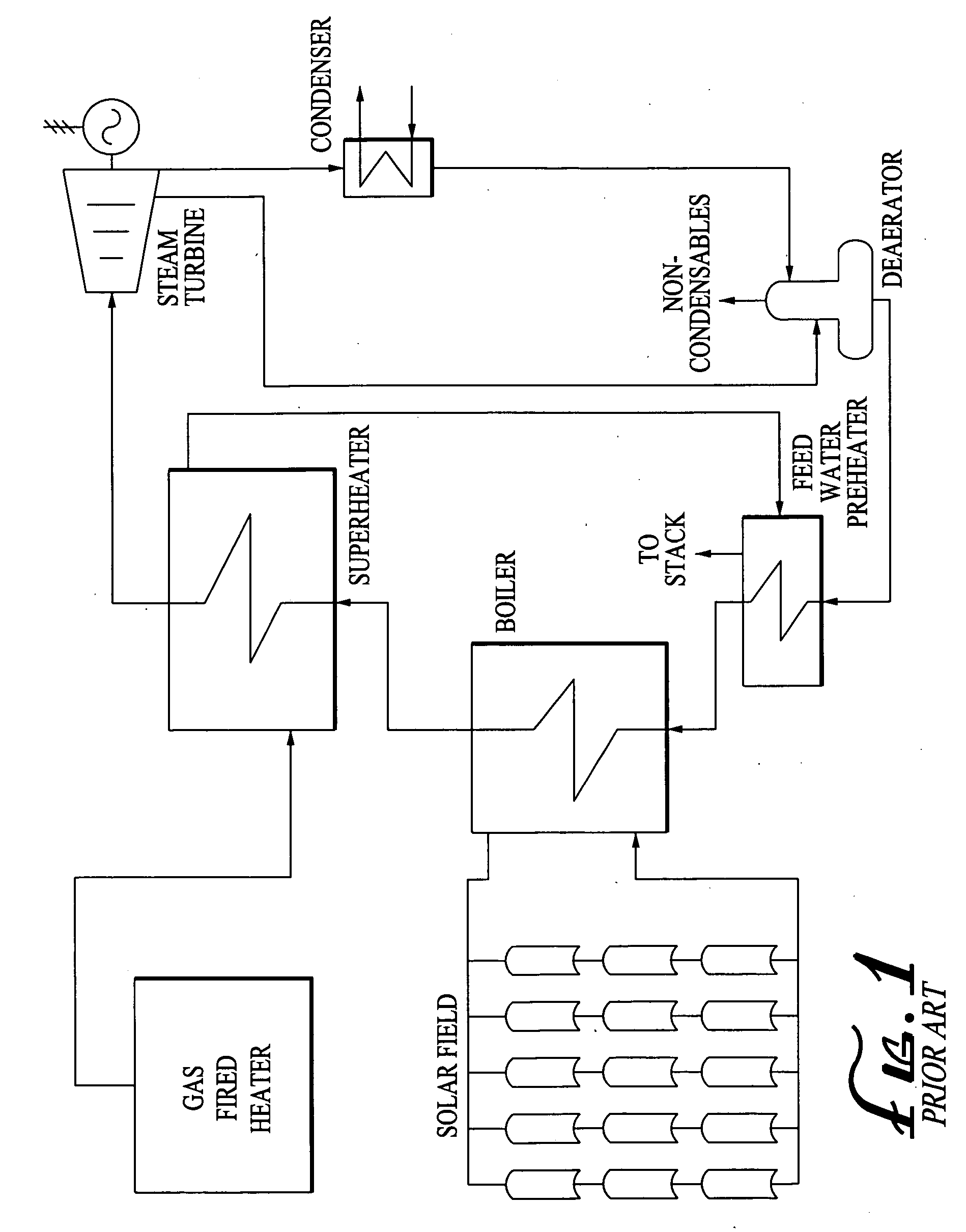
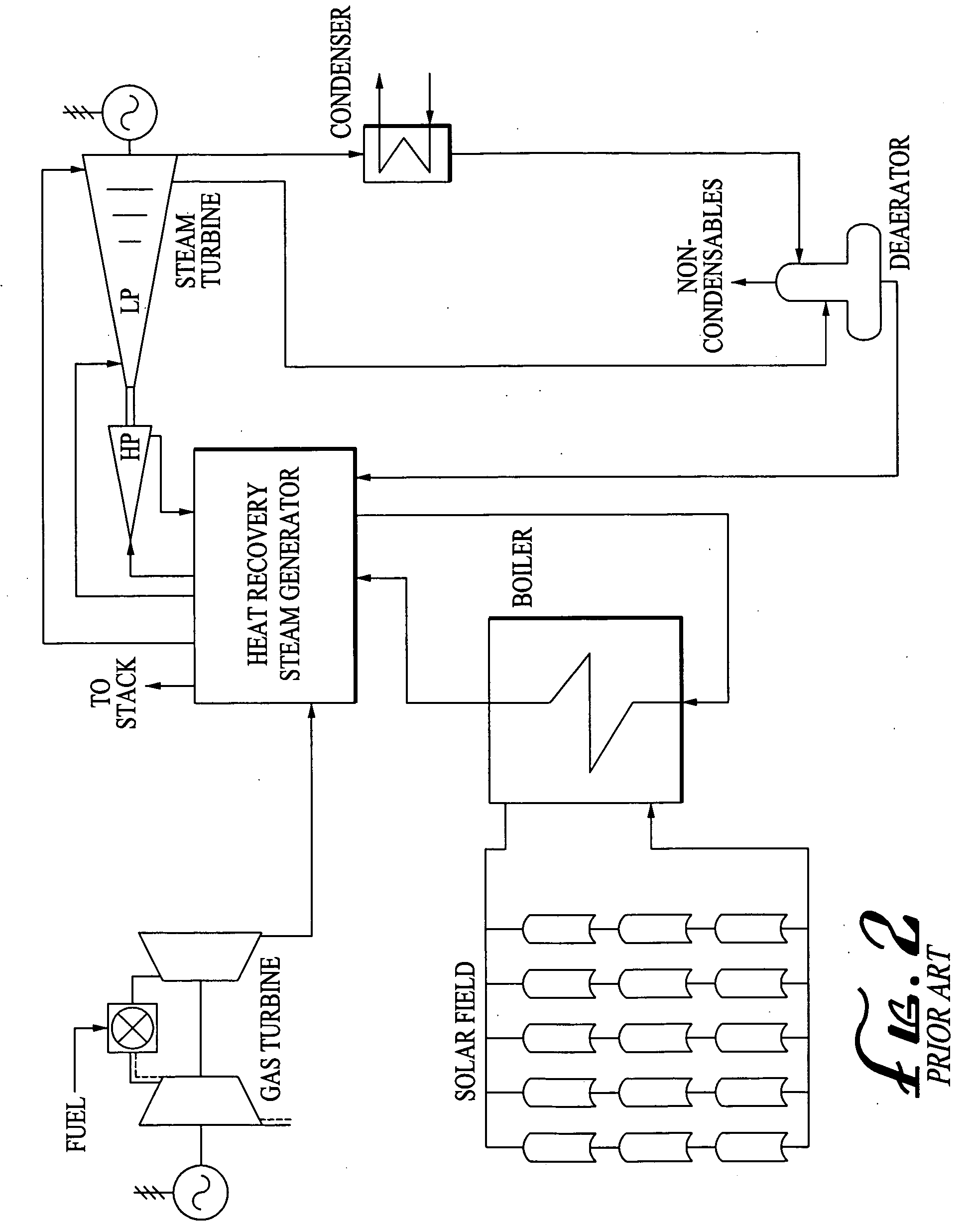
A generating facility is provided for generating electricity from both solar and non-solar energy sources. The solar generating portion of the facility includes capability to directly generate electricity from solar insolation, or to store the solar energy in a tangible medium, including stored heat, or solar generating fuel. The generating facility is configured to generate electricity simultaneously from both solar and non-solar sources, as well a solely from immediate solar insolation and from solar energy stored in a tangible medium. Additionally, the solar generating capacity may be segregated; such that separate spectra of solar insolation are used to capture heat for steam turbine based electrical generation, capture light energy for photovoltaic based electrical generation, and to grow biomass to generate a solar fuel.
Owner:BRIGHTSOURCE ENERGY
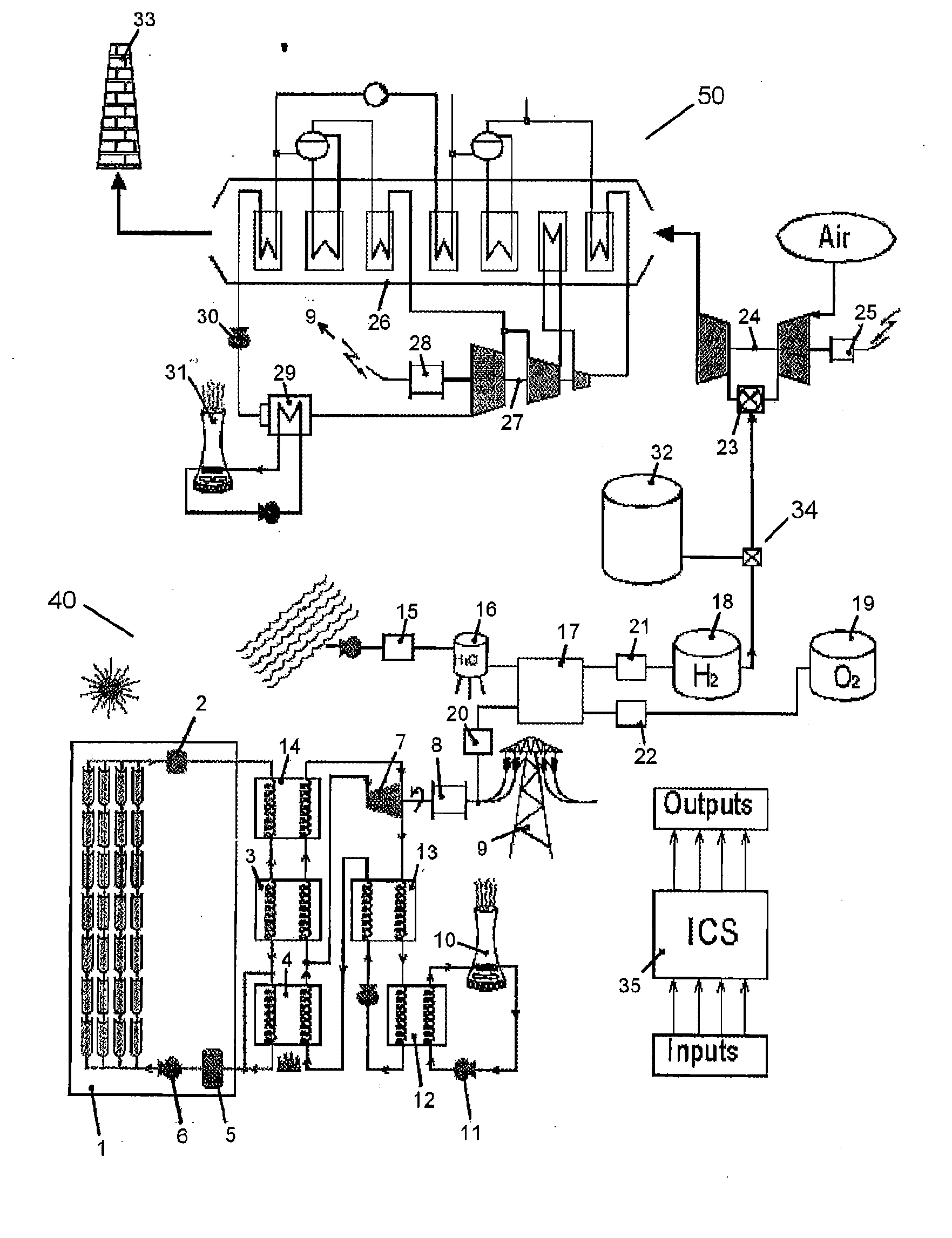
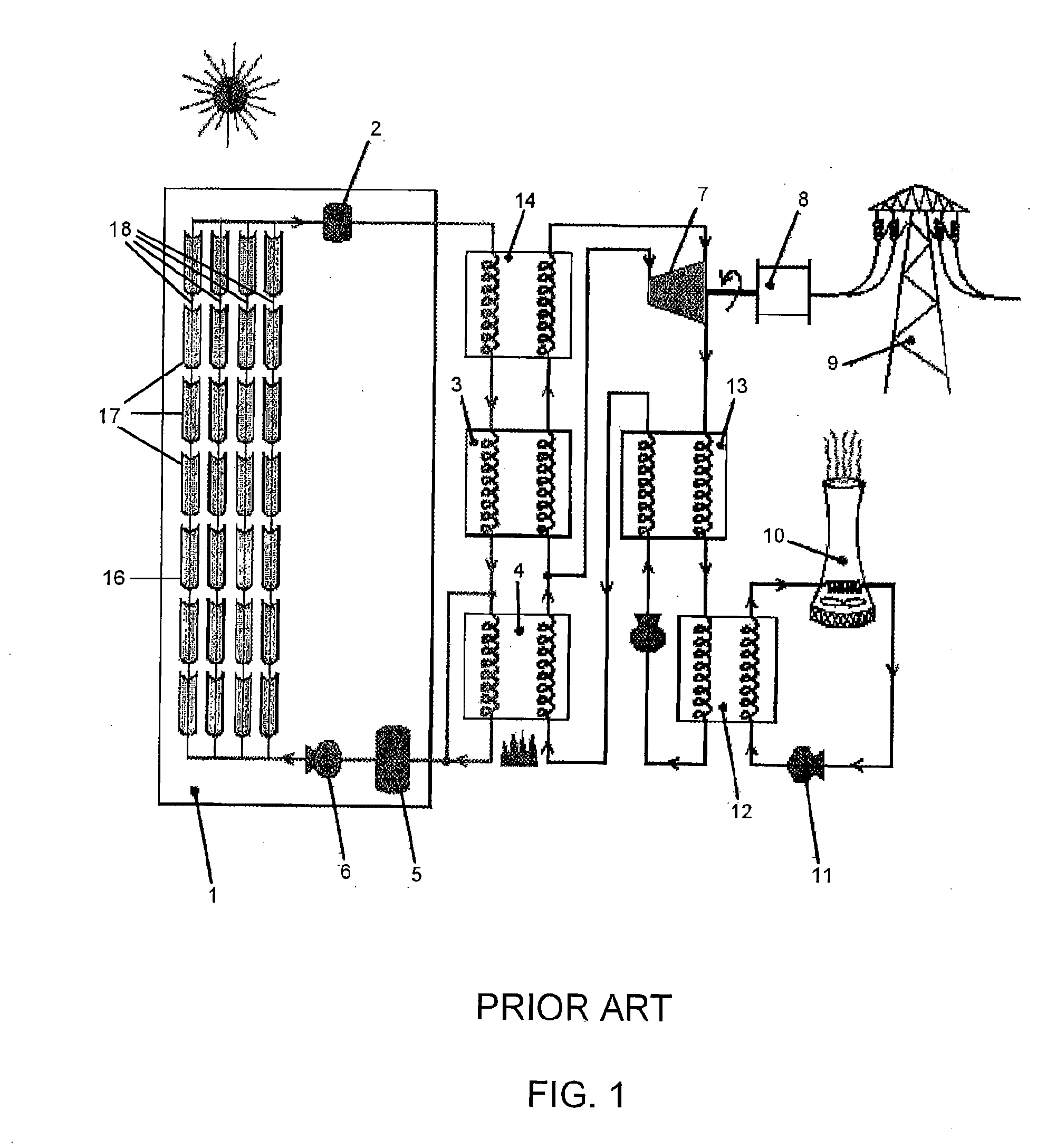
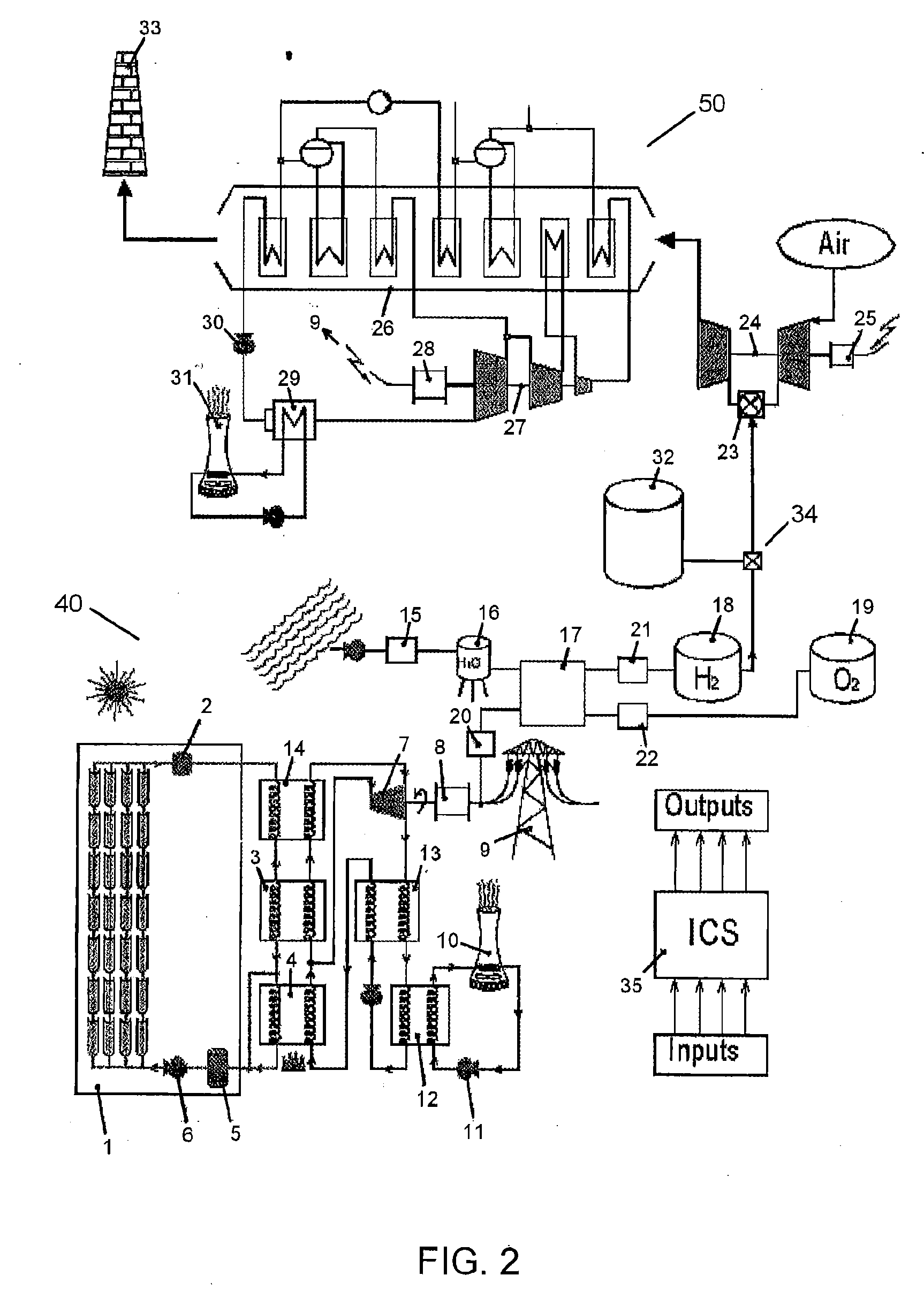
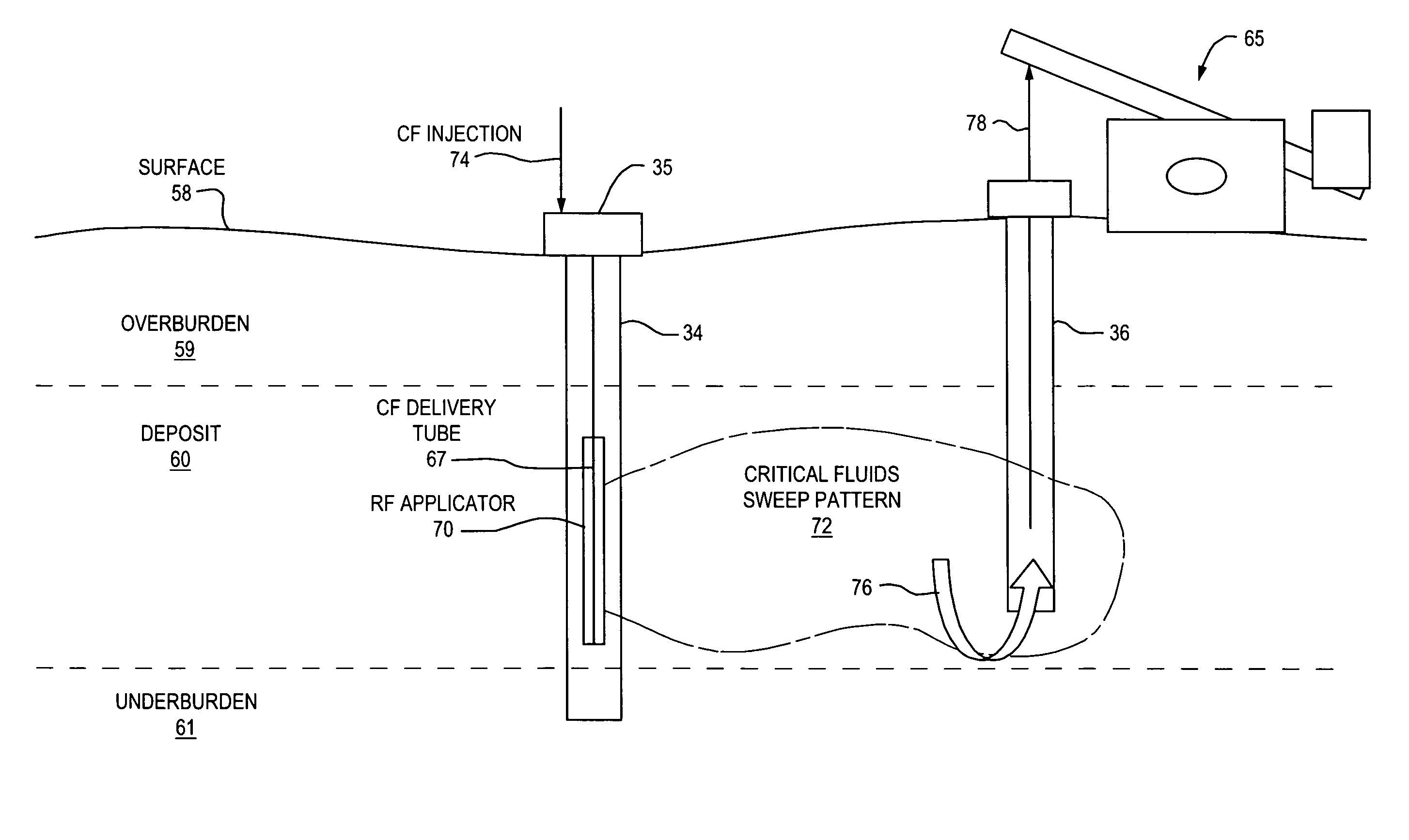
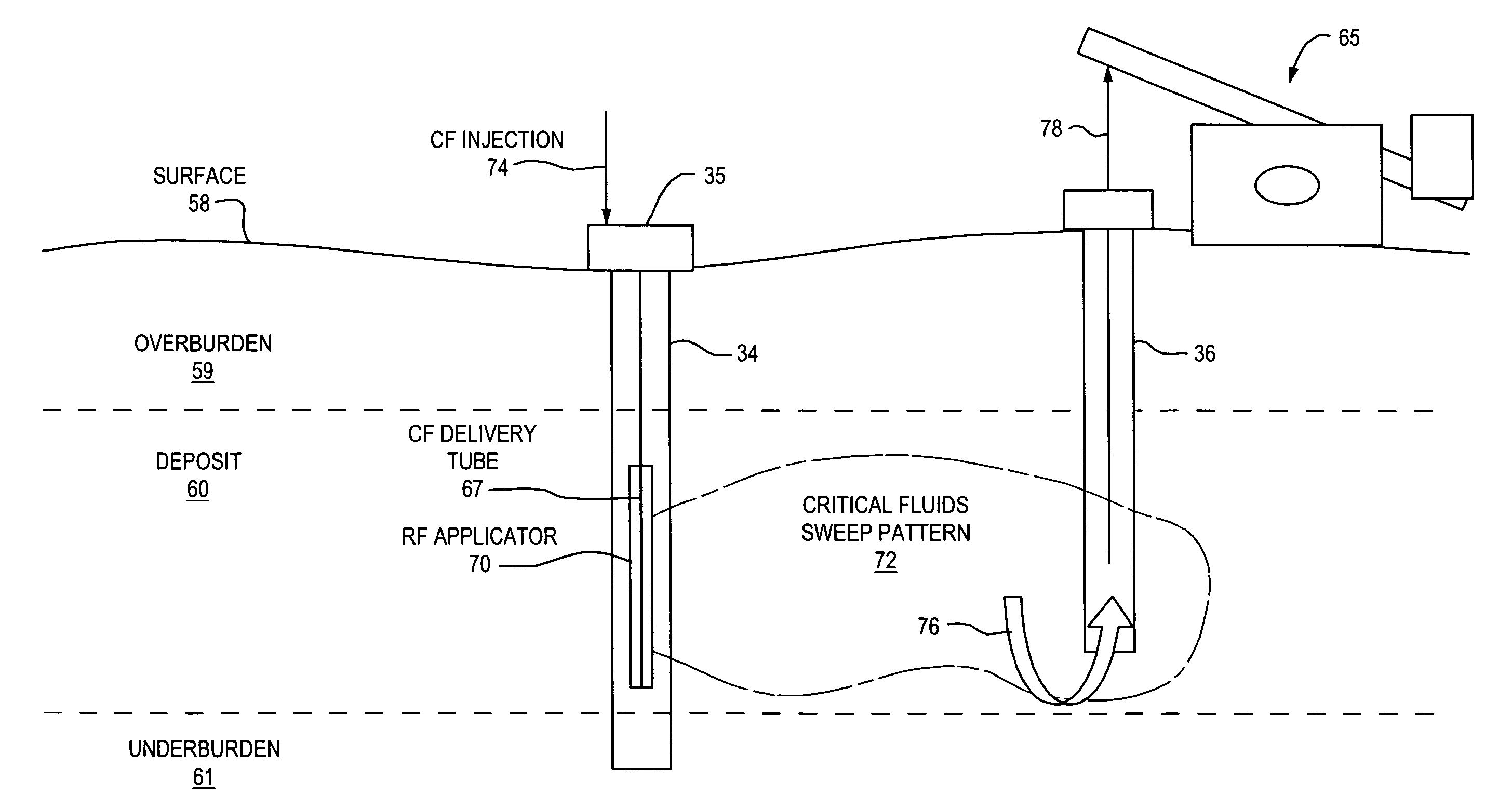
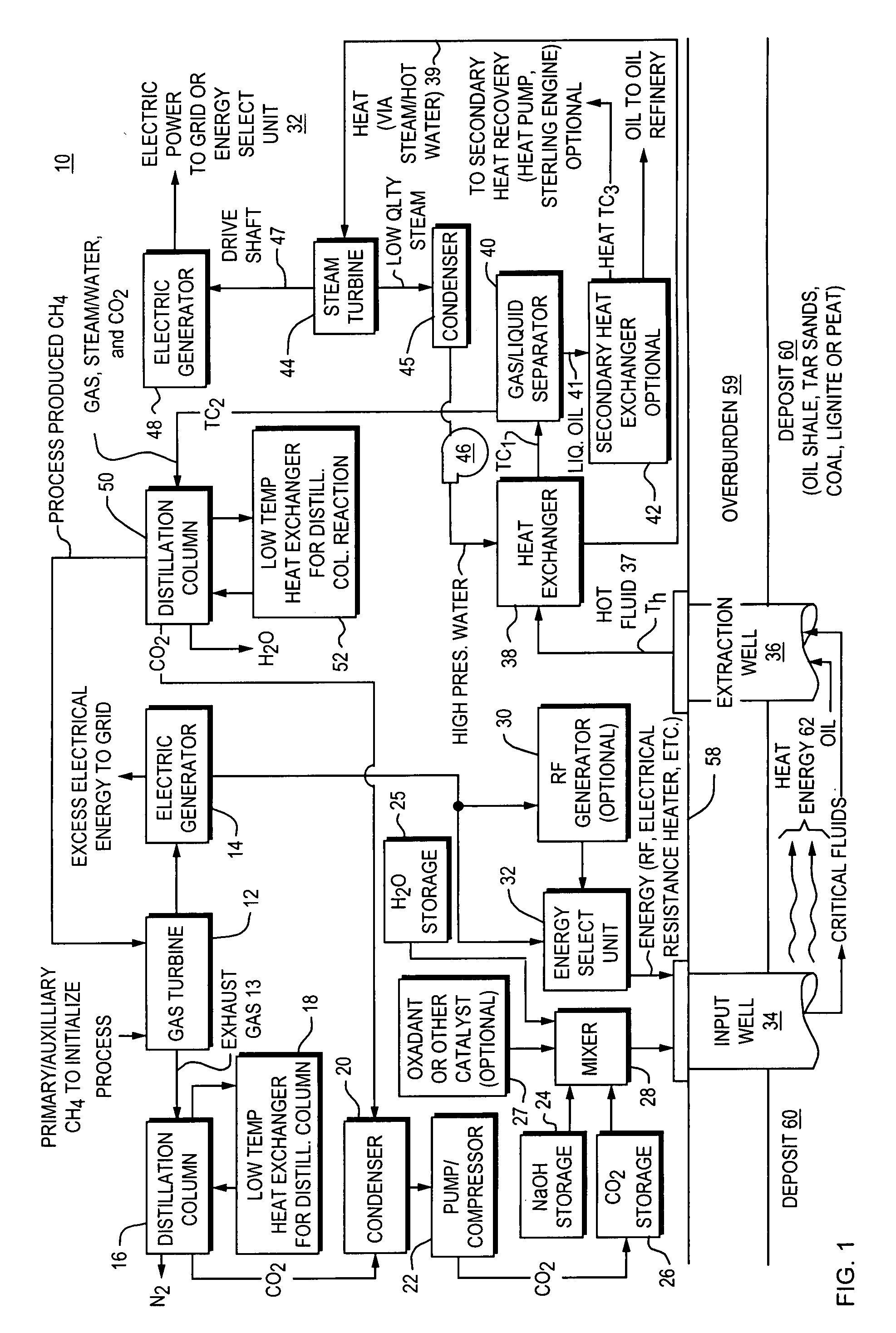
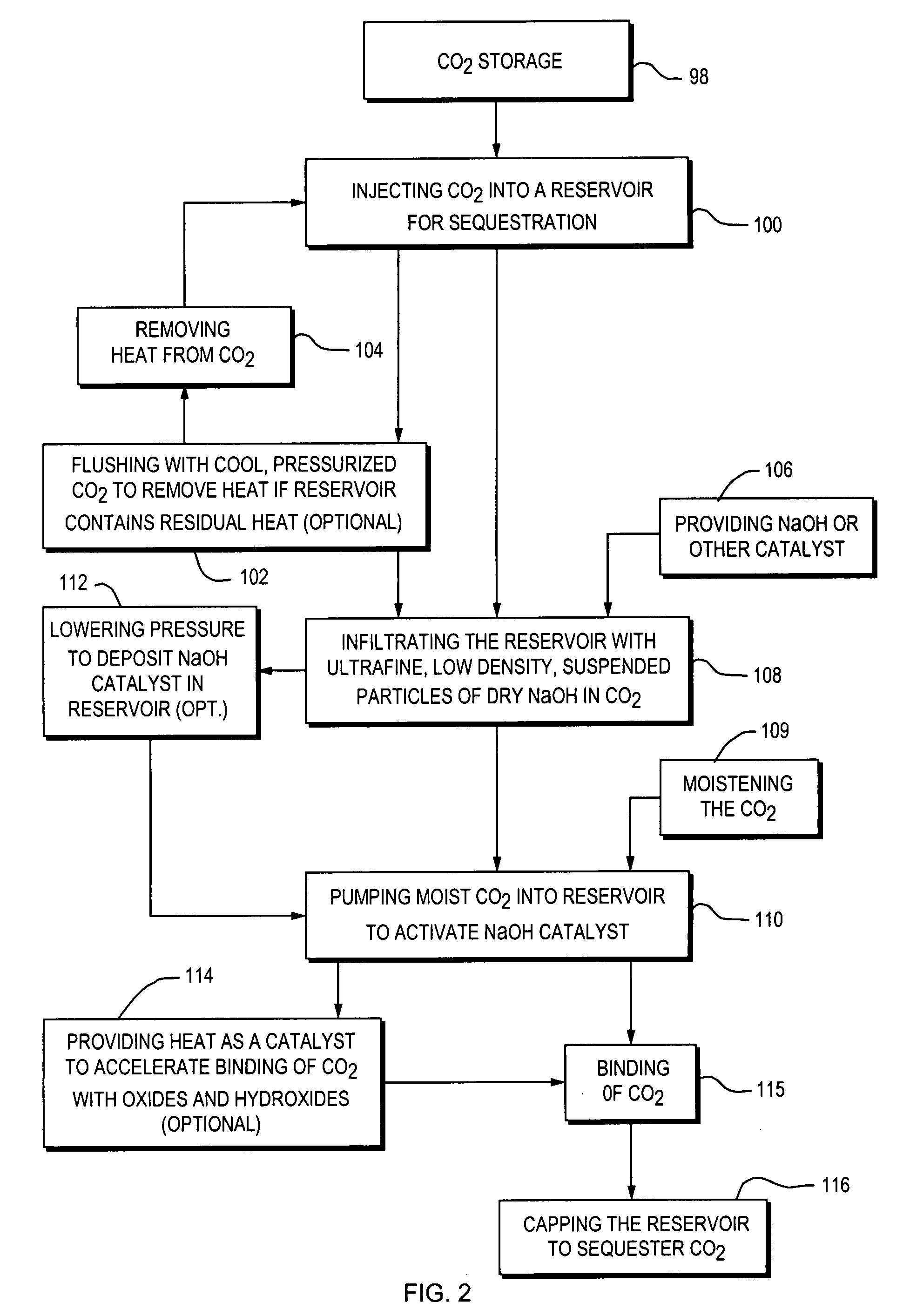
Method and apparatus for capture and sequester of carbon dioxide and extraction of energy from large land masses during and after extraction of hydrocarbon fuels or contaminants using energy and critical fluids
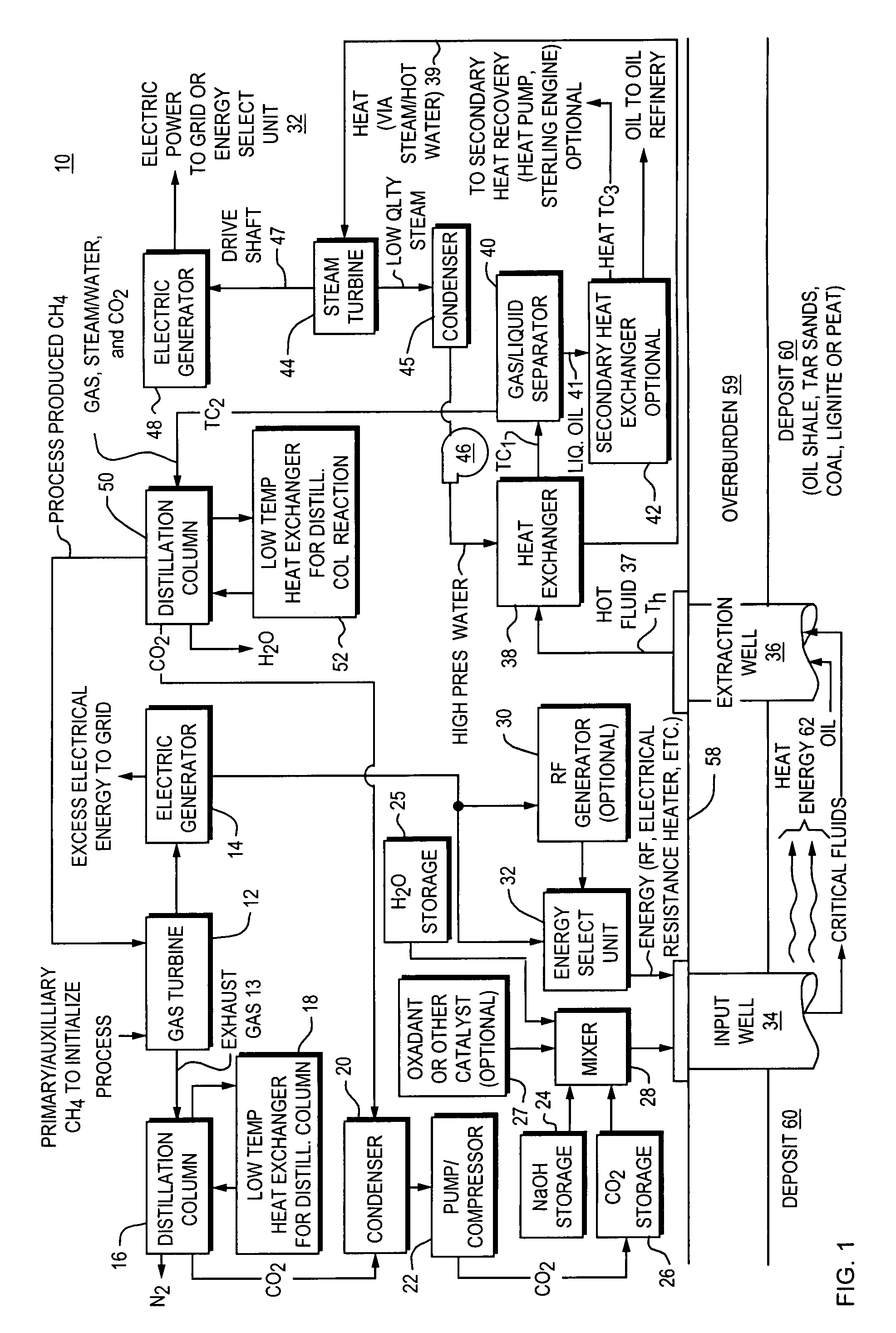
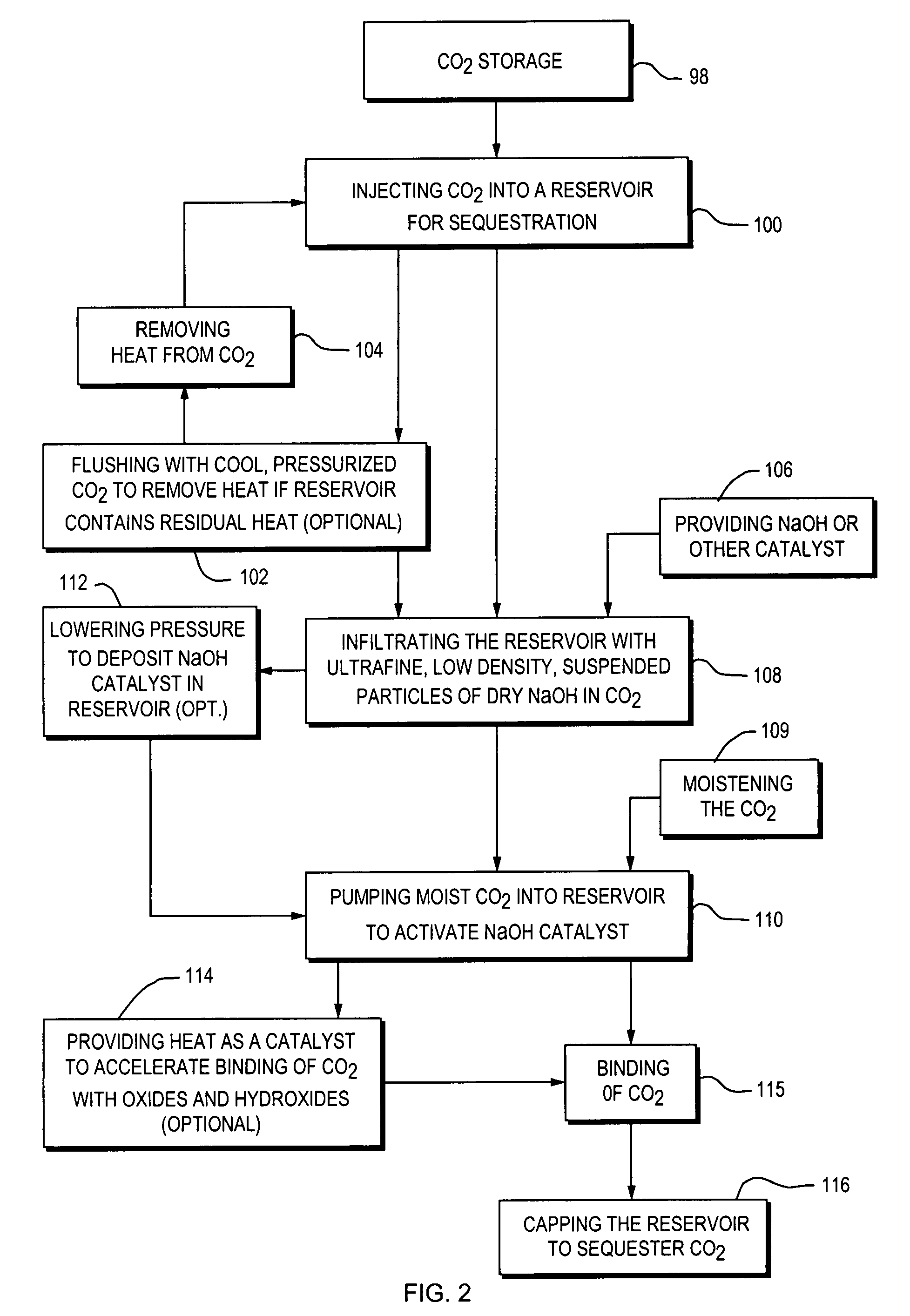
ActiveUS7562708B2Reduce energy consumptionMinimal pollutionSurveyOther gas emission reduction technologiesClosed loopUltra fine
A closed loop system for increasing yield, reducing post process pollution, reducing energy consumed during and after extraction of fuels or contaminants in formations and for sequestering of carbon dioxide C02 from various sources is converted to a critical fluid for use as a flushing and cooling medium. Electrical energy heats a hydrocarbon rich formation resulting in the extraction of hot fluids which are fed to heat exchangers, gas / liquid separator, and steam turbine whereby oil, electric power, carbon dioxide and methane are produced for reuse in the system or for external use. Further, a method for sequestering of carbon dioxide in a formation comprises the steps of injecting CO2 into the reservoir, flushing with cool pressurized CO2 for heat removal, infiltrating with ultra-fine low density suspended catalyst particles of dry sodium hydroxide in CO2, pumping water moistened CO2 into the reservoir to activate the catalysts, binding the CO2 with reacting materials and capping the reservoir.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Power plant with emissions recovery
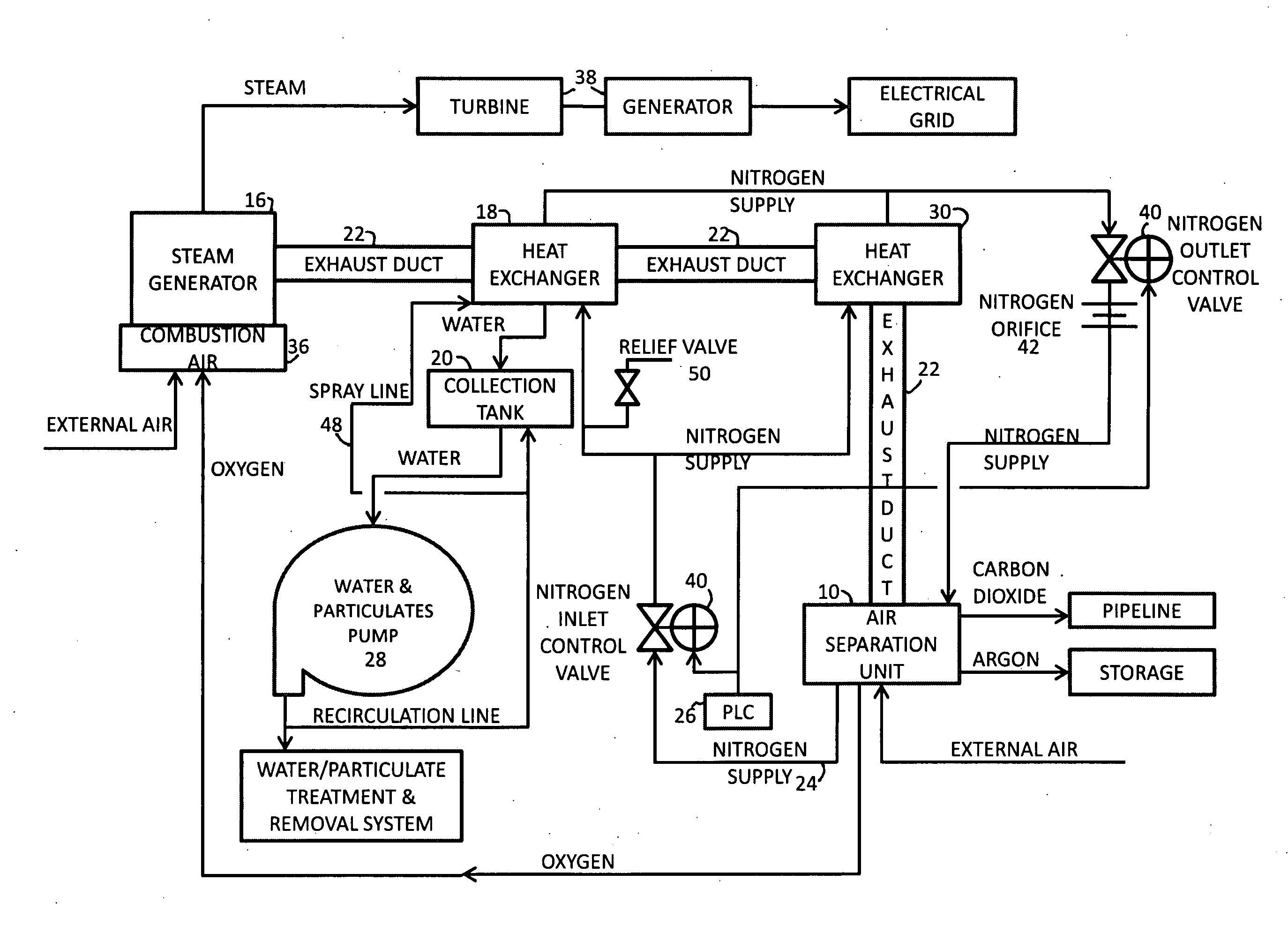
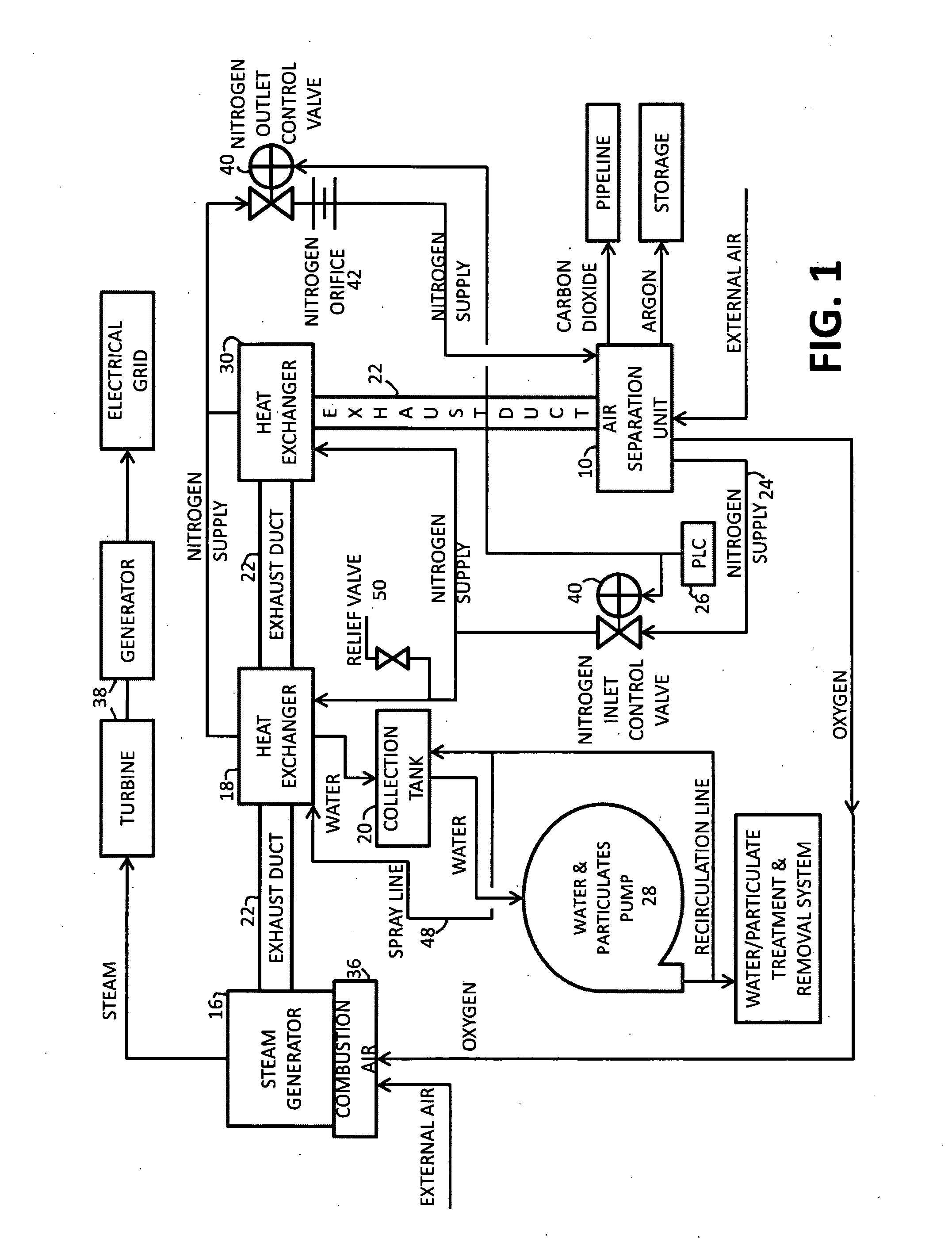
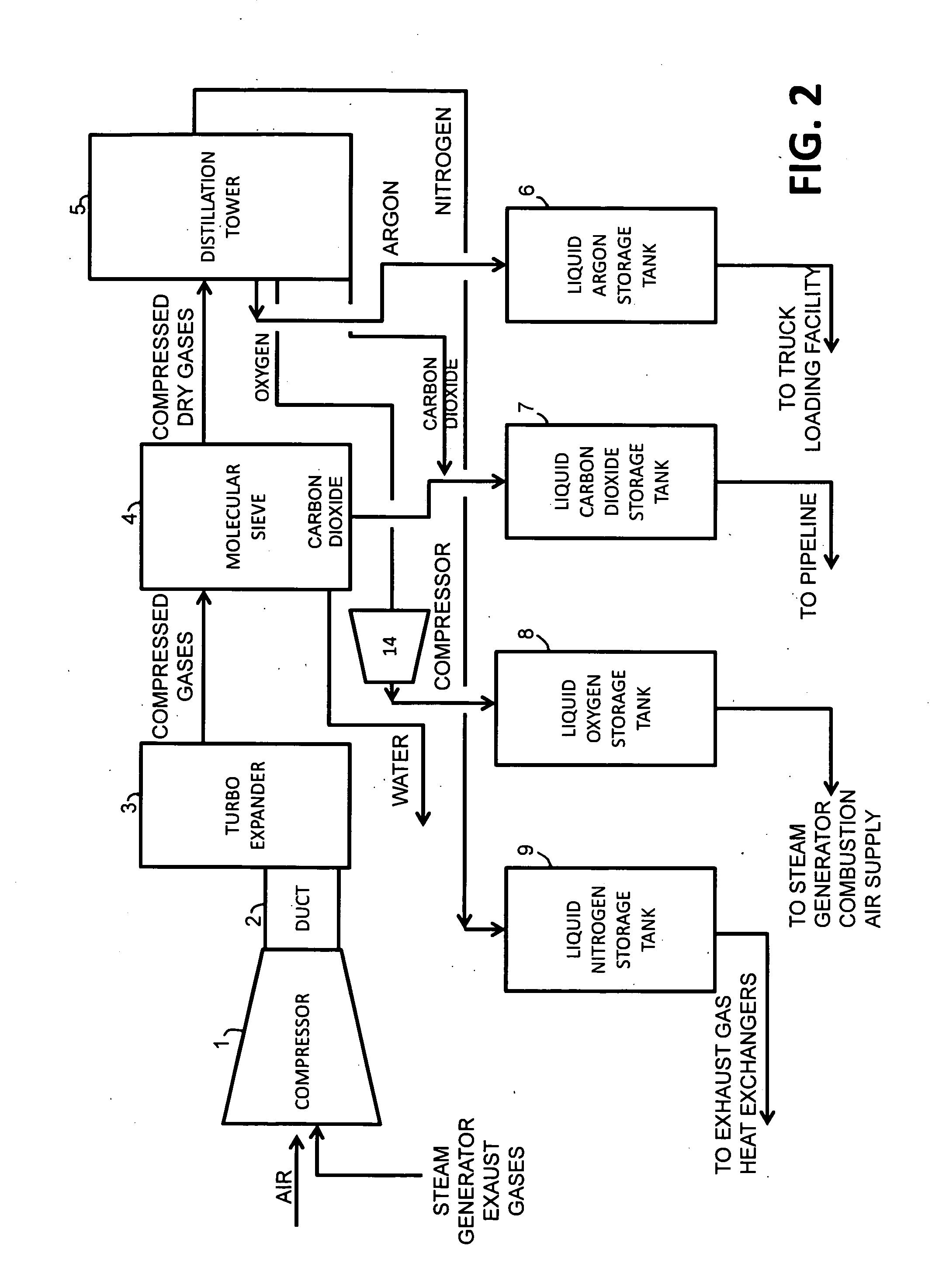
InactiveUS20100018218A1Reduce deliveryEnvironment safetySolidificationLiquefactionParticulatesNitrogen gas
A power plant including an air separation unit (ASU) arranged to separate nitrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide and argon from air and produce a stream of substantially pure liquid oxygen, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and argon; a steam generator, fired or unfired, arranged to combust a fuel, e.g., natural gas, liquefied natural gas, synthesis gas, coal, petroleum coke, biomass, municipal solid waste or any other gaseous, liquid or solid fuel in the presence of air and a quantity of substantially pure oxygen gas to produce an exhaust gas comprising water, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides and other trace gases, and a steam-turbine-generator to produce electricity, a primary gas heat exchanger unit for particulate / acid gas / moisture removal and a secondary heat exchanger arranged to cool the remainder of the exhaust gases from the steam generator. Exhaust gases are liquefied in the ASU thereby recovering carbon dioxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, sulfur oxides, oxygen, and all other trace gases from the steam generator exhaust gas stream. The cooled gases are liquefied in the ASU and separated for sale or re-use in the power plant. Carbon dioxide liquid is transported from the plant for use in enhanced oil recovery or for other commercial use. Carbon dioxide removal is accomplished in the ASU by cryogenic separation of the gases, after directing the stream of liquid nitrogen from the air separation unit to the exhaust gas heat exchanger units to cool all of the exhaust gases including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur oxides, and other trace gases.
Owner:TRIENCON SERVICES
Method and apparatus for capture and sequester of carbon dioxide and extraction of energy from large land masses during and after extraction of hydrocarbon fuels or contaminants using energy and critical fluids
ActiveUS20070261844A1Weaken energyReducing critical fluid requirementSurveyOther gas emission reduction technologiesClosed loopUltra fine
A closed loop system for increasing yield, reducing post process pollution, reducing energy consumed during and after extraction of fuels or contaminants in formations and for sequestering of carbon dioxide C02 from various sources is converted to a critical fluid for use as a flushing and cooling medium. Electrical energy heats a hydrocarbon rich formation resulting in the extraction of hot fluids which are fed to heat exchangers, gas / liquid separator, and steam turbine whereby oil, electric power, carbon dioxide and methane are produced for reuse in the system or for external use. Further, a method for sequestering of carbon dioxide in a formation comprises the steps of injecting CO2 into the reservoir, flushing with cool pressurized CO2 for heat removal, infiltrating with ultra-fine low density suspended catalyst particles of dry sodium hydroxide in CO2, pumping water moistened CO2 into the reservoir to activate the catalysts, binding the CO2 with reacting materials and capping the reservoir.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
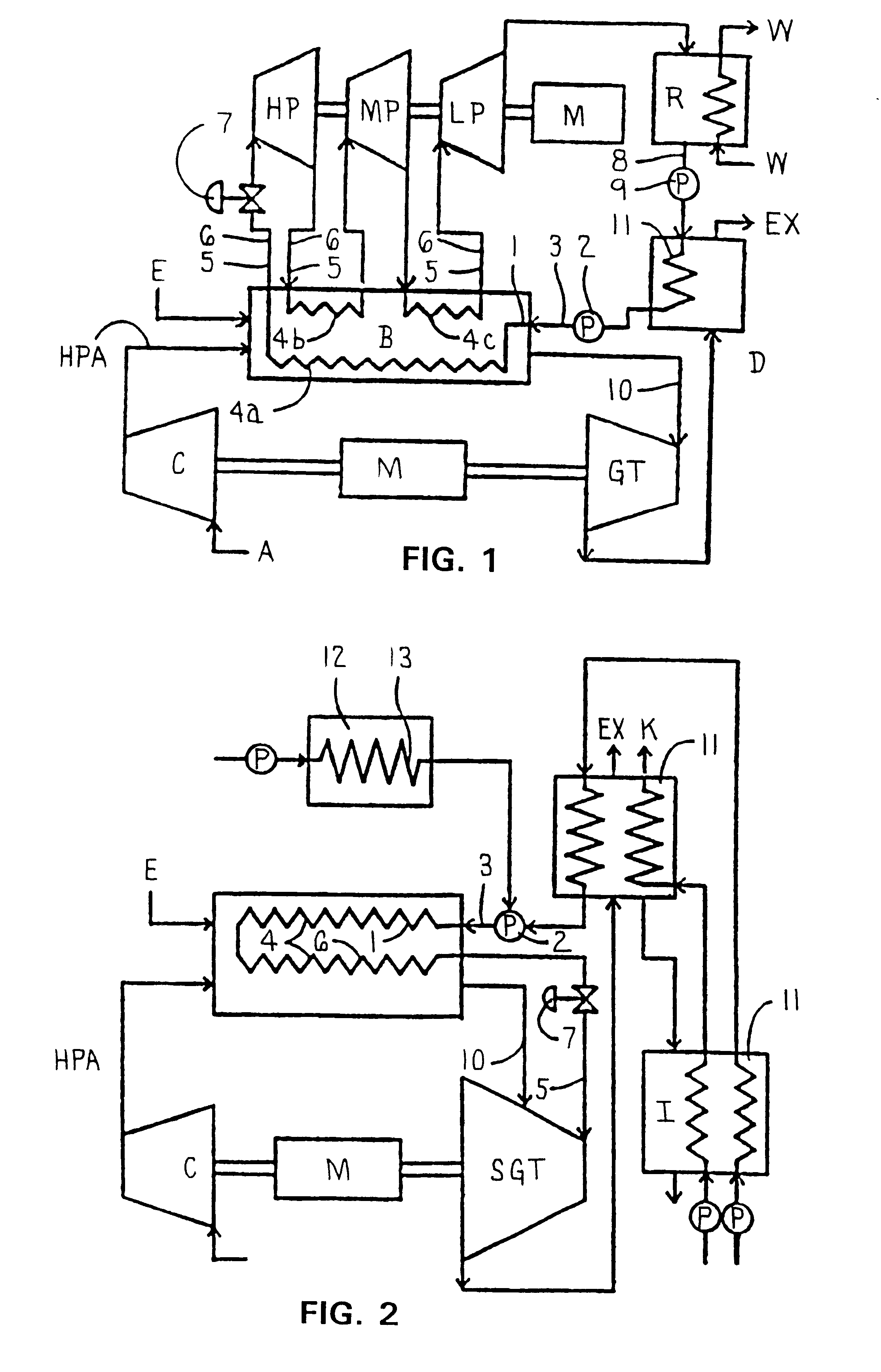
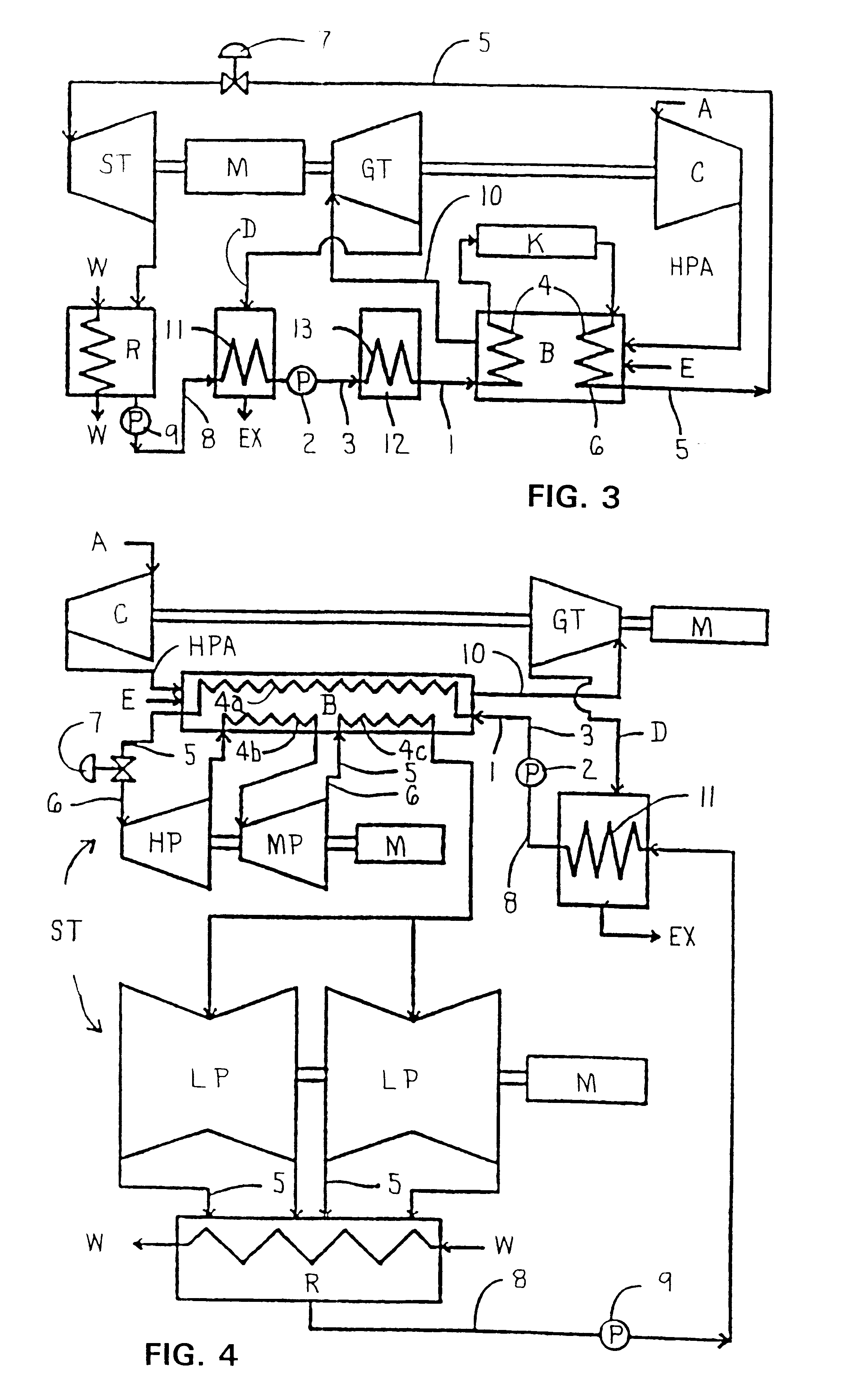
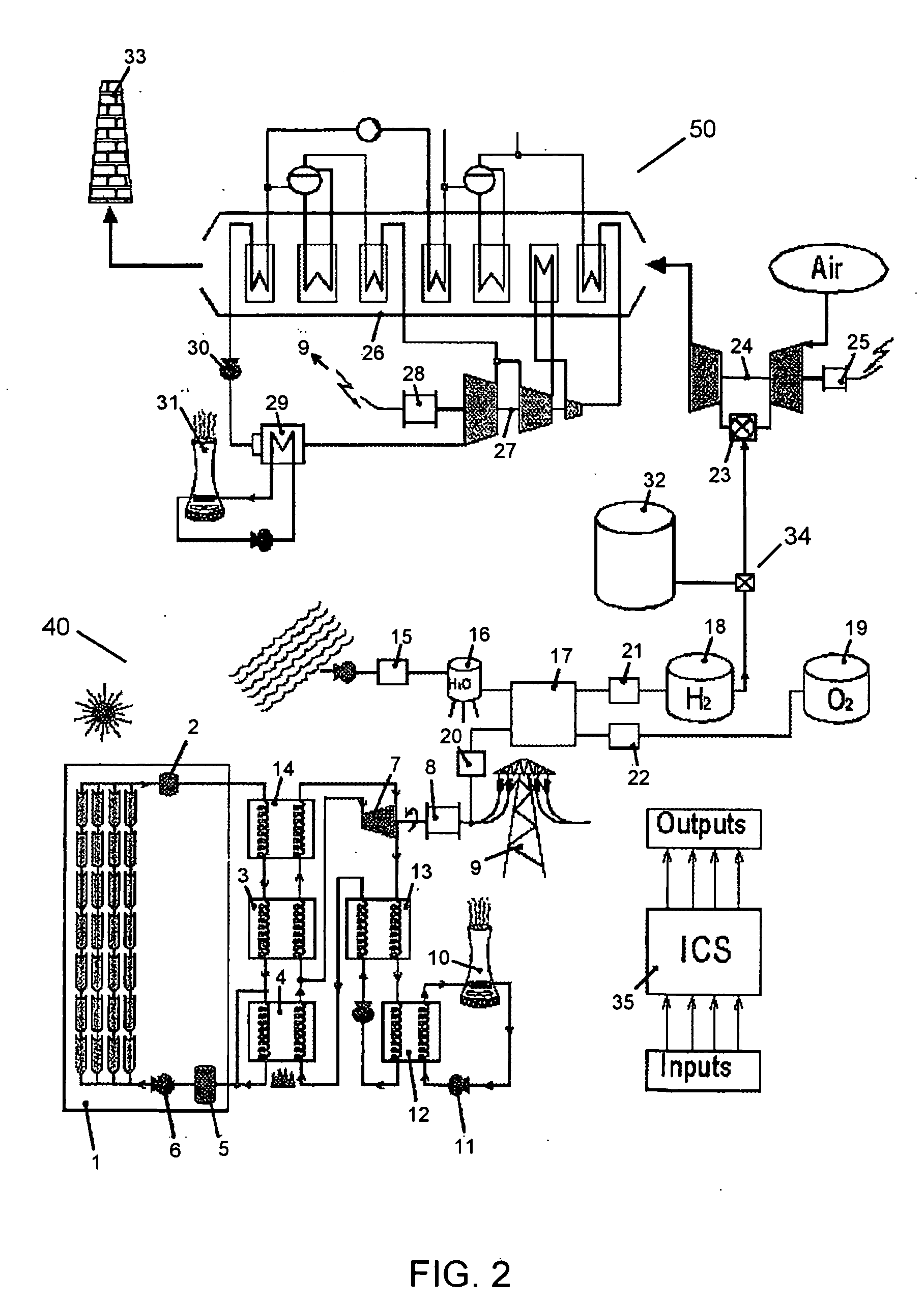
Methods and apparatus for starting up emission-free gas-turbine power stations
InactiveUS6945052B2Large capacityGas turbine plantsIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationPower stationCombustion chamber
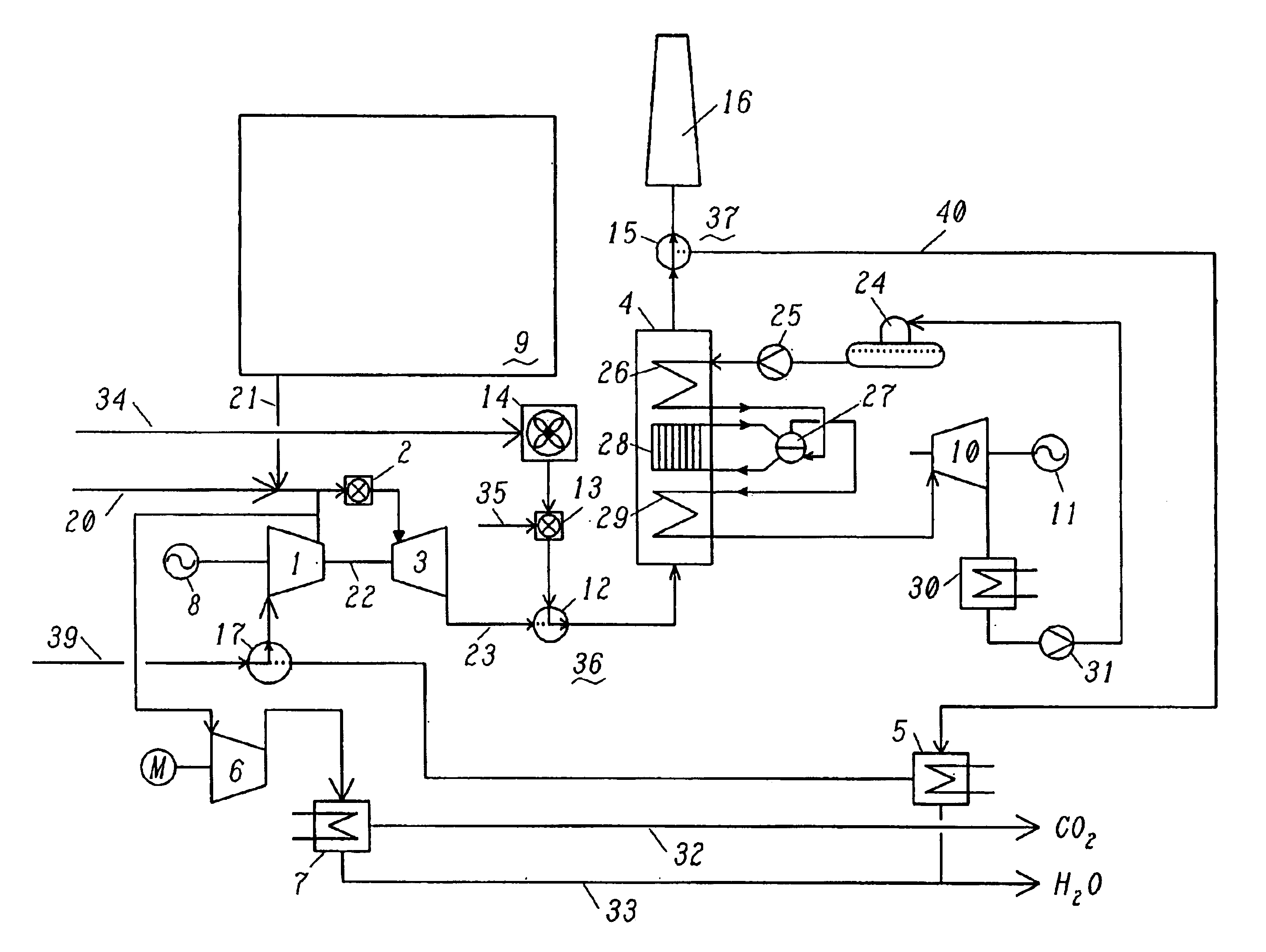
In a power generation plant having at least one gas turbine cycle with heat-recovery boiler (4) and at least one steam turbine cycle operated via the heat-recovery boiler (4), the gas turbine cycle being designed to be semi-closed and essentially free of emissions and essentially comprising a compressor (1), a combustion chamber (2) arranged downstream of the compressor (1), a gas turbine (3) arranged downstream of the combustion chamber (2), a heat-recovery boiler (4) arranged downstream of the gas turbine (3), and at least one generator (8) coupled to the gas turbine (3), modes of operation with the gas turbine cycle stopped and start-up using fresh air are made possible by first means (12) being arranged which alternatively or additionally allow hot gas to be fed into the hot-gas path (23) between gas turbine (3) and heat-recovery boiler (4), and by second means (15) being arranged which alternatively or additionally allow exhaust gas to be expelled from the exhaust-gas path (40) downstream of the heat-recovery boiler (4).
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
Hybrid generation with alternative fuel sources
Owner:BRIGHTSOURCE ENERGY
Methods and systems for enhancing operation of power plant generating units and systems
ActiveUS20160281607A1Programme controlTurbine/propulsion engine ignitionPower stationControl engineering
A method for controlling and enhancing a startup operation for a combined cycle power block (block) having at least one gas turbine and at least one steam turbine, wherein operating parameters define performance and operational characteristics for the startup operation, the method comprising: receiving measured operating parameters from a plurality of reference blocks and, for each of the plurality of reference blocks, a plurality of types of the startup operations; given the measured operating parameters, developing one or more reference transfer functions between two of the measured operating parameters; receiving measured operating parameters from the startup operation of a target block; given the measured operating parameters from the target block, developing one or more transfer functions for the target block between two of the operating parameters; selecting one of the reference transfer functions; and normalizing the transfer function of the target block per the selected reference transfer function.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
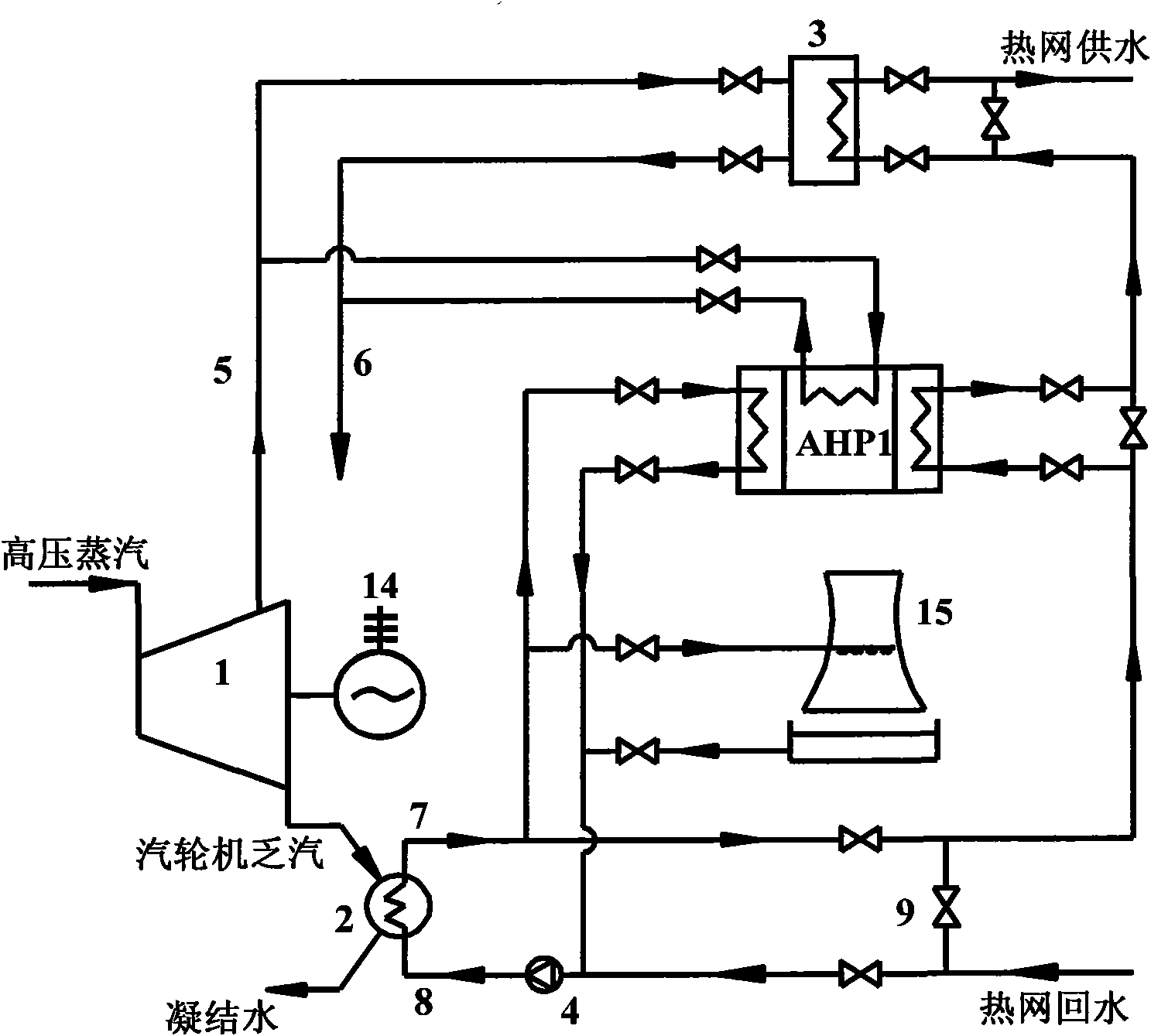
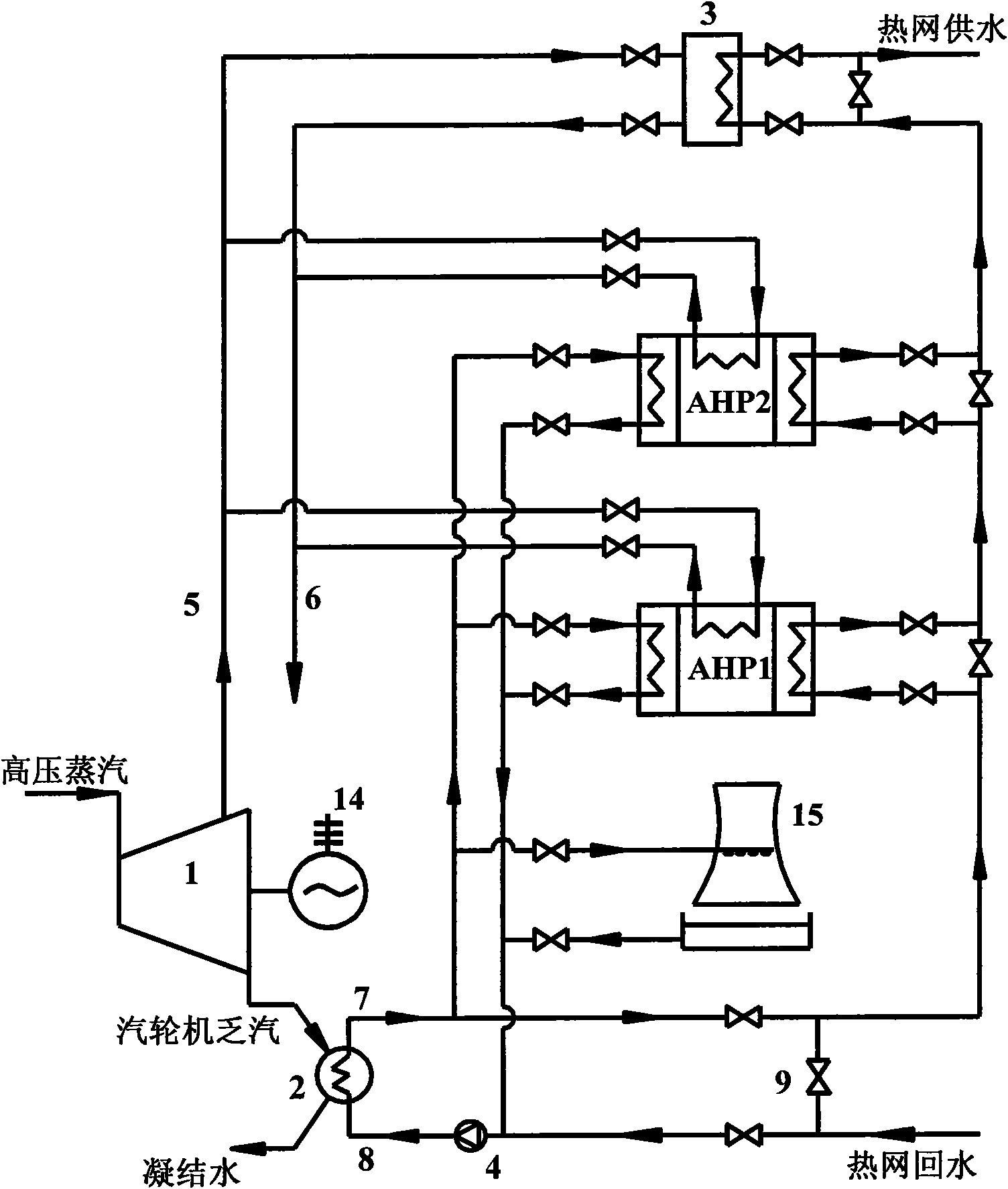
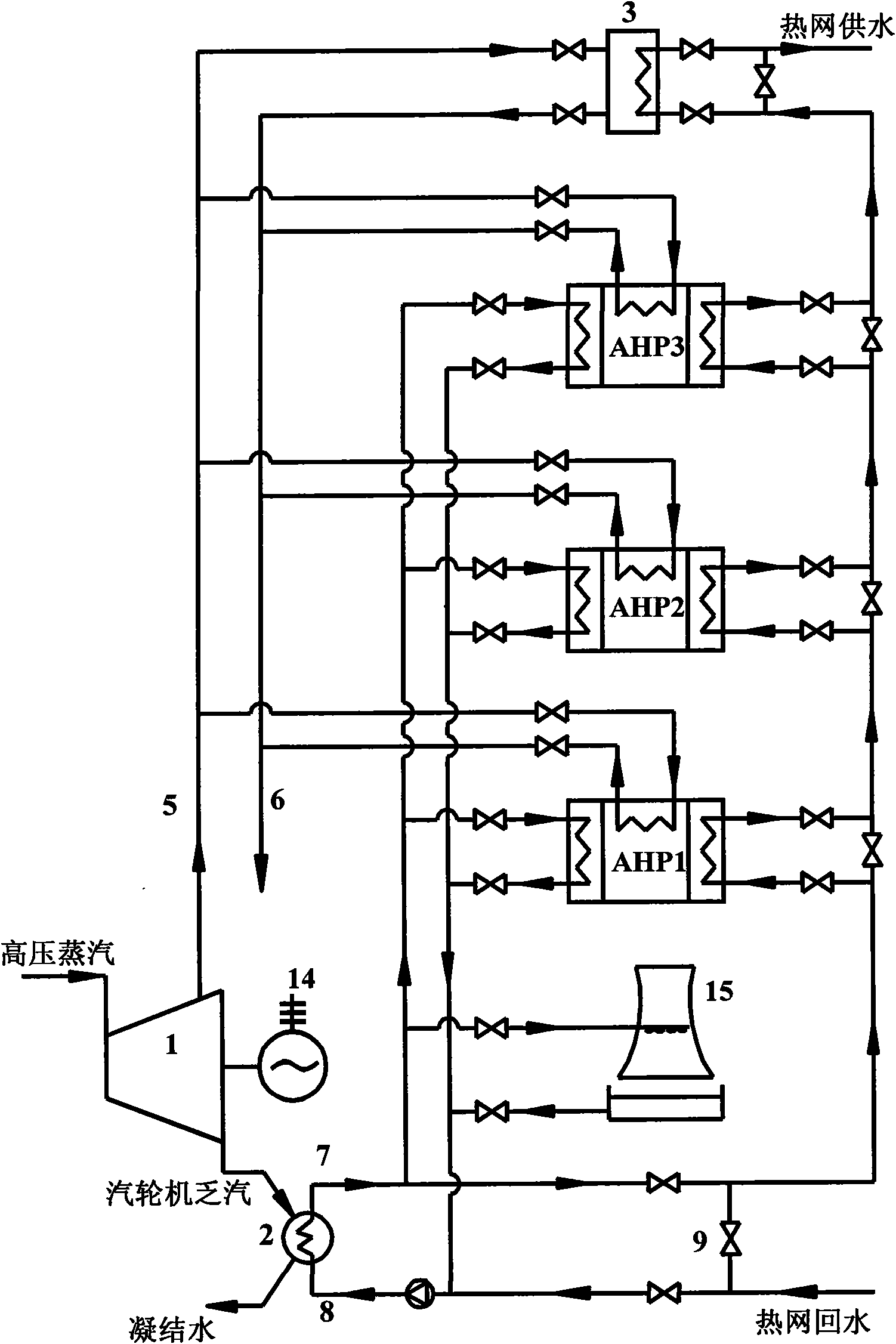
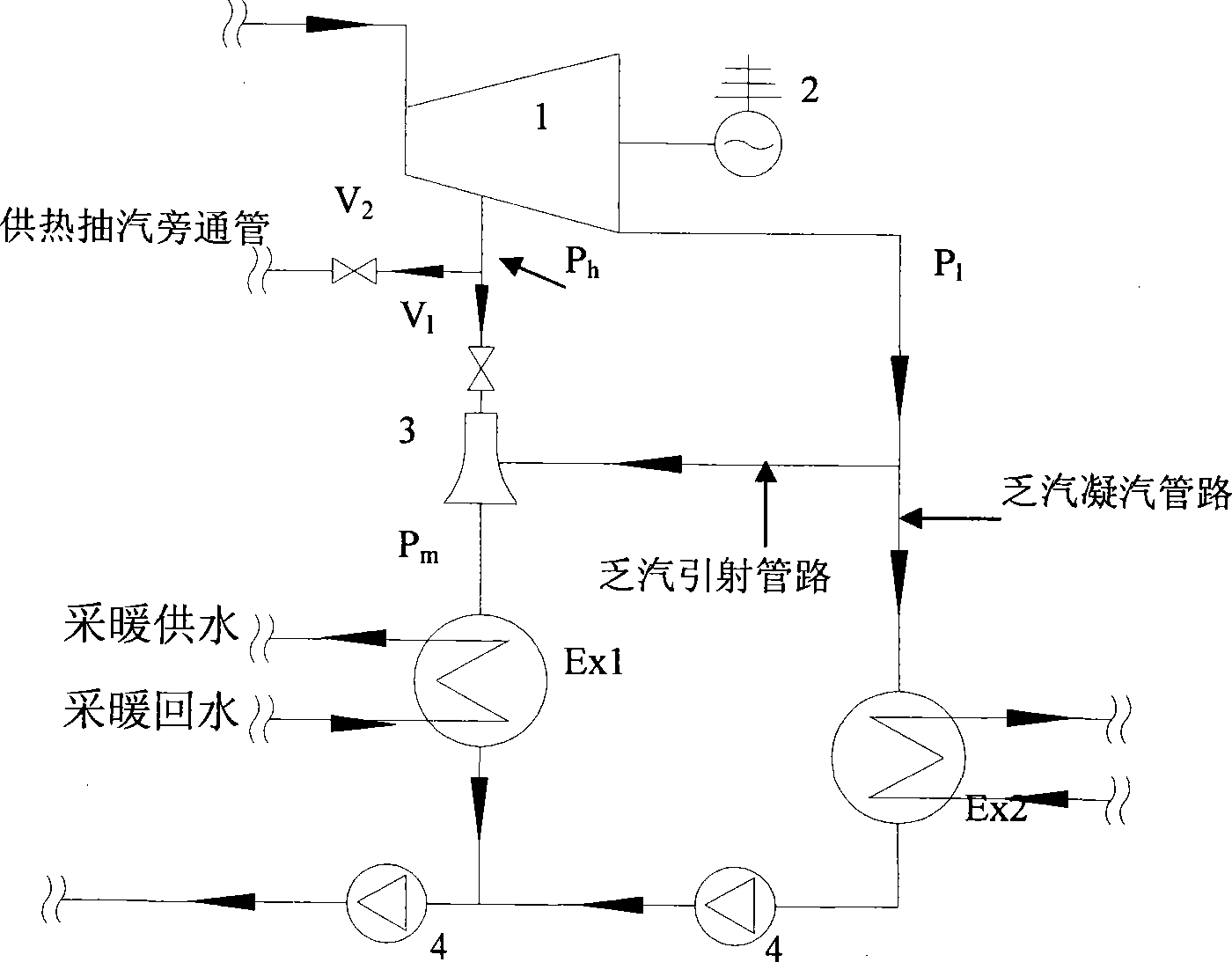
Large temperature-difference central heating system
ActiveCN101231004ALarge heating temperature differenceImprove delivery capacityHeat recovery systemsLighting and heating apparatusElectricityExternal energy
The invention relates to a central heating system with large temperature difference, which belongs to the energy field. The system comprises a steam turbine, a condenser, a steam absorption heat pump, a steam-water heat exchanger, a hot water absorption heat pump, a water-water heat exchanger as well as a connecting pipe and accessories. The invention is characterized in that the temperature difference of the heat net supply is large, and is about one time higher than the conventional heat net operation, thus the transmission capacity of the heat net is greatly increased, and at the same time, no heat preservation and thermal stress compensation problems exist as the backwater temperature of the heating is low, thereby reducing the investment of the backwater pipeline network and the whole pipeline network; the steam turbine is utilized to discharge steam and preheat the backwater of the large heat net, and circulating cooling water is utilized to be taken as the low level heat energy of the absorption heat pumps. The invention has the advantages that the residual heat produced in the electricity generating process of a power plant is recycled to the greatest extent as much as possible, the combination mode of the hot water absorption heat pump and the water-water heat exchanger is adopted at the end to heat the hot water of the secondary heat net supply, and the temperature difference of the supply-water and the backwater of the large heat net are increased, at the same time, the heat net does not need external energy to be the driving force.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Process for superheated steam
InactiveUS20070245736A1Chemical industryCombustible gas catalytic treatmentElectricityPartial oxidation
Disclosed is a process for the preparation of superheated of steam by transferring heat from at least a fraction of a high pressure steam to a lower pressure steam to produce a superheated, lower pressure steam. The high pressure steam can be generated by recovering heat from a heat producing chemical process such as, for example, the partial oxidation of carbonaceous materials. The lower pressure steam can be generated by reducing the pressure of a portion of the high pressure steam or by recovering heat from one or more chemical processes. The superheated, lower pressure steam may used to generate electricity in a steam turbine, operate a steam turbine drive, or as a heat source. Also disclosed is a process for driving a steam turbine using superheated steam produced by the process of the invention.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Optimized control of power plants having air cooled condensers
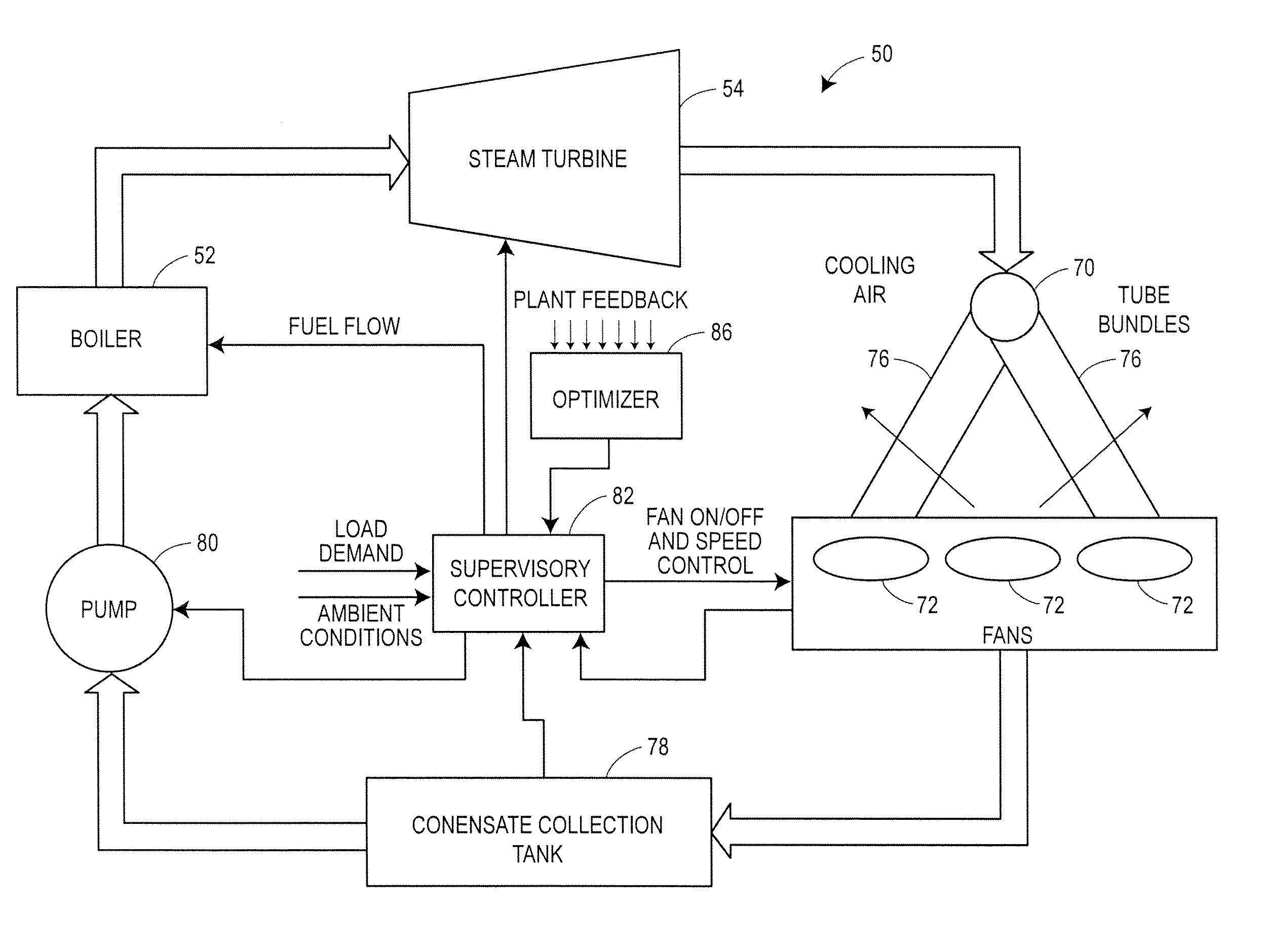
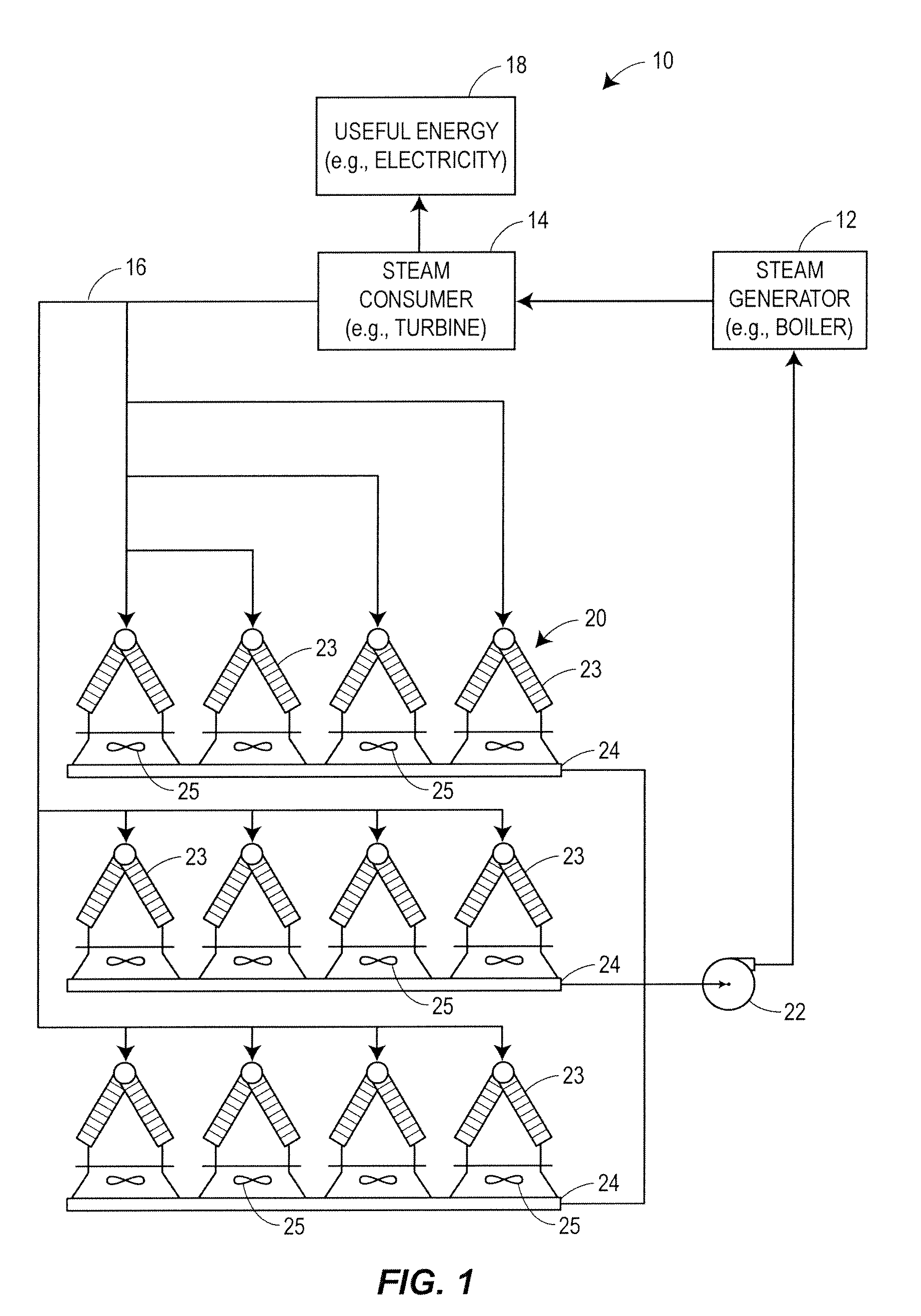
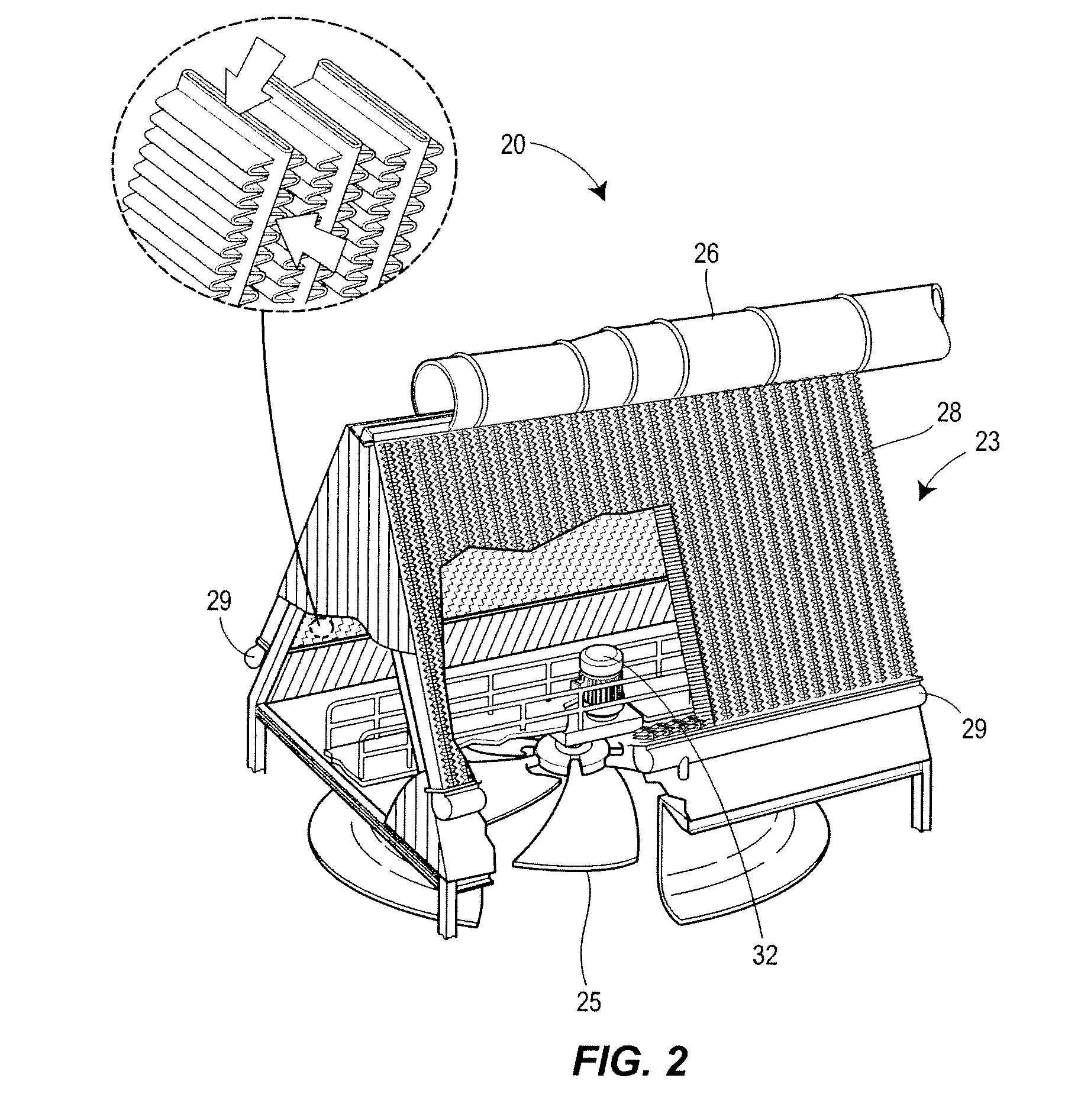
ActiveUS20110066298A1Cost can be reduced and minimizedLow costMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlOperating pointControl variable
An optimization and control system for a utility plant that uses fan based air cooled condensers controls the operation of the power generation system at the plant in conjunction with the operation of the air cooled condensers so as to run the power plant at an optimum operating point associated with minimizing or reducing the cost of each kilowatt-hour of energy or other useful energy produced by the plant. The optimization and control system includes an optimizer having a numerical solver that determines values for a set of control variables associated with an optimal operating point of the plant and an expert system that oversees and modifies the control variable settings prior to providing these settings to a plant controller. The numerical solver uses an objective function and one or more models of plant equipment to determine the operating point of the plant that minimizes the cost per unit of useful energy generated by the plant. As part of determining the optimal plant operating point, the numerical solver may determine the number of fans to run within the air cooled condensers of the plant and / or the speed of the fans to use in the air cooled condensers in conjunction with the amount of fuel to burn in the boiler, the desired temperature of the steam at the input of the steam turbine, etc., all required to produce a given amount of power (load demand) at the particular environmental conditions currently experienced at the plant. The expert system may modify these outputs by determining which fans to actually use at any particular time based on, for example, the availability of or the operational status of the fans, the wear of the fans and fan motors, etc.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
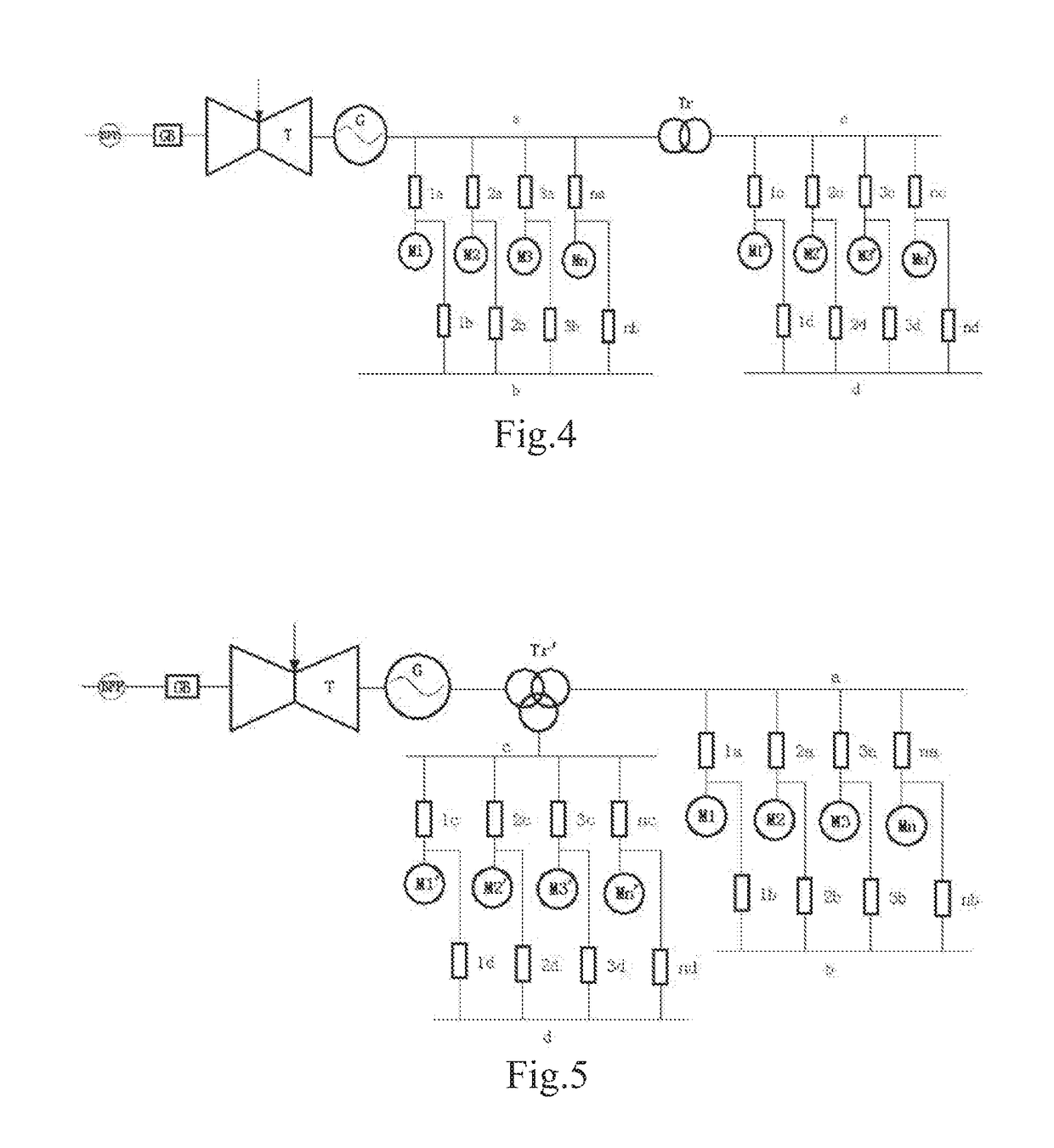
Generalized frequency conversion system for steam turbine generator unit
InactiveUS20190071992A1Low costImprove reliabilityAC motor controlEnergy industryFrequency changerFrequency conversion
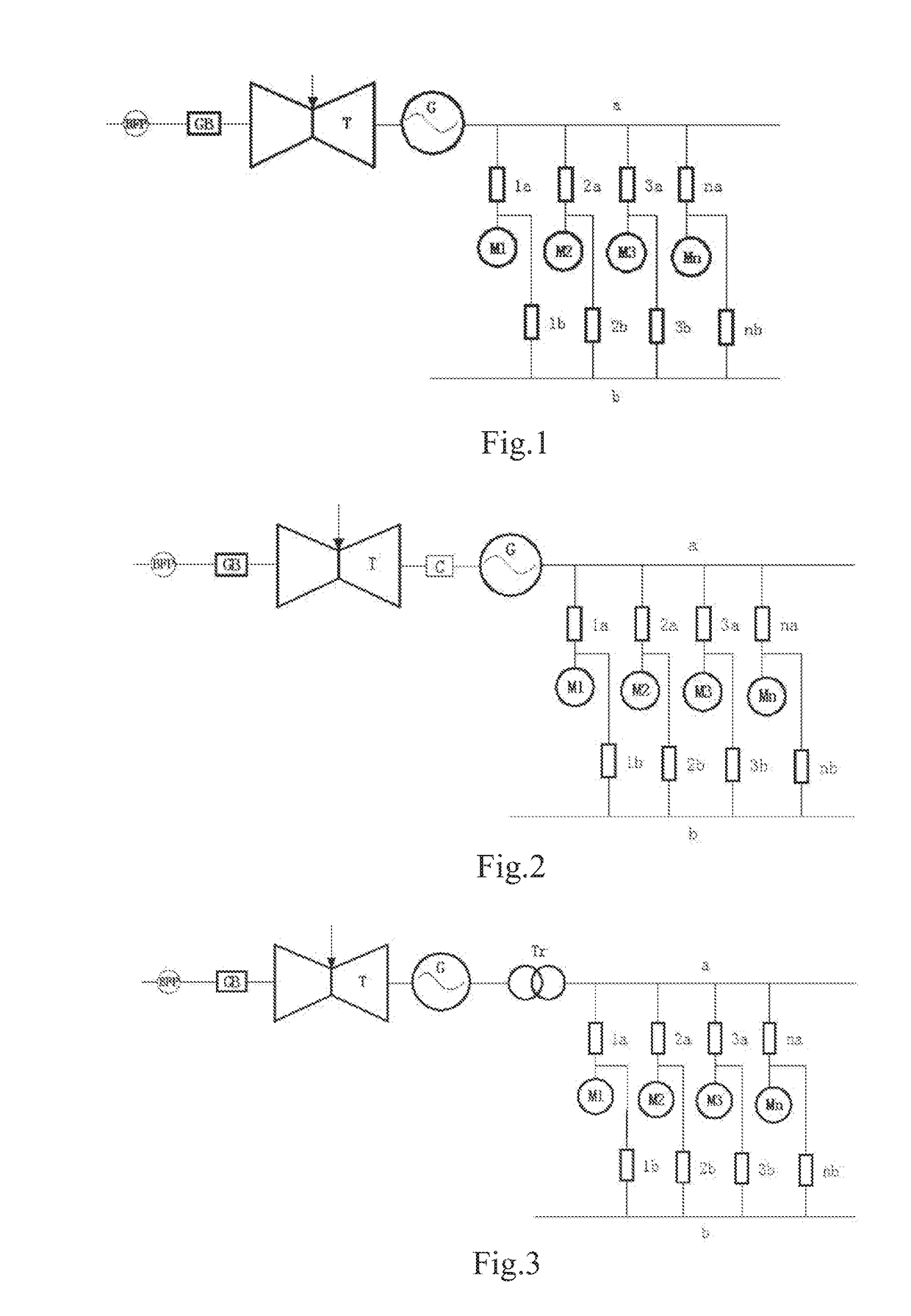
The present invention provides a generalized frequency conversion system for a steam turbine generator unit. The system comprises at least a steam turbine (T) with an adjustable rotating speed, a water feeding pump (BFP), a generator (G), a speed increasing gearbox (GB), a variable frequency bus (a, c) and an auxiliary machine connected thereto. With a change in load of the unit, parameters of steam entering the steam turbine (T) and an extracted steam amount are correspondingly adjusted (changed), so that the rotating speed of the steam turbine (T) changes correspondingly; and thus the rotating speed of the water feeding pump (BFP) is changed through the speed increasing gearbox (GB) on the one hand, and the frequency of an alternating current outputted by the generator (G) is changed on the other hand. Other types of frequency converters do not need to be additionally provided. The system is simple, reliable, low in cost, and high in efficiency.
Owner:FENG
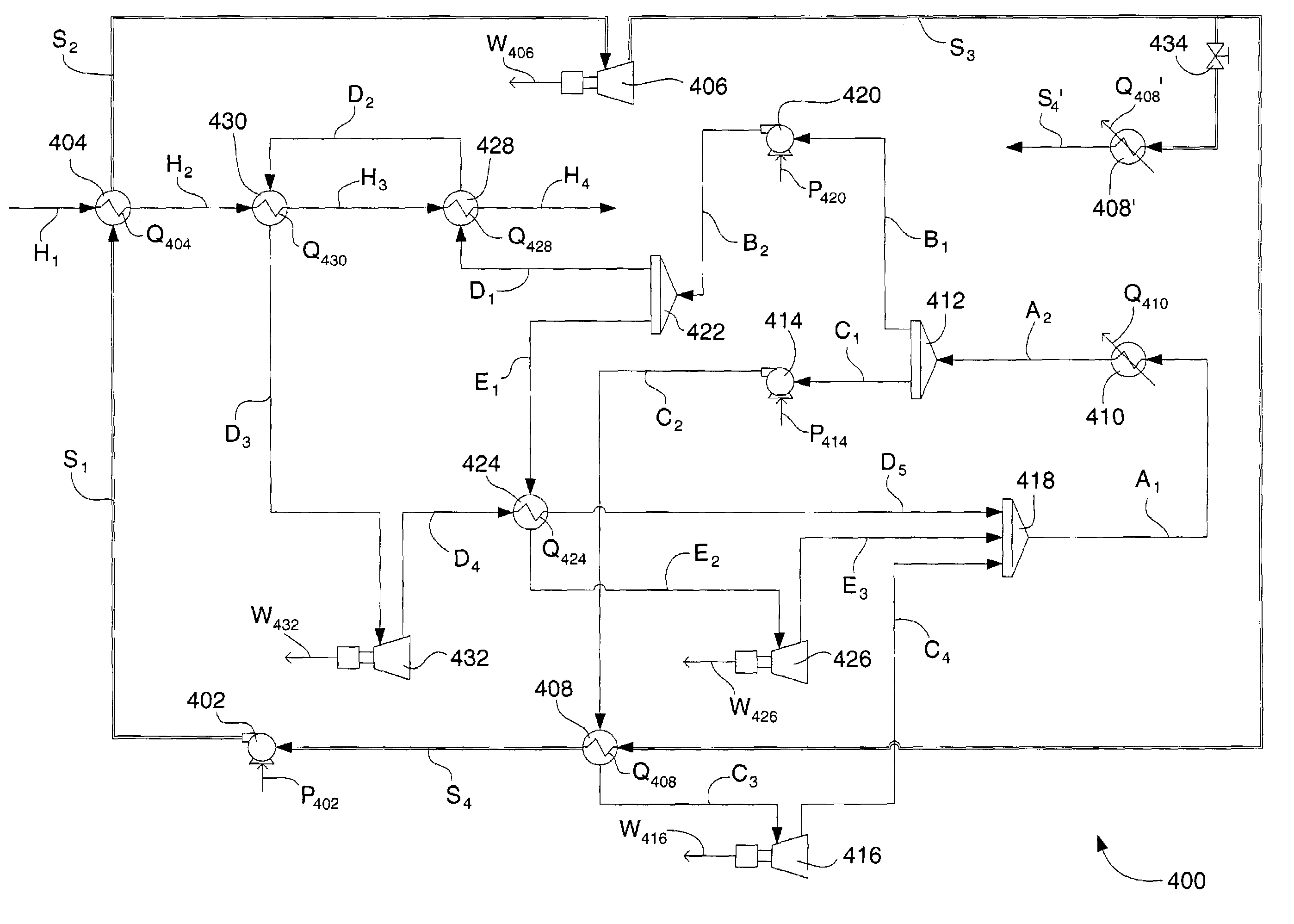
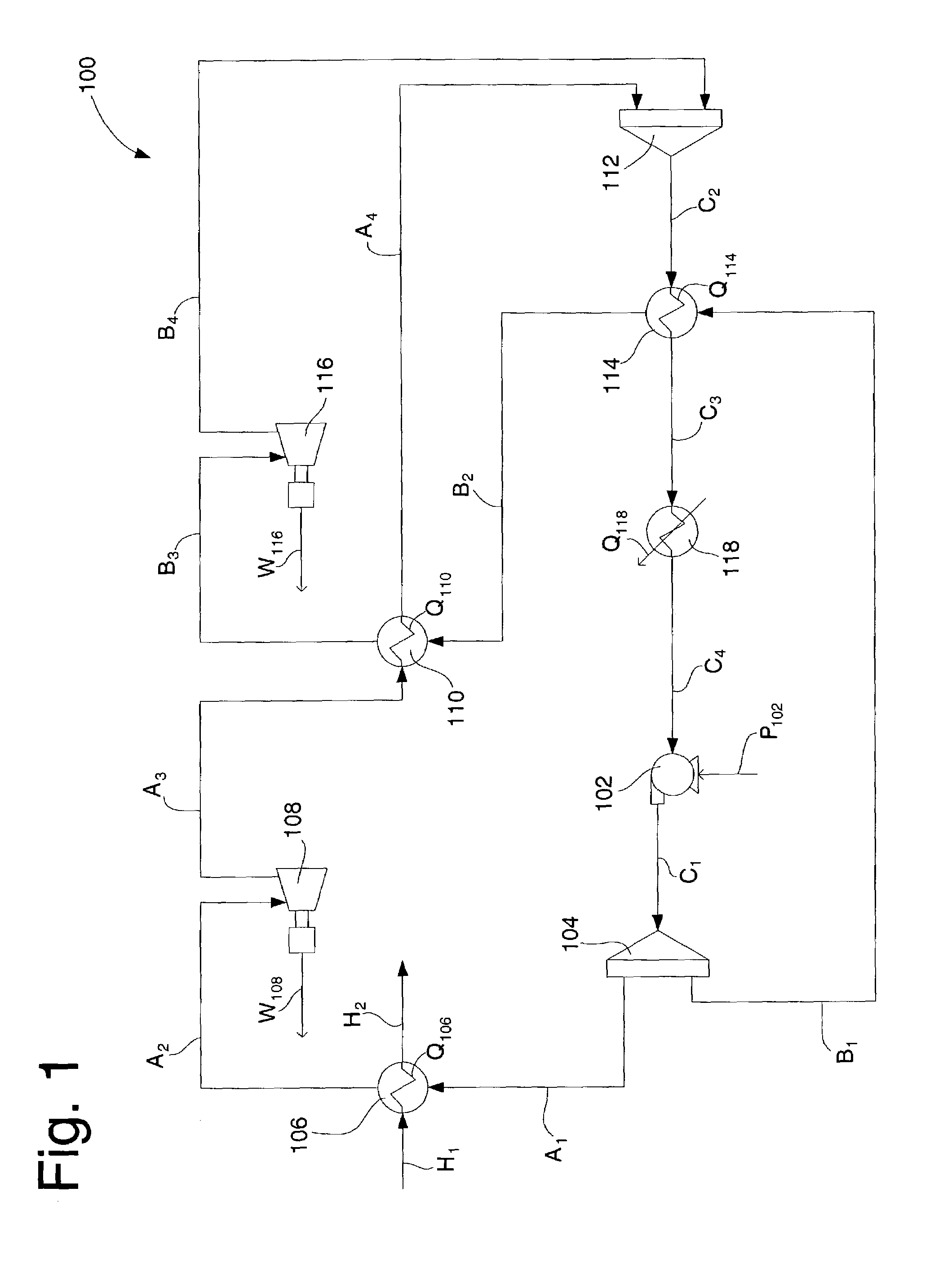
Cascading closed loop cycle power generation
InactiveUS7096665B2Improve power efficiencyIncrease pressureEnergy industrySteam accumulatorsLiquid propaneSteam condensation
Owner:UNIVERSAL TECH
Electrical power generation method
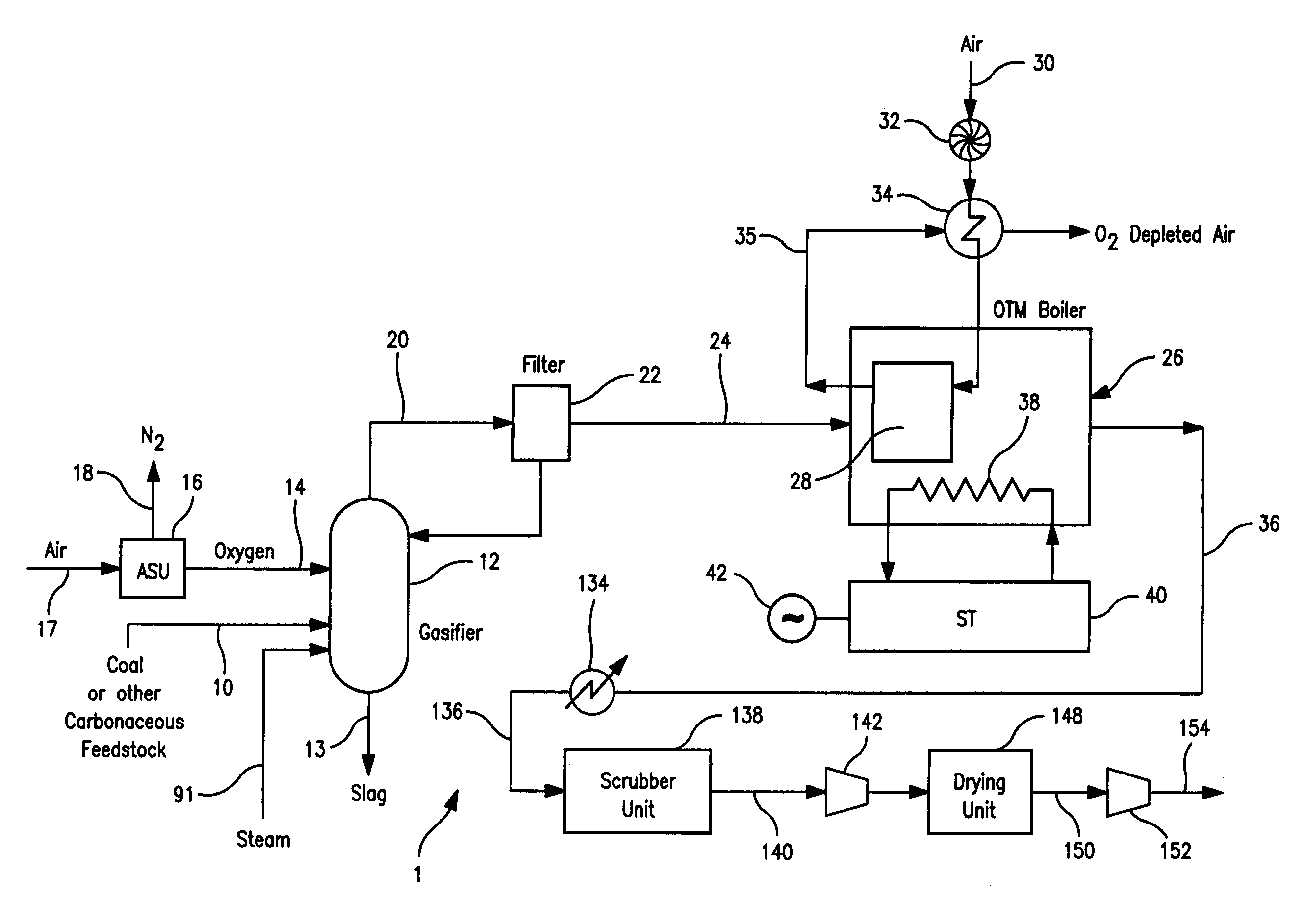
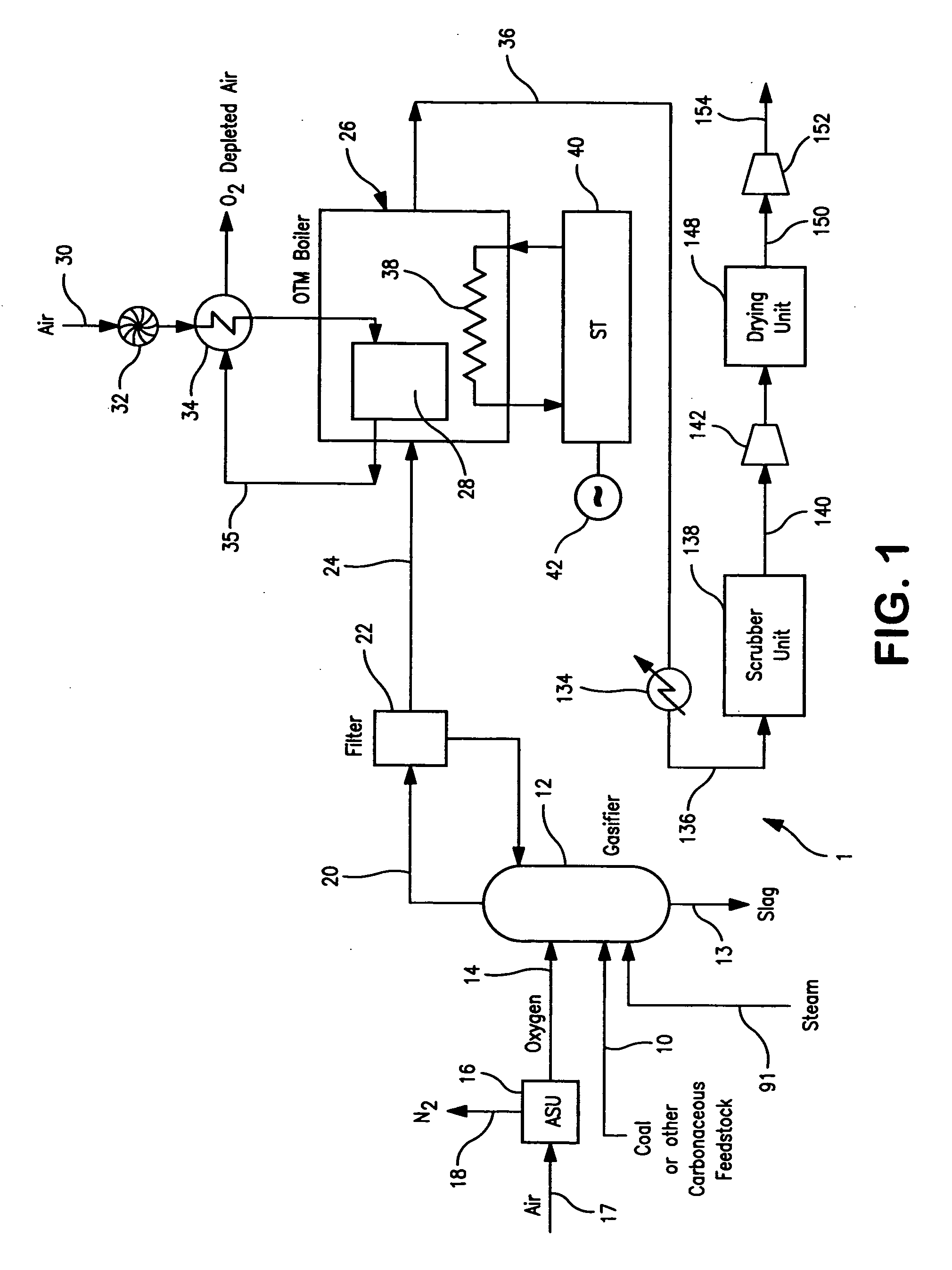
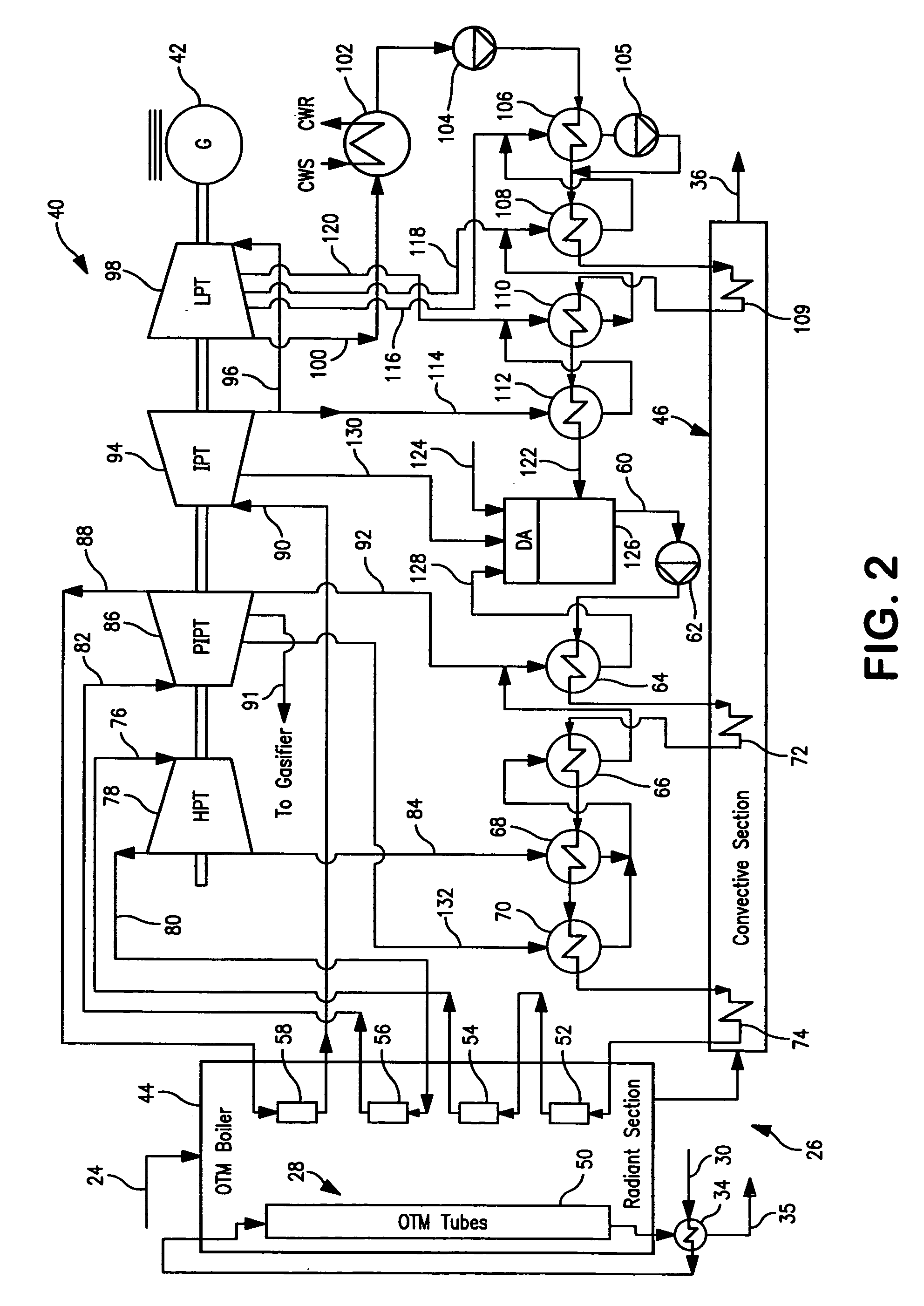
A method of generating electrical power in which a synthesis gas stream generated in a gasifier is combusted in an oxygen transport membrane system of a boiler. The combustion generates heat to raise steam to in turn generate electricity by a generator coupled to a steam turbine. The resultant flue gas can be purified to produce a carbon dioxide product.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
Power generation system and method of operating same
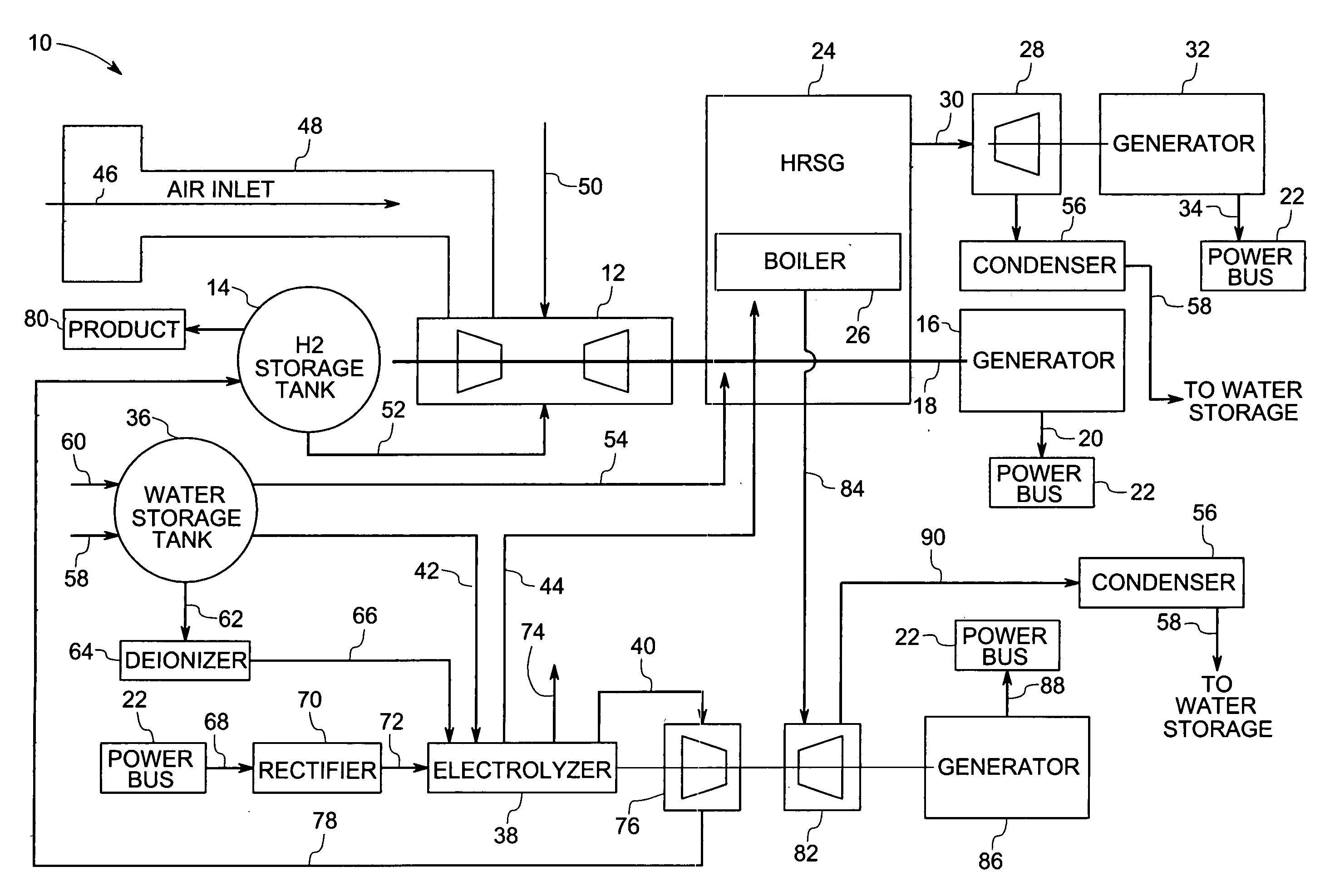
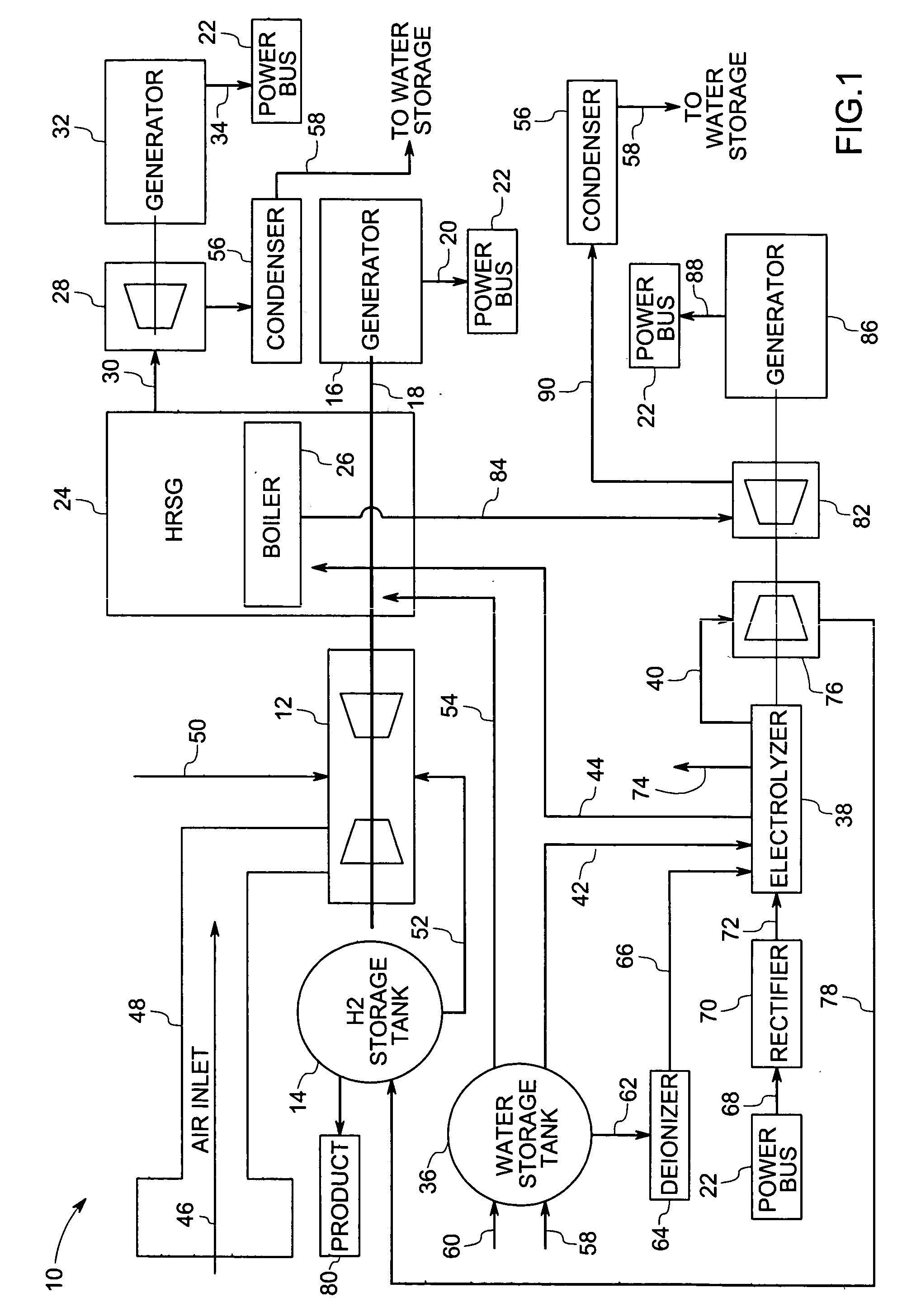
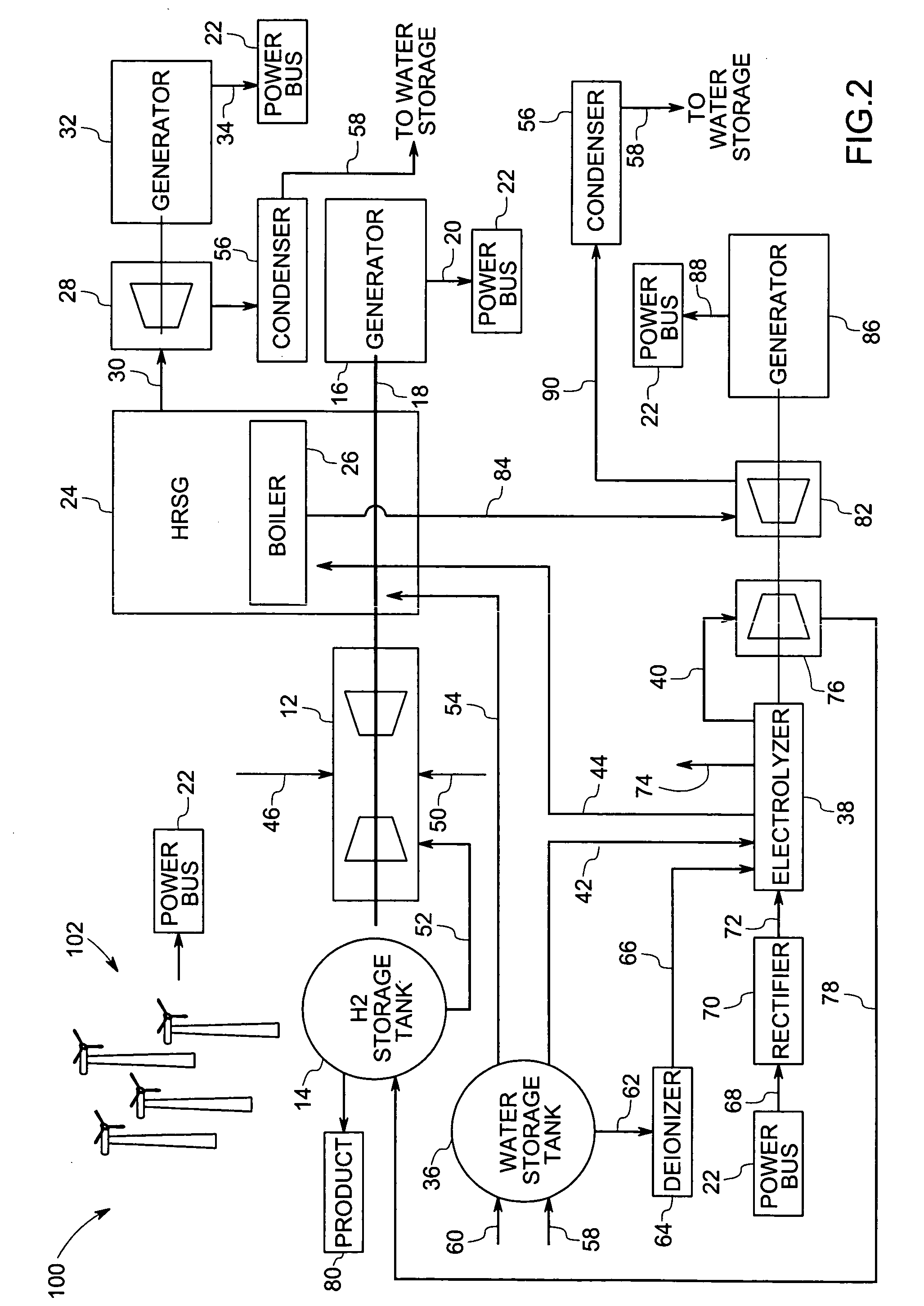
A power generation system comprising a liquid-cooled electrolyzer operable to produce a supply of hydrogen from water is provided. The power generation system may also comprise a steam turbine and a steam production device operable to produce a supply of steam to the steam turbine. The power generation system may also comprise a system operable to provide cooling liquid to the liquid-cooled electrolyzer and to couple heated cooling liquid from the liquid-cooled electrolyzer to the steam production device.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
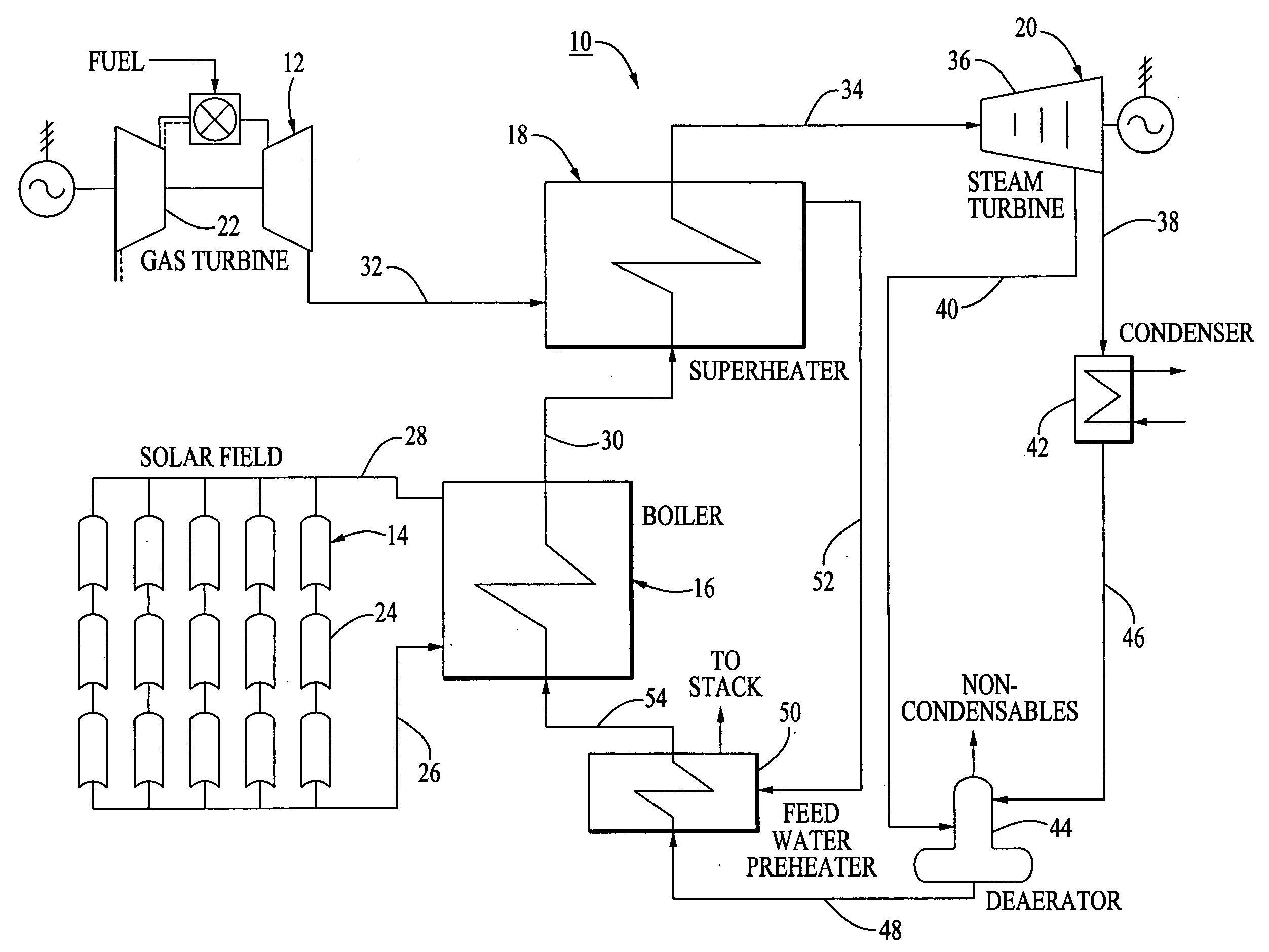
High power density combined cycle power plant
InactiveUS6230480B1Reduce installation costsService degradationEnergy industryGas turbine plantsPower stationCogeneration
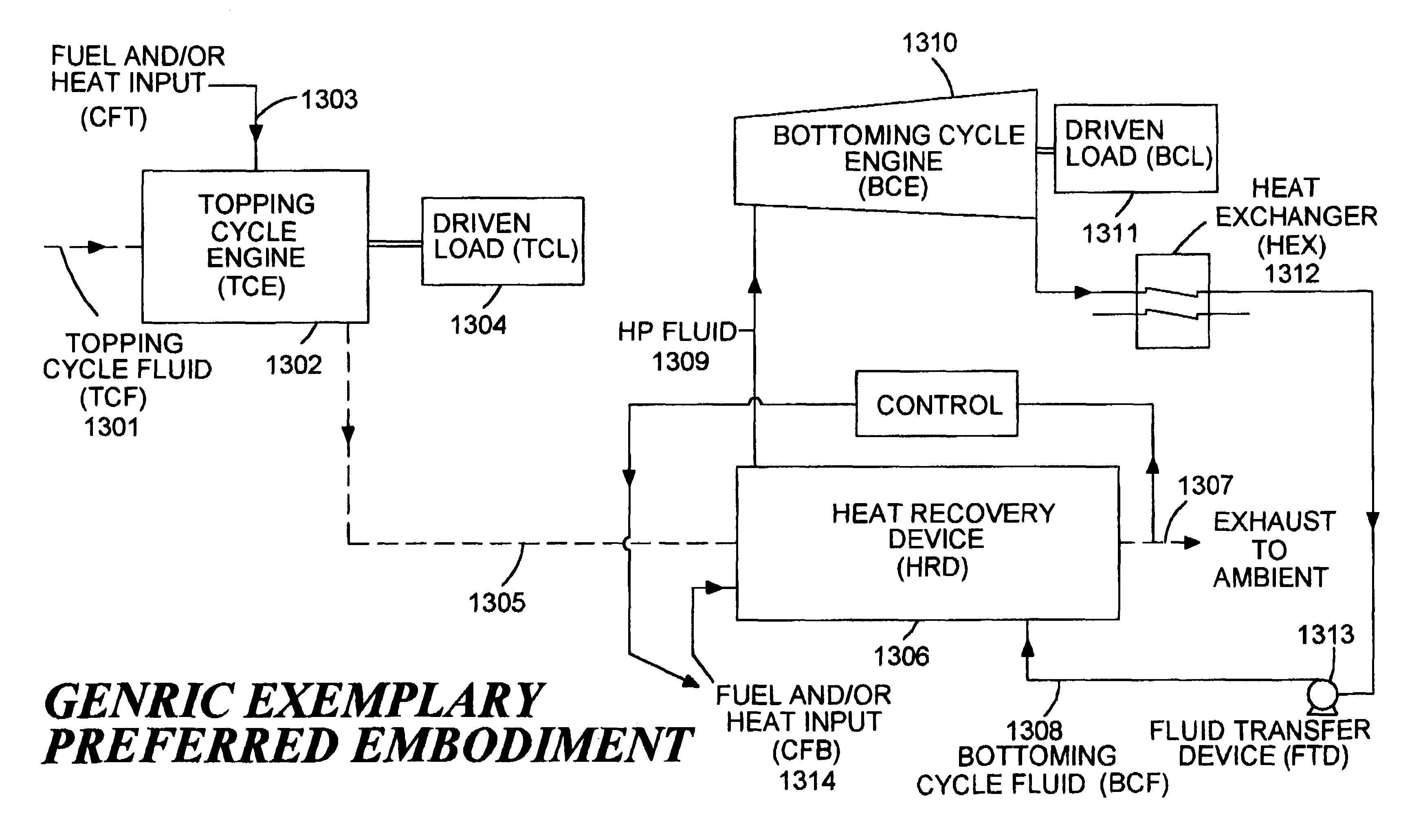
A system and method for increasing the specific output of a combined cycle power plant and providing flexibility in the power plant rating, both without a commensurate increase in the plant heat rate, is disclosed. The present invention demonstrates that the process of upgrading thermal efficiencies of combined cycles can often be accomplished through the strategic use of additional fuel and / or heat input. In particular, gas turbines that exhaust into HRSGs, can be supplemental fired to obtain much higher steam turbine outputs and greater overall plant ratings, but without a penalty on efficiency. This system and method by in large defines a high efficiency combined cycle power plant that is predominantly a Rankine (bottoming) cycle. Exemplary embodiments of the present invention include a load driven by a topping cycle engine (TCE), powered by a topping cycle fluid (TCF) which exhausts into a heat recovery device (HRD). The HRD is fired with a supplementary fuel or provided an additional heat source to produce more energetic and / or a larger quantity of the bottoming cycle fluid (BCF) which is used to power a bottoming cycle engine, (BCE) which drives a load (potentially the same load as the topping cycle engine). Energy contained in either the TCF or BCF is used to power the TCE and BCE respectively, but these fluids, and / or their respective engine exhausts, may also be used to support a wide variety of cogeneration applications.
Owner:ROLLINS III WILLIAM SCOTT
Method of and power plant for generating power by oxyfuel combustion
InactiveUS7874140B2Costs lossesLosses of powerGas turbine plantsHeat recoveryPower stationCombustion
Owner:AMEC FOSTER WHEELER POWER EQUIP CO INC
System and method for oxygen separation in an integrated gasification combined cycle system
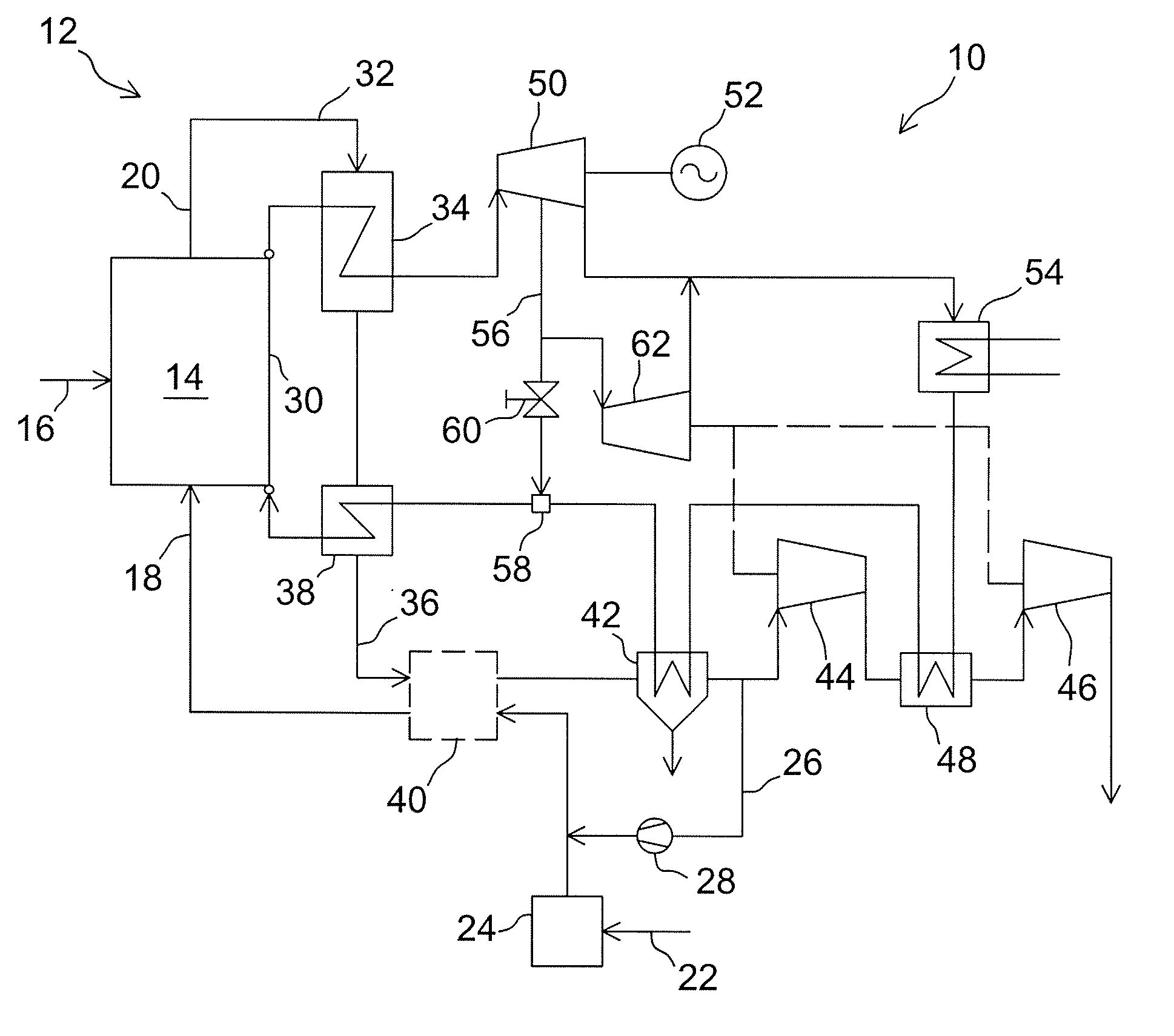
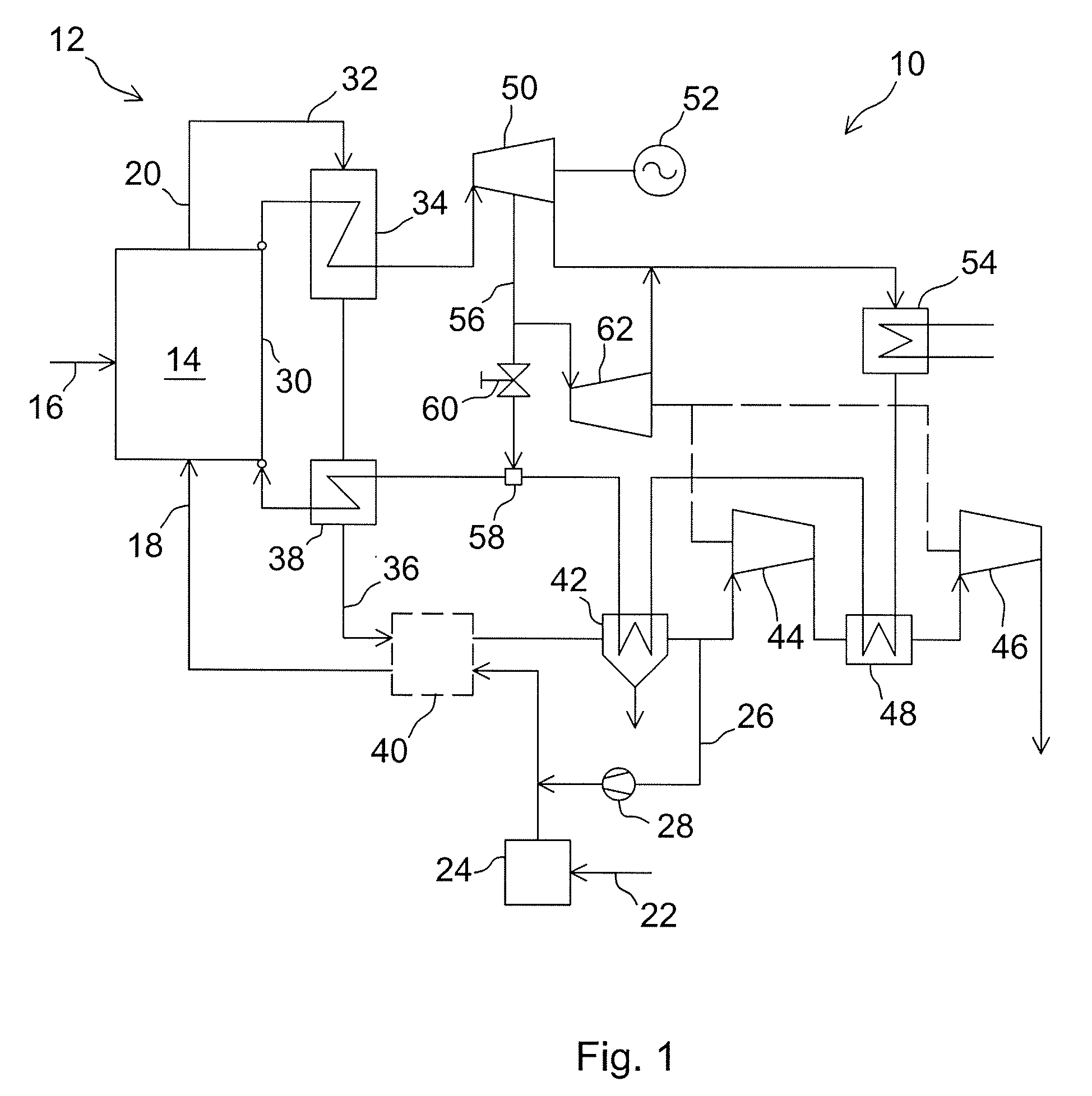
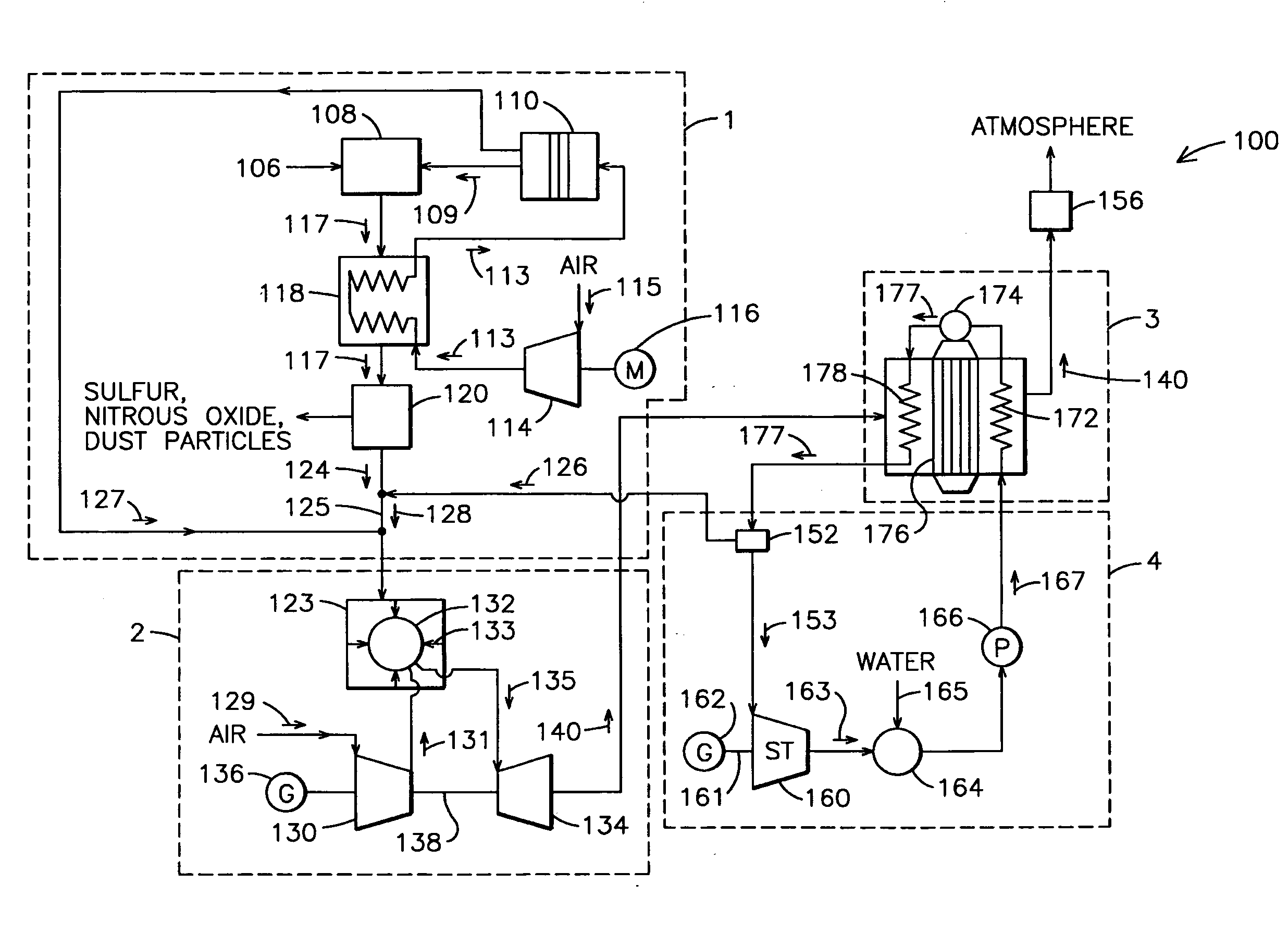
An integrated gasification combined cycle power generation system (100). In one embodiment, shown in FIG. 1, a gasifier (108) is configured to generate synthetic gas (117) from a carbonaceous material (106) and an oxygen supply (109) with a cleaning stage (120) positioned to receive synthetic gas (117) from the gasifier (108) and remove impurities therefrom. A gas turbine combustion system (2) including a turbine (123) is configured to receive fuel (128) from the gasifier (108) and a first air supply (131) from a first air compressor (130). A steam turbine system (4) is configured to generate power with heat recovered from exhaust (140) generated by the gas turbine system (2) and an ion transport membrane air separation unit (110) includes a second air compressor (114) for generating a second air supply (113). A first heat exchanger (118) is configured to cool the synthetic gas (117) prior to removal of impurities in the cleaning stage (120) by flowing the second air supply (113) through the first heat exchanger (118) so that the second air supply (113) receives heat from the synthetic gas (117).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Hybrid generation with alternative fuel sources
InactiveUS7191597B2Increase rangeIncreasing total rated powerPhotovoltaic supportsAuxillary drivesElectricityAlternative fuels
A generating facility is provided for generating electricity from both solar and non-solar energy sources. The solar generating portion of the facility includes capability to directly generate electricity from solar insolation, or to store the solar energy in a tangible medium, including stored heat, or solar generating fuel. The generating facility is configured to generate electricity simultaneously from both solar and non-solar sources, as well a solely from immediate solar insolation and from solar energy stored in a tangible medium. Additionally, the solar generating capacity may be segregated; such that separate spectra of solar insolation are used to capture heat for steam turbine based electrical generation, capture light energy for photovoltaic based electrical generation, and to grow biomass to generate a solar fuel.
Owner:LOS ANGELES ADVISORY SERVICES +1
Steam jet type heat pump heat distribution system for recovering thermal power plant condensing residual heat
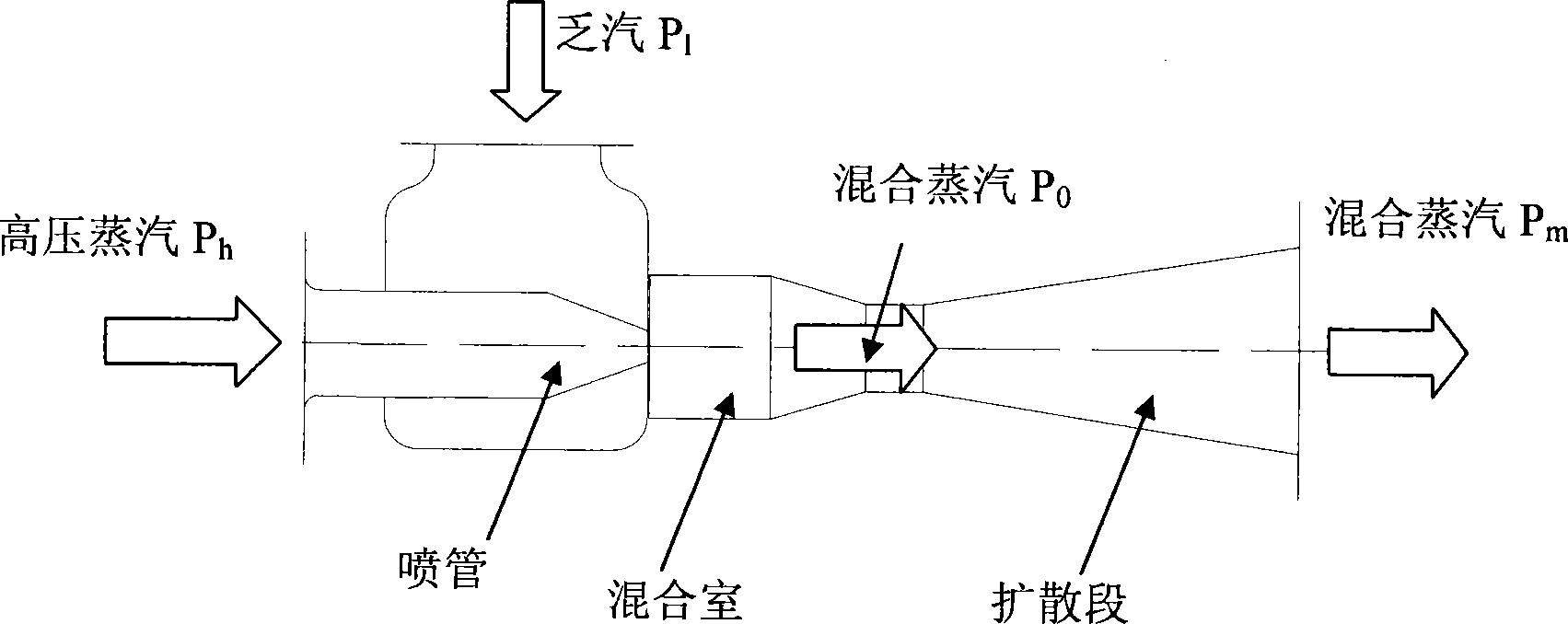
InactiveCN101240909AEasy to manufactureImprove heat transfer effectFeed water supplyEnergy efficient heating/coolingLow voltageCore component
The present invention provides a steam injection heatpump heating system. The technical solution is that the system is composed of a steam injector, a high voltage steam pipeline, a low voltage steam pipeline, a throttling gear and a bypass connecting pipe. The high voltage steam enters in the heat exchanger heaing backwater after injecting lower steam turbine voltage condensing in low temperature, this realises waste heat recovery in low temperature condensing steam of the steam turbine. The core component is the steam injector, the high voltage heat supplying pumping is used as high-velocity jet acceleratively formed in the injecting tube of the working steam, and lower voltage steam turbine is rolled in the mixing room as injected flow, mixing steam in the expanding section of the steam injector is decelerately compressed in a certain back pressure, then sending to the heat interchanger for heating backwater, a certian back pressure mixing steam condenses to water after heat releasing in the exchanger, returning to the backwater system of electrical factory, completing thermal circuit of the combined heat and power generation set.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
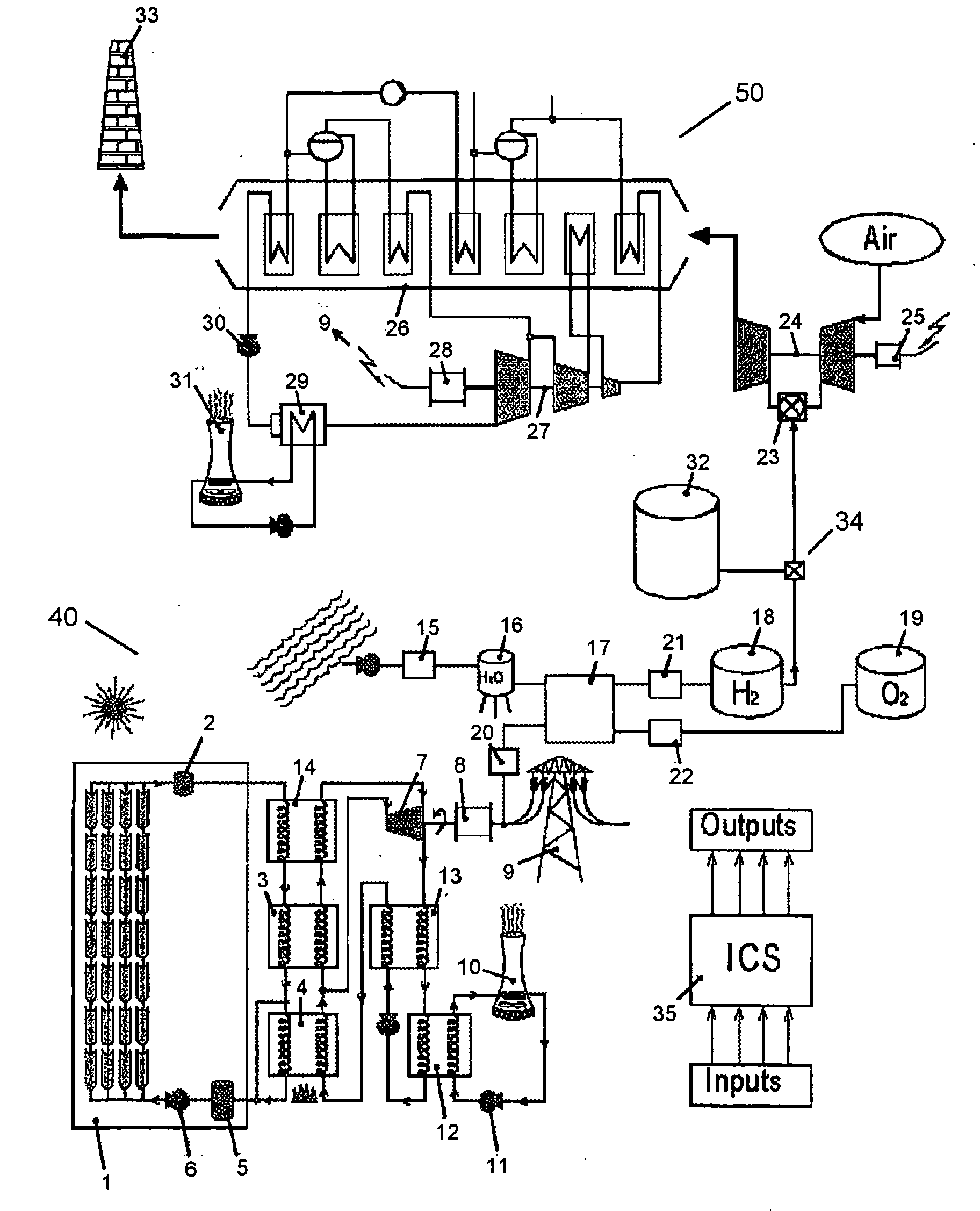
Electrical generating system using solar energy and gas turbine
An apparatus for generating electricity using both solar energy and a gas turbine includes (a) a gas turbine electric generator; (b) a solar energy collector array; (c) a vaporizer for vaporizing a working fluid liquid, such as water, using thermal energy derived from the solar energy collector array; (d) one or more superheaters for superheating working fluid vapor produced in the vaporizer; and (e) a working fluid vapor turbine electric generator, such as a steam turbine electric generator, the working fluid vapor turbine electric generator being driven by the superheated working fluid vapor. The apparatus is configured such that all of the working fluid vapor exiting the one or more superheaters is that which is produced in the vaporizer.
Owner:SKOWRONSKI MARK
Method and system for controlling a powerplant during low-load operations
The present invention provides a system and method of operating a combined-cycle powerplant at part-load without shutting down an HRSG and steam turbine. The present invention may apply to a powerplant operating in an open-cycle mode. The present invention may also apply to a powerplant operating in a closed-cycle mode.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for treatment of waste
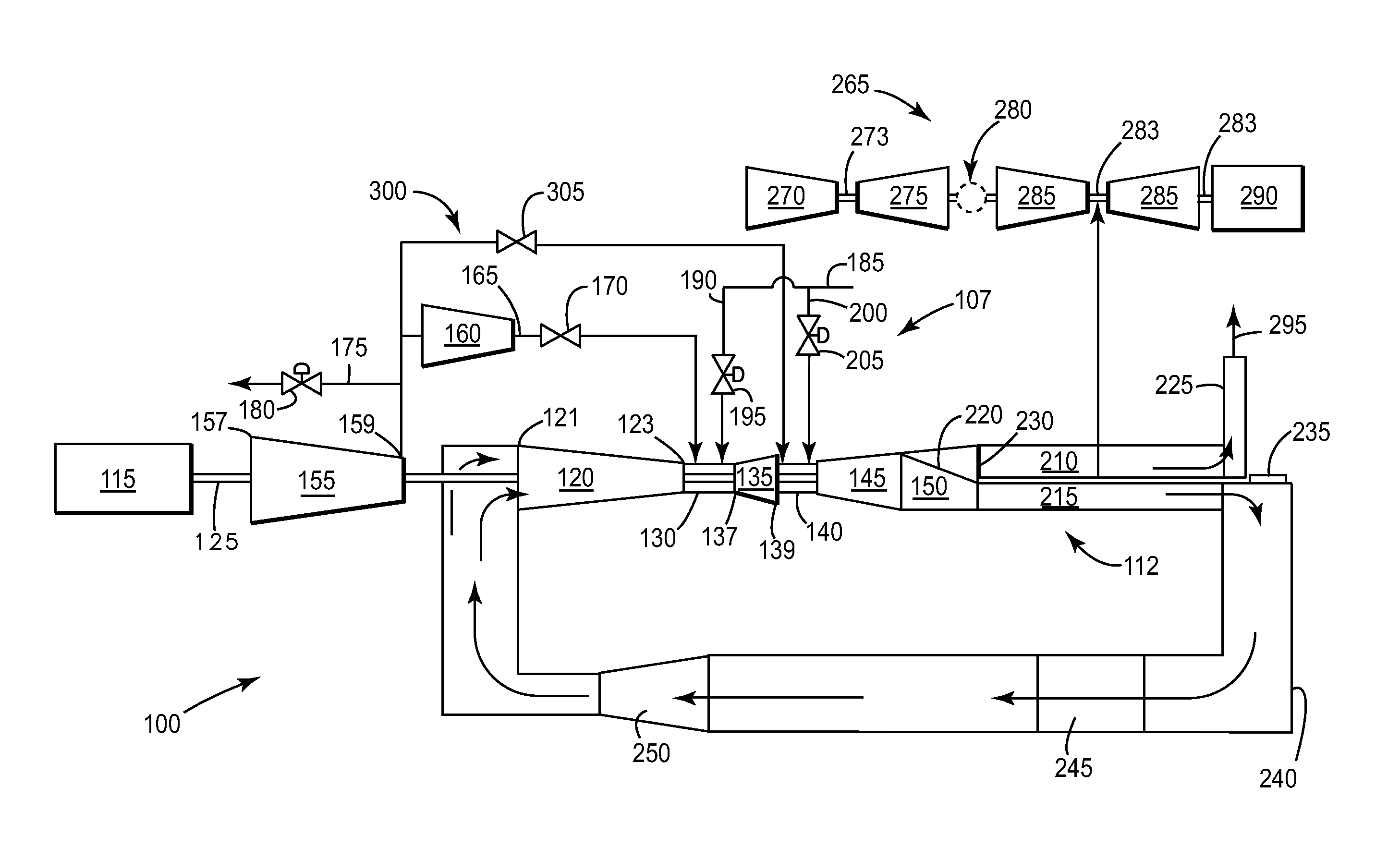
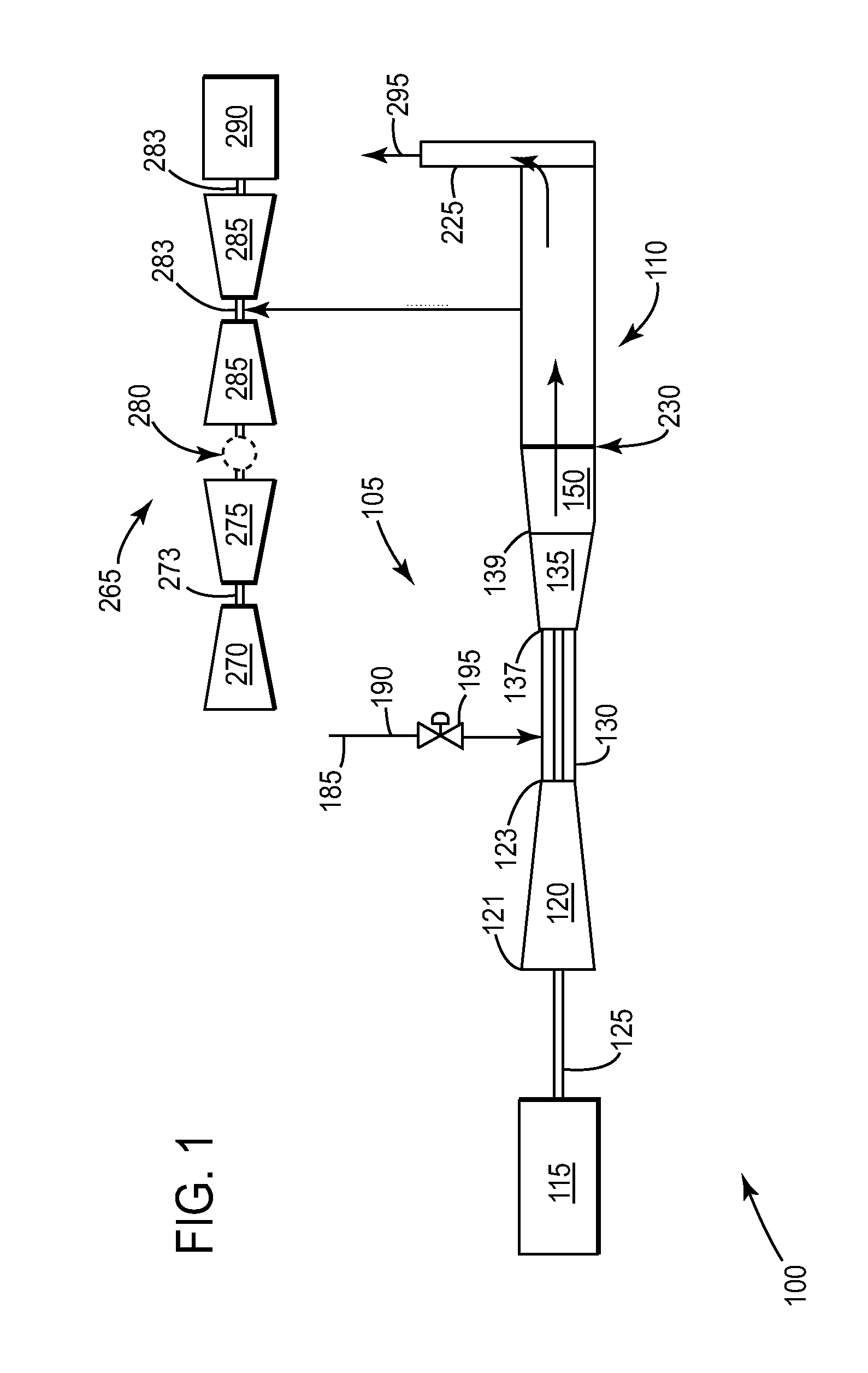
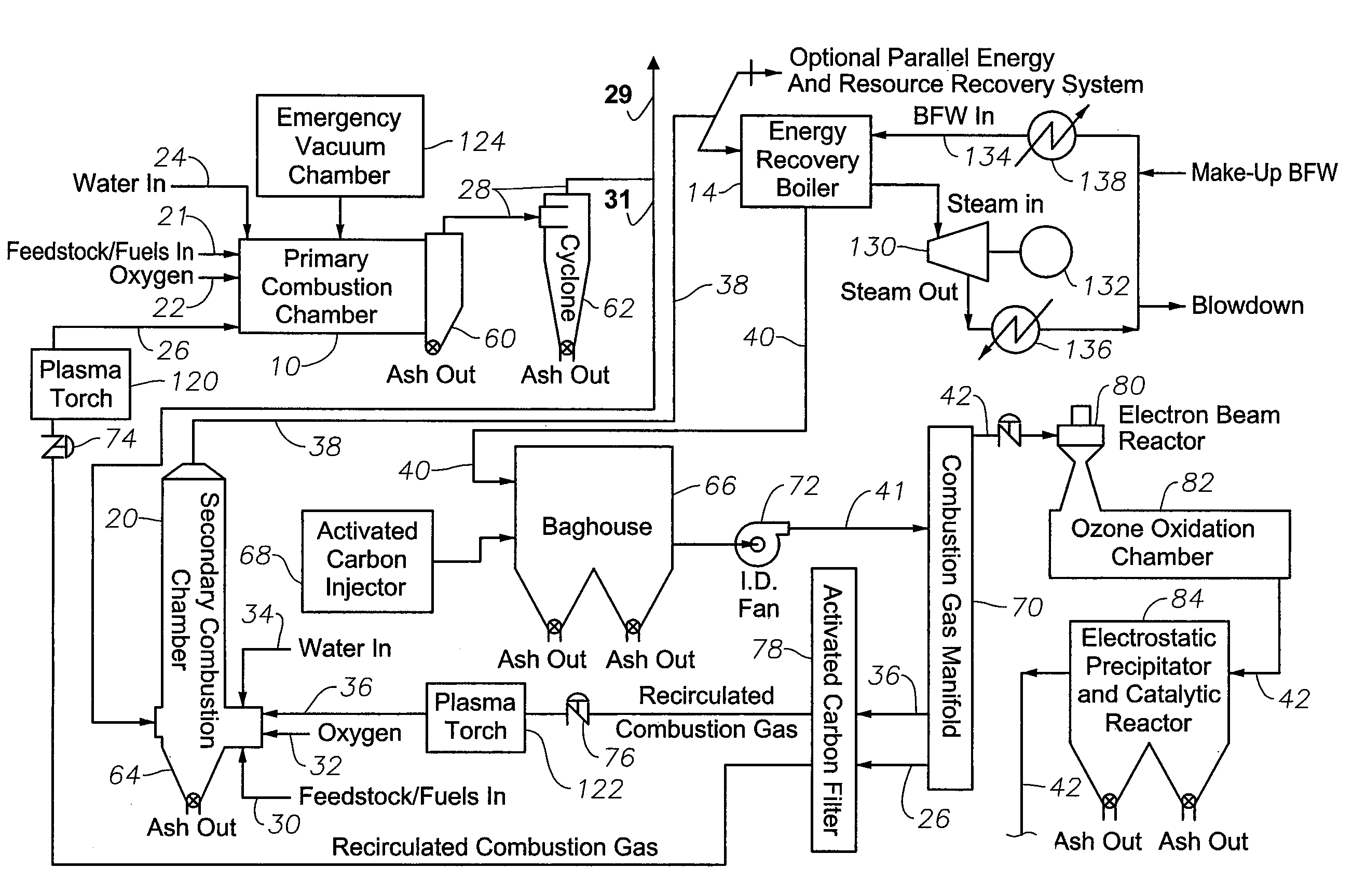
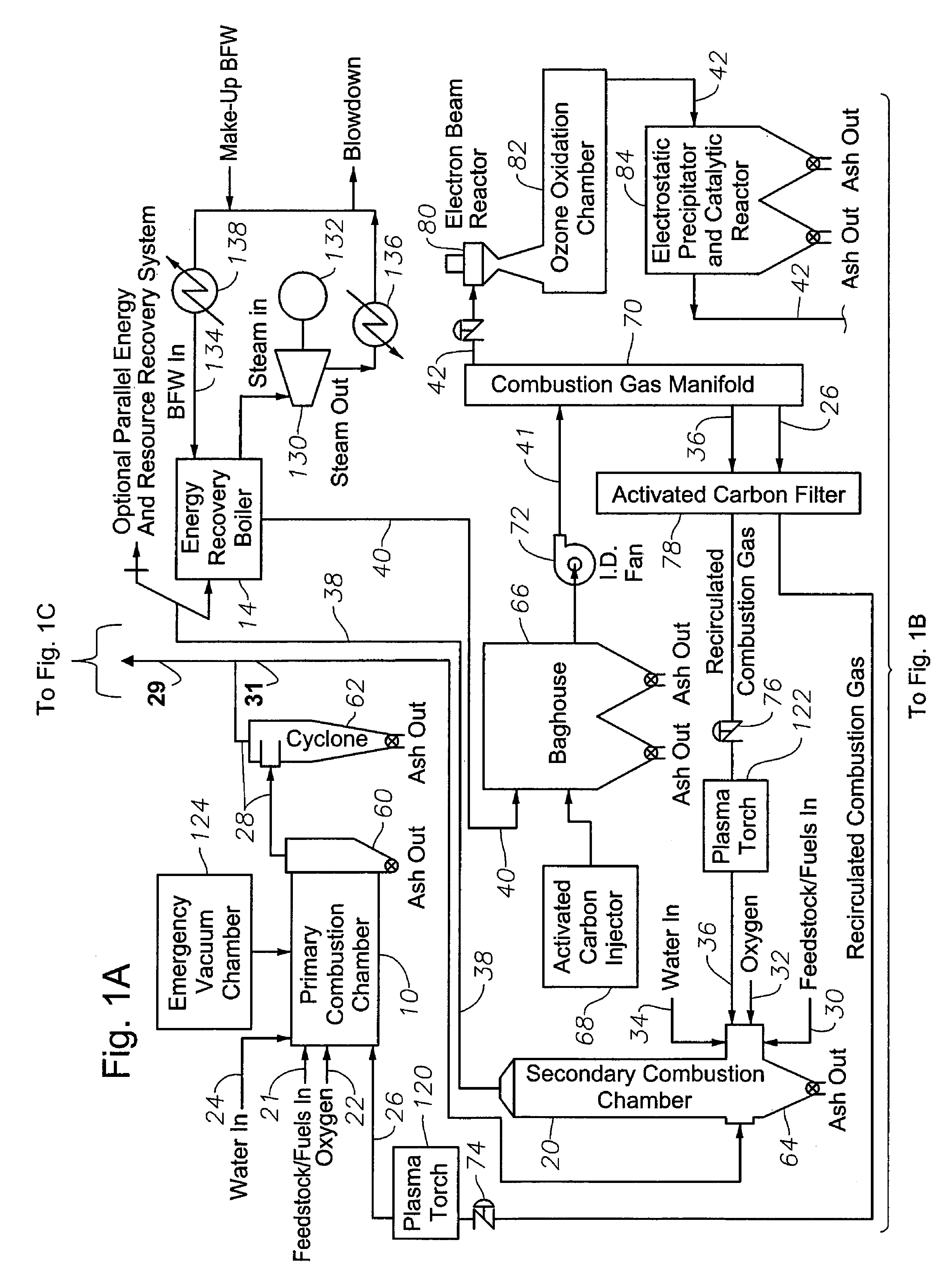
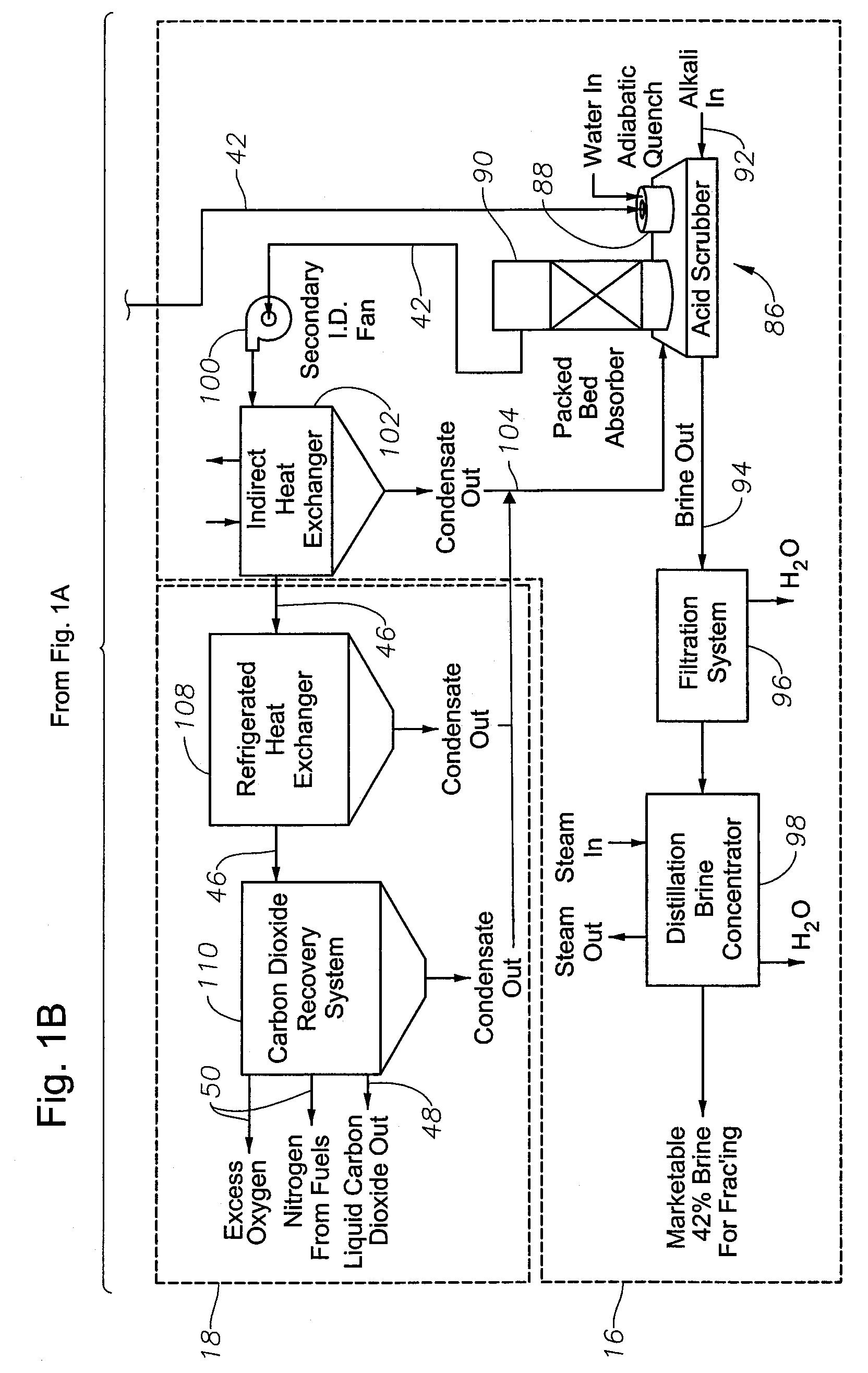
InactiveUS6619214B2Efficient and reliable in operationEasy maintenanceSolid fuel combustionIncinerator apparatusEngineeringTransfer mechanism
An apparatus for treating waste material that comprises four major cooperating subsystems, namely a pyrolytic converter, a two-stage thermal oxidizer, a steam generator and a steam turbine driven by steam generated by the steam generator. In operation, the pyrolytic converter is uniquely heated without any flame impinging on the reactor component and the waste material to be pyrolyzed is transported through the reaction chamber of the pyrolytic converter by a pair of longitudinally extending, side-by-side material transfer mechanisms. Each of the transfer mechanisms includes a first screw conveyor section made up of a plurality of helical flights for conveying the heavier waste and a second paddle conveyor section interconnected with the first section for conveying the partially pyrolyzed waste, the second section comprising a plurality of paddle flights. Once operating, the apparatus is substantially self-sustaining and requires a minimum use of outside energy sources for pyrolyzing the waste materials.
Owner:APS IP HLDG
Reduced-emission gasification and oxidation of hydrocarbon materials for liquid fuel production
InactiveUS8038746B2Reduce system sizeHigh heat transfer rateHydrogenGas modification by gas mixingLiquid hydrocarbonsLiquid fuel
Owner:CLARK STEVE L
Hybrid generation with alternative fuel sources
InactiveUS20070012041A1Increase rangeIncreasing total rated powerPhotovoltaic supportsAuxillary drivesAlternative fuelsLight energy
A generating facility is provided for generating electricity from both solar and non-solar energy sources. The solar generating portion of the facility includes capability to directly generate electricity from solar insolation, or to store the solar energy in a tangible medium, including stored heat, or solar generating fuel. The generating facility is configured to generate electricity simultaneously from both solar and non-solar sources, as well a solely from immediate solar insolation and from solar energy stored in a tangible medium. Additionally, the solar generating capacity may be segregated; such that separate spectra of solar insolation are used to capture heat for steam turbine based electrical generation, capture light energy for photovoltaic based electrical generation, and to grow biomass to generate a solar fuel.
Owner:LOS ANGELES ADVISORY SERVICES +1
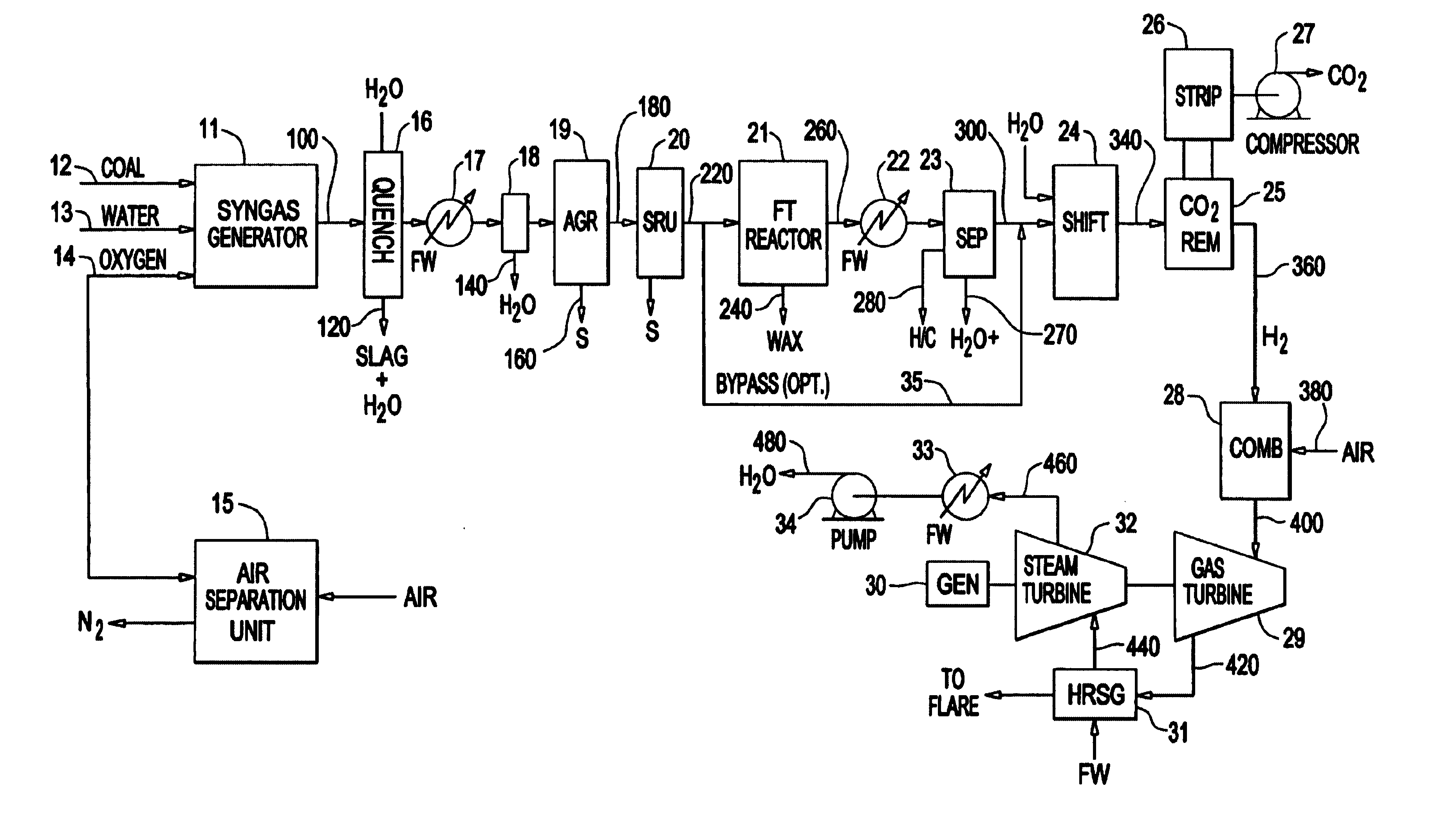
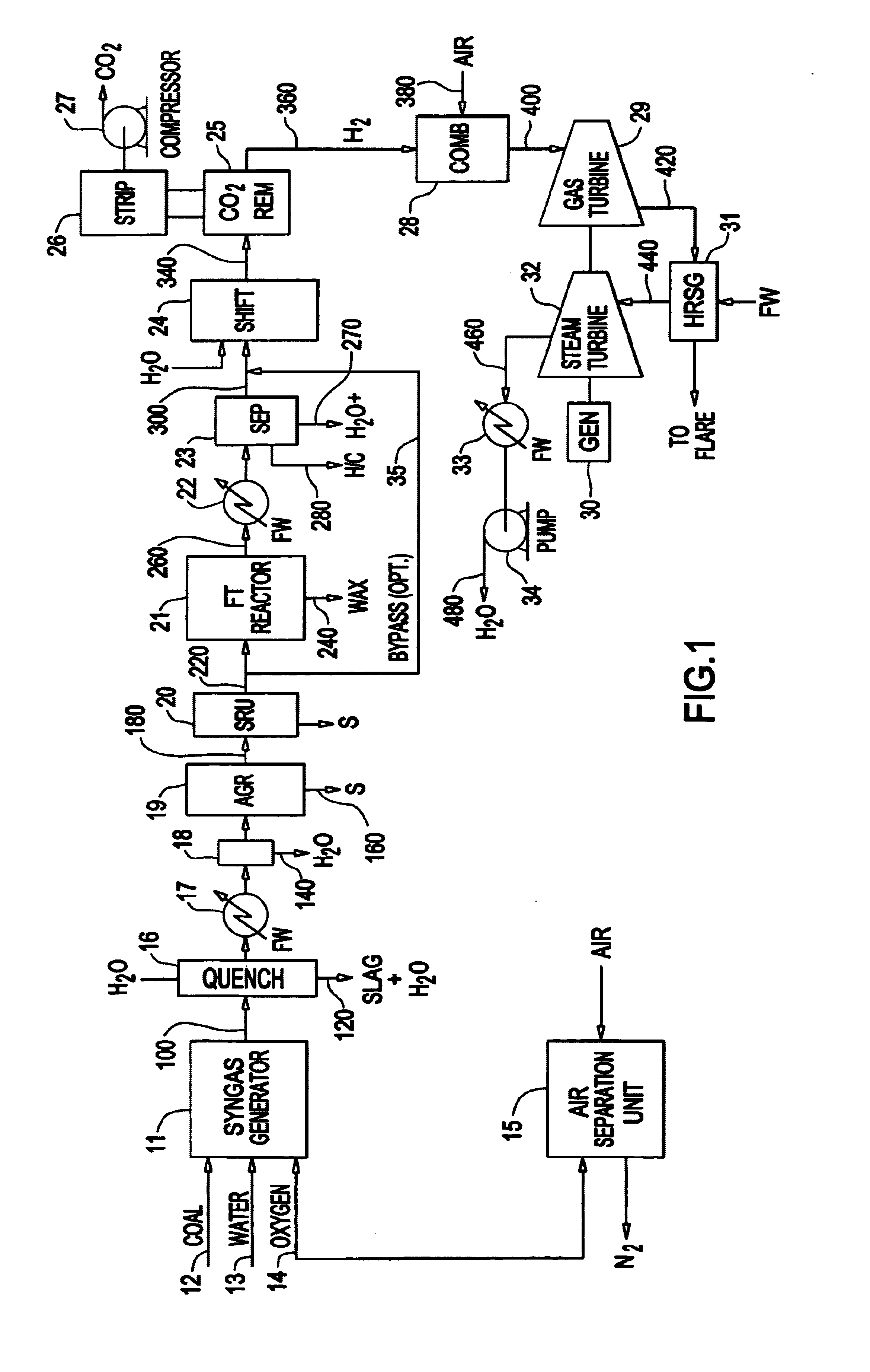
Integrated Fischer-Tropsch and power production plant with low CO2 emissions
A plant for producing Fischer-Tropsch liquids and electrical power with greatly reduced emissions of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere is made up of a syngas generator unit, an air separation unit, a Fischer-Tropsch unit, a CO2 removal unit, and a combined cycle electricity generation unit. Each of Fischer-Tropsch liquids, carbon dioxide, and electrical power can be recoverable under proper economic conditions. Electrical power is recoverable by the use of a gas turbine fueled by predominantly hydrogen and a steam turbine powered by steam generated by cooling exhaust gases from the gas turbine. Sequestration of CO2 and fueling the gas turbine with hydrogen reduces the amount of greenhouse gases emitted to the atmosphere.
Owner:RES USA LLC
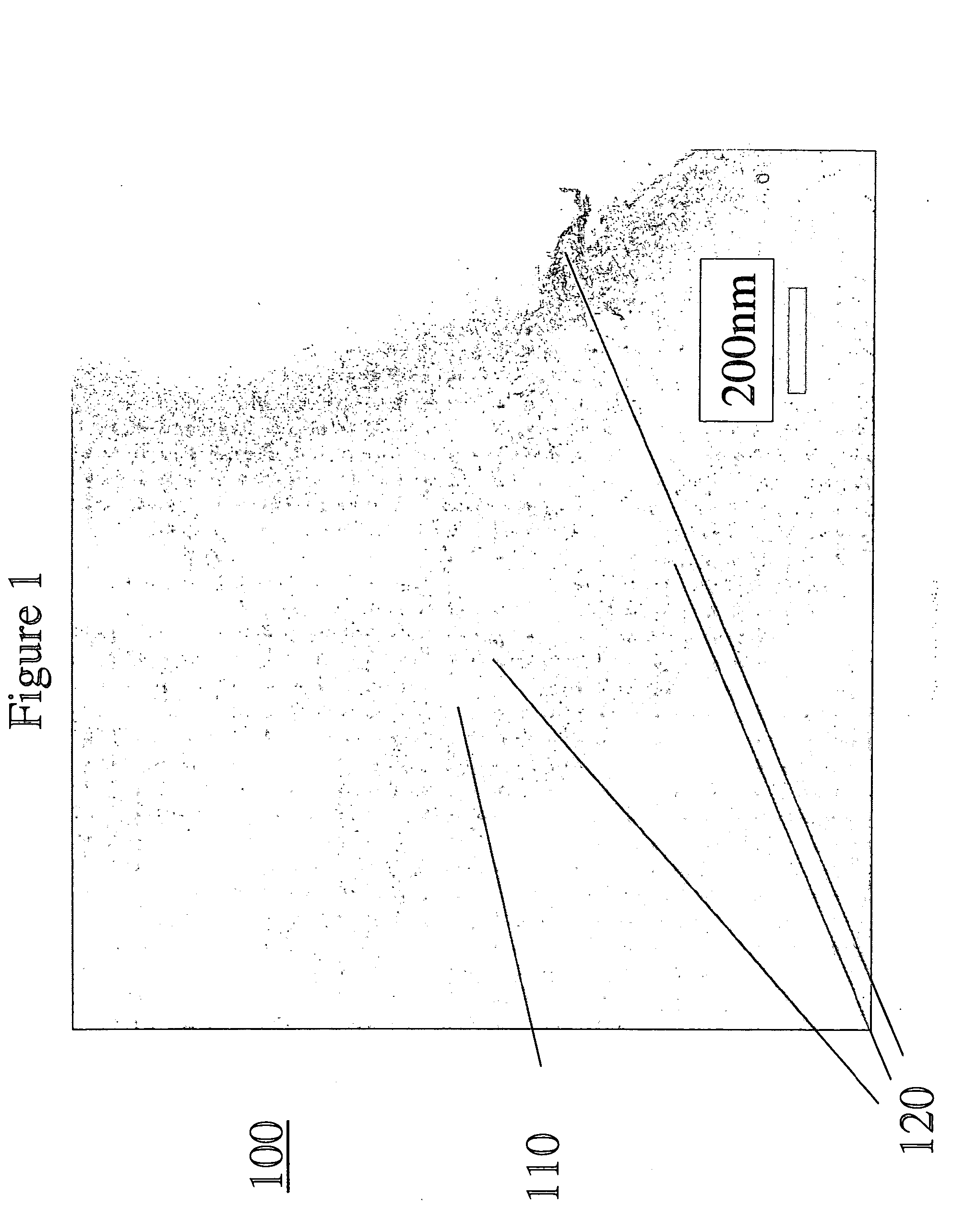
Metallic alloy nanocomposite for high-temperature structural components and methods of making
InactiveUS20050133121A1Increase volume fractionTransportation and packagingMetal-working apparatusNanocompositeAirplane
A nanocomposite comprising a plurality of nanoparticles dispersed in a metallic alloy matrix, and a structural component formed from such a nanocomposite. The metallic matrix comprises at least one of a nickel-based alloy and an iron-based alloy. The nanocomposite contains a higher volume fraction of nanoparticle dispersoids than those presently available. The structural component include those used in hot gas path assemblies, such as steam turbines, gas turbines, and aircraft turbine. A method of making such nanocomposites is also disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com