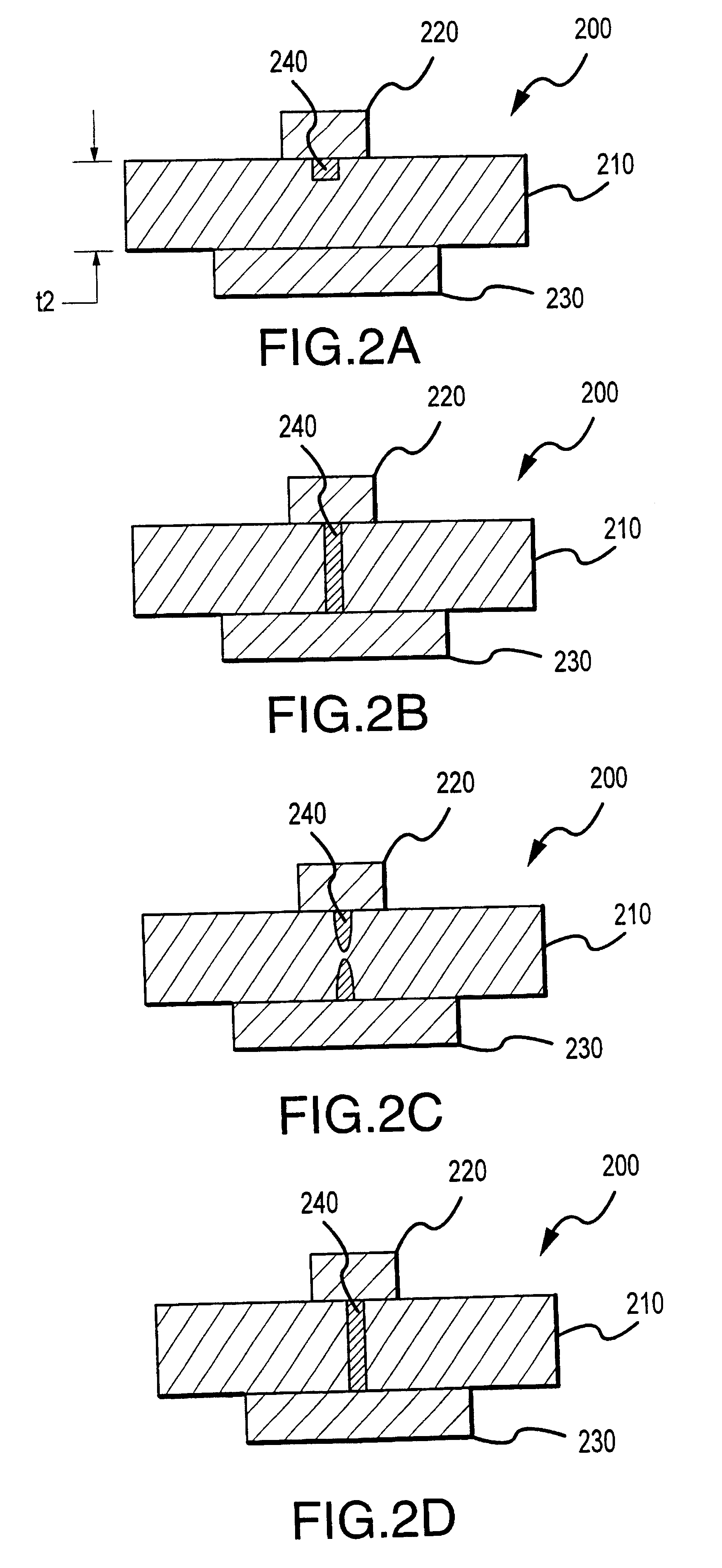
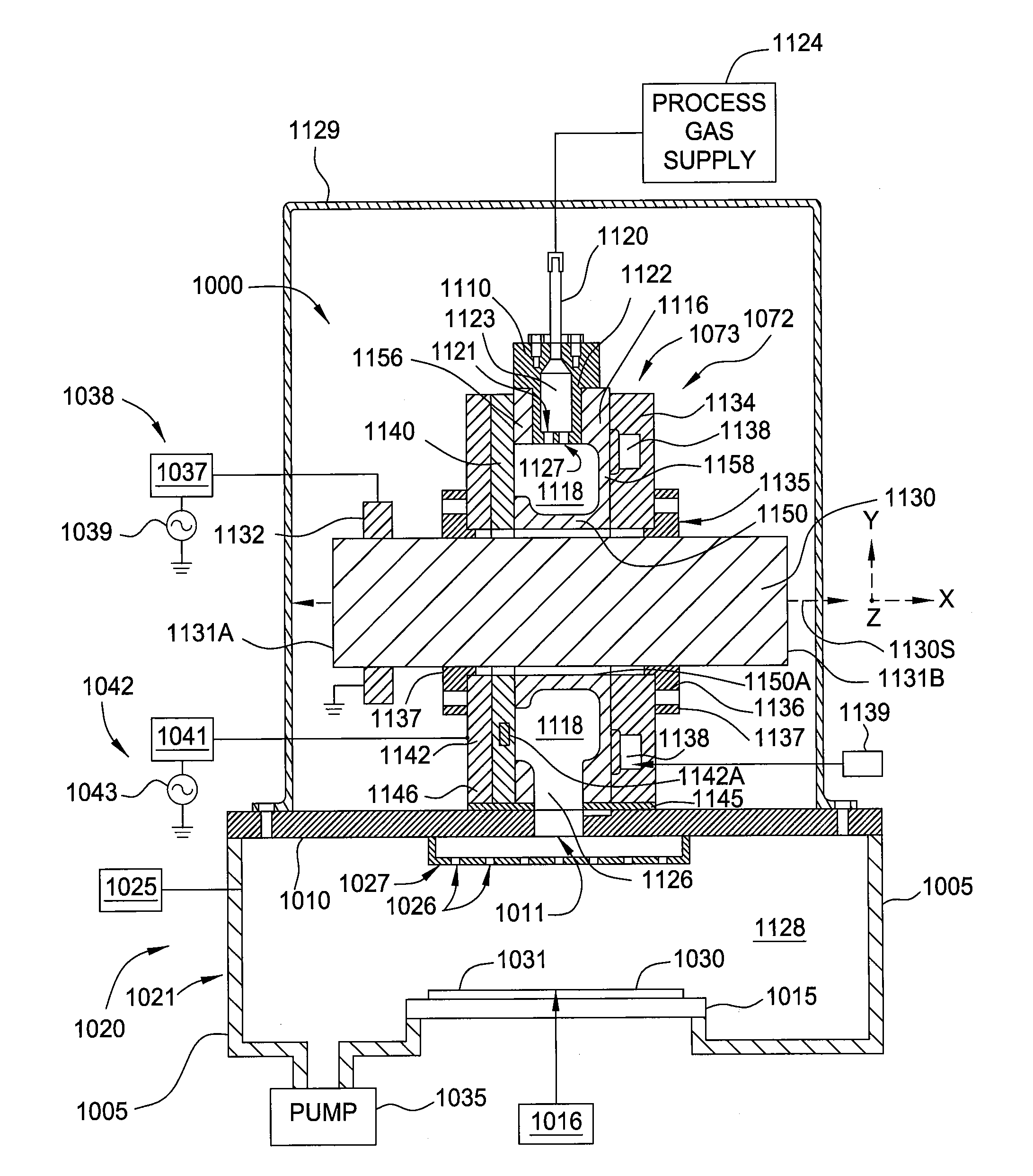
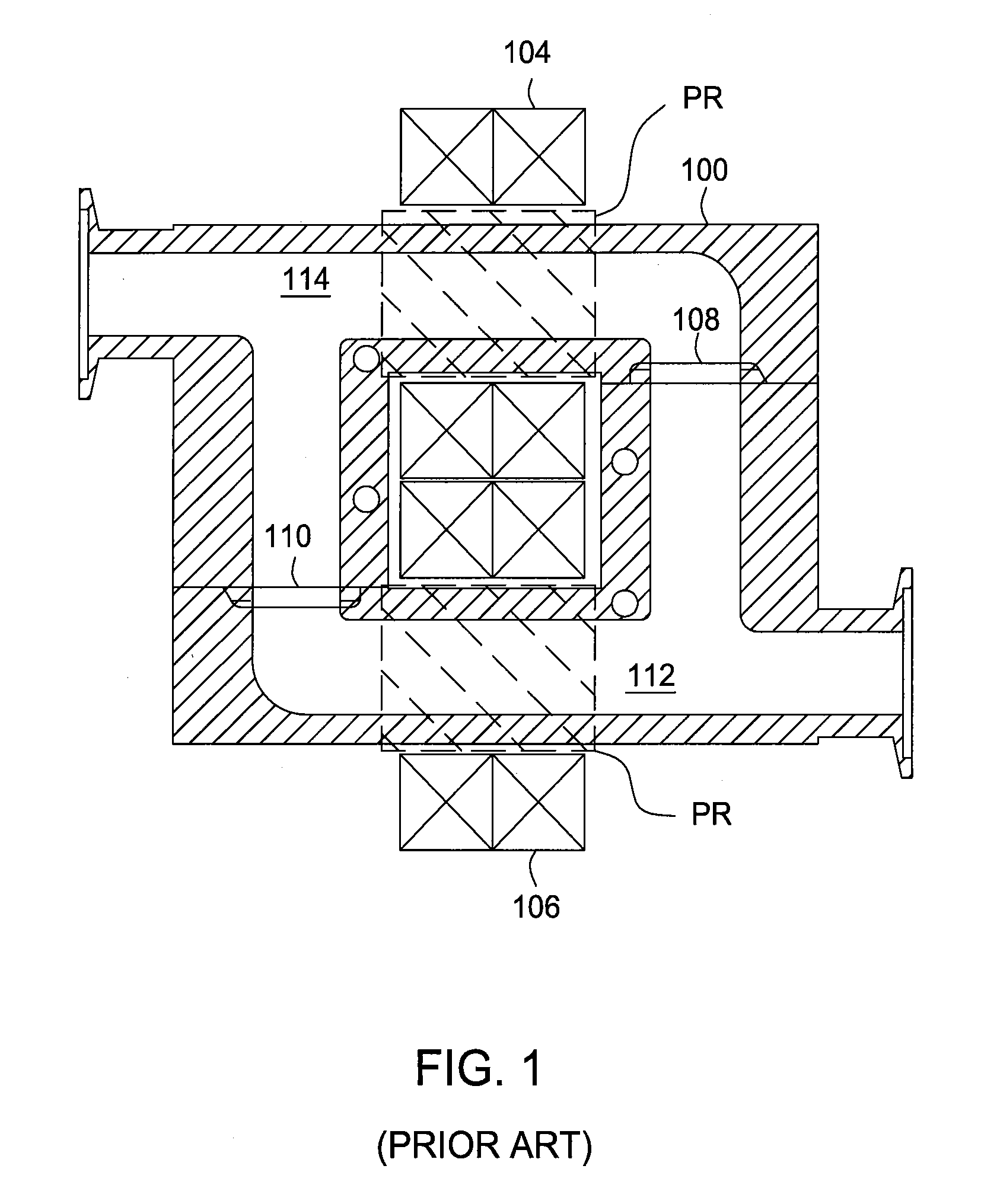
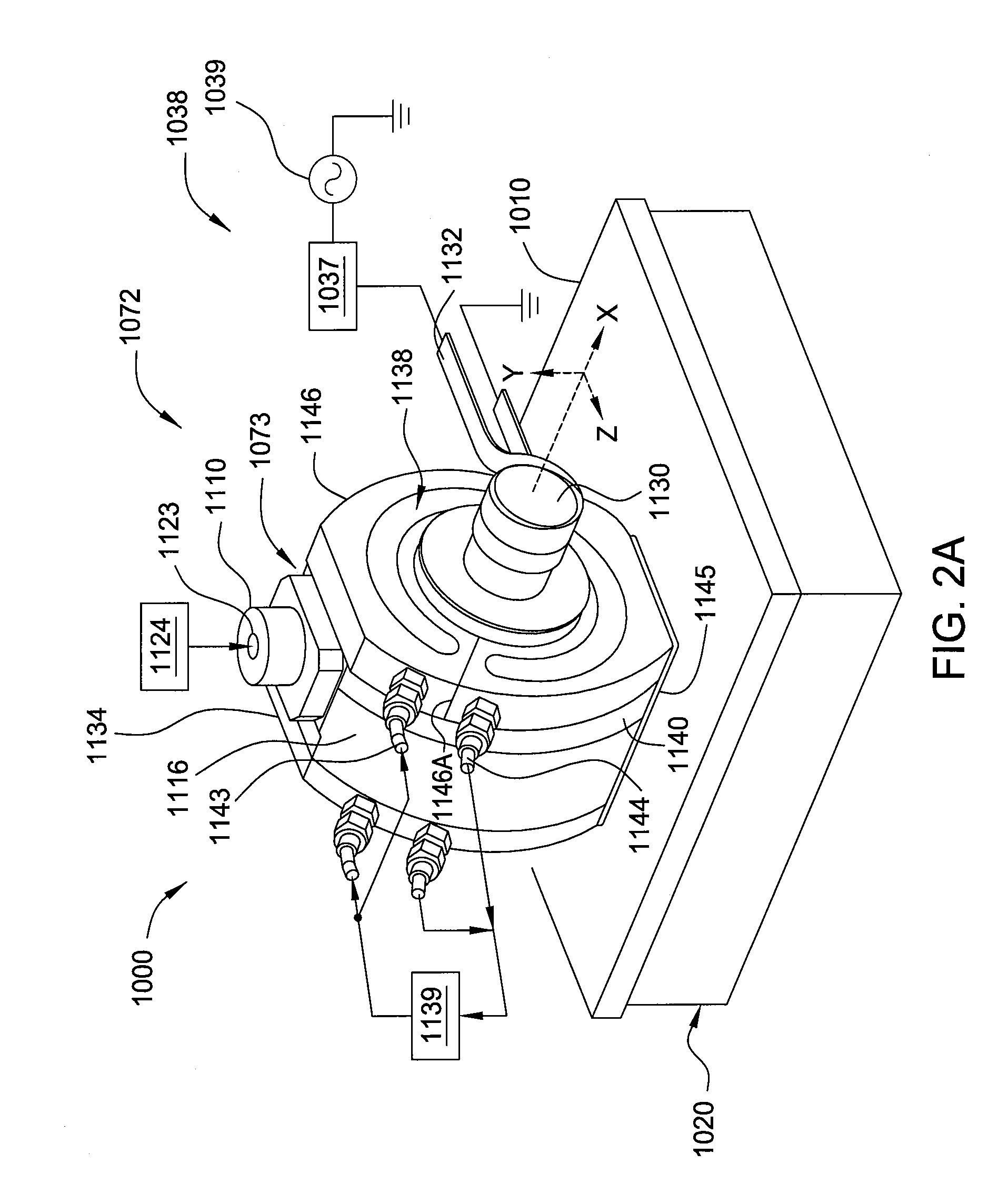
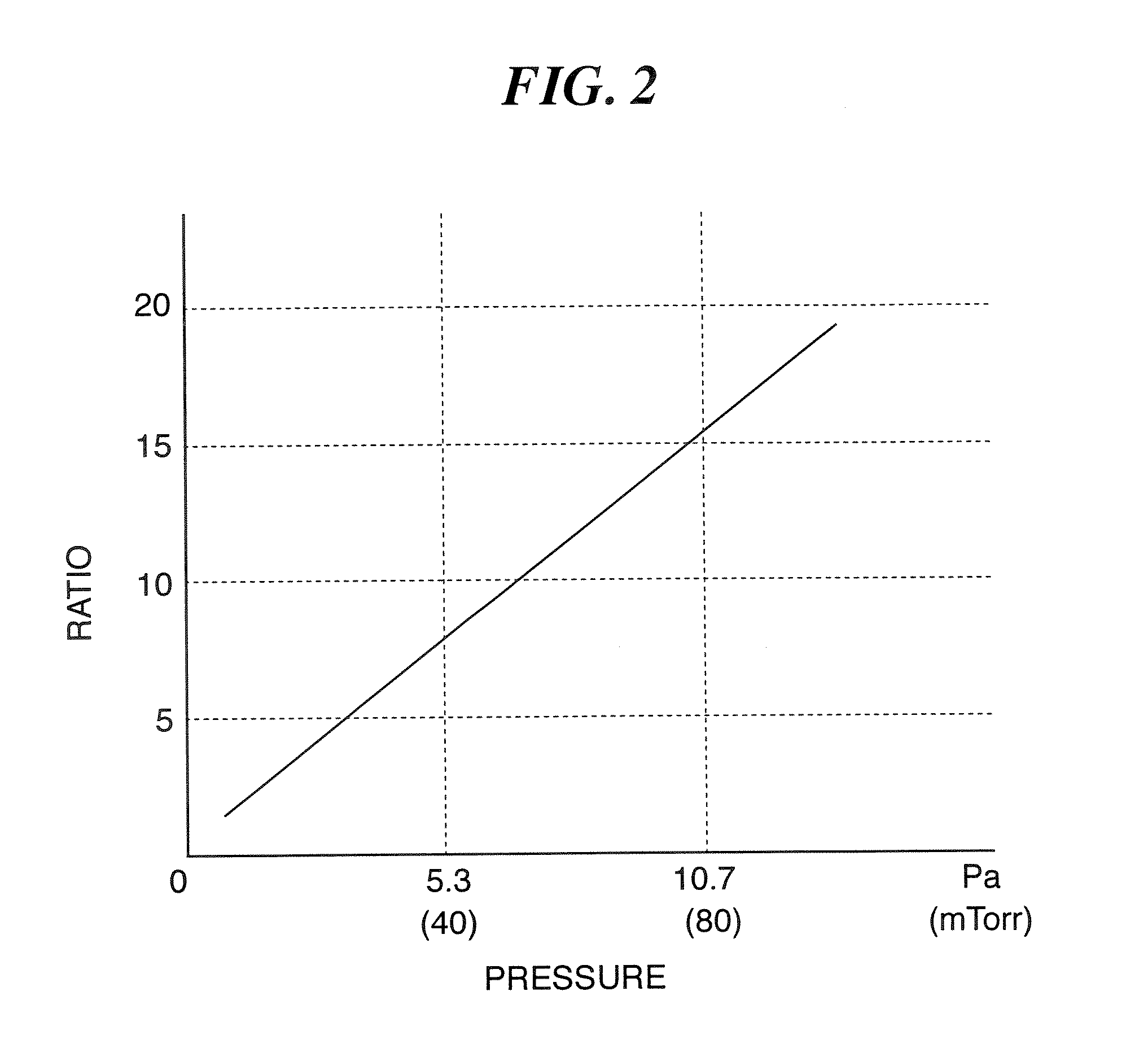
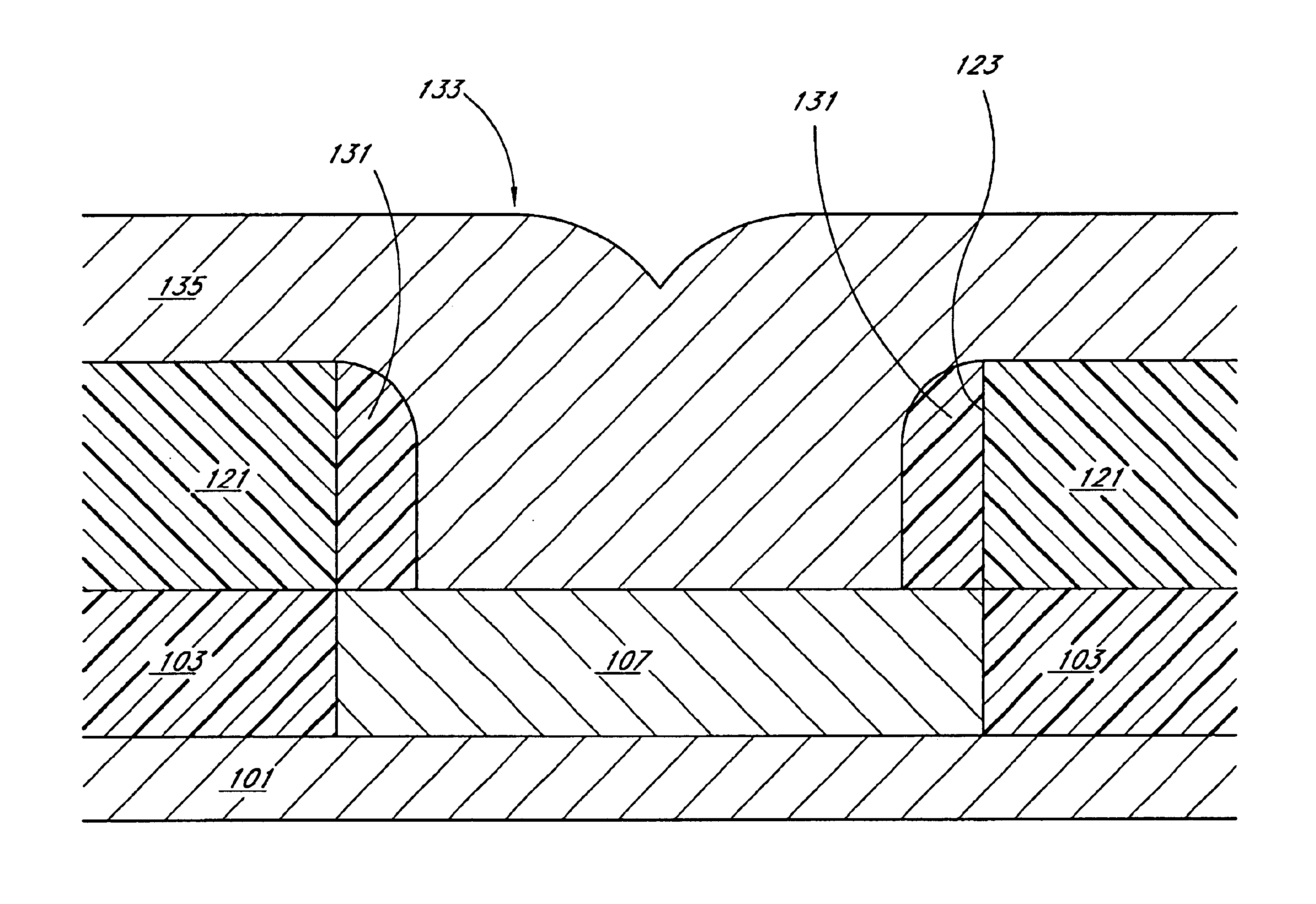
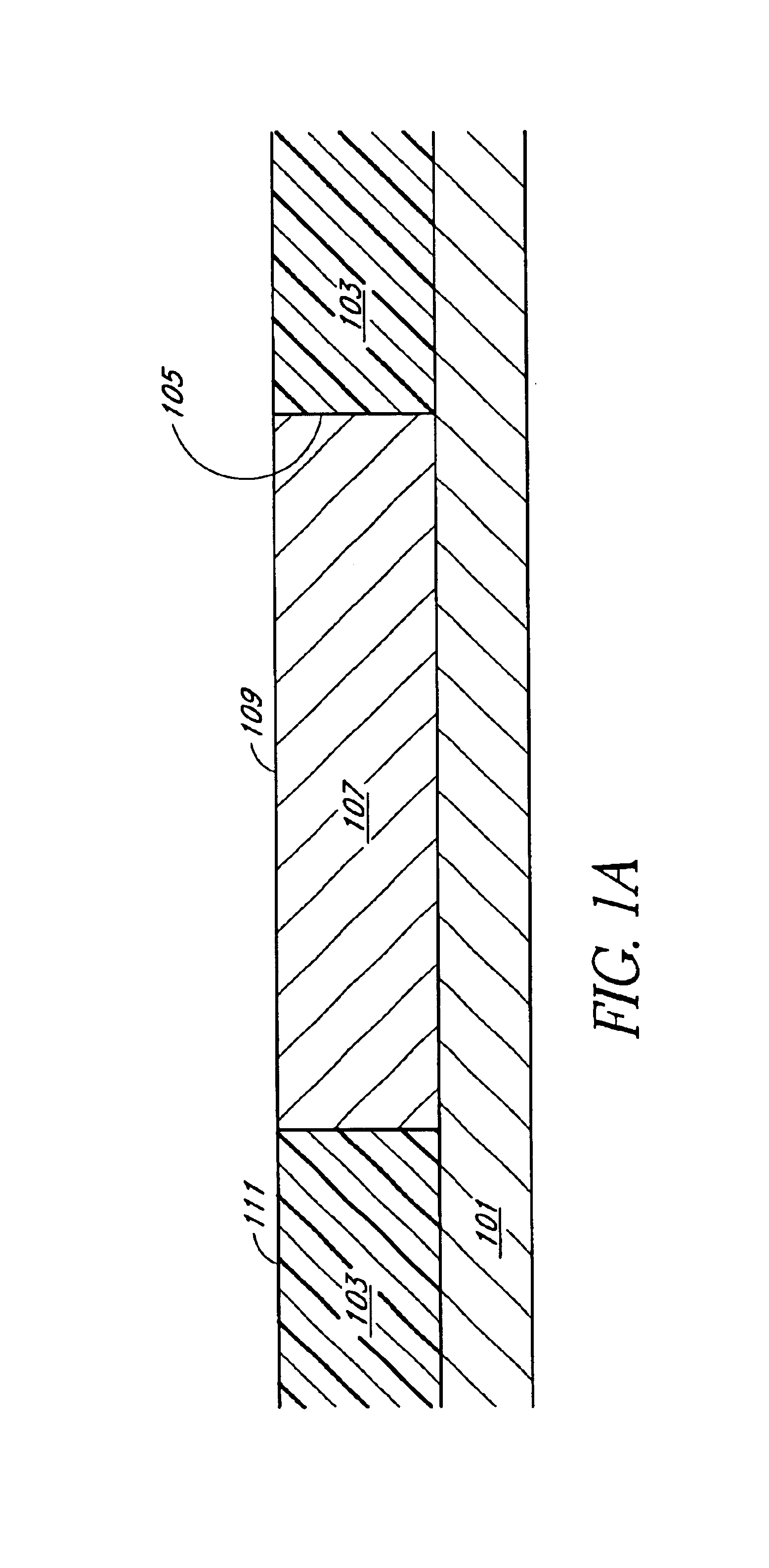
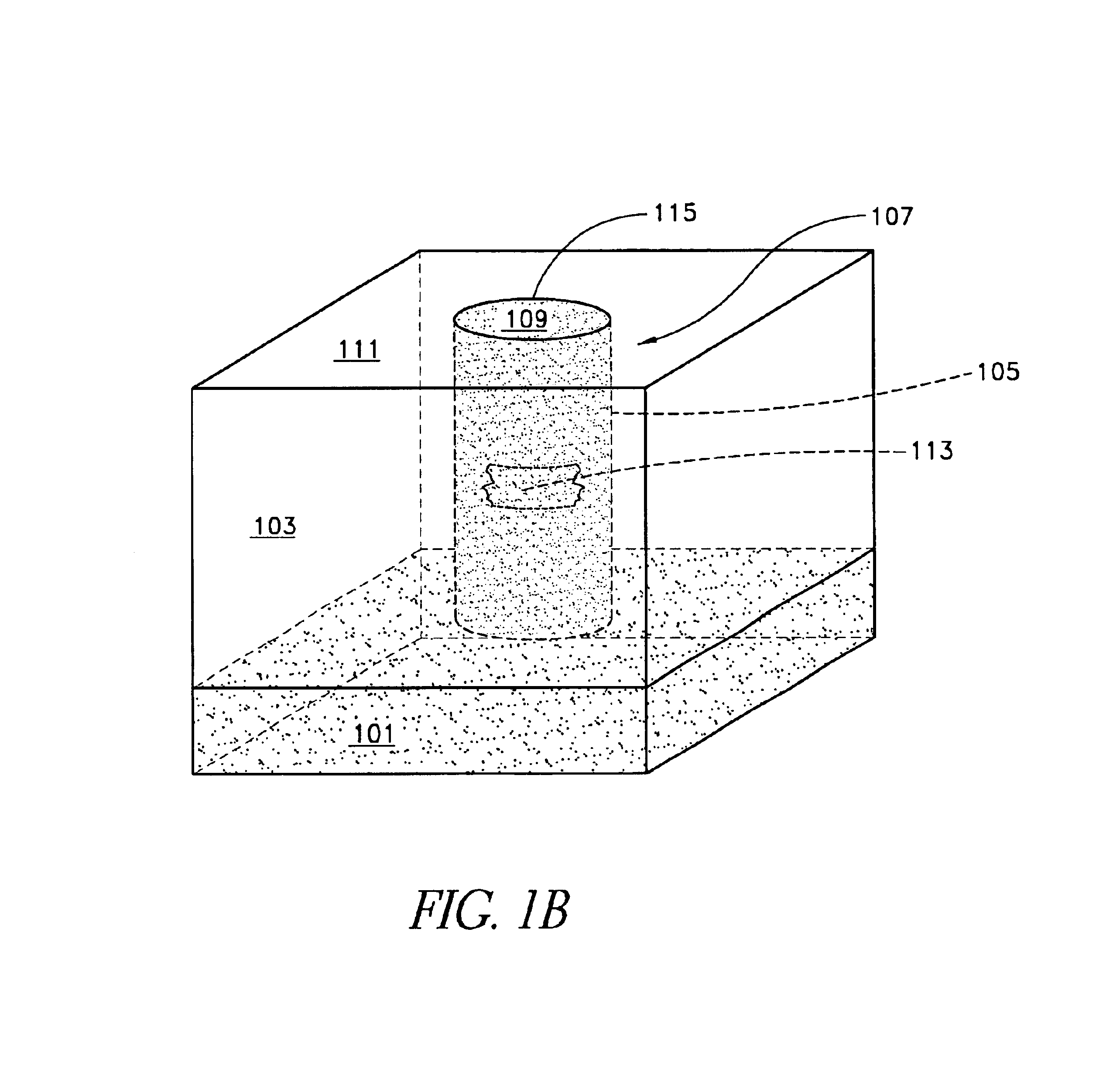
Patents
Literature
118961 results about "Ion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An ion (/ˈaɪɒn, -ən/) is an atom or molecule that has a net electrical charge. Since the charge of the electron (considered negative by convention) is equal and opposite to that of the proton (considered positive by convention), the net charge of an ion is non-zero due to its total number of electrons being unequal to its total number of protons. A cation is a positively charged ion, with fewer electrons than protons, while an anion is negatively charged, with more electrons than protons. Because of their opposite electric charges, cations and anions attract each other and readily form ionic compounds.
Low energy carbonylation process
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
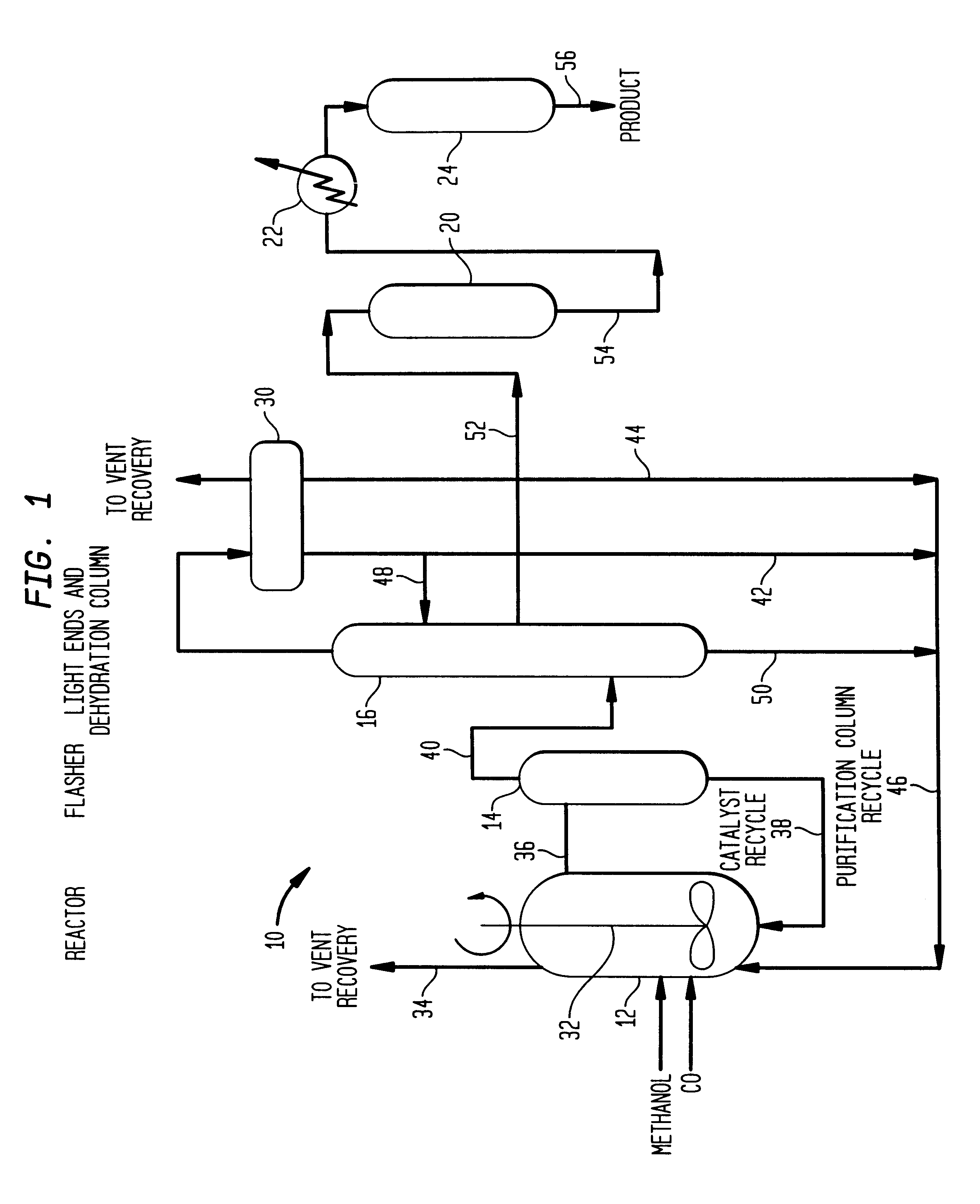
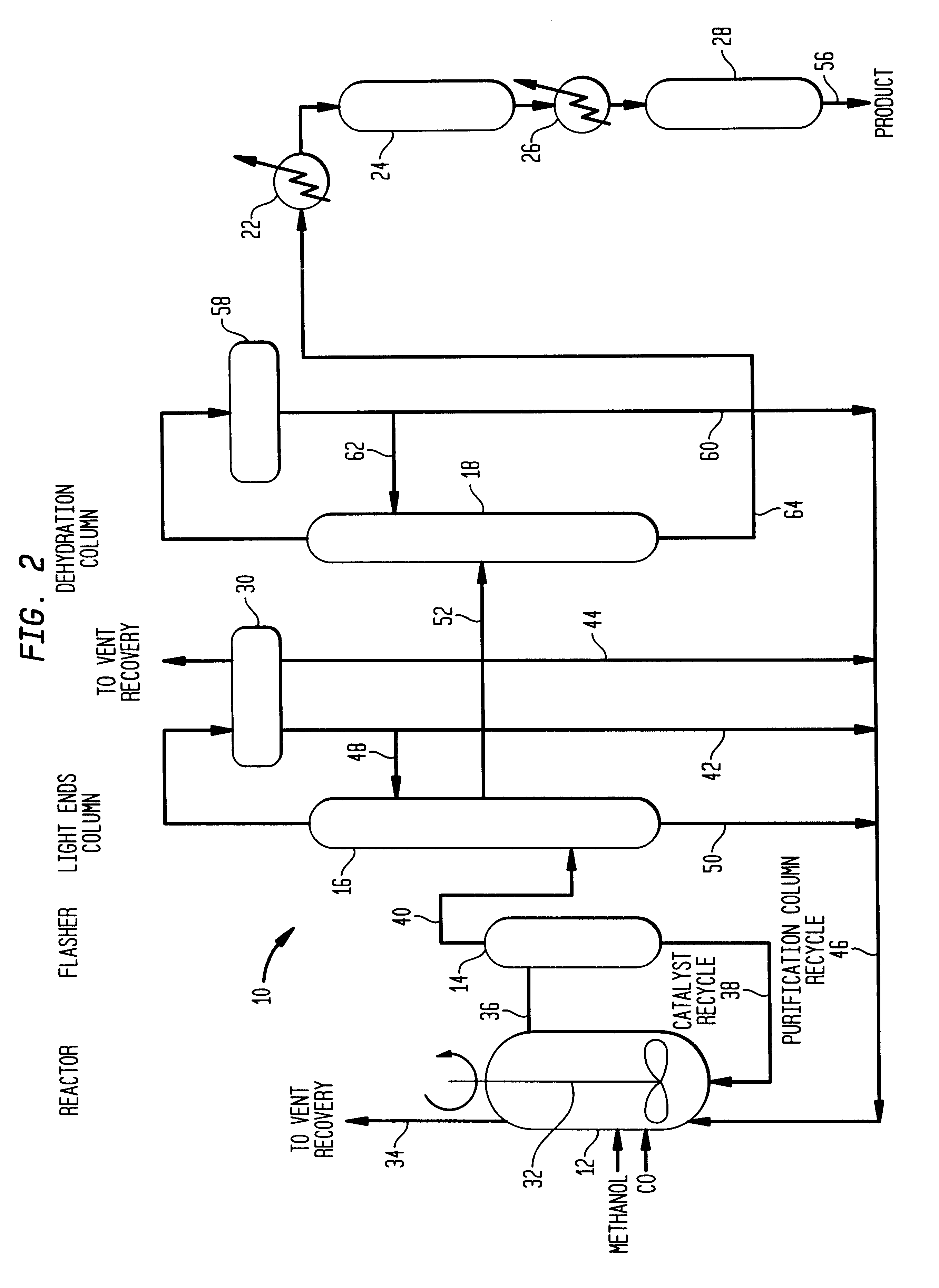
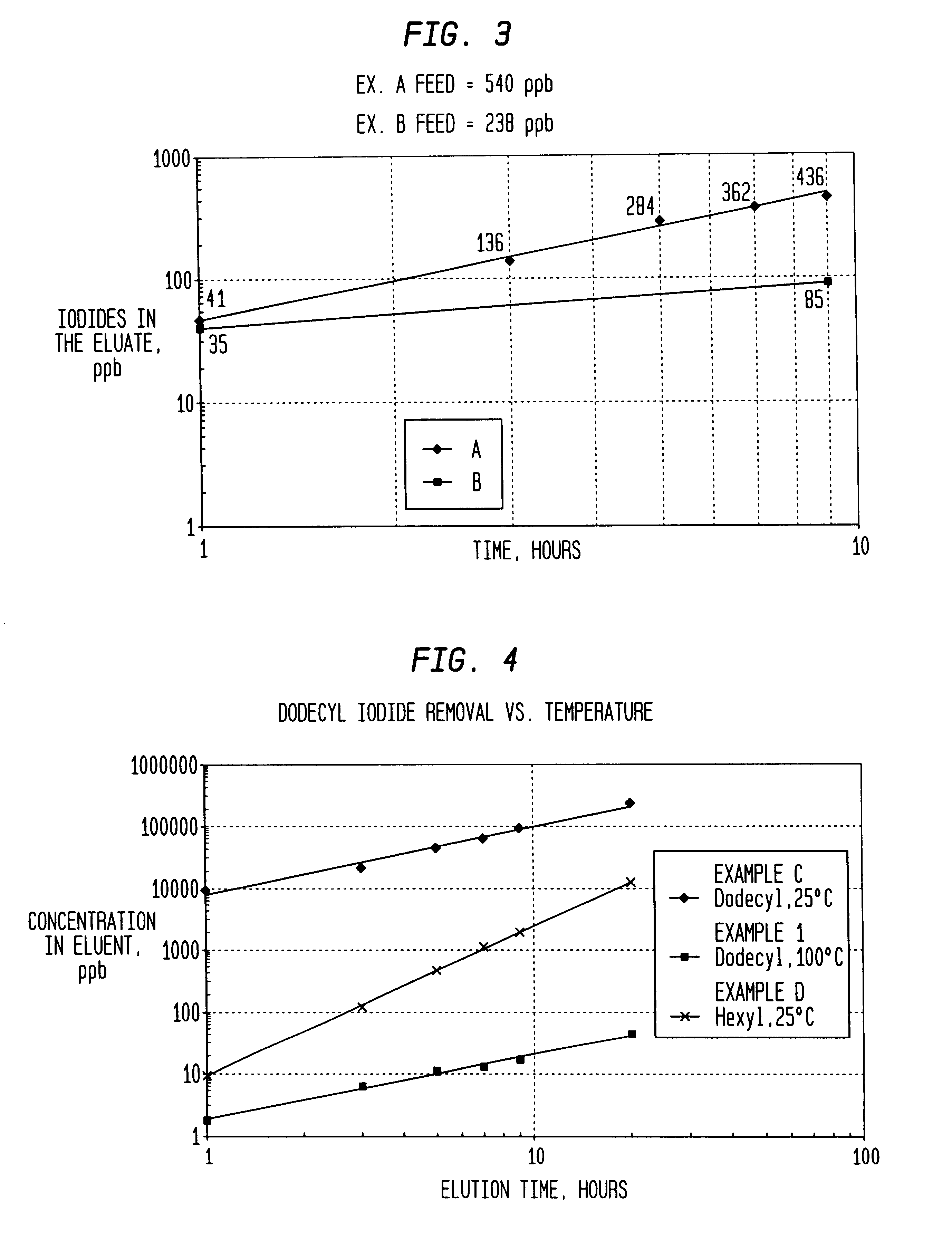
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Sequential method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6428859B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingSequential methodHigh density
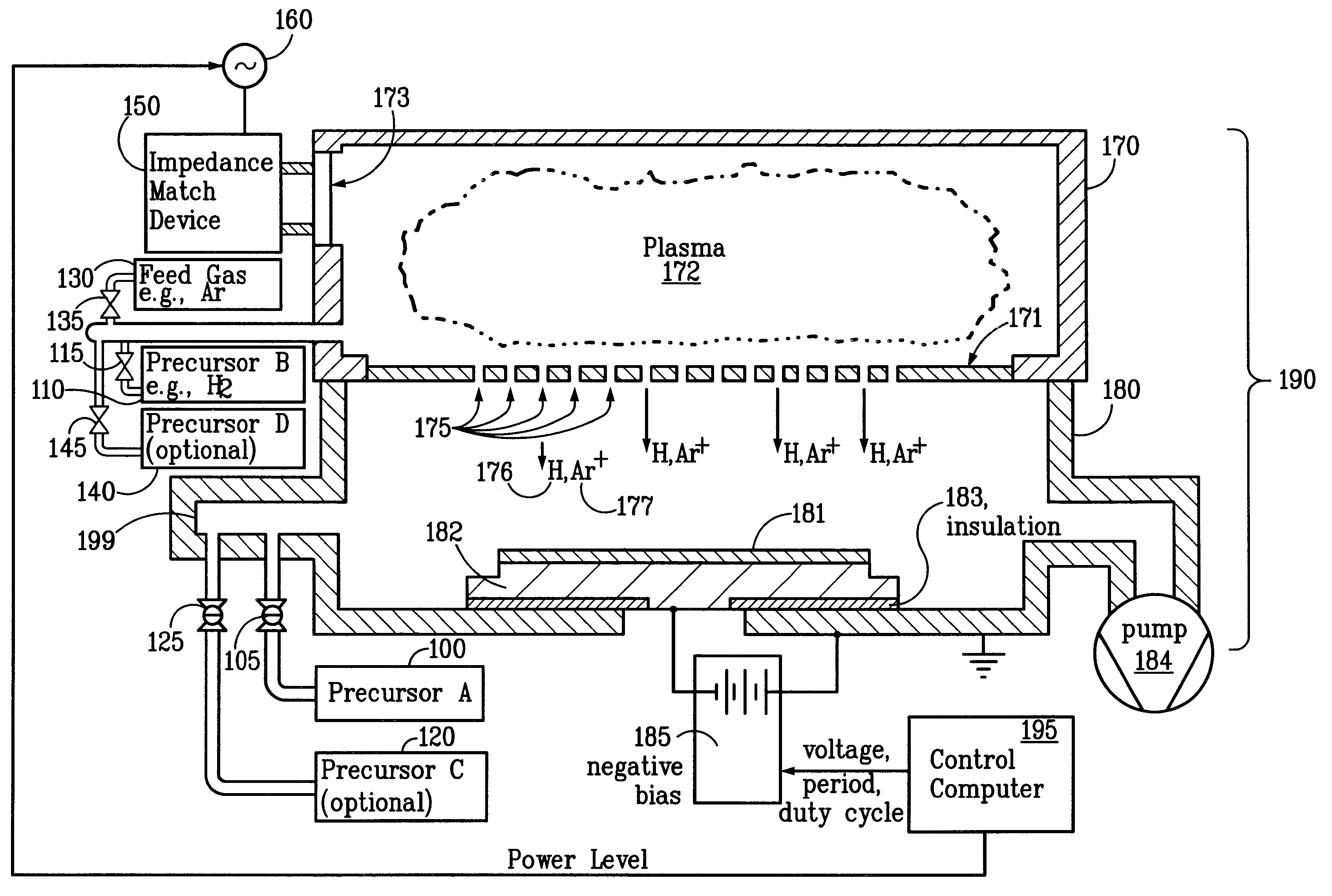
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Methods of removing silicon oxide and gaseous mixtures for achieving same
ActiveUS20090275205A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical treatmentPartial oxidation
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Support for high performance affinity chromatography and other uses
Multilayered particulate materials are formed by coating a particulate substrate with a metal and adsorbing an organic layer comprising a recognition moiety onto the metal film. The recognition moiety interacts with an analyte of interest allowing for its detection, purification, etc. Suitable recognition moieties can be selected from a range of species including, small molecules, polymers and biomolecules and the like. The novel particulate materials of the invention can be utilized in an array of methods including, ion-exchange, ion-selective ion-exchange, assays, affinity dialysis, size exclusion dialysis, as supports in solid phase synthesis, combinatorial synthesis and screening of compound libraries and the like.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Programmable metallization cell structure and method of making same
InactiveUS6084796ASolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A programmable metallization cell ("PMC") comprises a fast ion conductor such as a chalcogenide-metal ion and a plurality of electrodes (e.g., an anode and a cathode) disposed at the surface of the fast ion conductor and spaced a set distance apart from each other. Preferably, the fast ion conductor comprises a chalcogenide with Group IB or Group IIB metals, the anode comprises silver, and the cathode comprises aluminum or other conductor. When a voltage is applied to the anode and the cathode, a non-volatile metal dendrite grows from the cathode along the surface of the fast ion conductor towards the anode. The growth rate of the dendrite is a function of the applied voltage and time. The growth of the dendrite may be stopped by removing the voltage and the dendrite may be retracted by reversing the voltage polarity at the anode and cathode. Changes in the length of the dendrite affect the resistance and capacitance of the PMC. The PMC may be incorporated into a variety of technologies such as memory devices, programmable resistor / capacitor devices, optical devices, sensors, and the like. Electrodes additional to the cathode and anode can be provided to serve as outputs or additional outputs of the devices in sensing electrical characteristics which are dependent upon the extent of the dendrite.
Owner:AXON TECH +1
Porous polymeric matrices made of natural polymers and synthetic polymers and optionally at least one cation and methods of making
A porous polymeric matrix containing at least one natural polymer and at least one synthetic polymer and optionally at least one cation. Furthermore, a method of making a porous polymeric matrix involving mixing at least one natural polymer and inorganic salts with a solution comprising at least one solvent and at least one synthetic polymer to form a slurry, casting the slurry in a mold and removing the solvent to form solid matrices, immersing the solid matrices in deionized water to allow natural polymer cross-linking and pore creation to occur simultaneously, and drying the matrices to create a porous polymeric matrix; wherein the matrix contains a cation. Also, a method of making a porous polymeric matrix, involving mixing at least one natural polymer in an aqueous solvent and mixing at least one synthetic polymer in an organic solvent, combining the mixtures and casting in a mold, and separately removing said aqueous solvent and said organic solvent to form a porous polymeric matrix; wherein the porous polymeric matrix does not contain a cation.
Owner:US SEC AGRI
System and method for modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20020104481A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingHigh densitySubject matter
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential or non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) apparatus and technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method; and, 4) providing a means of improved radical generation and delivery. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract that will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or meaning of the claims. [37 C.F.R. § 1.72(b)].
Owner:ANGSTRON SYST
Method of depositing barrier layer for metal gates
InactiveUS6858524B2Eliminate the problemEasy to controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricRemote plasma
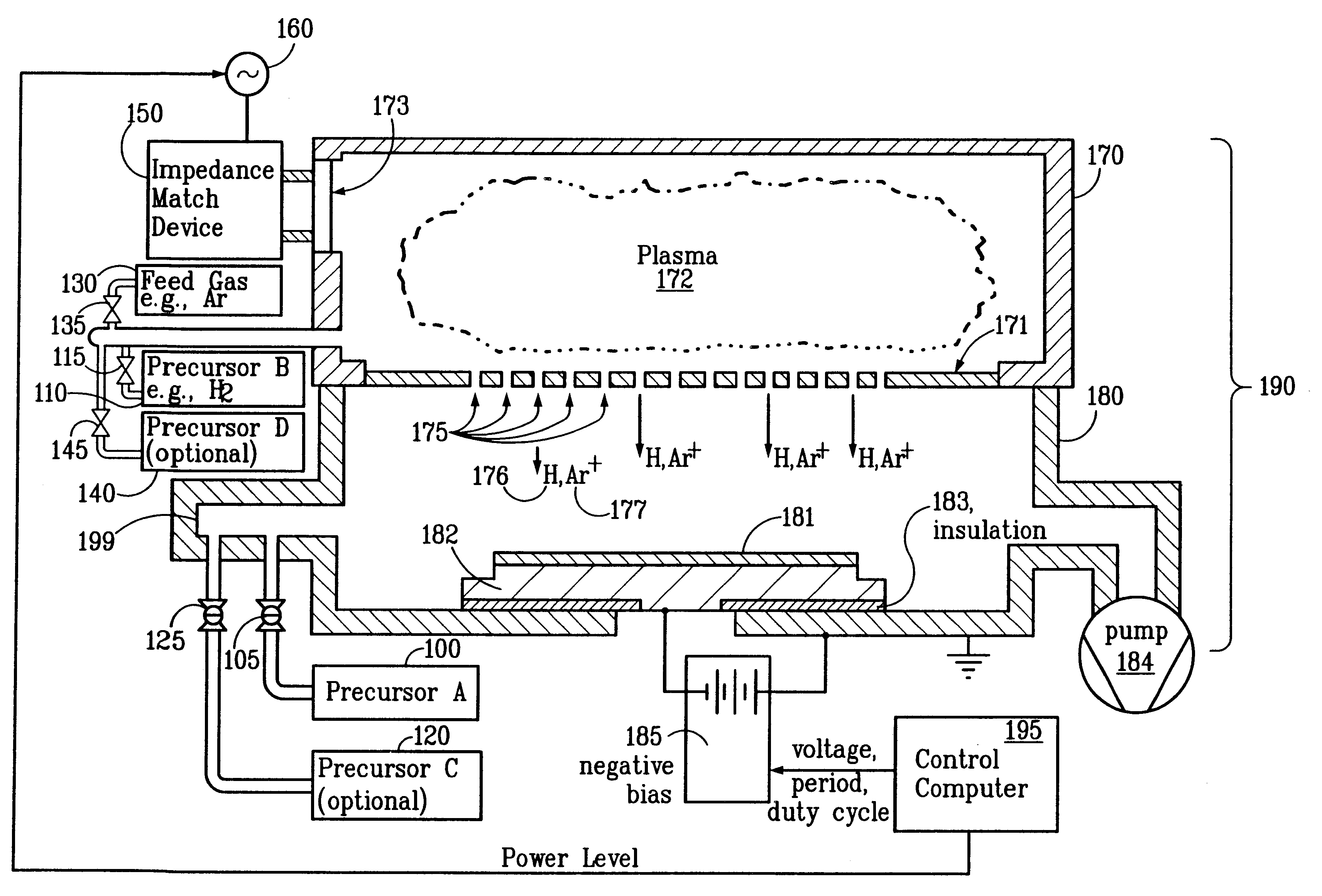
A method of manufacturing a high performance MOS device and transistor gate stacks comprises forming a gate dielectric layer over a semiconductor substrate; forming a barrier layer over the gate dielectric layer by an ALD type process; and forming a gate electrode layer over the barrier layer. The method enables the use of hydrogen plasma, high energy hydrogen radicals and ions, other reactive radicals, reactive oxygen and oxygen containing precursors in the processing steps subsequent to the deposition of the gate dielectric layer of the device. The ALD process for forming the barrier layer is performed essentially in the absence of plasma and reactive hydrogen radials and ions. This invention makes it possible to use oxygen as a precursor in the deposition of the metal gates. The barrier film also allows the use of hydrogen plasma in the form of either direct or remote plasma in the deposition of the gate electrode. Furthermore, the barrier film prevents the electrode material from reacting with the gate dielectric material. The barrier layer is ultra thin and, at the same time, it forms a uniform cover over the entire surface of the gate dielectric.
Owner:ASM INTERNATIONAL
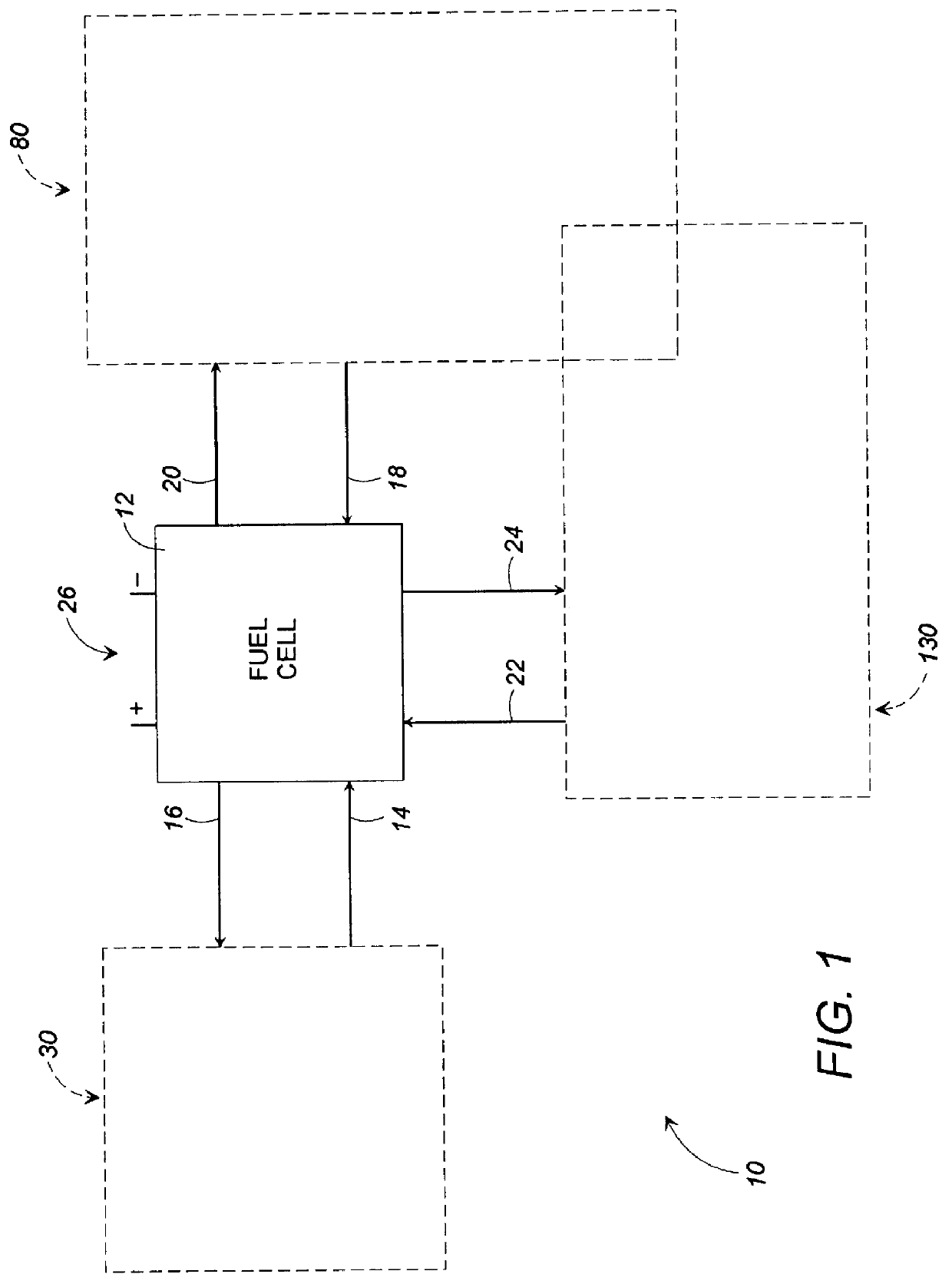
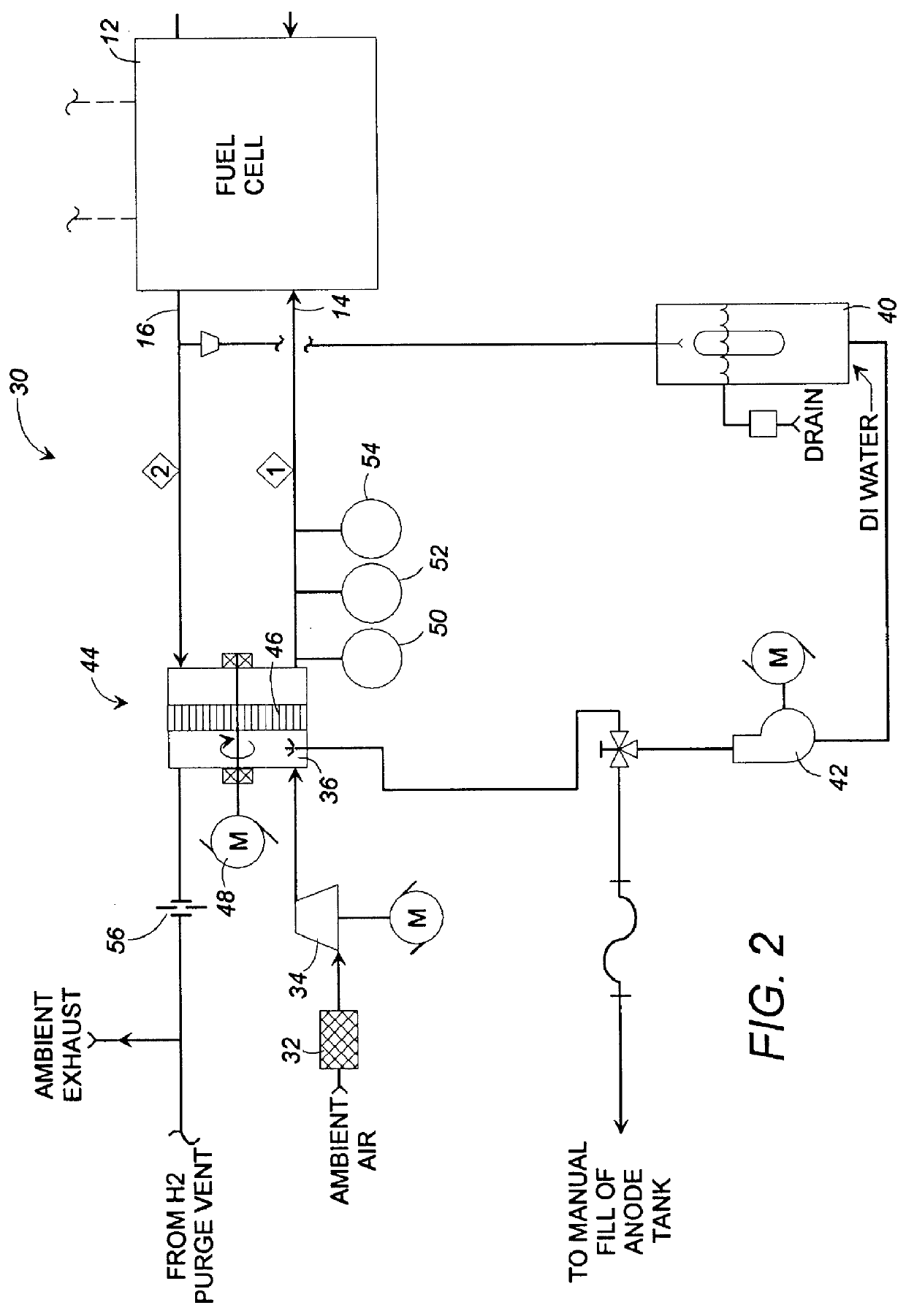
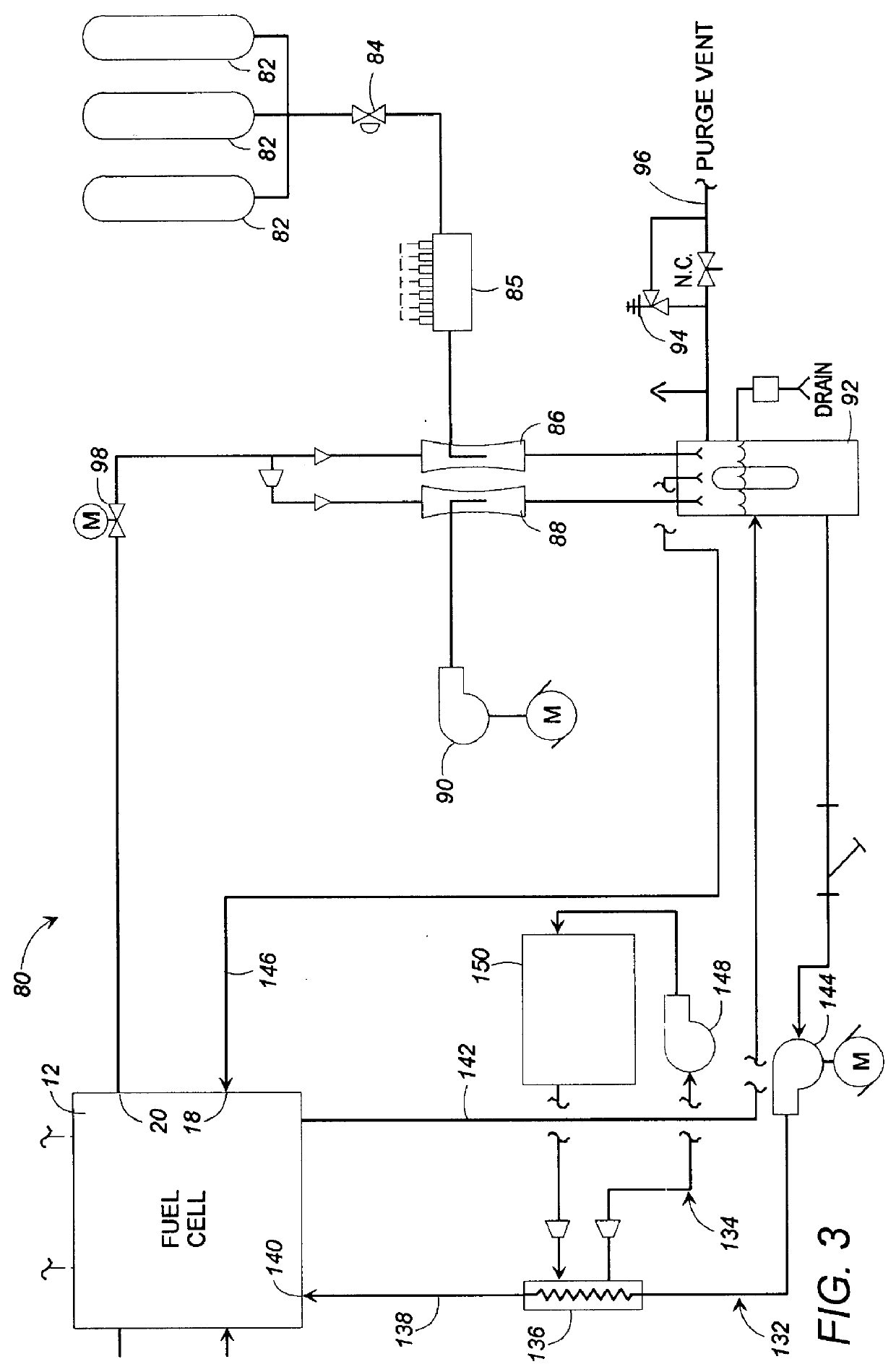
Fuel cell gas management system
InactiveUS6013385AImprove battery efficiencyMinimize the possibilityFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cell controlIonEnthalpy
A fuel cell gas management system including a cathode humidification system for transferring latent and sensible heat from an exhaust stream to the cathode inlet stream of the fuel cell; an anode humidity retention system for maintaining the total enthalpy of the anode stream exiting the fuel cell equal to the total enthalpy of the anode inlet stream; and a cooling water management system having segregated deionized water and cooling water loops interconnected by means of a brazed plate heat exchanger.
Owner:EMPRISE TECH ASSOC
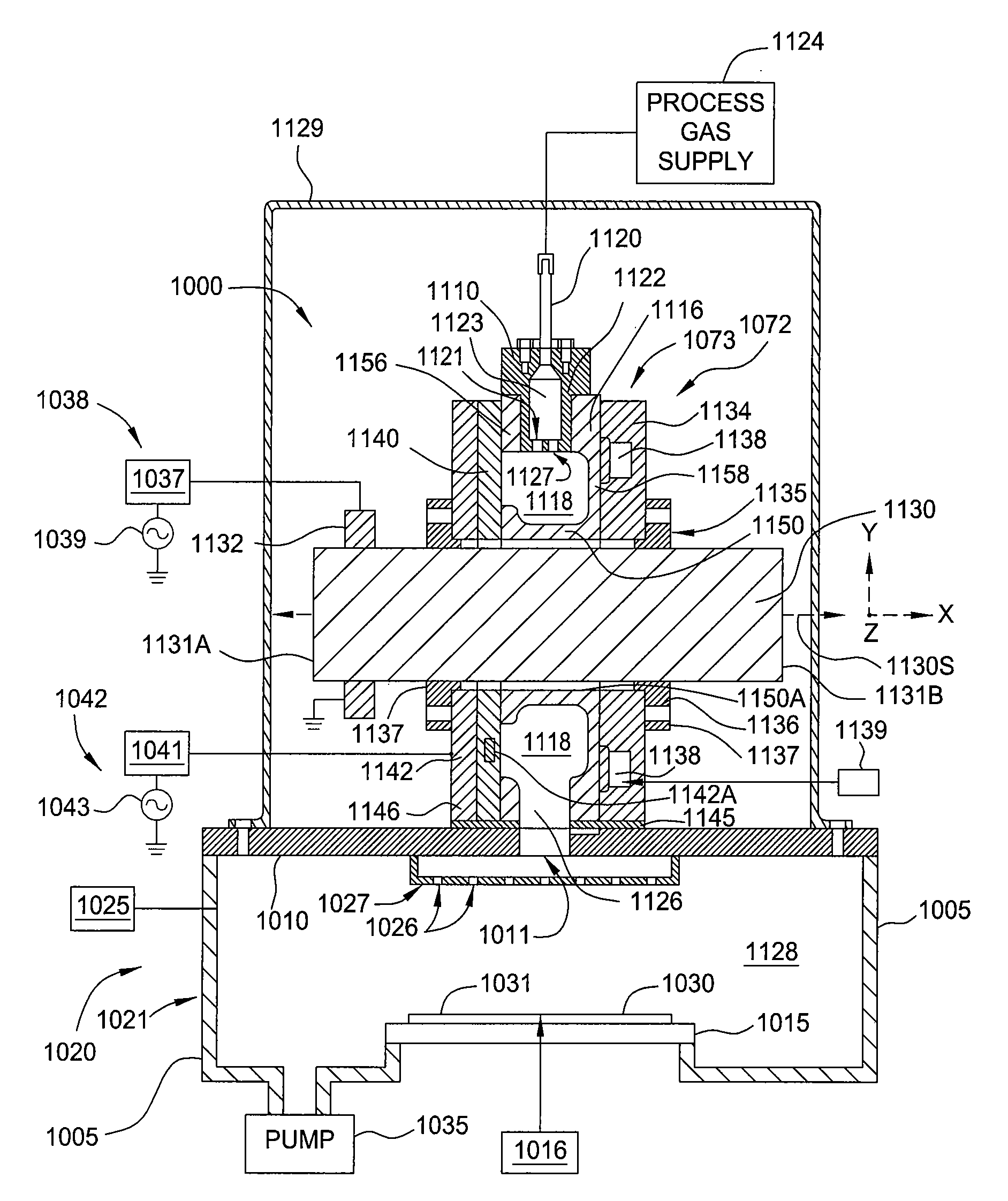
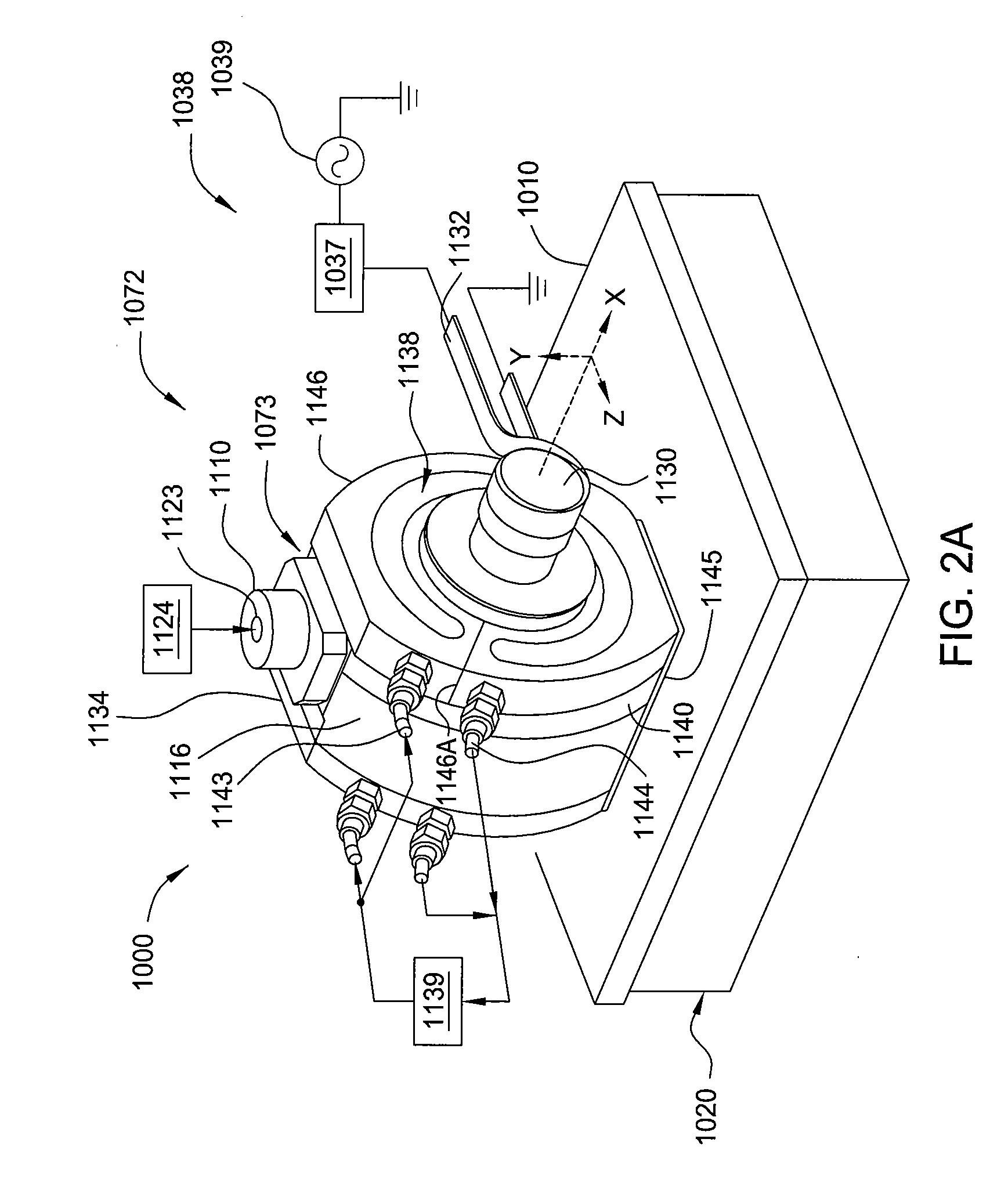
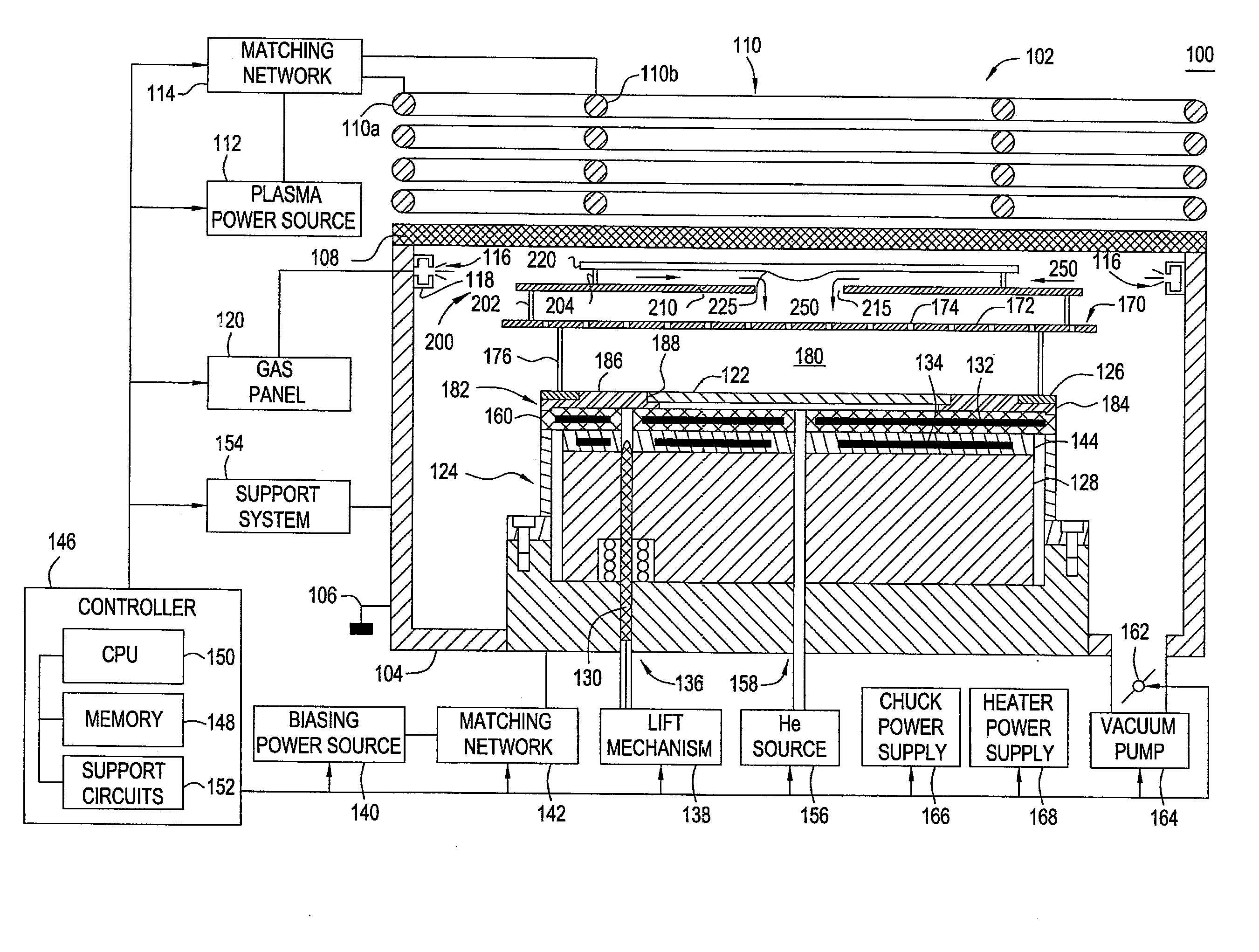
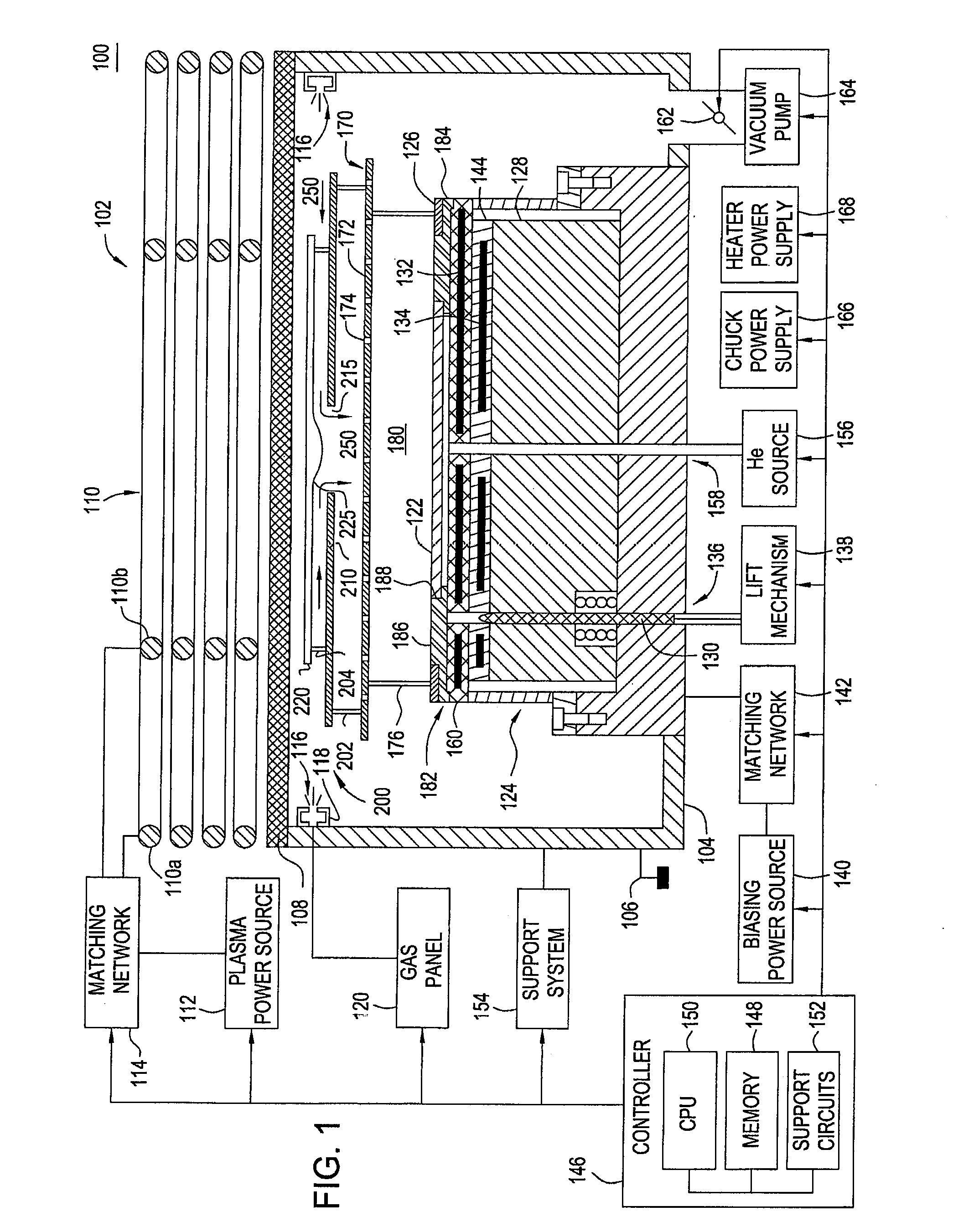
Plasma source design
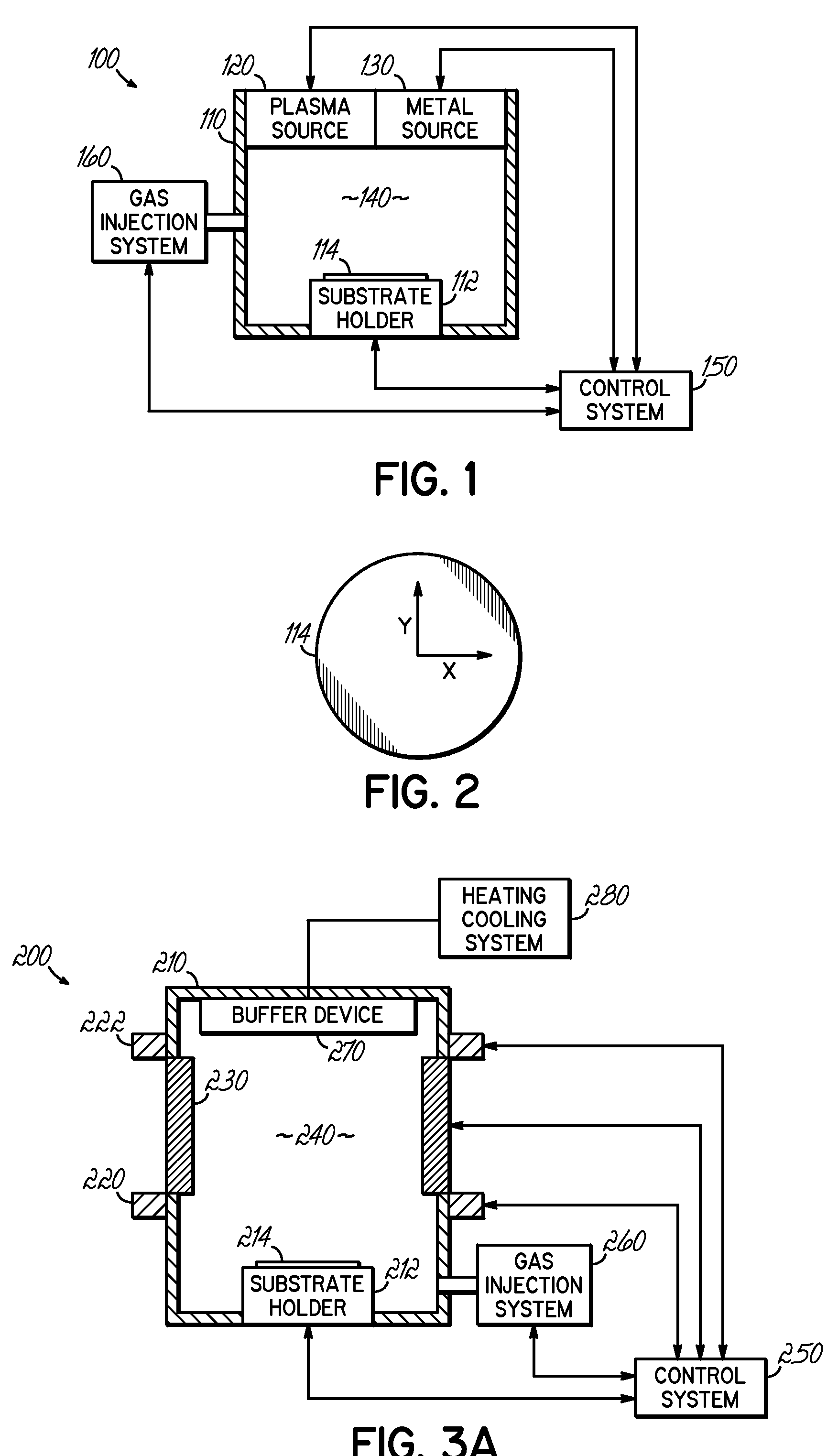
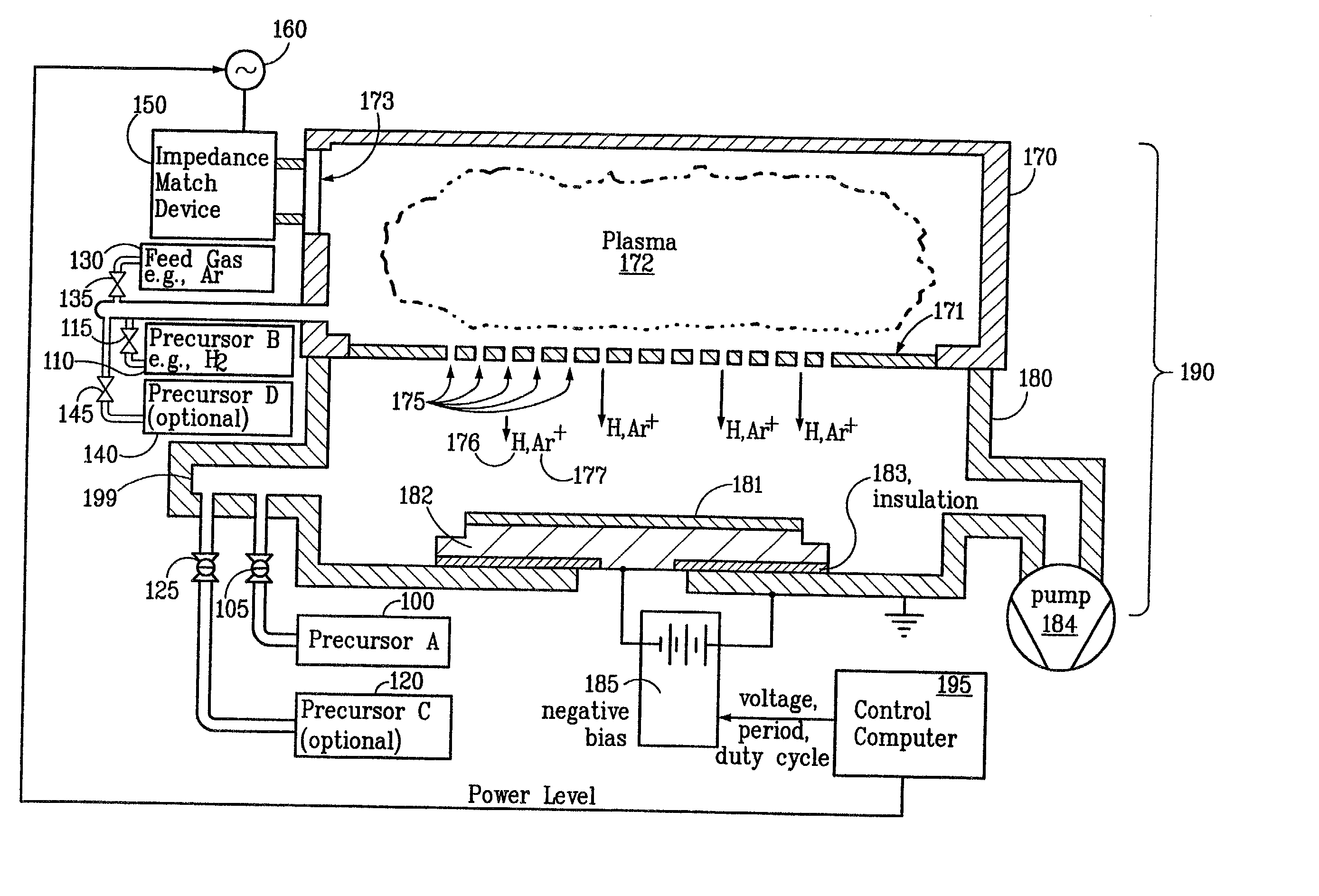
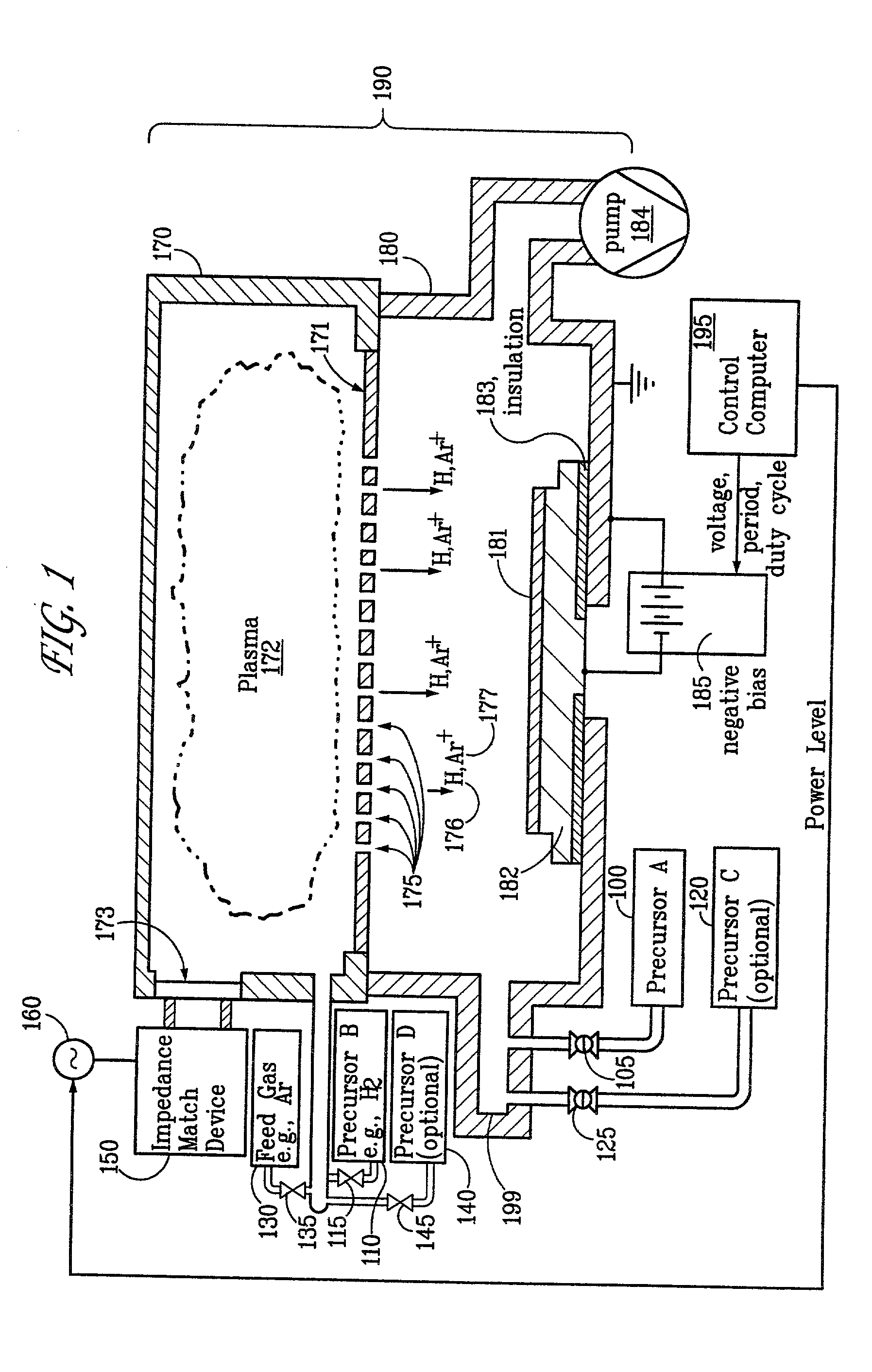
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a plasma source apparatus, and method of using the same, that is able to generate radicals and / or gas ions in a plasma generation region that is symmetrically positioned around a magnetic core element by use of an electromagnetic energy source. In general, the orientation and shape of the plasma generation region and magnetic core allows for the effective and uniform coupling of the delivered electromagnetic energy to a gas disposed in the plasma generation region. In general, the improved characteristics of the plasma formed in the plasma generation region is able to improve deposition, etching and / or cleaning processes performed on a substrate or a portion of a processing chamber that is disposed downstream of the plasma generation region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Long persistent phosphors and persistent energy transfer technique
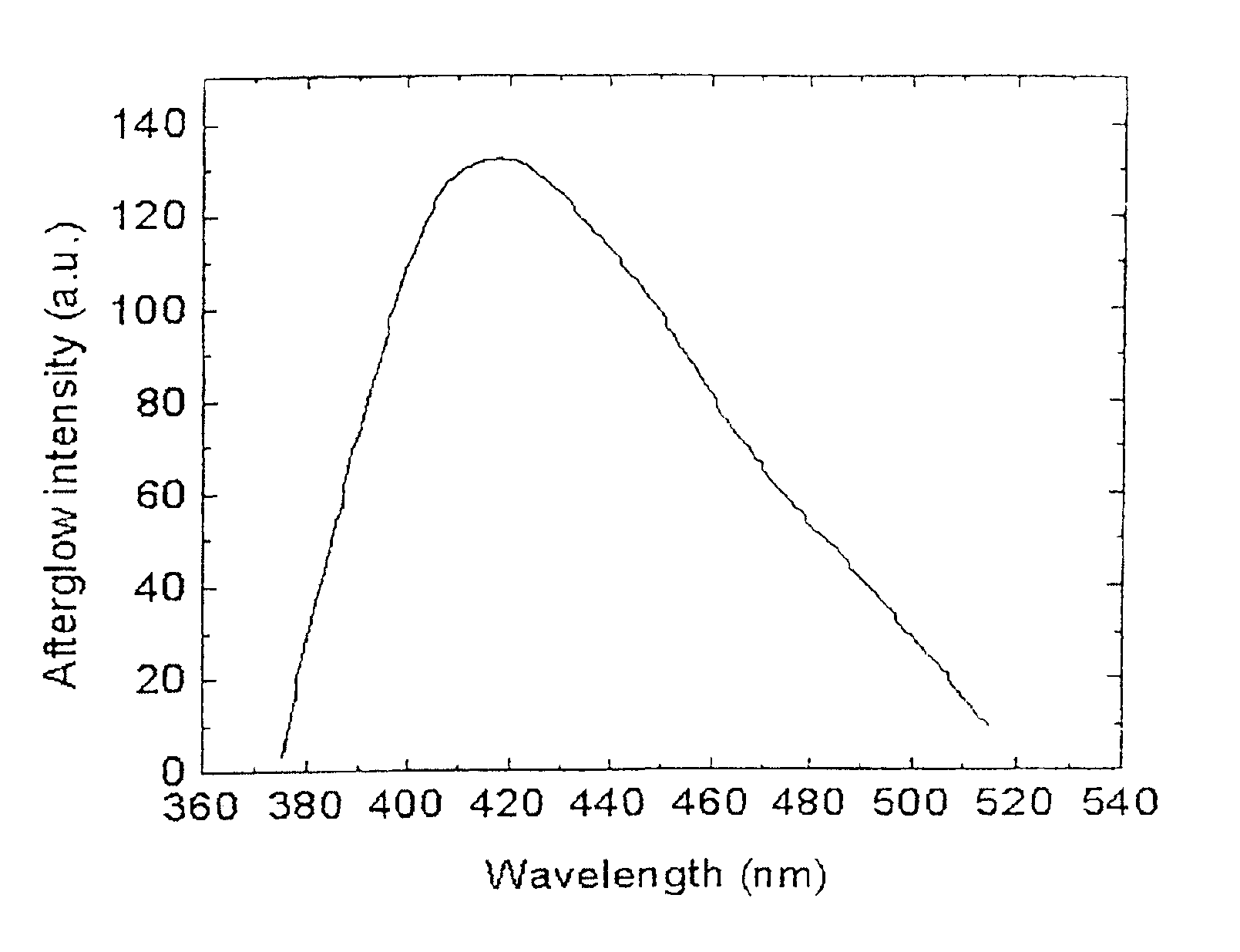
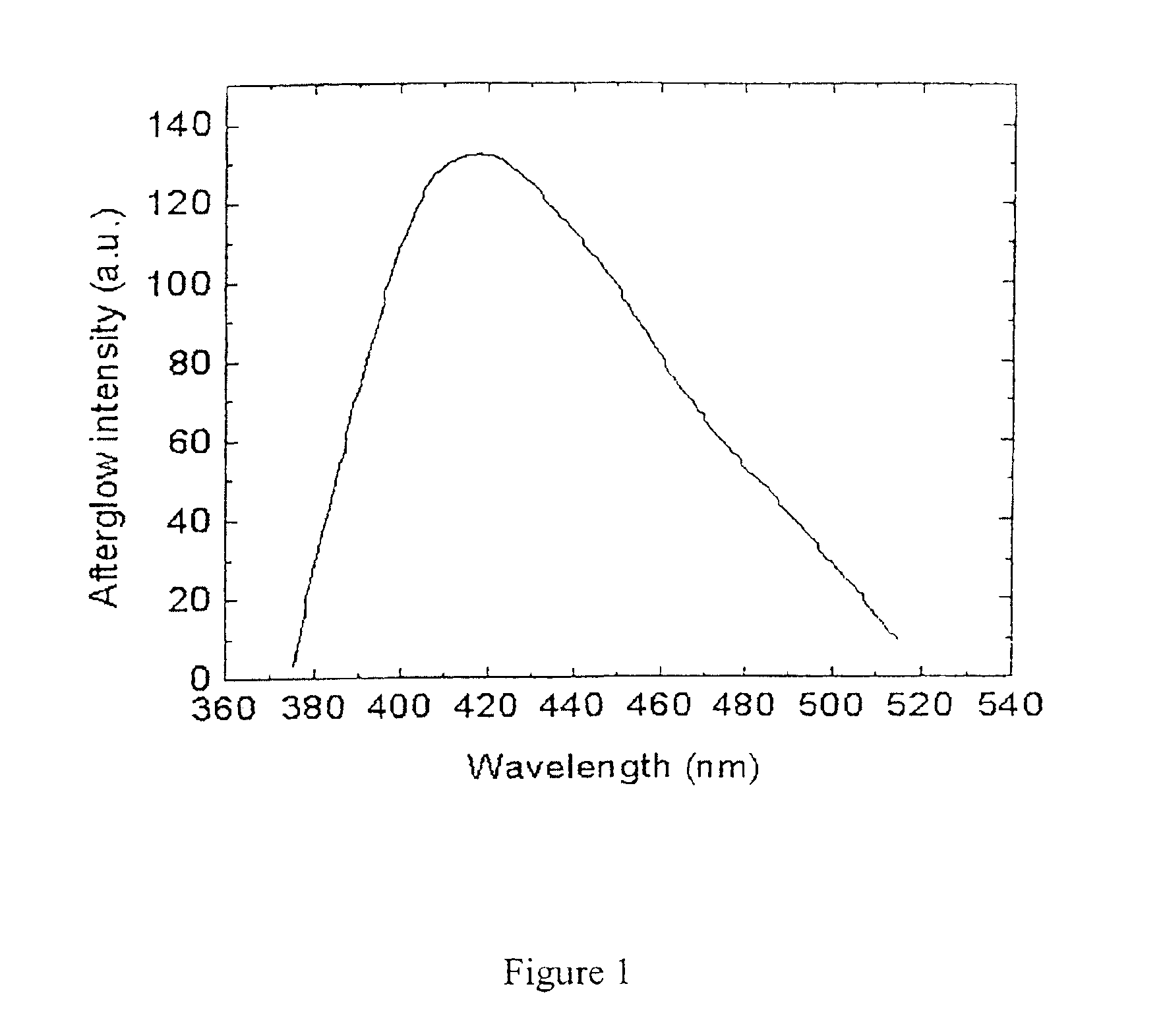
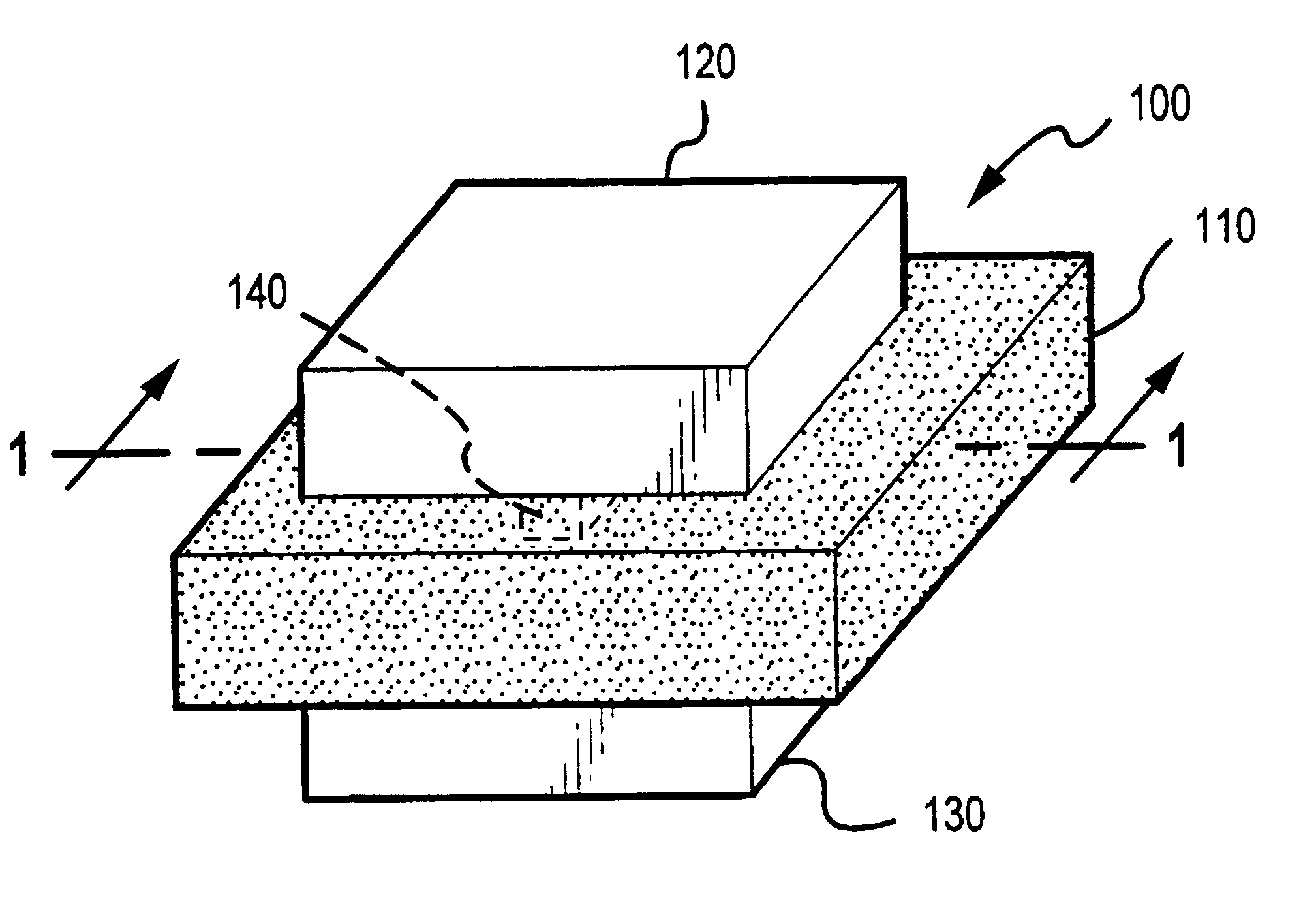
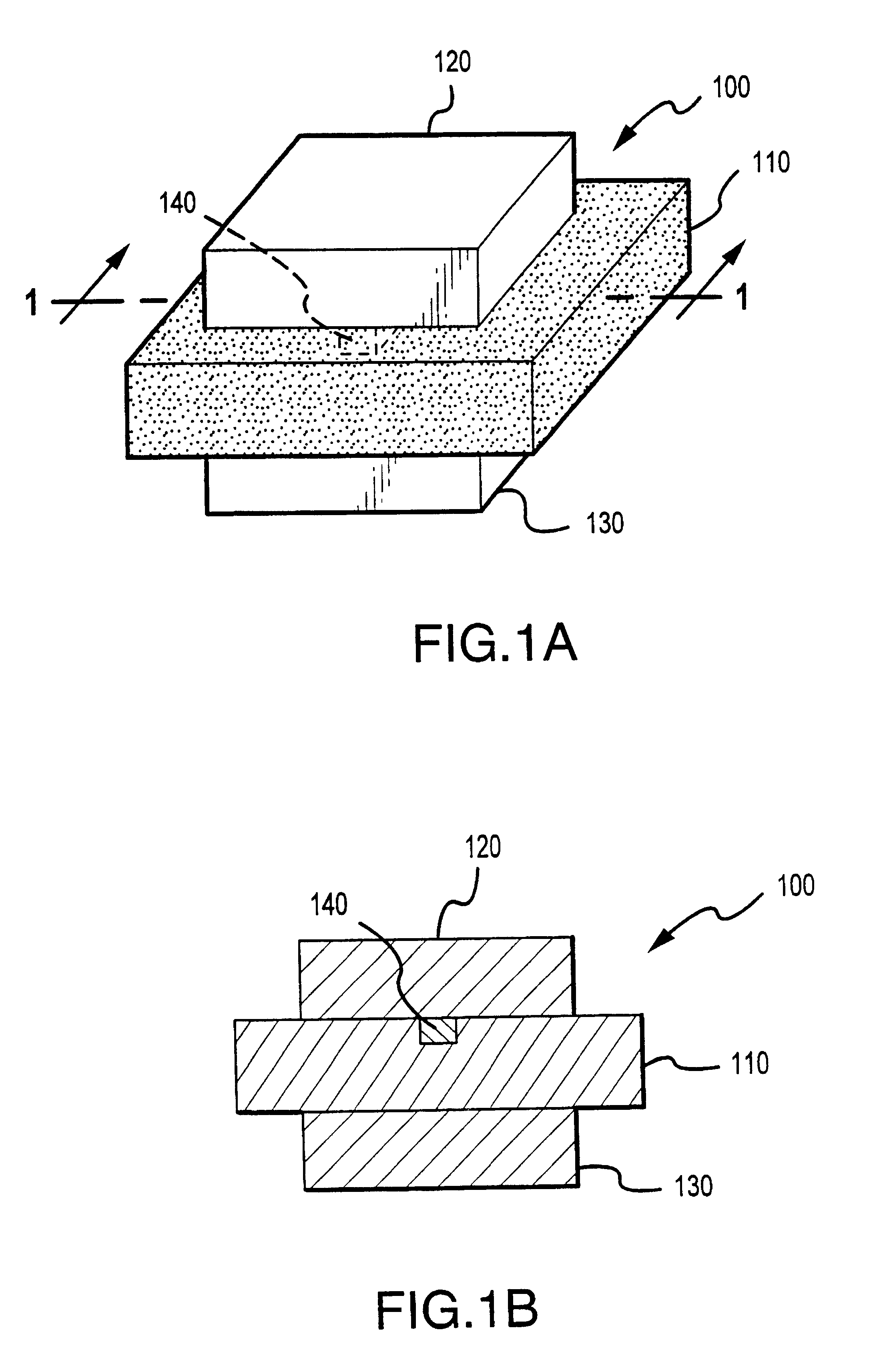
The invention provides long-persistent phosphors, methods for their manufacture and phosphorescent articles. The invention also provides a method for generating a long-persistent phosphorescence at a selected color. The phosphors of the invention may be alkaline earth aluminates, alkaline earth silicates, and alkaline earth aluminosilicates. The phosphors include those activated by cerium. The phosphors also include those in which persistent energy transfer occurs from a donor ion to an acceptor ion, producing persistent emission largely characteristic of the acceptor ion.
Owner:UNIV OF GEORGIA RES FOUND INC +1
Programmable sub-surface aggregating metallization structure and method of making same
InactiveUS6418049B1Low costHighly manufacturableNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceElectrical conductor
A programmable sub-surface aggregating metallization sructure ("PSAM") includes an ion conductor such as a chalcogenide-glass which includes metal ions and at least two electrodes disposed at opposing surfaces of the ion conductor. Preferably, the ion conductor includes a chalcogenide material with Group IB or Group IIB metals. One of the two electrodes is preferably configured as a cathode and the other as an anode. When a voltage is applied between the anode and cathode, a metal dendrite grows from the cathode through the ion conductor towards the anode. The growth rate of the dendrite may be stopped by removing the voltage or the dendrite may be retracted back towards the cathode by reversing the voltage polarity at the anode and cathode. When a voltage is applied for a sufficient length of time, a continuous metal dendrite grows through the ion conductor and connects the electrodes, thereby shorting the device. The continuous metal dendrite then can be broken by applying another voltage. The break in the metal dendrite can be reclosed by applying yet another voltage. Changes in the length of the dendrite or the presence of a break in the dendrite affect the resistance, capacitance, and impedance of the PSAM.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA +1
Plasma source design
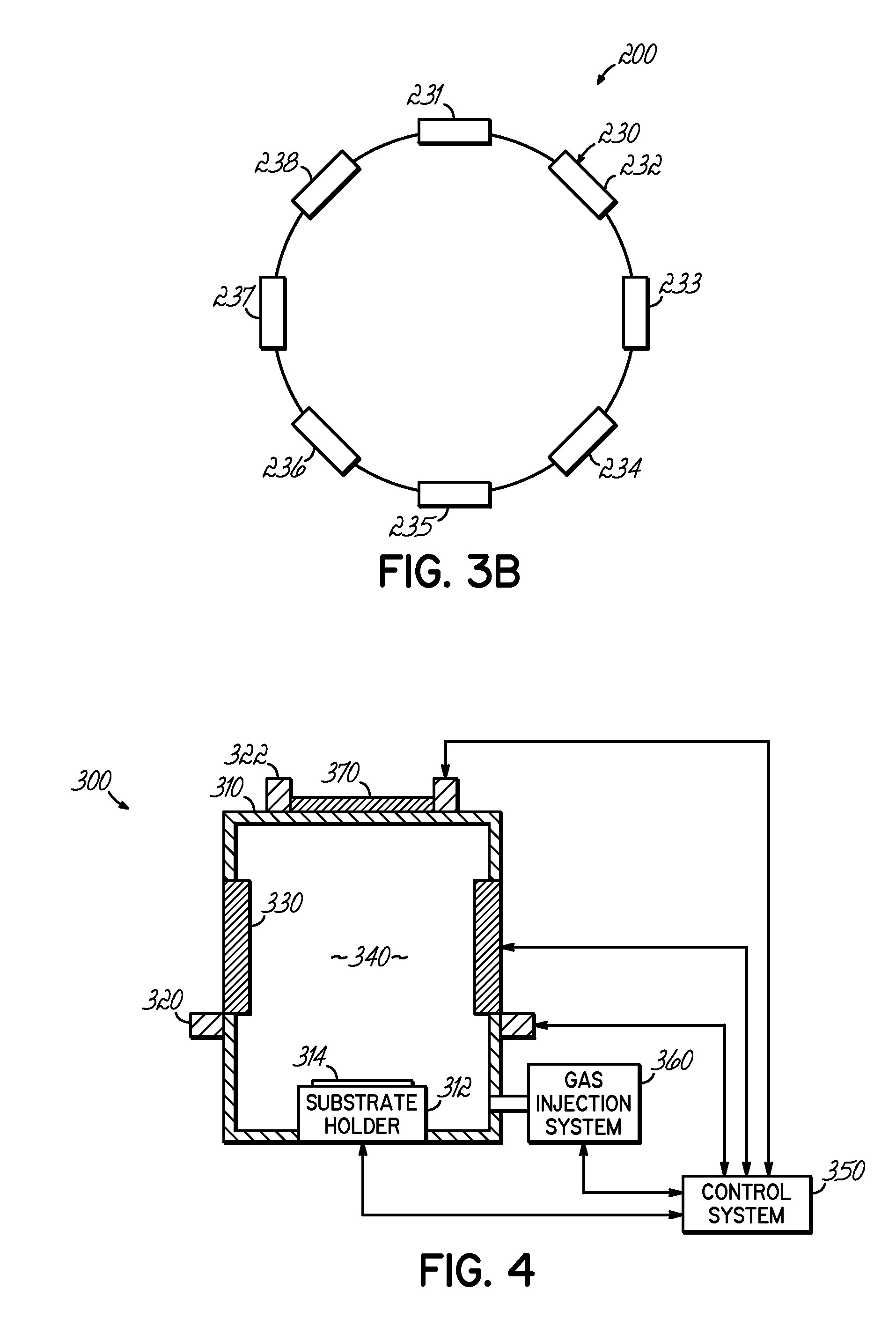
Embodiments of the present invention generally provide a plasma source apparatus, and method of using the same, that is able to generate radicals and / or gas ions in a plasma generation region that is symmetrically positioned around a magnetic core element by use of an electromagnetic energy source. In general, the orientation and shape of the plasma generation region and magnetic core allows for the effective and uniform coupling of the delivered electromagnetic energy to a gas disposed in the plasma generation region. In general, the improved characteristics of the plasma formed in the plasma generation region is able to improve deposition, etching and / or cleaning processes performed on a substrate or a portion of a processing chamber that is disposed downstream of the plasma generation region.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Systems and methods for thin-film deposition of metal oxides using excited nitrogen—oxygen species
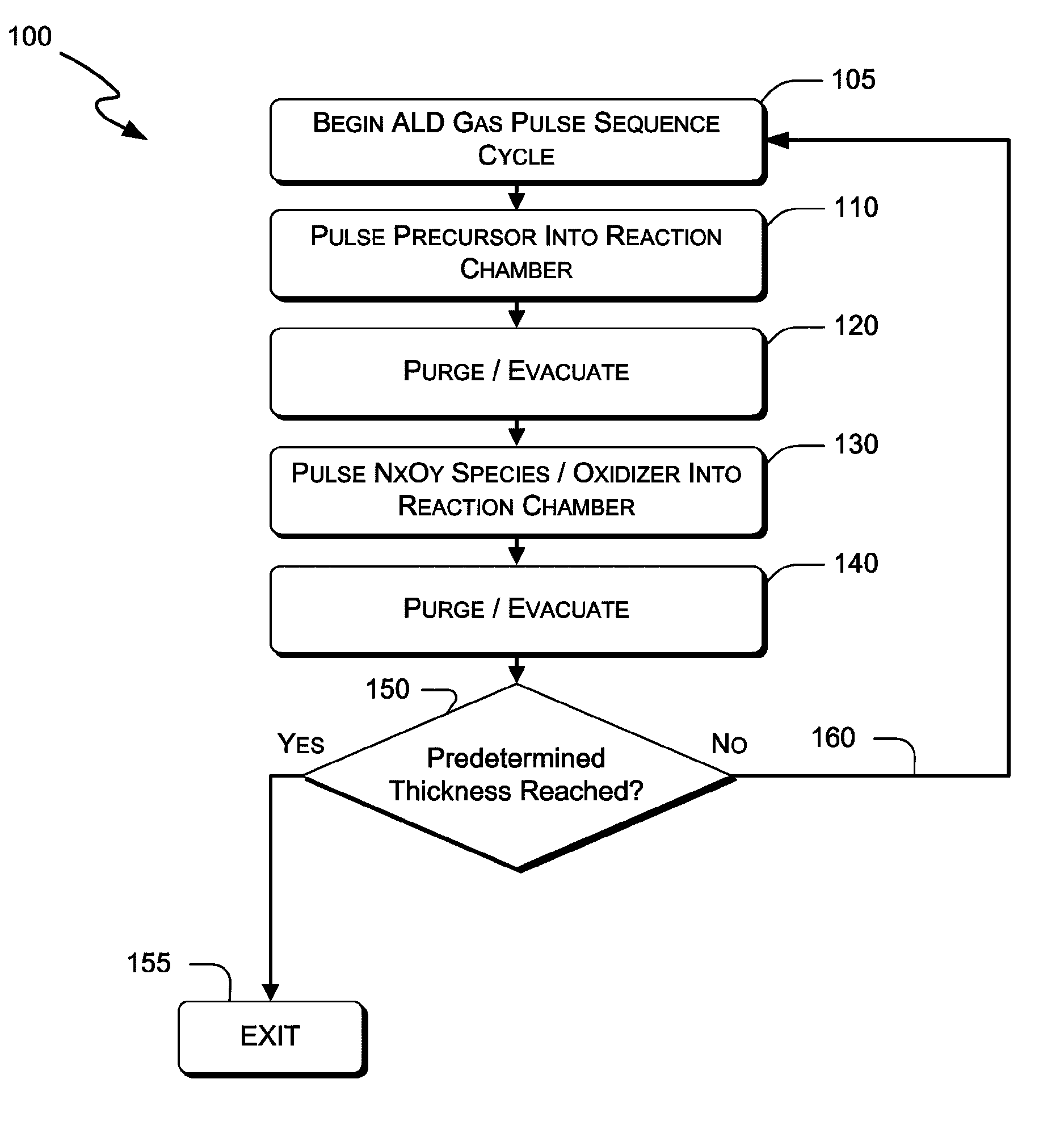
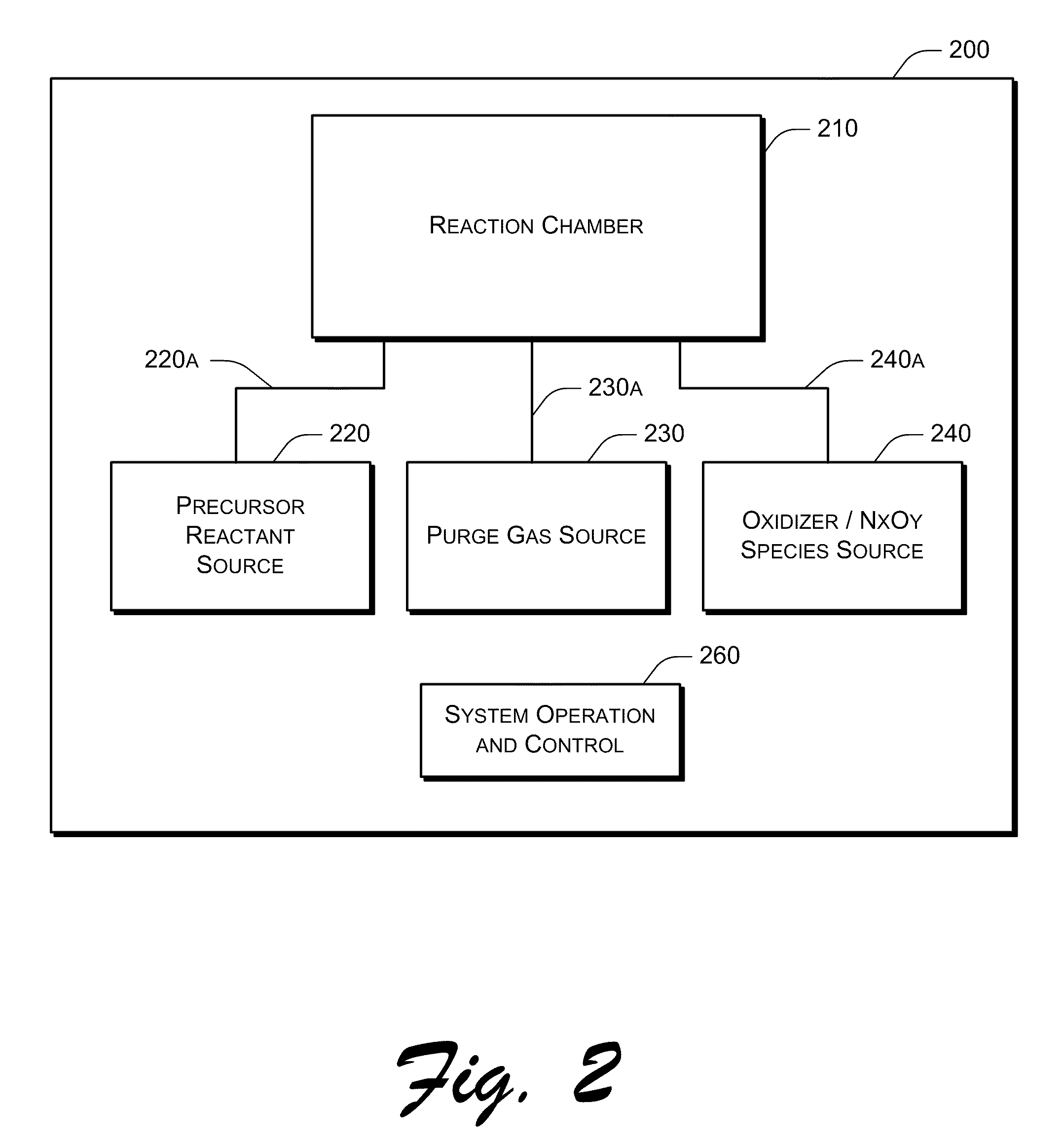
ActiveUS8883270B2Improve deposition efficiencyEnhance growth rate and uniformitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical discharge ozone preparationOxygenAtomic layer deposition
Systems and methods are delineated which, among other things, are for depositing a film on a substrate that is within a reaction chamber. In an exemplary method, the method may comprise applying an atomic layer deposition cycle to the substrate, wherein the cycle may comprise exposing the substrate to a precursor gas for a precursor pulse interval and then removing the precursor gas thereafter, and exposing the substrate to an oxidizer comprising an oxidant gas and a nitrogen-containing species gas for an oxidation pulse interval and then removing the oxidizer thereafter. Aspects of the present invention utilize molecular and excited nitrogen-oxygen radical / ionic species in possible further combination with oxidizers such as ozone. Embodiments of the present invention also include electronic components and systems that include devices fabricated with methods consistent with the present invention.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Continuous method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS6416822B1Faster efficient meanSimple methodPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityVolumetric Mass Density
The present invention relates to an enhanced non-sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Light-Emitting Element, Light-Emitting Device, Electronic Appliance, and Lighting Device
InactiveUS20140183503A1Reduce the driving voltageImprove current efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesLow voltageQuinoline
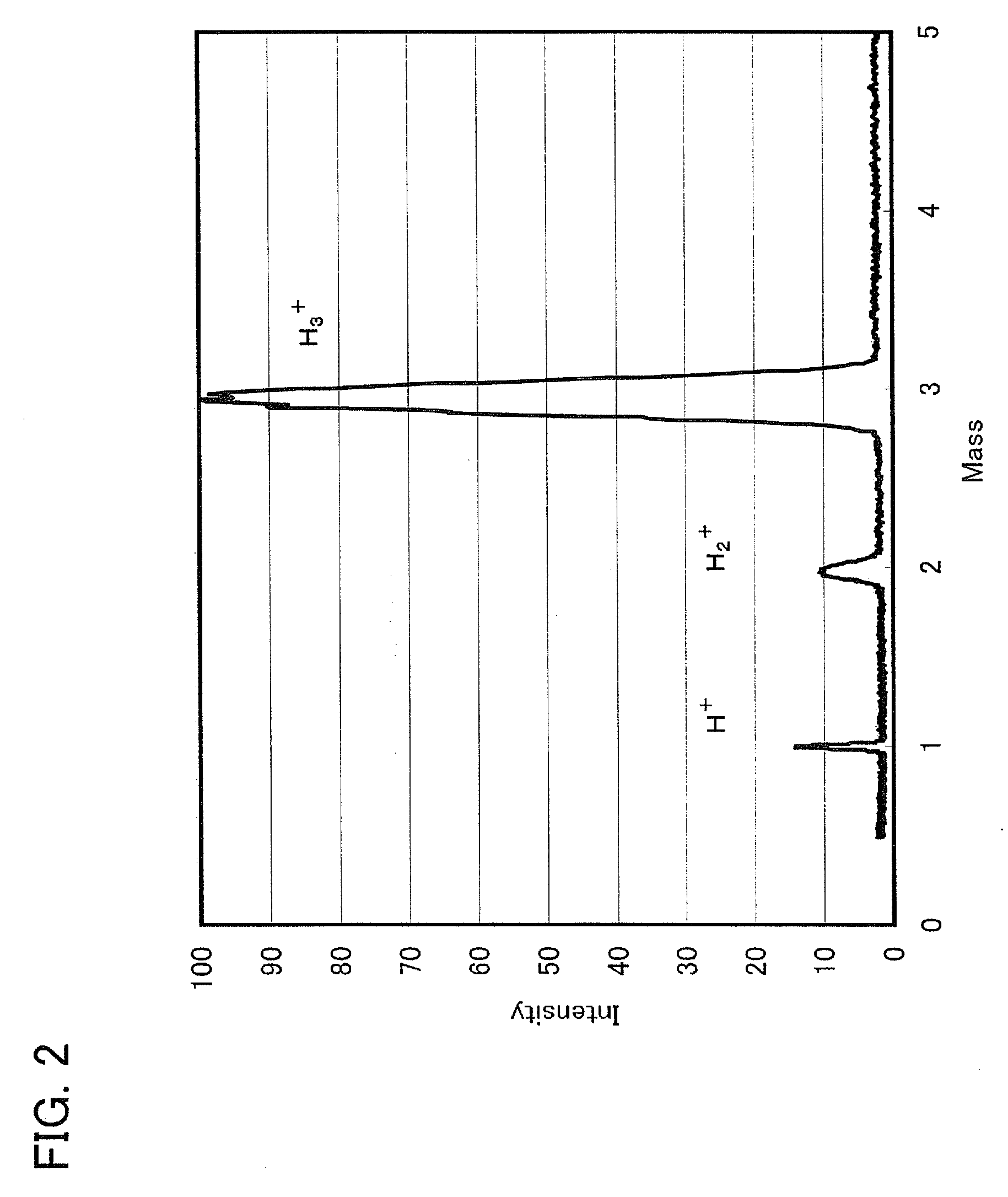
Disclosed is a light-emitting element having high emission efficiency, capable of driving at low voltage, and showing a long lifetime. The light-emitting element contains a compound between a pair of electrodes, and the compound is configured to give a first peak of m / z around 202 and a second peak of m / z around 227 in a mass spectrum. The first and second peaks are product ions of the compound and possess compositions of C16H9 and C17H10N, respectively, which are derived from a dibenzo[f,h]quinoline unit.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for producing carbon surface films by plasma exposure of a carbide compound
InactiveUS20060068125A1Reduce frictionEasy to controlChemical vapor deposition coatingFlexible microstructural devicesCarbon filmCarbon coating
Reactive halogen-ion plasmas, having for example, generating chloride ions, generated from low-pressure halogen gases using a radio-frequency plasma are employed for producing low-friction carbon coatings, such as a pure carbon film, at or near room temperature on a bulk or thin film of a compound, such as titanium carbide.
Owner:THE AEROSPACE CORPORATION
Method and apparatus of distributed plasma processing system for conformal ion stimulated nanoscale deposition process
InactiveUS20080026574A1Good coverageHigh aspect ratio (HAR) featuresVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingPlasma densityHigh density
A deposition system and method of operating thereof is described for depositing a conformal metal or other similarly responsive coating material film in a high aspect ratio feature using a high density plasma is described. The deposition system includes a plasma source, and a distributed metal source for forming plasma and introducing metal vapor to the deposition system, respectively. The deposition system is configured to form a plasma having a plasma density and generate metal vapor having a metal density, wherein the ratio of the metal density to the plasma density proximate the substrate is less than or equal to unity. This ratio should exist at least within a distance from the surface of the substrate that is about twenty percent of the diameter of the substrate. A ratio that is uniform within plus or minus twenty-five percent substantially across the surface of said substrate is desirable. The ratio is particularly effective for plasma density exceeding 1012 cm−3, and for depositing film on substrates having nanoscale features with maximum film thickness less than half of the feature width, for example, at ten percent of the feature width.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method of cleaning substrate processing chamber, storage medium, and substrate processing chamber
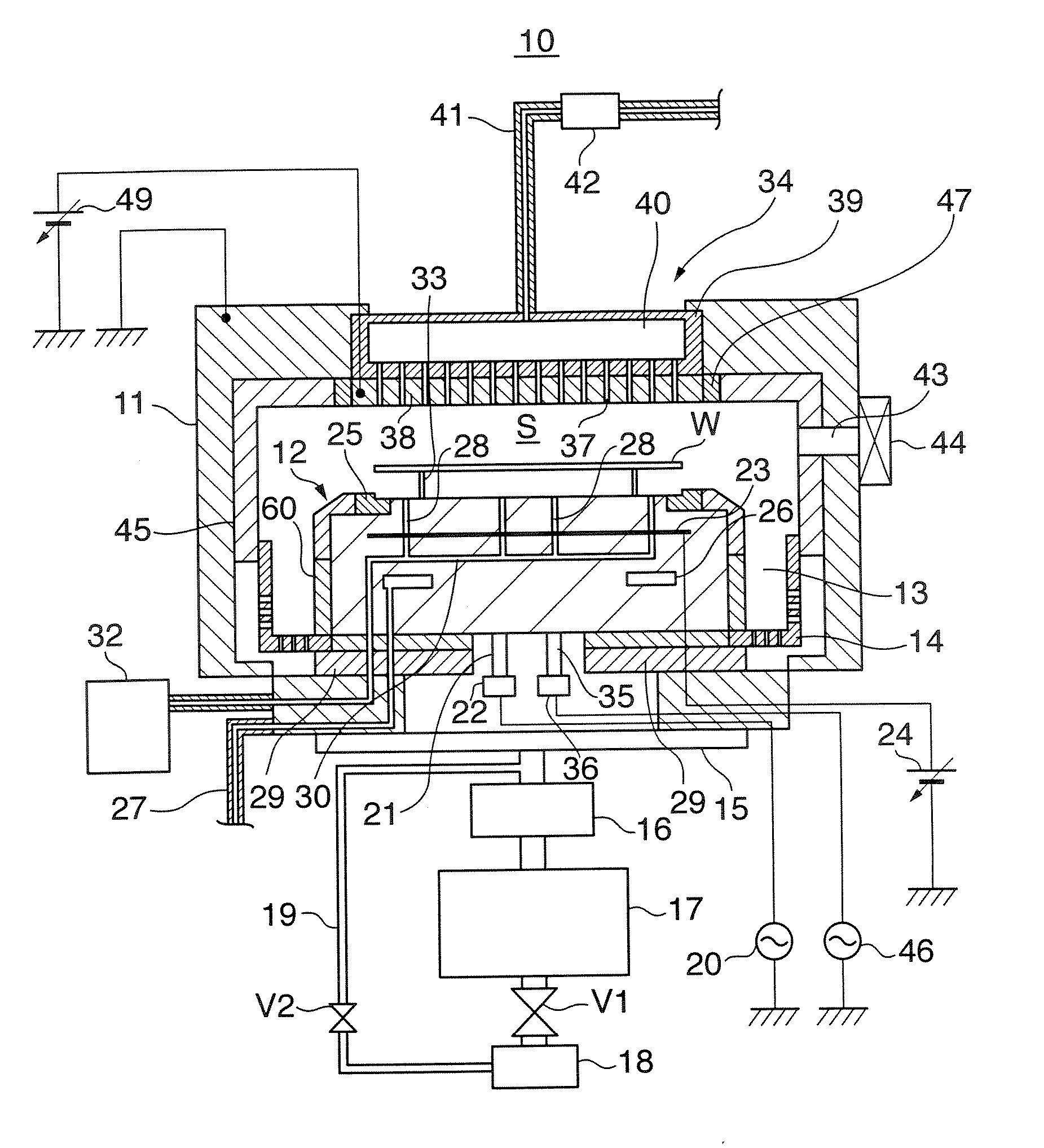
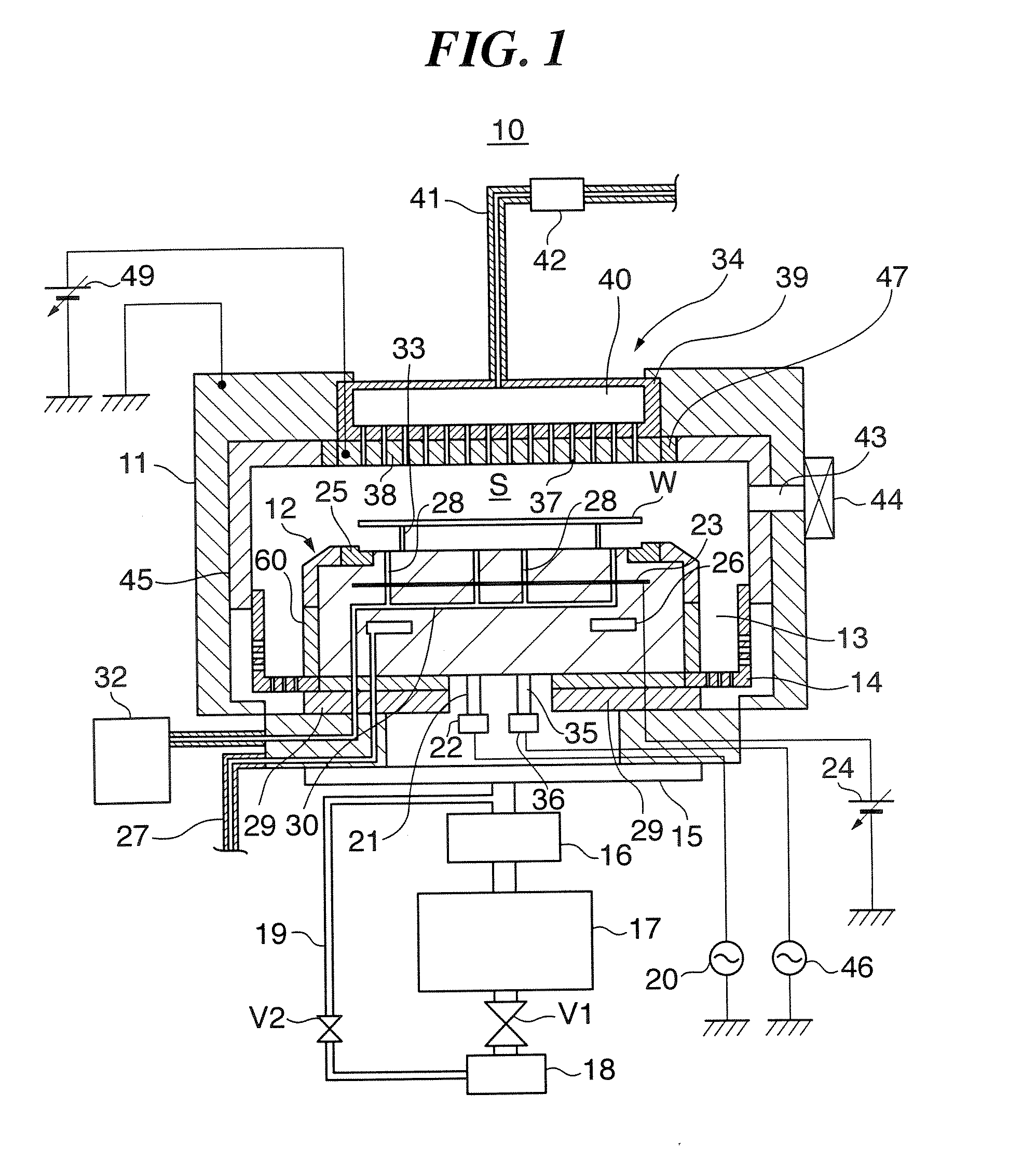
ActiveUS20070186952A1Inhibition formationElectric discharge tubesHollow article cleaningElectricityReactive-ion etching
A method of cleaning a substrate processing chamber that enables formation of an oxide film on a surface of a processing chamber inside component to be prevented. A substrate processing chamber 11 has therein a processing space S into which a wafer W is transferred and carries out reactive ion etching on the wafer W in the processing space S. The substrate processing chamber 11 has an upper electrode plate 38 that comprises silicon and a lower surface of which is exposed to the processing space S. A dry cleaning is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using oxygen radicals produced from oxygen gas introduced into the processing space S. An oxide removal processing is carried out on the upper electrode plate 38 using fluorine ions and fluorine radicals produced from carbon tetrafluoride gas introduced into the processing space S.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Programmable conductor memory cell structure
In programmable conductor memory cells, metal ions precipitate out of a glass electrolyte element in response to an applied electric field in one direction only, causing a conductive pathway to grow from cathode to anode. The amount of conductive pathway growth, and therefore the programming, depends, in part, on the availability of metal ions. It is important that the metal ions come only from the solid solution of the memory cell body. If additional metal ions are supplied from other sources, such as the sidewall edge at the anode interface, the amount of metal ions may not be directly related to the strength of the electric field, and the programming will not respond consistently from cell to cell. The embodiments described herein provide new and novel structures that block interface diffusion paths for metal ions, leaving diffusion from the bulk glass electrolyte as the only supply of metal ions for conductive pathway formation.
Owner:OVONYX MEMORY TECH LLC
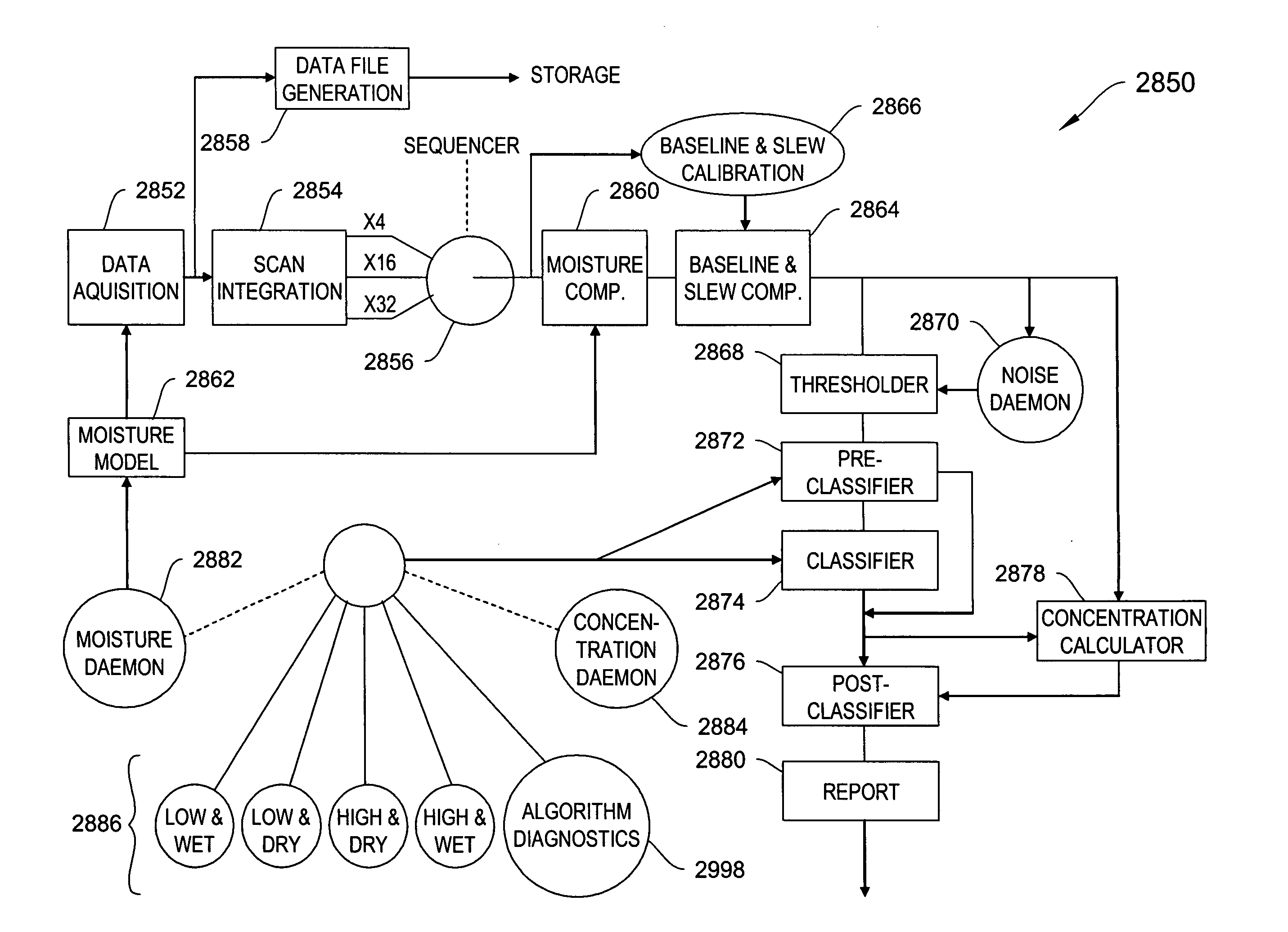
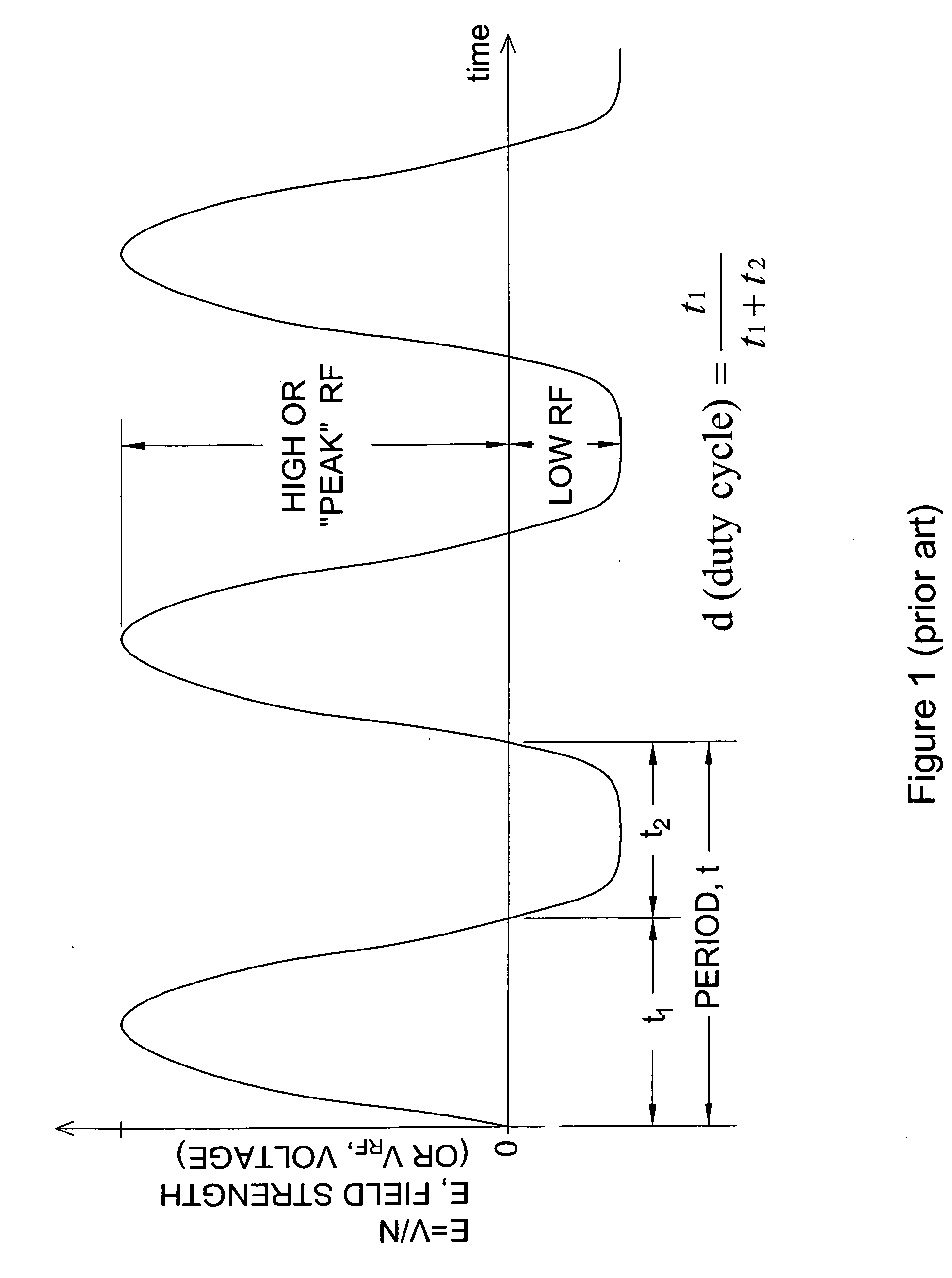
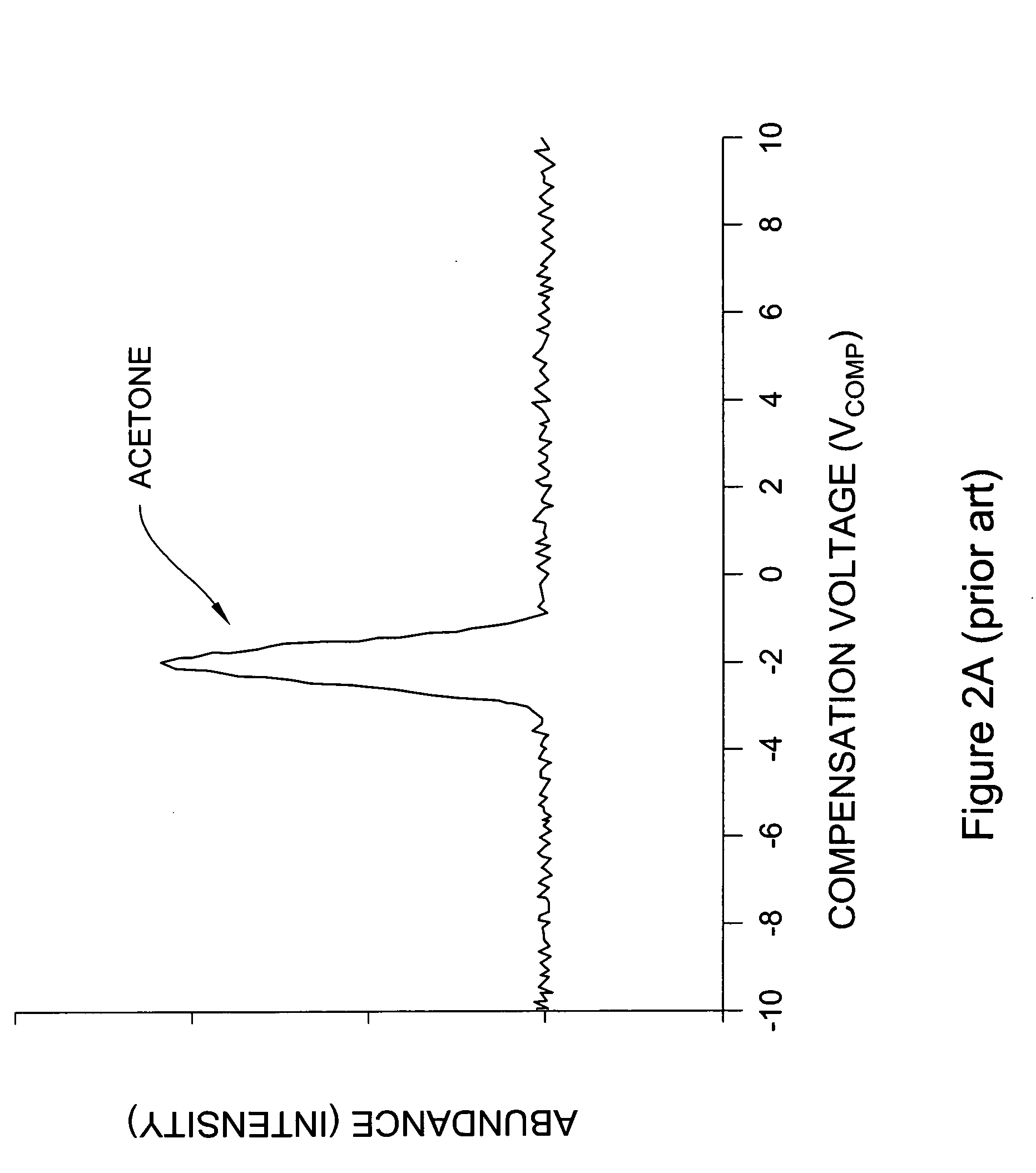
Systems and methods for ion species analysis with enhanced condition control and data interpretation
ActiveUS20050253061A1Reduces spectral peak overlapHigh resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSystems approachesComputer science
The invention relates generally to ion mobility based systems, methods and devices for analyzing samples and, more particularly, to sample detection using enhanced condition control and data interpretation.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
Sequential UV induced chemical vapor deposition
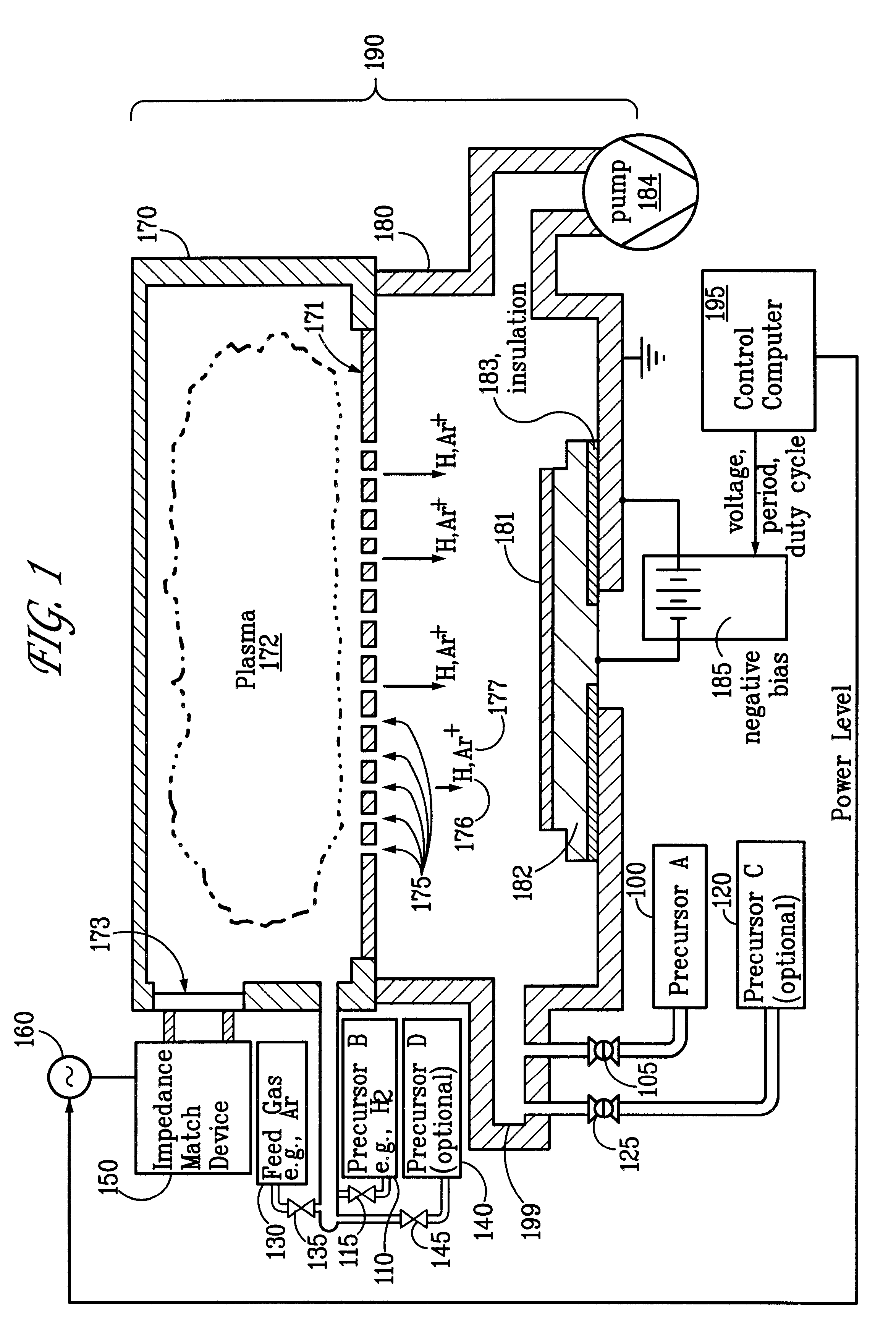
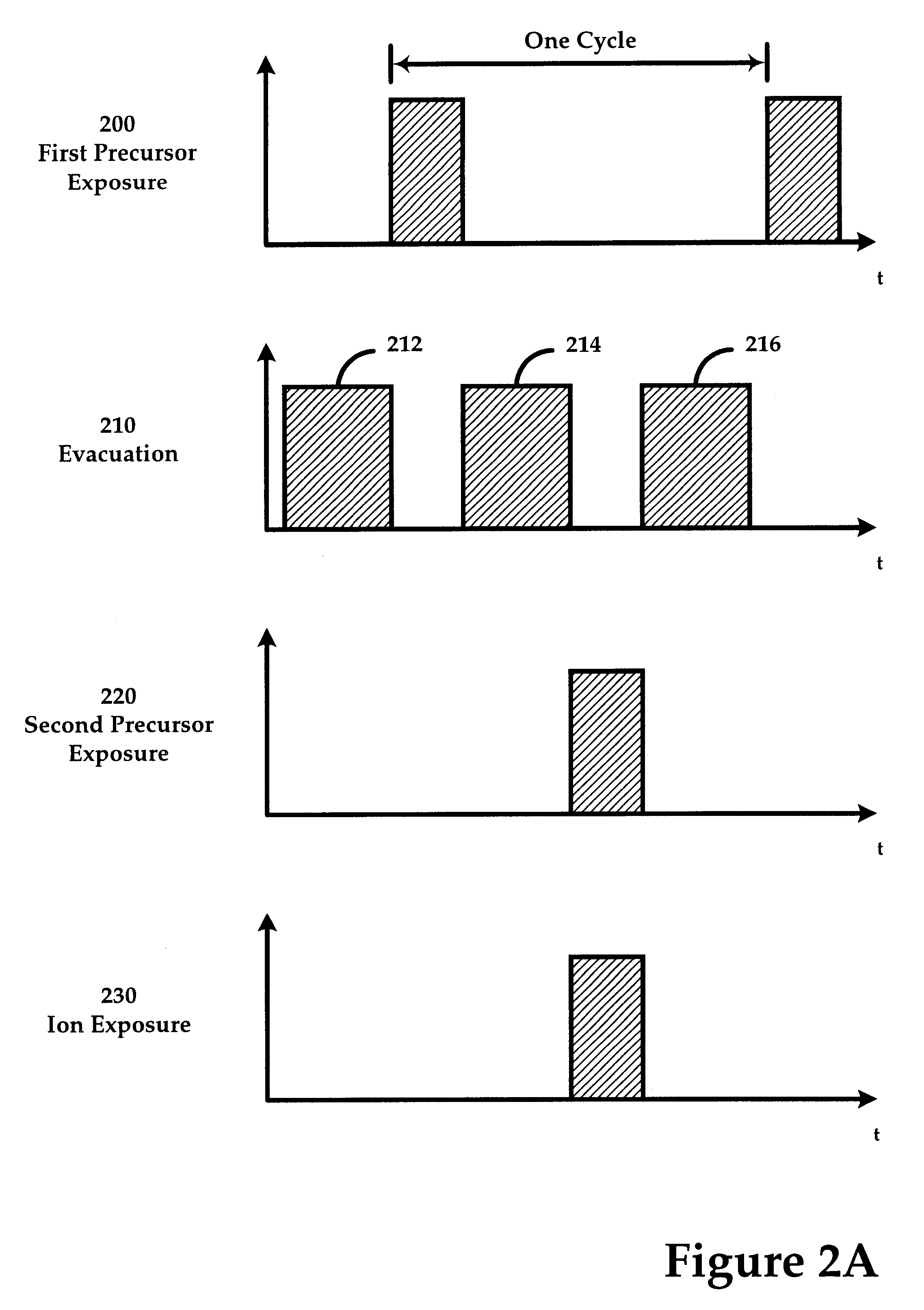
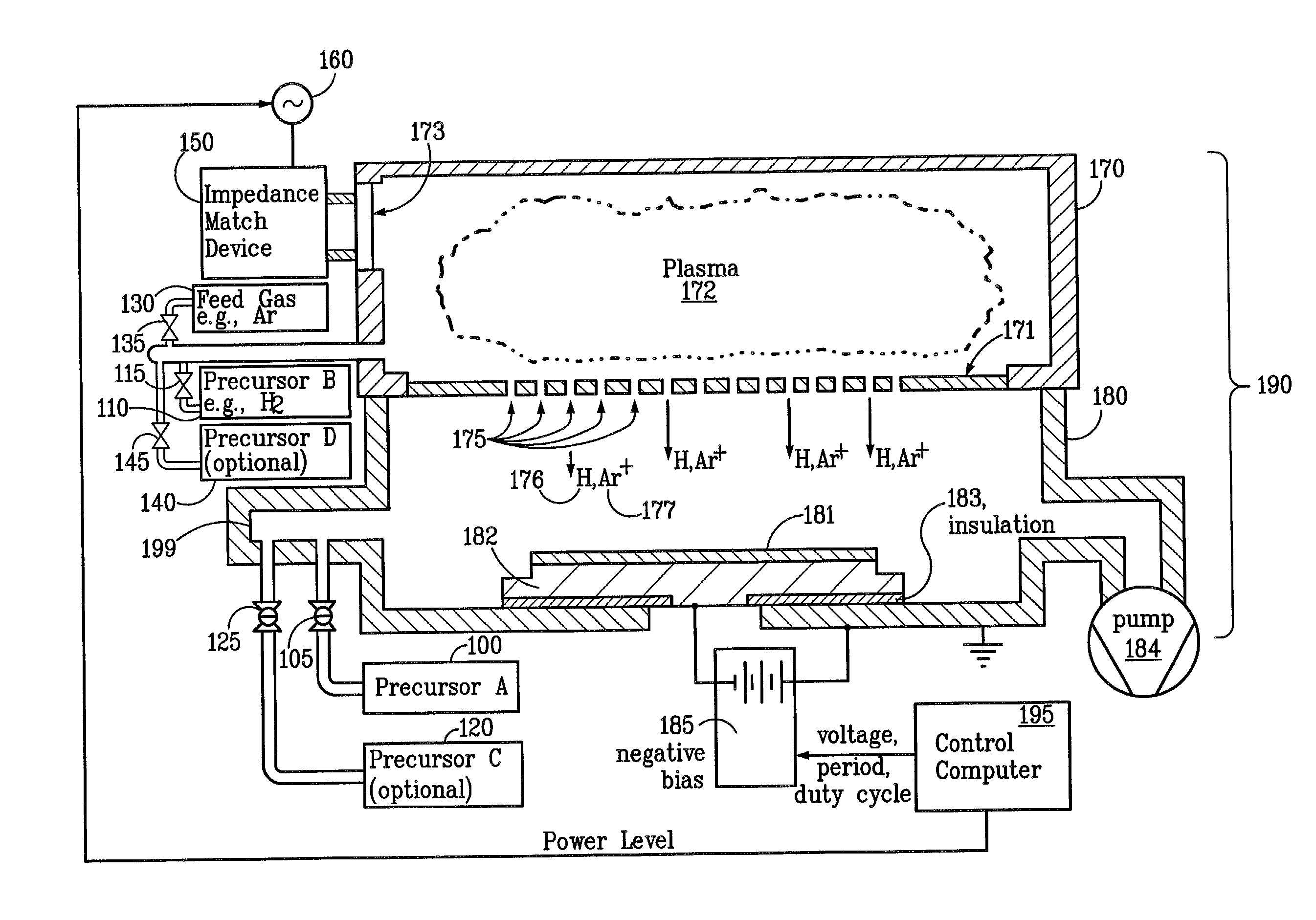
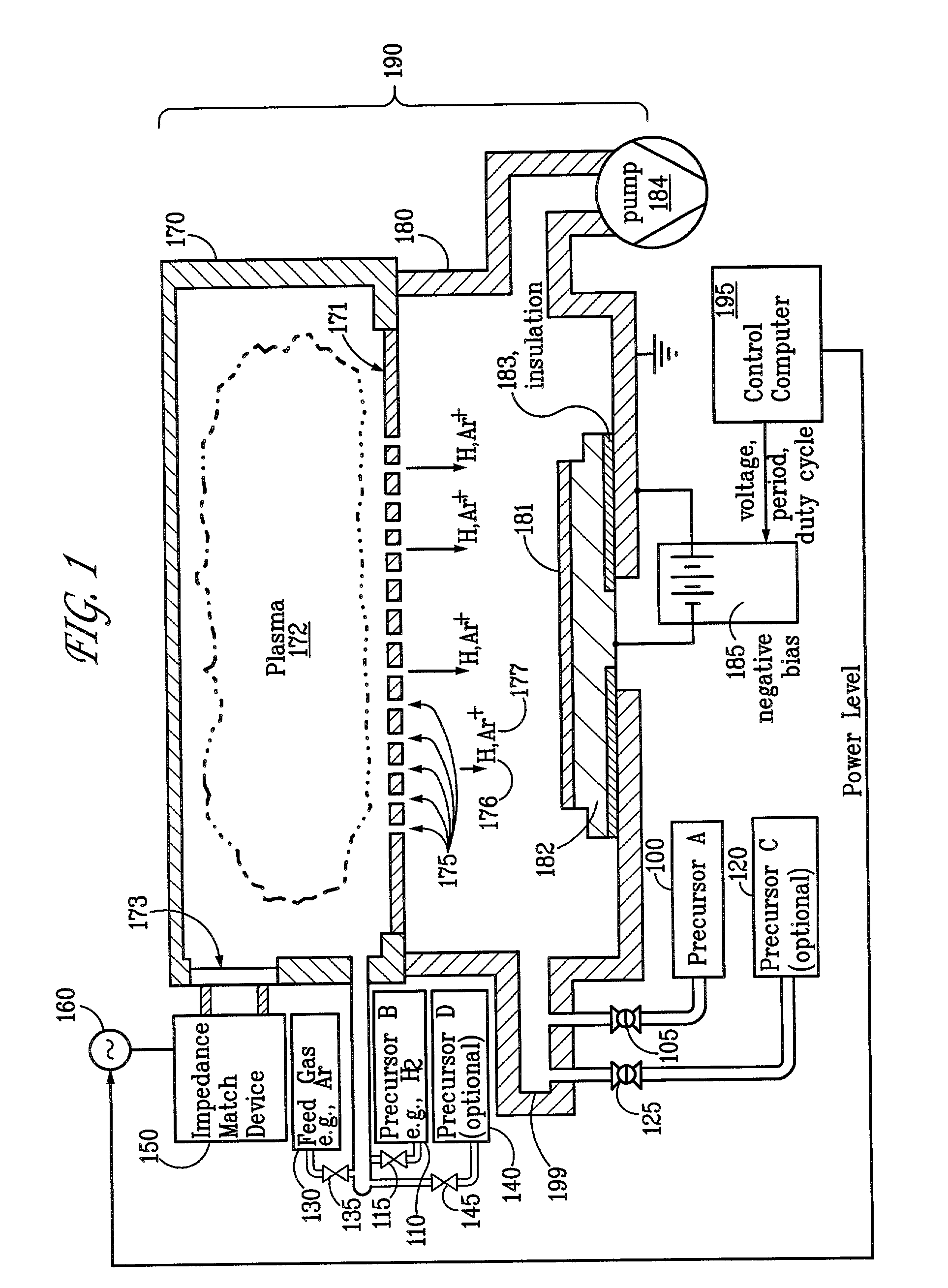
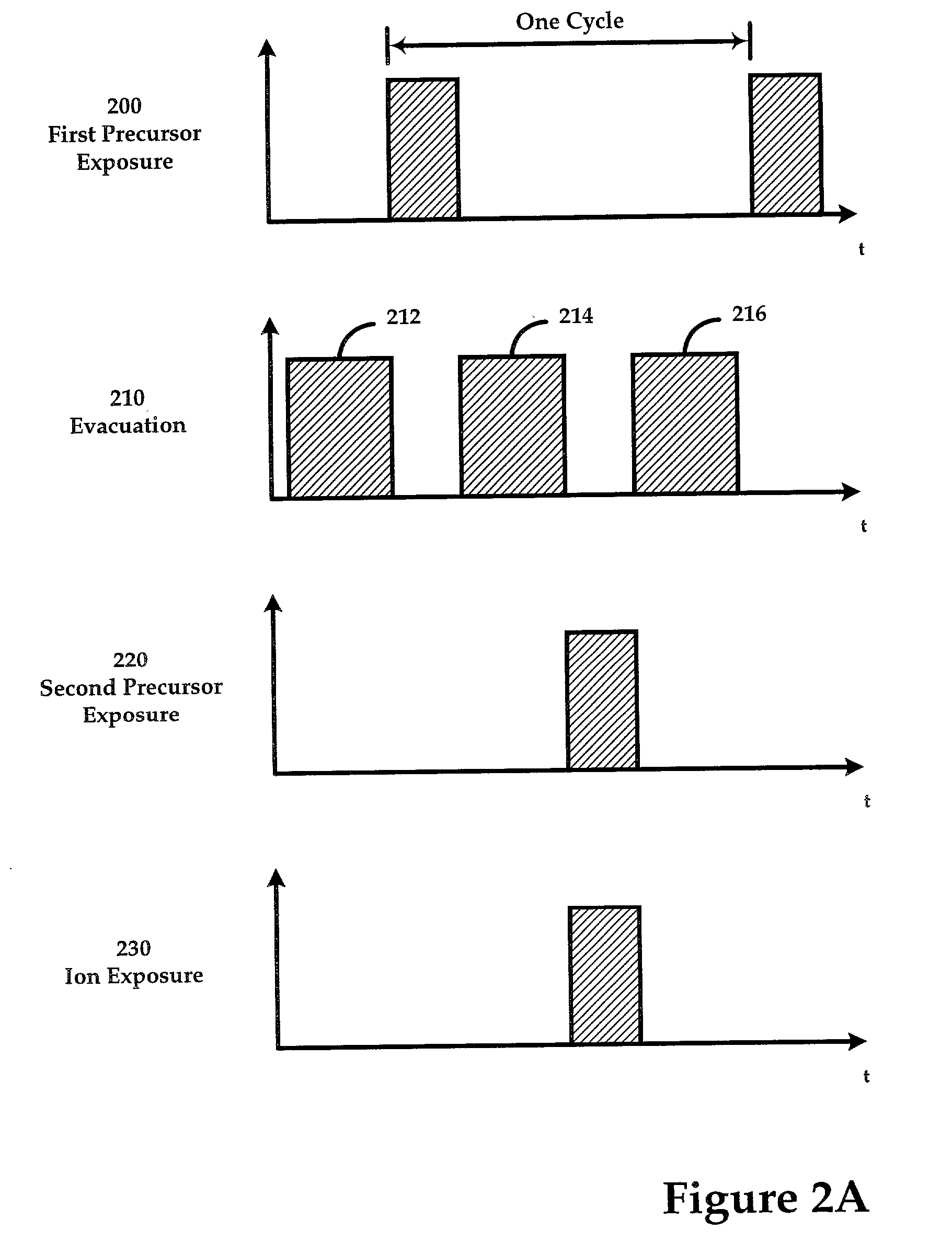
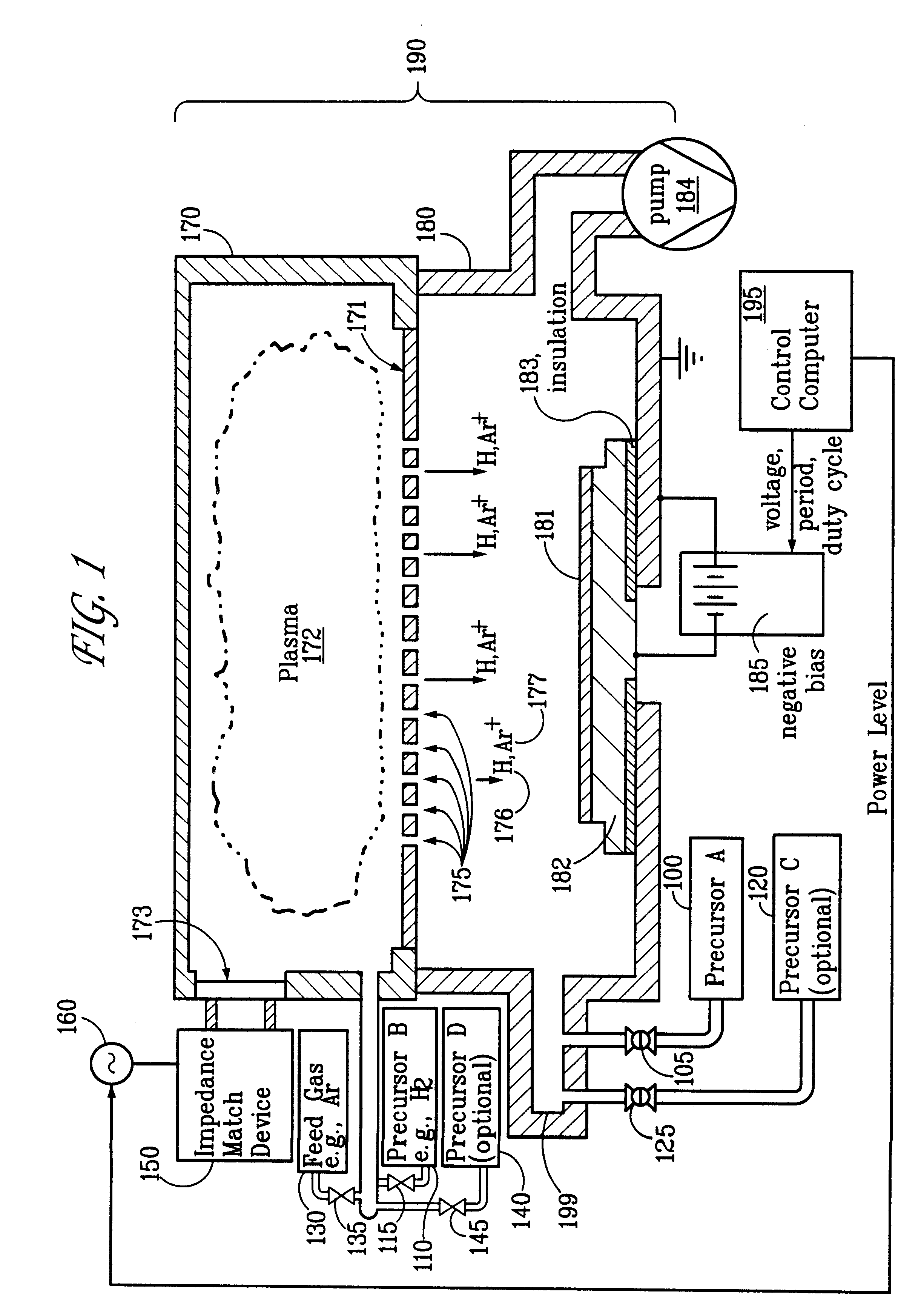
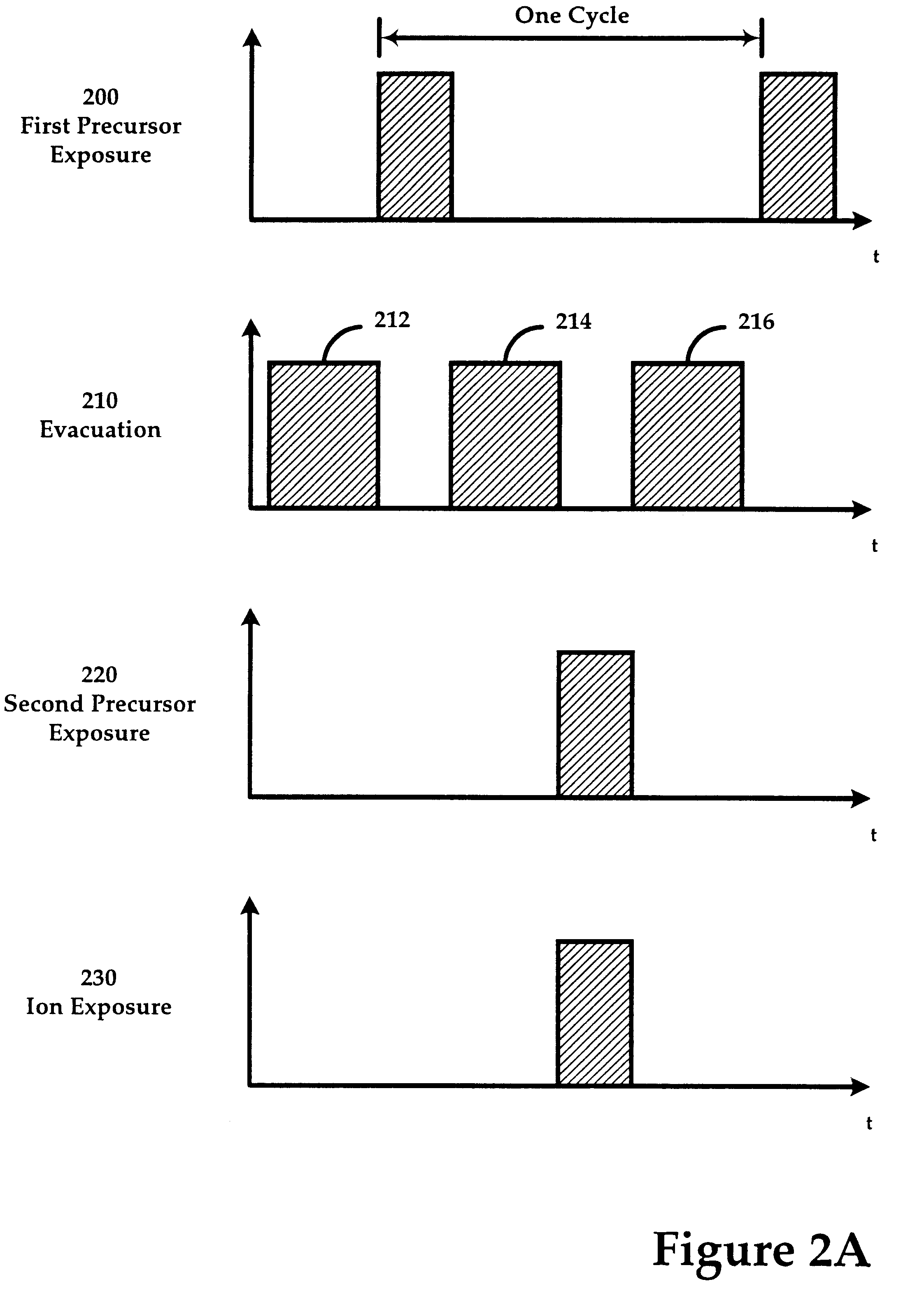
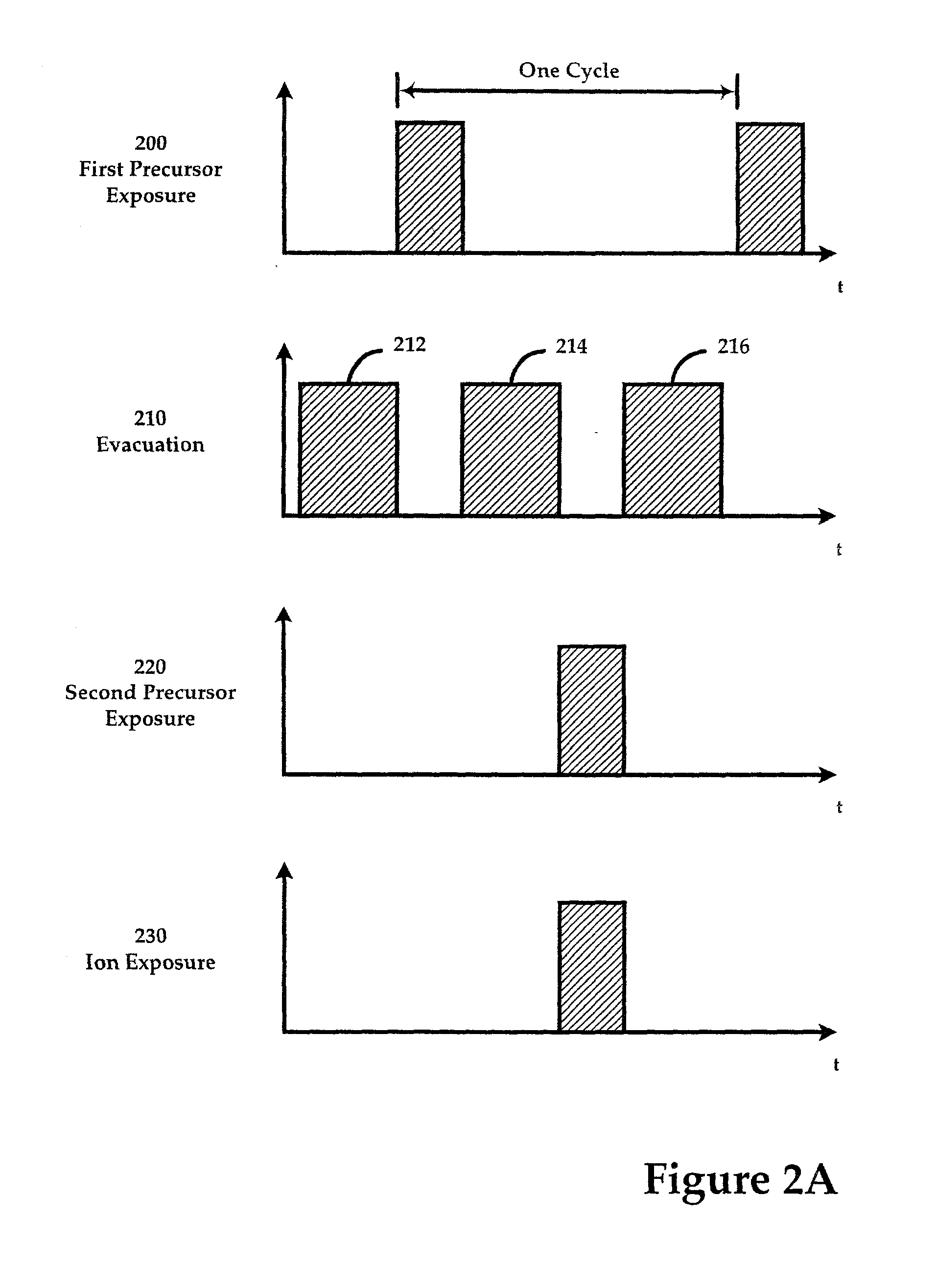
Ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential chemical vapor deposition (CVD) processes are disclosed where an ion flux, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or an electron flux, respectively, is used to induce the chemical reaction in the process. The process for depositing a thin film on a substrate includes introducing a flow of a first reactant gas in vapor phase into a process chamber where the gas forms an adsorbed saturated layer on the substrate and exposing the substrate to a flux of ions, a flux of ultra-violet radiation, or a flux of electrons for inducing a chemical reaction of the adsorbed layer of the first reactant gas to form the thin film. A second reactant gas can be used to form a compound thin film. The ion-induced, UV-induced, and electron-induced sequential CVD process of the present invention can be repeated to form a thin film of the desired thickness.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
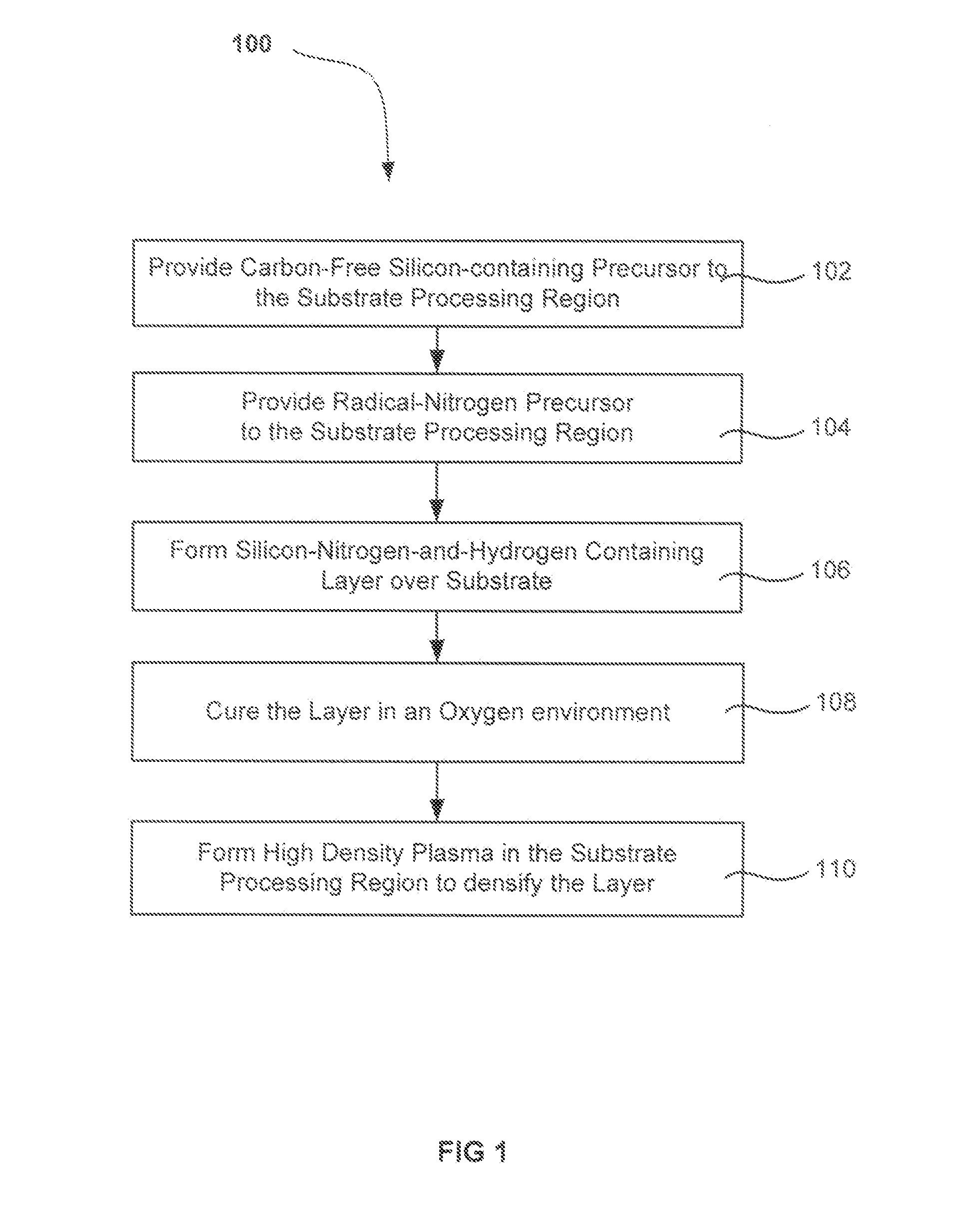
Densification for flowable films
InactiveUS20130288485A1Increase etch toleranceImprove toleranceElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh densityDielectric layer
A method of forming a dielectric layer is described. The method first deposits an initially-flowable layer on a substrate. The initially-flowable layer is then densified by exposing the substrate to a high-density plasma (HDP). Essentially no additional material is deposited on the initially-flowable layer, in embodiments, but the impact of the accelerated ionic species serves to condense the layer and increase the etch tolerance of the processed layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
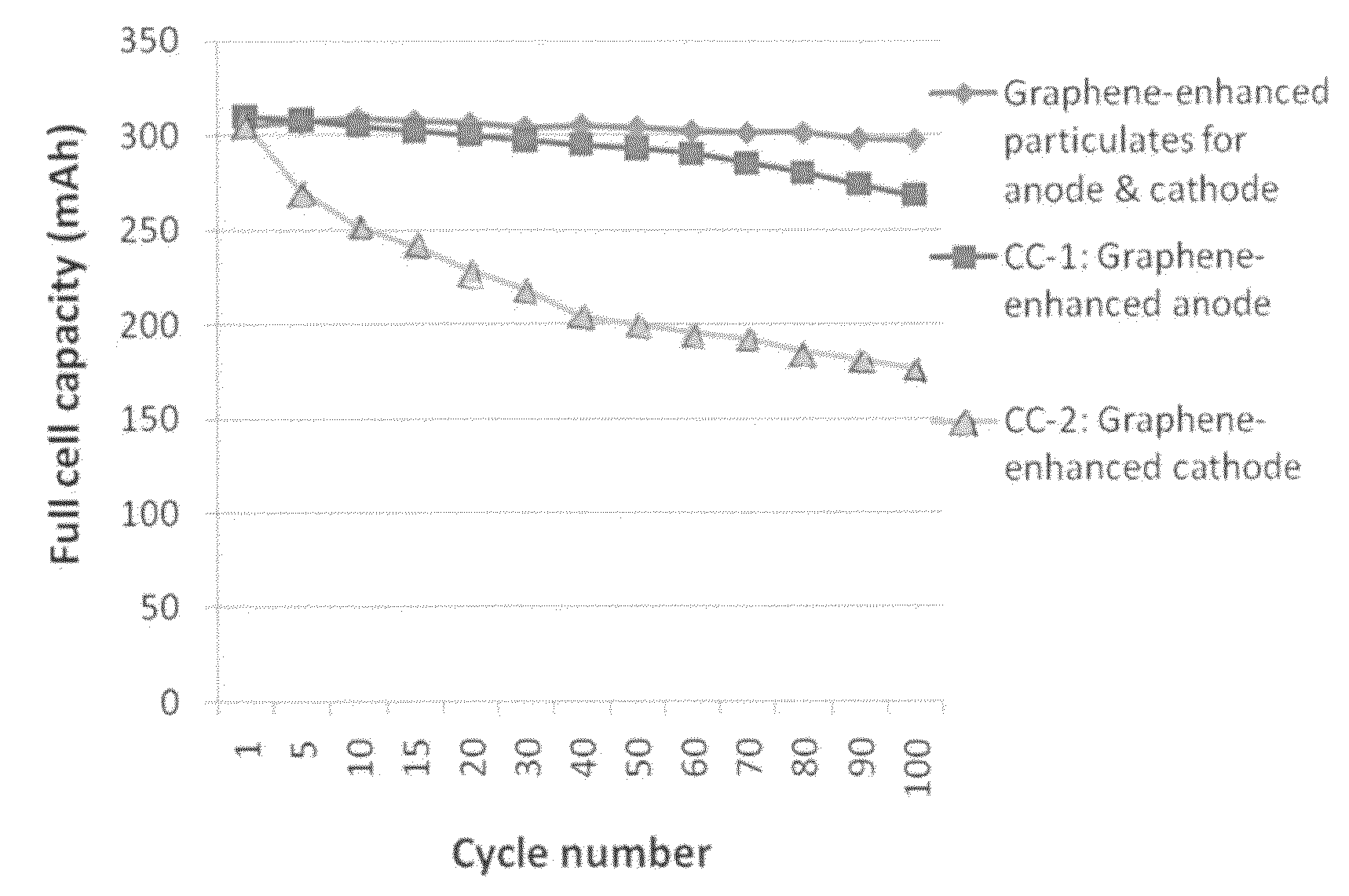
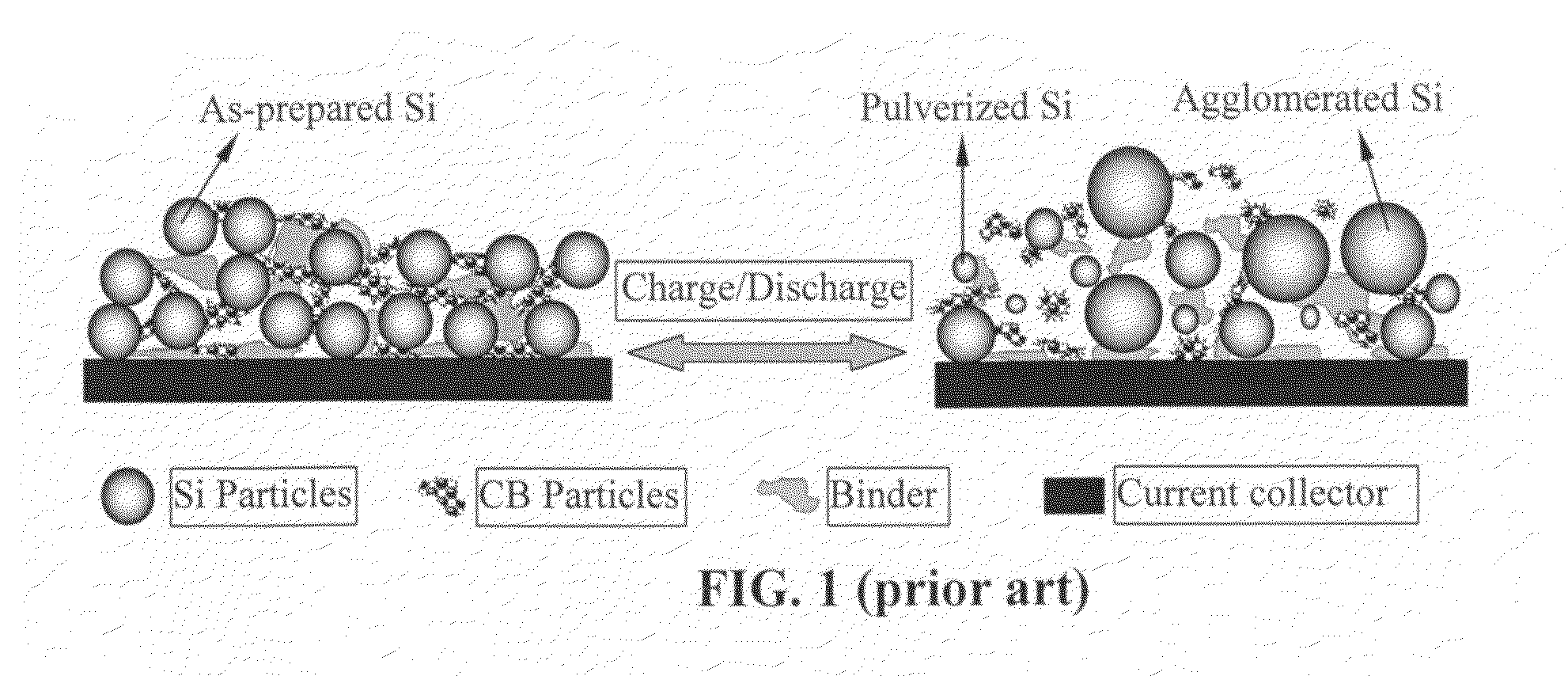
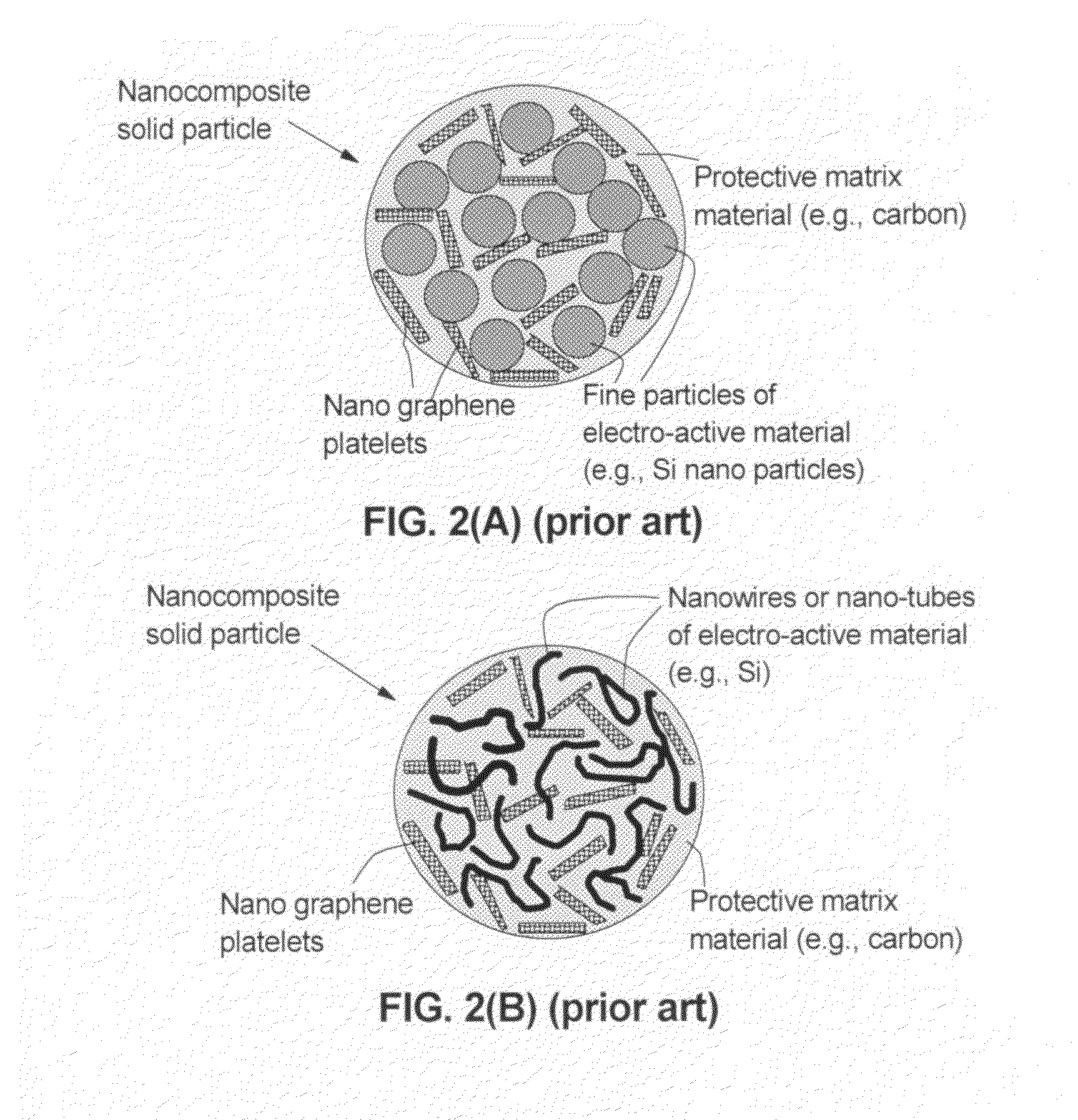
Graphene-enhanced anode particulates for lithium ion batteries
ActiveUS20120064409A1Enhanced Li-ion insertionIncrease capacityNon-metal conductorsMaterial nanotechnologyParticulatesMicroparticle
A nano graphene-enhanced particulate for use as a lithium-ion battery anode active material, wherein the particulate is formed of a single sheet of graphene or a plurality of graphene sheets and a plurality of fine anode active material particles with a size smaller than 10 μm. The graphene sheets and the particles are mutually bonded or agglomerated into the particulate with at least a graphene sheet embracing the anode active material particles. The amount of graphene is at least 0.01% by weight and the amount of the anode active material is at least 0.1% by weight, all based on the total weight of the particulate. A lithium-ion battery having an anode containing these graphene-enhanced particulates exhibits a stable charge and discharge cycling response, a high specific capacity per unit mass, a high first-cycle efficiency, a high capacity per electrode volume, and a long cycle life.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Atomic Layer Deposition of Oxides Using Krypton as an Ion Generating Feeding Gas
InactiveUS20070281105A1Improve abilitiesImprove efficiencyChemical vapor deposition coatingPlasma techniqueKryptonHigh density
An atomic layer deposition system and method utilizing radicals generated from a high-density mixed plasma for deposition is disclosed. A high-quality oxide or oxynitride can be deposited by exposing a substrate to a first precursor which is adsorbed onto the substrate during a first phase of one deposition cycle. After purging the deposition chamber, the substrate is exposed to a second precursor which includes oxygen radicals and krypton ions formed from the high-density mixed plasma. The ions and radicals are formed by introducing a radical generating feed gas (e.g., O2) and an ion generating feed gas into a plasma chamber and exciting the gases to form the high-density mixed plasma. The radicals and ions are then introduced to the substrate where they react with the first precursor to deposit a layer of the desired film. Krypton is preferably used as the ion generating feed gas because the metastable states of krypton lead to an efficient dissociation of oxygen into oxygen radicals when compared with other inert gases.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
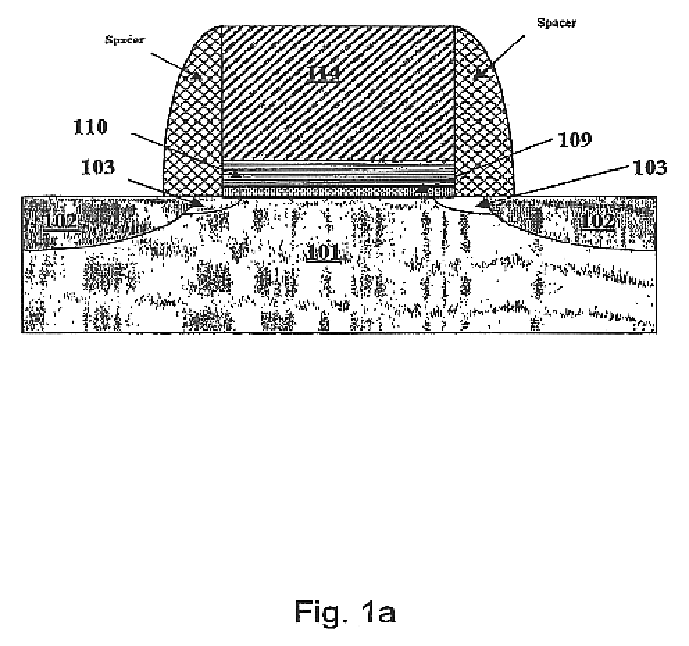
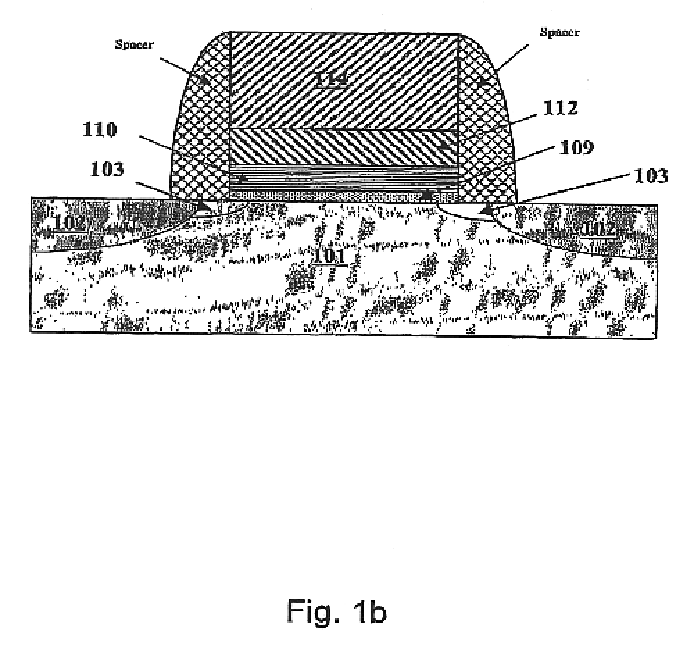
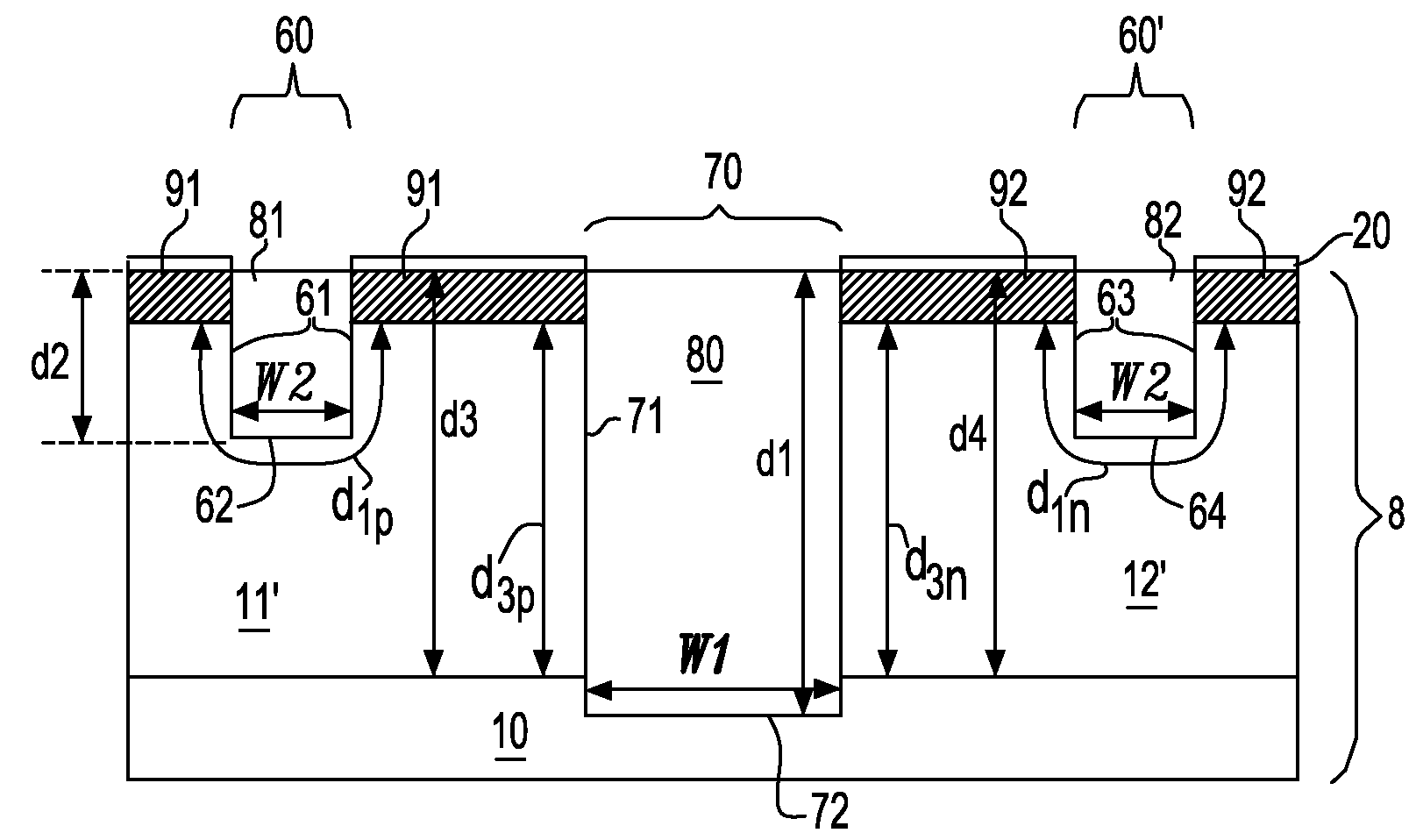
Self-aligned and extended inter-well isolation structure
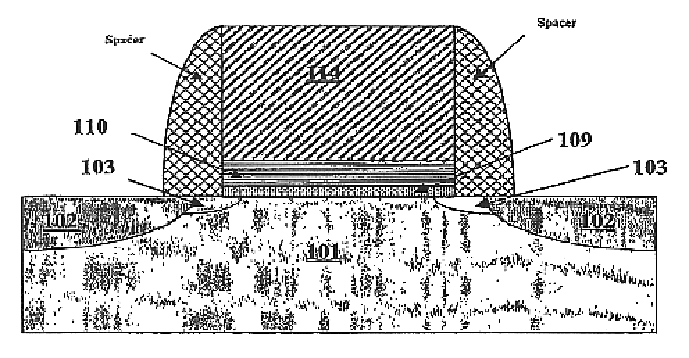
InactiveUS20080283962A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesEngineeringDielectric layer
A pedestal is formed out of the pad layer such that two edges of the pedestal coincide with a border of the wells as implanted. An extended pedestal is formed over the pedestal by depositing a conformal dielectric layer. The area of the extended pedestal is exposed the semiconductor surface below is recessed to a recess depth. Other trenches including at least one intra-well isolation trench are lithographically patterned. After a reactive ion etch, both an inter-well isolation trench and at least one intra-well isolation trench are formed. The width of the inter-well isolation trench may be reduced due to the deeper bottom surface compared to the prior art structures. The boundary between the p-well and the n-well below the inter-well isolation structure is self-aligned to the middle of the inter-well isolation structure.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
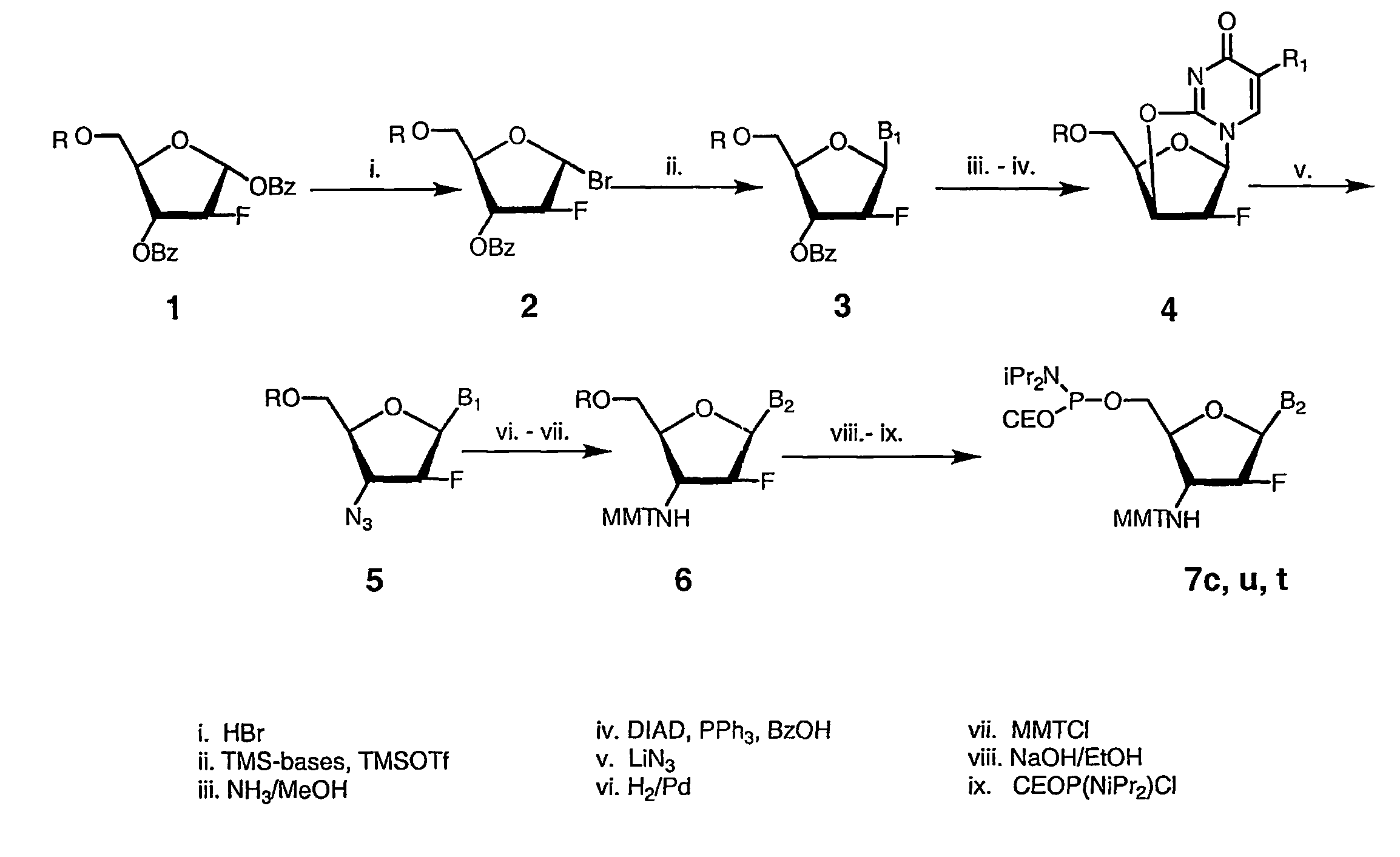
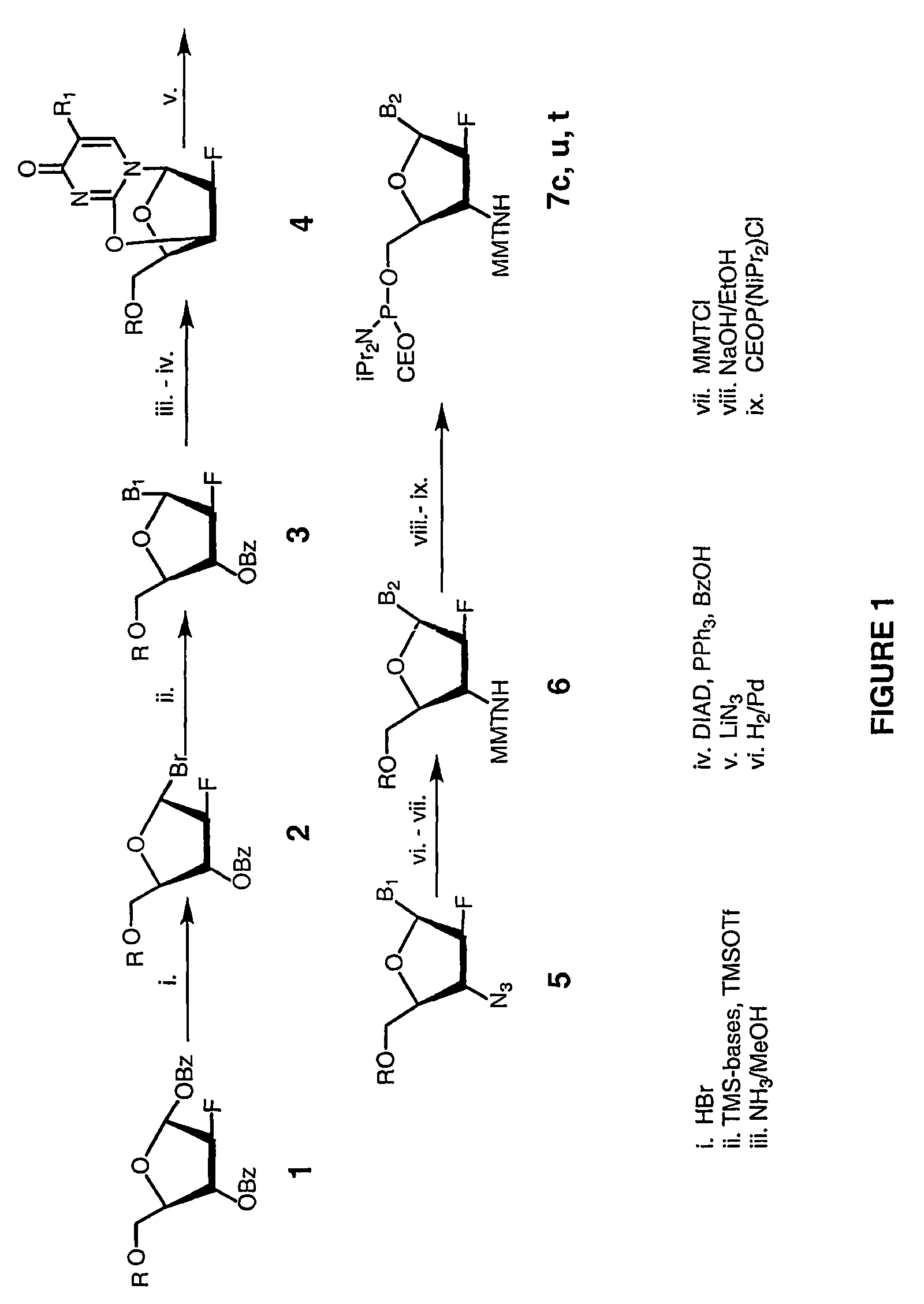
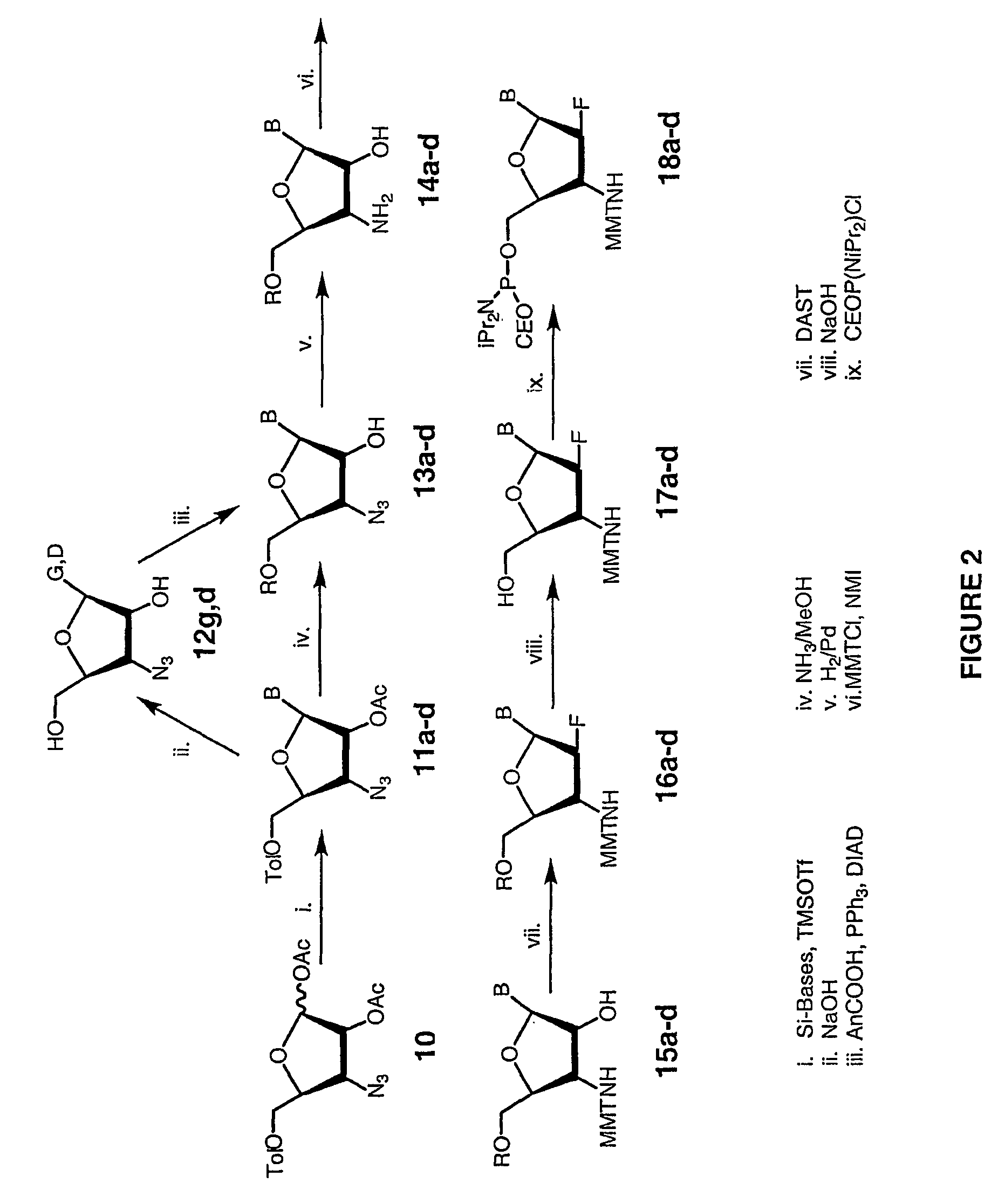
2'-arabino-fluorooligonucleotide N3'->P5' phosphoramidates: their synthesis and use
Oligonucleotides with a novel sugar-phosphate backbone containing at least one 2′-arabino-fluoronucleoside and an internucleoside 3′-NH—P(—O)(OR)—O-5′ linkage, where R is a positively charged counter ion or hydrogen, and methods of synthesizing and using the inventive oligonucleotides are provided. The inventive phosphoramidate 2′-arabino-fluorooligonucleotides have a high RNA binding affinity to complementary nucleic acids and are base and acid stable.
Owner:GERON CORPORATION
Method for manufacturing soi substrate
InactiveUS20090142905A1High bonding strengthImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptoelectronicsSingle crystal
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method and apparatus for photomask plasma etching
A method and apparatus for etching photomasks is provided herein. In one embodiment, the apparatus comprises a process chamber having a support pedestal adapted for receiving a photomask. An ion-neutral shield is disposed above the pedestal and a deflector plate assembly is provided above the ion-neutral shield. The deflector plate assembly defines a gas flow direction for process gases towards the ion-neutral shield, while the ion-neutral shield is used to establish a desired distribution of ion and neutral species in a plasma for etching the photomask.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Continuous method for depositing a film by modulated ion-induced atomic layer deposition (MII-ALD)
InactiveUS20020164423A1Faster efficient meanSimple methodPretreated surfacesSolid state diffusion coatingHigh densityOptoelectronics
The present invention relates to an enhanced sequential atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique suitable for deposition of barrier layers, adhesion layers, seed layers, low dielectric constant (low-k) films, high dielectric constant (high-k) films, and other conductive, semi-conductive, and non-conductive films. This is accomplished by 1) providing a non-thermal or non-pyrolytic means of triggering the deposition reaction; 2) providing a means of depositing a purer film of higher density at lower temperatures; and, 3) providing a faster and more efficient means of modulating the deposition sequence and hence the overall process rate resulting in an improved deposition method.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com