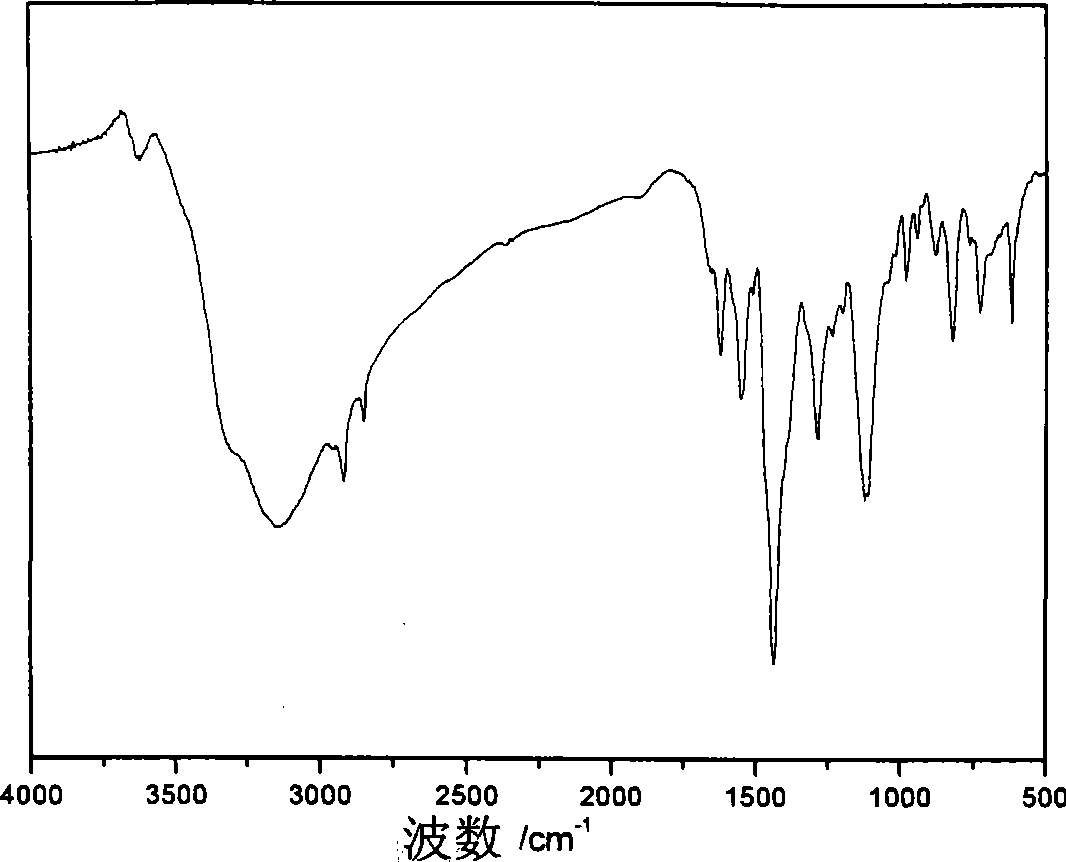
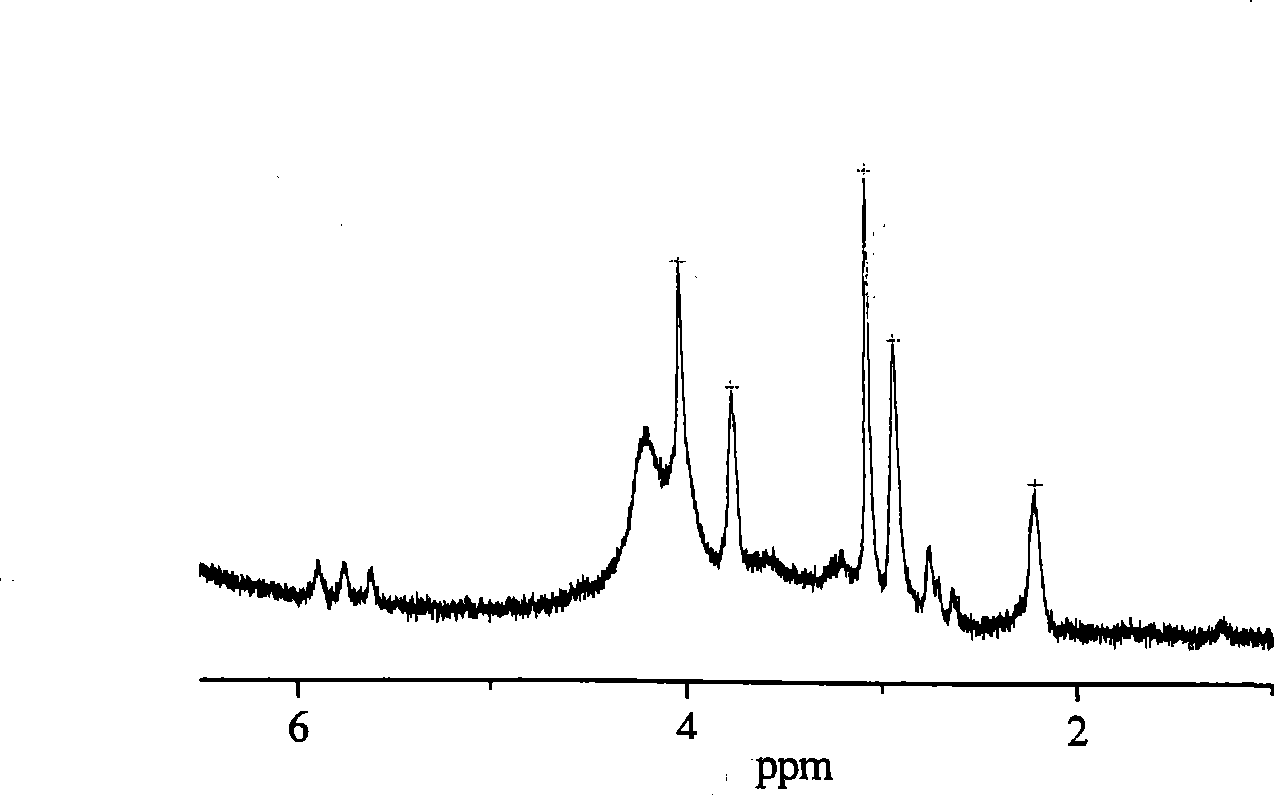
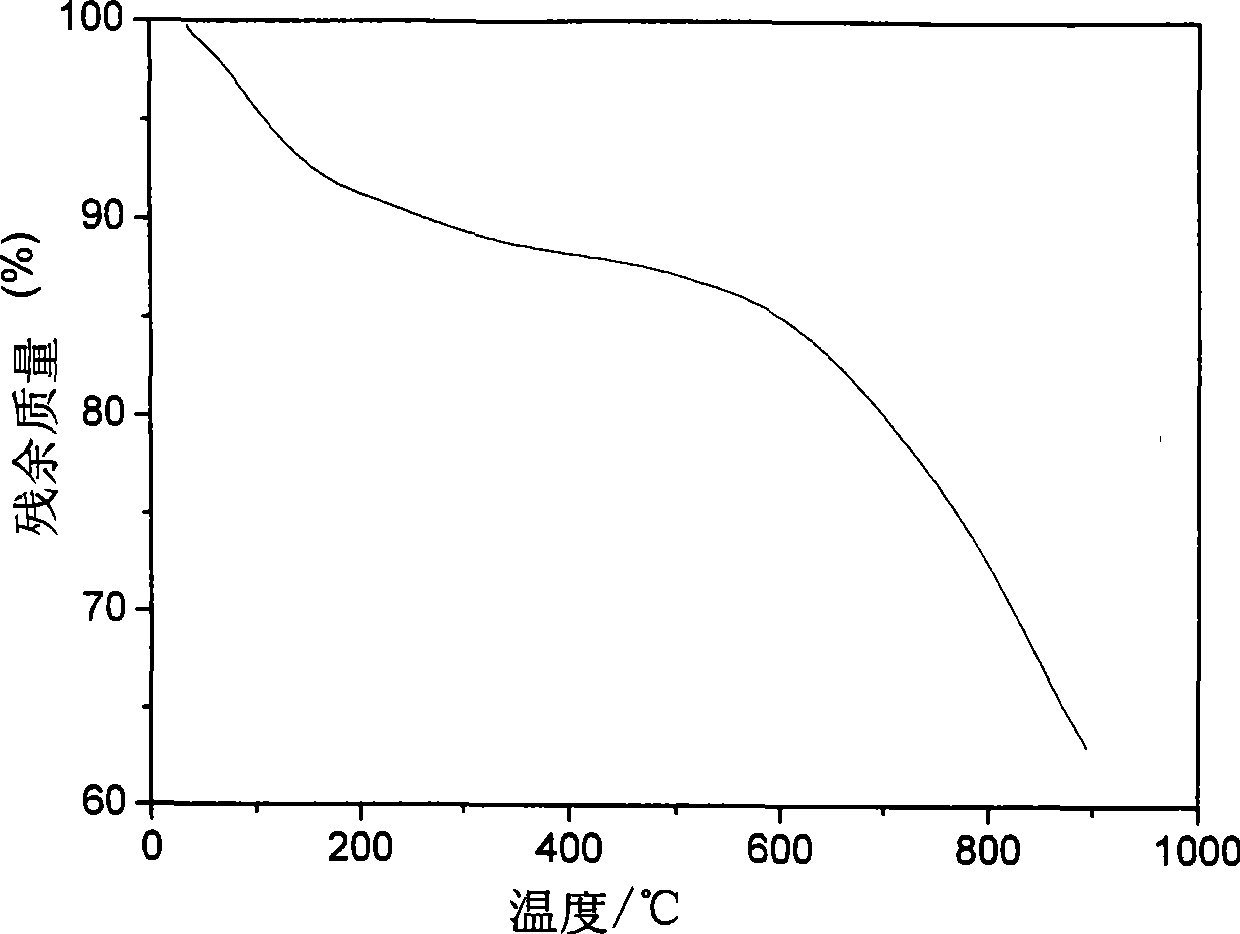
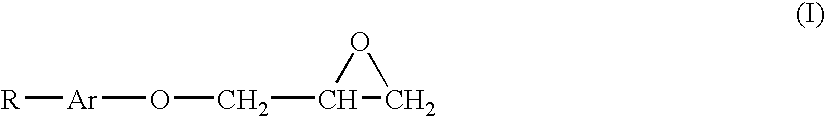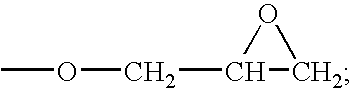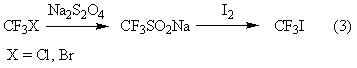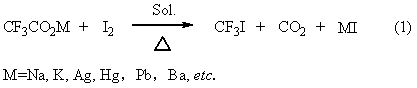Patents
Literature
727 results about "Methyl iodide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Methyl iodide, also called iodomethane, and commonly abbreviated "MeI", is the chemical compound with the formula CH₃I. It is a dense, colorless, volatile liquid. In terms of chemical structure, it is related to methane by replacement of one hydrogen atom by an atom of iodine. It is naturally emitted by rice plantations in small amounts. It is also produced in vast quantities estimated to be greater than 214,000 tons annually by algae and kelp in the world's temperate oceans, and in lesser amounts on land by terrestrial fungi and bacteria. It is used in organic synthesis as a source of methyl groups.
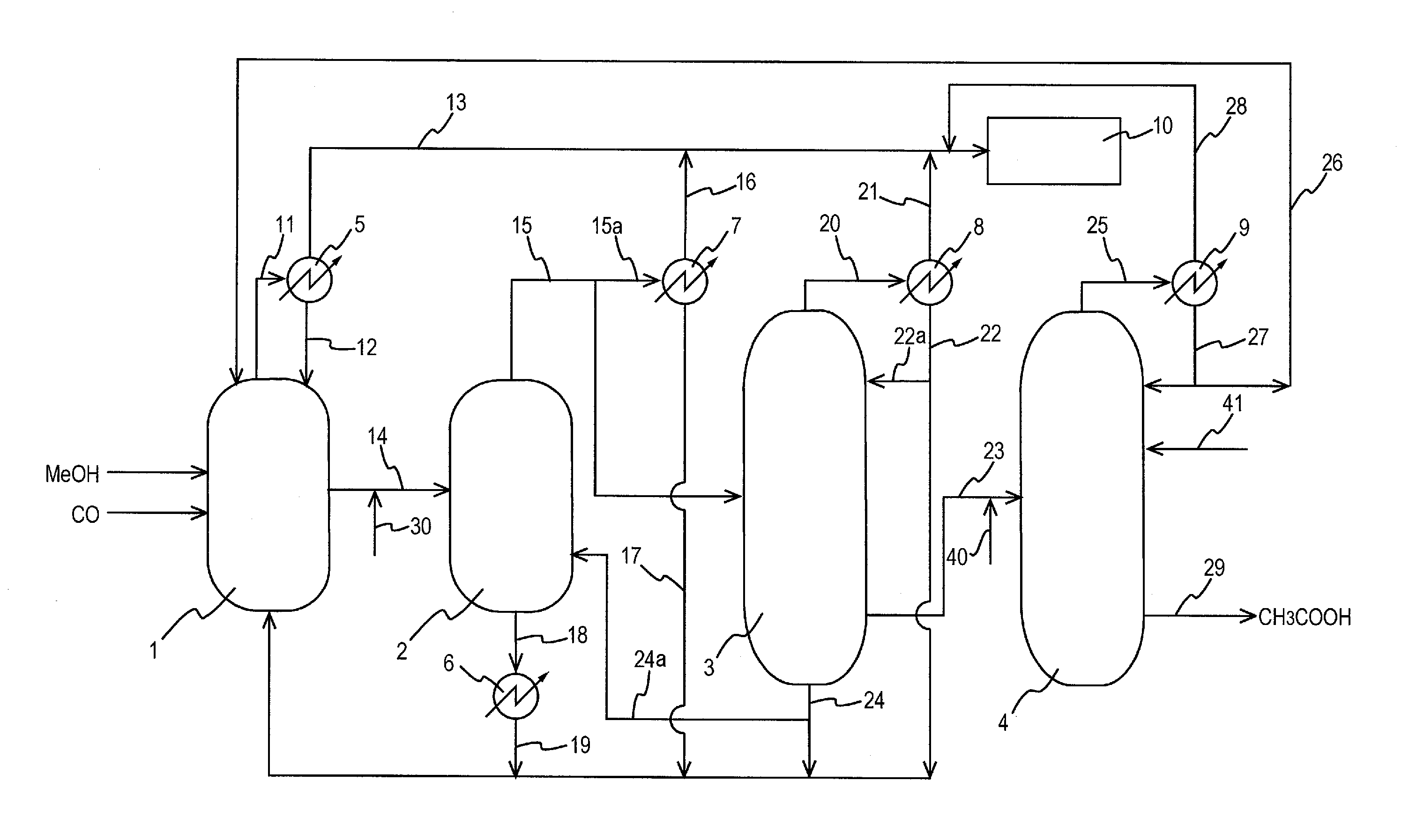
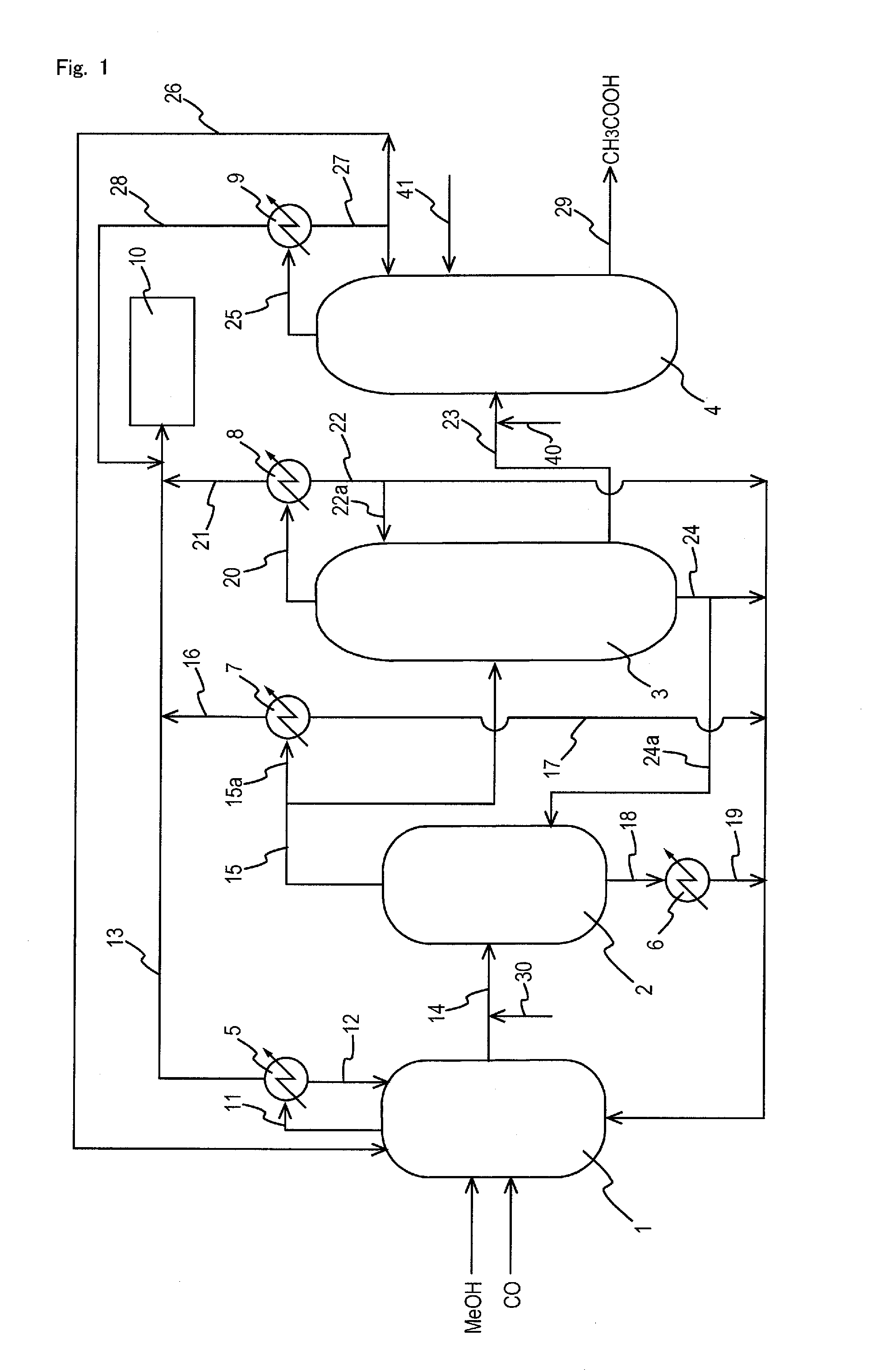
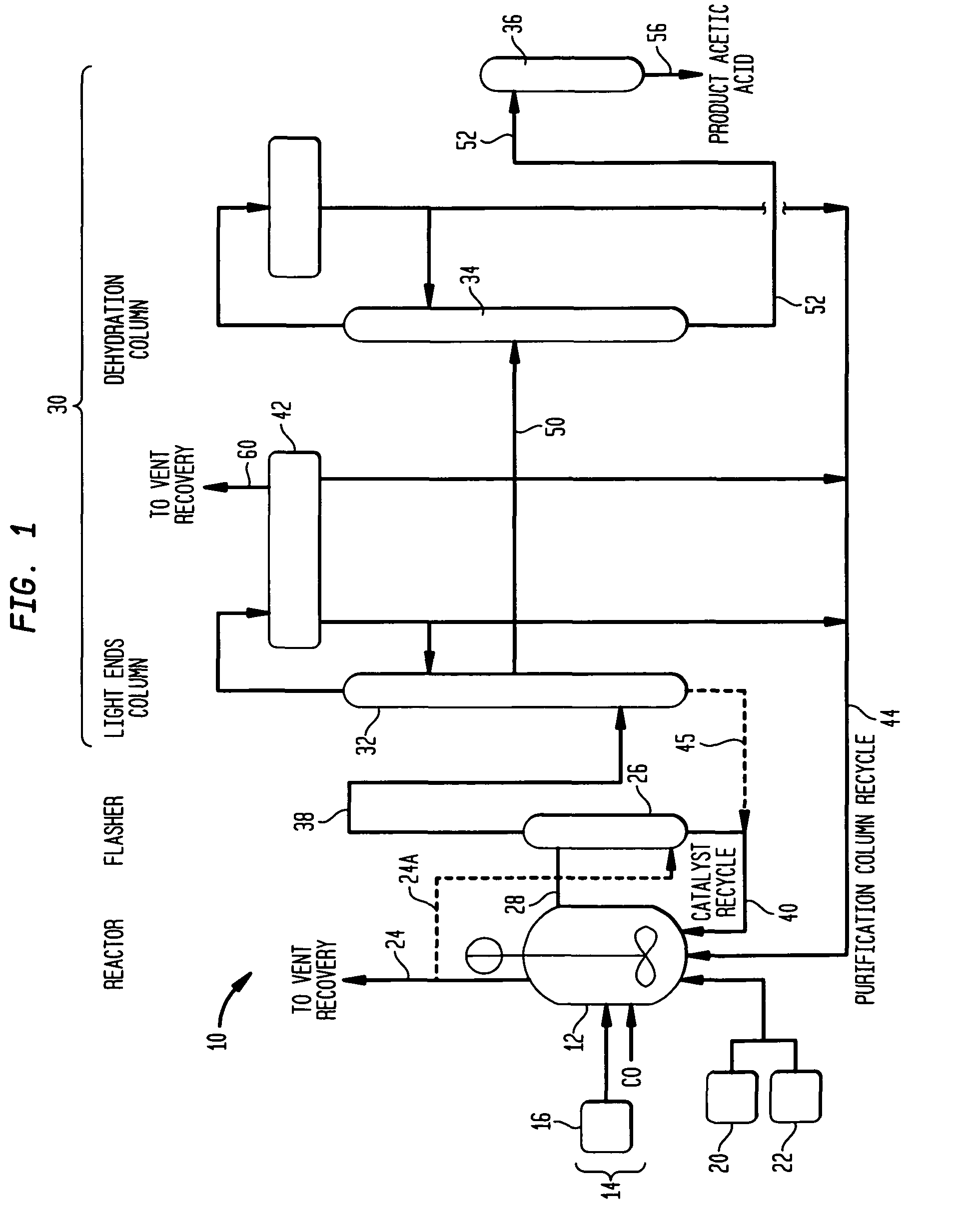
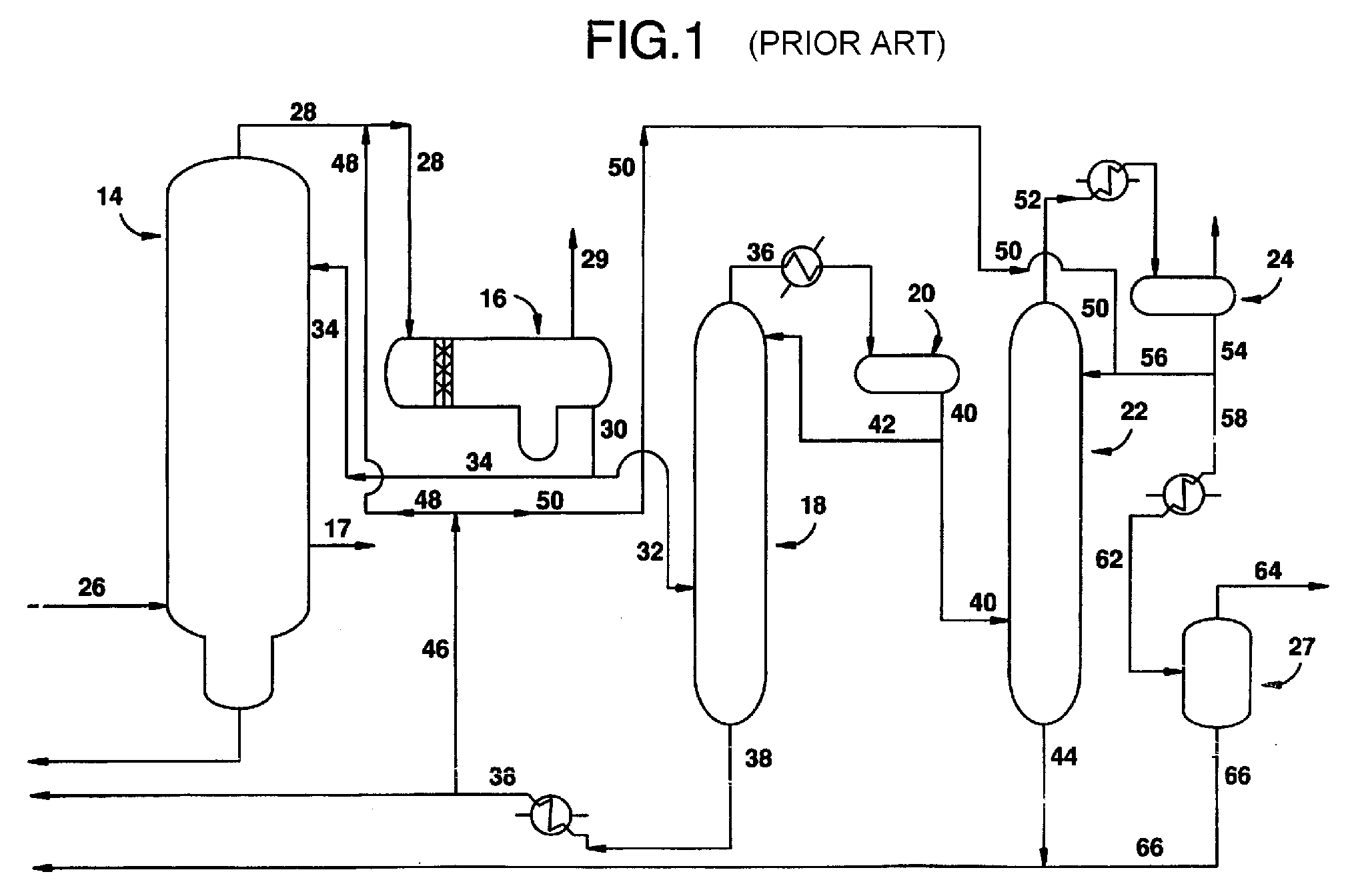
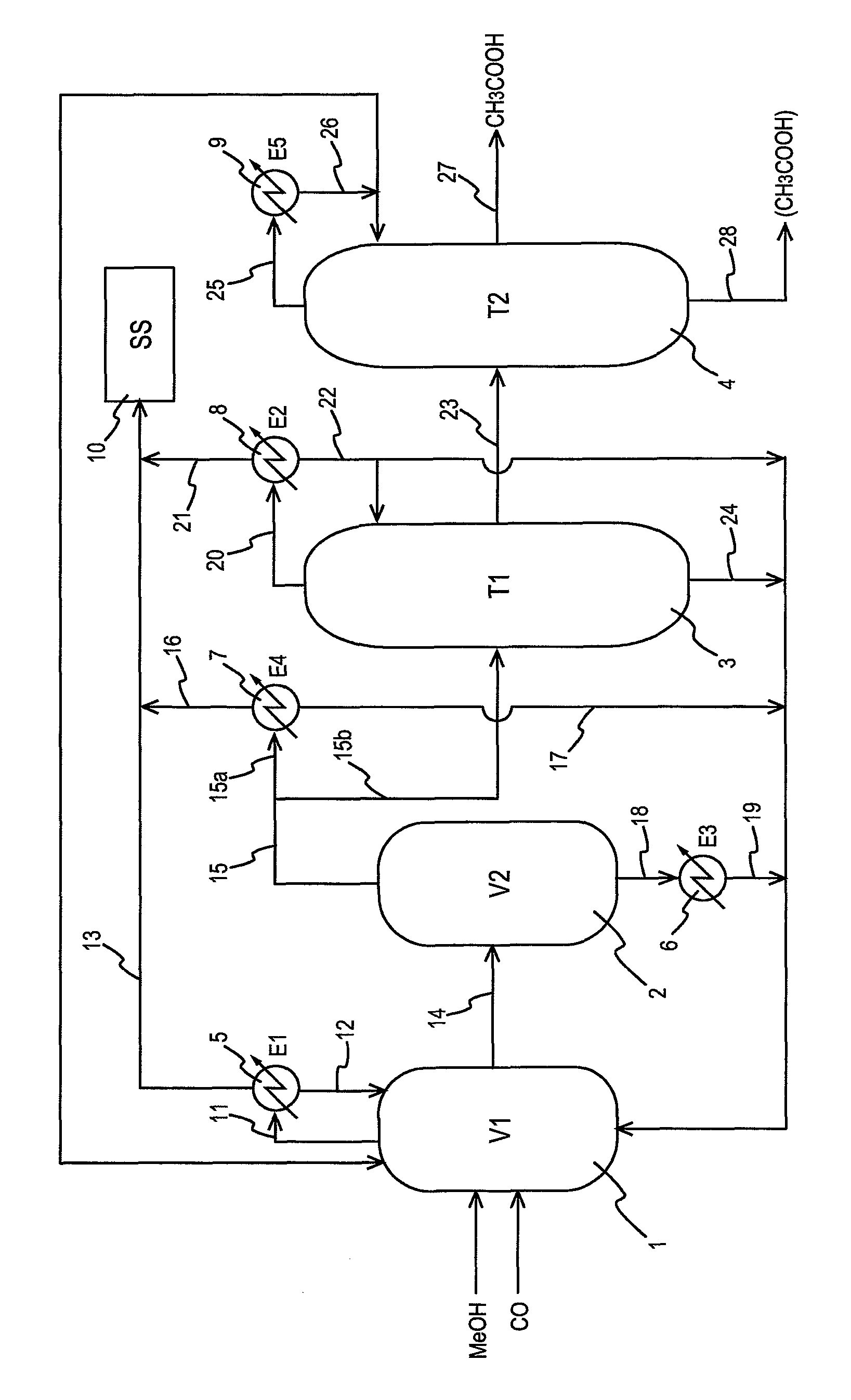
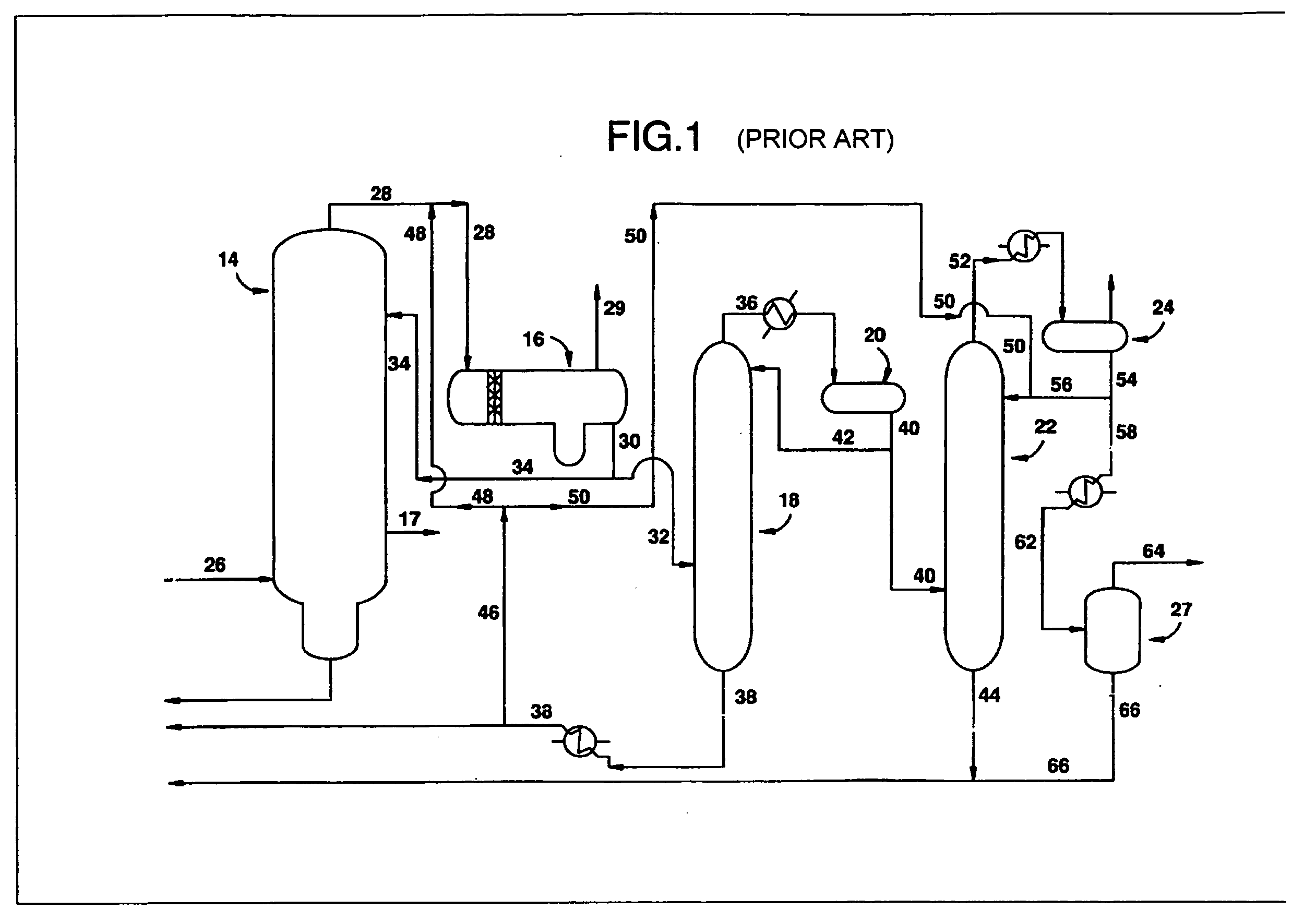
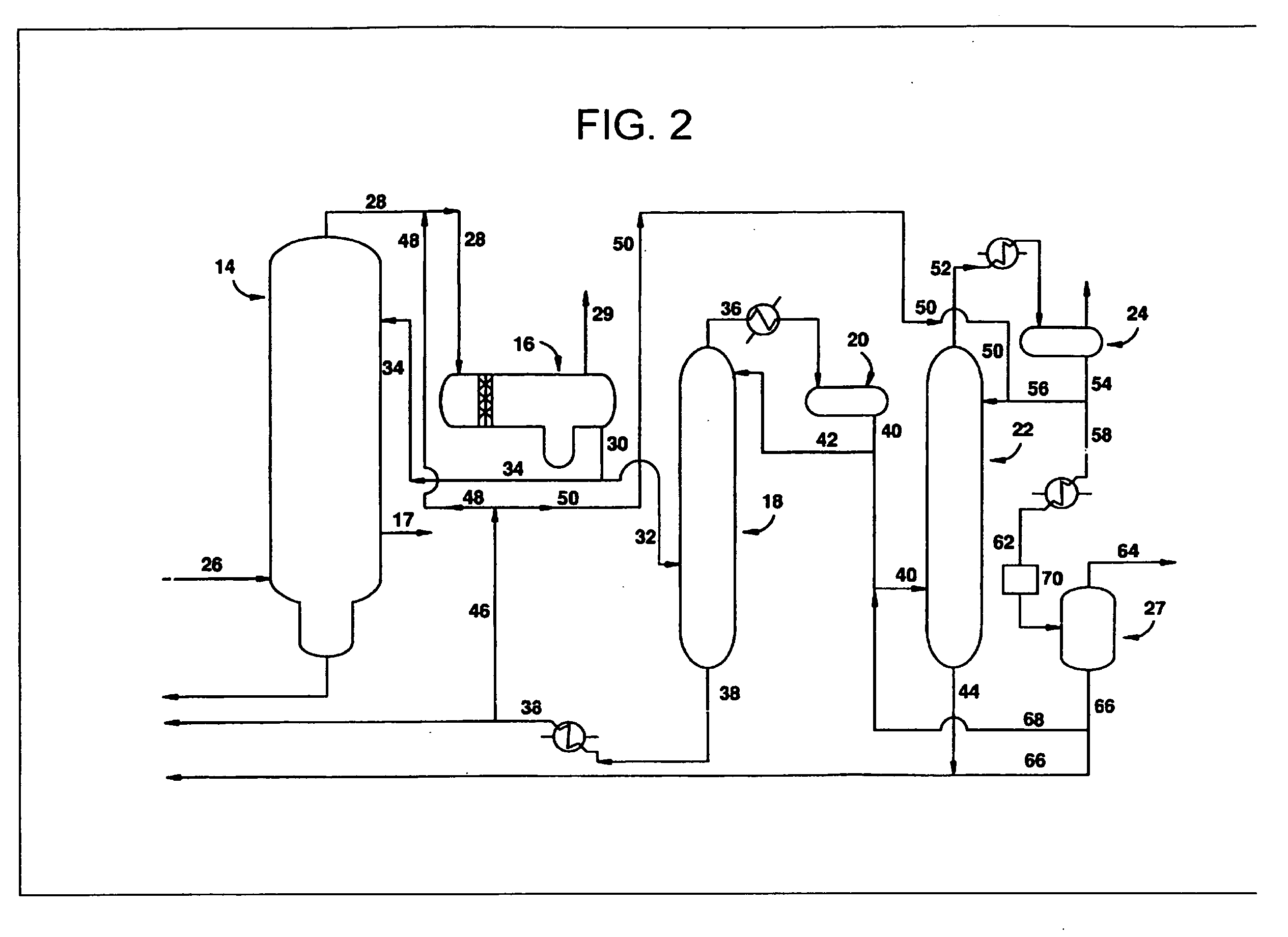
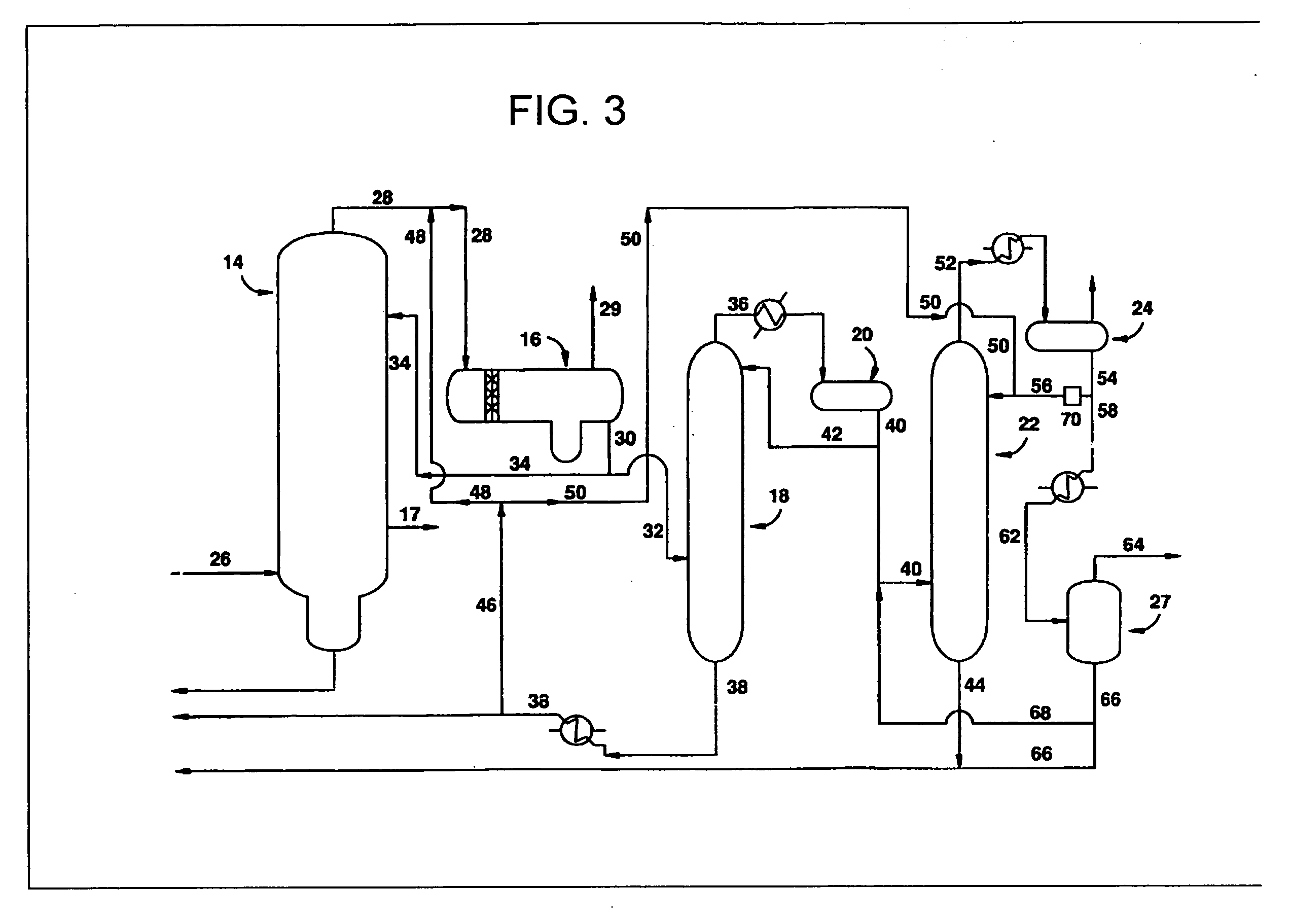
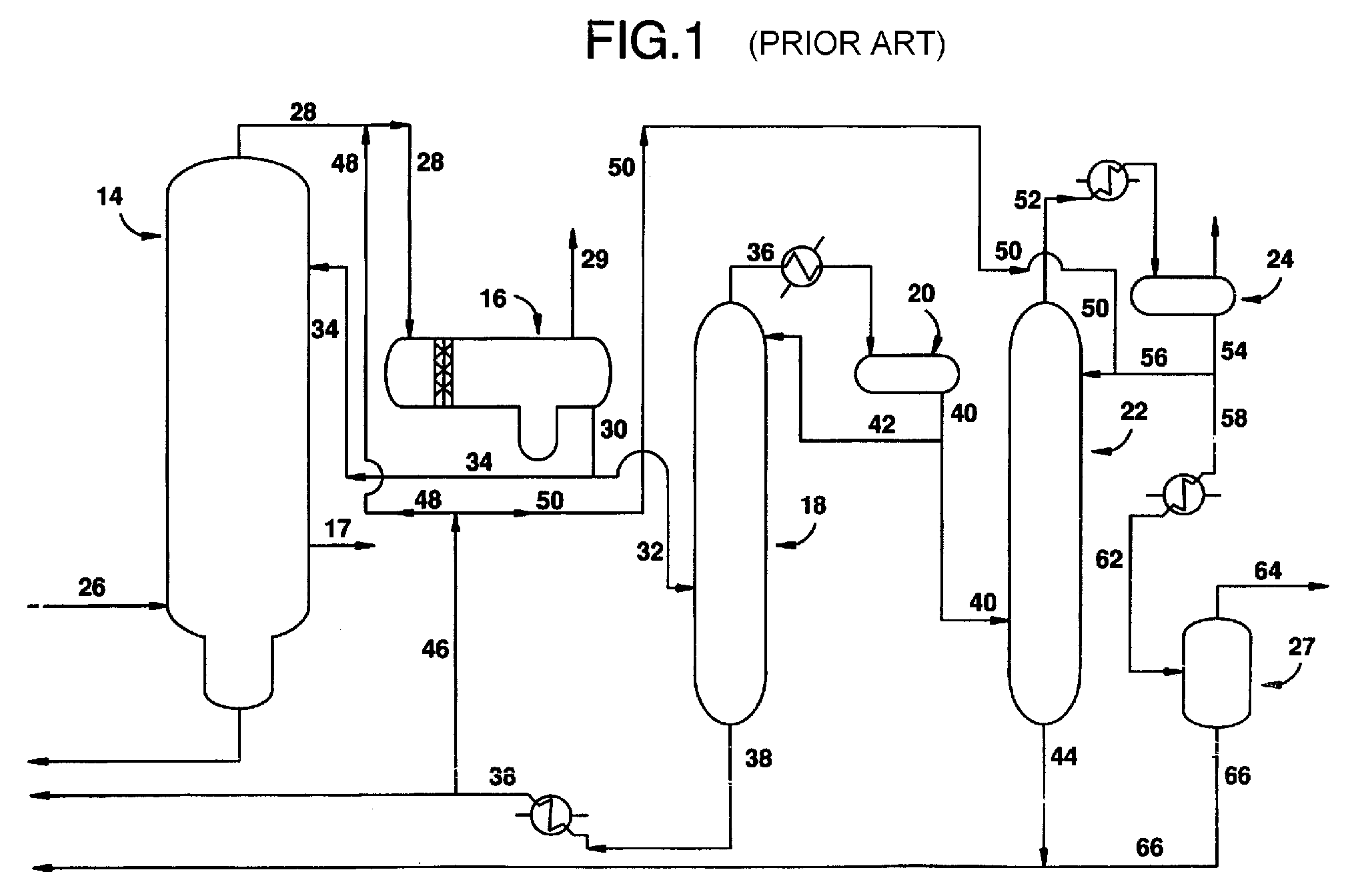
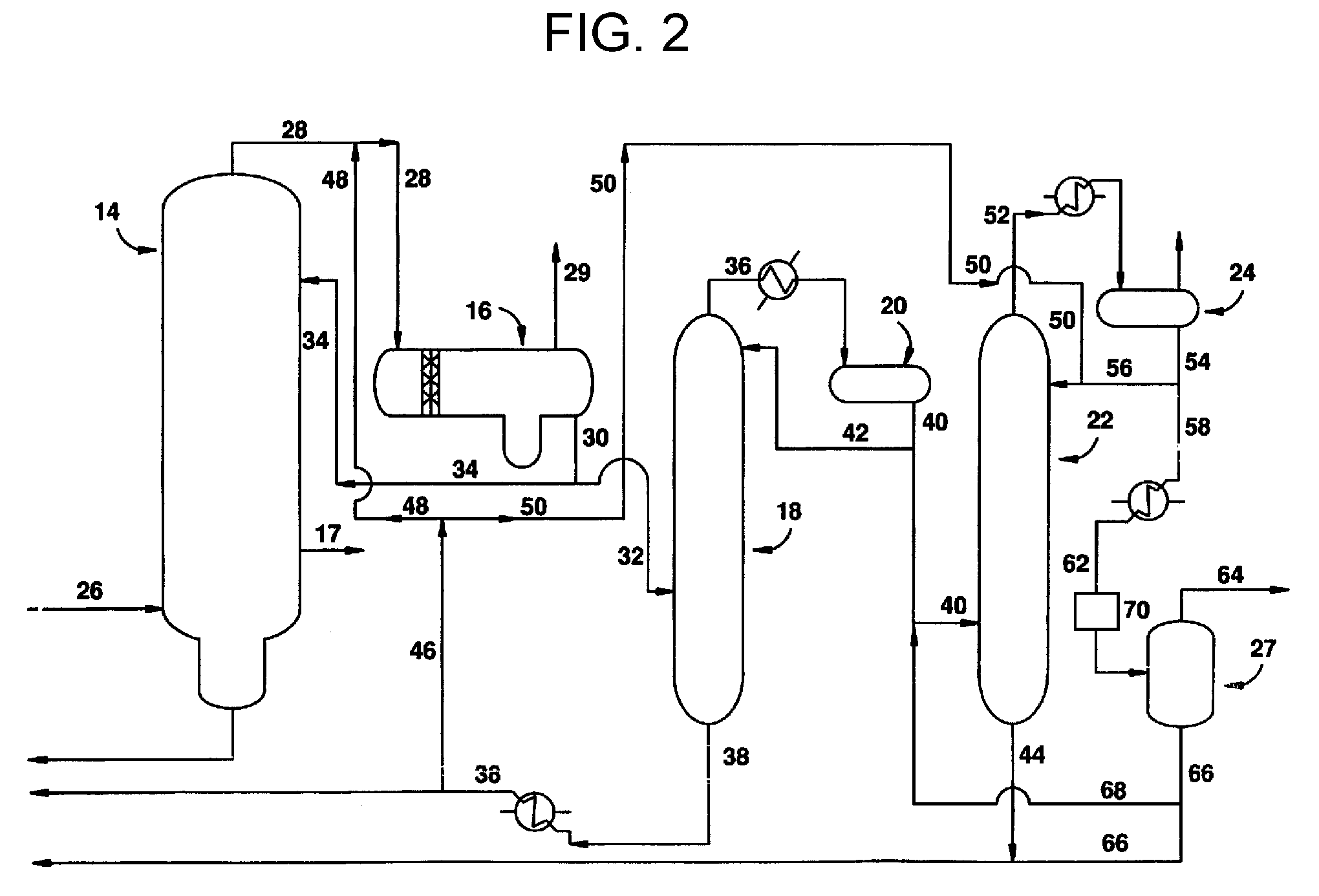
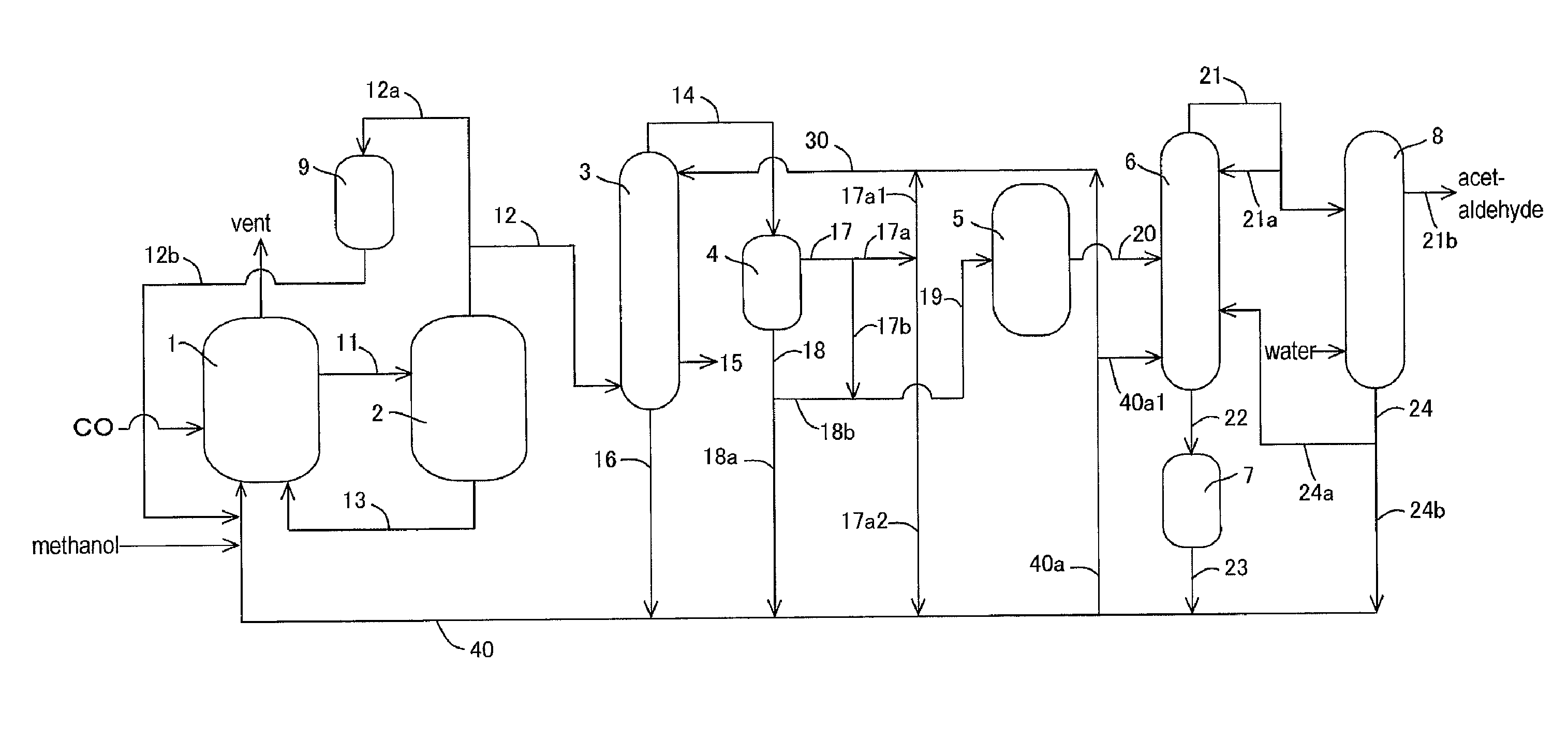
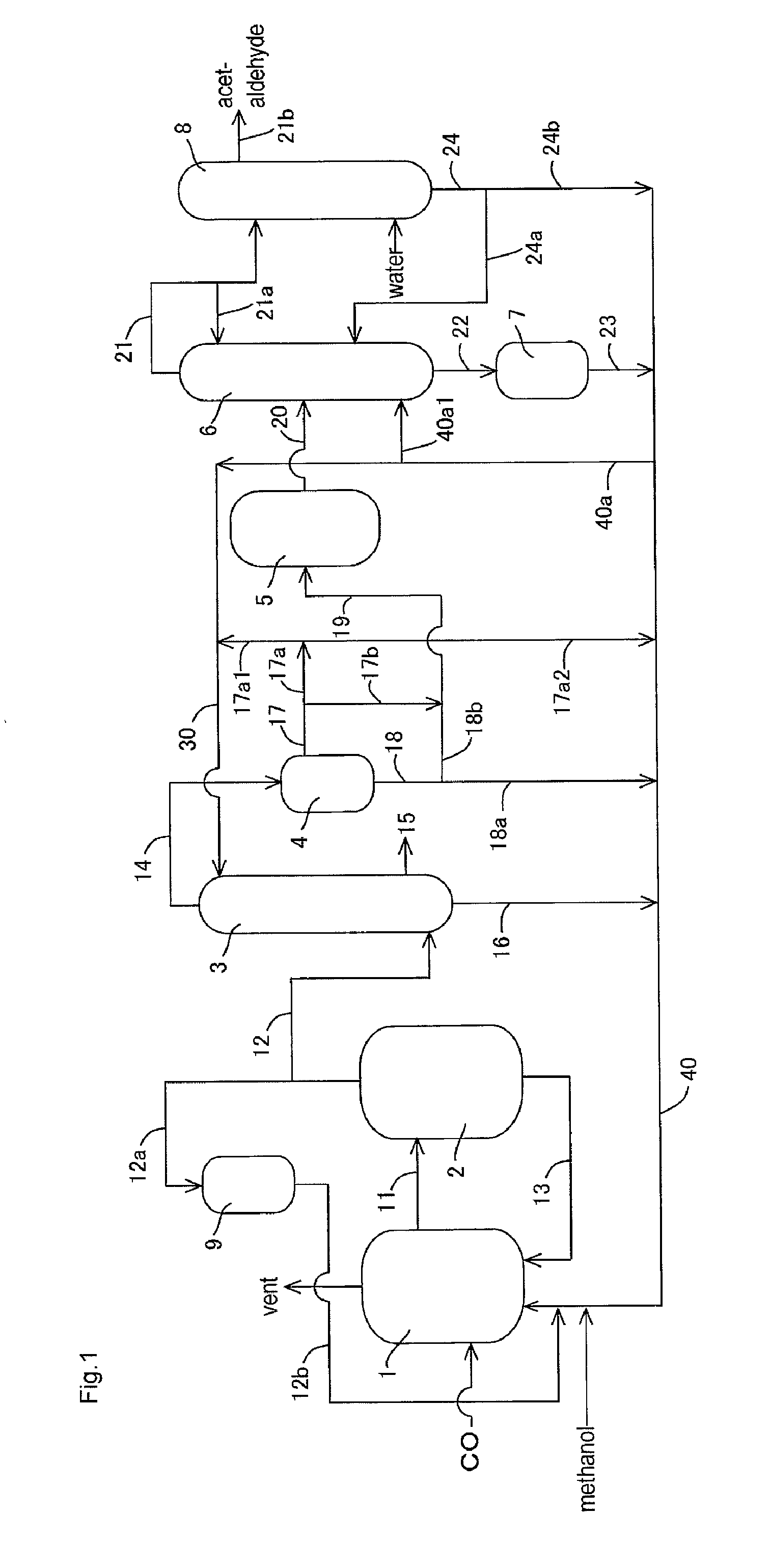
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7208624B2Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
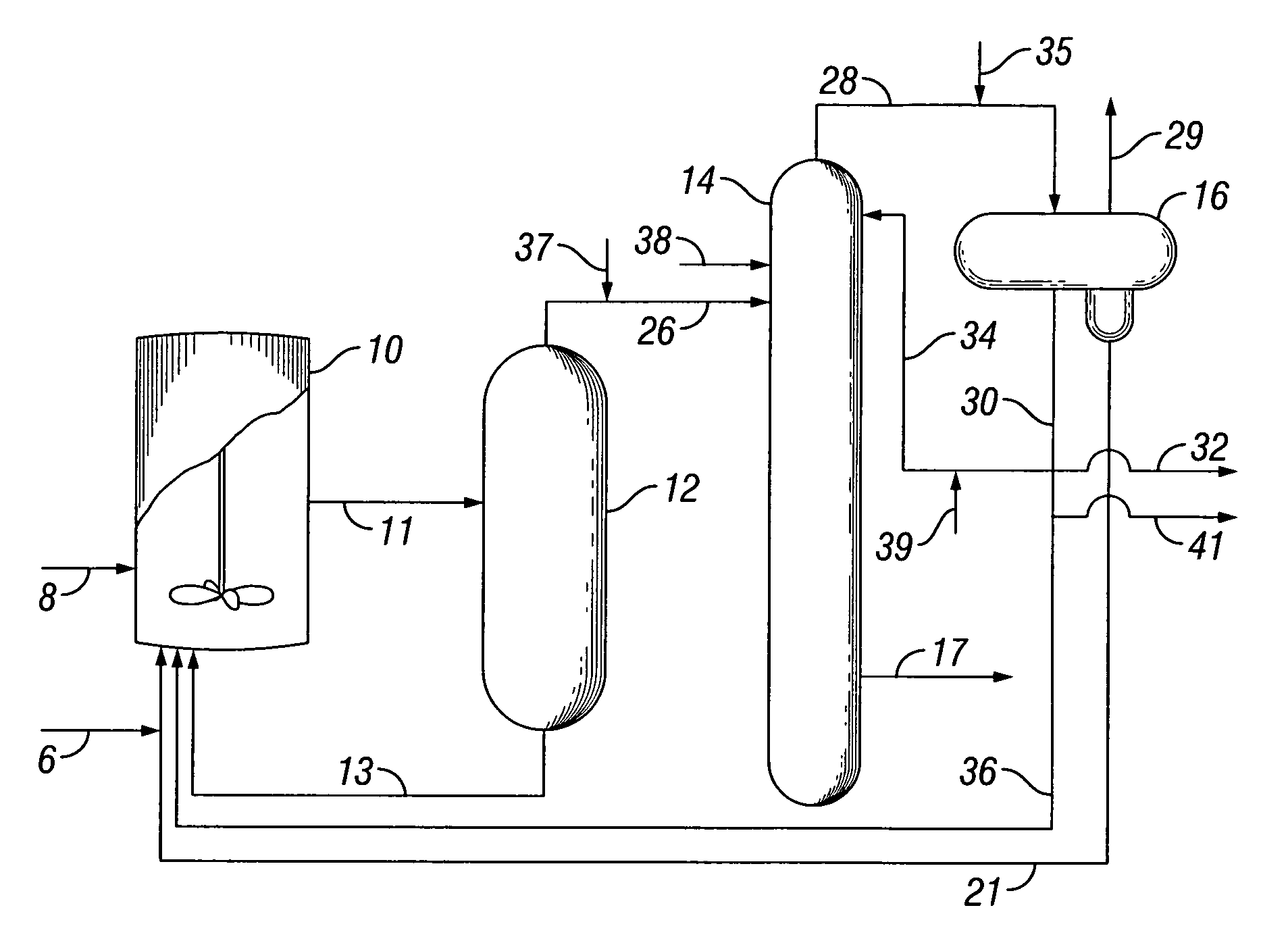
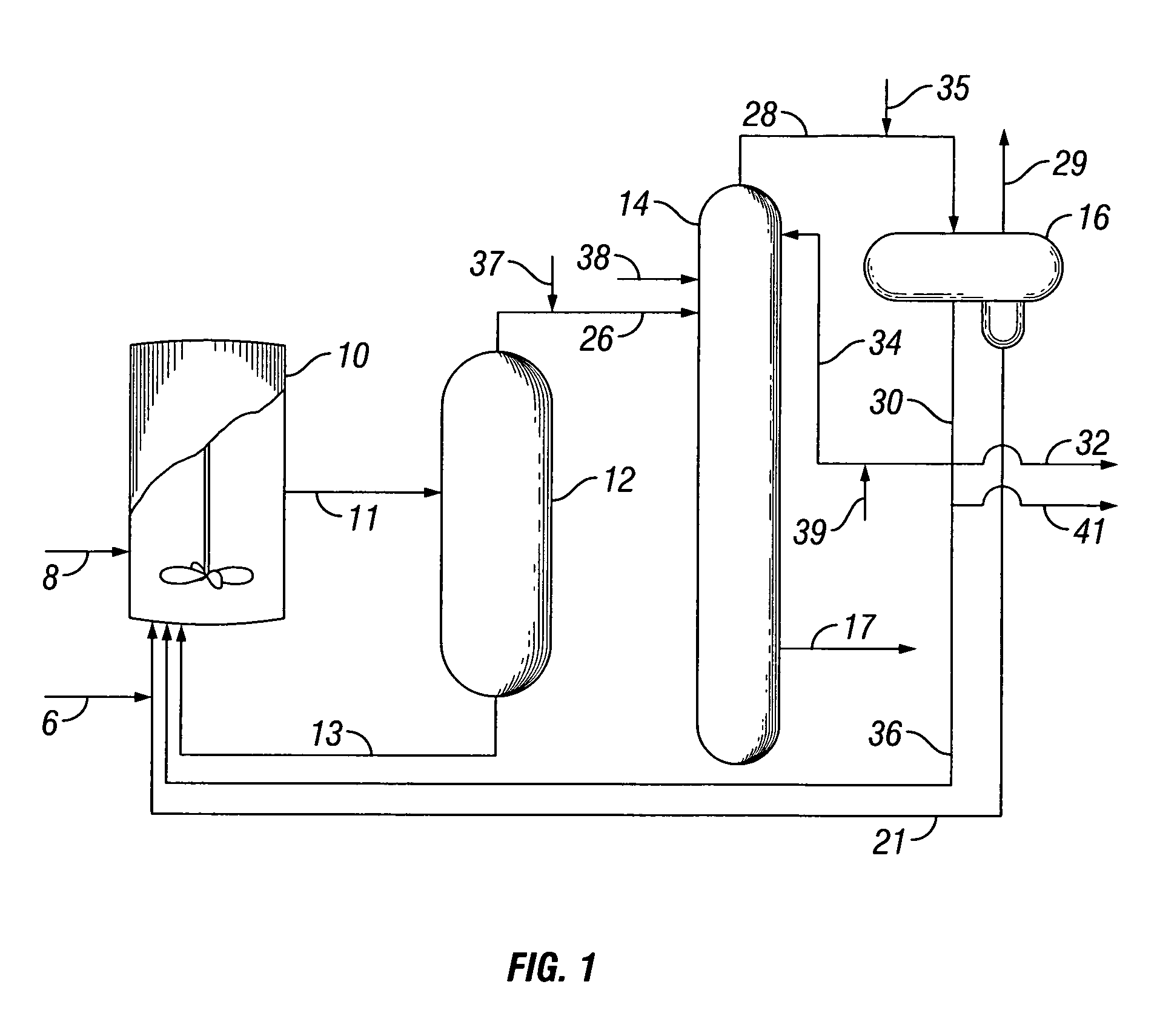
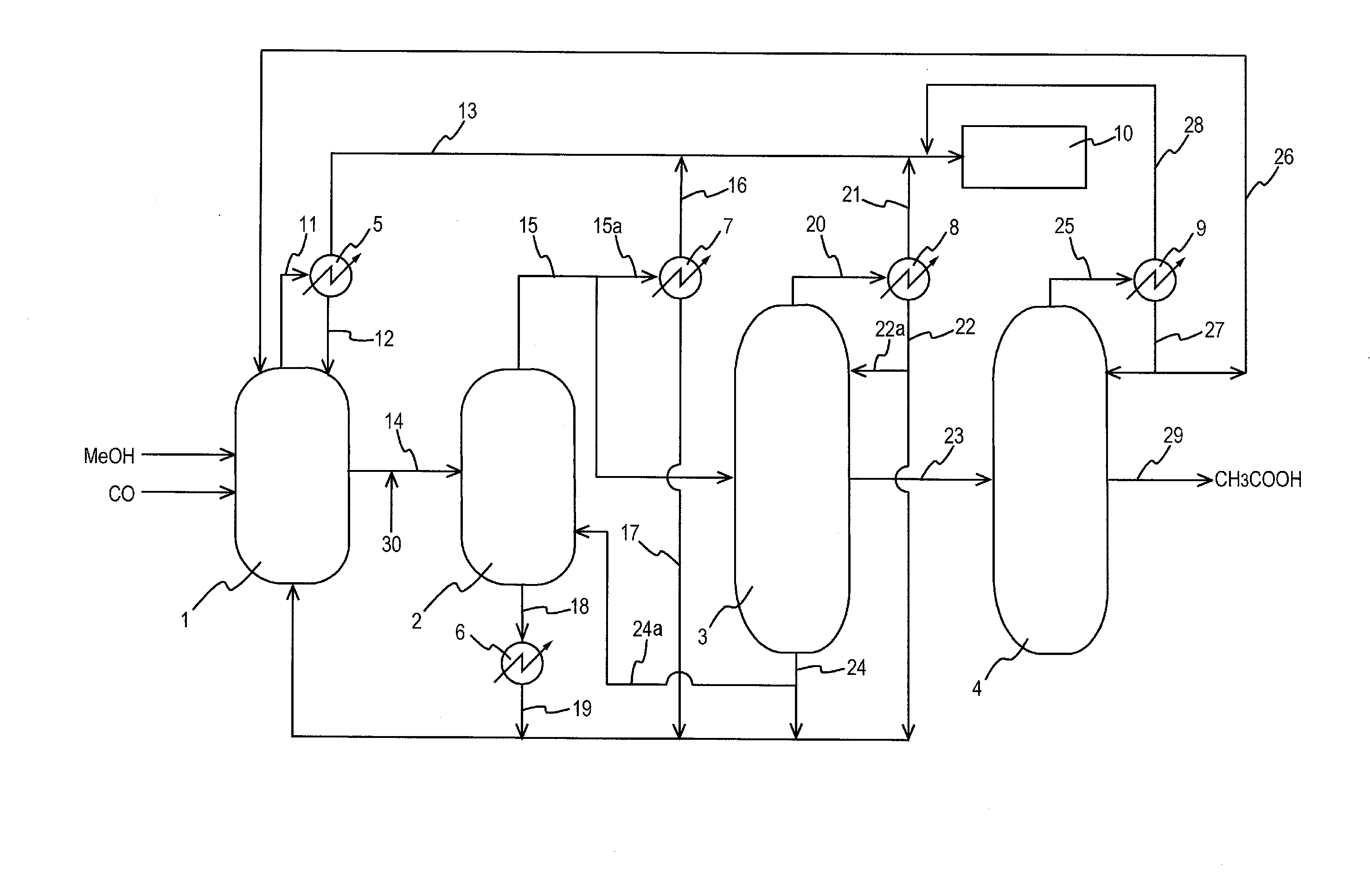
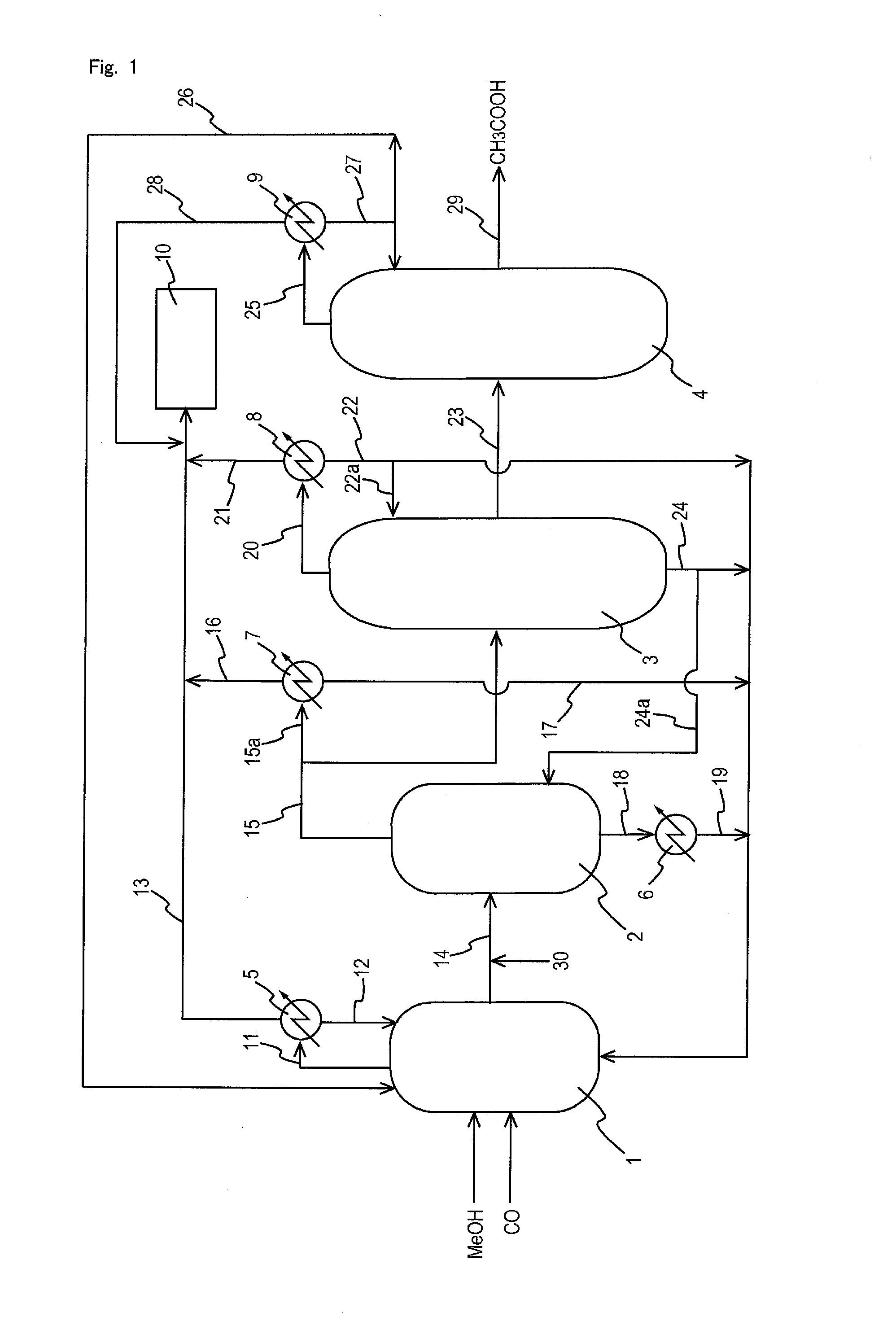
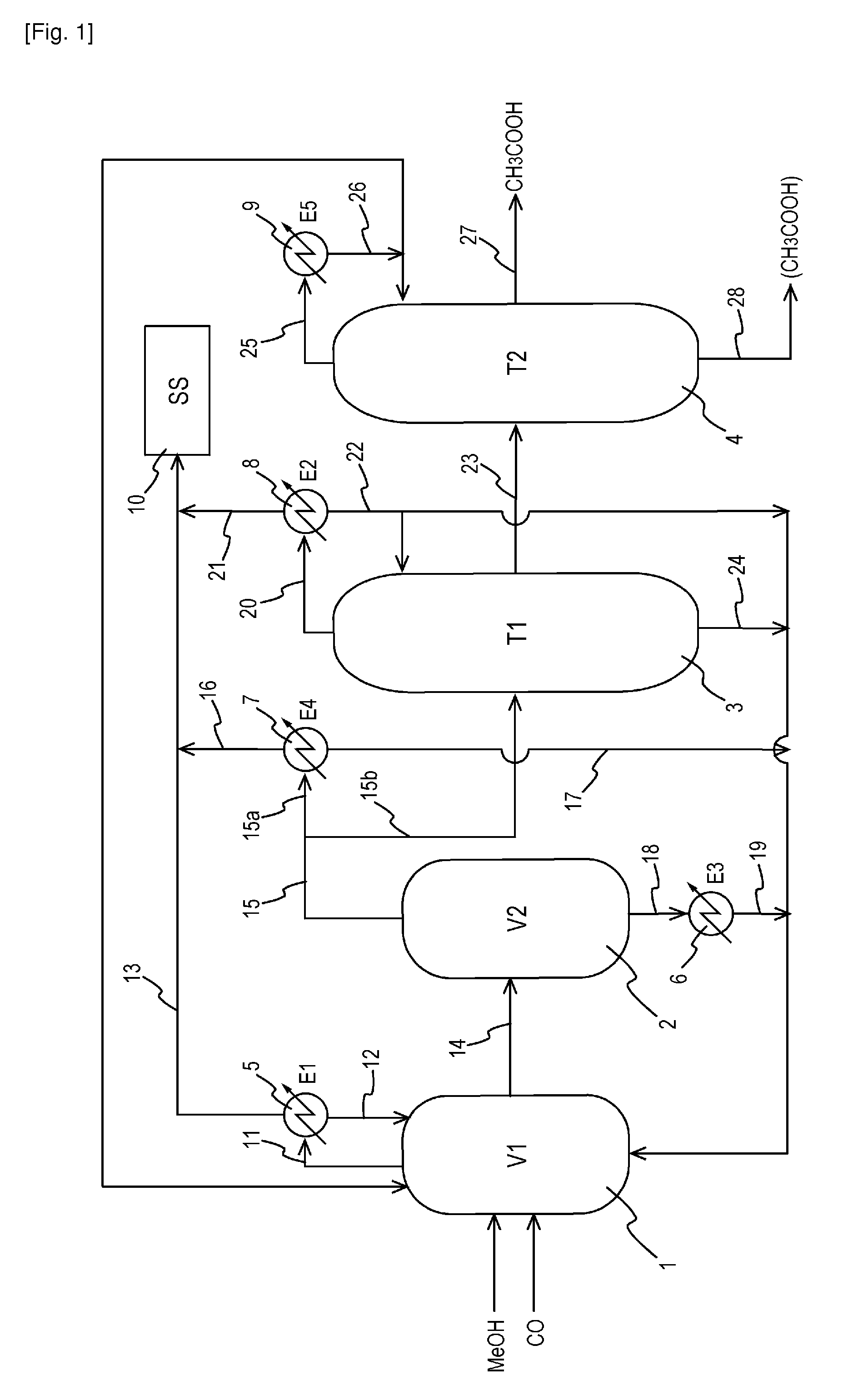
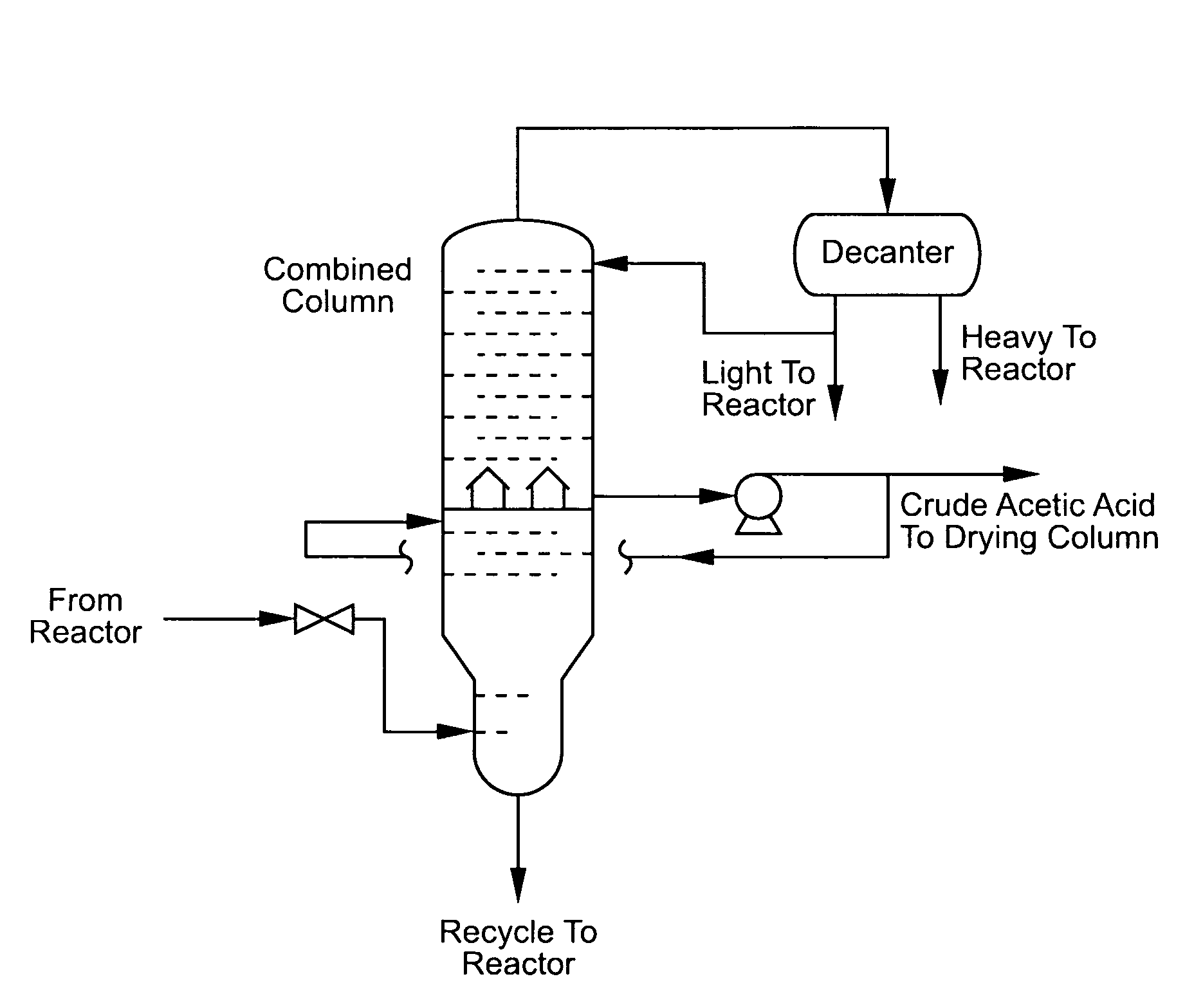
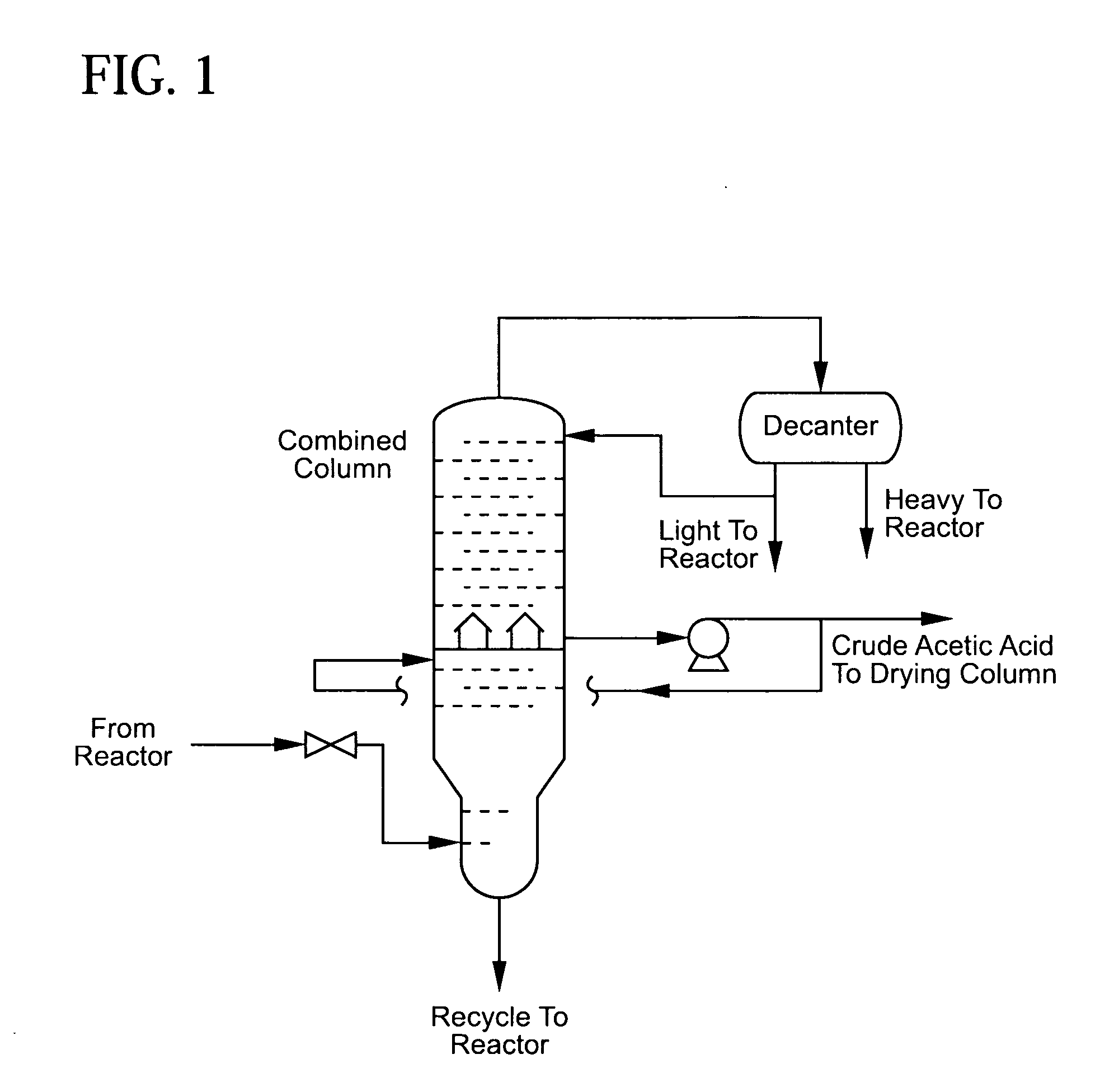
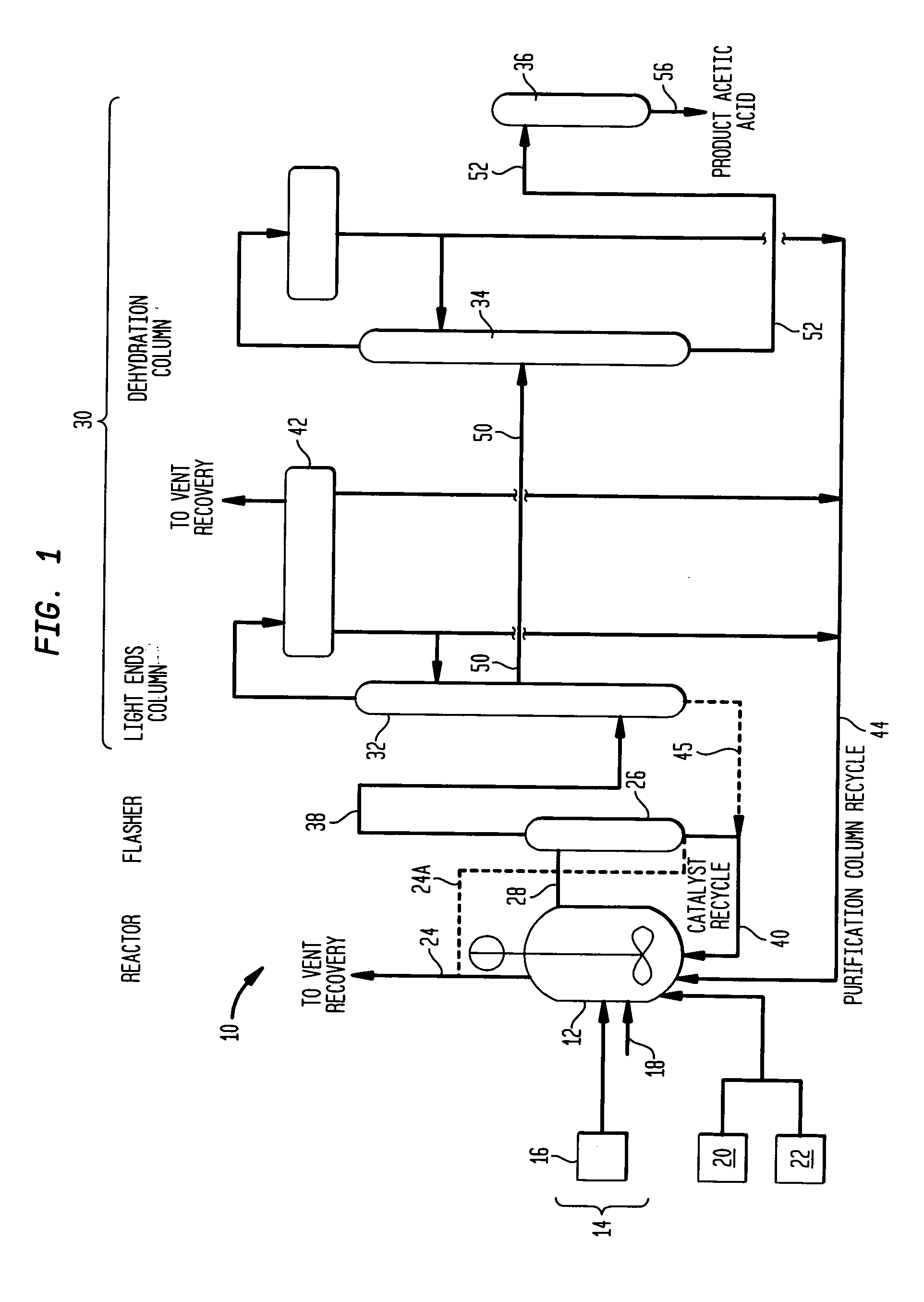
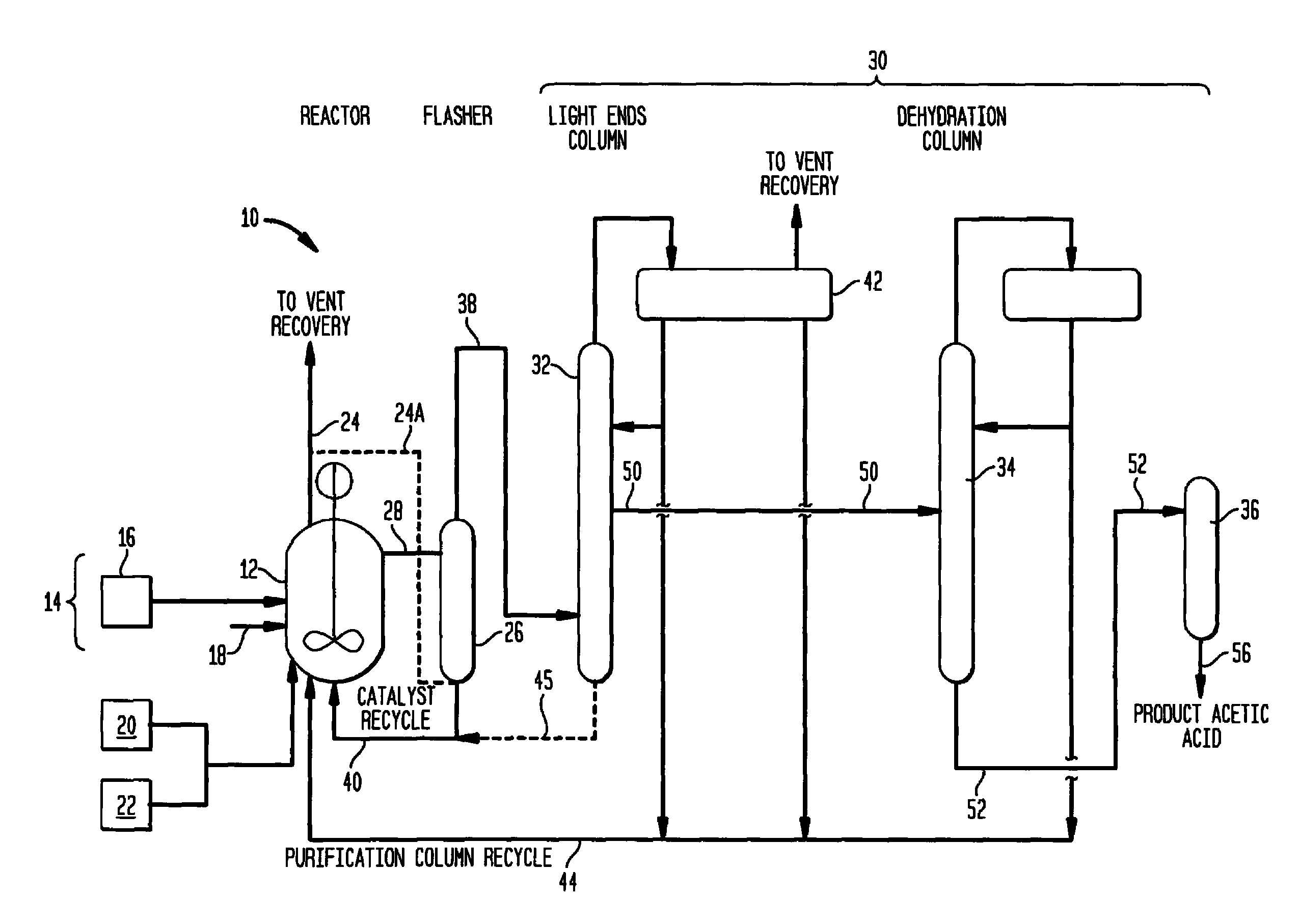
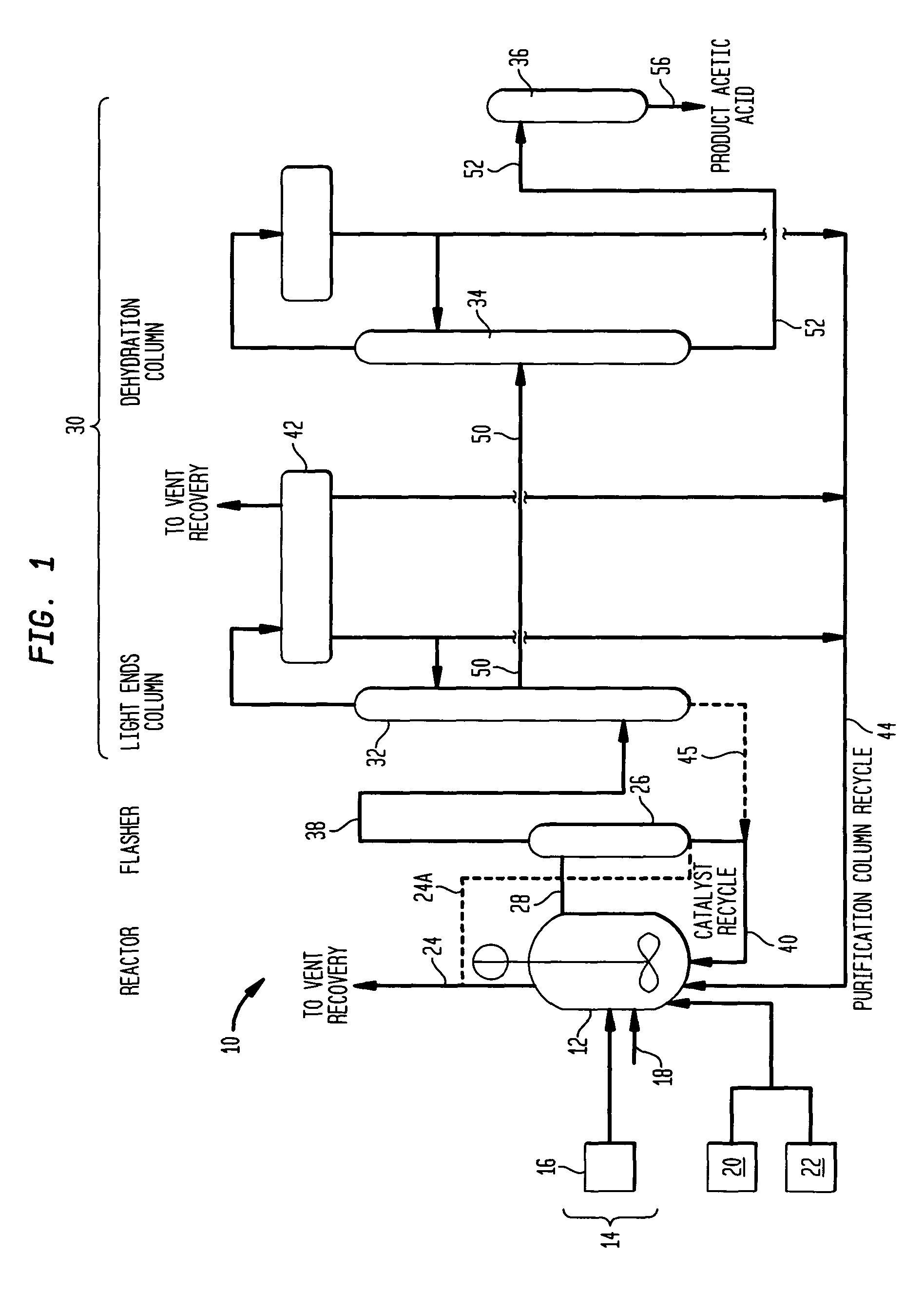
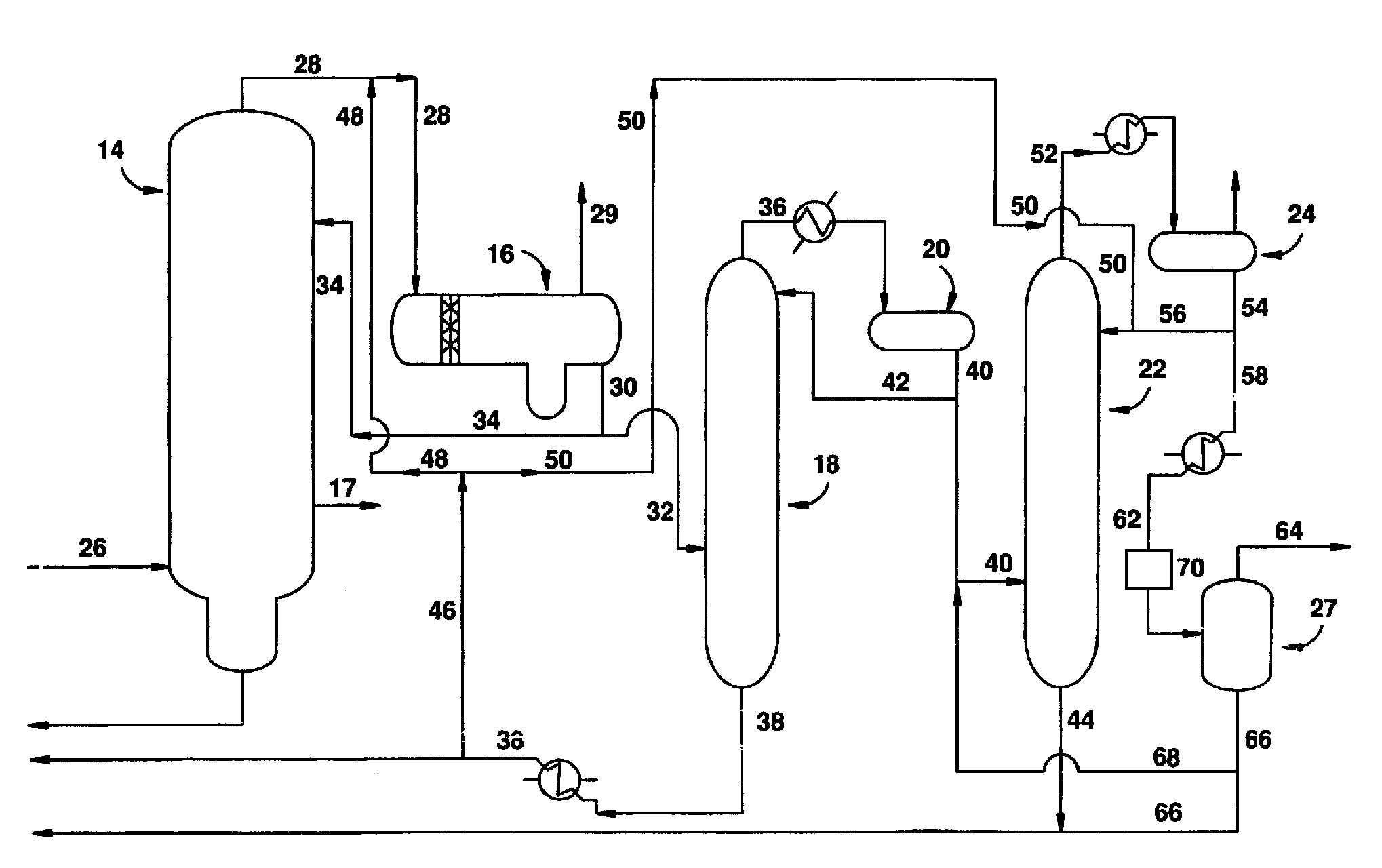
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
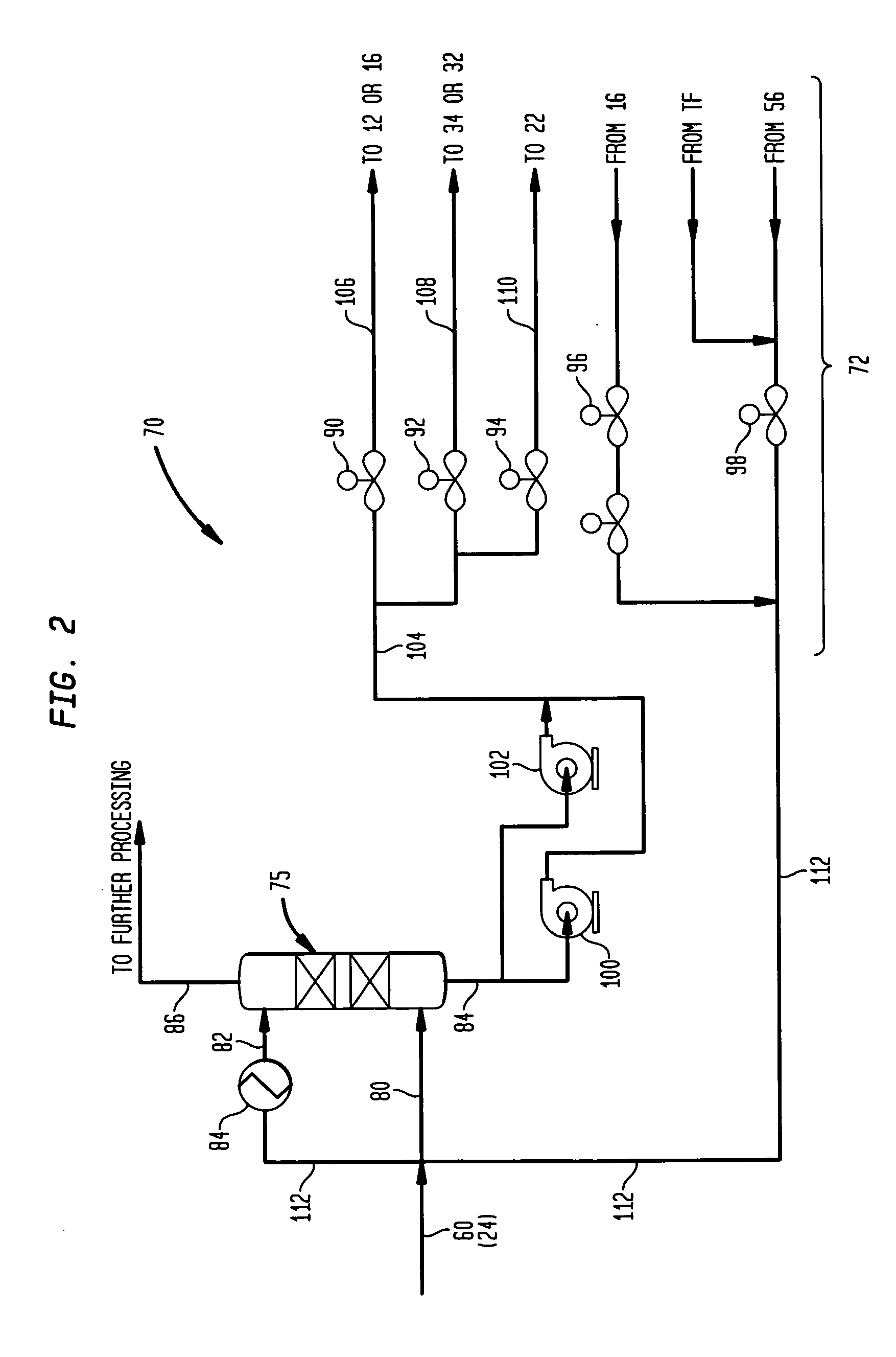
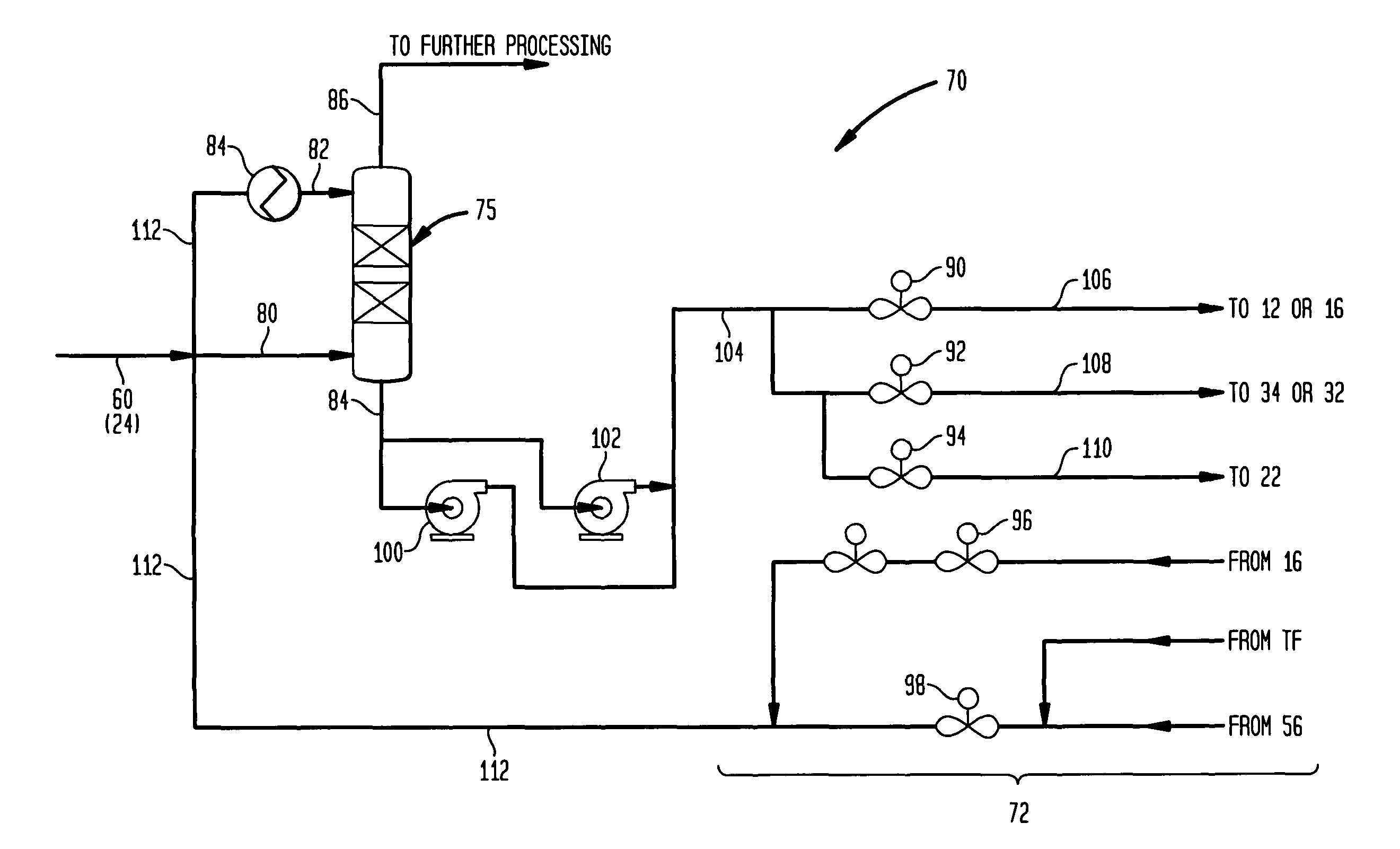
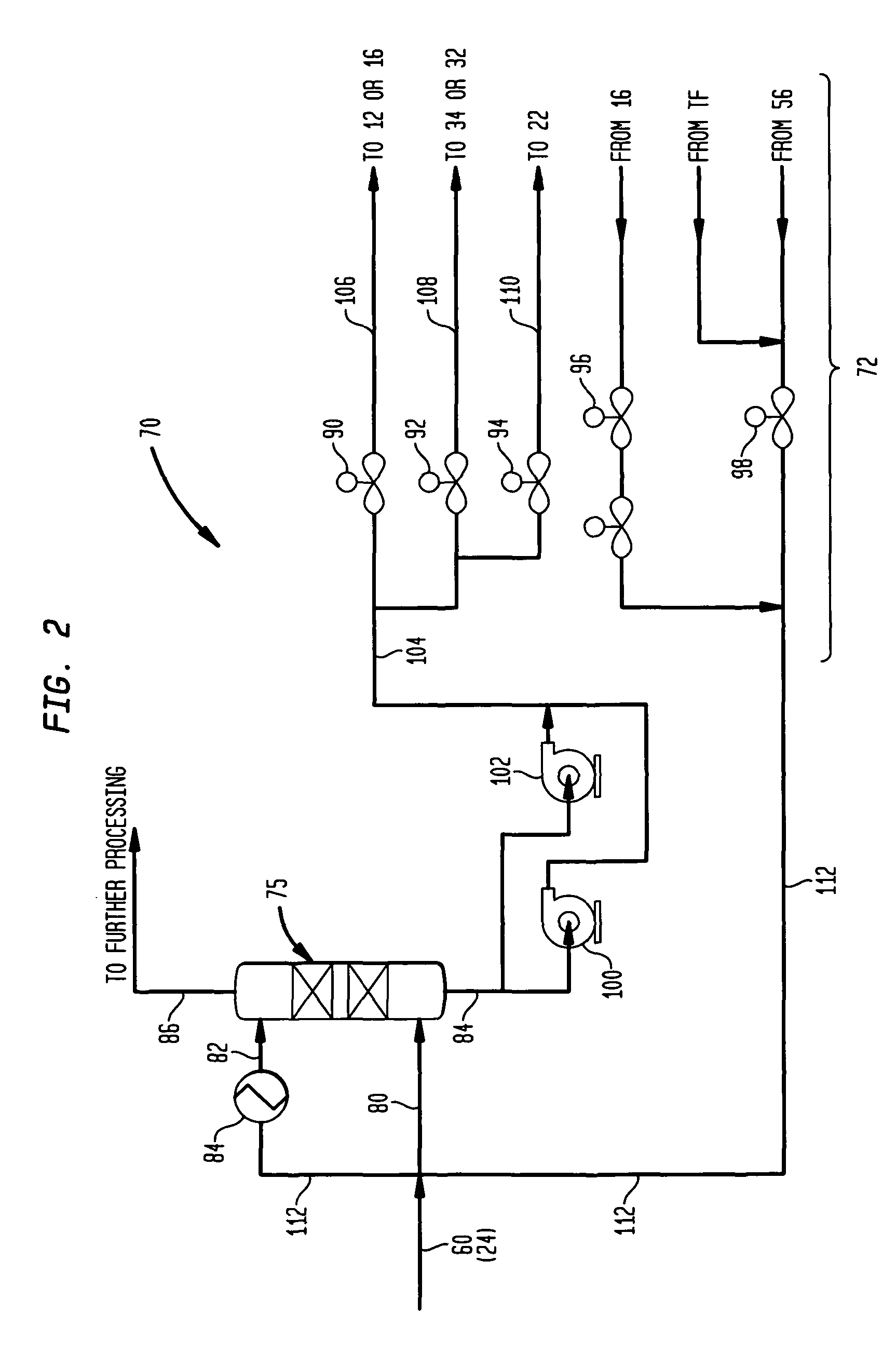
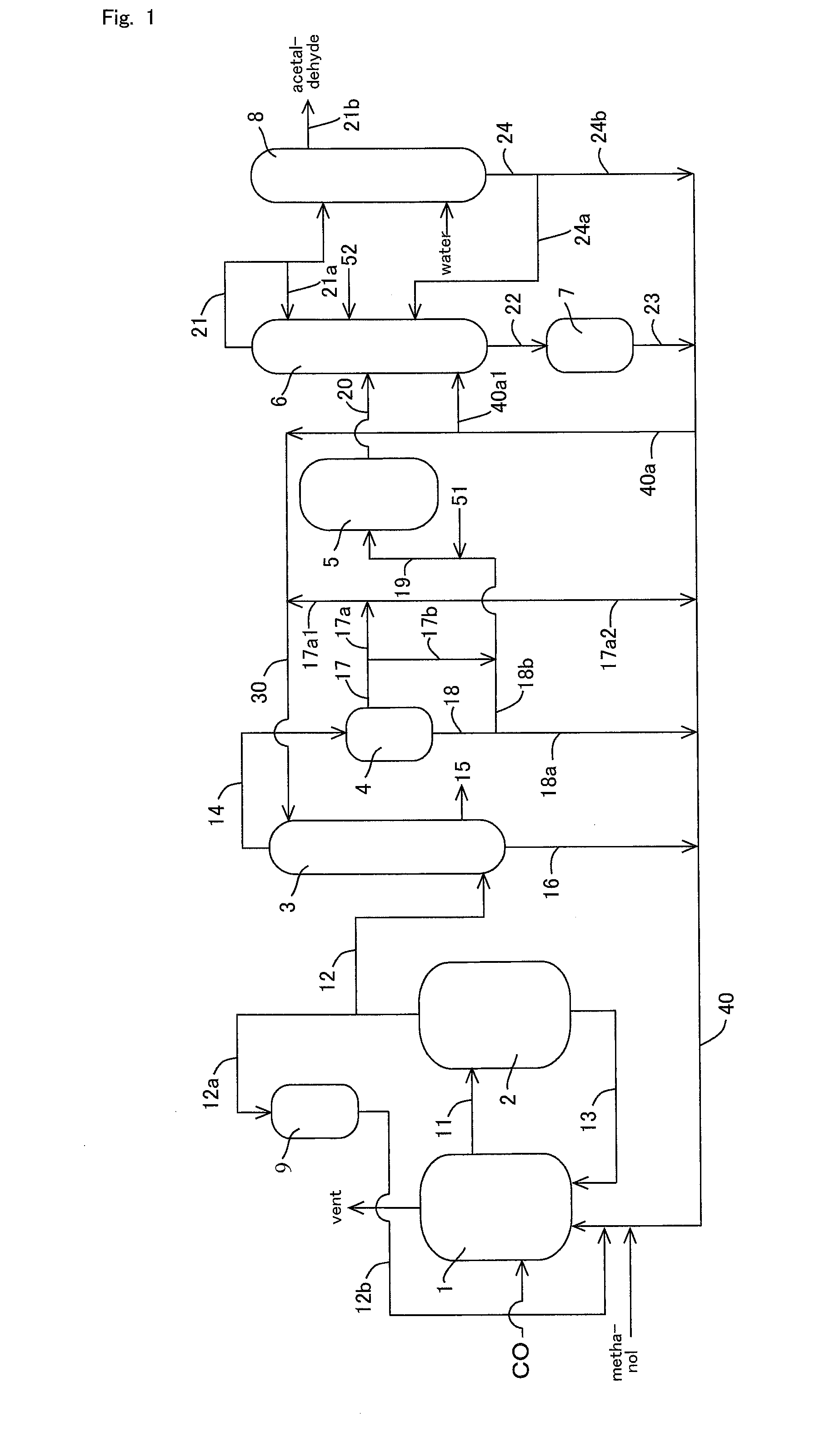
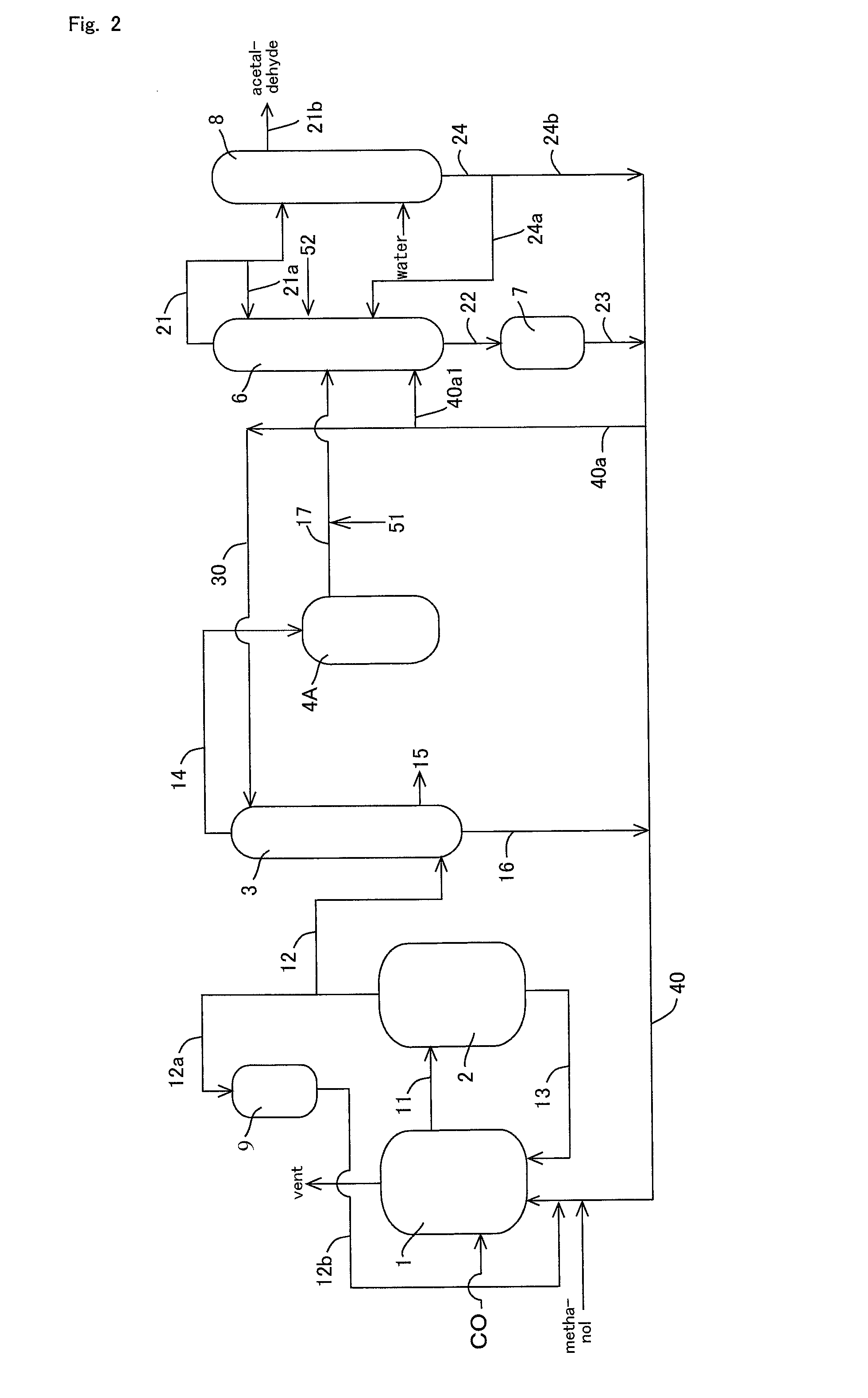
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
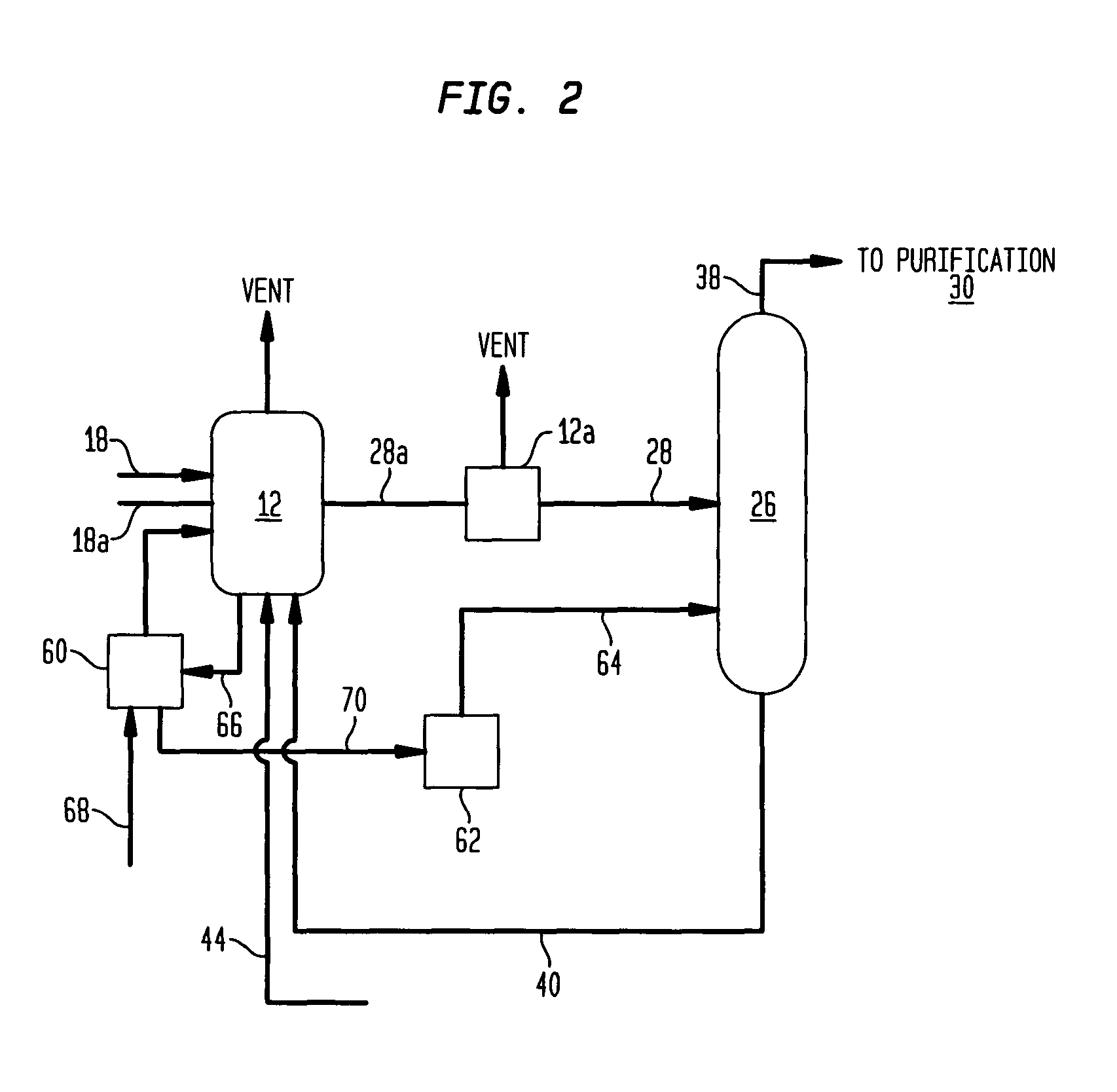
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Addition of iridium to the rhodium/inorganic iodide catalyst system
InactiveUS6211405B1High rateReduce productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of an alcohol, ether or ester to products comprising a carboxylic acid, the anhydride thereof or coproduction of the carboxylic acid and anhydride. More particularly, the present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of methanol to produce acetic acid by reacting methanol with carbon monoxide in a liquid reaction medium containing a catalyst comprising rhodium, iridium, iodide ion, and said reaction medium further comprising water, acetic acid, methyl iodide, and methyl acetate and subsequently recovering acetic acid from the resulting reaction product.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130264186A1Improve concentrationEfficient executionOrganic chemistry methodsDistillation separationBoiling pointFractionating column
Acetic acid is produced while efficiently inhibiting condensation of hydrogen iodide in a distillation column (second distillation column) for purifying crude acetic acid by further distillation.A process for producing acetic acid comprises an acetic acid collection step for feeding a first distillation column with a volatile component at least containing acetic acid, methyl acetate, methyl iodide, water, and hydrogen iodide, separating a first lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a first liquid stream mainly containing acetic acid, and an acetic acid purification step for feeding a second distillation column with the first liquid stream, further separating a second lower boiling point component as an overhead, and collecting a second liquid stream containing acetic acid, wherein an alkali component is added or mixed to the first liquid stream in the manners (1) and / or (2) for distilling a liquid object to be treated containing the first liquid stream and the alkali component in the second column: (1) the alkali component is added to or mixed with the first liquid stream before the first liquid stream is fed to the second column, (2) in the second column, the alkali component is added or mixed at the same height level as or at a height level upper than a height level at which the first liquid stream is fed.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Methanol carbonylation system having absorber with multiple solvent options
A methanol carbonylation system 10 includes an absorber tower 75 adapted for receiving a vent gas stream and removing methyl iodide therefrom with a scrubber solvent, the absorber tower being coupled to first and second scrubber solvent sources 16, 56 which are capable of supplying different first and second scrubber solvents. A switching system including valves 90, 92, 94, 96, 98 alternatively provides first or second scrubber solvents to the absorber tower and returns the used solvent and sorbed material to the carbonylation system to accommodate different operating modes.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Heat transfer compositions with a hydrofluoroalkene, an iodocarbon and additives
The invention pertains to heat transfer compositions, particularly to automobile refrigerants comprising a hydrofluoroalkene, an iodocarbon, a polyol ester and at least one compound comprising trifluoromethane, methyl iodide, heptafluorobutane or propene.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130310603A1Efficient productionEasy to save energyOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIodideReaction step
Acetic acid is produced while inhibiting an increased concentration or production of hydrogen iodide in a carbonylation reactor or corrosion of the carbonylation reactor.A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system comprising a metal catalyst (e.g., a rhodium catalyst), an ionic iodide (e.g., lithium iodide), and methyl iodide in a carbonylation reactor; and in the process, (i) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 860 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 15% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor, and / or (ii) the concentration of the metal catalyst is maintained at not less than 660 ppm on the basis of weight, the concentration of water is maintained at 0.8 to 3.9% by weight, the concentration of the ionic iodide is maintained at not more than 13% by weight, the concentration of methyl iodide is maintained at not more than 13.9% by weight, and the concentration of methyl acetate is maintained at not less than 0.1% by weight, in a whole liquid phase in the reactor.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
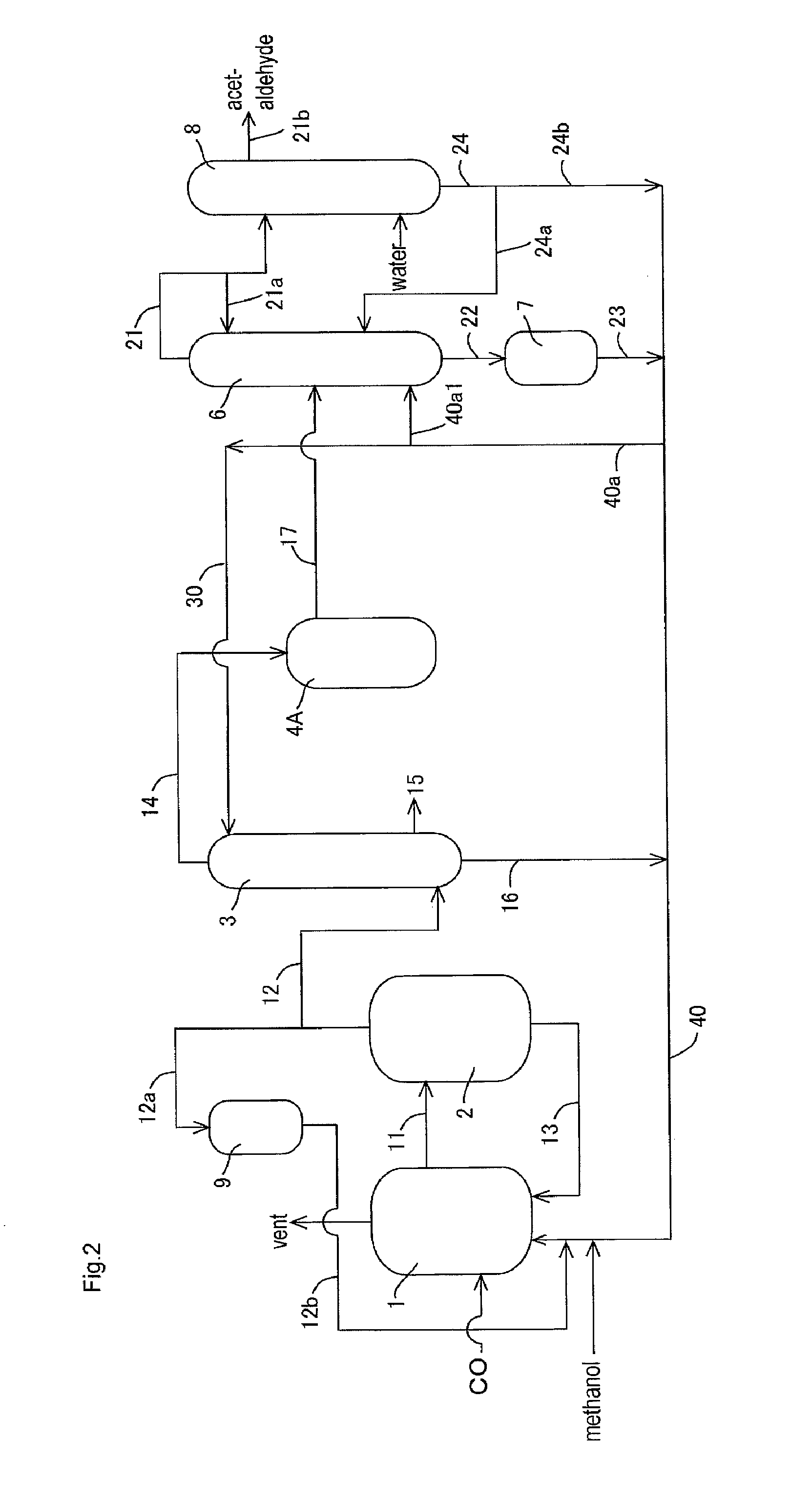
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130281735A1Efficient removalImprove corrosion resistanceOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsDistillationMethyl acetate
Acetic acid is produced while inhibiting increased concentrations of hydrogen iodide and acetic acid in an acetaldehyde distillation column.A production process of acetic acid comprises a step for allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide; a step for feeding a flasher with the reaction mixture to separate a volatile component (2A) and a low-volatile component (2B); a step for feeding a distillation column with the volatile component (2A), and separating an overhead (3A) containing methyl iodide, acetic acid, methyl acetate, water, acetaldehyde, and hydrogen iodide, and a stream (3B) containing acetic acid to collect acetic acid; and a separation step for feeding an acetaldehyde distillation column with at least part of the overhead (3A) and separating a liquid object to be treated containing the overhead (3A) into a lower boiling point component (4A) containing acetaldehyde and a higher boiling point component (4B); wherein, in the separation step, the liquid object contains methanol and / or dimethyl ether in a concentration of 0.1 to 50% by weight is subjected to distillation.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
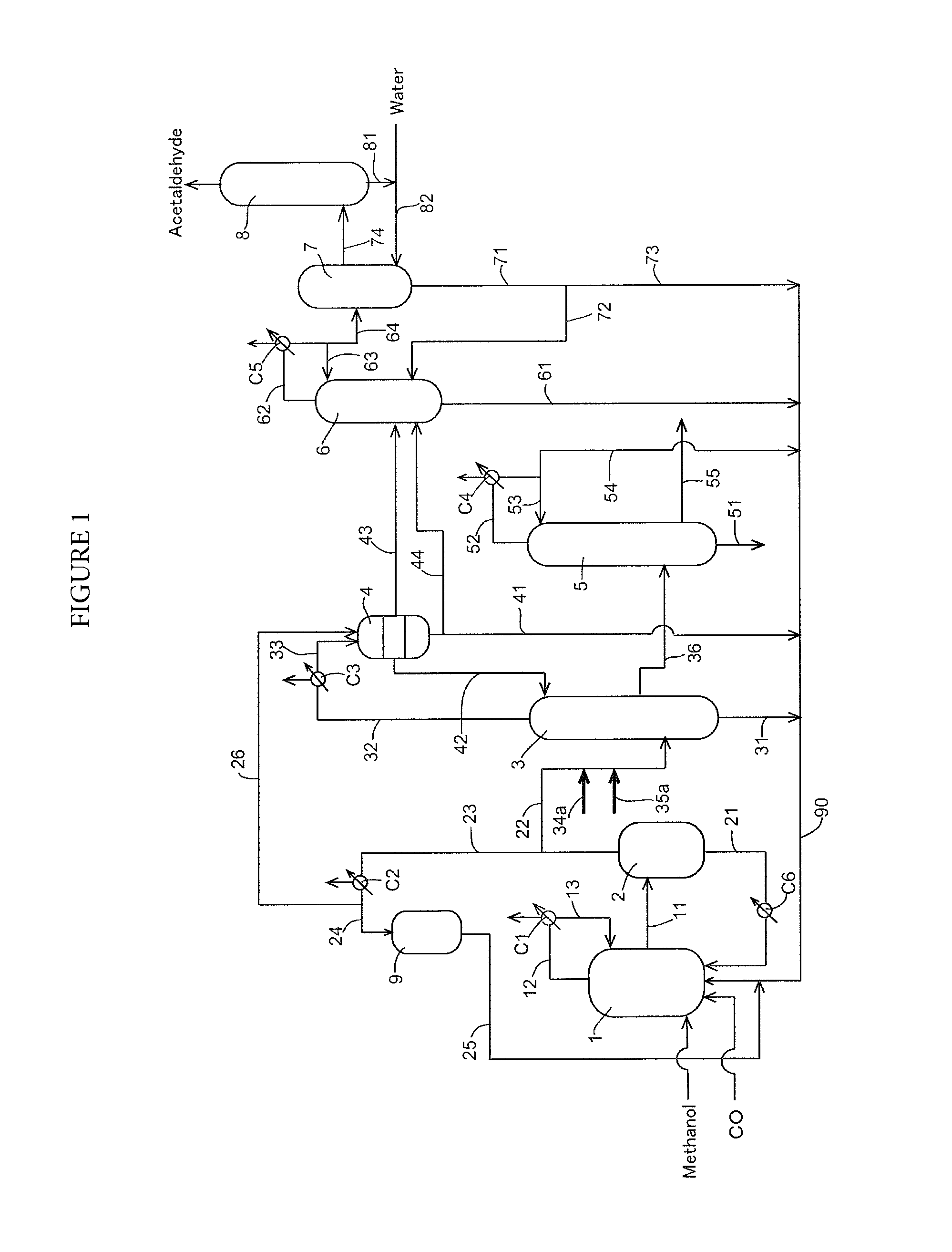
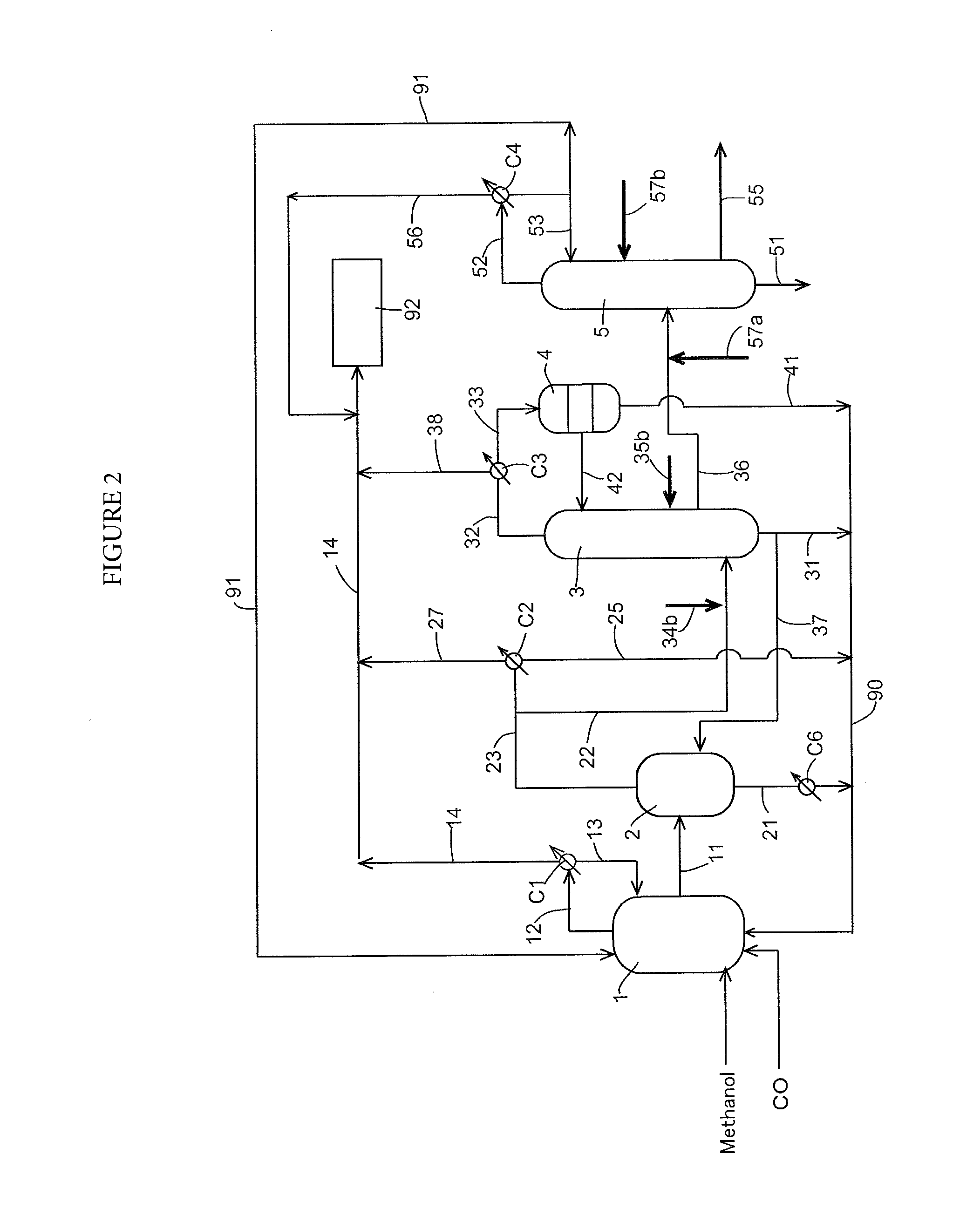
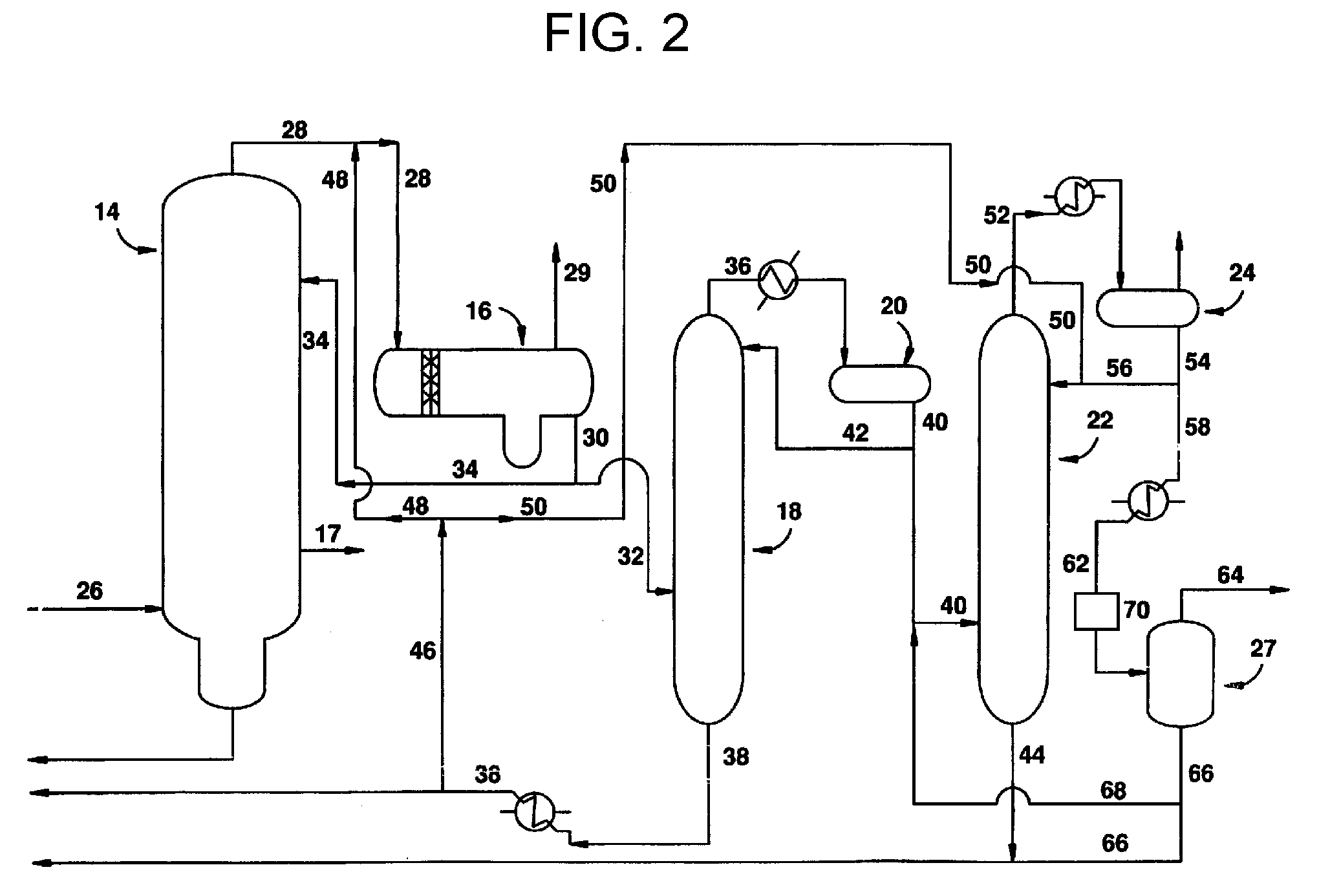
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS9006483B2Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130116470A1High purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationChemical industryDistillationResource saving
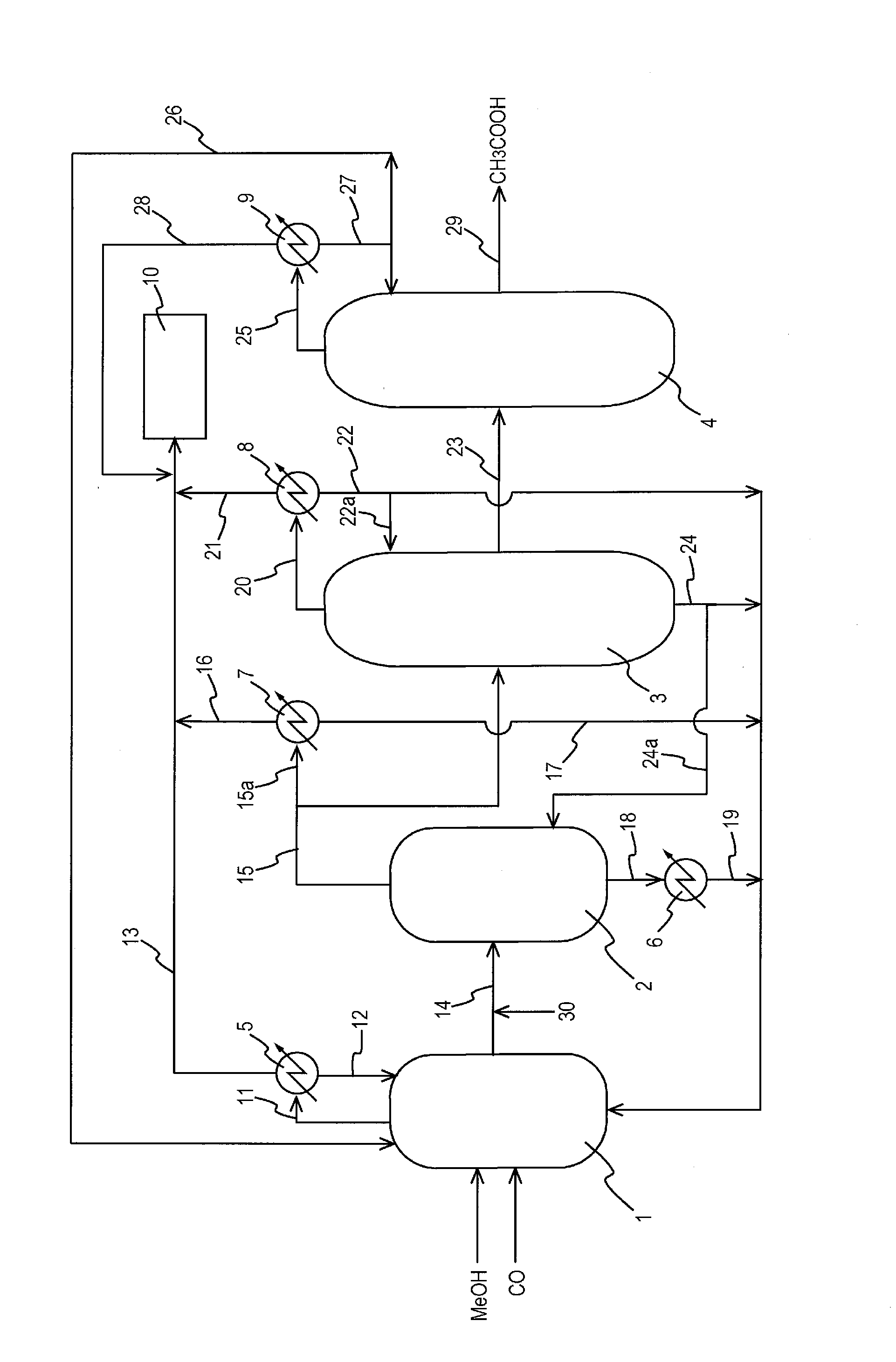
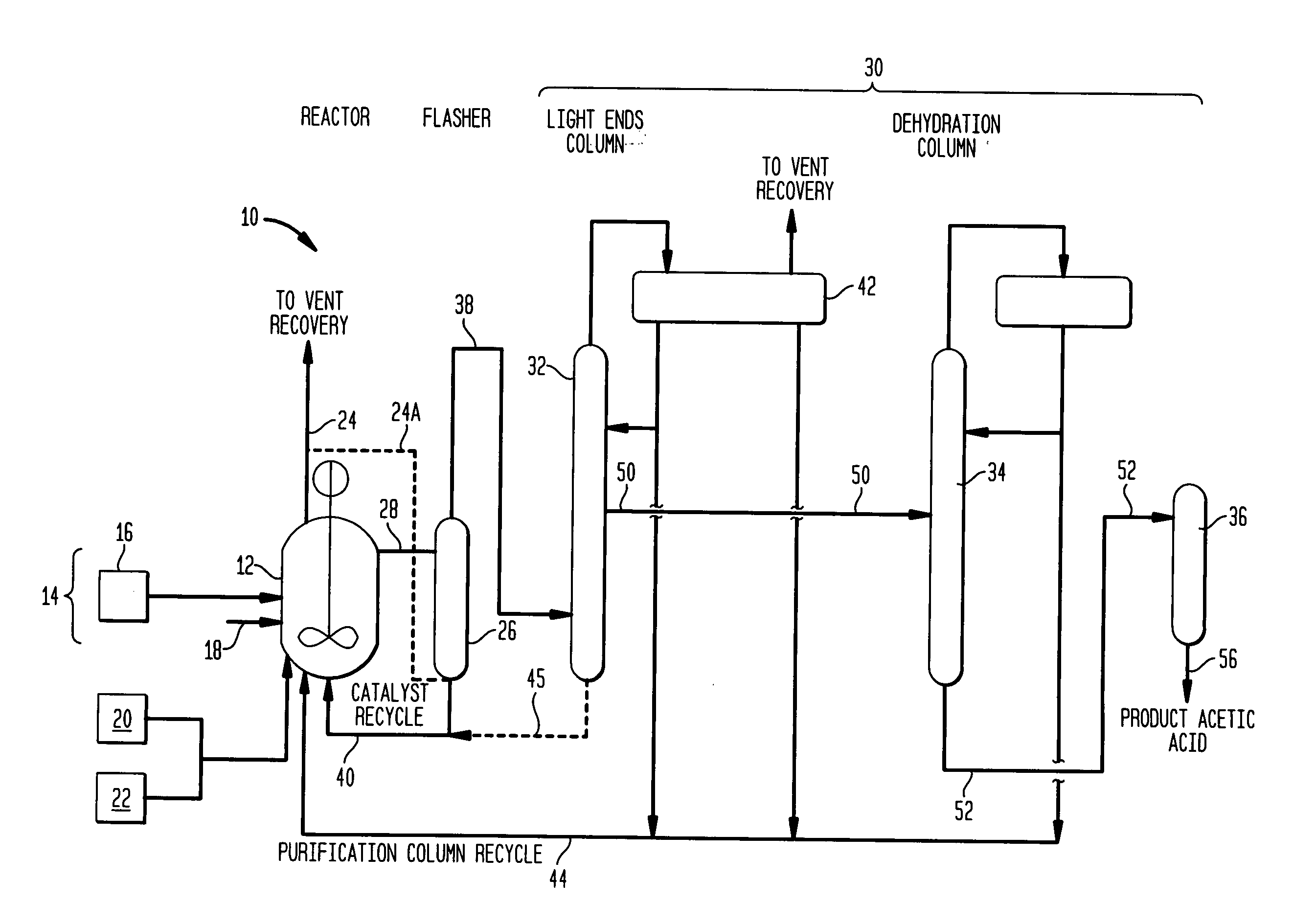
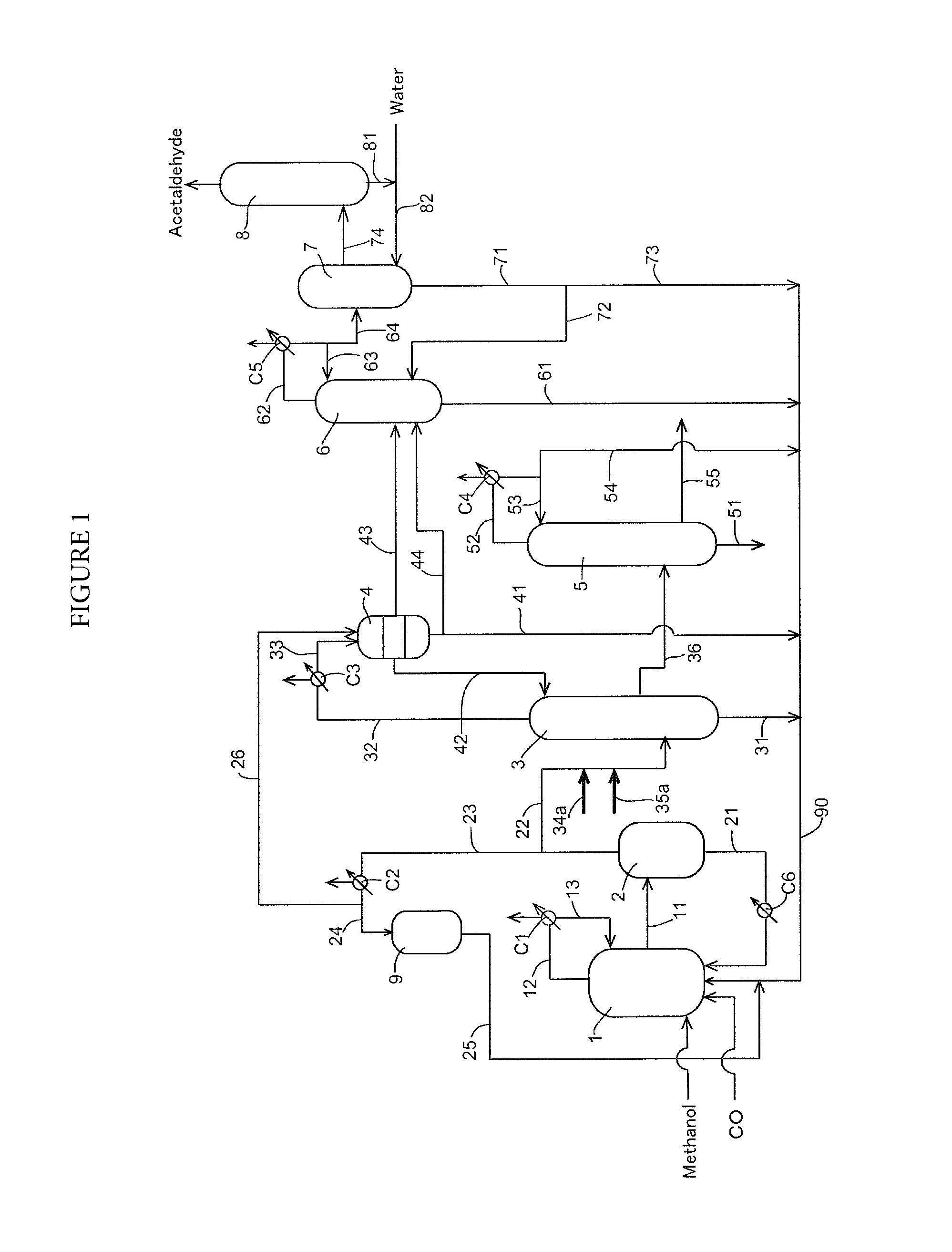
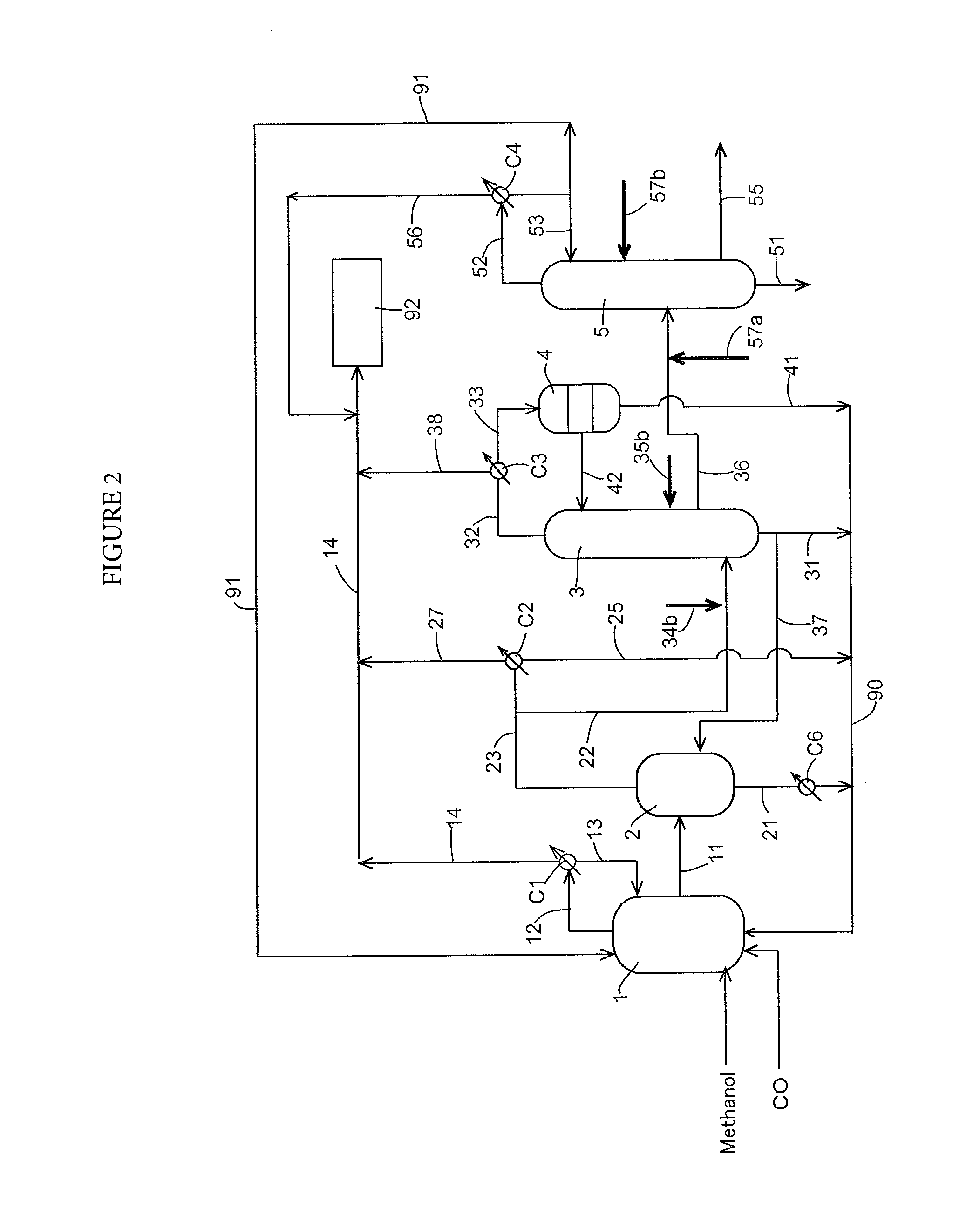
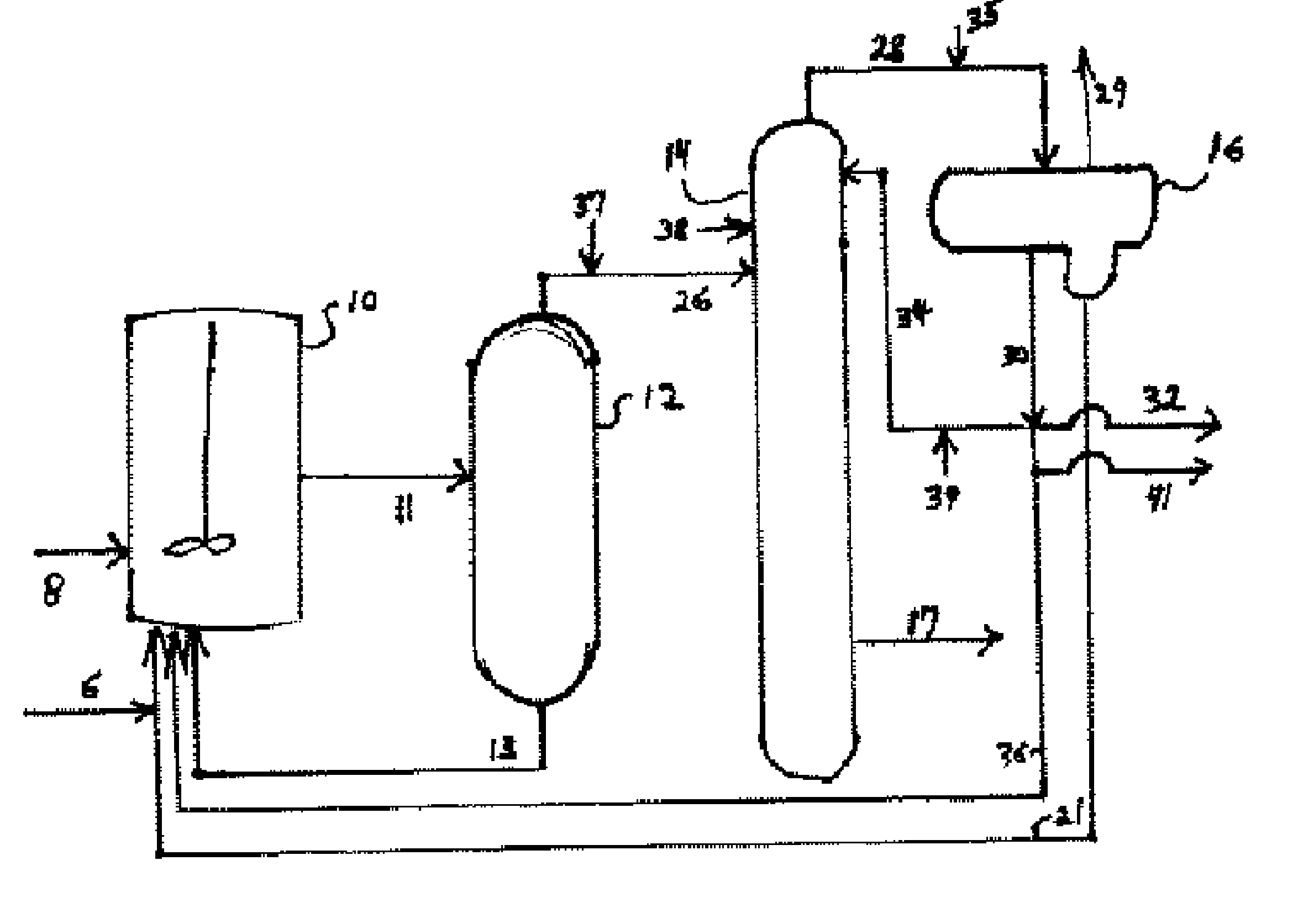
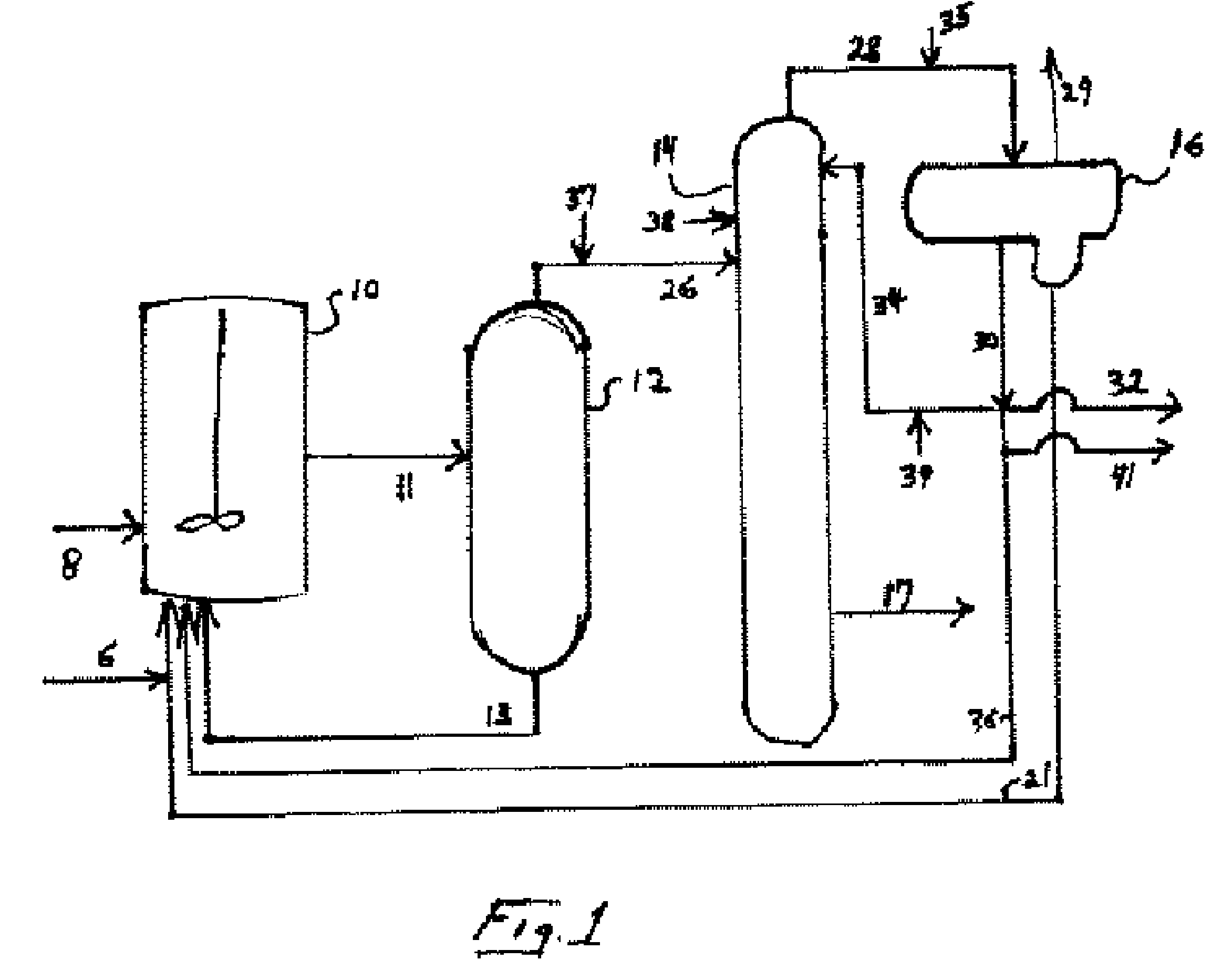
A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing at least one member selected from the group consisting of methanol, dimethyl ether, and methyl acetate to react with carbon monoxide in a catalyst system comprising a rhodium catalyst, an iodide salt, and methyl iodide in the presence of acetic acid and water in a plant compromising a reactor 1; a flasher 2; and a distillation column 3; wherein part of the vaporized stream is introduced into a heat exchanger 7. The process achieves a production of acetic acid with a high purity in a resource-saving and energy-saving equipment by efficiently removing a reaction heat even in a large-sized plant.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Methods for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS7683212B2Efficient productionReduce formationHydrogenOrganic compound preparationGas phaseReaction rate
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Carbonylation process
ActiveUS20070293695A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionHydrogen halideCarboxylic acid
Disclosed is a carbonylation process for the production of carboxylic acids, carboxylic acid esters and / or carboxylic acid anhydrides wherein a carbonylation feedstock compound selected from one or more organic oxygenates such as alcohols, ethers, and esters is contacted with carbon monoxide in the presence of a carbonylation catalyst and one or more onium compounds. The carbonylation process differs from known carbonylation processes in that a halide compound such as a hydrogen halide, typically hydrogen iodide, and / or alkyl halide, typically methyl iodide, extraneous or exogenous to the carbonylation process is not fed or supplied separately to the process.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130261334A1Increase concentrationEfficient executionOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsIodideDistillation
A process for producing acetic acid by: a reaction step for continuously allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst system comprising a metal catalyst, an ionic iodide, and methyl iodide in a carbonylation reactor, a flash distillation step for continuously feeding a flasher with a reaction mixture from the reactor and evaporating a volatile component at least containing product acetic acid, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide by flash distillation to separate the volatile component and a liquid catalyst mixture at least containing the metal catalyst and the ionic iodide, and an acetic acid collection step for separating a stream containing acetic acid from the volatile component to collect acetic acid; wherein, in the flash distillation step, the flash distillation is conducted under the condition that the concentration of methyl acetate in the liquid catalyst mixture is not less than 0.6% by weight.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Control method for process of removing permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process
ActiveUS20050197513A1Organic compound preparationCarbonyl compound preparationAcetic acidDistillation
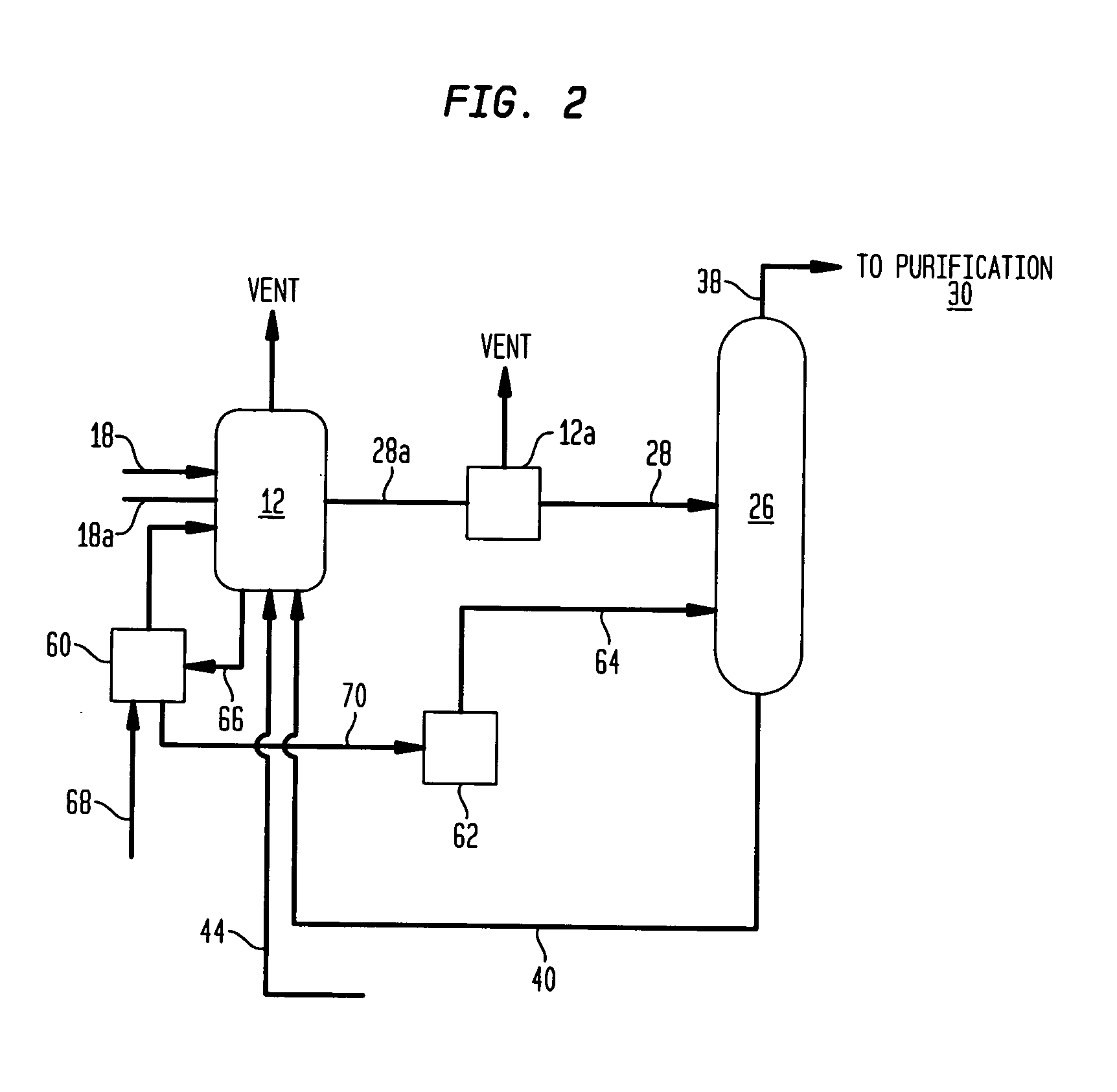
Disclosed is a method of controlling a separation process for removing moving permanganate reducing compounds from a process stream in the methanol carbonylation process for making acetic acid, where the method includes the steps of measuring the density of a stream containing acetaldehyde and methyl iodide, optionally calculating the relative concentrations of acetaldehyde and methyl iodide in the stream, and adjusting distillation or extraction process parameters based on the measured density or one or more relative concentrations calculated therefrom.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
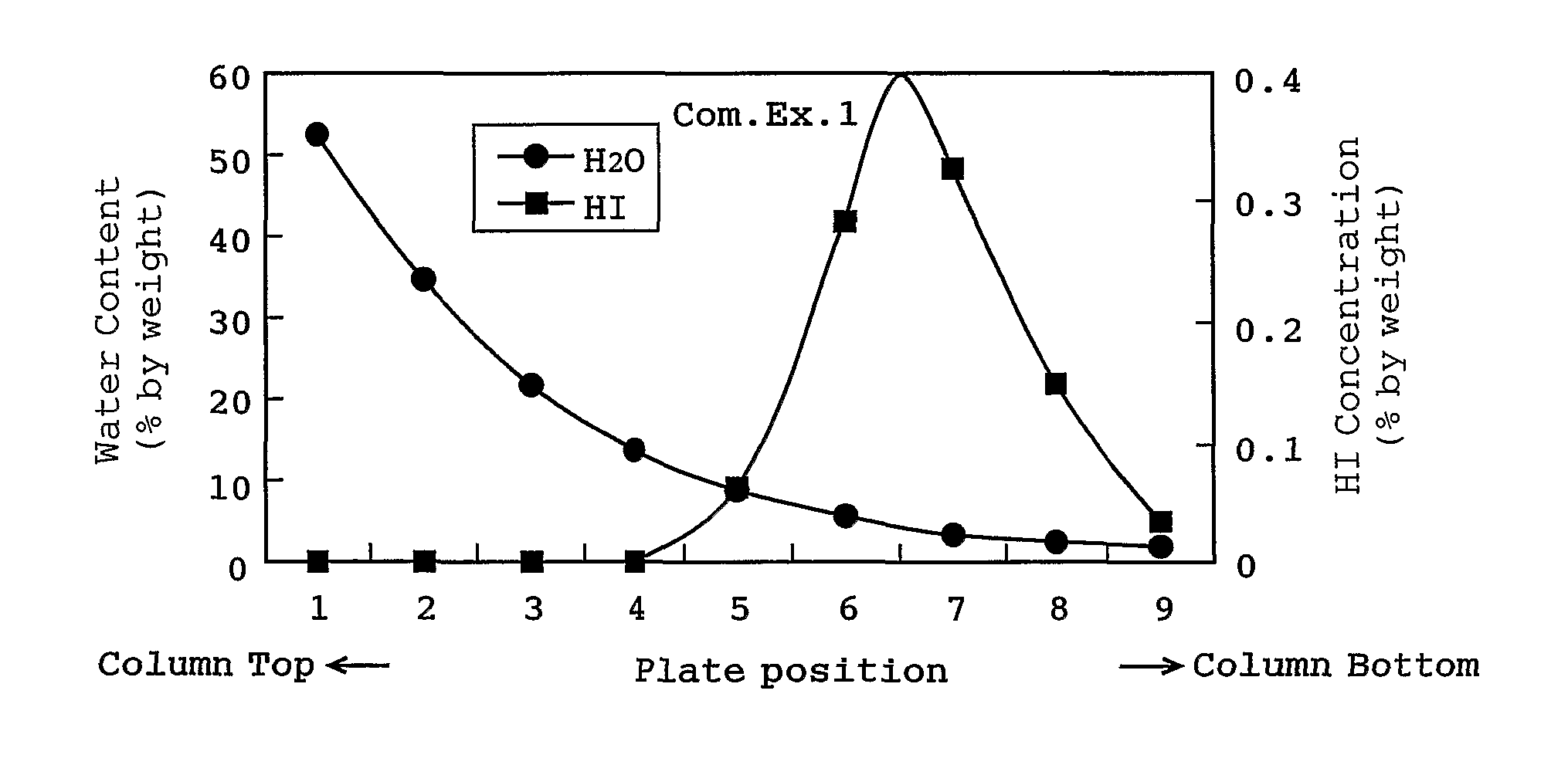
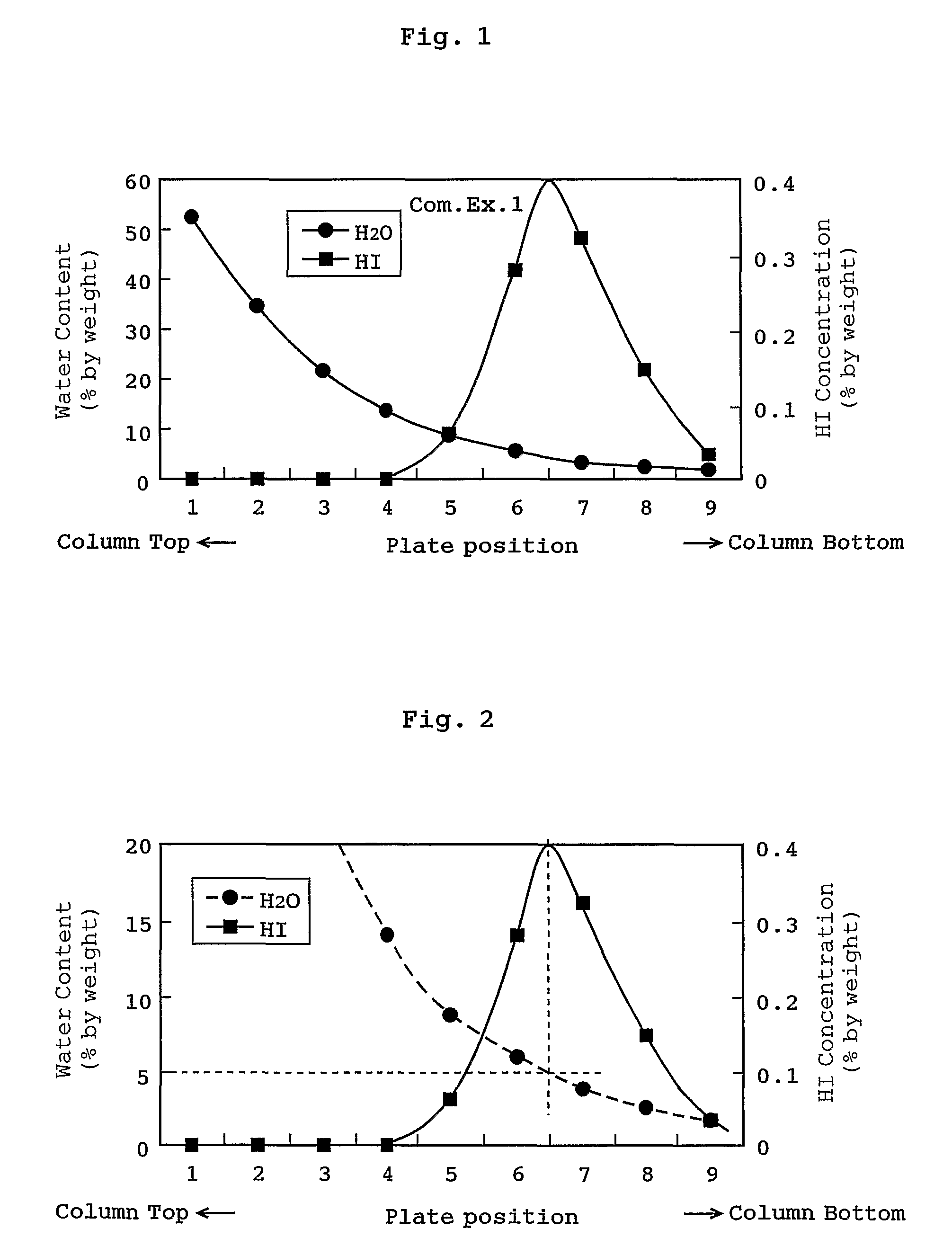
Distillation process
ActiveUS7884241B2Avoid condensationAvoid corrosionOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateDistillation method
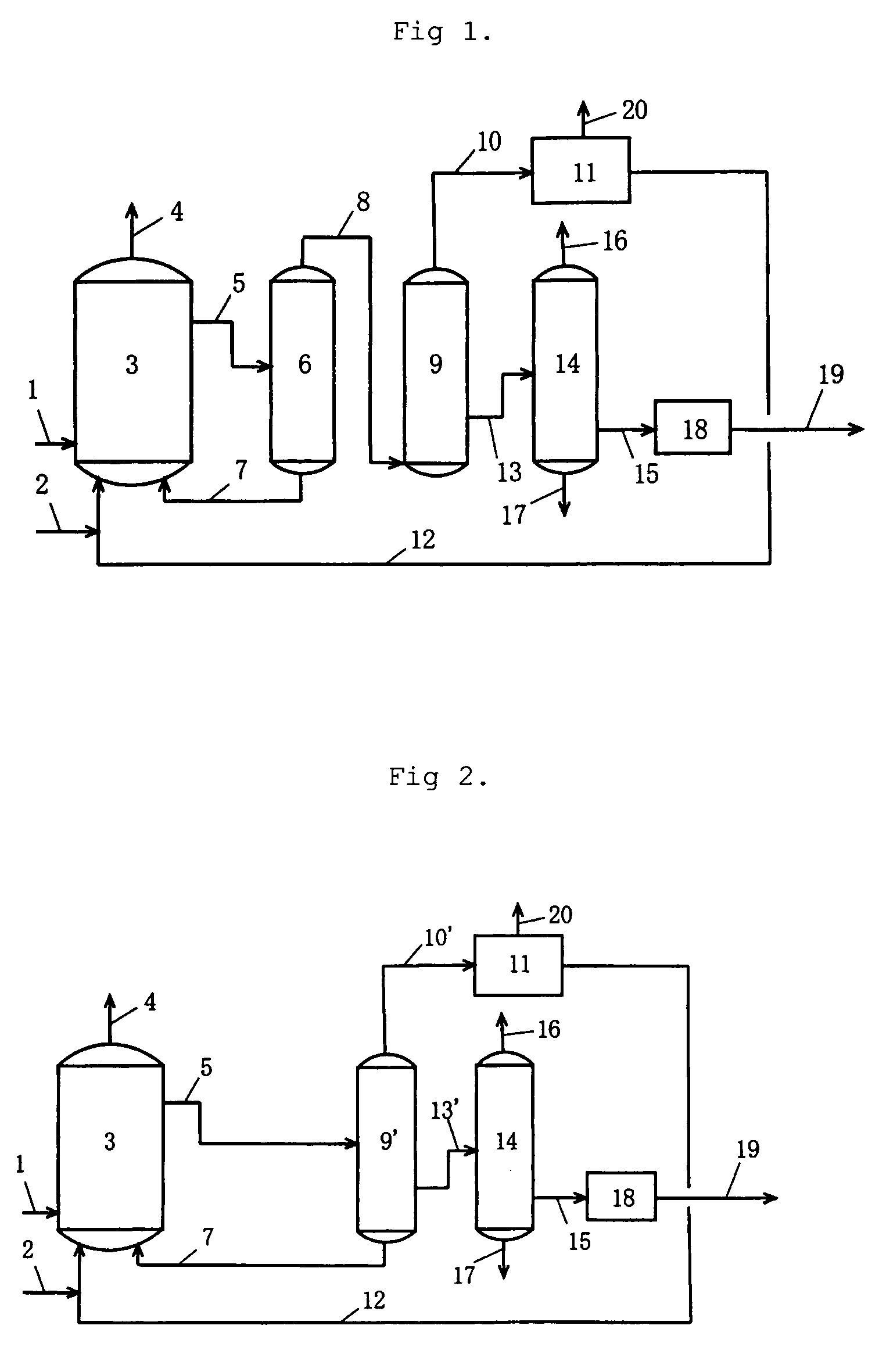
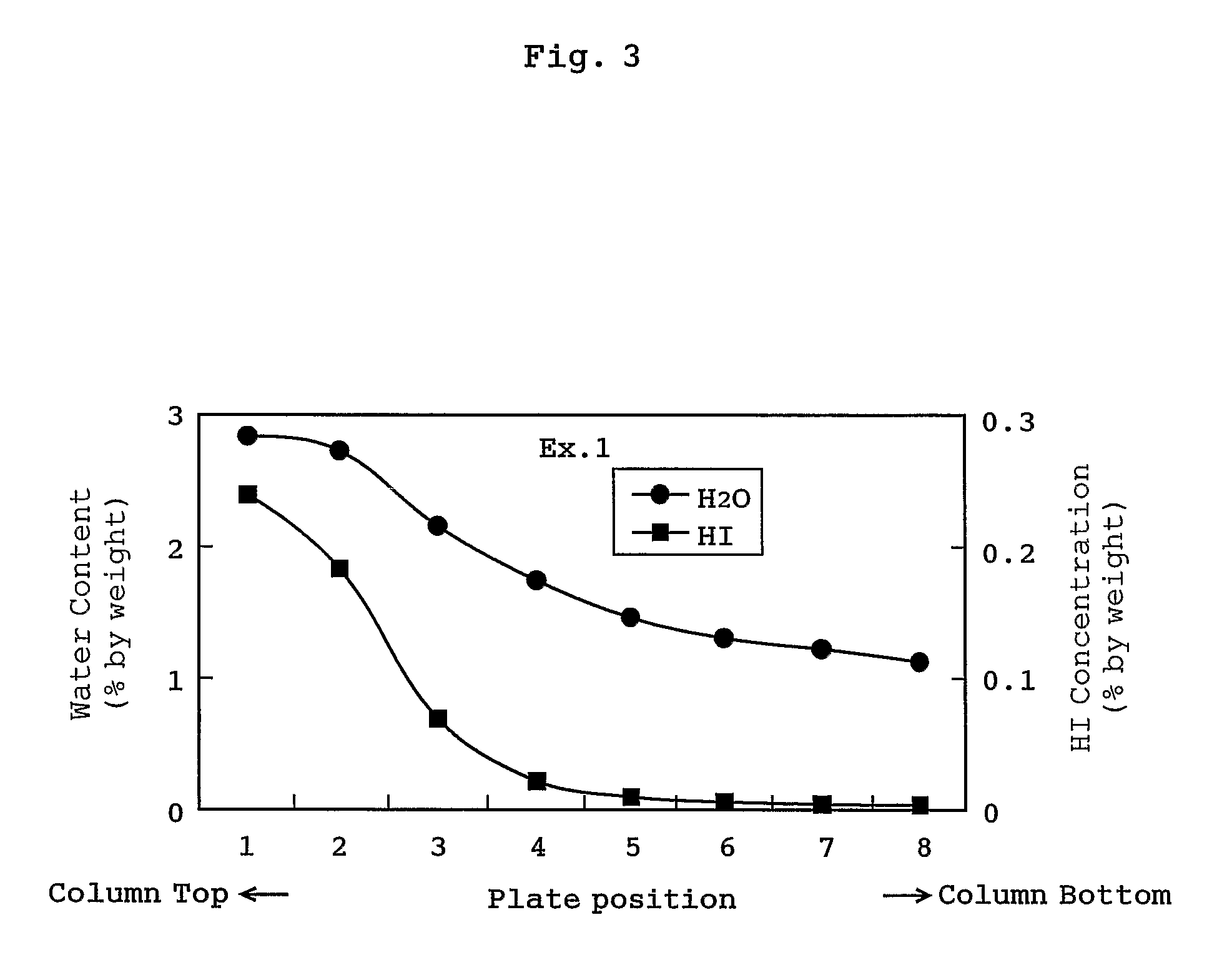
A mixture containing hydrogen iodide and water and having a water content of not more than 5% by weight (particularly not more than 3% by weight) in a distillation system is distilled to prevent condensation of hydrogen iodide in the distillation system. The mixture may comprise hydrogen iodide, water, methanol, methyl iodide, acetic acid, and methyl acetate. Even when the mixture contains hydrogen iodide at a concentration of 1 to 3000 ppm on the basis of weight, an acetic acid product having a concentration of hydrogen iodide of not more than 50 ppm can be obtained by withdrawing a fraction containing hydrogen iodide from the top of the column, and withdrawing acetic acid as a side-cut stream or a stream from the bottom of the column. Such a process (distillation process) effectively inhibits condensation of hydrogen iodide in the distillation system and corrosion in the distillation system.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Preparation of acetic acid
InactiveUS20100063319A1Eliminate useOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionFractionating columnMethyl acetate
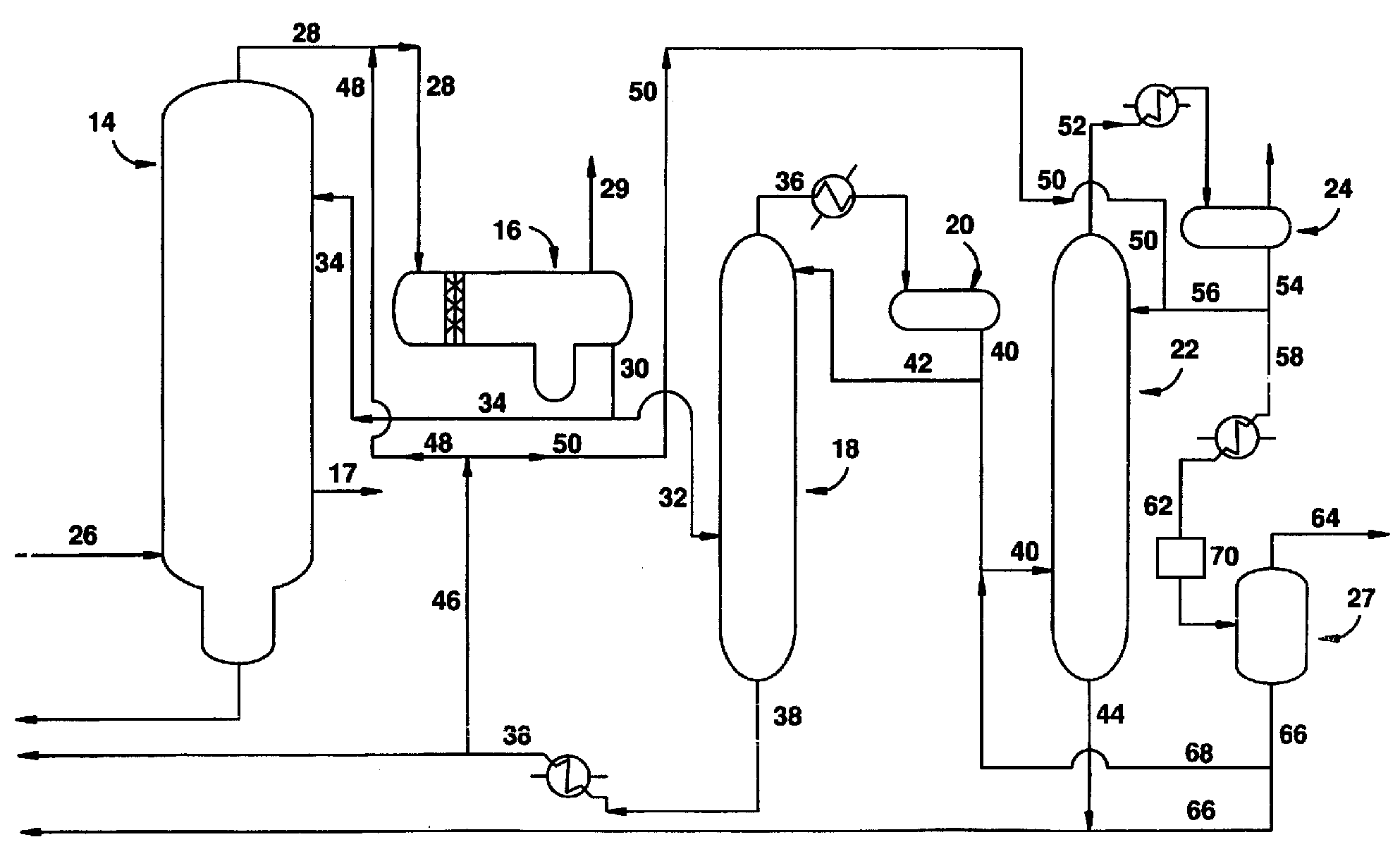
A process for producing acetic acid is disclosed. The process comprises carbonylating methanol to form a reaction mixture comprising a catalyst, catalyst stabilizer, acetic acid, methanol, methyl iodide, methyl acetate, water, and carbon monoxide and introducing at least a portion of the reaction mixture to a distillation column to separate into a bottom steam comprising the catalyst and catalyst stabilizer, a sidedraw stream comprising acetic acid and water, and an overhead stream comprising methanol, methyl acetate, methyl iodide, and water. The process of the invention eliminates the use of flash tank.
Owner:LYONDELLBASELL ACETYLS
Method and apparatus for carbonylating methanol with acetic acid enriched flash stream
ActiveUS20090270650A1Improve concentrationShorten the purification processOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal catalystMethyl acetate
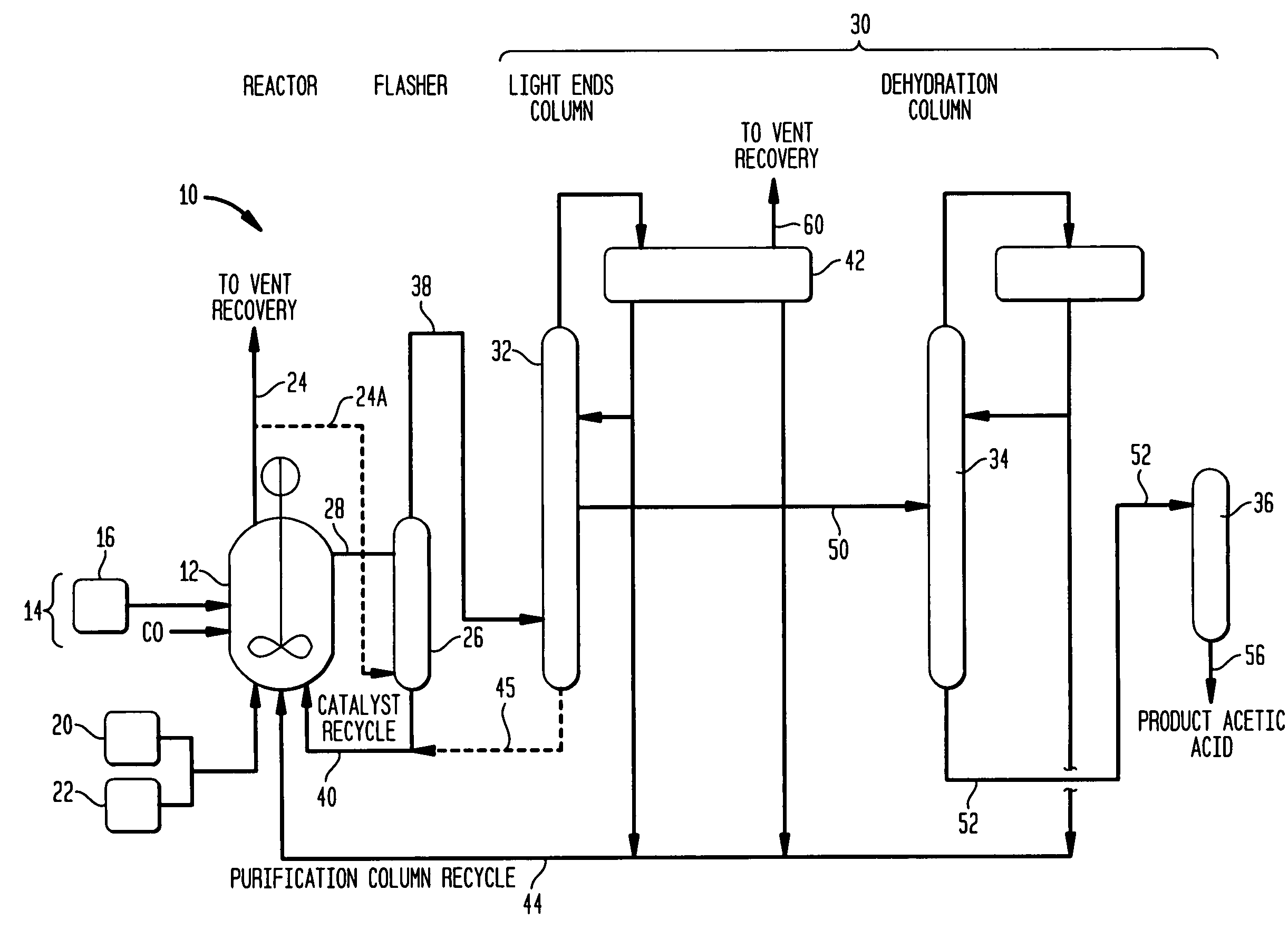
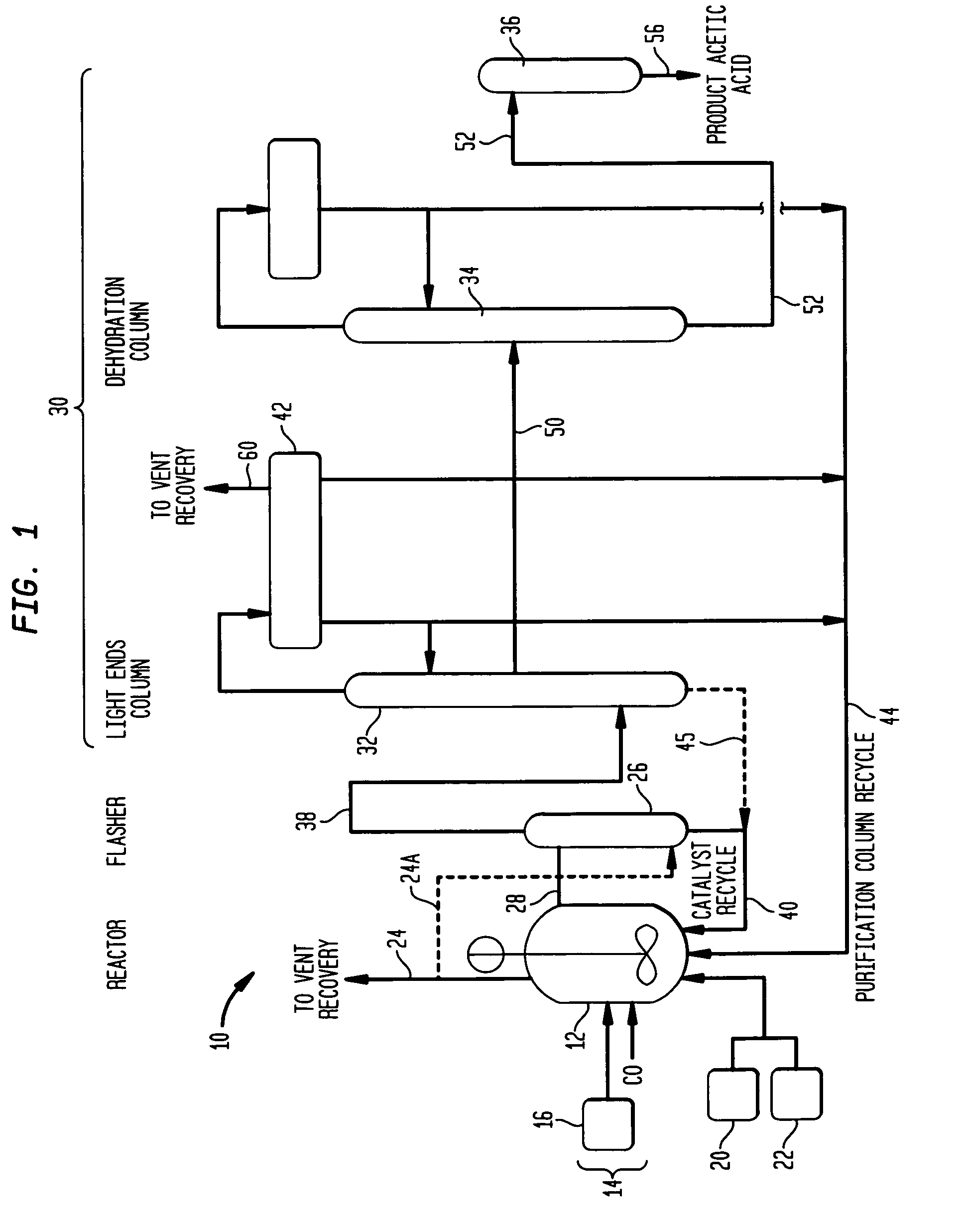
A carbonylation process for producing acetic acid including: (a) carbonylating methanol or its reactive derivatives in the presence of a Group VIII metal catalyst and methyl iodide promoter to produce a liquid reaction mixture including acetic acid, water, methyl acetate and methyl iodide; (b) feeding the liquid reaction mixture at a feed temperature to a flash vessel which is maintained at a reduced pressure; (c) heating the flash vessel while concurrently flashing the reaction mixture to produce a crude product vapor stream, wherein the reaction mixture is selected and the flow rate of the reaction mixture fed to the flash vessel as well as the amount of heat supplied to the flash vessel is controlled such that the temperature of the crude product vapor stream is maintained at a temperature less than 90° F. cooler than the feed temperature of the liquid reaction mixture to the flasher and the concentration of acetic acid in the crude product vapor stream is greater than 70% by weight of the crude product vapor stream.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20150025270A1Avoid pollutionEnsure stable and continuous operationOrganic compound preparationDistillation separationWater concentrationAcetic acid ear
A production process of acetic acid according to the present invention inhibits concentration of hydrogen iodide and improves a liquid-liquid separation of an overhead from a distillation column. Acetic acid is produced by distilling a mixture containing hydrogen iodide, water, acetic acid and methyl acetate in a first distillation column (3) to form an overhead and a side cut stream or bottom stream containing acetic acid, cooling and condensing the overhead in a condenser (C3) to form separated upper and lower phases in a decanter (4). According to this process, a zone having a high water concentration is formed in the distillation column above the feed position of the mixture by feeding a mixture having a water concentration of not less than an effective amount to not more than 5% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 4.5% by weight) and a methyl acetate concentration of 0.5 to 9% by weight (e.g., 0.5 to 8% by weight) as the mixture to the distillation column and distilling the mixture. In the zone having a high water concentration, hydrogen iodide is allowed to react with methyl acetate to produce methyl iodide and acetic acid.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS8957248B2High purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationChemical industryAcetic acid earResource saving
A production process of acetic acid comprises a reaction step for continuously allowing at least one member selected from the group consisting of methanol, dimethyl ether, and methyl acetate to react with carbon monoxide in a catalyst system comprising a rhodium catalyst, an iodide salt, and methyl iodide in the presence of acetic acid and water in a plant compromising a reactor 1; a flasher 2; and a distillation column 3; wherein part of the vaporized stream is introduced into a heat exchanger 7. The process achieves a production of acetic acid with a high purity in a resource-saving and energy-saving equipment by efficiently removing a reaction heat even in a large-sized plant.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Modular and reconfigurable multi-stage high temperature microreactor cartridge apparatus and system for using same
InactiveUS20080181829A1Improve efficiencyIncrease speedGaseous chemical processesLiquid-gas reaction of thin-film typeMicroreactorGas phase
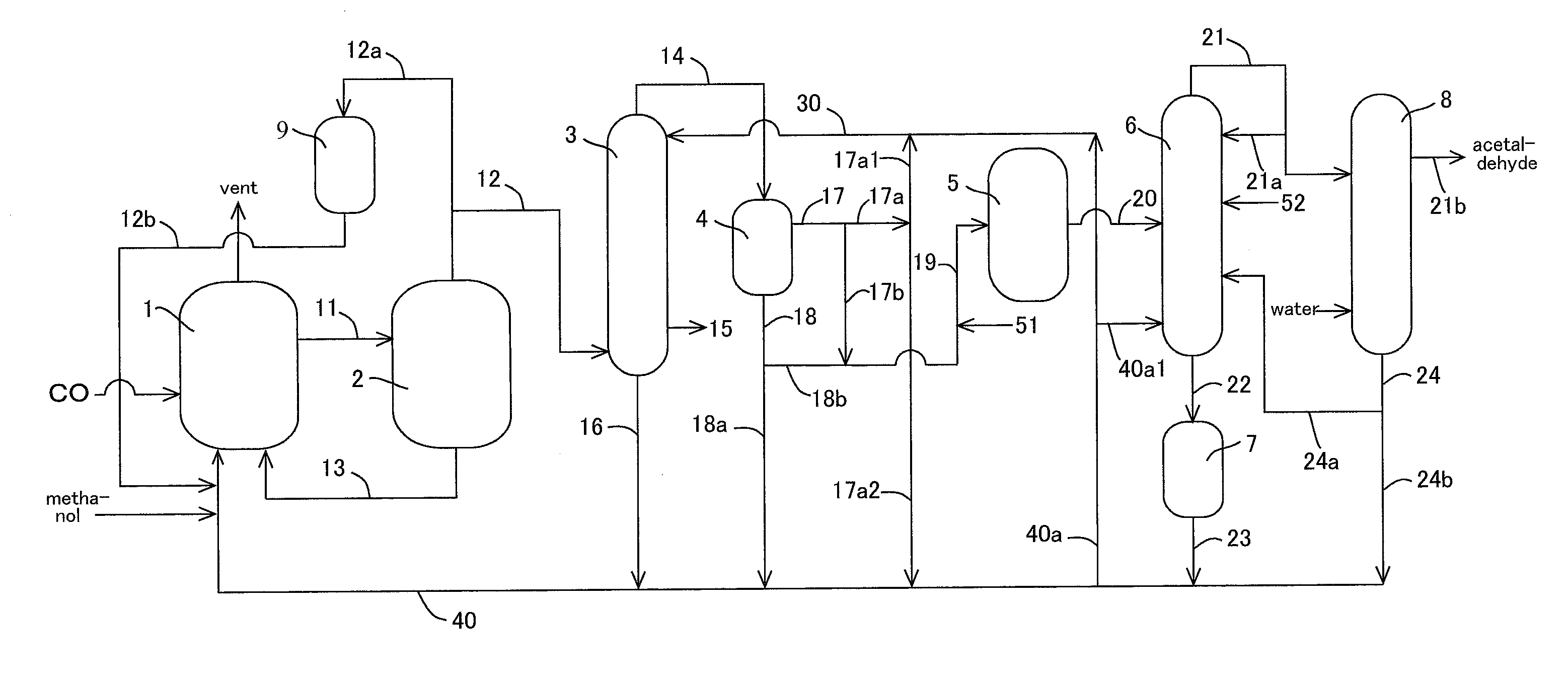
A microfluidic reactor cartridge having glass capillary tubing wound in a coil and surrounded by a ceramic housing capable use in high temperatures and method for using same. In another embodiment, the microfluidic cartridge is a serpentine reactor cartridge with a serpentine microreactor channel formed in a ceramic housing. The serpentine reactor cartridge has an inlet tube attached to its inlet port and an outlet tube attached to its outlet port. The inlet port is a macro / micro interface and the outlet port is a micro / macro interface useful in gas phase reactions where solids must be used to produce a reactant. The method for using a microfluidic reactor cartridge includes two phases, the first phase for producing a radioactive labeled gas such as methyl iodide and the second phase is a methylation reaction.
Owner:ADVION
Quaternized polybenzimidazoles and preparation method thereof
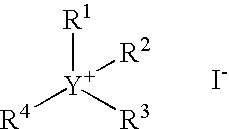
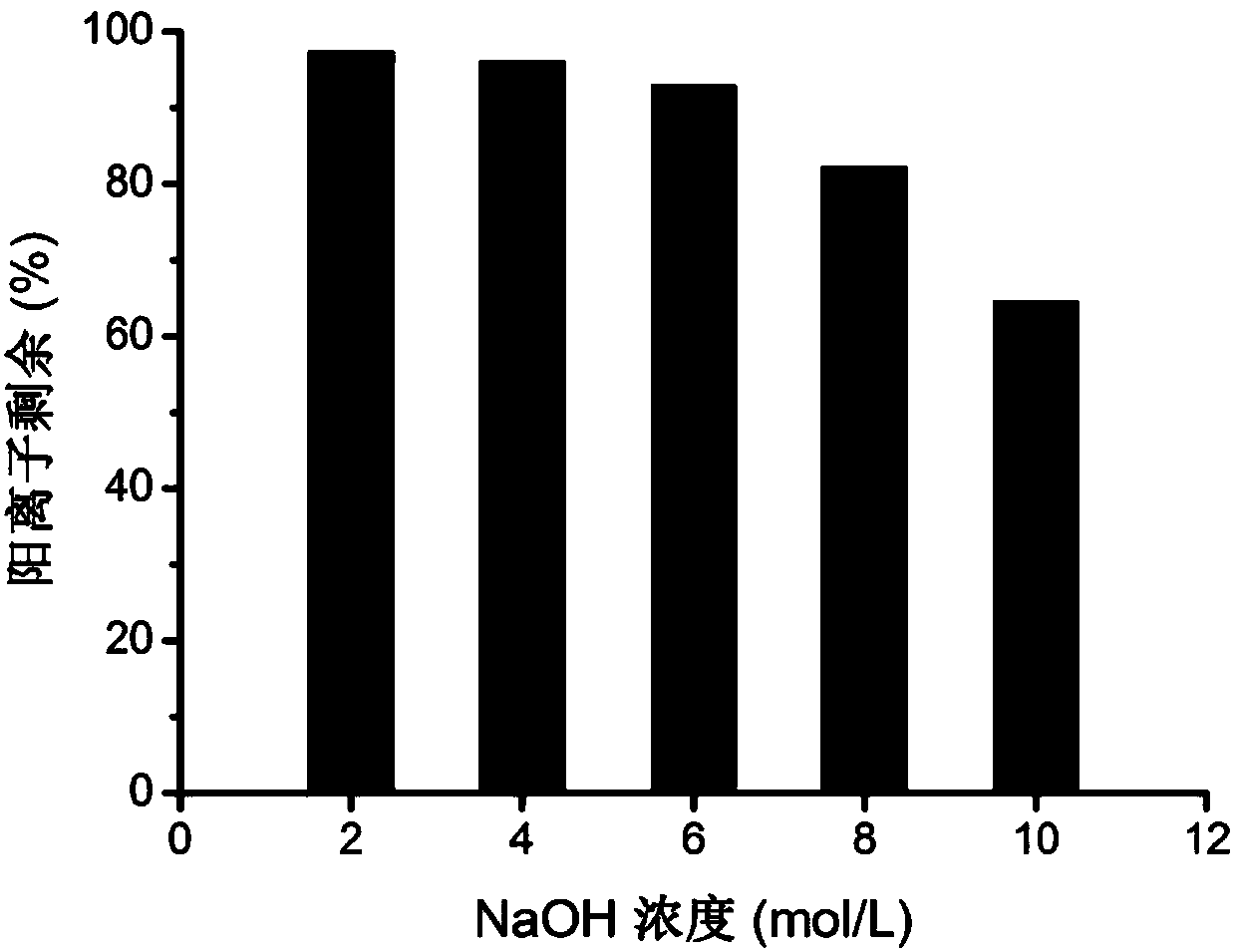
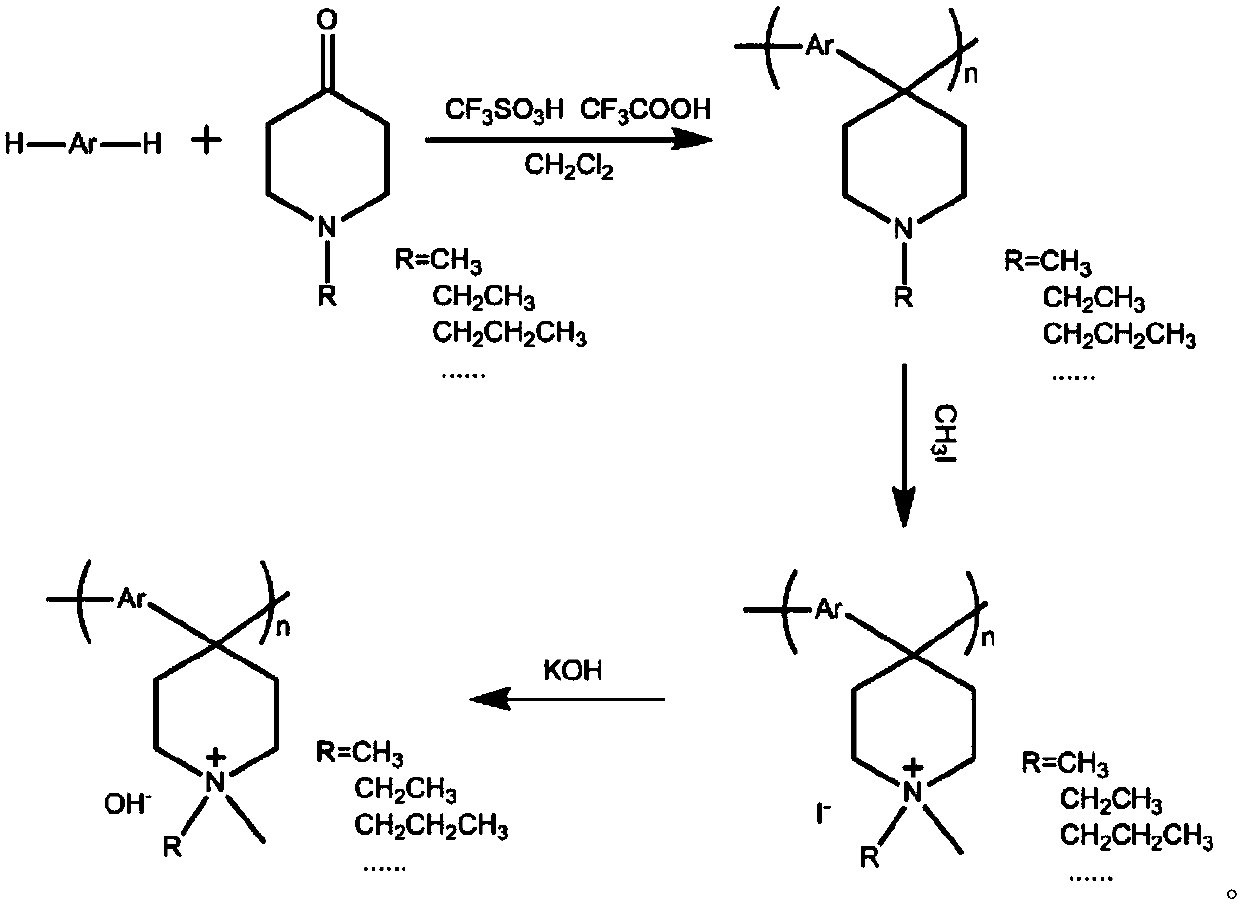
InactiveCN101392060ASolve the problem of brittleness and insolubleGood resistance to methanol penetrationAnion exchangersCell component detailsSolubilitySide chain
The invention provides quaternized polybenzimidazole and a preparation method thereof. Polyanions are formed by polybenzimidazole and derivatives thereof (PBIs) under the function of a dehydrogenized reagent and a solvent, small molecules such as tertiary amine halide, methyl iodide and the like are inoculated to the side chain of the polybenzimidazole molecule and ion exchange is carried out in an alkaline solution, therefore, the quaternized polybenzimidazole with good thermal stability, solubility and membrane forming performance can be prepared. The quaternized polybenzimidazole can be used as an OH<->ion-exchange membrane in alkali fuel cells and has broad application prospect.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Control method for process of removing permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process
ActiveUS20060293537A1Organic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionAcetic acidDistillation
Disclosed is a method of controlling a separation process for removing permanganate reducing compounds from a process stream in the methanol carbonylation process for making acetic acid, where the method includes the steps of measuring the density of a stream containing acetaldehyde and methyl iodide, optionally calculating the relative concentrations of acetaldehyde and methyl iodide in the stream, and adjusting distillation or extraction process parameters based on the measured density or one or more relative concentrations calculated therefrom.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Preparation method of anionic polymer membrane with high chemical stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of an anionic polymer membrane with the high chemical stability, and belongs to the field of ionic polymer membranes. The preparation method comprises thesteps that under catalysis of mixed superacid, an aryl compound and an N-alkyl-4-piperidone compound generate an addition condensation reaction to obtain a linear polymer with high molecular weight and narrow molecular weight distribution; and quaternization modification is conducted on a nitrogen heterocycle on a polymer chain with methyl iodide or alkyl bromide, the obtained quaternized ionic polymer is soaked in a concentrated strong alkaline solution for ion exchange, washing and drying are conducted, and finally the obtained ion polymer is subjected to dissolution casting. According to the preparation method, the experiment process is simple and efficient, and the obtained anionic polymer membrane has the high ionic conductivity and ionic exchange capacity and is very excellent in chemical and heat stability and mechanical strength. The anionic polymer membrane has the very good application prospect and development potential in the alkaline polymer fuel cell field and has the great advantage compared with an anionic polymer membrane applied to a fuel cell at the present stage.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for carbonylating methanol with acetic acid enriched flash stream
ActiveUS7820855B2Organic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsMetal catalystMethyl acetate
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Process for Producing Acetic Acid
ActiveUS20050197506A1Easy to separateFacilitate phase separationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionMethyl acetateFormate Esters
An improved process is disclosed for producing acetic acid, including the following steps: reacting a carbonylatable reactant such as methanol, methyl acetate, methyl formate or dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in a reaction medium containing water, methyl iodide, and a catalyst to produce a reaction product that contains acetic acid; separating the reaction product to provide a volatile phase containing acetic acid, water, and methyl iodide and a less volatile phase; distilling the volatile phase to produce a purified acetic acid product and a first overhead containing water, methyl acetate, and methyl iodide; phase separating the first overhead to provide a first liquid phase containing water and a second liquid phase containing methyl iodide; and adding dimethyl ether to the process in an amount effective to enhance separation of the first overhead to form the first and second liquid phases.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Control method for process of removing permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process
Disclosed is a method of controlling a separation process for removing permanganate reducing compounds from a process stream in the methanol carbonylation process for making acetic acid, where the method includes the steps of measuring the density of a stream containing acetaldehyde and methyl iodide, optionally calculating the relative concentrations of acetaldehyde and methyl iodide in the stream, and adjusting distillation or extraction process parameters based on the measured density or one or more relative concentrations calculated therefrom.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
Working medium for heat cycle, composition for heat cycle system, and heat cycle system
ActiveCN107614652AFully playLow greenhouse potentialHeat-exchange elementsCompression machinesKryptonEngineering
This working medium for a heat cycle contains trifluoroethylene and a first component comprising at least one substance selected from carbon dioxide, fluoromethane, trifluoroiodomethane, methane, ethane, propane, helium, neon, argon, krypton, xenon, nitrogen, and ammonia.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
Cation fluorine surfactant and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101293853AReduce surface tensionThe synthesis method is simpleOrganic compound preparationTransportation and packagingBenzoic acidSolvent
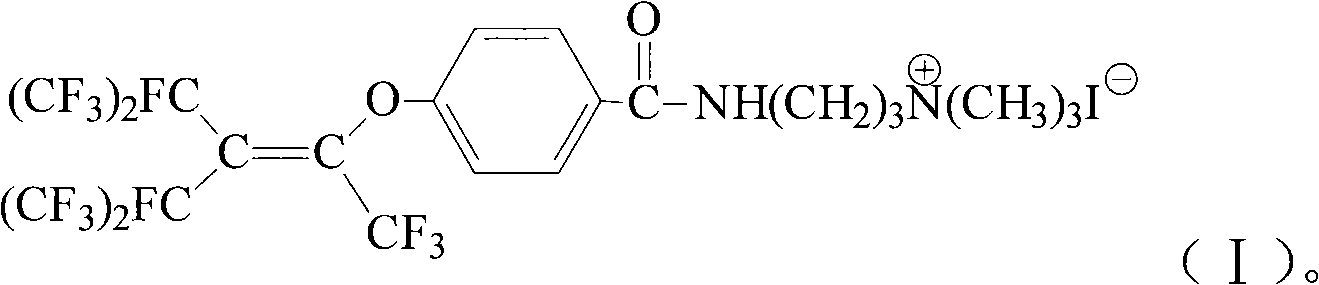
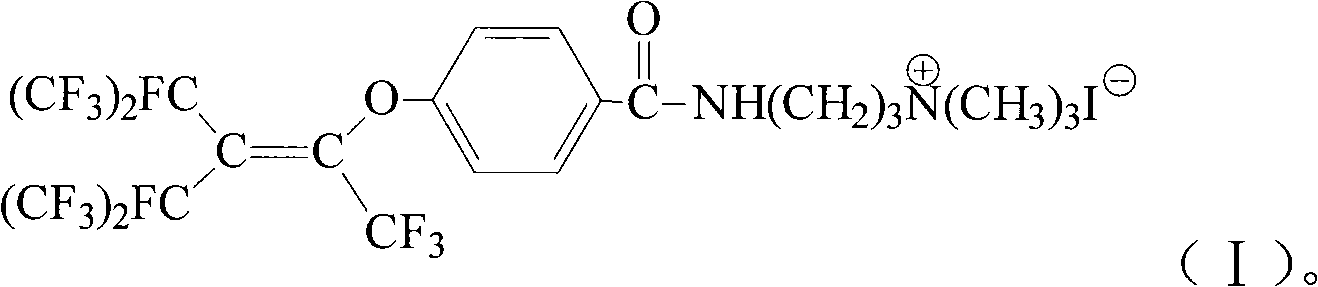
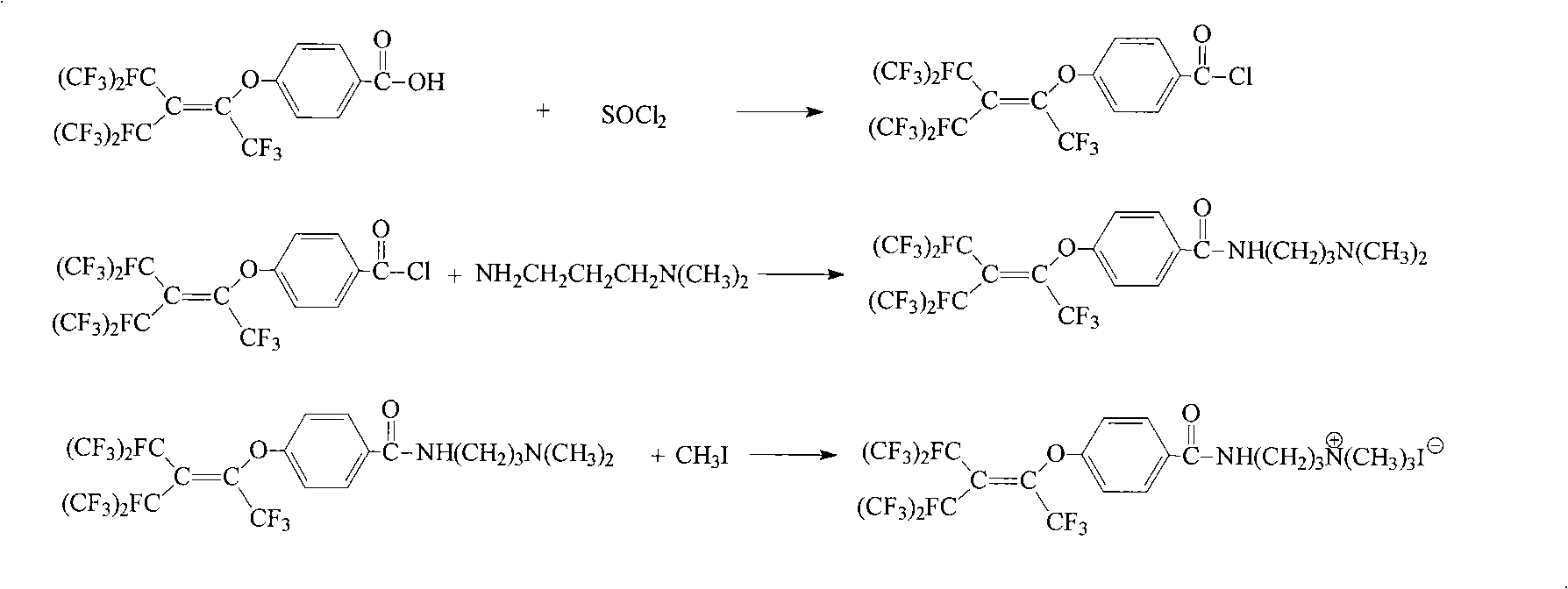
The invention provides a cationic fluorosurfactant (I) and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises adopting perfluorobutenyloxy benzoic acid and thionyl chloride as raw materials to perform a chloroacylation reaction at -30 DEC C to 70 DEC C in polar solvent, adding N,N-dimethyl propylene diamine and base catalyst, performing an amidation reaction at -20 DEC C to 120 DEC C, separating the reactant liquor to obtain N-[3-(p-perfluorobutenyloxybenzamido)propyl]-N, N-dimethyl amine, dissolving into non-proton polar solvent, adding iodomethane, performing a quaternization reaction at 0 DEC C to 100 DEC C, and filtering the reactant liquor to obtain N-[3-(p-butenyloxybenzamido)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethyl ammonium iodide. The method has simple synthetic method and high reaction yield. Aqueous solution prepared from the N-[3-(p-butenyloxybenzamido)propyl]-N,N,N-trimethyl ammonium iodide has low surface tension.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Process for producing acetic acid
ActiveUS20130303800A1Stable productionEfficient removalOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reactionPtru catalystDistillation
A process for stably producing high-purity acetic acid while efficiently removing acetaldehyde is provided.The process for producing acetic acid comprises a reaction step for allowing methanol to react with carbon monoxide in the presence of a metal catalyst, a halide salt, and methyl iodide; a step for continuously feeding a flasher with the reaction mixture and separating a lower boiling point component (2A) containing acetic acid and methyl iodide and a higher boiling point component (2B) containing the metal catalyst and the halide salt; a step for feeding a distillation column with the lower boiling point component (2A), and separating a lower boiling point component (3A) containing methyl iodide and acetaldehyde and a stream (3B) containing acetic acid to collect acetic acid; a condensation step for condensing and temporarily holding the lower boiling point component (3A) in a decanter and discharging the lower boiling point component (3A) from the decanter; and a step for separating the lower boiling point component (3A) discharged from the decanter into acetaldehyde and a liquid residue and recycling the liquid residue to the reaction system. In the condensation step, the amount of the lower boiling point component (3A) to be held is controlled based on a fluctuating flow rate of the lower boiling point component (3A) to be fed to the decanter.
Owner:DAICEL CHEM IND LTD
Trifluoroiodomethane preparation method
ActiveCN102992943AObvious cost advantageWorkmanship is feasibleChemical recyclingHalogenated hydrocarbon preparationActive agentEthylic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing trifluoroiodomethane through utilizing industrial waste trifluoroacetic acid and industrially recovered iodine. The method has the characteristics of low cost, simple operation, mild reaction, fast reaction speed, high yield, high selectivity, environmental protection and the like. The synthesized trifluoroiodomethane is an important fluorine-containing fine chemical engineering raw material, and can be used for producing fluorine-containing finishing agents, fluorine-containing surfactants and other fluorine-containing fine chemicals.
Owner:SINOCHEM LANTIAN +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com