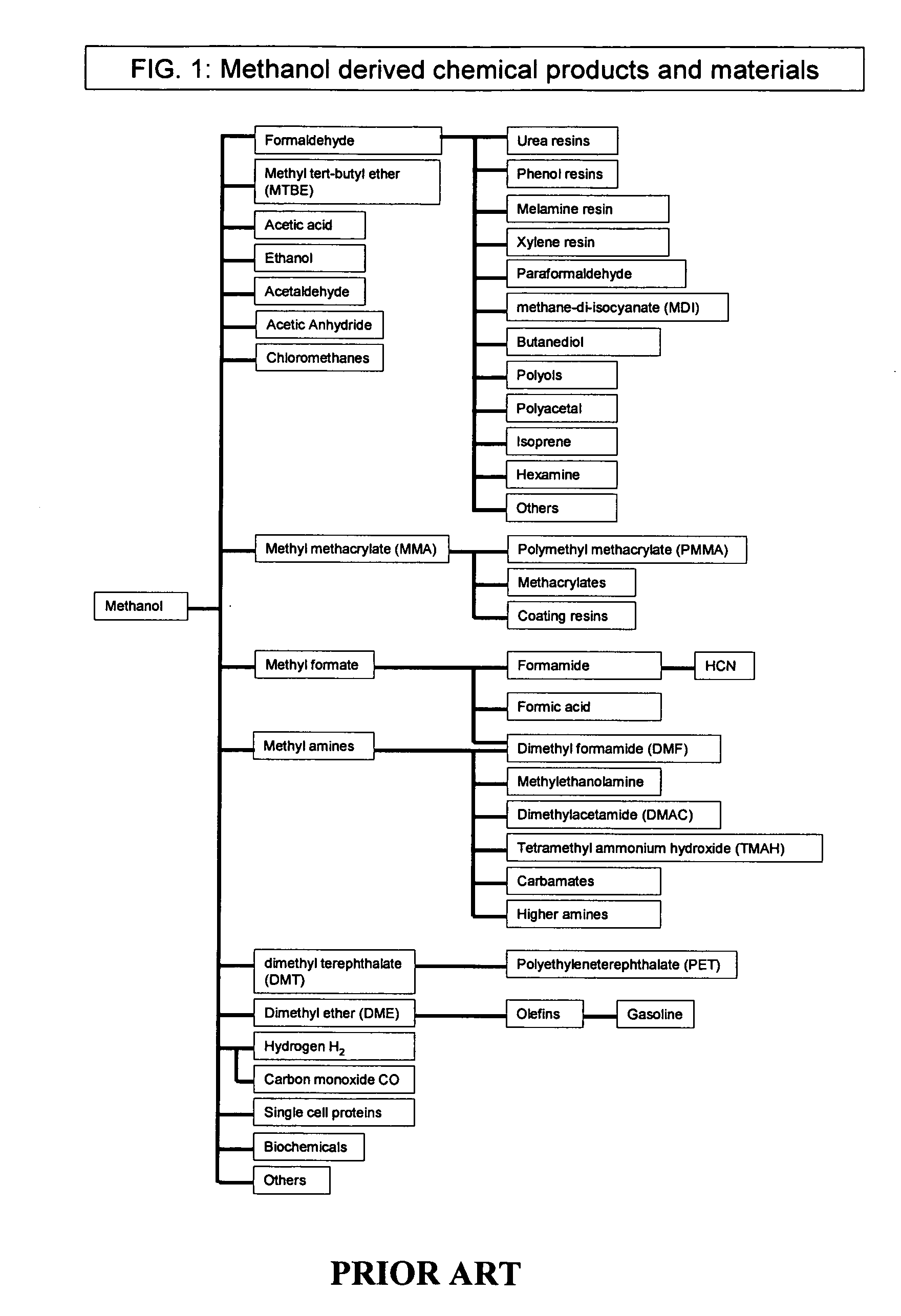
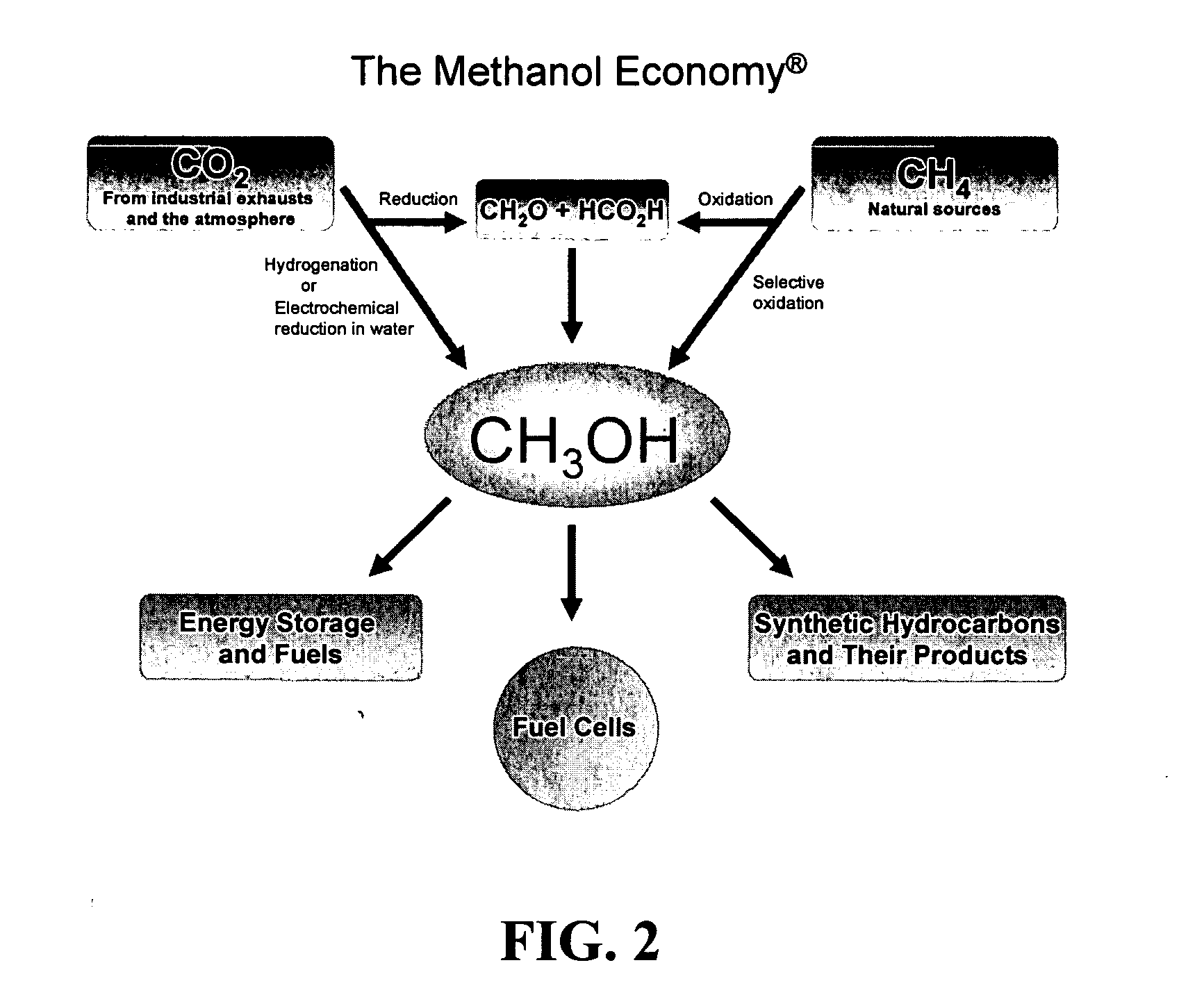
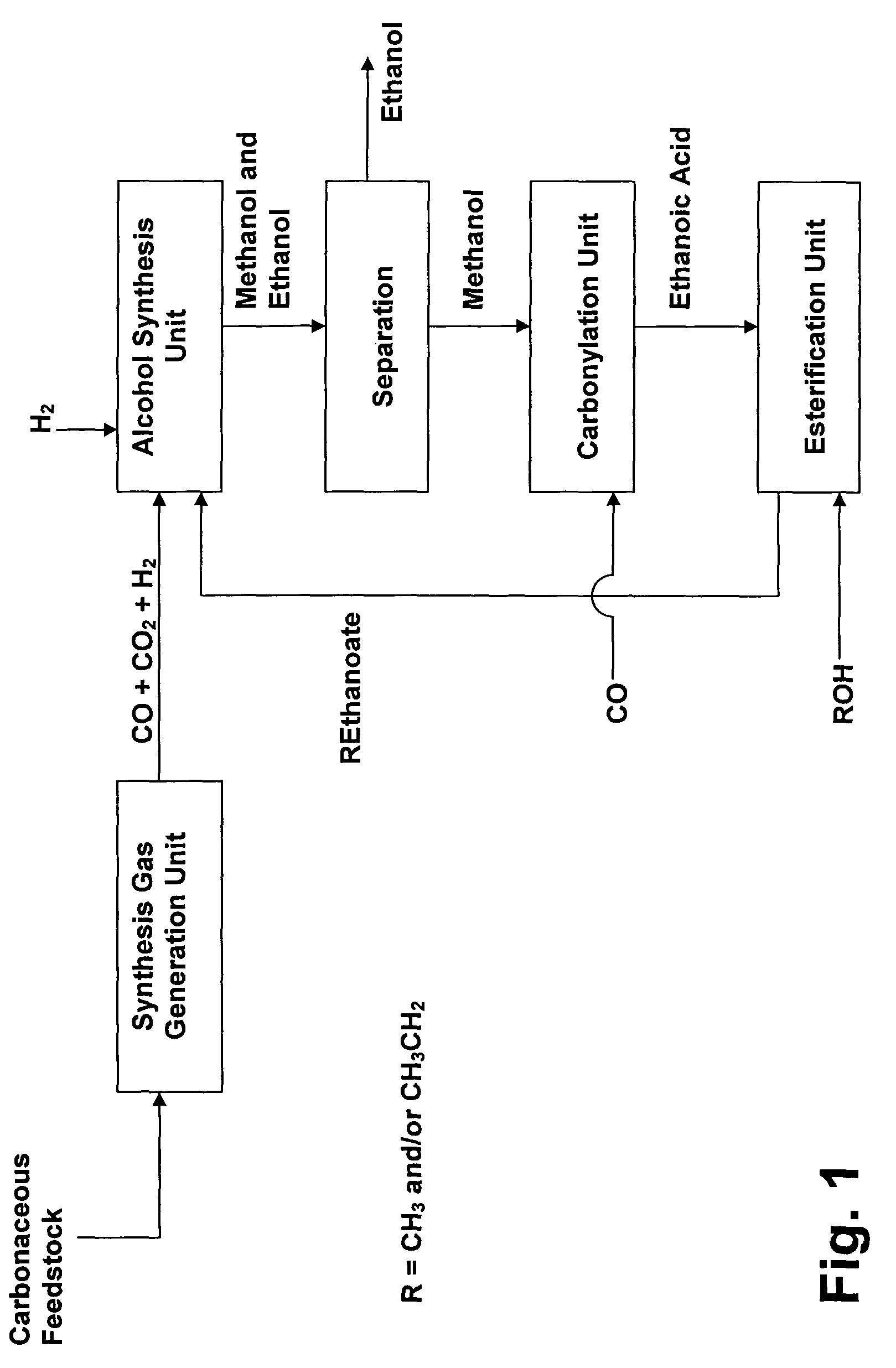
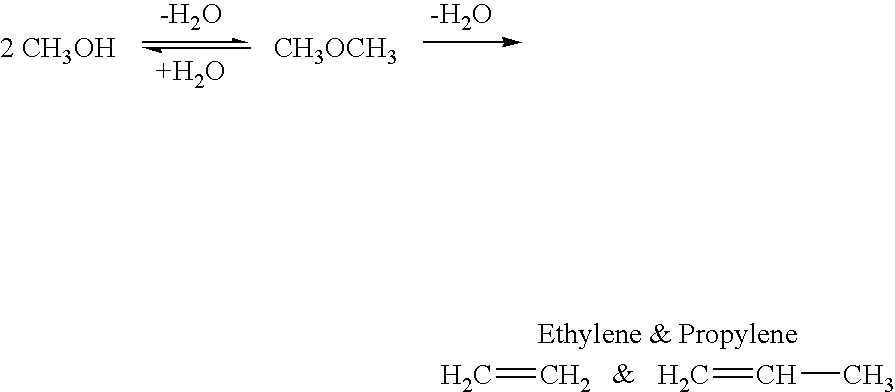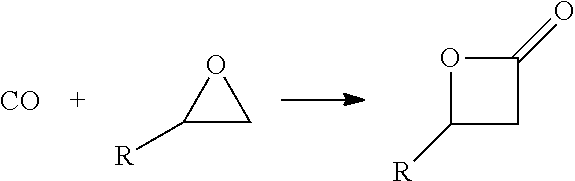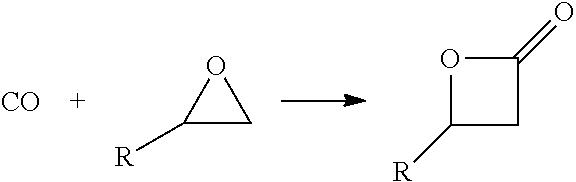Patents
Literature
1229results about "Preparation by carbon monoxide or formate reaction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
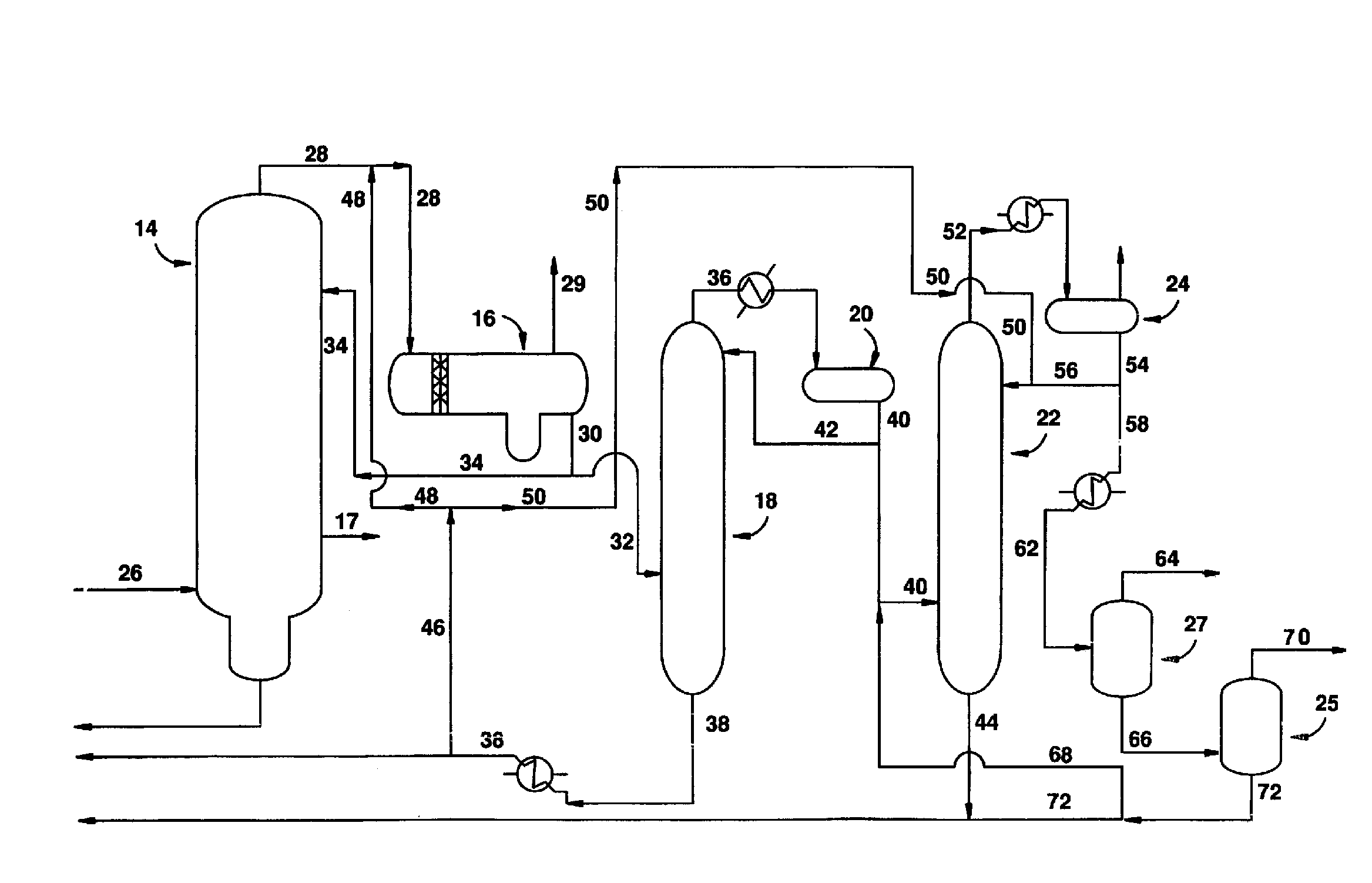
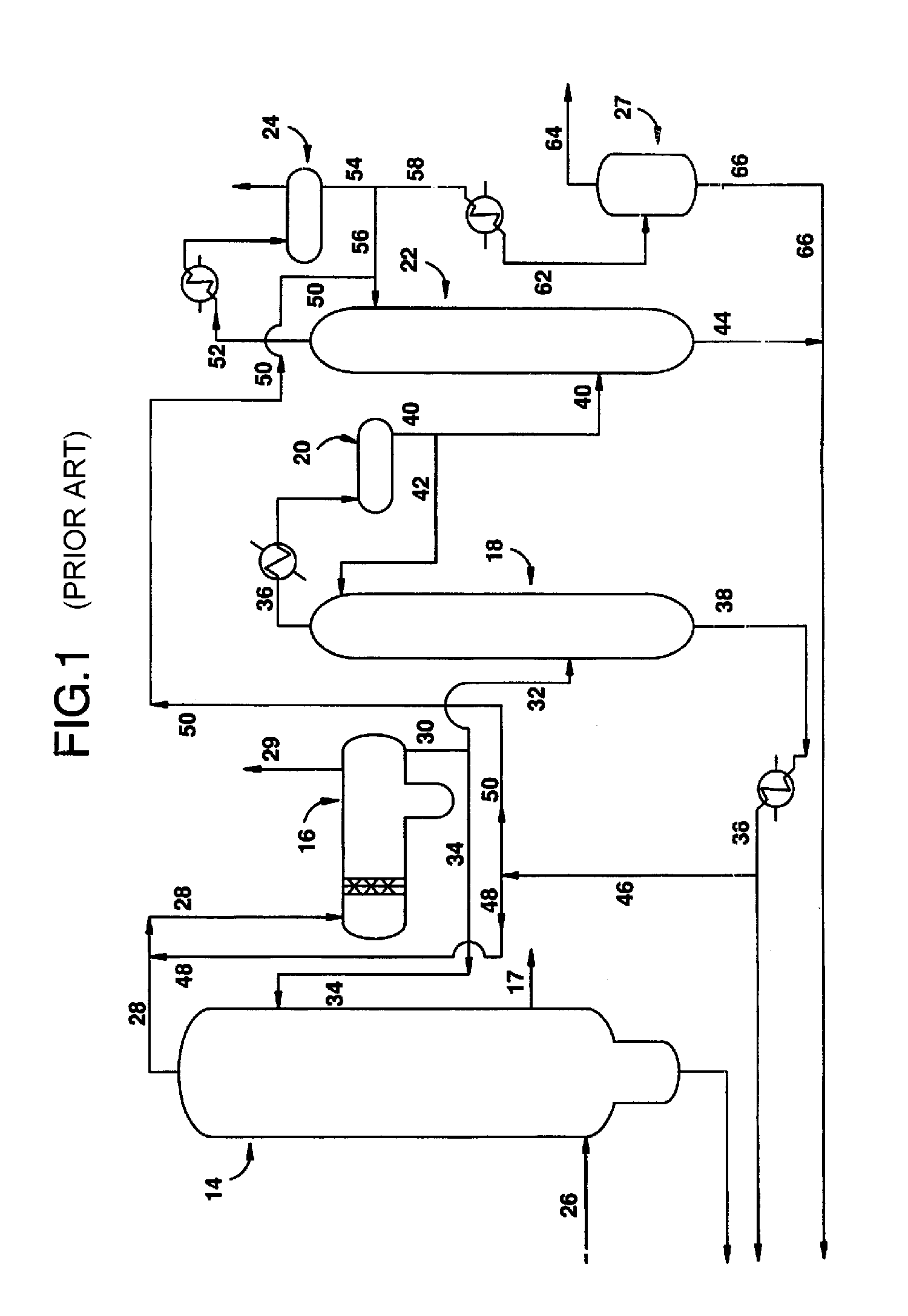
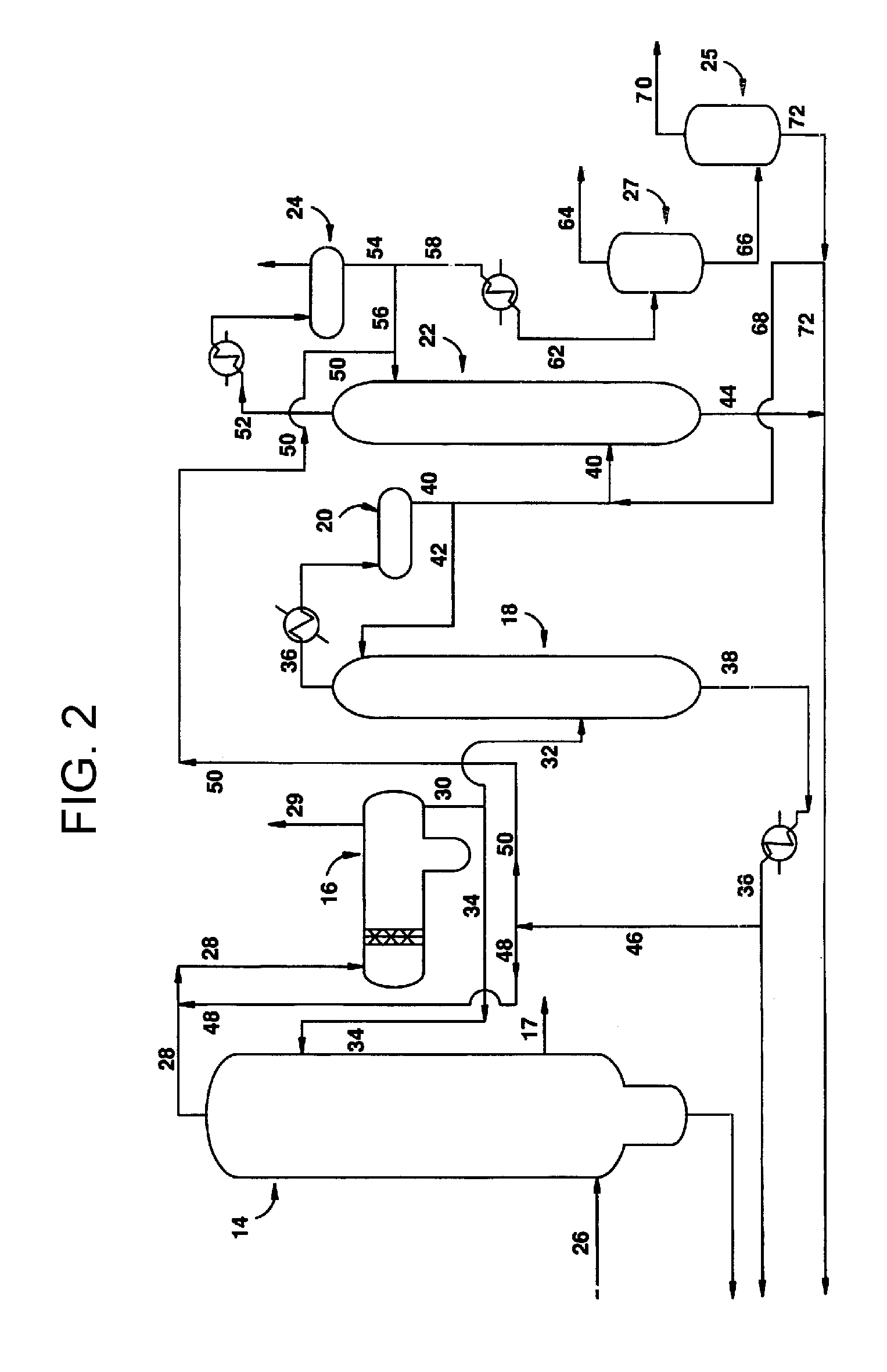
Removal of permanganate reducing compounds from methanol carbonylation process stream
ActiveUS7223886B2Reduce solubilitySimple methodOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionAcetic acidIodide
An improvement of the methanol carbonylation process for manufacturing acetic acid is disclosed. Specifically disclosed is a method for reducing the formation of alkyl iodides and C3-8 carboxylic acids by removing permanganate reducing compounds (“PRC's”) from the light phase of the condensed light ends overhead stream, including (a) distilling the light phase to yield a PRC enriched overhead stream; and (b) extracting the third overhead stream with water in at least two consecutive stages and separating therefrom one or more aqueous streams containing PRC's.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
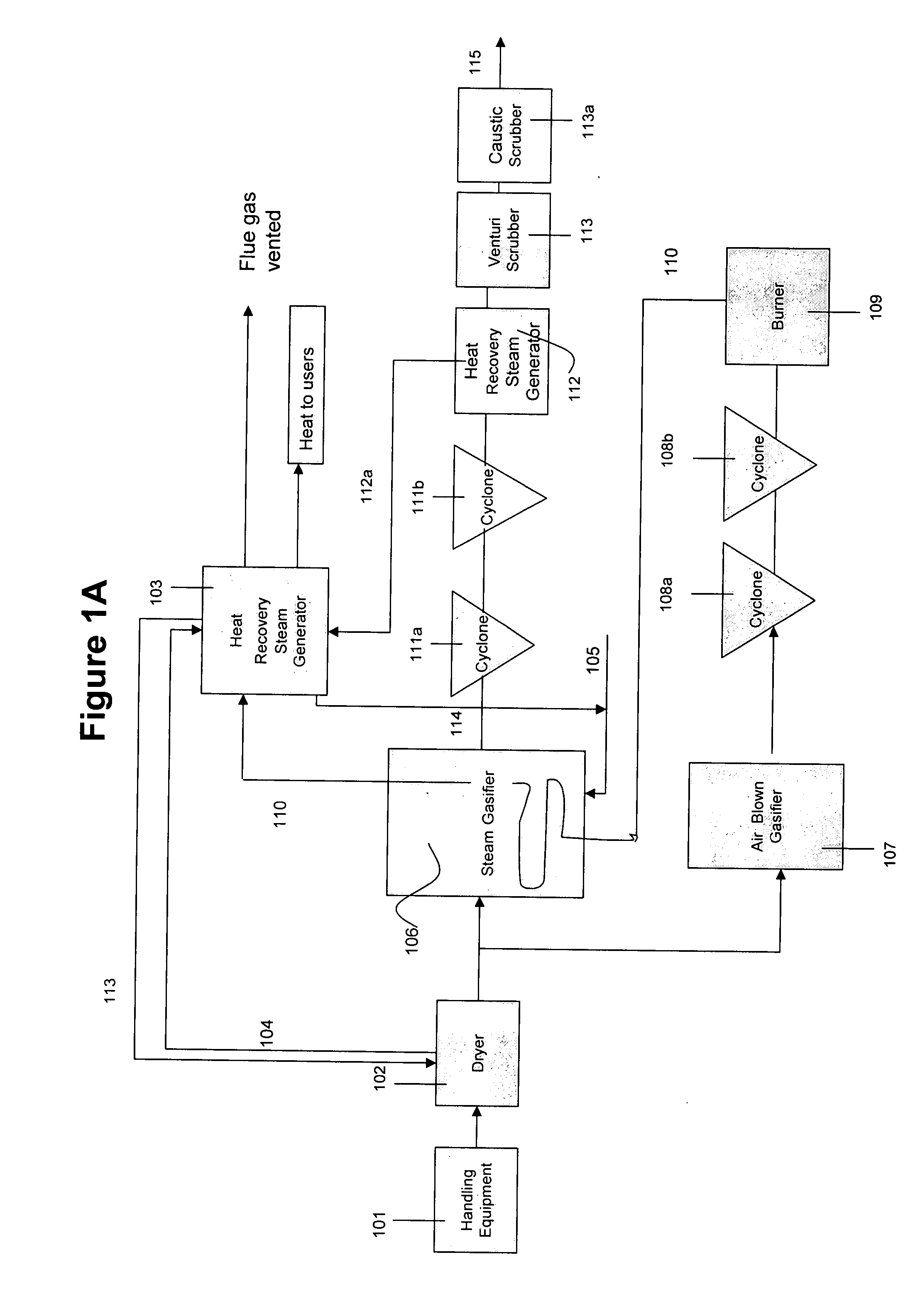
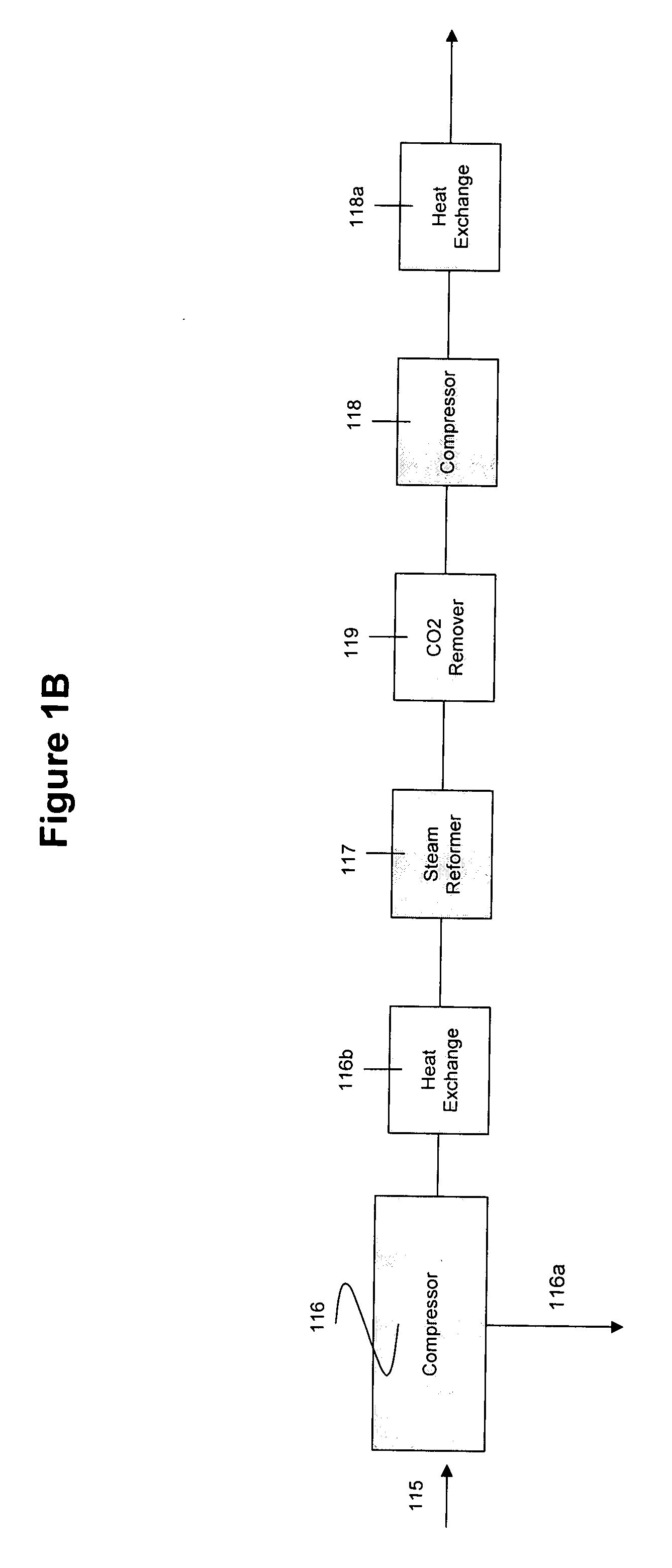
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
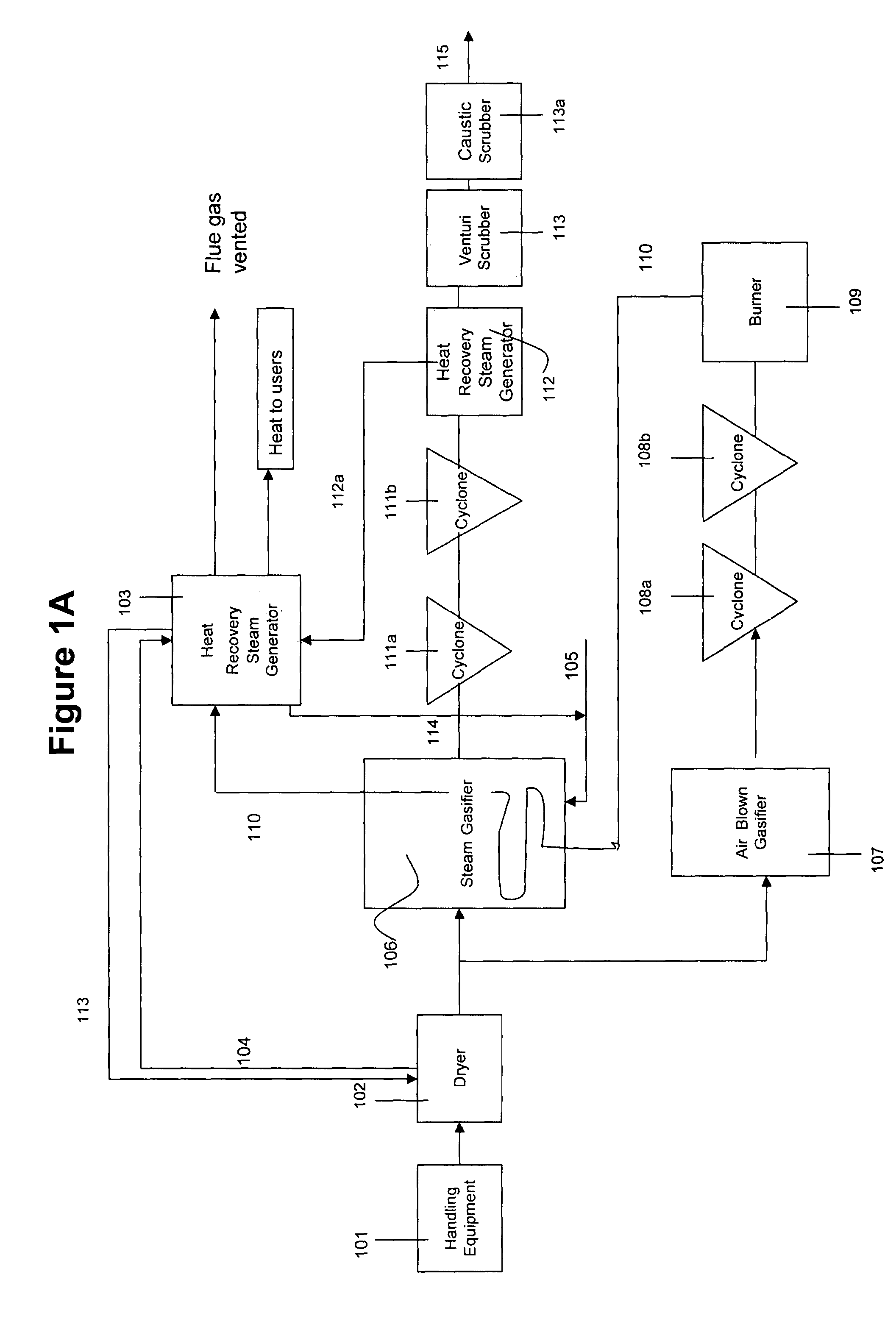
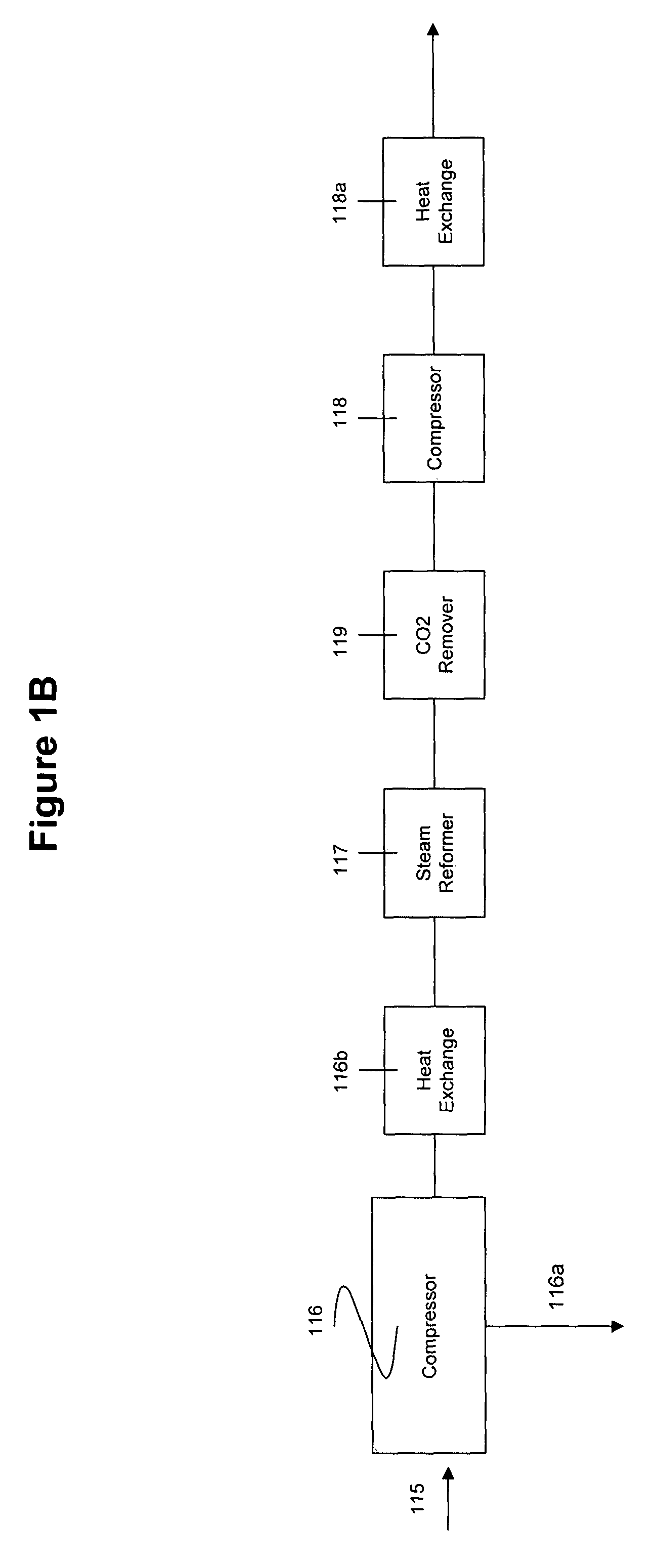
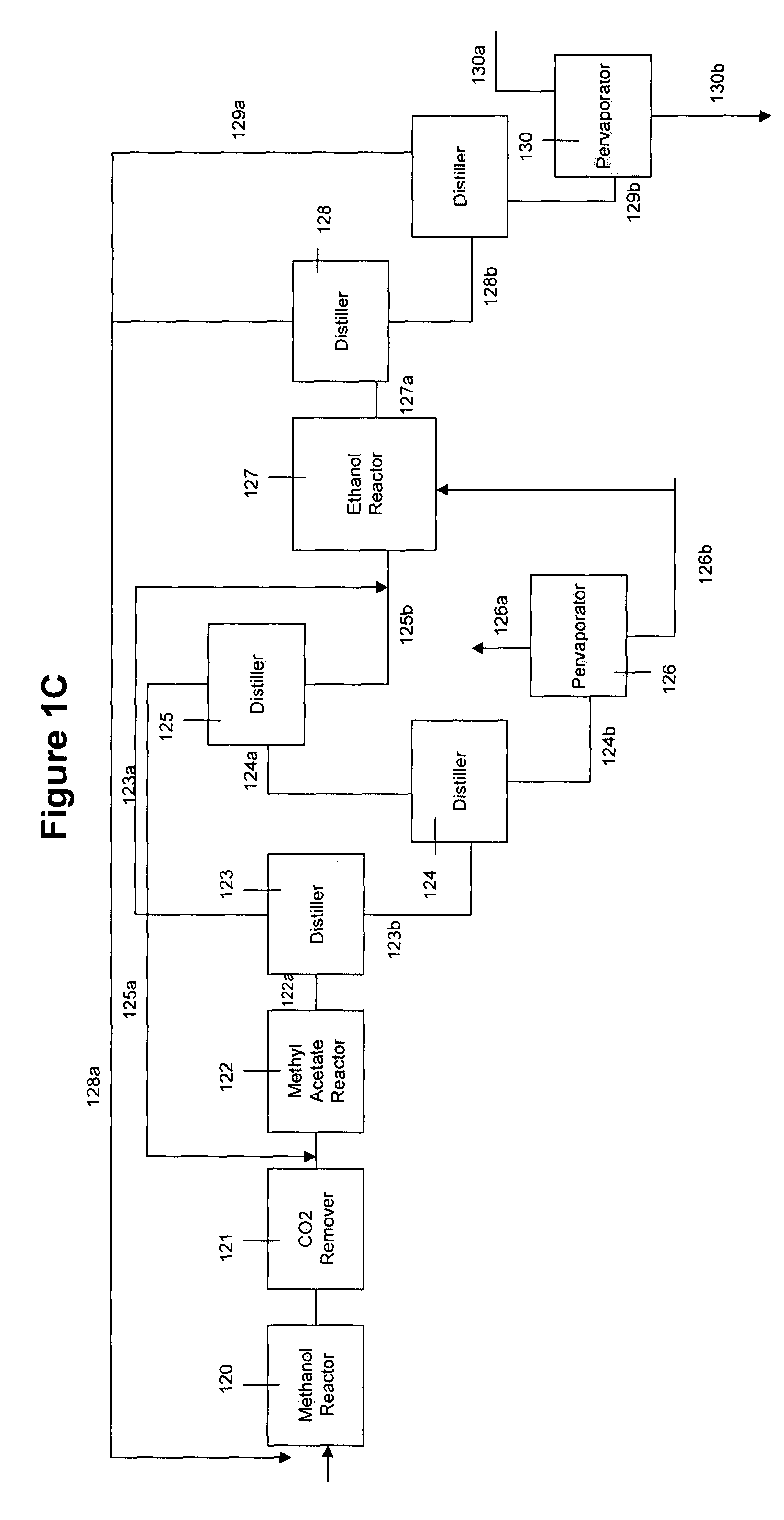
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
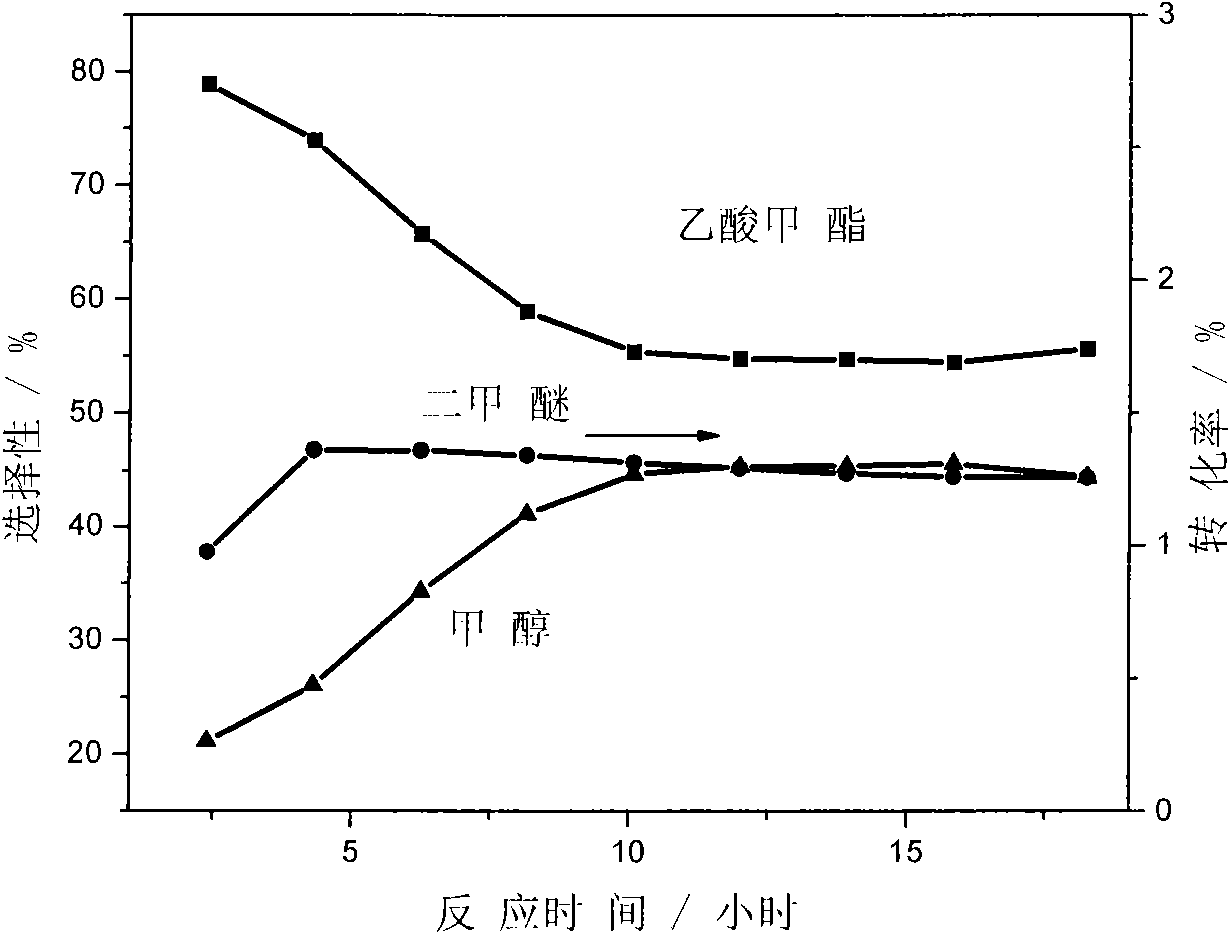
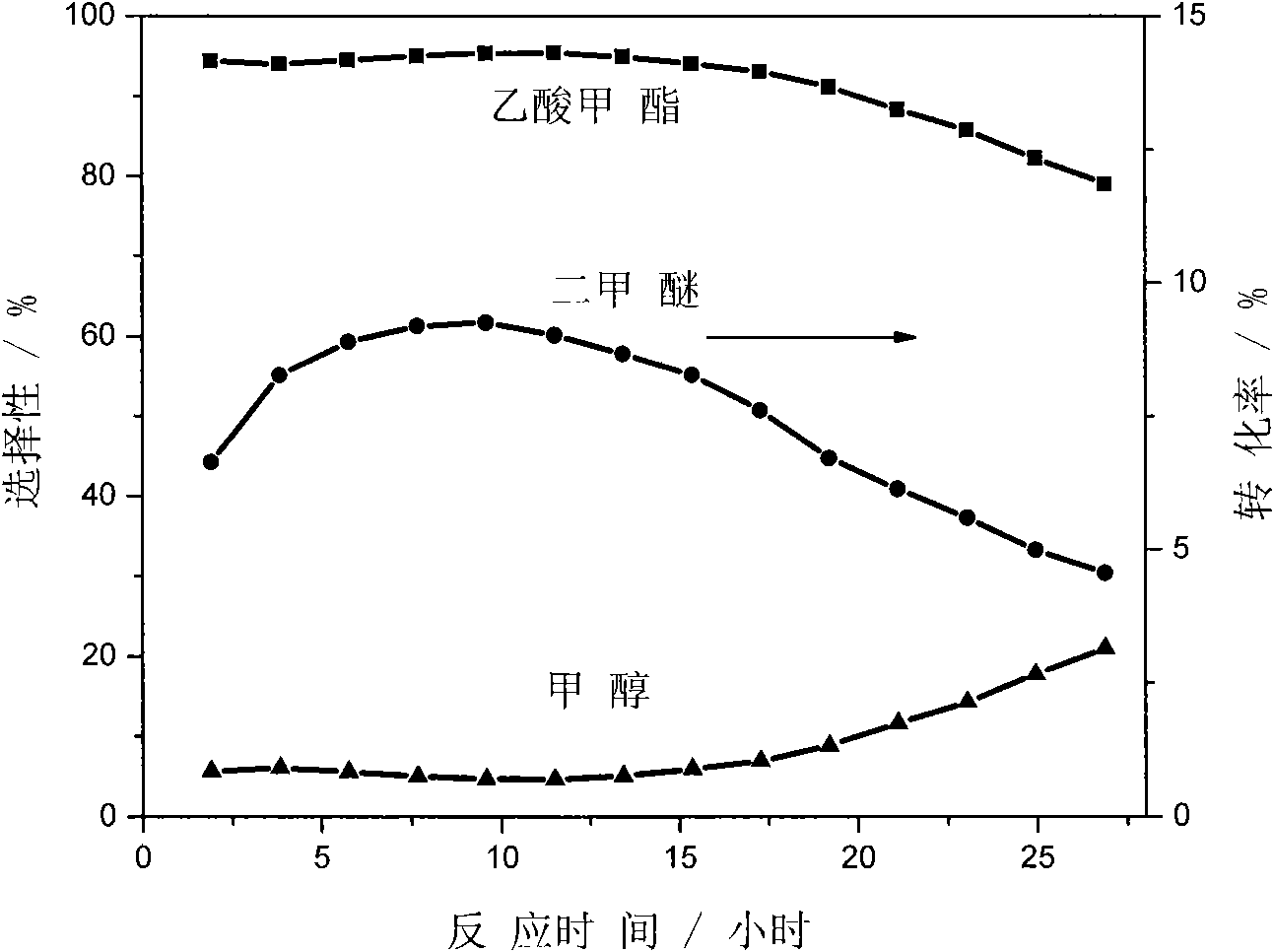
Method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether
ActiveCN101613274AImprove stabilityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMolecular sieveMethyl acetate
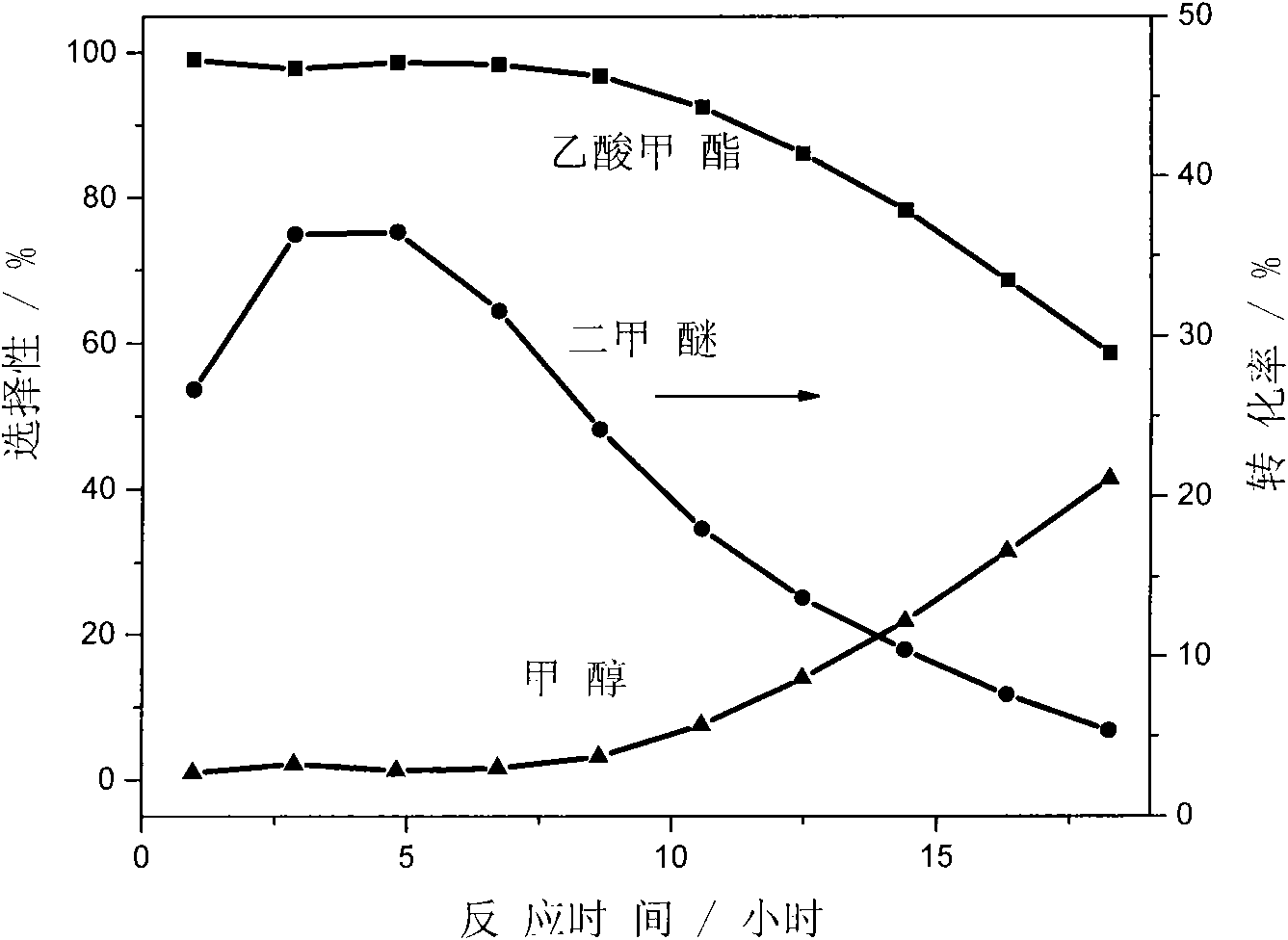
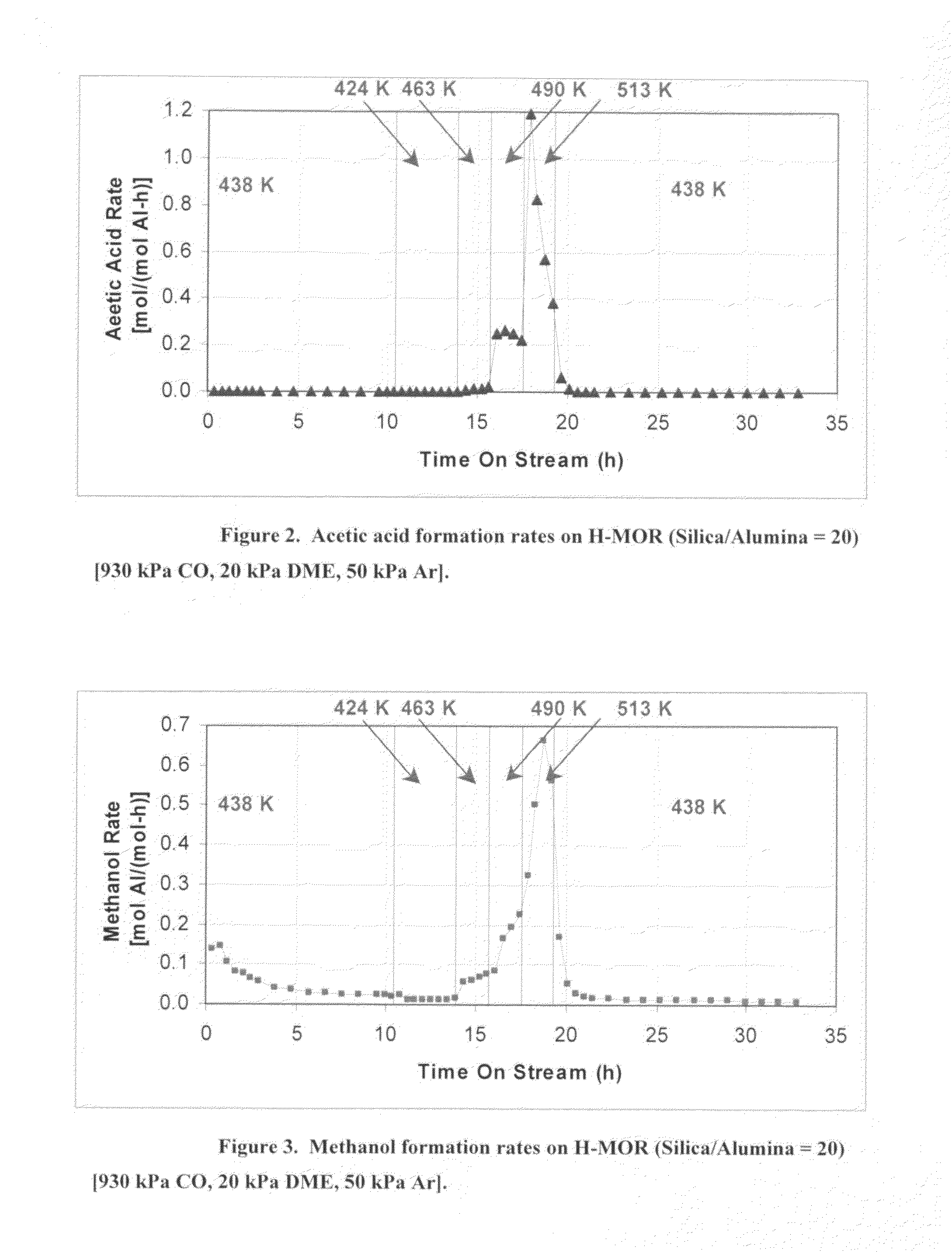
The invention discloses a catalyst modification method for preparing methyl acetate by carbonylating dimethyl ether. The method is applied to the reaction process in which the dimethyl ether reacts with the carbon monoxide to high selectively form methyl acetate in the presence of an acid molecular sieve catalyst, particularly a mordenite molecular sieve. Pyridine organic amines are utilized to modify the mordenite molecular sieve and modify a channel structure and the acidity of the molecular sieve, thereby effectively inhibiting carbon deposition and greatly improving the stability of catalysts. The use of the catalysts by the method can catalyze the carbonylation of dimethyl ether to obtain methyl acetate under mild conditions. The conversion rate of dimethyl ether is between 10 and 60percent, the selectivity of the methyl acetate is over 99 percent, and the activity of the catalysts is kept steady after the reaction is performed for 48 hours.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing diethyl oxalate by coupling CO
ActiveCN101143821ANo pollution in the processImprove efficiencyPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsCyclic processContinuous use
The invention discloses a method for preparing diethyl oxalate by CO coupling reaction. By applying a gas phase method, CO is coordinated with ethyl nitrite and is catalyzed by bimetallic supported catalyzer to couplingly generate crude diethyl oxalate, the reaction is a self-sealing circulation process, the CO gas mixed with the ethyl nitrite coming from a regeneration reactor is preheated and then enters into a coupling reactor, after the reaction, the gas is separated by condensation, so that the colorless and transparent condensed diethyl oxalate liquid is produced, and the uncondensed gas containing NO enters into the regeneration reactor to react with ethanol and oxygen in order to generate ethyl nitrite which is again circulated back to the coupling reactor for continuous use. The invention is carried out on the basis of previous laboratory research and under the background of industrial production and fulfils the continuous run examination of the bench scale test and pilot magnification under the condition of industrial operation, the temperature of the coupling reaction is low, and the concentration of products is increased. The method has the advantages of more energy saving, no pollution and high benefit. The total conversion rate of the CO generated by reaction is one hundred percent, and the selectivity of diethyl oxalate is over ninety six percent.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method of producing ethyl acetate
InactiveUS20090005588A1Good dispersionWell mixedOrganic compound preparationRotary stirring mixersAcetic acidReaction temperature
Methods and systems for the production of ethyl acetate are described herein. The methods and systems incorporate the novel use of a high shear device to promote dispersion and mixing of a carbonyl co-reactant (e.g. acetic acid, acetaldehyde) with ethanol. The high shear device may allow for lower reaction temperatures and pressures and may also reduce reaction time with existing catalysts.
Owner:HRD CORP
Noble metal support
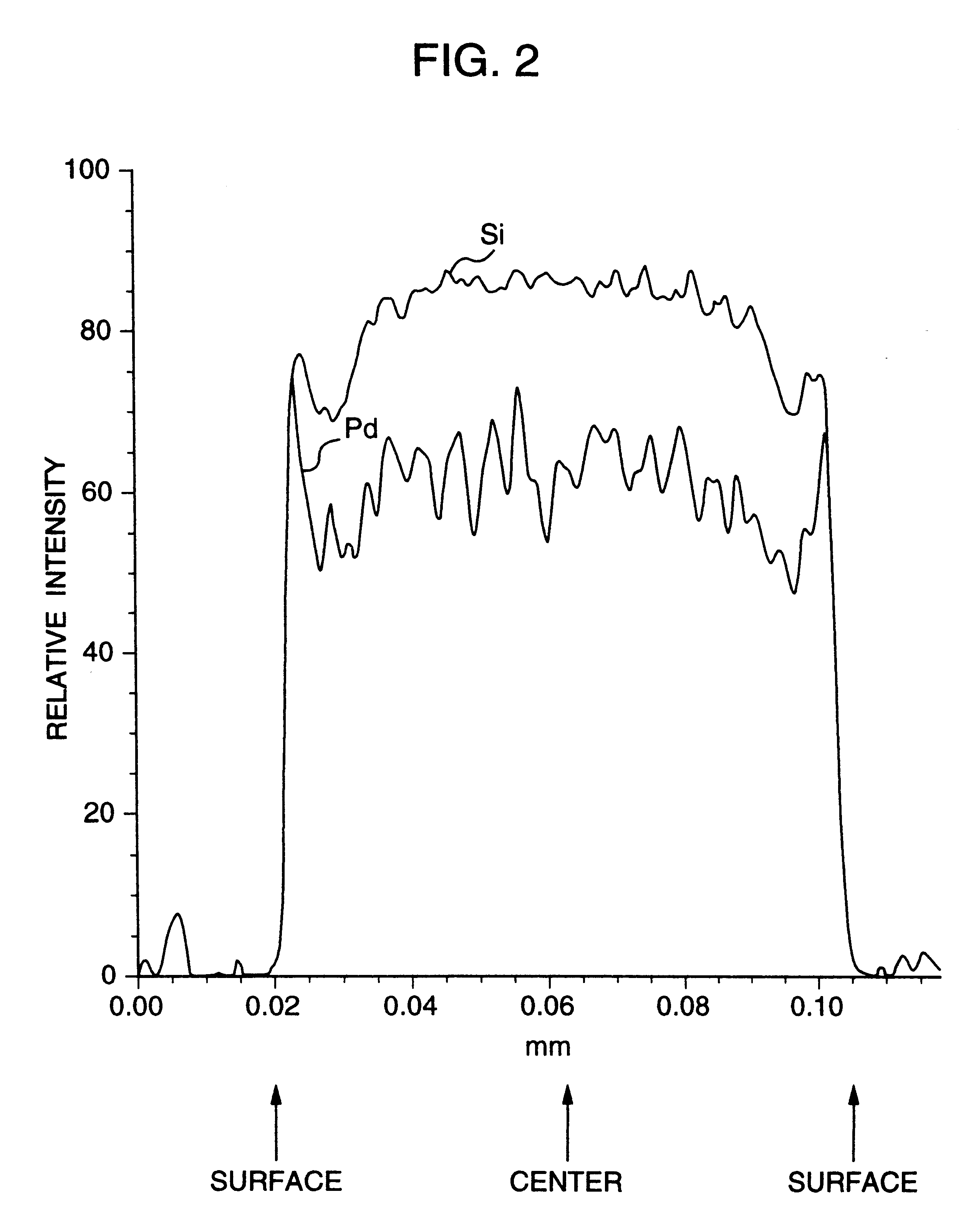
InactiveUS6228800B1Efficient use ofLong catalyst lifeOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationPalladiumChemistry
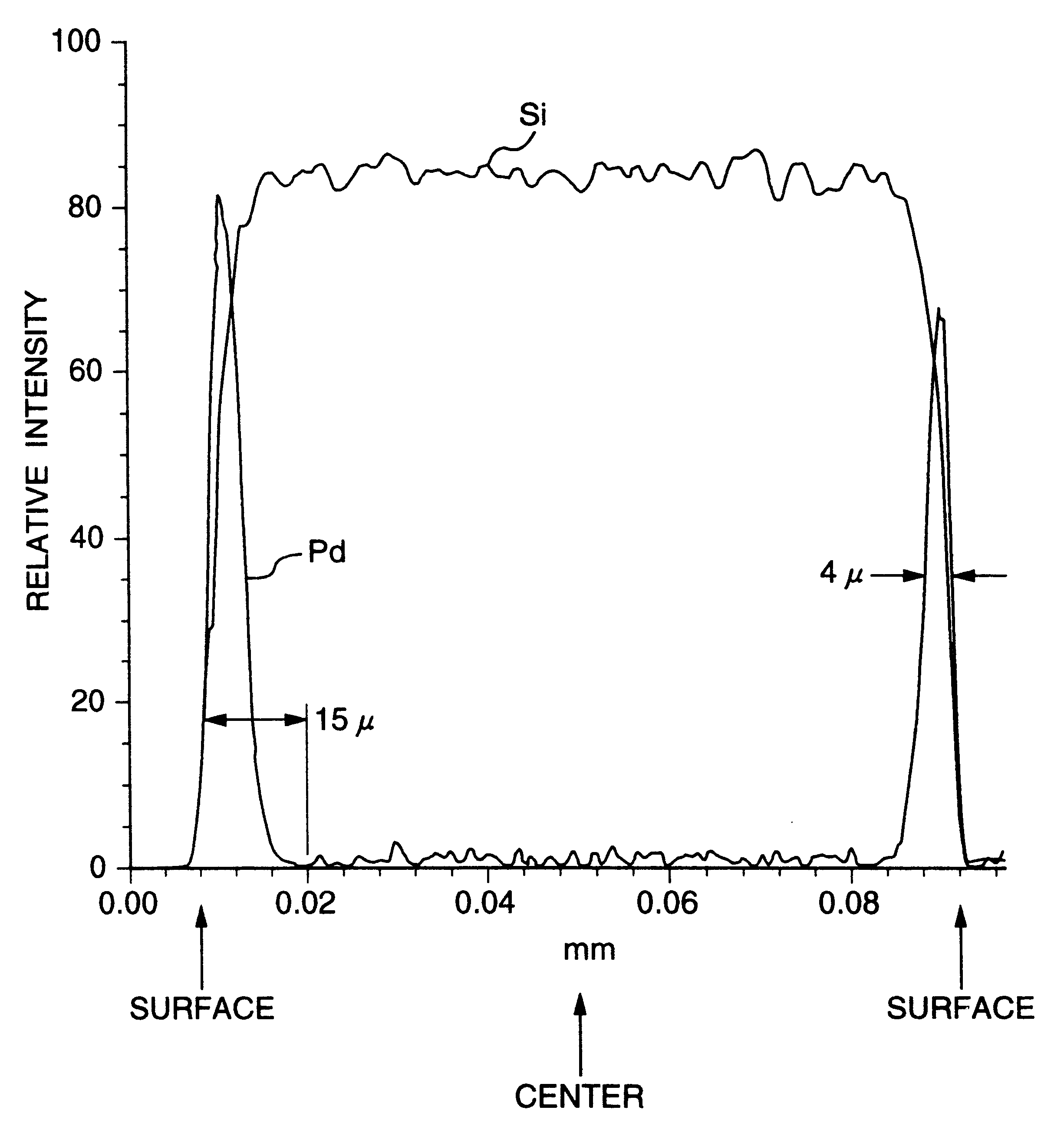
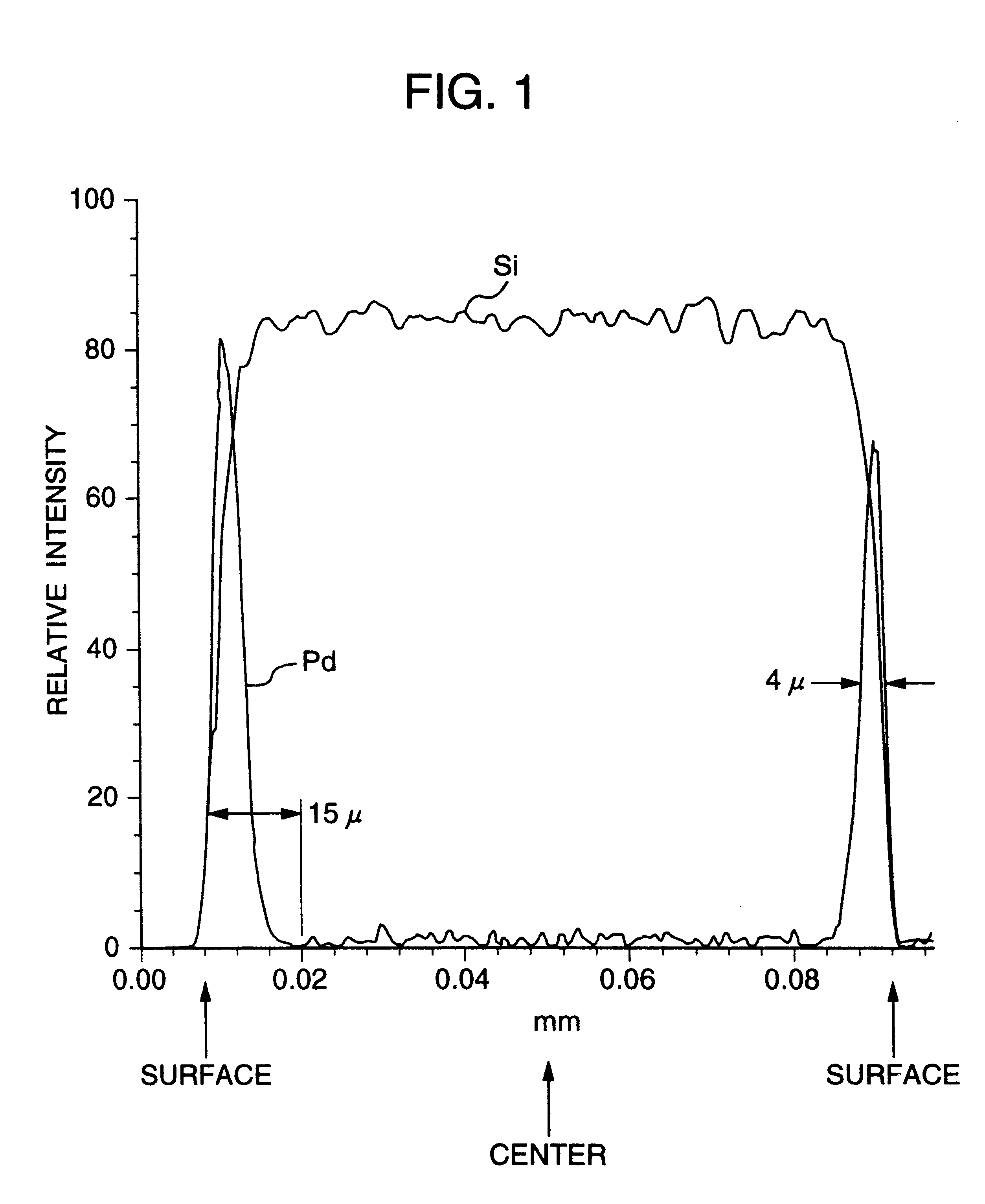
A noble metal-supported article which comprises a carrier and a palladium-containing metal component supported on the carrier, which article has (A) a layer in which substantially no palladium is supported in the interior of the carrier and (B) a layer in which palladium is supported in the region from the outer surface to a depth of less than 100 mum of the carrier.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
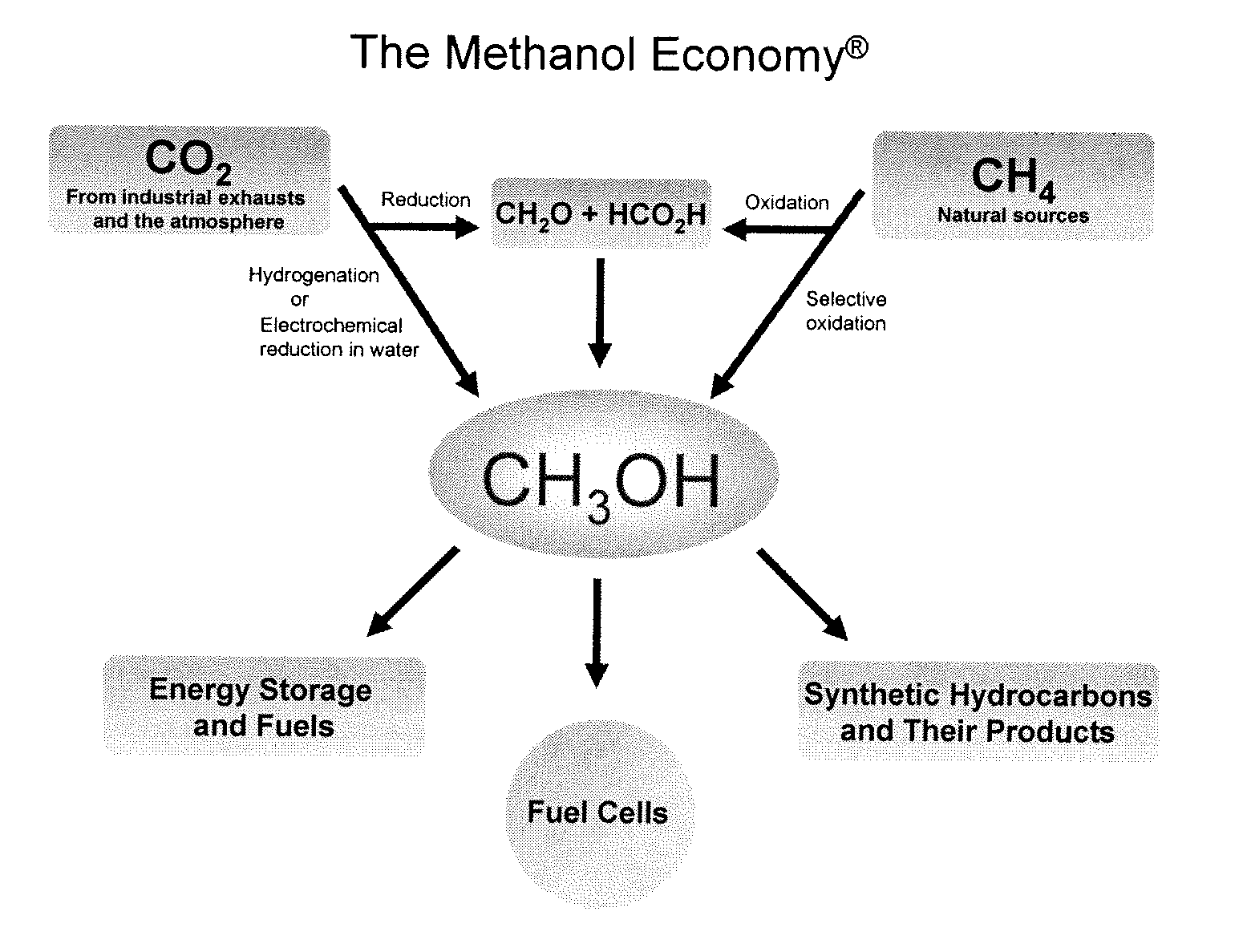
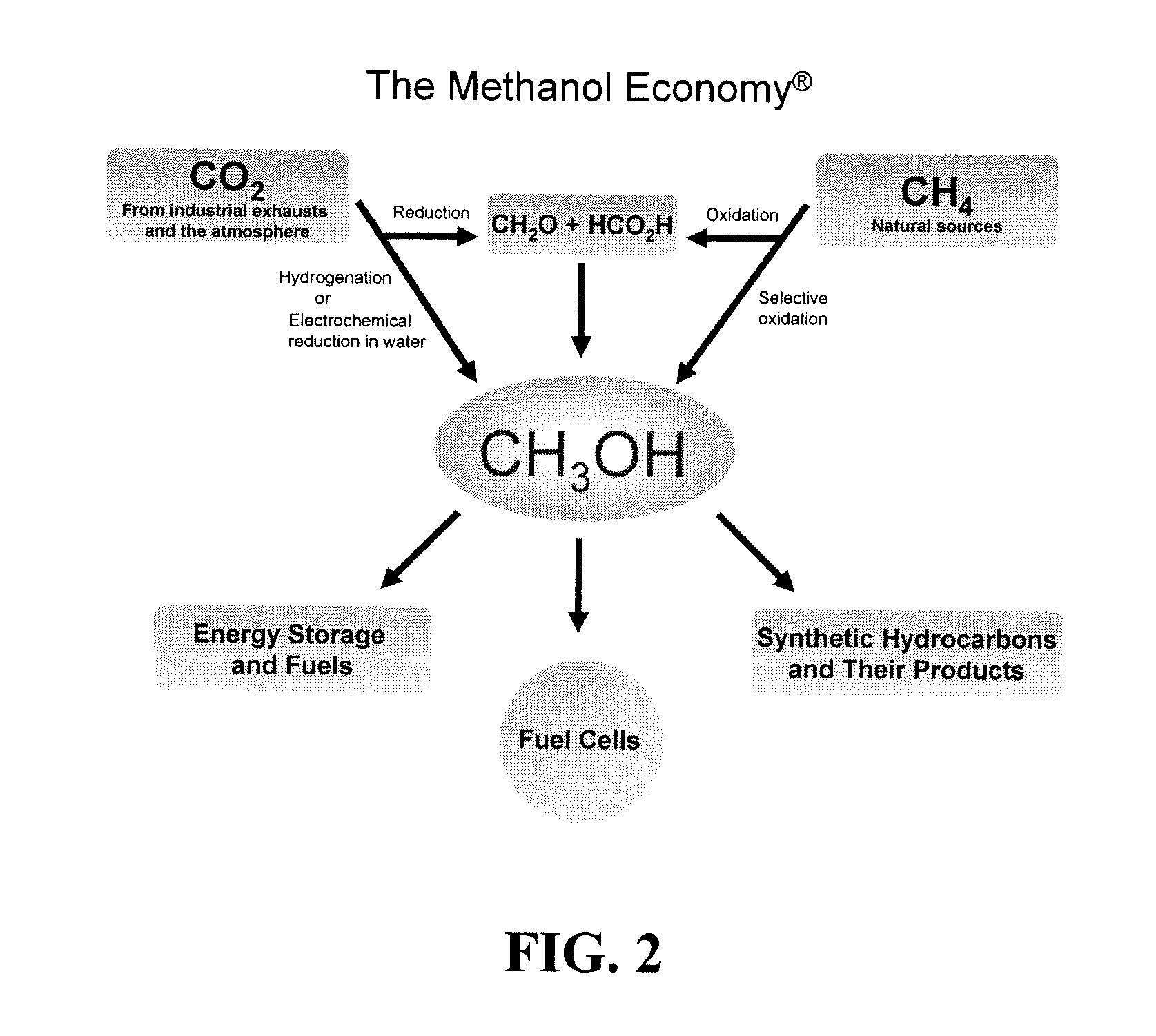
Efficient and selective chemical recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20070254969A1Avoid emissionsElectrolysis componentsOxygen compounds purification/separationElectrochemistryDimethyl ether
An efficient and environmentally beneficial method of recycling and producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by chemical or electrochemical reduction secondary treatment to produce essentially methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Efficient and selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20060235091A1Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsHydrogenFlue gas
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by electrochemical reduction produces formic acid acid and some formaldehyde and methanol mixtures. The formic acid can be used as source of carbon as well as hydrogen to produce methanol, dimethyl ether and other products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Process for the production of esters from alcohols using acetic acid as acetylating and clays as catalysts
InactiveUS6472555B2Easy to adaptLow reaction temperatureOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidAlcohol
The present invention relates to a process for the preparation of esters from alcohols using acetic acid as acetylating agent and clays as catalysts, which comprises the preparation of esters in a single step from the reaction of aliphatic, acyclic, cyclic, heterocyclic, alpha,beta-unsaturated and aromatic alcohols with carbon atoms in the range of C1 to C10 with acetic acid in a molar ratio of 1:3 to 11 using reusable natural montmorillonite / metal ion-exchanged clay catalysts in the solvent medium of aliphatic, aromatic, or chlorinated hydrocarbons at 30-140° C. for a period in the range of 0.02 to 3.0 hrs, and recovering the corresponding esters by simple work-up procedure.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Process for the conversion of hydrocarbons into ethanol
ActiveUS7947746B2Increased formationIncreased purge stepOrganic compound preparationOxygen compounds preparation by reductionAcetic acidAlcohol
Process for converting synthesis gas to ethanol, including the steps of 1) introducing synthesis gas, together with methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, into an alcohol synthesis unit to produce methanol and ethanol, 2) separating the methanol from the ethanol of step 1, 3) introducing methanol, from step 2, together with CO, into a carbonylation unit in the presence of a methanol carbonylation catalyst, to produce ethanoic acid, and 4) introducing ethanoic acid, from step 3, together with methanol and / or ethanol, into an esterification unit to produce methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate. In step 5), methyl ethanoate and / or ethyl ethanoate, produced in step 4, are fed into the alcohol synthesis unit of step 1, and in step 6) ethanol from step 2 is recovered.
Owner:INEOS ACETYLS UK LTD
Method for producing methanol, dimethyl ether, derived synthetic hydrocarbons and their products from carbon dioxide and water (moisture) of the air as sole source material
InactiveUS7378561B2High activityImprove surface activityOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsNano structuringWater source
A method for producing methanol and dimethyl ether using the air as the sole source of materials is disclosed. The invention relates to a method for separating the water (i.e., the moisture in the air) and carbon dioxide content of atmospheric air for their use in the subsequent production of methanol, dimethyl ether and derived synthetic hydrocarbons as products. The method includes the conversion of carbon dioxide and water under conditions sufficient to produce methanol and / or dimethyl ether. Methanol and / or dimethyl ether can be used as fuel or fuel additives or further converted to synthetic hydrocarbons and their products. Carbon dioxide is captured on a suitable absorbent, preferentially polyethyleneimine supported on nano-structured fumed silica. The process can also involve hydrogenation with hydrogen produced by electrolysis of water obtained from the air or from any other water source. Methanol can be dehydrated to produce dimethyl ether or further processed to produce synthetic hydrocarbons, polymers, and products derived from them by other known methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
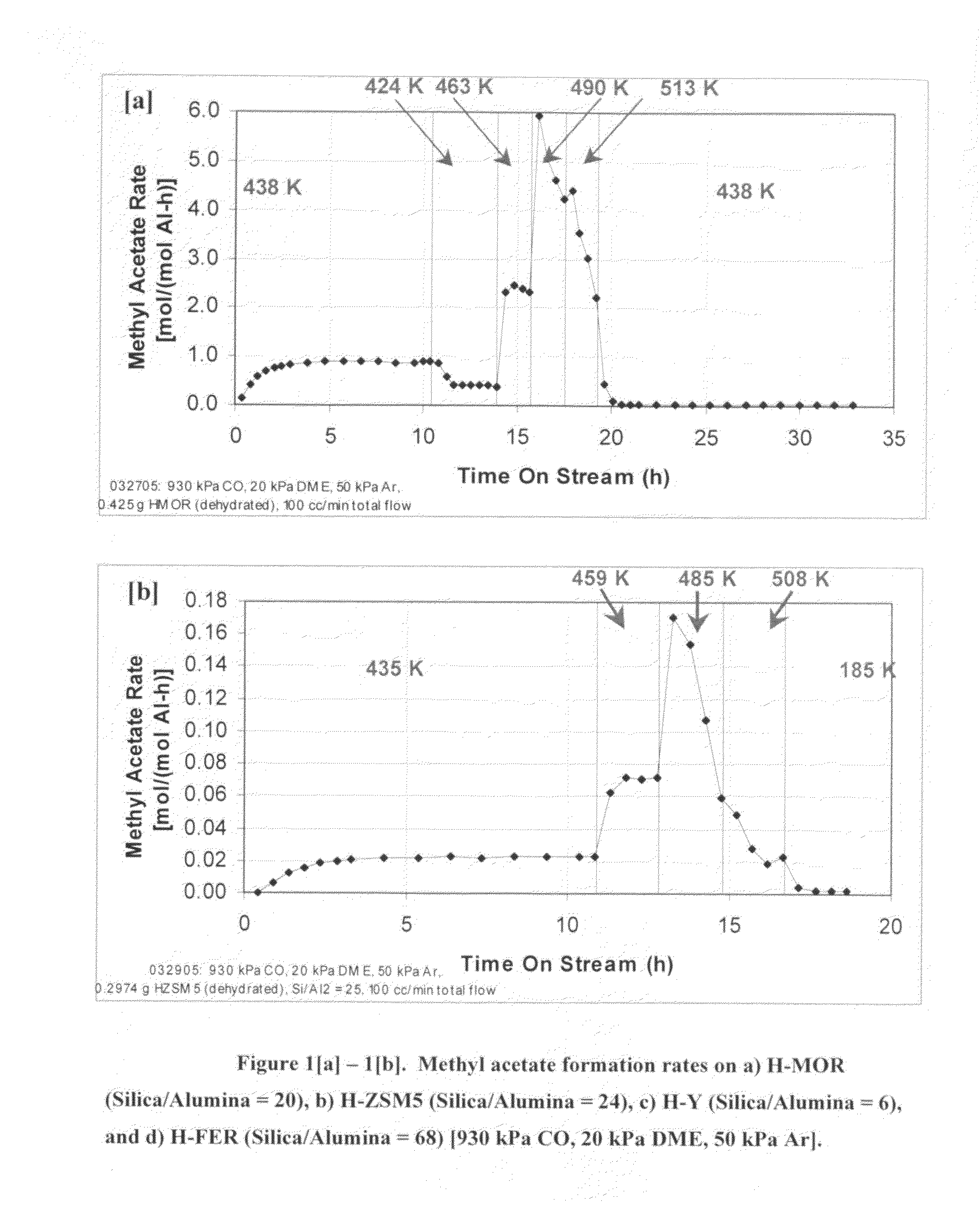
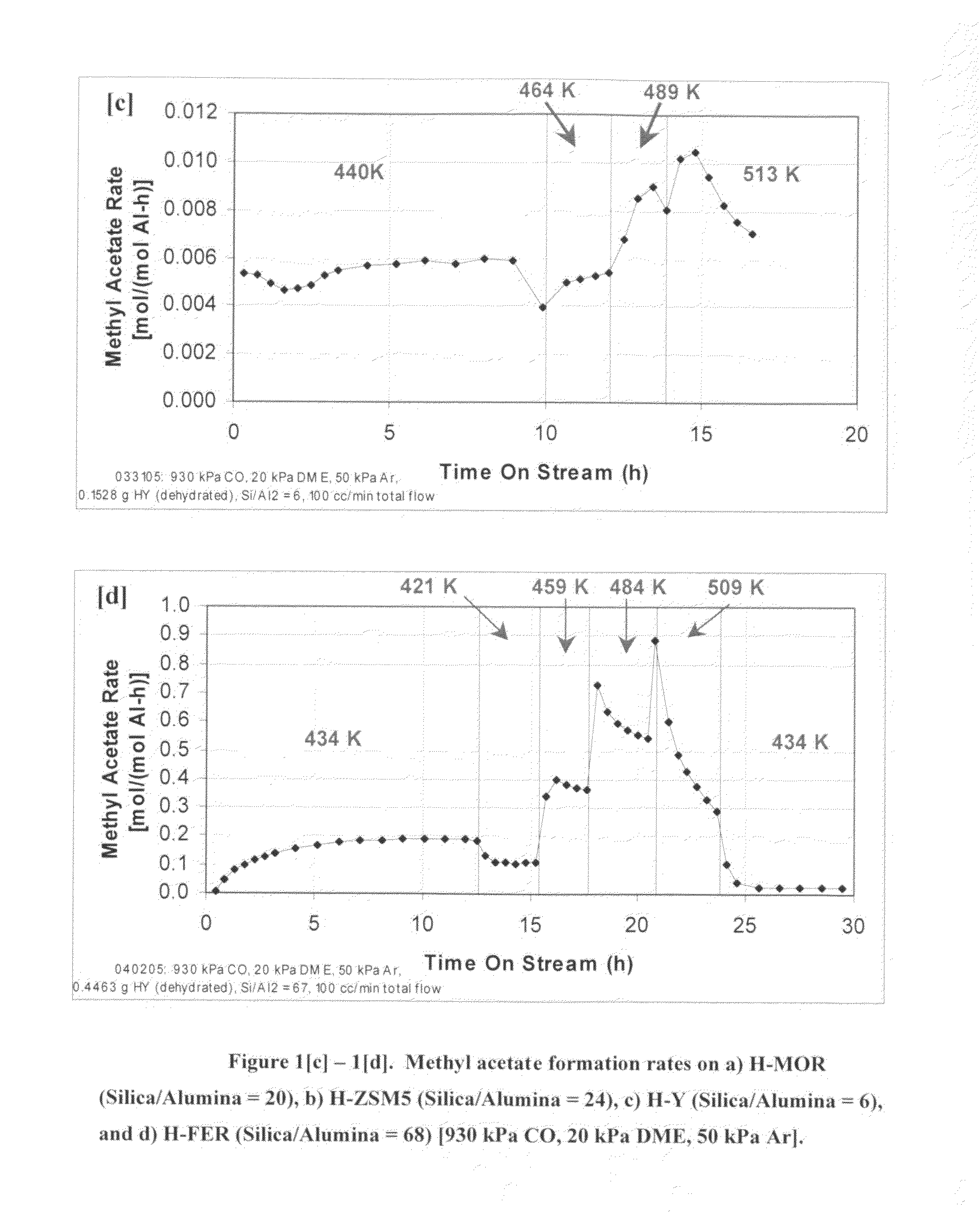
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS20070238897A1Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:THE BRITISH PETROLEUM CO LTD +1
Tin promoted platinum catalyst for carbonylation of lower alkyl alcohols
InactiveUS6903045B2Not volatileLess solubleIsocyanic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationSolid componentGas phase
A carbonylation catalyst useful for producing esters and carboxylic acids in a vapor phase carbonylation process, wherein the catalyst includes a solid component having a catalytically effective amount of platinum and tin associated with a solid catalyst support material and a vaporous halide promoter component.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Methods for the improvement of product yield and production in a microorganism through the addition of alternate electron acceptors
ActiveUS8956851B2Reduce formationSugar derivativesOrganic compound preparationBiotechnologyHeterologous
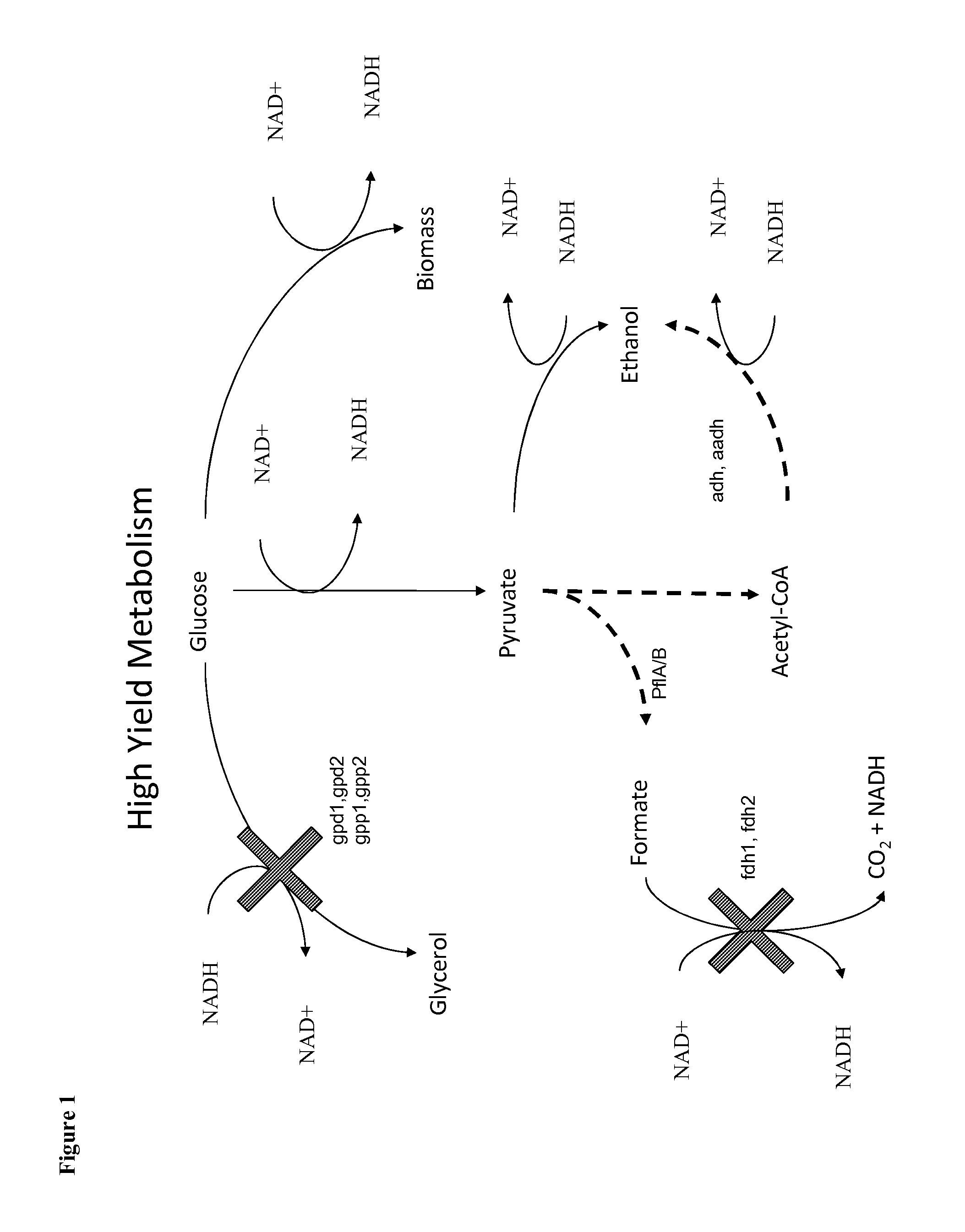
The present invention provides for novel metabolic pathways to reduce or eliminate glycerol production and increase product formation. More specifically, the invention provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising a deletion of one or more native enzymes that function to produce glycerol and / or regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source, such as lignocellulose, to a product, such as ethanol, wherein the one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated, or downregulated. The invention also provides for a recombinant microorganism comprising one or more heterologous enzymes that function to regulate glycerol synthesis and one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes that function in one or more engineered metabolic pathways to convert a carbohydrate source to ethanol, wherein said one or more native and / or heterologous enzymes is activated, upregulated or downregulated.
Owner:LALLEMAND HUNGARY LIQUIDITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Addition of iridium to the rhodium/inorganic iodide catalyst system
InactiveUS6211405B1High rateReduce productionPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationPtru catalystCarboxylic acid
The present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of an alcohol, ether or ester to products comprising a carboxylic acid, the anhydride thereof or coproduction of the carboxylic acid and anhydride. More particularly, the present invention provides a process for the carbonylation of methanol to produce acetic acid by reacting methanol with carbon monoxide in a liquid reaction medium containing a catalyst comprising rhodium, iridium, iodide ion, and said reaction medium further comprising water, acetic acid, methyl iodide, and methyl acetate and subsequently recovering acetic acid from the resulting reaction product.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
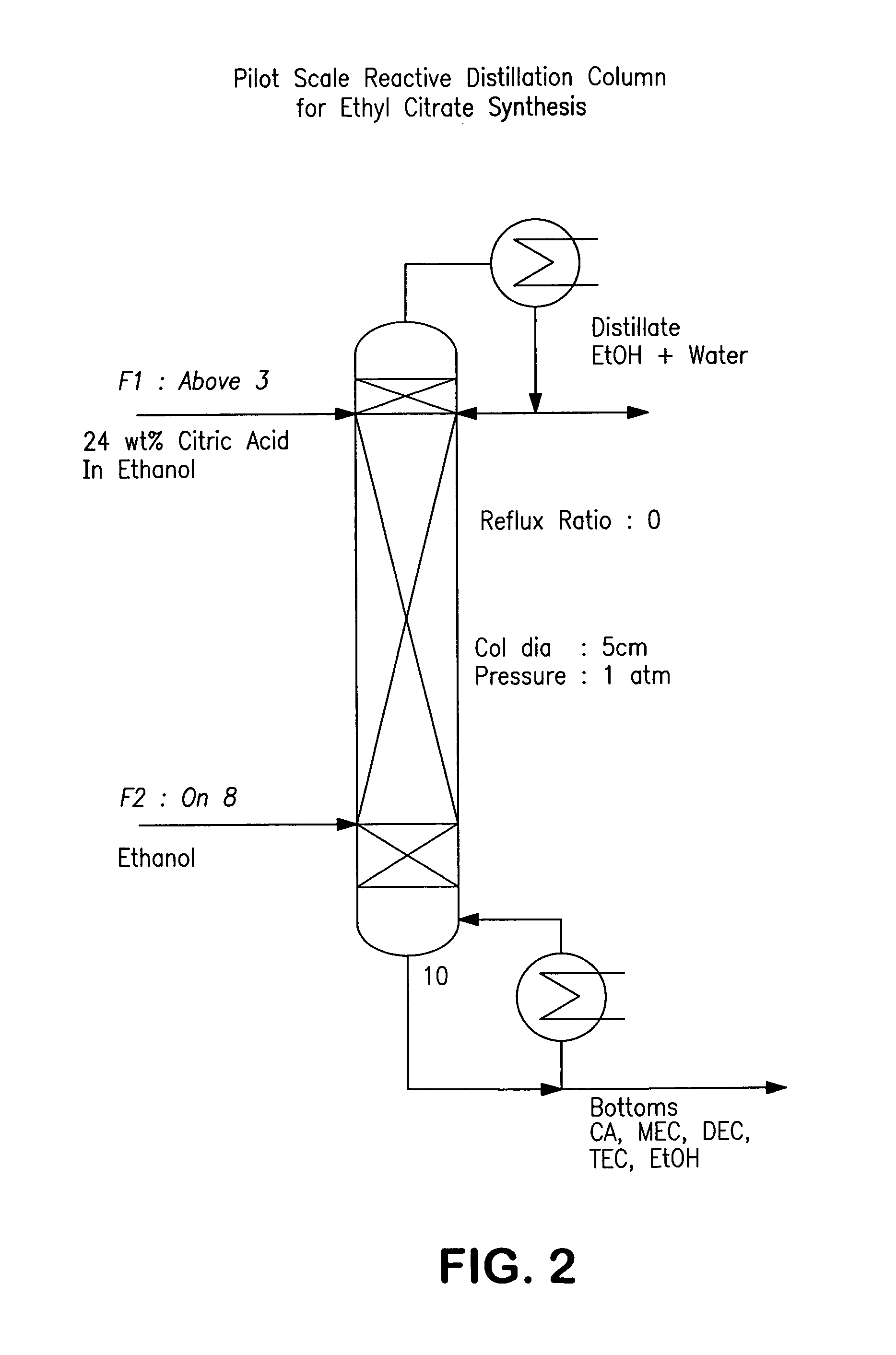
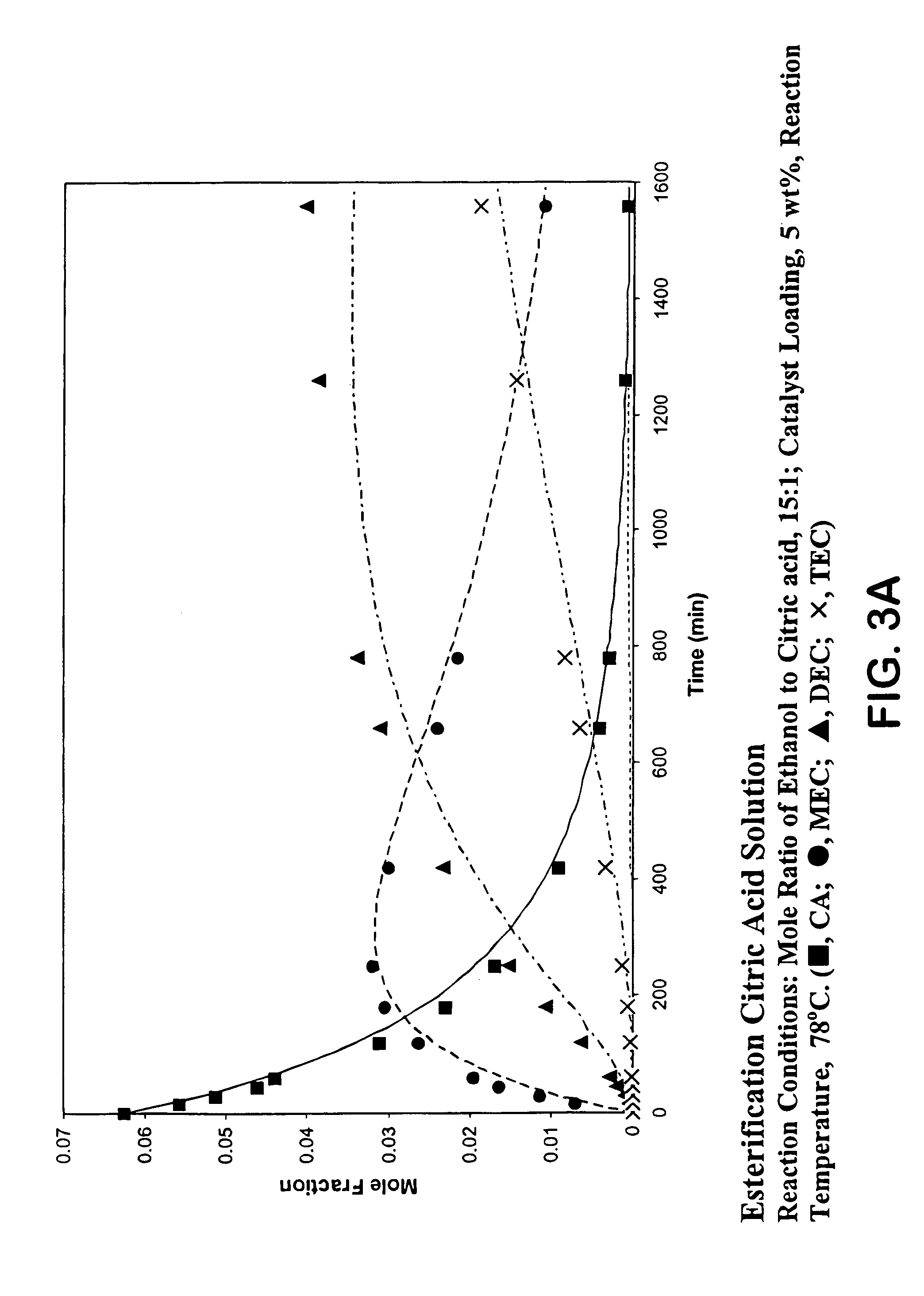
Process for reactive esterification distillation
ActiveUS20060252956A1Preparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationOrganic acidChemical reaction
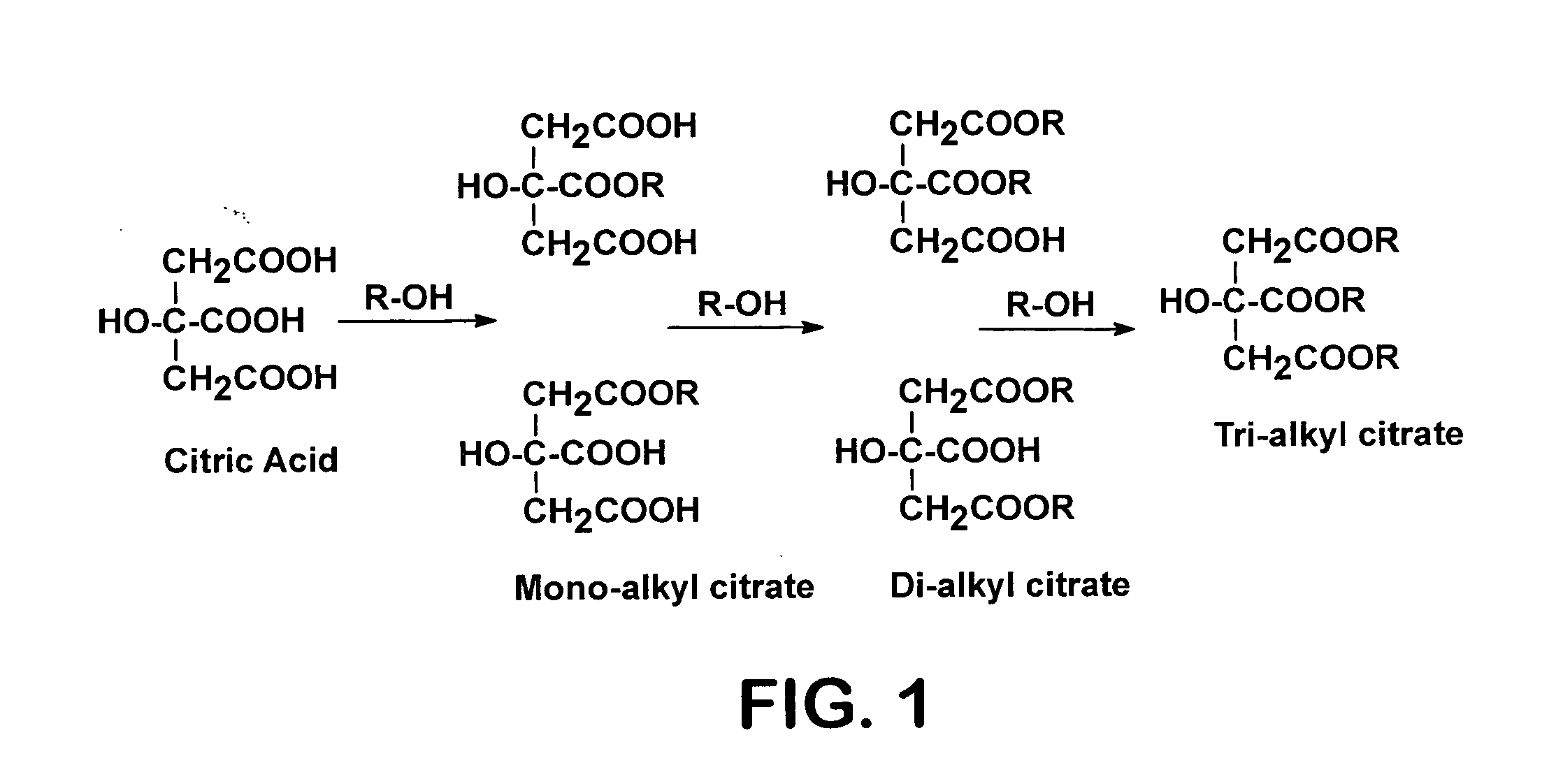
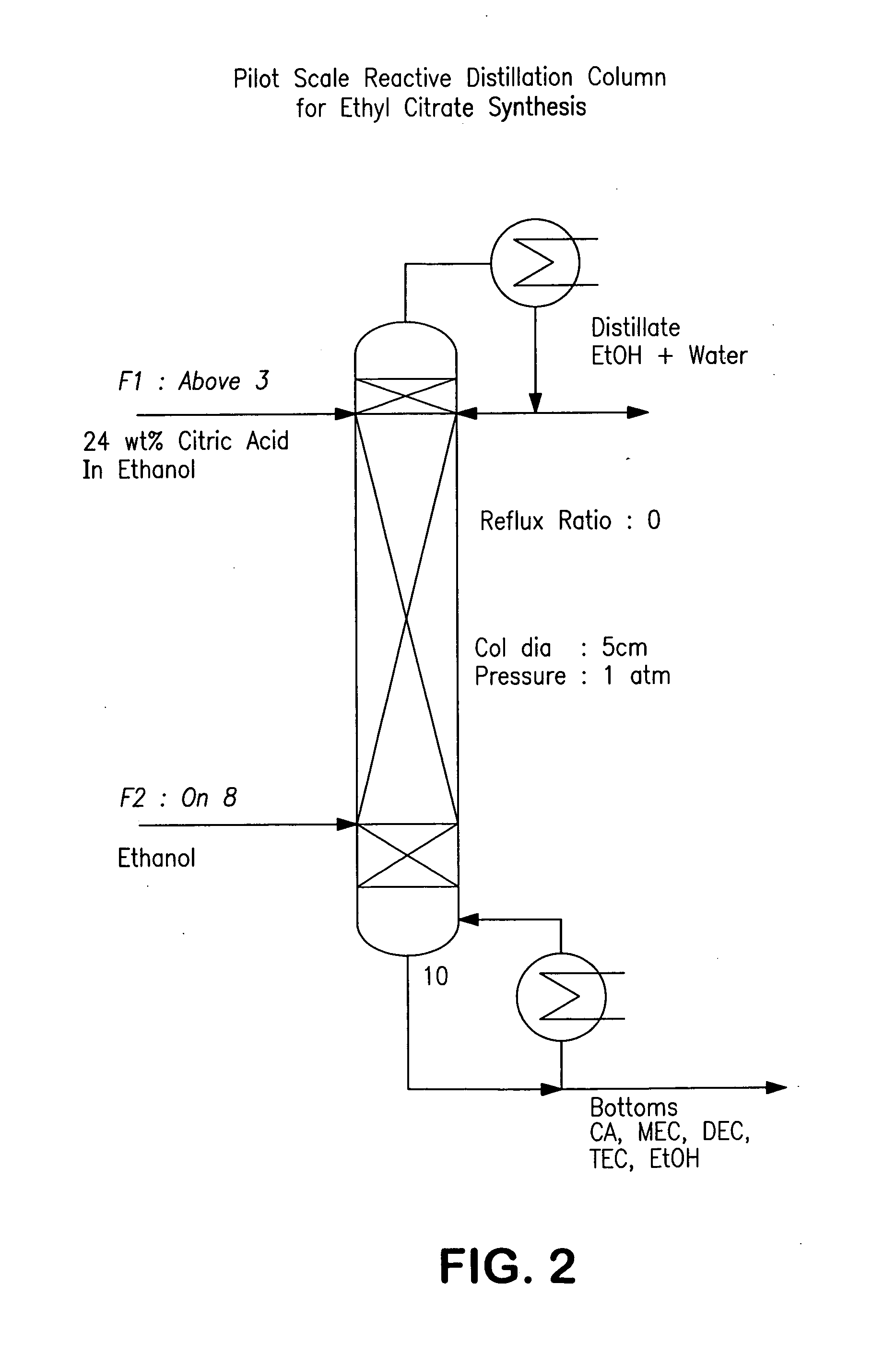
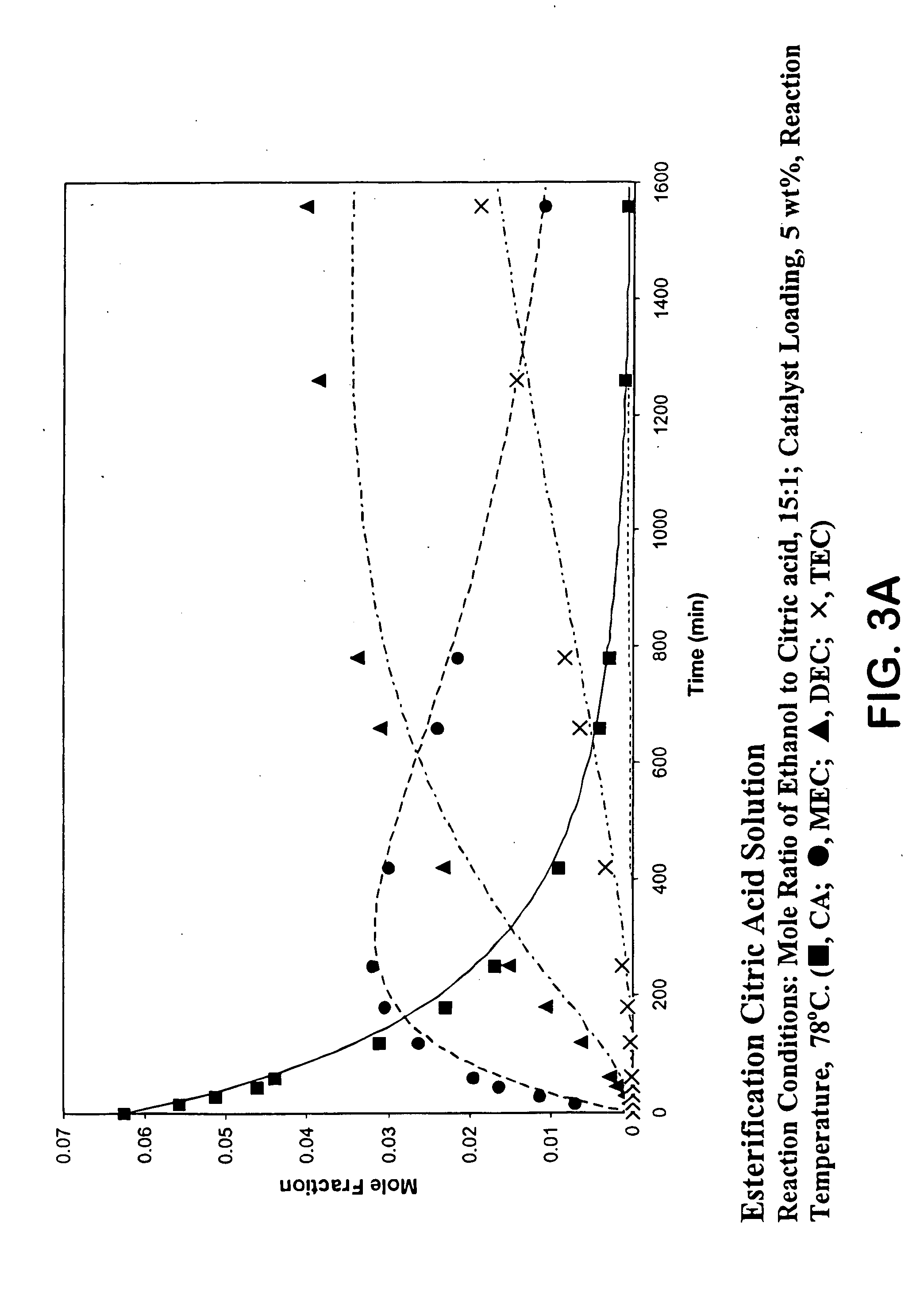
A process for producing organic acid di- or tri-esters, particularly citric acid tri-esters, with the available acid groups esterified using countercurrent reactive distillation using acid catalysts in a structured packing is described. In the reactive distillation an organic acid di- or tri-ester is formed by chemical reaction and purified to its final state within the single column. Organic acid di- or tri-esters are produced at relatively low cost, with less waste production in by-products of the reaction, and in a less complicated manner than prior processes. Organic acid di- and tri-esters have uses as solvents, as plasticizers and in conversion products.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Hydroformylation process
InactiveUS6049011AAvoid the needReduce processingPreparation by oxo-reaction and reductionPreparation by hydrogenationEthyleneHydrocarbon
PCT No. PCT / EP96 / 00163 Sec. 371 Date Oct. 15, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Oct. 15, 1997 PCT Filed Jan. 17, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 22265 PCT Pub. Date Jul. 25, 1996A dilute ethylene stream, e.g., one produced by steam cracking, is oxonated to yield propanal, without the need to separate other lower hydrocarbons.
Owner:EXXON CHEM PAT INC
Methylidene malonate process
ActiveUS20100286438A1High purityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMalonatePolymerization
An improvement in the production of methylidene malonates is attained by use of specific reaction phase and / or separation phase polymerization inhibitors and combinations thereof.
Owner:HB FULLER CO
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
ActiveUS7465822B2Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesCarboxylic acidCarbonylation
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting under substantially anhydrous conditions a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a zeolite catalyst having an 8-member ring channel which is interconnected with a channel defined by a ring with greater than or equal to 8 members, the 8-member ring having a window size of at least 2.5 Angstroms×at least 3.6 Angstroms and at least one Brønsted acid site and the zeolite having a silica:X2O3 ratio of at least 5, wherein X is selected from aluminum, boron, iron, gallium and mixtures thereof.
Owner:BP CHEM LTD +1
Continuous carbonylation process
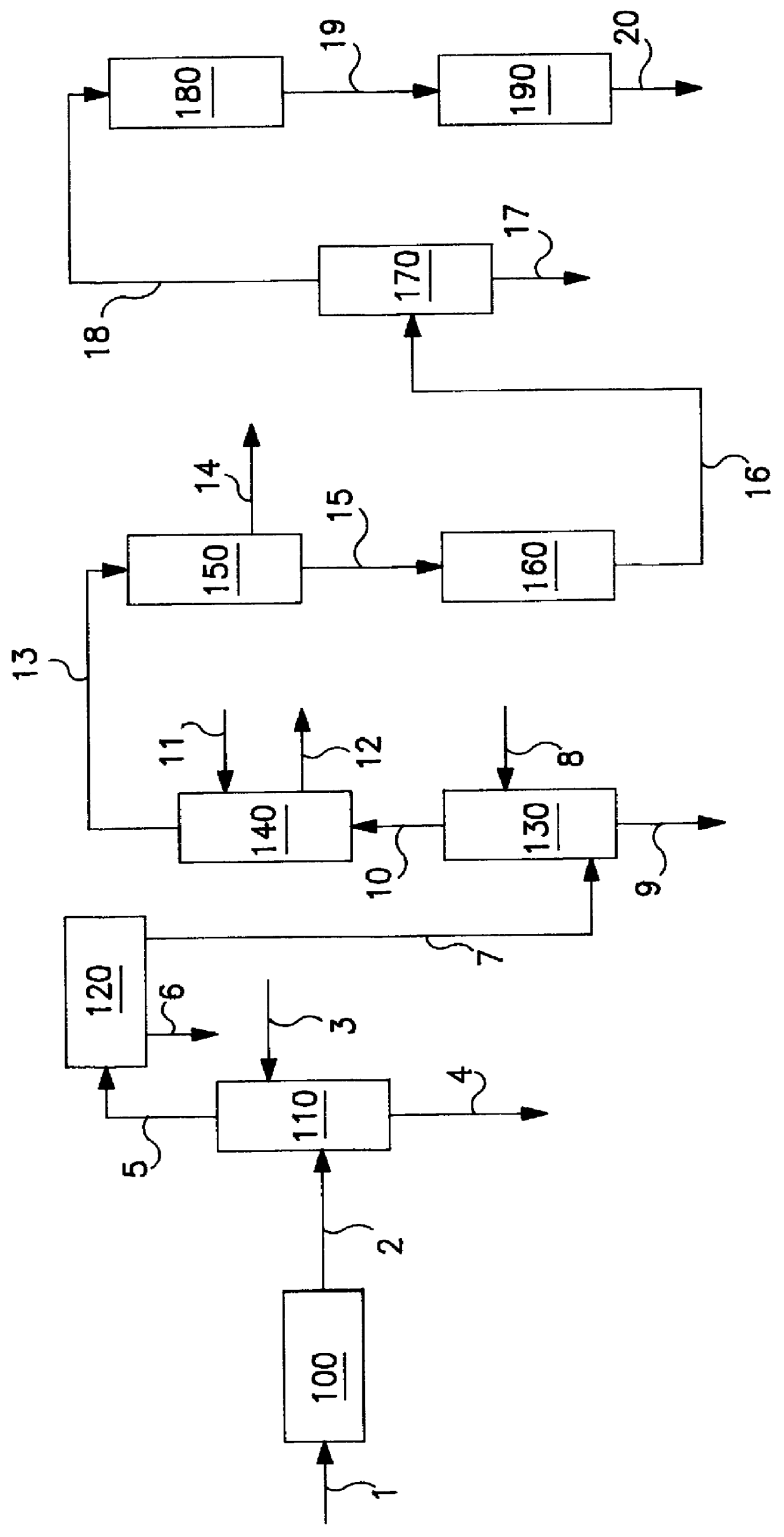
InactiveUS6916951B2Improve heat removal efficiencyStable catalyst environmentOrganic compound preparationOrganic chemistry methodsAcetic acidGas phase
Disclosed is a continuous process wherein carbon monoxide, a carbonylatable reactant, and a halide in the gas phase are contacted with a non-volatile catalyst solution comprising an ionic liquid and a Group VIII metal to produce a carbonylation product in the gas phase. The process is useful for the continuous preparation of acetic acid by the carbonylation of methanol.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Efficient and selective conversion of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS7605293B2Minimize or eliminate the disadvantages or dangers inherentElectrolysis componentsCarbon compoundsHydrogenFlue gas
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by electrochemical reduction produces formic acid acid and some formaldehyde and methanol mixtures. The formic acid can be used as source of carbon as well as hydrogen to produce methanol, dimethyl ether and other products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Process for production of acrylates from epoxides
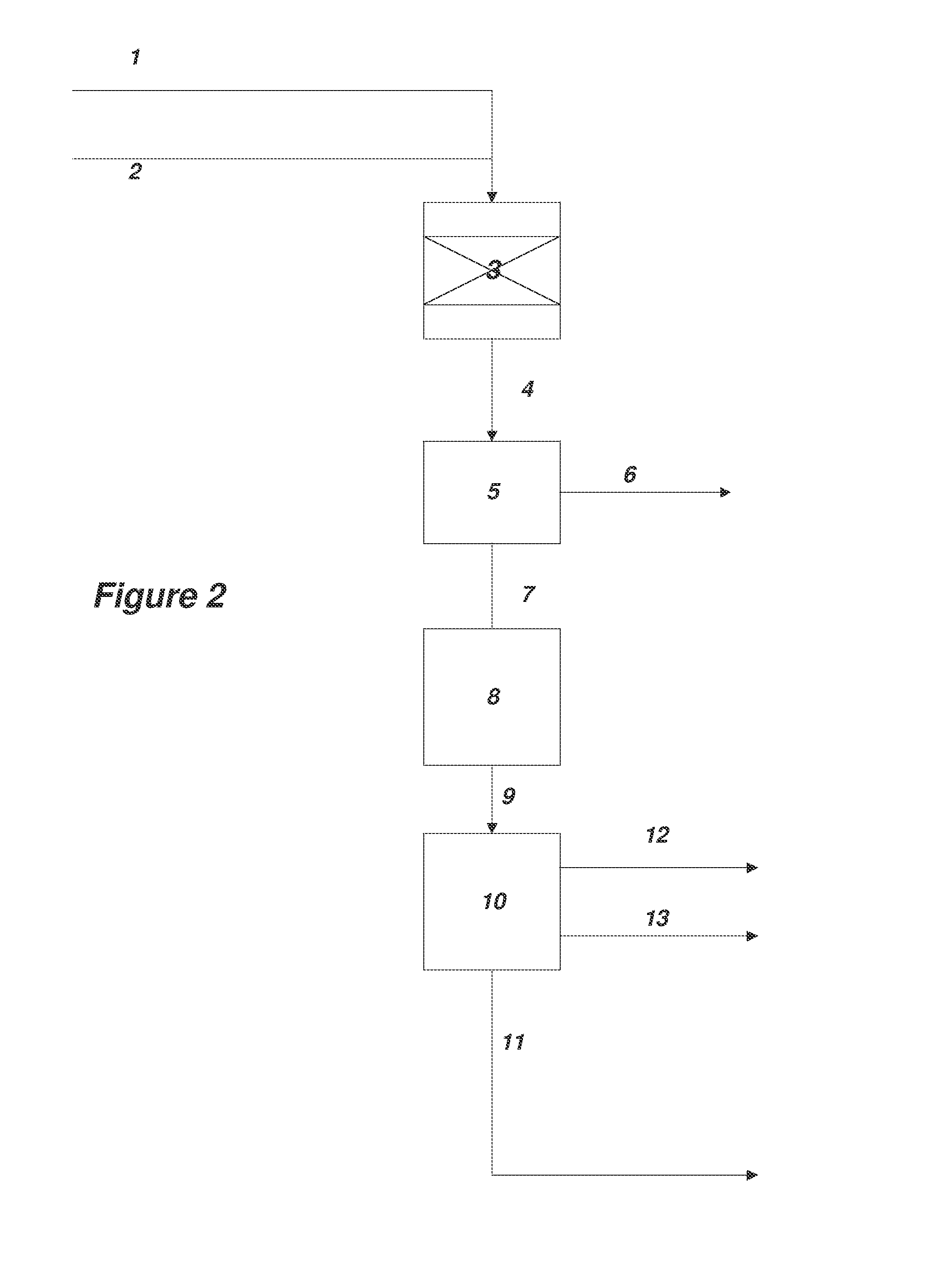
ActiveUS20140309399A1Low costAvoiding isolation and storageOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionReaction zoneMetal carbonyl
The methods of the present invention comprise the steps of: providing a feedstock stream comprising an epoxide and carbon monoxide; contacting the feedstock stream with a metal carbonyl in a first reaction zone to effect conversion of at least a portion of the provided epoxide to a beta lactone; directing the effluent from the first reaction zone to a second reaction zone where the beta lactone is subjected to conditions that convert it to a compound selected from the group consisting of: an alpha beta unsaturated acid, an alpha beta unsaturated ester, an alpha beta unsaturated amide, and an optionally substituted polypropiolactone polymer; and isolating a final product comprising the alpha-beta unsaturated carboxylic acid, the alpha-beta unsaturated ester, the alpha-beta unsaturated amide or the polypropiolactone.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Prepn process of 3-hydroxy propionate and propylene glycol
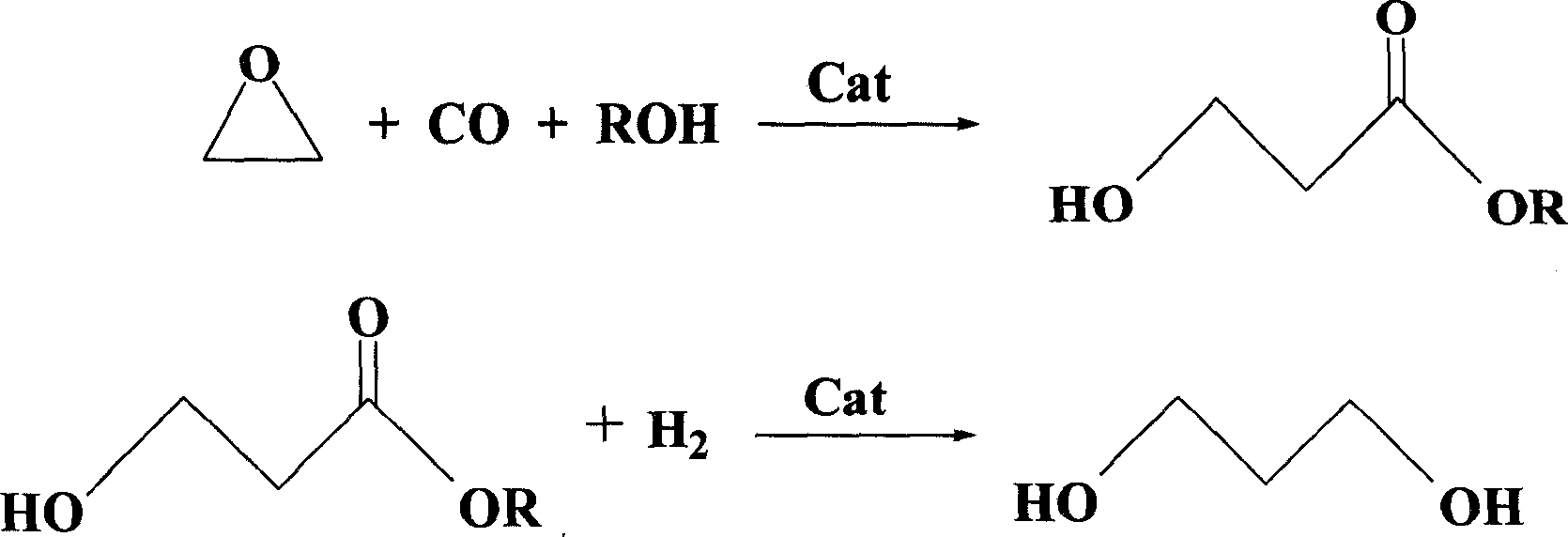
InactiveCN101020635AHigh activityImprove stabilityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsAccelerantCobalt catalyst
The present invention is process of preparing 3-hydroxy propionate and 1, 3-propylene glycol with epoxide as material. The present invention prepares 3-hydroxy propionate with epoxide, CO and alcohol under the action of cobalt catalyst and co-catalyst, and prepares 1, 3-propylene glycol under the action of 3-hydroxy propionate hydrogenating catalyst. The present invention has the advantages of simple reaction apparatus, simple operation, mild reaction condition, high catalyst activity, no environmental pollution, low production cost, etc.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process for production of acrylates from epoxides
ActiveUS9096510B2Low costAvoiding isolation and storageOrganic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionReaction zoneMetal carbonyl
The methods of the present invention comprise the steps of: providing a feedstock stream comprising an epoxide and carbon monoxide; contacting the feedstock stream with a metal carbonyl in a first reaction zone to effect conversion of at least a portion of the provided epoxide to a beta lactone; directing the effluent from the first reaction zone to a second reaction zone where the beta lactone is subjected to conditions that convert it to a compound selected from the group consisting of: an alpha beta unsaturated acid, an alpha beta unsaturated ester, an alpha beta unsaturated amide, and an optionally substituted polypropiolactone polymer; and isolating a final product comprising the alpha-beta unsaturated carboxylic acid, the alpha-beta unsaturated ester, the alpha-beta unsaturated amide or the polypropiolactone.
Owner:NOVOMER INC
Process for carbonylation of alkyl ethers
InactiveUS20060252959A1Organic compound preparationPreparation from carboxylic acid esters/lactonesMordeniteMethyl acetate
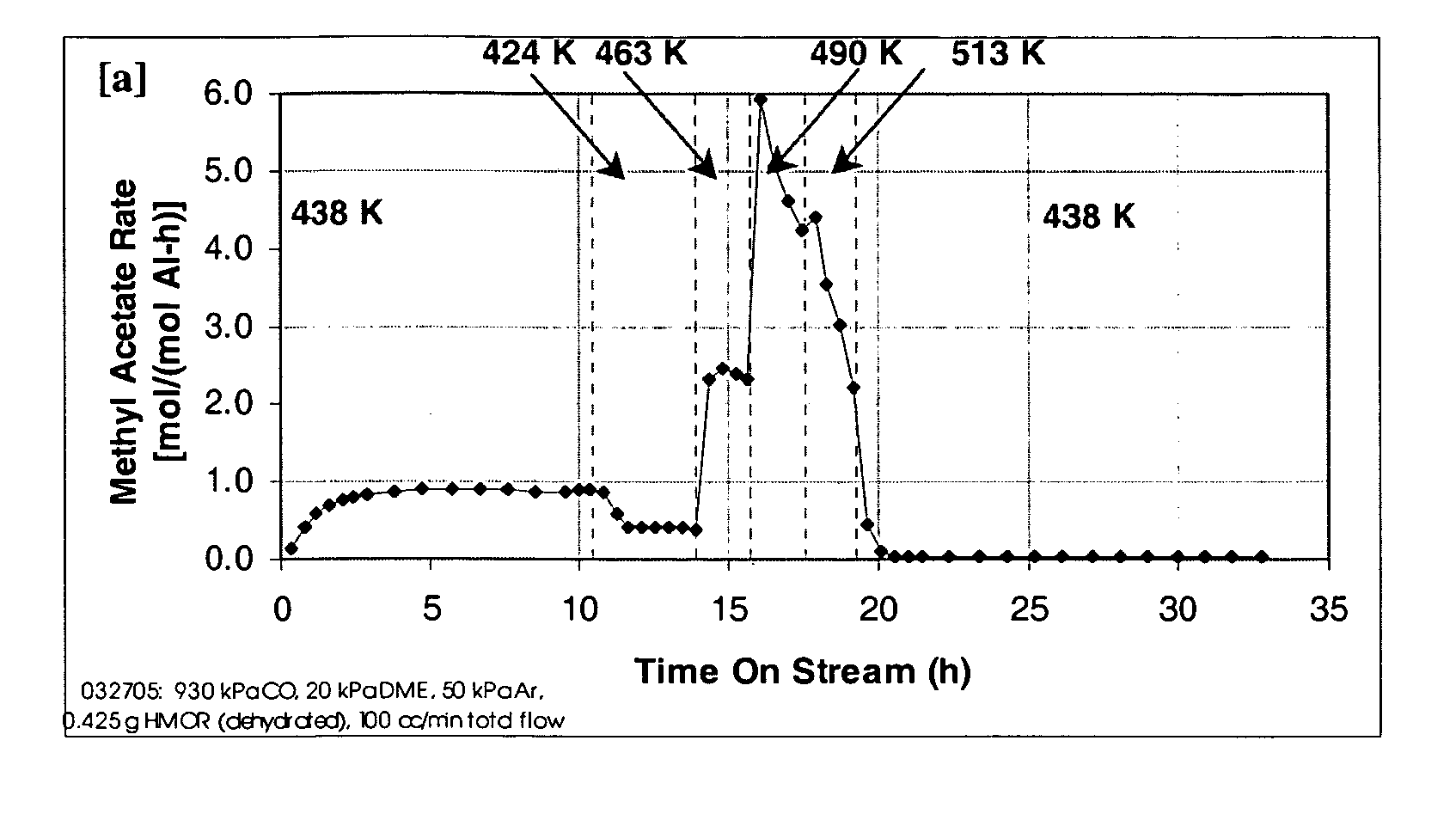
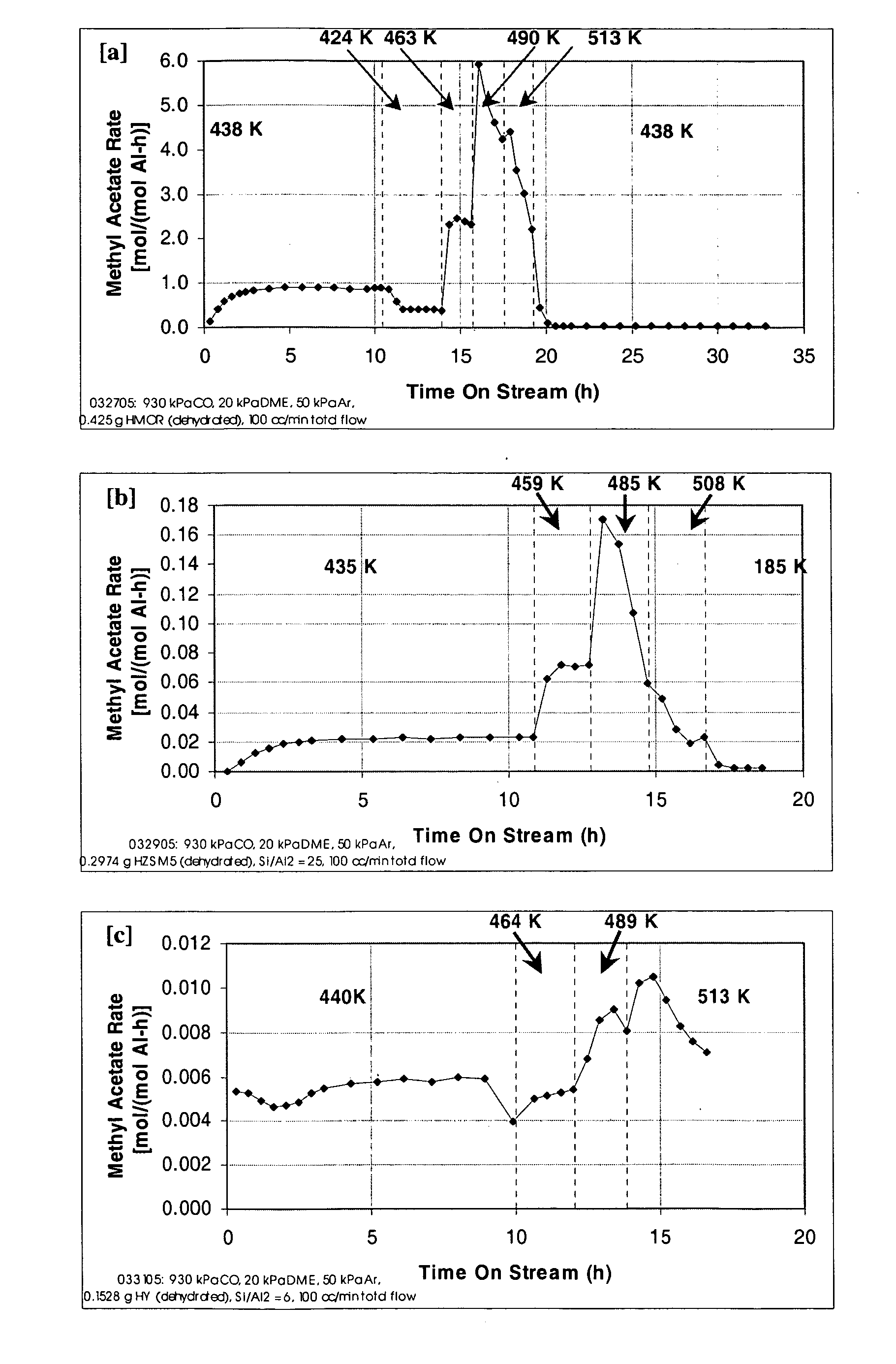
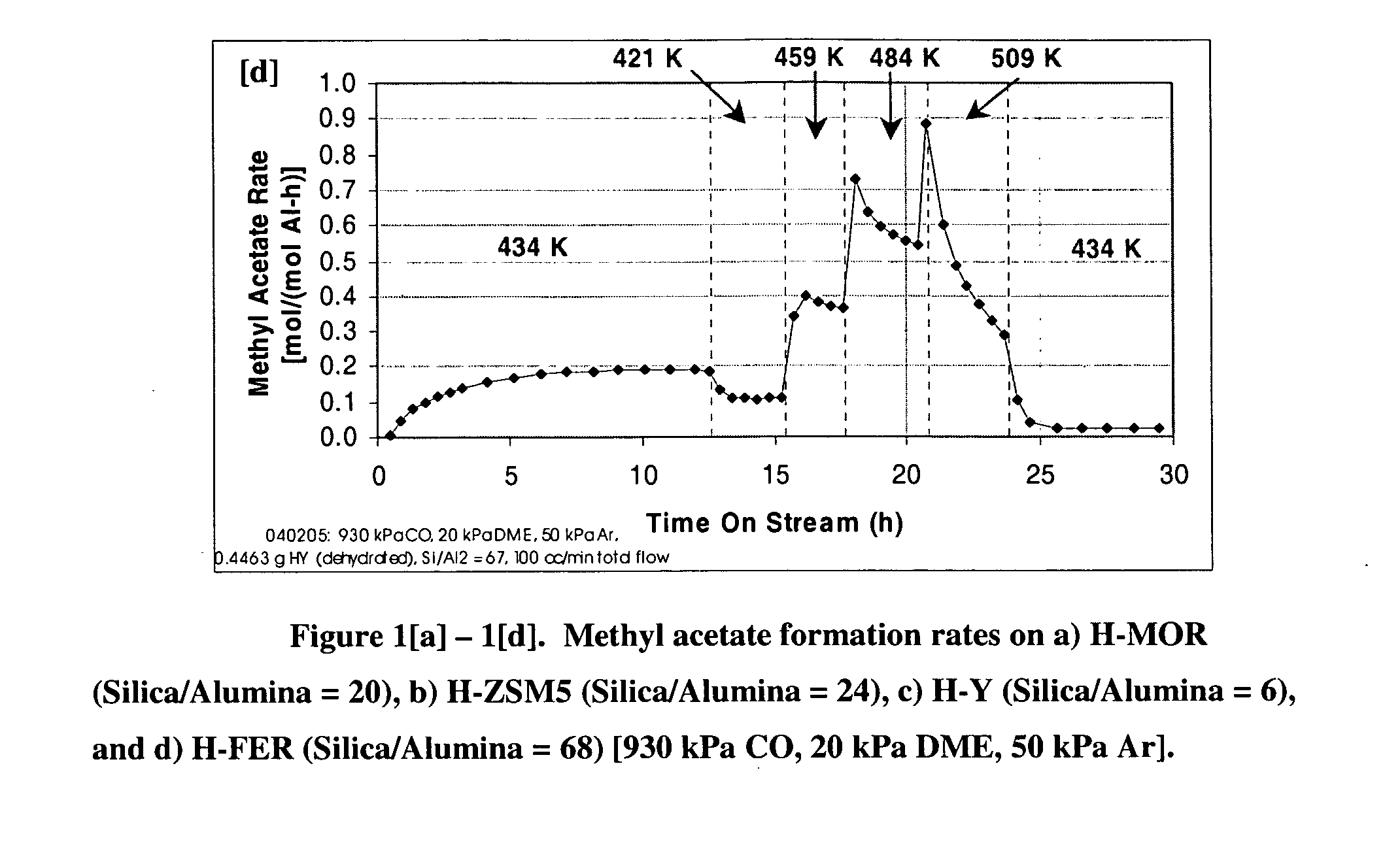
A product comprising a lower alkyl ester of a lower aliphatic carboxylic acid is produced by a process comprising reacting a lower alkyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst comprising mordenite and / or ferrierite, under substantially anhydrous conditions. More specifically, methyl acetate is selectively produced by reaction of dimethyl ether with carbon monoxide in the presence of a catalyst comprising mordenite or ferrierite, under substantially anhydrous conditions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Preparation method for catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase
ActiveCN101543784ALow costCatalyst activation/preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionGas phaseReaction temperature
The invention discloses a preparation method for a catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester by gas-phase. The catalyst takes alpha-alumina as a carrier, palladium as an active component and 2 MOxes as an additive, M is magnesium, titanium, zirconium, vanadium, manganese, iron, nickel, copper, zinc, molybdenum or tungsten, and components of the catalyst (calculated by carrier mass) are: 0.01 to 0.75 percent of the palladium and 0.1 to 20 percent of MOxes. The preparation method comprises the following steps that: firstly, an additive metal salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier, and a palladium salt solution is used to impregnate the carrier to obtain the catalyst after the carrier is dried and roasted. Before the use, pure hydrogen or H2-N2 mixed gas is activated by the catalyst at a temperature of between 150 and 450 DEG C. The catalyst can be used for synthesizing oxalic ester by the carbonylation of CO and nitrous acid ester, the using reaction temperature of the catalyst is between 70 and 150 DEG C, and the reaction space velocity is between 500 and 9,000h<-1>. The catalyst has higher reaction activity and selectivity; and the catalyst has low cost.
Owner:HAISO TECH
Process for reactive esterification distillation
ActiveUS7667068B2Organic compound preparationPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic acidChemical reaction
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Methods of making alkyl lactates and alkyl levulinates from saccharides
InactiveUS20150045576A1Organic compound preparationPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionLevulinic acidAlcohol
Unique methods have been developed to convert saccharides into value-added products such as alkyl lactates, lactic acid, alkyl levulinates, levulinic acid, and optionally alkyl formate esters and / or hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF). Useful catalysts include Lewis acid catalysts and Brønsted acid catalysts including mineral acids, metal halides, immobilized heterogeneous catalysts functionalized with a Brønsted acid group or a Lewis acid group, or combinations thereof. The saccharides are contacted with the catalyst in the presence of various alcohols.
Owner:BATTELLE MEMORIAL INST
Catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101596455ASmooth responseHigh reactivityPreparation by carbon monoxide or formate reactionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsActive componentDistilled water
The invention relates to a catalyst for synthesizing oxalic ester and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst contains active components of palladium and lanthanum which respectively account for 0.3-1.5 percent and 0.01-8 percent of the weight of a carrier, and the carrier is Alpha-Al2O3. The preparation method comprises the following steps: placing the Alpha-Al2O3 into alkaline solution, and processing the Alpha-Al2O3 in a high-pressure kettle under a temperature of 150-350 DEG C; washing the Alpha-Al2O3 with distilled water to neutral; drying the Alpha-Al2O3 under the temperature of 100-200 DEG C; dipping the Alpha-Al2O3 in solution with the concentration of lanthanum being 0.003-0.02 M, drying and baking; and dipping the Alpha-Al2O3 in solution with the concentration of palladium being 0.003-0.02 M, drying and baking under a temperature of 300-700 DEG C. The catalyst is applied to a reaction for synthesizing dimethyl oxalate by carbon monoxide and methyl nitrite and has the advantages of higher reacting activity and selectivity, long service life, stable reaction and easy control; and the space time yield of the dimethyl oxalate is 830g / L.h-1130g / L.h.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
Popular searches
Distillation separation Carboxylic preparation from carbon monoxide reaction Carbonyl compound separation/purification Carboxylic compound separation/purification Gas purification by liquid washing Bulk chemical production Preparation by carbon oxide reduction Combustible gas chemical modification Products Reagents
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com