Patents
Literature
328 results about "Mri imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
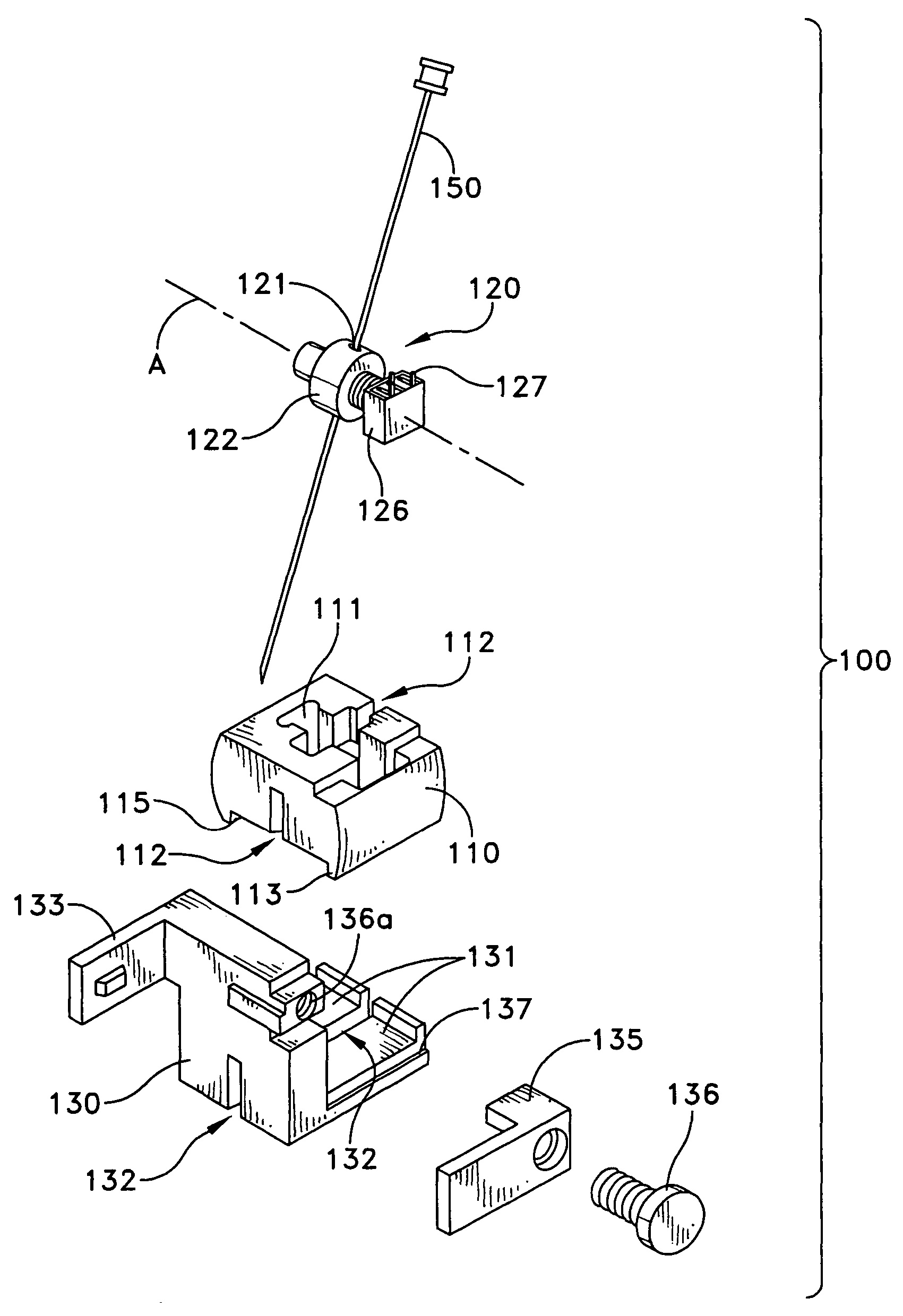
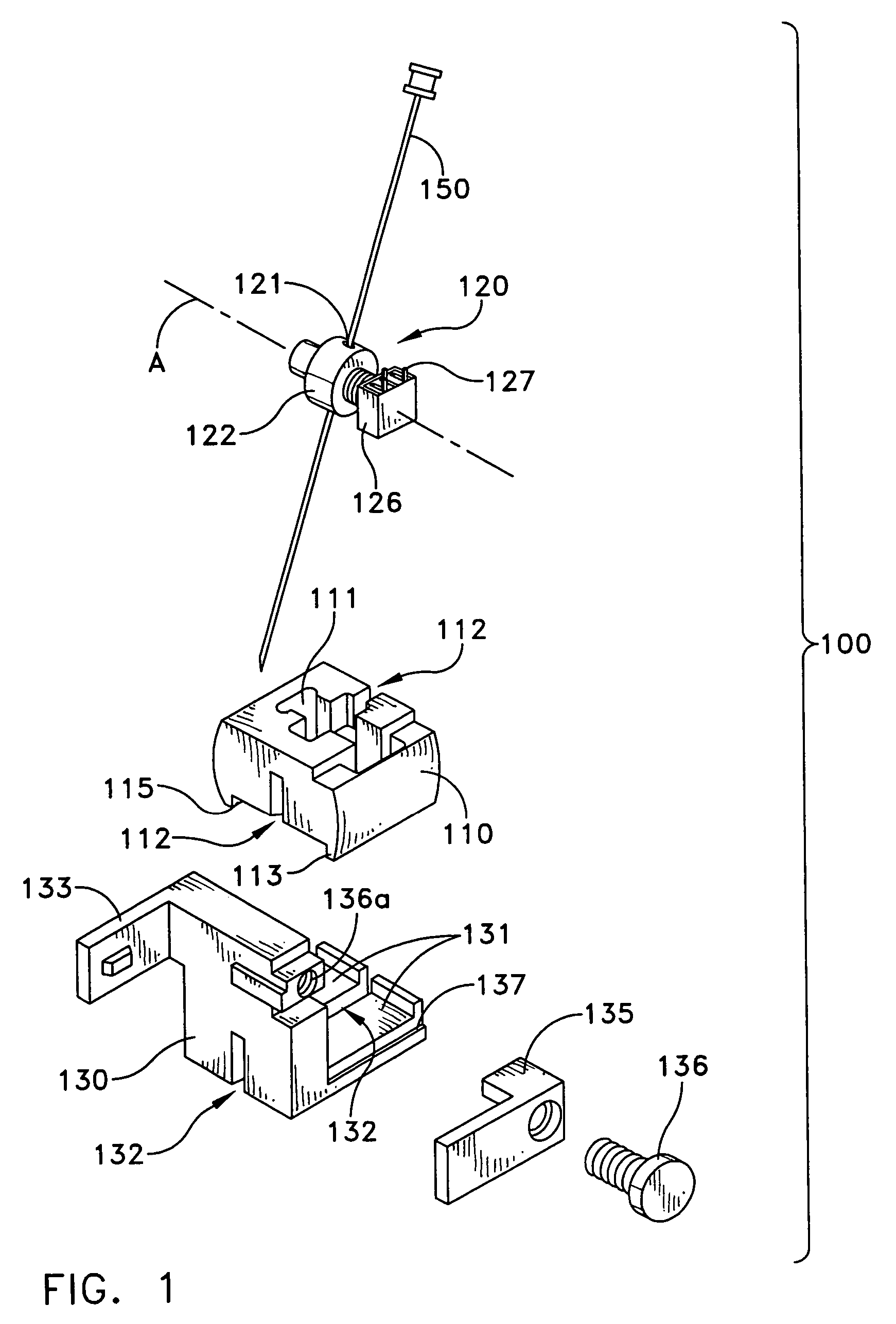
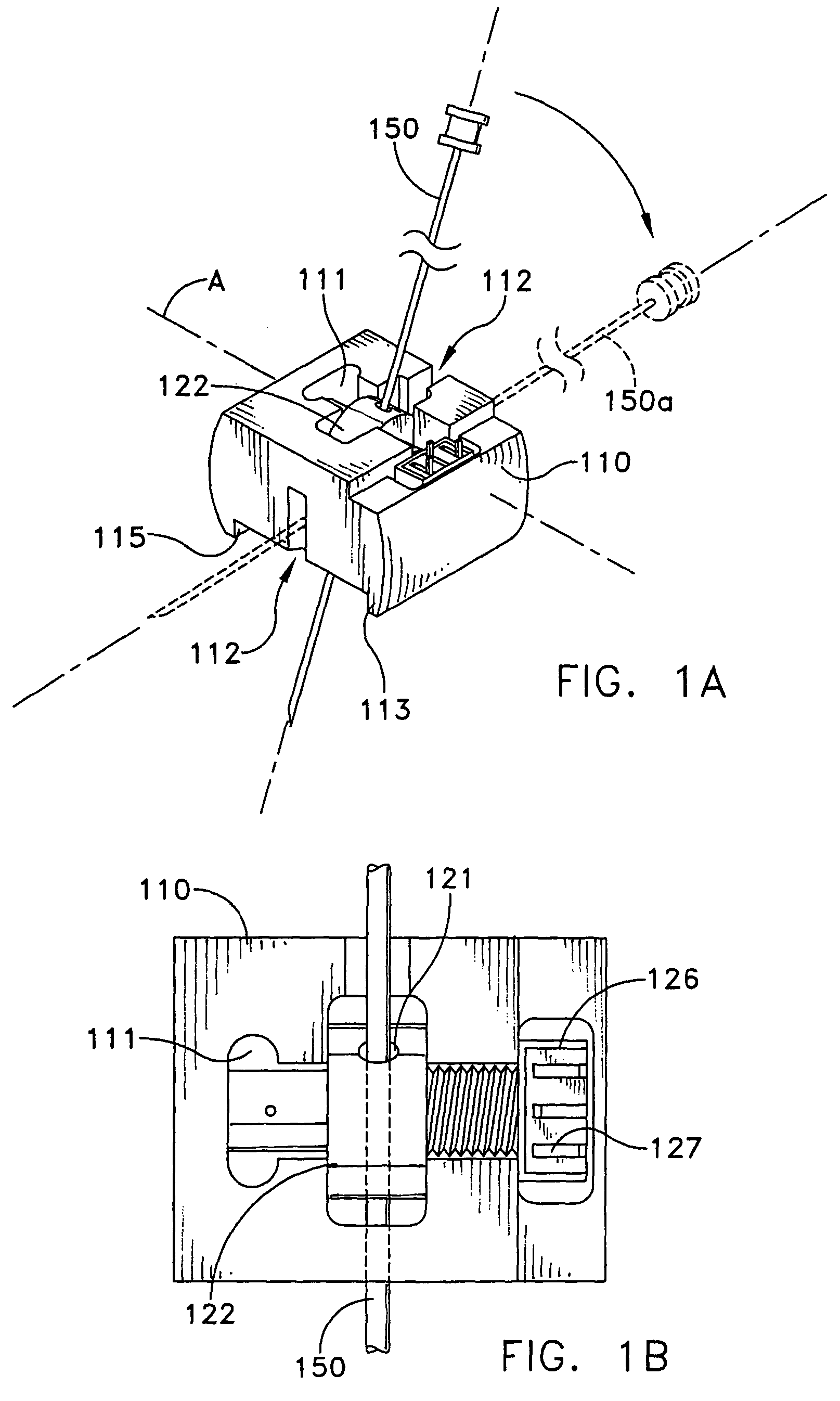
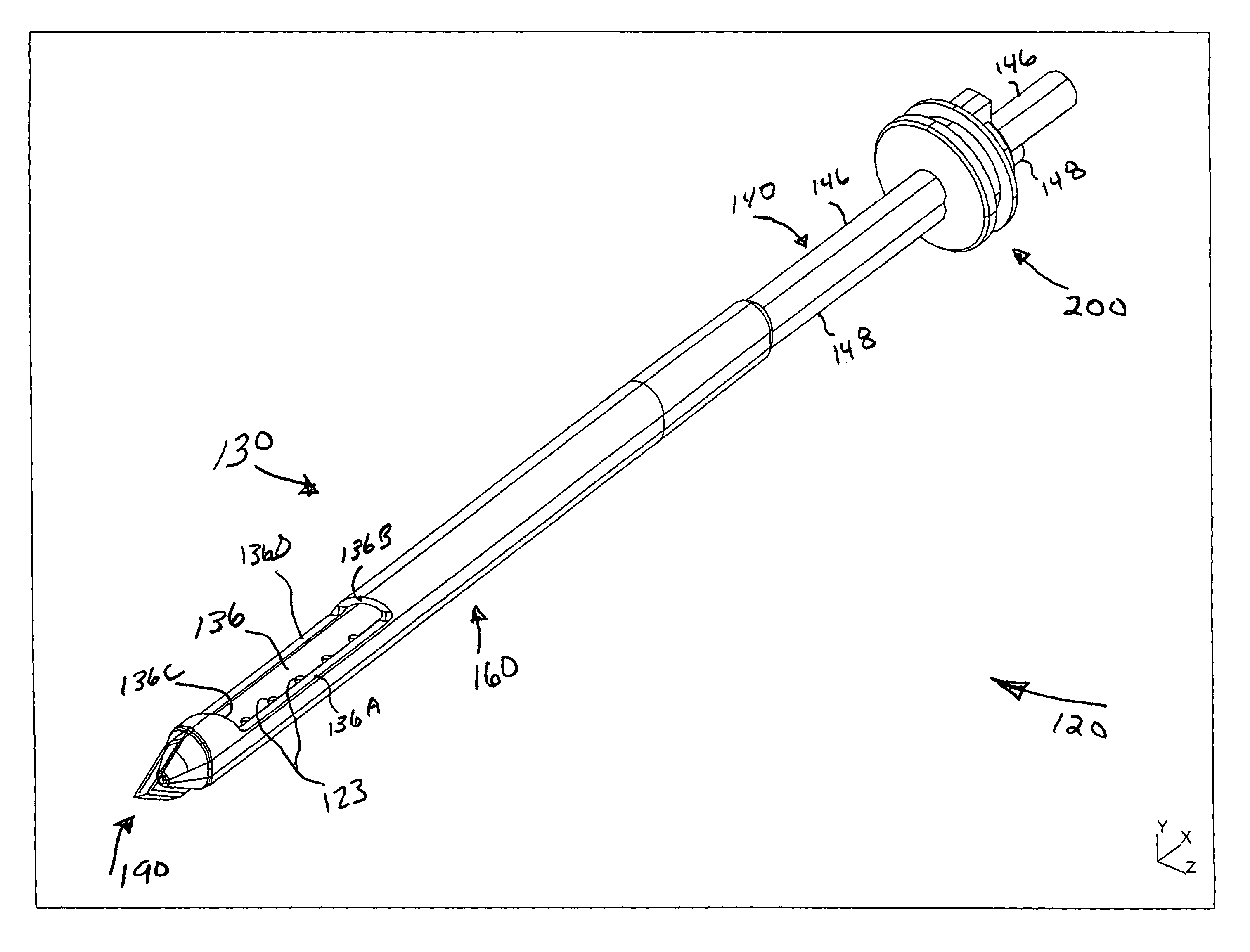
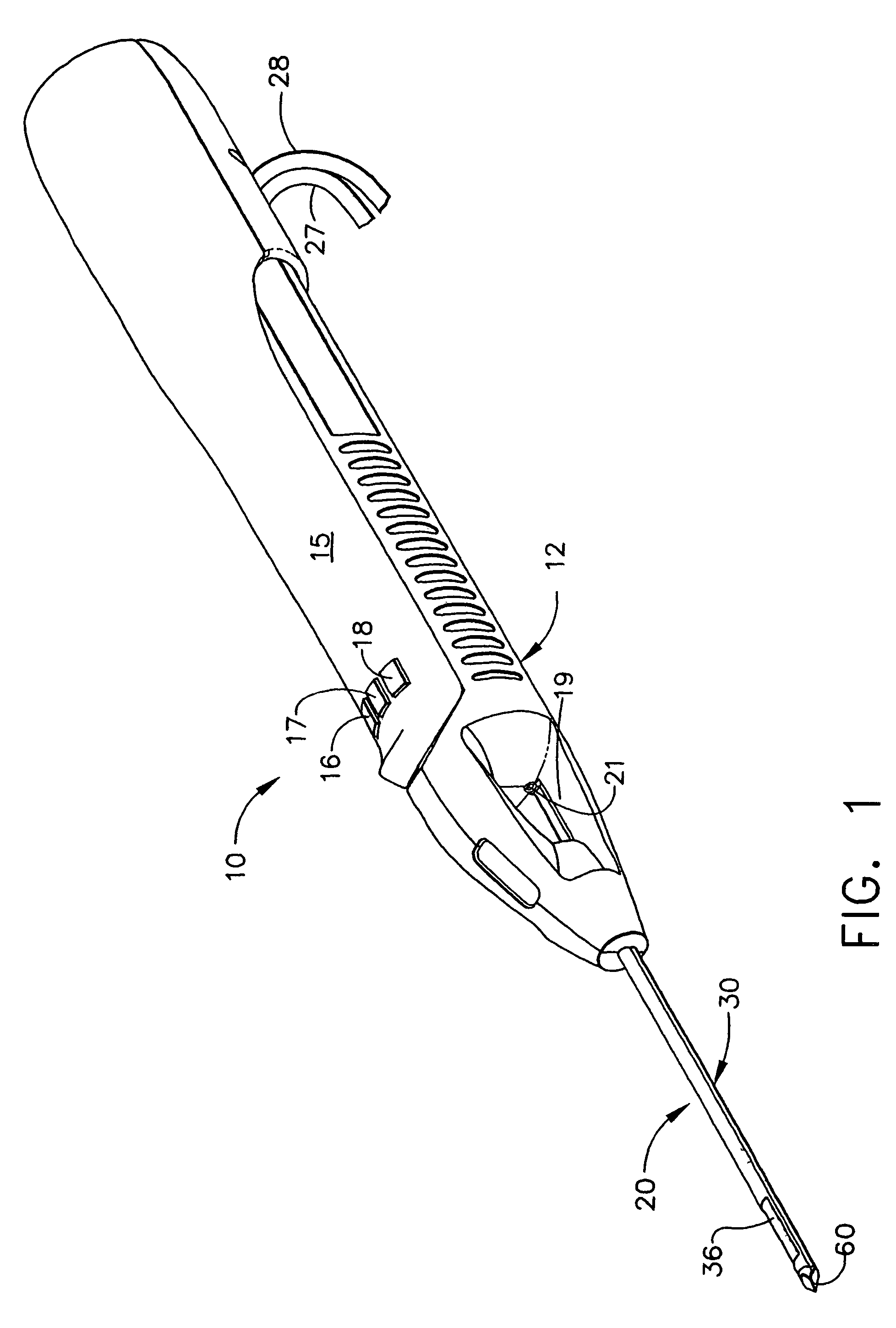
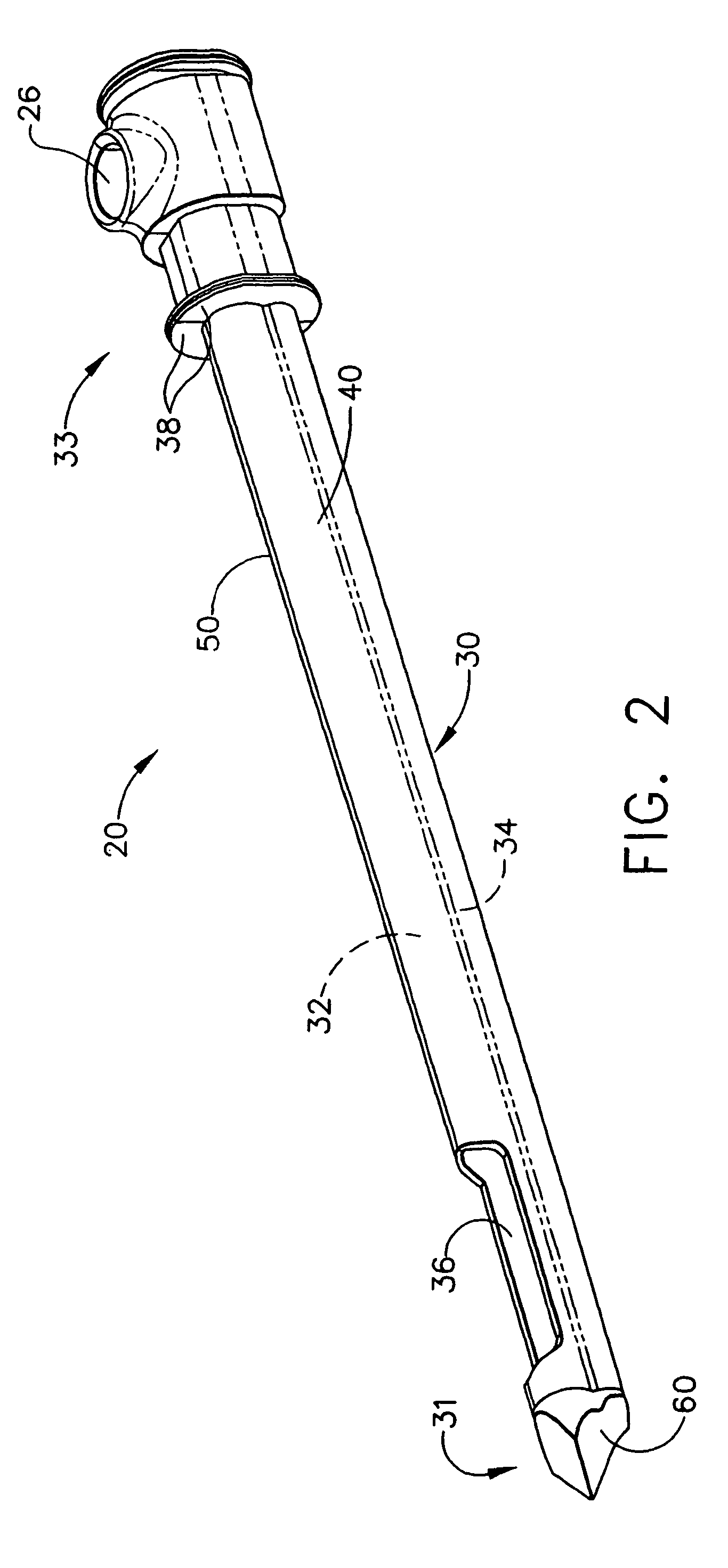
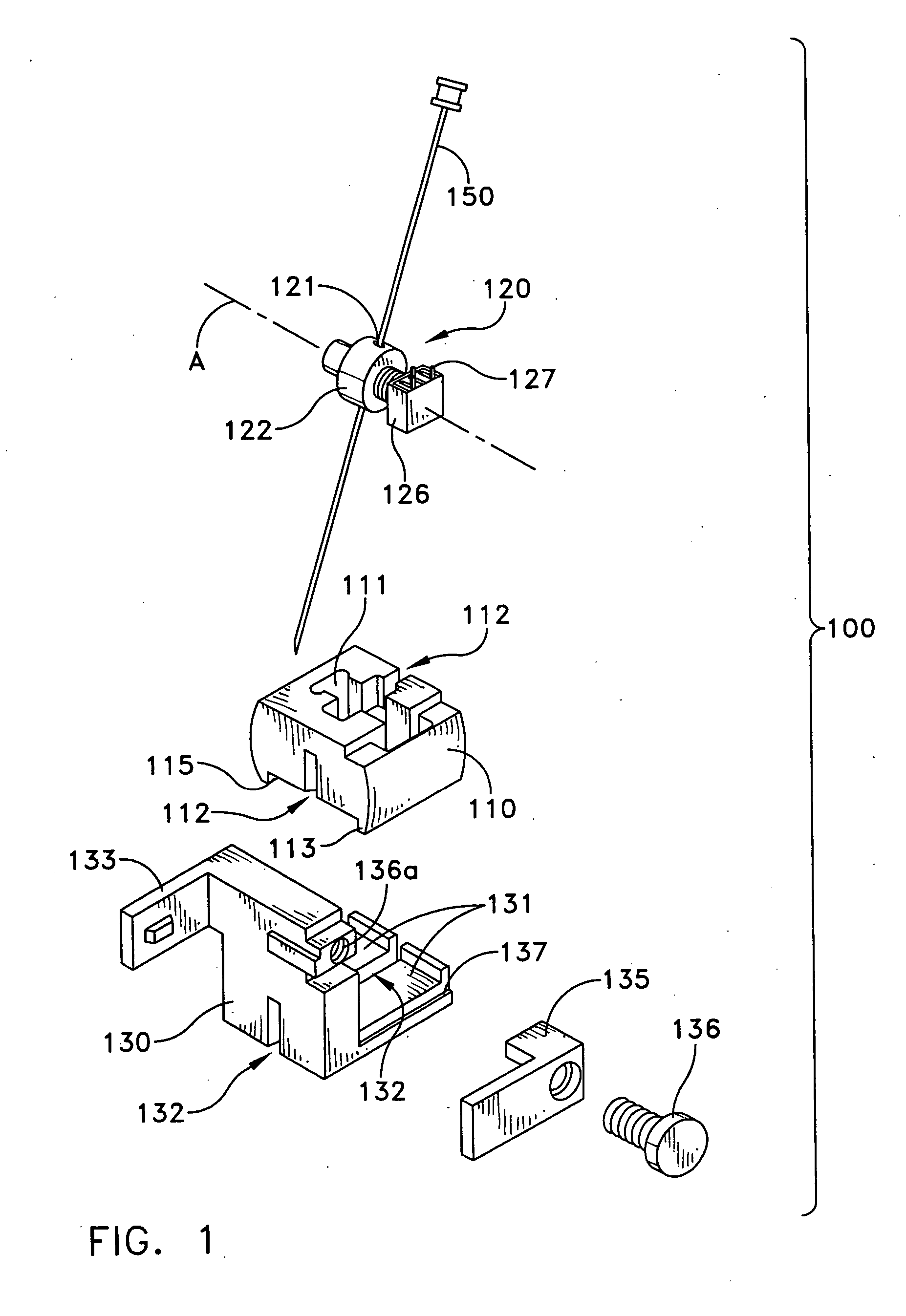
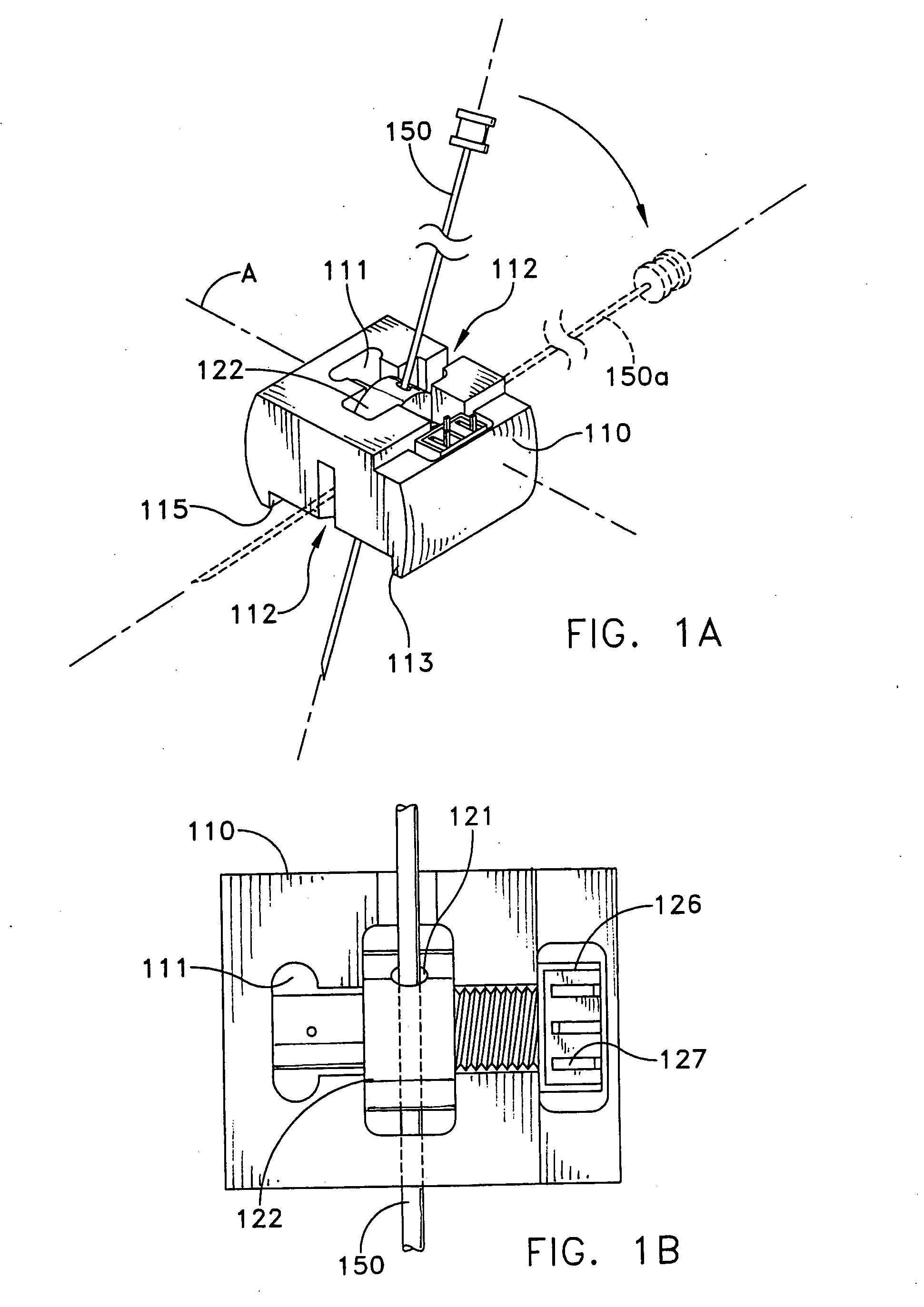
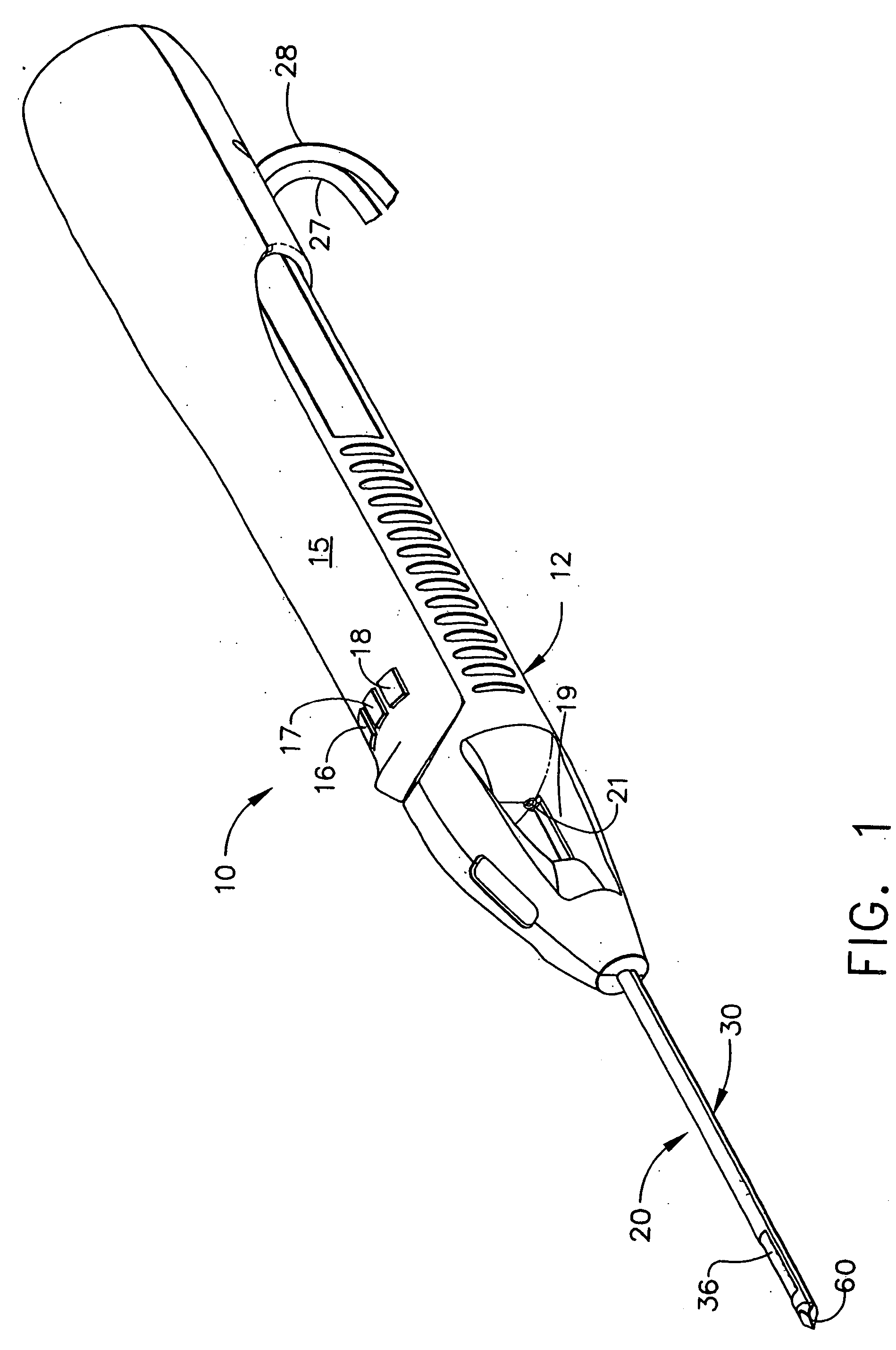
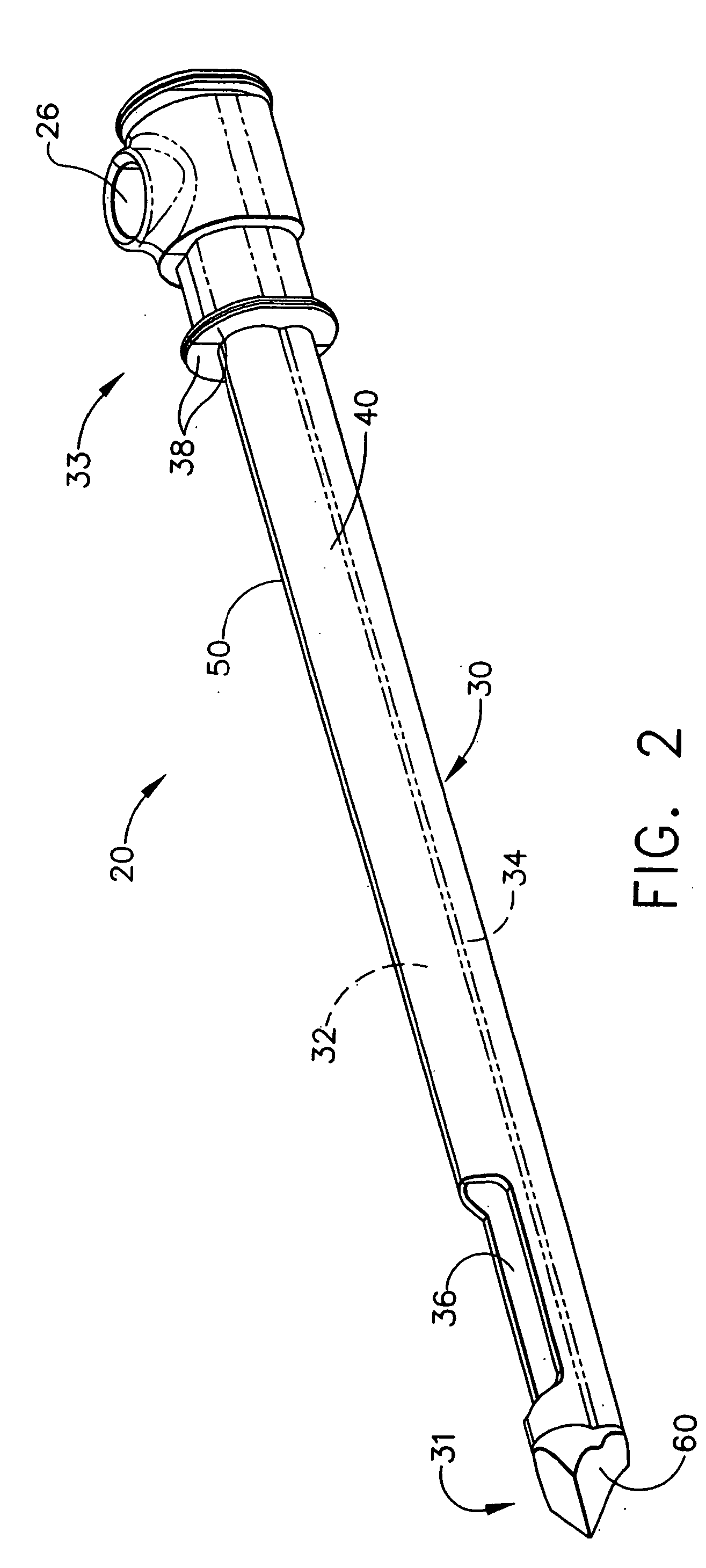
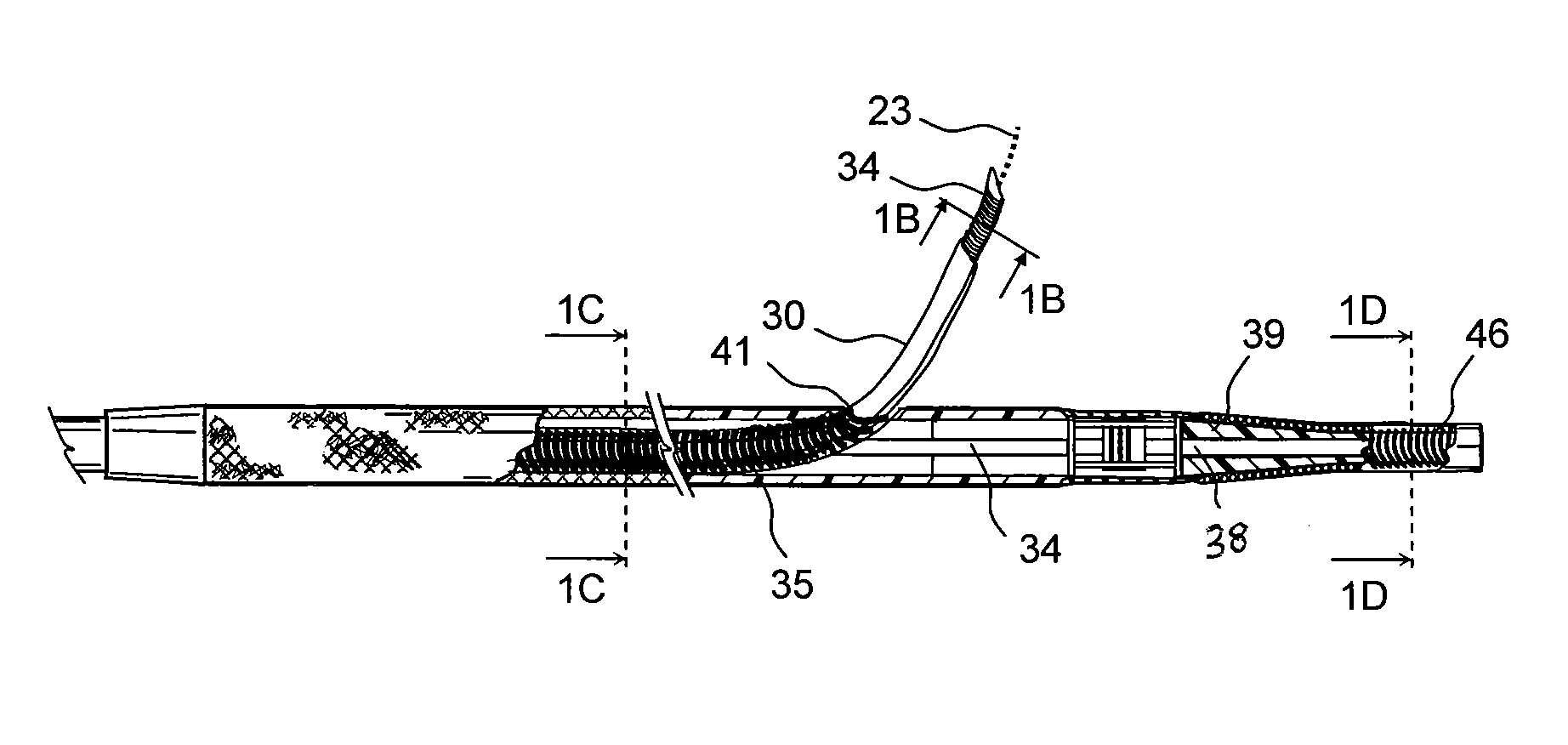
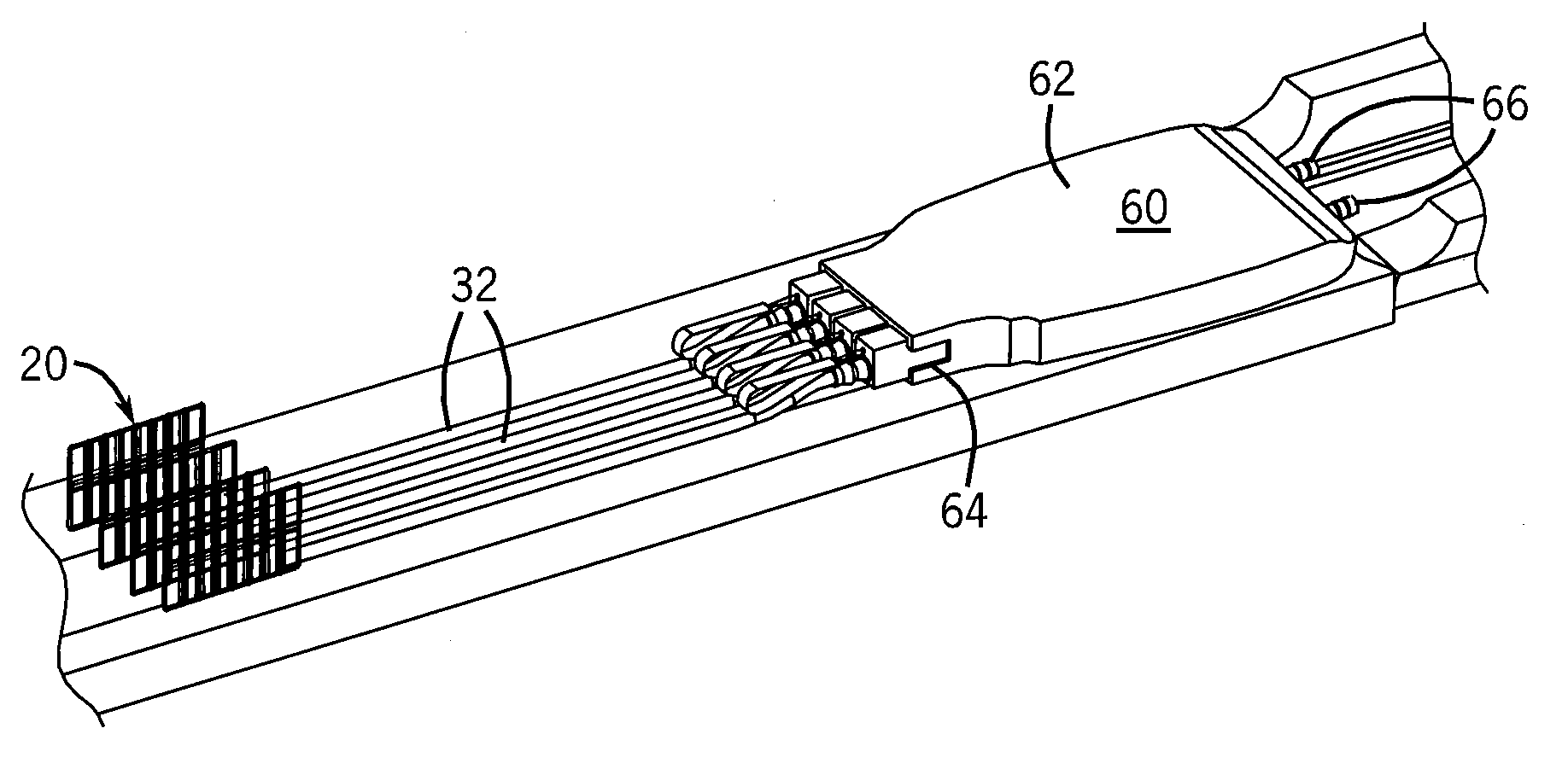
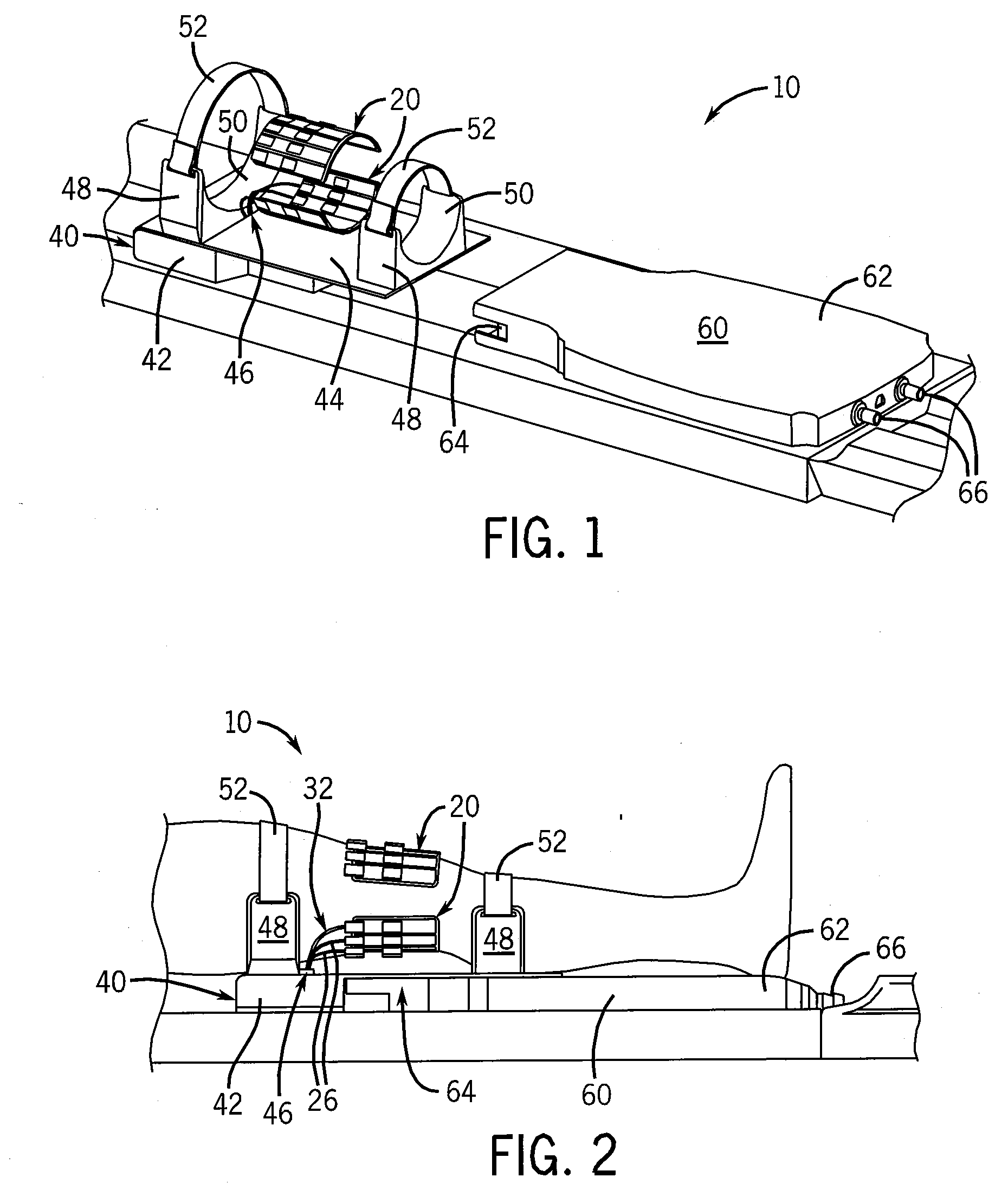
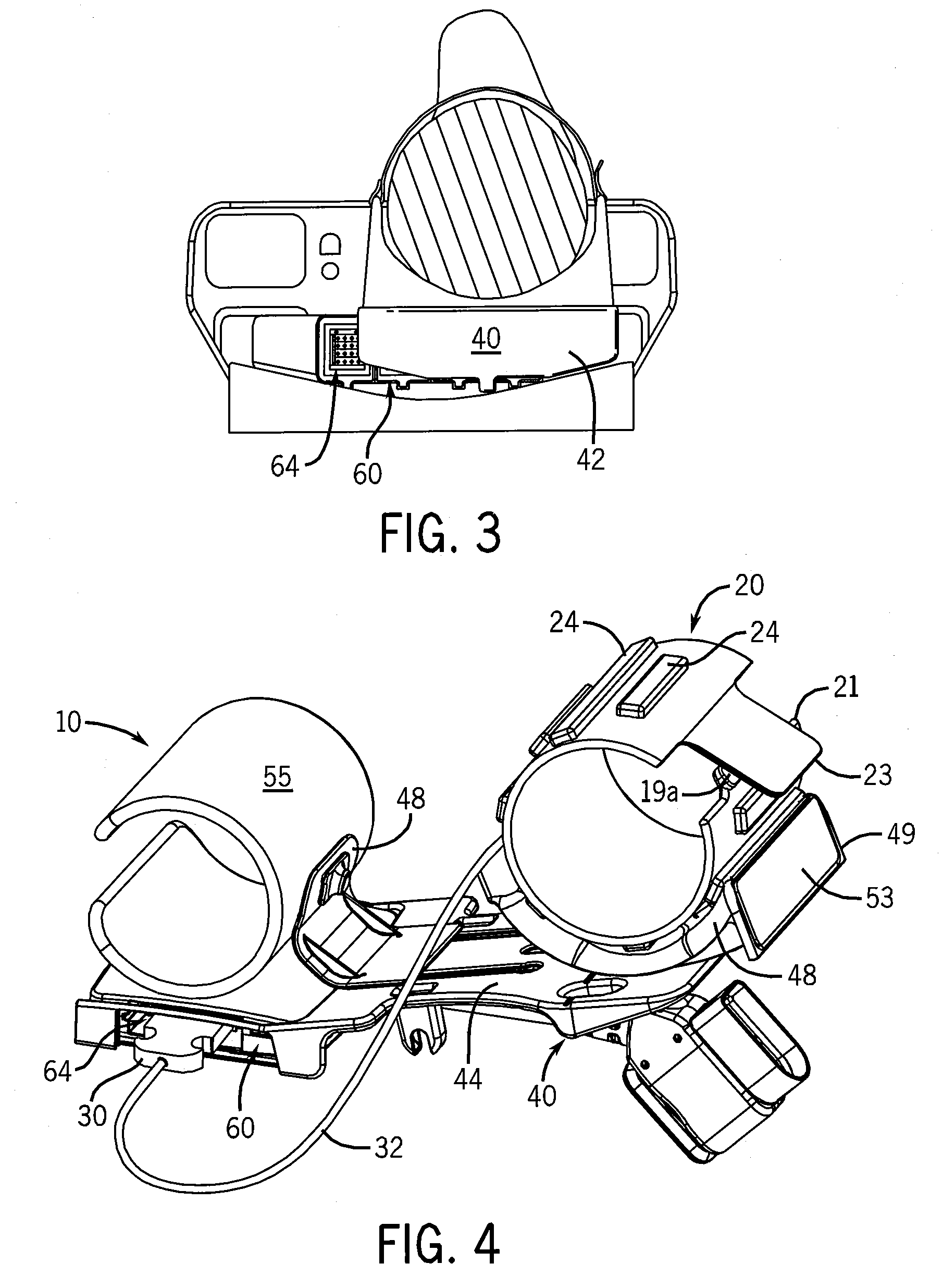
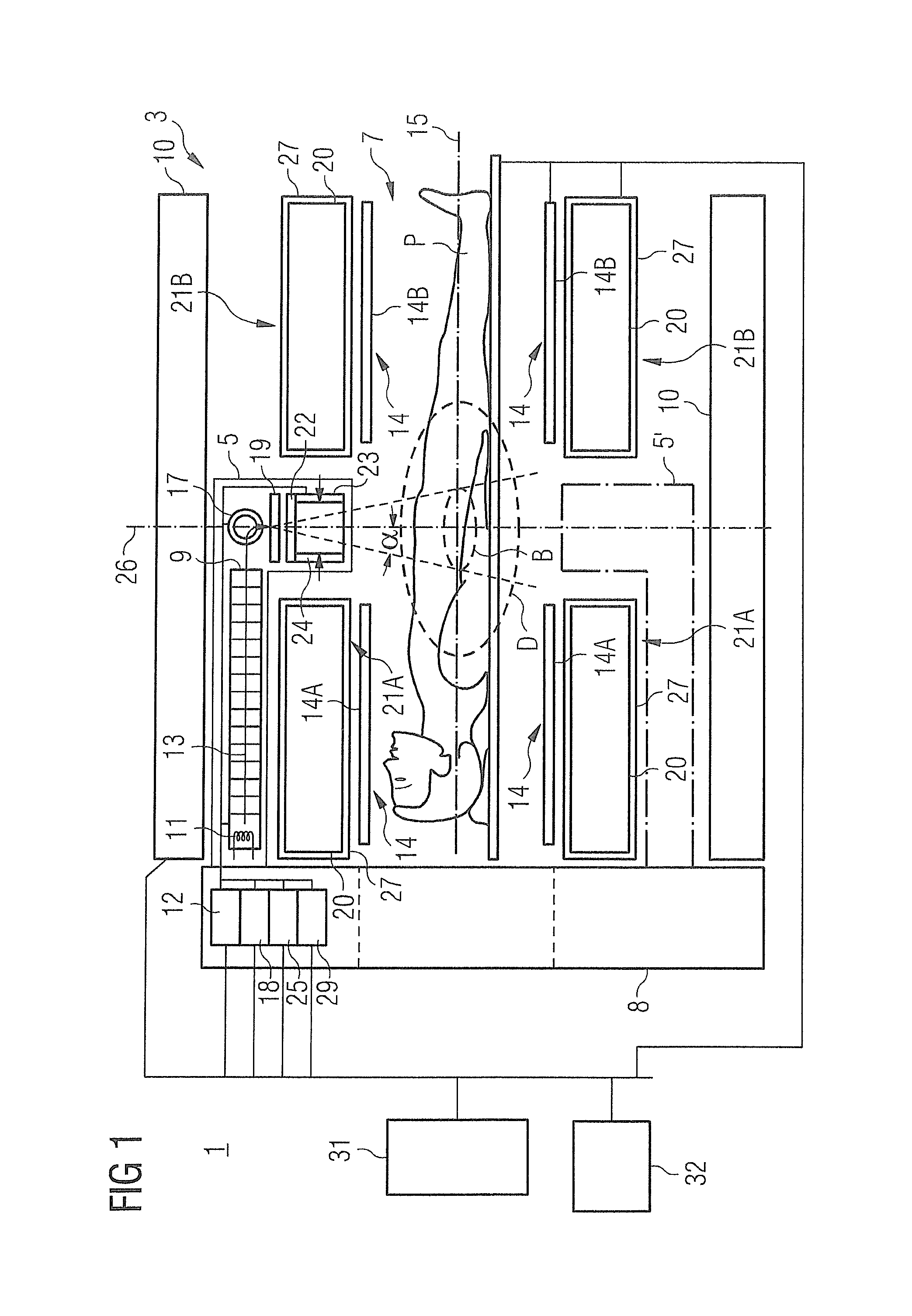
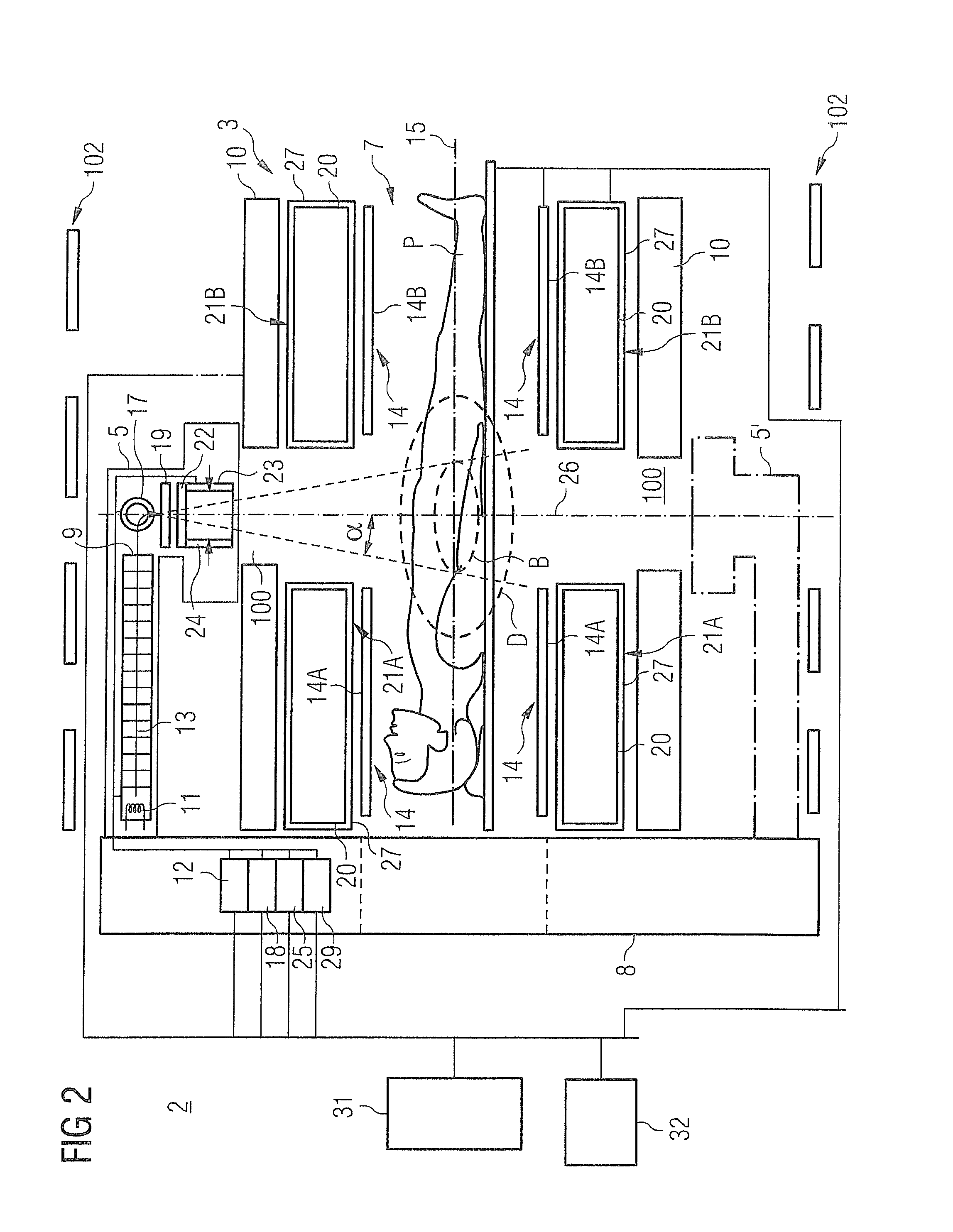
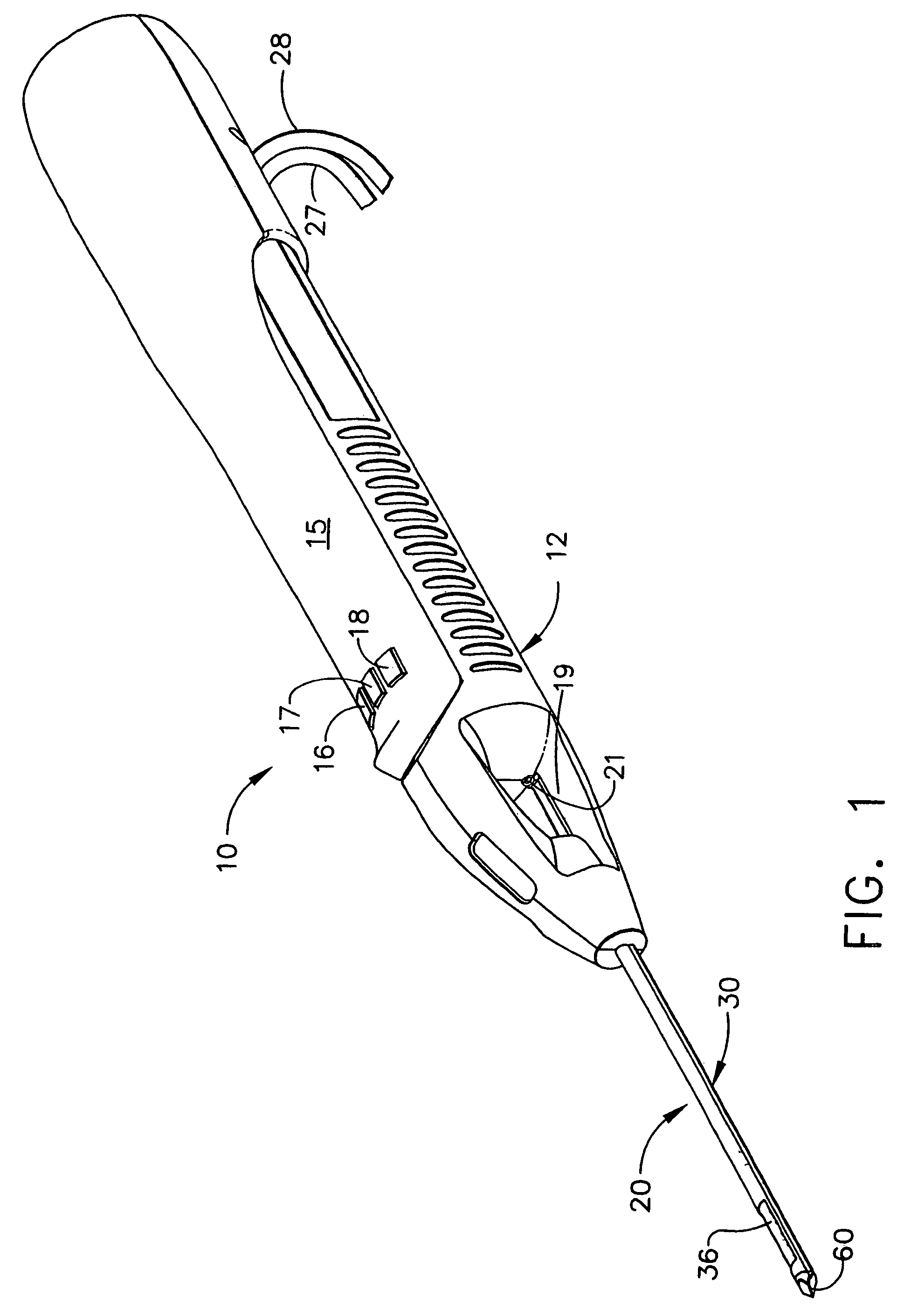
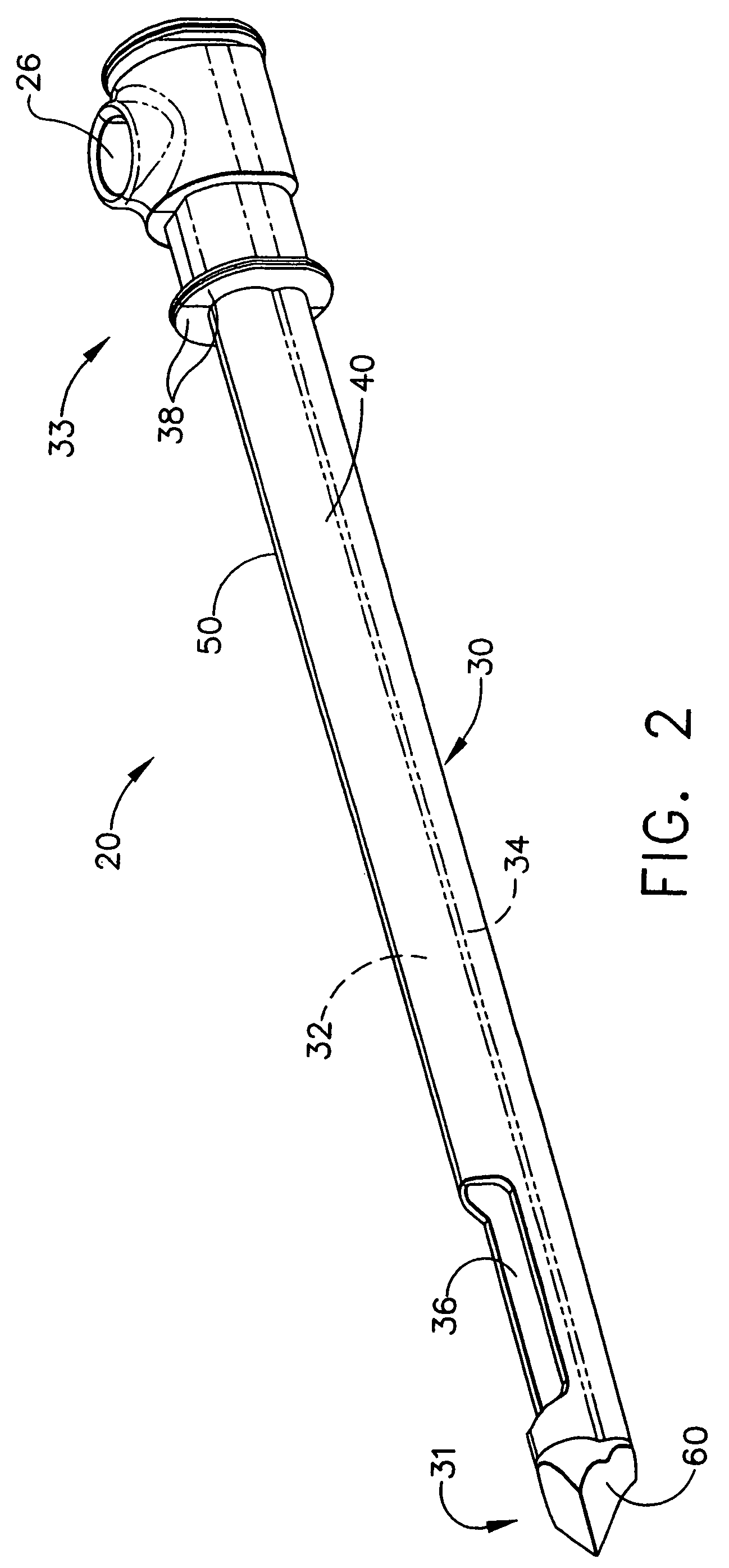
Probe guide for use with medical imaging systems
InactiveUS7846103B2Accurate placementEfficiently provide informationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesSingle imageCombined use
An improved probe guide and probe guide system for use in conjunction with a medical imaging device is disclosed. The medical imaging device may be any type of imaging device that generates a cross-sectional image of a portion of a patient's body in a single image plane, such as, ultrasound, CT, or MRI imaging devices. The probe guide allows maintaining the movement of the probe within the image plane and accurate placement of a probe, such as a biopsy needle, by allowing a range of angular translation of the probe. The probe guide system enables extrapolation of the penetration path of the probe held by the probe guide and superimpose it on to the cross-sectional image allowing the medical personnel to view the penetration path of the probe within the patient in advance.
Owner:MEDICAL EQUIP DIVERSIFIED SERVICES
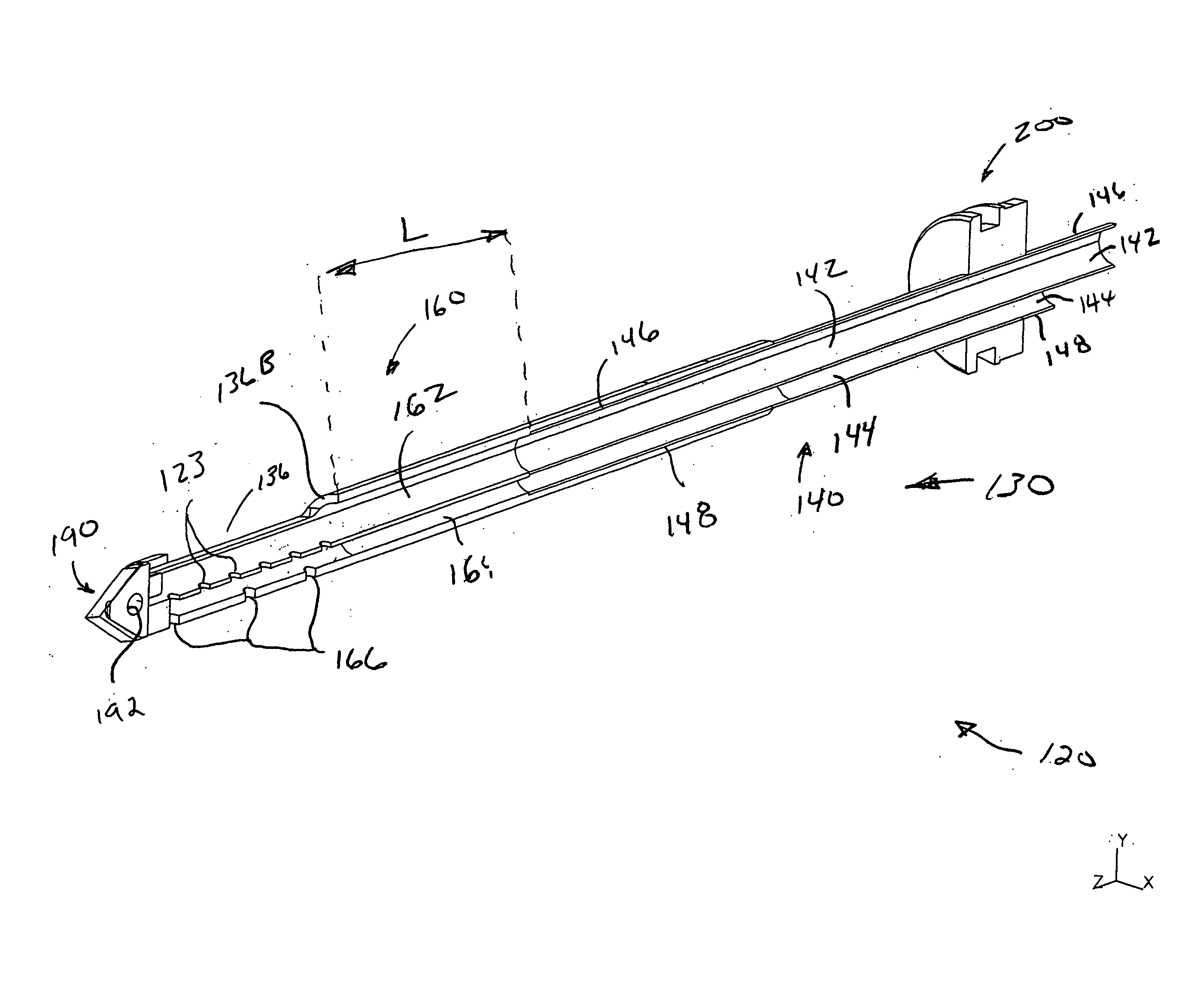
Biopsy device
InactiveUS9345456B2Maintain stiffnessMaintain strengthSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDistal portionBiopsy device
An improved needle assembly is provided. A distal portion of the needle can be formed of a first material which does not interfere with MRI imaging of a tissue receiving port disposed in the distal needle portion. A proximal needle portion can be formed of a second, different material. The proximal needle portion can provide strength and stiffness.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
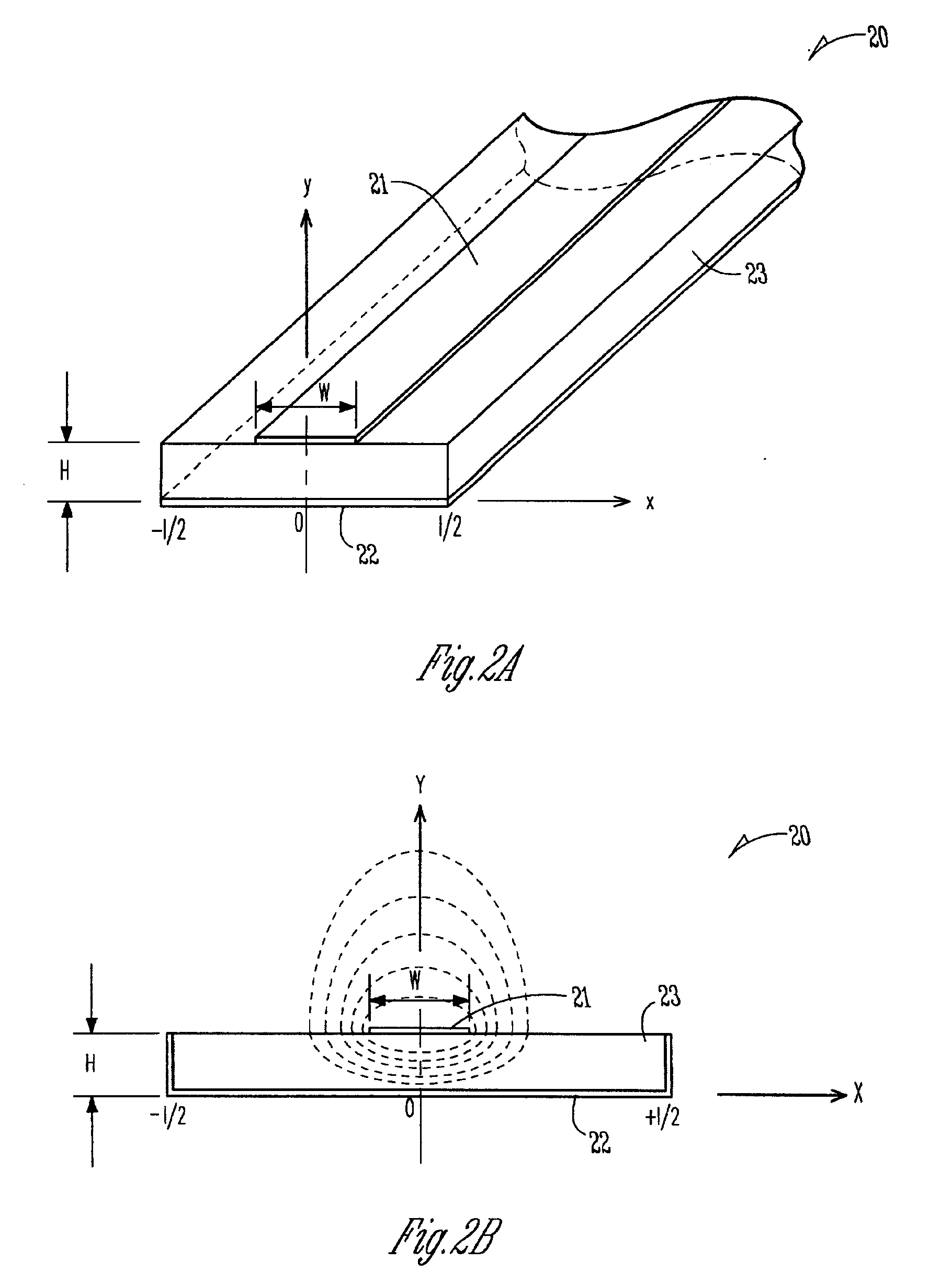
Method and apparatus for magnetic resonance imaging and spectroscopy using microstrip transmission line coils
InactiveUS7023209B2Easy to manufactureLow costMaterial analysis using microwave meansMagnetsSpectroscopyMri image
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
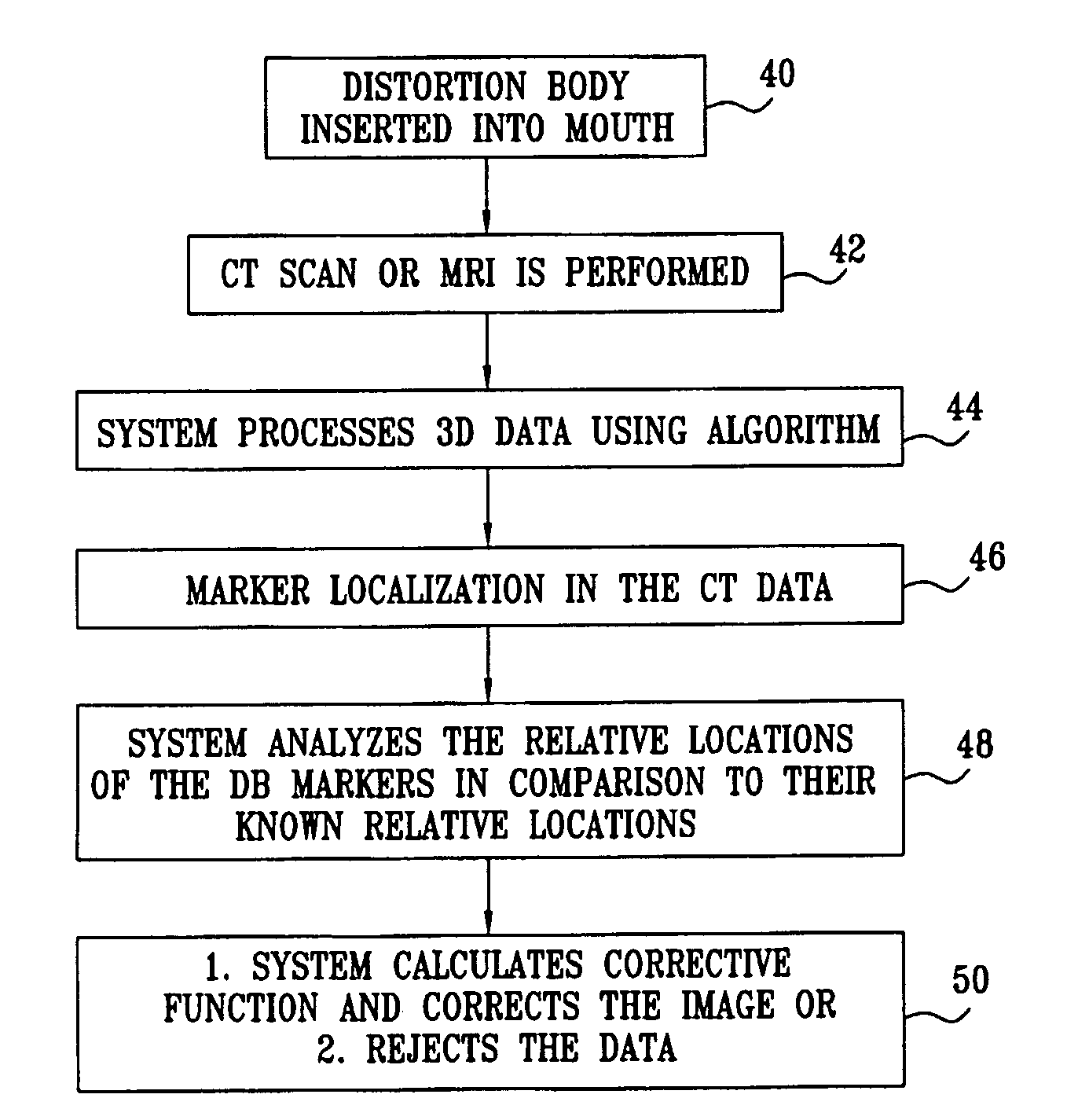
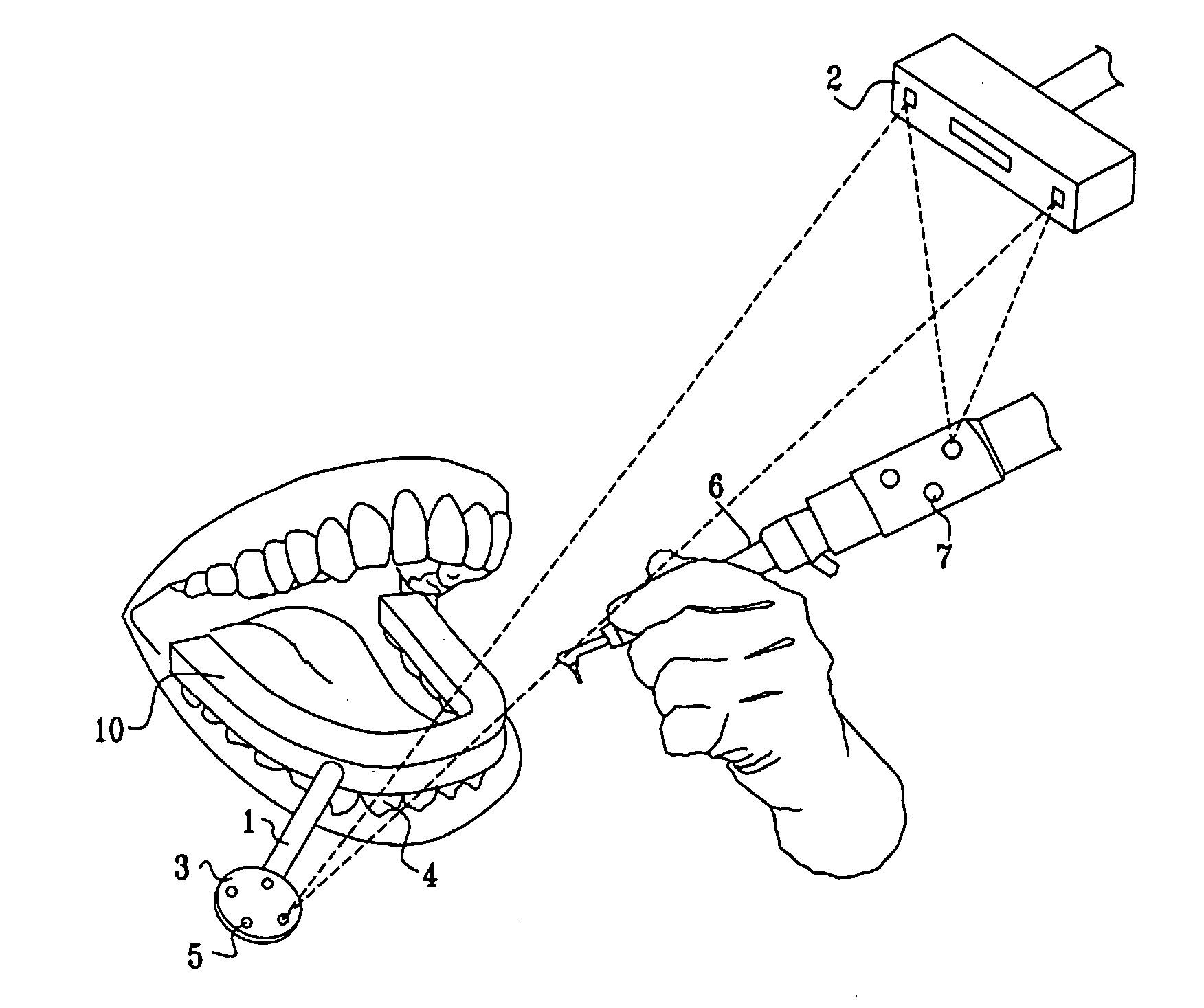
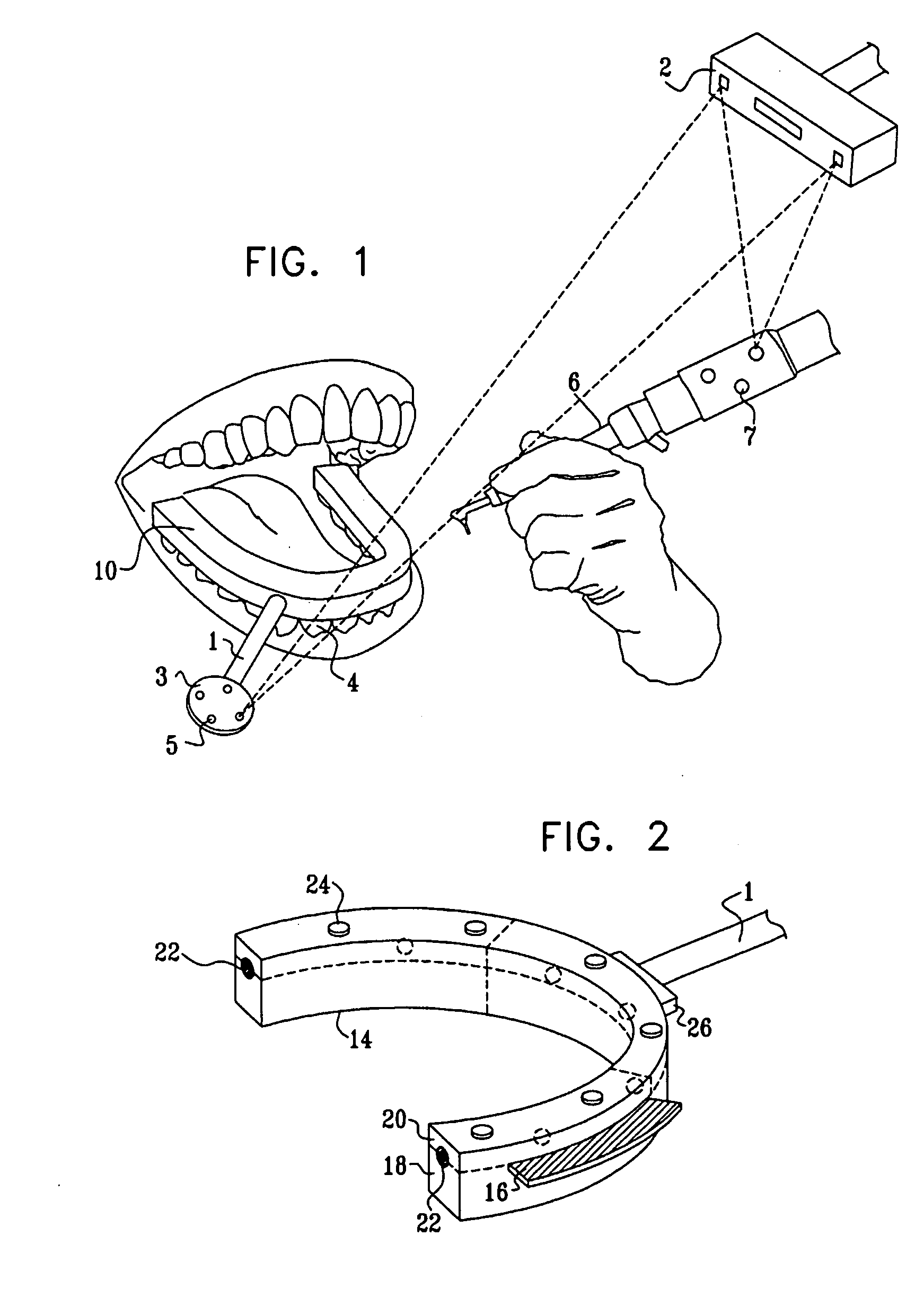
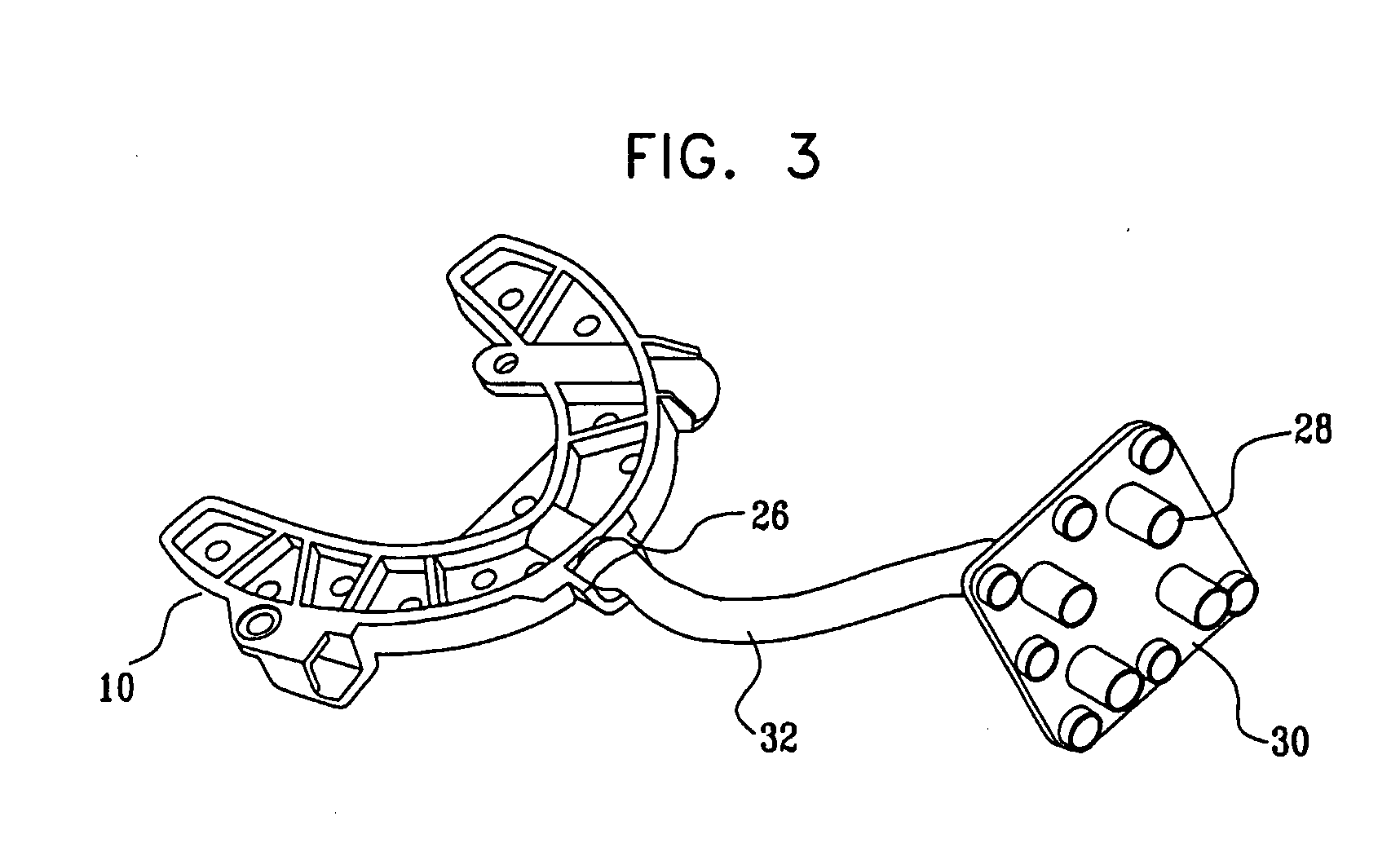
Image guided implantology methods
InactiveUS7457443B2Accurate dataEfficient use ofImpression capsImage analysisThree dimensional ctMri image
A method for correcting inherent distortions in a CT or MRI imaging process, or distortions arising from excessive patient movement during the scan by means of a registration device inserted into the mouth of the patient at the time the scan is being performed. The registration device incorporates a set of fiducial markers disposed in a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. The exact positions of the fiducial markers are known with respect to each other, thus providing a three-dimensional reference against which the resulting images can be compared. Additionally, a method whereby three-dimensional CT or MRI images taken prior to an operation, are accurately registered and integrated with real-time tracking positional data of the patient's body part and instruments operating thereon. Application is described for the drilling of a patient's jaw for the placement of dental implants.
Owner:IMAGE NAVIGATION LTD
Image guided implantology methods
InactiveUS20050163342A1Accurate dataEfficient use ofImpression capsImage analysisThree dimensional ctMri image
A method for correcting inherent distortions in a CT or MRI imaging process, or distortions arising from excessive patient movement during the scan by means of a registration device inserted into the mouth of the patient at the time the scan is being performed. The registration device incorporates a set of fiducial markers disposed in a predetermined three-dimensional pattern. The exact positions of the fiducial markers are known with respect to each other, thus providing a three-dimensional reference against which the resulting images can be compared. Additionally, a method whereby three-dimensional CT or MRI images taken prior to an operation, are accurately registered and integrated with real-time tracking positional data of the patient's body part and instruments operating thereon. Application is described for the drilling of a patient's jaw for the placement of dental implants.
Owner:IMAGE NAVIGATION LTD
Probe guide for use with medical imaging systems
InactiveUS20060064010A1Accurate placementEfficiently provide informationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical needlesSystems medicineSingle image
An improved probe guide and probe guide system for use in conjunction with a medical imaging device is disclosed. The medical imaging device may be any type of imaging device that generates a cross-sectional image of a portion of a patient's body in a single image plane, such as, ultrasound, CT, or MRI imaging devices. The probe guide allows maintaining the movement of the probe within the image plane and accurate placement of a probe, such as a biopsy needle, by allowing a range of angular translation of the probe. The probe guide system enables extrapolation of the penetration path of the probe held by the probe guide and superimpose it on to the cross-sectional image allowing the medical personnel to view the penetration path of the probe within the patient in advance.
Owner:MEDICAL EQUIP DIVERSIFIED SERVICES
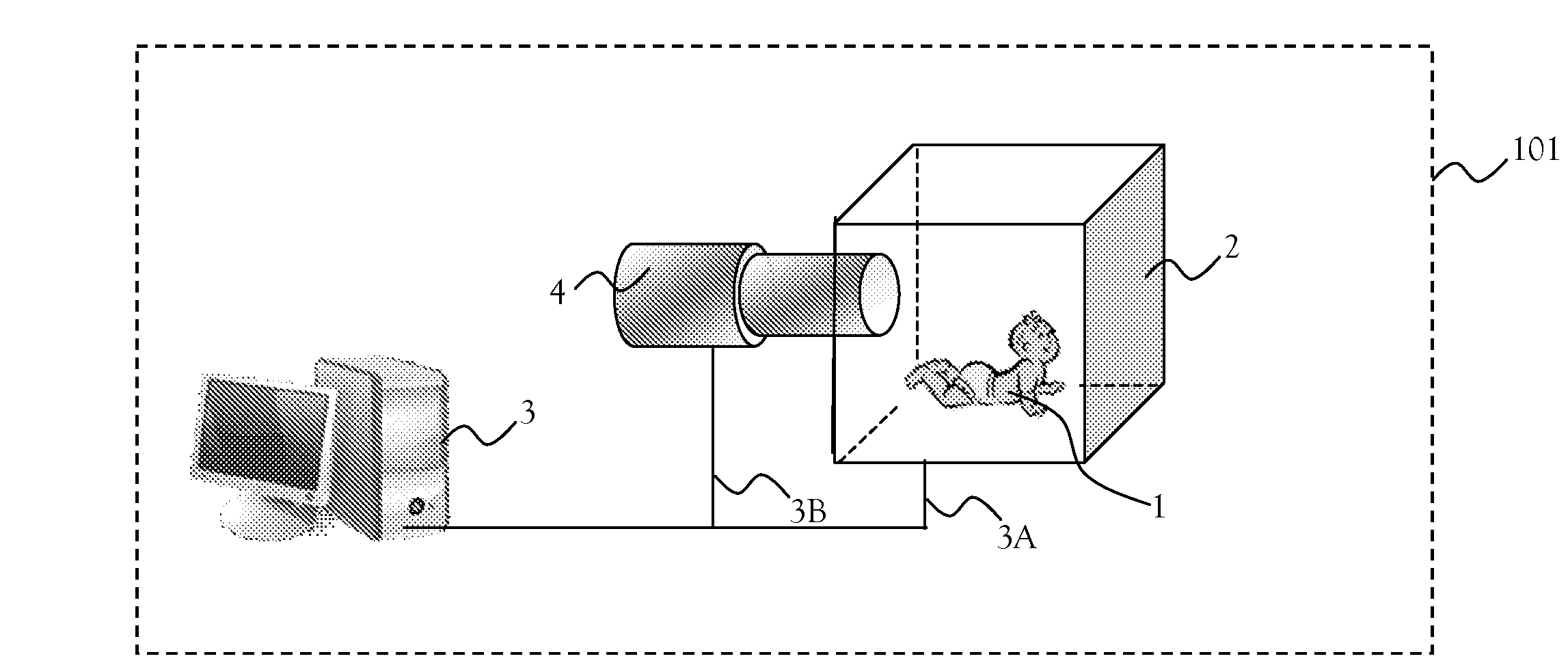
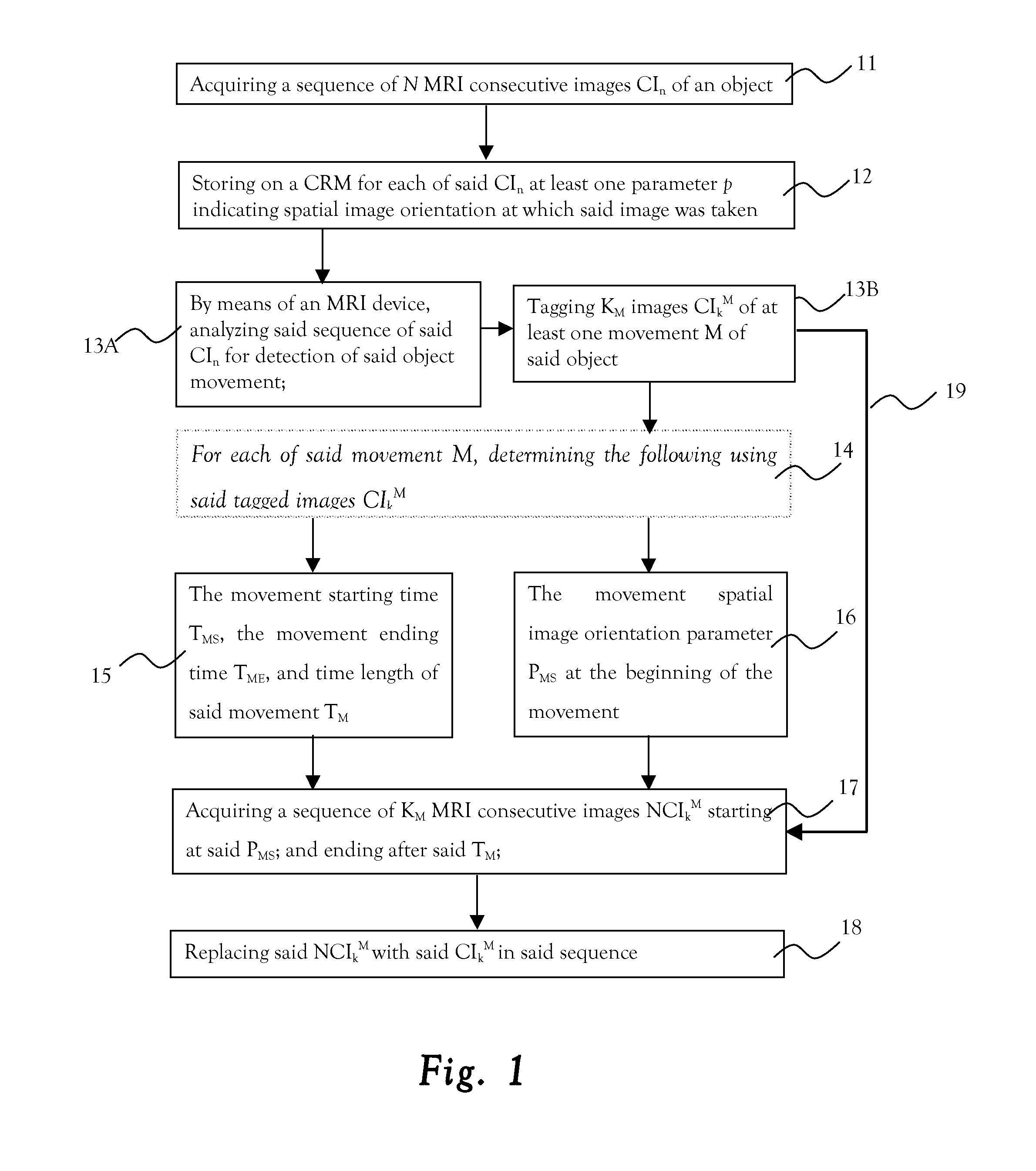
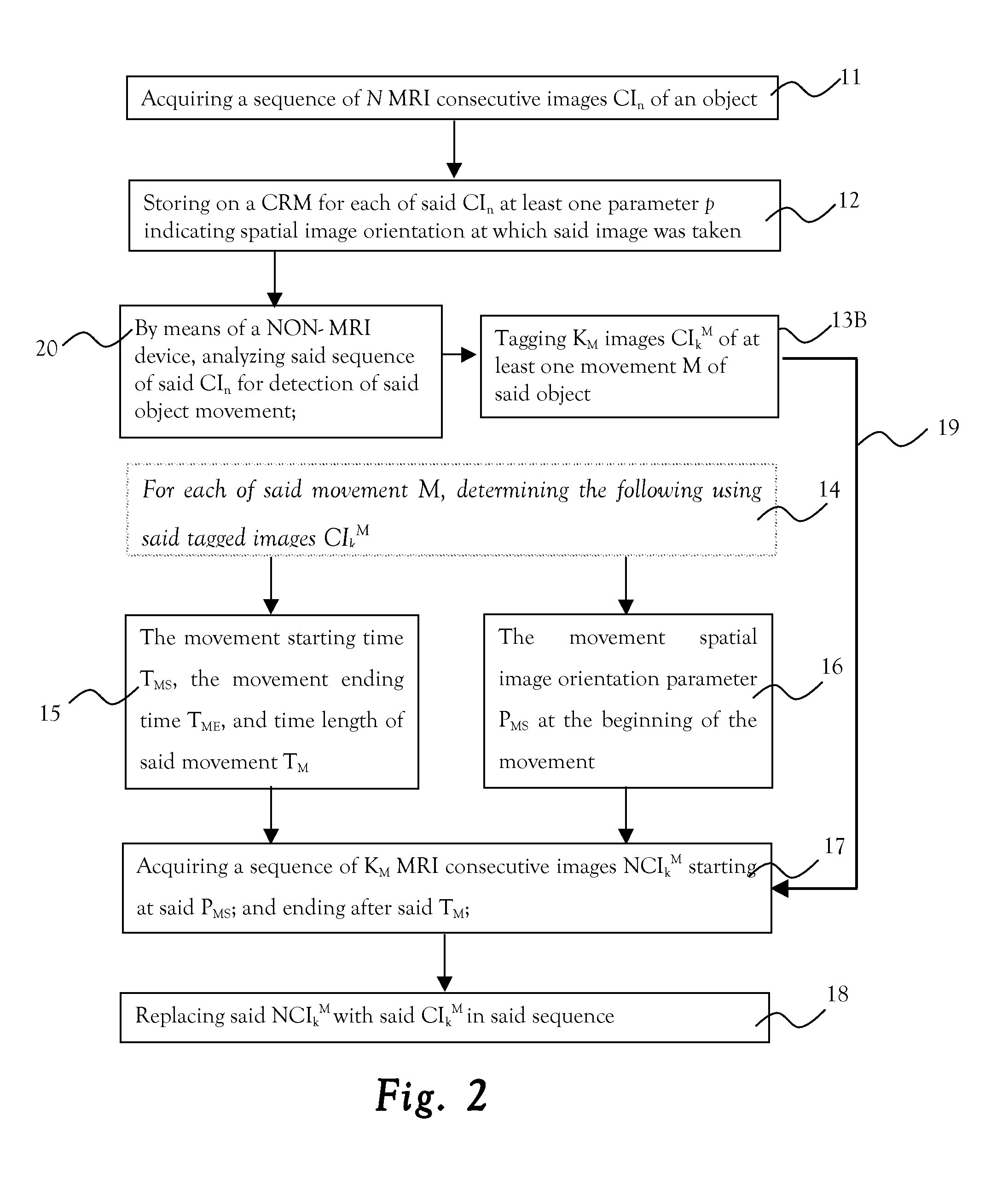
MRI system with means to eliminate object movement whilst acquiring its image
ActiveUS20140099010A1AvoidingReduced object-movementImage analysisMagnetic measurementsObject motionSpatial image
A method of reducing the effect of object movements along MRI imaging. The method includes: acquiring a sequence of MRI consecutive images of an object; storing on a computer readable medium, for each of the images, at least one parameter p indicating spatial image orientation at which the image was taken; analyzing the sequence of the images for detection of the object movement; and tagging images of at least one movement of the object.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Dedicated Superconductor MRI Imaging System
ActiveUS20100066368A1Quality improvementImprove image qualityElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceThermal isolationEngineering
The present invention relates to dedicated superconductor magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF apparatus and method of constructing the same. One Embodiment of the present invention provides an MRI breast imaging apparatus comprising an examination region, a patient support, at least one vacuum thermal isolation housing, a main magnet system, and a cryogenic system. The vacuum thermal isolation housing comprises a low vacuum space between at least one inner and an outer high vacuum enclosure. The low vacuum space hosts at least one superconductor RF coil and a heat sink assembly therein. The RF coil is in thermal contact with the heat sink assembly that is coupled to the cryogenic system through a heat pipe to achieve and maintain a desired low temperature at the superconductor RF coil. The system provides a local examination region substantially surrounded by the superconductor RF coil.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Biopsy device
InactiveUS20050215922A1Maintaining stiffness characteristicMaintain strengthSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDistal portionBiopsy device
An improved needle assembly is provided. A distal portion of the needle can be formed of a first material which does not interfere with MRI imaging of a tissue receiving port disposed in the distal needle portion. A proximal needle portion can be formed of a second, different material. The proximal needle portion can provide strength and stiffness.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
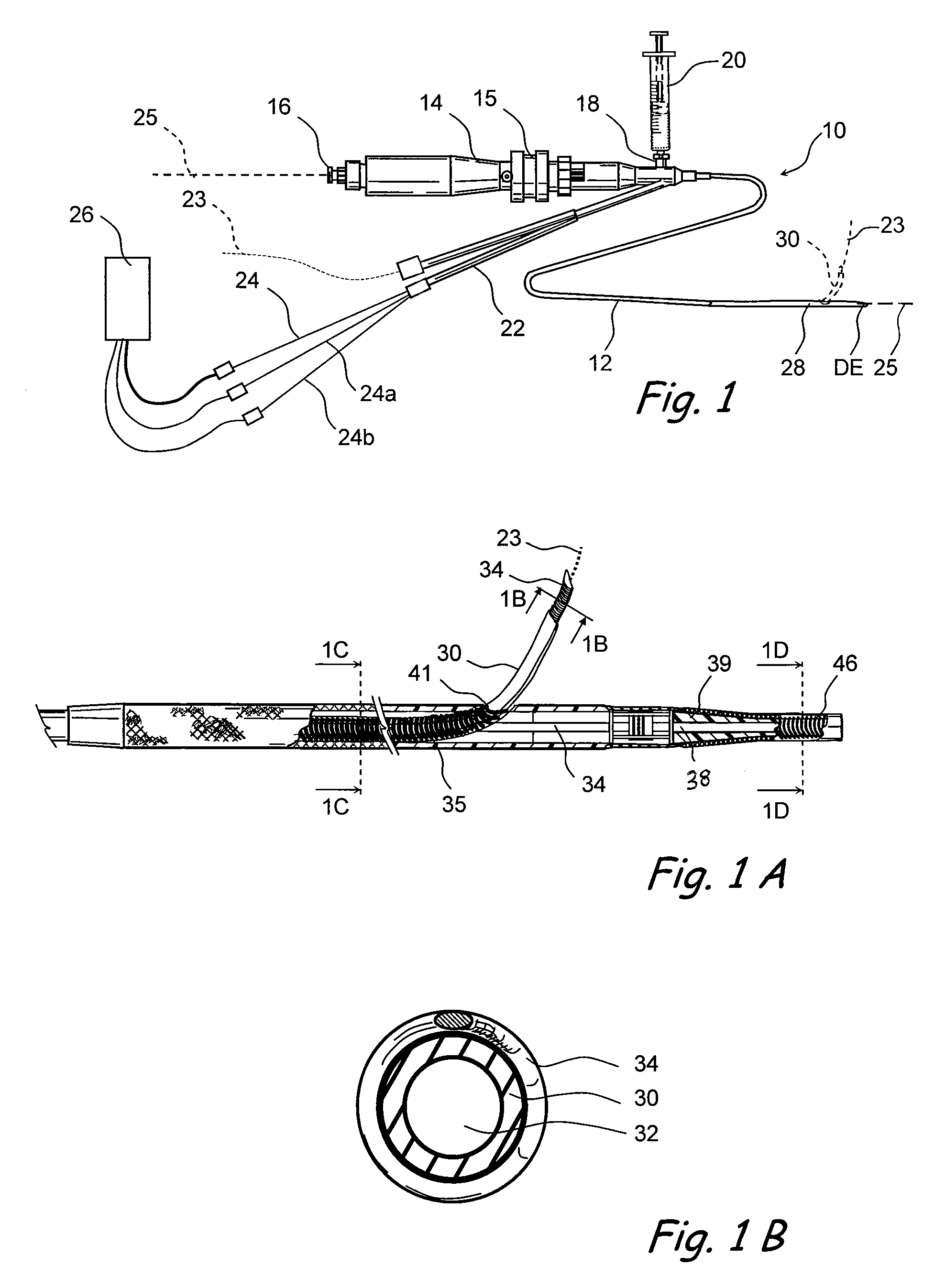
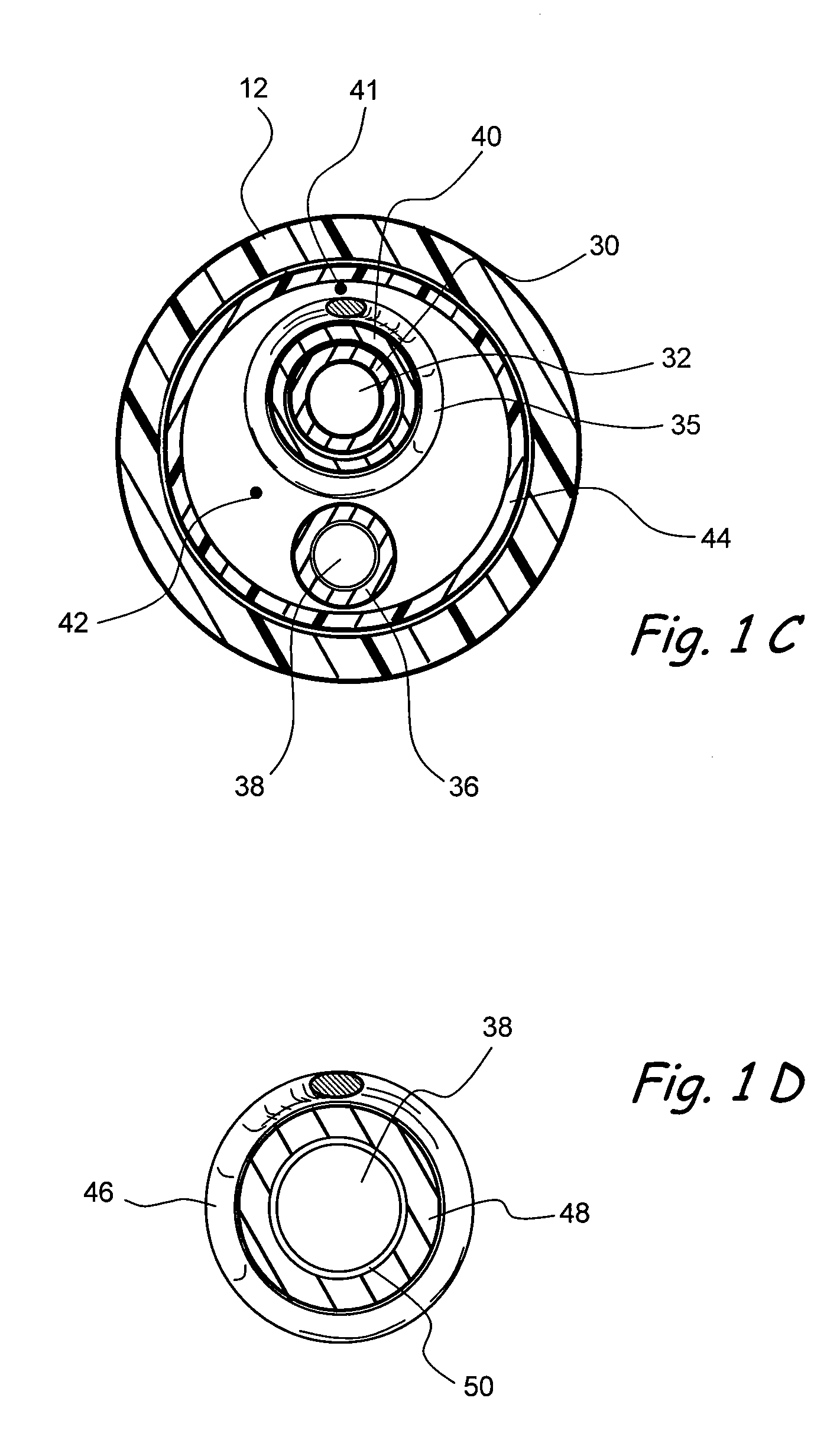
In vivo localization and tracking of tissue penetrating catheters using magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) guided tissue penetrating catheters and their methods of use. One or more MRI apparatus (e.g., one or more coils) are positioned on or in a catheter device that includes a tissue penetrator that may be used to form a penetration tract from a body lumen in which the catheter is positioned to a target location outside of that body lumen. The MRI apparatus (e.g., coil(s)) is / are used in conjunction with an MRI imaging system to indicate the position and / or rotational orientation of the penetrating catheter within the subject's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
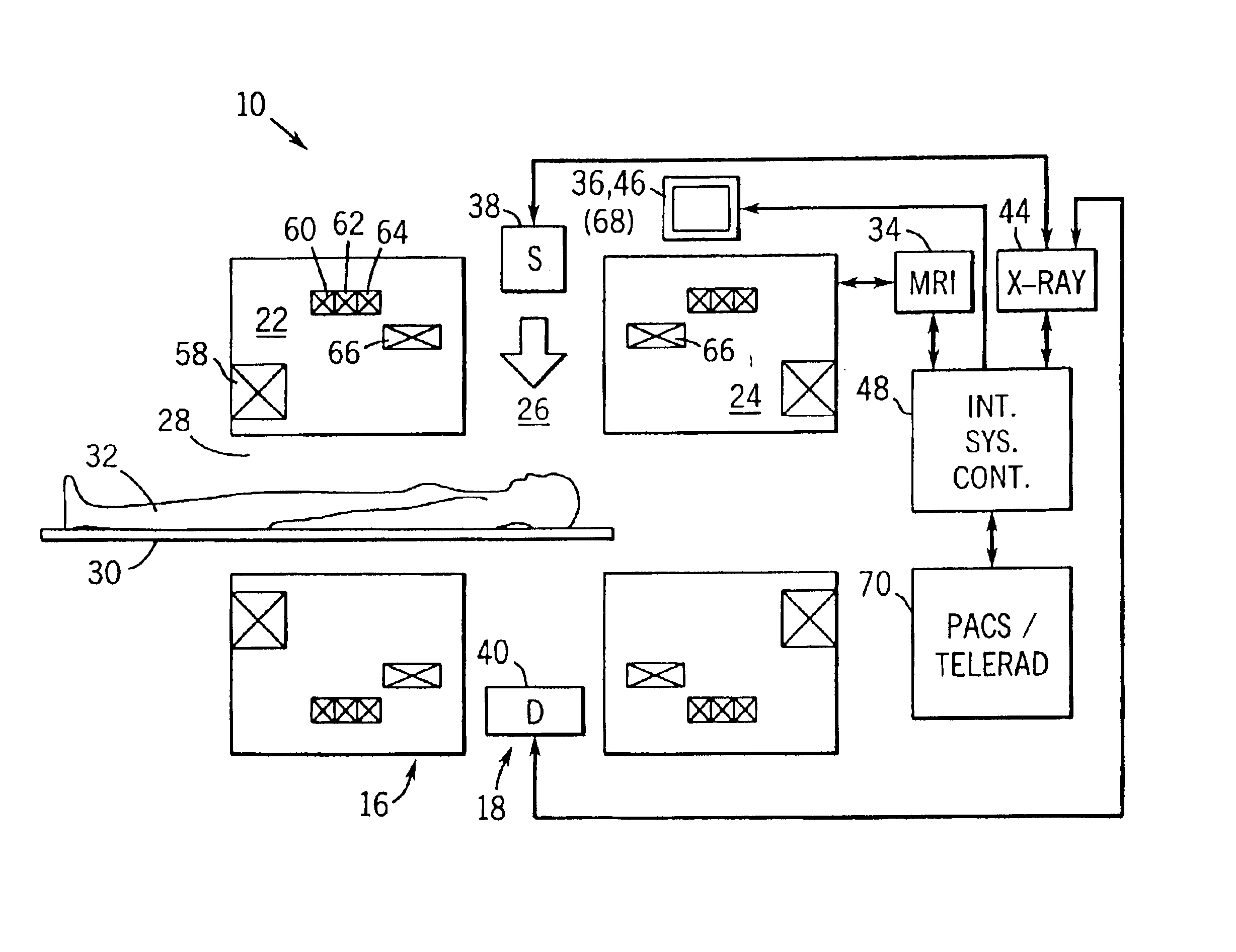
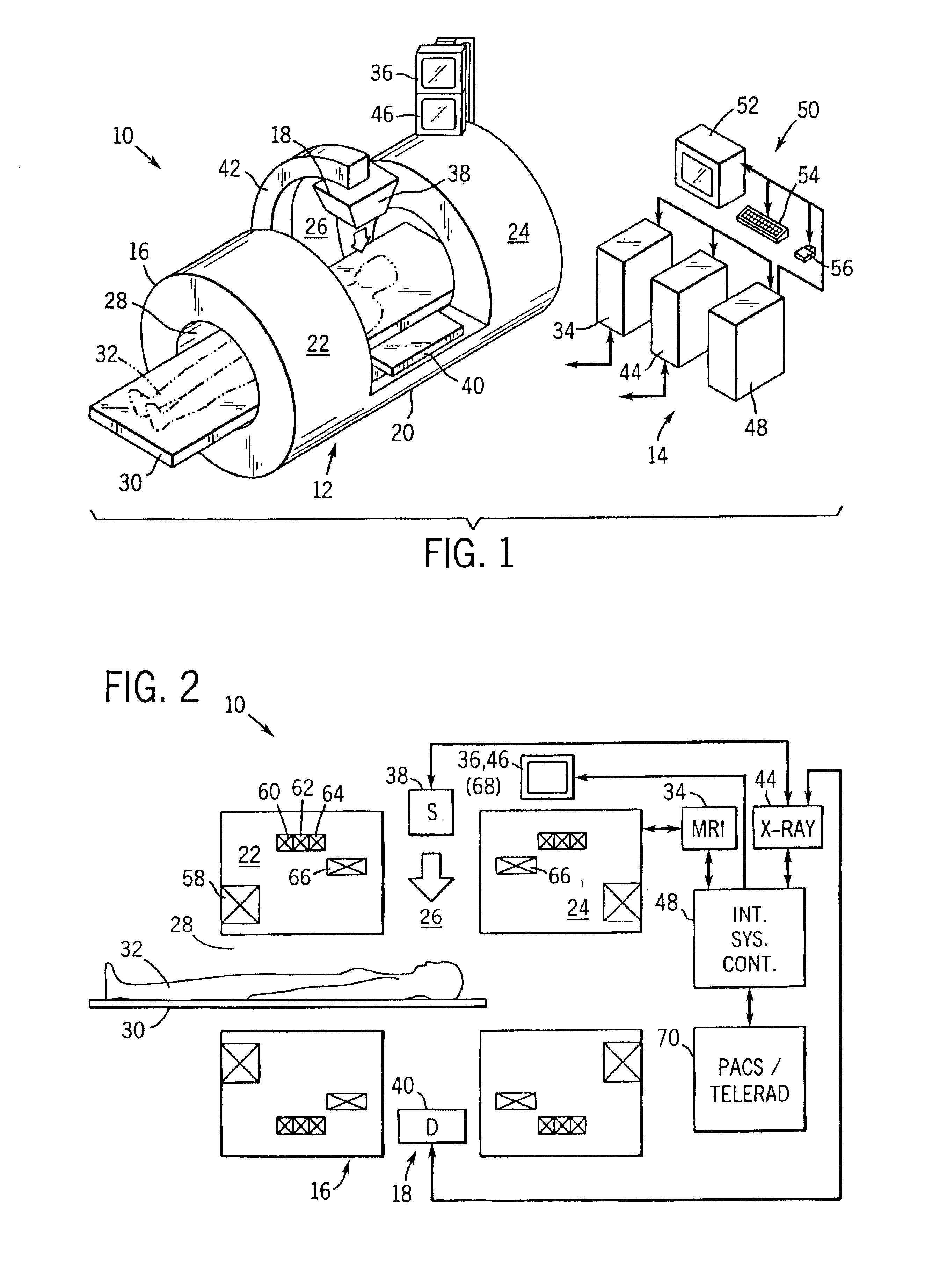
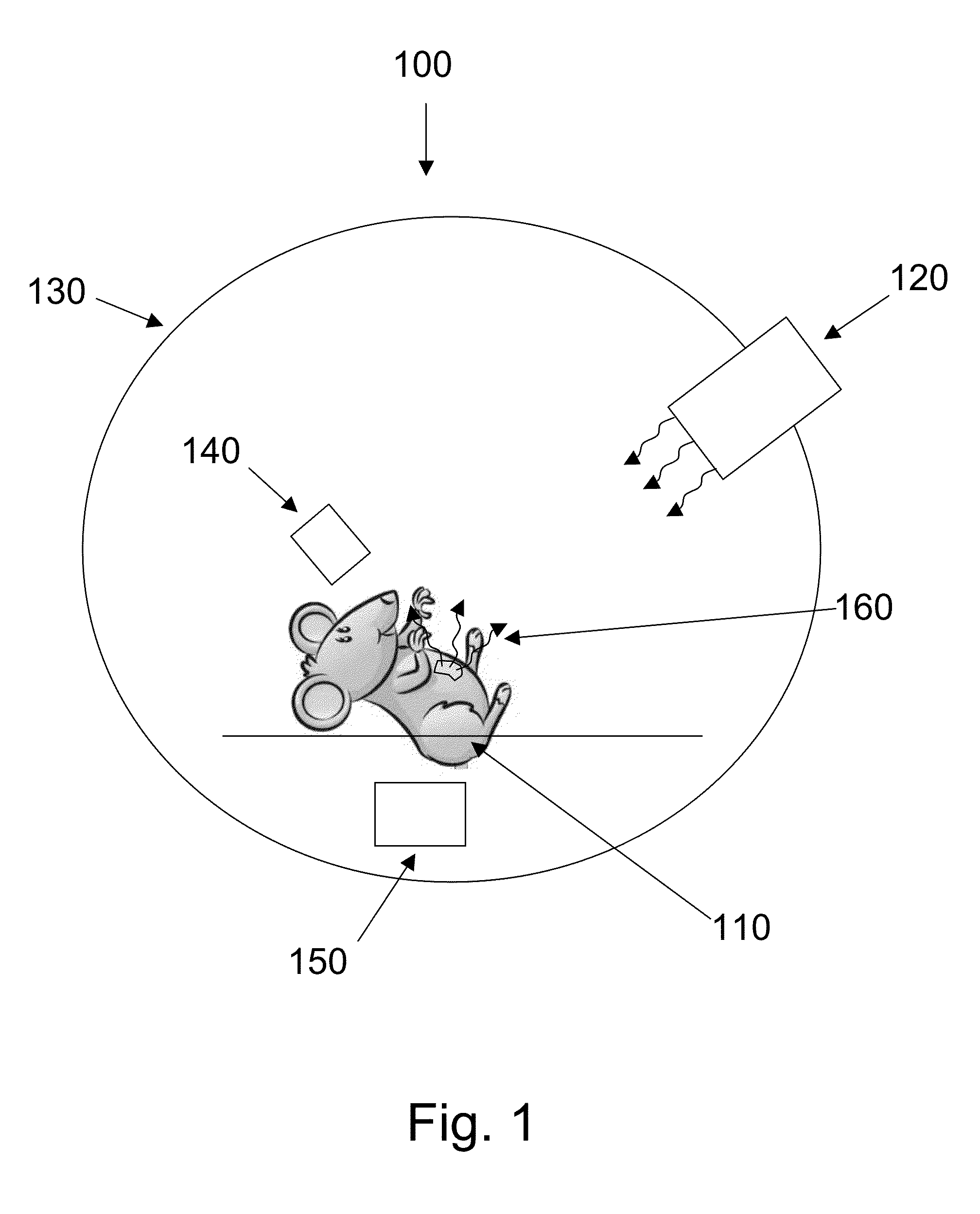
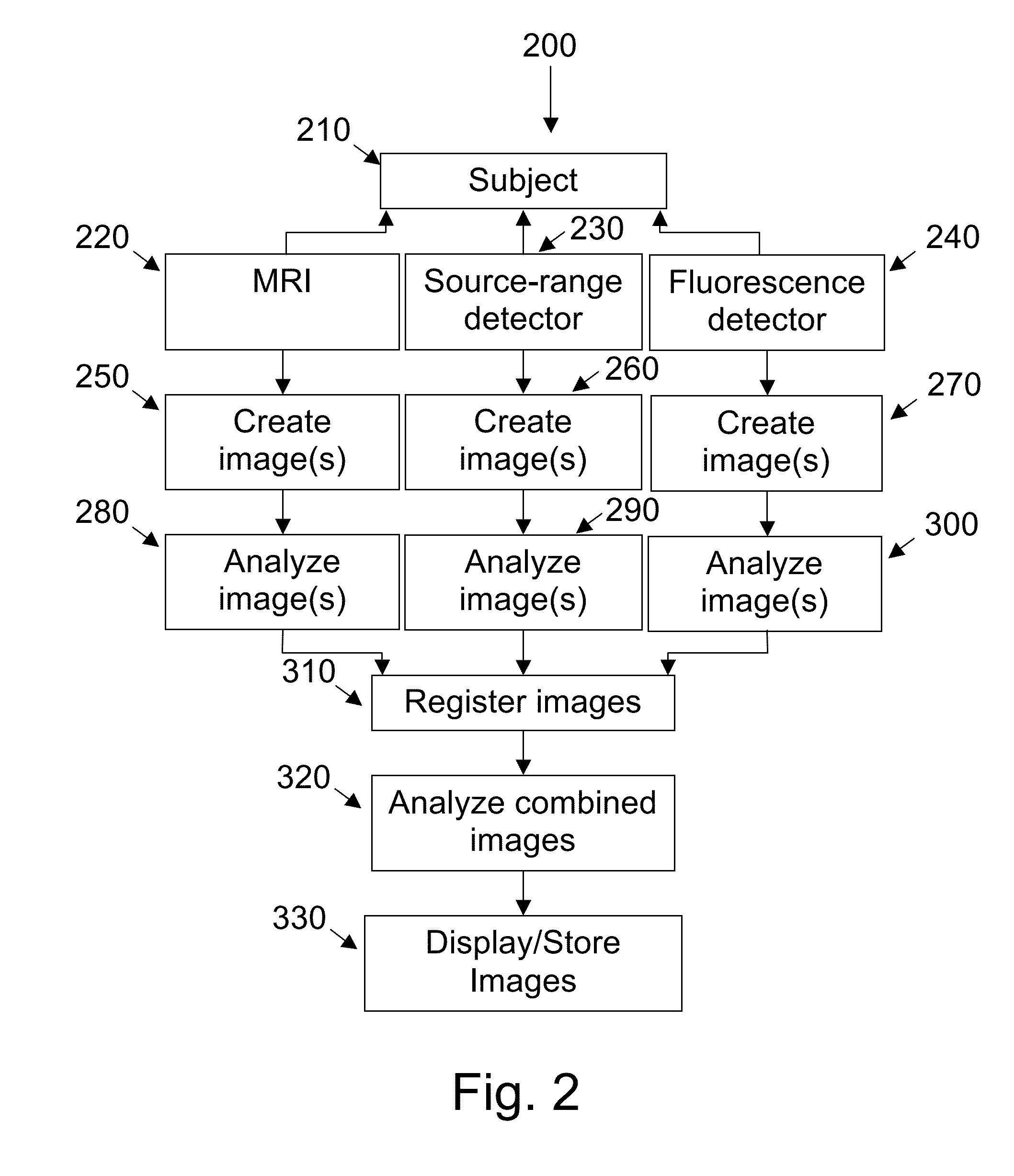
Integrated multi-modality imaging system
InactiveUS6925319B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMagnetic measurementsSplit magnetDiagnostic Radiology Modality
An integrated, multi-modality imaging technique is disclosed. The embodiment described combines a split-magnet MRI system with a digital x-ray system. The two systems are employed together to generate images of a subject in accordance with their individual physics and imaging characteristics. The images may be displaced in real time, such as during a surgical intervention. The images may be registered with one another and combined to form a composite image in which tissues or objects difficult to image in one modality are visible. By appropriately selecting the position of an x-ray source and detector, and by programming a desired corresponding slice for MRI imaging, useful combined images may be obtained and displayed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
In Vivo Localization and Tracking of Tissue Penetrating Catheters Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance image (MRI) guided tissue penetrating catheters and their methods of use. One or more MRI apparatus (e.g., one or more coils) are positioned on or in a catheter device that includes a tissue penetrator that may be used to form a penetration tract from a body lumen in which the catheter is positioned to a target location outside of that body lumen. The MRI apparatus (e.g., coil(s)) is / are used in conjunction with an MRI imaging system to indicate the position and / or rotational orientation of the penetrating catheter within the subject's body.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
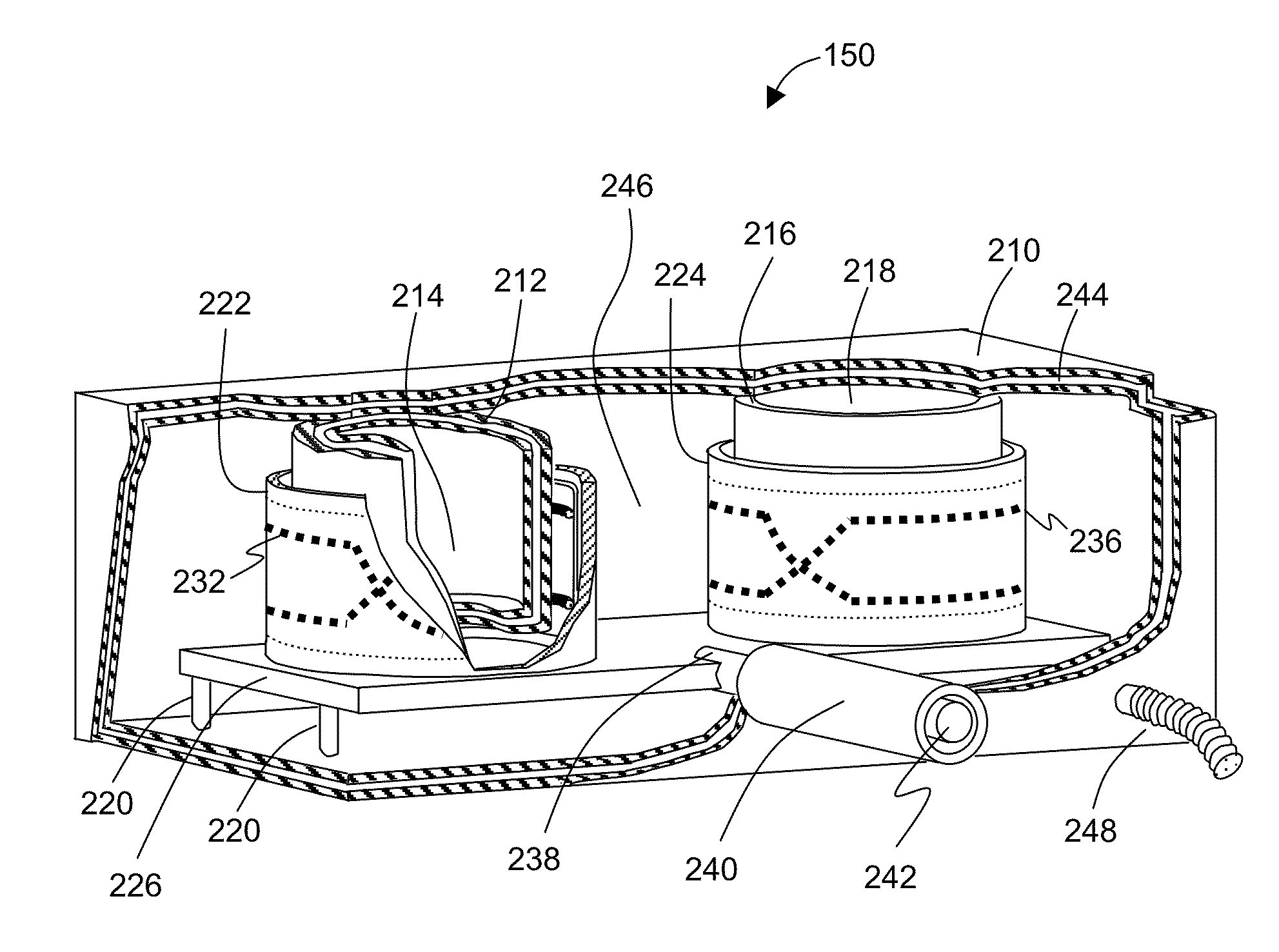
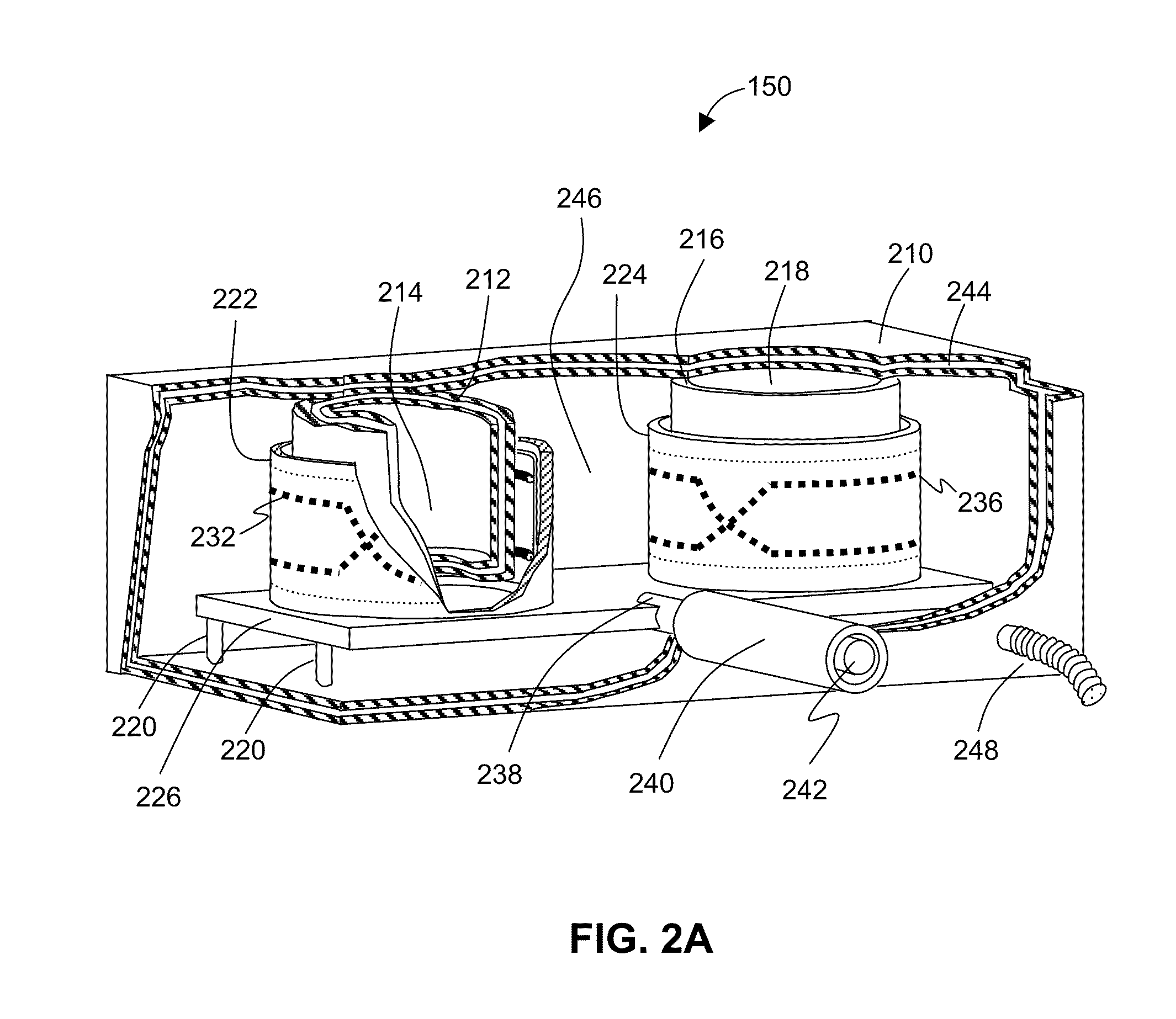
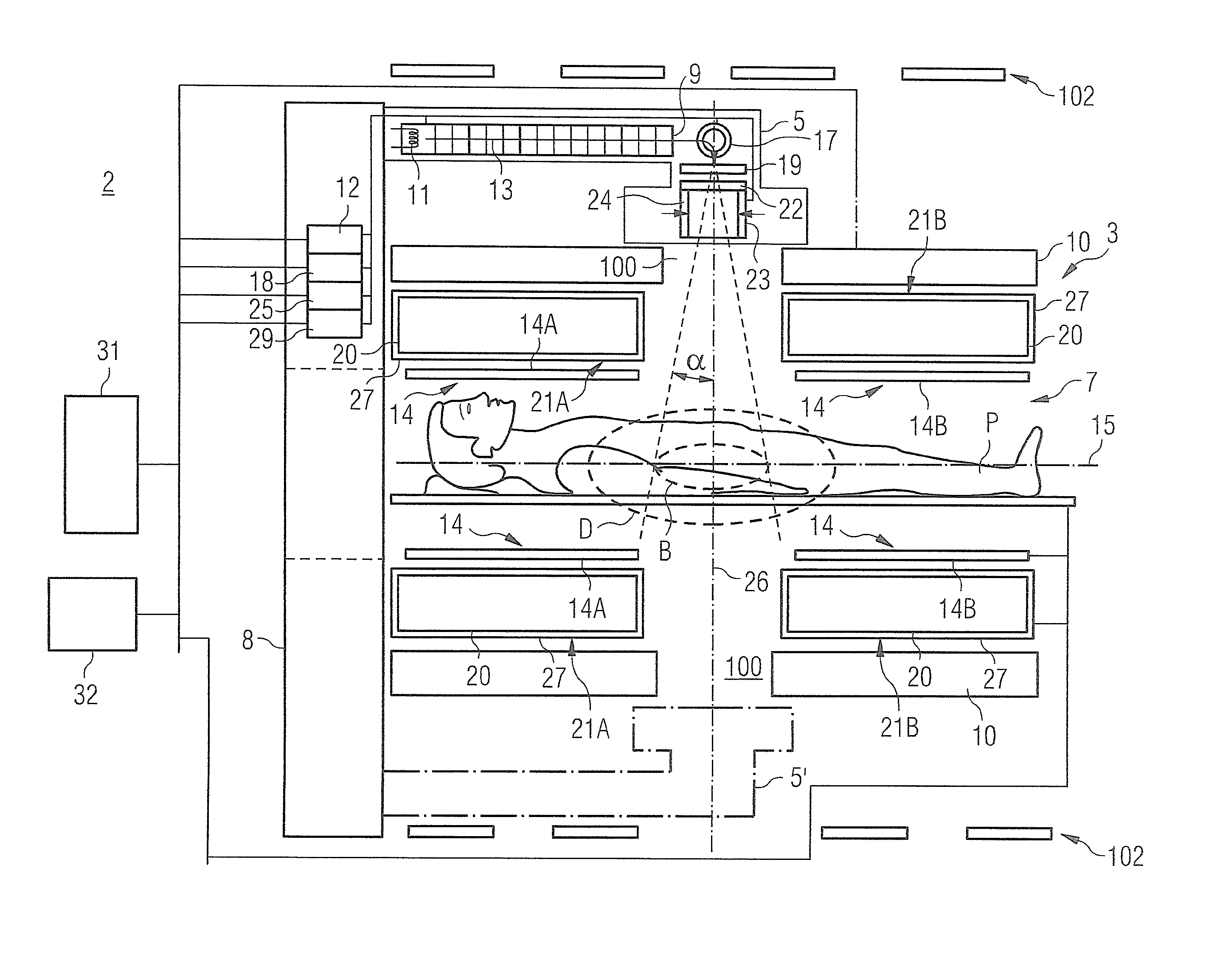
Modular Apparatus for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveUS20100315085A1Minimize couplingIncrease the useable field-of-viewDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsEngineeringRadio frequency
The present invention discloses a modular MRI imaging system. The imaging system includes MRI radio-frequency antenna arrays separate from the patient support structure. The antenna arrays are affixed to a thin, flexible film such that they may be located next to the anatomical region of interest. In addition, multiple antenna arrays may be configured in various planar or three-dimensional arrangements to optimize the FOV and SNR. Separate patient support structures are provided that enhance ergonomics and patient stabilization. By removing the antenna from the housing, the support structures may be designed without the constraints of supporting the antenna or the associated electronics. The MRI imaging system further employs a preamplifier module. The preamplifier module houses the preamplifier and much of the other associated circuitry for each of the antennae. The preamplifier module operates to combine the signals from the antenna arrays and pass the signals to the MRI system.
Owner:NEOCOIL
System and method for MRI imaging using polarized light
InactiveUS20140051974A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioIncrease contrastUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using lightPolarizerPhoton source
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) imaging system, including: an MRI device adapted to image at least a portion of an animal; a photon source; an imaging photon detector that detects photons emitted by the photon source; and an image processor that superimposes the MRI image and the photon detector image. The system also includes one or more polarizers located between the animal and the photon detector.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
Microcoil device with a forward field-of-view for large gain magnetic resonance imaging
Microcoils can be used in medical devices to enhance RF response signals and to create fields to enhance imaging capability in MRI imaging systems. An improved microcoil design includes a device to be inserted into a patient comprising a solid body having at least one pair of radially opposed microcoils physically associated with the solid body, each microcoil having an outside microcoil diameter of 6 mm or less, individual windings of each microcoil together defining a geometric plane for each microcoil, and the plane of each microcoil being parallel to the plane of another microcoil in the pair of radially opposed microcoils.
Owner:IMAGE GUIDED DRUG DELIVERY SYST
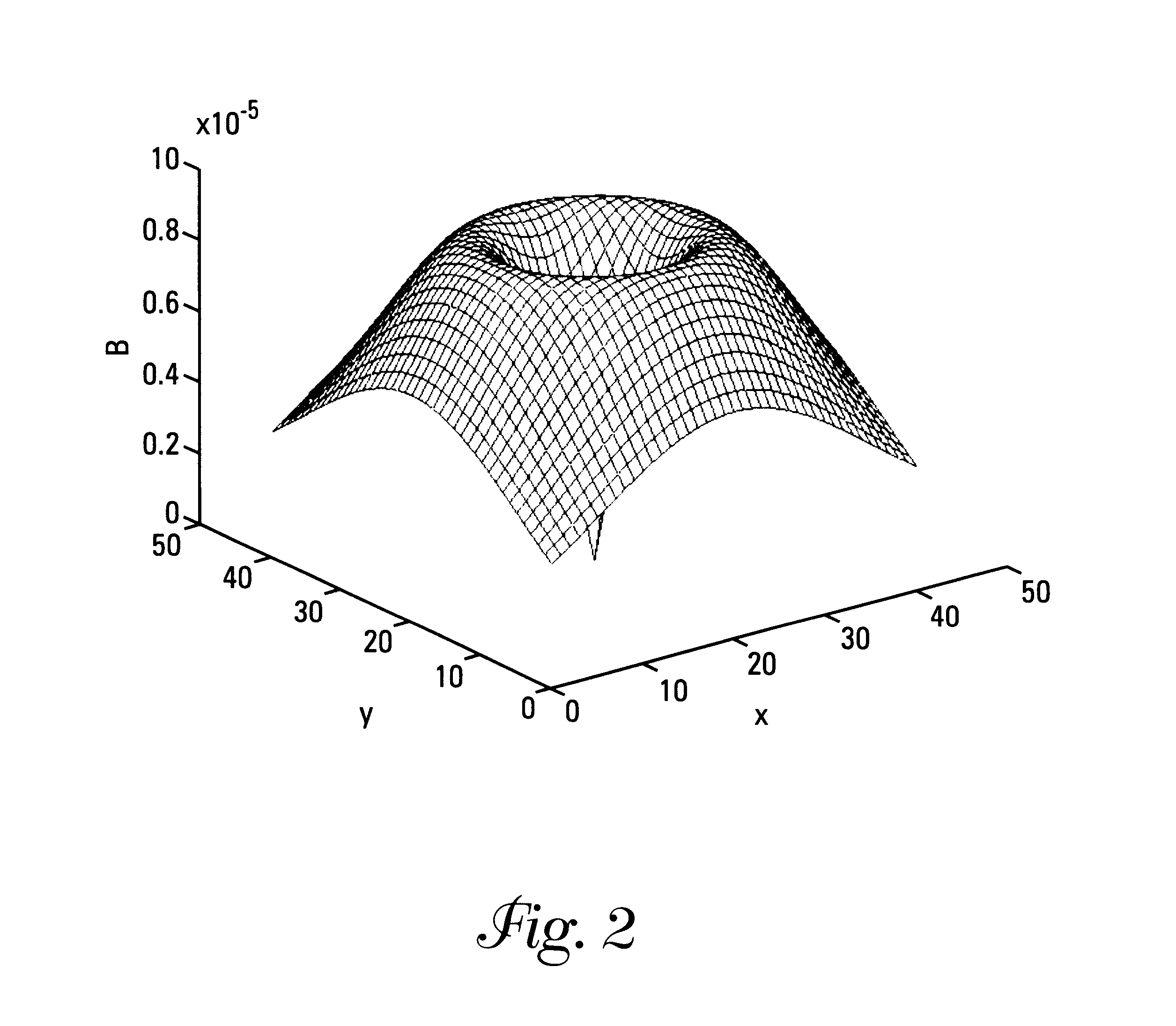
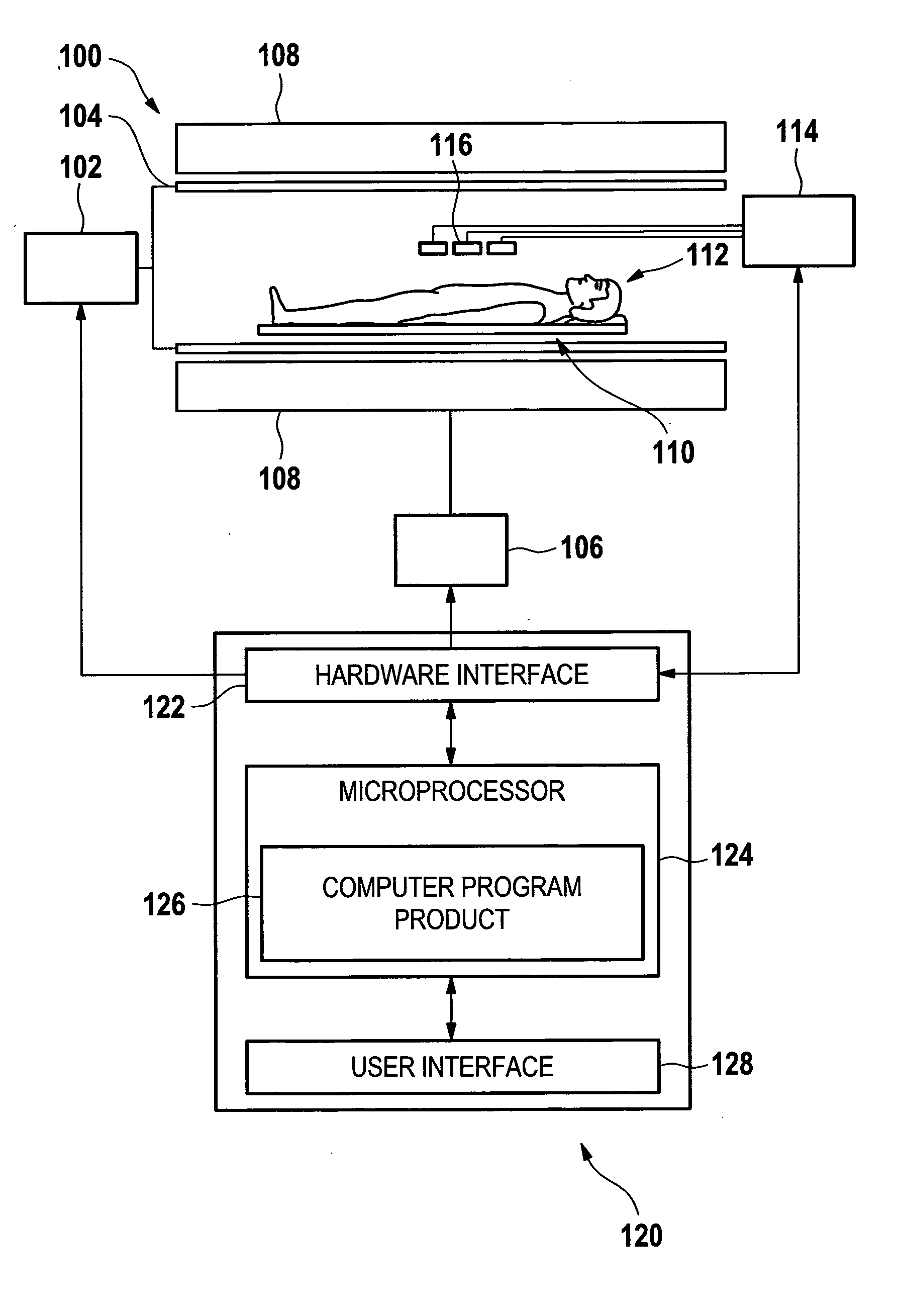
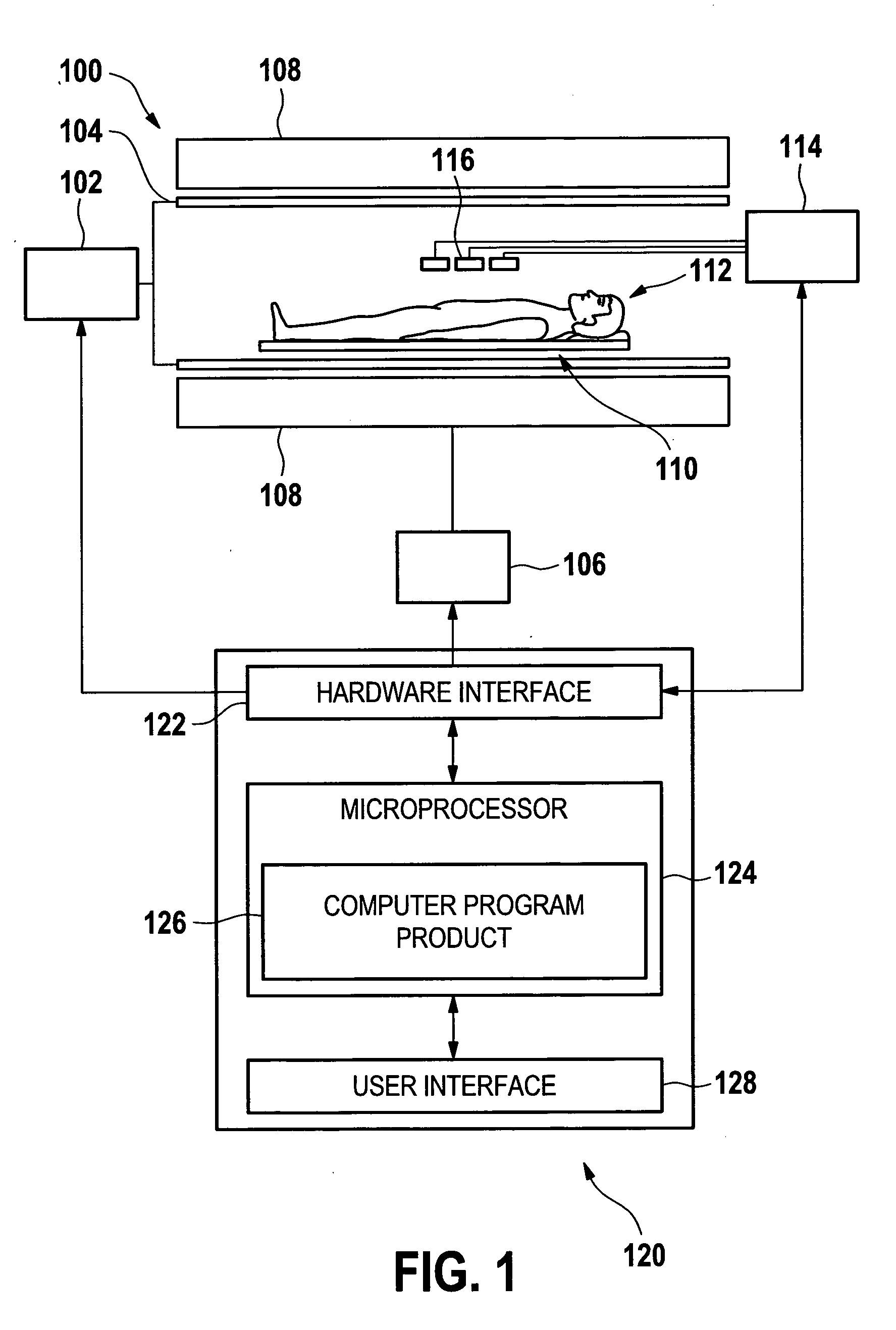
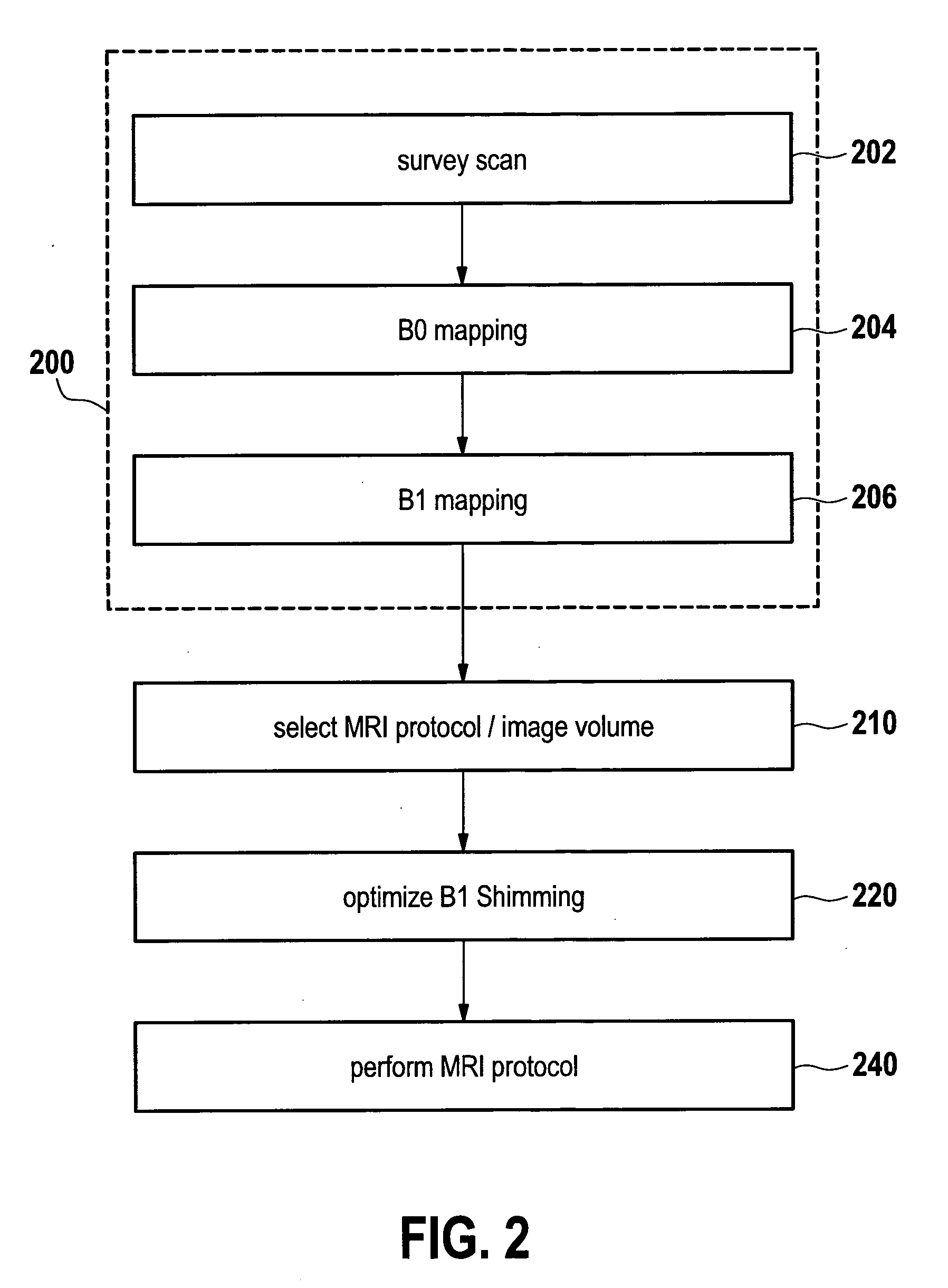
B1-mapping and b1l-shimming for MRI
ActiveUS20110156704A1Shorten the timeEfficient workflowElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMri imageVoxel size
The invention relates to a method of acquiring MRI image data comprising the following steps: performing a 3-dimensional B1 mapping of a first volume using a first voxel size, selecting an MRI protocol, performing the B1-shim in accordance with the MRI protocol, performing the MRI protocol to acquire MRI imaging data of a second volume using a second voxel size, wherein the first voxel size is larger than the second voxel size, wherein the first volume is larger than the second volume, and wherein the second volume is contained within the first volume.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
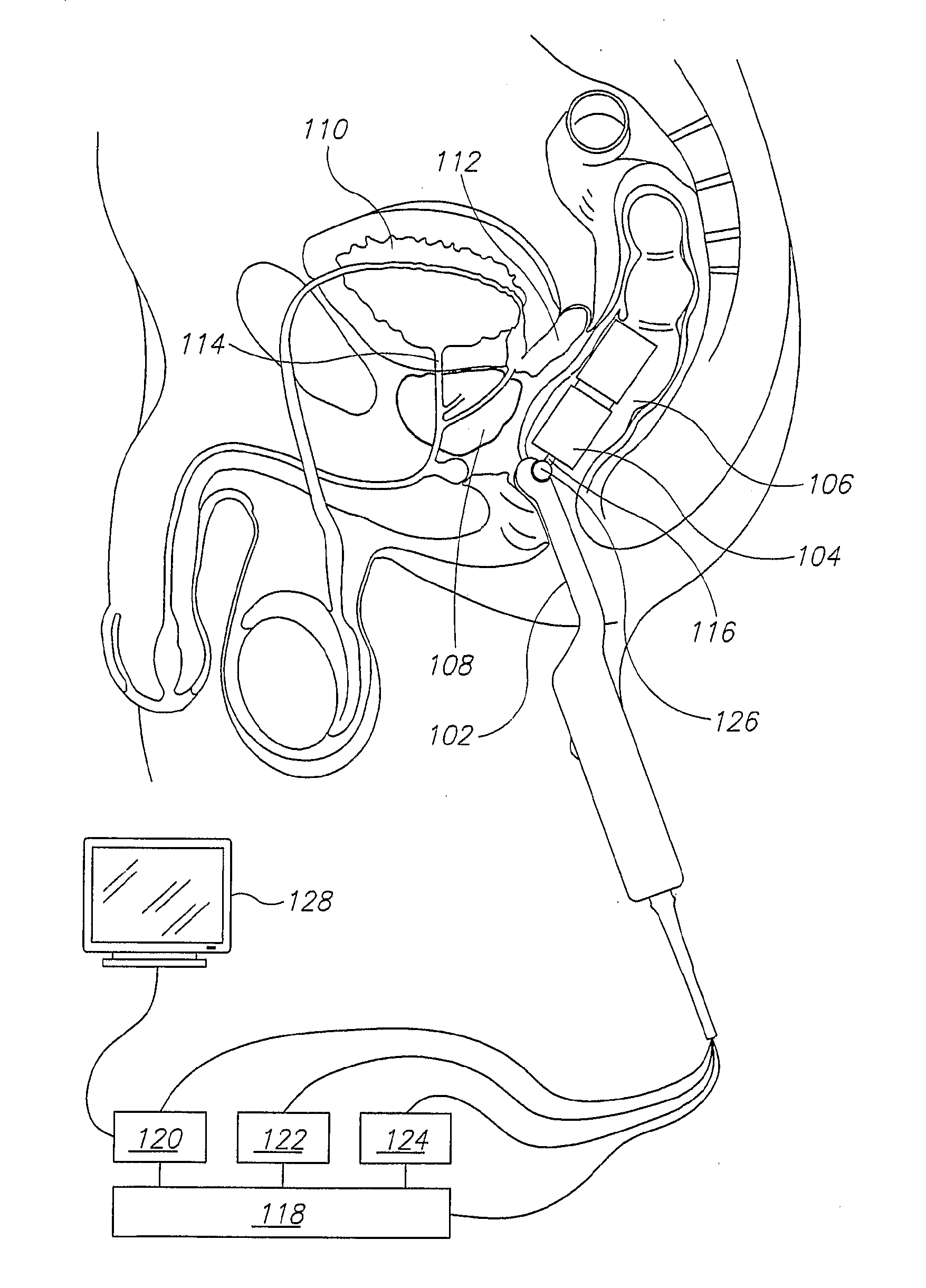
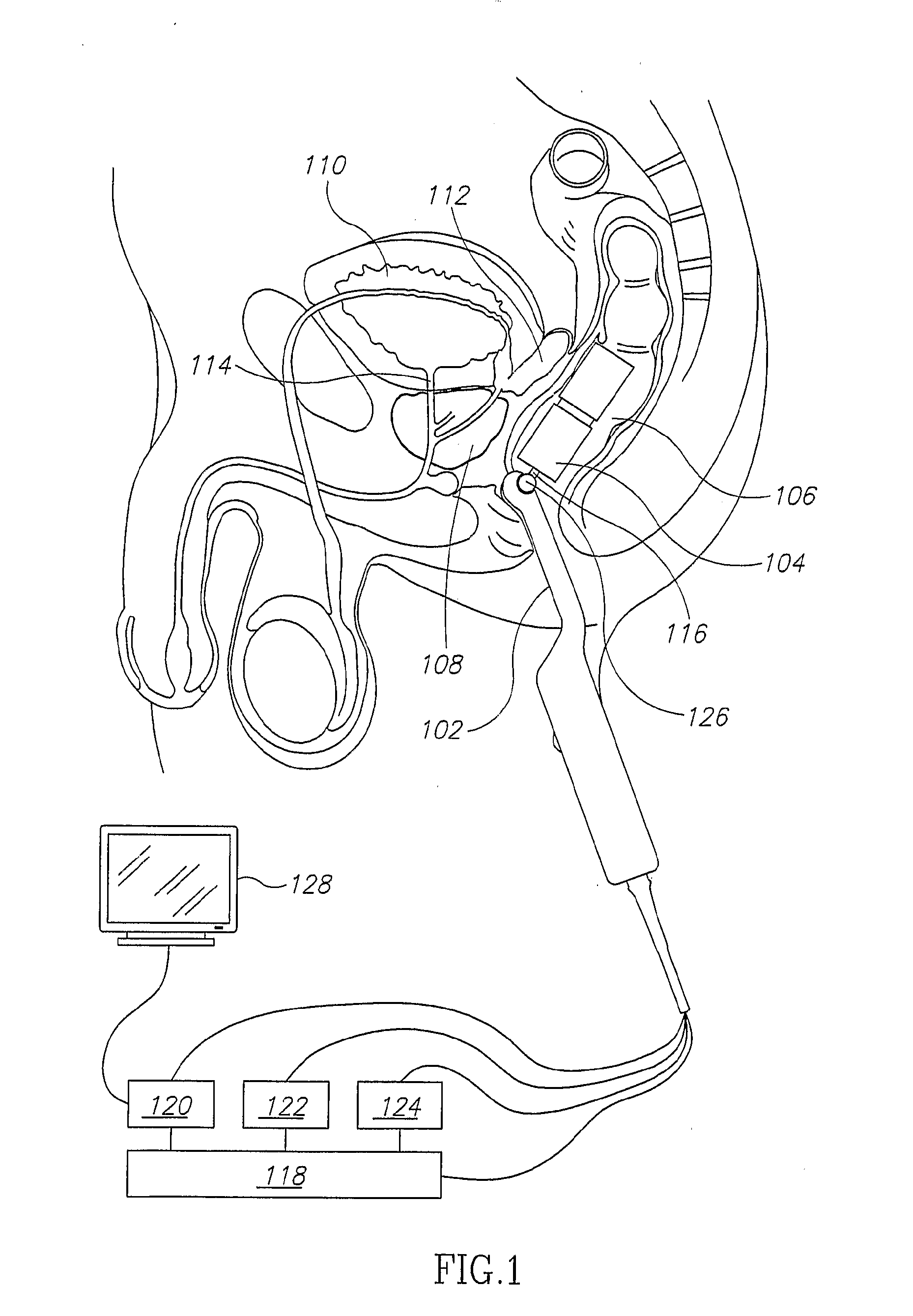
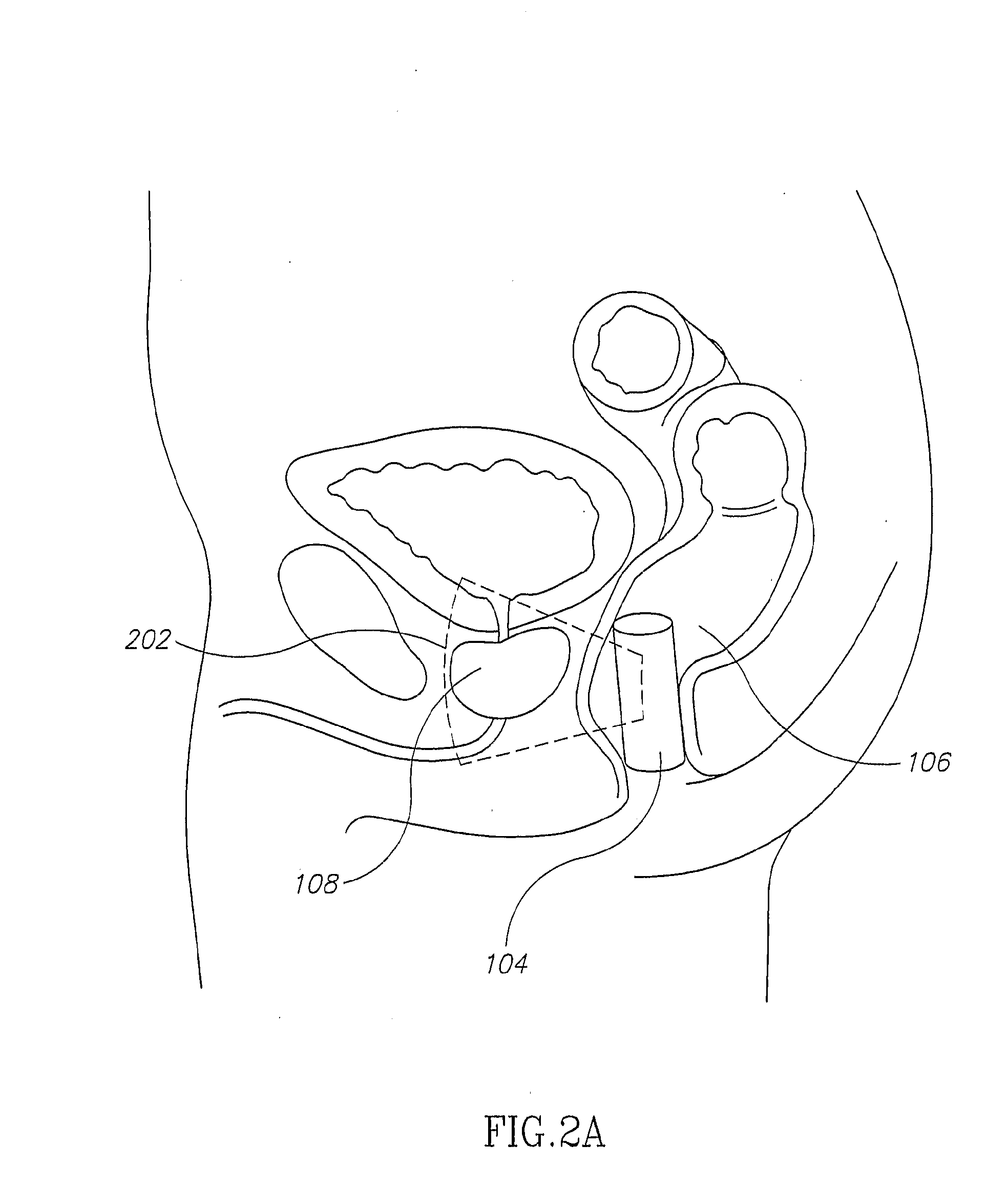
Mri Probe for Prostate Imaging
InactiveUS20080234569A1Reduce probabilityHigh resolutionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingMri image
A rectal probe adapted for ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate, comprising: a) an ultrasound imaging probe; b) an MRI probe comprising a first magnetic field source for creating a static magnetic field in an MRI imaging region outside the rectal probe, a second magnetic field source for creating a time-varying magnetic field which excites nuclei in the MRI imaging region, and a receiver for receiving NMR signals from the excited nuclei and generating MRI imaging data indicative thereof; and c) a link joining the ultrasound probe and the MRI probe.
Owner:TOPSPIN MEDICAL ISRAEL
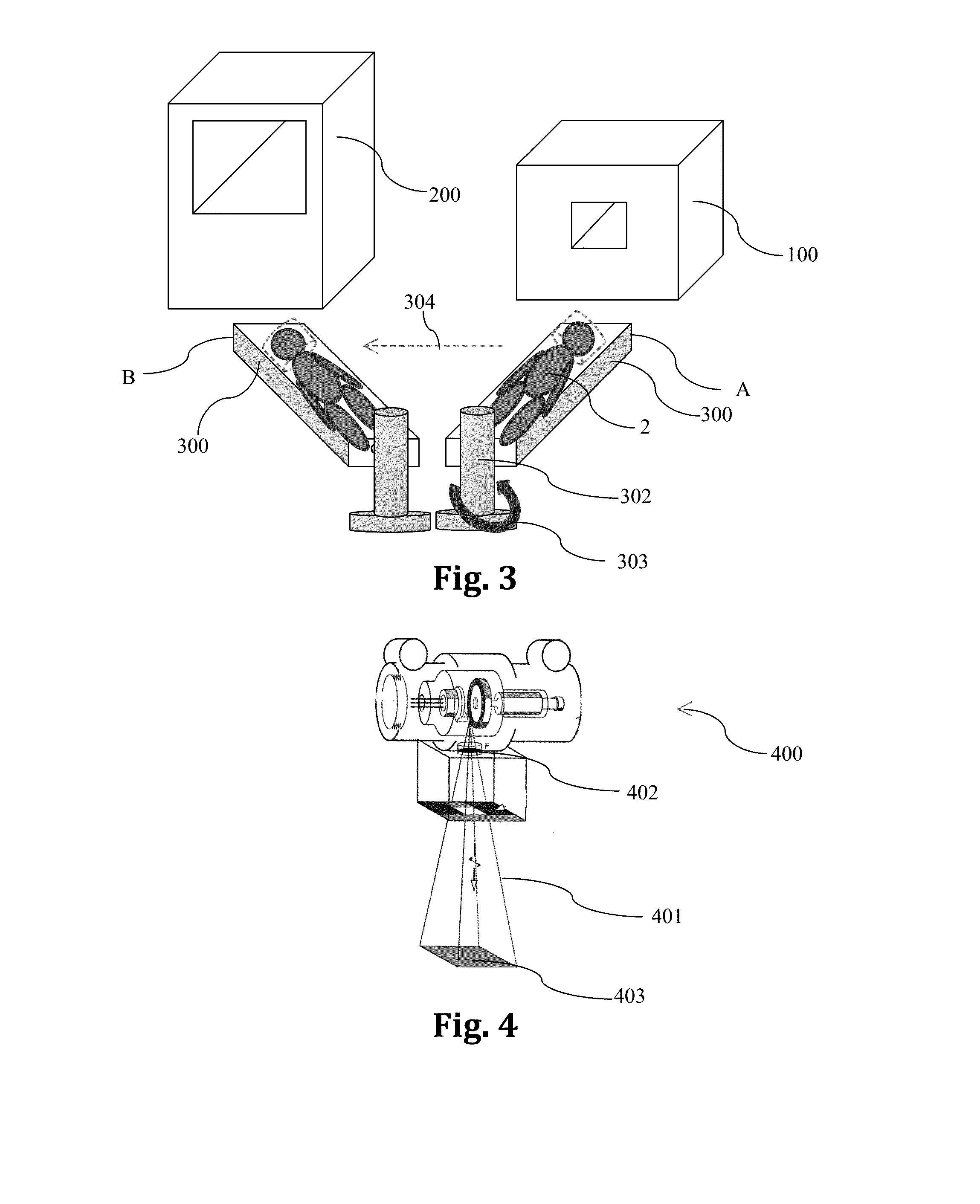
Combined MRI and radiation therapy system
ActiveUS20140135615A1Reduce the overall diameterWeakening rangeMagnetic measurementsScreening apparatusTherapeutic radiationElectron
A combined MRI and radiation therapy system has MRI imaging equipment and radiation therapy equipment. The MRI imaging equipment includes a shielded solenoidal magnet including a number of main magnet coils arranged coaxially along an axis, and a shielding arrangement arranged coaxially with the axis, at a greater radius from the axis than the main magnet coils. The radiation therapy equipment includes a LINAC assembly, that includes a linear electron accelerator arranged with an electron beam path parallel to the axis, and electron beam deflection arrangement and a target for generating a beam of therapeutic radiation. The linear electron accelerator is located at a position radially between the main magnet coils and the shielding arrangement.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Integrated Superconductor MRI Imaging System
ActiveUS20100066367A1Quality improvementImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsWave amplification devicesThermal isolationEngineering
The present invention relates to an integrated magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) RF apparatus and method of constructing the same. One Embodiment of the present invention provides an MRI apparatus comprising an examination region, a patient support, at least one vacuum thermal isolation housing, a main magnet system for generating a main magnetic field in the examination region, and a cryogenic system. The vacuum thermal isolation housing comprises a hermetically sealed high vacuum jacket that encloses a low vacuum space hosting at least one superconductor RF coil and a heat sink assembly therein. The RF coil is in thermal contact with the heat sink assembly that is coupled to the cryogenic system through a heat pipe to achieve and maintain a desired low temperature at the superconductor RF coil.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
Technique for parallel MRI imaging (k-t grappa)
InactiveUS20060050981A1Magnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionMissing dataImaging quality
The subject invention relates to a method for reconstructing a dynamic image series. Embodiments of the subject invention can be considered and / or referred to as a parallel imaging-prior-information imaging (parallel-prior) hybrid method. A specific embodiment can be referred to as k-t GRAPPA. The subject method can involve linear interpolation of data in k-t space. Linear interpolation of missing data in k-t space can exploit the correlation of the acquired data in both k-space and time. Several extra auto-calibration signal (ACS) lines can be acquired in each k-space scan and the correlation of the acquired data can be calculated based on the extra ACS lines. In an embodiment, ACS lines can be calculated based on other acquired data, such that values in an ACS line can be partially acquired and the unacquired values can be calculated and filled in based on the acquired values. In a preferred embodiment, no extra training data is used and no sensitivity map is used. In an embodiment, the extra ACS lines can be directly applied in the k-space to improve the image quality. Because the correlations exploited via the subject method are local and intrinsic, the subject method does not require that the sensitivity maps have no change during the acquisition. Advantageously, the subject method can be utilized when sensitivity maps change, preferably slowly, during the acquisition of the data.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Portable system and method for MRI imaging and tissue analysis
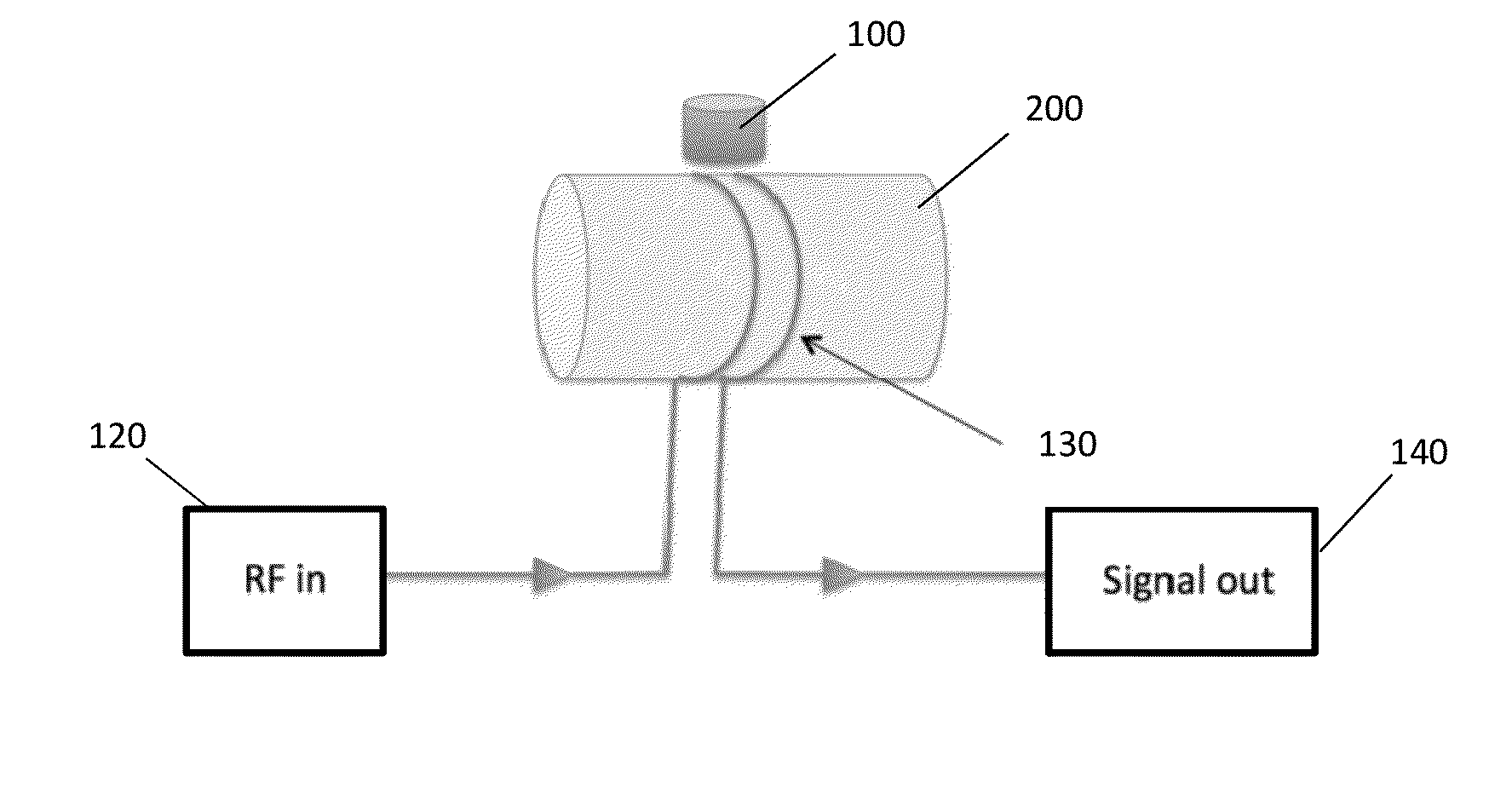
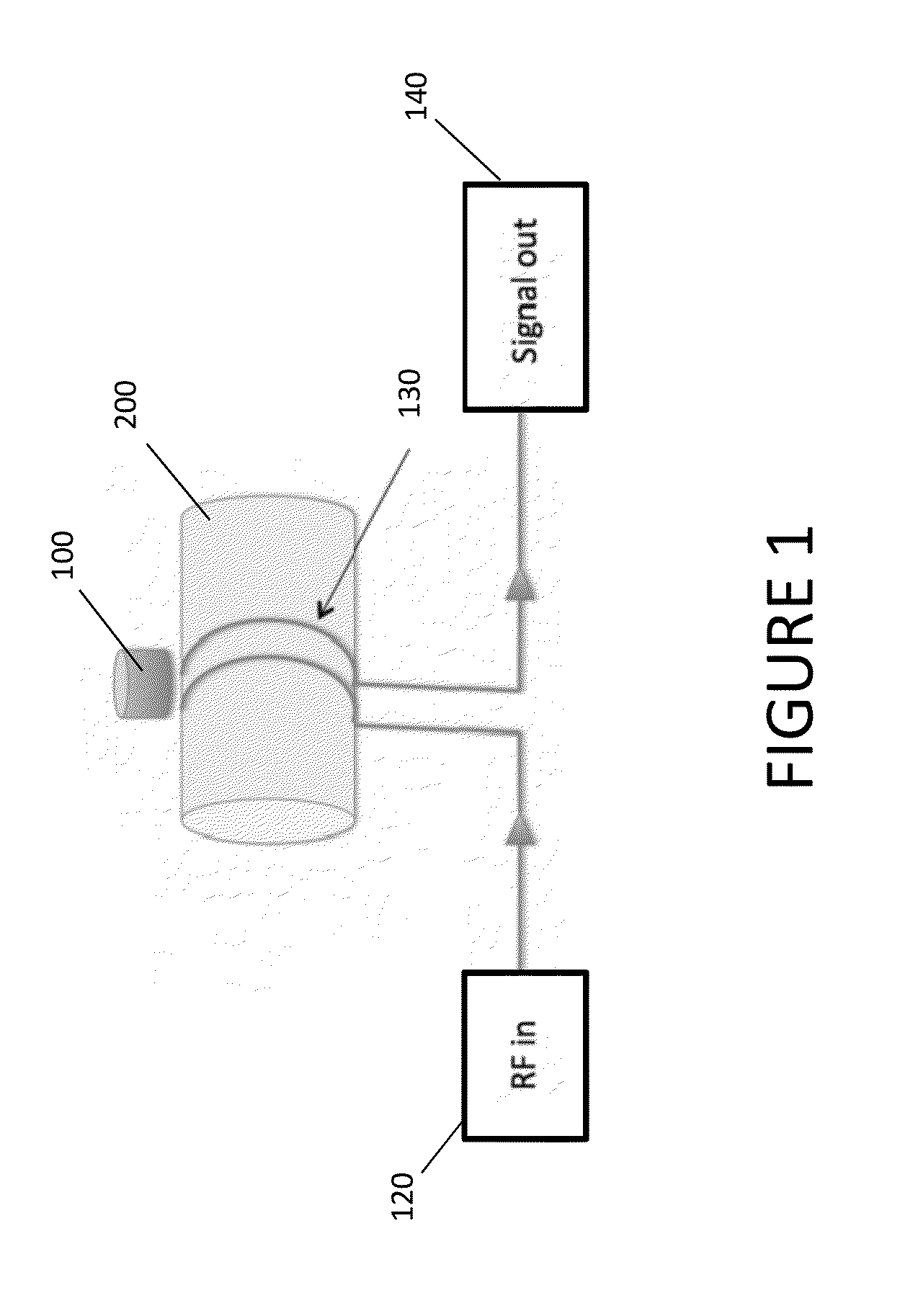
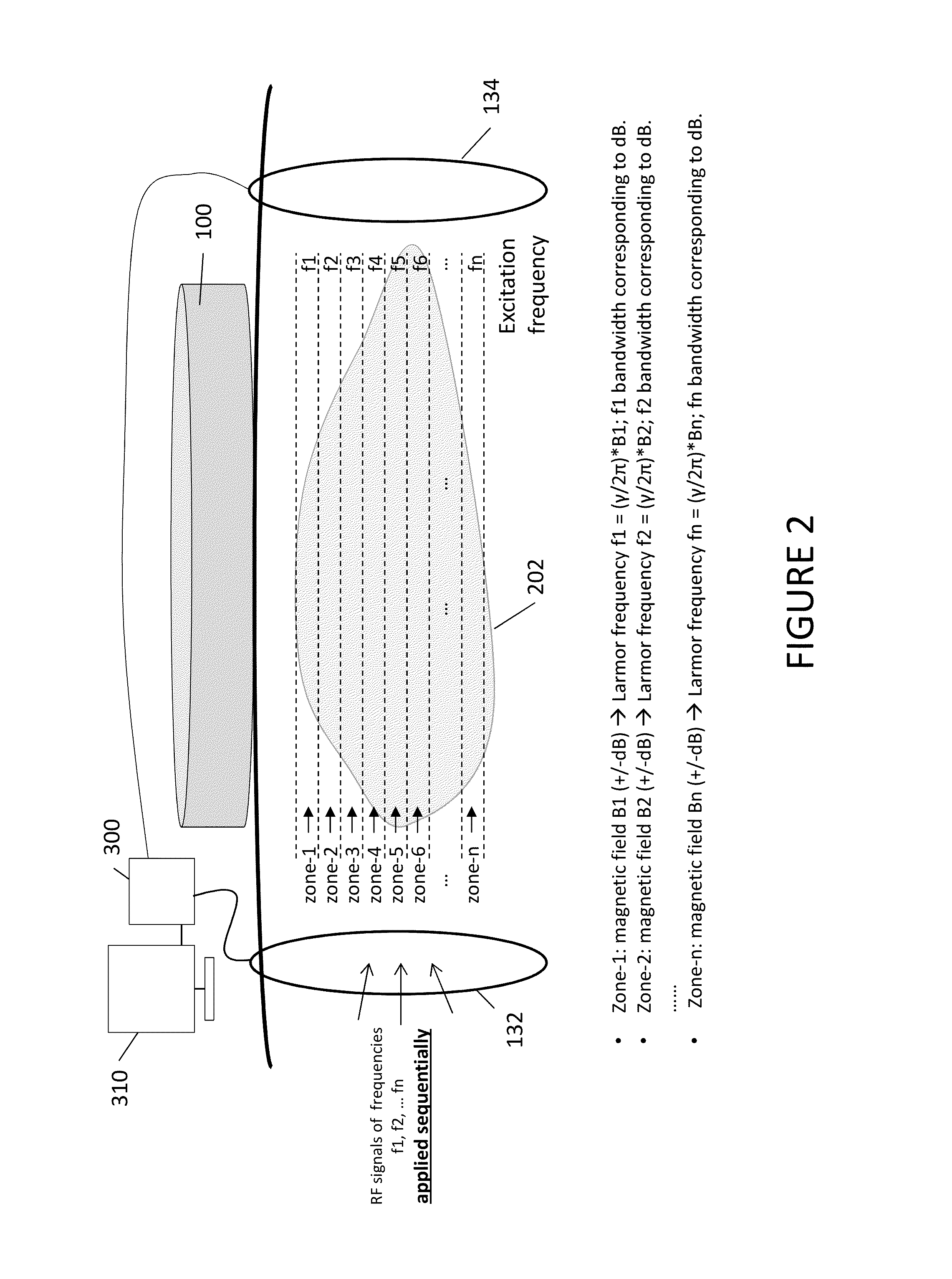
The present invention discloses a portable magnetic resonance method and device for tissue analysis including a magnetic field generator, a radio frequency source, a radio frequency detector, a power source, and a processor configured for receiving radio frequency signals and for analyzing those signals to determine discriminatory tissue characteristics in a planar section of a region of interest within a patient's body, with the magnetic field generator positioned outside of the patient's body, and more preferably hand held in proximity to the patient's body. The processor is configured to direct the radio frequency source to produce a radio frequency field in varying planar sections of the region of interest at Larmor frequencies such that spins resonant with the Larmor frequency in the particular planar section of the region of interest are excited. The processor is further configured to direct the radio frequency detector to receive magnetic resonance signals produced in each planar section of the region of interest in response to the applied radio frequency field, to compute from the acquired magnetic resonance signals a quantitative metric indicative of discriminatory characteristics of differing tissues or other materials within each such planar section, and to produce human discernable output indicative of such quantitative metric.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE
Method of forming a biopsy device
InactiveUS7445739B2Maintain stiffnessMaintain strengthButtonsSurgical needlesDistal portionBiopsy device
A method for forming a needle assembly is provided. A distal portion of the needle can be formed of a first material which does not interfere with MRI imaging of a tissue receiving port disposed in the distal needle portion. A proximal needle portion can be formed of a second, different material, such as a metal. The proximal needle portion can provide strength and stiffness.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
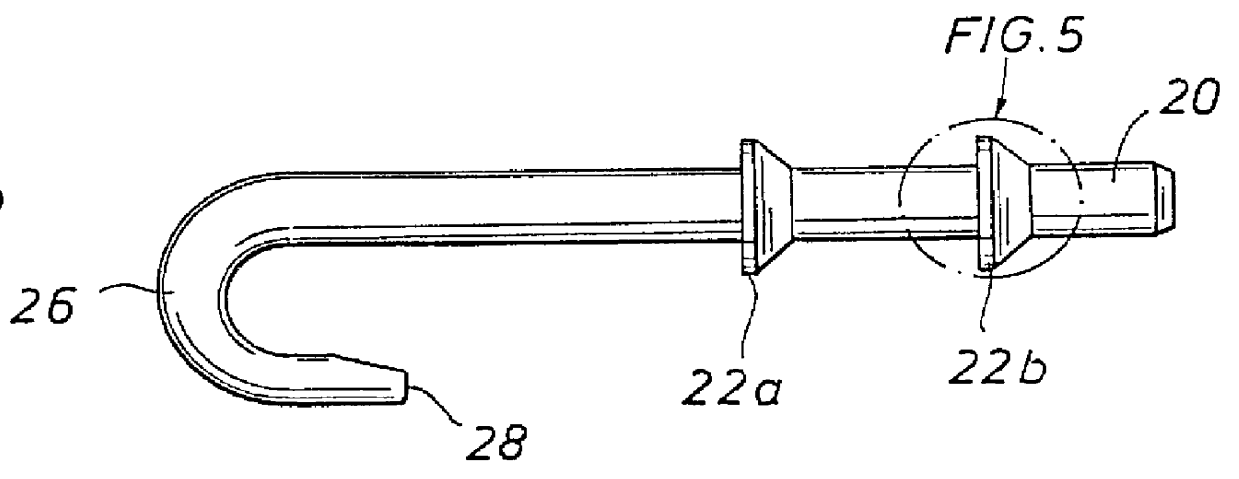
Plastic stay assembly for use with MRI and X-ray imaging systems
An improved surgical retractor stay having a plastic hook member such that the entire surgical retractor stay is substantially non-interfering with X-ray and MRI imaging techniques.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
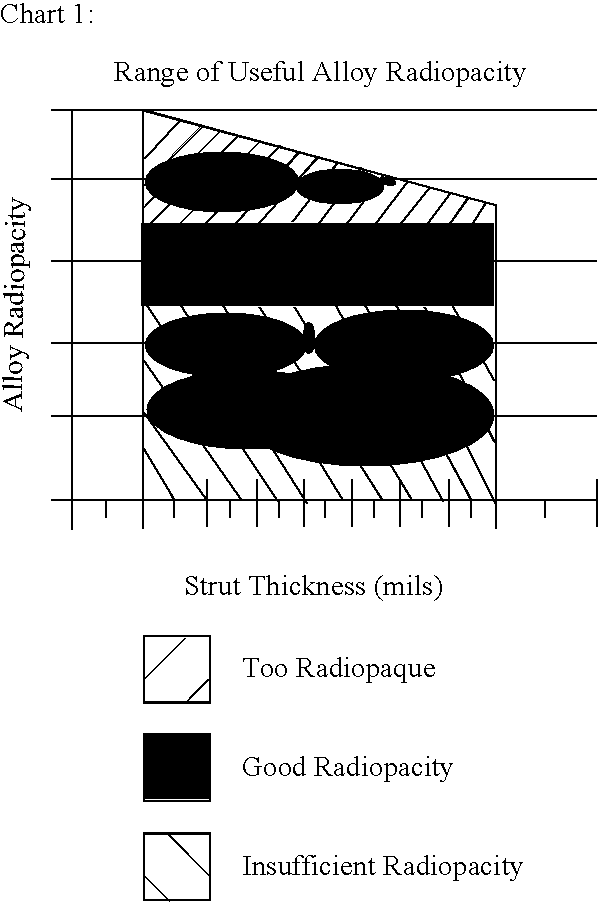
MRI compatible, radiopaque alloys for use in medical devices
A metallic alloy whose primary constituent elements are a relatively higher volume fraction of titanium and a relatively lower volume fraction of an added element or elements generally selected from the transition elements (excluding mercury, cadmium, osmium and copper). Medical devices formed from the metallic alloy are visible under MRI imaging and are sufficiently radiopaque for viewing by x-ray fluoroscopy. The alloy may be embodied in a multitude of medical devices.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Shortened Carbon Nanotubes
InactiveUS20080003182A1Low toxicityEasy to relaxMaterial nanotechnologyPowder deliveryCarbon nanotubeX-ray
A shortened carbon nanotube and methods for preparing the same and contrast agents are disclosed. One embodiment includes a shortened carbon nanotube. The shortened carbon nanotube has a length of about 100 nm or less with a cargo. The shortened carbon nanotube is suitable for use in x-ray and MRI imaging as a contrast agent.
Owner:RICE UNIV +1
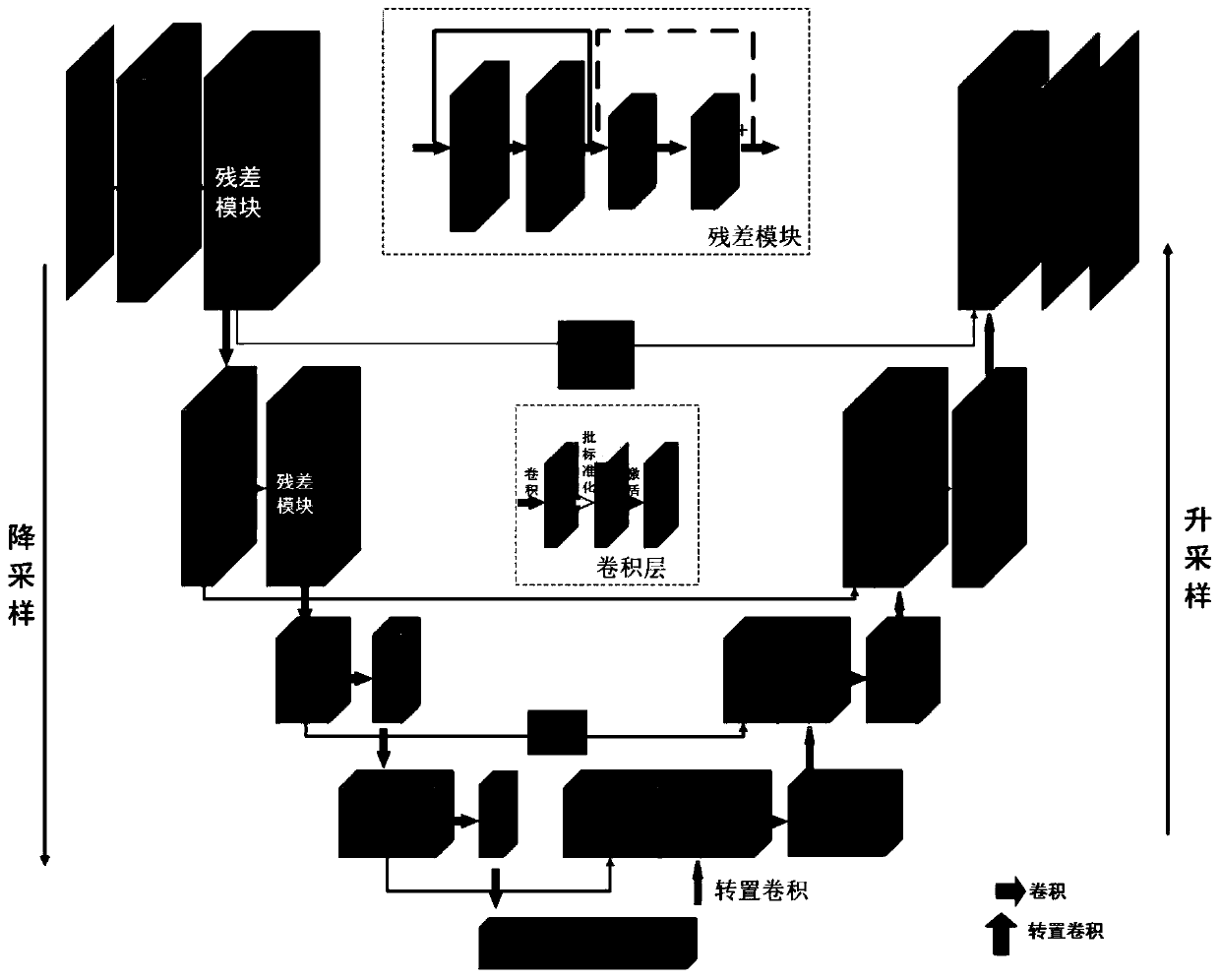
Fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on residual U-net convolutional neural network
ActiveCN109993809AReduce the number of collection pointsReduce acquisition timeReconstruction from projectionDiagnostic recording/measuringFast mriRate of convergence
The invention discloses a fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on residual U-net convolutional neural network and the method comprises three steps of preparing training data, carrying out training based on the residual U-net convolutional neural network, and carrying out image reconstruction based on the residual U-net convolutional neural network. By adding the residual module into the U-net convolutional neural network, the problems of gradient disappearance, overfitting, low convergence speed and the like of the U-net convolutional neural network can be solved, and the quality of rapid MRI imaging based on the U-net convolutional neural network is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Wireless in-bore patient monitor for MRI
InactiveUS20060206024A1Reduce error rateHigh bandwidthElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsEngineeringMri image
A wireless in bore sensor for magnet resonance imaging provides radio frequency communication of physiological and other data signals from a battery powered unit held adjacent to the patient within the bore by using multiple diversity techniques to overcome the interfering environment of the MRI imaging system and to prevent interference with the MRI system.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Entertainment system for use during the operation of a magnetic resonance imaging device
InactiveUS20100238362A1Reduce anxietyReduce noiseTelevision system detailsEar treatmentLow-pass filterEyewear
An entertainment system for use with a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device that includes video glasses and headphones. A Faraday shield encloses the entertainment system to reduce adequately RF signals from entering or leaving the entertainment system. The entertainment system may have non-ferromagnetic RF low-pass filters between parts of the system, such as the control unit and the video glasses, to reduce higher RF signals from entering or leaving those parts. To replace the battery and or entertainment media, a person opens the entertainment system's Faraday shield when not MRI imaging or outside the MRI magnet room. The door has an Faraday shield overlapping the system Faraday shield and making low resistance RF contact. The entertainment system has a minimal amount of ferromagnetic material so that it may operate within the high magnetic field of the MRI magnet bore with minimal performance degradation. The entertainment system uses non-ferromagnetic speakers in the headphone. Passive ear protection and noise cancellation reduce the loud noise of the MRI system heard by the patient to a level where the patient can hear the entertainment. The entertainment system includes a charger for the rechargeable batteries.
Owner:HUGHES BRIAN
Ct/mri integrated system for the diagnosis of acute strokes and methods thereof
InactiveUS20150208994A1Magnetic measurementsPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputed tomographyRisk stroke
A dual modality CT / MRI integrated system for the diagnosis of acute strokes and treating a patient and methods thereof. The method includes: immobilizing a patient or a portion thereof to a support; accommodating the patient or portion thereof in a CT device; scanning the same; placing the patient or portion thereof within an MRI device and imaging the same such that the orientation of the patient or portion thereof in the CT scanning and the MRI imaging is identical or at least spatially (2D or 3D) retrievable.
Owner:ASPECT IMAGING
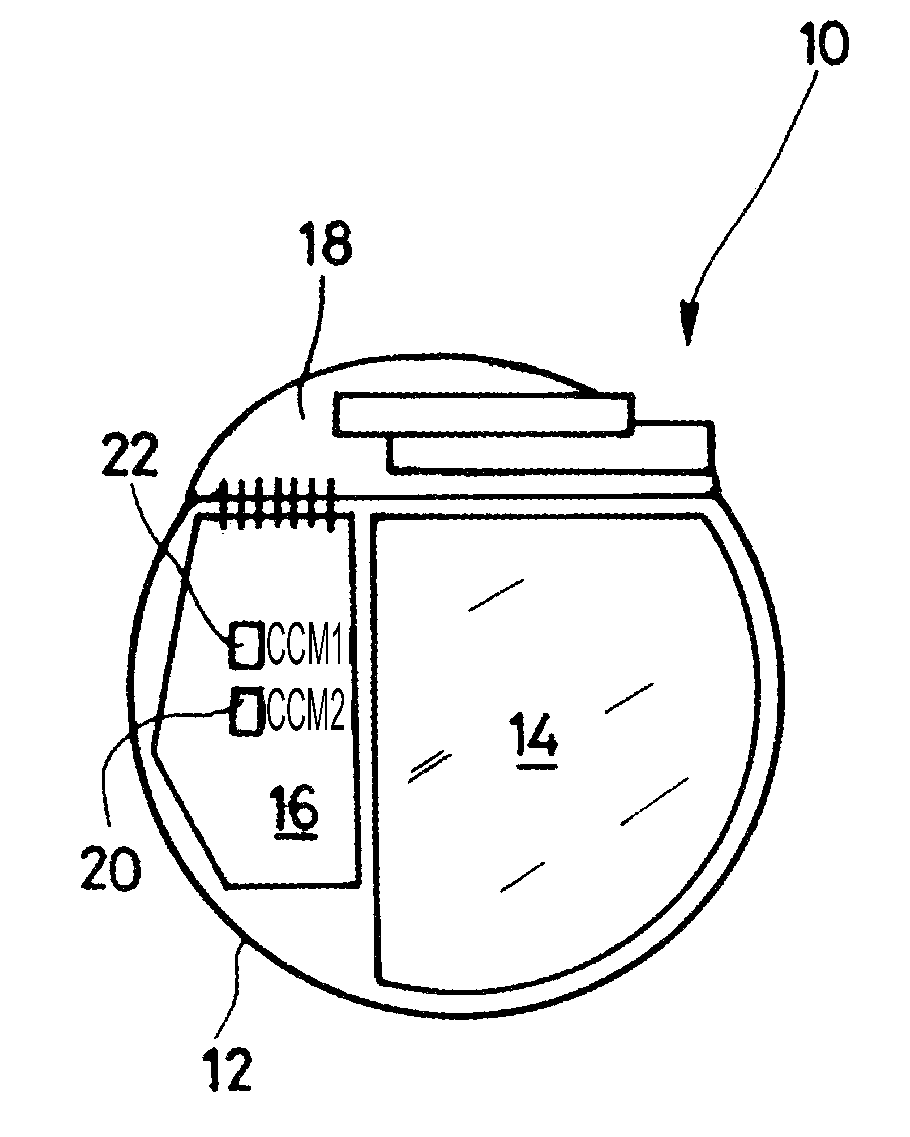
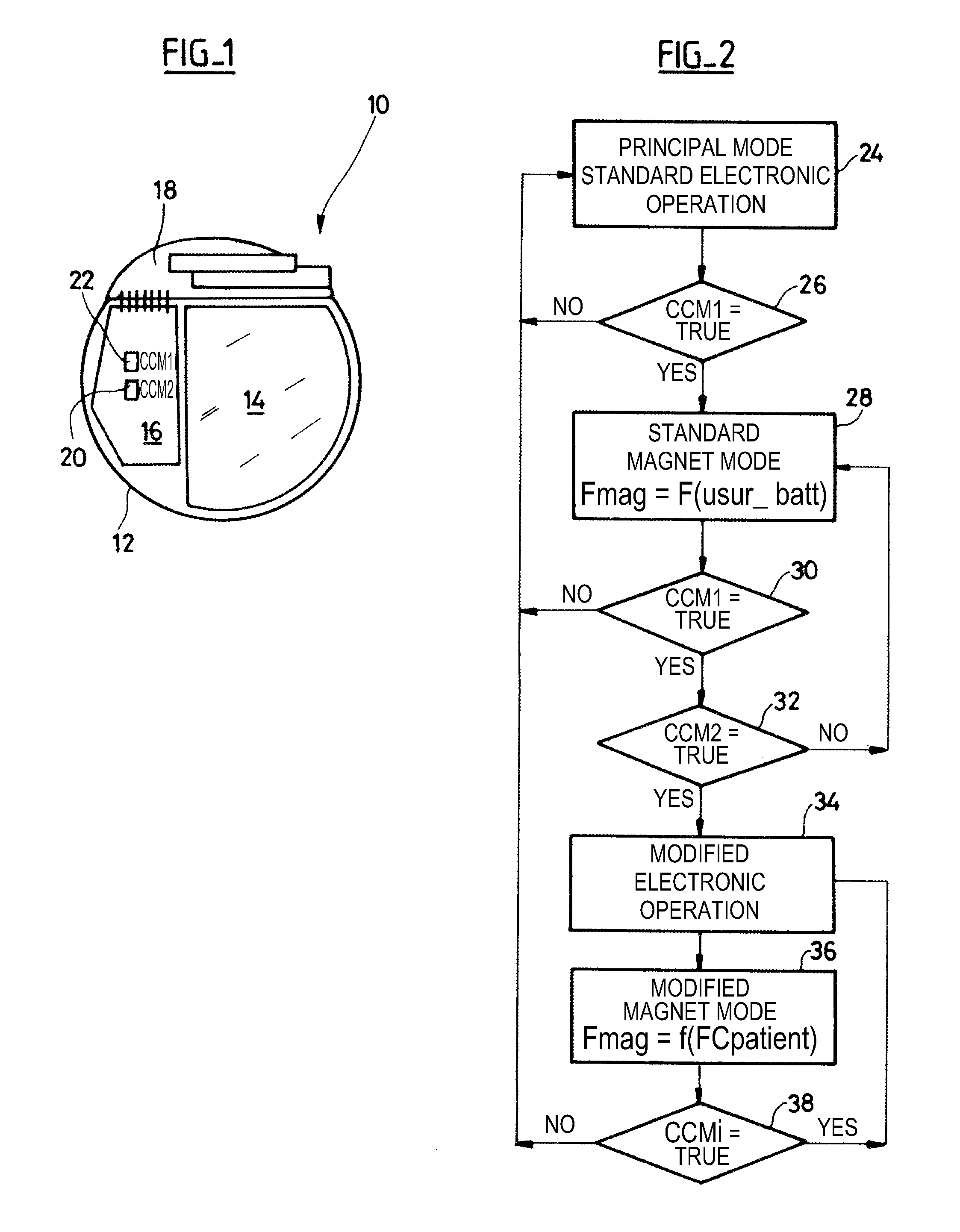
Detection of strong static magnetic fields and MRI examination safekeeping for an implantable cardiac prosthesis
An implantable medical device detects a strong static magnetic field associated with an MRI imaging instrument and operates in a safekeeping operating mode. The device (10) includes an electronic circuit for the detection / stimulation of a cardiac activity (16), a weak field sensor (22) detecting the presence of a first magnetic field of a permanent magnet being located in proximity to the device, a strong field sensor (20) detecting the presence of a second magnetic field of an MRI imaging instrument during the course of an MRI examination. The electronic circuit is placed in a safekeeping operating mode protected from the magnetic field of an MRI imaging instrument when the weak field sensor detects the first magnetic field and the strong field sensor detects the second magnetic field. The strong field sensor is a sensor that is selectively activated on detection of a magnetic field by the weak field sensor.
Owner:SORIN CRM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com