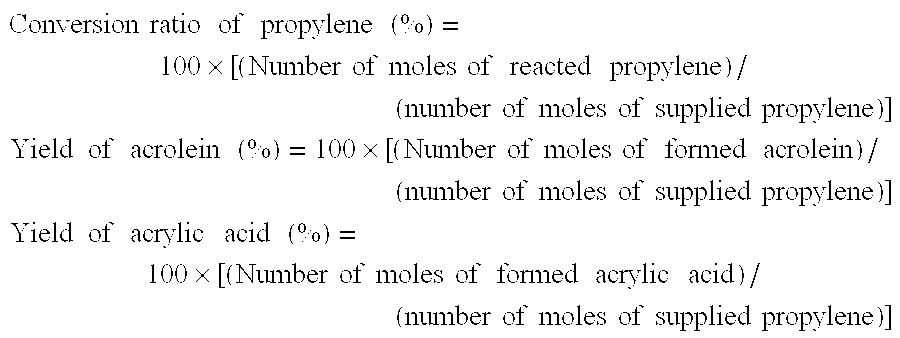Patents
Literature
458 results about "Water concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The standard state for a liquid is the pure liquid, so the standard state of water is pure water, whose concentration is 55.5 M (in a liter, there are 55.5 moles of water, so its concentration is 55.5 mol/L). In dilute aqueous solutions, the concentration of water is very close to 55.5 M. So in this calculation,...
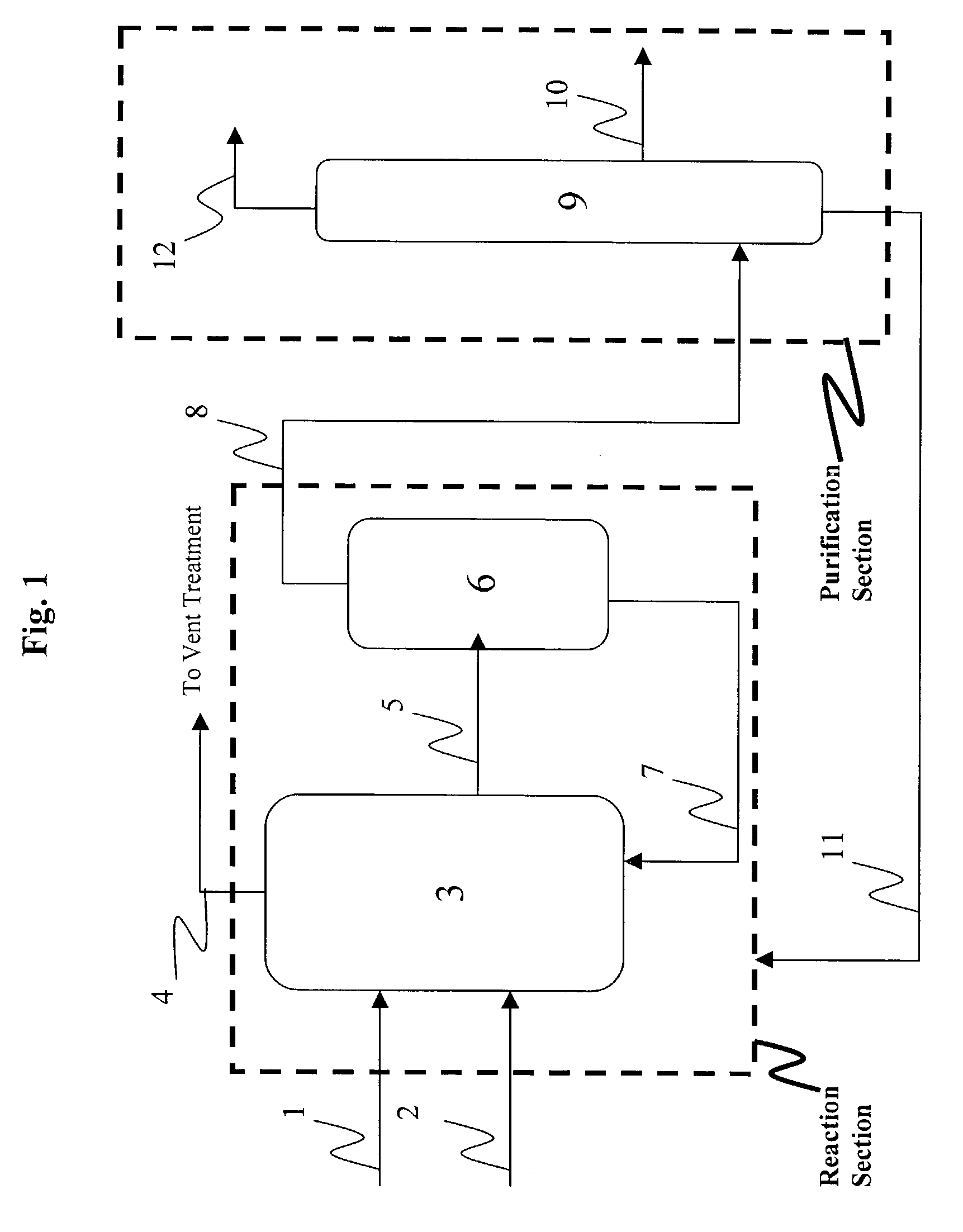
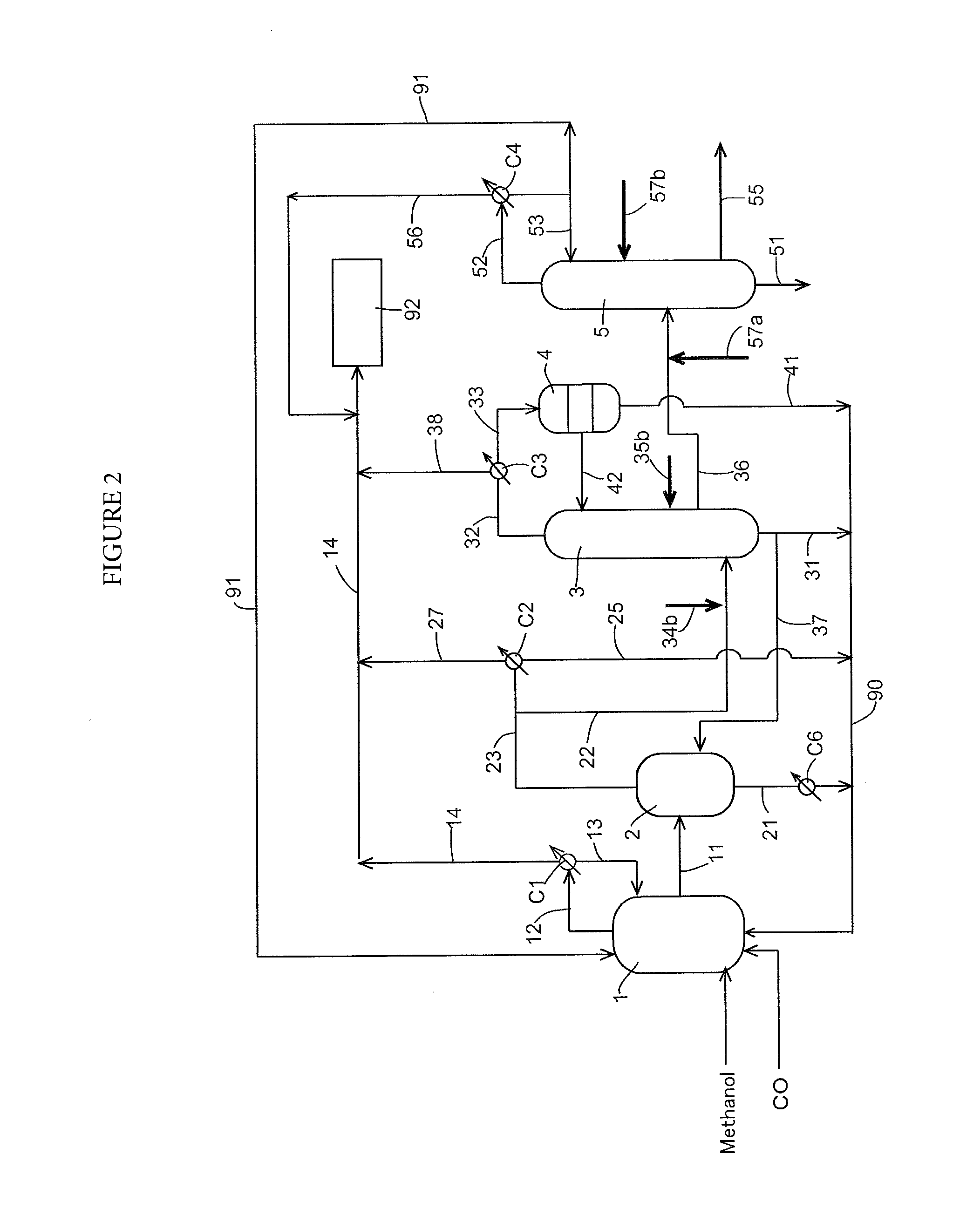
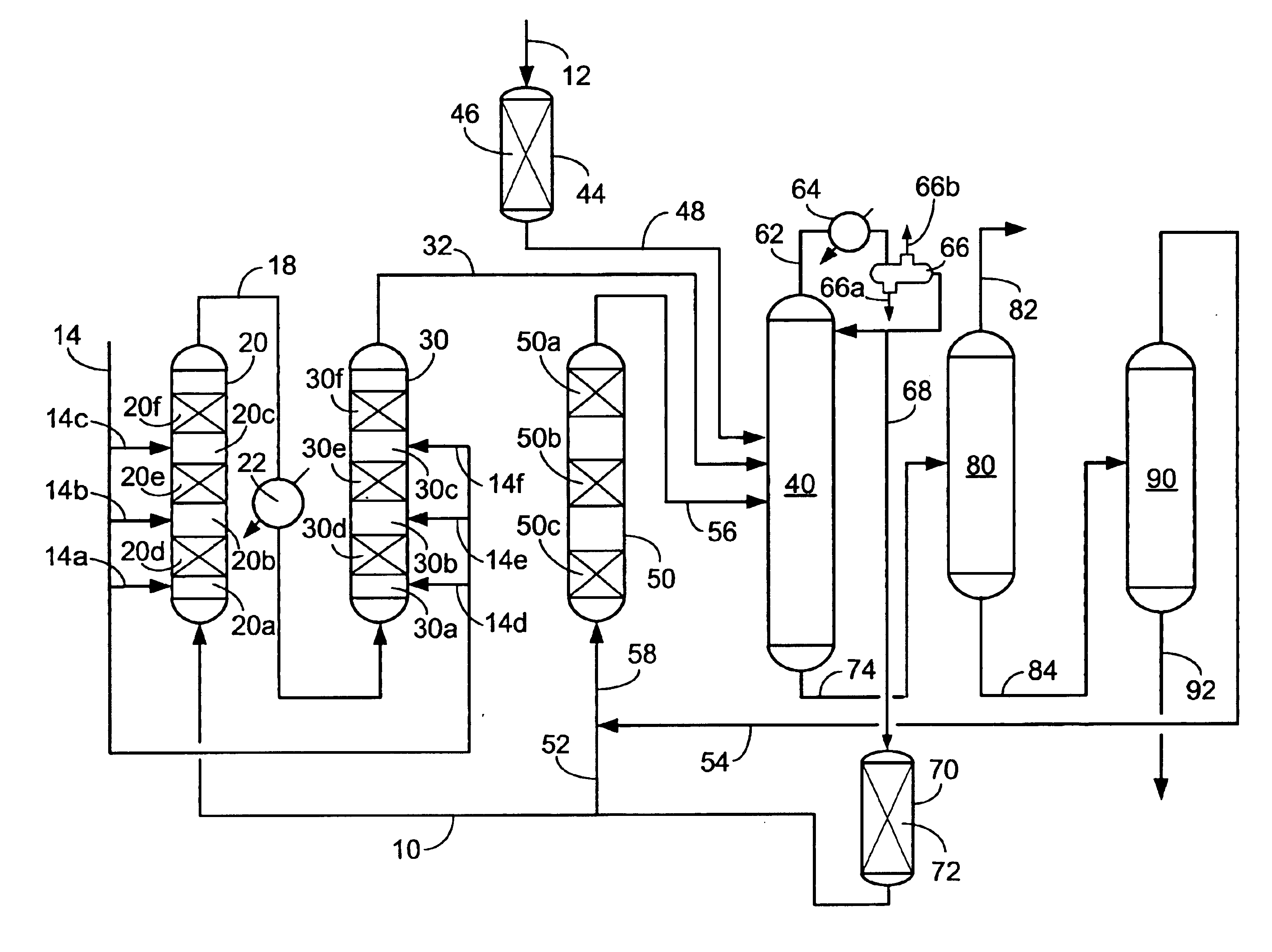
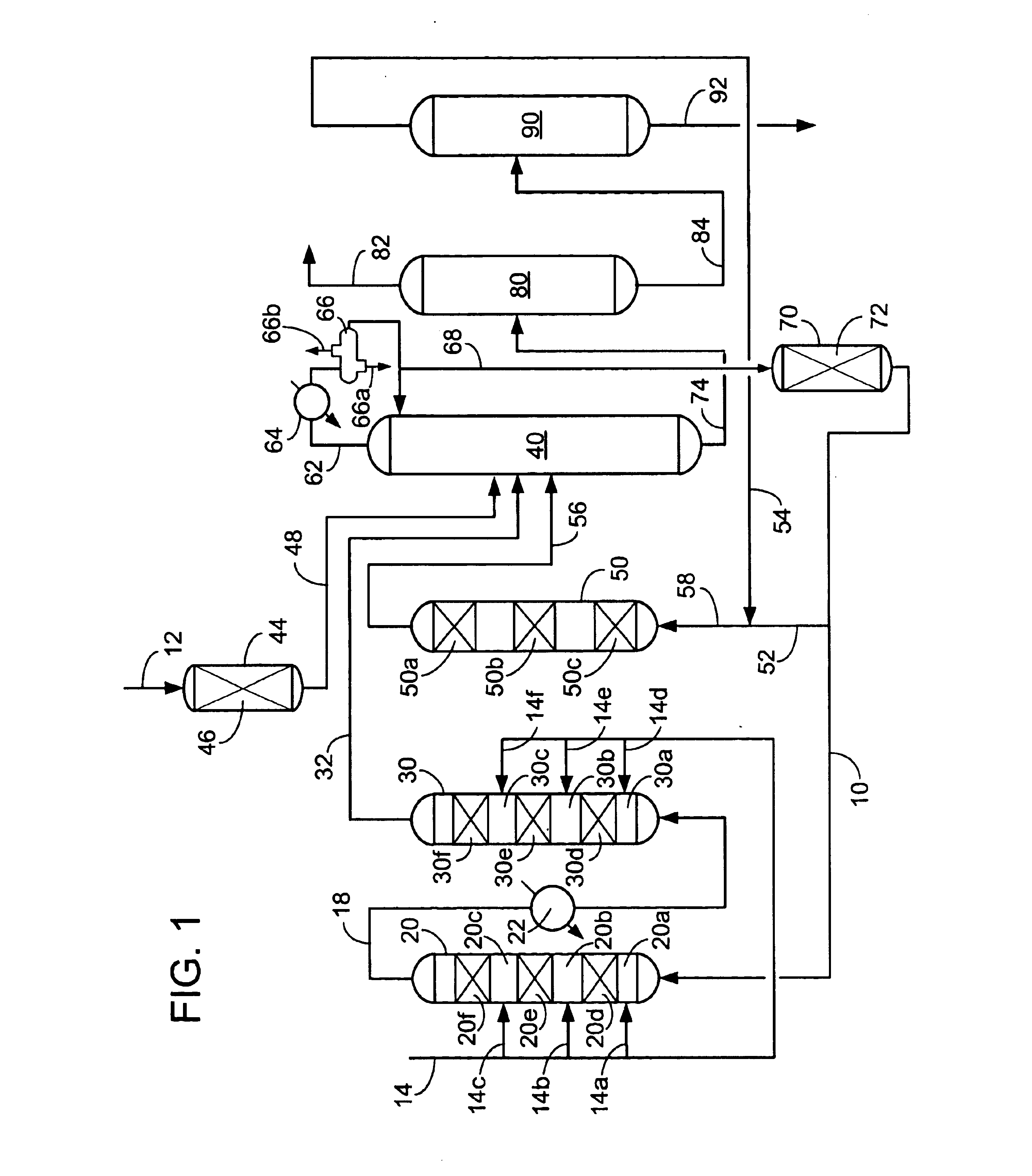
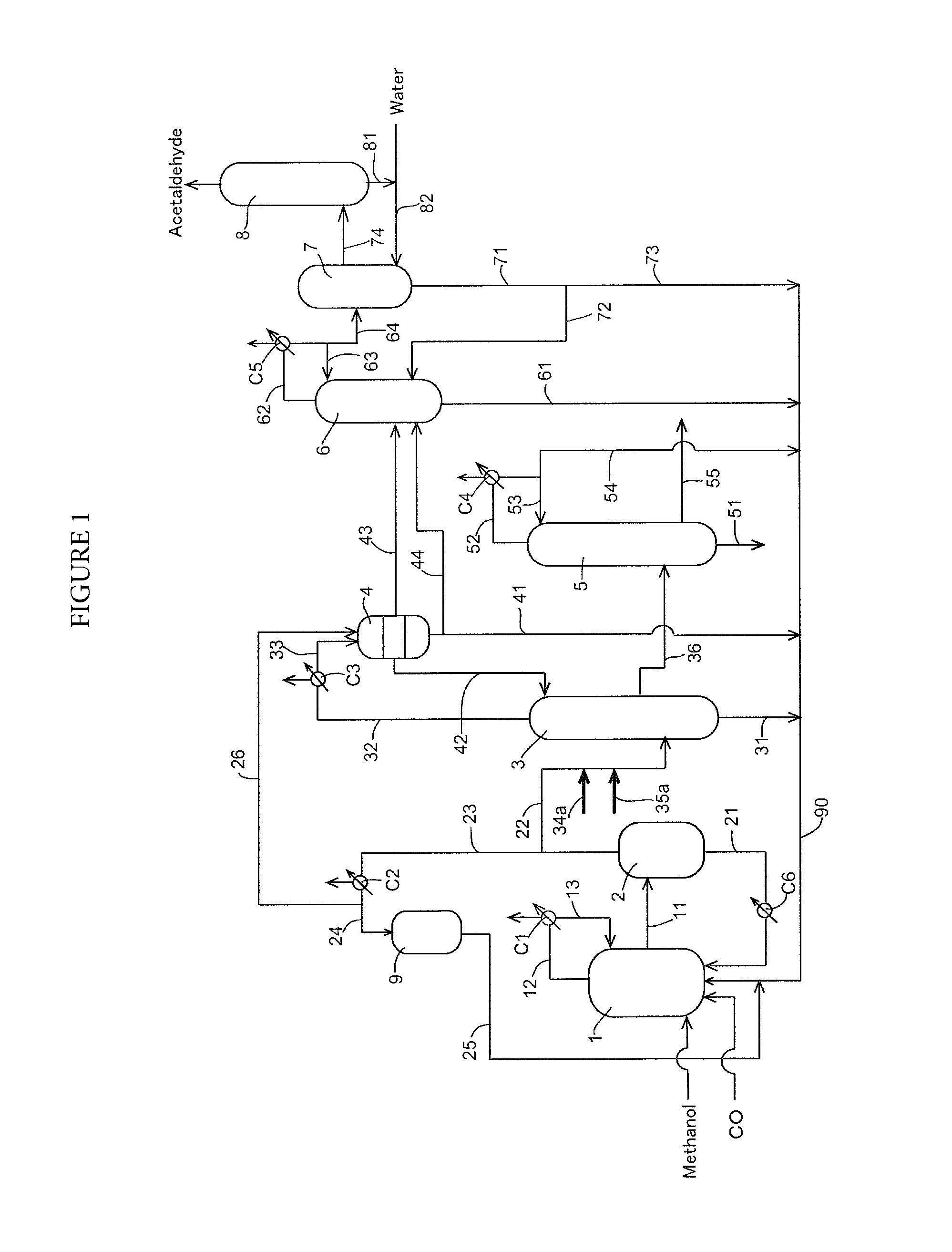
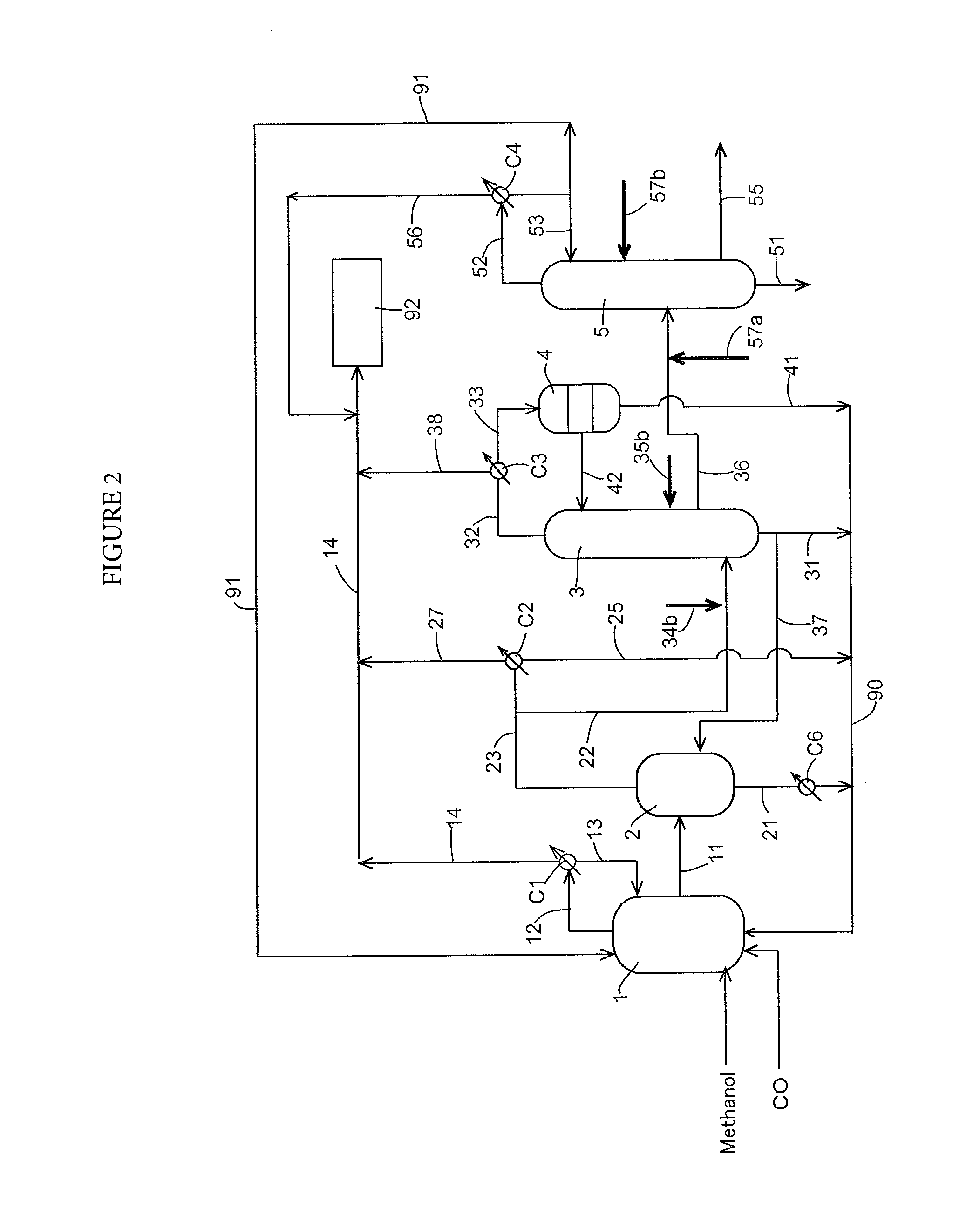
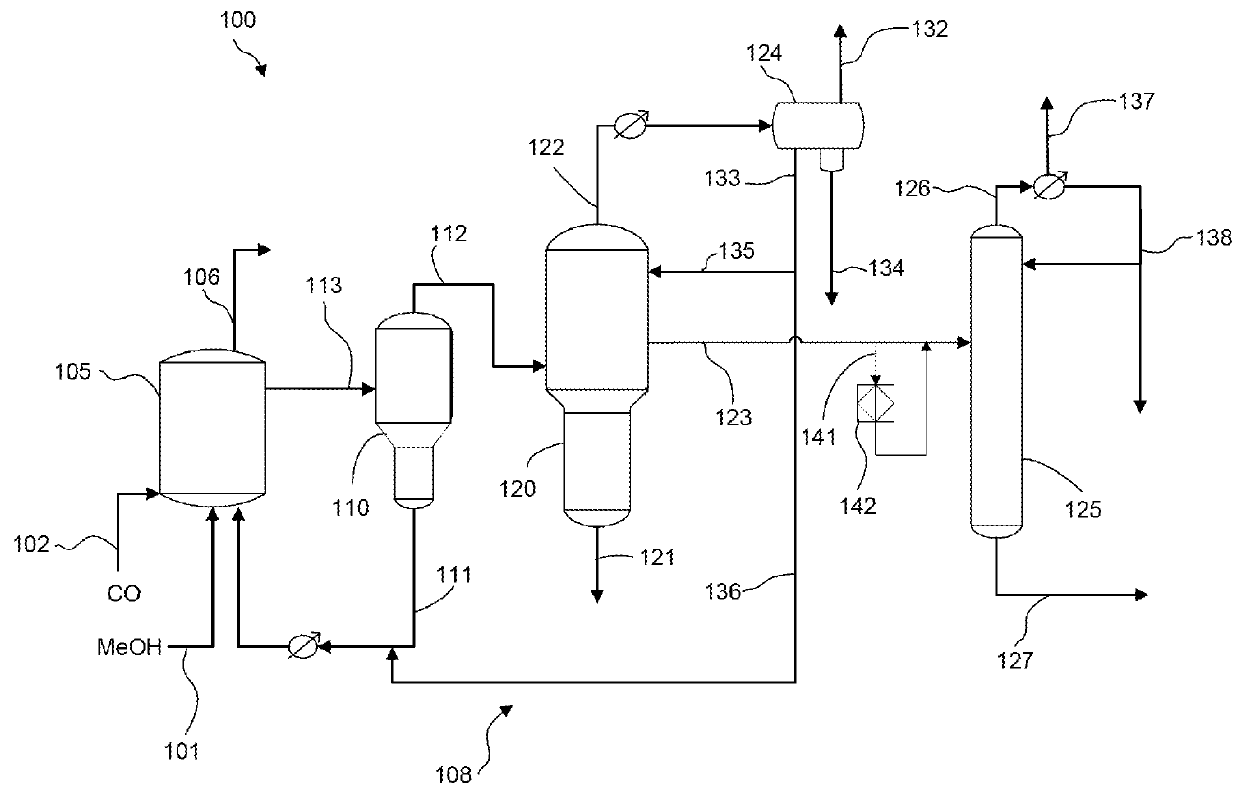
Low water methanol carbonylation process for high acetic acid production and for water balance control
ActiveUS7005541B2High acetic acid production rateIncrease chanceOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionWater methanolAcetic anhydride
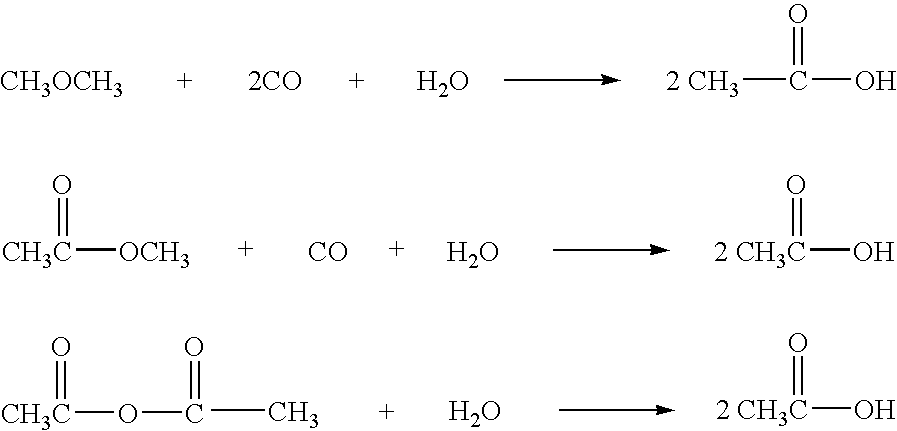
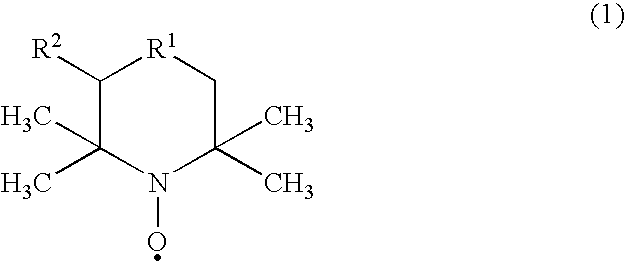
The invention relates to a process for the production of acetic acid by carbonylation of methanol, and reactive derivatives thereof, in a reaction mixture using a rhodium-based catalyst in low water conditions. The process is used to achieve reaction rates of at least 15 g mol / l / hr. The high rate reactions proceed at water concentrations of less than 2.0 wt. %. Under certain conditions, the water concentration in the reaction mixture of the process is maintained at a desired concentration by at least one process step including adding a compound such as methyl acetate, dimethyl ether, acetic anhydride, or mixtures of these compounds to the reaction system. The process step of adding the components to the reaction mixture may be combined with other process steps for controlling water concentrations in reaction mixtures for the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
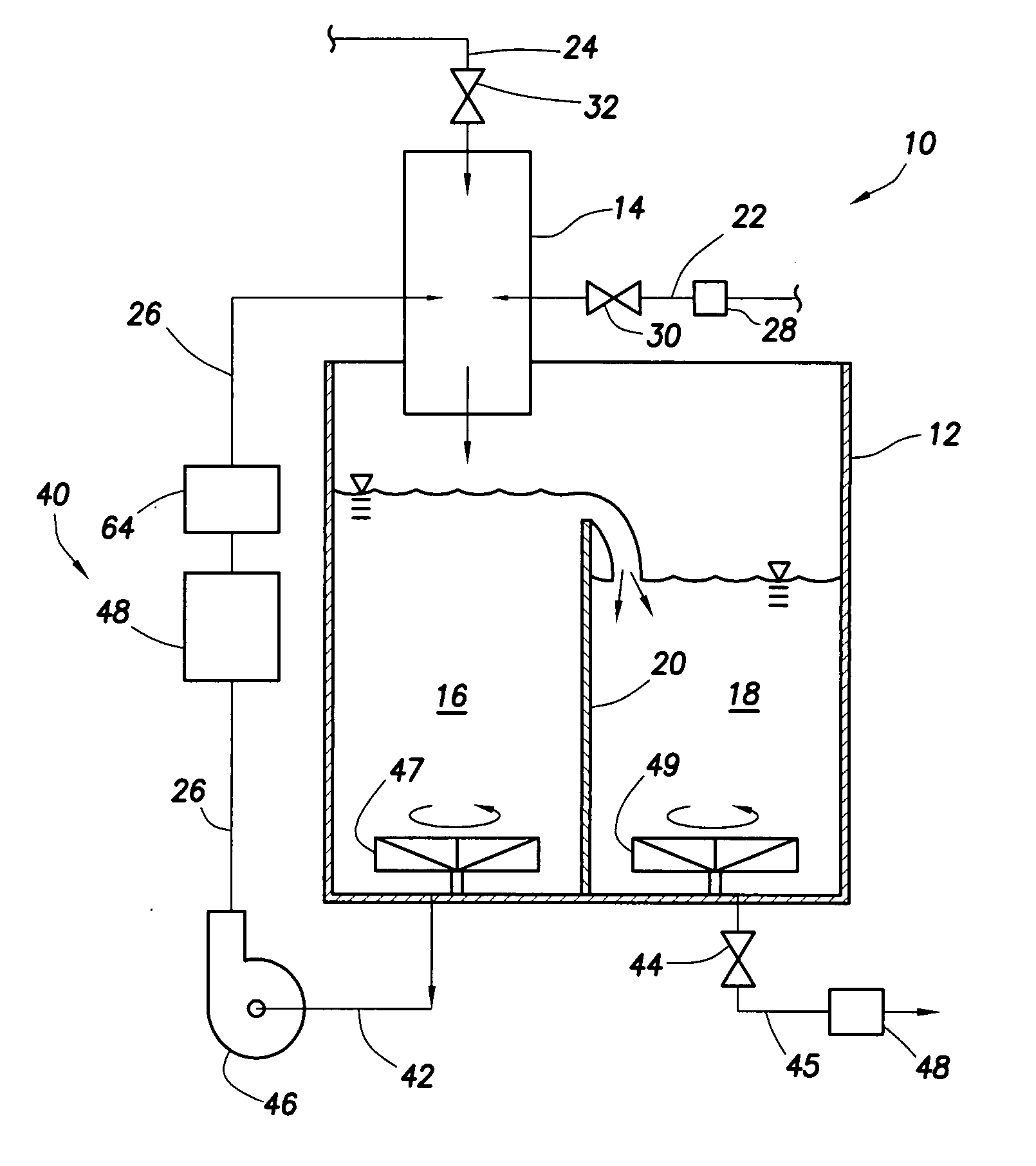
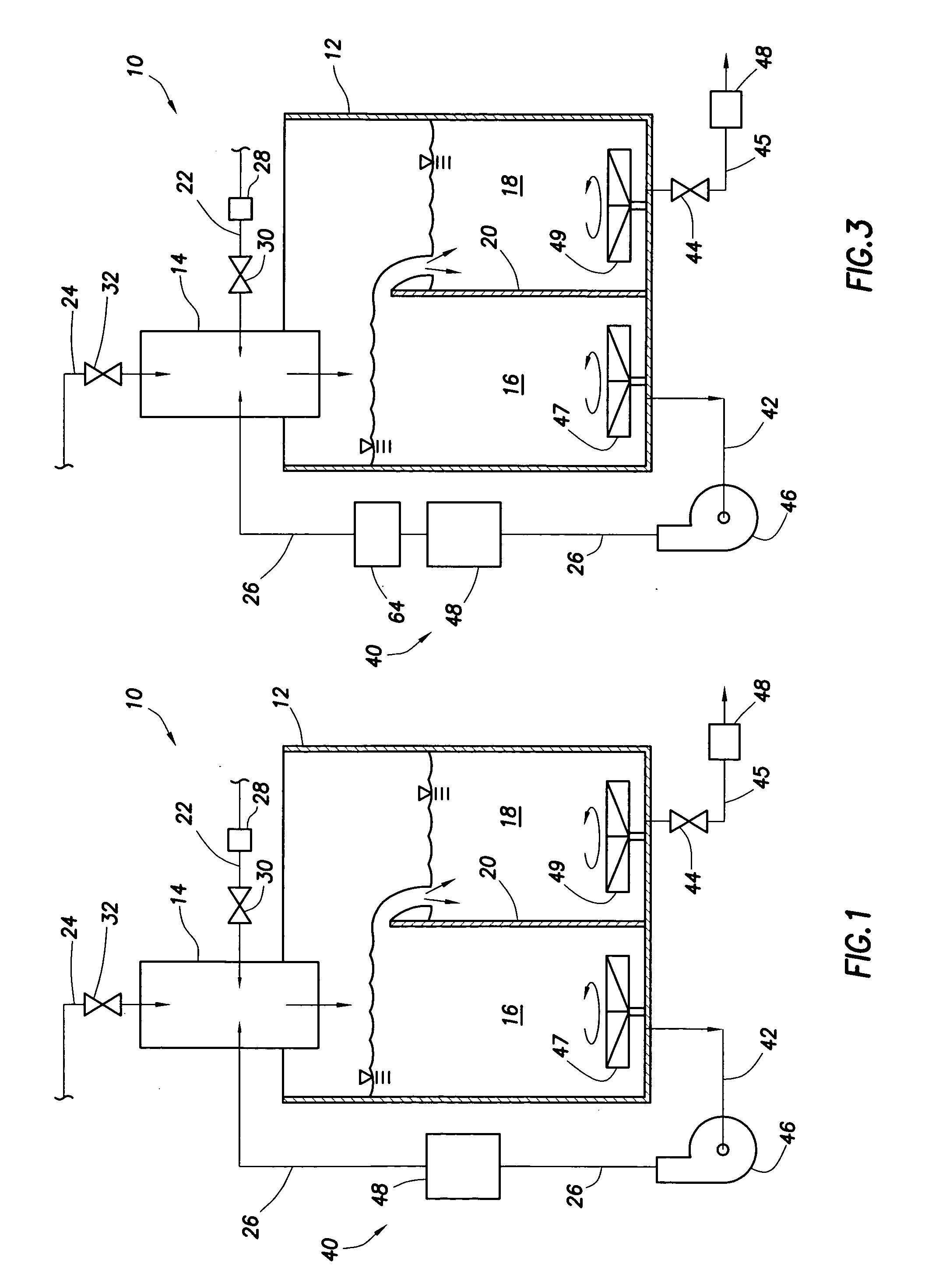
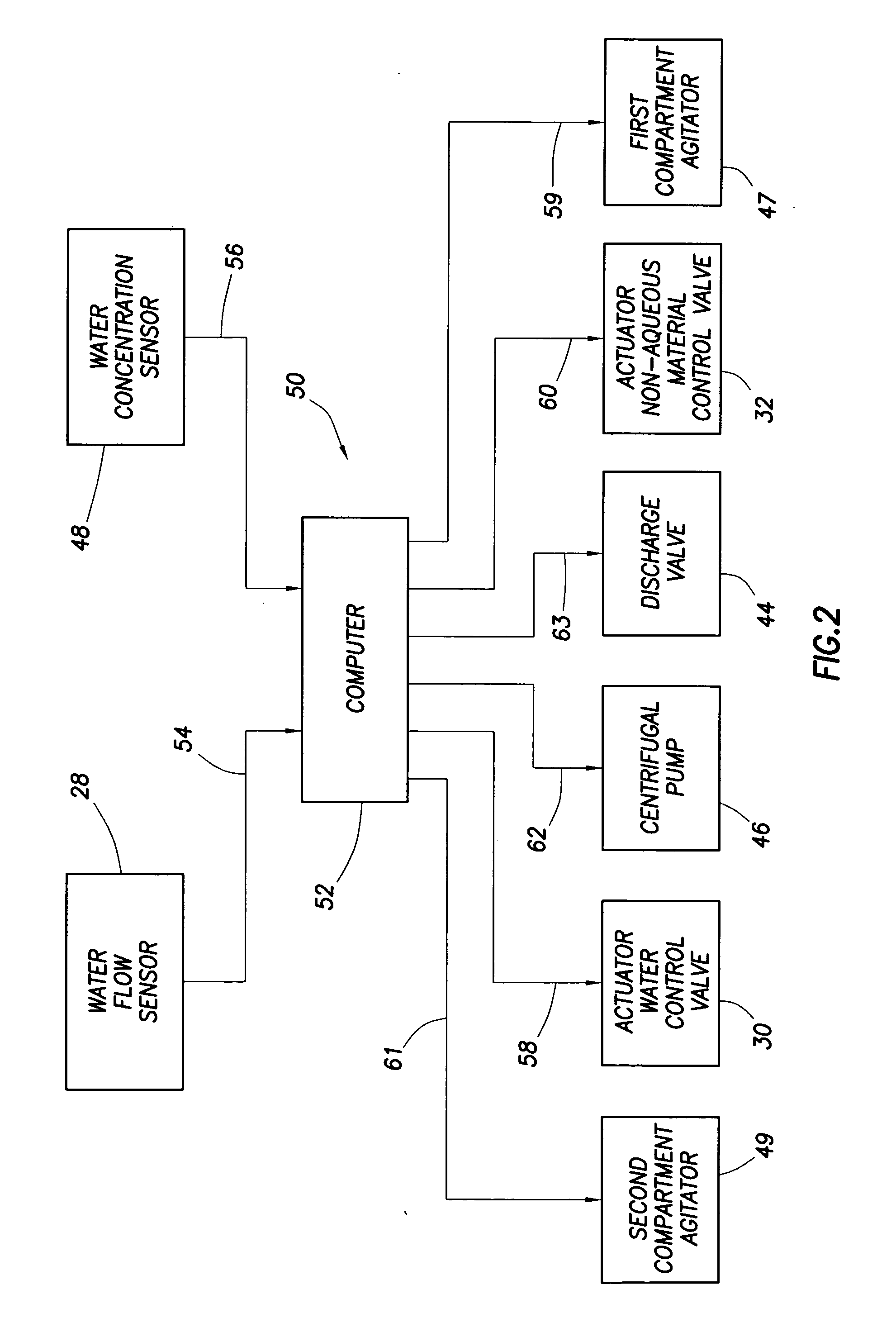
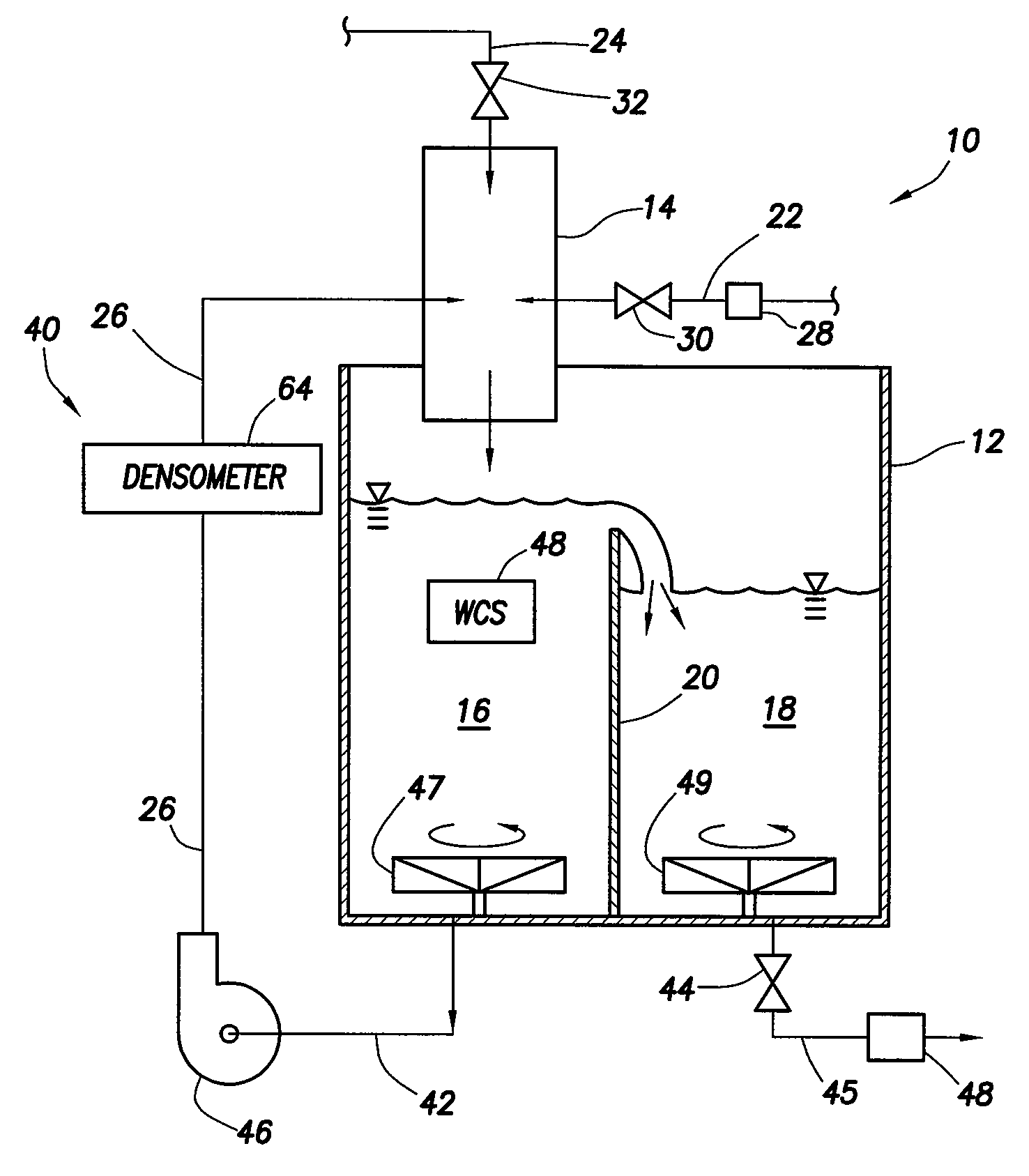
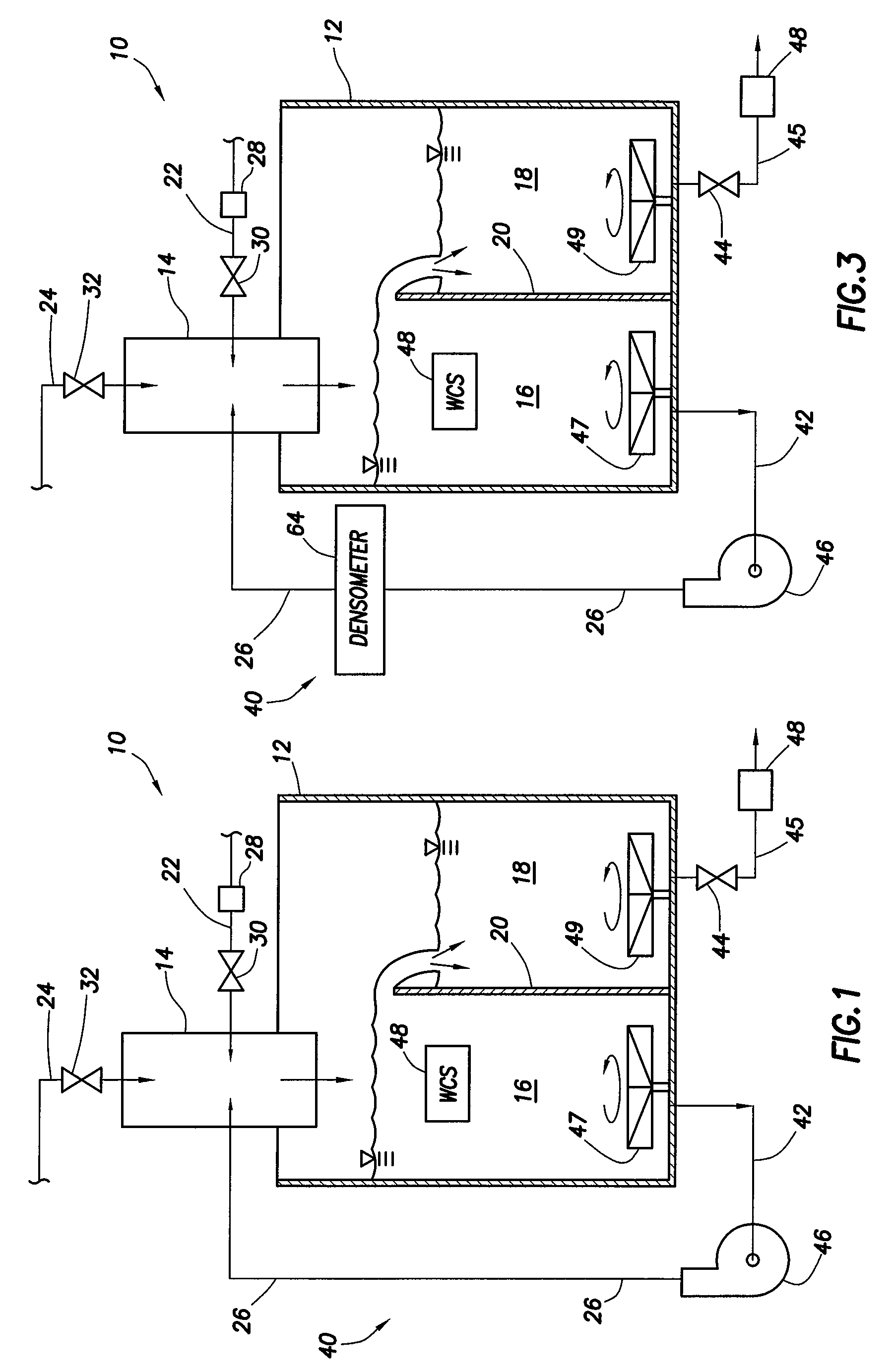
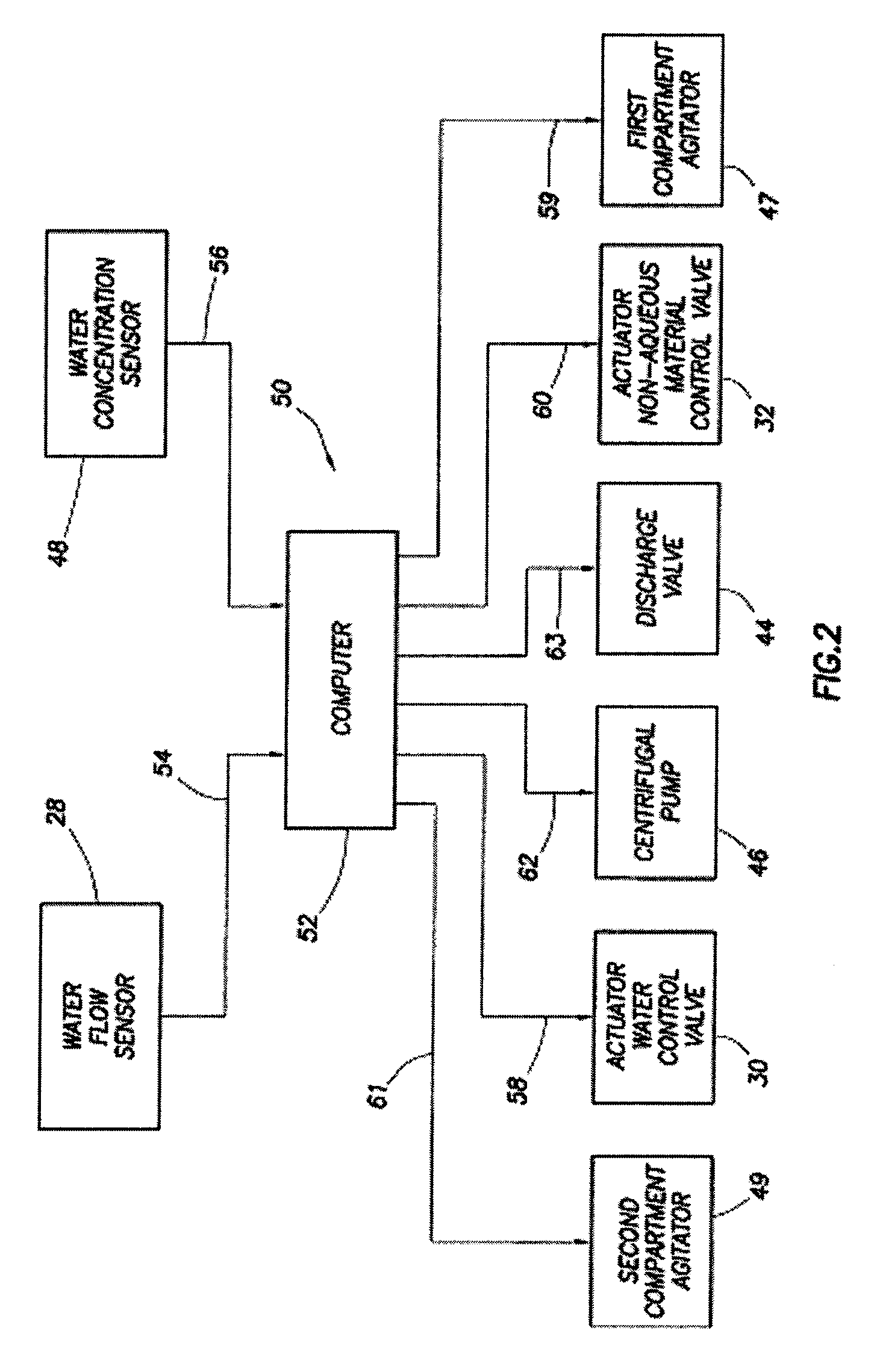
System and method for mixing water and non-aqueous materials using measured water concentration to control addition of ingredients
ActiveUS20050201197A1Eliminates and at least minimizes drawbackReduce stepsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow mixersWater concentrationAdditive ingredient
The present invention is directed to a system and method for mixing a fluid comprising water and at least one non-aqueous material. The system comprises a mixing tub and mixing head adapted to inject the fluid into the mixing tub. It also includes a plurality of lines connected to the mixing head that supply the mixing head with water and the at least one non-aqueous material and a recirculation circuit that delivers the fluid from the mixing tub back to the mixing head. The system further includes a sensor connected to the recirculation circuit that measures the concentration of water in the fluid. An automatic controller uses the concentration measurement data to control the amount of each of the ingredients injected into the mixing tub.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
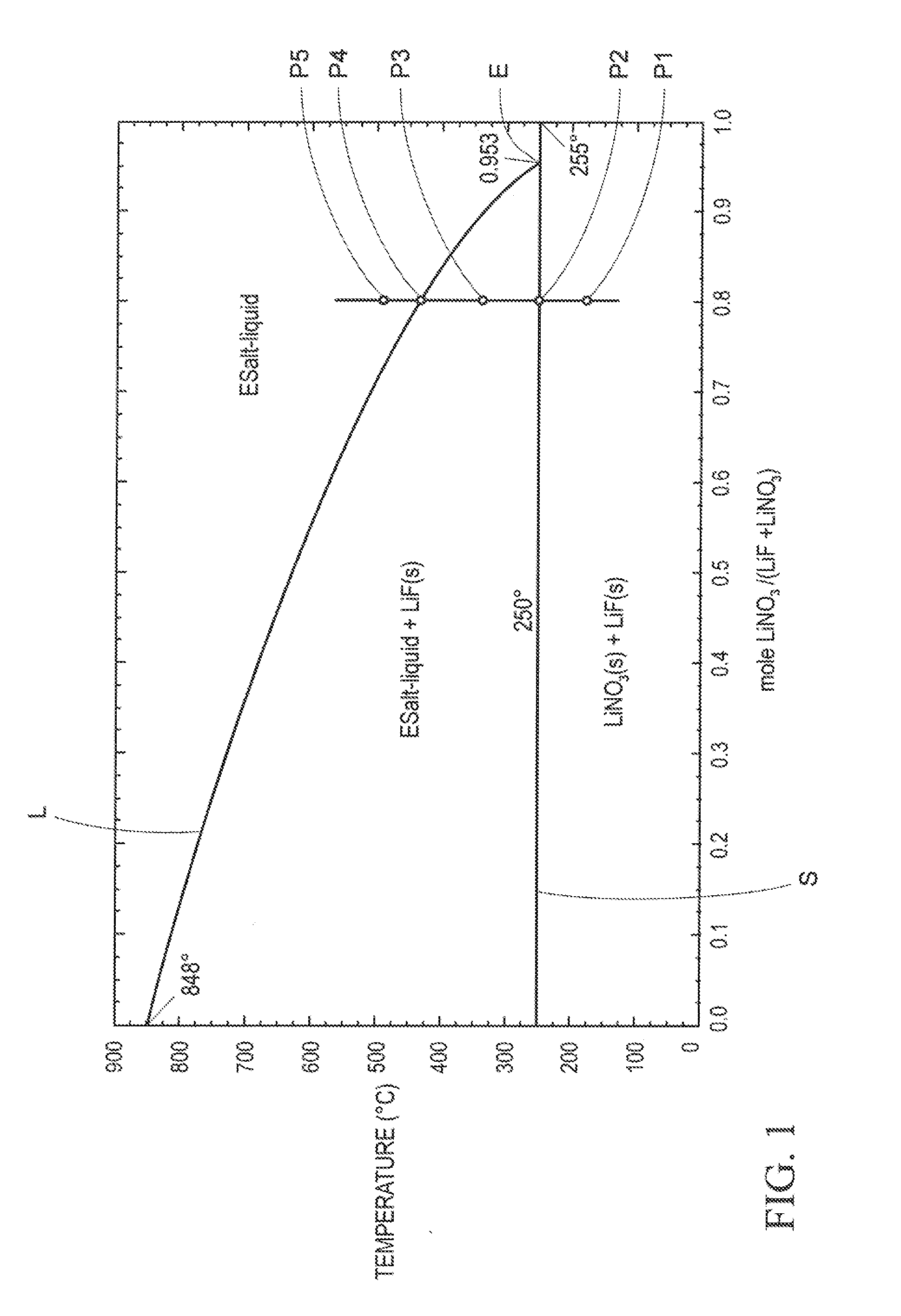
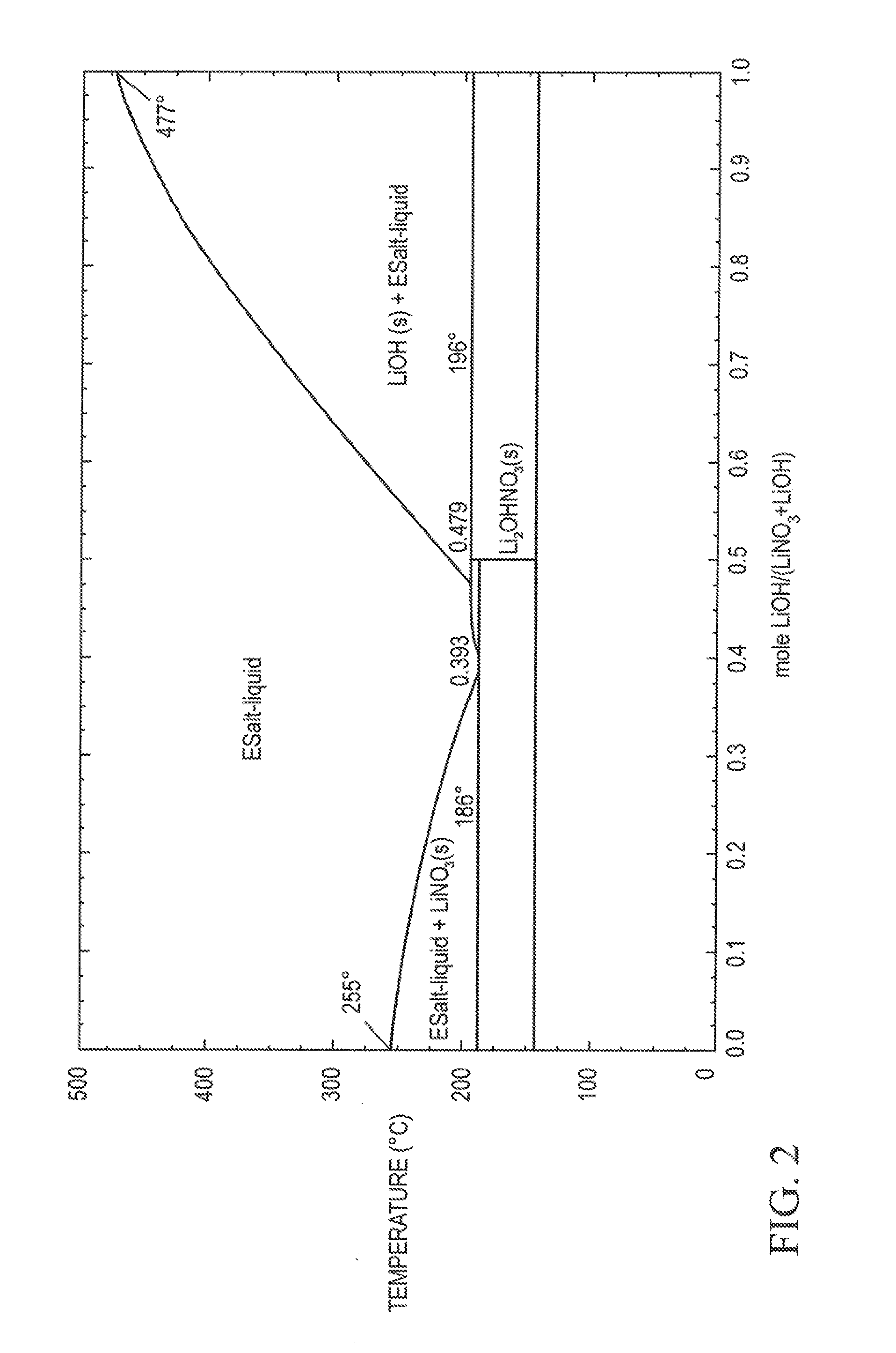
Thermal energy storage materials
A thermal energy storage material (TESM) system (and associated methods) that reproducibly stores and recovers latent heat comprising i) at least one first metal containing material including at least one first metal compound that includes a nitrate ion, a nitrite ion, or both; ii) at least one second metal containing material including at least one second metal compound; and iii) optionally including water, wherein the water concentration if any is present is less than about 10 wt. %; wherein the TESM has a liquidus temperature, TL, from about 100° C. to about 250° C.; and wherein the TESM exhibits a heat storage density from 300° C. to 80° C. of at least about 1 MJ / l; so that upon being used in a system that generates heat, at least a portion of the heat is captured and stored by the TESM and subsequently released for use, and the system is generally resistant to corrosion at temperatures of about 300° C.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
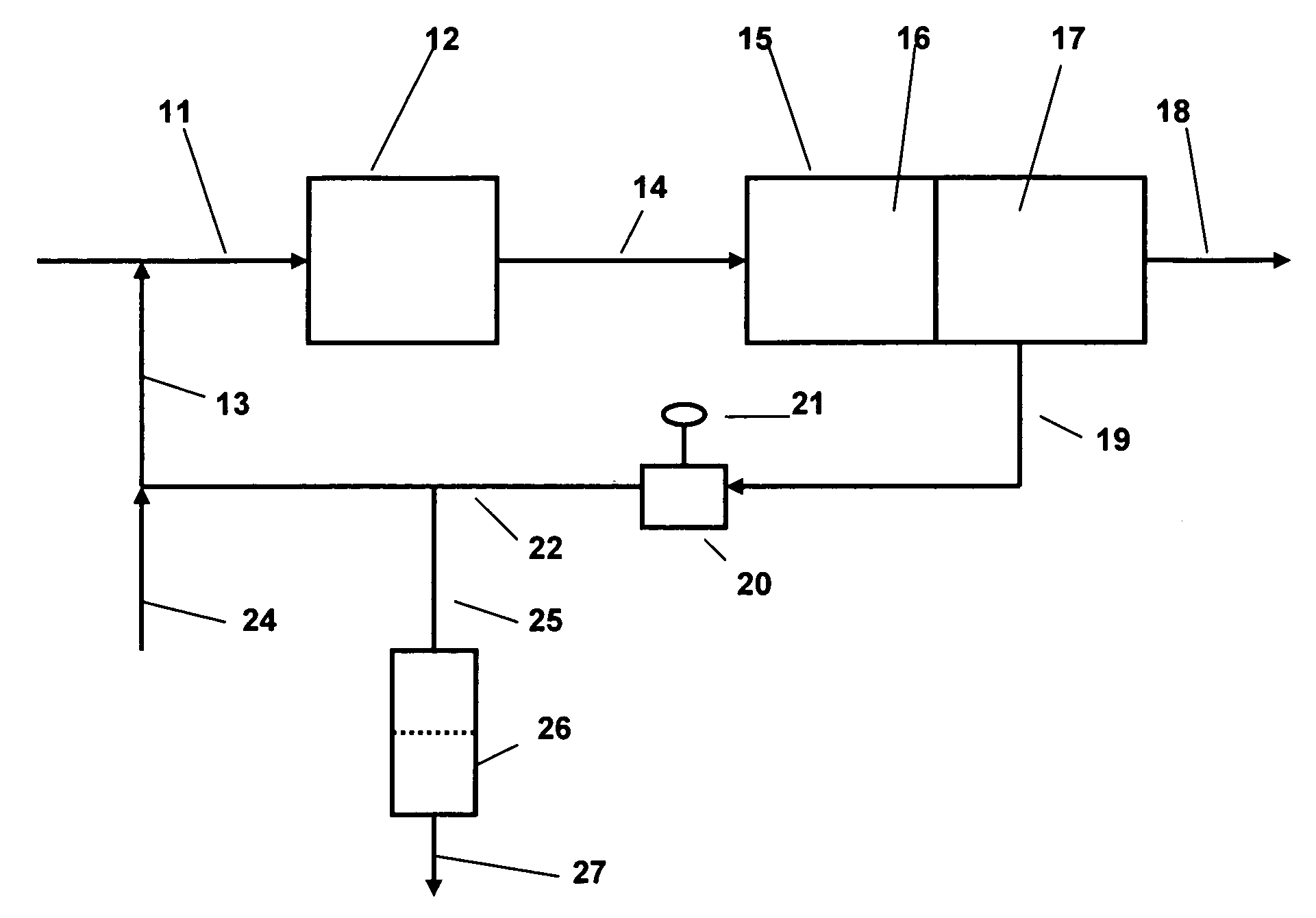
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS9006483B2Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process and apparatus for the removal of nitrogen compounds from a fluid stream
InactiveUS6894201B1Increase capacityImprove adsorption capacityHydrocarbonsAdsorption purification/separationAlkyl transferMolecular sieve
Disclosed is a process and apparatus for removing nitrogen compounds from an alkylation substrate such as benzene. A conventional adsorbent bed can be used to adsorb basic organic nitrogen compounds and a hot adsorbent bed of acidic molecular sieve can adsorb the weakly basic nitrogen compounds such as nitrites. Water facilitates the adsorption of the weakly basic nitrogen compounds. Running an alkylation substrate stream from a fractionation column of elevated temperature and suitable water concentration to the hot adsorbent bed may be advantageous.
Owner:UOP LLC
Inferred water analysis in polyphenylene sulfide production
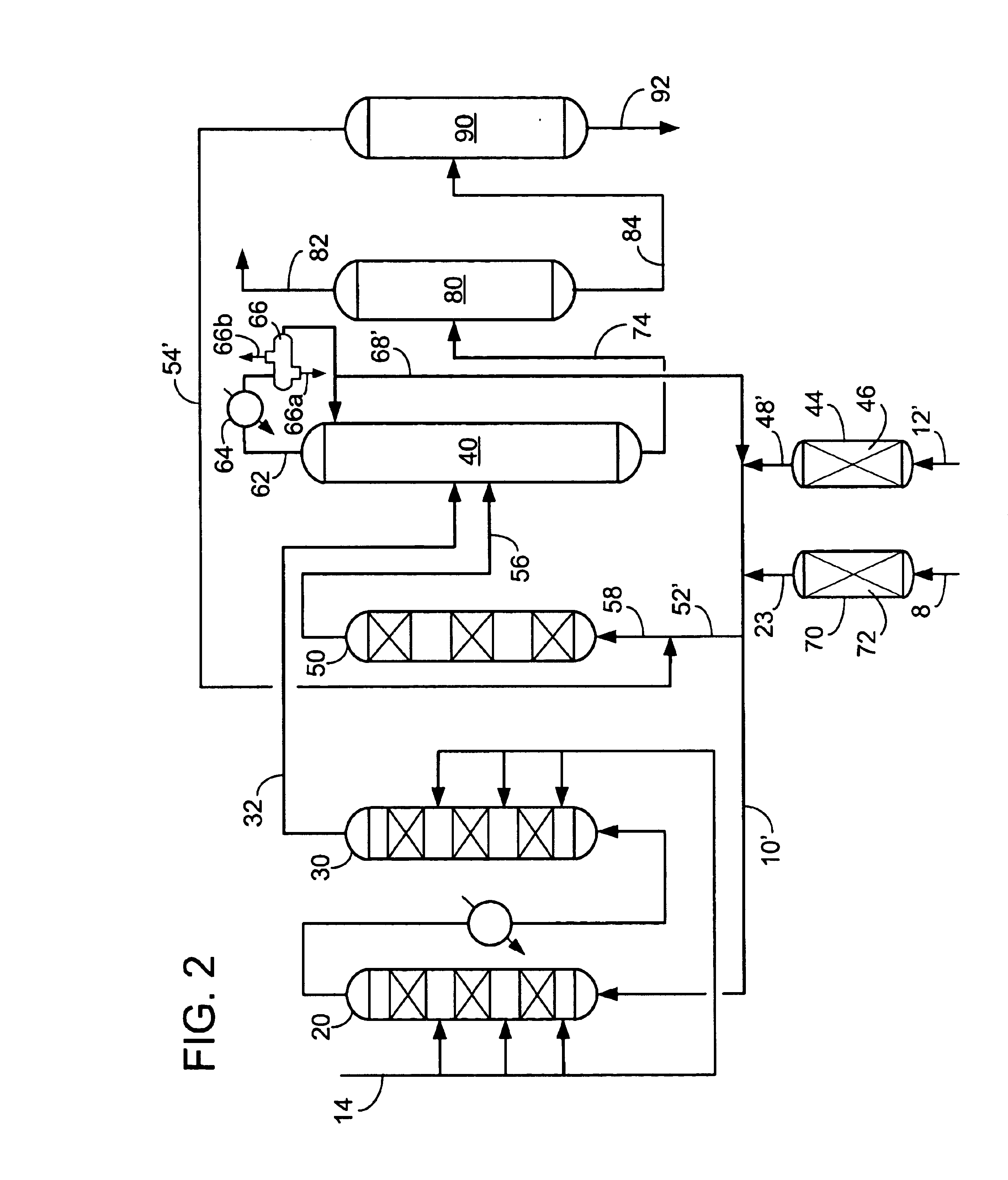
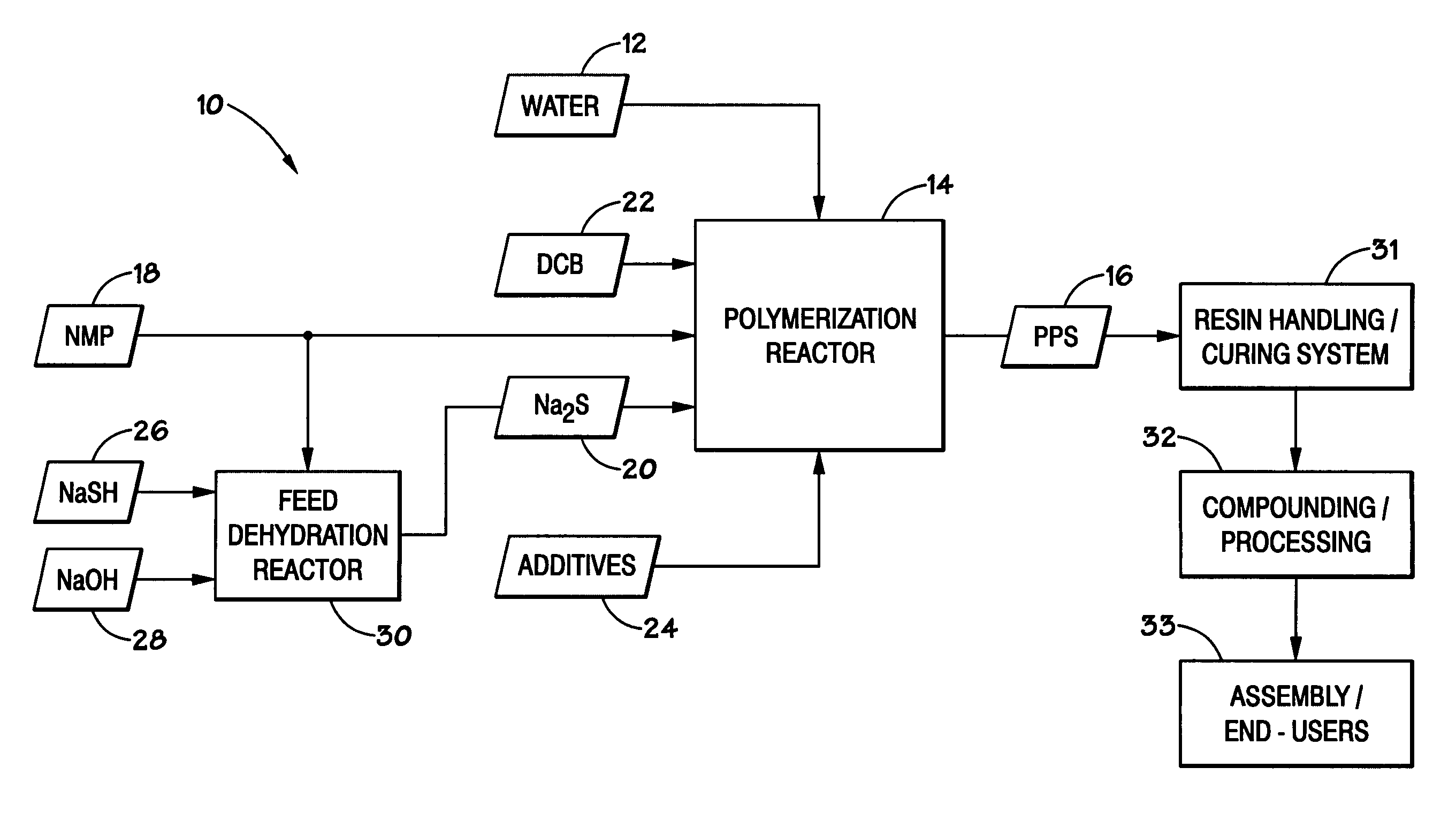
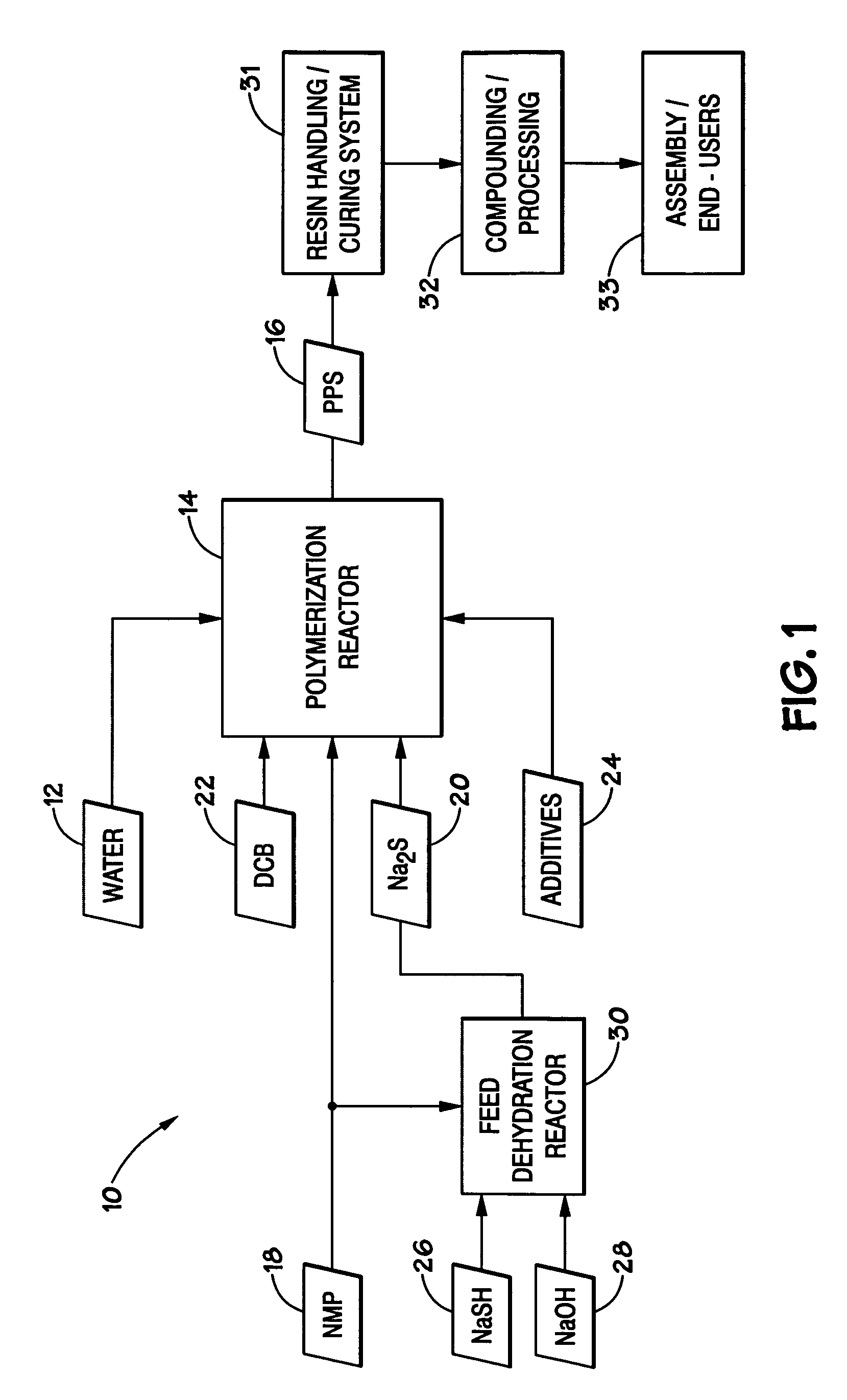
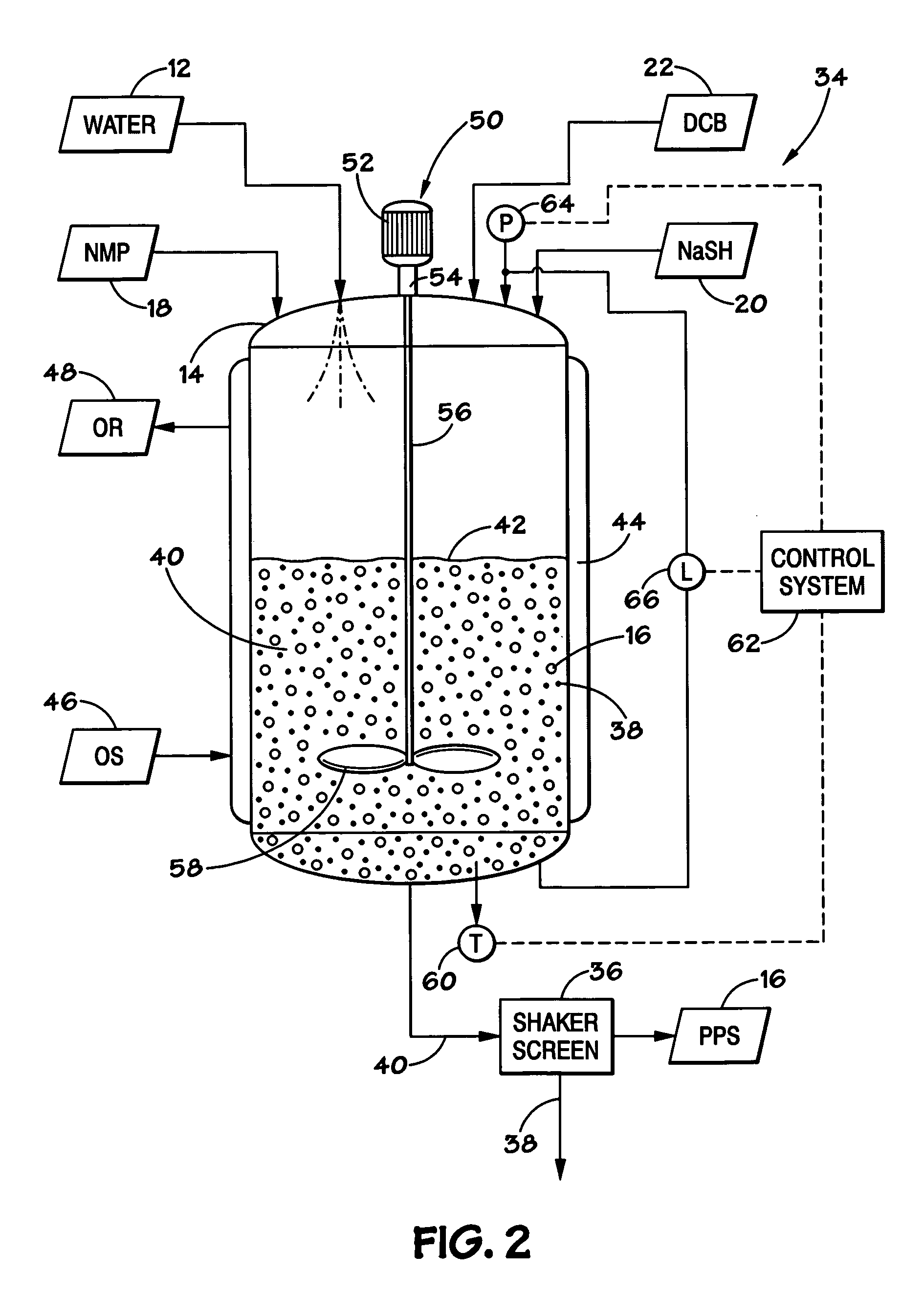
A method for producing polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) polymer, including polymerizing reactants in a reaction mixture in a vessel to form PPS polymer in the vessel, measuring values of operating variables of the vessel and / or PPS process, and determining the amount of quench fluid to add to the vessel based on the values of the operating variables. The technique may rely on the vapor liquid equilibrium (VLE) of the mixture to calculate the concentration of water existing in the reactor prior to quench, and accounts for the effectiveness of the upstream dehydration process and in the amount of water produced during the polymerization. The technique is a striking improvement over the trial-and-error estimation of the amount of quench water based on human operating experience, and avoids direct measurements of the existing water concentration in the reactor. The result is improved control of PPS particle size and other properties.
Owner:SOLVAY SA
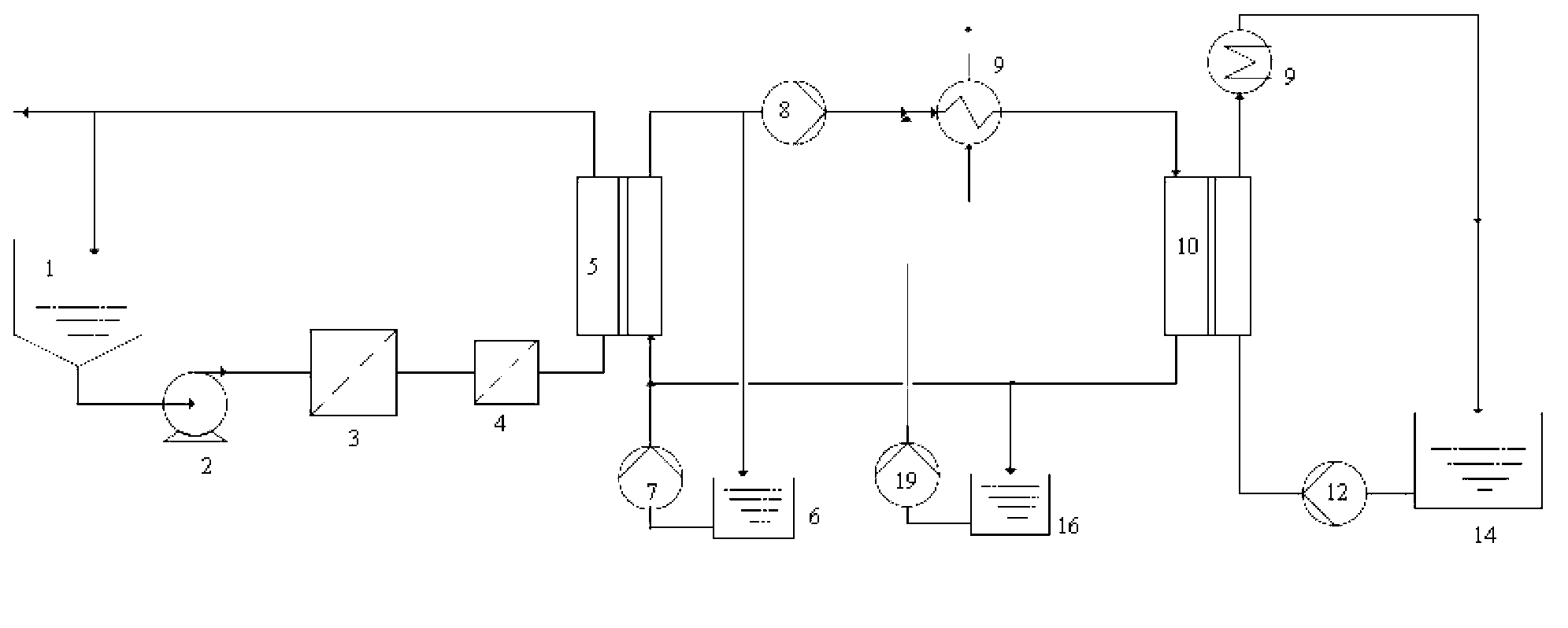
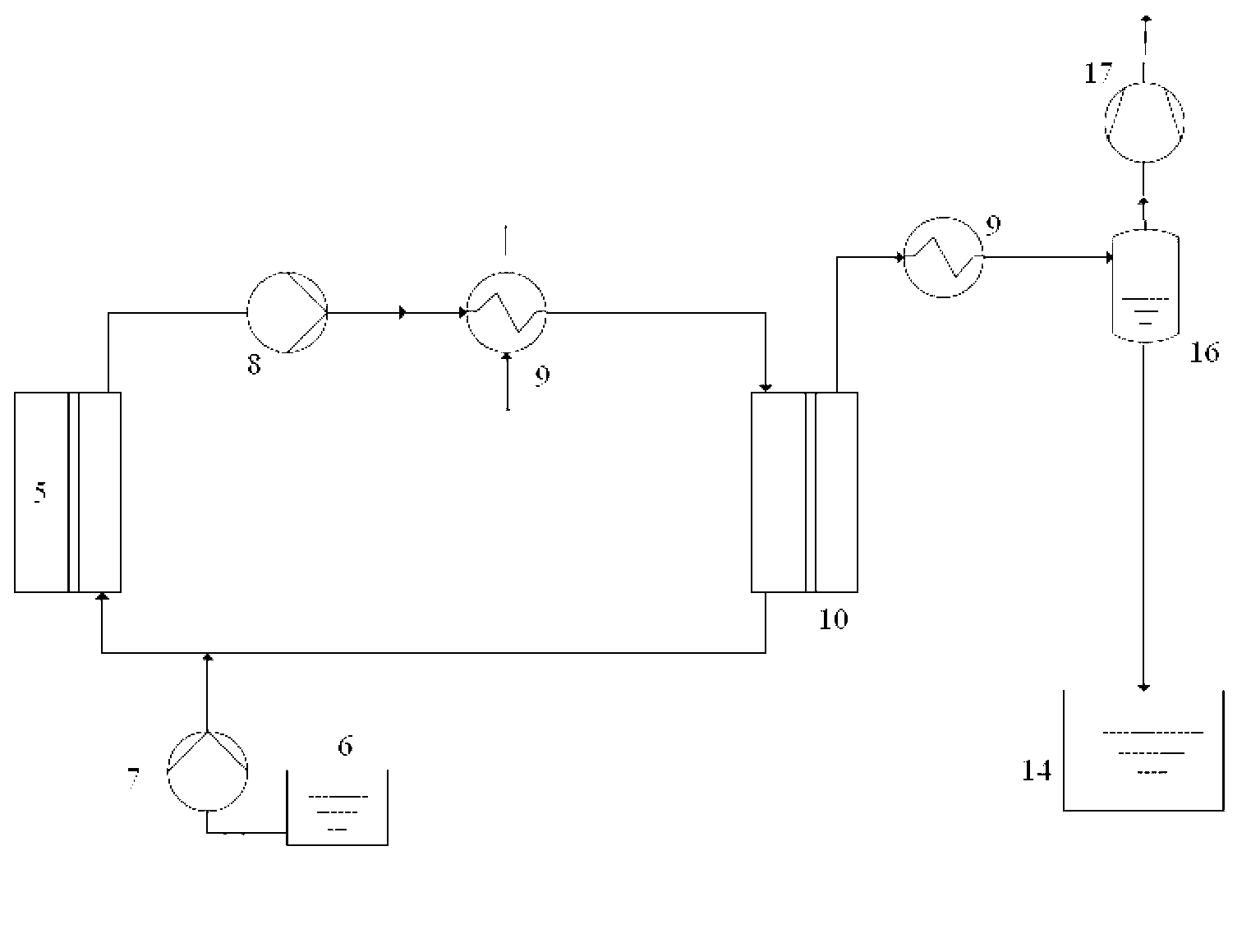
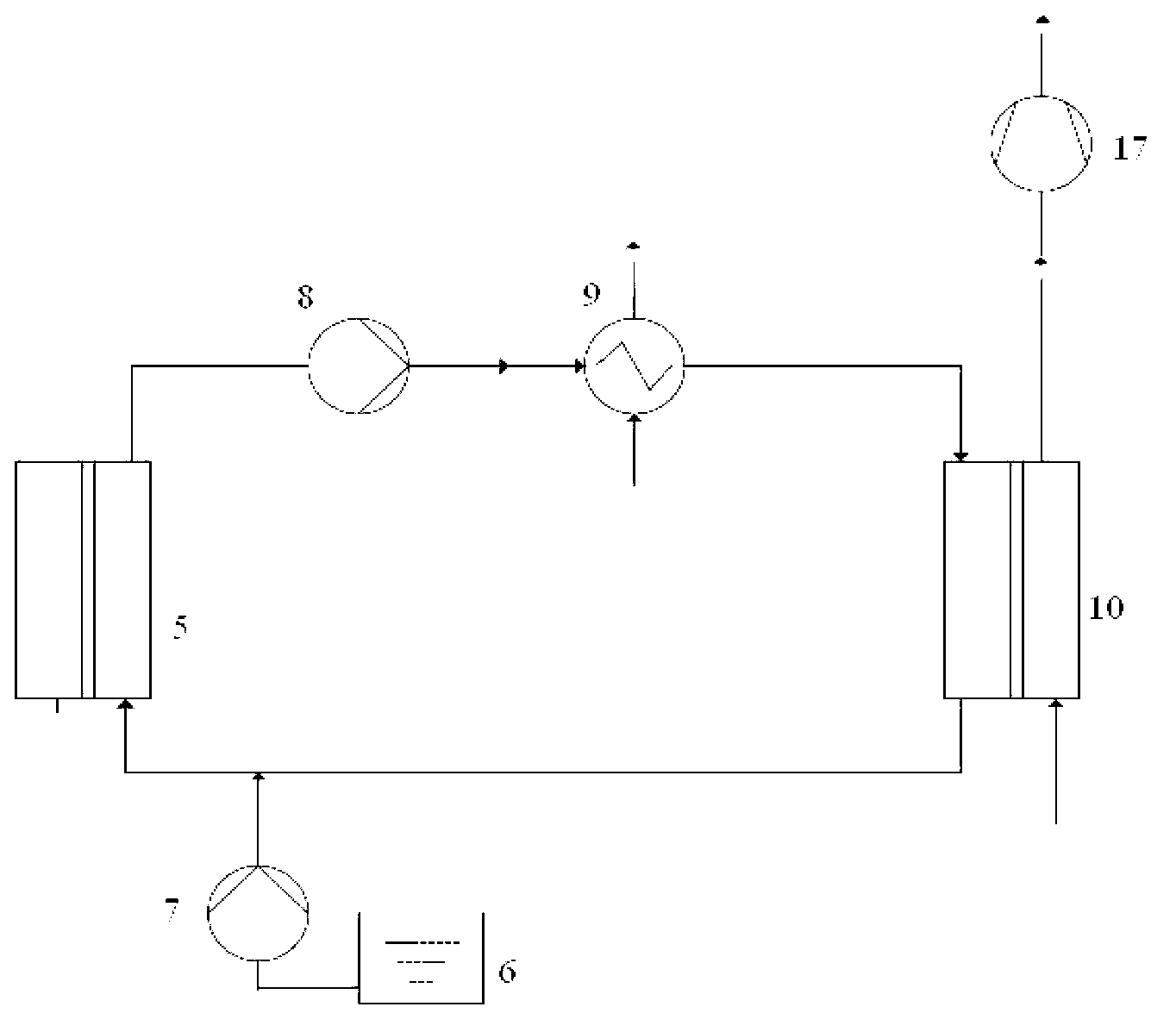
Waste water treatment method and device based on forward osmosis and membrane distillation
InactiveCN103073146AReduced operating temperature rangeLow costSemi-permeable membranesWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisSalt contentWater concentration
The invention belongs to the field of sewage treatment, and particularly relates to a waste water treatment method and device based on forward osmosis and membrane distillation. The waste water treatment method based on the forward osmosis and membrane distillation comprises a waste water concentration process and a drive liquid circulation process, wherein the waste water concentration process adopts a forward osmosis technology to concentrate waste water with high salt content and high chemical oxide demand (COD) concentration through drive liquid so as to obtain the concentrated waste water and diluted drive liquid; the drive liquid circulation process adopts a membrane distillation technology to dehydrate the diluted drive liquid so as to obtain the purified water and renewable drive liquid; and the renewable drive liquid is repeatedly used for the waste water concentration process so as to continuously concentrate the waste water. Due to the adoption of the method and device for treating the waste water with high salt content and high COD concentration, the waste water of different sources and fields can be treated, and the advantages such as wide applicability for waste water, stability in running and low treatment cost can be realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADVANCED RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Dehumidification process and apparatus using collodion membrane
InactiveUS6497749B2High gradientAvoid flowSemi-permeable membranesLighting and heating apparatusWater concentrationGlycerol
Owner:ARTHUR S KESTEN
Method and apparatus for performing qualitative and quantitative analysis of burn extent and severity using spatially structured illumination
Frequent monitoring of early-stage burns is necessary for deciding optimal treatment and management. Superficial-partial thickness and deep-partial thickness burns, while visually similar, differ dramatically in terms of clinical treatment and are known to progress in severity over time. The disclosed method uses spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) far noninvasively mapping quantitative changes in chromophore and optical properties that may be an indicative of burn wound severity. A controlled protocol of graded burn severity is developed and applied to 17 rats. SFDI data is acquired at multiple near-infrared wavelengths over a course of 3 h. Burn severity is verified using hematoxylin and eosin histology. Changes in water concentration (edema), deoxygenated hemoglobin concentration, and optical scattering (tissue denaturation) are statistically significant measures, which are used to differentiate superficial partial-thickness burns from deep-partial thickness burns.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dehydrogenation process with water and temperature control
ActiveUS7687676B1Long catalyst lifeLower inlet temperatureHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalytic naphtha reformingTemperature controlAlkane
The activity of a dehydrogenation catalyst is improved by increasing the water concentration maintained in the reactants toward the start of the catalyst's life, but after the catalyst has deactivated to the extent that the temperature required to maintain the conversion per pass of paraffinic hydrocarbon through the reaction zone increases by at least 2° C.
Owner:UOP LLC
Cultivation method of anammox granular sludge
ActiveCN103043788AAccelerated enrichment growthPromote formationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesWater concentrationNitrogen
The invention discloses a cultivation method of anammox granular sludge, and belongs to the field of water treatment. The cultivation method solves the technical problems that the existing high-efficiency anammox granular sludge is difficult to cultivate, and the cultivation time is long. The method comprises the following steps that 1, aerobic granular sludge and anammox seed sludge are simultaneously inoculated into an EGSB (expanded granular sludge bed) reactor; 2, nitrogenous simulated waste water is supplied to the EGSB reactor, the hydraulic retention time is kept for 12h, and concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in intake water are gradually increased until successful start when the synchronous removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen is above 80%; and 3, intake water concentrations of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen are kept stable, the hydraulic retention time is gradually shortened up to 2.6h when the synchronous removal rate of ammonia nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen is above 80%, and then the cultivation of the anammox granular sludge is completed. With the method, the reactor can be started successfully within about 20 days, and the high-efficiency anammox granular sludge can be obtained within about 89 days.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CIVIL ENG & ARCHITECTURE
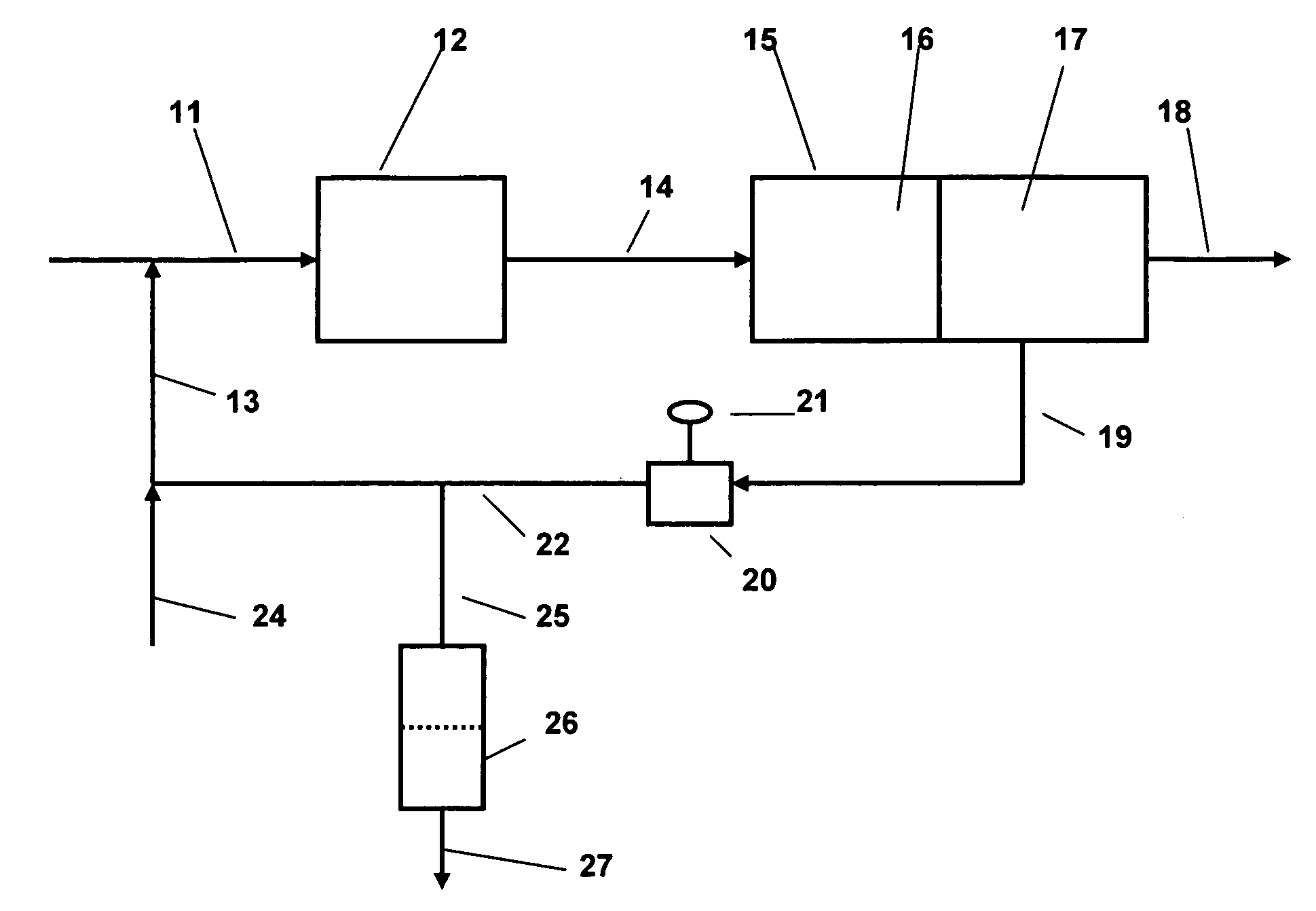
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20150025270A1Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
System and method for mixing water and non-aqueous materials using measured water concentration to control addition of ingredients
ActiveUS7284898B2Eliminates and at least minimizes drawbackReduce stepsControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFlow mixersAdditive ingredientWater concentration
The present invention is directed to a system and method for mixing a fluid comprising water and at least one non-aqueous material. The system comprises a mixing tub and mixing head adapted to inject the fluid into the mixing tub. It also includes a plurality of lines connected to the mixing head that supply the mixing head with water and the at least one non-aqueous material and a recirculation circuit that delivers the fluid from the mixing tub back to the mixing head. The system further includes a sensor connected to the recirculation circuit that measures the concentration of water in the fluid. An automatic controller uses the concentration measurement data to control the amount of each of the ingredients injected into the mixing tub.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
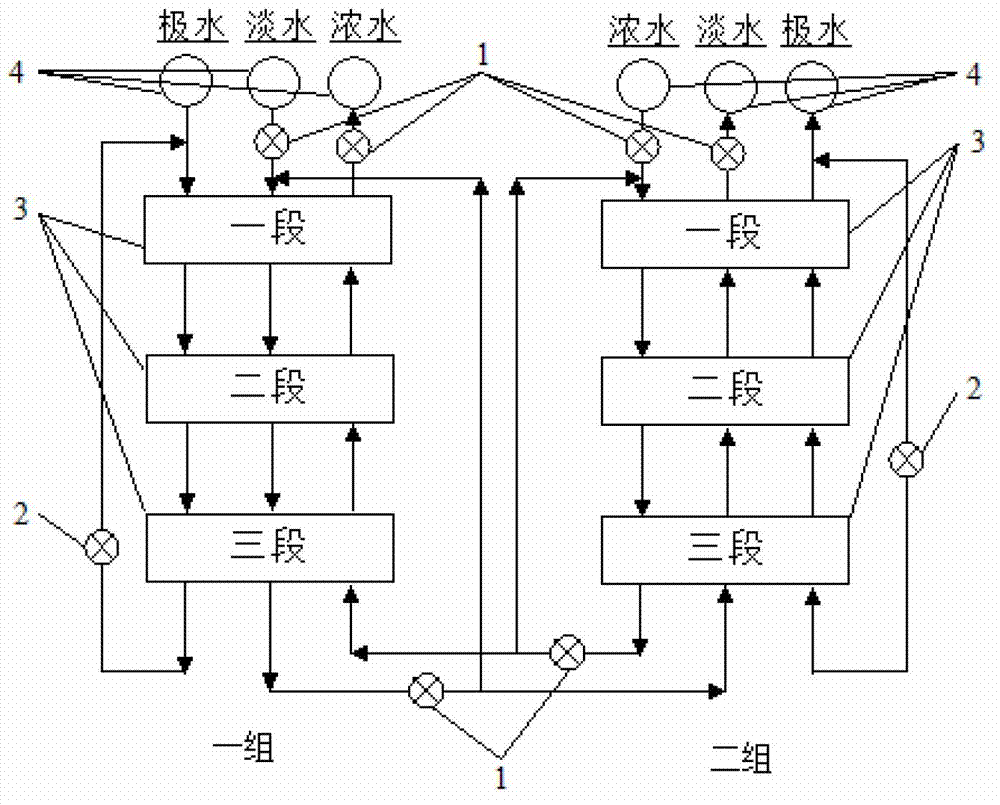
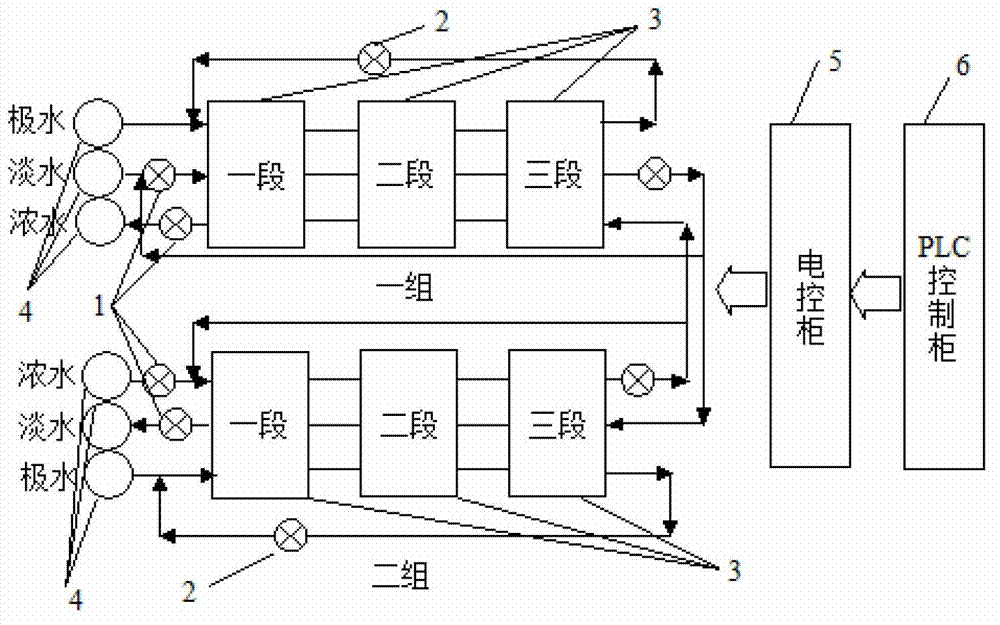
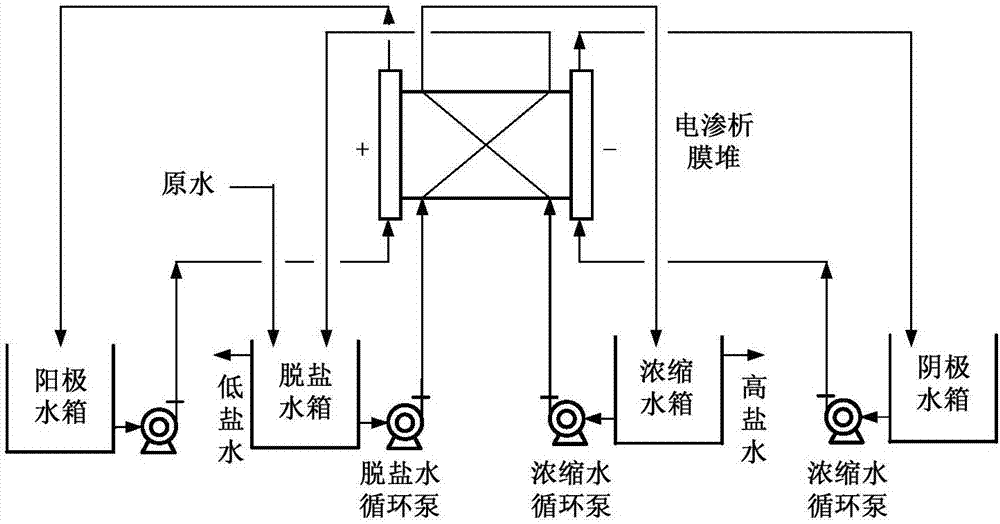
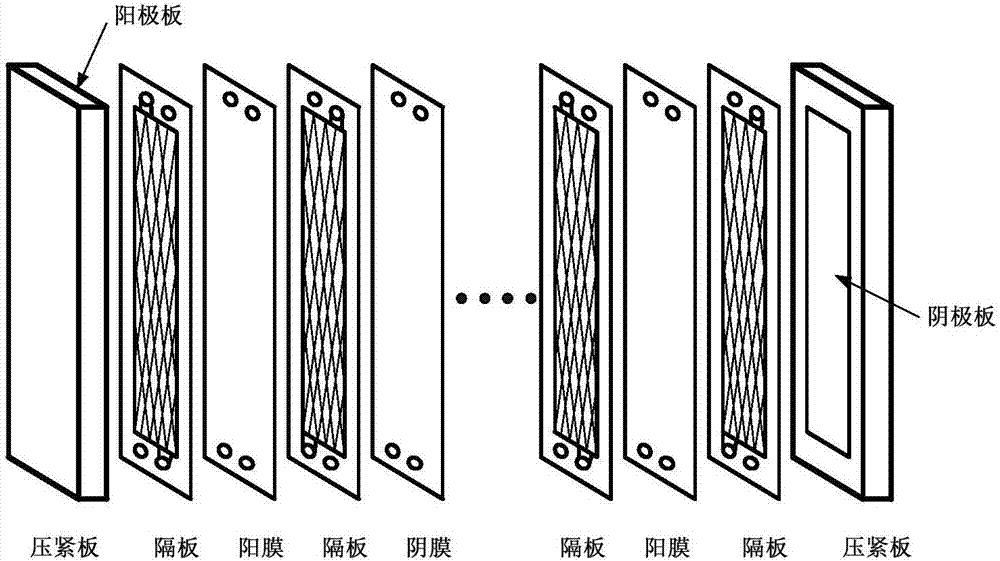
Electrodialysis device applicable to treatment on high-salinity wastewater from industries such as coal chemical industry
InactiveCN102963966AOvercome recoveryOvercoming the low concentration ratio of concentrated waterGeneral water supply conservationDispersed particle separationUltrafiltrationHigh energy
The invention relates to an electrodialysis device applicable to treatment on high-salinity wastewater from industries such as coal chemical industry. The electrodialysis device comprises an electrodialysis membrane stack unit, a frequent polarity conversion control unit and an online monitoring and process control unit, wherein the electrodialysis membrane stack unit consists of a plurality of membrane stacks which are connected with one another in series through pipelines in a desalted department, a concentrated department and a pole compartment respectively and form a multi-level inversion system with solution flow direction control; a programmable logic controller (PLC) unit, a rectifier and a solenoid valve are used for implementing frequent polarity conversion; and solutions in the desalted department and the concentrated department can be cycled or partially cycled, thereby obtaining a high fresh water recovery rate and a high concentrated water concentration multiple. The electrodialysis device can fundamentally solve the problems of low fresh water recovery rate, low concentrated water concentration multiple, high energy consumption and difficulty in long-term and stable operation in the process of treating the high-salinity wastewater in the coal chemical industry and the like by an ultrafiltration-reverse osmosis method, and thus the engineering application of the electrodialysis treatment technology for the high-salinity wastewater in the industries such as the coal chemical industry is promoted.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
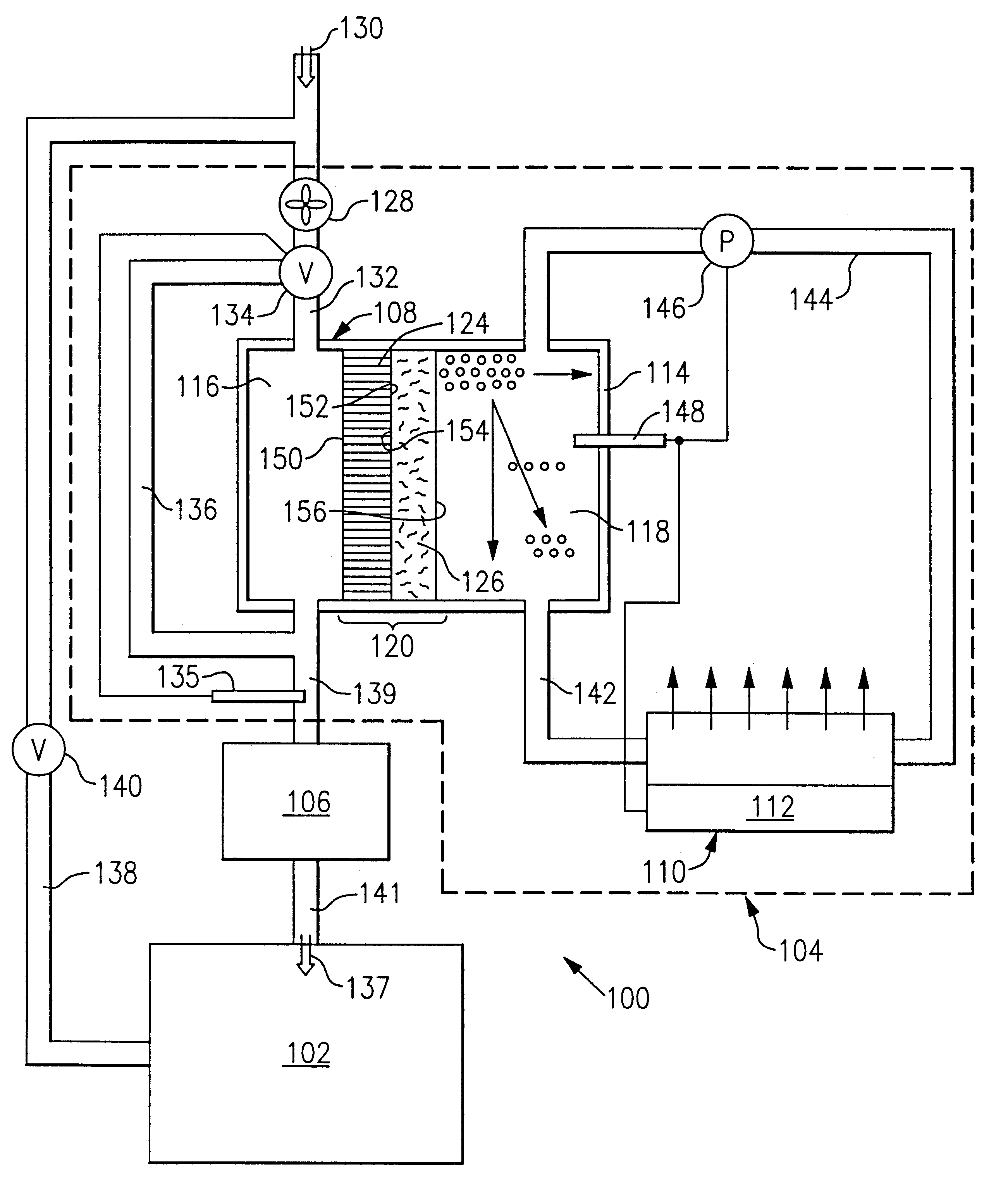
Dehumidification process and apparatus
InactiveUS20020139127A1Inhibit microbial growthHigh gradientDispersed particle separationCompression machines with cascade operationWater concentrationMembrane configuration
A humid gas stream is dehumidified by bringing that stream into contact with the front surface of a hydrophilic capillary condenser layer that captures the water and moves it adjacent the rear surface of the capillary layer. An osmotic layer, such as a semi-permeable membrane, is disposed on the rear surface of the condenser layer, and an osmotic fluid having a low concentration of water therein, is disposed adjacent the osmotic layer. An osmotic driving force, resulting from the water concentration gradient across the osmotic layer, transports the condensed water from the condensing layer through the thickness of the osmotic layer and into an osmotic fluid. The osmotic layer also inhibits the osmotic fluid from flowing into the condenser layer.
Owner:ARTHUR S KESTEN
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS9382186B1Stay focusedPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionAcetic acidWater concentration
A process for producing acetic acid is disclosed in which the water concentration is controlled in the side stream between two columns. Controlling the water concentration by the liquid light phase recycle controls the hydrogen iodide concentration in the side stream to be less than or equal to 50 wppm.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Separation of water from hydrocarbons
A method for the removal of dissolved water or water and ice from hydrocarbon liquids such as petroleum refinery fuels or natural gas liquids in a manner which enables the fuels to be readily treated by the coalescence / separation technique while reducing the potential for plugging filters and other equipment with ice crystals. Free water or water / ice is removed from the liquid hydrocarbons by contacting the hydrocarbon feed with a treating agent which as an affinity for water prior to subjecting the mixture to coalescence / separation. The treating agent is preferably a co-solvent for the water and the hydrocarbon such as an alcohol e.g. methanol. The treating agent and water are separated from the hydrocarbon component during the coalescence / separation and recirculated to the feed with the composition of the recycle aqueous phase being controlled to achieve the desired level of water removal to meet relevant product specifications. Consistent with the removal of the water during the coalescence / separation, the water concentration of the recycle loop containing the co-solvent / water blend gradually increases with removal of the water from the feed. This progressive increase in water level can be compensated by controlled addition of pure co-solvent to the recycle coupled with continuous or periodic dumping of excess mixture. Alternatively, the circulating mixture may be subjected to continuous or batch regeneration or disposed of in any other way which is convenient and economical.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Rake-free thickener with rotary annular channels
ActiveCN105944407AEnsure stabilityImprove settlement performanceSedimentation regulating devicesSettling tanks feed/dischargeWater concentrationEngineering
The invention relates to the field of slime water concentration and clarification, in particular to a rake-free thickener with rotary annular channels. The rake-free thickener at least comprises a thickener body, and further comprises rotary annular channels, wherein the rotary annular channels are used for constraining upper-layer ore pulp inside the thickener to do reciprocatory motion; the rotary annular channels consist of a plurality groups of annular channels of which the diameters are increased gradually; adjacent annular channels are mutually communicated through connecting channels; each group of the annular channels comprises an upper annular partitioning plate and a lower inclined settlement plate; overflowing ore pulp is discharged out from overflow weirs; the overflow weirs comprise annular overflow weirs and composite overflow weirs; settled granules are fed into a bottom flow discharge system; the bottom flow discharge system consist of bottom flow collecting cabins, bottom flow holes and corresponding bottom flow pumps; the rake-free thickener further comprises a feeding pipeline and a driving stirring mechanism; a stirring machine is driven by residual power of the feeding pipeline conveying the ore pulp to rotate so as to uniformly mix the ore pulp with medicines. The rake-free thickener has the characteristics of being low in energy consumption, low in repairing workload, low in medicine consumption and free of rake.
Owner:ANHUI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
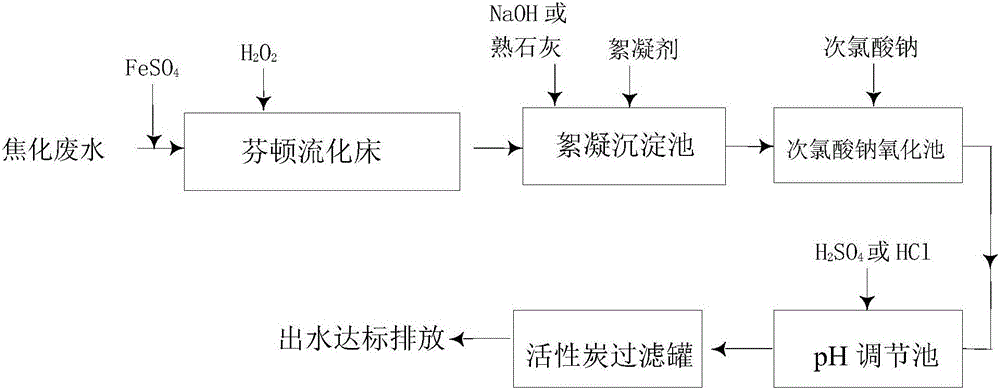
Method and system for deeply treating coking wastewater to decarbonize, decolor and remove cyanide
ActiveCN106745961AGood effectImprove reaction efficiencyWater treatment compoundsWater contaminantsActivated carbon filtrationWater quality
The invention provides a method and system for deeply treating coking wastewater to decarbonize, decolor and remove cyanide. The method comprises the following steps: 1) introducing the coking wastewater into a Fenton fluidized bed, and adding a mixed solution of ferrous sulfate, sulfuric acid and water into a solution; 2) adding hydrogen peroxide into the solution of the Fenton fluidized bed and sufficiently reacting; 3) leading out a reaction solution in the Fenton fluidized bed, adjusting the pH (Potential of Hydrogen) value of the reaction solution, adding a flocculating agent, and after precipitating, taking supernatant; 4) mixing the supernatant with sodium hypochlorite, and carrying out an oxidization reaction; and 5) adjusting the pH of the reaction solution, and carrying out adsorption treatment by active carbon to obtain a deeply treated water body. According to the method and the system, the Fenton fluidized bed, flocculation and sedimentation, sodium hypochlorite oxidization, and active carbon filtering and adsorption are effectively combined; the Fenton fluidized bed and the flocculation and sedimentation are carried out, residual cyanide in output water mainly exists in a CN<-> form, the oxidization efficiency of the sodium hypochlorite is higher, and the cyanide can be removed; and the adsorption effect of the active carbon is combined, so that the water concentration of the output water is lower.
Owner:CISDI ENG CO LTD
Preparation method for graphene-based film and application of graphene-based film to oil-water separation
ActiveCN103768960AEasy to prepareSimple manufacturing methodSemi-permeable membranesLiquid separationPolymer scienceWater concentration
The invention relates to a preparation method for a graphene-based film and application of the graphene-based film to oil-water separation. The graphene-based film is obtained by preparing gel from oxidized graphene and a crosslinking agent, drying the gel, compacting the gel under the pressure of 10-200 kPa, and reducing. The preparation method for the graphene-based oil-water separation film is simple, feasible and low in cost and can be applied to batch industrial production; the film is light in mass and stable and can be cyclically used at high efficiency; the graphene-based oil-water separation film material can separate oil from an oil-water mixture at high efficiency, low energy consumption and ultrahigh speed in various environments, the water content is lower than 200ppm, the minimum water concentration is up to 10ppm, and the water concentration is different slightly according to different oil phases.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Monolayer films of semiconducting metal dichalcogenides, methods of making same, and uses of same
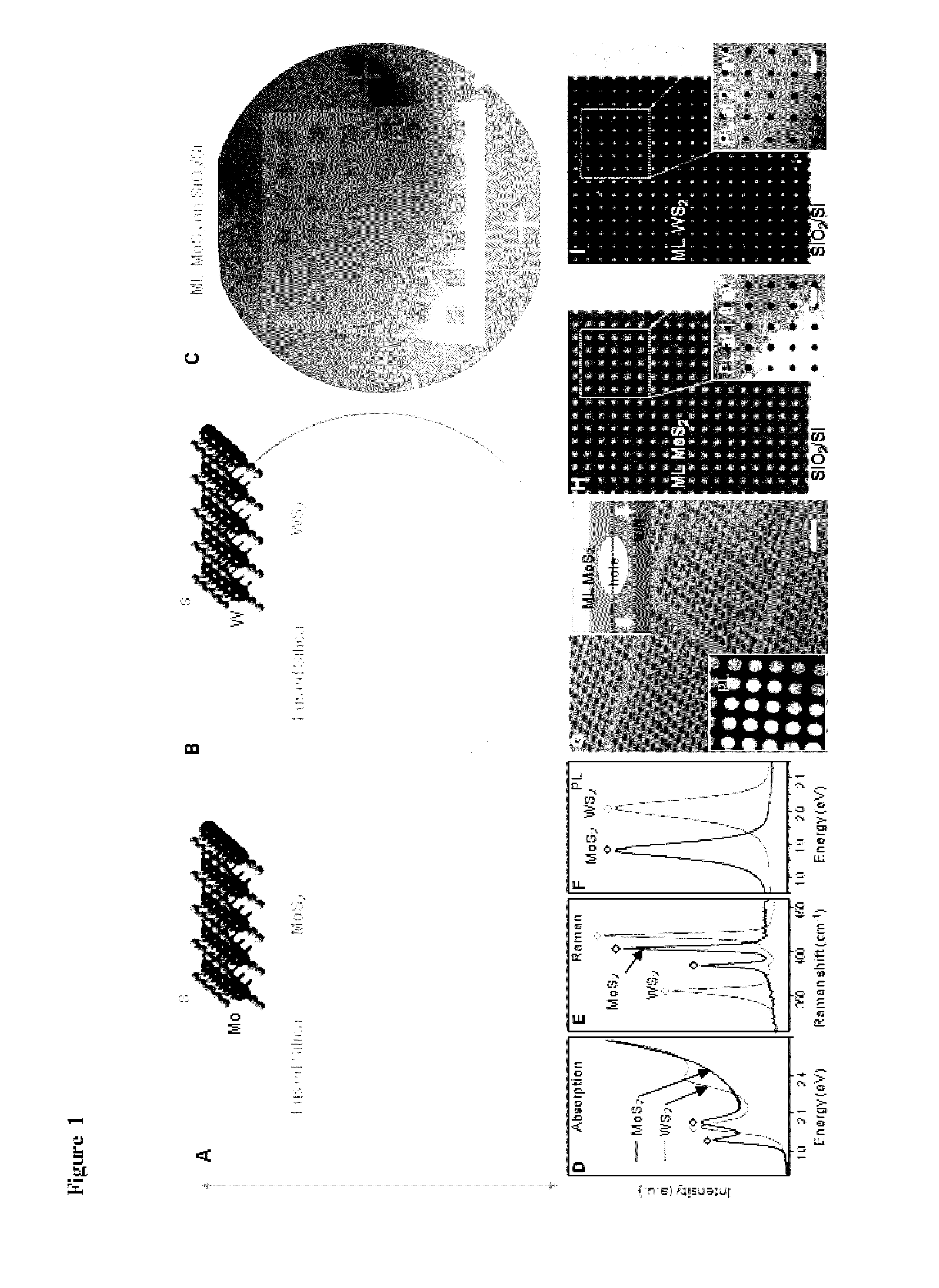
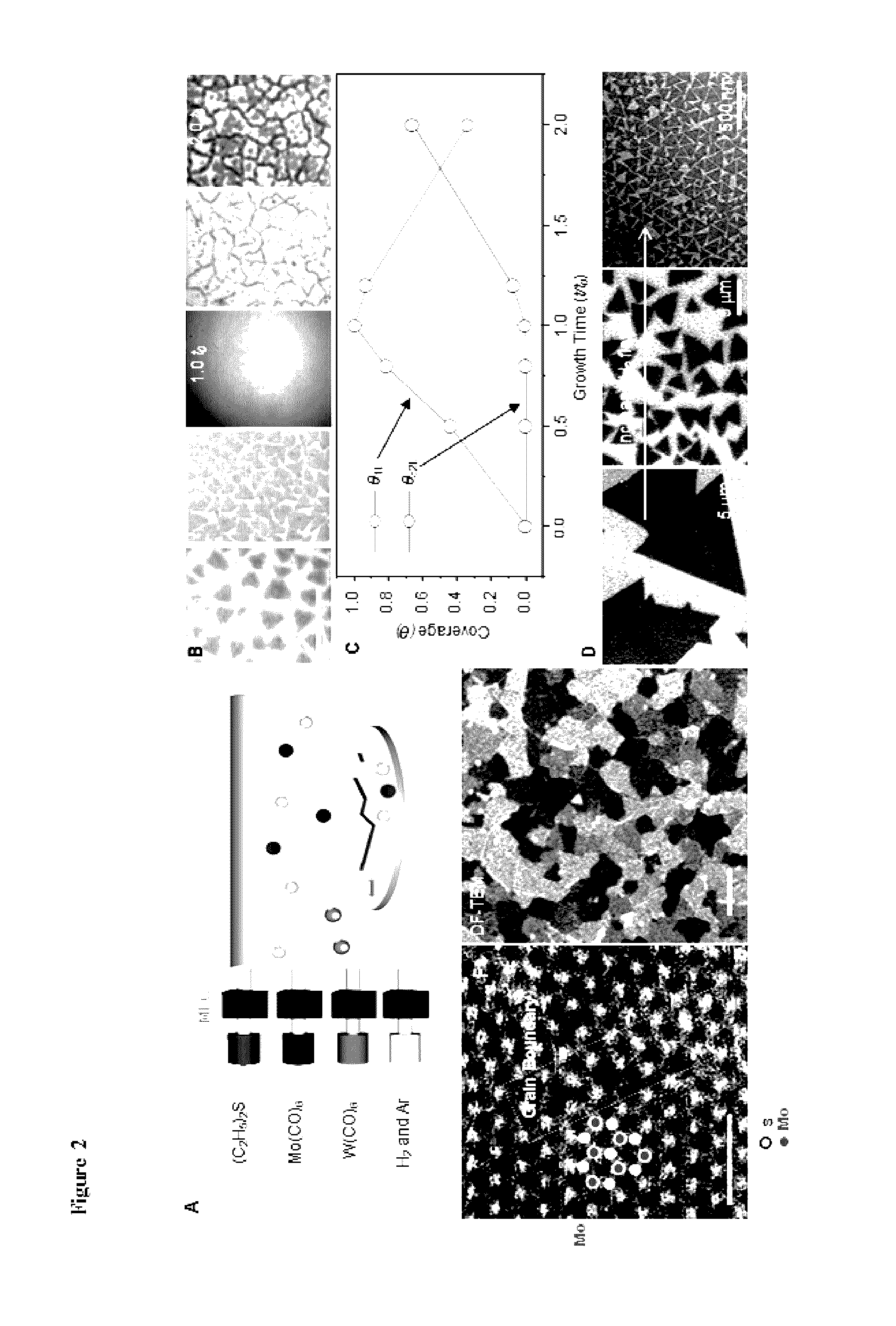
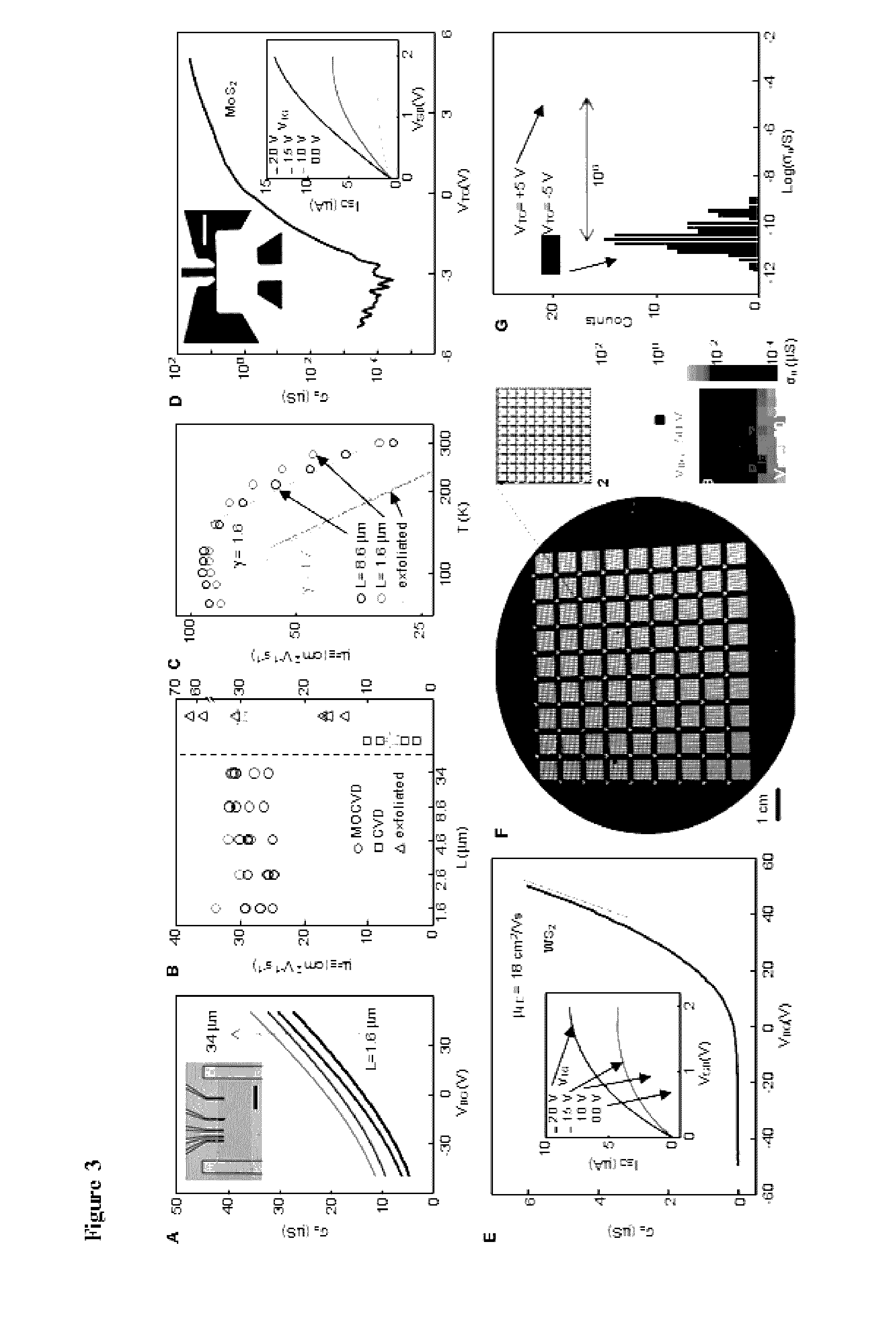
ActiveUS20160308006A1High carrier mobilityFunction increaseTransistorPolycrystalline material growthWater concentrationSulfur
Metal-chalcogenide films disposed on a substrate comprising at least one monolayer (e.g., 1 to 10 monolayers) of a metal-chalcogenide. The films can be continuous (e.g., structurally and / or electrically continuous) over 80% or greater of the substrate that is covered by the film. The films can be made by methods based on low metal precursor concentration relative to the concentration of chalcogenide precursor. The methods can be carried out at low water concentration. The films can be used in devices (e.g., electrical devices and electronic devices).
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Process for separating 2-butanol from tert-butanol/water mixtures
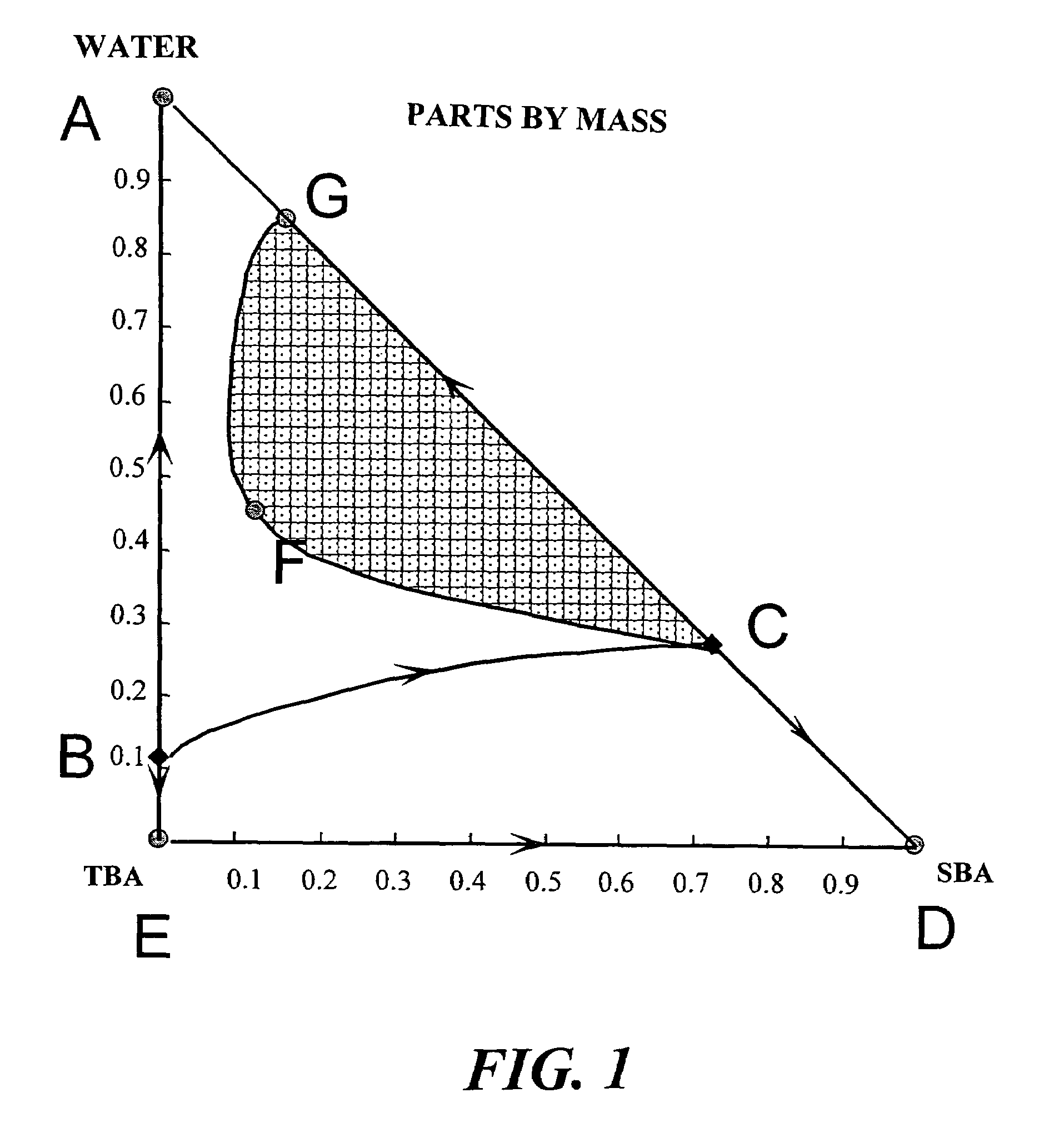
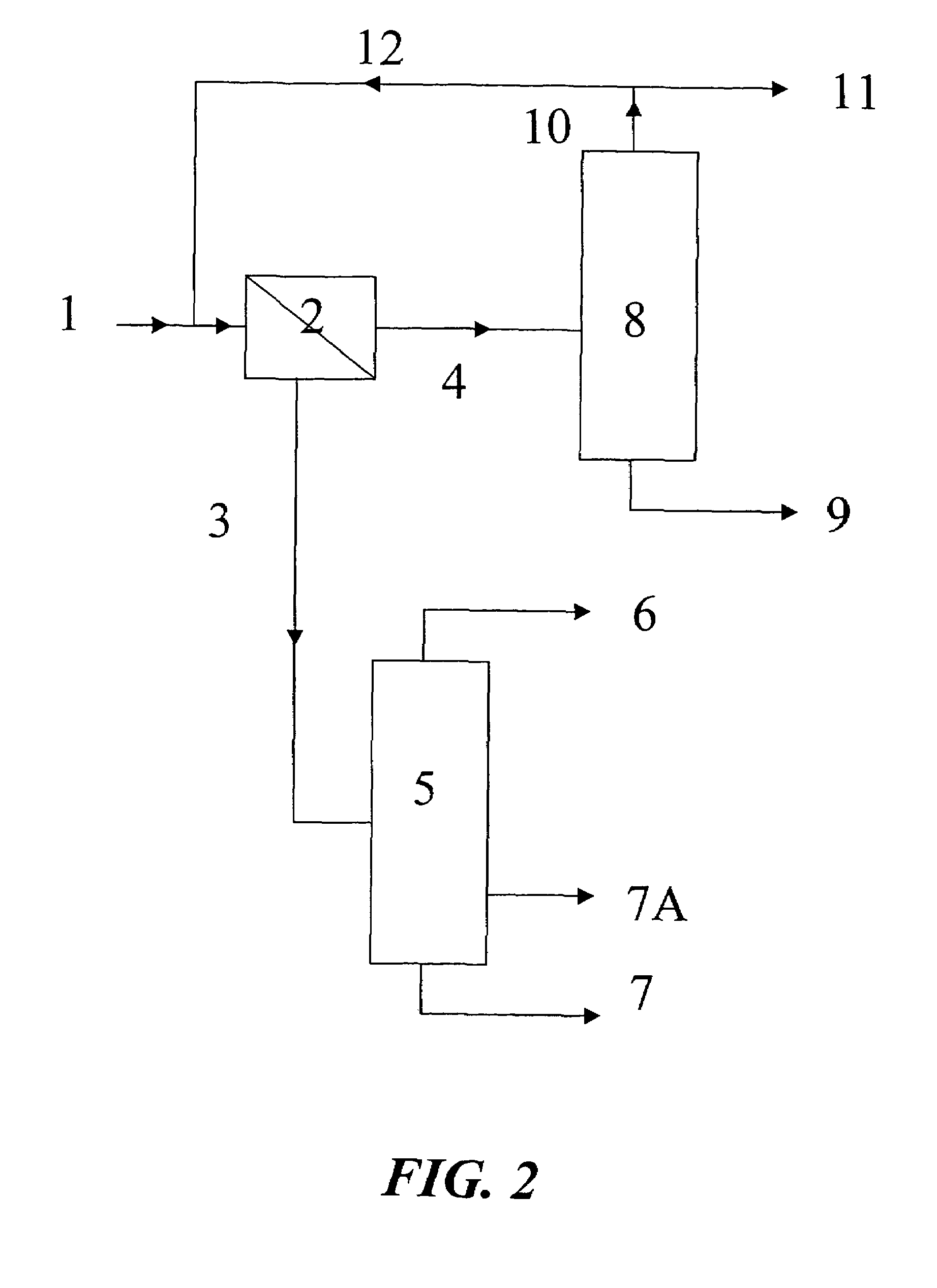
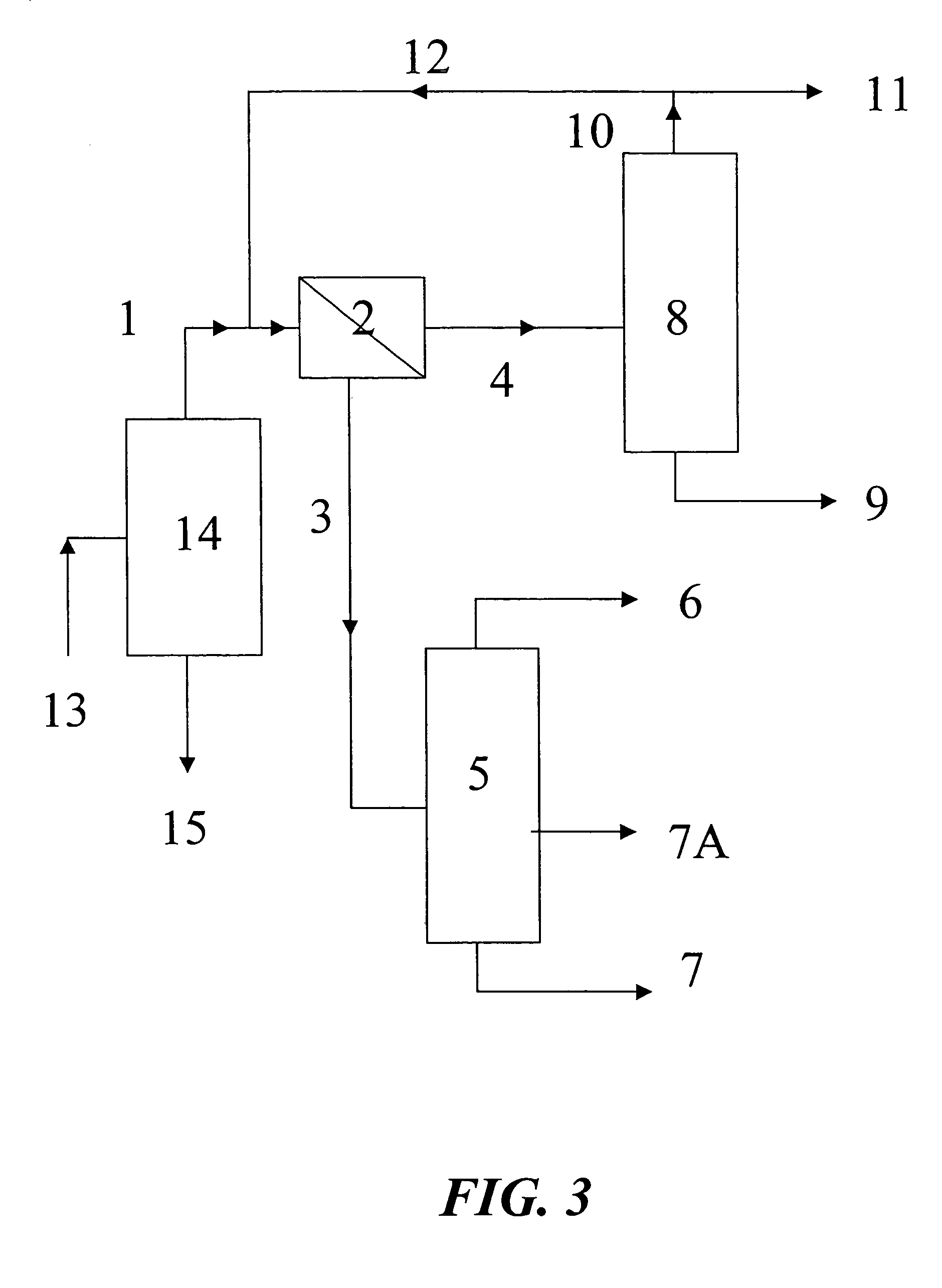
The present invention relates to a process for separating 2-butanol from tert-butanol / water mixtures using a membrane to reduce a water concentration to less than the limit concentration of the distillation boundary line connecting the two azeotropes TBA / water and SBA / water and is subsequently worked up by distillation.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for manufacturing nonaqueous secondary battery electrode
ActiveUS20110239446A1Low input-output resistanceImprove input and output performanceFinal product manufacturePrimary cellsInorganic particleOrganic solvent
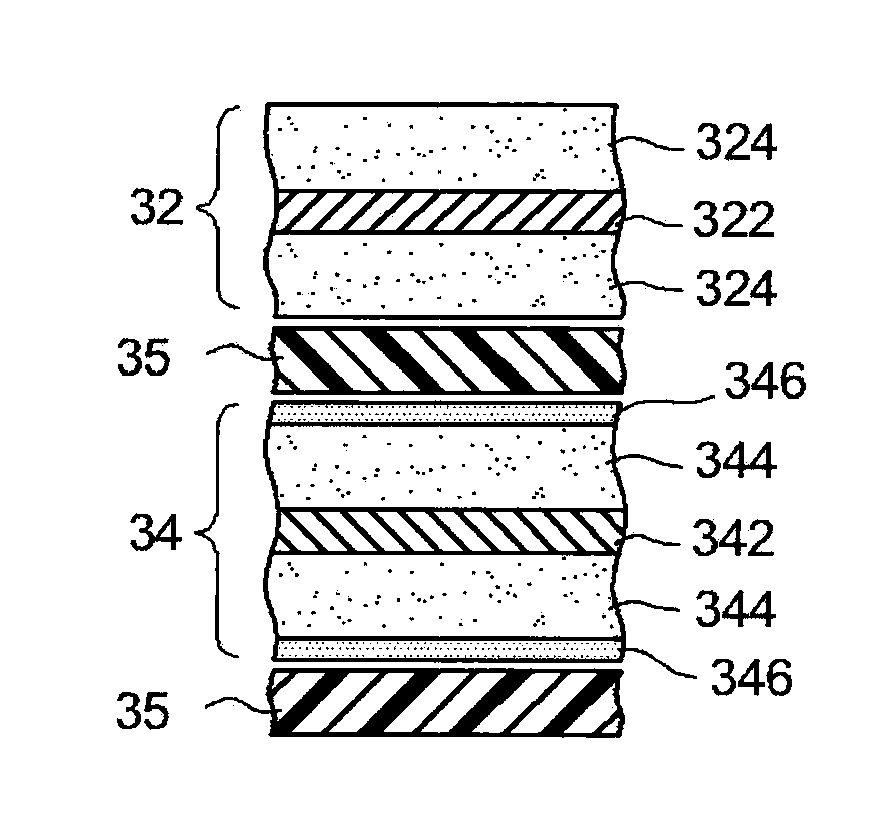
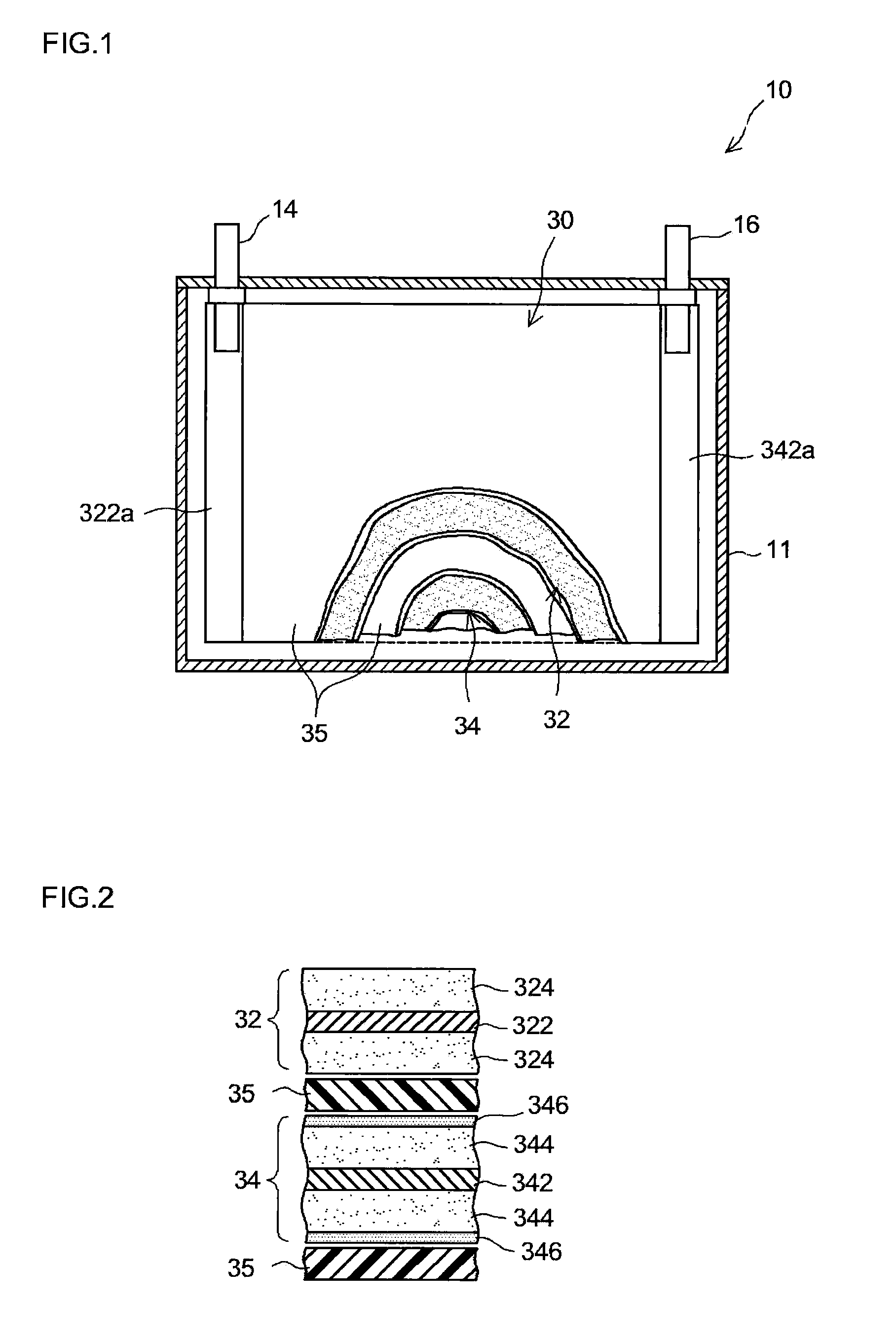
A method is provided for manufacturing an electrode that has a porous inorganic layer on the surface of an active material layer and is suitable for constructing a nonaqueous secondary battery with excellent input-output performance. In this manufacturing method, an electrode perform, which has an active material layer (344) consisting primarily of active material particles (42) and supported on a collector (342), is prepared. The water concentration of at least the surface (344a) of the active material layer (344) is adjusted to 100 ppm to 500 ppm. A slurry (S) containing inorganic particles (44), a binder and an organic solvent is coated on the surface (344a) of the active material layer with the water concentration thus adjusted, to form a porous inorganic layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Method for production of acrylic acid
InactiveUS7038079B2Improve productivityEasy to operateOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAbsorption columnWater concentration
A method is disclosed which produces acrylic acid in a high yield as maintaining the conditions for purifying acrylic acid in constant ranges and preventing the acrylic acid from polymerization. By using a reactor which has first reaction zone and second reaction zone formed of different reaction tubes, propylene concentration adjusting in the range of 7–15 vol. % and water concentration adjusting in the range of 0–10 vol. % are introduced thereto thereby obtaining an acrylic acid-containing gas. Then the gas is introduced to an acrylic acid absorption column to adjust water concentration in the range of 1–45 wt. %, thereby preventing from polymerization.
Owner:NIPPON SHOKUBAI CO LTD
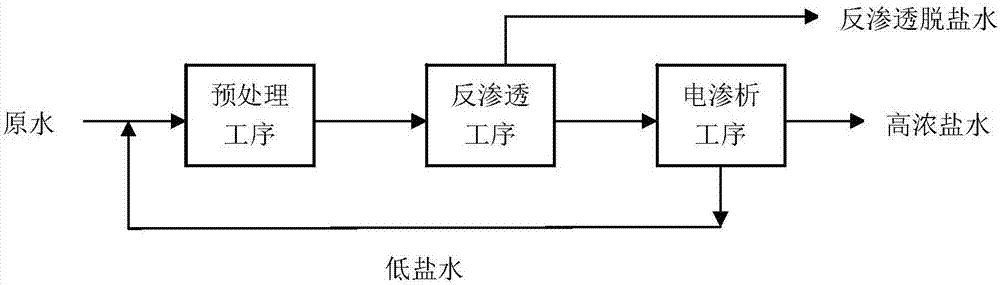
High-hardness salt-containing water concentration method based on monovalent cationic selective electrodialysis
ActiveCN107055713AHigh desalination rateAchieve separationGeneral water supply conservationDispersed particle separationPermeationPrecipitation
The invention discloses a high-hardness salt-containing water concentration method based on monovalent cationic selective electrodialysis. The method comprises the following steps: 1, performing chemical precipitation hardness removal and pretreatment on raw water; 2, performing reverse osmosis desalination treatment; and 3, regulating the pH value of reverse osmosis concentrated saltwater with hydrochloric acid or sulfuric acid to be 4-6 so as to serve as raw electrodialysis water, and enabling the water to respectively enter a desalting chamber and a concentration chamber formed by an anode membrane and a cathode membrane at an interval in an electrodialysis membrane stack, thereby obtaining high-salt electrodialysis water and low-salt electrodialysis water. According to the method disclosed by the invention, extra equipment and devices are not needed, and two ions forming a scale forming matter are separated under the condition that the recovery rate is not changed, so that a scaling phenomenon caused by simultaneous interception or simultaneous permeation is avoided.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
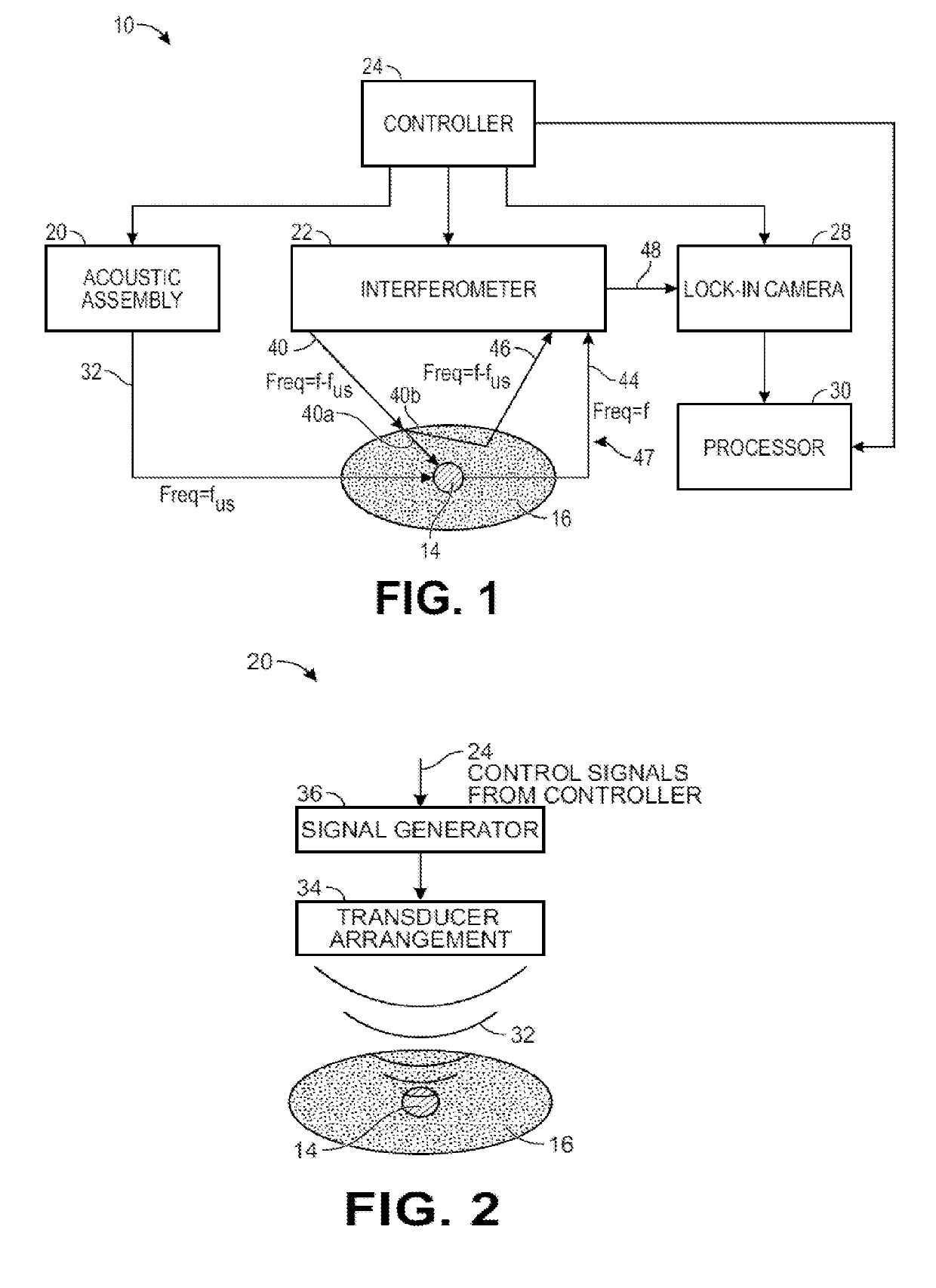
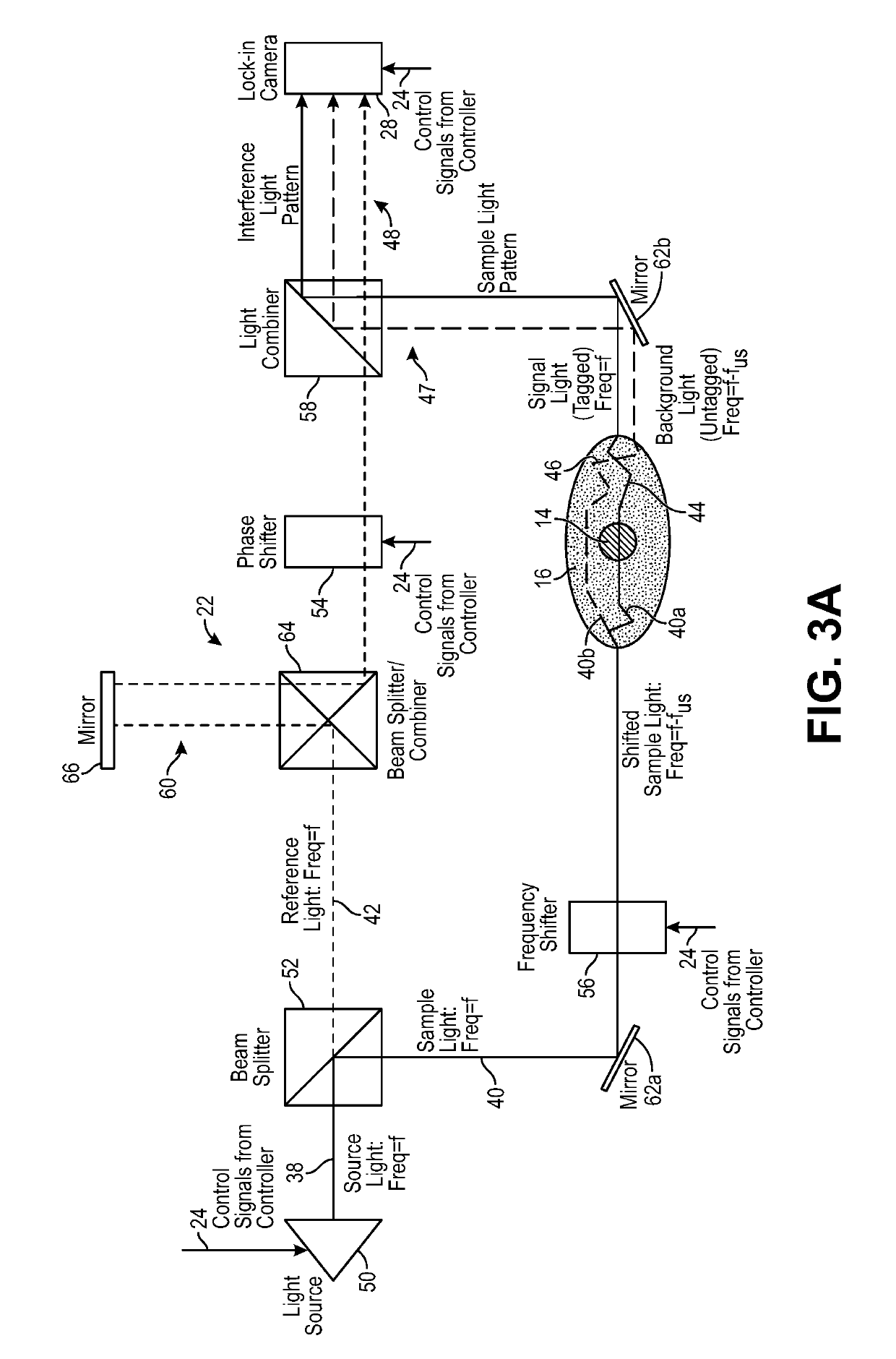
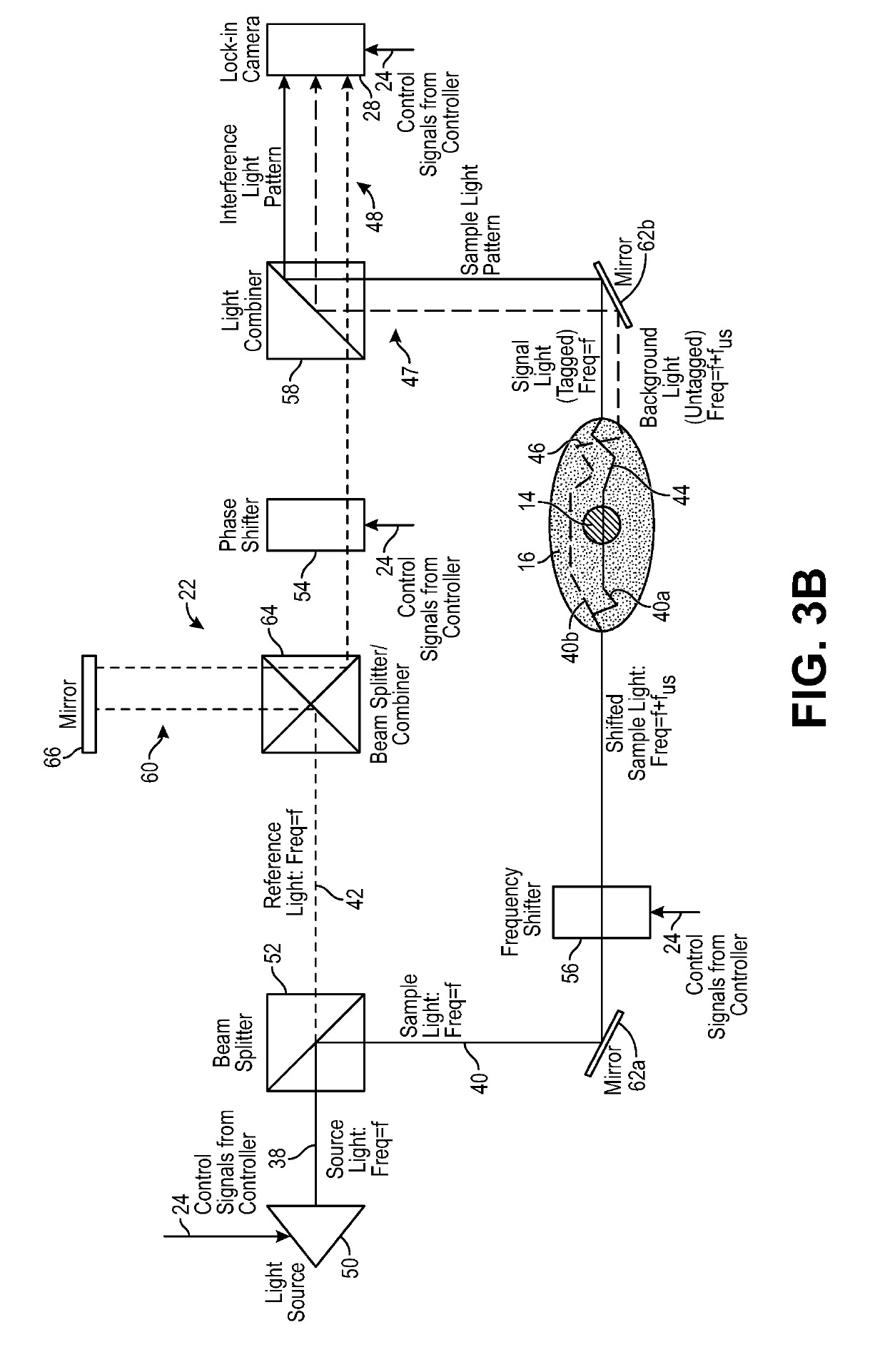
Optical detection system for determining neural activity in brain based on water concentration
ActiveUS20190150745A1Improved Axial ResolutionReduce signal to noise ratioMedical imagingMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAnatomical structuresVoxel
A non-invasive system and method. Sample light is delivered into an anatomical structure, such that a portion of the sample light passes through a target voxel comprising brain matter in the head and is scattered by the head as signal light. The signal light is detected, changes in the level of water concentration or relative water concentration of the target voxel are detected based on the detected signal light, and a level of neural activity is determined within the target voxel based on the determined changes level of the water concentration or relative water concentration of the target voxel.
Owner:HI LLC
Reconstructed tobacco leaves containing basic incense substances in tobaccos prepared by water extraction method and ethanol extraction method and cigarettes produced by reconstructed tobacco leaves
ActiveCN103462205AReduce pollutionReduce drynessTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentWater concentrationFiltration
The invention relates to reconstructed tobacco leaves containing basic incense substances in tobaccos prepared by a water extraction method and an ethanol extraction method. 40kg of waste and second-rate tobacco powders are added with 320L of water and are stirred and extracted for 2h at 60 DEG C. The extraction is carried out for twice. After filtration, the extraction liquid is concentrated to the density of 1.2g / mL. The concentration liquid is reserved. 10kg of waste and second-rate tobacco powders are extracted by 70L 60% of ethanol at 70 DEG C for 1.5h. The extraction is carried out for twice. The extraction liquid is concentrated to the density of 1.2g / mL. 10000g of water concentration liquid and 500g of ethanol concentration liquid are mixed uniformly and added to 10kg of reconstructed tobacco leaves. According to the reconstructed tobacco leaves, used tobacco raw materials are wastes including small-grain tobacco powders, tobacco ashes or tobacco stems and the like generated in a processing process of the tobacco leaves, cut tobaccos or the tobaccos; the wastes are changed into valuable things so as to reduce pollution to the environment; according to the reconstructed tobacco leaves, the sensory quality is improved, the aroma amount is increased, the fragrance is improved, the natural tobacco aroma is set off, the dry feeling of smoke is reduced, the body fluid production feeling of the smoke is enhanced and the smoking comfort level is improved.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO ZHEJIANG IND +1
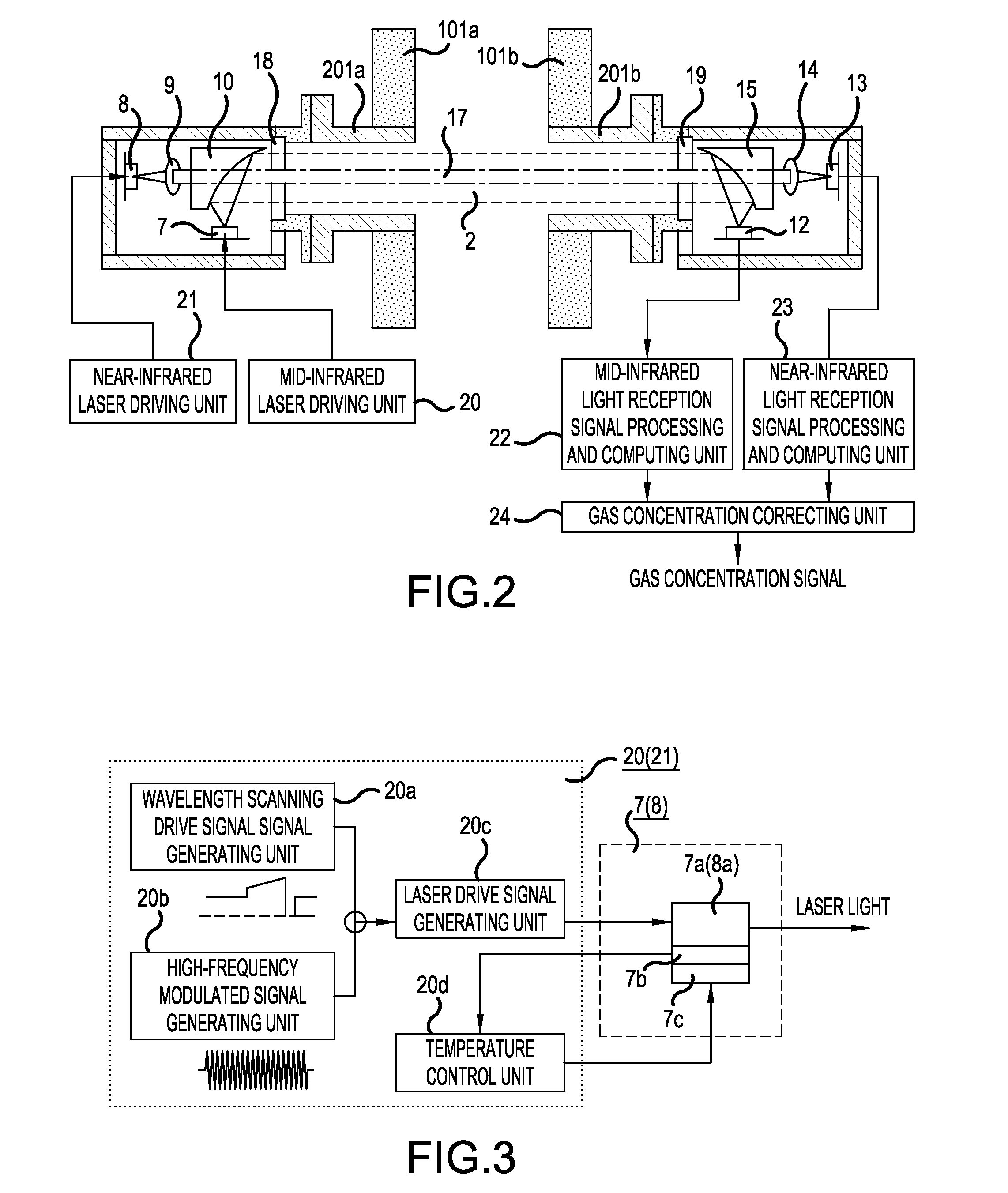
Laser-type gas analyzer
ActiveUS20150268159A1Improve accuracyHigh precision measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsWater concentrationMid infrared
Aspects of a laser-type gas analyzer can include a mid-infrared light reception signal processing and computing unit that calculates a gas concentration of the first gas to be measured on the basis of a mid-infrared light reception signal, a near-infrared light reception signal processing and computing unit that detects, at respective times, the gas concentration of the second gas to be measured, water concentration in a space, and alight amount decrement due to dust, on the basis of near-infrared light reception signal. Also included can be a gas concentration correcting unit that corrects the gas concentrations of the first and second gases to be measured using the water concentration and the light amount decrement.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Thermal energy storage materials
InactiveUS20120216981A1Improve performanceHeat storage plantsHeat-exchange elementsThermal energyThermal energy storage
The present invention relates to a thermal energy storage material (TESM) system (and associated methods). The TESM system comprises i) a container having a wall surface; and ii) a TESM in at least partial contact with the wall surface. The TESM may include, consist essentially of, or consist of a metal containing compound comprising at least two different metal cations and one or more polyatomic anions. The at least two metal cations may include lithium cations. The TESM may have a liquidus temperature, TL, from about 100° C. to about 250° C. The TESM may exhibits a heat storage density from 300° C. to 80° C. of at least 1 MJ / l. The TESM system may be free of water. If any water is present in the TESM system, the water concentration preferably is less than about 10 wt. %. Preferably, the TESM system is generally resistant to corrosion at temperatures of about 300° C.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
System and process for trapping sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide by ammonia absorption at atmospheric pressure
InactiveUS20140050651A1High desulfurizationHigh carbon reduction efficiencyCombination devicesGas treatmentCo2 absorptionWater concentration
A system and a process for capture and absorption of sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide by an ammonia method at normal pressure are disclosed. The system has a dilute ammonia water supply device connected with sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide absorption devices; an induced draft fan is connected with a heat exchanger connected with the sulfur dioxide absorption device; a sulfur dioxide absorption tower is connected with a carbon dioxide absorption tower; cooling devices in the sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide absorption towers share a cooling water inlet and outlet pipe; the sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide absorption devices respectively restore ammonia concentration to original ammonia water concentration by supplementing concentrated ammonia water; the sulfur dioxide and carbon dioxide absorption devices respectively pump solutions into the heat exchangers, then the solutions enter crystallization tanks; solid-liquid separation is performed through centrifuges, and the liquid continues to circulate in the system.
Owner:ANHUI HUAIHUA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com