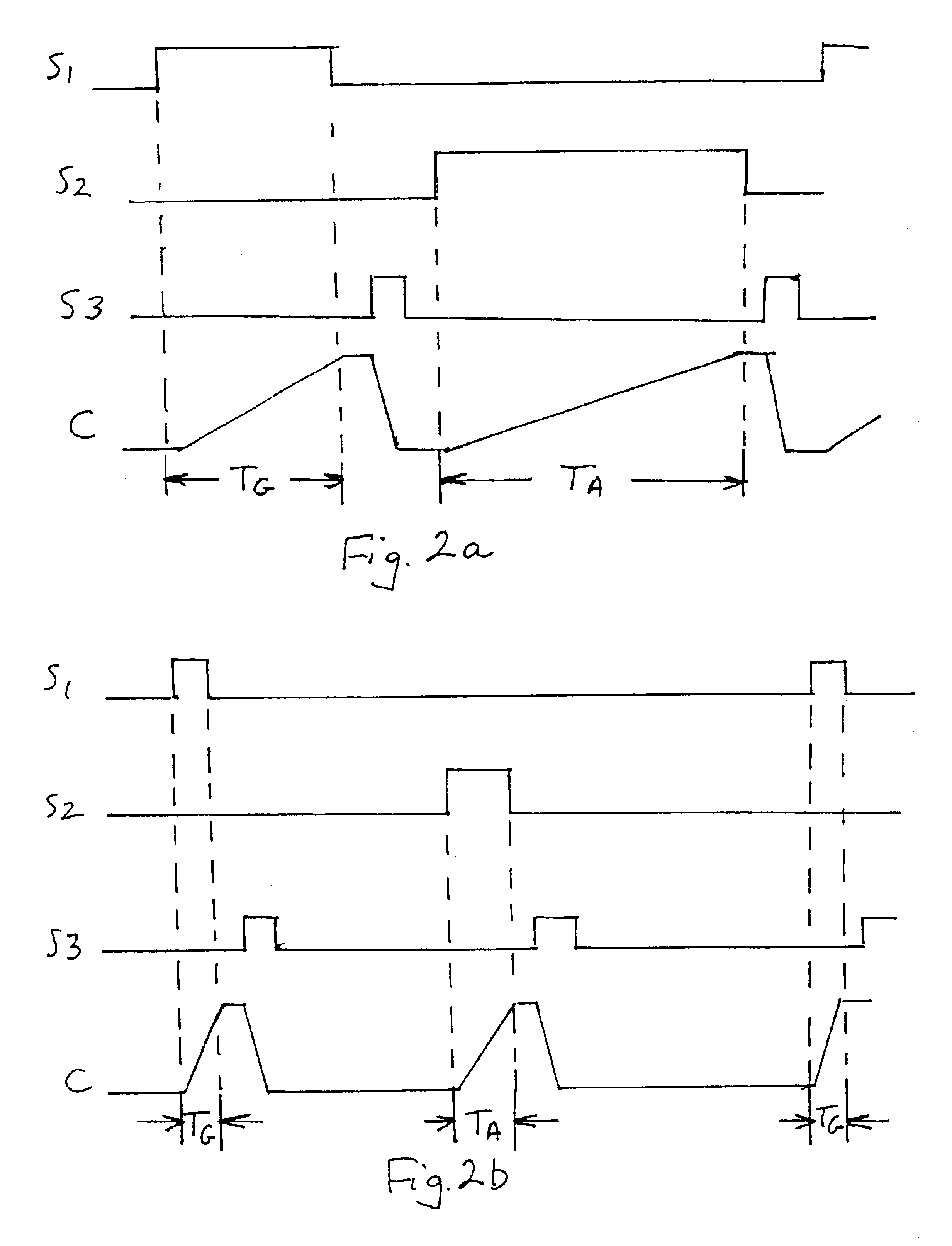
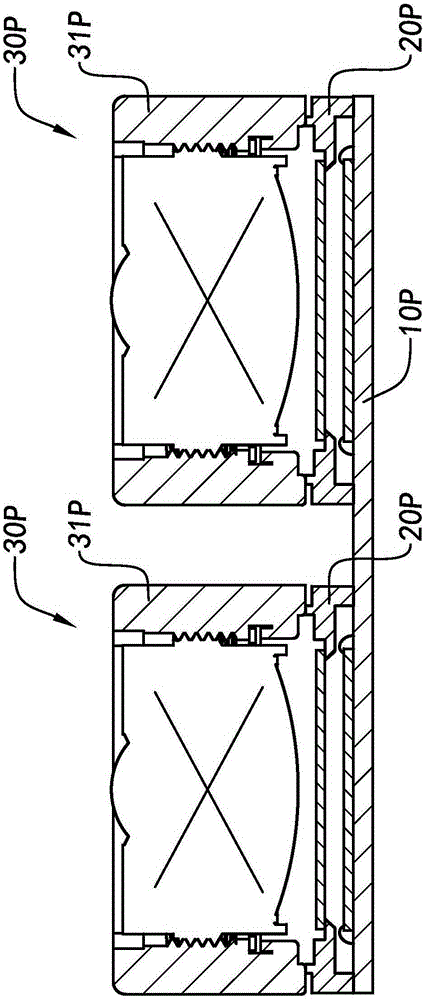
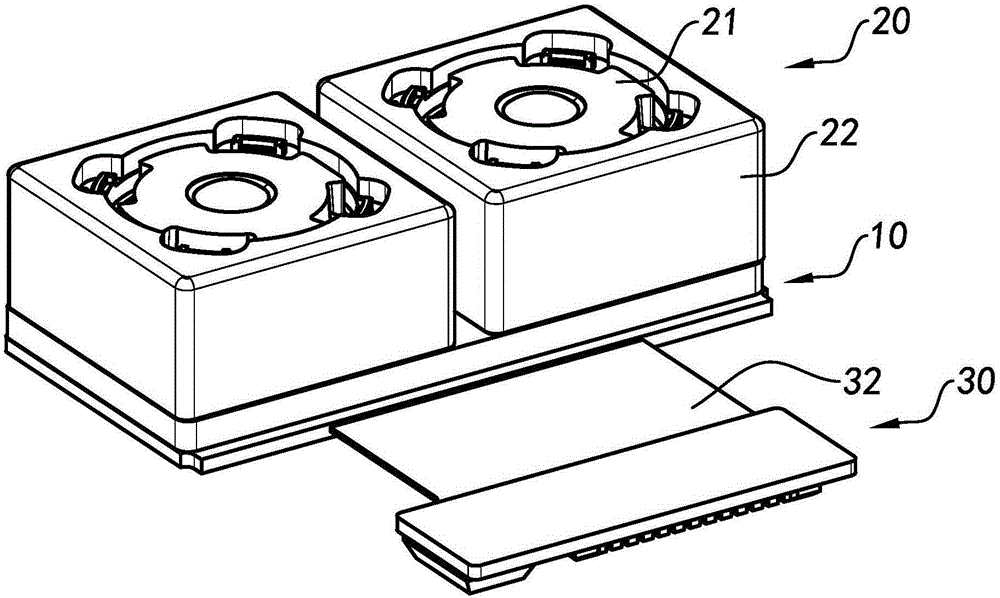
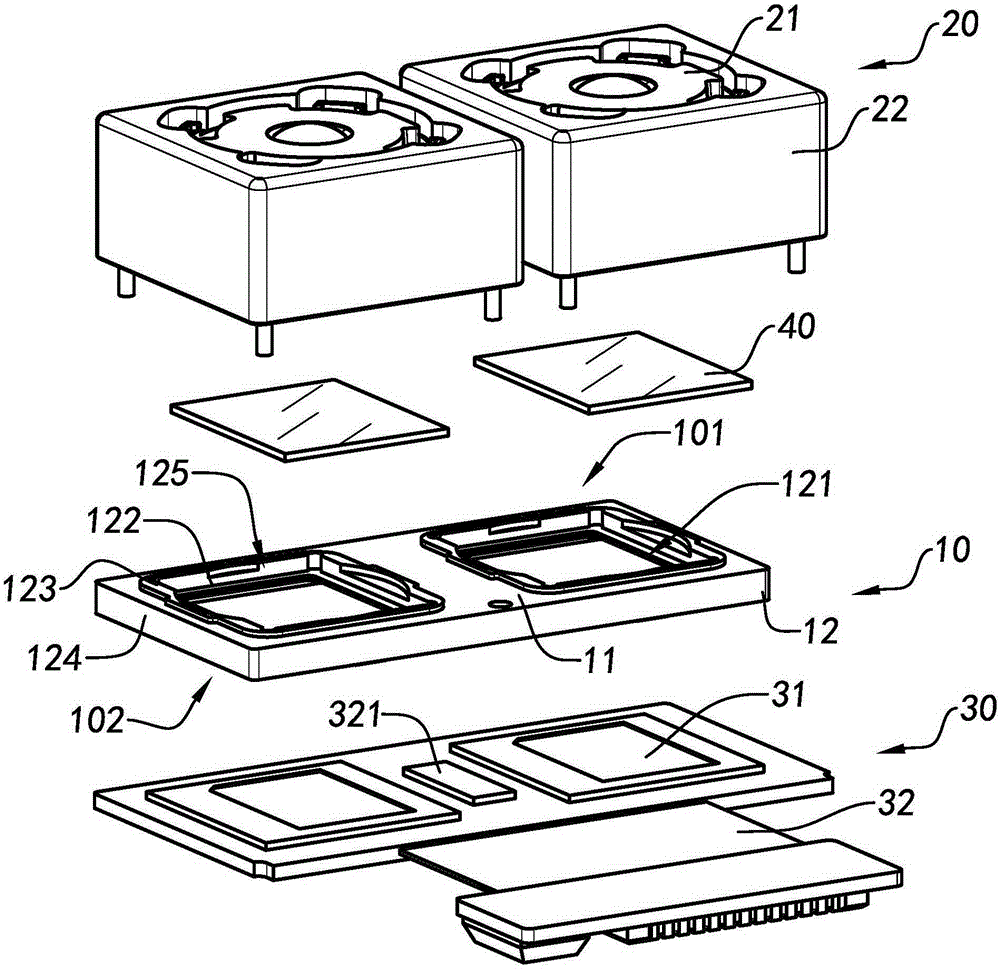
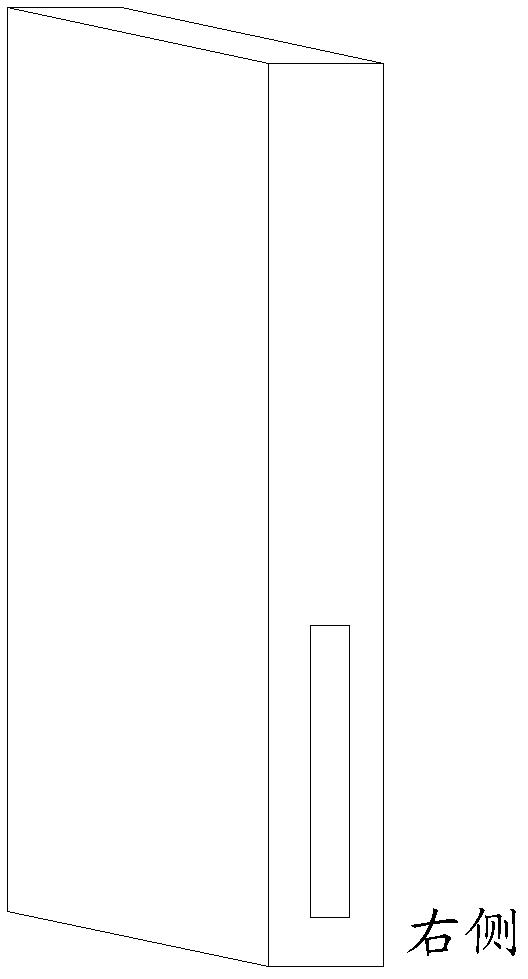Patents
Literature
5161 results about "Light sensing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
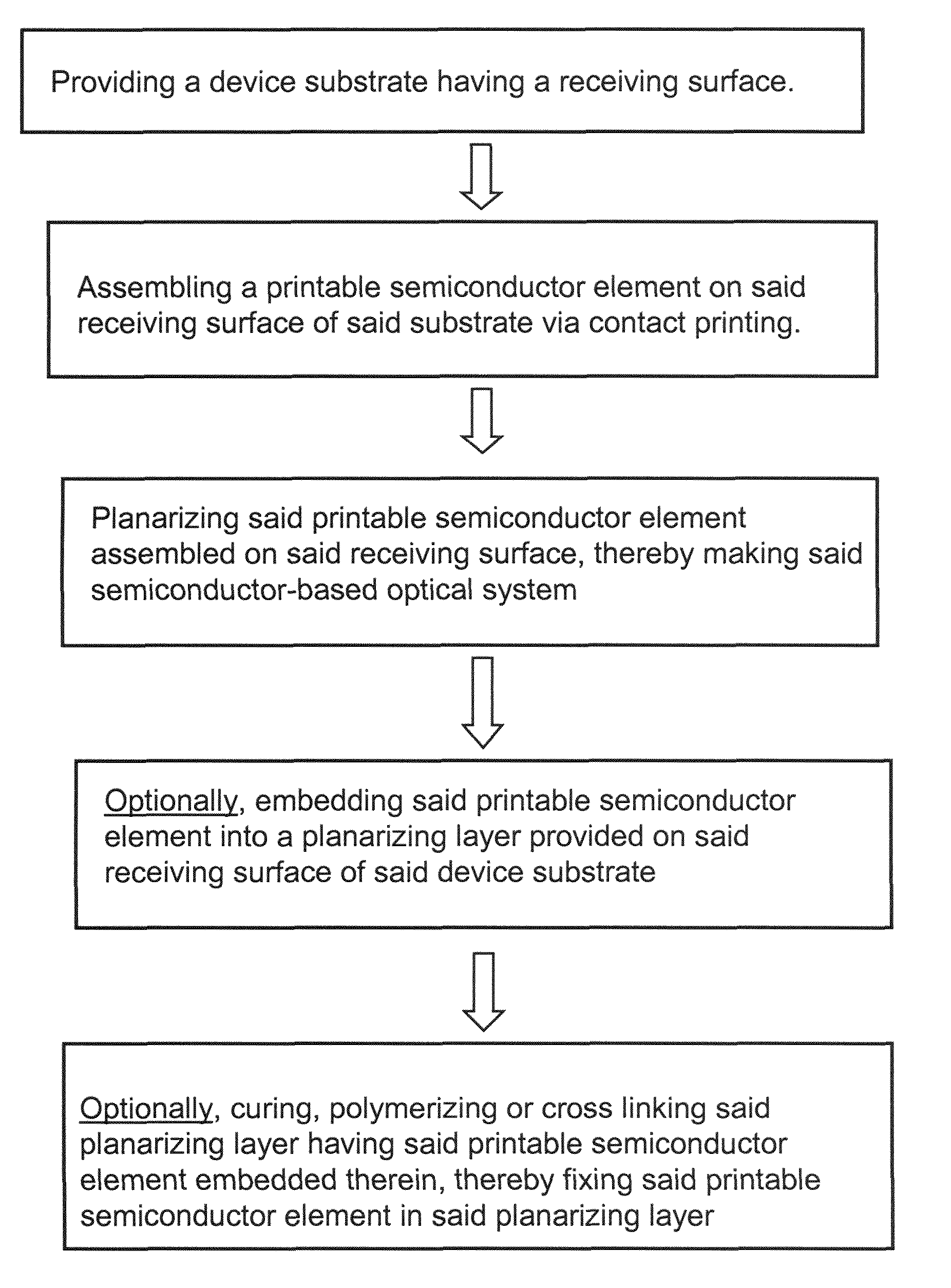
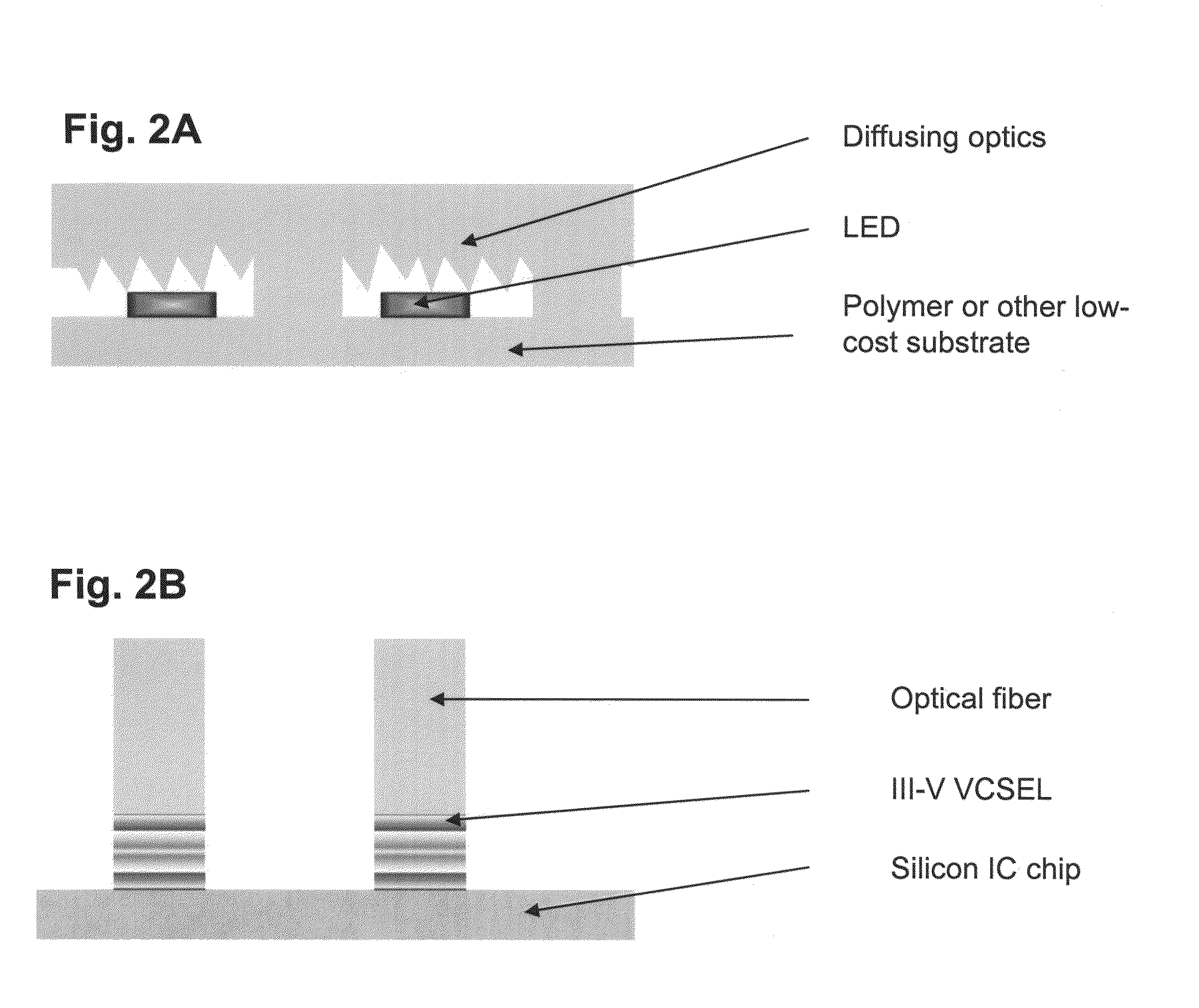
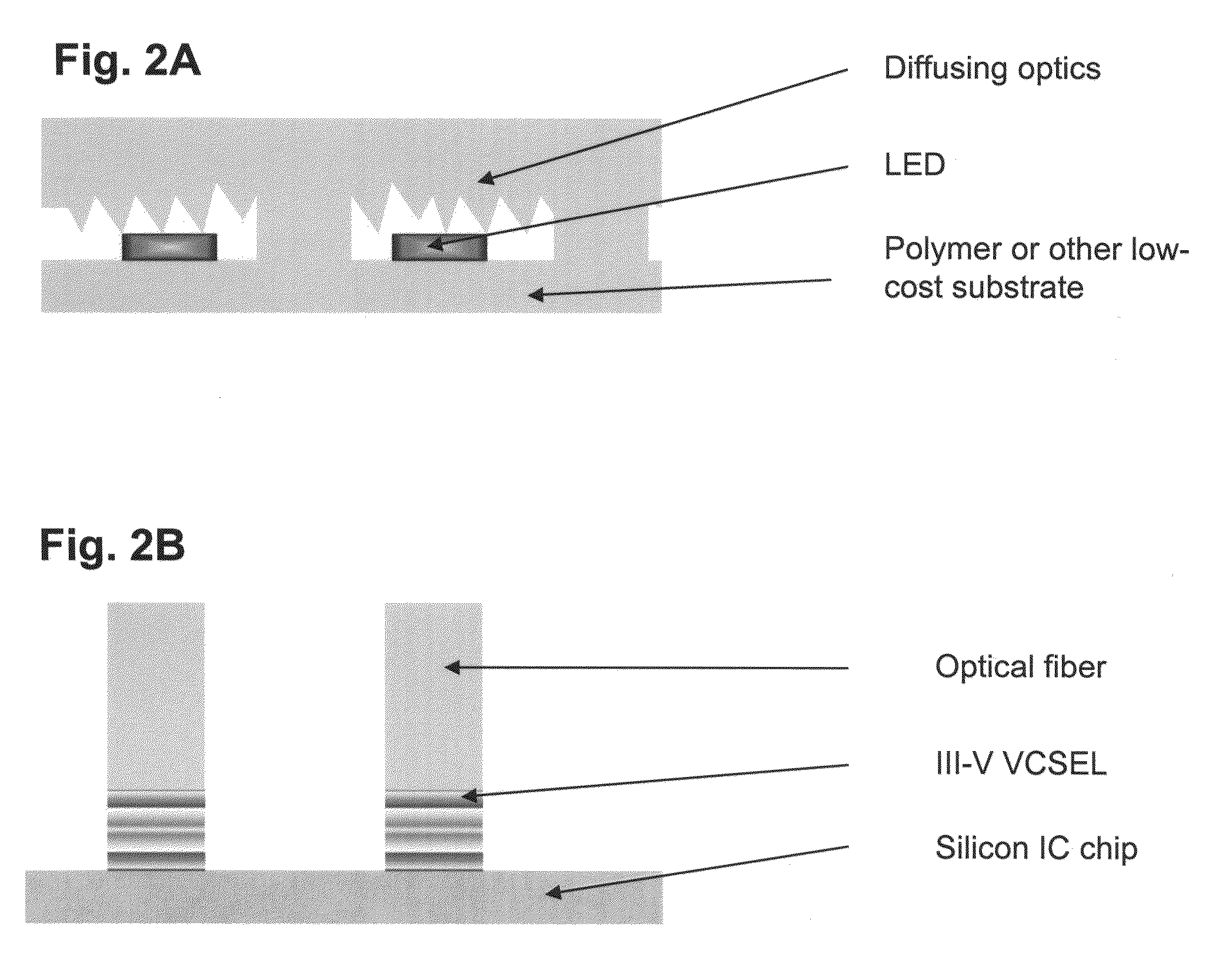
Optical systems fabricated by printing-based assembly
ActiveUS7972875B2Low costImprove performanceFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsLight sensingSingle crystal
Provided are optical devices and systems fabricated, at least in part, via printing-based assembly and integration of device components. In specific embodiments the present invention provides light emitting systems, light collecting systems, light sensing systems and photovoltaic systems comprising printable semiconductor elements, including large area, high performance macroelectronic devices. Optical systems of the present invention comprise semiconductor elements assembled, organized and / or integrated with other device components via printing techniques that exhibit performance characteristics and functionality comparable to single crystalline semiconductor based devices fabricated using conventional high temperature processing methods. Optical systems of the present invention have device geometries and configurations, such as form factors, component densities, and component positions, accessed by printing that provide a range of useful device functionalities. Optical systems of the present invention include devices and device arrays exhibiting a range of useful physical and mechanical properties including flexibility, shapeability, conformability and stretchablity.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
Network based multiple sensor and control device with temperature sensing and control
InactiveUS20050043907A1Minimize adverse effectsPartial latencyThermometer detailsElectric devicesMultiple sensorControl equipment
A multifunction sensor device which provides various transducer functions including means for performing temperature sensing, humidity sensing, ambient light sensing, motion detection, thermostat functions, switching functions, load switching and dimming functions, displaying actual and set temperature values, displaying time of day values and a means to put the device in an on, off or auto mode. The device has utility in environments such as that found in offices, schools, homes, industrial plants or any other type of automated facility in which sensors are utilized for energy monitoring and control, end user convenience or artificial or natural cooling, heating and HVAC control. The device can be used as a switch or dimmer, sensor or thermostat as well as to adjust and control all natural and artificial lighting, temperature and humidity devices. Key elements of the invention include overcoming the difficulty of mounting diverse sensors or transducers within the same device or housing; permitting these various sensors to exist in a single package that can be mounted to a wall in a substantially flush manner; and eliminating the requirement of an air flow channel in the device, thus minimizing any adverse effects on the motion detecting element or sensor as well as providing built in partial hysteresis. The device may include additional transducers or sensors and is constructed such that the temperature and humidity sensors are neither exposed to the flow of air in a room or area nor in an airflow channel whereby a chimney effect may occur. The device can transmit and receive real time data, relative data and actual discrete data in addition to switching and controlling loads locally or remotely. An embodiment utilizing airflow channels to direct air over the temperature and humidity sensors is also disclosed.
Owner:ECKEL DAVID P +2
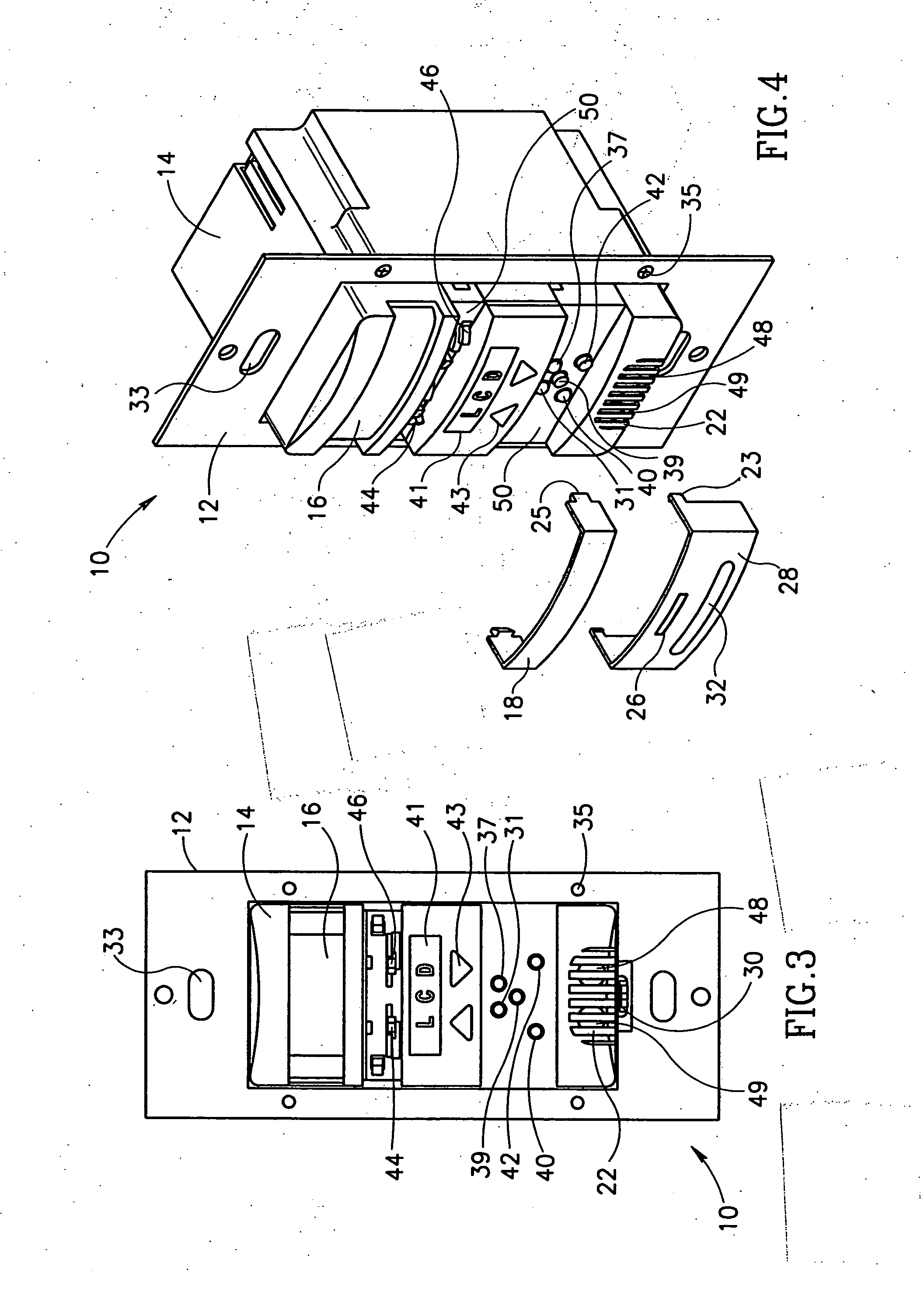
Display with infrared backlight source and multi-touch sensing function
A touch-sensing display screen includes an upper transparent substrate, a lower substrate opposite the upper substrate, and a backlight unit having an infrared light source configured to radiate infrared light through the upper substrate in a first direction. A transparent window is disposed in alignment with the infrared light source and between the upper and lower transparent substrates. A portion of the infrared light radiated in the first direction is reflected back through the upper substrate and through the transparent window in a second direction by an object touching a surface of the upper transparent substrate. A pixel thin-film transistor on the lower substrate is configured to activate a pixel electrode, and an infrared light-sensing thin-film transistor is configured to sense the infrared light received through the upper substrate in the second direction, and output an infrared light-sense signal in response thereto.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
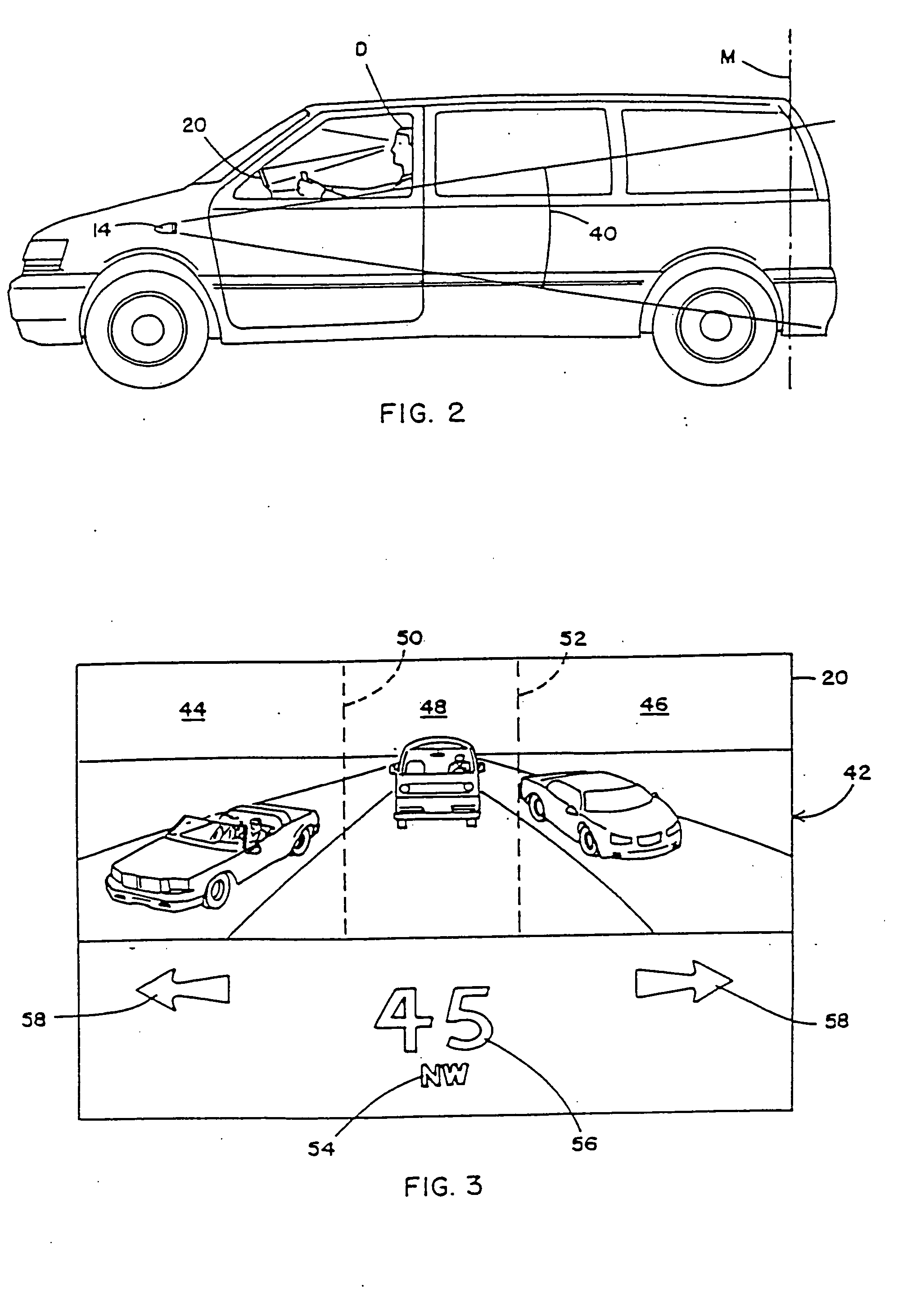
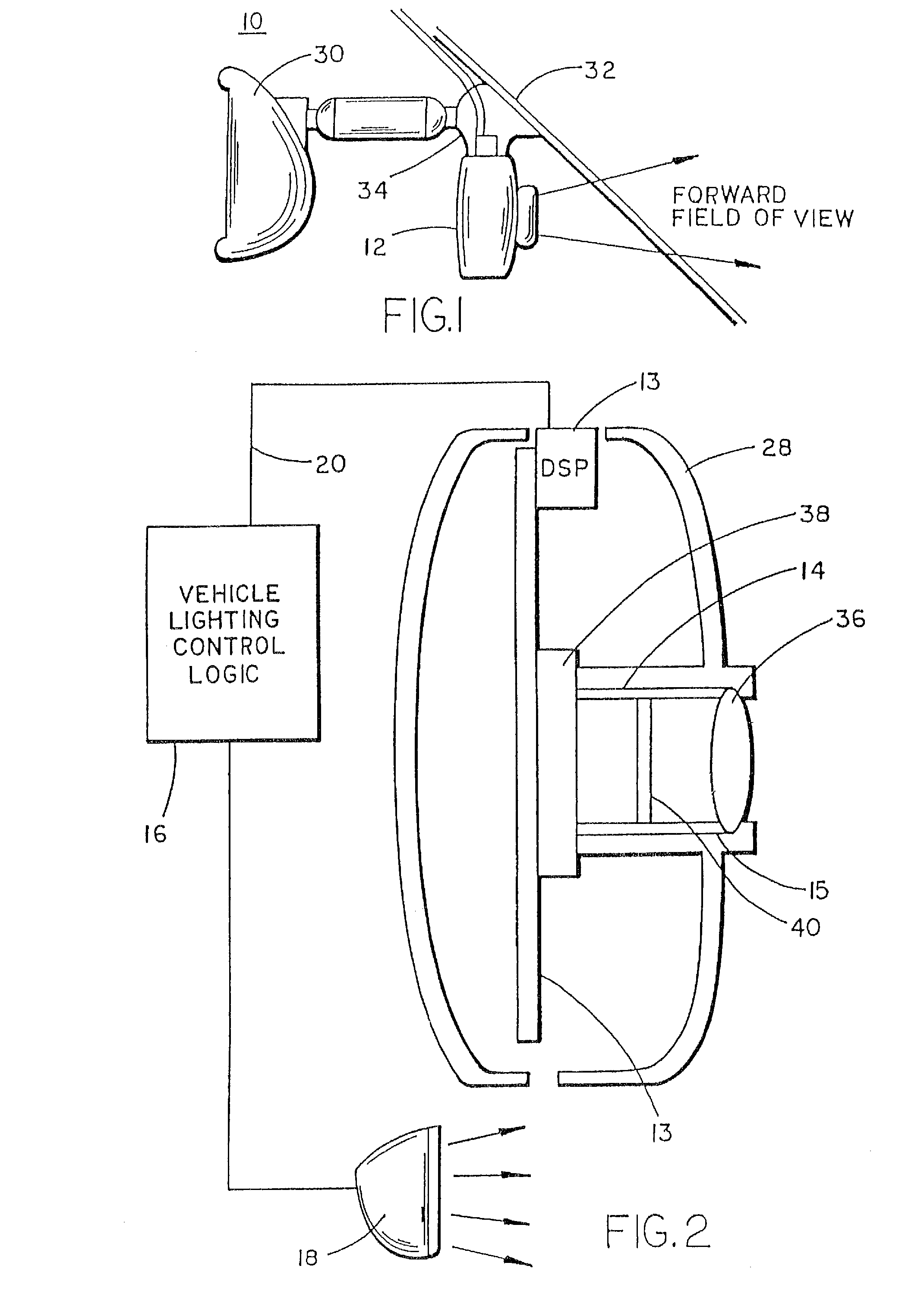
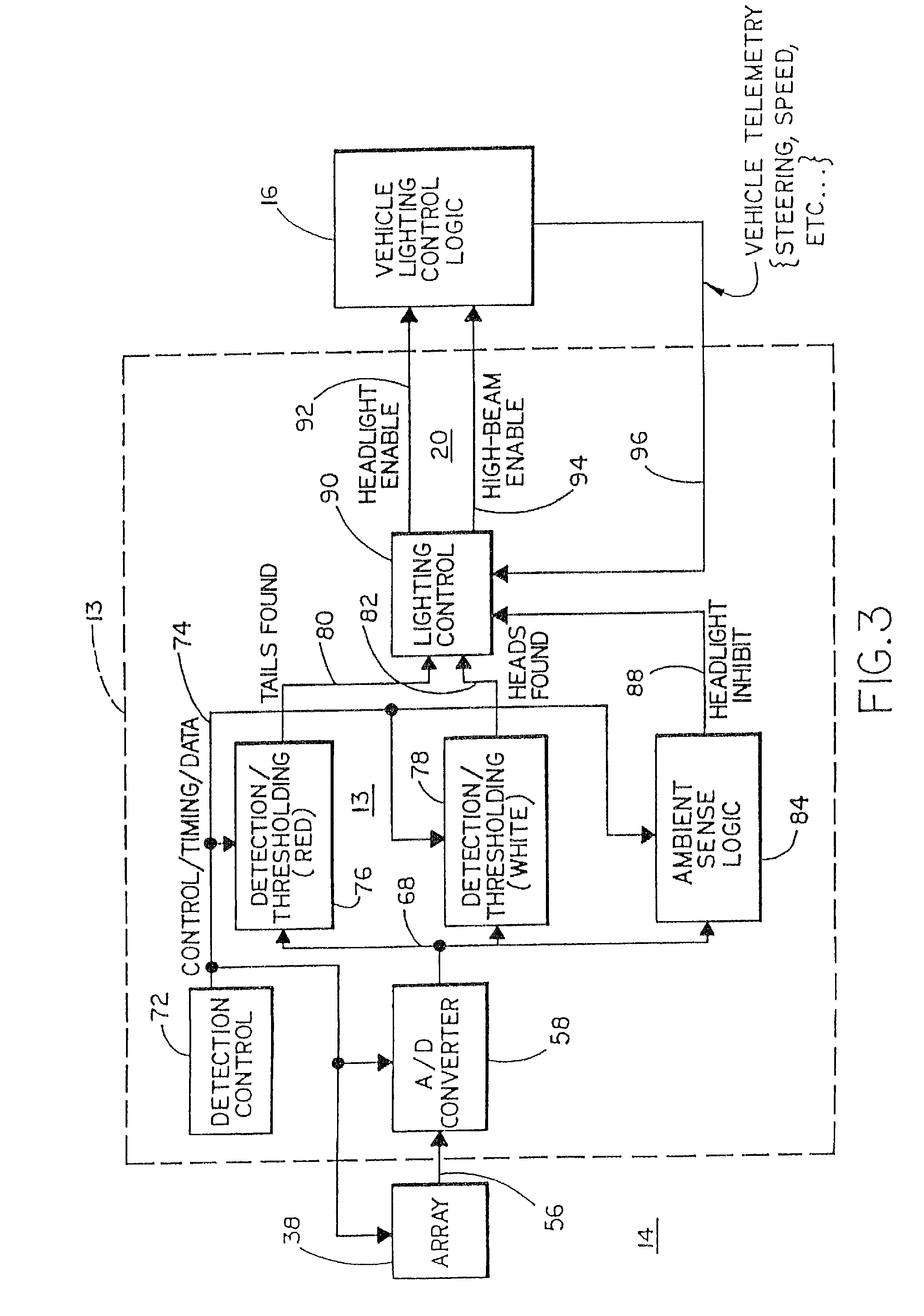
Image sensing system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20070120657A1Easy to explainRemove distortionVehicle seatsVehicle headlampsDriver/operatorDisplay device
An image sensing system for a vehicle includes an imaging sensor and a logic and control circuit. The imaging sensor comprises a two-dimensional array of light sensing photosensor elements formed on a semiconductor substrate, and has a field of view exterior of the vehicle. The logic and control circuit comprises an image processor for processing image data derived from the imaging sensor. The image sensing system may generate an indication of the presence of an object within the field of view of the imaging sensor. Preferably, video images may be captured by said imaging sensor and may be displayed by a display device for viewing by the driver when operating the vehicle. The logic and control circuit may generate at least one control output, and the at least control output may control an enhancement of the video images.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
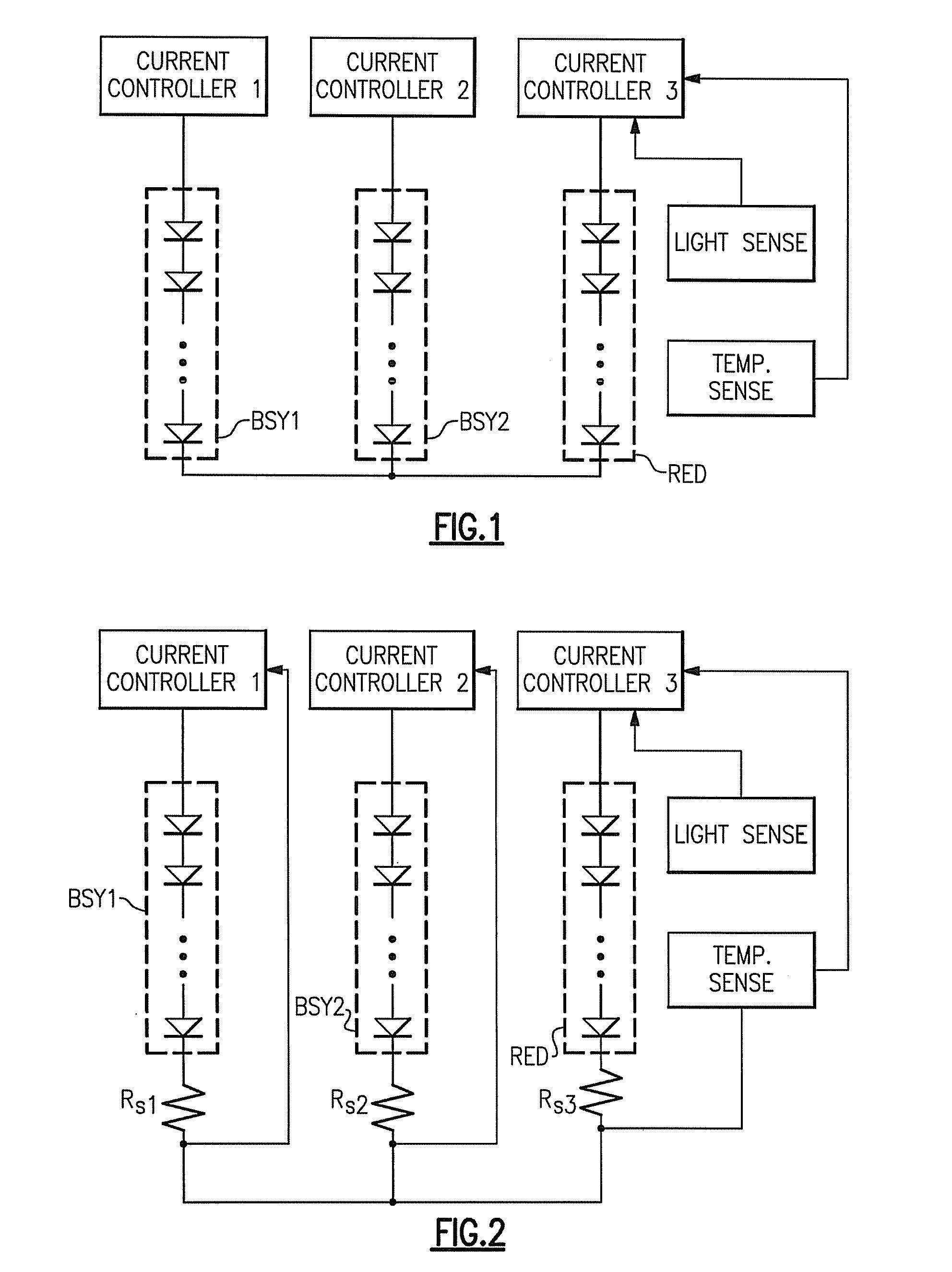
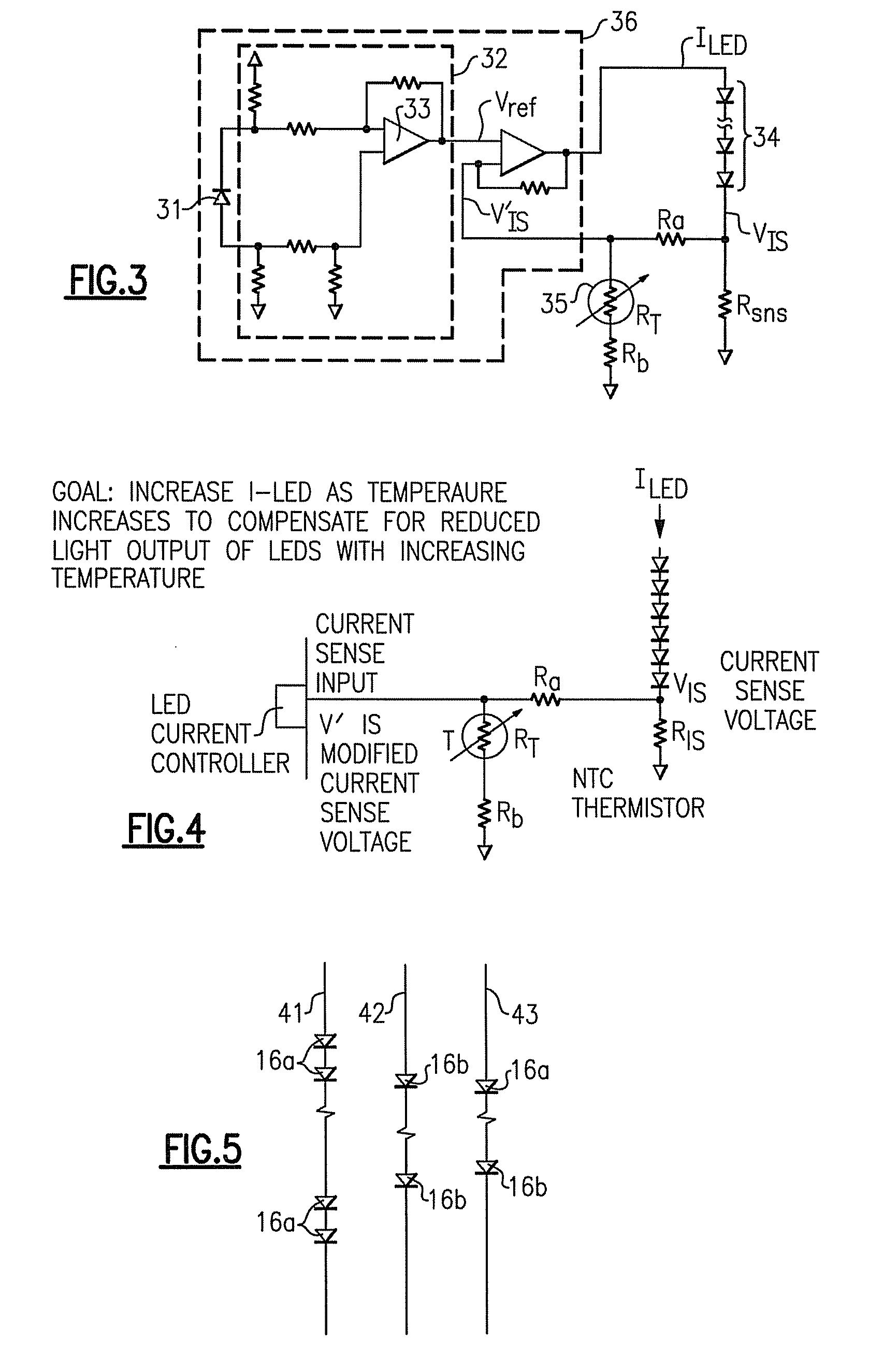
Lighting devices and methods for lighting
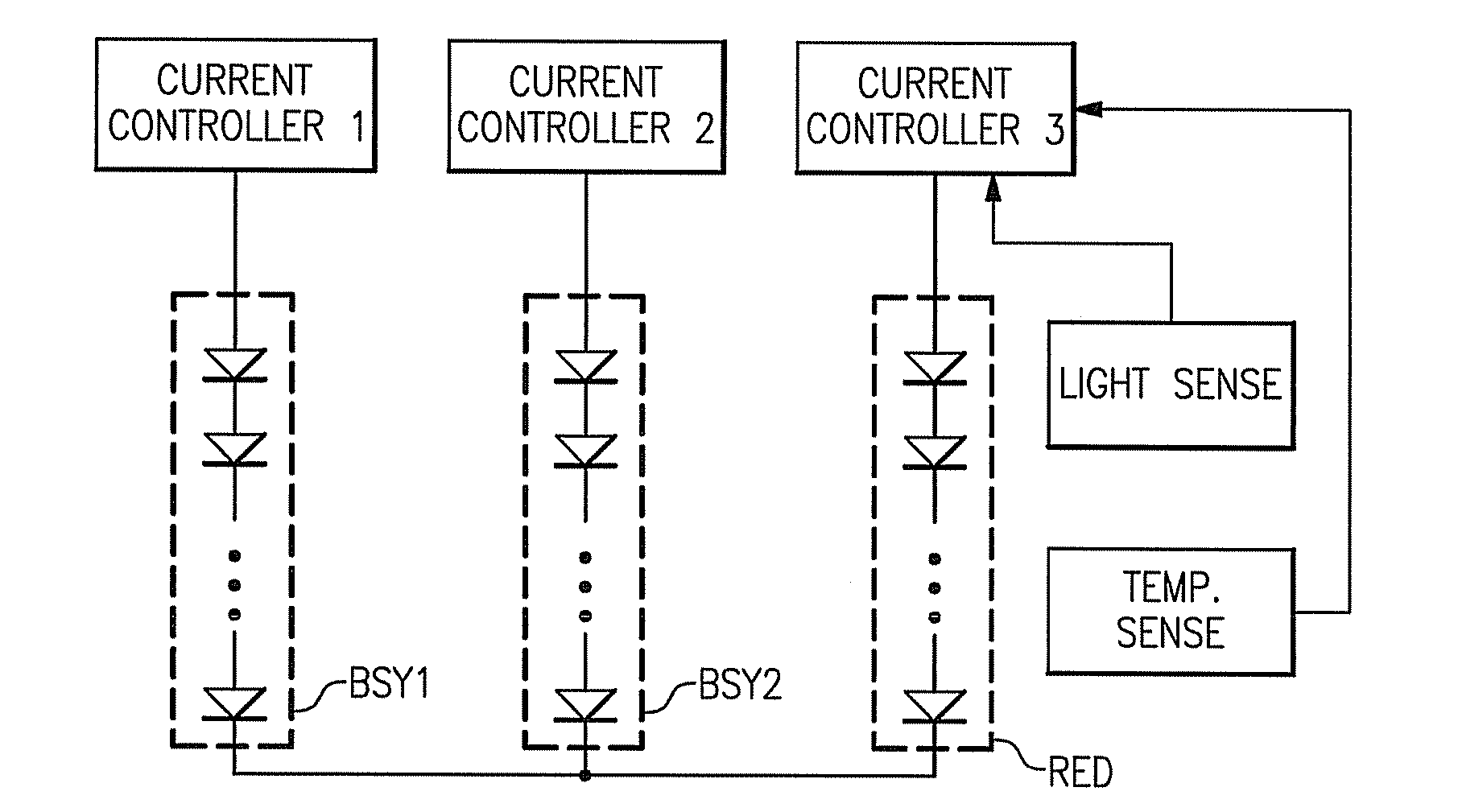
ActiveUS20080309255A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesLight sensingLight equipment
A lighting device comprises groups of solid state light emitters, a sensor and circuitry. If the emitters are illuminated, the sensor is exposed to combined light from the groups, and senses only a portion of the combined light. The circuitry adjusts current applied to at least one of the emitters based on an intensity of the light sensed. Also, a device comprising emitters, a circuit board and a sensor, at least one of the emitters being positioned on the first circuit board and the sensor being spaced from the circuit board. Also, a lighting device comprising emitters, a sensor, and circuitry which adjusts current applied an emitters based on detection by the first sensor, the circuitry comprising a differential amplifier circuit. Also, a lighting device, comprising light emitters and circuitry which adjusts current applied to only some of the emitters based on ambient temperature. Also, methods of lighting.
Owner:IDEAL IND LIGHTING LLC
Image sensing system for a vehicle
InactiveUS20070109406A1Easy to explainRemove distortionVehicle seatsVehicle headlampsLight sensingControl circuit
An image sensing system for a vehicle includes an imaging sensor comprising a two-dimensional array of light sensing photosensor elements. The system includes a logic and control circuit comprising an image processor for processing image data derived from the imaging sensor. The logic and control circuit generates at least one control output for controlling at least one accessory of the vehicle. The imaging sensor is disposed at an interior portion of the cabin of the vehicle and preferably has a field of view exterior of the vehicle through a window of the vehicle.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Ambient light rejection for non-imaging contact sensors
ActiveUS20130120760A1Reduce the amount requiredEnhance the imagePerson identificationUsing optical meansLight sensingMagnification
A sensor for capturing images of skin topology is provided having a platen, and a one or two-dimensional array of light sensing pixel elements for receiving light representative of skin topology when skin, such as finger(s), are present upon the platen. Such sensor being improved by structures, layers, or methods for reducing or blocking ambient light which would hinder the light sensing pixel elements from sensing the light representative of skin topology. The sensors are non-imaging contact sensors as they have platen to contact skin to be imaged, and do not require optics, such as lenses for focusing and / or magnification, to enable proper capture of light representative of skin topology on the sensor's light sensing pixel elements.
Owner:HID GLOBAL CORP
Apparatus and method for high dynamic range imaging using spatially varying exposures
InactiveUS6864916B1Minimize the numberSubstantial lossTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsHigh-dynamic-range imagingUltrasound attenuation
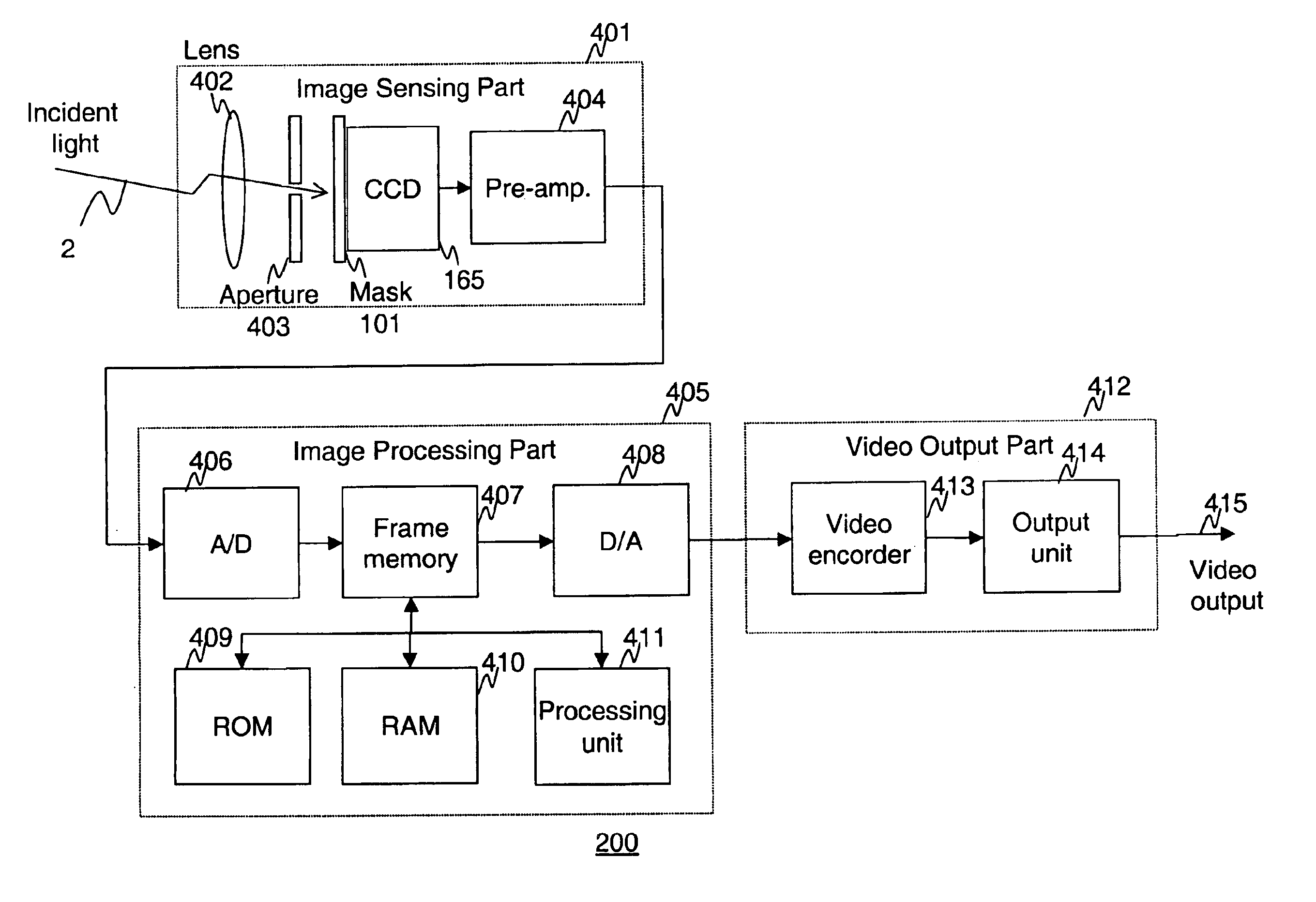
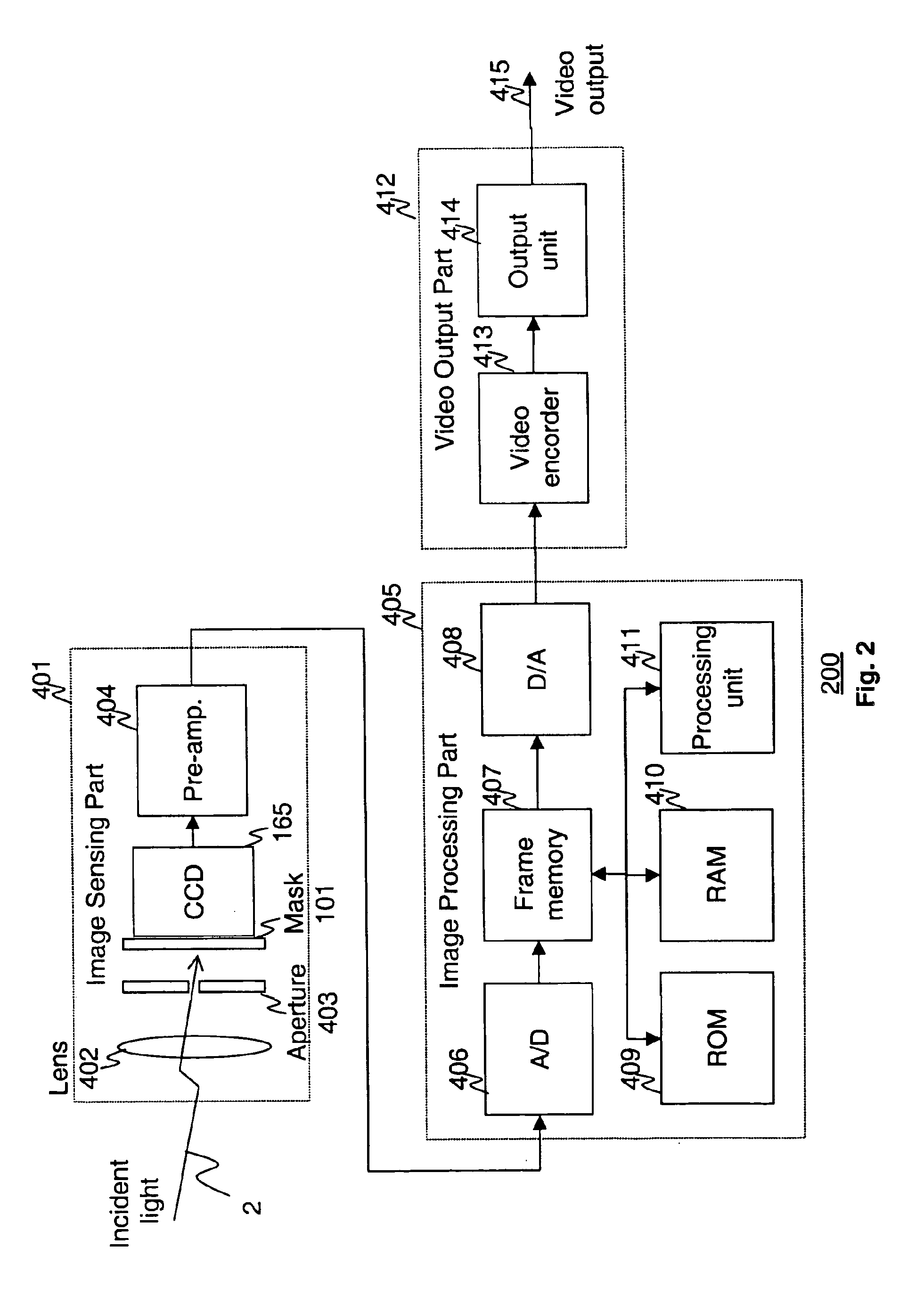
Apparatus and methods are provided for obtaining high dynamic range images using a low dynamic range image sensor. The image of a scene is captured with an image sensor using a spatially varying exposure function. The spatially varying exposure function can be implemented in a number of ways, such as by using as an optical mask with a fixed spatial attenuation pattern or by using an array of light sensing elements having spatially varying photosensitivities. The captured image is then normalized with respect to the spatially varying exposure function. The normalized image data can be interpolated to account for pixels that are either saturated or blackened to enhance the dynamic range of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
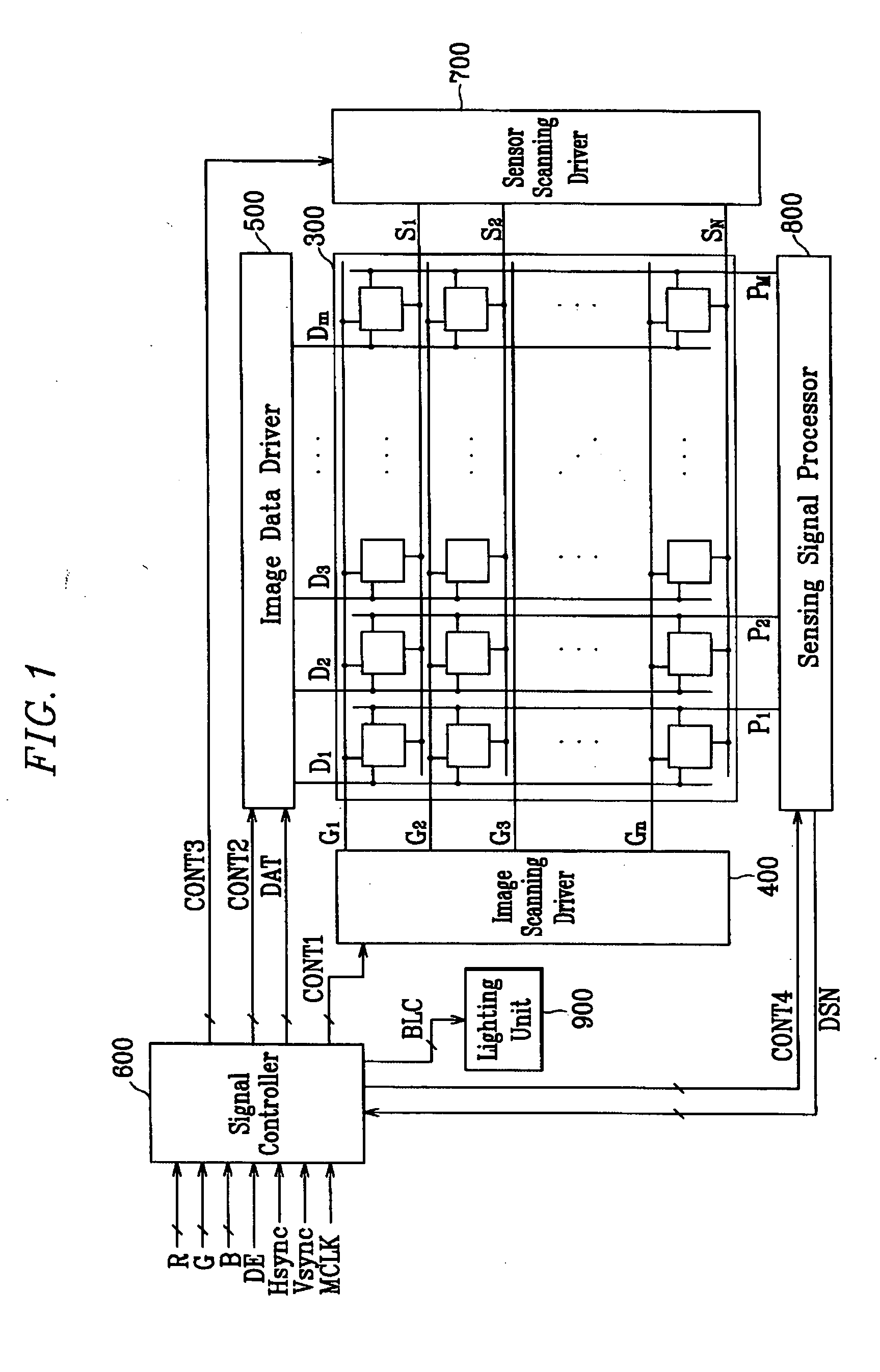
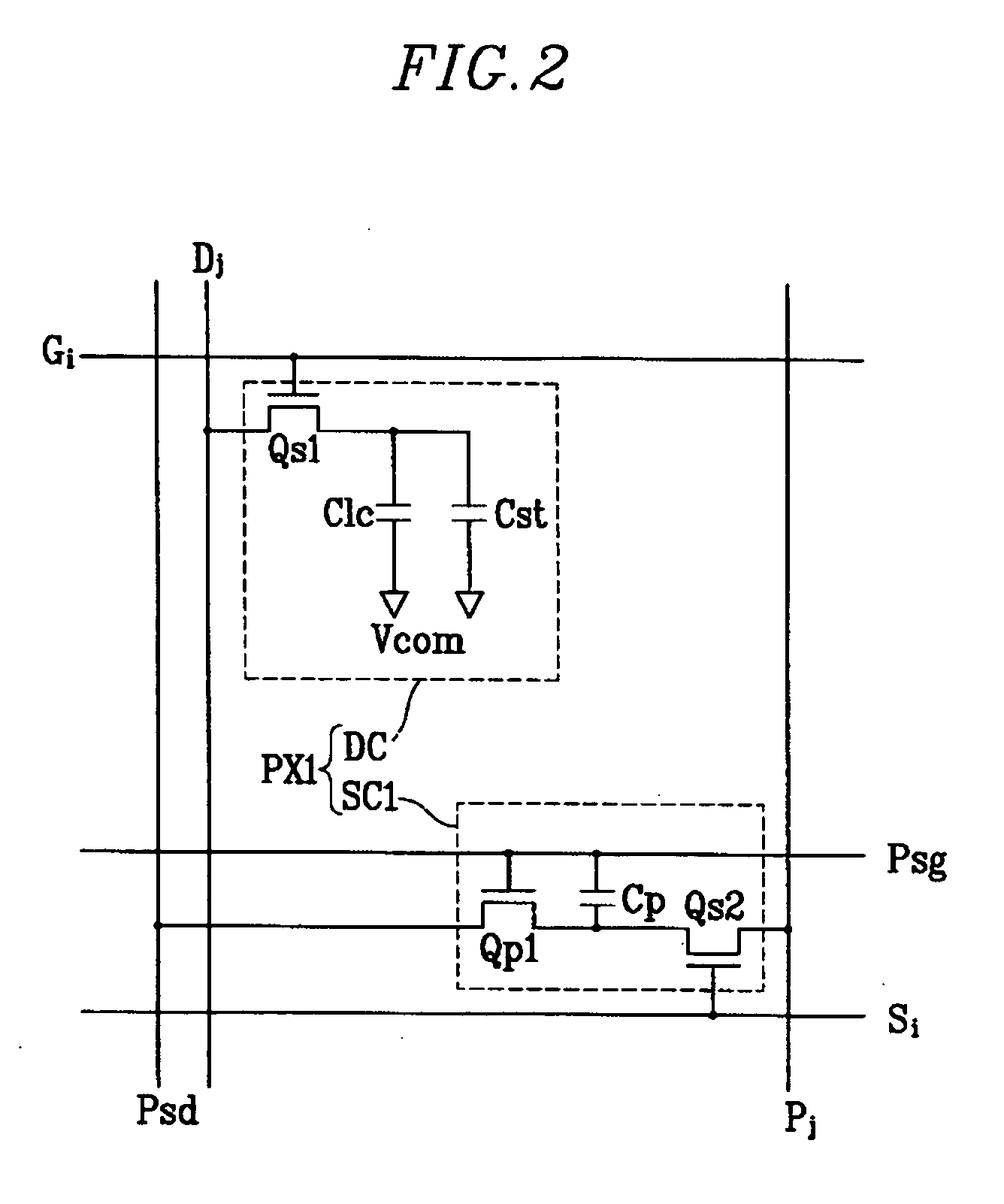
Touch detectable display device and driving method thereof
A display device is disclosed which includes: a display panel; a lighting unit to illuminate the display panel and having a state in response to a lighting control signal; a pressure sensing unit generating a first sensor output signal according to a touch on the display panel; a light sensing unit receiving light from the lighting unit and ambient light and generating a second sensor output signal according to the touch on the display panel; a sensor scanning driver outputting sensor scanning signals to the pressure sensing unit and the light sensing unit in response to a sensor scanning control signal; and a sensing controller generating the lighting control signal and the sensor scanning control signal based on the first and the second sensor output signals and outputting the lighting control signal to the lighting unit and the sensor scanning control signal and the sensor scanning driver.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
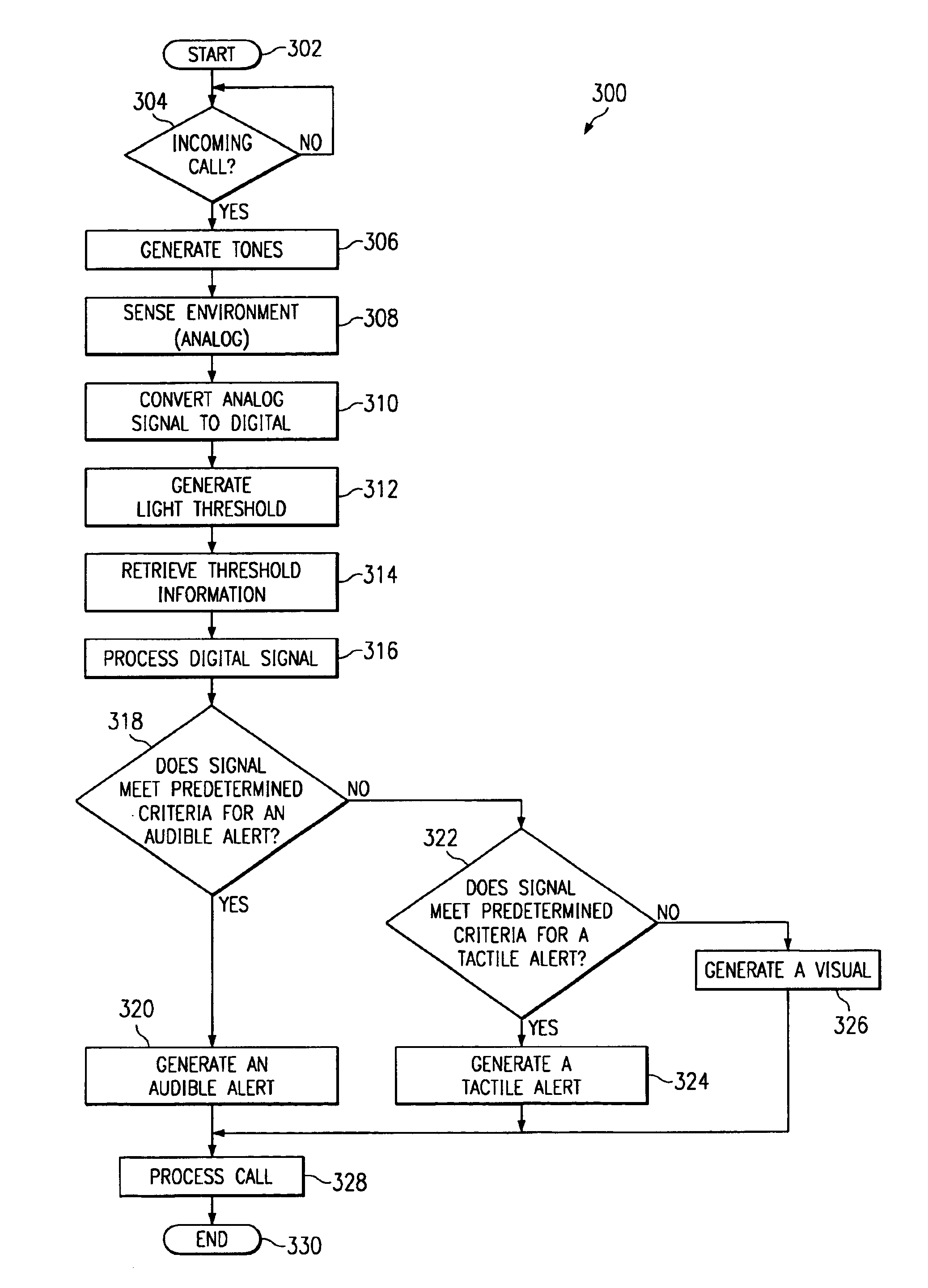
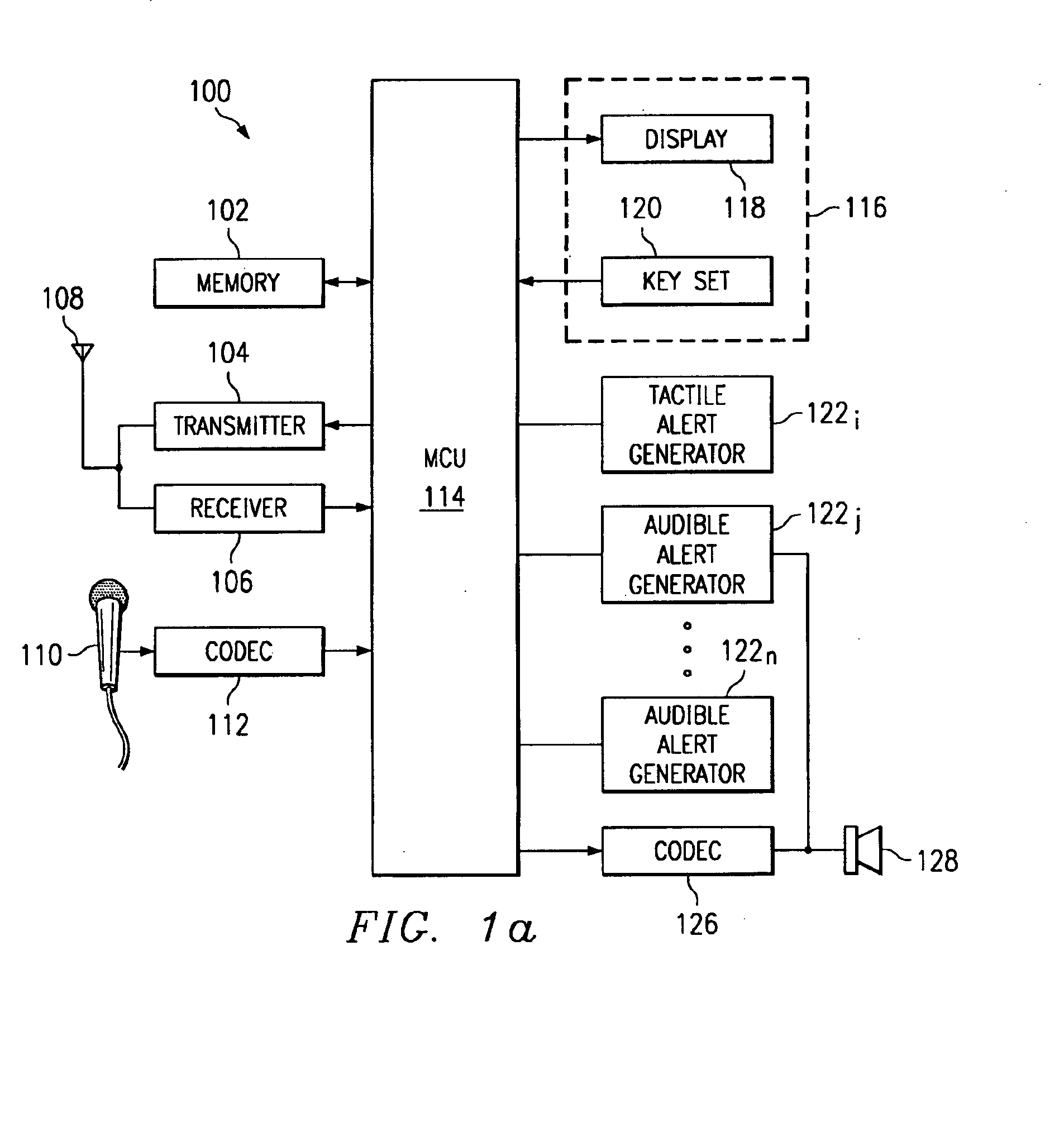
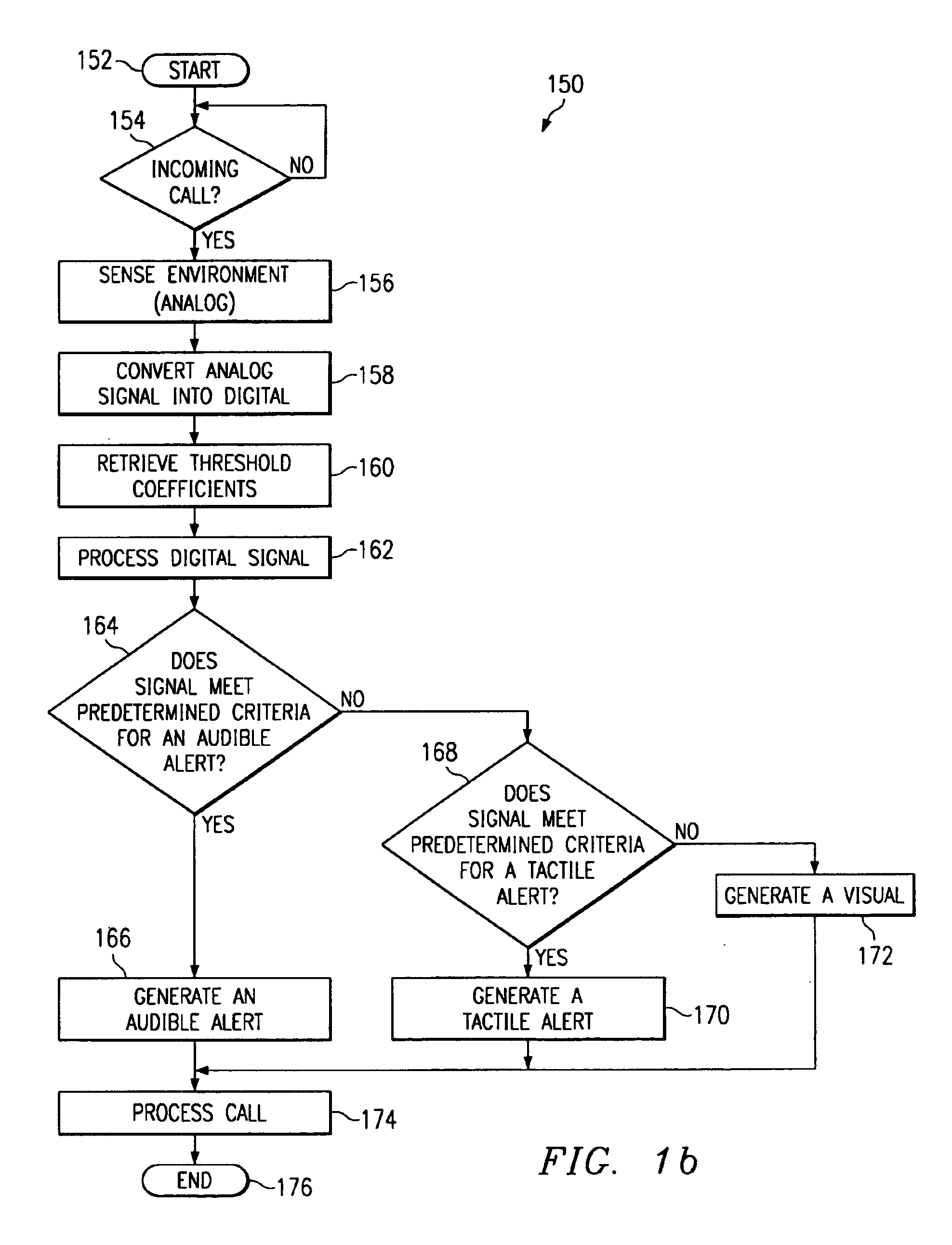
Wireless communication device having intelligent alerting system
InactiveUS6954657B2Cordless telephonesDevices with GPS signal receiverBluetoothGlobal Positioning System
A wireless device (100) having an optimum alert sequence definition analyzes its environment, including time and type of incoming call, and selects an appropriate alert signal sequence. A central processing unit (114) included within the device (100) is responsive to a transmitted signal from an external communications device to generate active and passive sonic sensing. The reflected signal received through the microphone (110) and a predetermined set of values or ranges stored in a memory (102) coupled to the central processing unit (114) are used as input for a program of instructions tangibly embodied in a programmable storage device executable by the central processing unit (114). Based upon processing of this reflected signal, the central processing unit (114) determines which alert signal is optimum given the environment.The device (100) may further include characterization of the environment based on processing of the ambient noise within the environment and several inputs including: manual inputs (user indication / selection), real time clock (including date), light sensing, temperature sensing, cellular receiver indications (RSSI and local network ID), motion sensing, caller identification, global positioning system data, and radio link reception (i.e. Bluetooth: office / home network, etc.).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
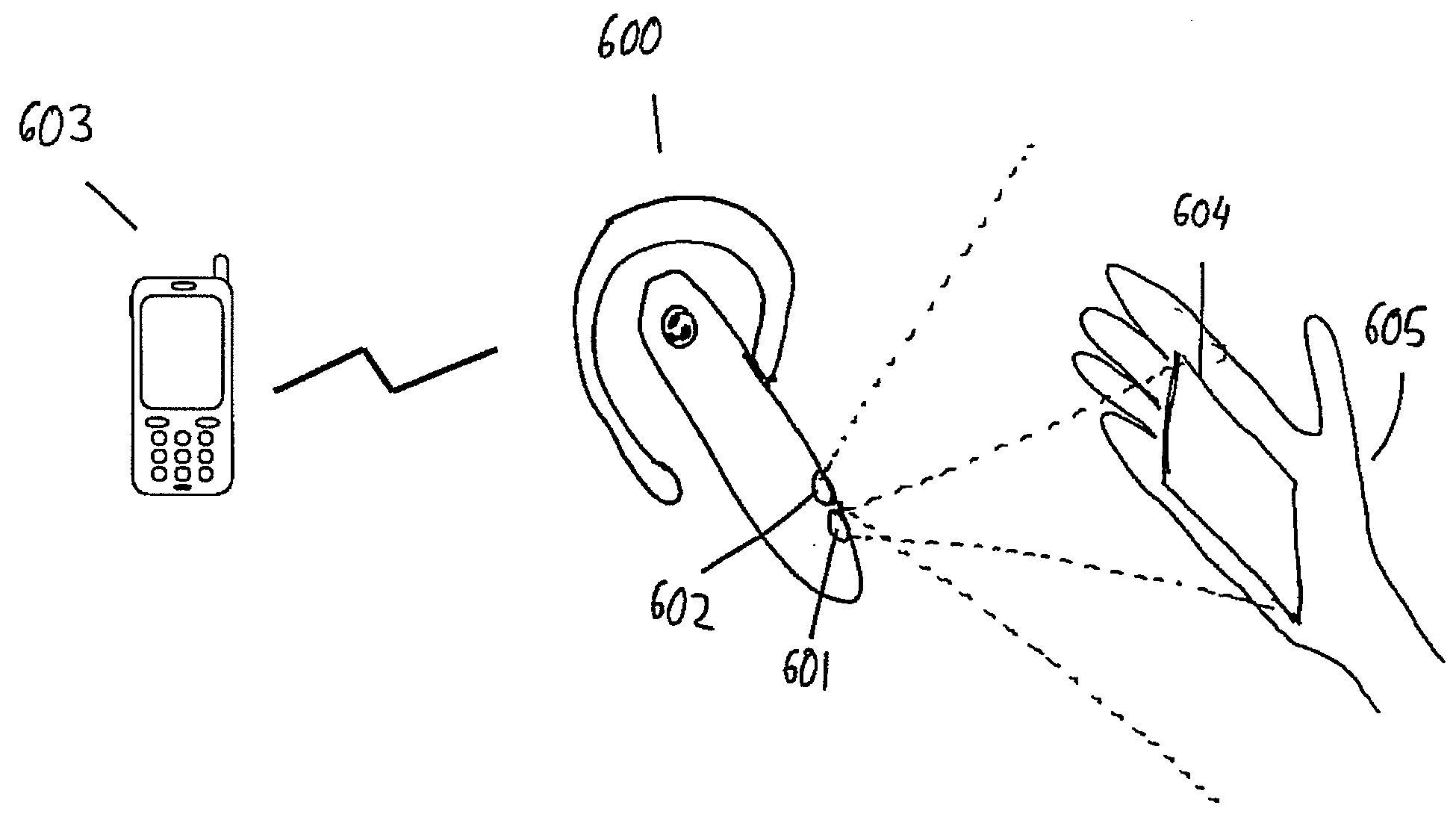
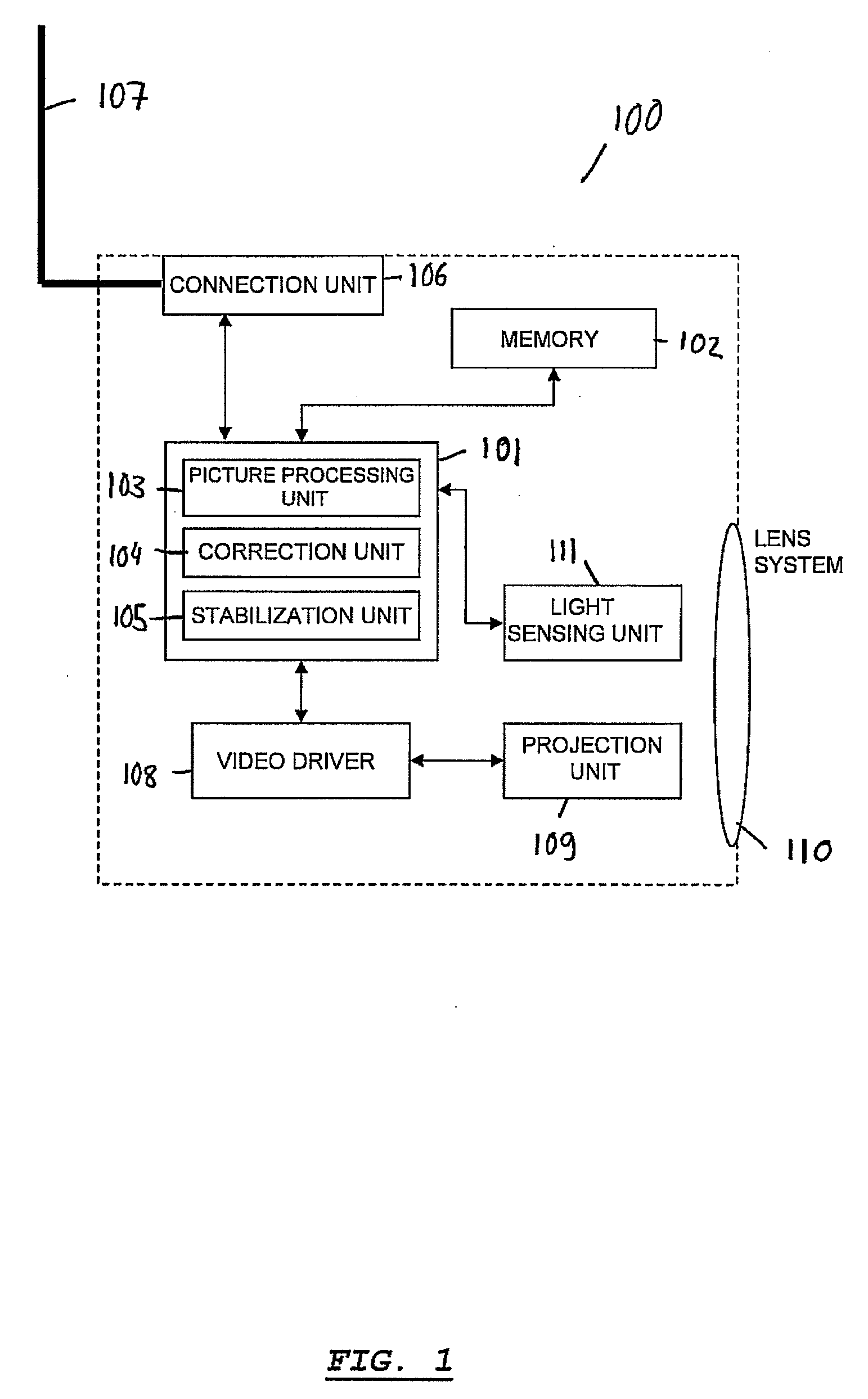
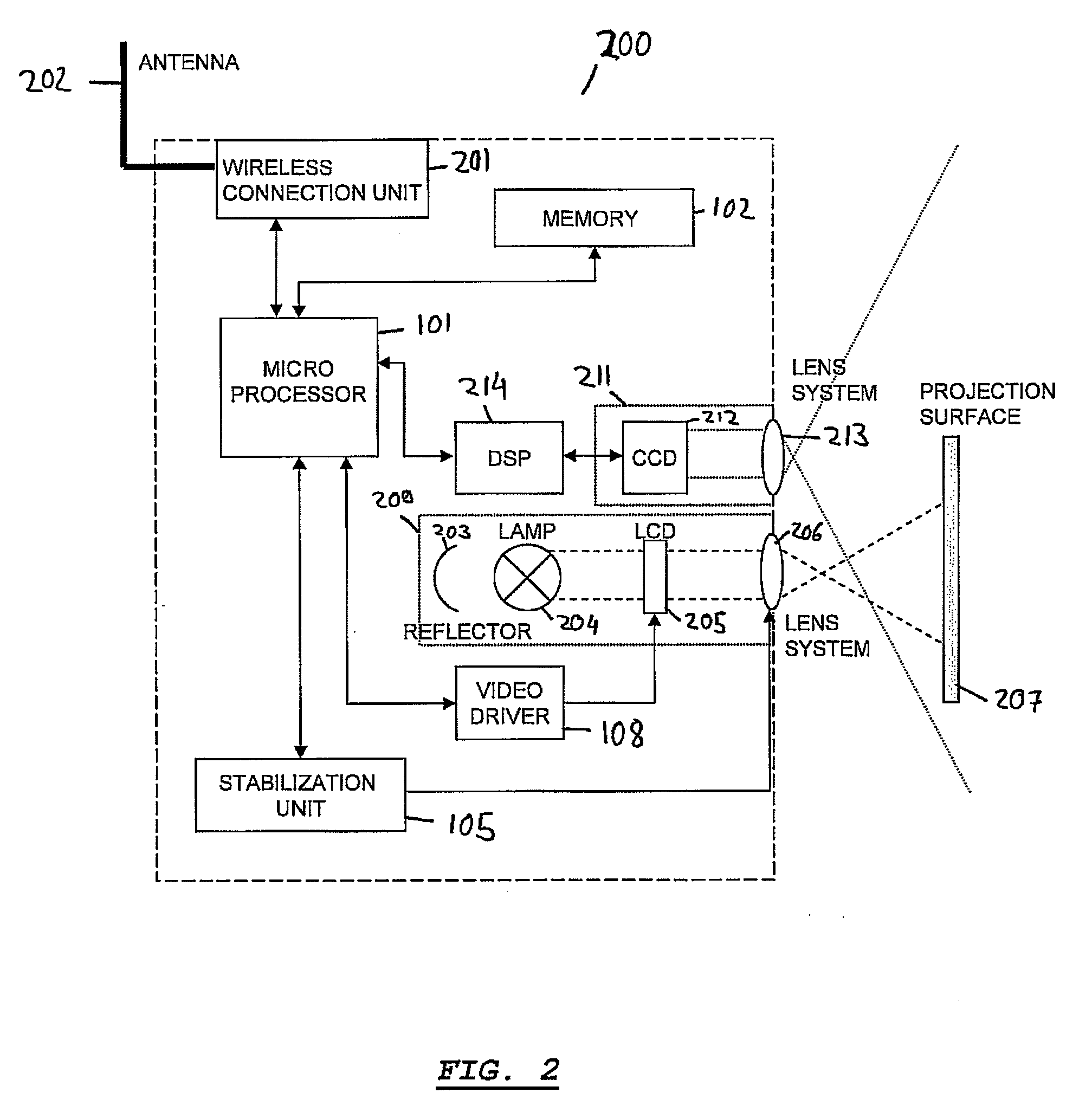
Portable projector and method of operating a portable projector
InactiveUS20090295712A1User interfaceFacilitate user inputCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsLight sensingComputer science
A portable projector comprising a projection unit for projecting an image onto a projection surface. The portable projector comprises a stabilization unit for stabilizing the projecting of the image. The portable projector further comprises a light sensing unit for scanning a region surrounding the portable projector.
Owner:SONY ERICSSON MOBILE COMM AB
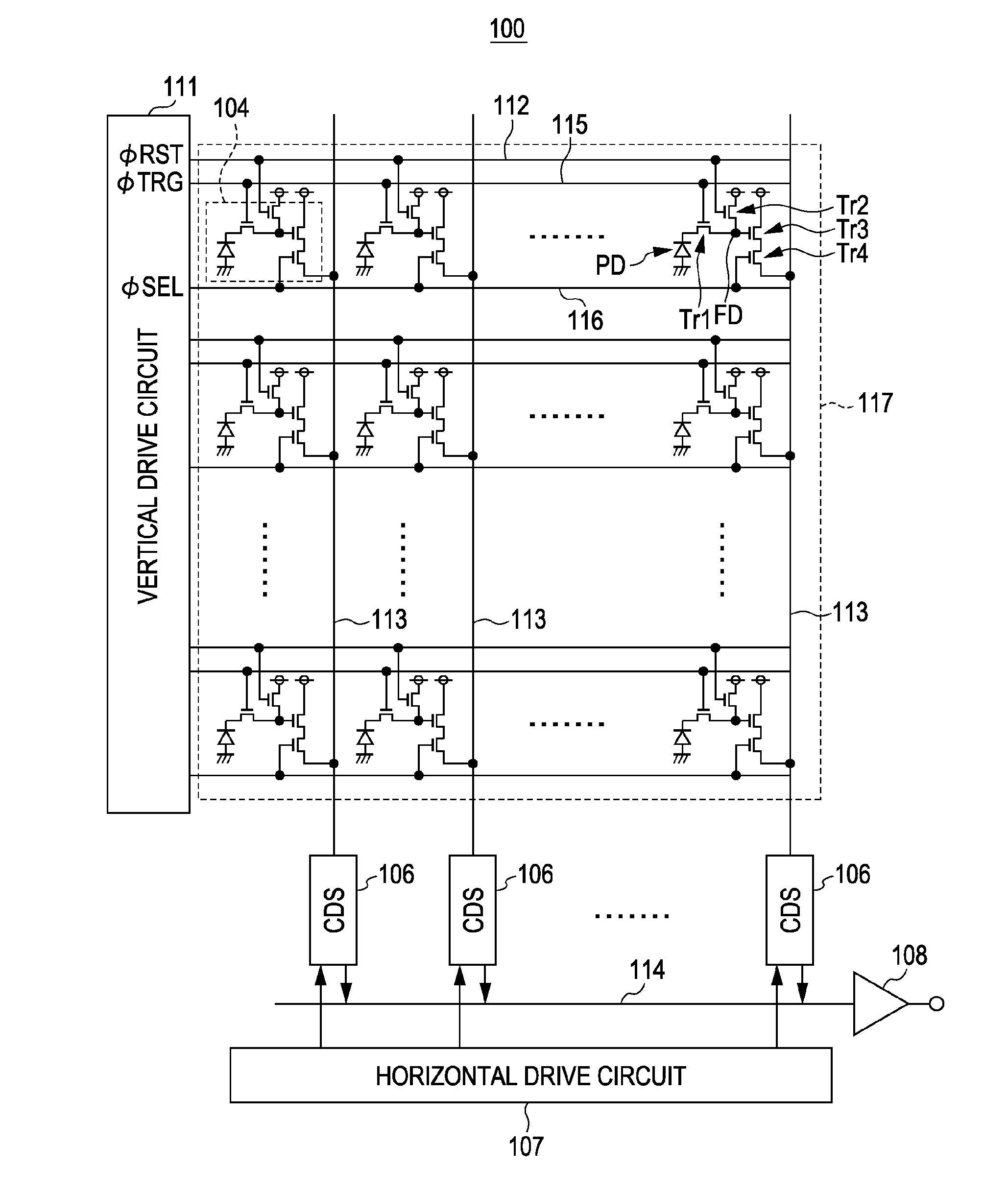
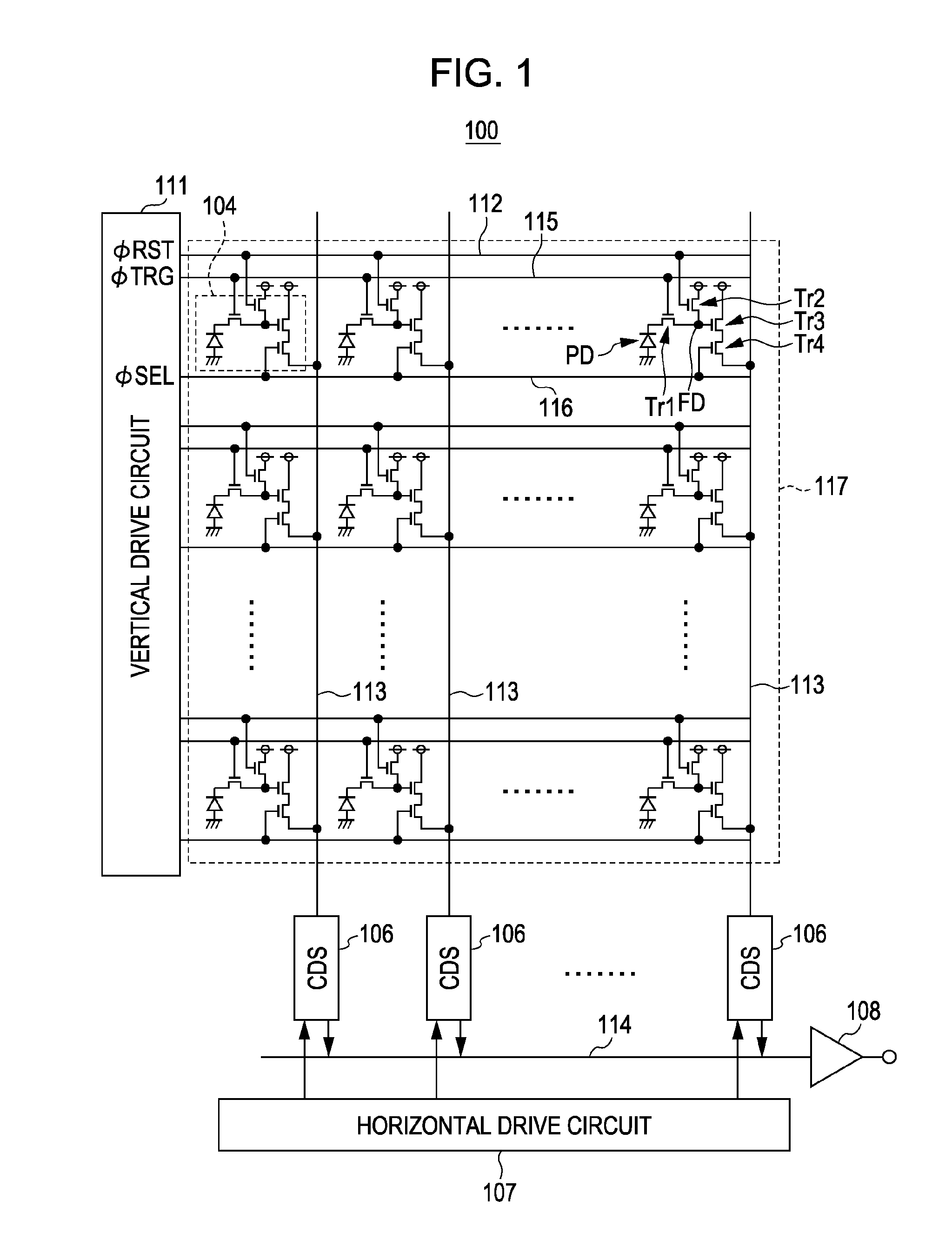
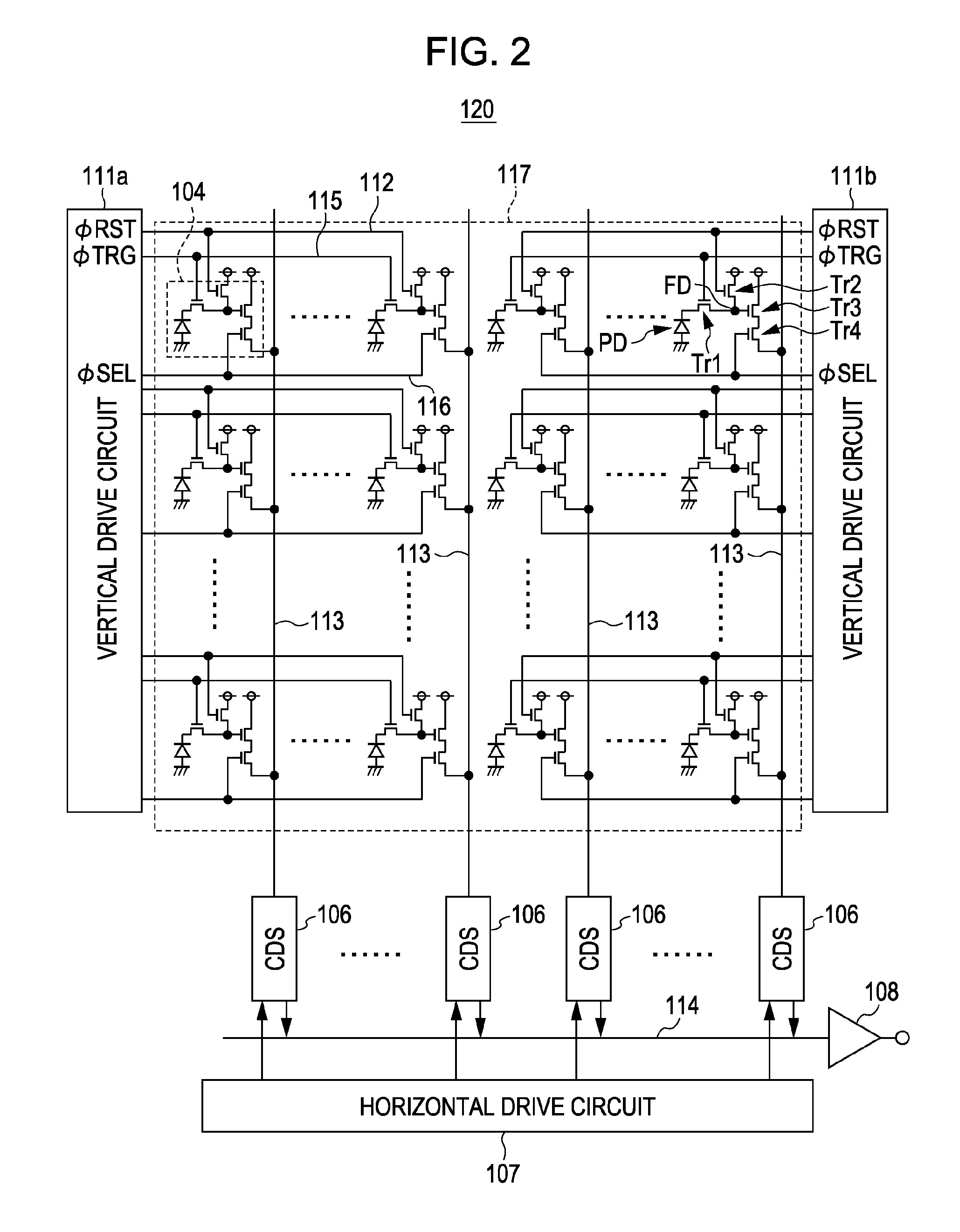
Solid-state imaging device, driving method of solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS20100245647A1Reduce blurImprove pressure resistanceTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight sensingTransistor
A solid-state imaging device includes a first chip including a plurality of pixels, each pixel including a light sensing unit generating a signal charge responsive to an amount of received light, and a plurality of MOS transistors reading the signal charge generated by the light sensing unit and outputting the read signal charge as a pixel signal, a second chip including a plurality of pixel drive circuits supplying desired drive pulses to pixels, the second chip being laminated beneath the first chip in a manner such that the pixel drive circuits are arranged beneath the pixels formed in the first chip to drive the pixels, and a connection unit for electrically connecting the pixels to the pixel drive circuits arranged beneath the pixels.
Owner:SONY CORP
Optical systems fabricated by printing-based assembly
ActiveUS20100283069A1Low costImprove performanceFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsLight sensingPliability
The present invention provides optical devices and systems fabricated, at least in part, via printing-based assembly and integration of device components. In specific embodiments the present invention provides light emitting systems, light collecting systems, light sensing systems and photovoltaic systems comprising printable semiconductor elements, including large area, high performance macroelectronic devices. Optical systems of the present invention comprise semiconductor elements assembled, organized and / or integrated with other device components via printing techniques that exhibit performance characteristics and functionality comparable to single crystalline semiconductor based devices fabricated using conventional high temperature processing methods. Optical systems of the present invention have device geometries and configurations, such as form factors, component densities, and component positions, accessed by printing that provide a range of useful device functionalities. Optical systems of the present invention include devices and device arrays exhibiting a range of useful physical and mechanical properties including flexibility, shapeability, conformability and stretchability. Optical systems of the present invention include, however, devices and device arrays provided on conventional rigid or semi-rigid substrates, in addition to devices and device arrays provided on flexible, shapeable and / or stretchable substrates.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD +1
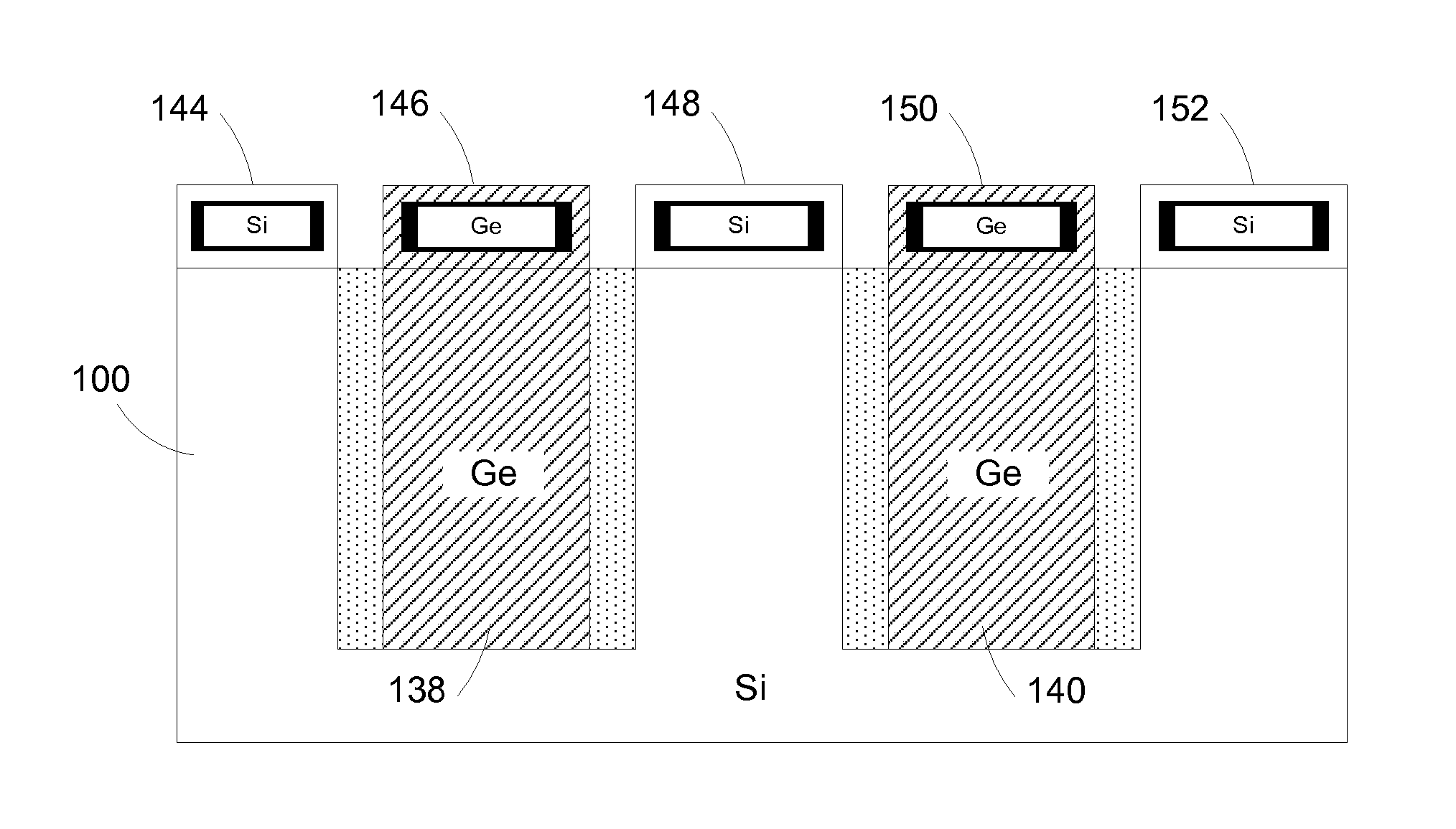
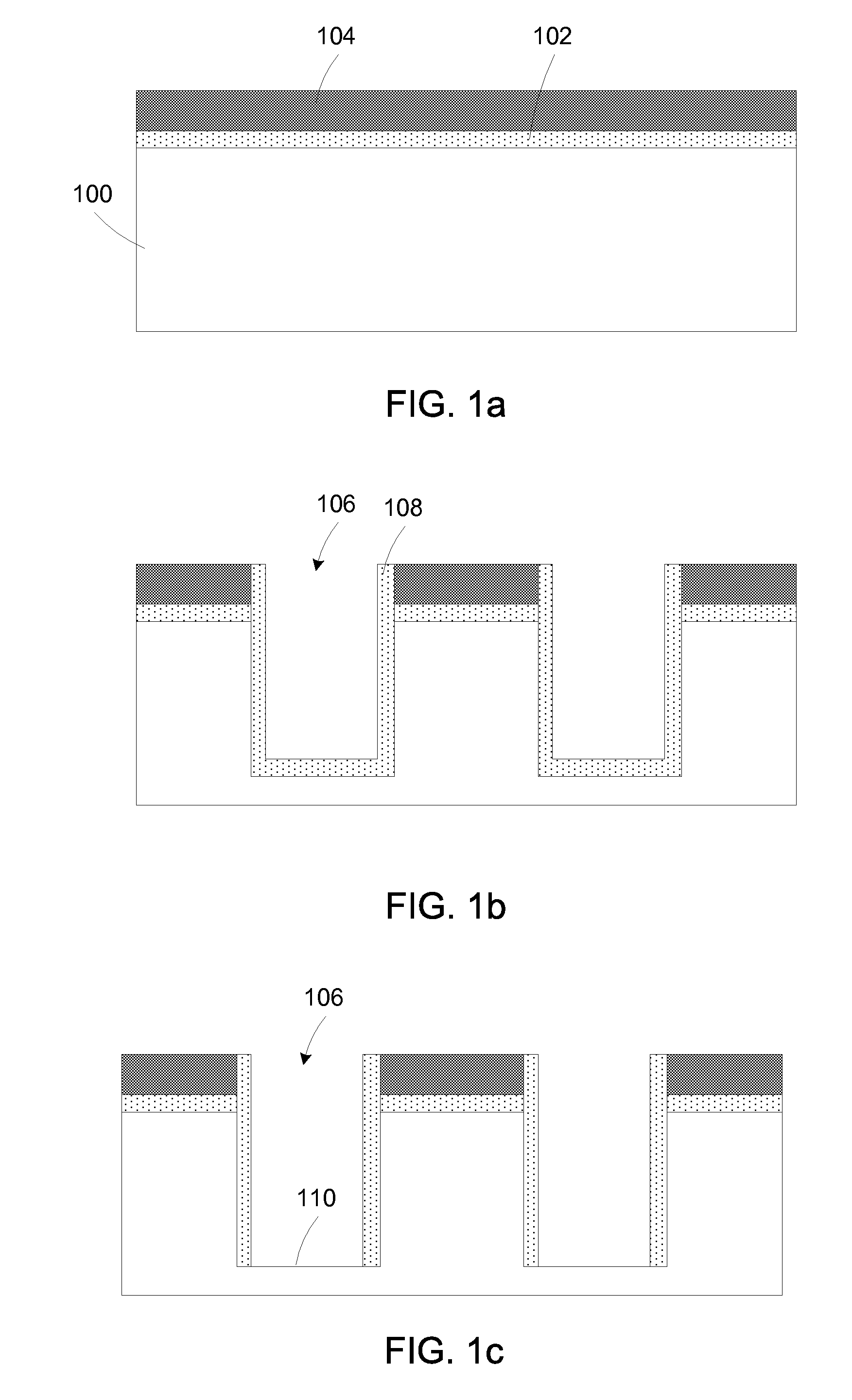
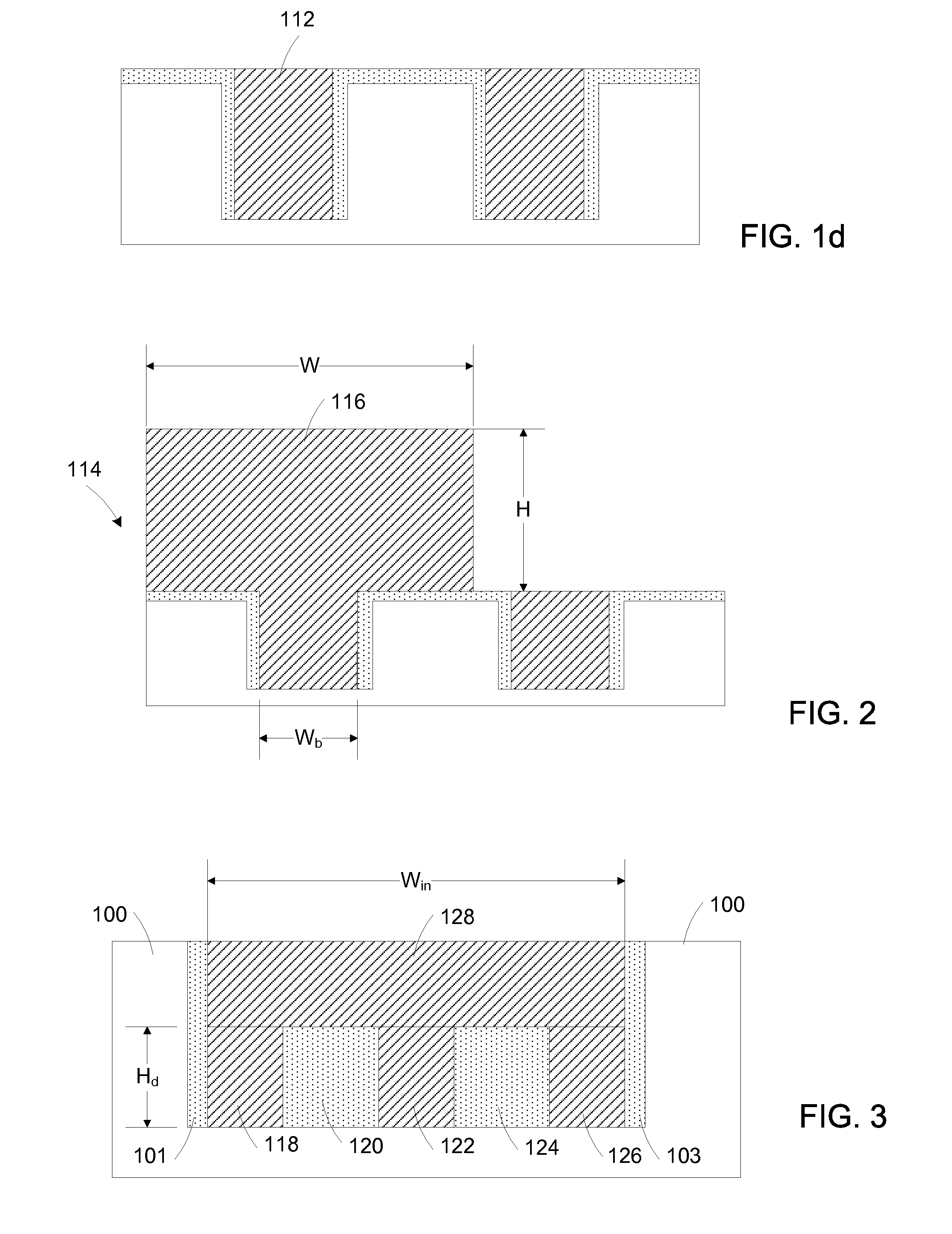
Semiconductor sensor structures with reduced dislocation defect densities and related methods for the same
Non-silicon based semiconductor devices are integrated into silicon fabrication processes by using aspect-ratio-trapping materials. Non-silicon light-sensing devices in a least a portion of a crystalline material can output electrons generated by light absorption therein. Exemplary light-sensing devices can have relatively large micron dimensions. As an exemplary application, complementary-metal-oxide-semiconductor photodetectors are formed on a silicon substrate by incorporating an aspect-ratio-trapping technique.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
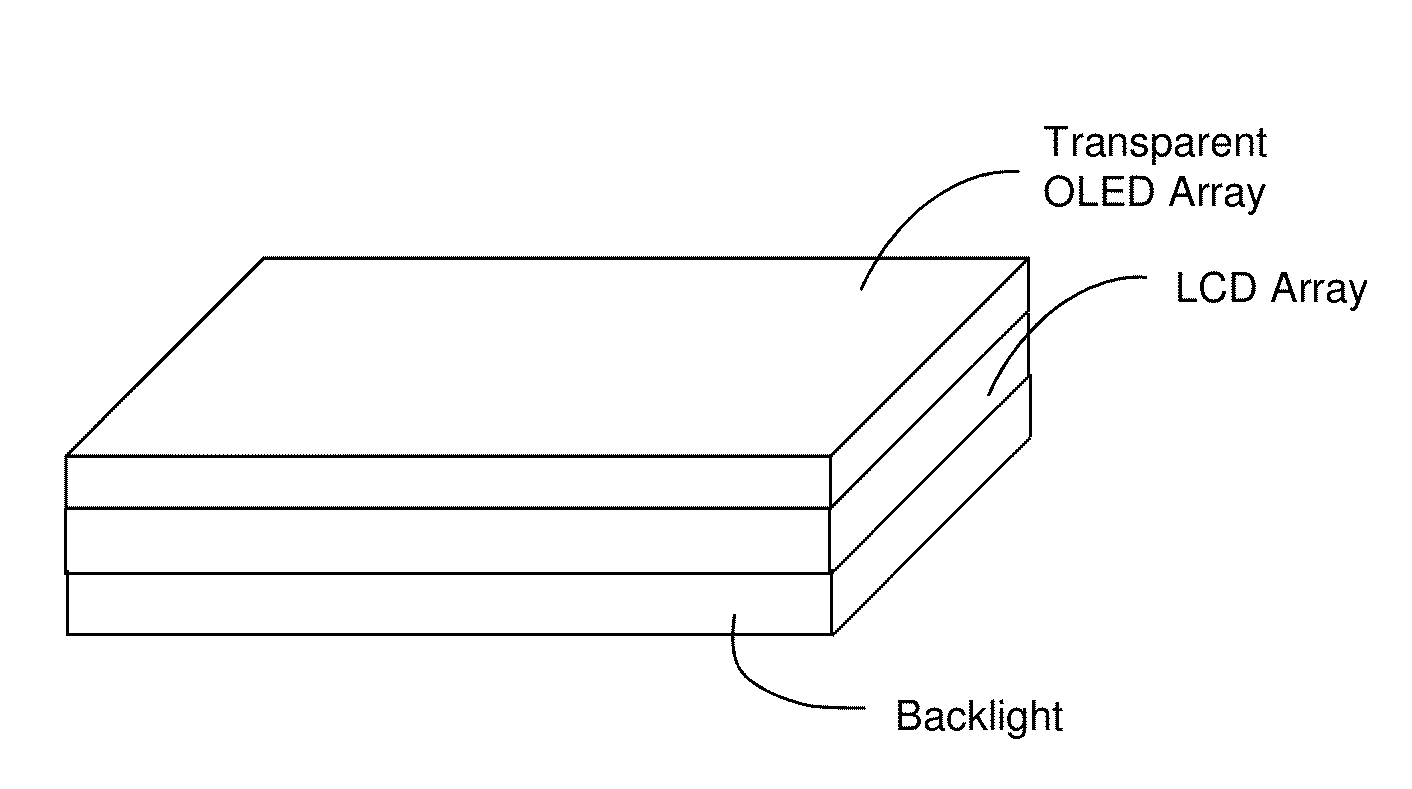
Use of LED or OLED Array to Implement Integrated Combinations of Touch Screen Tactile, Touch Gesture Sensor, Color Image Display, Hand-Image Gesture Sensor, Document Scanner, Secure Optical Data Exchange, and Fingerprint Processing Capabilities
InactiveUS20140036168A1Easy to useCharacter and pattern recognitionNon-linear opticsColor imageTablet computer
A system and method for implementing a display which also serves as one or more of a tactile user interface touchscreen, proximate hand gesture sensor, light field sensor, lensless imaging camera, document scanner, fingerprint scanner, and secure optical communications interface. In an implementation, an OLED array can be used for light sensing as well as light emission functions. In one implementation a single OLED array is used as the only optoelectronic user interface element in the system. In another implementation two OLED arrays are used, each performing and / or optimized from different functions. In another implementation, an LCD and an OLED array are used in various configurations. The resulting arrangements allow for sharing of both optoelectric devices as well as associated electronics and computational processors, and are accordingly advantageous for use in handheld devices such as cellphone, smartphones, PDAs, tablet computers, and other such devices.
Owner:NRI R&D PATENT LICENSING LLC
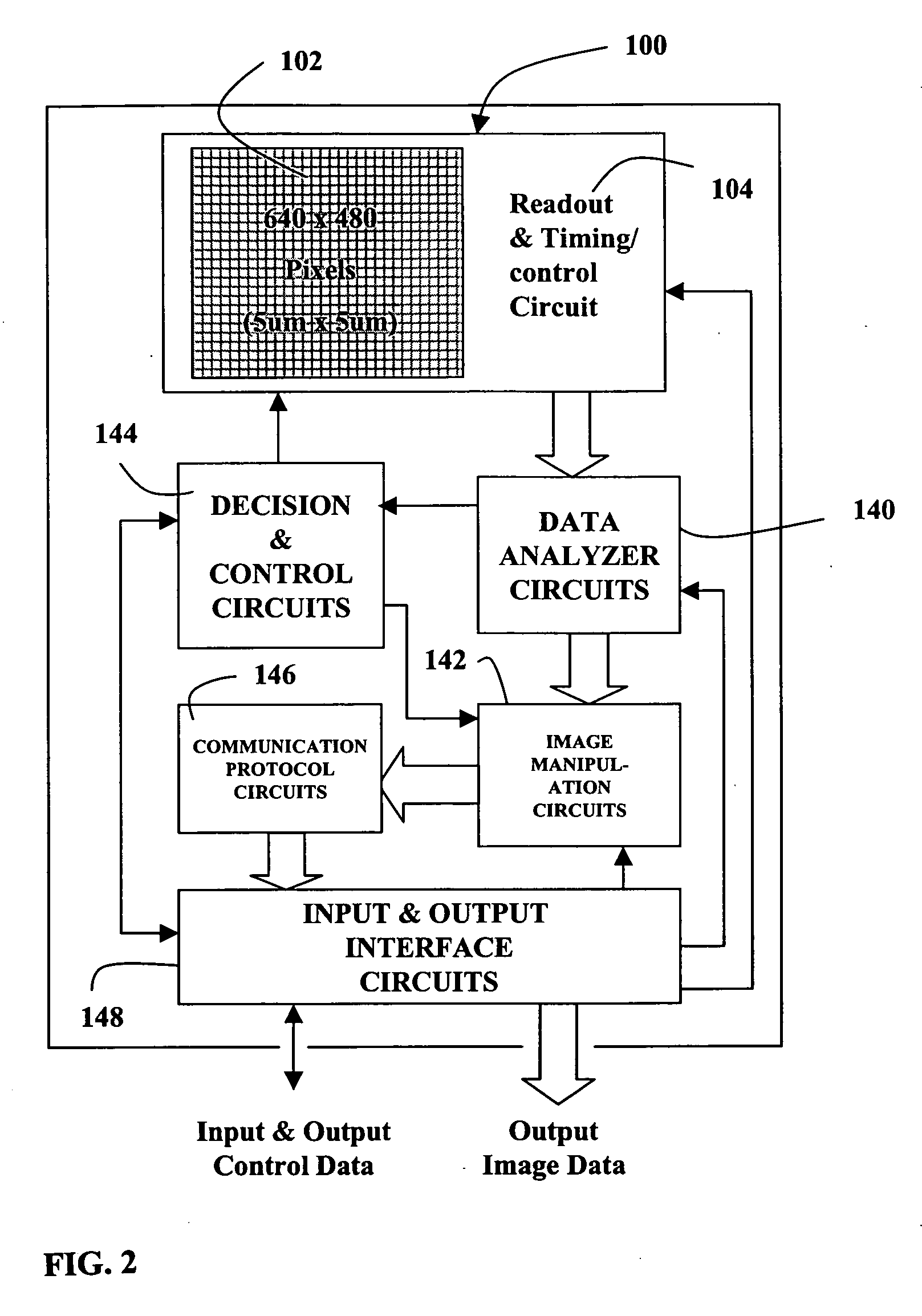
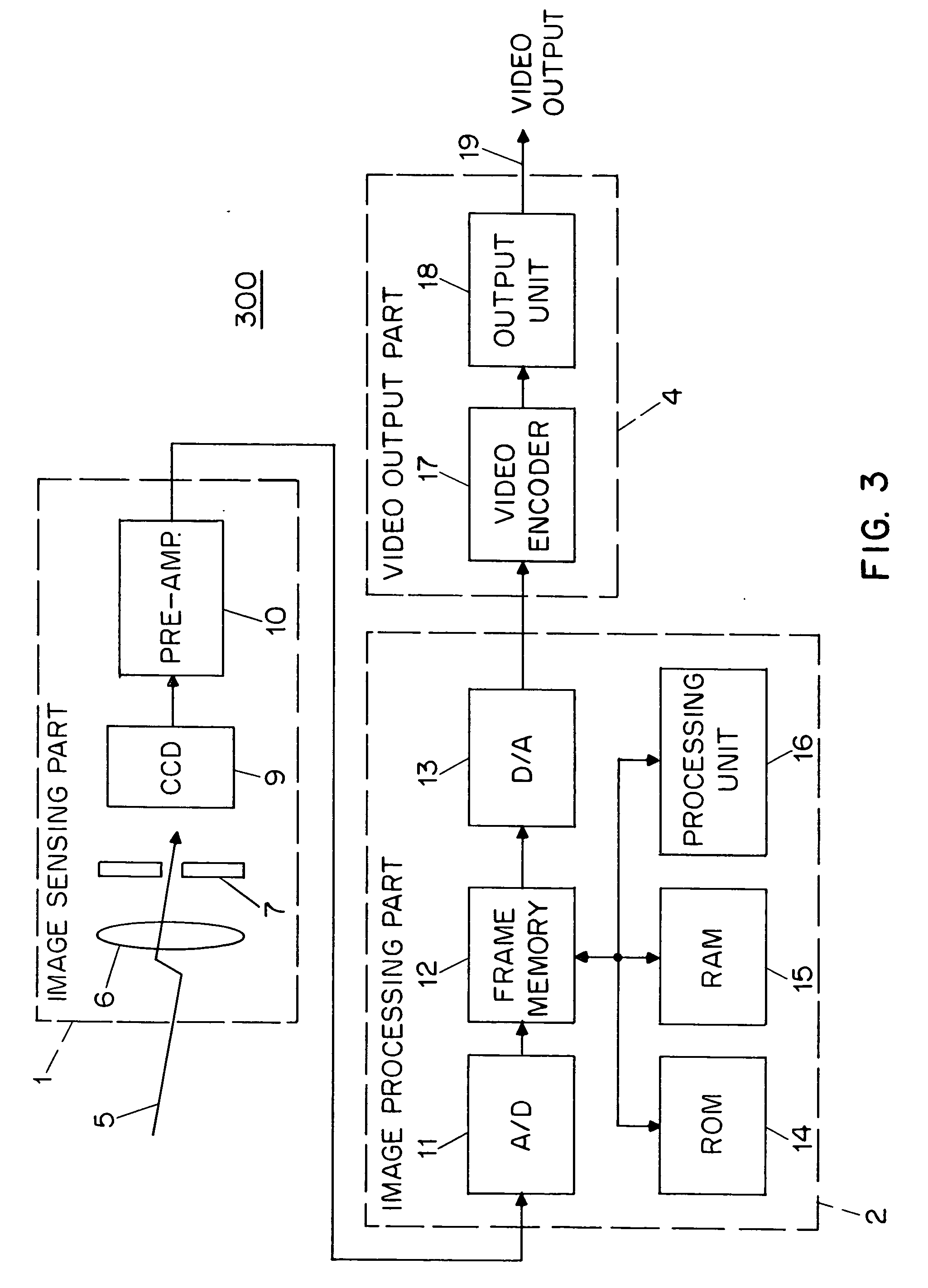
Electronic image sensor
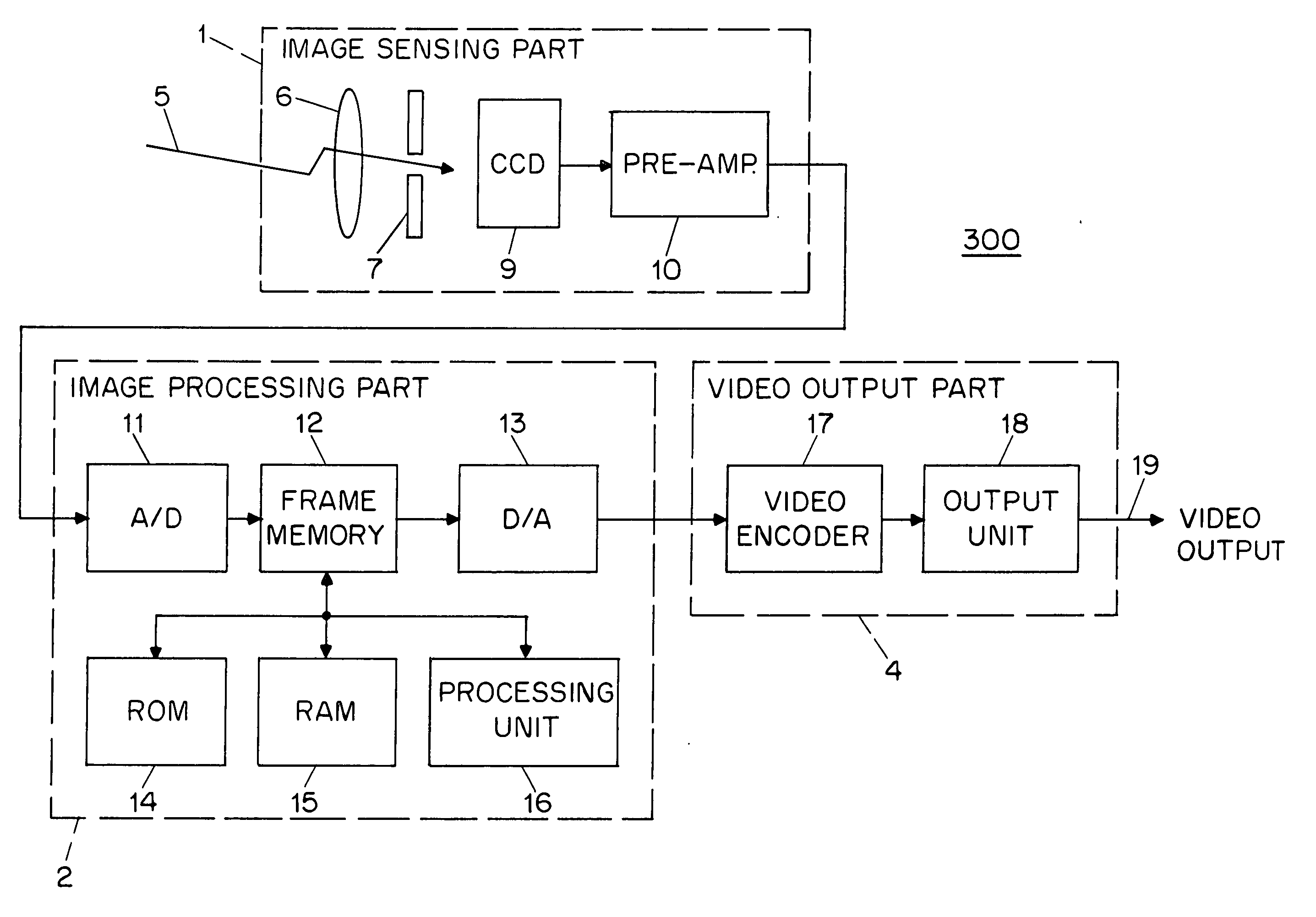
InactiveUS20060164533A1Avoid complicationsAccurate exposureTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringFrame rate
An electronic imaging sensor. The sensor includes an array of photo-sensing pixel elements for producing image frames. Each pixel element defines a photo-sensing region and includes a charge collecting element for collecting electrical charges produced in the photo-sensing region, and a charge storage element for the storage of the collected charges. The sensor also includes charge sensing elements for sensing the collected charges, and charge-to-signal conversion elements. The sensor also includes timing elements for controlling the pixel circuits to produce image frames at a predetermined normal frame rate based on a master clock signal (such as 12 MHz or 10 MHz). This predetermined normal frame rate which may be a video rate (such as about 30 frames per second or 25 frames per second) establishes a normal maximum per frame exposure time. The sensor includes circuits (based on prior art techniques) for adjusting the per frame exposure time (normally based on ambient light levels) and novel frame rate adjusting features for reducing the frame rate below the predetermined normal frame rate, without changing the master clock signal, to permit per frame exposure times above the normal maximum exposure time. This permits good exposures even in very low light levels. (There is an obvious compromise of lowering of the frame rate in conditions of very low light levels, but in most cases this is preferable to inadequate exposure.) These adjustments can be automatic or manual.
Owner:E PHOCOS
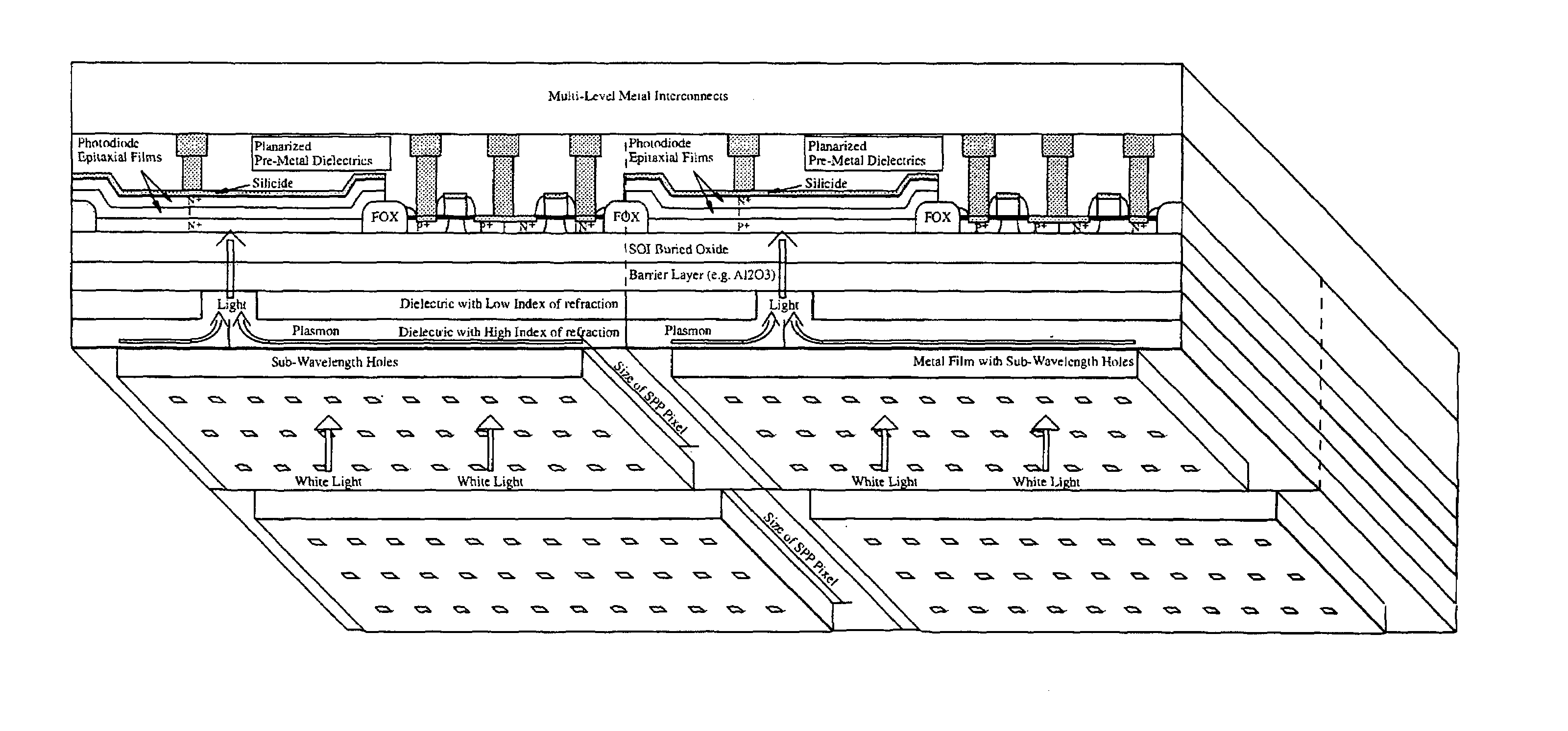
CMOS image sensor
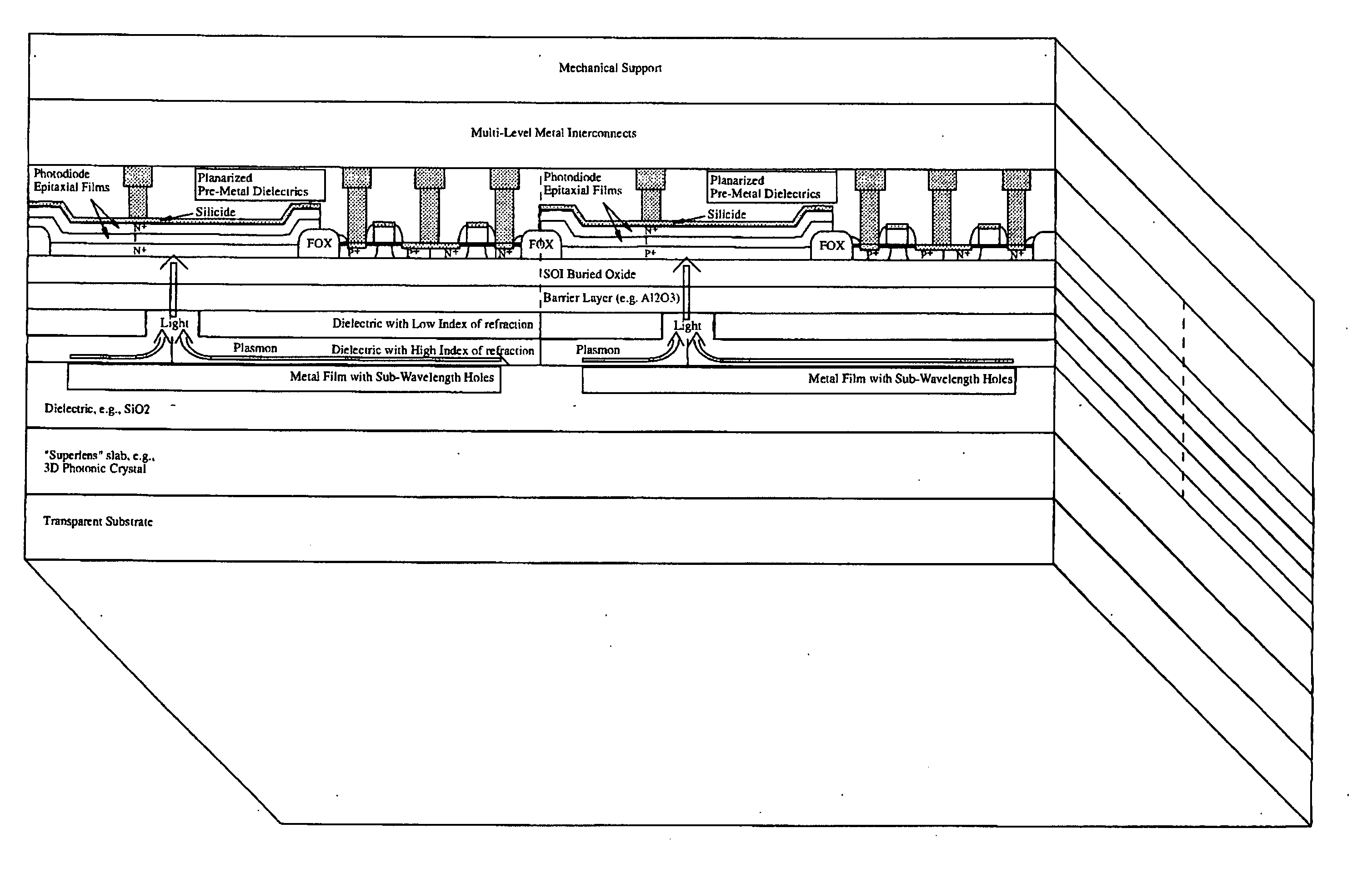
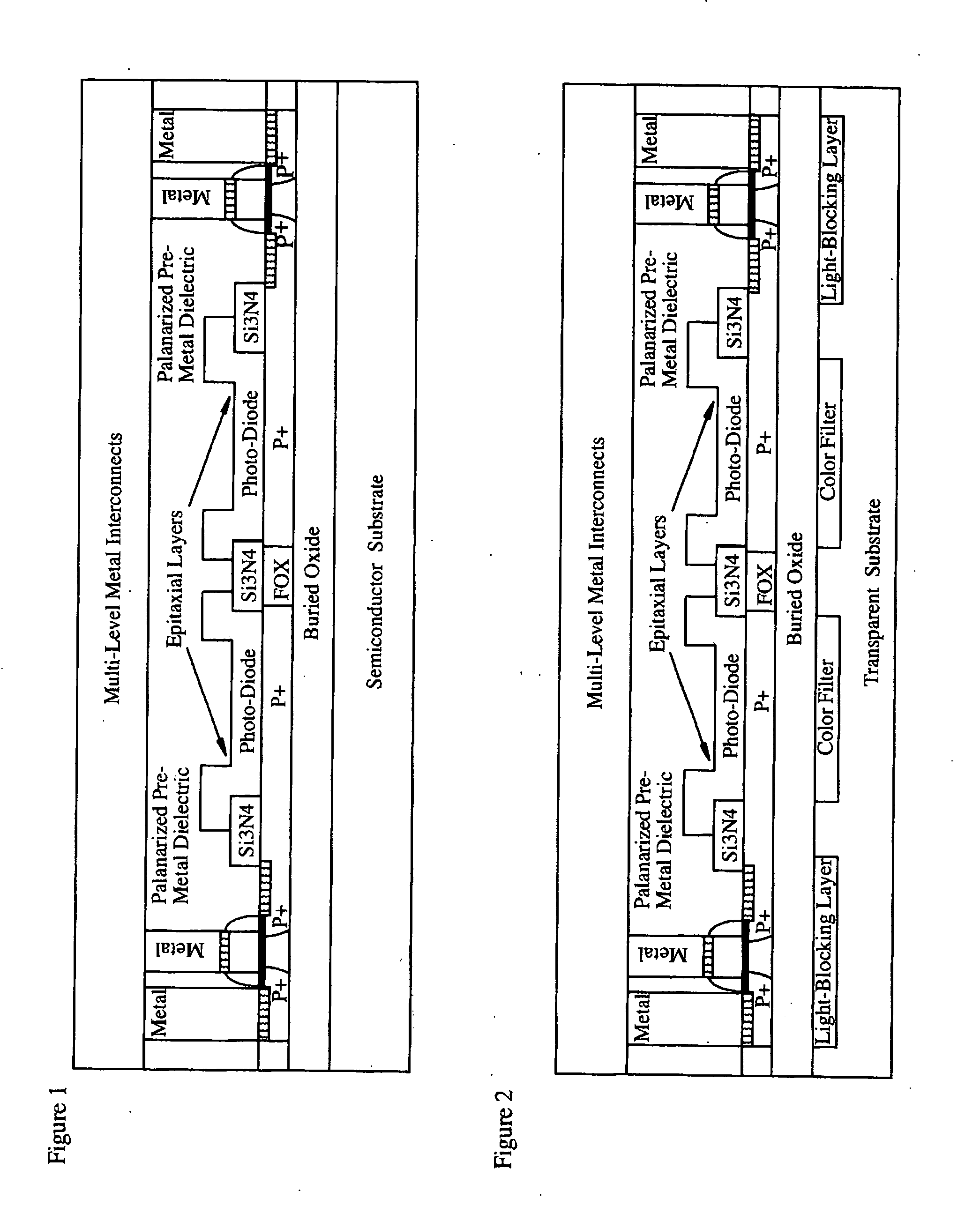
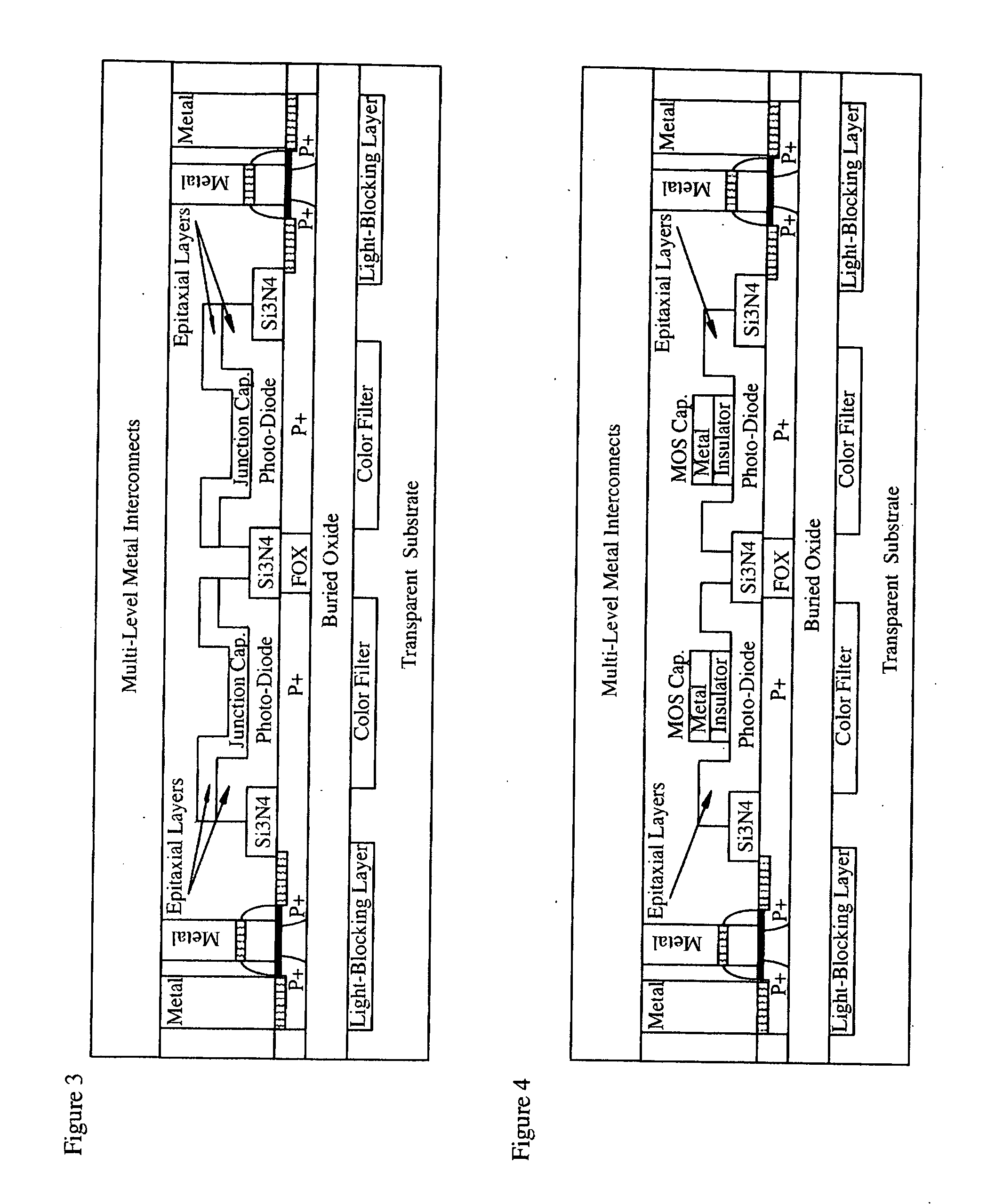
Light sensing devices are monolithically integrates with CMOS devices on Thin-Film Silicon-On-insulator (TF-SOI) or Thin-Film Germanium-On-Insulator (TF-GeOI) substrates. Photo-diode active layers are epitaxially grown on the front-side of the substrate and after full processing of the front-side of the substrate, the substrate material is removed under the buried insulator (buried oxide). Monolithically integrated structures are then fabricated on the back of the buried oxide. The back-side is then bonded to a new substrate that is transparent to the wavelengths of interest. For example, quartz, sapphire, glass, or plastic, are suitable for the visible range. Back-side illumination of the sensor matrix is thereby allowed, with light traveling through the structures fabricated on the back of the substrate, opposite to the side on which CMOS is made.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
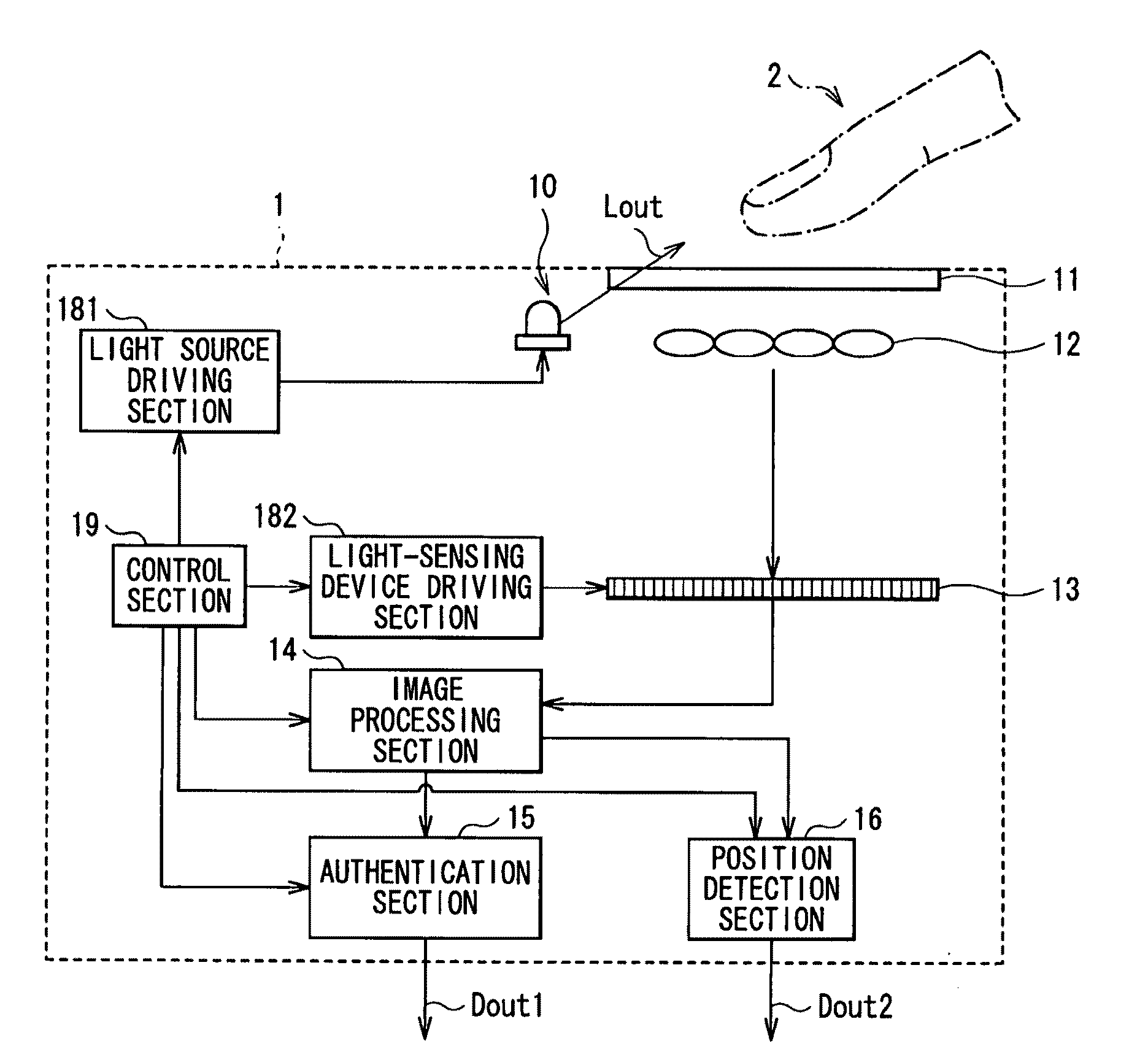
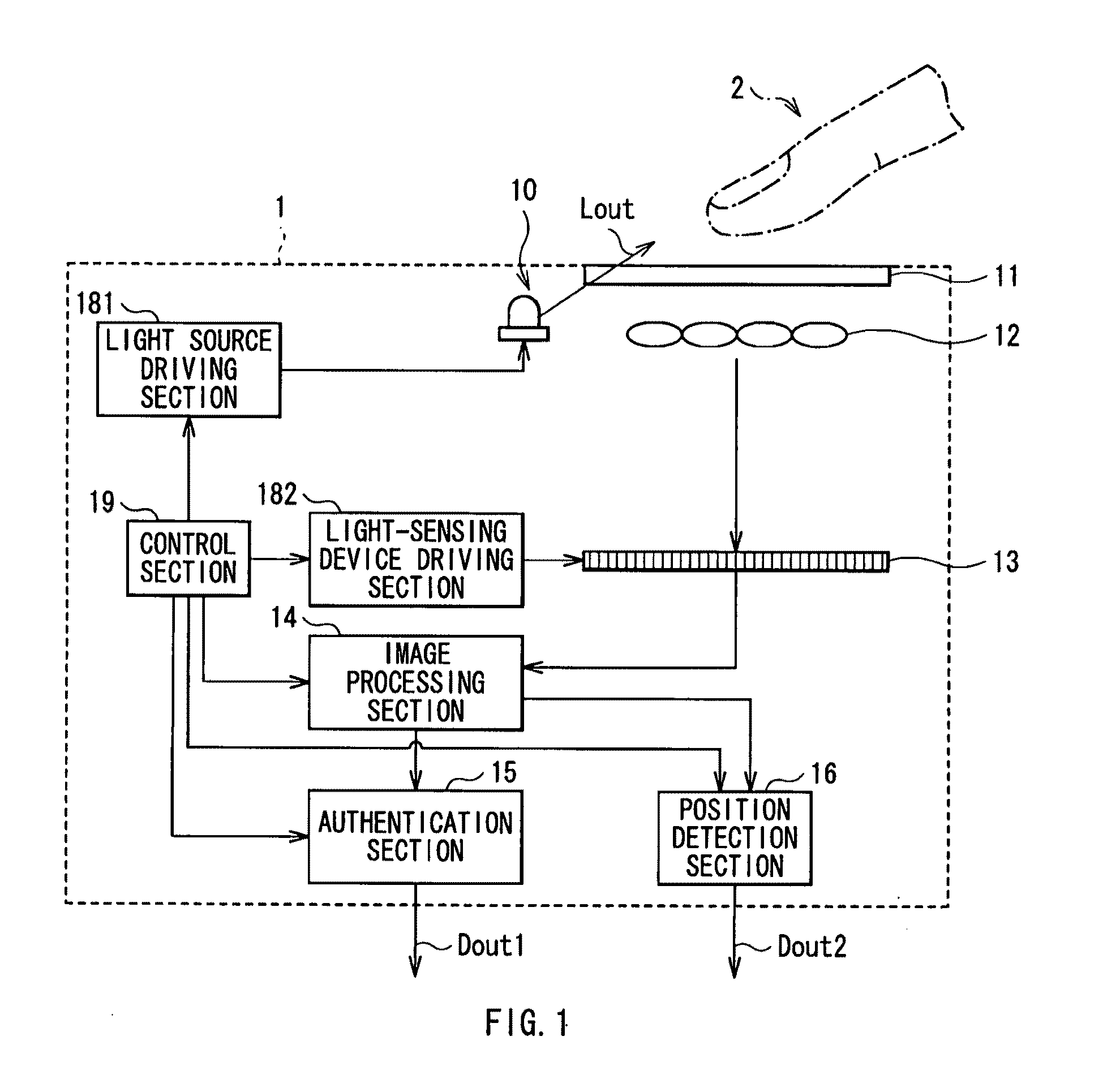
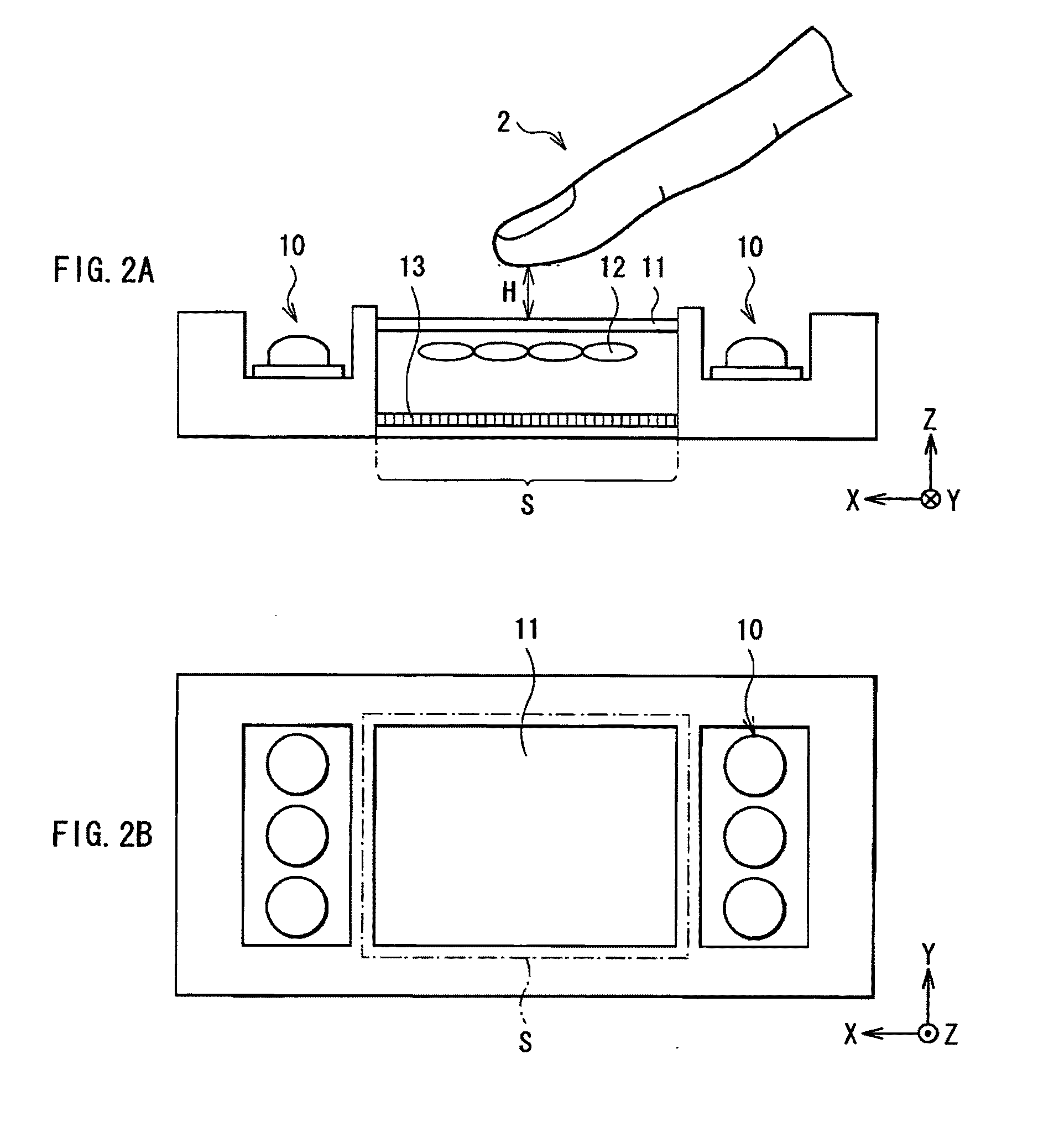
Biometrics authentication system
InactiveUS20100026453A1Small and simple configurationSimple configurationElectric signal transmission systemsImage analysisLight sensingLiving body
A biometrics authentication system having a small and simple configuration and being capable of implementing both of biometrics authentication and position detection is provided. A biometrics authentication system includes: a light source emitting light to an object; a microlens array section condensing light from the object; a light-sensing device obtaining light detection data of the object on the basis of the light condensed by the microlens array section; a position detection section detecting the position of the object on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device; and an authentication section, in the case where the object is a living body, performing authentication of the living body on the basis of the light detection data obtained in the light-sensing device.
Owner:SONY CORP
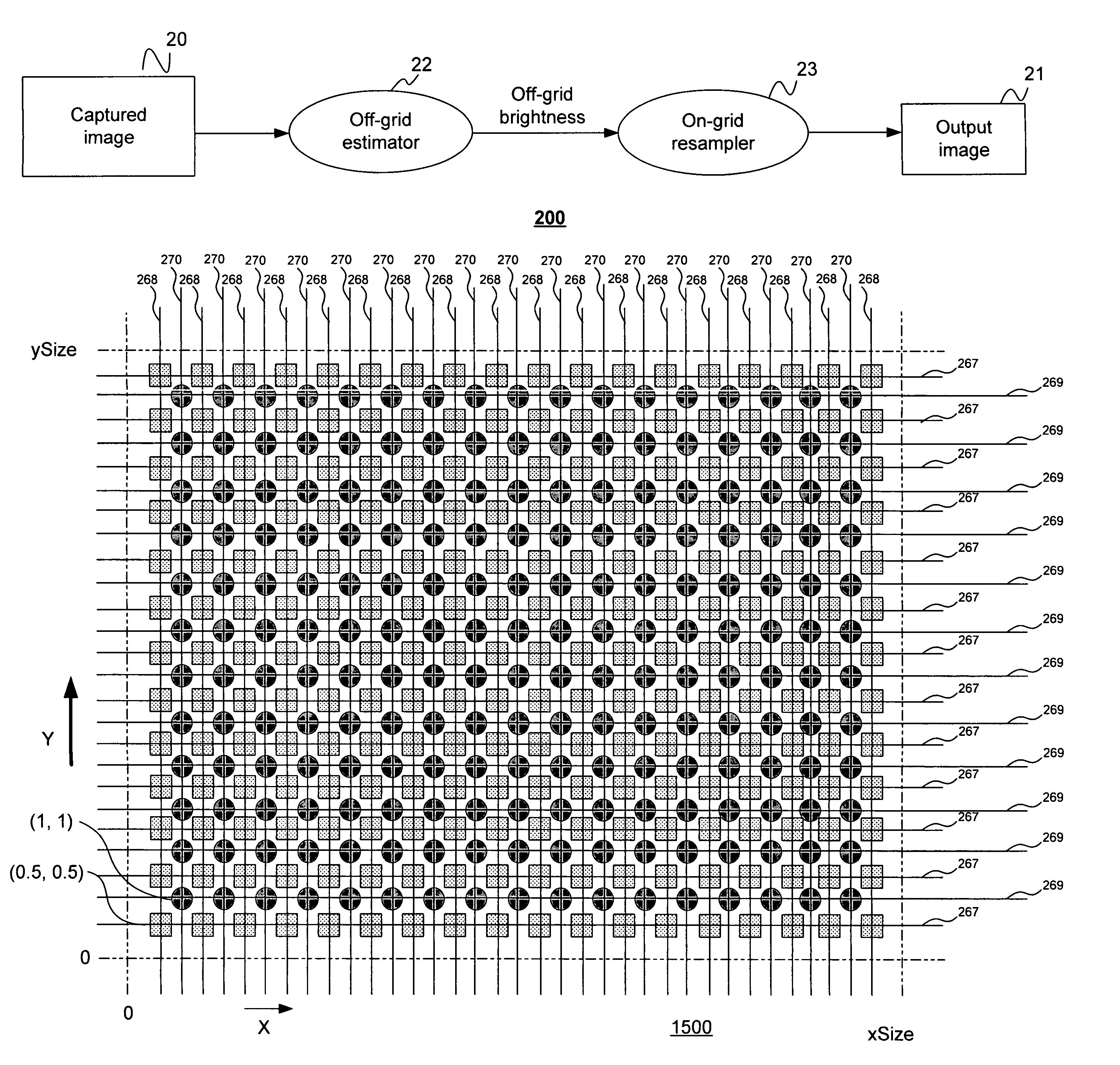
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
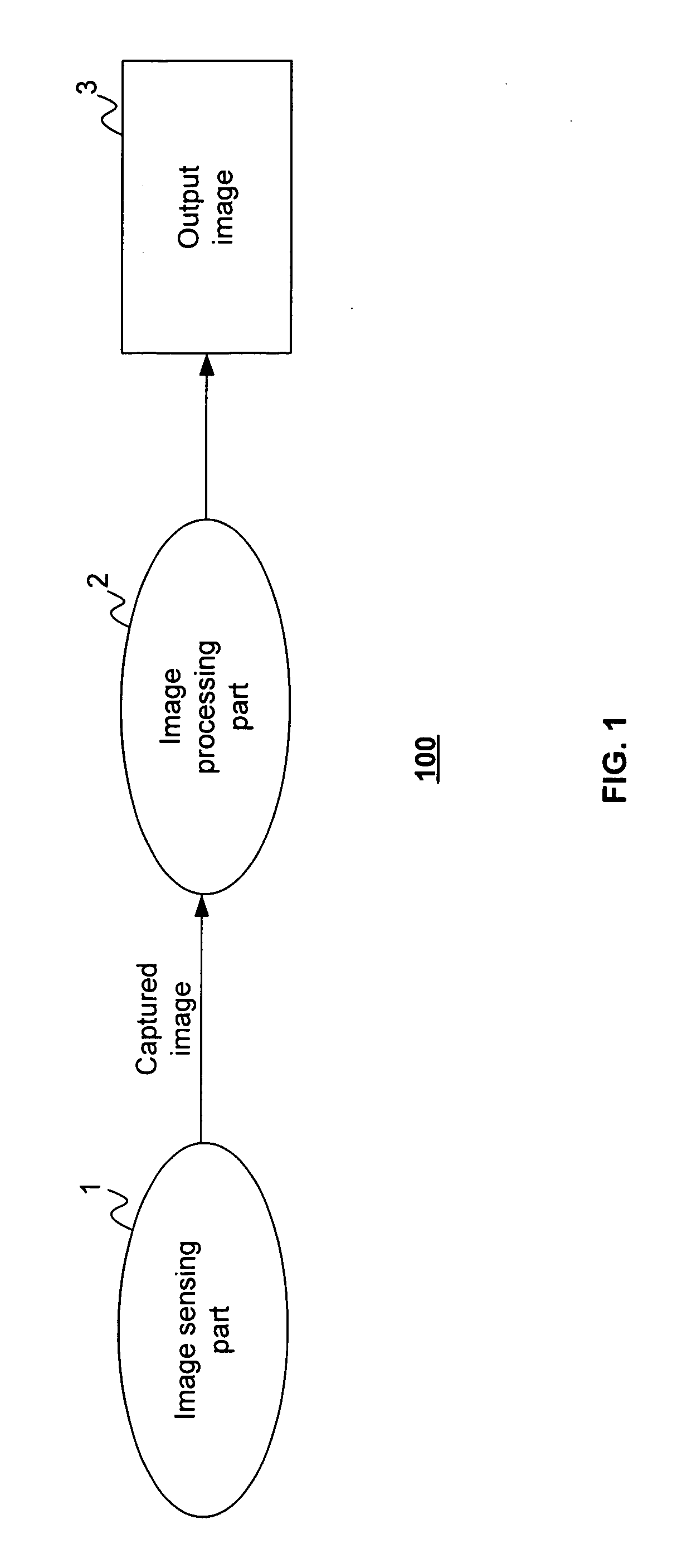
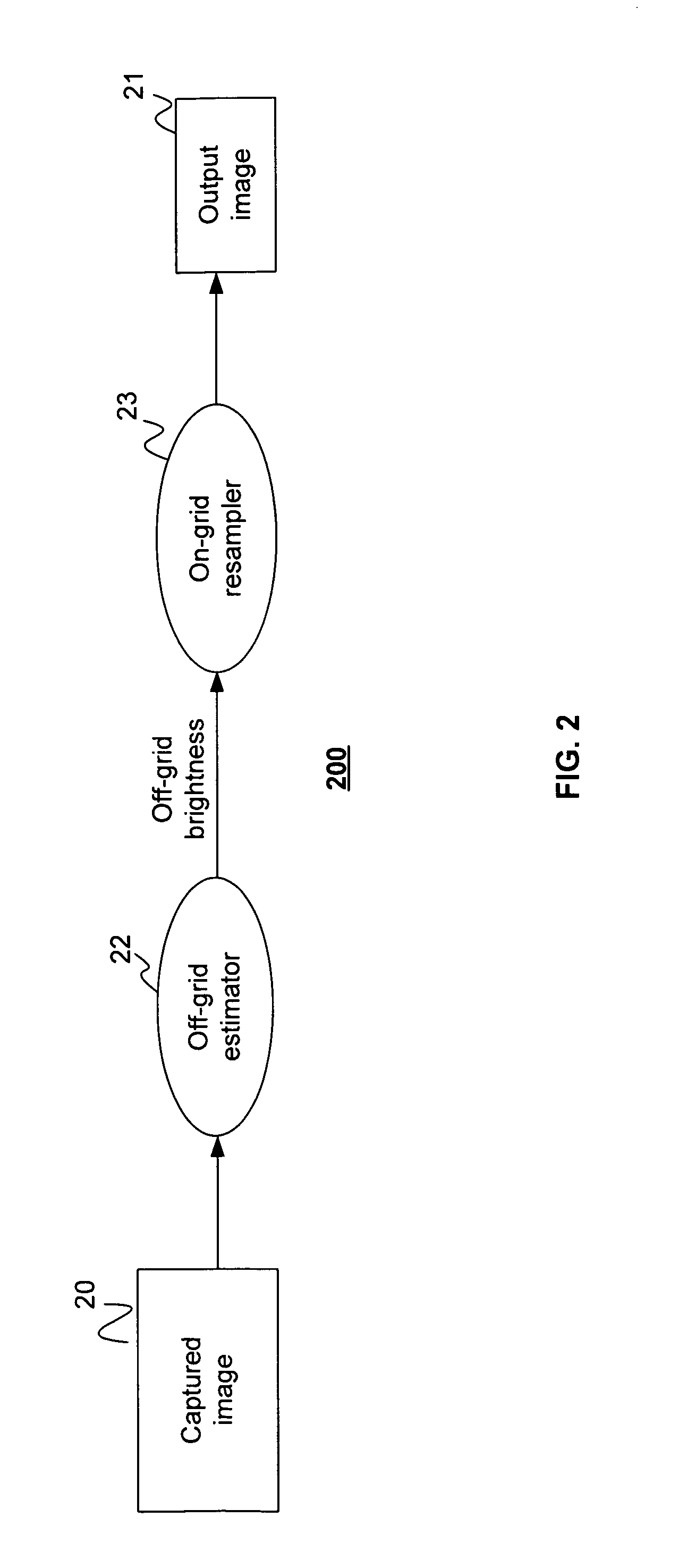
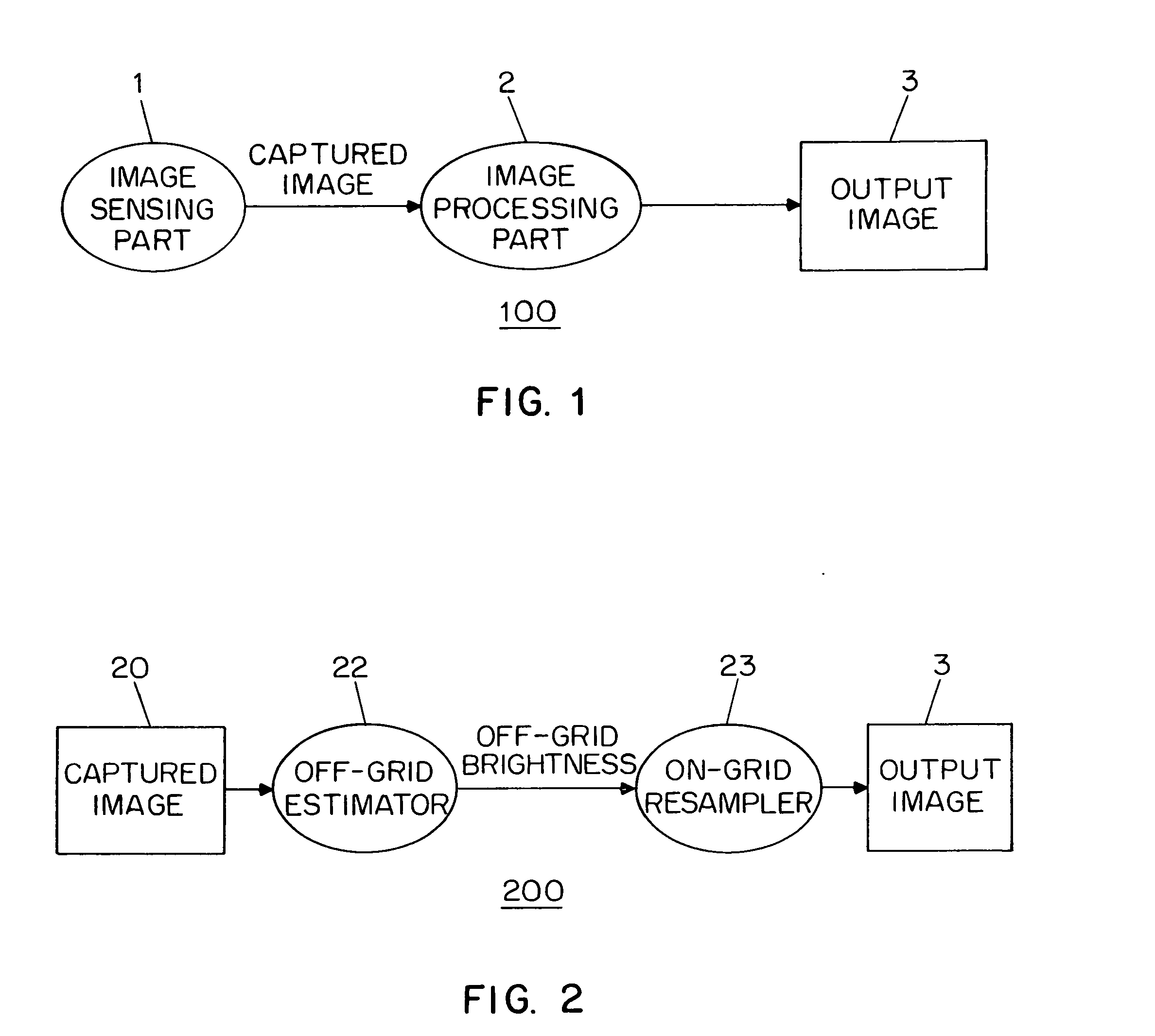
InactiveUS7084905B1Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLight sensingImage resolution
Disclosed are method and apparatus for obtaining relatively high dynamic range images using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor without significant loss of resolution. The image sensor has an array of light-sensing elements with different sensitivity levels in accordance with a predetermined spatially varying sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements. An image of a scene is captured with the image sensor and stored as brightness values at respective pixel positions in a linear or two-dimensional uniform grid. The brightness values of the captured image at the pixel positions are then used to estimate the brightness values at off-grid positions of a uniform off-grid array located at respective interstices of the pixel position grid. The estimated off-grid brightness values are either used directly as the pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic output image or interpolated to derive resampled on-grid brightness values at the pixel positions of the pixel position grid to provide a relatively high dynamic range output image. Alternatively, the brightness values of the captured image are interpolated by an on-grid interpolation filter to derive pixel brightness values of a relatively high dynamic range output image, each pixel brightness value of the output image being derived from a corresponding plurality of the captured image brightness values. In each instance, either the captured image brightness values or the pixel brightness values of the output image may be compensated for non-linearities of the radiometric response function of the light-sensing elements of the image sensor.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
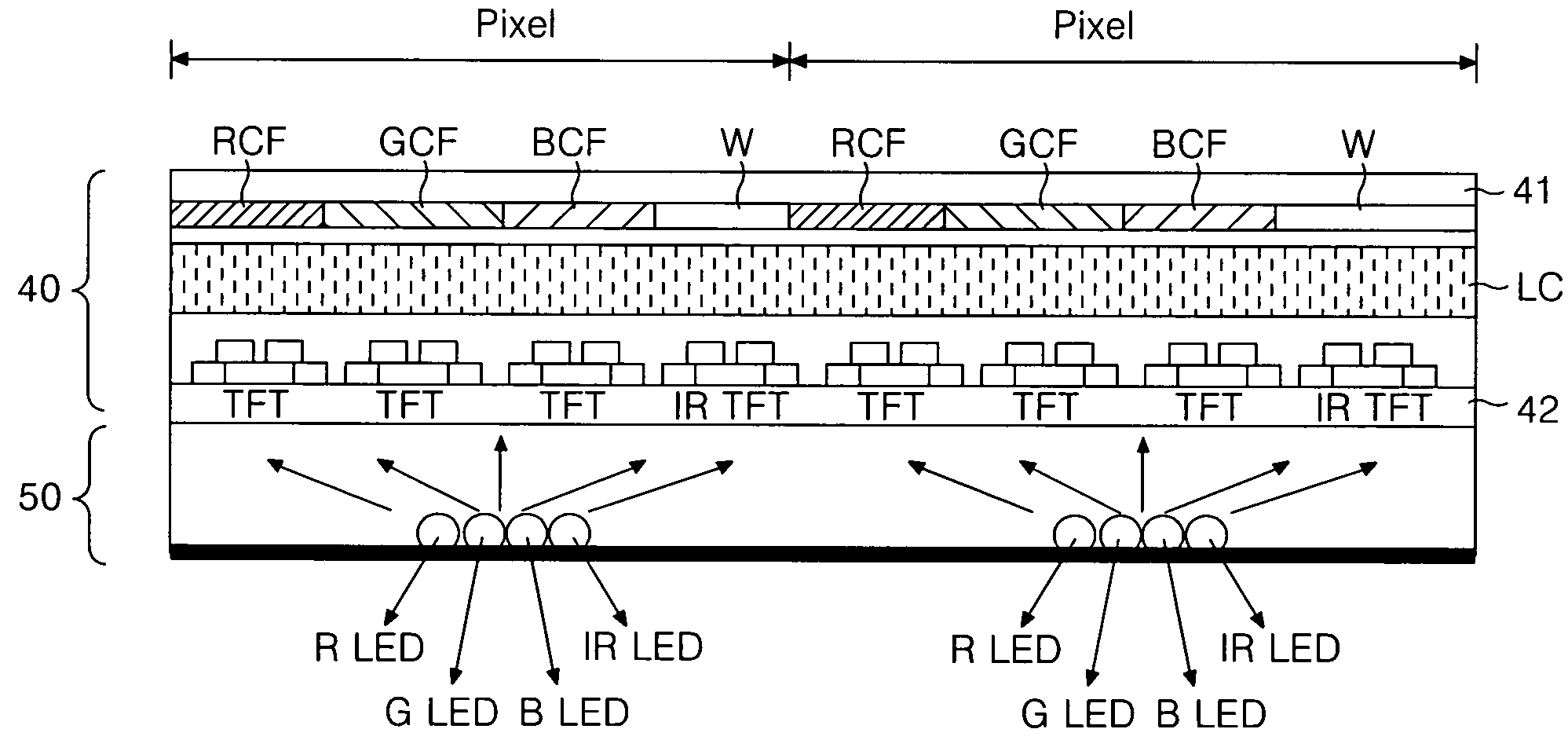
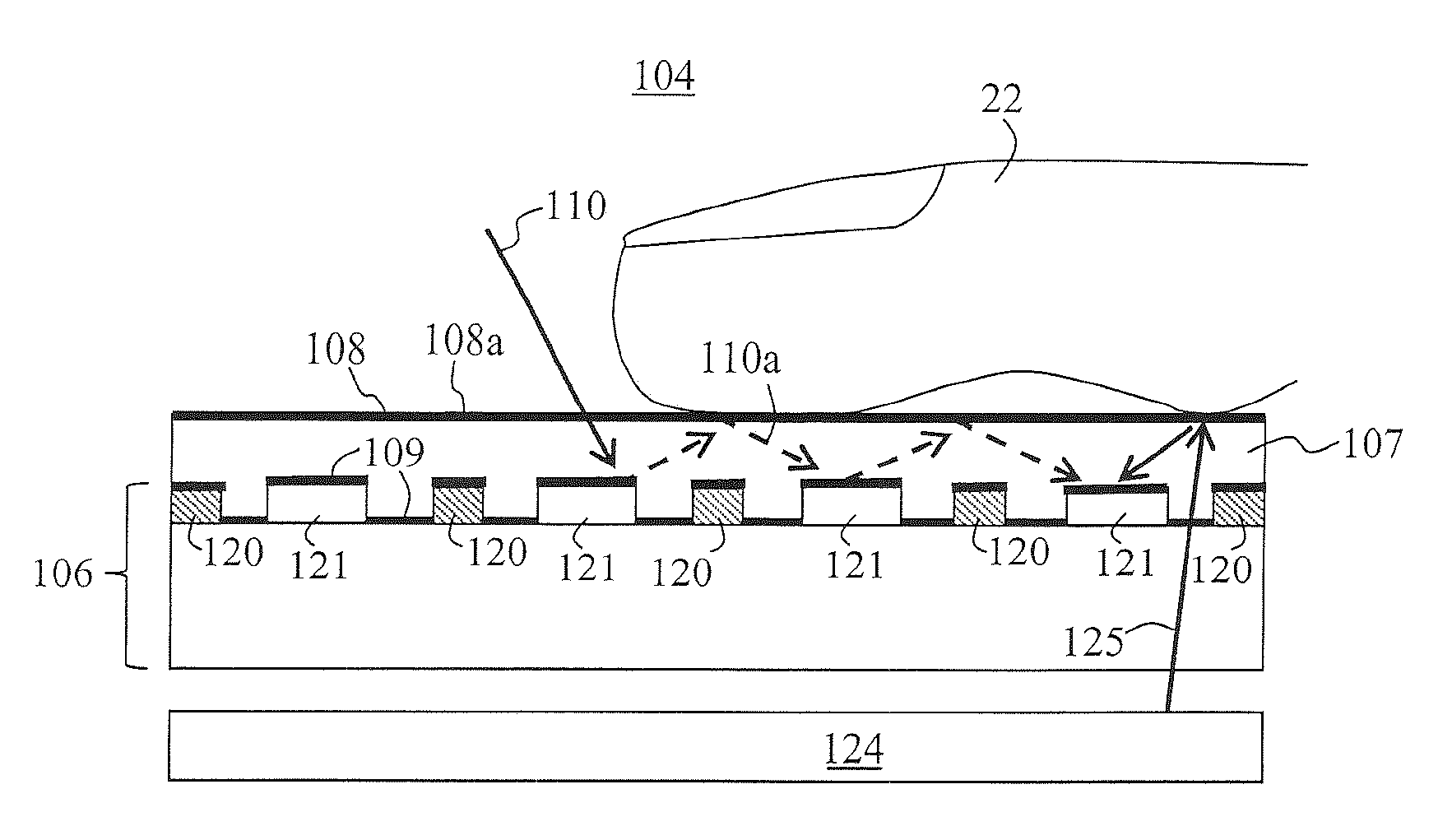
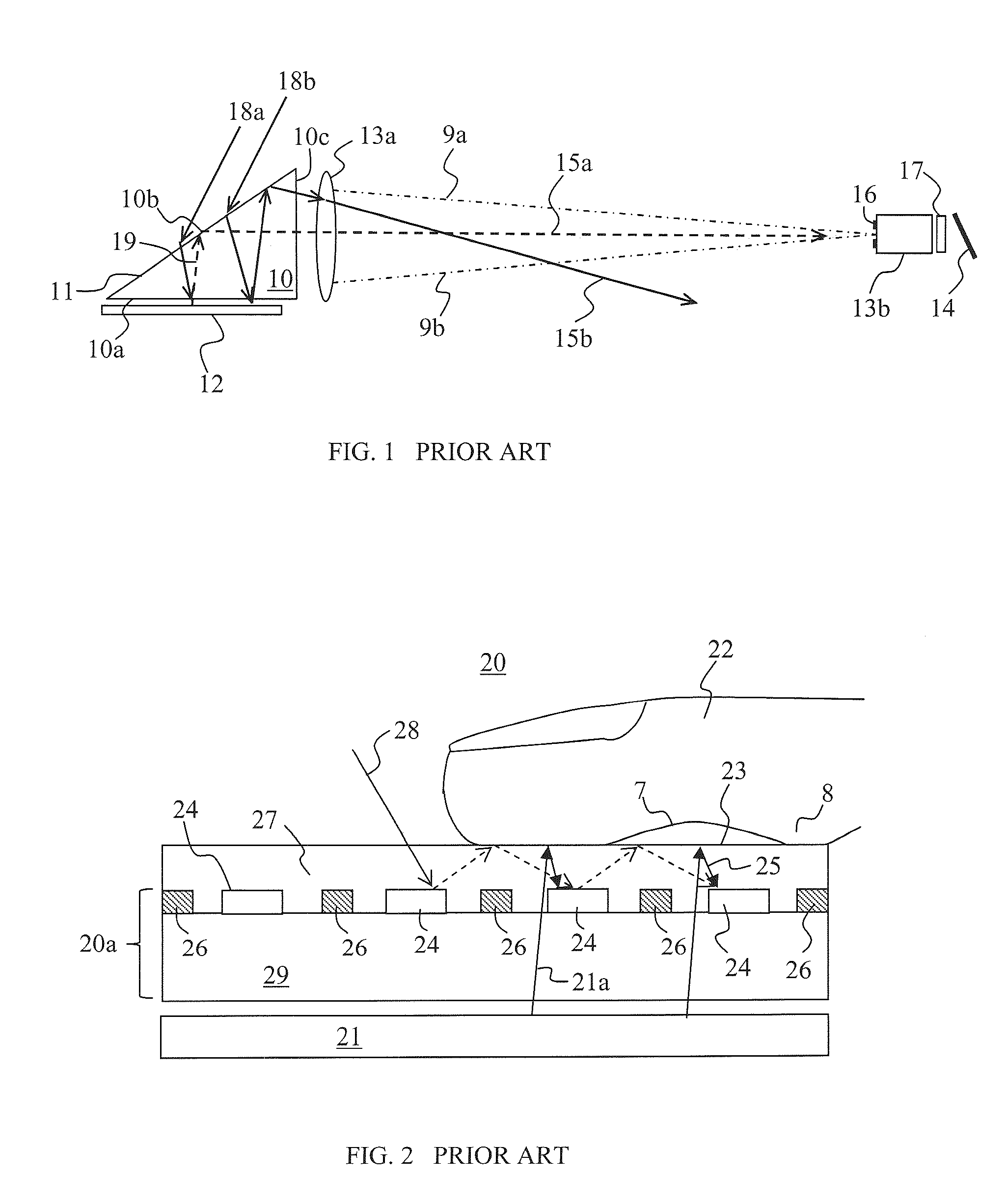
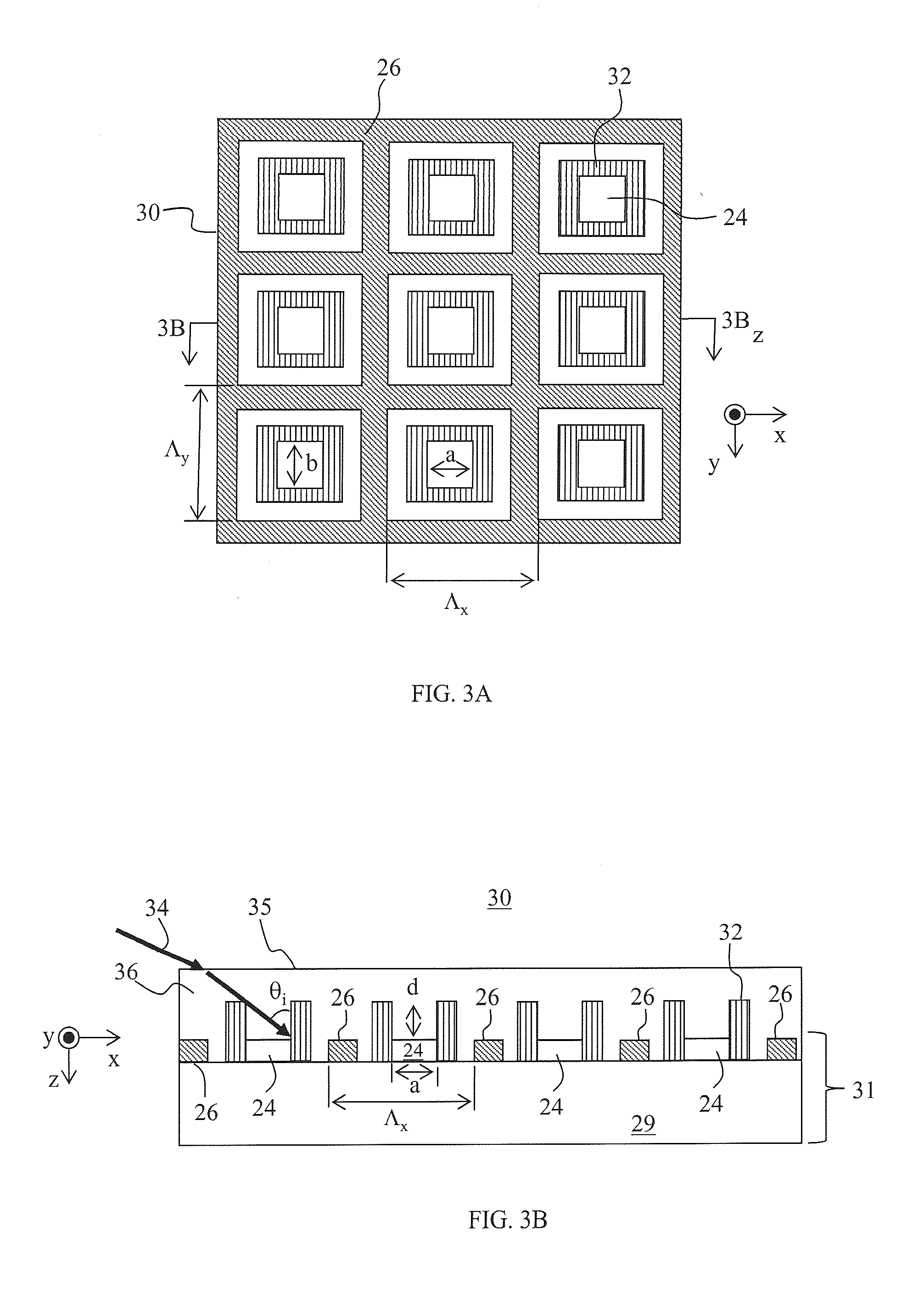
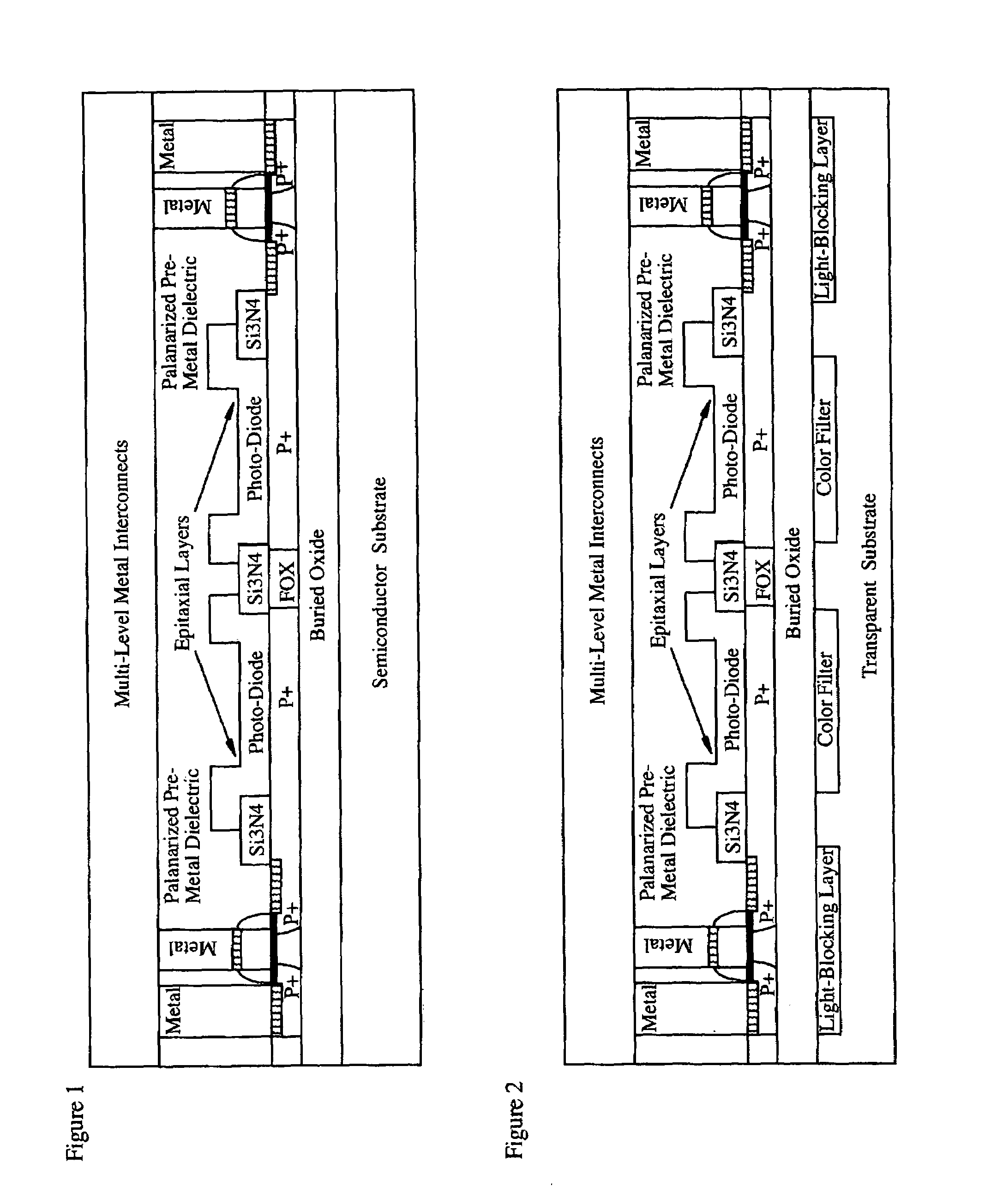
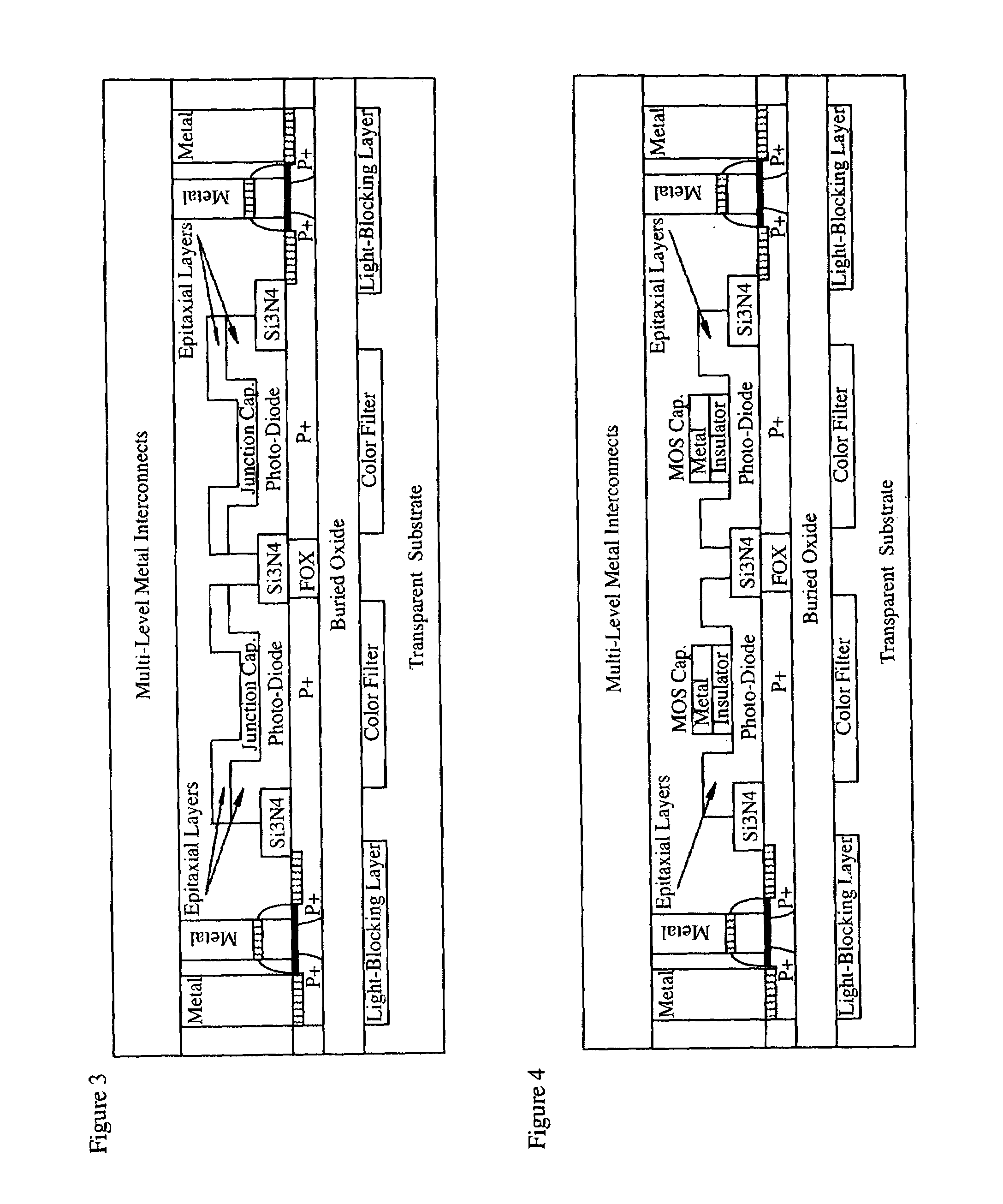
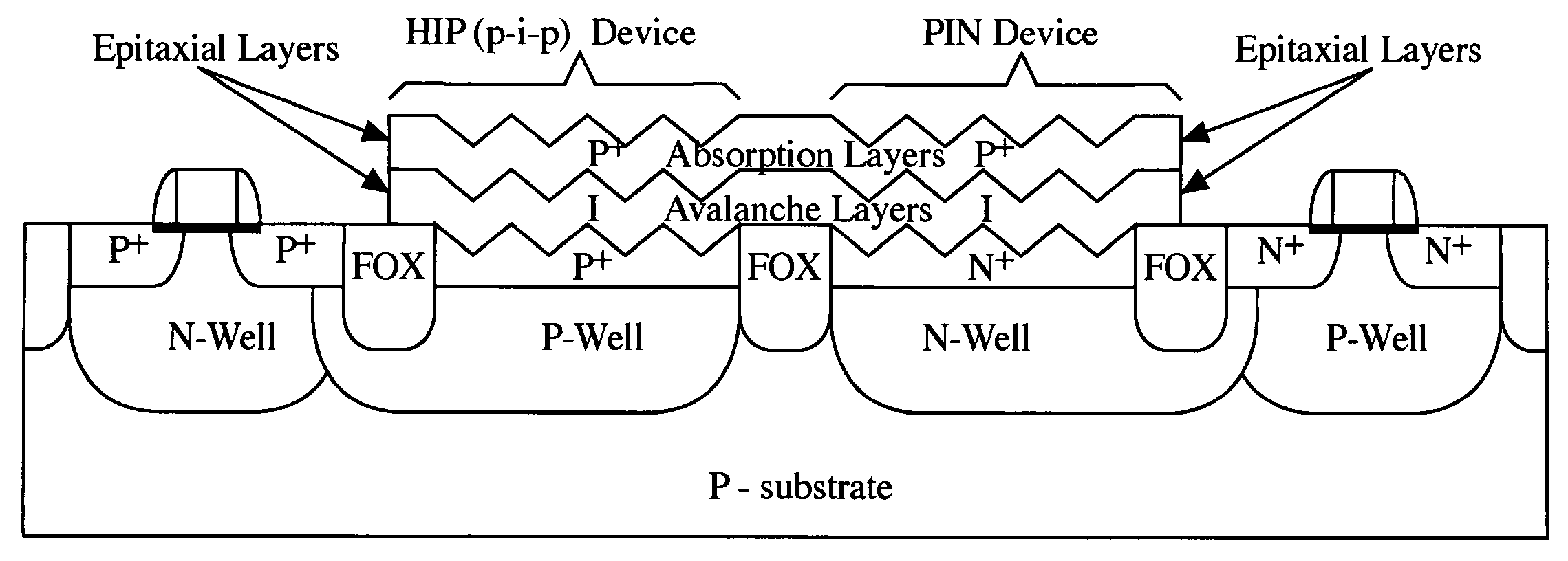
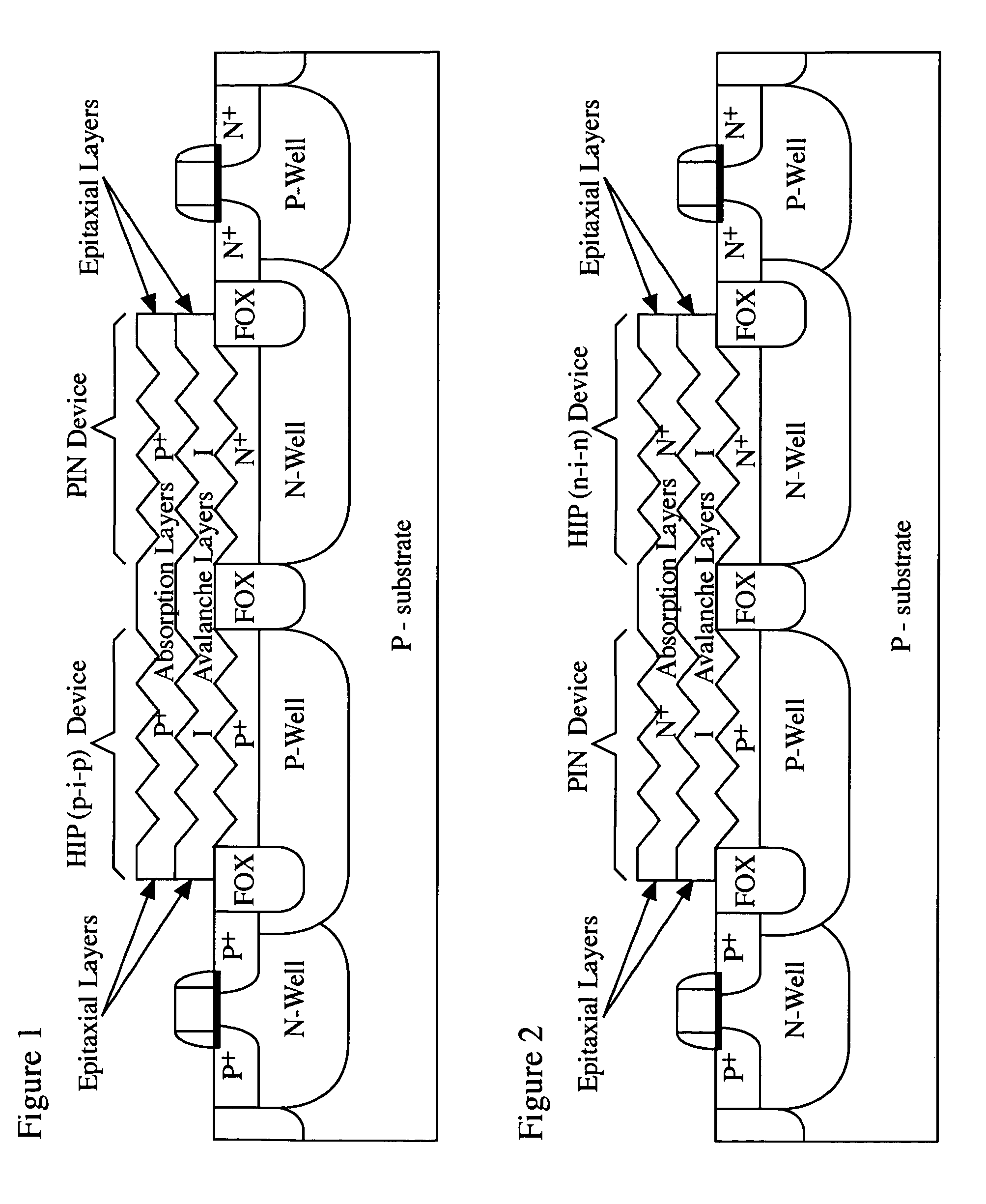
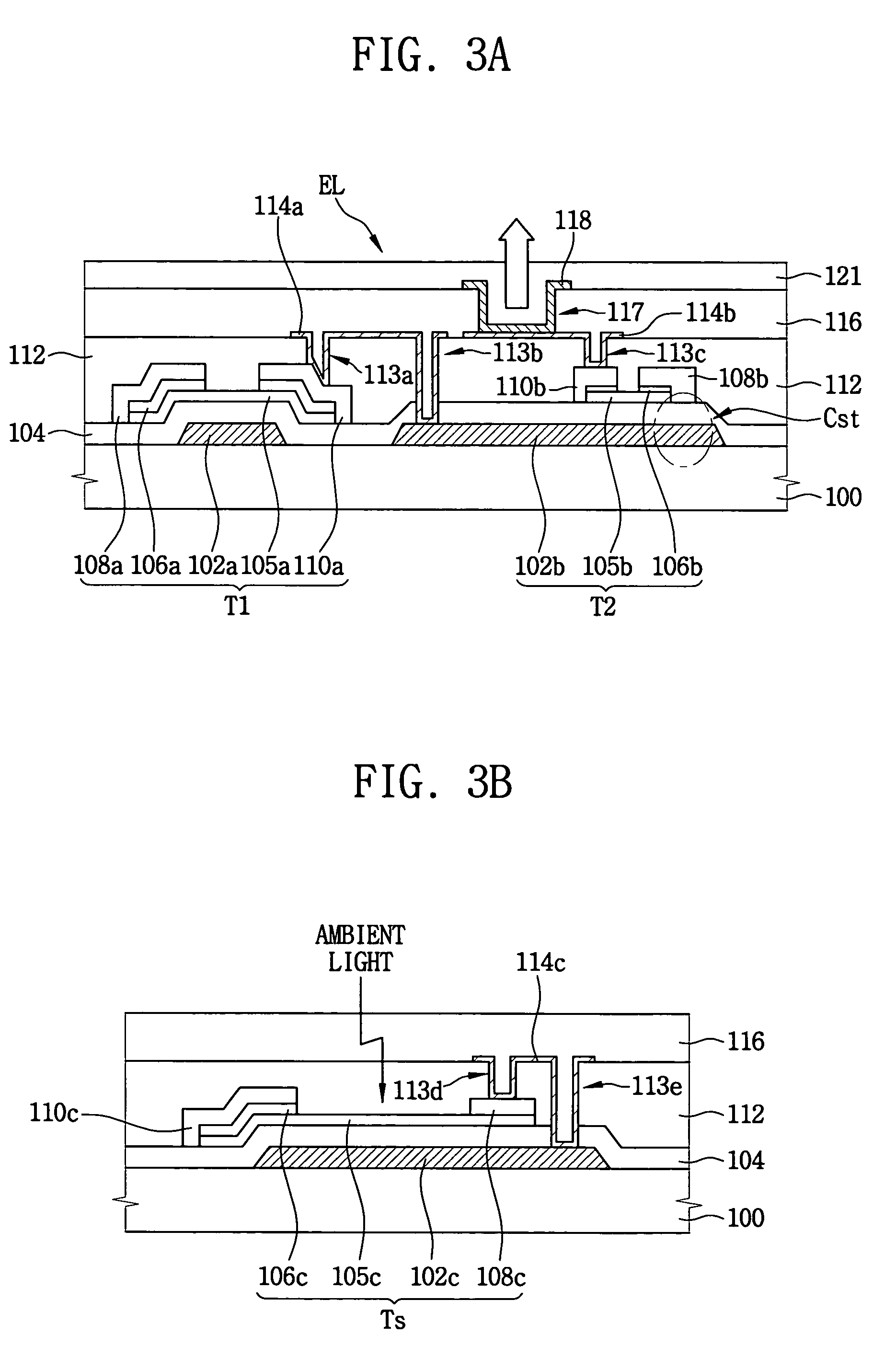
Light-sensing device
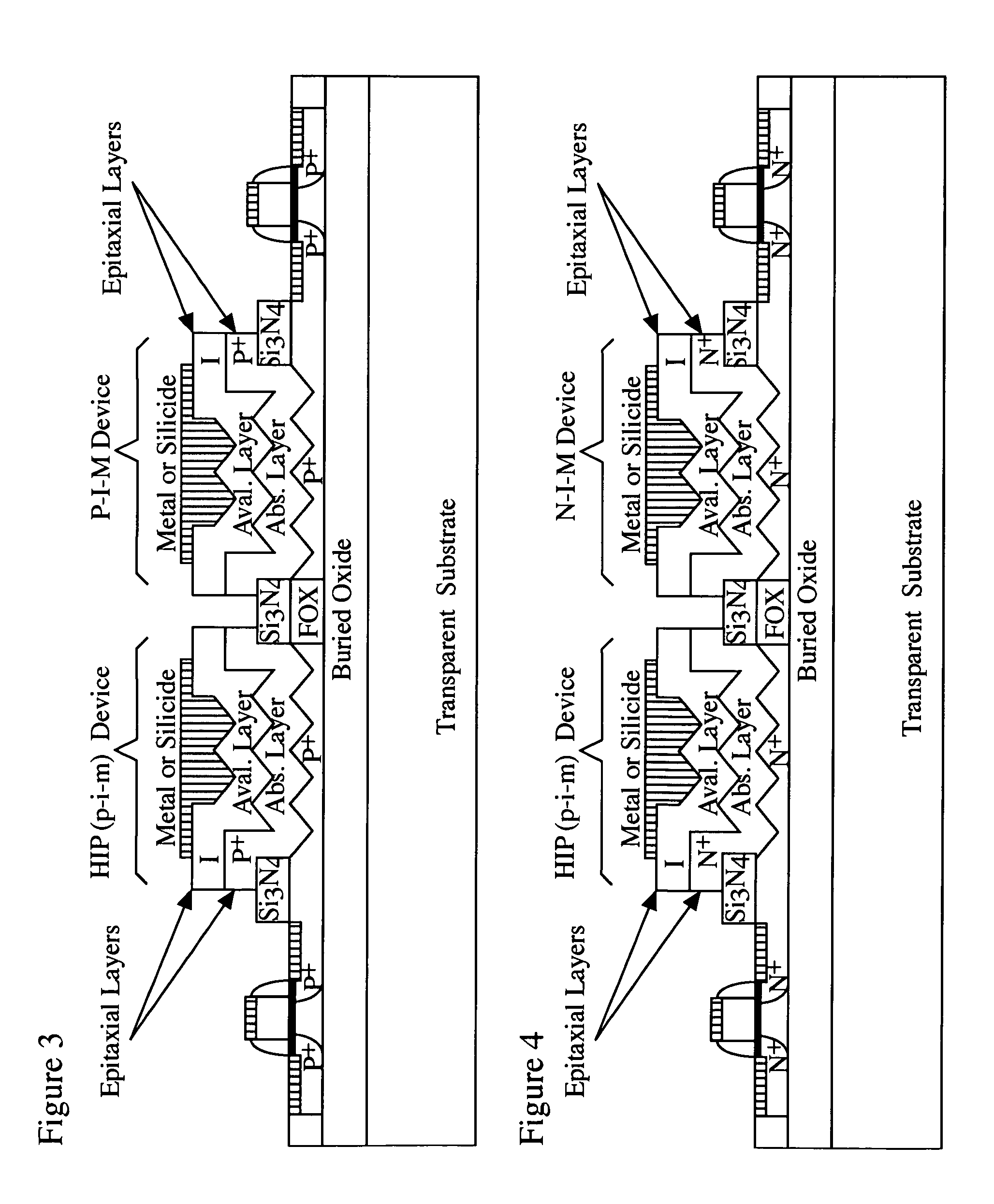
ActiveUS7521737B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeterojunctionPixel density
A method of fabricating light-sensing devices including photodiodes monolithically integrated with CMOS devices. Several types of photodiode devices (PIN, HIP) are expitaxially grown in one single step on active areas implanted in a common semiconductor substrate, the active areas having defined polarities. The expitaxially grown layers for the photodiode devices may be either undoped or in-situ doped with profiles suitable for their respective operation. With appropriate choice of substrate materials, device layers and heterojunction engineering and process architecture, it is possible to fabricate silicon-based and germanium-based multi-spectral sensors that can deliver pixel density and cost of fabrication comparable to the state of the art CCDs and CMOS image sensors. The method can be implemented with epitaxially deposited films on the following substrates: Silicon Bulk, Thick-Film and Thin-Film Silicon-On-Insulator (SOI), Germanium Bulk, Thick-Film and Thin-Film Geranium-On-Insulator (GeOI).
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
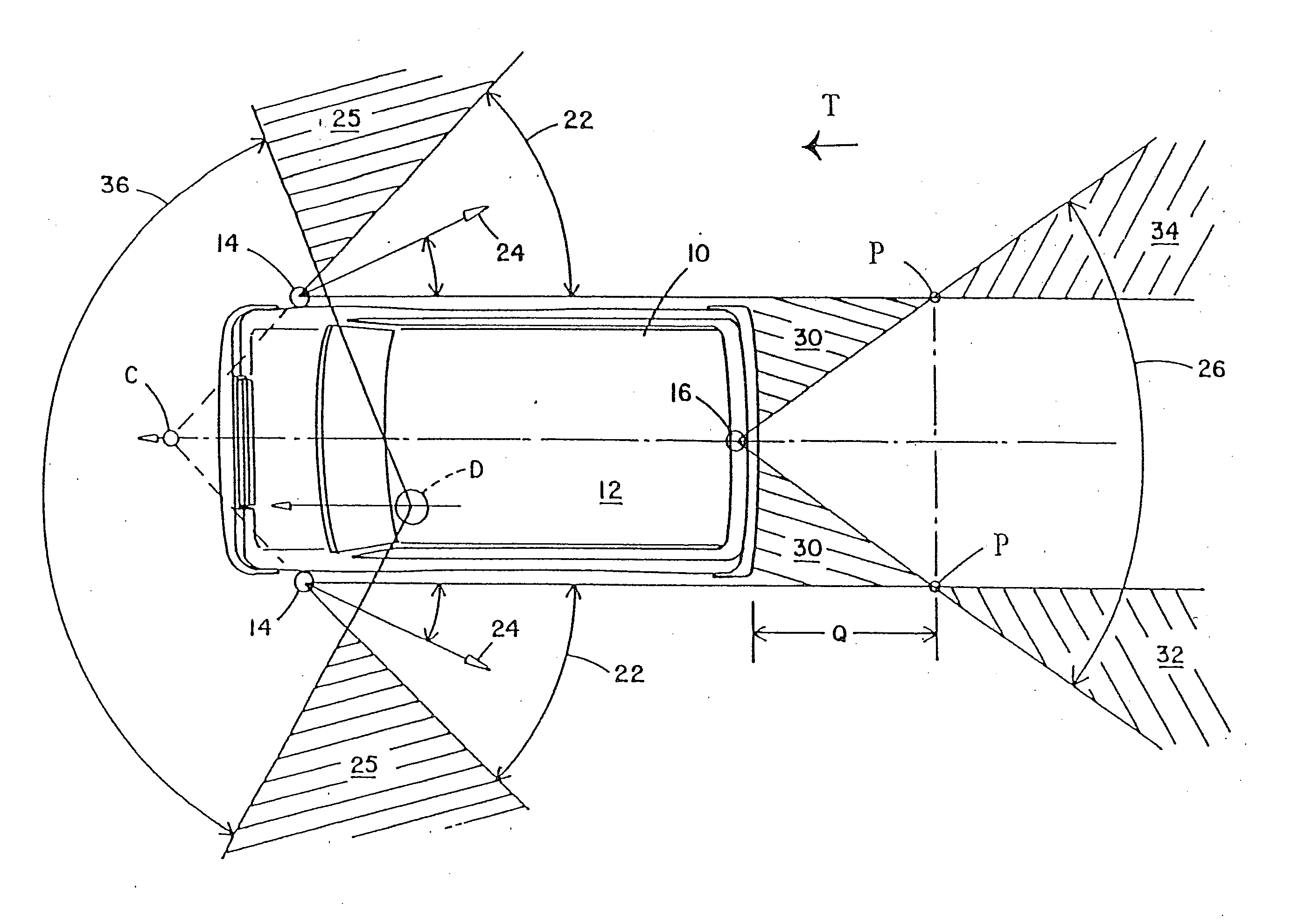
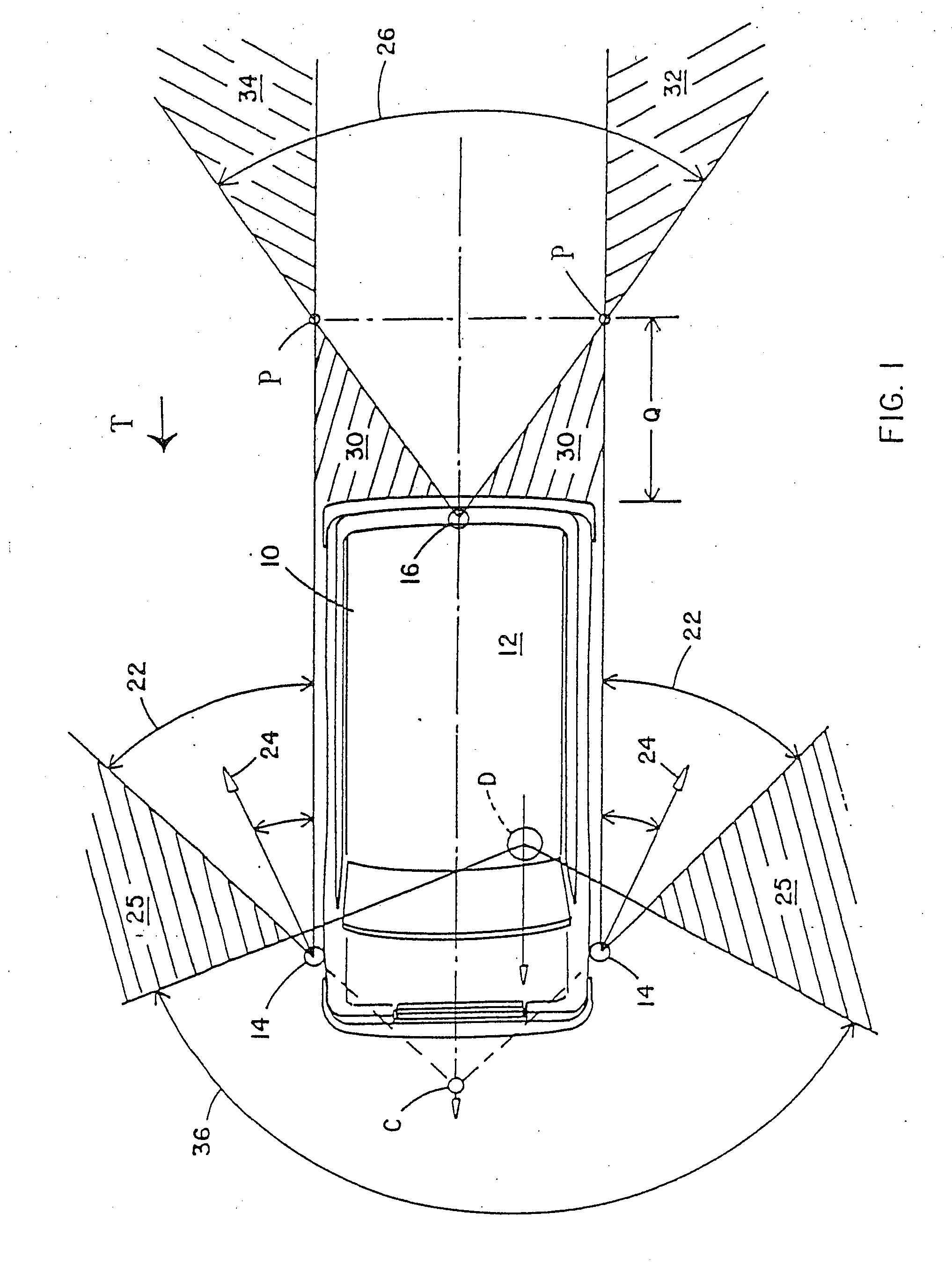
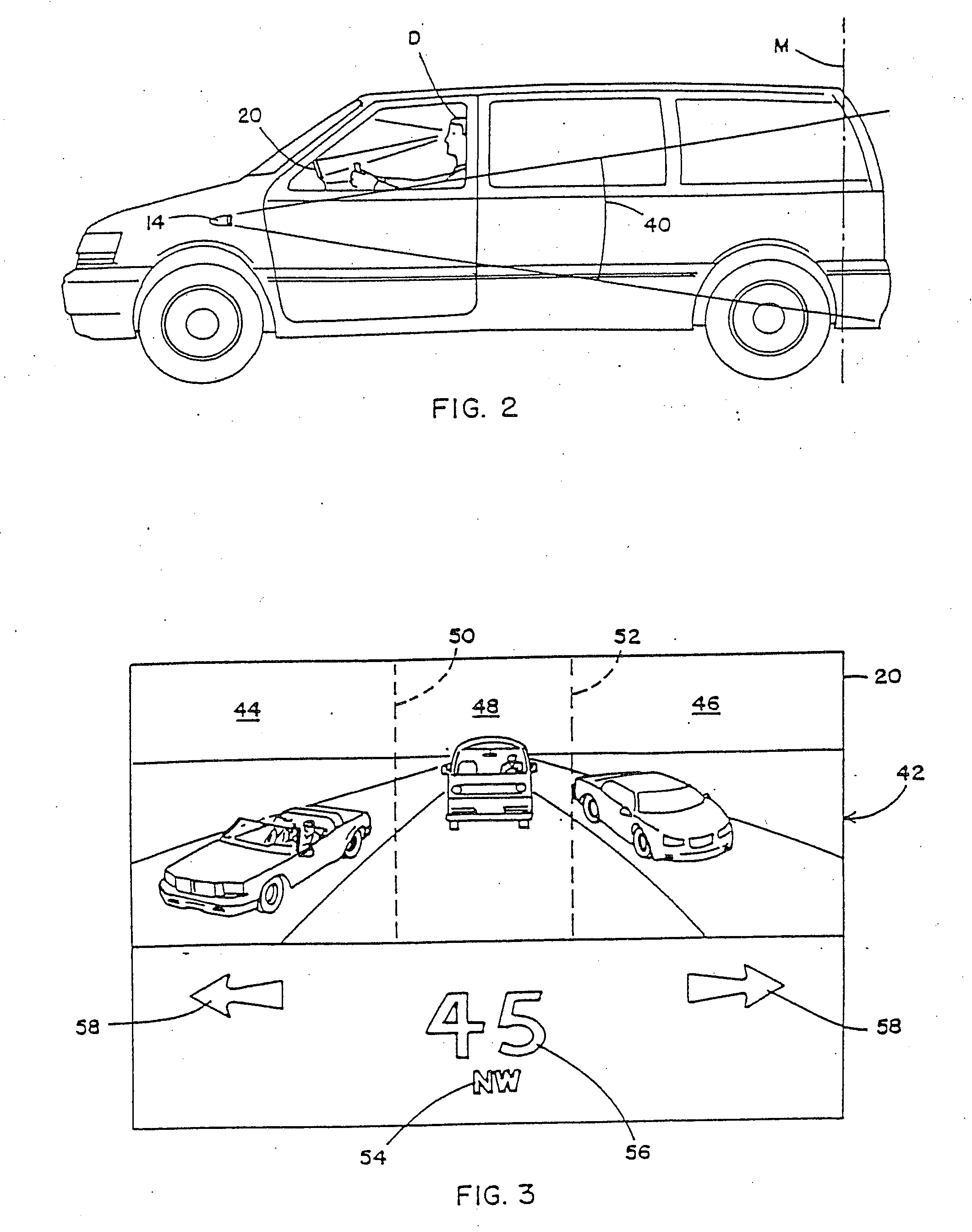
Vehicular image sensing system
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
CMOS image sensor
Light sensing devices are monolithically integrates with CMOS devices on Thin-Film Silicon-On-insulator (TF-SOI) or Thin-Film Germanium-On-Insulator (TF-GeOI) substrates. Photodiode active layers are epitaxially grown on the front-side of the substrate and after full processing of the front-side of the substrate, the substrate material is removed under the buried insulator (buried oxide). Monolithically integrated structures are then fabricated on the back of the buried oxide. The back-side is then bonded to a new substrate that is transparent to the wavelengths of interest. For example, quartz, sapphire, glass, or plastic, are suitable for the visible range. Back-side illumination of the sensor matrix is thereby allowed, with light traveling through the structures fabricated on the back of the substrate, opposite to the side on which CMOS is made.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Method and apparatus for obtaining high dynamic range images
InactiveUS20050099504A1High imagingTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLight sensingBrightness perception
The application provides techniques for obtaining a relatively high dynamic range image of a scene using a relatively low dynamic range image sensor exposed to incident light from the scene for capturing an image. The image sensor has a multiplicity of light-sensing elements in an array and each light sensing element has a particular one of a plurality of sensitivity levels to incident light in accordance with a predetermined sensitivity pattern for the array of light-sensing elements and has a response function. Each light sensing element is responsive to incident light from the scene for producing a captured image brightness value at a corresponding one of a multiplicity of pixel positions of a pixel position array. Each one of the multiplicity of pixel positions corresponds to a particular one of the plurality of sensitivity levels of the light sensing elements.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK +1
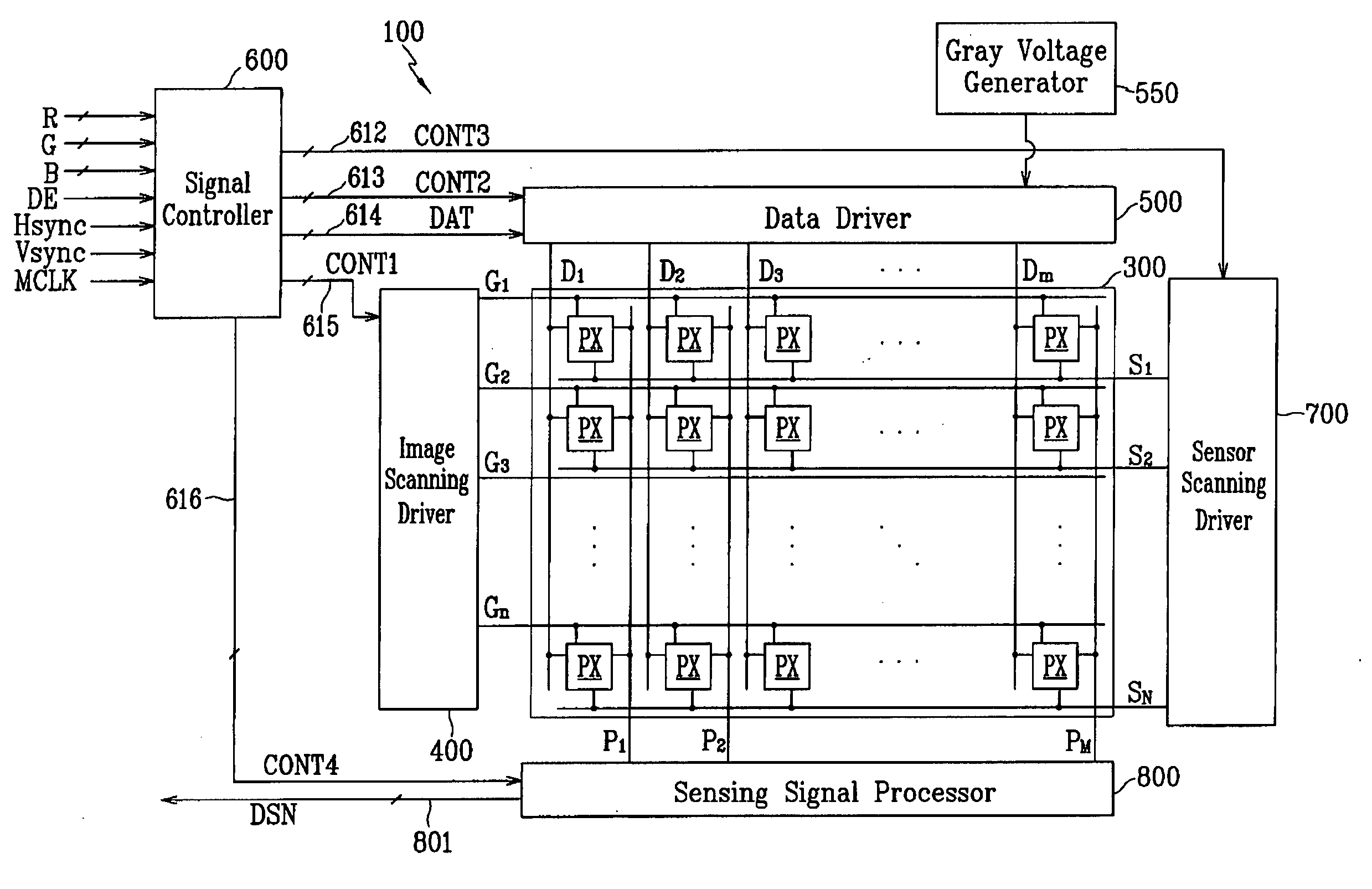
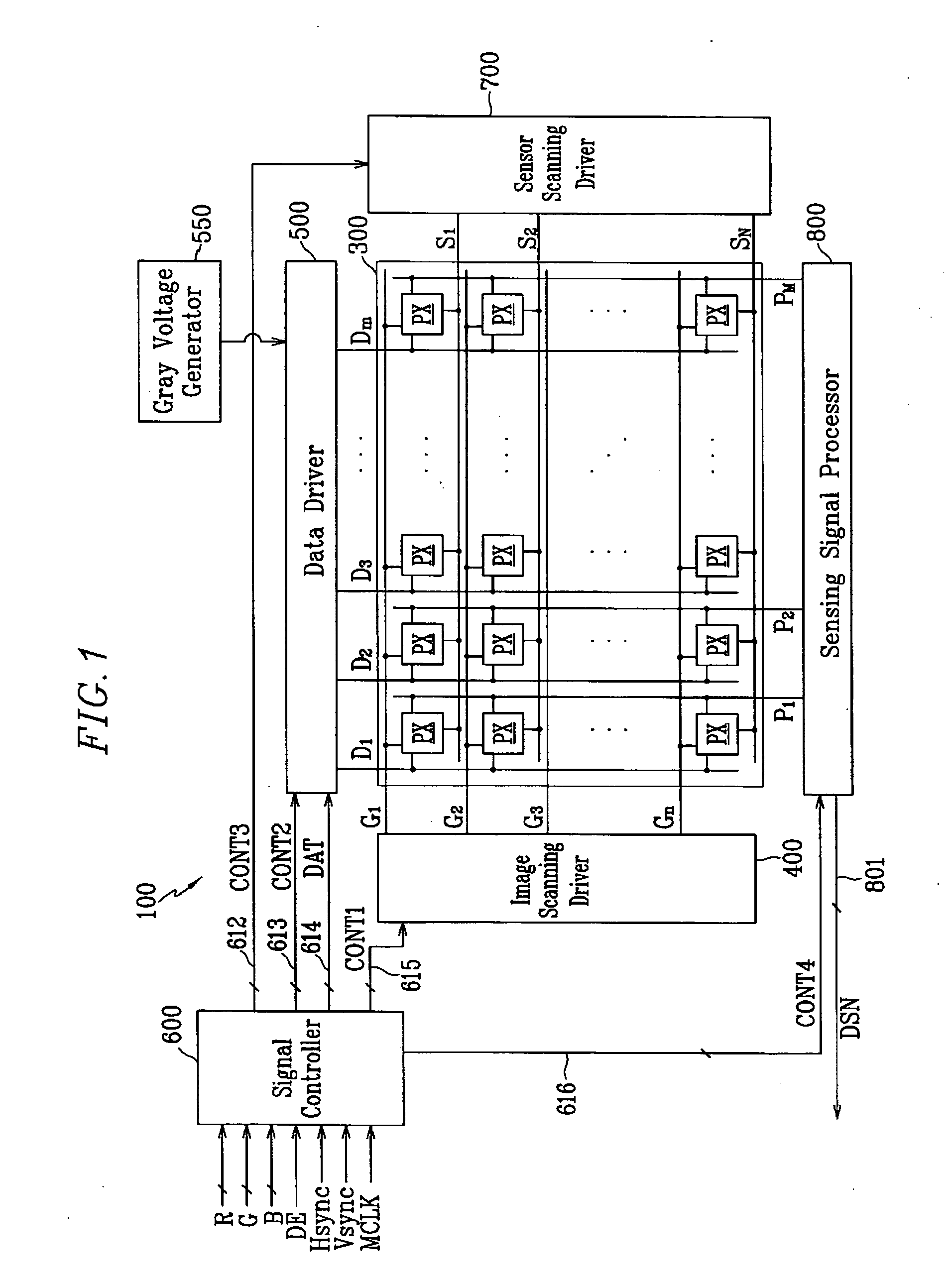
Display device and driving apparatus thereof
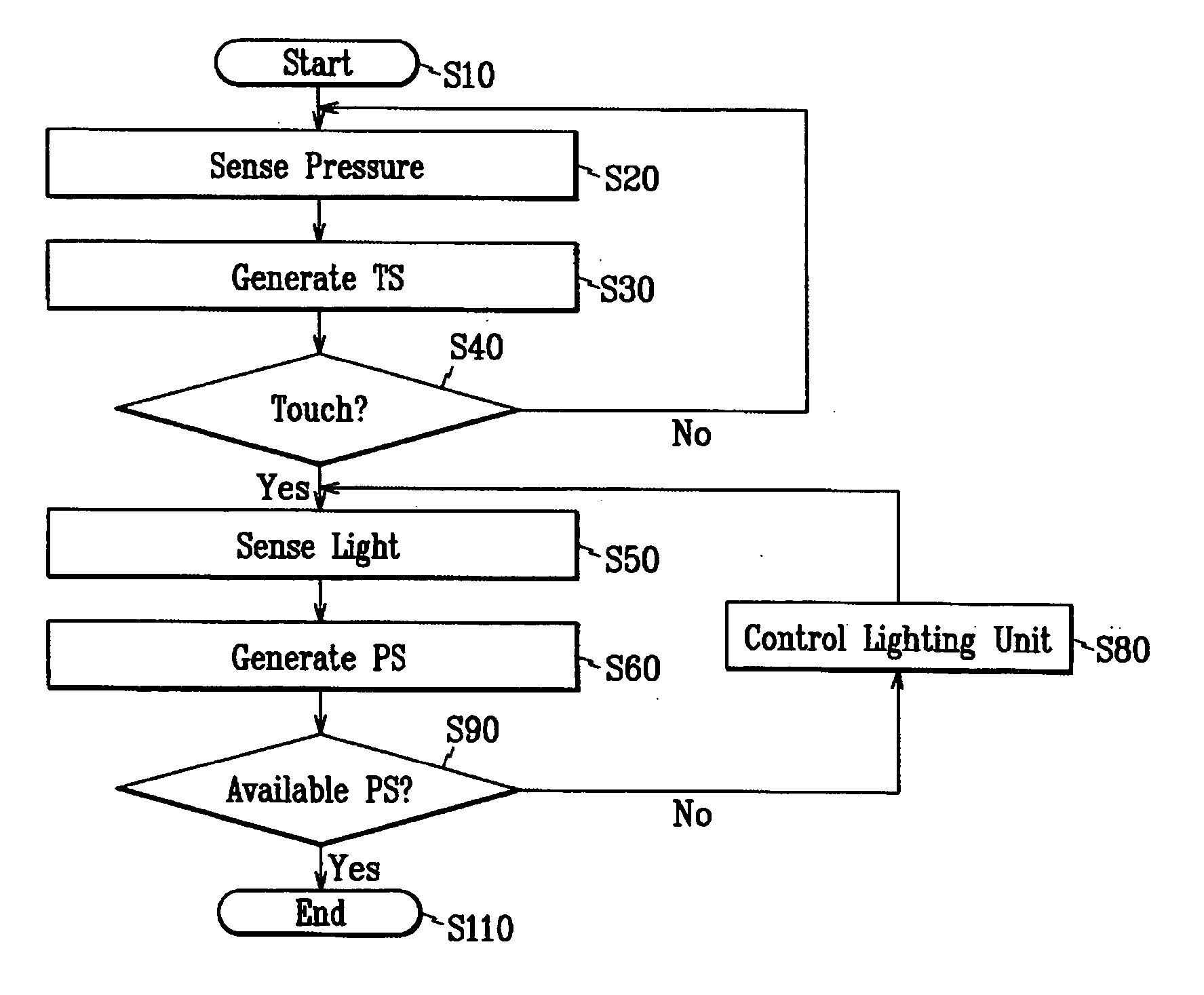
ActiveUS20060138983A1Reliable and accurate touch sensingReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTStatic indicating devicesLight sensingA d converter
A display apparatus may include touch detection circuitry including a light sensing circuit and a physical parameter sensing circuit (e.g., a pressure sensing circuit). The display apparatus may further include processing circuitry implementing a power-saving mode and a normal mode, and configured to generate touch information. An display driver may include a photo sensing circuit and a pressure sensing circuit. An embodiment of the display driver may include: an amplifying unit amplifying a photo sensing signal and a pressure sensing signal; a parallel-to-serial converting unit converting the amplified photo sensing signal and the amplified pressure sensing signal into serial sensing signals; and an analog-to-digital converter converting the serial sensing signals into digital sensing signals, wherein the amplifying unit, the parallel-to-serial converting unit, and the analog-to-digital converter operate in one of a normal mode and a power saving mode according to the pressure sensing signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Integrated ambient light sensor and distance sensor
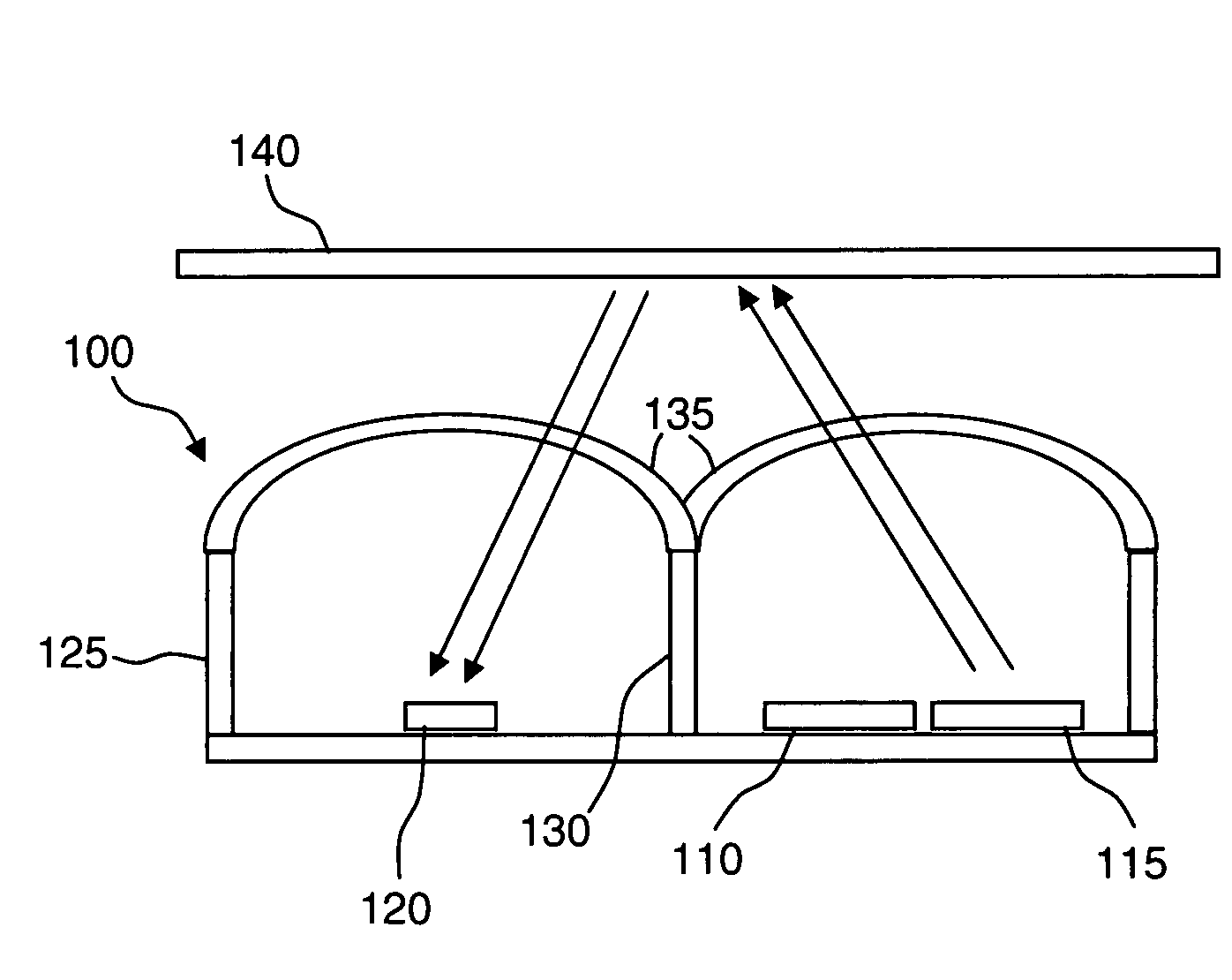
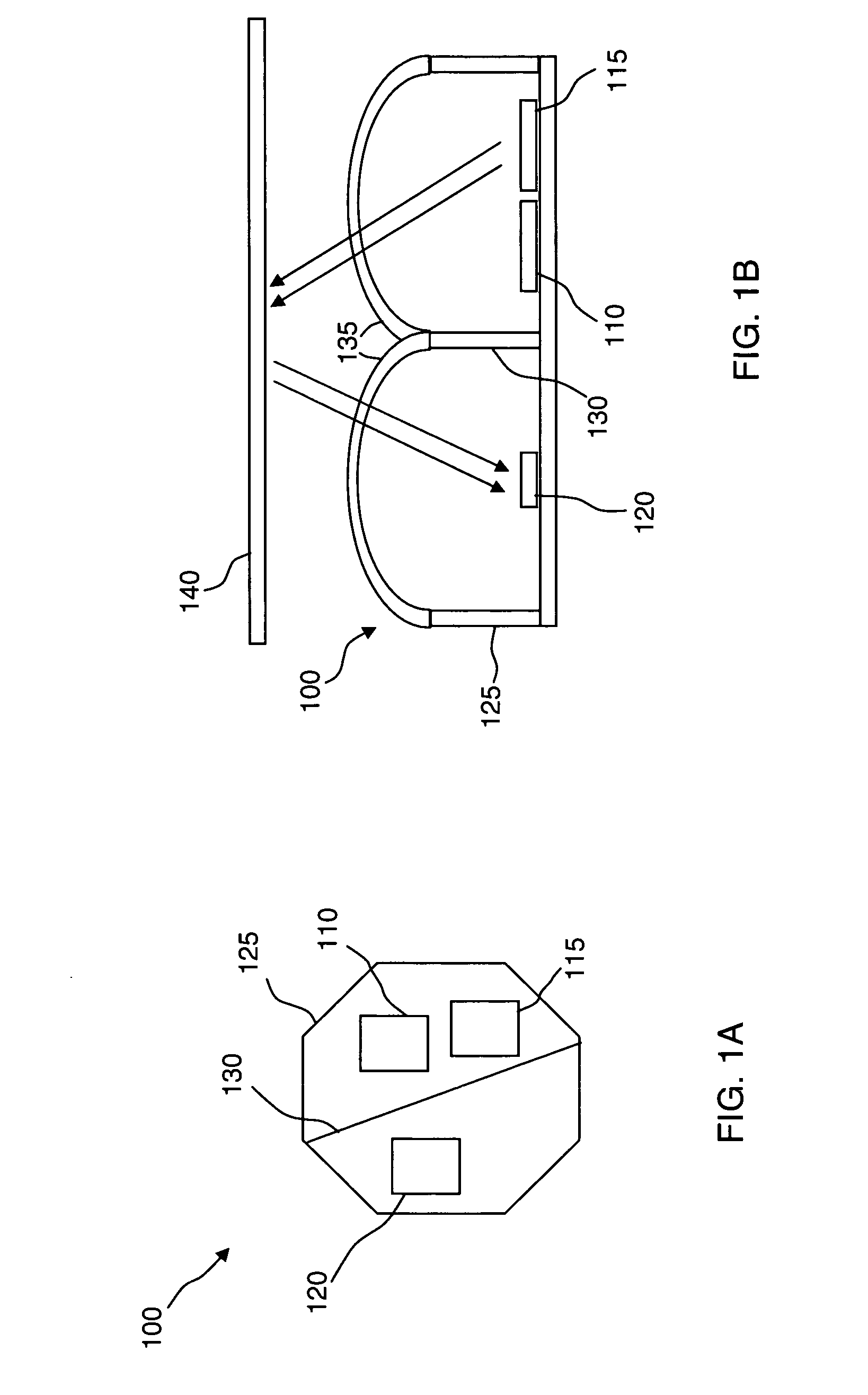
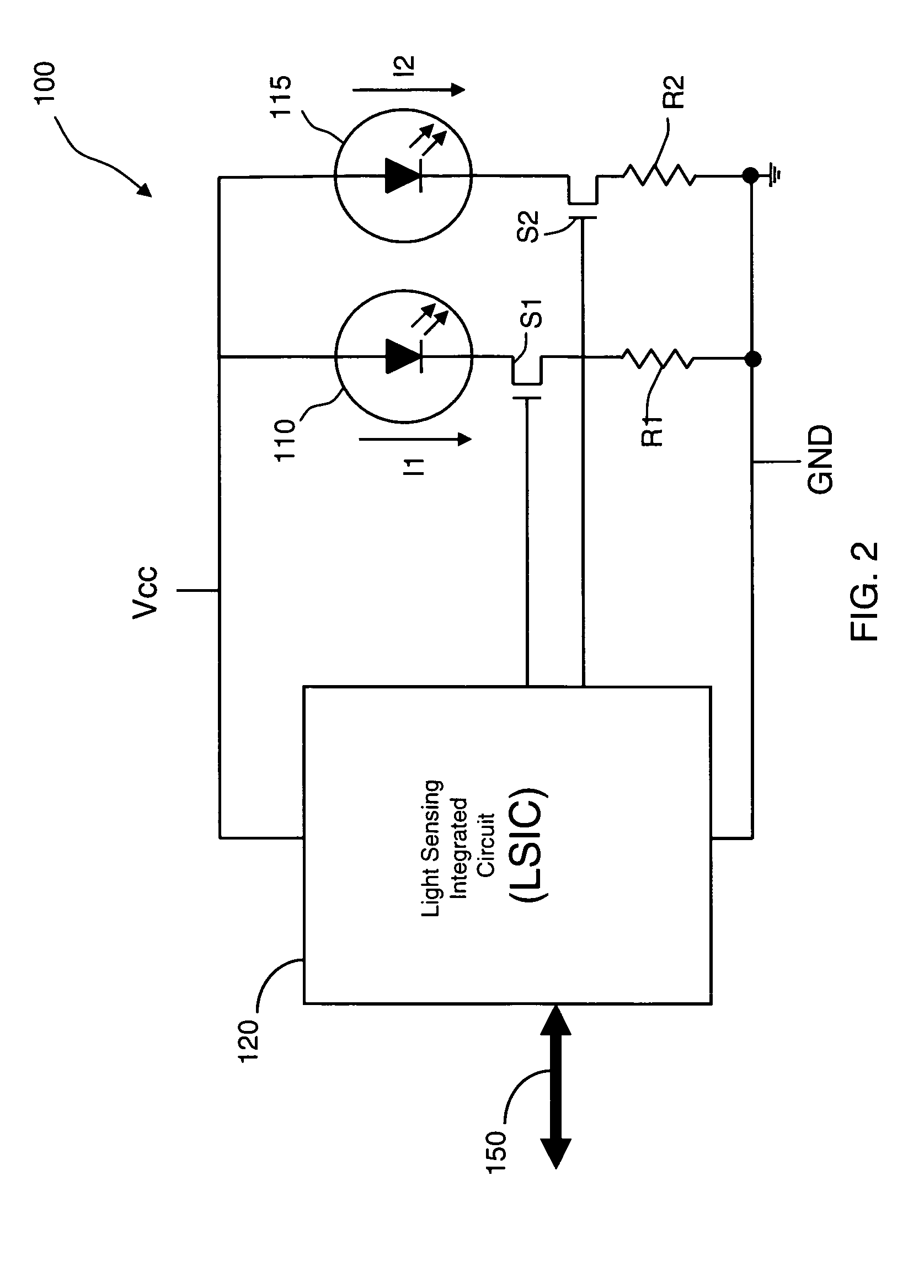
ActiveUS20090027652A1Multiple functionsOptical rangefindersScattering properties measurementsLight sensingDistance sensors
An integrated proximity and light sensor includes an indicating light-emitting device (“ILD”), a projecting light-emitting device (“PLD”), and a light sensing integrated circuit (“LSIC”) configured as a single package. The LSIC controls each of the ILD and the PLD to emit light therefrom and the LSIC is configured to detect an ambient light level and also to detect a reflection of the light projected by the PLD from a surface for proximity detection.
Owner:EMINENT ELECTRONICS TECH
Light sensing in display device
InactiveUS20100201275A1Static indicating devicesElectroluminescent light sourcesLight sensingDisplay device
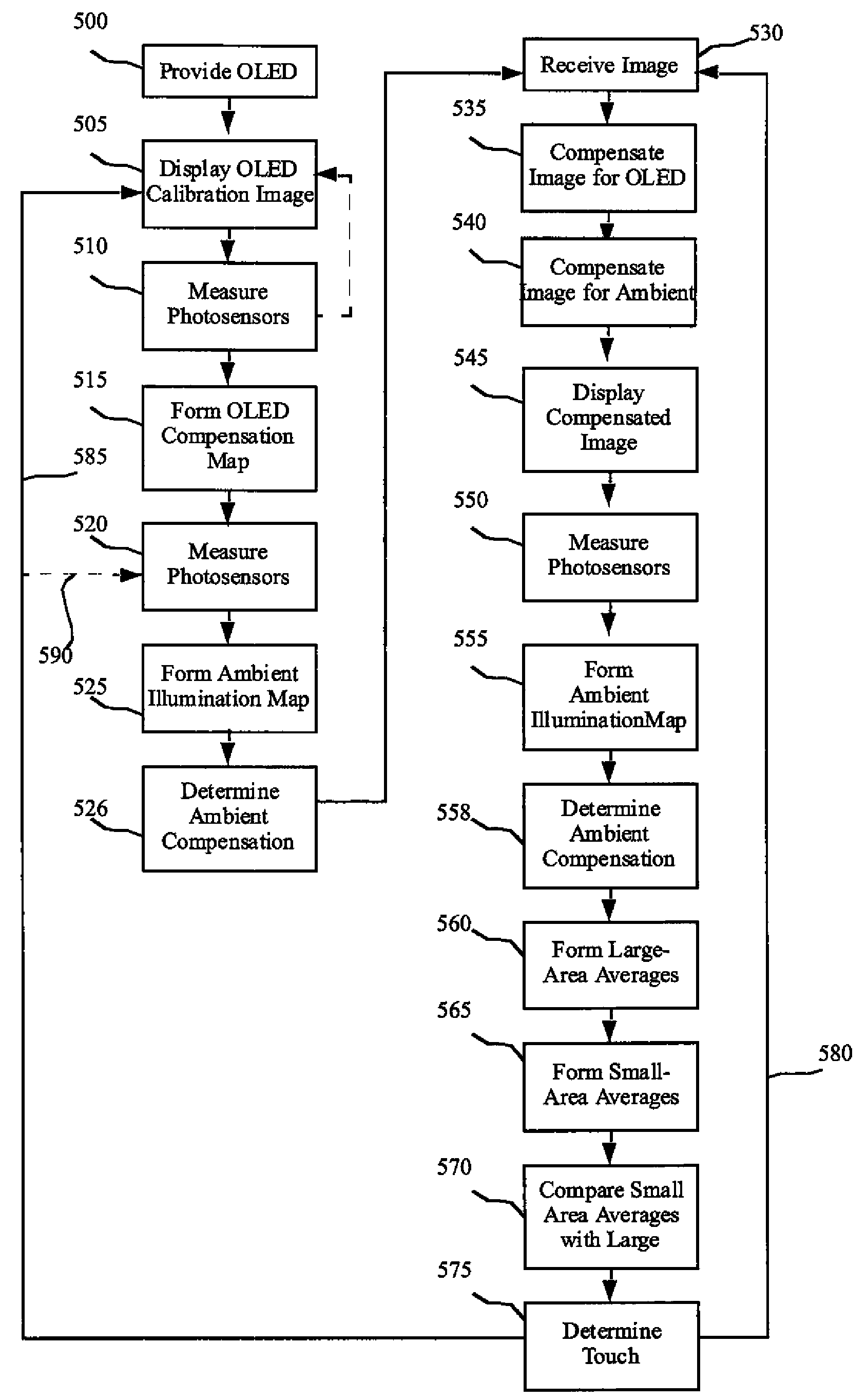
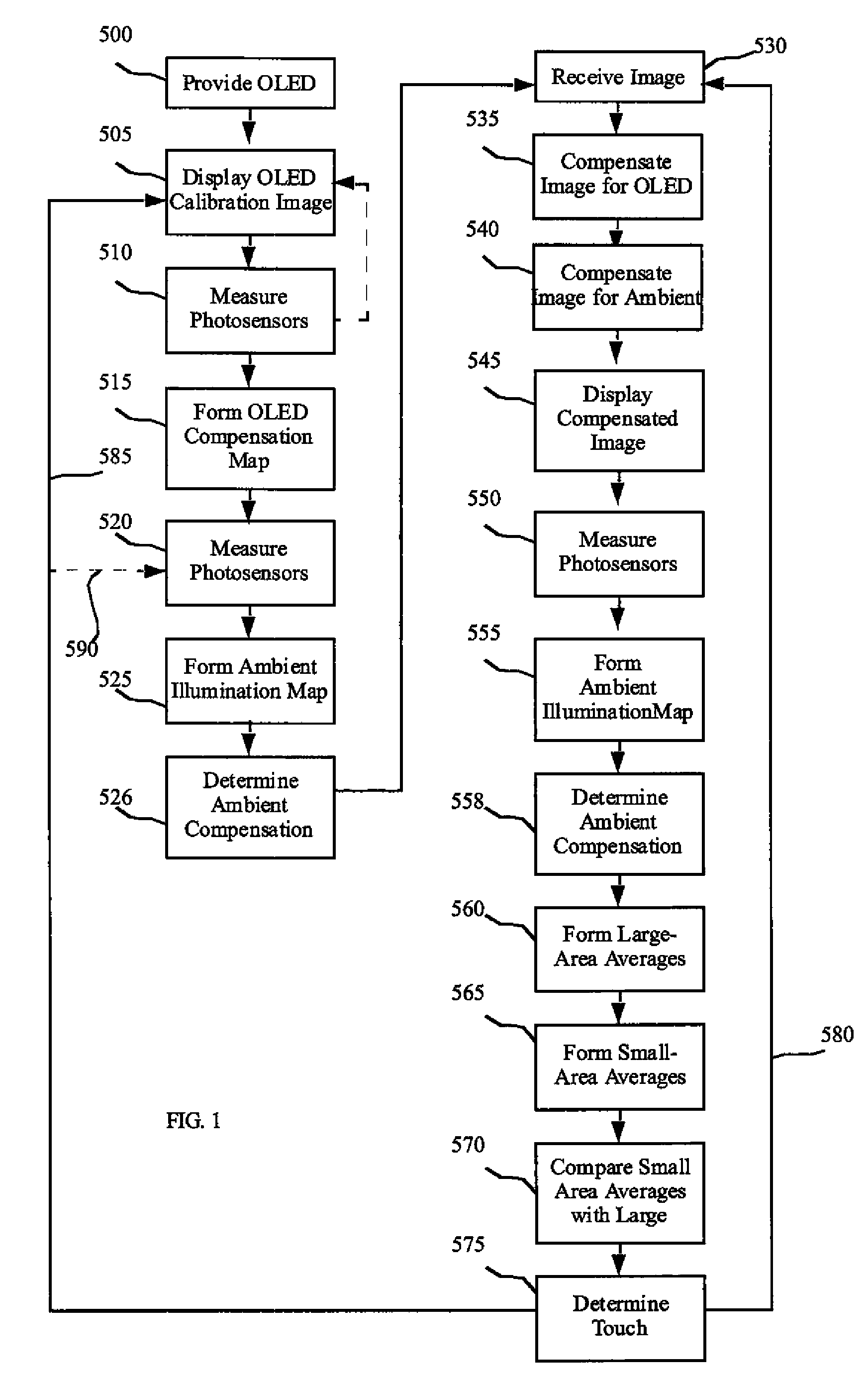
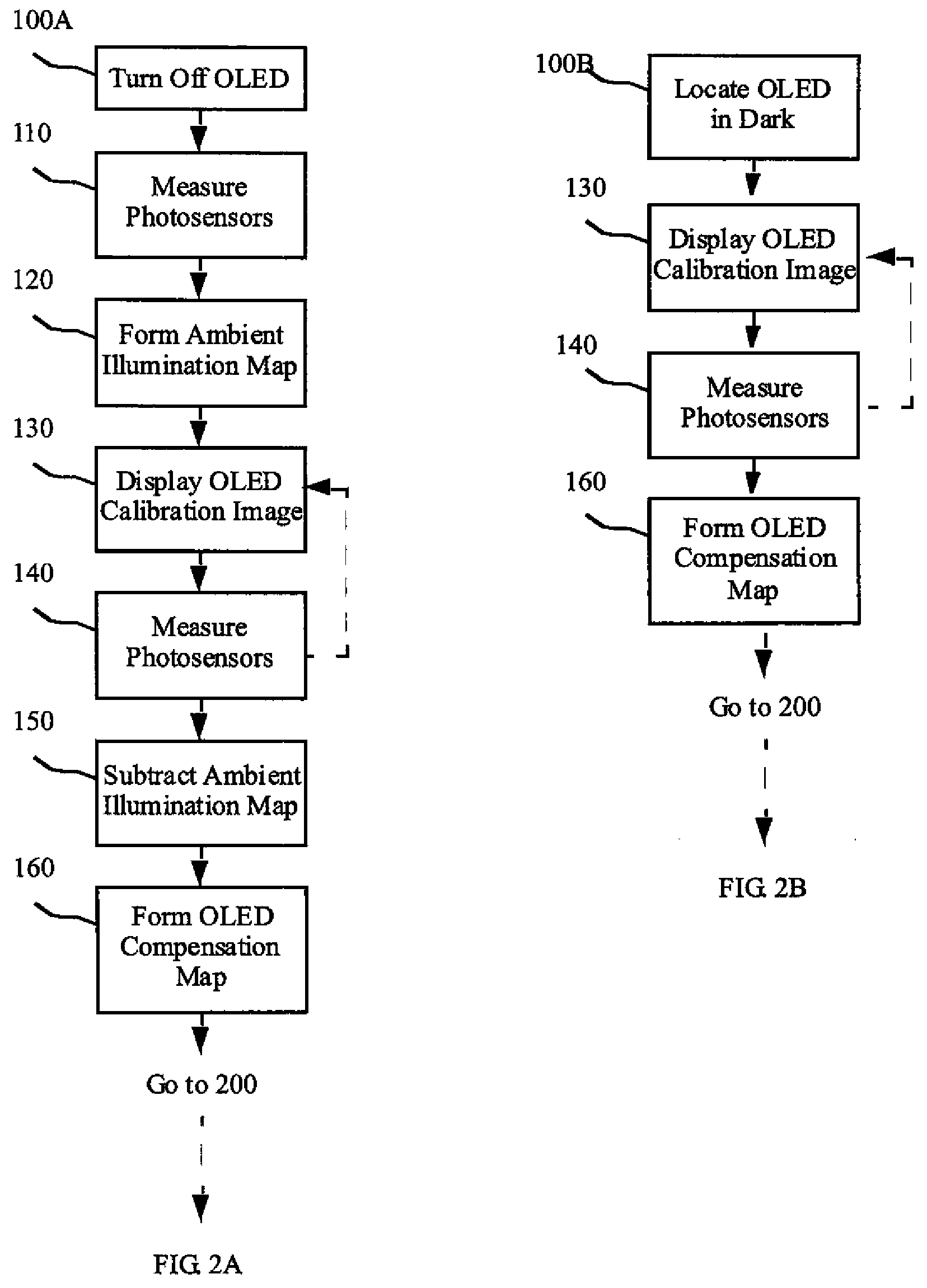
A method for controlling an OLED display includes providing an OLED device and a controller, measuring and communicating the amount of ambient and emitted OLED light incident upon an array of photosensors distributed over the display area for measuring the incident light, operating the OLED pixels with at least one calibration image and forming an OLED compensation map in response to a first measured incident light, receiving a second incident light measurement and forming an ambient illumination map, receiving and compensating an image and driving the OLED pixels with the compensated image, receiving a third incident light measurement and forming large-area average values and small-area average values, and comparing the large-area average values and the small-area average values to a predetermined criterion, and determining the location of one or more light occlusions or reflections.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Display apparatus having photo sensor
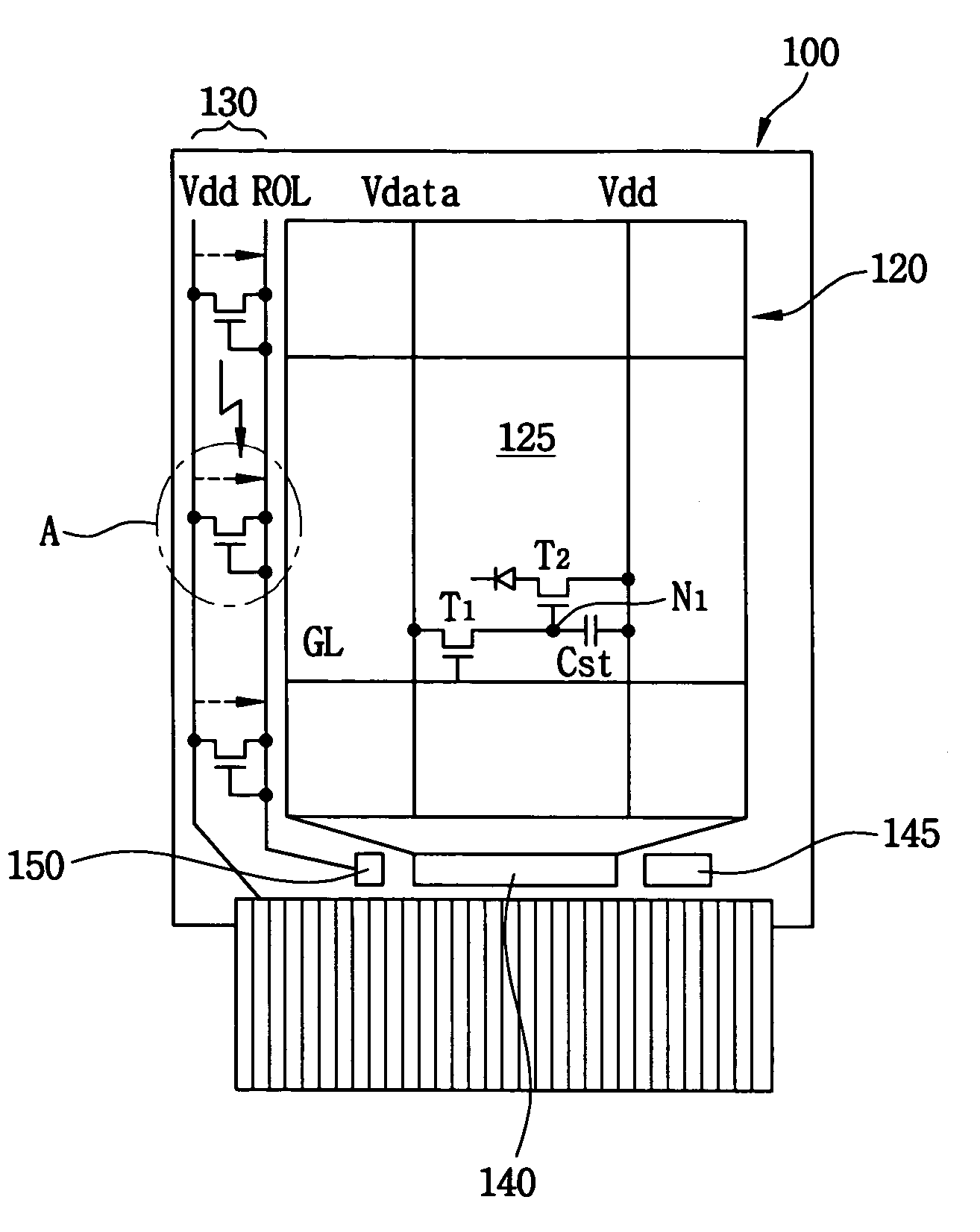
ActiveUS7218048B2Brightness adjustableDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesLight sensingElectron
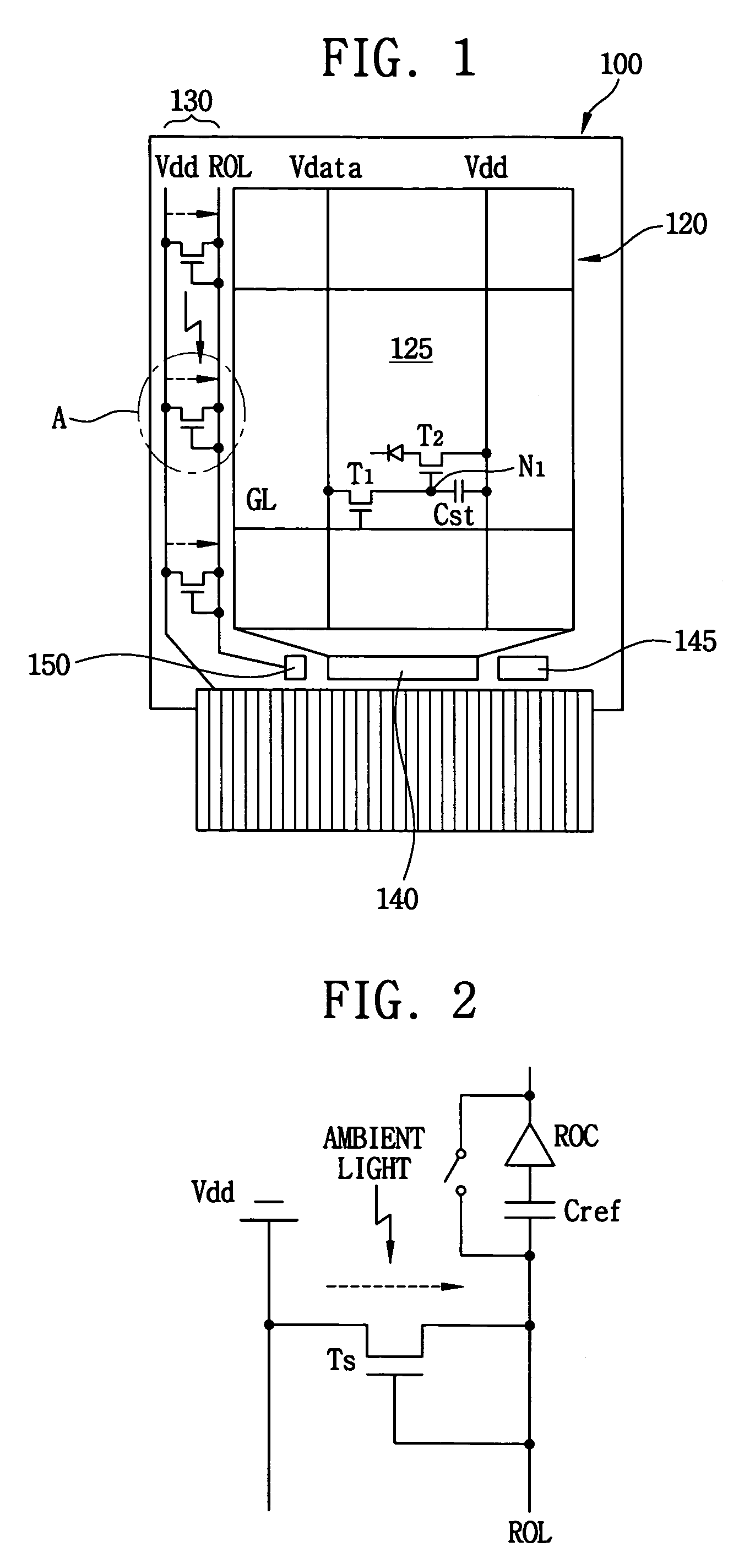
An electronic display apparatus includes a substrate, pixels and light sensing parts. The substrate includes a display region and a peripheral region adjacent the display region, and the substrate includes a plurality of gate lines extended in a first direction and a plurality of data lines extended in a second direction that is substantially perpendicular to the first direction. The pixels defined by each of the data and gate lines are formed in the display region to display an image. The light sensing part is formed in the peripheral region, and the light sensing part senses an intensity of an ambient light. The light sensing part that senses an intensity of an ambient light is formed on the array substrate, so that a luminance of the display apparatus may be adjusted in accordance with the intensity of the ambient light.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
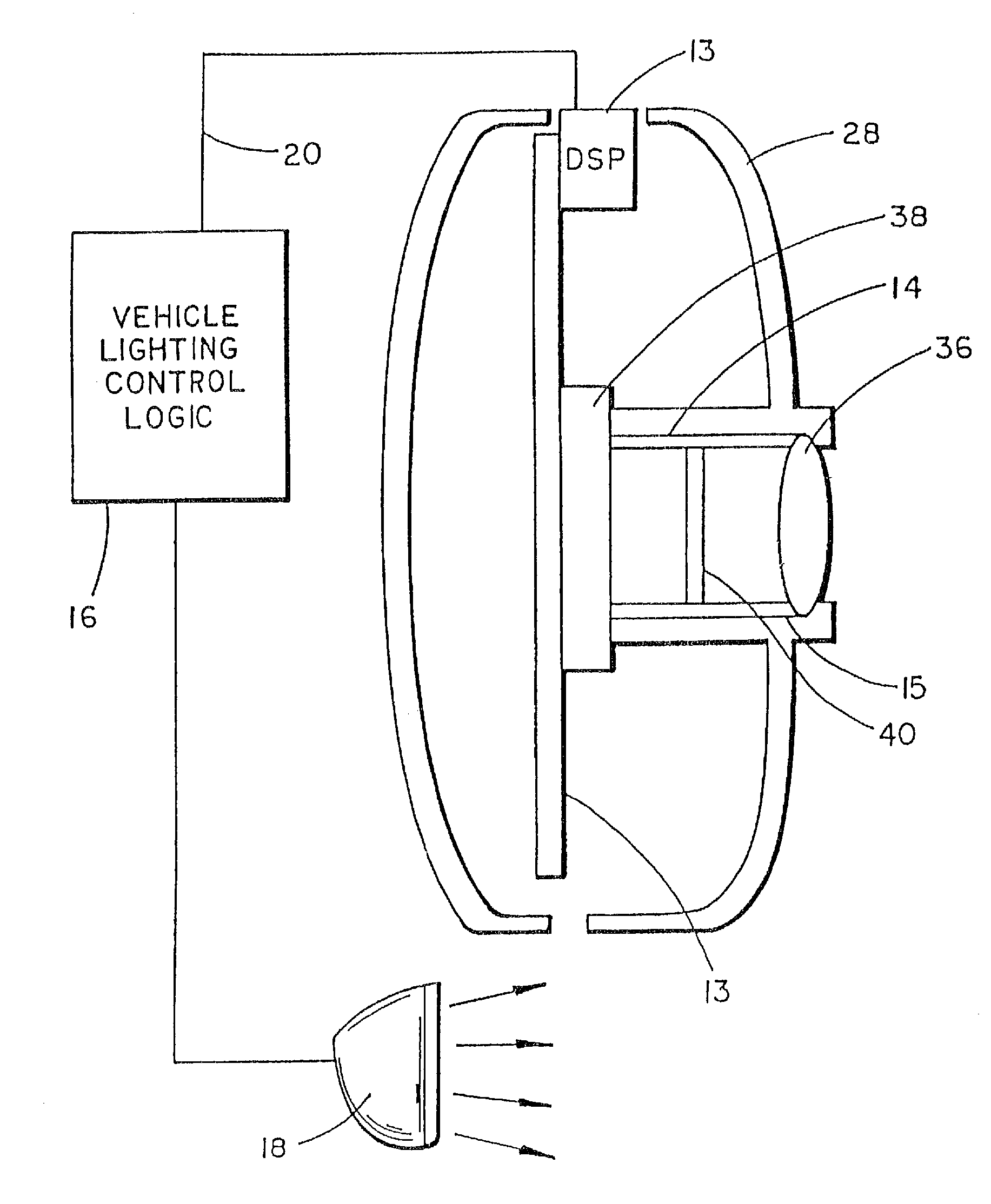
Vehicle rearview mirror system
InactiveUS6918674B2Low costEasy to usePhotometry using reference valueMirrorsLight sensingDisplay device
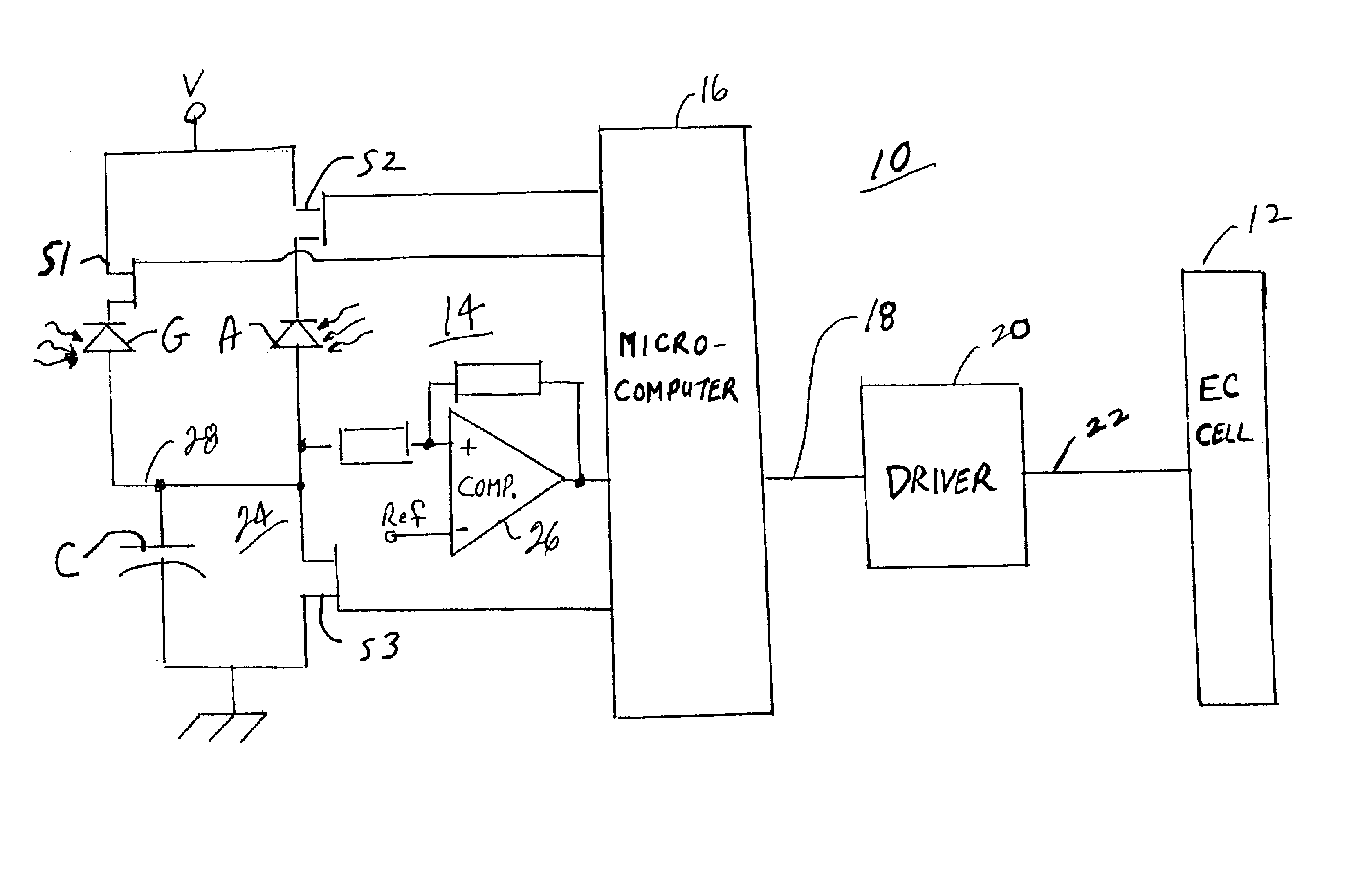
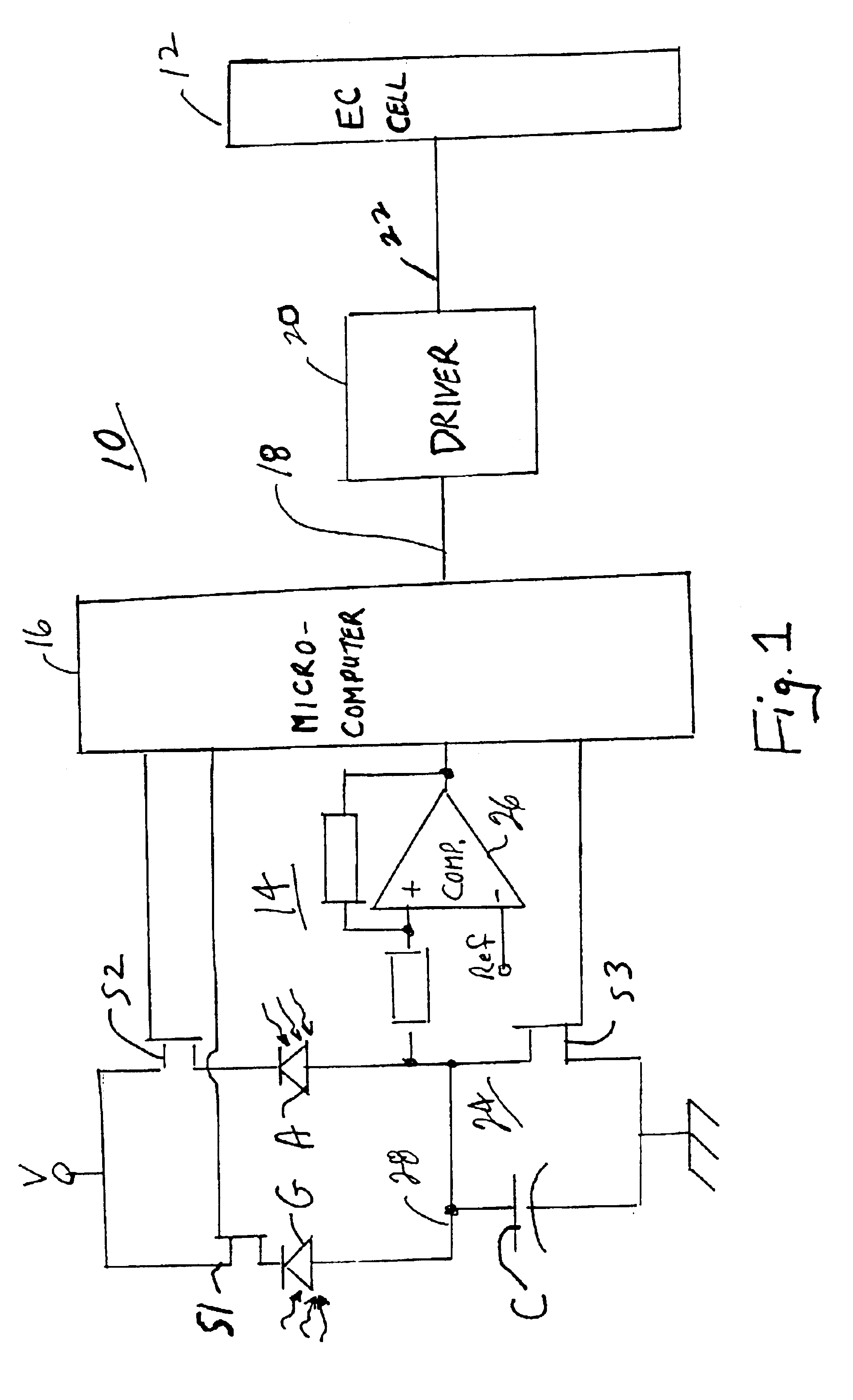
A vehicle rearview mirror system includes an electro-optic reflective element, an ambient light sensor that is operable to sense ambient light, a glare light sensor that is operable to sense glare light and a circuit that is responsive to the ambient glare light sensors which establishes a reflectance level of the reflective element. The circuit includes a sensor-responsive device and a controller. The sensor-responsive device produces an output that is a function of light sensed by glare and ambient light sensors. The controller connects one of the glare and ambient light sensors at a time with the sensor-responsive device to establish glare and ambient light levels and thereby the reflectance level of the reflective element. The mirror system may include a display operable to project light through the reflective element and may control the intensity of the display as a function of the glare light and ambient light.
Owner:DONNELLY CORP
Multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket, multi-lens camera module and application of multi-lens camera module
The invention discloses a multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket, a multi-lens camera module and an application of the multi-lens camera module. The multi-lens camera module comprises at least two lens assemblies, at least two light-sensing assemblies and an integrally-molded multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket, wherein the multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket is provided with an upper side part and a lower side part; each lens assembly is connected to the upper side part of the multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket; each light-sensing assembly is connected to the lower side part of the multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket; and the lens assemblies are positioned on light sensing paths of the light-sensing assemblies. Through adoption of the multi-lens camera module one-piece bracket and the multi-lens camera module, the technical defect of deviations in positions, angles and the like among brackets during connection of every independent bracket in the prior art can be overcome, so that the imaging quality of the multi-lens camera module is ensured.
Owner:NINGBO SUNNY OPOTECH CO LTD
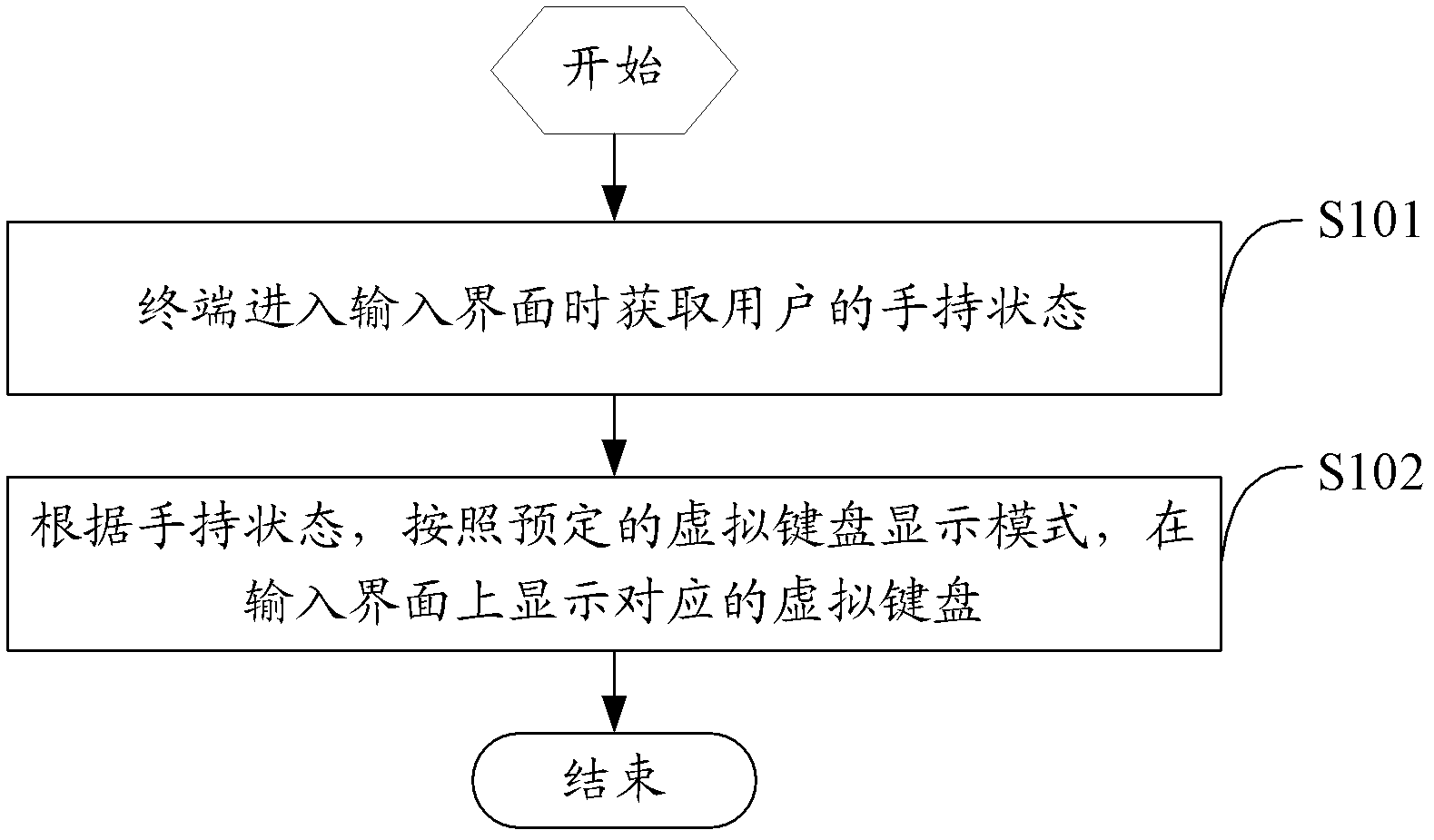
Left or right hand adapting virtual keyboard display method and terminal
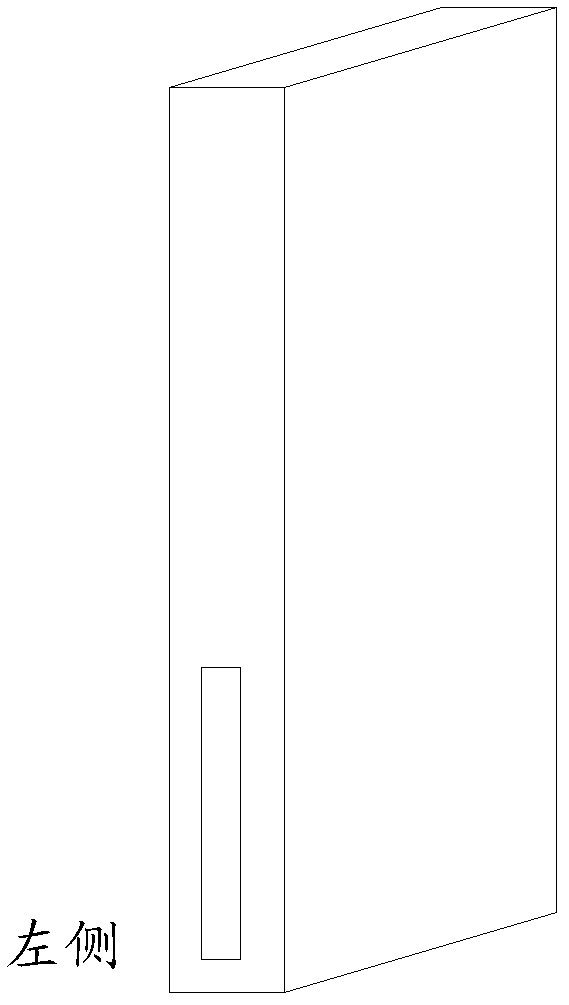
InactiveCN102810039AEasy inputAvoid the problem of not being able to use one hand for virtual keyboard inputAlphabetical characters enteringTelephone set constructionsLight sensingComputer terminal
The invention relates to a left or right hand adapting virtual keyboard display method and terminal. The left and right hand adapting virtual keyboard display method comprises the following steps: acquiring the state of holding the terminal by the user by hand when the terminal enters the input interface, and displaying the corresponding virtual keyboard on the input interface according to the state of holding the terminal by the user by hand and the preset virtual keyboard display mode. Because the state of holding the terminal by the user by hand is judged automatically by light-sensing modules arranged on two sides of the terminal and the layout mode of the virtual keyboard is adjusted automatically according to the acquired state of holding the terminal by the user by hand, the virtual keyboard which is used by the user to input by left or right hand can be displayed on the input interface conveniently, the user can input conveniently, and the problem that the user can be not input by single hand through the virtual keyboard of the large-size touch screen terminal is avoided.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com