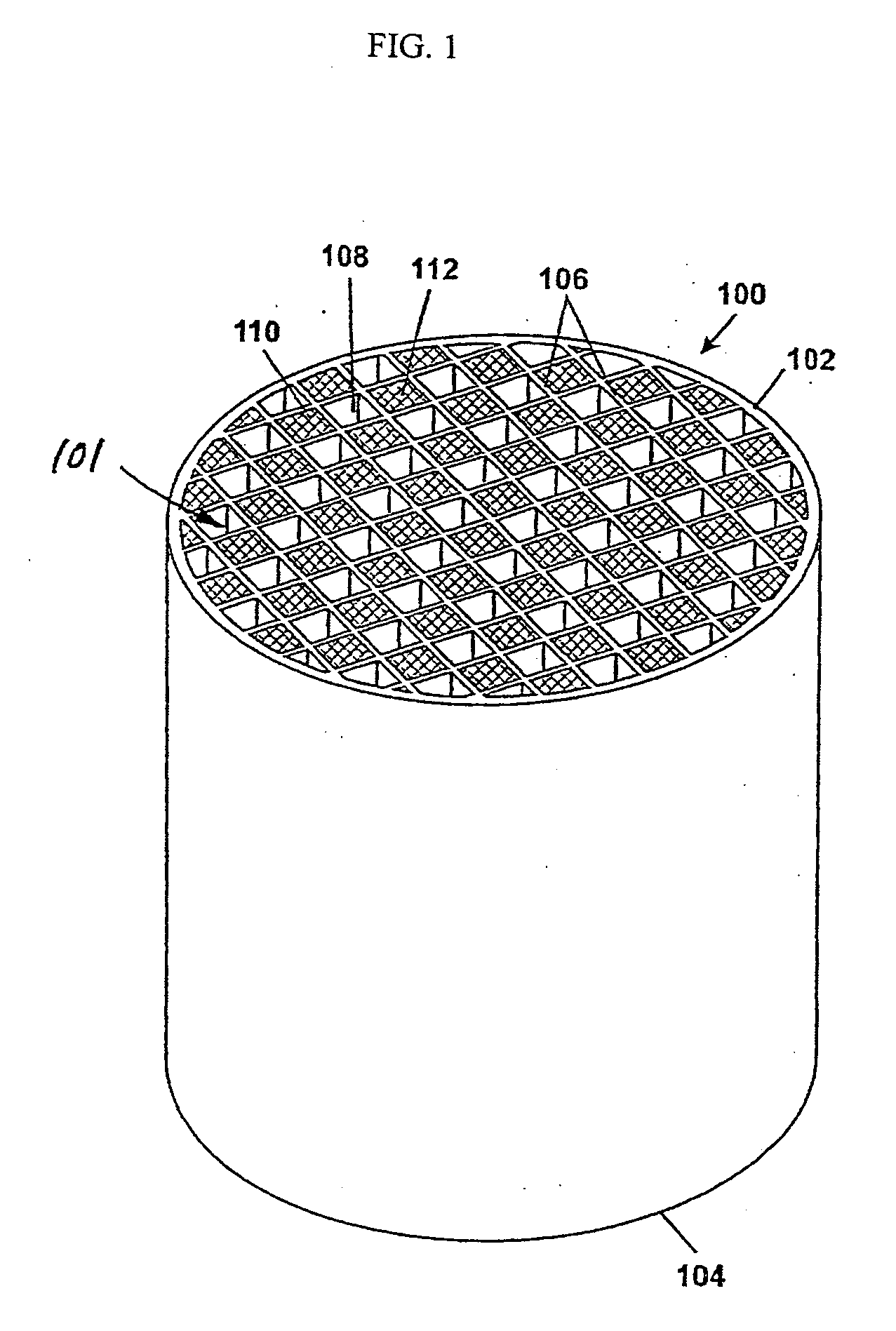
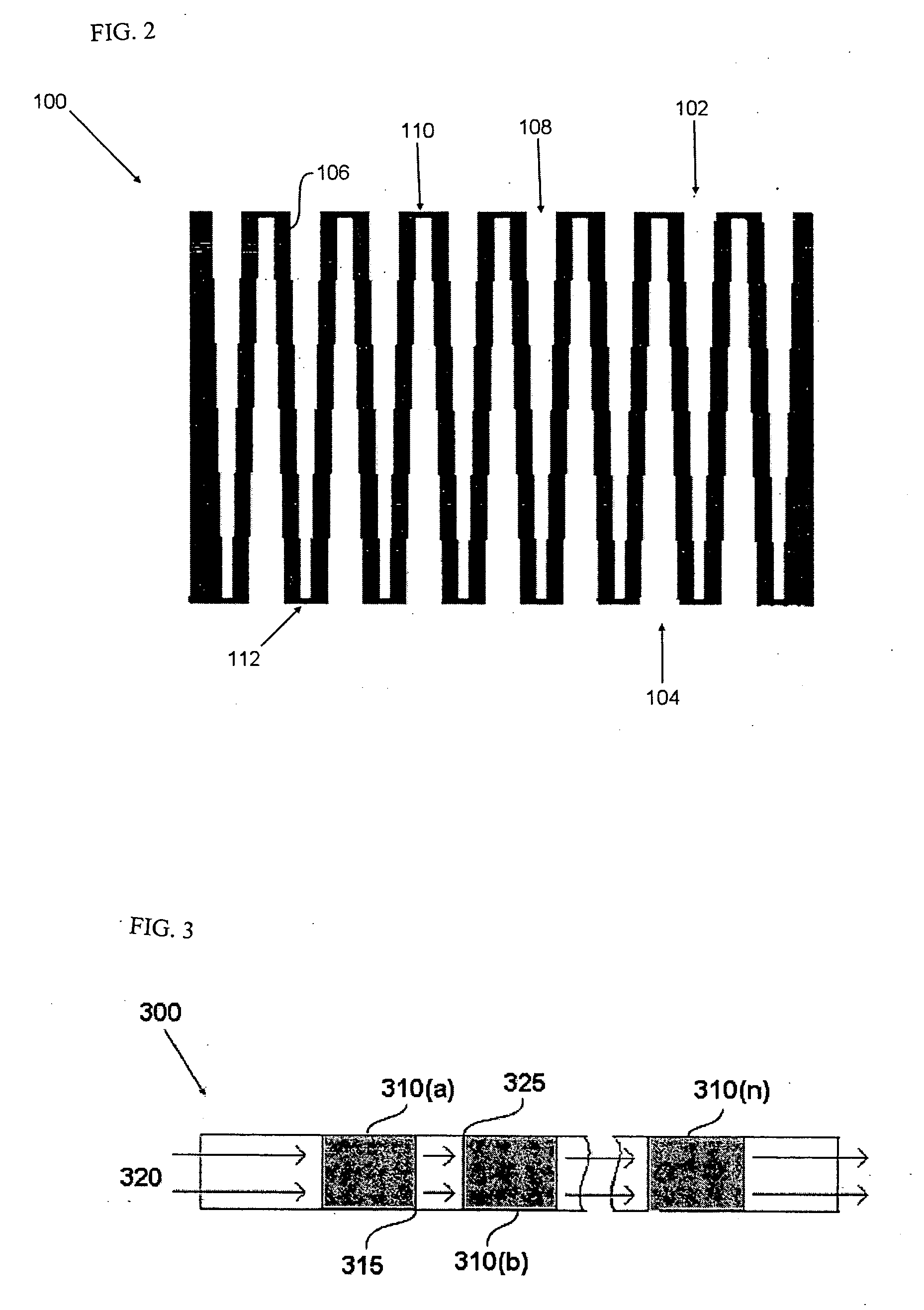
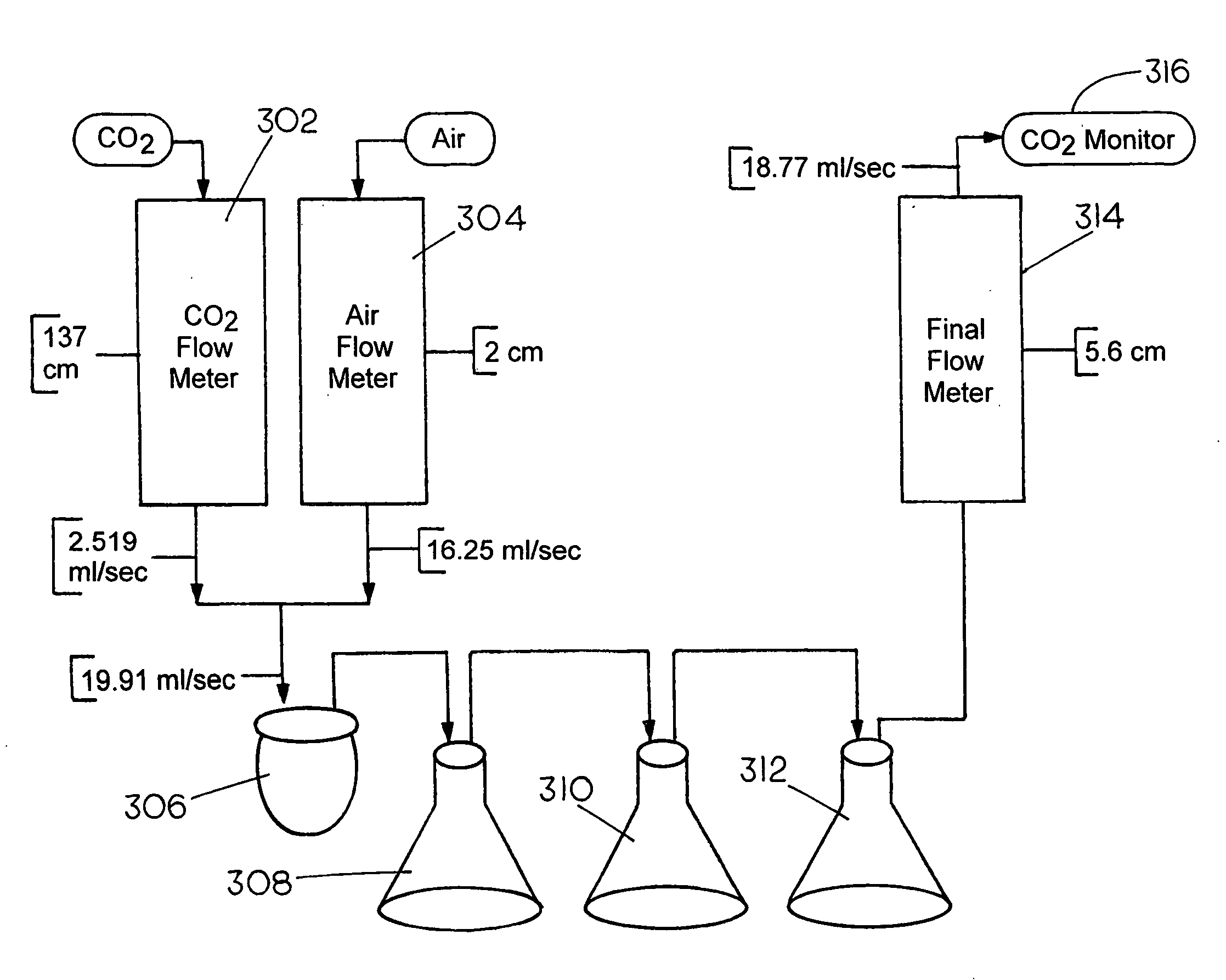
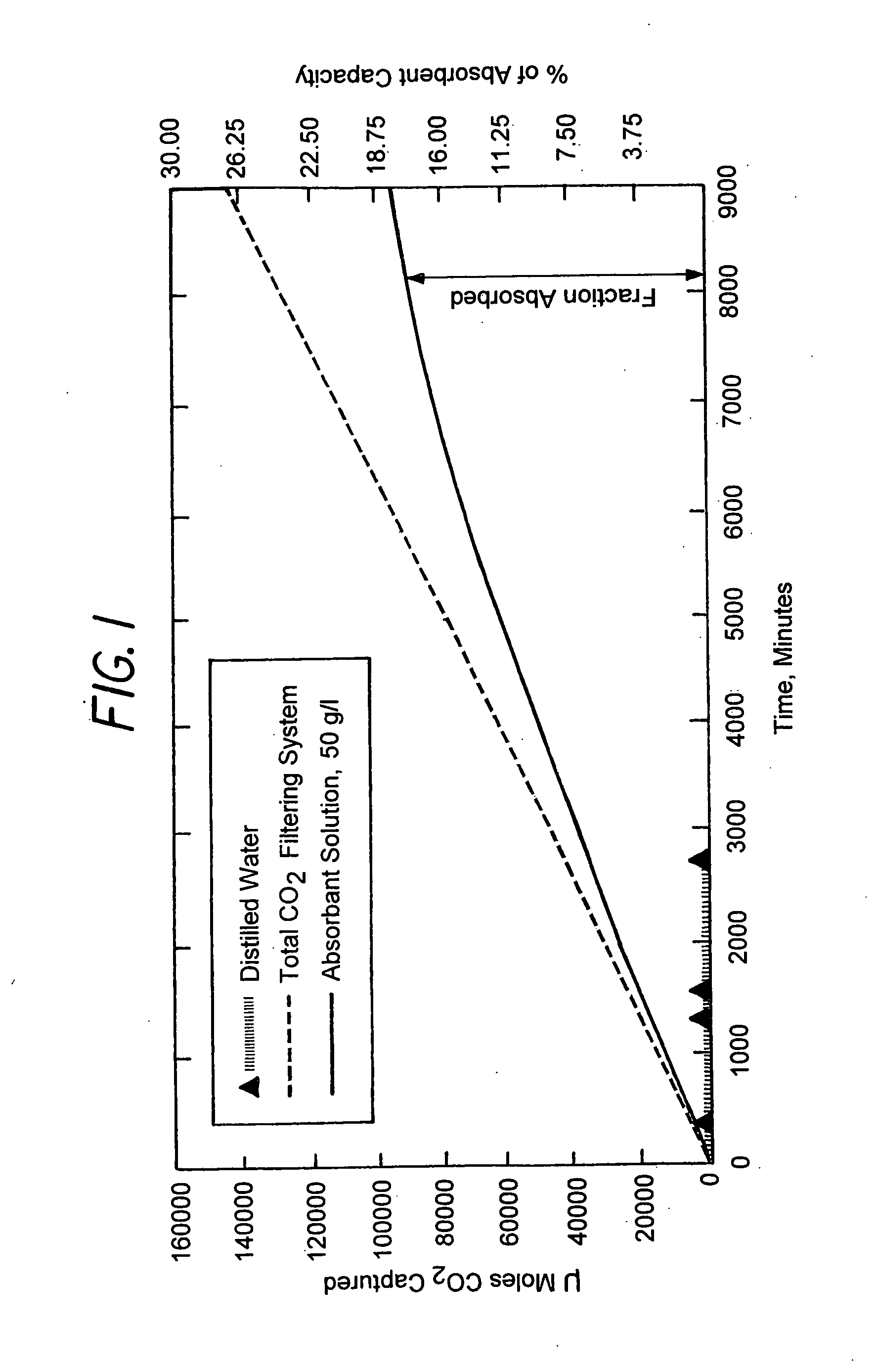
Patents
Literature
23298 results about "Flue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A flue is a duct, pipe, or opening in a chimney for conveying exhaust gases from a fireplace, furnace, water heater, boiler, or generator to the outdoors. Historically the term flue meant the chimney itself. In the United States, they are also known as vents for boilers and as breeching for water heaters and modern furnaces. They usually operate by buoyancy, also known as the stack effect, or the combustion products may be 'induced' via a blower. As combustion products contain carbon monoxide and other dangerous compounds, proper 'draft', and admission of replacement air is imperative. Building codes, and other standards, regulate their materials, design, and installation.
Tobacco processing
InactiveUS6895974B2Lower Level RequirementsInhibition formationTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentTobacco-specific nitrosaminesEngineering
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
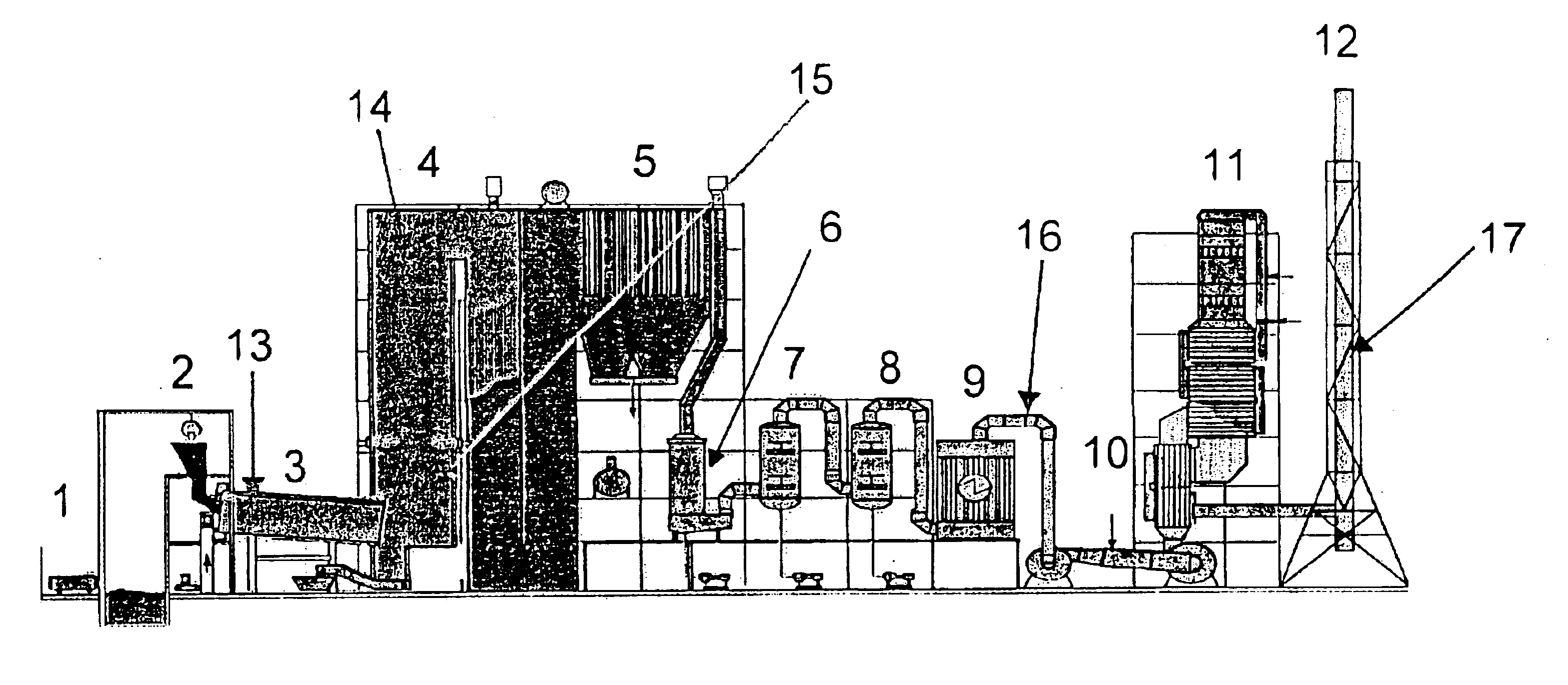
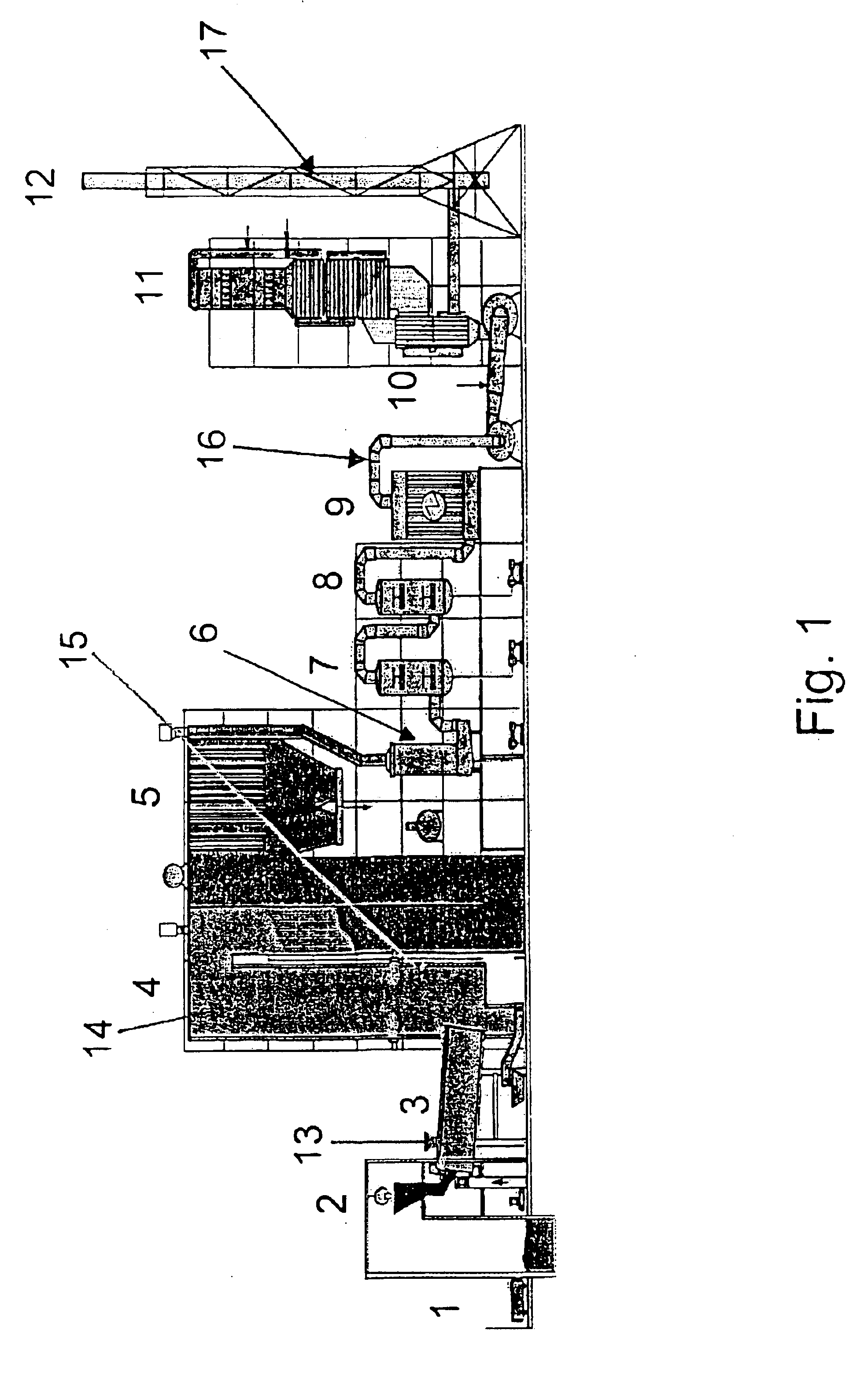
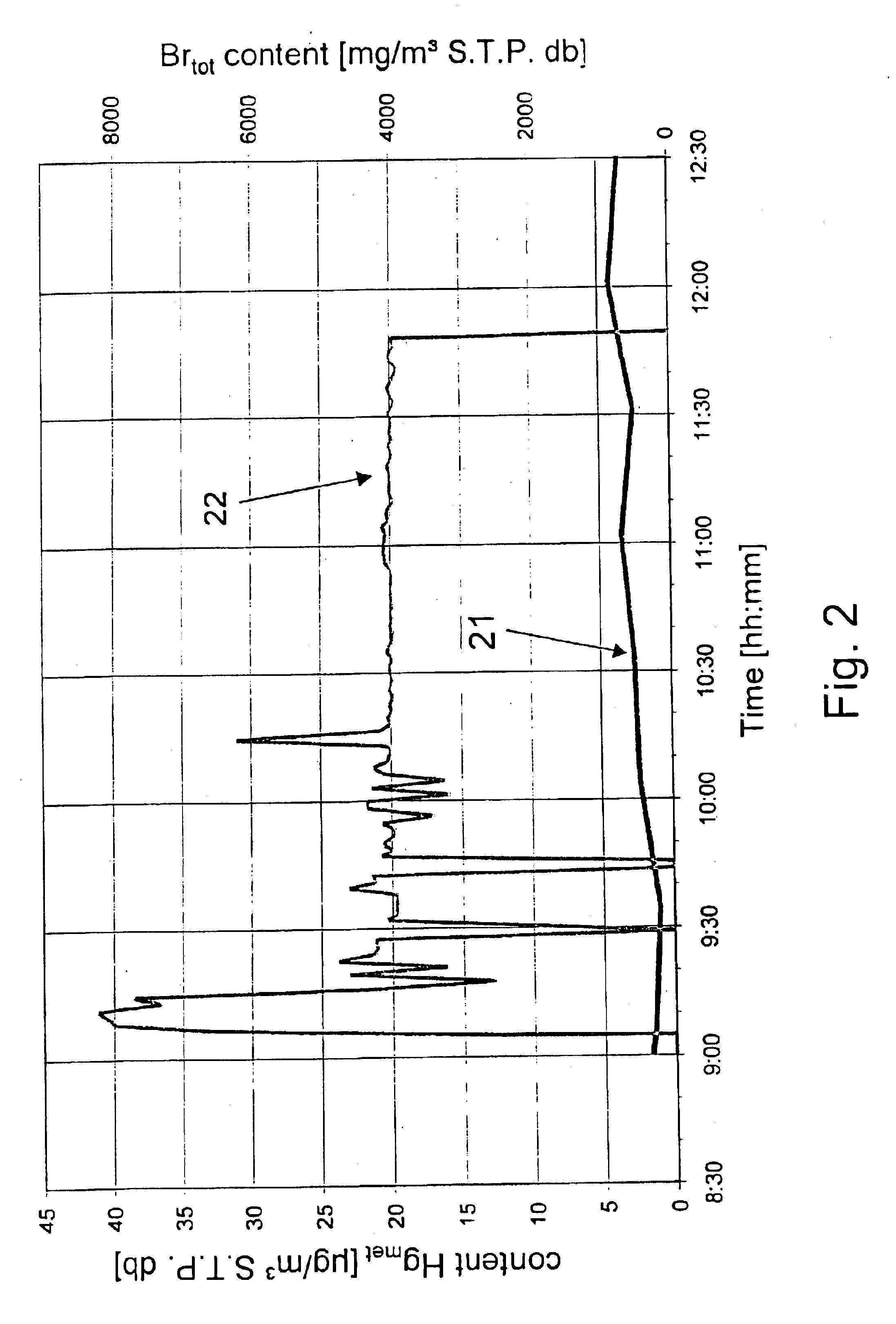
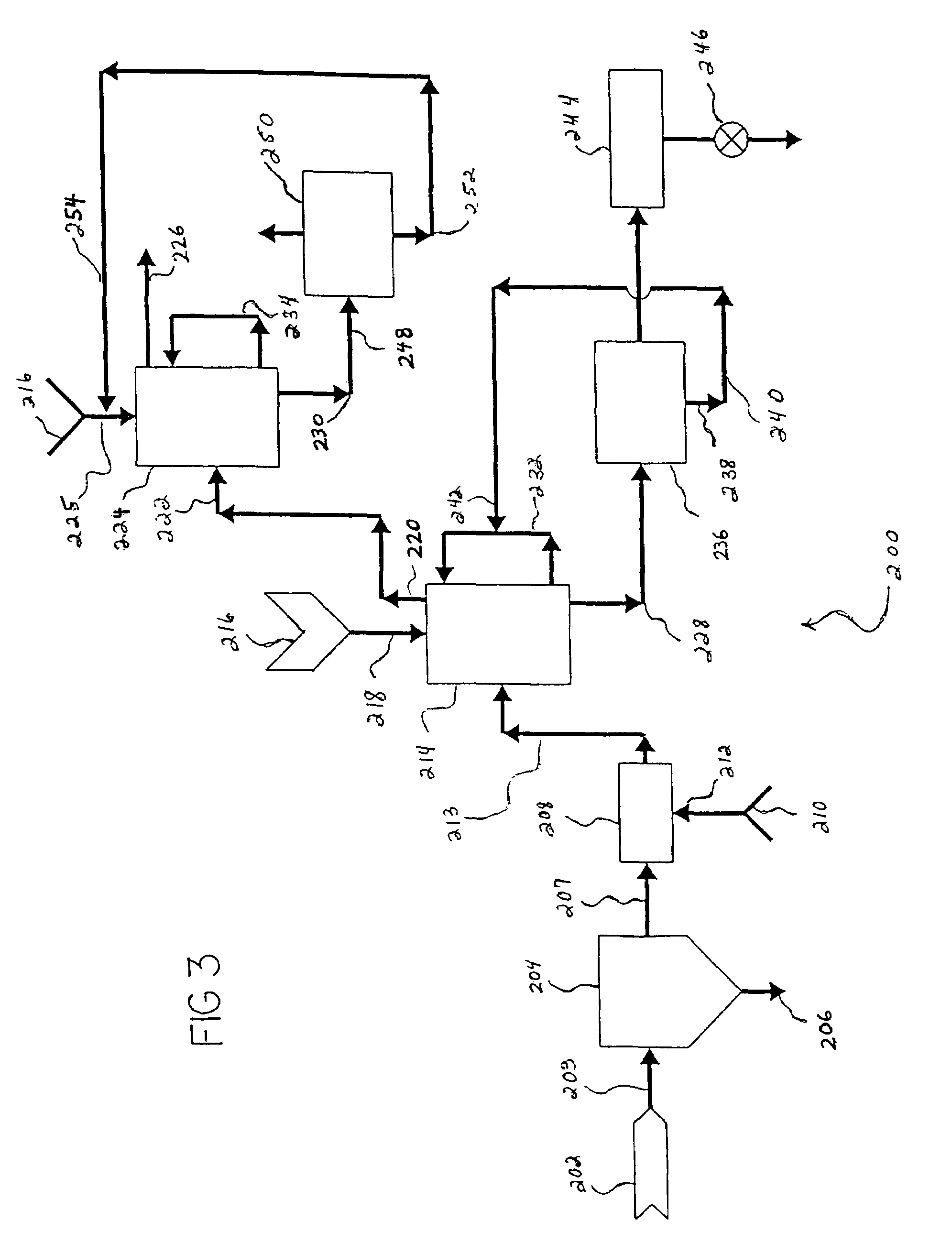
Process for removing mercury from flue gases
InactiveUS6878358B2Reduce operating costsSmall amountUsing liquid separation agentChemical/physical processesPower stationCombustion
Process for removing mercury from flue gases of high-temperature plants, in particular power stations and waste incineration plants in which a bromine compound is fed to the multistage furnace and / or the flue gas in a plant section downstream of the furnace, the temperature during contact of the bromine compound with the flue gas being at least 500° C., preferably at least 800° C. The combustion is carried out in the presence of a sulphur compound, in particular sulphur dioxide. Subsequently to the furnace, the flue gas is subjected to an optional multistage cleanup for removing mercury from the flue gas, which cleanup comprises a wet scrubber and / or a dry cleanup.
Owner:BROMERC
Enhanced mercury control in coal-fired power plants
InactiveUS6808692B2Easy to captureEliminate dischargeChloride preparationUsing liquid separation agentPulverized fuel ashElemental mercury
A method of treating a coal combustion flue gas, which includes injecting a molecular halogen or thermolabile molecular halogen precursor, such as calcium hypochlorite, able to decompose to form molecular halogen at flue gas temperature. The molecular halogen converts elemental mercury to mercuric halide, which is adsorbable by alkaline solids such as subbituminous or lignite coal ash, alkali fused bituminous coal ash, and dry flue gas desulphurization solids, capturable in whole or part by electrostatic precipitators (ESPs), baghouses (BHs), and fabric filters (FFs), with or without subsequent adsorption by a liquid such as a flue gas desulphurization scrubbing liquor.
Owner:HAZELMERE RES
Thief process for the removal of mercury from flue gas
InactiveUS6521021B1Low costQuench oxidationGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentParticulatesCombustion chamber
A system and method for removing mercury from the flue gas of a coal-fired power plant is described. Mercury removal is by adsorption onto a thermally activated sorbent produced in-situ at the power plant. To obtain the thermally activated sorbent, a lance (thief) is inserted into a location within the combustion zone of the combustion chamber and extracts a mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas. The semi-combusted coal has adsorptive properties suitable for the removal of elemental and oxidized mercury. The mixture of semi-combusted coal and gas is separated into a stream of gas and semi-combusted coal that has been converted to a stream of thermally activated sorbent. The separated stream of gas is recycled to the combustion chamber. The thermally activated sorbent is injected into the duct work of the power plant at a location downstream from the exit port of the combustion chamber. Mercury within the flue gas contacts and adsorbs onto the thermally activated sorbent. The sorbent-mercury combination is removed from the plant by a particulate collection system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
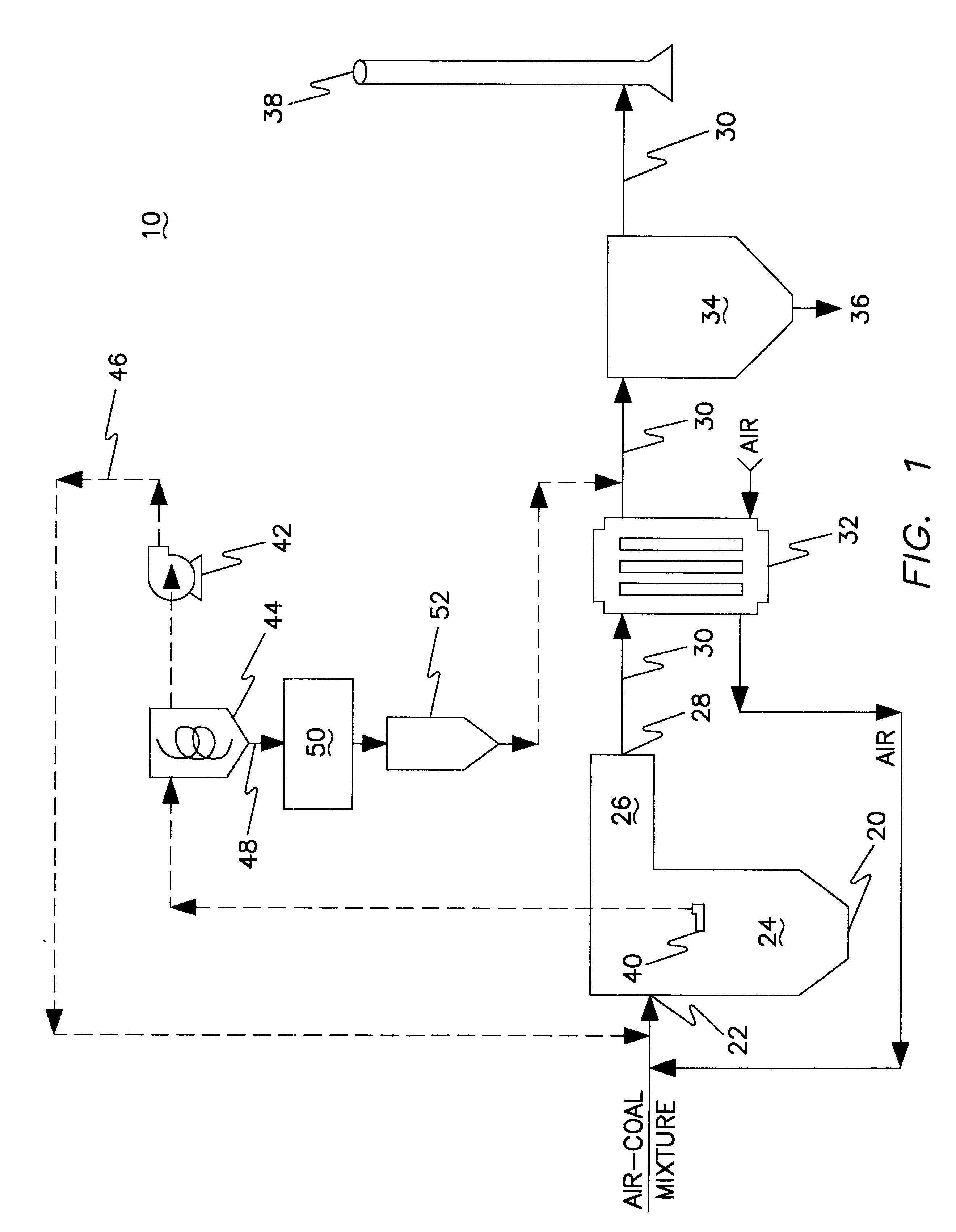
System and method for converting biomass to ethanol via syngas
A method and apparatus for synthesizing ethanol using synthetic routes via synthesis gas are disclosed. A method and apparatus for gasifying biomass, such as biomass, in a steam gasifier that employs a fluidized bed and heating using hot flue gases from the combustion of synthesis gas is described. Methods and apparatus for converting synthesis gas into ethanol are also disclosed, using stepwise catalytic reactions to convert the carbon monoxide and hydrogen into ethanol using catalysts including iridium acetate.
Owner:WOODLAND BIOFUELS
Flue gas mercury control
ActiveUS8080088B1Enhance particulate collectionReducing fly ash resistivityGas treatmentIsotope separationActivated carbonHalogen
An adsorbent composition for removing mercury from a flue gas stream, and a method of its use. The composition is a powdered activated carbon having at least one of a halogen-containing component and an alkaline component dispersed thereon. A flow agent can be composited with the material to maintain flowability in situ.
Owner:SRINIVASACHAR SRIVATS
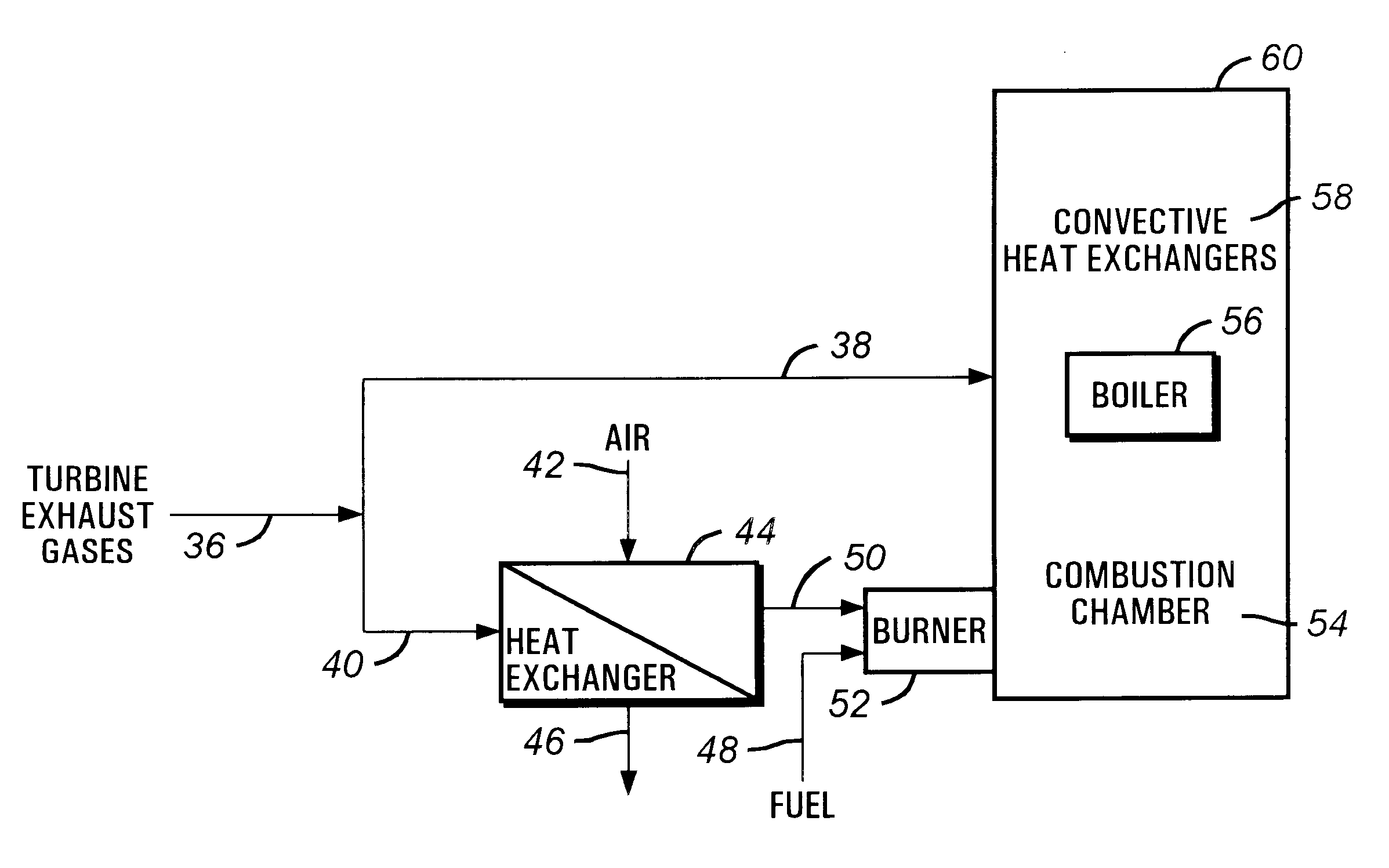
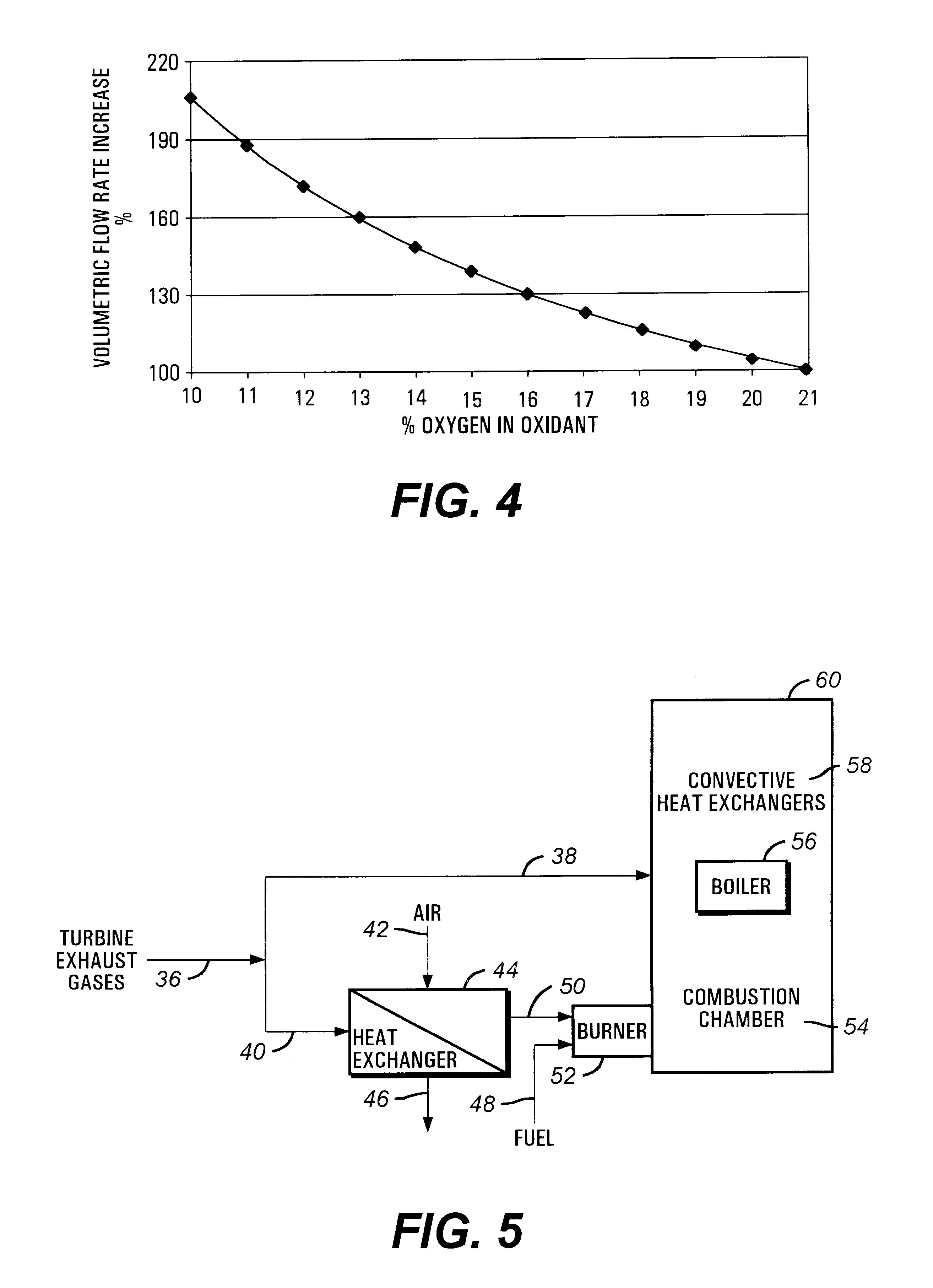
Oxidant control in co-generation installations
InactiveUS6247315B1Steam regenerationIndirect carbon-dioxide mitigationControl system designCogeneration
This invention is related to so-called combined cycle co-generation installations, and it addresses present concerns of the industry. Among these, combustion stability, corrosion (due to large water content in the flue gases), large heat transfer areas, and the like. In some embodiments, an additional heat exchanger is added to heat combustion air with a portion of the exhaust gases resulting from an engine, preferably a gas turbine. As a result, the efficiency of the cycle will improve, the oxidant will be enriched by above 50% oxygen, the combustion process will be enhanced, and the dimensions of the boiler may be reduced. It is considered that the combustion air will require between 10% and 80% of the total flue gas volume, more preferably between 20% and 40%. This is the portion of the flue gases sent through the heat exchanger. A control system designed to optimize the flow of the different streams is also presented. Other inventive embodiments forego heat exchanges in lieu of precise control of two flows of exhaust gas, with preferred addition of additional oxidant to the boiler bumers.
Owner:LAIR LIQUIDE SA POUR LETUDE & LEXPLOITATION DES PROCEDES GEORGES CLAUDE +1
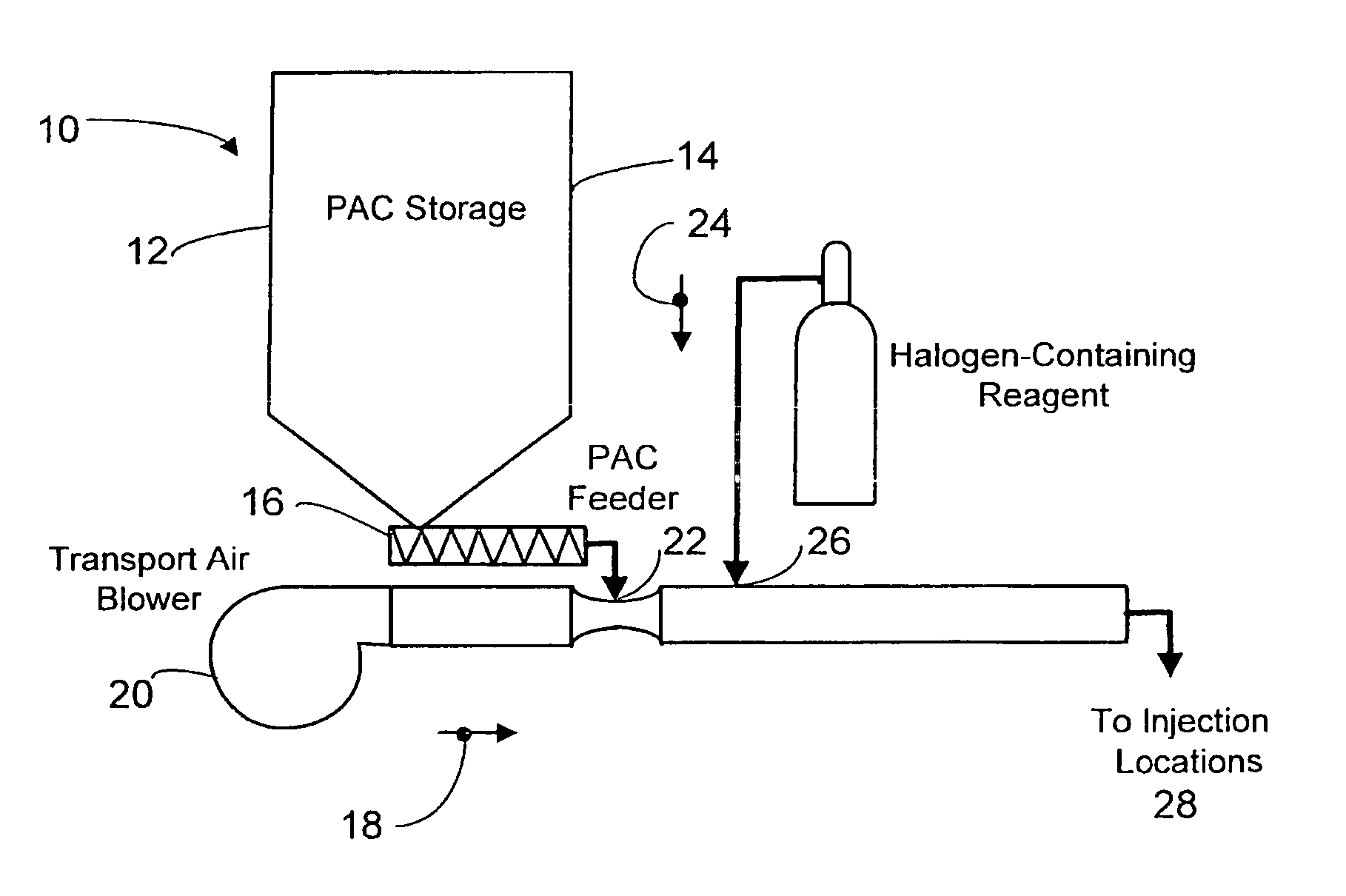
Dynamic halogenation of sorbents for the removal of mercury from flue gases
InactiveUS20070180990A1Efficient ConcentrationEasy to captureGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentHalogenSorbent
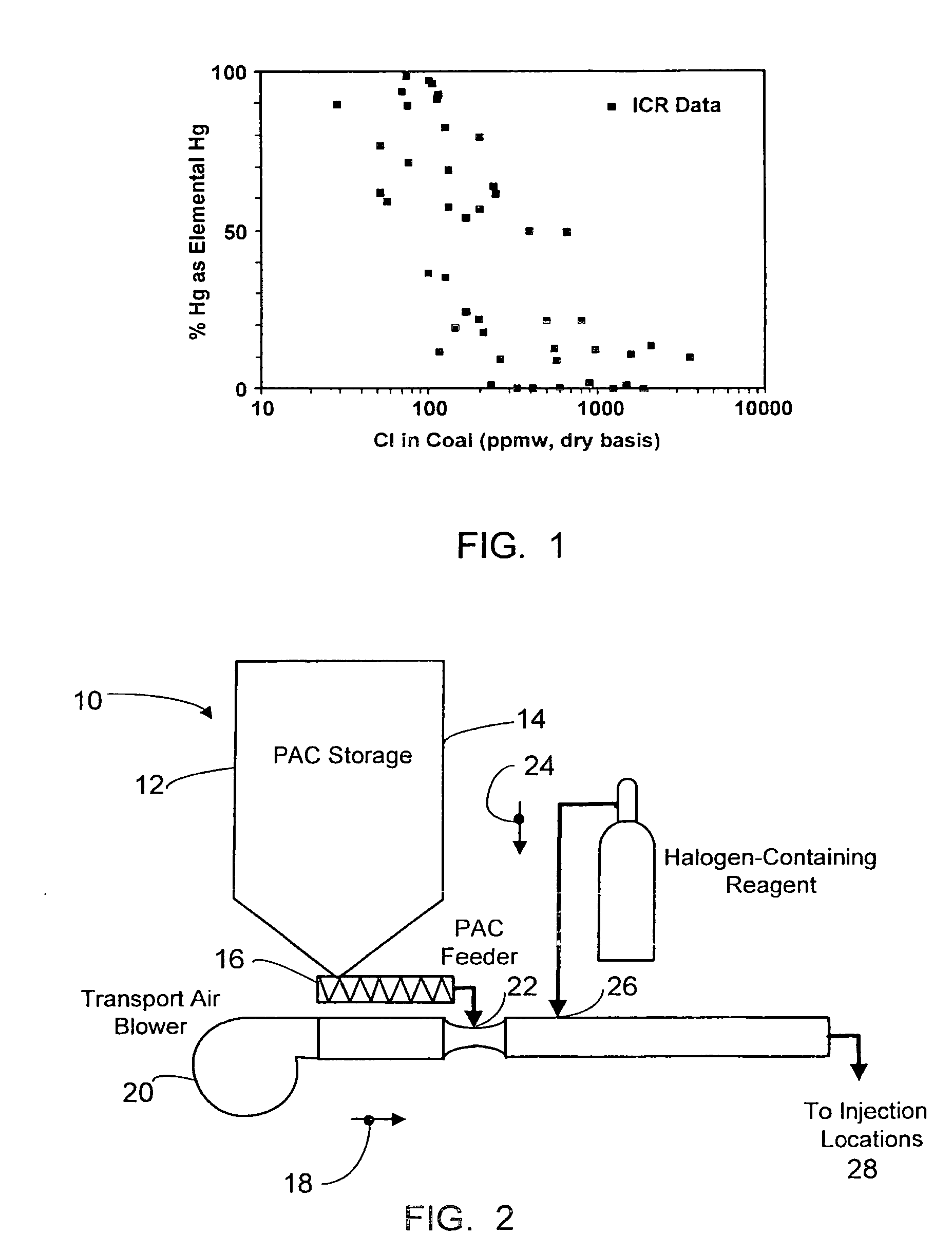
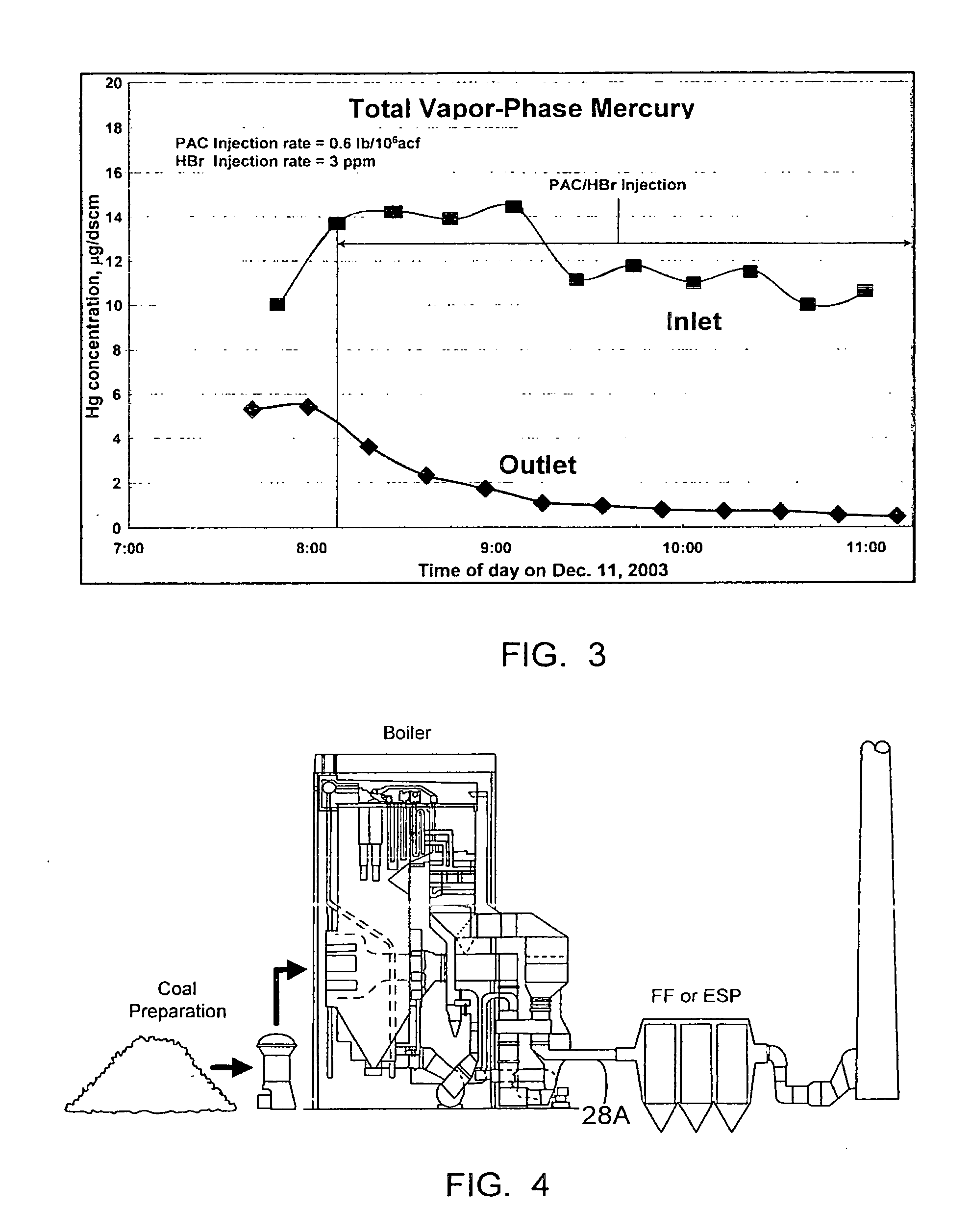
A halogen-containing gas is injected into a flowing transport air / sorbent stream at a point close to the point where the sorbent and transport air first mix to maximize the residence time available for the halogen-containing compound to be adsorbed onto the sorbent surface prior to the sorbent being injected into a flue gas containing mercury. This process maximizes the benefit and utilization of the halogen-containing reagent by placing it exactly where it is needed to facilitate elemental mercury removal—on the surface of the sorbent. The sorbent particles with their loading of adsorbed halogen-containing reagent enter the flue gas with a high reactivity for the removal of elemental mercury.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
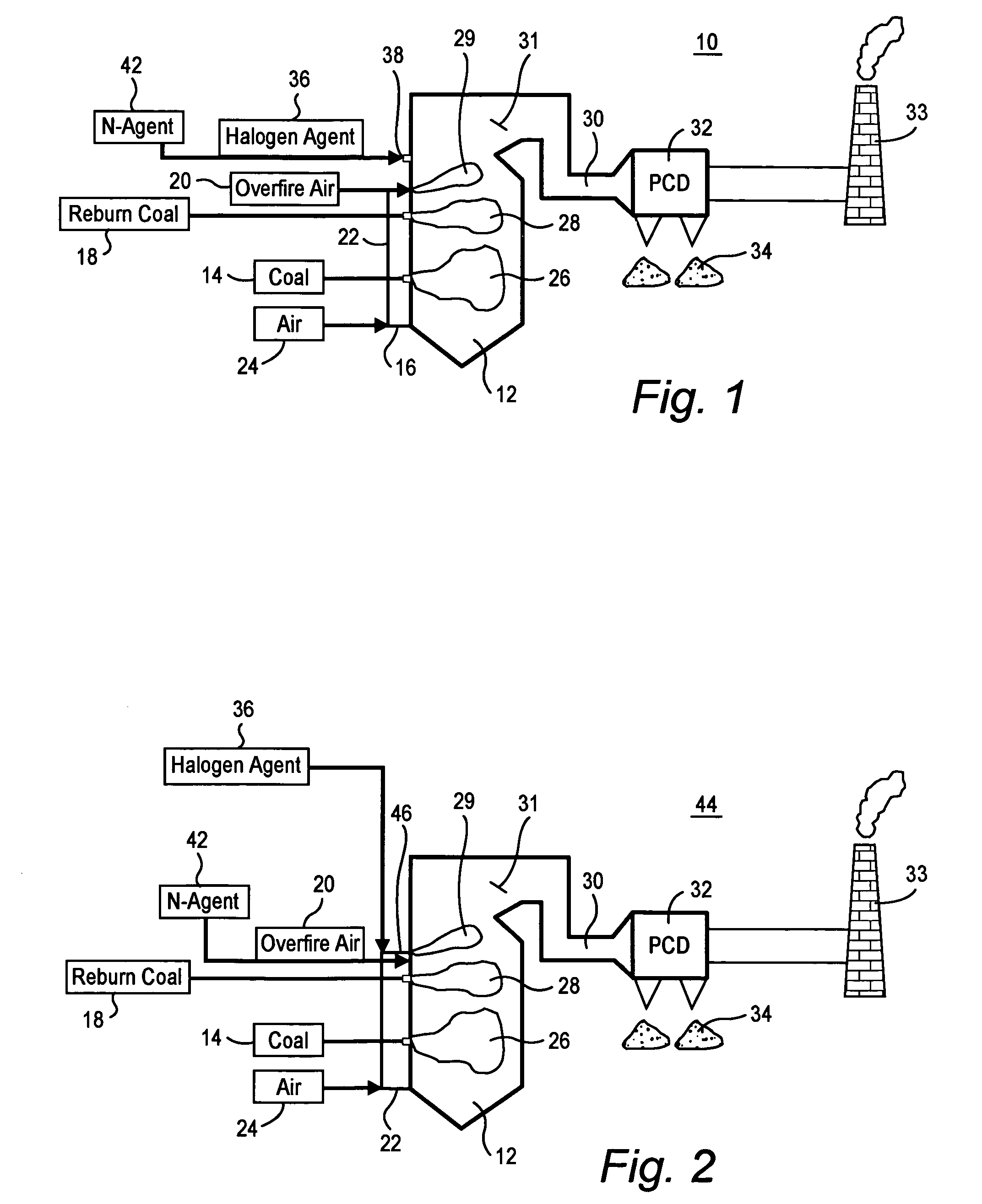
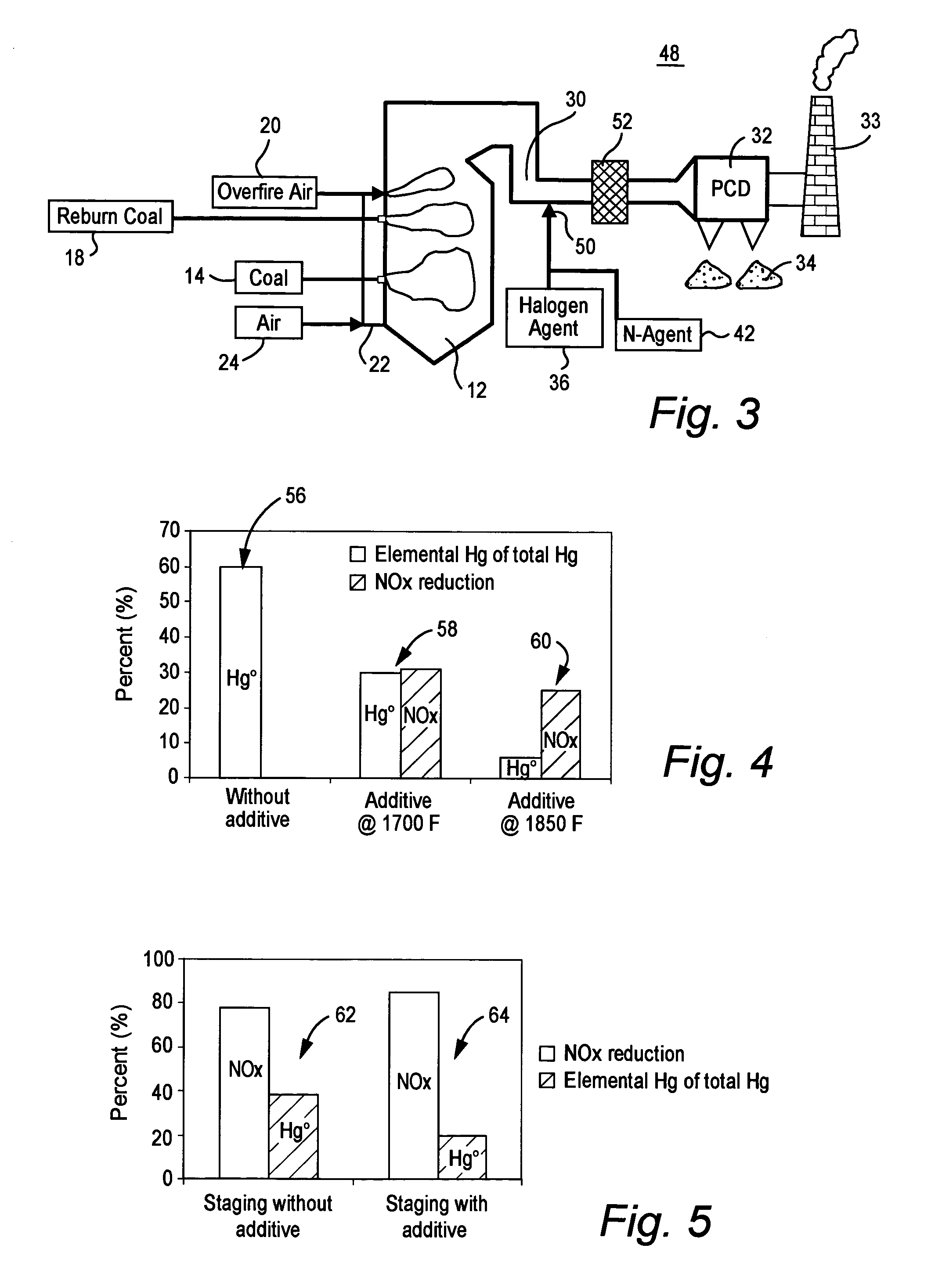
Method for reducing NOX in combustion flue gas using metal-containing additives
InactiveUS6206685B1Improved control deviceSure easyDispersed particle separationSolid fuel combustionAtmospheric airNitric oxide
Various methods for decreasing the amount of nitrogen oxides released to the atmosphere as a component of combustion gas mixtures are provided. The methods specifically provide for the removal of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide (NOx) from gas mixtures emitted from stationary combustion systems. In particular, methods for improving efficiency of nitrogen oxide reduction from combustion systems include injecting metal-containing compounds into the main combustion zone and / or the reburning zone of a combustion system. The metal containing compounds react with active combustion species, and these reactions change radical concentrations and significantly improve NOx conversion to molecular nitrogen. The metal-containing additives can be injected with the main fuel, in the main combustion zone, with secondary or reburning fuel addition, or at several locations in the main combustion zone and reburning zone. Optionally, nitrogenous reducing agents and / or overfire air can be injected downstream to further increase NOx reduction.
Owner:GE ENERGY & ENVIRONMENTAL RES
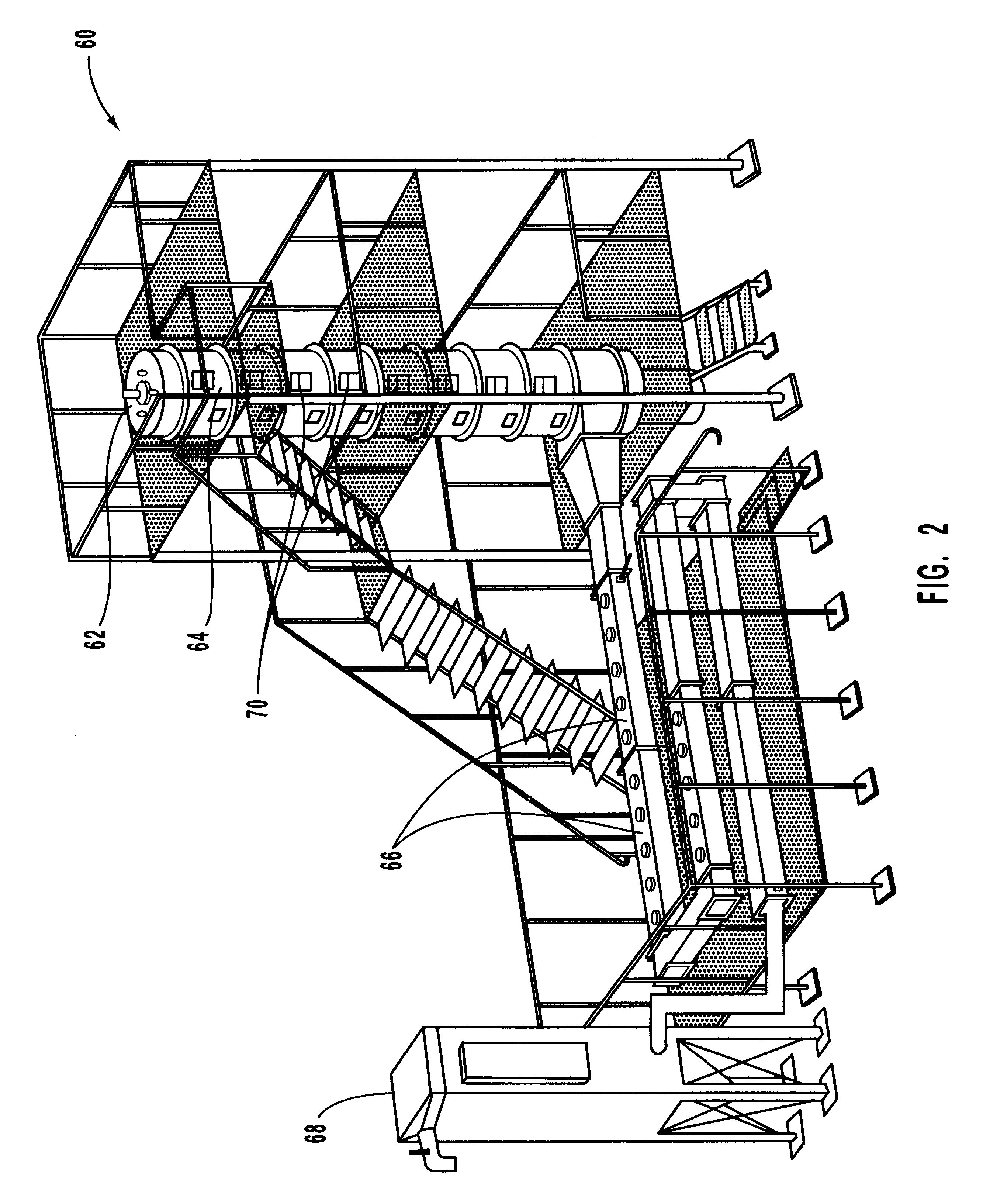
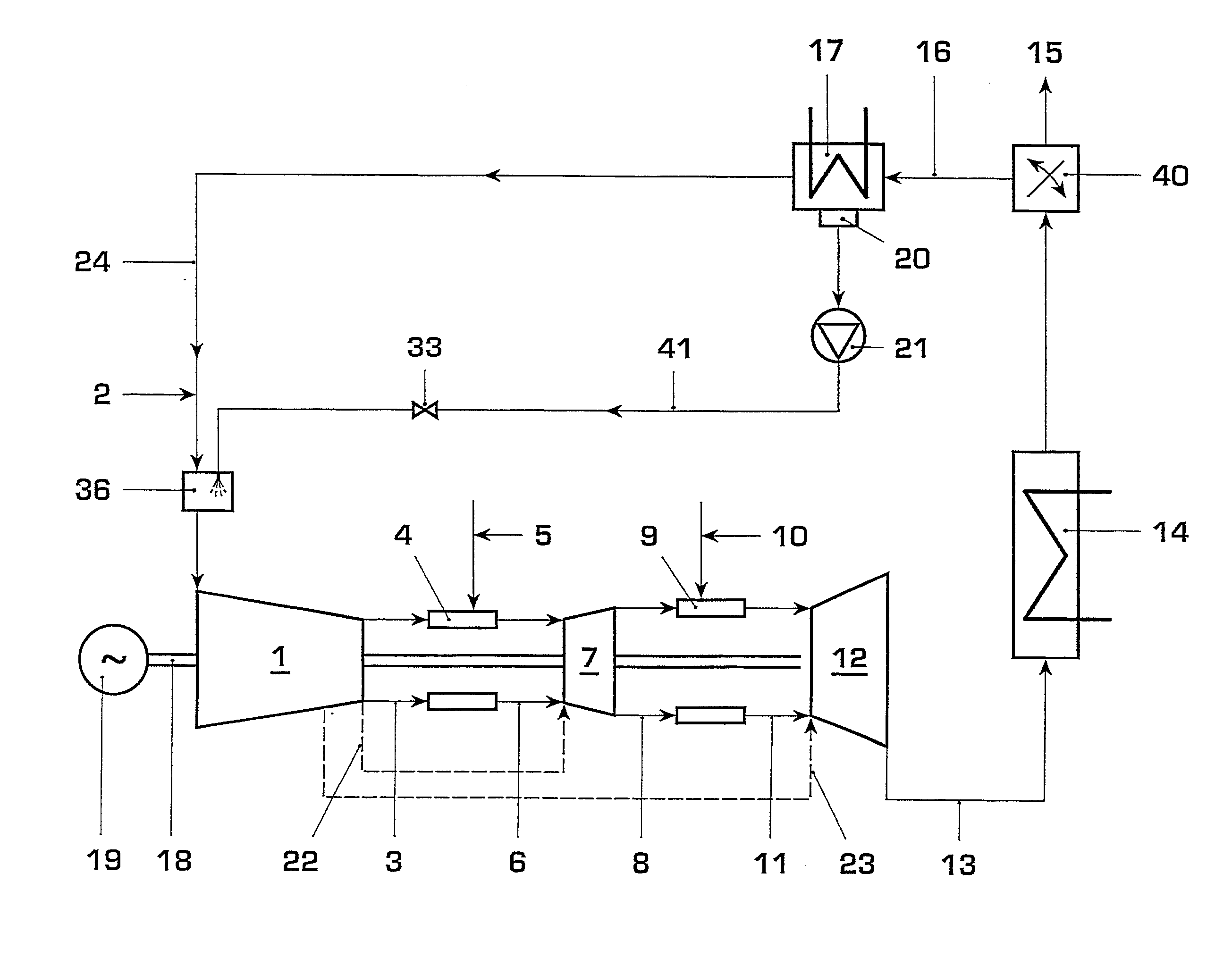
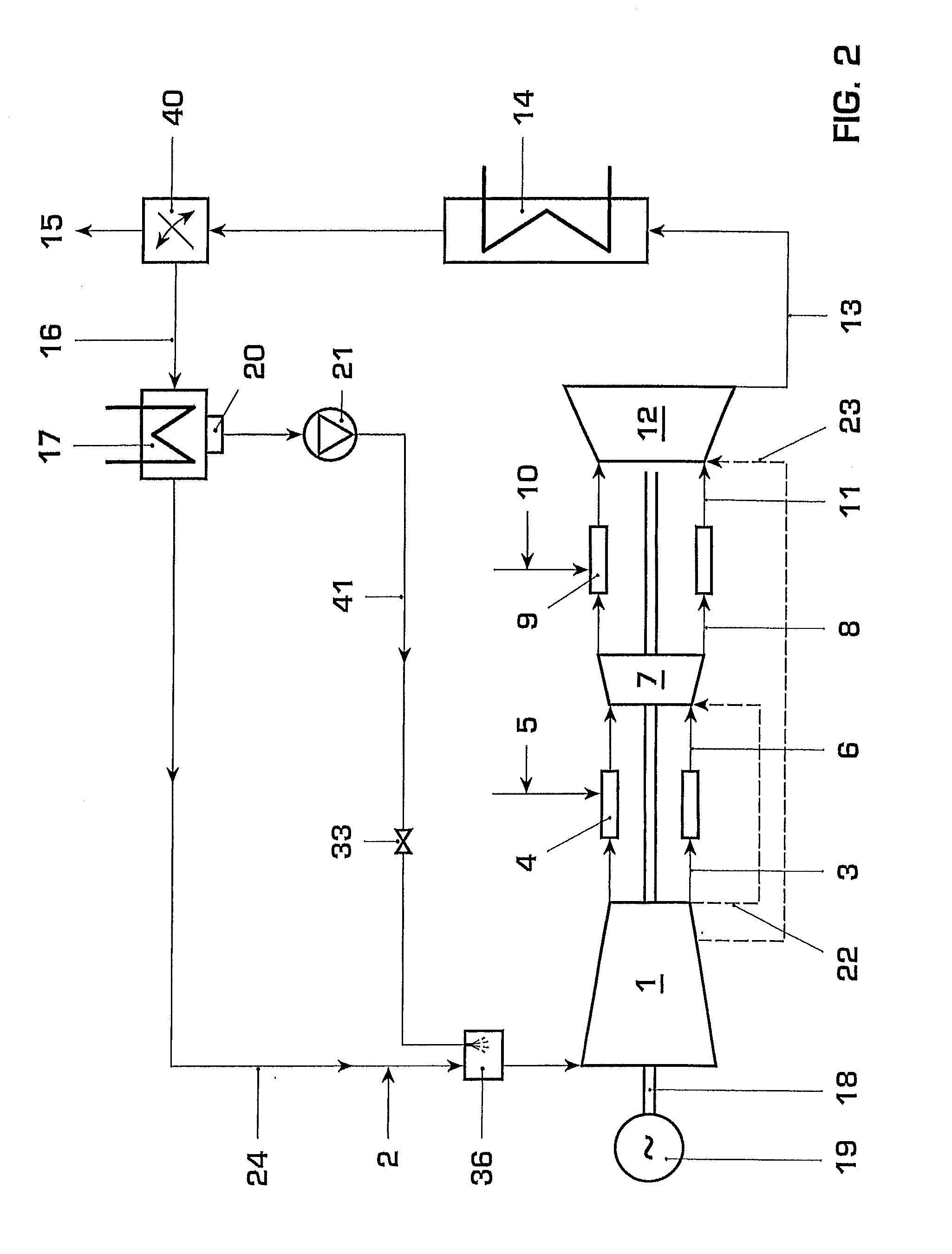
Gas Turbine Installation with Flue Gas Recirculation
A method and installation are disclosed which can, for example, provide for reliable, low-Nox-emission operation of a gas turbine installation with hydrogen-rich fuel gas. An exemplary gas turbine installation includes an arrangement for flue gas recirculation into a compressor inlet and for fuel gas dilution. Oxygen content in combustion air can be reduced by recirculation of recooled flue gas, and the fuel gas can be diluted with compressed flue gas. The oxygen reduction in the combustion air can lead to minimum residual oxygen in the flue gas which can be used for fuel gas dilution. As a result of the flue gas recirculation, water content in the combustion air can be increased by feedback of the water which results as a combustion product. The oxygen reduction, increased water content, and fuel dilution can reduce the flame velocity of hydrogen-rich fuel gases and enable a robust, reliable and low-emission combustion.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
Sorbents for the oxidation and removal of mercury
ActiveUS20060048646A1Reduce the amount requiredHigh activityGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbonHalogen
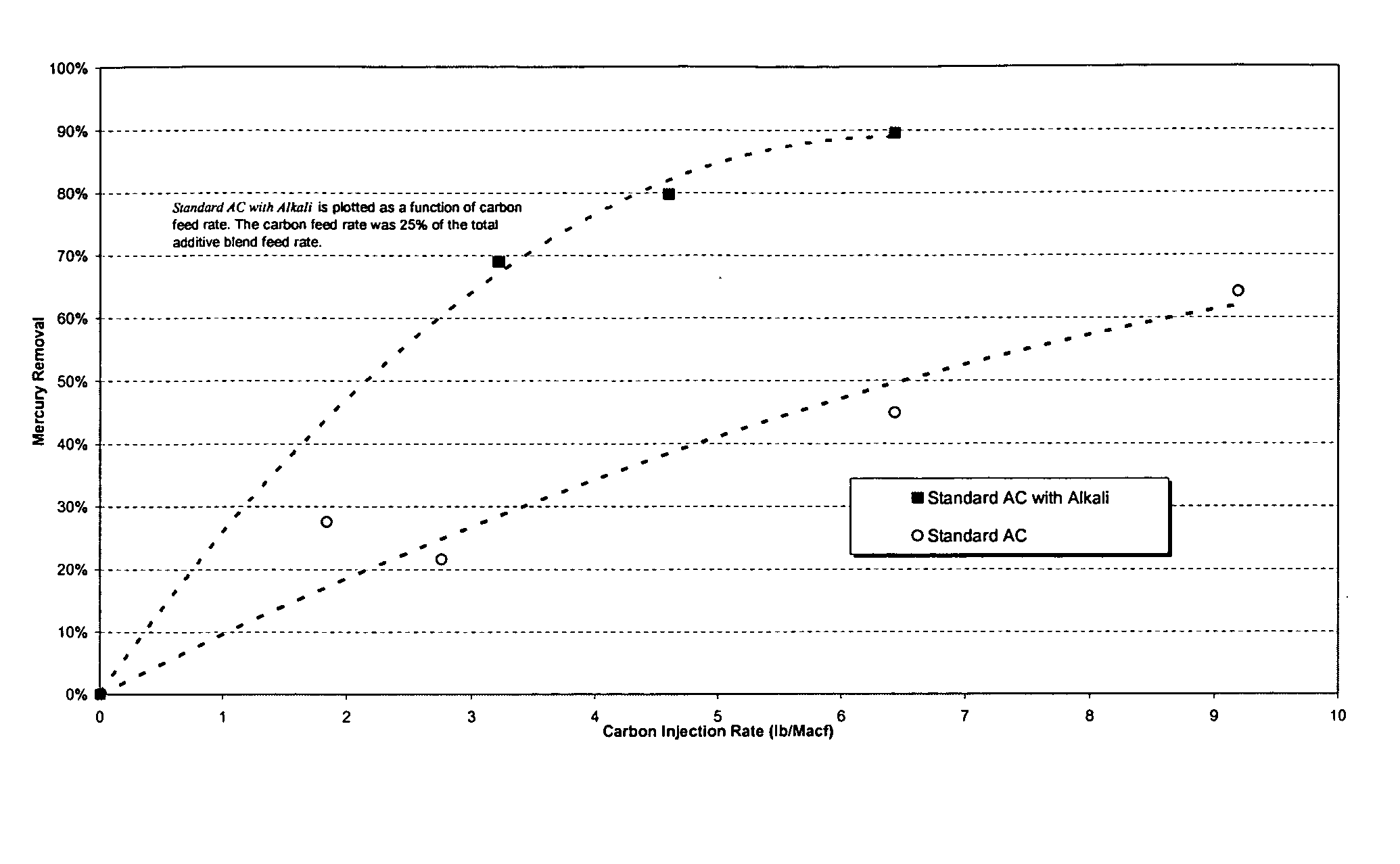
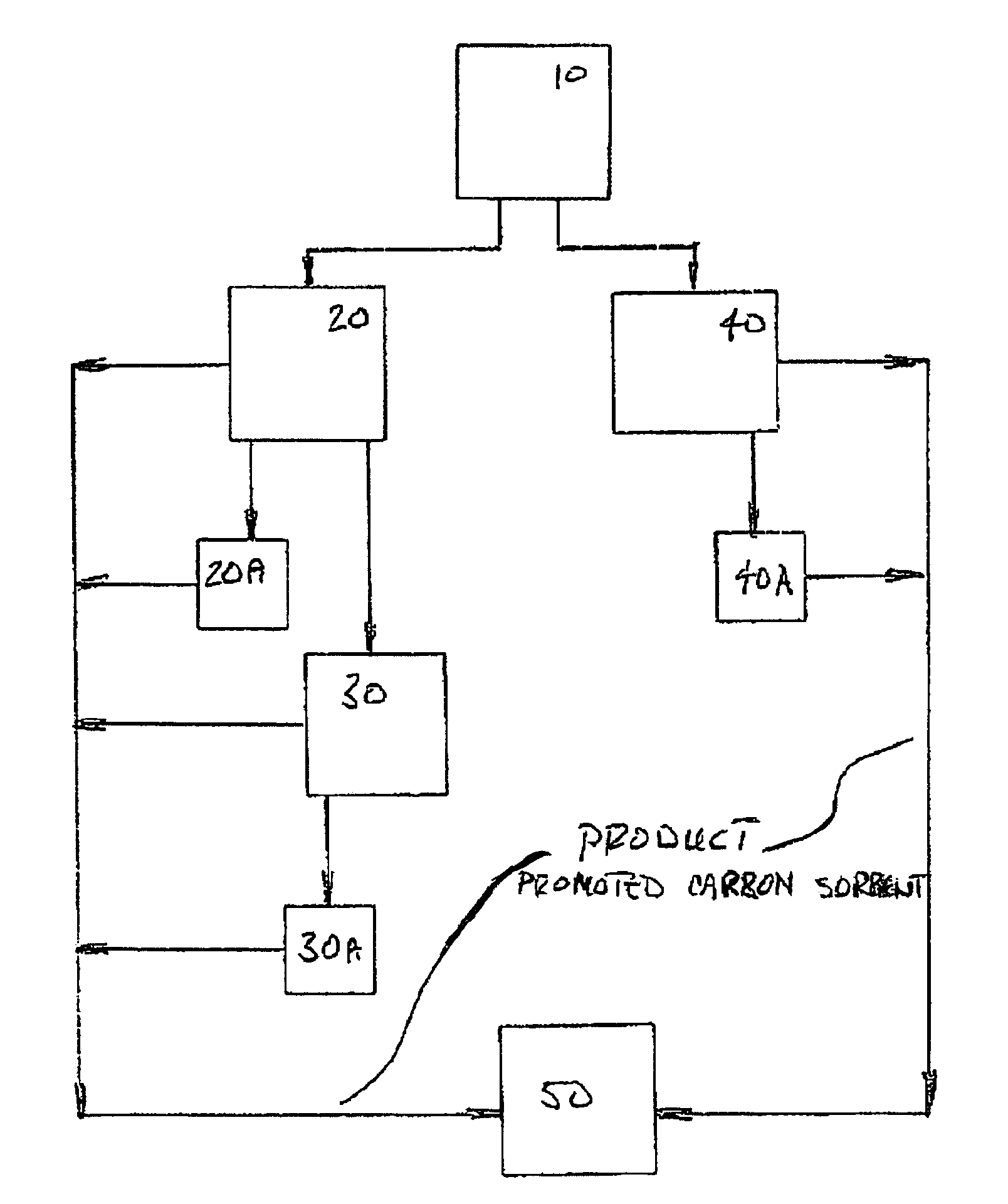
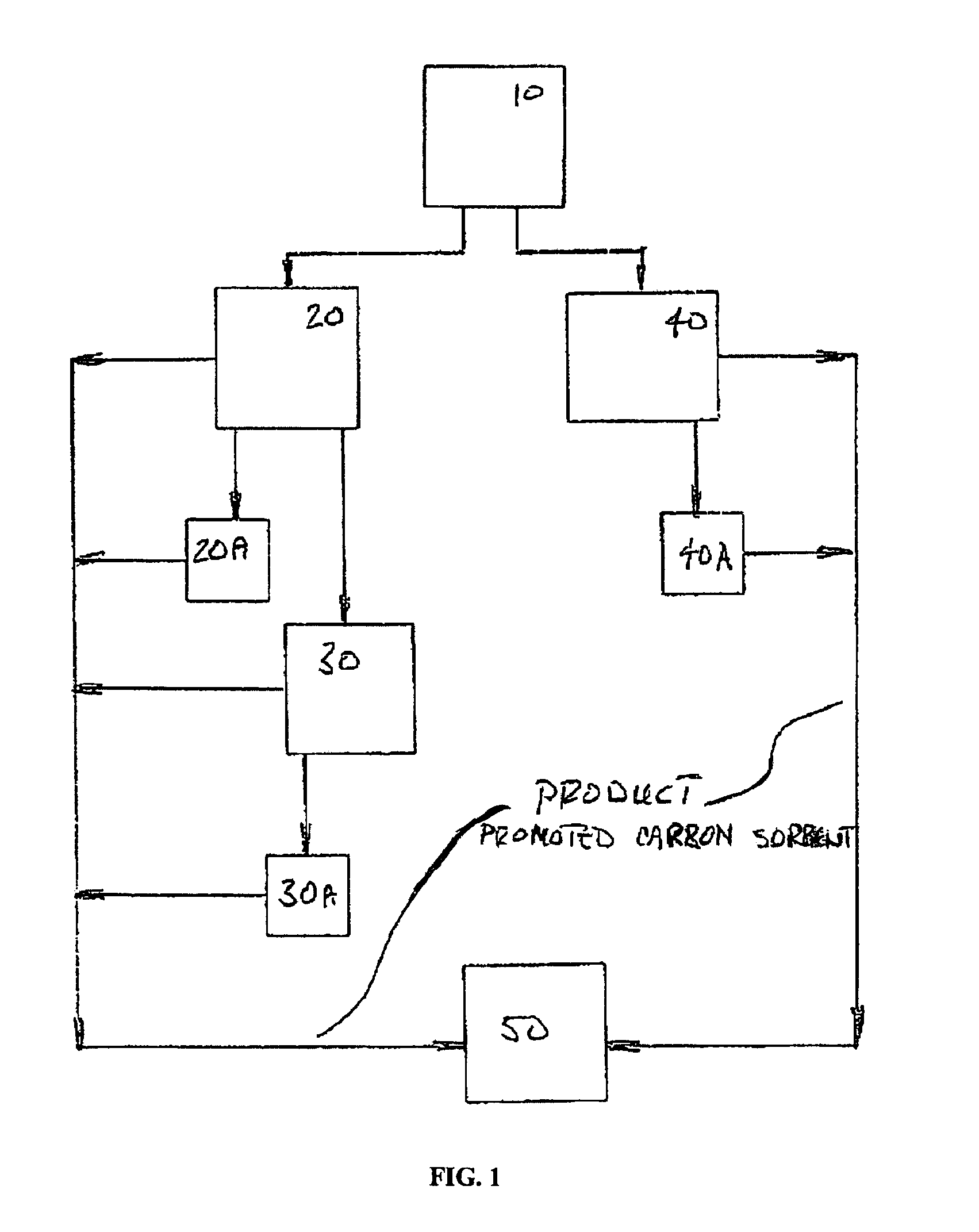
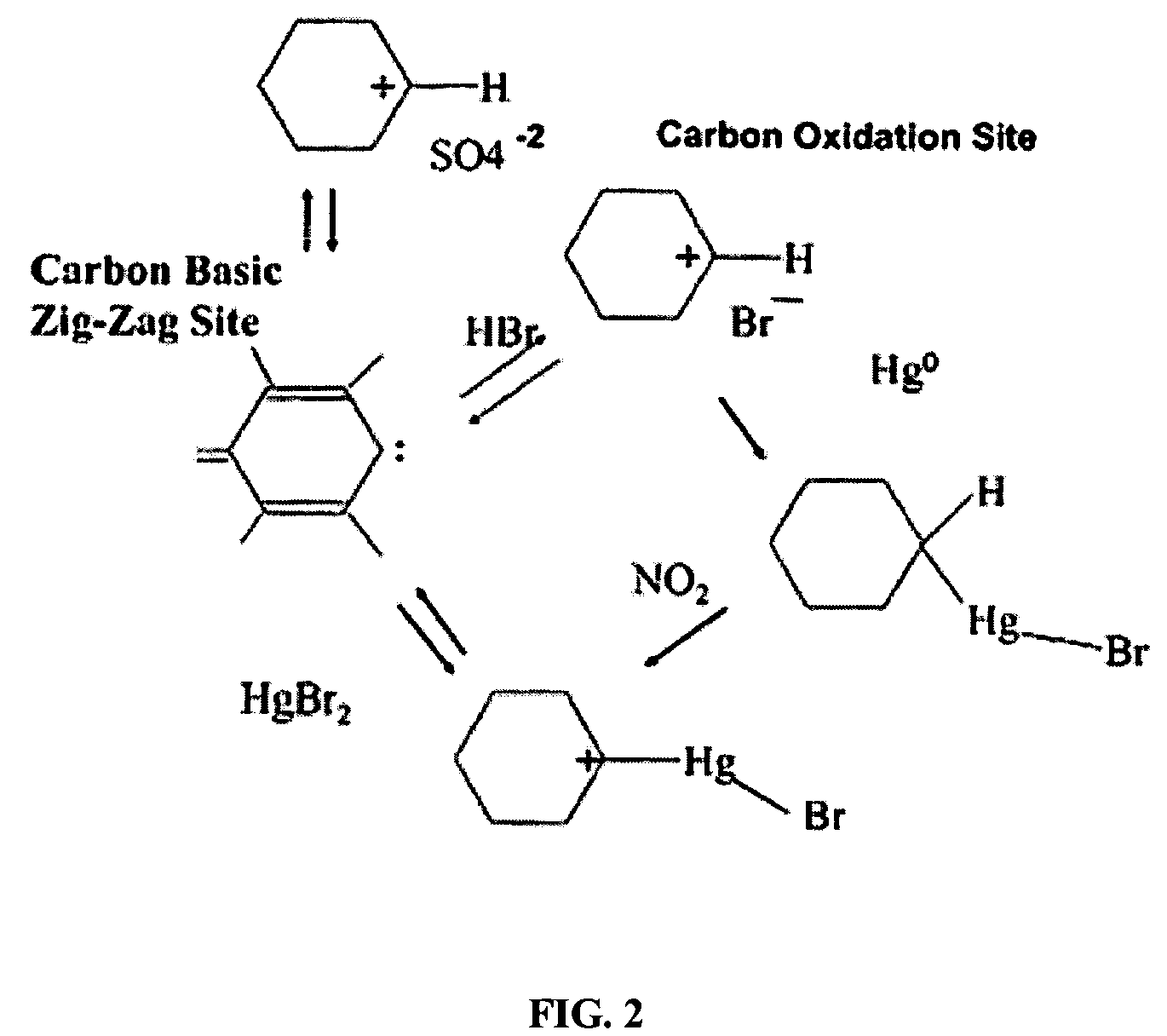
A promoted activated carbon sorbent is described that is highly effective for the removal of mercury from flue gas streams. The sorbent comprises a new modified carbon form containing reactive forms of halogen and halides. Optional components may be added to increase reactivity and mercury capacity. These may be added directly with the sorbent, or to the flue gas to enhance sorbent performance and / or mercury capture. Mercury removal efficiencies obtained exceed conventional methods. The sorbent can be regenerated and reused. Sorbent treatment and preparation methods are also described. New methods for in-flight preparation, introduction, and control of the active sorbent into the mercury contaminated gas stream are described.
Owner:MIDWEST ENERGY EMISSIONS CORP
Cigarette comprising dark air-cured tobacco
ActiveUS8186360B2Less-costly to produceImprove sensory propertiesTobacco treatmentCigar manufactureActivated carbonEngineering
Owner:R J REYNOLDS TOBACCO COMPANY
Multi-component removal in flue gas by aqua ammonia
InactiveUS7255842B1Regeneration process is less-costlyIncrease load capacityGas treatmentNitrogen compoundsNitric oxideSlurry
A new method for the removal of environmental compounds from gaseous streams, in particular, flue gas streams. The new method involves first oxidizing some or all of the acid anhydrides contained in the gas stream such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitric oxide (NO) and nitrous oxide (N2O) to sulfur trioxide (SO3) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). The gas stream is subsequently treated with aqua ammonia or ammonium hydroxide which captures the compounds via chemical absorption through acid-base or neutralization reactions. The products of the reactions can be collected as slurries, dewatered, and dried for use as fertilizers, or once the slurries have been dewatered, used directly as fertilizers. The ammonium hydroxide can be regenerated and recycled for use via thermal decomposition of ammonium bicarbonate, one of the products formed. There are alternative embodiments which entail stoichiometric scrubbing of nitrogen oxides and sulfur oxides with subsequent separate scrubbing of carbon dioxide.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Pollutant emission control sorbents and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20070122327A1Small particle sizePromotes Hg-captureGas treatmentOther chemical processesSorbentFlue gas
Sorbents for removal of mercury and other pollutants from gas streams, such as a flue gas stream from coal-fired utility plants, and methods for their manufacture and use are disclosed. The methods include mixing sorbent substrate particles with a sulfide salt and a metal salt to form a metal sulfide on the outer surface of the sorbent particles.
Owner:BASF CATALYSTS LLC
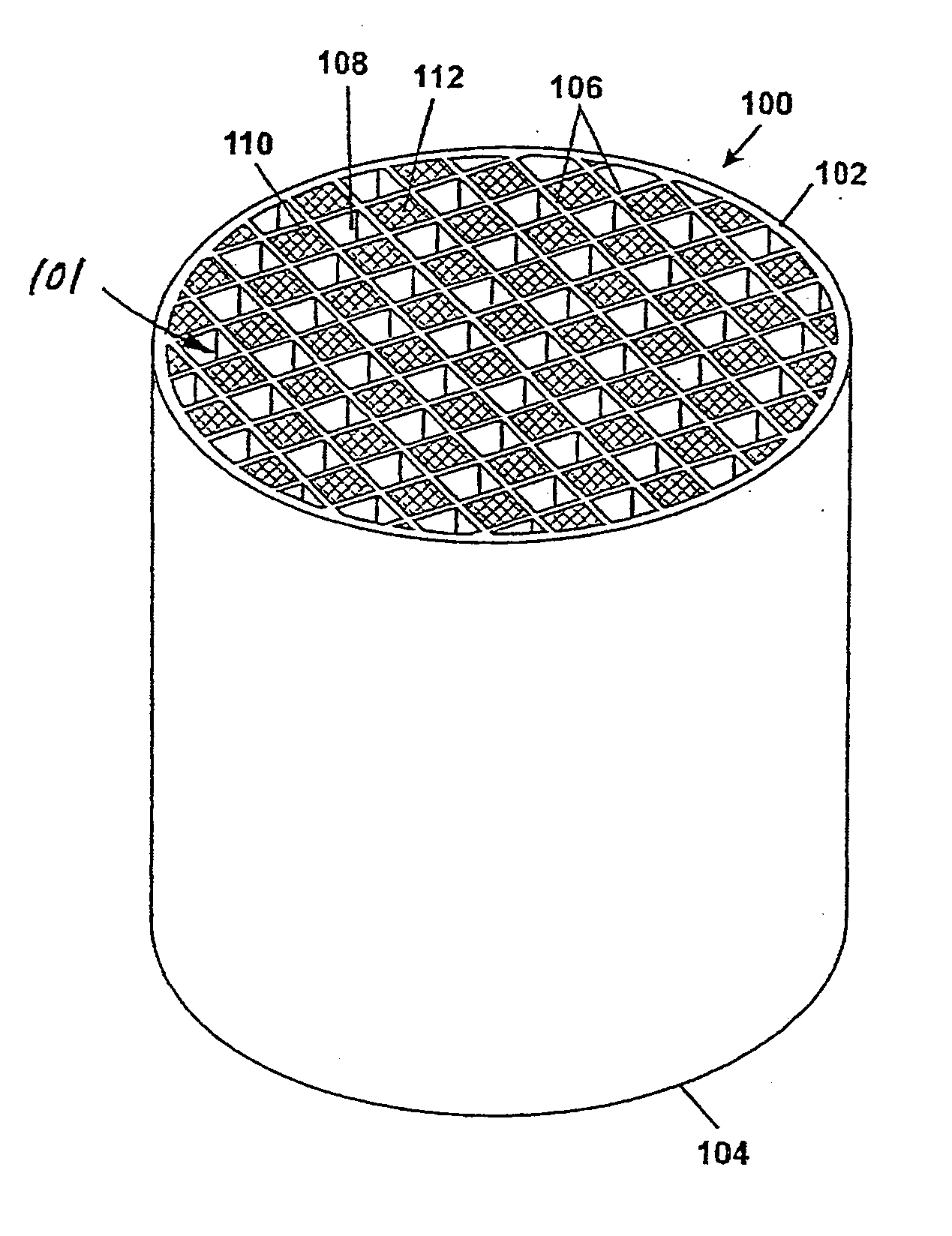
Activated carbon honeycomb catalyst beds and methods for the use thereof
InactiveUS20070261557A1Simple designLow costGas treatmentCarbon compoundsActivated carbonCombustion system
Disclosed herein, without limitation, are activated carbon honeycomb catalyst beds and systems for removing mercury and other toxic metals from a process stream, i.e, from flue gas of a coal combustion system. The activated carbon honeycomb can for example remove greater than 90% mercury from flue gas with a simple design and without adding material to the flue gas. Also disclosed herein, and without limitation, are methods for manufacturing and using the disclosed honeycomb catalyst beds and systems.
Owner:CORNING INC
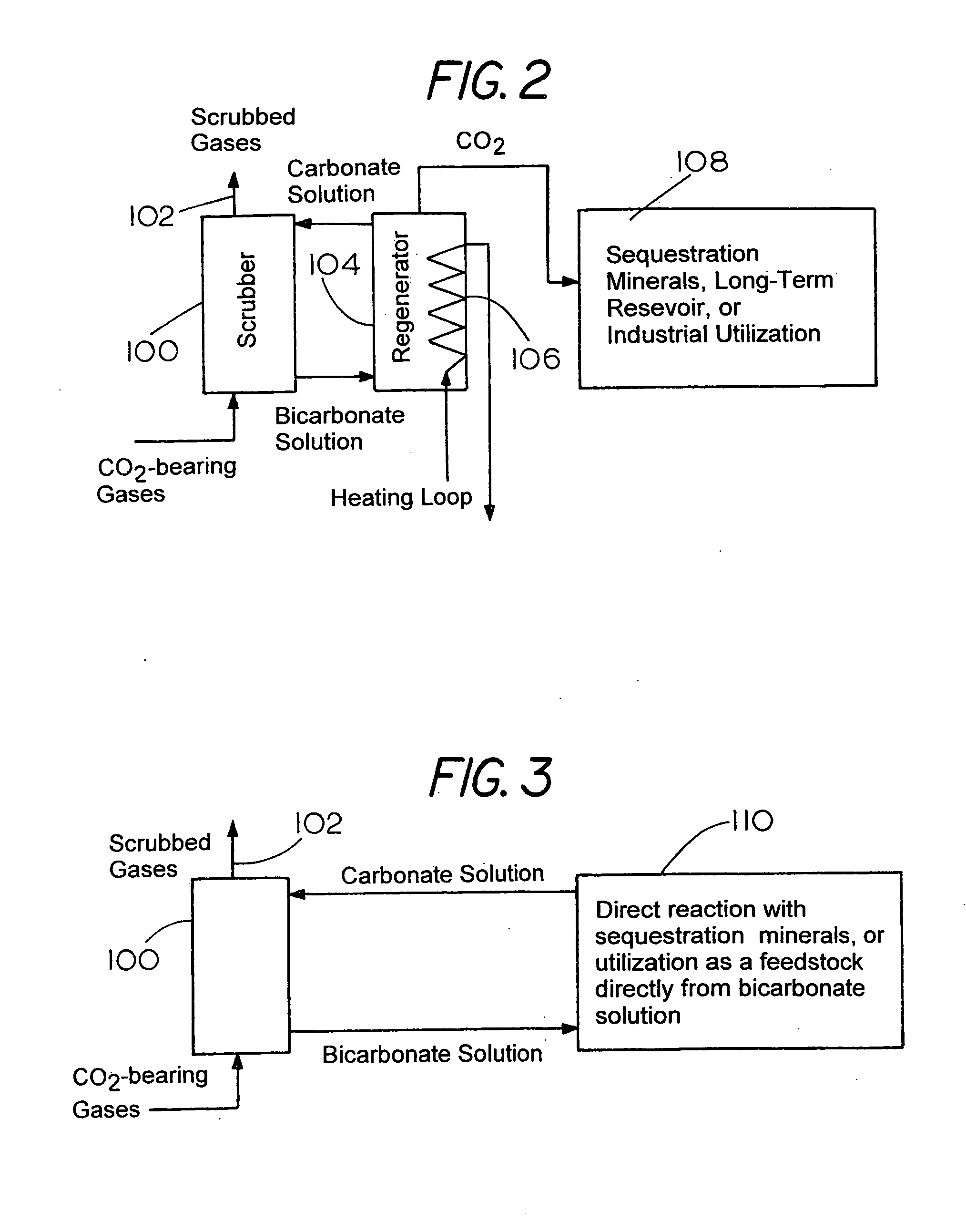
Capture and Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide in Flue Gases
ActiveUS20090202410A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentAlkaline earth metalOxidation state
There is provided a process for the capture and sequestration of carbon dioxide that would otherwise enter the atmosphere and contribute to global warming and other problems. CO2 capture is accomplished by reacting carbon dioxide in flue gas with an alkali metal carbonate, or a metal oxide, particularly containing an alkaline earth metal or iron, to form a carbonate salt. A preferred carbonate for CO2 capture is a dilute aqueous solution of additive-free (Na2CO3). Other carbonates include (K2CO3) or other metal ion that can produce both a carbonate and a bicarbonate salt. Examples of suitable metal oxides include several alkaline earths including CaO and MgO. The captured CO2 is preferably sequestered using any available mineral or industrial waste that contains calcium magnesium or iron in non-carbonate forms, or iron in the Fe+2 oxidation state.
Owner:MICHIGAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
Sorbents for the oxidation and removal of mercury
ActiveUS7435286B2Efficient use ofEasy to controlGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentActivated carbonHalogen
A promoted activated carbon sorbent is described that is highly effective for the removal of mercury from flue gas streams. The sorbent comprises a new modified carbon form containing reactive forms of halogen and halides. Optional components may be added to increase reactivity and mercury capacity. These may be added directly with the sorbent, or to the flue gas to enhance sorbent performance and / or mercury capture. Mercury removal efficiencies obtained exceed conventional methods. The sorbent can be regenerated and reused. Sorbent treatment and preparation methods are also described. New methods for in-flight preparation, introduction, and control of the active sorbent into the mercury contaminated gas stream are described.
Owner:MIDWEST ENERGY EMISSIONS CORP
Method for removing mercury from flue gas after combustion
InactiveUS7727307B2Simple and economical methodGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentPower stationCombustion
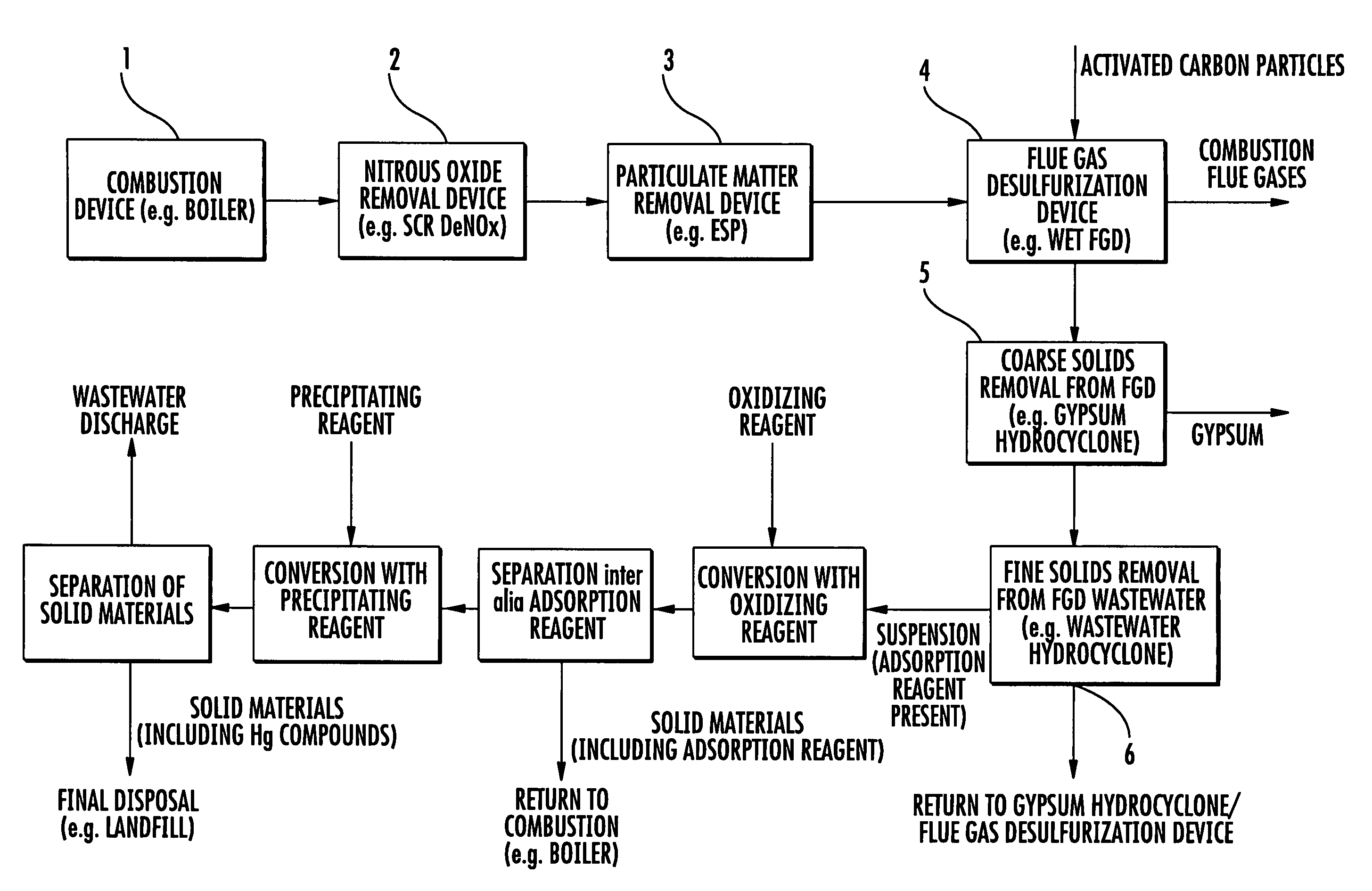
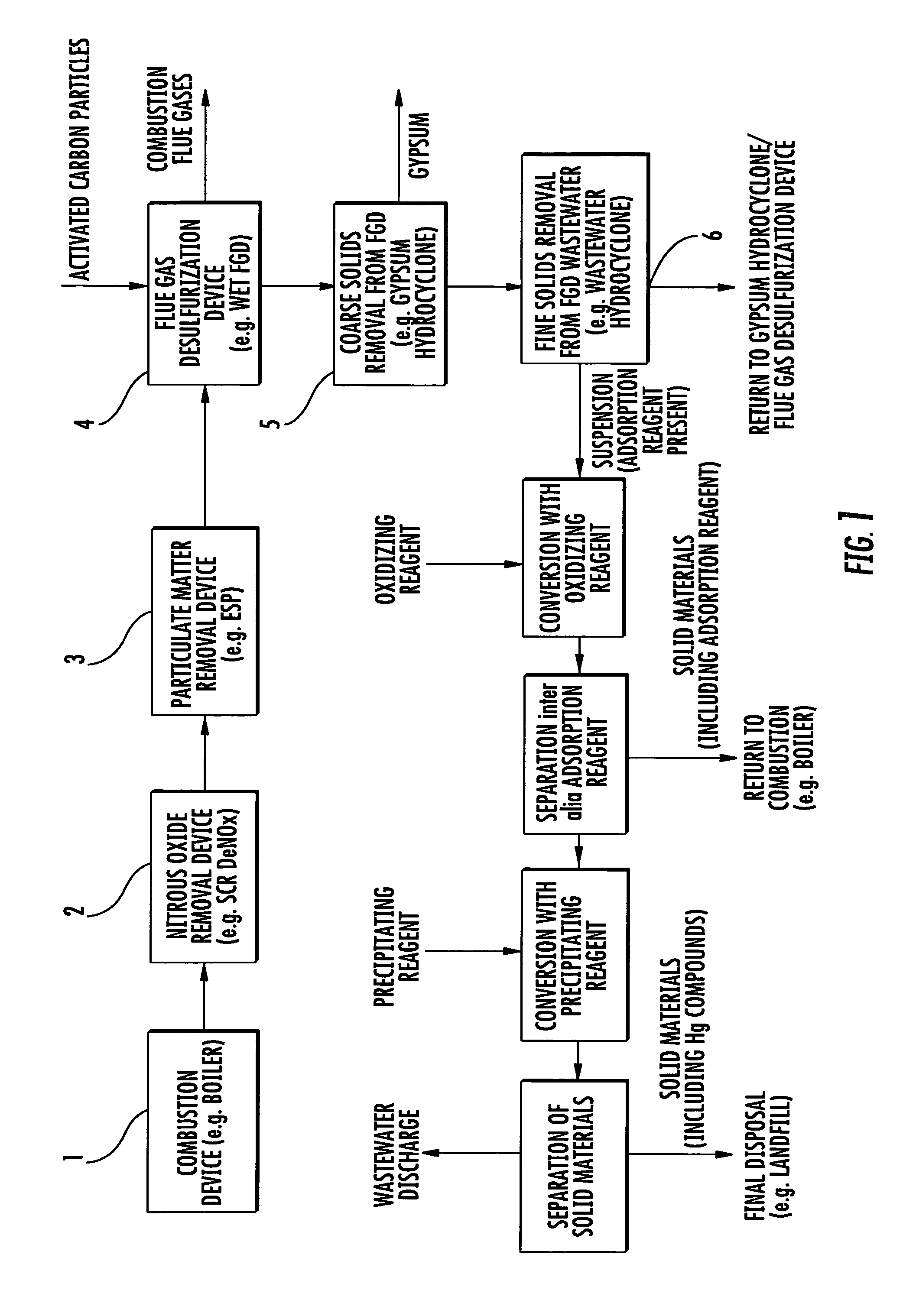
A method of removing mercury from flue gases from combustion plants, such as for example power plants or waste incineration plants, is achieved in which mercury-containing flue gases are brought into contact with an adsorption reagent either directly or indirectly by being contained in an absorption reagent, whereby mercury is substantially adsorbed by the adsorption reagent during this contact. After adsorption has occurred the adsorption reagent is separated from the flue gases and subsequently from the absorption reagent and added to an aqueous solution containing an oxidizing agent, whereby the adsorbed mercury dissolves as Hg2+. The Hg2+-containing solution is subsequently separated from the adsorption agent and the Hg2+ then is removed from the solution. This method enables the mercury to be removed from flue gas in a simple and economical manner.
Owner:STEAG ENERGY SERVICES
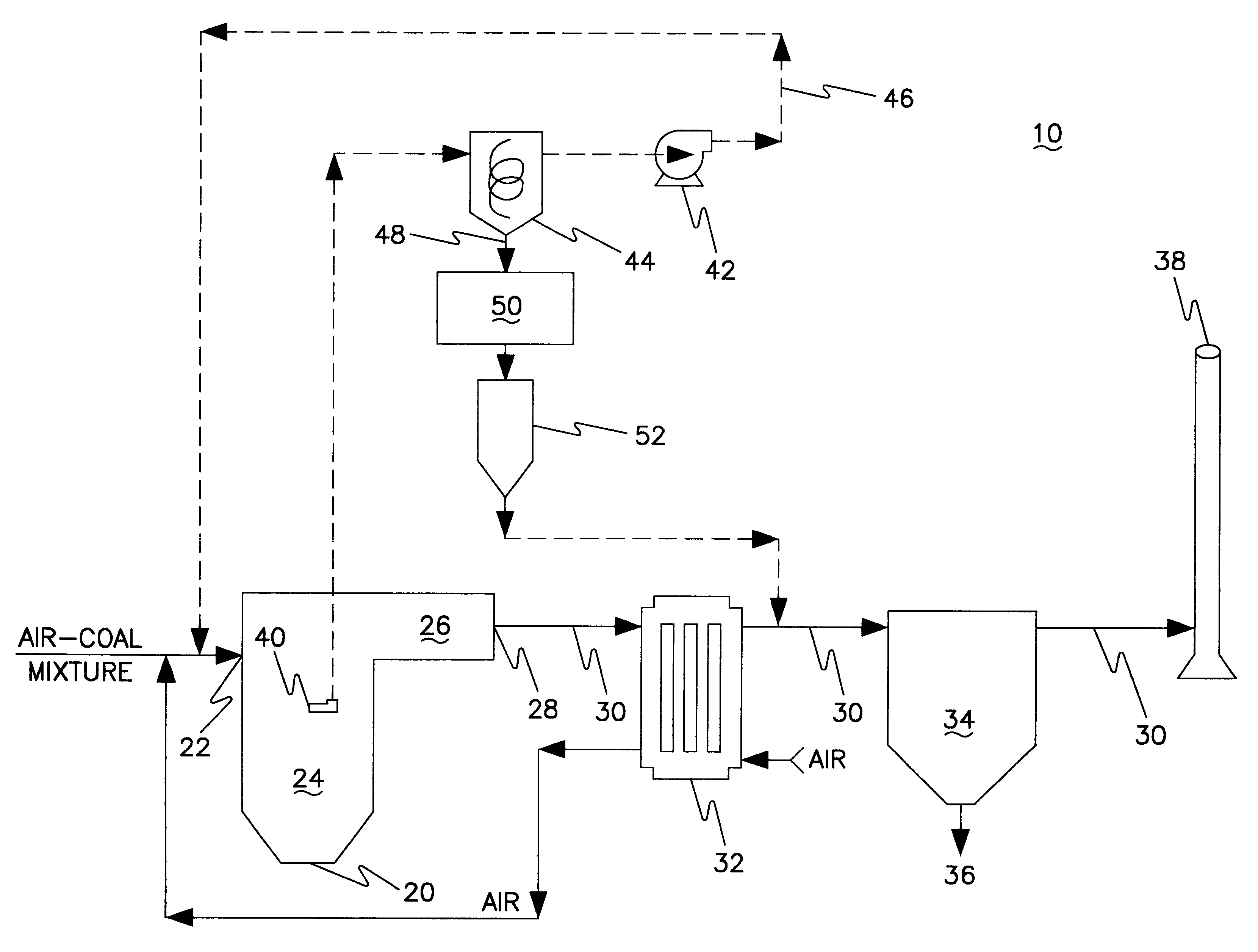
Method to control mercury emissions from exhaust gases
InactiveUS6136281AElimination of mercury in flue gas emissionsEasy to collectCombination devicesExhaust apparatusSolid massGas phase
The present invention relates to a method to catalyze the oxidation of Hg(0) in a flue gas stream prior to standard emissions control equipment. The oxidized mercury has been found to be more condensable than Hg(0) and consequently more easily removed from the gas phase. Accordingly, mercury in its oxidized form can be trapped from a flue gas stream or the like by absorption onto a solid mass or can be more efficiently removed from flue gas streams by wet processes such as a two-stage wet FGD. The gist underlying the inventive concept of the instant invention relates to the use of a porous bed of gold-coated material that is saturated with Hg(0) to the point that the gold in the presence of HCl in the exhaust stream catalyses the oxidation of Hg(0).
Owner:TENNESEE VALLEY AUTHORITY
Method of simultaneously reducing CO2 and SO2 emissions in a combustion installation
InactiveUS6737031B2Reduce carbon dioxide emissionsFluidized bed combustionGas treatmentCombustionFlue gas
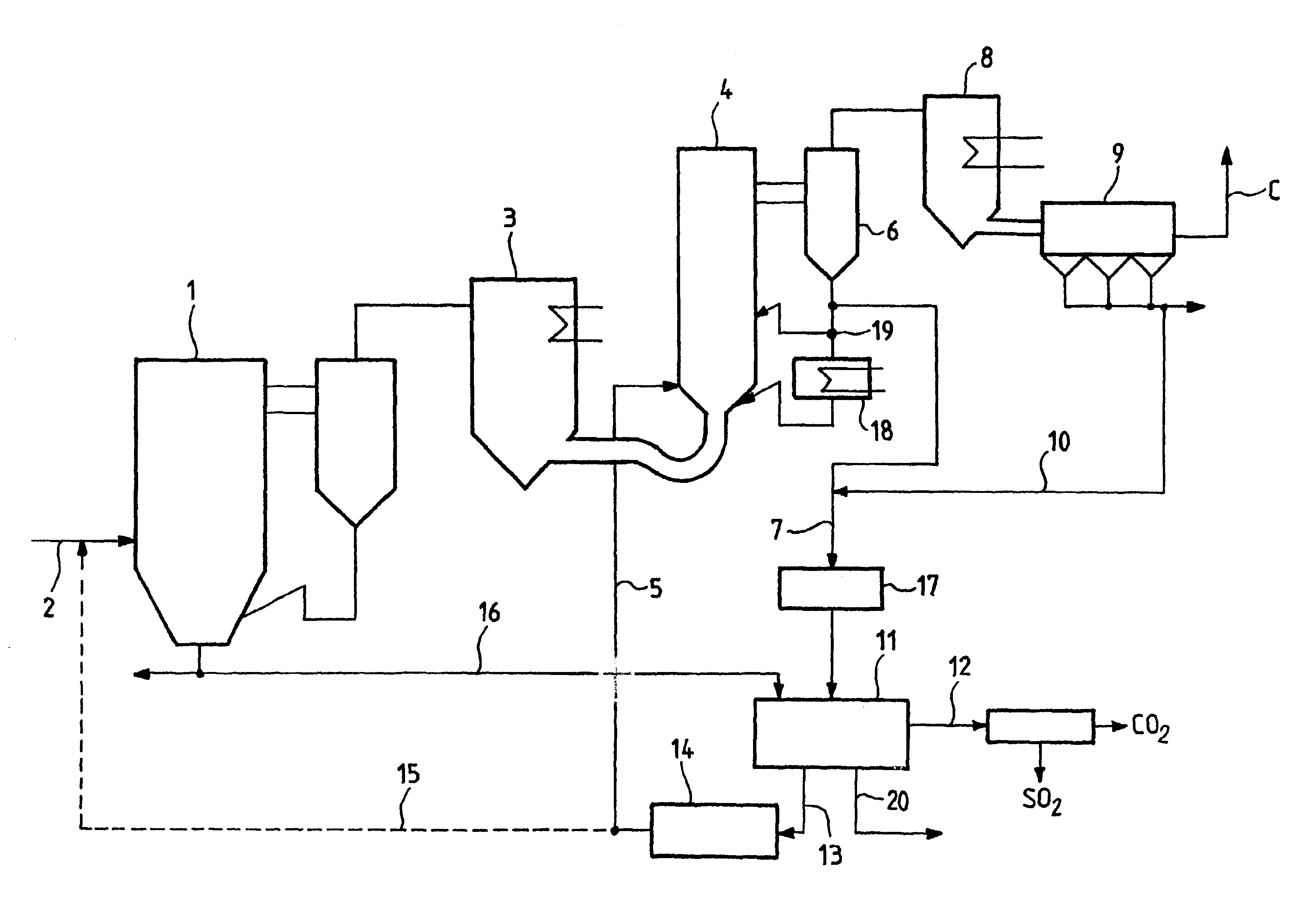
The method of simultaneously reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions and sulfur dioxide (SO2) emissions produced by the combustion of carbon-containing matter in a hearth consists in injecting into the hearth a calcium-based agent, a fraction of which absorbs SO2 after decarbonization, and then, after the flue gases have been subjected to intermediate cooling, in causing them to transit via a first reactor and in putting them in contact therein with the other fraction of the absorbant that has not reacted with SO2 so as to capture CO2 from the flue gases by carbonization, then, in a separator, in extracting the solids contained in the flue gases output from the first reactor so as to subject them to heat treatment in a second reactor in order to extract CO2 therefrom by decarbonization and in order to recycle the resulting regenerated CO2 absorbant to the first reactor.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC TECH GMBH
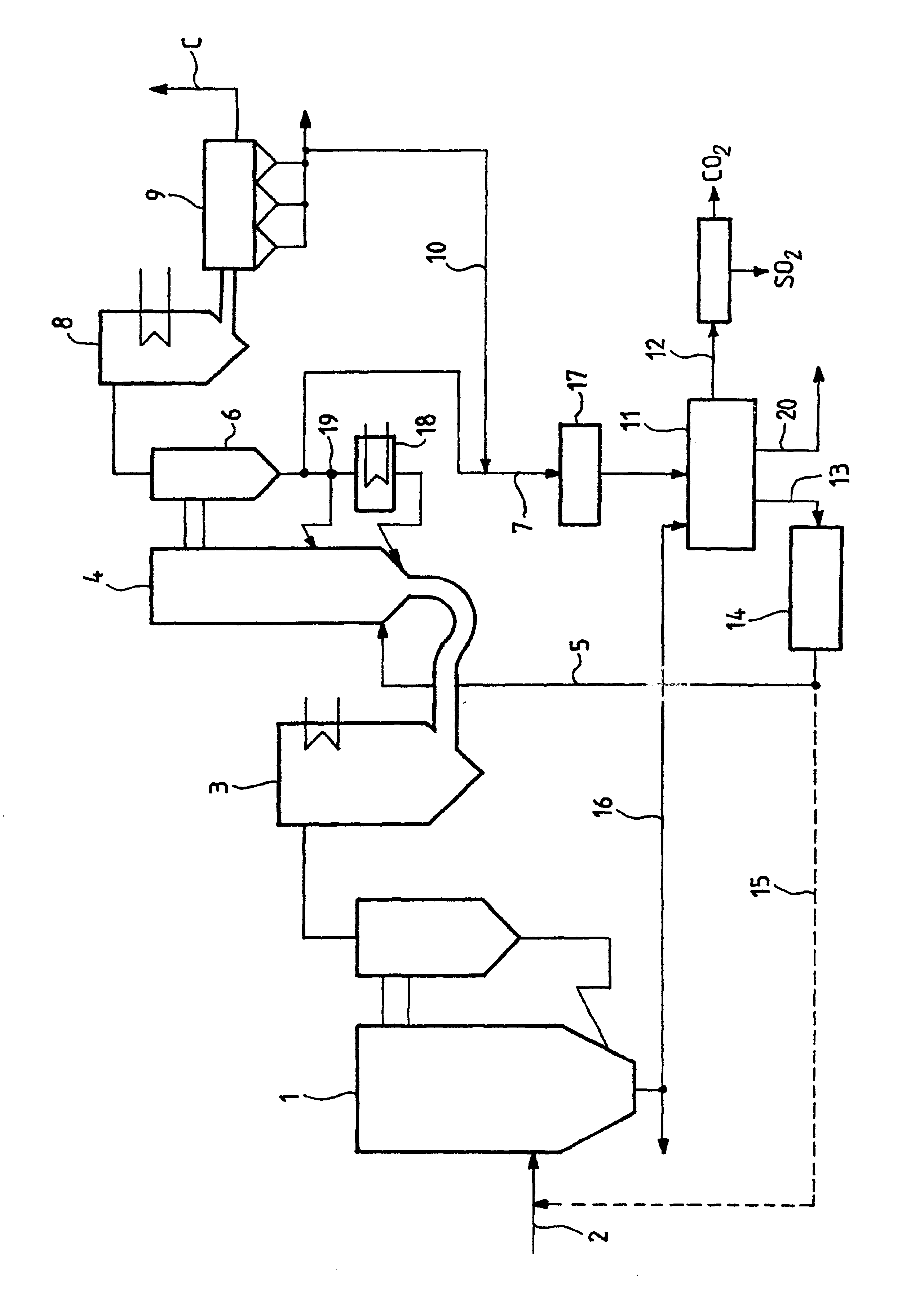
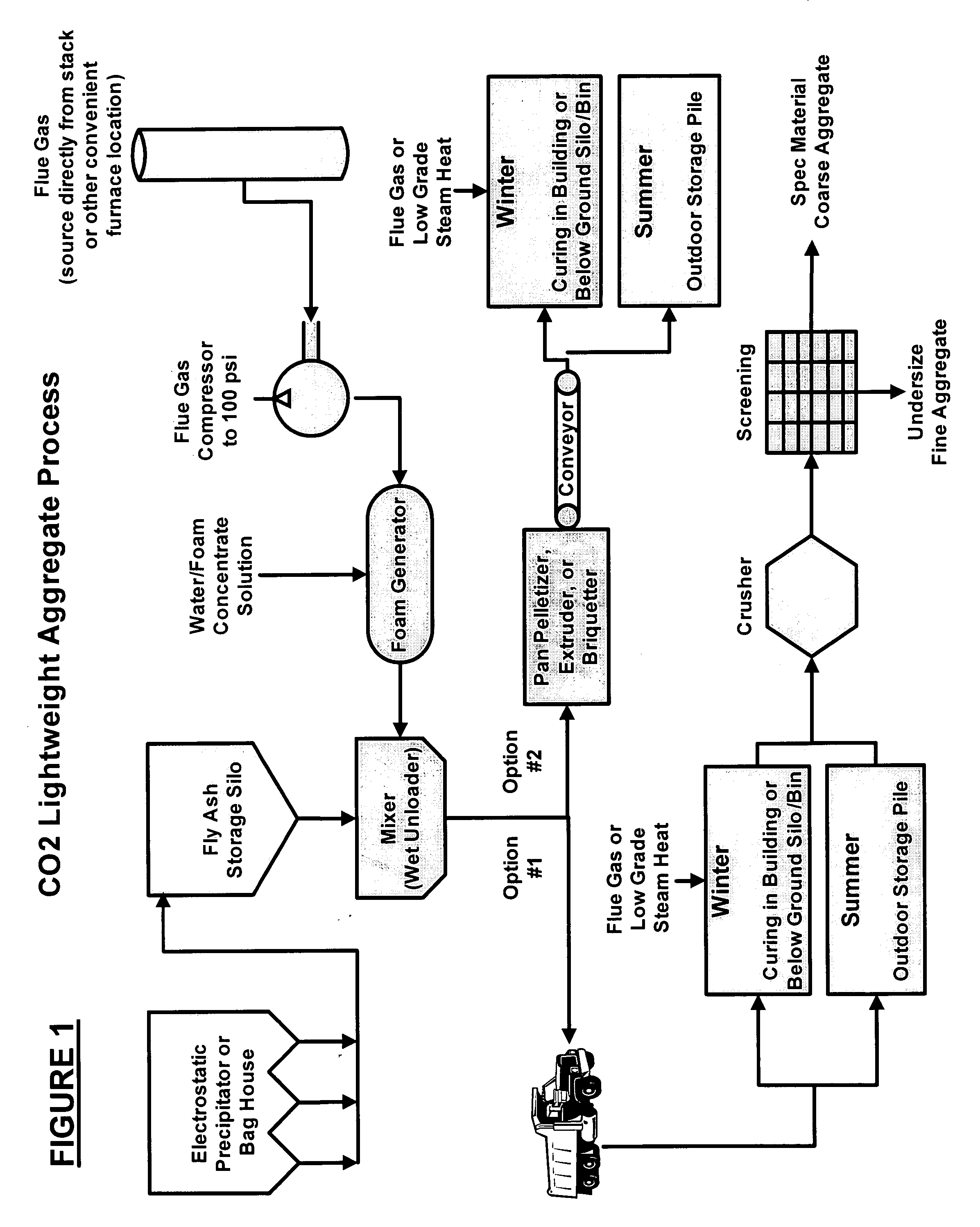
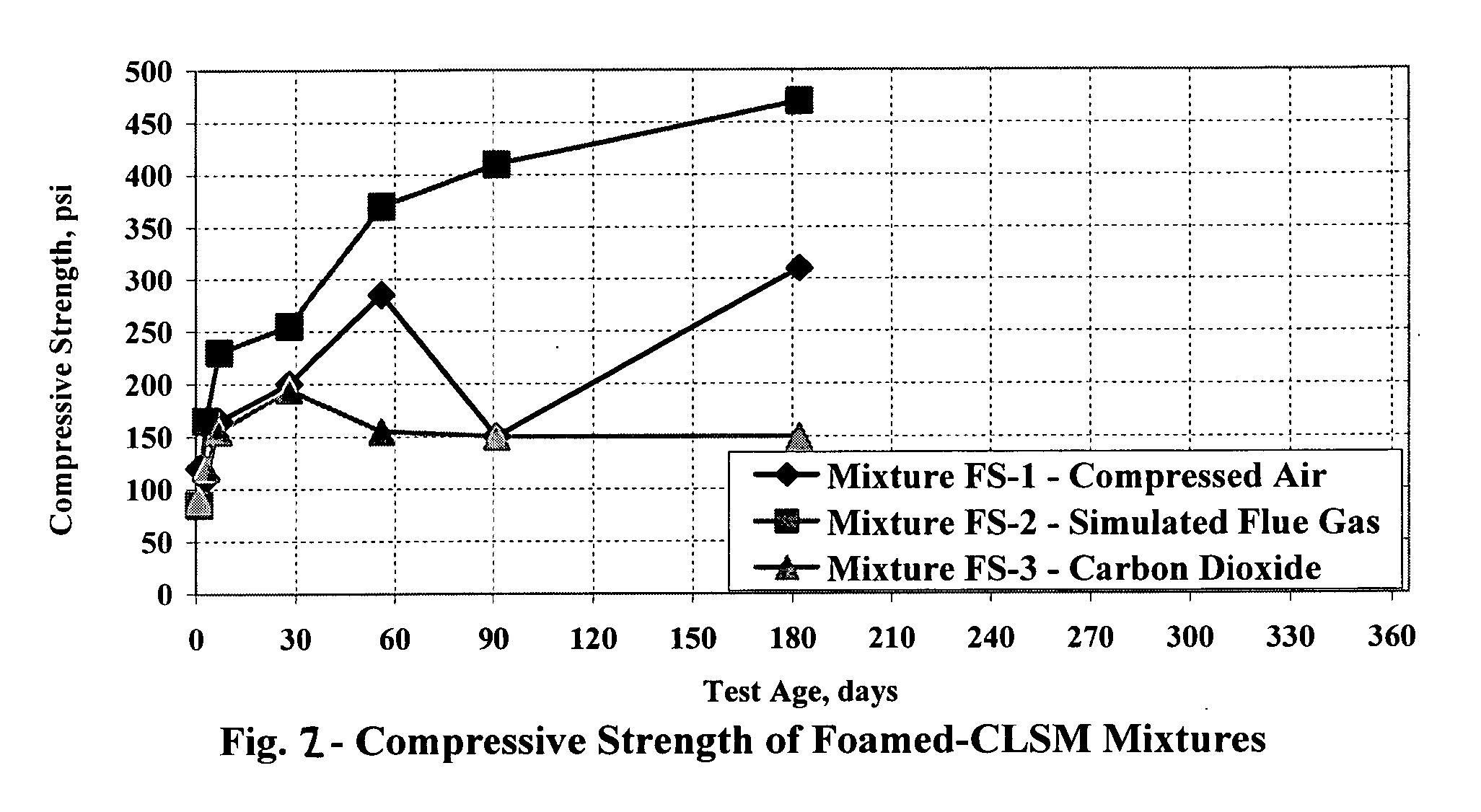
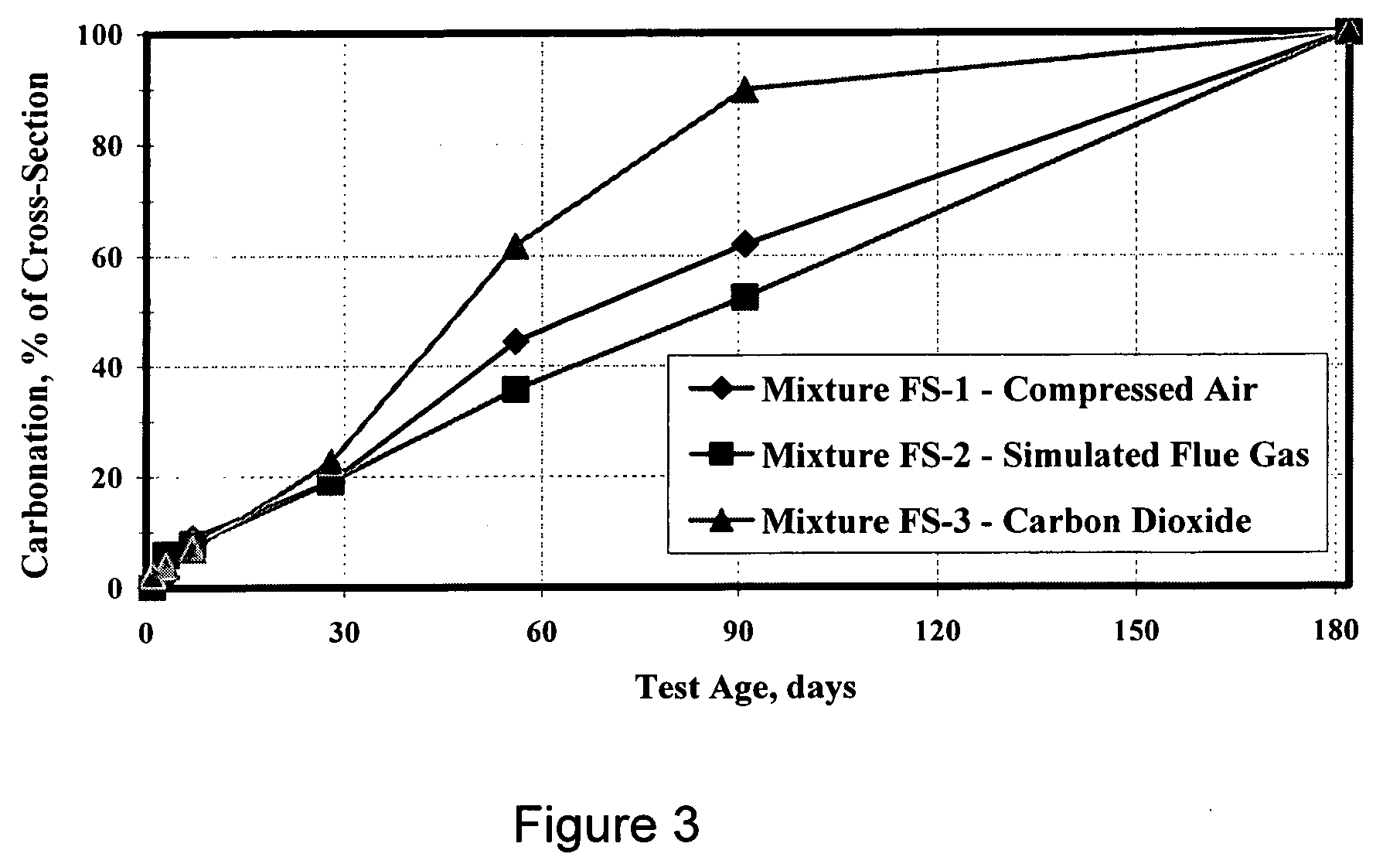
Carbon dioxide sequestration in foamed controlled low strength materials
InactiveUS20060185560A1Improve the environmentEasy to useProductsReagentsCombustion chamberMaterials science
A process for sequestering carbon dioxide from the flue gas emitted from a combustion chamber is disclosed. In the process, a foam including a foaming agent and the flue gas is formed, and the foam is added to a mixture including a cementitious material (e.g., fly ash) and water to form a foamed mixture. Thereafter, the foamed mixture is allowed to set, preferably to a controlled low-strength material having a compressive strength of 1200 psi or less. The carbon dioxide in the flue gas and waste heat reacts with hydration products in the controlled low-strength material to increase strength. In this process, the carbon dioxide is sequestered. The CLSM can be crushed or pelletized to form a lightweight aggregate with properties similar to the naturally occurring mineral, pumice.
Owner:WISCONSIN ELECTRIC POWER
Electrical power generation method
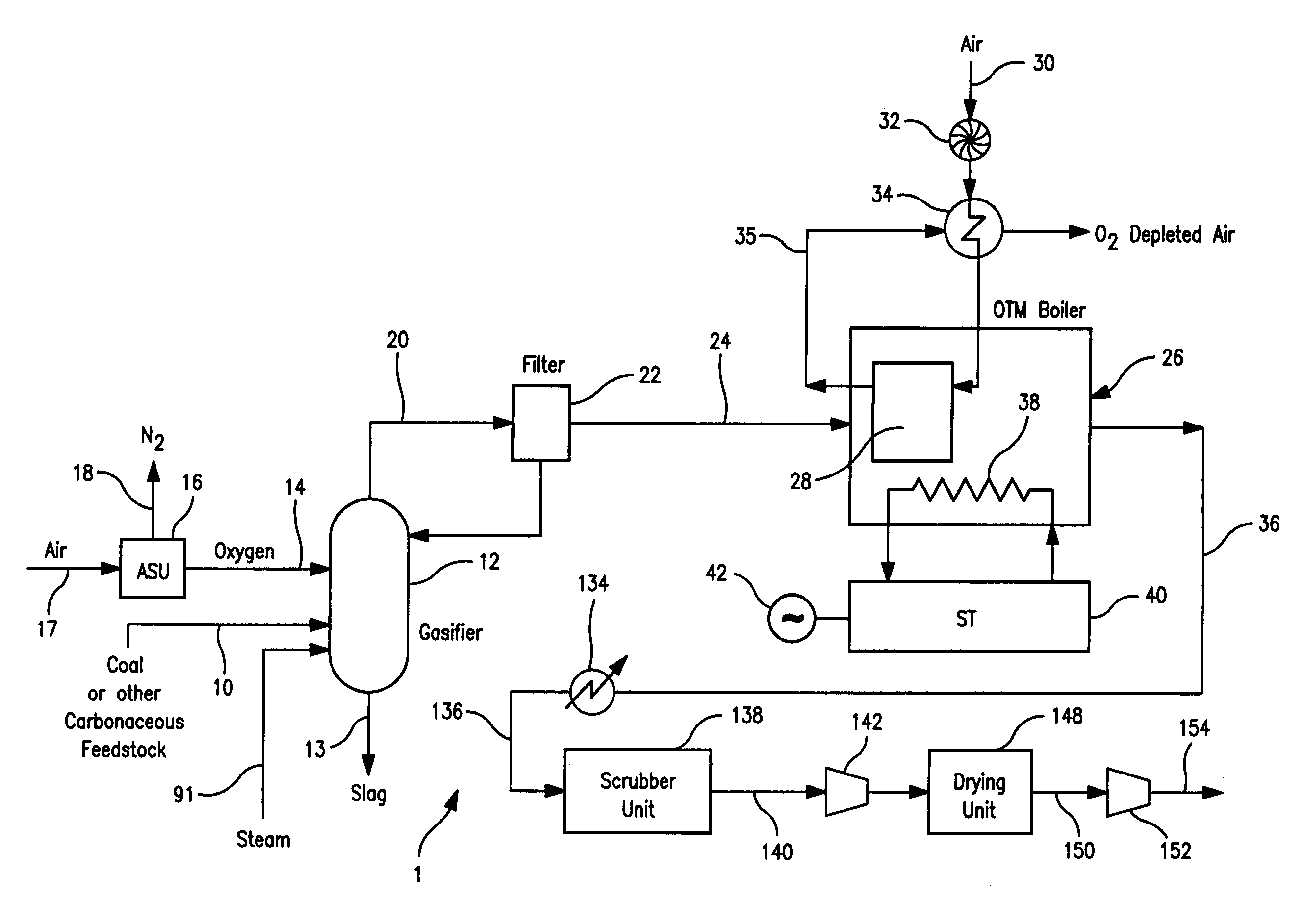
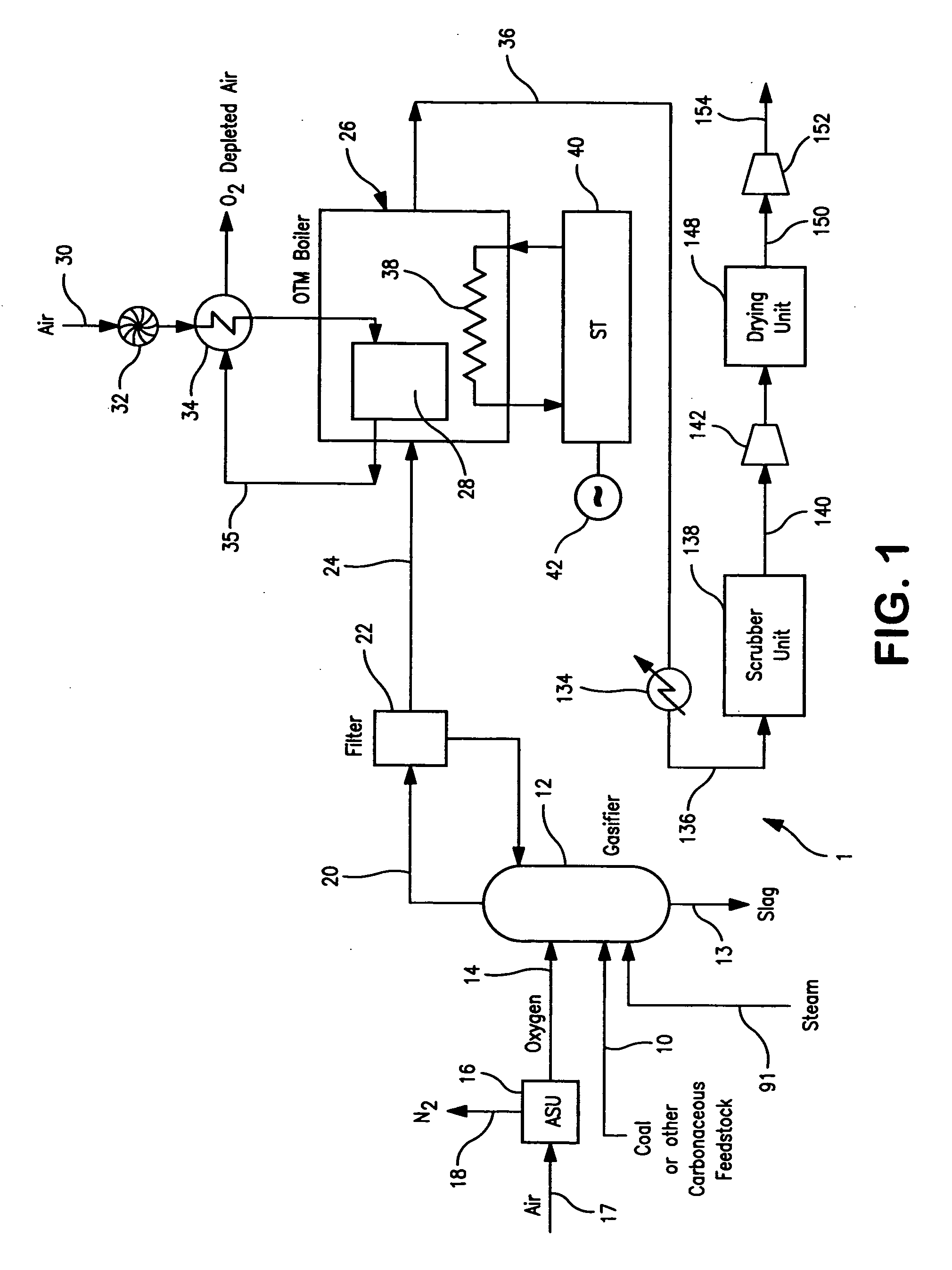
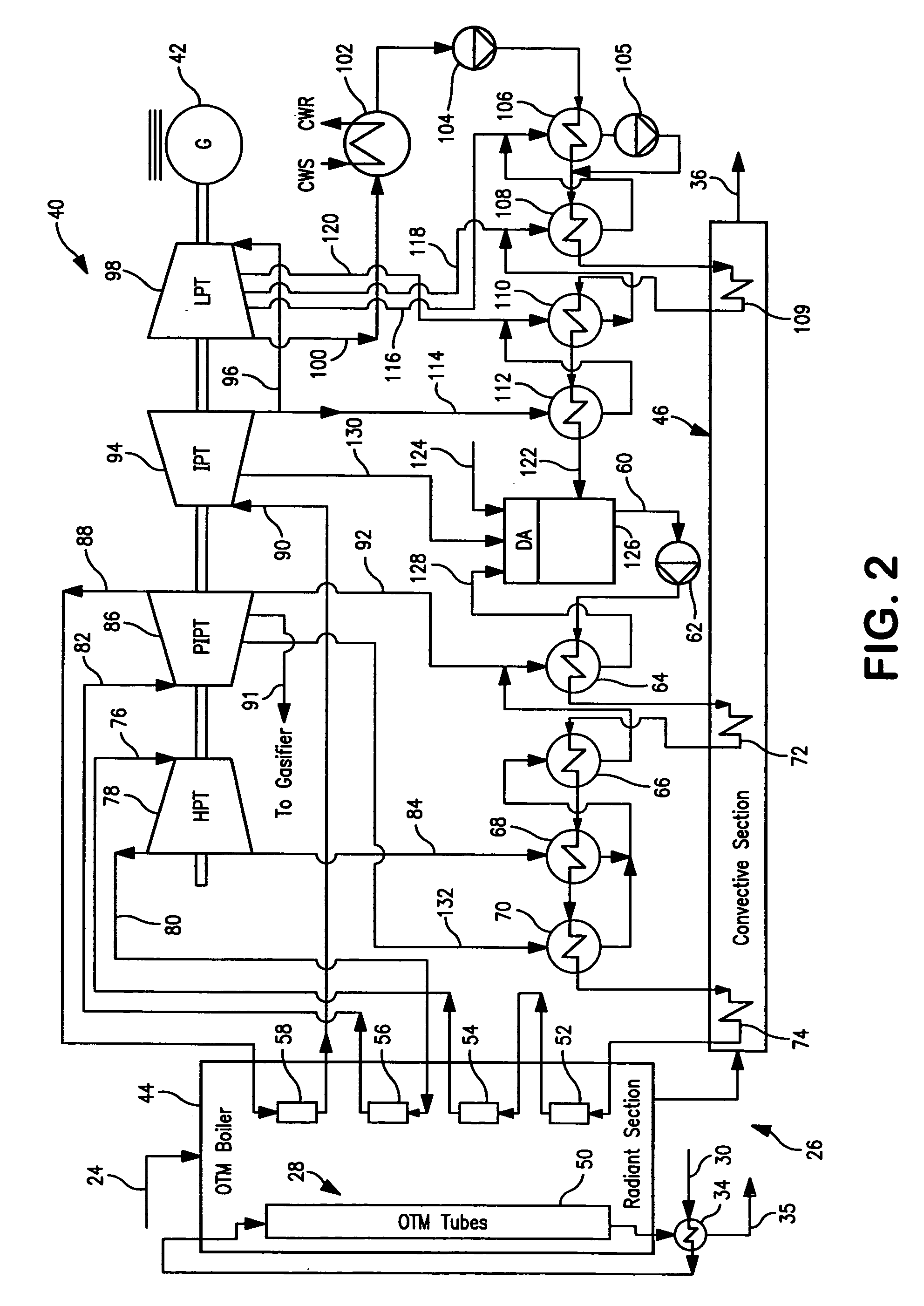
A method of generating electrical power in which a synthesis gas stream generated in a gasifier is combusted in an oxygen transport membrane system of a boiler. The combustion generates heat to raise steam to in turn generate electricity by a generator coupled to a steam turbine. The resultant flue gas can be purified to produce a carbon dioxide product.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC
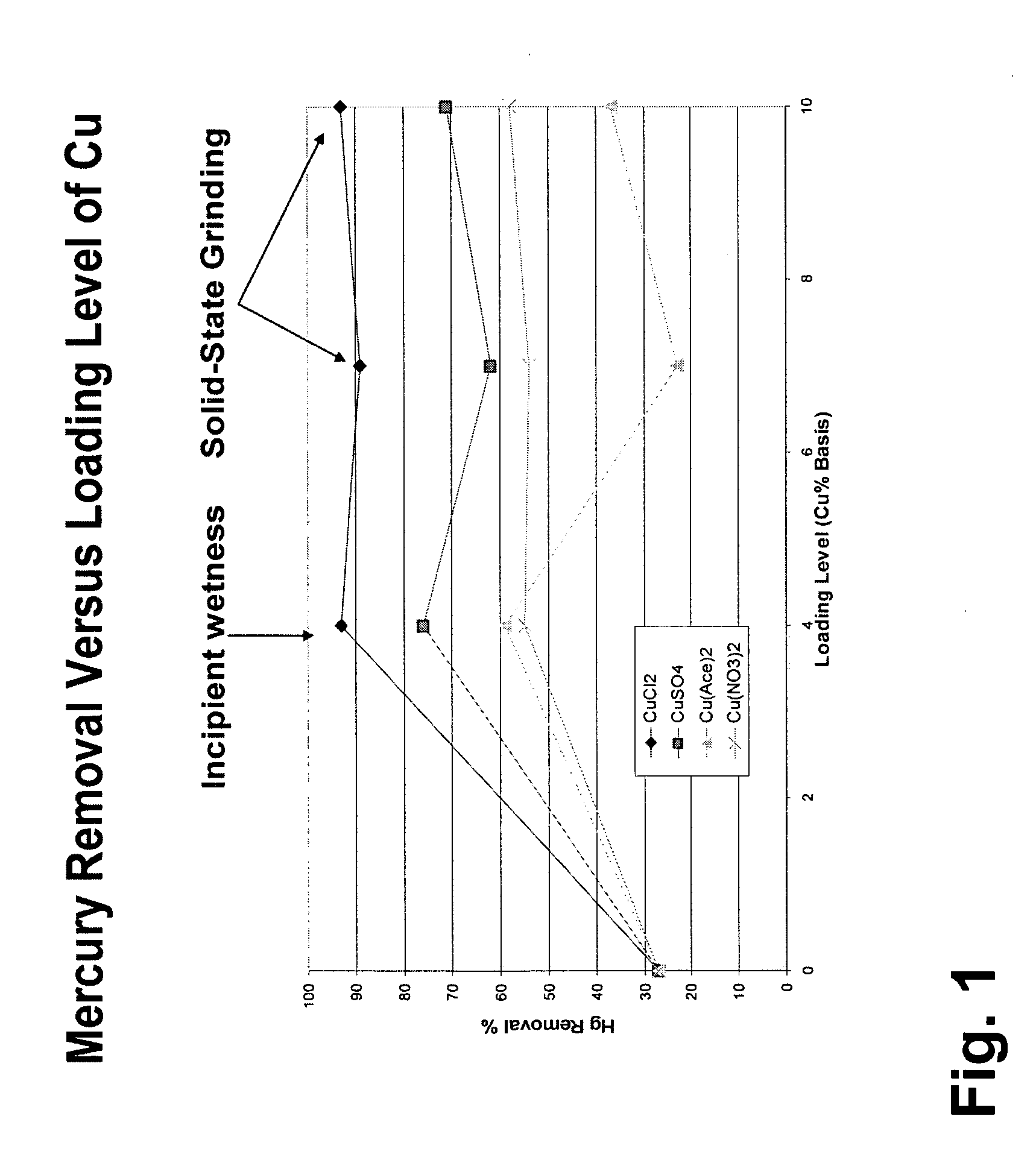
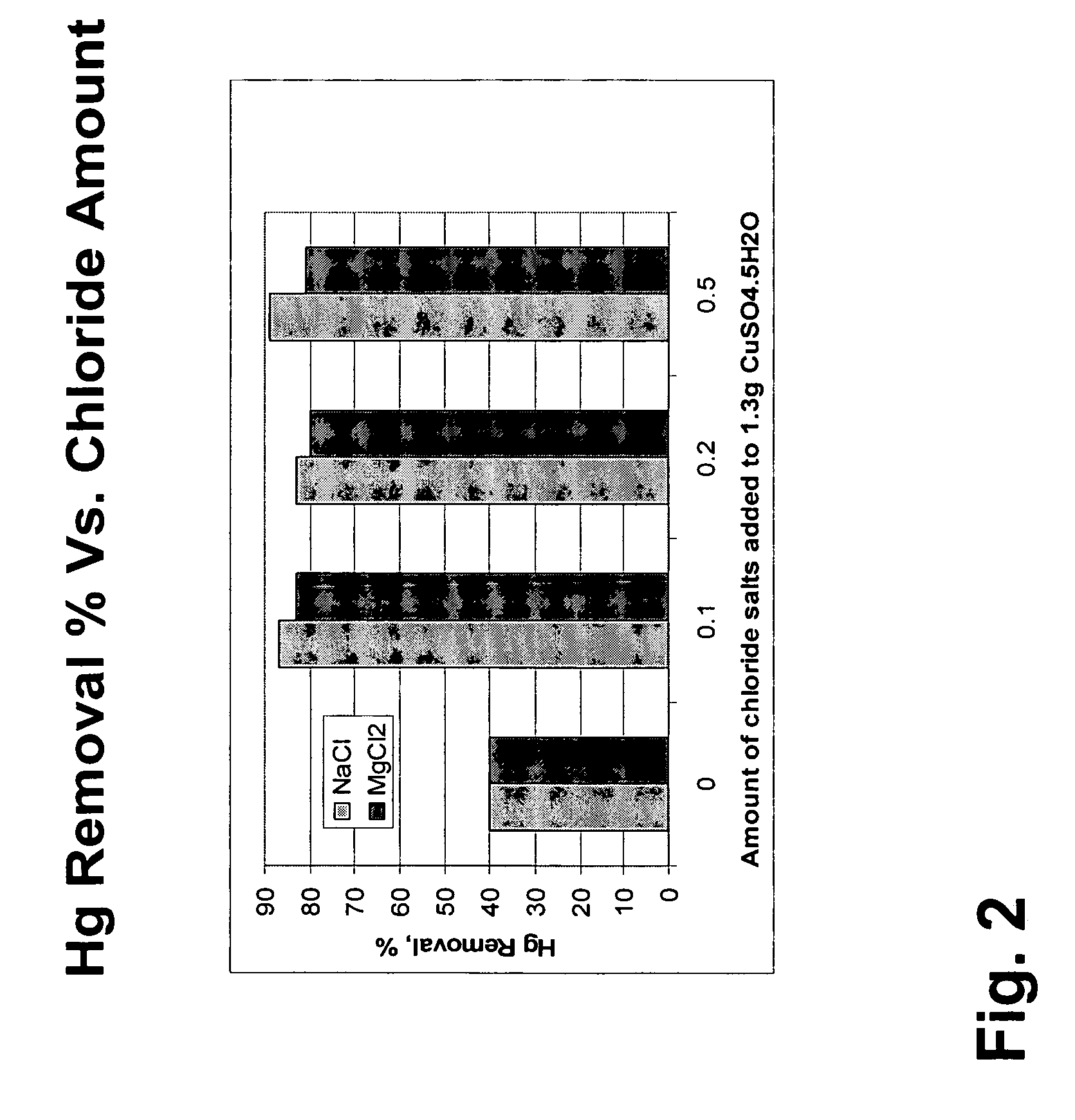
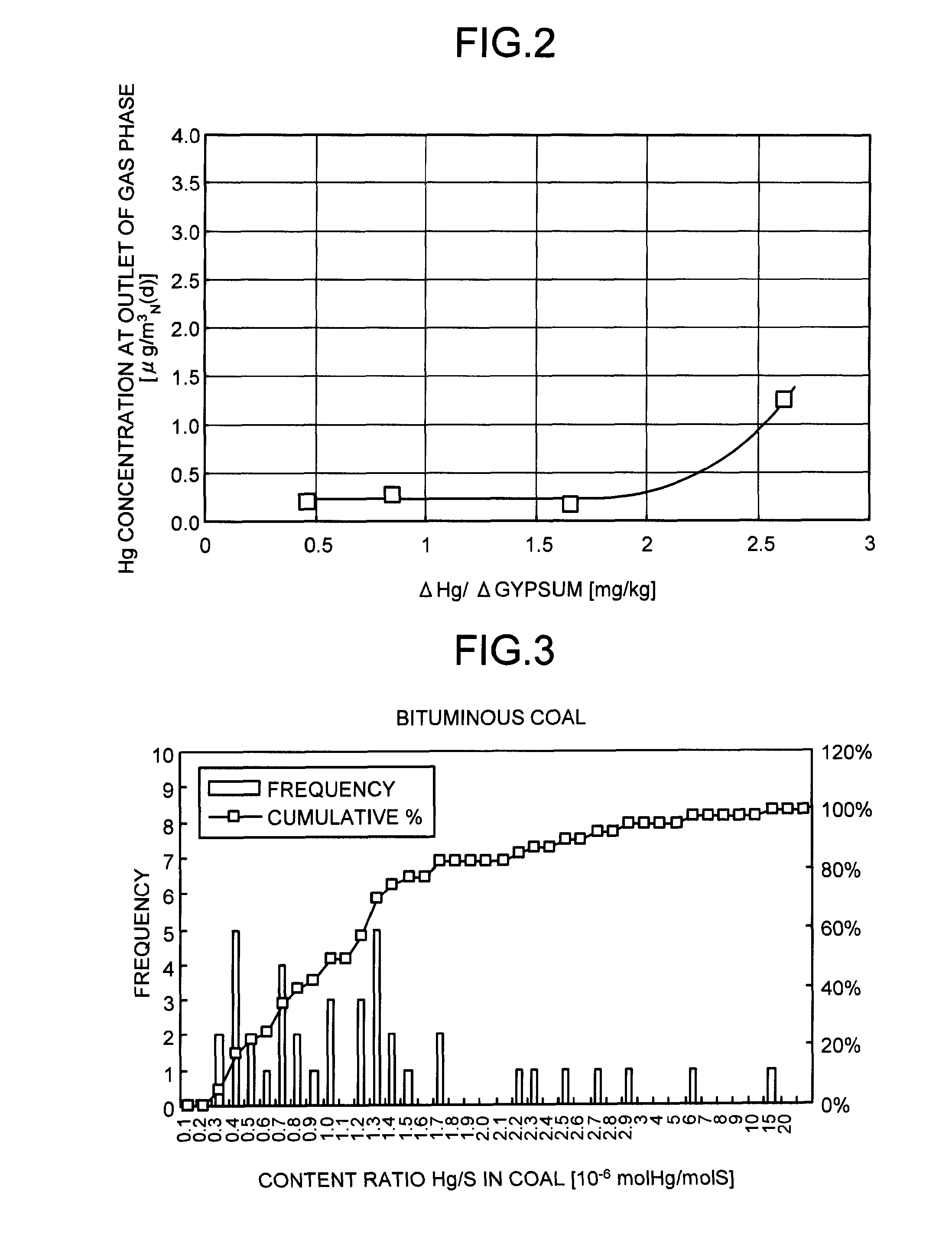
Reducing mercury emissions from the burning of coal
Processes and compositions are provided for decreasing emissions of mercury upon combustion of fuels such as coal. Various sorbent compositions are provided that contain components that reduce the level of mercury and / or sulfur emitted into the atmosphere upon burning of coal. In various embodiments, the sorbent compositions are added directly to the fuel before combustion; are added partially to the fuel before combustion and partially into the flue gas post combustion zone; or are added completely into the flue gas post combustion zone. In preferred embodiments, the sorbent compositions comprise a source of halogen and preferably a source of calcium. Among the halogens, iodine and bromine are preferred. In various embodiments, inorganic bromides make up a part of the sorbent compositions.
Owner:NOX II LTD
Method for mercury removal from flue gas streams
The method for removing mercury from a flue gas stream of the present invention is comprised of first treating a sorbent with a metal halide, and then contacting a sufficient amount of the sorbent with a gas stream for a sufficient amount of time to bind with a desired amount of the mercury in said gas stream. The metal is selected from Groups I and II of the periodic table of the elements. The halide is selected from the group consisting of I, Br, Cl. The metal halide comprises from about 0.5% to 25% by weight of said treated sorbent.
Owner:CALGON CARBON
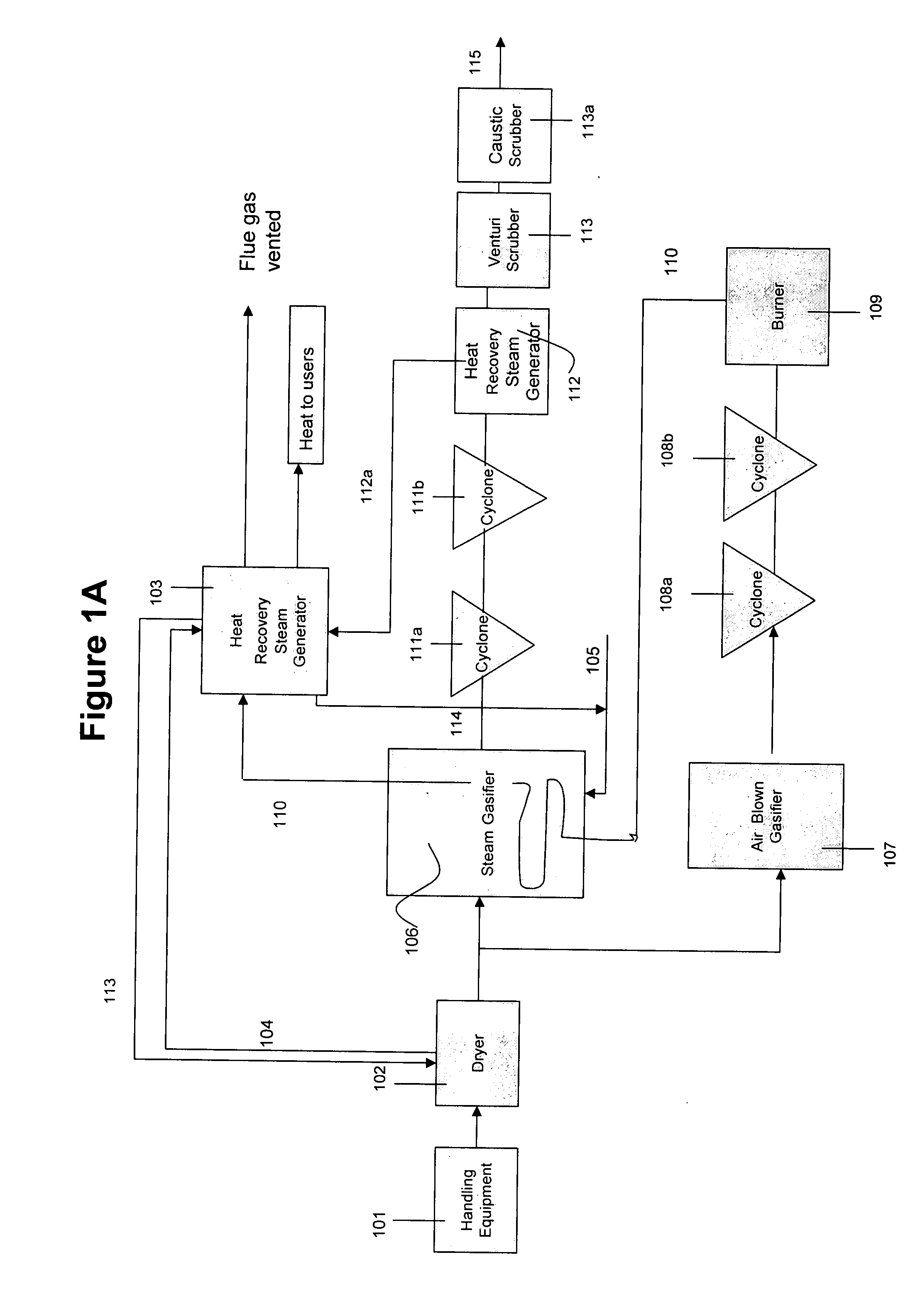
Thermal decomposition device of oil field waste
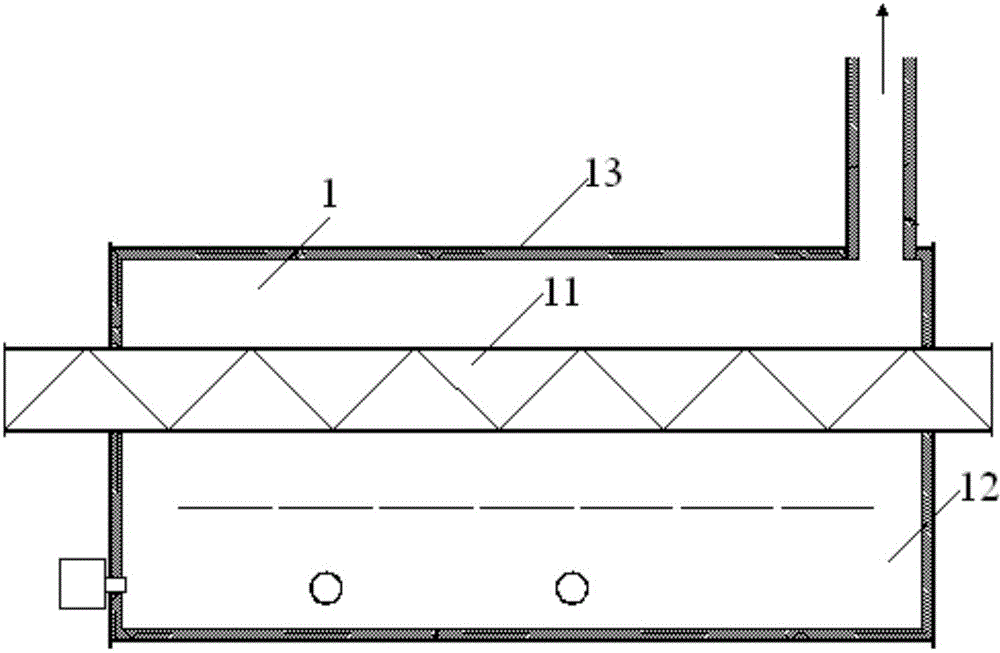
InactiveCN104402186AImprove heat transfer efficiencyIncrease the effective heat transfer areaWaste water treatment from quariesSpecific water treatment objectivesOil fieldEngineering
The invention discloses a thermal decomposition device of oil field wastes. The thermal decomposition device comprises a casing, wherein a flue and a heating cavity are formed inside the casing; the heating cavity is isolated from the flue; ribs are arranged on the casing with the heating cavity. Fume inside the flue flashes the casing with the heating cavity, so that the heat can be conducted; due to adoption of the ribs on the casing with the heating cavity, the heat exchange area is effectively increased when being compared with that of the prior art, and the heat exchange efficiency of the thermal decomposition device is improved.
Owner:JEREH ENERGY SERVICES
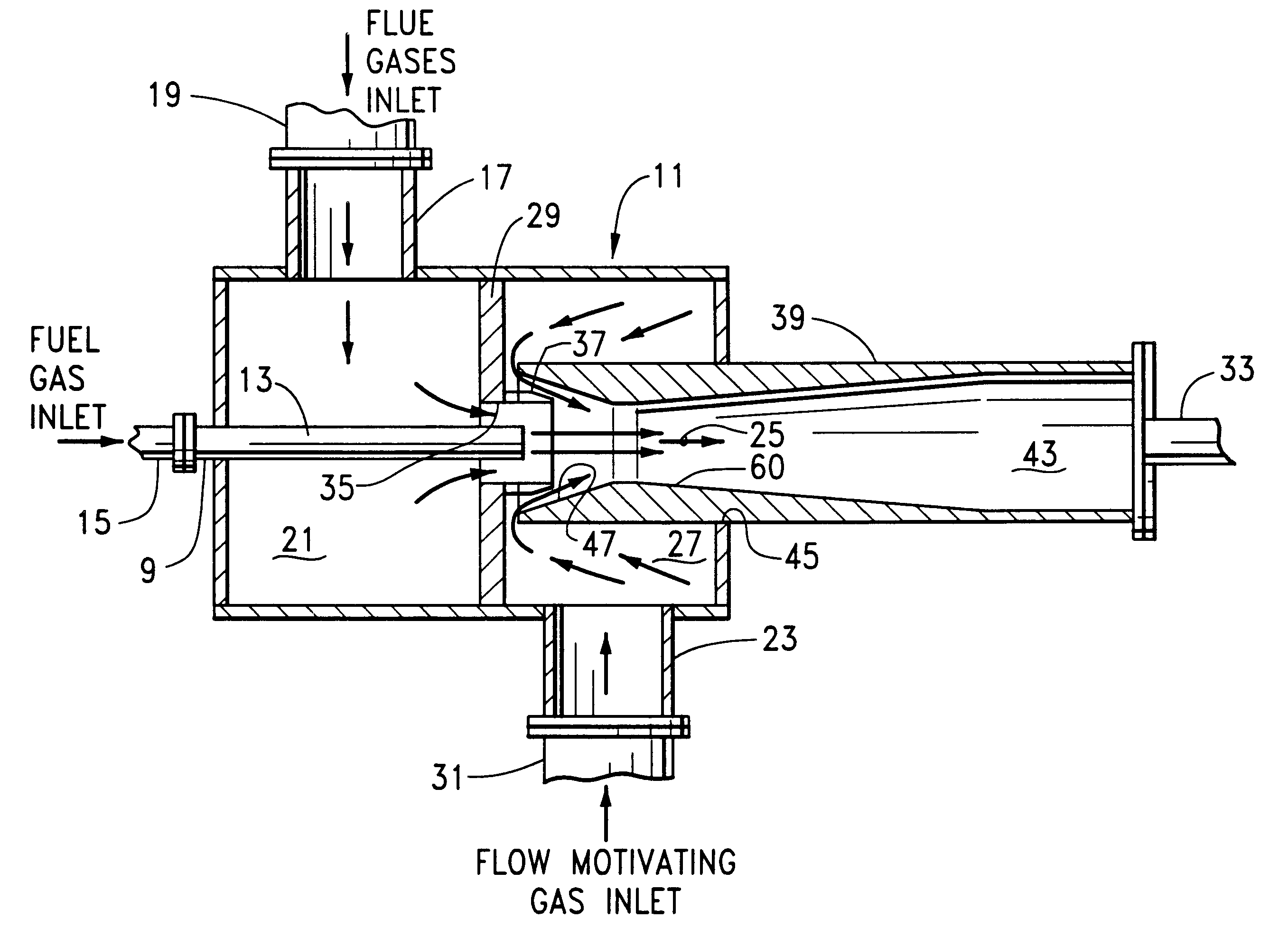
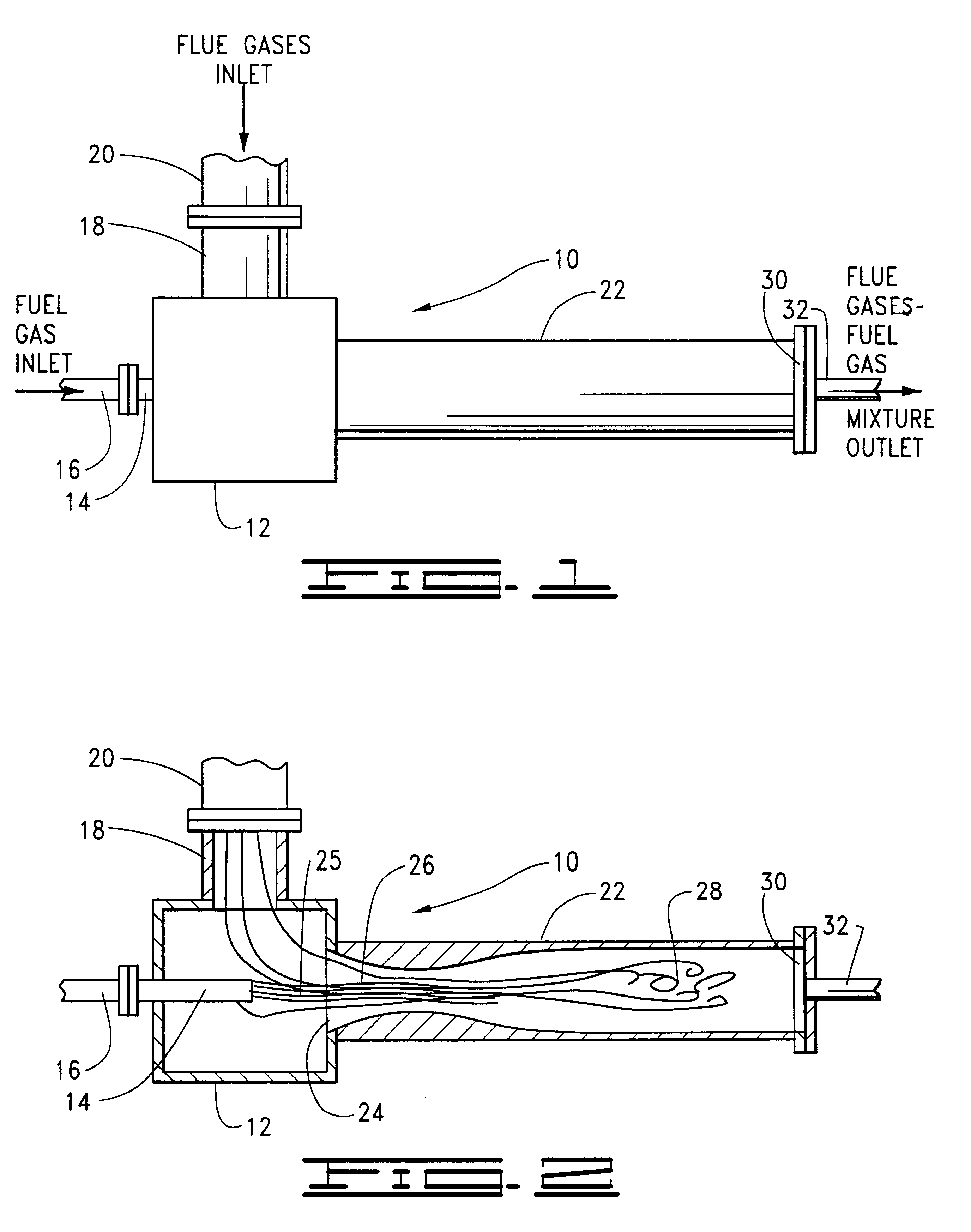
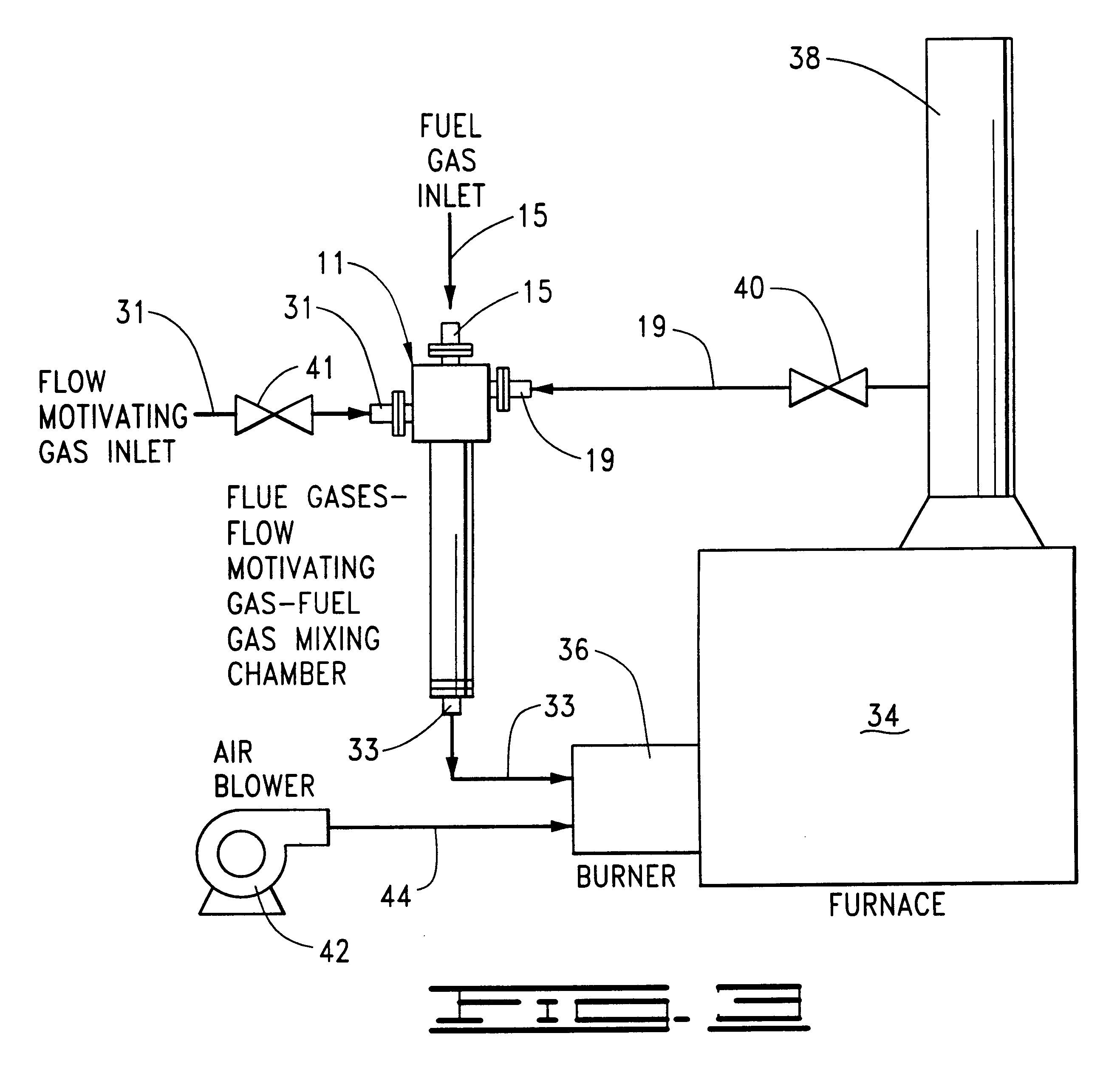
Fuel dilution methods and apparatus for NOx reduction
Methods and apparatus for reducing the content of nitrogen oxides in the flue gases produced by the combustion of fuel gas and combustion air introduced into a burner connected to a furnace are provided. The methods basically comprise the steps of conducting the combustion air to the burner, providing a chamber outside of the burner and furnace for mixing flue gases from the furnace with the fuel gas, discharging the fuel gas in the form of a fuel jet into the mixing chamber so that flue gases from the furnace are drawn into the chamber and mixed with and dilute the fuel gas therein and conducting the resulting mixture of flue gases and fuel gas to the burner wherein the mixture is combined with the combustion air and burned in the furnace.
Owner:JOHN ZINK CO LLC
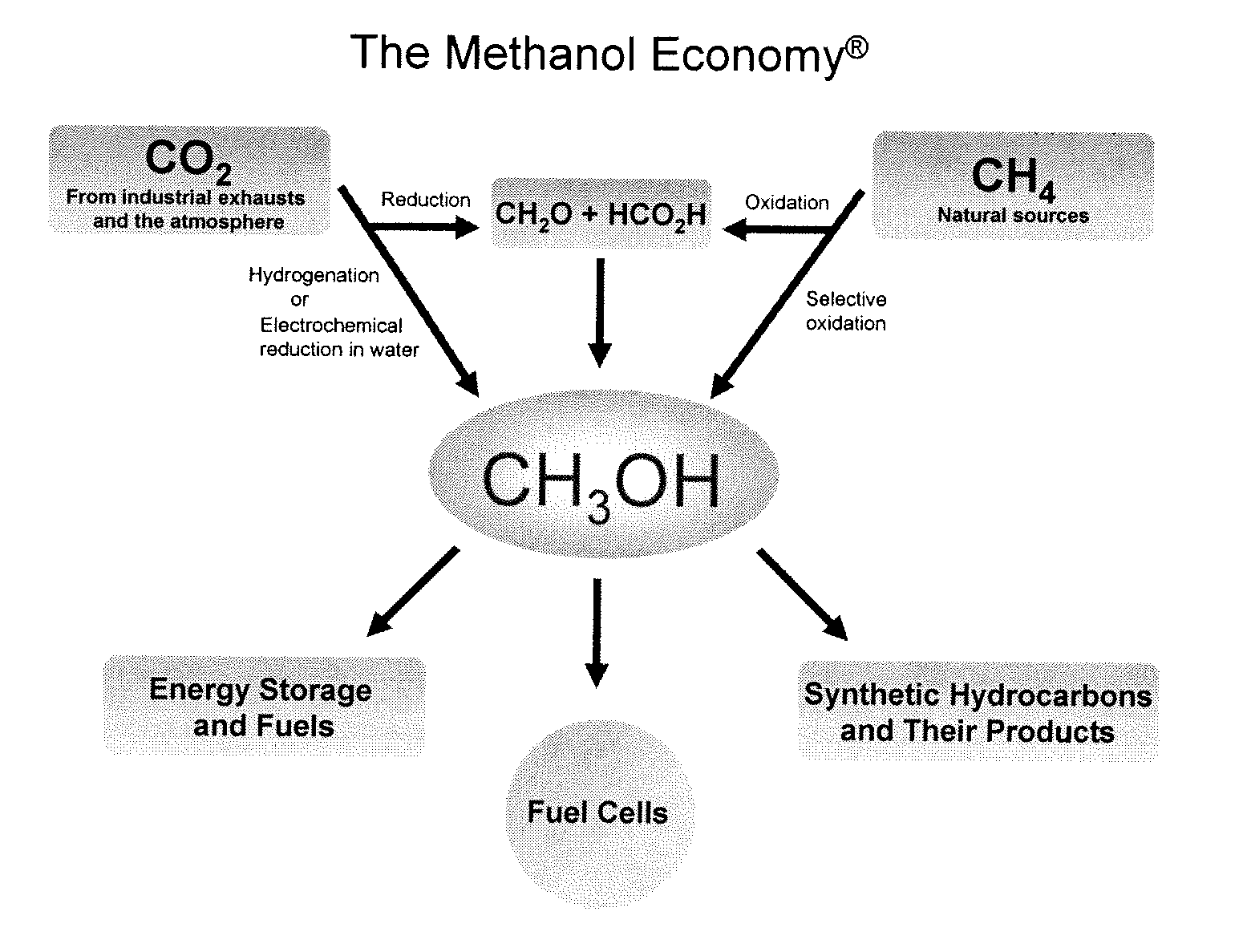
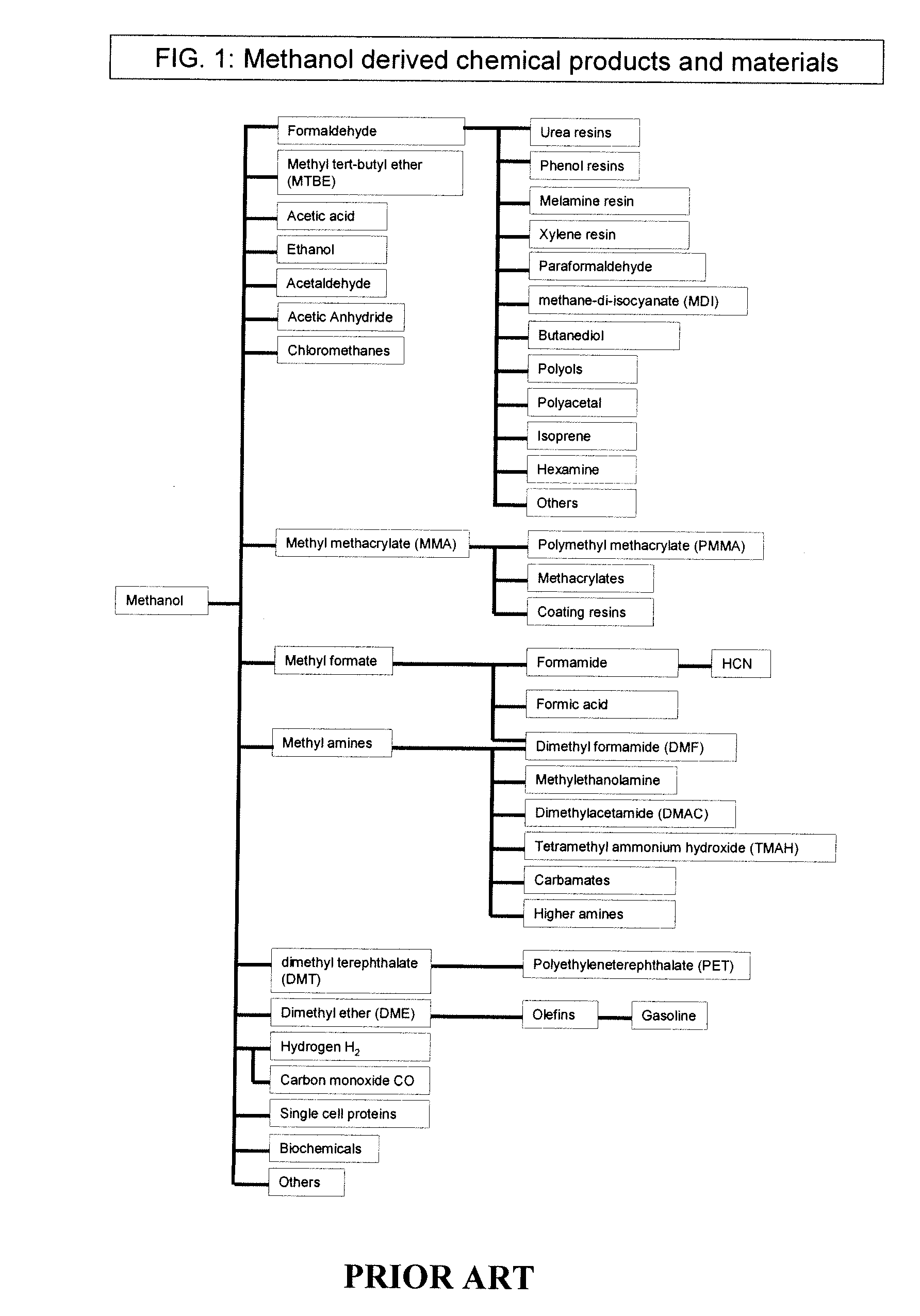
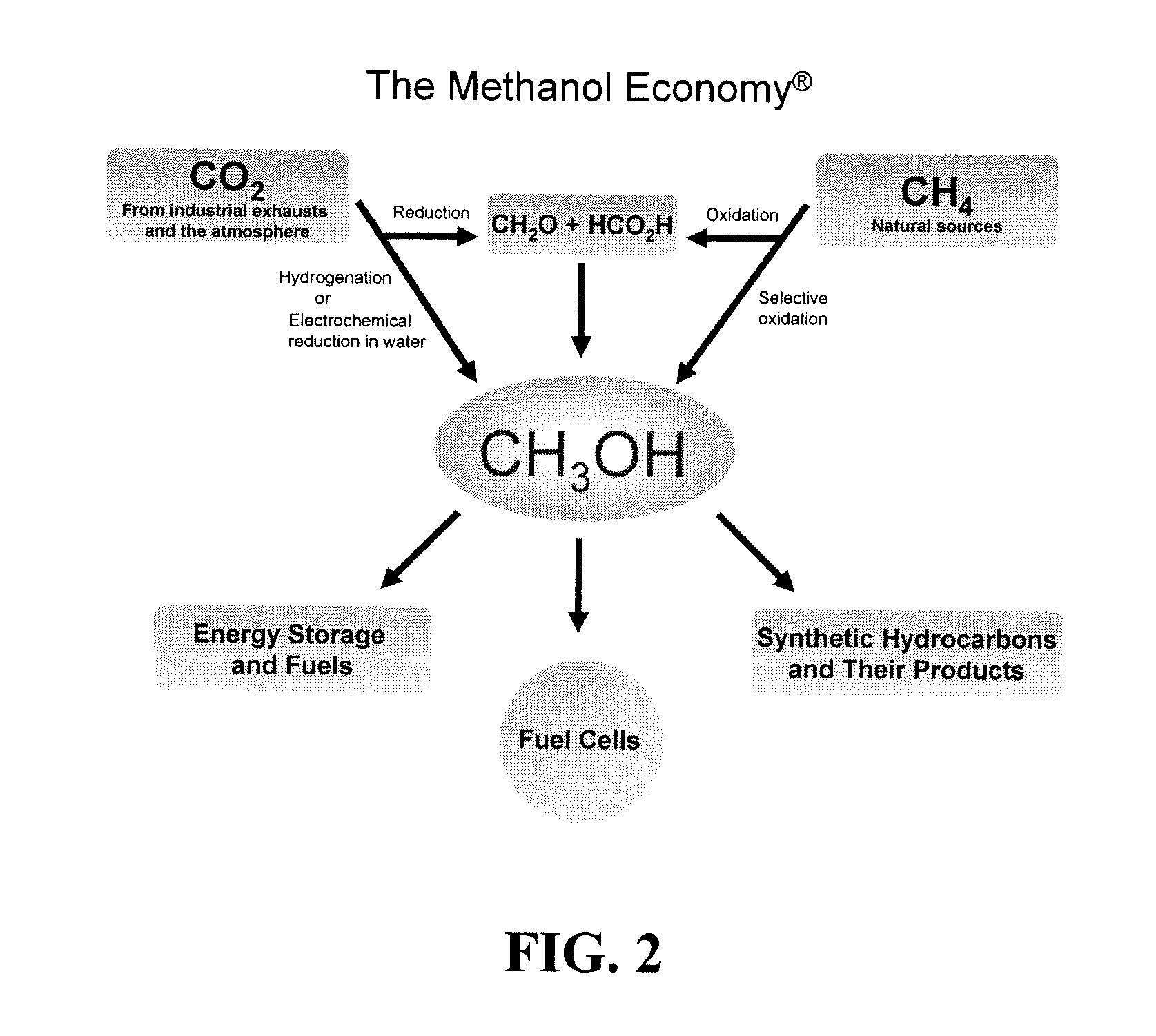
Efficient and selective chemical recycling of carbon dioxide to methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products
ActiveUS20070254969A1Avoid emissionsElectrolysis componentsOxygen compounds purification/separationElectrochemistryDimethyl ether
An efficient and environmentally beneficial method of recycling and producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning powerplants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by chemical or electrochemical reduction secondary treatment to produce essentially methanol, dimethyl ether and derived products.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
System and method for carbon dioxide capture and sequestration
A method and a system capable of removing carbon dioxide directly from ambient air, and obtaining relatively pure CO2. The method comprises the steps of generating usable and process heat from a primary production process;applying the process heat from said primary process to water to co-generate substantially saturated steam, alternately repeatedly exposing a sorbent to removal and to capture and regeneration system phases, wherein said sorbent is alternately exposed to a flow of ambient air during said removal phase, thereby enabling said sorbent to sorb, and therefore remove, carbon dioxide from said ambient air, and to a flow of the co-generated steam during the regeneration and capture phase, after the sorbent has adsorbed the carbon dioxide, thereby enabling regeneration of such sorbent, and the resultant capture in relatively pure form of the adsorbed carbon dioxide. This process can also be carried out in more efficient form by admixing with the air a minor amount of a flue gas or an effluent gas containing a higher concentration of carbon dioxide than exists in the atmosphere, most preferably following a pre-treatment. The carbon dioxide can be stored for further use, or sequestered permanently following the capture: The adsorbent is exposed to air at substantially ambient conditions and the adsorbent is exposed to the co-generated steam at a temperature in the range of not greater than about 130° C. The system provides the sorbent substrate and equipment for carrying out the above method, and provides for obtaining purified carbon dioxide for further use in agriculture and chemical processes, including manufacturing hydrocarbon fuels, or for permanent sequestration, as needed.
Owner:GLOBAL THERMOSTAT OPERATIONS LLC
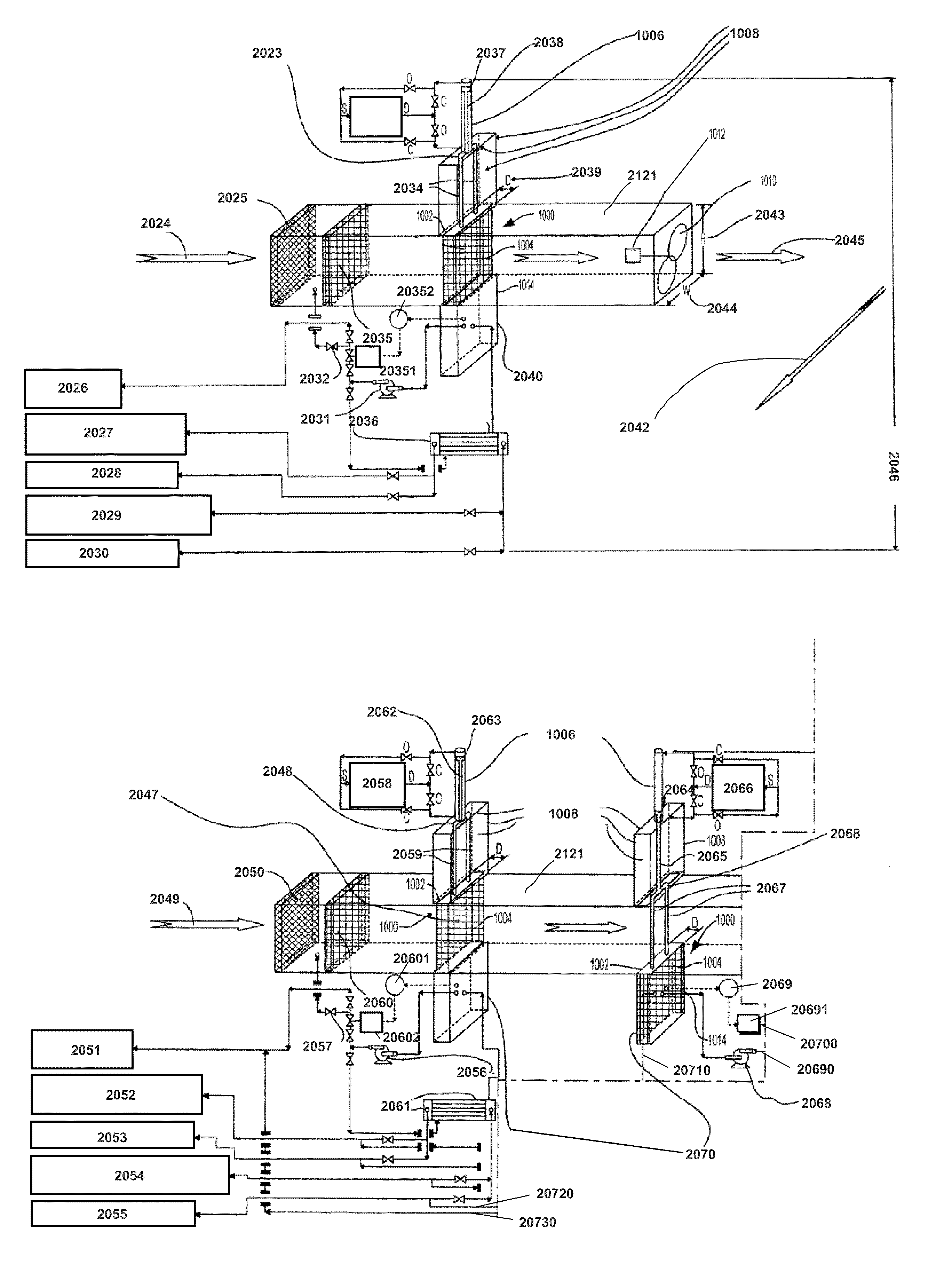
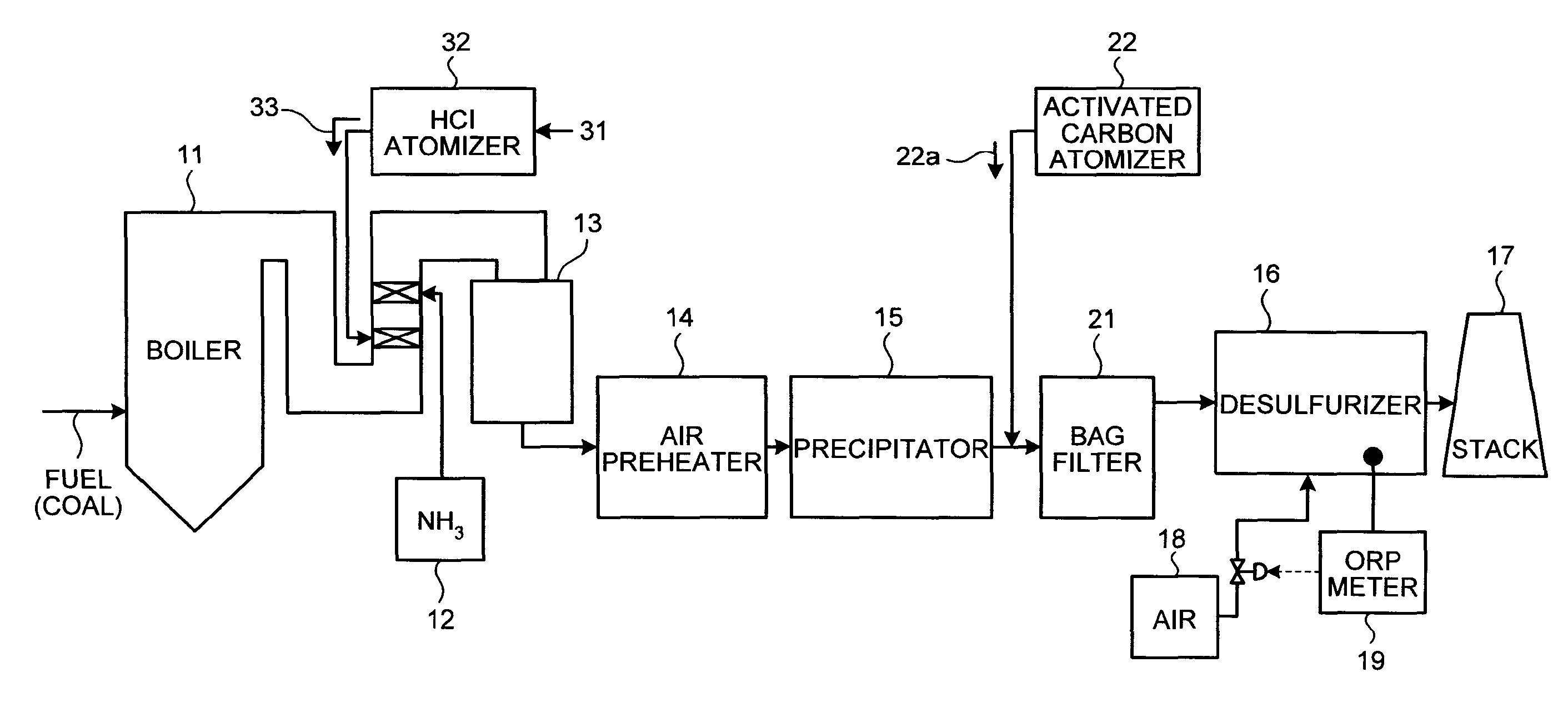
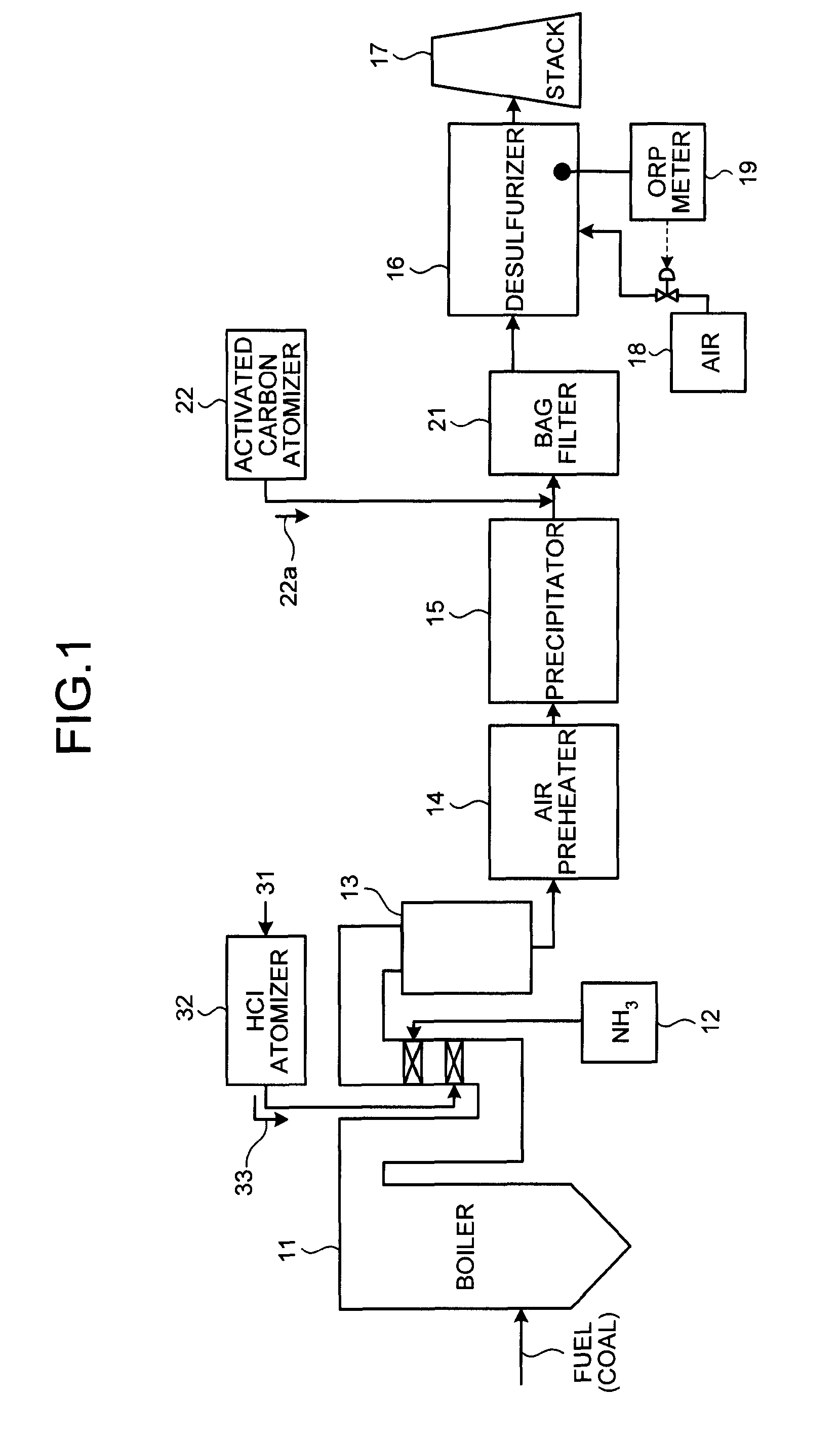
Flue gas control system of coal combustion boiler and operating method thereof
ActiveUS8071060B2Reduce operating costsCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsAir preheaterParticulates
A flue gas control system of a coal combustion boiler comprises an HCl atomizer that sprays hydrogen chloride to flue gas from a coal combustion boiler that uses coal as a fuel; NOx removing apparatus that removes nitrogen oxides by ammonia denitration by adding ammonia to the flue gas after spraying hydrogen chloride and oxidizes mercury; an air preheater that recovers heat in the gas after removal of nitrogen oxides; a precipitator that removes particulates in the gas; an activated carbon atomizer that sprays activated carbon into the gas after particulate collection; a bag filter that collects activated carbon having adsorbed mercury; a desulfurizer that removes sulfur oxides in the flue gas after removal of activated carbon; a stack that discharges the gas which has undergone desulfurization to outside; and an ORP meter that measures an oxidation reduction potential for feeding air to a slurry absorbent in the desulfurizer.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Method for removal of mercury emissions from coal combustion
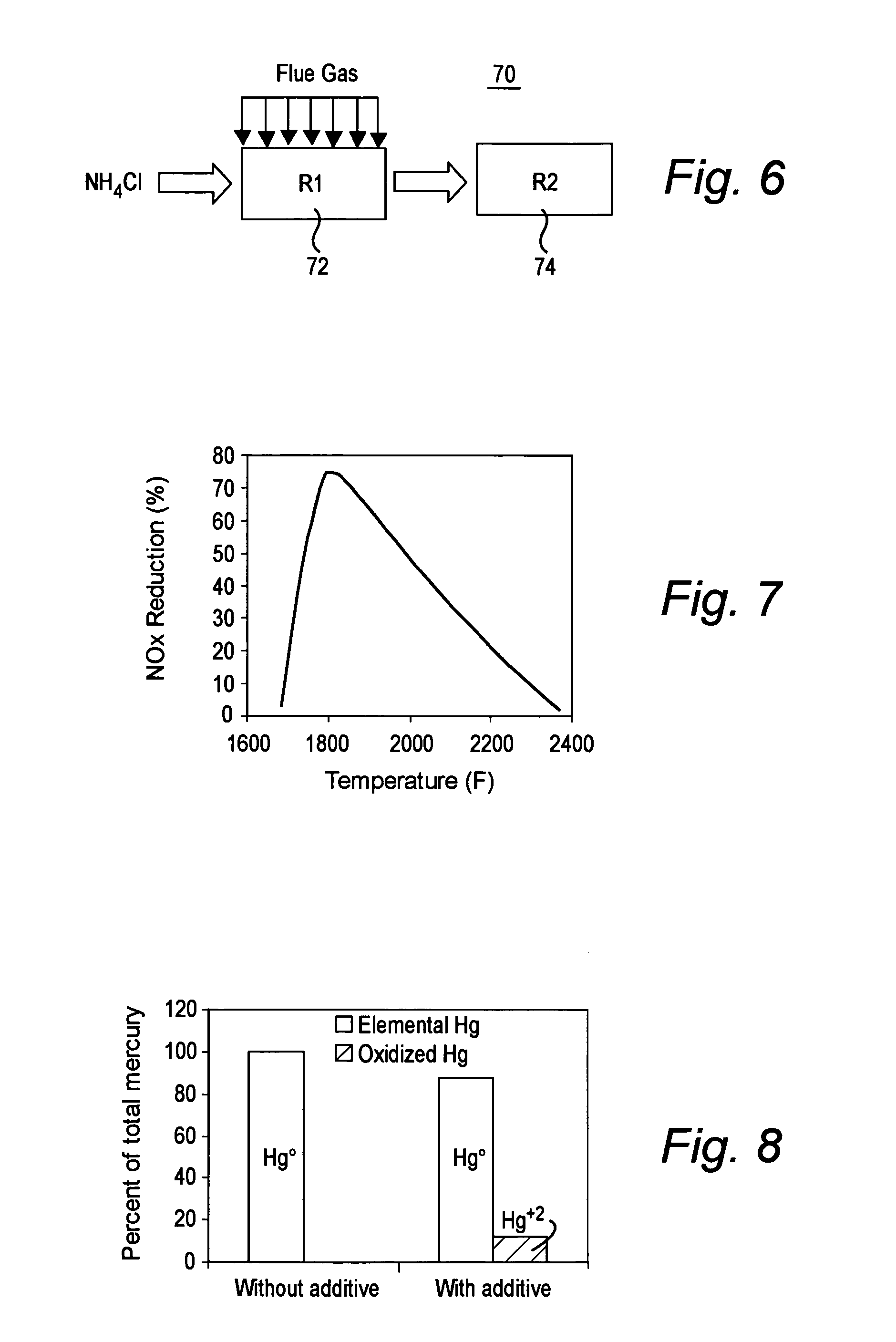
A method to reduce emissions in flue gas due to combustion of coal in a combustion unit including the steps of: combusting coal in a primary combustion zone of the combustion unit; releasing elemental mercury from the combustion into the flue gas; injecting NH4Cl, NH4Br, or NH4I into the flue gas; oxidizing the elemental mercury with halogen from the additive; adsorbing the oxidized mercury generated by the combustion of the coal with an adsorbent in the flue gas, and collecting the adsorbent with the oxidized mercury in a combustion waste treatment system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com