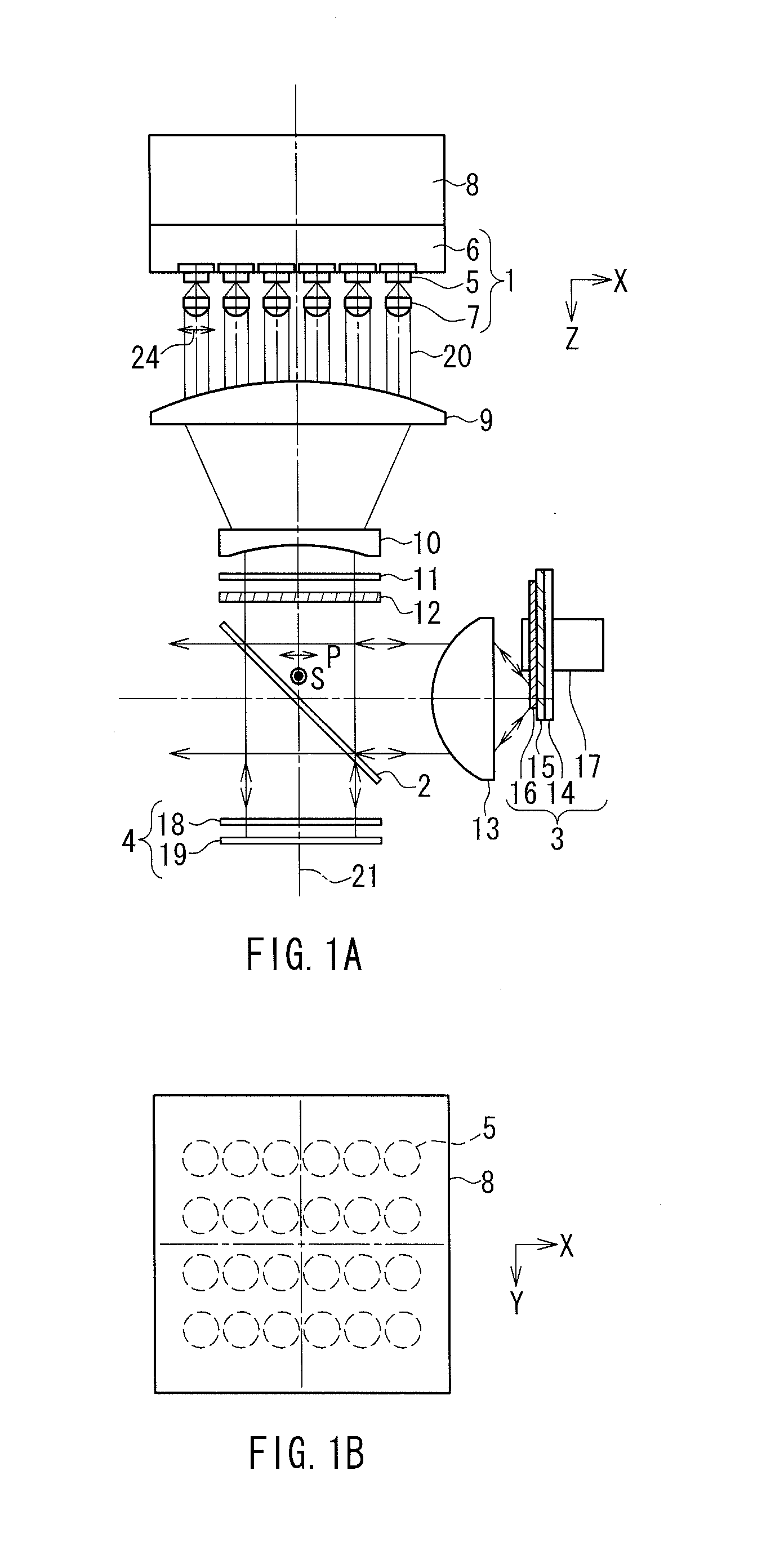
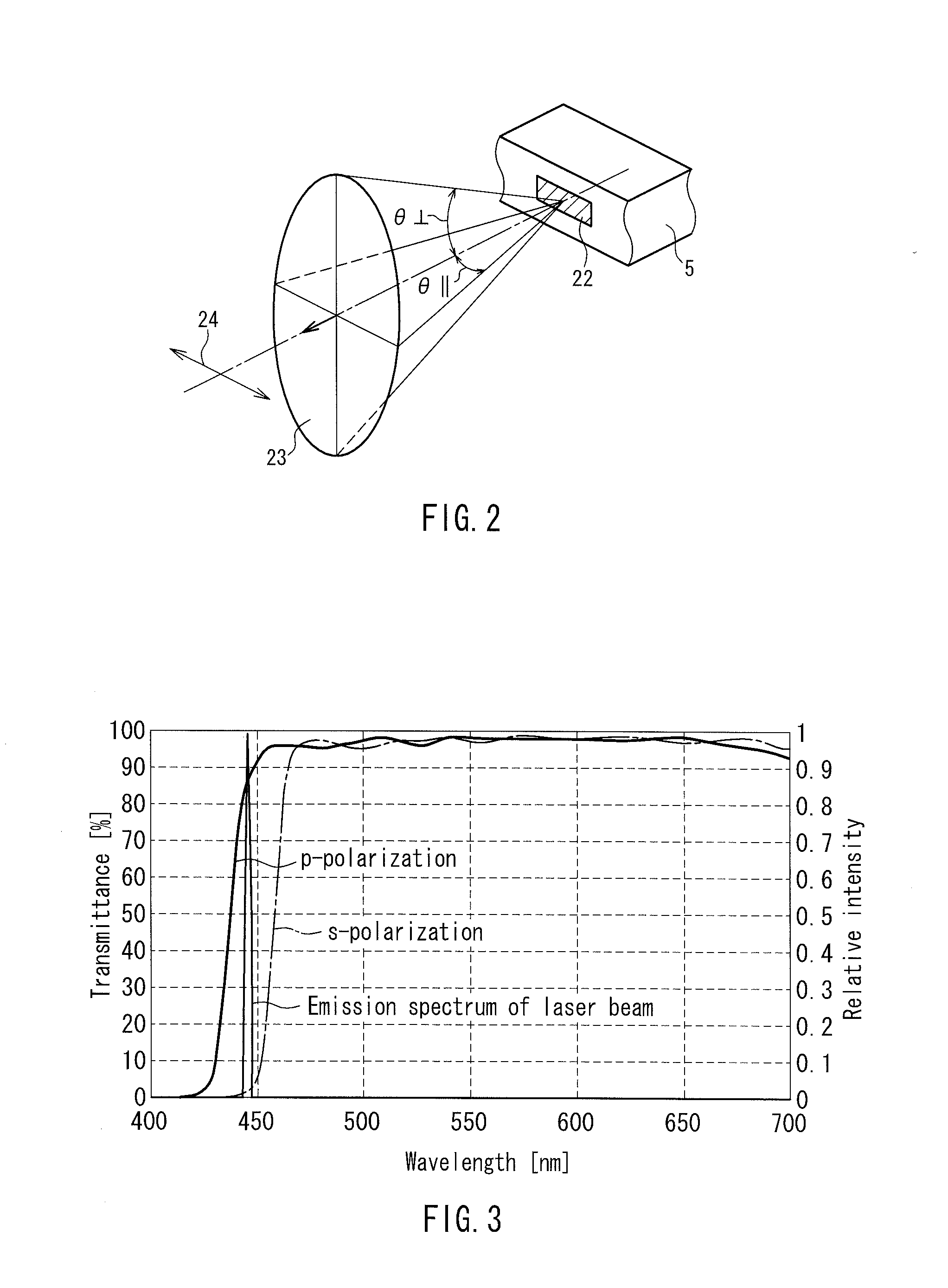
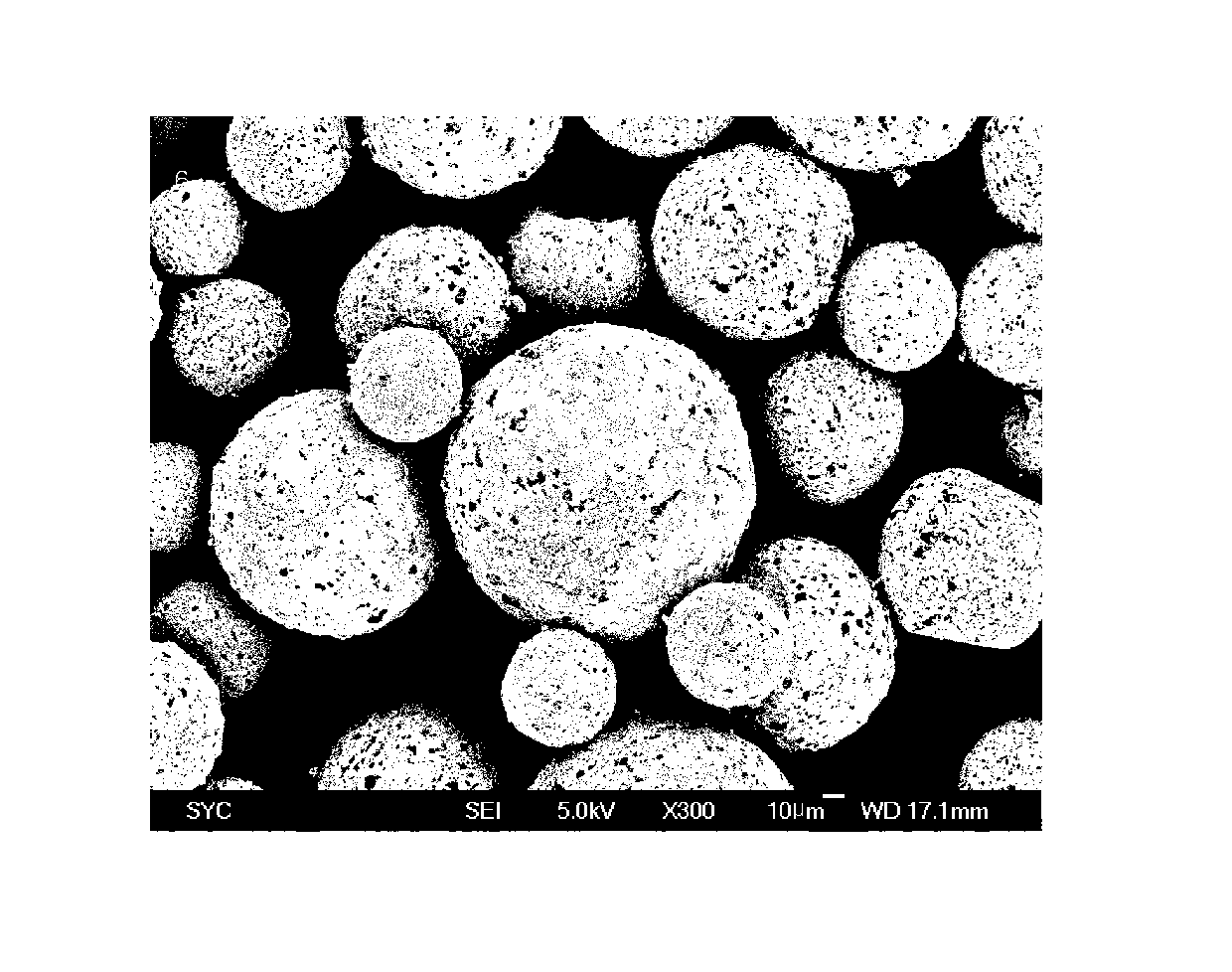
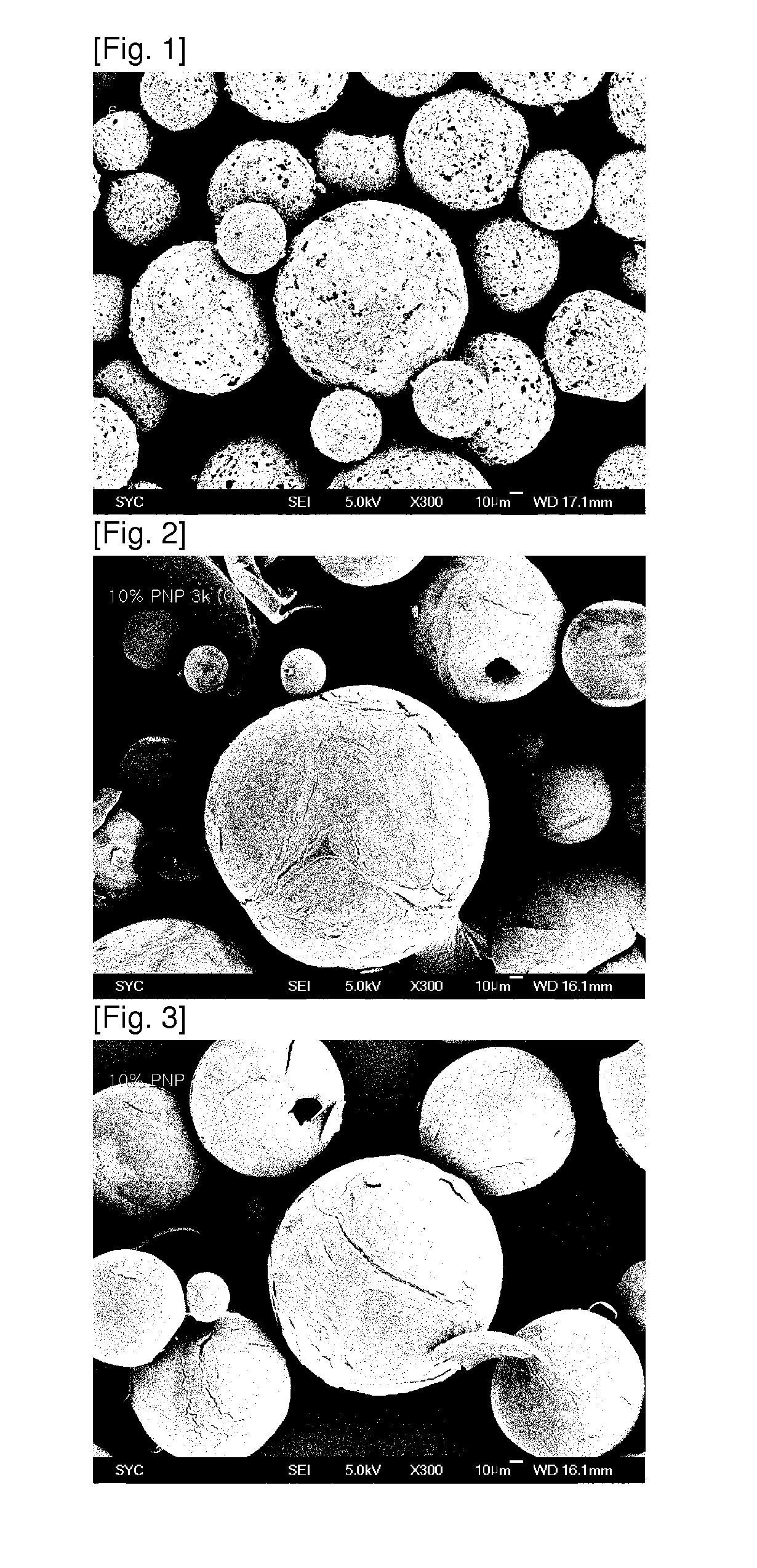
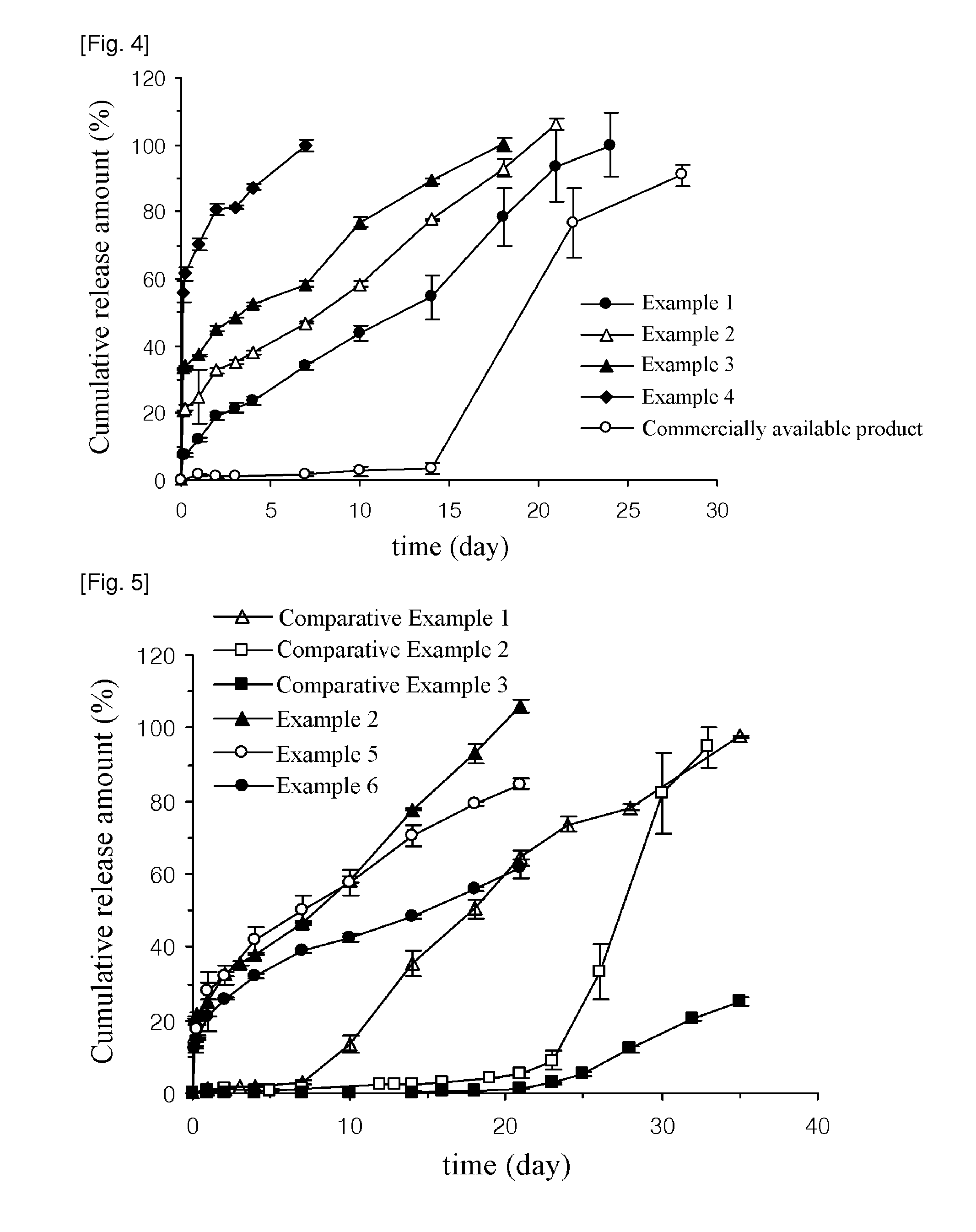
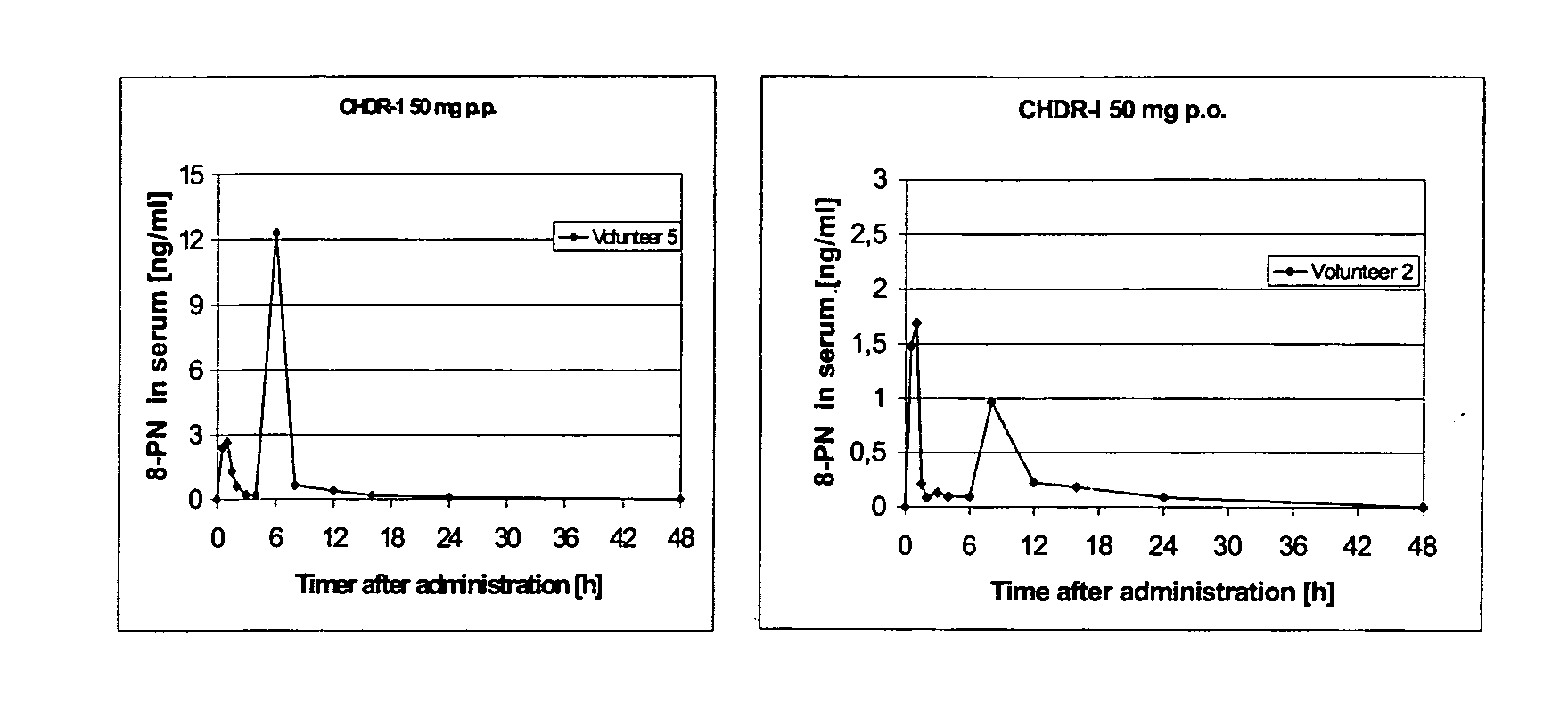
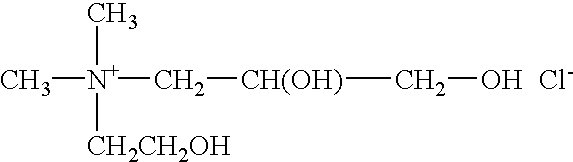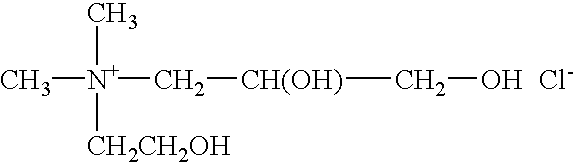Patents
Literature
754results about How to "Efficient Concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
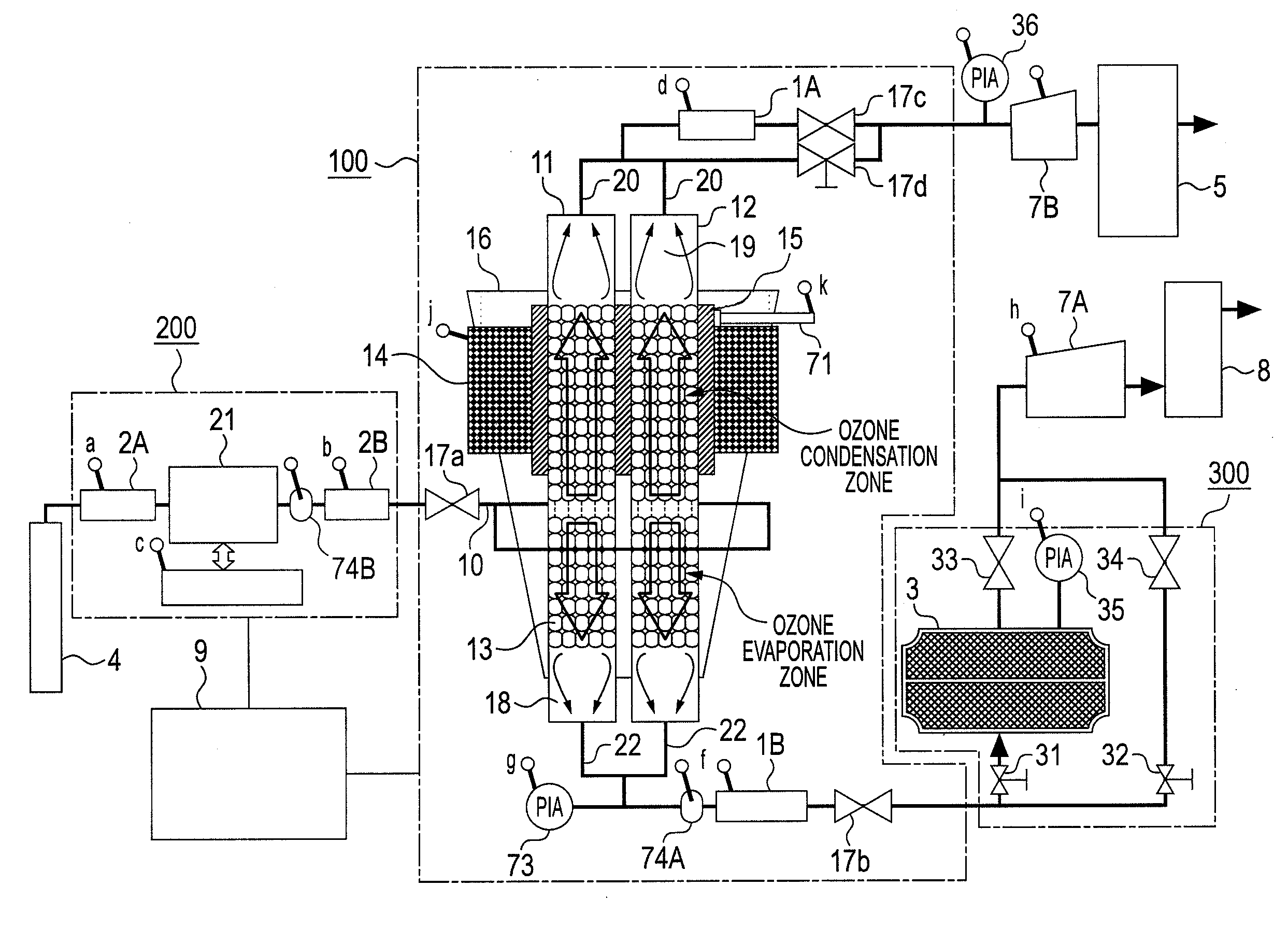
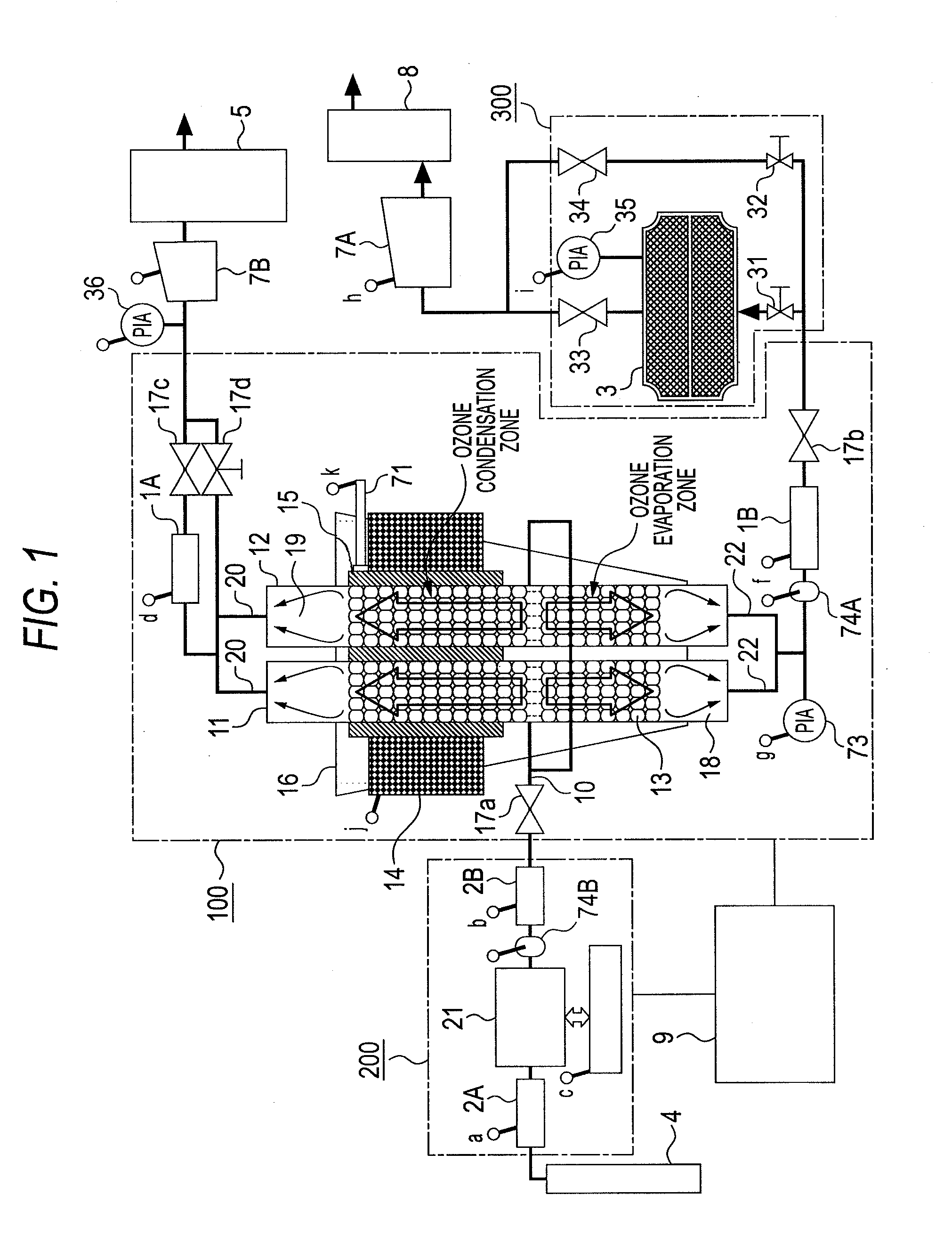
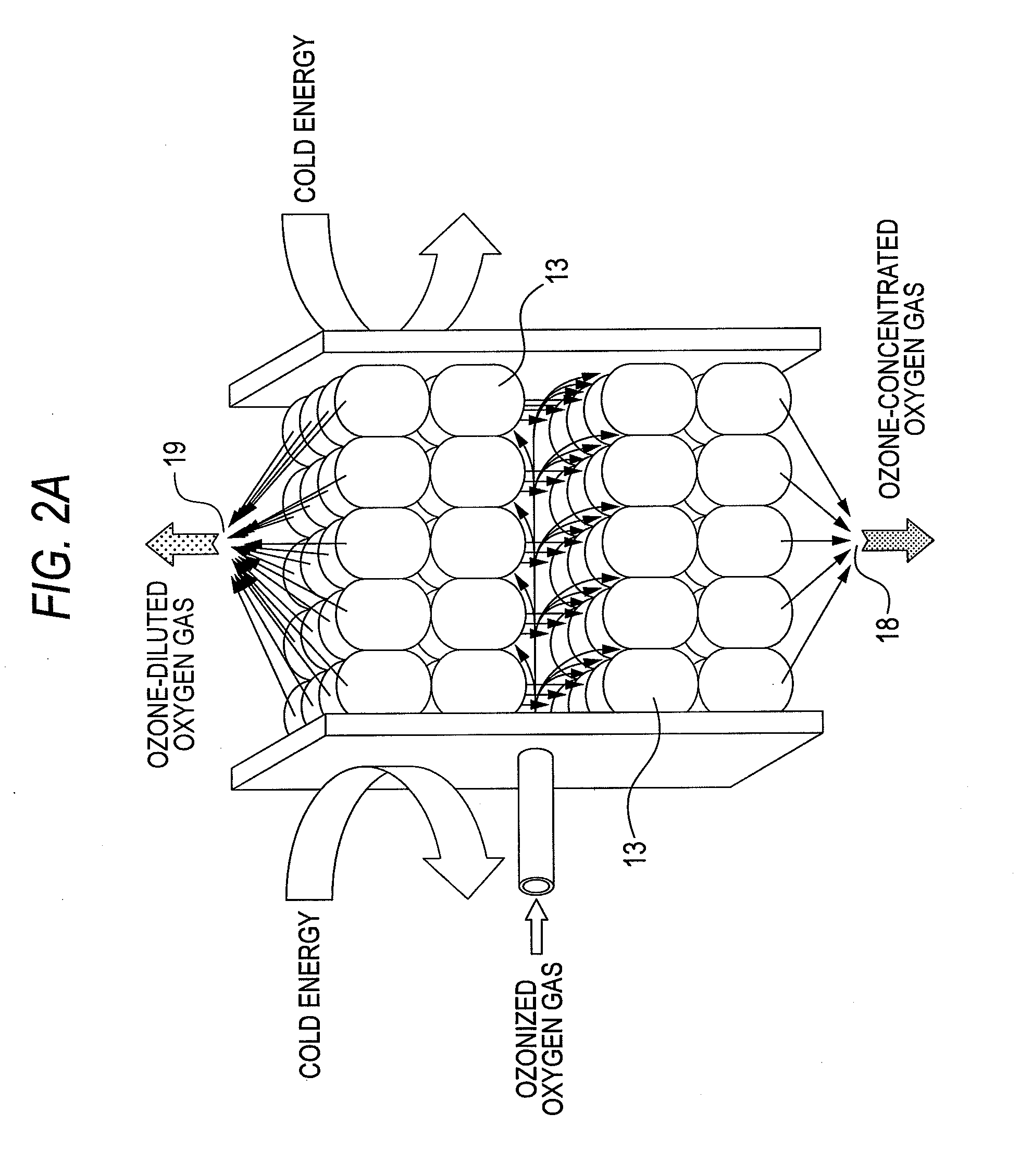
Apparatus for concentrating and diluting specific gas and method for concentrating and diluting specific gas
ActiveUS20100162752A1Improve processing efficiencySmall sizeSolidificationGas treatmentSpherical shapedVaporization
One ozone concentrating chamber is provided therein with a part of a cooling temperature range where ozone can be selectively condensed or an oxygen gas can be selectively removed by transmission from an ozonized oxygen gas, and a part of a temperature range where condensed ozone can be vaporized, and condensed ozone is vaporized by moving condensed ozone with flow of a fluid or by gravitation to the part where condensed ozone can be vaporized, whereby the ozonized oxygen gas can be increased in concentration. Such a constitution is provided that a particle material 13 for condensation and vaporization filled in the ozone concentrating chambers 11 and 12 has a spherical shape of a special shape with multifaceted planes on side surfaces, or an oxygen transmission membrane 130 capable of selectively transmitting an oxygen gas in an ozone gas is provided.
Owner:TOSHIBA MITSUBISHI-ELECTRIC IND SYST CORP
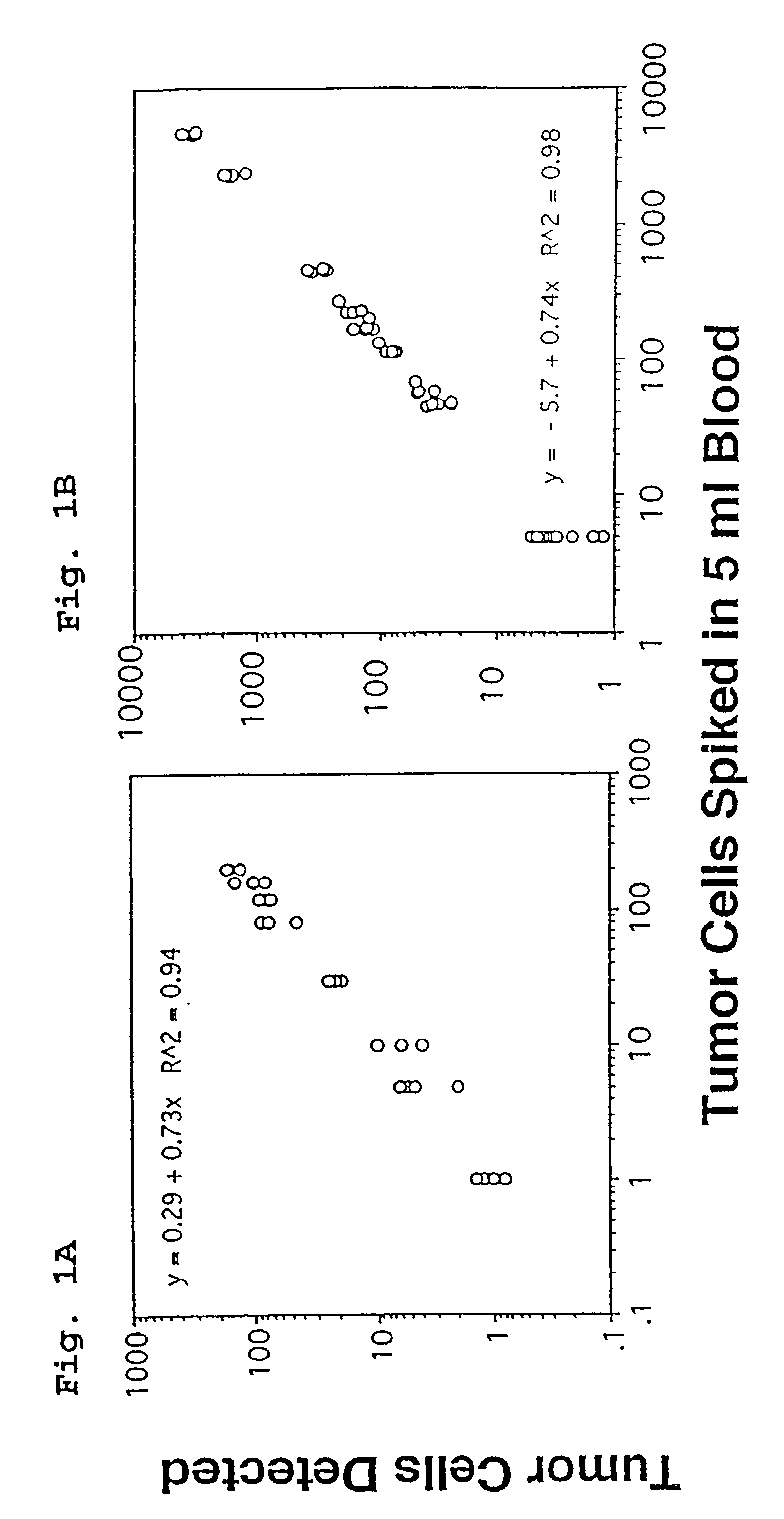
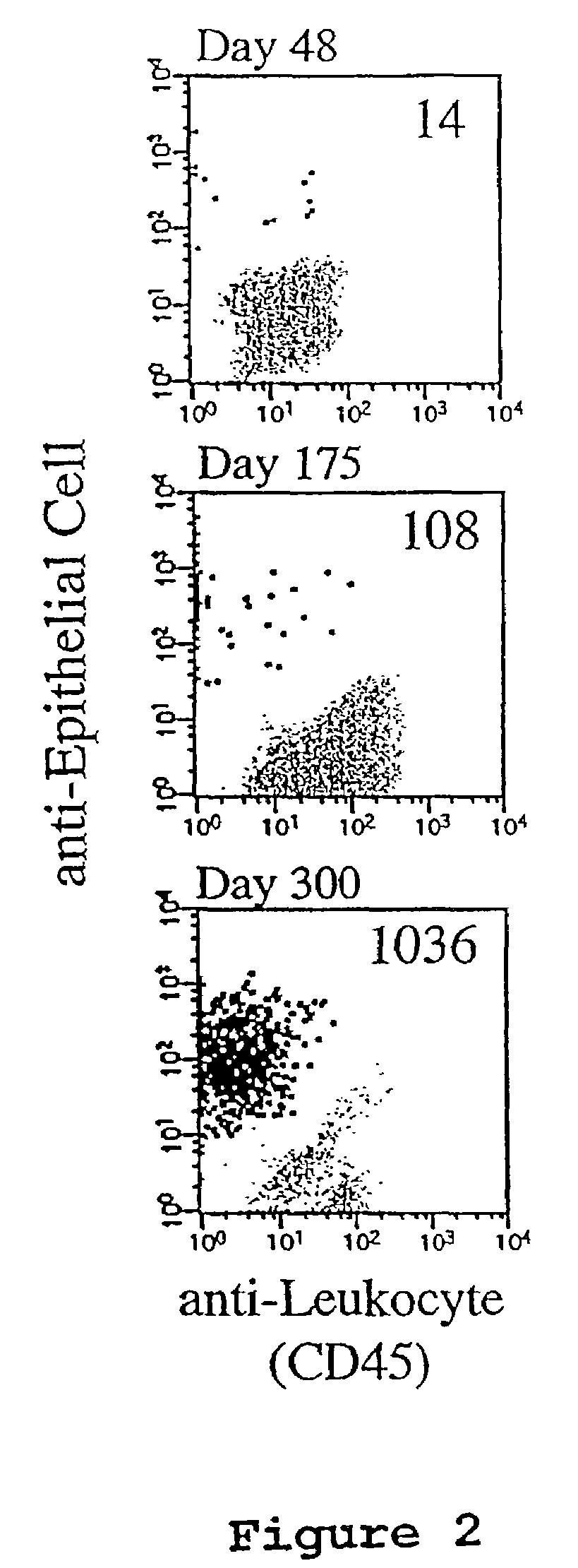
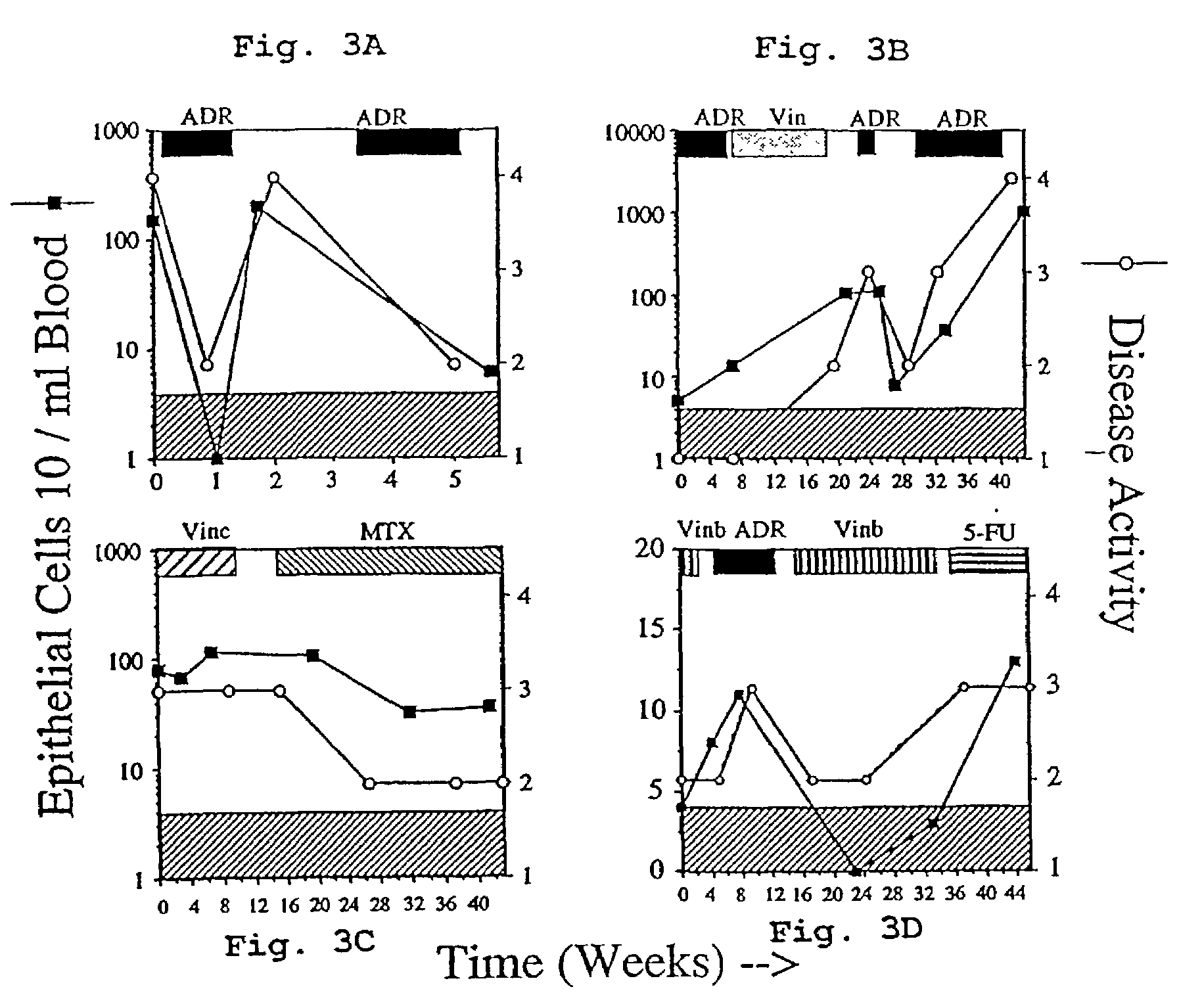
Methods and reagents for the rapid and efficient isolation of circulating cancer cells
InactiveUS7332288B2Efficient ConcentrationEasy to detectNanomagnetismMicrobiological testing/measurementCirculating cancer cellCell sensitivity
A highly sensitive assay is disclosed which combines immunomagnetic enrichment with multiparameter flow cytometric and immunocytochemical analysis to detect, enumerate and characterize carcinoma cells in the blood. The assay can detect one epithelial cell or less in 1 ml of blood and has a greater sensitivity than conventional PCR or immunohistochemistry by 1-2 orders of magnitude. In addition, the assay facilitates the biological characterization and staging of carcinoma cells.
Owner:MENARINI SILICON BIOSYSTEMS SPA
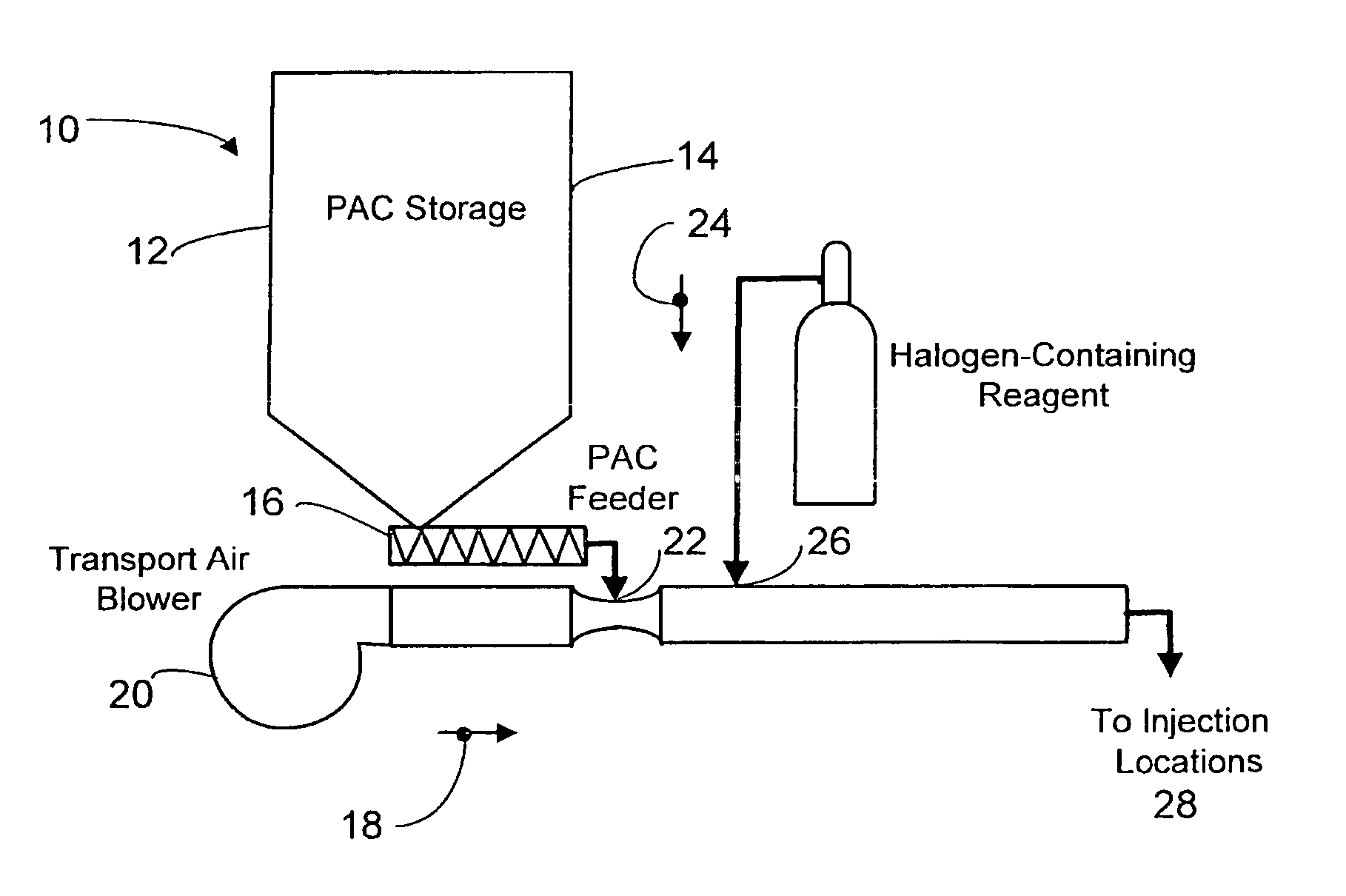
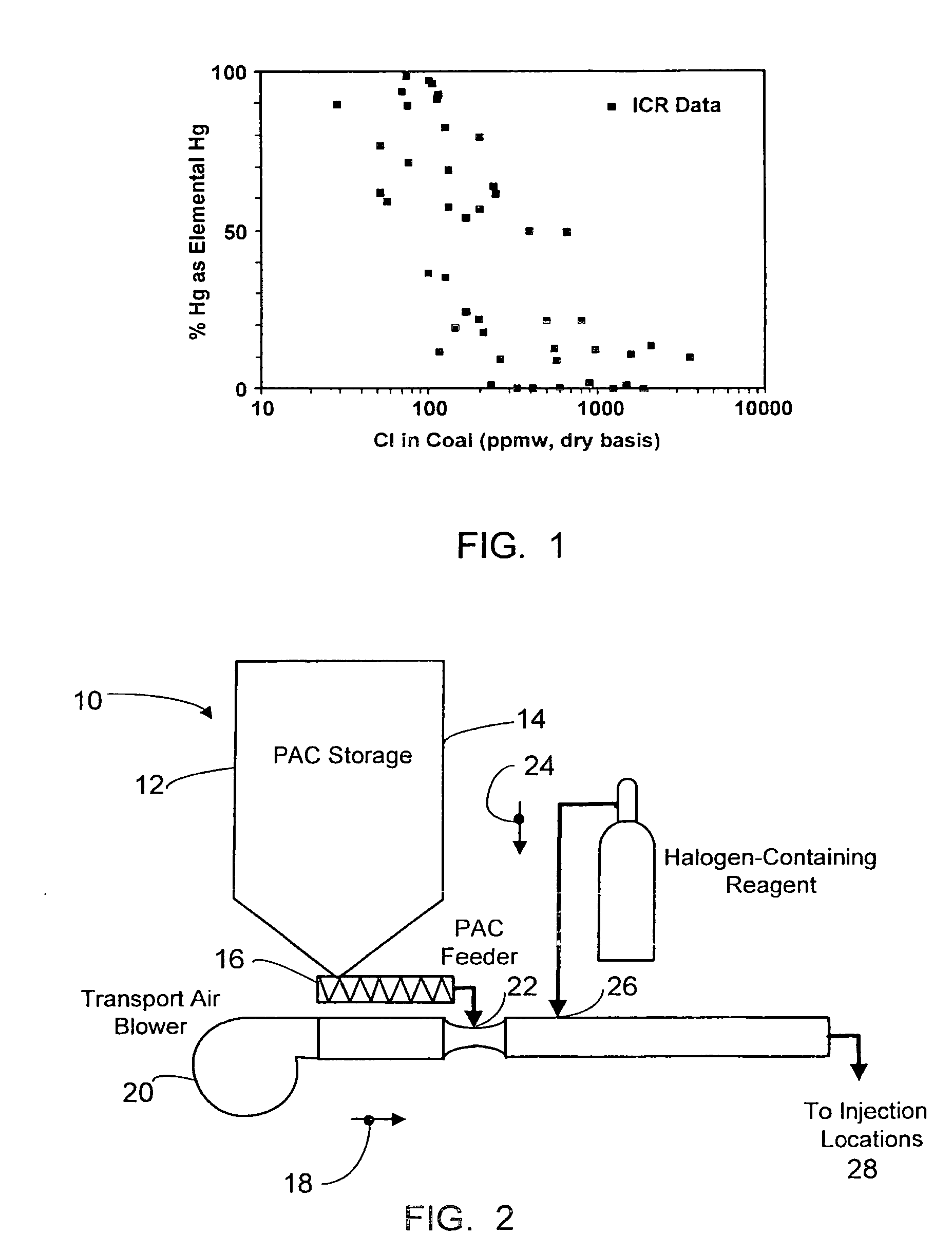
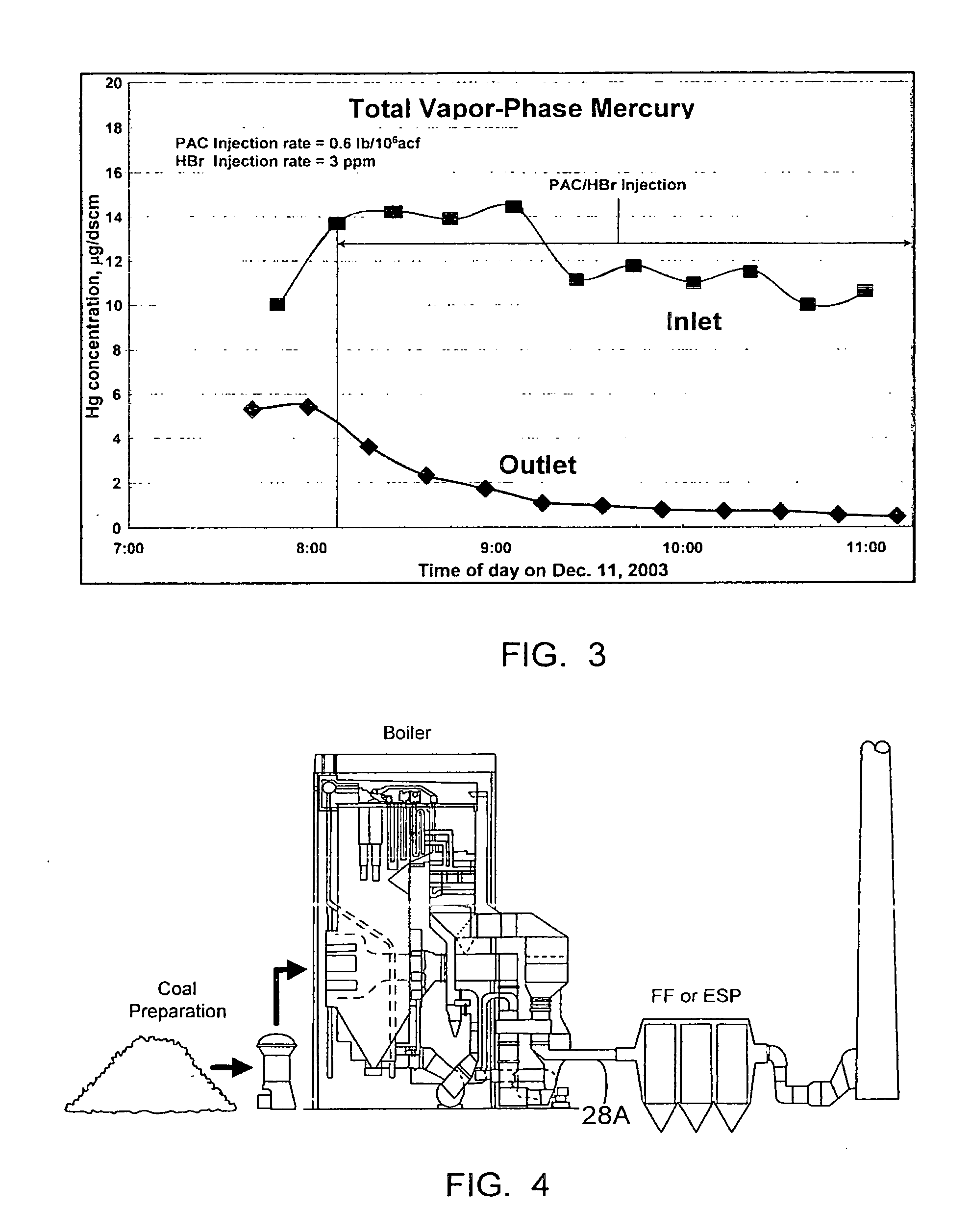
Dynamic halogenation of sorbents for the removal of mercury from flue gases
InactiveUS20070180990A1Efficient ConcentrationEasy to captureGas treatmentUsing liquid separation agentHalogenSorbent
A halogen-containing gas is injected into a flowing transport air / sorbent stream at a point close to the point where the sorbent and transport air first mix to maximize the residence time available for the halogen-containing compound to be adsorbed onto the sorbent surface prior to the sorbent being injected into a flue gas containing mercury. This process maximizes the benefit and utilization of the halogen-containing reagent by placing it exactly where it is needed to facilitate elemental mercury removal—on the surface of the sorbent. The sorbent particles with their loading of adsorbed halogen-containing reagent enter the flue gas with a high reactivity for the removal of elemental mercury.
Owner:THE BABCOCK & WILCOX CO
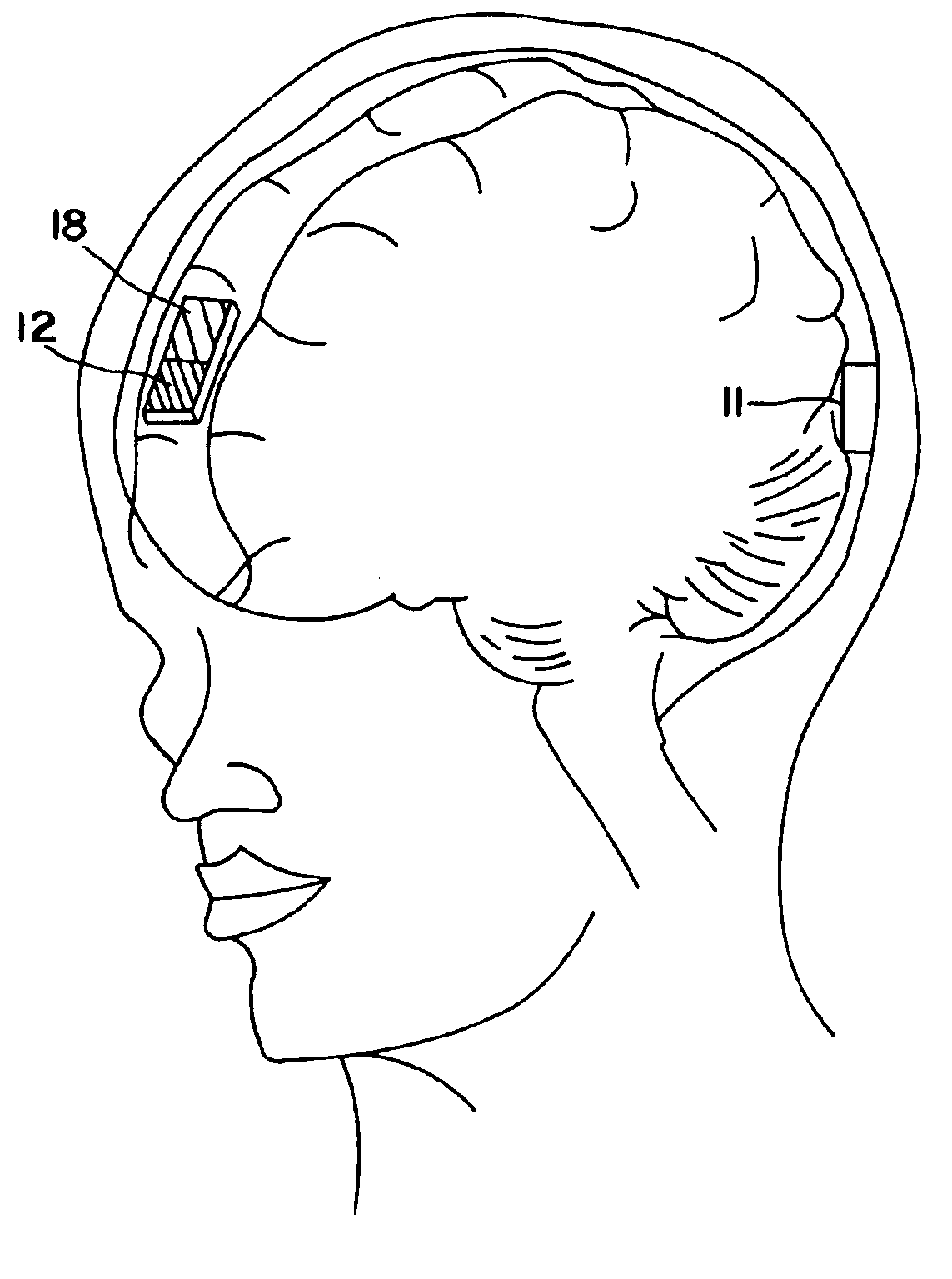
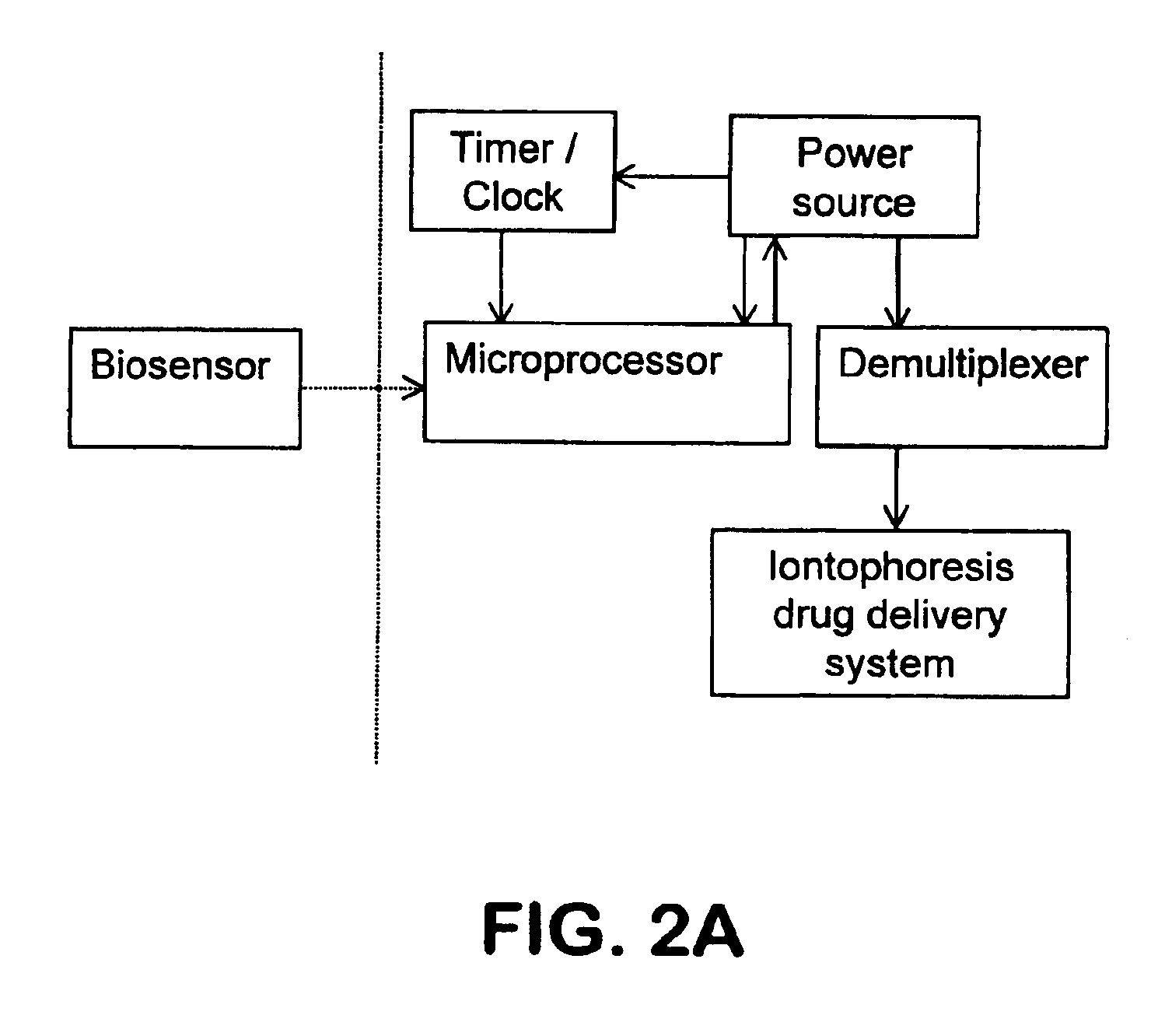
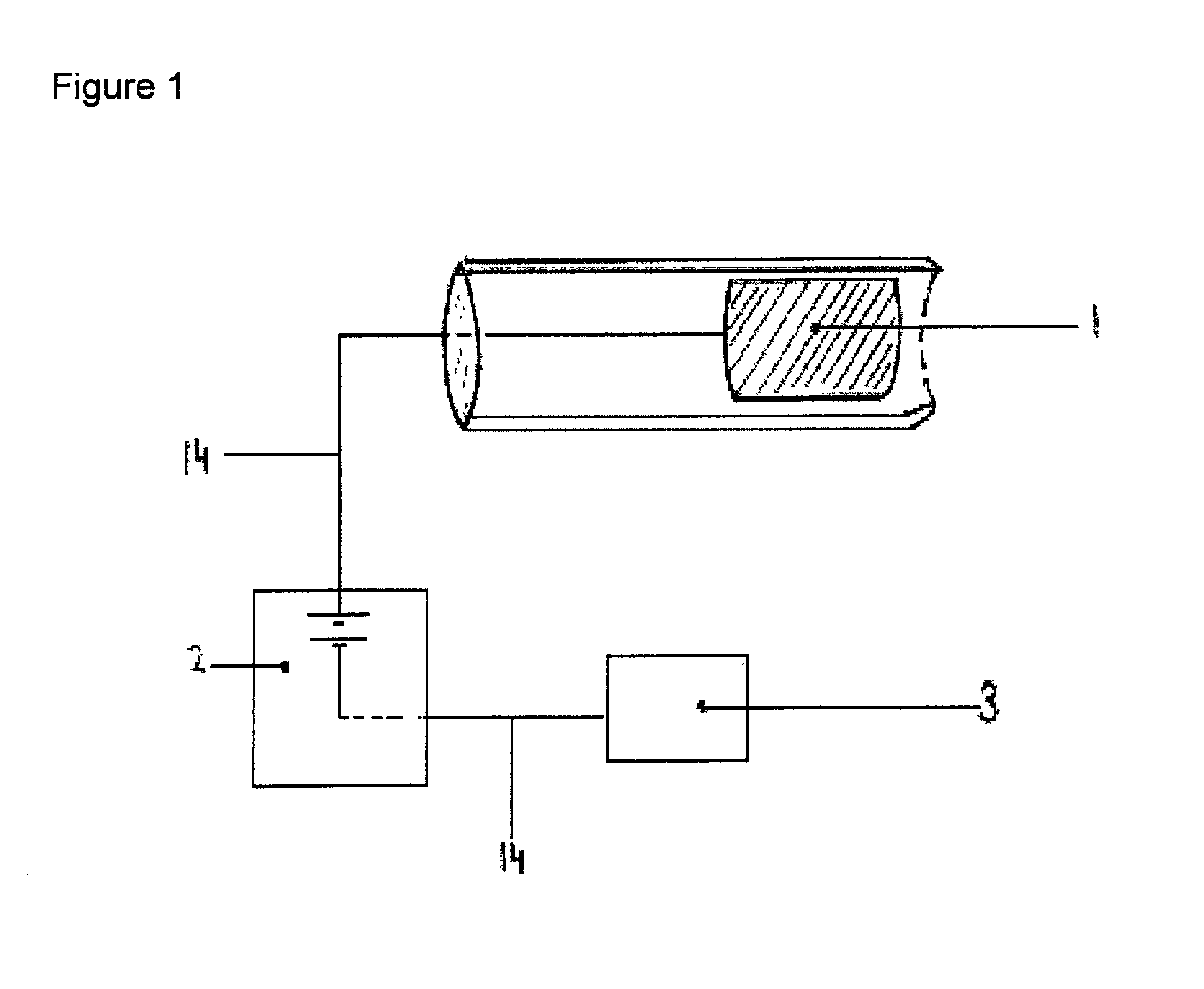
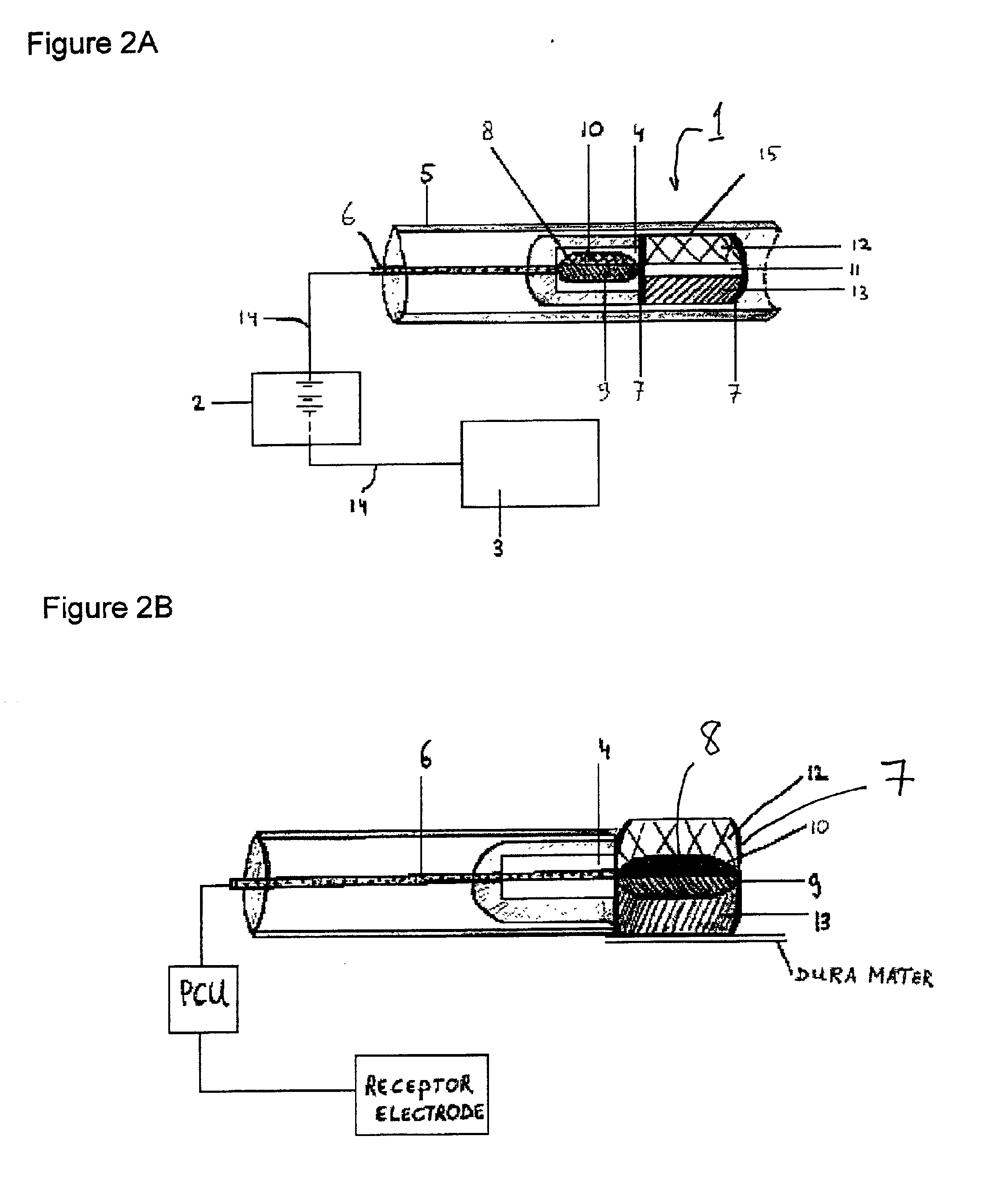
Methods and apparatus for enhanced and controlled delivery of a biologically active agent into the central nervous system of a mammal
InactiveUS7033598B2Enhanced and controlled deliveryReduce applicationsElectrotherapyPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNervous systemActive agent
Disclosed are invasive and non-invasive central nervous system (CNS) drug delivery methods and devices for use in these methods that essentially circumvent the blood-brain barrier. More specifically, the disclosed methods and devices utilize iontophoresis as delivery technique that allows for enhanced delivery of a biologically active agent into the CNS of a mammal as well as for (pre)-programmable and controlled transport.
Owner:INTRABRAIN INT
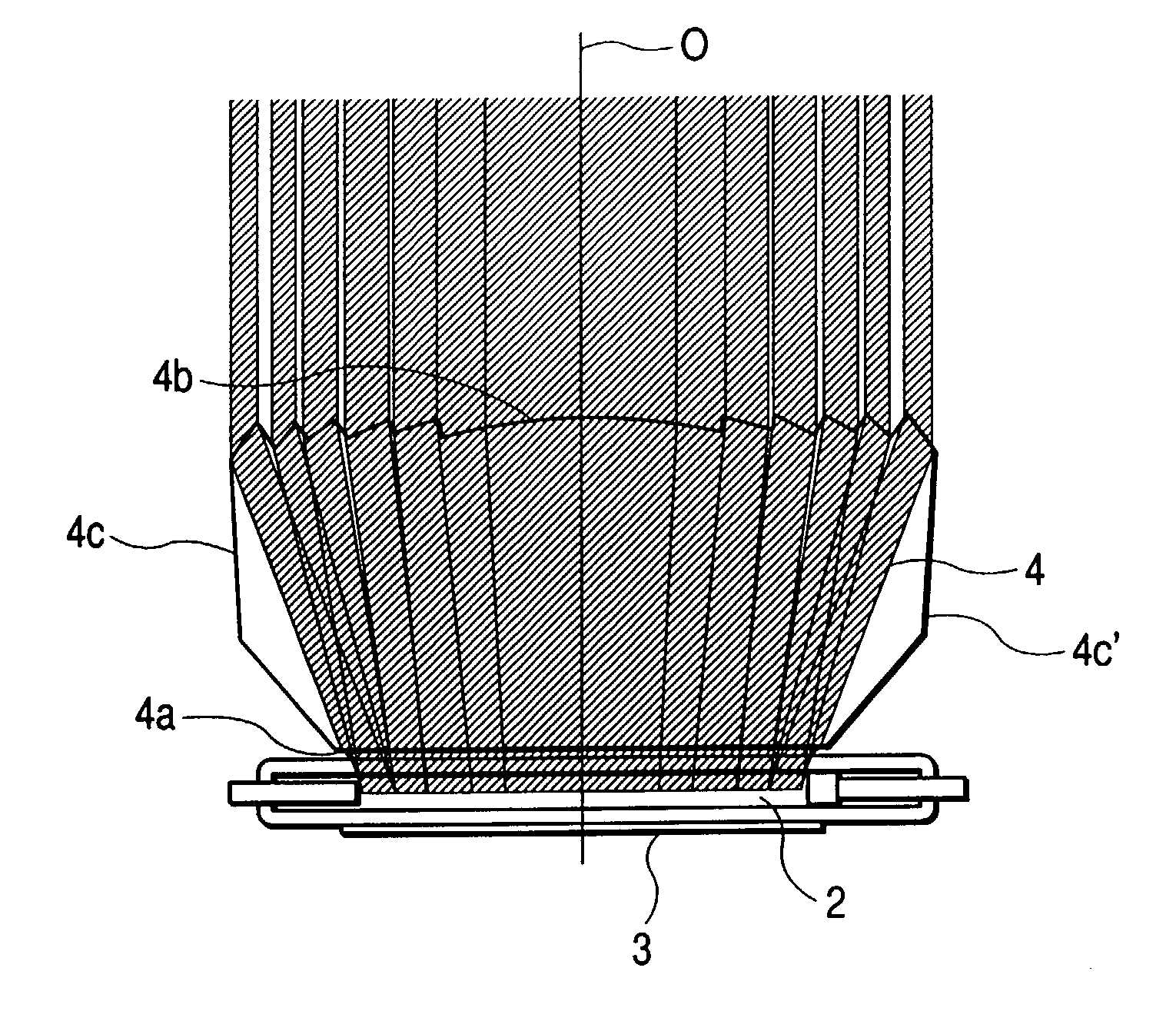
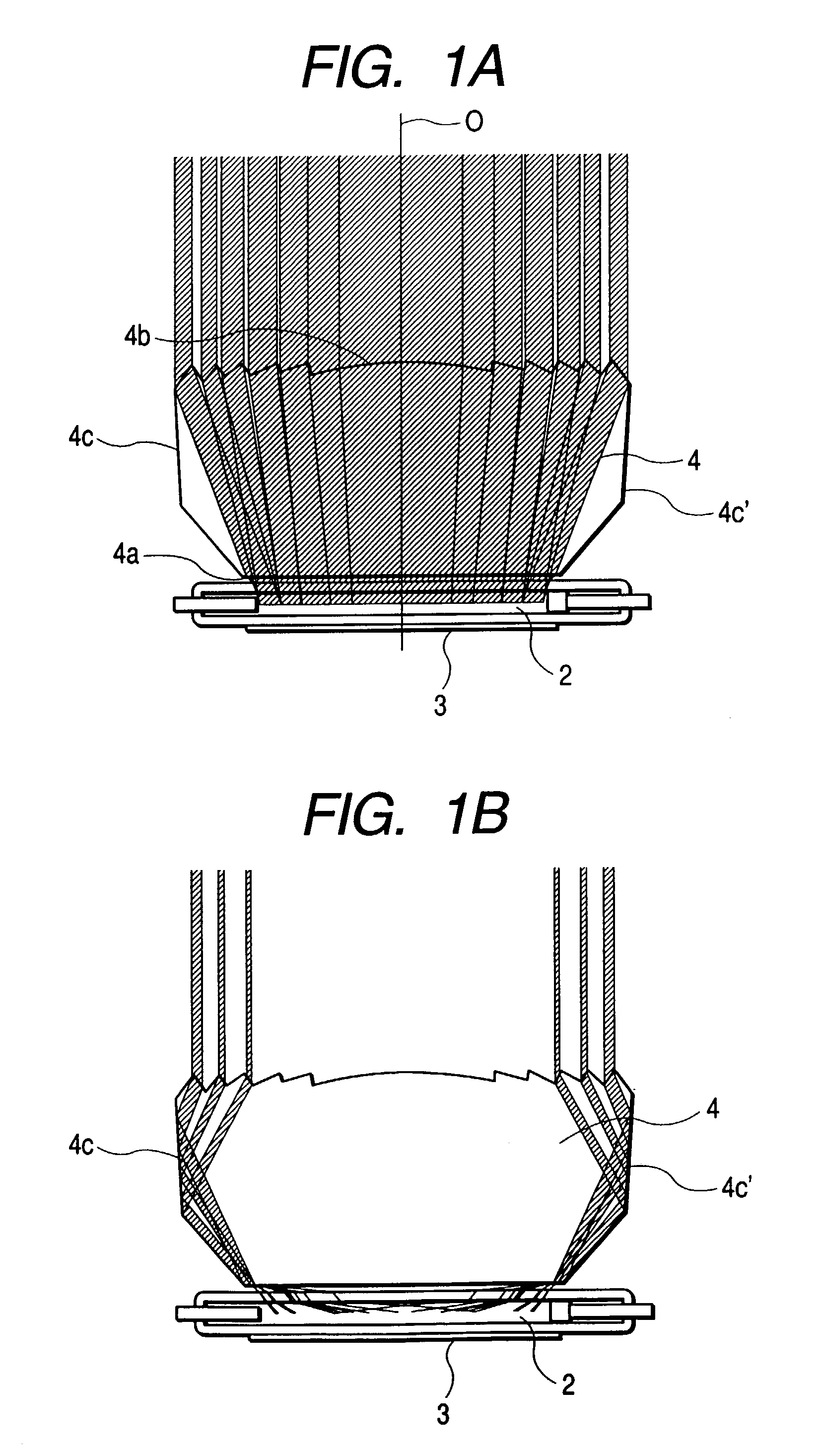
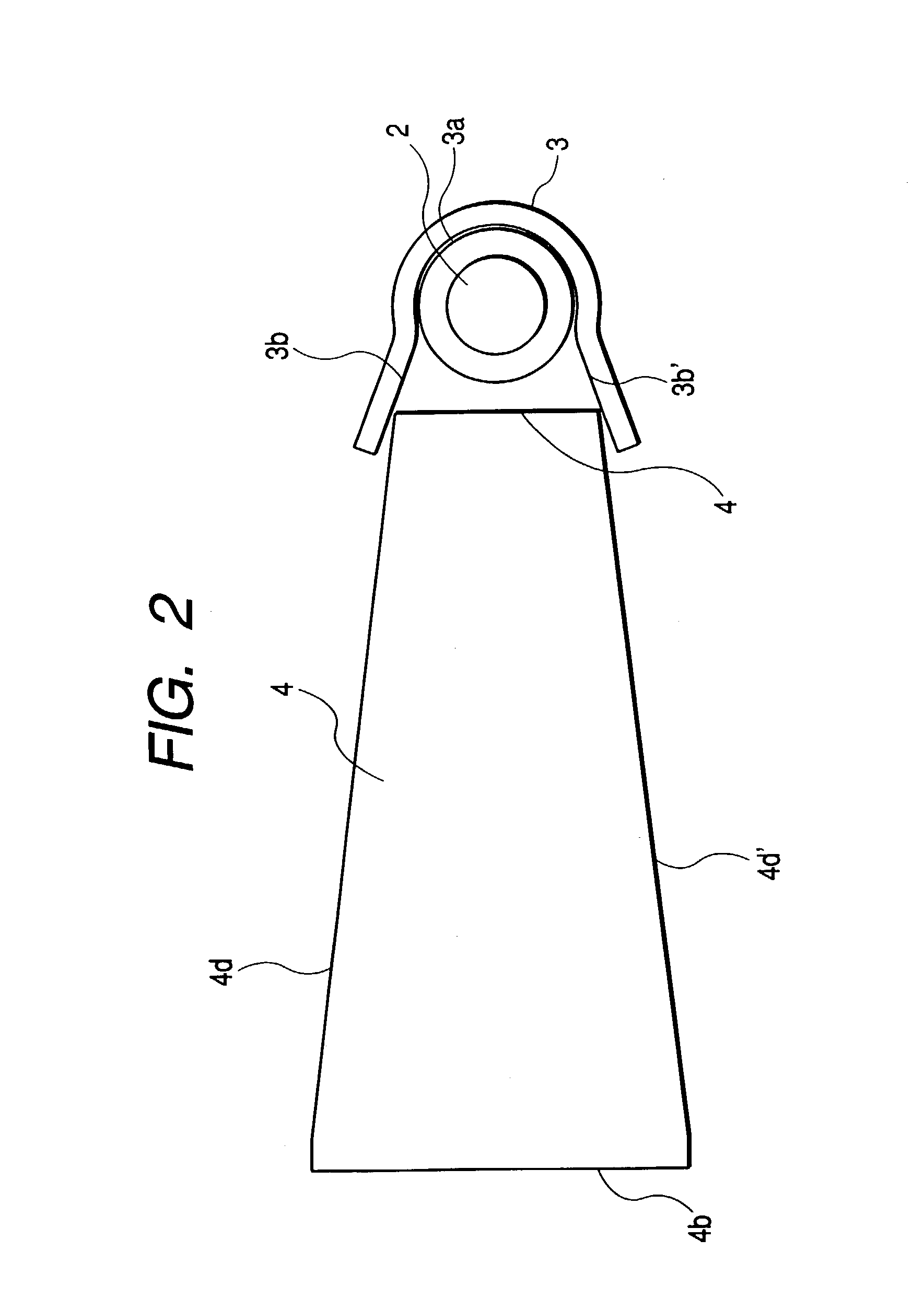
Illuminating apparatus
InactiveUS6974236B2Efficient ConcentrationImprove propertiesMachines/enginesEngine cooling apparatusPhysicsFresnel lens
This specification discloses an illuminating apparatus having a light source and an optical unit disposed forwardly on the object side of the light source, the optical unit being provided with an incidence surface on which light from the light source is incident, a light emergence surface provided with a Fresnel lens, and a side reflecting surface for totally reflecting the light incident on the incidence surface toward the Fresnel lens, wherein the light totally reflected by the side reflecting surface is refracted by the Fresnel lens and efficiently irradiates the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Method and device for enhanced delivery of a biologically active agent through the spinal spaces into the central nervous system of a mammal
InactiveUS6913763B2Promotes high patient compliancePromotes acceptanceElectrotherapyMedical devicesDiseaseNervous system
A delivery method and implantable apparatus that allows for controlled, enhanced and (pre)-programmable administration of a biologically active agent into the spinal structures and / or the brain via the epidural space of a mammal, particularly of a human being and including a feedback regulated delivery method and apparatus specifically in the treatment of neurological diseases and chronic pain.
Owner:INTRABRAIN INT
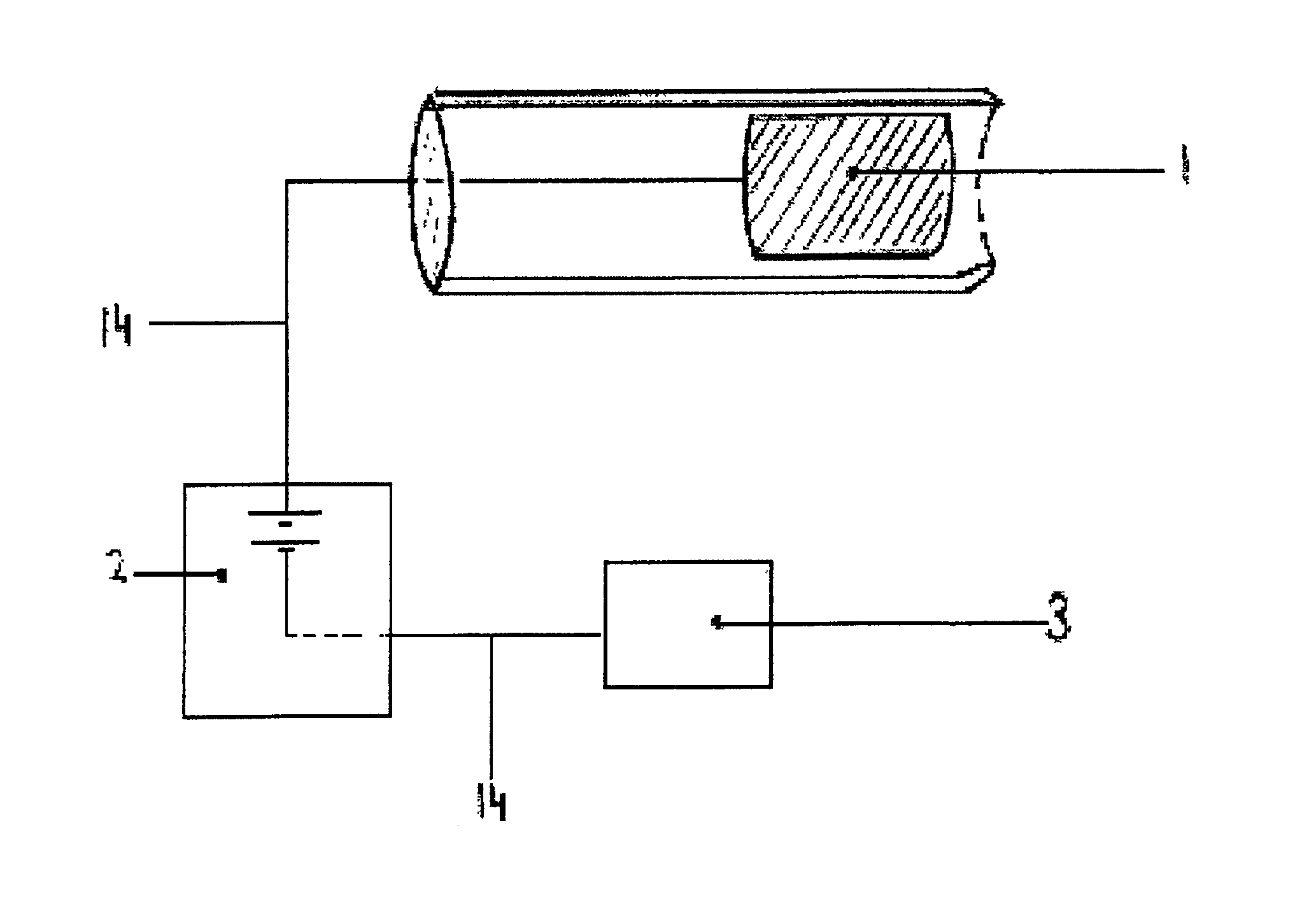
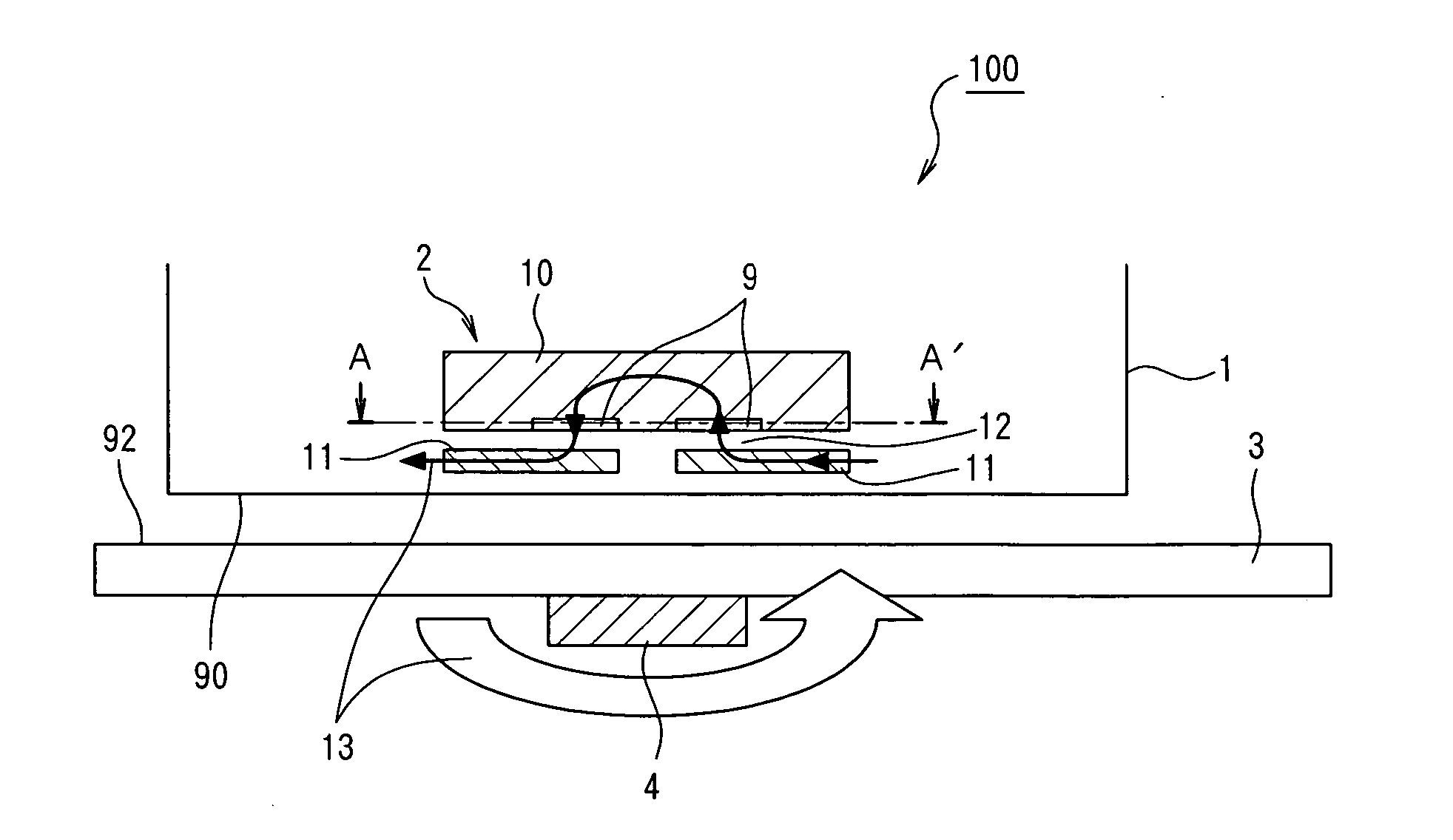
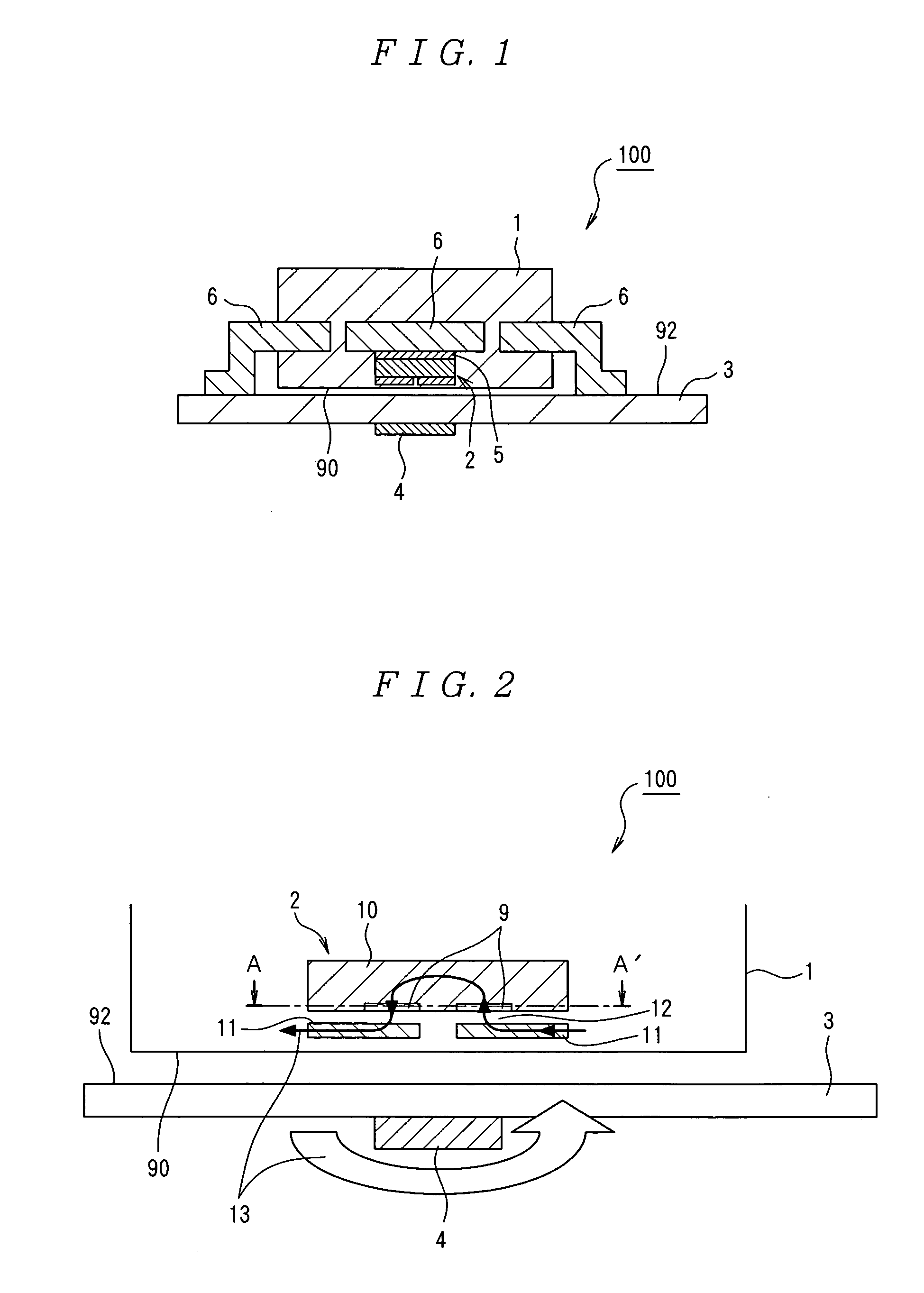
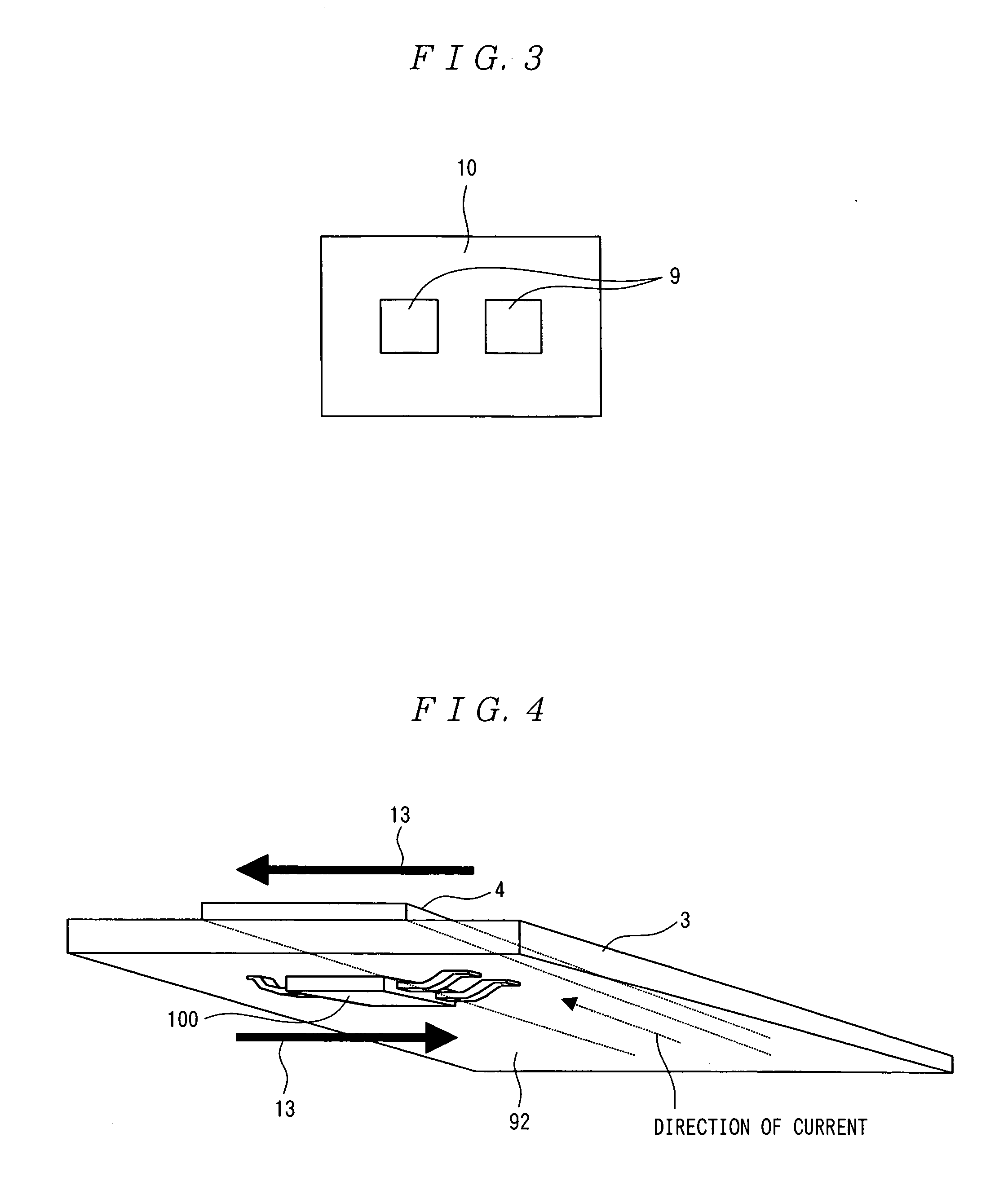
Current measuring method and current measuring device
InactiveUS20060033487A1Easy to detectEasy to reachMagnetic measurementsVoltage/current isolationElectricityElectrical conductor
A current measuring method capable of reducing the size of a current sensor while ensuring electric insulation easily and suitable for enhancing reliability by preventing heat generation. A current measuring device comprises a printed board (3) having a conductor for measurement (4), and a noncontact current sensor (100) being mounted on the printed board (3), wherein the current sensor (100) is mounted on the surface (92) of the printed board (3) opposite to the side provided with the conductor for measurement (4). Since the current sensor (100) is mounted on the rear surface (92), electric insulation between the secondary conductor of the current sensor (100) and the conductor for measurement (4) can be ensured relatively easy.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Methods for concentrating microalgae
InactiveUS20090162919A1Efficient ConcentrationEfficient separationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism separationNannochloropsisBiology
The present invention provides commercially viable, large-scale methods for concentrating microalgae with an average diameter of about 20 μm or less. The methods find use in concentrating microalgae with an average diameter of about 5 μm or less, for example, Nannochloropsis.
Owner:AURORA ALGAE
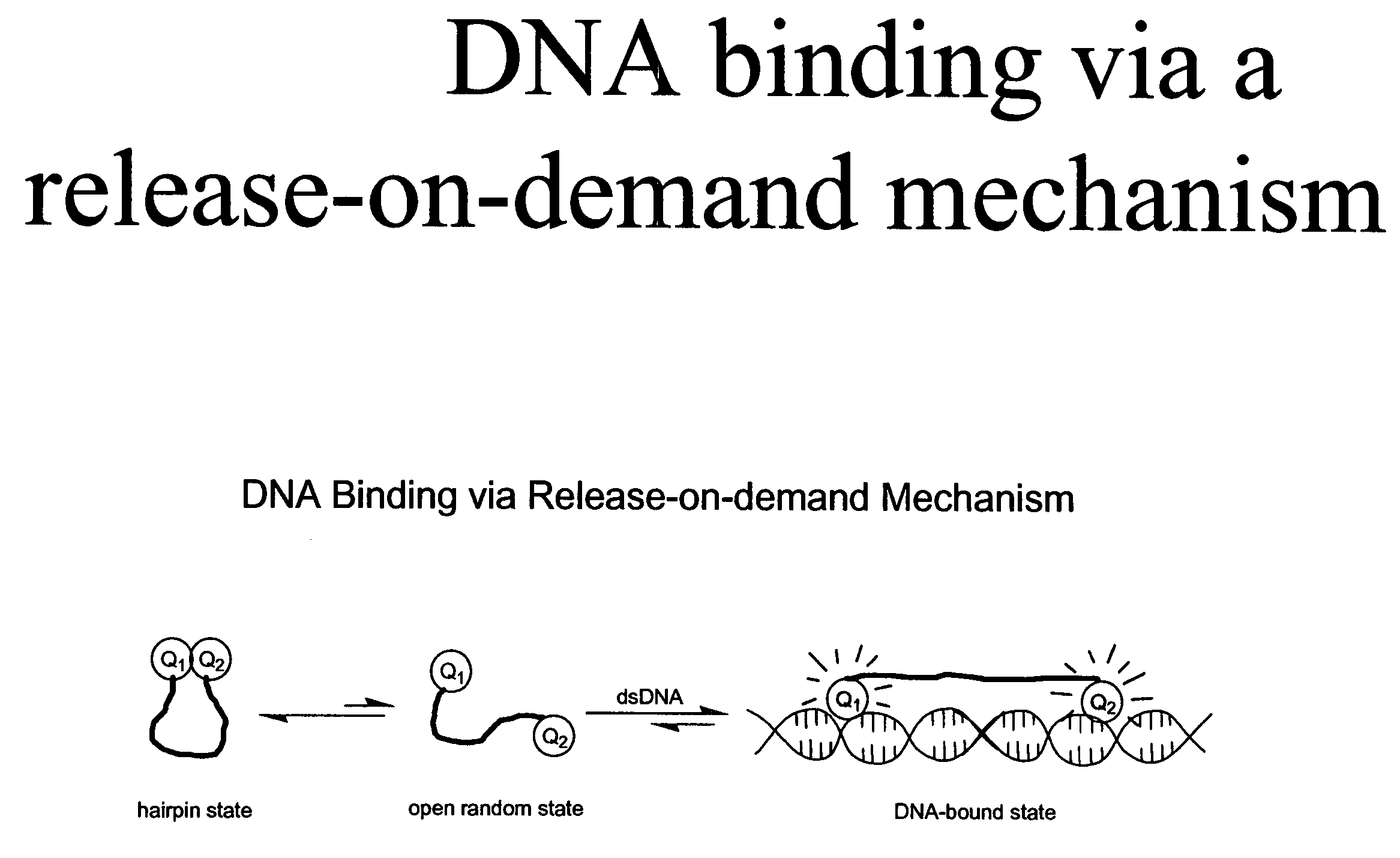
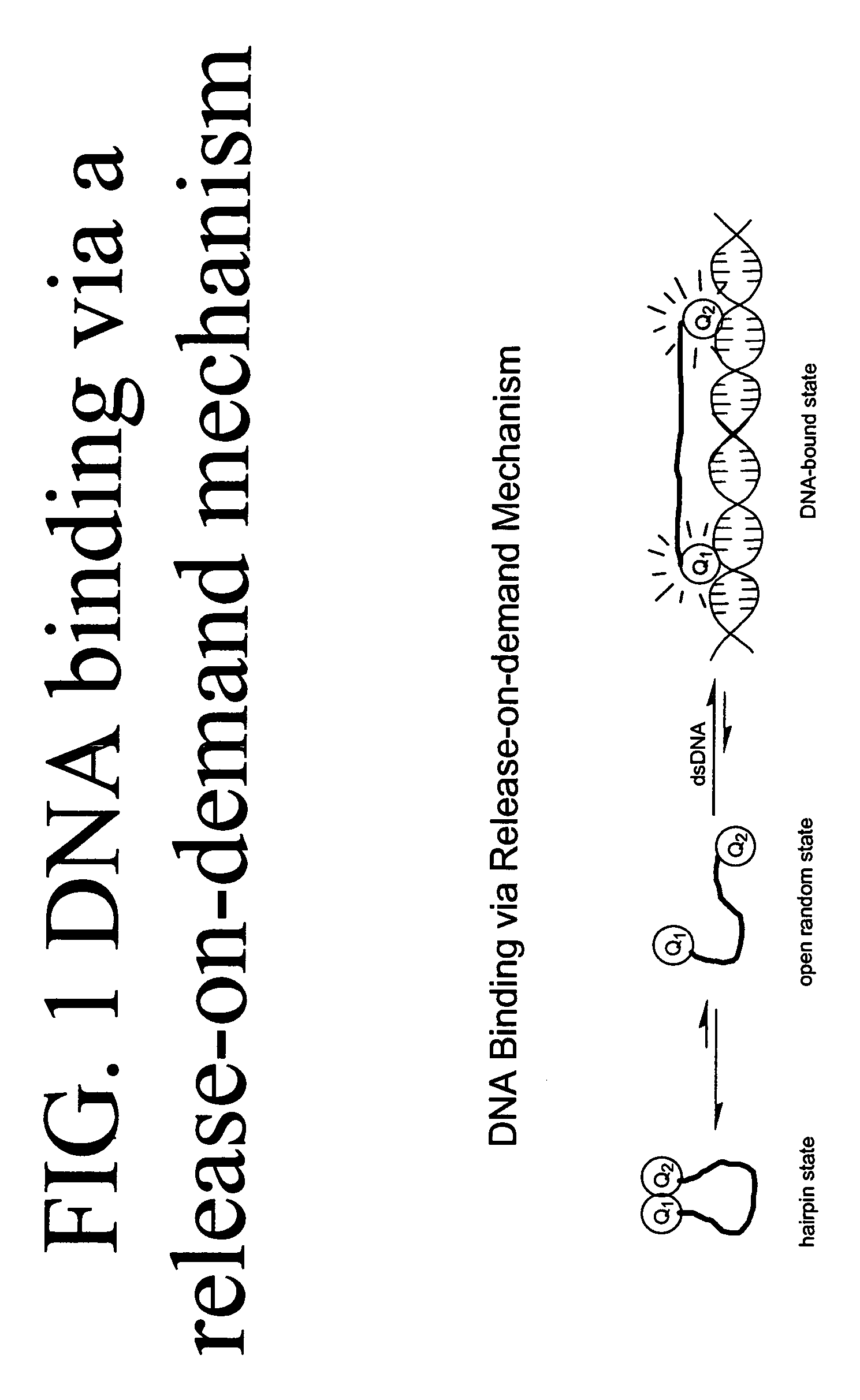
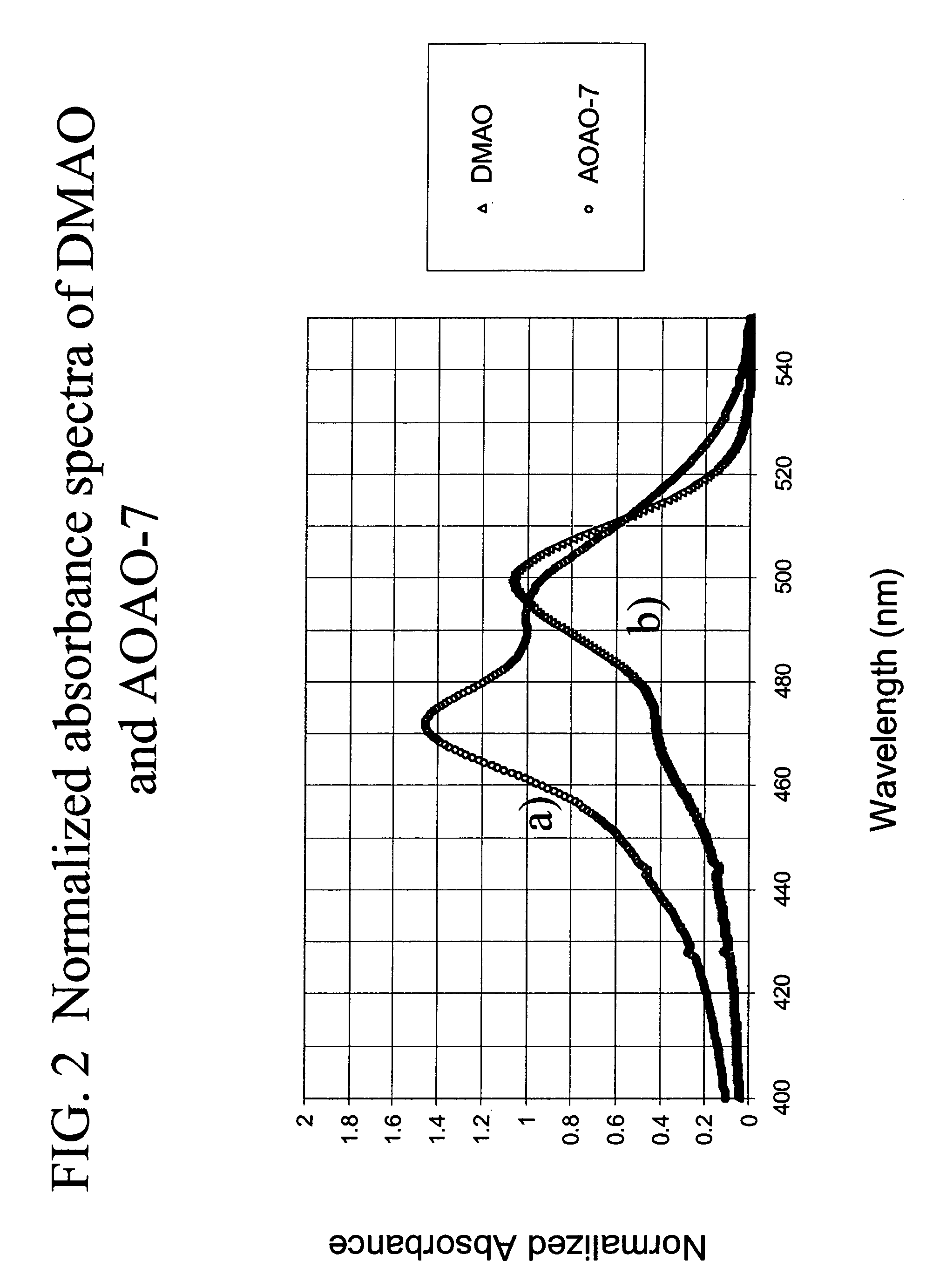
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS7601498B2Low toxicityIncrease signal strengthMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionStaining
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Assembly with osmolality-increasing fluid
InactiveUS20050137582A1Low friction characteristicSimple procedureWound drainsMixingUrologyReady to use
A catheter assembly is disclosed comprising: a hydrophilic catheter; a wetting fluid for wetting of the catheter; and a receptacle enclosing at least the insertable part of the catheter and the wetting fluid. Further, the wetting fluid is a solution incorporating at least one osmolality-increasing compound, and the total concentration of the osmolality-increasing compound(s) is very high, preferably exceeding 600 mOsm / dm3. The wetting fluid could either be arranged in contact with the hydrophilic surface layer of the catheter in the receptacle, for preservation of the hydrophilic surface layer in a wetted state during accommodation in said receptacle and provision of a ready-to-use catheter assembly, or be arranged to keep the wetting fluid separated from the hydrophilic surface layer of the catheter during storage, but to be brought into contact with said hydrophilic surface layer upon activation before an intended use of the catheter. A similar method and wetting fluid is disclosed as well. The provision of the osmolality-increasing compound in the wetting fluid provides several advantages per se, such as a improved properties of the hydrophilic coating, a more predictable and controllable wetting process, a more expedient and cost efficient production, etc. Further, the use of this very high concentration of osmolality-increasing compound in the wetting fluid has proven remarkably efficient.
Owner:ASTRA TECH SE
Adsorbent-Containing Hemostatic Devices
InactiveUS20070154510A1Minimal clean-upGood coagulationNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersFiberMontmorillonite
The present invention utilizes a combination of a porous carrier and inorganic material is selected from the group consisting of diatomaceous earth, glass powder or fibers, precipitated or fumed silica, kaolin and montmorillonite clays, and Ca exchanged permutites to make a more effective hemostatic device to treat wounds in mammalian animals. These hemostatic devices provide a lower heat rise to the skin as compared to direct application of zeolites to the skin.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
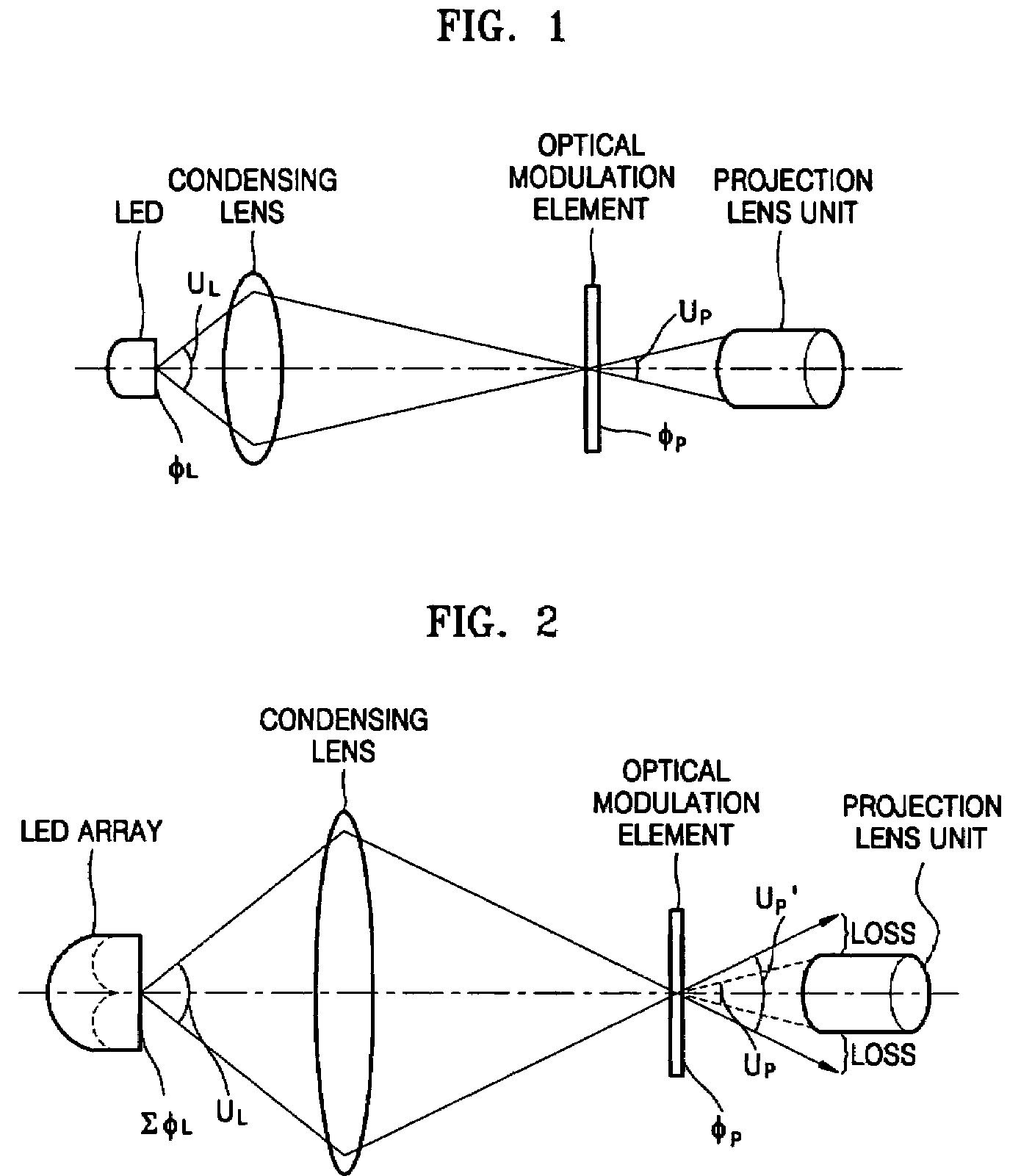
Light source device and projection display apparatus
ActiveUS20120140183A1Improve spectrum utilizationEfficient ConcentrationProjectorsColor photographyFluorescenceOptoelectronics
A light source device has: a light source unit including solid-state light sources emitting blue-color light and a condensing lens; a dichroic mirror polarization separating color light into first and second polarization components; a fluorescence emission plate excited with the first polarization component, emitting fluorescence of green and red components to enter the dichroic mirror; a first retardation plate converting the second polarization component to a circularly polarized light; and a reflection plate reflecting a light passed through the first retardation plate to reenter the same. The color lights from the fluorescence emission plate and the first retardation plate are combined at the dichroic mirror. A second retardation plate converts the polarization direction of the light from the light source unit, so as to control the ratio of p-polarization and s-polarization components. Lights from solid-state light sources are condensed efficiently and a high spectrum-utilization factor is obtained.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Nerve cell protective agents
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 01828 Sec. 371 Date Jan. 30, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Jan. 30, 1998 PCT Filed May 29, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 45410 PCT Pub. Date Dec. 4, 1997The invention provides novel benzindole derivatives, processes for producing them, as well as a neuroprotective agent, an agent to prevent or treat diseases involving the degeneration, retraction or death of neurons, and an analgesic, each containing the benzindole derivatives as an active ingredient.
Owner:MOCHIDA PHARM CO LTD
Adsorbent-Containing Hemostatic Devices
InactiveUS20070154509A1Minimal clean-upGood coagulationNon-adhesive dressingsPlastersMolecular sieveTissue skin
The present invention utilizes a combination of a porous carrier and an adsorbent such as a molecular sieve to make a more effective hemostatic device to treat wounds in mammalian animals. These hemostatic devices provide a lower heat rise to the skin as compared to direct application of zeolites to the skin.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
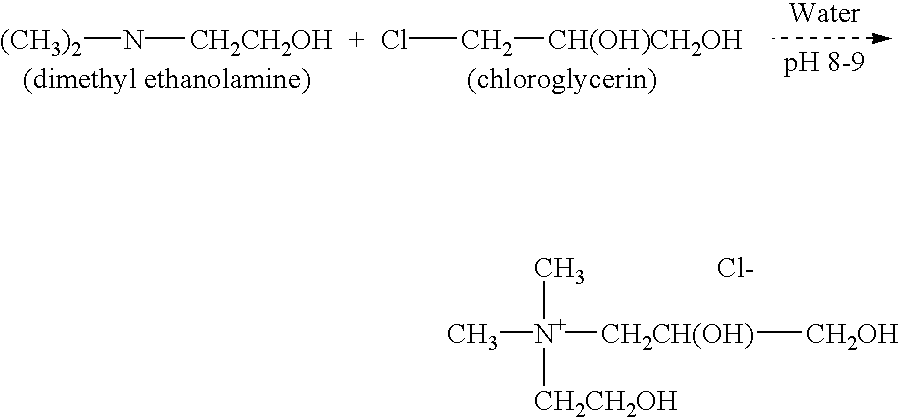
Skin moisturization compound
The present invention discloses a series of quaternary nitrogen compounds in which the four groups surrounding nitrogen are (a) one glyceryl portion, (b) two methyl groups and (c) a hydroxy ethyl group. The compound of the present invention is an outstanding moisturizer when applied to skin.
Owner:SURFATECH
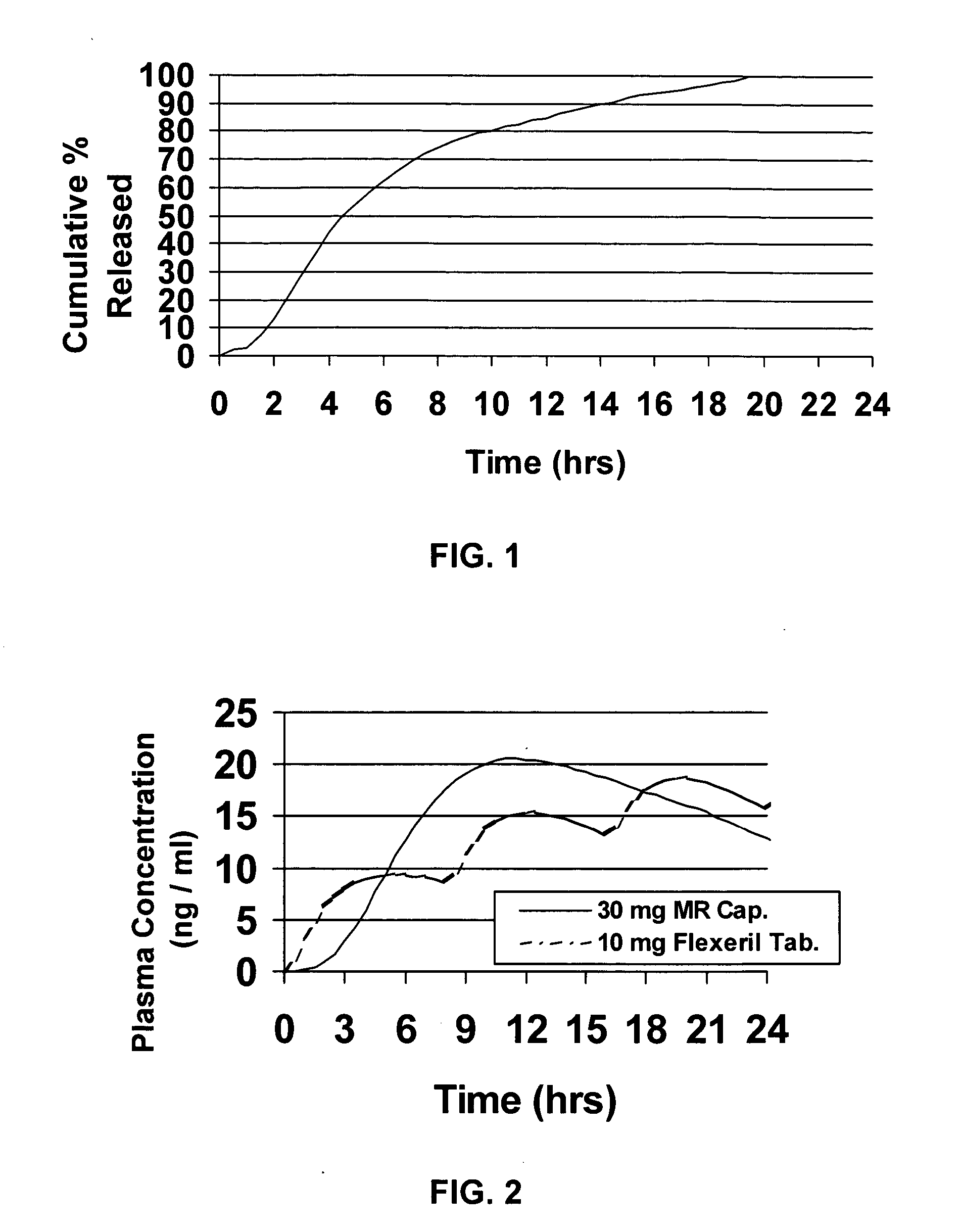
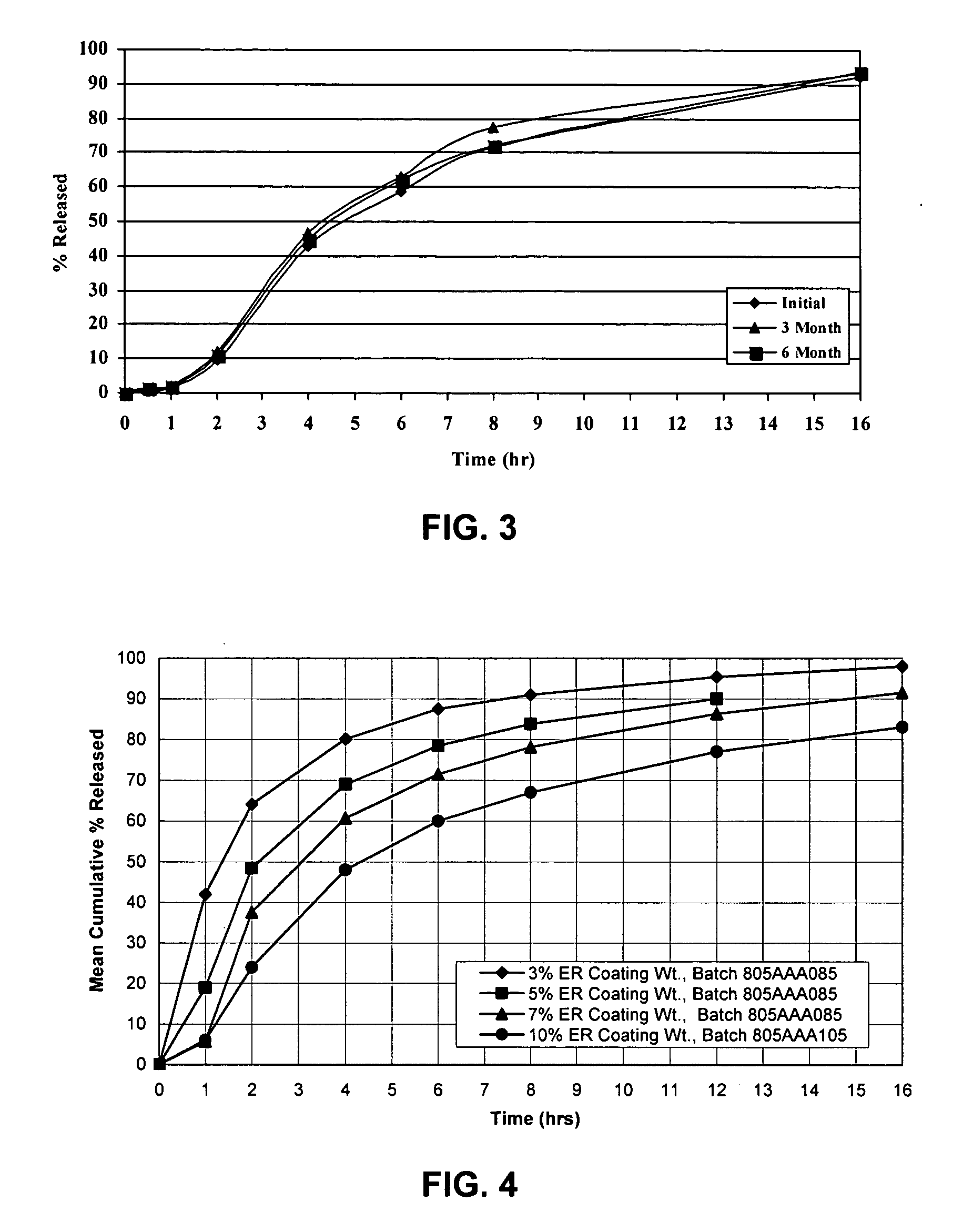
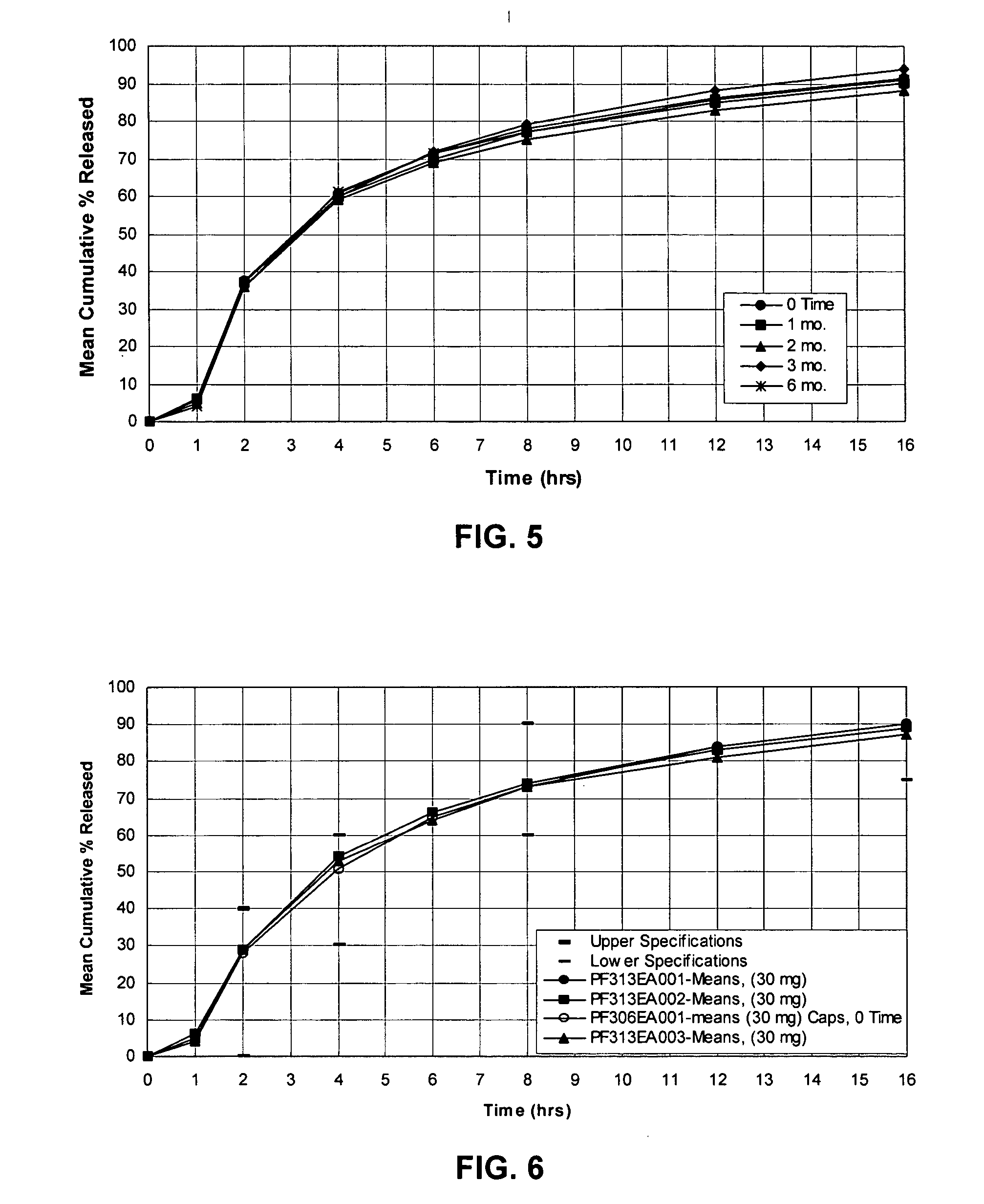
Modified release dosage forms of skeletal muscle relaxants
InactiveUS20050106247A1Patient compliance is goodEfficient ConcentrationBiocidePowder deliveryDiseaseModified Release Dosage Form
A unit dosage form, such as a capsule or the like, for delivering a skeletal muscle relaxant, such as cyclobenzaprine hydrochloride, into the body in an extended or sustained release fashion comprising one or more populations of drug-containing particles (beads, pellets, granules, etc.) is disclosed. At least one bead population exhibits a pre-designed sustained release profile. Such a drug delivery system is designed for once-daily oral administration to maintain an adequate plasma concentration—time profile, thereby providing relief of muscle spasm associated with painful musculoskeletal conditions over a 24 hour period.
Owner:ADARE PHARM INC
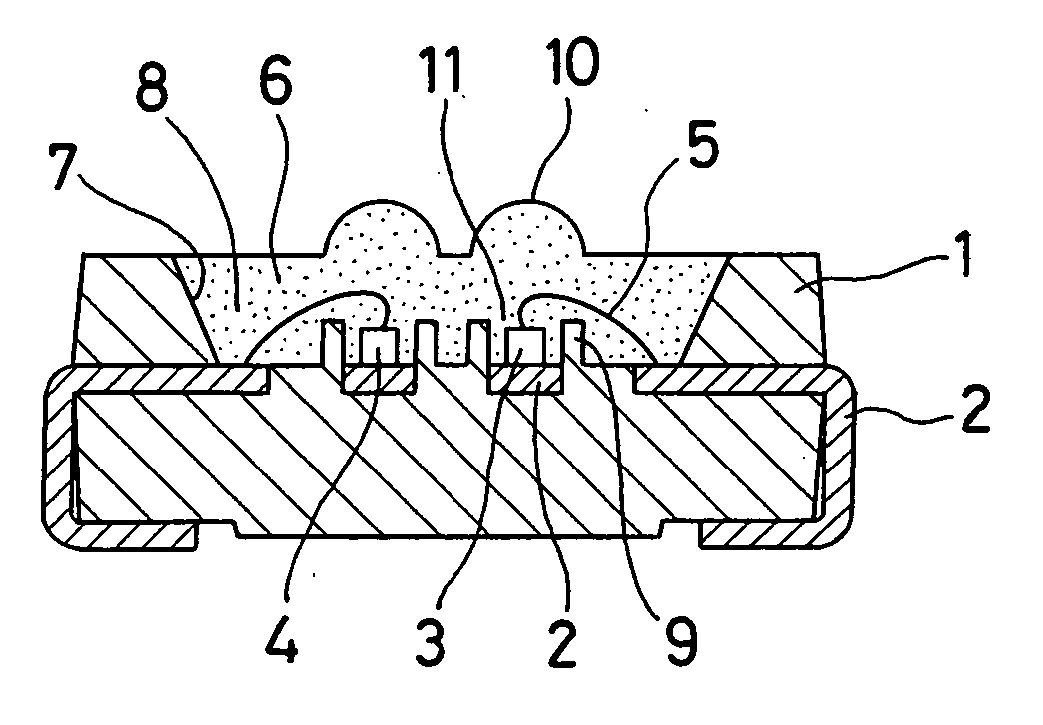
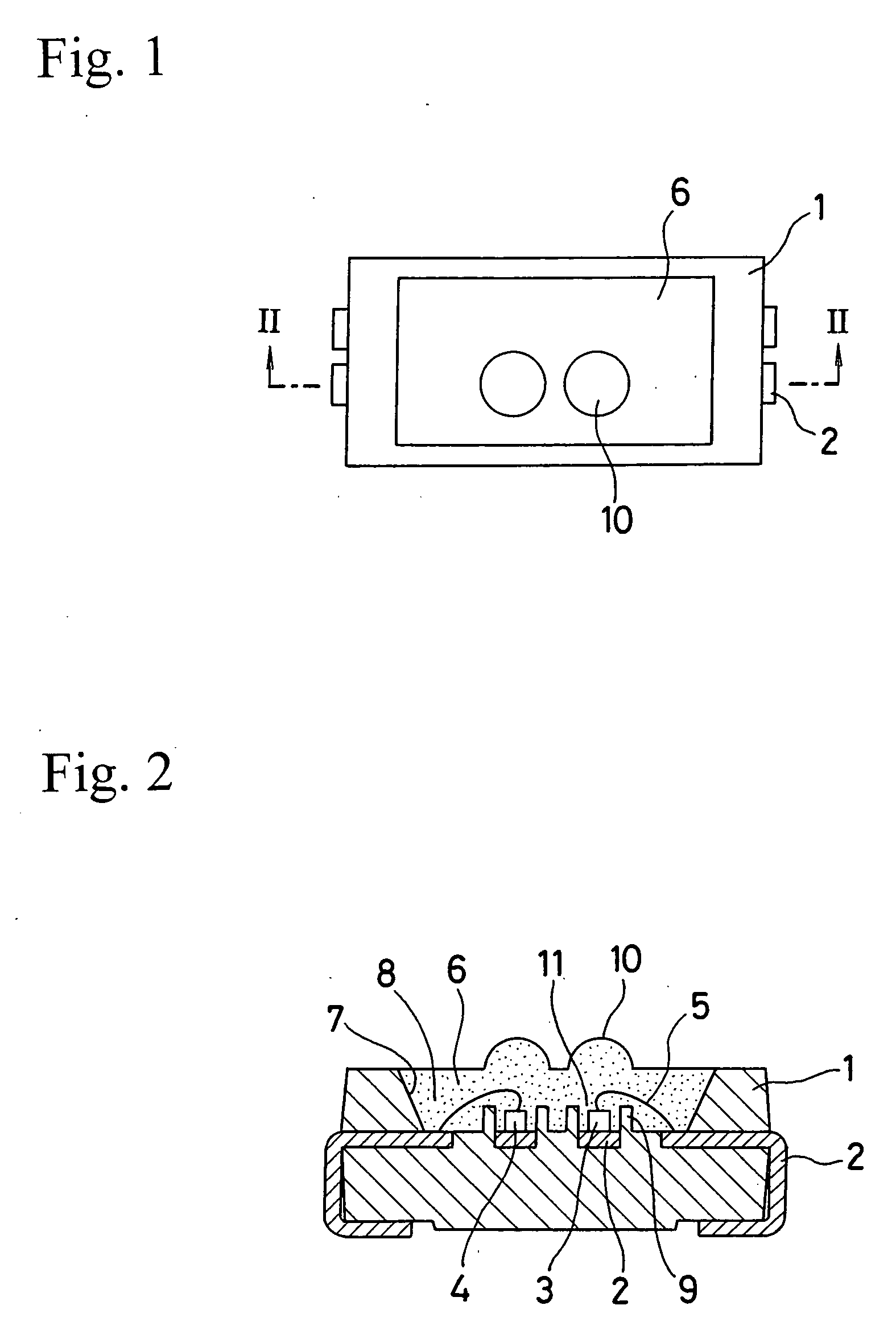
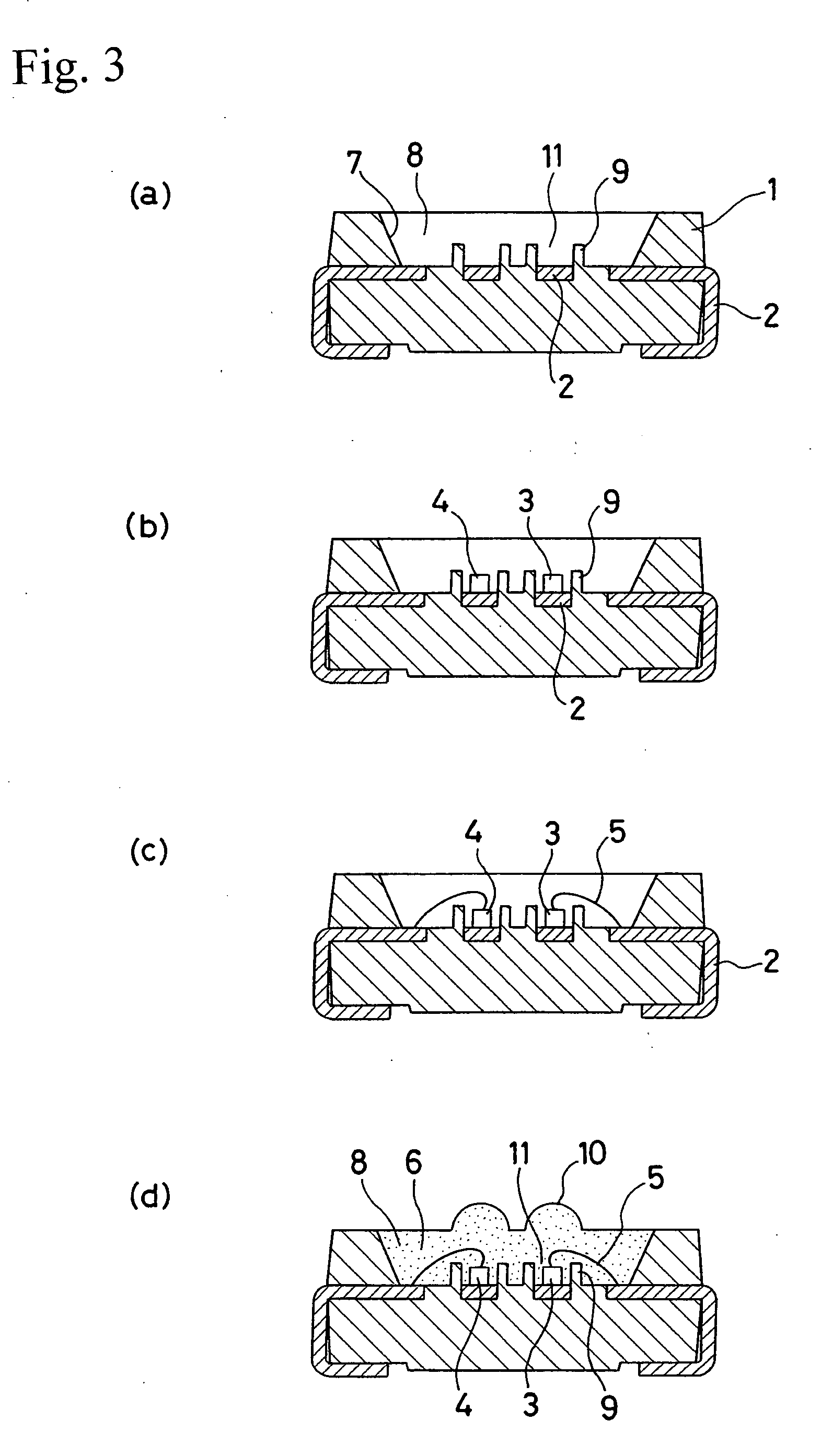
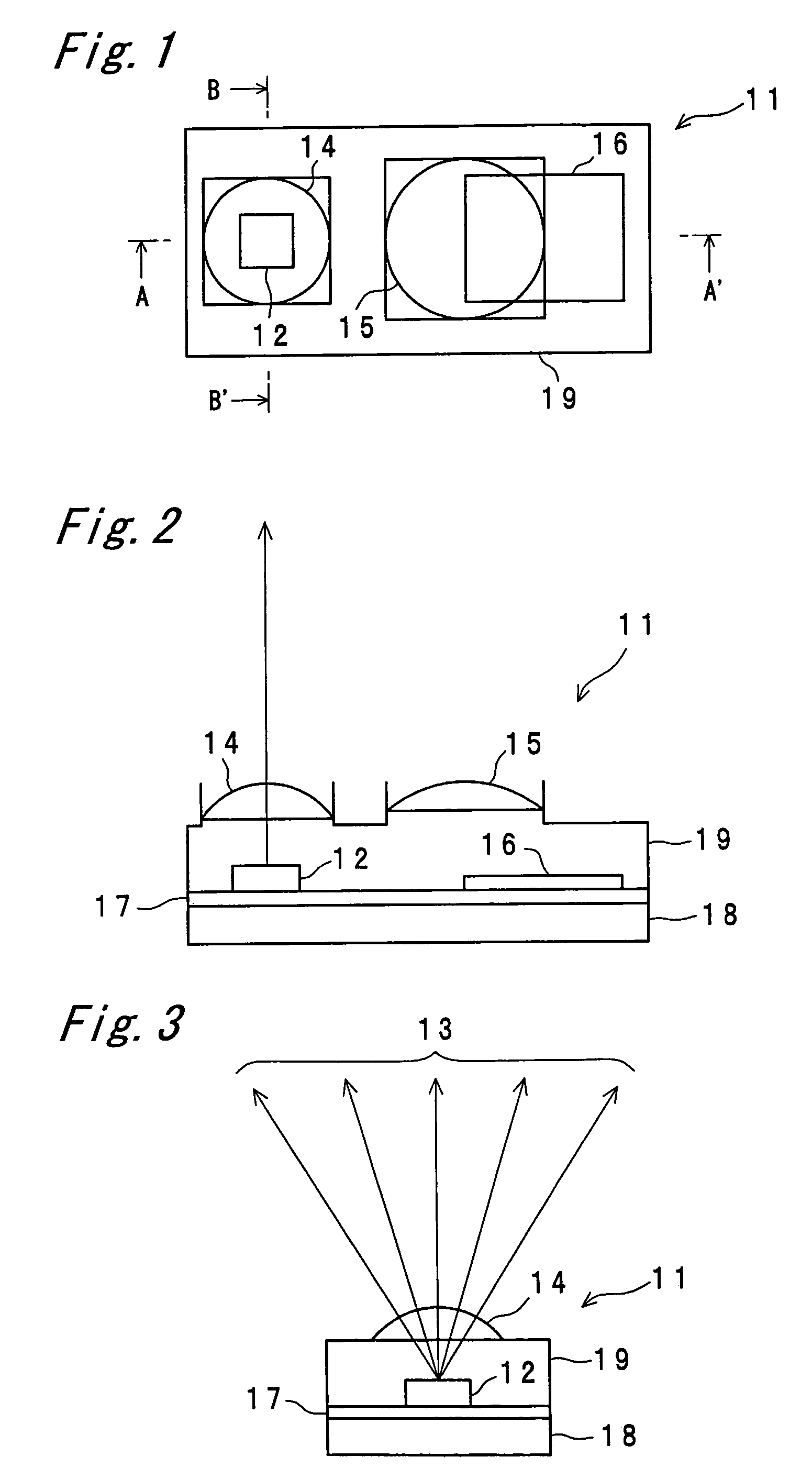
Light emitting diode device
InactiveUS20060065957A1Efficient ConcentrationDistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringLead frame
A plurality of separate lead frames can be insert-molded in a reflector composed of a white resin having a high reflectivity to form a package for an LED device. A cavity is formed in the reflector. The cavity can have an inner circumferential surface that opens wider in an upward direction. Cups can be located in the cavity. Each cup has an outer wall that can be in the form of a cylinder with the bottom formed of each of two separate lead frames. A red LED chip and a green LED chip can be adhesively fixed to the lead frames located on the bottoms of the respective cups. The LED chips can have lower electrodes, which are electrically brought into conduction with the lead frames one by one. The LED chips can also have upper electrodes, which are electrically brought into conduction with the lead frames one by one via bonding wires. A light transmissive resin can be filled in the cavity.
Owner:STANLEY ELECTRIC CO LTD
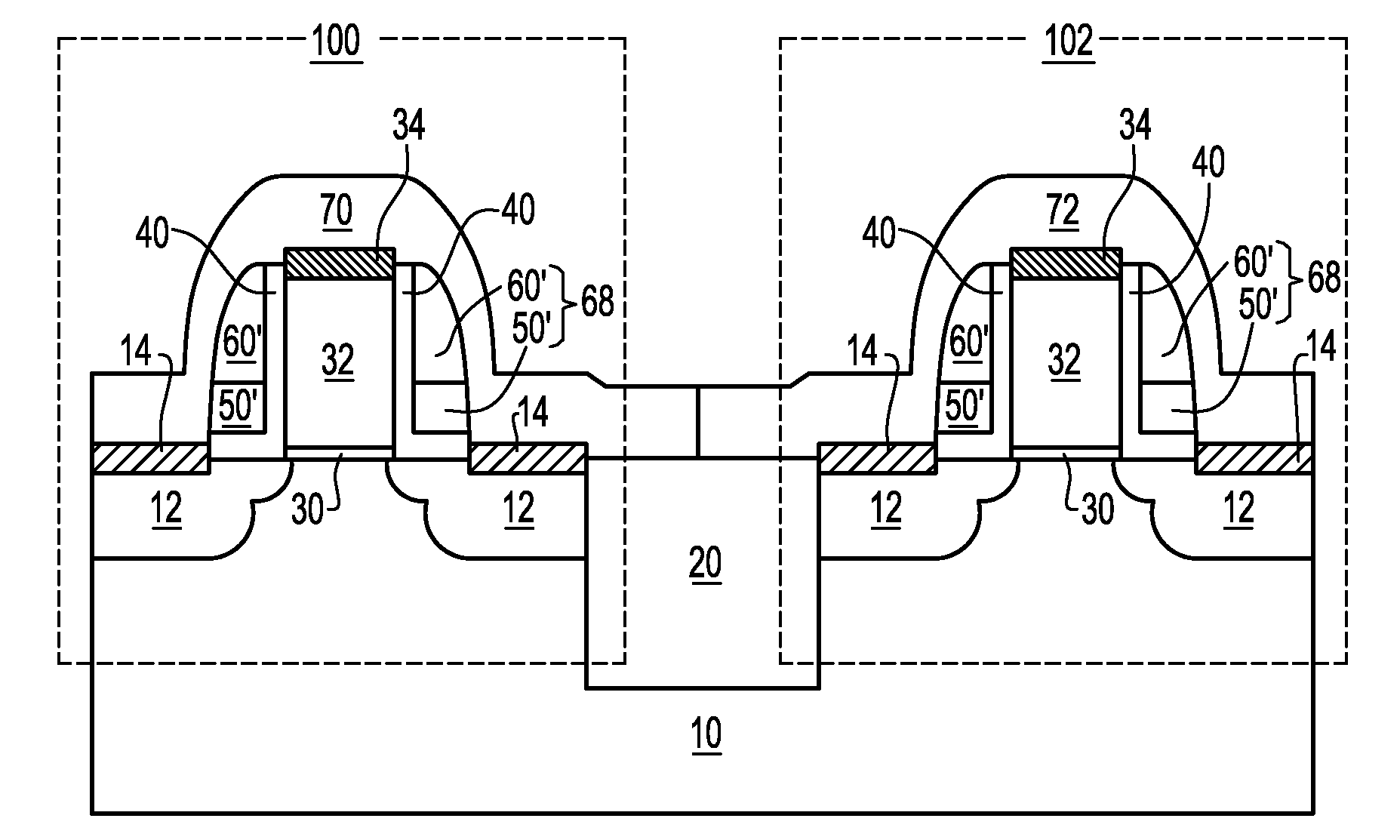
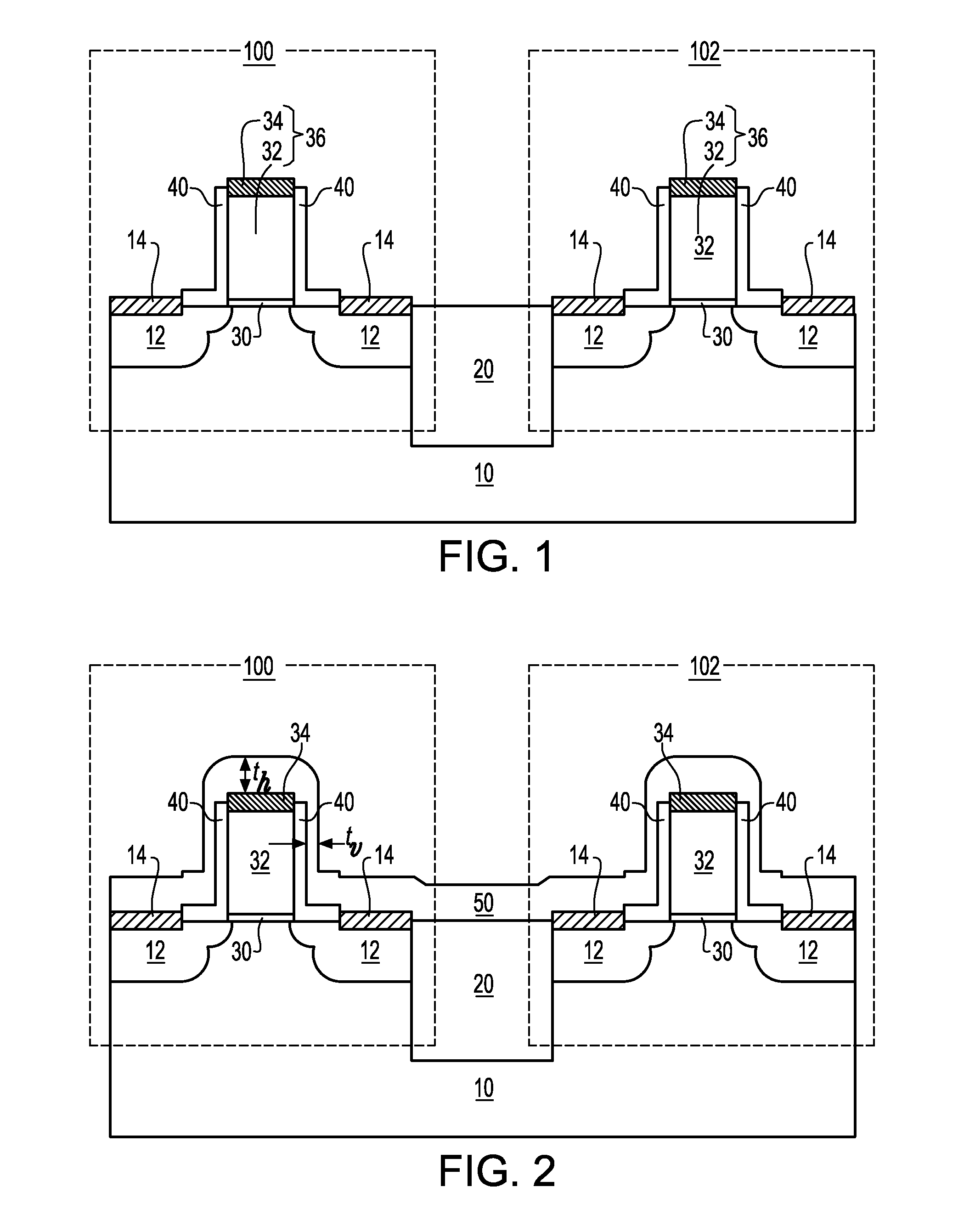
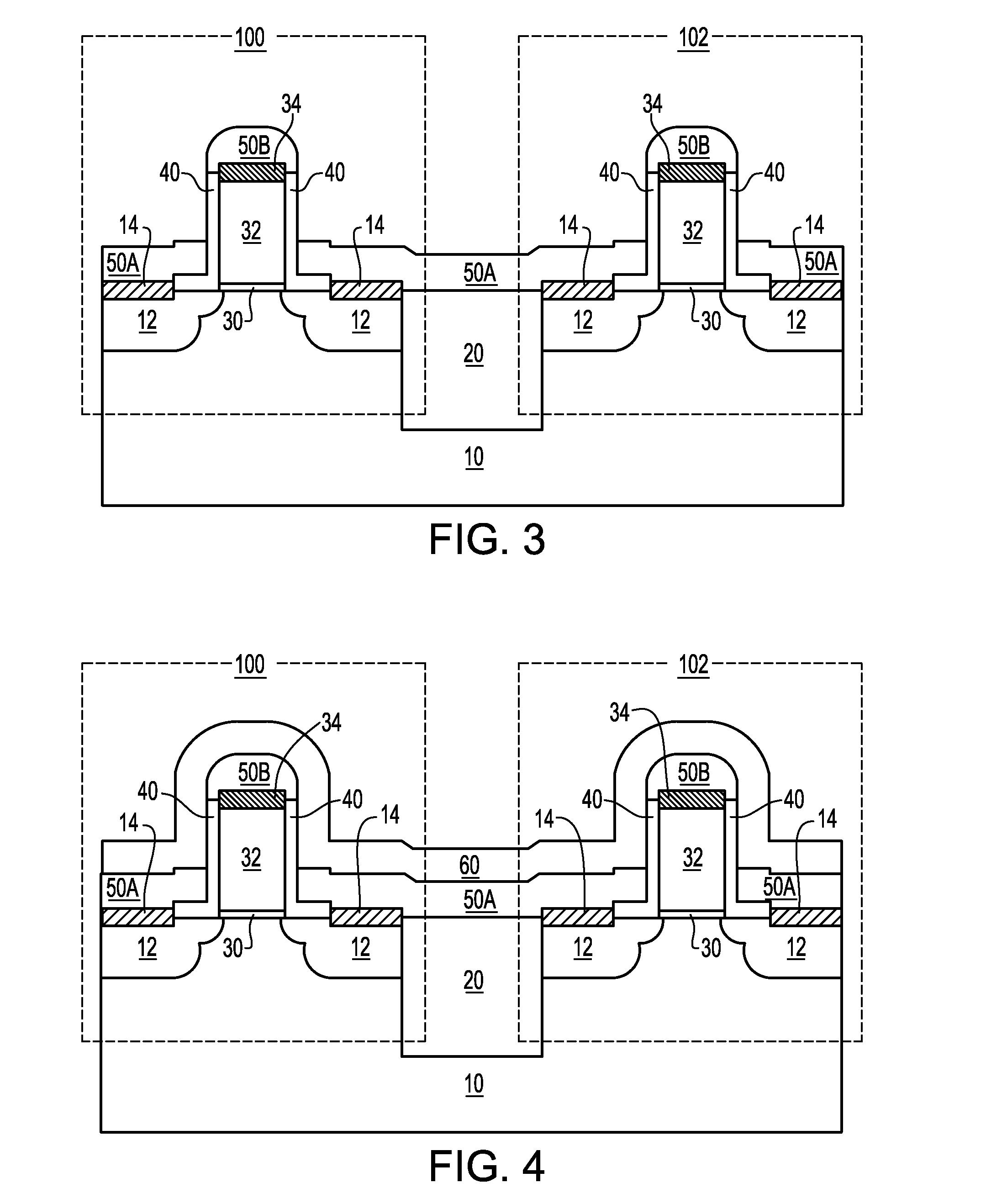
Structure and methods for stress concentrating spacer
InactiveUS20080237726A1Efficient ConcentrationImprove transmission efficiencyTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMOSFETEngineering
A stress-concentrating spacer structure is a stack of an upper gate spacer with a low Young's modulus and a lower gate spacer with a high Young's modulus. The stacked spacer structure surrounds the gate electrode. The stress-concentrating spacer structure may contact an inner gate spacer that contacts the gate electrode or may directly contact the gate electrode. The upper gate spacer deforms substantially more than the lower gate spacer. The stress generated by the stress liner is thus transmitted primarily through the lower gate spacer to the gate electrode and subsequently to the channel of the MOSFET. The efficiency of the transmission of the stress from the stress liner to the channel is thus enhanced compared to conventional MOSFETs structure with a vertically uniform composition within a spacer.
Owner:IBM CORP
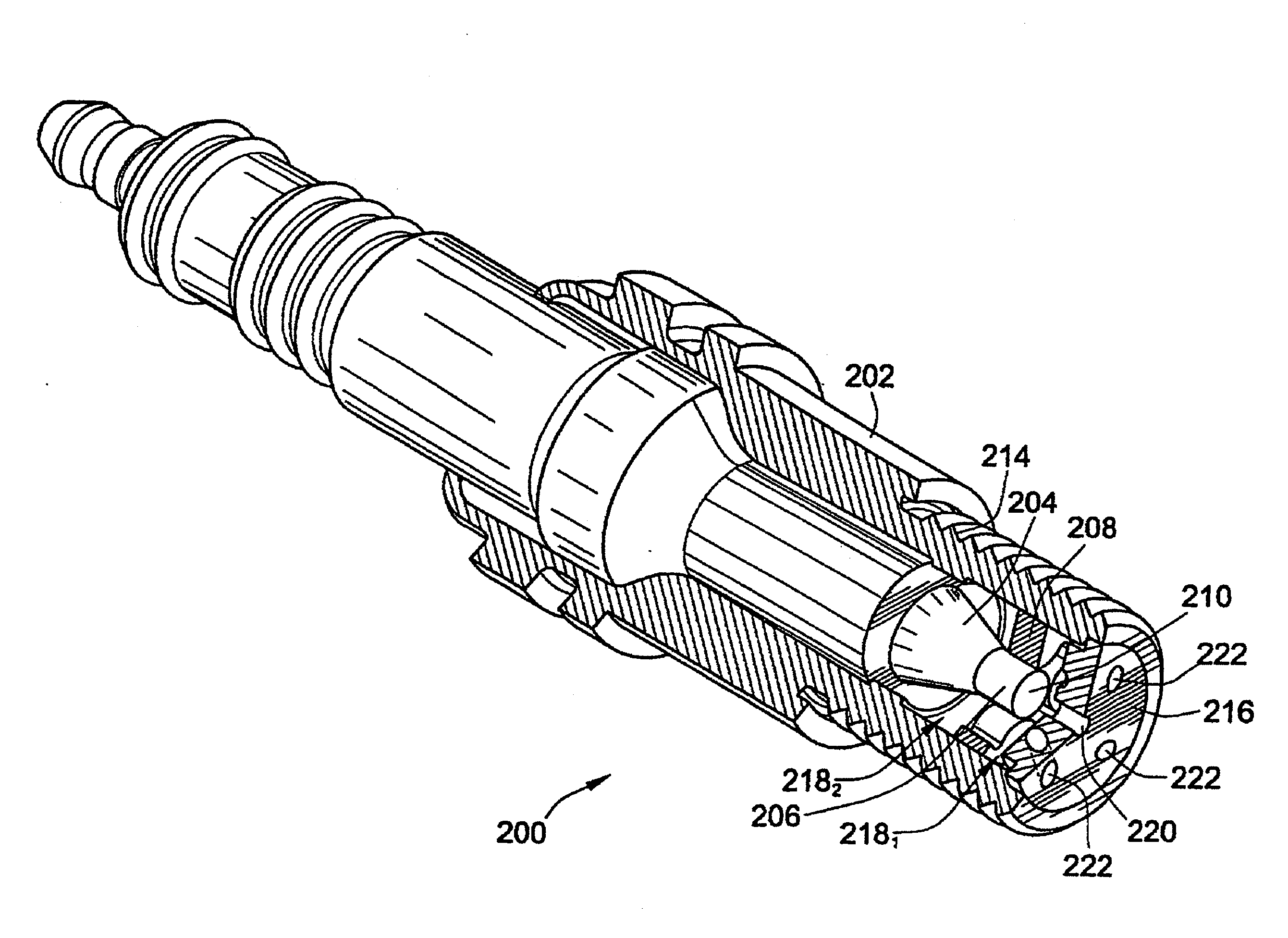
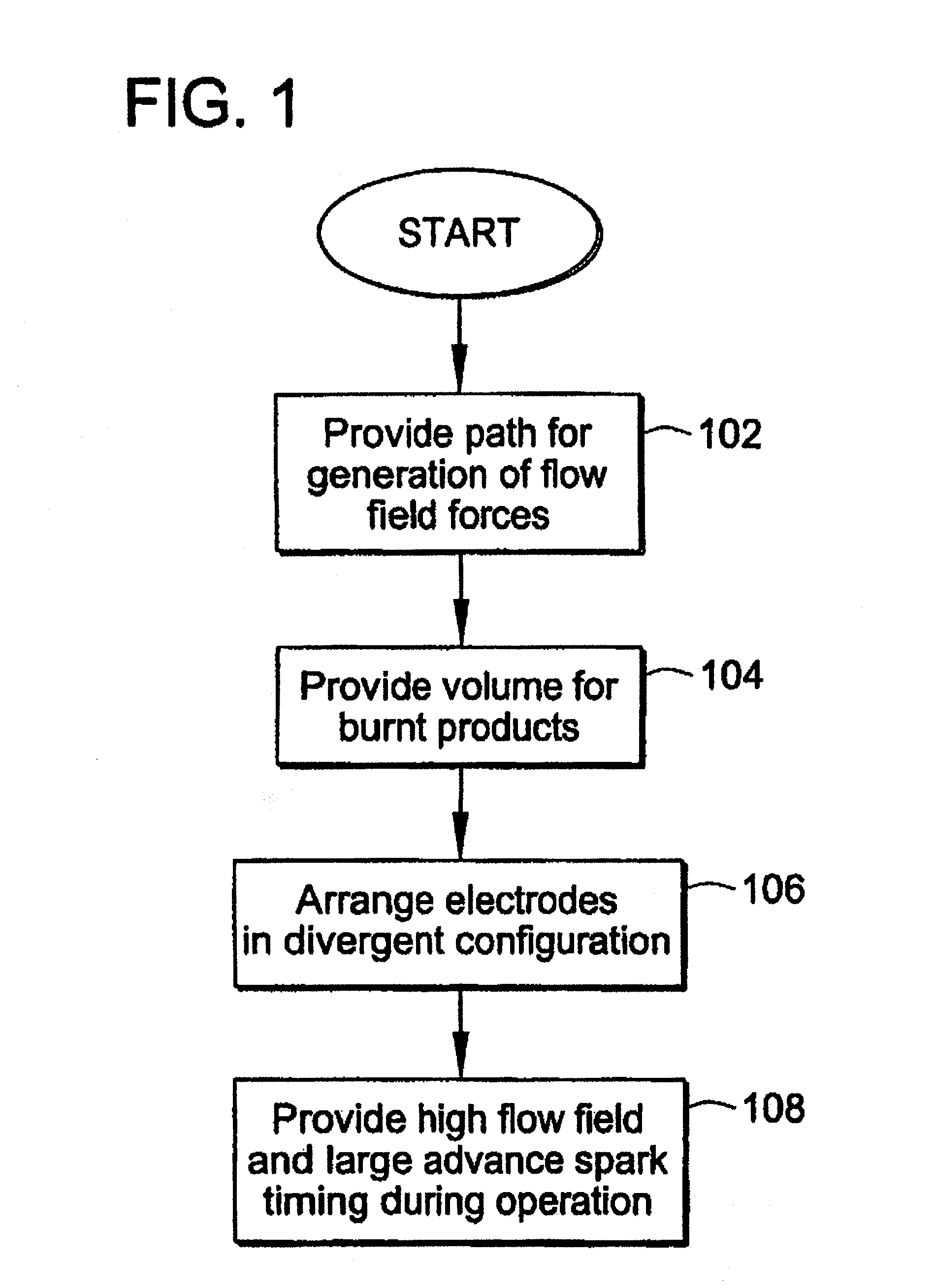
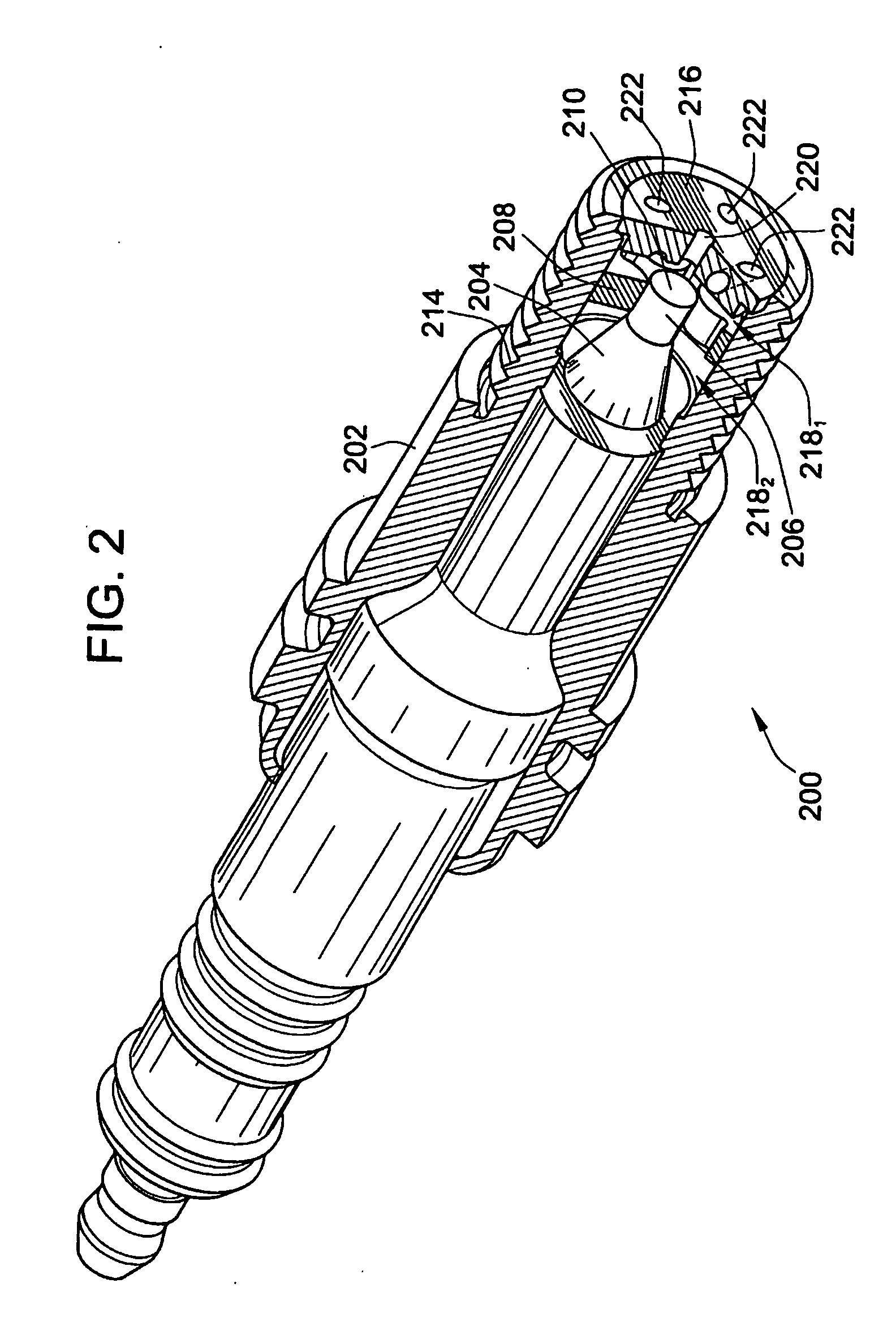
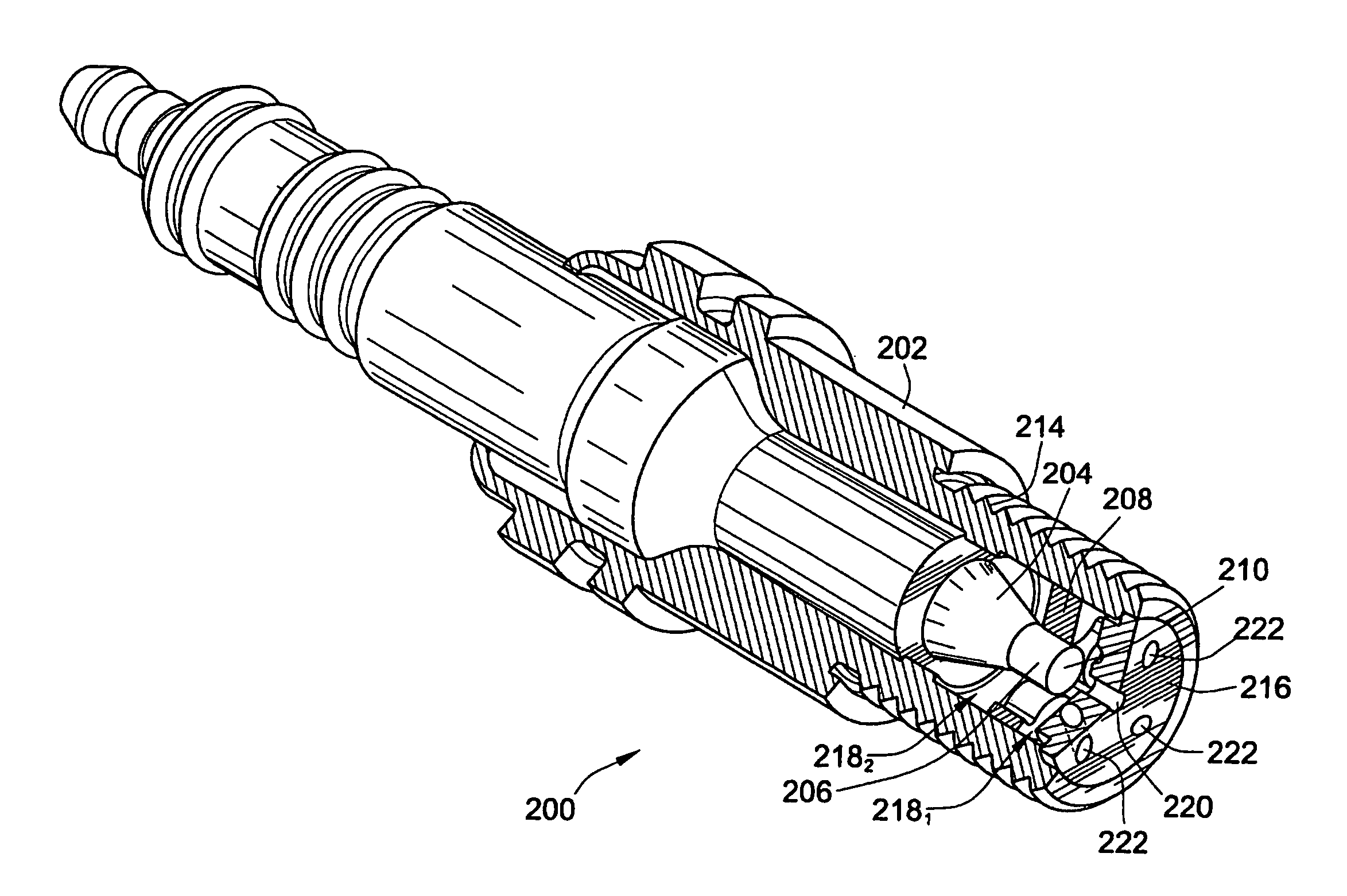
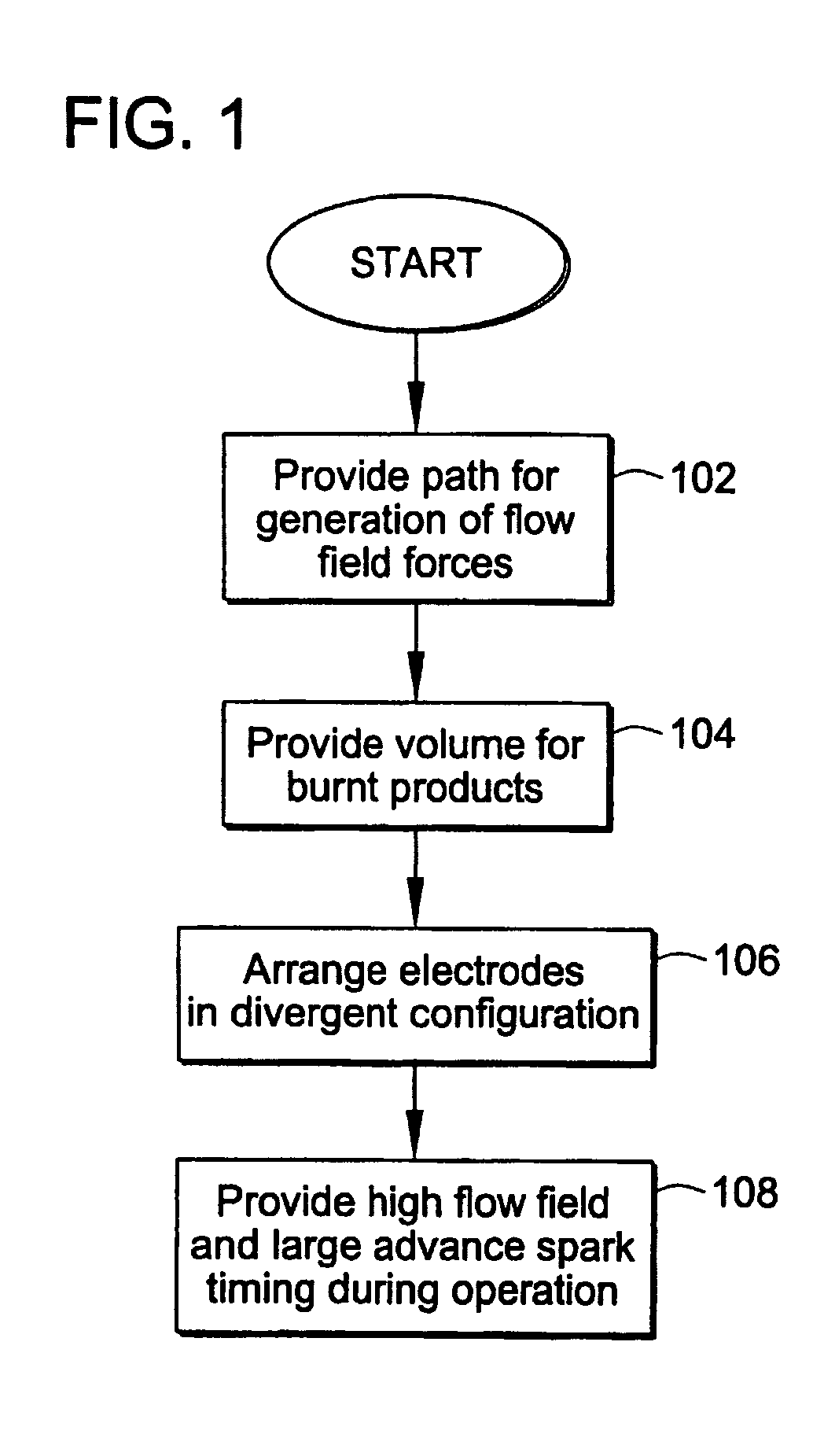
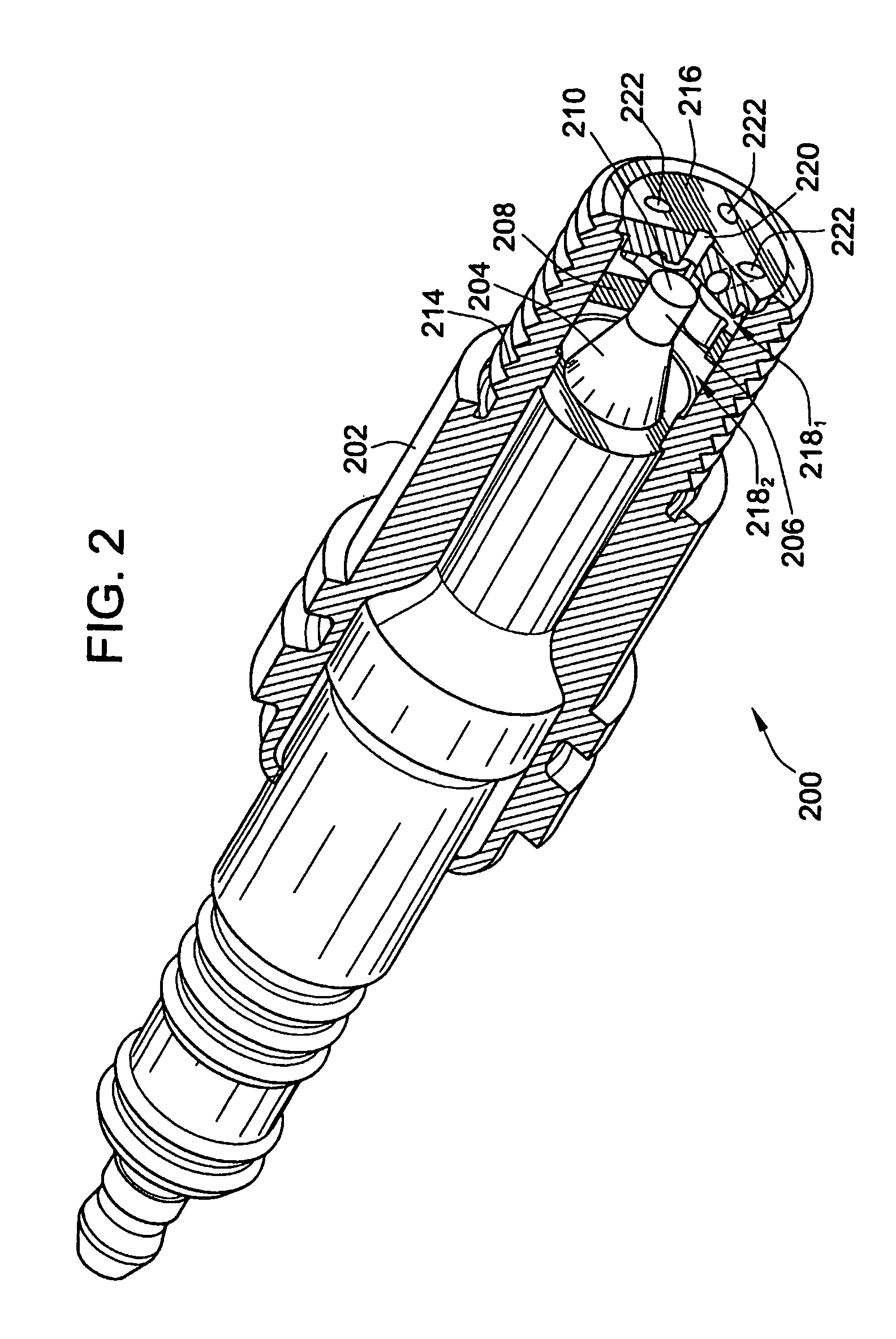
Pre-Chamber Spark Plug
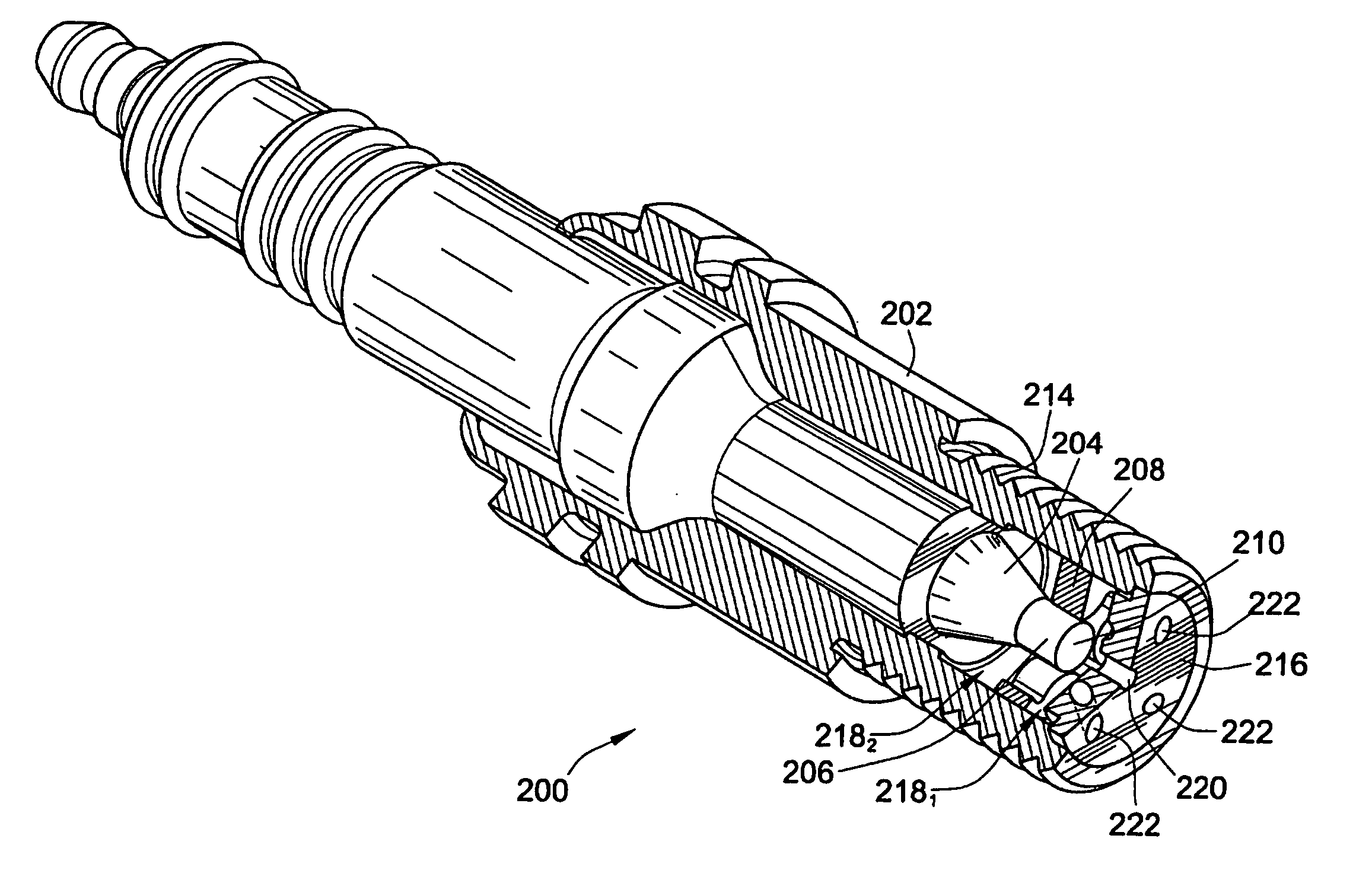
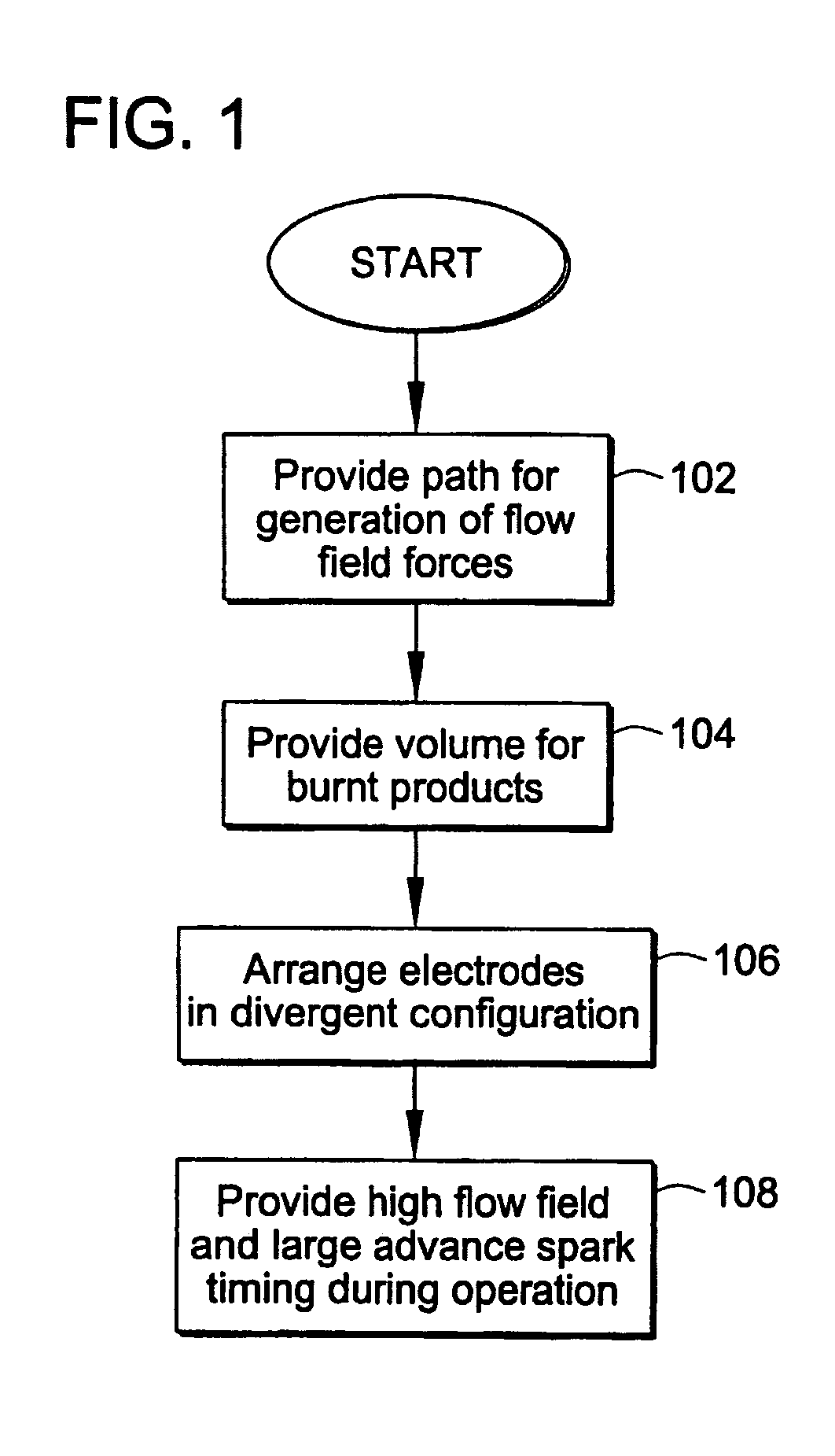
ActiveUS20090309475A1Maximize spark plug lifeReduce erosionSpark gapsInternal combustion piston enginesElectricityElectrode erosion
A method and apparatus to maximize spark plug life in pre-chamber spark plugs operating with ultra-lean mixtures and / or elevated engine BMEP is presented. Electrode erosion is reduced by spreading discharge energy over a wider surface area, maintaining fuel concentration in the spark gap, controlling gas static pressure during discharge, and maintaining safe electrode temperature. Energy is spread via a swirling effect created by periphery holes in an end cap, resulting in a lower specific energy discharge at the electrodes. Divergently configured electrodes reduce the spark voltage at high operating pressures and the energy required for ignition. The flow field generated at the electrodes prevents electrical shorts due to water condensation and avoids misfire. The center electrode insulation provides an effective heat transfer path to prevent electrode overheating and pre-ignition. The volume behind the electrodes provides a volume for burnt products from previous combustion cycles and leads to more reliable ignition.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Hologram element, production method thereof, and optical header
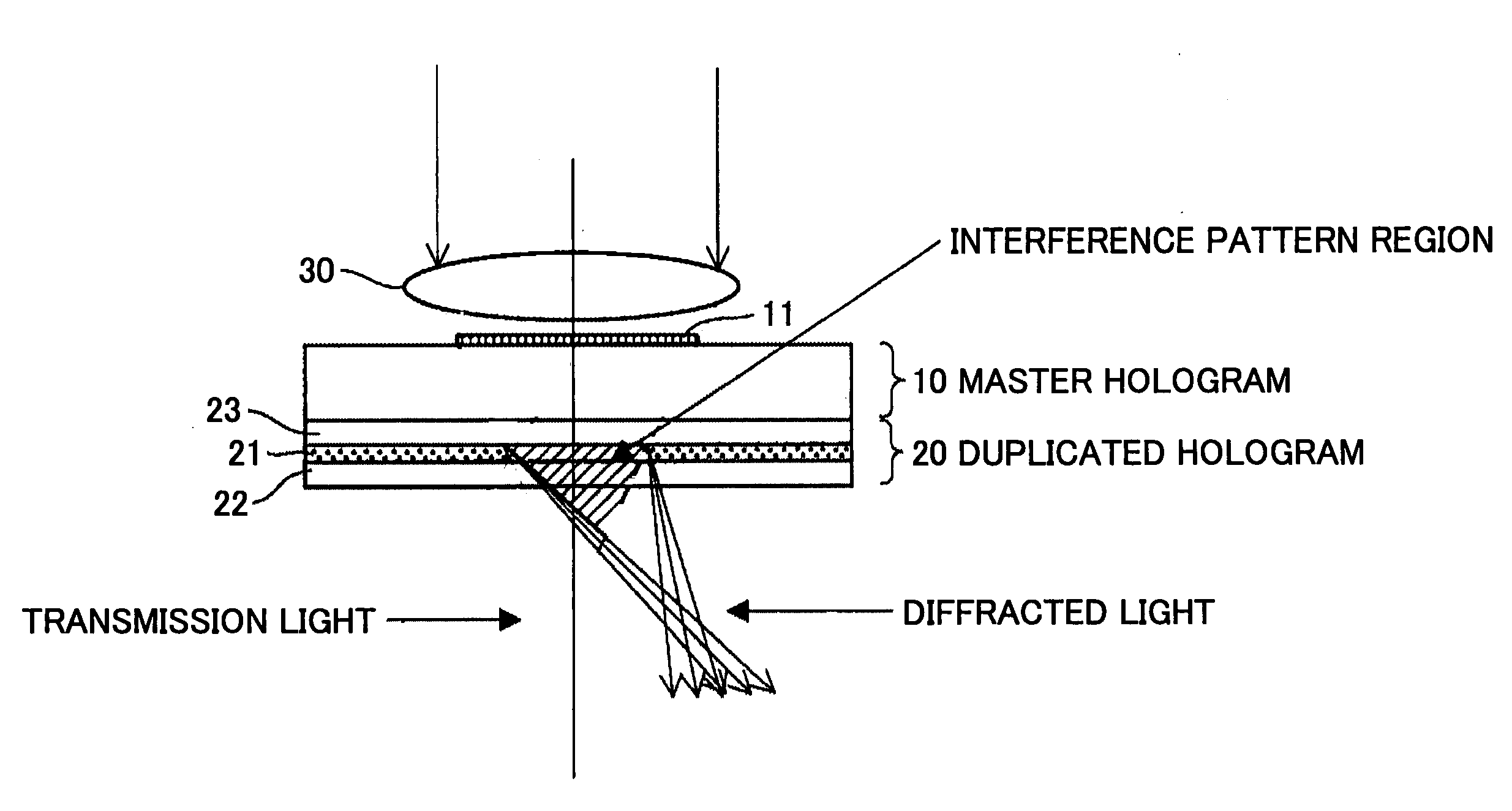
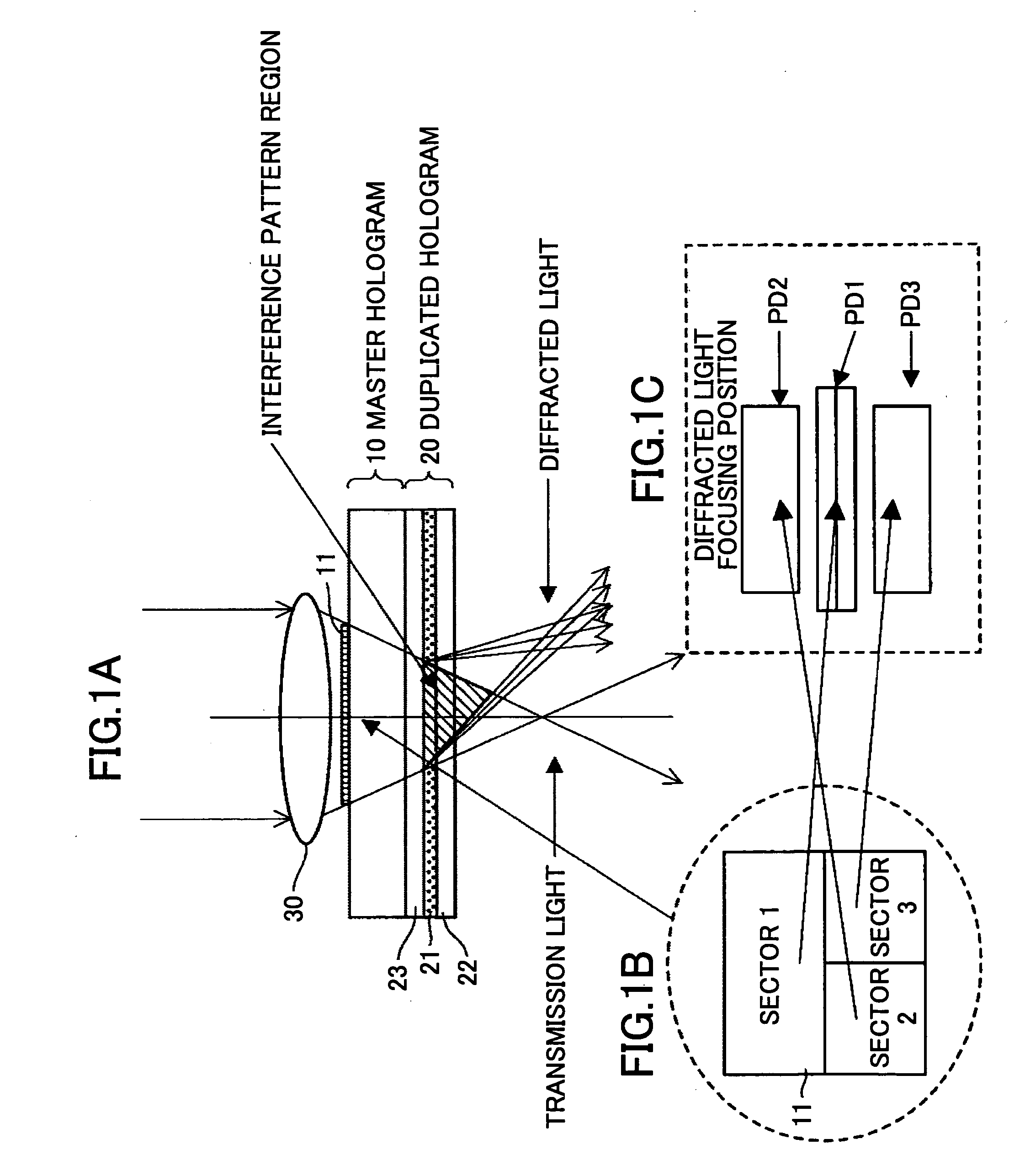
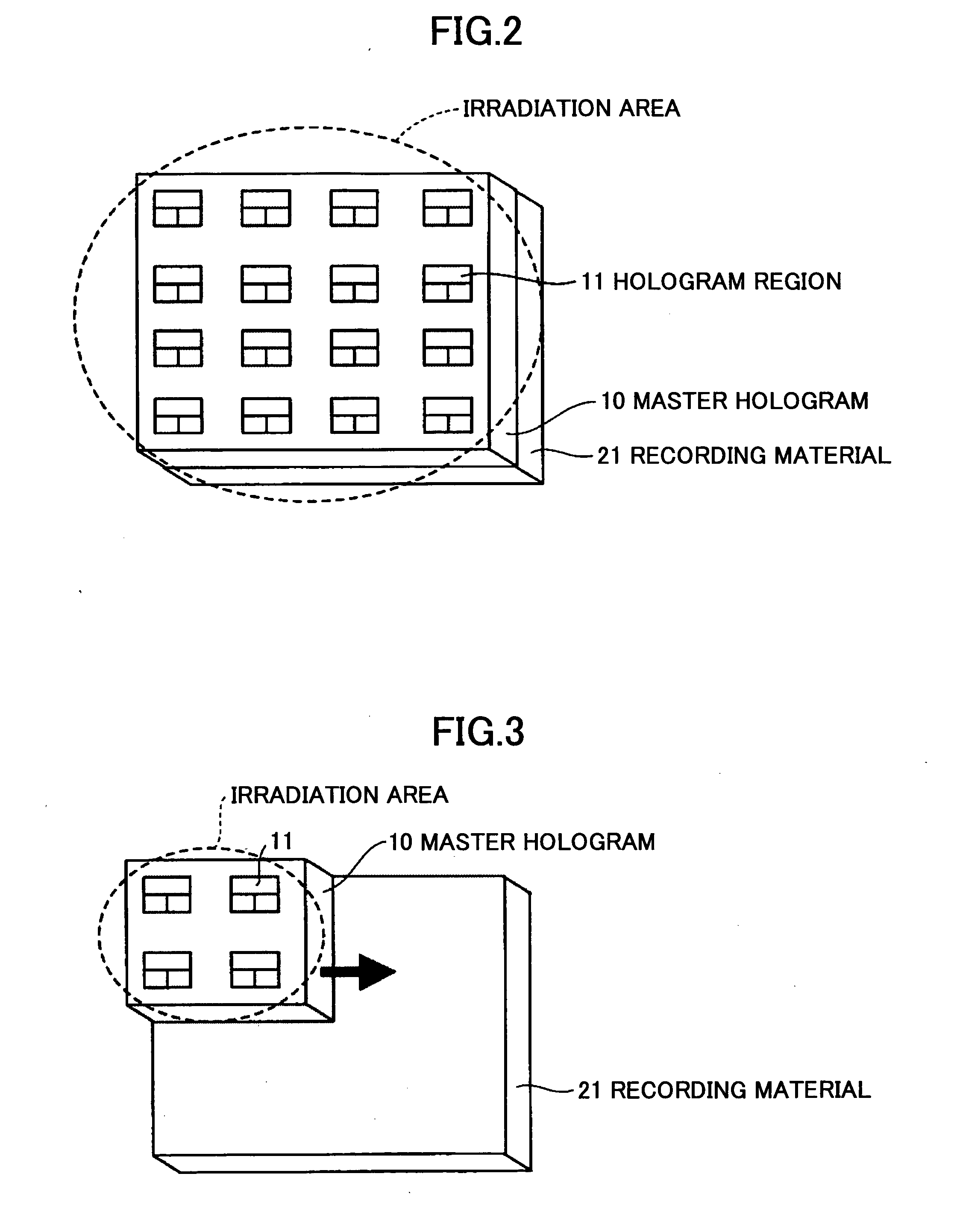
InactiveUS20060055993A1High film thicknessImprove productivityHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesRecord information storageProduction rateLight beam
A method of producing a hologram element is disclosed that is able to prevent spread of a polymerization reaction and light leakage during exposure with interference light, and improve productivity in mass production. The hologram element is for transmitting, reflecting, diffracting, or scattering incident light, and includes a pair of substrates, an isolation member between the substrates that forms an isolated region, and a photo-sensitive recording material sealed in the isolated region. The hologram element includes a periodic structure formed by exposing the recording material to interference light. The interference light is generated by two or more light beams, or by using a master hologram. The recording material is formed from a composite material including a polymerized polymer or a polymerized liquid crystal. The periodic structure is formed by exposing the recording material to the interference light to induce the polymerization reaction and phase separation in the composite material.
Owner:RICOH KK
Methods and compositions for treating ocular disorders
InactiveUS20060293270A1Efficient ConcentrationEffective maintenanceGenetic material ingredientsGene therapyCompound (substance)Vascular endothelial growth factor
This invention relates to methods of treating ocular disease. The method of the invention is directed to the administration of an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (anti-VEGF) compound to treat such disease.
Owner:EYETECH
Pre-chamber spark plug
ActiveUS20070069617A1Maximize spark plug lifeReduce erosionSparking plugsInternal combustion piston enginesSpecific energyElectricity
A method and apparatus to maximize spark plug life in pre-chamber spark plugs operating with ultra-lean mixtures and / or elevated engine BMEP is presented. Electrode erosion is reduced by spreading discharge energy over a wider surface area, maintaining fuel concentration in the spark gap, controlling gas static pressure during discharge, and maintaining safe electrode temperature. Energy is spread via a swirling effect created by periphery holes in an end cap, resulting in a lower specific energy discharge at the electrodes. Divergently configured electrodes reduce the spark voltage at high operating pressures and the energy required for ignition. The flow field generated at the electrodes prevents electrical shorts due to water condensation and avoids misfire. The center electrode insulation provides an effective heat transfer path to prevent electrode overheating and preignition. The volume behind the electrodes provides a volume for burnt products from previous combustion cycles and leads to more reliable ignition.
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
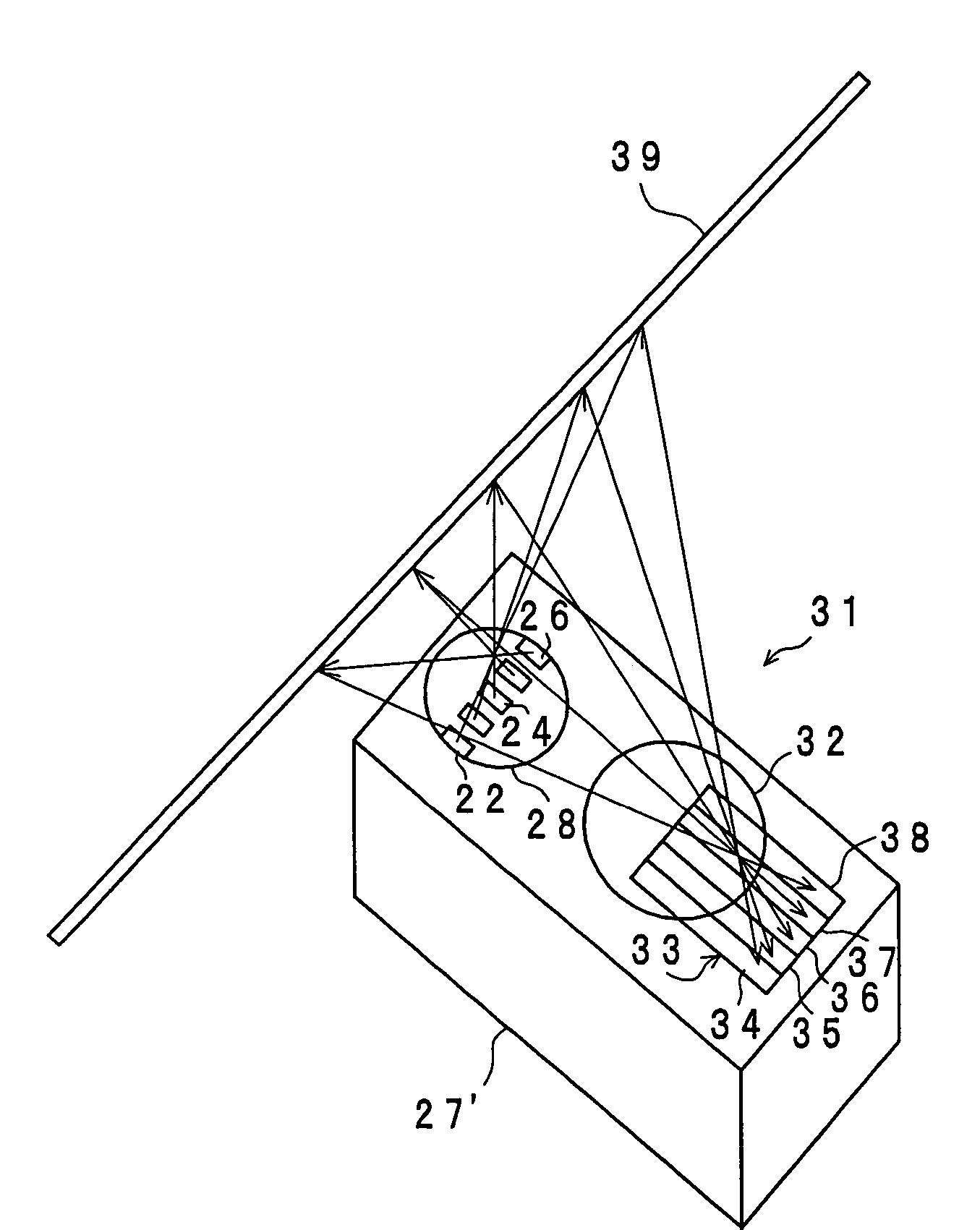
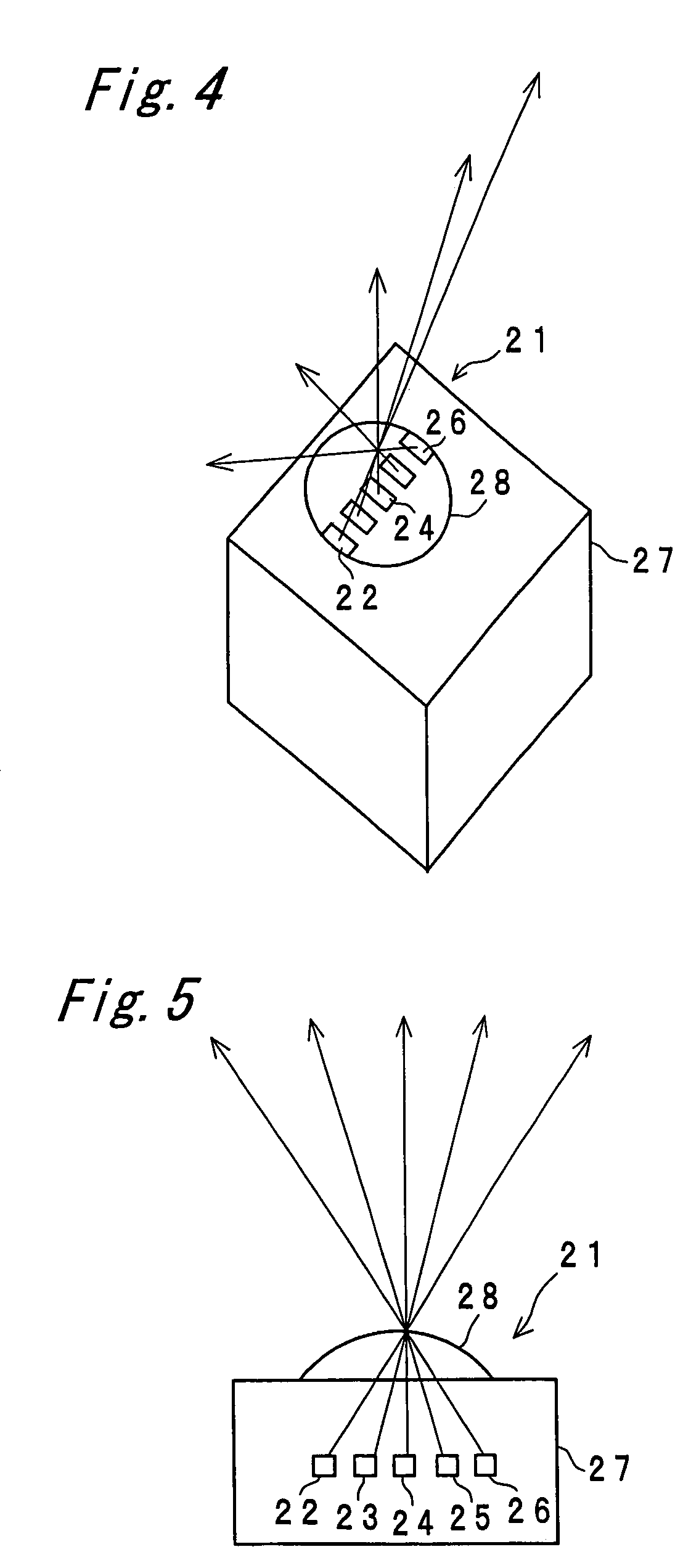
Multiple ranging apparatus
InactiveUS7417716B2Efficient ConcentrationOptical rangefindersSolid-state devicesLength waveInstrumentation
A multiple ranging apparatus has a light emitting section constituted by a plurality of aligned LEDs which emit light rays of wavelengths different from one another, and a light receiving section constituted by a plurality of aligned PSD parts which have wavelength sensitivities corresponding to the different wavelengths of the light rays emitted from the LEDs. Thus, even when ranging of respective points is simultaneously measured in multiple ranging measurement, it is possible to identify which LED the light is emitted from, and therefore, to simultaneously measure the distances of two or more points.
Owner:SHARP KK
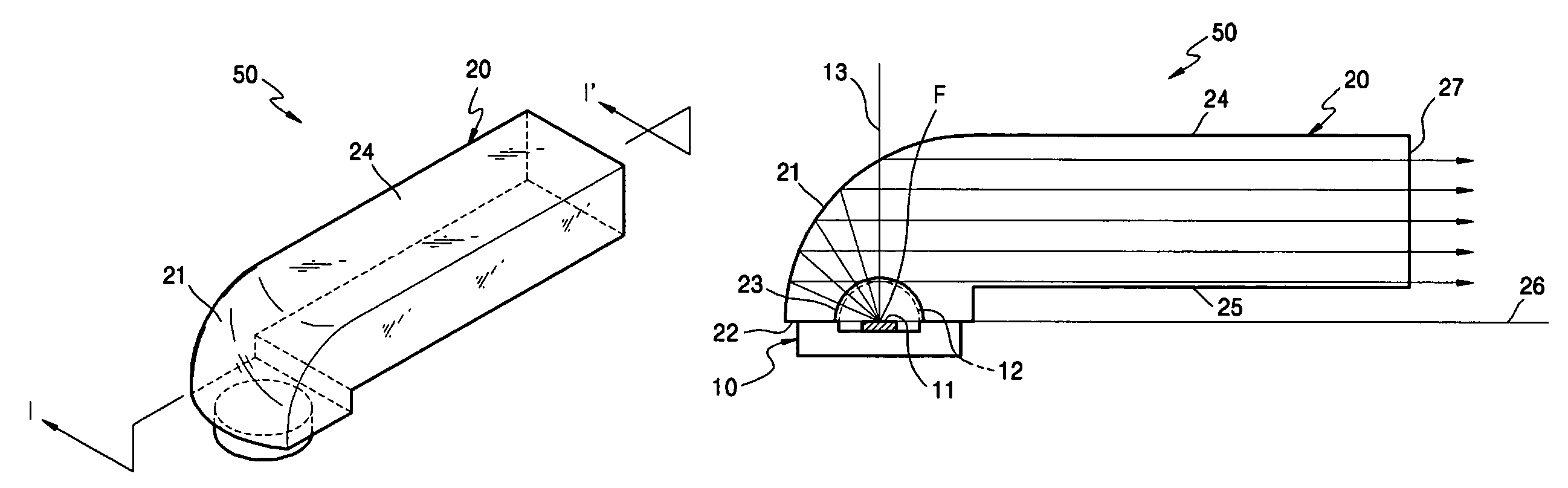
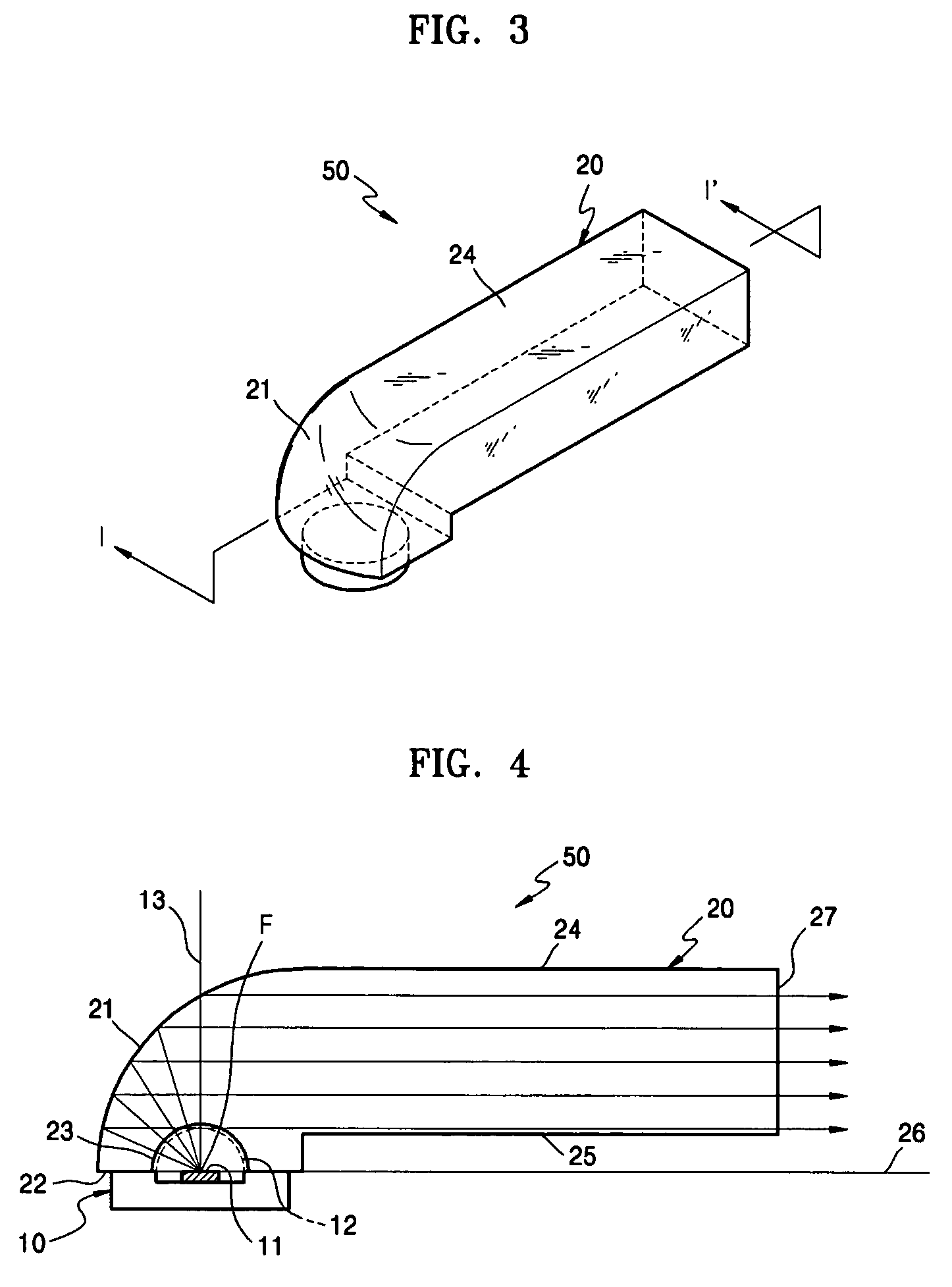
Illumination unit using LED and image projecting apparatus employing the same
ActiveUS7182497B2Efficient ConcentrationTelevision system detailsMechanical apparatusLight guideOptoelectronics
An illumination unit is provided which includes a glass rod including a parabolic reflection surface, a light incident surface facing the parabolic reflection surface, a concave portion formed inwardly in the light incident surface at a position of a focal point of the parabolic reflection surface, and a light guide portion facing the parabolic reflection surface and having a rectangular section. An LED module is disposed at the focal point of the parabolic reflection surface and emitting light to the parabolic reflection surface through the concave portion. A surface of the light guide portion parallel to the light incident surface is stepped from the light incident surface in a direction in which the rectangular section of the light guide portion decreases.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
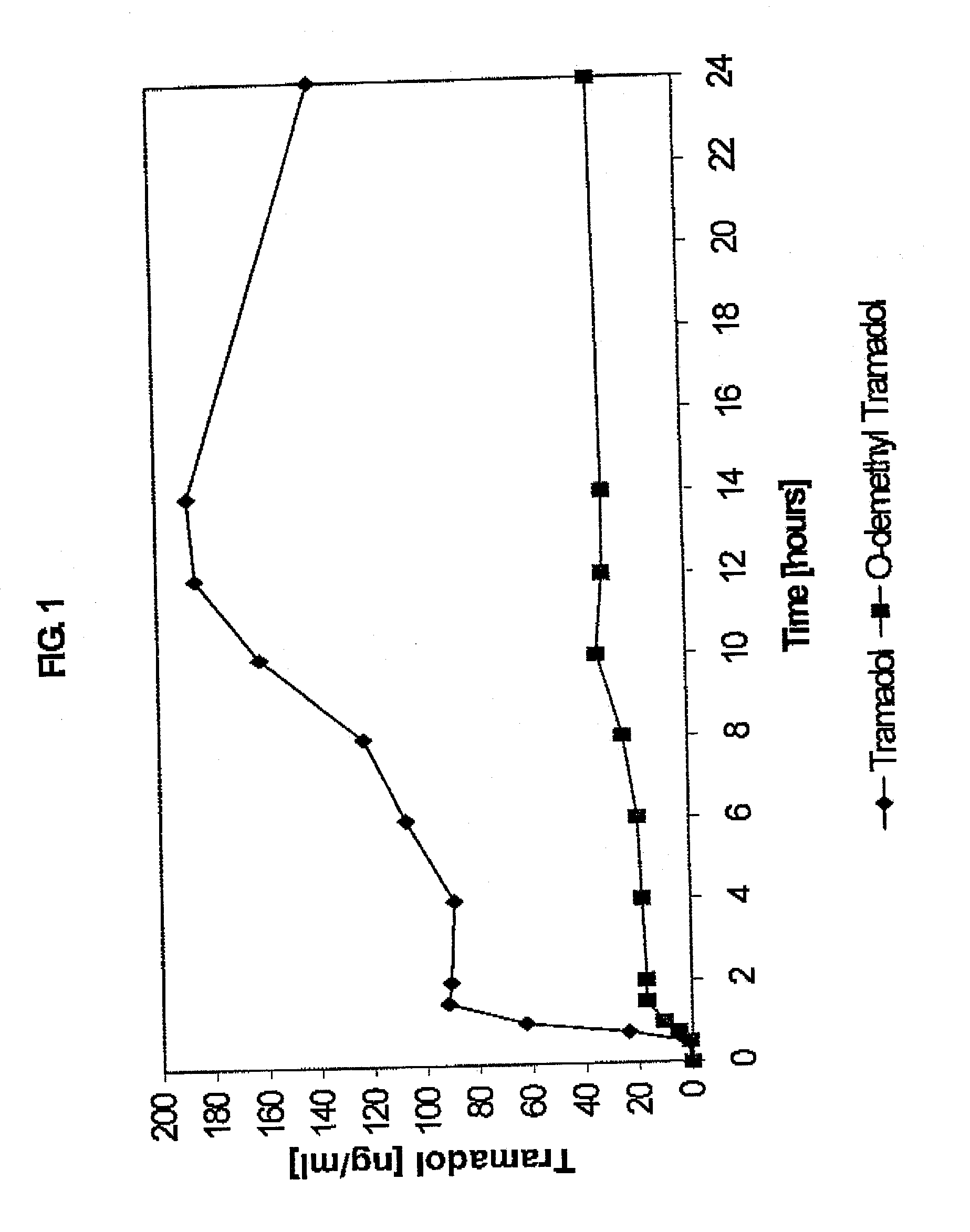
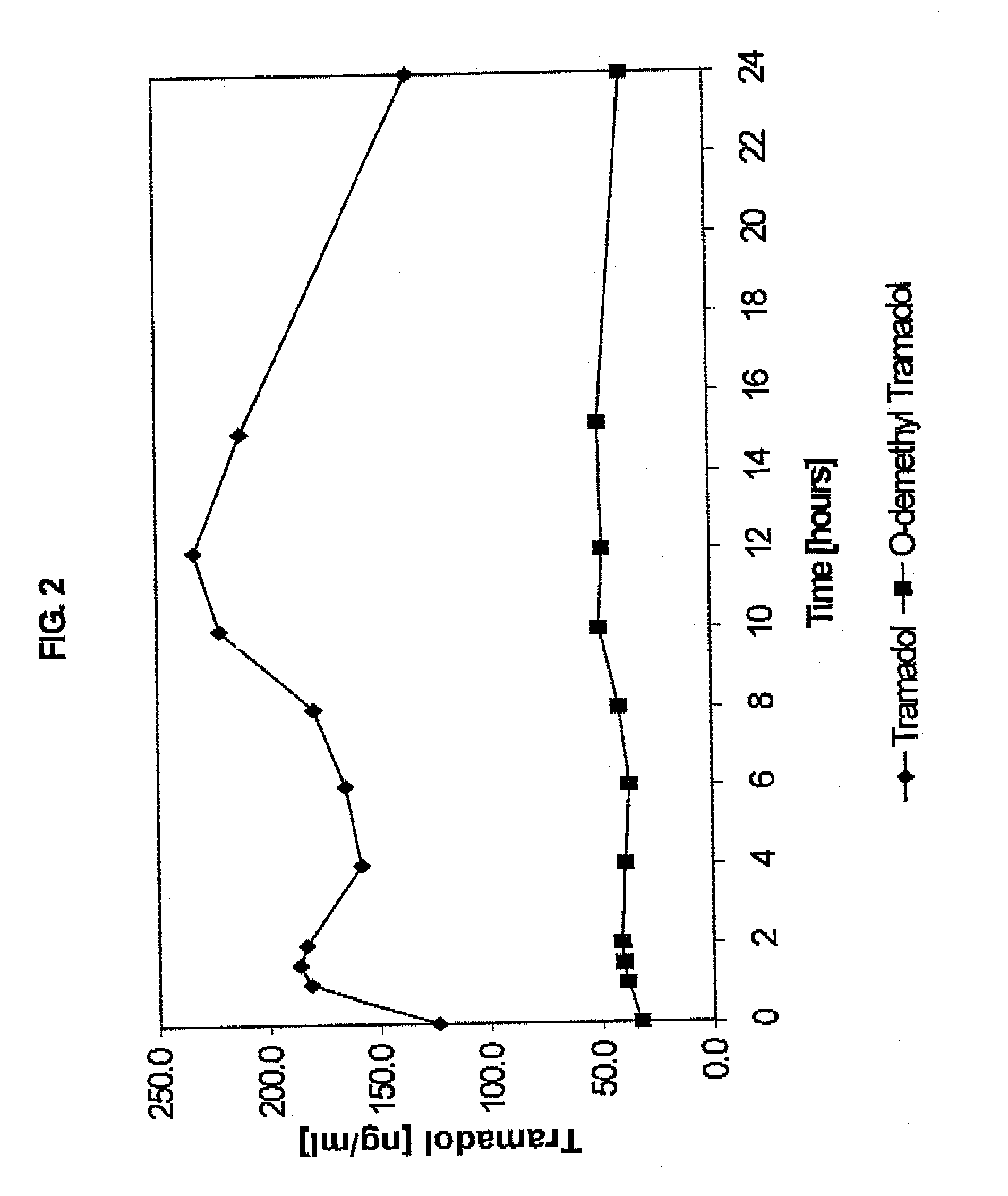
Extended release composition containing Tramadol
InactiveUS20030143270A1Effective controlRelieve painPowder deliveryBiocideBlood concentrationPeak concentration
The present invention relates to a once daily extended release pharmaceutical preparation of Tramadol or its acceptable pharmaceutical salts. The preparation provides, effective blood concentration for a period of about 24 hours with reduced peak concentrations. It is characterized that effective Tramadol levels appear within the first hours after administration, the time to maximal Tramadol content Tmax is at least 10 hours and the peak Tramadol concentration is less than three times the concentration obtained after 24 hours of said administration.
Owner:GALEPHAR PHARMA RES
Pre-chamber spark plug
ActiveUS7659655B2Life maximizationReduce erosionSparking plugsInternal combustion piston enginesElectricityElectrode erosion
Owner:WOODWARD GOVERNOR CO
Sustained-release polymeric microparticles containing poorly water-soluble drug and method for preparing the same
ActiveUS20130273167A1Easy to controlEffective drug concentrationBiocidePowder deliveryWater soluble drugWater soluble
Disclosed are sustained-release polymeric microparticles containing a poorly water-soluble drug and a method for preparing the same.
Owner:SAMYANG HLDG CORP
Oral modified release formulations
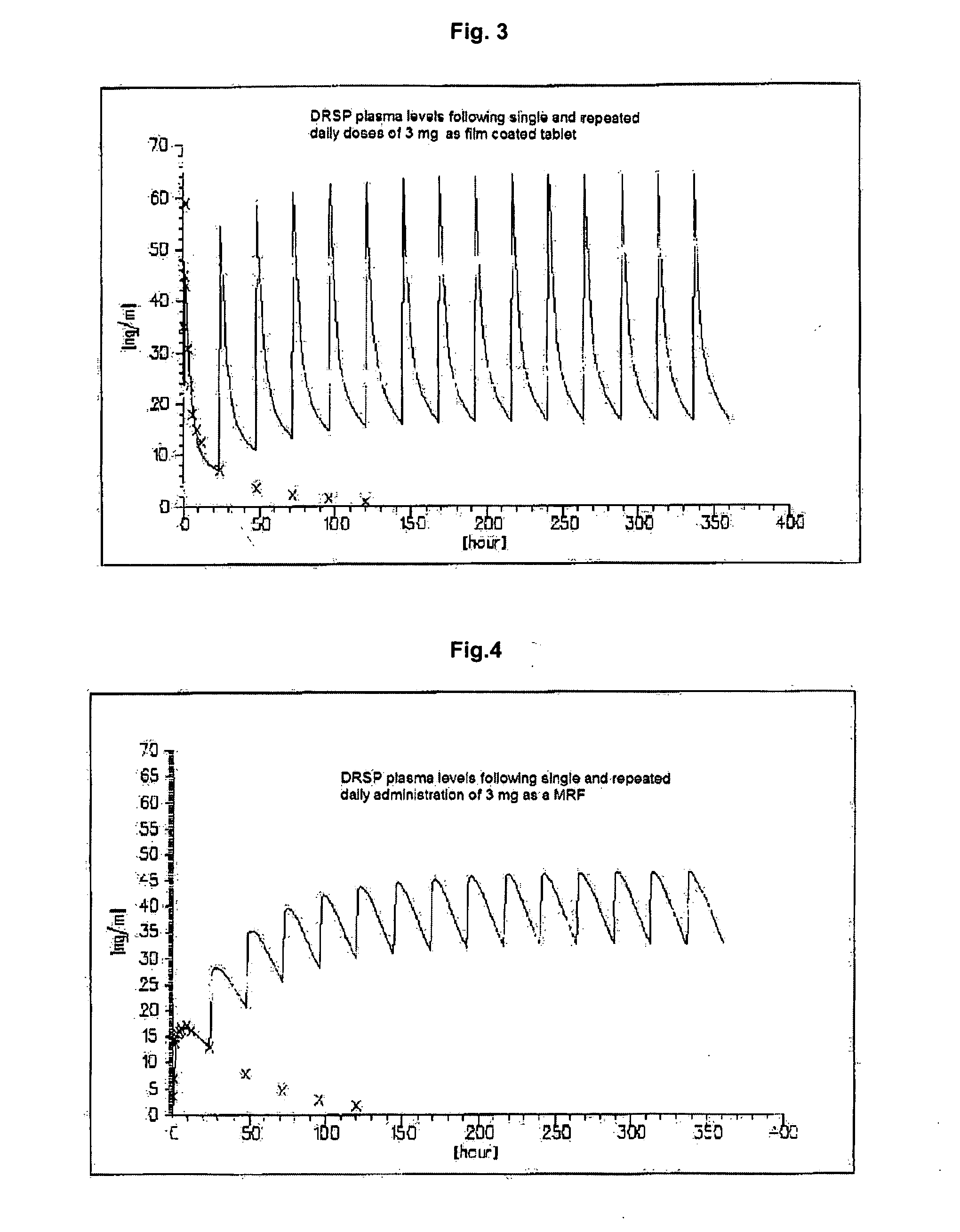
InactiveUS20100086599A1High dose of drugReduce doseBiocidePowder deliveryDrospirenoneImmediate release
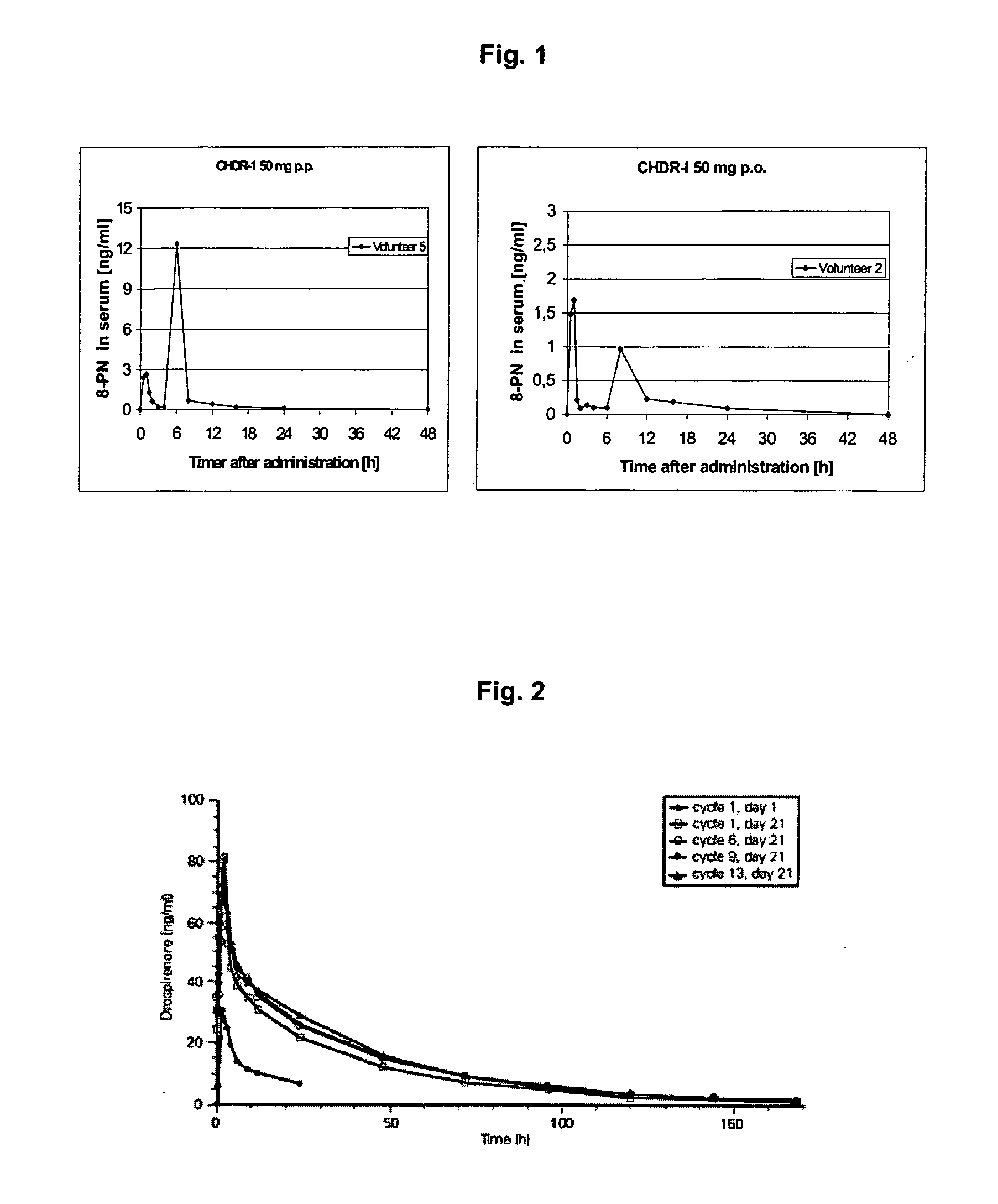
This invention is directed to an oral modified release formulation of the phytoestrogen 8-Prenylnaringenin in combination with a progestin, preferably with Drospirenone, and several uses thereof. In another aspect of the invention an oral modified formulation of 8-Prenylnaringenin with an immediately releasing progestin, like Drospirenone, is provided as well as several uses thereof.
Owner:BAYER INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY GMBH
Highly simplified lateral flow-based nucleic acid sample preparation and passive fluid flow control
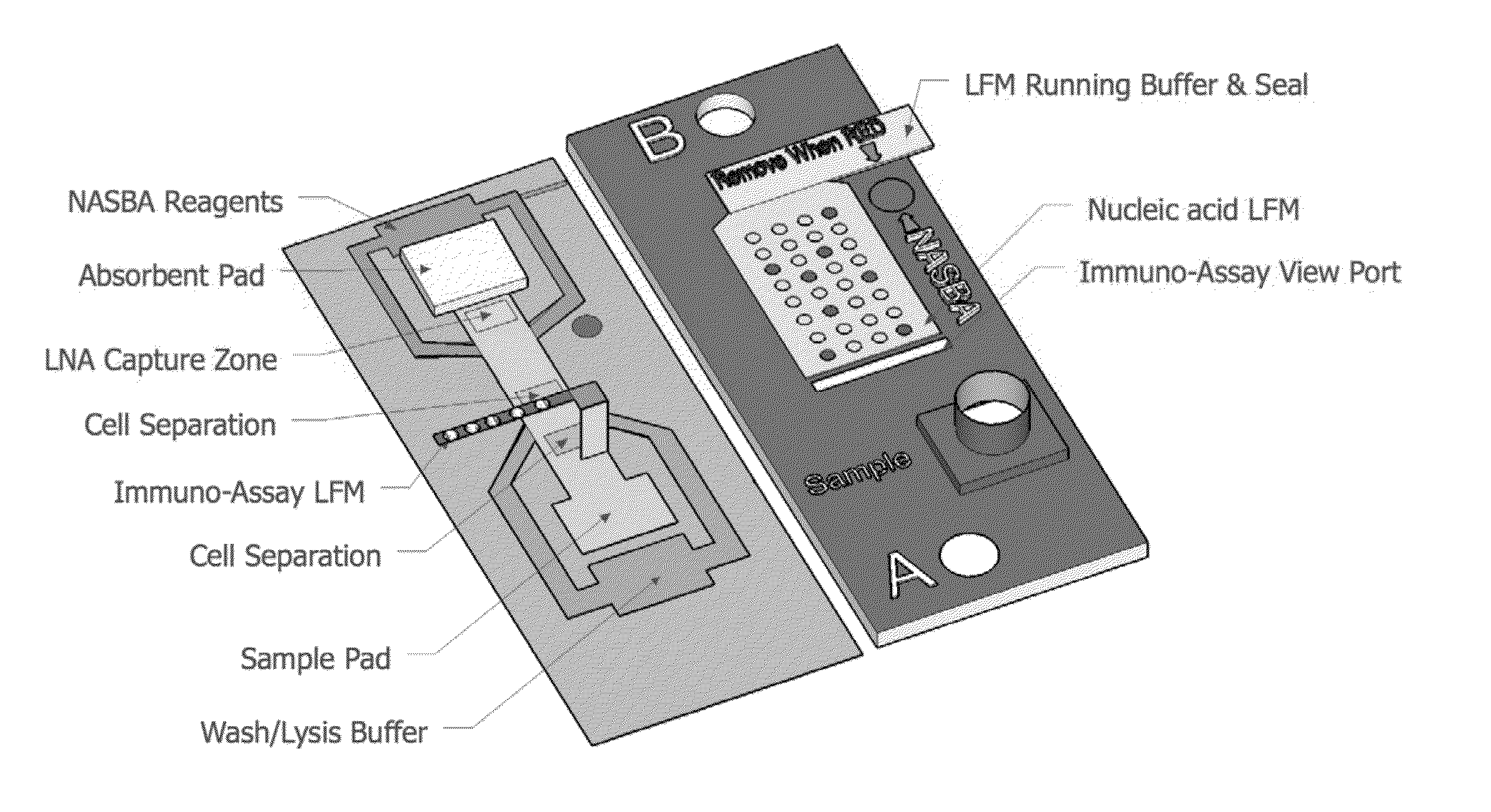
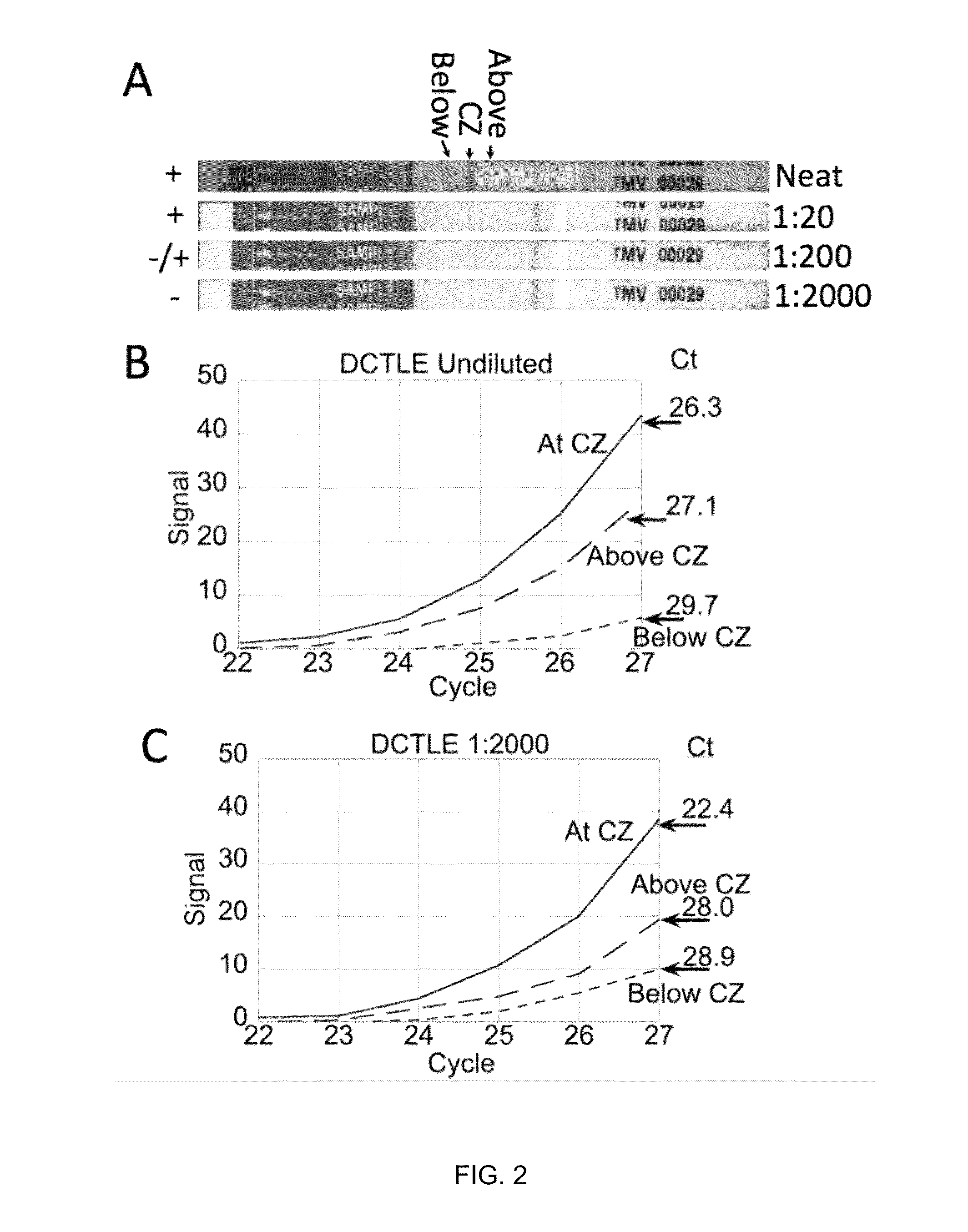
ActiveUS9207236B2Rapid immuno-affinity captureEfficient ConcentrationPreparing sample for investigationDNA preparationFluid controlHumic acid
Highly simplified lateral flow chromatographic nucleic acid sample preparation methods, devices, and integrated systems are provided for the efficient concentration of trace samples and the removal of nucleic acid amplification inhibitors. Methods for capturing and reducing inhibitors of nucleic acid amplification reactions, such as humic acid, using polyvinylpyrrolidone treated elements of the lateral flow device are also provided. Further provided are passive fluid control methods and systems for use in lateral flow assays.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Superabrasive electrodeposited cutting edge and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS6098609AGood precisionImprove working precisionRevolution surface grinding machinesBonded abrasive wheelsBiomedical engineeringThin walled
PCT No. PCT / JP96 / 00206 Sec. 371 Date Jul. 30, 1997 Sec. 102(e) Date Jul. 30, 1997 PCT Filed Feb. 1, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO96 / 23630 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 8, 1996A cutting edge comprising a mass of superabrasive particles (2) electrodeposited on a thin-walled metallic base member (1) along a border (6) of said base member, wherein said mass (2) forms one or more layers at said border of said base member and fixed thereto, and each layer contains parts comprising at least five superabrasive particles (3) in a row in an extending direction of said base member from said border, so as to improve free-cut performance, decrease kerf width and prolong the life of cutting tool.
Owner:ISHIZUKA HIROSHI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com