Patents
Literature
68763 results about "Zinc" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a blue-silvery appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. In some respects zinc is chemically similar to magnesium: both elements exhibit only one normal oxidation state (+2), and the Zn²⁺ and Mg²⁺ ions are of similar size. Zinc is the 24th most abundant element in Earth's crust and has five stable isotopes. The most common zinc ore is sphalerite (zinc blende), a zinc sulfide mineral. The largest workable lodes are in Australia, Asia, and the United States. Zinc is refined by froth flotation of the ore, roasting, and final extraction using electricity (electrowinning).
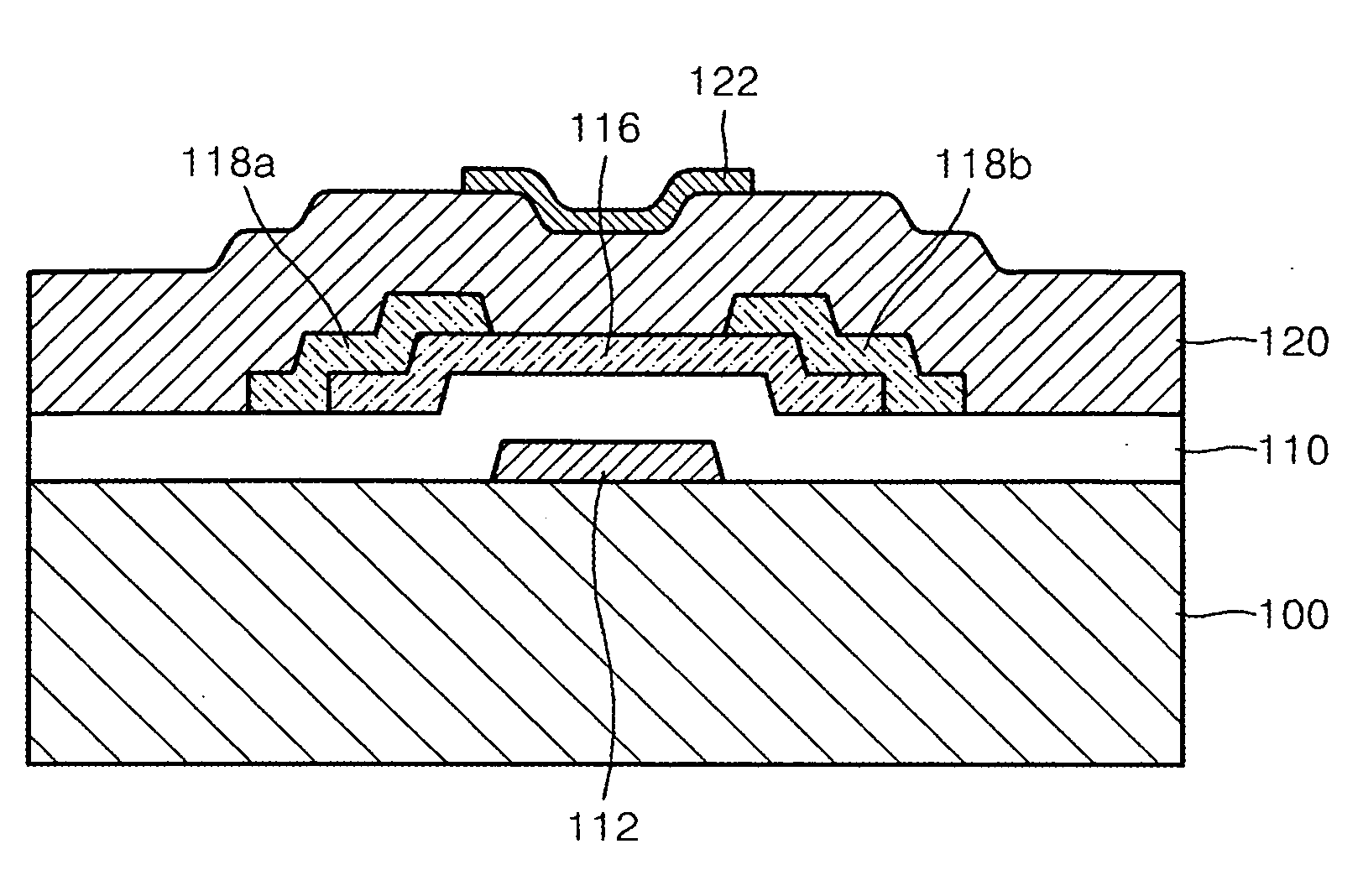
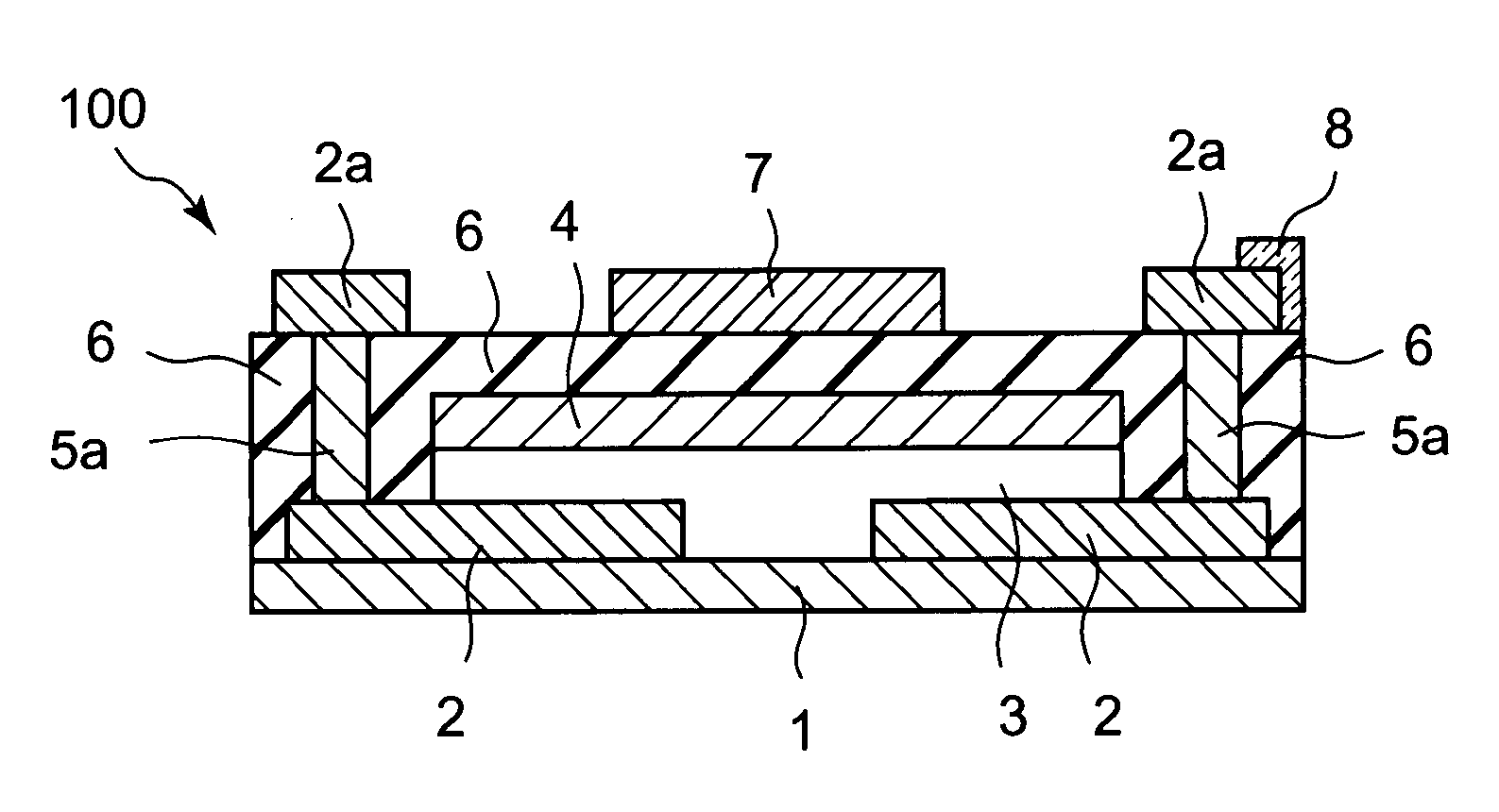
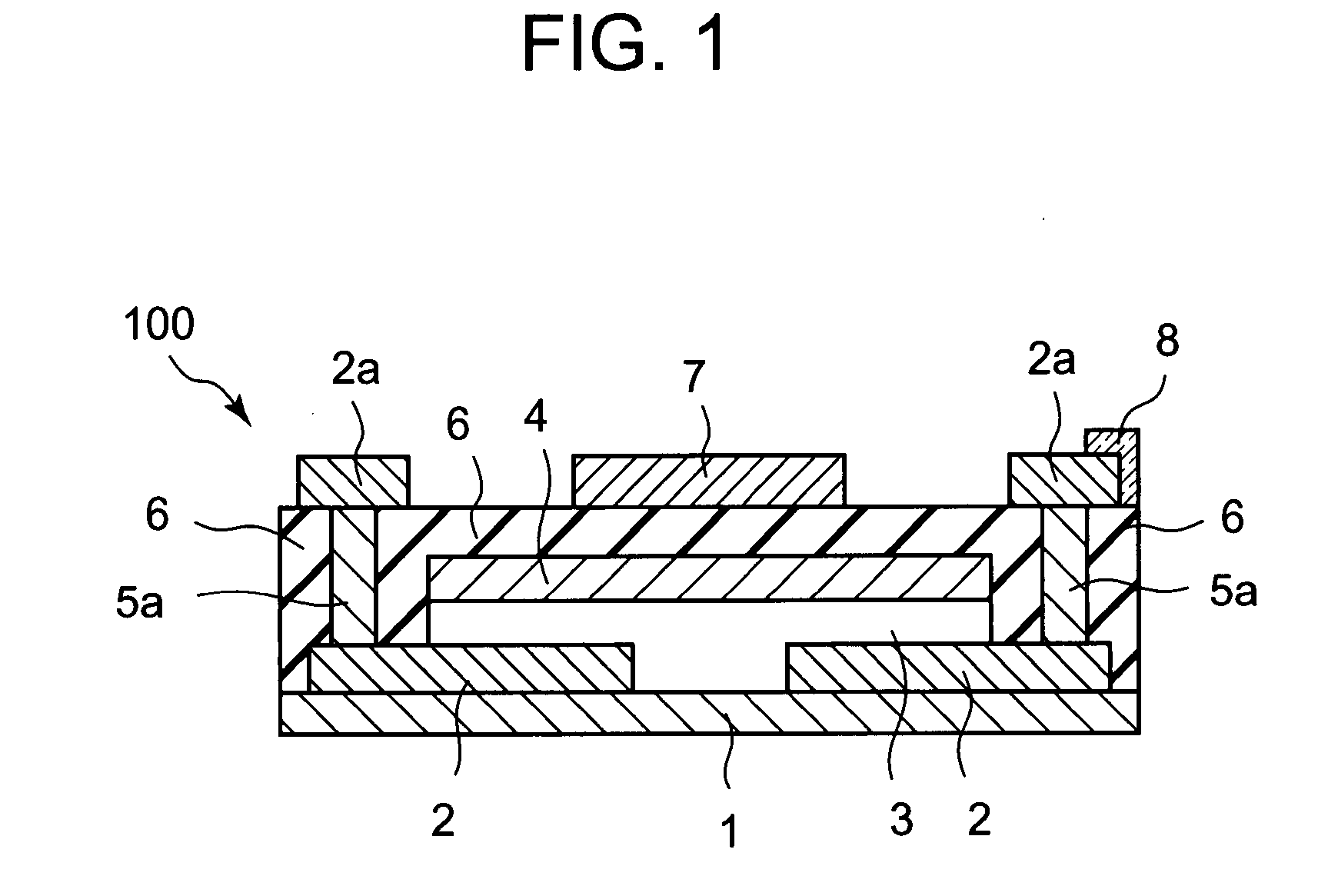
Semiconductor device, manufacturing method, and electronic device
ActiveUS20060244107A1Stabilize element propertyEasy to manufactureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSurface levelIntrinsic resistance
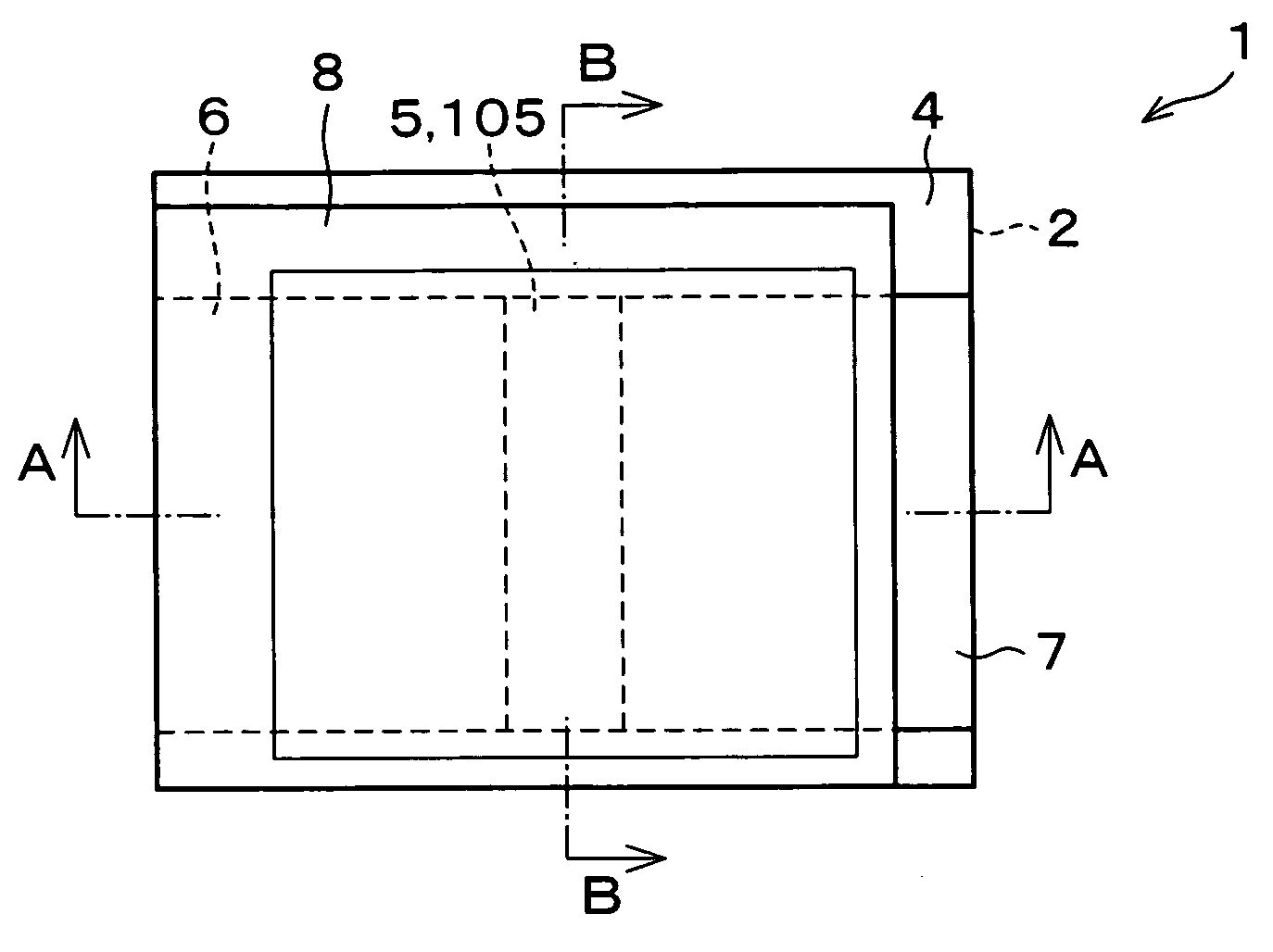
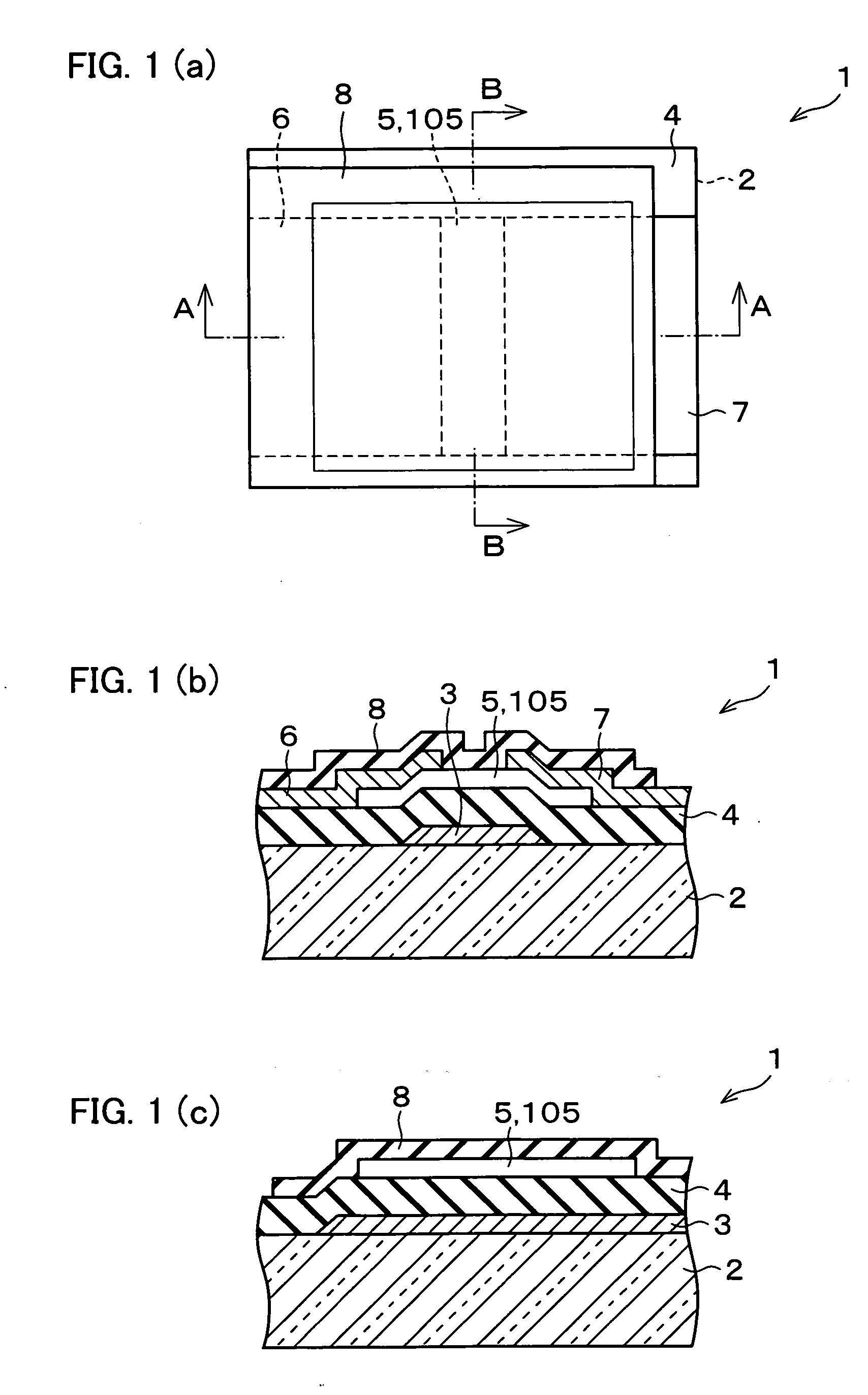
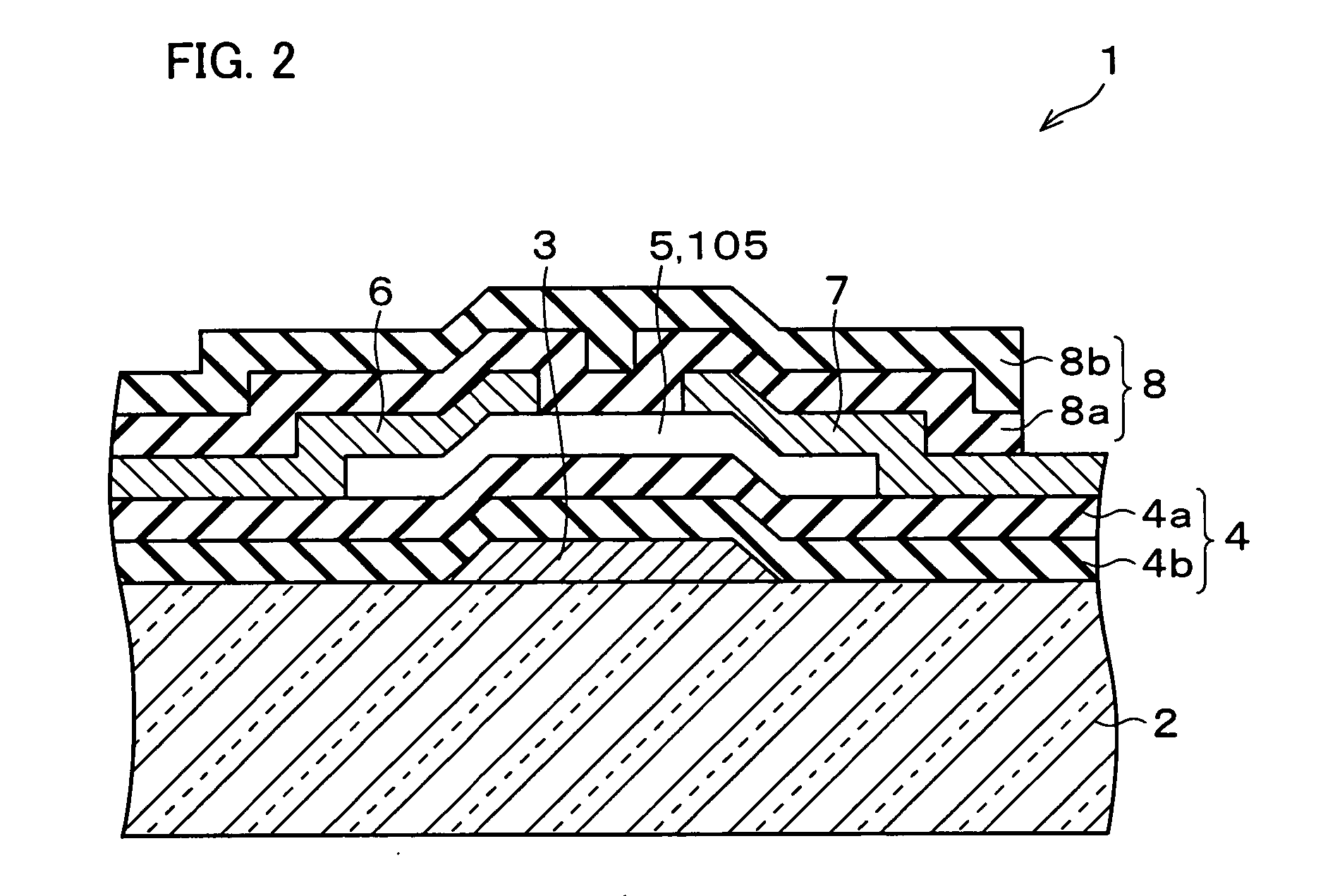
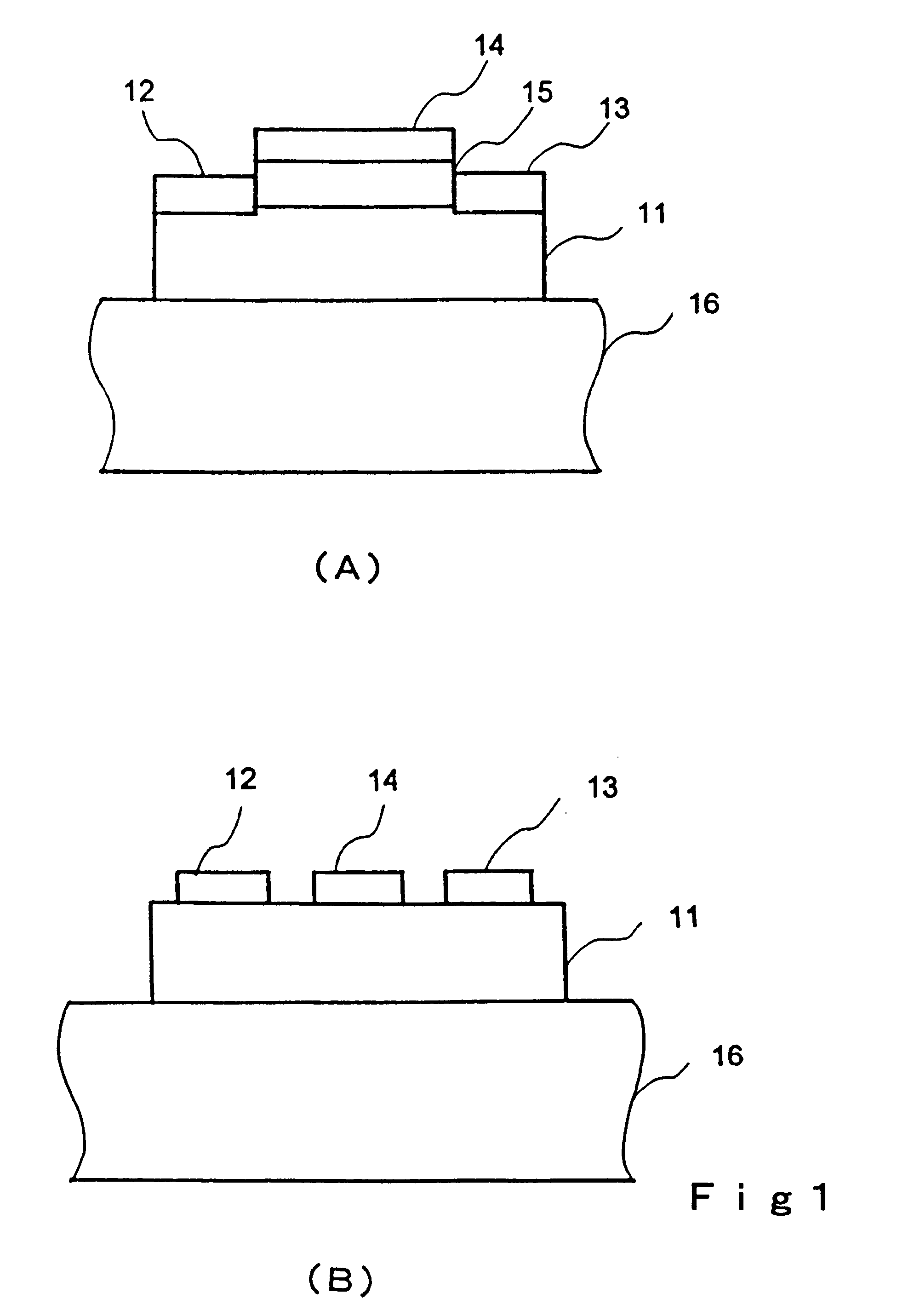
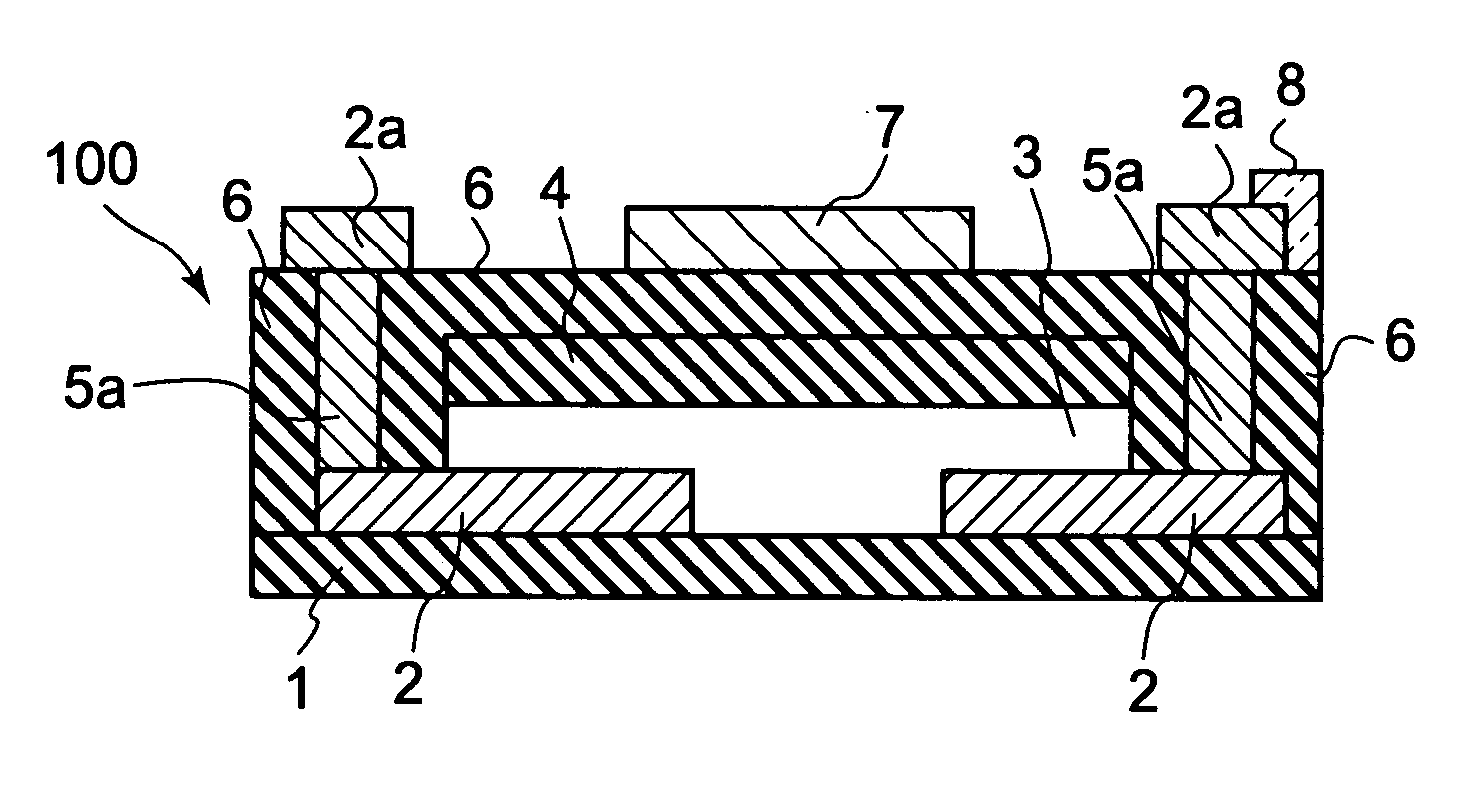
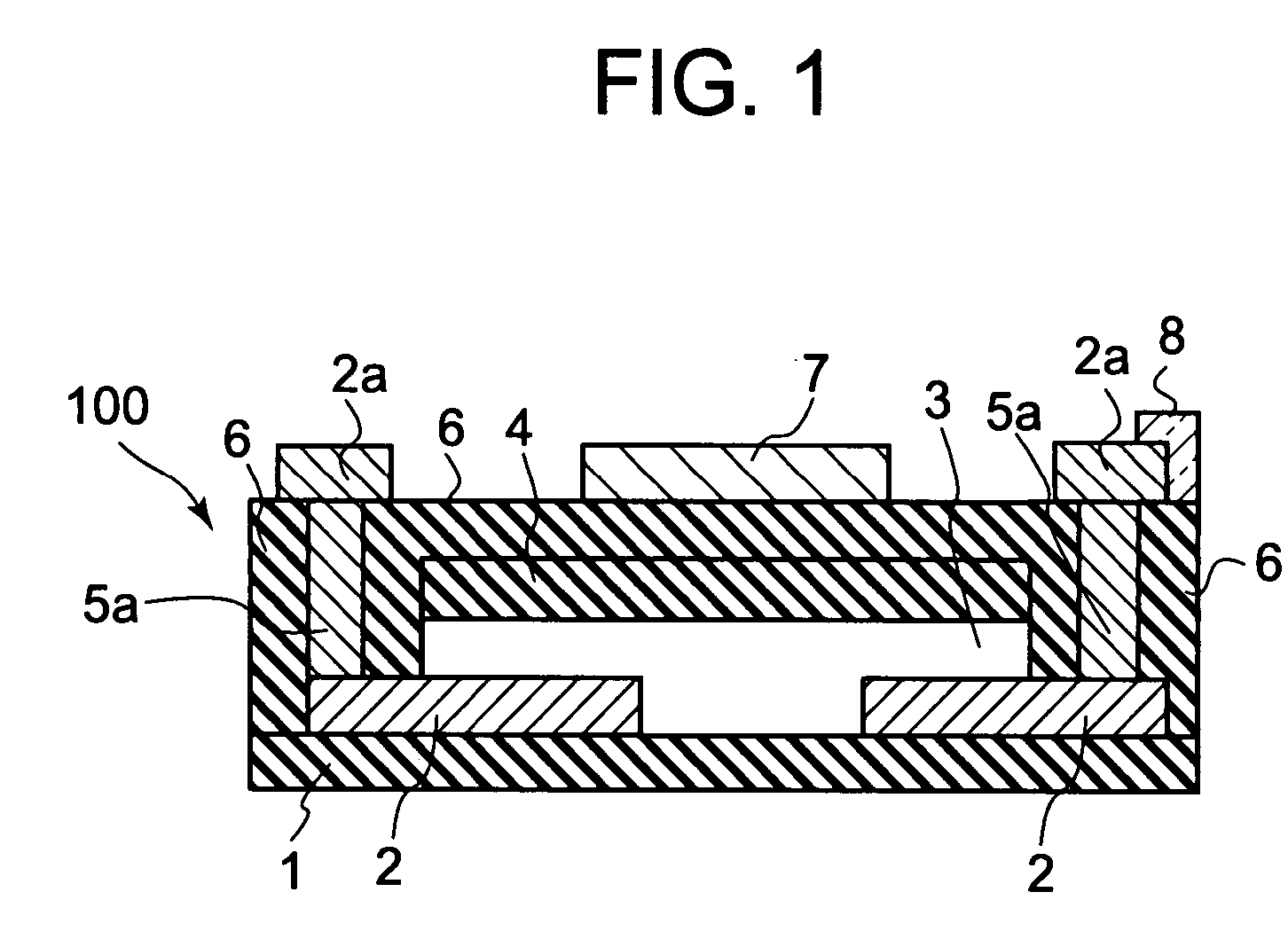
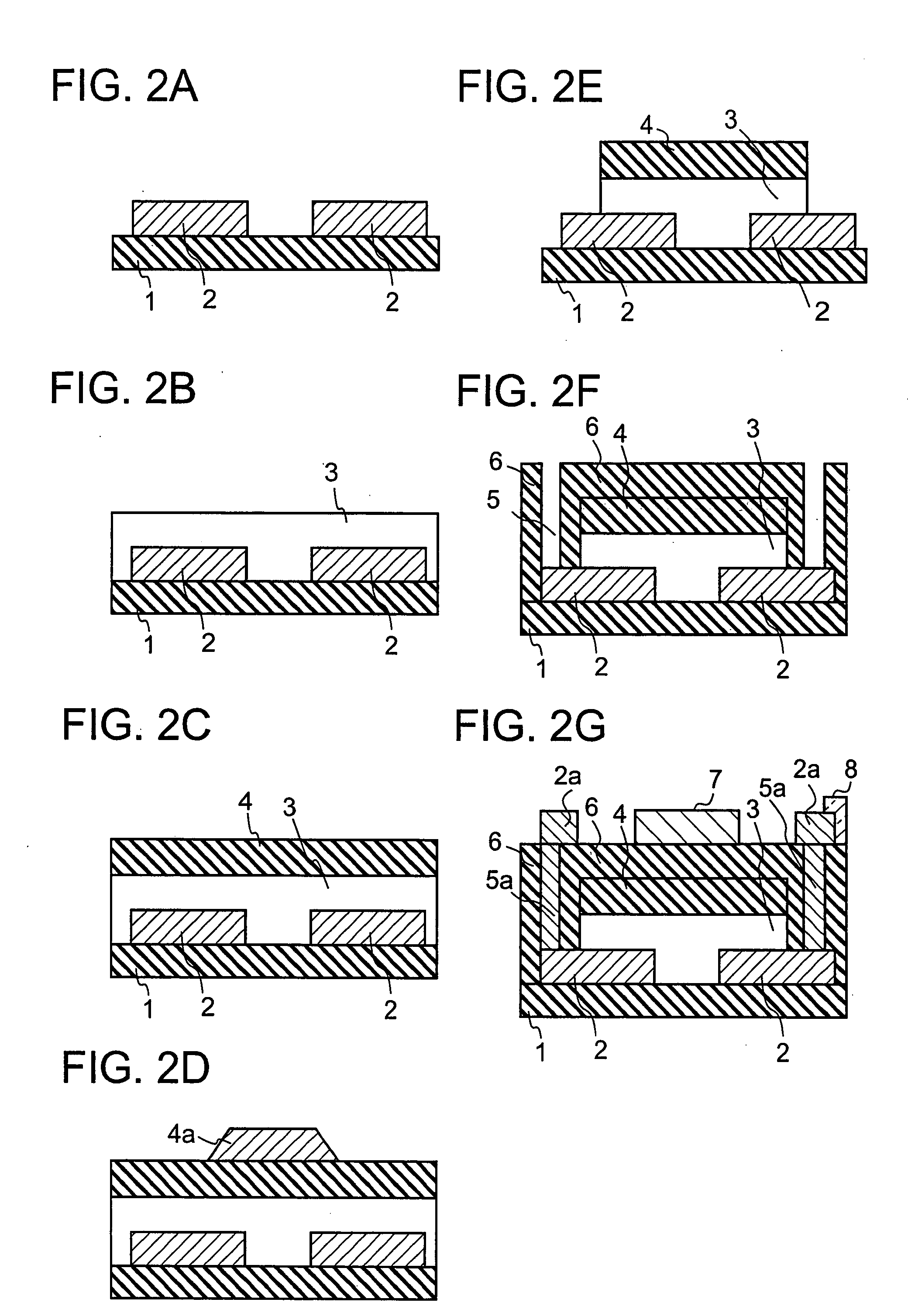
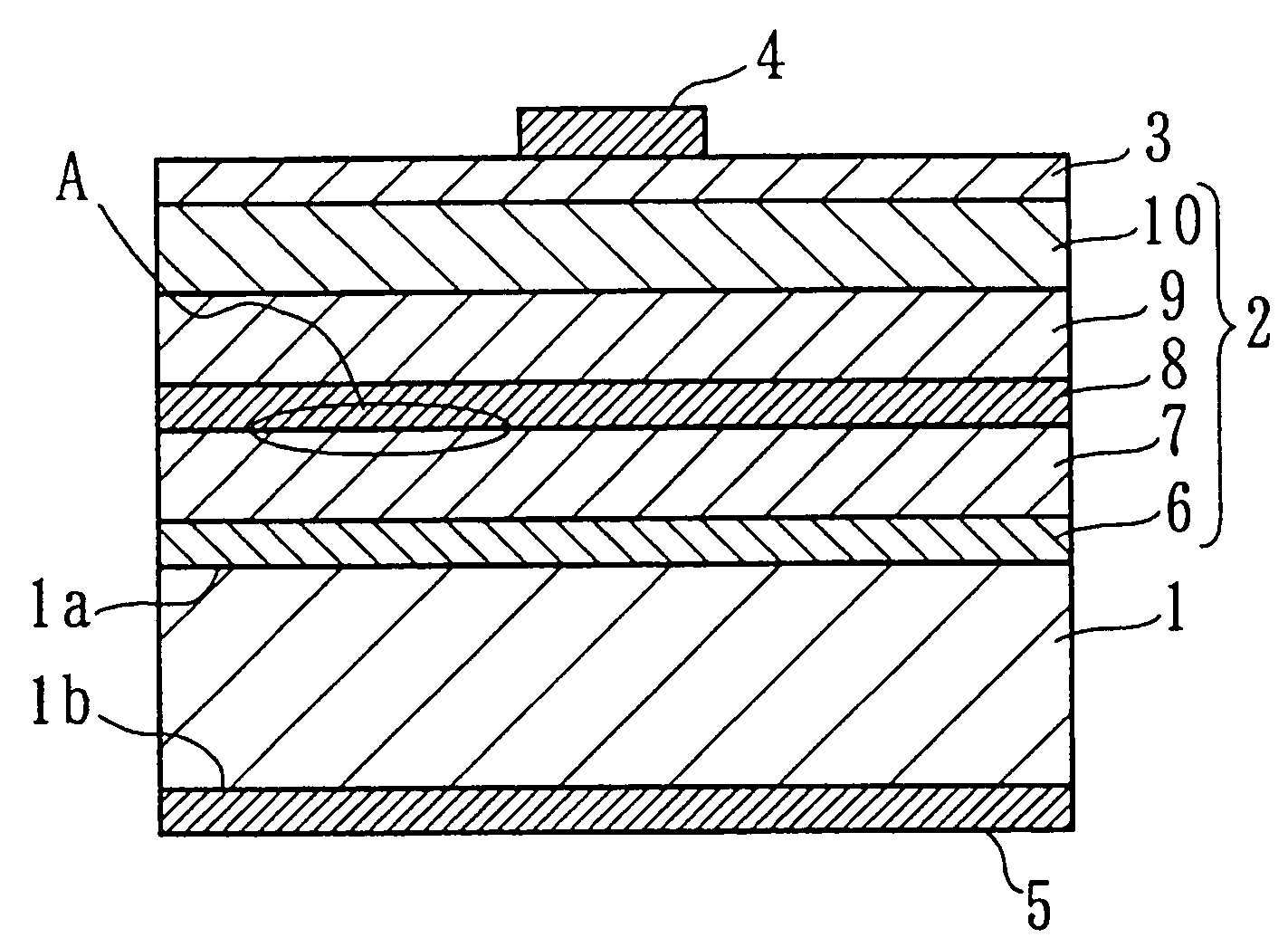
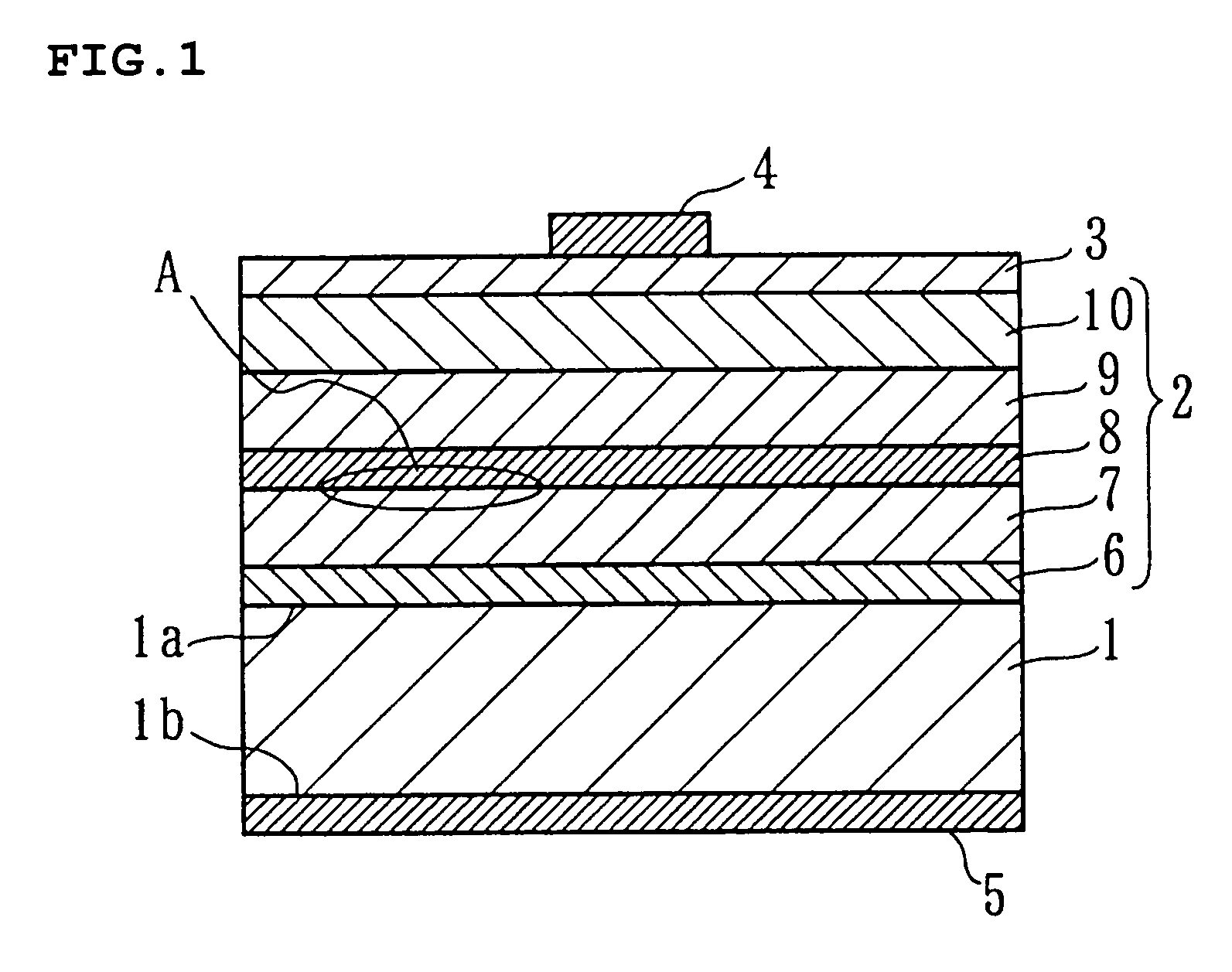
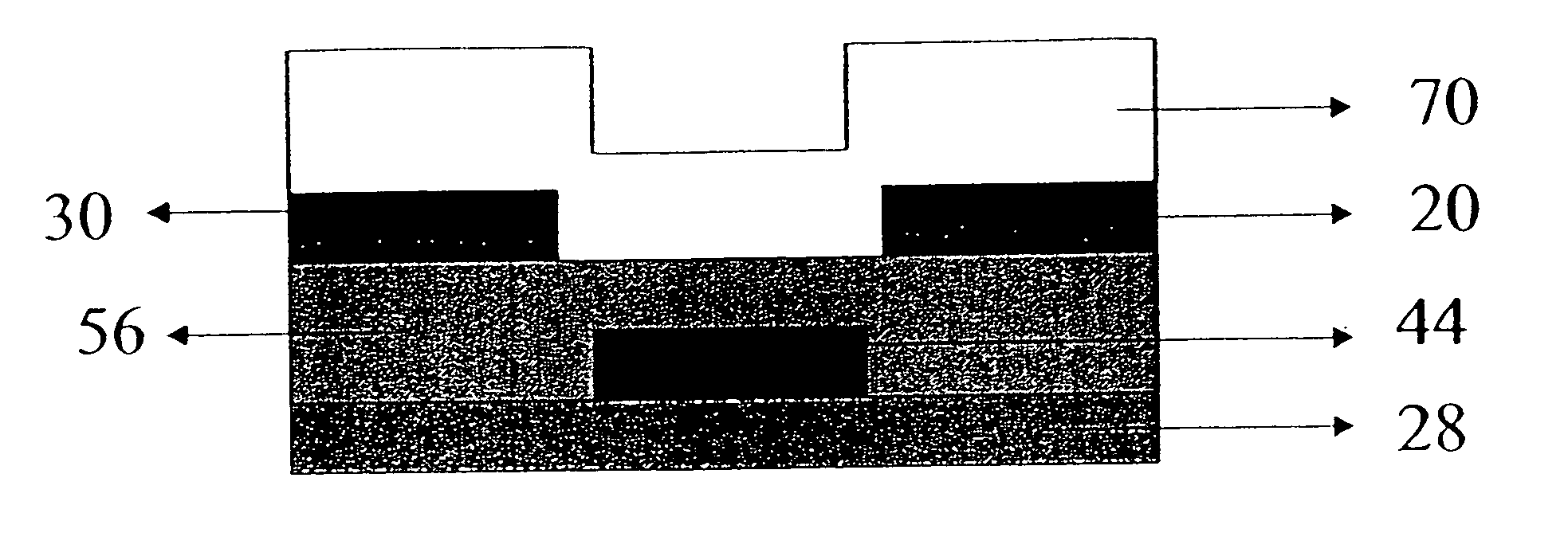
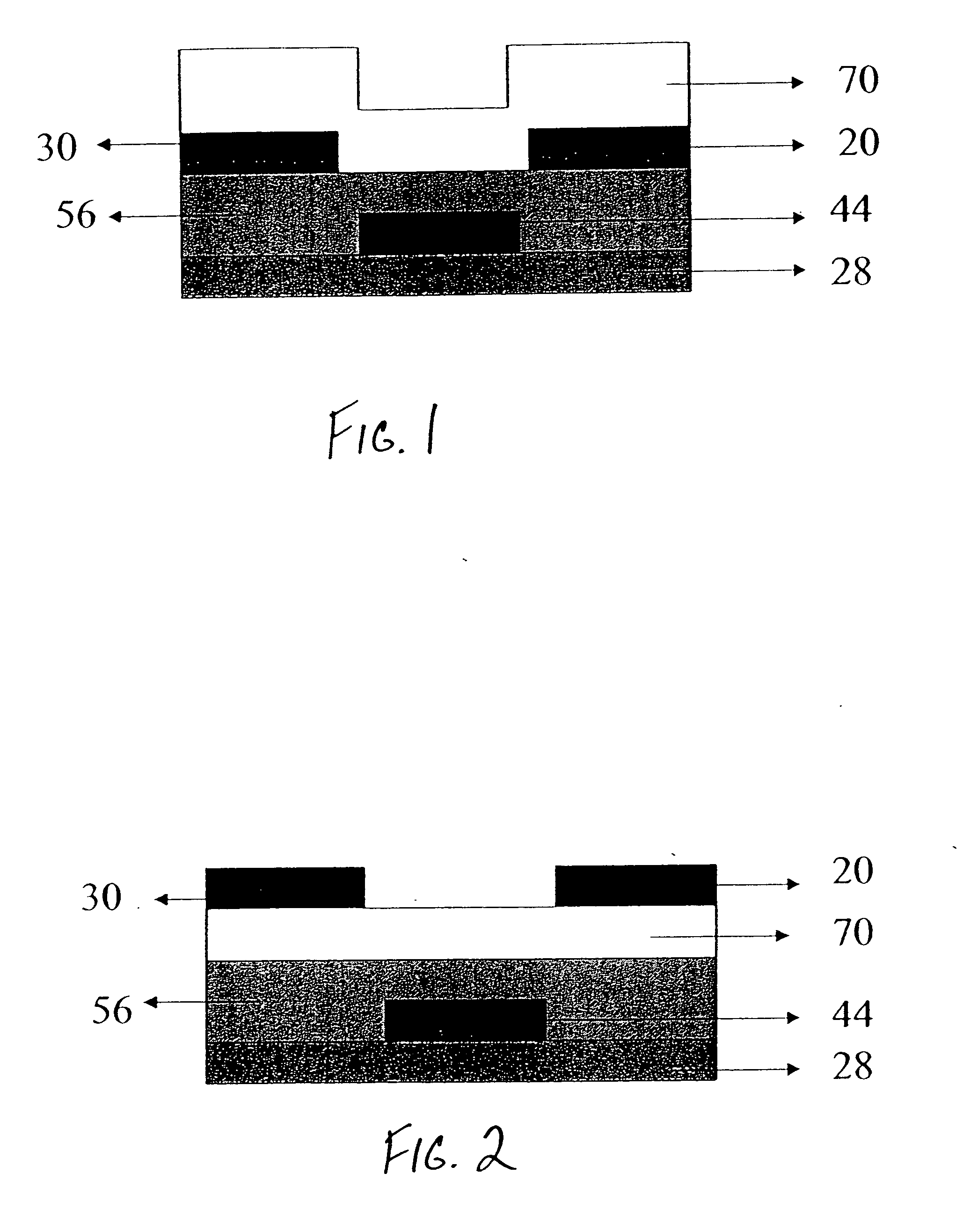
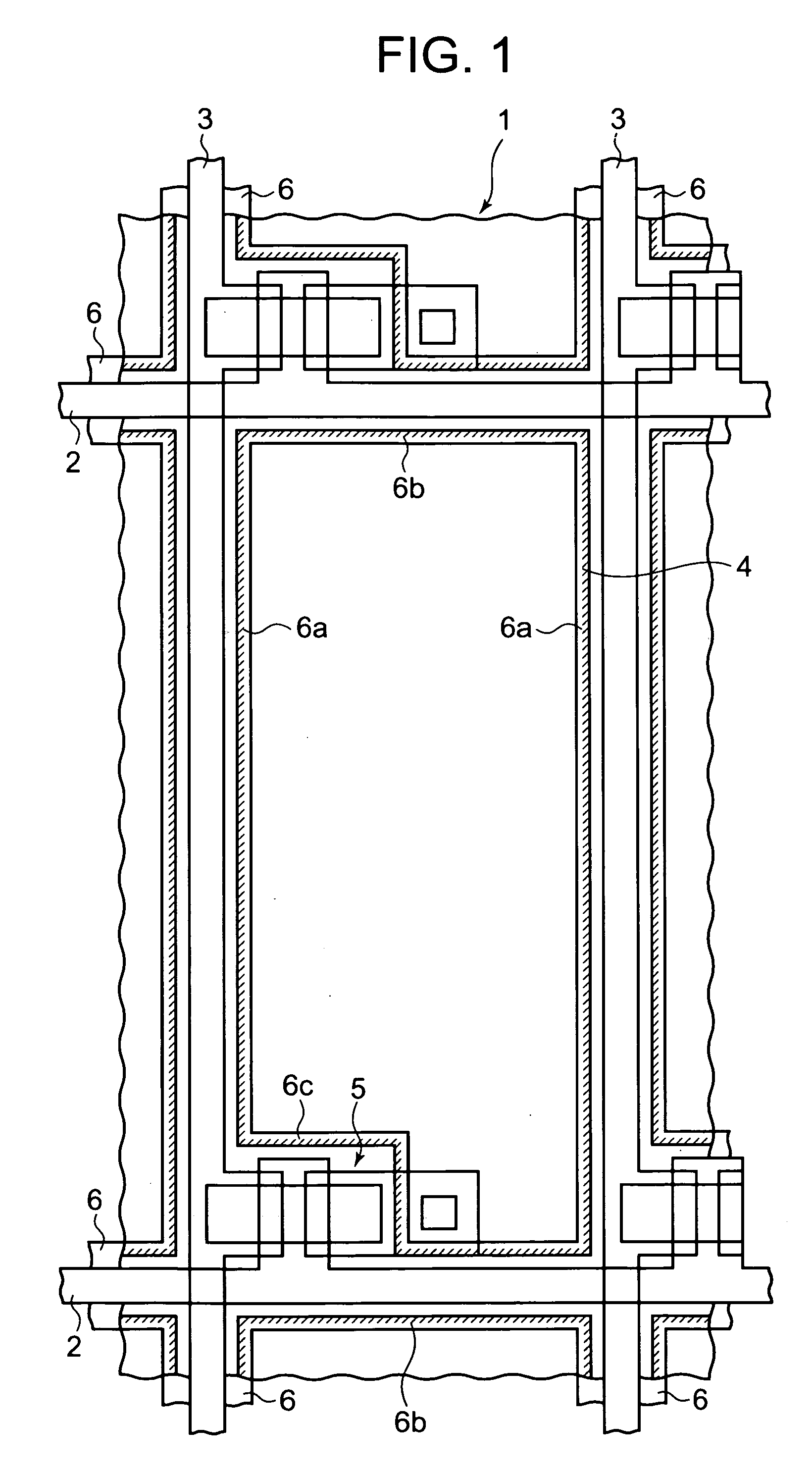
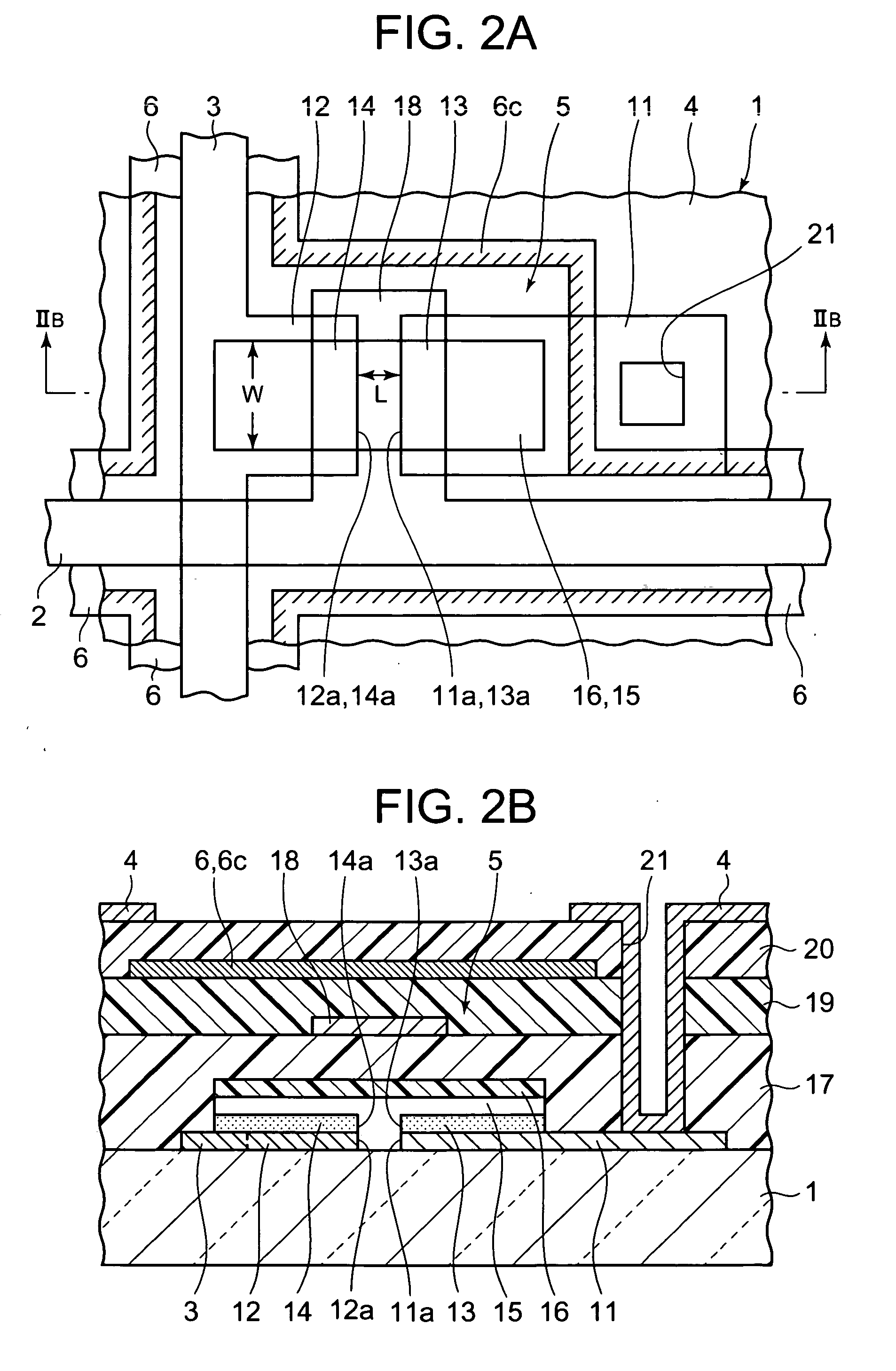
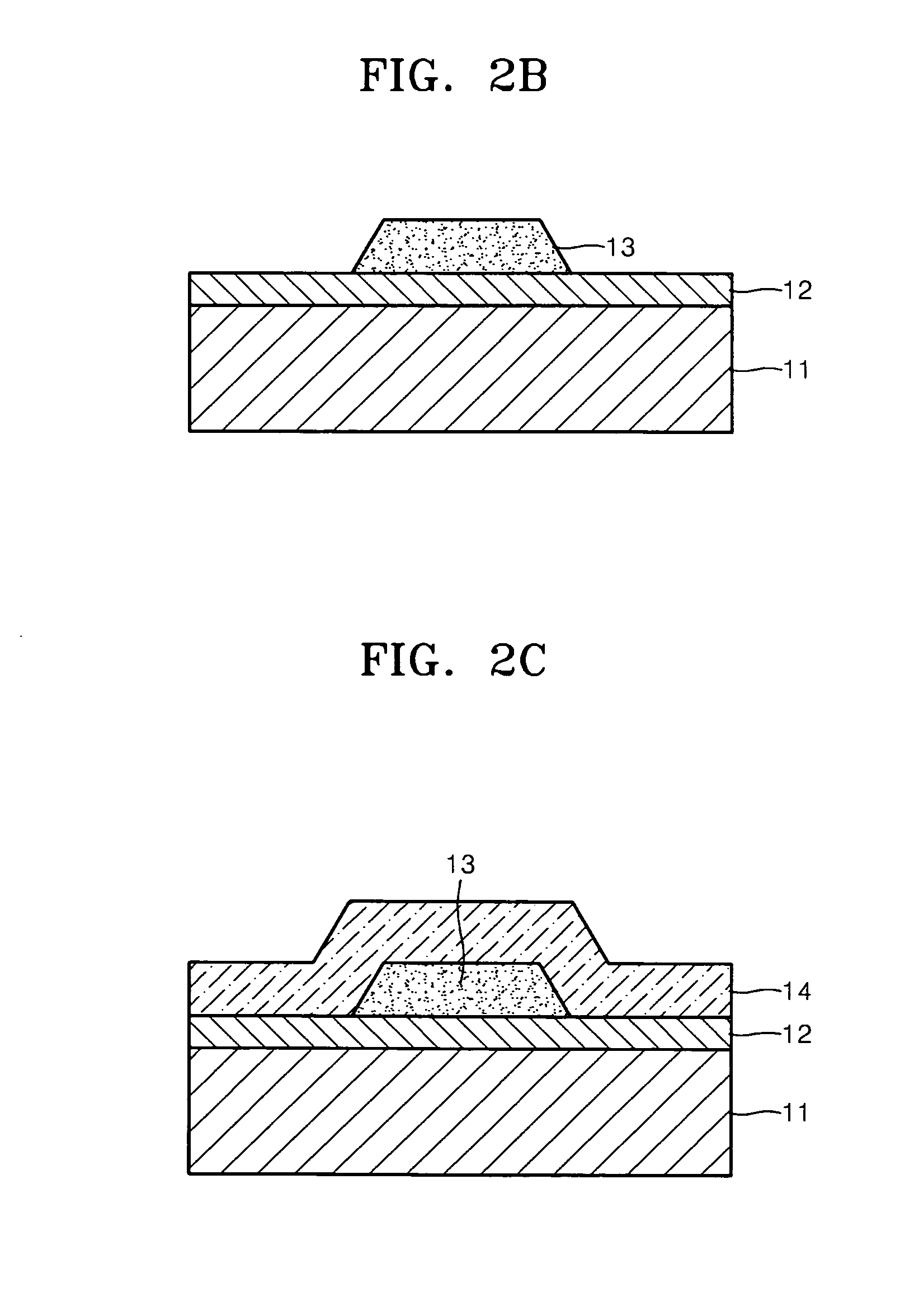
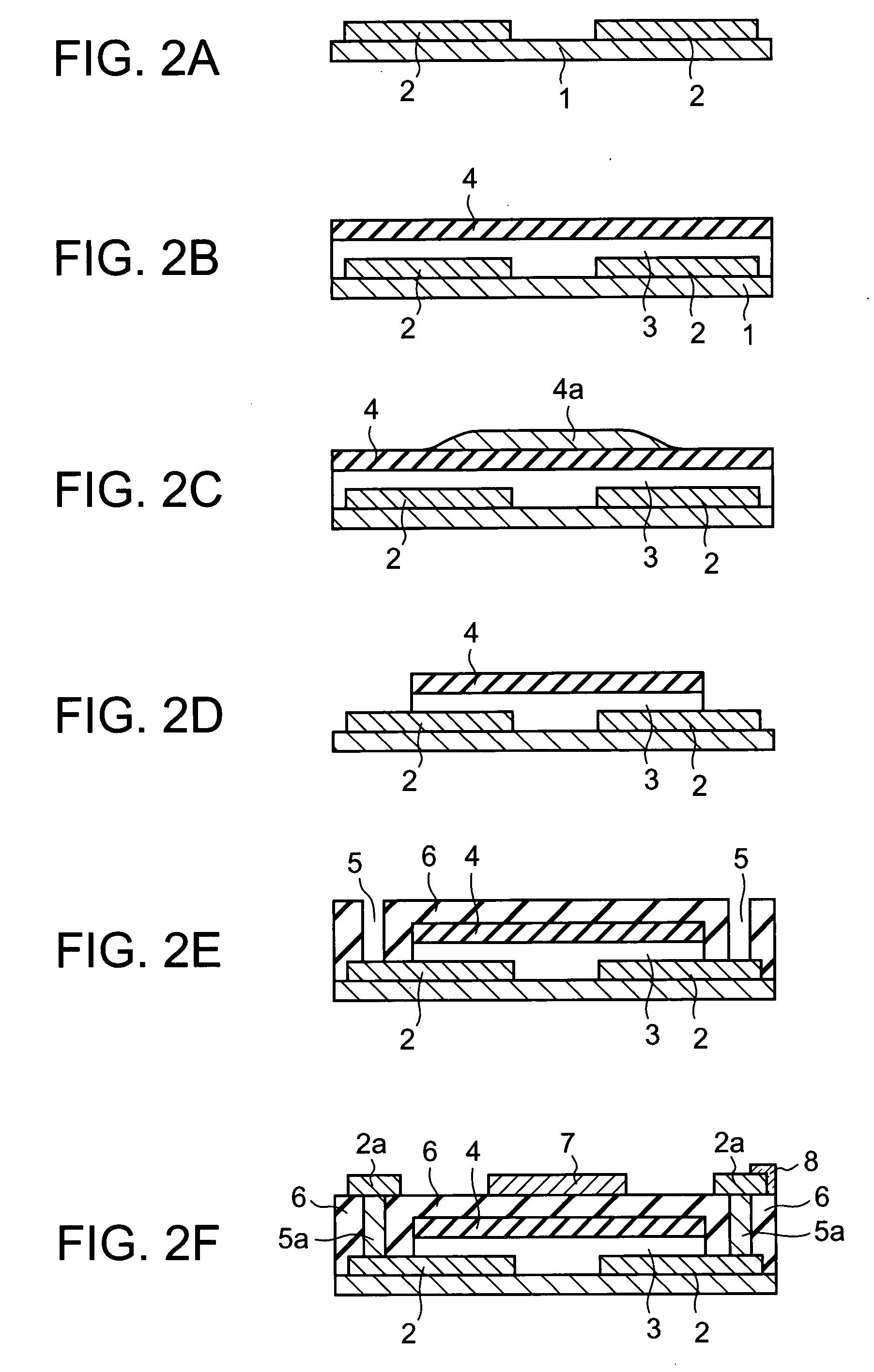
In a thin film transistor (1), a gate insulating layer (4) is formed on a gate electrode (3) formed on an insulating substrate (2). Formed on the gate insulating layer (4) is a semiconductor layer (5). Formed on the semiconductor layer (5) are a source electrode (6) and a drain electrode (7). A protective layer (8) covers them, so that the semiconductor layer (5) is blocked from an atmosphere. The semiconductor layer (5) (active layer) is made of, e.g., a semiconductor containing polycrystalline ZnO to which, e.g., a group V element is added. The protective layer (8) thus formed causes decrease of a surface level of the semiconductor layer (5). This eliminates a depletion layer spreading therewithin. Accordingly, the ZnO becomes an n-type semiconductor indicating an intrinsic resistance, with the result that too many free electrons are generated. However, the added element works on the ZnO as an accepter impurity, so that the free electrons are reduced. This decreases a gate voltage required for removal of the free electrons, so that the threshold voltage of the thin film transistor (1) becomes on the order of 0V. This allows practical use of a semiconductor device which has an active layer made of zinc oxide and which includes an protective layer for blocking the active layer from an atmosphere.
Owner:SHARP KK +2
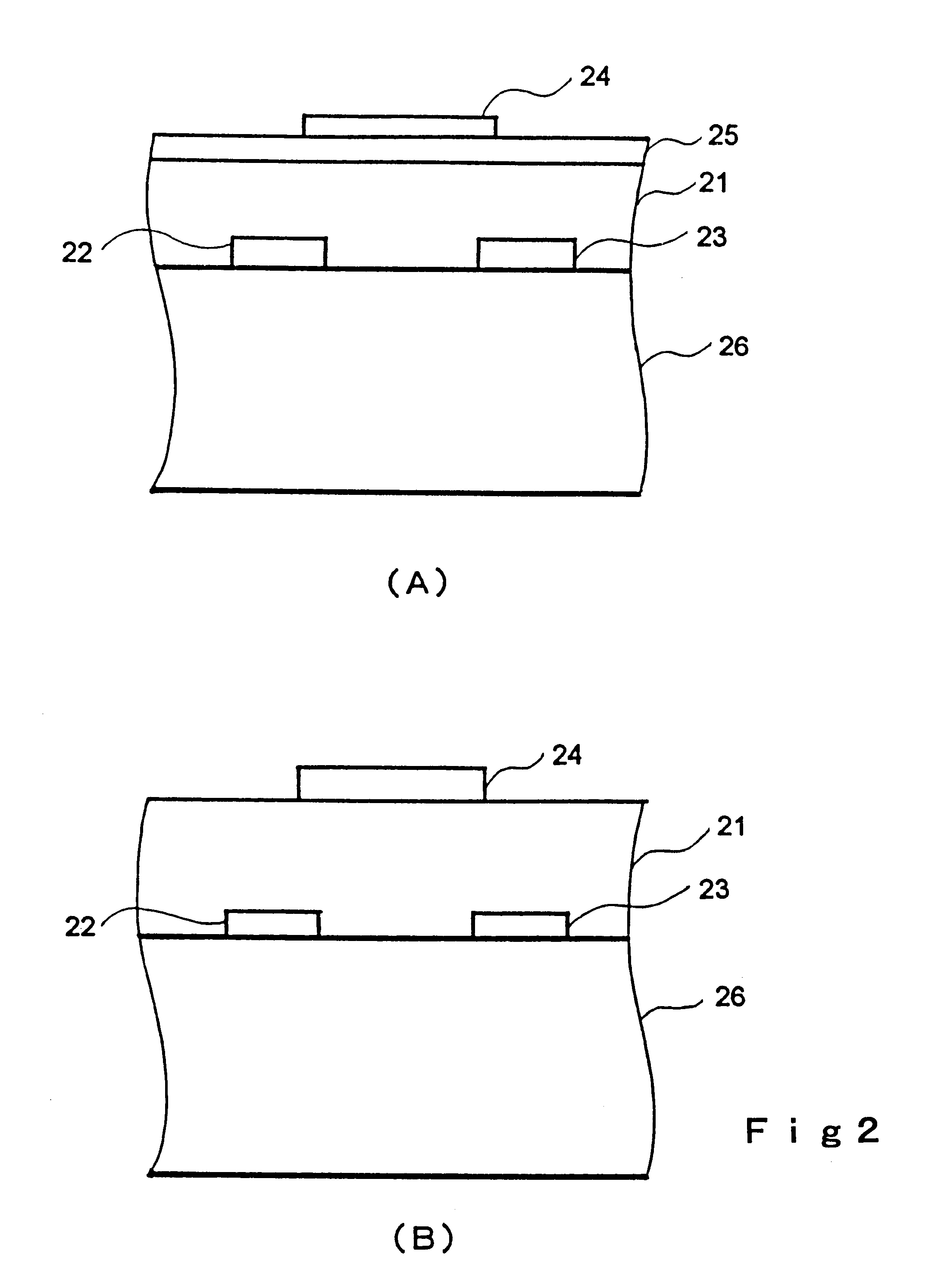
Transistor and semiconductor device
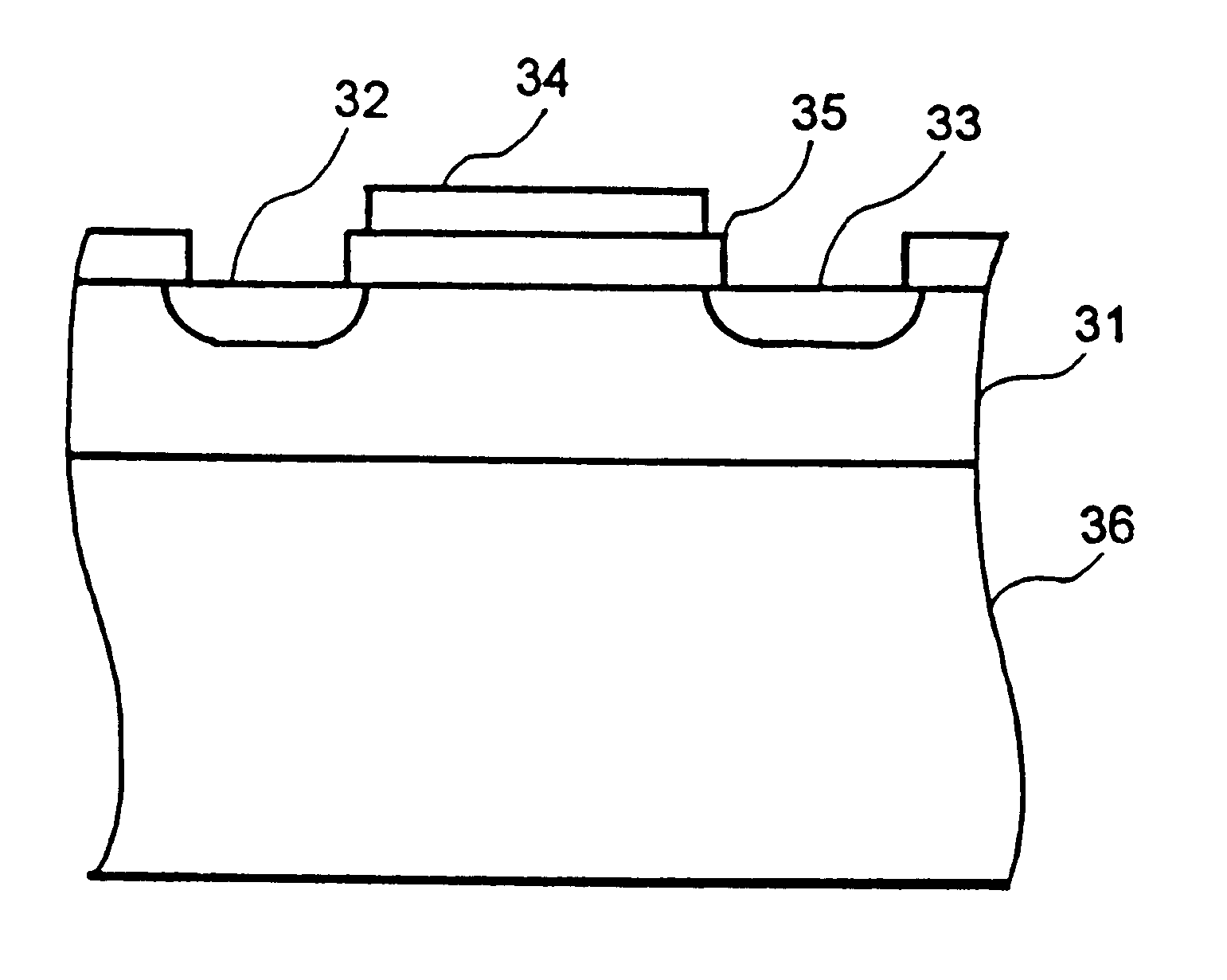
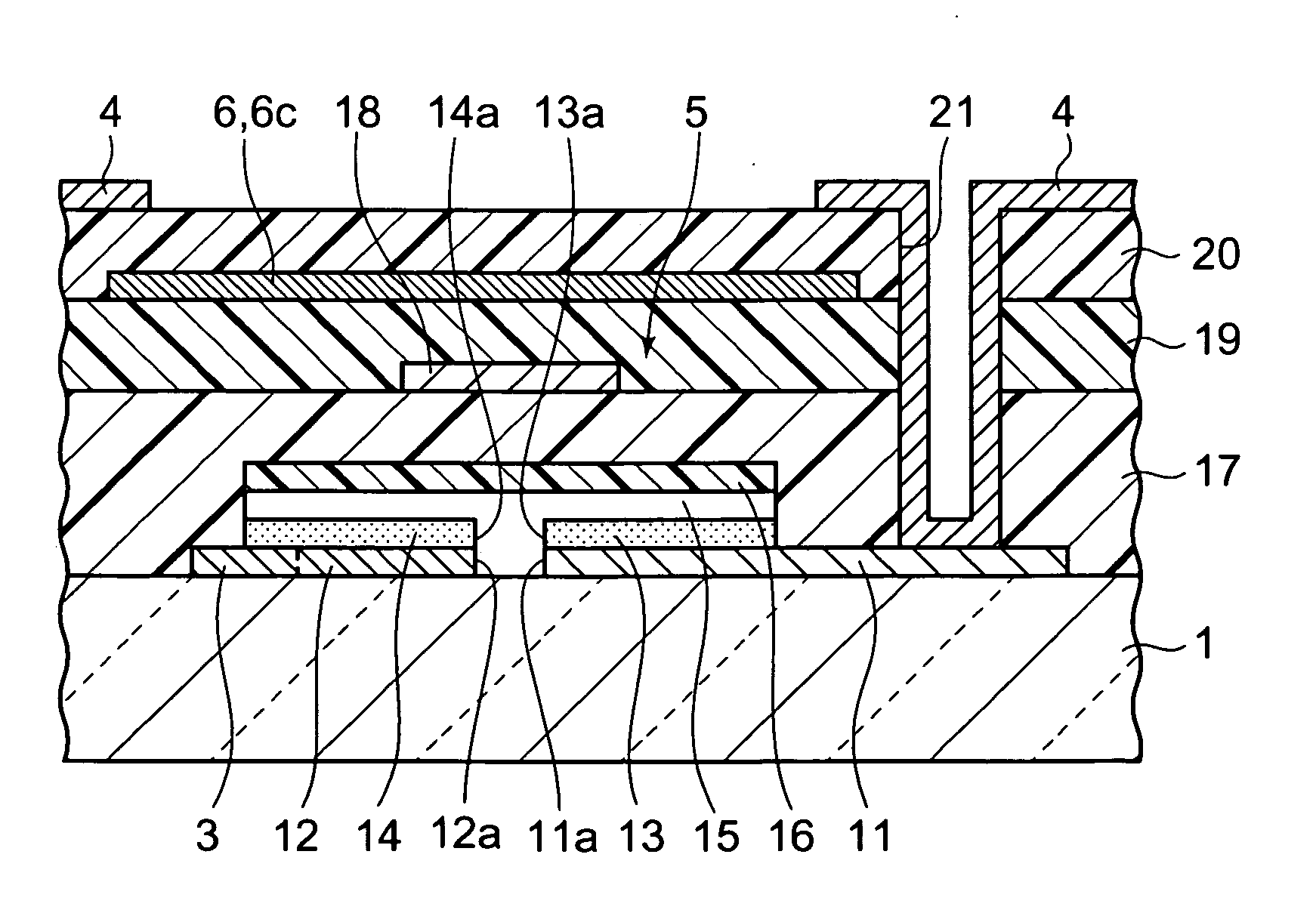
A transistor is provided, which is entirely and partially transparent by the use of a transparent channel layer made of zinc oxide or the like. A channel layer 11 formed of a transparent semiconductor such as zinc oxide ZnO. A transparent electrode is used for all of a source 12, a drain 13 and a gate 14, or a part of them. As the transparent electrode, a transparent conductive material such as conductive ZnO doped with, for example, group III elements is used. As a gate insulating layer 15, a transparent insulative material such as insulative ZnO doped with elements capable of taking a valence of one as a valence number or group V elements is used. If a substrate 16 must be transparent, for example, glass, sapphire, plastic or the like can be used as a transparent material.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
ActiveUS7402506B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsZinc
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
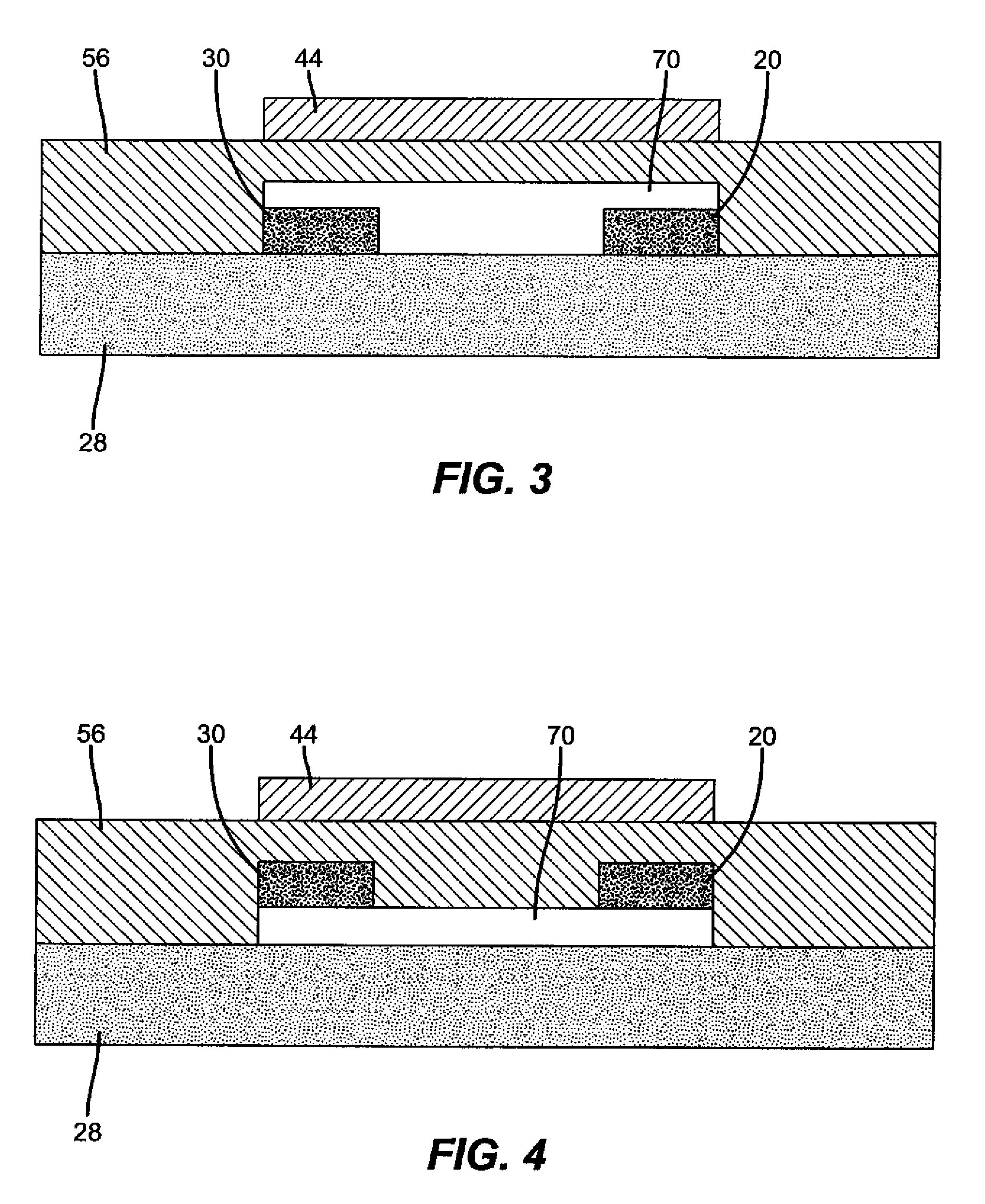
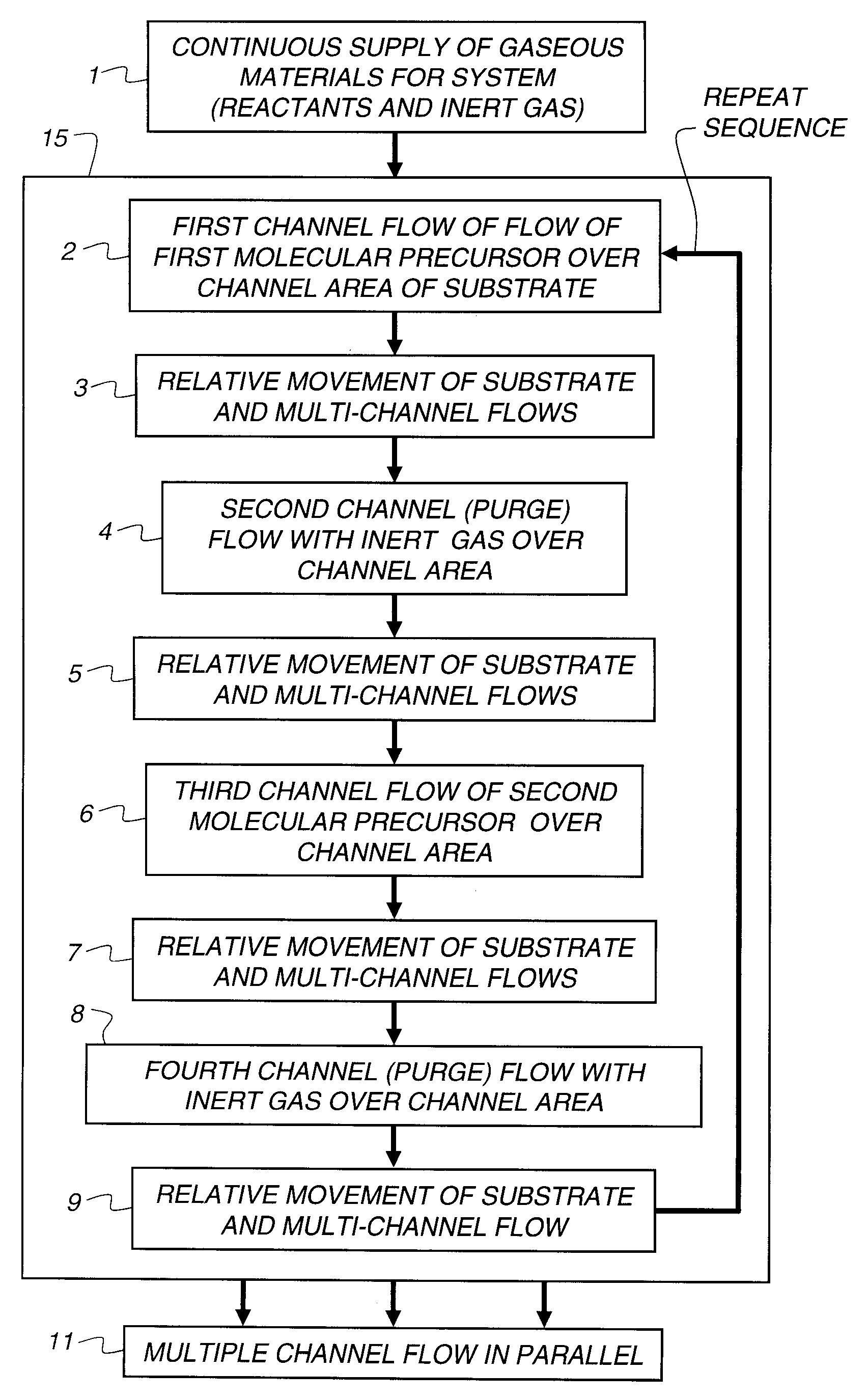
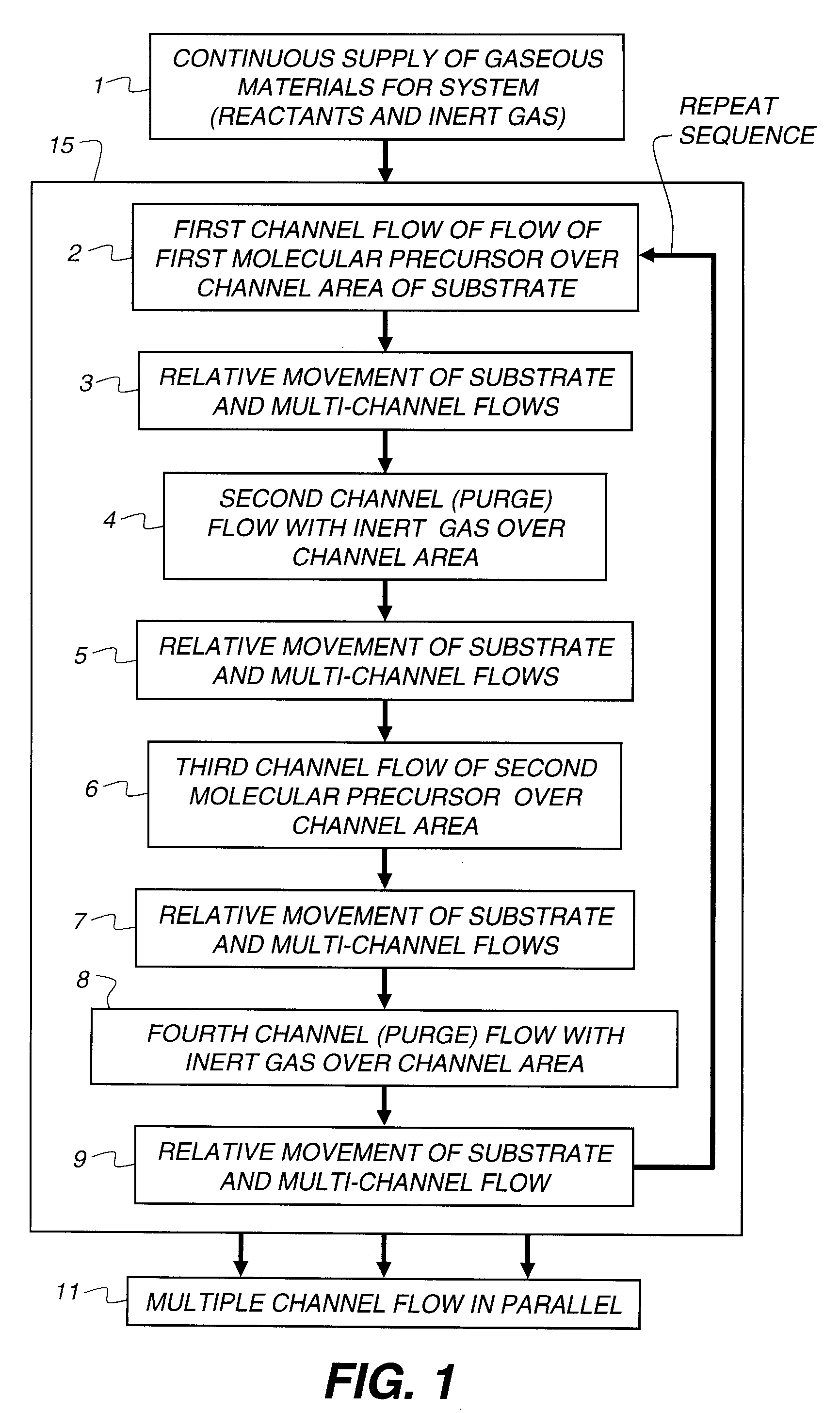
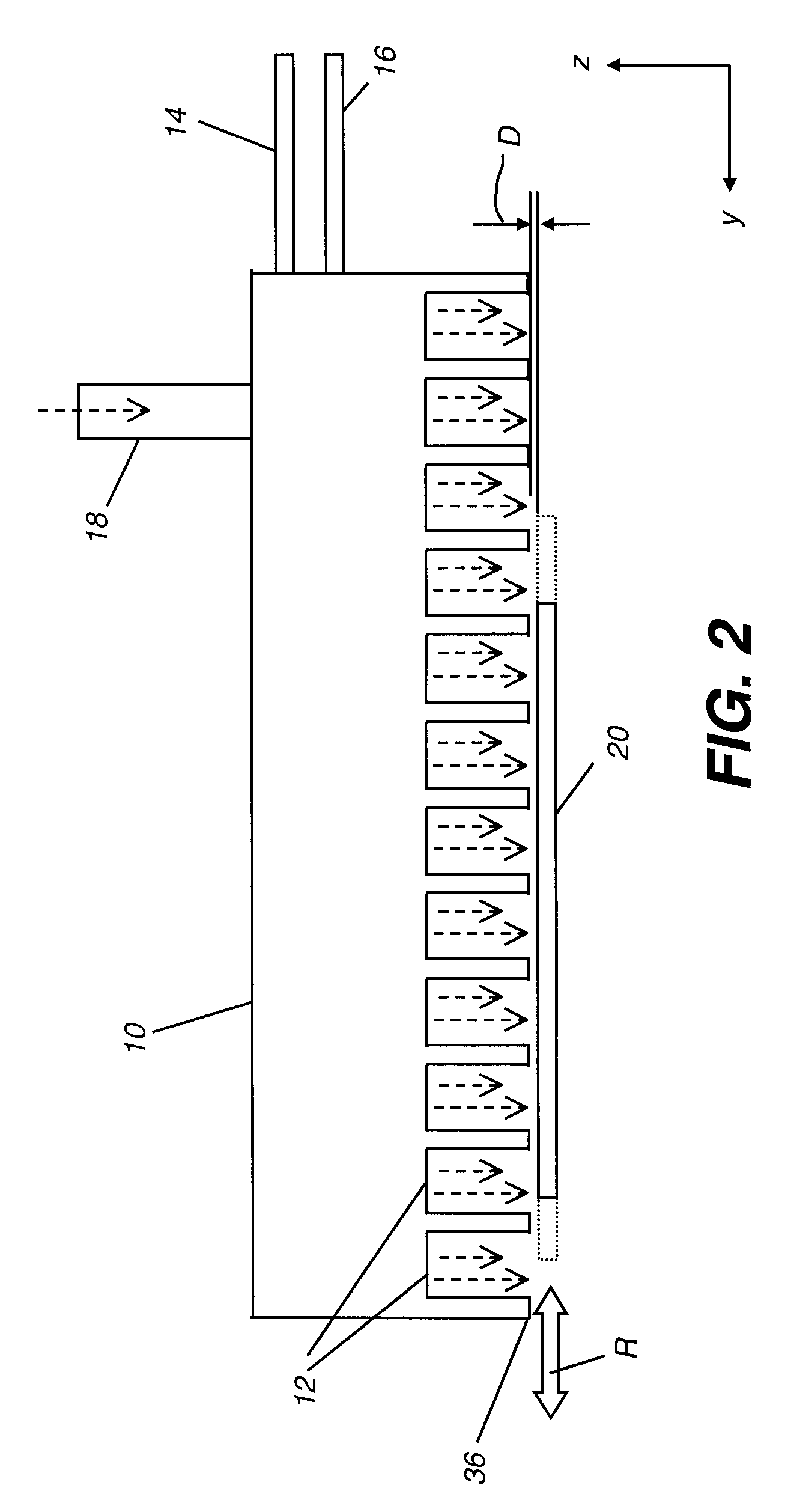
Process for atomic layer deposition
ActiveUS20080182358A1Suitable for processingAllowed to operateAdditive manufacturing apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincAtomic layer deposition
The present invention relates to a process of making a zinc-oxide-based thin film semiconductor, for use in a transistor, comprising thin film deposition onto a substrate comprising providing a plurality of gaseous materials comprising at least first, second, and third gaseous materials, wherein the first gaseous material is a zinc-containing volatile material and the second gaseous material is reactive therewith such that when one of the first or second gaseous materials are on the surface of the substrate the other of the first or second gaseous materials will react to deposit a layer of material on the substrate and wherein the third gaseous material is inert with respect to reacting with the first or second gaseous materials.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
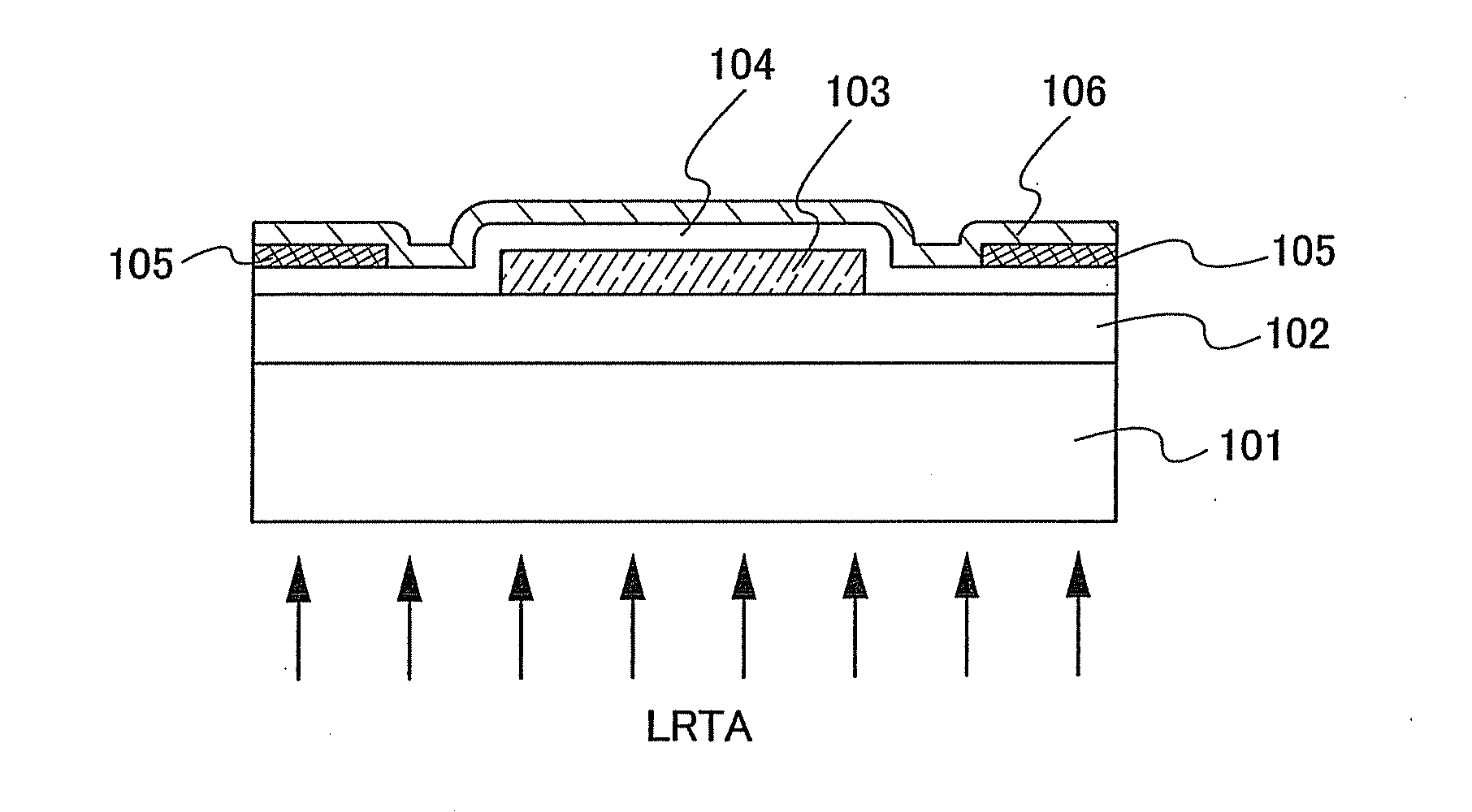
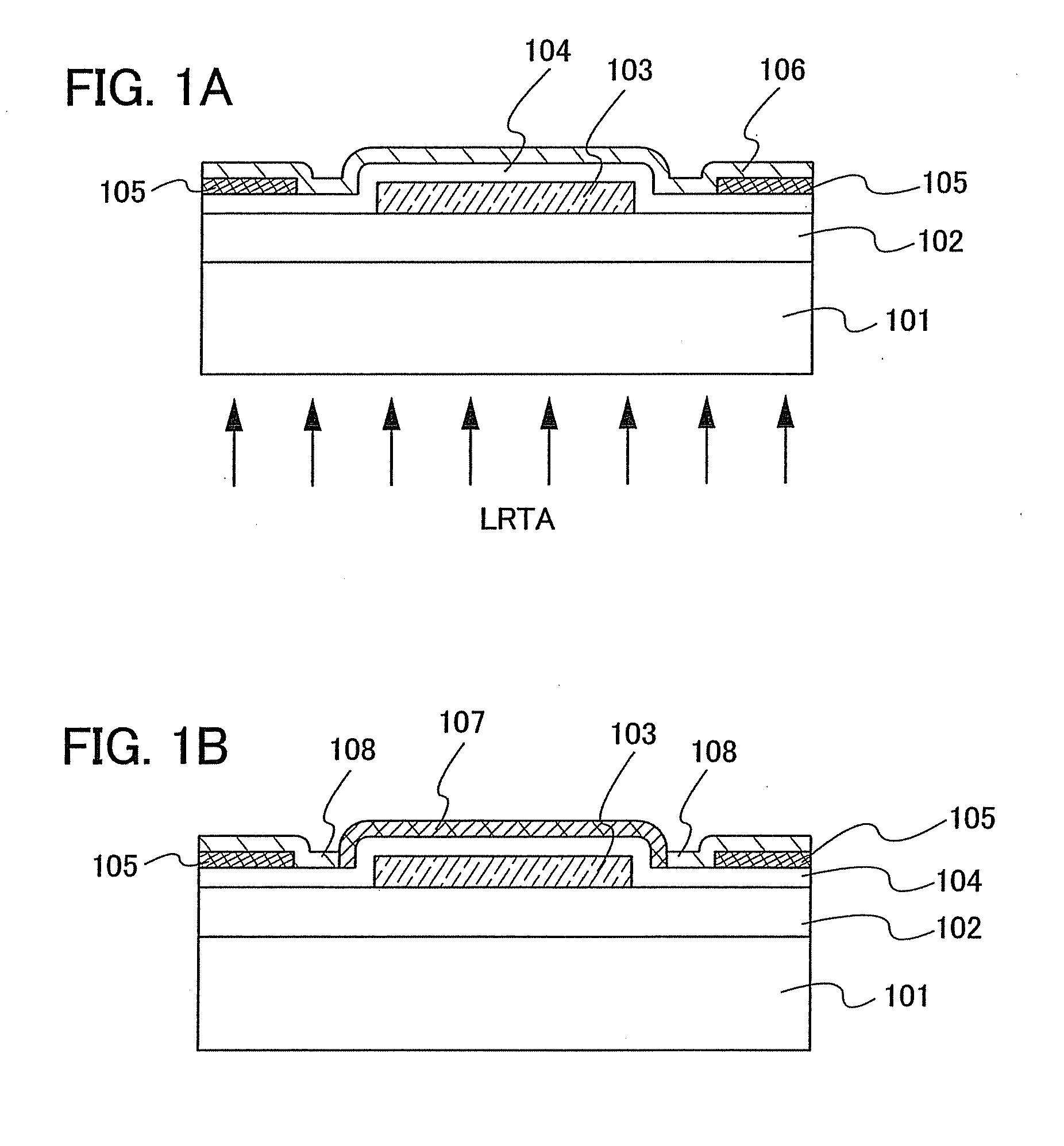
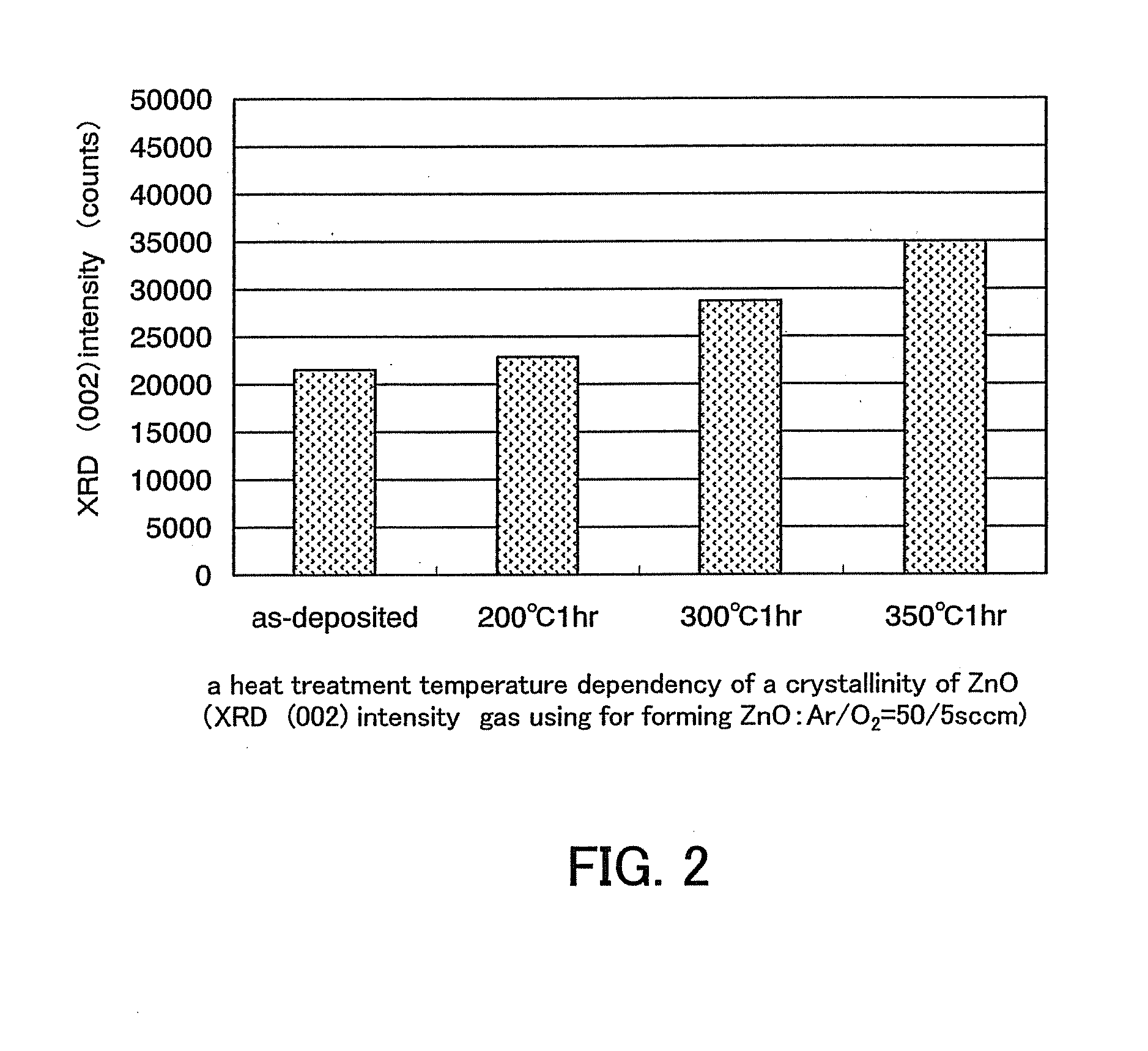
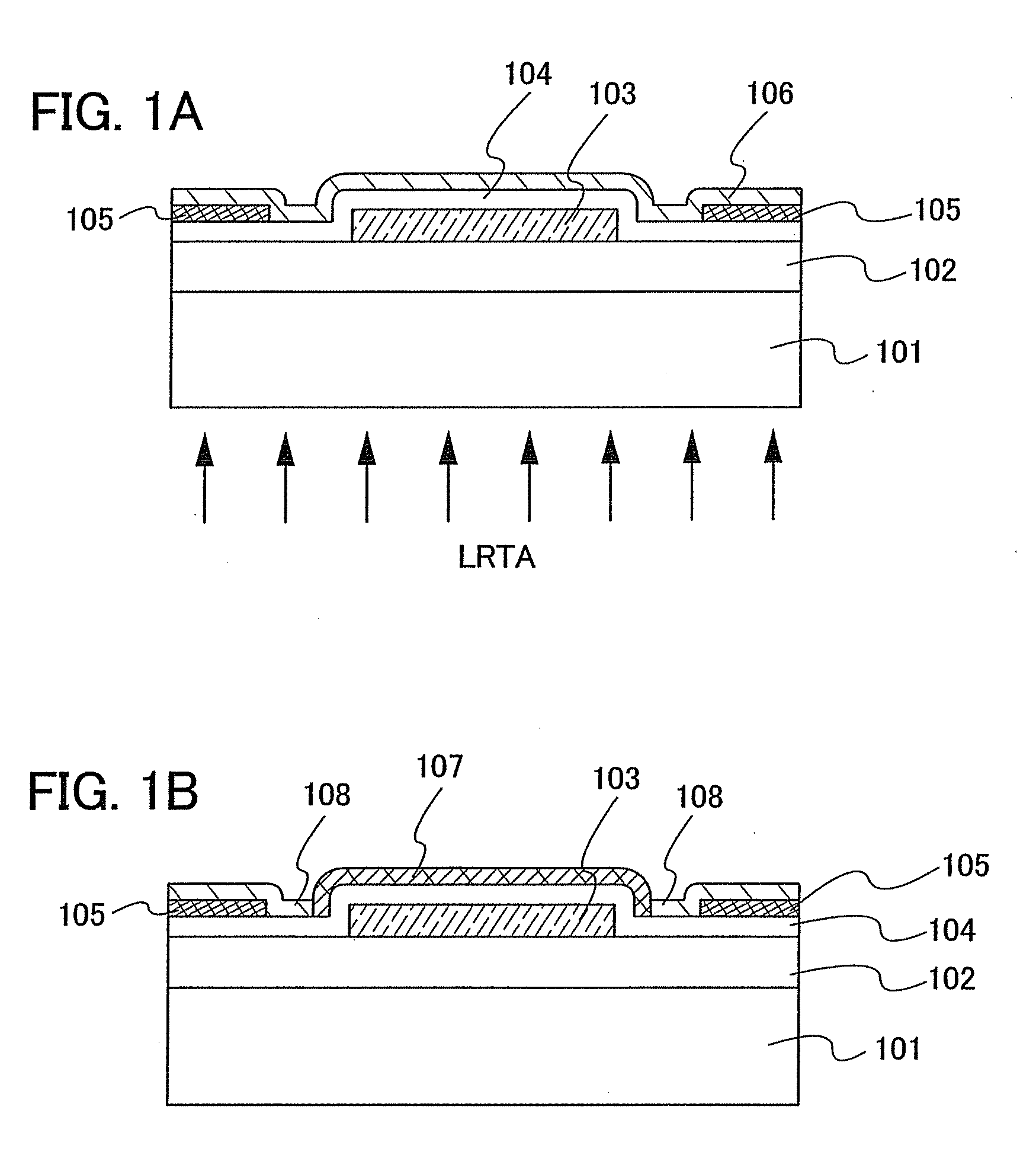
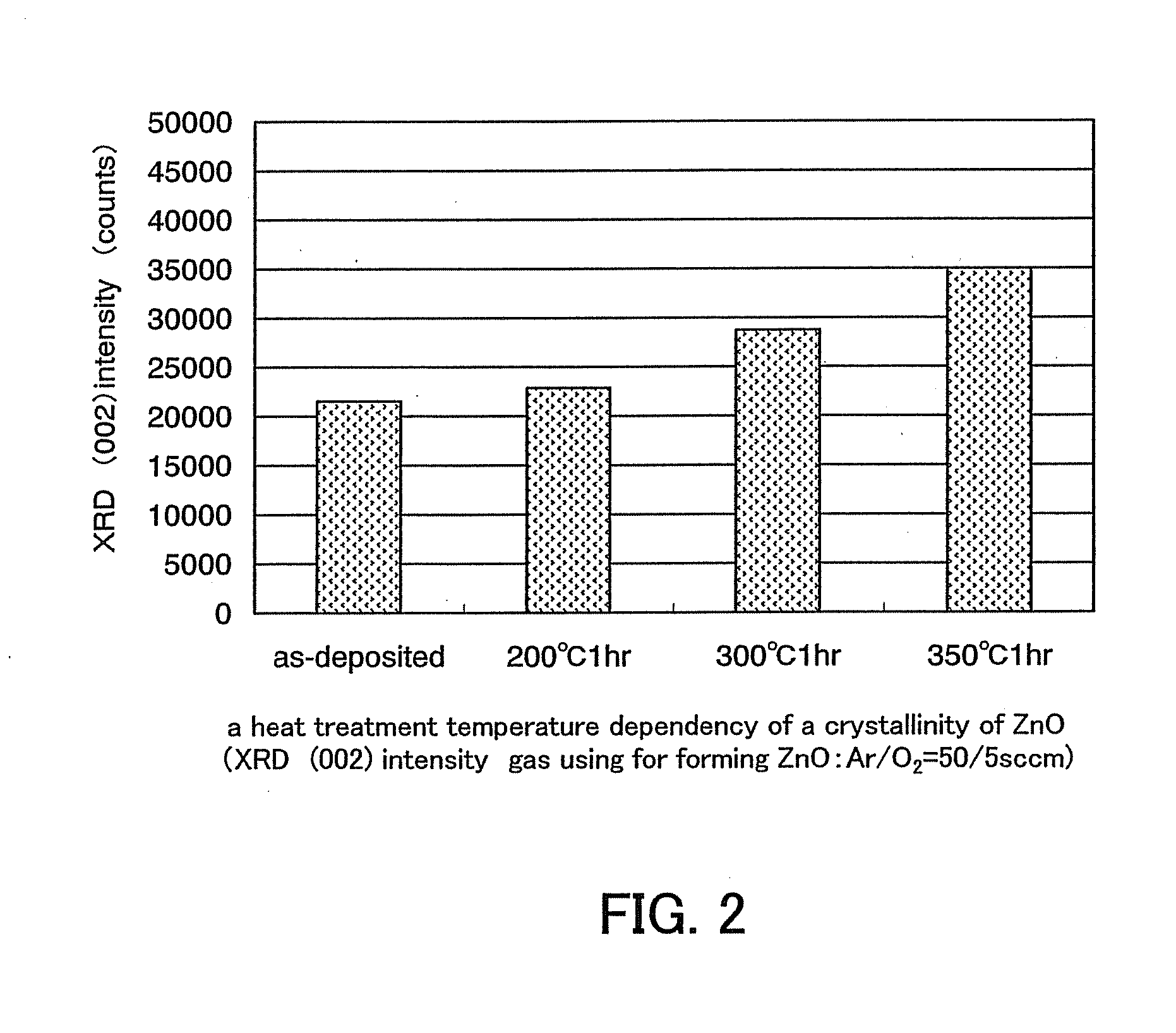
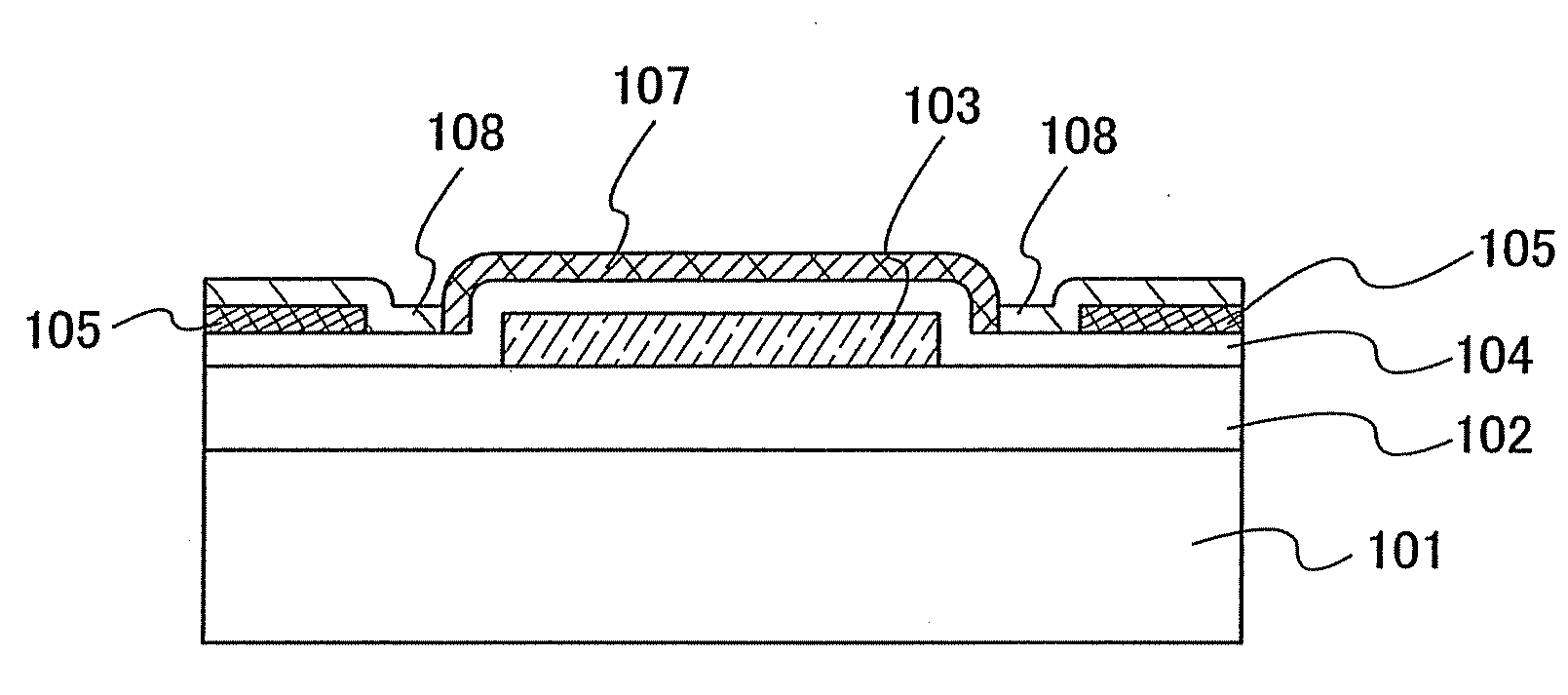
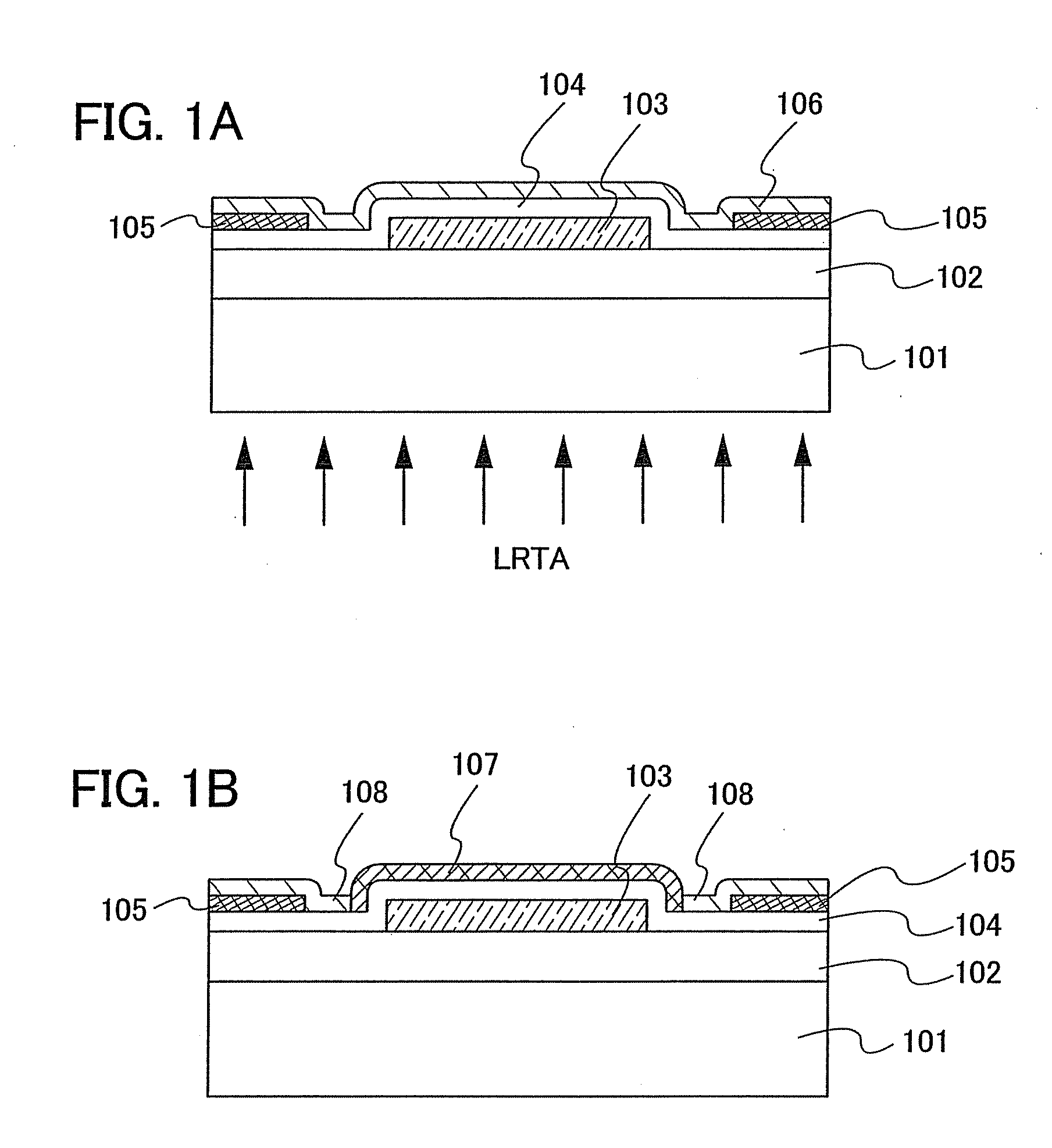
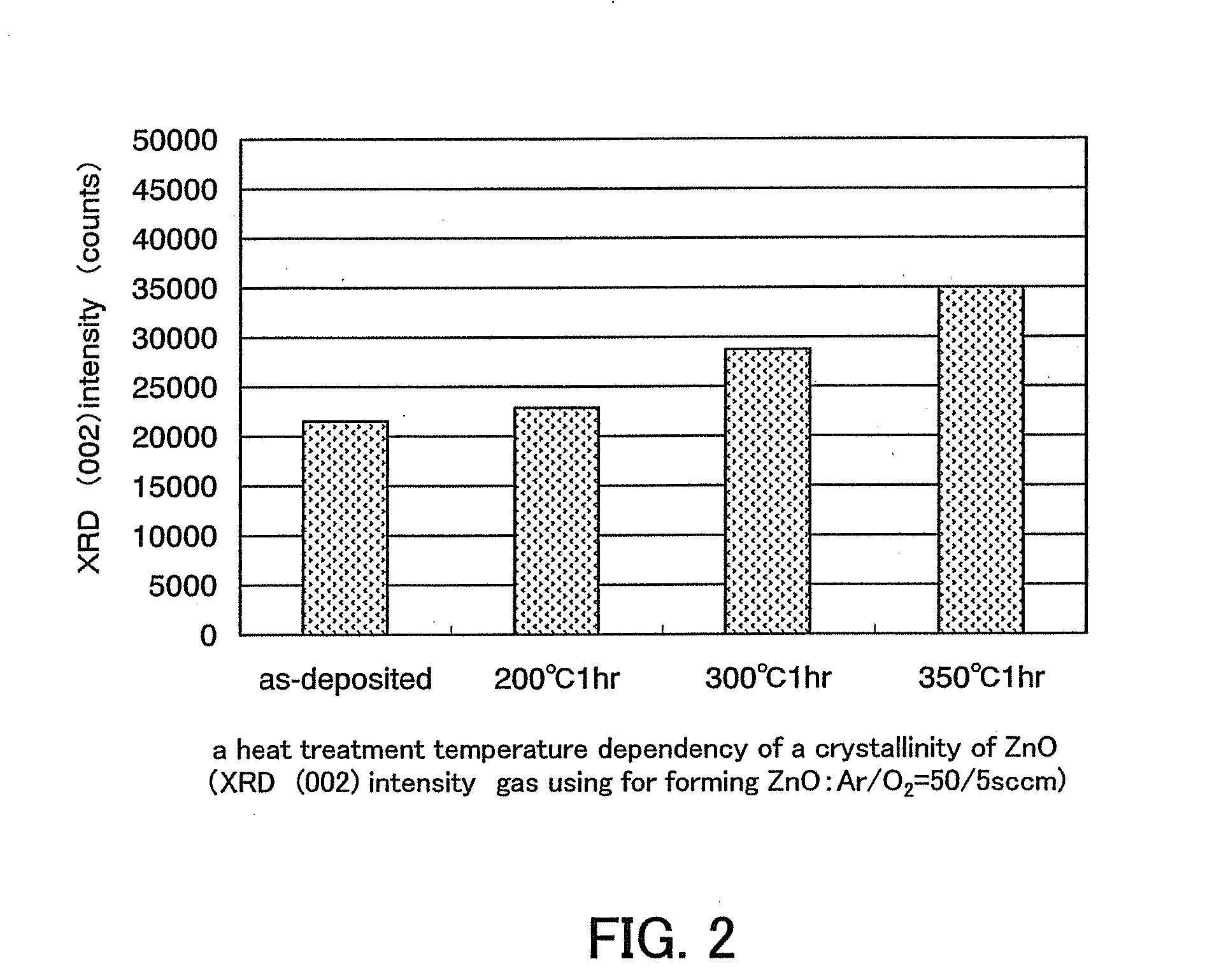
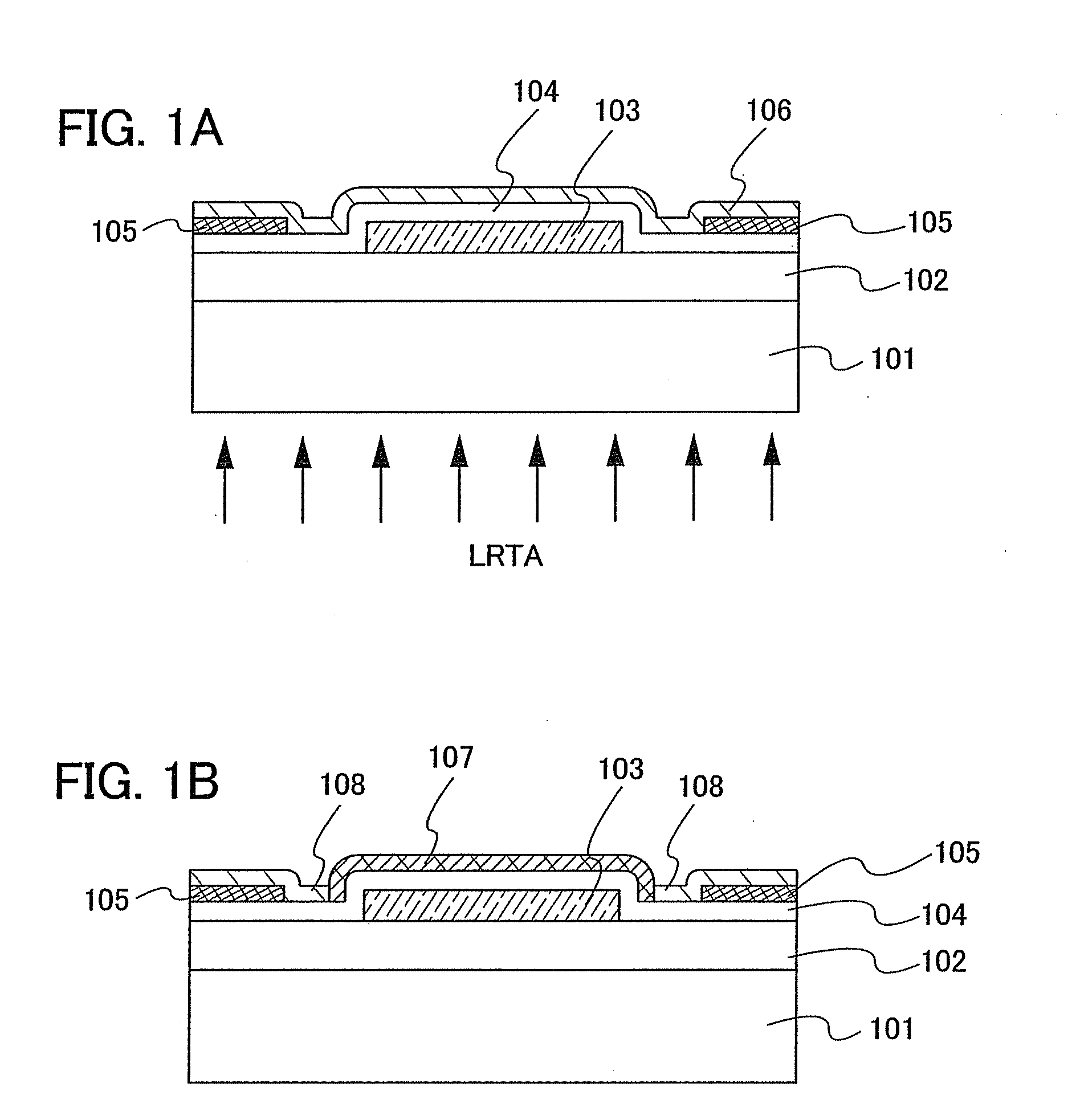
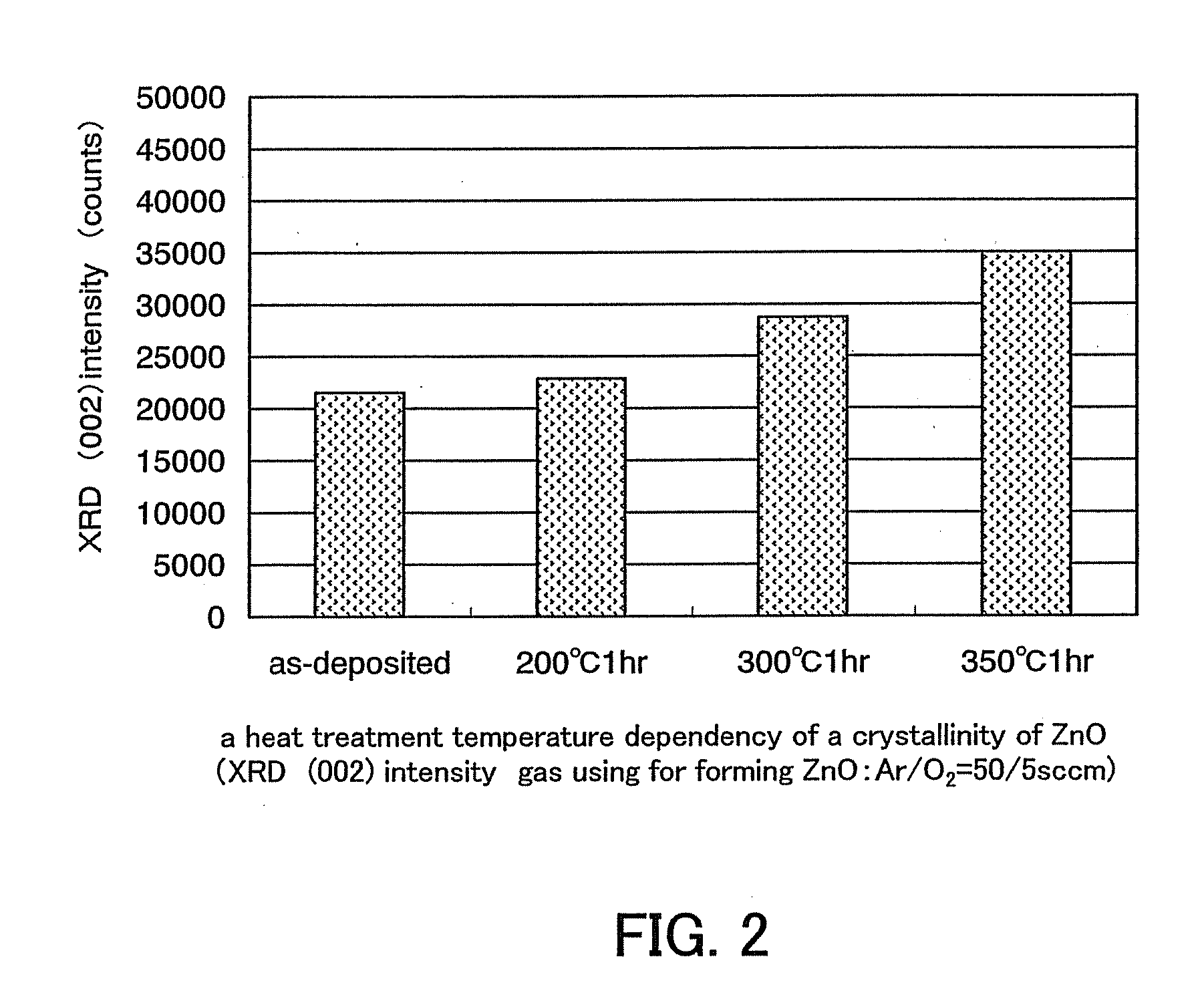
Semiconductor device including active layer made of zinc oxide with controlled orientations and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070187678A1Improve heat resistanceImprove propertiesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesZincActive layer
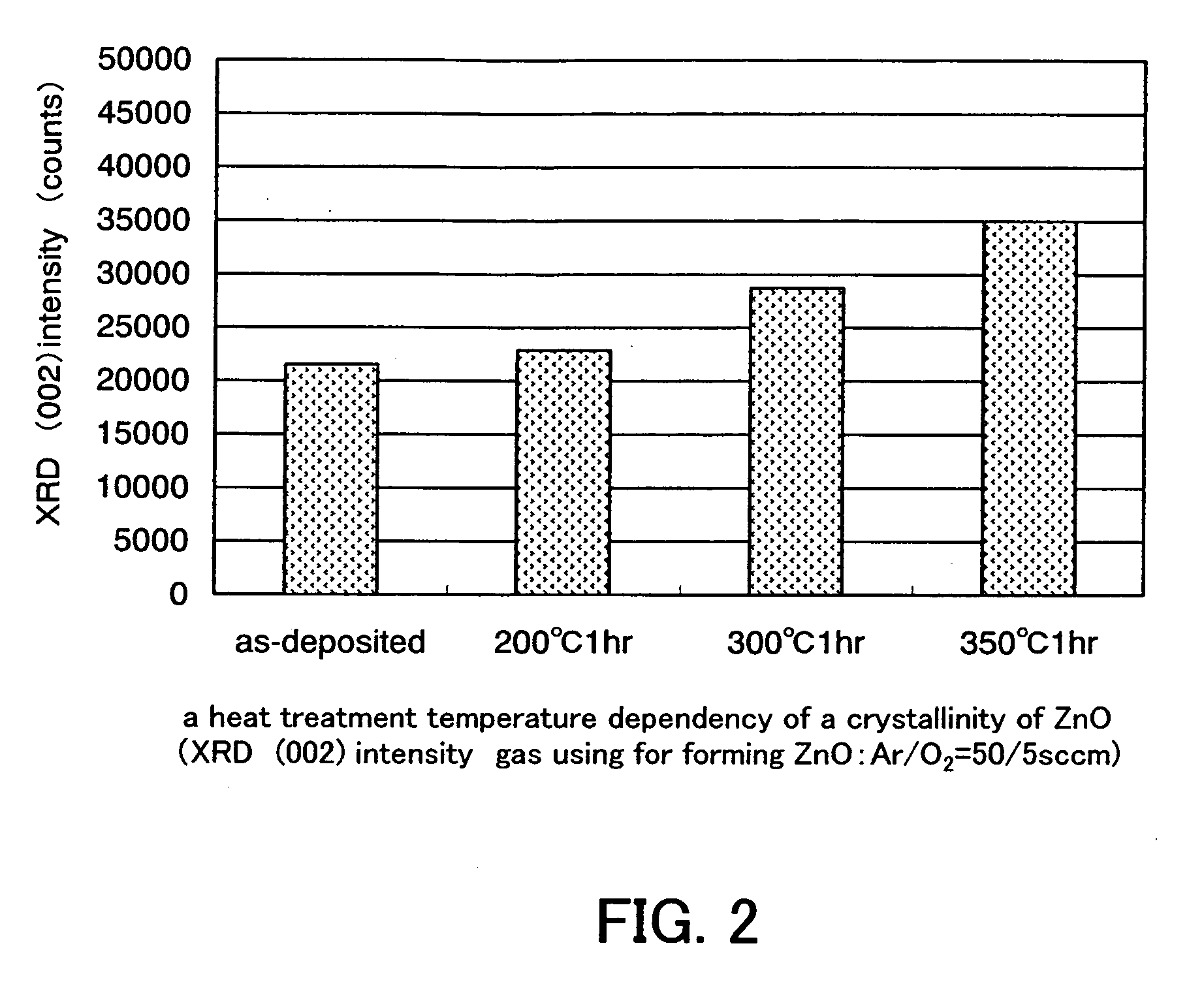
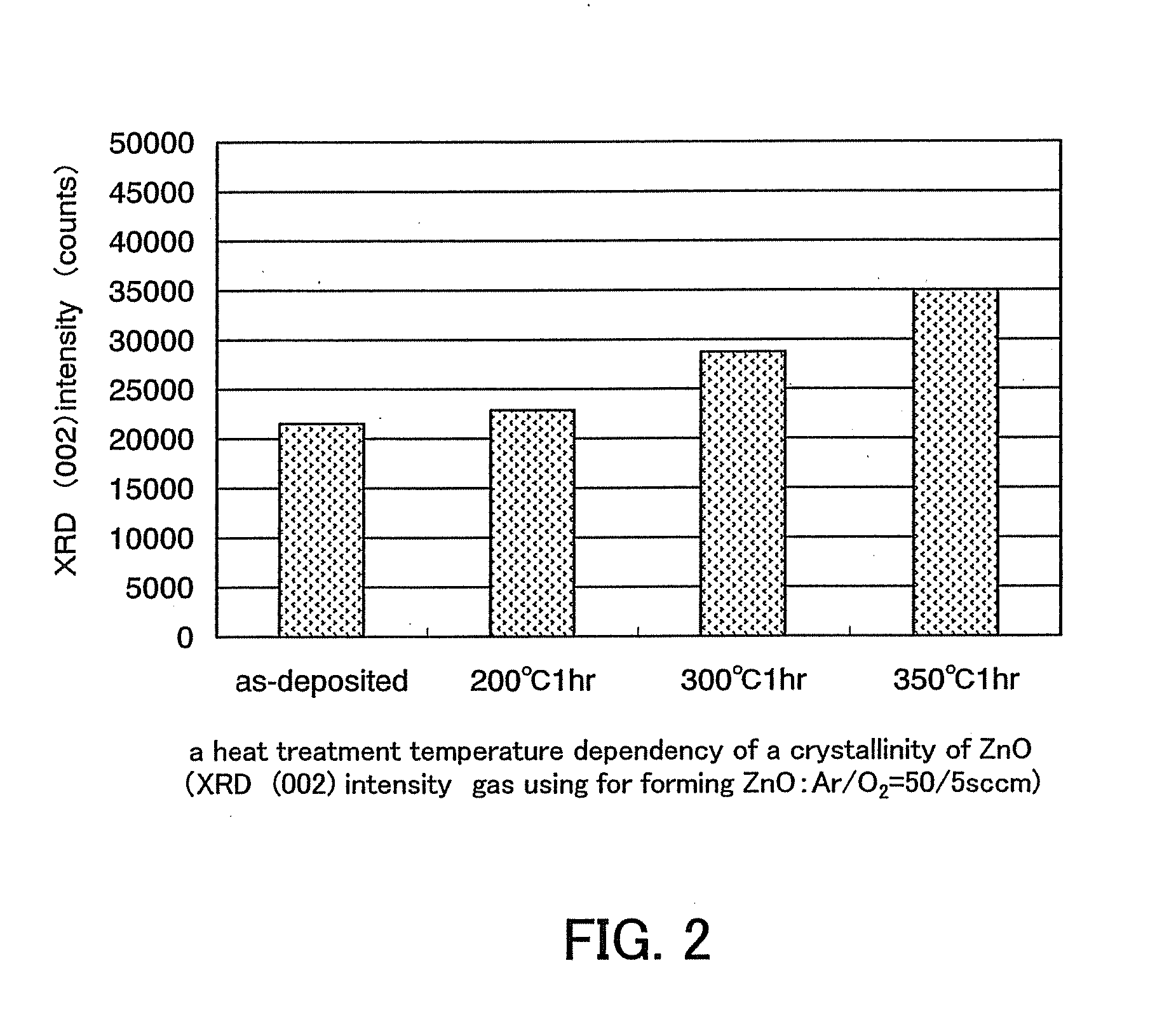
A semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor thin film layer primarily including zinc oxide having at least one orientation other than (002) orientation. The zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (002) orientation and (101) orientation. Alternatively, the zinc oxide may have a mixed orientation including (100) orientation and (101) orientation.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Semiconductor device in which zinc oxide is used as a semiconductor material and method for manufacturing the semiconductor device
ActiveUS7501293B2Improve surface smoothnessHigh crystallinityTransistorLaser detailsSemiconductor materialsDevice material
A semiconductor device having excellent crystallinity and excellent electric characteristics includes a ZnO thin film having excellent surface smoothness. ZnO-based thin films (an n-type contact layer, an n-type clad layer, an active layer, a p-type clad layer, and a p-type contact layer) primarily including ZnO are formed sequentially by an ECR sputtering method or other suitable method on a zinc-polar surface of a ZnO substrate. A transparent electrode and a p-side electrode are formed by an evaporation method or other suitable method on a surface of the p-type contact layer, and an n-side electrode is formed on an oxygen-polar surface of the ZnO substrate.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Thin film transistor and organic light-emitting display device having the thin film transistor
InactiveUS20080224133A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenDisplay device
Disclosed is a thin film transistor including a P-type semiconductor layer, and an organic light-emitting display device having the thin film transistor. The present invention provides a thin film transistor including a substrate, a semiconductor layer, and a gate electrode and a source / drain electrode formed on the substrate, wherein the semiconductor layer is composed of P-type ZnO:N layers through a reaction of a mono-nitrogen gas with a zinc precursor, and the ZnO:N layer includes an un-reacted impurity element at a content of 3 at % or less.
Owner:SAMSUNG MOBILE DISPLAY CO LTD
High-electron mobility transistor with zinc oxide
InactiveUS7105868B2Increase heightHigh electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSchottky barrierField-effect transistor
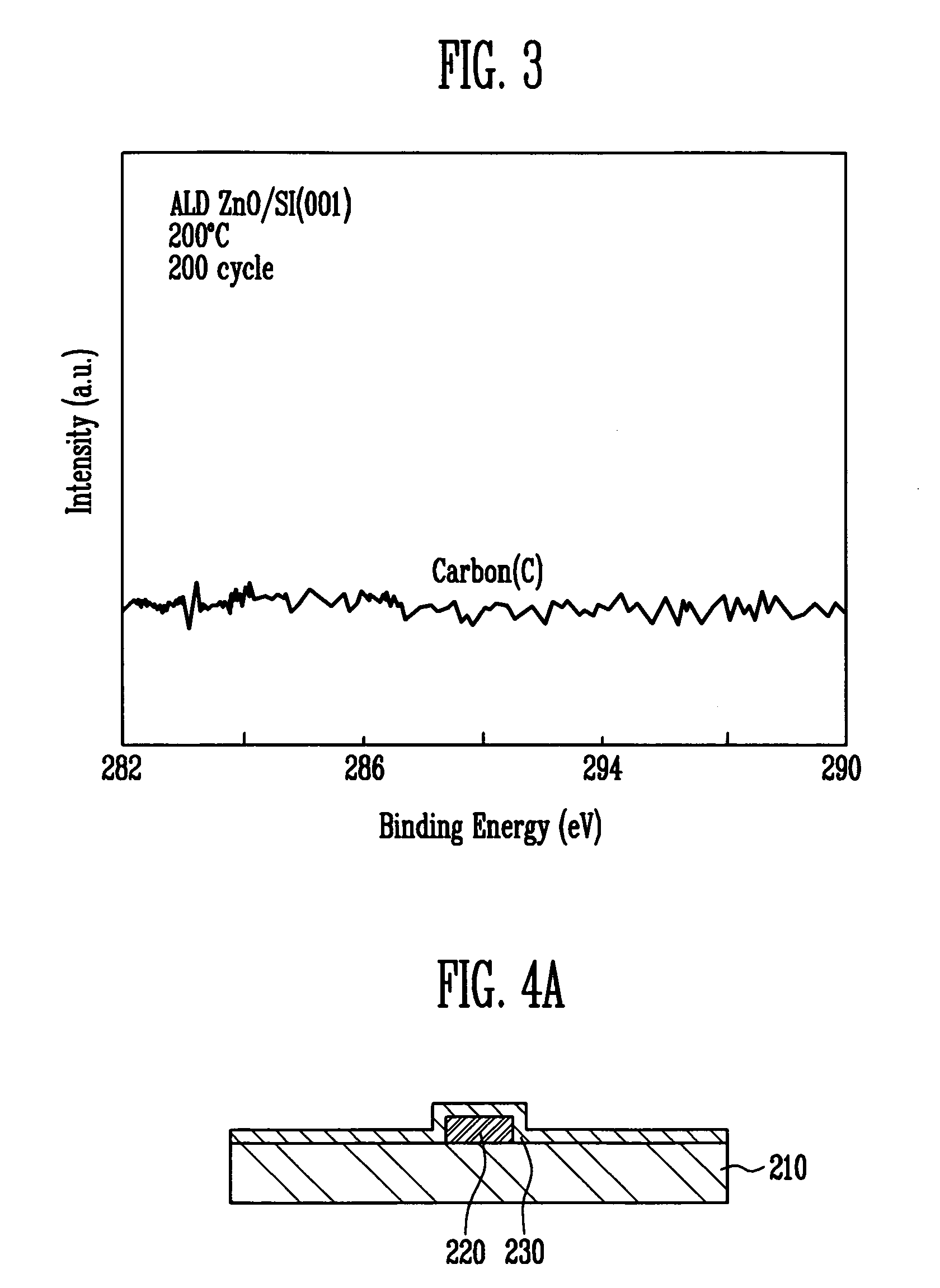
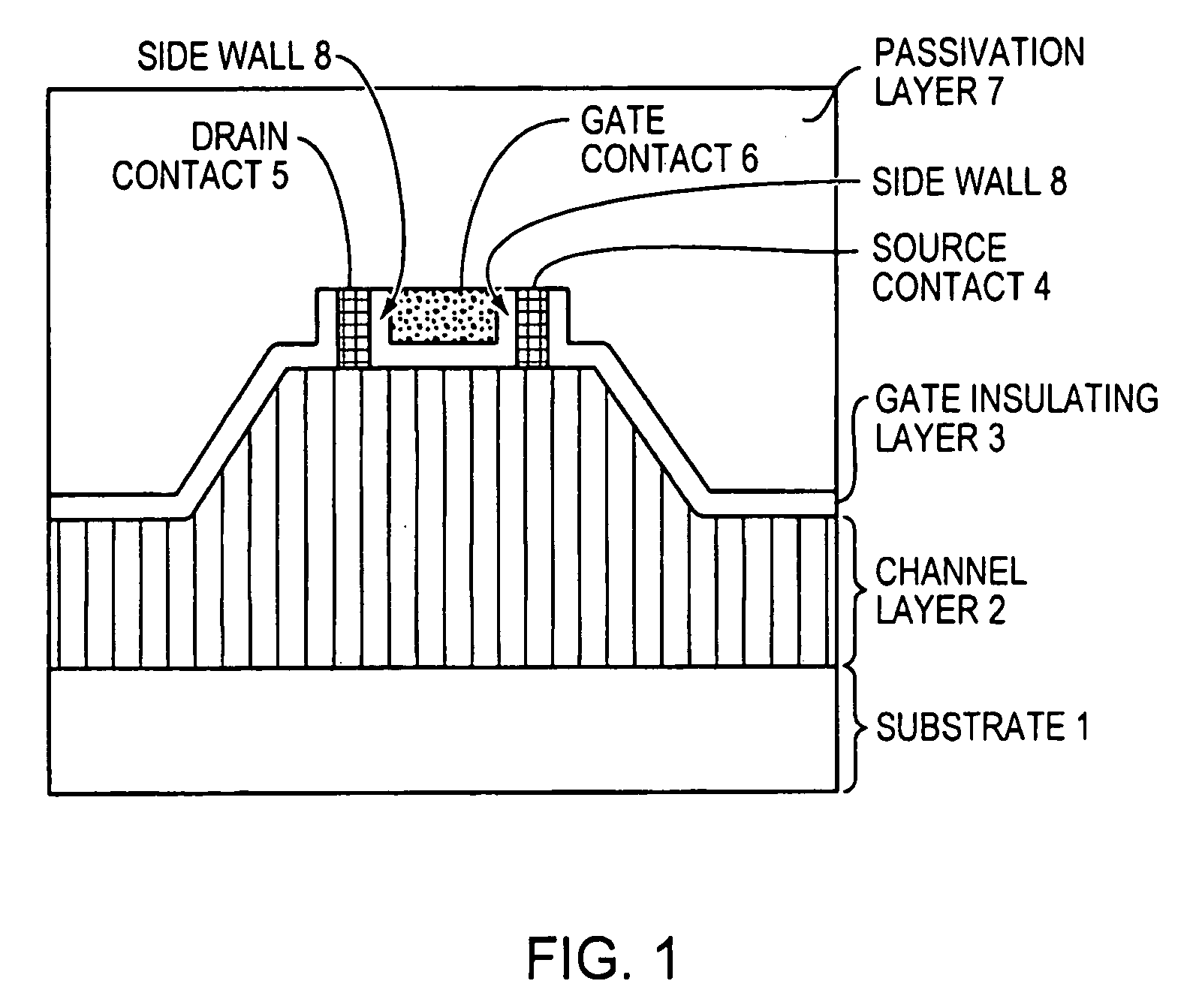
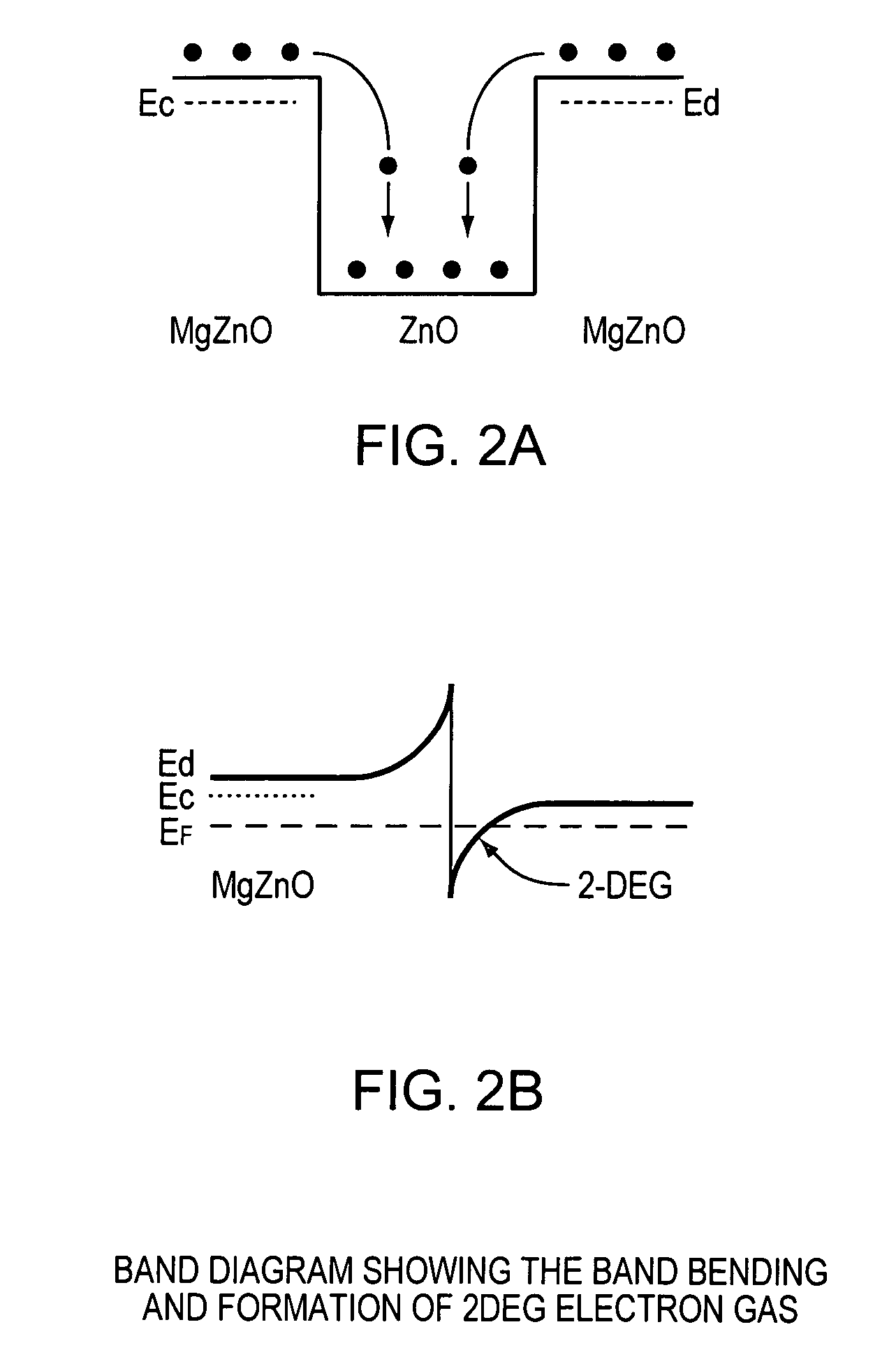
A zinc oxide (ZnO) field effect transistor exhibits large input amplitude by using a gate insulating layer. A channel layer and the gate insulating layer are sequentially laminated on a substrate. A gate electrode is formed on the gate insulating layer. A source contact and a drain contact are disposed at the both sides of the gate contact and are electrically connected to the channel layer via openings. The channel layer is formed from n-type ZnO. The gate insulating layer is made from aluminum nitride / aluminum gallium nitride (AlN / AlGaN) or magnesium zinc oxide (MgZnO), which exhibits excellent insulation characteristics, thus increasing the Schottky barrier and achieving large input amplitude. If the FET is operated in the enhancement mode, it is operable in a manner similar to a silicon metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (Si-MOS-type FET), resulting in the formation of an inversion layer.
Owner:NAUSE CATHERINE D
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
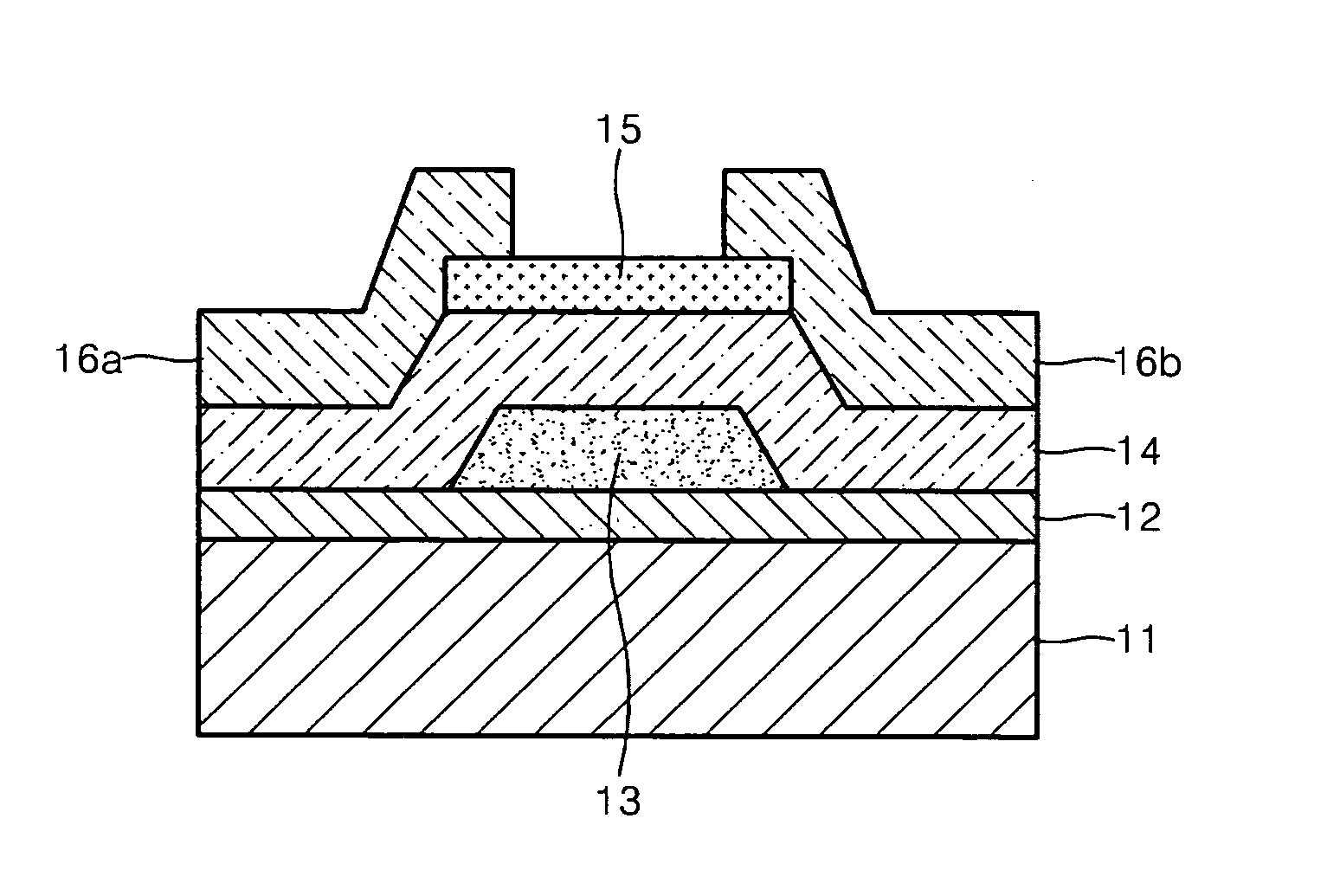
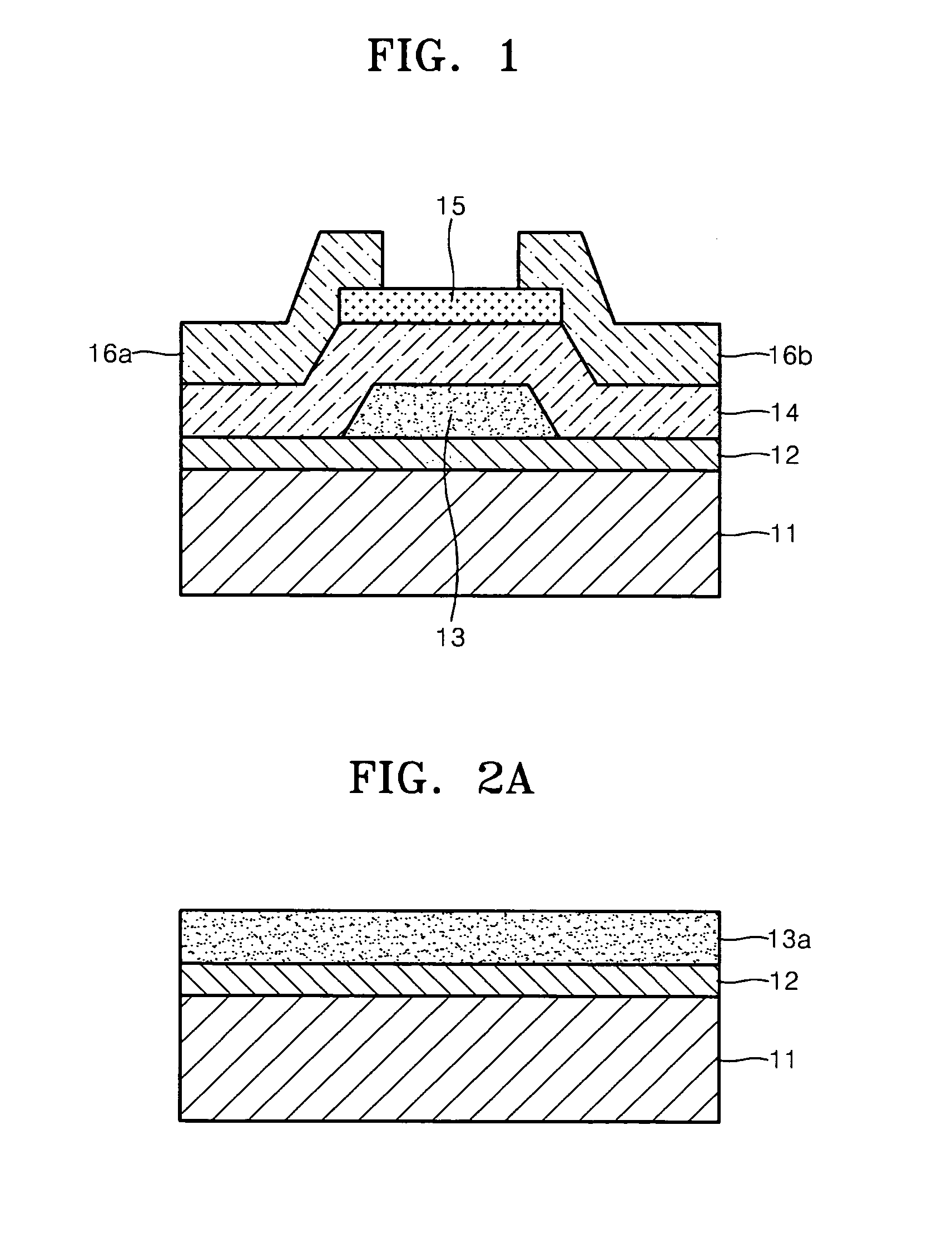
Thin film transistor having oxide semiconductor layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20060284172A1Etch resistance of resist is lowPromote meltingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingZincSemiconductor
A thin film transistor has a semiconductor thin film including zinc oxide, a protection film formed on entirely the upper surface of the semiconductor thin film, a gate insulating film formed on the protection film, a gate electrode formed on the gate insulating film above the semiconductor thin film, and a source electrode and drain electrode formed under the semiconductor thin film so as to be electrically connected to the semiconductor thin film.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
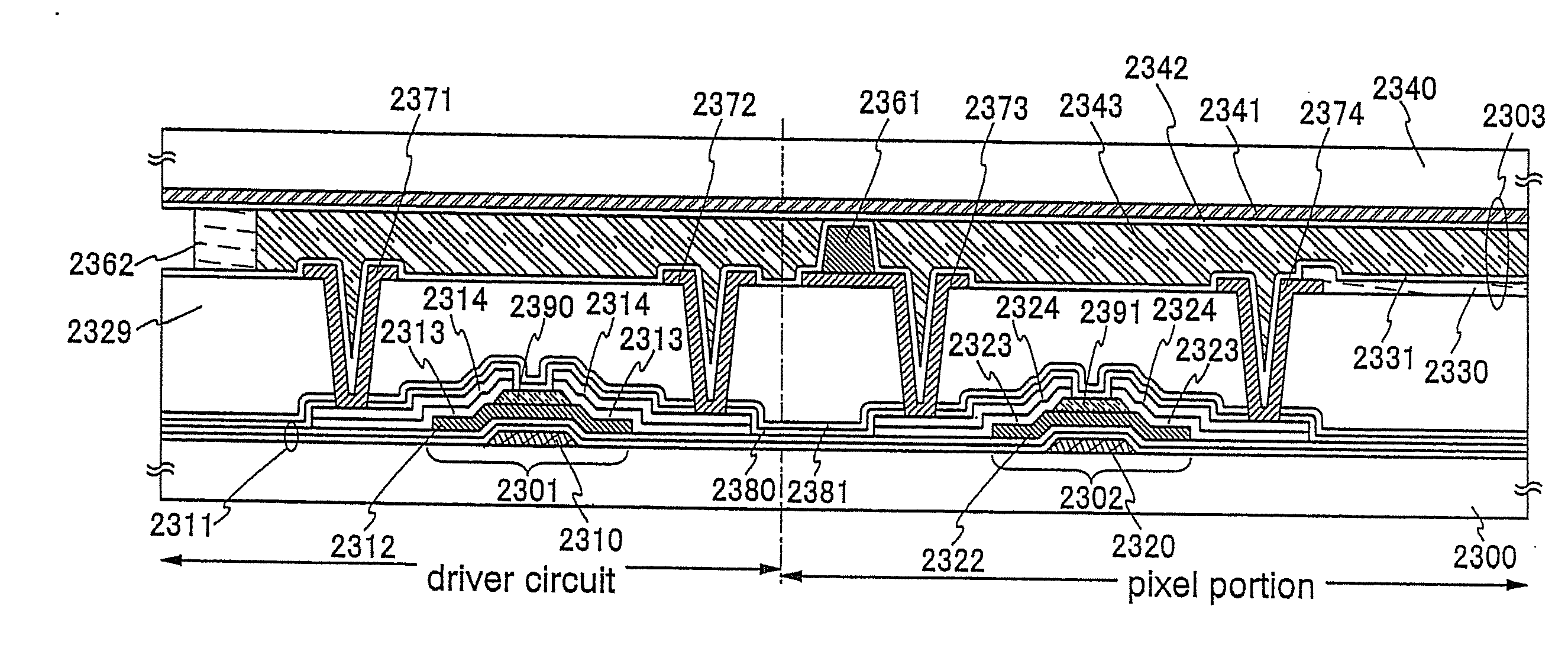
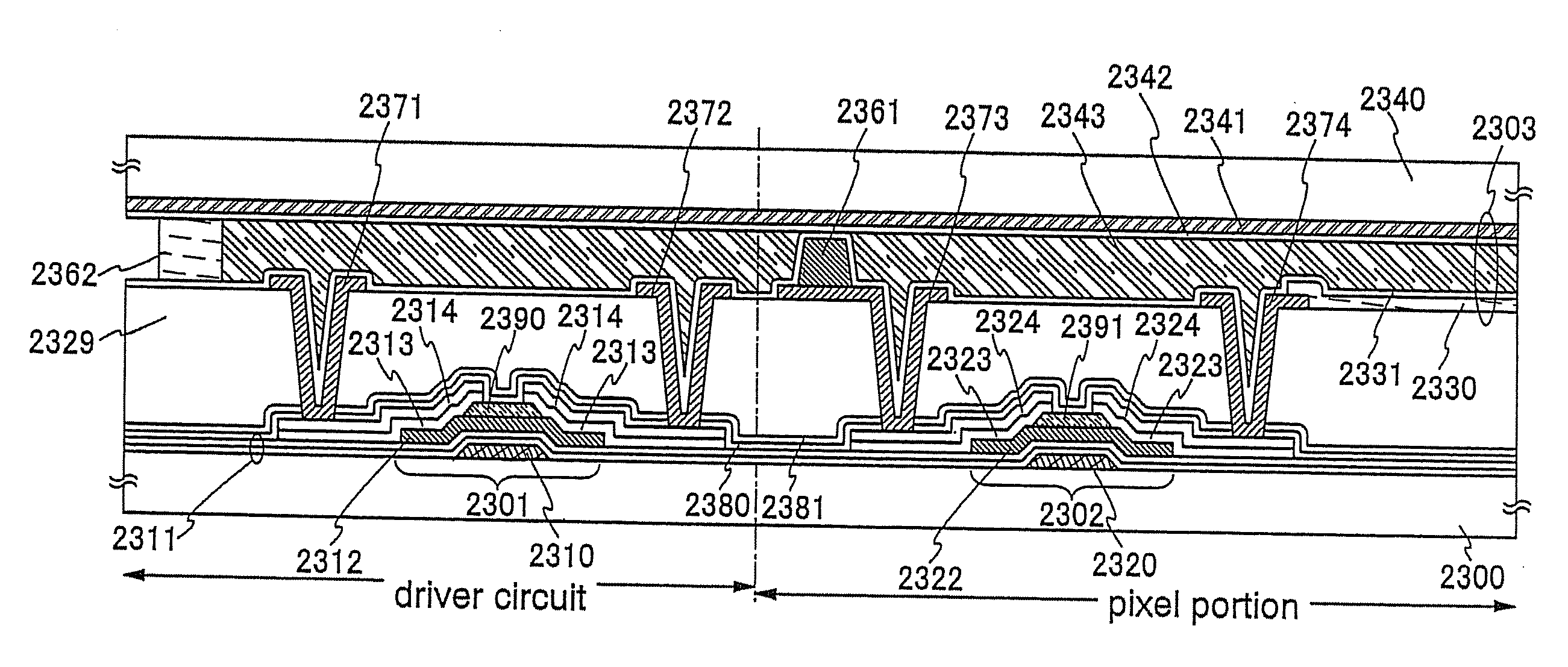
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
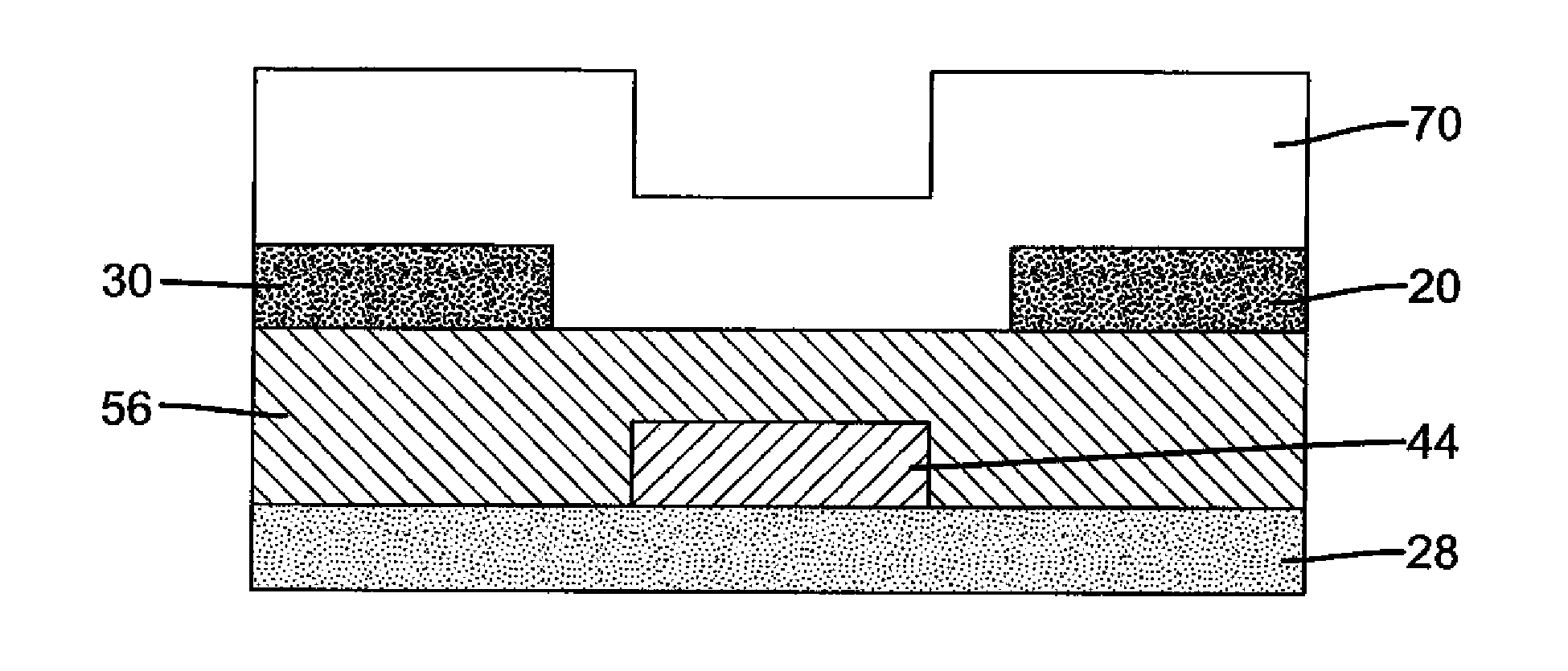
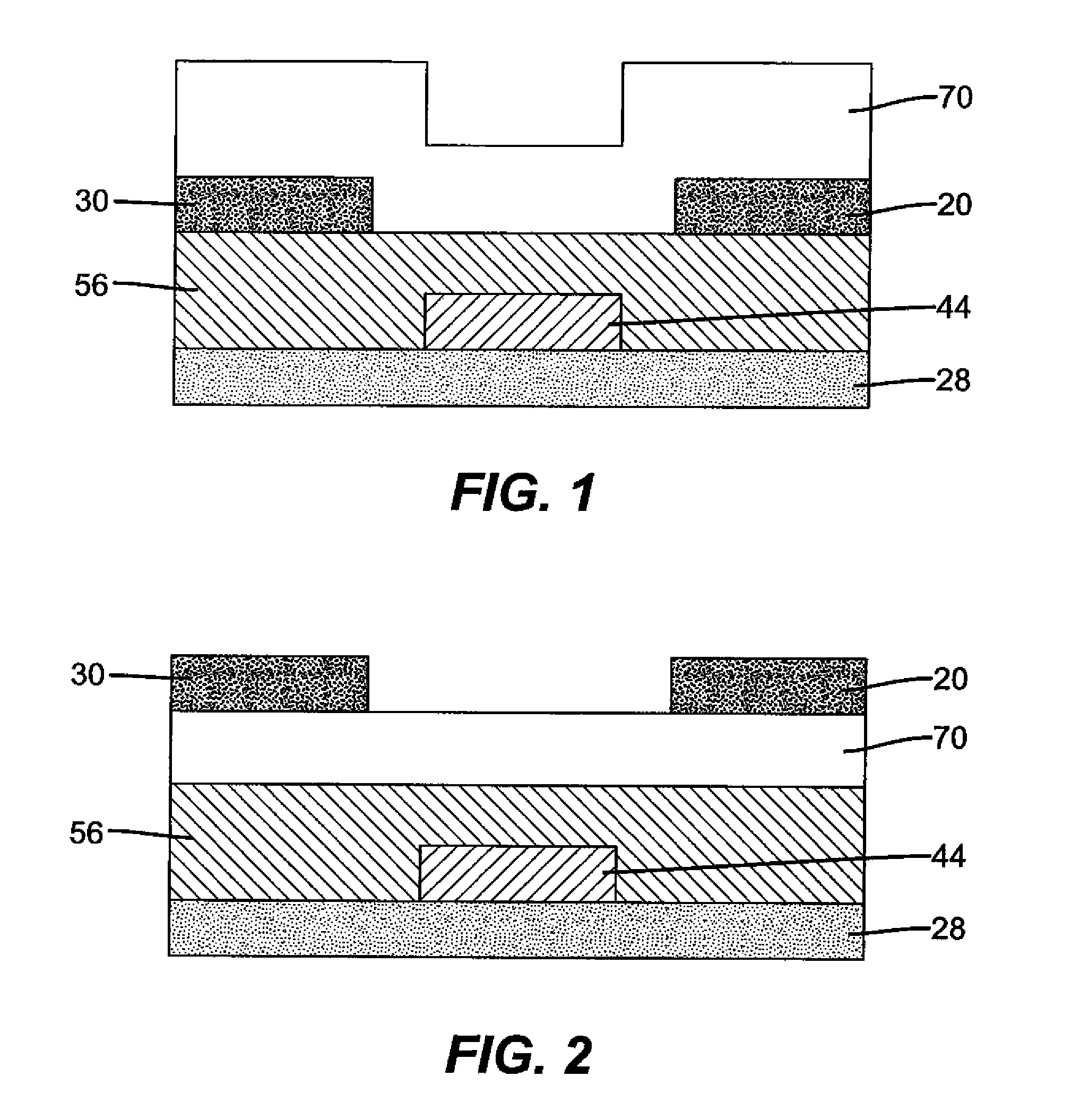
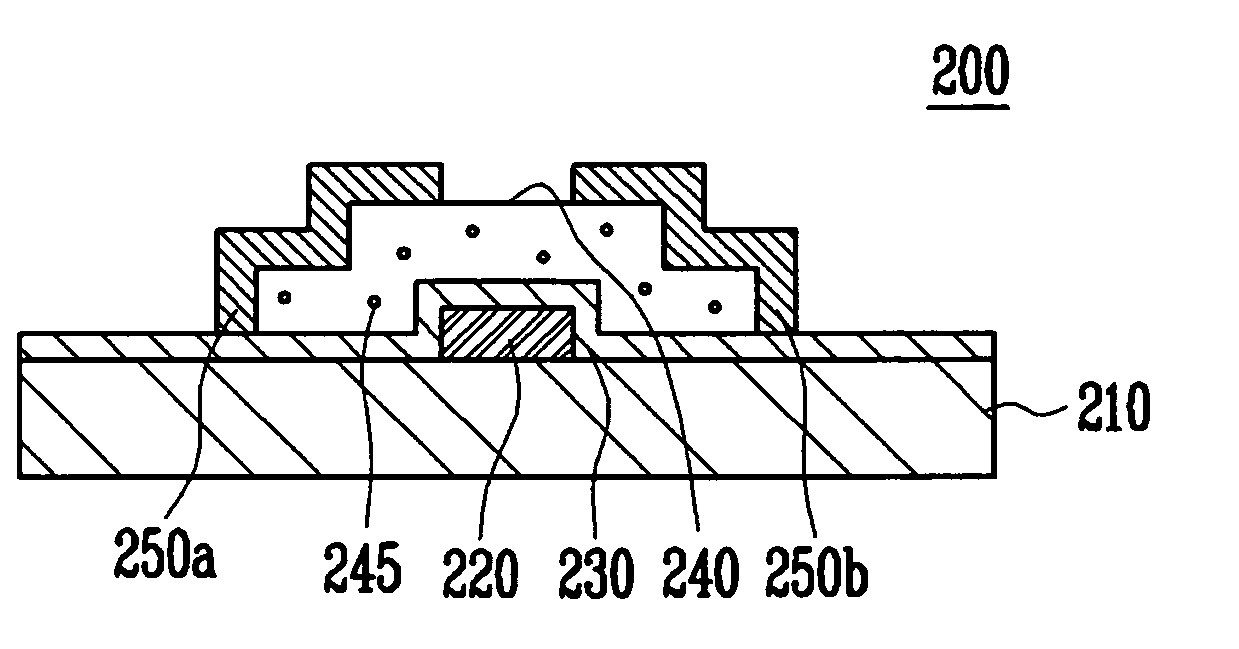
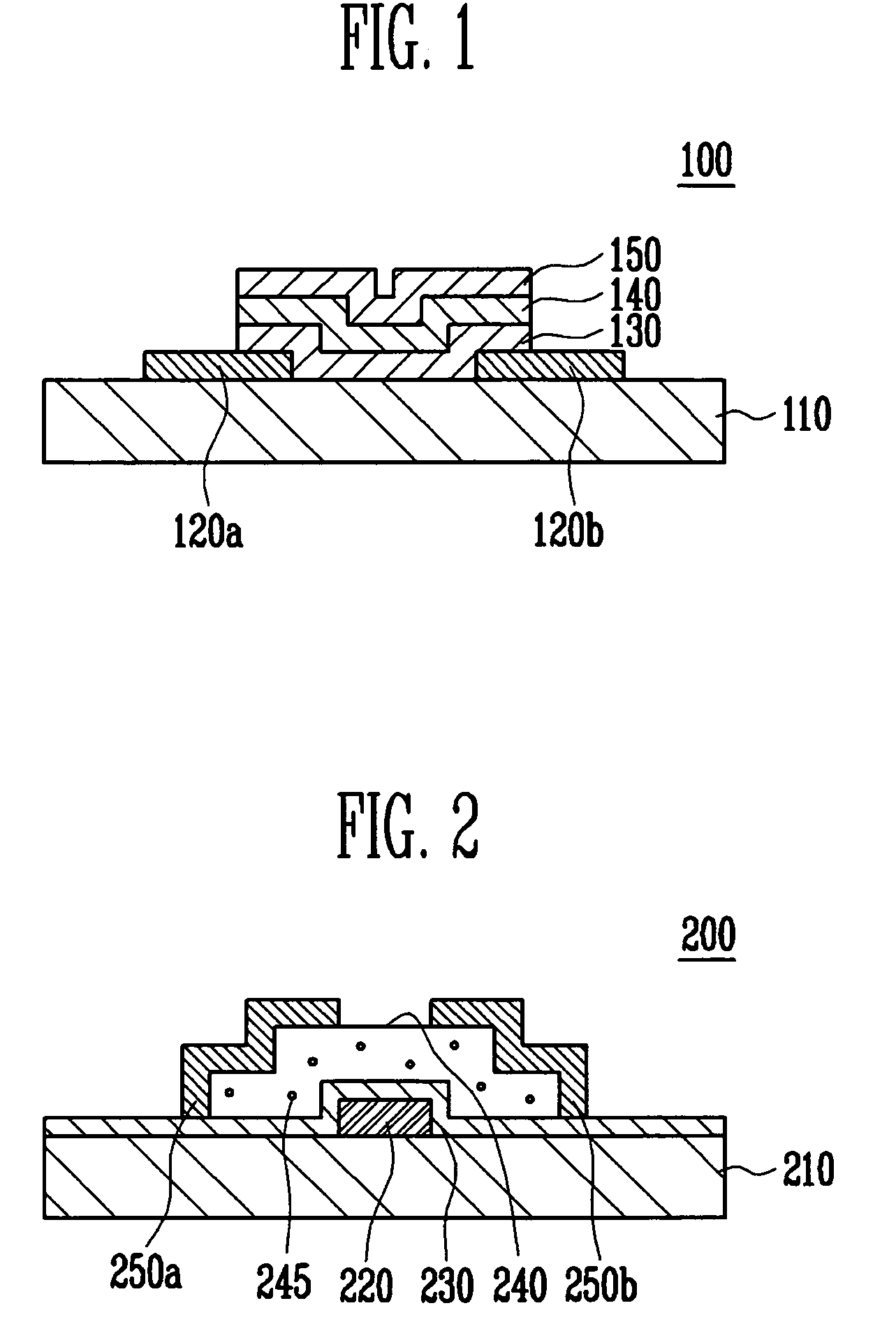
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method of producing a sustained-release preparation
InactiveUS6197350B1Reduce the number of stepsSuitable for industrializationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood concentrationOrganic solvent
A method of producing sustained-release microcapsules which comprises dispersing a physiologically active polypeptide into a solution of a biodegradable polymer and zinc oxide in an organic solvent, followed by removing the organic solvent; which provides a sustained-release preparation showing a high entrapment ratio of the physiologically active polypeptide and its constant high blood concentration levels over a long period of time.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
ActiveUS20080308797A1High yieldReduce the ratioTransistorDischarge tube luminescnet screensEngineeringZinc
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
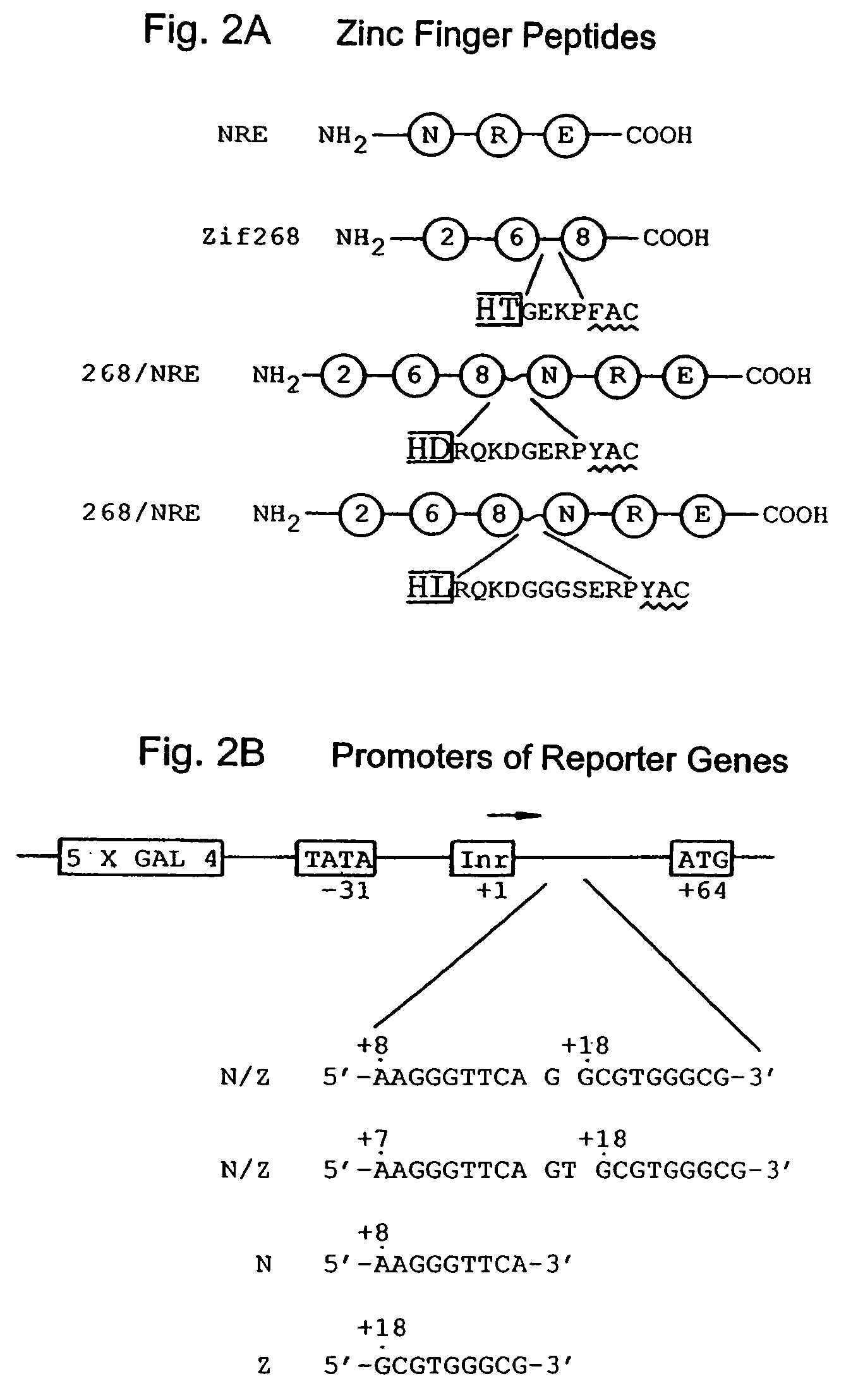
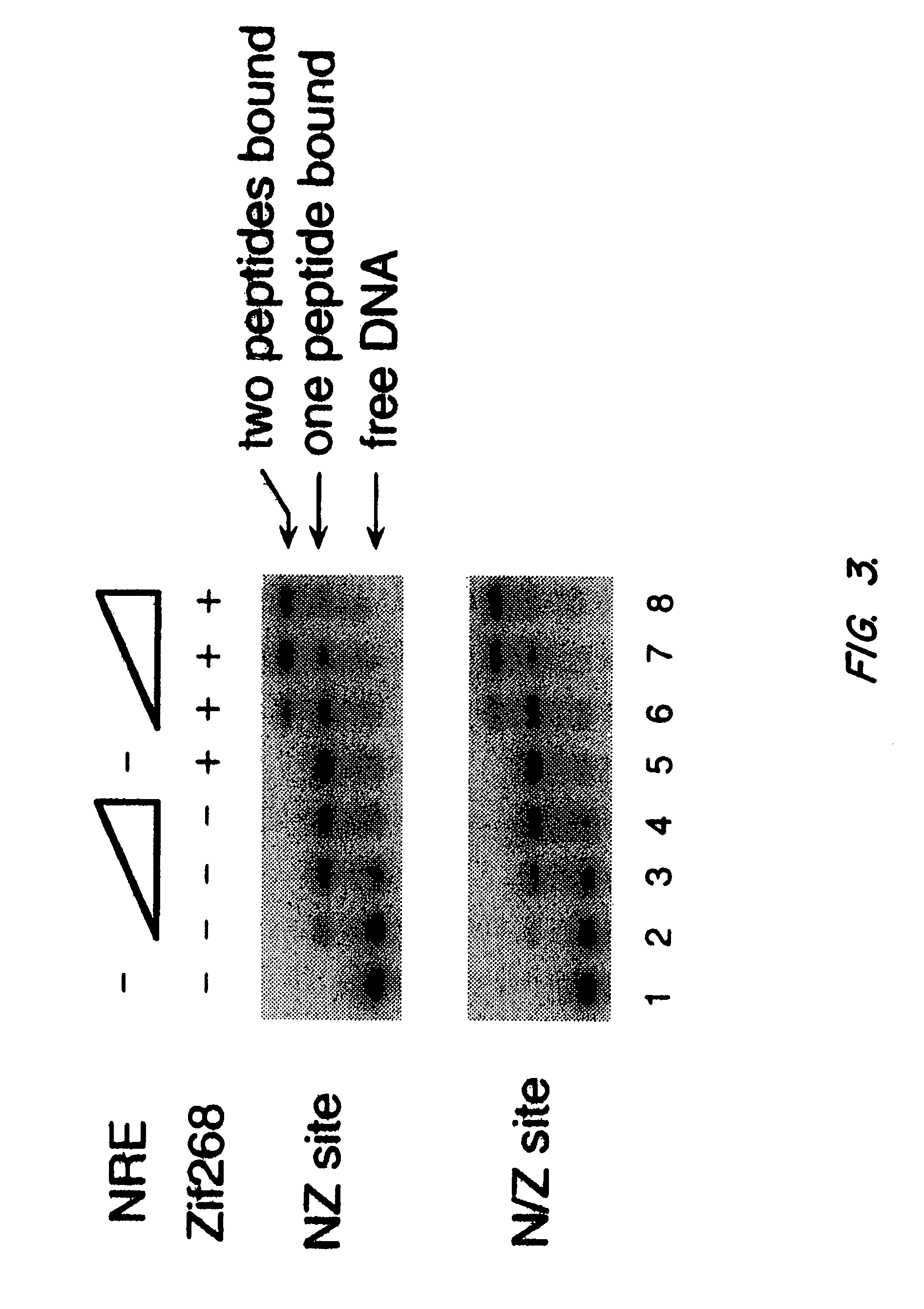
Nucleic acid encoding poly-zinc finger proteins with improved linkers
InactiveUS7153949B2Enhanced affinity and specificityImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA-binding domainNucleotide
Polynucleotides encoding chimeric proteins, and methods for their production and use are disclosed. The chimeric proteins comprise a flexible linker between two zinc finger DNA-binding domains, wherein the linker contains eight or more amino acids between the second conserved histidine residue of the carboxy-terminal zinc finger of the first domain and the first conserved cysteine residue of the amino-terminal zinc finger of the second domain.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Semiconductor Device and Manufacturing Method Thereof
An object is to provide a semiconductor device of which a manufacturing process is not complicated and by which cost can be suppressed, by forming a thin film transistor using an oxide semiconductor film typified by zinc oxide, and a manufacturing method thereof. For the semiconductor device, a gate electrode is formed over a substrate; a gate insulating film is formed covering the gate electrode; an oxide semiconductor film is formed over the gate insulating film; and a first conductive film and a second conductive film are formed over the oxide semiconductor film. The oxide semiconductor film has at least a crystallized region in a channel region.
Owner:MOLECULAR DEVICES
Treatment of neuropathic pain with zinc finger proteins
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC
Oxide semiconductor device and surface treatment method of oxide semiconductor
InactiveUS20090166616A1Effectively suppressing the threshold potential shift and occurrence of leak currentPhysical property is lessSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseThreshold potential
Oxygen defects formed at the boundary between the zinc oxide type oxide semiconductor and the gate insulator are terminated by a surface treatment using sulfur or selenium as an oxygen group element or a compound thereof, the oxygen group element scarcely occurring physical property value change. Sulfur or selenium atoms effectively substitute oxygen defects to prevent occurrence of electron supplemental sites by merely applying a gas phase or liquid phase treatment to an oxide semiconductor or gate insulator with no remarkable change on the manufacturing process. As a result, this can attain the suppression of the threshold potential shift and the leak current in the characteristics of a thin film transistor.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
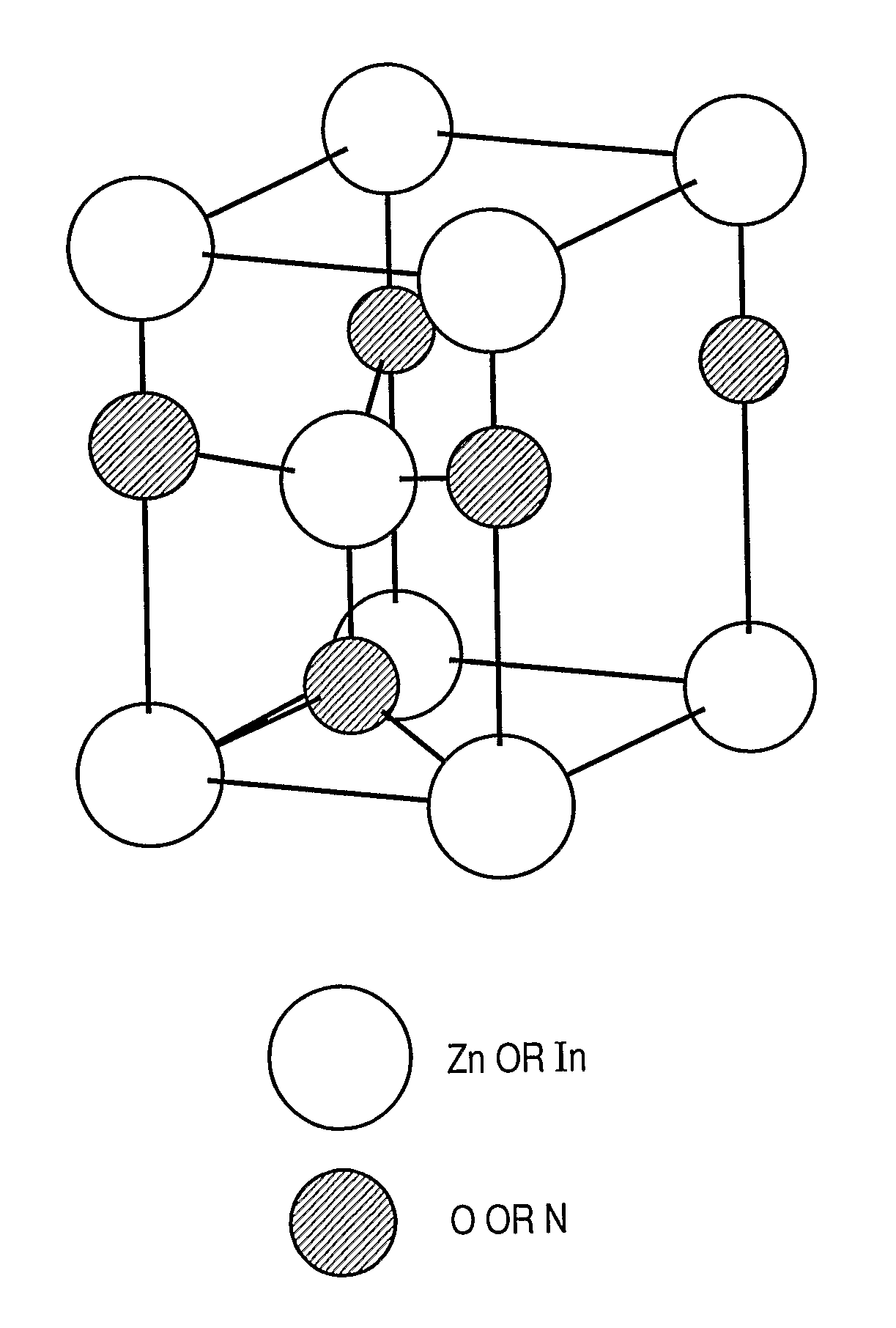
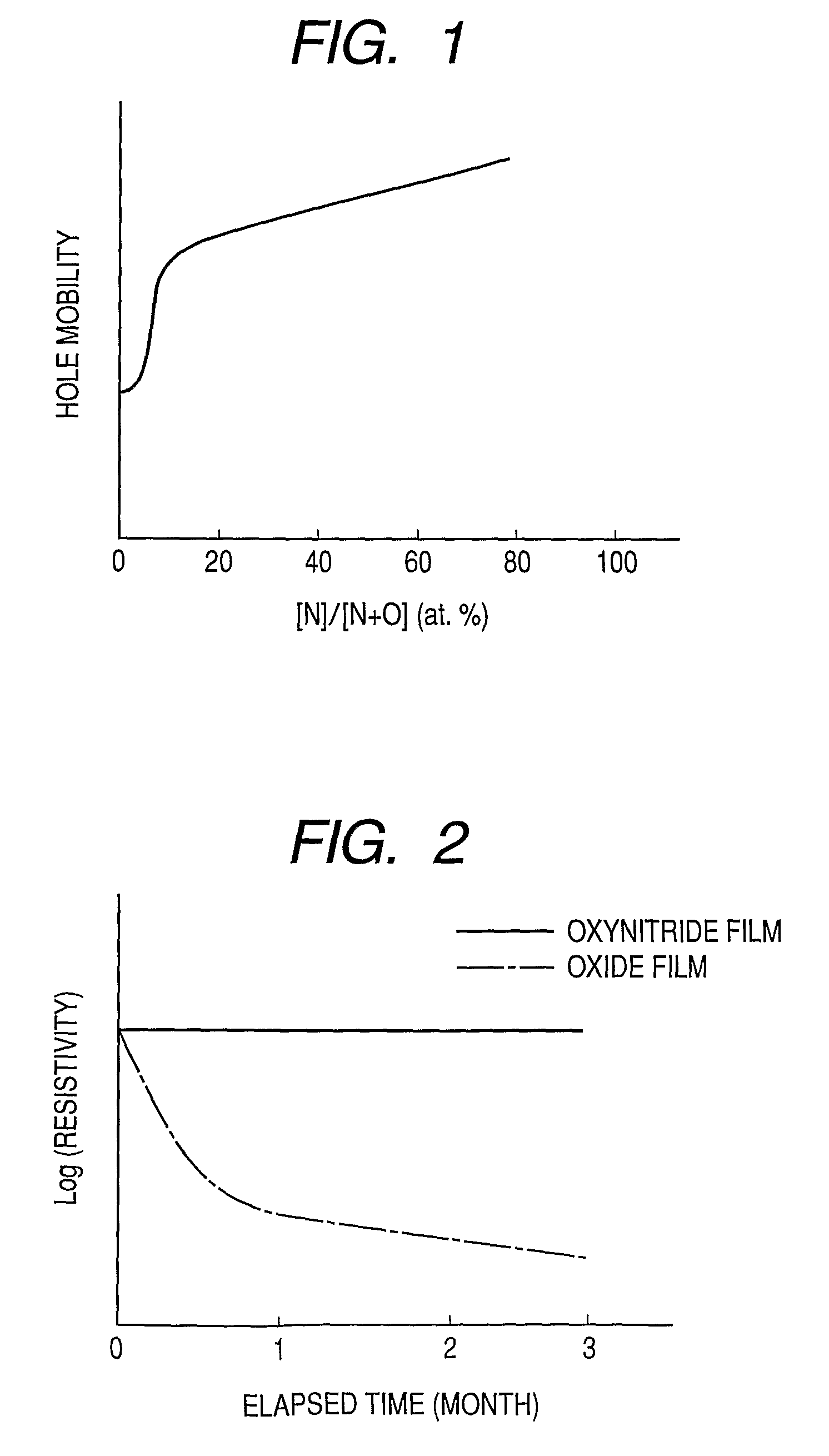
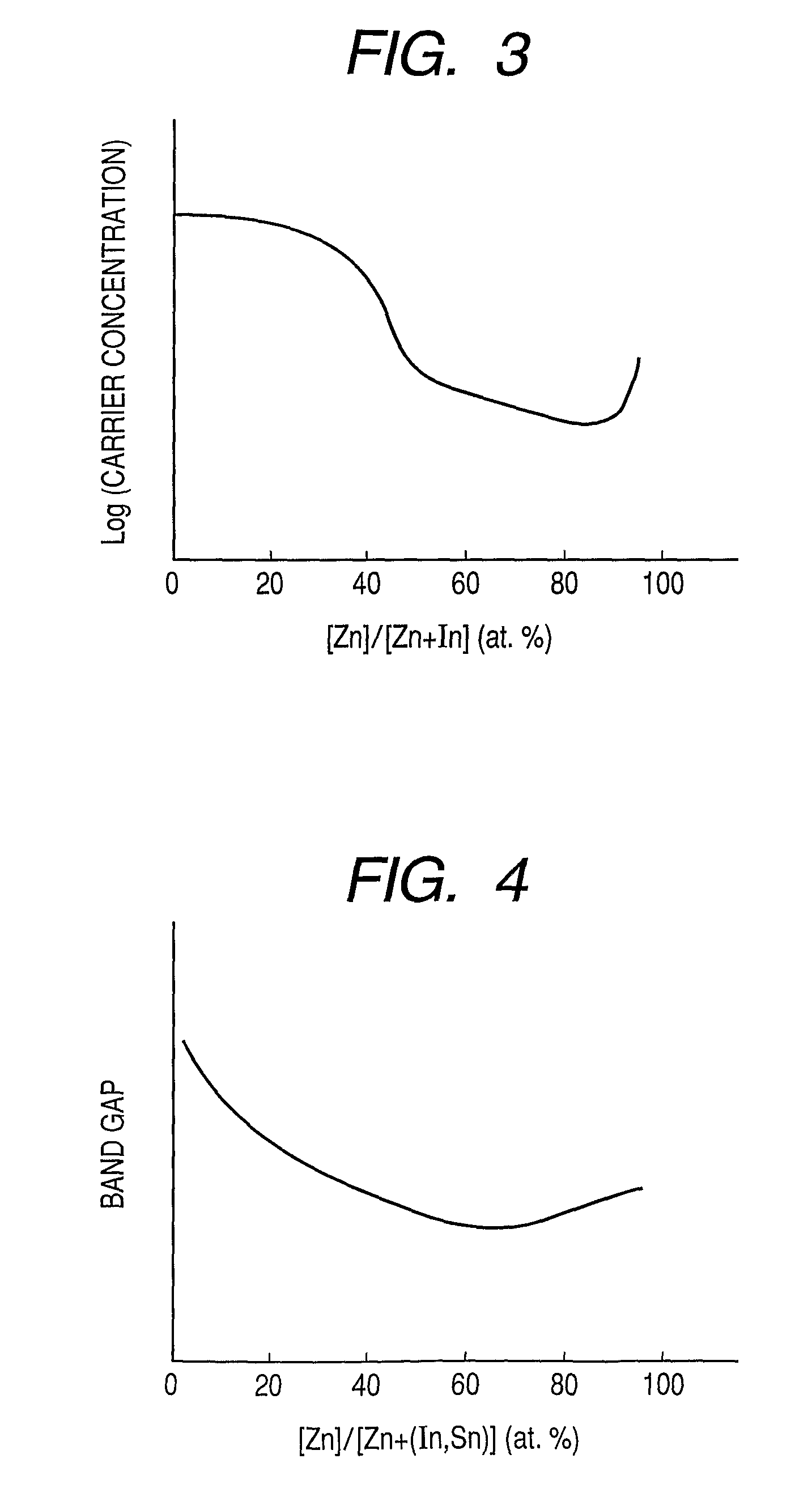
Metal oxynitride semiconductor containing zinc
ActiveUS8274078B2High mobility and environmental stabilityImprove mobilityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesNitrogen oxideOxygen
Provided is an oxynitride semiconductor comprising a metal oxynitride. The metal oxynitride contains Zn and In and at least one element selected from the group consisting of Ga, Sn, Mg, Si, Ge, Y, Ti, Mo, W, and Al. The metal oxynitride has an atomic composition ratio of N, N / (N+O), of 7 atomic percent or more to 80 atomic percent or less.
Owner:CANON KK
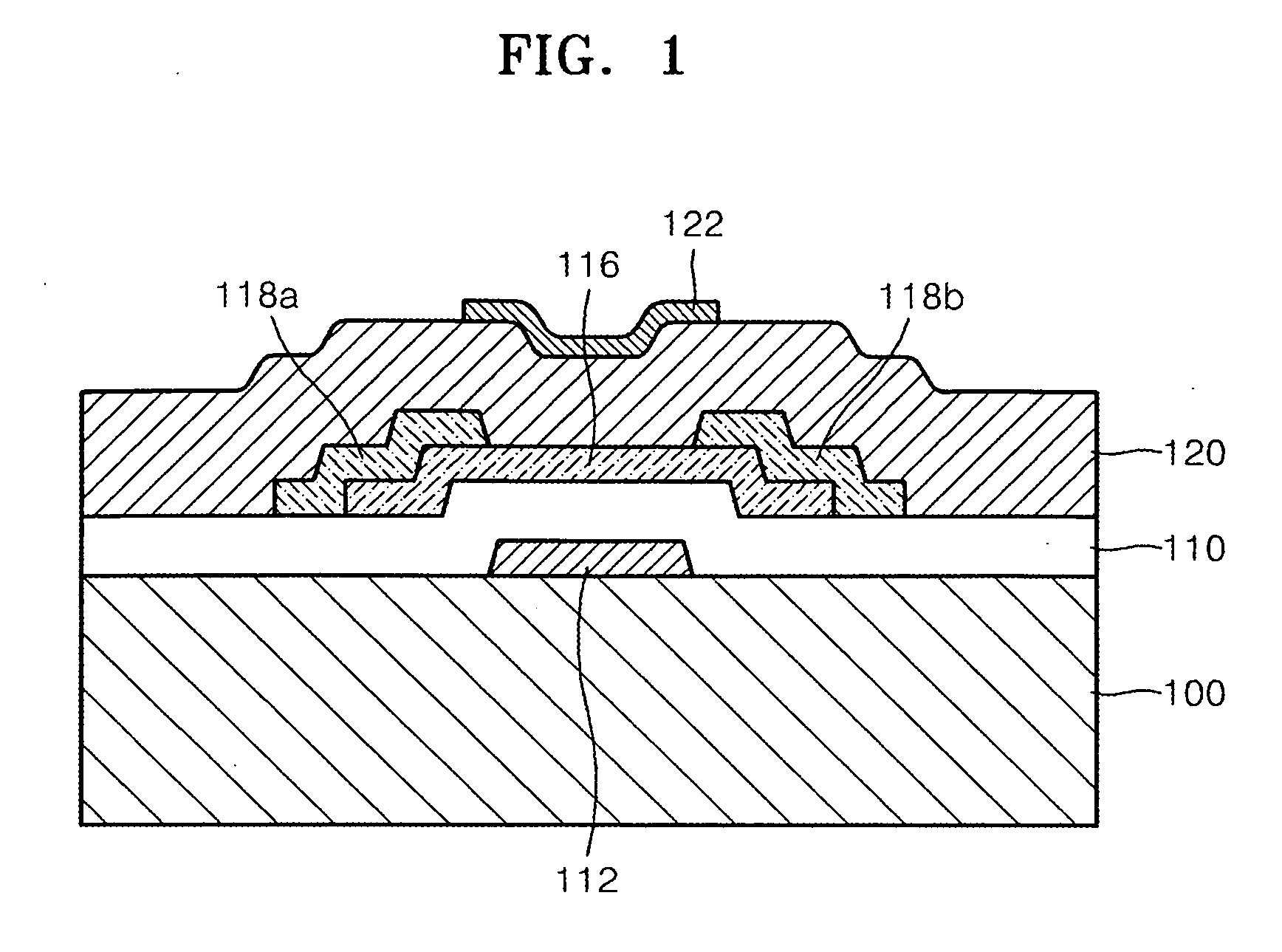
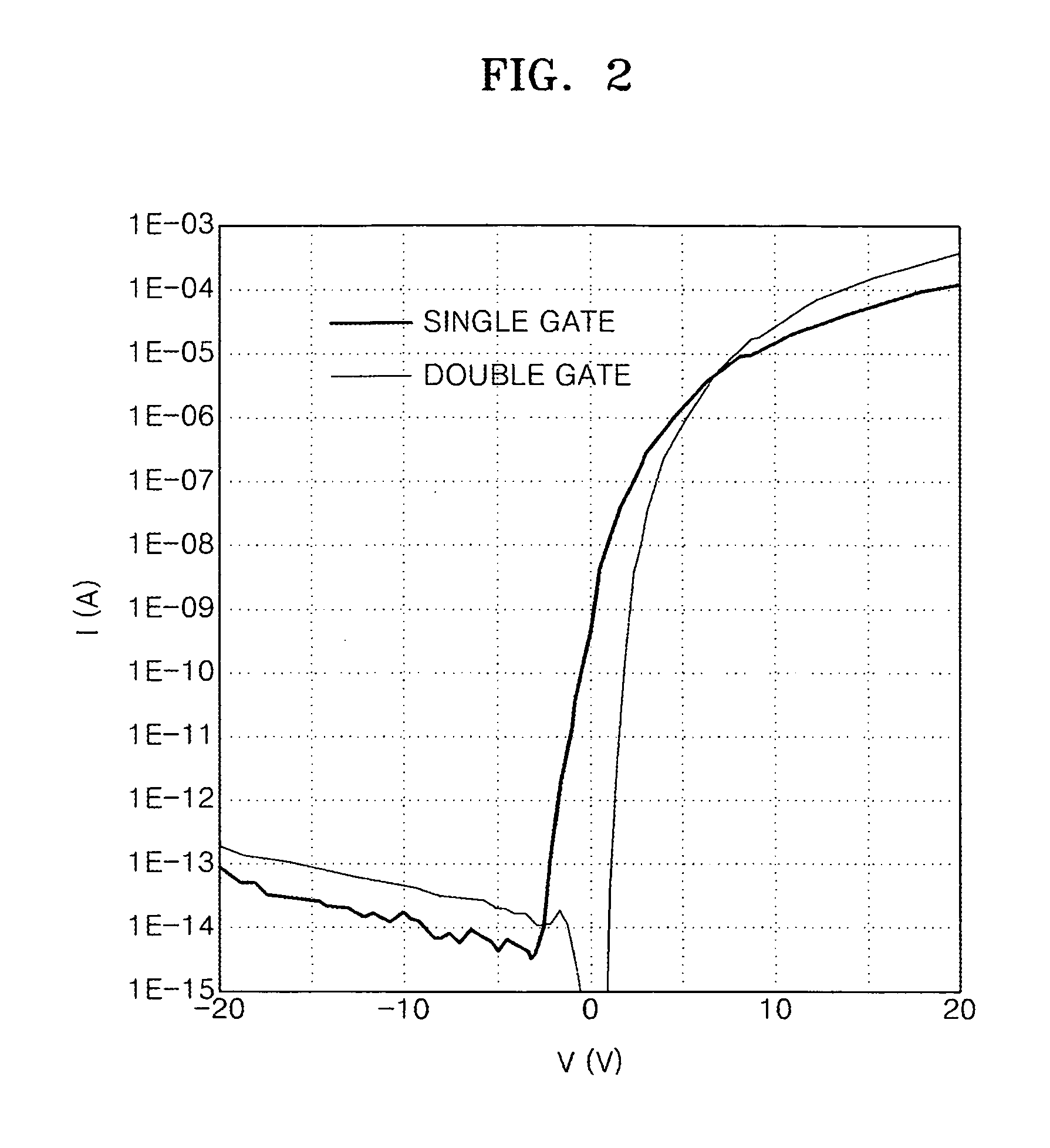
Oxide semiconductor transistor and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20090206332A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringSilicon oxide
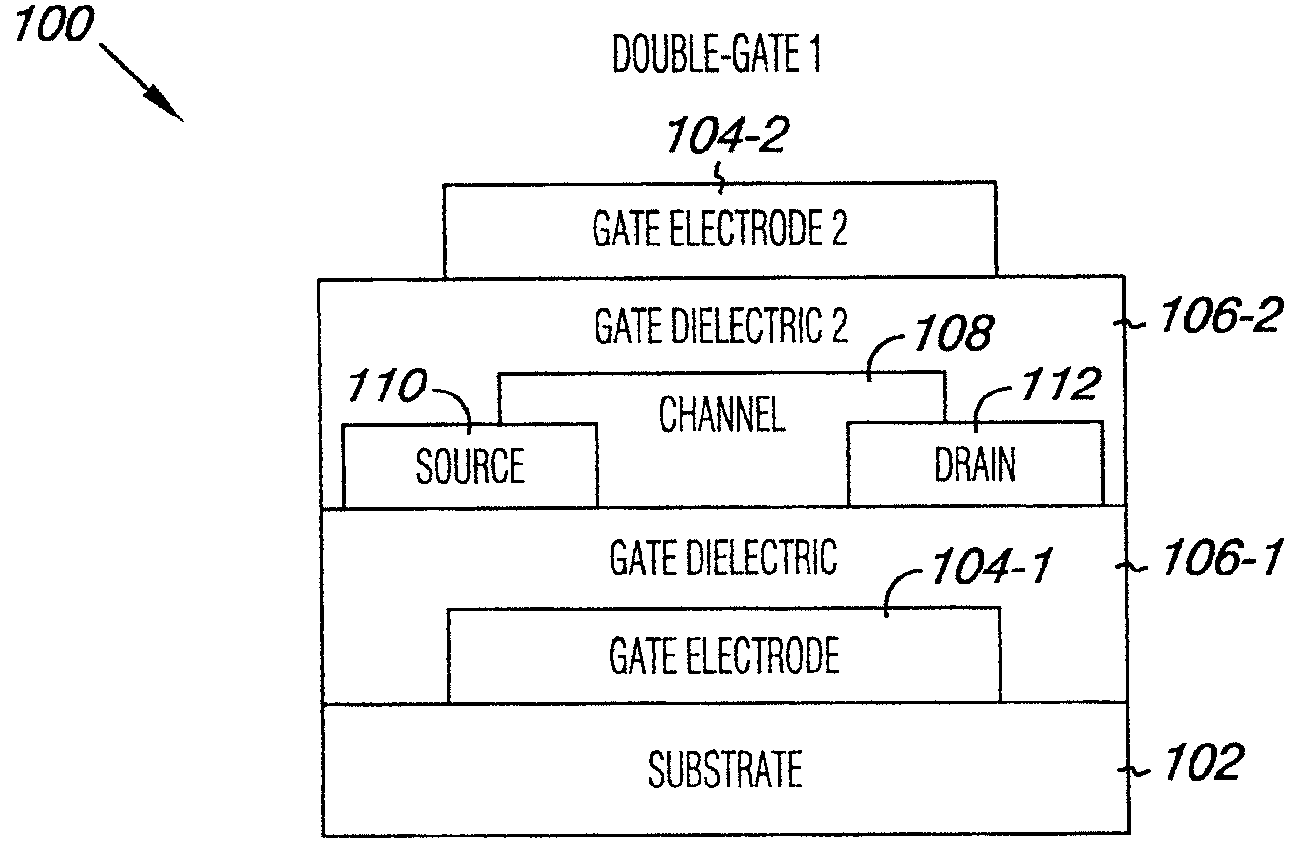
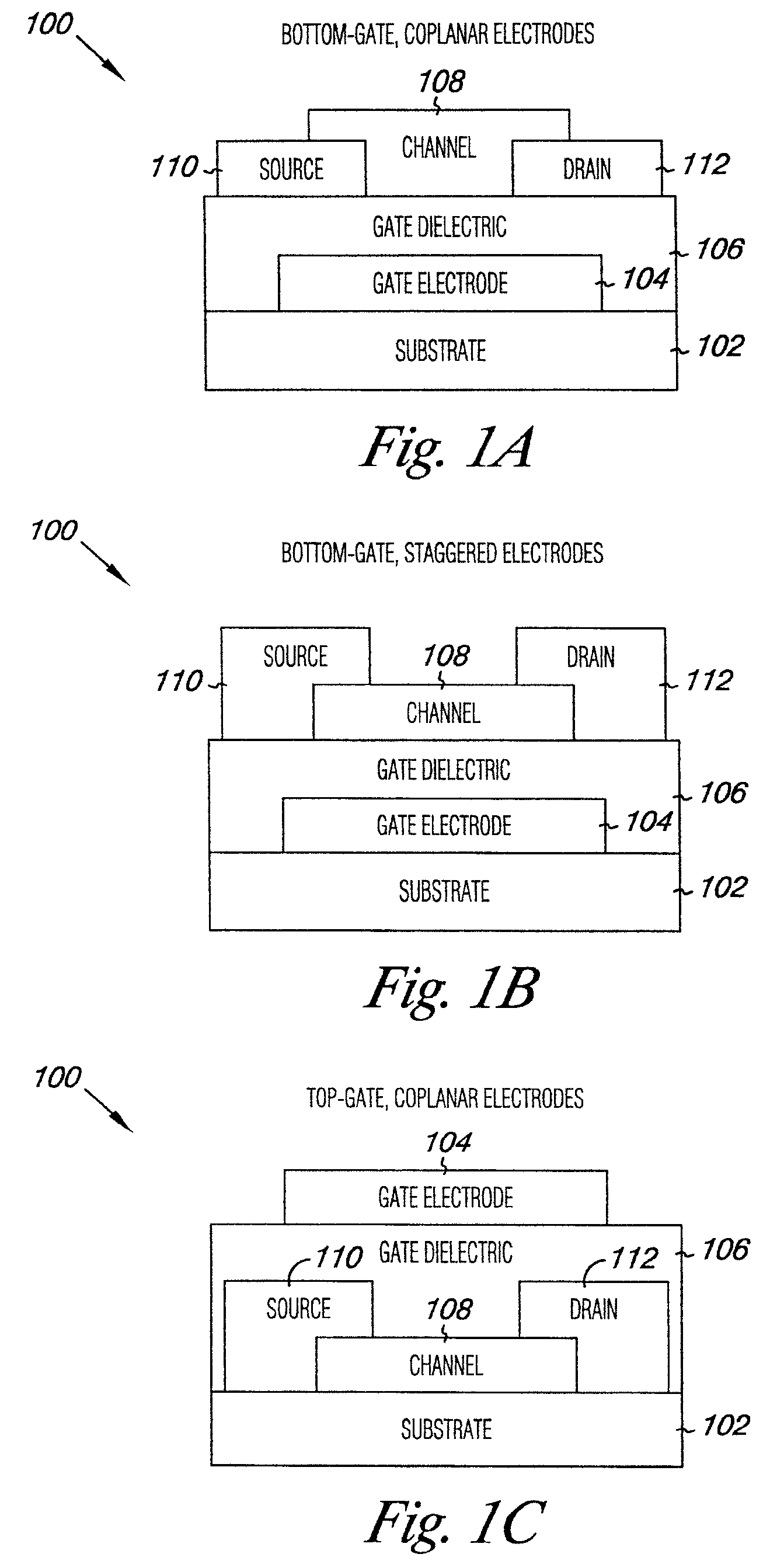
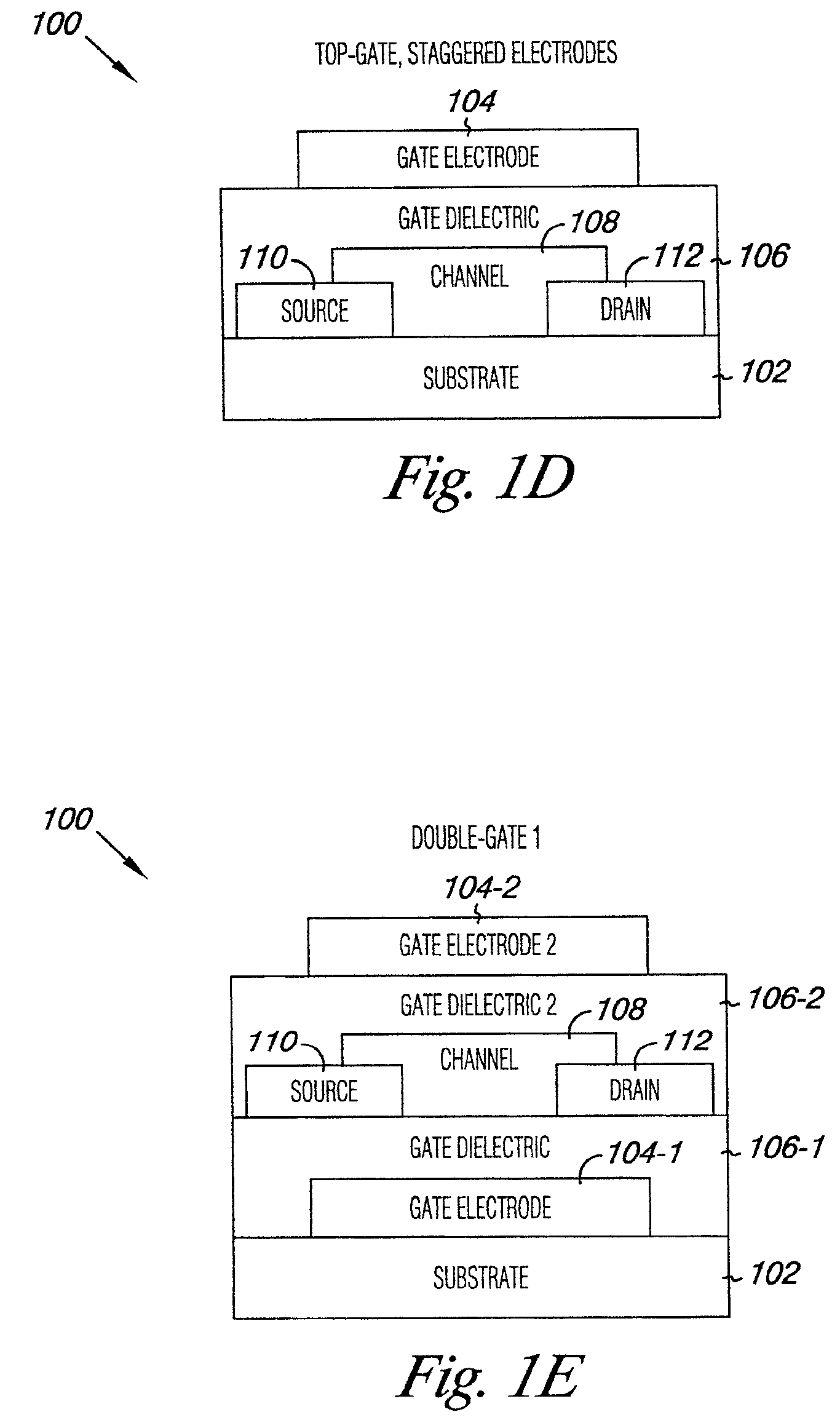
An oxide semiconductor thin film transistor (TFT) and a method of manufacturing the oxide semiconductor TFT. The oxide semiconductor TFT includes a first gate insulating layer arranged between an oxide semiconductor channel layer and a first gate and a second gate insulating layer arranged between the channel layer and a second gate. The first and second gate insulating layers are made out of different materials and have different thicknesses. Preferably, the second gate insulating layer is silicon oxide and is thinner than the first gate insulating layer which is preferably silicon nitride. Oxide semiconductor refers to an oxide material such as Zinc Oxide, Tin Oxide, Ga—In—Zn Oxide, In—Zn Oxide, In—Sn Oxide, and one of Zinc Oxide, Tin Oxide, Ga—In—Zn Oxide, In—Zn Oxide and In—Sn Oxide.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Oxide semiconductor, thin film transistor including the same and method of manufacturing a thin film transistor
InactiveUS20090008638A1Improve electrical performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRare-earth elementGroup element
Example embodiments relate to an oxide semiconductor including zinc oxide (ZnO), a thin film transistor including a channel formed of the oxide semiconductor and a method of manufacturing the thin film transistor. The oxide semiconductor may include a GaxInyZnz oxide and at least one material selected from the group consisting of a 4A group element, a 4A group oxide, a rare earth element and combinations thereof.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of making a semiconductor device having a multicomponent oxide
One exemplary embodiment includes a semiconductor device. The semiconductor device can include a channel including one or more of a metal oxide including zinc-gallium, cadmium-gallium, cadmium-indium.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Field effect transistor using oxide semicondutor and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS8384077B2Easy to produceLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeIndiumField-effect transistor
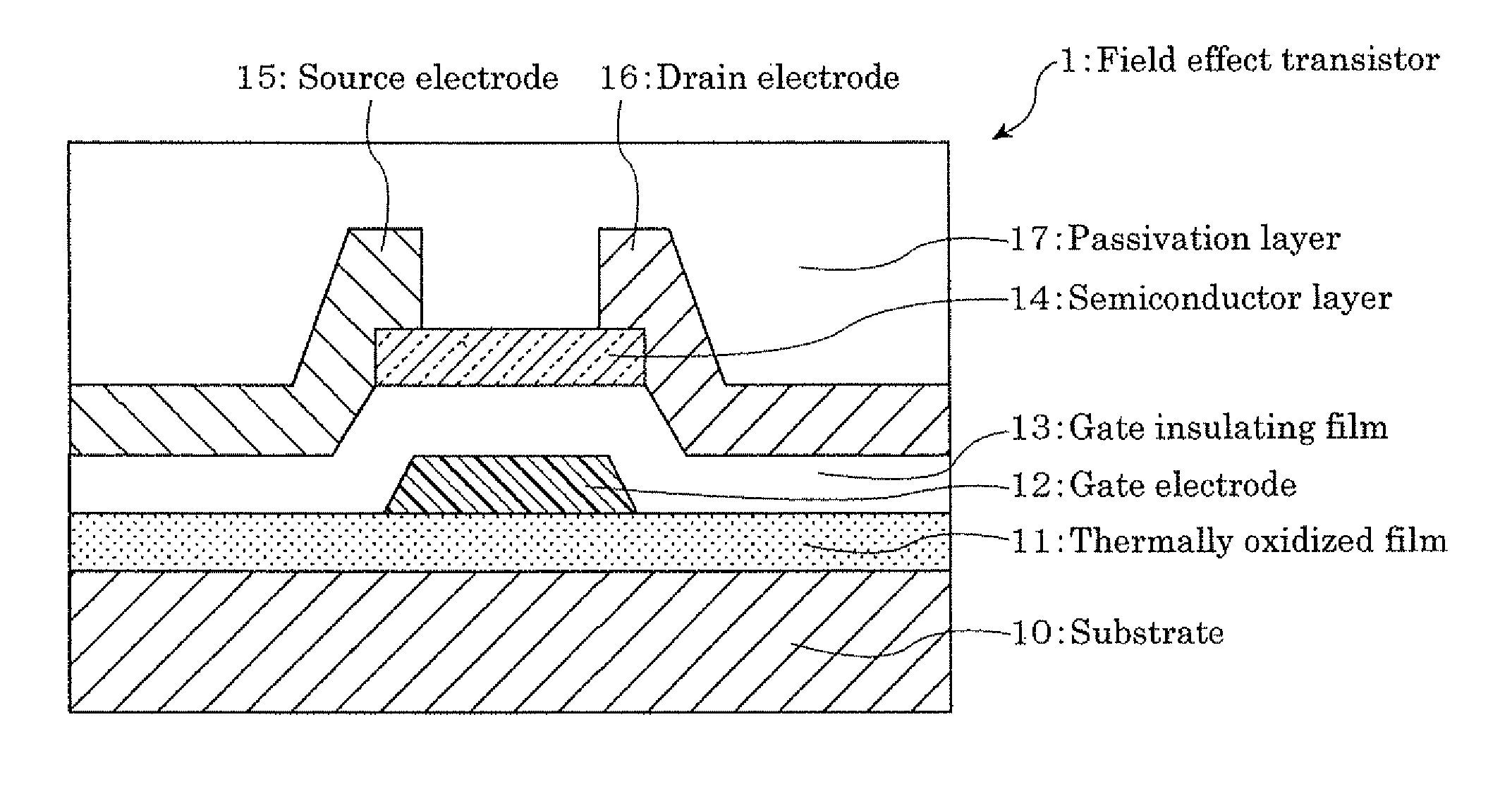
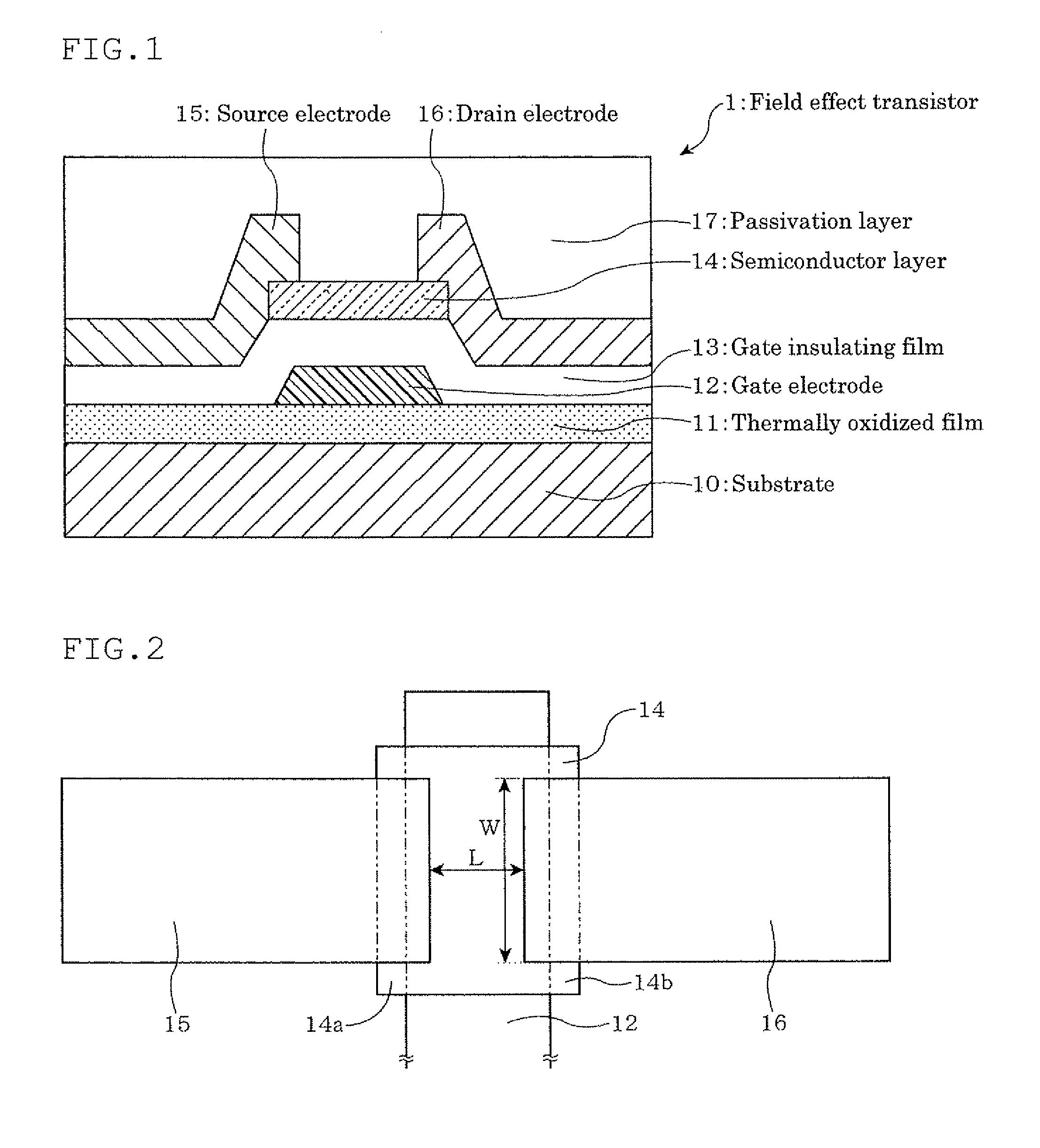
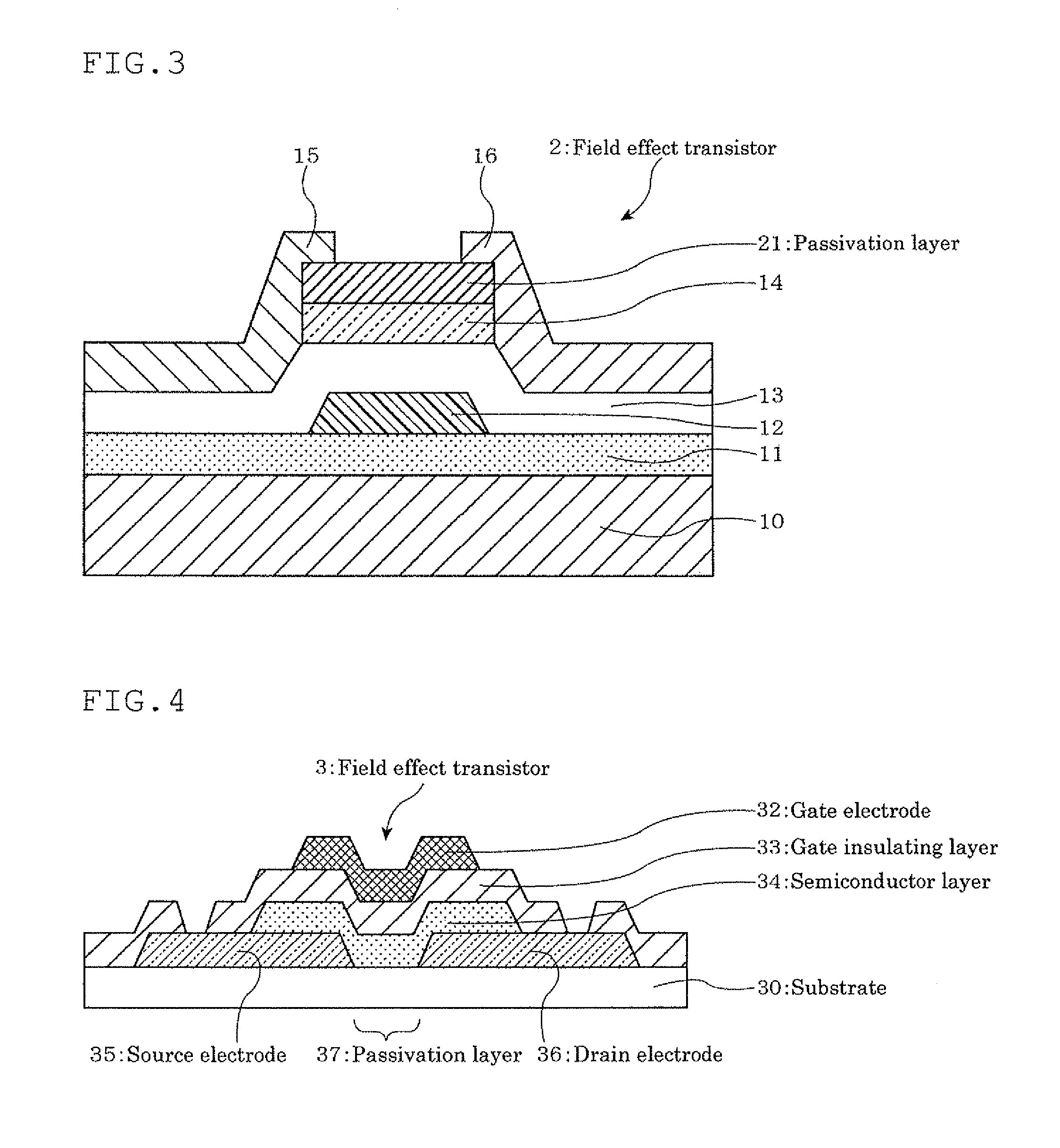
A field effect transistor which includes, on a substrate, at least a semiconductor layer, a passivation layer for the semiconductor layer, a source electrode, a drain electrode, a gate insulating film and a gate electrode, the source electrode and the drain electrode being connected through the semiconductor layer, the gate insulating film being present between the gate electrode and the semiconductor layer, the passivation layer being at least on one surface side of the semiconductor layer, and the semiconductor layer including a composite oxide which comprises In (indium), Zn (zinc) and Ga (gallium) in the following atomic ratios (1) to (3):In / (In+Zn)=0.2 to 0.8 (1)In / (In+Ga)=0.59 to 0.99 (2)Zn / (Ga+Zn)=0.29 to 0.99 (3).
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
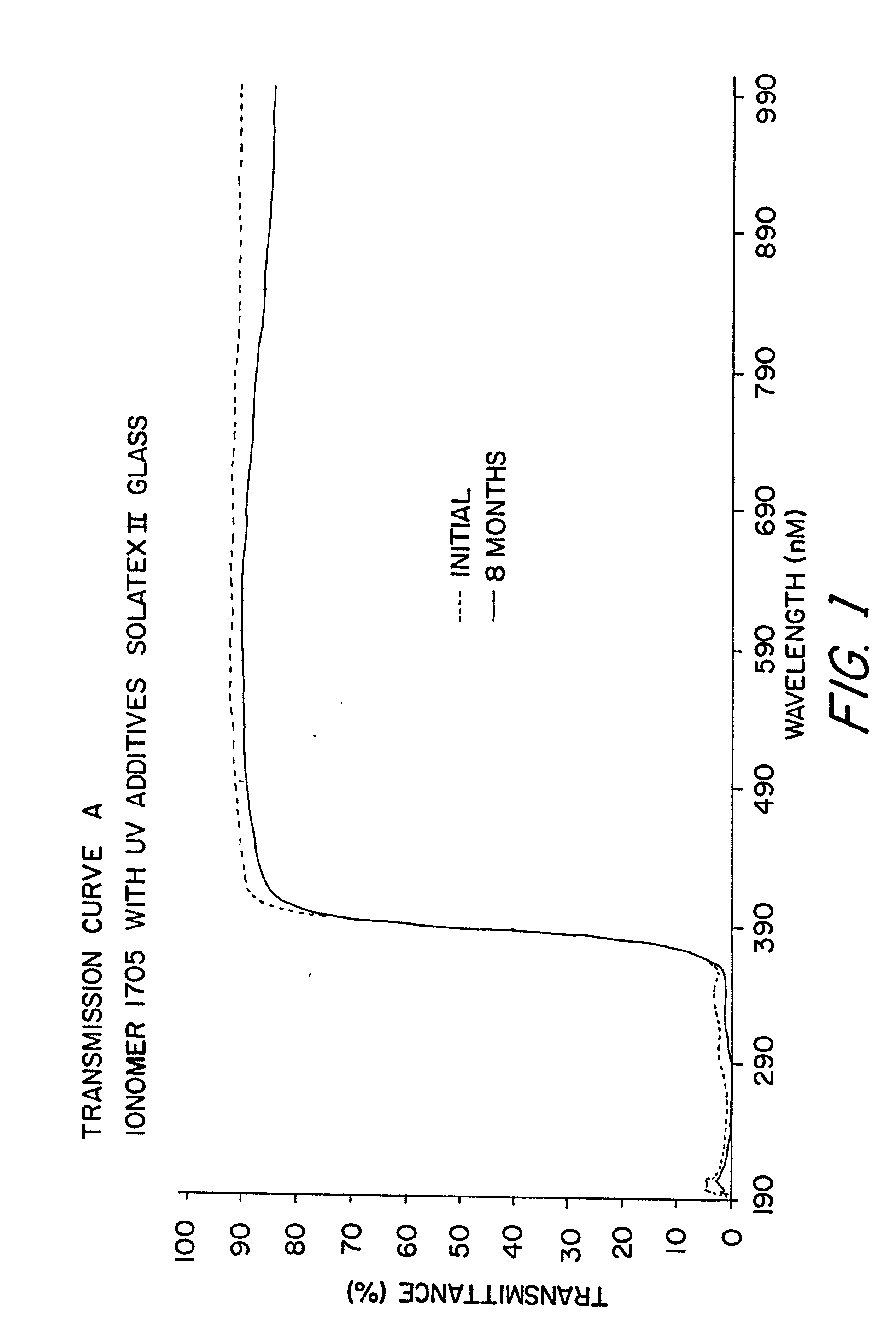
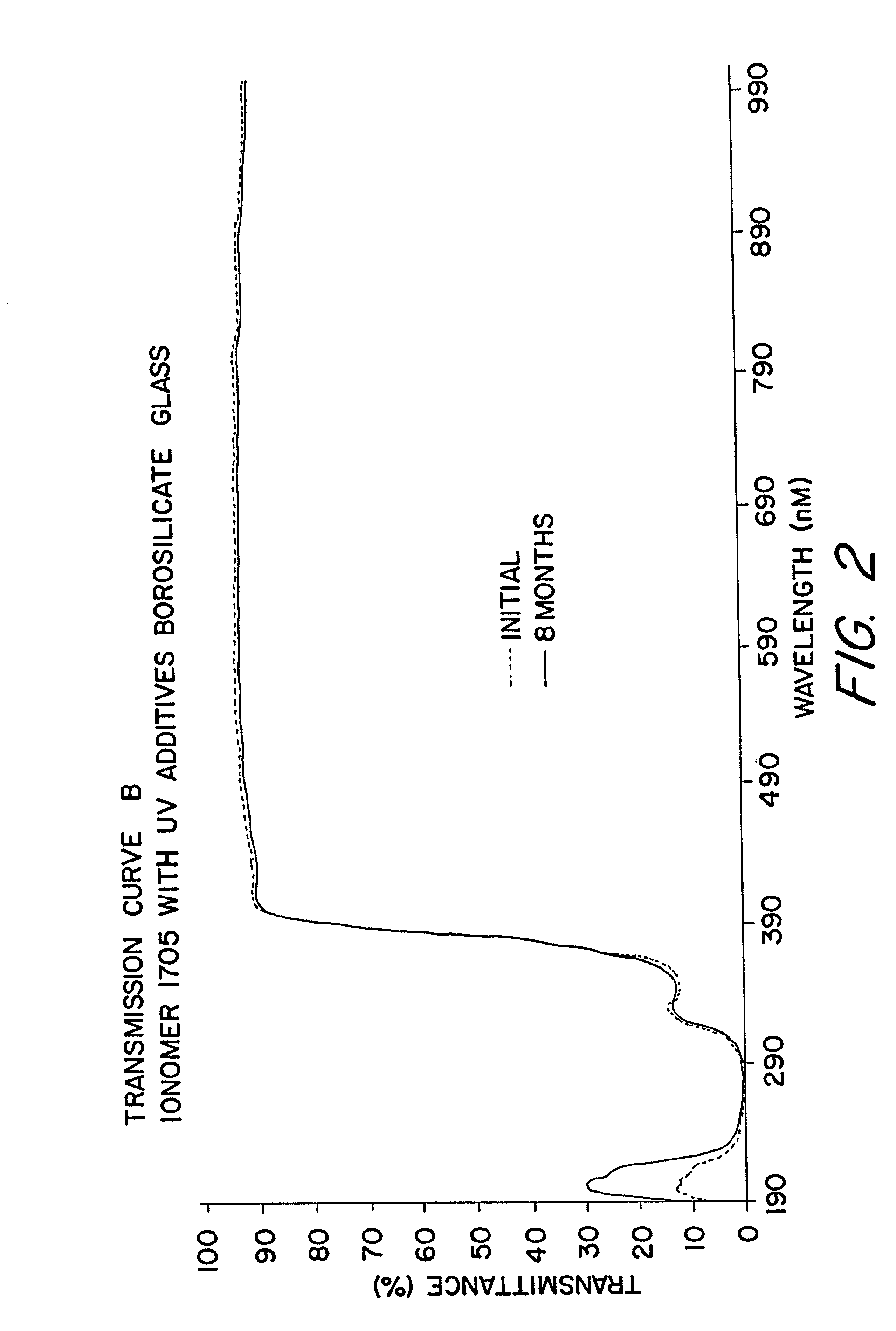
Encapsulated photovoltaic modules and method of manufacturing same
InactiveUS20030000568A1Extended service lifeLong useful lifePV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsIonomerChemical reaction
An improved laminated photovoltaic solar cell module and method of manufacture are provided which are characterized by use of a zinc-based ionomer encapsulant to avoid chemical reaction degradation by residues of acidic solder flux at soldered solar cell connections.
Owner:RWE SCHOTT SOLAR
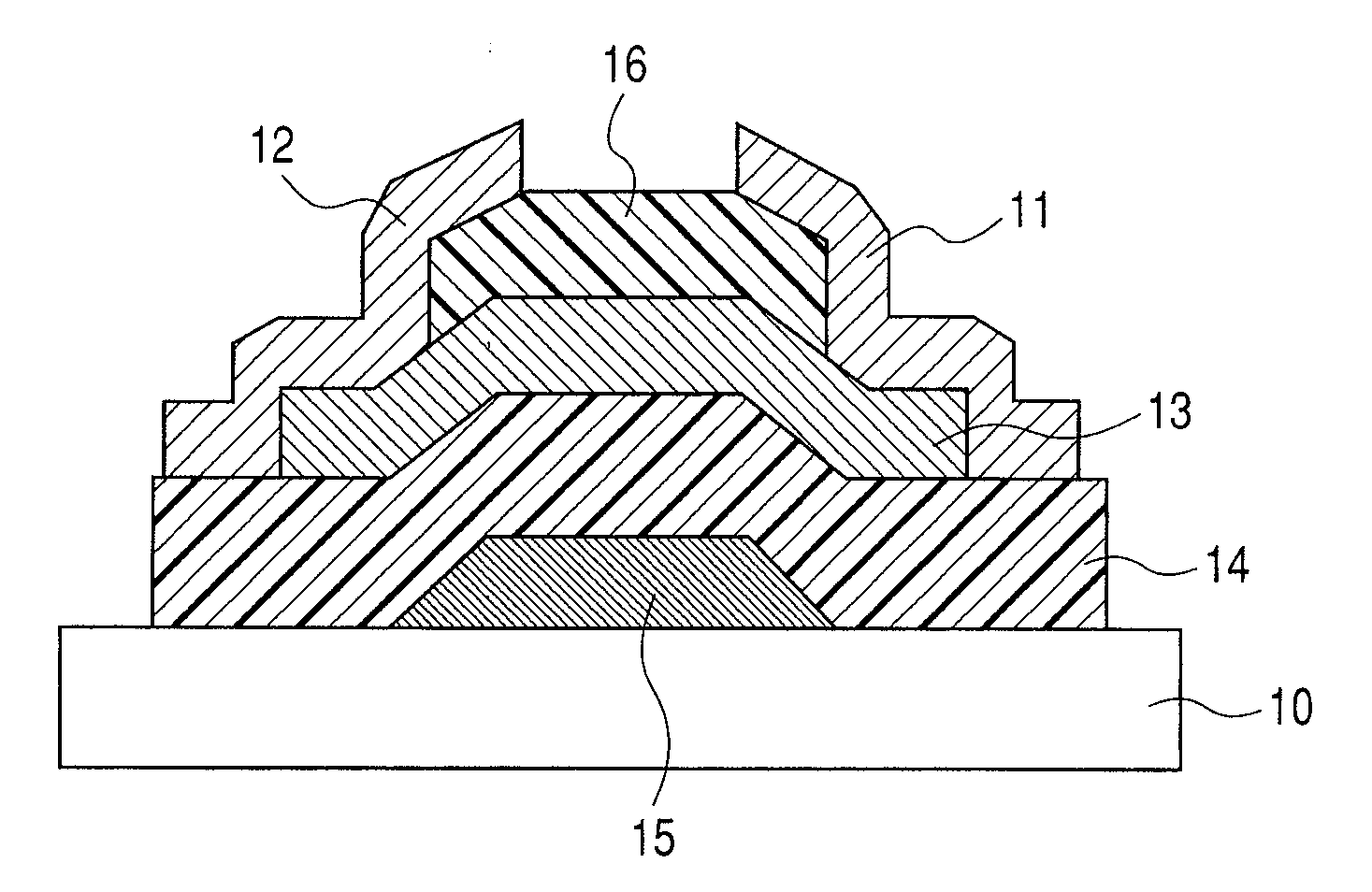
Semiconductor device including active layer of zinc oxide with controlled crystal lattice spacing and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20070278490A1Improve performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLattice planeActive layer
A semiconductor device includes an oxide semiconductor thin film layer of zinc oxide. The (002) lattice planes of at least a part of the oxide semiconductor thin film layer have a preferred orientation along a direction perpendicular to a substrate of the semiconductor device and a lattice spacing d002 of at least 2.619 Å.
Owner:KOICHI IND PROMOTION CENT +1
Lead free reduced ricochet limited penetration projectile
A frangible projectile with a specific gravity similar to a lead projectile. The projectile comprises 34-94%, by weight, binder. The binder comprises poly ether block amide resin. The projectile further comprises 6-66%, by weight, ballast. The ballast comprises at least one member selected from a group consisting of tungsten, tungsten carbide, molybdenum, tantalum, ferro-tungsten, copper, bismuth, iron, steel, brass, aluminum bronze, beryllium copper, tin, aluminum, titanium, zinc, nickel silver alloy, cupronickel and nickel. The projectile can be prepared with a particularly preferred specific gravity of 5-14 and more preferably 11-11.5.
Owner:ACCUTEC USA
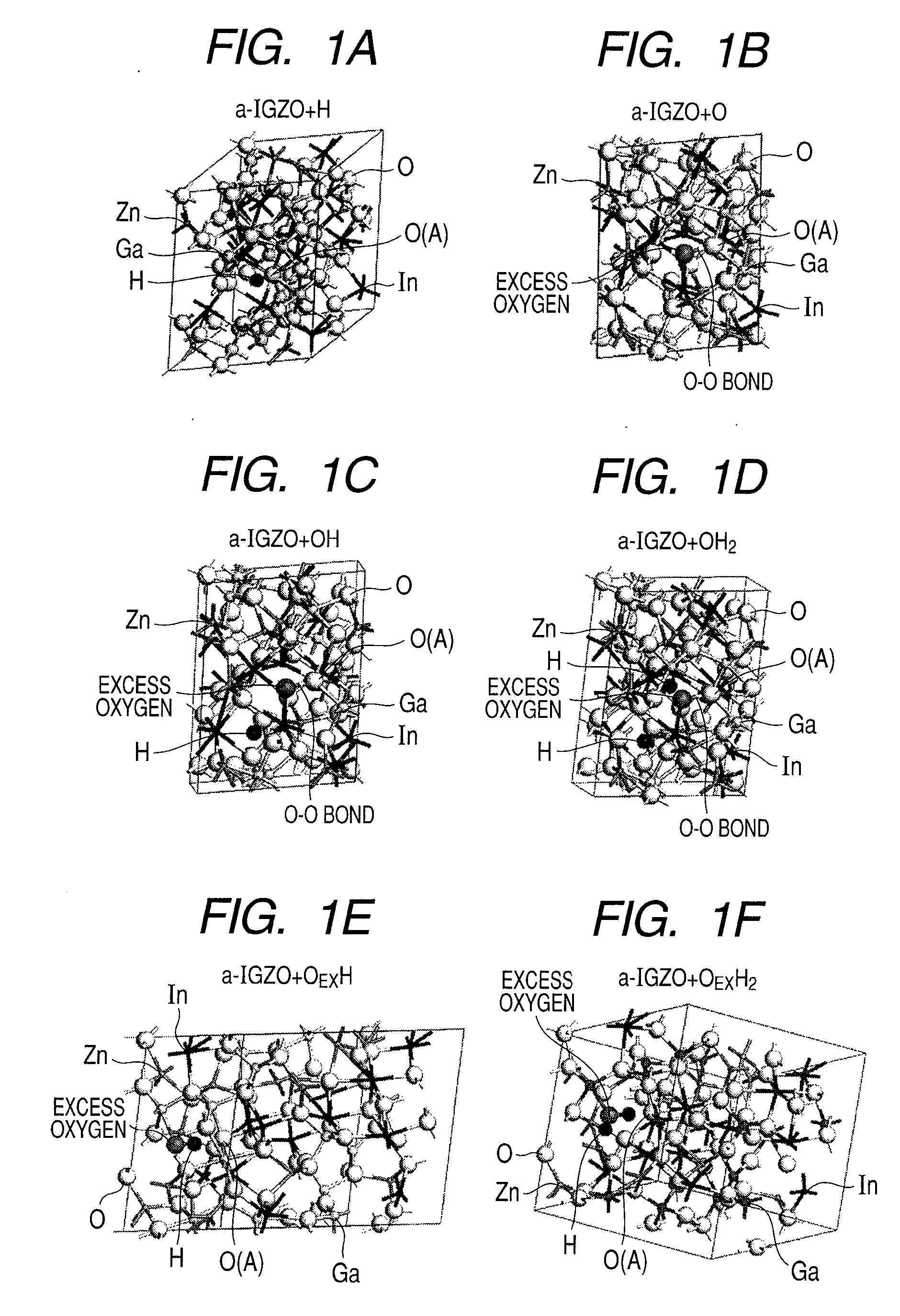
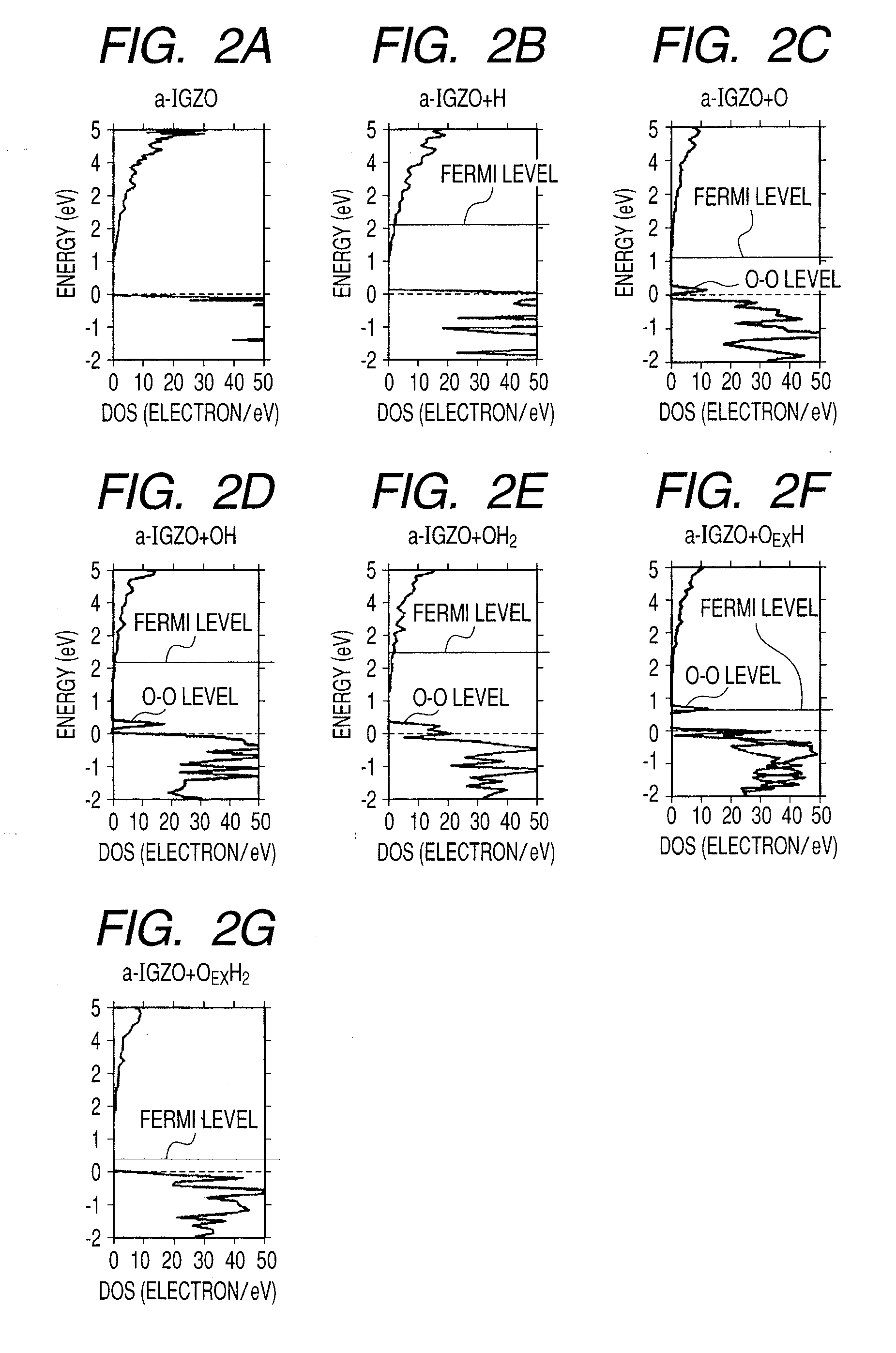
Amorphous oxide semiconductor and thin film transistor using the same
InactiveUS20100051938A1Improve transistor characteristicsLow costTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIndiumHydrogen
There is provided an amorphous oxide semiconductor including hydrogen and at least one element of indium (In) and zinc (Zn), the amorphous oxide semiconductor containing one of hydrogen atoms and deuterium atoms of 1×1020 cm−3 or more to 1×1022 cm−3 or less, and a density of bonds between oxygen and hydrogen except bonds between excess oxygen (OEX) and hydrogen in the amorphous oxide semiconductor being 1×1018 cm−3 or less.
Owner:CANON KK
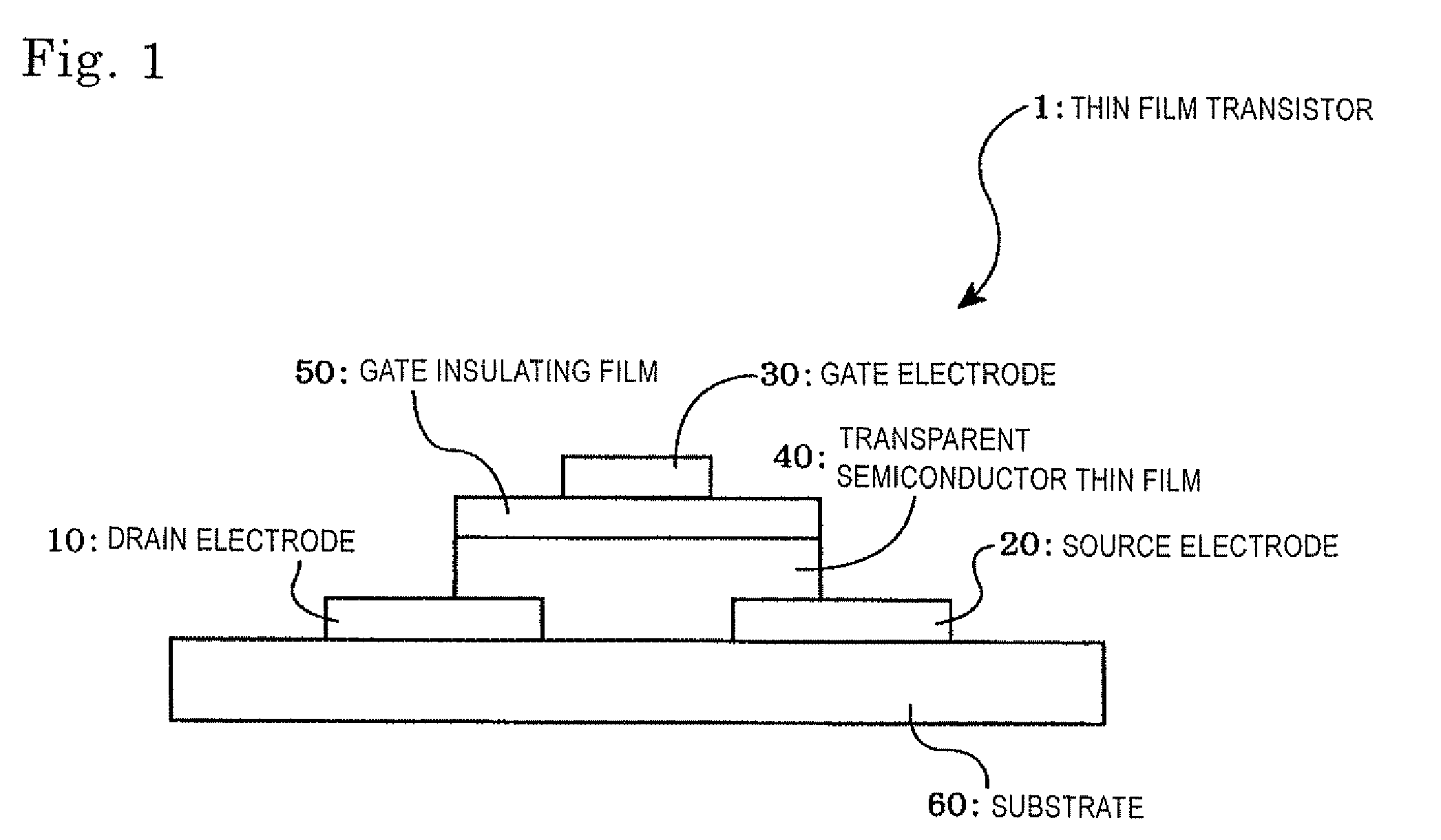
Semiconductor thin film, method for manufacturing the same, thin film transistor, and active-matrix-driven display panel
ActiveUS7998372B2Hardly erroneously operatesSmall currentNanotechConductive materialIndiumActive matrix
Disclosed is a semiconductor thin film which can be formed at a relatively low temperature even on a flexible resin substrate. Since the semiconductor thin film is stable to visible light and has high device characteristics such as transistor characteristics, in the case where the semiconductor thin film is used as a switching device for driving a display, even when overlapped with a pixel part, the luminance of a display panel does not deteriorate. Specifically, a transparent semiconductor thin film 40 is produced by forming an amorphous film containing zinc oxide and indium oxide and then oxidizing the film so that the resulting film has a carrier density of 10+17 cm−3 or less, a Hall mobility of 2 cm2 / V·sec or higher, and an energy band gap of 2.4 EV or more.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com