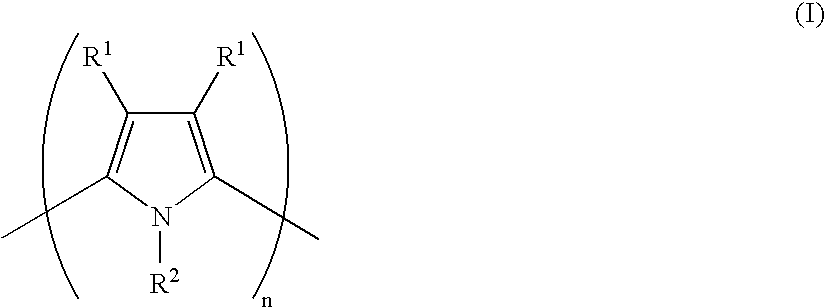Patents
Literature
19312results about "Nanoinformatics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
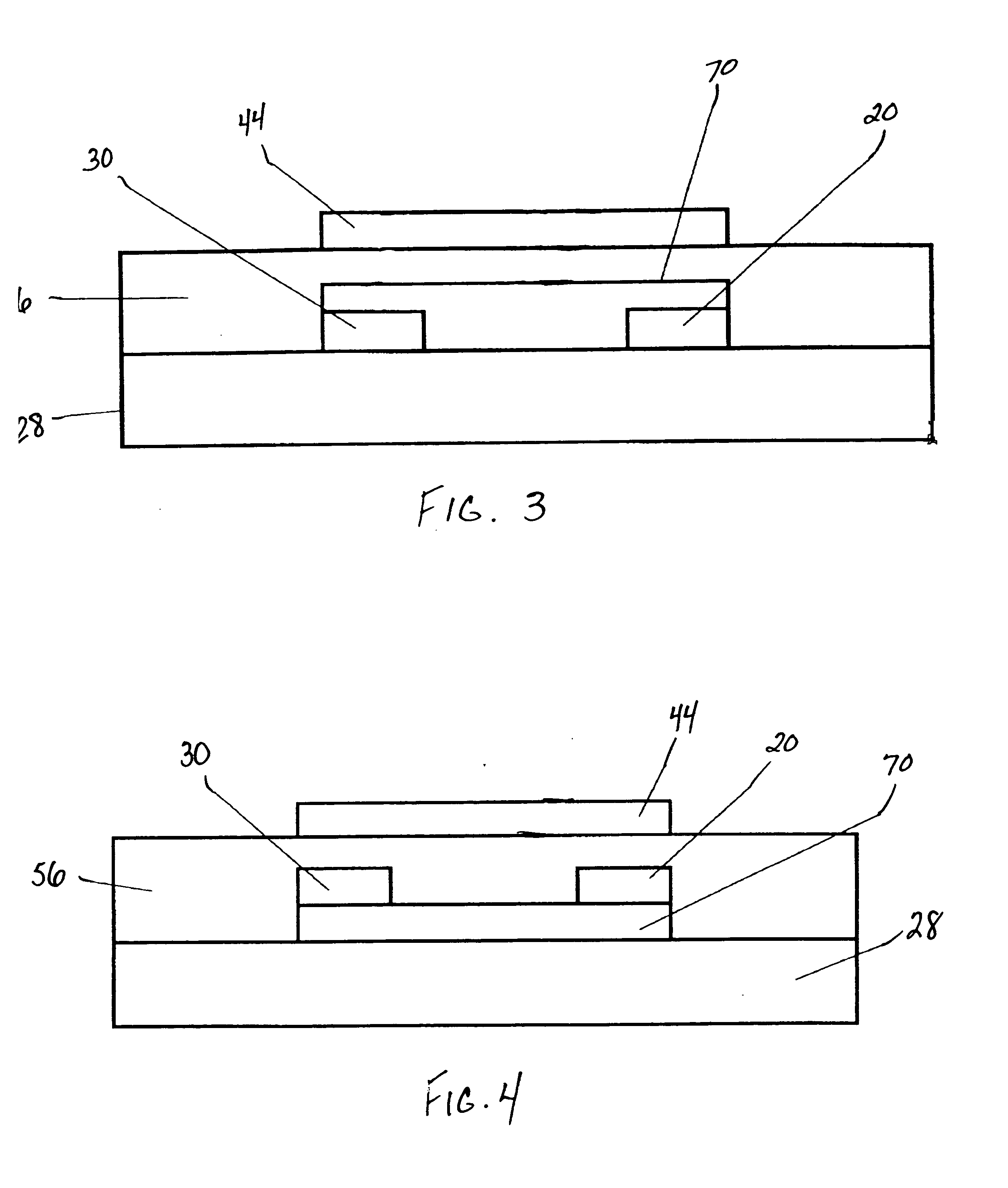
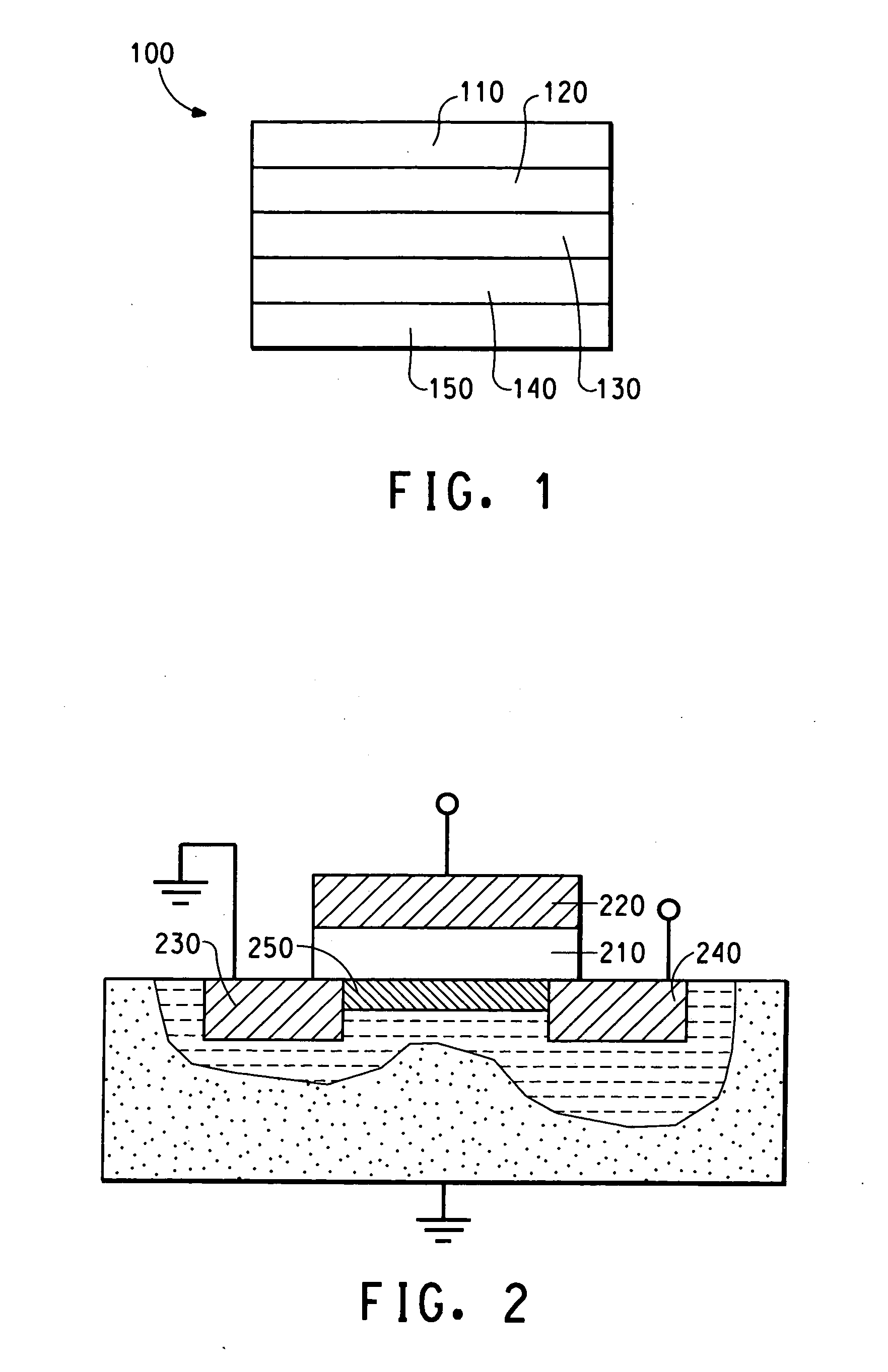
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
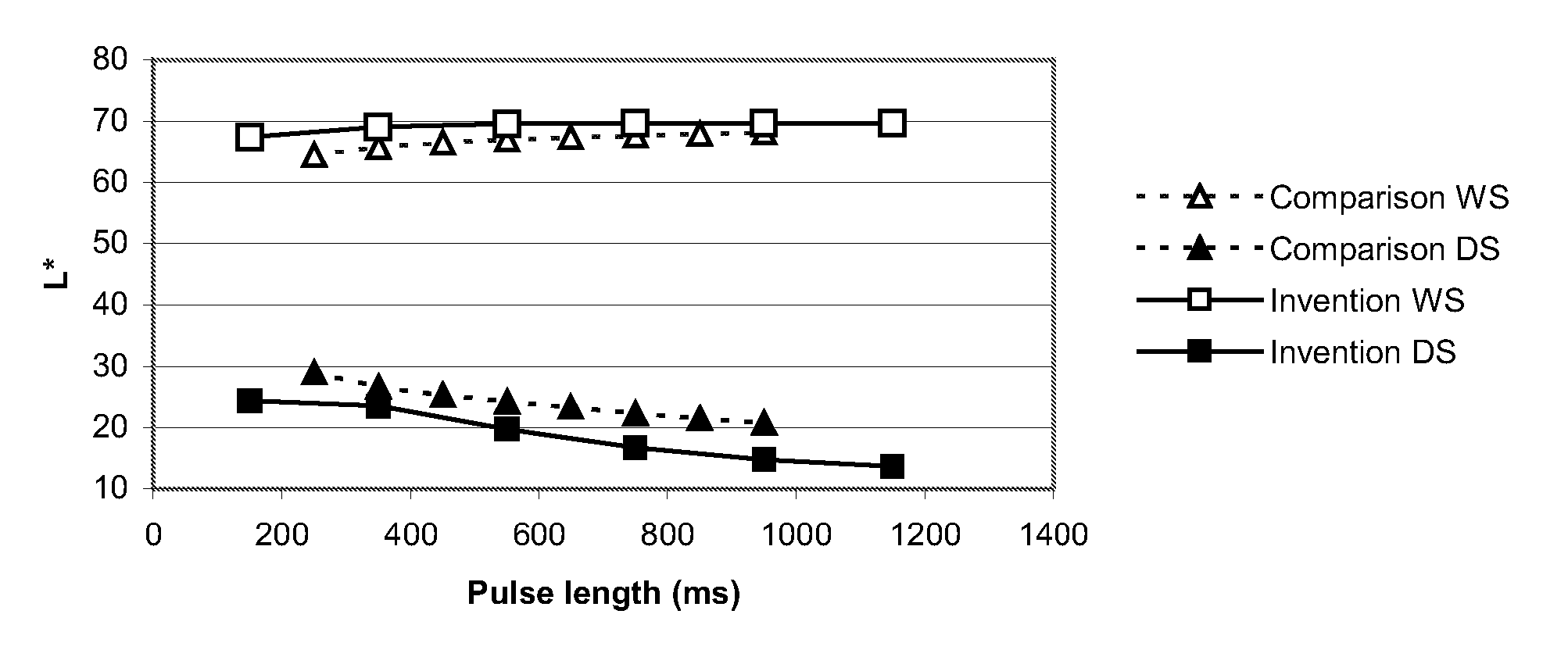
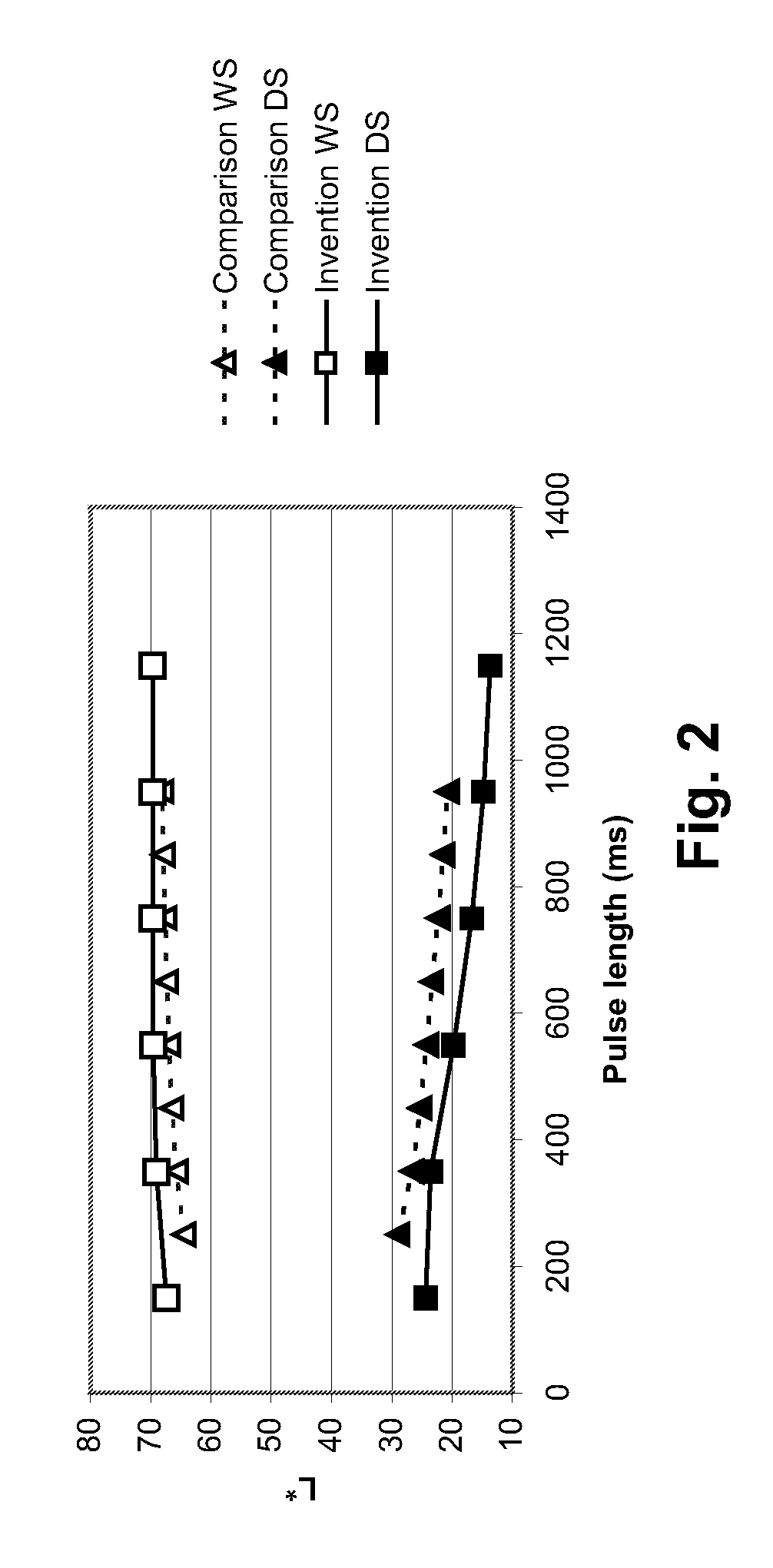
ActiveUS7402506B2NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsZinc
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
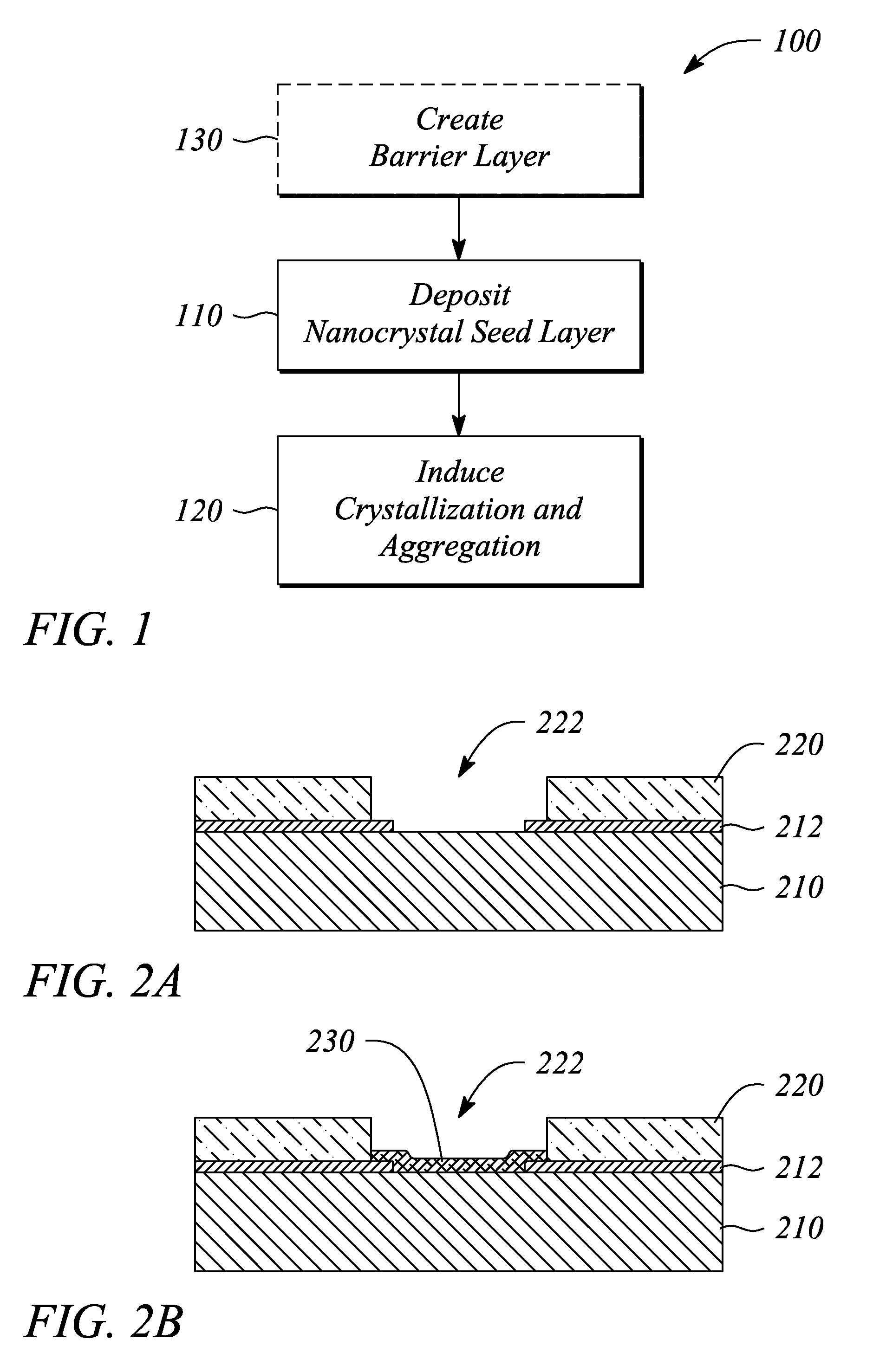
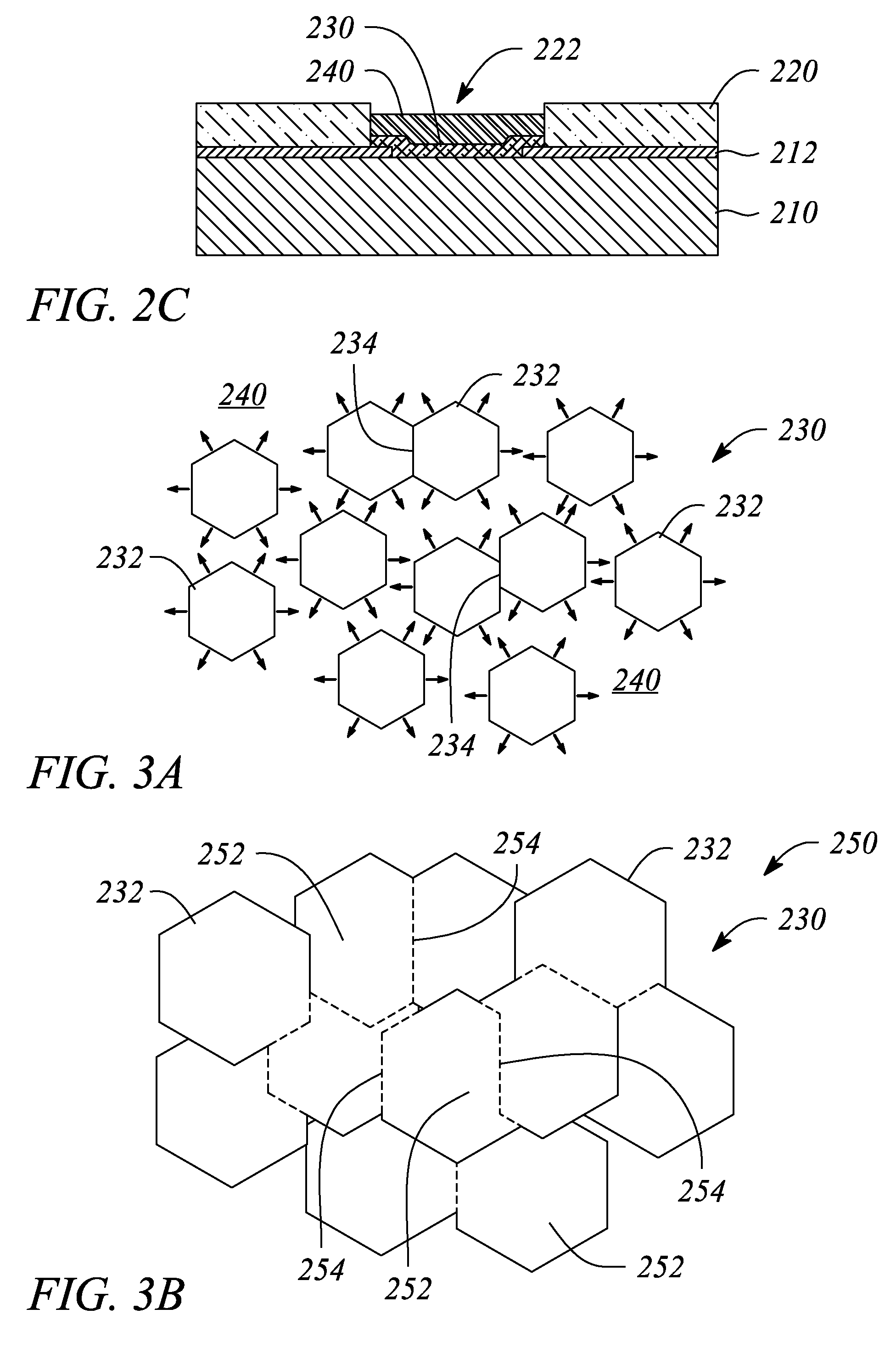
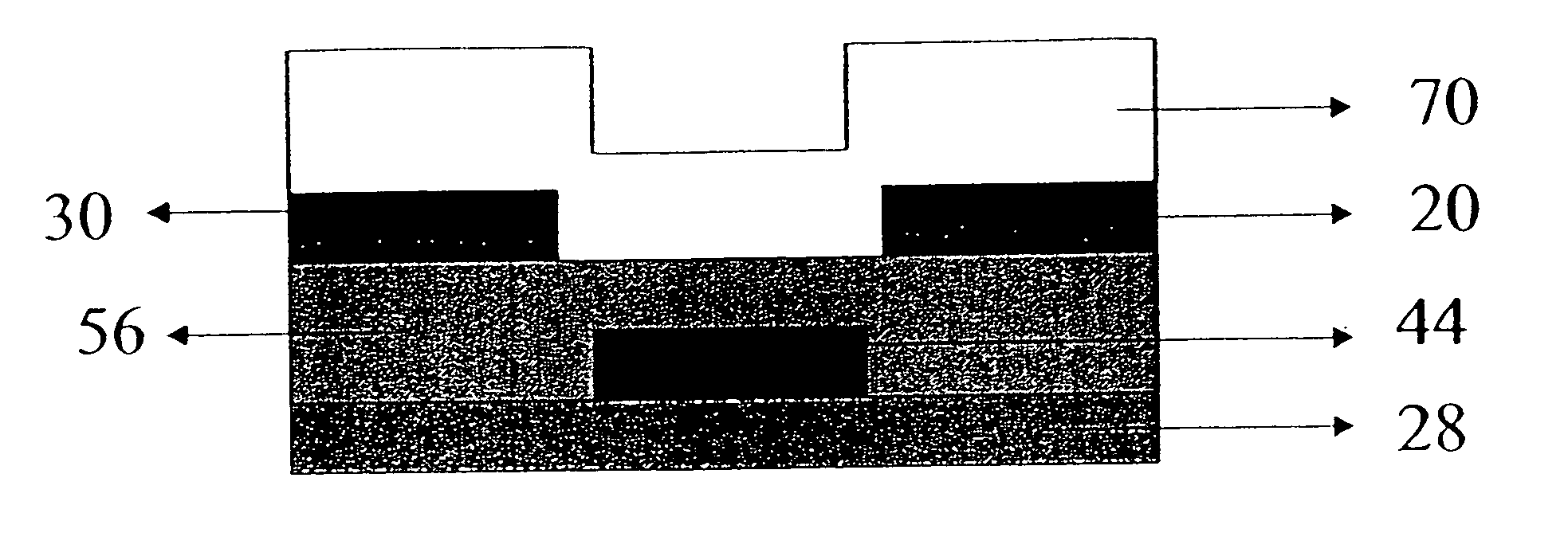
Fused nanocrystal thin film semiconductor and method
A thin film semiconductor and a method of its fabrication use induced crystallization and aggregation of a nanocrystal seed layer to form a merged-domain layer. The nanocrystal seed layer is deposited onto a substrate surface within a defined boundary. A reaction temperature below a boiling point of a reaction solution is employed. A thin film metal-oxide transistor and a method of its production employ the thin film semiconductor as a channel of the transistor. The merged-domain layer exhibits high carrier mobility.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Methods of making thin film transistors comprising zinc-oxide-based semiconductor materials and transistors made thereby
A thin film transistor comprises a zinc-oxide-containing semiconductor material. Such transistors can further comprise spaced apart first and second contact means or electrodes in contact with said material. Further disclosed is a process for fabricating a thin film transistor device, wherein the substrate temperature is no more than 300° C. during fabrication.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
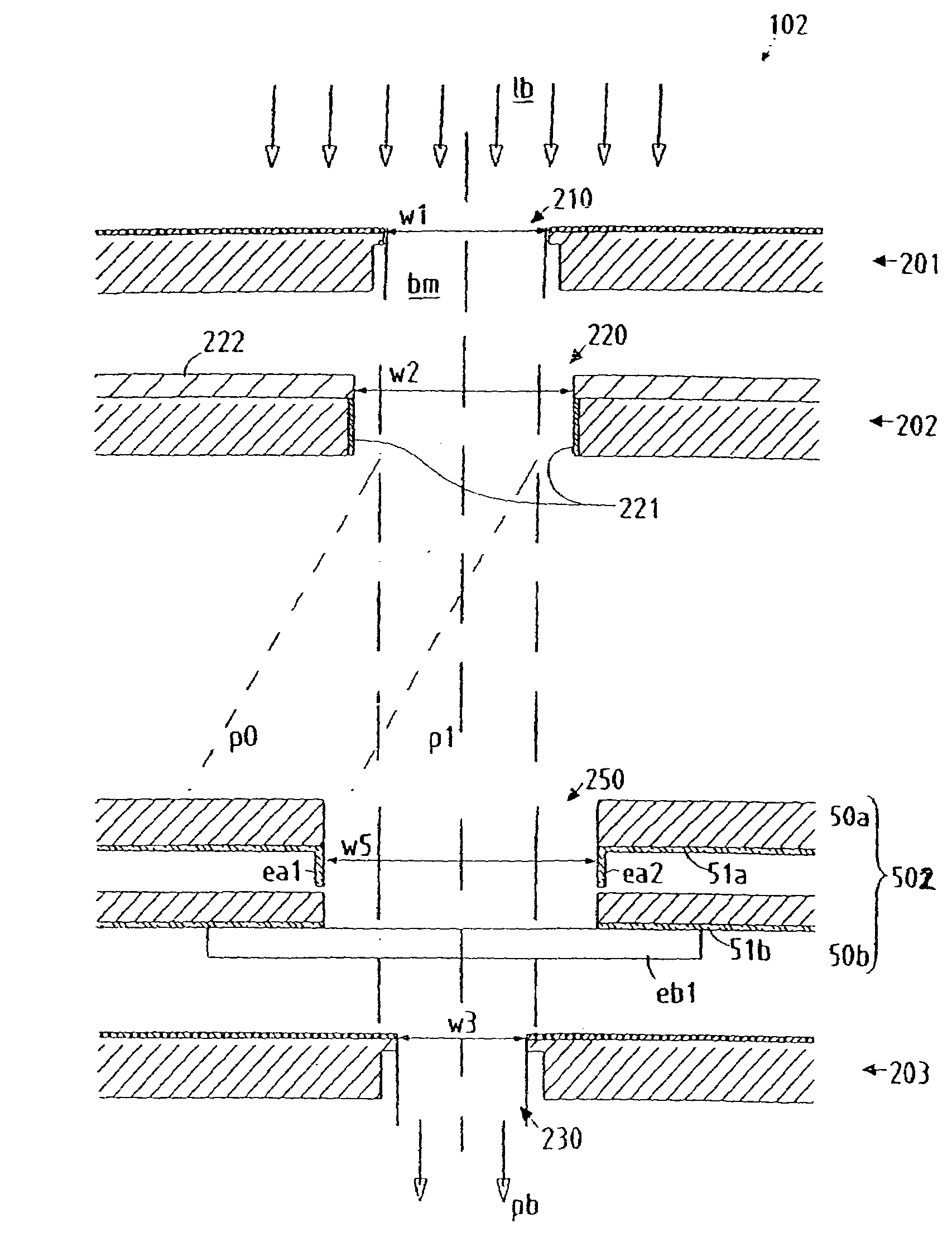
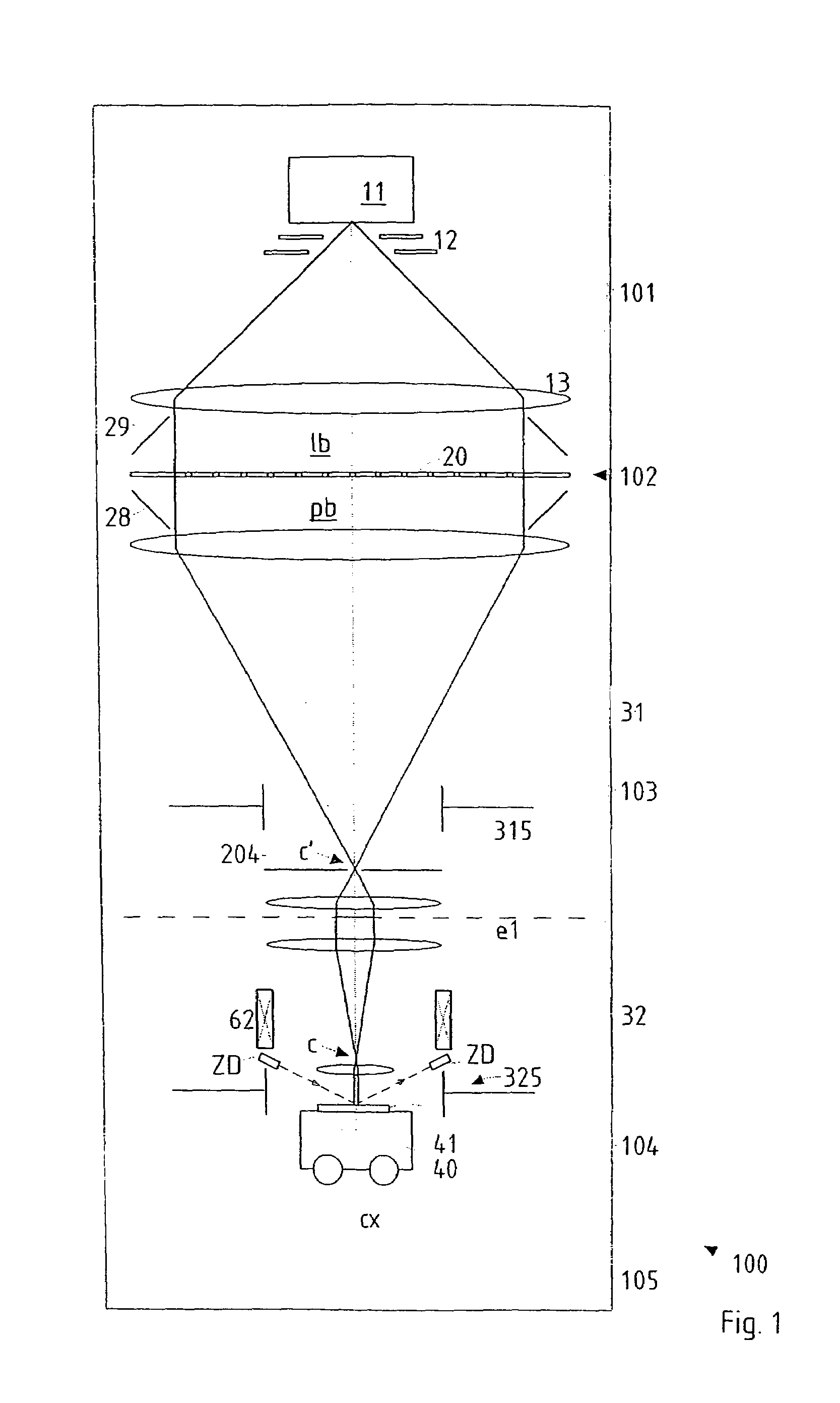
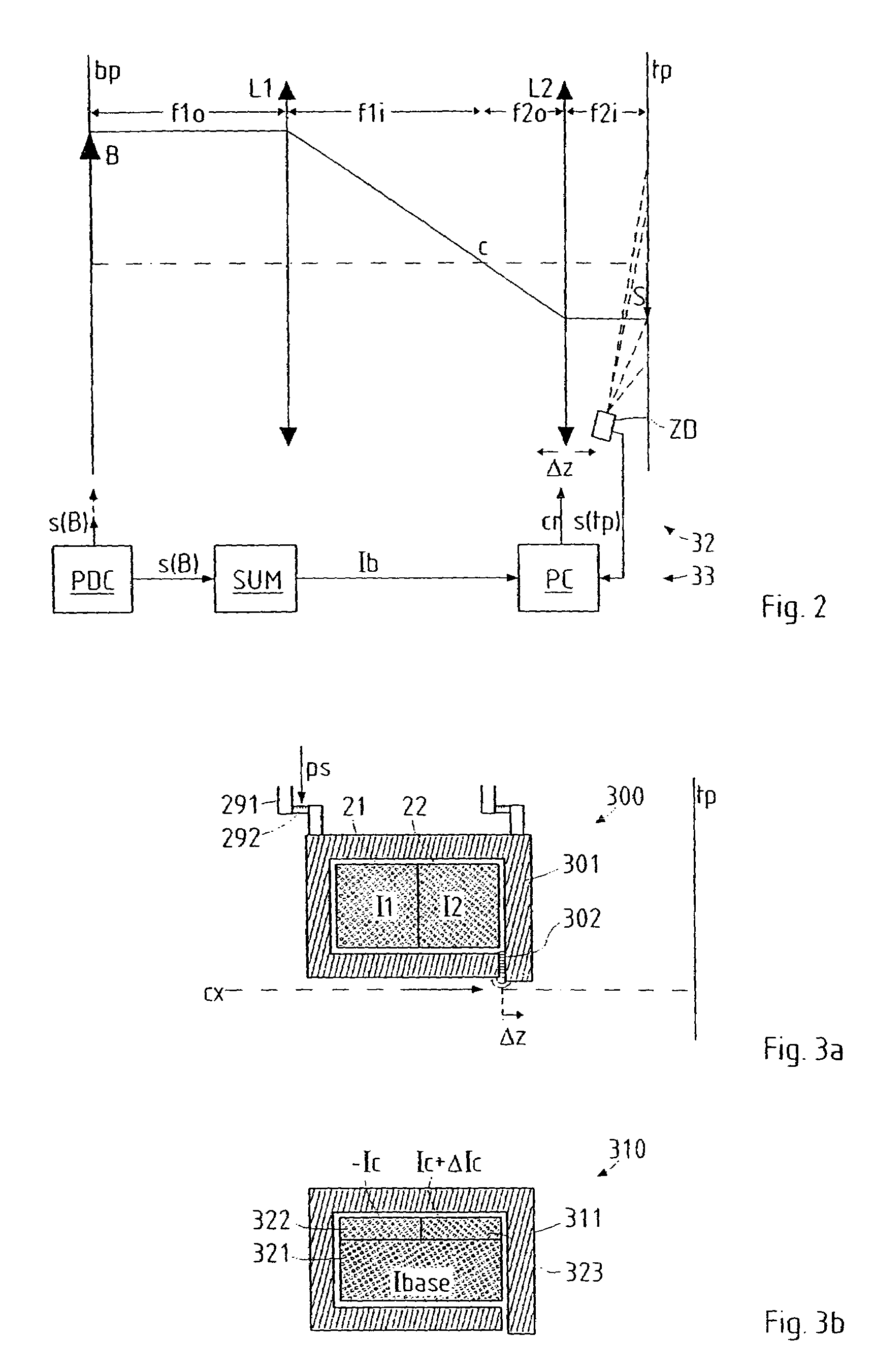
Particle-optical projection system
ActiveUS7388217B2Minimize distortionCompensation deviationElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsOptical axisProjection system
In a particle-optical projection system a pattern is imaged onto a target by means of energetic electrically charged particles. The pattern is represented in a patterned beam of said charged particles emerging from the object plane through at least one cross-over; it is imaged into an image with a given size and distortion. To compensate for the Z-deviation of the image position from the actual positioning of the target (Z denotes an axial coordinate substantially parallel to the optical axis), without changing the size of the image, the system includes a position detector for measuring the Z-position of several locations of the target, and a controller for calculating modifications of selected lens parameters of the final particle-optical lens and controlling said lens parameters according to said modifications.
Owner:IMS NANOFABTION
Demultiplexer for a molecular wire crossbar network (MWCN DEMUX)
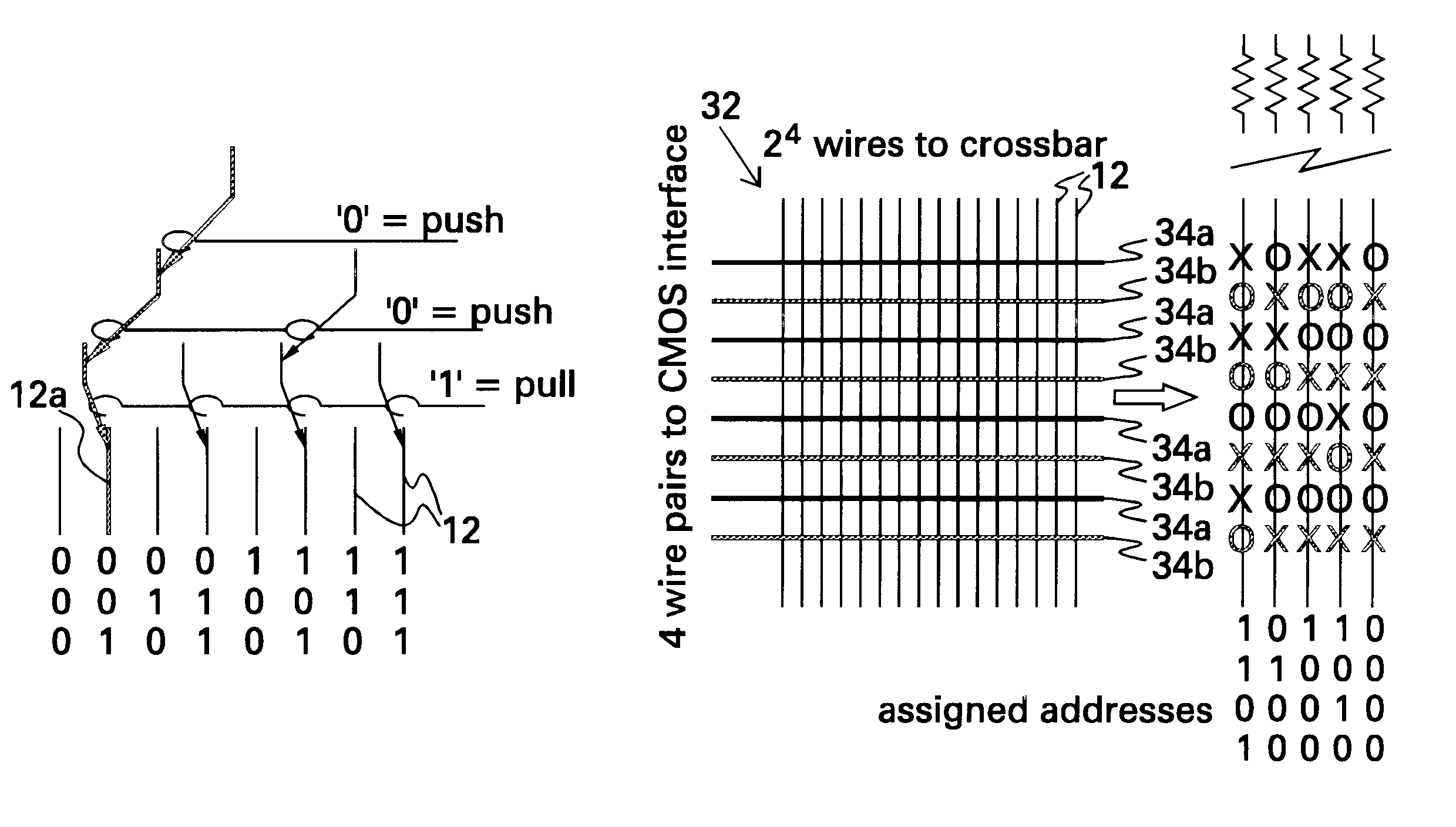
A demultiplexer for a two-dimensional array of a plurality of nanometer-scale switches (molecular wire crossbar network) is disclosed. Each switch comprises a pair of crossed wires which form a junction where one wire crosses another and at least one connector species connecting said pair of crossed wires in said junction. The connector species comprises a bi-stable molecule. The demultiplexer comprises a plurality of address lines accessed by a first set of wires in the two-dimensional array by randomly forming contacts between each wire in the first set of wires to at least one of the address lines. The first set of wires crosses a second set of wires to form the junctions. The demultiplexer solves both the problems of data input and output to a molecular electronic system and also bridges the size gap between CMOS and molecules with an architecture that can scale up to extraordinarily large numbers of molecular devices. Further, the demultiplexer is very defect tolerant, and can work despite a large number of defects in the system.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Projection exposure method and projection exposure system
InactiveUS20050030506A1Avoid defocusing errorProvides adequateNanoinformaticsMaterial analysis by optical meansLithographic artistHigh numerical aperture
In a method for manufacturing semiconductor devices and other finely structured parts, a projection objective (5) is used in order to project the image of a pattern arranged in the object plane of the projection objective onto a photosensitive substrate which is arranged in the region of the image plane (12) of the projection objective. In this case, there is set between an exit surface (15), assigned to the projection objective, for exposing light and an incoupling surface (11), assigned to the substrate, for exposing light a small finite working distance (16) which is at least temporarily smaller in size and exposure time interval than a maximum extent of an optical near field of the light emerging from the exit surface. As a result, projection objectives with very high numerical apertures in the region of NA>0.8 or more can be rendered useful for contactless projection lithography.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
Doped elongated semiconductors, growing such semiconductors, devices including such semiconductors and fabricating such devices
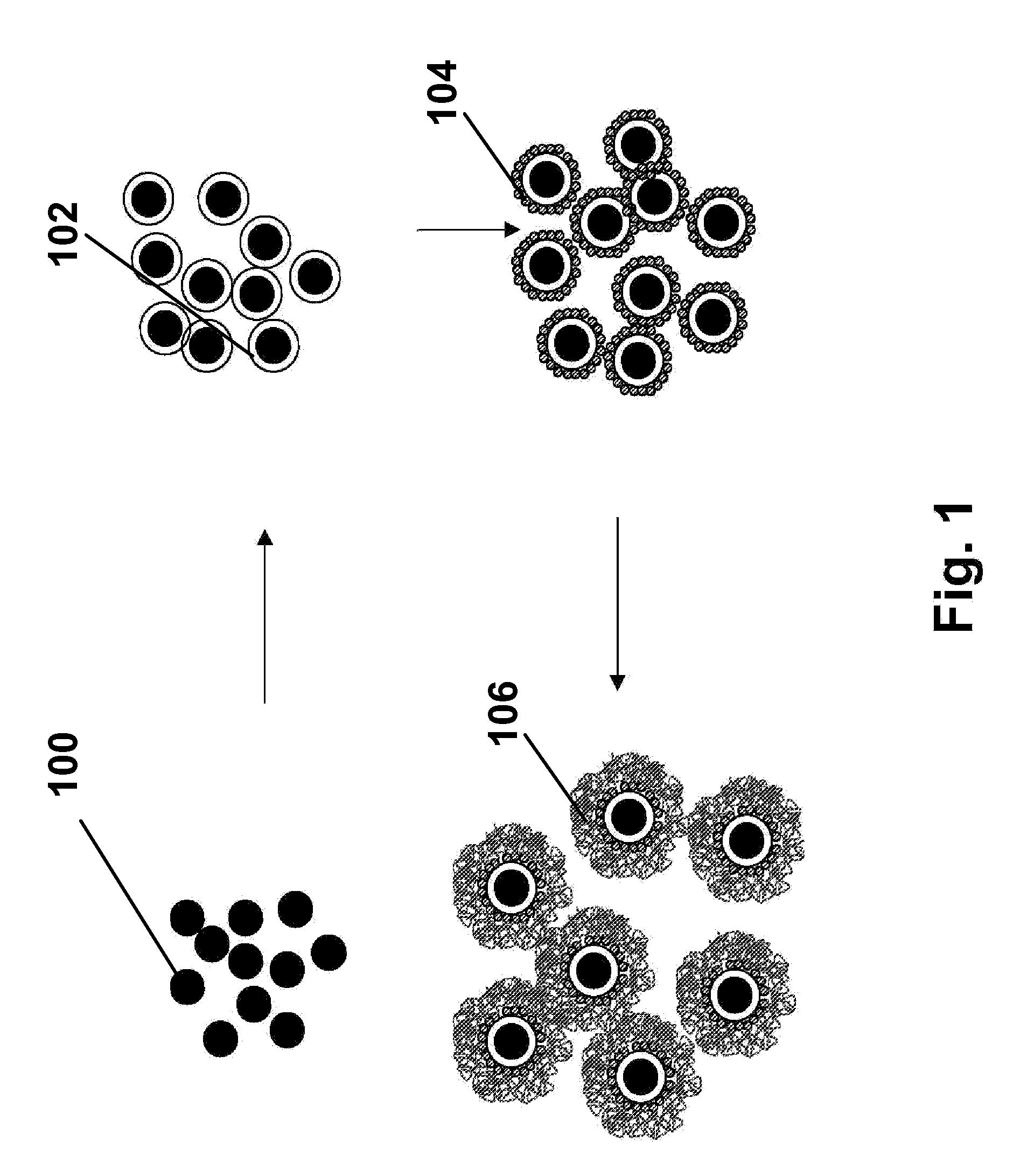
A bulk-doped semiconductor that is at least one of the following: a single crystal, an elongated and bulk-doped semiconductor that, at any point along its longitudinal axis, has a largest cross-sectional dimension less than 500 nanometers, and a free-standing and bulk-doped semiconductor with at least one portion having a smallest width of less than 500 nanometers. Such a semiconductor may comprise an interior core comprising a first semiconductor; and an exterior shell comprising a different material than the first semiconductor. Such a semiconductor may be elongated and my have, at any point along a longitudinal section of such a semiconductor, a ratio of the length of the section to a longest width is greater than 4:1, or greater than 10:1, or greater than 100:1, or even greater than 1000:1. At least one portion of such a semiconductor may a smallest width of less than 200 nanometers, or less than 150 nanometers, or less than 100 nanometers, or less than 80 nanometers, or less than 70 nanometers, or less than 60 nanometers, or less than 40 nanometers, or less than 20 nanometers, or less than 10 nanometers, or even less than 5 nanometers. Such a semiconductor may be a single crystal and may be free-standing. Such a semiconductor may be either lightly n-doped, heavily n-doped, lightly p-doped or heavily p-doped. Such a semiconductor may be doped during growth. Such a semiconductor may be part of a device, which may include any of a variety of devices and combinations thereof, and, and a variety of assembling techniques may be used to fabricate devices from such a semiconductor. Two or more of such a semiconductors, including an array of such semiconductors, may be combined to form devices, for example, to form a crossed p-n junction of a device. Such devices at certain sizes may exhibit quantum confinement and other quantum phenomena, and the wavelength of light emitted from one or more of such semiconductors may be controlled by selecting a width of such semiconductors. Such semiconductors and device made therefrom may be used for a variety of applications.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
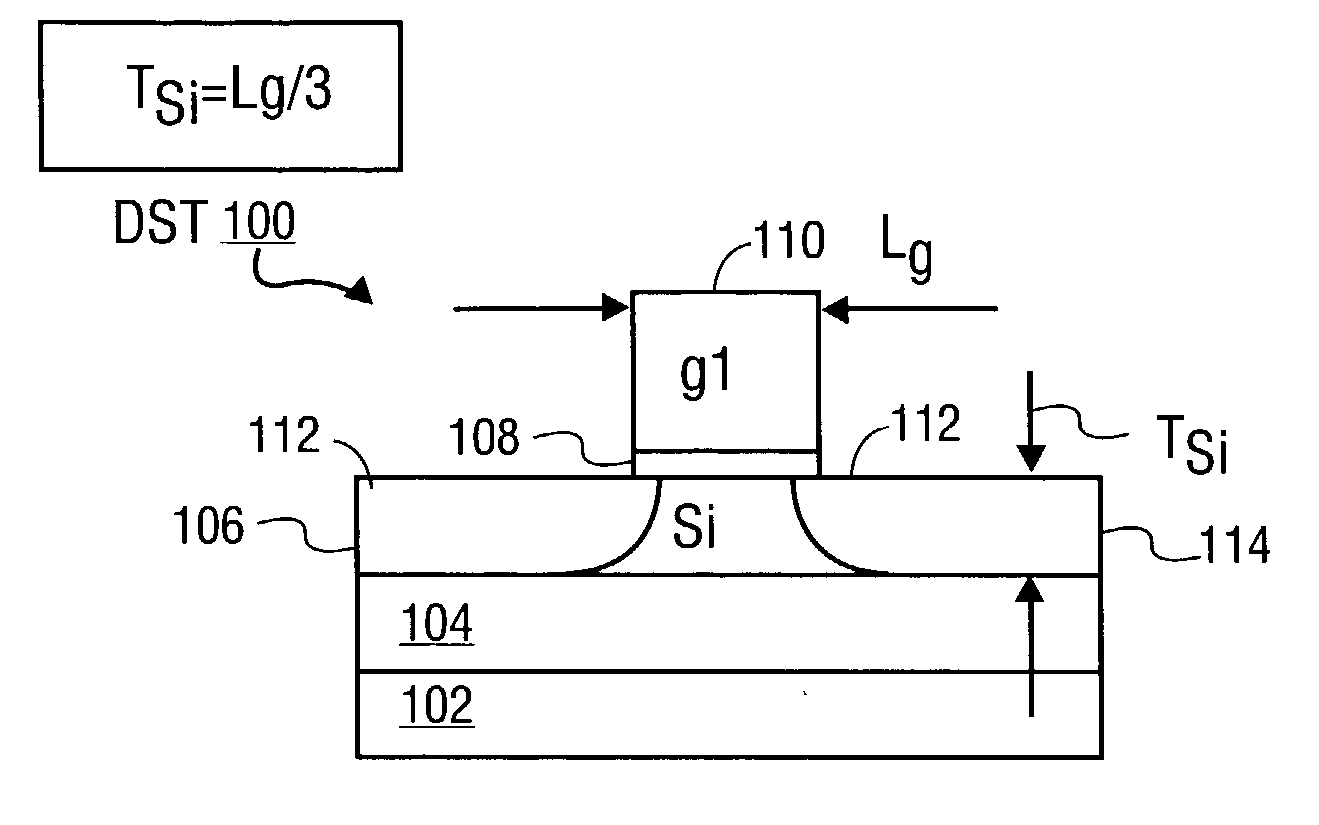
Non-planar gate all-around device and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS20140225065A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNanowireGate dielectric
A non-planar gate all-around device and method of fabrication thereby are described. In one embodiment, the device includes a substrate having a top surface with a first lattice constant. Embedded epi source and drain regions are formed on the top surface of the substrate. The embedded epi source and drain regions have a second lattice constant that is different from the first lattice constant. Channel nanowires having a third lattice are formed between and are coupled to the embedded epi source and drain regions. In an embodiment, the second lattice constant and the third lattice constant are different from the first lattice constant. The channel nanowires include a bottom-most channel nanowire and a bottom gate isolation is formed on the top surface of the substrate under the bottom-most channel nanowire. A gate dielectric layer is formed on and all-around each channel nanowire. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric layer and surrounding each channel nanowire.
Owner:SONY CORP
Nanostructure and nanocomposite based compositions and photovoltaic devices
InactiveUS6878871B2Improve equipment efficiencyMaterial nanotechnologyFinal product manufactureSemiconductor nanocrystalsNanostructure
Nanocomposite photovoltaic devices are provided that generally include semiconductor nanocrystals as at least a portion of a photoactive layer. Photovoltaic devices and other layered devices that comprise core-shell nanostructures and / or two populations of nanostructures, where the nanostructures are not necessarily part of a nanocomposite, are also features of the invention. Varied architectures for such devices are also provided including flexible and rigid architectures, planar and non-planar architectures and the like, as are systems incorporating such devices, and methods and systems for fabricating such devices. Compositions comprising two populations of nanostructures of different materials are also a feature of the invention.
Owner:NANOSYS INC
Touch screen sensor
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
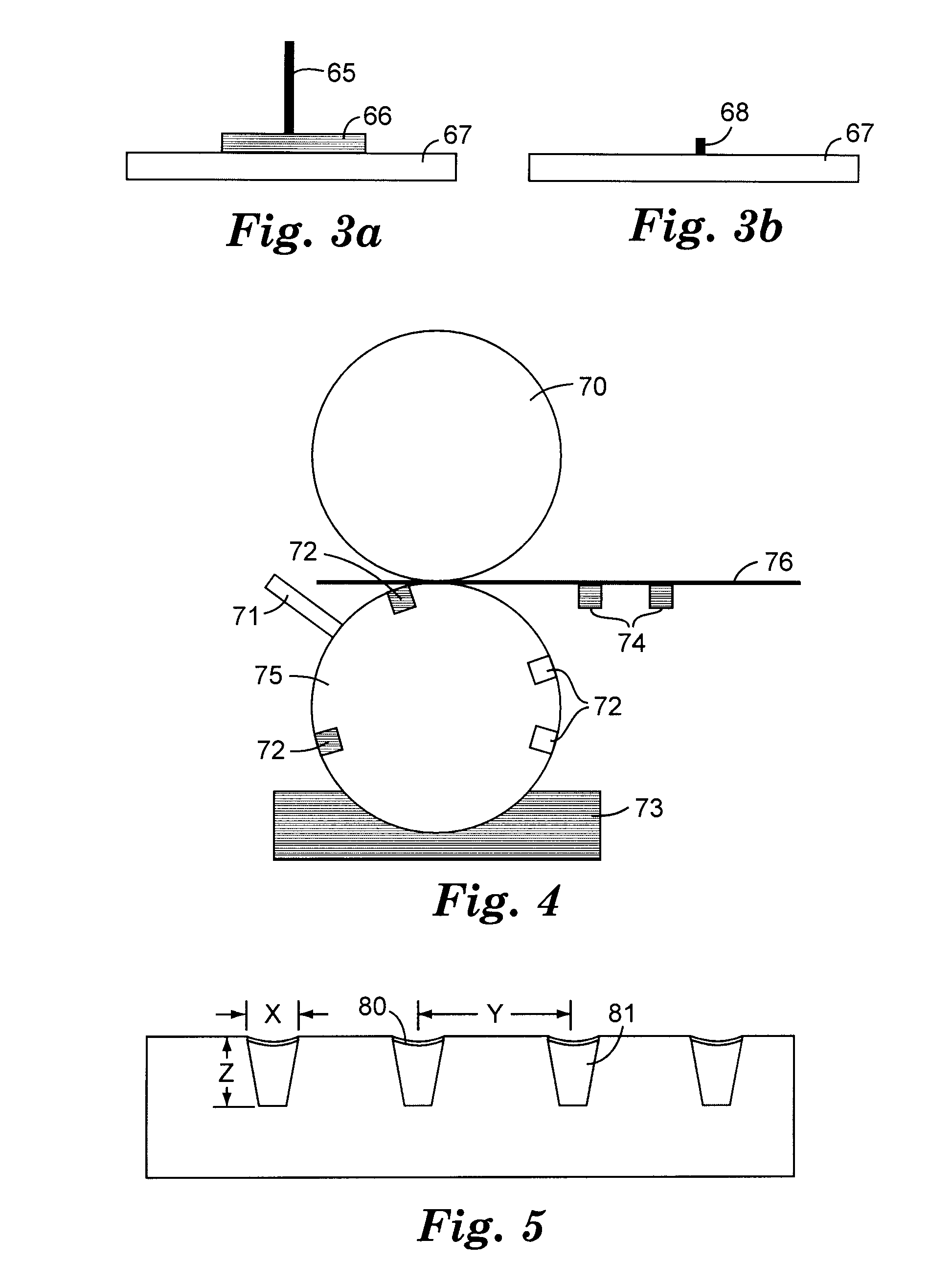
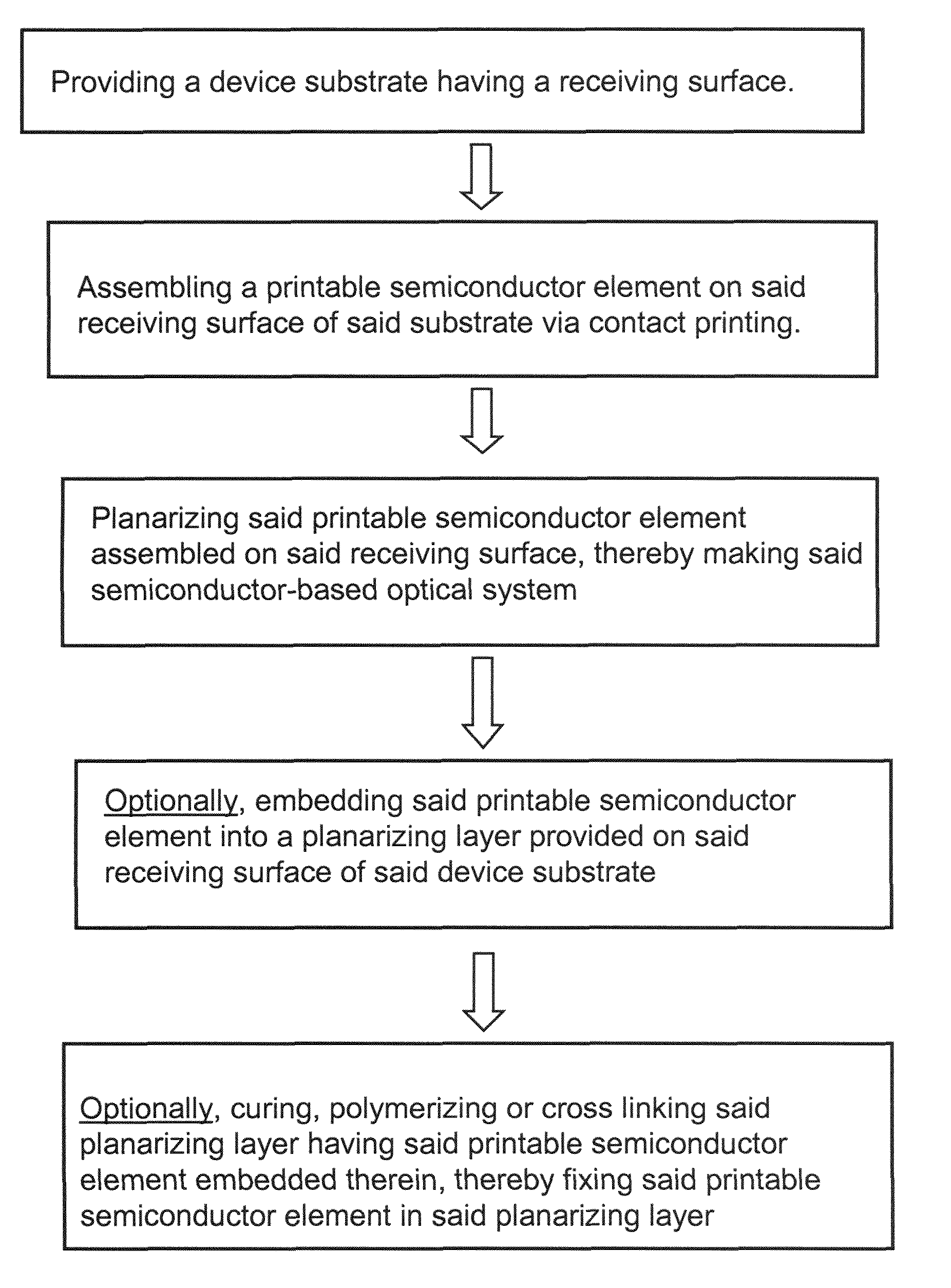
Optical systems fabricated by printing-based assembly
ActiveUS7972875B2Low costImprove performanceFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsLight sensingSingle crystal
Provided are optical devices and systems fabricated, at least in part, via printing-based assembly and integration of device components. In specific embodiments the present invention provides light emitting systems, light collecting systems, light sensing systems and photovoltaic systems comprising printable semiconductor elements, including large area, high performance macroelectronic devices. Optical systems of the present invention comprise semiconductor elements assembled, organized and / or integrated with other device components via printing techniques that exhibit performance characteristics and functionality comparable to single crystalline semiconductor based devices fabricated using conventional high temperature processing methods. Optical systems of the present invention have device geometries and configurations, such as form factors, component densities, and component positions, accessed by printing that provide a range of useful device functionalities. Optical systems of the present invention include devices and device arrays exhibiting a range of useful physical and mechanical properties including flexibility, shapeability, conformability and stretchablity.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
Tri-gate devices and methods of fabrication
The present invention is a semiconductor device comprising a semiconductor body having a top surface and laterally opposite sidewalls formed on a substrate. A gate dielectric layer is formed on the top surface of the semiconductor body and on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body. A gate electrode is formed on the gate dielectric on the top surface of the semiconductor body and adjacent to the gate dielectric on the laterally opposite sidewalls of the semiconductor body.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Dielectrophoretic displays
A dielectrophoretic display comprises a substrate having walls defining at least one cavity, the cavity having a viewing surface and a side wall inclined to the viewing surface; a suspending fluid contained within the cavity; a plurality of at least one type of particle suspended within the suspending fluid; and means for applying to the substrate an electric field effect effective to cause dielectrophoretic movement of the particles to the side wall of the cavity.
Owner:E INK CORPORATION
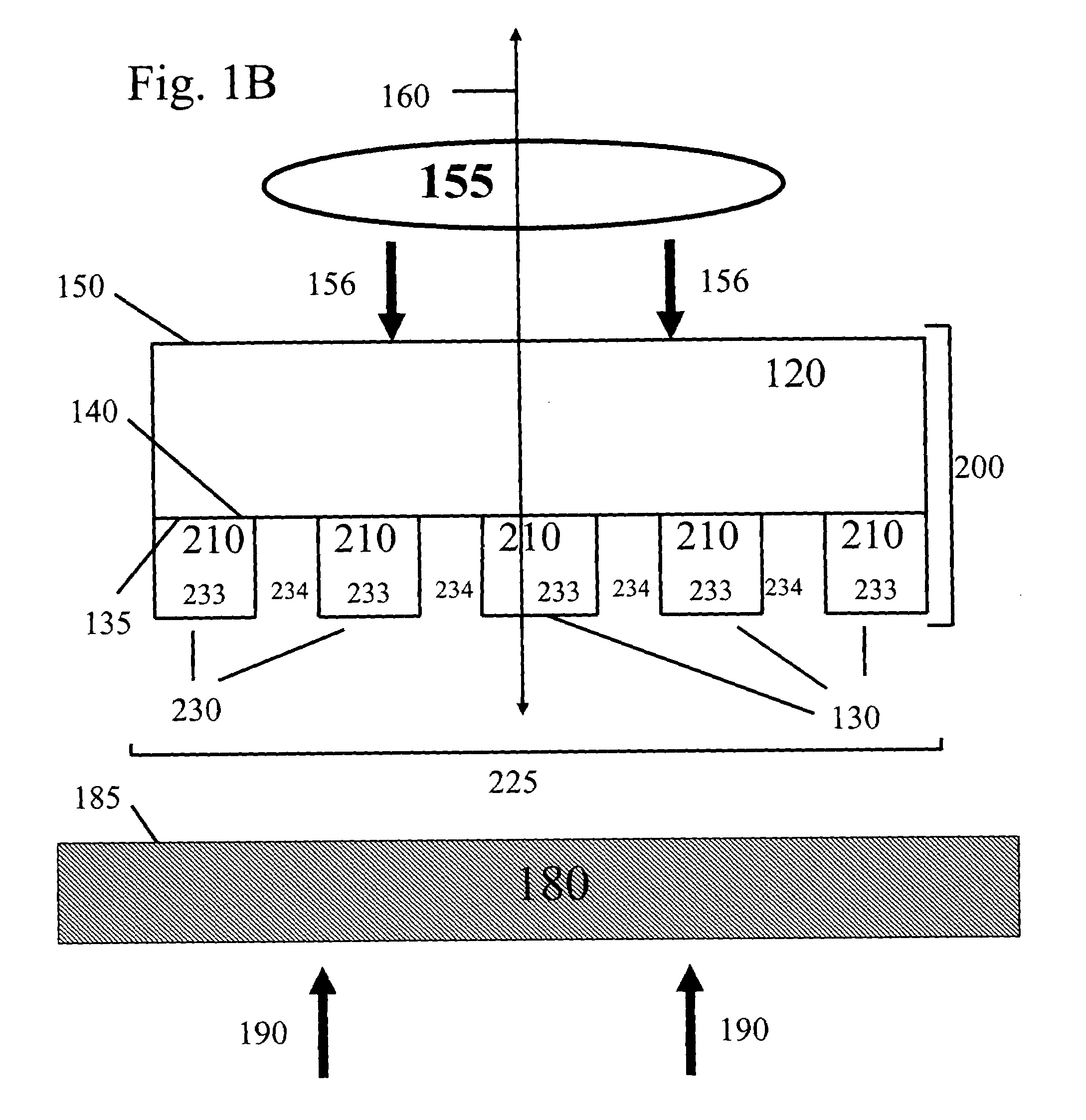
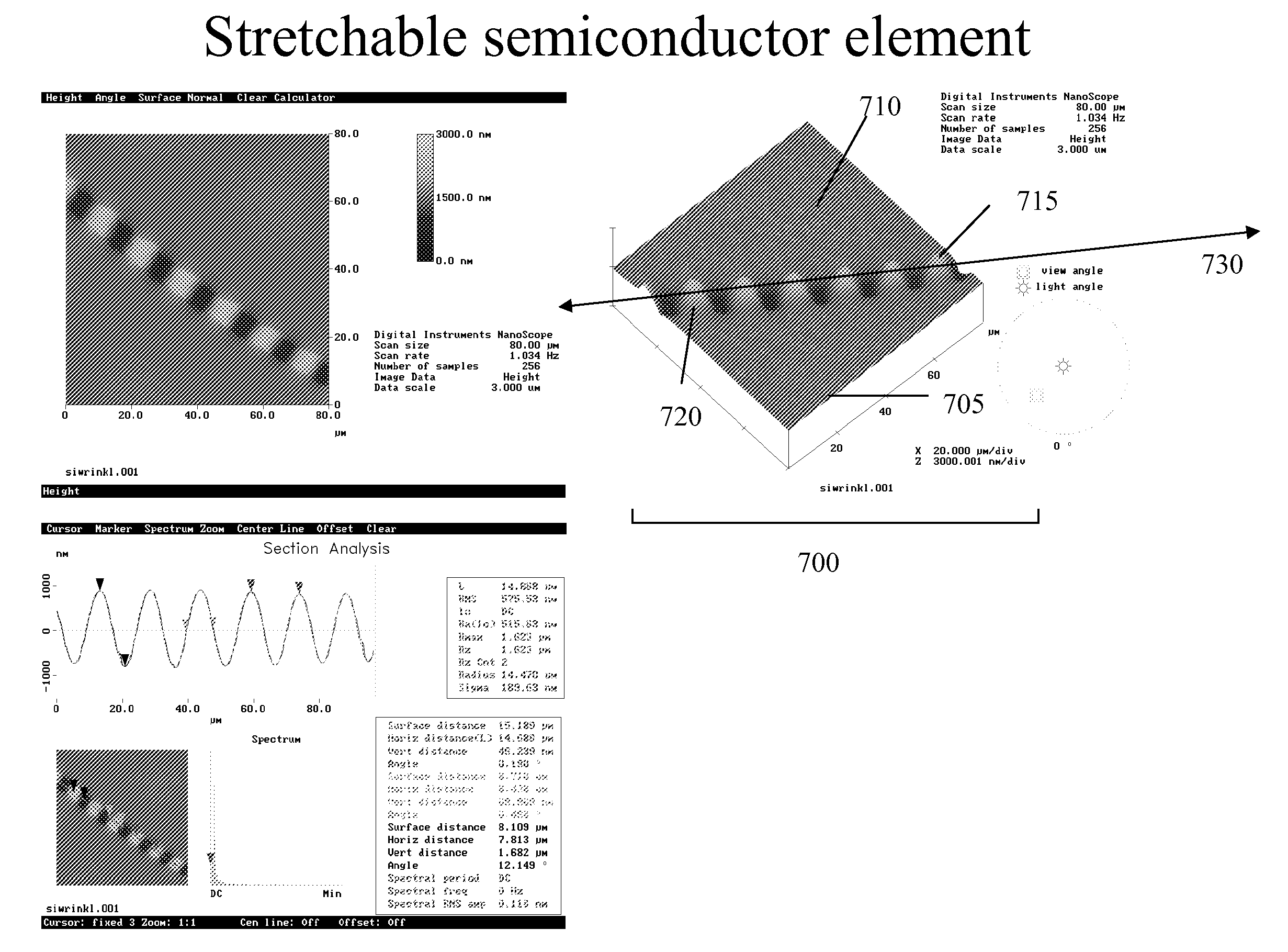
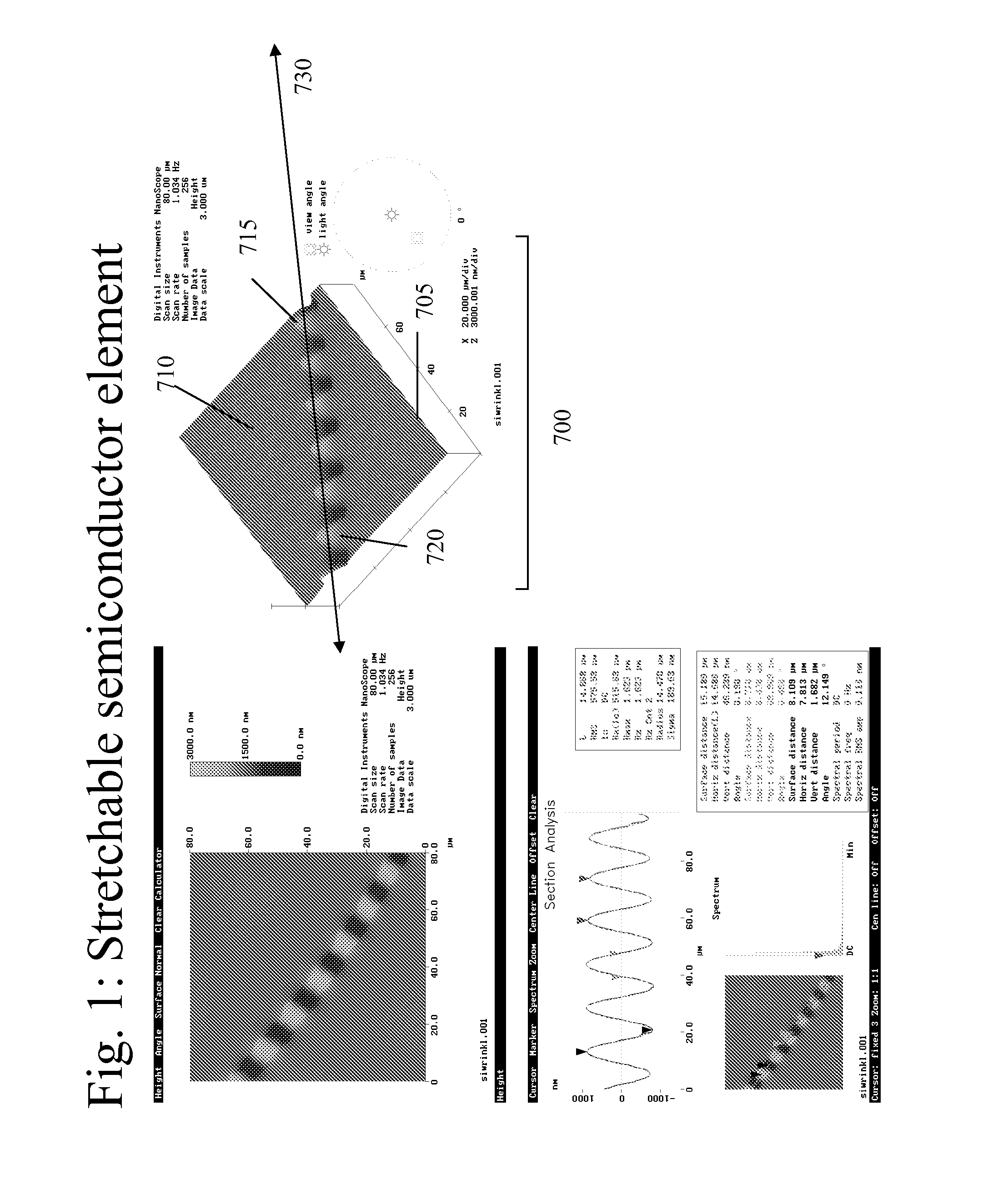
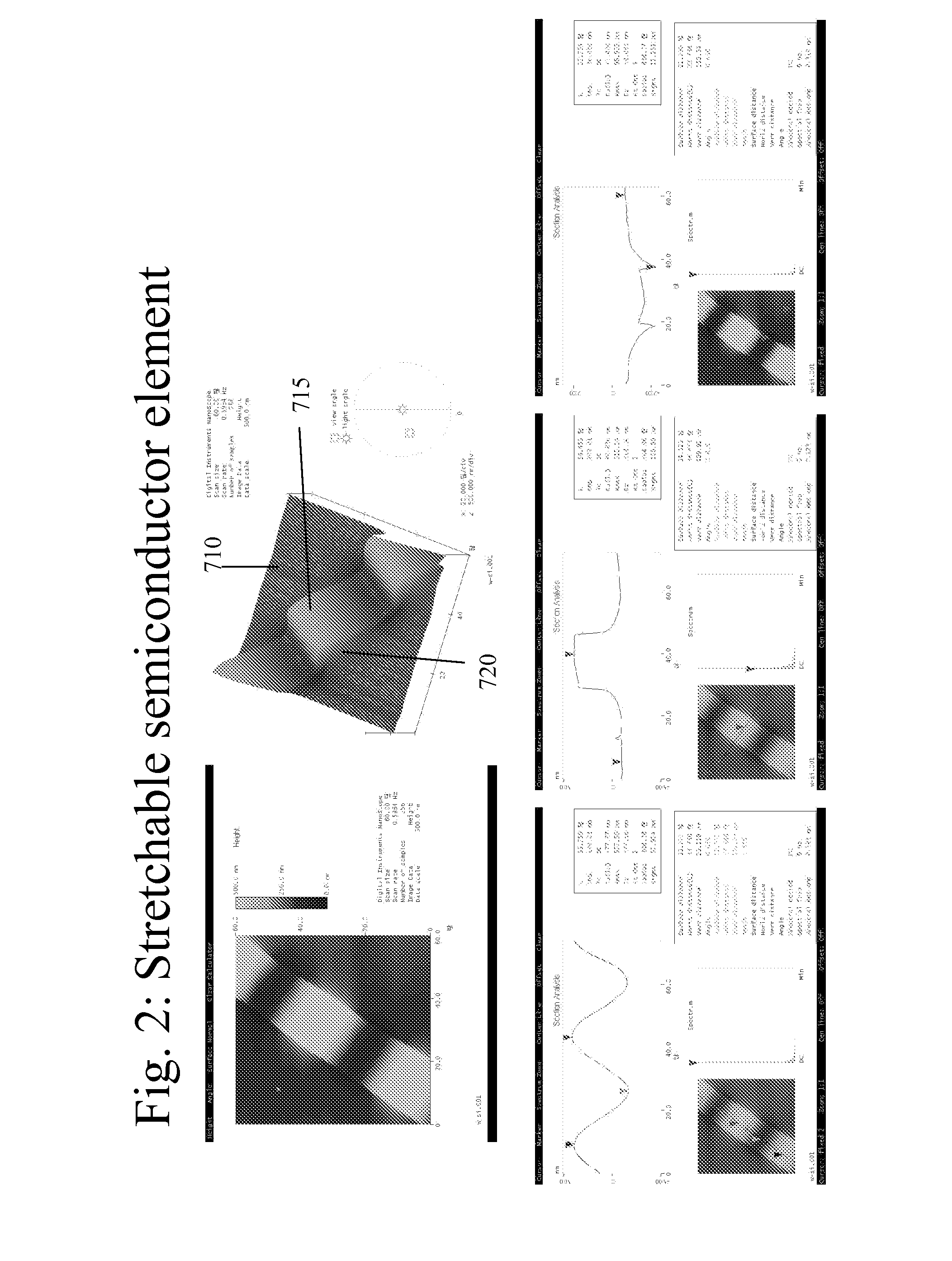
Stretchable semiconductor elements and stretchable electrical circuits
ActiveUS20060038182A1Complete release is preventedLow costTransistorDecorative surface effectsStretchable electronicsSemiconductor structure
The invention provides methods and devices for fabricating printable semiconductor elements and assembling printable semiconductor elements onto substrate surfaces. Methods, devices and device components of the present invention are capable of generating a wide range of flexible electronic and optoelectronic devices and arrays of devices on substrates comprising polymeric materials. The present invention also provides stretchable semiconductor structures and stretchable electronic devices capable of good performance in stretched configurations.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Nanowire-based transparent conductors and applications thereof
A transparent conductor including a conductive layer coated on a substrate is described. More specifically, the conductive layer comprises a network of nanowires that may be embedded in a matrix. The conductive layer is optically clear, patternable and is suitable as a transparent electrode in visual display devices such as touch screens, liquid crystal displays, plasma display panels and the like.
Owner:CHAMP GREAT INTL
Composite patterning devices for soft lithography
ActiveUS7195733B2Improve fidelityIncrease resistanceMaterial nanotechnologyNanoinformaticsNano sizeYoung's modulus
The present invention provides methods, devices and device components for fabricating patterns on substrate surfaces, particularly patterns comprising structures having microsized and / or nanosized features of selected lengths in one, two or three dimensions. The present invention provides composite patterning devices comprising a plurality of polymer layers each having selected mechanical properties, such as Young's Modulus and flexural rigidity, selected physical dimensions, such as thickness, surface area and relief pattern dimensions, and selected thermal properties, such as coefficients of thermal expansion, to provide high resolution patterning on a variety of substrate surfaces and surface morphologies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Stretchable form of single crystal silicon for high performance electronics on rubber substrates
ActiveUS7521292B2Large elongationSignificant flexingTransistorCircuit bendability/stretchabilityEngineeringFlexible electronics
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Solar cells using fullerenes
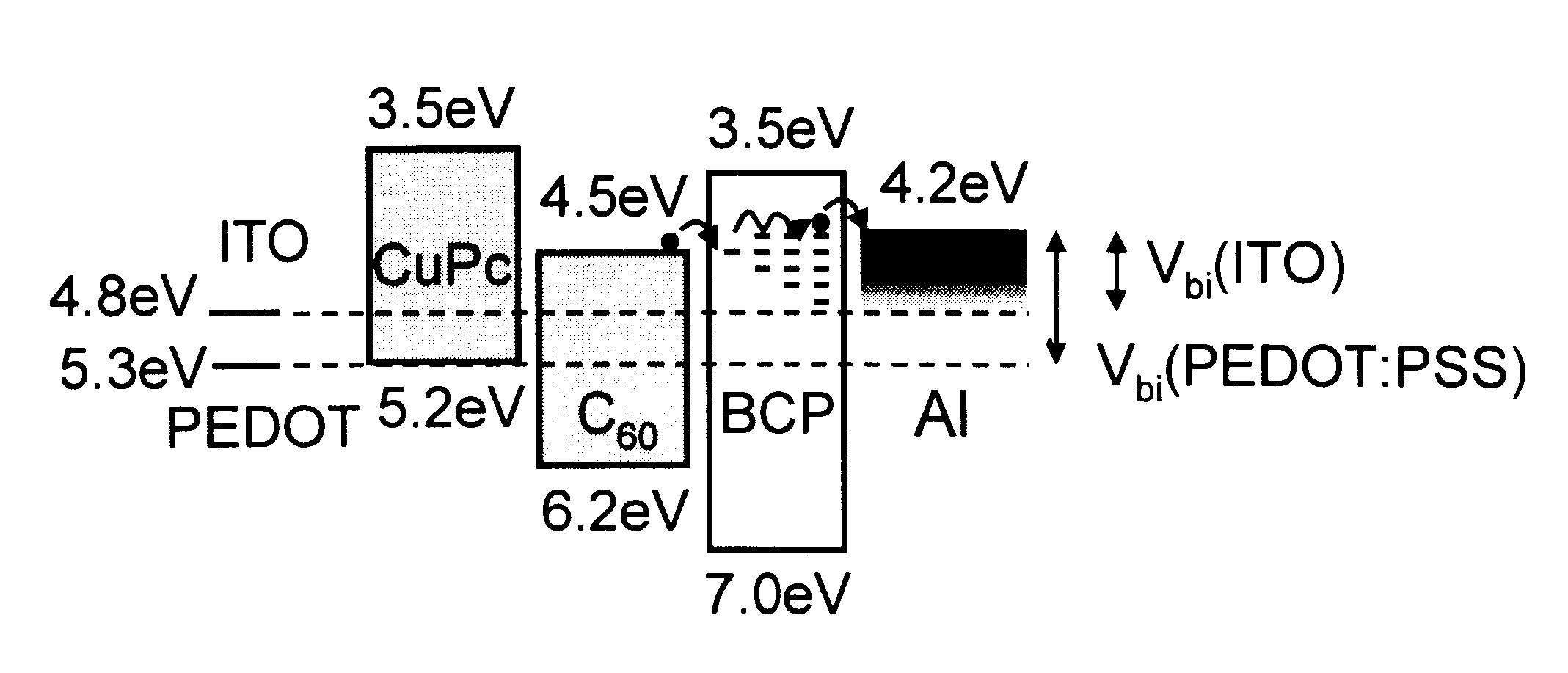
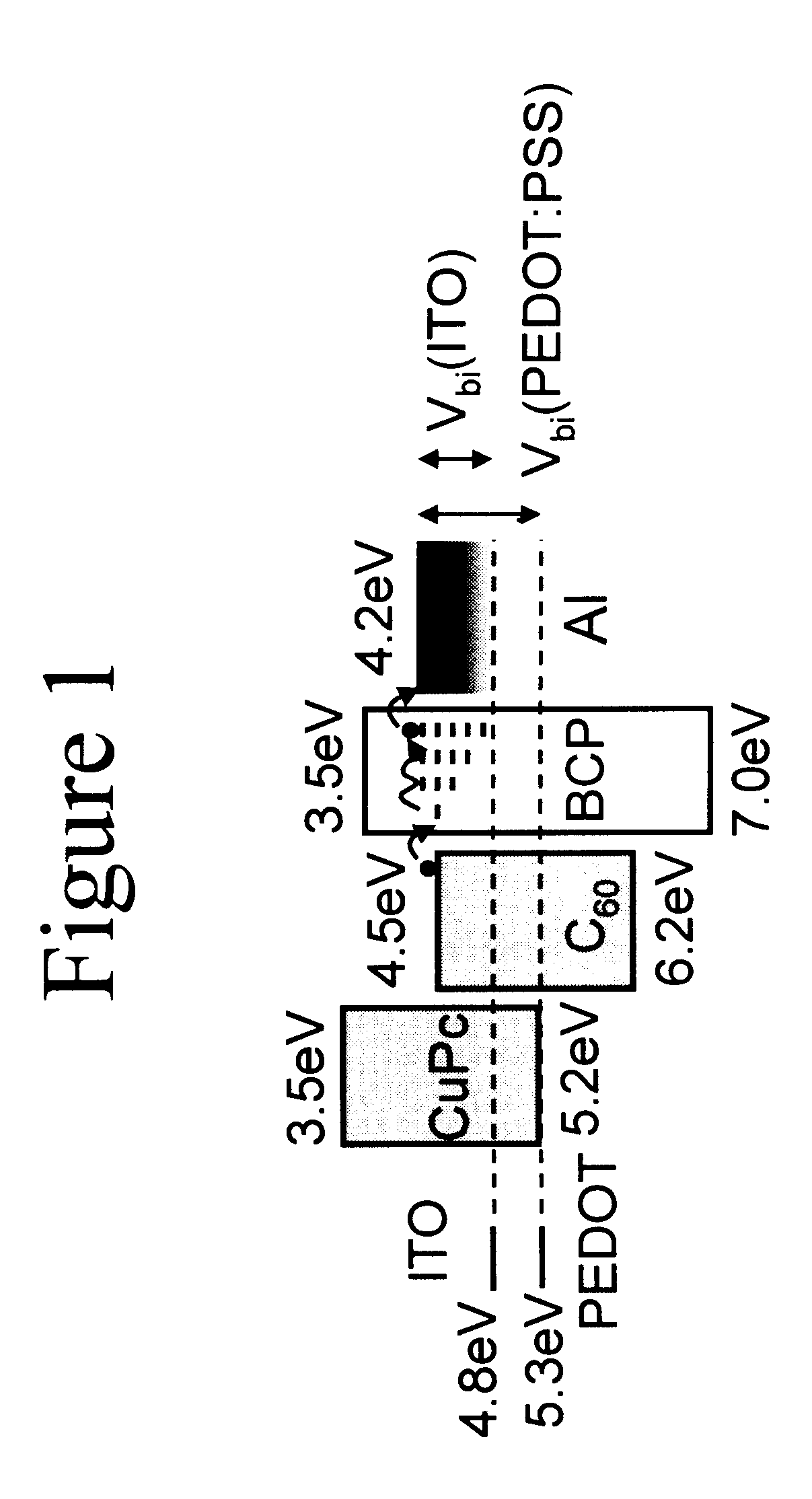
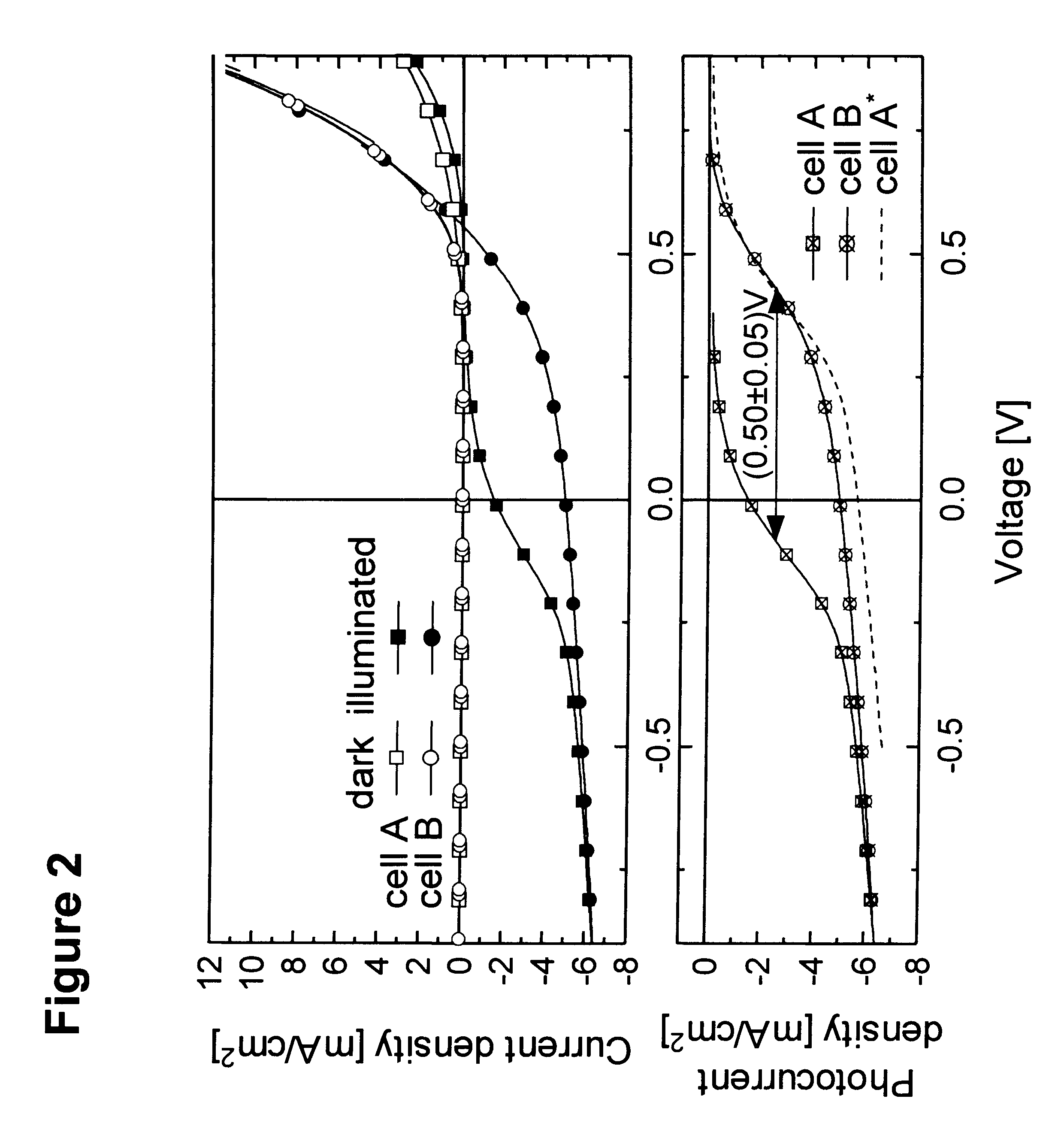
InactiveUS6580027B2Improve efficiencyIncrease the electric field strengthPV power plantsNanoinformaticsSolar cellFullerene
Organic photosensitive optoelectronic devices are disclosed. The devises comprise photoconductive organic thin films in a heterostructure, which include an exciton blocking layer to enhance device efficiency. The use of fullerenes in the electron conducting layer has lead to devices with high efficiency. Single heterostructure, stacked and wave-guide type embodiments are disclosed. Devices having multilayer structures and an exciton blocking layer are also disclosed. Guidelines for selection of exciton blocking layers are provided.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
High precision orientation alignment and gap control stages for imprint lithography processes
InactiveUS6873087B1Achieve separationPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesNanoinformaticsLithography processEngineering
Processes and associated devices for high precision positioning of a template an substrate during imprint lithography includes a calibration system with a course calibration stage and a fine orientation stage capable of maintaining a uniform gap between the template and substrate. The fine orientation stage includes a pair of flexure members having flexure joints for motion about a pivot point intersected by first and second orientation axes. Actuators lengthen or shorten to expand or contract the flexure members. Separation of the template is achieved using a peel-and-pull method that avoids destruction of imprinted features from the substrate.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST +1
Charge transport layers and organic electron devices comprising same
InactiveUS20070181874A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensNanoinformaticsTransport layerHole transport layer
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Molecular-wire crossbar interconnect (MWCI) for signal routing and communications
InactiveUS6314019B1Easy to manufactureSaving circuit areaNanoinformaticsDigital storageSignal routingActive switch
A molecular-wire crossbar interconnect for signal routing and communications between a first level and a second level in a molecular-wire crossbar is provided. The molecular wire crossbar comprises a two-dimensional array of a plurality of nanometer-scale switches. Each switch is reconfigurable and self-assembling and comprises a pair of crossed wires which form a junction where one wire crosses another and at least one connector species connecting the pair of crossed wires in the junction. The connector species comprises a bi-stable molecule. Each level comprises at least one group of switches and each group of switches comprises at least one switch, with each group in the first level connected to all other groups in the second level in an all-to-all configuration to provide a scalable, defect-tolerant, fat-tree networking scheme. The primary advantage is ease of fabrication, because an active switch is formed any time two wires cross. This saves tremendously on circuit area (a factor of a few times ten), since no other wires or ancillary devices are needed to operate the switch or store the required configuration. This reduction of the area of a configuration bit and its switch to just the area of two crossing wires is a major advantage in constructing a defect-tolerant interconnect network.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD CO +1
Acrylic microchannels and their use in electrophoretic applications
Microchannels having at least an acrylic inner surface and methods of their use in electrophoretic applications are provided. The subject microchannels may be in the form of a variety of configurations suitable for holding an electrophoretic medium. The subject microchannels give rise to substantially reduced EOF and / or adsorption as compared to fused silica under conditions of electrophoresis and find use in a variety of electrophoretic applications in which charged entities are moved through a medium under the influence of the an applied electric field.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Release strategies for making transferable semiconductor structures, devices and device components
ActiveUS20080108171A1Low cost structureLow costFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsSemiconductor structureDevice Subassembly
Provided are methods for making a device or device component by providing a multilayer structure having a plurality of functional layers and a plurality of release layers and releasing the functional layers from the multilayer structure by separating one or more of the release layers to generate a plurality of transferable structures. The transferable structures are printed onto a device substrate or device component supported by a device substrate. The methods and systems provide means for making high-quality and low-cost photovoltaic devices, transferable semiconductor structures, (opto-)electronic devices and device components.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Multivalent immunoglobulin-based bioactive assemblies
ActiveUS7527787B2Efficacious for arrestingInhibition formationPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseDiagnostic agent
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Methods and compositions for generating bioactive assemblies of increased complexity and uses
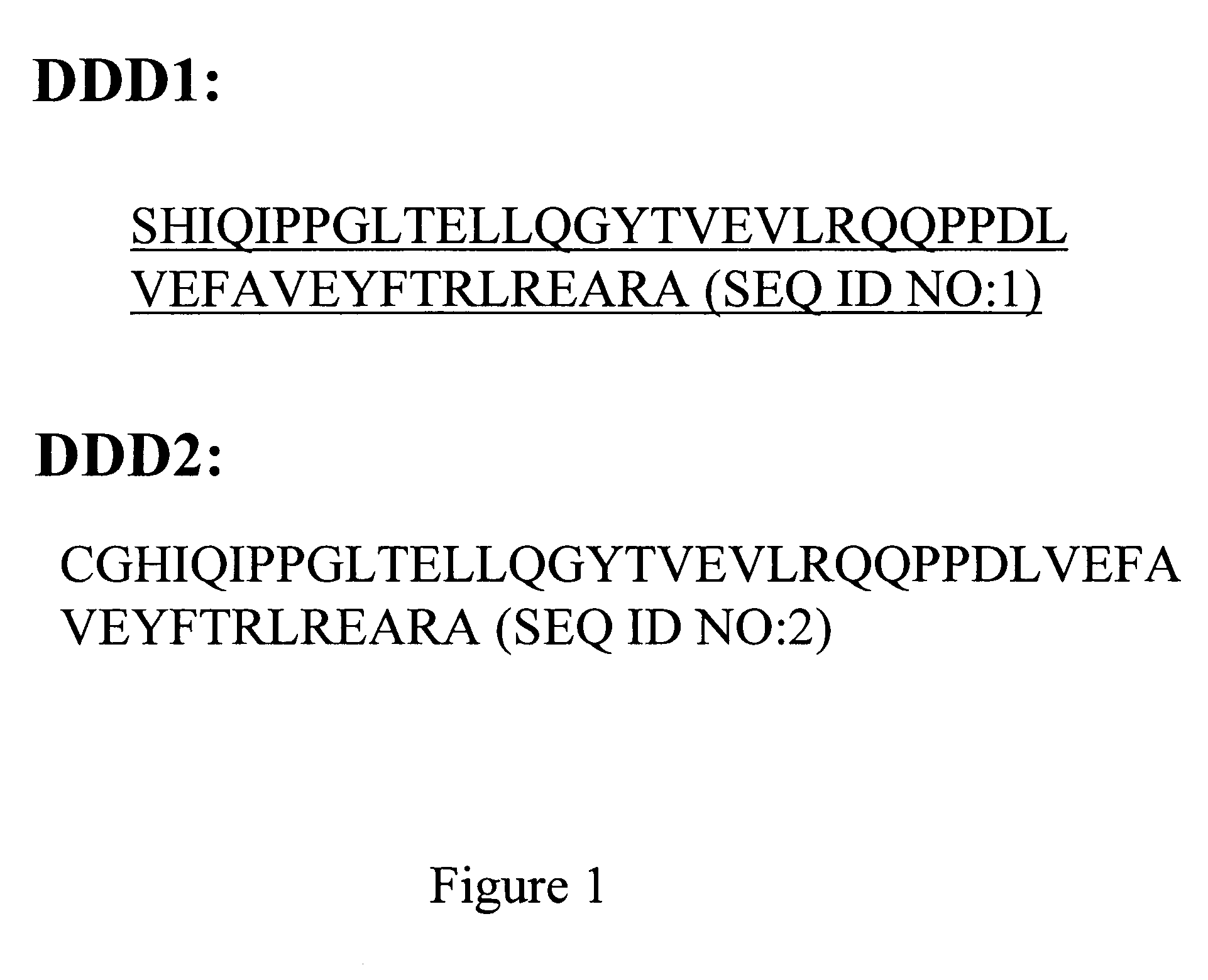
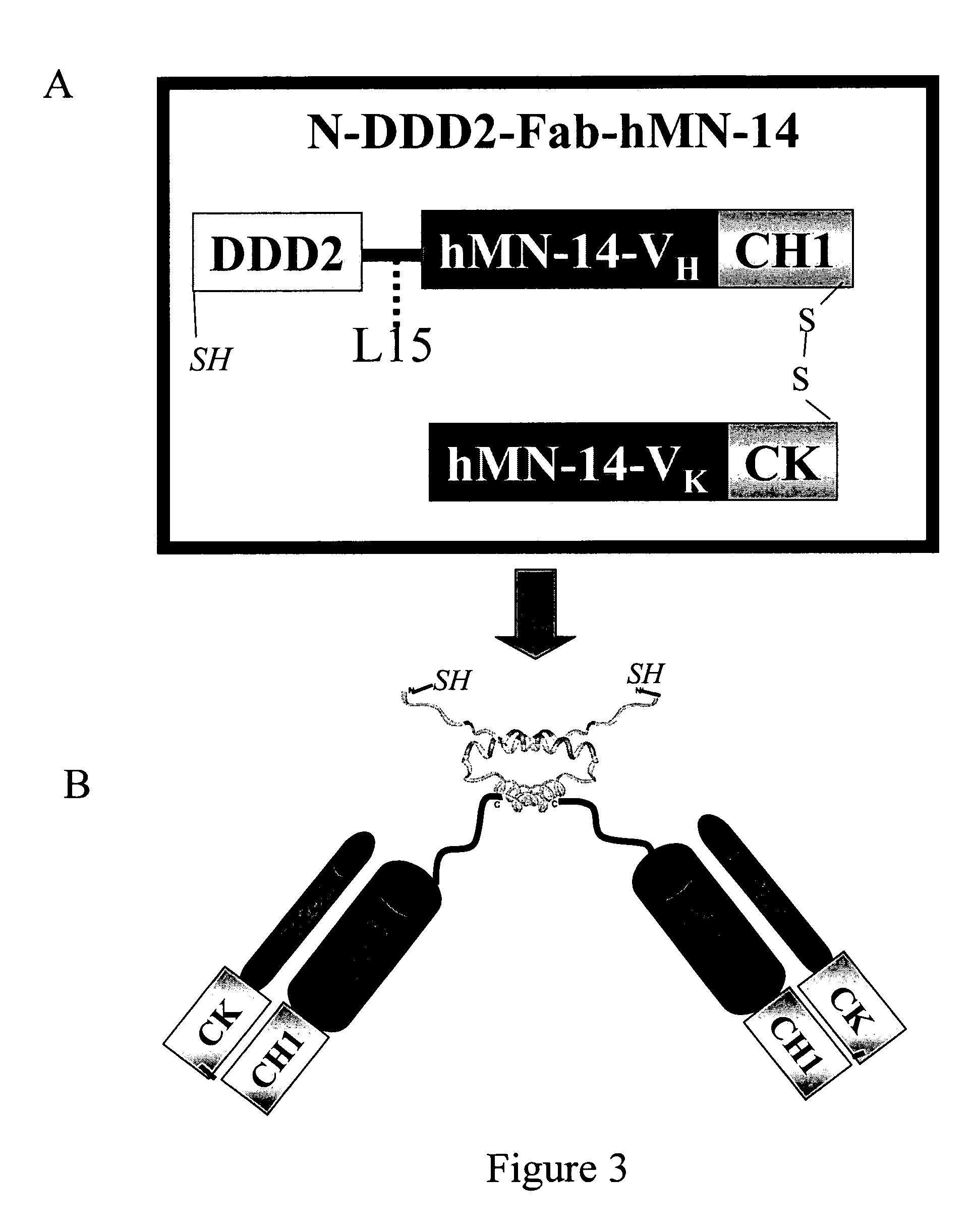
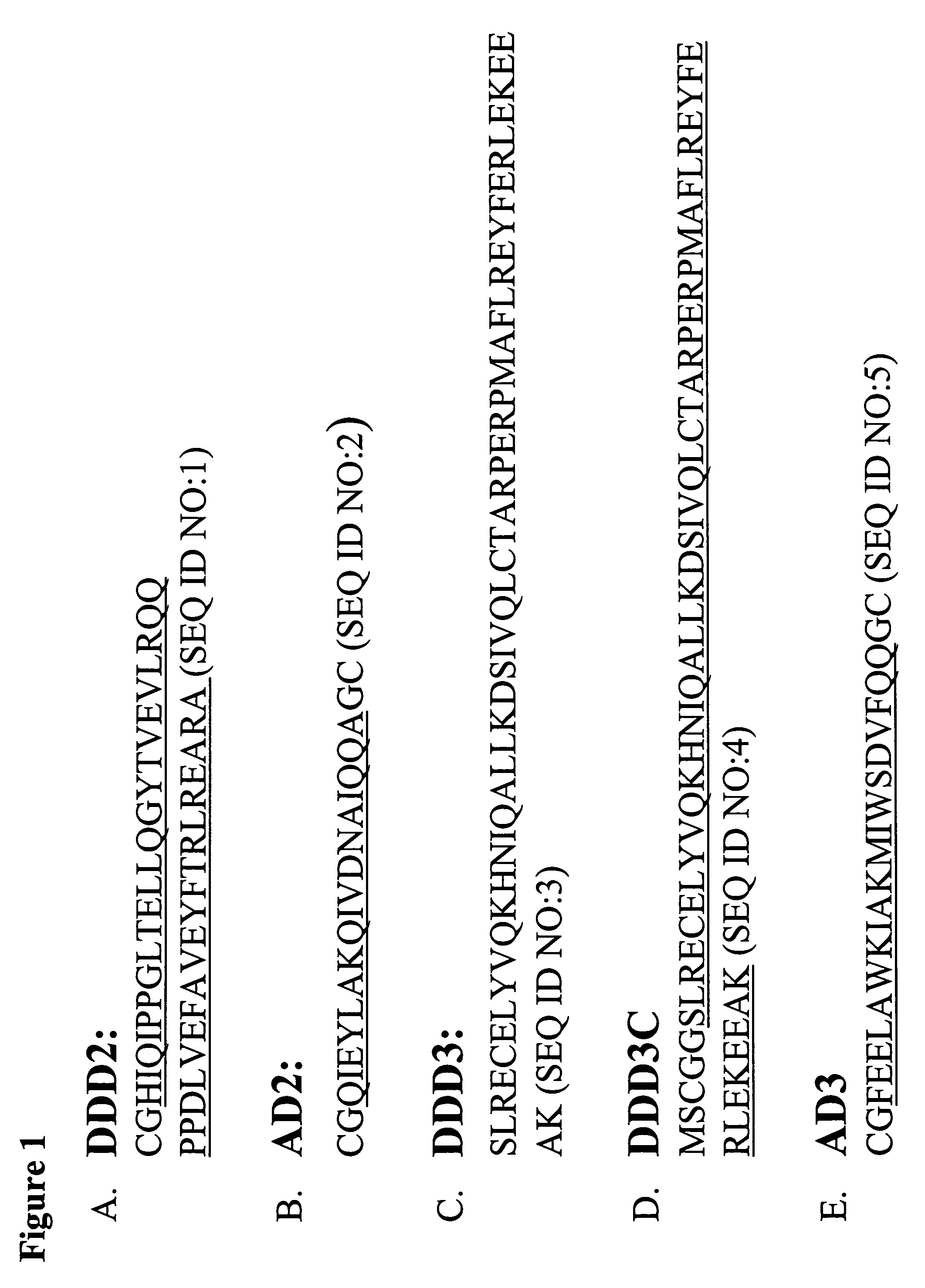
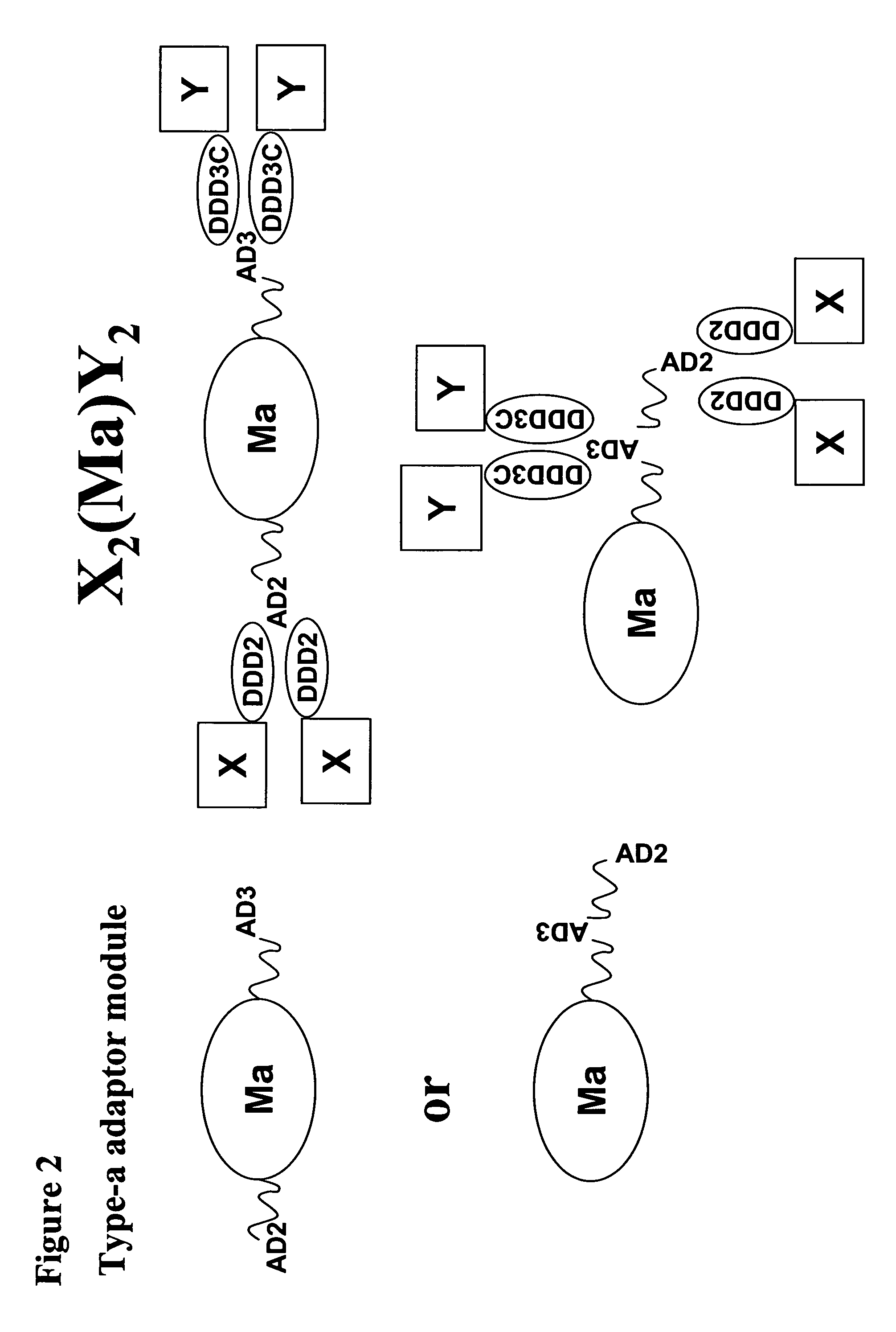
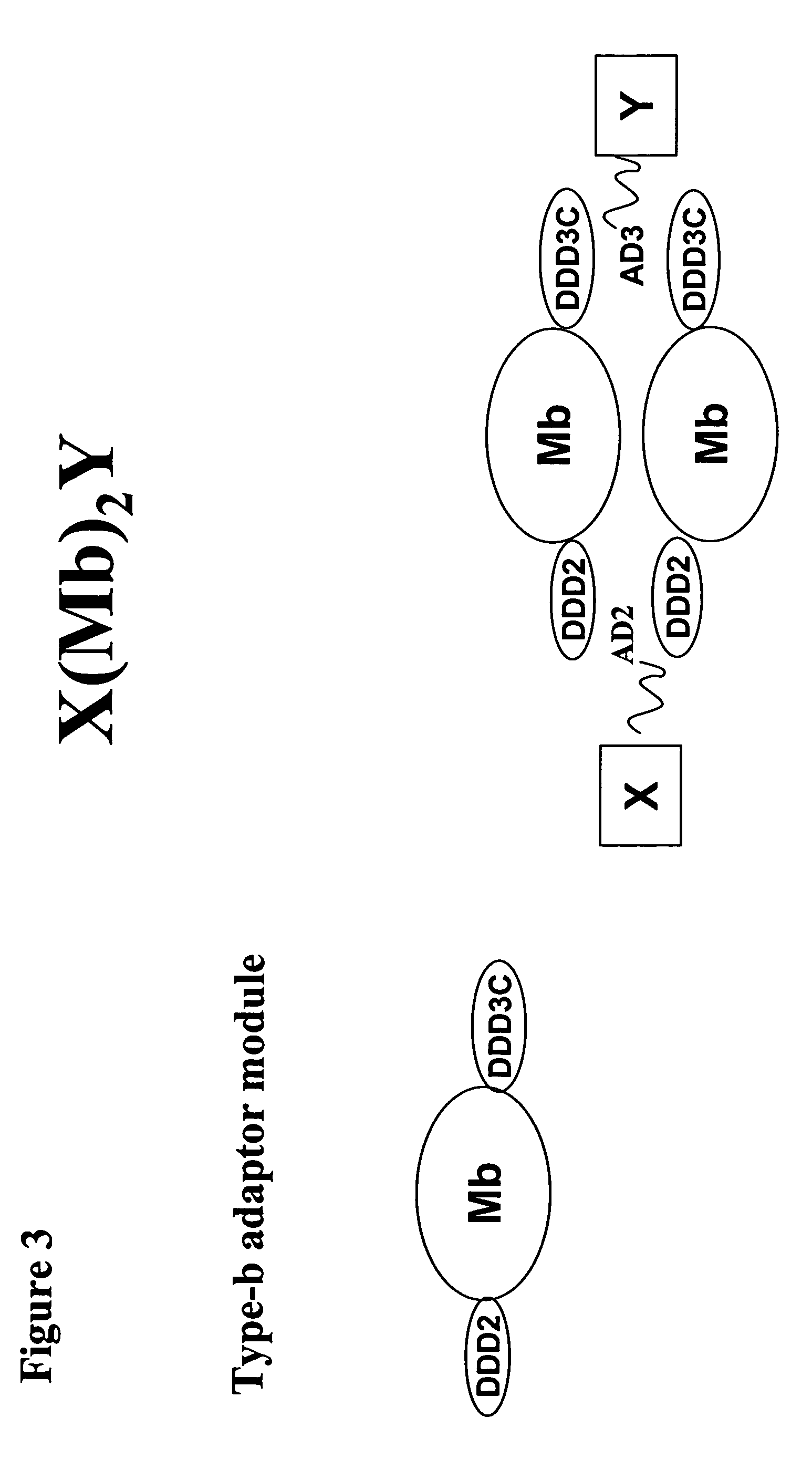
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for making and using bioactive assemblies of defined compositions, which may have multiple functionalities and / or binding specificities. In particular embodiments, the bioactive assembly is formed using dock-and-lock (DNL) methodology, which takes advantage of the specific binding interaction between dimerization and docking domains (DDD) and anchoring domains (AD) to form the assembly. In various embodiments, one or more effectors may be attached to a DDD or AD sequence. Complementary AD or DDD sequences may be attached to an adaptor module that forms the core of the bioactive assembly, allowing formation of the assembly through the specific DDD / AD binding interactions. Such assemblies may be attached to a wide variety of effector moieties for treatment, detection and / or diagnosis of a disease, pathogen infection or other medical or veterinary condition.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Water dispersible polypyrroles made with polymeric acid colloids for electronics applications
InactiveUS20050205860A1Material nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrolytesWater dispersiblePolypyrrole
Compositions are provided comprising aqueous dispersions of at least one polypyrrole and at least one colloid-forming polymeric acids at methods of making such compositions. The new compositions are useful in electronic devices including organic electronic devices such as organic light emitting diode displays, memory storage, electromagnetic shielding, electrochromic displays,and thin film transistors, field effect resistance devices.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Free-standing and aligned carbon nanotubes and synthesis thereof
One or more highly-oriented, multi-walled carbon nanotubes are grown on an outer surface of a substrate initially disposed with a catalyst film or catalyst nano-dot by plasma enhanced hot filament chemical vapor deposition of a carbon source gas and a catalyst gas at temperatures between 300° C. and 3000° C. The carbon nanotubes range from 4 to 500 nm in diameter and 0.1 to 50 μm in length depending on growth conditions. Carbon nanotube density can exceed 104 nanotubes / mm2. Acetylene is used as the carbon source gas, and ammonia is used as the catalyst gas. Plasma intensity, carbon source gas to catalyst gas ratio and their flow rates, catalyst film thickness, and temperature of chemical vapor deposition affect the lengths, diameters, density, and uniformity of the carbon nanotubes. The carbon nanotubes of the present invention are useful in electrochemical applications as well as in electron emission, structural composite, material storage, and microelectrode applications.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
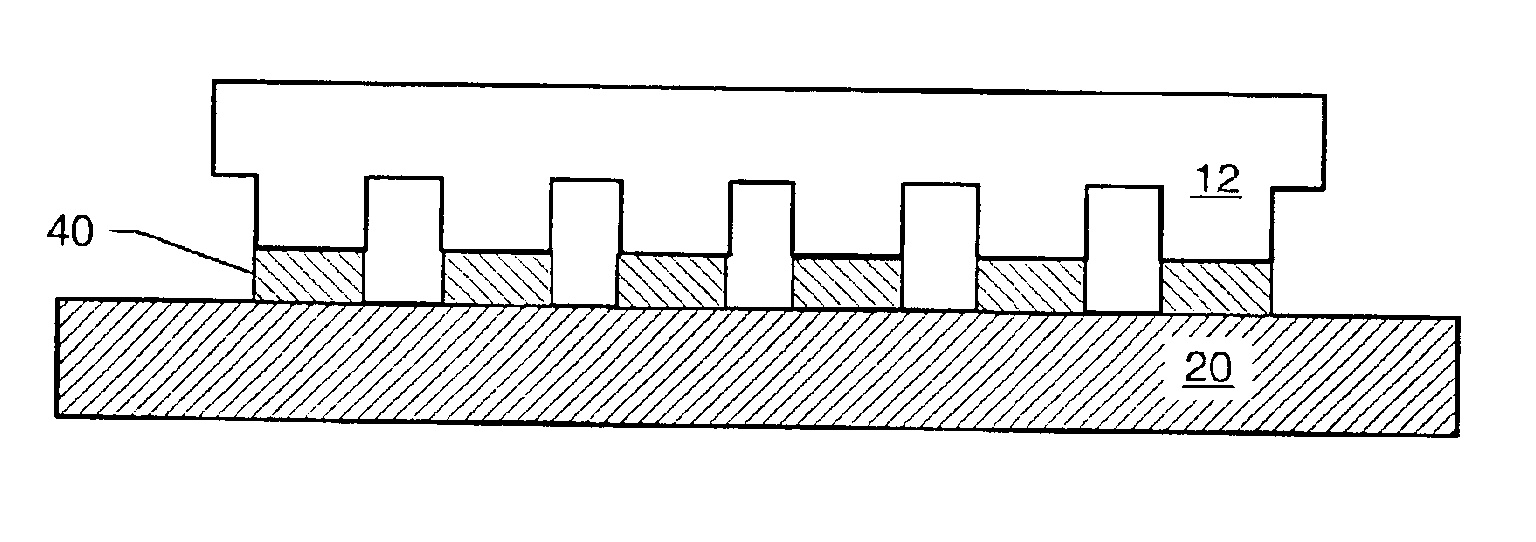
Formation of discontinuous films during an imprint lithography process
ActiveUS6932934B2Low viscosityMaterial nanotechnologyDecorative surface effectsLithography processLithographic artist
The present invention is directed to methods for patterning a substrate by imprint lithography. An imprint lithography method includes placing a curable liquid on a substrate. A template may be contacted with the curable liquid. Surface forces at the interface of the curable liquid and the template cause the curable liquid to gather in an area defined by a lower surface of the template. Alternately, the curable liquid may fill one or more relatively shallow recesses in the template and the area under the template lower surface. Activating light is applied to the curable liquid to form a patterned layer on the substrate.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods of positioning and/or orienting nanostructures
Methods of positioning and orienting nanostructures, and particularly nanowires, on surfaces for subsequent use or integration. The methods utilize mask based processes alone or in combination with flow based alignment of the nanostructures to provide oriented and positioned nanostructures on surfaces. Also provided are populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, devices that include populations of positioned and / or oriented nanostructures, systems for positioning and / or orienting nanostructures, and related devices, systems and methods.
Owner:ONED MATERIAL INC
Popular searches
Semiconductor devices Photomechanical exposure apparatus Microlithography exposure apparatus Disposition/mounting of heads Irradiation devices Time-pieces with integrated devices Pigment treatment with macromolecular organic compounds Pigment treatment with organosilicon compounds Electrophoretic coatings Liquid/solution decomposition chemical coating
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com