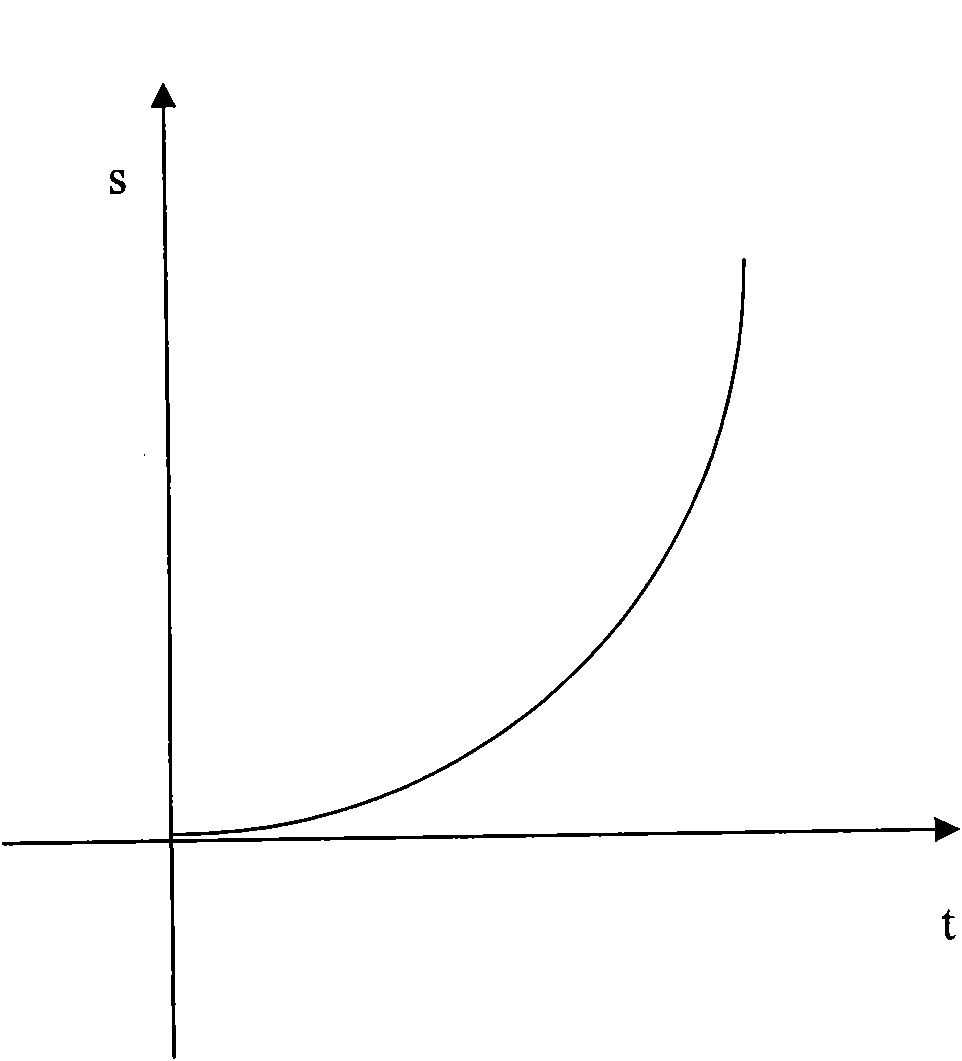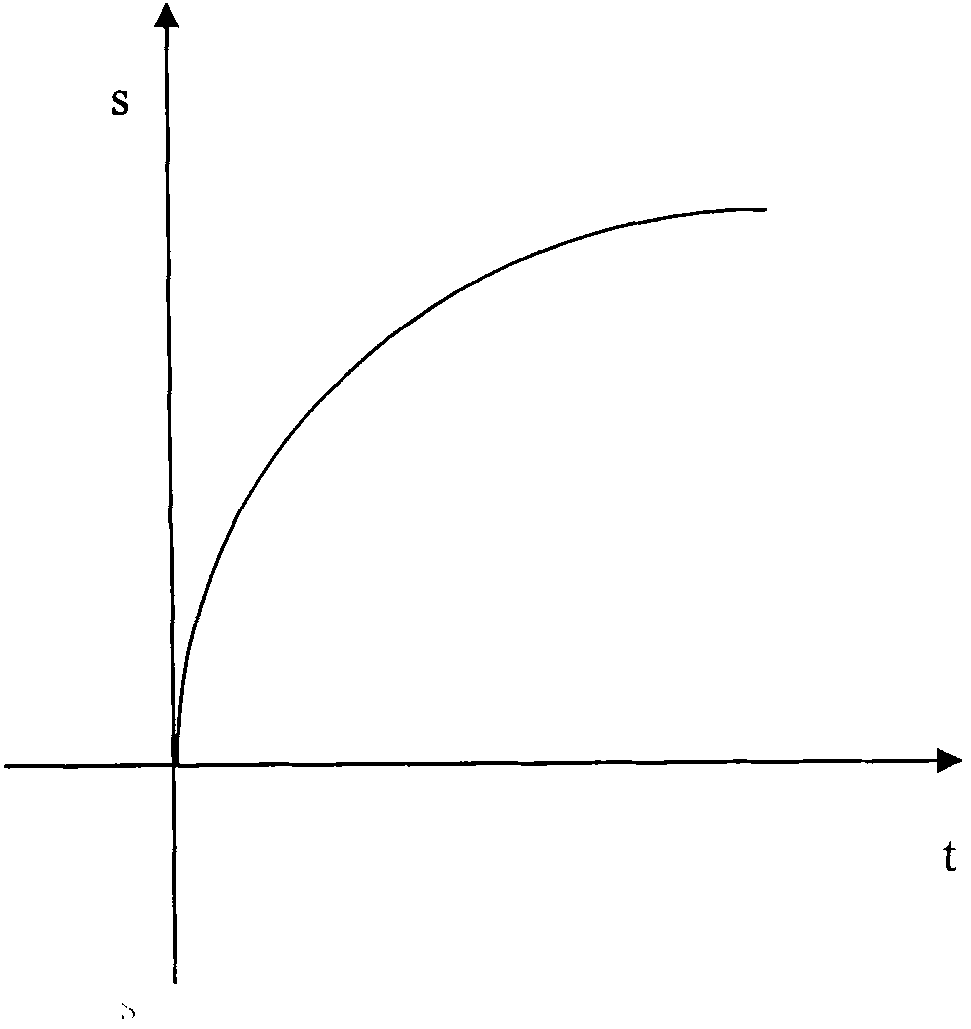Patents
Literature
784 results about "Object motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
An object translates , or changes location, from one point to another. And an object rotates , or changes its attitude . In general, the motion of any object involves both translation and rotation. The translations are in direct response to external forces . The rotations are in direct response to external torques or moments (twisting forces).
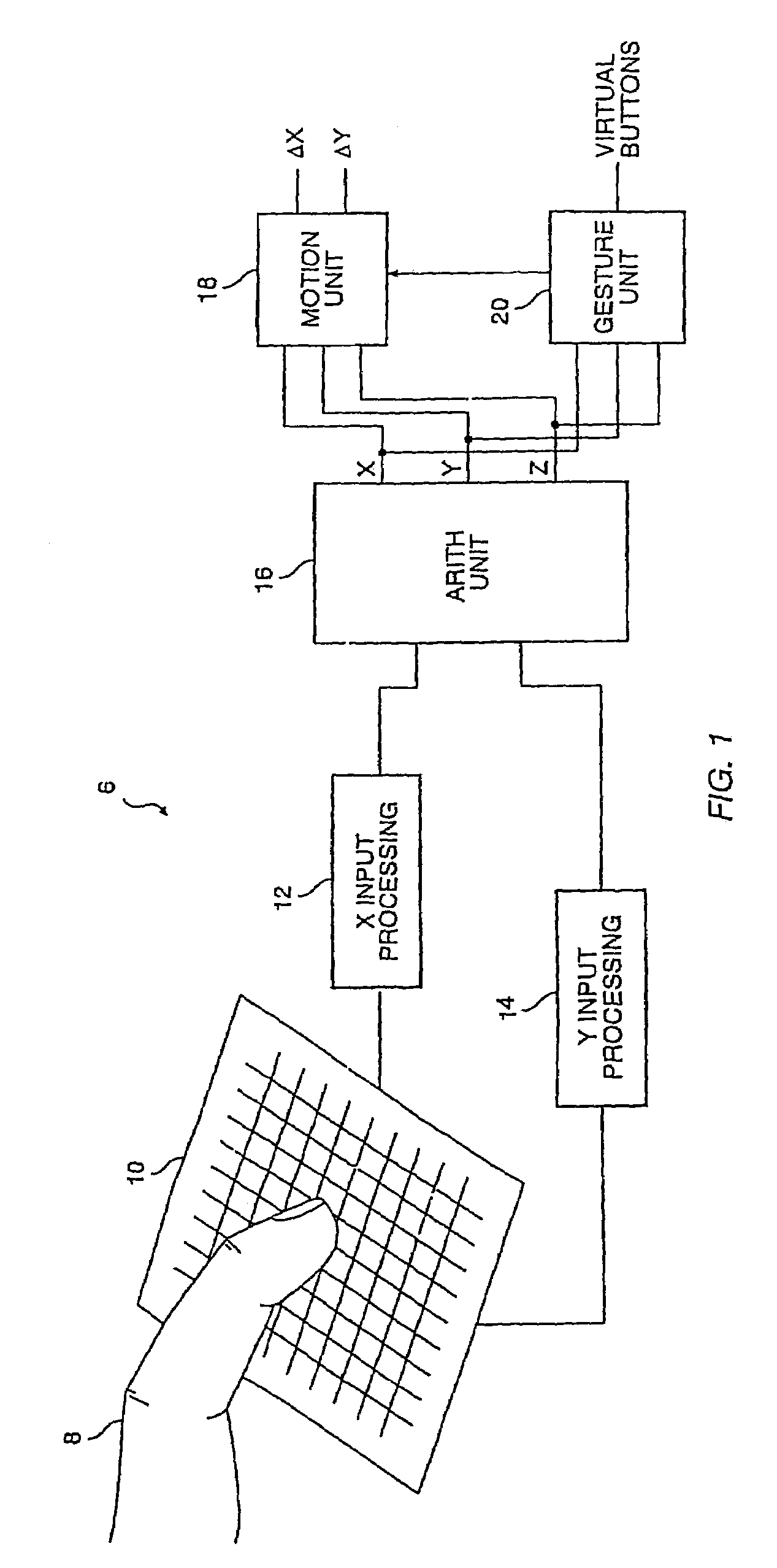
Graphical scroll wheel
ActiveUS20070236475A1Facilitates improved system usabilityEasily causedData processing applicationsCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsObject motion
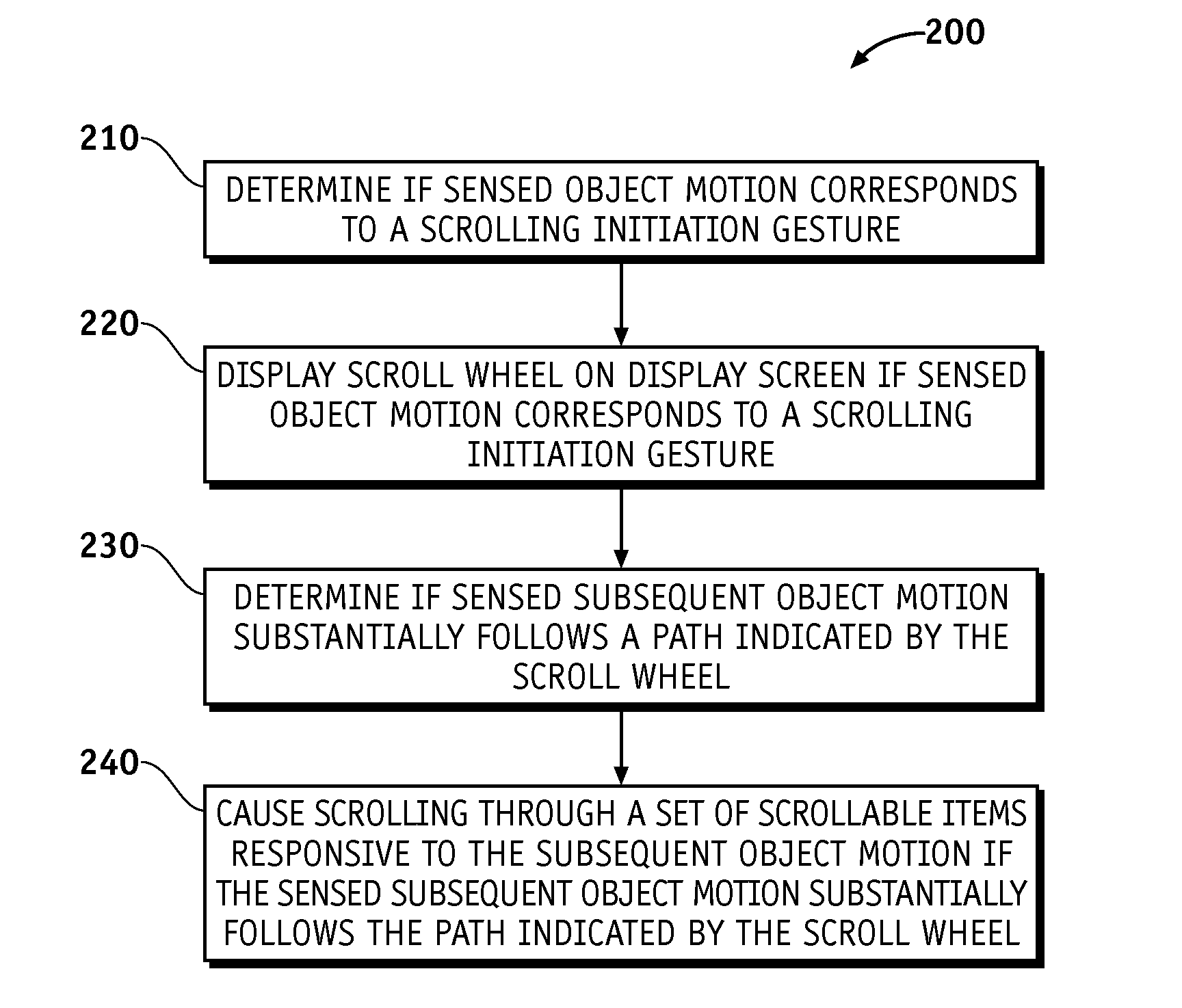
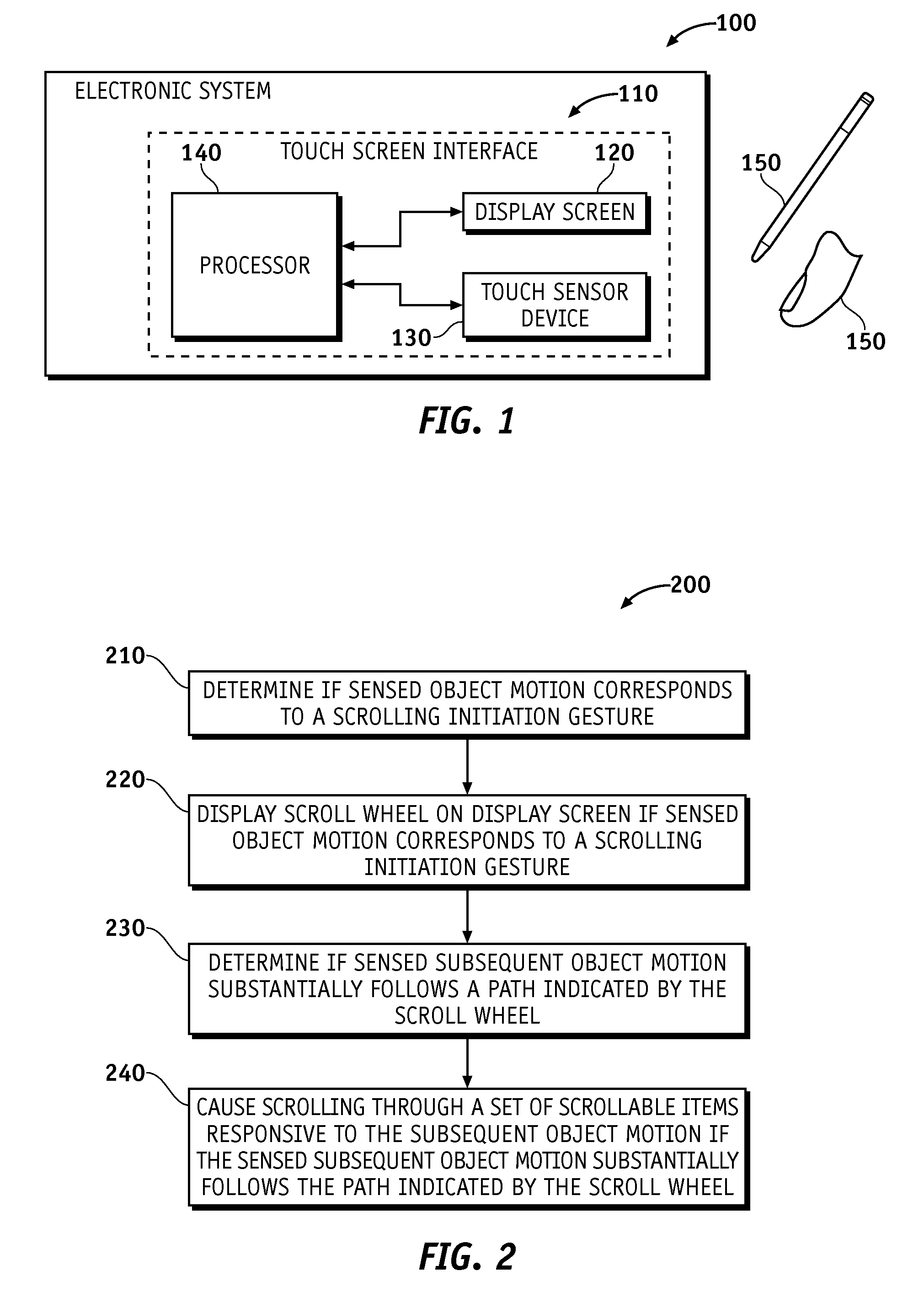
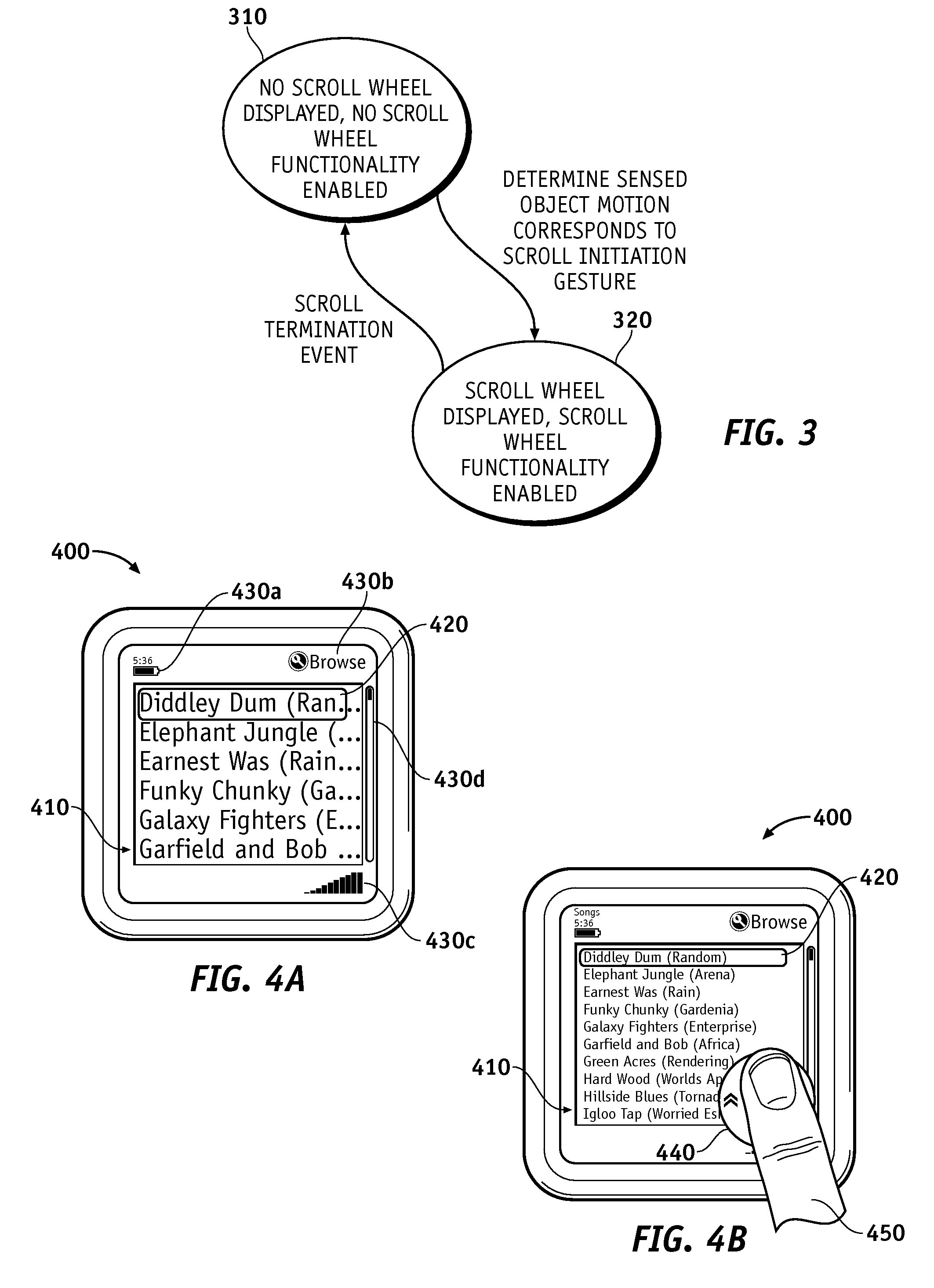
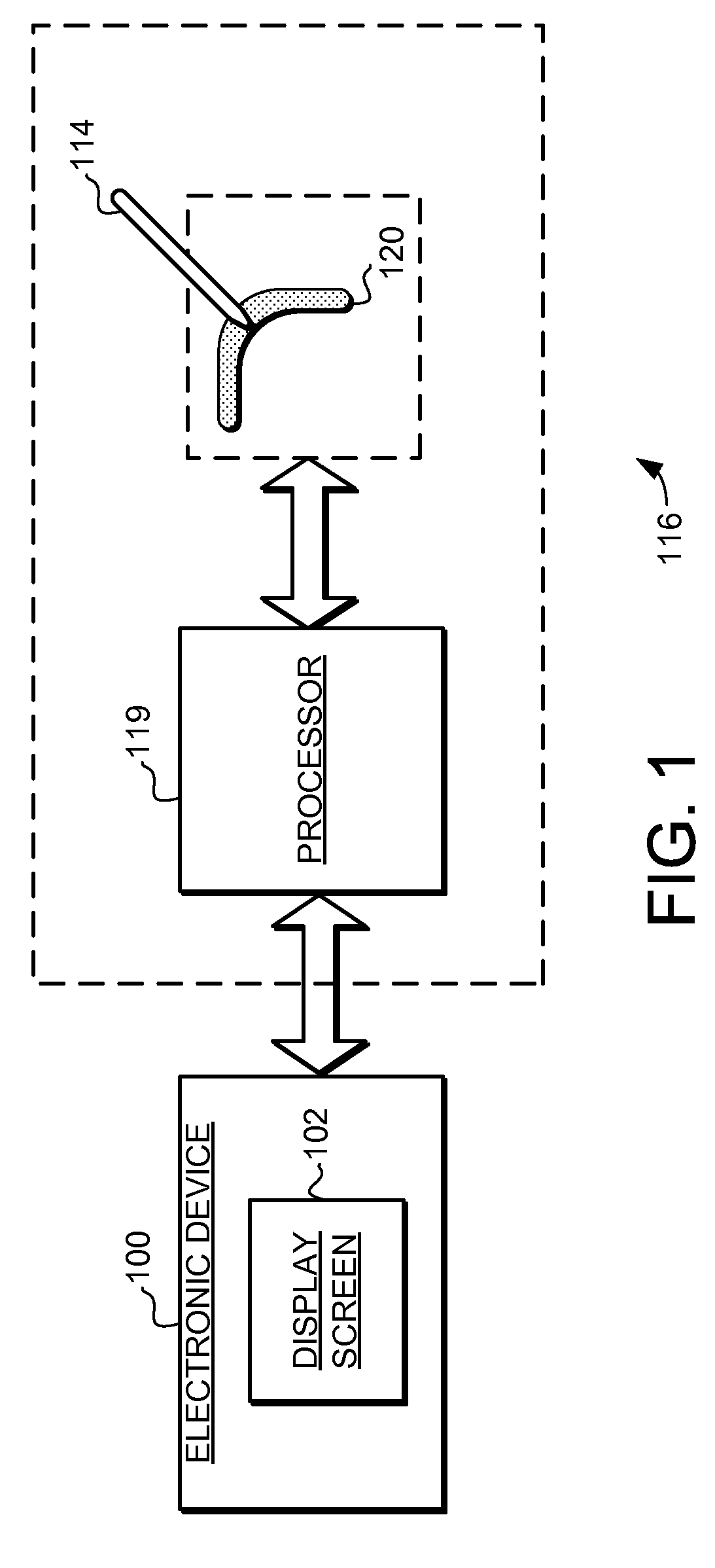
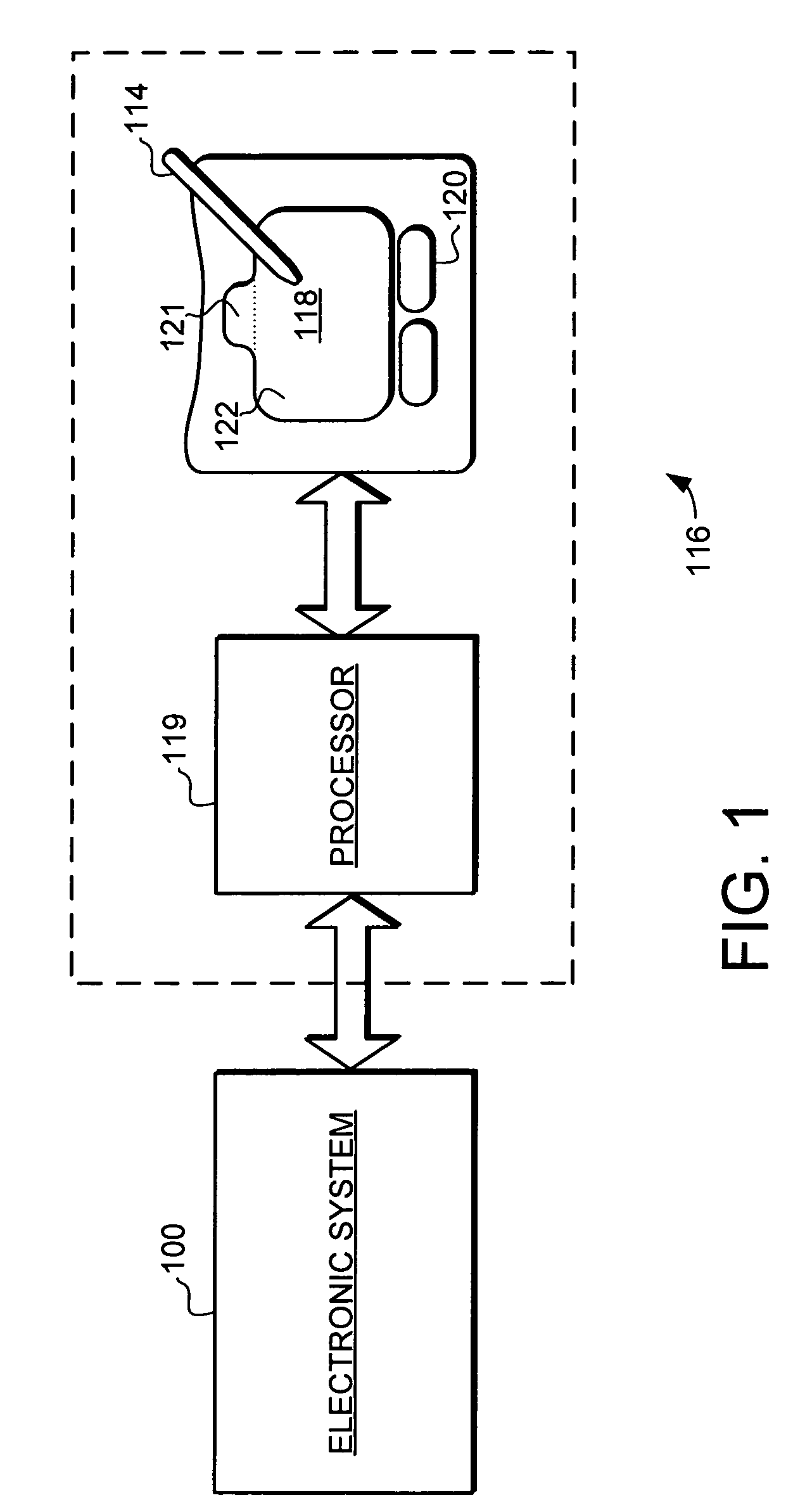
A touch screen interface including a display screen, a touch sensor device, and a processor coupled to the display screen and the touch sensor is described. The touch sensor device is adapted to sense object motion in a sensing region that overlaps at least part of the display screen. The processor is adapted to cause a scroll wheel that indicates a scrolling path to appear on the display screen selectively, such as in response to the touch sensor sensing object motion that corresponds to a scrolling initiation gesture. The processor is further adapted to cause scrolling on a display screen selectively, such as in response to the touch sensor sensing subsequent object motion along the scrolling path after the touch sensor has sensed the object motion corresponding to the scrolling initiation gesture.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Method and apparatus for determining orientation and position of a moveable object
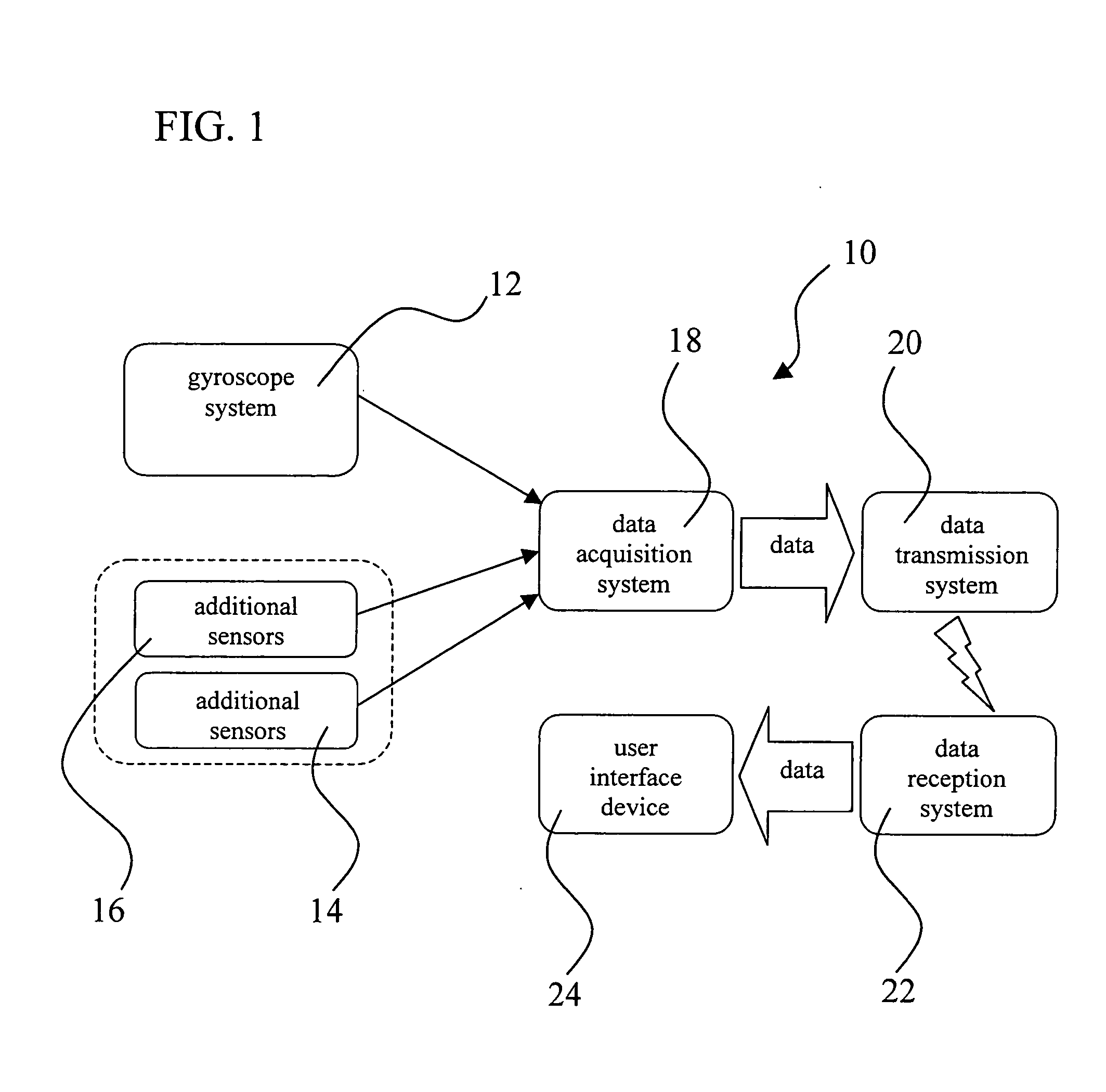
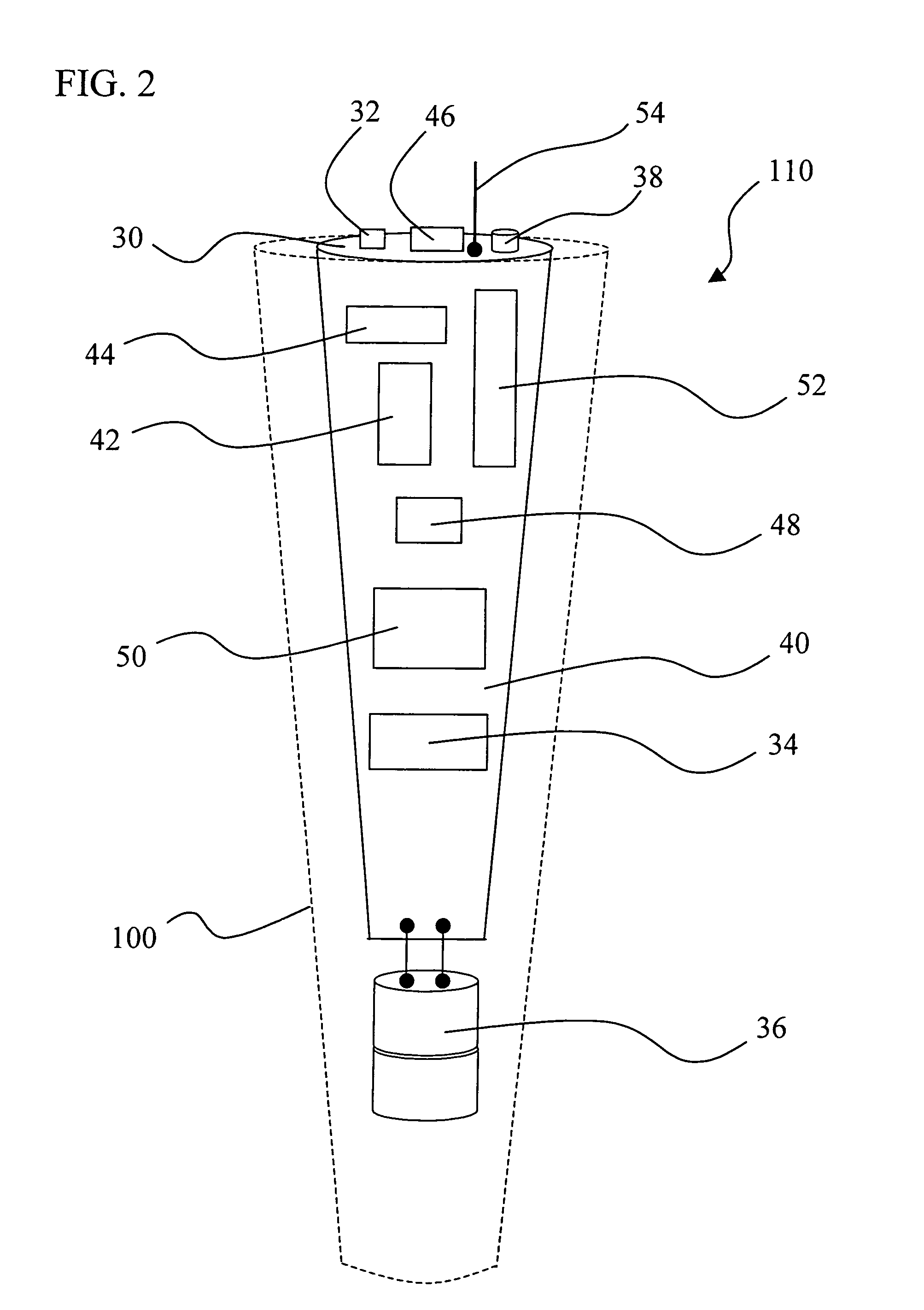
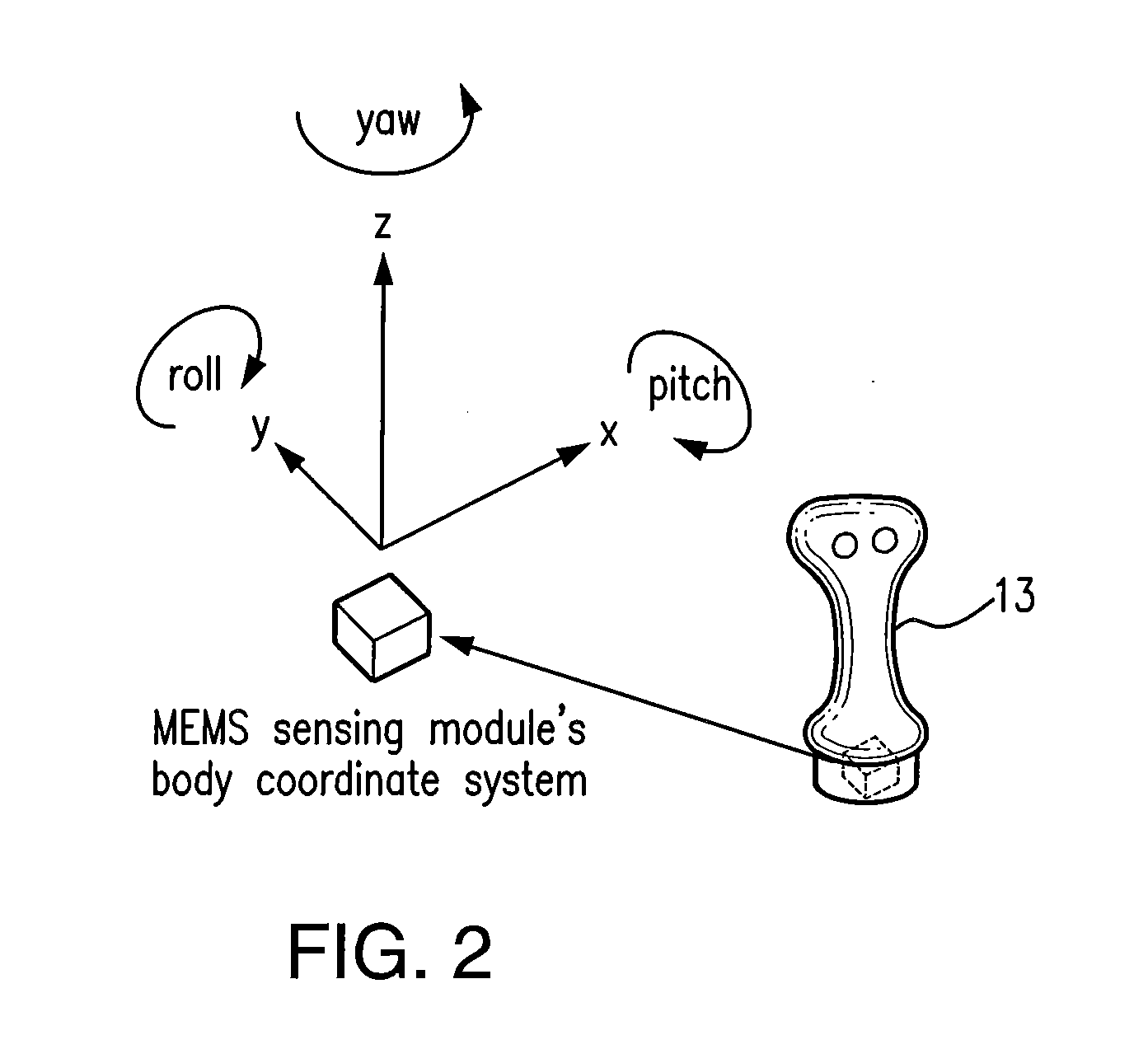
InactiveUS20050032582A1Gymnastic exercisingNavigation by speed/acceleration measurementsMicrocontrollerObject motion
An orientation and position tracking system in three-dimensional space and over a period of time utilizing multiple inertial and other sensors for determining motion parameters to measure orientation and position of a moveable object. The sensors, for example vibrational and angular velocity sensors, generate signals characterizing the motion of the moveable object. The information is received by a data acquisition system and processed by a microcontroller. The data is then transmitted via wireless communication to an external data reception system (locally based or a global network). The information can then be displayed and presented to the user through a variety of means including audio, visual, and tactile.
Owner:FORTESCUE CORP
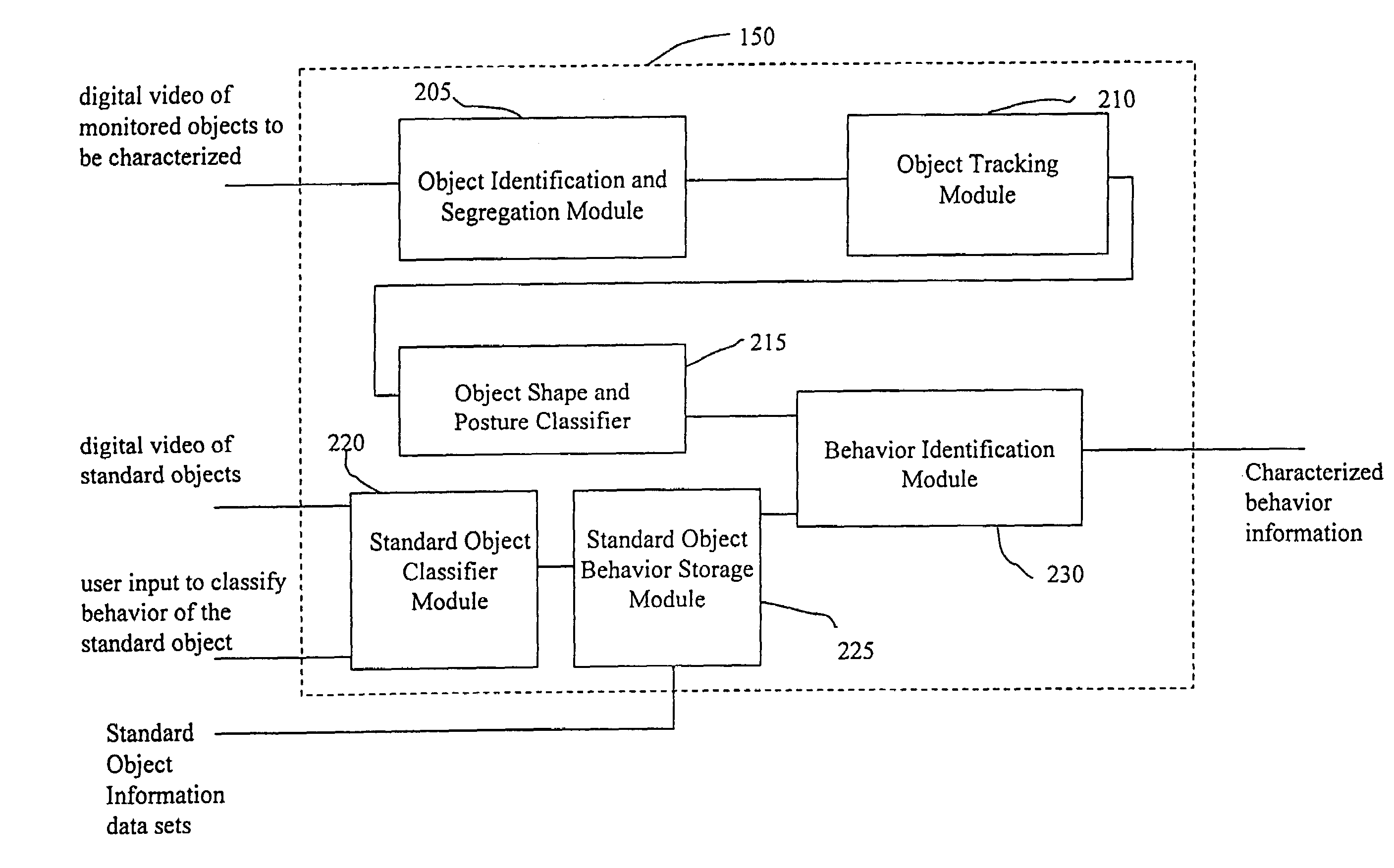
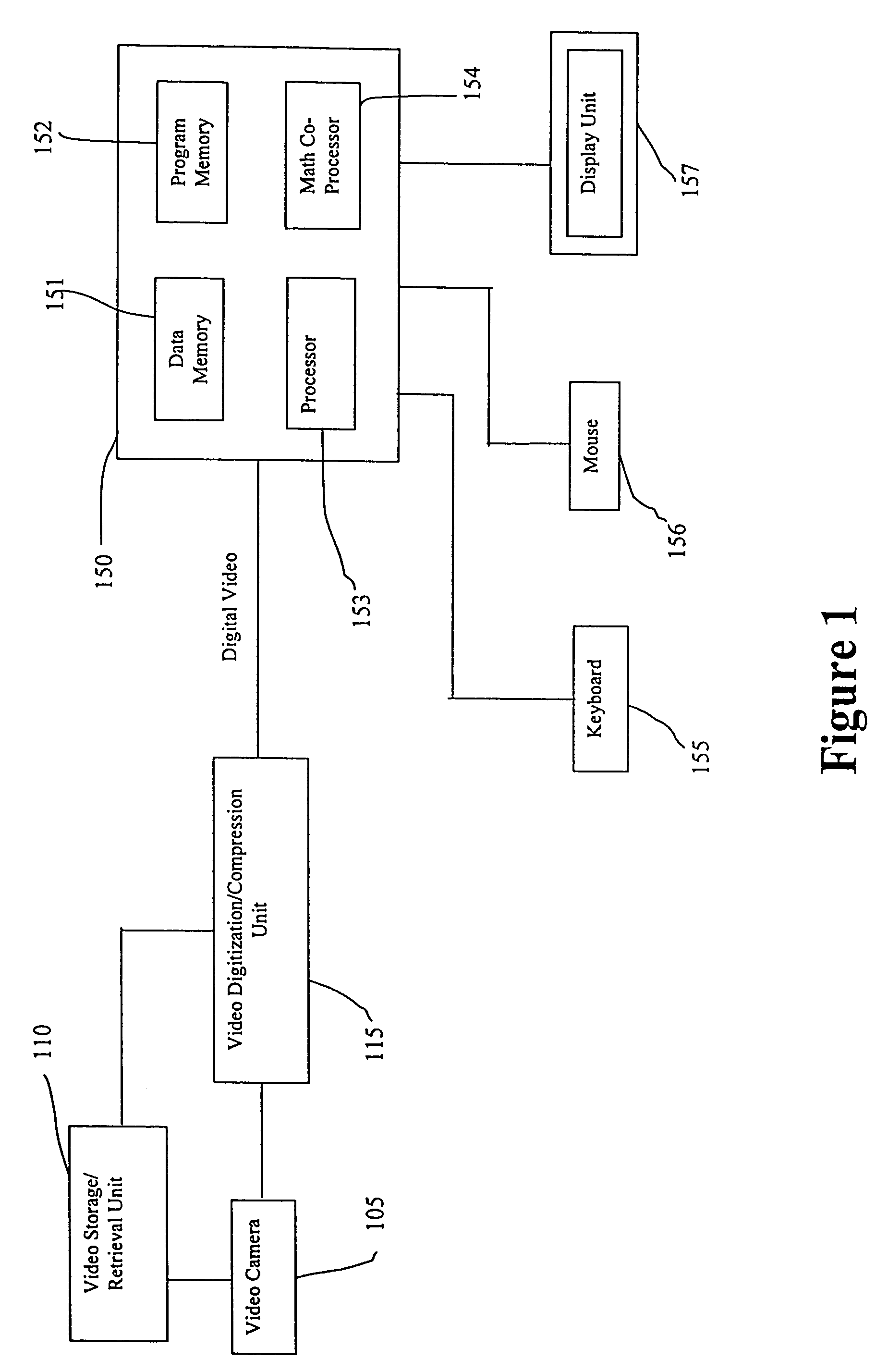
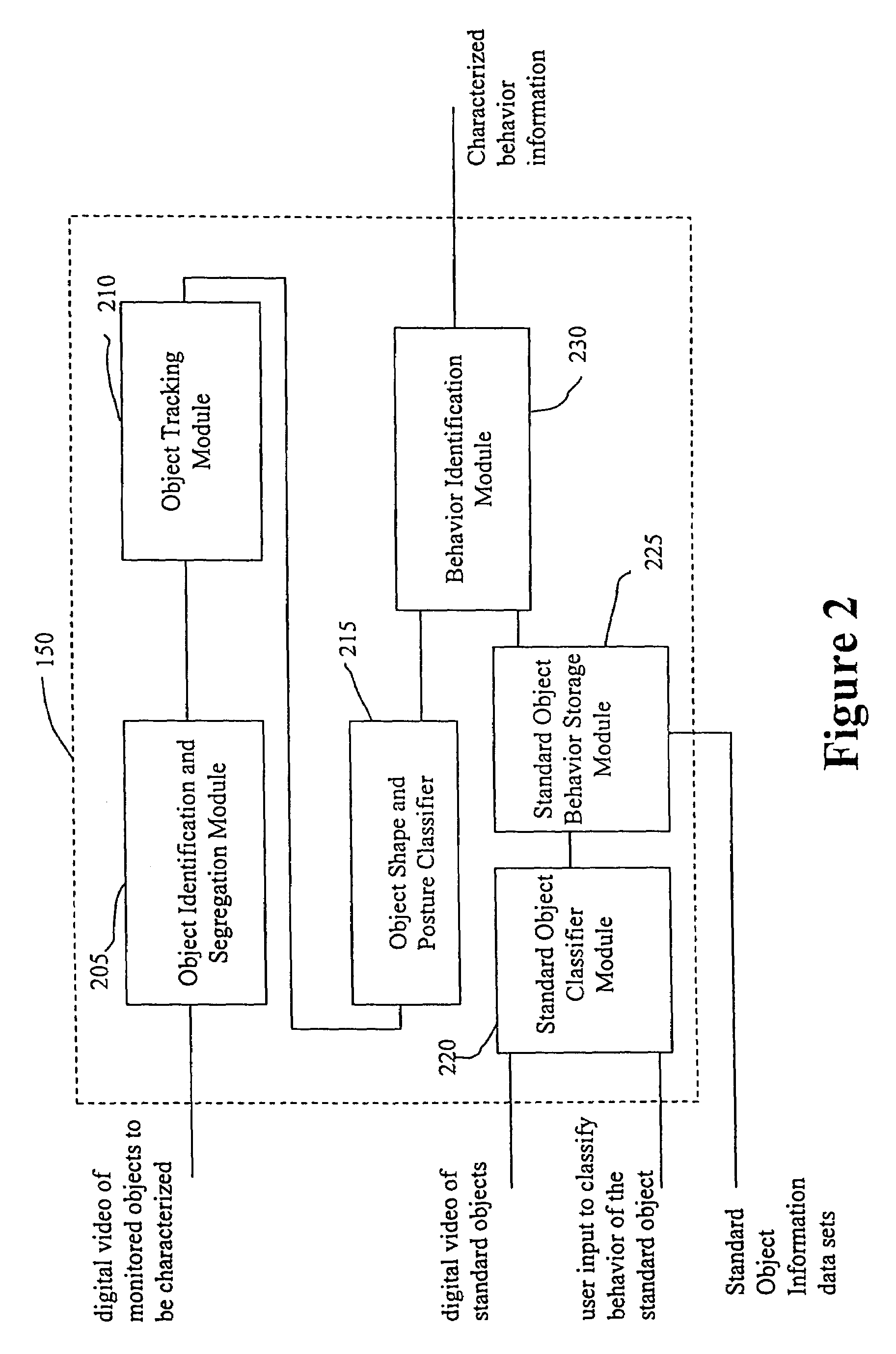
System and method for object identification and behavior characterization using video analysis
InactiveUS7068842B2Accurate identificationEfficient detectionImage enhancementImage analysisProbabilistic methodAnimal behavior
In general, the present invention is directed to systems and methods for finding the position and shape of an object using video. The invention includes a system with a video camera coupled to a computer in which the computer is configured to automatically provide object segmentation and identification, object motion tracking (for moving objects), object position classification, and behavior identification. In a preferred embodiment, the present invention may use background subtraction for object identification and tracking, probabilistic approach with expectation-maximization for tracking the motion detection and object classification, and decision tree classification for behavior identification. Thus, the present invention is capable of automatically monitoring a video image to identify, track and classify the actions of various objects and the object's movements within the image. The image may be provided in real time or from storage. The invention is particularly useful for monitoring and classifying animal behavior for testing drugs and genetic mutations, but may be used in any of a number of other surveillance applications.
Owner:CLEVER SYS
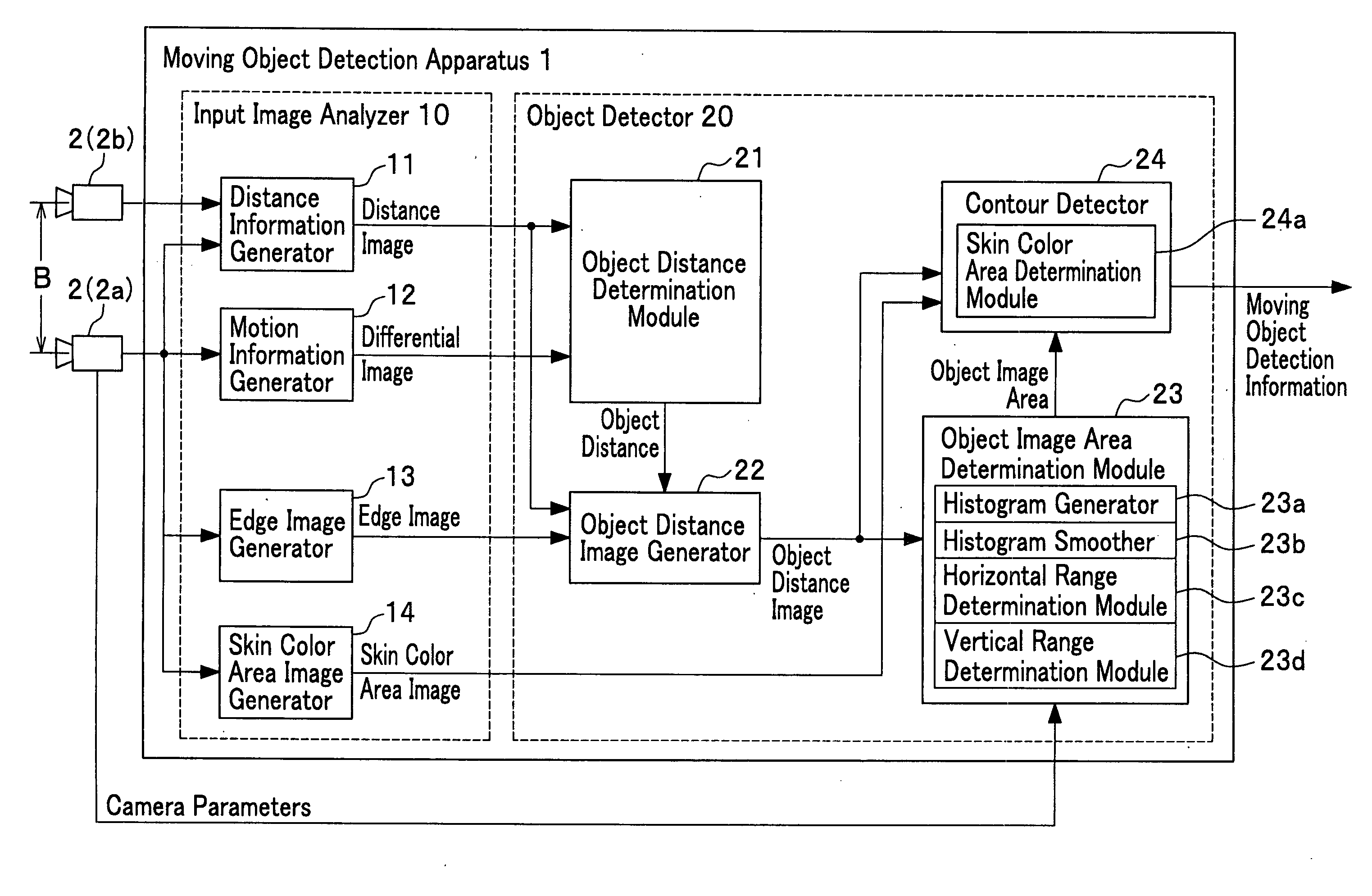
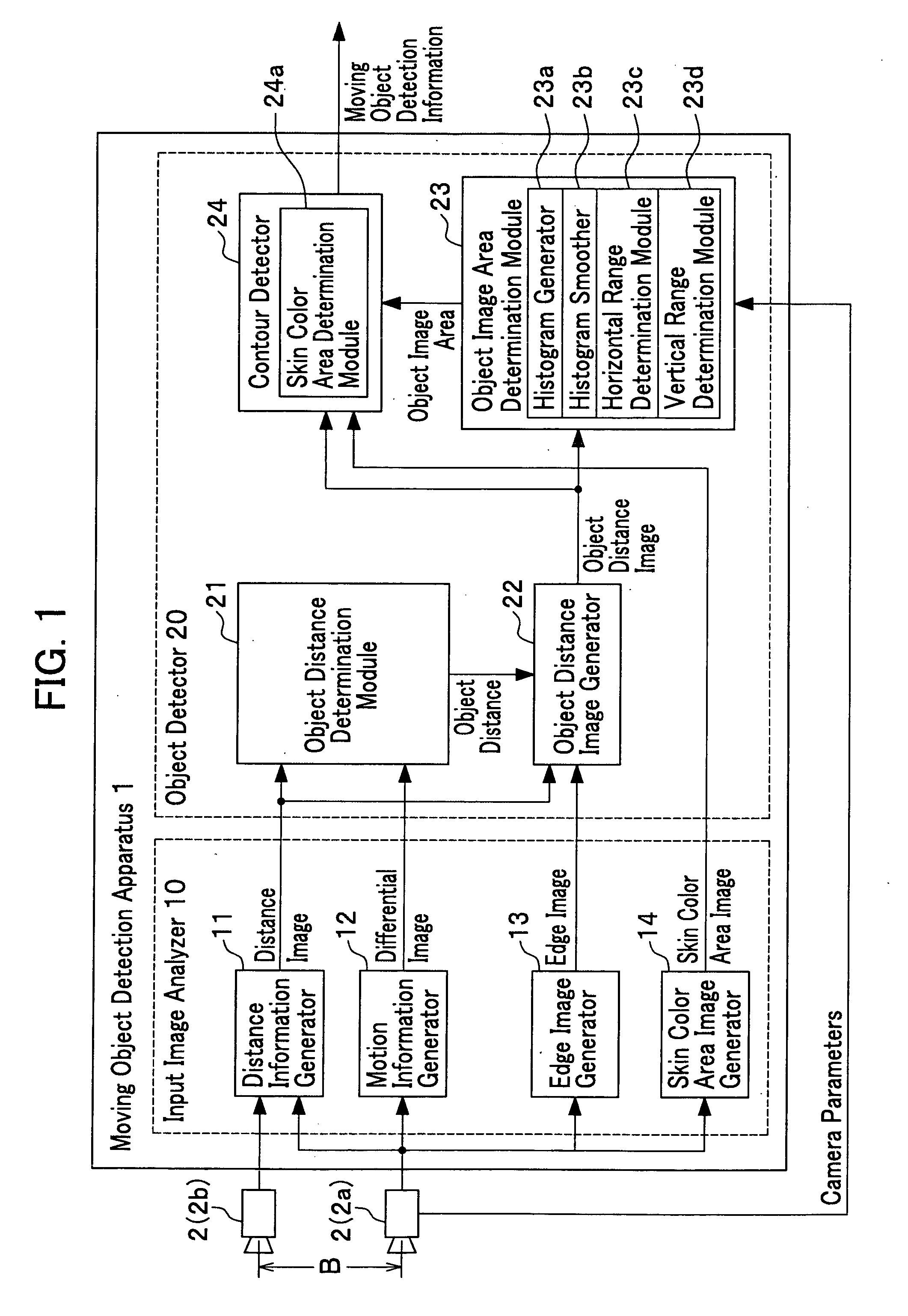
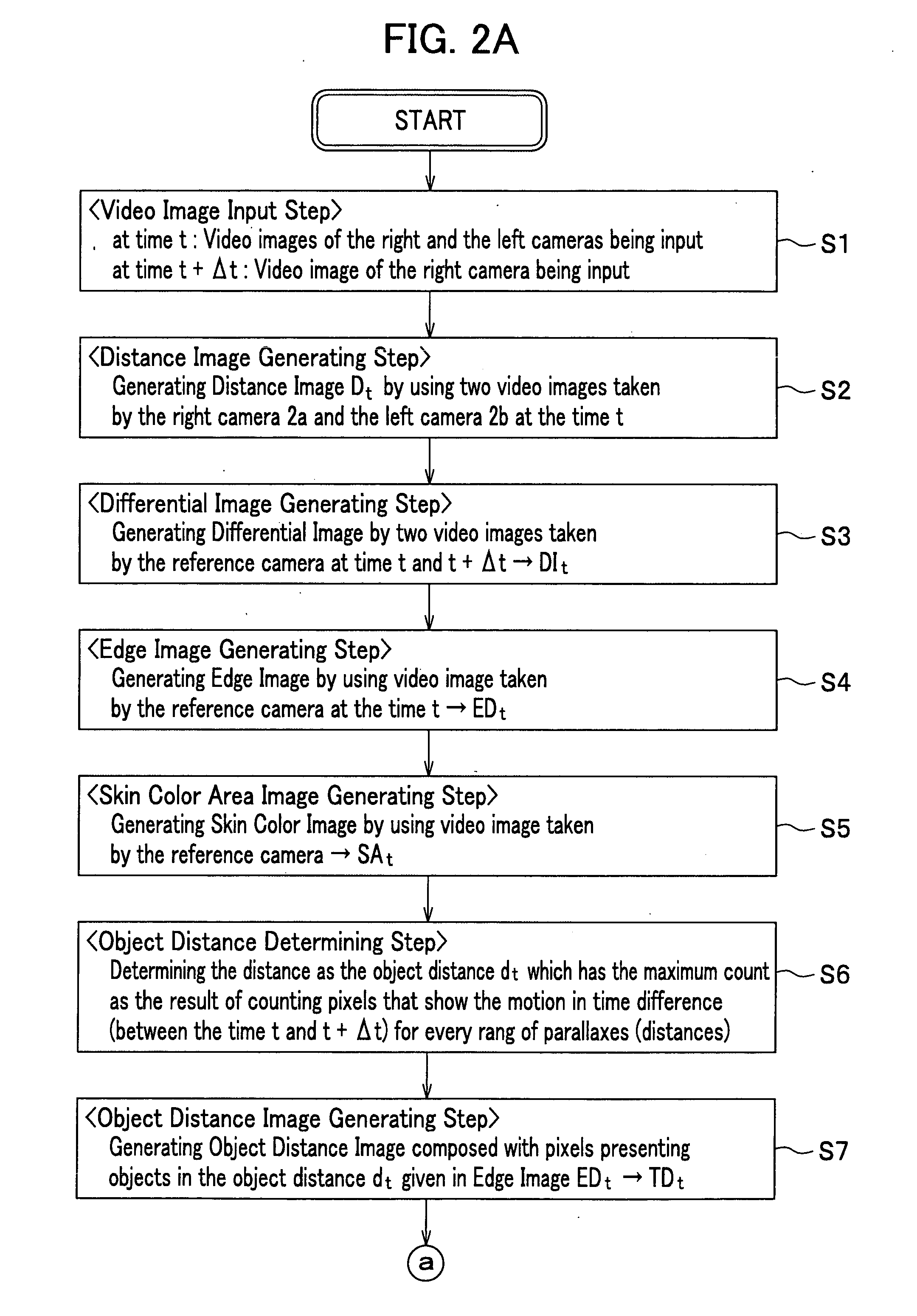
Apparatus, method and program for moving object detection
ActiveUS20050147277A1Improve accuracyEasy determine symmetryImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionVideo image
The present invention detects a moving object by generating the distance information of the moving object, detecting the object motion, determining the object distance, detecting the object image area and the object contour from the video image that includes the object image and contour, and provides a moving object detection apparatus to carry out such detection as well as detecting a contour of the specific moving object by detecting the center of the moving object in high precision.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
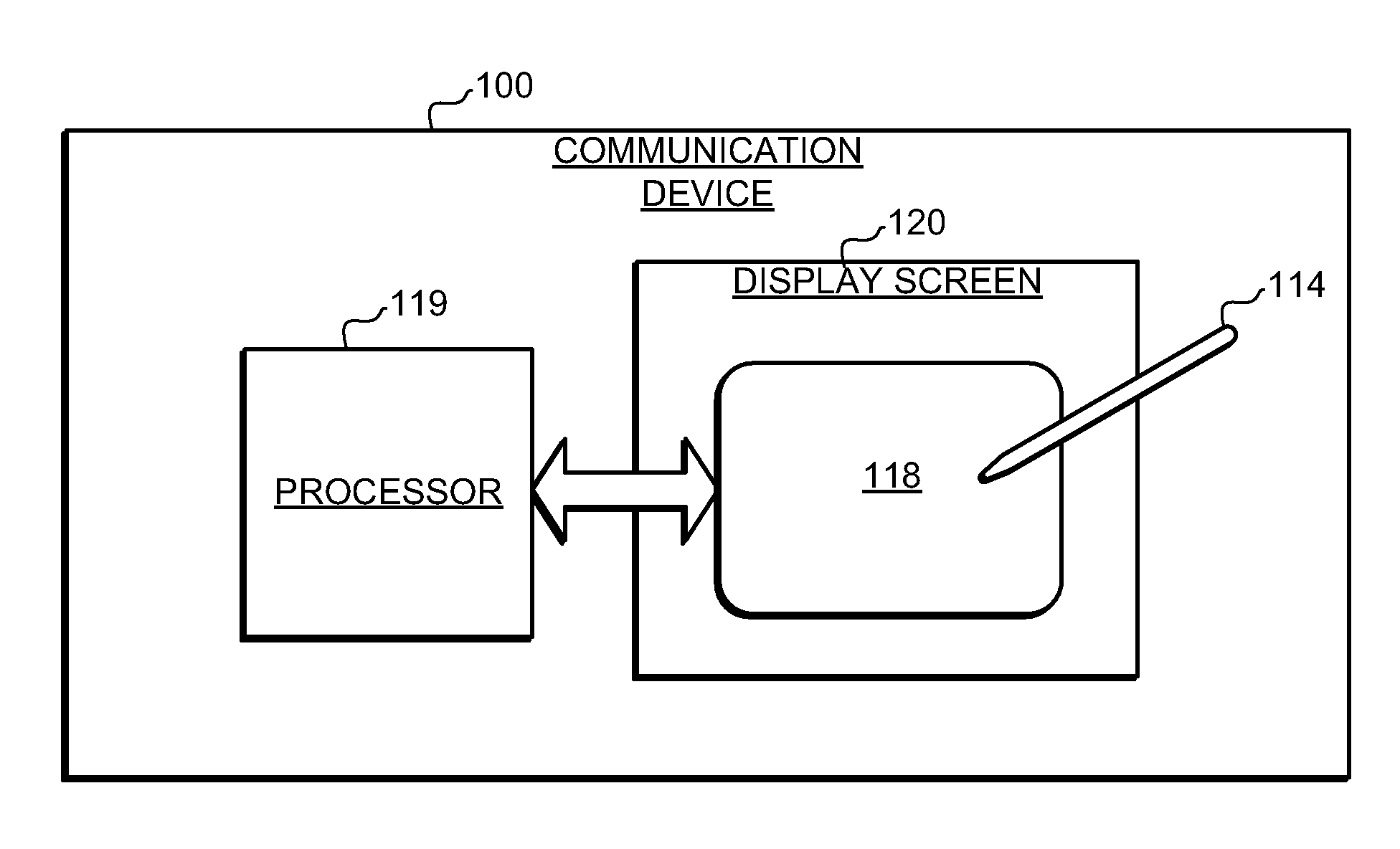
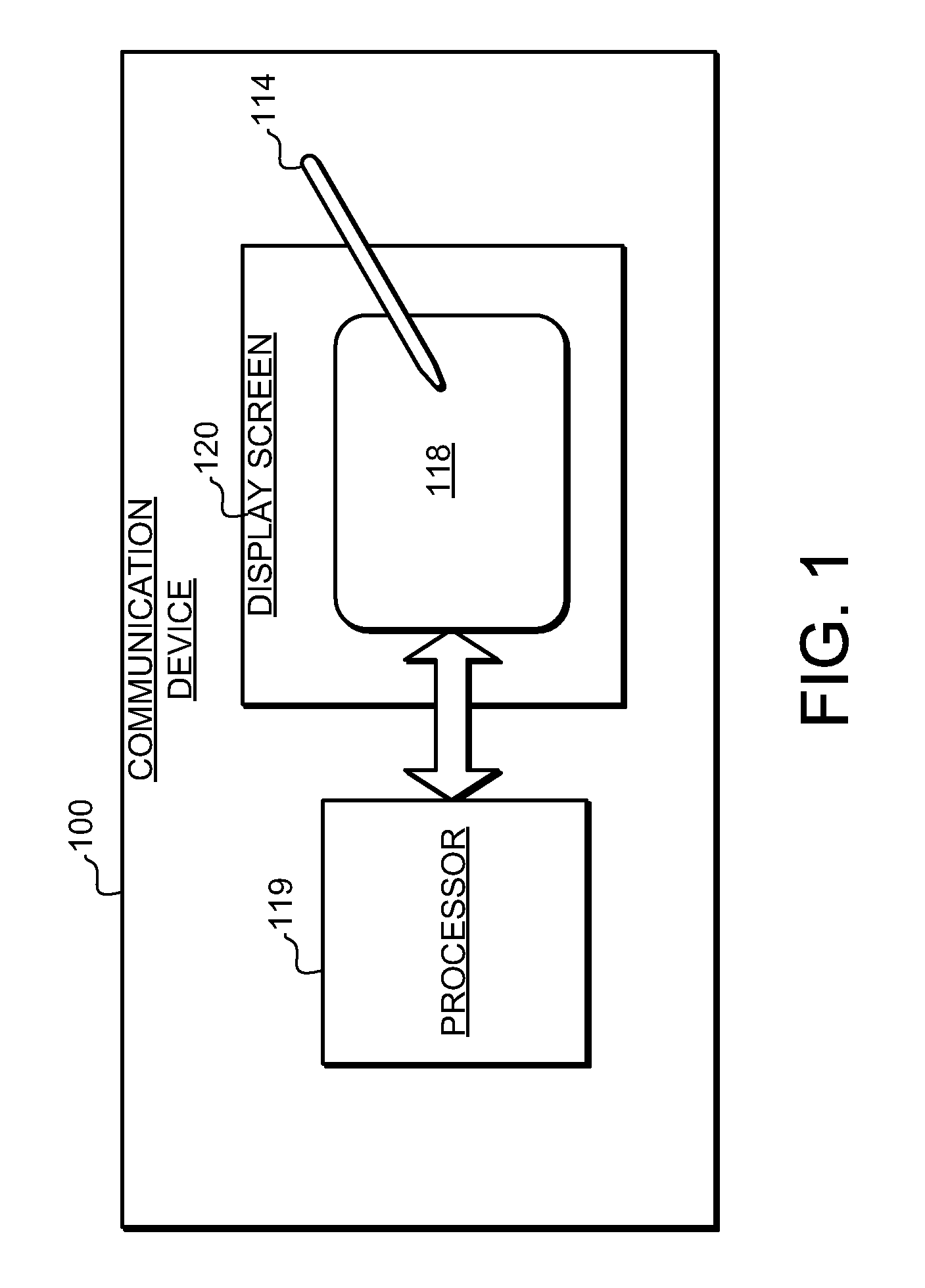
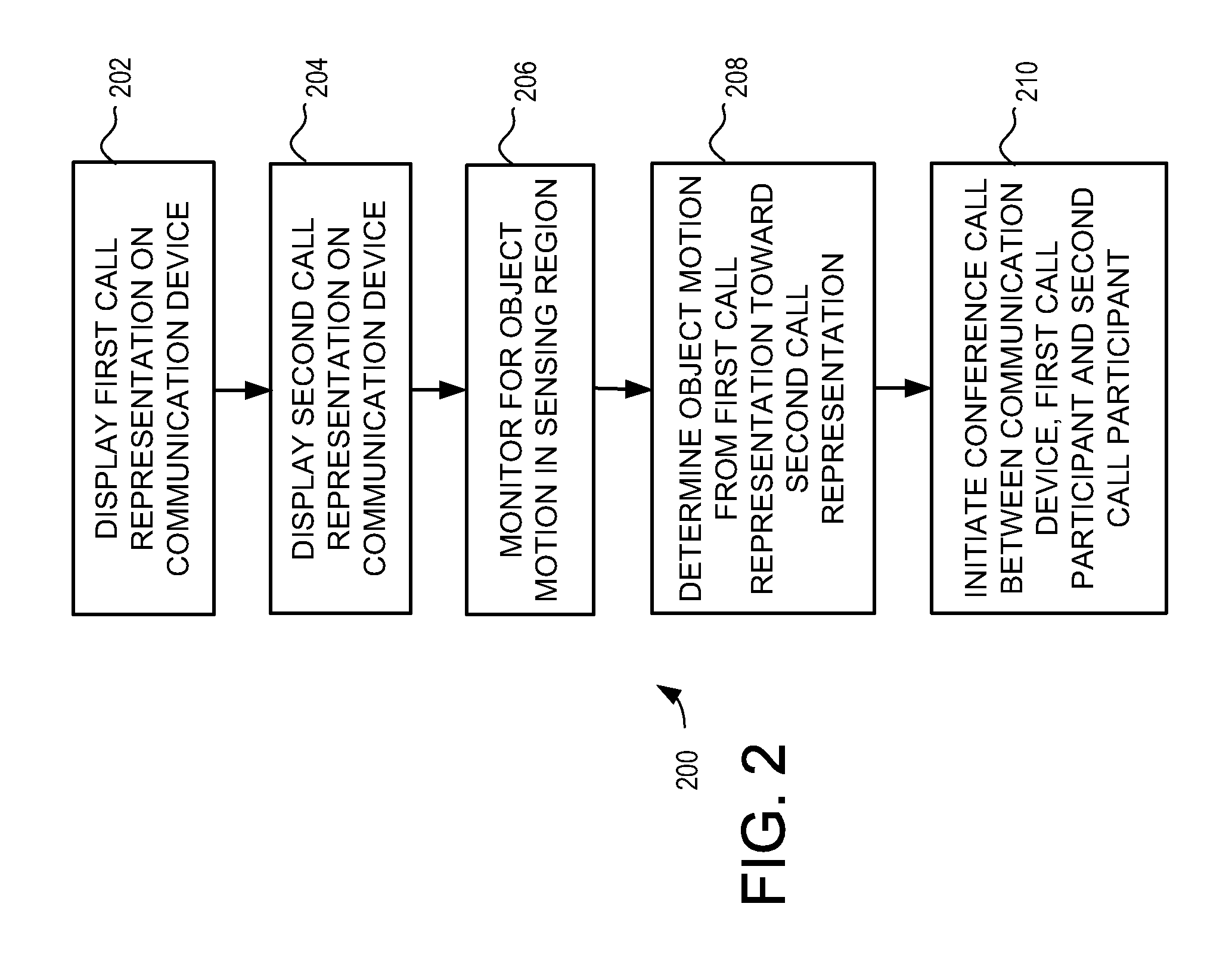
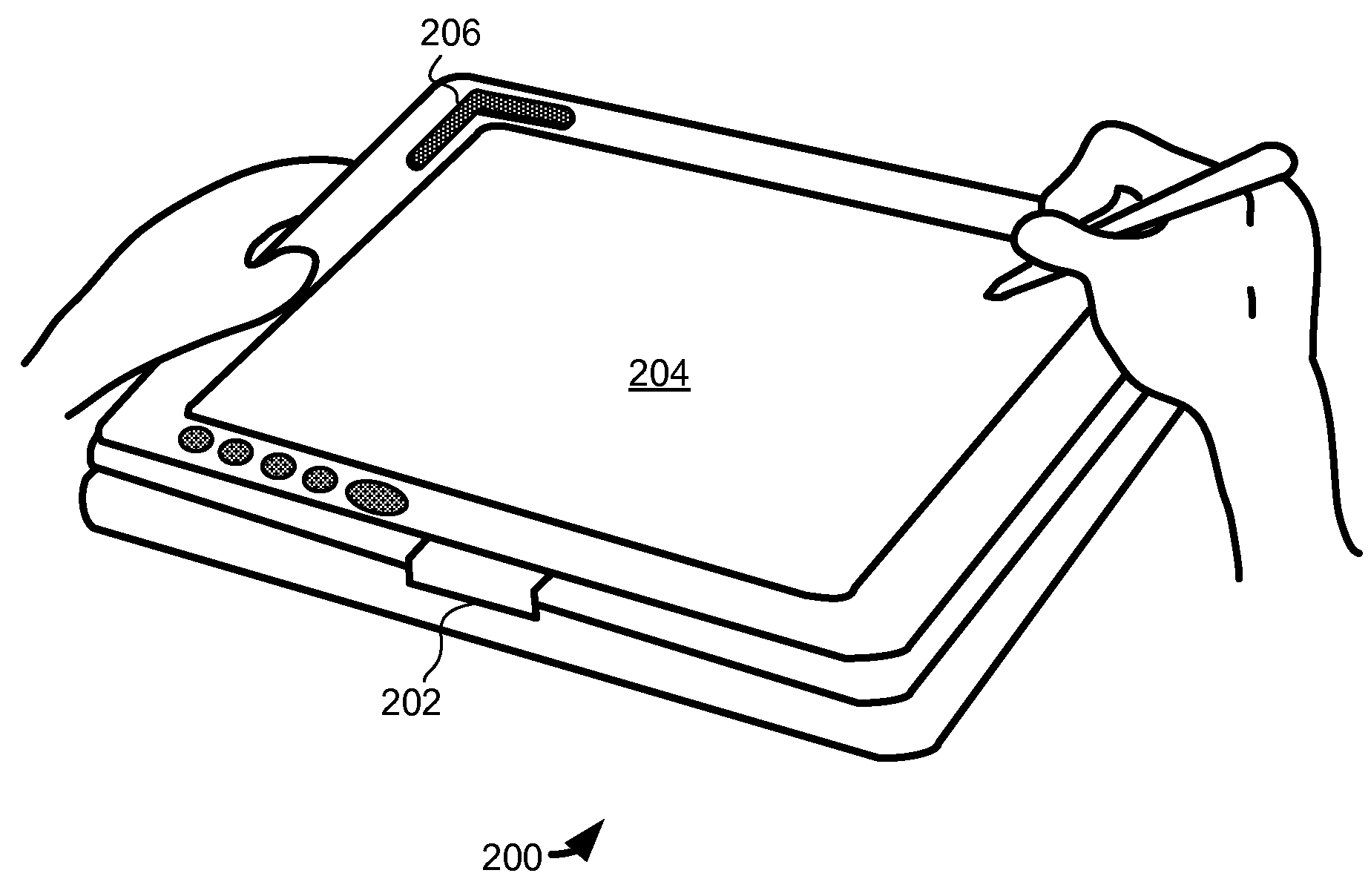
Handheld communication device and method for conference call initiation
InactiveUS20090054107A1Facilitate initiationImproved user interface functionalityServices signallingSubstation equipmentProximity sensorObject motion
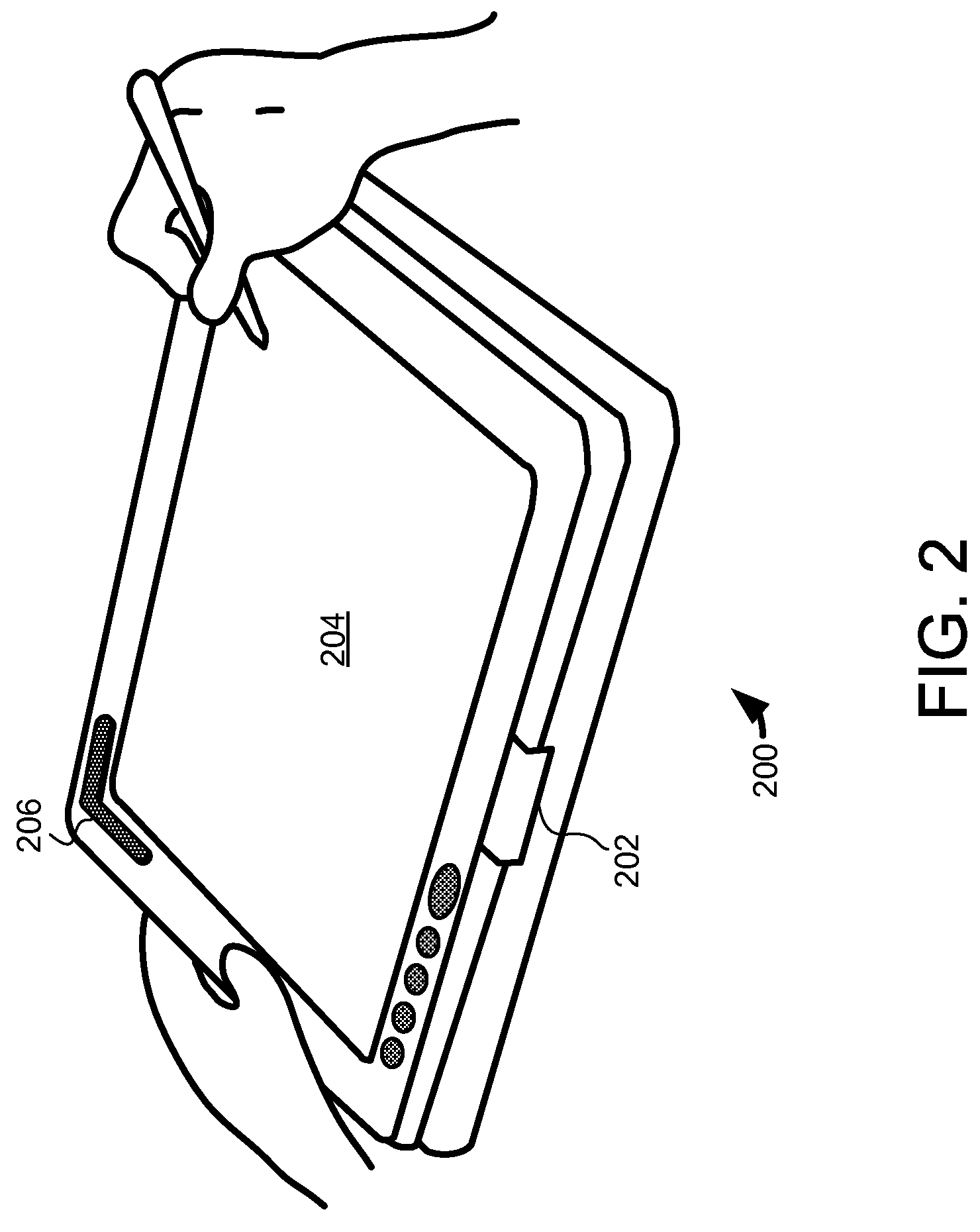
A handheld communication device and method is provided that facilitates improved device usability. The handheld communication device and method uses a touch screen interface, where the touch screen comprises a proximity sensor adapted to detect object motion in a sensing region, a display screen overlapping the sensing region, and a processor. The touch screen is adapted to provide user interface functionality on the communication device by facilitating the display of user interface elements and the selection and activation of corresponding functions. The handheld communication device and method are configured to display representations of calls on the display screen, and are further configured to initiate conference calls responsive to sensed object motion beginning at a first call representation and continuing toward a second call representation. Thus, a user can initiate a conference call with a relatively simple and easy to perform gesture on the touch screen.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Proximity sensor and method for indicating a display orientation change
InactiveUS7884807B2Easy to change directionsEasily causedTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsProximity sensorObject motion
A proximity sensor device and method is provided that facilitates orientation changes in displays. The proximity sensor device and method provide a user with the ability to indicate an orientation change in a display using the sensing region of a proximity sensor device as a user interface. In one specific embodiment, proximity sensor device is implemented to indicate an orientation change in a first way responsive to detected object motion along the sensing region in a first direction, and is further implemented to indicate an orientation change in a second way responsive to detected object motion along the sensing region in a second direction. Thus, a user can cause orientation changes of different ways through the use of object motions in different directions along the sensing region.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
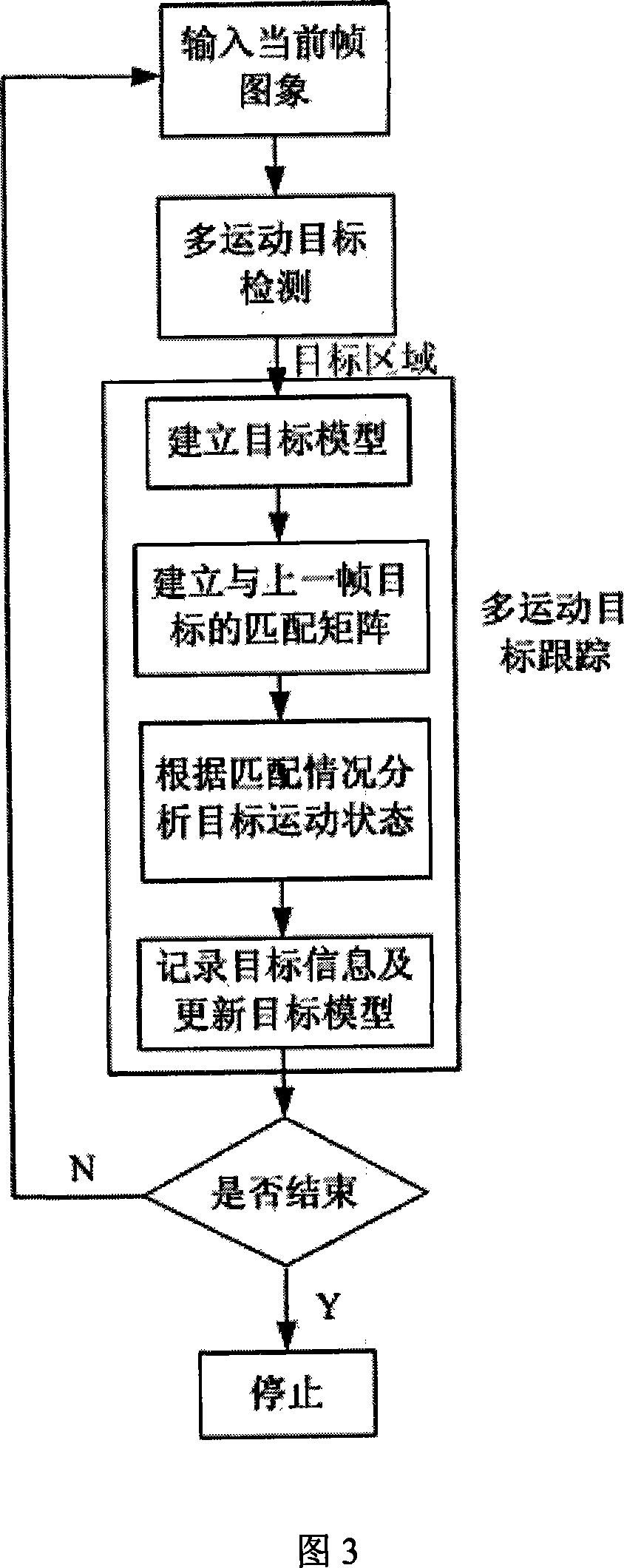
Moving object detecting and tracing method in complex scene
InactiveCN101141633AImprove accuracySuppress interferenceImage analysisClosed circuit television systemsObject motionVisual monitoring
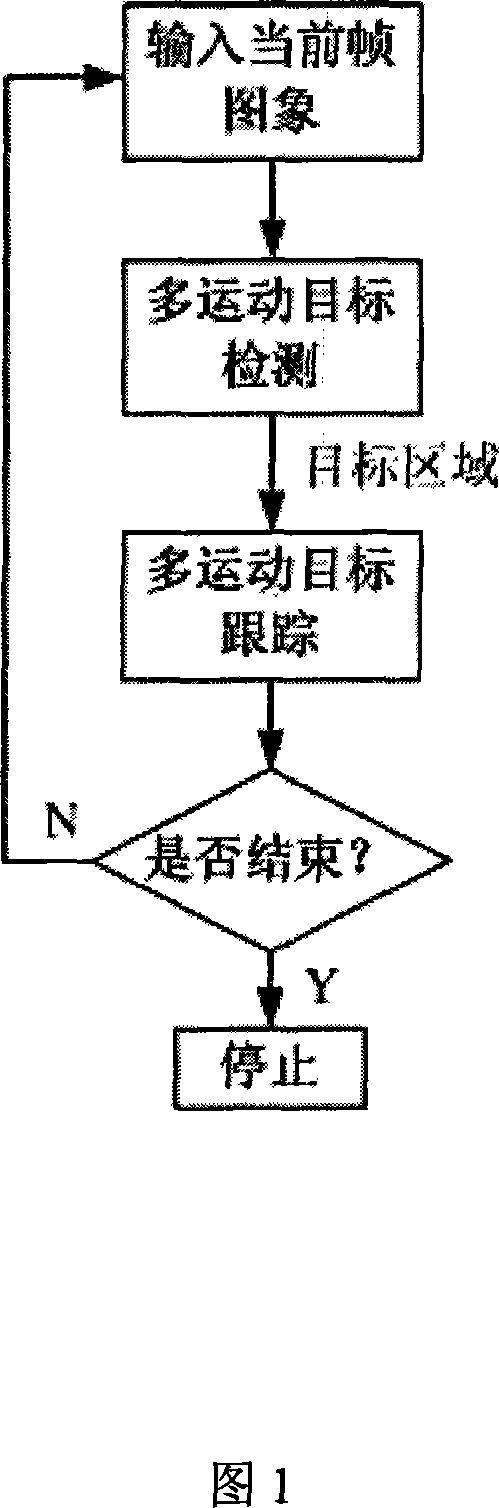
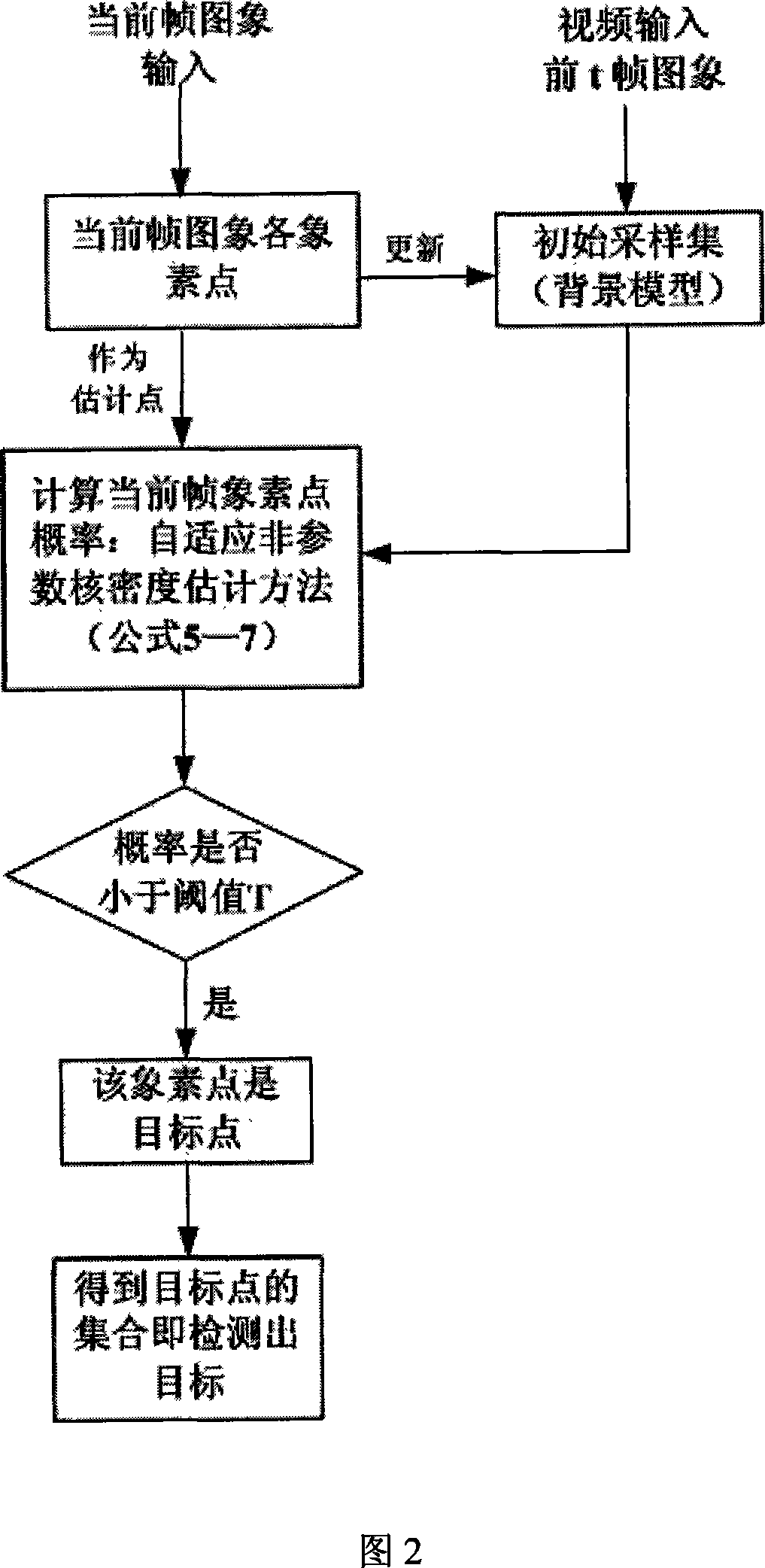
The present invention discloses method for moving target detection and tracking in a complex scene. The method comprises two steps of multiple moving target detection and multiple moving target tracking: in the multiple moving target detection, a background model based on self adapting nonparametric kernel density estimation is established with the aim at the monitoring of the complex scene, therefore the disturbance of the movement of tiny objects can be effectively suppressed, the target shadow is eliminated, and the multiple moving target is detected; in the multiple moving target tracking, the target model is established, the moving state of the target is confirmed through ''matching matrix'', and corresponding tracking strategy is adopted according to the different movement condition of the target. Target information is ''recovered'' through the probabilistic reasoning method, and the target screening degree of the target is analyzed with the aim at the problem that multiple targets screen mutually. The algorithm of the present invention can well realize the moving target tracking, obtains the trace of the moving target, and has good real time and ability of adapting to the environmental variation. The present invention has wide application range and high accuracy, therefore being a core method for intelligent vision monitoring with versatility.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Proximity sensor and method for indicating a display orientation change
InactiveUS20080284738A1Easy to change directionsEasily causedCathode-ray tube indicatorsDetails for portable computersProximity sensorObject motion
A proximity sensor device and method is provided that facilitates orientation changes in displays. The proximity sensor device and method provide a user with the ability to indicate an orientation change in a display using the sensing region of a proximity sensor device as a user interface. In one specific embodiment, proximity sensor device is implemented to indicate an orientation change in a first way responsive to detected object motion along the sensing region in a first direction, and is further implemented to indicate an orientation change in a second way responsive to detected object motion along the sensing region in a second direction. Thus, a user can cause orientation changes of different ways through the use of object motions in different directions along the sensing region.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
Vehicular image sensing system
Owner:MAGNA ELECTRONICS INC
High dynamic range & depth of field depth camera
ActiveUS20130201288A1Add depthImprove dynamic rangeElectromagnetic wave reradiationSteroscopic systemsObject motionFrame time
In order to maximize the dynamic range and depth of field for a depth camera used in a time of flight system, the light source is modulated at a plurality of different frequencies, a plurality of different peak optical powers, a plurality of integration subperiods, a plurality of lens foci, aperture and zoom settings during each camera frame time. The different sets of settings effectively create subrange volumes of interest within a larger aggregate volume of interest, each having their own frequency, peak optical power, lens aperture, lens zoom and lens focus products consistent with the distance, object reflectivity, object motion, field of view, etc. requirements of various ranging applications.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
Proximity sensor device and method with improved indication of adjustment
InactiveUS20070262951A1Improve usabilityEasy to adjustCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingProximity sensorElectronic systems
A proximity sensor device and method is provided that facilitates improved system usability. Specifically, the proximity sensor device and method provide the ability for a user to easily cause adjustments in an electronic system using a proximity sensor device as a user interface. For example, it can be used to facilitate user interface navigation, such as scrolling. As another example, it can be used to facilitate value adjustments, such as changing a device parameter. To facilitate adjustment, the embodiments of the present invention provide a proximity sensor device that is adapted to indicate adjustment in a first way responsive to object motion in both of two opposite directions along a path proximate the touch sensor device. This facilitates use of the proximity sensor device by a user to indicate adjustments to an electronic device, and is particularly useful for indicating continuing adjustments.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Video surveillance using stationary-dynamic camera assemblies for wide-area video surveillance and allow for selective focus-of-attention
InactiveUS20060203090A1Wide-area coverageSelective focus-of-attentionCharacter and pattern recognitionColor television detailsVideo monitoringObject motion
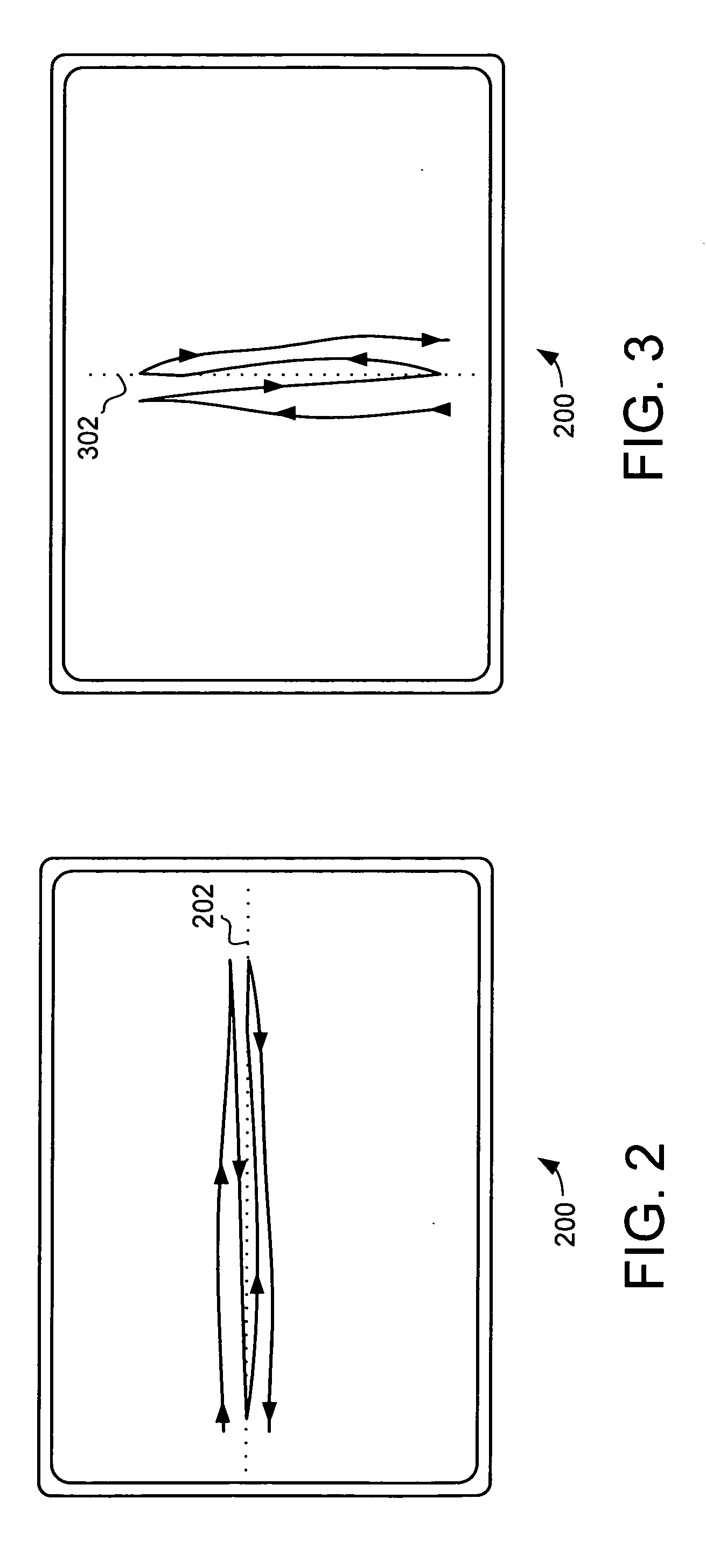
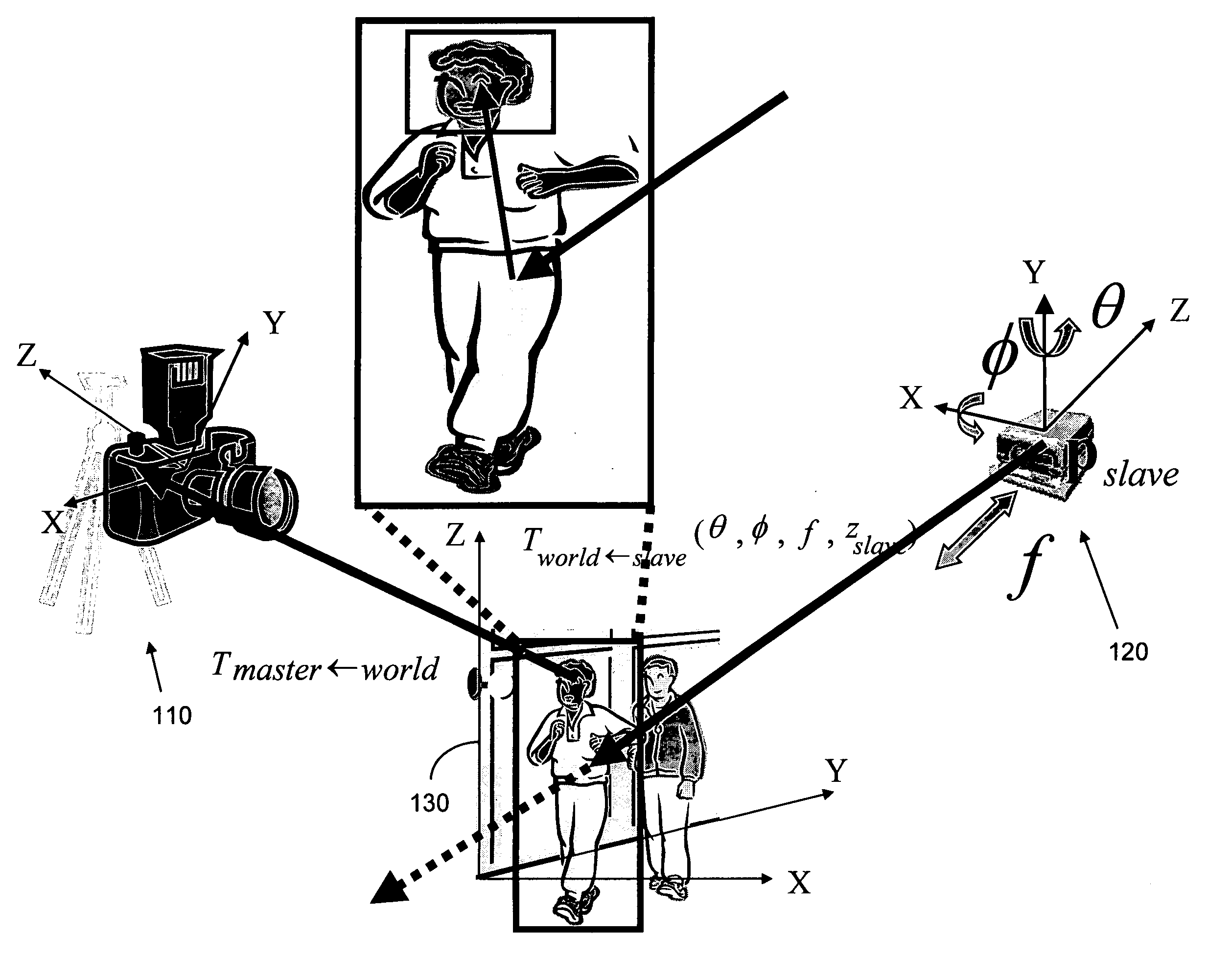
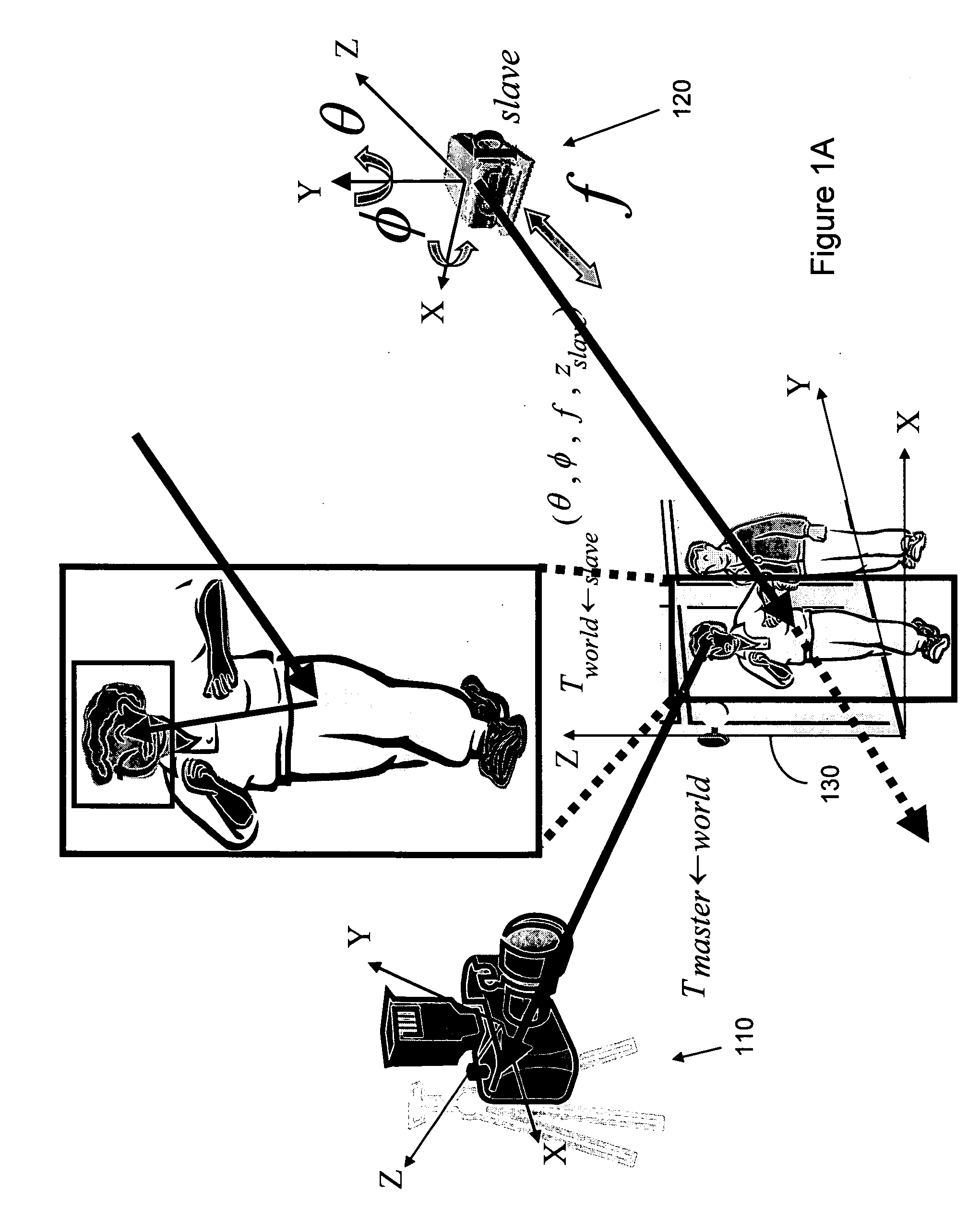
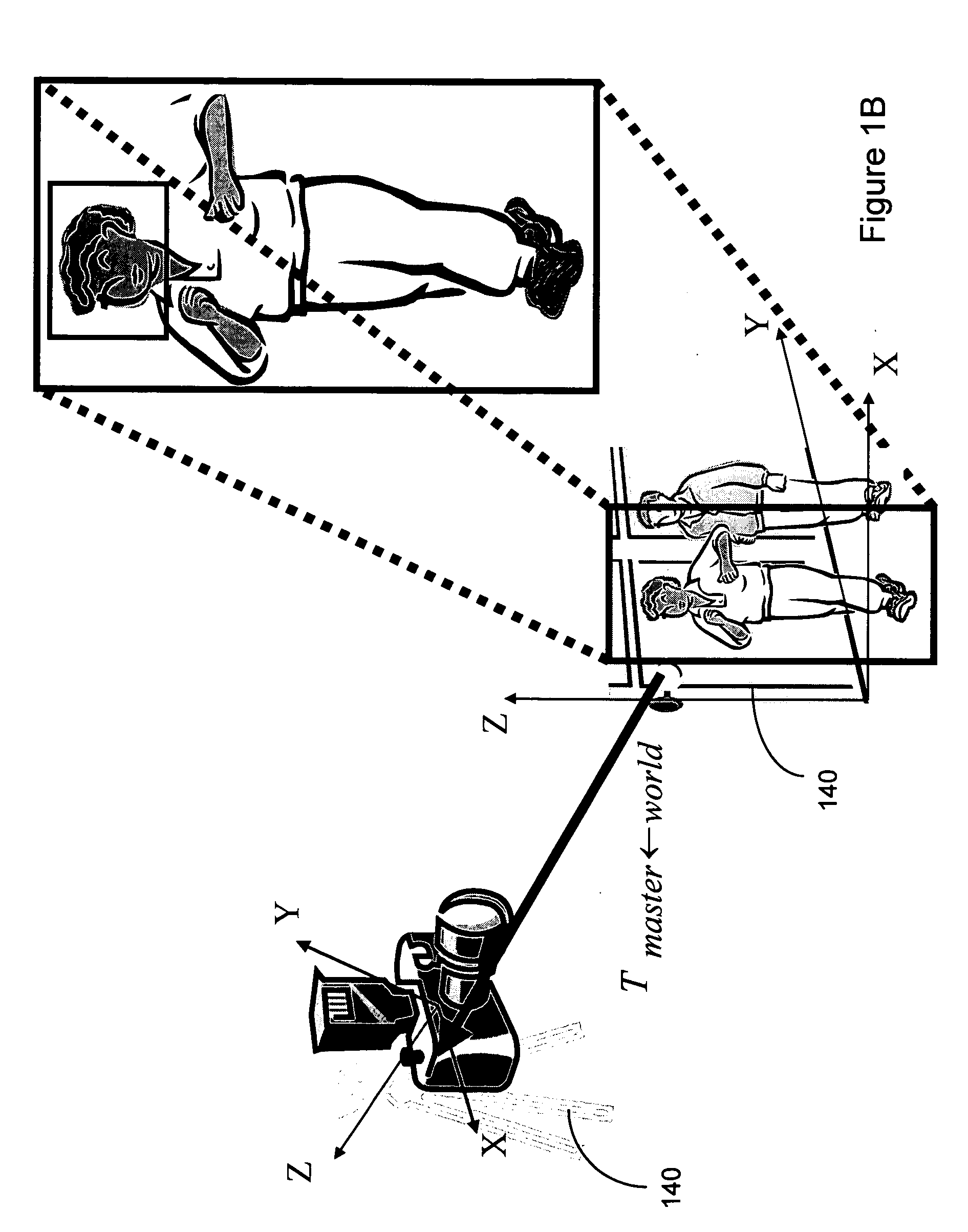
A video surveillance system includes multiple video cameras. The surveillance system is configured with an arrangement to separate the surveillance functions and assign different surveillance functions to different cameras. A master camera is assigned the surveillance of large area surveillance and tracking of object movement while one or more slave cameras are provided to dynamically rotate and adjust focus to obtain clear image of the moving objects as detected by the master camera. Algorithms to adjust the focus-of-attention are disclosed to effectively carry out the tasks by a slave camera under the command of a master camera to obtain images of a moving object with clear feature detections.
Owner:PROXIMEX CORP
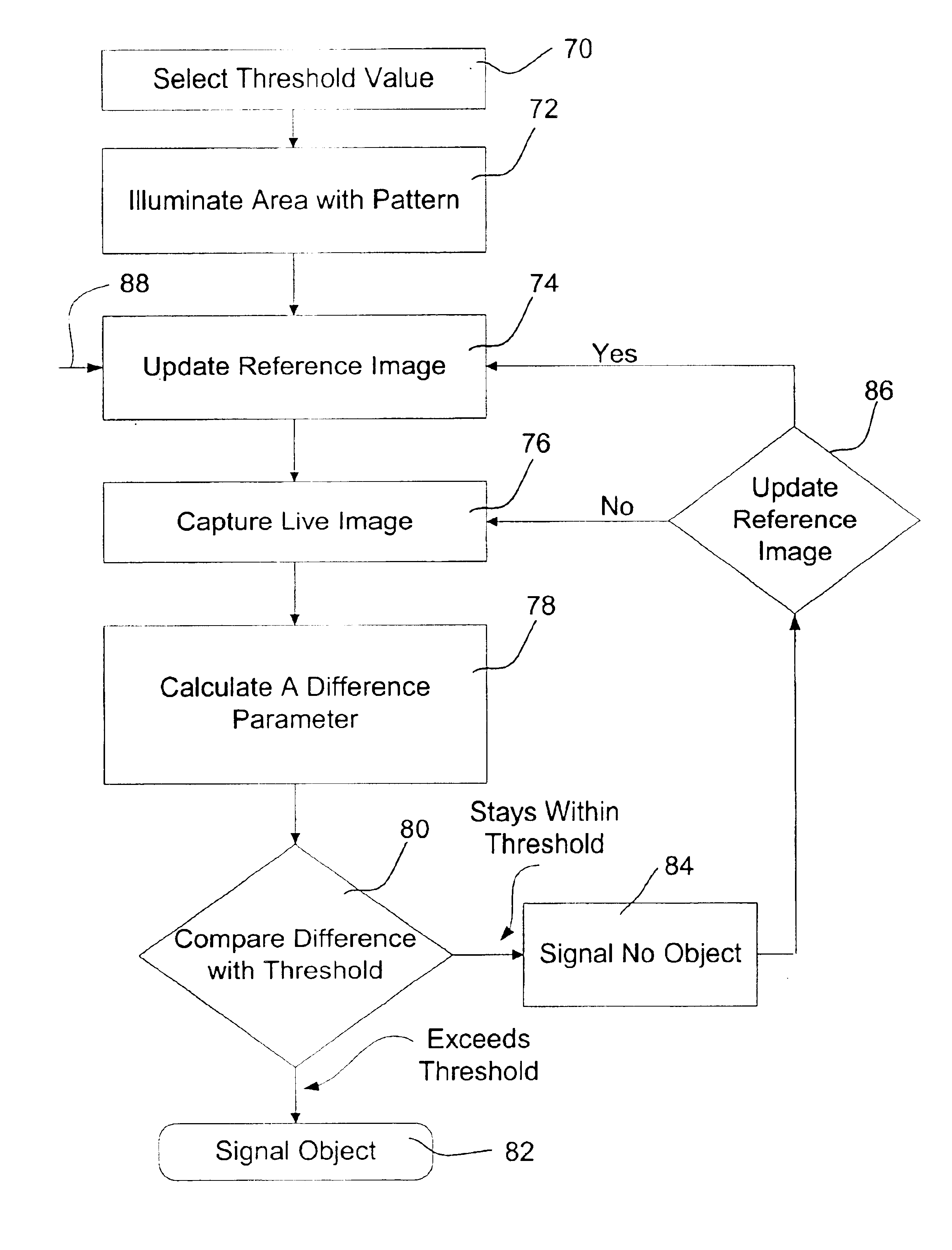
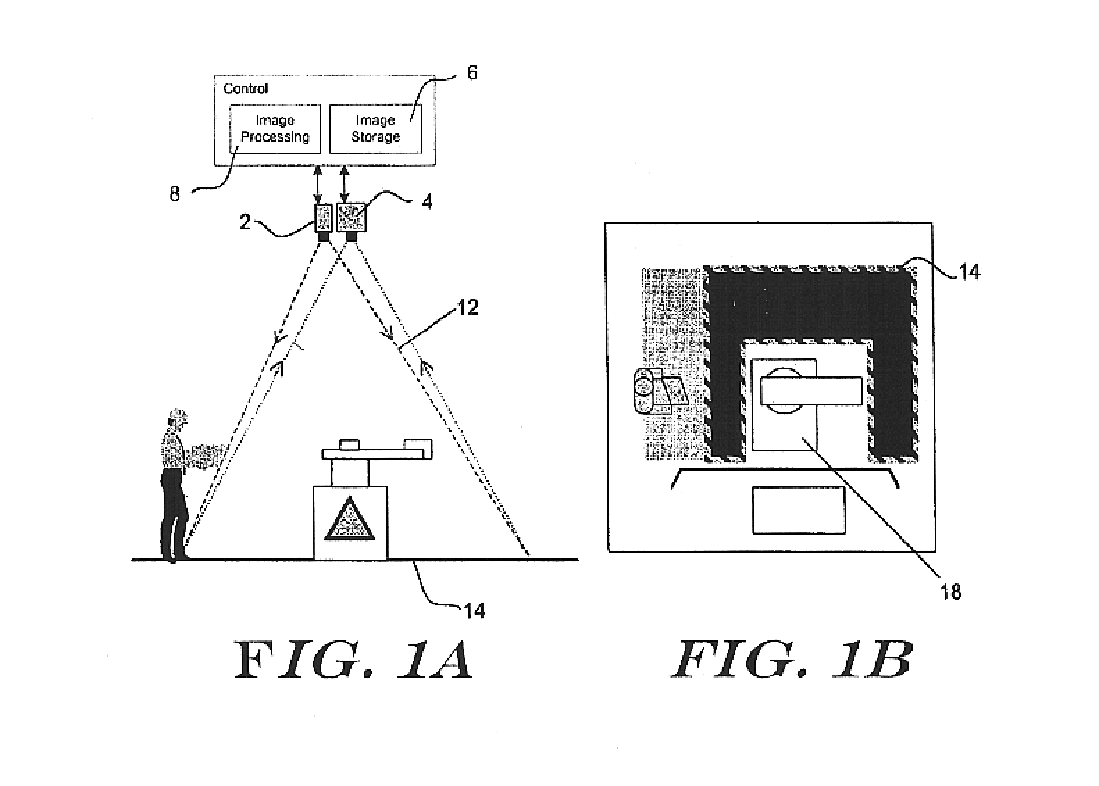
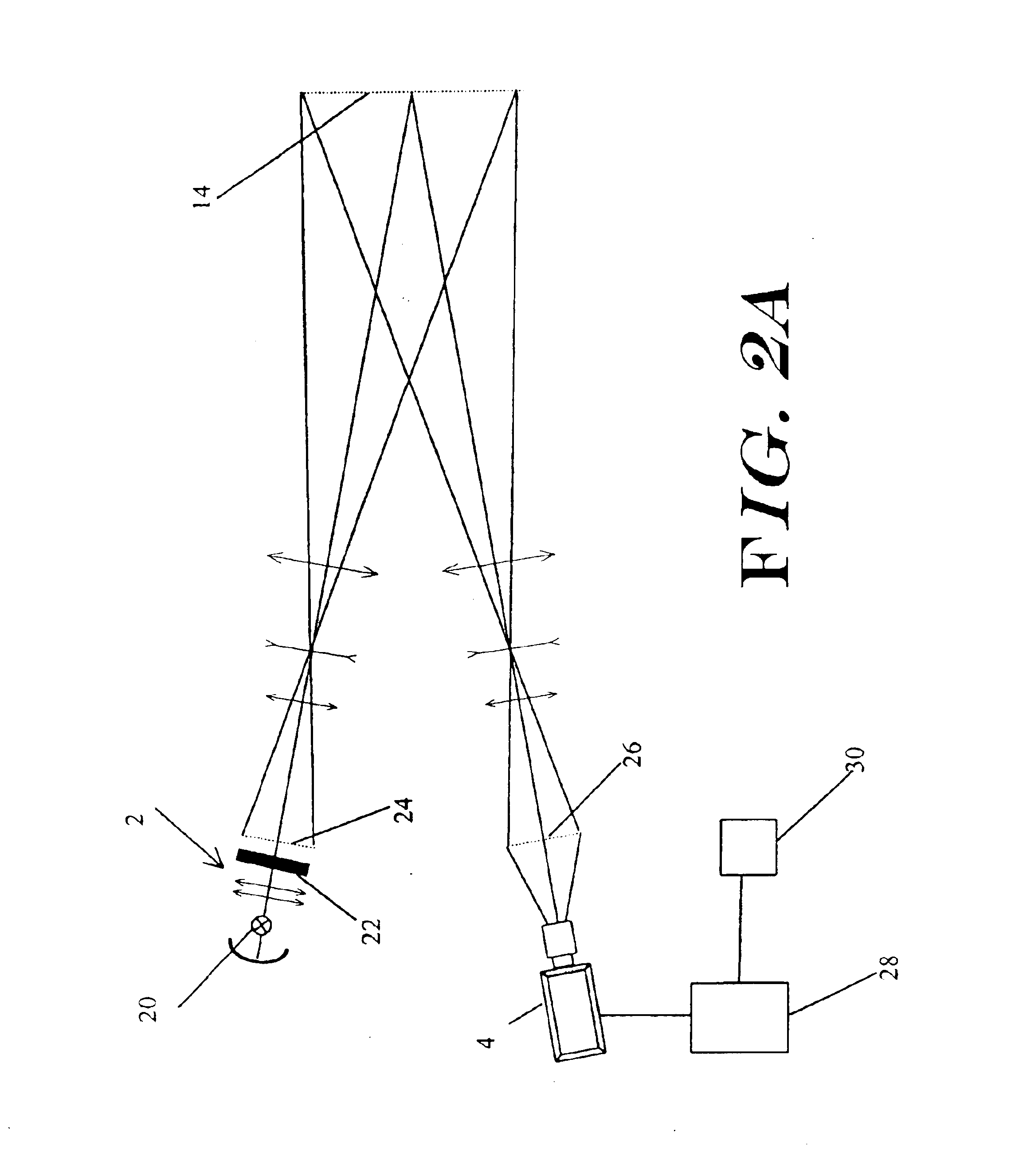
Method and apparatus for detecting objects
InactiveUS6841780B2Less effect efficacyHighly effectiveRadiation pyrometryImage analysisObject motionComputer science
An object detection system is provided that projects one or more patterns onto a monitored area, captures one or more live images of the monitored area, and detects objects that enter the monitored area by detecting changes in the one or more patterns in the live images. Such an object detection system may be less susceptible to dynamic lighting conditions, and more sensitive to object motion and / or presence.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Integrated sensor and video motion analysis method
ActiveUS20150324636A1Conserve camera powerConserve video memoryTelevision system detailsImage enhancementObject motionSensor fusion
A method that integrates sensor data and video analysis to analyze object motion. Motion capture elements generate motion sensor data for objects of interest, and cameras generate video of these objects. Sensor data and video data are synchronized in time and aligned in space on a common coordinate system. Sensor fusion is used to generate motion metrics from the combined and integrated sensor data and video data. Integration of sensor data and video data supports robust detection of events, generation of video highlight reels or epic fail reels augmented with metrics that show interesting activity, and calculation of metrics that exceed the individual capabilities of either sensors or video analysis alone.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
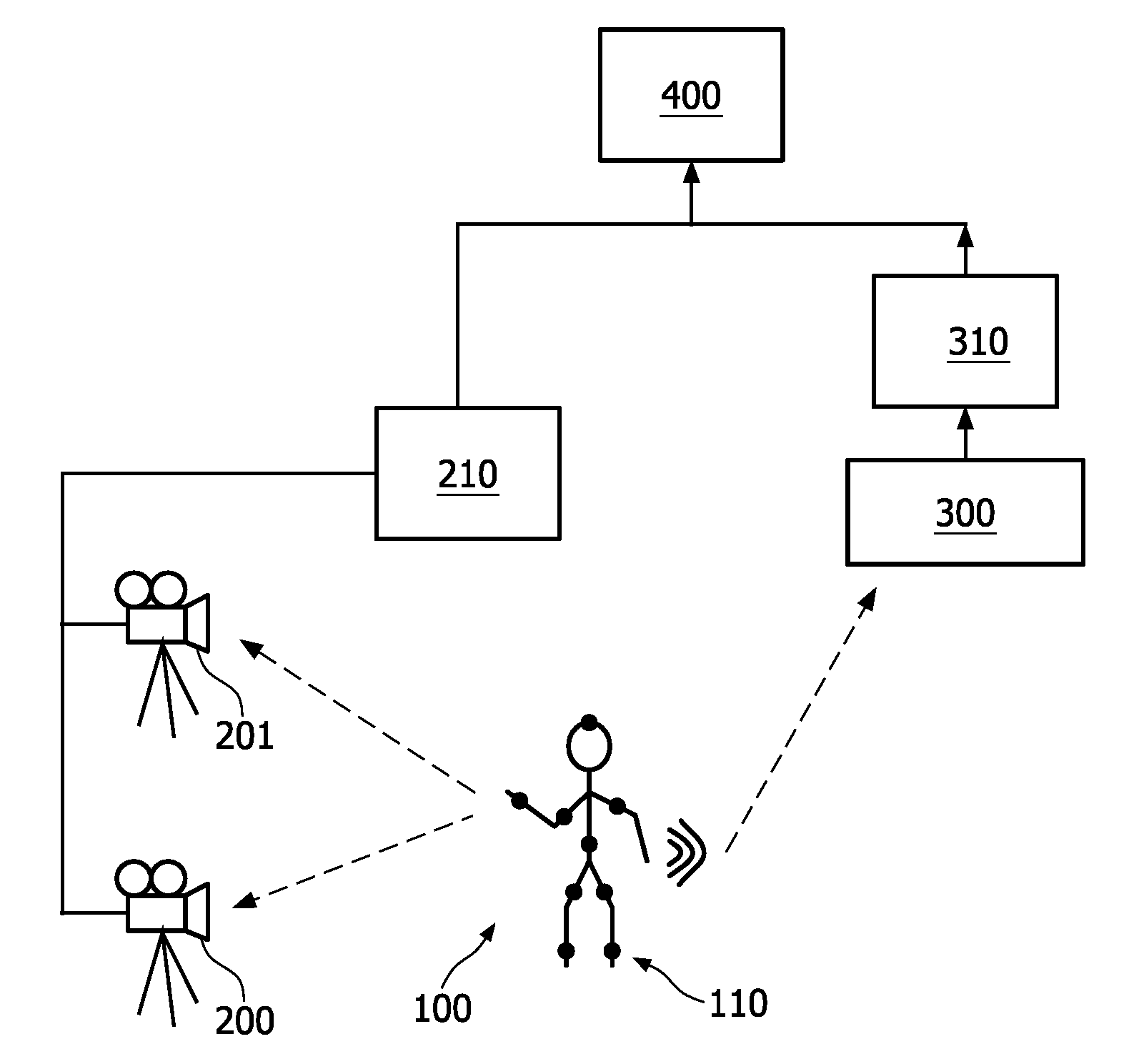
Intuitive multiple degrees of freedom portable control device
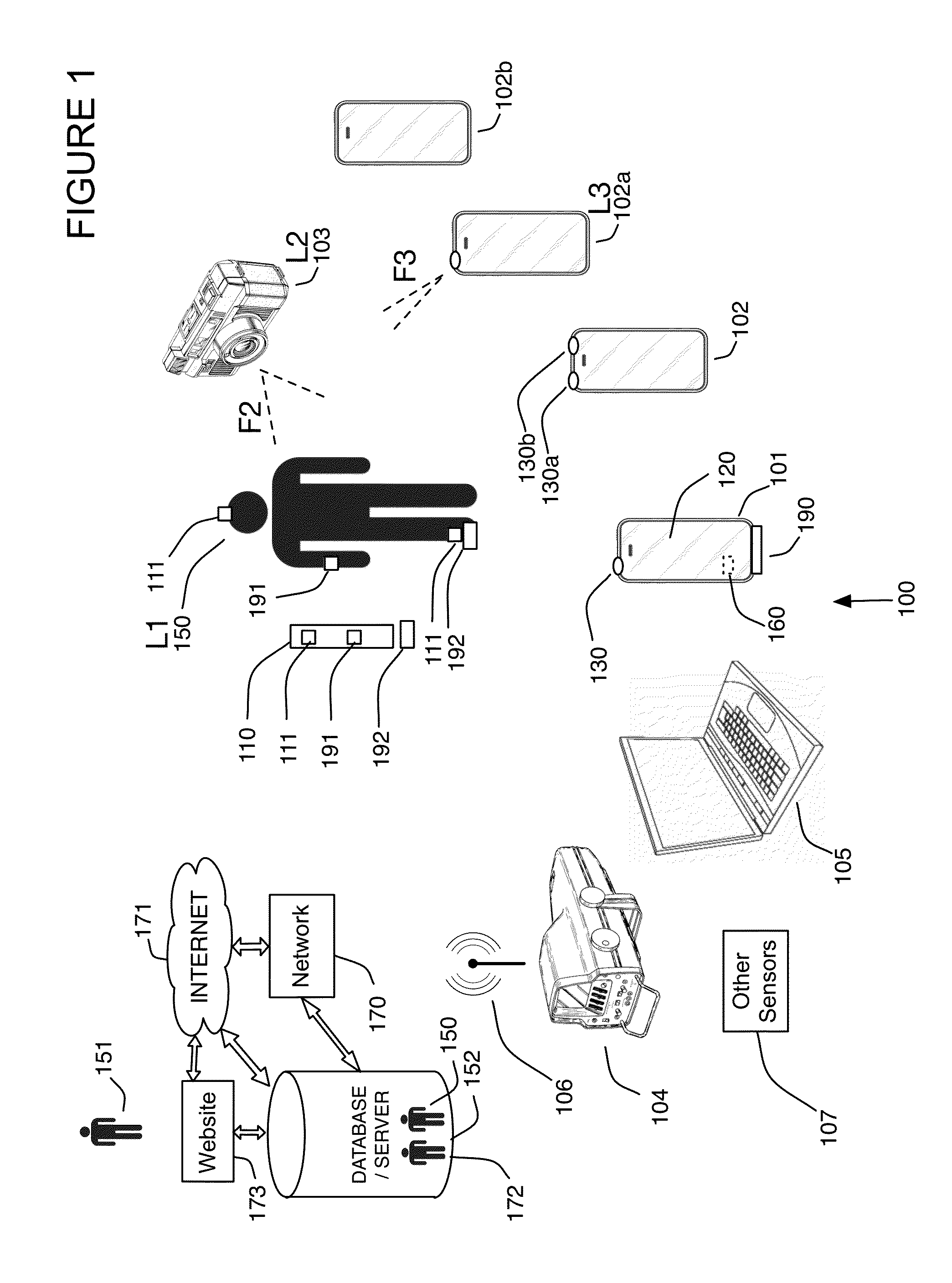
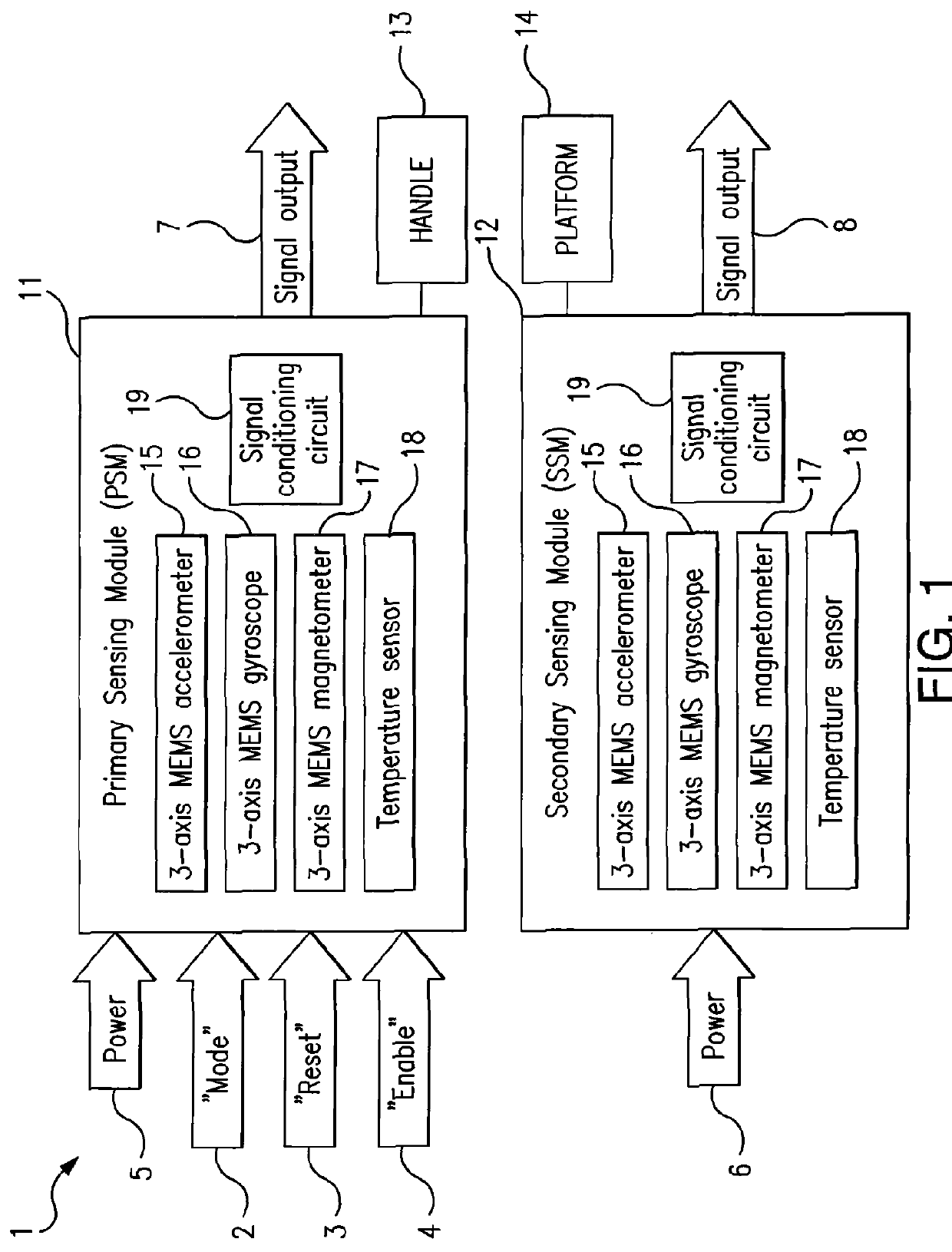
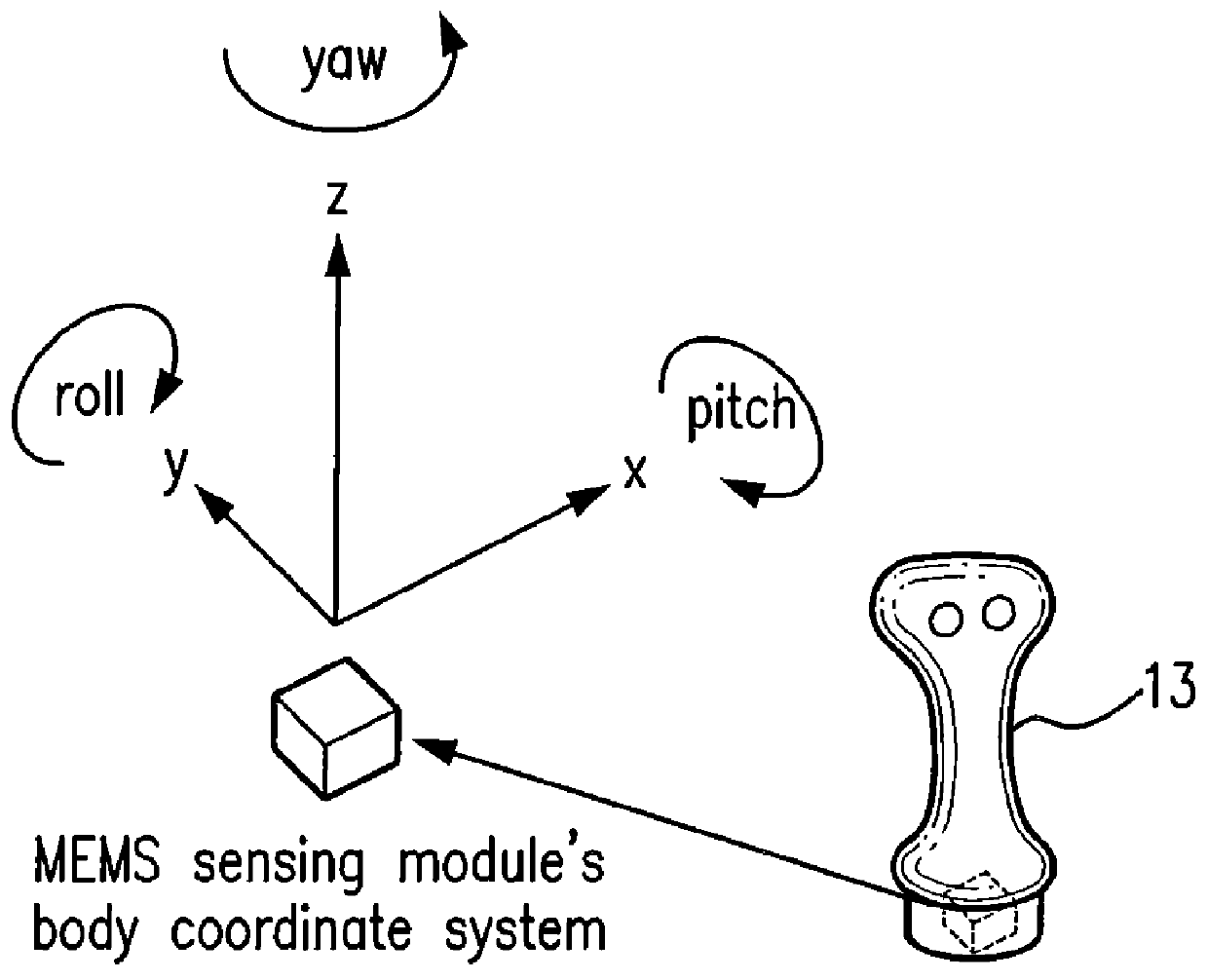
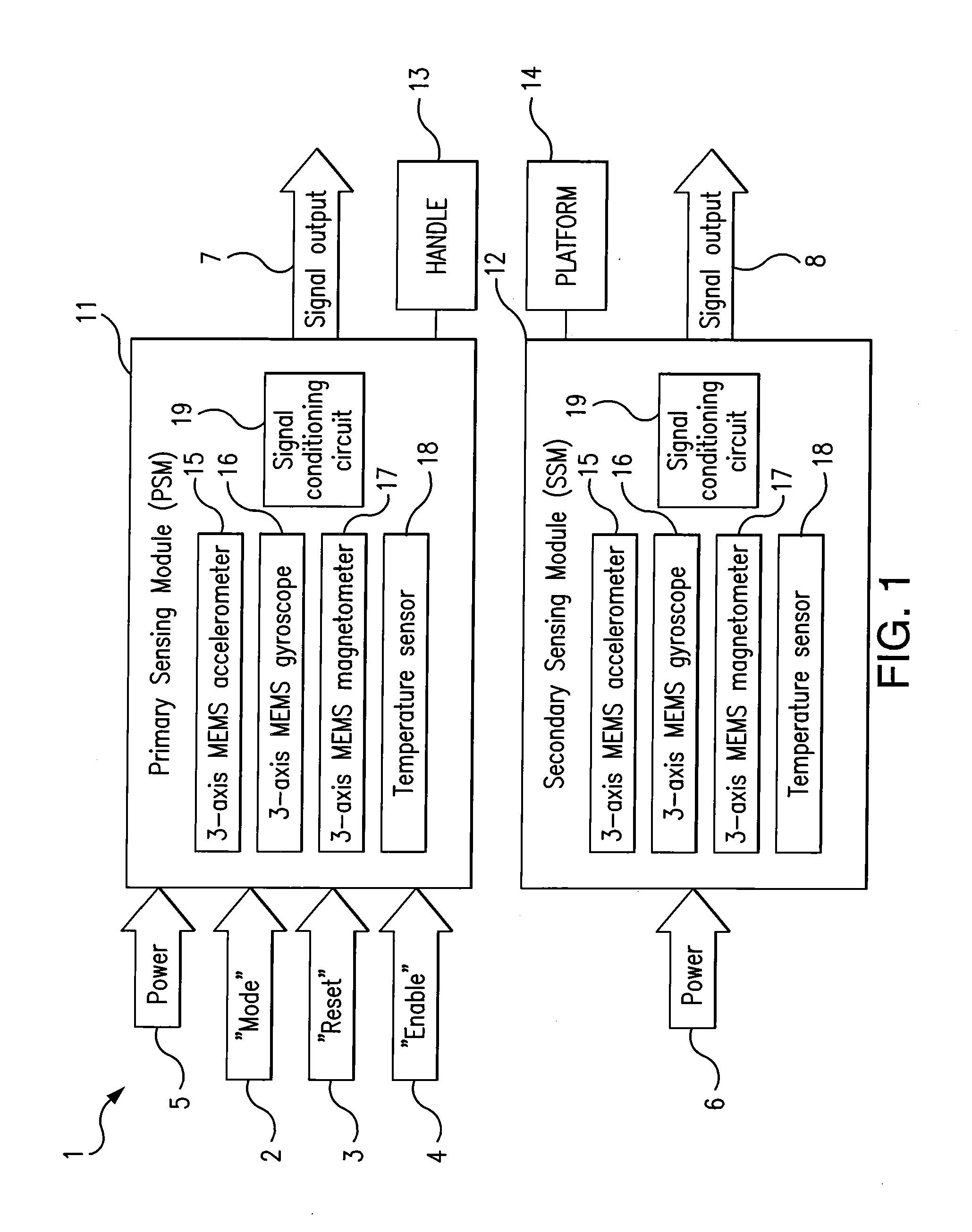
A control device for a vehicle or mechanism includes a portable displacement controller which permits a non-technical user to achieve effective control of the vehicle or mechanism, by moving the portable displacement controller intuitively with little learning effort. A first sensing device, attached to the displacement controller, detects the user's controlling motion. A second sensing device, attached to the object being controlled, detects motion thereof. An interface device receives signals from the sensing devices, processes those signals to determine relative motion of the controlling motion and the object's motion and outputs a control signal in accordance with the processed signals. The sensing devices each detect motion in six degrees of freedom; the sensing devices each include a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. In specific embodiments, the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers include micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SYST
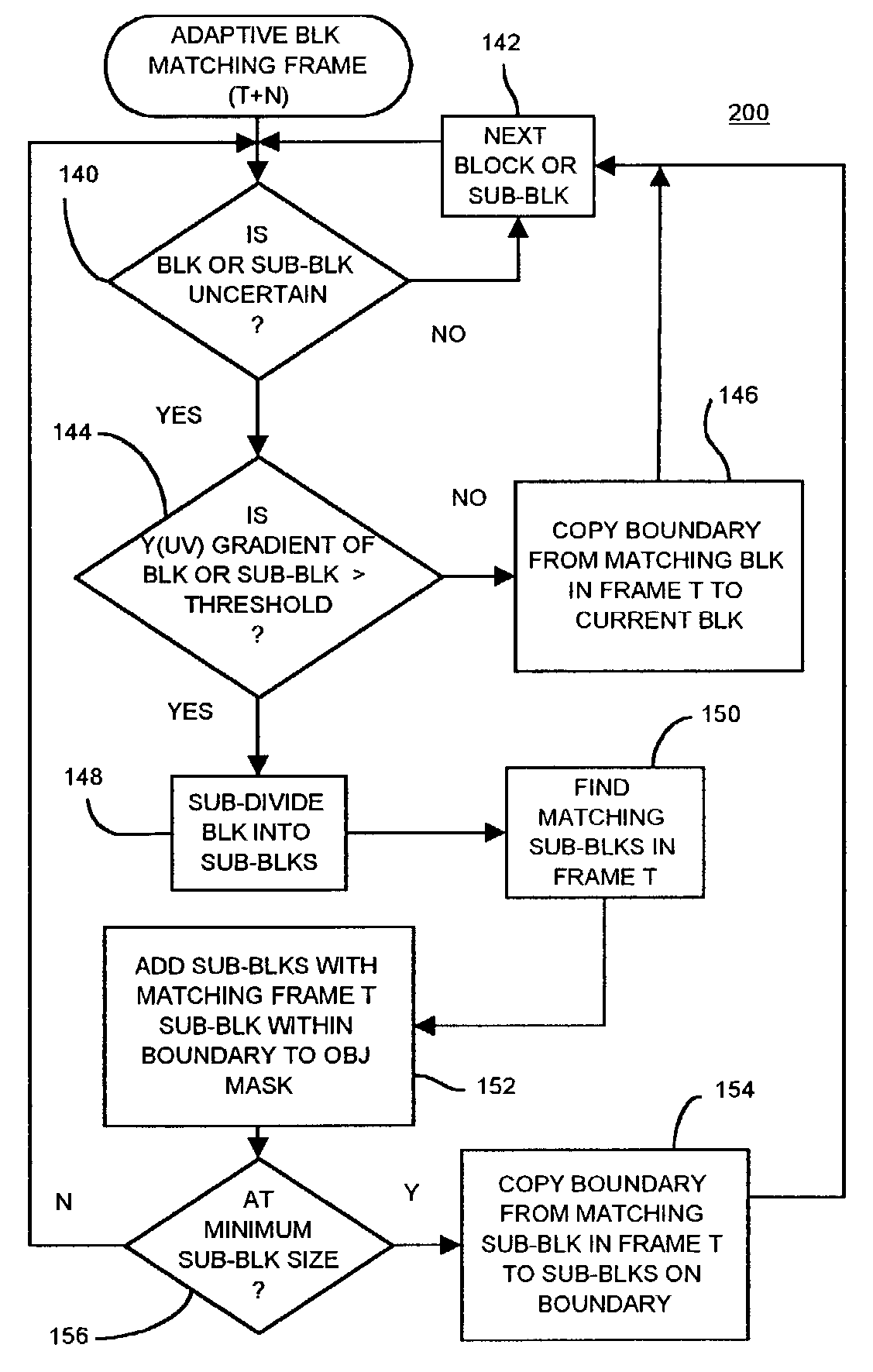
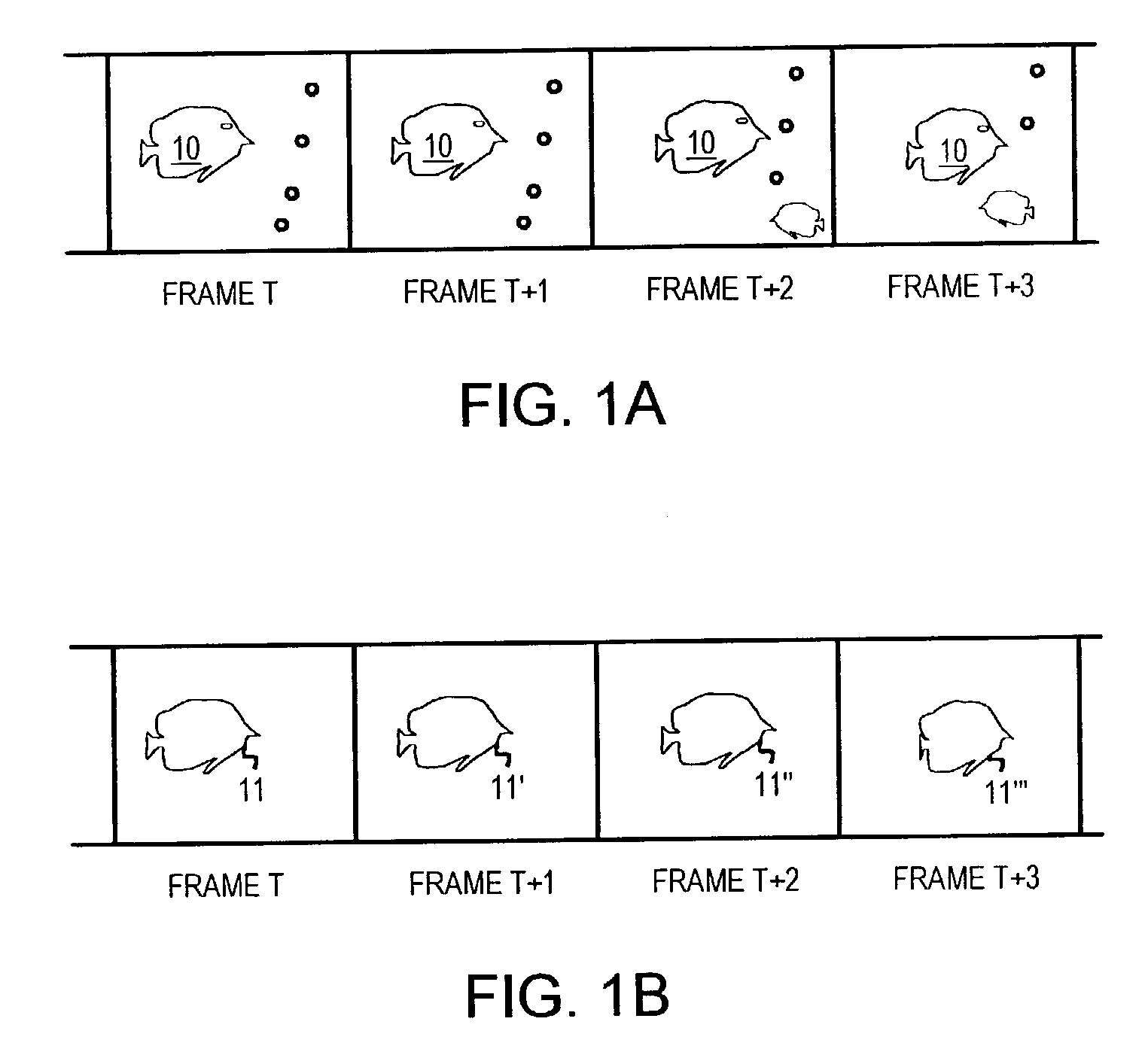
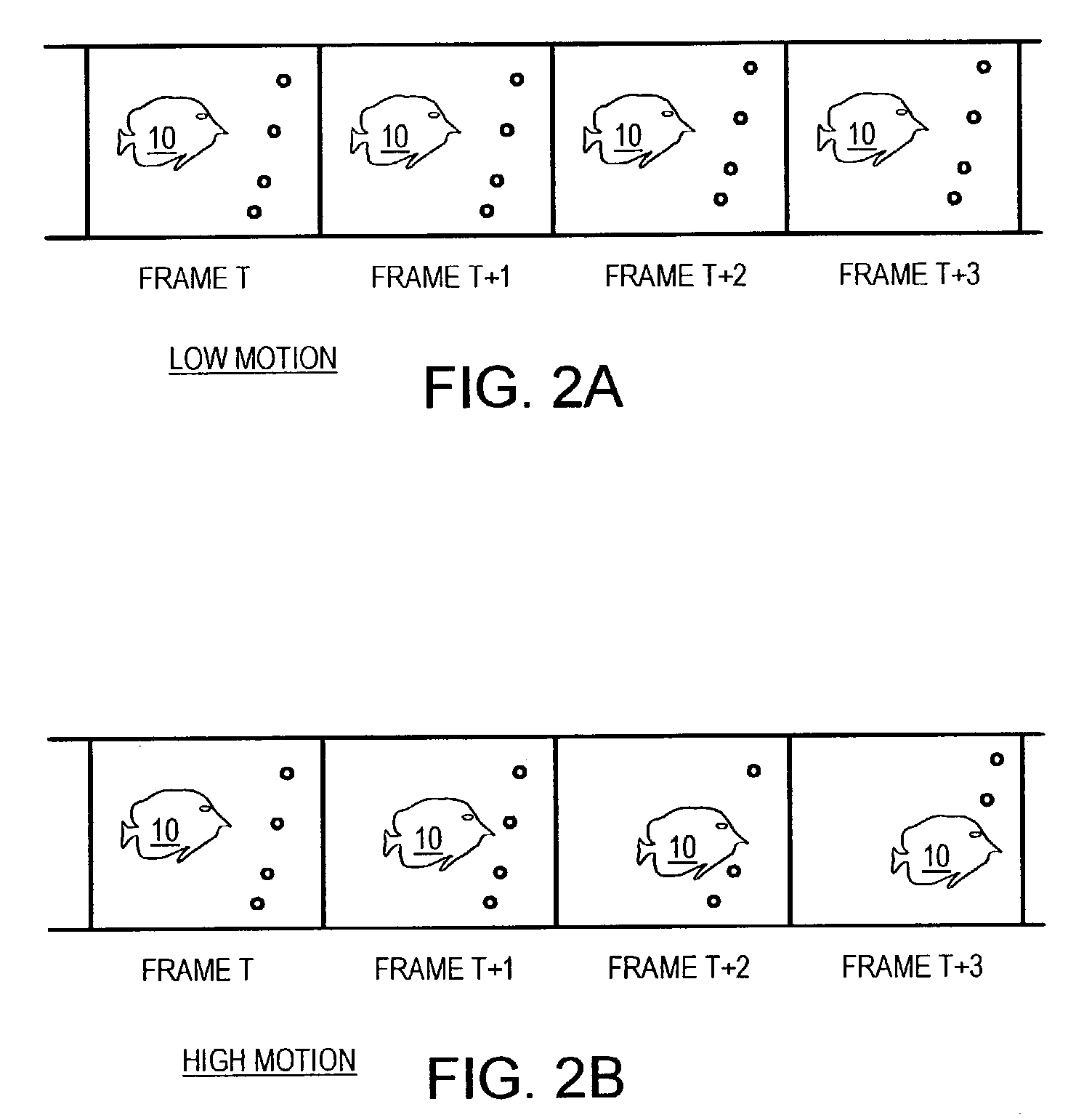
Object tracking using adaptive block-size matching along object boundary and frame-skipping when object motion is low
InactiveUS7095786B1Image analysisPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesObject motionVideo sequence
An object in a video sequence of frames is tracked by object masks generated for frames in the sequence. Macroblocks are motion compensated. Blocks matching entirely within a prior-frame object mask are used to generate an average object motion. When the average motion is below a motion threshold, frames are skipped at larger intervals, but more frequent frames are processed when high motion occurs. When the macroblock best matches a prior-frame block that has the object's boundary passing through the block, the macroblock is uncertain and is sub-divided into smaller sub-blocks that are again motion compensated. Sub-blocks matching blocks within the object mask in the base frame are added to the new object mask for the current frame while sub-blocks matching a block containing the object boundary are uncertain and can again be sub-divided to further refine the object boundary. Frame skipping and adaptive-size blocks on the object boundary reduce computational load.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES I LLC
Vehicle control based on perception uncertainty
InactiveUS20130197736A1Uncertainty in valueAutonomous decision making processDistance measurementObject motionPerception system
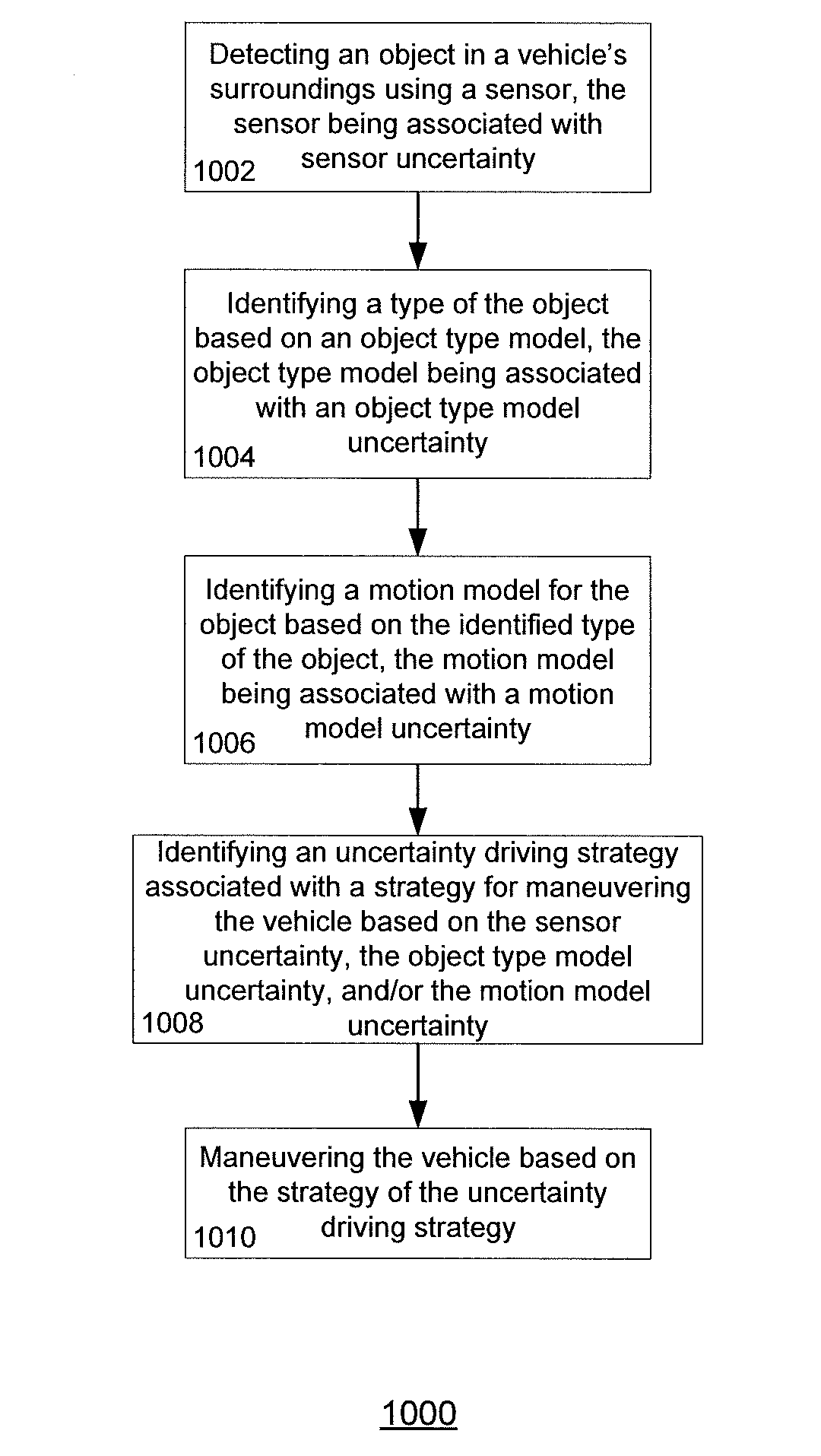
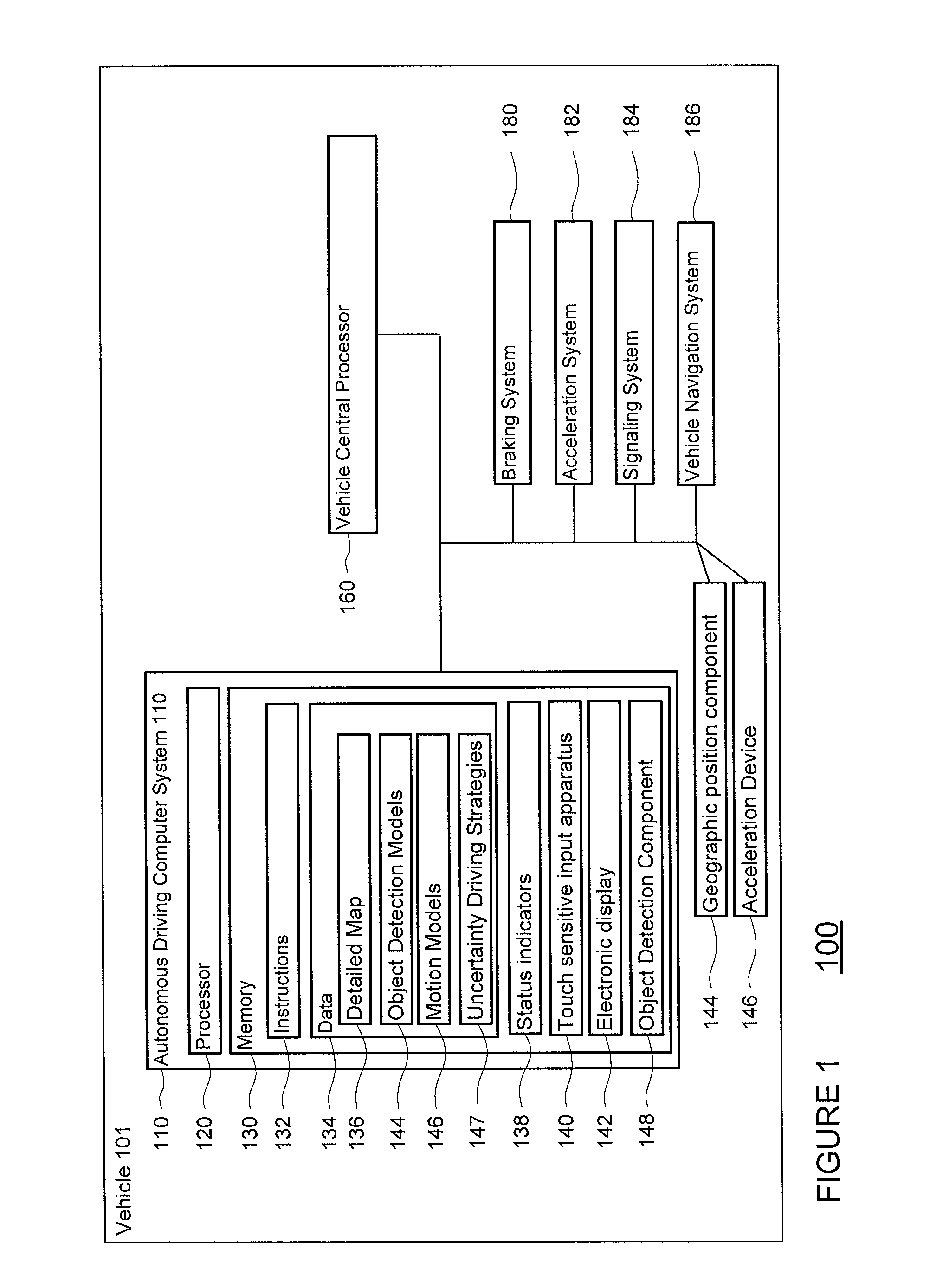
Aspects of the disclosure relate generally to maneuvering autonomous vehicles. Specifically, the vehicle may determine the uncertainty in its perception system and use this uncertainty value to make decisions about how to maneuver the vehicle. For example, the perception system may include sensors, object type models, and object motion models, each associated with uncertainties. The sensors may be associated with uncertainties based on the sensor's range, speed, and / or shape of the sensor field. The object type models may be associated with uncertainties, for example, in whether a perceived object is of one type (such as a small car) or another type (such as a bicycle). The object motion models may also be associated with uncertainties, for example, not all objects will move exactly as they are predicted to move. These uncertainties may be used to maneuver the vehicle.
Owner:WAYMO LLC
Proximity sensor device and method with adjustment selection tabs
ActiveUS20070283263A1Avoid difficult choicesImprove usabilityFrequency-division multiplex detailsTime-division multiplexProximity sensorObject motion
A proximity sensor device and method is provided that facilitates improved usability. Specifically, the proximity sensor device and method provides the ability for a user to easily select the type of adjustment inputted by the proximity sensor device. In one embodiment, the proximity sensor device includes an adjustment region and one or more start tabs adjacent to the adjustment region. The proximity sensor also includes a processor adapted to indicate adjustment of a first type responsive to sensed object motion originating in a first start tab and continuing in the adjustment region. Thus, a user can cause an adjustment of the first type by introducing an object proximate the first start tab, and moving the object from the first start tab and into the adjustment region.
Owner:WACOM CO LTD
Optical motion tracking of an object
InactiveUS20130093866A1Limited resolutionIncrease heightMagnetic measurementsColor television detailsImaging processingObject motion
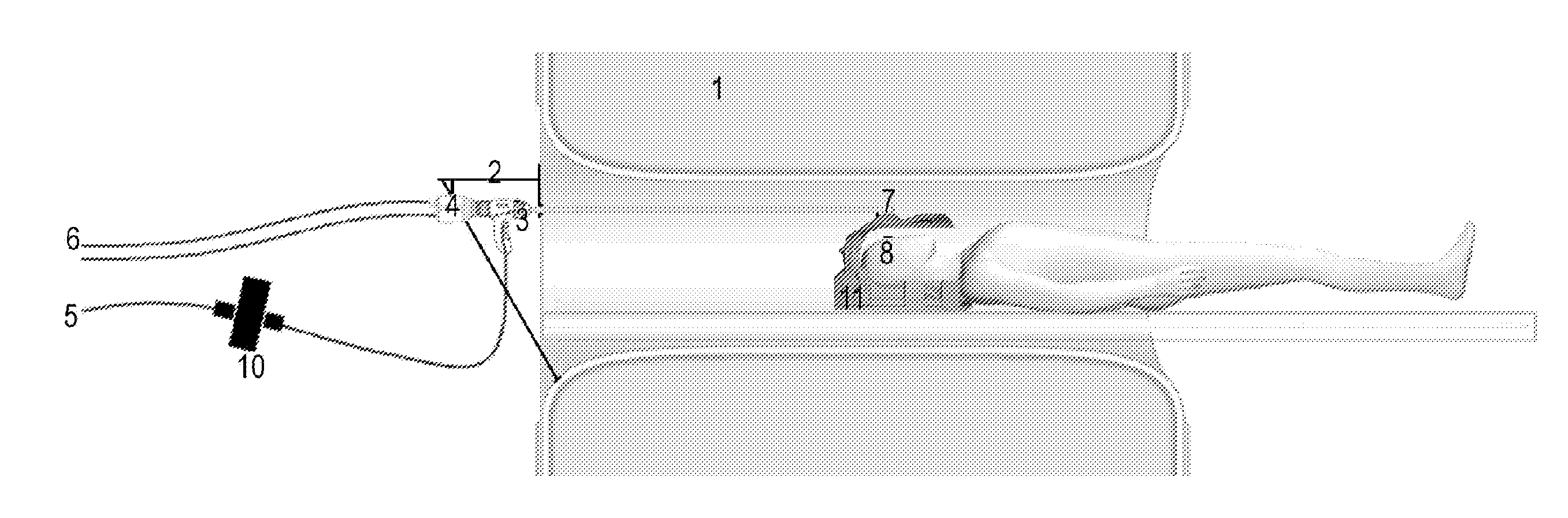
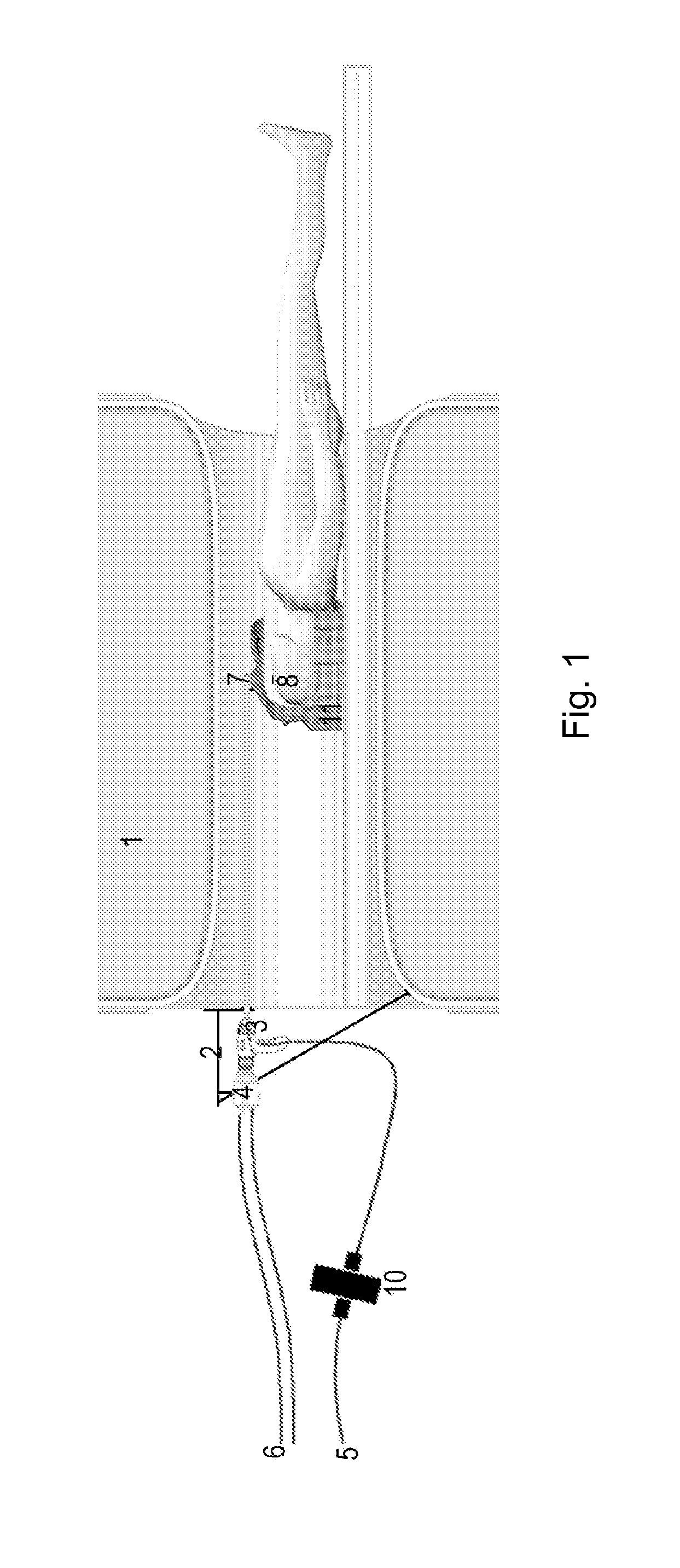
The present invention relates to a system and a method for monitoring / tracking the movement of an object in a location which is difficult to access, such as the movement of a patient in a clinical MRI scanner. This is achieved by an optical motion tracking system for determining the movement of an object at least partly located in a volume of difficult access and / or at least partly located in an electromagnetic field, said system comprising a borescope for imaging a pattern on the object or a surface part of the object with a camera, said pattern or surface part located adjacent to a distal end of the borescope and said camera attached to a proximal end of said borescope, and image processing means for calculating the movement of said pattern or surface part relative to the distal end of the borescope based on a plurality of frames / images captured by the camera. The invention further relates to the use of a borescope for motion tracking of an object and a marker plate suitable for use in the motion tracking system.
Owner:RIGSHOSPITALET
Advance video coding with perceptual quality scalability for regions of interest
ActiveUS20120177121A1Amenable to multithread/multi-processor architecturesEfficient compressionImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionMotion parameter
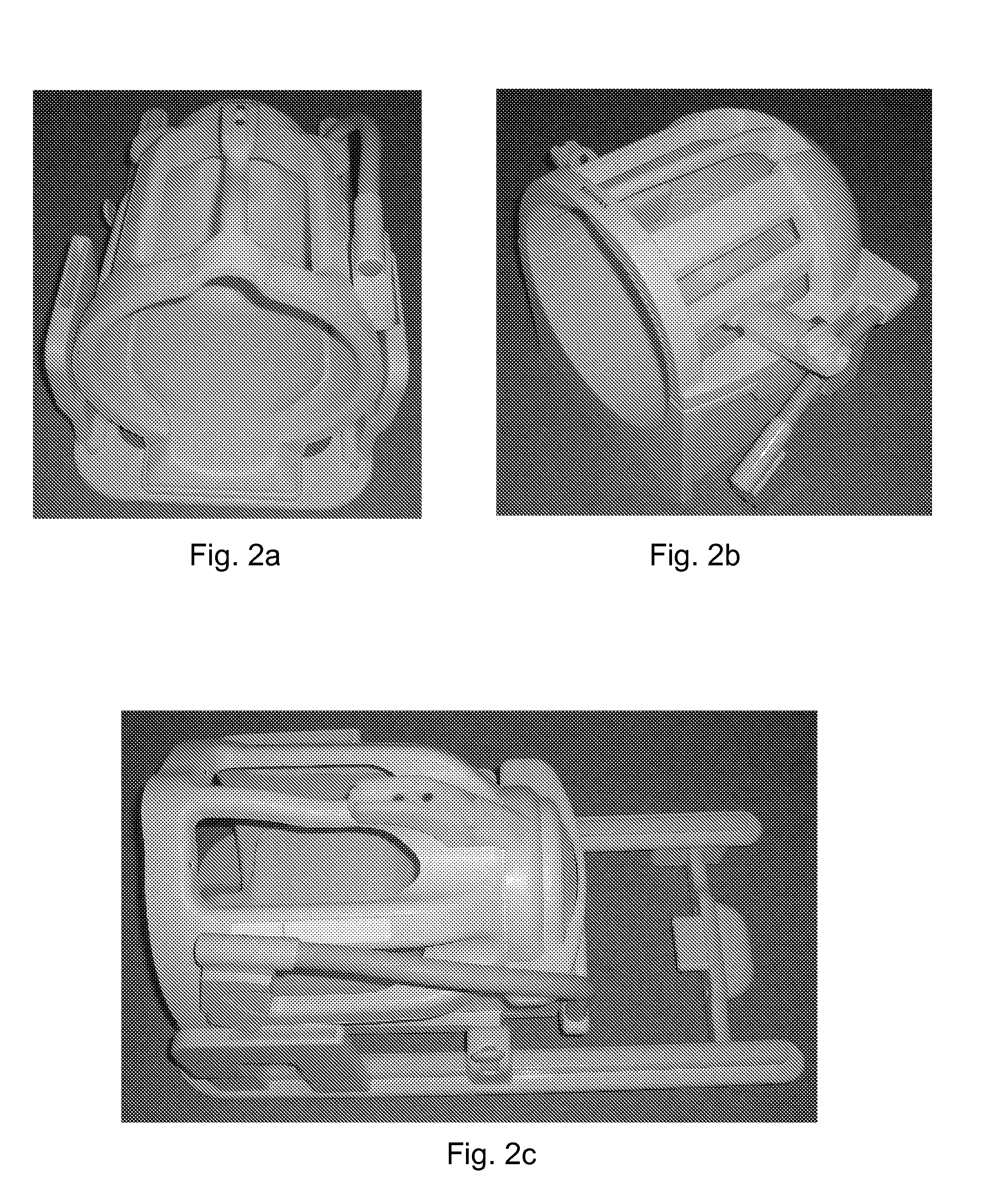
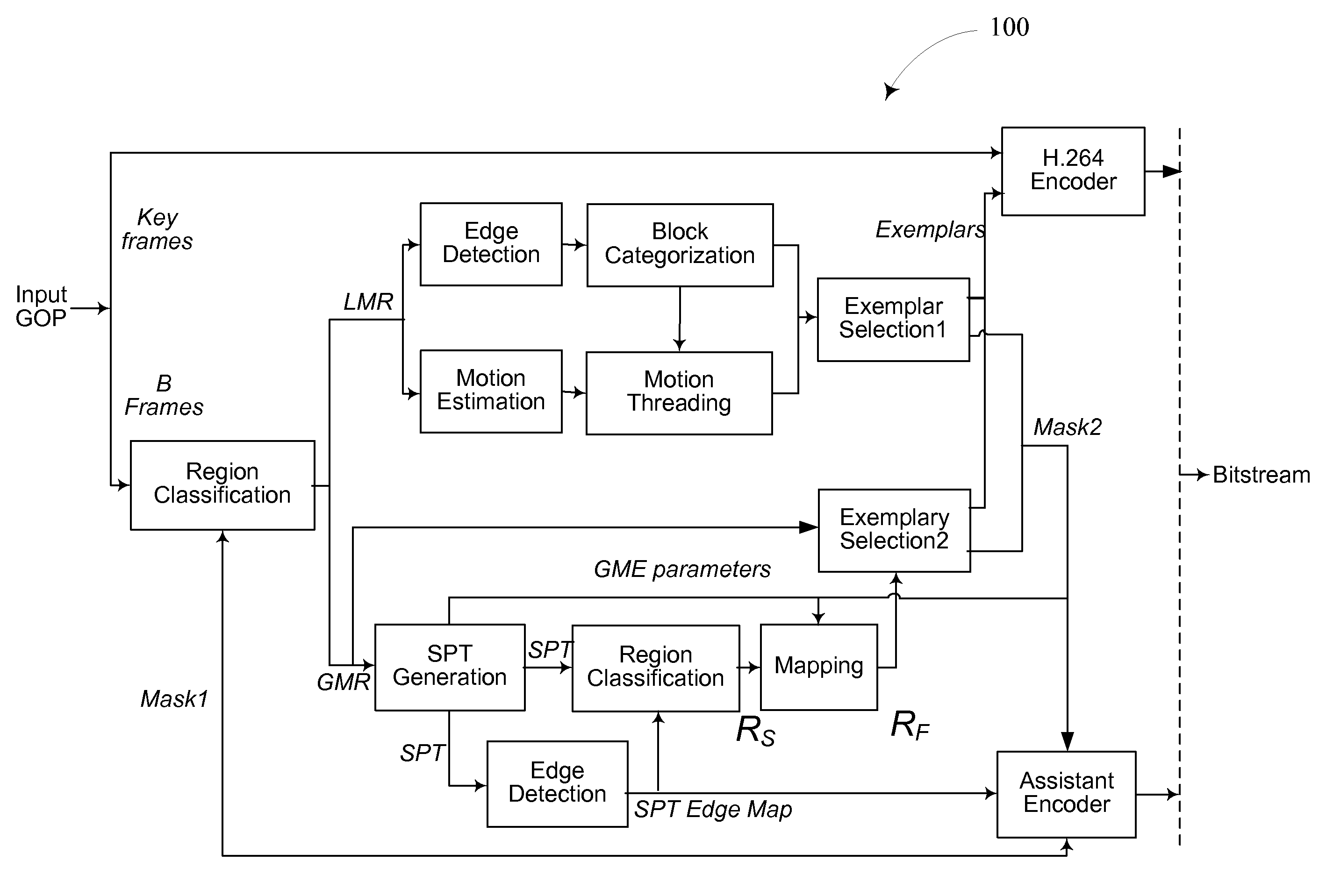
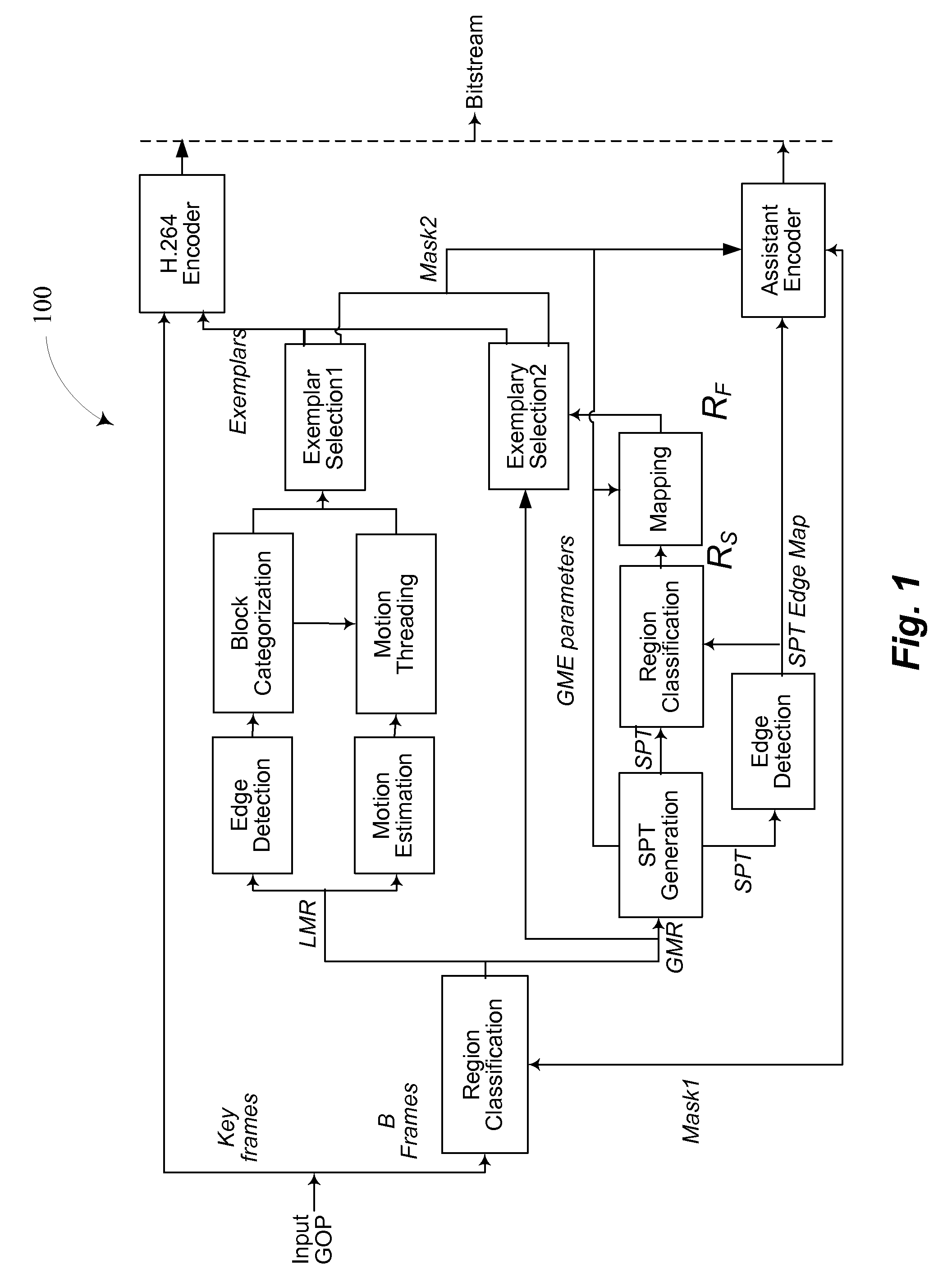
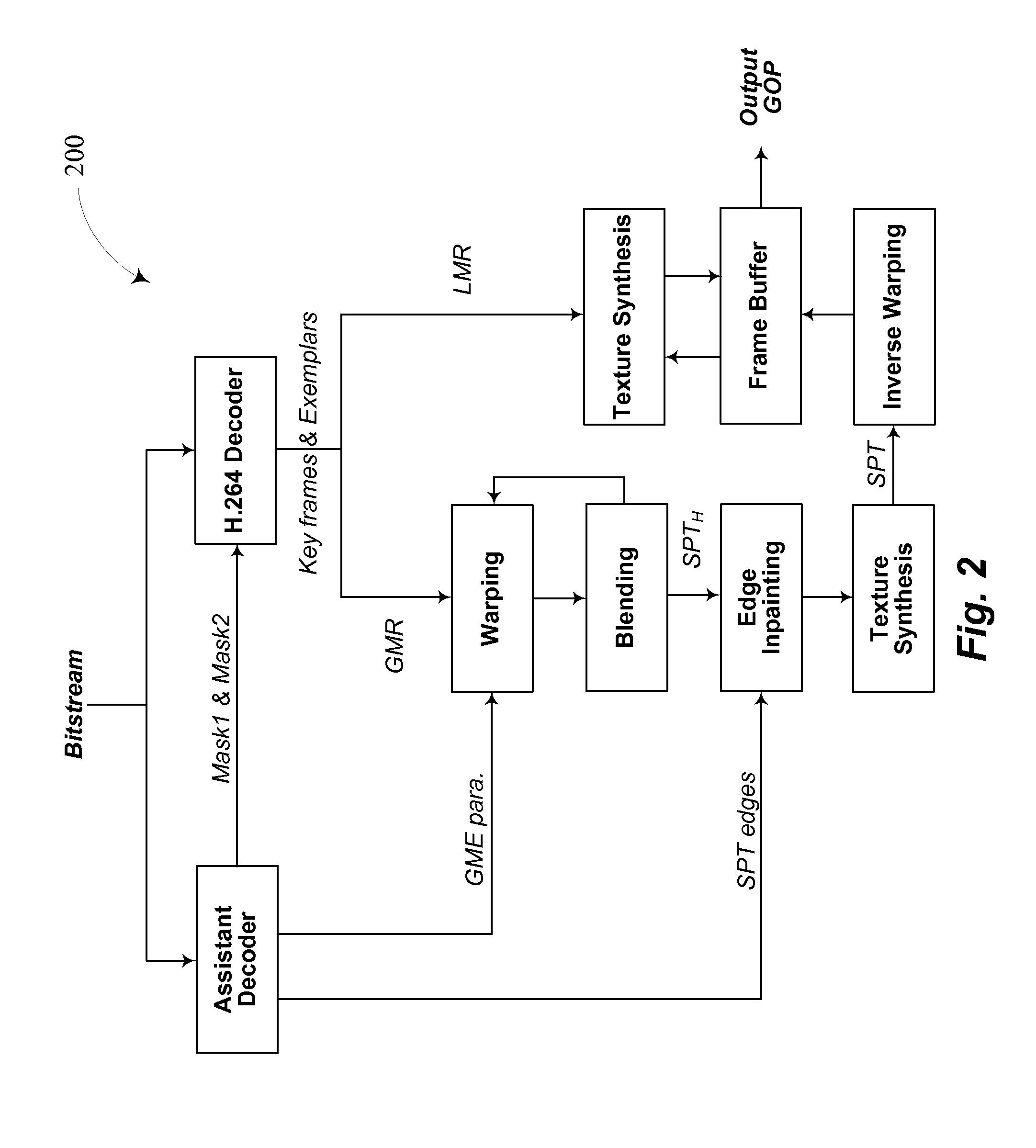
A video compression framework based on parametric object and background compression is proposed. At the encoder, an object is detected and frames are segmented into regions corresponding to the foreground object and the background. The encoder generates object motion and appearance parameters. The motion or warping parameters may include at least two parameters for object translation; two parameters for object scaling in two primary axes and one object orientation parameter indicating a rotation of the object. Particle filtering may be employed to generate the object motion parameters. The proposed methodology is the formalization of the concept and usability for perceptual quality scalability layer for Region(s) of Interest. A coded video sequence format is proposed which aims at “network friendly” video representation supporting appearance and generalized motion of object(s).
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS INT NV
Object motion capturing system and method
InactiveUS20100194879A1Reliable and accurate measurementPrecise positioningImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionMotion capture
In a system and method of capturing movement of an object, a tracking device is used having an optical marker and a motion sensor providing motion data representative of the position and orientation of the tracking device. The tracking device is connected to the object, and motion of the optical marker is registered by a camera to thereby provide video data representative of the position of the tracking device. The motion data and the video data are processed in combination to determine the position and orientation of the tracking device in space over time.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Intuitive multiple degrees of freedom portable control device
A control device for a vehicle or mechanism includes a portable displacement controller which permits a non-technical user to achieve effective control of the vehicle or mechanism, by moving the portable displacement controller intuitively with little learning effort. A first sensing device, attached to the displacement controller, detects the user's controlling motion. A second sensing device, attached to the object being controlled, detects motion thereof. An interface device receives signals from the sensing devices, processes those signals to determine relative motion of the controlling motion and the object's motion and outputs a control signal in accordance with the processed signals. The sensing devices each detect motion in six degrees of freedom; the sensing devices each include a three-axis accelerometer, a three-axis gyroscope, and a three-axis magnetometer. In specific embodiments, the accelerometers, gyroscopes, and magnetometers include micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SYST
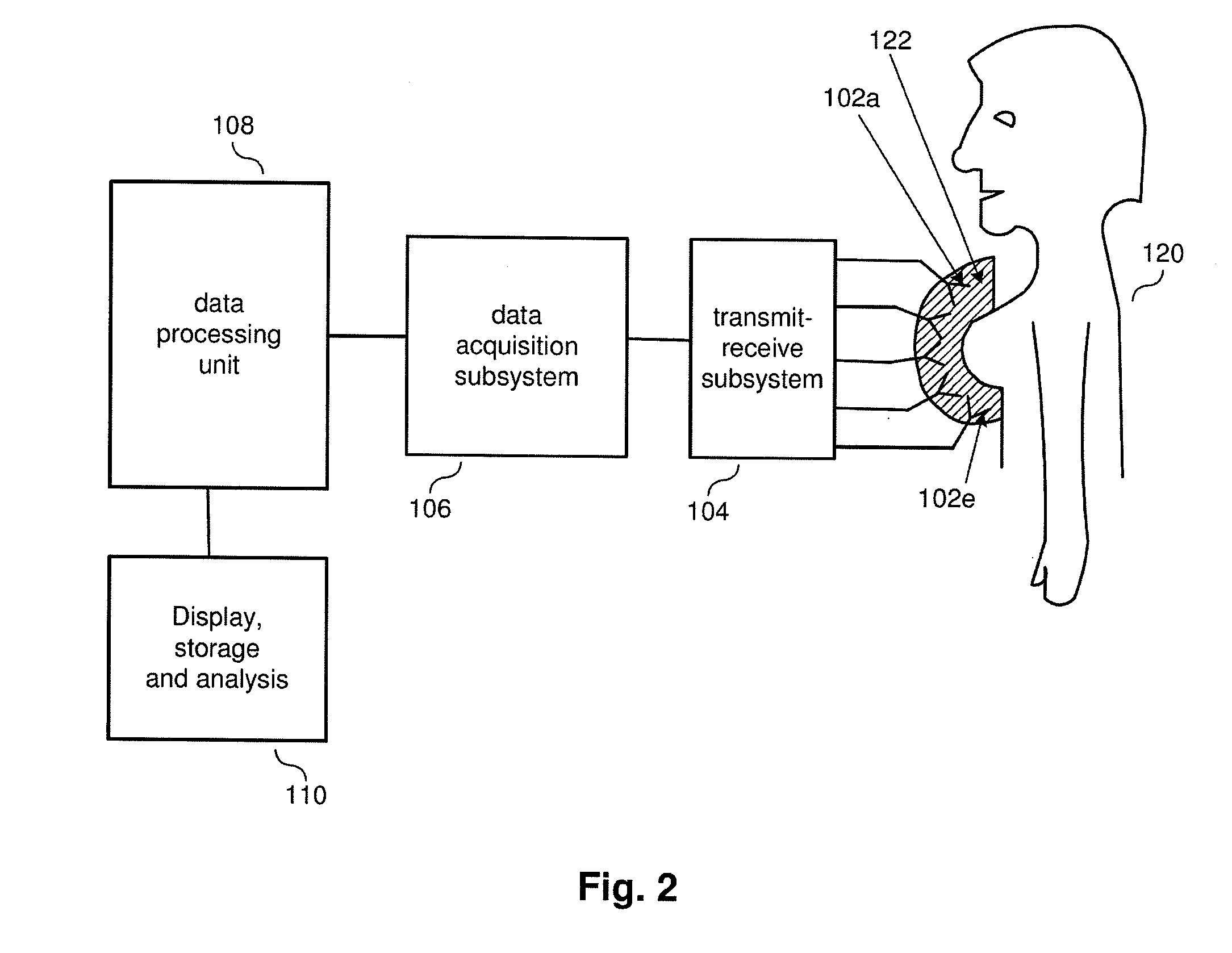
Apparatus and method for doppler-assisted MIMO radar microwave imaging
ActiveUS20110237939A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionMicrowave imaging
A method and apparatus for enhanced microwave imaging of an object collects microwave responses for multiple combinations of transmit antennas, receive antennas, and object movement states. The responses are grouped into sets of responses corresponding to at least two object movement states. An image is reconstructed from the set of responses for each movement state, and a differential image representative of object movement is generated from the reconstructed image for each of the at least two object movement states. The differential image is overlaid on a reconstructed image to obtain an enhanced composite image of the object.
Owner:VAYYAR IMAGING LTD
Screen display-controlling method facing to slide body of touch screen
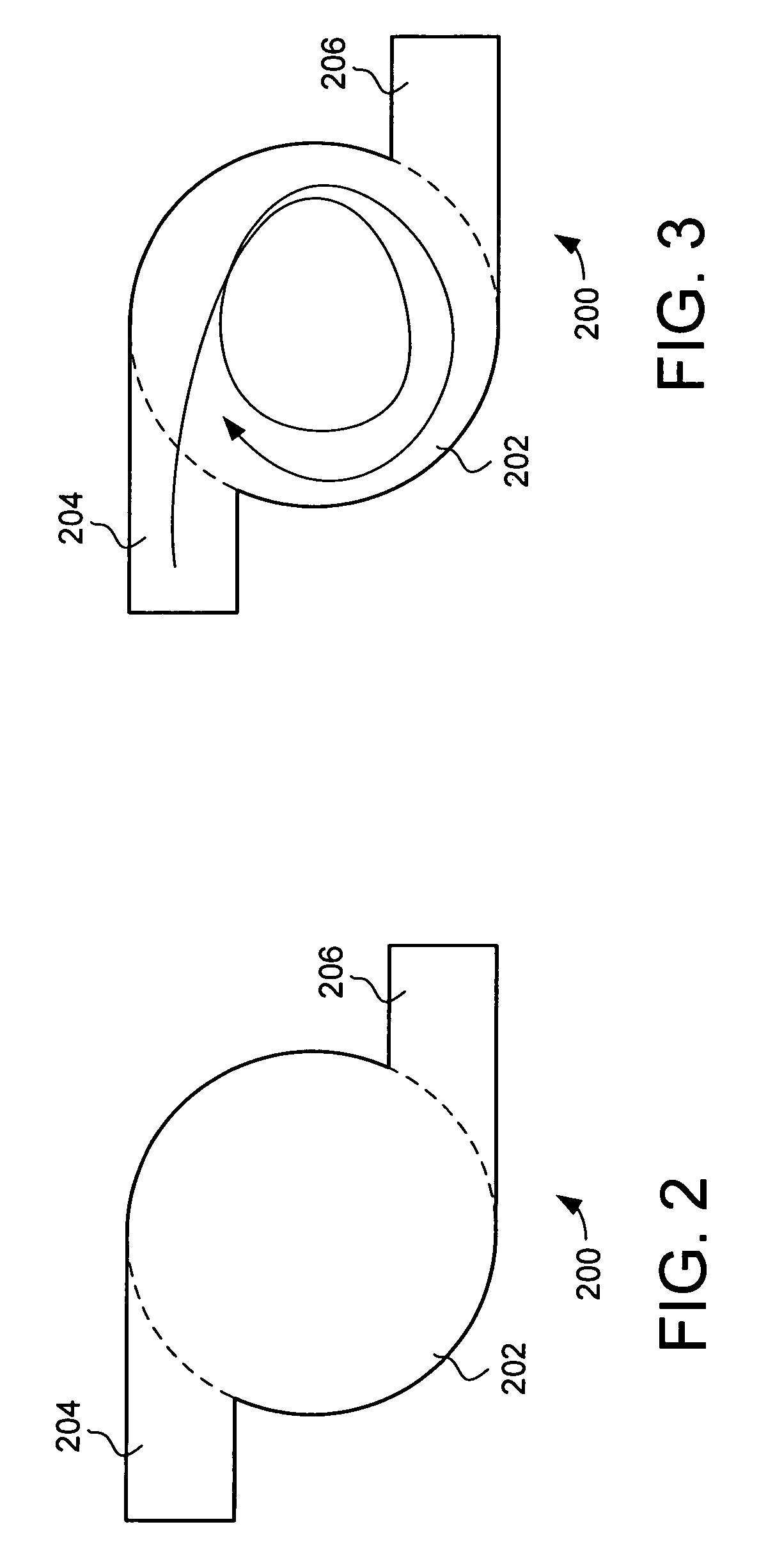
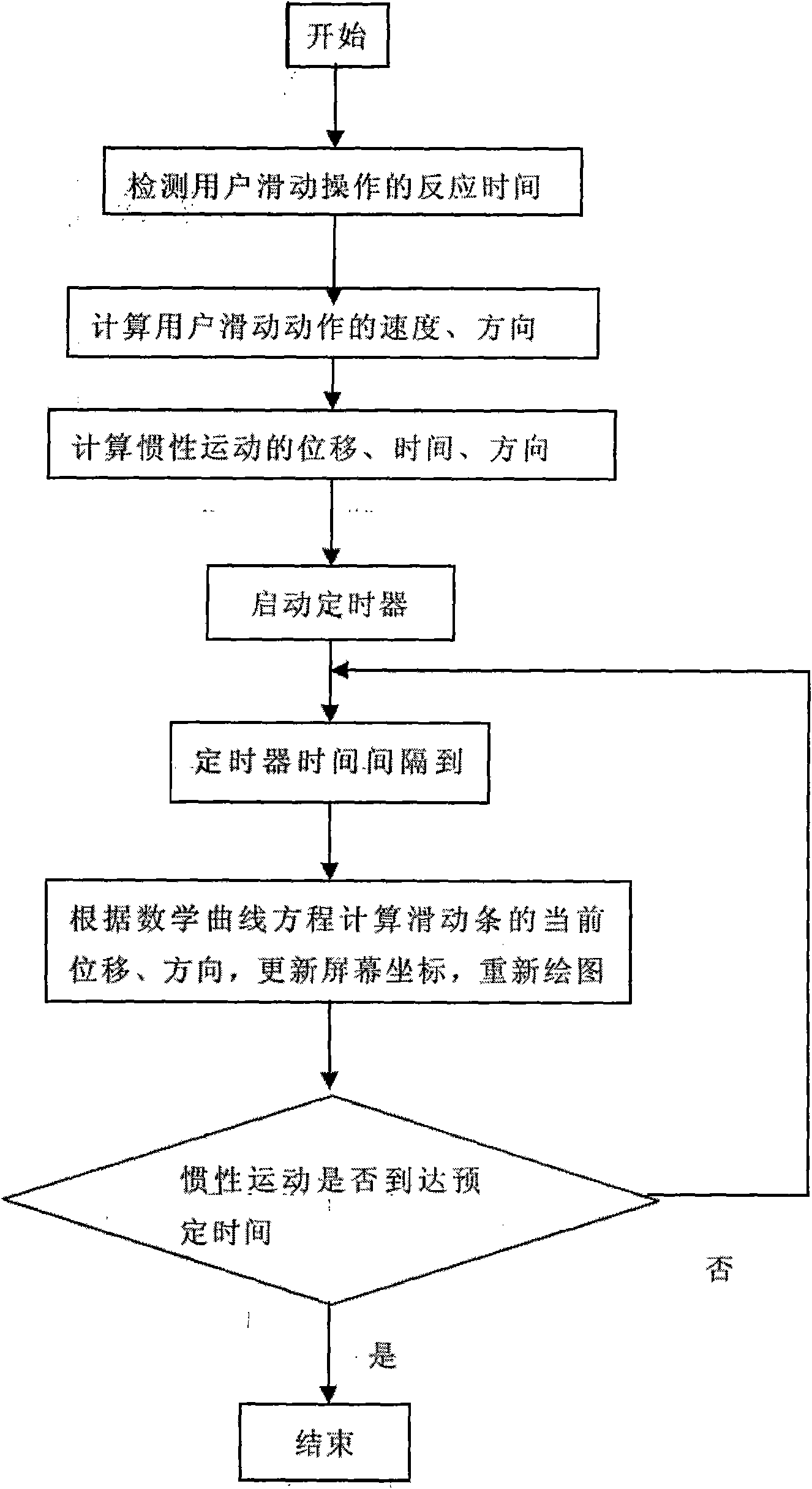
The invention discloses a screen display-controlling method facing to a slide body of a touch screen, which comprises the following steps of: (1) setting a coordinate system on a touch screen; (2) detecting the sliding action of a user on the touch screen with the coordinate system, and recoding parameters correlative to the sliding action; and (3) controlling the moving direction, speed and displacement of the slide body displayed on the screen according to the parameters, wherein the motion of the slide body is an inertial motion which consists of a positive acceleration stage and a negative acceleration stage. The method can control the display status of the slide body in the screen according to the sliding operation of the user on the slide body of the touch screen, reflects the factors such as the moving direction, speed, acceleration and the like of the slide body, and leads the user to obtain the visual effect which is close to the motion of objects in the real world.
Owner:CIENET COMM BEIJING CO LTD
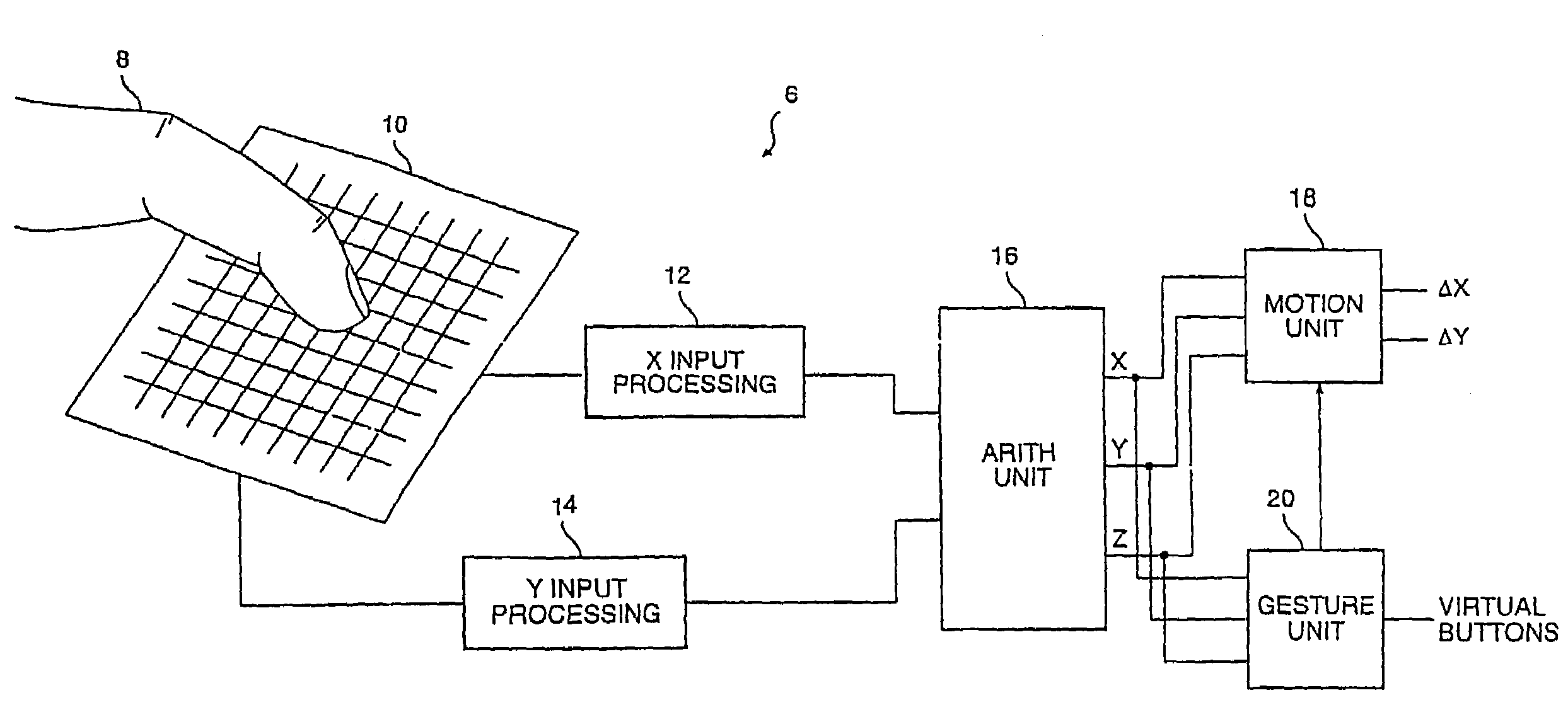
Object position detector with edge motion feature and gesture recognition
InactiveUS7532205B2Highly integratedRapid responseTransmission systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsObject motionDisplay device
A method of generating cursor motion signals for improved usability is provided. In one embodiment, the method comprises detecting object motion in a sensing region and providing cursor motion signals in accordance with cursor motion values generated responsive to continuation of the object motion in the inner region. This embodiment further comprises providing cursor motion signals configured to generate cursor motion that combines incremental cursor motion with additional cursor motion responsive to the object moving from the inner region into the outer region, where the incremental cursor motion comprises motion toward an edge of the display correlating to an edge of the sensing region proximate the object, and where the additional cursor motion comprises cursor motion indicated by cursor motion values generated responsive to continuation of the object motion in the outer region of the sensing region.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC
Method and apparatus for motion invariant imaging
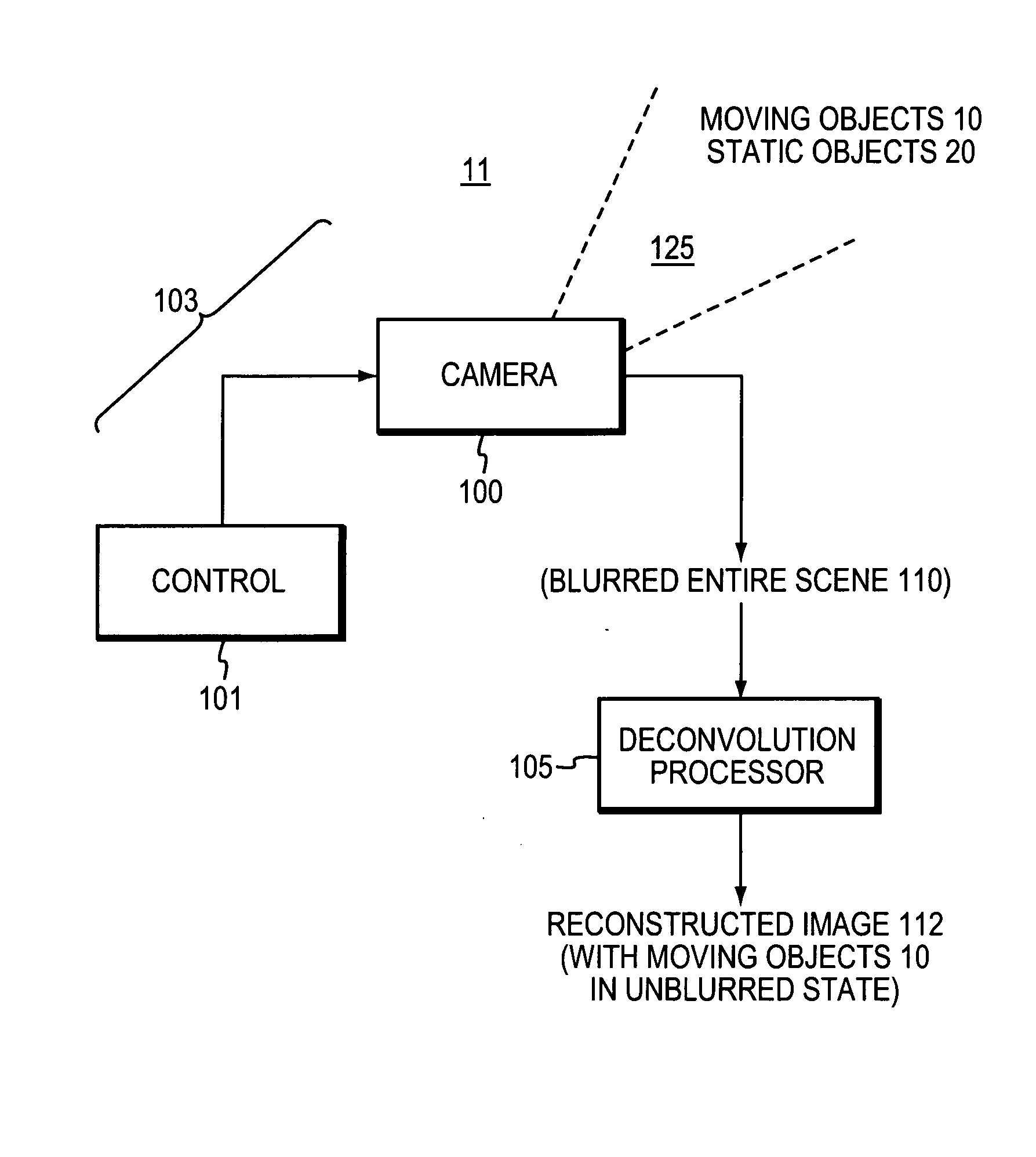
ActiveUS20090244300A1Easily invertedImage enhancementTelevision system detailsObject motionRange of motion
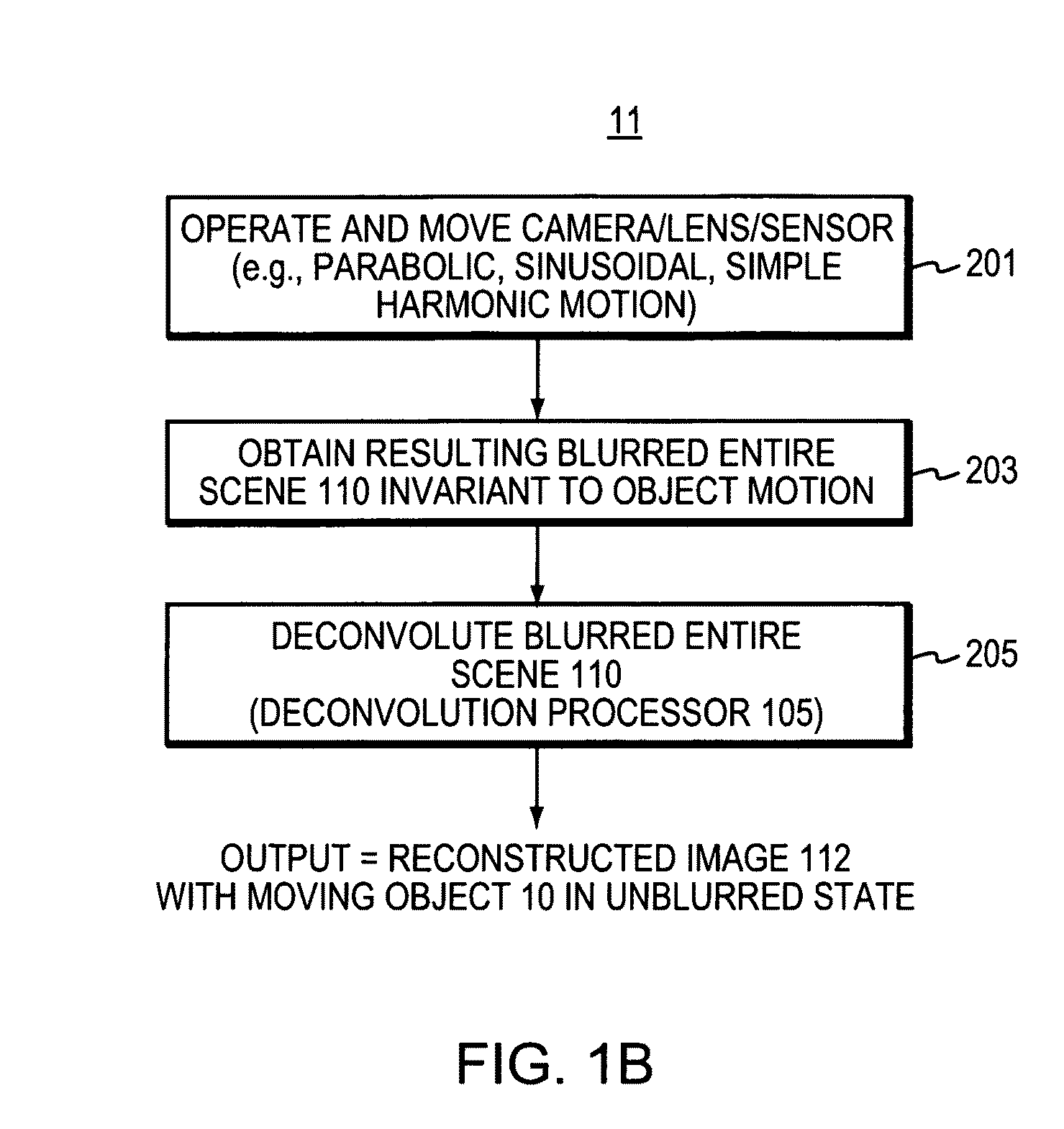
Object motion during camera exposure often leads to noticeable blurring artifacts. Proper elimination of this blur is challenging because the blur kernel is unknown, varies over the image as a function of object velocity, and destroys high frequencies. In the case of motions along a 1D direction (e.g. horizontal), applicants show that these challenges can be addressed using a camera that moves during the exposure. Through the analysis of motion blur as space-time integration, applicants show that a parabolic integration (corresponding to constant sensor acceleration) leads to motion blur that is not only invariant to object velocity, but preserves image frequency content nearly optimally. That is, static objects are degraded relative to their image from a static camera, but all moving objects within a given range of motions reconstruct well. A single deconvolution kernel can be used to remove blur and create sharp images of scenes with objects moving at different speeds, without requiring any segmentation and without knowledge of the object speeds.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Visualization, measurement and analysis of vibrating objects
InactiveUS20050279172A1Low costReduce the numberVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesObject motionFull field
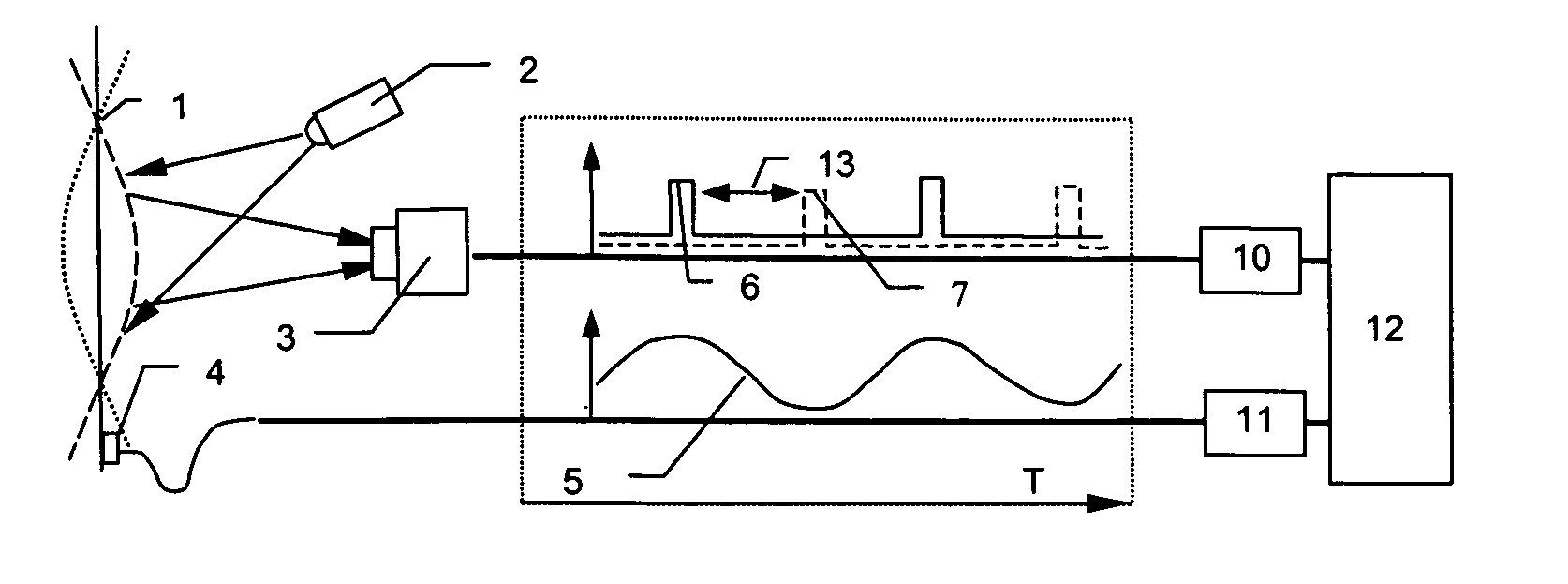
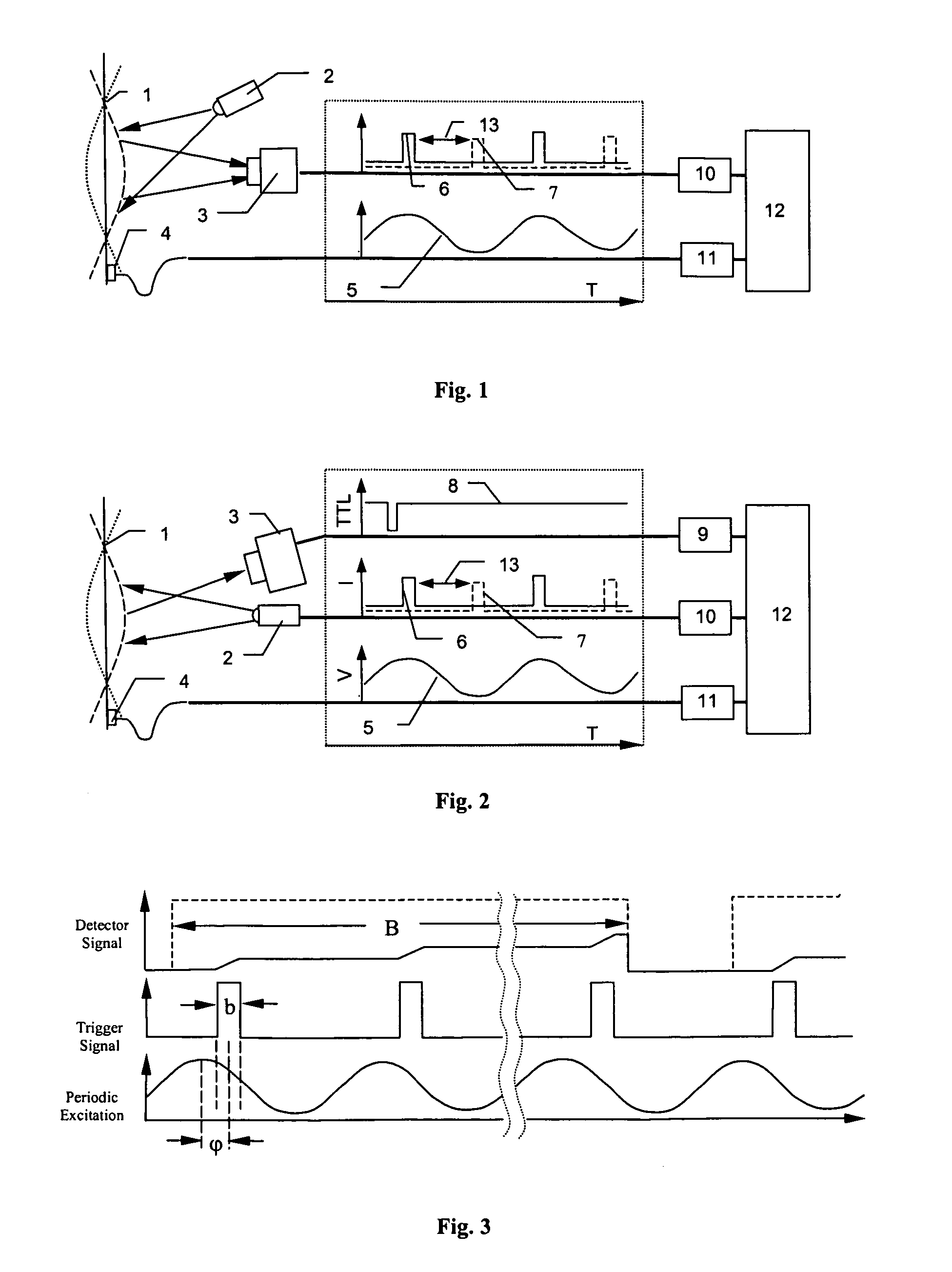
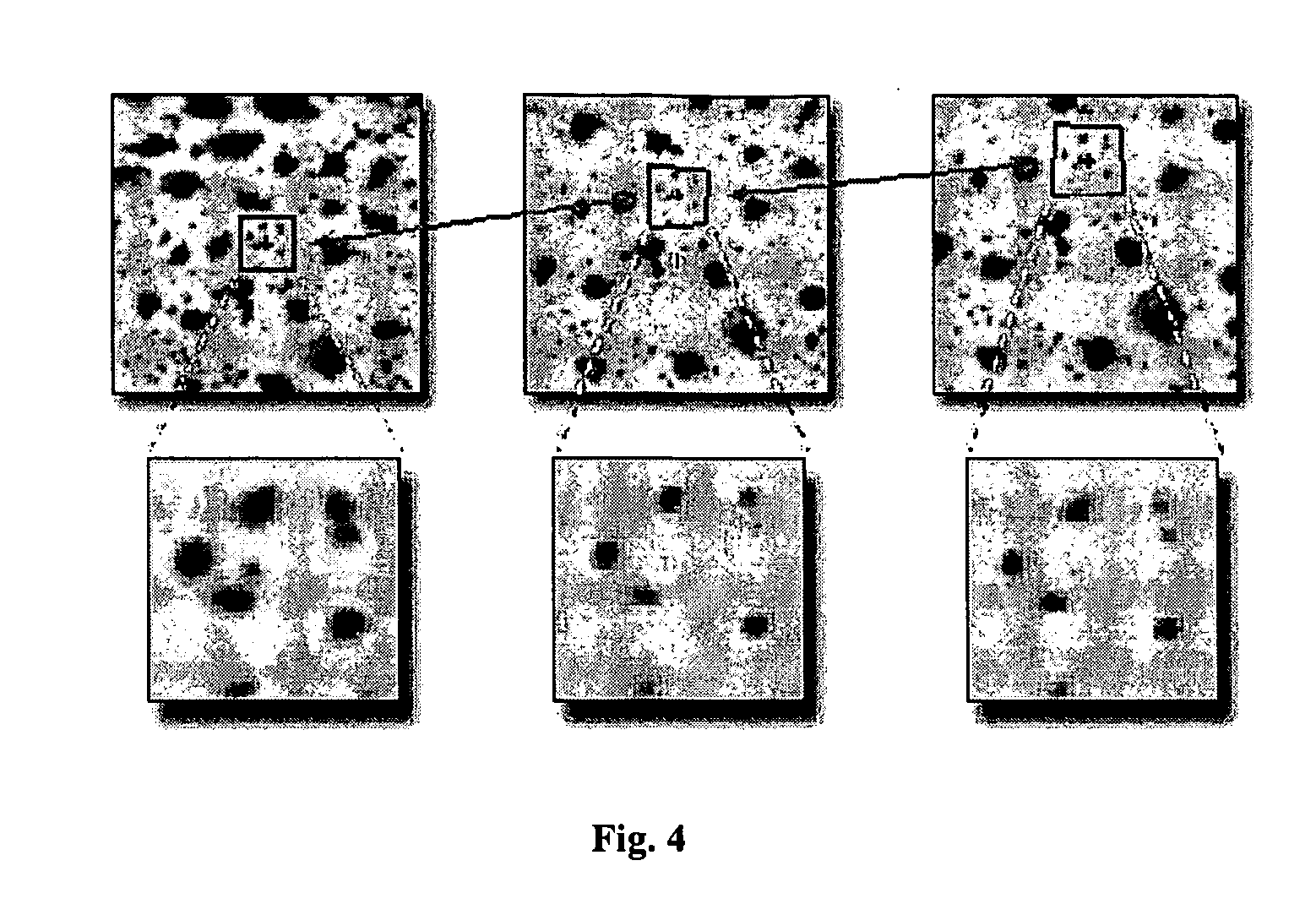
A simple, relatively inexpensive, non-contacting, full-field (total visible surface) measurement and visualization methodology is described to measure the object motions and the object stretches and object distortions (deformations) during oscillation of an object. The method is capable of full-field measurement of 1D, 2D and / or 3D object motions and the associated object surface deformations on vibrating objects. The methodology is based on a combination of stroboscopic image ascuisition and / or controlled image exposure time with a synchronization system to acquire the images at appropriate times during periodic oscillation of an object; the periodicity of the applied excitation is used to mitigate the requirement for high speed imaging. Then, image matching procedures, such as 3D digital image correlation, are used with software to extract full-field object motions and surface deformations at each time of interest.
Owner:CORRELATED SOLUTIONS
MRI system with means to eliminate object movement whilst acquiring its image
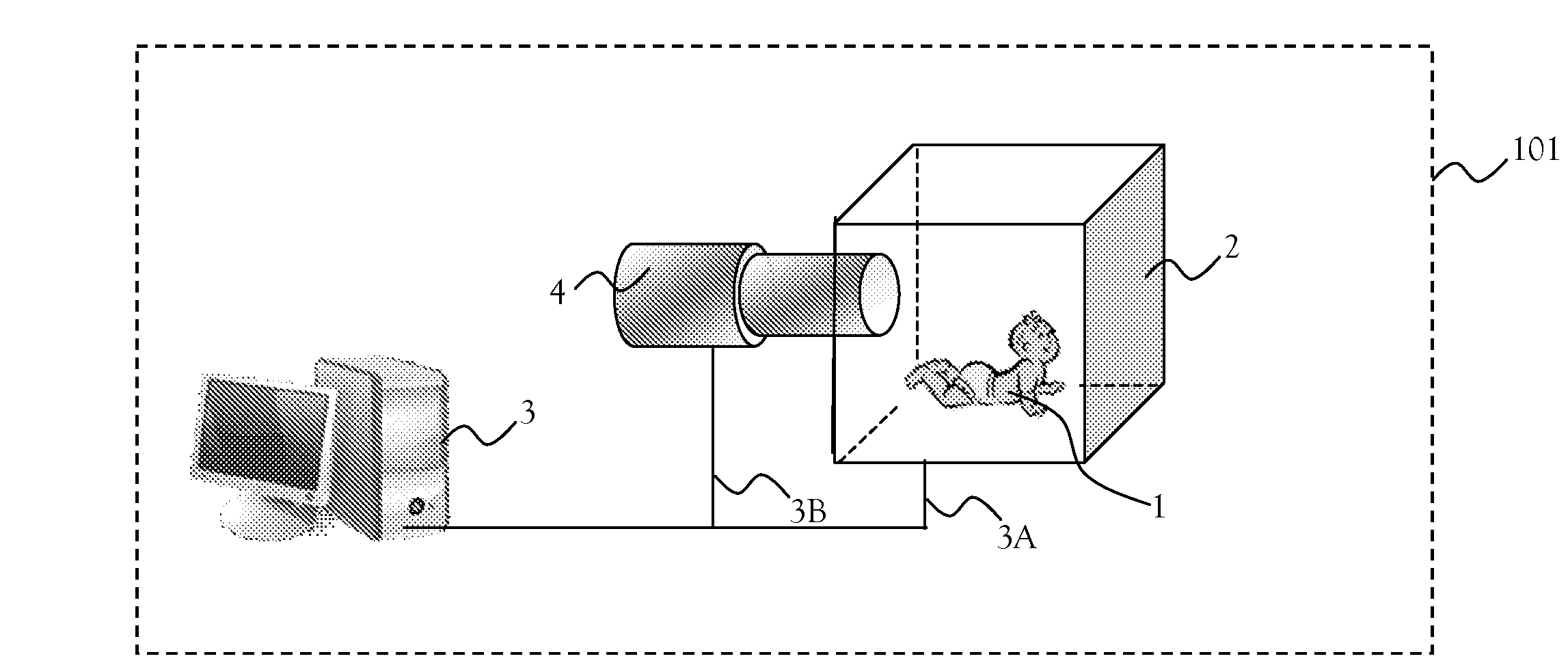
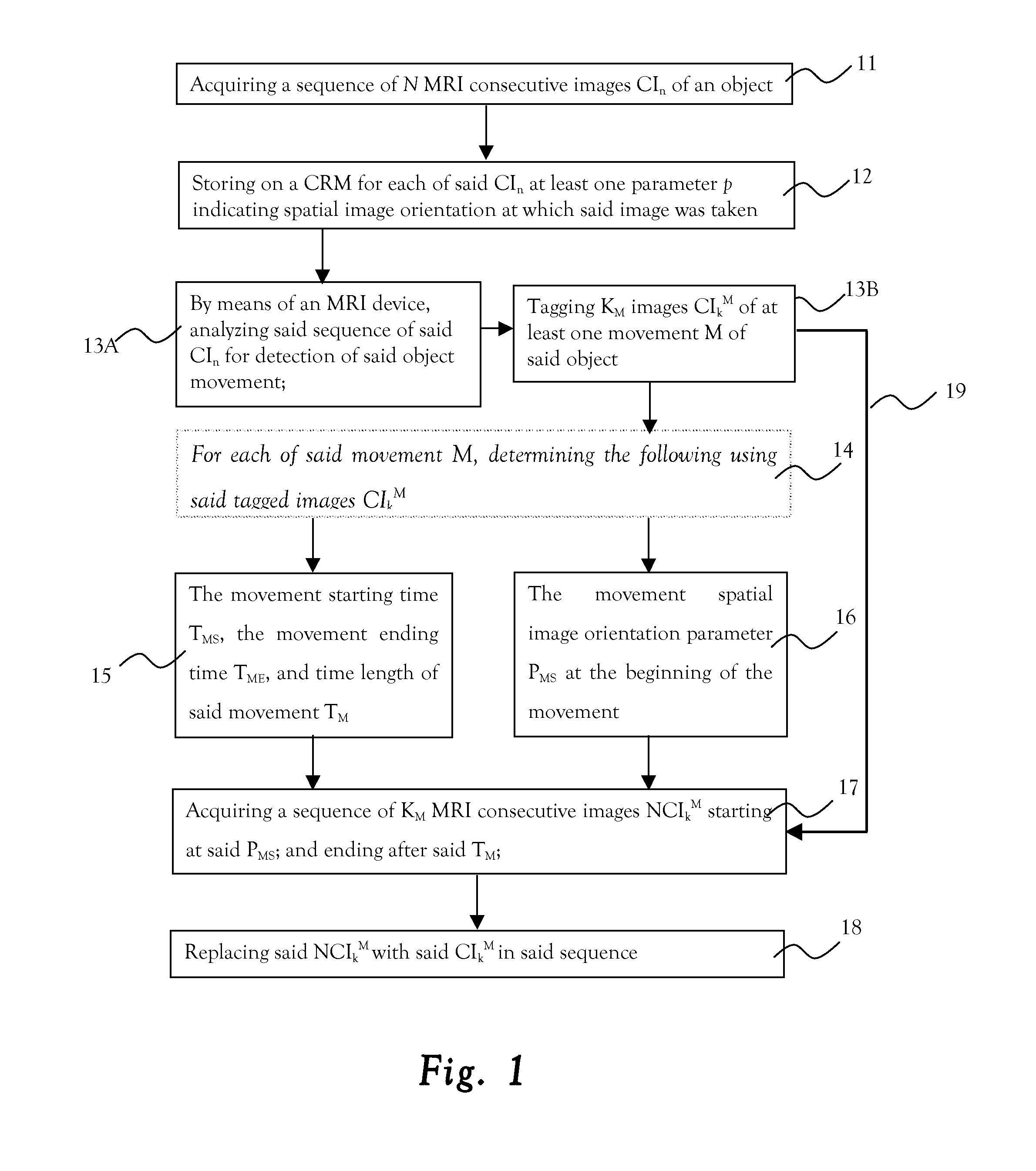
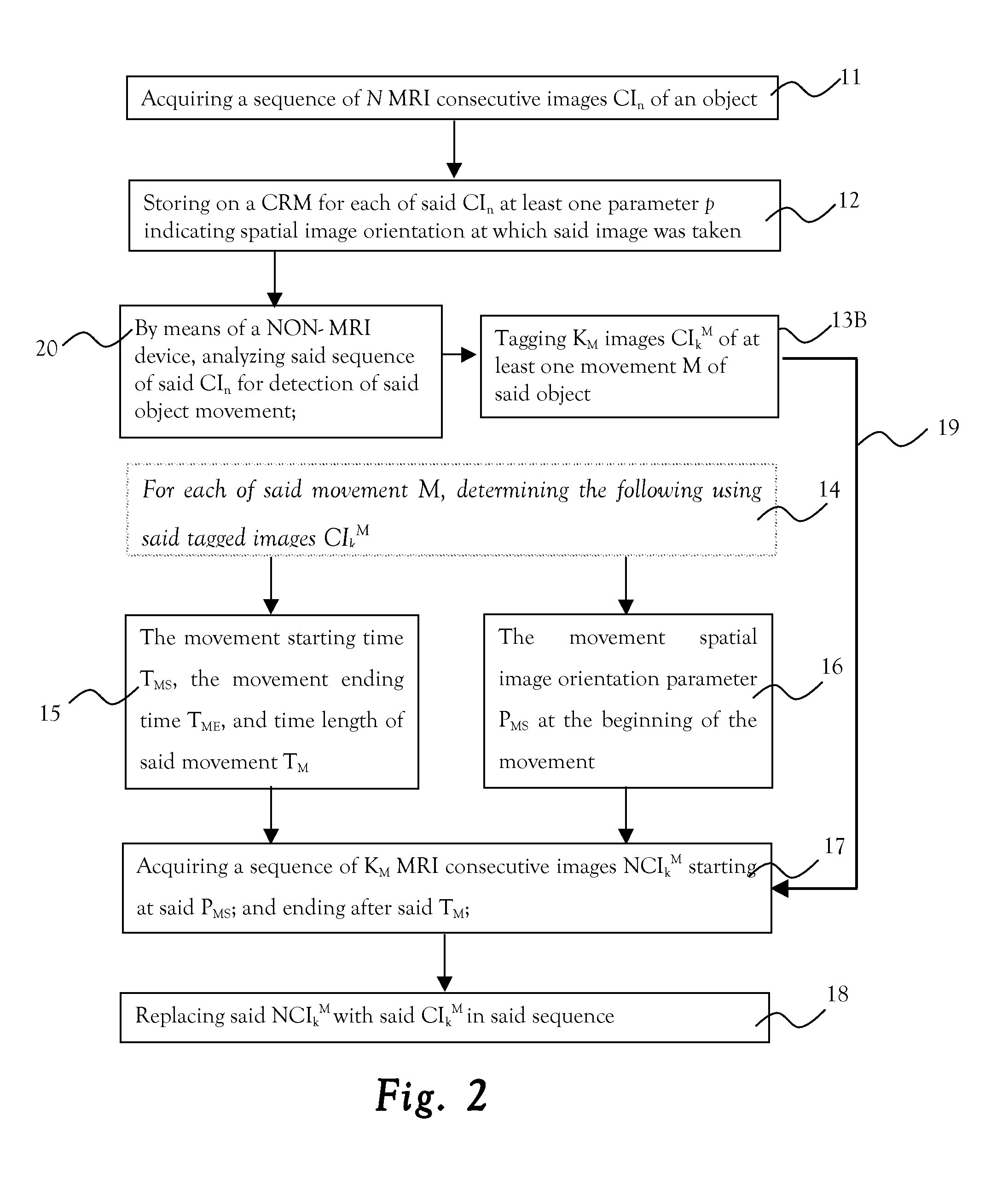
ActiveUS20140099010A1AvoidingReduced object-movementImage analysisMagnetic measurementsObject motionSpatial image
A method of reducing the effect of object movements along MRI imaging. The method includes: acquiring a sequence of MRI consecutive images of an object; storing on a computer readable medium, for each of the images, at least one parameter p indicating spatial image orientation at which the image was taken; analyzing the sequence of the images for detection of the object movement; and tagging images of at least one movement of the object.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Integrated sensor and video motion analysis method
ActiveUS9396385B2Low utilizationSave on storageImage enhancementImage analysisObject motionSensor fusion
A method that integrates sensor data and video analysis to analyze object motion. Motion capture elements generate motion sensor data for objects of interest, and cameras generate video of these objects. Sensor data and video data are synchronized in time and aligned in space on a common coordinate system. Sensor fusion is used to generate motion metrics from the combined and integrated sensor data and video data. Integration of sensor data and video data supports robust detection of events, generation of video highlight reels or epic fail reels augmented with metrics that show interesting activity, and calculation of metrics that exceed the individual capabilities of either sensors or video analysis alone.
Owner:NEWLIGHT CAPITAL LLC
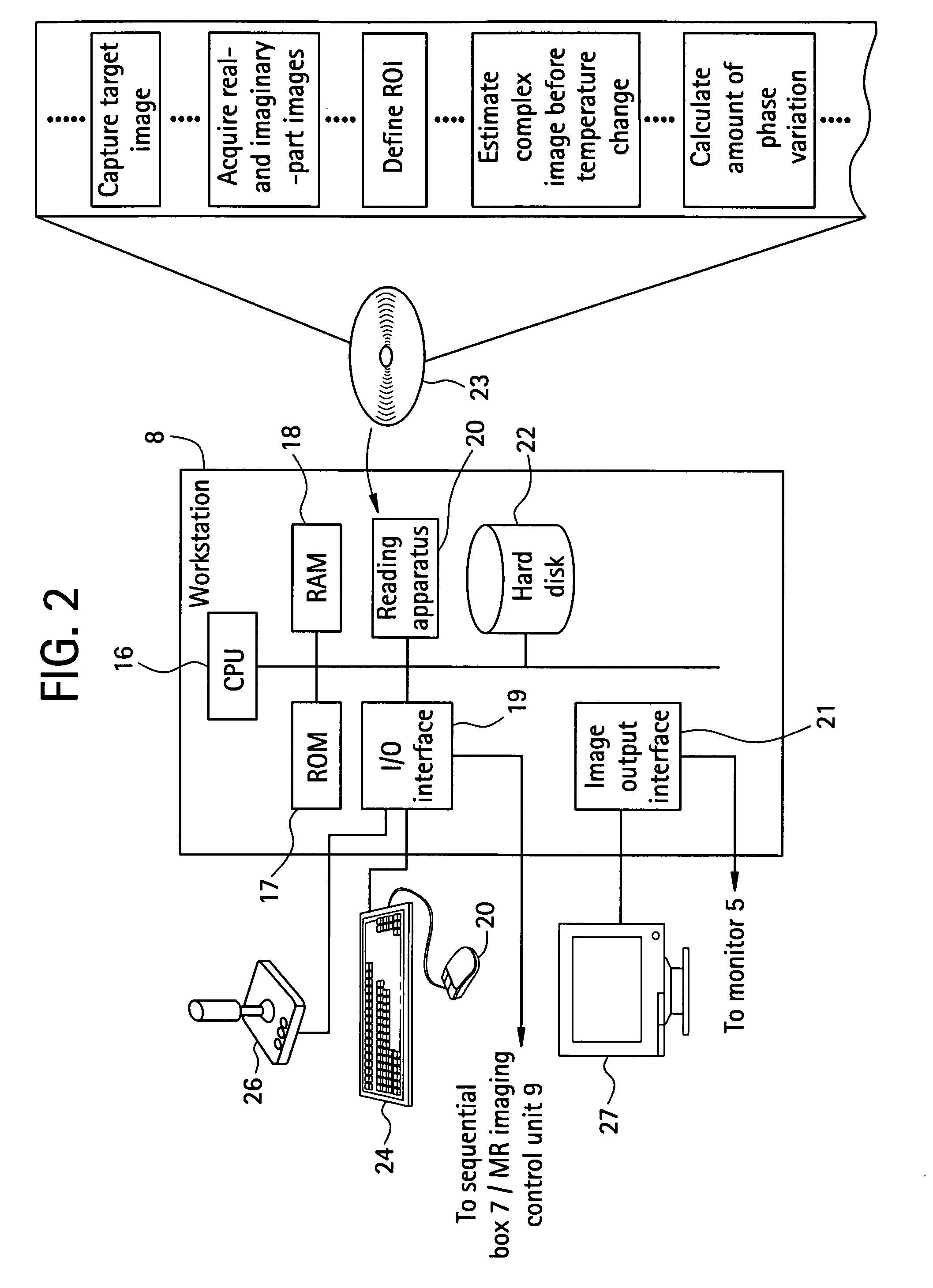
Self-referencing/body motion tracking non-invasive internal temperature distribution measurement method and apparatus using magnetic resonance tomographic imaging technique
InactiveUS7505805B2AdvantageousGood for observationChiropractic devicesEye exercisersObject motionPhase difference
A noninvasive image measuring method of measuring internal organ / tissue temperature using an MRI system. Temperature measurement insusceptible to body motion and spatial variation of magnetic field is realized by utilizing the position and size of a temperature change region as a priori information to determine the phase distribution of the complex magnetic resonance signal of water proton at a given temperature point and by subtracting the phase distribution before the temperature change estimated (self-referred) from the phase distribution in the peripheral region for each pixel of the image, thereby eliminating the subtraction process of image before and after temperature change. The precision of temperature measurement can be enhanced by estimating a complex curved surface formed of the peripheral region in each temperature change region of the real-part and imaginary-part images of the complex magnetic resonance signal, and calculating the phase difference between an actually measured complex signal distribution and the estimated complex signal distribution of the complex signal distribution for each pixel, thereby reducing the estimation error due to phase transition from −π to +π occurring in a phase distribution. Furthermore, temperature can be measured through optimal imaging following up body motion by using an optical positioning system in combination even if the part being measured is shifted.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com