Patents
Literature
1154 results about "Protein carbonyl" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
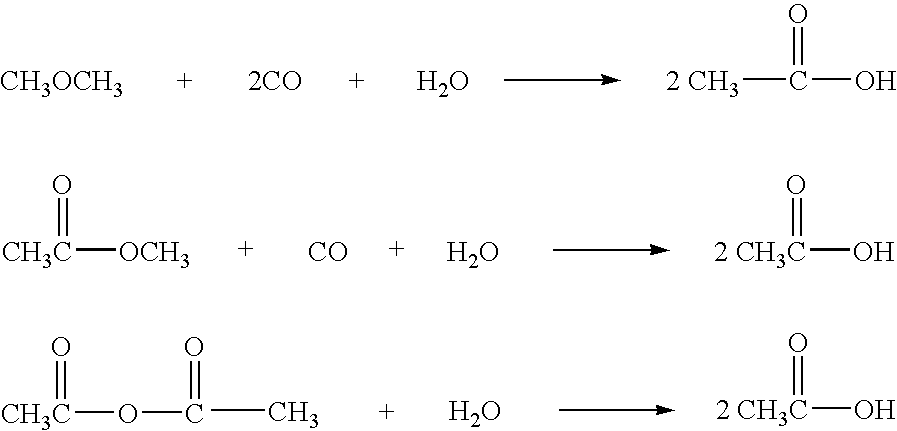
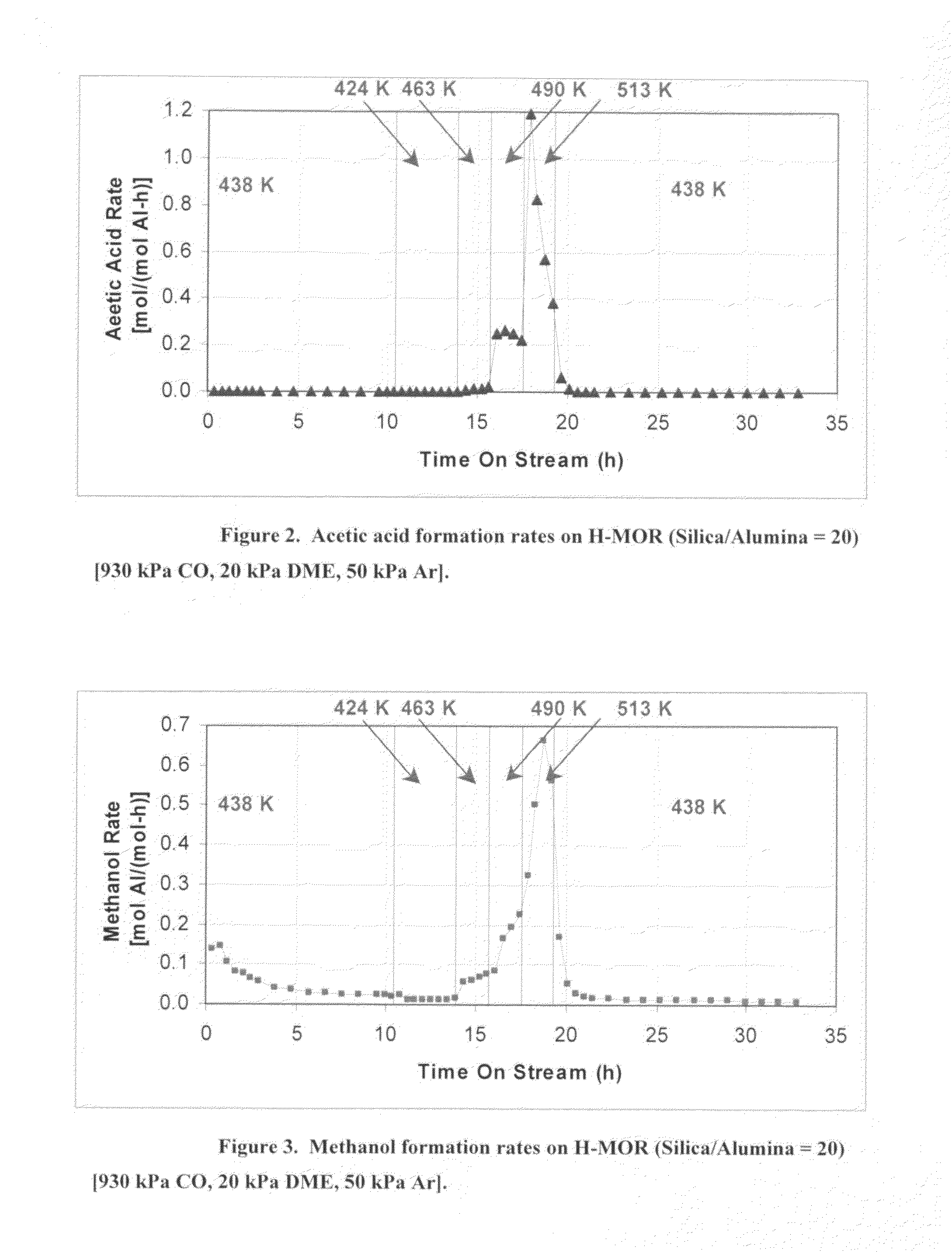
Protein carbonylation. The modification of side chains in a few native amino acids such as histidine, cysteine, and lysine in proteins to carbonyl derivatives (aldehydes and ketones) is known as protein carbonylation. Oxidative stress, often metal catalyzed, leads to protein carbonylation.
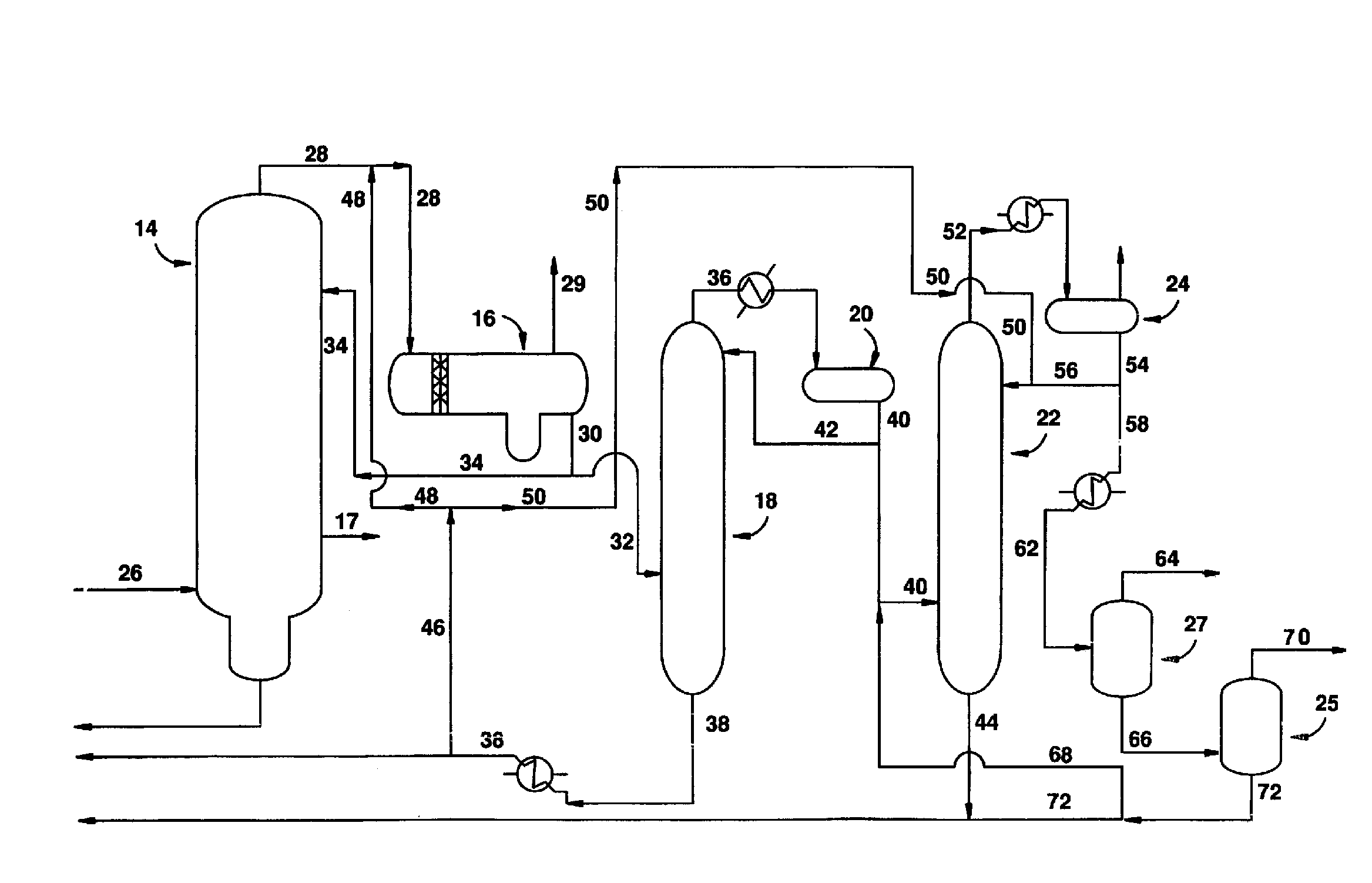
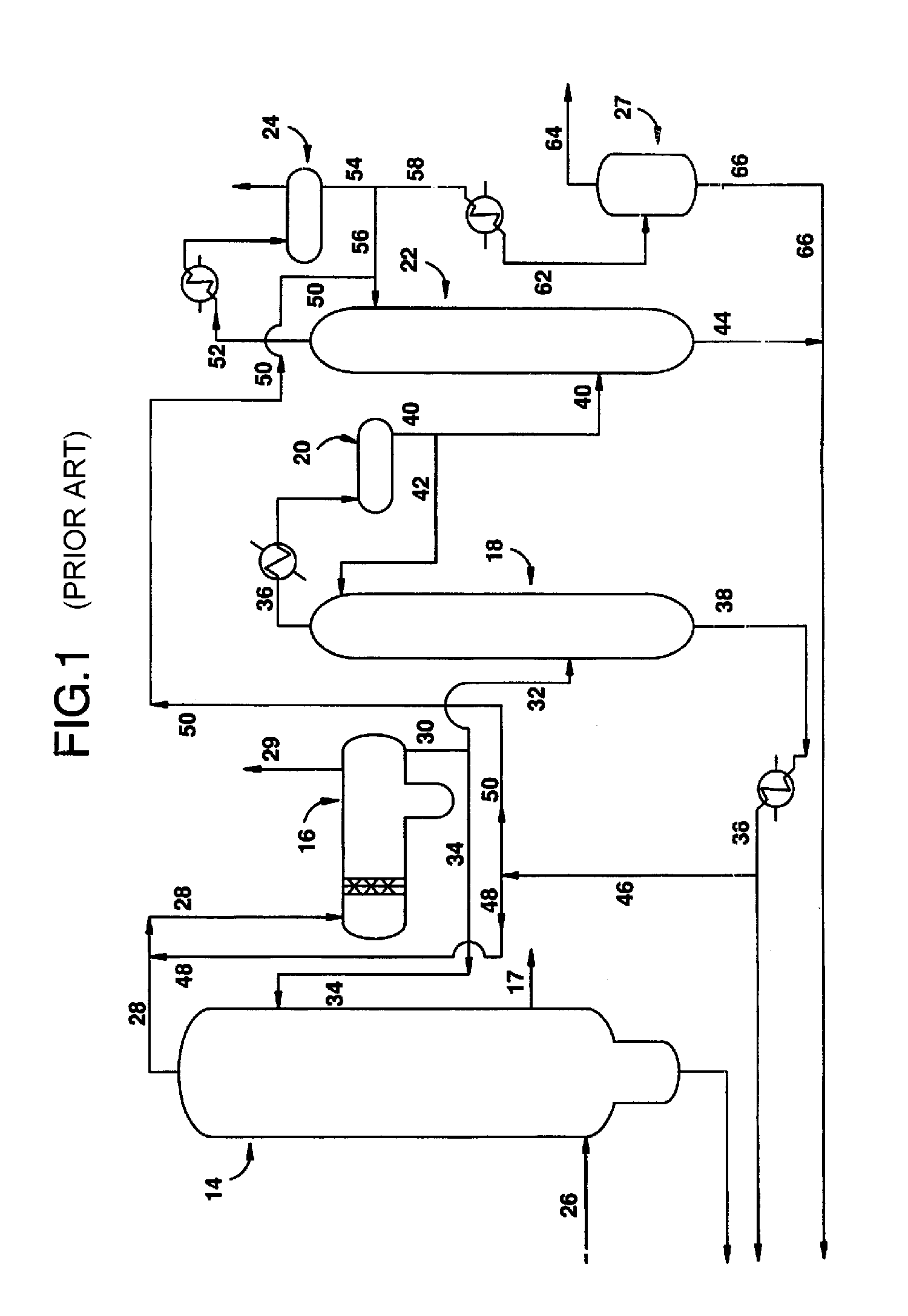
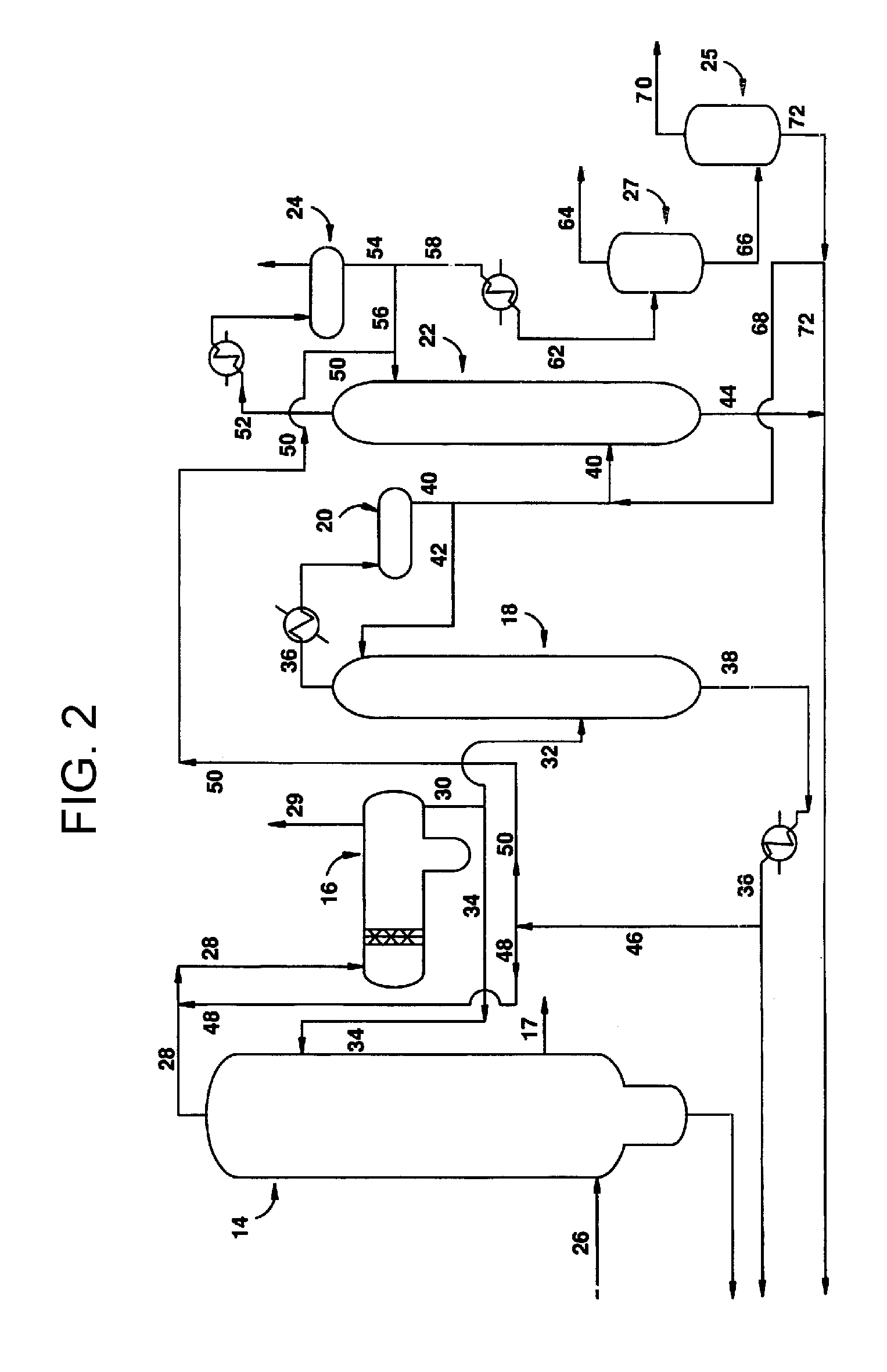
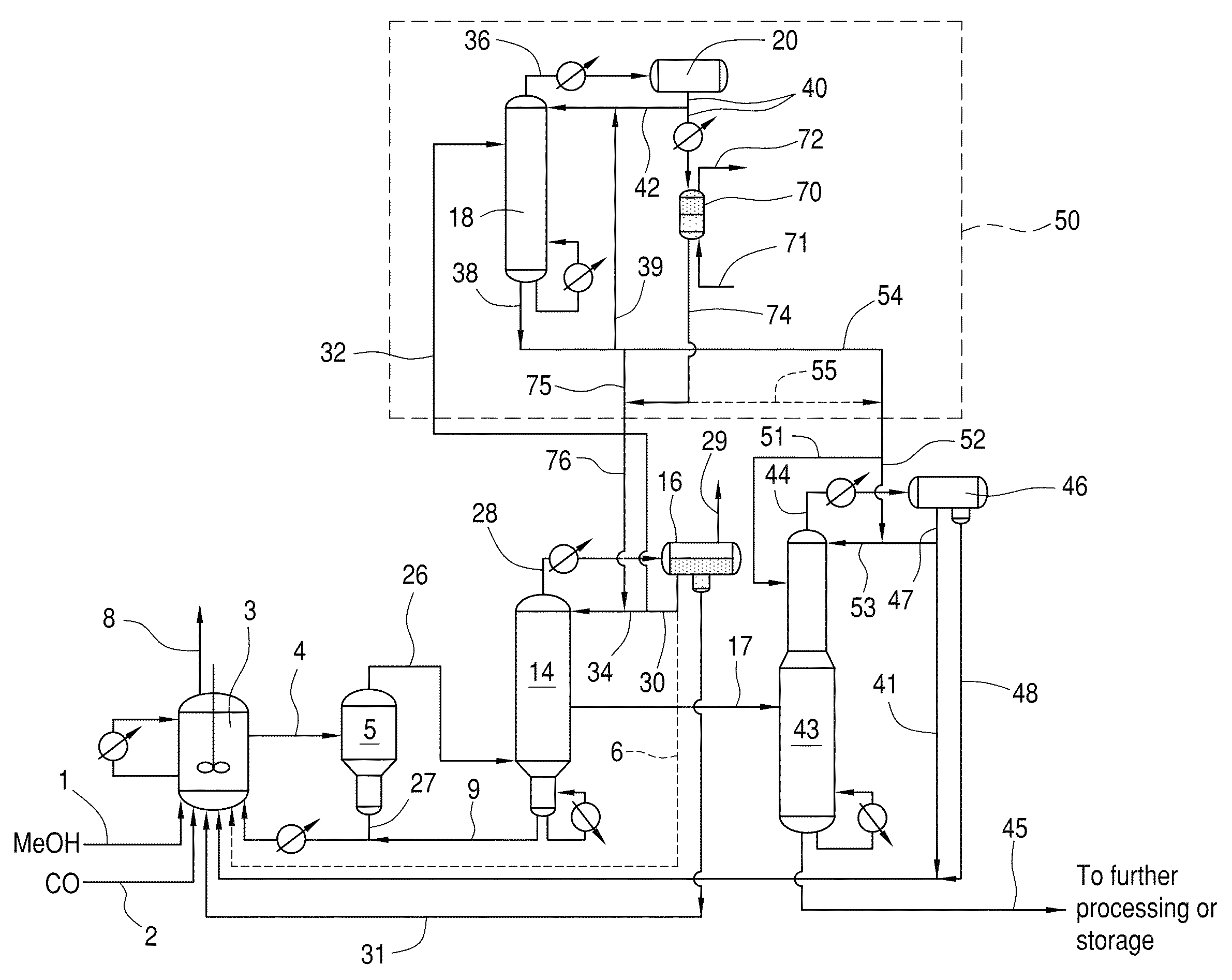
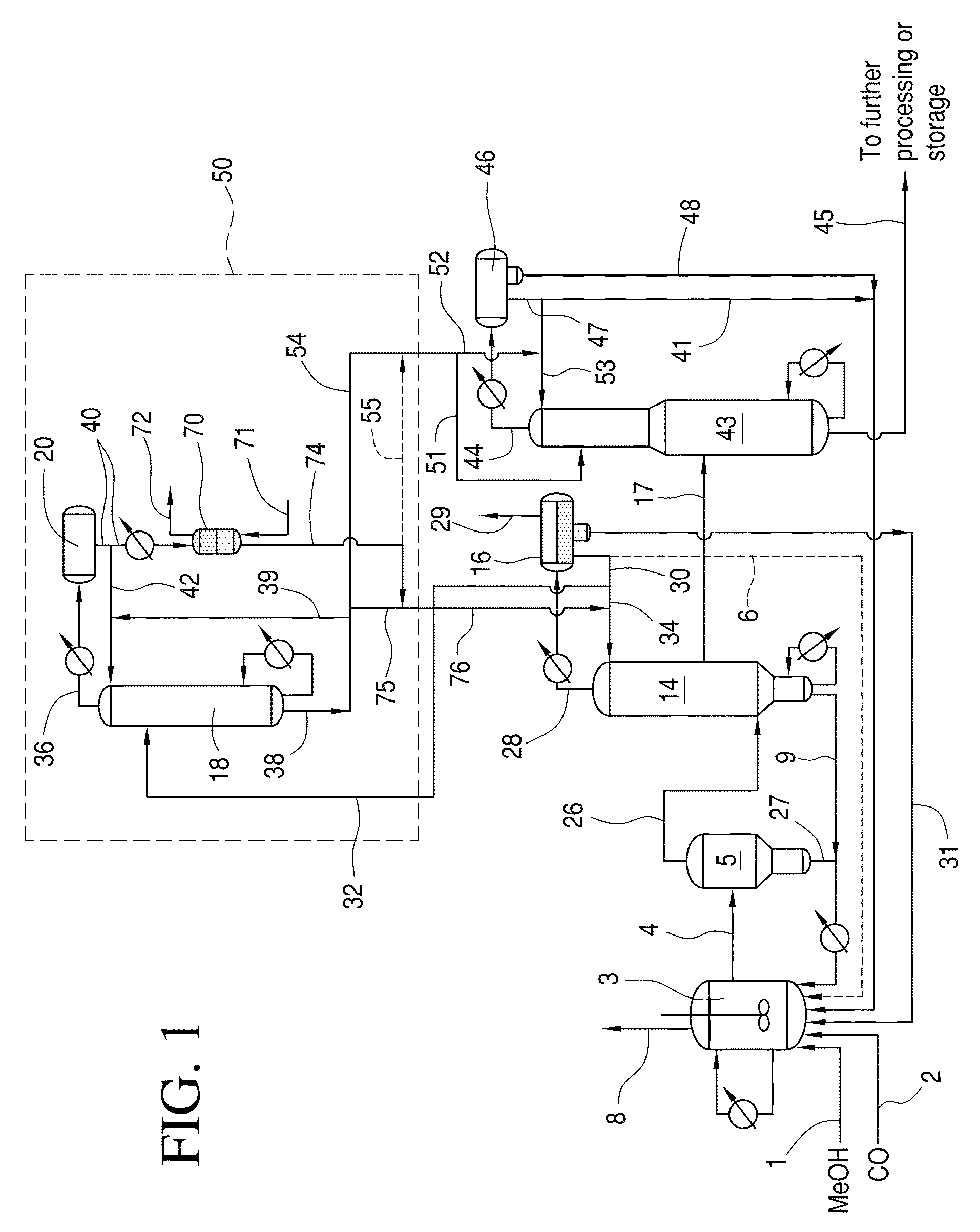
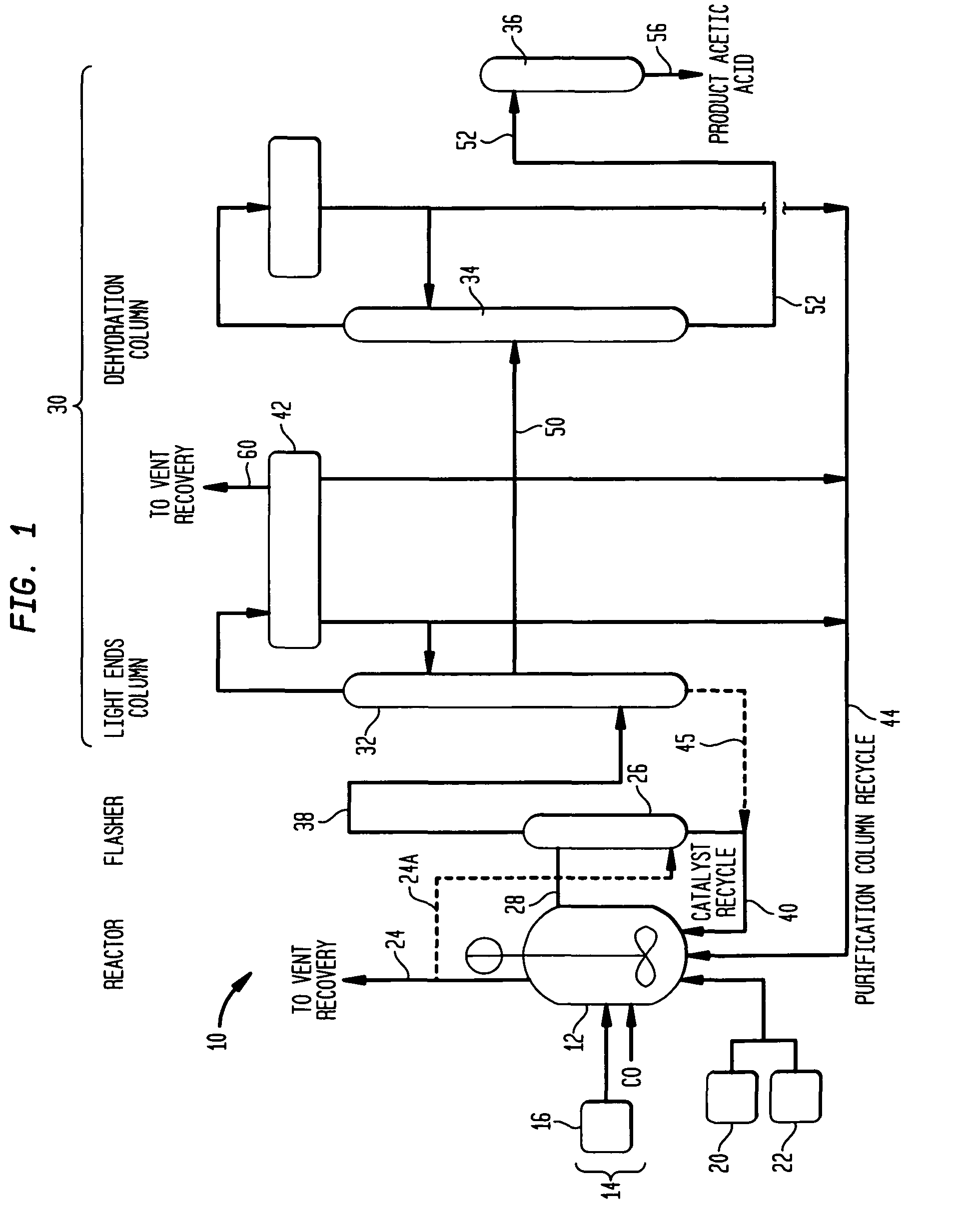
Low energy carbonylation process
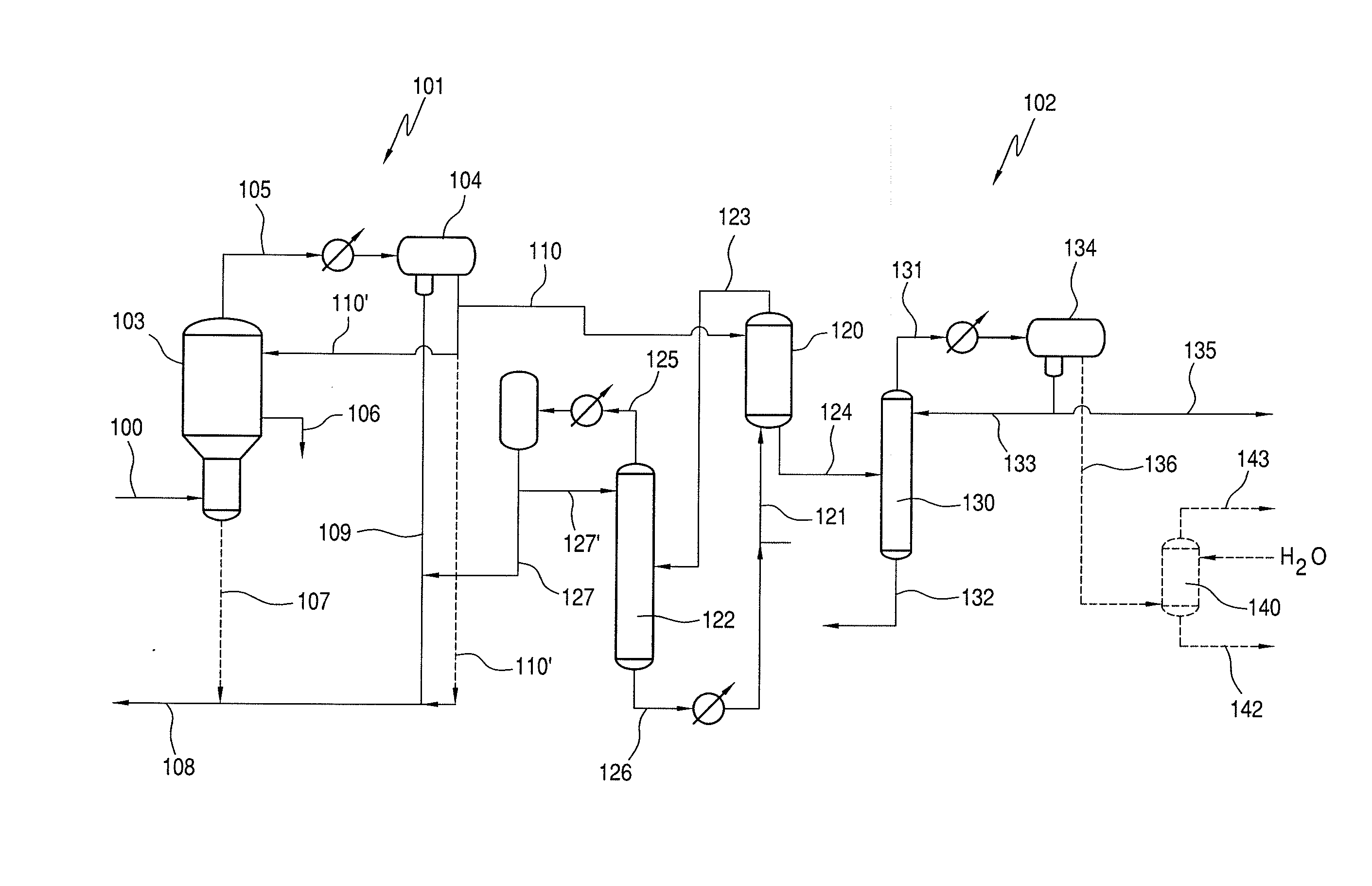
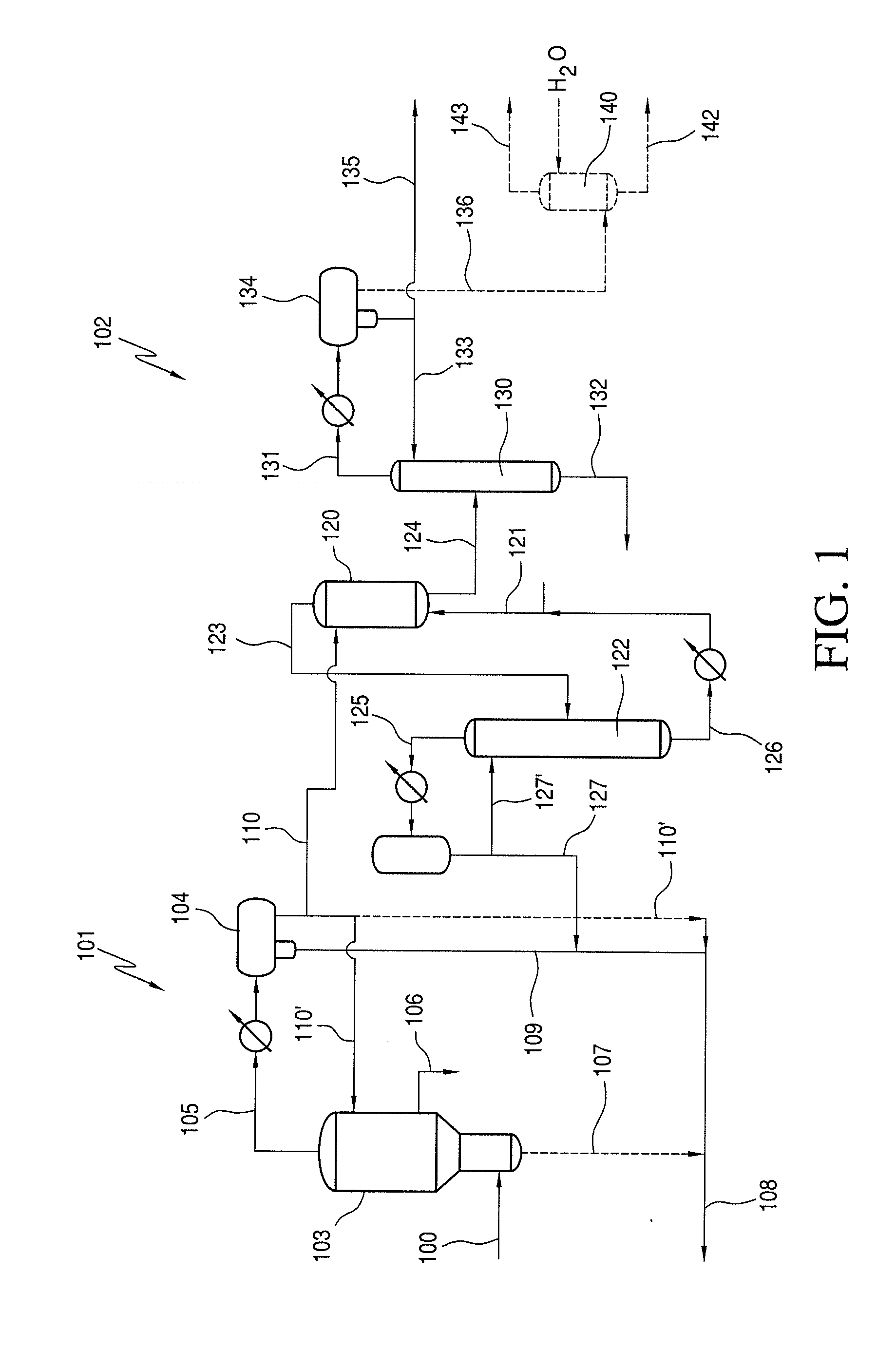
InactiveUS6657078B2Weaken energyHigh purityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsPropanoic acidIodide
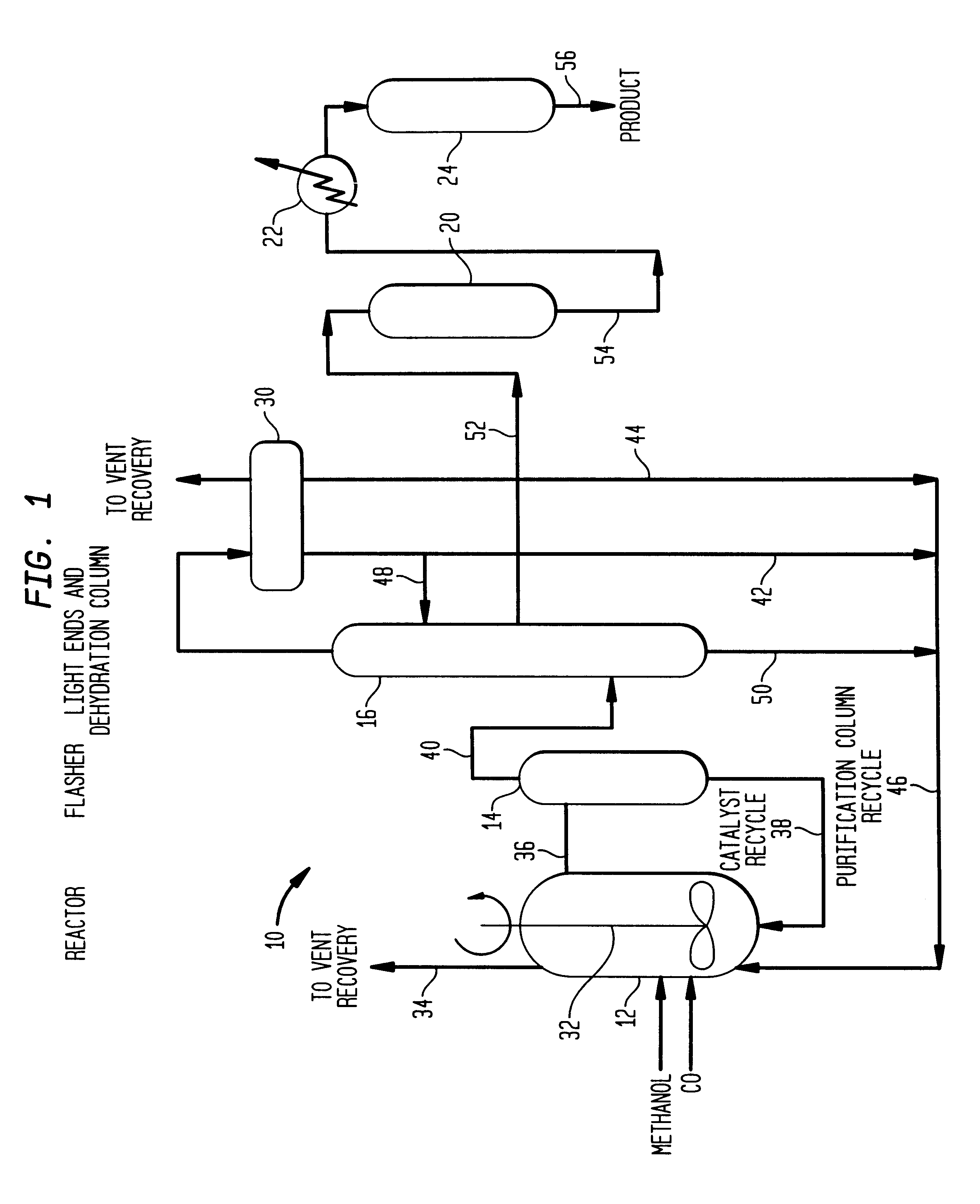
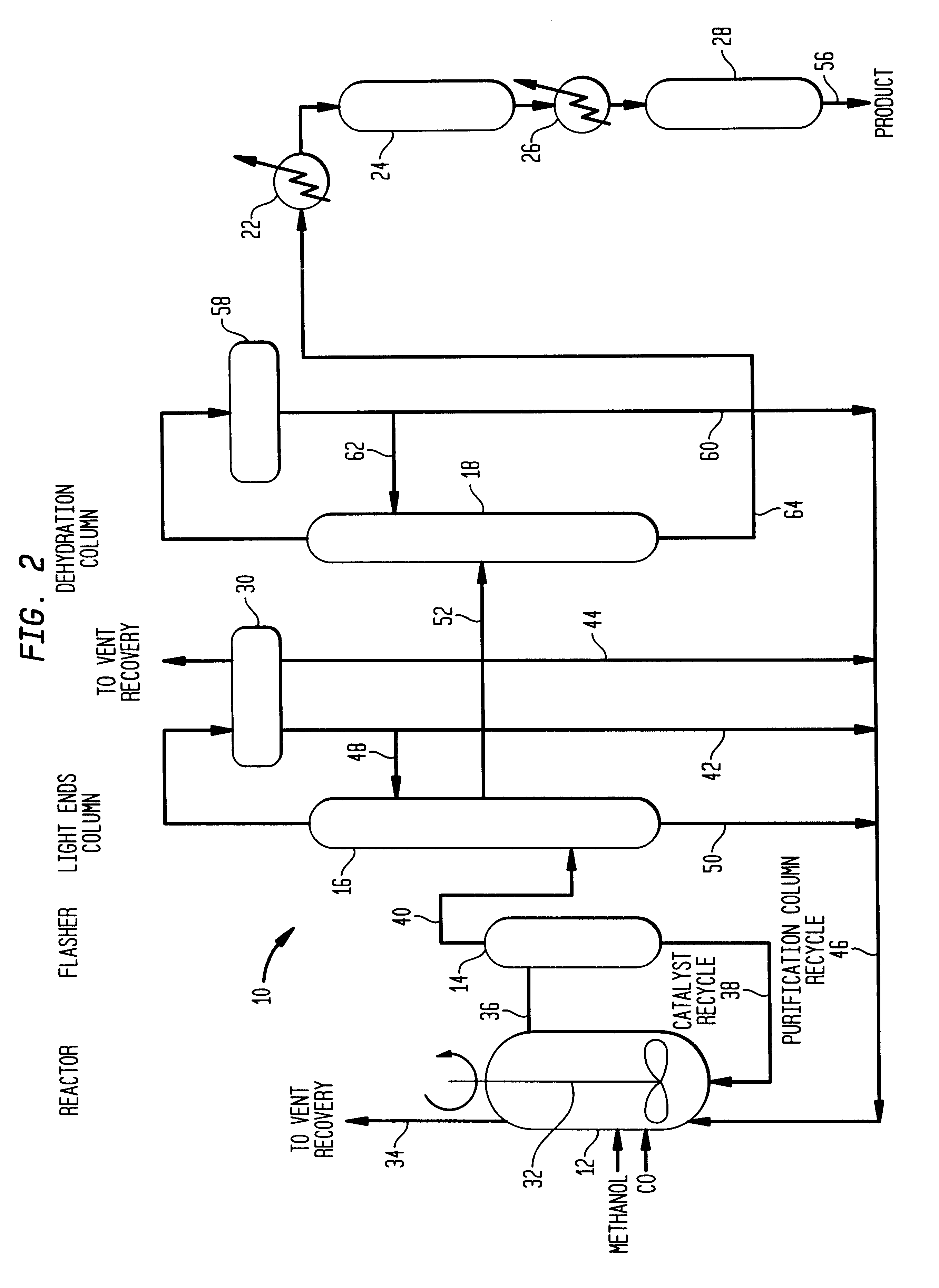
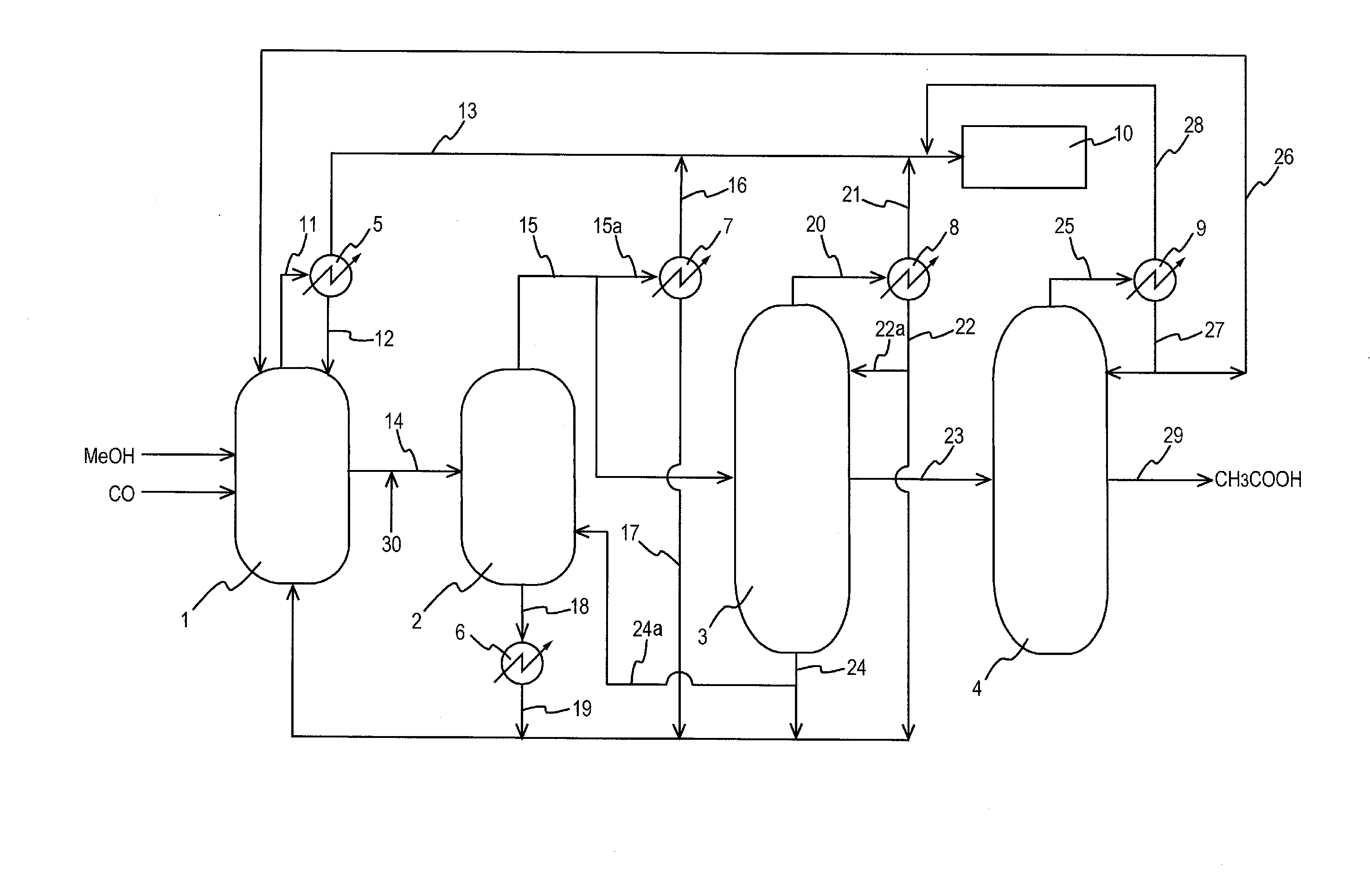
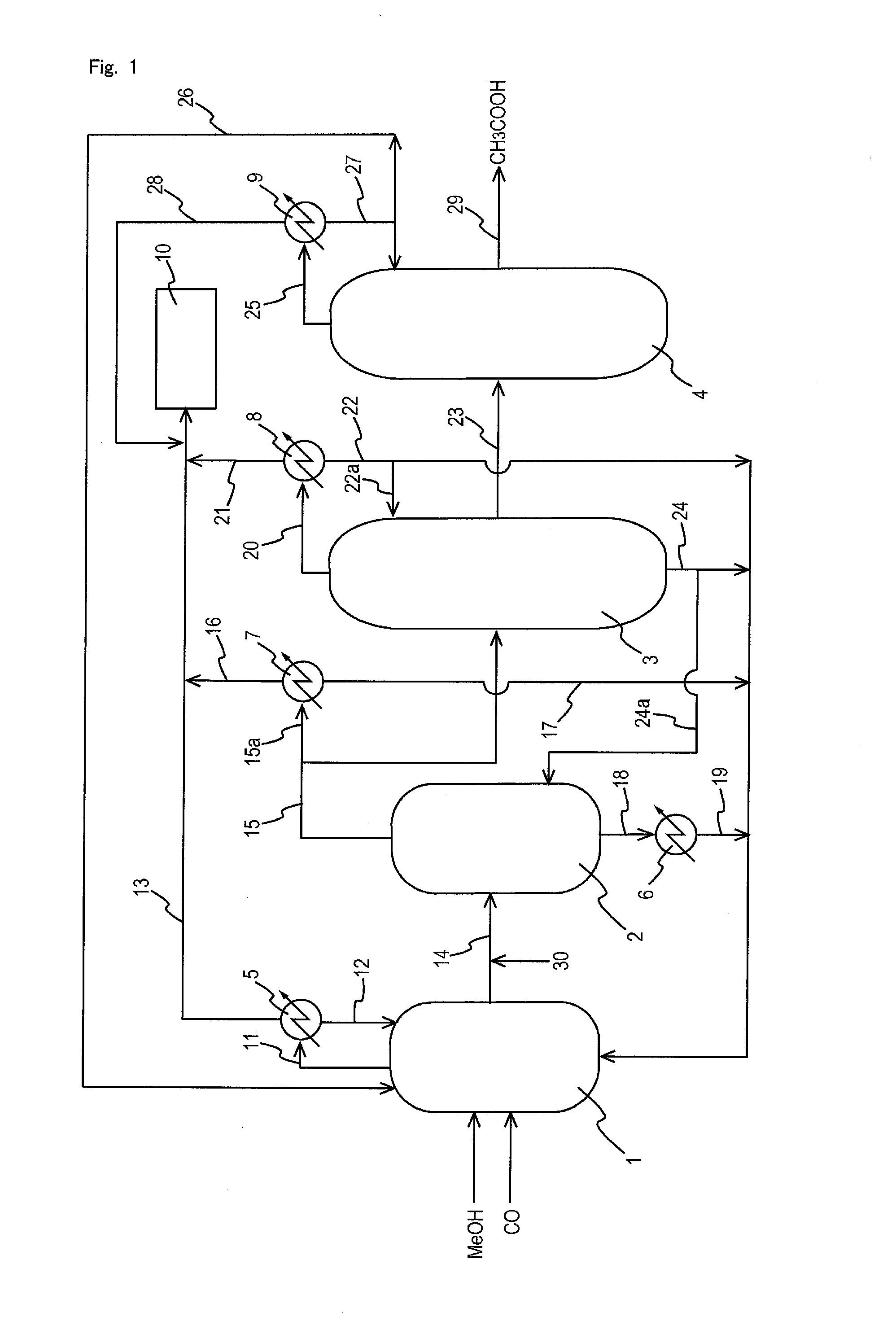
A low energy process for producing acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol is disclosed. The process involves a rhodium-catalyzed system operated at less than about 14% water utilizing up to 2 distillation columns. The process is preferably controlled such that the product stream has a low level of propionic acid impurity and the level of aldehyde impurities is minimized by way of aldehyde removal or minimizing aldehyde generation. The level of iodides is controlled by contacting the product, at elevated temperatures, with ion exchange resins. In preferred embodiments, at least one silver or mercury exchanged macroreticular strong acid ion exchange resin is used to purify the product. The high temperature treatment provides the added benefit of controlling the Color Value (Pt-Co units) of the product stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223886B2Reduce solubilitySimple methodOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionAcetic acidIodide
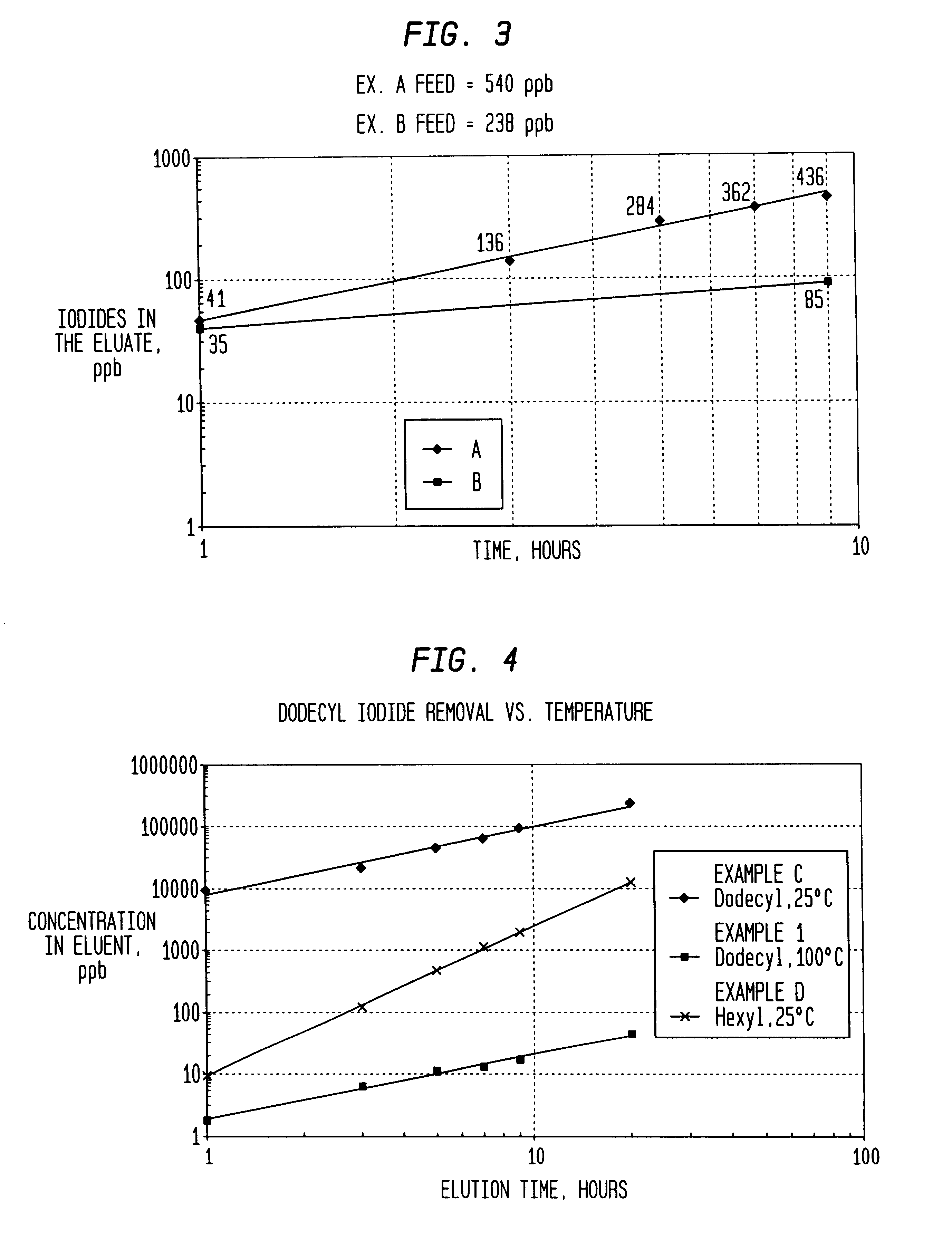
An improvement of the methanol carbonylation process for manufacturing acetic acid is disclosed. Specifically disclosed is a method for reducing the formation of alkyl iodides and C3-8 carboxylic acids by removing permanganate reducing compounds (“PRC's”) from the light phase of the condensed light ends overhead stream, including (a) distilling the light phase to yield a PRC enriched overhead stream; and (b) extracting the third overhead stream with water in at least two consecutive stages and separating therefrom one or more aqueous streams containing PRC's.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101613274AImprove stabilityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMolecular sieveMethyl acetate
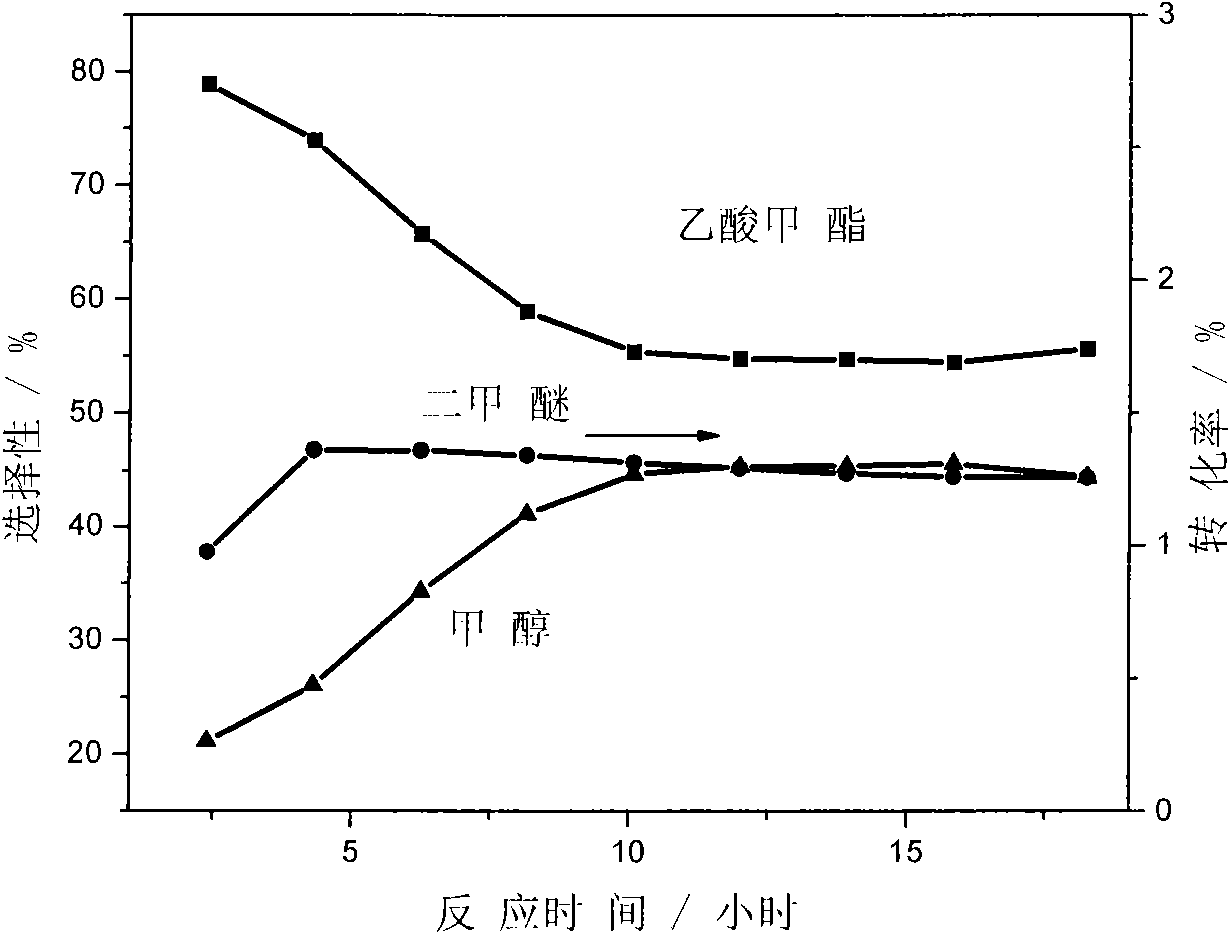
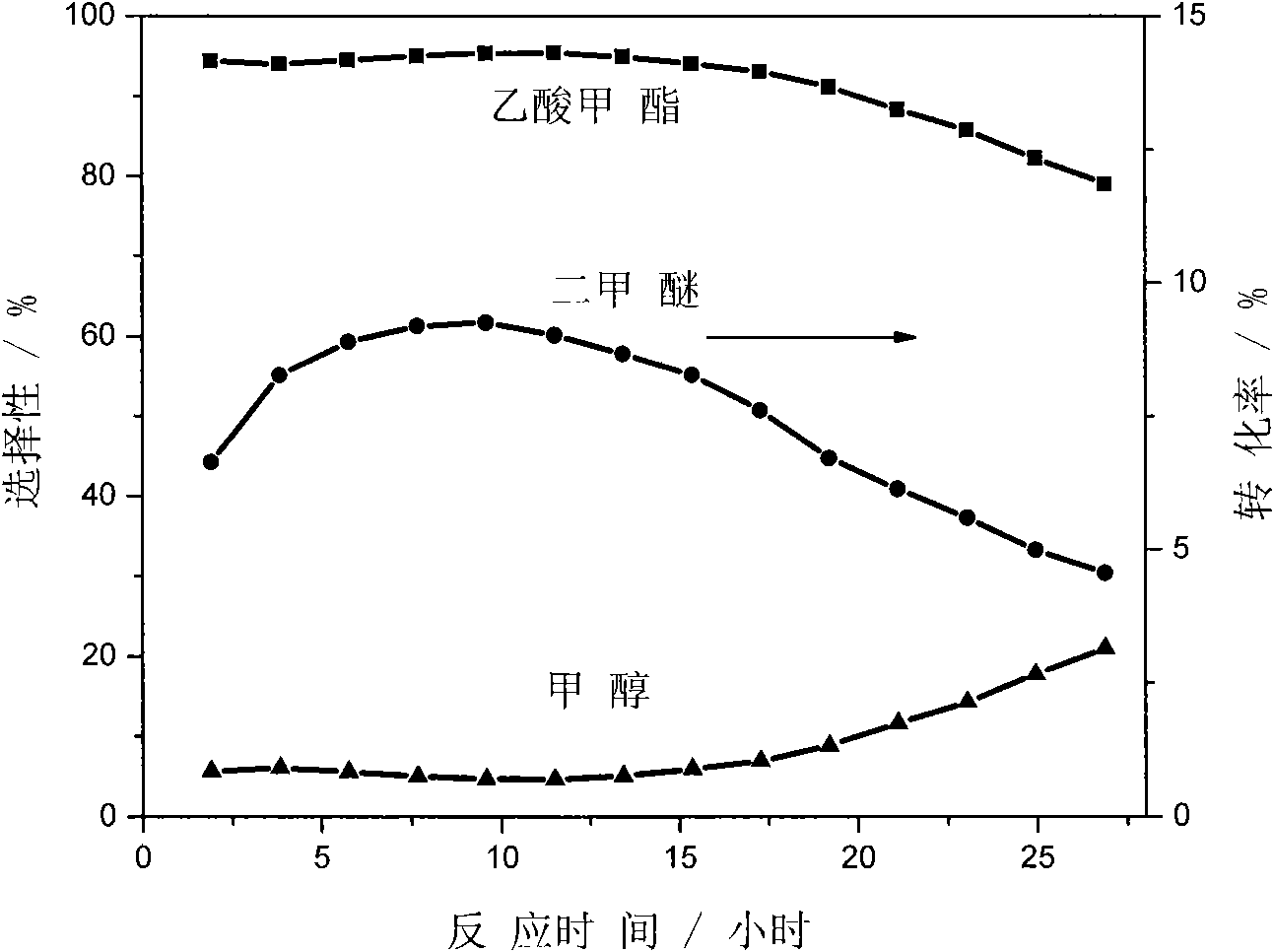
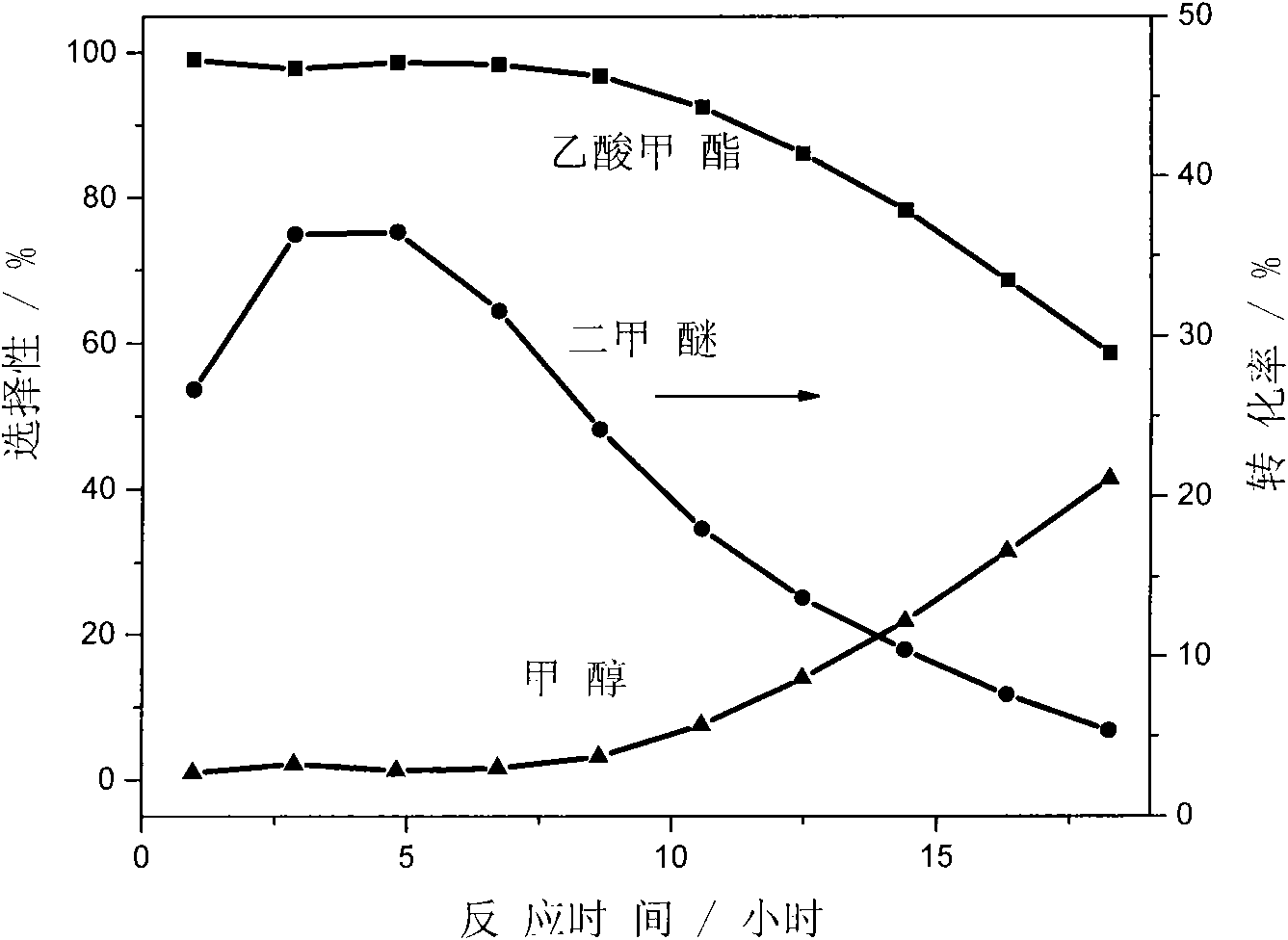
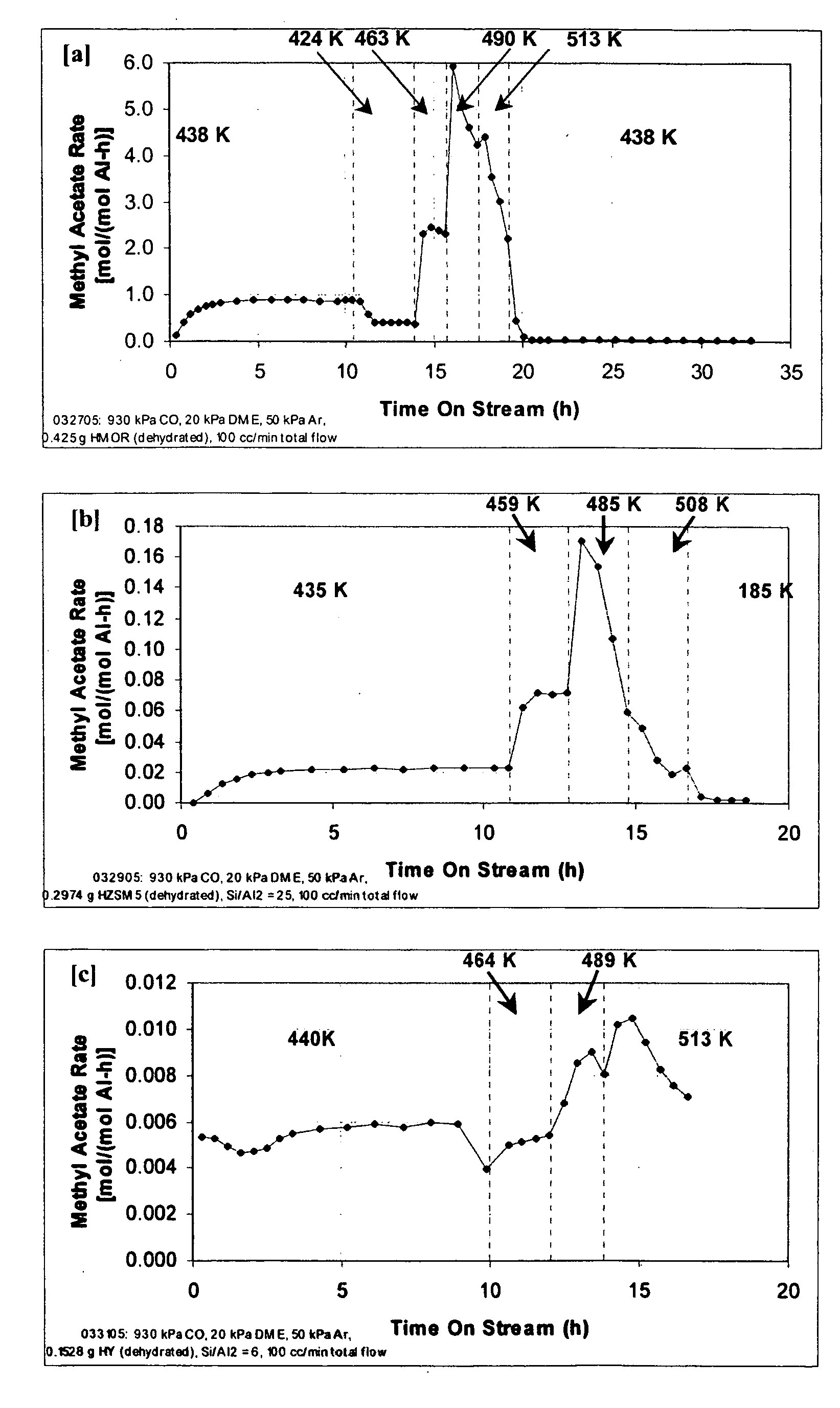
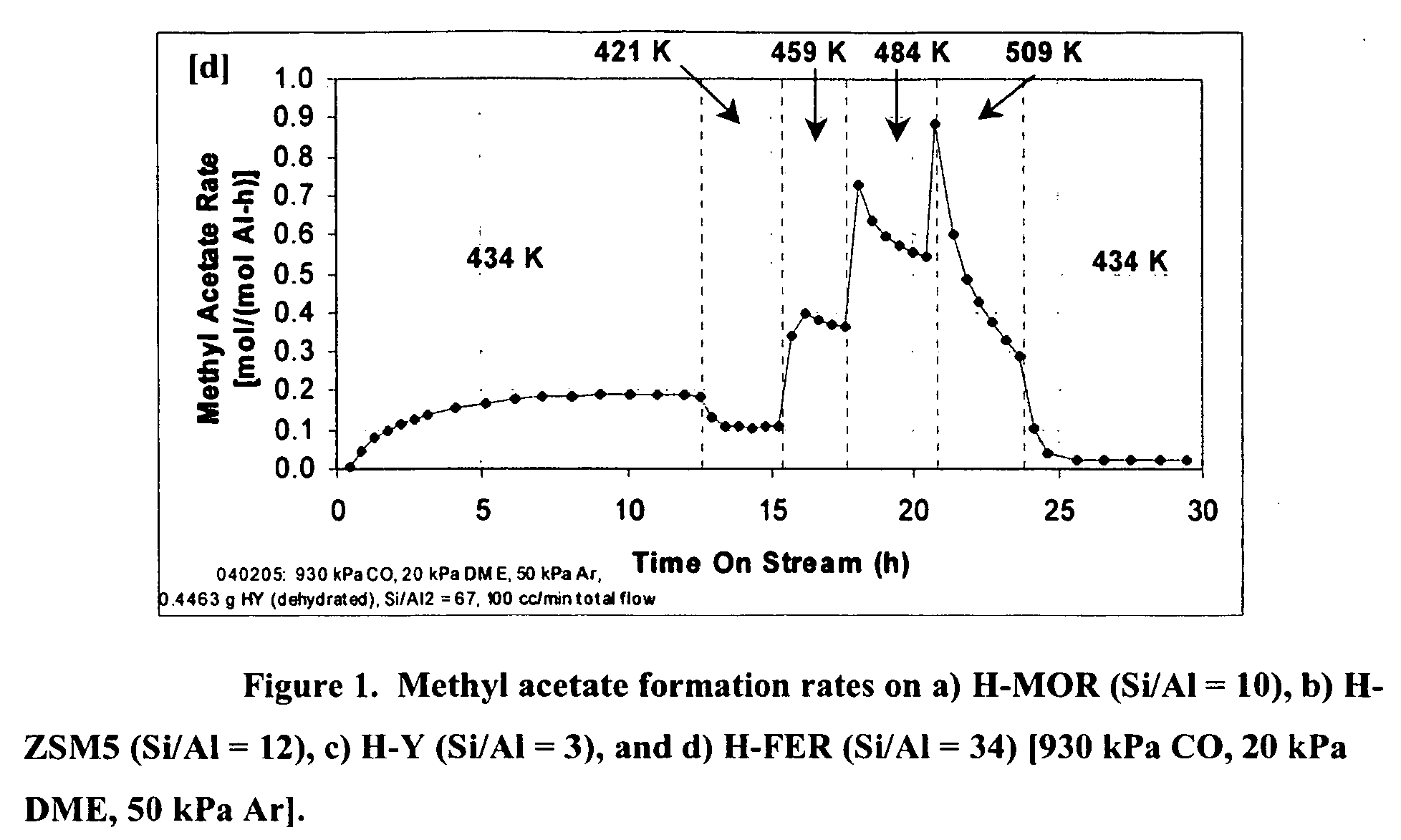
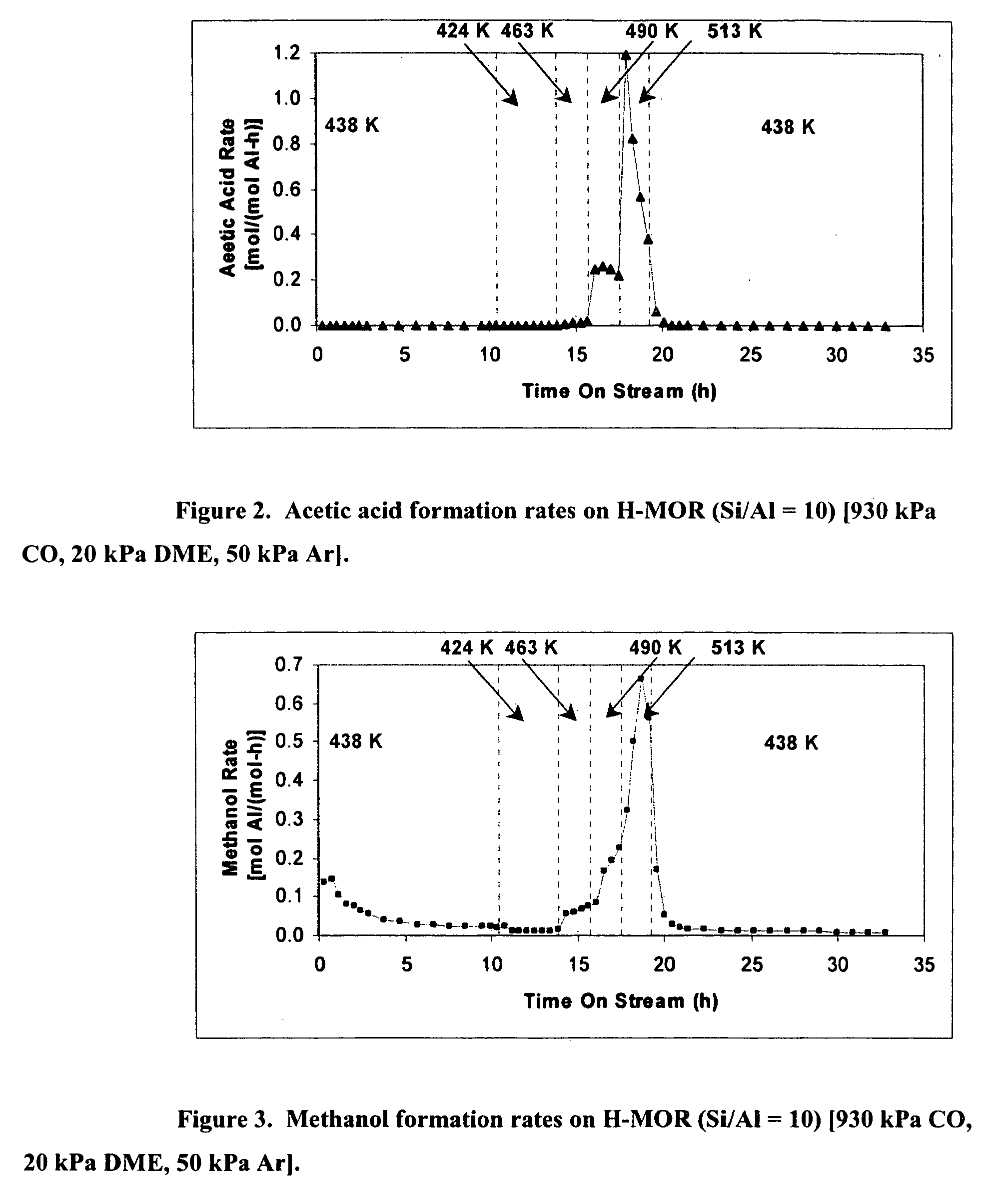
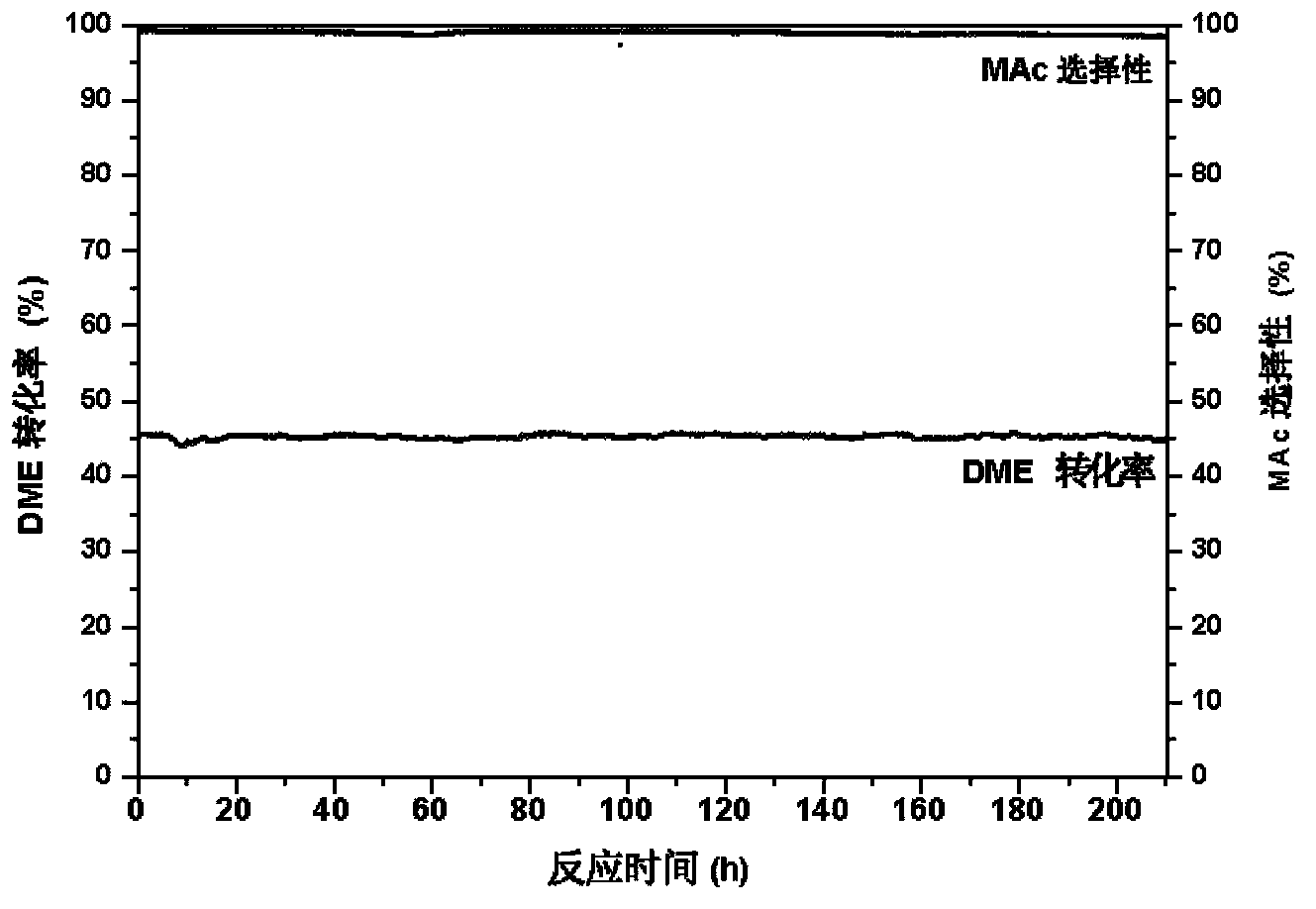
The invention discloses a catalyst modification method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether. The method is applied to the reaction process in which the dimethyl ether reacts with the carbon monoxide to high selectively form methyl acetate in the presence of an acid molecular sieve catalyst, particularly a mordenite molecular sieve. Pyridine organic amines are utilized to modify the mordenite molecular sieve and modify a channel structure and the acidity of the molecular sieve, thereby effectively inhibiting carbon deposition and greatly improving the stability of catalysts. The use of the catalysts by the method can catalyze the carbonylation of dimethyl ether to obtain methyl acetate under mild conditions. The conversion rate of dimethyl ether is between 10 and 60percent, the selectivity of the methyl acetate is over 99 percent, and the activity of the catalysts is kept steady after the reaction is performed for 48 hours.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for the production of acetic acid
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Control of impurities in reaction product of rhodium-catalyzed methanol carbonylation
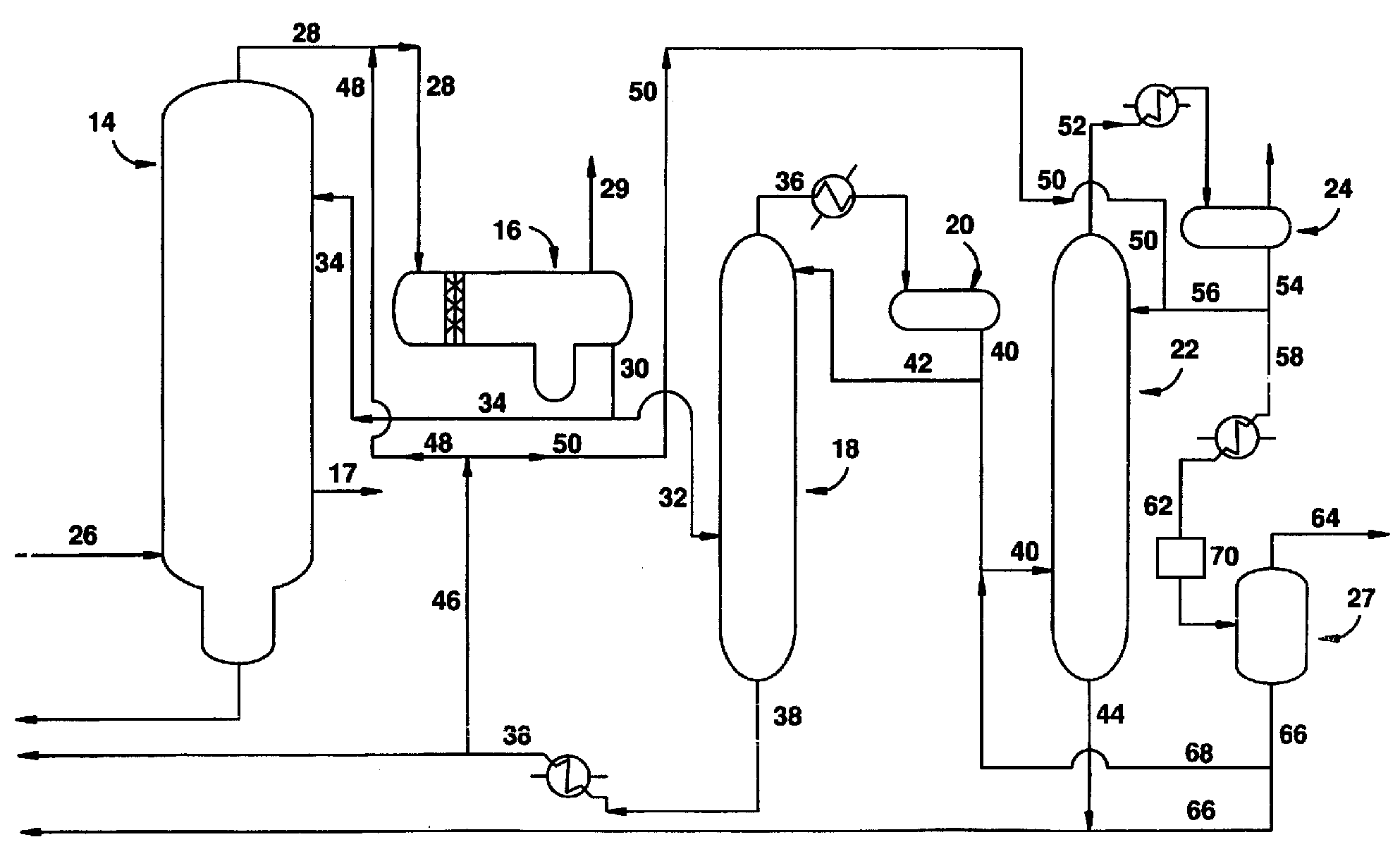
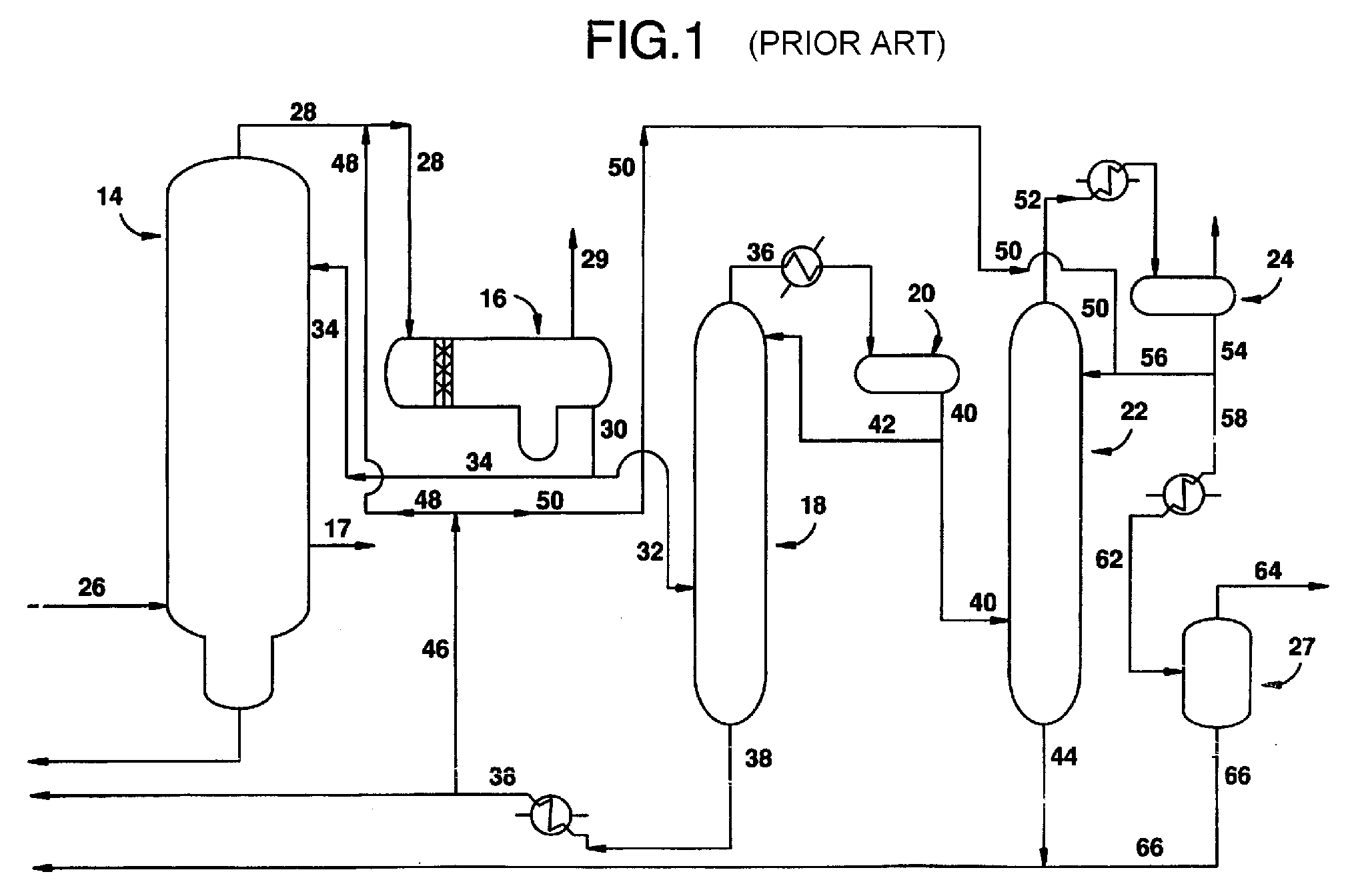
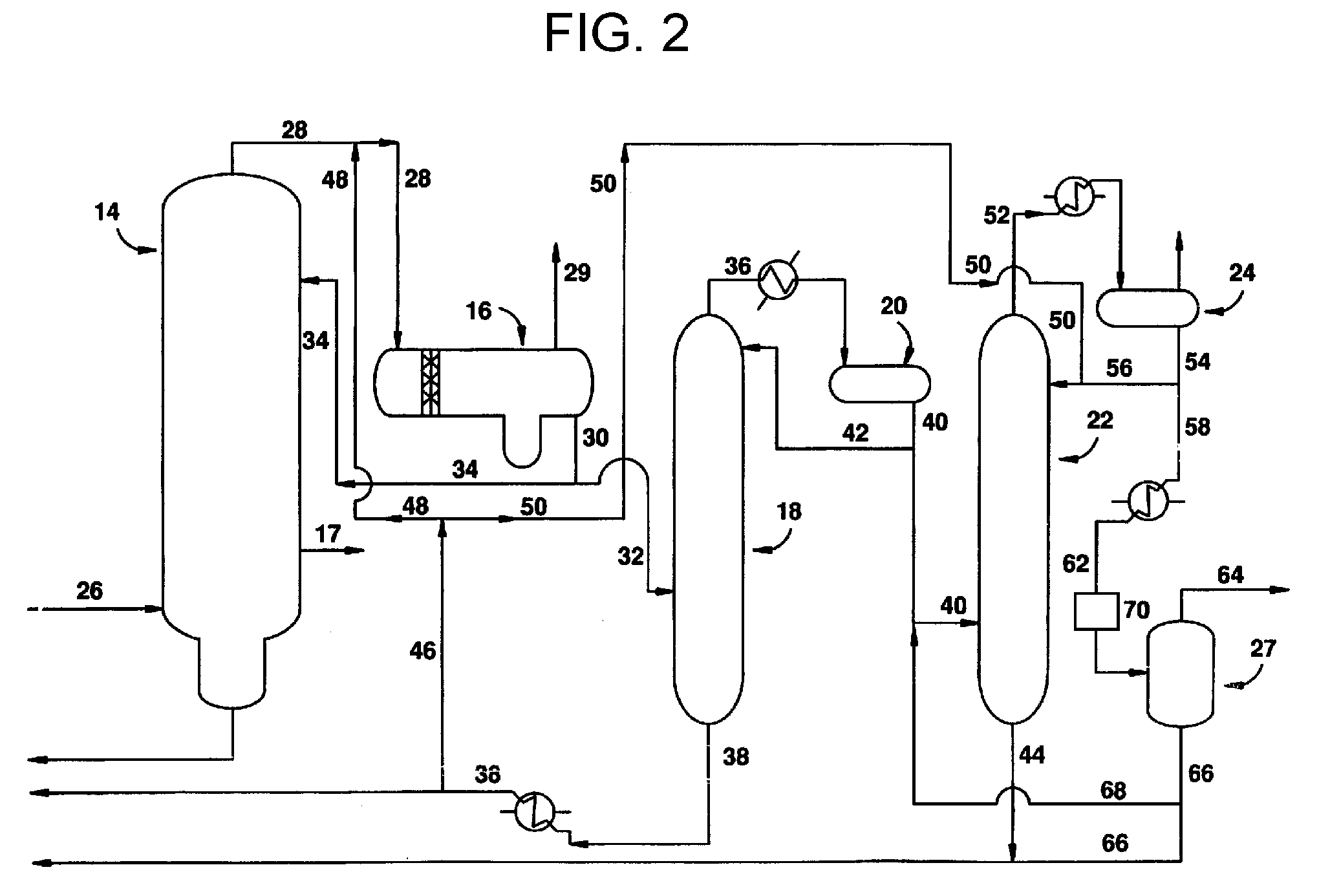
InactiveUS20080293966A1Improve the level ofHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionProtein carbonylCarbonylation
The present invention relates to carbonylation of methanol, methyl acetate, dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof to produce glacial acetic acid, and more specifically to the manufacture of glacial acetic acid by the reaction of methanol, methyl acetate, dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof with carbon monoxide wherein the product glacial acetic acid contains low impurities.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
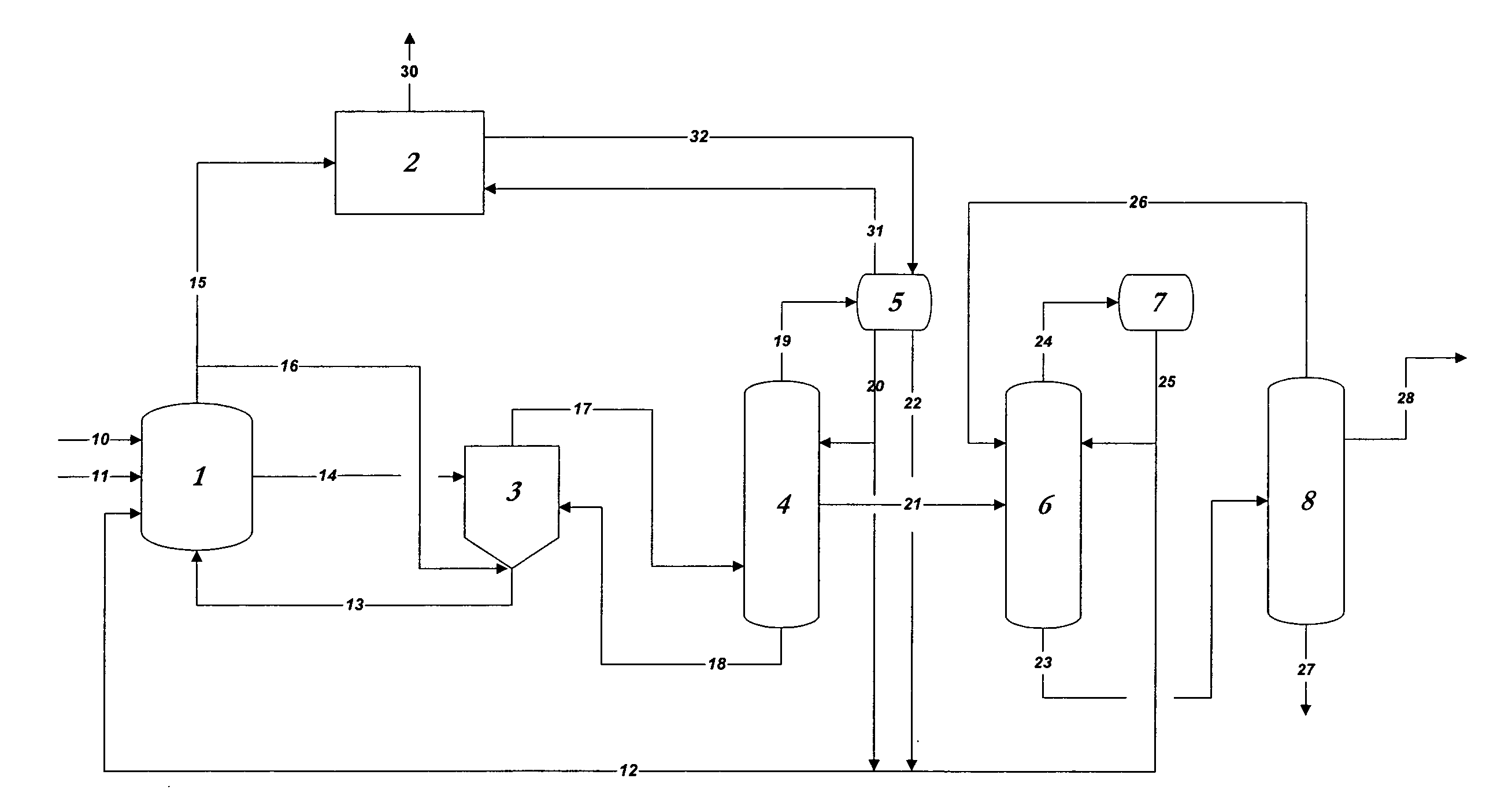
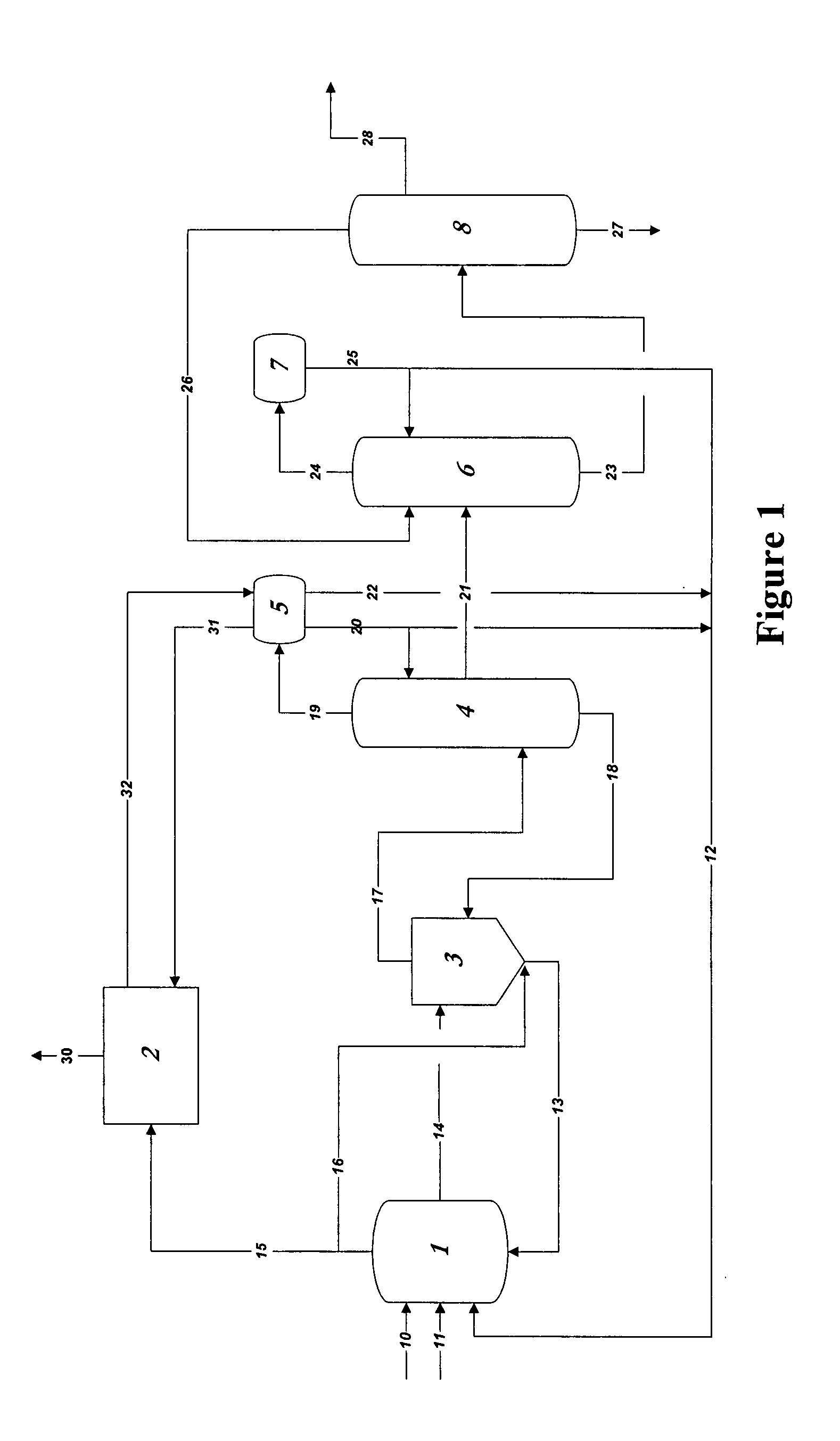
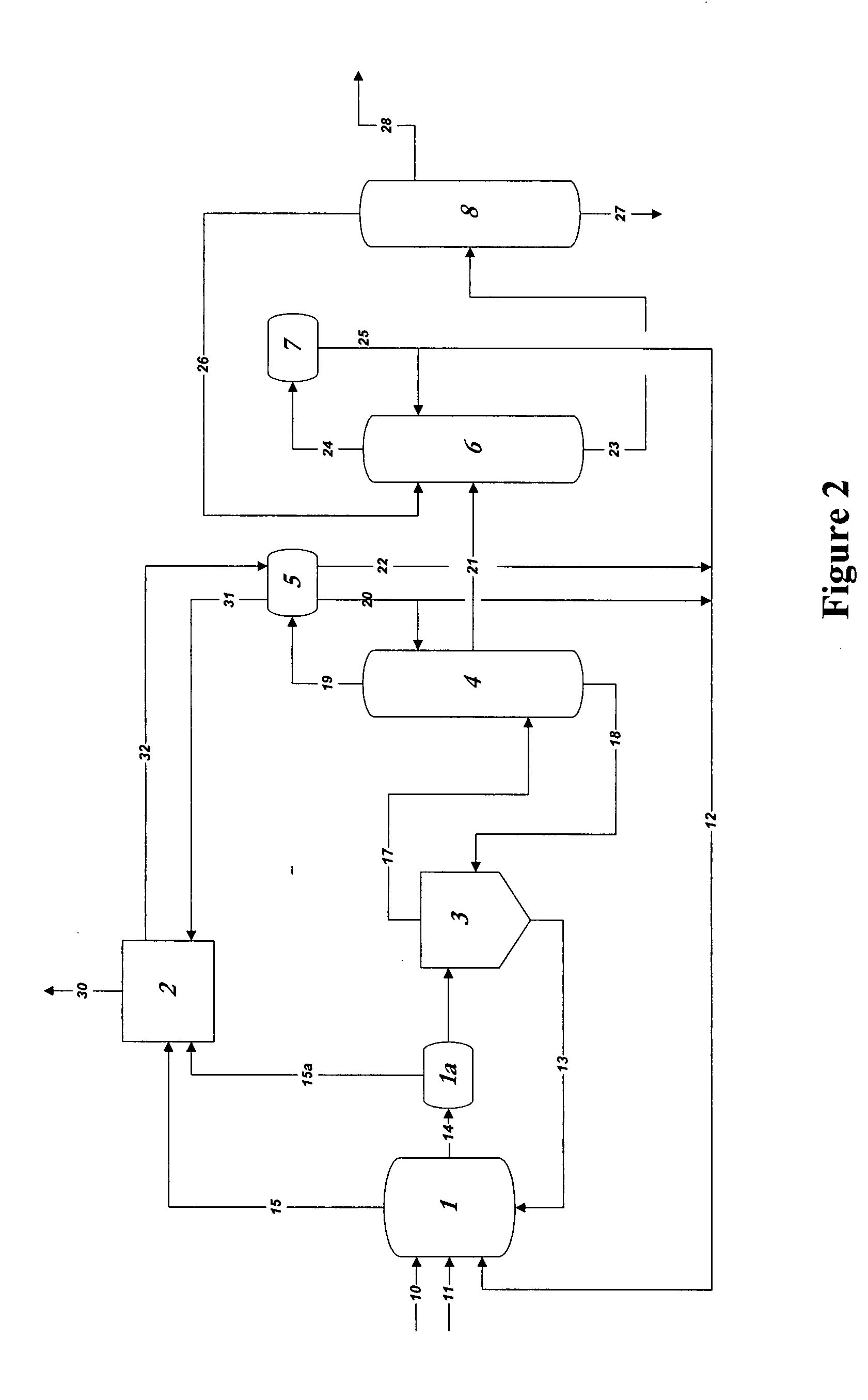
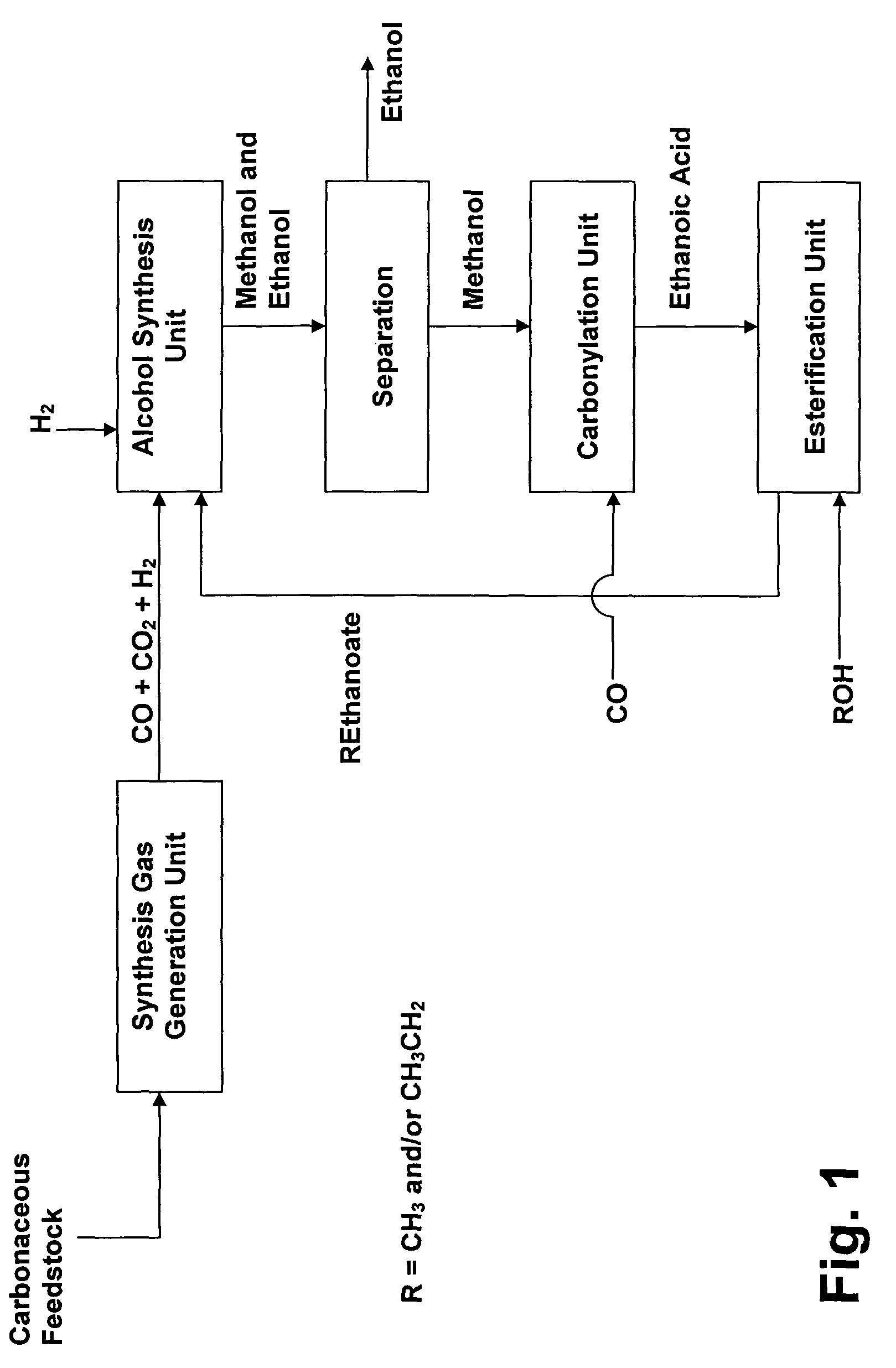
Process for the conversion of hydrocarbons into ethanol
ActiveUS7947746B2Increased formationIncreased purge stepOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidAlcohol
Process for converting synthesis gas to ethanol, including the steps of 1) introducing synthesis gas, together with methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, into an alcohol synthesis unit to produce methanol and ethanol, 2) separating the methanol from the ethanol of step 1, 3) introducing methanol, from step 2, together with CO, into a carbonylation unit in the presence of a methanol carbonylation catalyst, to produce ethanoic acid, and 4) introducing ethanoic acid, from step 3, together with methanol and / or ethanol, into an esterification unit to produce methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate. In step 5), methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, produced in step 4, are fed into the alcohol synthesis unit of step 1, and in step 6) ethanol from step 2 is recovered.
Owner:INEOS ACETYLS UK LTD
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223883B2Reduce solubilityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionAcetic acidCarbonylation
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS20070238897A1Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:THE BRITISH PETROLEUM CO LTD +1
Tin promoted platinum catalyst for carbonylation of lower alkyl alcohols
InactiveUS6903045B2Not volatileLess solubleIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentGas phase
A carbonylation catalyst useful for producing esters and carboxylic acids in a vapor phase carbonylation process, wherein the catalyst includes a solid component having a catalytically effective amount of platinum and tin associated with a solid catalyst support material and a vaporous halide promoter component.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
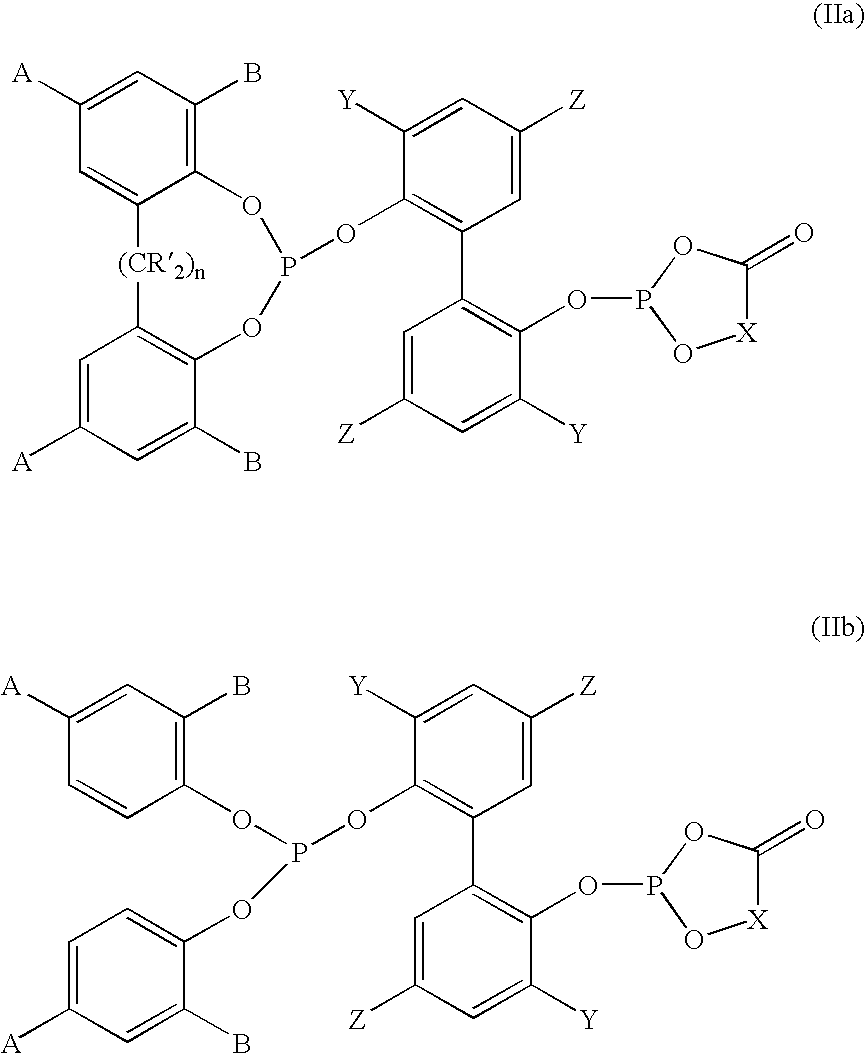
Phosoxophite ligands and use thereof in carbonylation processes
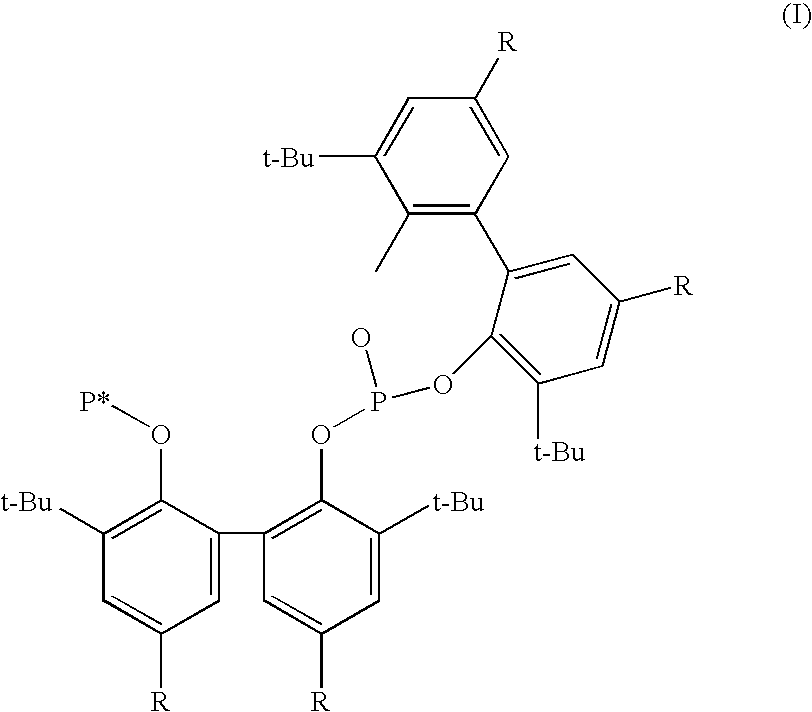
ActiveUS7196230B2High activityHigh selectivitySilicon organic compoundsRhodium organic compoundsCarbonylationProtein carbonyl
A novel organophosphorus composition and synthesis thereof, the composition being characterized by one phosphite moiety, one phosoxophite moiety, and a plurality of sterically bulky substituents. The novel composition finds utility as a ligand in Group VIII transition metal phosoxophite complex catalysts and complex catalyst precursors that are used in carbonylation processes, preferably, hydroformylation processes. Additionally, there is disclosed a novel method of preparing a phosphoromonochloridite composition that finds utility as a precursor to the novel phosoxophite composition.
Owner:DOW TECH INVESTMENTS
Process for the carbonylation of epoxides
InactiveUS20050014977A1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationLanthanideCobalt
The present invention pertains to a process for the carbonylation of an epoxide by reacting it with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system containing two components, wherein the first component is a source of one or more metals selected from the group consisting of cobalt, ruthenium and rhodium, and the second component is a coordination complex of a tetrapyrrole compound with one or more of the metals belonging to the group consisting of groups IIIA and IIIB of the periodic system, lanthanides and actinides. The present invention also pertains a process for the preparation of a catalyst system.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
Processes for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS8889904B2Reduce loadEasy to separateSolvent extractionOrganic compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
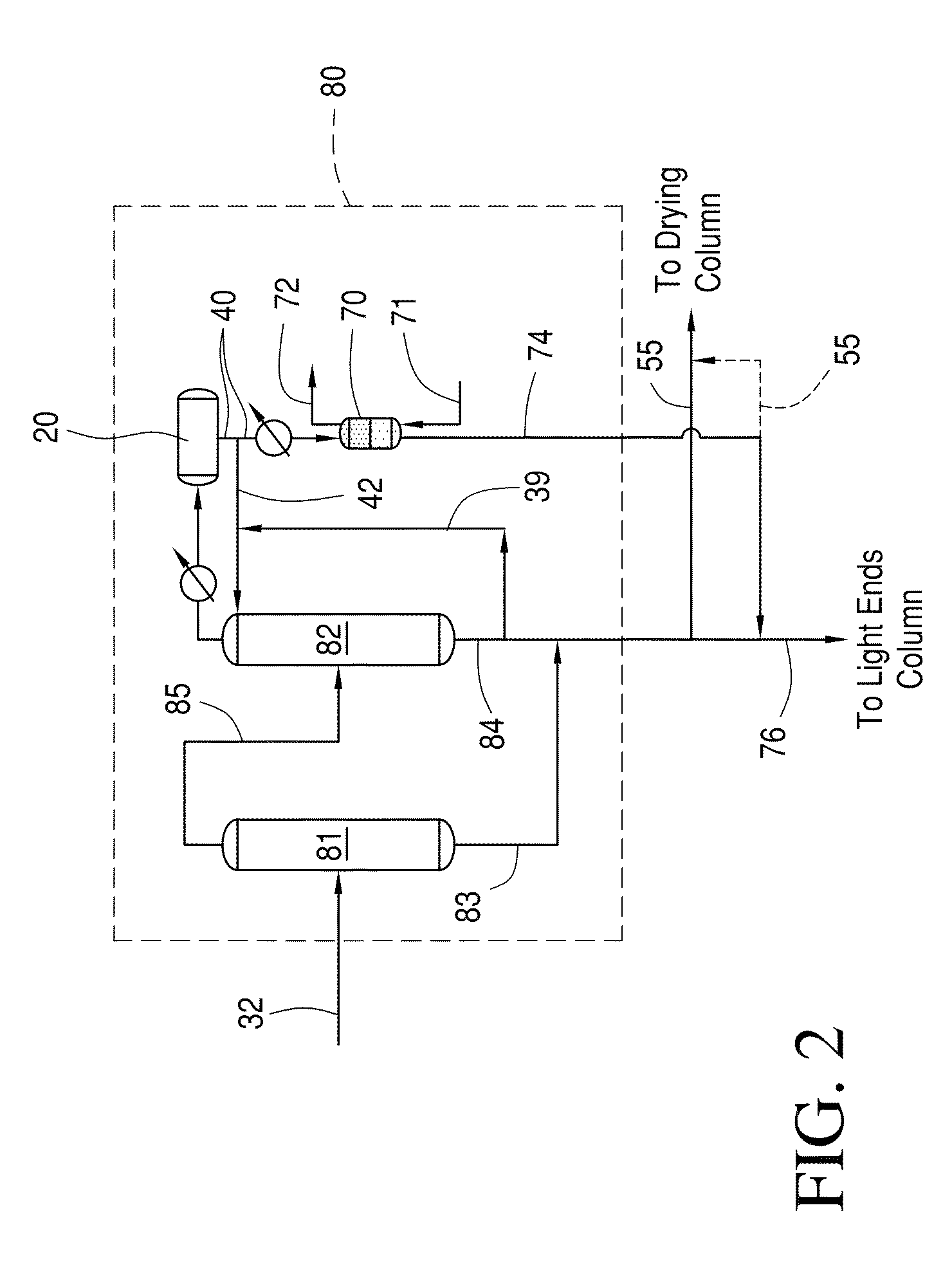
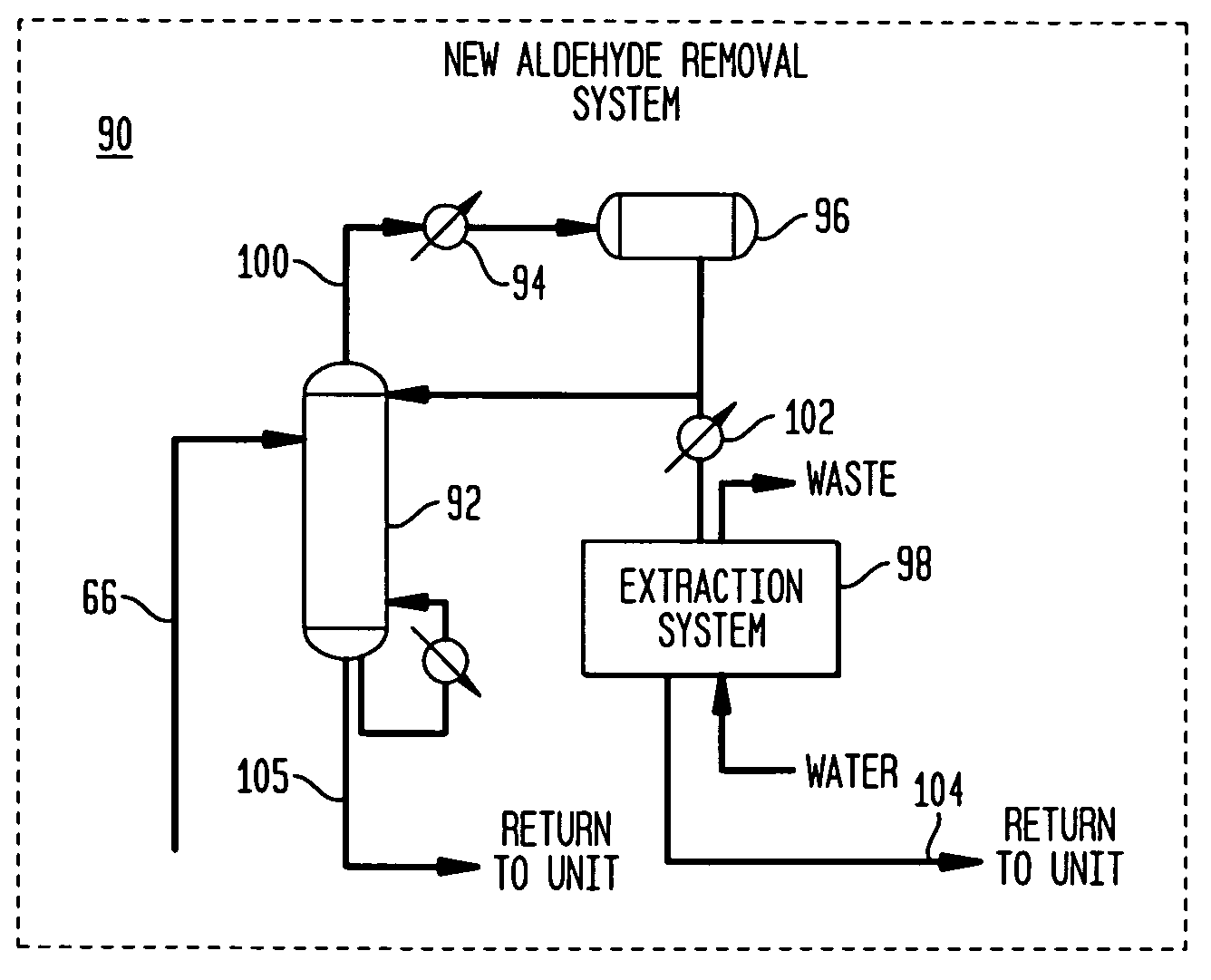
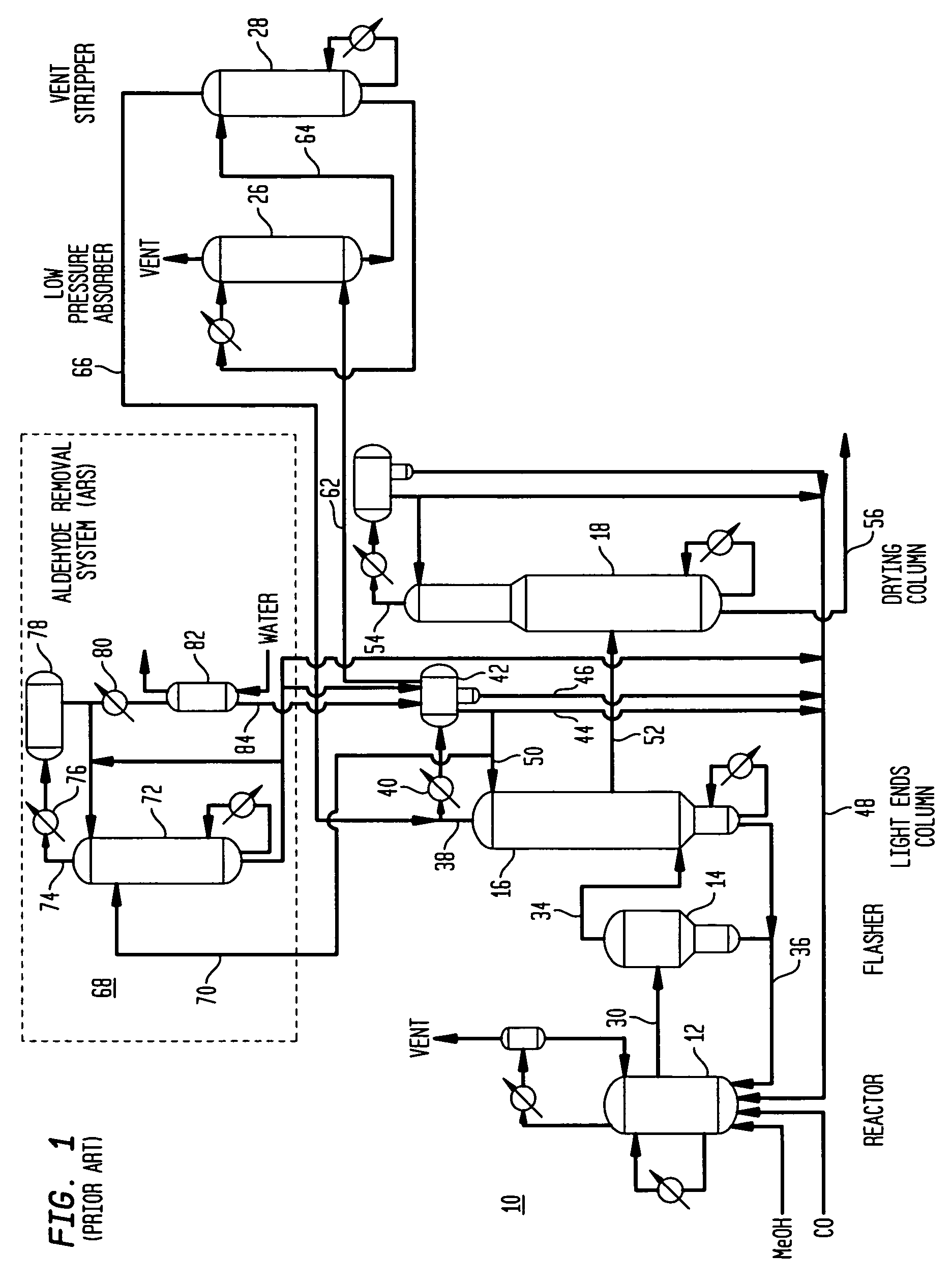
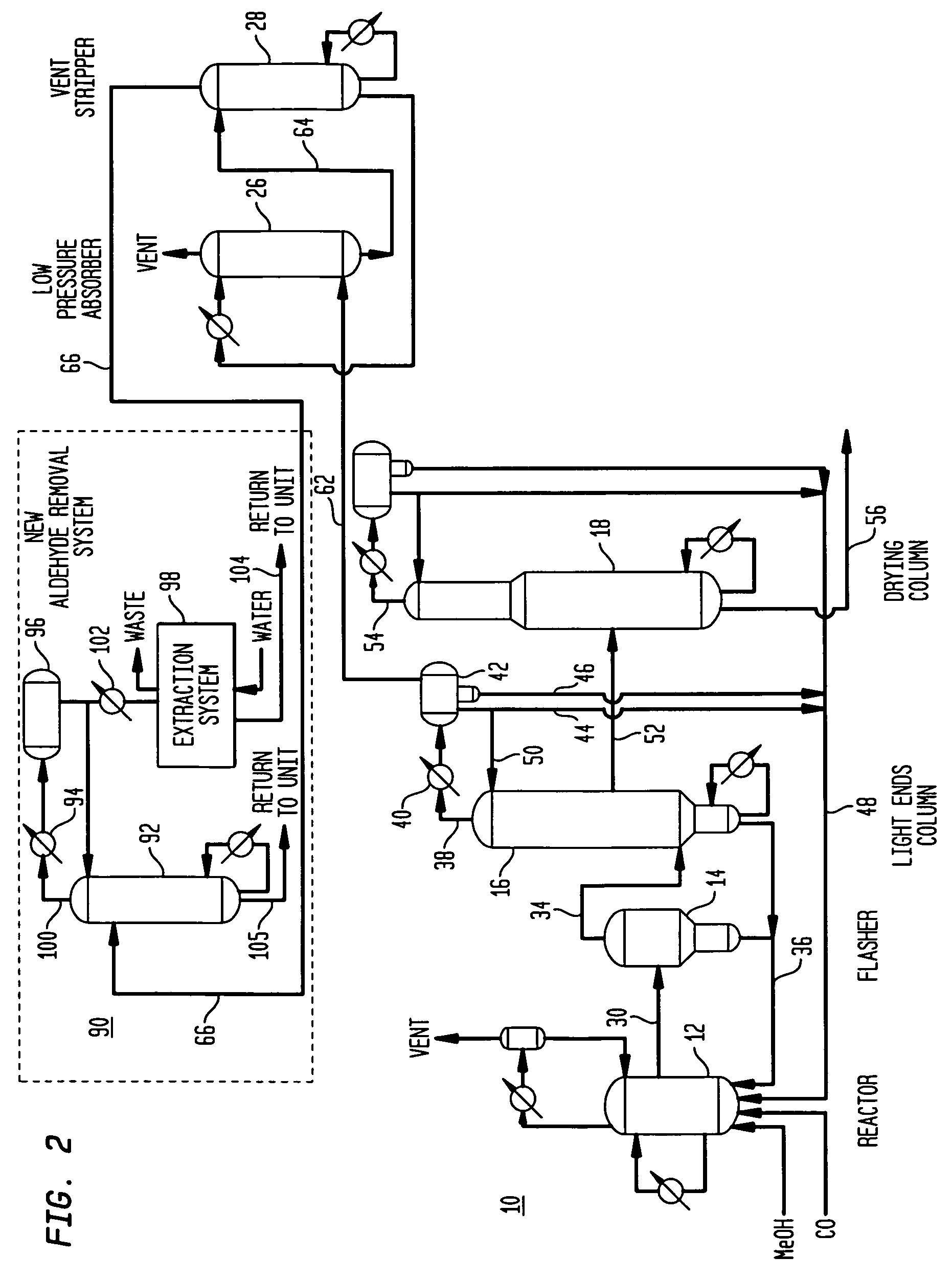
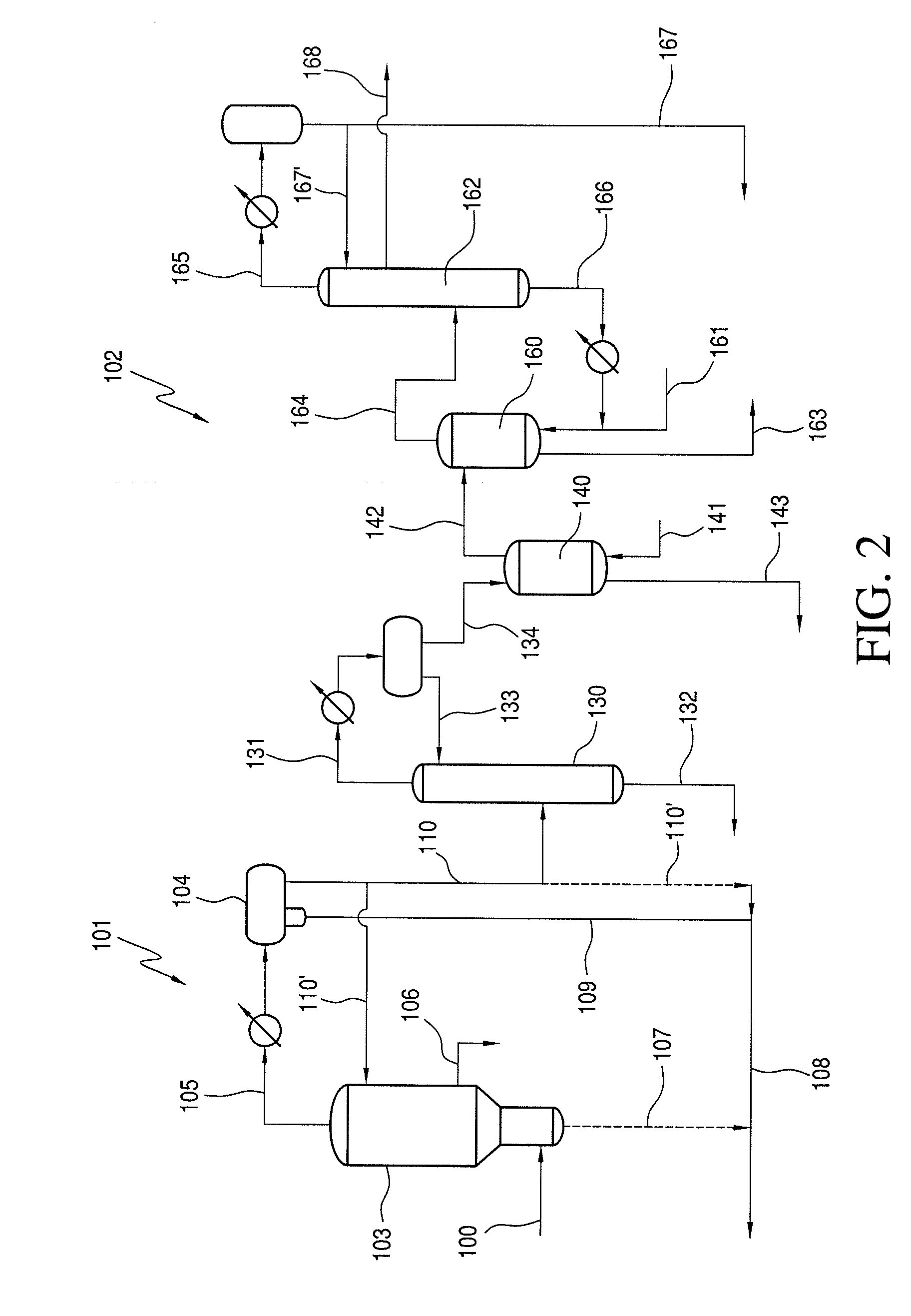
Methanol carbonylation with improved aldehyde removal
ActiveUS7884237B2Operating and capital costLower the volumeOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationOrganic compound preparationCarbonylationSolvent
Methanol carbonylation with improved aldehyde removal includes: (a) scrubbing light ends and aldehyde impurity from vent gas with an absorber solvent; (b) stripping absorbed light ends and aldehyde impurity from the absorber solvent to provide a vent-recovered light ends stream; (c) purifying the vent-recovered light ends stream to remove aldehyde impurity; and (d) recycling purified light ends from the vent-recovered light ends stream to the production system.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
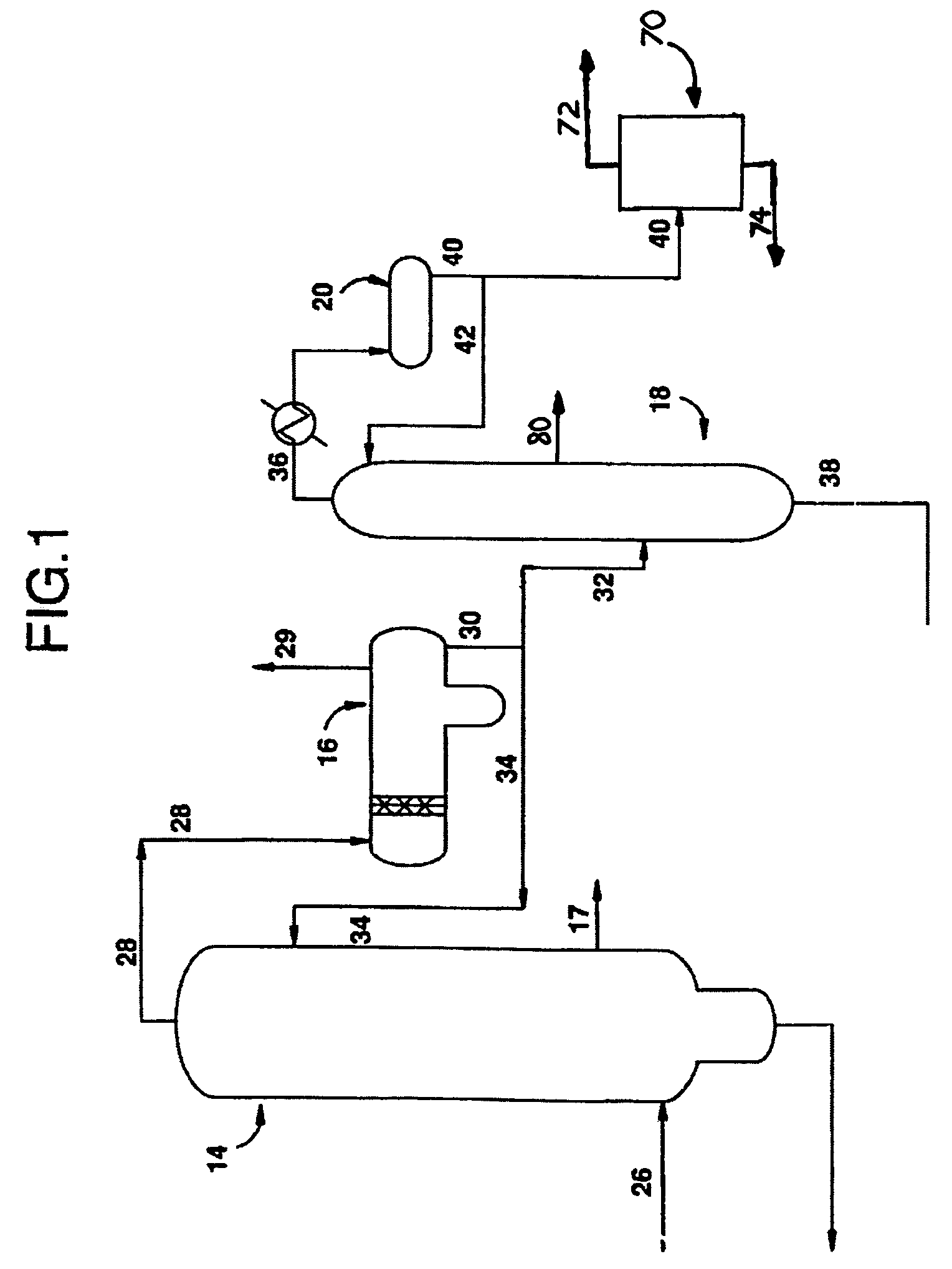
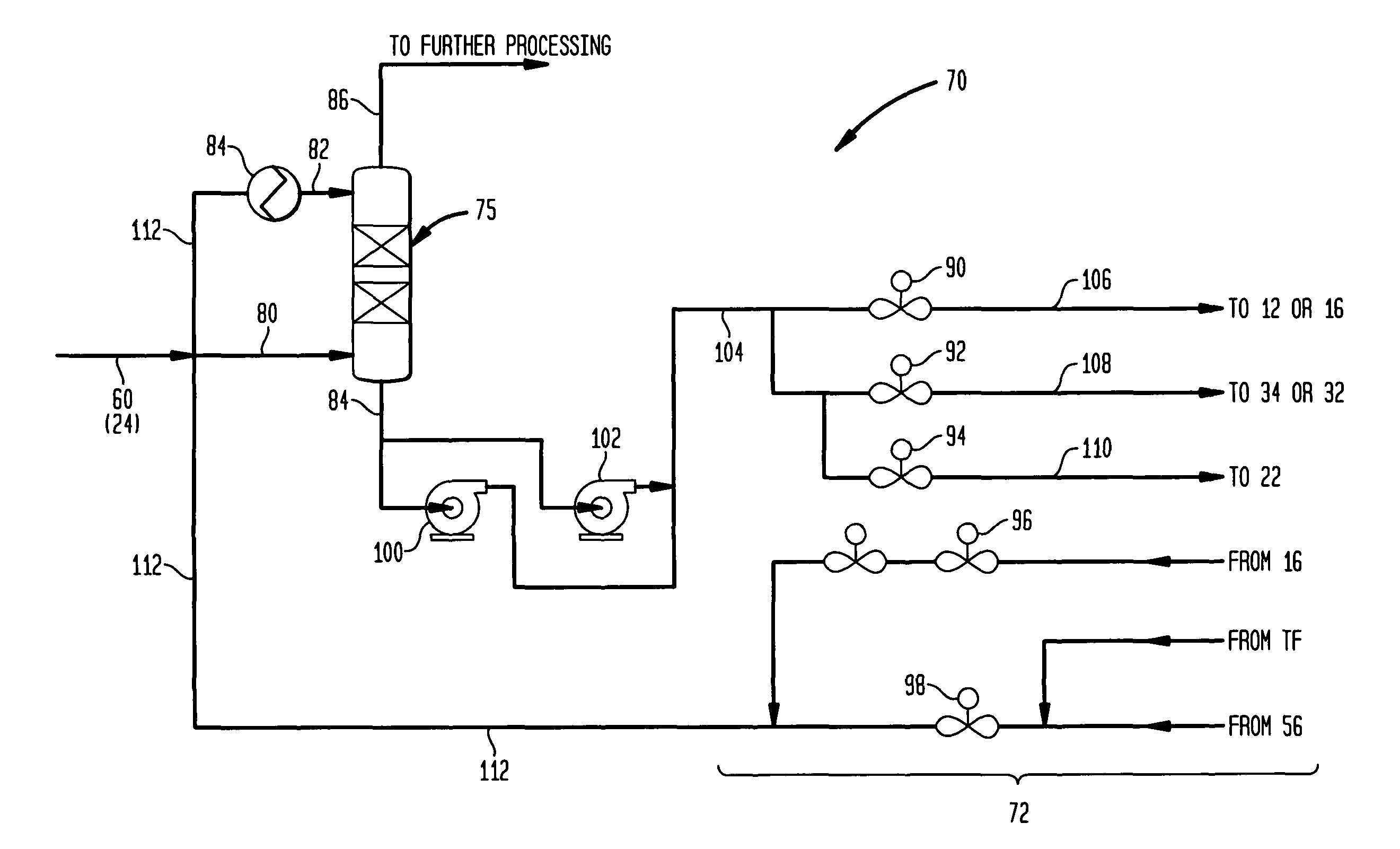
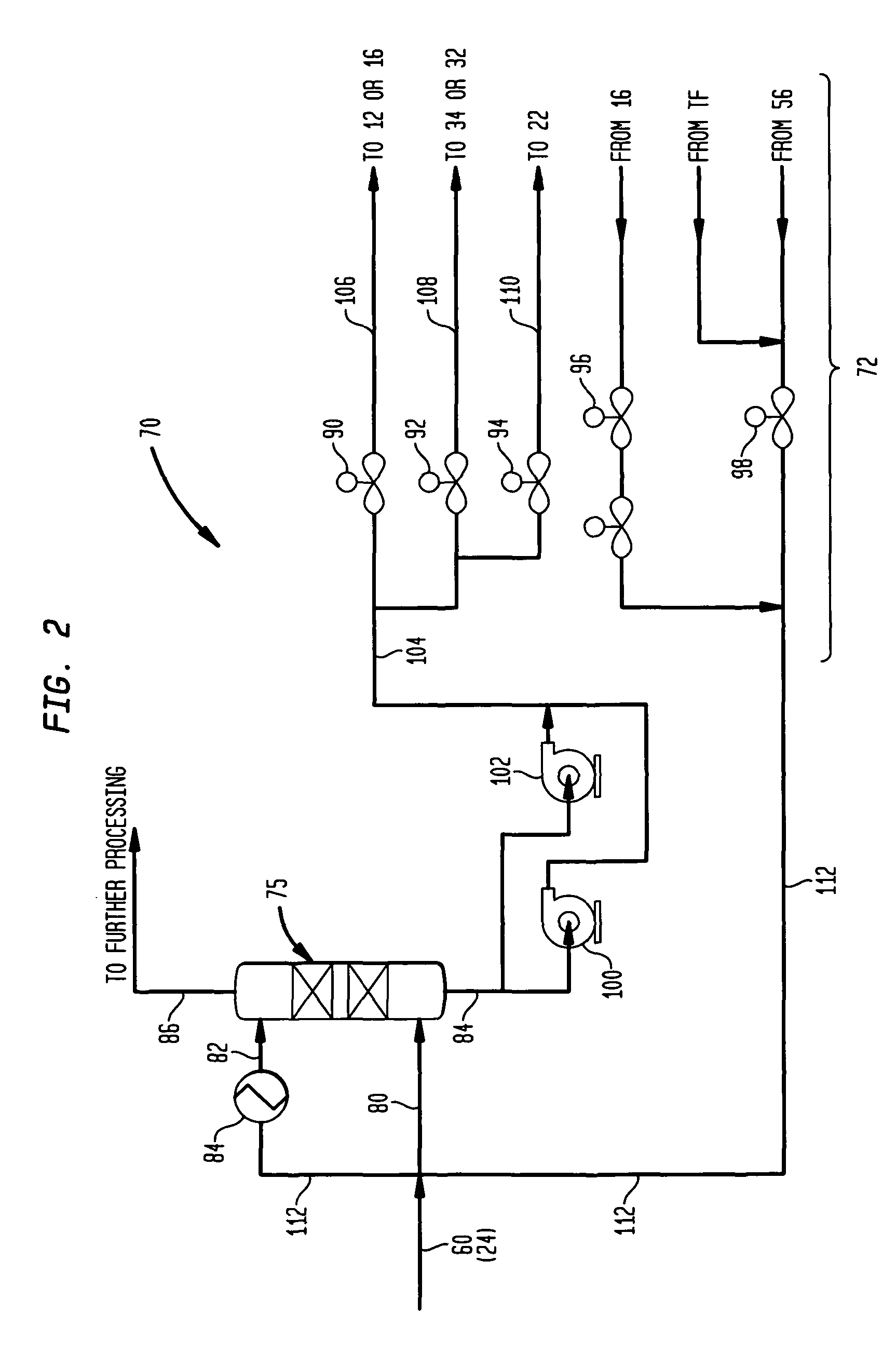
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS7465822B2Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:BP CHEM LTD +1
Continuous carbonylation process
InactiveUS6916951B2Improve heat removal efficiencyStable catalyst environmentOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidGas phase
Disclosed is a continuous process wherein carbon monoxide, a carbonylatable reactant, and a halide in the gas phase are contacted with a non-volatile catalyst solution comprising an ionic liquid and a Group VIII metal to produce a carbonylation product in the gas phase. The process is useful for the continuous preparation of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130310603A1Efficient productionEasy to save energyOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIodideReaction step
Acetic acid is produced while inhibiting an increased concentration or production of hydrogen iodide in a carbonylation reactor or corrosion of the carbonylation reactor.A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system comprising a metal catalyst (e.g., a rhodium catalyst), an ionic iodide (e.g., lithium iodide), and methyl iodide in a carbonylation reactor; and in the process, (i) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 860 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 15% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor, and / or (ii) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 660 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 3.9% by weight, the concentration of the ionic iodide is maintained at not more than 13% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
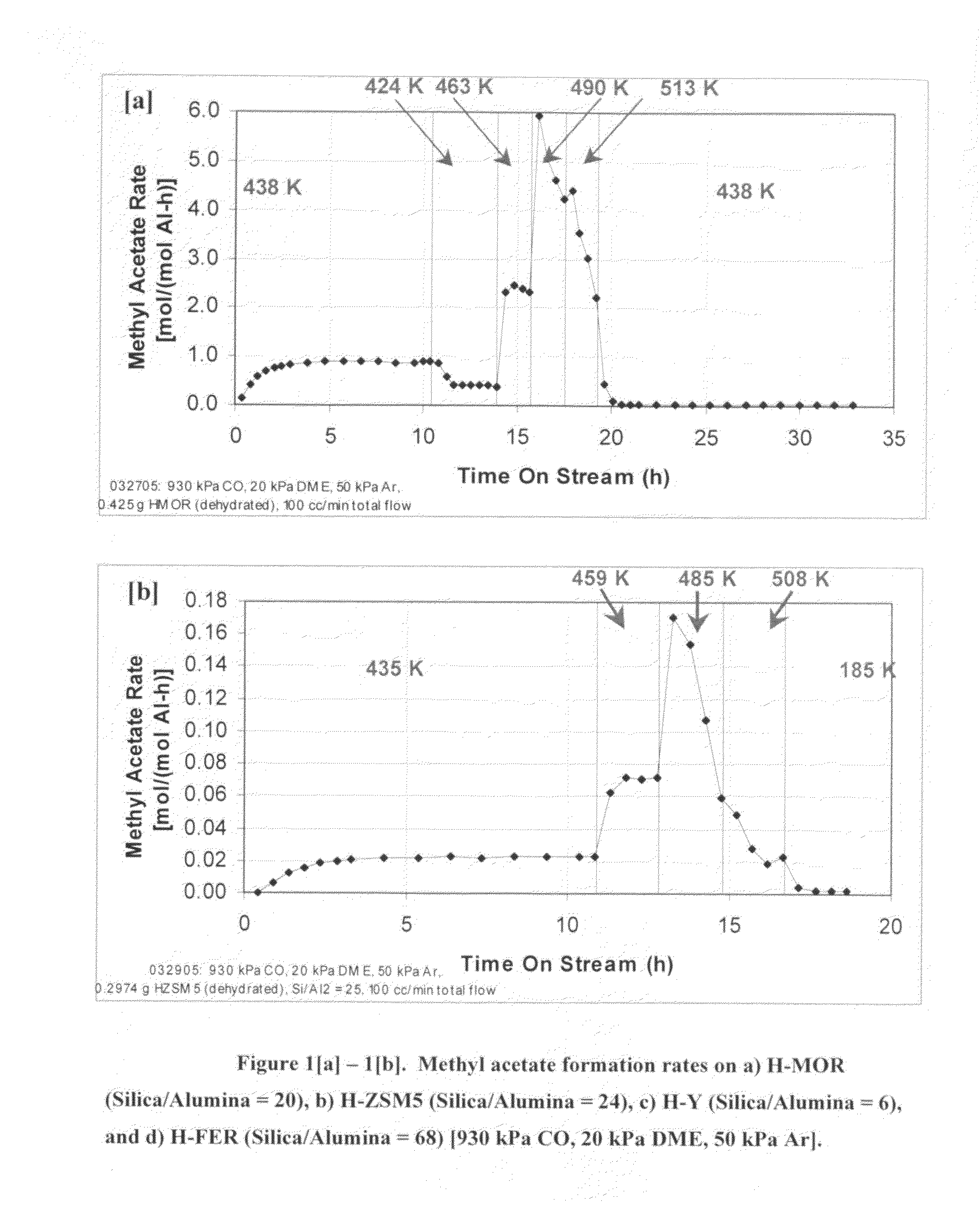
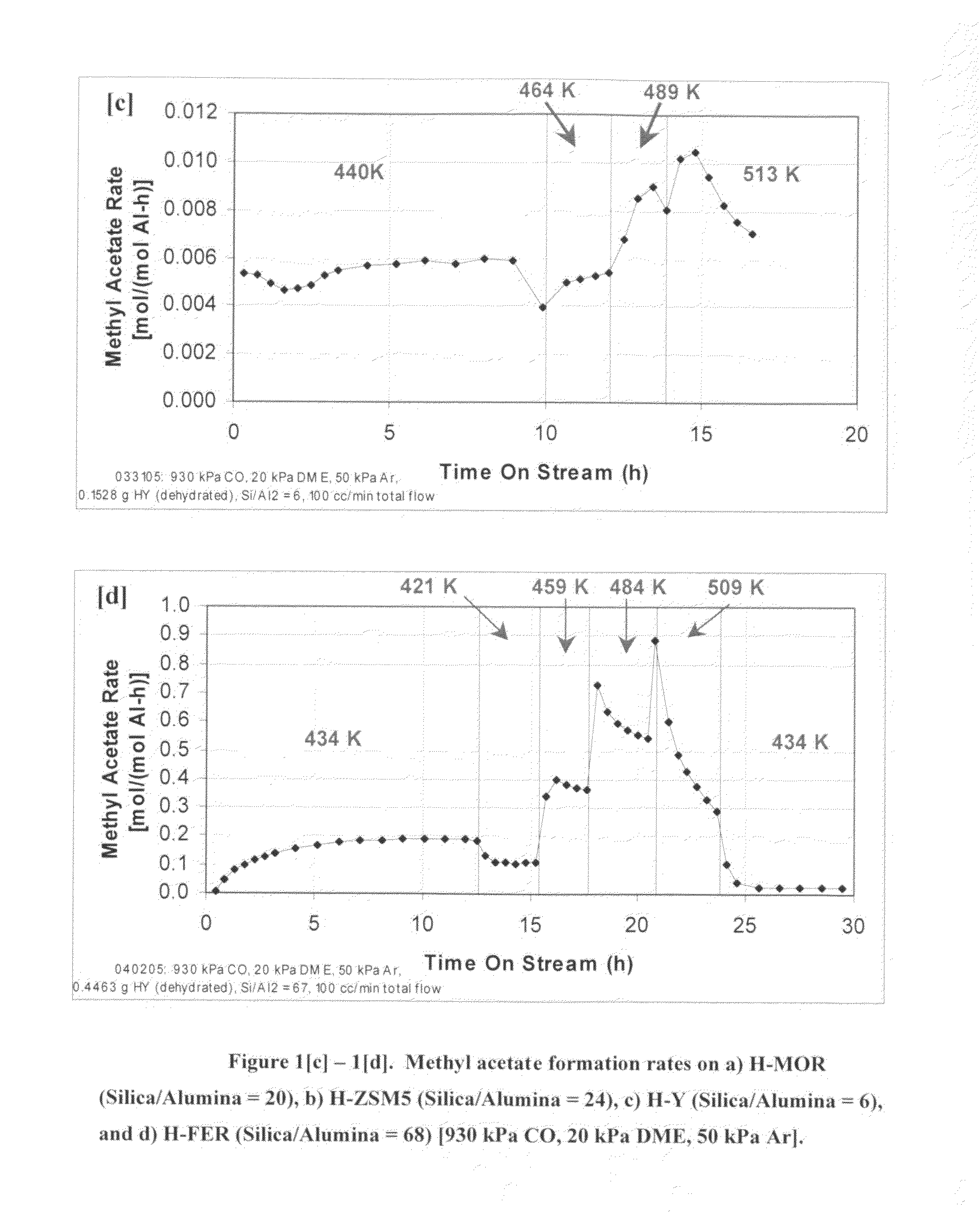
InactiveUS20060252959A1Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesMordeniteMethyl acetate
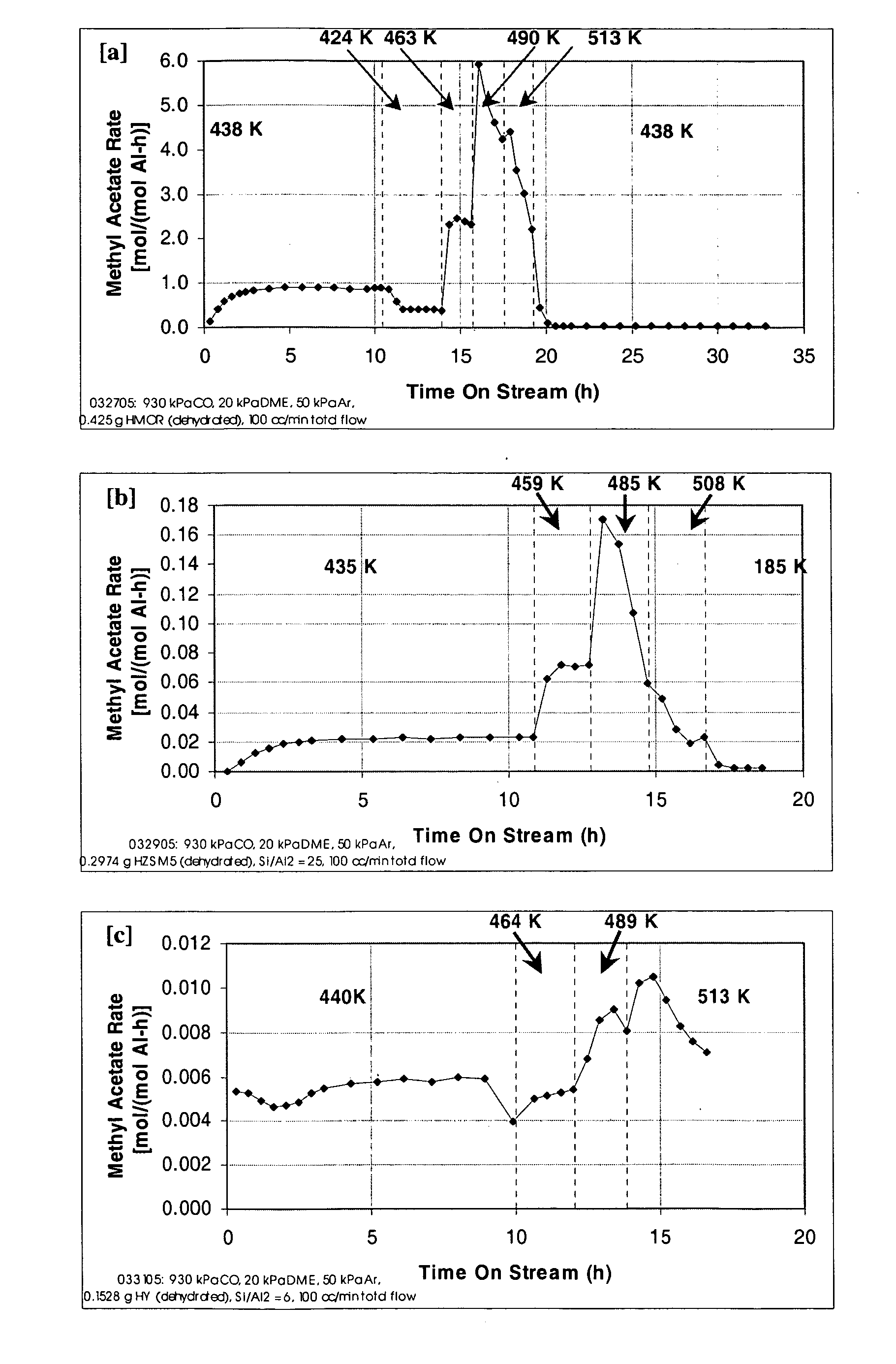
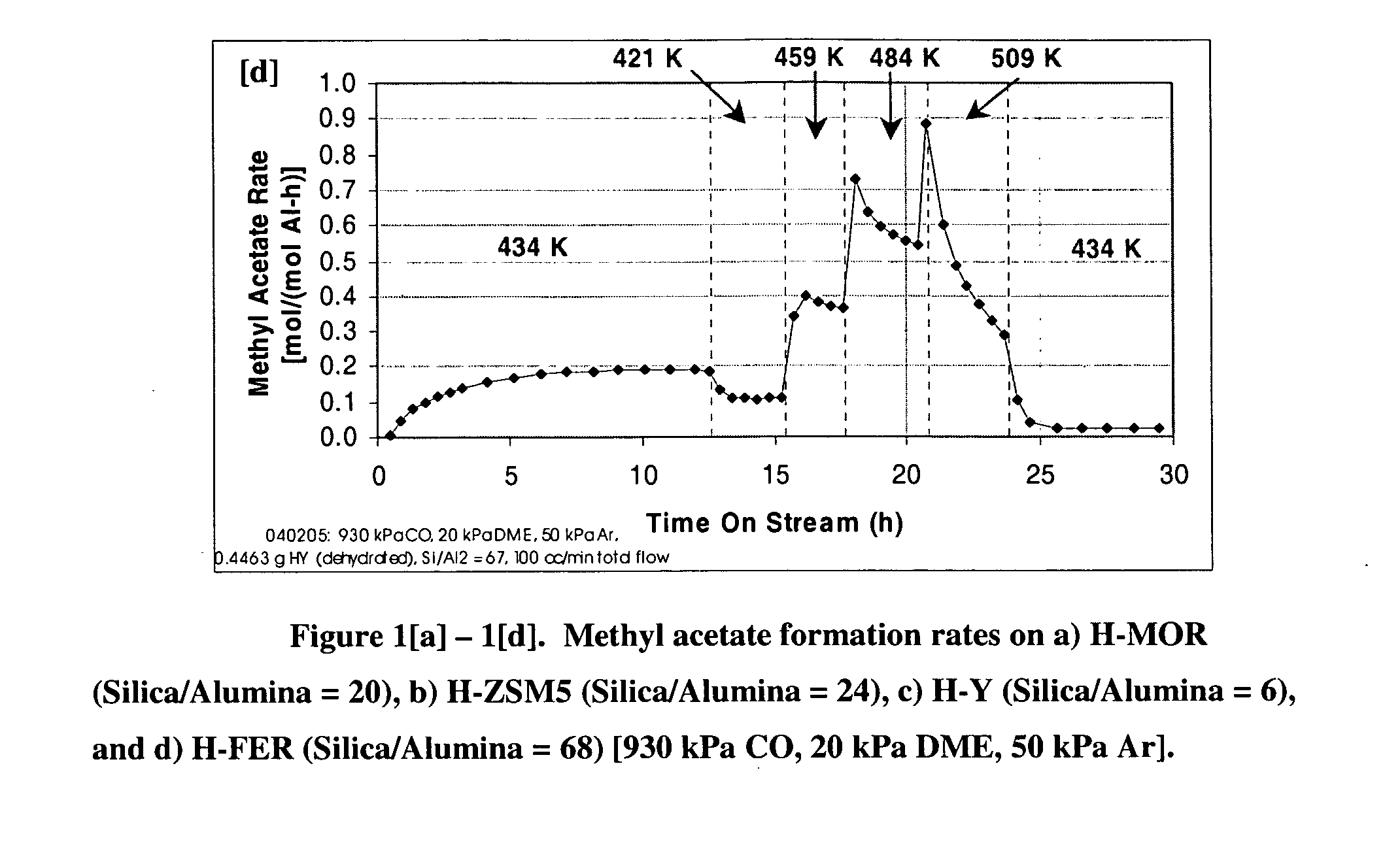
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst comprising mordenite and / or ferrierite, under substantially anhydrous conditions. More specifically, methyl acetate is selectively produced by reaction of dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst comprising mordenite or ferrierite, under substantially anhydrous conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Preparation method for catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase
ActiveCN101543784ALow costCatalyst activation/preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionGas phaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method for a catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase. The catalyst takes alpha-alumina as a carrier, palladium as an active component and 2 MOxes as an additive, M is magnesium, titanium, zirconium, vanadium, manganese, iron, nickel, copper, zinc, molybdenum or tungsten, and components of the catalyst (calculated by carrier mass) are: 0.01 to 0.75 percent of the palladium and 0.1 to 20 percent of MOxes. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: firstly, an additive metal salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier, and a palladium salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier to obtain the catalyst after the carrier is dried and roasted. Before the use, pure hydrogen or H2-N2 mixed gas is activated by the catalyst at a temperature of between 150 and 450 DEG C. The catalyst can be used for synthesizing oxalic ester by the carbonylation of CO and nitrous acid ester, the using reaction temperature of the catalyst is between 70 and 150 DEG C, and the reaction space velocity is between 500 and 9,000h<-1>. The catalyst has higher reaction activity and selectivity; and the catalyst has low cost.
Owner:HAISO TECH
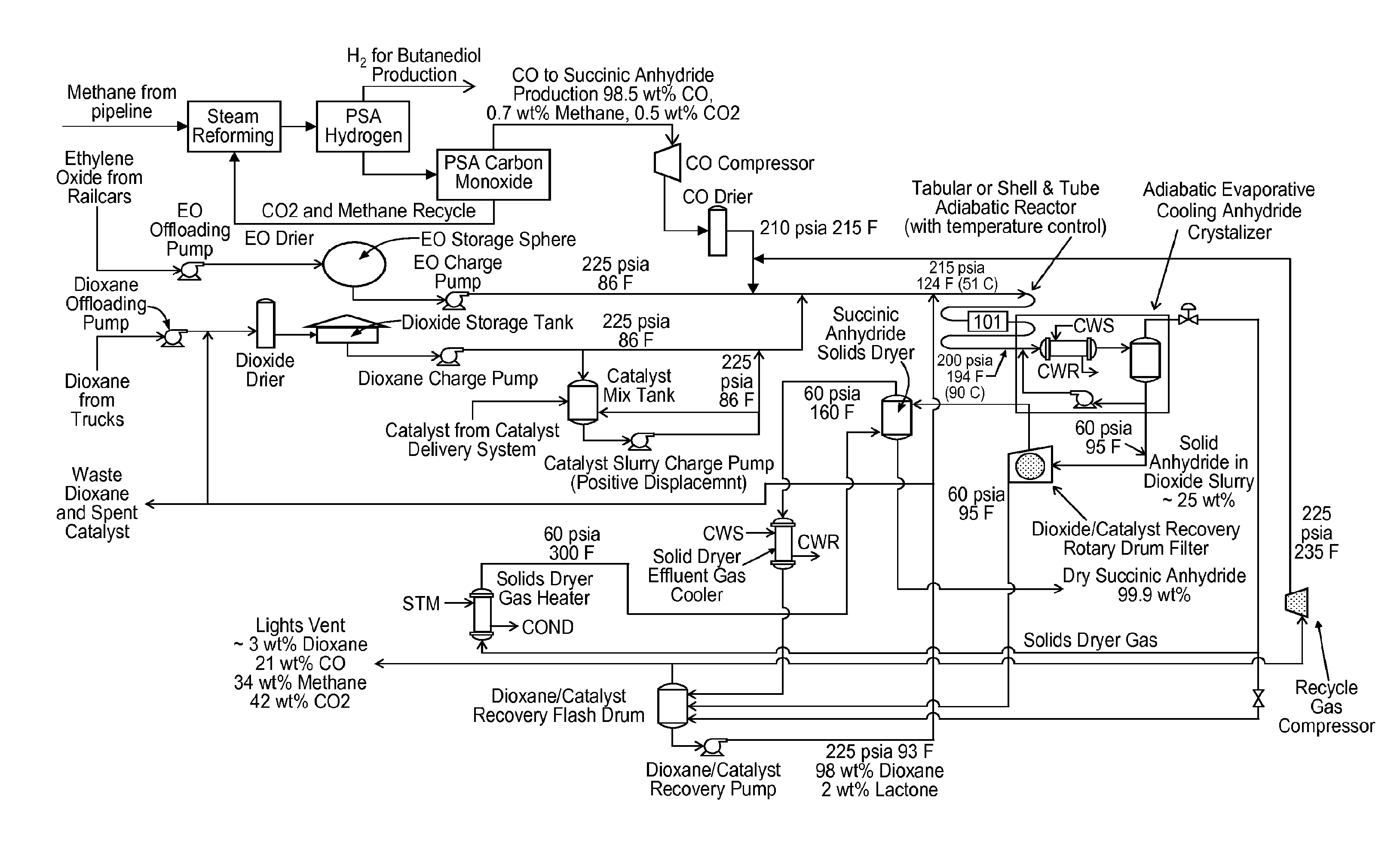
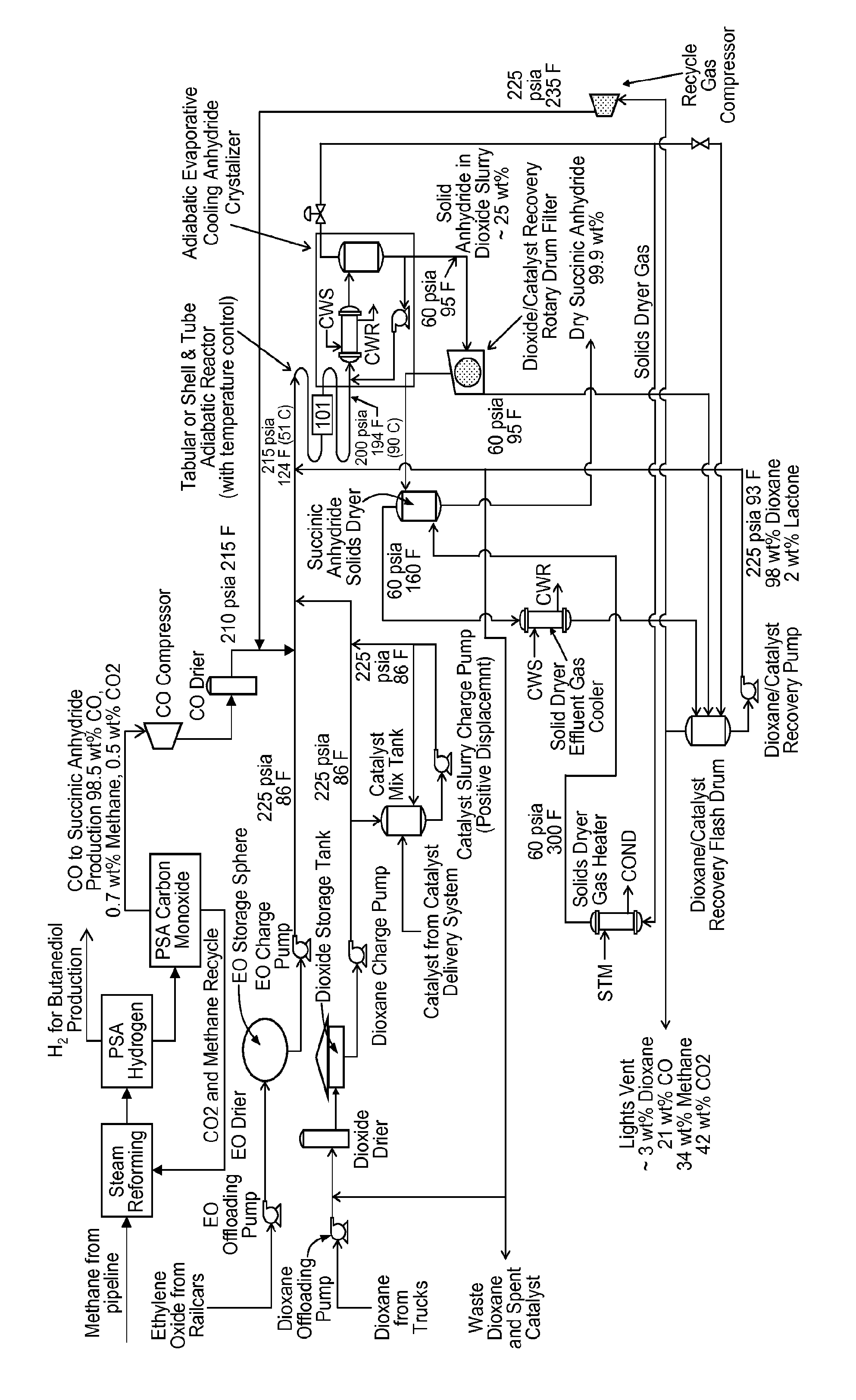
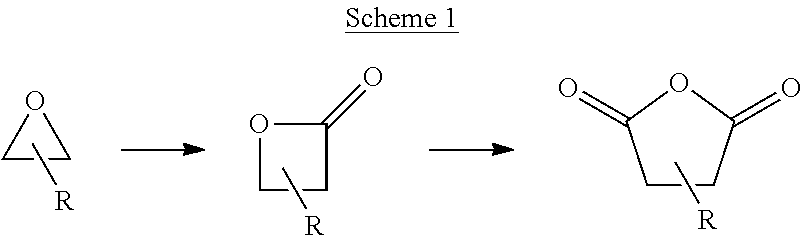
Succinic anhydride from ethylene oxide
ActiveUS9156803B2Organic chemistryOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsEthylene oxideContinuous flow
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Process for Recovering Halogen Promoters and Removing Permanganate Reducing Compounds
ActiveUS20120090981A1Solvent extractionCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionAcetic acidHalogen
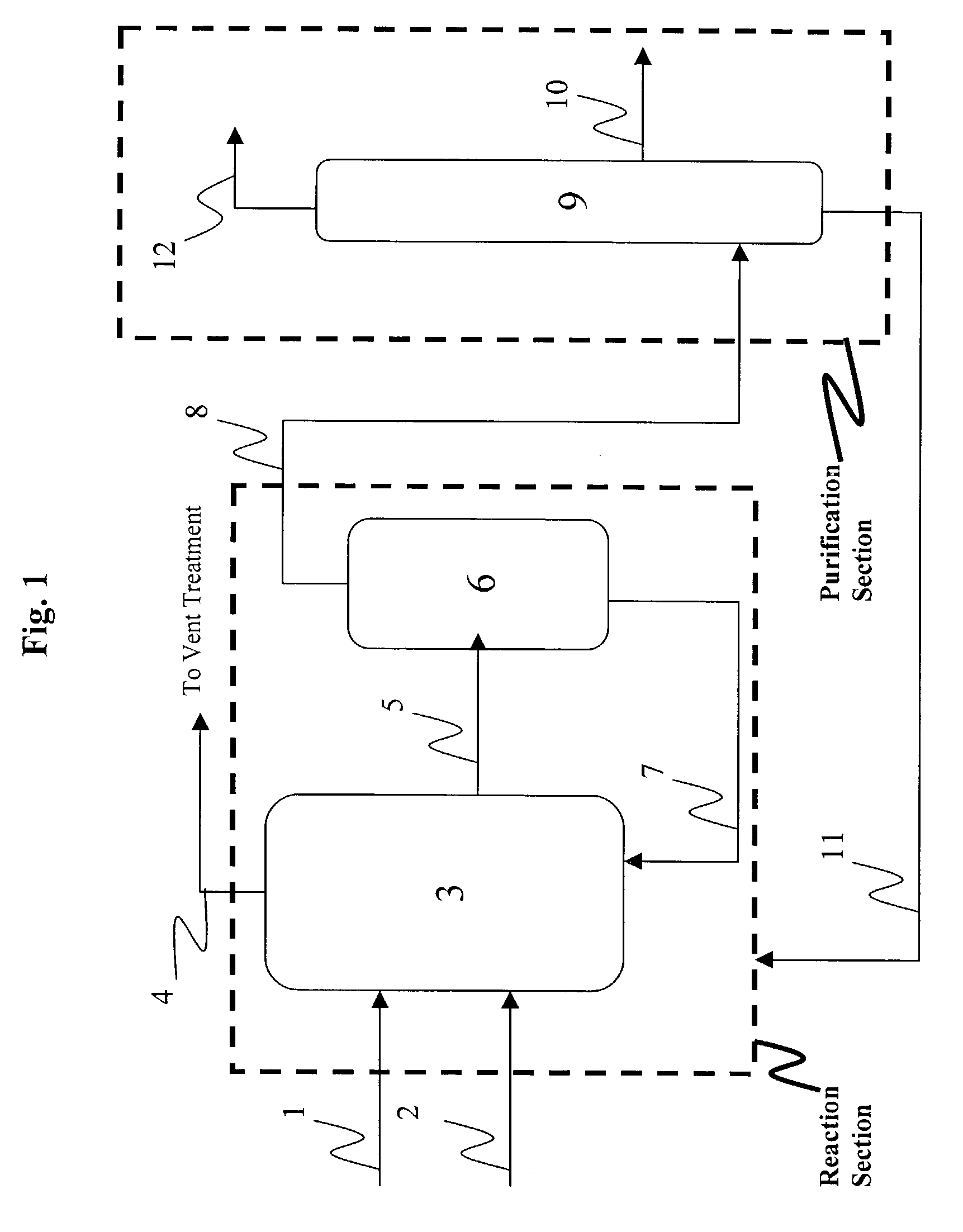
This invention relates to processes for producing acetic acid and, in particular, to improved processes for recovering C2+ alkyl halides and removing permanganate reducing compounds formed during the carbonylation of methanol in the presence of a Group VIII metal carbonylation catalyst to produce acetic acid.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Carbonylation process
ActiveUS20070293695A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogen halideCarboxylic acid
Disclosed is a carbonylation process for the production of carboxylic acids, carboxylic acid esters and / or carboxylic acid anhydrides wherein a carbonylation feedstock compound selected from one or more organic oxygenates such as alcohols, ethers, and esters is contacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a carbonylation catalyst and one or more onium compounds. The carbonylation process differs from known carbonylation processes in that a halide compound such as a hydrogen halide, typically hydrogen iodide, and / or alkyl halide, typically methyl iodide, extraneous or exogenous to the carbonylation process is not fed or supplied separately to the process.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Control of formic acid impurities in industrial glacial acetic acid
InactiveUS20080293967A1High purityLess impuritiesOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionProtein carbonylChemistry
This invention relates to carbonylation of methanol, methyl acetate, dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof to produce glacial acetic acid, and more specifically to the manufacture of glacial acetic acid by the reaction of methanol, methyl acetate dimethyl ether or mixtures thereof with carbon monoxide wherein the product glacial acetic acid contains low formic acid impurities.
Owner:SCATES MARK O +1
Process for producing acetic acid
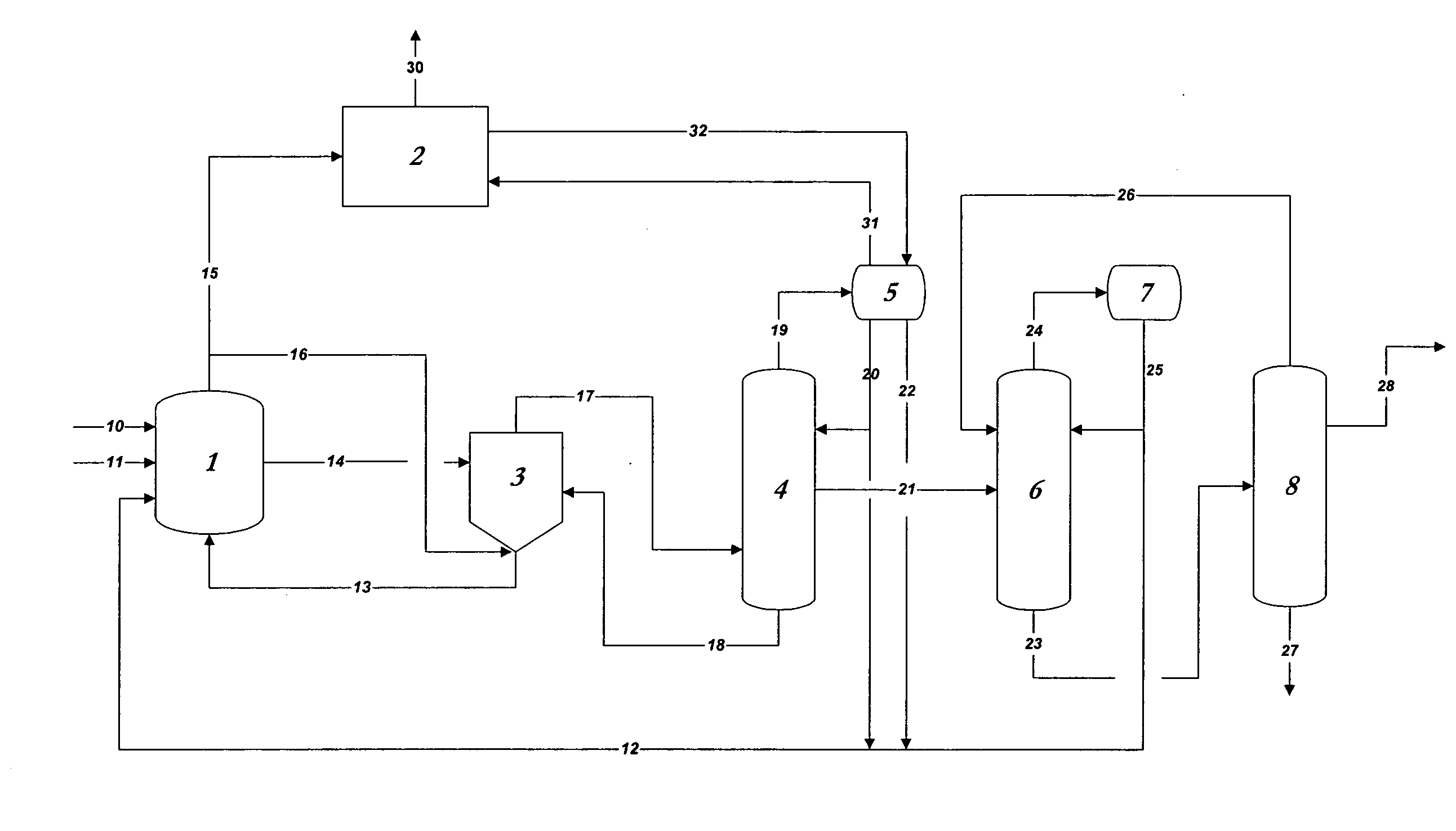
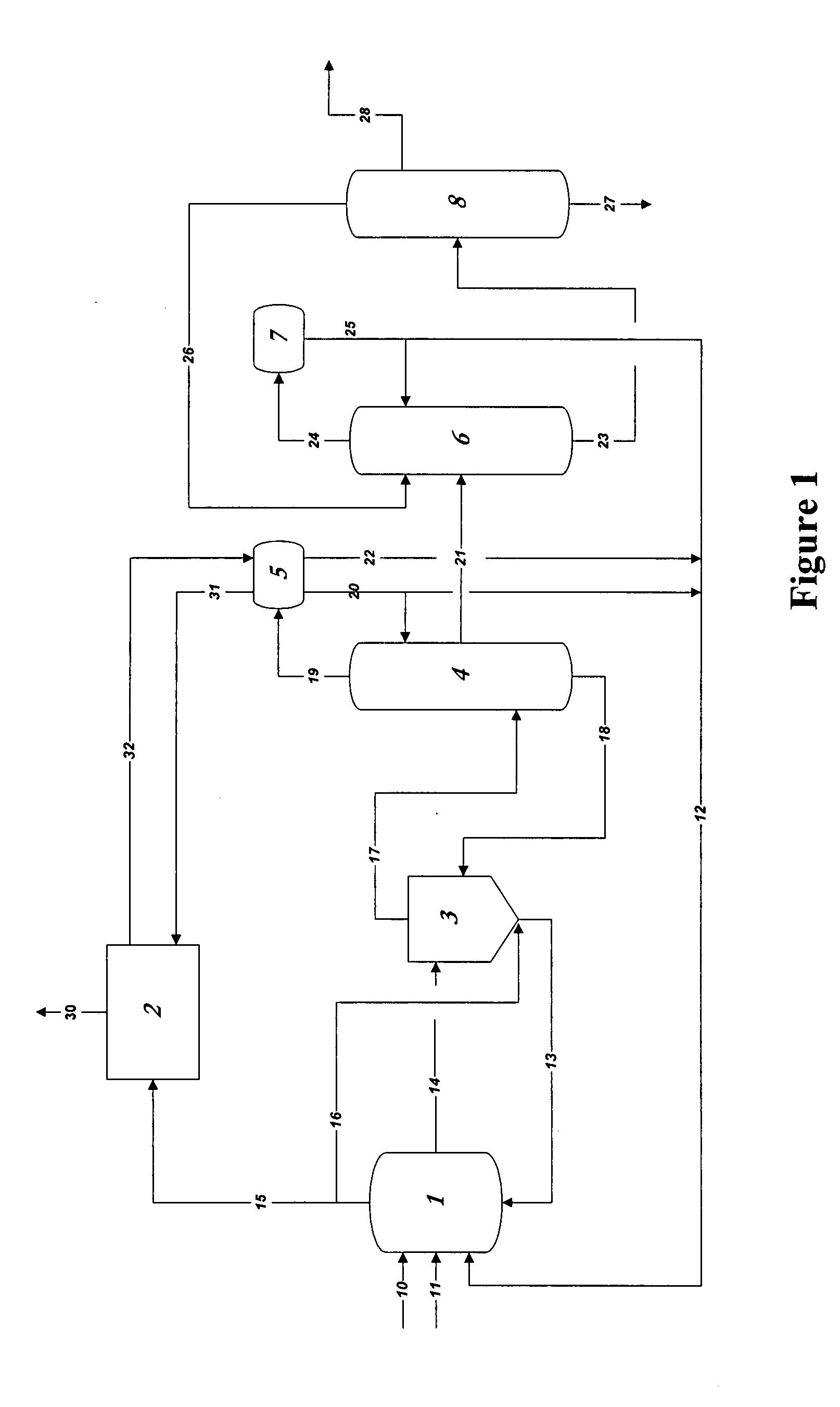
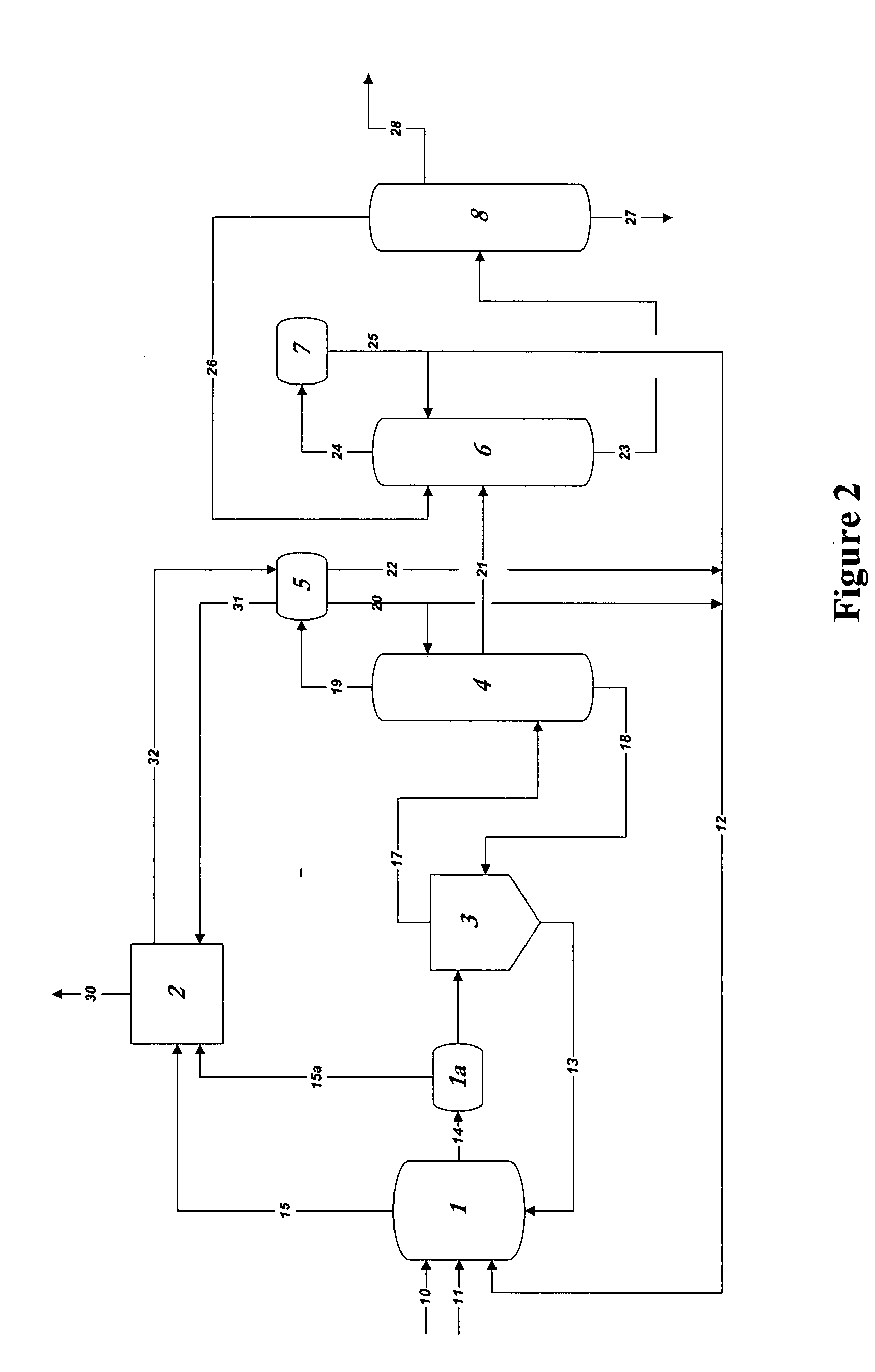
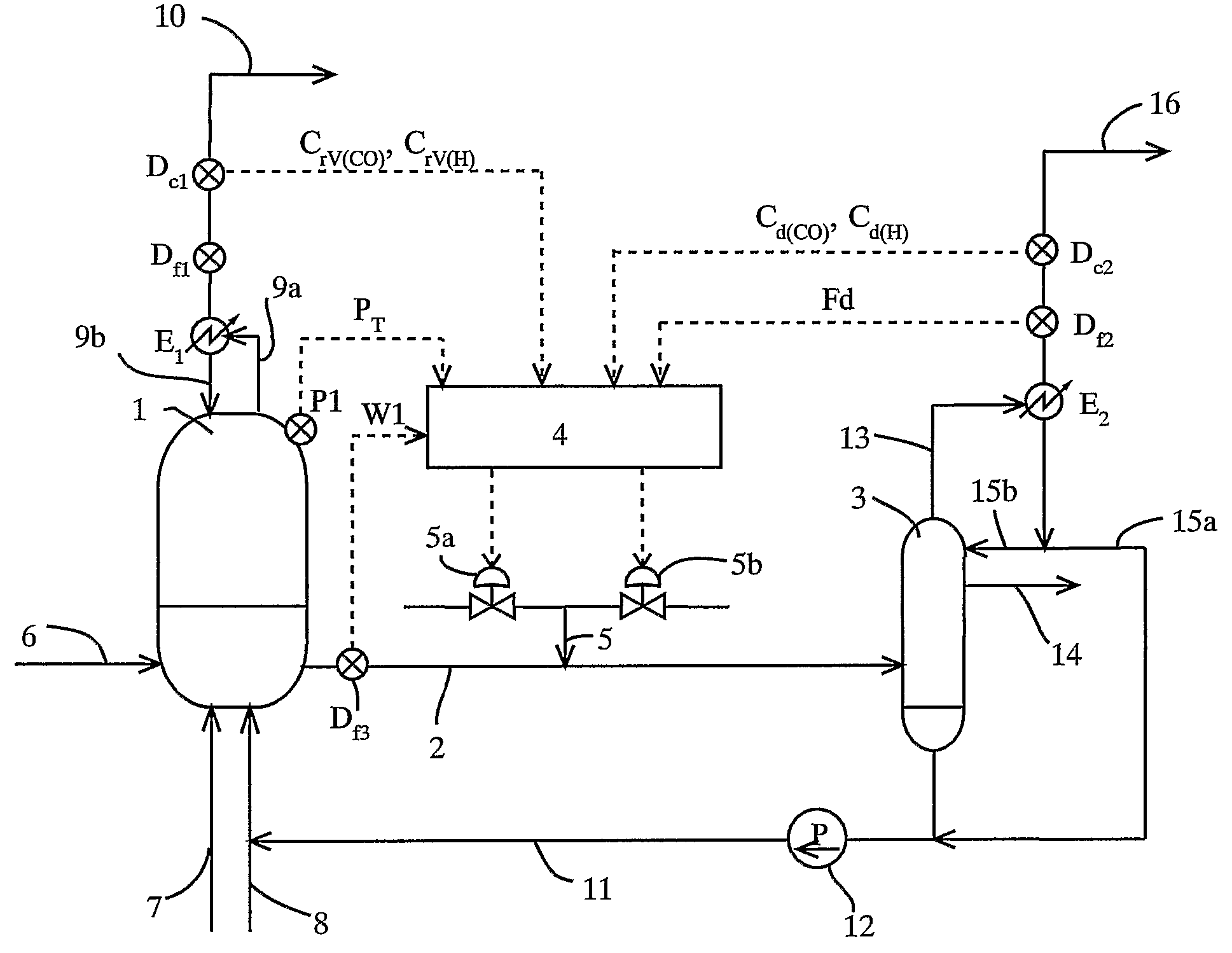
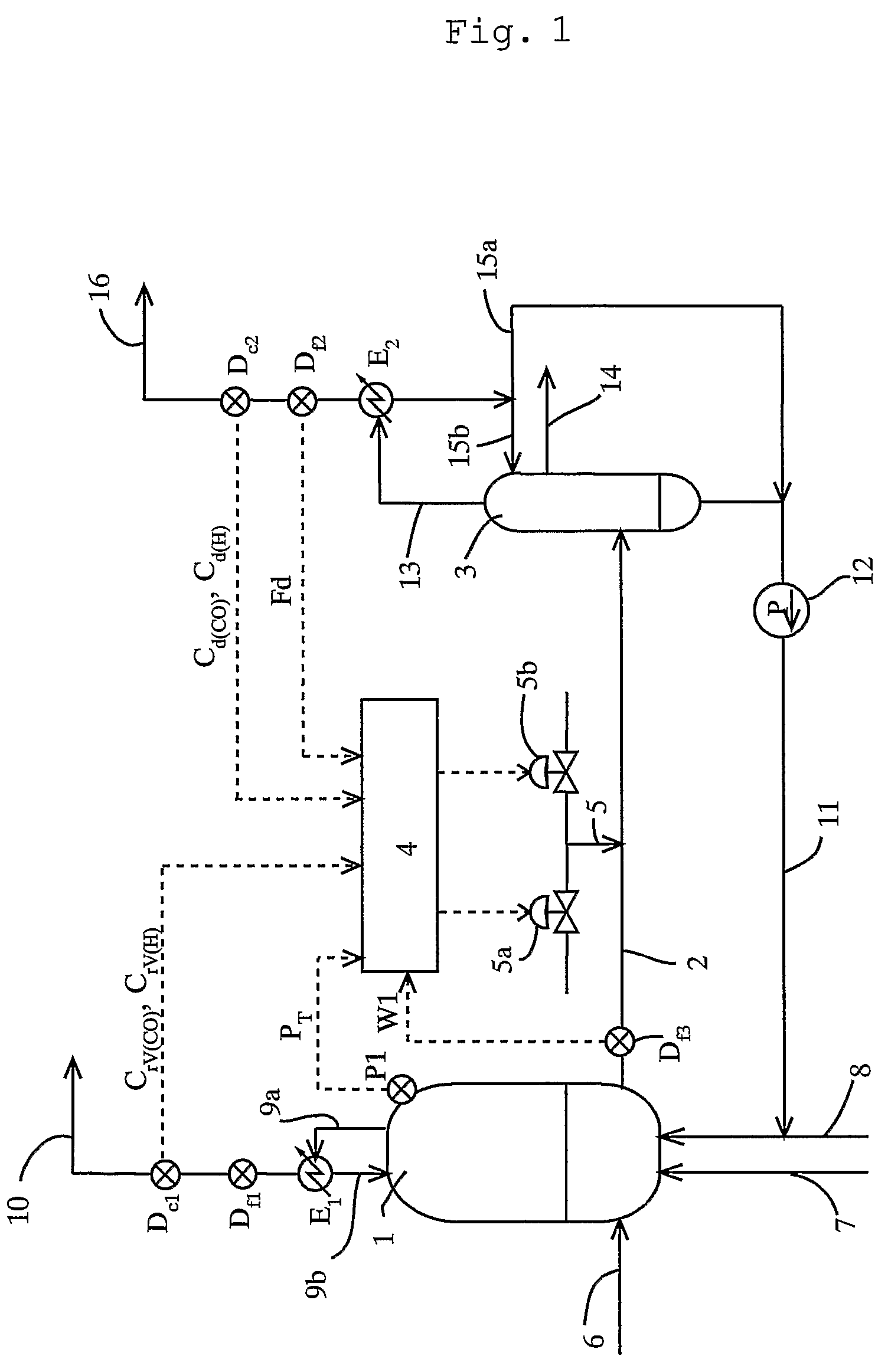
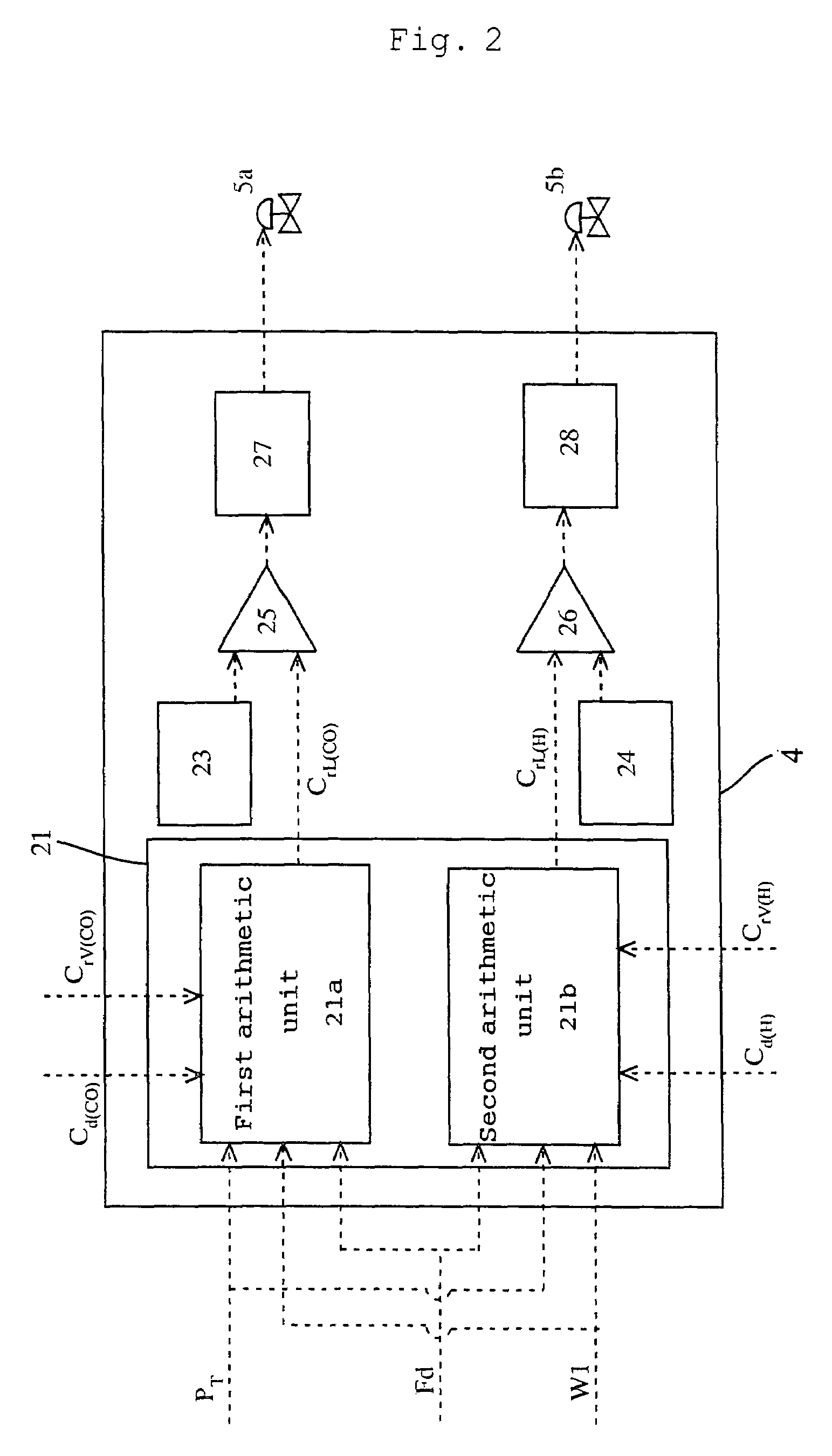
ActiveUS7476761B2Decrease in reaction rate can be inhibitedIncrease hydrogen partial pressurePreparation from carboxylic acid saltsOrganic compound preparationCarbon numberReaction rate
A process for producing a carboxylic acid comprises allowing an alcohol having a carbon number of “n” to continuously react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a carbonylation catalyst system, and a limited amount of water, continuously withdrawing the reaction mixture from the reaction system 1, introducing the withdrawn reaction mixture into a distillation step (distillation columns 3a and 3b), and separating a higher-boiling component and a lower-boiling component containing a carboxylic acid having a carbon number of “n+1”, respectively. In the process, the amount of carbon monoxide and / or hydrogen contained in a liquid phase of the reaction system is adjusted to at least one of the following conditions (i) and (ii): (i) the amount of carbon monoxide relative to 1 kilogram of the liquid phase by weight is at least 2 mmol per 1 MPa of carbon monoxide partial pressure of the reaction system, and (ii) the amount of hydrogen relative to 1 kilogram of the liquid phase by weight is at least 50 mmol per 1 MPa of hydrogen partial pressure of the reaction system. Such a process inhibits deactivation of a metal catalyst and deterioration in a reaction rate, and decreases formation of by-products in producing a carboxylic acid under a low water content.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Method used for preparing methyl acetate
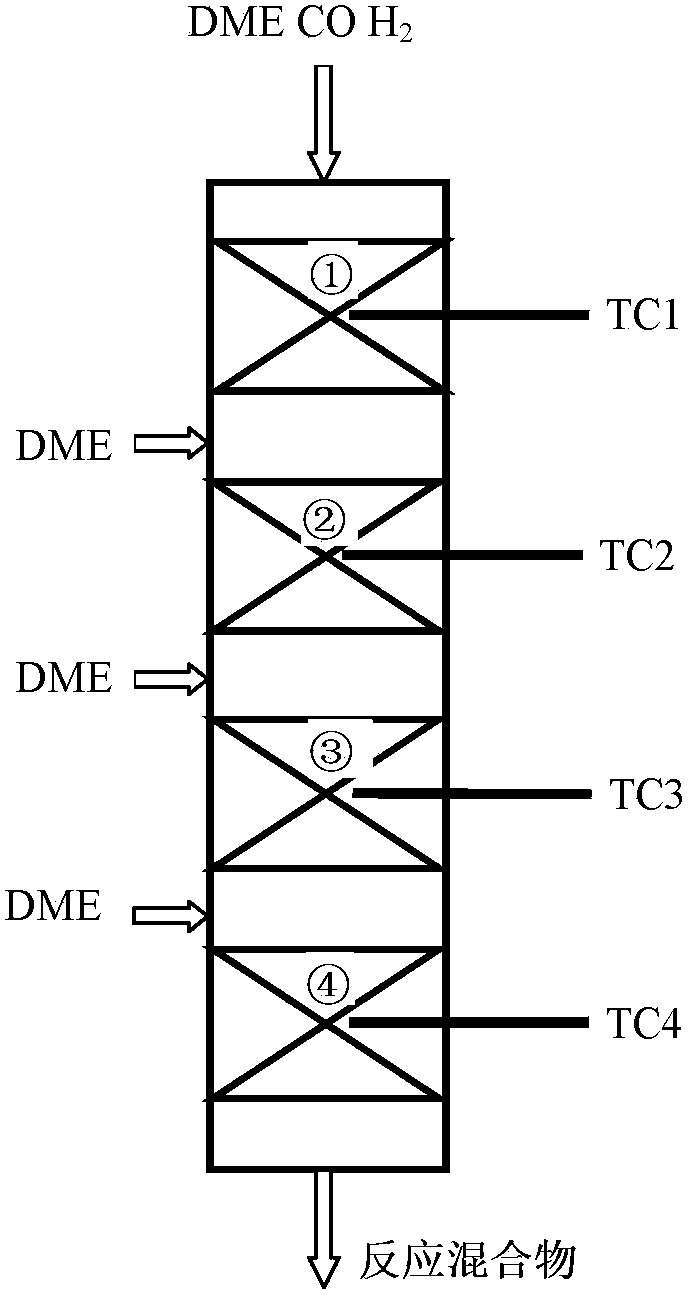
ActiveCN103896768AExtend your lifeControl temperature distributionMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationMolecular sieveHydrogen
Provided in the present invention is a process for preparing methyl acetate through carbonylation of dimethyl ether, comprising: passing a feed gas containing dimethyl ether, carbon monoxide, and optional hydrogen gas through a reactor loaded with a mordenite molecular sieve catalyst, and preparing methyl acetate by reacting same at a reaction temperature of 19 to 320°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5 to 20.0 Mpa, and a gas volume space velocity of 500 to 5000 h-1; wherein the mordenite molecular sieve catalyst is a hydrogen-type mordenite molecular sieve catalyst with an adsorbed organic amine, the molar ratio of the dimethyl ether to carbon monoxide in the feed gas is DME / CO = 1 / 1 to 1 / 15, the molar ratio of the hydrogen gas to carbon monoxide is H2 / CO = 0 to 10 / 1, and the dimethyl ether in the feed gas is charged into the reactor by means of feeding in stages. The present invention is characterized in that: through treatment by organic amine adsorption, the temperature distribution of catalyst bed can be effectively controlled so as to avoid the occurrence of hot points, and thereby side reactions are reduced, the selectivity of target product is improved, and the lifetime of the catalyst is greatly extended.
Owner:YANCHANG ZHONGKE (DALIAN) ENERGY TECH CO LTD
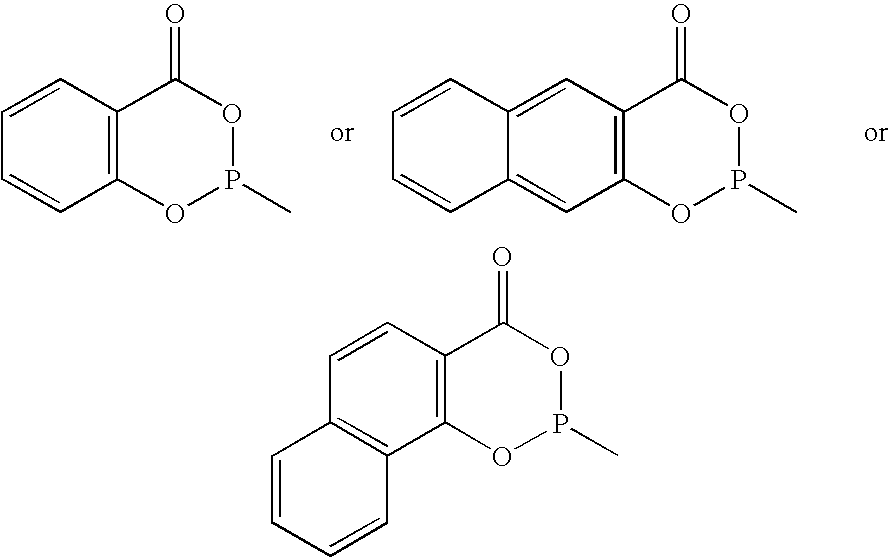
Methyl methoxyacetate (MMAC) synthesis method
InactiveCN104119228AEfficient synthesisMolecular sieve catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMolecular sieveHydrogen
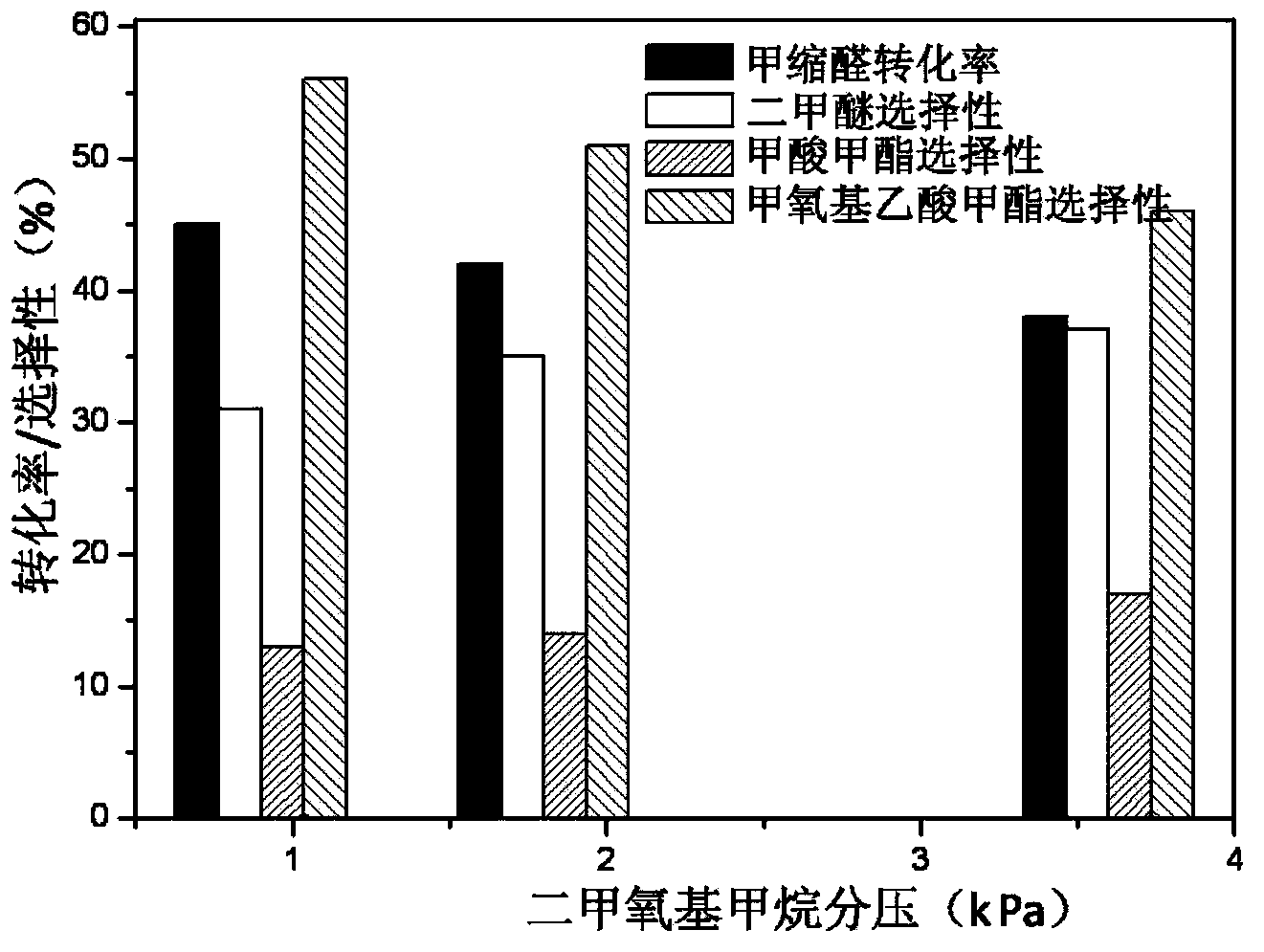
The invention discloses a catalyst for synthesis of methyl methoxyacetate (MMAC) by use of dimethoxymethane (DMM) and CO as raw materials, the catalyst is a molecular sieve with twelve membered ring cavity, ten membered ring channel and supercage structures, the International Zeolite Association (IZA) defines the topological structure of the catalyst as MWW type such as MCM-22 and MCM-49, the molecular formula is SixAlyOz, and the molecular sieve is hydrogen type. The molecular sieve SiO2 / Al2O3 ratio is 10-200. Carbonylation reaction is performed in a gas-solid phase fixed bed reactor, the reaction pressure is 1-50*105Pa, a reaction raw material gas comprises the dimethoxymethane with the partial pressure of 1-50kPa and balance of CO (1-49*105Pa) or CO / He (1-49* 105Pa), the reaction temperature is 60-180 DEG C, and the space velocity is 20-500L .g<-1>.h<-1>. Compared with a MFI type molecular sieve (HZSM-5) only having a crossed ten membered ring structure and a BEA type molecular sieve (Hbeta) only having a twelve membered ring structure, the MWW type molecular sieve has higher methyl methoxyacetate selectivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method used for preparing methyl acetate via carbonylation of dimethyl ether
ActiveCN103896769AExtend your lifeControl temperature distributionPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogenReaction temperature
Provided is a method for preparing methyl acetate by dimethyl ether carbonylation, comprising passing a feed gas including dimethyl ether, carbon monoxide and optional hydrogen through a reactor filled with a mordenite and / or ferrierite molecular sieve based catalyst and reacting at a reaction temperature of 190-320°C, a reaction pressure of 0.5-20.0 MPa and a gas space velocity of 500-5000 h-1 so as to prepare methyl acetate, wherein the molar ratio of dimethyl ether to carbon monoxide is DME / CO=1 / 1-1 / 15, the molar ratio of hydrogen to carbon monoxide is H2 / CO=0-10 / 1, and the feed gas is distributed into each catalyst bed layer in a segmental feeding manner. A feed gas including dimethyl ether and carbon monoxide is uniformly distributed into each catalyst bed layer via a gas distributor, in a segmental feeding manner, which can remarkably improve the conversion rate of dimethyl ether, effectively control or adjust the temperature distribution of a catalyst bed layer, avoid the appearance of a hot spot, and prolong the service life of a catalyst.
Owner:YANCHANG ZHONGKE (DALIAN) ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Control method for process of removing permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process
ActiveUS20050197513A1Organic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
Disclosed is a method of controlling a separation process for removing moving permanganate reducing compounds from a process stream in the methanol carbonylation process for making acetic acid, where the method includes the steps of measuring the density of a stream containing acetaldehyde and methyl iodide, optionally calculating the relative concentrations of acetaldehyde and methyl iodide in the stream, and adjusting distillation or extraction process parameters based on the measured density or one or more relative concentrations calculated therefrom.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for indirectly producing alcohol with synthetic gas and application of process
ActiveCN103012062AReduce energy consumptionMild reaction conditionsOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationHydrogenMethyl acetate
The invention relates to a process for indirectly producing alcohol with synthetic gas. The process comprises the steps that the synthetic gas formed by mixing industrial carbon monoxide with hydrogen is taken as a raw material to synthesize methanol; methanol is dehydrated to prepare dimethyl ether; dimethyl ether, carbon monoxide and hydrogen are mixed for carbonylation reaction to prepare methyl acetate; methyl acetate is purified and hydrogenated; a hydrogenated product is purified; and an alcohol product is obtained. An adopted catalyst, the process and a device have the characteristics of high conversion per pass and high effective utilization rate of reaction heat; the load of separating a crude product is reduced greatly; the production flow is shortened; and the production energy consumption is reduced greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI WUZHENG ENG TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com