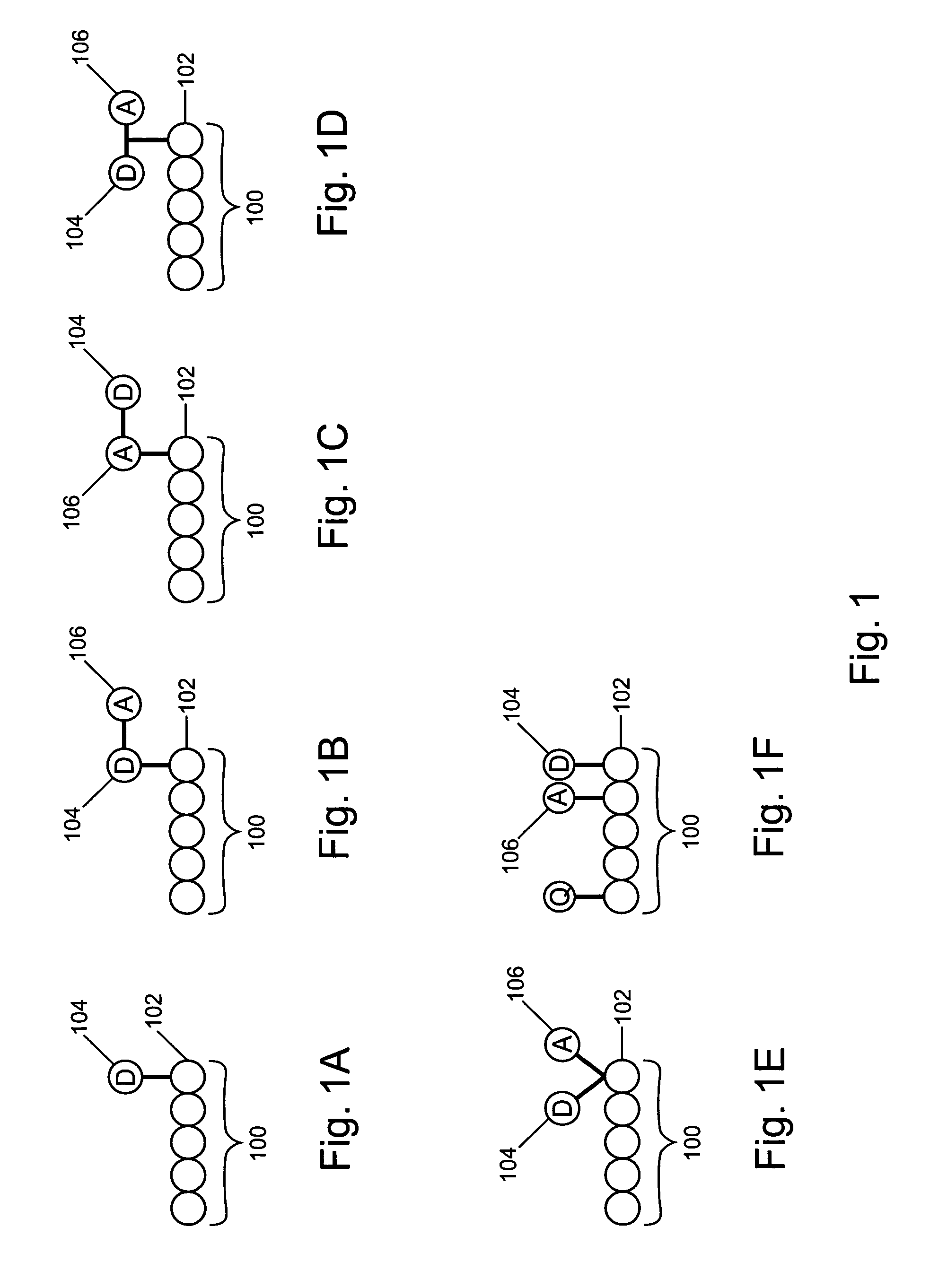
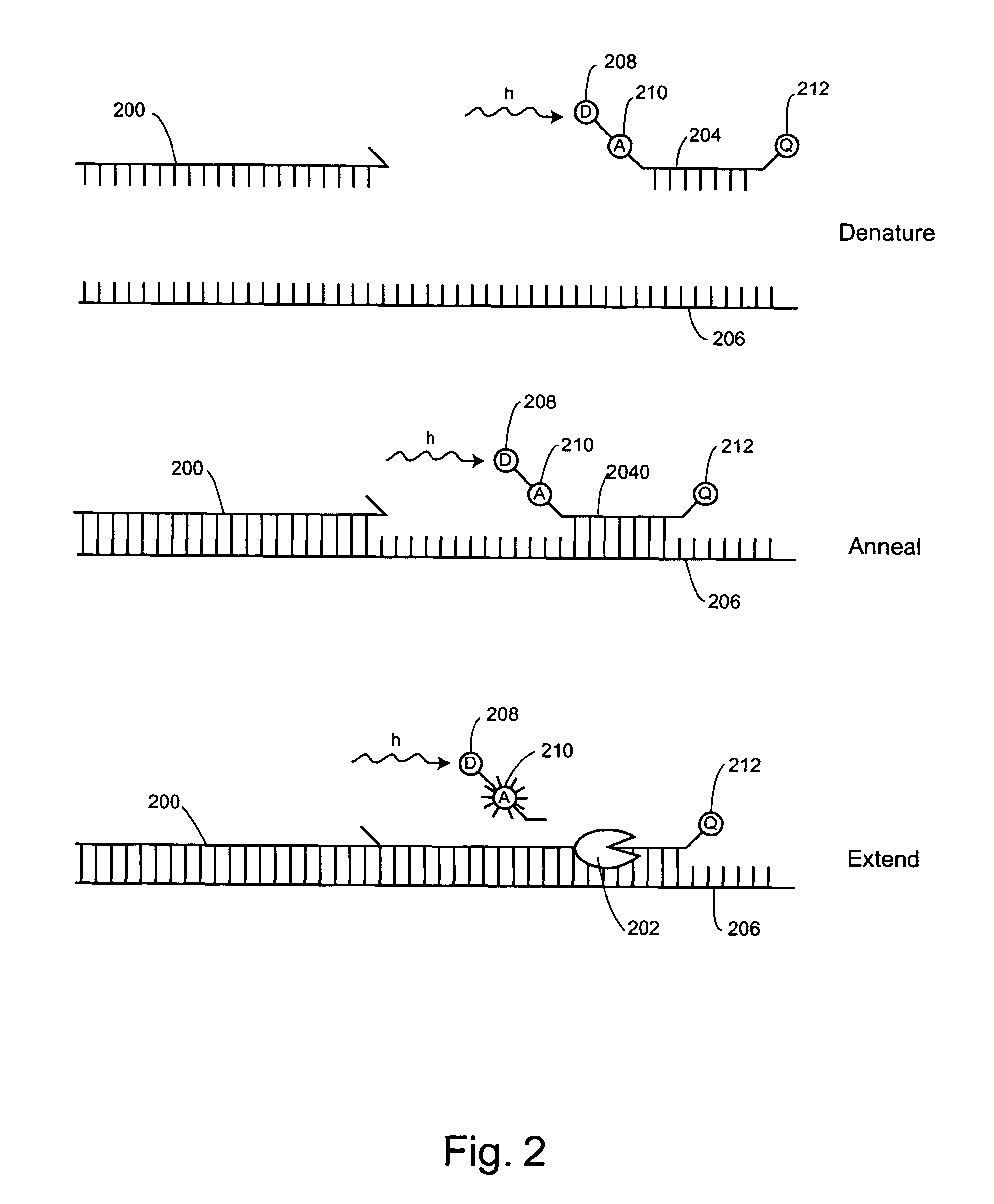
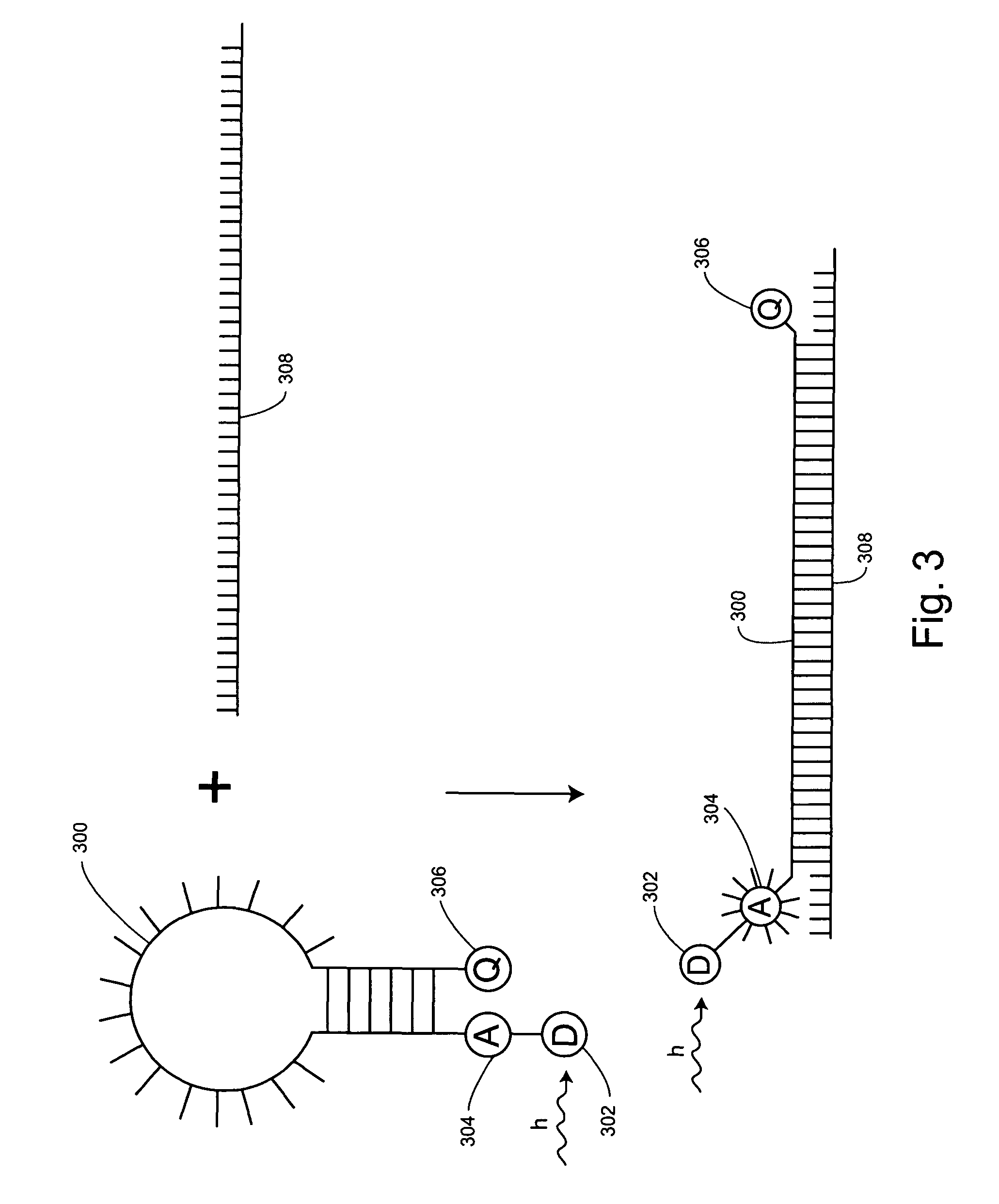
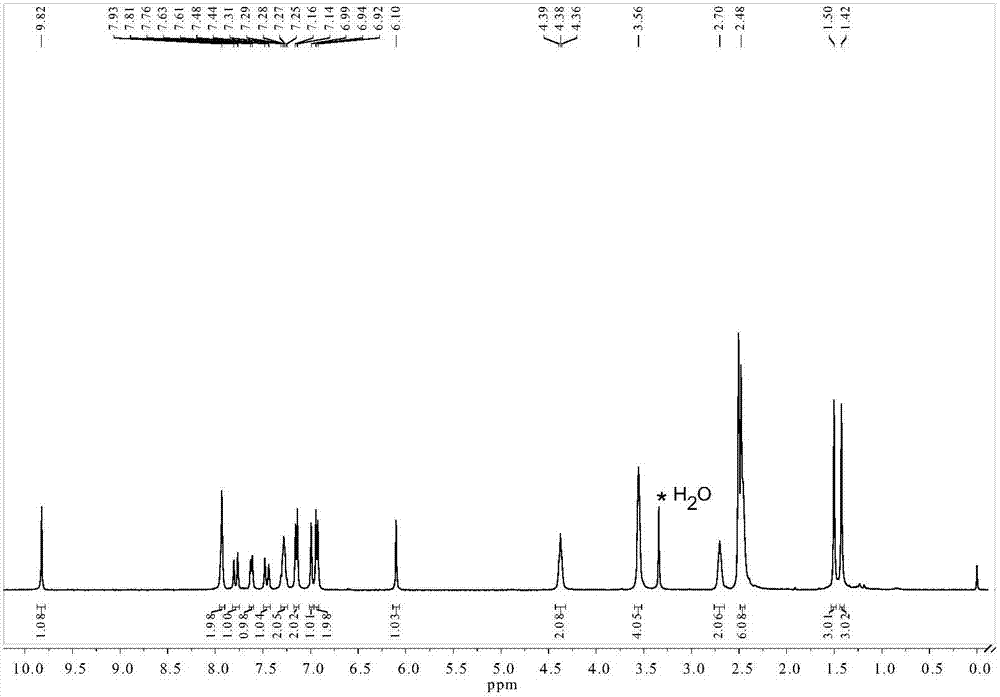
Patents
Literature
428 results about "Background fluorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
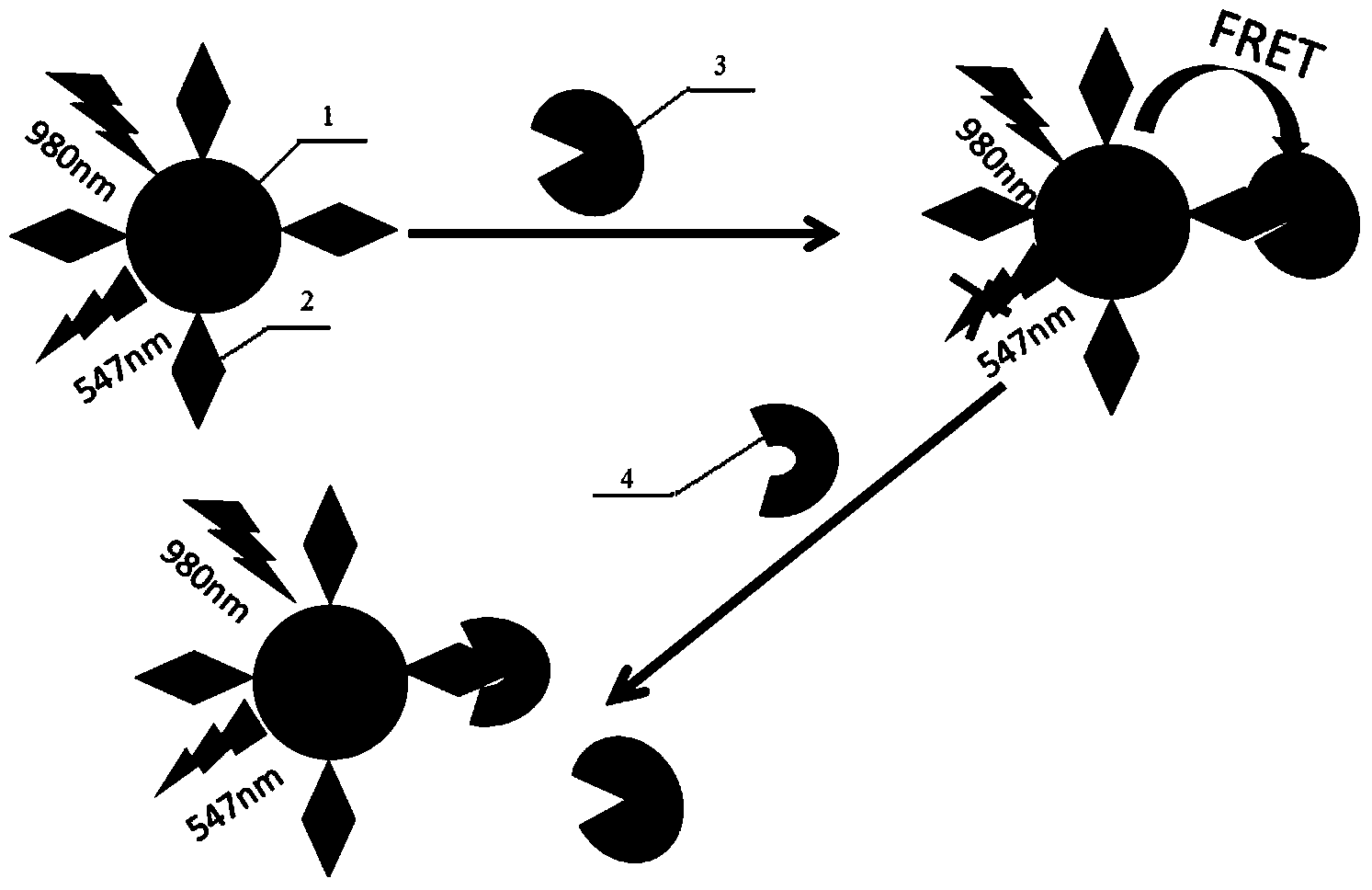
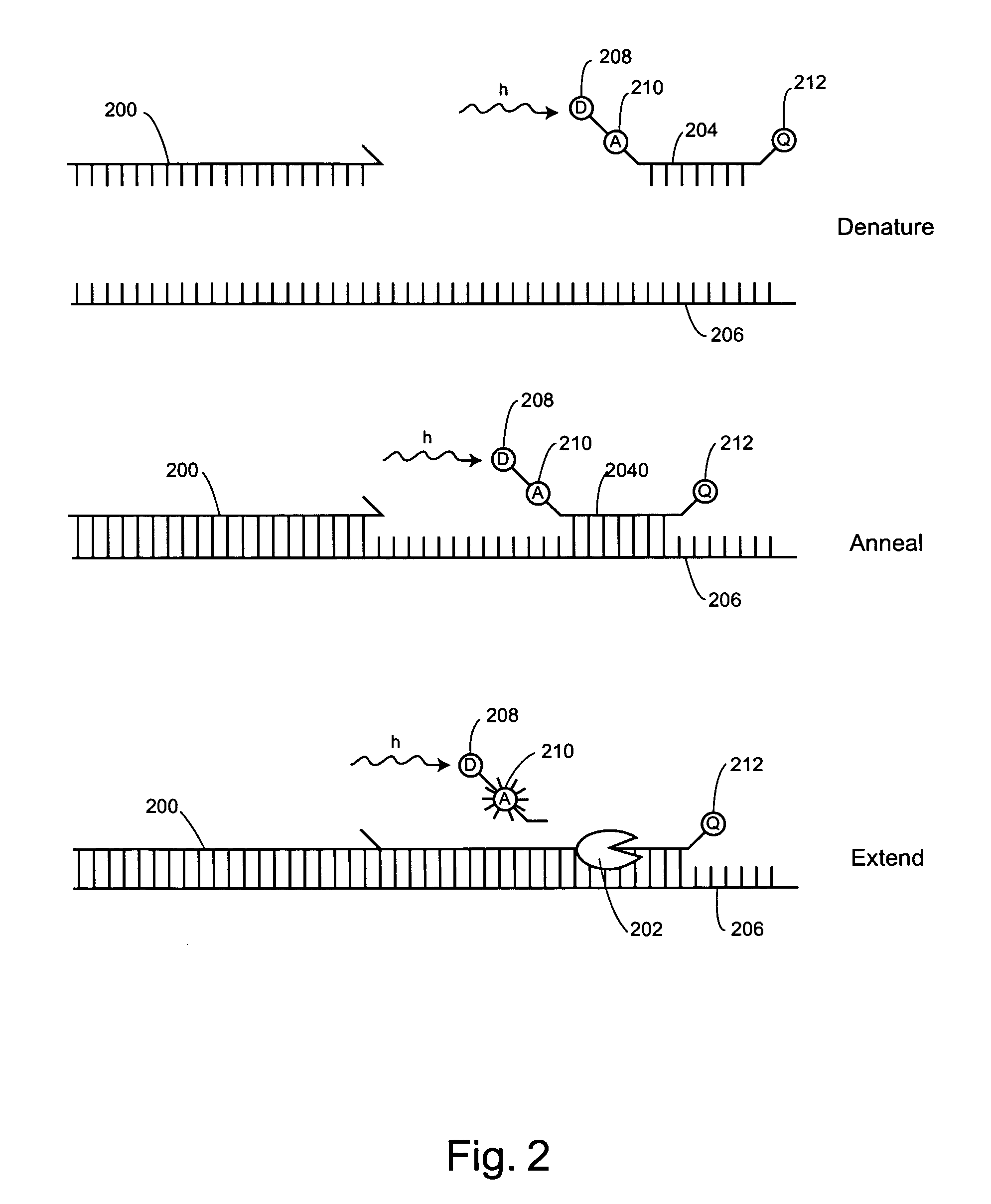
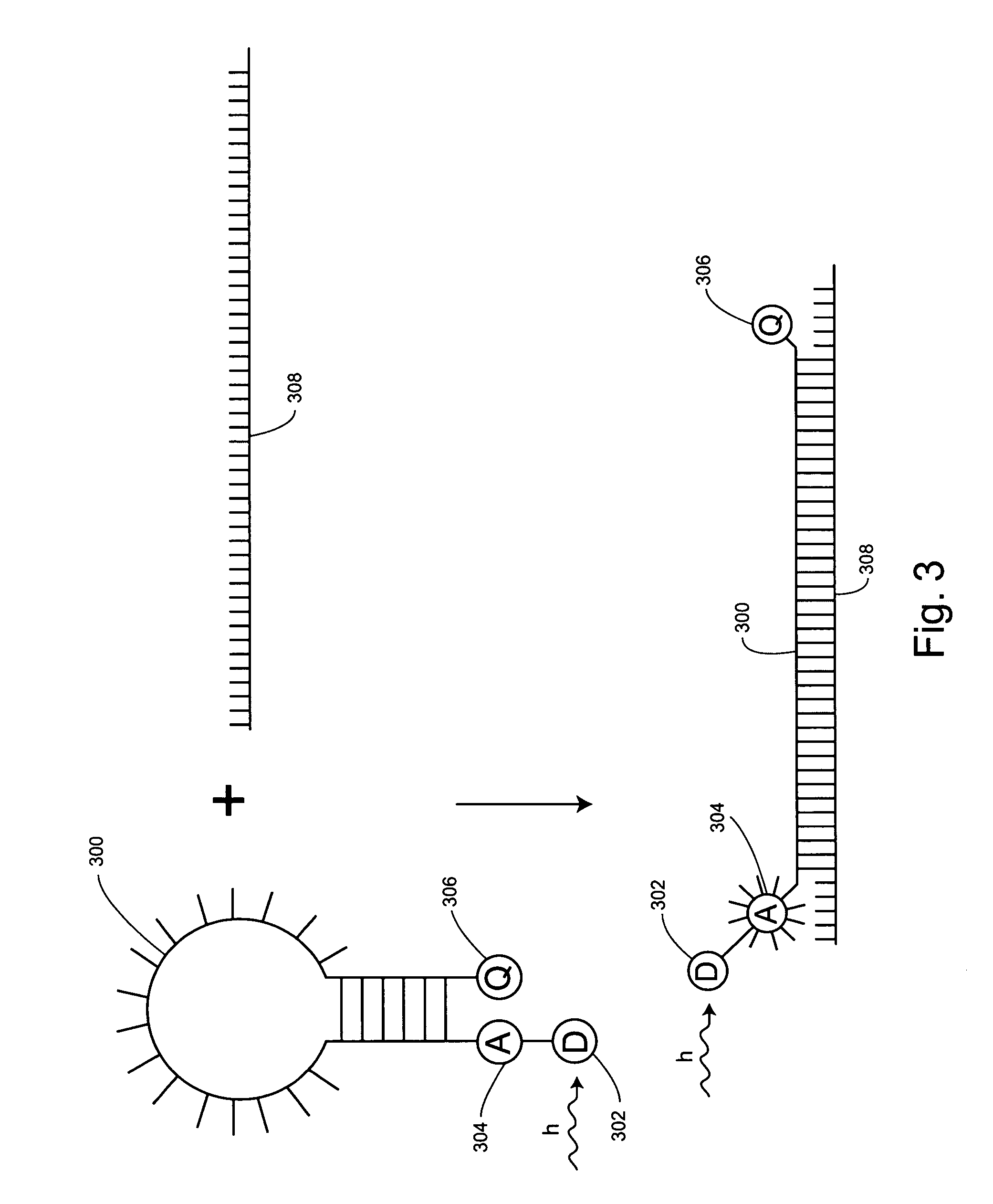
Background fluorescence that is due to the instrument setup and imaging parameters—for example, light from the excitation source, camera noise, and ambient light. Background fluorescence that is due to autofluorescence of samples, vessels, and imaging media, or the fluorescence resulting from fluorophores not bound to specific targets.
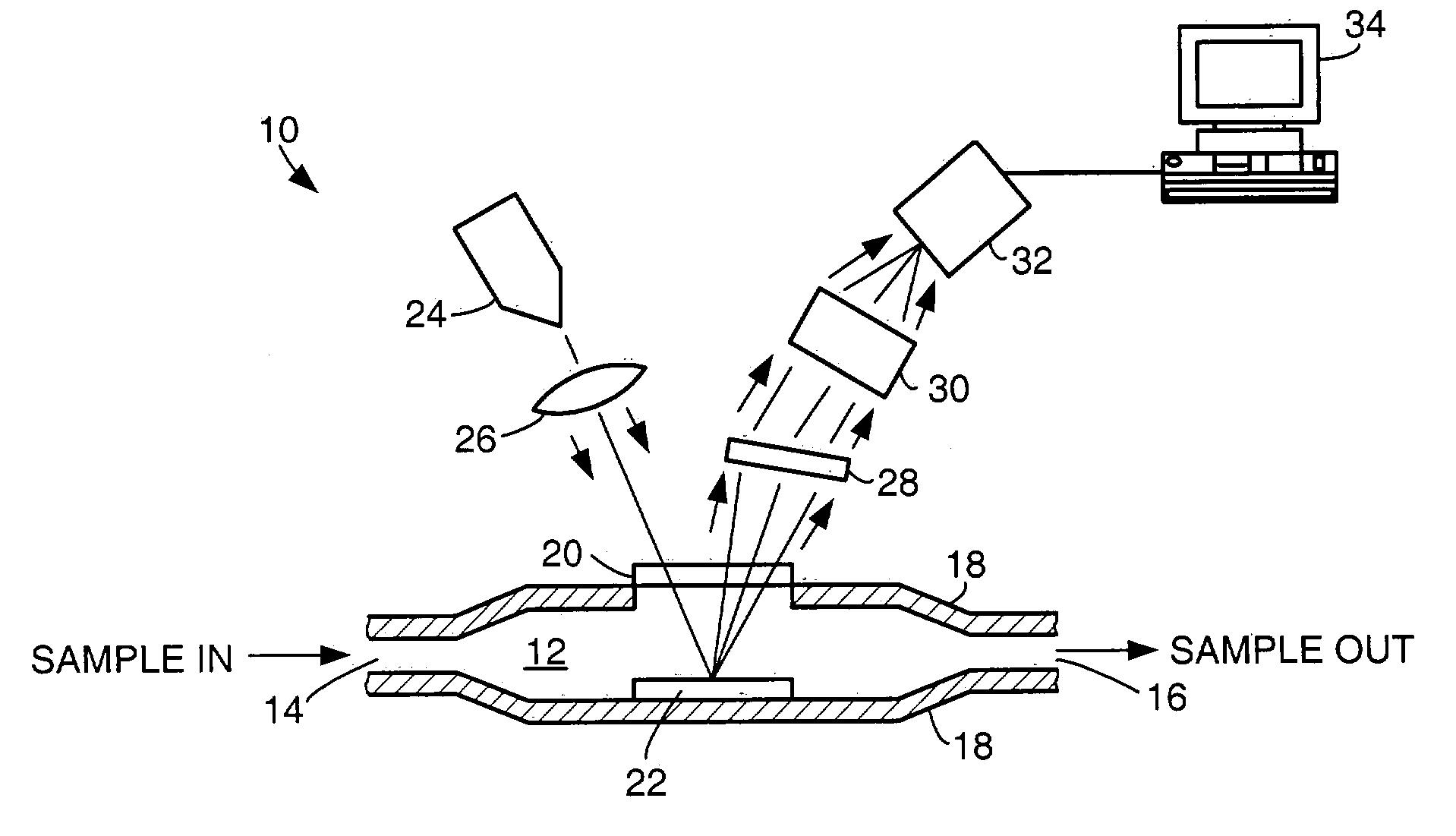
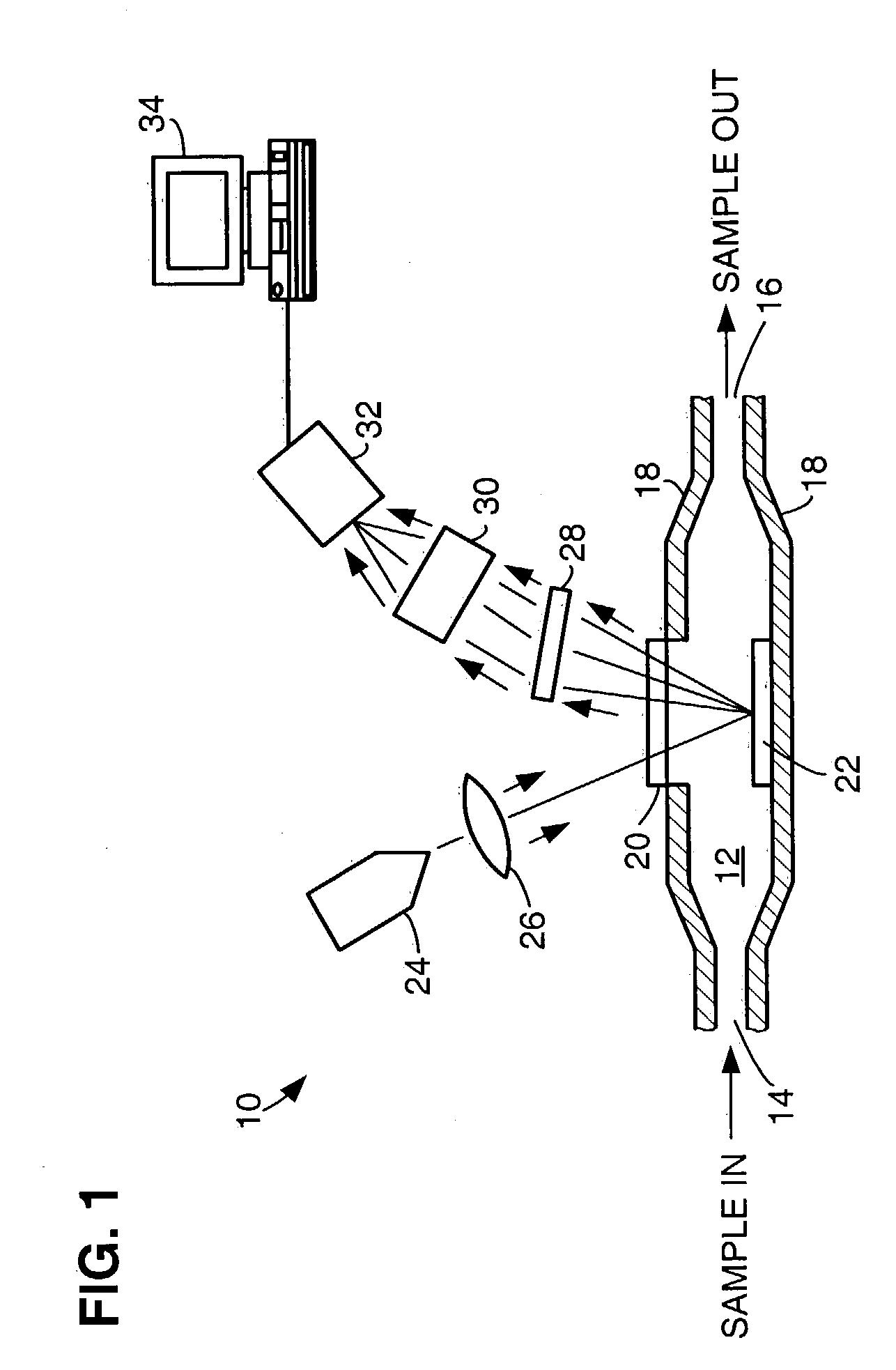
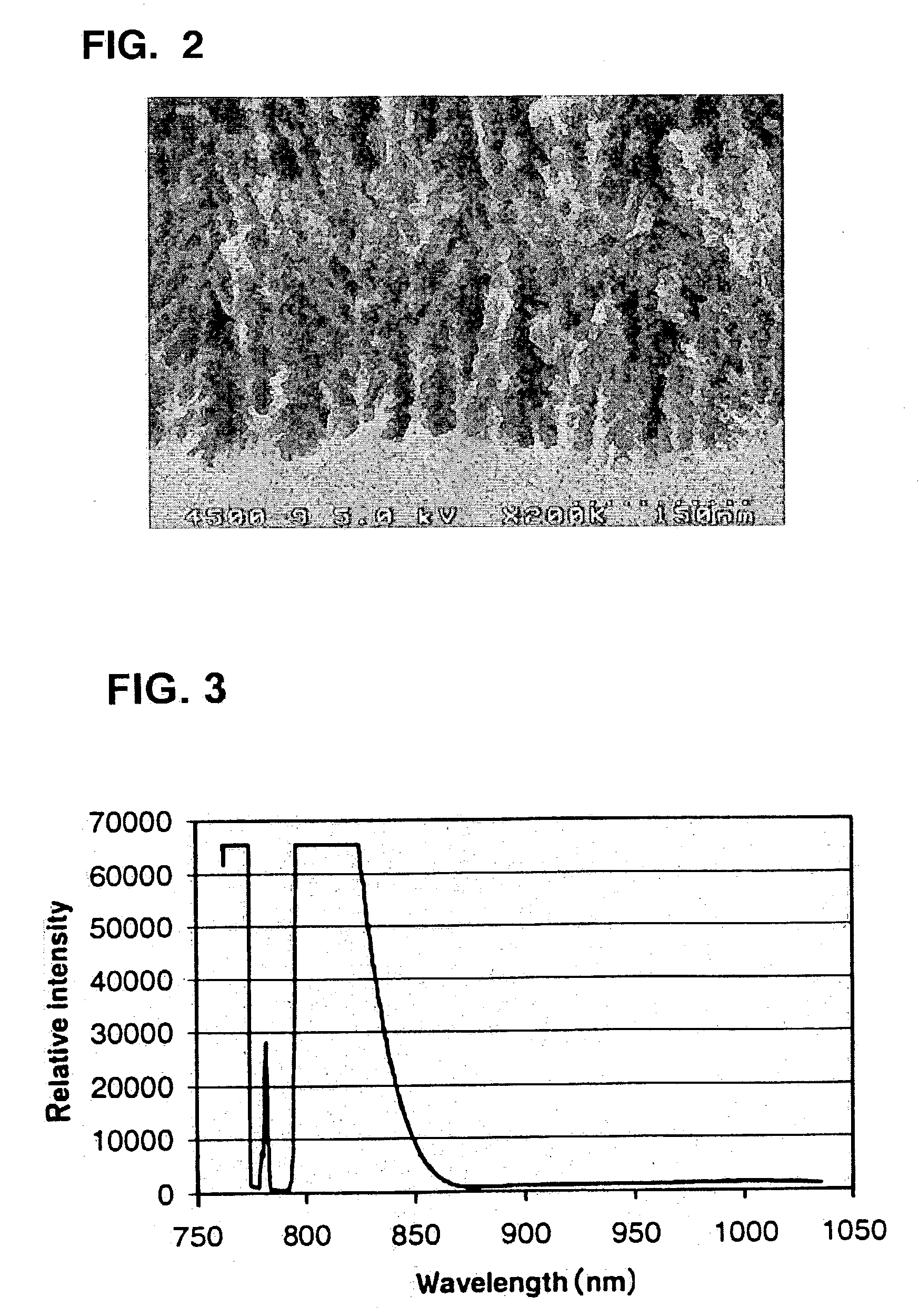
Method and apparatus for noninvasive measurement of carotenoids and related chemical substances in biological tissue
InactiveUS6205354B1Rapid and noninvasive and quantitative measurementRiskRadiation pyrometrySurgeryResonance Raman spectroscopyAntioxidant
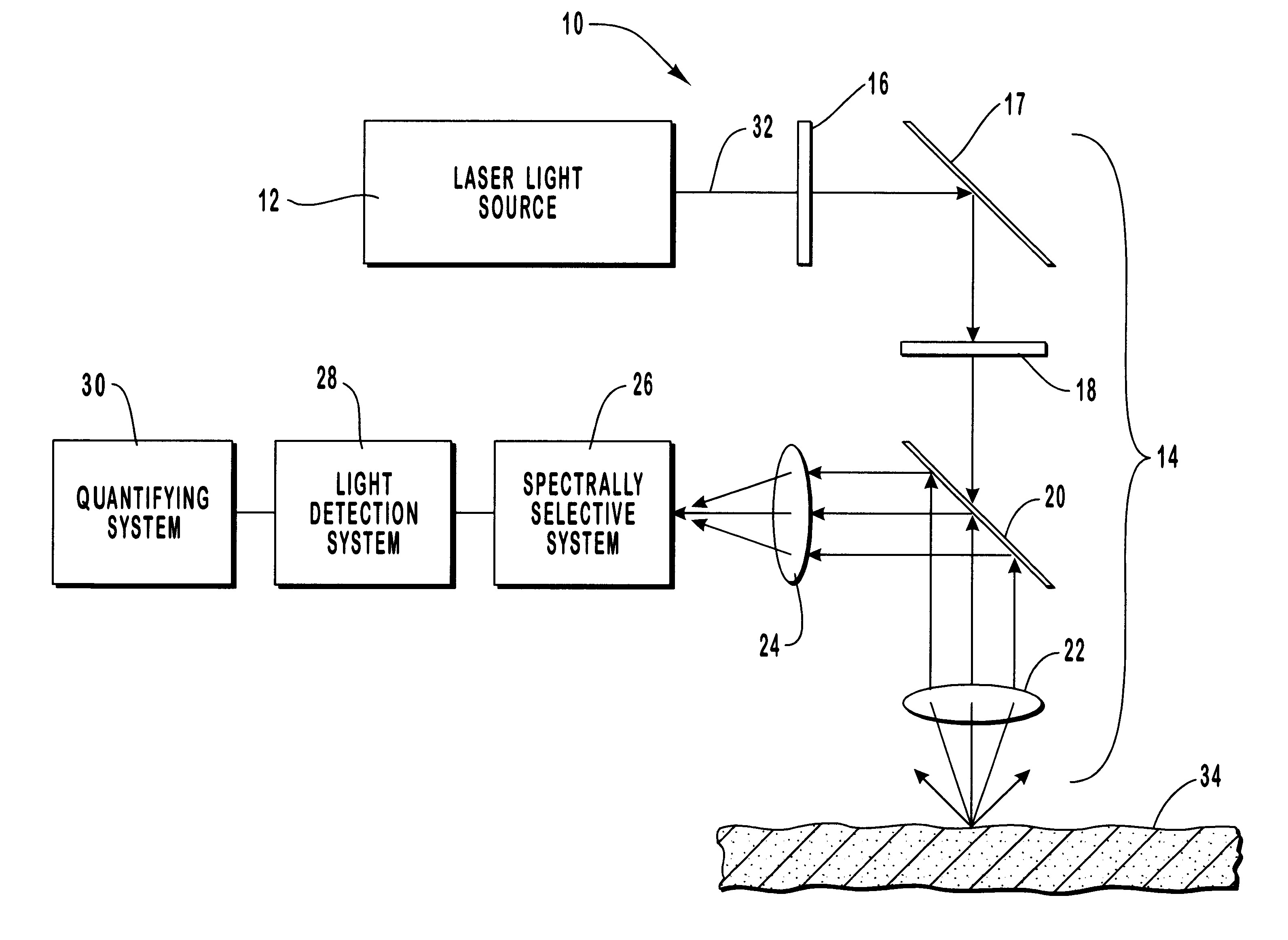
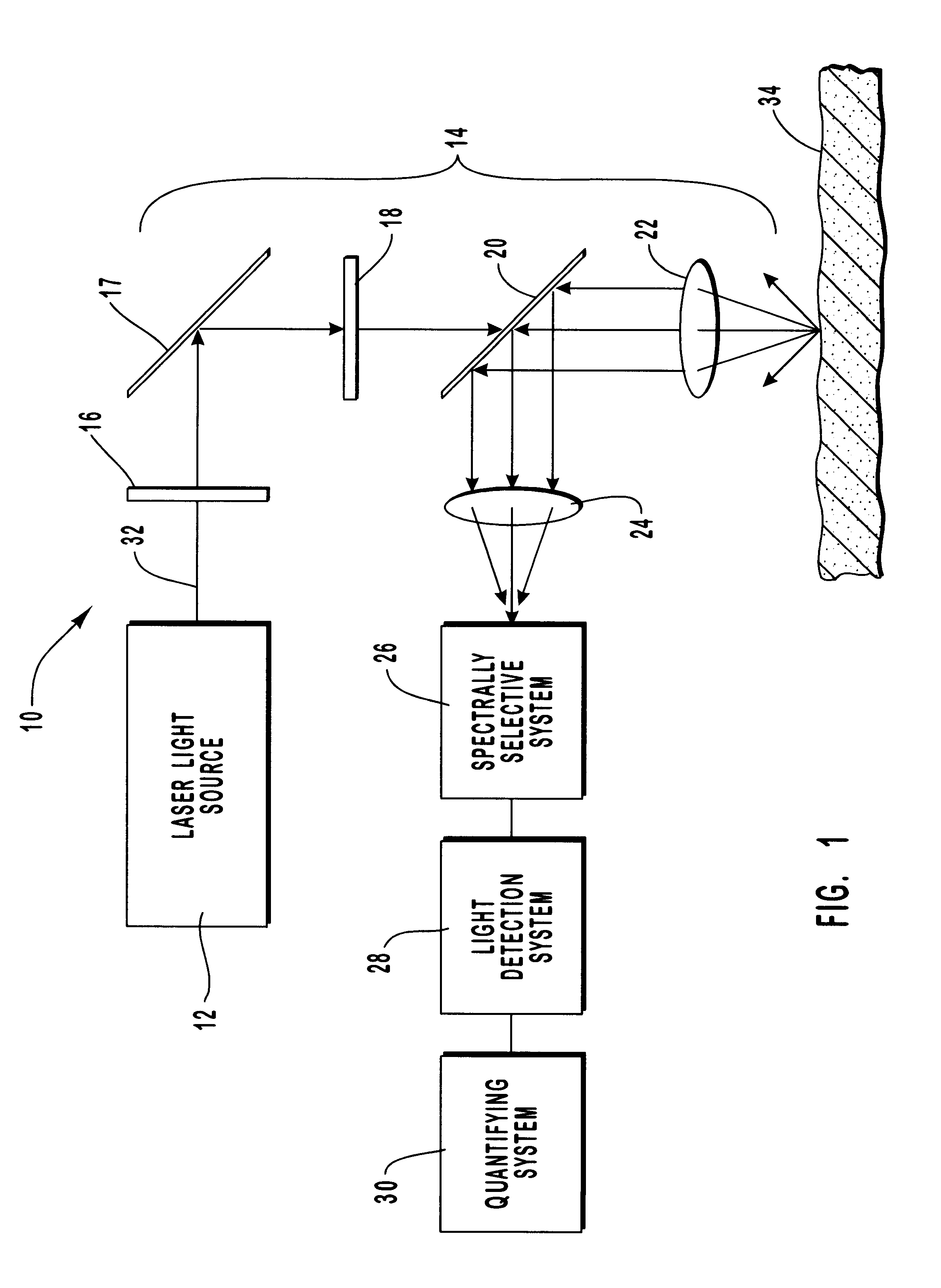
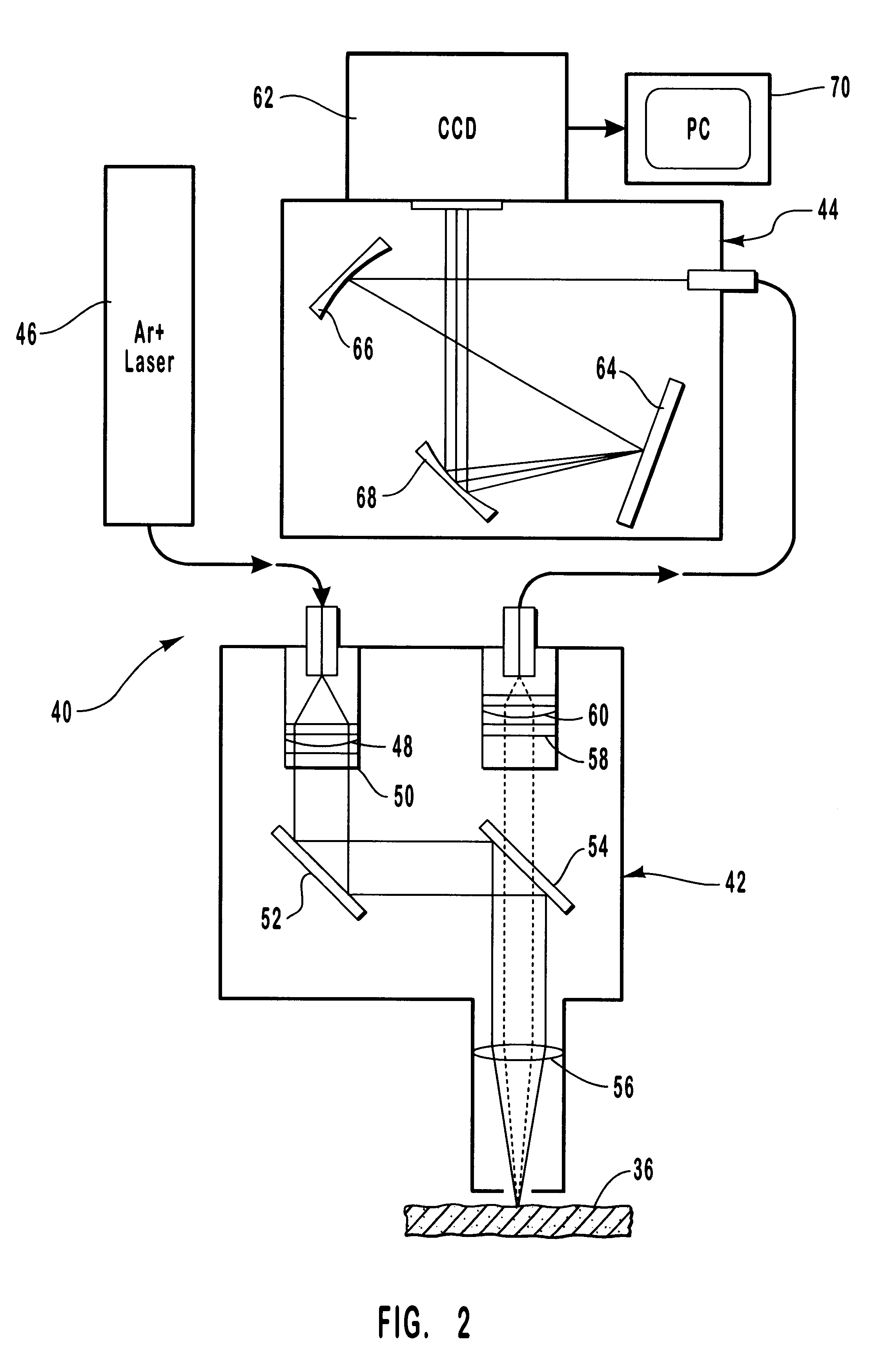
A method and apparatus are provided for the determination of levels of carotenoids and similar chemical compounds in biological tissue such as living skin. The method and apparatus provide a noninvasive, rapid, accurate, and safe determination of carotenoid levels which in turn can provide diagnostic information regarding cancer risk, or can be a marker for conditions where carotenoids or other antioxidant compounds may provide diagnostic information. Such early diagnostic information allows for the possibility of preventative intervention. The method and apparatus utilize the technique of resonance Raman spectroscopy to measure the levels of carotenoids and similar substances in tissue. In this technique, laser light is directed upon the area of tissue which is of interest. A small fraction of the scattered light is scattered inelastically, producing the carotenoid Raman signal which is at a different frequency than the incident laser light, and the Raman signal is collected, filtered, and measured. The resulting Raman signal can be analyzed such that the background fluorescence signal is subtracted and the results displayed and compared with known calibration standards.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Quenching oligonucleotides
InactiveUS6323337B1Decreasing background fluorescenceReducing background fluorescenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferQuenching
The invention relates to oligonucleotides labeled with an energy transfer acceptor useful in conjunction with fluorescent nucleic acid stains. The resulting oligonucleotides are useful for decreasing background fluorescence during amplification assays and in ligation assays, and for detecting hybridization.
Owner:MOLECULAR PROBES
Homogeneous fluorassay methods employing fluorescent background rejection and water-soluble rare earth metal chelates
InactiveUS6242268B1High binding constantNon-metal conductorsGlass making apparatusHalf-lifeMetal chelate
Homogeneous assays for determining quantitatively the extent of a specific binding reaction can be carried out effectively on very dilute solutions using measurements of fluorescence if a fluorescence measurement scheme that is capable of rejecting short-lived background fluorescence is employed and if the fluorescent group being measured has the following properties: a. the group being measured must be a rare earth metal chelate complex combination; b. the chelate must be water-soluble; c. the complex combination must also be stable in extremely dilute aqueous solutions, that is, the measured chelate must have at least one ligand having a metal-to-ligand binding constant of at least about 1013M-1 or greater and it must have a fluorescent emission that is long-lived compared to the longest decay lifetime of ambient substances and have a half life of from 0.01 to 50 msec.
Owner:EG&G WALLAC
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS7601498B2Low toxicityIncrease signal strengthMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesNucleic acid detectionStaining
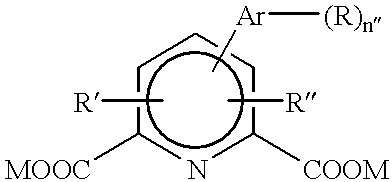
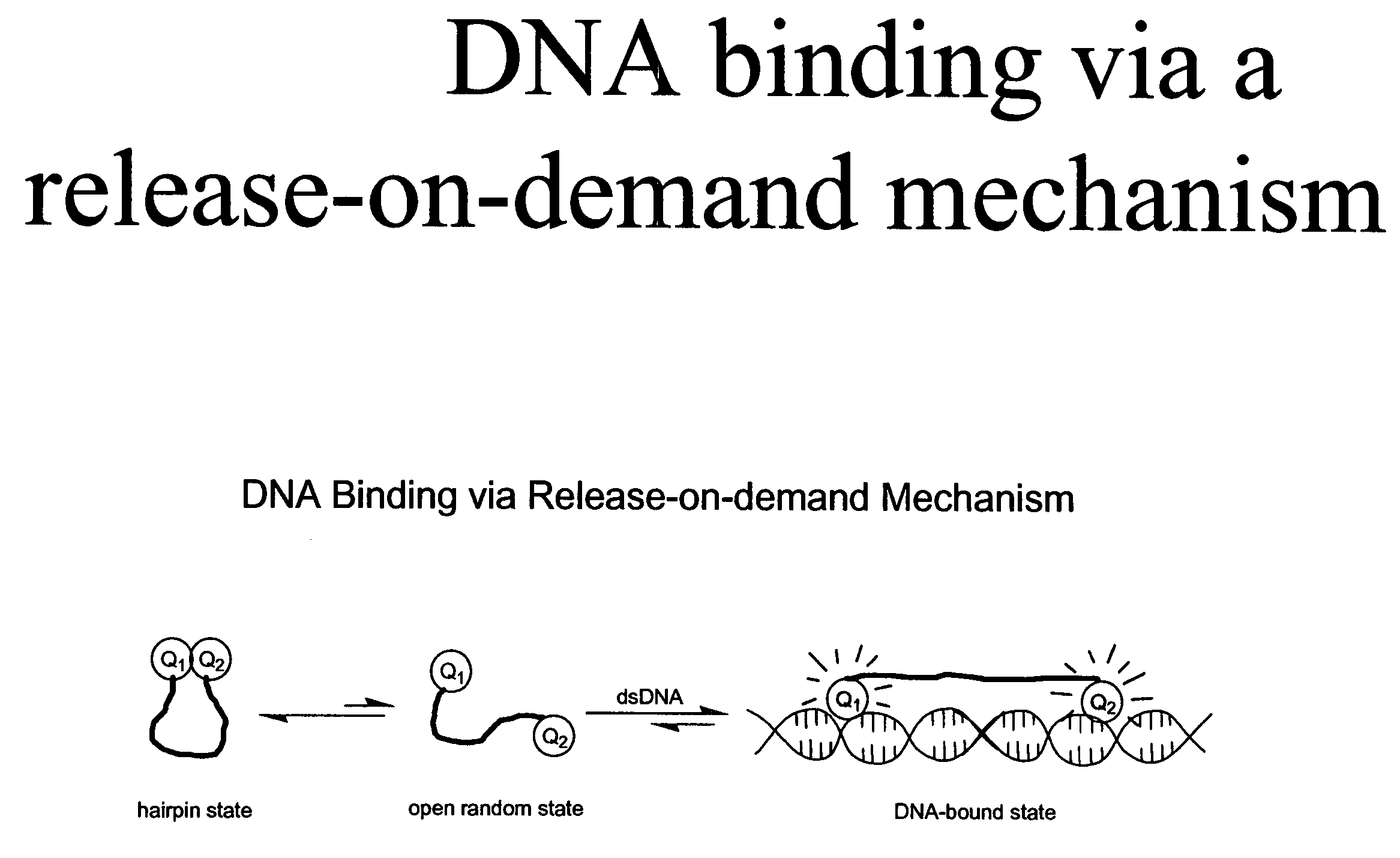
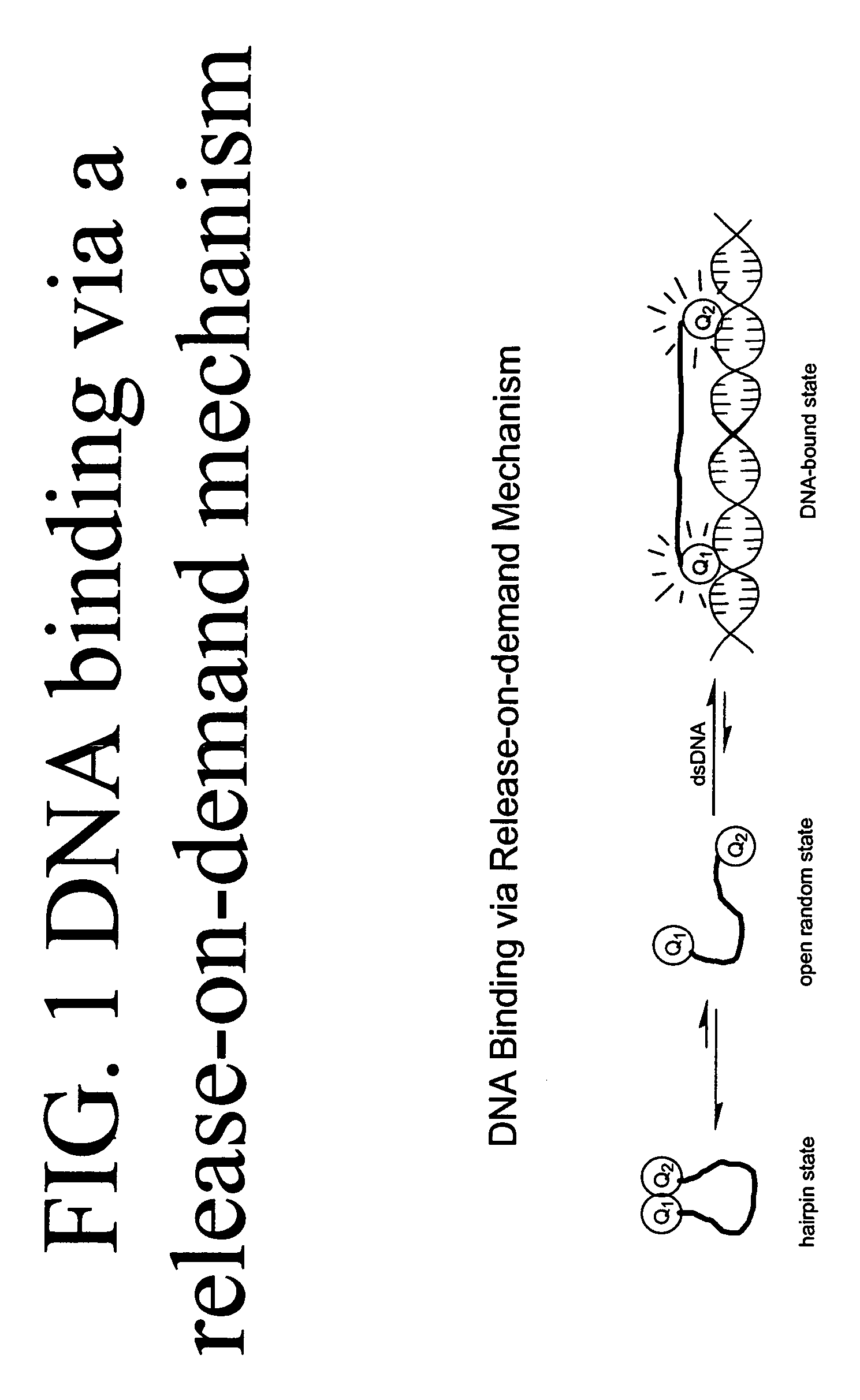
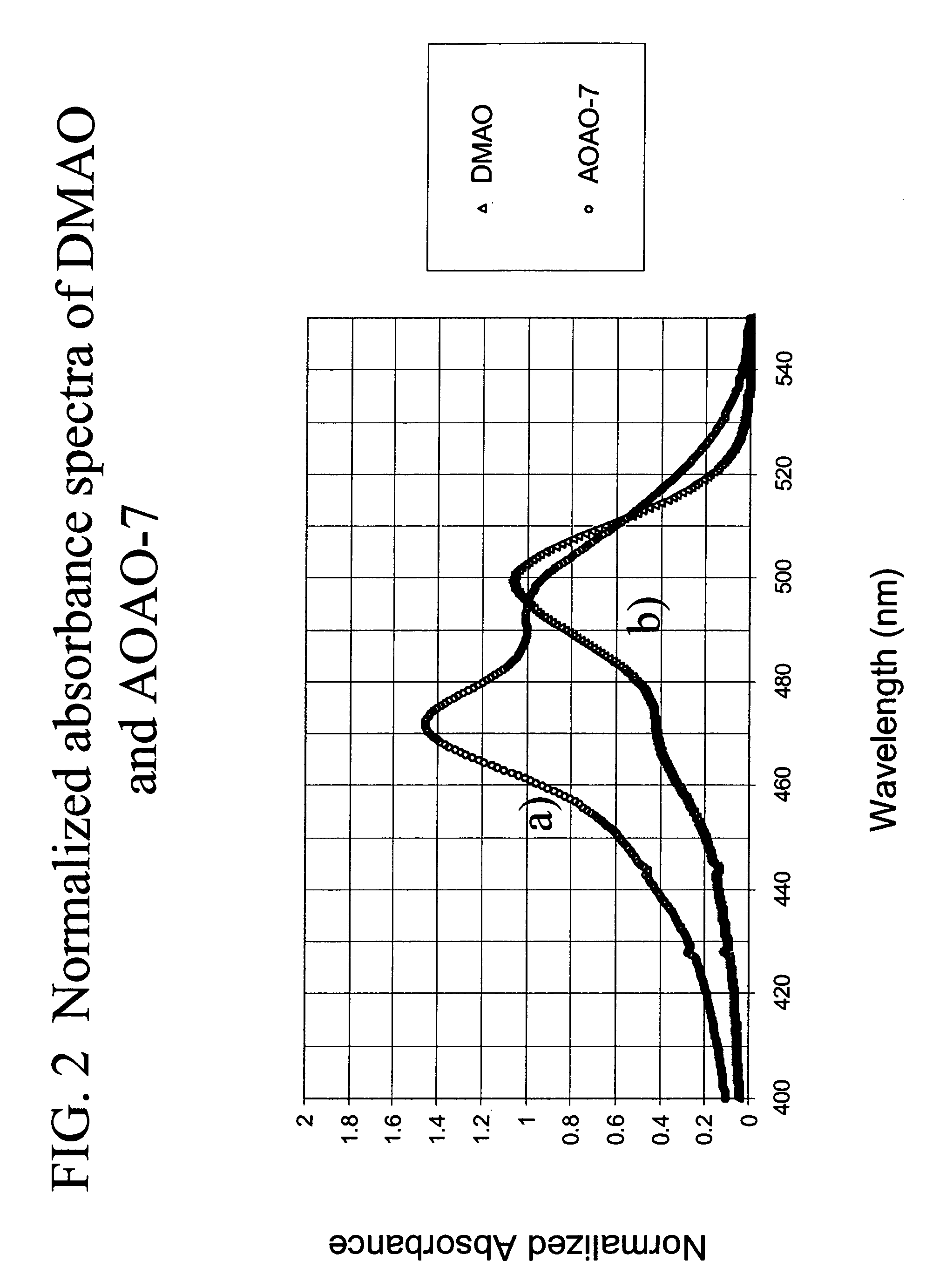
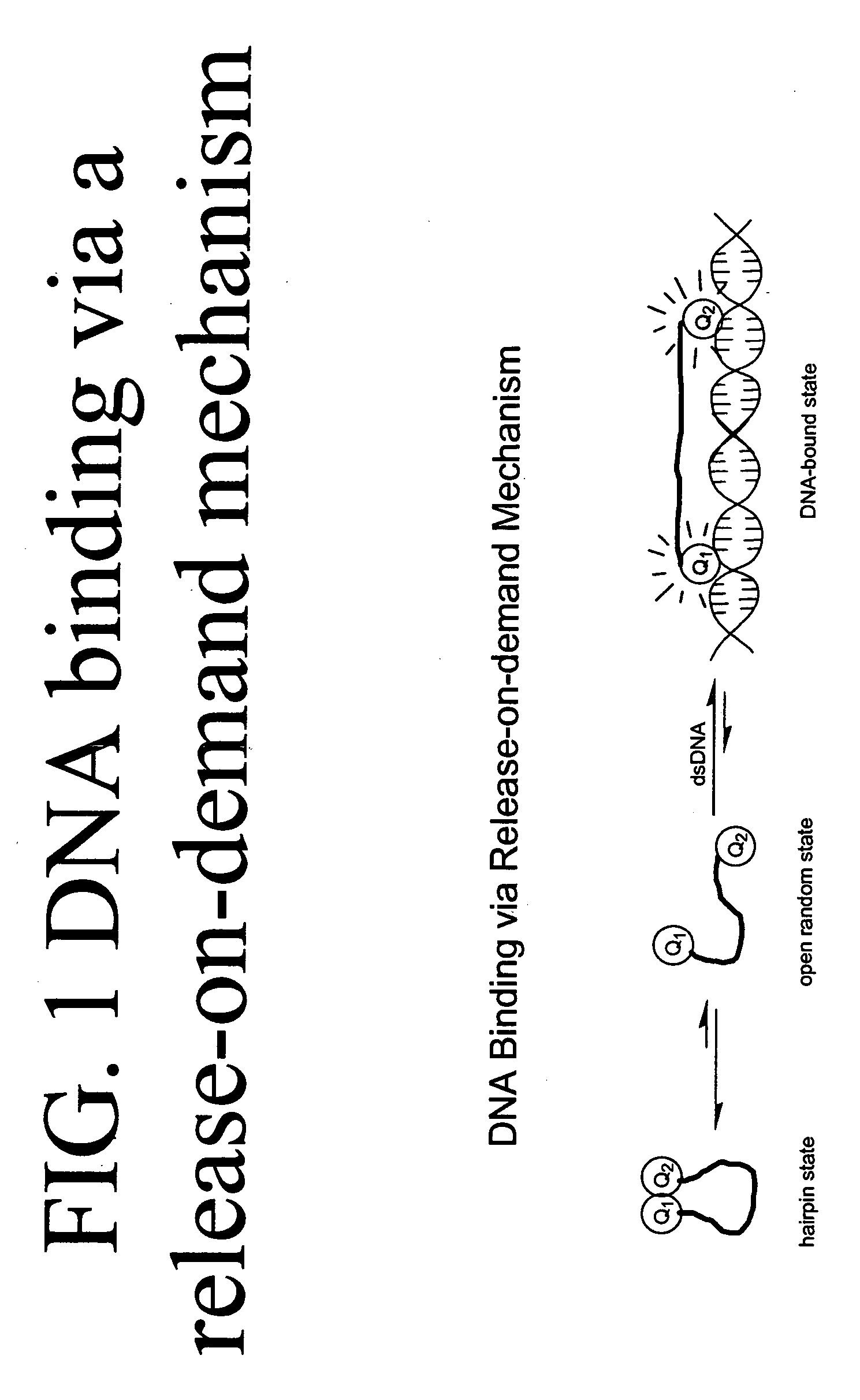
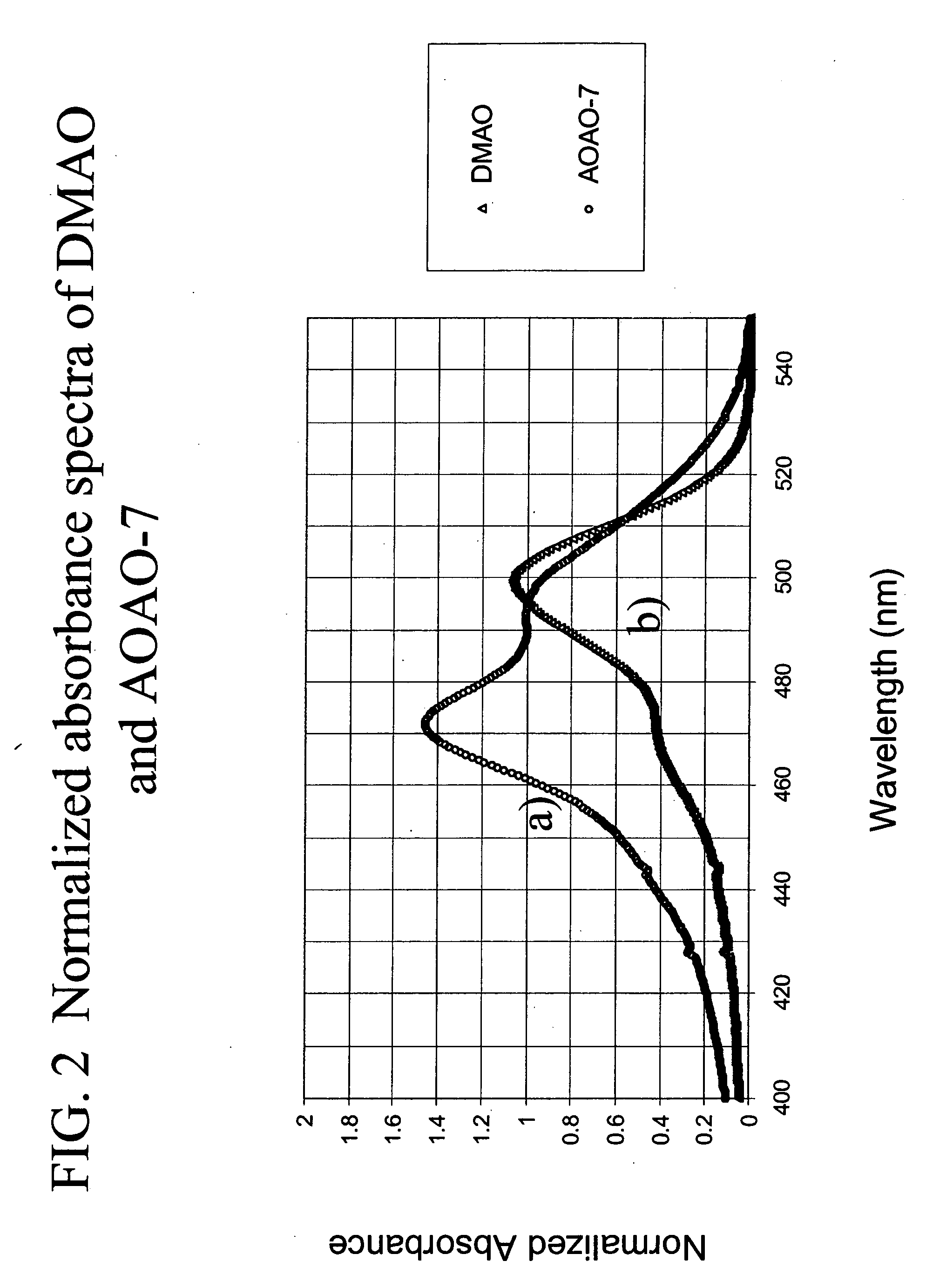
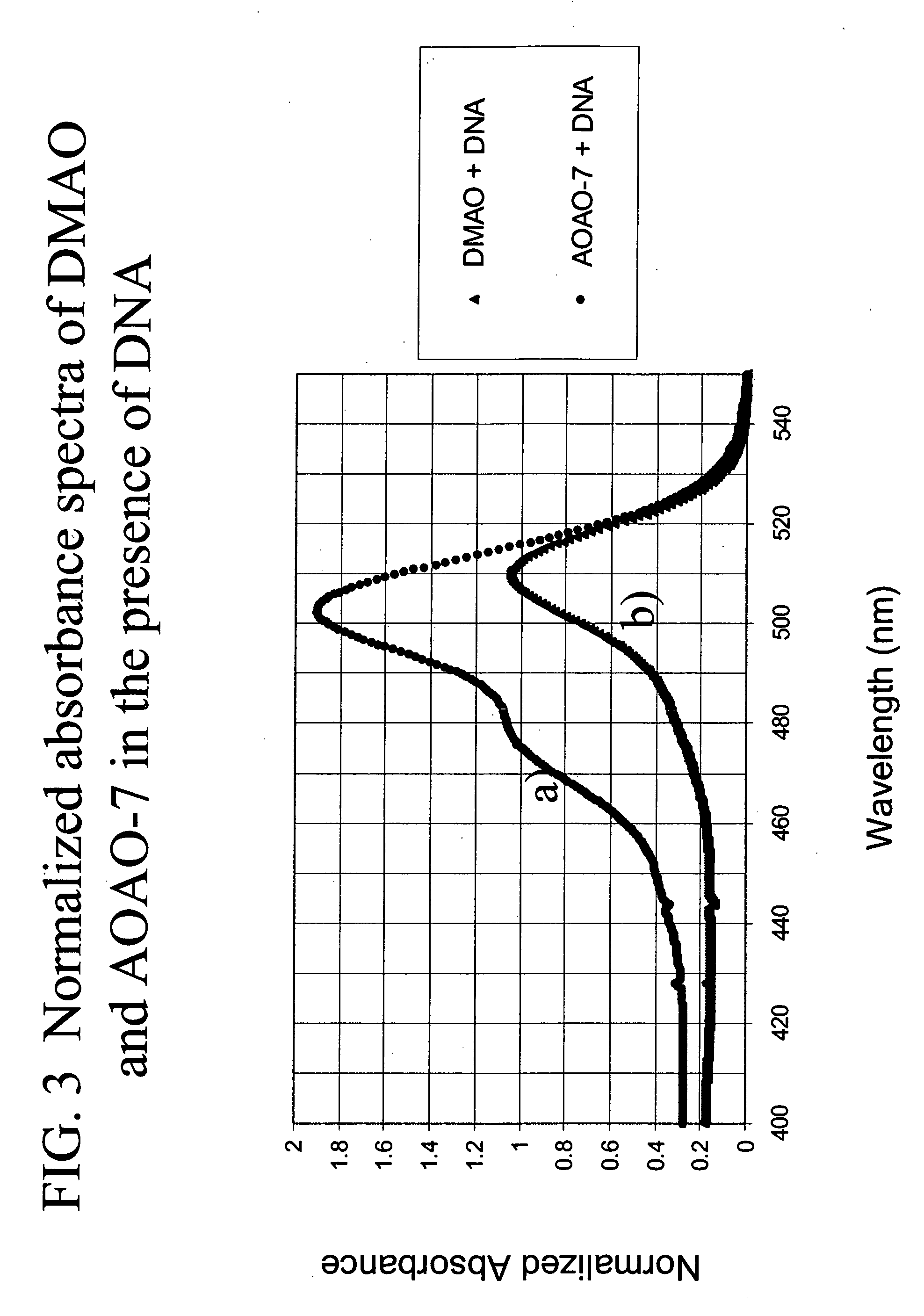
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
Non-fluorescent energy transfer
InactiveUS7741467B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferPhotochemistry
The present invention relates generally to the transfer of non-fluorescent energy between donor and acceptor moieties. In certain embodiments, the invention provides biomolecules that include substantially non-fluorescent donor moieties. Processes involving these donor moieties typically entail reduced background fluorescence relative to applications that involve conventional fluorescent donor moieties. In addition to reaction mixtures and methods that include the use of these biomolecules, the invention also provides related kits and systems.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
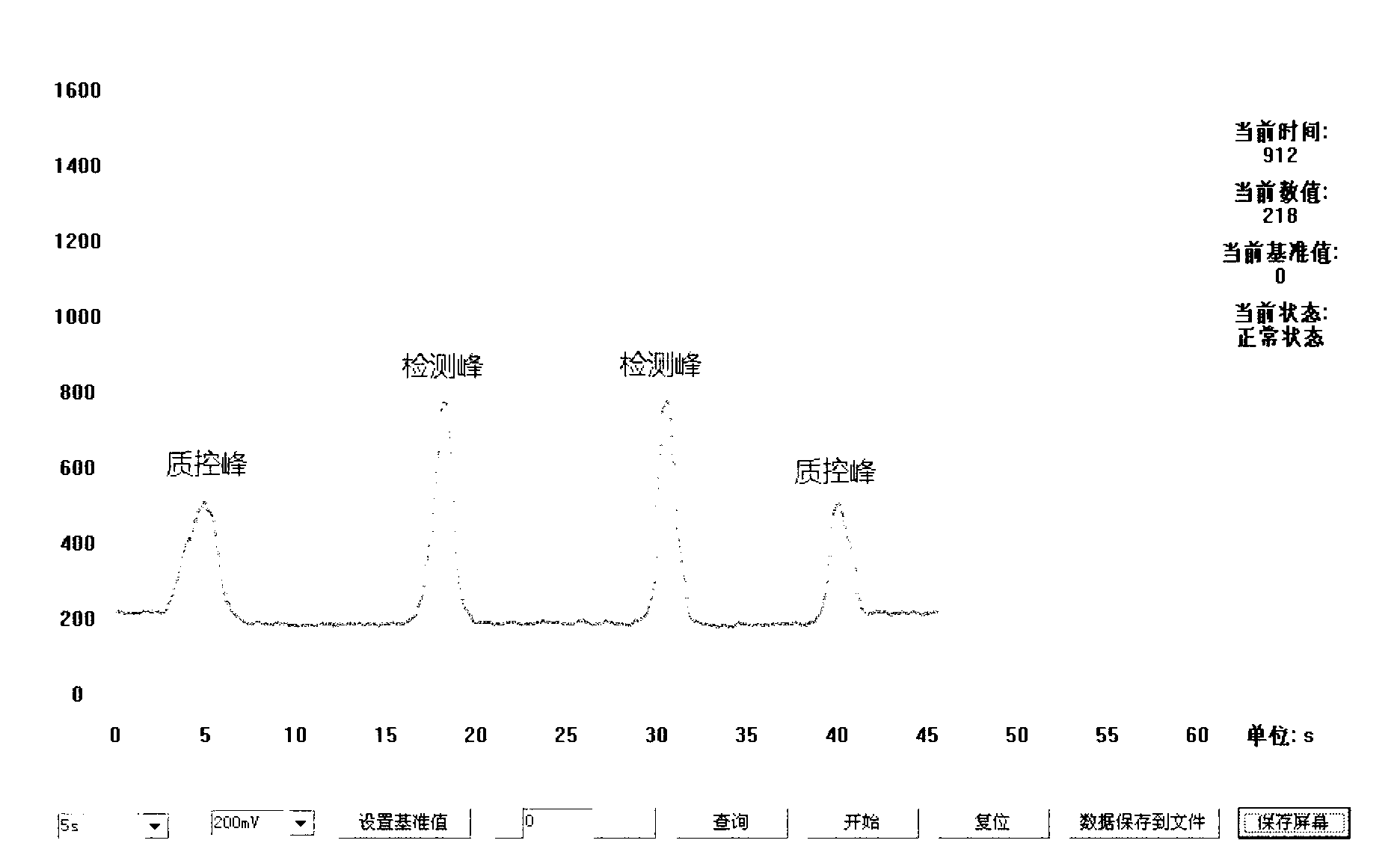
Immunochromatography quantitative determination reagent based on near infrared fluorescence nanoparticle markers
ActiveCN103197074AImprove chromatography propertiesHigh detection sensitivityMaterial analysisMicrosphereChemical products
The invention relates to a method based on near infrared fluorescence molecules and nano particle marks as well as an immunochromatography quantitative detection reagent based on near infrared fluorescence nanoparticles. According to the invention, infrared fluorescence is connected with nanoparticles to prepare an immunochromatography test strip based on the near infrared fluorescence nanoparticles. During the detection, an infrared light scanner is utilized, and a quality control line and a sample line are respectively scanned by utilizing near infrared light; and after the fluorescence intensity of a detection line is rectified by utilizing the fluorescence intensity of a quality control line, and a standard curve in a fluorescence analyzer is taken in, the concentration of a to-be-detected matter in a sample can be analyzed and detected. Compared with the direct connection of the near infrared fluorescence molecules and detecting molecules, the near infrared fluorescence nanoparticle immunochromatography improves the detection flexibility obviously, and the lowers the background fluorescence intensity. The marking method and the reagent can be applied to microorganism detection, food safety detection, poison detection as well as rapid dangerous chemical product detection.
Owner:BEIJING RUNBO FUDE BIOLOGICAL TECH DEV
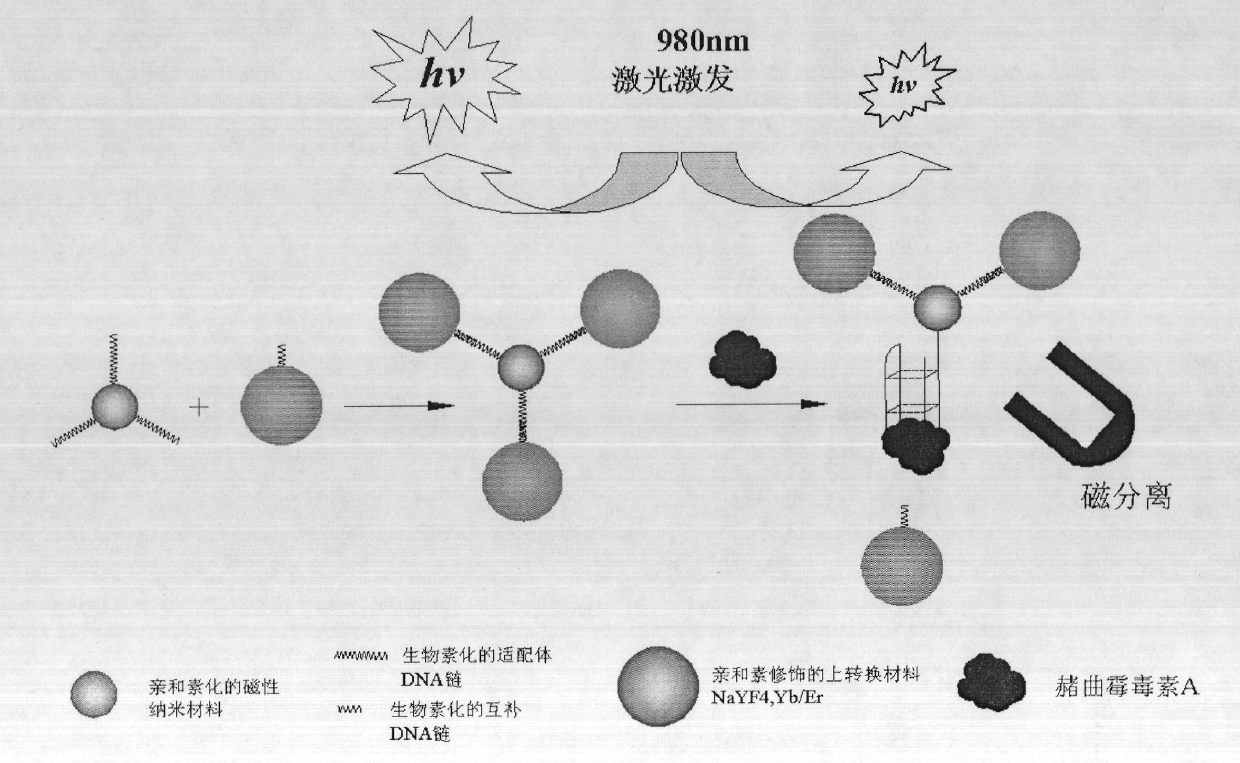
Method for detecting ochratoxin A by magnetic separation of aptamer-functionalized magnetic nano material and marking of up-conversion fluorescent nano material
ActiveCN102023147AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceBulk samplesUp conversion
The invention discloses a method for detecting ochratoxin A by the magnetic separation of an aptamer-functionalized magnetic nano material and the marking of an up-conversion fluorescent nano material, which is used for detecting the ochratoxin A content of wheat, grains, feeds and products thereof, and the like. In the method, the ochratoxin-specific aptamer-functionalized magnetic nano material is utilized to perform magnetic separation and enrichment reaction on a sample to rapidly condense bulk samples, effectively increase the condensation of the samples by thousands of times, greatly shorten a detection period and improve the detection sensitivity; and simultaneously, the novel ochratoxin A analysis method for realizing rapid sample treatment, analysis and detection is constructed by combining the characteristics of high sensitivity of laser induced fluorescence of the up-conversion fluorescent nano material and capability of effectively avoiding the interference of biological background fluorescence of the samples.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Methods and systems of optical imaging for target detection in a scattering medium
ActiveUS20120128264A1Increase contrastDiagnostics using lightPhotometryContrast ratioBackground fluorescence
A method for enhancing contrast in fluorescence imaging is provided. The method comprises providing a patterned illumination source for illuminating one or more regions corresponding to a scan step, scanning at least a portion of a surface of a subject using a plurality of scan steps, acquiring image frames corresponding to two or more scan steps, deducting a background fluorescence from the image frames corresponding to the two or more scan steps to form one or more processed image frames, and reconstructing an image using one or more of the processed image frames.
Owner:GLOBAL LIFE SCI SOLUTIONS USA LLC
Method for detecting upconversion fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using carbon nanomaterial as receptor
InactiveCN103487418ACarbon source is easy to getEasy to prepareFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsSurface markerQuenching
The invention discloses a method for detecting fluorescence resonance energy transfer by using a water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial as a fluorescence donor and using a carbon nanomaterial as a fluorescence receptor. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) preparing the water-soluble upconversion fluorescence nanomaterial and performing surface marker to obtain a fluorescence donor solution; (2) preparing the carbon nanomaterial to obtain a fluorescence receptor solution; (3) mixing the fluorescence donor solution and the fluorescence receptor solution for incubation and measuring the fluorescence intensity to obtain a fluorescence quenching curve; (4) mixing certain-concentration fluorescence donor solution and certain-concentration fluorescence receptor solution for incubation, adding a target object with different concentrations for continuous incubation, measuring the fluorescence intensity and drawing a standard curve; (5) calculating the concentration of the target object in an actual sample according to the standard curve. According to the method, interference of the background fluorescence of a biological sample can be avoided, detection to serum or the target object in a whole blood sample can be directly realized, the washing and separation processes are not needed, the detection speed is high, and the cost is low.
Owner:GUANGZHOU IMPROVE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Time resolved fluorescent imaging system
InactiveUS20100090127A1Reduce dispersionReduce the amount requiredPhotometrySolid-state devicesFluorescent imagingPhysics
This invention provides a system and method that allows for time-resolved fluorescent imaging of fluorescent samples. The user is able to receive temporally filtered pictures of the sample with a reduced amount of the scattered excitation light and the short lived background fluorescence. The system allows for adjustment of fluorescent gating time and delay time.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Multi-wavelength excitation-based fluorescence elimination method for Raman spectrum
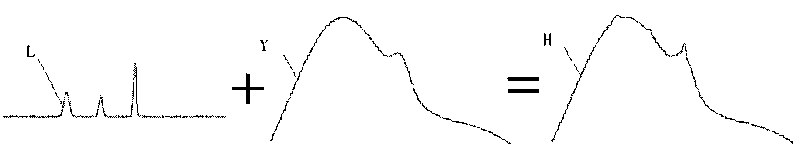
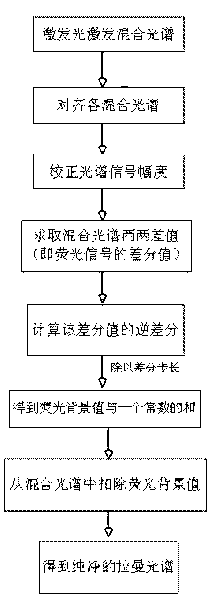
InactiveCN101692045AReasonable methodEliminate background fluorescenceRaman scatteringMixed spectrumOpto electronic
The invention discloses a multi-wavelength excitation-based fluorescence elimination method for Raman spectrum, which relates to a method of chemical analysis and photoelectric signal processing and comprises the steps of: sequentially exciting mixed spectra consisting of fluorescence and Raman light by irradiating a plurality of similar wavelength lasers sequentially generated by a laser source to the same measured sample; when a spectrograph acquires various mixed spectrum signals, aligning the mixed spectra, and normalizing and correcting the amplitude of the spectrum signals through a full spectrum integral value to obtain spectra of which the X-coordinates are aligned and the amplitude of the Y-coordinates is corrected; evaluating a difference value between each two mixed spectra, wherein the difference value is a differential value of a fluorescence signal; calculating an inverse difference of the differential value, wherein the inverse difference is divided by a differential step to obtain the sum of a fluorescence background value and a constant; and finally, deducting the fluorescence background value from the mixed spectra to separate a pure Raman spectrum so as to achieve the aim of fluorescence elimination of the Raman spectrum. The method is reasonable, can eliminate background fluorescence effectively, has low cost and convenient use, and is easy to popularize and use.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method, structure, and apparatus for Raman spectroscopy
Disclosed herein are a Raman spectroscopy structure comprising a porous material substrate, and a method of performing Raman spectroscopy of a sample disposed adjacent to the structure comprising the porous material substrate. Generally, the substrate includes one or more layers of a porous material such as porous silicon, porous polysilicon, porous ceramics, porous silica, porous alumina, porous silicon-germanium, porous germanium, porous gallium arsenide, porous gallium phosphide, porous zinc oxide, and porous silicon carbide. It has been discovered that such a substrate material, when excited with near-infrared light, does not exhibit undesired background fluorescence characteristic of other known Raman spectroscopy substrates.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Methods of using dyes in association with nucleic acid staining or detection and associated technology
ActiveUS20060211029A1Increase DNA detection sensitivity“effective dye concentrationMethine/polymethine dyesSugar derivativesStainingStrong acids
Methods of using dyes and associated technology are provided. A dye, such as a monomeric dye or a dimeric dye, may be used in a nucleic acid gel staining application and / or a nucleic acid detection application. Such a dye and a salt that comprises an anion that is associated with a strong acid and a cation that is associated with a strong base may be used in such an application. A dimeric dye, such as a dimeric dye capable of forming a hairpin-like structure, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids via a release-on-demand mechanism. A dimeric dye having low background fluorescence in the absence of nucleic acids and high fluorescence in the presence of nucleic acids, upon binding therewith, may be used to stain and / or detect nucleic acids.
Owner:BIOTIUM INC
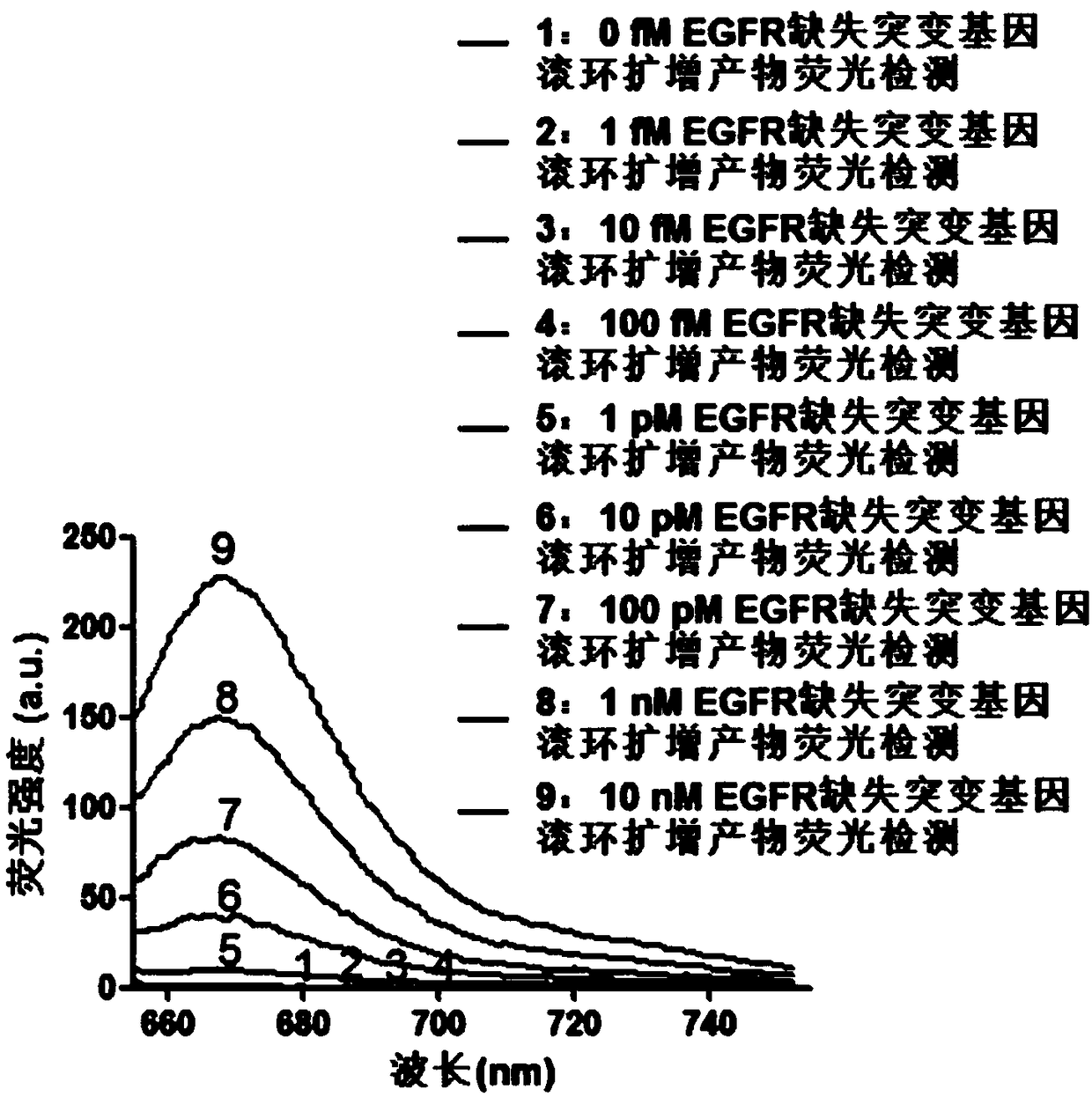
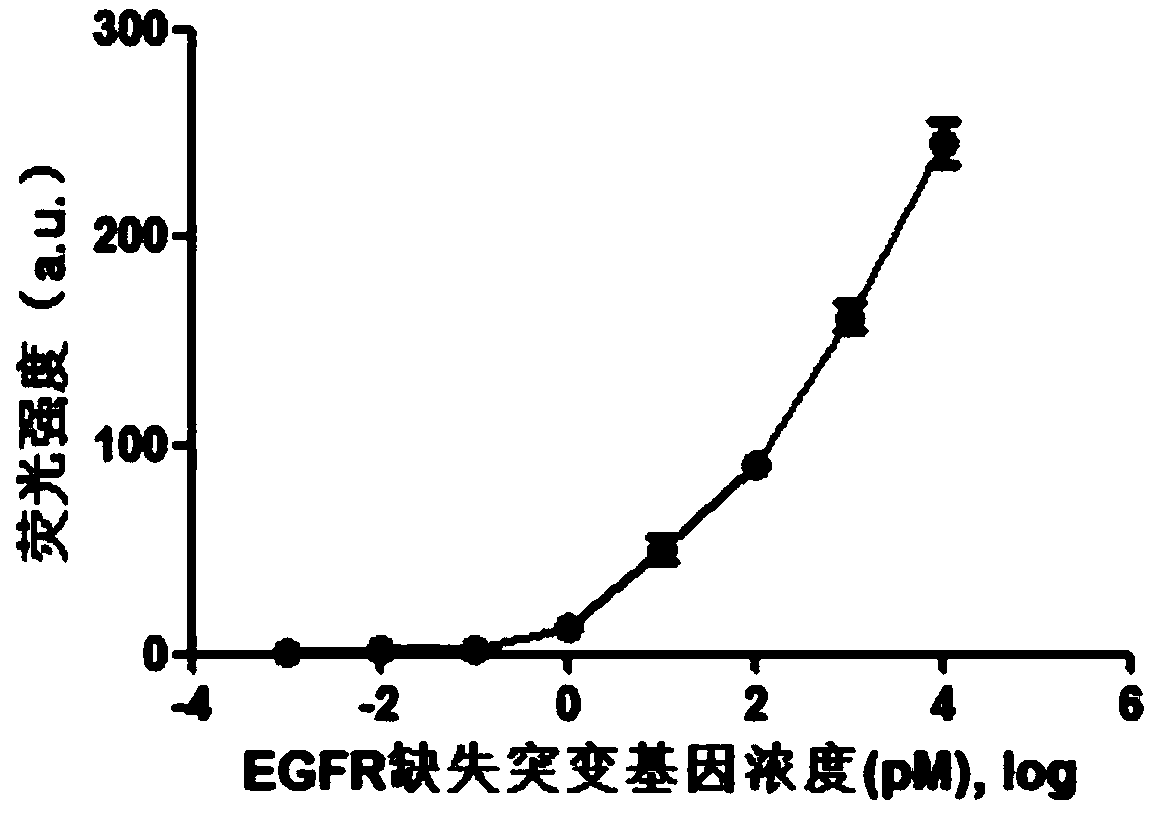
Fluorescence detection kit and fluorescence detection method for deletion mutation of gene
ActiveCN108949924AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LA-DNA
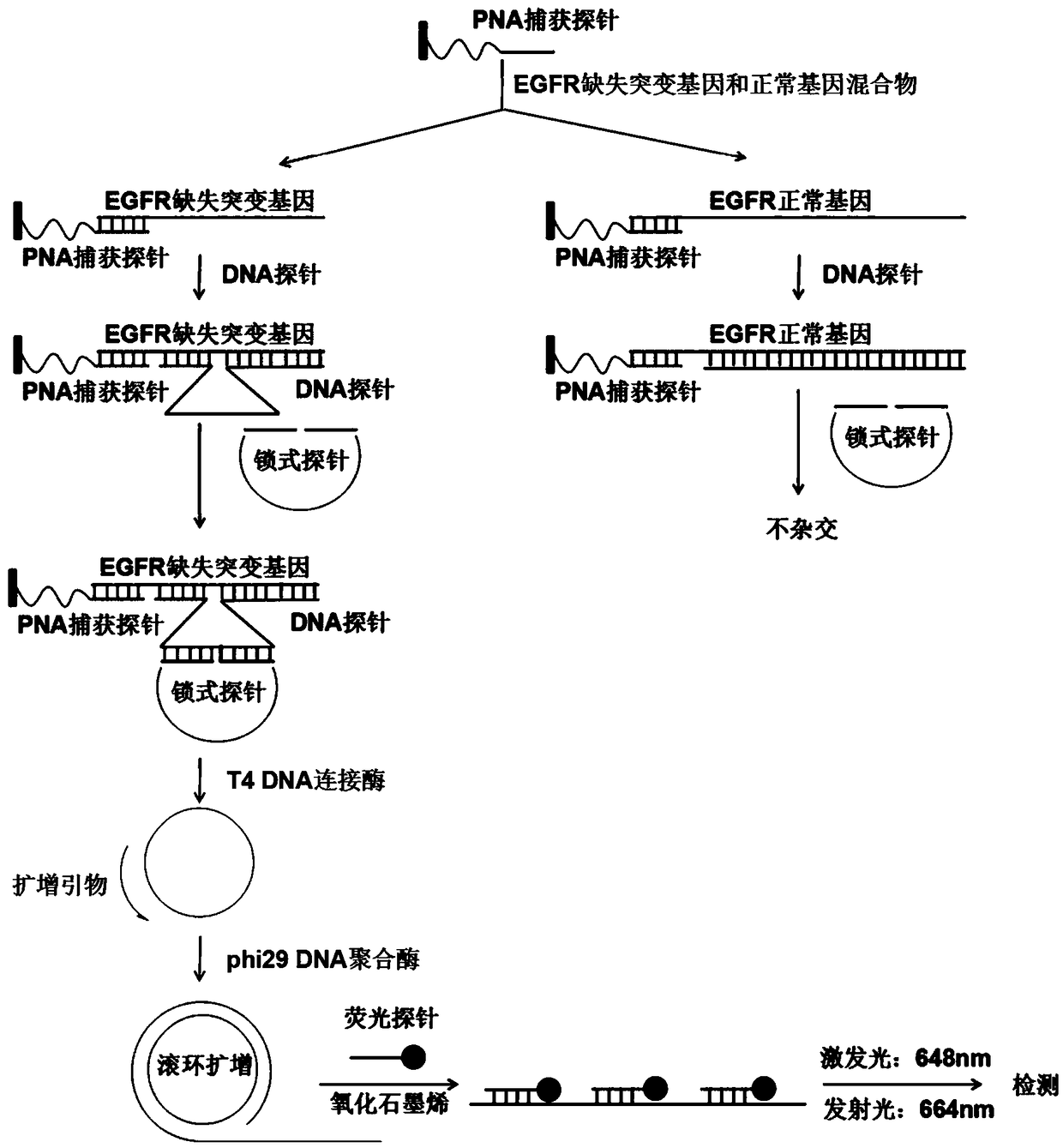
The invention provides a fluorescence detection kit for a deletion mutation gene. The kit includes: a PNA capture probe, a DNA probe, a padlock probe, a DNA polymerase, a DNA ligase, a rolling circleamplification primer, and a fluorescence probe. The invention also provides a method of using the kit to perform the fluorescence detection on the deletion mutation gene, wherein the method includes:1) immobilizing the PNA capture probe on the bottom of a pore plate, and hybridizing the probe with a target gene with a buffer solution; 2) hybridizing the target gene immobilized on the bottom of the pore plate with the DNA probe; 3) hybridizing a single chain section on the DNA probe, which is hybridized with the target gene, with the padlock probe, cyclizing the hybridized product with the DNAligase, and performing rolling circle amplification under effect of the rolling circle amplification primer and the DNA polymerase; 4) hybridizing the fluorescence probe with a rolling circle amplification product, quenching background fluorescence, and detecting the change on fluorescence intensity.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
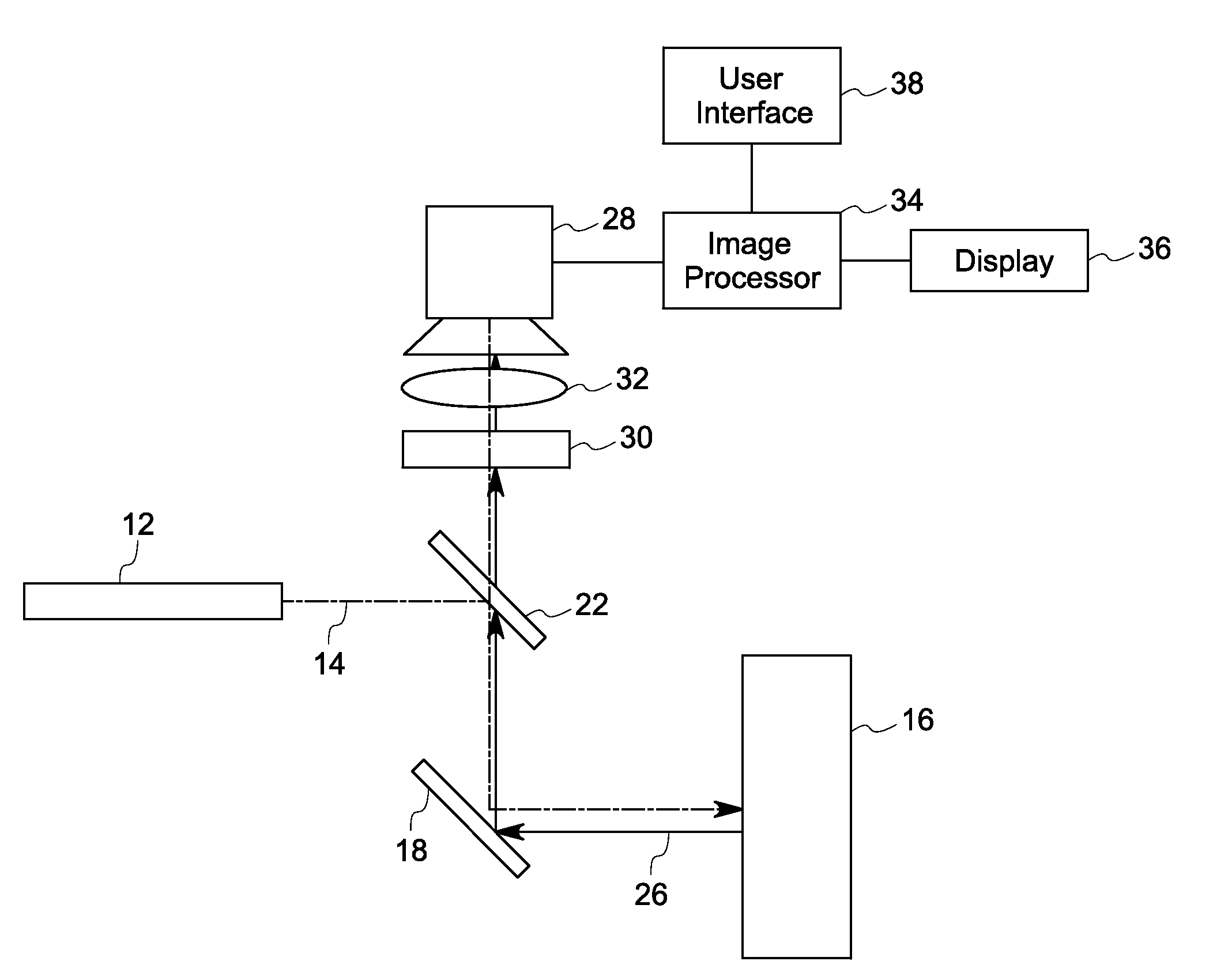
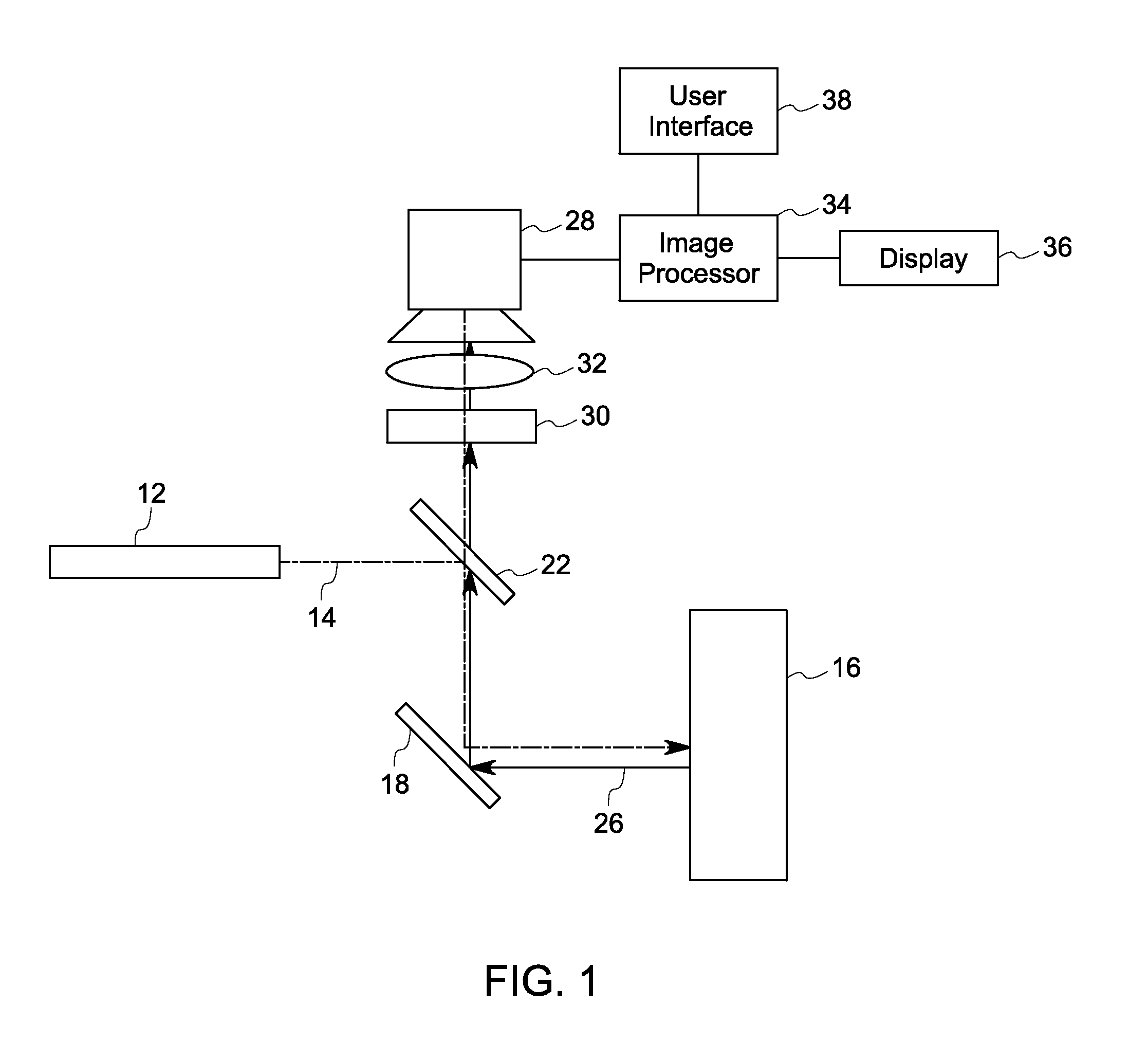
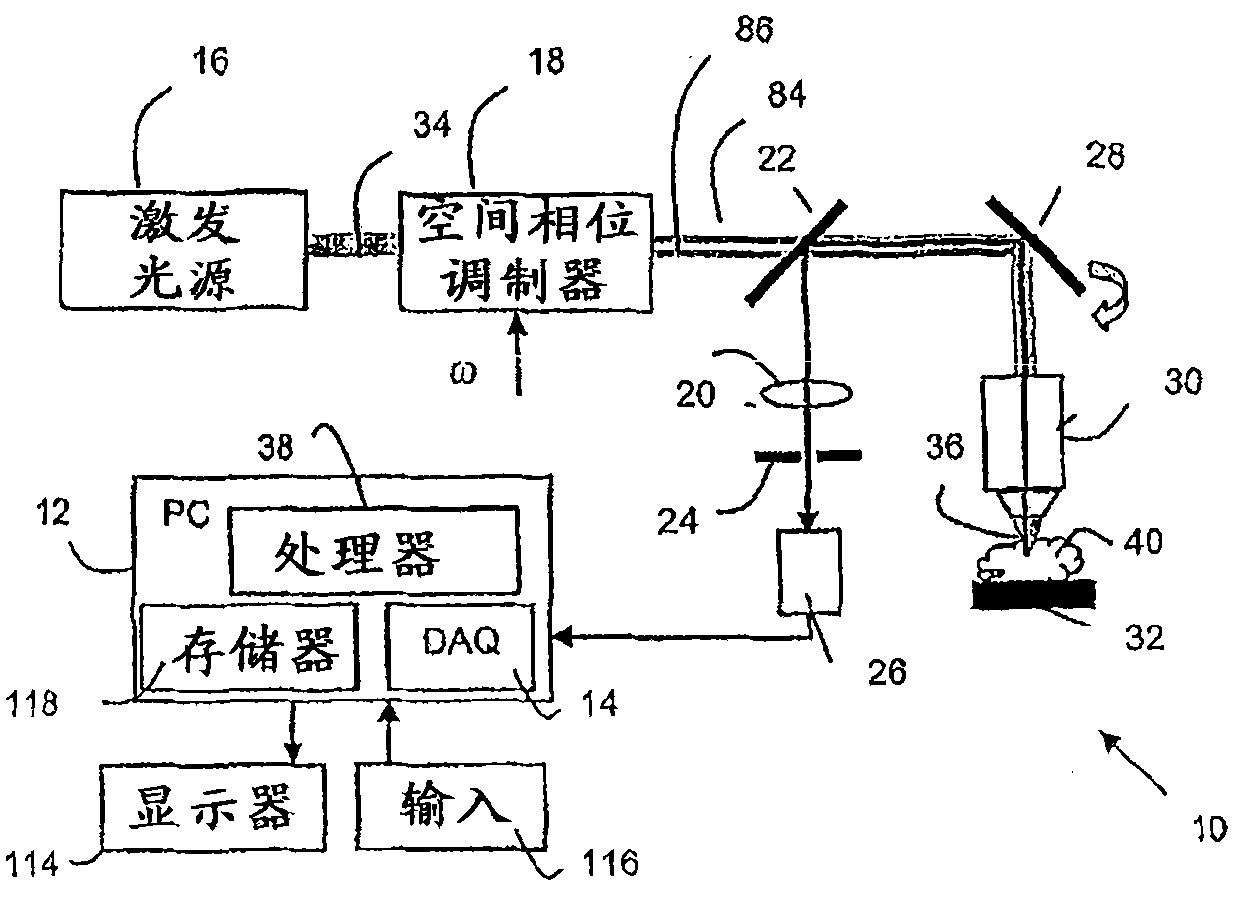
Fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system and method
A fluorescence focal modulation microscopy system (10) and method (200) is disclosed for high resolution molecular imaging of thick biological tissues (40) with single photon excited fluorescence. Optical sectioning and diffraction limited spatial resolution are retained for imaging inside a multiple-scattering medium by the use of focal modulation, a technique for suppressing the background fluorescence signal excited by the scattered light. The focal modulation microscopy system has a spatial phase modulator (18) inserted in the excitation light path (34), which varies the spatial distribution of coherent excitation light around the focal volume periodically at a preset frequency. A fluorescence focal modulation image (122,142) is formed on a display (114) with the demodulated fluorescence, while a confocal image (120,140) is available simultaneously.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
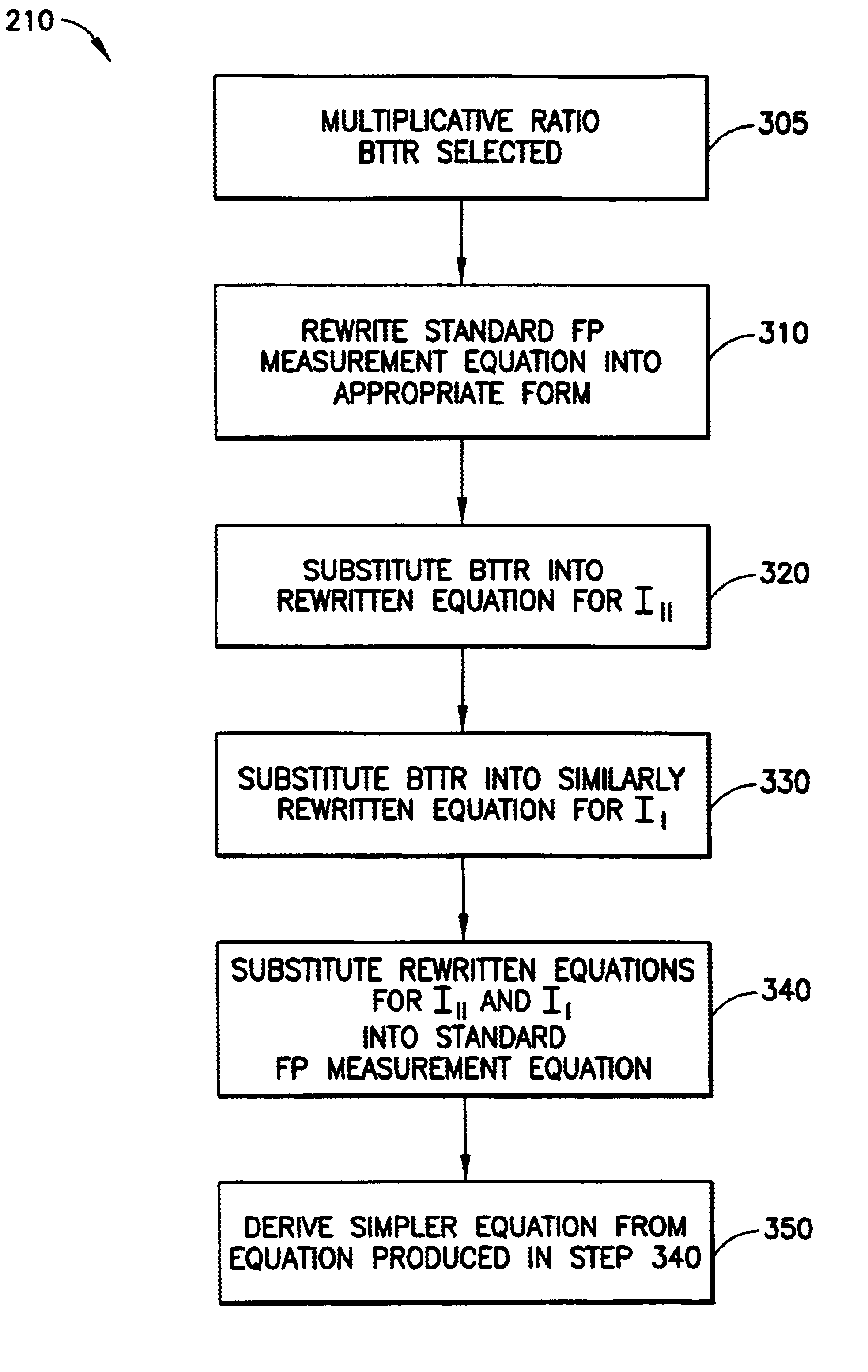
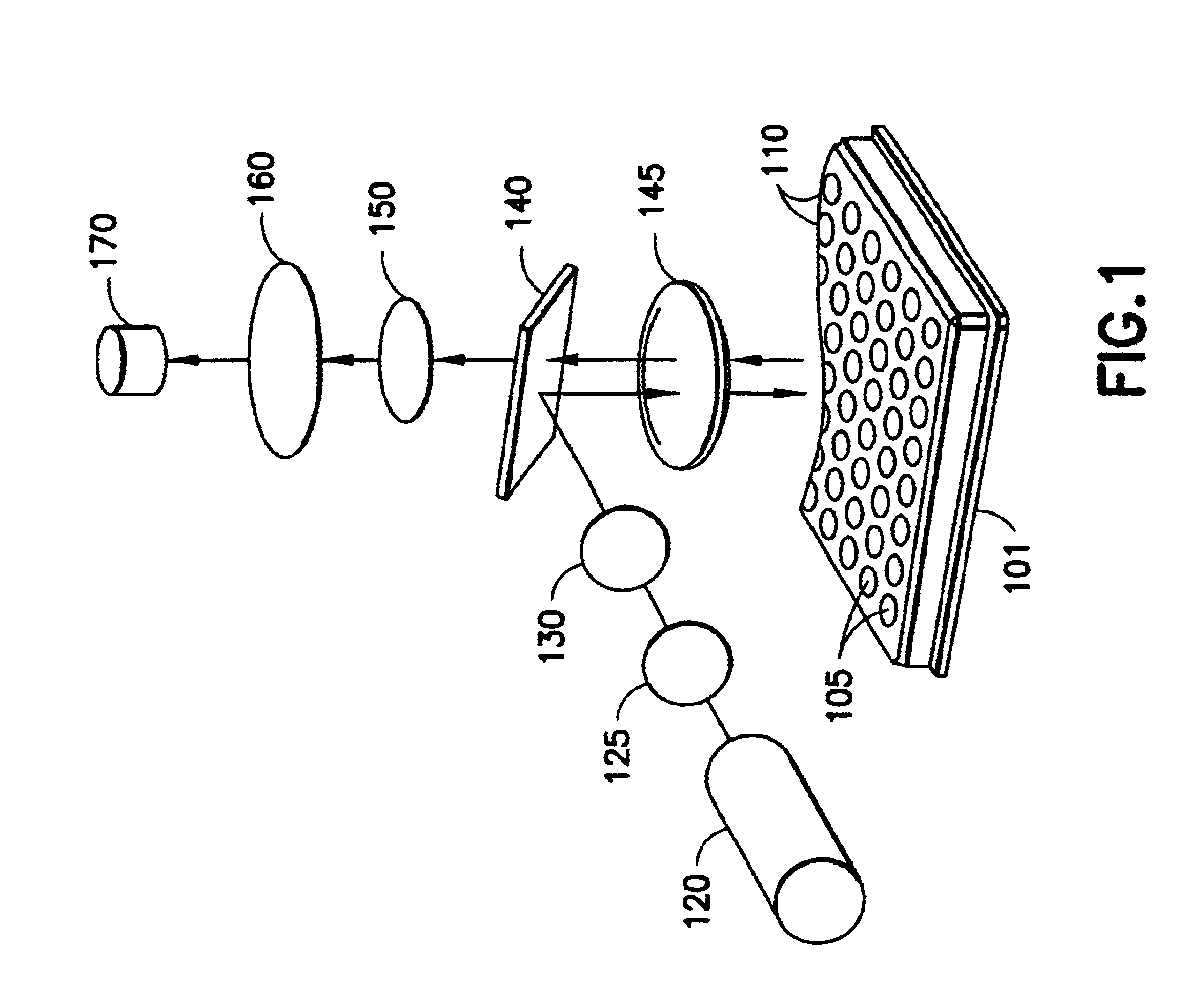
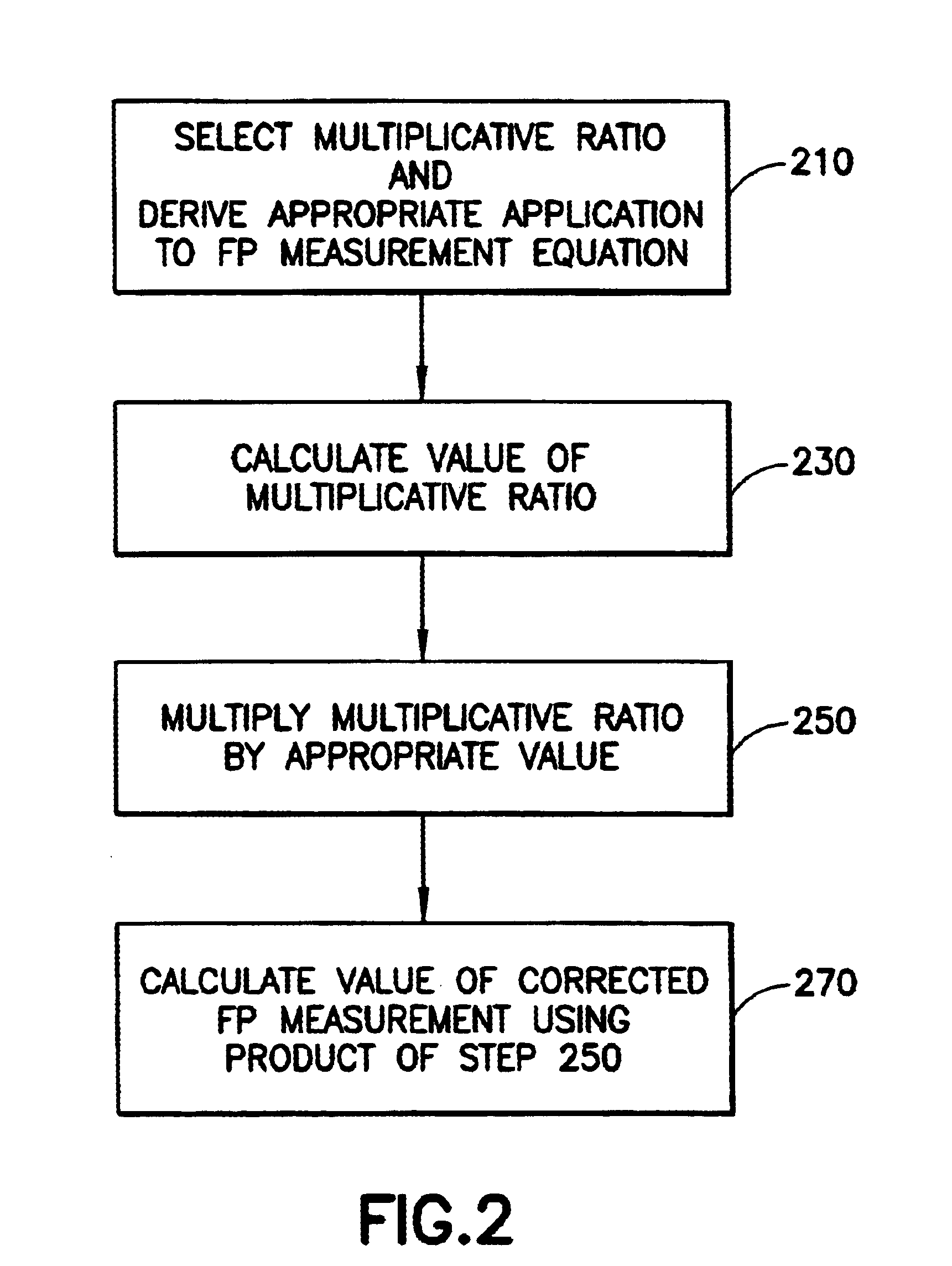
Ratiometric background correction for fluorescence polarization assays
InactiveUS6674527B2Accurate methodCalibration accuracyRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryBackground noiseFluorescent polarization assay
Owner:CAMBRIDGE RES & INSTR
Disposable optical cuvette cartridge with low fluorescence material
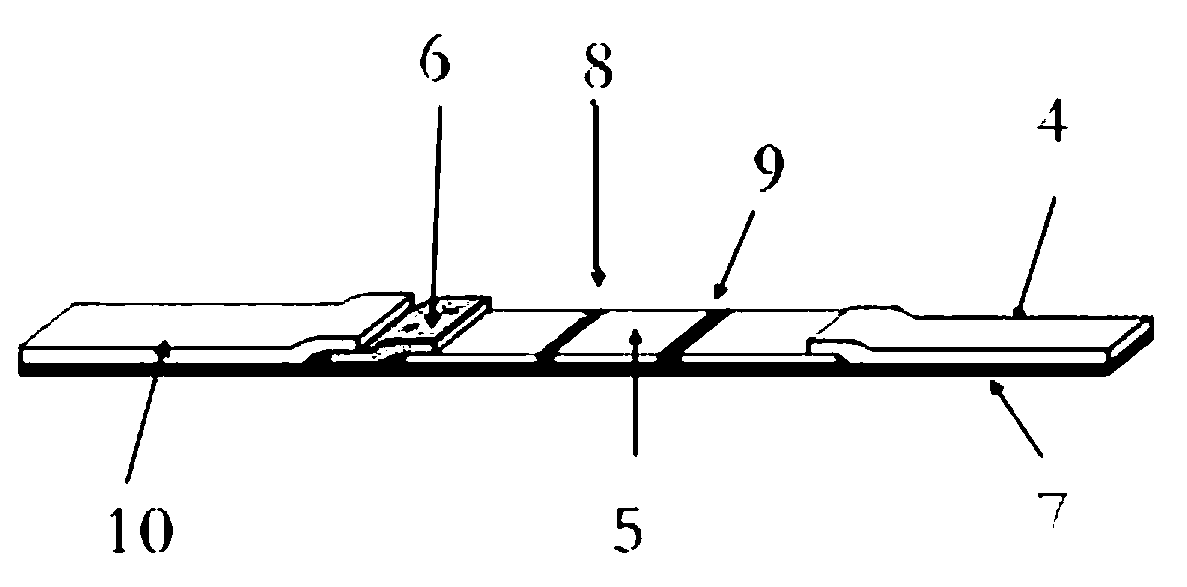
A disposable cuvette cartridge for optical measurements is formed from three flexible thin layers. The middle layer is an adhesive sheet with cut out regions, typically between 30 and 50, serving as optical chambers bounded by the two outer layers. Inlet and vent holes in one of the outer sheets provide access to the optical chambers. At least one of the outer sheets is made of a material having low fluorescence, such as a cyclo-olefin copolymer. With its low background fluorescence, the cuvette cartridge is useful for high-throughput fluorescence measurements of biological samples.
Owner:PPD BIOMARKER DISCOVERY SCI
Specific fluorescent probe for identifying hydrogen sulfide and application of probe
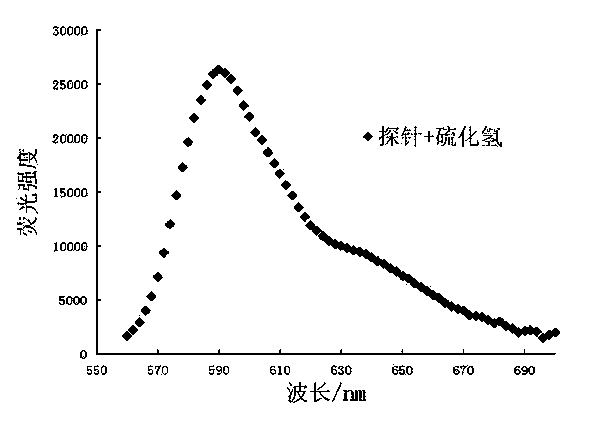
ActiveCN103805170AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisFluoProbes
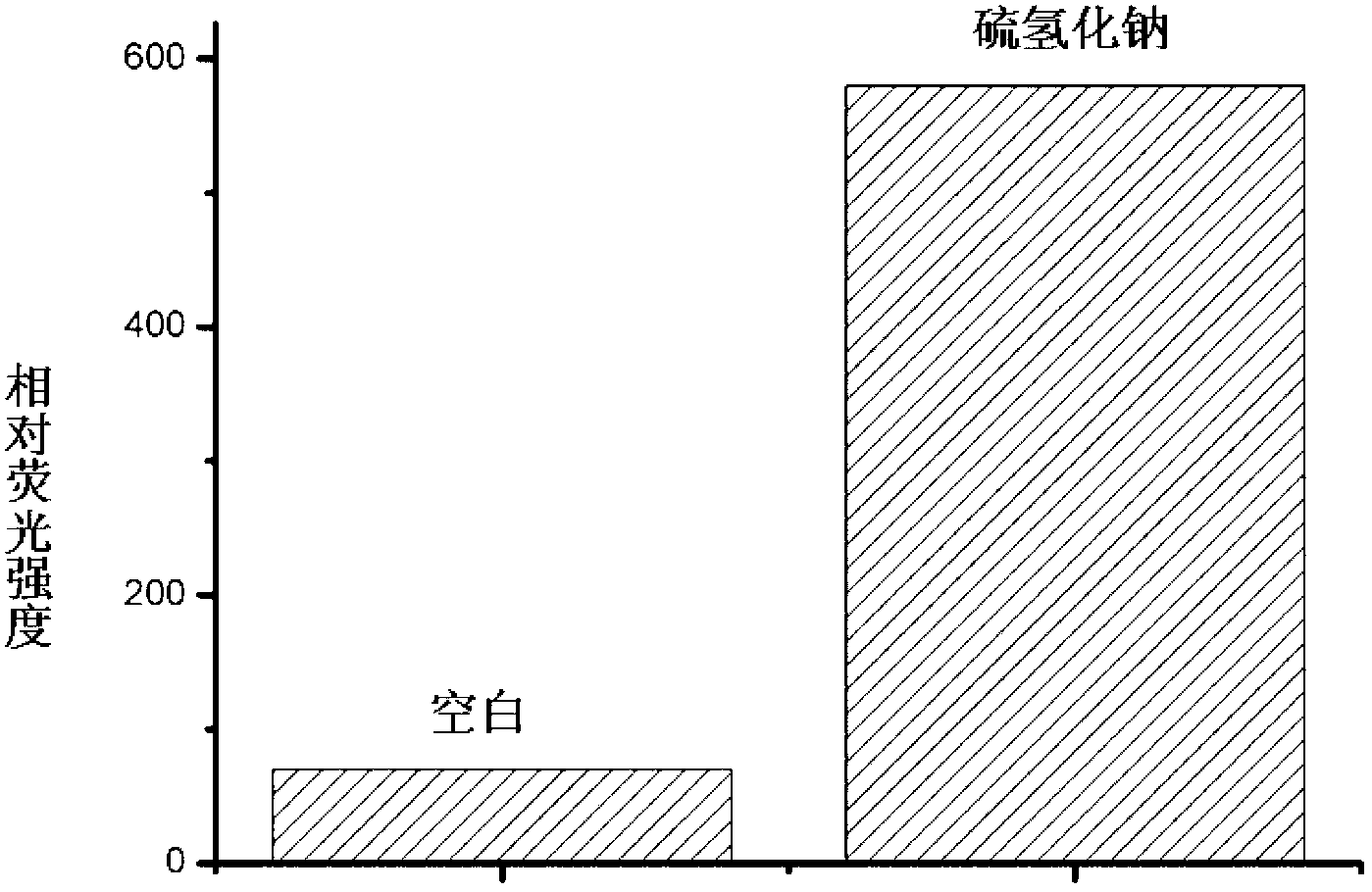
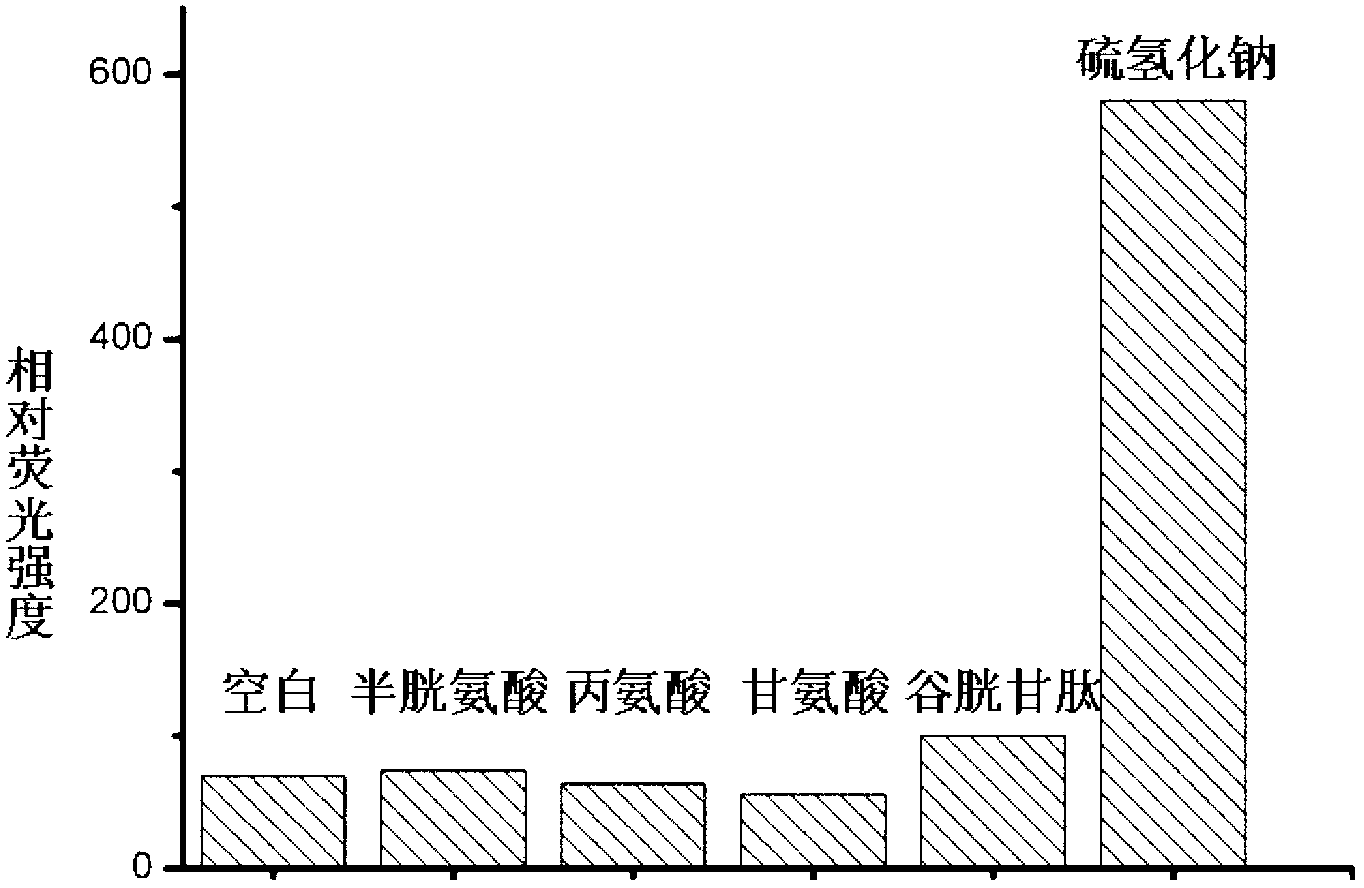
The invention relates to a specific fluorescent probe for identifying hydrogen sulfide and an application of the probe, belonging to the field of fine chemical engineering. The fluorescent probe is a resorufin derivative. Resorufin sodium salt, potassium carbonate and 2, 4-binitro bromobenzene are mixed in proportion in acetonitrile liquor to be heated, and finally are purified by silica gel chromatography to obtain the fluorescent probe. The fluorescent probe and a corresponding hydrogen sulfide content detection process are not interfered by matrixes and impurities in a biosystem and can be used for quantitative determination of hydrogen sulfide content in various biosystems. The fluorescent probe has high specificity and can be hydrolyzed with hydrogen sulfide after being specifically cyclized to obtain a hydrolysate with broken ether bonds. The probe is low in cost and feasible, can be obtained by chemical synthesis and is simple and feasible in synthetic process. The probe is high in sensitivity, and has good fluorescence emission spectrum characteristics (600-650nm). In the wavelength range, the background fluorescence of a biological sample is weak, so that the probe is suitable for detecting hydrogen sulfide content in cells. Hydrogen sulfide is quantitively detected by drawing a standard curve.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INST OF DALIAN UNIV OF TECH CO LTD
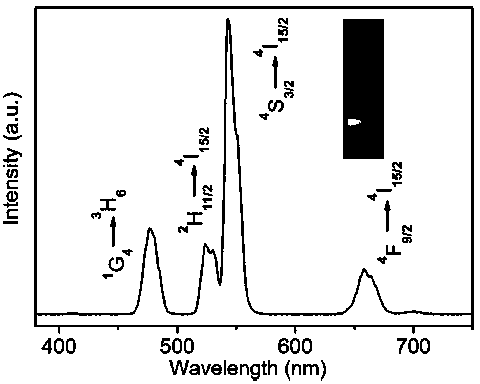
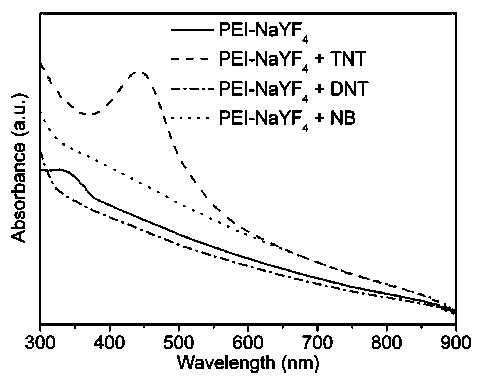
Composite upconversion nanoprobe with multicolor luminescent spectrums and preparation method and application of composite upconversion nanoprobe
InactiveCN104059669ALow costAvoid interferenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsMass ratioRare earth
The invention discloses a composite upconversion nanoprobe with multicolor luminescent spectrums and a preparation method and an application of the composite upconversion nanoprobe. PEI-NaYF4:Yb,Tm and PAA-NaYF4:Yb,Er of which the mass ratio is 3:1 are evenly mixed, so that the composite upconversion nanoprobe with the multicolor luminescent spectrums is obtained. The nanoprobe is made of a rare-earth-based upconversion luminescent nano-material and has the multiple visible luminescent zone spectrums, and therefore proportional fluorescence visual detection can be achieved. According to TNT test paper prepared by using the nanoprobe as a host material, under excitation by a light source with the wavelength being 980 nm, whether TNT exists or not is judged by observing whether a fluorescence color of the test paper changes or not. The upconversion luminescent nano-material is excited on the basis of the near-infrared light source, background fluorescence interference can be well overcome, and therefore detection sensitivity can be improved to a great extent. A synthetic method of the host material is simple and practicable, a substrate of the test paper is low in price, the TNT test paper and the excitation light source thereof are convenient to carry, operation is simple, reliability is high, and therefore the TNT test paper is very suitable for a security check site.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method for detecting enoxacin in biological body fluid with Mn doping ZnS quantum point room temperature phosphorescent
InactiveCN101281131AAvoid interferenceAvoid preprocessingFluorescence/phosphorescenceUrine sampleHigh selectivity
The invention relates to a method of a Mn doped ZnS quantum dots room temperature phosphorescence detecting an enoxacin in the biological body fluids. The invention uses the room temperature phosphorescence properties of the Mn doped ZnS quantum dots, and provides a simple, fast, economical, keen and highly selective method to detect the enoxacin in the biology body fluids; the Mn doped ZnS quantum dots are dissolved to be a solution, a urine sample or a serum sample is diluted into 30, 50 or 80 times for detecting the linear equation of the enoxacin, whose linear range is 0.2-7.2 mu mol / L, and detection limit is 58.6 nmol / L; when the method is used to detect the enoxacin in the biological body fluids, an oxygen scavenger and a inducer are not need to add, and the background fluorescence and the interference of scattered light can be avoided. Simultaneously, due to the high selectivity of the method, when the enoxacin is detected in the biological body fluids, a complex sample pretreatment process is not needed.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Specific fluorescence probe for identifying thiophenol and application of specific fluorescence probe
ActiveCN104531136AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceChemical synthesisN dimethylformamide
The invention discloses a specific fluorescence probe for identifying thiophenol and application of the specific fluorescence probe and belongs to the field of fine chemical industry. The specific fluorescence probe is a derivative of 2-benzothiazole-6-naphthol and is prepared by the following steps: mixing the 2-benzothiazole-6-naphthol and 2, 4-dinitrobenzene into an N, N-dimethylformamide solution according to a proportion, heating, and finally, purifying by adopting silica gel chromatography to obtain the fluorescence probe. The fluorescence probe and a corresponding thiophenol content detecting process can not be interfered by matrixes and impurities in a biological system and can be used for quantitatively determining the thiophenol content in various biological systems. The specific fluorescence probe is high in specificity, can be hydrolyzed after being acted with the thiophenol, namely an ether bond is fractured; is cheap and is easy in acquisition, can be obtained by chemical synthesis, is simple and feasible in synthetic process; is high in sensitivity, is good in fluorescence attribute. A hydrolysate can be excited by a two-photon laser with 800nm as an excitation light source, a biological sample is weak in background fluorescence, and the specific fluorescence probe is suitable for detecting the thiophenol content in cells and is capable of quantitatively determining the thiophenol by drawing a standard curve.
Owner:CHANGSHU RES INST OF DALIAN UNIV OF TECH CO LTD
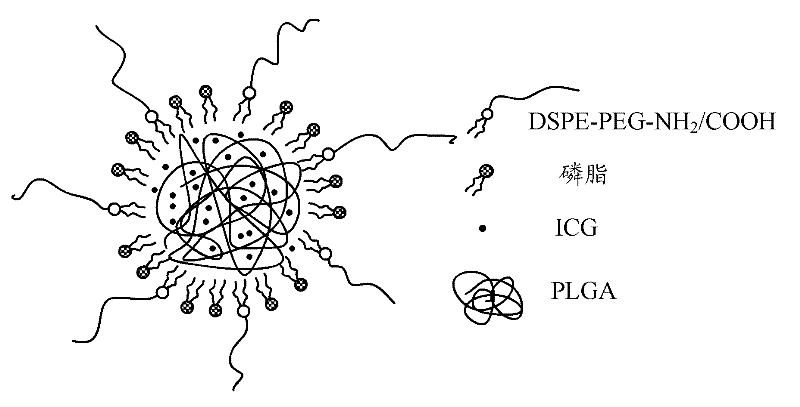
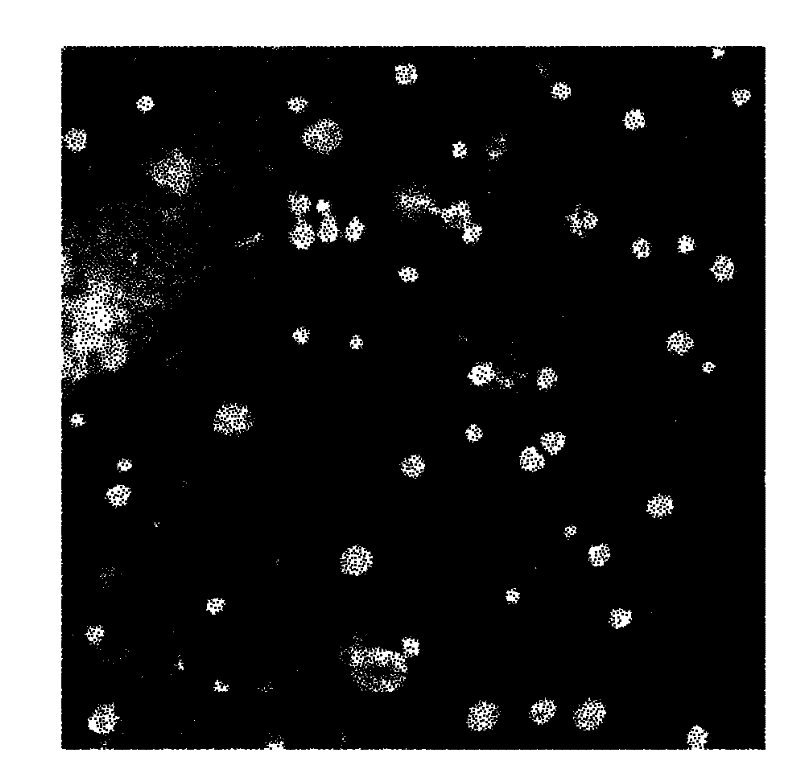
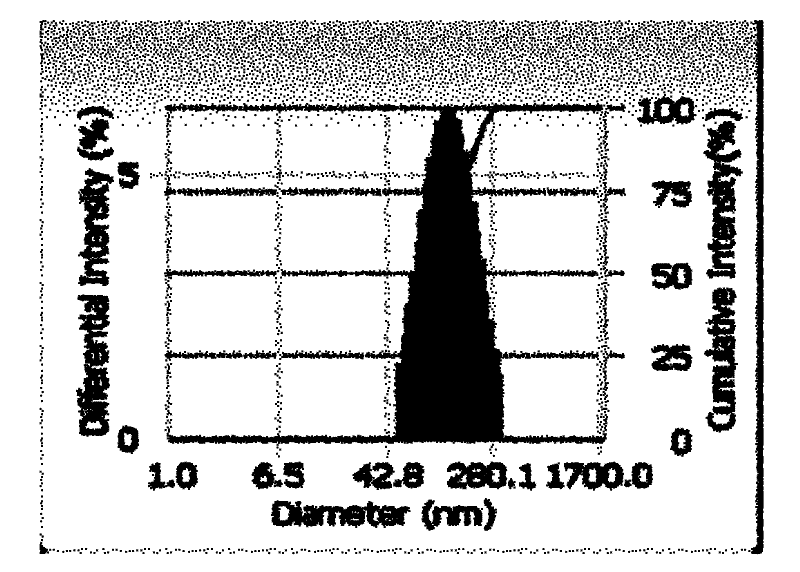
Fluorescence nanometer probe and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a fluorescence nanometer probe, comprising an inner core formed by polyglycolide lactide, a middle layer formed by phospholipid surrounding on the surface of the inner core and a shell formed by distearoyl phosphatidyl ethanolamine-polyethylene glycol which contains amino or carboxyl and partially penetrates through the middle layer, wherein indocyanine green is dispersed in the inner core. According to the invention, a core-shell structure is formed to ensure that the indocyanine green is wrapped in the polyglycolide lactide, therefore, the indocyanine green is effectively avoided from being aggregated and decomposed and the stability is increased; and the wrapped indocyanine green has a near-infrared fluorescence characteristic to ensure that the background fluorescence penetrating tissues is small and then can be relatively accurately applied to bioluminescence labeling.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
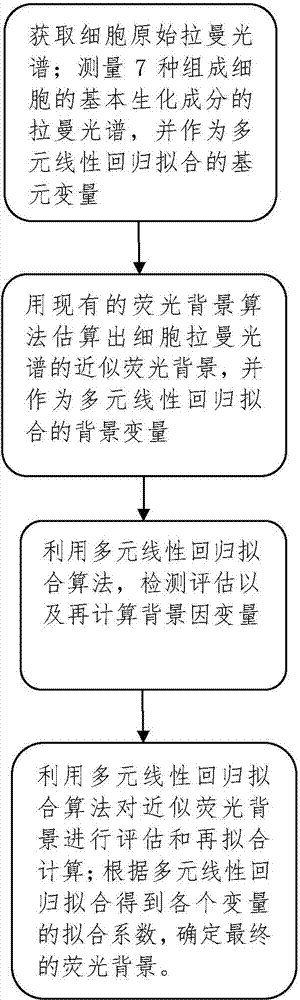
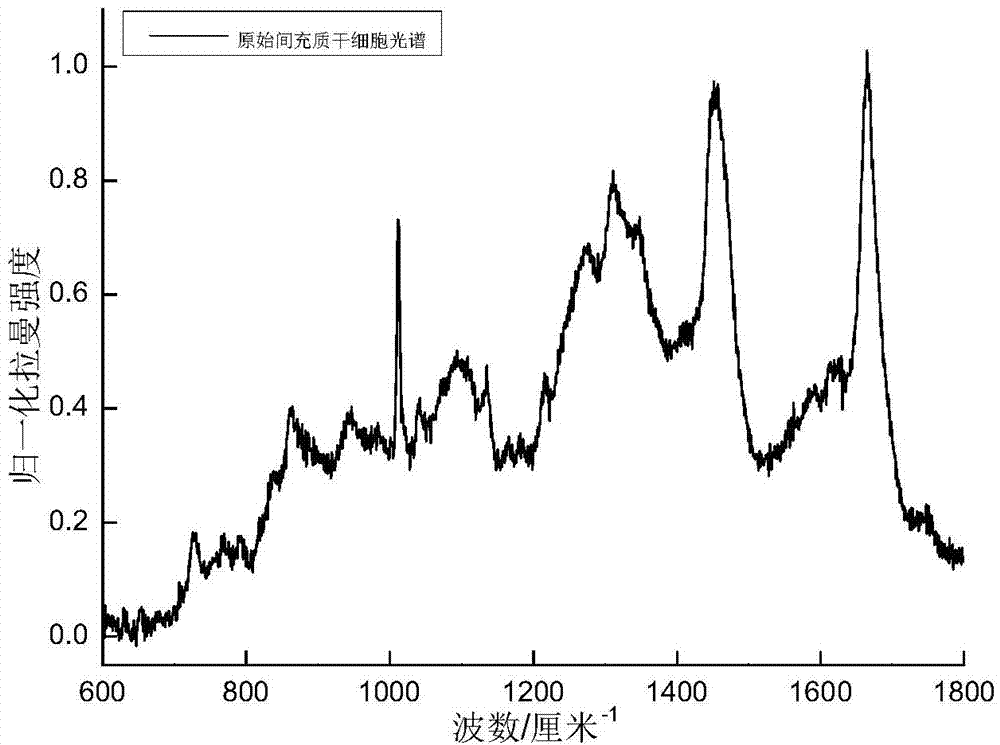
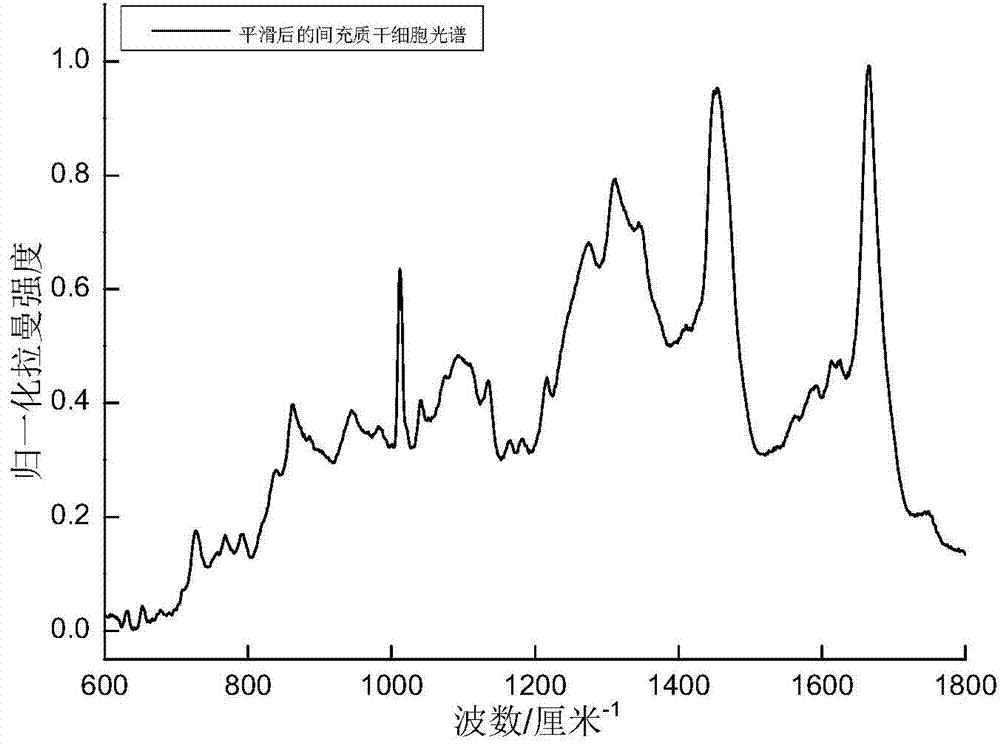
Method for obtaining true Raman spectrum of cell by multiple linear regression fitting
ActiveCN103901014ARemove fluorescent backgroundExact fitRaman scatteringLinear regressionComputer science
The invention discloses a method for obtaining a true Raman spectrum of a cell by multiple linear regression fitting. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the original Raman spectrum of the cell; acquiring a smooth Raman spectrum after smoothing; acquiring primitive-variable Raman spectrums of all primitive variables in the cell; initially fitting and calculating an approximate fluorescence background Raman spectrum of the cell; obtaining a fitting coefficient corresponding to each primitive variable and background variable by multiple linear regression fitting; finally determining the fluorescence background Raman spectrum of the cell by the sum of products of the background variable Raman spectrums and corresponding fitting coefficients; deducting the obtained fluorescence background Raman spectrum by using smoothing Raman spectrum and obtaining the true Raman spectrum of the cell. The method disclosed by the invention is used for eliminating the background fluorescence of the Raman spectrum of the cell, can fit out the fluorescence background of the Raman spectrum of the cell more accurately than other methods, and can realize fast elimination of the fluorescence background of the Raman spectrum of the cell so as to obtain the true Raman spectrum of the cell.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
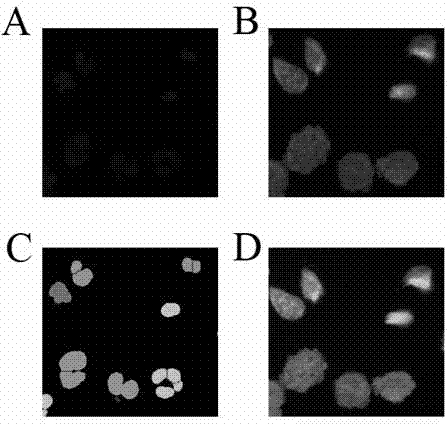
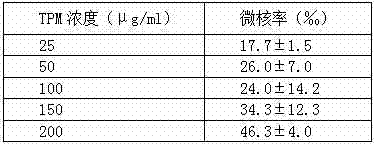
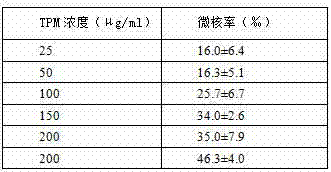
In-vitro cell micronuclei method for detecting total particulate matters of main stream smoke of cigarettes
ActiveCN104122189ALong storage timeThe detection process is fastImage analysisPreparing sample for investigationTotal particulate matterBiology
The invention discloses an in-vitro cell micronuclei method for detecting total particulate matters of main stream smoke of cigarettes. The method comprises the steps of seeding cells on a 96-hole plate for cigarette smoke contamination, directly fixing, dyeing, and feeding the cells into a high-connotation imaging system for detection; setting fluorescence intensity parameters of main nucleuses and the micronuclei of the cells according to the difference between a fluorescence value of cell nucleuses and a background fluorescence value, measuring the sizes of the main nucleuses and the micronuclei of the cells so as to set nucleus diameter parameters, and setting distance parameters according to distances between the cell nucleuses; performing analysis on images according to the setting, and selecting the number of binucleated cells with the micronuclei and the total number of the binucleated cells from a result lead-out column so as to calculate the micronucleus rate. According to the method, the number of required cells is small, the cells are not need to be used, and micronuclei sheets are not required to be manufactured; furthermore, the in-vitro cell micronuclei method is high in detection speed, large in sampling quantity and high in accuracy.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO YUNNAN IND
Optical ion sensing film for detecting metal ions, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102495038AHigh quantum yieldHigh Intensity FluorescenceFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldPolyvinyl chloride
The invention discloses an optical ion sensing film for detecting metal ions. The optical ion sensing film comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 0.34 to 0.38 percent of ETH5418, 0.46 to 0.91 percent of quadri[3,5-bi-( trifluoromethyl)benzene]-sodium-tetraborate, 0.43 to 2.17 percent of metal ion carrier, 2.01 to 2.17 percent of up-conversion nanorod, 31.41 to 32.71 percent of polrvinyl chloride and the balance of bis(2-ethylhexyl)decandeionate or o-npoe 2-nitrophenyl octyl ether or dioctyl phthalate. The invention also discloses a preparation method for the sensing film and application of the sensing film to detection of the metal ions. The sensing film is excited by light with wavelength of 980 nanometers and the light of the sensing film is transmitted in a near infrared region, so that the sensor is not interfered with background absorption and background fluorescence; furthermore, compared with the conventional organic system, the system has higher quantum yield, and can produce high-intensity fluorescence.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Fluorescent probe for detecting biological hydrogen sulfide as well as preparation and application of fluorescent probe
InactiveCN103173212AReduce volumeImprove permeabilityGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceSulfideBiological macromolecule
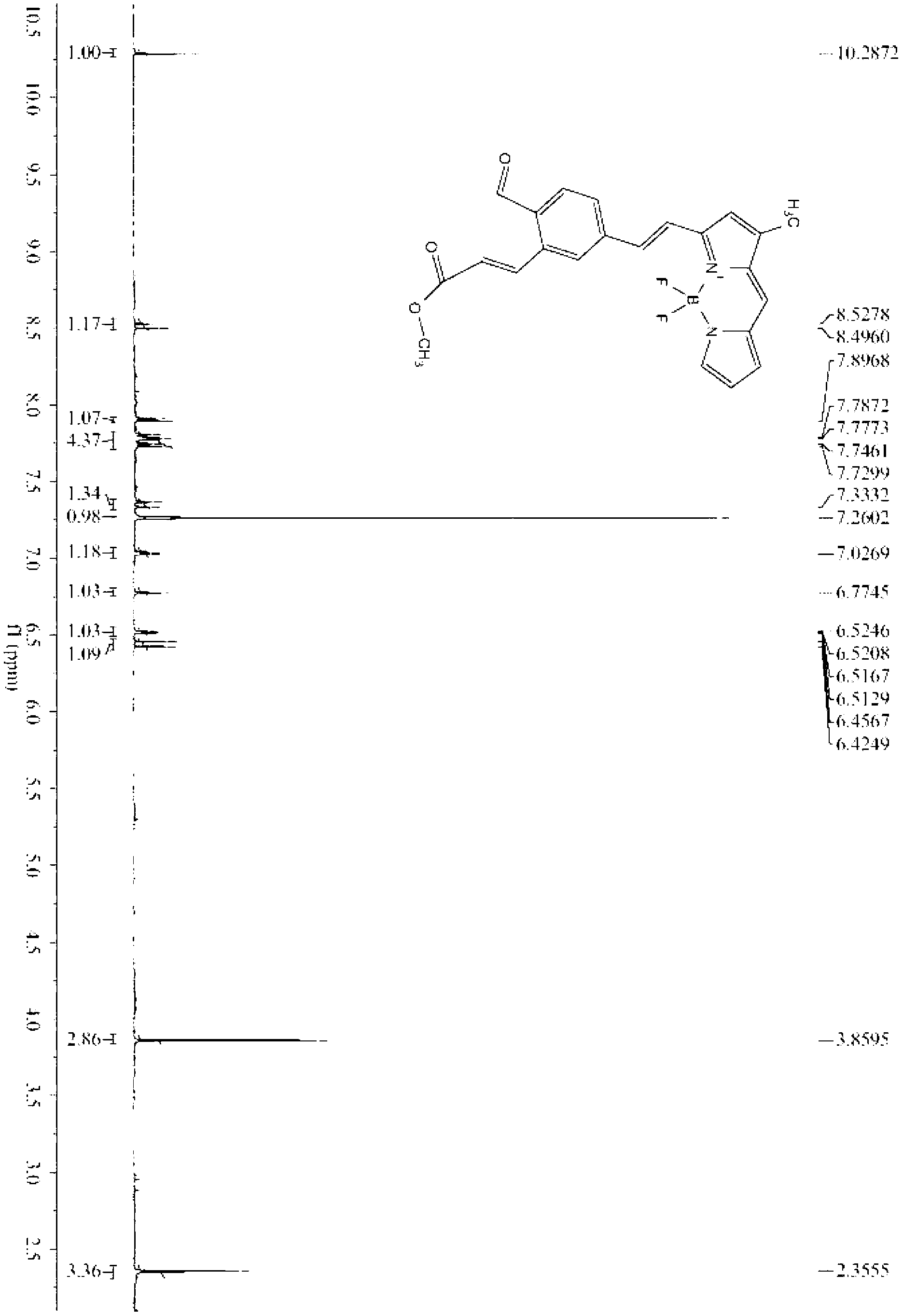
The invention provides a fluorescent probe for detecting biological hydrogen sulfide, with a structure as shown in a formula (I). The fluorescent probe, though not fluorescing by self in a physiological environment, can specifically and rapidly react with the hydrogen sulfide to generate a product with strong fluorescence, thereby achieving specific detection on the hydrogen sulfide. The fluorescent probe is good in stability and can be preserved for long time to use; the fluorescent probe has a long fluorescence excitation wavelength (>500nm), thereby causing no damage to an organism and being capable of effectively avoiding interference from biological macromolecule background fluorescence; and the fluorescent probe is high in detection signal-to-noise ratio, good in sensitivity, excellent in selectivity, capable of specifically detecting the hydrogen sulfide in a complicated biological sample, and good in biological membrane permeability, so that the fluorescent probe can be used for detecting the hydrogen sulfide in living cells.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Non-fluorescent energy transfer
InactiveUS20070077588A1Reduced background fluorescenceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEnergy transferPhotochemistry
The present invention relates generally to the transfer of non-fluorescent energy between donor and acceptor moieties. In certain embodiments, the invention provides biomolecules that include substantially non-fluorescent donor moieties. Processes involving these donor moieties typically entail reduced background fluorescence relative to applications that involve conventional fluorescent donor moieties. In addition to reaction mixtures and methods that include the use of these biomolecules, the invention also provides related kits and systems.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
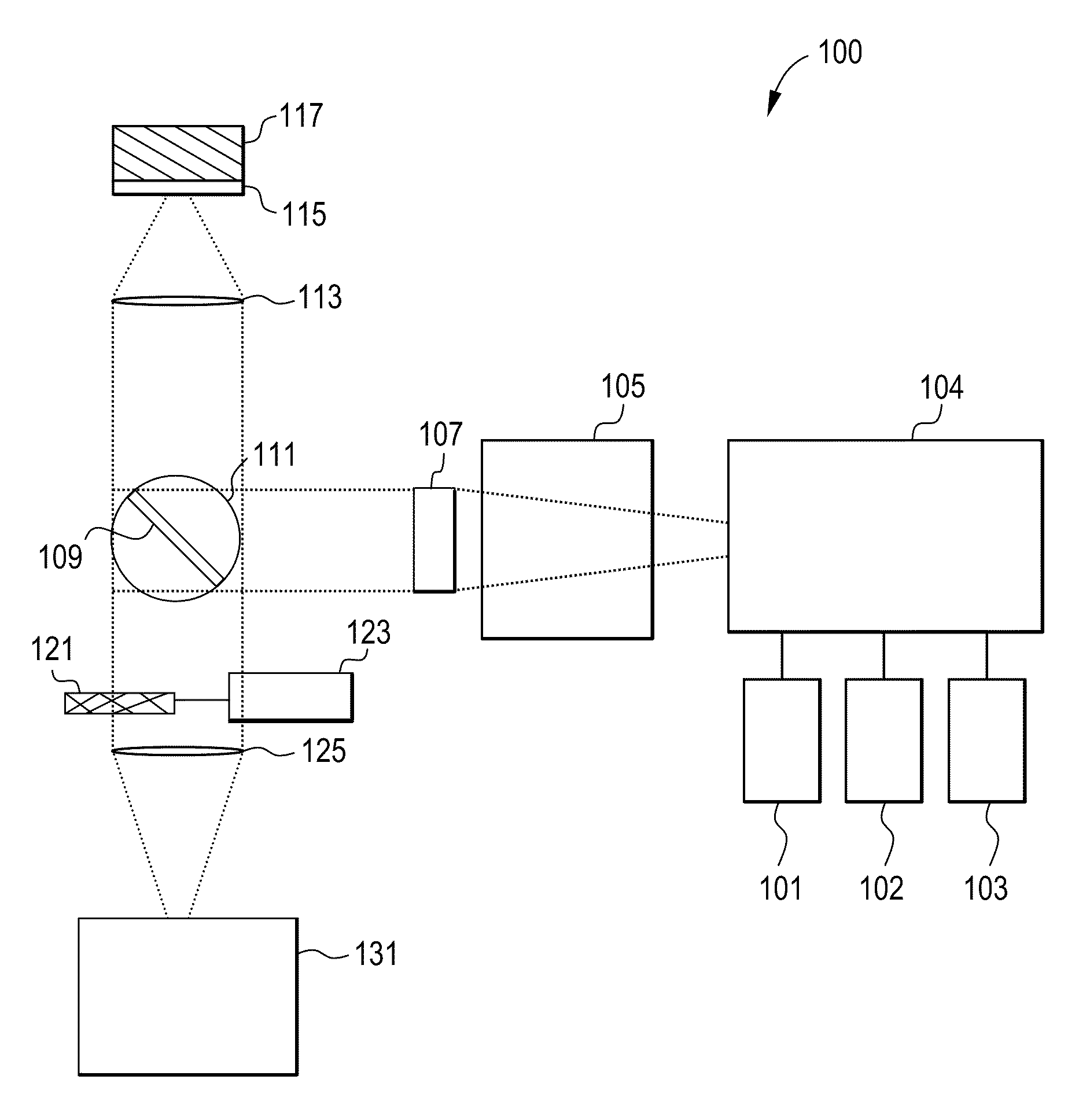
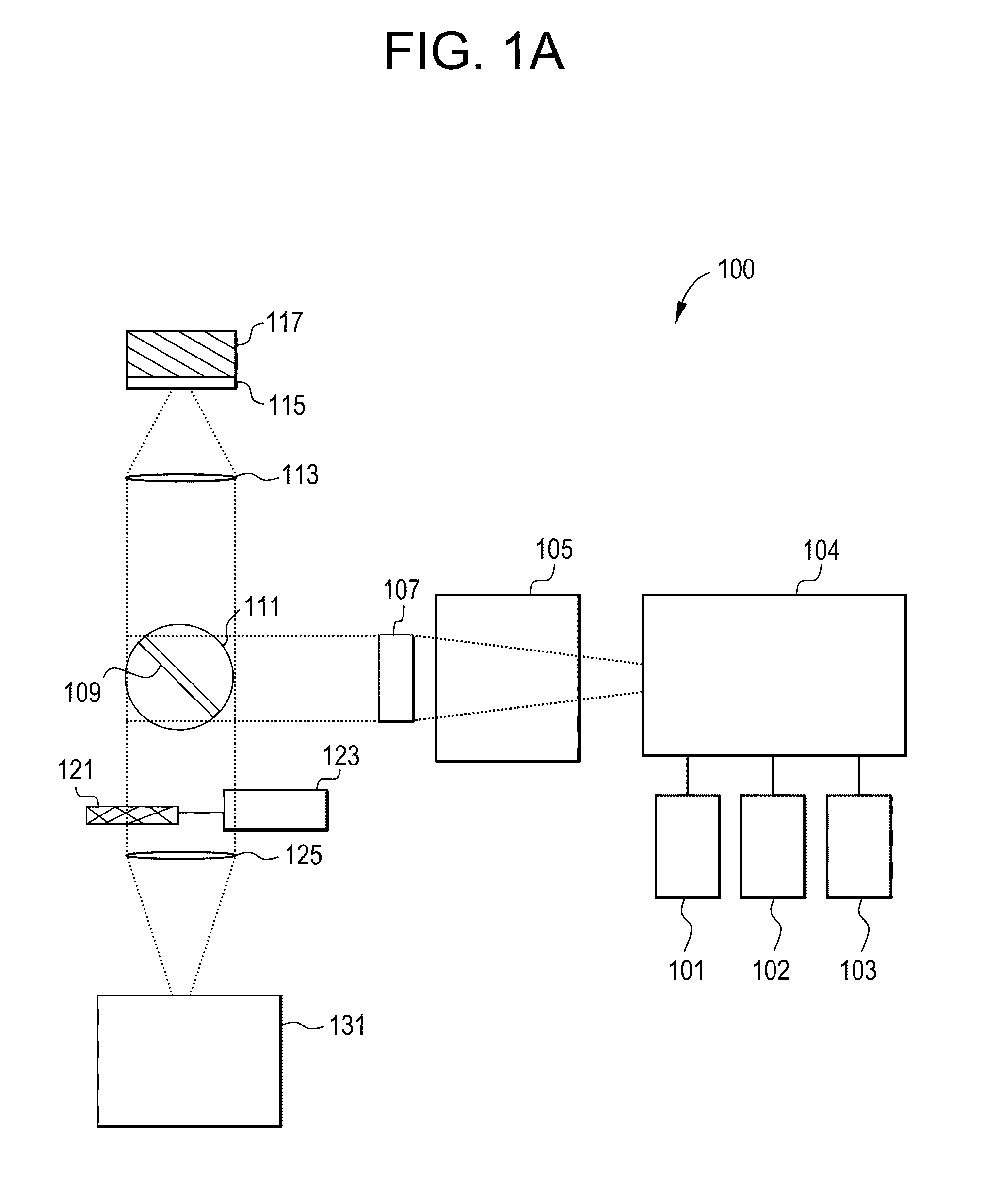
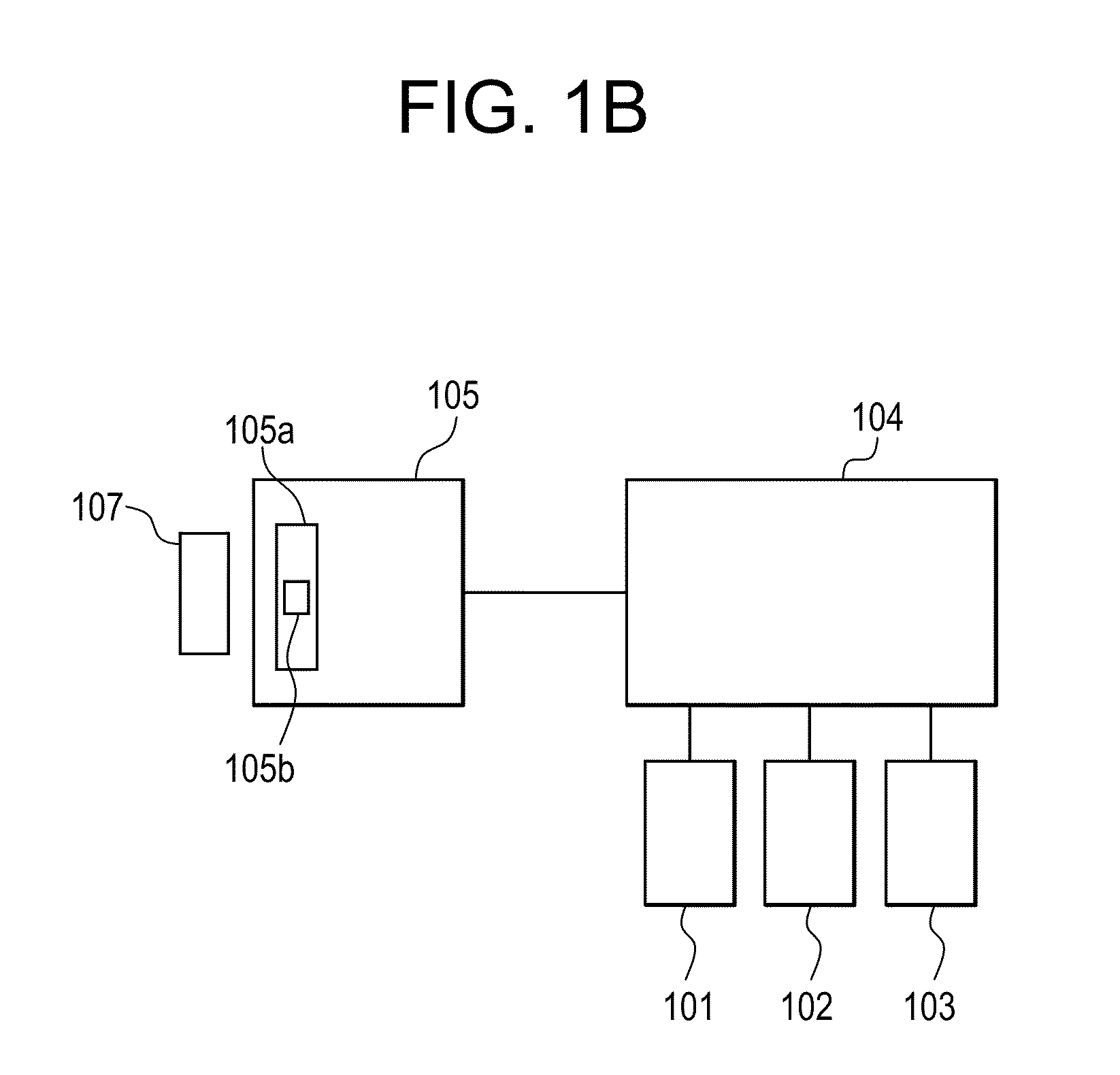
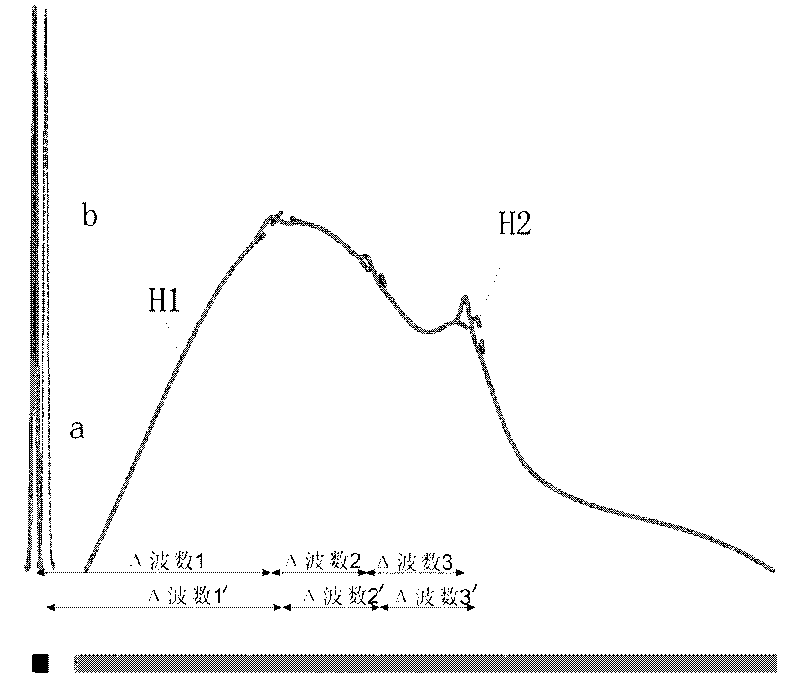
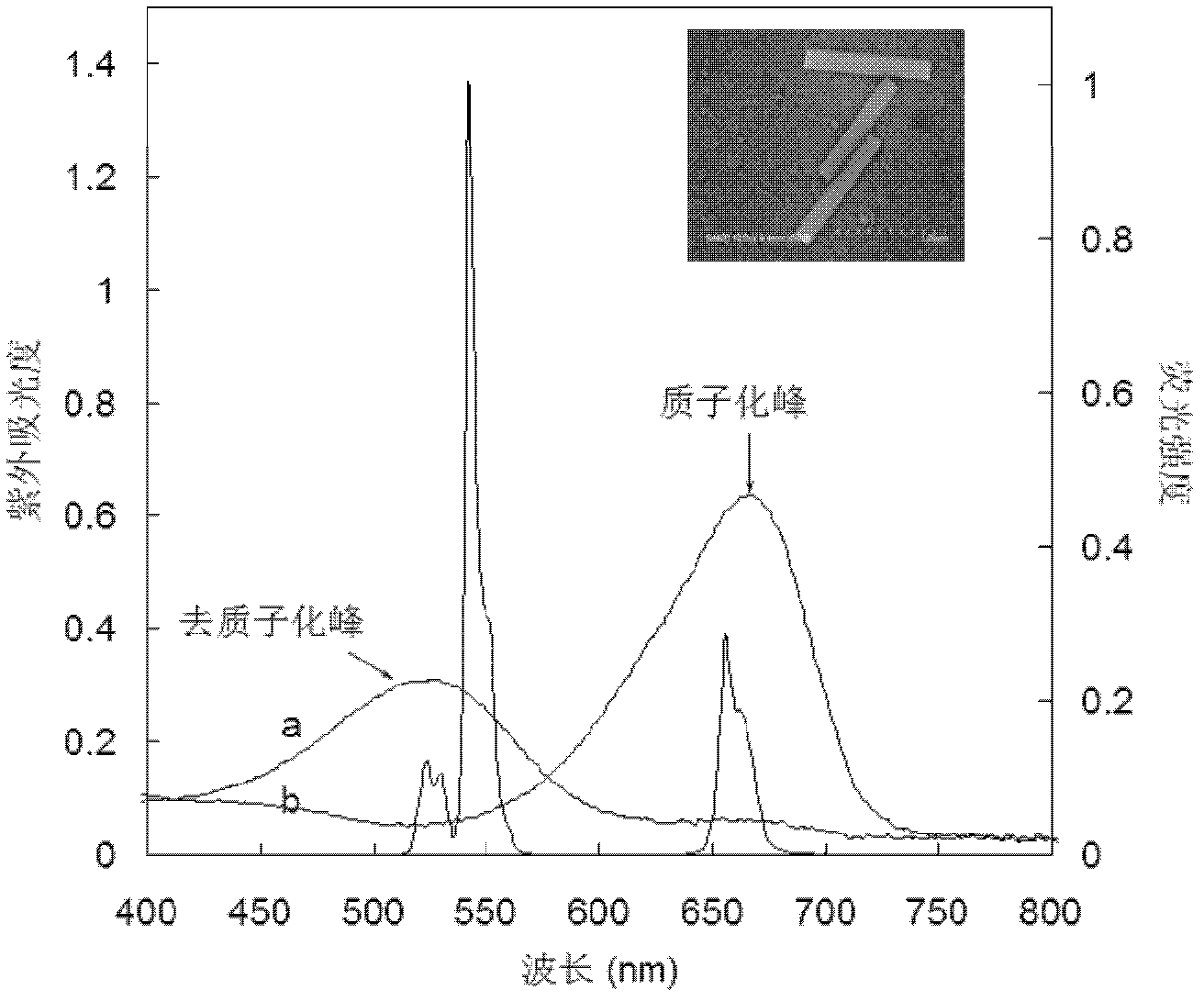
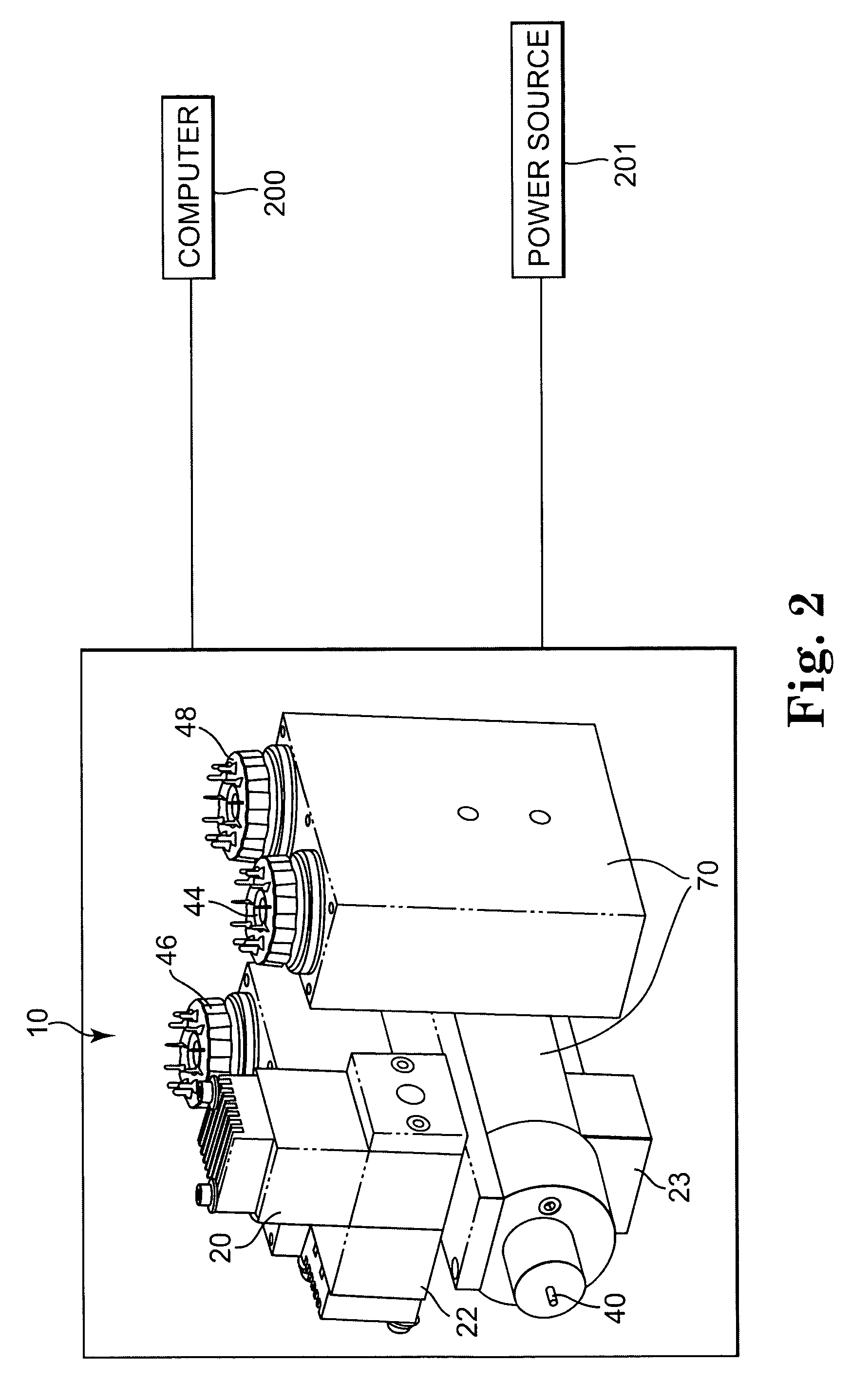
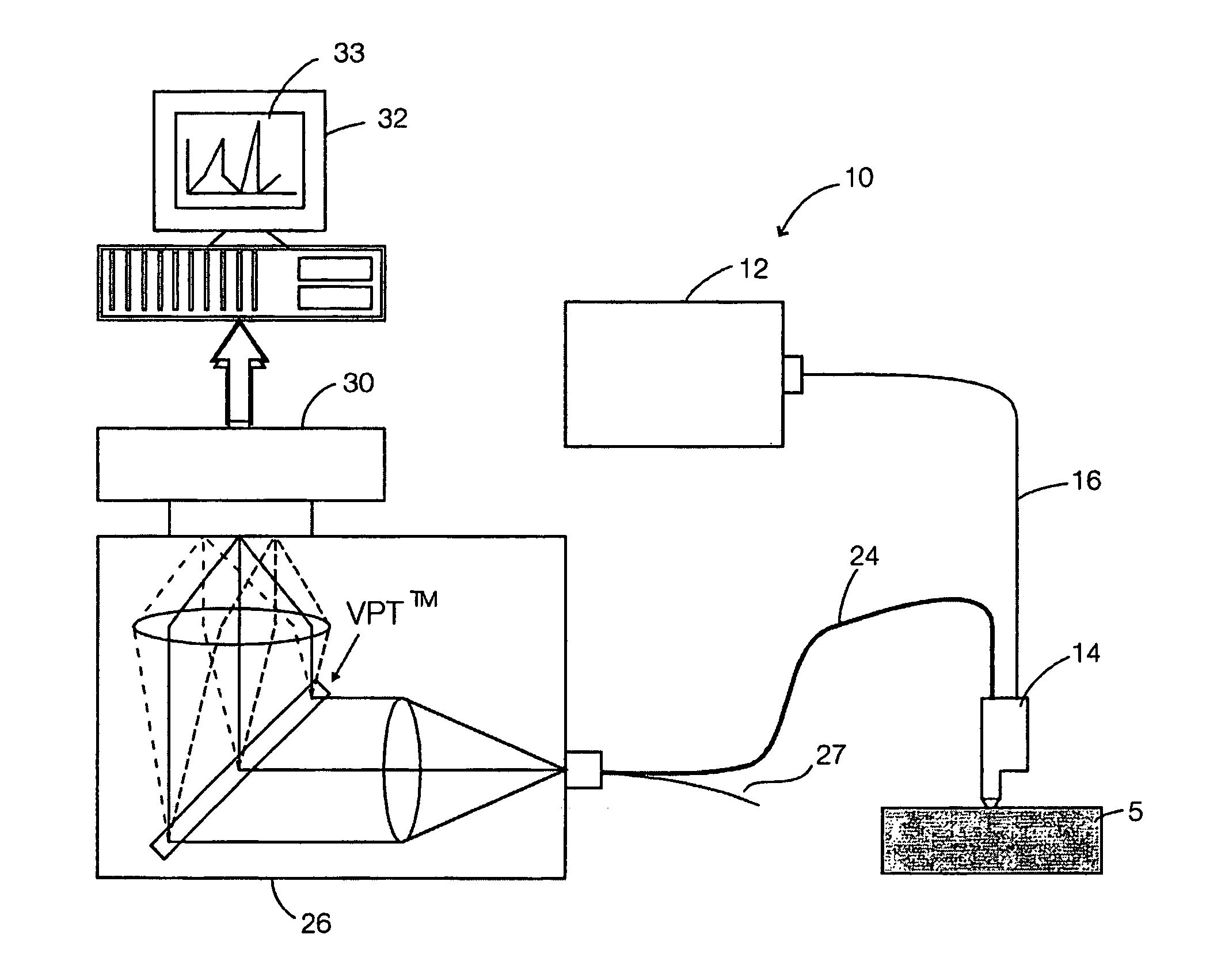
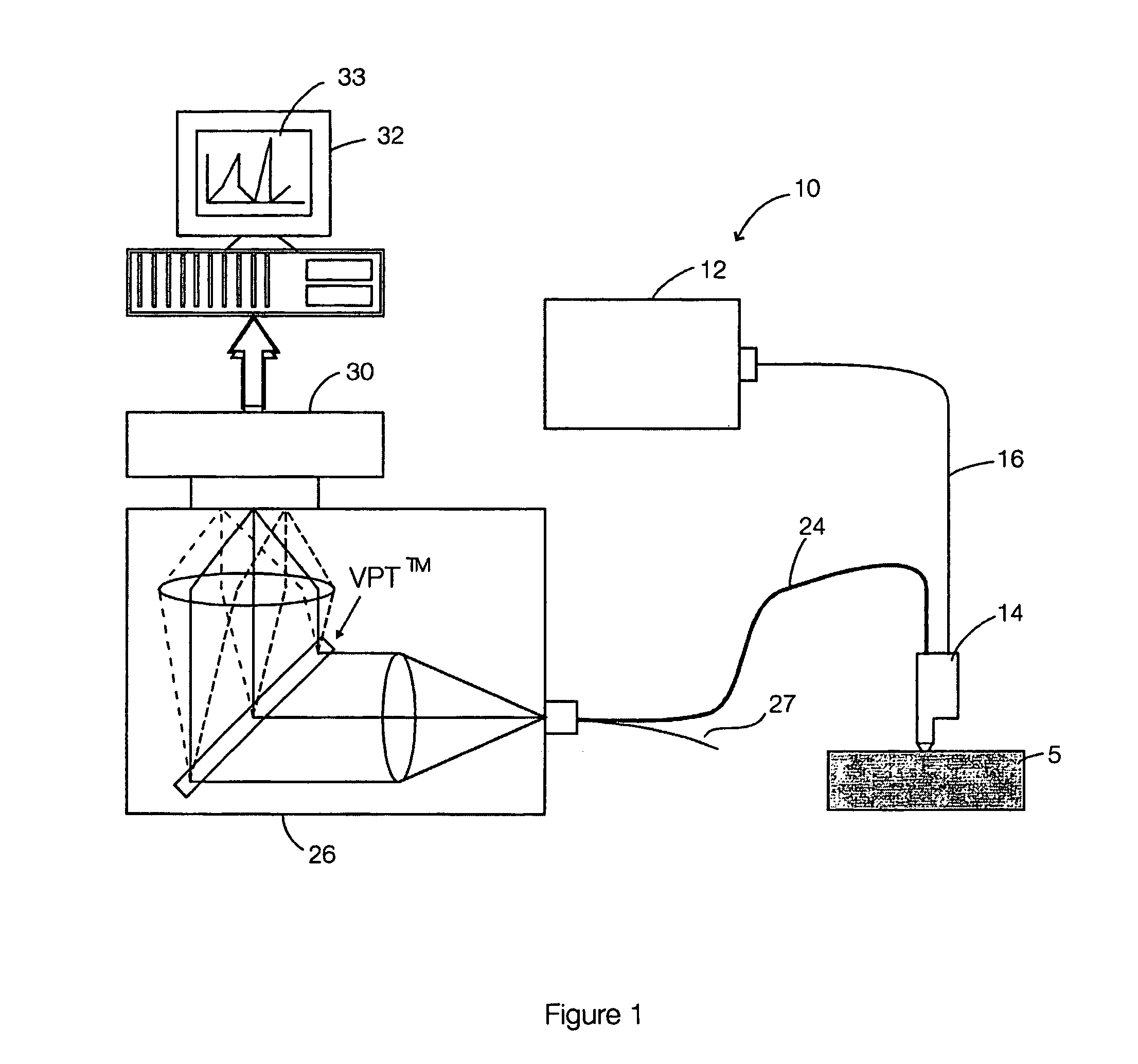
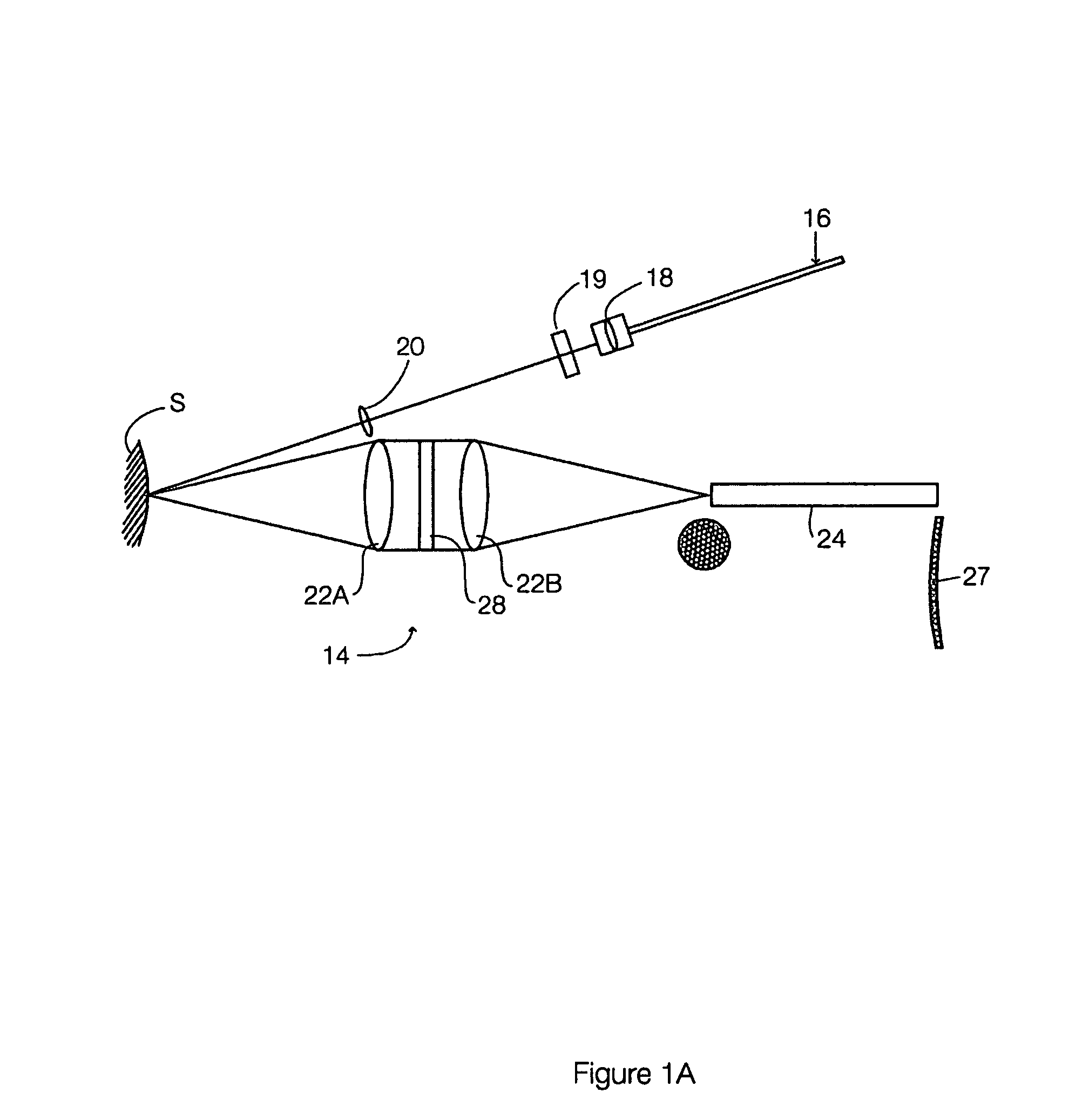
Raman instrument for measuring weak signals in the presence of strong background fluorescence
A method for measuring a chemical concentration in tissue has two measurement steps. First, generating a first light and illuminating a portion of the tissue with the first light; capturing a first reflected light from the tissue; directing the first reflected light to a plurality of light sensors, each light sensor measuring light at a different wavelength, that wavelength being proximate to a wavelength of an expected Raman shift wavelength for the chemical in the tissue; and obtaining a measurement from each of the light sensors, each measurement being specific to the first reflected light through that light sensor. Second, generating a second light and illuminating a portion of the tissue with the second light; capturing a second reflected light from the tissue; directing the second reflected light to the plurality of light sensors, each light sensor measuring light at a different wavelength that wavelength being proximate to a wavelength of an expected Raman shift wavelength for the chemical in the tissue; and obtaining a measurement from each of the light sensors, each measurement being specific to the second reflected light through that light sensor. The measurements of the first reflected light and the measurements of the second reflected light are used to calculate a concentration of the chemical in the tissue.
Owner:NU SKIN INT
Multimodal detection of tissue abnormalities based on raman and background fluorescence spectroscopy
Owner:BRITISH COLUMBIA CANCER AGENCY BRANCH
Lysosome-targeted fluorescent dye capable of realizing red emission and near-infrared emission, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107098923AImprove targetingStable structureAzo dyesGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLysosomal targetingReaction temperature
The invention discloses a lysosome-targeted fluorescent dye capable of realizing red emission and near-infrared emission, and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the field of bioluminescence analysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving a compound with the substituent R in an anhydrous organic solvent and adding morpholinoindolal and a catalyst under the condition of introduction of nitrogen, wherein a mol ratio of morpholinoindolal to the compound with the substituent R is 1-10: 1; and carrying out a reaction at a reaction temperature of 25 to 200 DEG C for 1 to 24 h, concentrating an obtained solution and carrying out silica-gel column chromatography so as to obtain the target fluorescent dye. The fluorescent dye prepared in the invention is applicable to targeted imaging of lysosomes in cells, fluorescent probes or laser dyes. The fluorescent dye has the advantages that the emission wavelength of the fluorescent dye is in a range from red zone to near-infrared zone; the fluorescent dye can prevent interference of biological background fluorescence and has high fluorescence quantum efficiency and good light stability; and the fluorescent dye can be specifically localized in lysosomes, so the fluorescent dye has high application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com