Patents
Literature
101 results about "Microcoil" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microcoil is a tiny electrical conductor such as a wire in the shape of a spiral or helix which could be a solenoid or a planar structure. One field where these are found is nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, where it identifies radio frequency (RF) coils that are smaller than 1 mm.
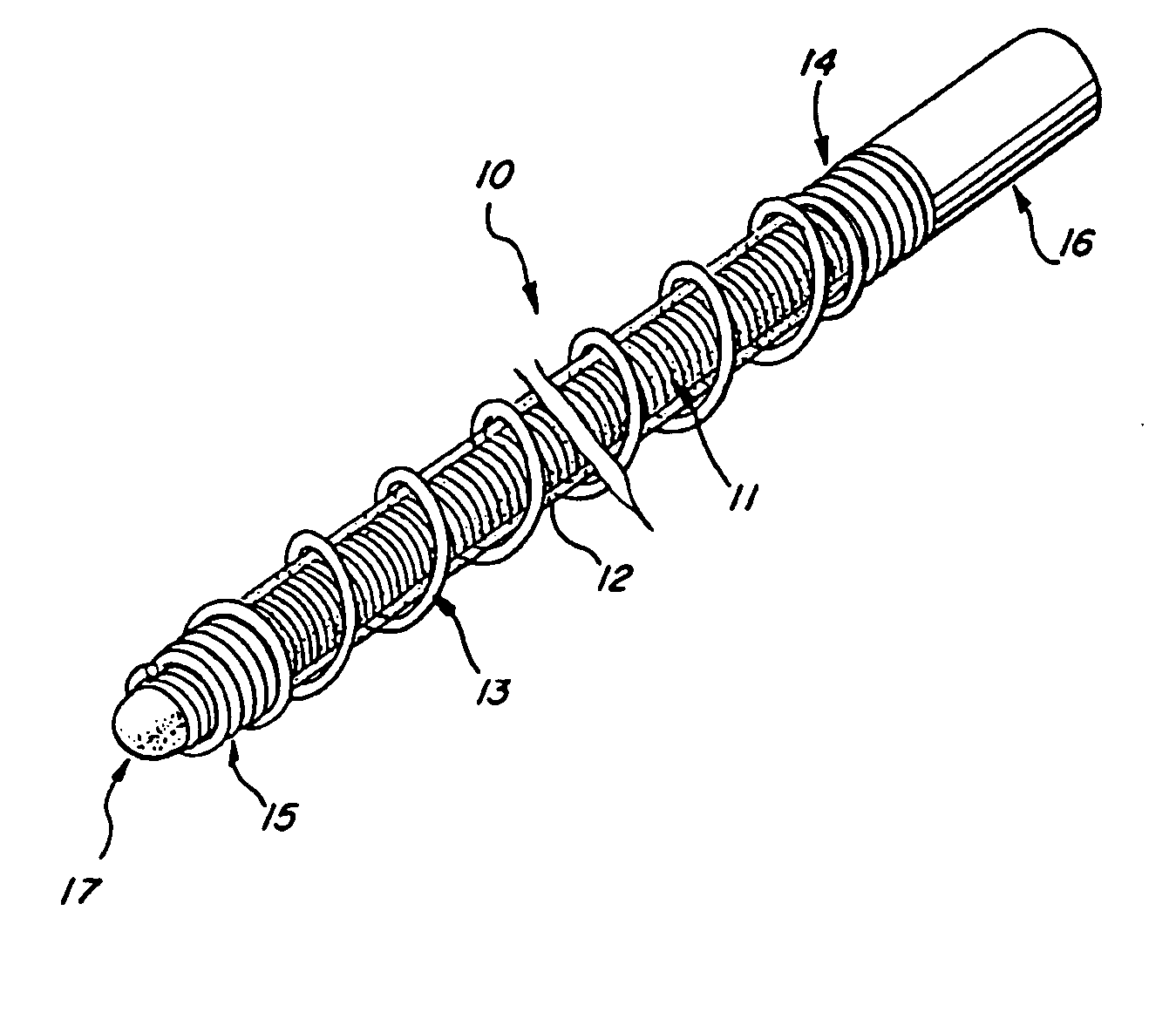
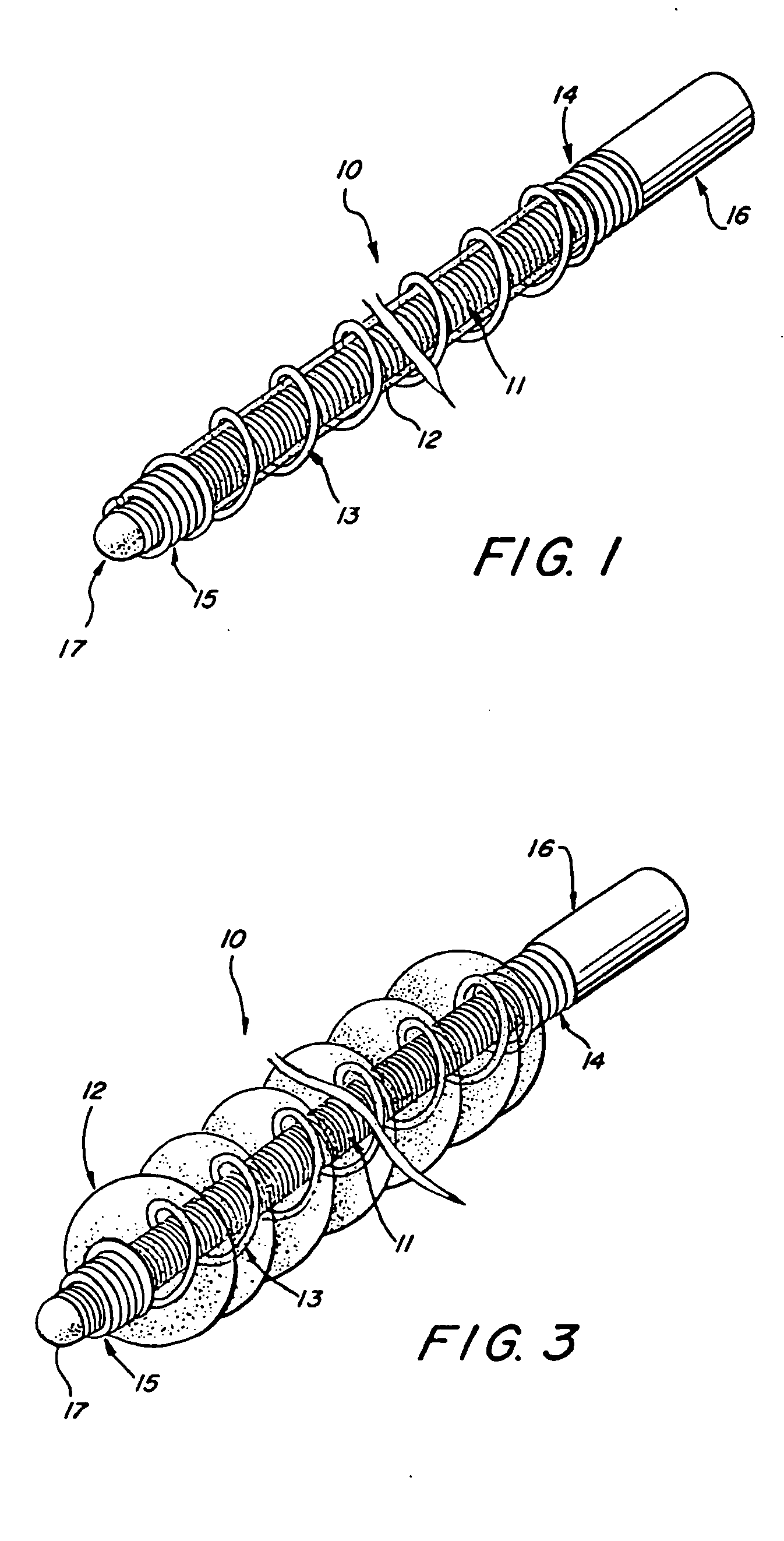
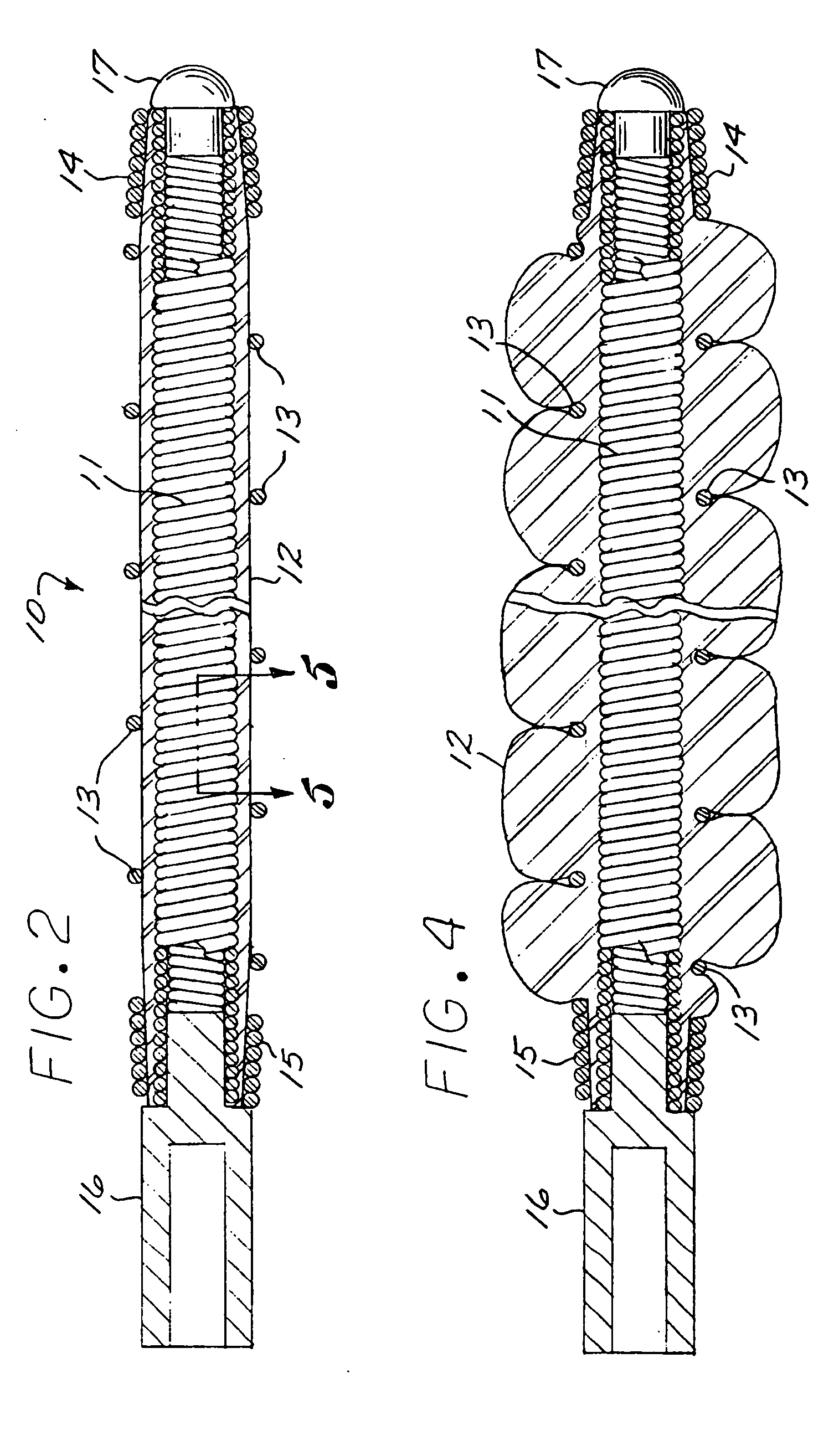
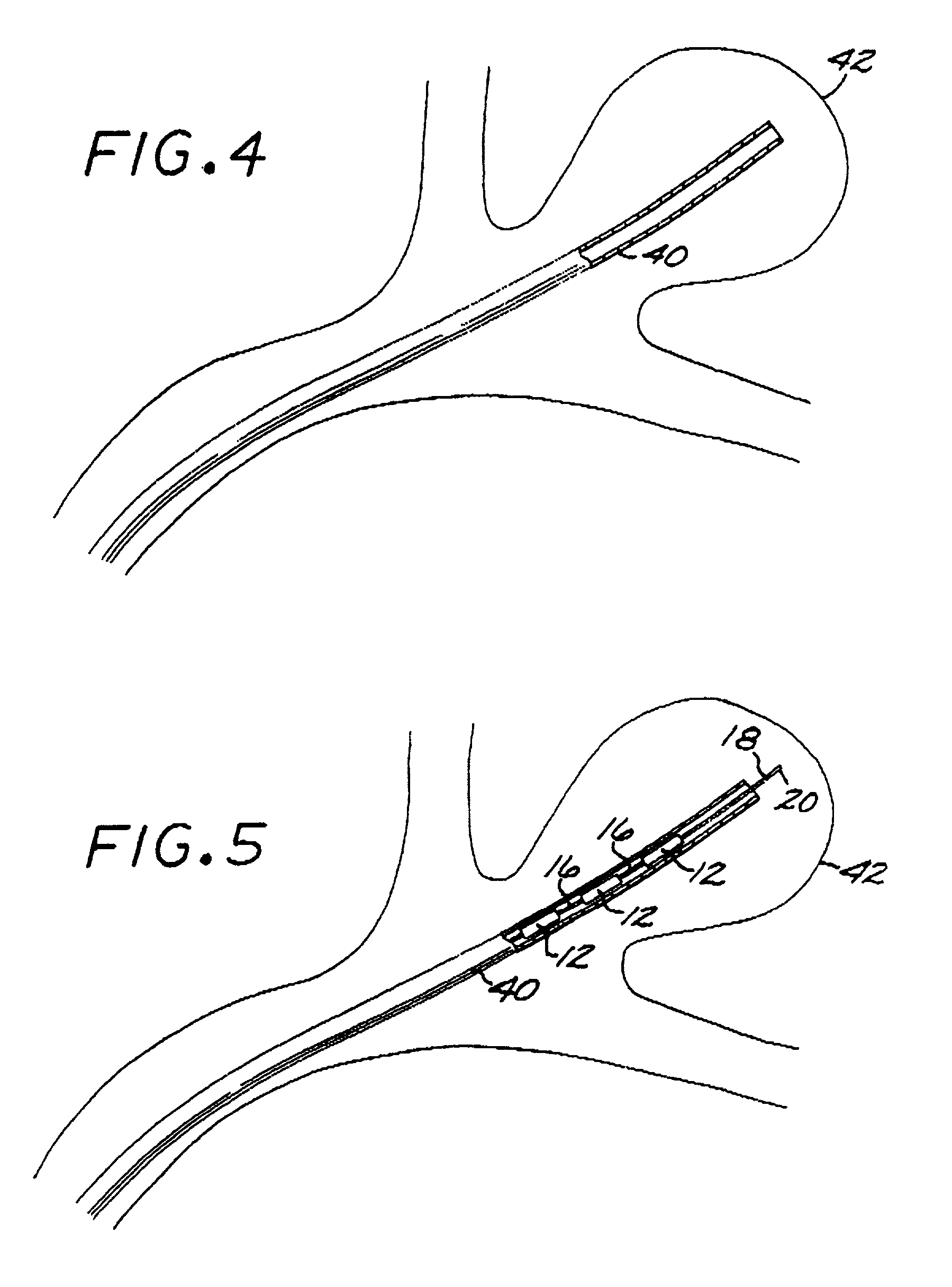
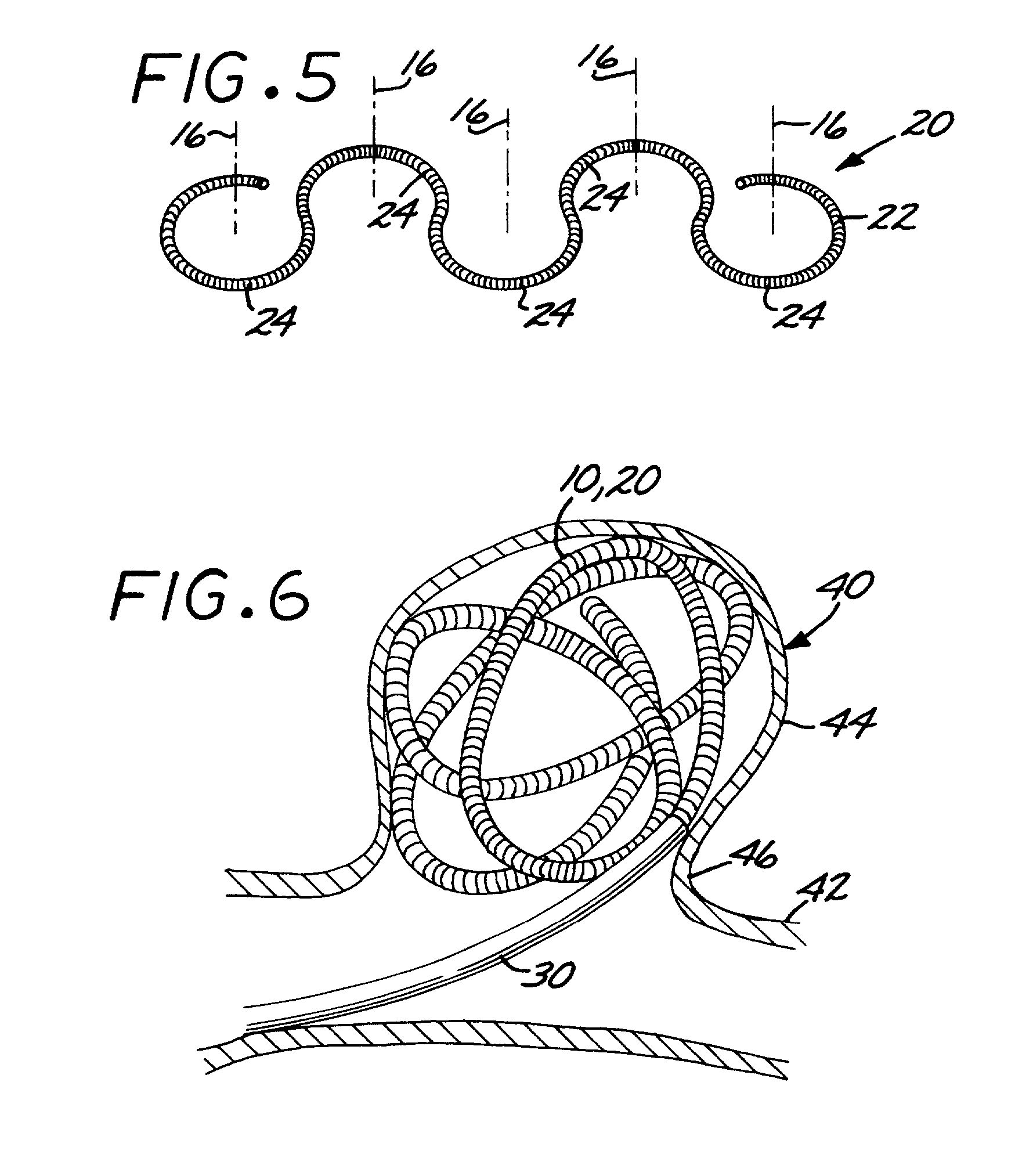
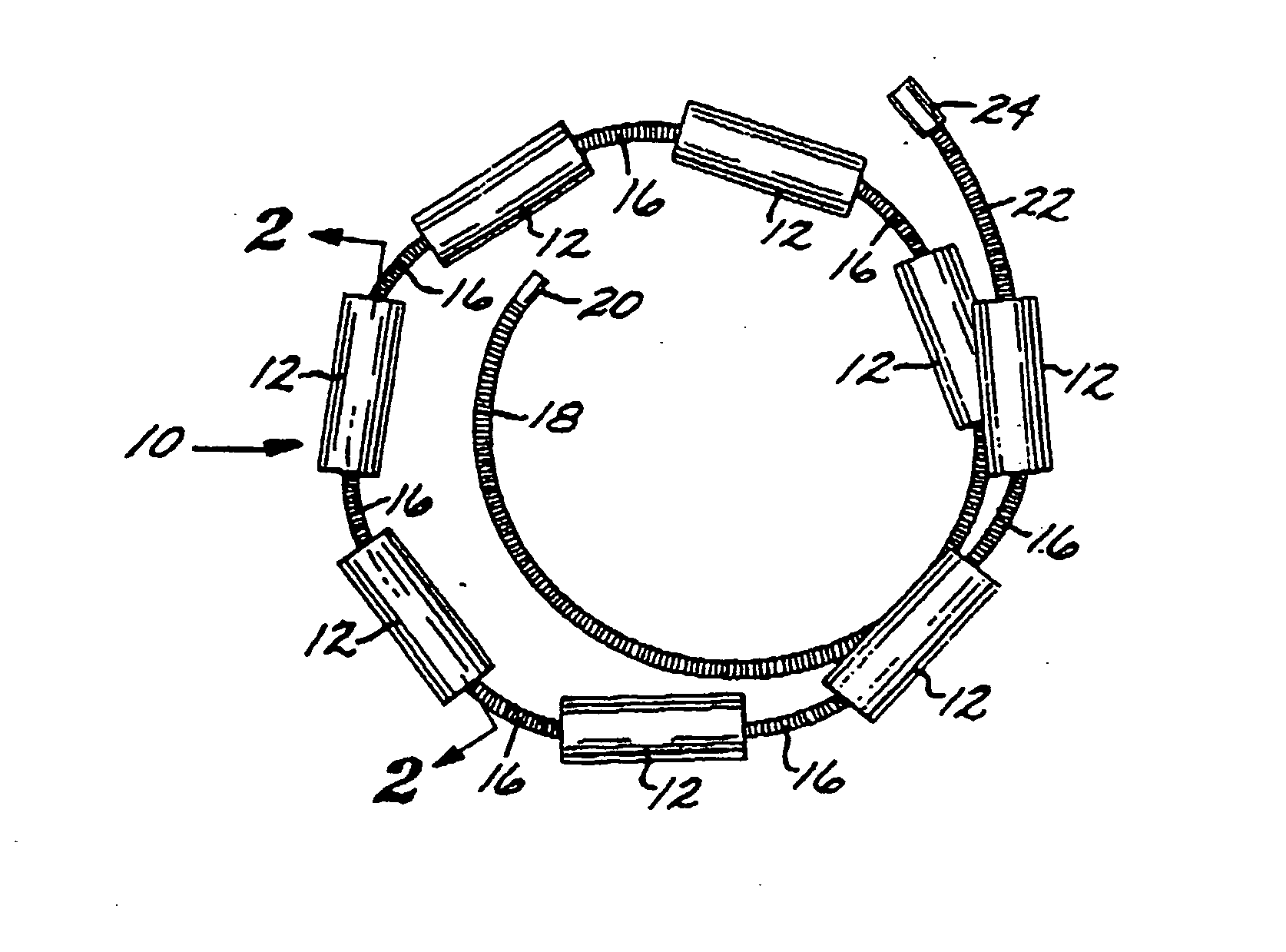
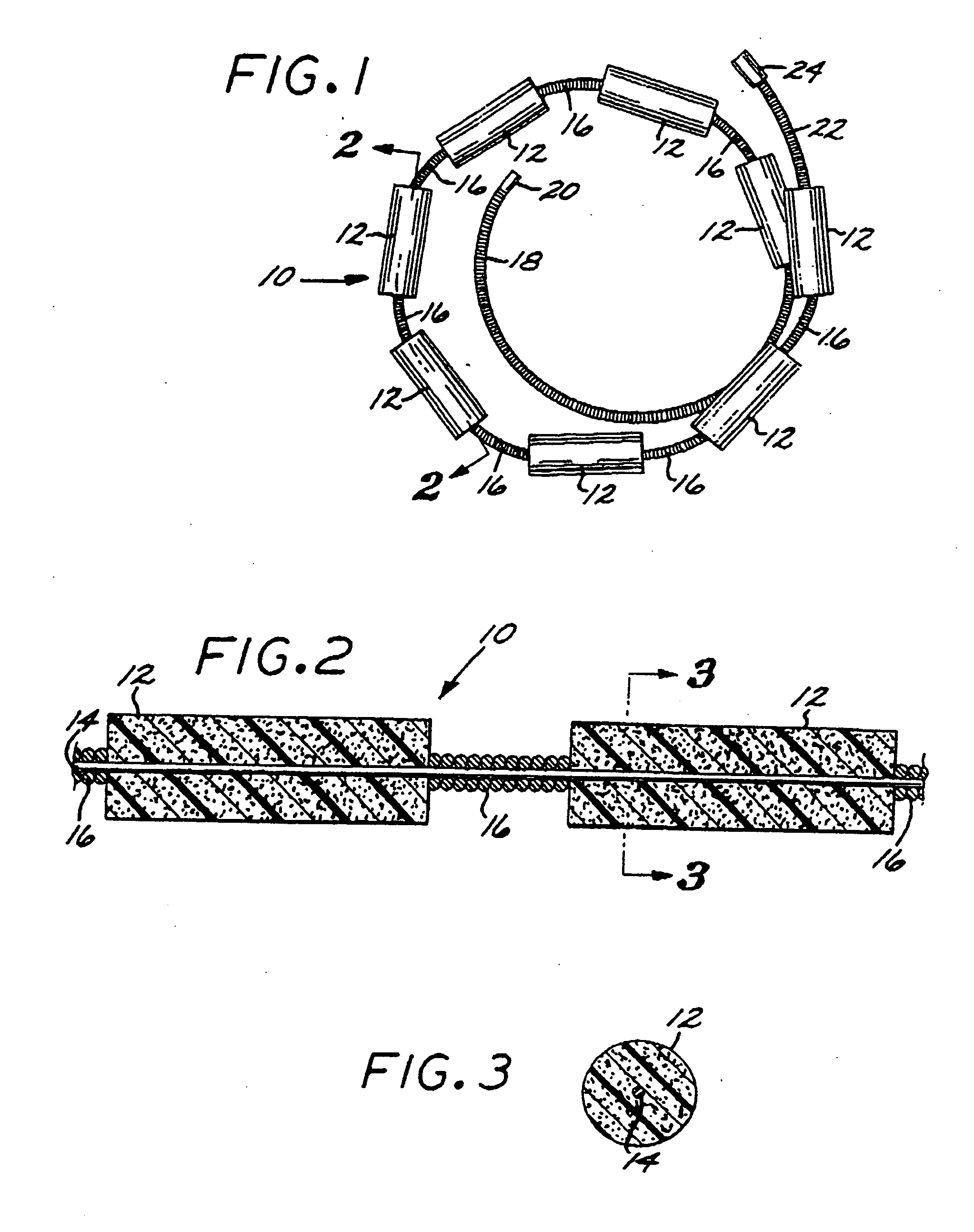
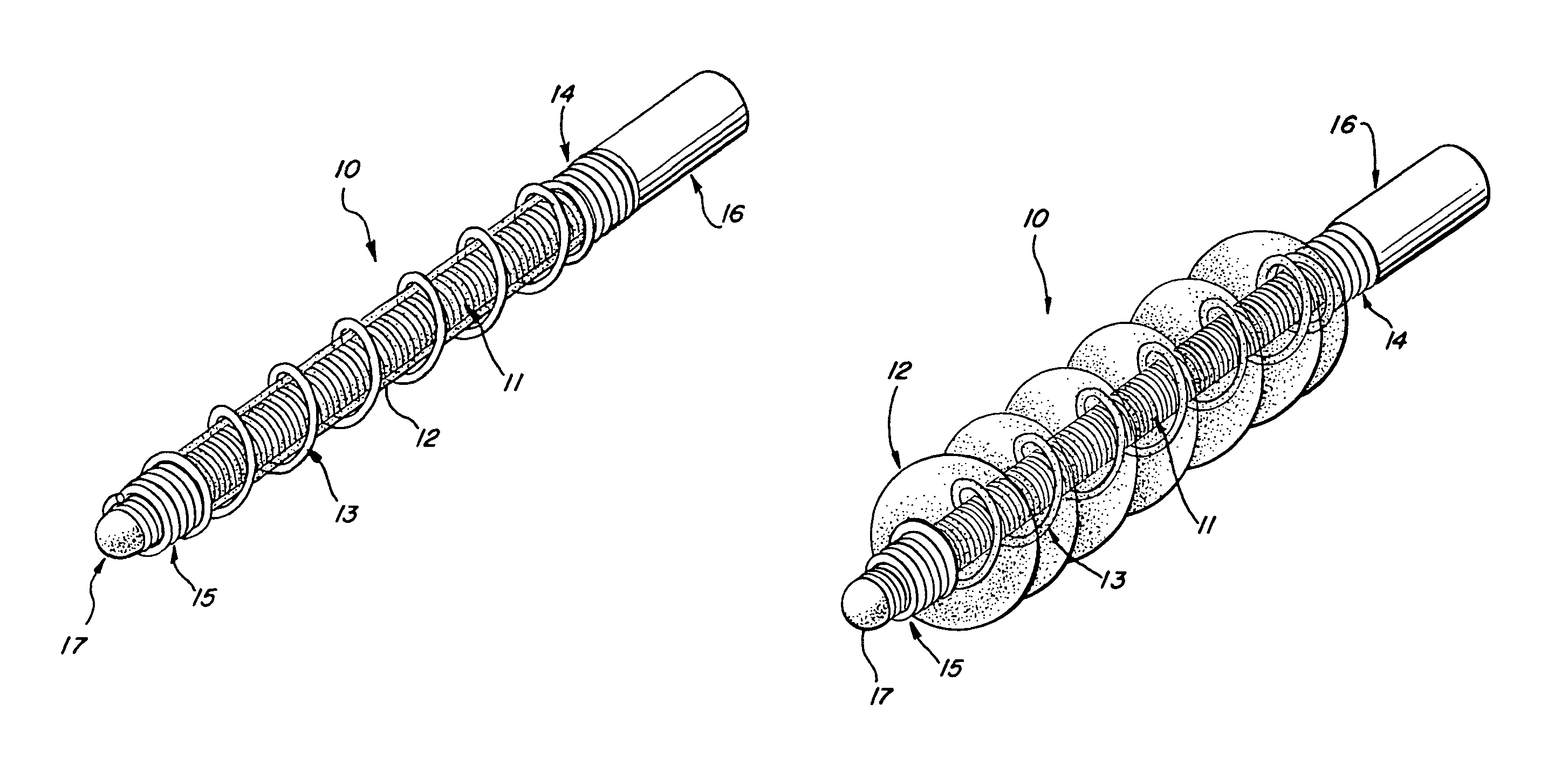
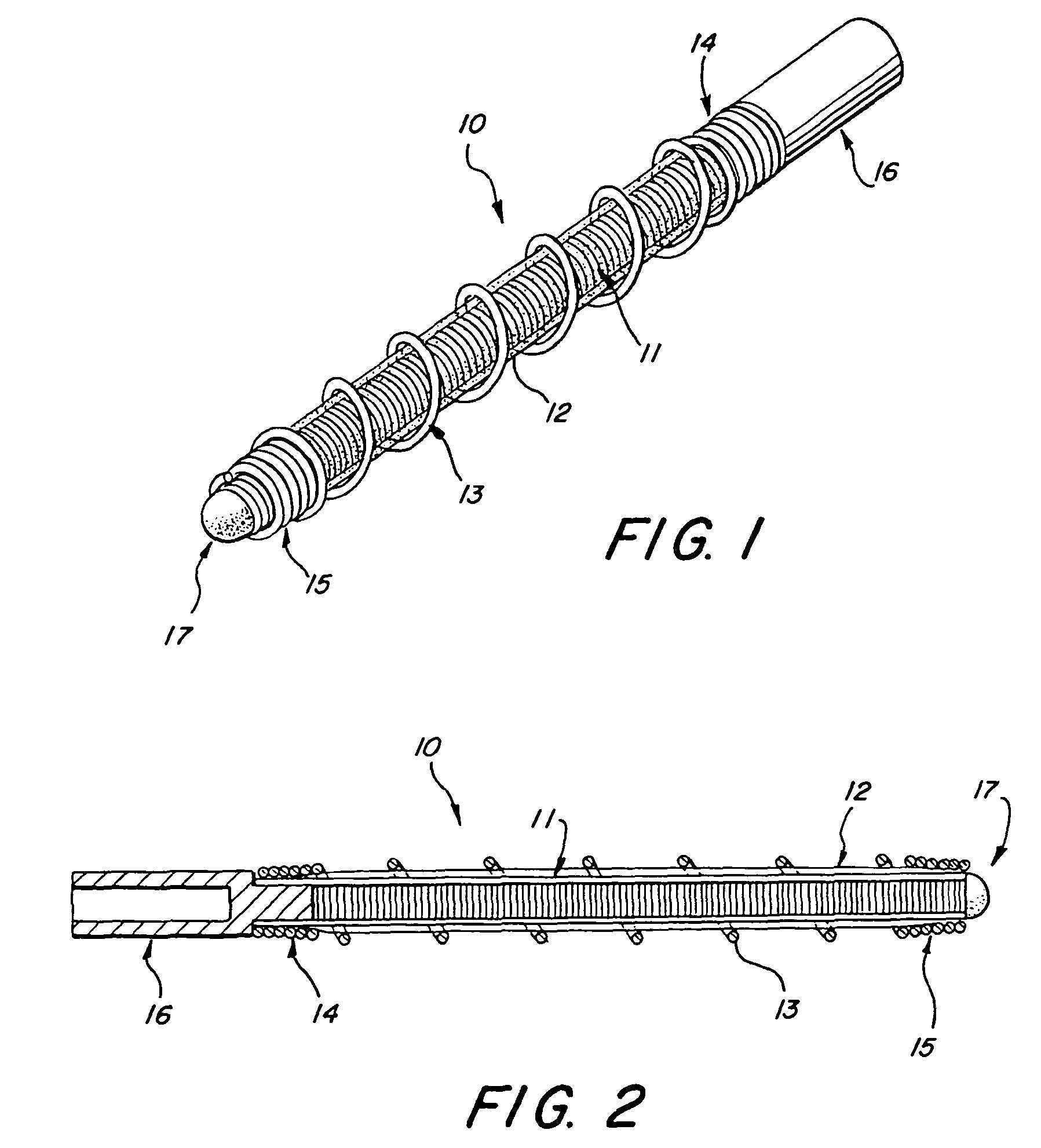
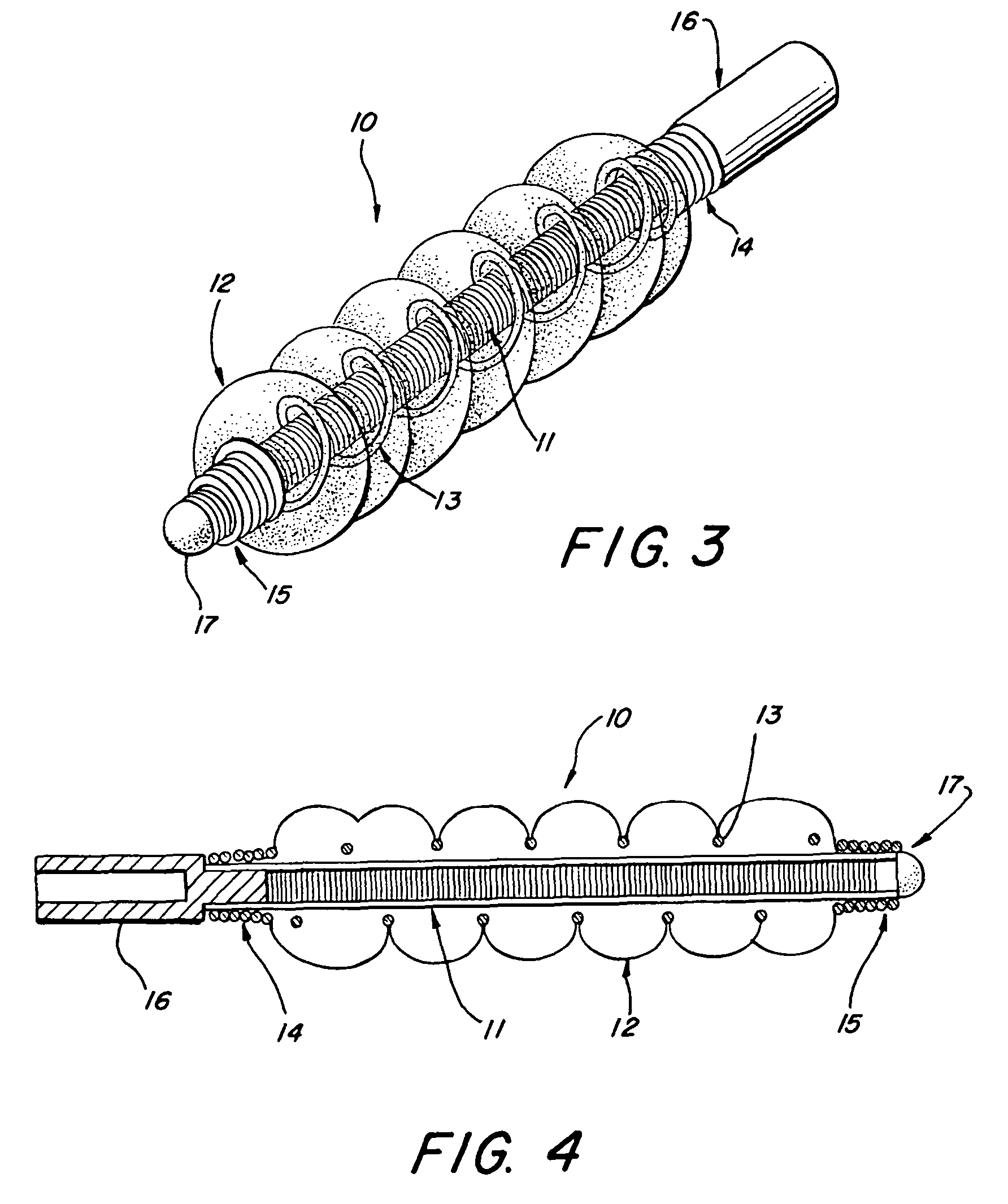
Multi-layer coaxial vaso-occlusive device
InactiveUS20050171572A1Reduces aggregate frictionDecreasing resistance to manipulationDilatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionMetallic materialsPliability
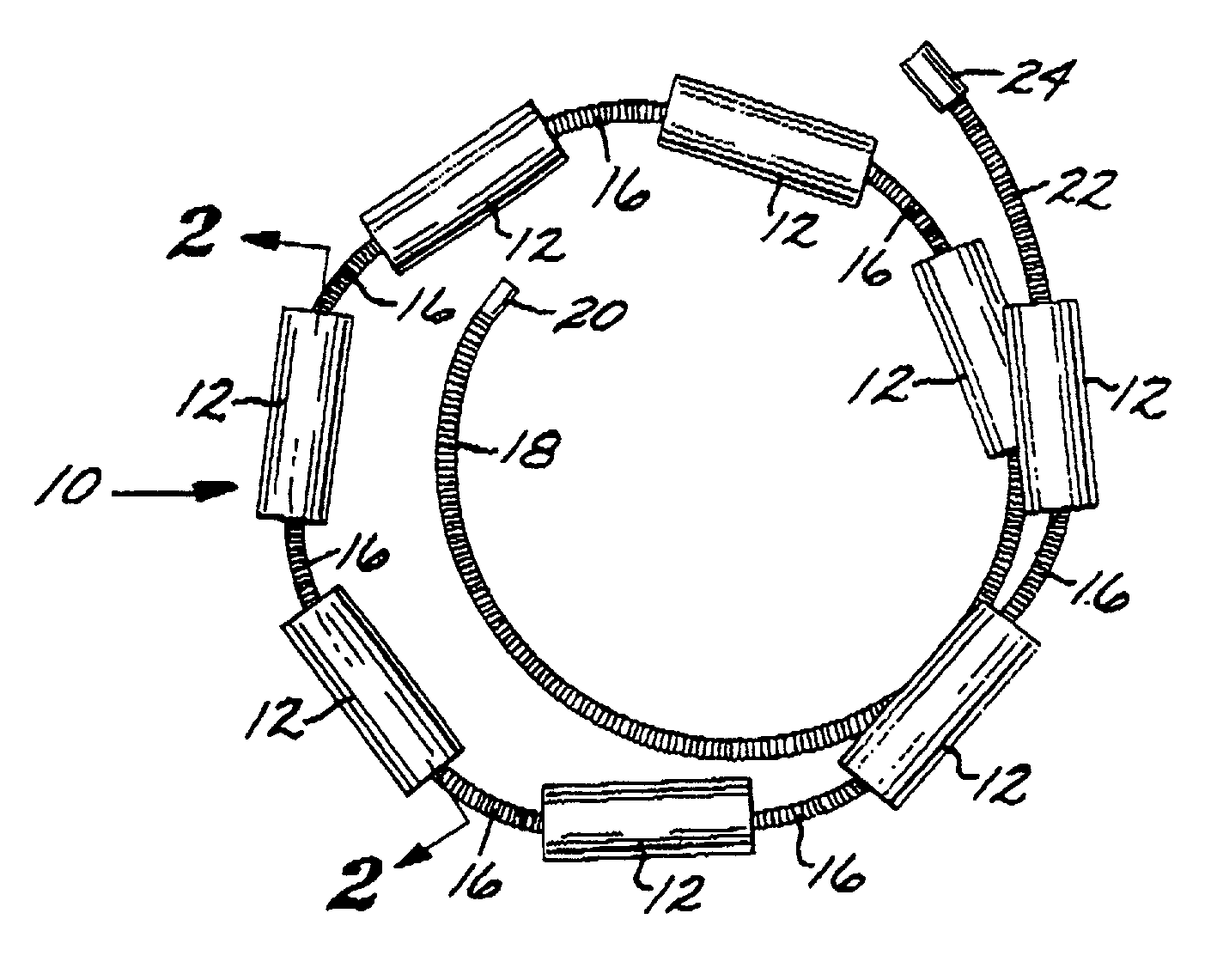
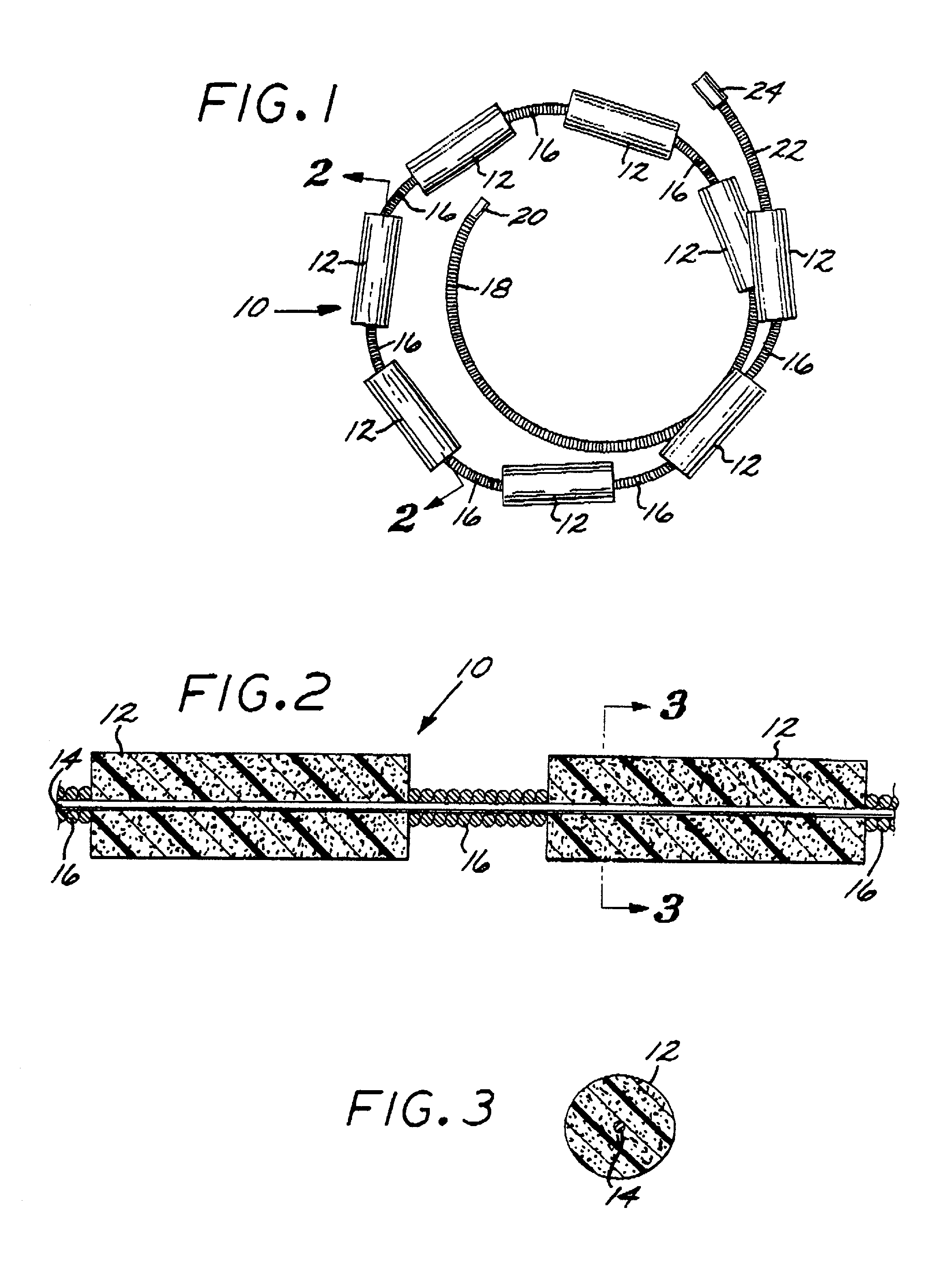
A vaso-occlusive device includes inner, intermediate, and outer elements arranged coaxially. The inner element is a filamentous element, preferably a microcoil. The intermediate element is made of a non-metallic material, preferably an expansile polymer. The outer element is substantially non-expansile and defines at least one gap or opening through which the intermediate element is exposed. In a preferred embodiment, when the intermediate element is expanded, it protrudes through the at least one gap or opening in the outer element and assumes a configuration with an undulating, convexly-curved outer surface defining a chain of arcuate segments, each having a diameter significantly greater than the diameter of the outer element. The expanded configuration of the intermediate element minimizes friction when the device is deployed through a microcatheter, thereby reducing the likelihood of buckling while maintaining excellent flexibility. The result is a device with enhanced pushability and trackability when deployed through a microcatheter.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
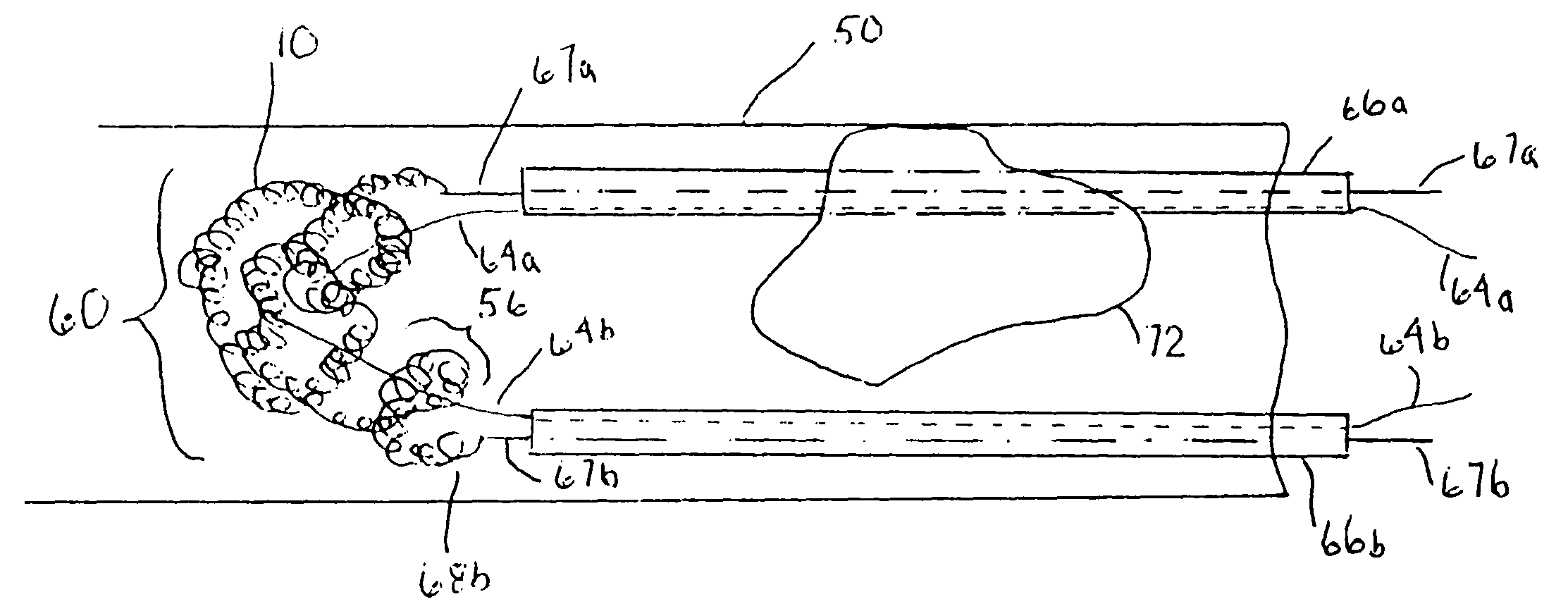
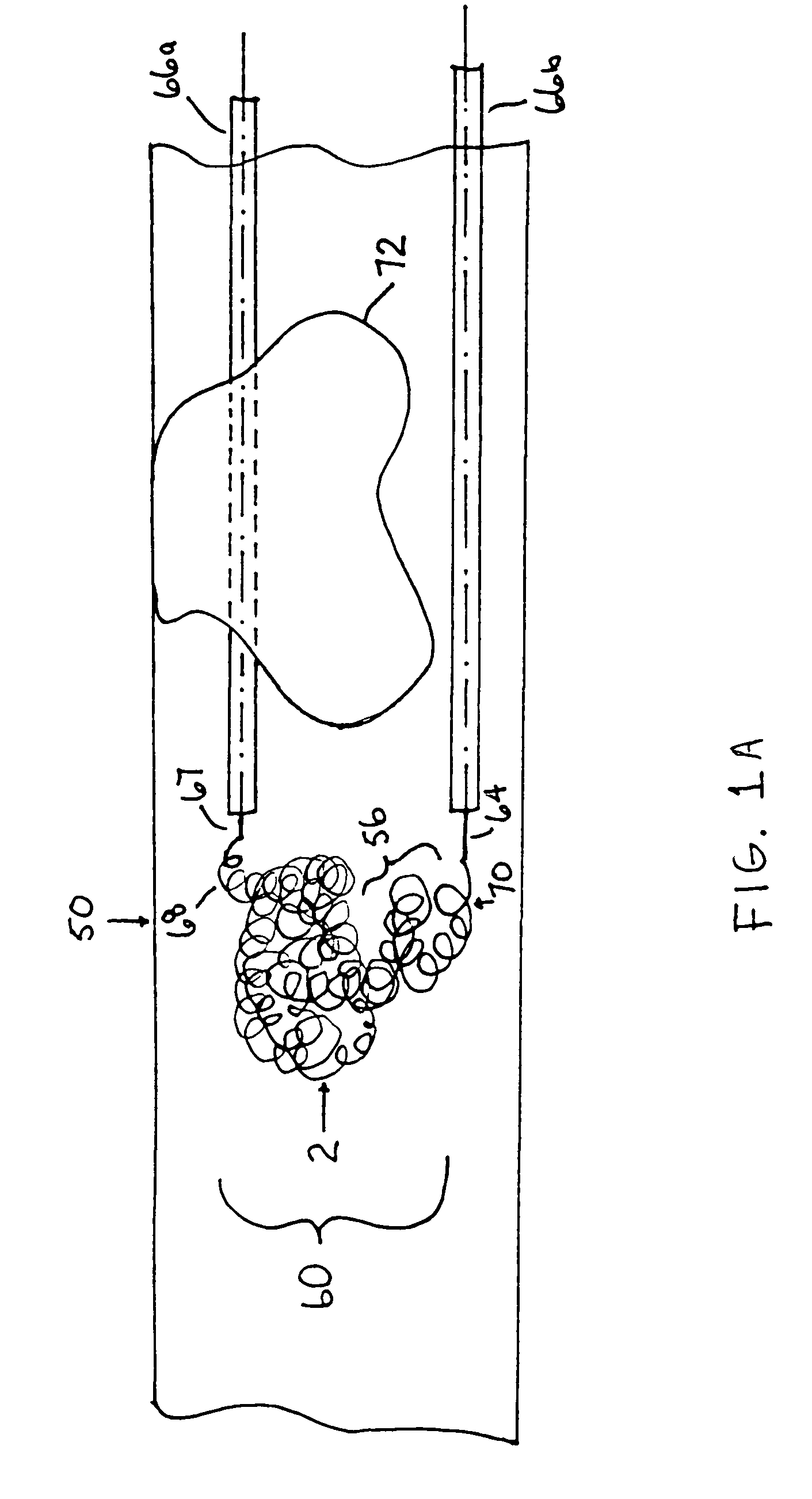
Thrombus removal system and process
InactiveUS20060224177A1Reducing non-rigid contactReduce contactCannulasDilatorsGrip forceSmall artery
A device captures and assists in the removal of a thrombus in arteries, even in small arteries. The device uses a soft coil mesh to engage the surface of a thrombus, and a guidewire is used to retract the soft coil mesh with the captured thrombus. The soft coil is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical element forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
Method of manufacturing expansile filamentous embolization devices
InactiveUS7014645B2Convenient position controlLow of tissue damageEar treatmentCatheterTitanium alloyBiomedical engineering
An embolization device for occluding a body cavity includes one or more elongated, expansible, hydrophilic embolizing elements non-releasably carried along the length of an elongated filamentous carrier that is preferably made of a very thin, highly flexible filament or microcoil of nickel / titanium alloy. At least one expansile embolizing element is non-releasably attached to the carrier. A first embodiment includes a plurality of embolizing elements fixed to the carrier at spaced-apart intervals along its length. In second, third and fourth embodiments, an elongate, continuous, coaxial embolizing element is non-releasably fixed to the exterior surface of the carrier, extending along a substantial portion of the length of the carrier proximally from a distal tip, and optionally includes a lumenal reservoir for delivery of therapeutic agents. Exemplary methods for making these devices include skewering and molding the embolizing elements. In any of the embodiments, the embolizing elements may be made of a hydrophilic, macro-porous, polymeric, hydrogel foam material. In the second, third and fourth embodiments, the elongate embolizing element is preferably made of a porous, environmentally-sensitive, expansile hydrogel, which can optionally be made biodegradable and / or bioresorbable, having a rate of expansion that changes in response to a change in an environmental parameter, such as the pH or temperature of the environment.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
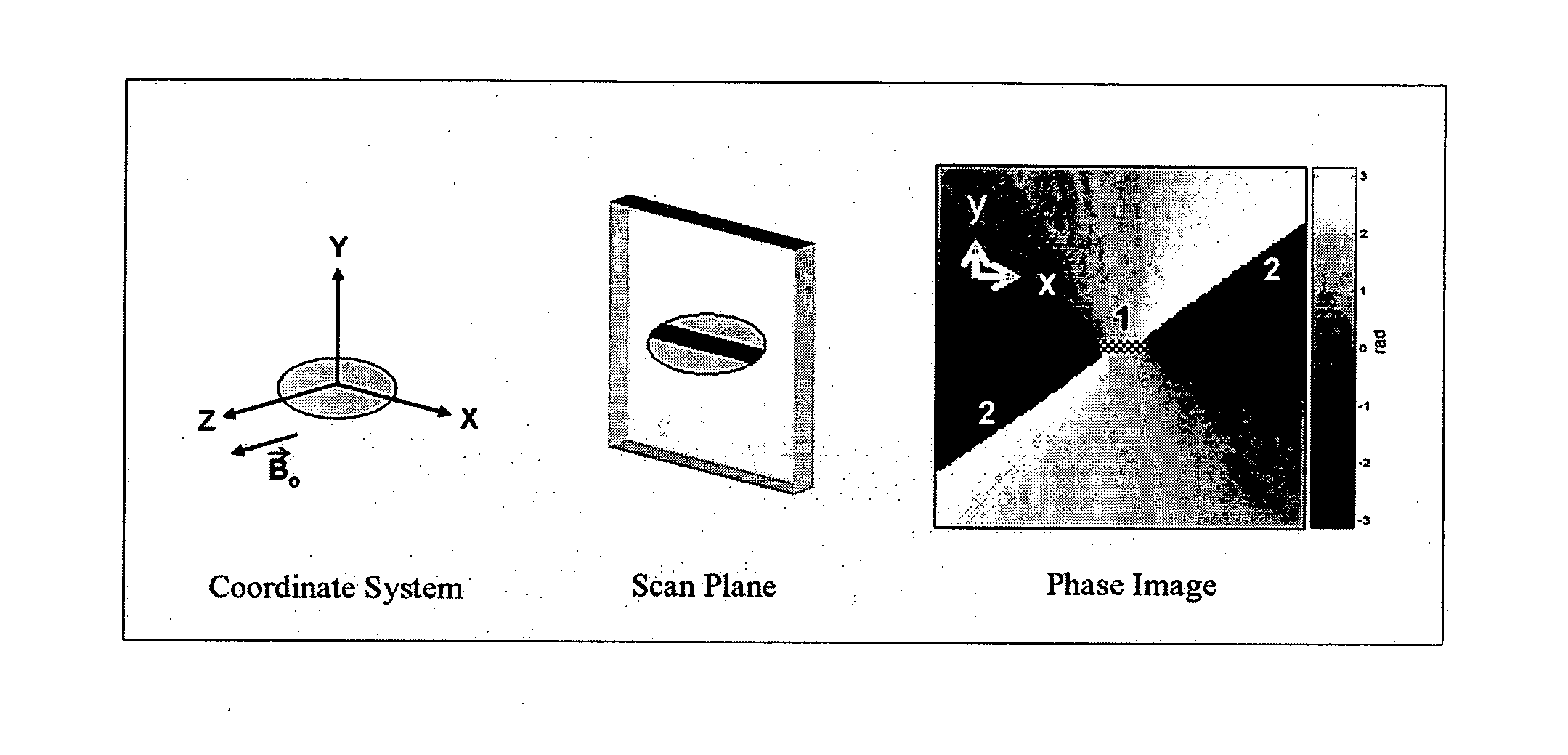
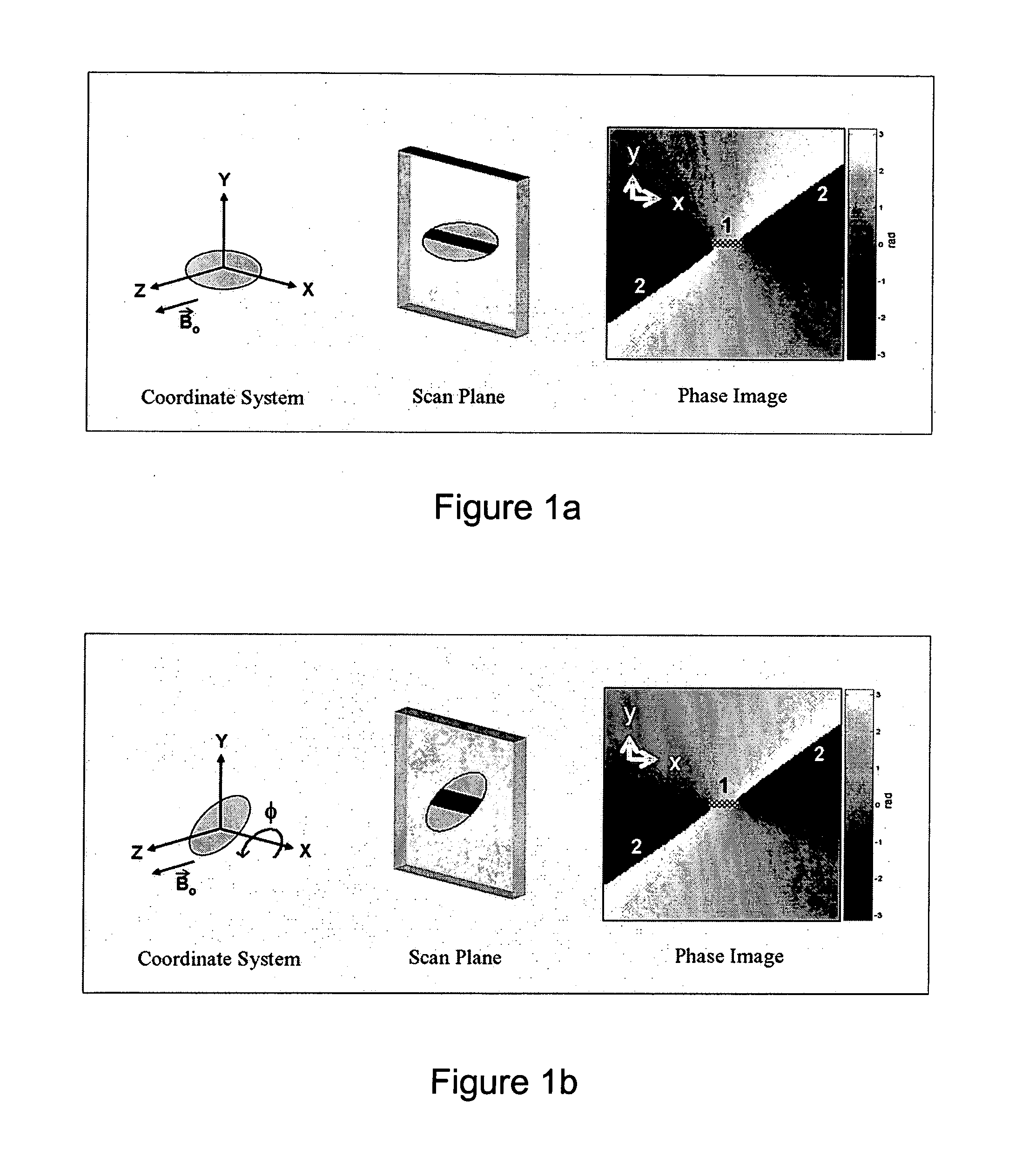
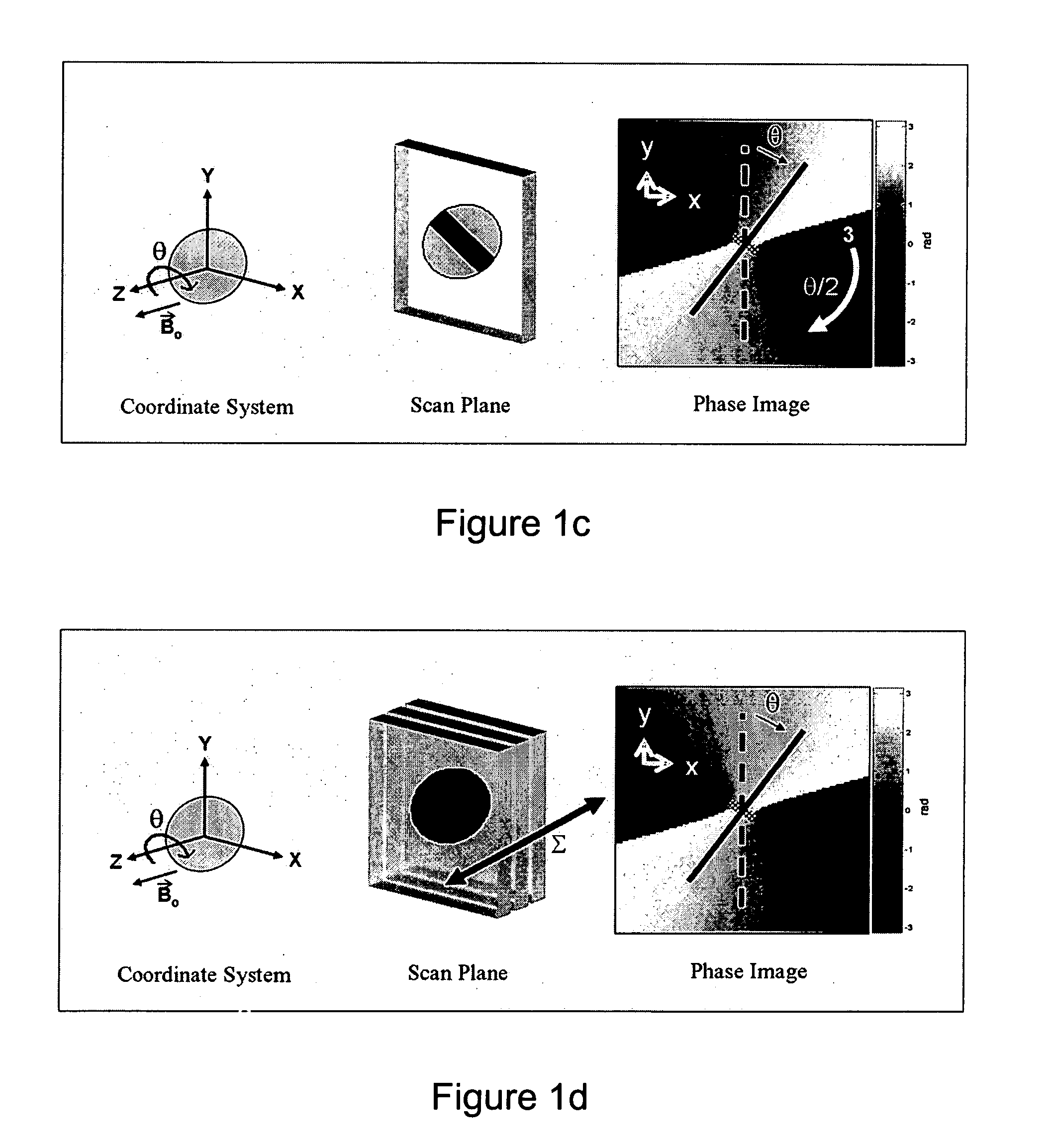
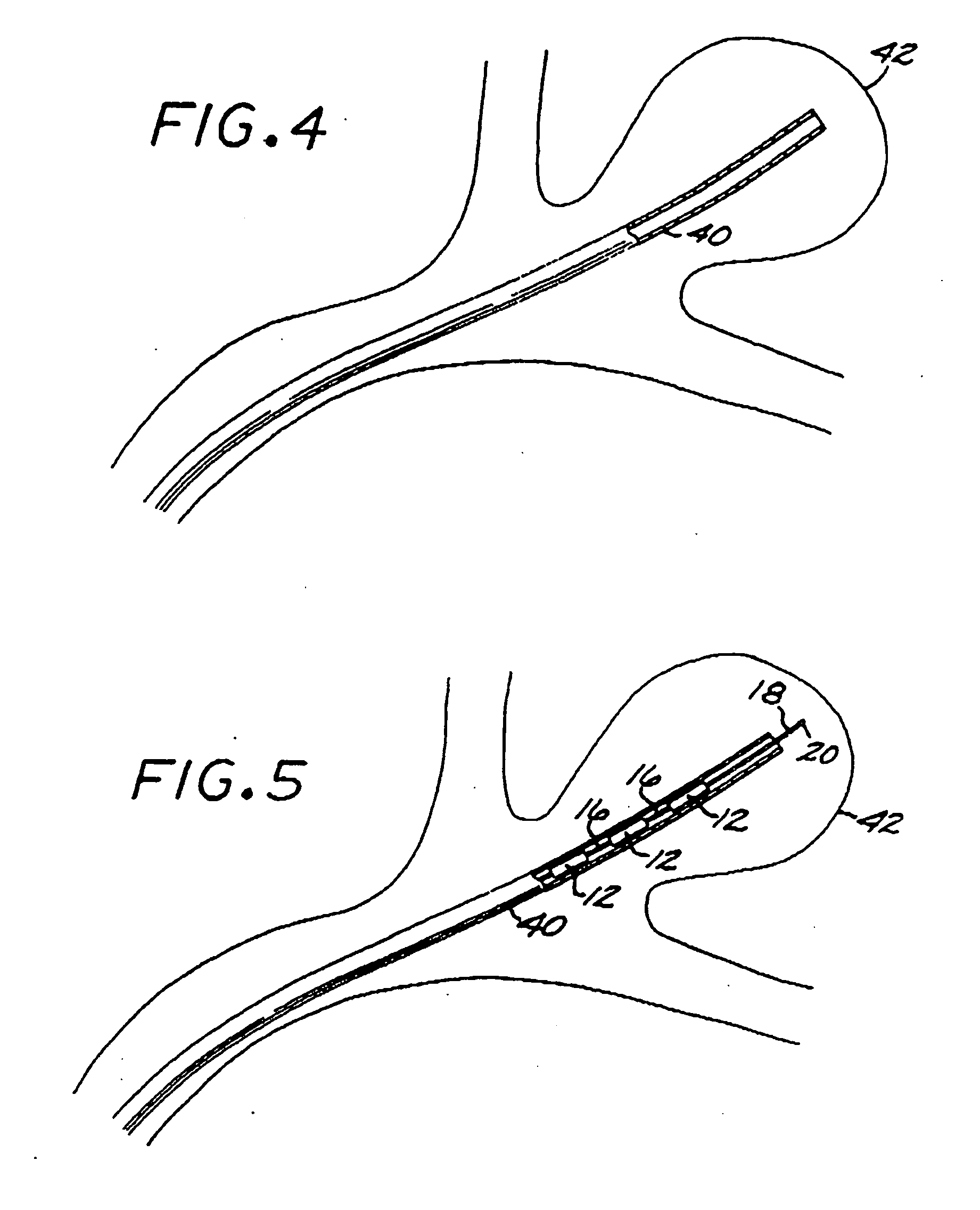
Catheter tracking with phase information
ActiveUS20050245814A1Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesBiopsy
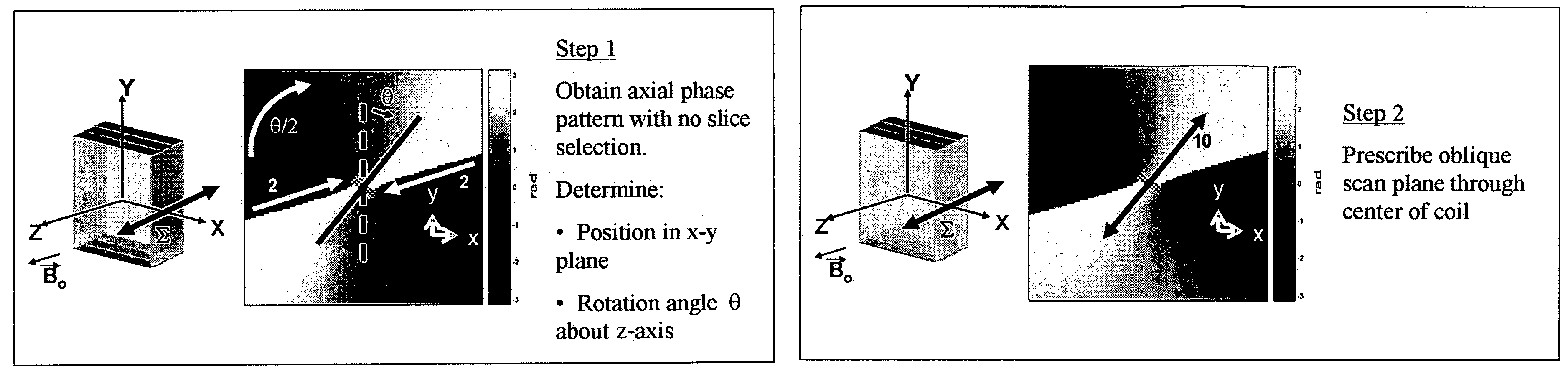
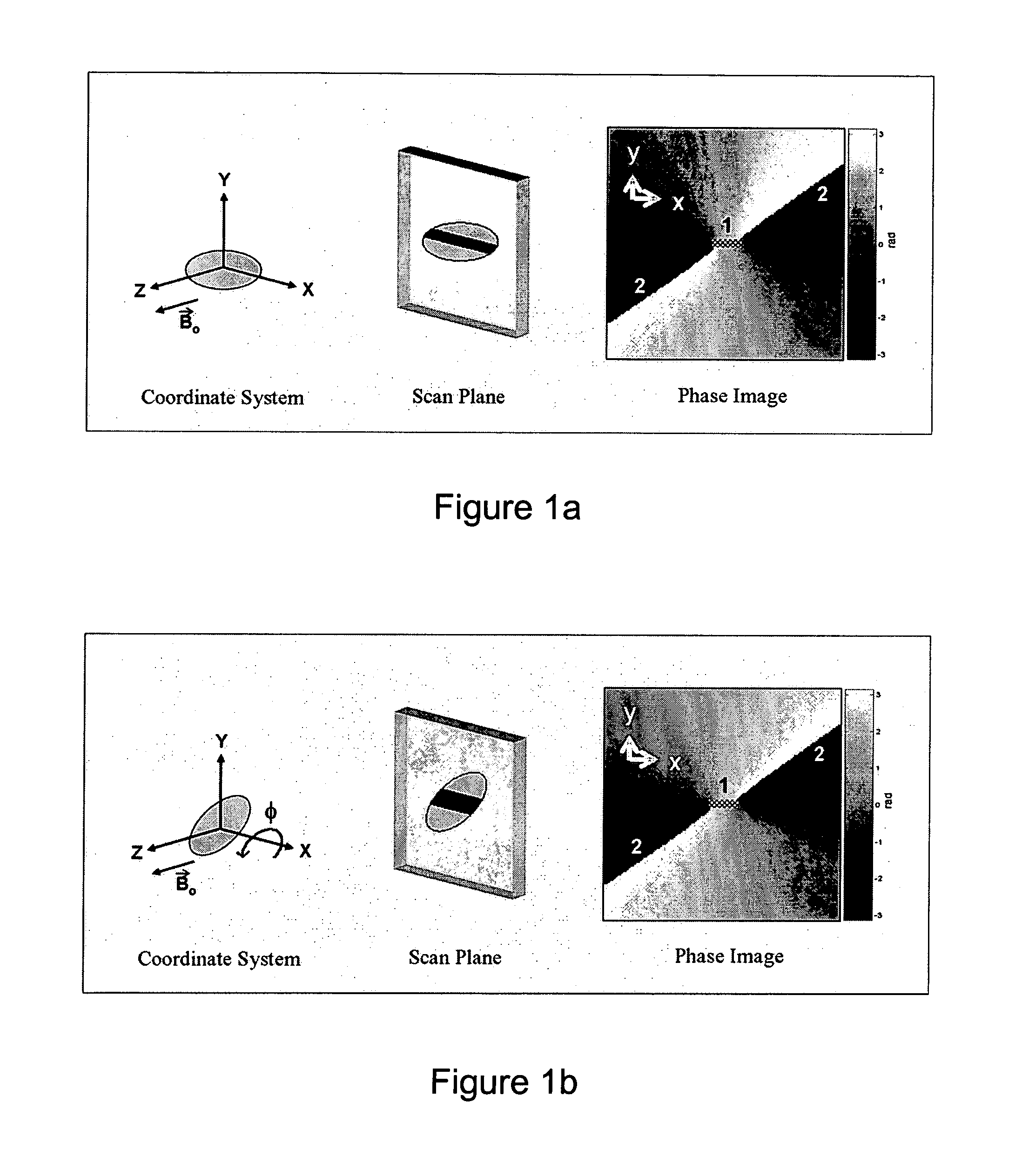
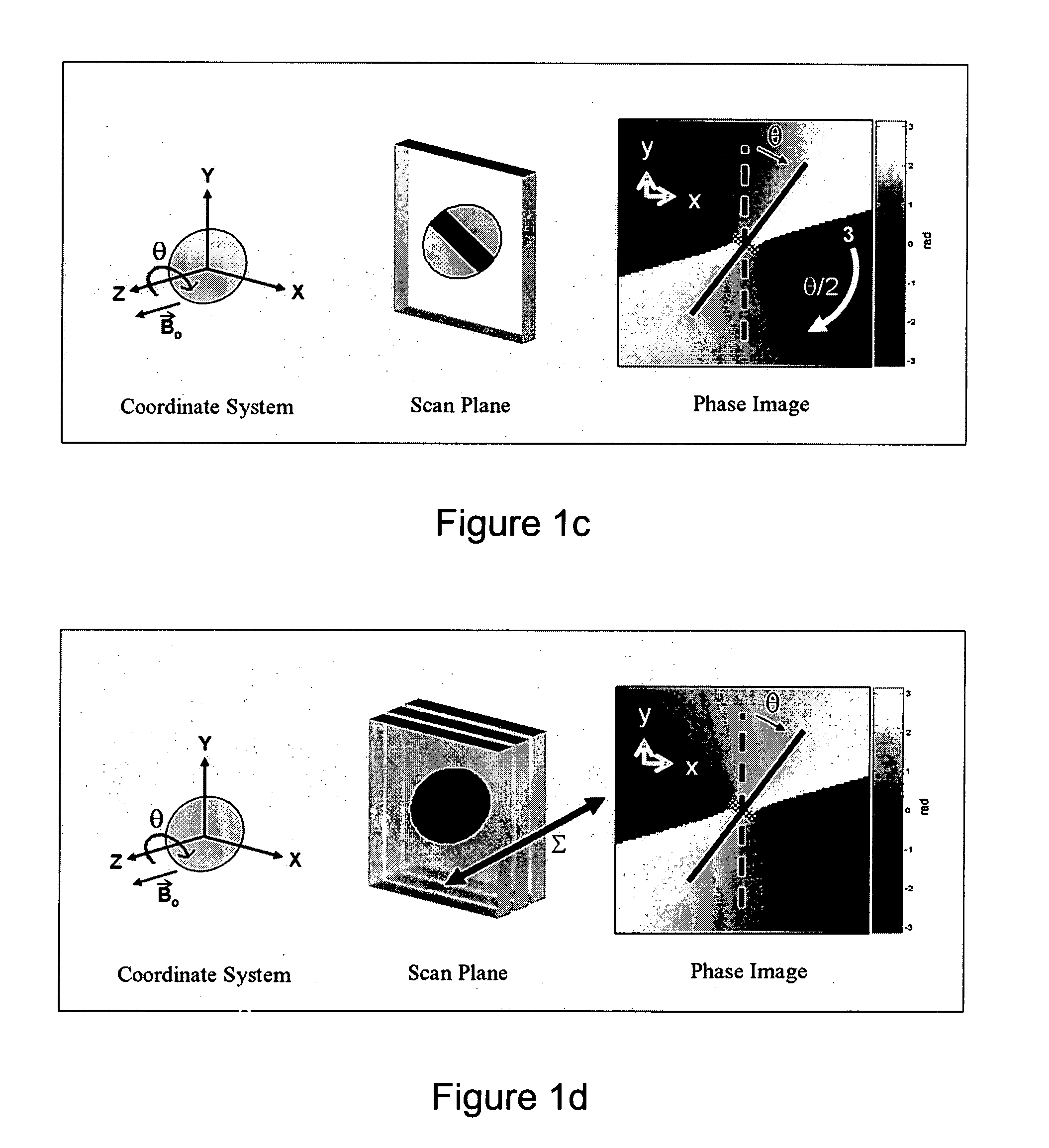
The present invention discloses a method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern and orientation of individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, tracking of interventional devices is performed by one integrated phase image projected onto the axial plane and a second image in an oblique plane through the center of the coil and normal to the coil plane. In another preferred embodiment, the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further preferred embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular access devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
Thrombus removal system and process
A device capable of capturing and facilitating the removal of a thrombus in blood vessels (or stones in biliary or urinary ducts, or foreign bodies) uses a soft coil mesh with the aid of a pull wire or string to engage the surface of a thrombus, and remove the captured thrombus. The soft coil mesh is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical elements forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls. The use of multiple coil mesh elements, delivered through a single lumen or multiple lumens, preferably with separate control of at least one end of each coil, provides a firm grasp on a distal side of a thrombus, assisting in non-disruptive or minimally disrupted removal of the thrombus upon withdrawal of the device.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
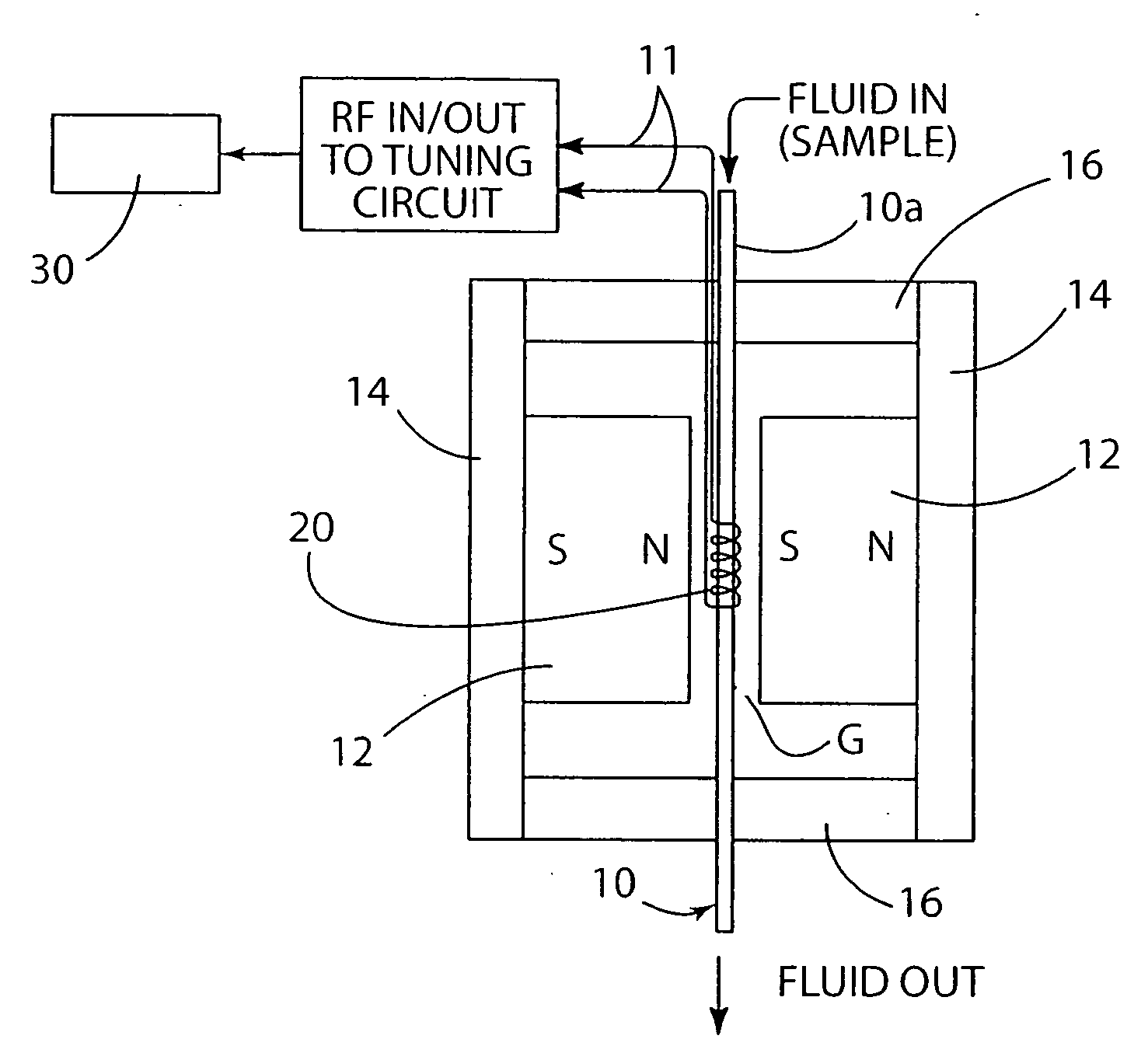
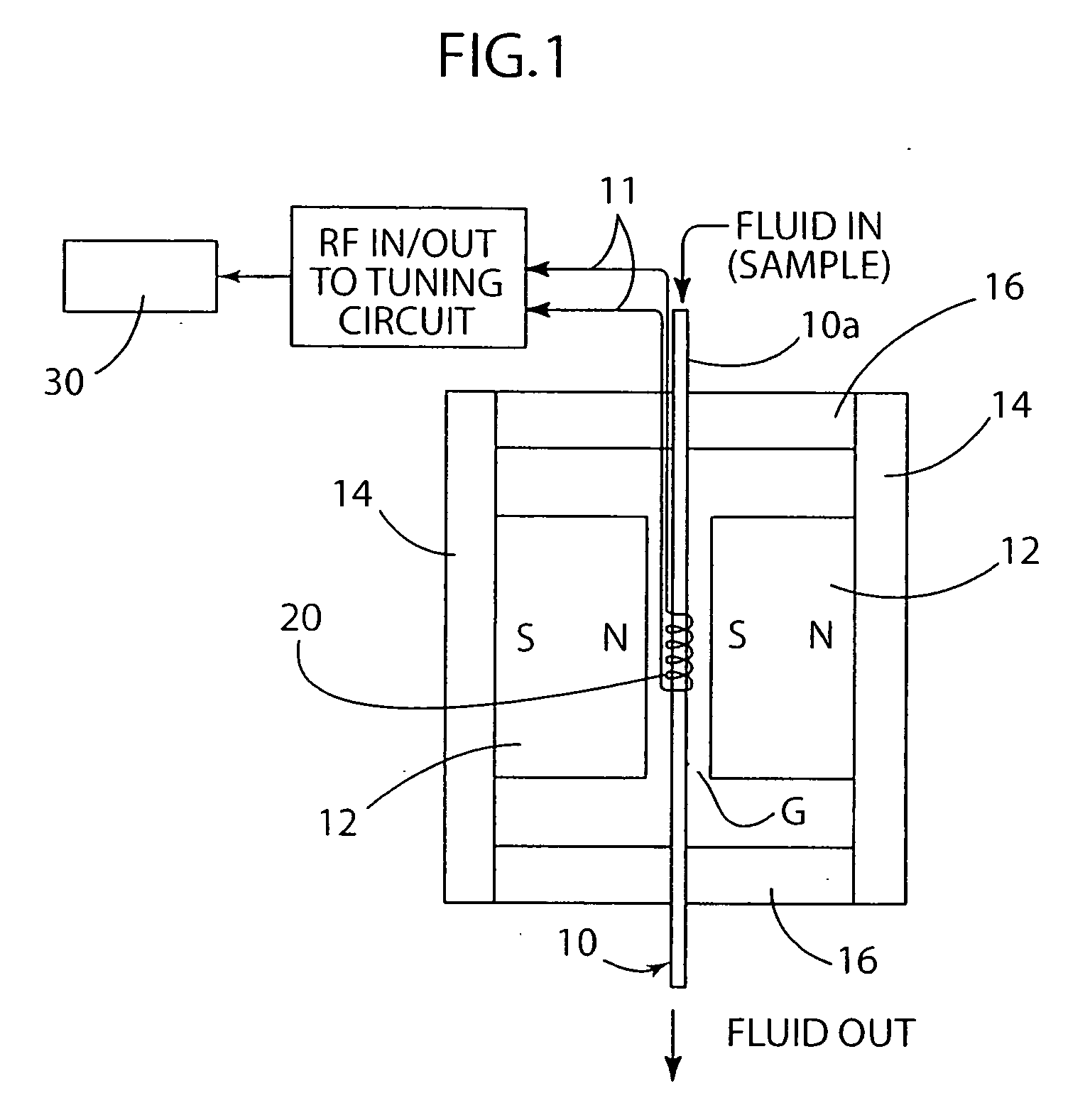
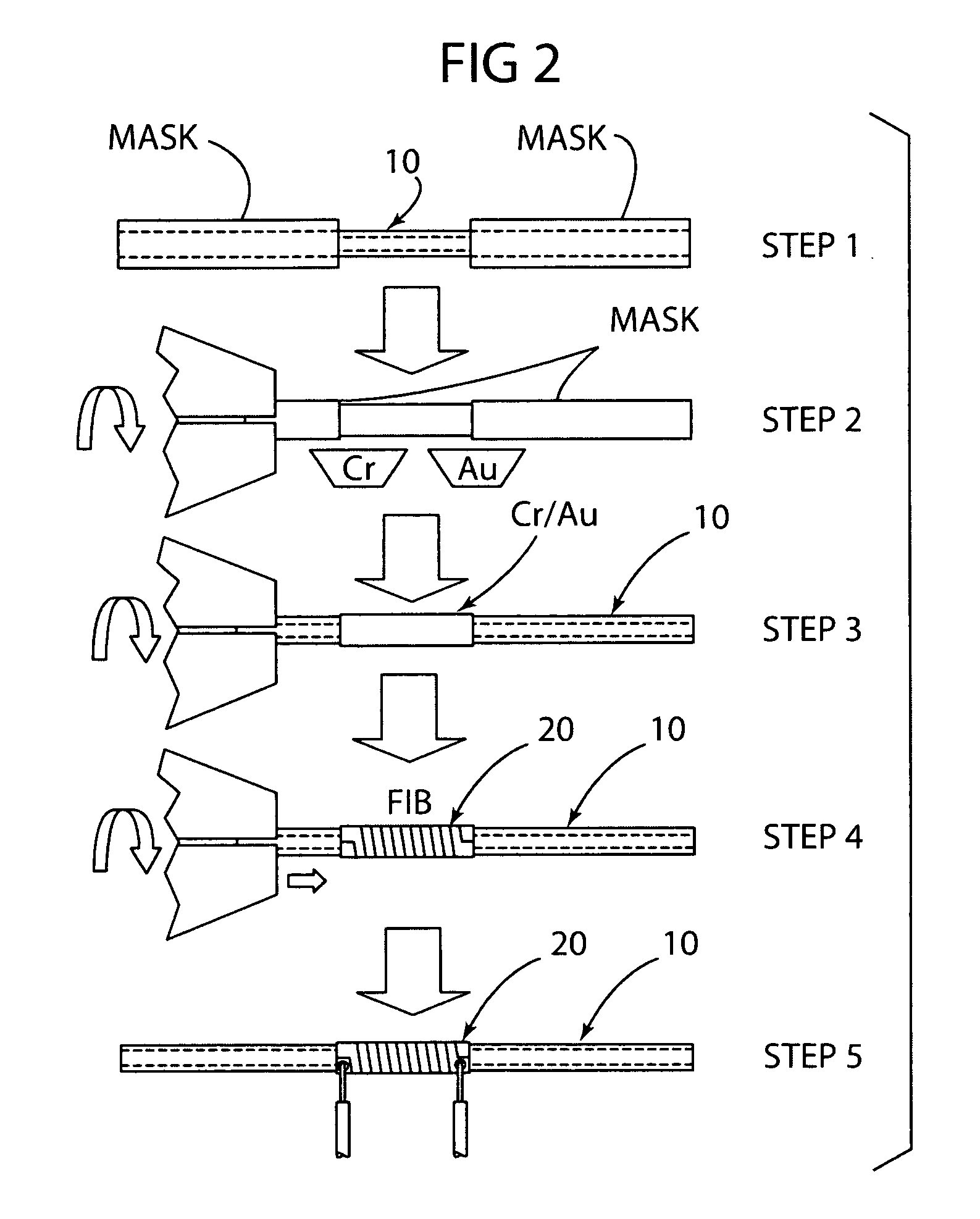
Biological detector and method
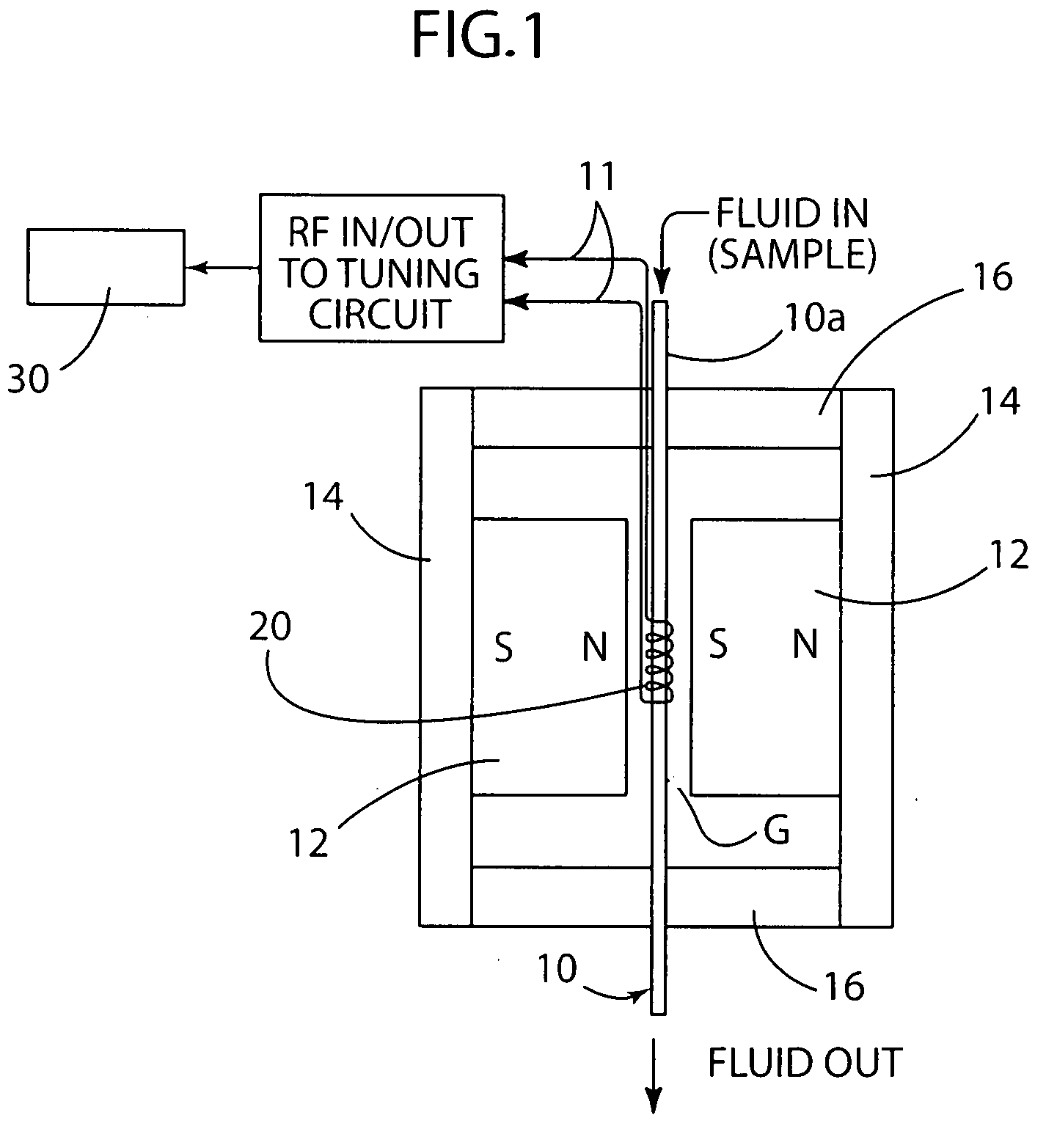
ActiveUS20080204022A1Low costCompact assemblyNanosensorsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceProximateSpectroscopy
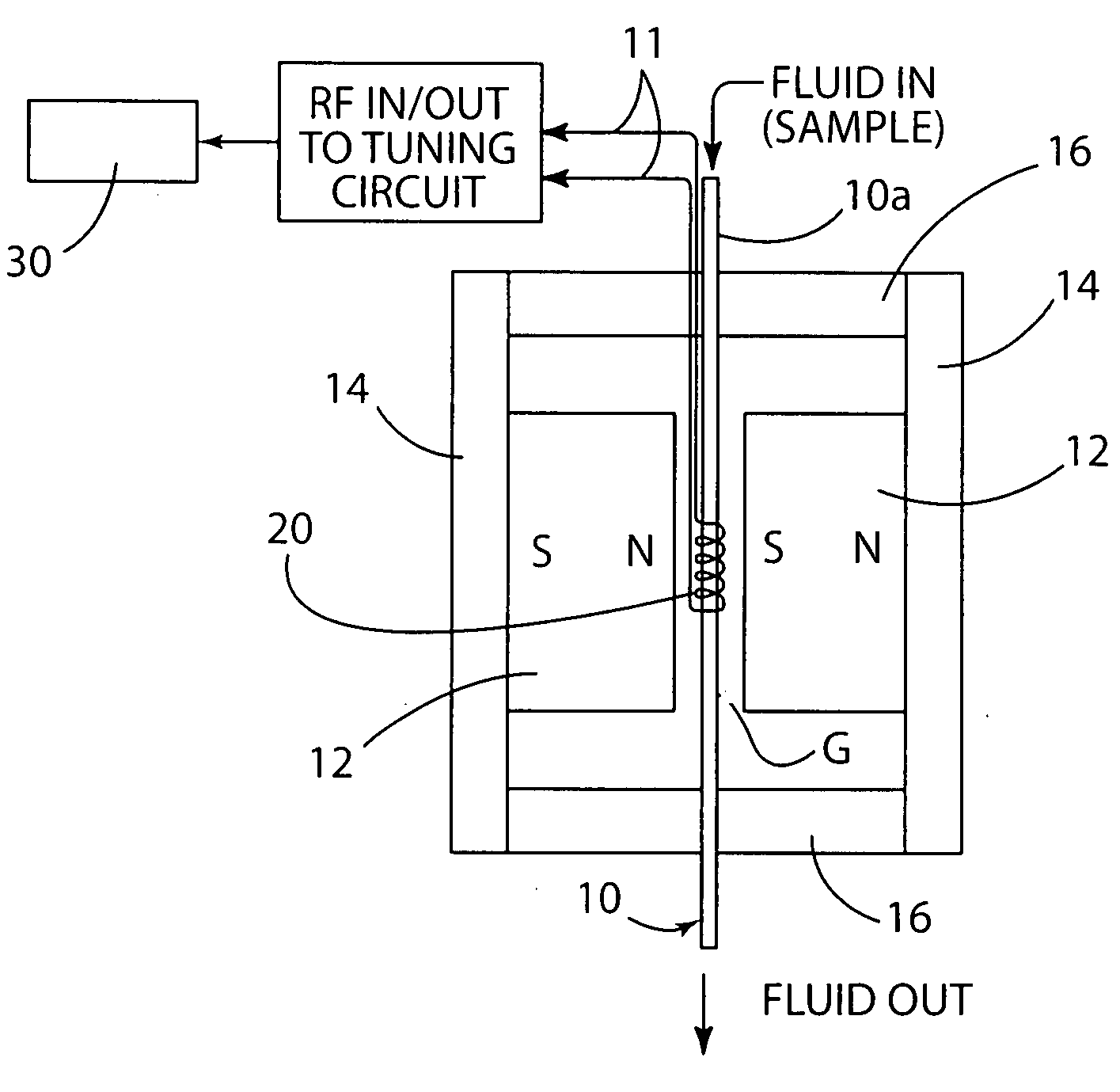
A biological detector includes a conduit for receiving a fluid containing one or more magnetic nanoparticle-labeled, biological objects to be detected and one or more permanent magnets or electromagnet for establishing a low magnetic field in which the conduit is disposed. A microcoil is disposed proximate the conduit for energization at a frequency that permits detection by NMR spectroscopy of whether the one or more magnetically-labeled biological objects is / are present in the fluid.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +2
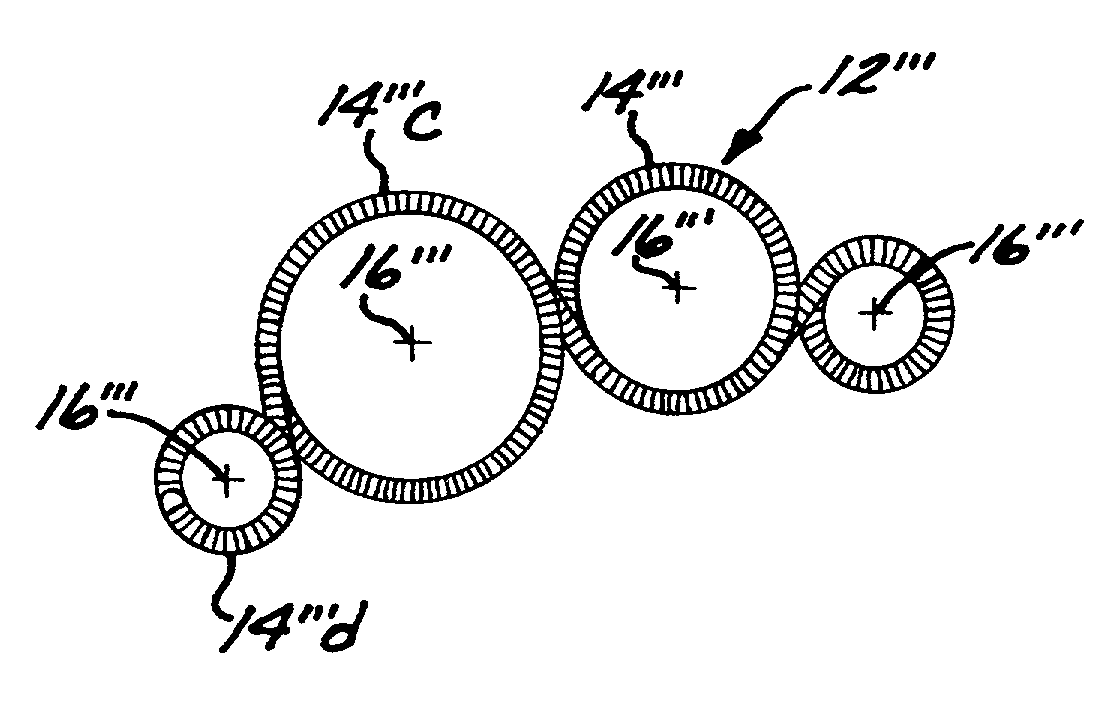
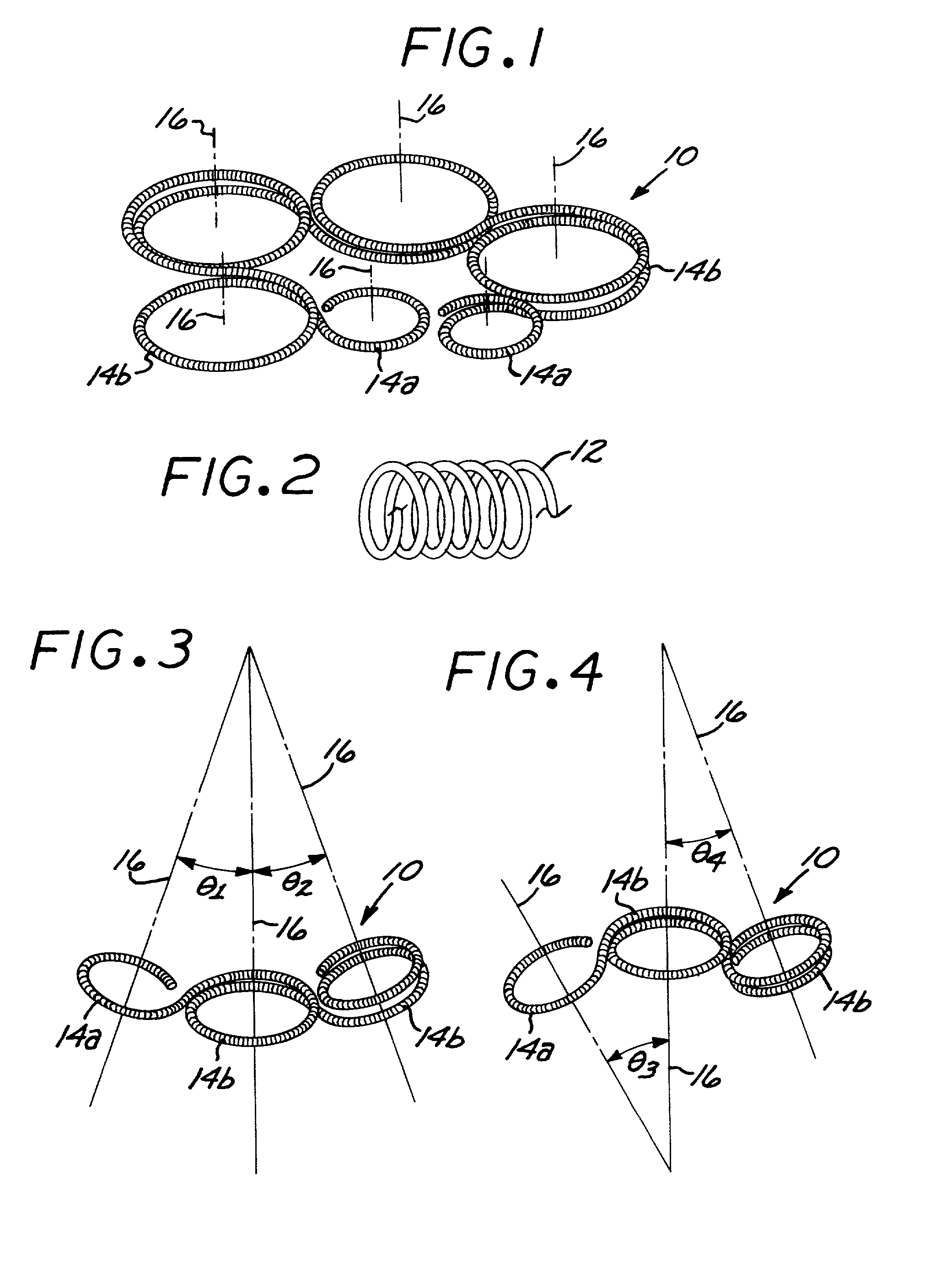
Microcoil vaso-occlusive device with multi-axis secondary configuration
InactiveUS7033374B2Minimizing shifting and tumblingMinimizing degree of compactionDilatorsOcculdersHigh energyClosed loop
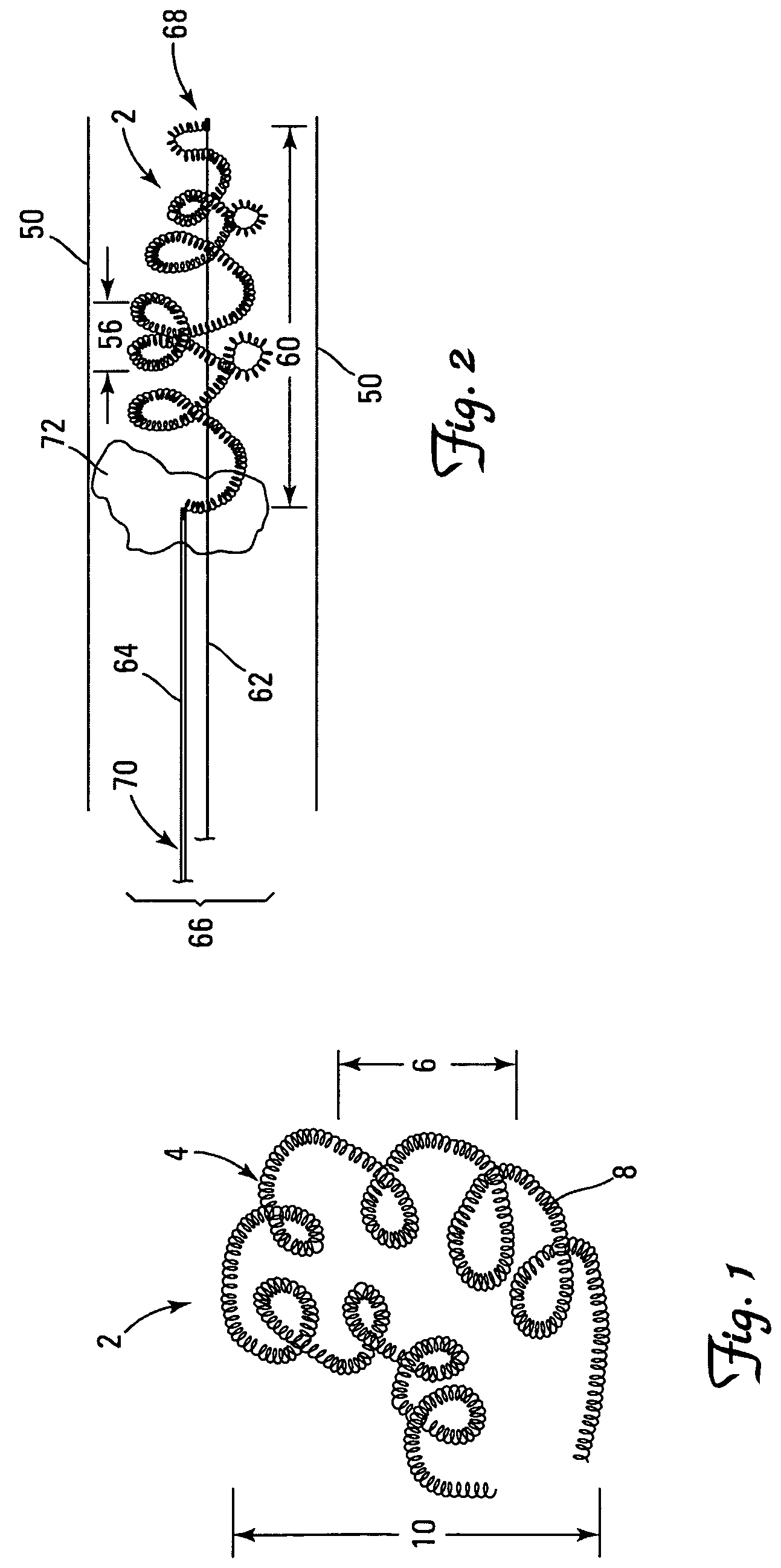
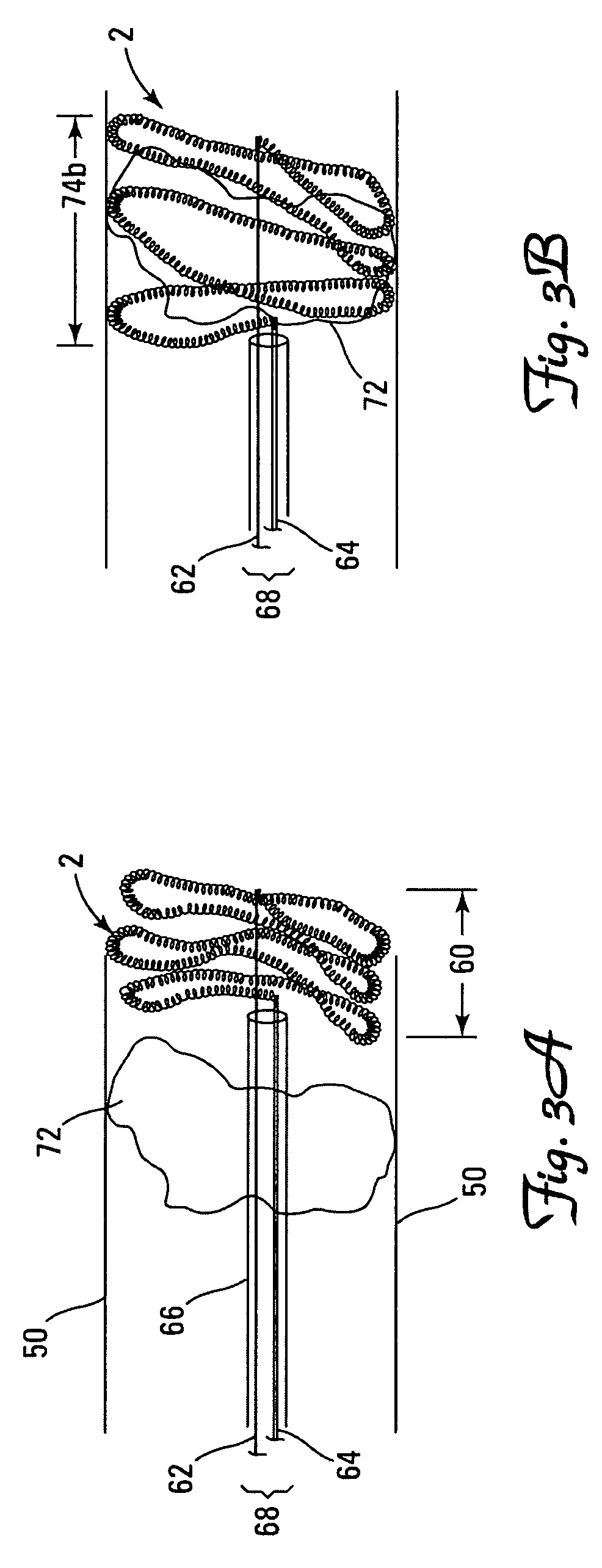
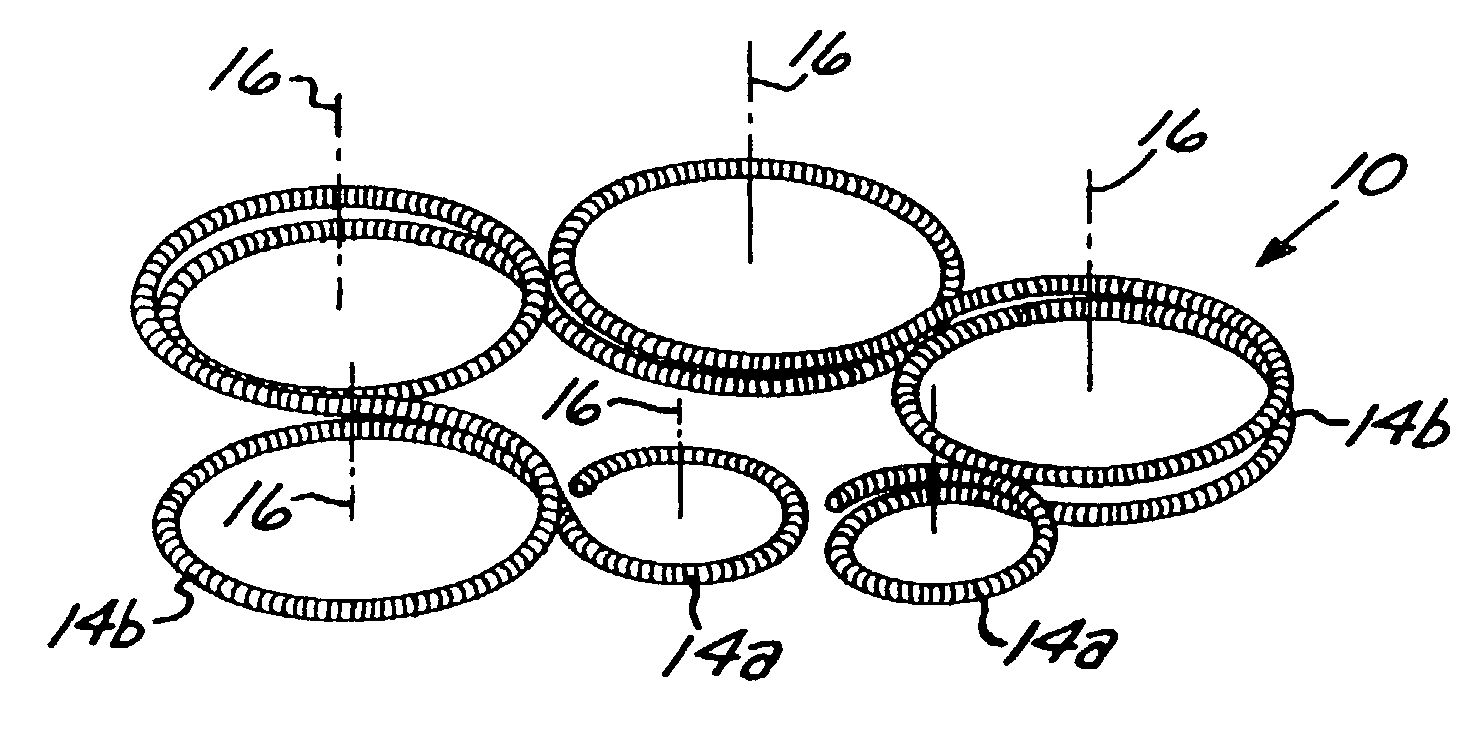
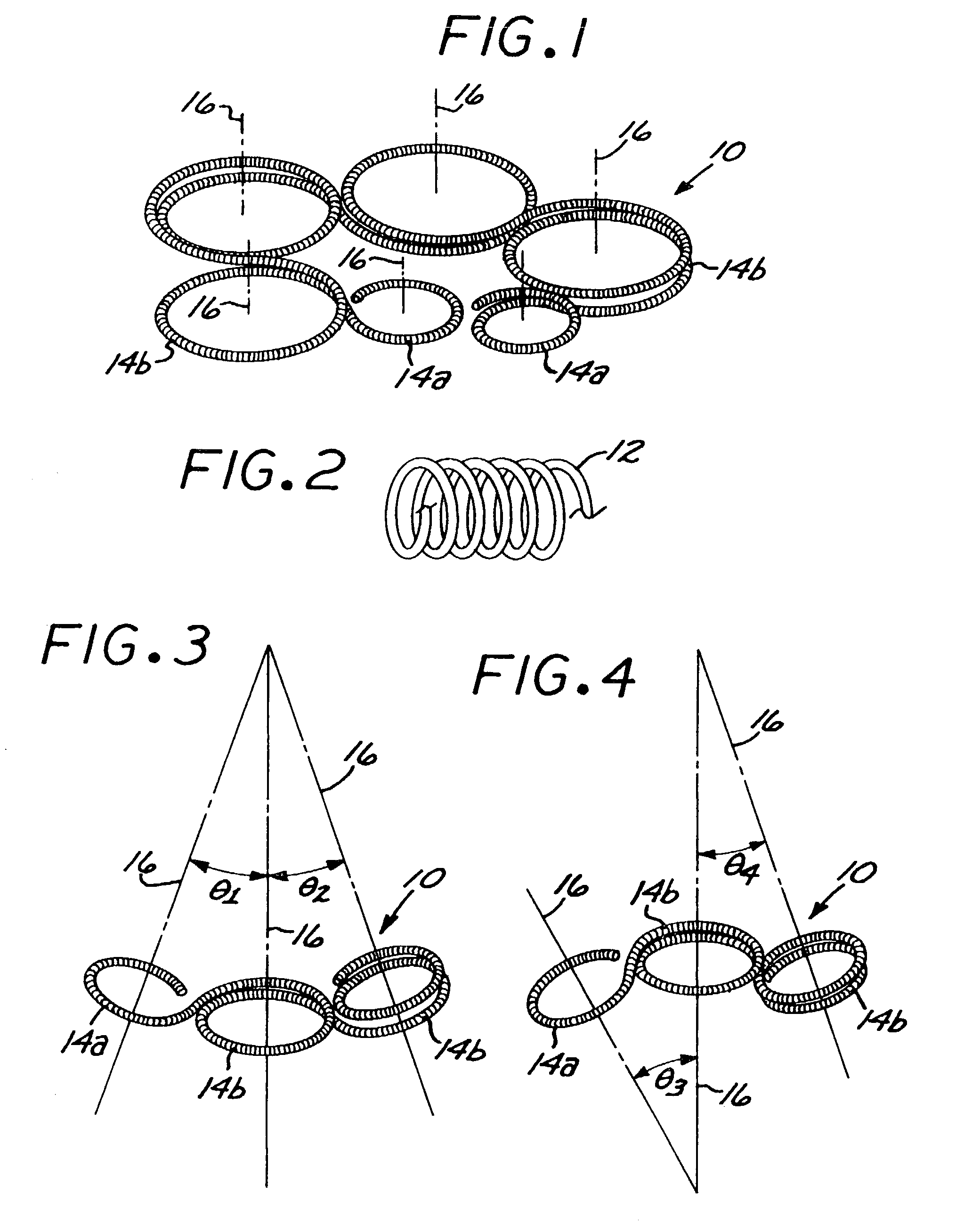
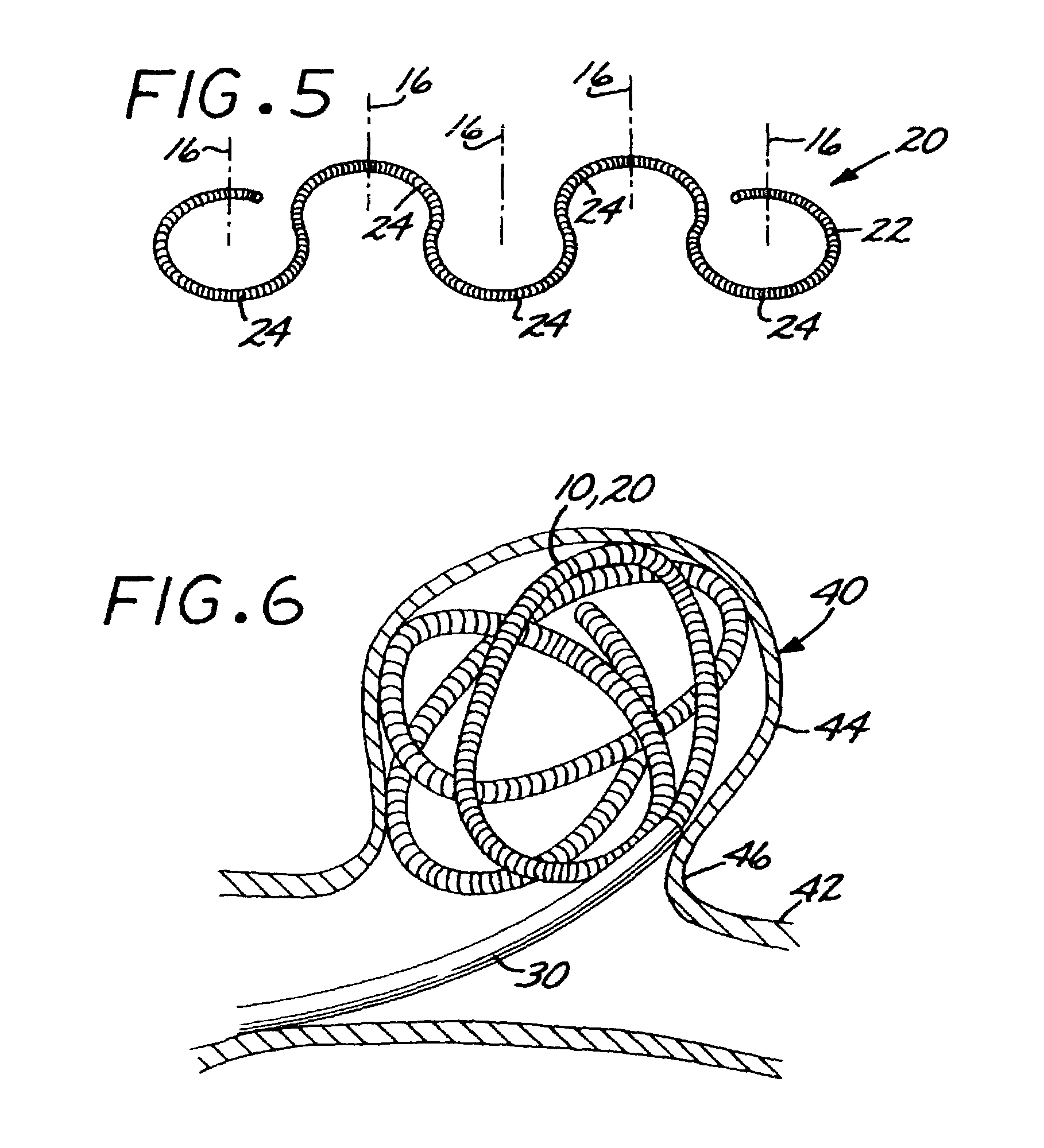
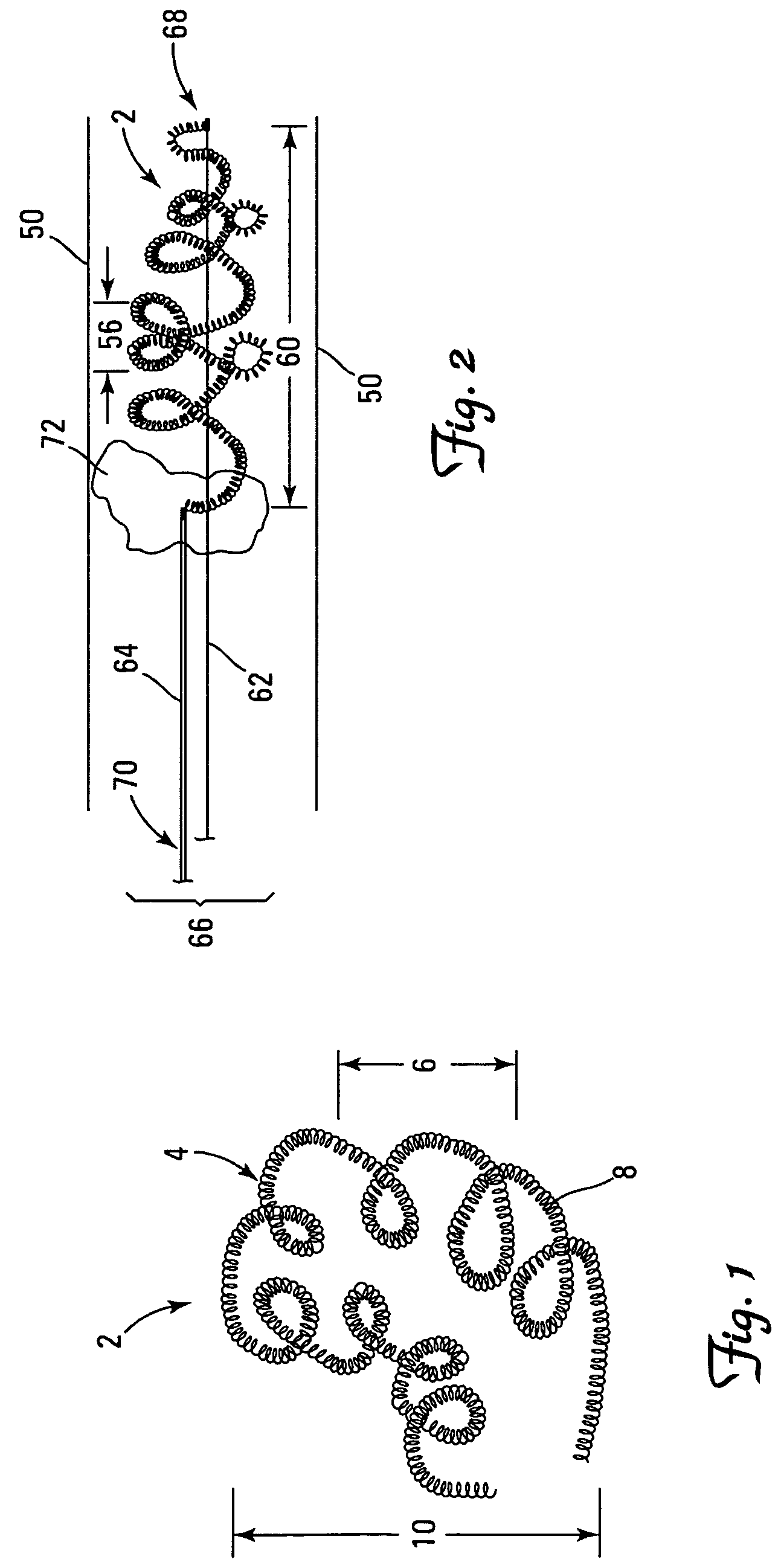
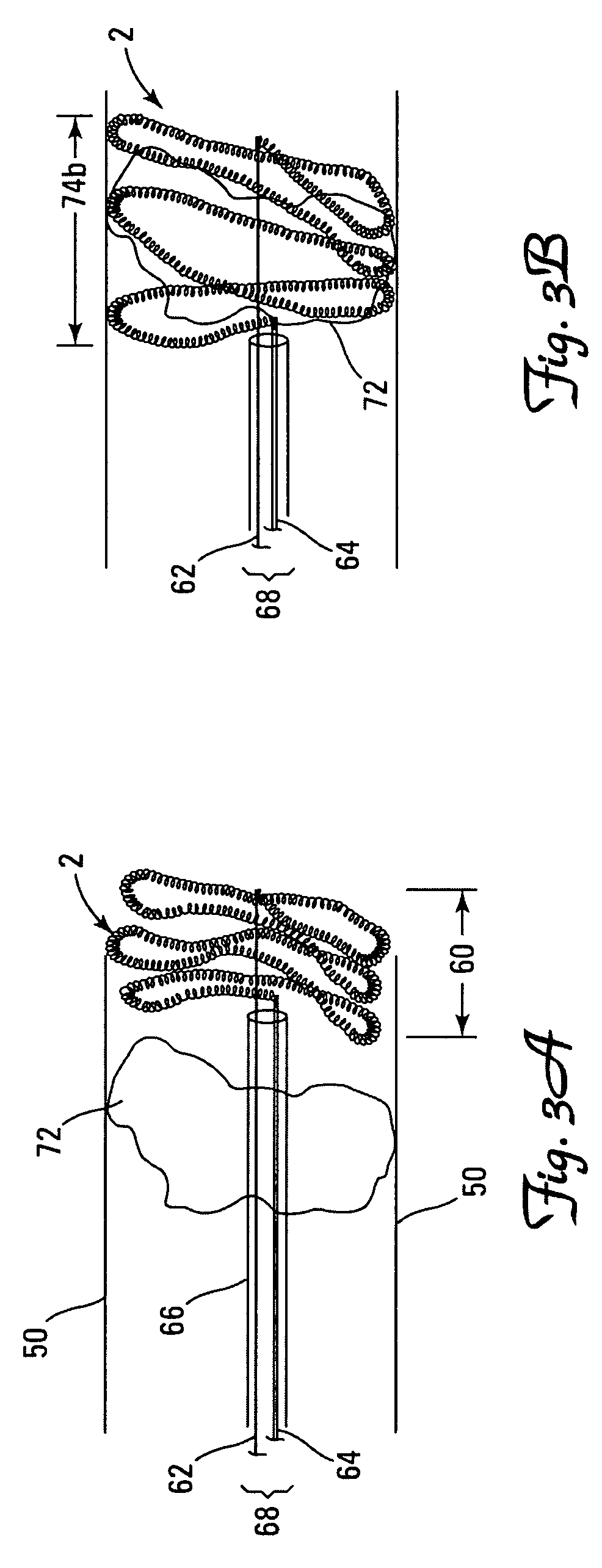
A vaso-occlusive device includes a microcoil formed into a minimum energy state secondary configuration comprising a plurality of curved segments, each defining a discrete axis, whereby the device, in its minimum energy state configuration, defines multiple axes. In a preferred embodiment, the secondary configuration-comprises a plurality of interconnected closed loops defining a plurality of discrete axes. In a second embodiment, the secondary configuration defines a wave-form like structure comprising an array of laterally-alternating open loops defining a plurality of separate axes. In a third embodiment, the secondary configuration forms a series of tangential closed loops, wherein the entire structure subtends a first angle of arc, and wherein each adjacent pair of loops defines a second angle of arc. In a fourth embodiment, the secondary configuration forms a logarithmic spiral. In all embodiments, the device, in its secondary configuration, has a dimension that is substantially larger than the largest dimension of the vascular site (i.e., aneurysm) in which it is to be deployed. Thus, confinement of the device within an aneurysm causes it to assume a three-dimensional configuration with a higher energy state than the minimum energy state. Because the minimum energy state configuration of the device is larger (in at least one dimension) than the aneurysm, the deployed device is constrained by its contact with the walls of the aneurysm from returning to its minimum energy state configuration. The engagement of the device with the aneurysm wall minimizes shifting or tumbling due to blood flow. Furthermore, the secondary configuration is not conducive to “coin stacking,” thereby minimizing the compaction experienced.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Thrombus removal system and process
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
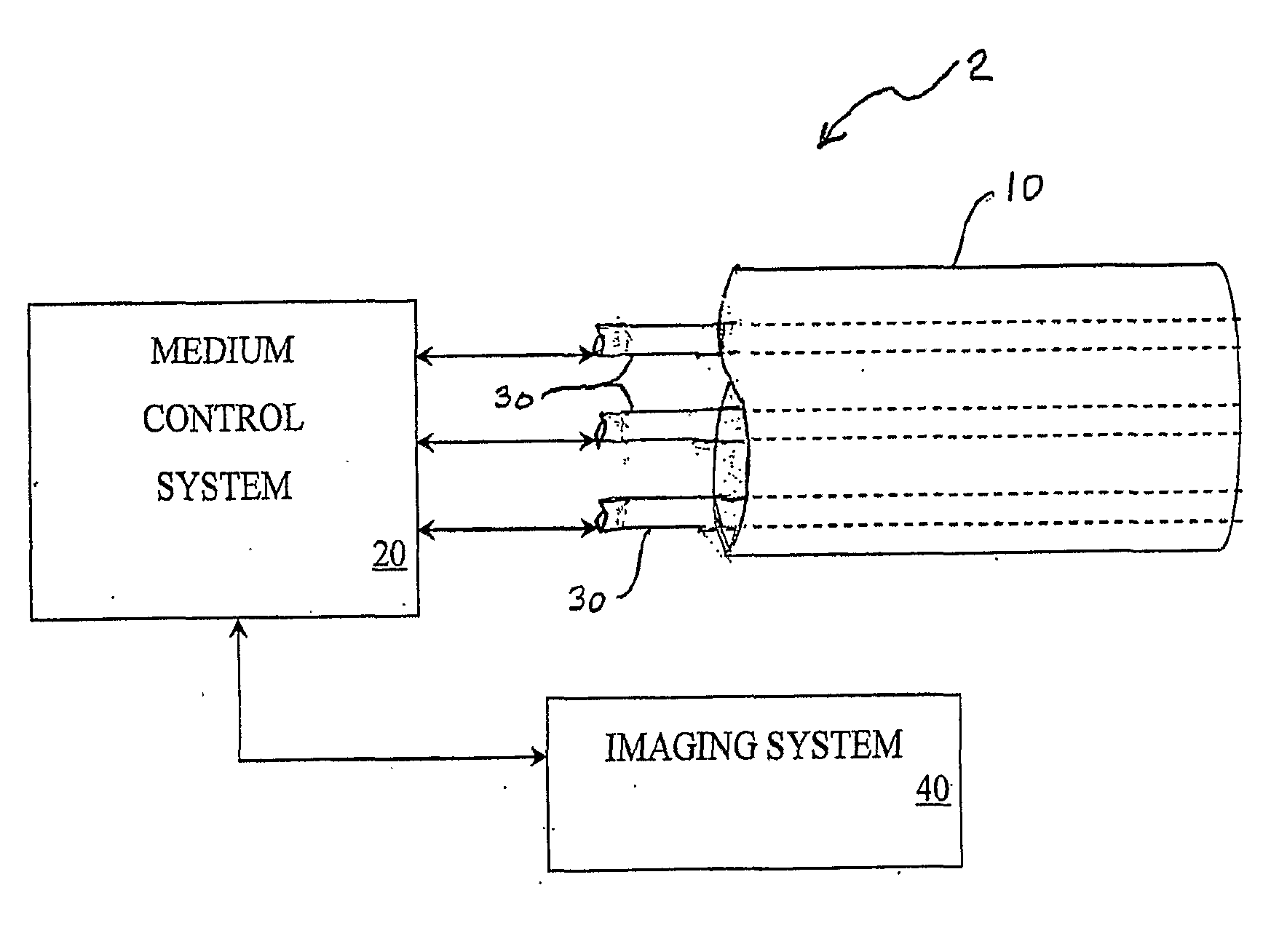
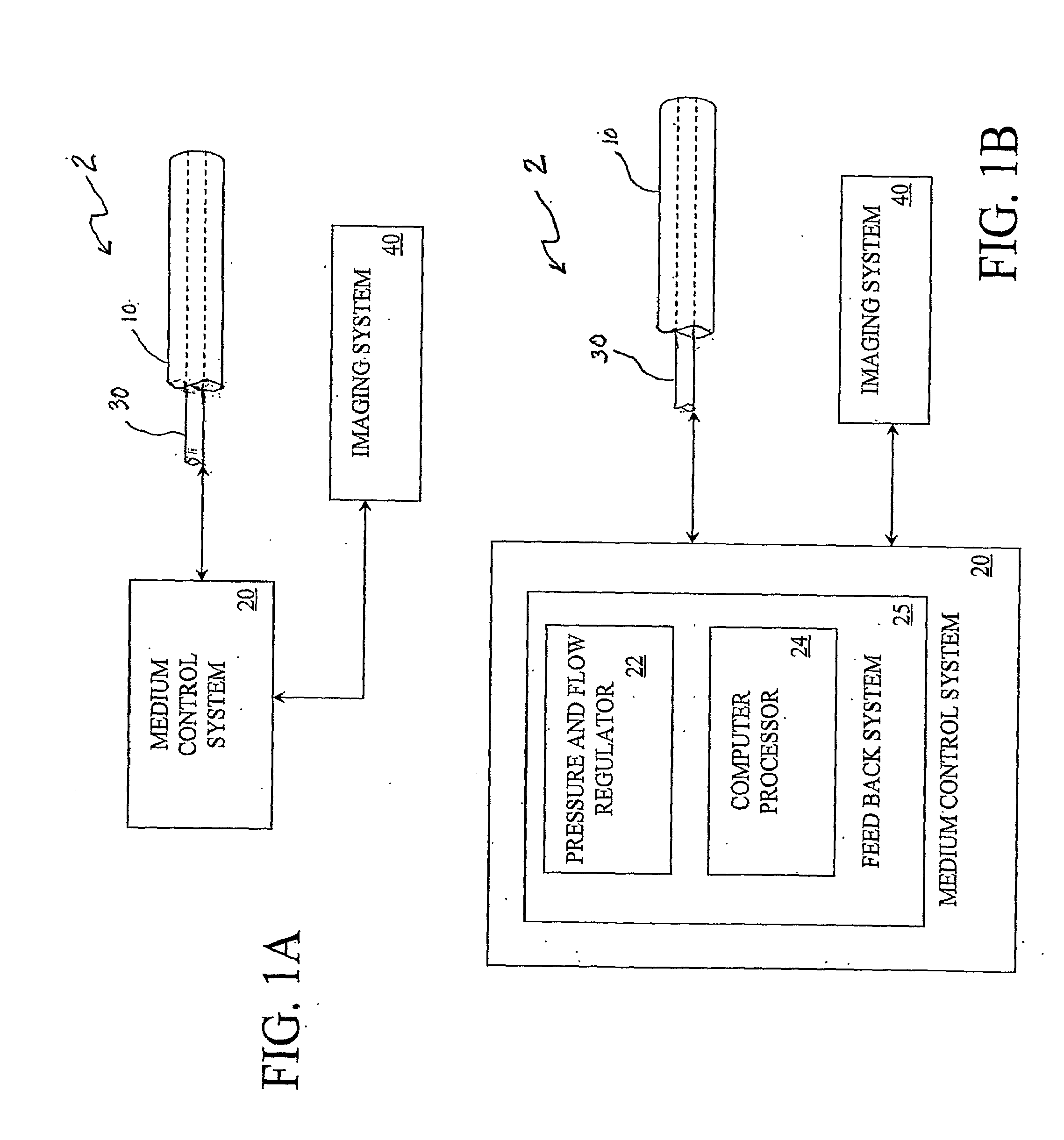
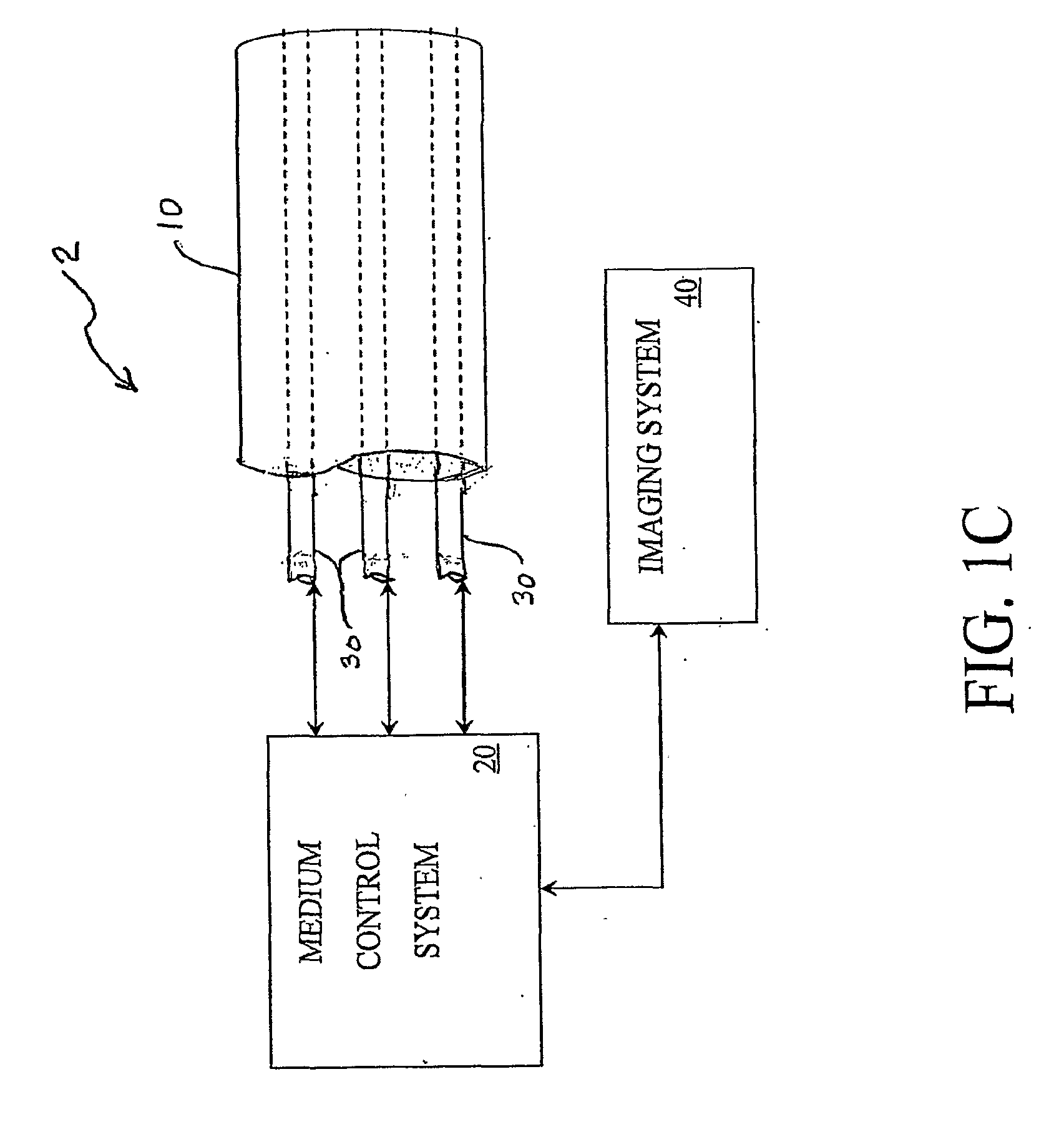
Multi-Port Catheter System with Medium Control and Measurement Systems for Therapy and Diagnosis Delivery
A series of embodiments of multi-lumen, multisegmented (or variable diameter) catheters and associated multi-channel flow control and measurement systems and methods for simultaneous delivery of a medium to a plurality of locations is described. The need for precise, stable reliable, and repeatable flow control in therapy delivery catheters is crucial to the efficacious treatment of the clinical manifestations of peripheral vascular disease (PVD) and other such maladies. Such treatments may involve the placement of multi-lumen catheters into peripheral arterial trees, with the subsequent need to govern the flow dynamics within each individual lumen of the multi-lumen device in such a way that an optimum distribution of the agent is achieved intra-arterially. Combinations of pumps, flow monitors, pressure monitors, feedback loops and related hardware and software collectively capable of achieving this goal are described. In other embodiments, this device and method could be used for infusions into tissues and solid organs, and microcoil systems can be added to the various components of the catheter systems to improve the imaging quality during MR-guided procedures.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Catheter tracking with phase information
ActiveUS7505808B2Precise positioningTrack positionCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringLaparoscopesIn vivo
A method for determining the position and / or orientation of a catheter or other interventional access device or surgical probe using phase patterns in a magnetic resonance (MR) signal. In the method of the invention, global two-dimensional correlations are used to identify the phase pattern around individual microcoils, which is unique for each microcoil's position and orientation. In one embodiment the position and orientation of a catheter tip can be reliably tracked using low resolution MR scans clinically useful for real-time interventional MRI applications. In a further embodiment, the invention provides real-time computer control to track the position of endovascular devices and interventional treatment systems, including surgical tools and tissue manipulators, devices for in vivo delivery of drugs, angioplasty devices, biopsy and sampling devices, devices for delivery of RF, thermal, microwave or laser energy or ionizing radiation, and internal illumination and imaging devices, such as catheters, endoscopes, laparoscopes, and related instruments.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT +1
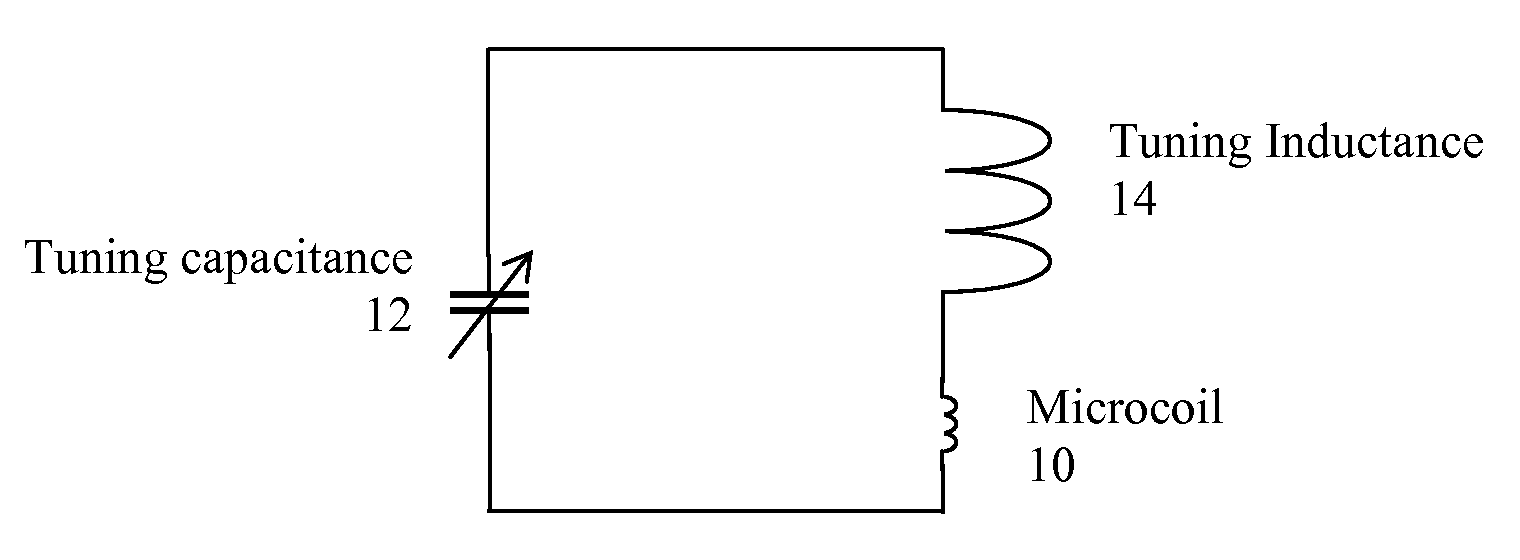
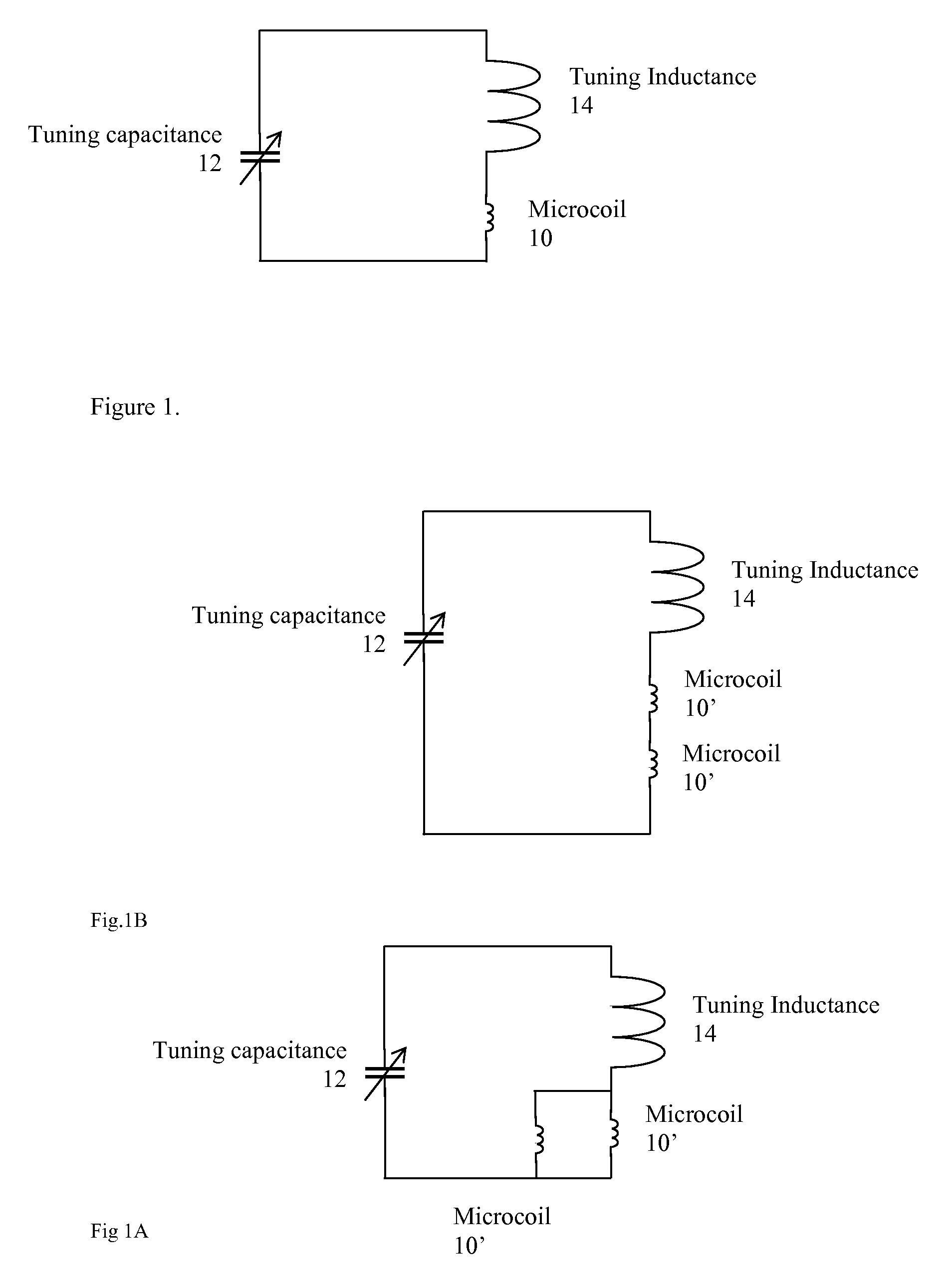
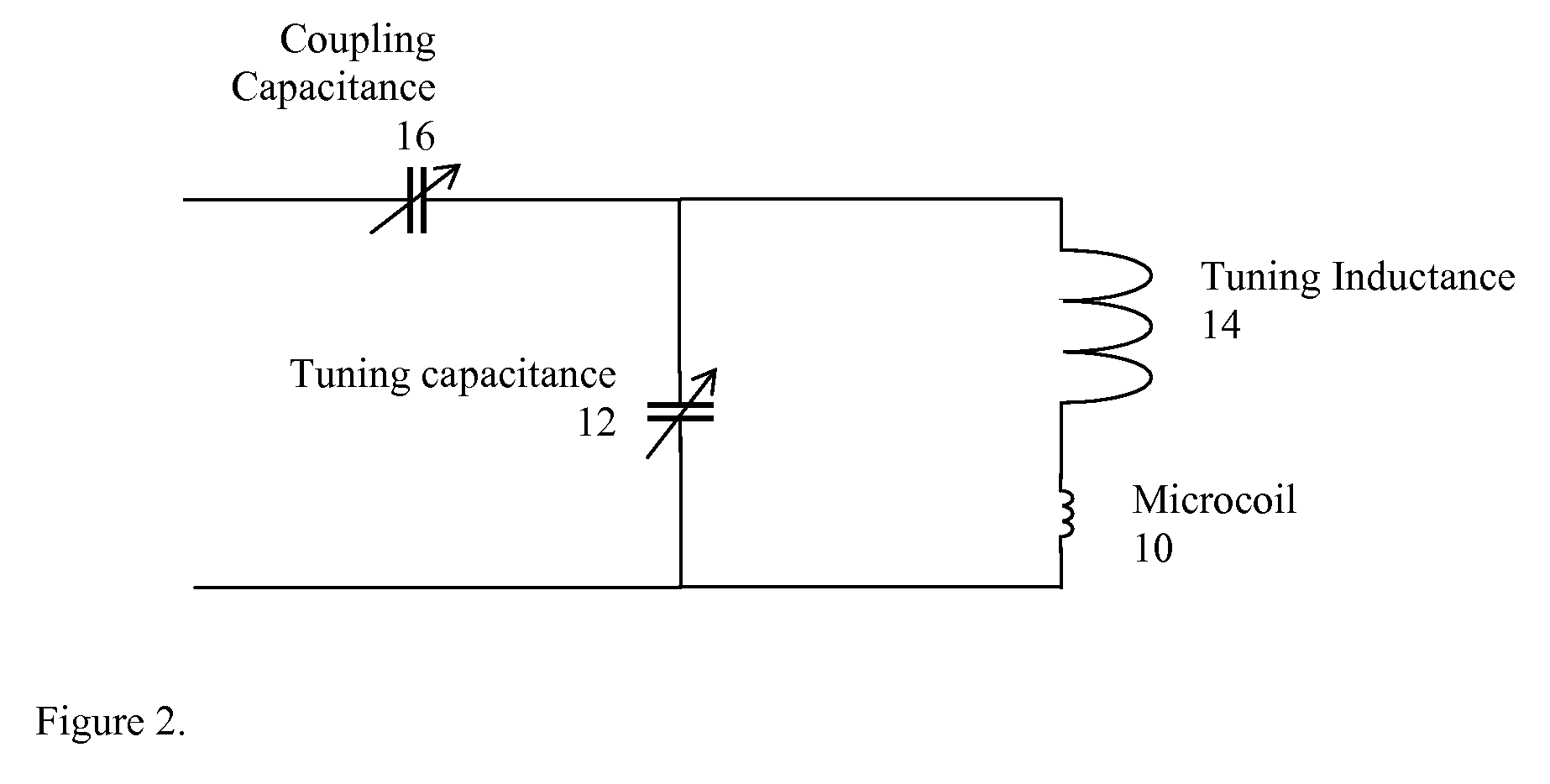
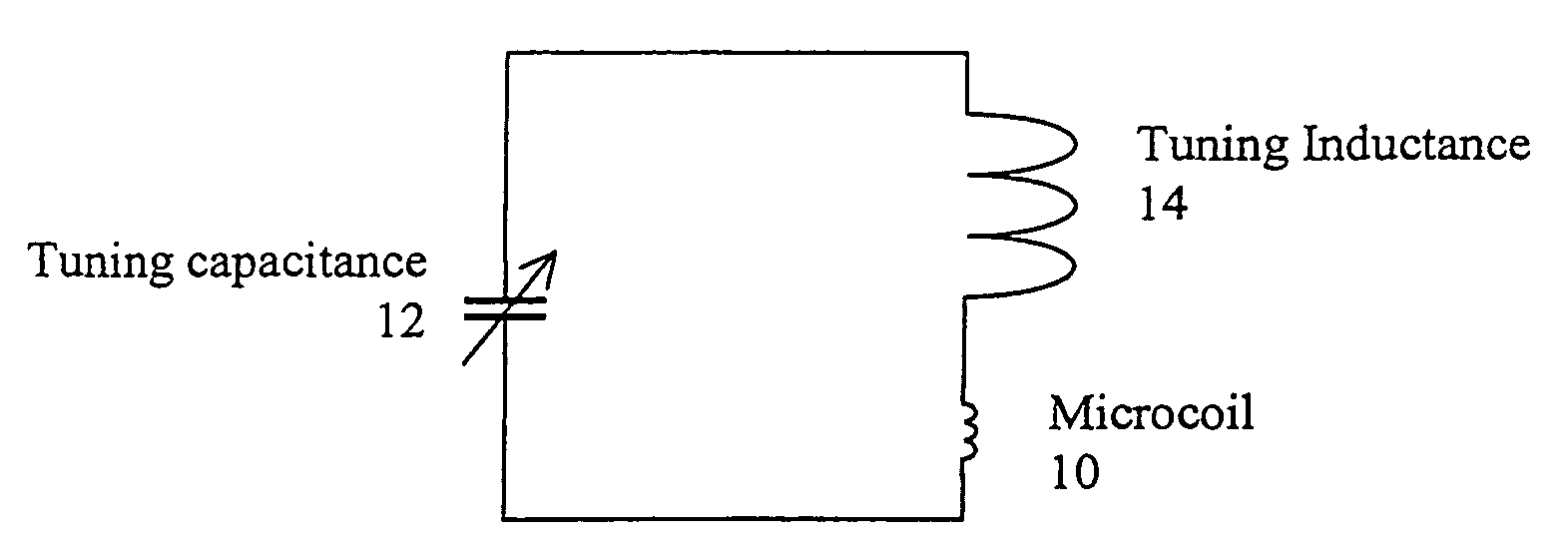
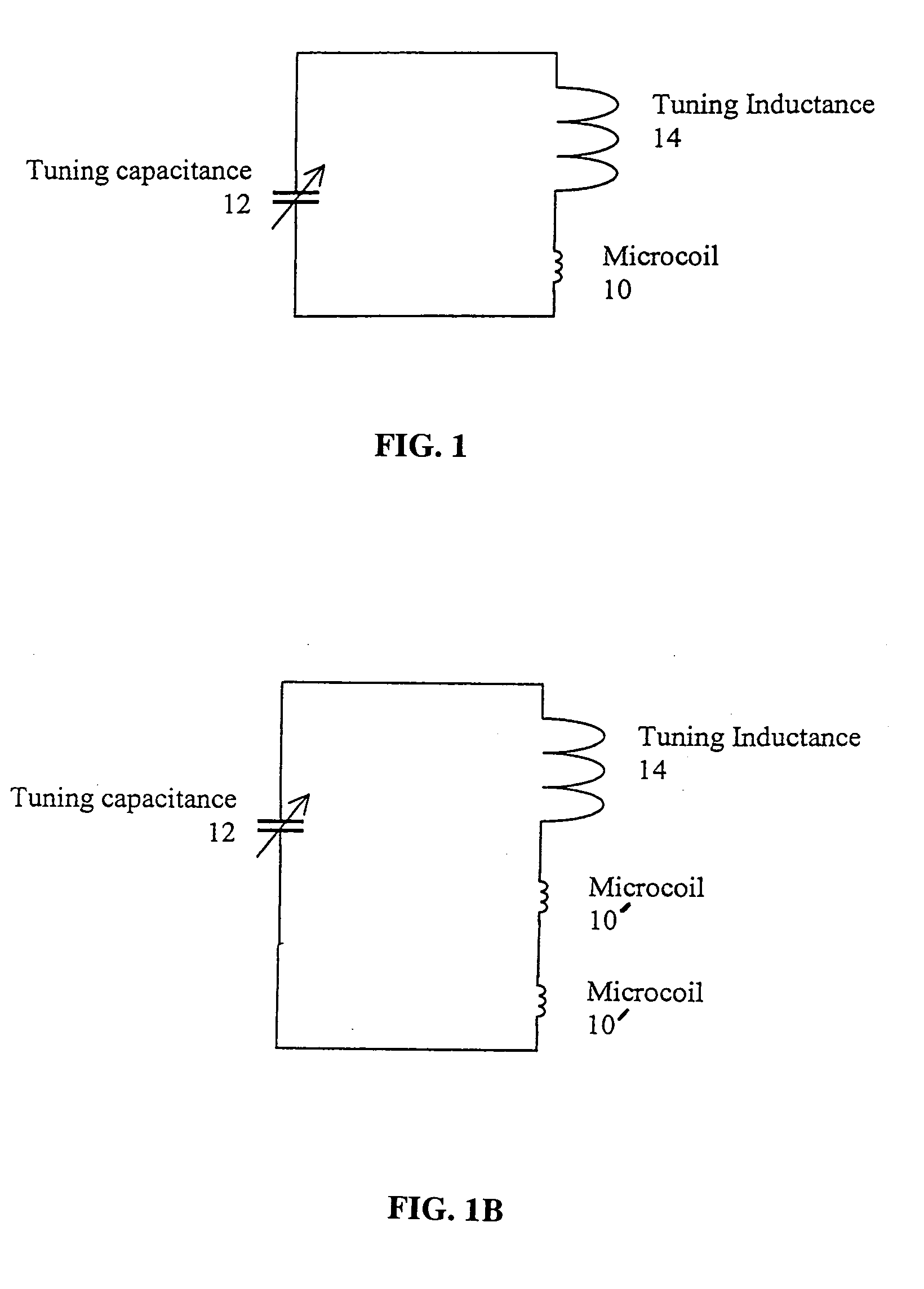
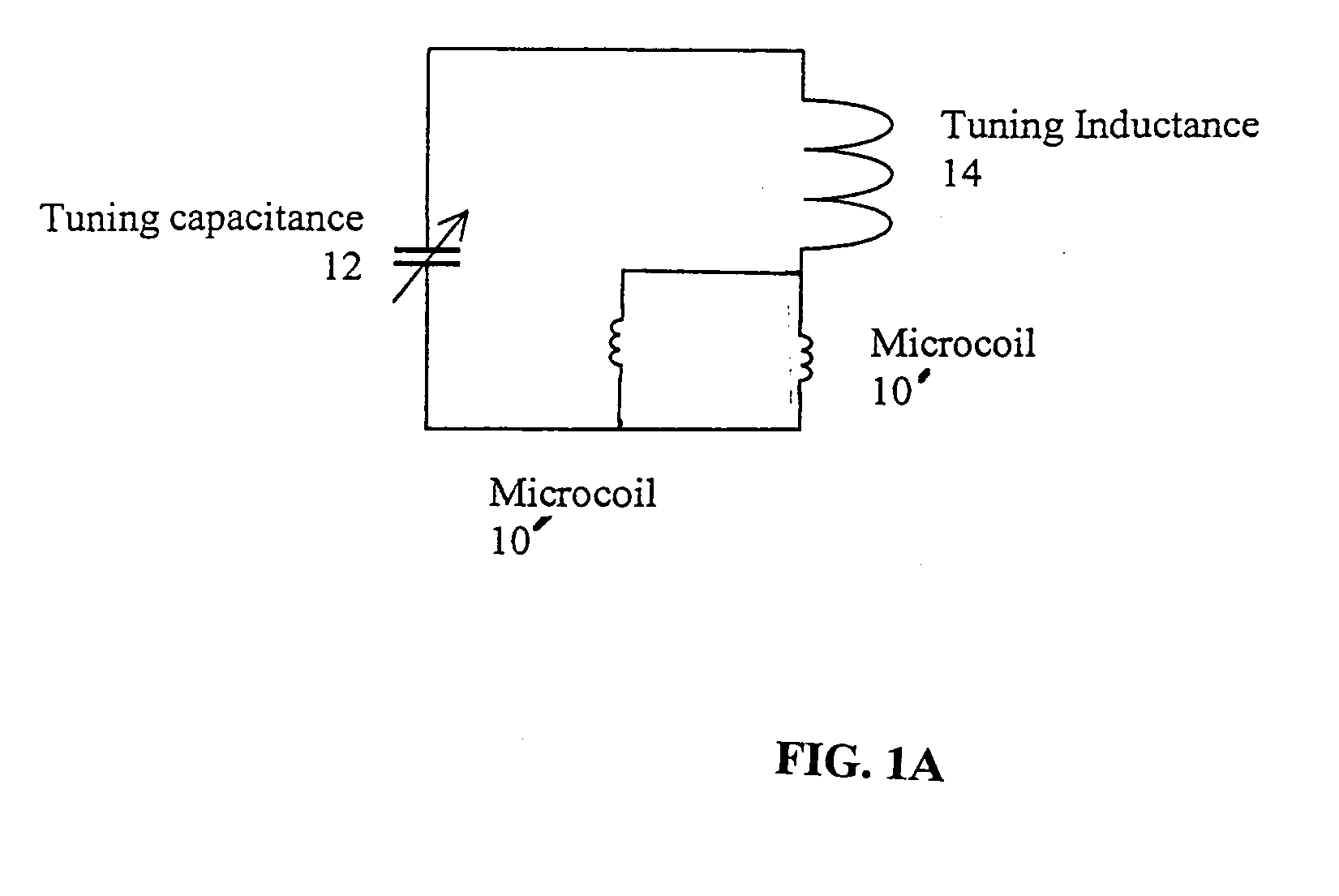
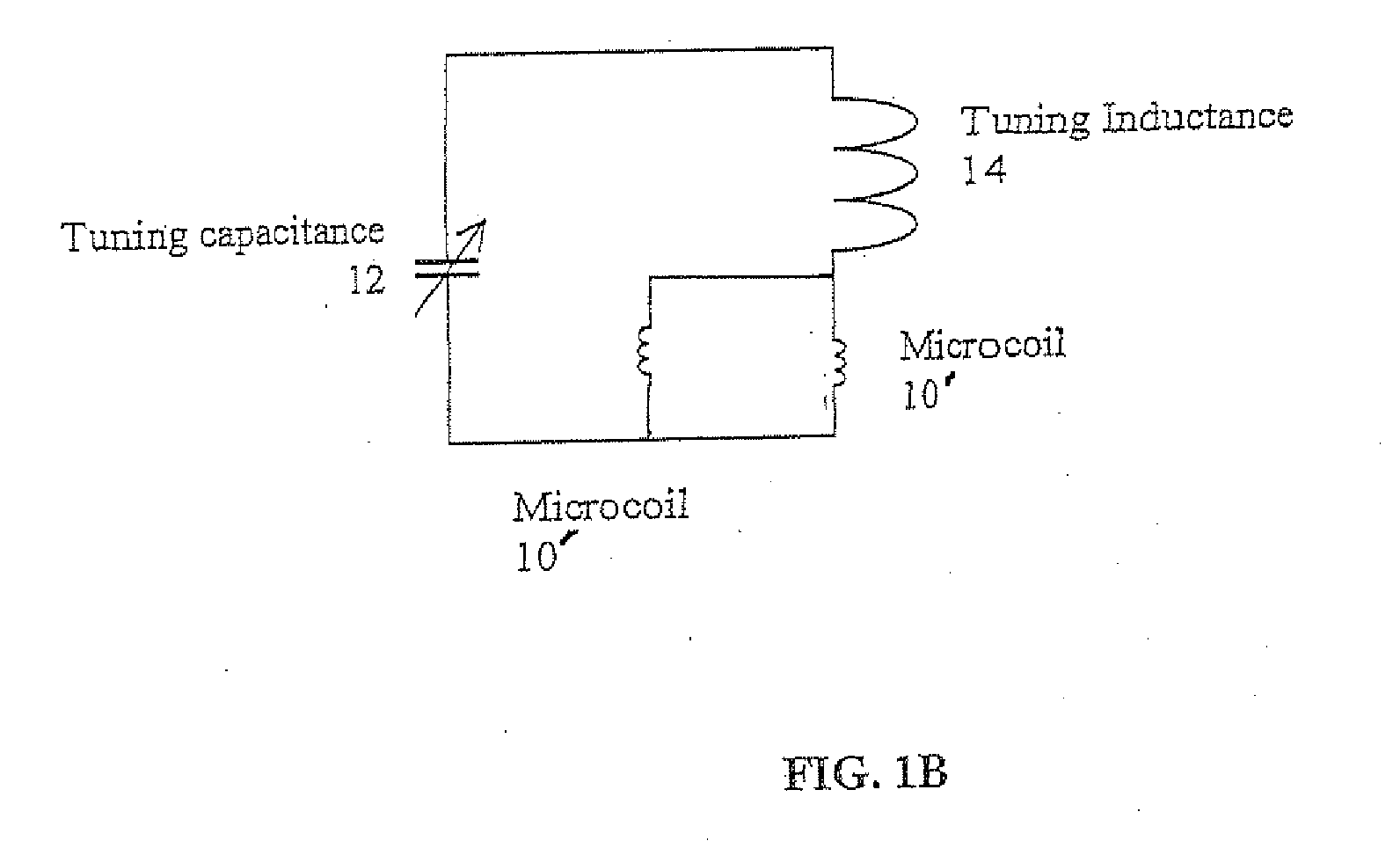
Tuning low-inductance coils at low frequencies
InactiveUS7405567B2Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceElectricity
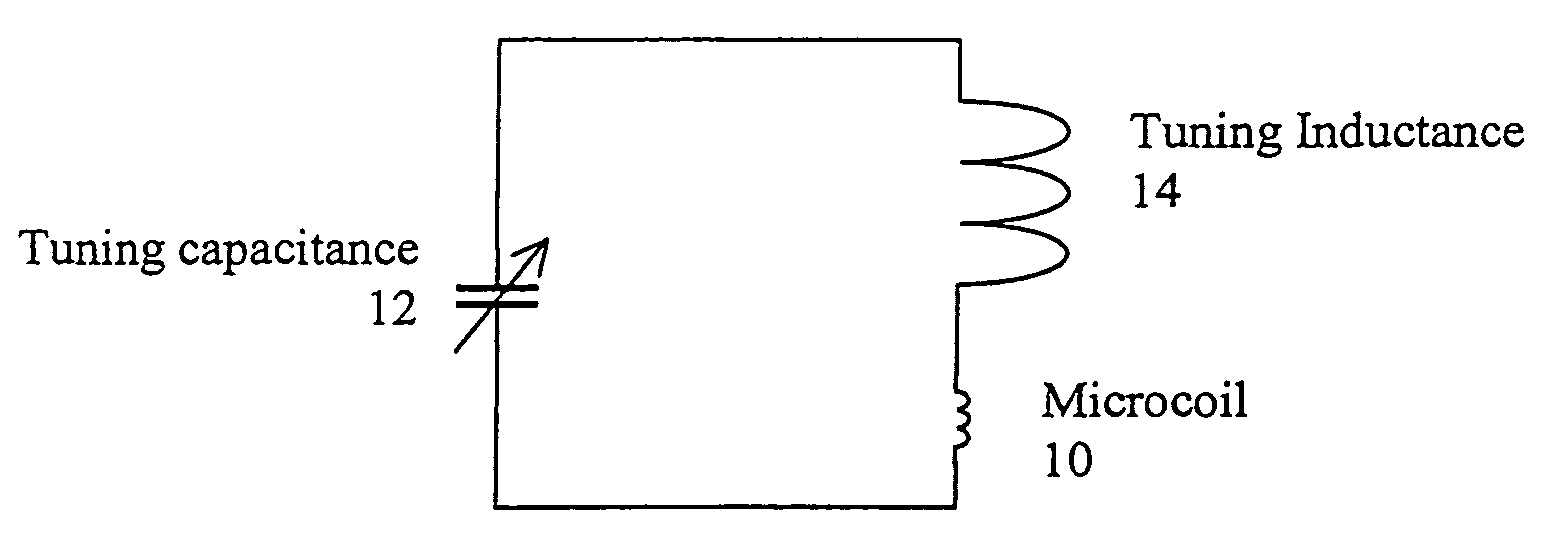
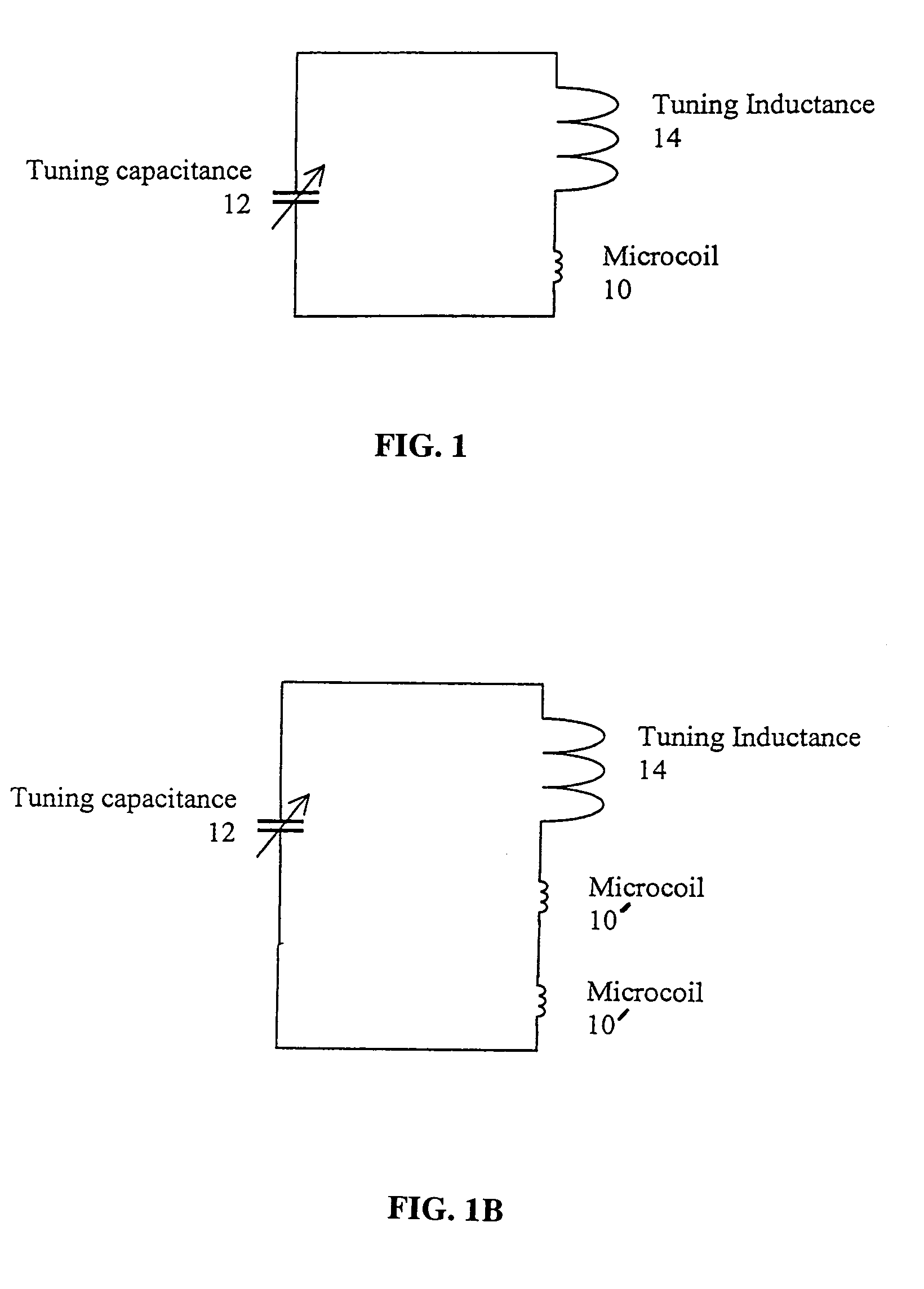
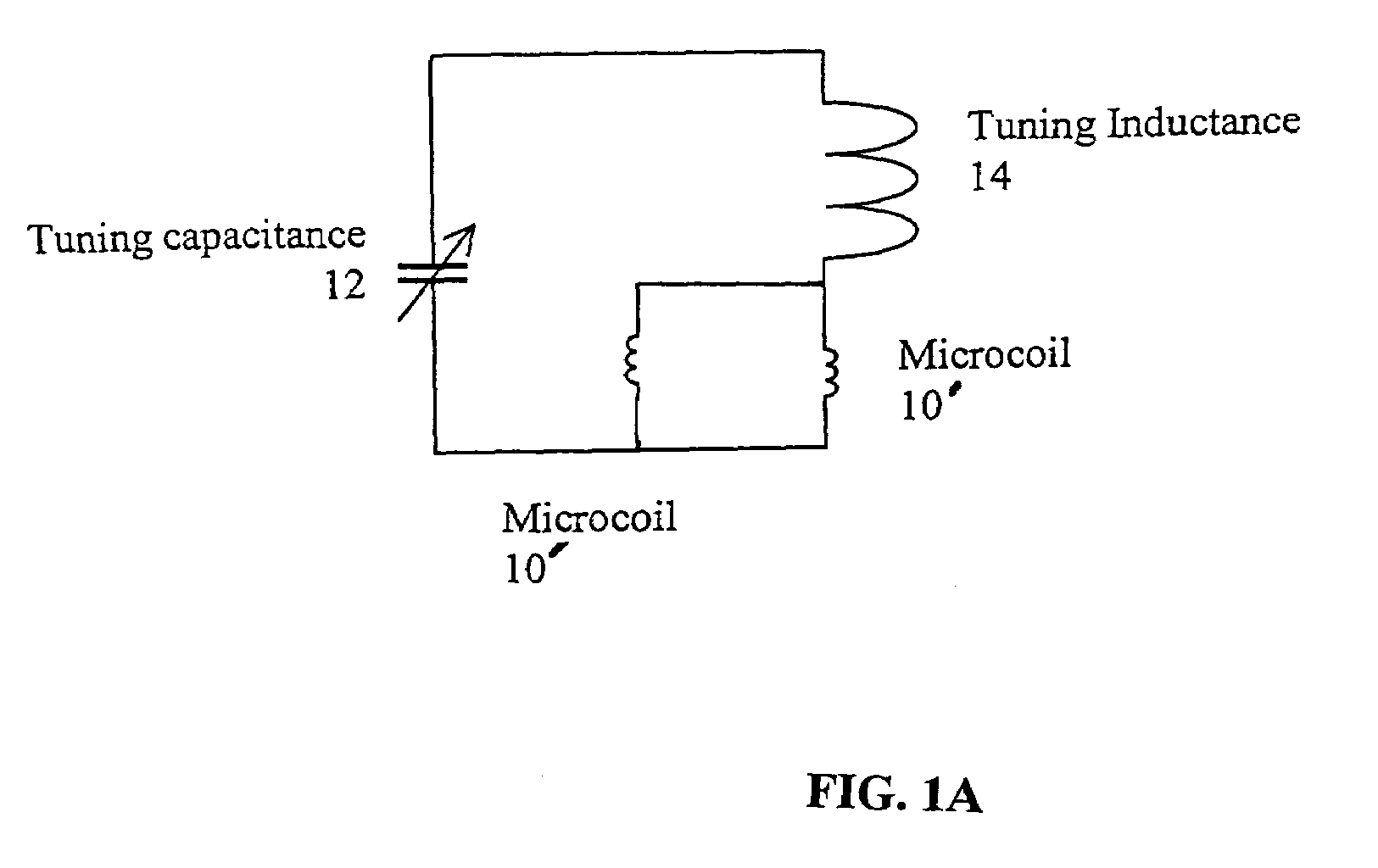
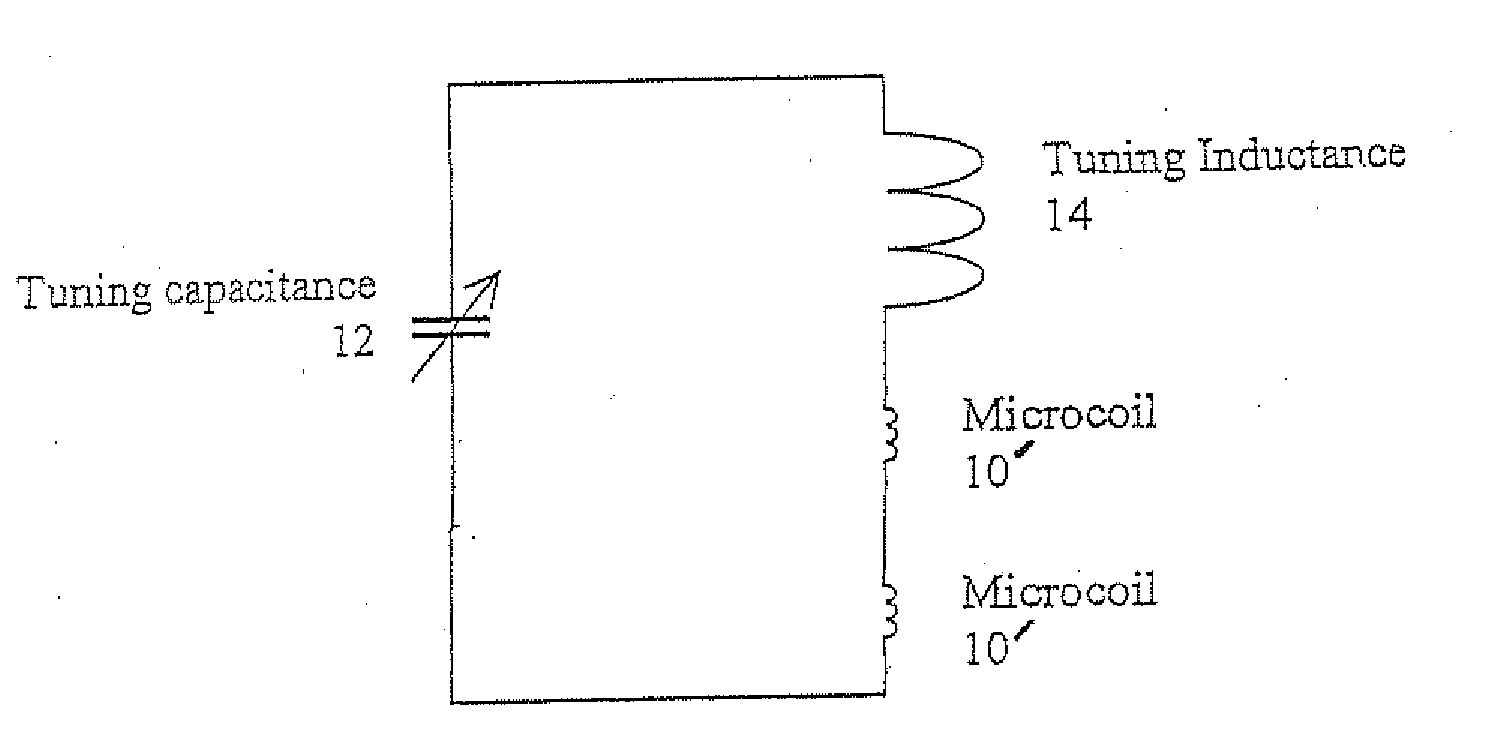
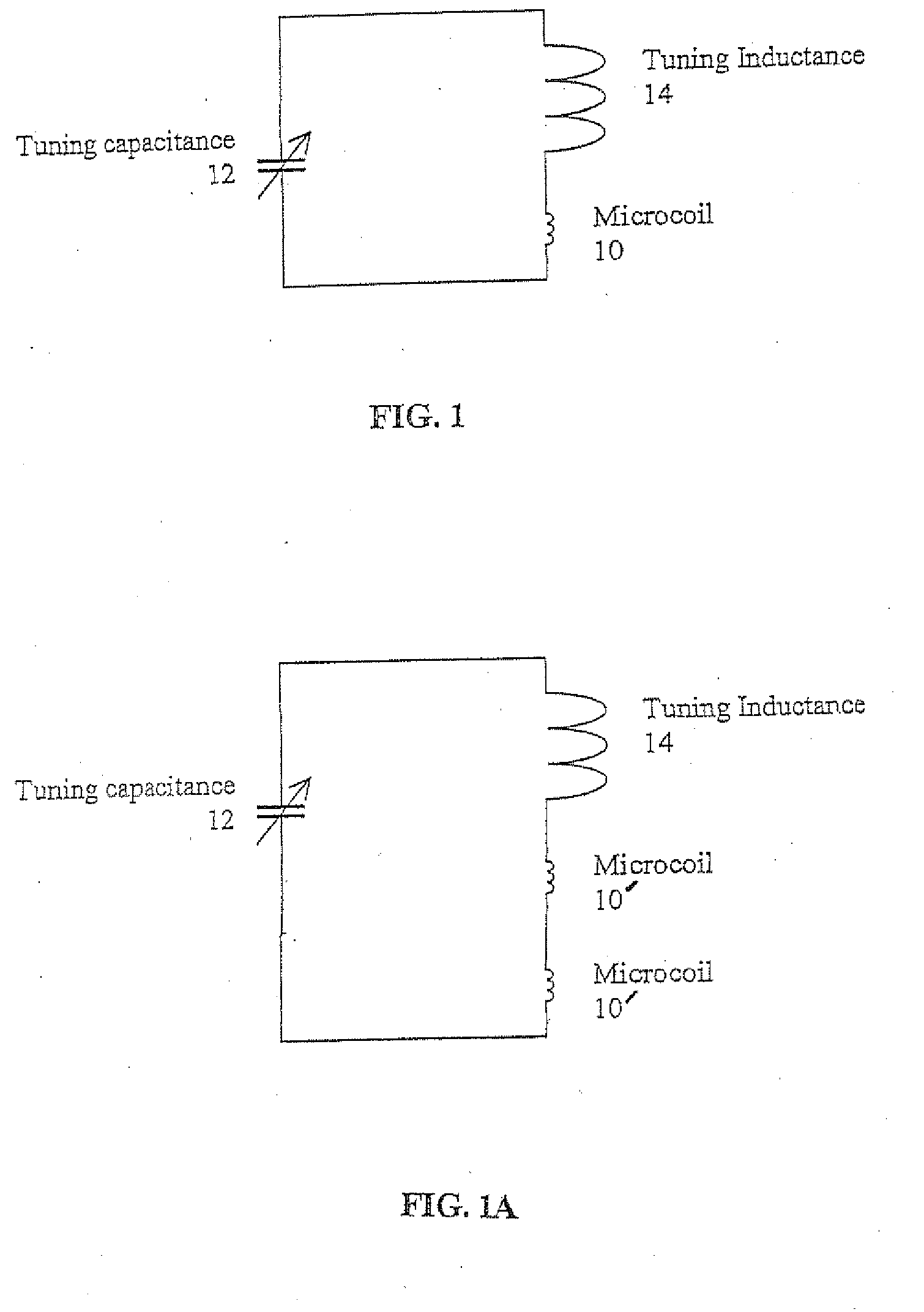
A method and apparatus for tuning and matching extremely small sample coils with very low inductance for use in magnetic resonance experiments conducted at low frequencies. A circuit is disclosed that is appropriate for performing measurements in fields where magnetic resonance is beneficially utilized. The circuit has a microcoil, an adjustable tuning capacitance, and added inductance in the form of a tuning inductor. The microcoil is an electrical coil having an inductance of about 25 nanohenries (nH) or less. Because additional inductance is purposefully added, the capacitance required for resonance and apparatus function is proportionally and helpfully reduced. The apparatus and method permit the resonant circuit and the magnet to be made extremely small, which is crucial for new applications in portable magnetic resonance imaging, for example.
Owner:ABQMR
Instrumented antifriction bearing and electrical motor equipped therewith
InactiveUS20060104558A1Satisfactory axial compactnessAccurate detectionBearing assemblyShaftsBall bearingRolling-element bearing
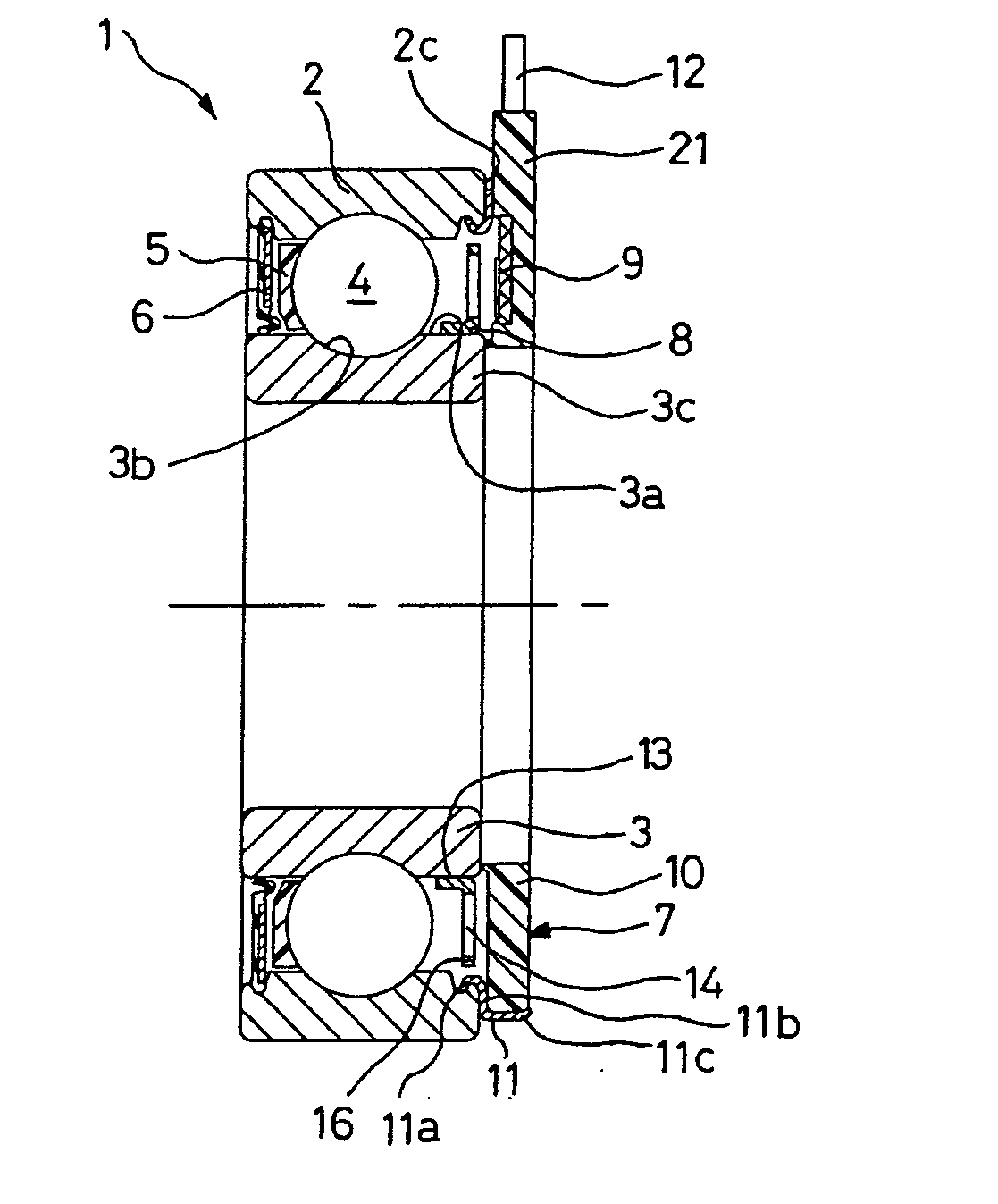
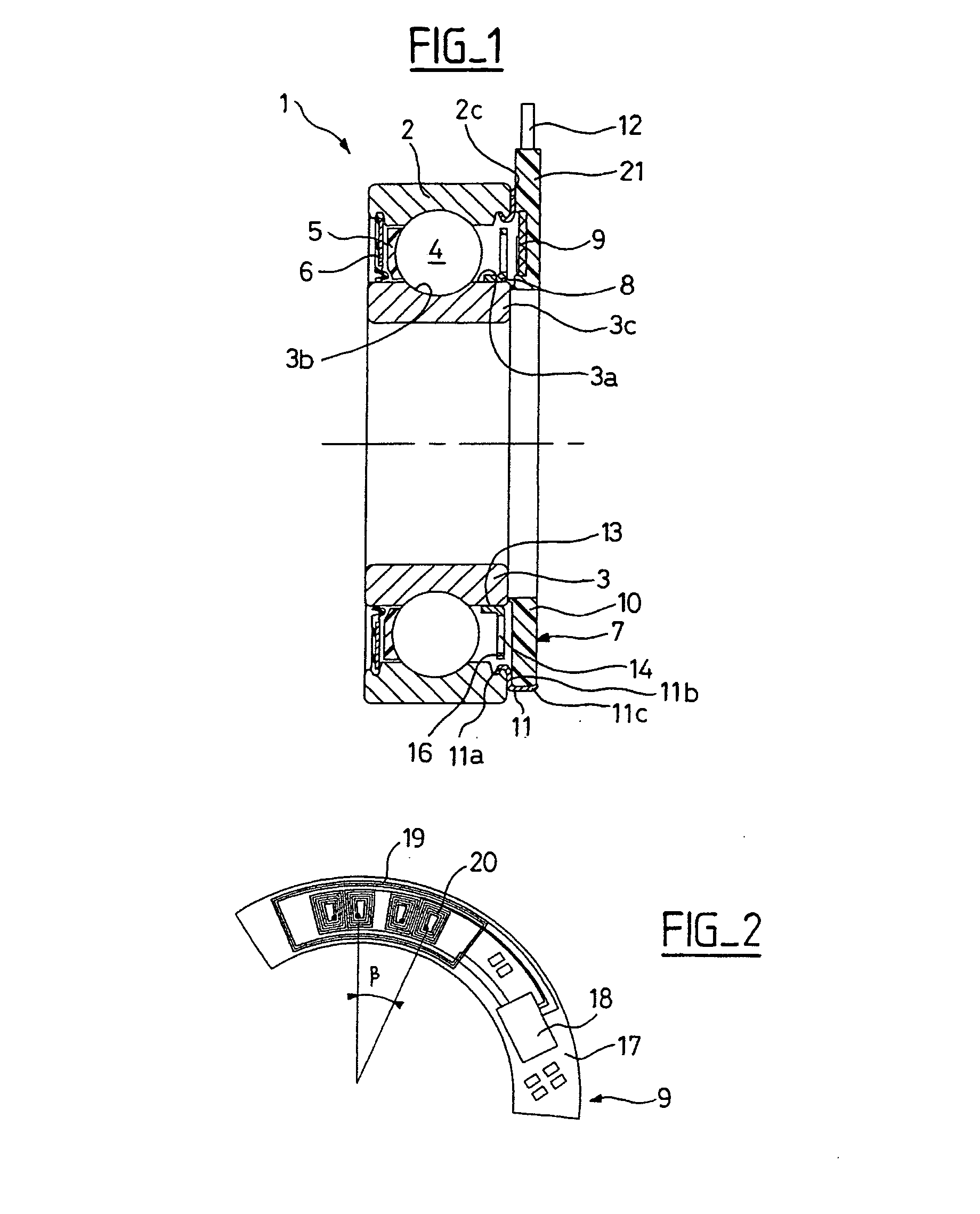
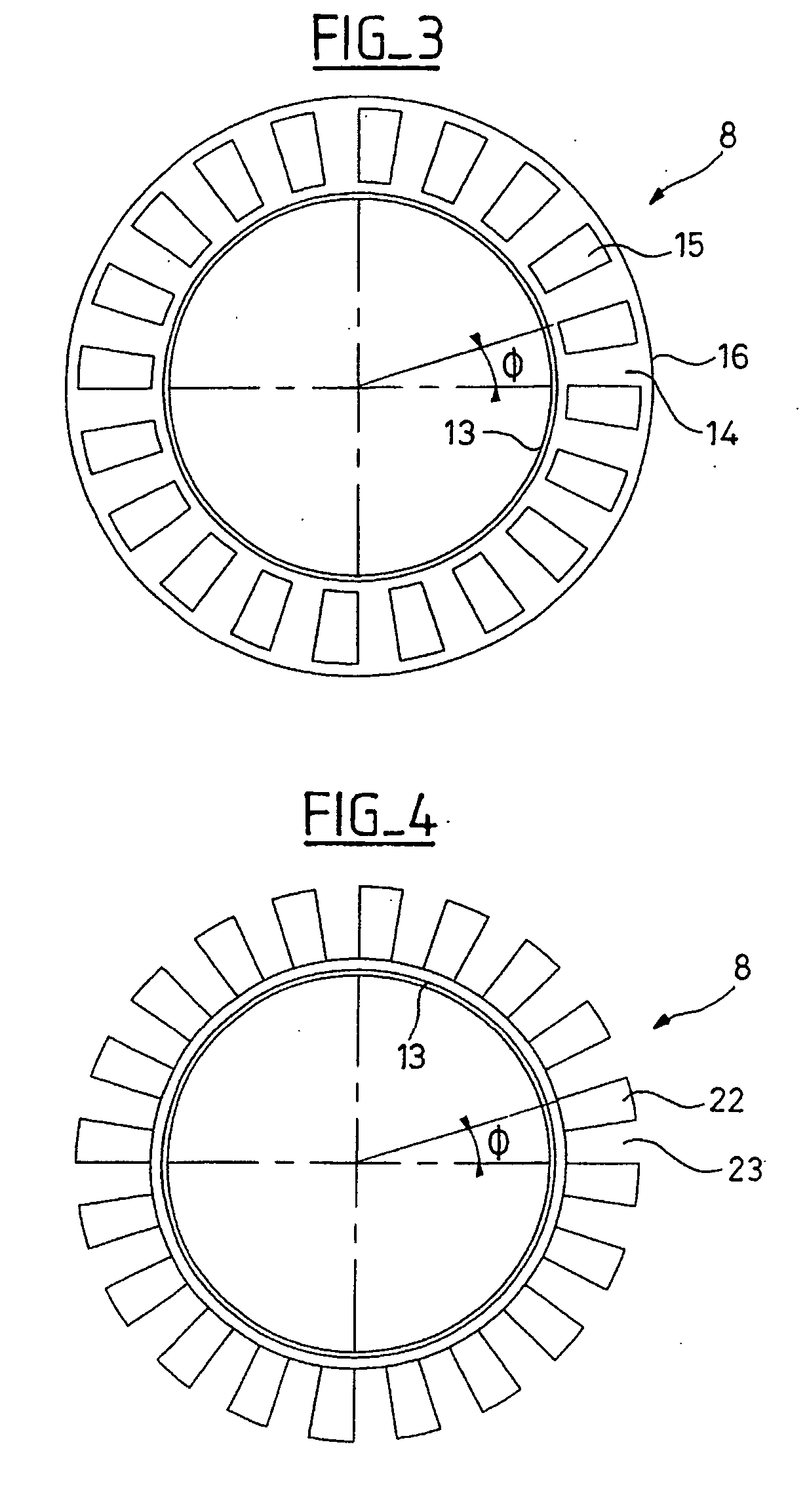
An instrumented ball-bearing may include a rotating part, a non-rotating part, and an assembly for detecting rotation parameters. The assembly for detecting rotation parameters may include an encoder and a sensor. The sensor may be integrated with the non-rotating part. The sensor may include a sensor unit and at least a microcoil. The microcoil may have a substantially planar winding. The microcoil may be positioned in the sensor unit of the non-rotating part such that the microcoil may be positioned axially opposite the encoder.
Owner:AB SKF
Microcoil device with a forward field-of-view for large gain magnetic resonance imaging
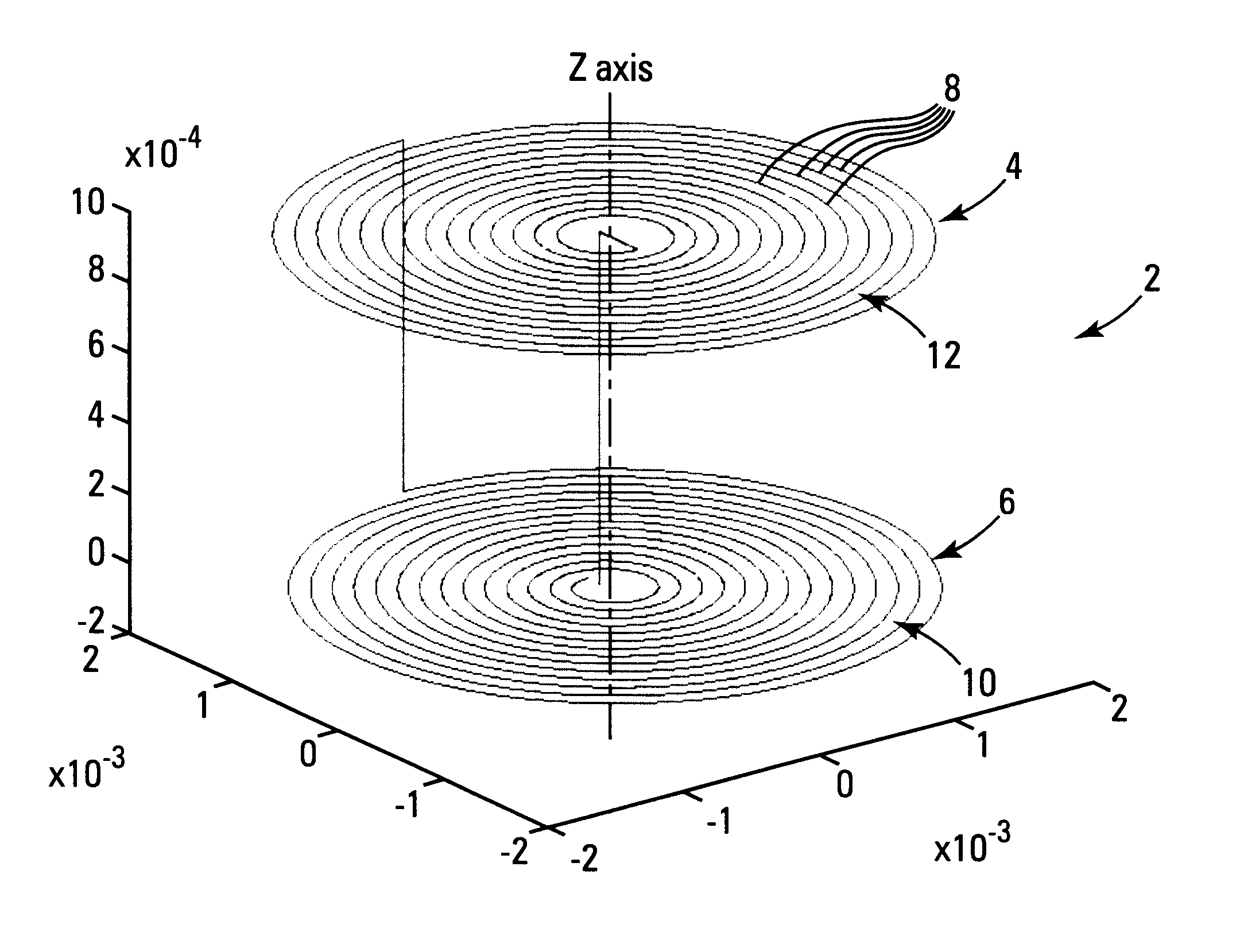
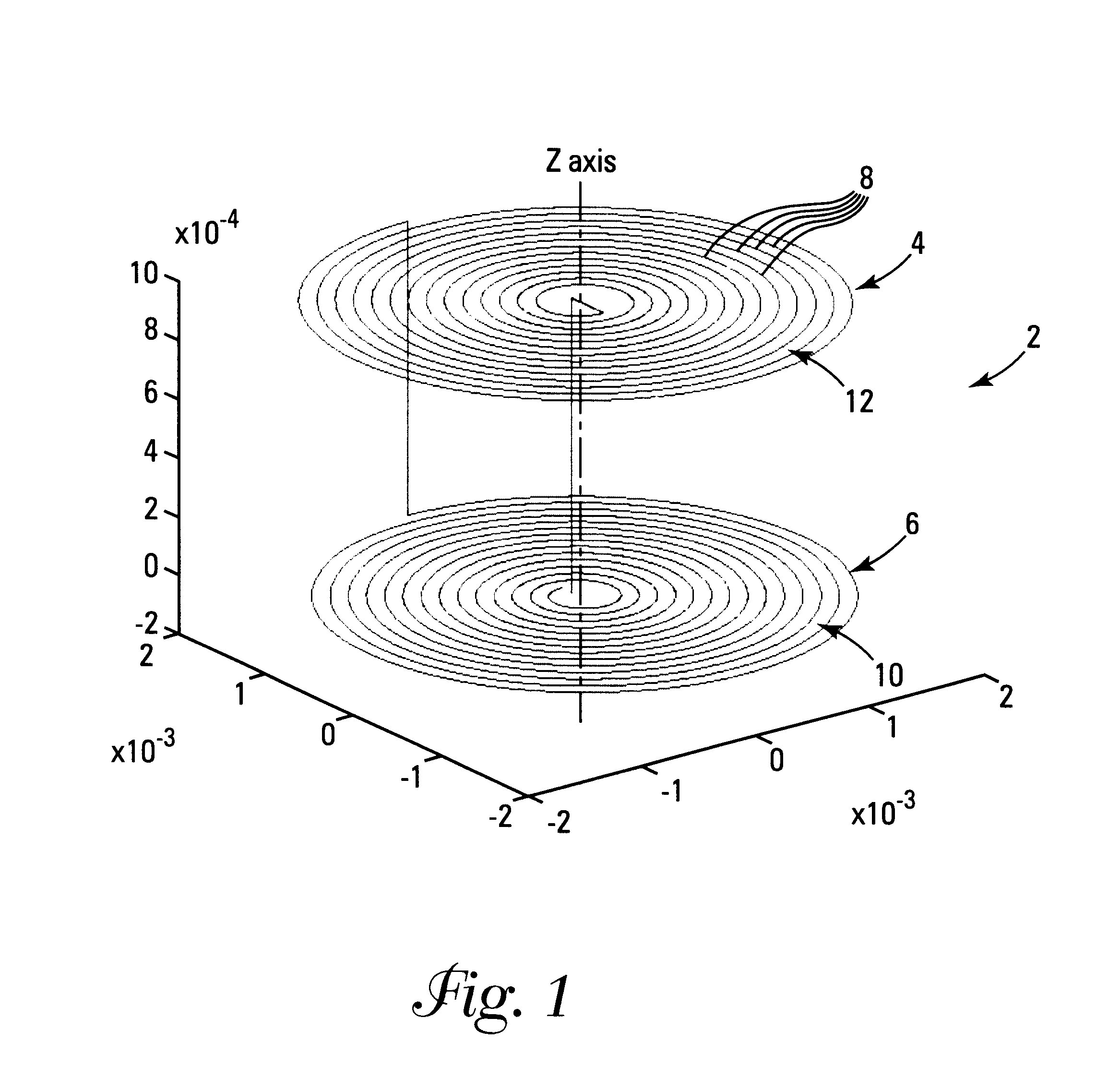
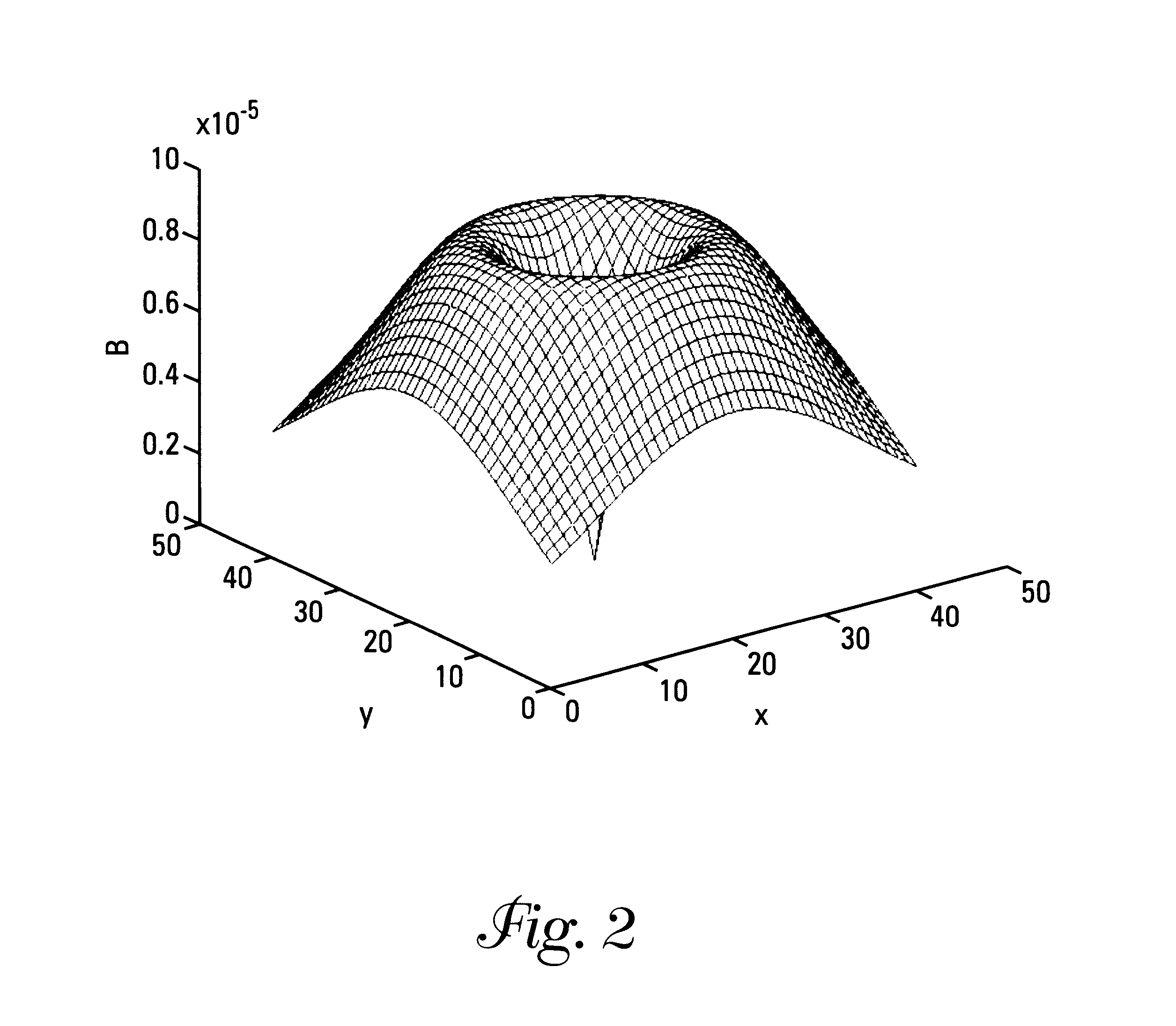
Microcoils can be used in medical devices to enhance RF response signals and to create fields to enhance imaging capability in MRI imaging systems. An improved microcoil design includes a device to be inserted into a patient comprising a solid body having at least one pair of radially opposed microcoils physically associated with the solid body, each microcoil having an outside microcoil diameter of 6 mm or less, individual windings of each microcoil together defining a geometric plane for each microcoil, and the plane of each microcoil being parallel to the plane of another microcoil in the pair of radially opposed microcoils.
Owner:IMAGE GUIDED DRUG DELIVERY SYST
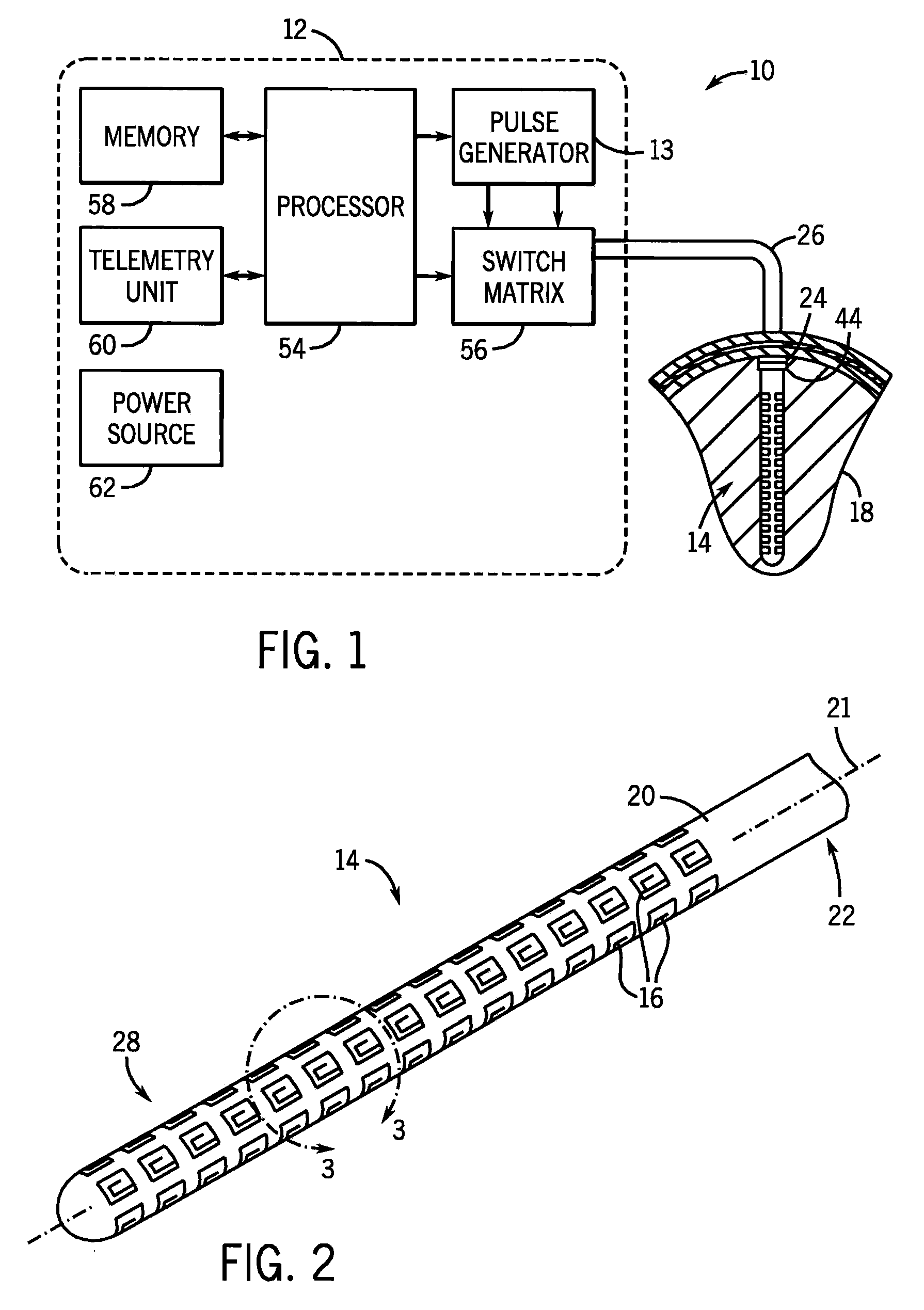
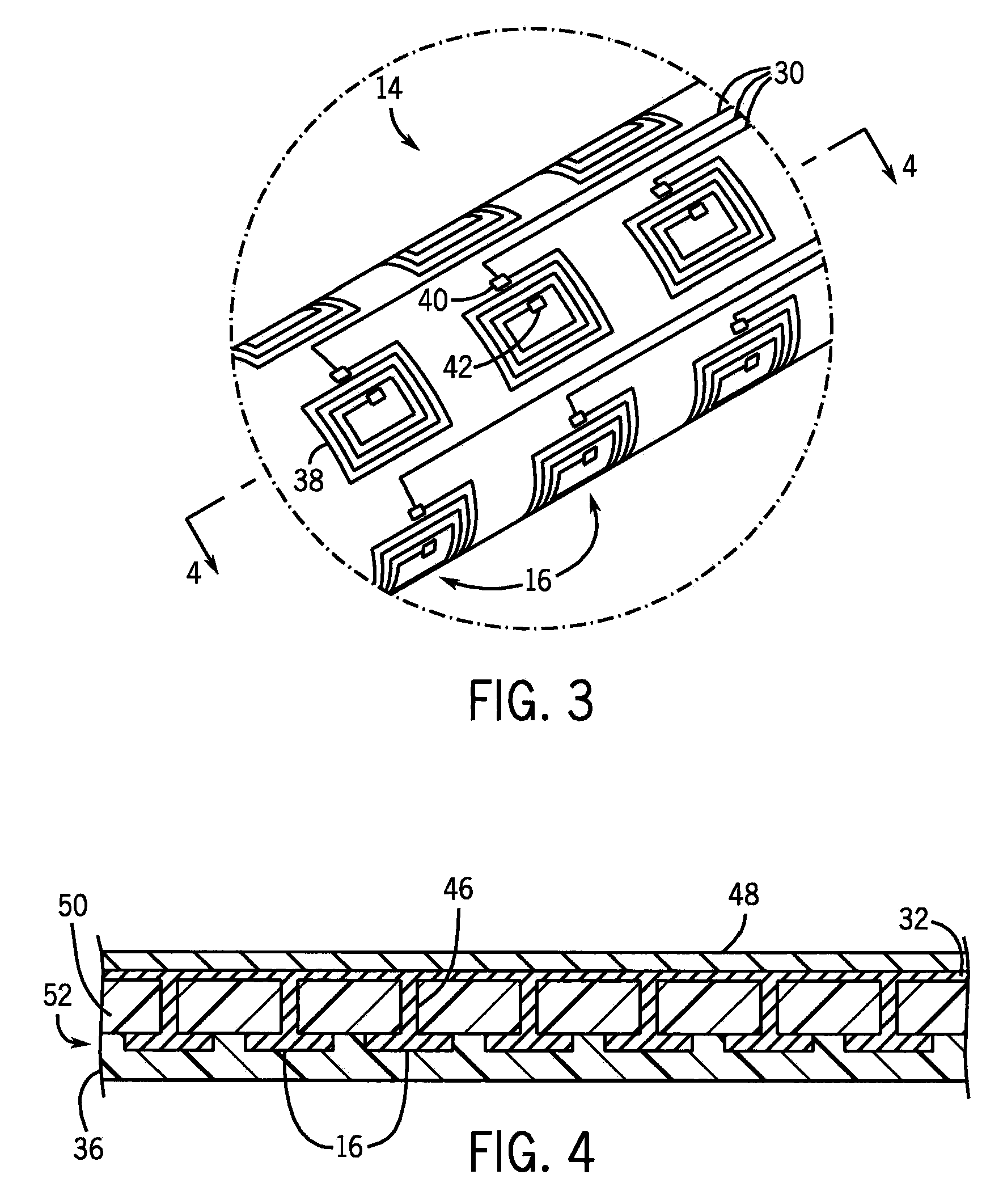
Deep brain stimulation implant with microcoil array
An implant for deep brain stimulation (DBS) has an array of electromagnetic microcoils dispersed over the length of the implant. The microcoils produce magnetic fields that are directed into, and induce current in, the adjacent brain tissue. The microcoils may be selectively operated to direct and focus electrical stimulation to targeted areas of the brain. The implant is useful in studying or treating neurophysiological conditions associated with the deep regions of the brain such as Parkinson's disease, drug addiction, and depression.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Tuning Low-Inductance Coils at Low Frequencies
InactiveUS20090256572A1Narrow downElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceElectricity
A method and apparatus for tuning and matching extremely small sample coils with very low inductance for use in magnetic resonance experiments conducted at low frequencies. A circuit is disclosed that is appropriate for performing measurements in fields where magnetic resonance is beneficially utilized. The circuit has a microcoil, an adjustable tuning capacitance, and added inductance in the form of a tuning inductor. The microcoil is an electrical coil having an inductance of about 25 nanohenries (nH) or less. Because additional inductance is purposefully added, the capacitance required for resonance and apparatus function is proportionally and helpfully reduced. The apparatus and method permit the resonant circuit and the magnet to be made extremely small, which is crucial for new applications in portable magnetic resonance imaging, for example.
Owner:ABQMR
Biological detector and method
InactiveUS20080315875A1Low costReduced cost and maintenance and space requirementMagnetic property measurementsNanosensorsMagnetite NanoparticlesSpectroscopy
Owner:SILLERUD LAUREL O
Method of manufacturing expansile filamentous embolization devices
InactiveUS20060149299A1High strengthReduced hydration rateCatheterTissue regenerationTitanium alloyBiomedical engineering
An embolization device for occluding a body cavity includes one or more elongated, expansible, hydrophilic embolizing elements non-releasably carried along the length of an elongated filamentous carrier that is preferably made of a very thin, highly flexible filament or microcoil of nickel / titanium alloy. At least one expansile embolizing element is non-releasably attached to the carrier. A first embodiment includes a plurality of embolizing elements fixed to the carrier at spaced-apart intervals along its length. In second, third and fourth embodiments, an elongate, continuous, coaxial embolizing element is non-releasably fixed to the exterior surface of the carrier, extending along a substantial portion of the length of the carrier proximally from a distal tip, and optionally includes a lumenal reservoir for delivery of therapeutic agents. Exemplary methods for making these devices include skewering and molding the embolizing elements. In any of the embodiments, the embolizing elements may be made of a hydrophilic, macroporous, polymeric, hydrogel foam material. In the second, third and fourth embodiments, the elongate embolizing element is preferably made of a porous, environmentally-sensitive, expansile hydrogel, which can optionally be made biodegradable and / or bioresorbable, having a rate of expansion that changes in response to a change in an environmental parameter, such as the pH or temperature of the environment.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
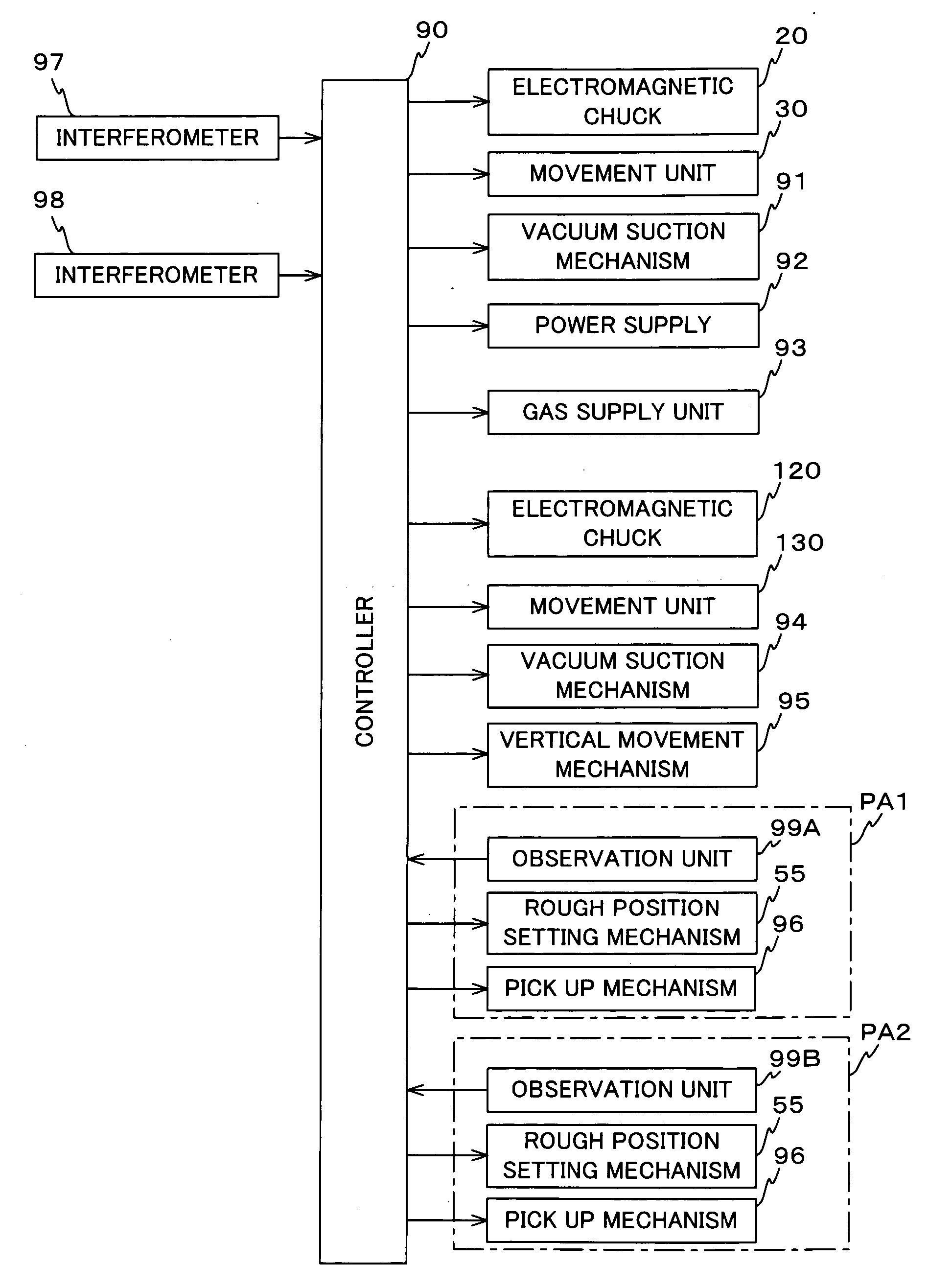
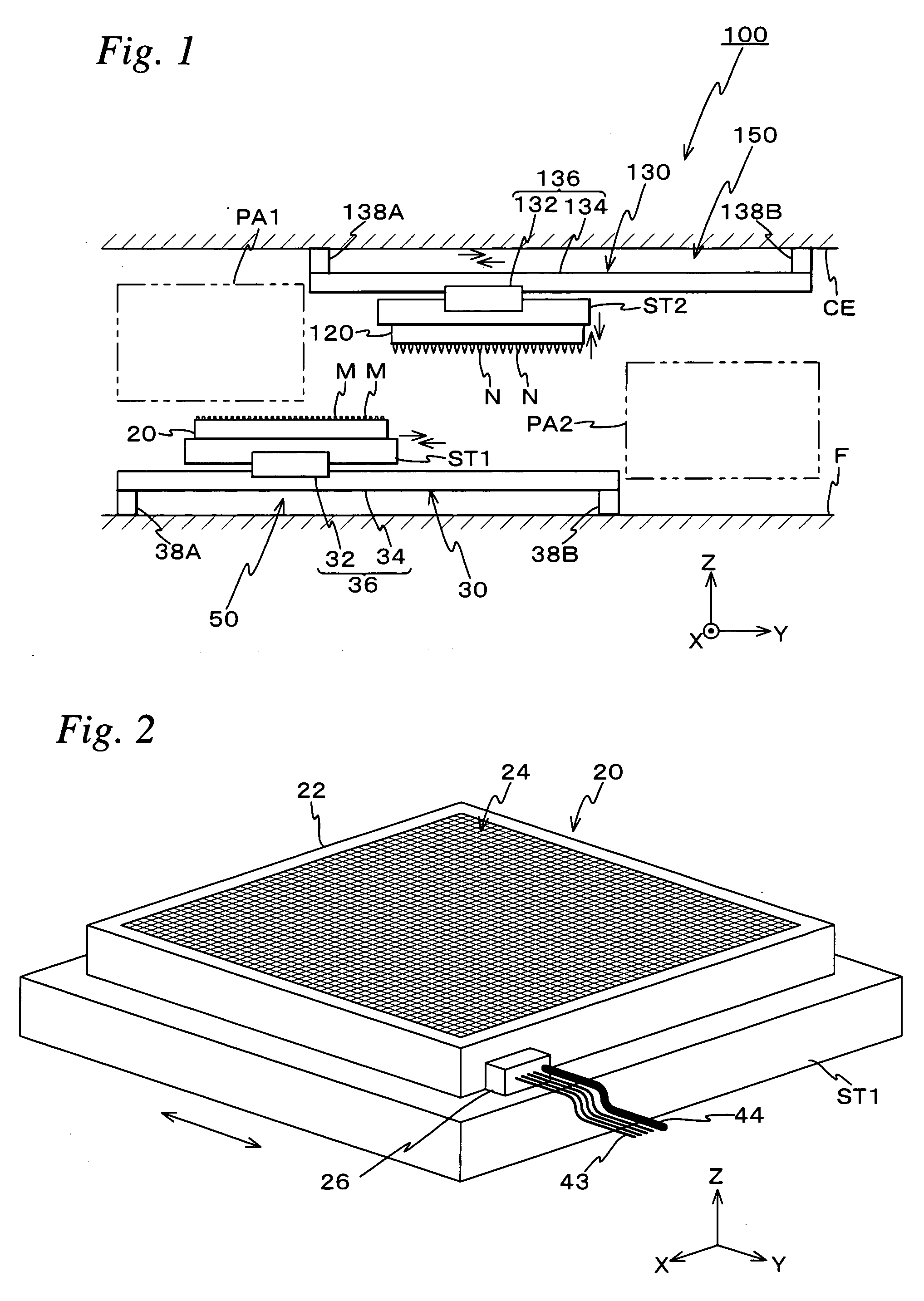
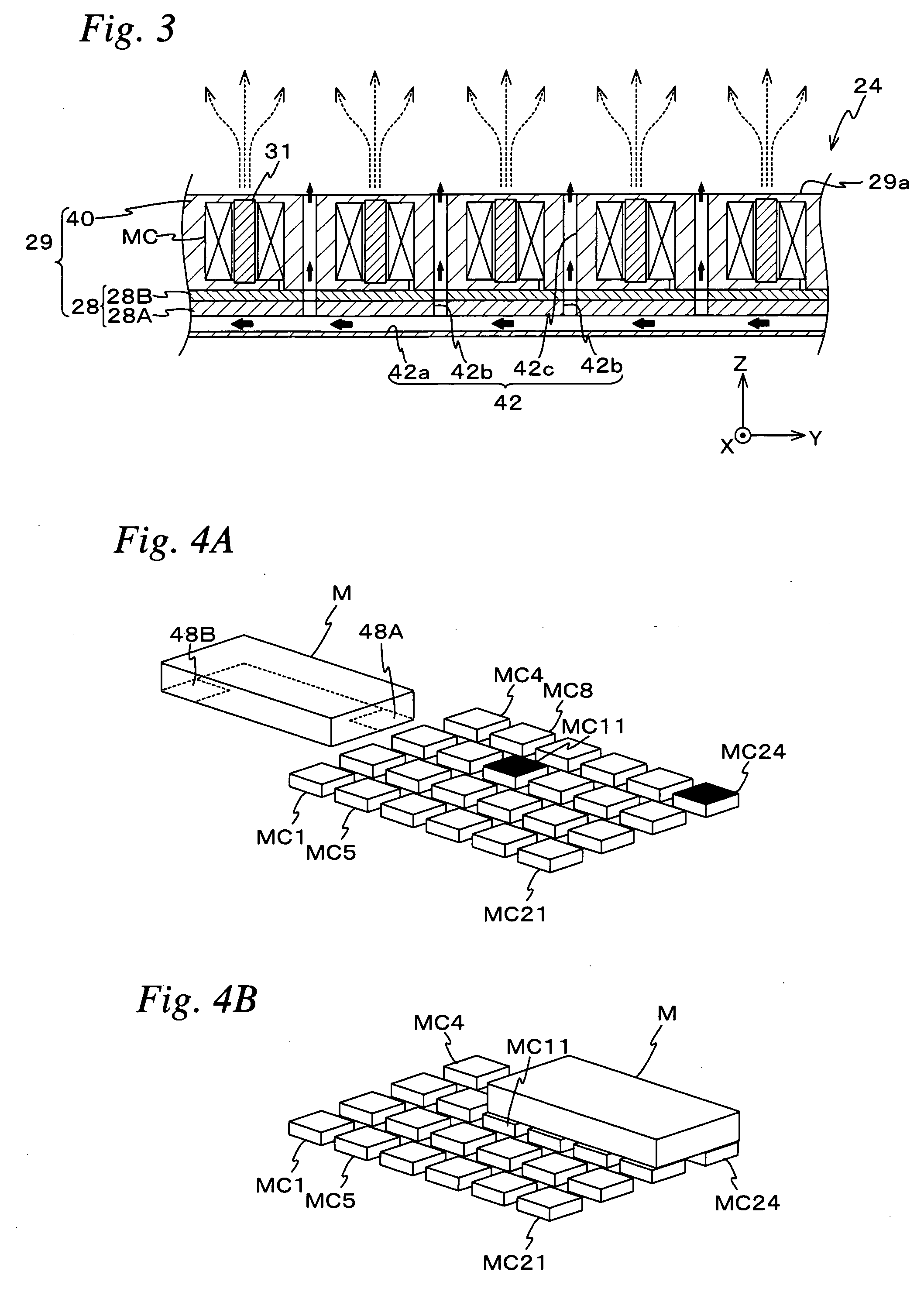
Holding unit, assembly system, sputtering unit, and processing method and processing unit
Because an electromagnetic chuck supplies current to a specific microcoil among a plurality of microcoils and makes an object exert an electromagnetic force working together with a magnet of the object, the object can be held in a state where the object is set at a desired position (a position that corresponds to the microcoil to which current has been supplied) on a base surface. Further, by gas that blows out from a gas supply passage, a levitation force is given to the object, which can reduce effects of a friction force that acts between the object and an upper surface of the electromagnetic chuck when the position of the object is set.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Tuning low-inductance coils at low frequencies
InactiveUS20080042650A1Narrow downElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceCapacitanceElectricity
A method and apparatus for tuning and matching extremely small sample coils with very low inductance for use in magnetic resonance experiments conducted at low frequencies. A circuit is disclosed that is appropriate for performing measurements in fields where magnetic resonance is beneficially utilized. The circuit has a microcoil, an adjustable tuning capacitance, and added inductance in the form of a tuning inductor. The microcoil is an electrical coil having an inductance of about 25 nanohenries (nH) or less. Because additional inductance is purposefully added, the capacitance required for resonance and apparatus function is proportionally and helpfully reduced. The apparatus and method permit the resonant circuit and the magnet to be made extremely small, which is crucial for new applications in portable magnetic resonance imaging, for example.
Owner:ABQMR
Microcoil vaso-occlusive device with multi-axis secondary configuration
InactiveUS7029486B2Minimizing shifting and tumblingMinimizing degree of compactionDilatorsOcculdersHigh energyClosed loop
A microcoil vaso-occlusive device has a minimum energy state secondary configuration having a plurality of curved segments, each defining a discrete axis. The secondary configuration may be a plurality of interconnected closed loops; an array of laterally-alternating open loops; a series of tangential closed loops; or a logarithmic spiral. The device, in its secondary cofiguration, has a dimension that is substantially larger than the largest dimension of the vascular site in which it is to be deployed. Thus, confinement of the device within the site causes it to assume a configuration with a higher energy state than the minimum energy state. Because the secondary configuration is larger (in at least one dimension) than the site, the device is constrained, by contact with the walls of the site, from returning to its secondary configuration, and shifting of the device due to blood flow is minimized.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
Three element coaxial vaso-occlusive device
ActiveUS8273100B2Reduces aggregate frictionDecreasing resistance to manipulationDilatorsCharacter and pattern recognitionMetallic materialsEngineering
A vaso-occlusive device includes inner, intermediate, and outer elements arranged coaxially. The inner element is a filamentous element, preferably a microcoil. The intermediate element is made of a non-metallic material, preferably an expansile polymer. The outer element is substantially non-expansile and defines at least one gap or opening through which the intermediate element is exposed. In a preferred embodiment, when the intermediate element is expanded, it protrudes through the at least one gap or opening in the outer element and assumes a configuration with an undulating, convexly-curved outer surface defining a chain of arcuate segments, each having a diameter significantly greater than the diameter of the outer element. The expanded configuration of the intermediate element minimizes friction when the device is deployed through a microcatheter, thereby reducing the likelihood of buckling while maintaining excellent flexibility. The result is a device with enhanced pushability and trackability when deployed through a microcatheter.
Owner:MICROVENTION INC
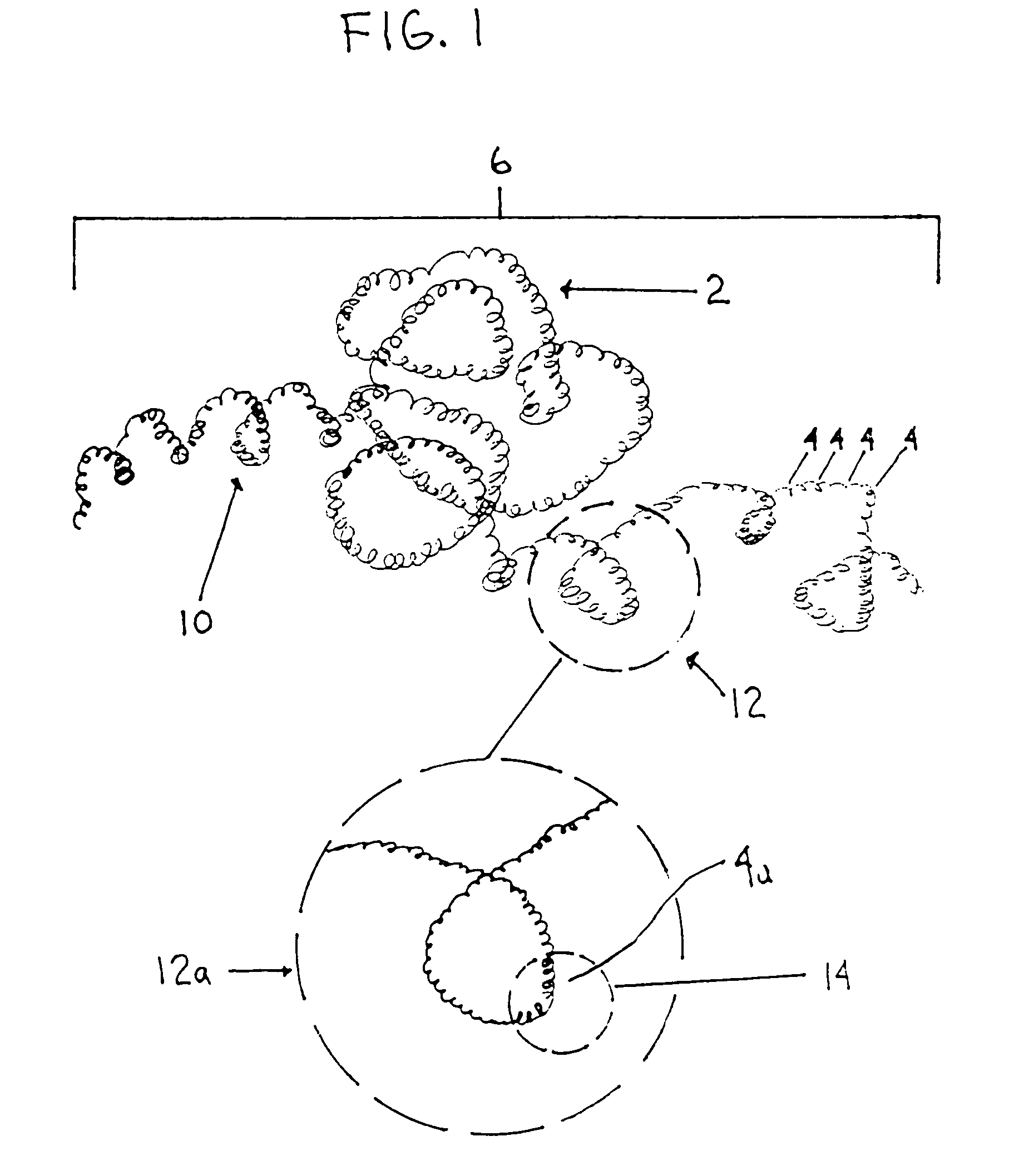
Method for efficient transport of small liquid volumes to, from or within microfluidic devices
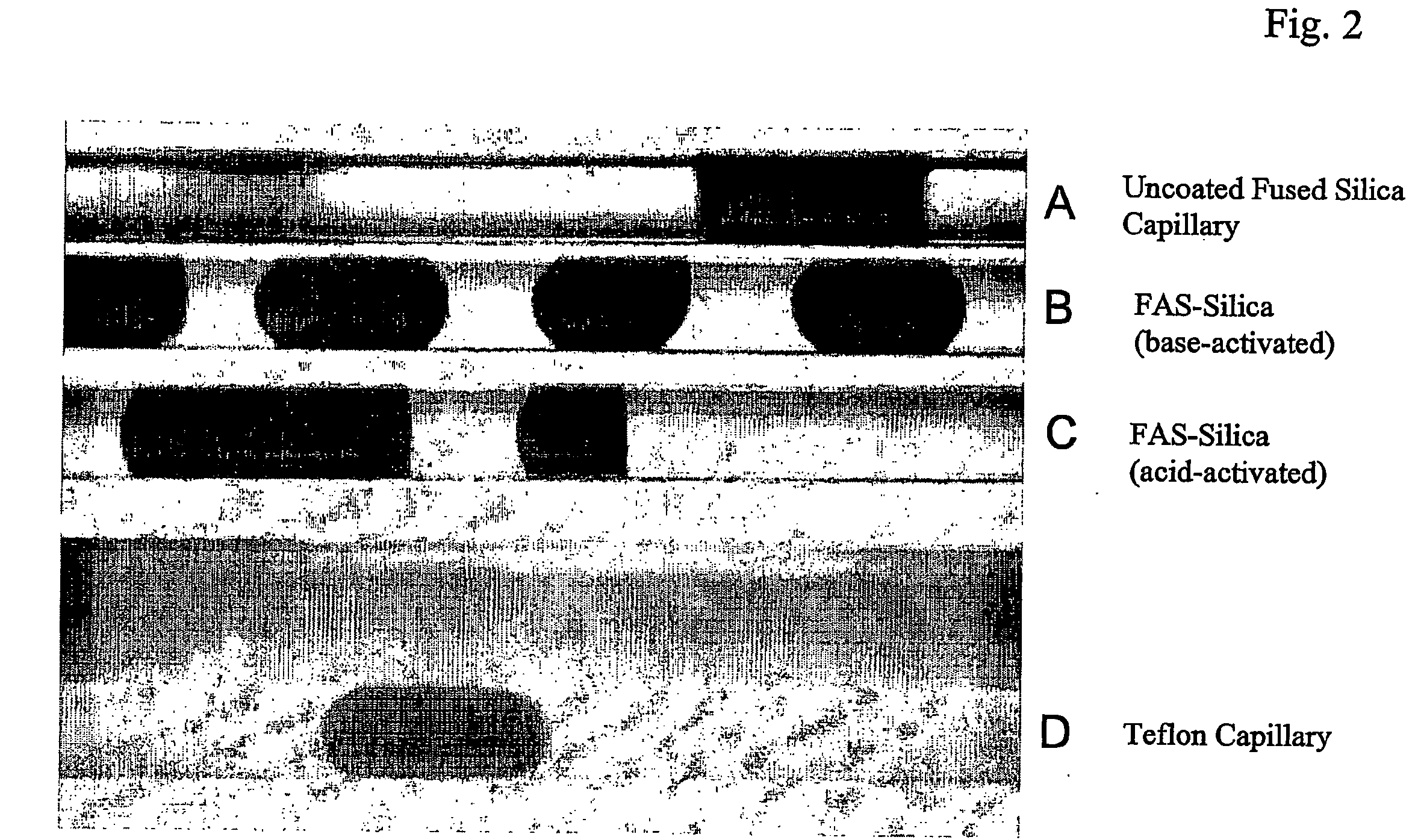
InactiveUS20070117212A1Avoid lostReduce lossOrganic chemistryFatty/oily/floating substances removal devicesCapillary TubingEngineering
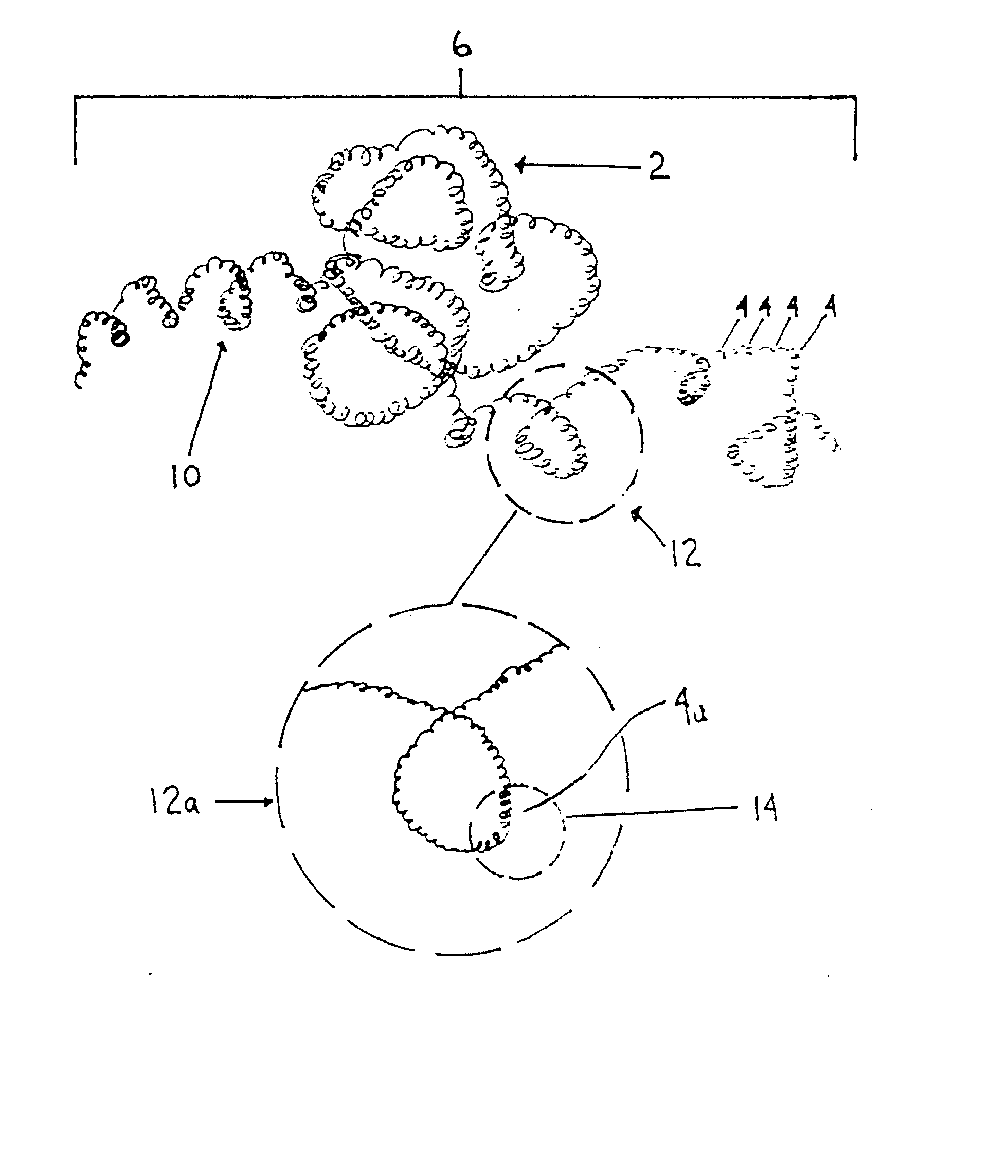
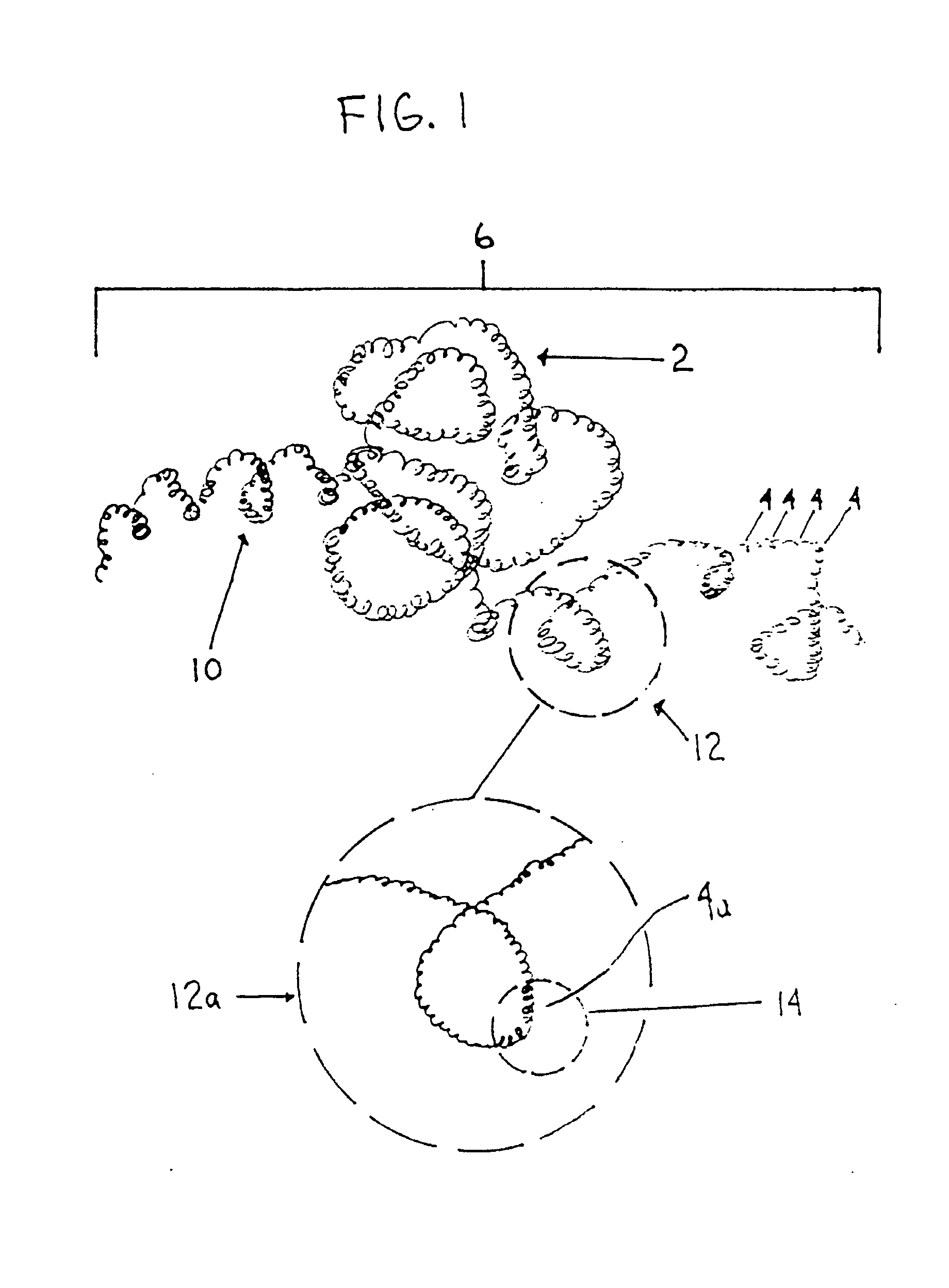
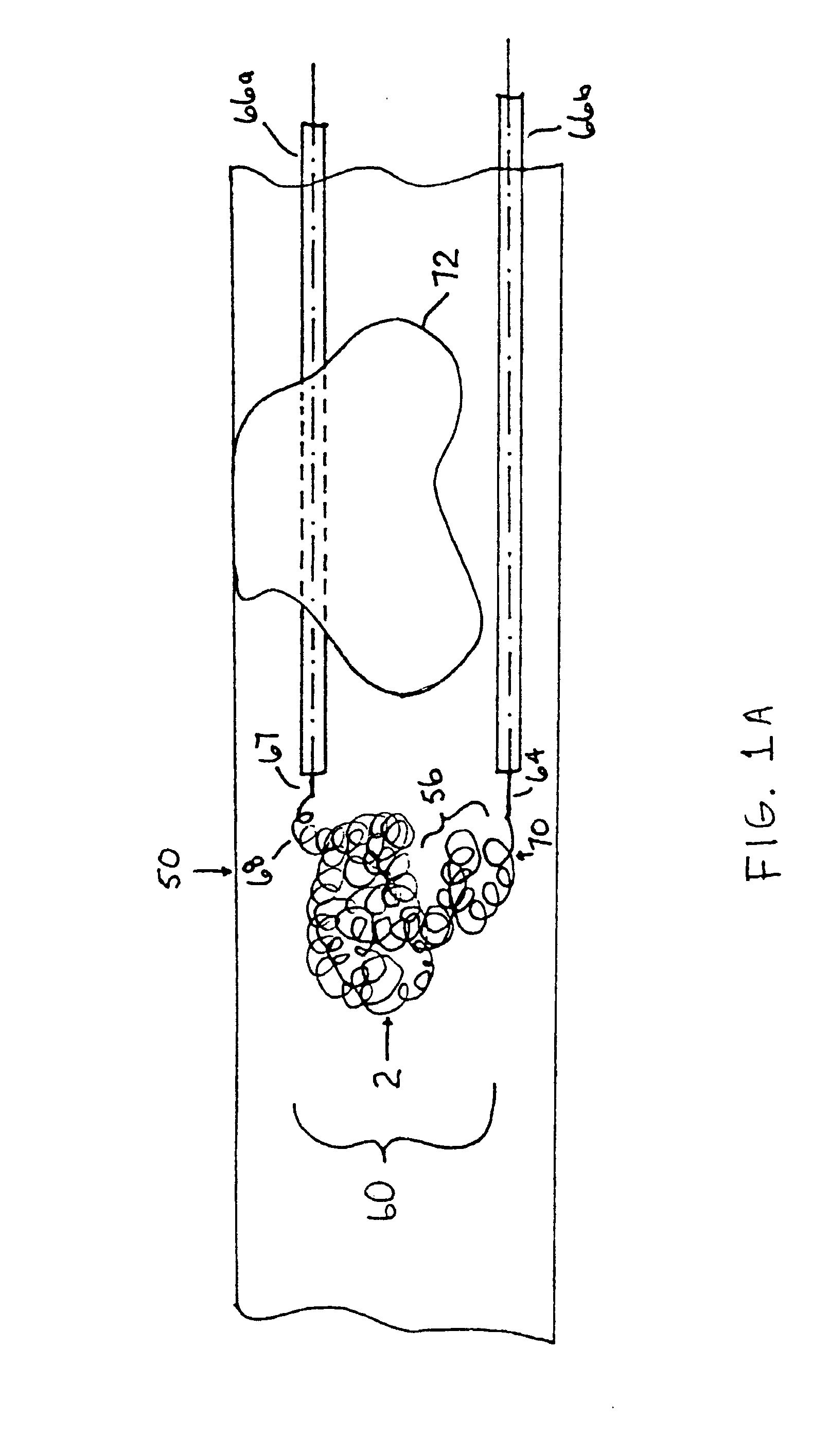
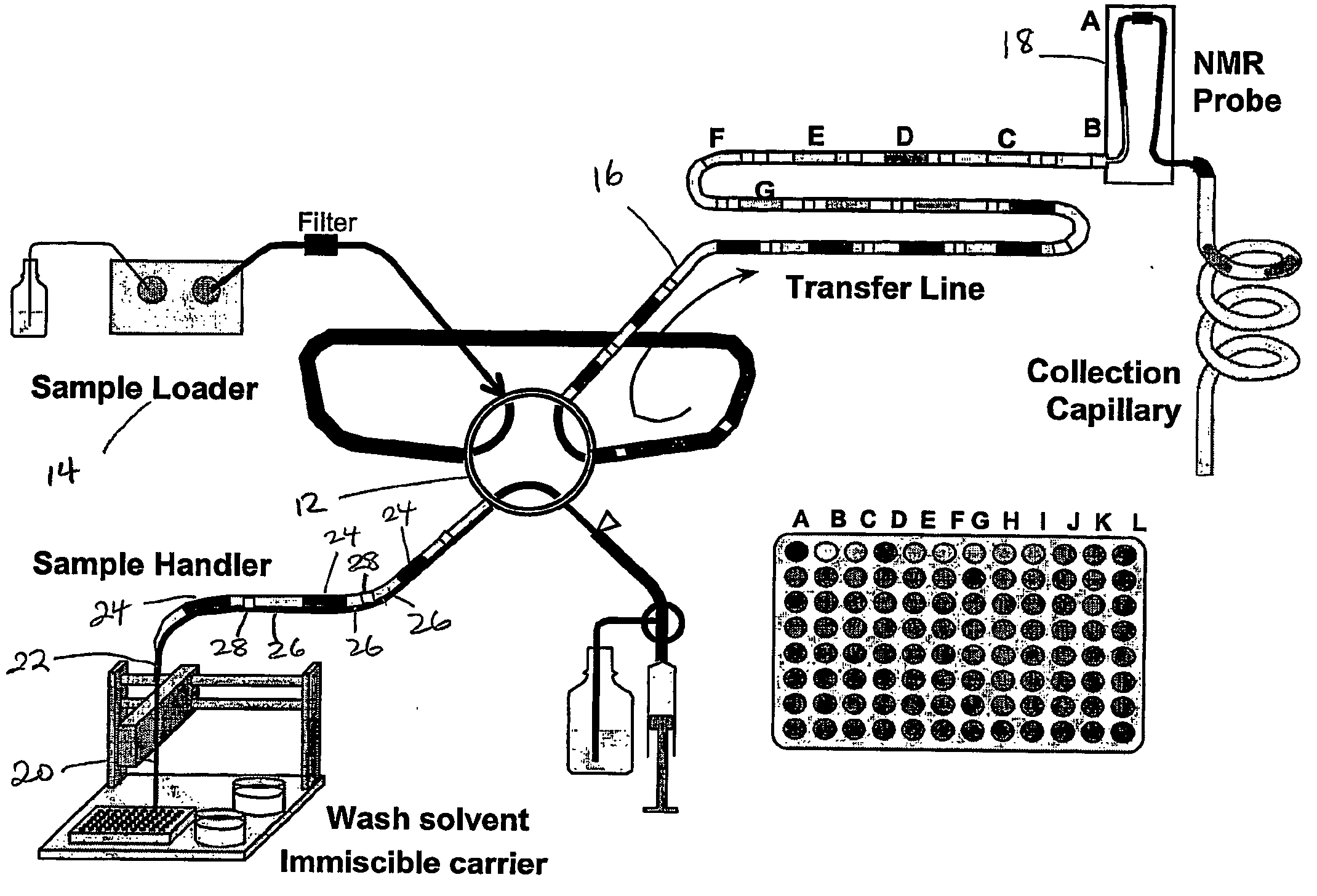
Methods are presented for realizing zero-dispersion segmented flow for transfer of small microfluidic samples onto or within microfluidic analysis or processing devices. Where fluidic systems are in whole or in part made of materials favorable to the zero-dispersion conditions for an indicated solvent / carrier fluid system, the system may be covalently coated to impart the necessary surface properties. This invention is demonstrated in an embodiment where 1 microliter samples (6) are robotically prepared and transferred through 3 meters of capillary tubing (4) to a microcoil NMR probe.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Thrombus removal system and process
InactiveUS20160220265A1Reliable dynamic compliance matchingReliably and safely navigate tortuous blood vesselSurgeryGrip forcePull force
A device capable of capturing and facilitating the removal of a solid obstruction in a vessel or tube, such as a thrombus in blood vessels (or stones in biliary or urinary ducts, or foreign bodies) uses a soft coil mesh with the aid of a pull wire or string to engage the surface of a thrombus, and remove the captured thrombus. The soft coil mesh is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical elements forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls. The use of multiple coil mesh elements, delivered through a single lumen or multiple lumens, preferably with separate control of at least one end of each coil, provides a firm grasp on a distal side of a thrombus, assisting in non-disruptive or minimally disrupted removal of the thrombus upon withdrawal of the device, with an extendable braid provided distally from the macrocoil to capture material distal of a deployed macrocoil.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
Method of tracking a vehicle using microradios
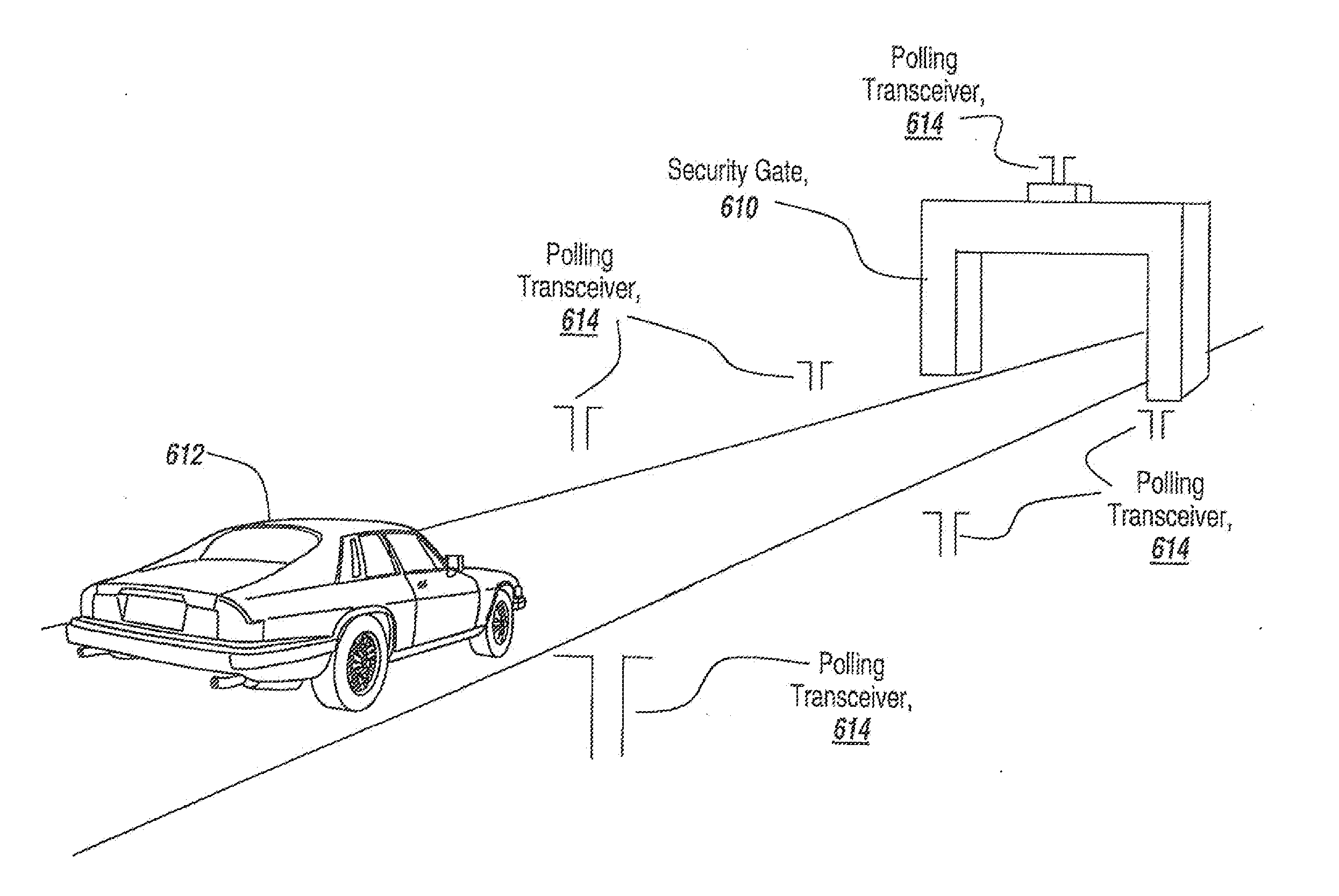
InactiveUS20110267235A1Cost-effectiveLow powerDirection finders using radio wavesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsRadio equipmentTerrain
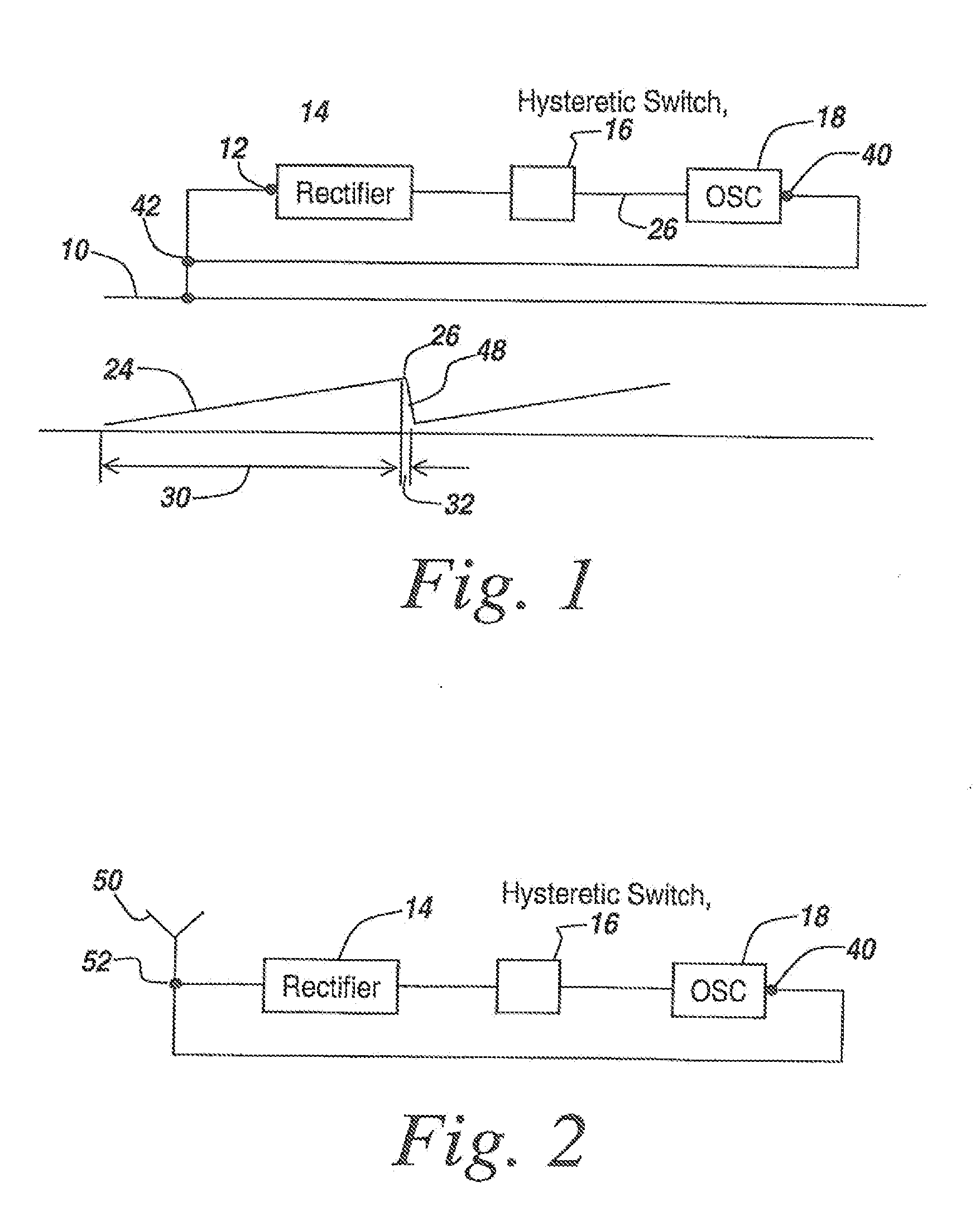
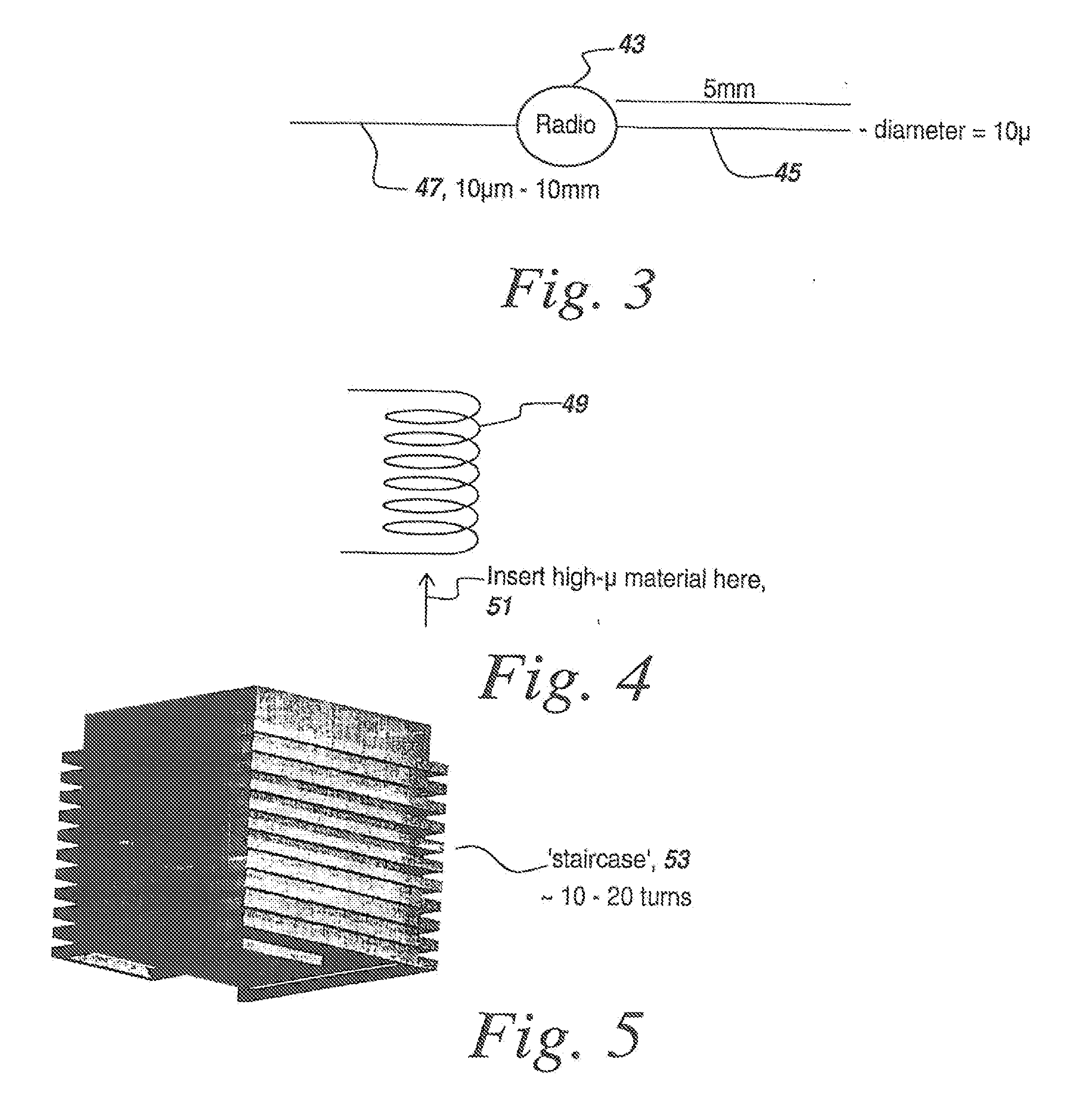
A microradio is provided with a hysteretic switch to permit an optimum range increasing charging cycle, with the charging cycle being long relative to the transmit cycle. Secondly, an ensemble of microradios permits an n2 power enhancement to increase range with coherent operation. Various multi-frequency techniques are used both for parasitic powering and to isolate powering and transmit cycles. Applications for microradios and specifically for ensembles of microradios include authentication, tracking, fluid flow sensing, identification, terrain surveillance including crop health sensing and detection of improvised explosive devices, biohazard and containment breach detection, and biomedical applications including the use of microradios attached to molecular tags to destroy tagged cells when the microradios are activated. Microradio deployment includes the use of paints or other coatings containing microradios, greases and aerosols. Moreover, specialized antennas, including microcoils, mini dipoles, and staircase coiled structures are disclosed, with the use of nano-devices further reducing the size of the microradios.
Owner:RADIOFIDO
Thrombus removal system and process
A device captures and assists in the removal of a thrombus in arteries, even in small arteries. The device uses a soft coil mesh to engage the surface of a thrombus, and a guidewire is used to retract the soft coil mesh with the captured thrombus. The soft coil is formed by an elongated microcoil element that forms the helical elements of a macrocoil element. The microcoil element provides a relatively elastic effect to the helical element forming the macrocoil and allows for control of gripping forces on the thrombus while reducing non-rigid contact of the device with arterial walls.
Owner:NEXGEN MEDICAL SYST
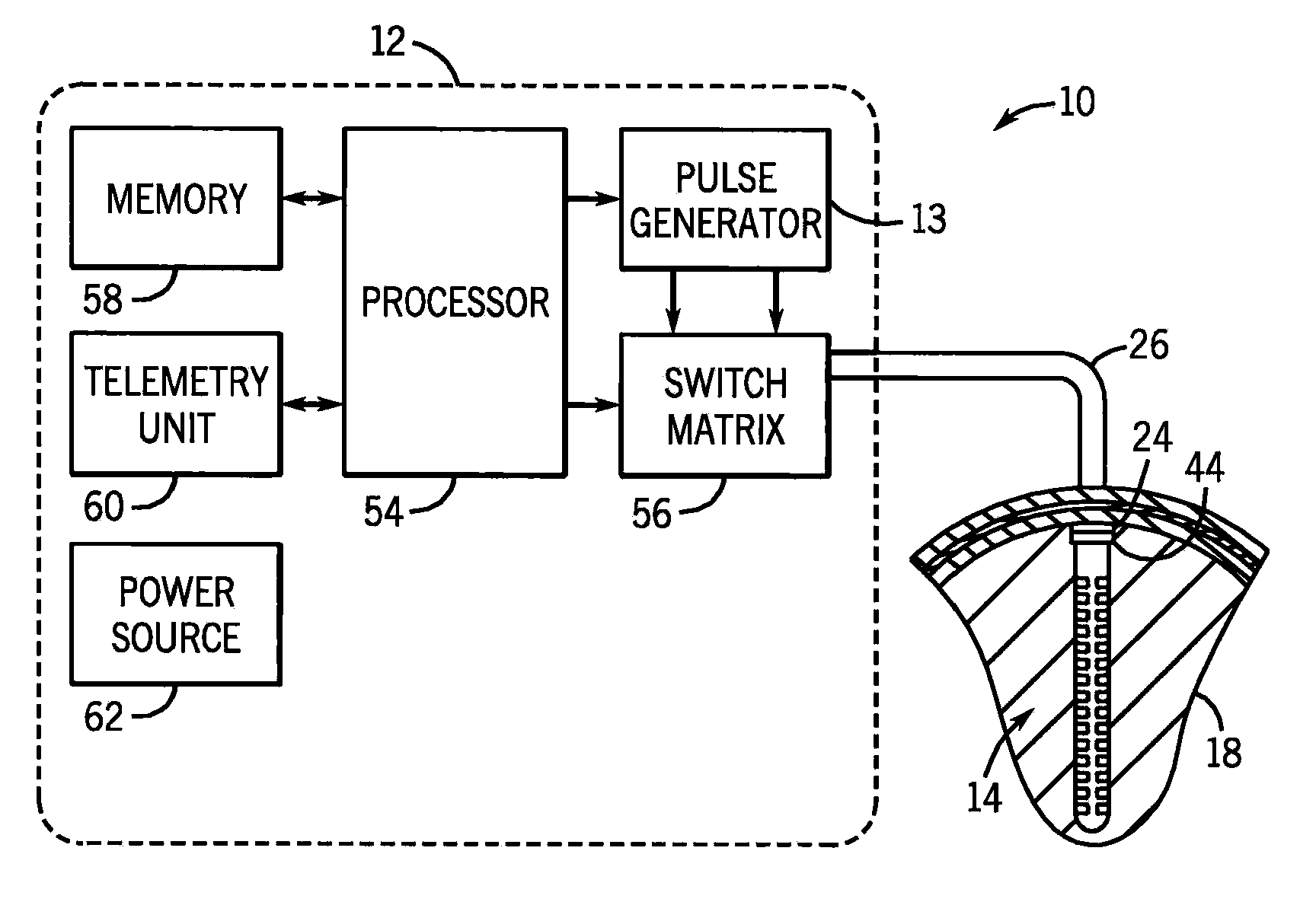
Apparatus for treating a patient
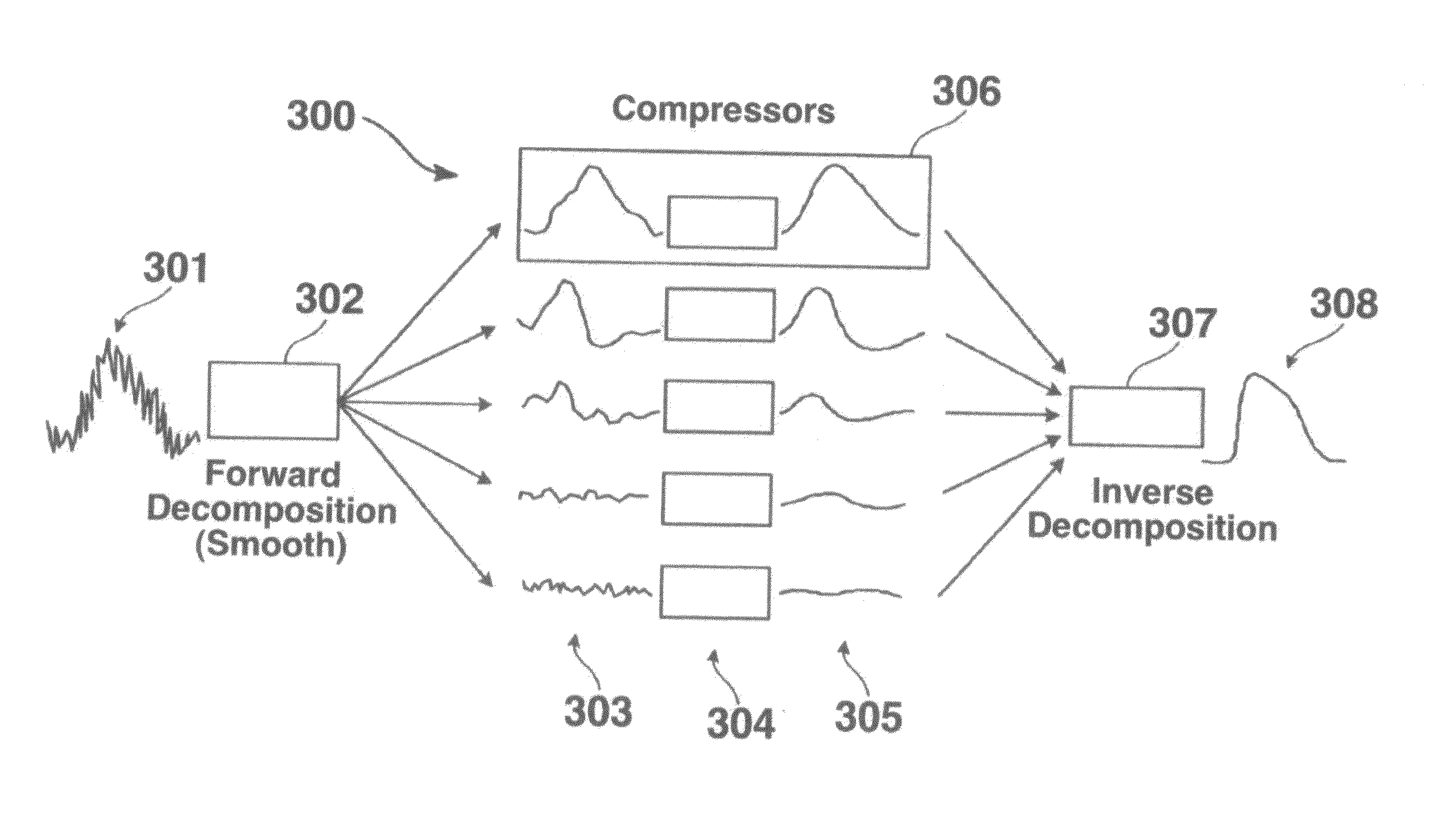
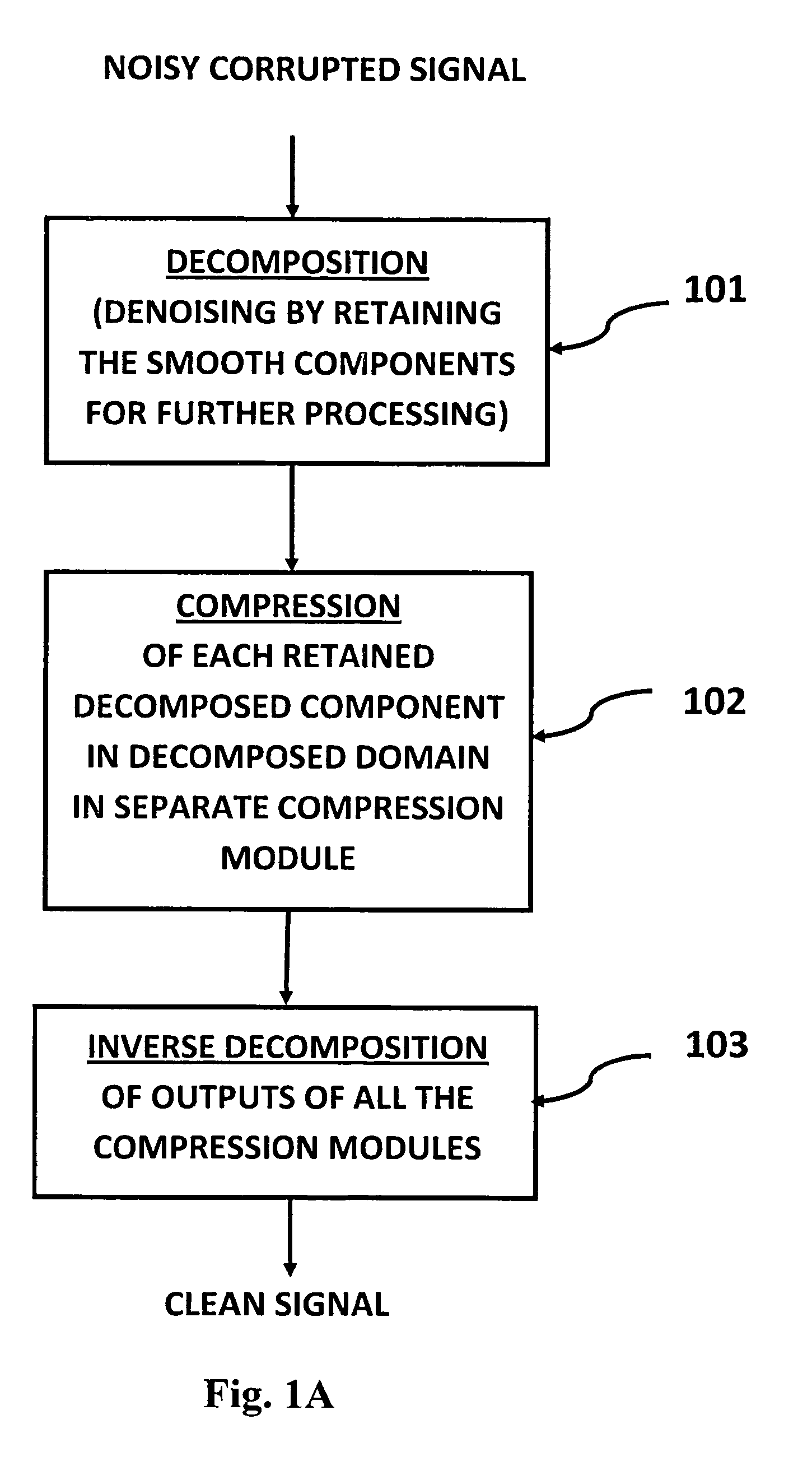
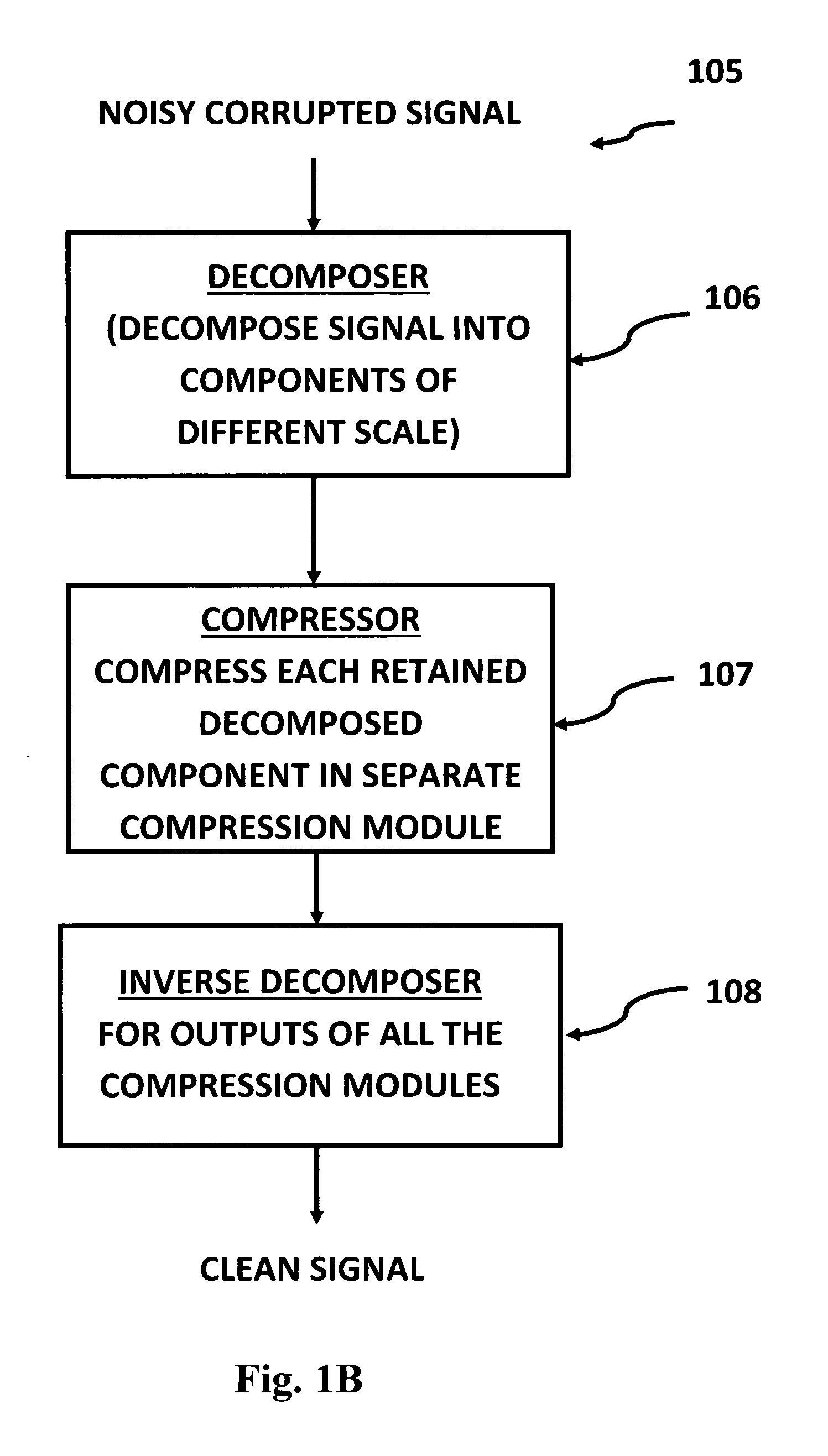
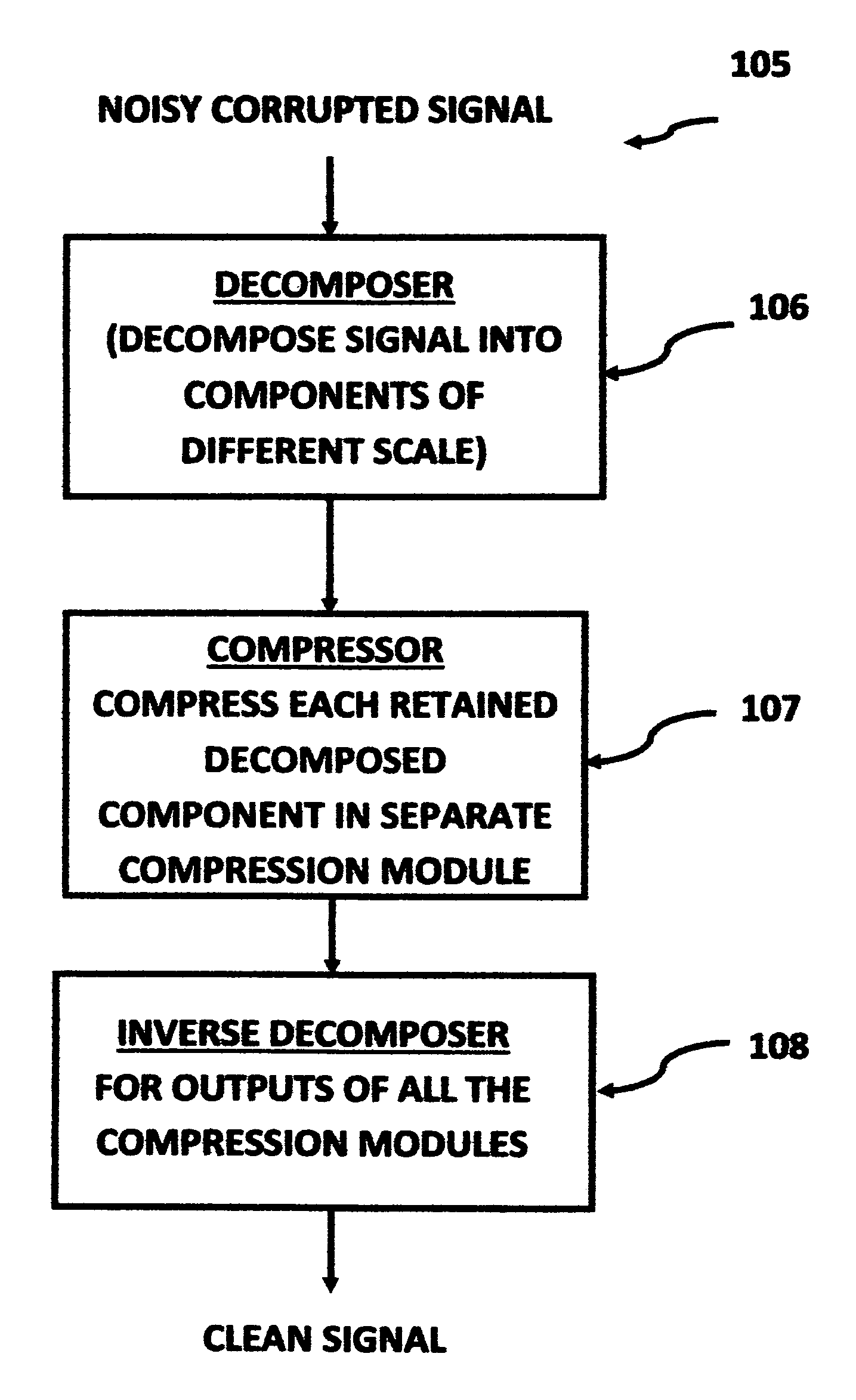
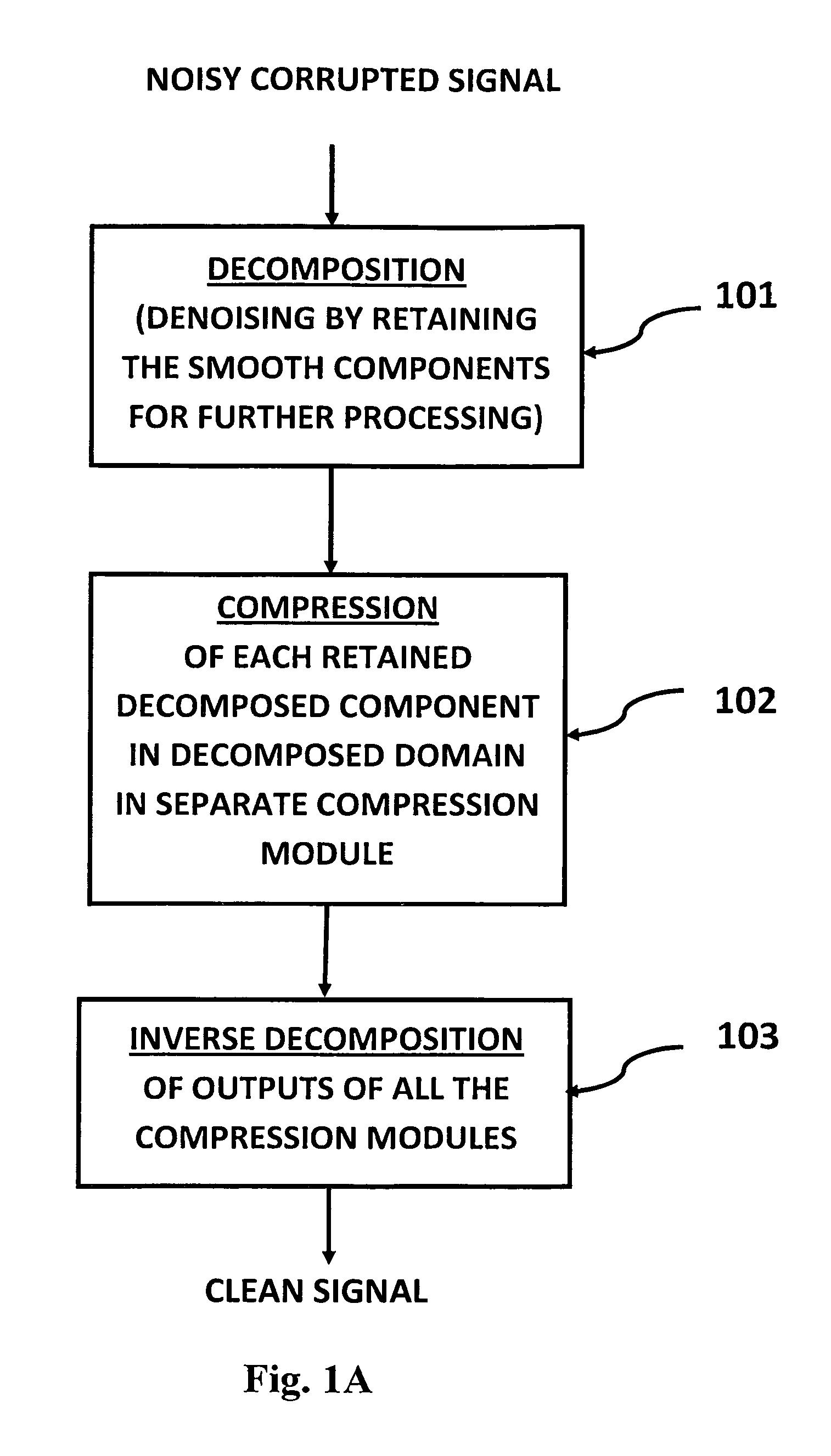
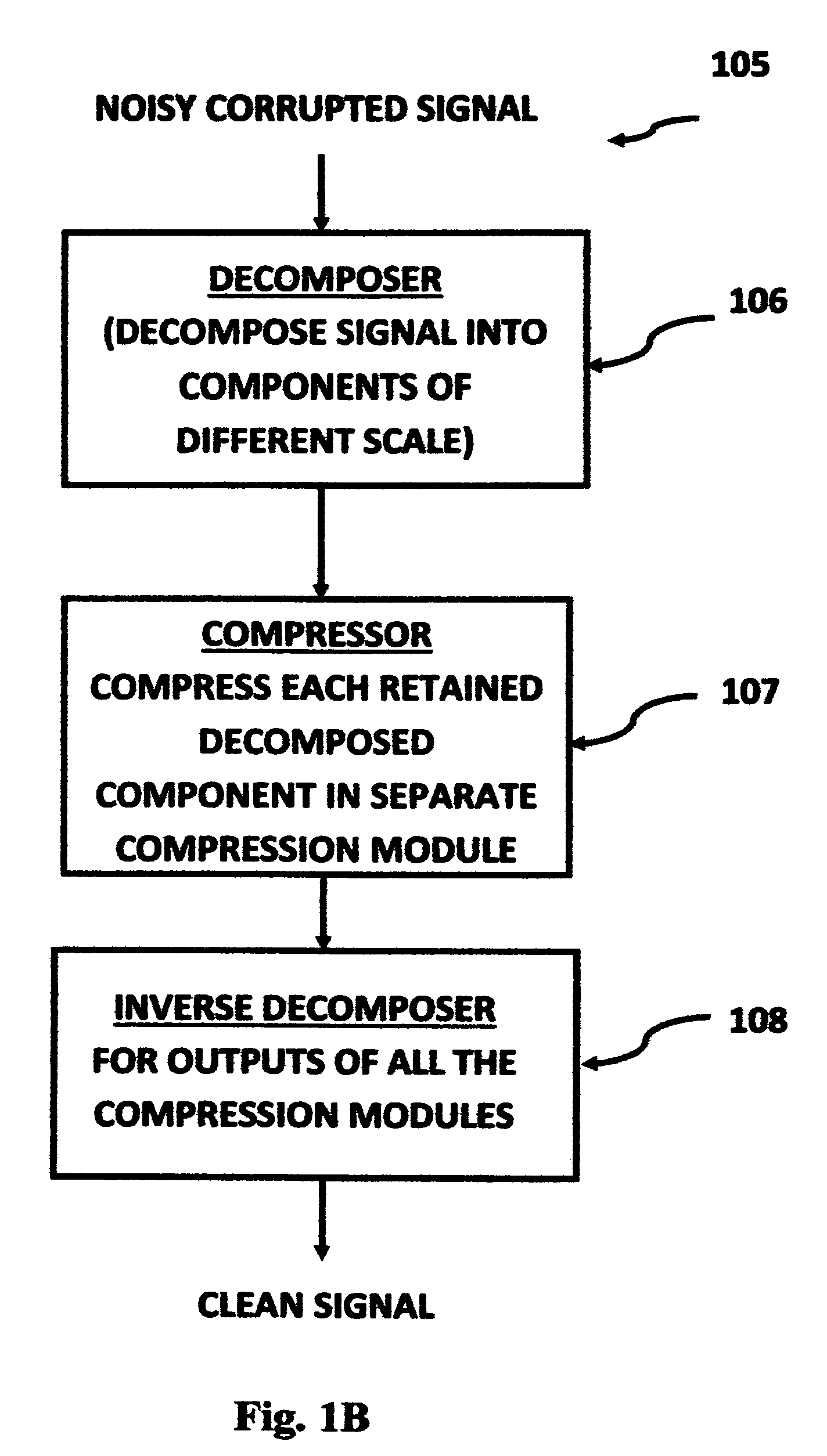
A signal processing method and system combines multi-scale decomposition, such as wavelet, pre-processing together with a compression technique, such as an auto-associative artificial neural network, operating in the multi-scale decomposition domain for signal denoising and extraction. All compressions are performed in the decomposed domain. A reverse decomposition such as an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined outputs from all the compression modules to recover a clean signal back in the time domain. A low-cost, non-drug, non-invasive, on-demand therapy braincap system and method are pharmaceutically non-intrusive to the body for the purpose of disease diagnosis, treatment therapy, and direct mind control of external devices and systems. It is based on recognizing abnormal brainwave signatures and intervenes at the earliest moment, using magnetic and / or electric stimulations to reset the brainwaves back to normality. The feedback system is self-regulatory and the treatment stops when the brainwaves return to normal. The braincap contains multiple sensing electrodes and microcoils; the microcoils are pairs of crossed microcoils or 3-axis triple crossed microcoils.
Owner:FU CHI YUNG
Method of manufacturing magnetic micro-structure
InactiveCN101108721AReduce manufacturing costEasy and quick to makeSemi-permeable membranesVolume/mass flow by thermal effectsMicro structureMicrometer
The invention relates to a fabrication method of the magnetic microstructure, which is characterized in that the invention comprises the fabrication of multilayer mould and the fabrication of the magnetic microstructure. The former is that the standard RCA cleaning process is used to clean silicon chips; multi layers of SU-8 photoresist are coated by rotating on the silicon chip surfaces and the multi layers of SU-8 mould are gotten after prebaking, photoetching, post baking and developing, and then the invention forms the magnetic microcolumn structure in the chip while molding dying the PDMS chip through directly filling the magnetic powders in the multilayer mould. Adopting the provided fabrication method can dispense with the electroplating process and fabricate the magnetic microstructure in the microfluid chip rapidly. The microstructure height is fabricated between micrometers less than ten and hundred of micrometers, which is determined by the photoresist layers of the rotating coating SU-8 and the magnetic microstructure is any one of the microcolumn, microline, microring or microcoil.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
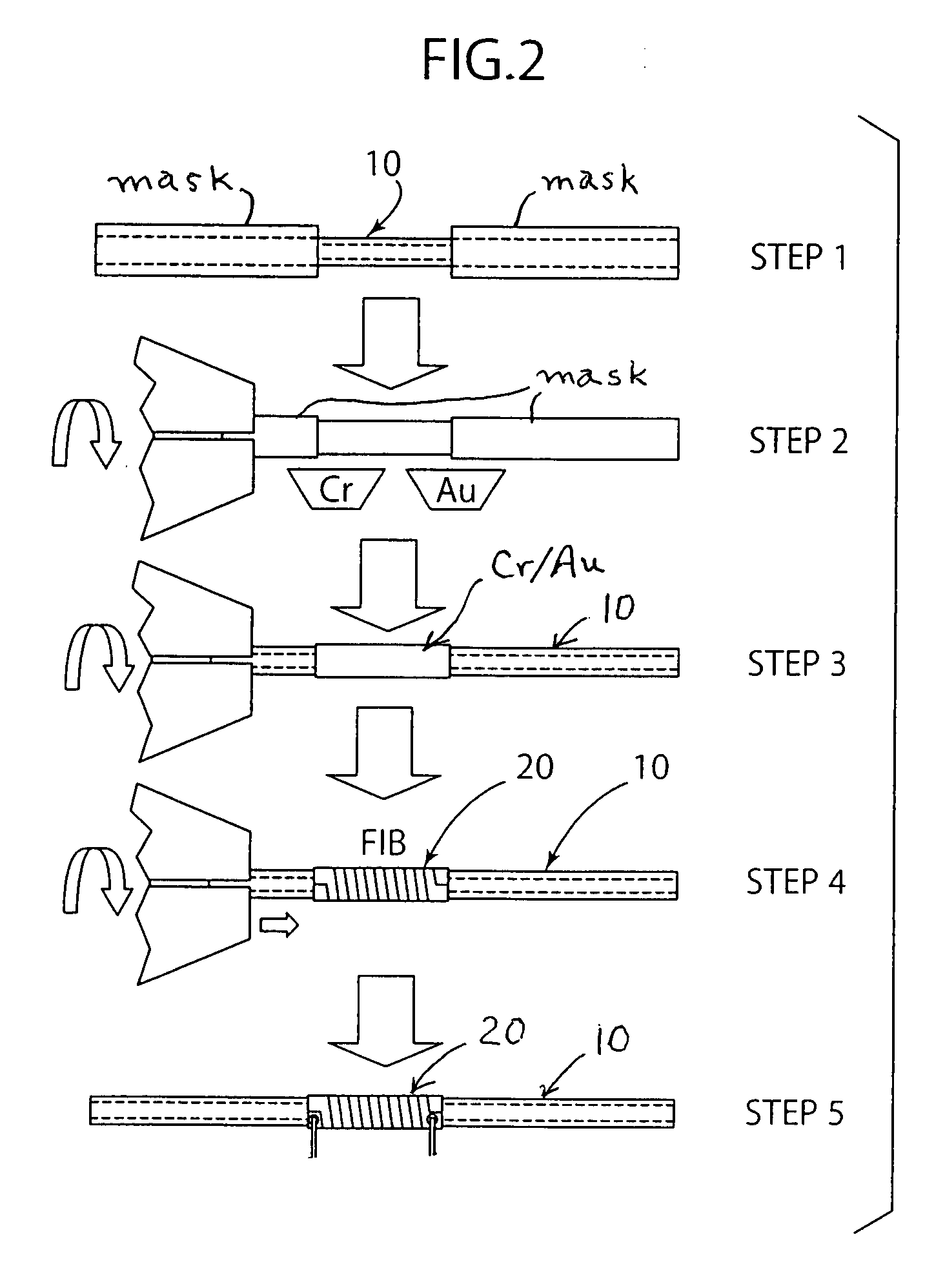
Optical fiber microcoil, resonant structure and method of making the same
ActiveUS7266259B1Transmission characteristicWell formedLaser detailsCladded optical fibreResonanceFiber diameter
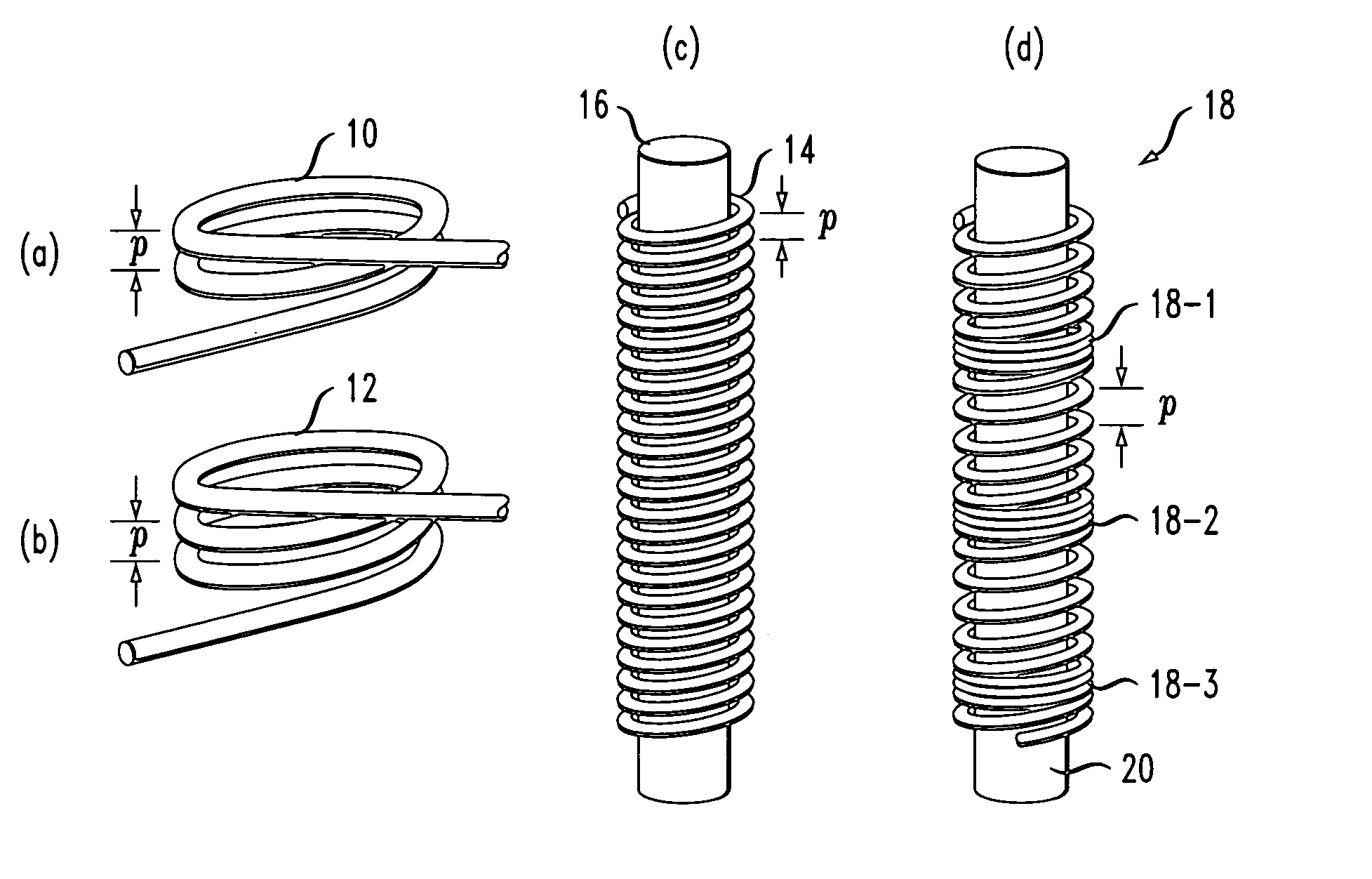
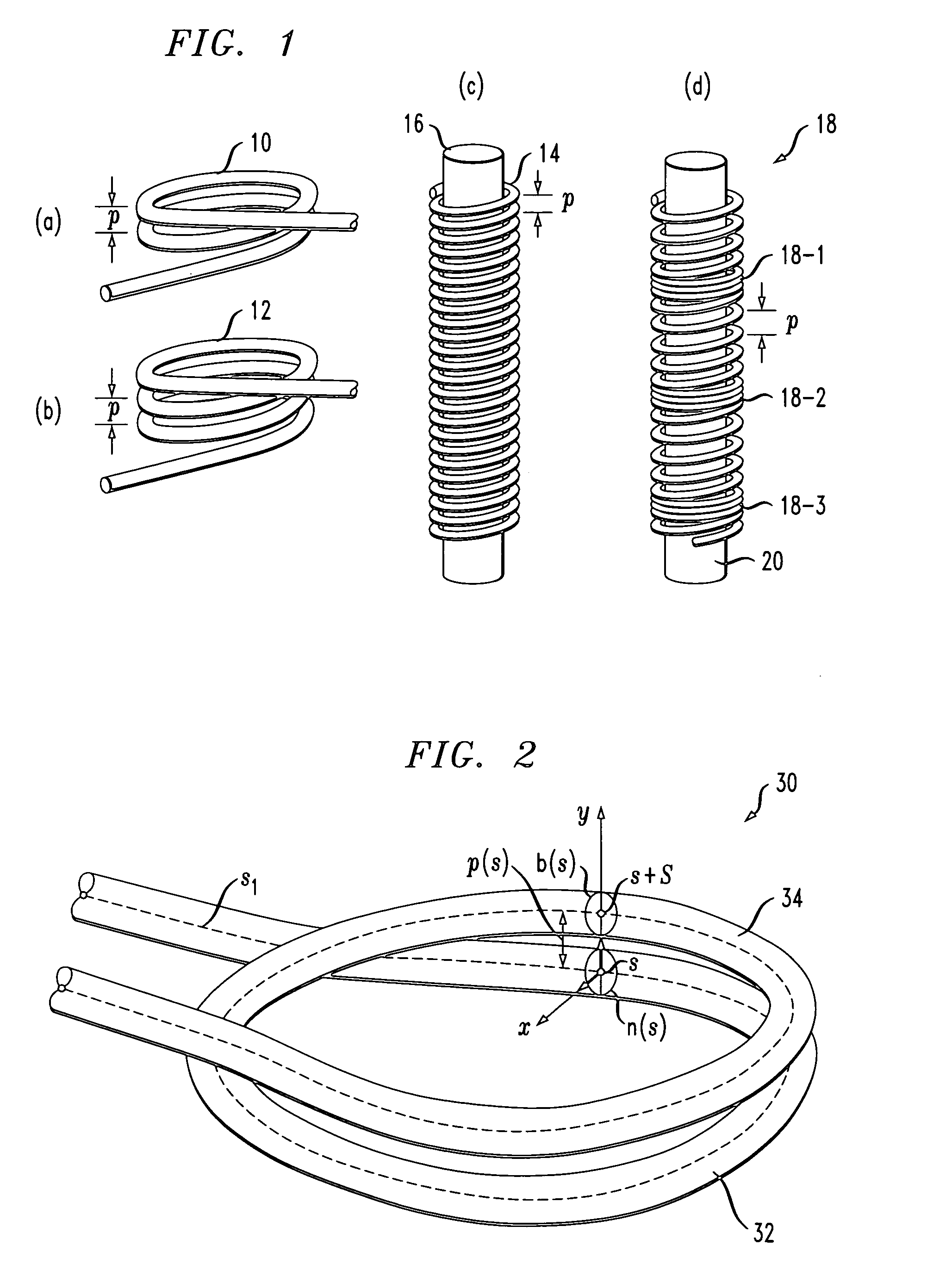
An optical fiber coil of sub-micron diameter is shown to exhibit self-coupling between adjacent turns so as to form a three-dimensional optical resonator of relatively low loss and high Q. As long as the pitch of the coil and propagating wavelength remain on the same order (or less than) the fiber diameter, resonance may occur. Resonances can be induced by allowing adjacent turns of the coil to touch each other. Optical devices such as resonators and interferometers may then be formed from such “microcoils” that exhibit superior characteristics to conventional planar devices. A method of forming such a microfiber using indirect laser heating is also disclosed.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Tuning Low-Inductance Coils at Low Frequencies
A method and apparatus for tuning and matching extremely small sample coils with very low inductance for use in magnetic resonance experiments conducted at low frequencies. A circuit is disclosed that is appropriate for performing measurements in fields where magnetic resonance is beneficially utilized. The circuit has a microcoil, an adjustable tuning capacitance, and added inductance in the form of a tuning inductor. The microcoil is an electrical coil having an inductance of about 25 nanohenries (nH) or less. Because additional inductance is purposefully added, the capacitance required for resonance and apparatus function is proportionally and helpfully reduced. The apparatus and method permit the resonant circuit and the magnet to be made extremely small, which is crucial for new applications in portable magnetic resonance imaging, for example.
Owner:ABQMR
Signal processing method and apparatus
A signal processing method and system combines multi-scale decomposition, such as wavelet, pre-processing together with a compression technique, such as an auto-associative artificial neural network, operating in the multi-scale decomposition domain for signal denoising and extraction. All compressions are performed in the decomposed domain. A reverse decomposition such as an inverse discrete wavelet transform is performed on the combined outputs from all the compression modules to recover a clean signal back in the time domain. A low-cost, non-drug, non-invasive, on-demand therapy braincap system and method are pharmaceutically non-intrusive to the body for the purpose of disease diagnosis, treatment therapy, and direct mind control of external devices and systems. It is based on recognizing abnormal brainwave signatures and intervenes at the earliest moment, using magnetic and / or electric stimulations to reset the brainwaves back to normality. The feedback system is self-regulatory and the treatment stops when the brainwaves return to normal. The braincap contains multiple sensing electrodes and microcoils; the microcoils are pairs of crossed microcoils or 3-axis triple crossed microcoils.
Owner:FU CHI YUNG
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com