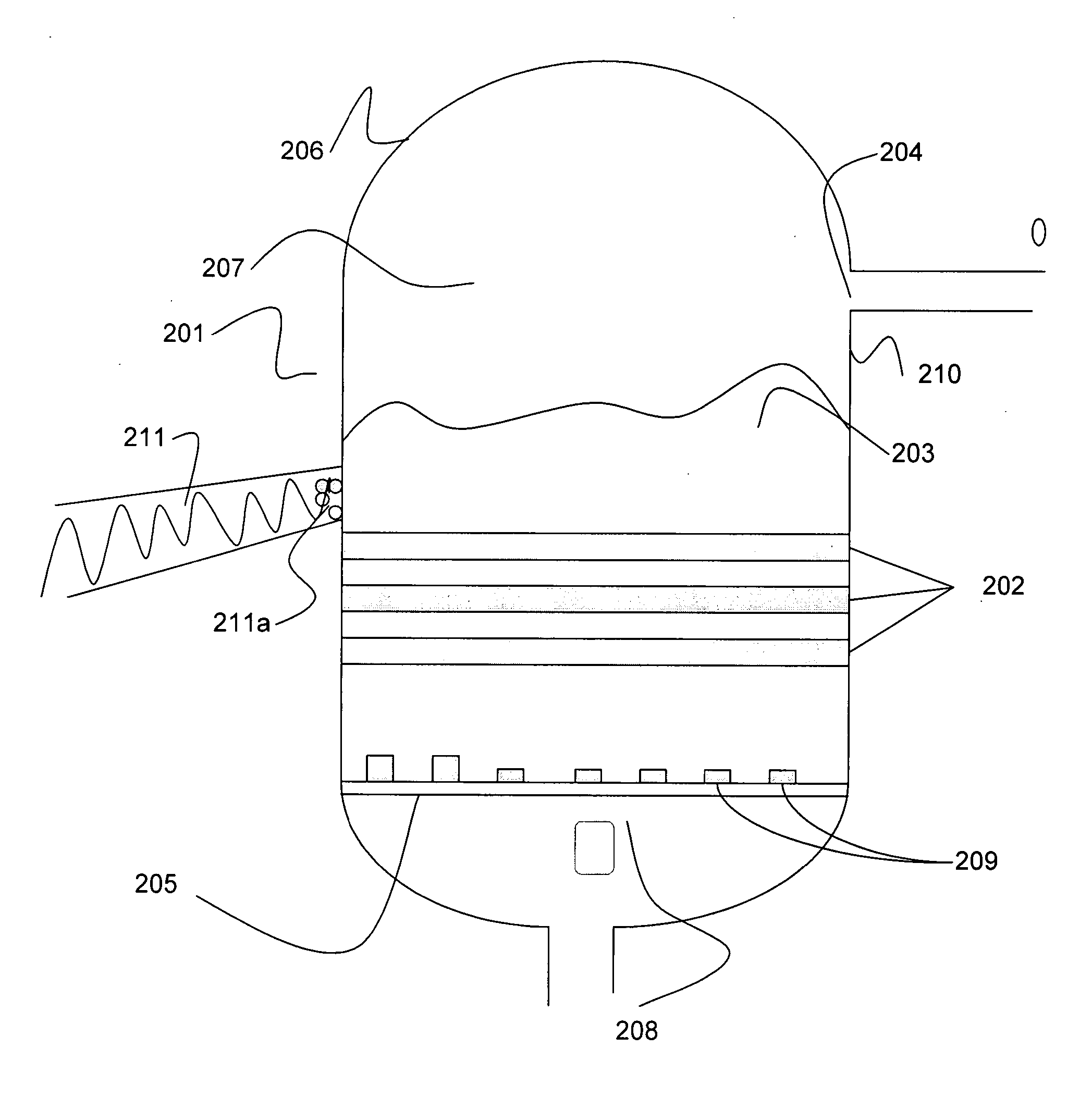
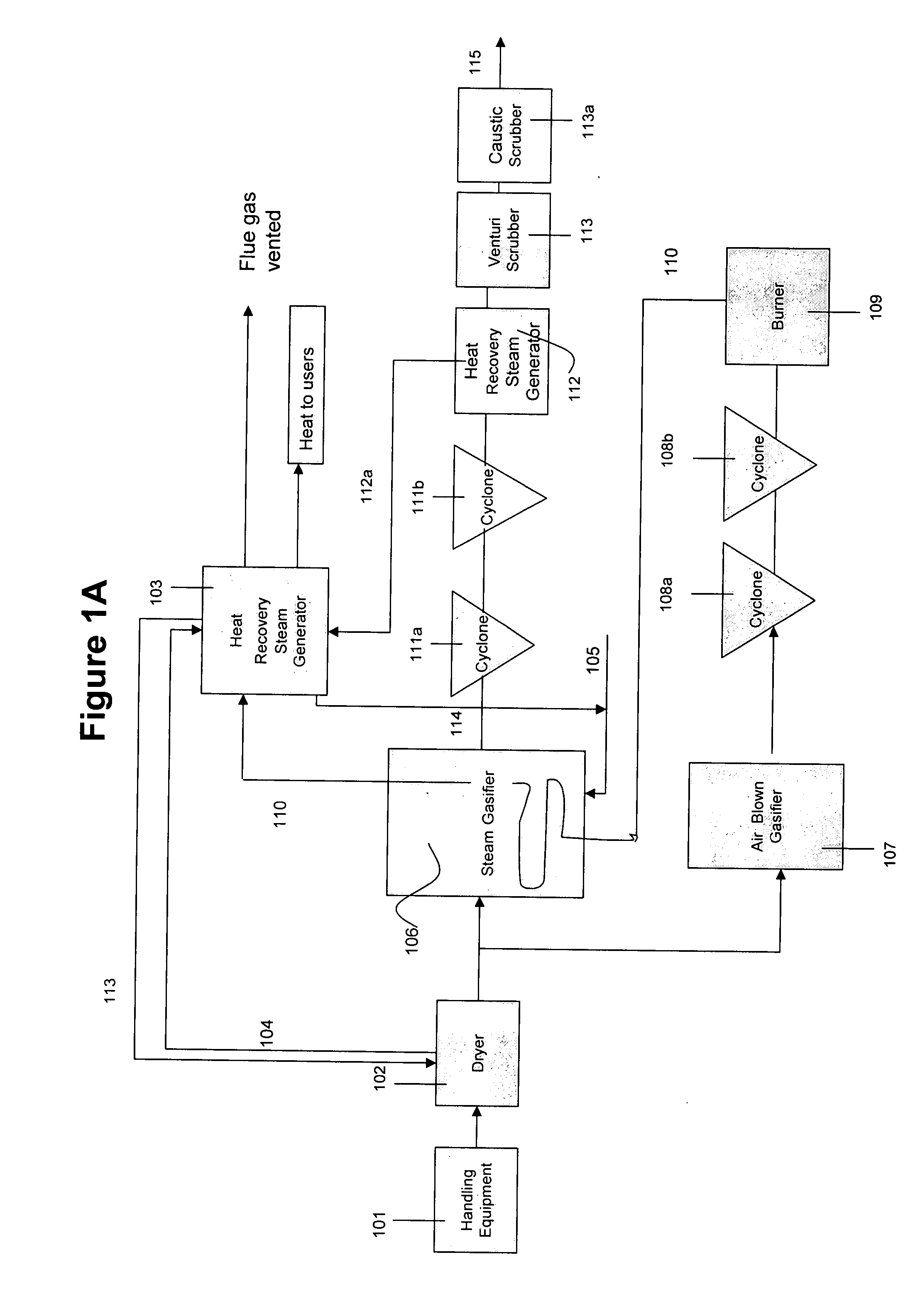
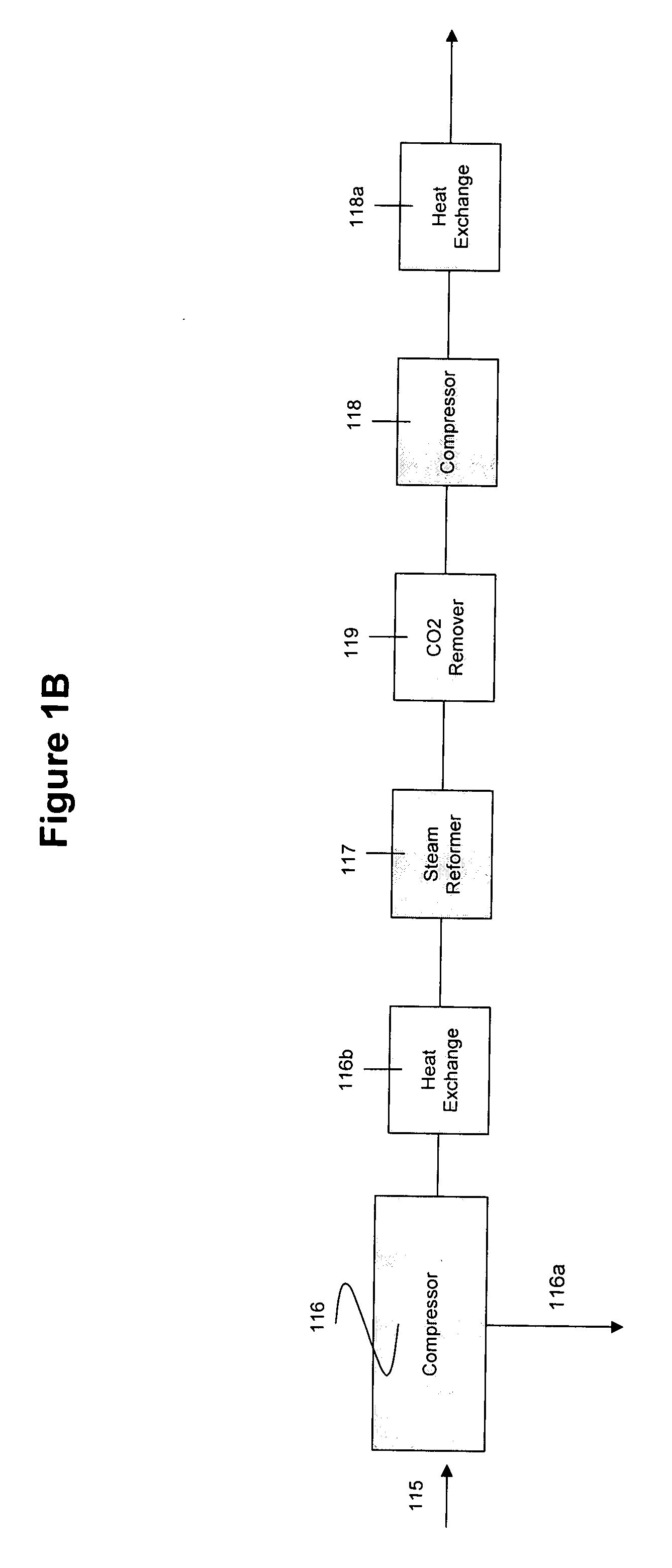
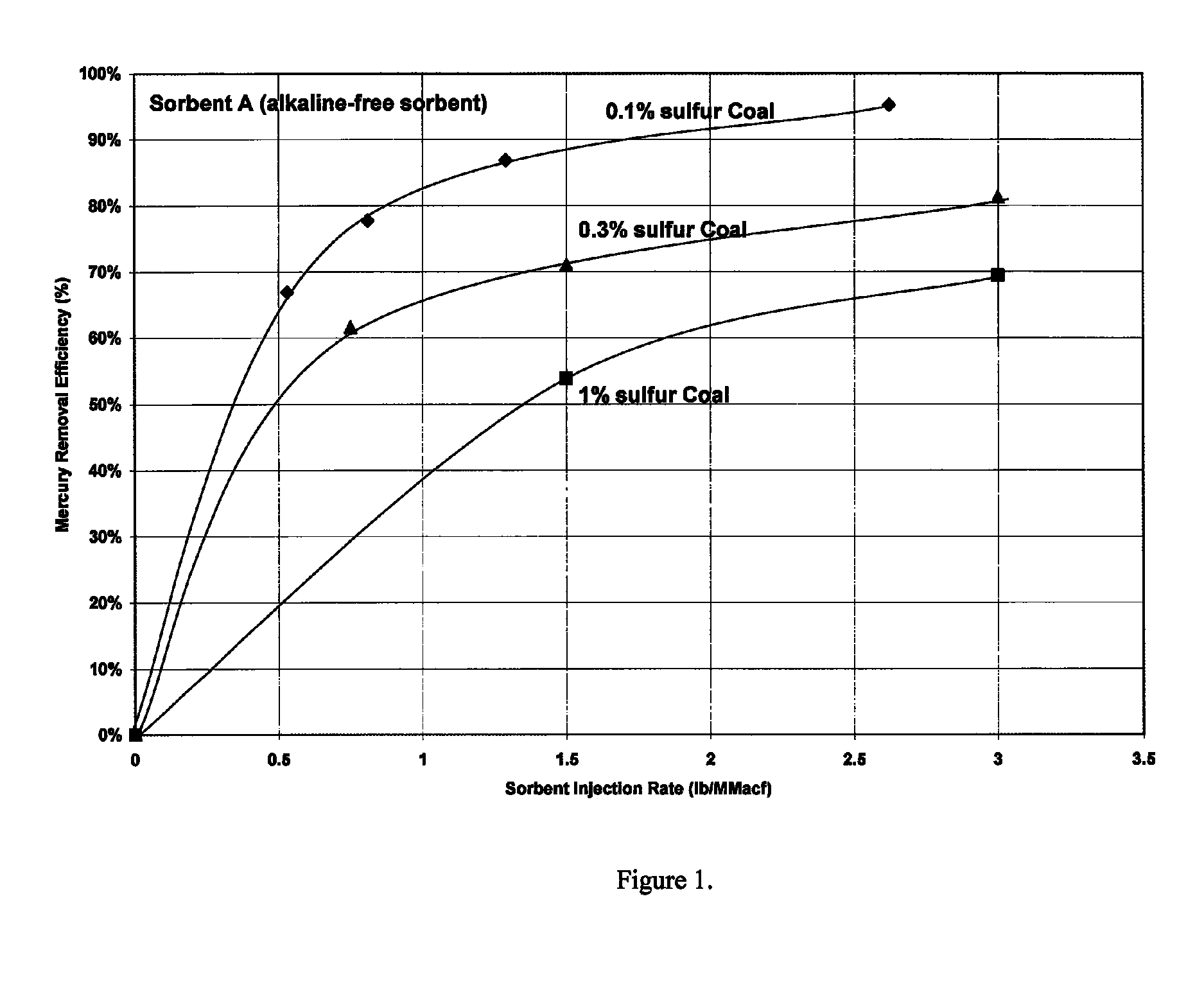
Patents
Literature
42670 results about "Flue gas" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flue gas is the gas exiting to the atmosphere via a flue, which is a pipe or channel for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, oven, furnace, boiler or steam generator. Quite often, the flue gas refers to the combustion exhaust gas produced at power plants. Its composition depends on what is being burned, but it will usually consist of mostly nitrogen (typically more than two-thirds) derived from the combustion of air, carbon dioxide (CO2), and water vapor as well as excess oxygen (also derived from the combustion air). It further contains a small percentage of a number of pollutants, such as particulate matter (like soot), carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and sulfur oxides.
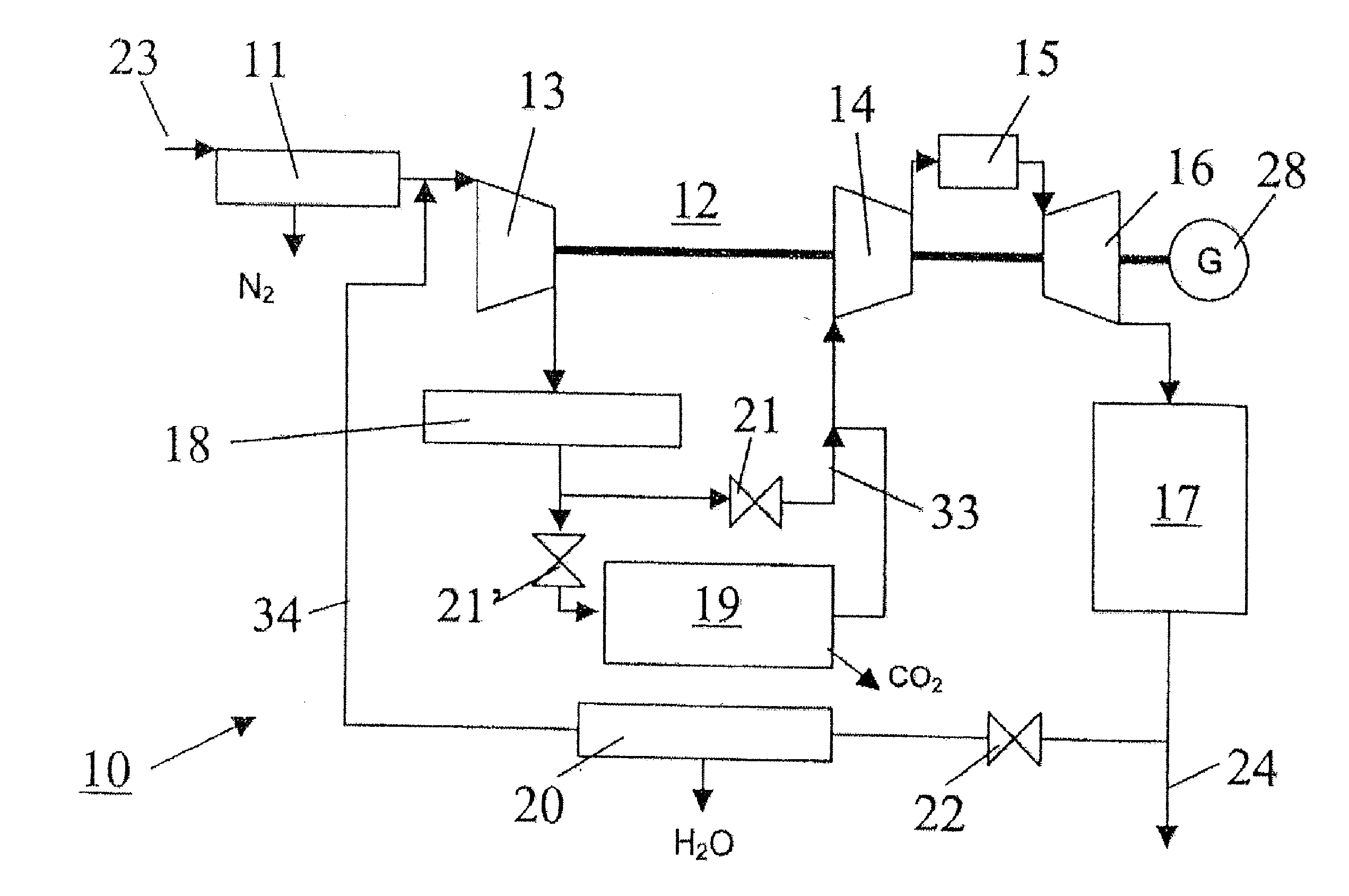
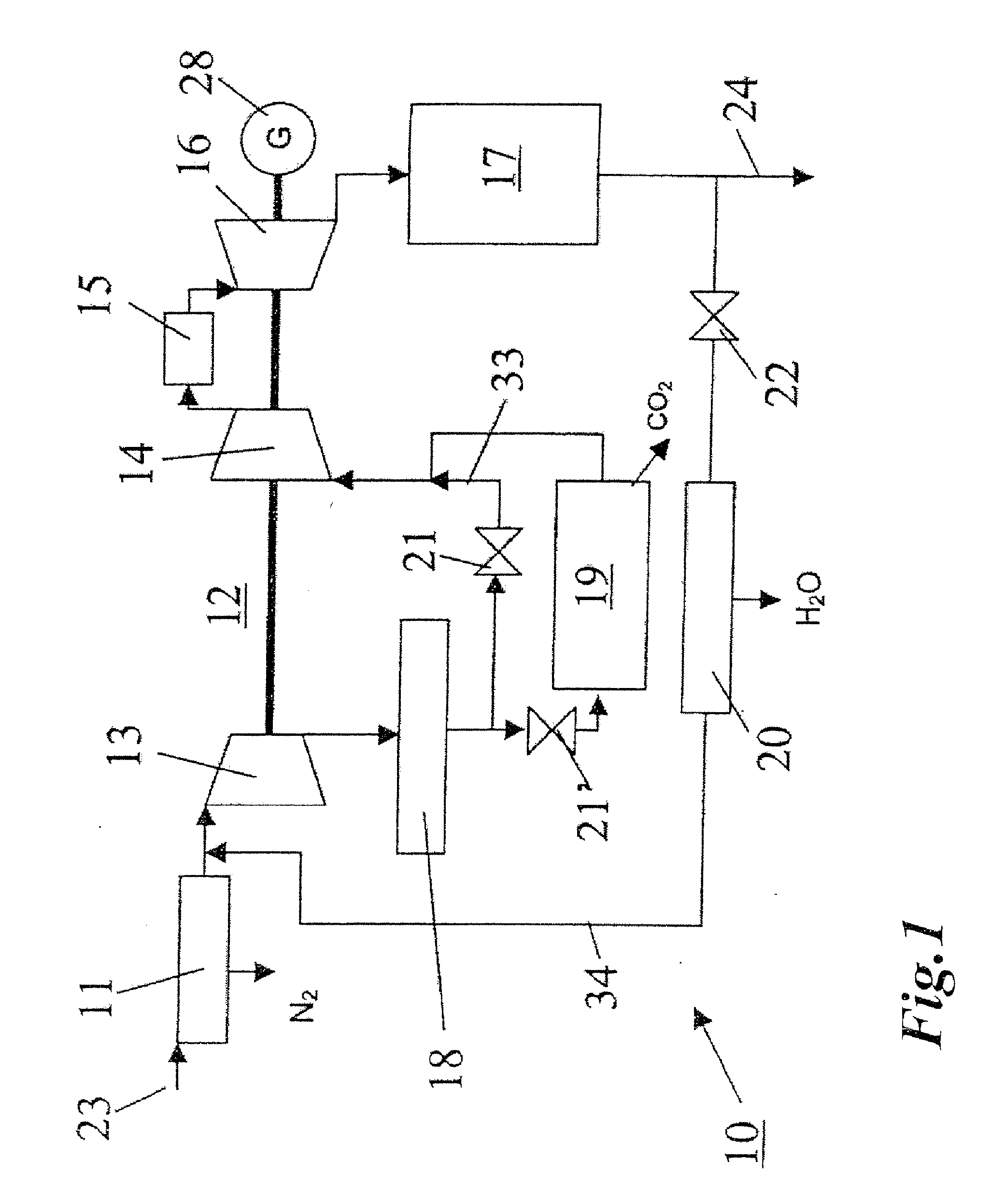
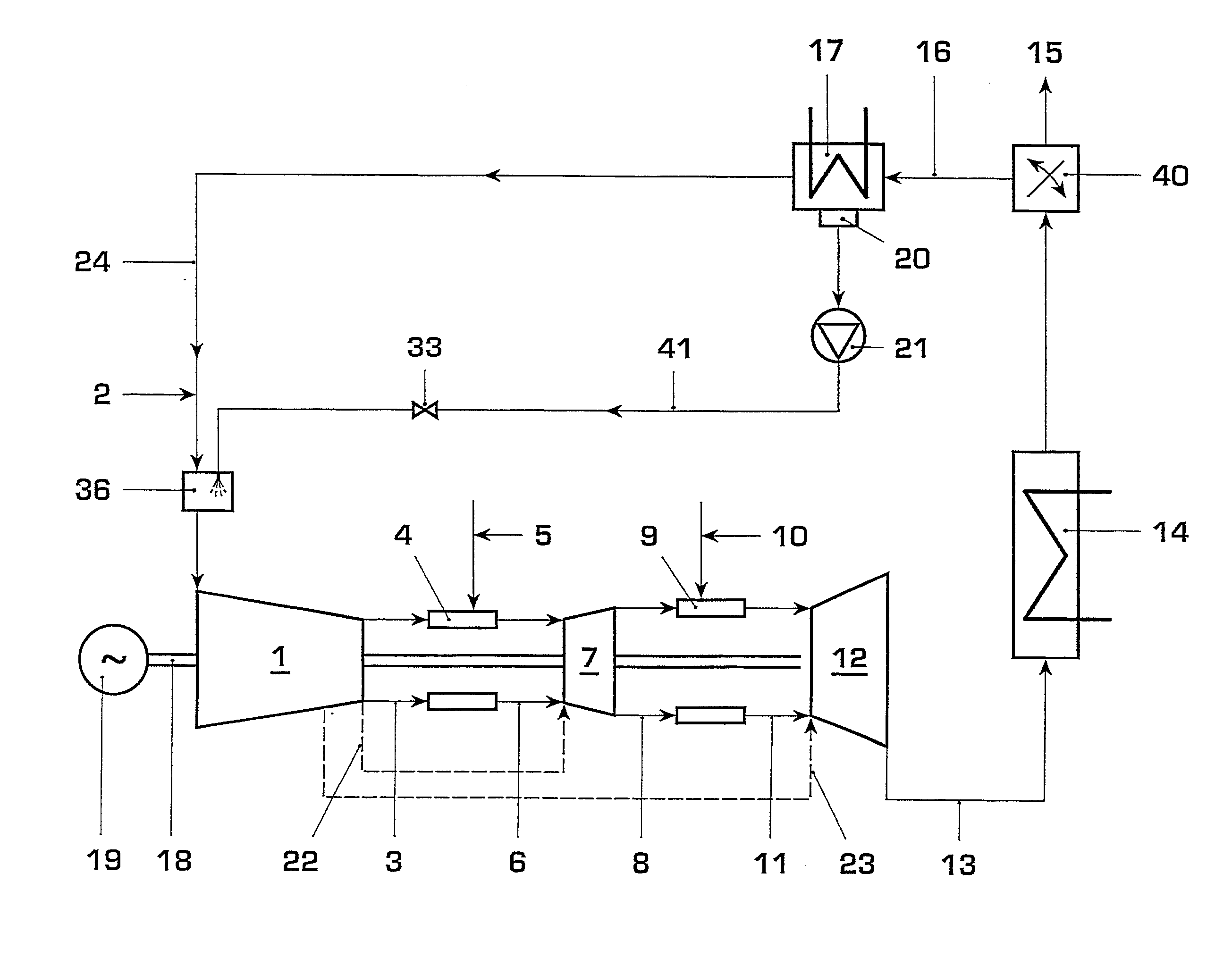
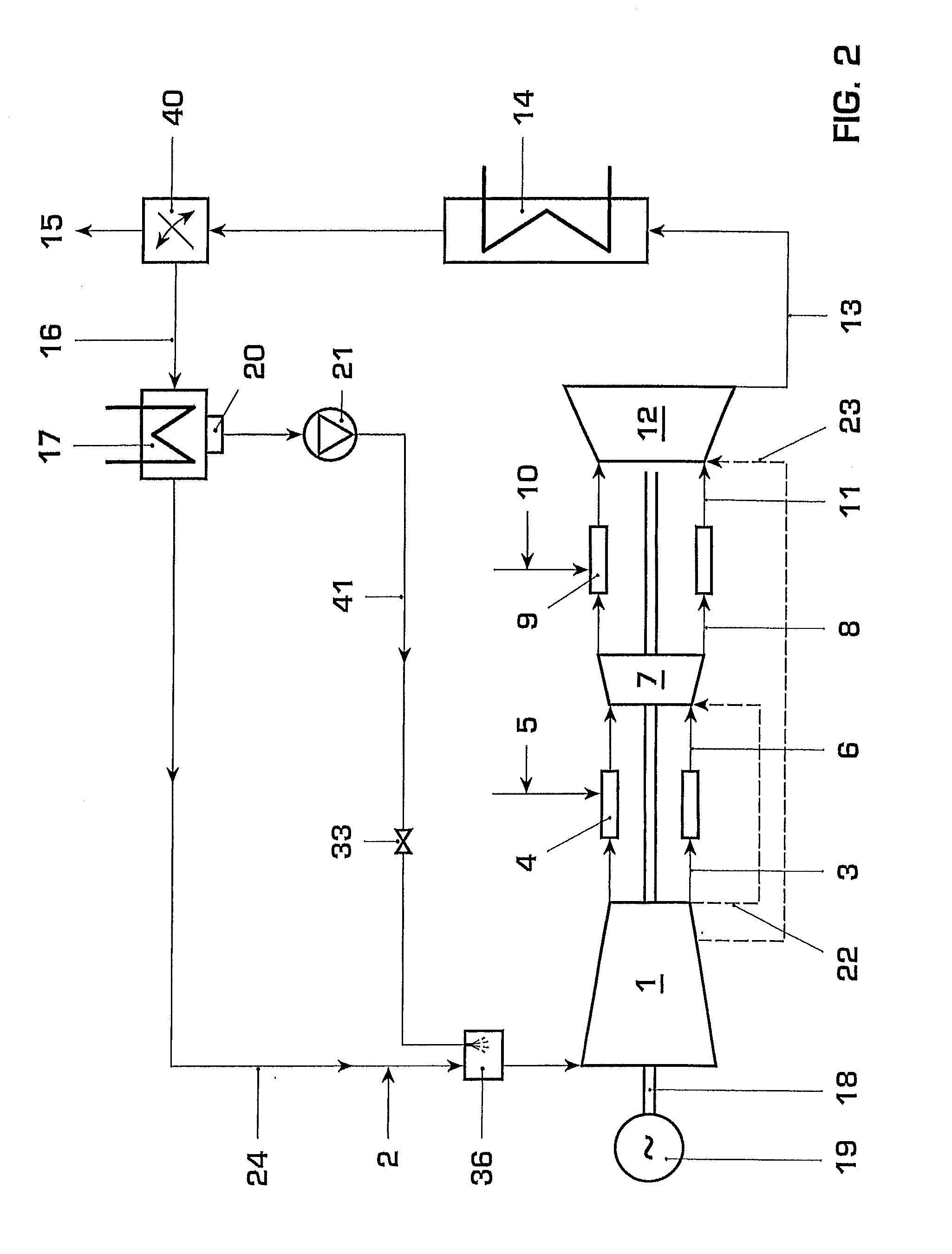
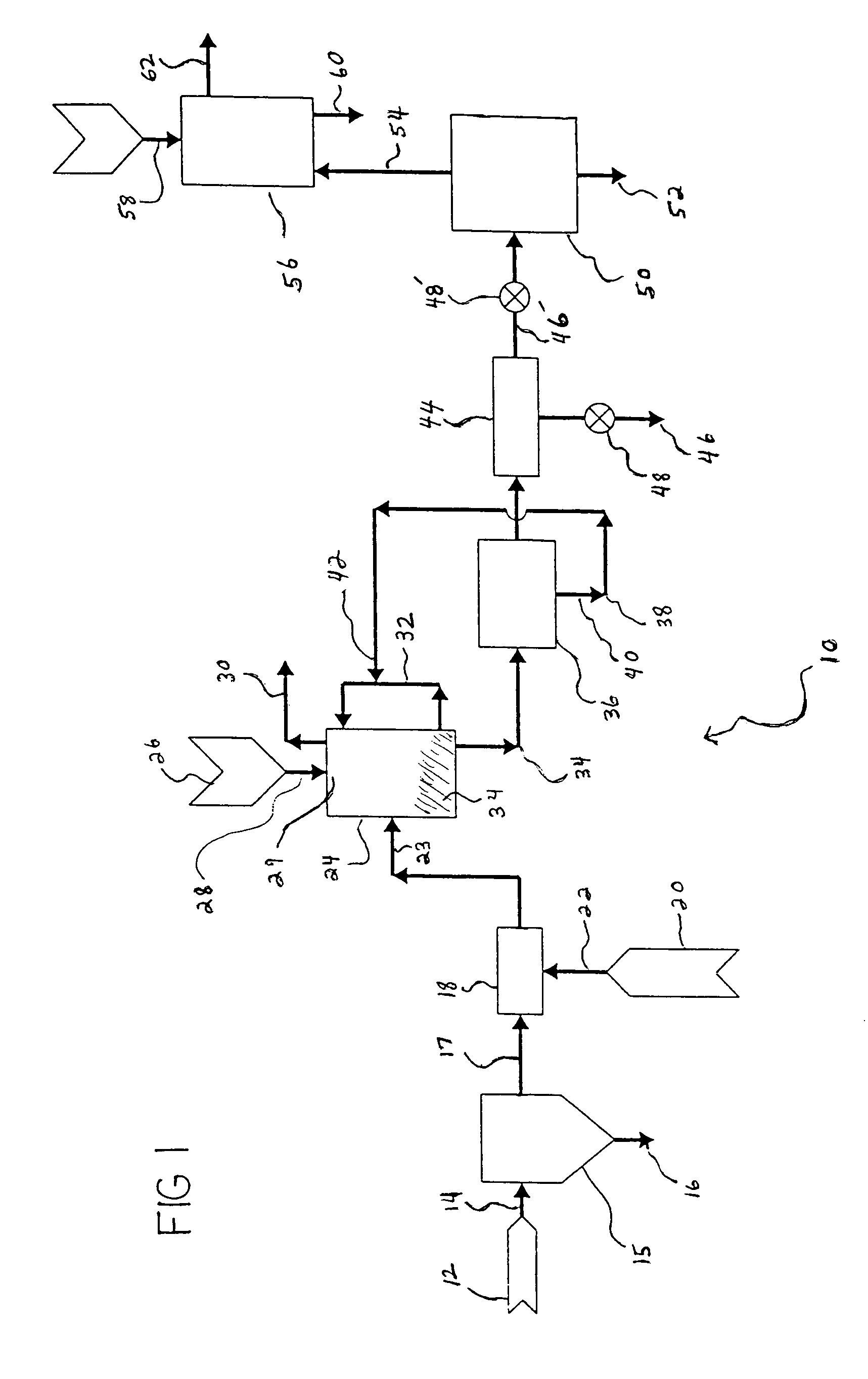
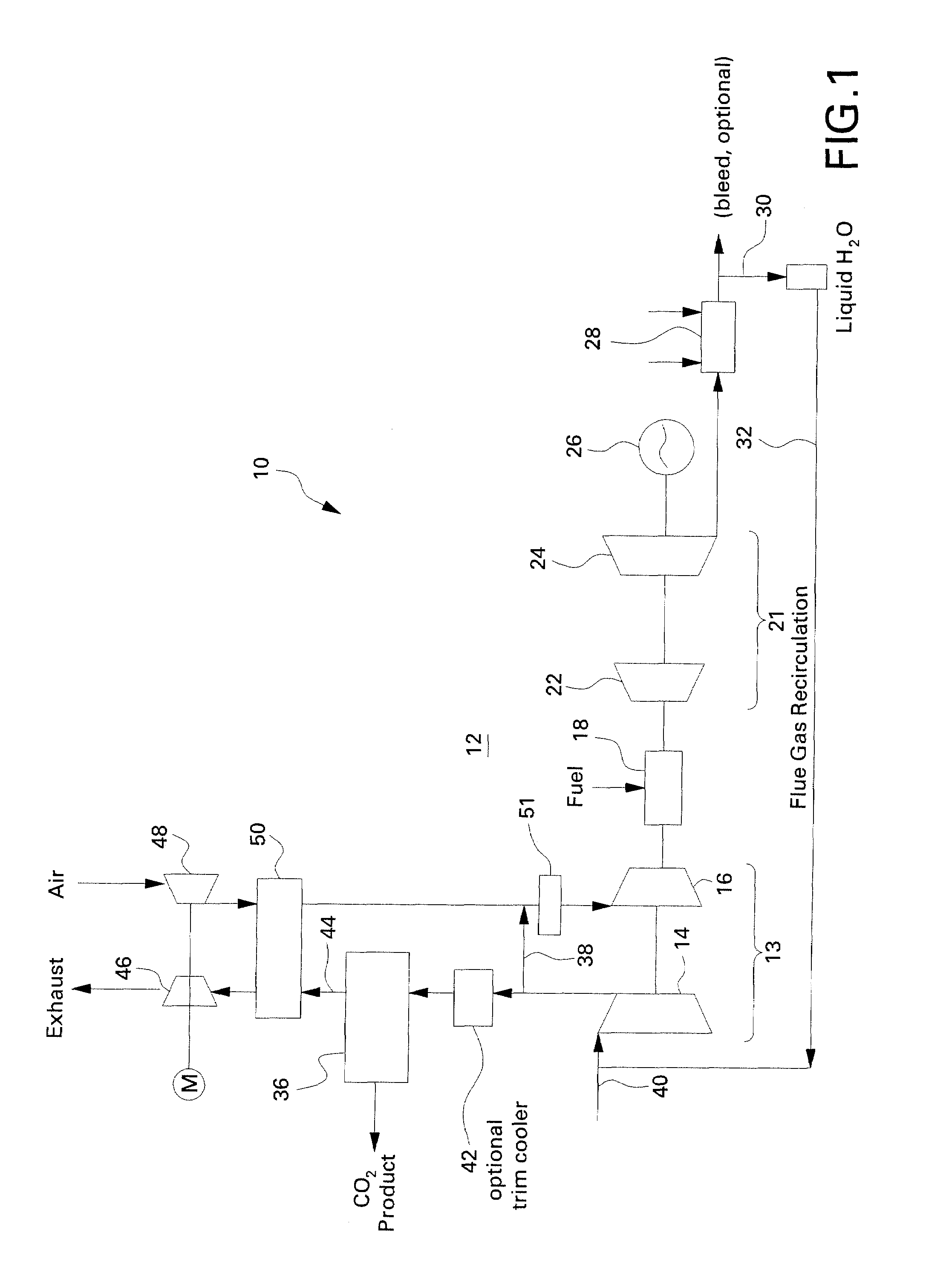
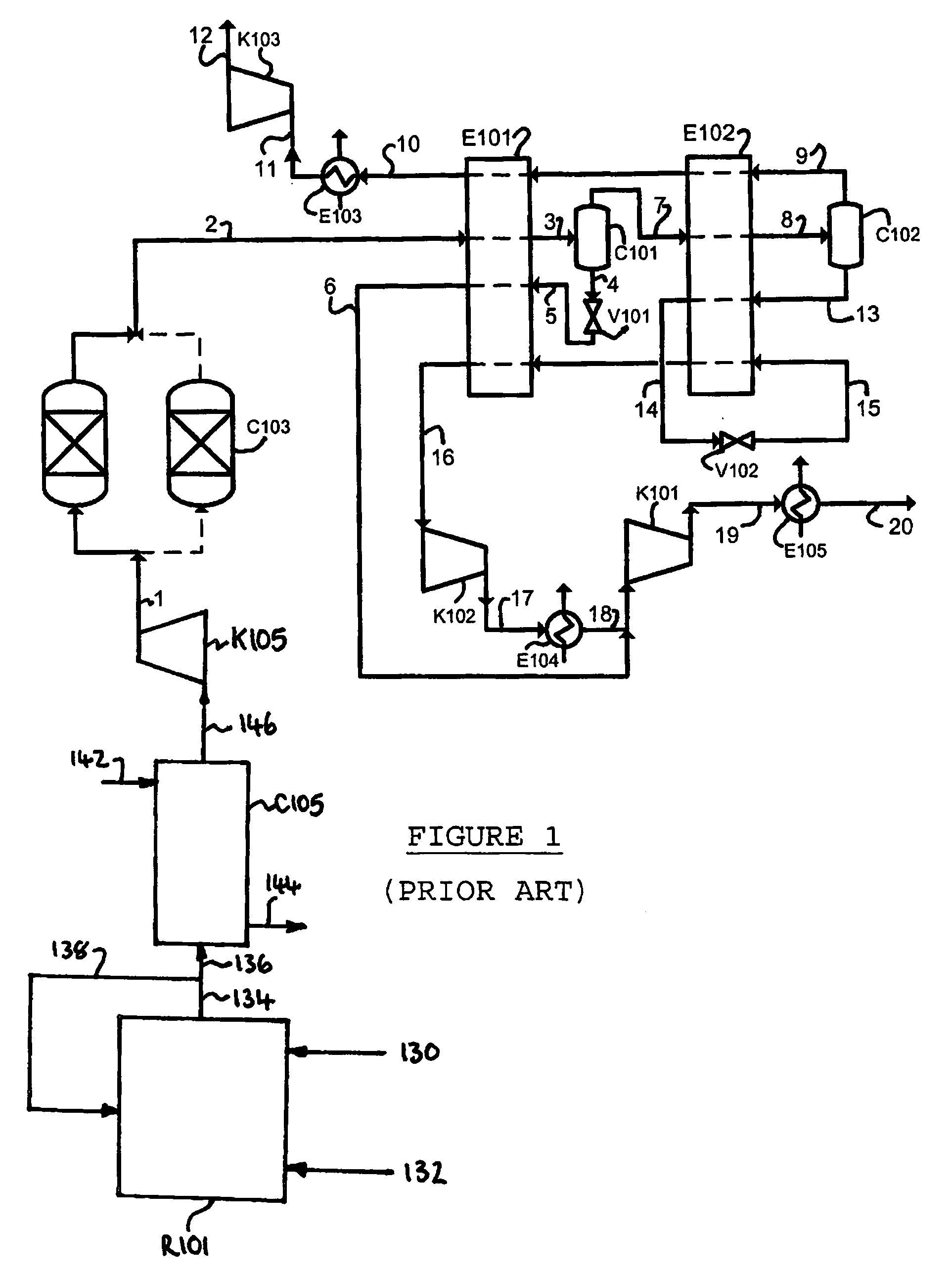
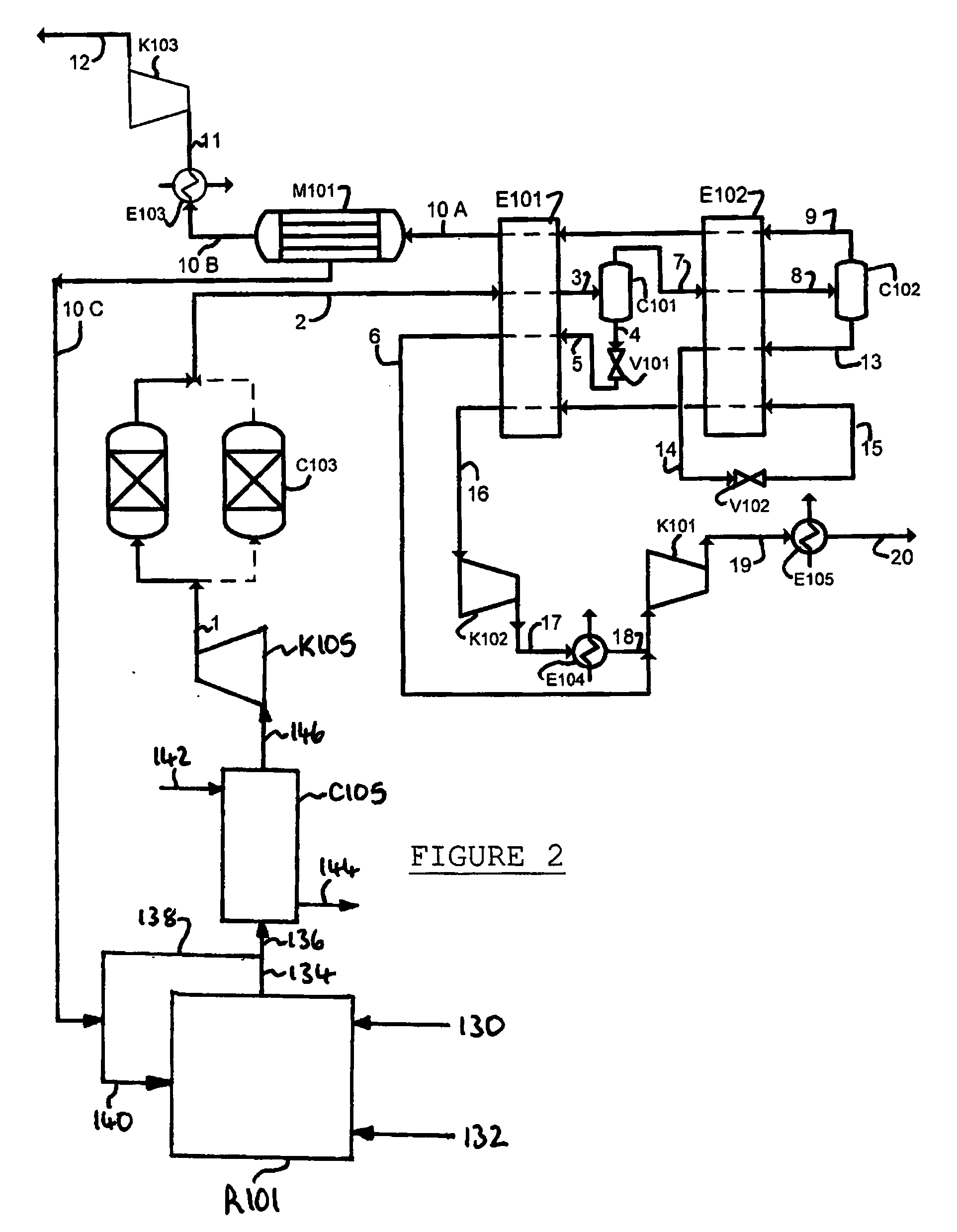
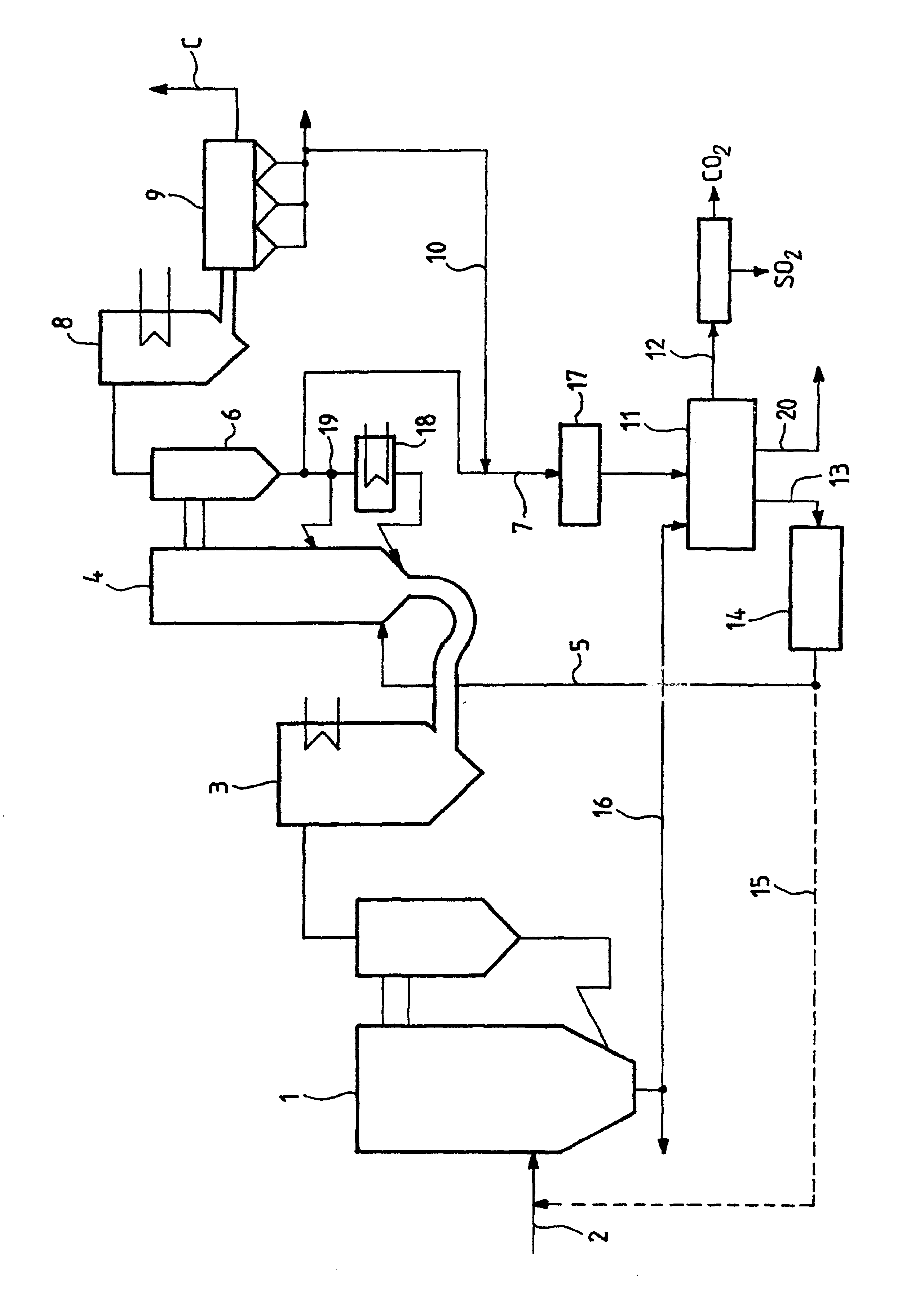
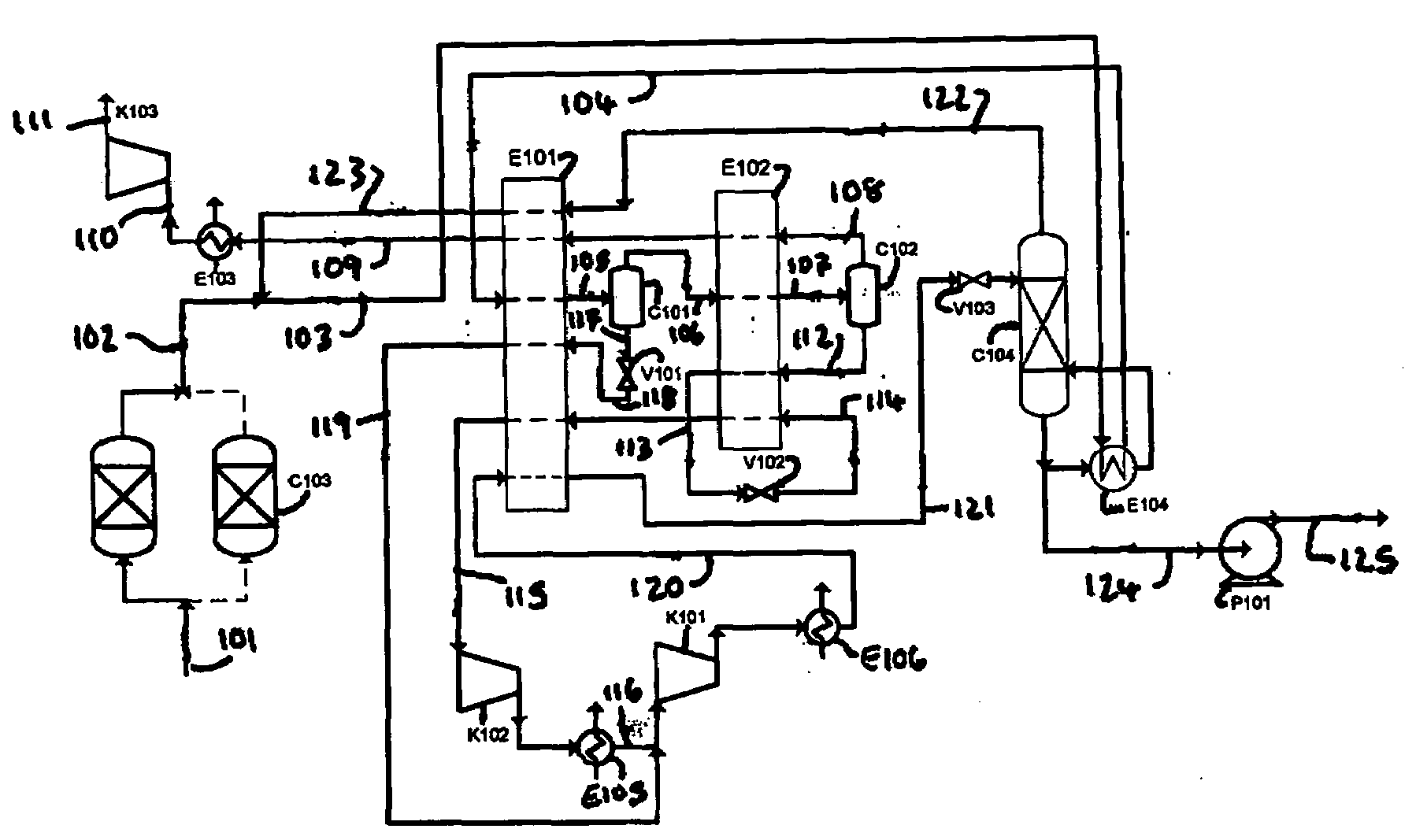
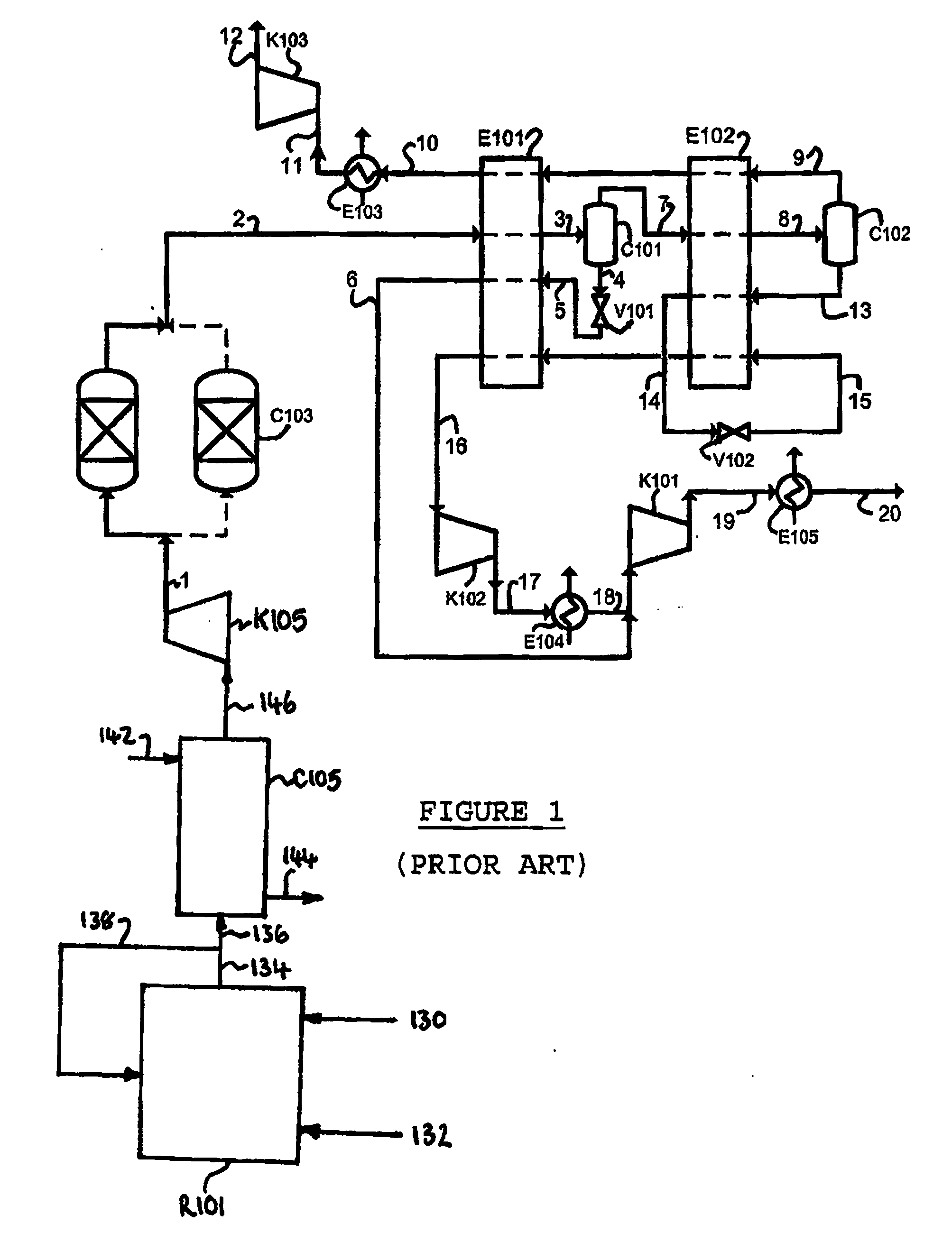
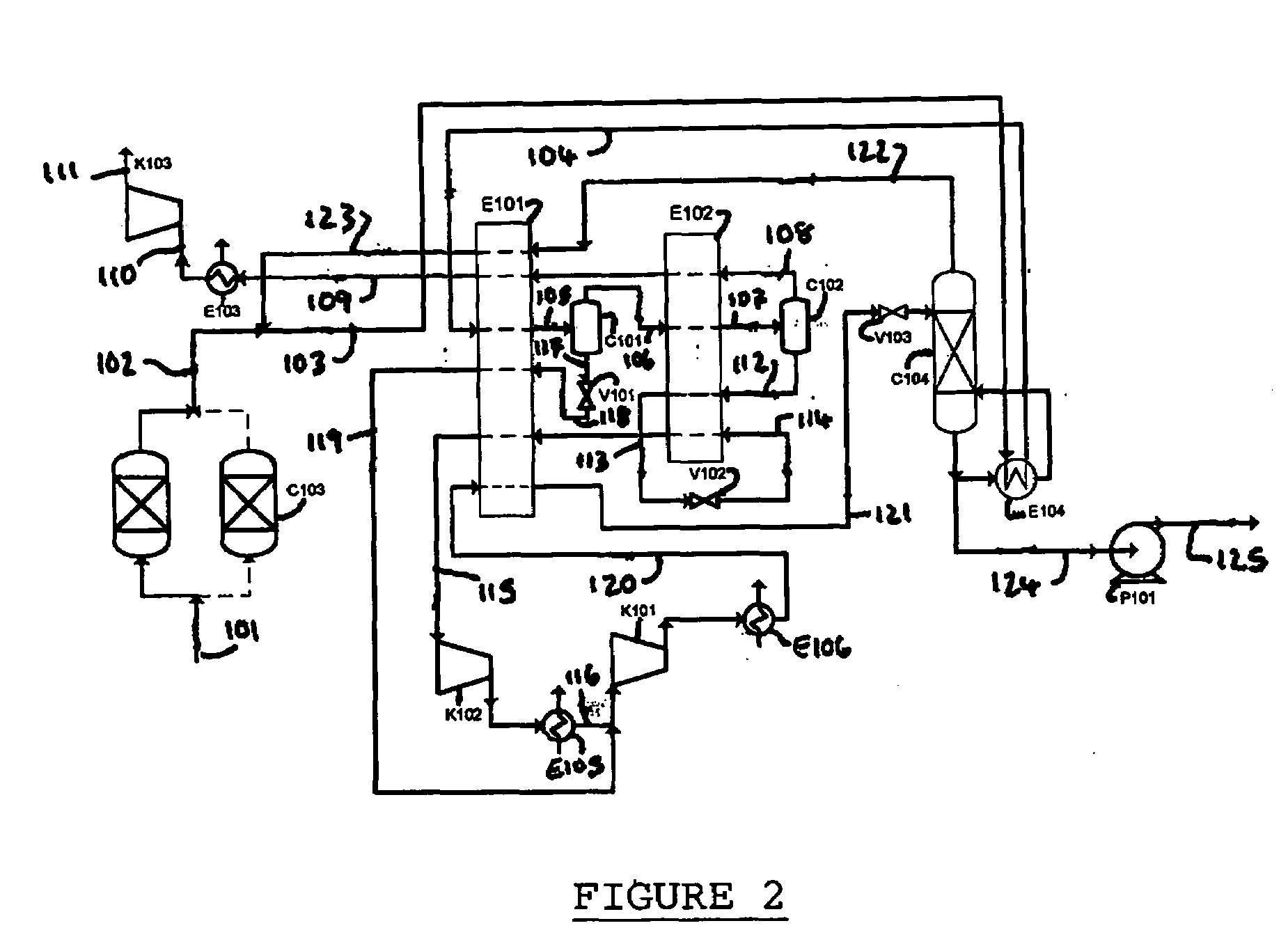
Method for Generating Energy in an Energy Generating Installation Having a Gas Turbine, and Energy Generating Installation Useful for Carrying Out the Method
InactiveUS20080010967A1Efficient removalImprove efficiencyDispersed particle separationGas turbine plantsCyclic processCombustion chamber
In a method for generating energy in an energy generating installation (10) having a gas turbine (12), in a first step, an oxygen-containing gas is compressed in a compressor (13, 14) of the gas turbine (12), in a second step the compressed gas is supplied, with the addition of fuel, for combustion in a combustion chamber (15), in a third step the hot flue gas from the combustion chamber (15) is expanded in a turbine (16) of the gas turbine (12) so as to perform work, and, in a fourth step, a branched-off part stream of the expanded flue gas is recirculated into a part of the gas turbine (12) lying upstream of the combustion chamber (15) and is compressed. A reduction in the CO2 emission, along with minimal losses of efficiency, is achieved in that carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the circulating gas in a CO2 separator (19), and in that measures are taken to compensate for the efficiency losses in the gas turbine cyclic process which are associated with the CO2 separation.
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
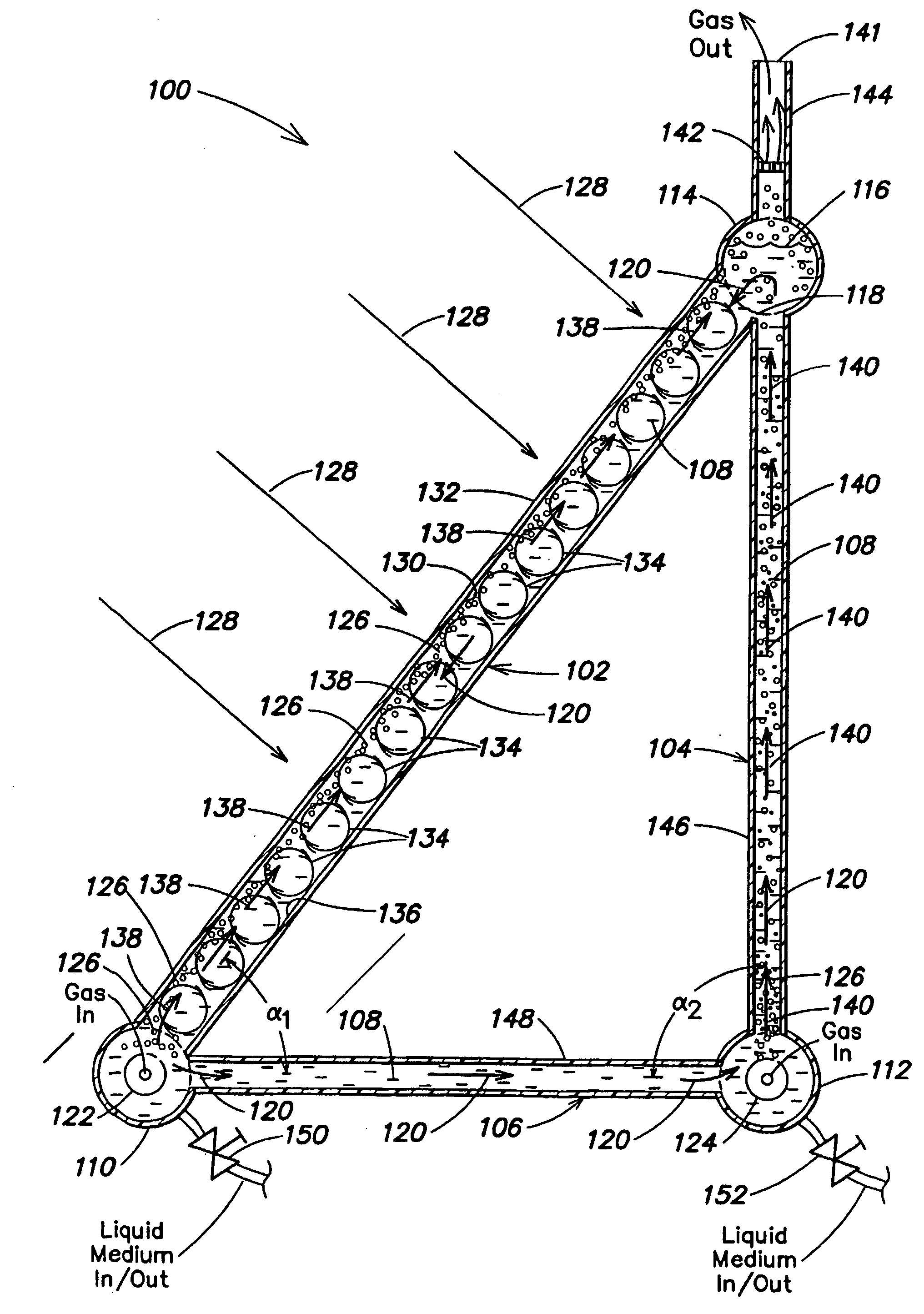
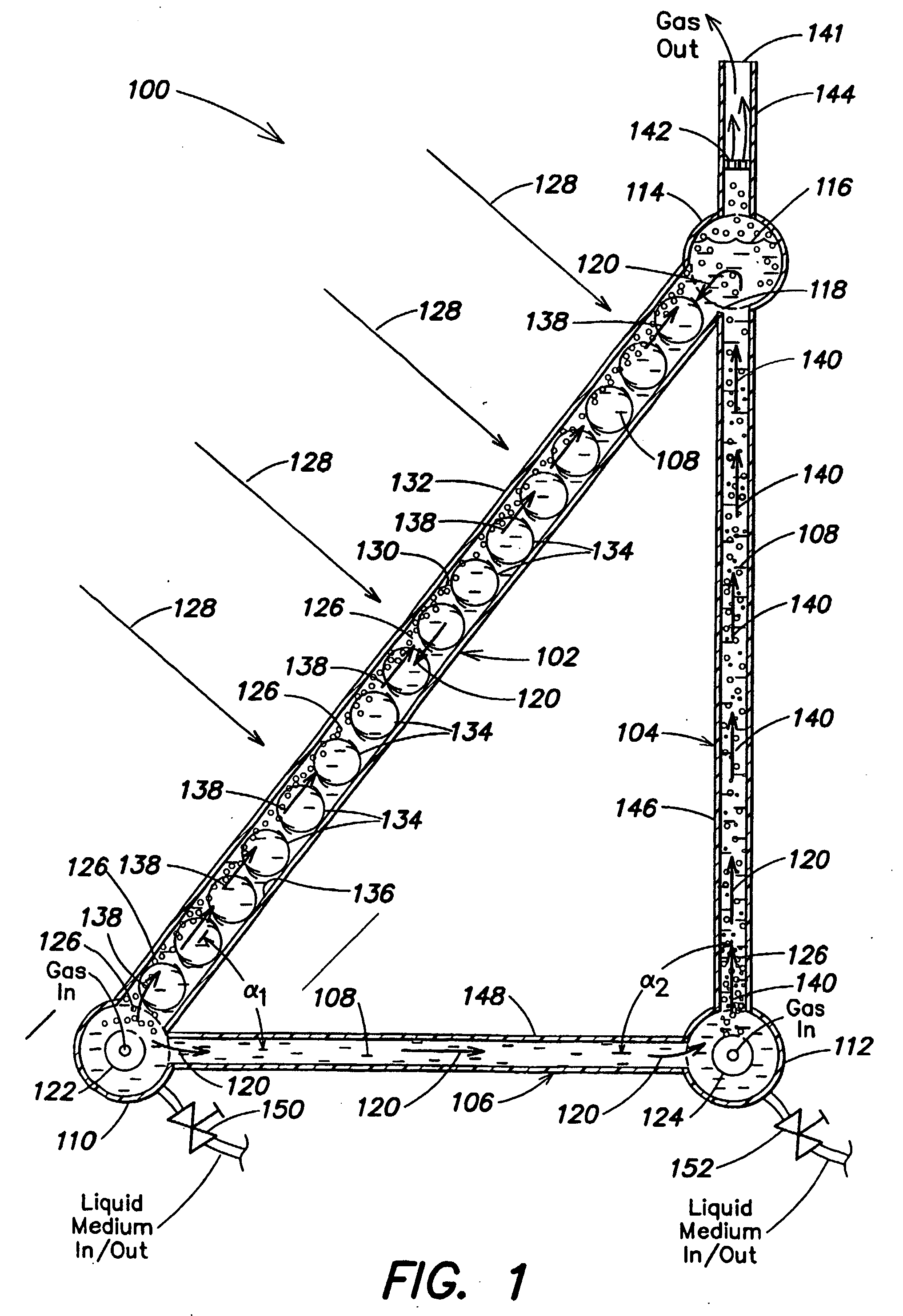
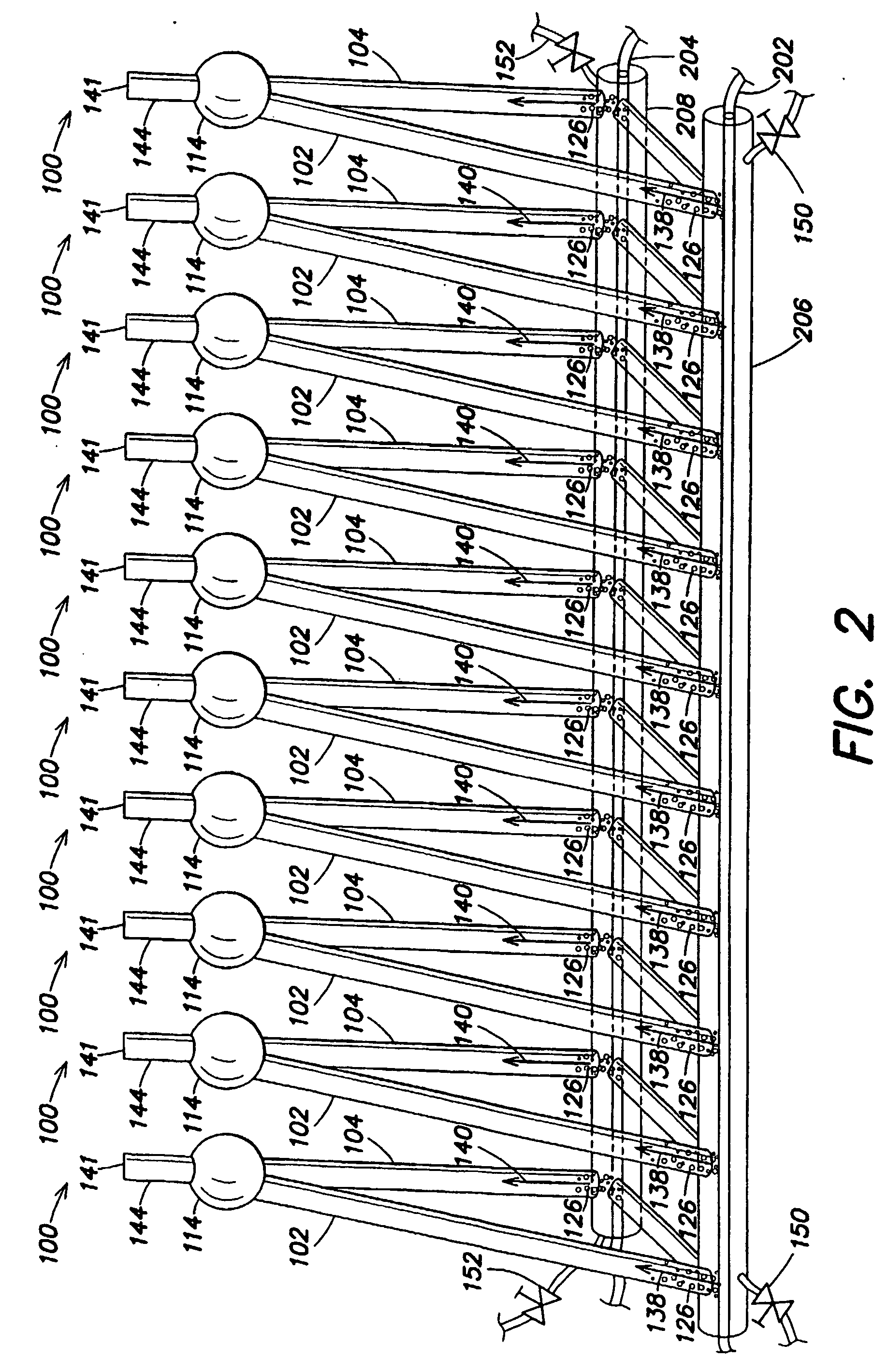
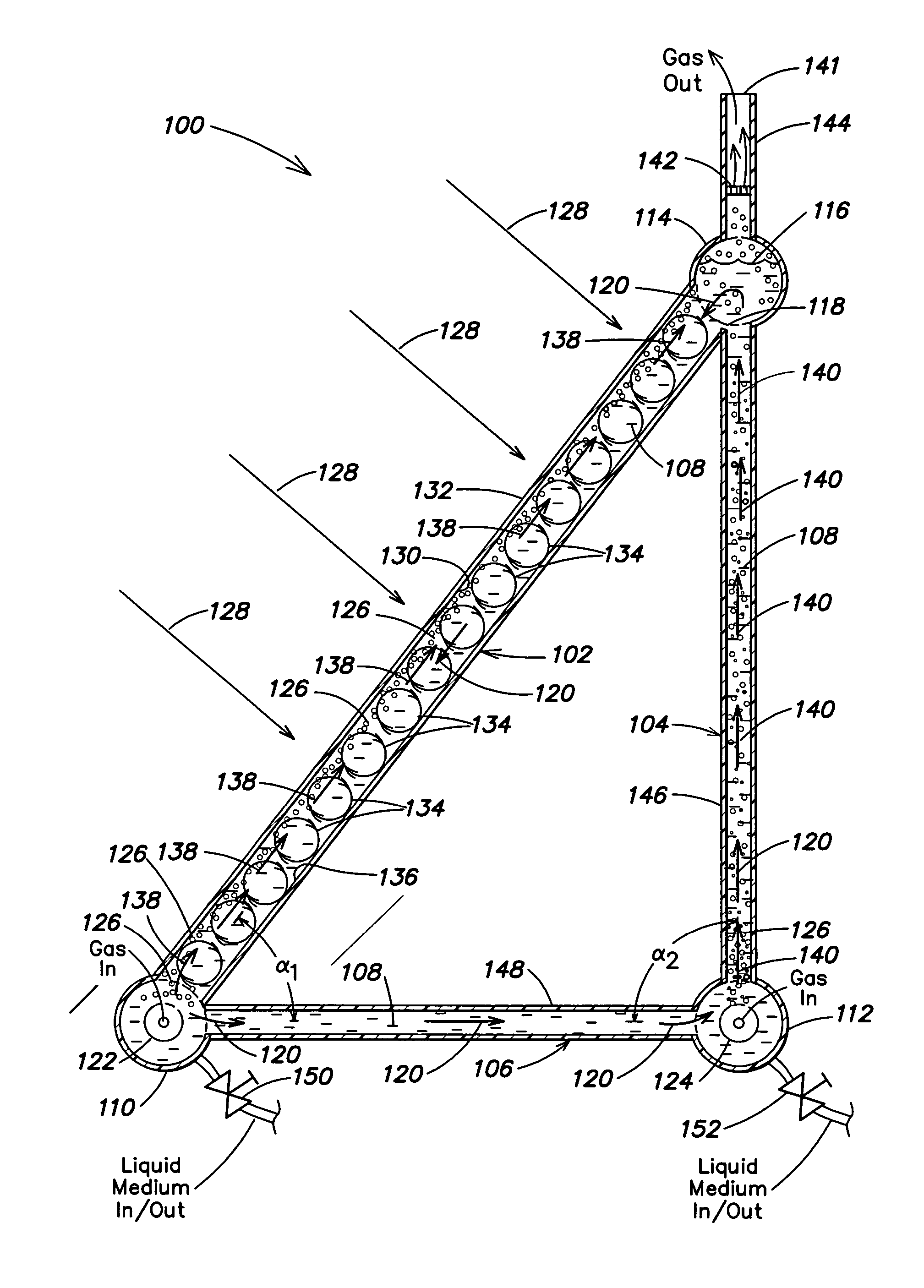
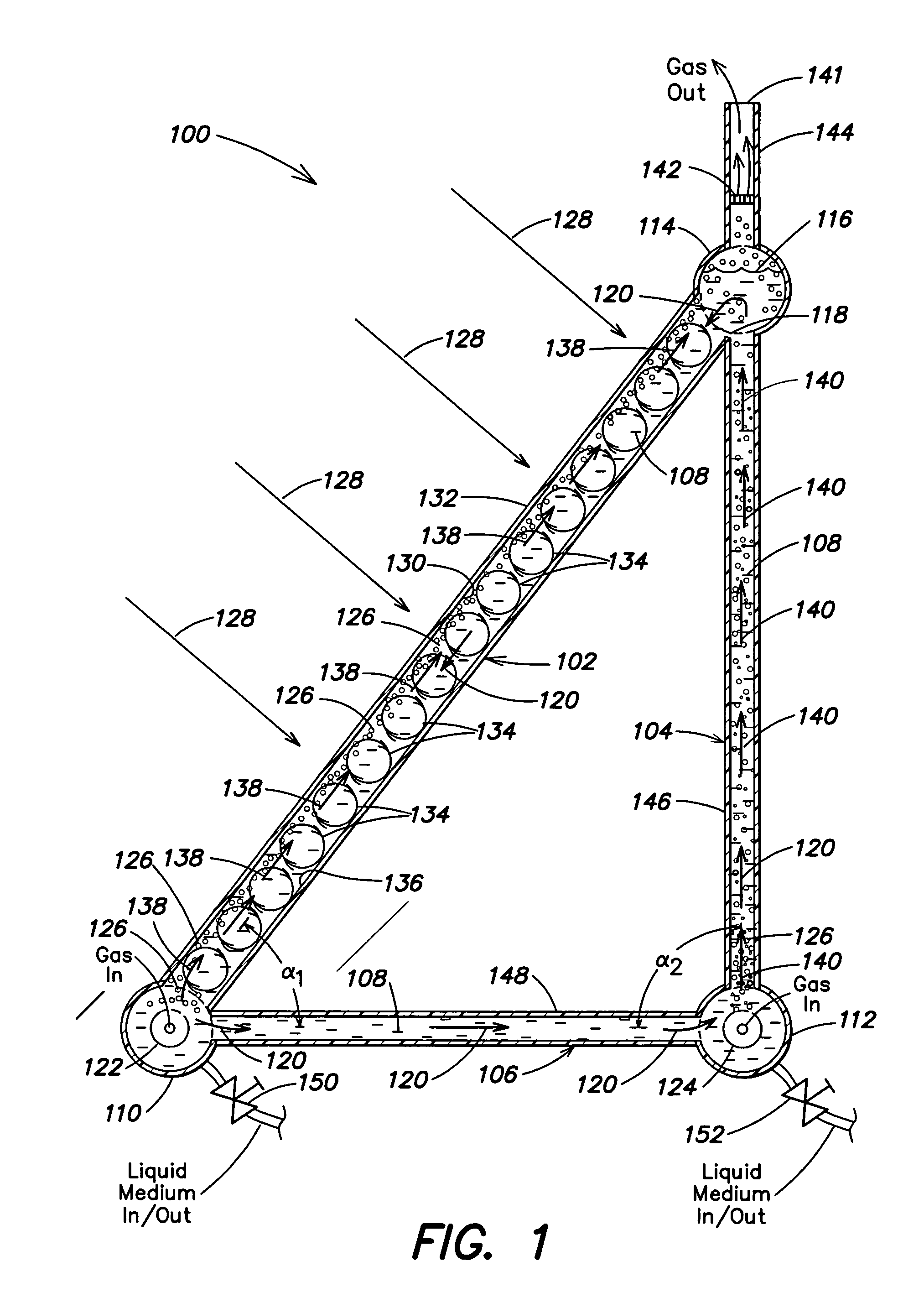
Photobioreactor and process for biomass production and mitigation of pollutants in flue gases
InactiveUS20050260553A1Easy to operateBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiquid mediumEngineering
Certain embodiments and aspects of the present invention relate to photobioreactor apparatus (100) designed to contain a liquid medium (108) comprising at least one species of photosynthetic organism therein, and to methods of using the photobioreactor apparatus (100) as part of a gas-treatment process and system able to at least partially remove certain undesirable pollutants from a gas stream (608). In certain embodiments, the disclosed photobioreactor apparatus (100 can be utilized as part of an integrated combustion method and system, wherein photosynthetic organisms utilized within the photobioreactor (100) at least partially remove certain pollutant compounds contained within combustion gases, e.g. CO2 and / or NOX, and are subsequently harvested from the photobioreactor (100), processed, and utilized as a fuel source for a combustion device (e.g. an electric power plant generator and / or incinerator).
Owner:GREENFUEL TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
Synthetic and biologically-derived products produced using biomass produced by photobioreactors configured for mitigation of pollutants in flue gases
InactiveUS20050239182A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiodieselLiquid medium
Certain embodiments and aspects of the present invention relate to photobioreactor apparatus designed to contain a liquid medium comprising at least one species of photosynthetic organisms therein, and to methods of using the photobioreactor apparatus as part of a production process for forming an organic molecule-containing product, such as a polymeric material and / or fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel), from biomass produced in the photobioreactor apparatus. In certain embodiments, the disclosed organic molecule / polymer production systems and methods, photobioreactor apparatus, methods of using such apparatus, and / or gas treatment systems and methods provided herein can be utilized as part of an integrated combustion and polymer and / or fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel) production method and system, wherein photosynthetic organisms utilized within the photobioreactor are used to at least partially remove certain pollutant compounds contained within combustion gases, e.g. CO2 and / or NOx, and are subsequently harvested from the photobioreactor, processed, and utilized as a source for generating polymers and / or organic molecule-containing products (e.g. fuel-grade oil (e.g. biodiesel)) and / or as a fuel source for a combustion device (e.g. an electric power plant generator and / or incinerator).
Owner:GREENFUEL TECHNOLOGIES CORPORATION
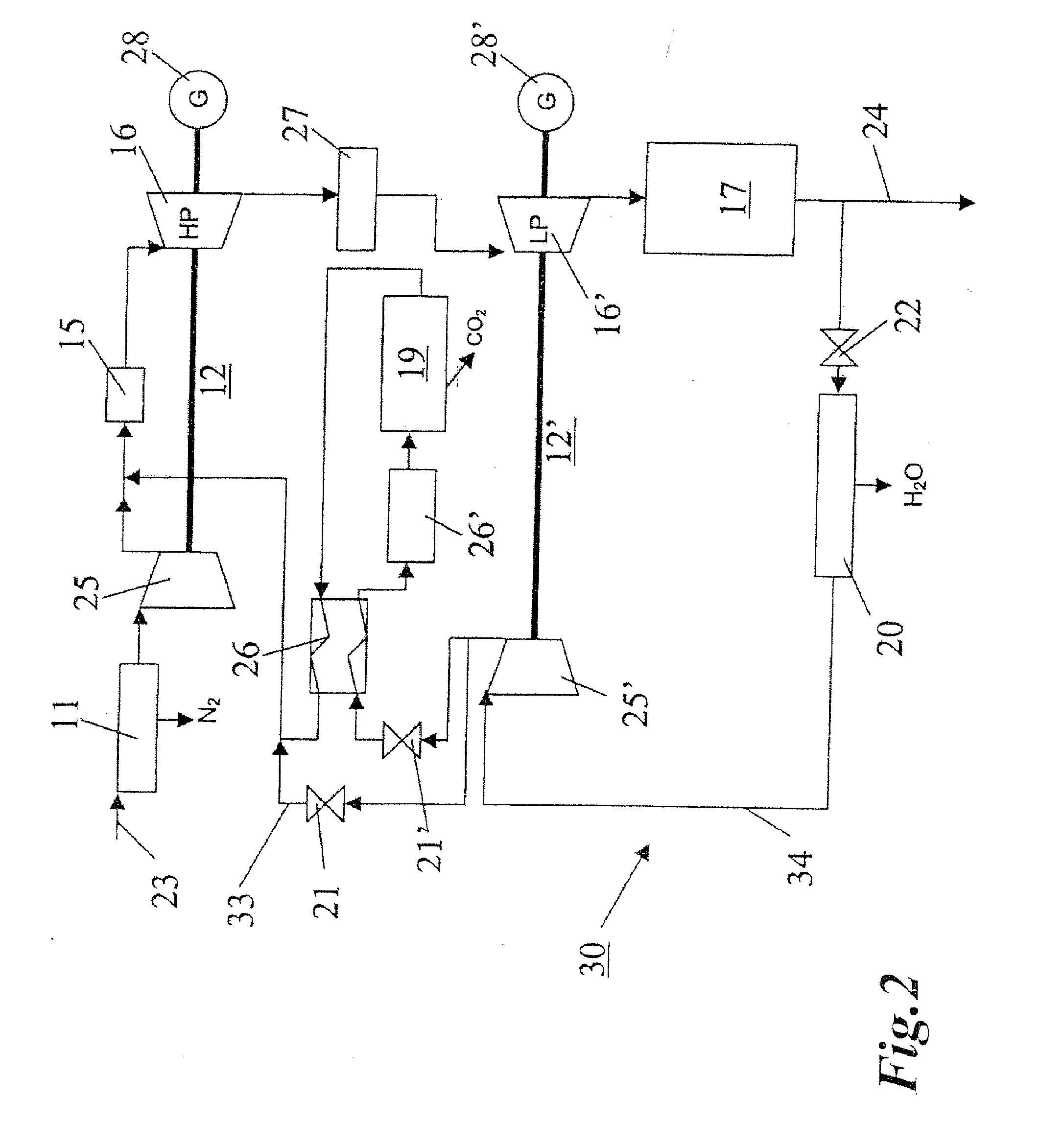
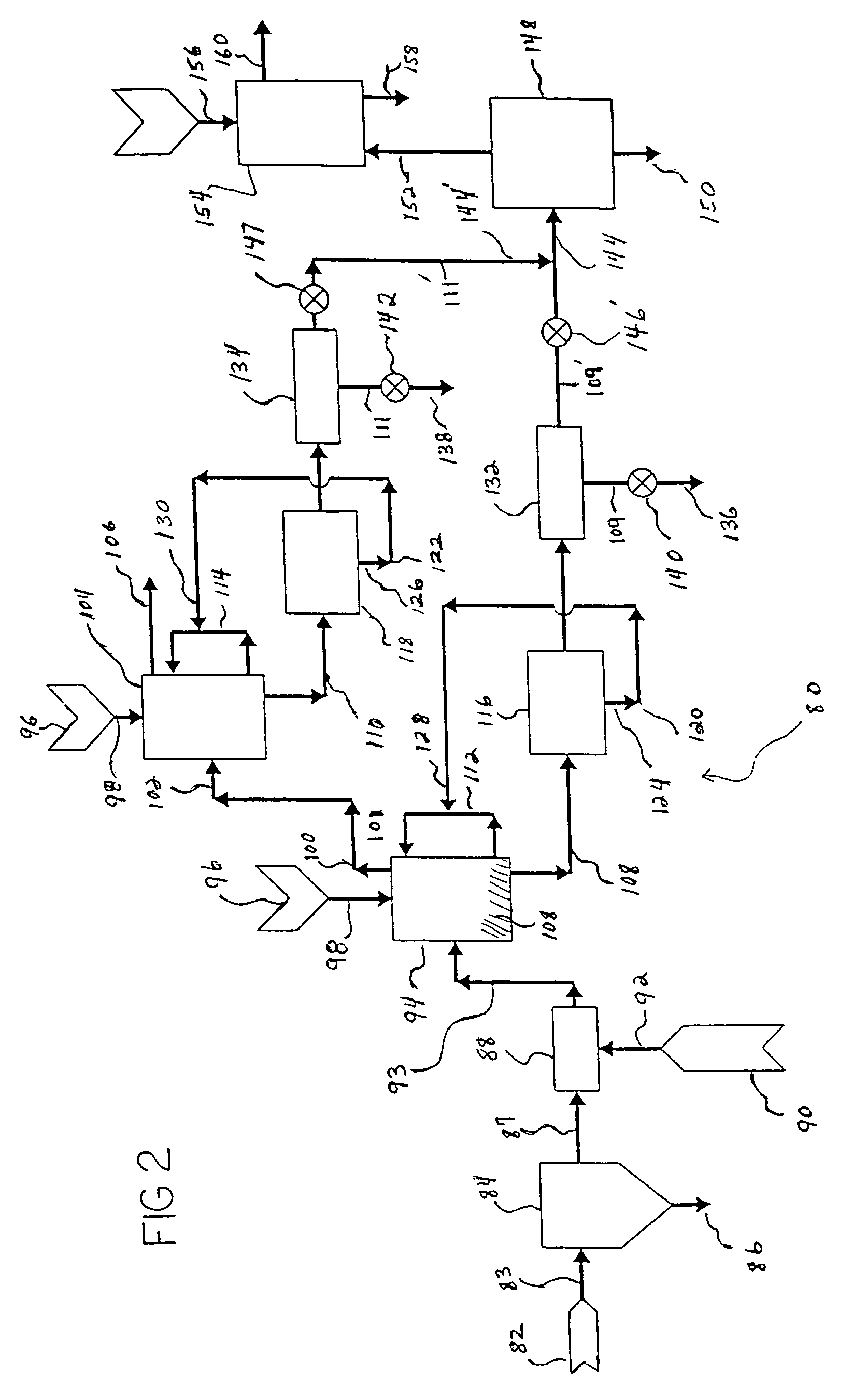
Method of generating energy in a power plant comprising a gas turbine, and power plant for carrying out the method
InactiveUS20050028529A1Small sizeLow costContinuous combustion chamberDispersed particle separationPower stationCombustor
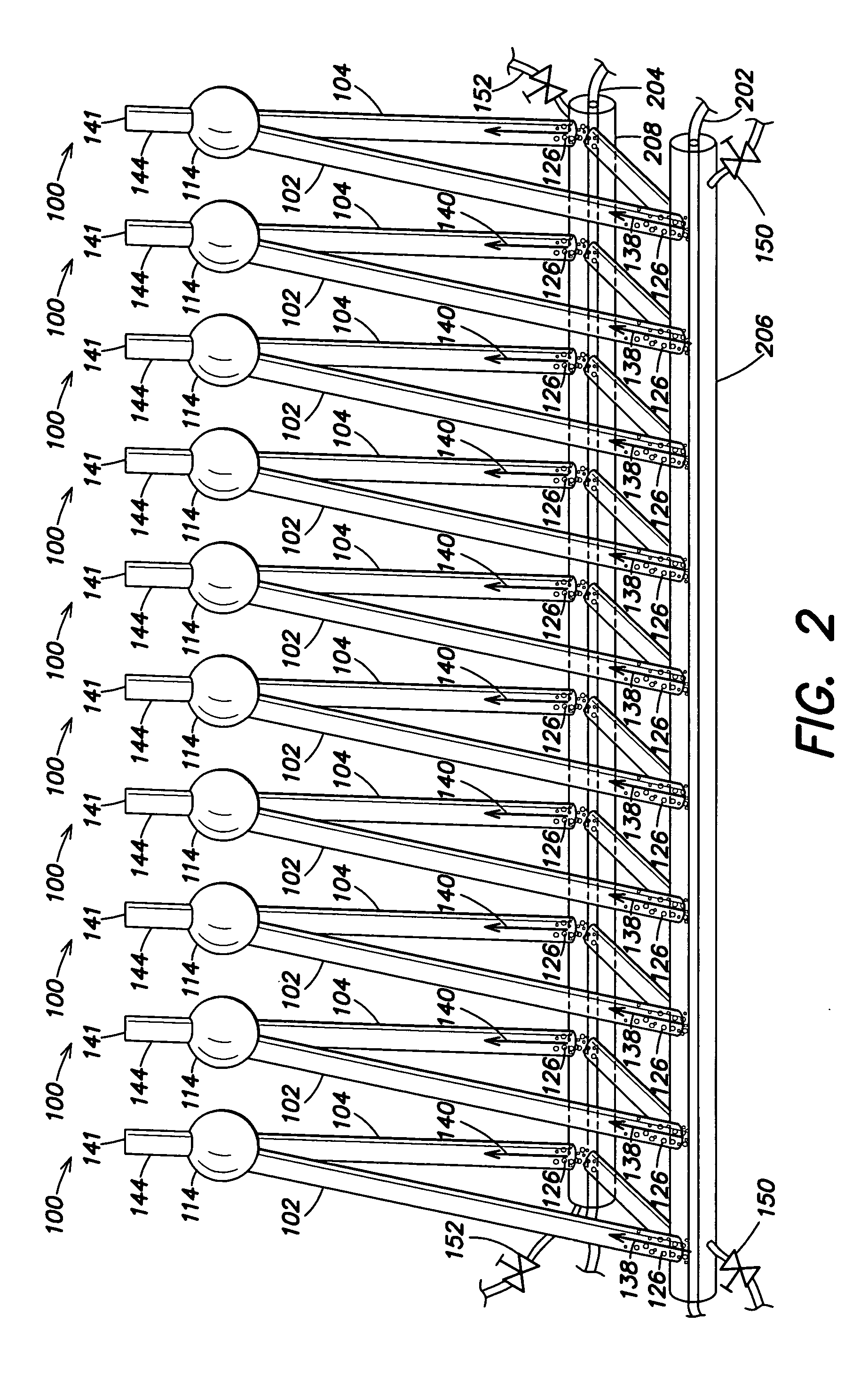
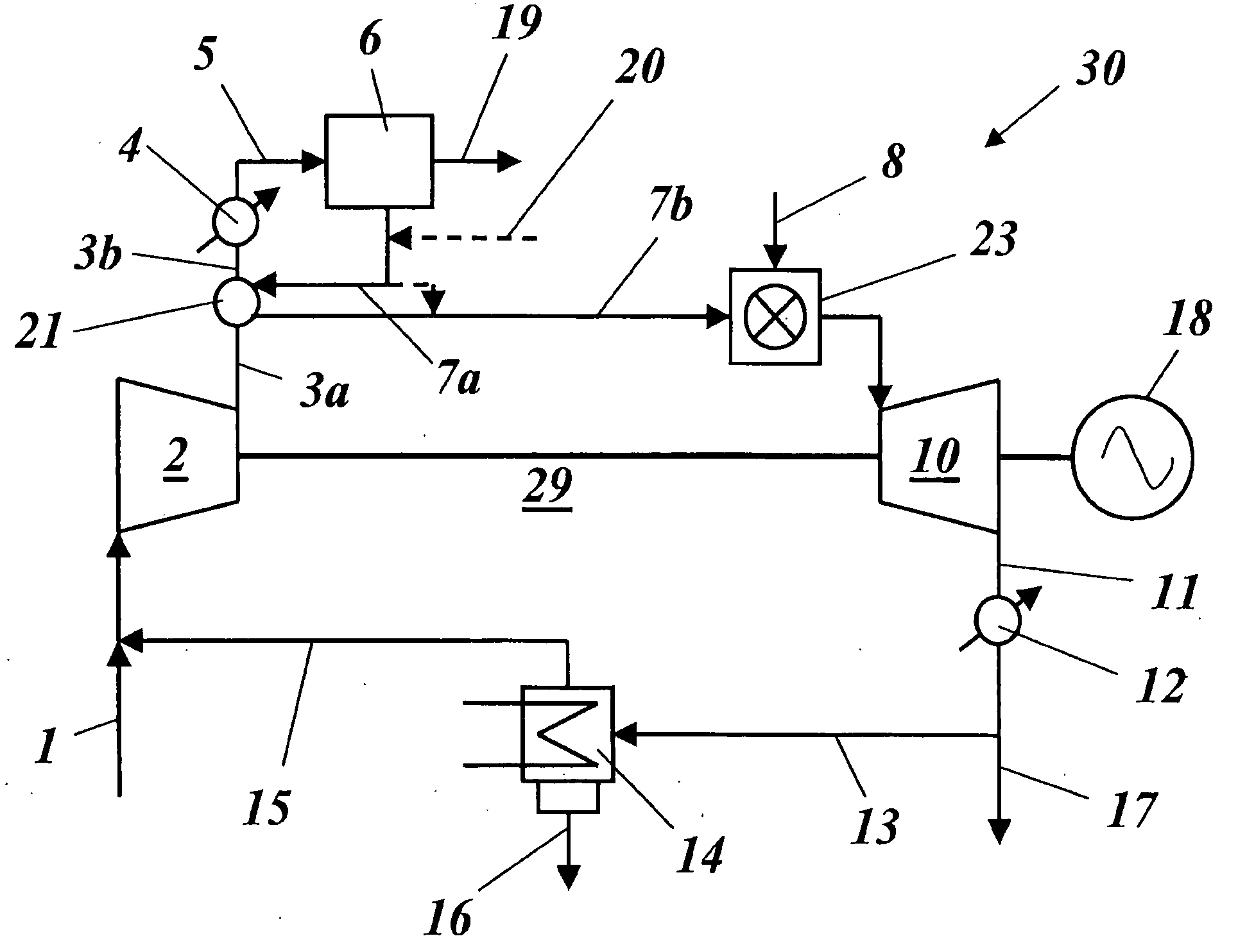
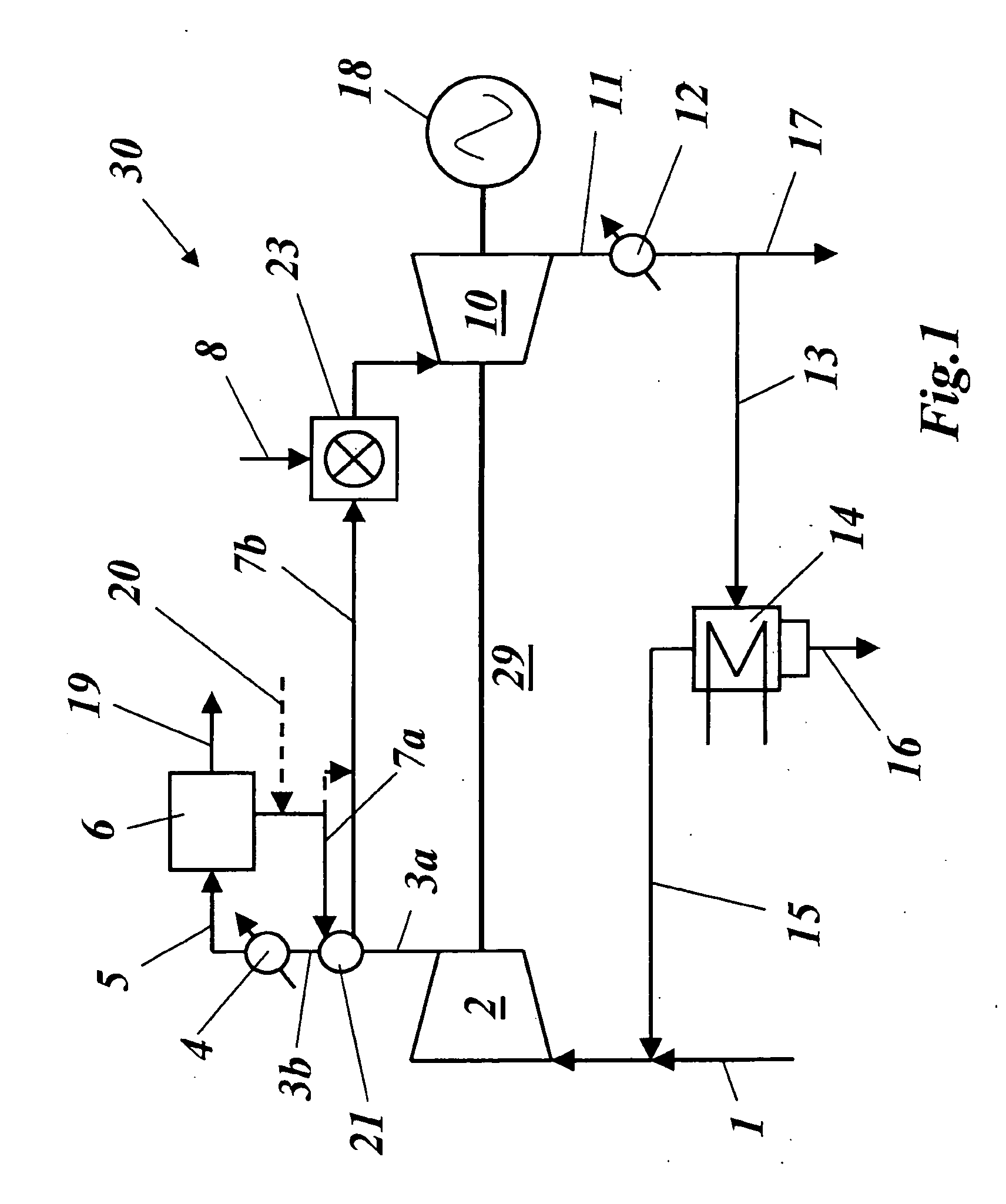
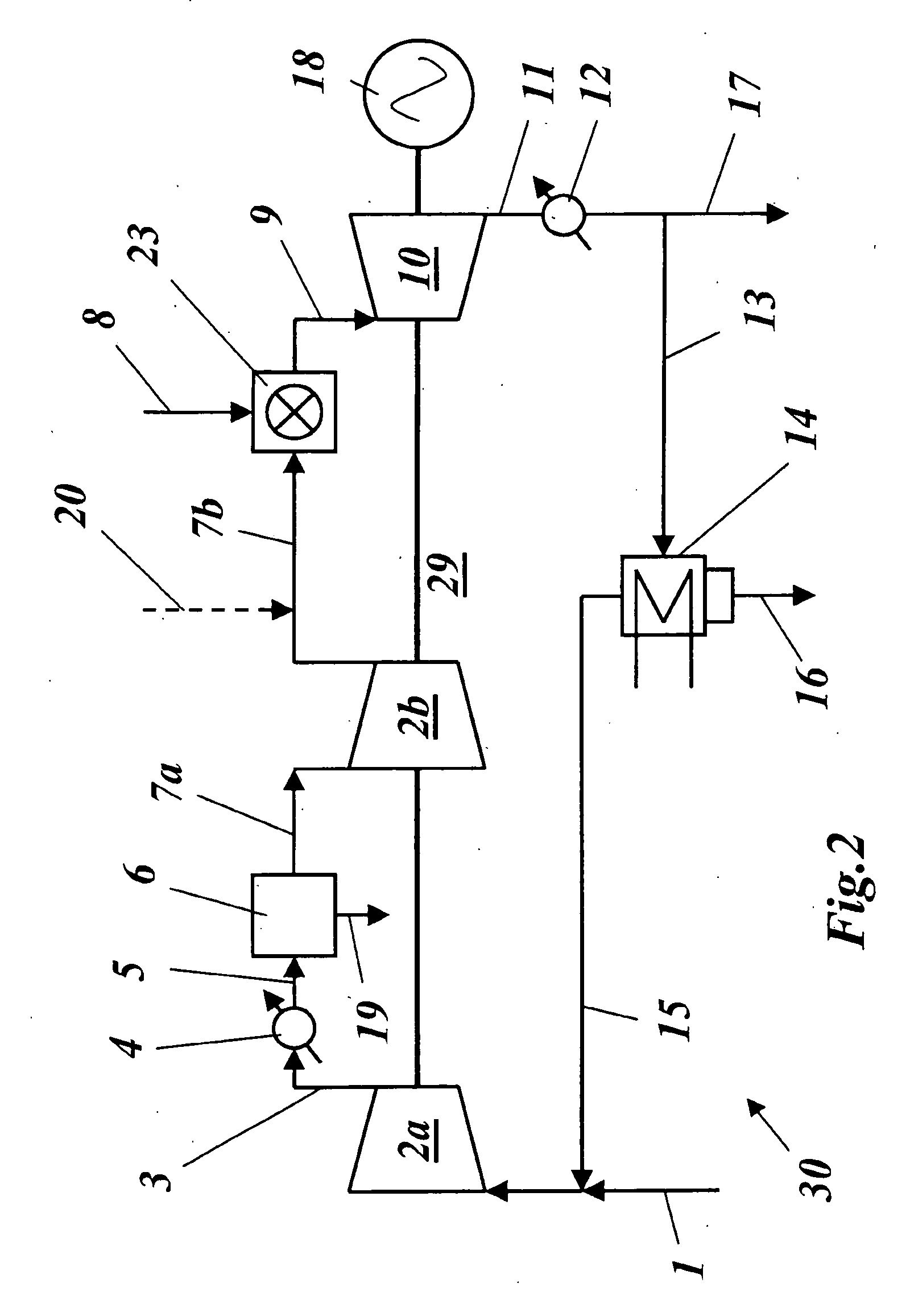
A method of generating energy in a power plant (30) having a gas turbine (29), includes a first step a gas containing air (1) is compressed in a first compressor (2) of the gas turbine (29), a second step the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) is fed to a combustion process with the addition of fuel (8) in a combustor (23), a third step the hot flue gas (9) from the combustor (23) is expanded in an expander or a turbine (10), driving a generator (18), of the gas turbine (29) while performing work, and a fourth step a partial flow of the expanded flue gas (11) is recirculated to the inlet of the first compressor (2) and admixed with the gas containing air (1). Carbon dioxide (CO2) is separated from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5; 7a, 7b) in a CO2 separator (6) before the third step. In such a method, the overall size and energy costs are reduced by virtue of the fact that, to permit increased CO2 concentrations in the CO2 separator (6), not more than about 70% of the carbon dioxide contained in the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b) is removed from the compressed gas (3, 3a, 3b; 5, 5a, 5b; 7a, 7b).
Owner:ALSTOM TECH LTD
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
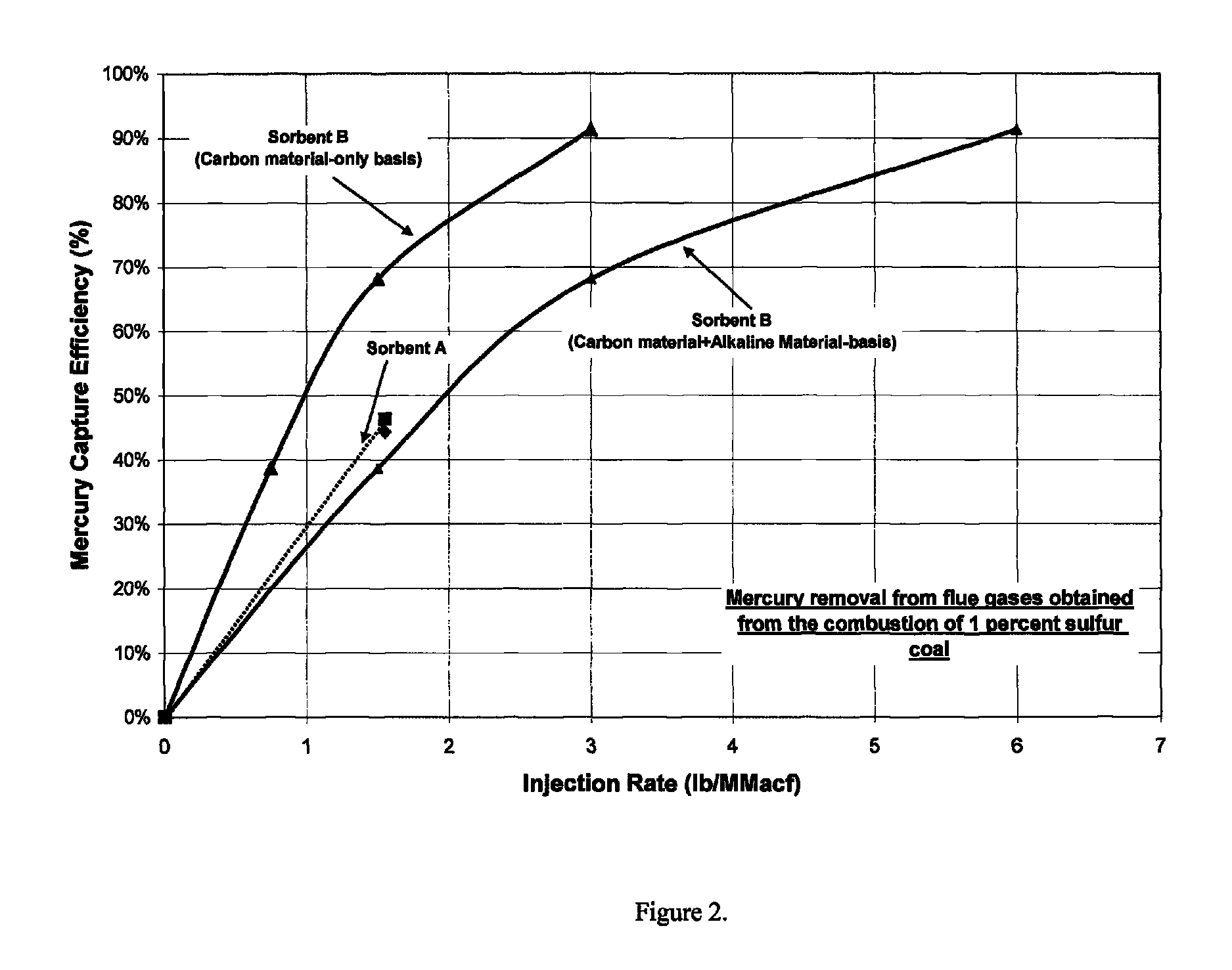
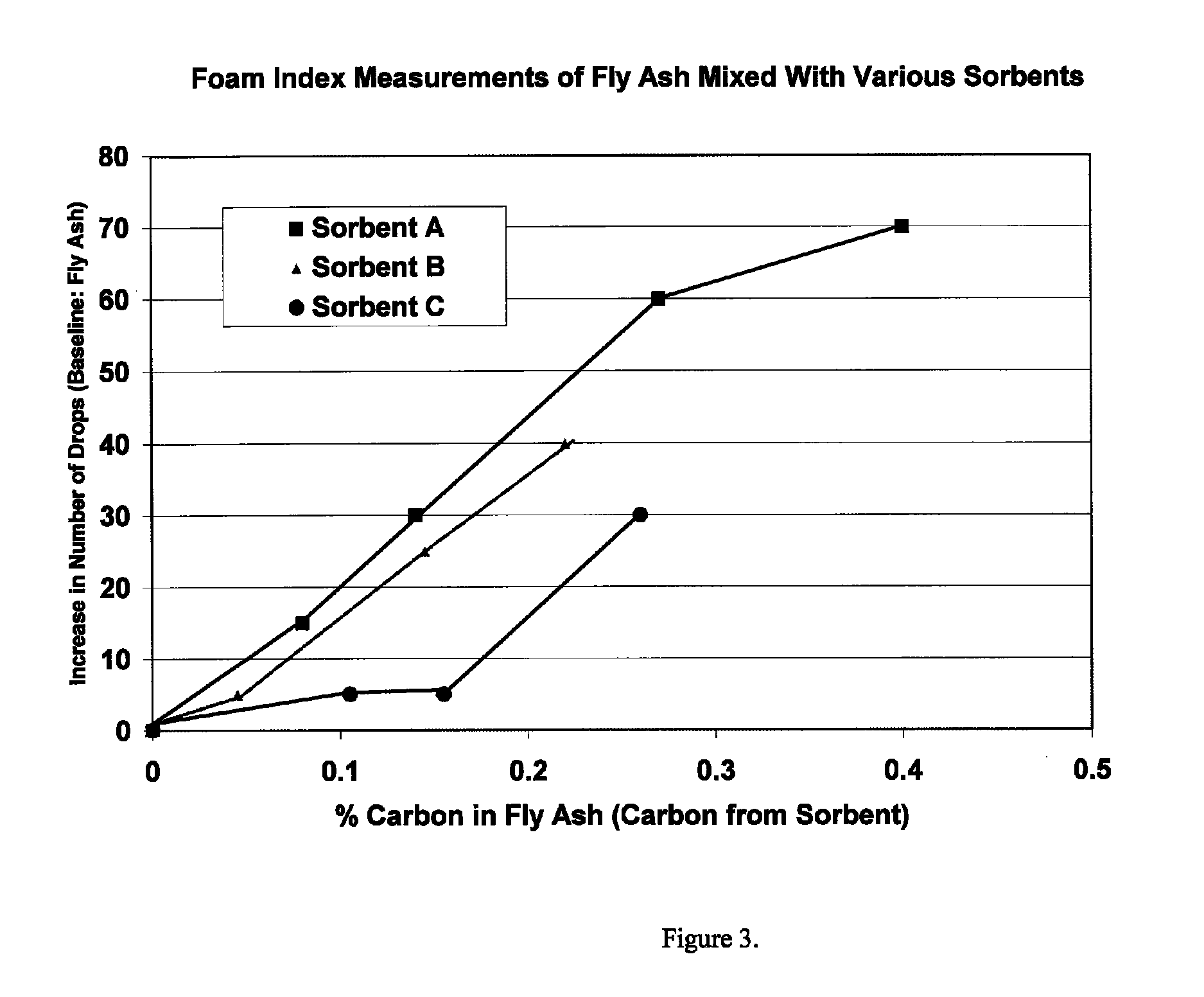
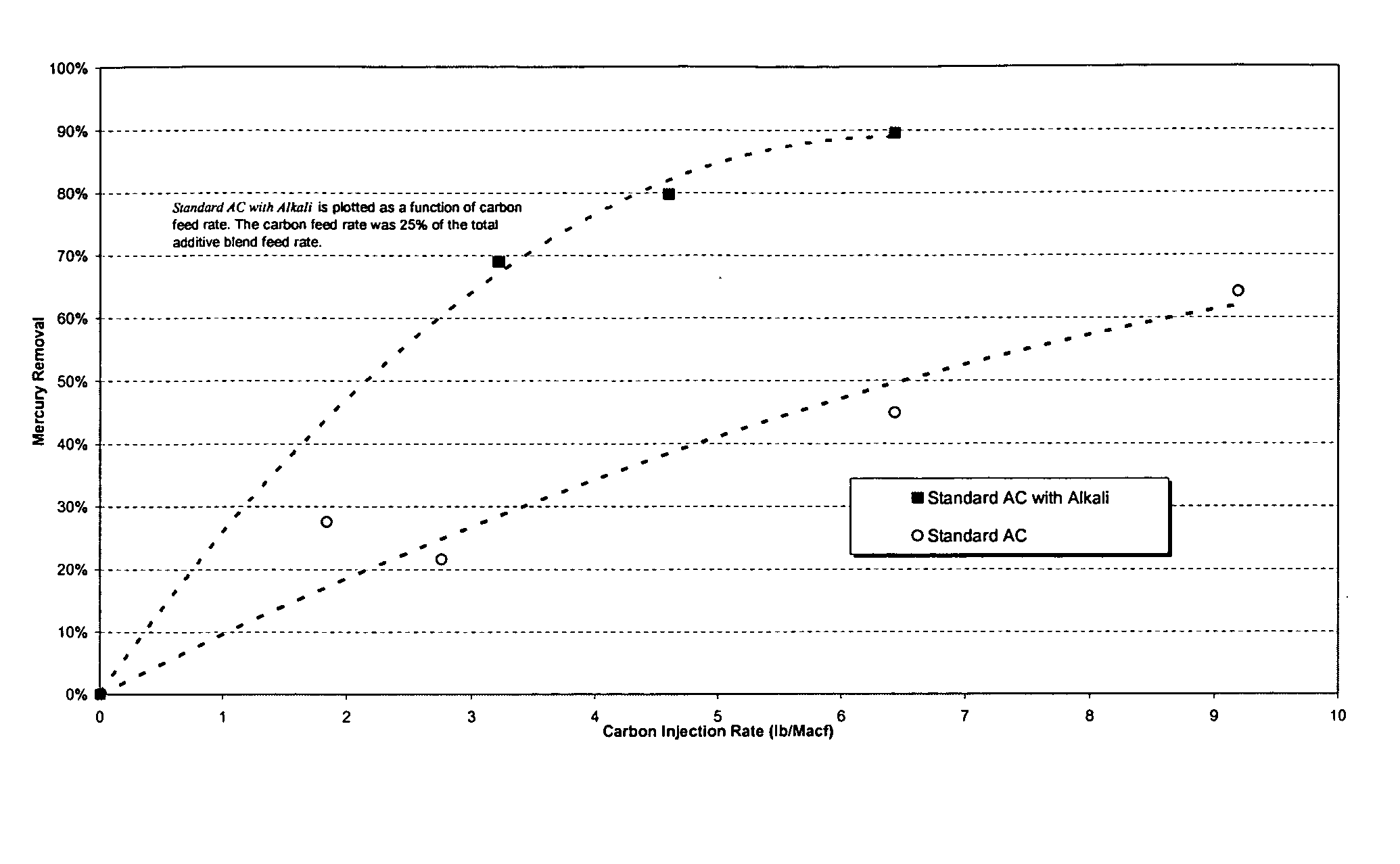
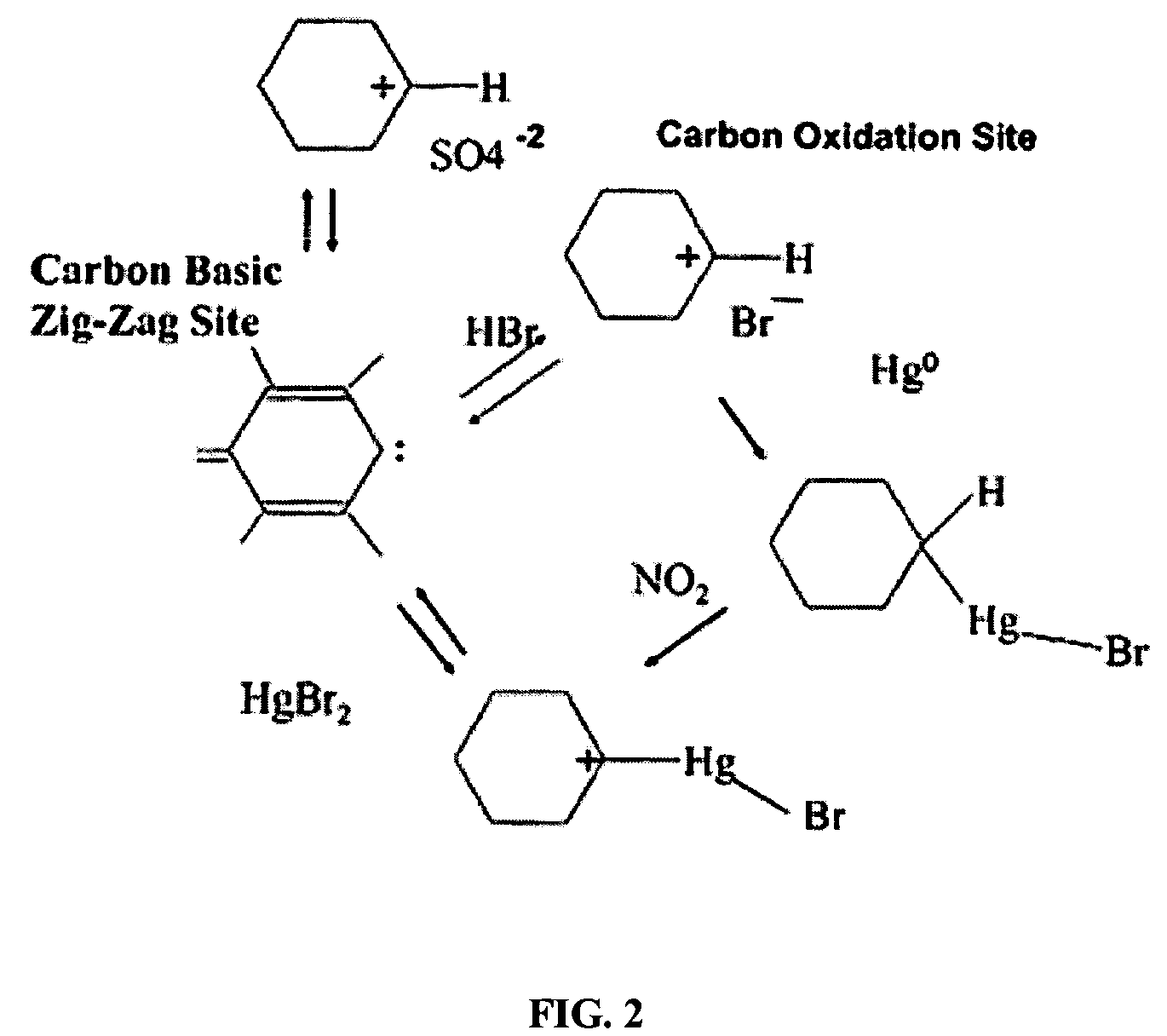
Flue gas mercury control
ActiveUS8080088B1Enhance particulate collectionReducing fly ash resistivityGas treatmentIsotope separationActivated carbonHalogen
An adsorbent composition for removing mercury from a flue gas stream, and a method of its use. The composition is a powdered activated carbon having at least one of a halogen-containing component and an alkaline component dispersed thereon. A flow agent can be composited with the material to maintain flowability in situ.
Owner:SRINIVASACHAR SRIVATS
Oxidant control in co-generation installations
InactiveUS6247315B1Steam regenerationIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationControl system designCogeneration
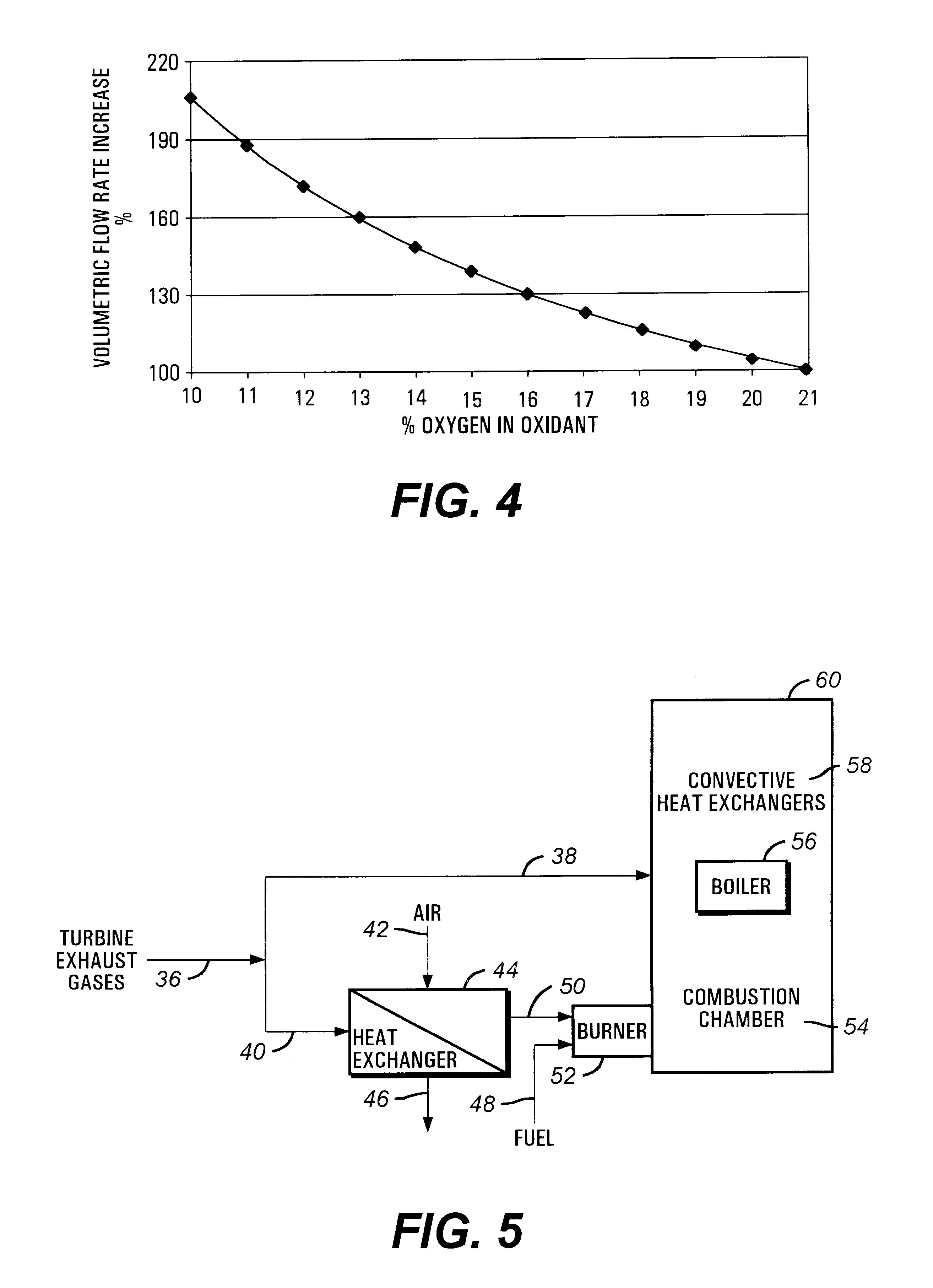
This invention is related to so-called combined cycle co-generation installations, and it addresses present concerns of the industry. Among these, combustion stability, corrosion (due to large water content in the flue gases), large heat transfer areas, and the like. In some embodiments, an additional heat exchanger is added to heat combustion air with a portion of the exhaust gases resulting from an engine, preferably a gas turbine. As a result, the efficiency of the cycle will improve, the oxidant will be enriched by above 50% oxygen, the combustion process will be enhanced, and the dimensions of the boiler may be reduced. It is considered that the combustion air will require between 10% and 80% of the total flue gas volume, more preferably between 20% and 40%. This is the portion of the flue gases sent through the heat exchanger. A control system designed to optimize the flow of the different streams is also presented. Other inventive embodiments forego heat exchanges in lieu of precise control of two flows of exhaust gas, with preferred addition of additional oxidant to the boiler bumers.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
Method for reducing NOX in combustion flue gas using metal-containing additives
InactiveUS6206685B1Improved control deviceSure easyDispersed particle separationSolid fuel combustionAtmospheric airNitric oxide
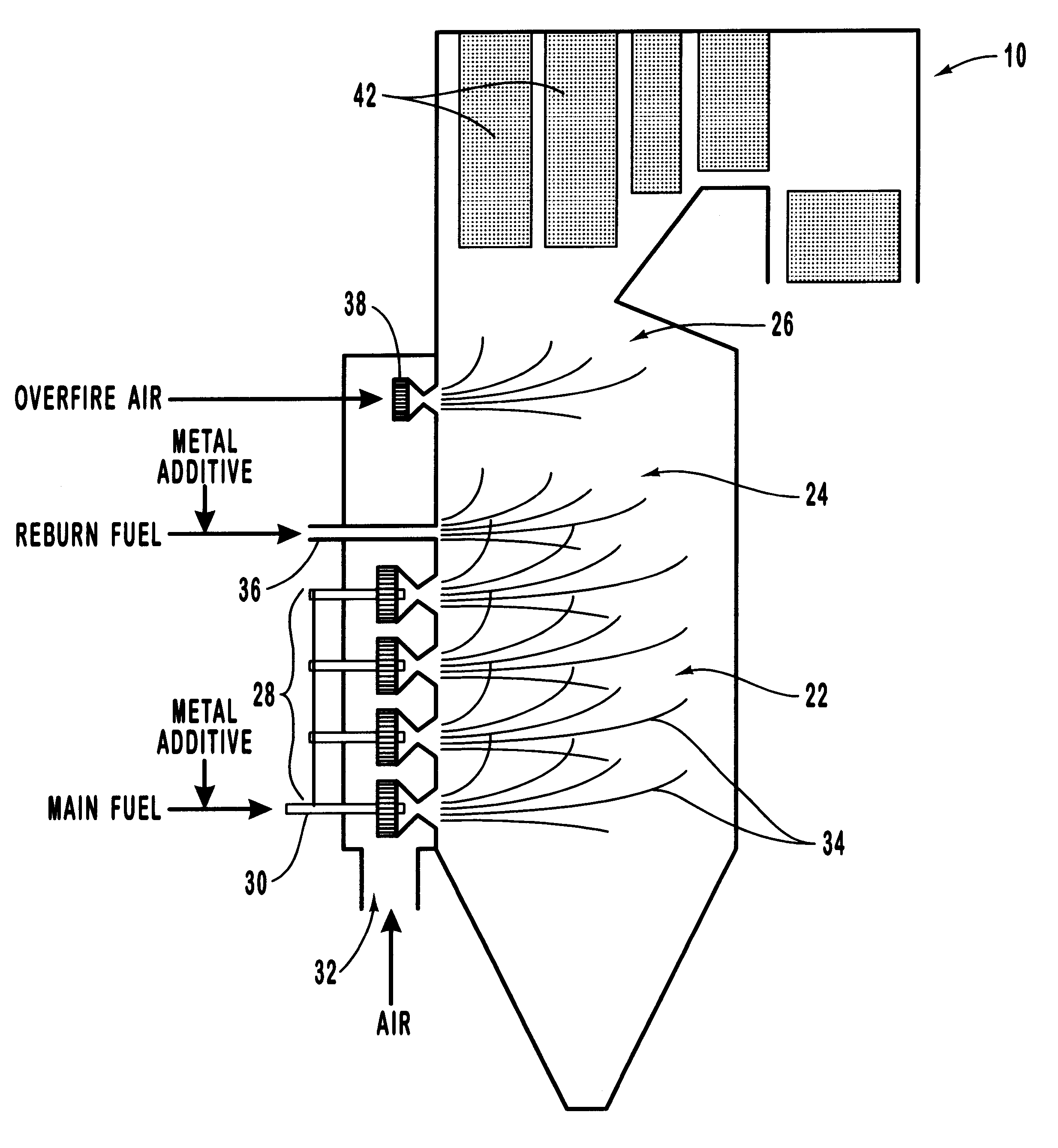
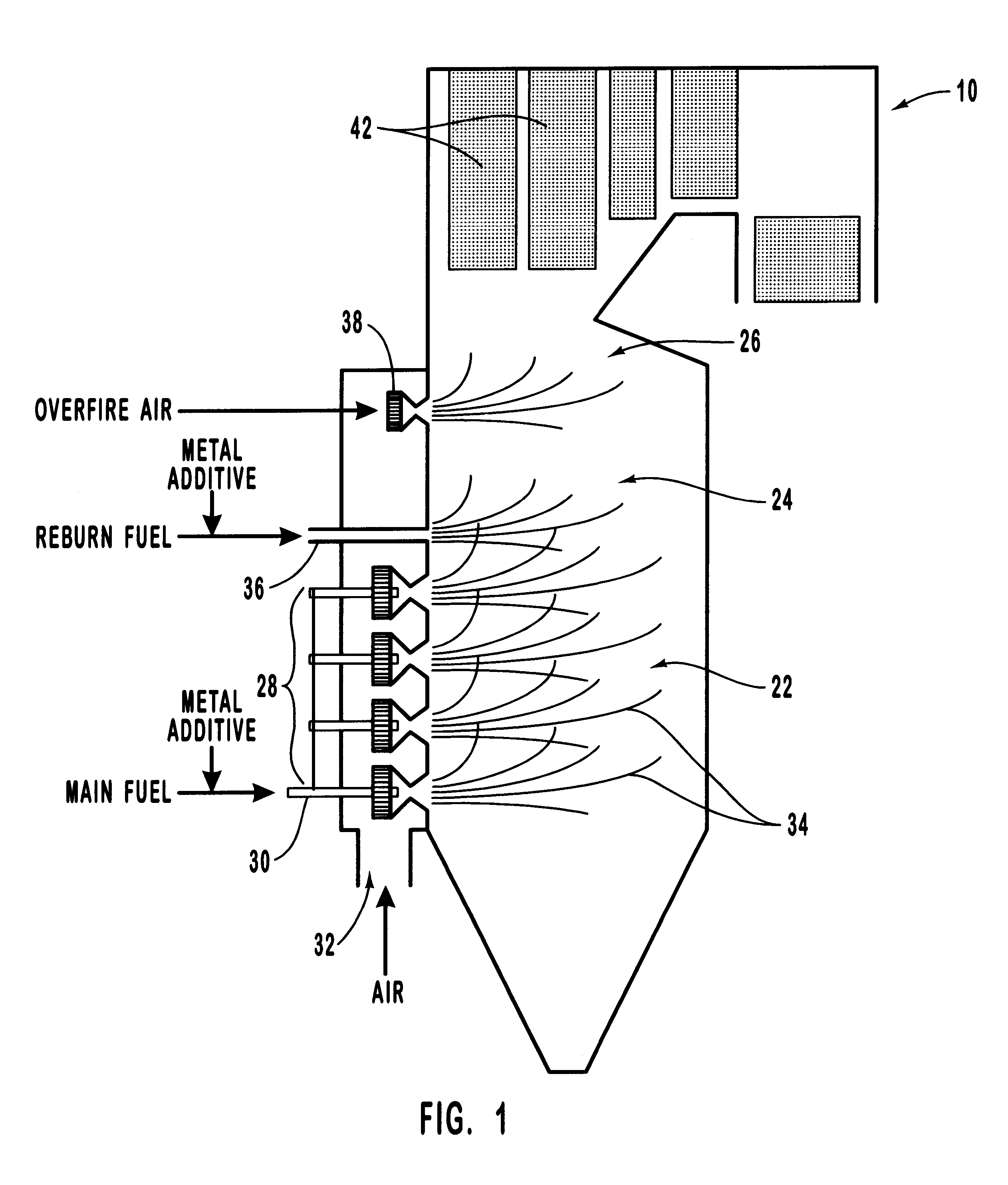
Various methods for decreasing the amount of nitrogen oxides released to the atmosphere as a component of combustion gas mixtures are provided. The methods specifically provide for the removal of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) from gas mixtures emitted from stationary combustion systems. In particular, methods for improving efficiency of nitrogen oxide reduction from combustion systems include injecting metal-containing compounds into the main combustion zone and / or the reburning zone of a combustion system. The metal containing compounds react with active combustion species, and these reactions change radical concentrations and significantly improve NOx conversion to molecular nitrogen. The metal-containing additives can be injected with the main fuel, in the main combustion zone, with secondary or reburning fuel addition, or at several locations in the main combustion zone and reburning zone. Optionally, nitrogenous reducing agents and / or overfire air can be injected downstream to further increase NOx reduction.
Owner:GE ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES
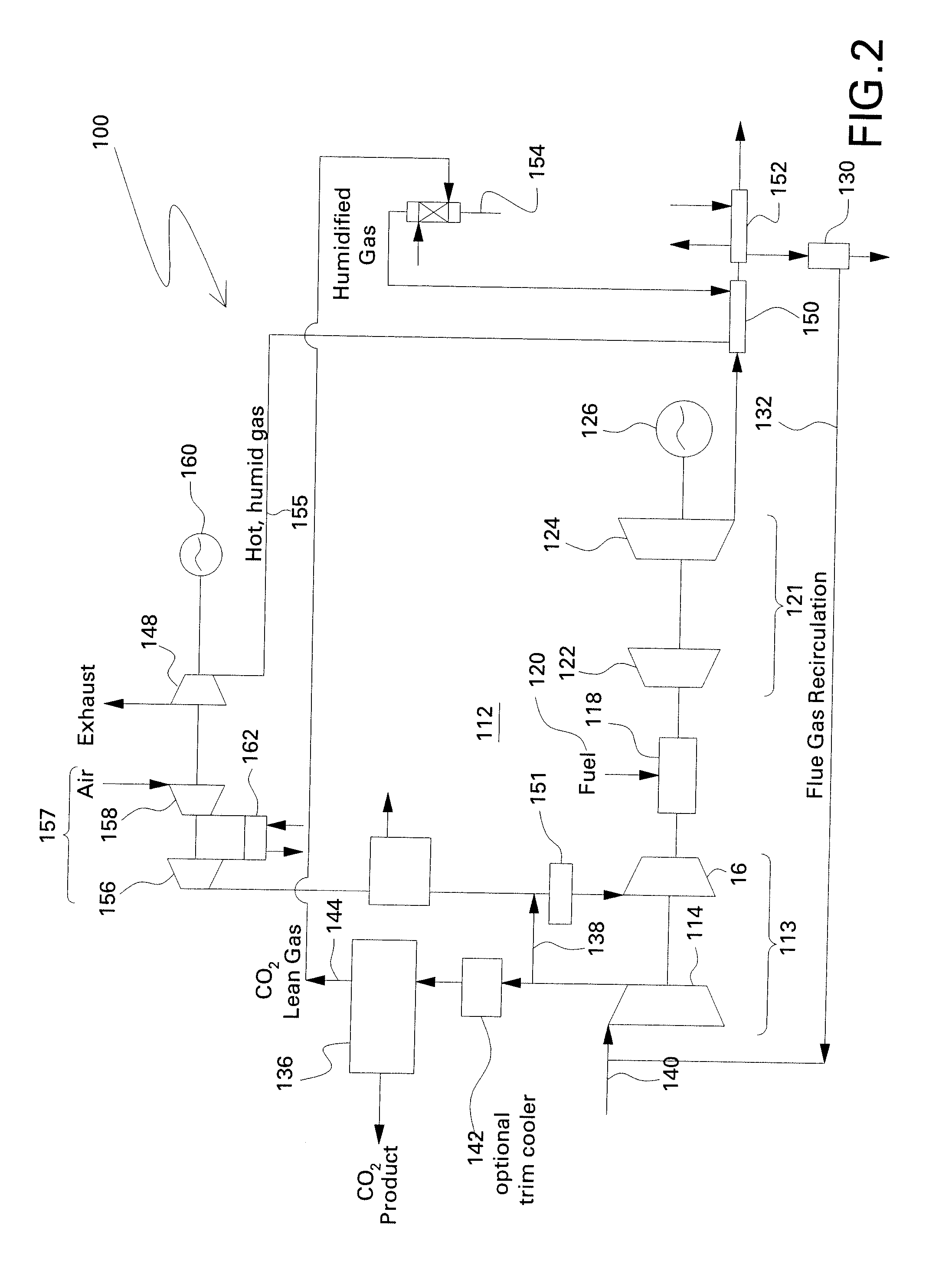
Gas Turbine Installation with Flue Gas Recirculation
A method and installation are disclosed which can, for example, provide for reliable, low-Nox-emission operation of a gas turbine installation with hydrogen-rich fuel gas. An exemplary gas turbine installation includes an arrangement for flue gas recirculation into a compressor inlet and for fuel gas dilution. Oxygen content in combustion air can be reduced by recirculation of recooled flue gas, and the fuel gas can be diluted with compressed flue gas. The oxygen reduction in the combustion air can lead to minimum residual oxygen in the flue gas which can be used for fuel gas dilution. As a result of the flue gas recirculation, water content in the combustion air can be increased by feedback of the water which results as a combustion product. The oxygen reduction, increased water content, and fuel dilution can reduce the flame velocity of hydrogen-rich fuel gases and enable a robust, reliable and low-emission combustion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
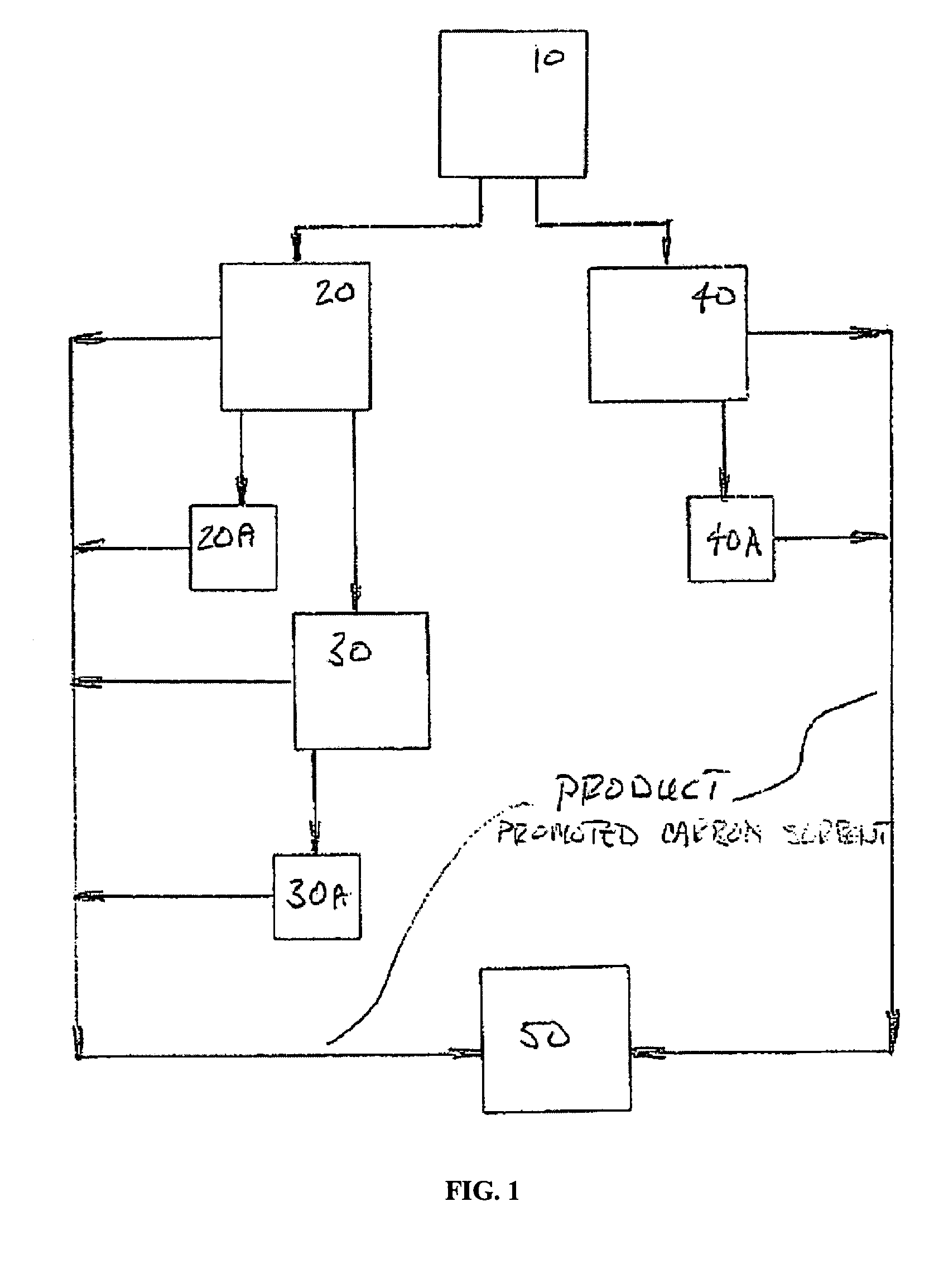
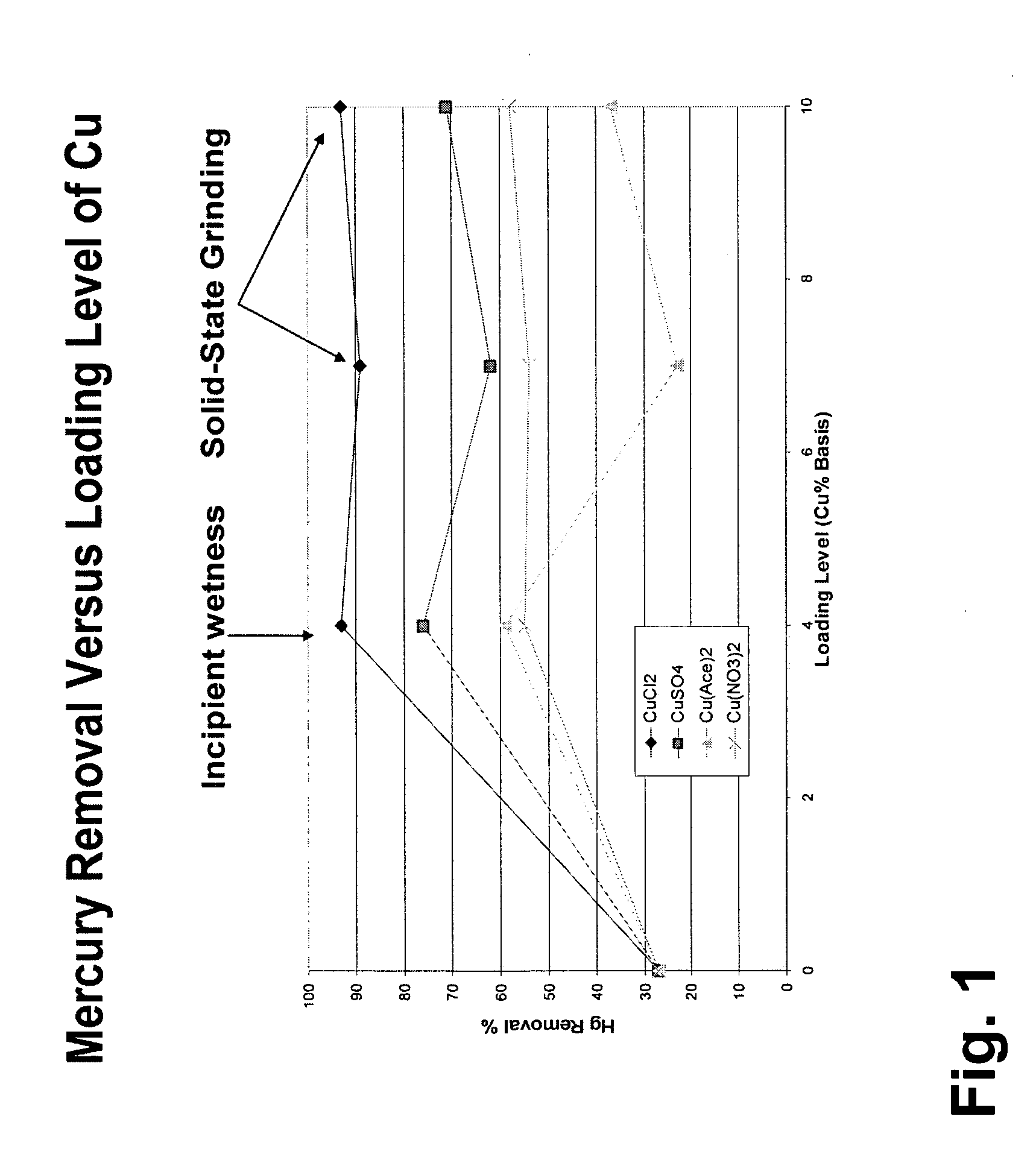
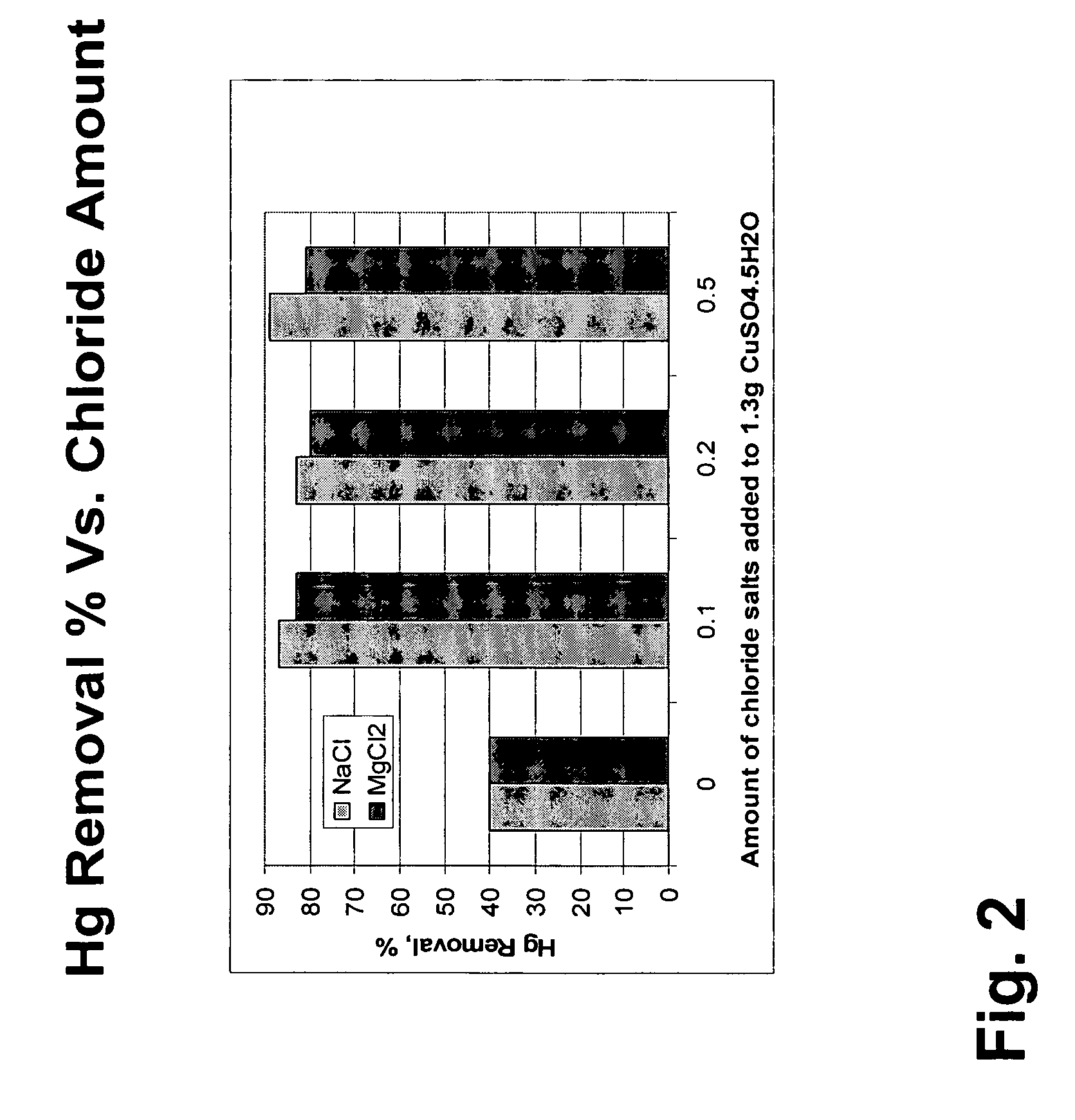
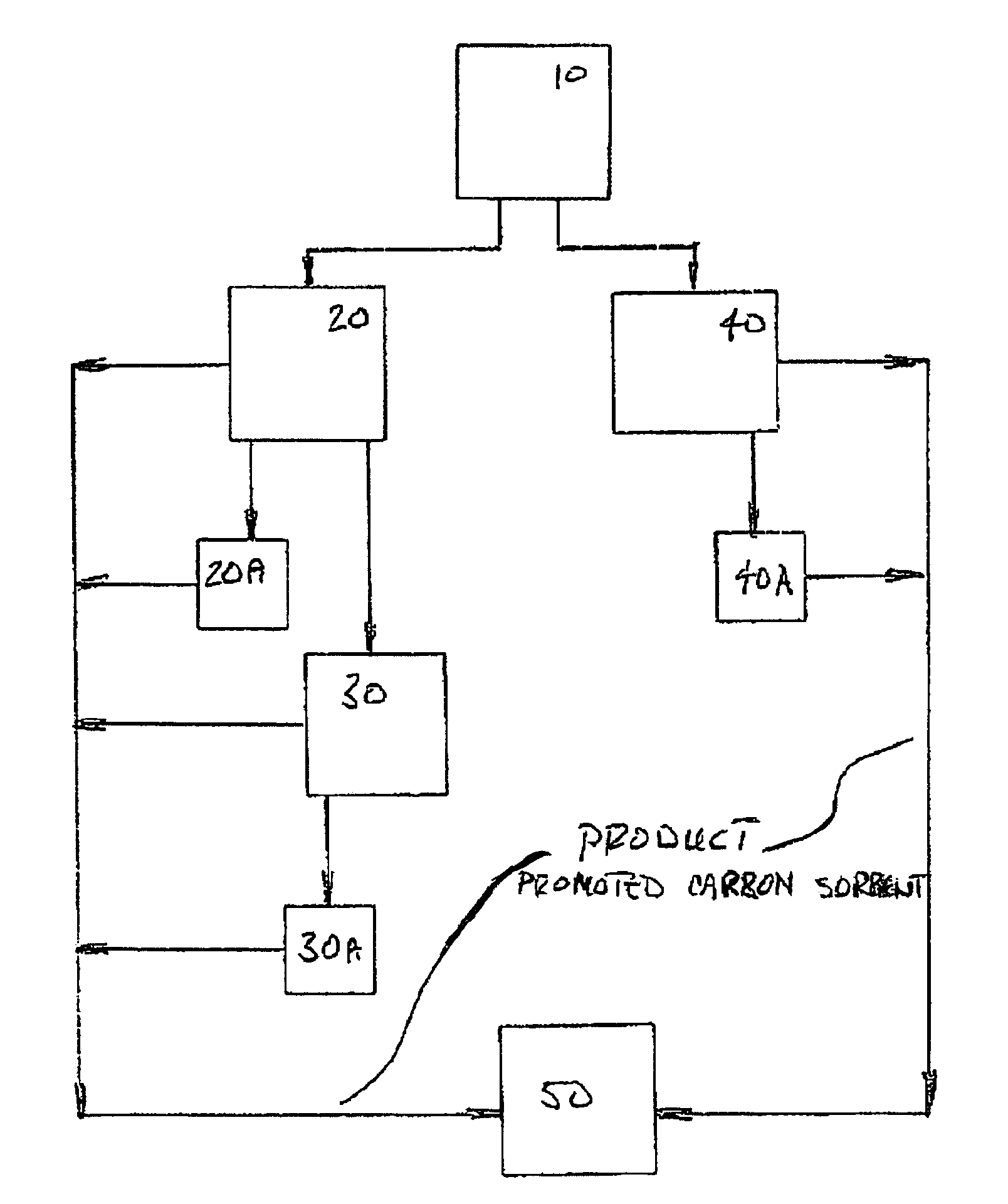
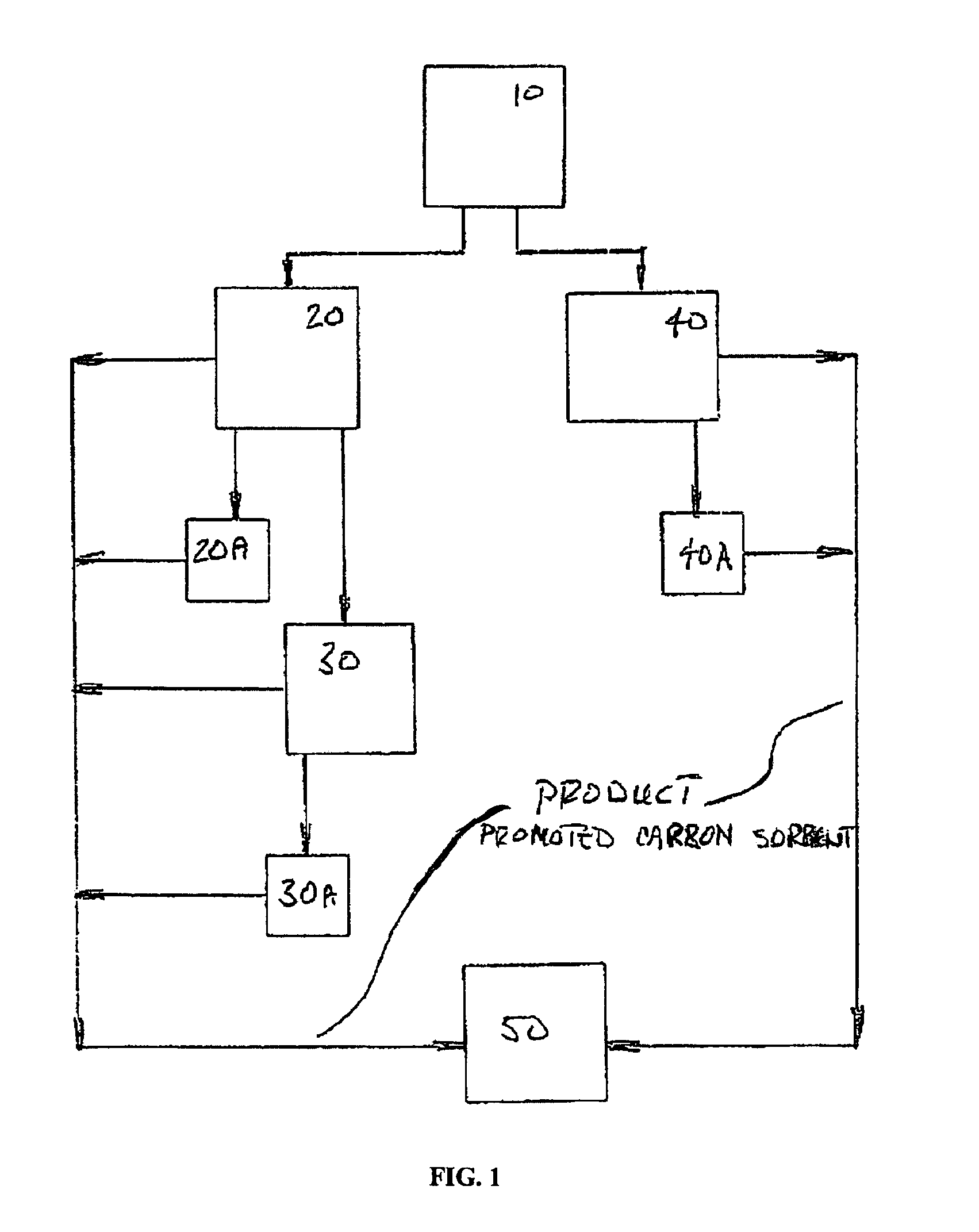
Sorbents for the oxidation and removal of mercury
ActiveUS20060048646A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh activityGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbonHalogen
A promoted activated carbon sorbent is described that is highly effective for the removal of mercury from flue gas streams. The sorbent comprises a new modified carbon form containing reactive forms of halogen and halides. Optional components may be added to increase reactivity and mercury capacity. These may be added directly with the sorbent, or to the flue gas to enhance sorbent performance and / or mercury capture. Mercury removal efficiencies obtained exceed conventional methods. The sorbent can be regenerated and reused. Sorbent treatment and preparation methods are also described. New methods for in-flight preparation, introduction, and control of the active sorbent into the mercury contaminated gas stream are described.
Owner:MIDWEST ENERGY EMISSIONS CORP
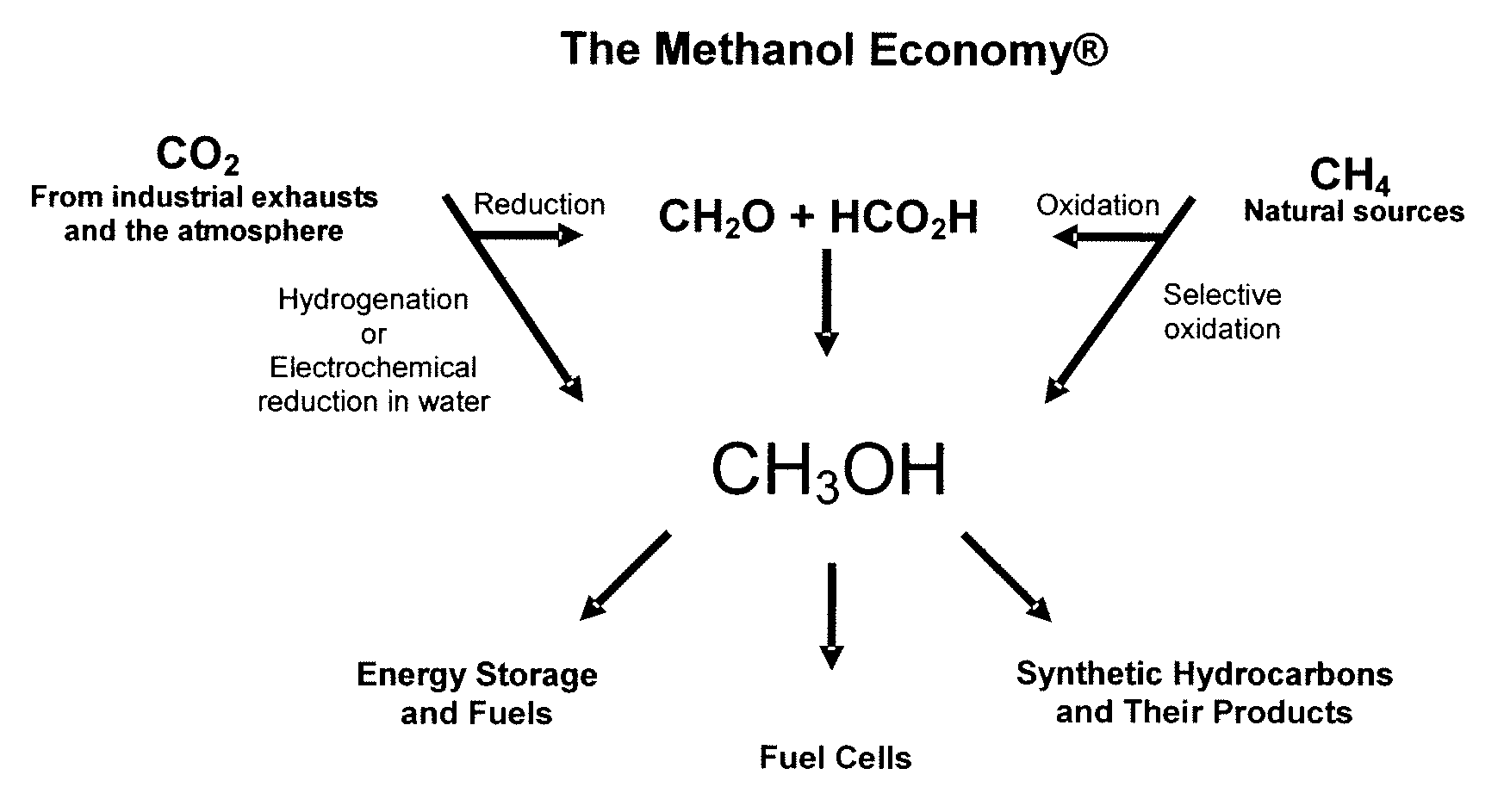
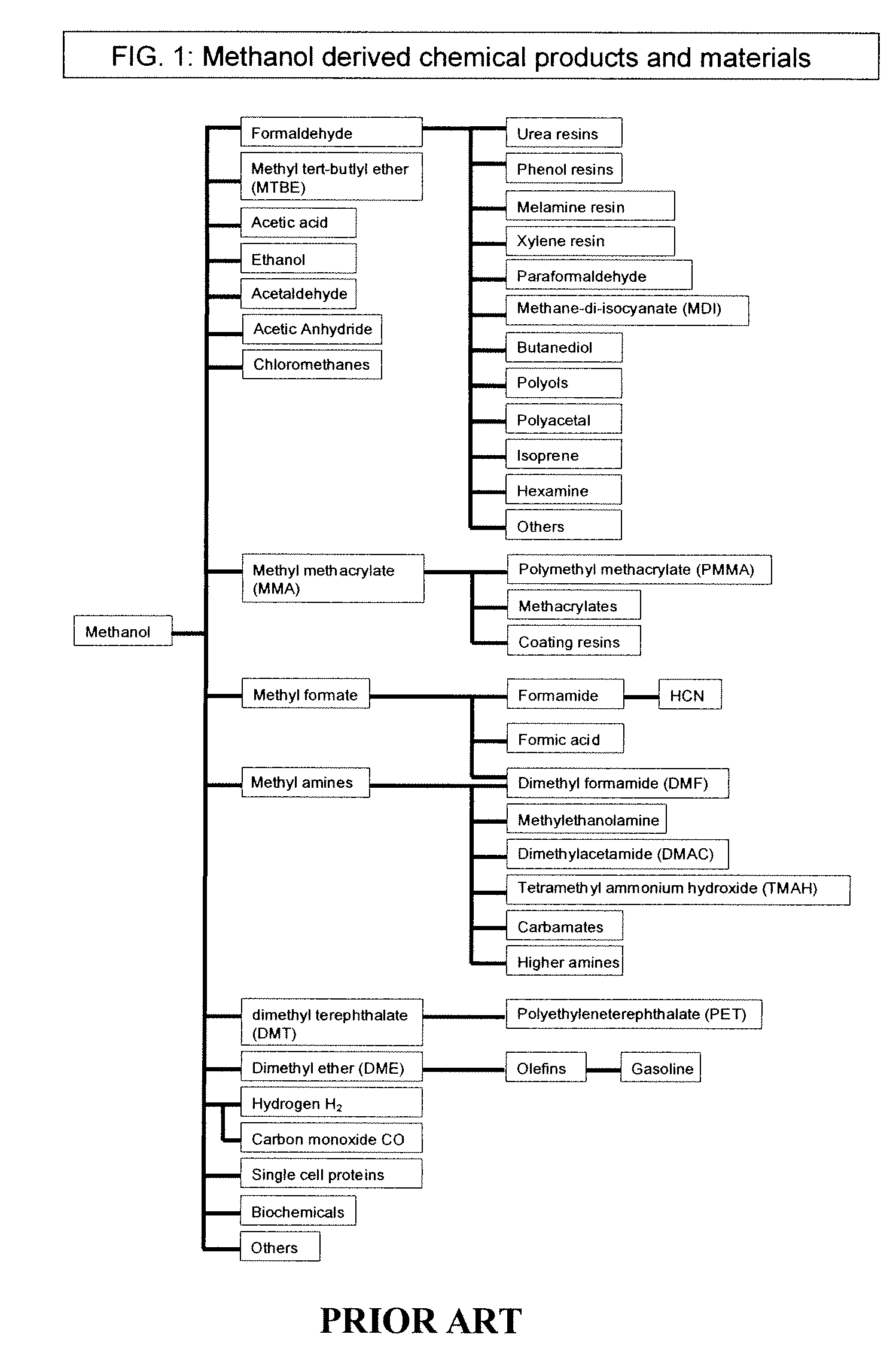
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
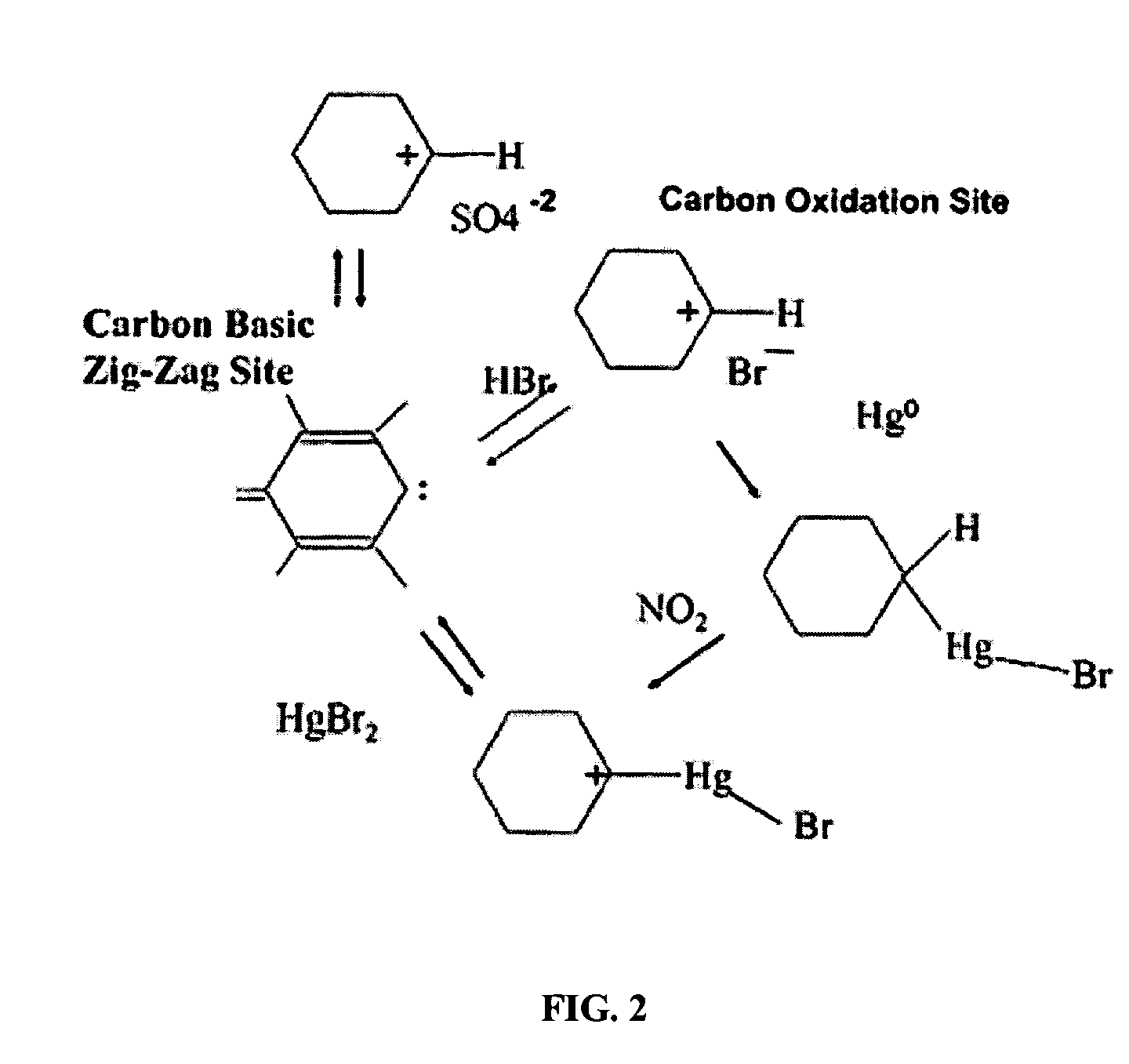
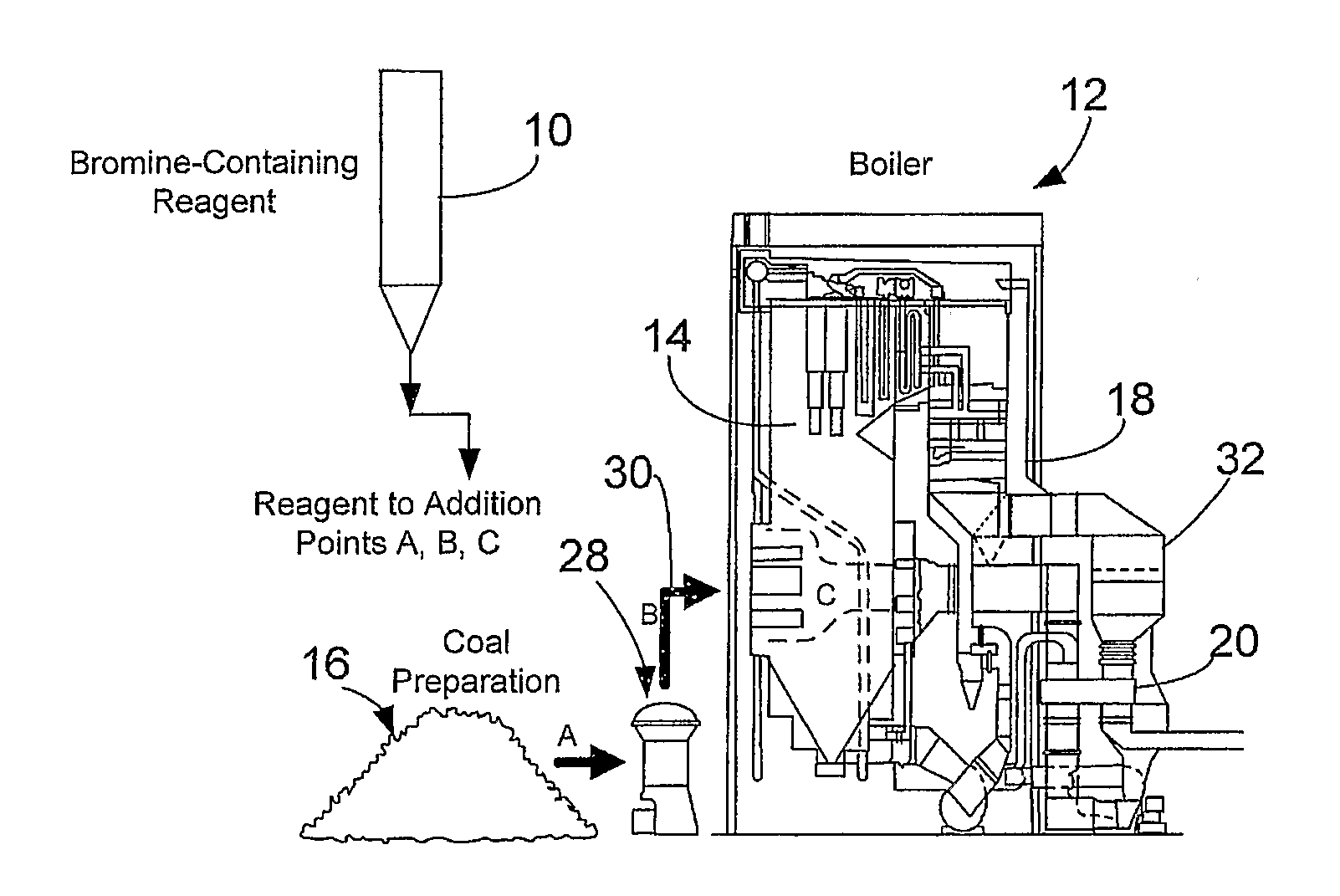
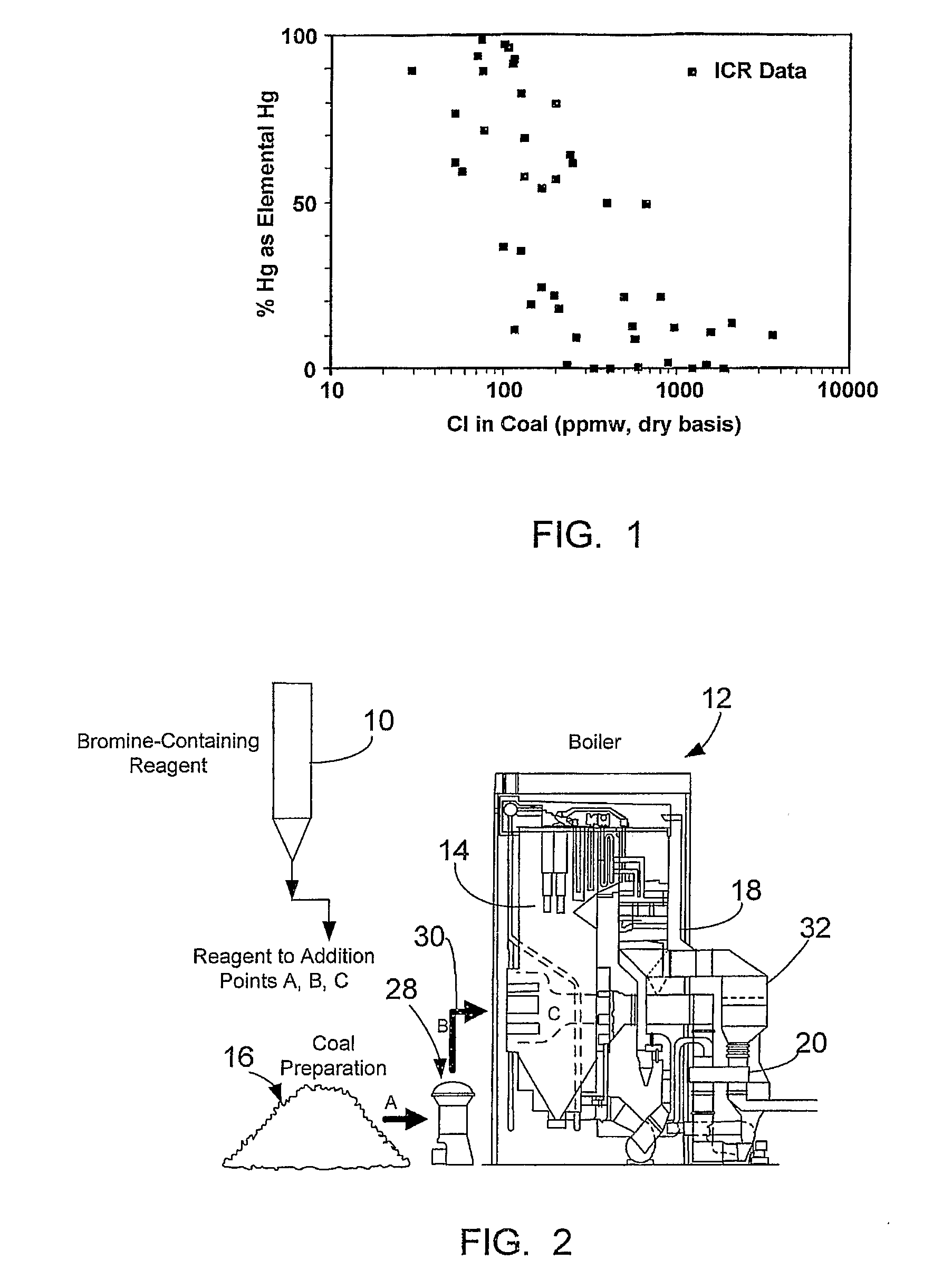
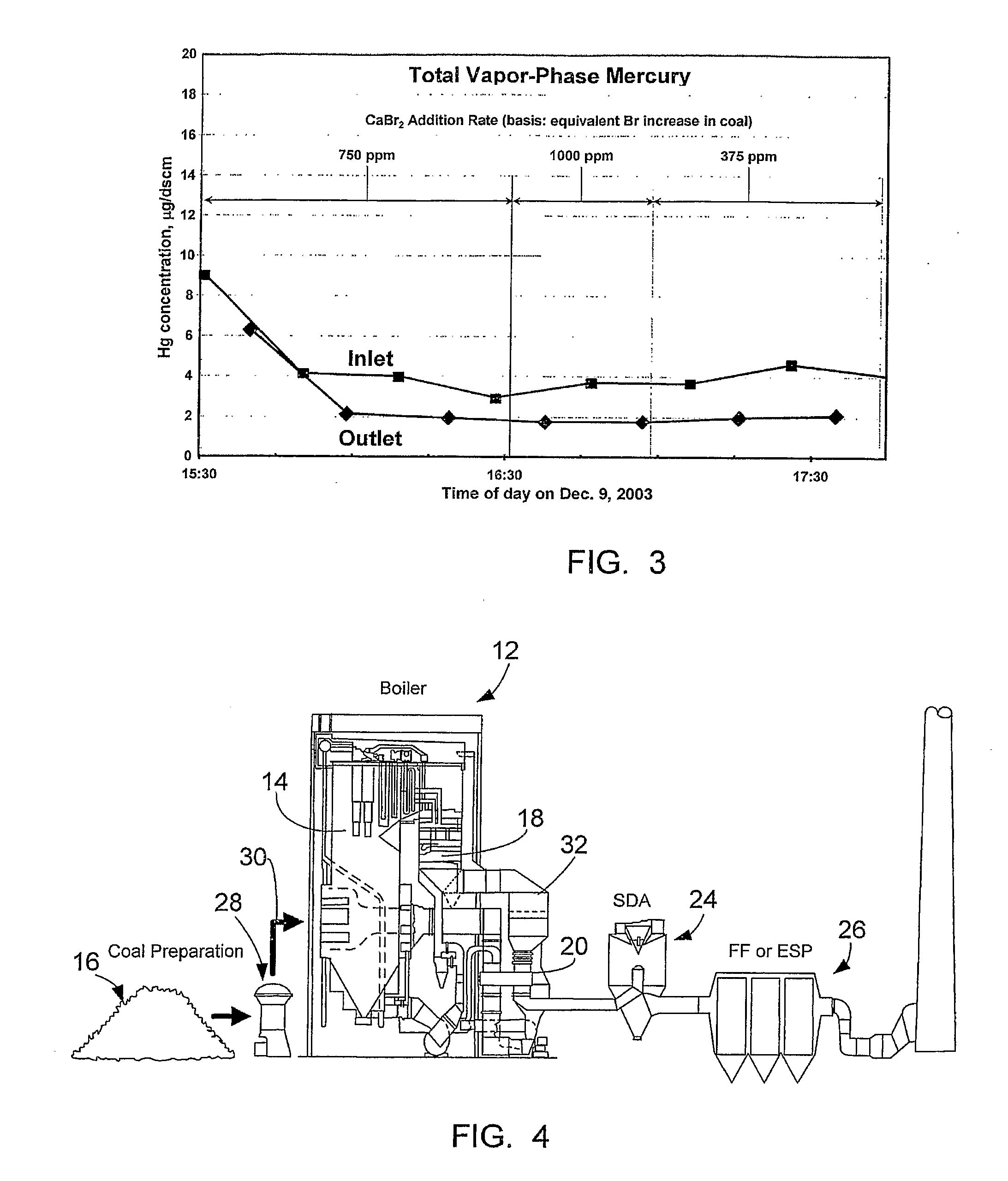
Bromine Addition for the Improved Removal of Mercury from Flue Gas
InactiveUS20080107579A1Significant technicalSignificant commercial advantageGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentCombustionFlue gas
Bromine-containing compounds, added to the coal, or to the boiler combustion furnace, are used to enhance the oxidation of mercury, thereby enhancing the overall removal of mercury in downstream pollution control devices. The method is applicable to utility power plants equipped with wet FGD systems, as well as those plants equipped with spray dryer absorber FGD systems.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
Multi-component removal in flue gas by aqua ammonia
InactiveUS7255842B1Regeneration process is less-costlyIncrease load capacityGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsNitric oxideSlurry
A new method for the removal of environmental compounds from gaseous streams, in particular, flue gas streams. The new method involves first oxidizing some or all of the acid anhydrides contained in the gas stream such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O) to sulfur trioxide (SO3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The gas stream is subsequently treated with aqua ammonia or ammonium hydroxide which captures the compounds via chemical absorption through acid-base or neutralization reactions. The products of the reactions can be collected as slurries, dewatered, and dried for use as fertilizers, or once the slurries have been dewatered, used directly as fertilizers. The ammonium hydroxide can be regenerated and recycled for use via thermal decomposition of ammonium bicarbonate, one of the products formed. There are alternative embodiments which entail stoichiometric scrubbing of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides with subsequent separate scrubbing of carbon dioxide.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
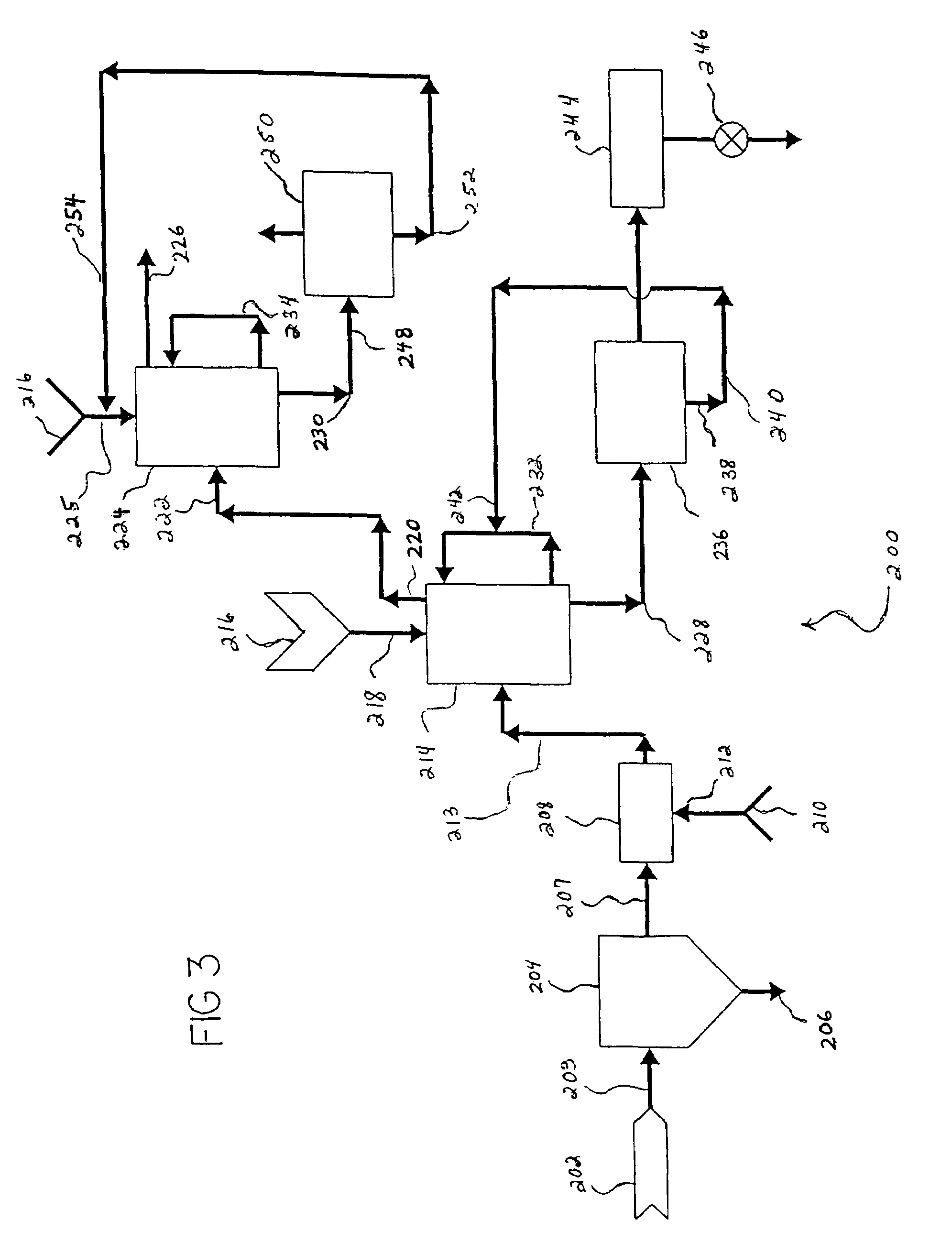
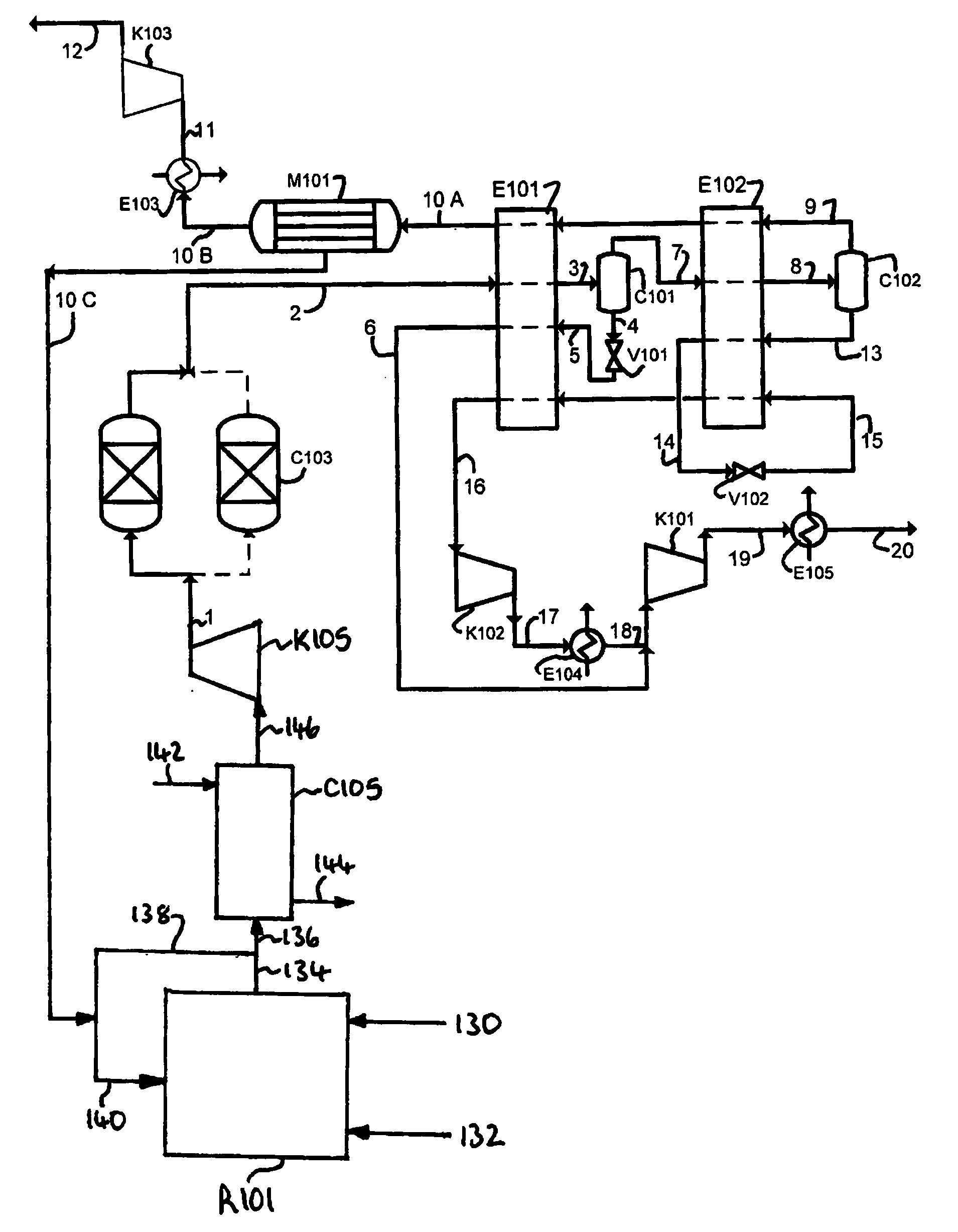
Power plants that utilize gas turbines for power generation and processes for lowering co2 emissions
ActiveUS20080104958A1Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsEmission reductionGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesPower stationWorking fluid
Power plants and process for lowering CO2 emissions generally includes extracting a portion of the recirculated CO2-rich flue gas mid-way through the compression pathway of a gas turbine and removing the CO2 in a separation unit. The remaining portion of the CO2 rich flue gas (i.e., the portion of the recirculated flue gas that was not fed to the separation unit) is mixed with fresh air coming from an additional compressor-expander and then fed back to the compression pathway. As a result, flue gas recirculation increases the CO2 concentration within the working fluid, leading to an additional increase in CO2 partial pressure. As the concentration and partial pressure of CO2 is increased, a lower energy penalty is observed to remove the CO2. Moreover, a reduced volume is fed to the CO2 separation unit during operation. Consequently, the size of the separation equipment can be reduced as well as the energy required for the separation process.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO +1
Ultra Cleaning of Combustion Gas Including the Removal of Co2
ActiveUS20080072762A1Reduce evaporationMinimize energy consumptionUsing liquid separation agentEmission preventionCo2 removalCombustion
Ultra cleaning of combustion gas to near zero concentration of residual contaminants followed by the capture of CO2 is provided. The high removal efficiency of residual contaminants is accomplished by direct contact cooling and scrubbing of the gas with cold water. The temperature of the combustion gas is reduced to 0-20 degrees Celsius to achieve maximum condensation and gas cleaning effect. The CO2 is captured from the cooled and clean flue gas in a CO2 absorber (134) utilizing an ammoniated solution or slurry in the NH3—CO2H2O system. The absorber operates at 0-20 degrees Celsius. Regeneration is accomplished by elevating the pressure and temperature of the CO2-rich solution from the absorber. The CO2 vapor pressure is high and a pressurized CO2 stream, with low concentration of NH3 and water vapor is generated. The high pressure CO2 stream is cooled and washed to recover the ammonia and moisture from the gas.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Pollutant emission control sorbents and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20070122327A1Small particle sizePromotes Hg-captureGas treatmentOther chemical processesSorbentFlue gas
Sorbents for removal of mercury and other pollutants from gas streams, such as a flue gas stream from coal-fired utility plants, and methods for their manufacture and use are disclosed. The methods include mixing sorbent substrate particles with a sulfide salt and a metal salt to form a metal sulfide on the outer surface of the sorbent particles.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
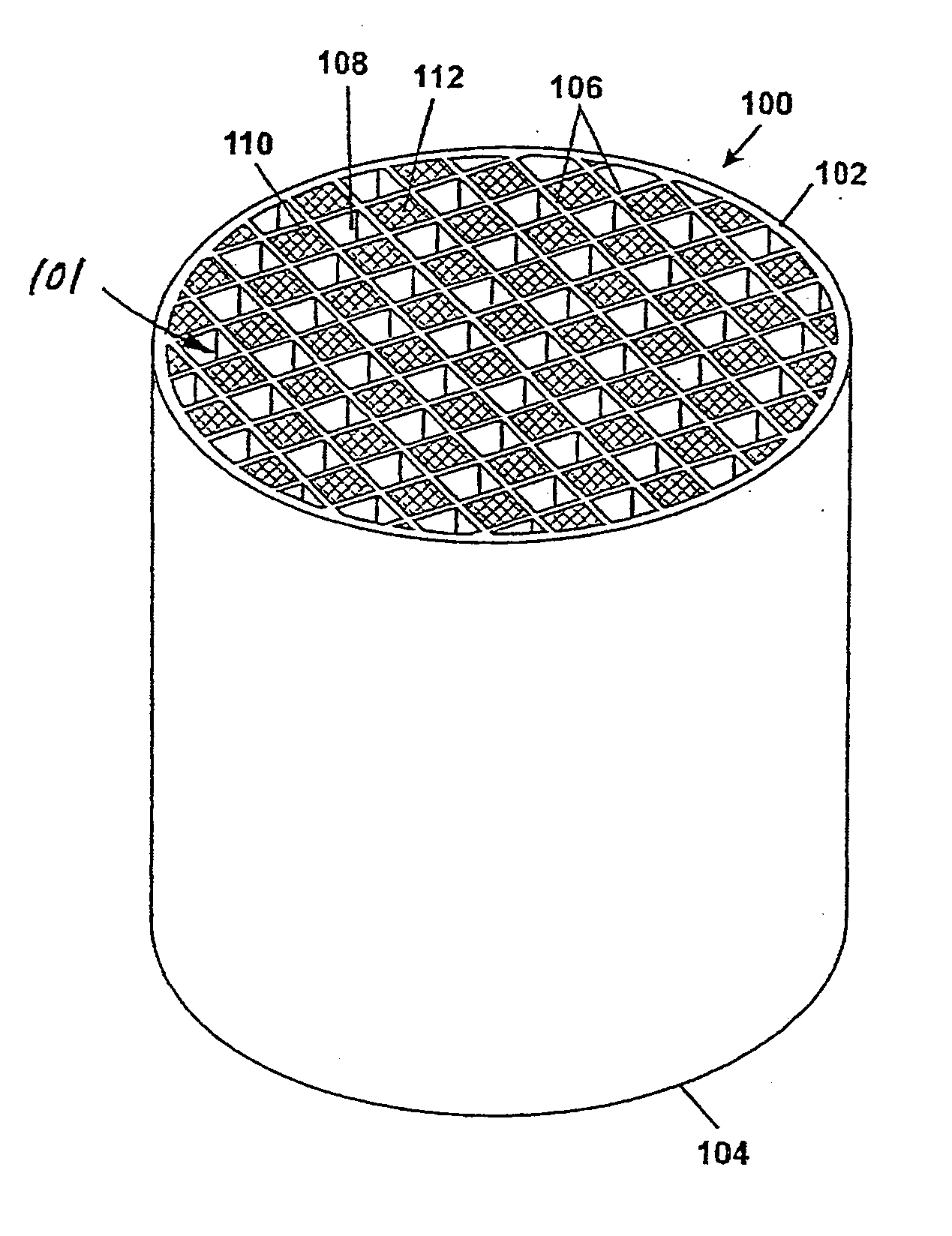
Activated carbon honeycomb catalyst beds and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070261557A1Simple designLow costGas treatmentCarbon compoundsActivated carbonCombustion system
Disclosed herein, without limitation, are activated carbon honeycomb catalyst beds and systems for removing mercury and other toxic metals from a process stream, i.e, from flue gas of a coal combustion system. The activated carbon honeycomb can for example remove greater than 90% mercury from flue gas with a simple design and without adding material to the flue gas. Also disclosed herein, and without limitation, are methods for manufacturing and using the disclosed honeycomb catalyst beds and systems.
Owner:CORNING INC
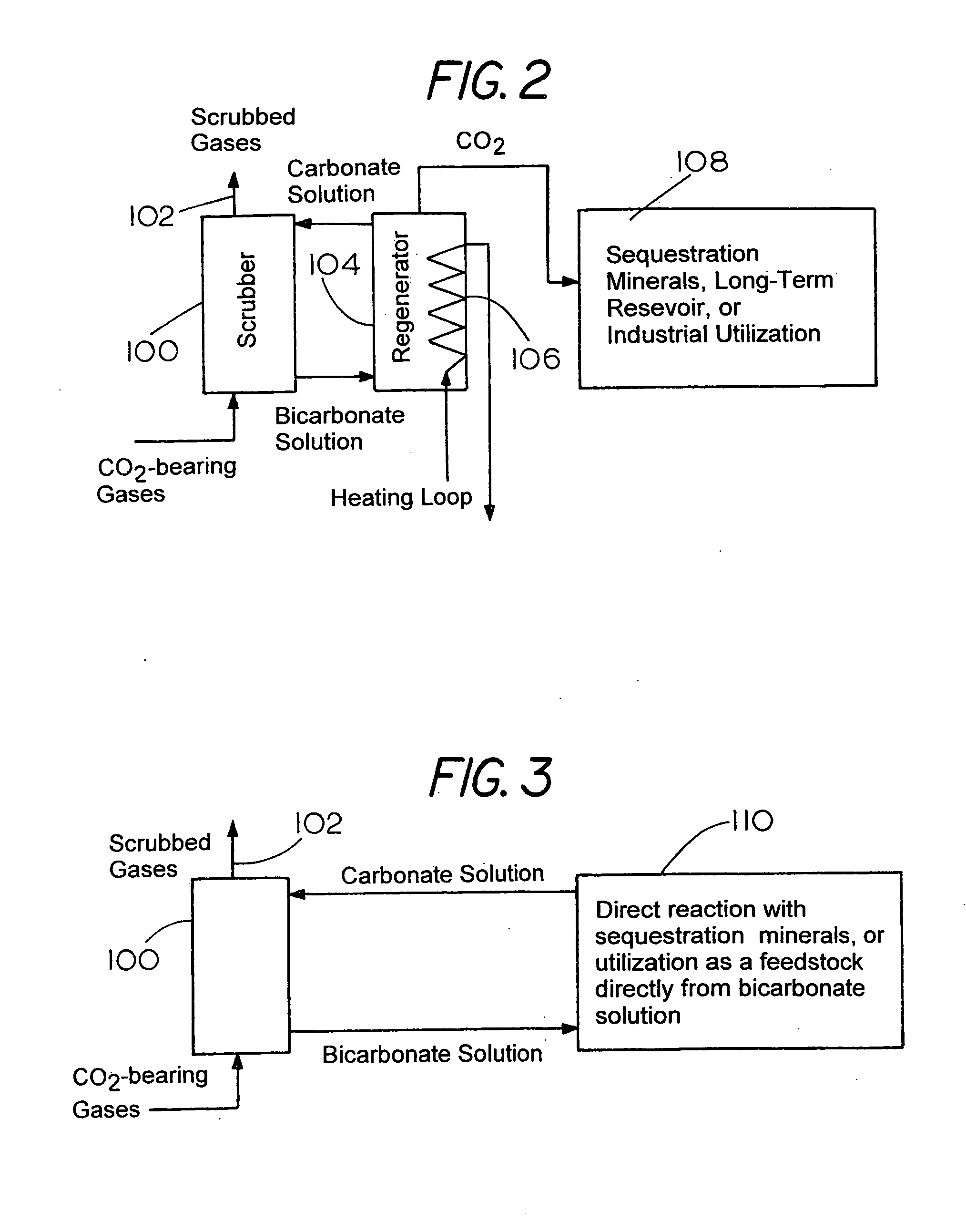
Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in Flue Gases
ActiveUS20090202410A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentAlkaline earth metalOxidation state
There is provided a process for the capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide that would otherwise enter the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and other problems. CO2 capture is accomplished by reacting carbon dioxide in flue gas with an alkali metal carbonate, or a metal oxide, particularly containing an alkaline earth metal or iron, to form a carbonate salt. A preferred carbonate for CO2 capture is a dilute aqueous solution of additive-free (Na2CO3). Other carbonates include (K2CO3) or other metal ion that can produce both a carbonate and a bicarbonate salt. Examples of suitable metal oxides include several alkaline earths including CaO and MgO. The captured CO2 is preferably sequestered using any available mineral or industrial waste that contains calcium magnesium or iron in non-carbonate forms, or iron in the Fe+2 oxidation state.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
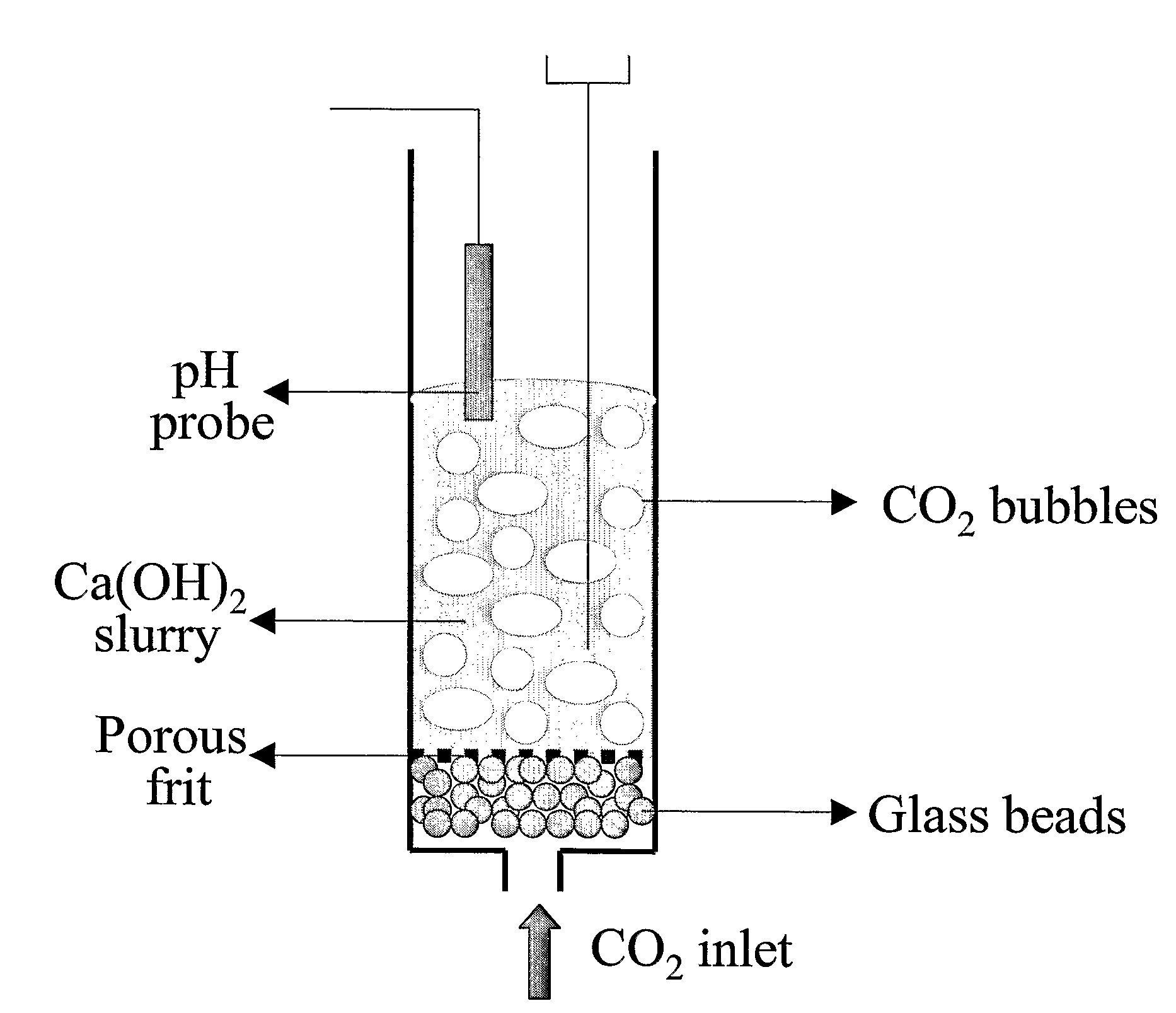
Sorbent for separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from gas mixtures
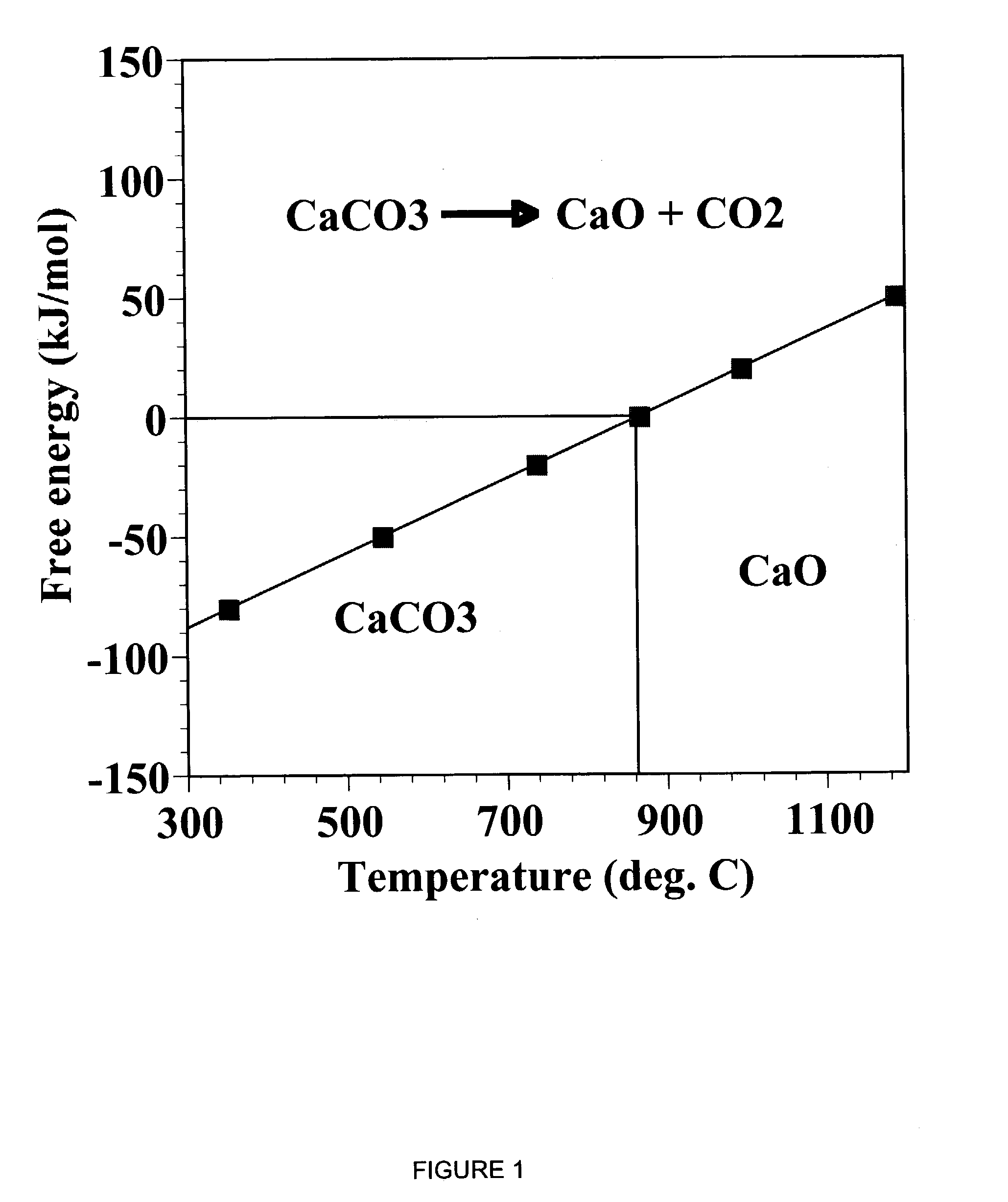
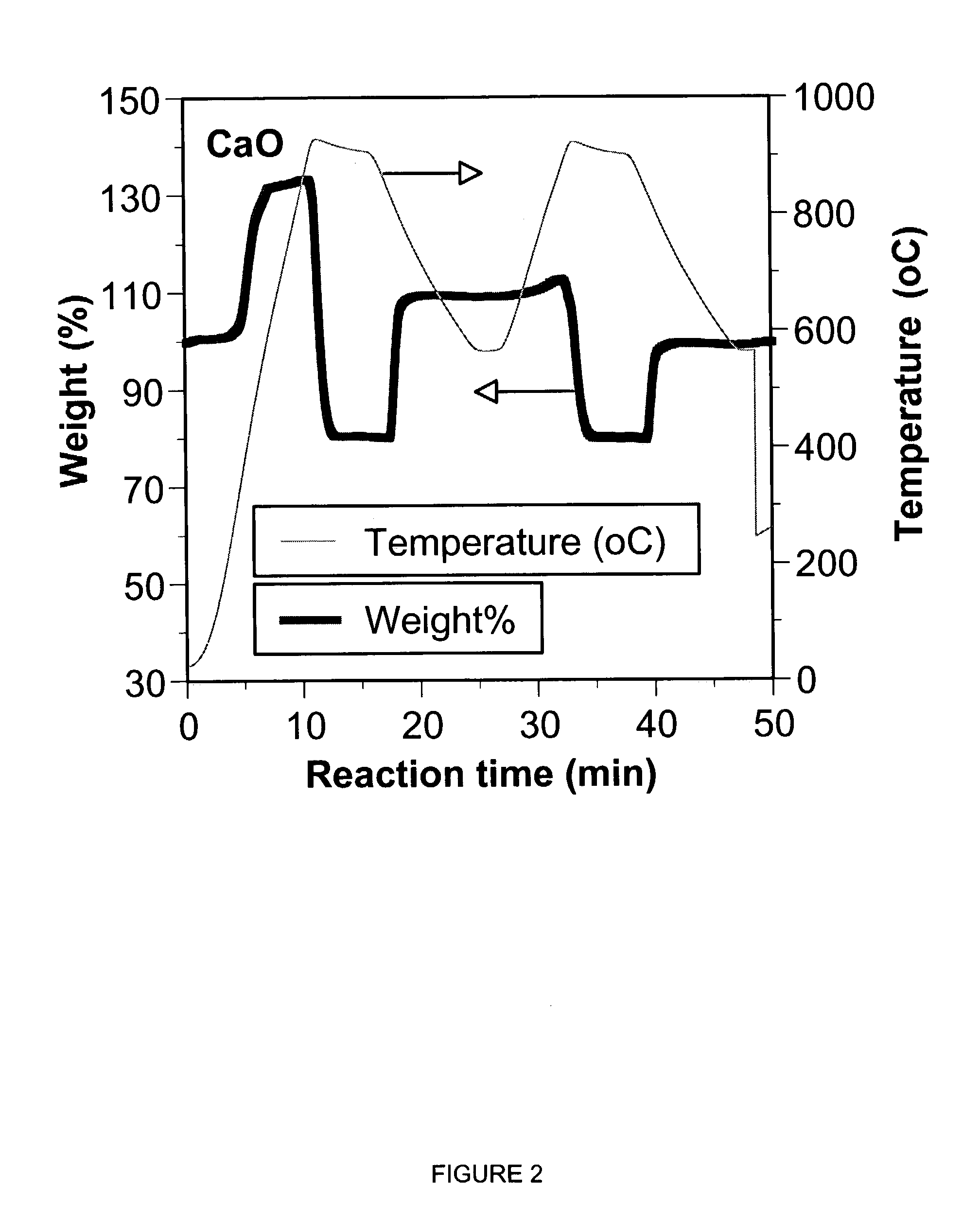
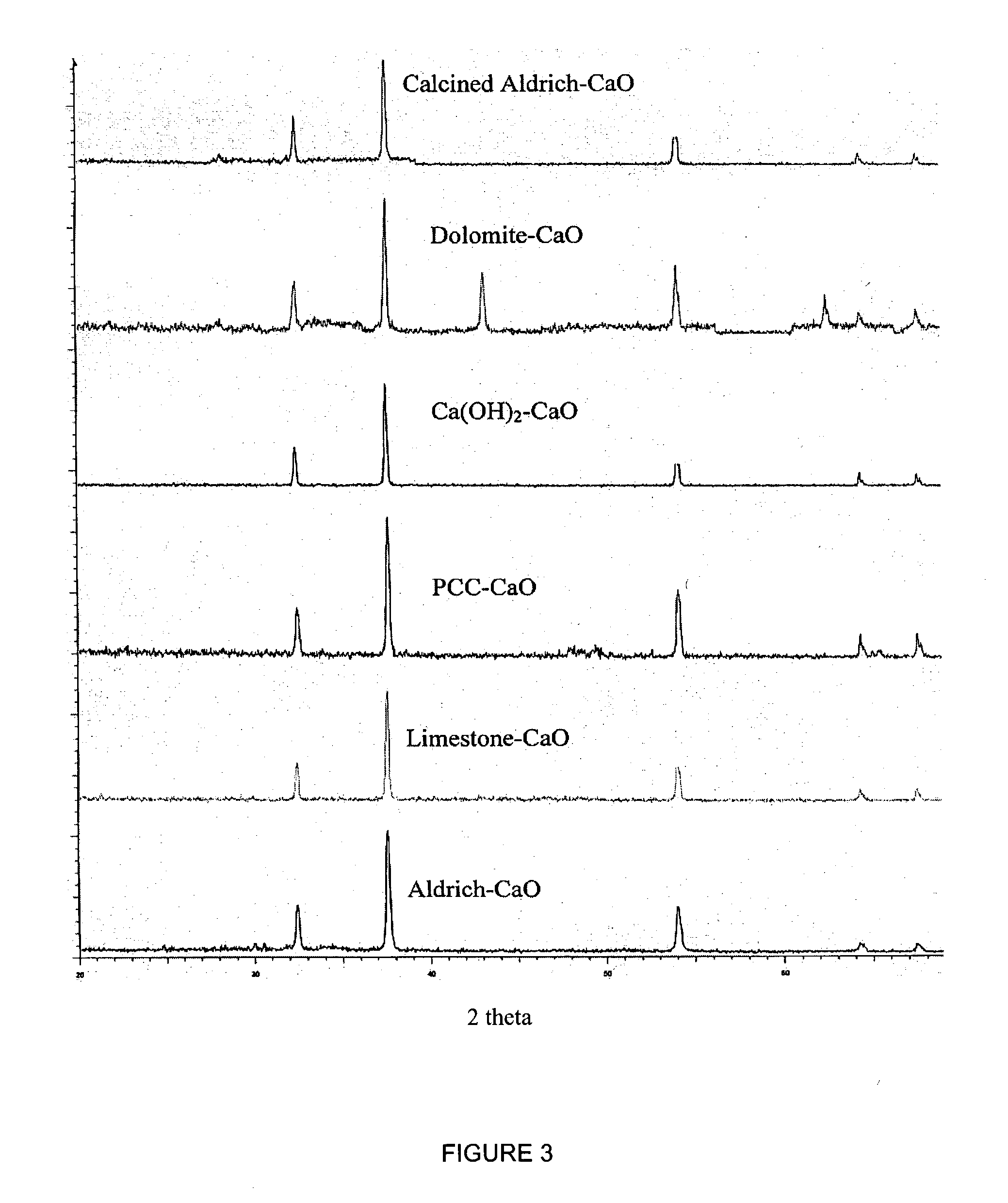
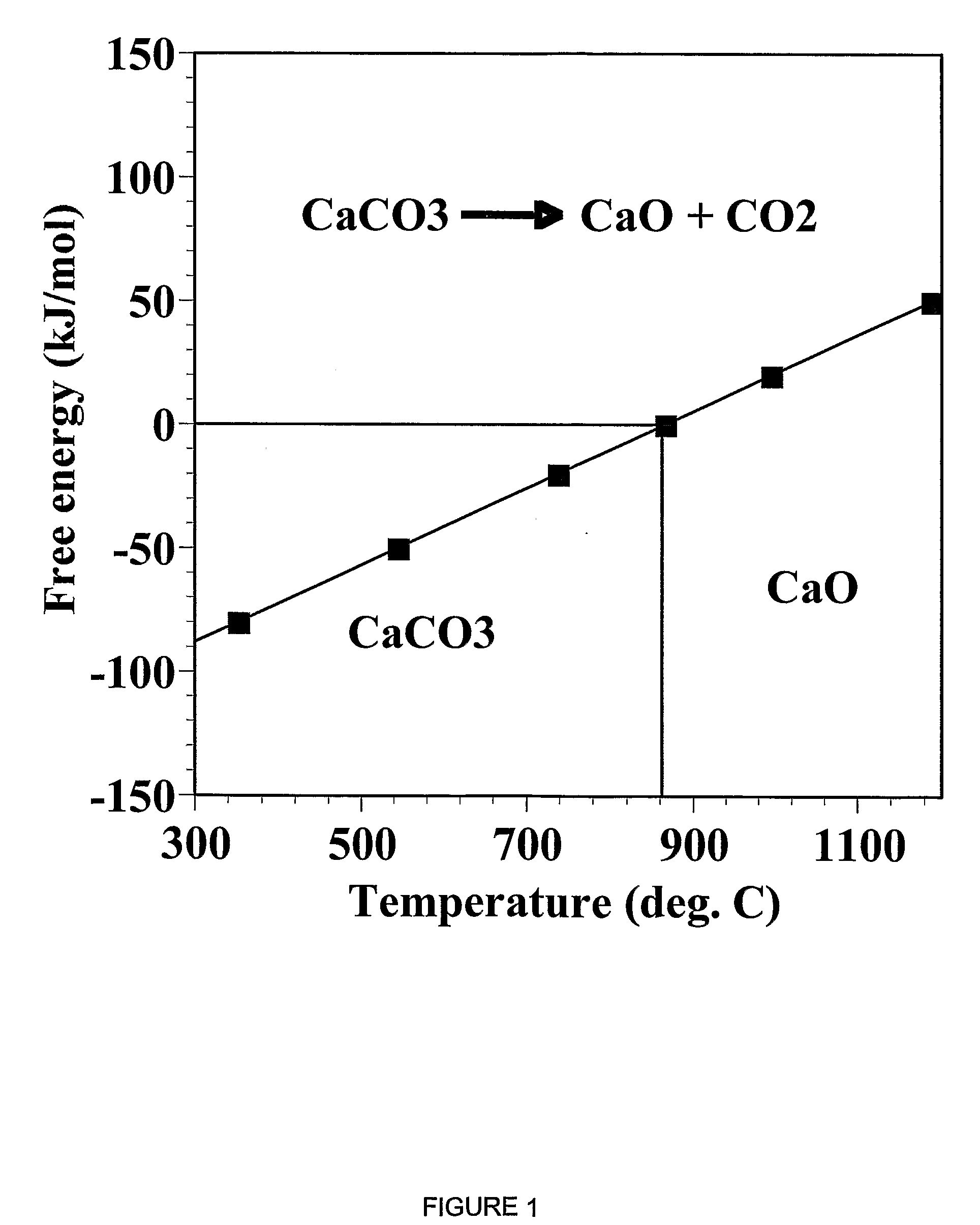
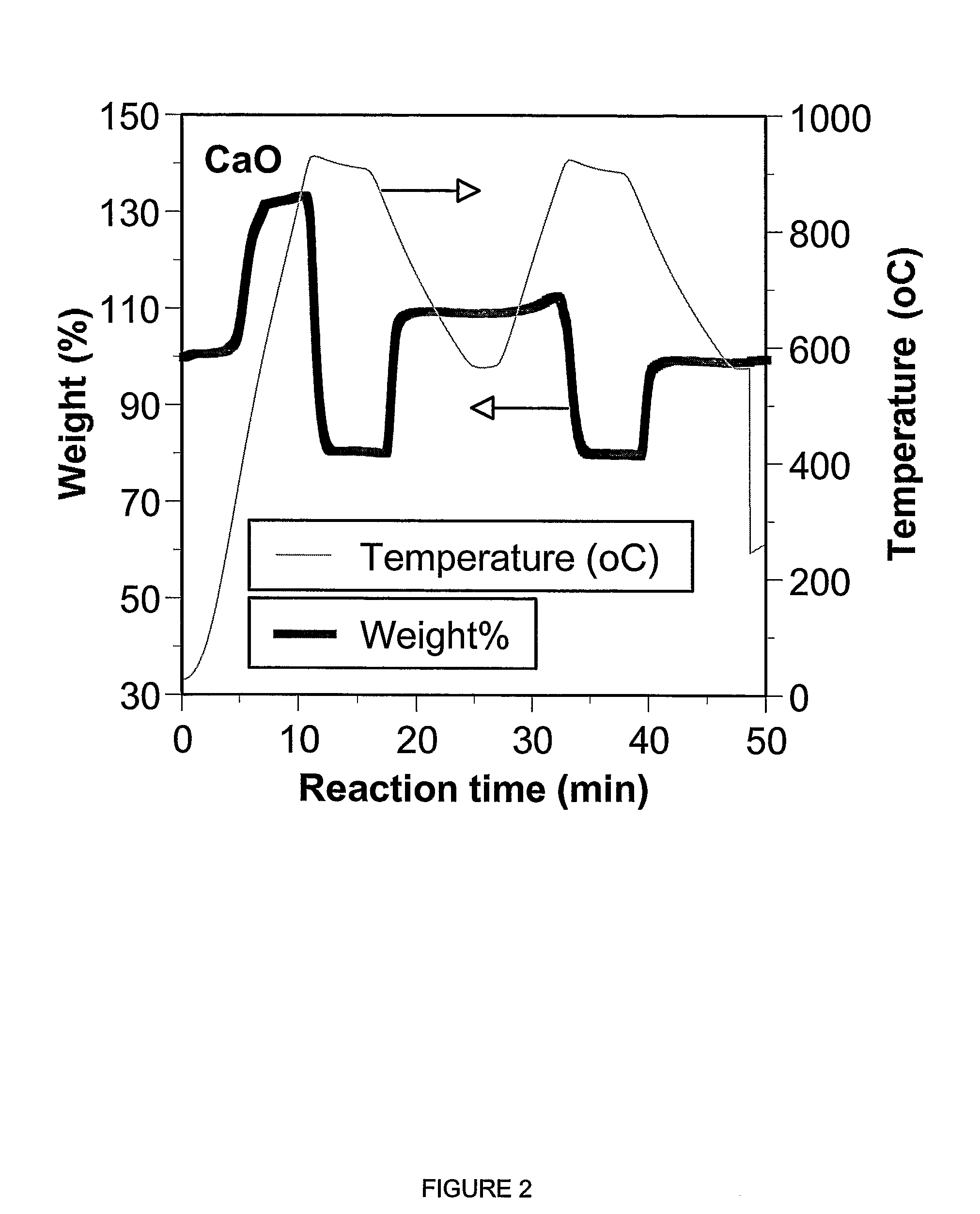
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from a multicomponent gas mixture to provide a gaseous stream depleted in CO2 compared to the inlet CO2 concentration in the stream. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases (such as flue gas / fuel gas) by its reaction with metal oxides (such as calcium oxide). The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 (CaRS-CO2) process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide (CaO) in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent and the evolution of a concentrated stream of CO2. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This carbonation-calcination cycle forms the basis of the CaRS-CO2 process. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, developed by a process detailed elsewhere, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Sorbents for the oxidation and removal of mercury
ActiveUS7435286B2Efficient use ofEasy to controlGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbonHalogen
A promoted activated carbon sorbent is described that is highly effective for the removal of mercury from flue gas streams. The sorbent comprises a new modified carbon form containing reactive forms of halogen and halides. Optional components may be added to increase reactivity and mercury capacity. These may be added directly with the sorbent, or to the flue gas to enhance sorbent performance and / or mercury capture. Mercury removal efficiencies obtained exceed conventional methods. The sorbent can be regenerated and reused. Sorbent treatment and preparation methods are also described. New methods for in-flight preparation, introduction, and control of the active sorbent into the mercury contaminated gas stream are described.
Owner:MIDWEST ENERGY EMISSIONS CORP
Separation of Carbon Dioxide (Co2) From Gas Mixtures By Calcium Based Reaction Separation (Cars-Co2) Process
InactiveUS20080233029A1Good repeatabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCombustible gas catalytic treatmentSorbentTransformation ratio
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from a multicomponent gas mixture to provide a gaseous stream depleted in CO2 compared to the inlet CO2 concentration in the stream. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases (such as flue gas / fuel gas) by its reaction with metal oxides (such as calcium oxide). The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 (CaRS—CO2) process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide (CaO) in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCOa). Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent and the evolution of a concentrated stream of CO2. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This carbonation-calcination cycle forms the basis of the CaRS—CO2 process. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, developed by a process detailed elsewhere, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
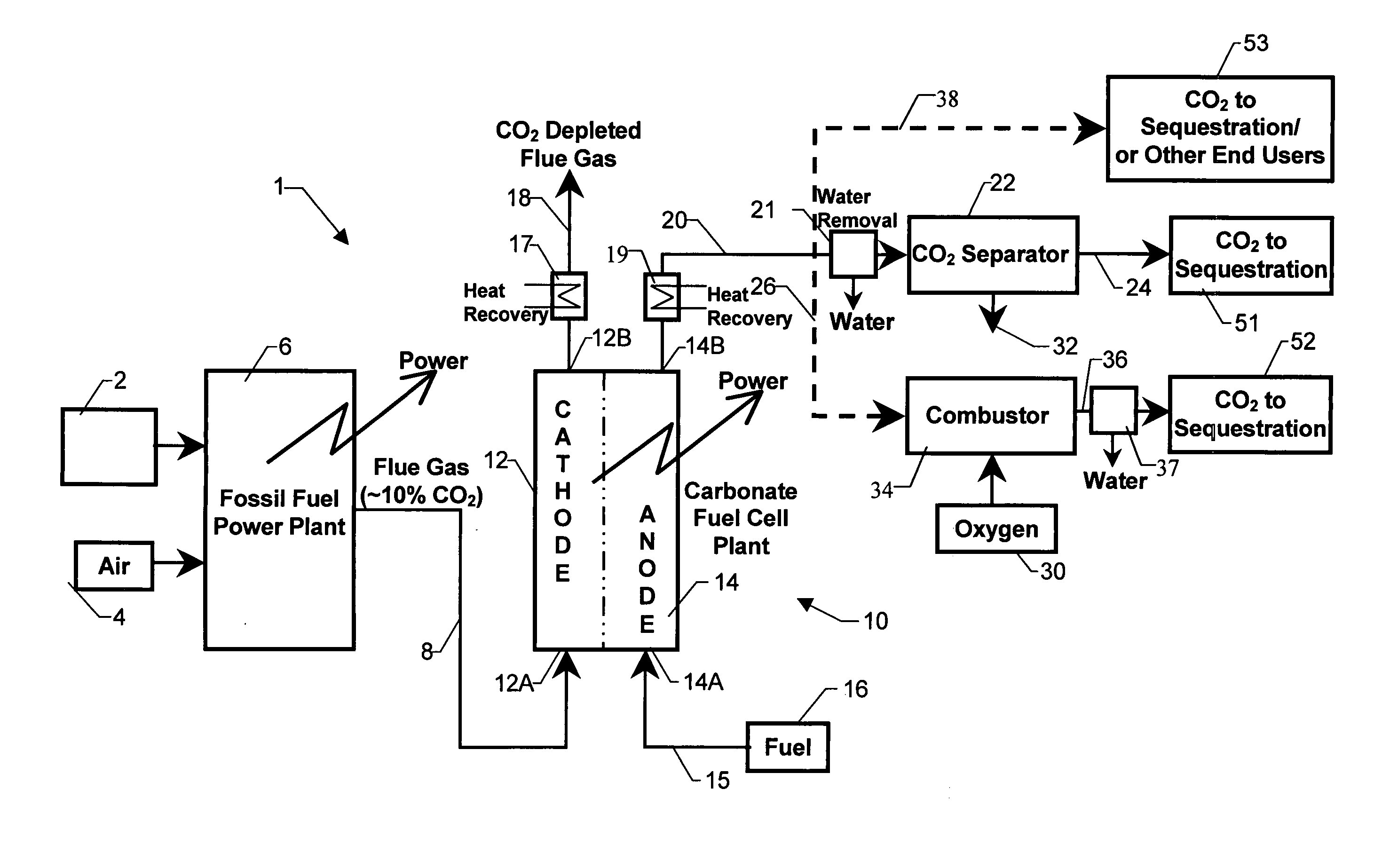
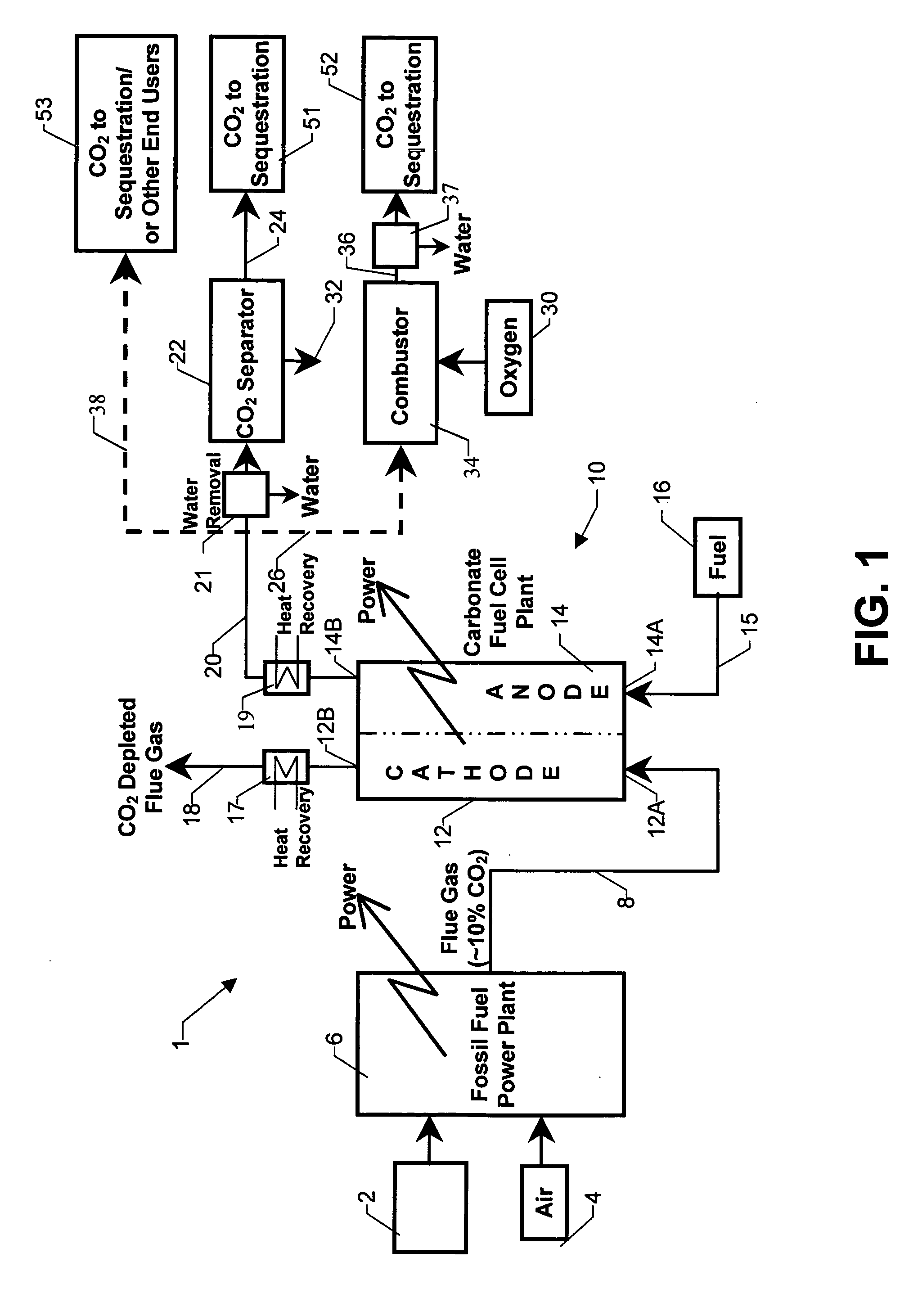
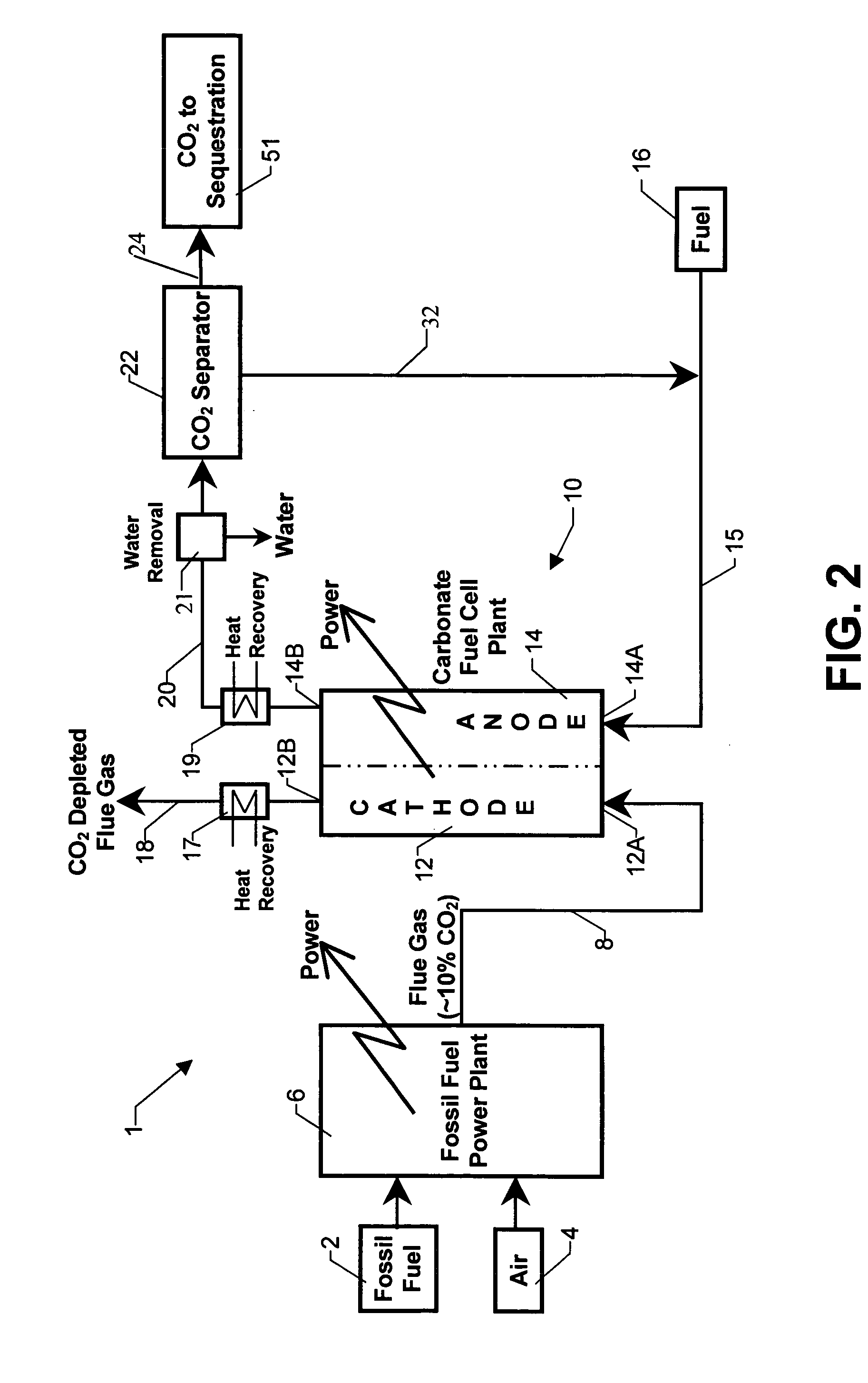
Integrated high efficiency fossil fuel power plant/fuel cell system with CO2 emissions abatement
An integrated power production system including a fossil fuel power plant for processing fossil based fuel such as coal or natural gas arranged in tandem with a carbonate fuel cell having an anode and a cathode section. The flue gas of the power plant serves exclusively as the inlet gas for the cathode section of the fuel cell. Anode exhaust gas leaving the anode section of the fuel cell is subjected to processing including sequestration of the carbon dioxide in the exhaust gas.
Owner:FUELCELL ENERGY INC
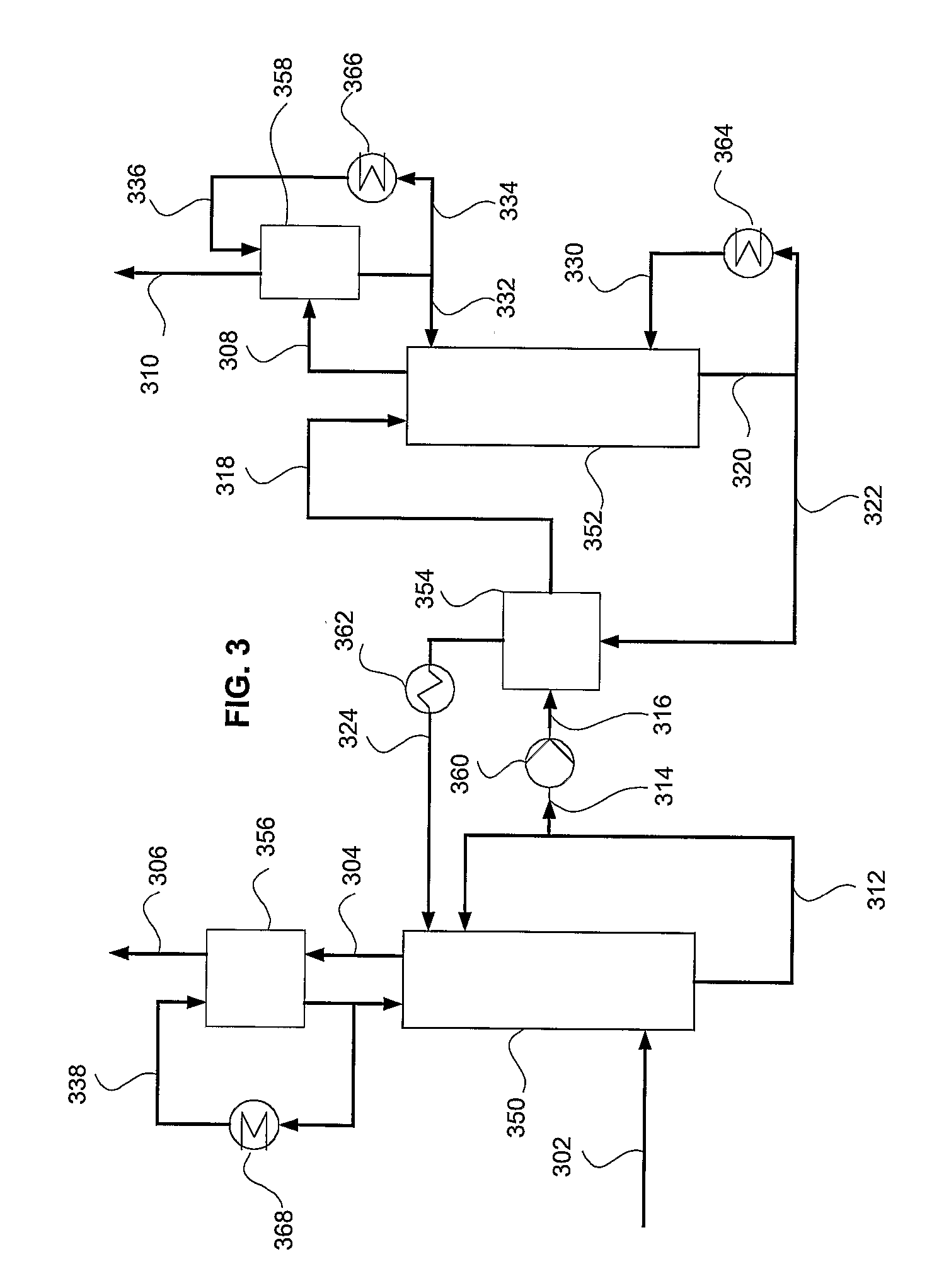
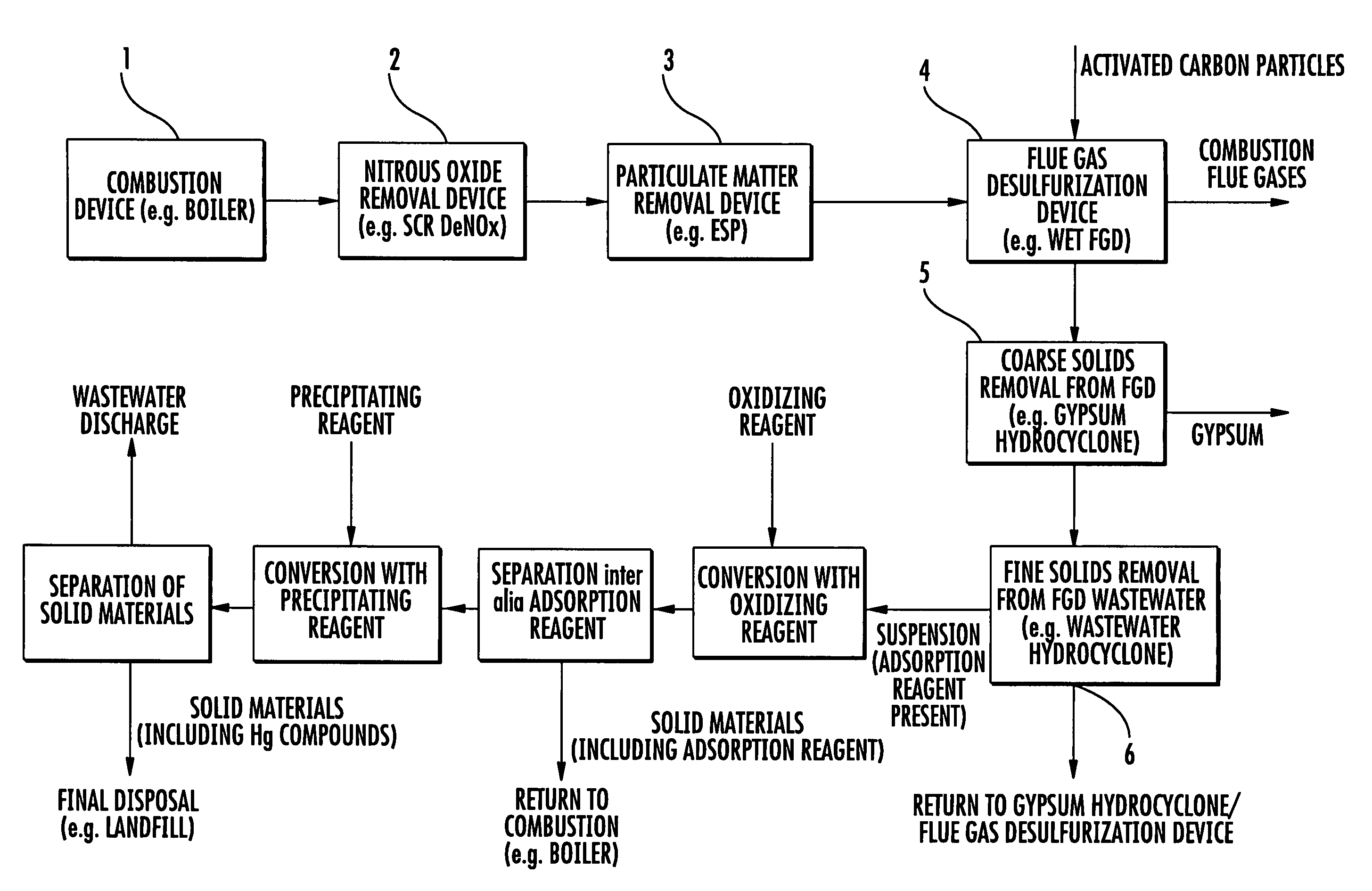
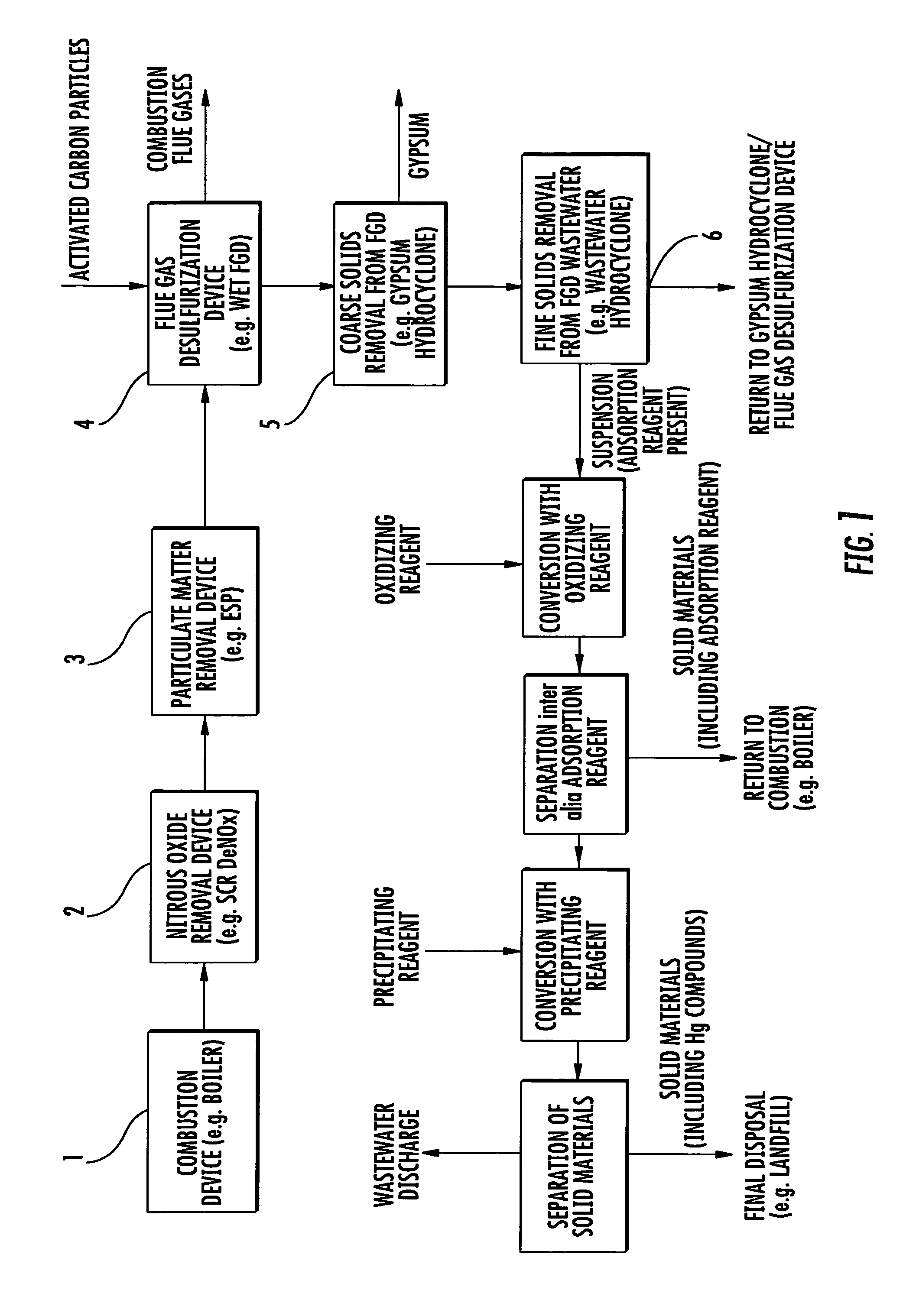
Method for removing mercury from flue gas after combustion
InactiveUS7727307B2Simple and economical methodGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentPower stationCombustion
A method of removing mercury from flue gases from combustion plants, such as for example power plants or waste incineration plants, is achieved in which mercury-containing flue gases are brought into contact with an adsorption reagent either directly or indirectly by being contained in an absorption reagent, whereby mercury is substantially adsorbed by the adsorption reagent during this contact. After adsorption has occurred the adsorption reagent is separated from the flue gases and subsequently from the absorption reagent and added to an aqueous solution containing an oxidizing agent, whereby the adsorbed mercury dissolves as Hg2+. The Hg2+-containing solution is subsequently separated from the adsorption agent and the Hg2+ then is removed from the solution. This method enables the mercury to be removed from flue gas in a simple and economical manner.
Owner:STEAG ENERGY SERVICES
Purification of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is separated from a feed gas, preferably derived from flue gas from an oxyfuel combustion process, in a membrane separation system to produce separated carbon dioxide gas which is fed to the oxyfuel combustion process to improve the performance of the process.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Method to control mercury emissions from exhaust gases
InactiveUS6136281AElimination of mercury in flue gas emissionsEasy to collectCombination devicesExhaust apparatusSolid massGas phase
The present invention relates to a method to catalyze the oxidation of Hg(0) in a flue gas stream prior to standard emissions control equipment. The oxidized mercury has been found to be more condensable than Hg(0) and consequently more easily removed from the gas phase. Accordingly, mercury in its oxidized form can be trapped from a flue gas stream or the like by absorption onto a solid mass or can be more efficiently removed from flue gas streams by wet processes such as a two-stage wet FGD. The gist underlying the inventive concept of the instant invention relates to the use of a porous bed of gold-coated material that is saturated with Hg(0) to the point that the gold in the presence of HCl in the exhaust stream catalyses the oxidation of Hg(0).
Owner:TENNESEE VALLEY AUTHORITY
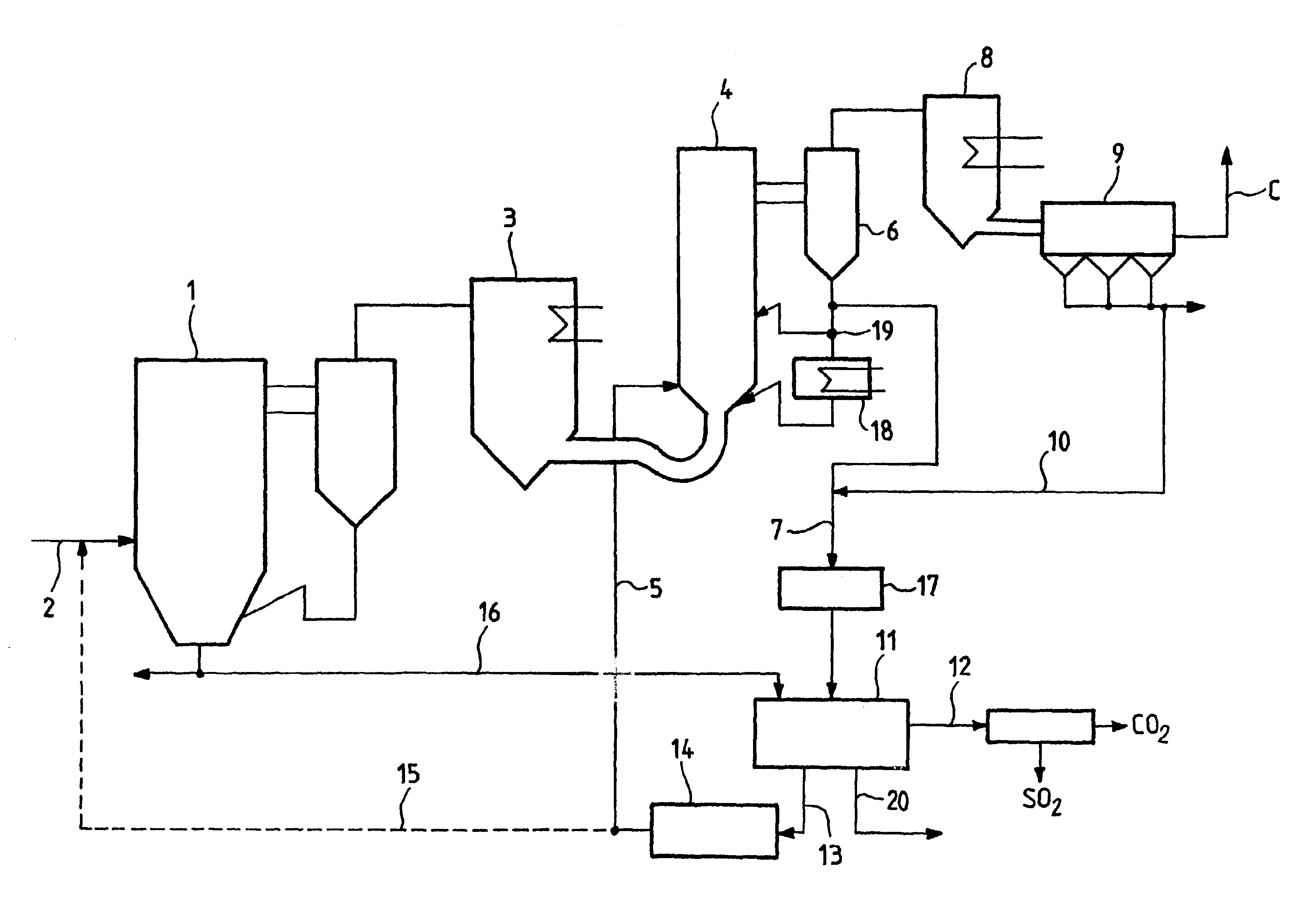
Method of simultaneously reducing CO2 and SO2 emissions in a combustion installation
InactiveUS6737031B2Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsFluidized bed combustionGas treatmentCombustionFlue gas
The method of simultaneously reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions produced by the combustion of carbon-containing matter in a hearth consists in injecting into the hearth a calcium-based agent, a fraction of which absorbs SO2 after decarbonization, and then, after the flue gases have been subjected to intermediate cooling, in causing them to transit via a first reactor and in putting them in contact therein with the other fraction of the absorbant that has not reacted with SO2 so as to capture CO2 from the flue gases by carbonization, then, in a separator, in extracting the solids contained in the flue gases output from the first reactor so as to subject them to heat treatment in a second reactor in order to extract CO2 therefrom by decarbonization and in order to recycle the resulting regenerated CO2 absorbant to the first reactor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
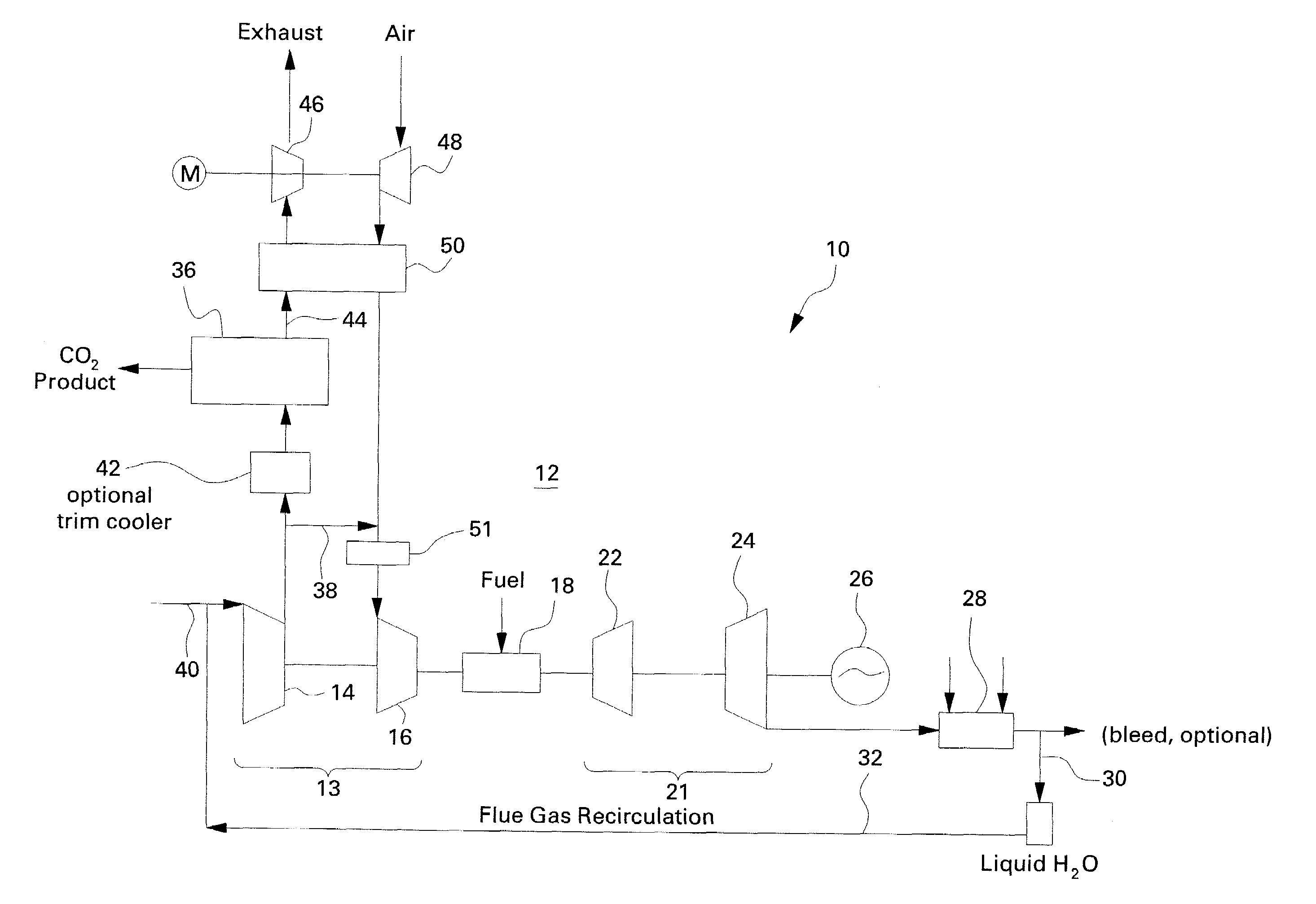
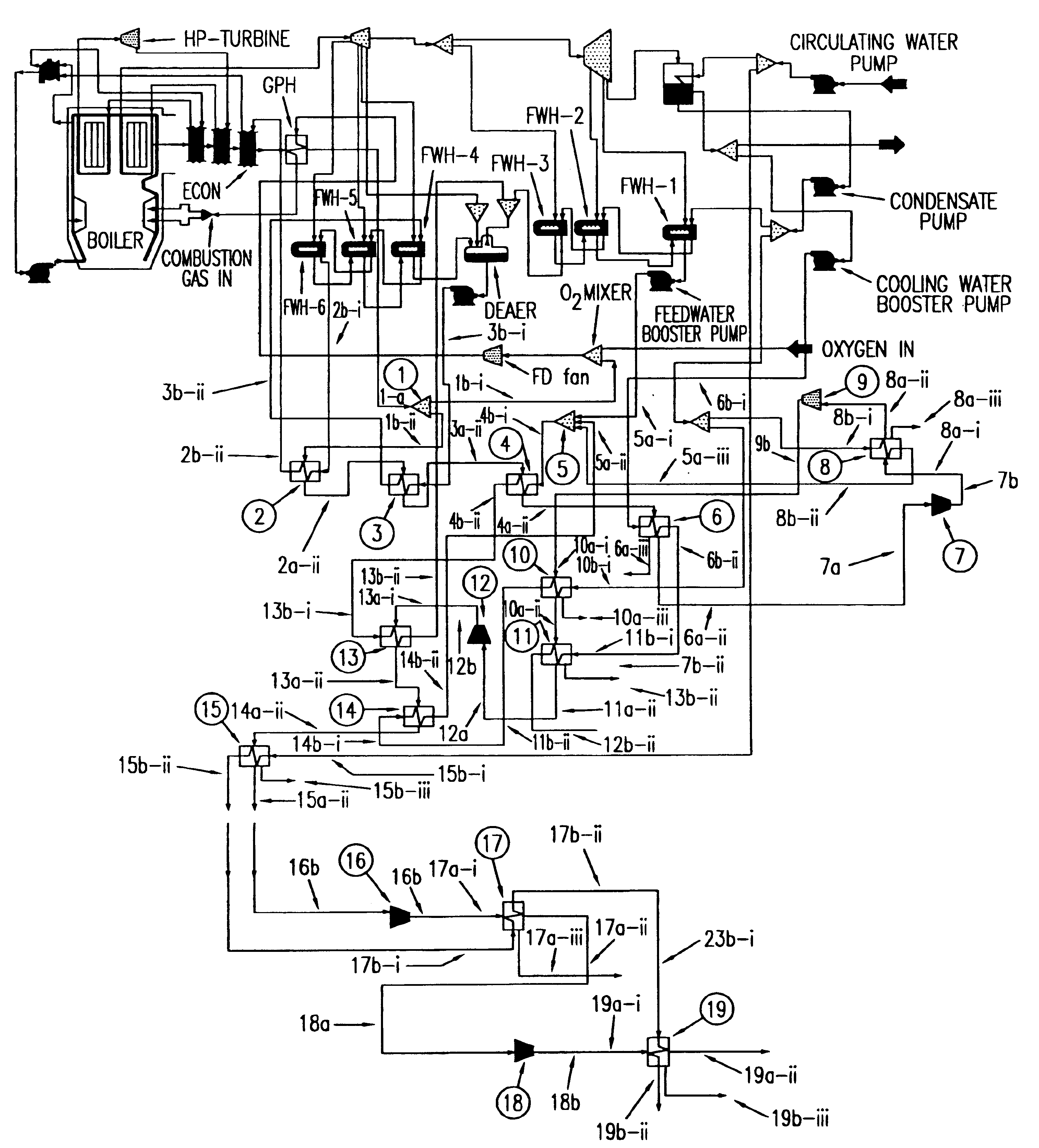
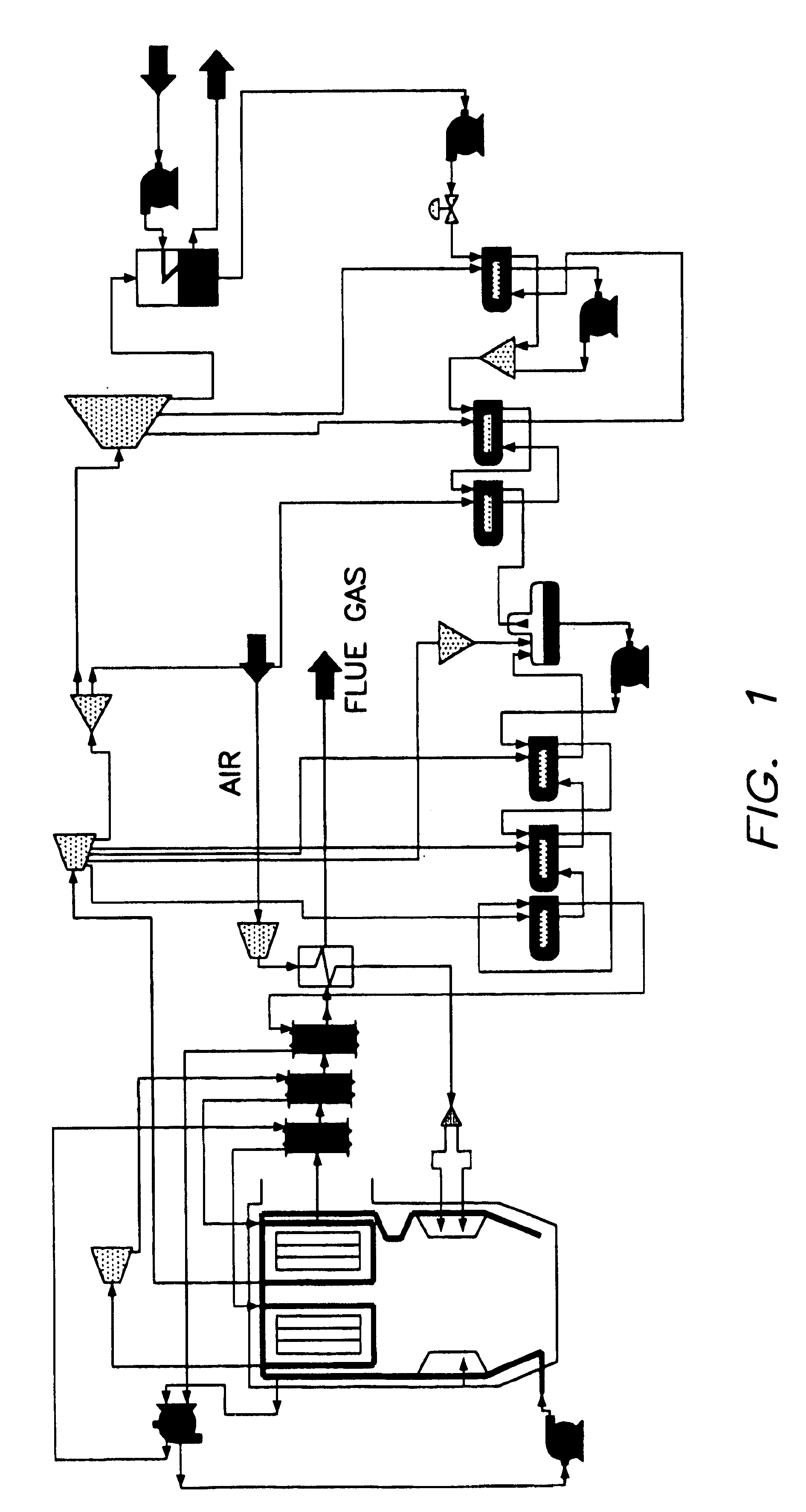
Compression stripping of flue gas with energy recovery
InactiveUS6898936B1Low costReduced Power RequirementsLiquid degasificationSteam regenerationWorking fluidWater vapor
A method of remediating and recovering energy from combustion products from a fossil fuel power plant having at least one fossil fuel combustion chamber, at least one compressor, at least one turbine, at least one heat exchanger and a source of oxygen. Combustion products including non-condensable gases such as oxygen and nitrogen and condensable vapors such as water vapor and acid gases such as SOX and NOX and CO2 and pollutants are produced and energy is recovered during the remediation which recycles combustion products and adds oxygen to support combustion. The temperature and / or pressure of the combustion products are changed by cooling through heat exchange with thermodynamic working fluids in the power generation cycle and / or compressing and / or heating and / or expanding the combustion products to a temperature / pressure combination below the dew point of at least some of the condensable vapors to condense liquid having some acid gases dissolved and / or entrained and / or directly condense acid gas vapors from the combustion products and to entrain and / or dissolve some of the pollutants while recovering sensible and / or latent heat from the combustion products through heat exchange between the combustion products and thermodynamic working fluids and / or cooling fluids used in the power generating cycle. Then the CO2, SO2, and H2O poor and oxygen enriched remediation stream is sent to an exhaust and / or an air separation unit and / or a turbine.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Purification of carbon dioxide
Impure carbon dioxide (“CO2”) comprising a first contaminant selected from the group consisting of oxygen (“O2”) and carbon monoxide (“CO”) is purified by separating expanded impure carbon dioxide liquid in a mass transfer separation column system. The impure carbon dioxide may be derived from, for example, flue gas from an oxyfuel combustion process or waste gas from a hydrogen (“H2”) PSA system.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Flue gas purification process using a sorbent polymer composite material
ActiveUS20050019240A1Easy to fixImprove removal efficiencyGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsSorbentFluoropolymer
This invention provides a process of removing sulfur oxides, mercury vapor, and fine particulate matters from industrial flue gases that contain such pollutants. The pollutants are removed by modules, which contain microporous adsorbent (i.e., sorbent) material that is held within a polymer matrix. The preferred polymers are fluoropolymers. The composite material that contains the microporous absorbent material held within a polymer matrix removes sulfur oxides by converting them into high concentration sulfuric acids. It also removes mercury vapor by chemically adsorbing the mercury into the matrix. It also removes fine particulate matters by surface filtration. The sulfuric acid that is produced inside the composite material is automatically expelled onto the external surfaces of the composite material and is drained into an acid reservoir together with the fine particulate matters which are washed from the external surfaces of the composite material by the constant dripping of the sulfuric acid along the external surfaces of the composite material.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Carbon dioxide sequestration in foamed controlled low strength materials
InactiveUS20060185560A1Improve the environmentEasy to useProductsReagentsCombustion chamberMaterials science
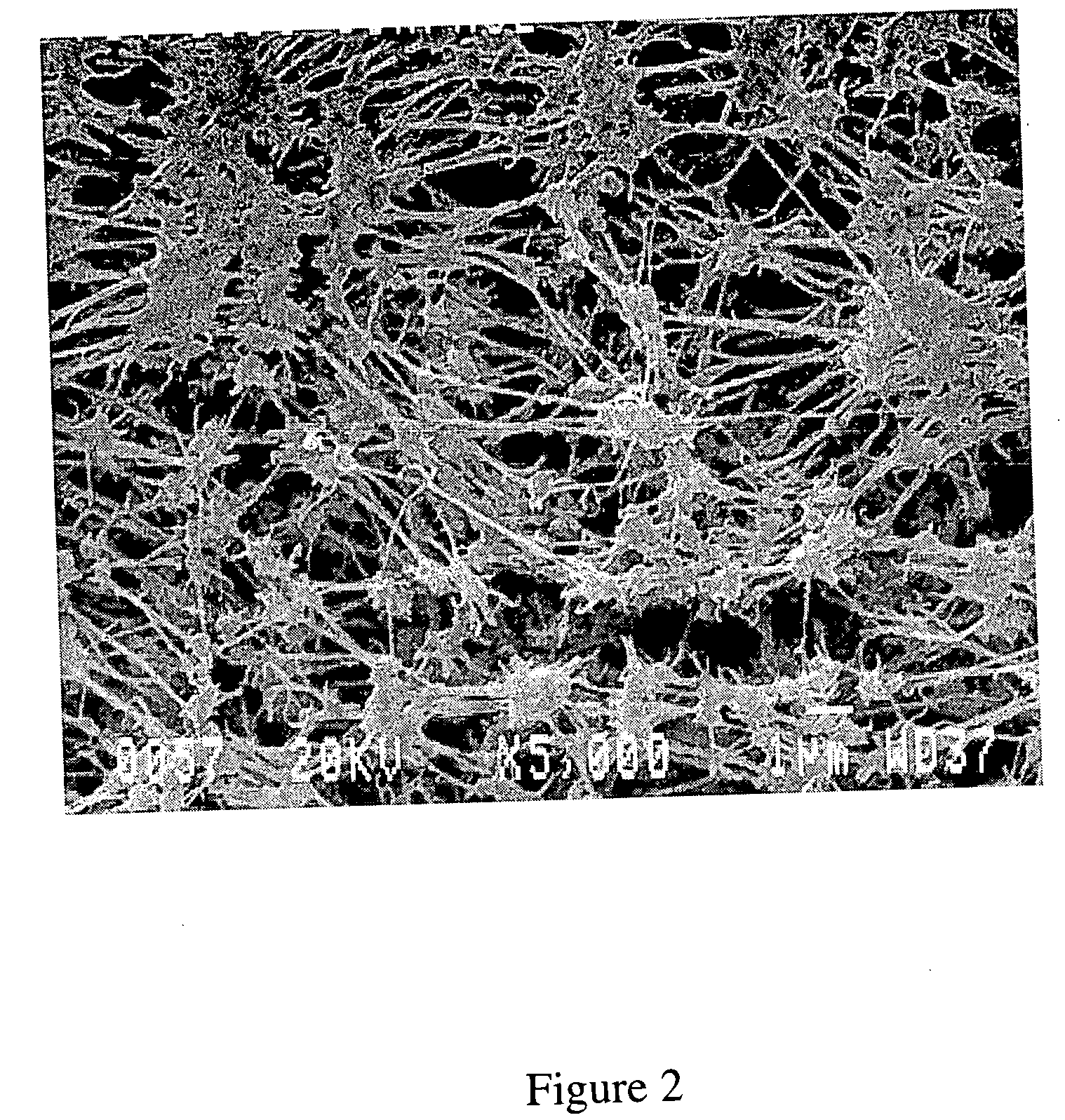
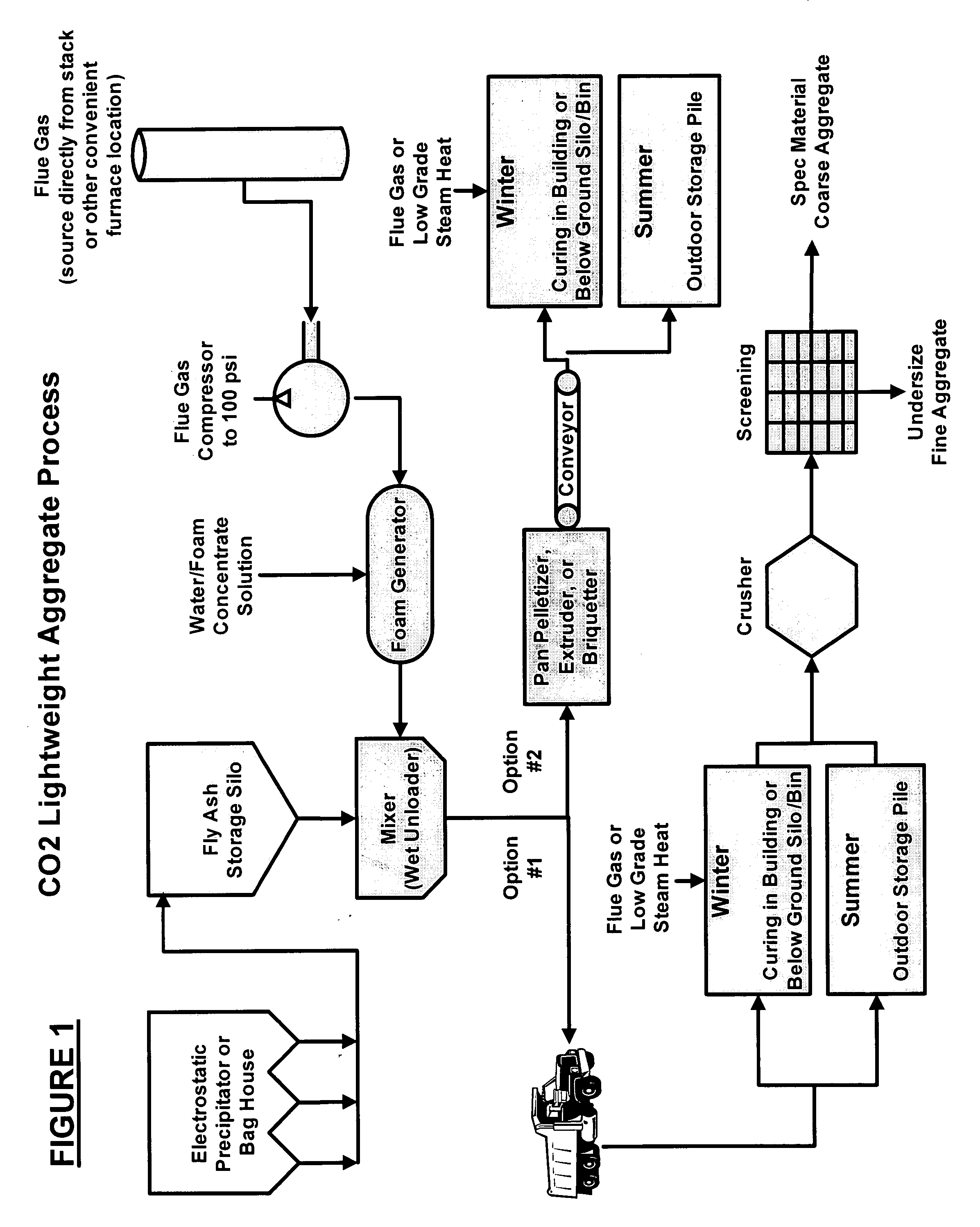
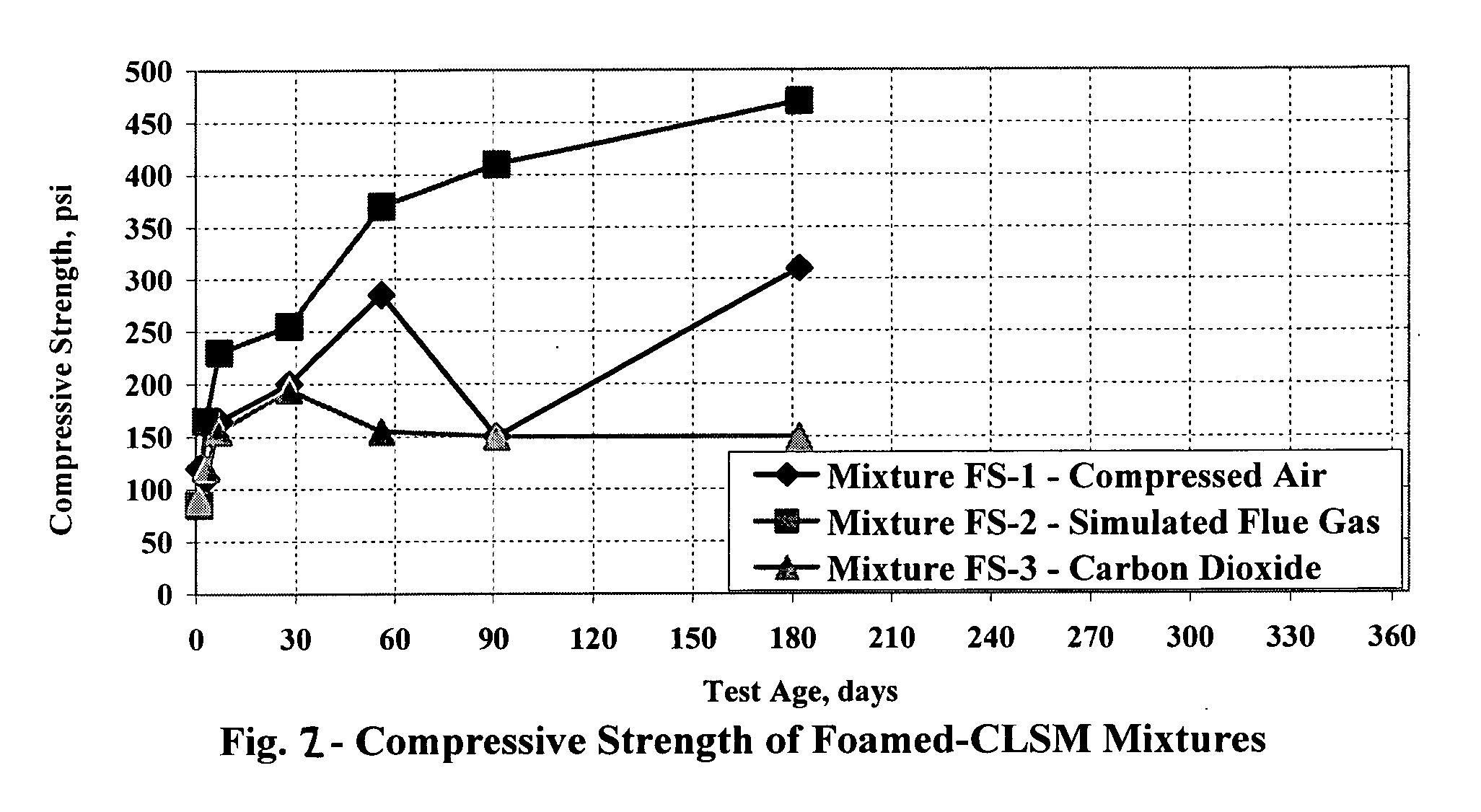
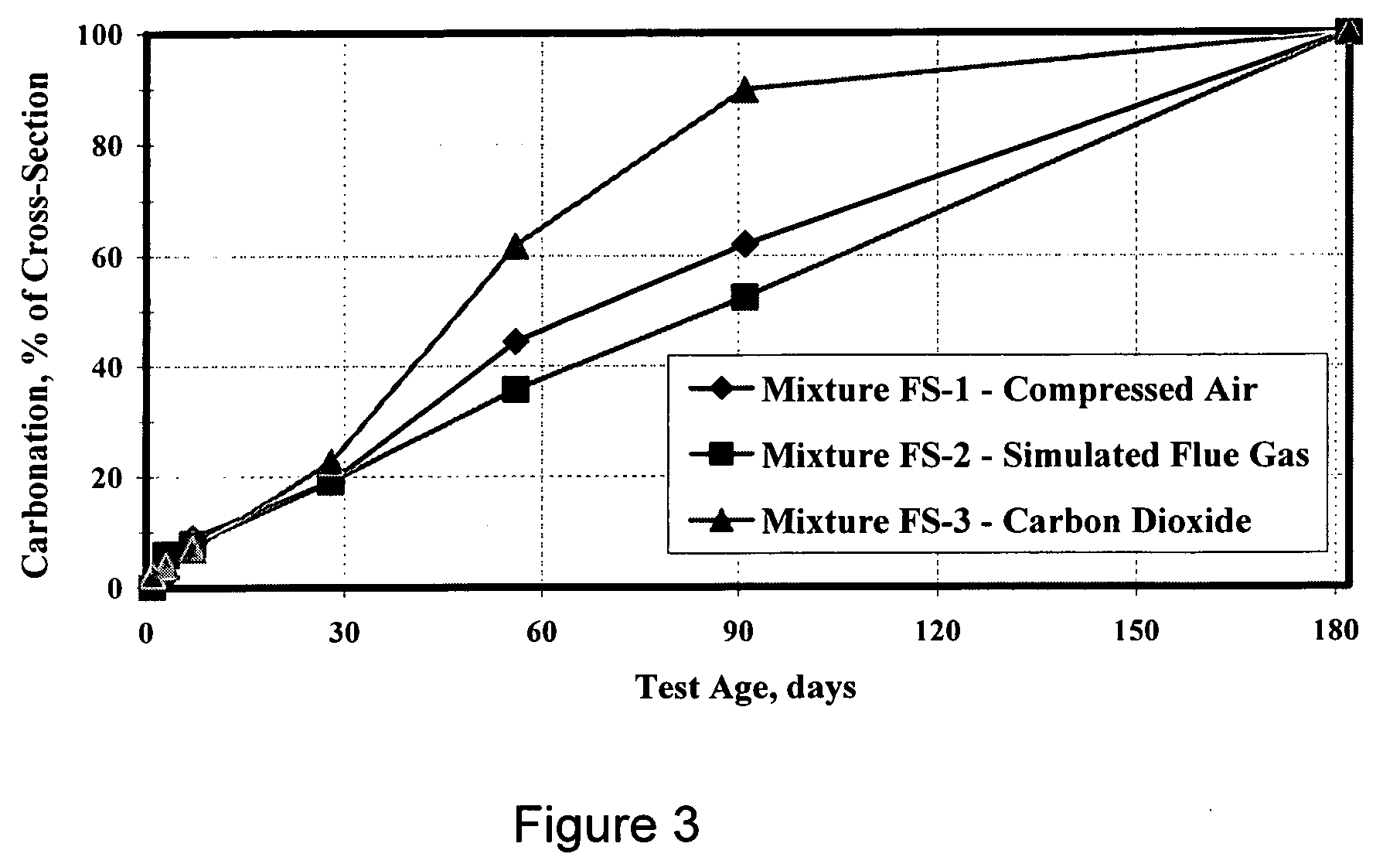
A process for sequestering carbon dioxide from the flue gas emitted from a combustion chamber is disclosed. In the process, a foam including a foaming agent and the flue gas is formed, and the foam is added to a mixture including a cementitious material (e.g., fly ash) and water to form a foamed mixture. Thereafter, the foamed mixture is allowed to set, preferably to a controlled low-strength material having a compressive strength of 1200 psi or less. The carbon dioxide in the flue gas and waste heat reacts with hydration products in the controlled low-strength material to increase strength. In this process, the carbon dioxide is sequestered. The CLSM can be crushed or pelletized to form a lightweight aggregate with properties similar to the naturally occurring mineral, pumice.
Owner:WISCONSIN ELECTRIC POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com