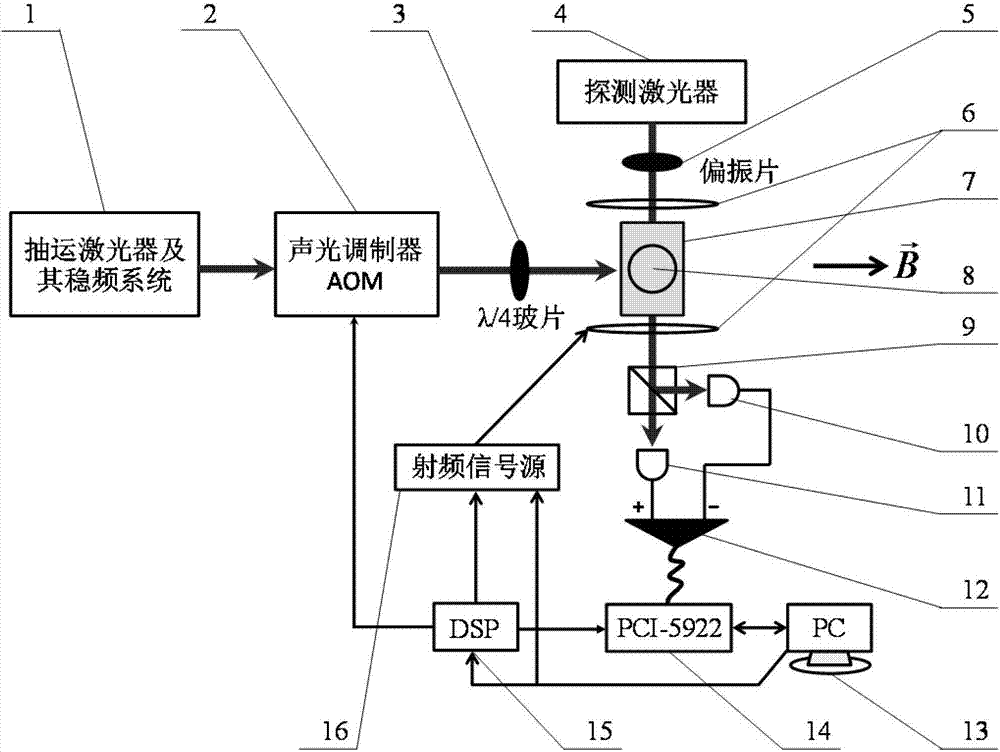
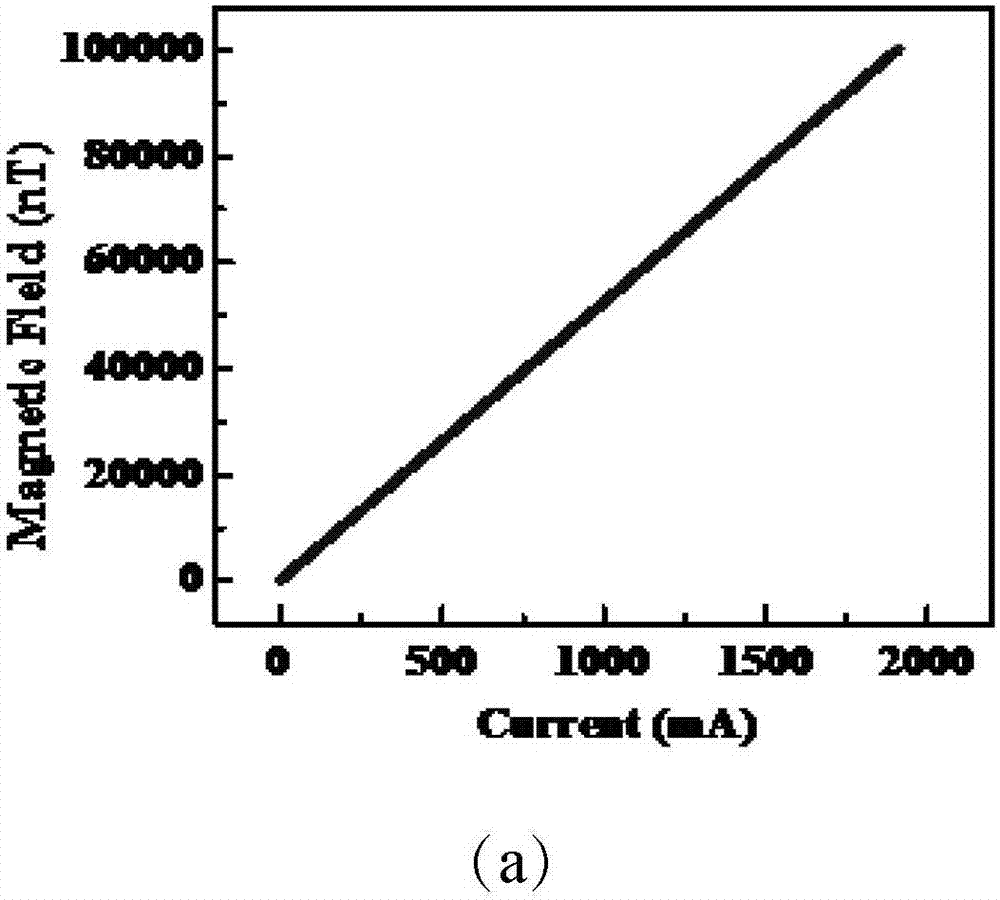
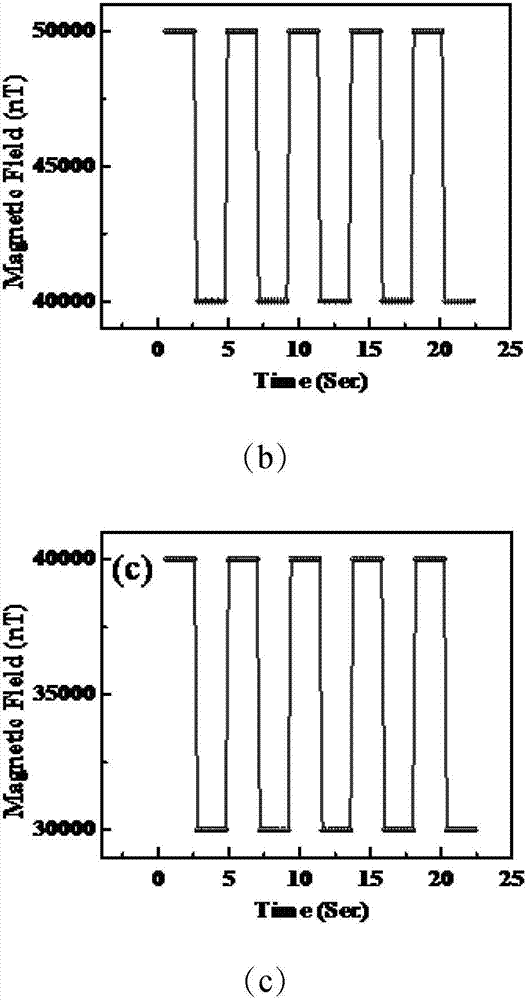
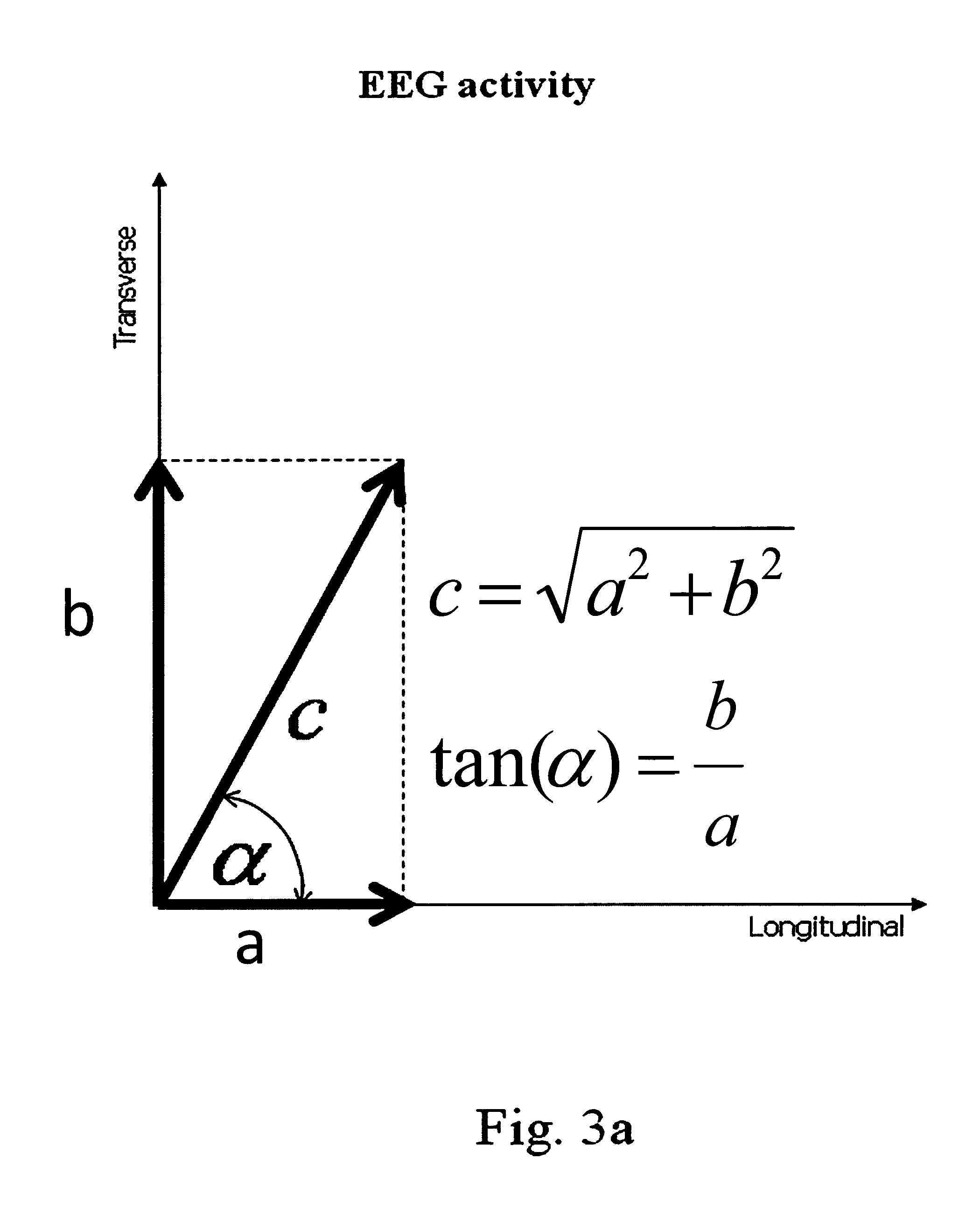Patents
Literature
373 results about "Low magnetic field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
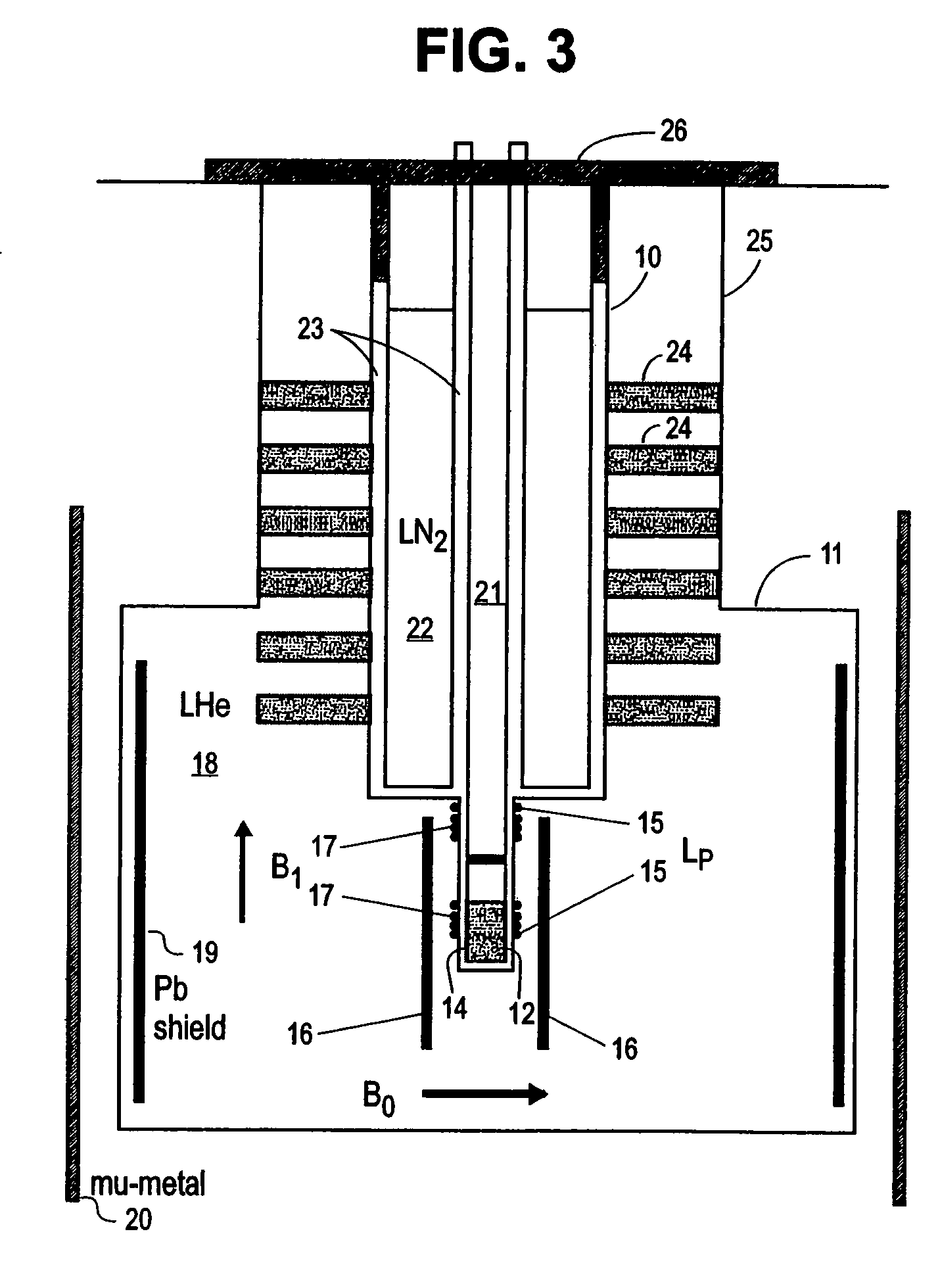
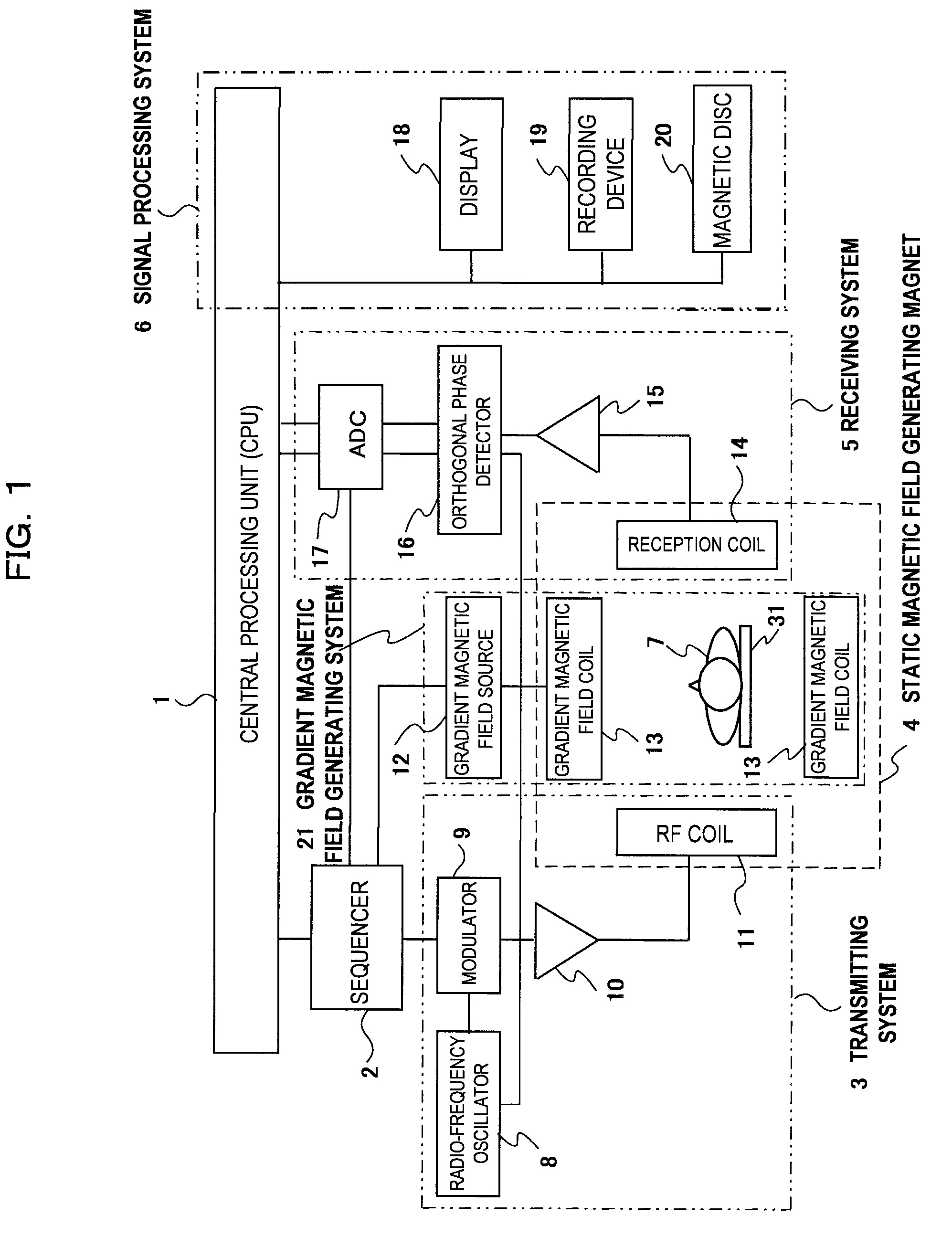
Apparatus and method for generating a magnetic field
InactiveUS20060114088A1Less trainingMinimizing x-raySurgical navigation systemsMagnetsTip positionDisplay device
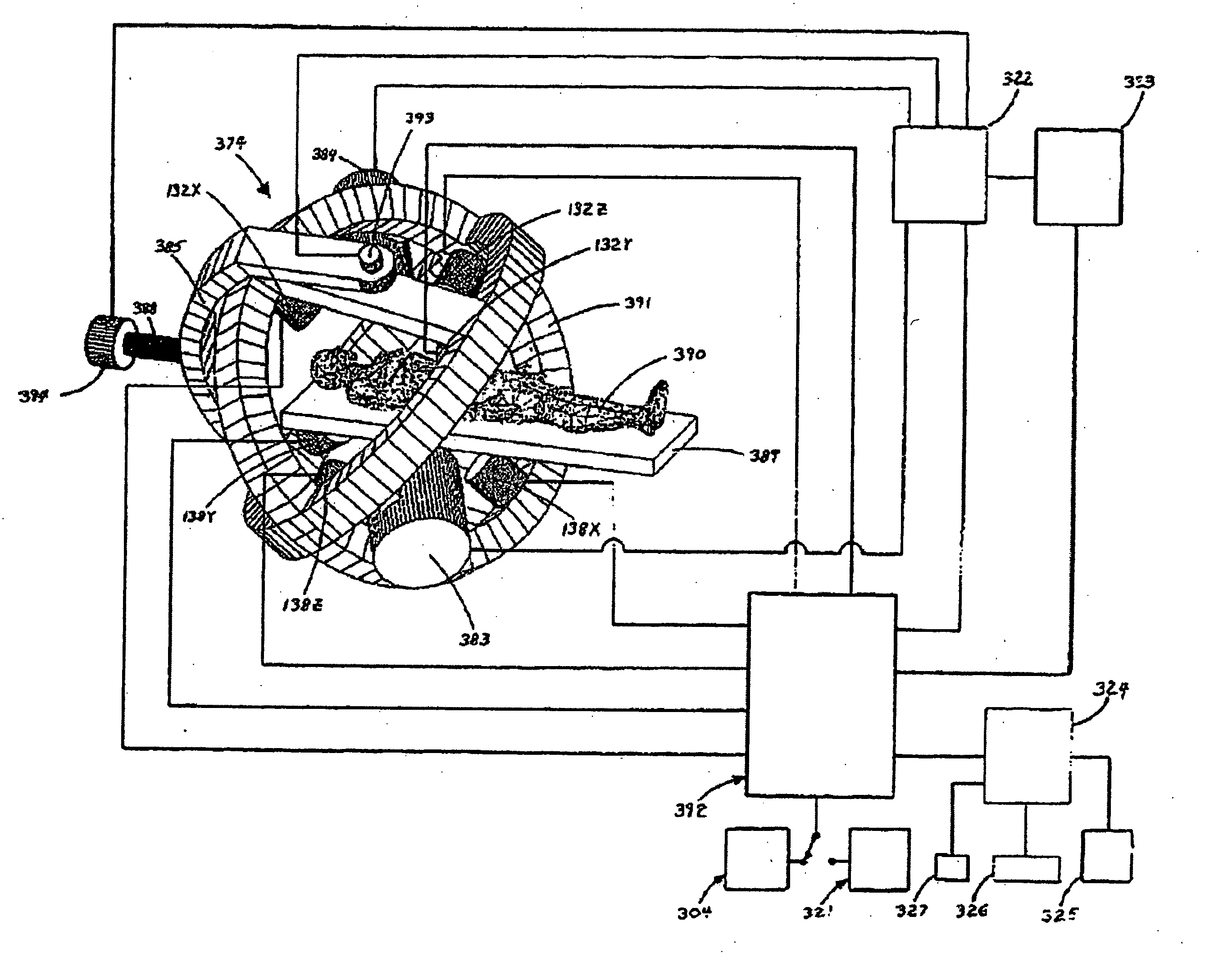
A system whereby a magnetic tip attached to a surgical tool is detected, displayed and influenced positionally so as to allow diagnostic and therapeutic procedures to be performed rapidly, accurately, simply, and intuitively is described. The tools that can be so equipped include catheters, guidewires, and secondary tools such as lasers and balloons, in addition biopsy needles, endoscopy probes, and similar devices. The magnetic tip allows the position and orientation of the tip to be determined without the use of x-rays by analyzing a magnetic field. The magnetic tip further allows the tool tip to be pulled, pushed, turned, and forcefully held in the desired position by applying an appropriate magnetic field external to the patient's body. A Virtual Tip serves as an operator control. Movement of the operator control produces corresponding movement of the magnetic tip inside the patient's body. Additionally, the control provides tactile feedback to the operator's hand in the appropriate axis or axes if the magnetic tip encounters an obstacle. The output of the control combined with the magnetic tip position and orientation feedback allows a servo system to control the external magnetic field by pulse width modulating the positioning electromagnet. Data concerning the dynamic position of a moving body part such as a beating heart offsets the servo systems response in such a way that the magnetic tip, and hence the secondary tool is caused to move in unison with the moving body part. The tip position and orientation information and the dynamic body part position information are also utilized to provide a display that allows three dimensional viewing of the magnetic tip position and orientation relative to the body part.
Owner:NEURO KINESIS CORP
Method and structure for controlling plasma uniformity
InactiveUS6110395AMinimal effectIncrease inertiaDecorative surface effectsVacuum evaporation coatingElectron temperatureHeat flux
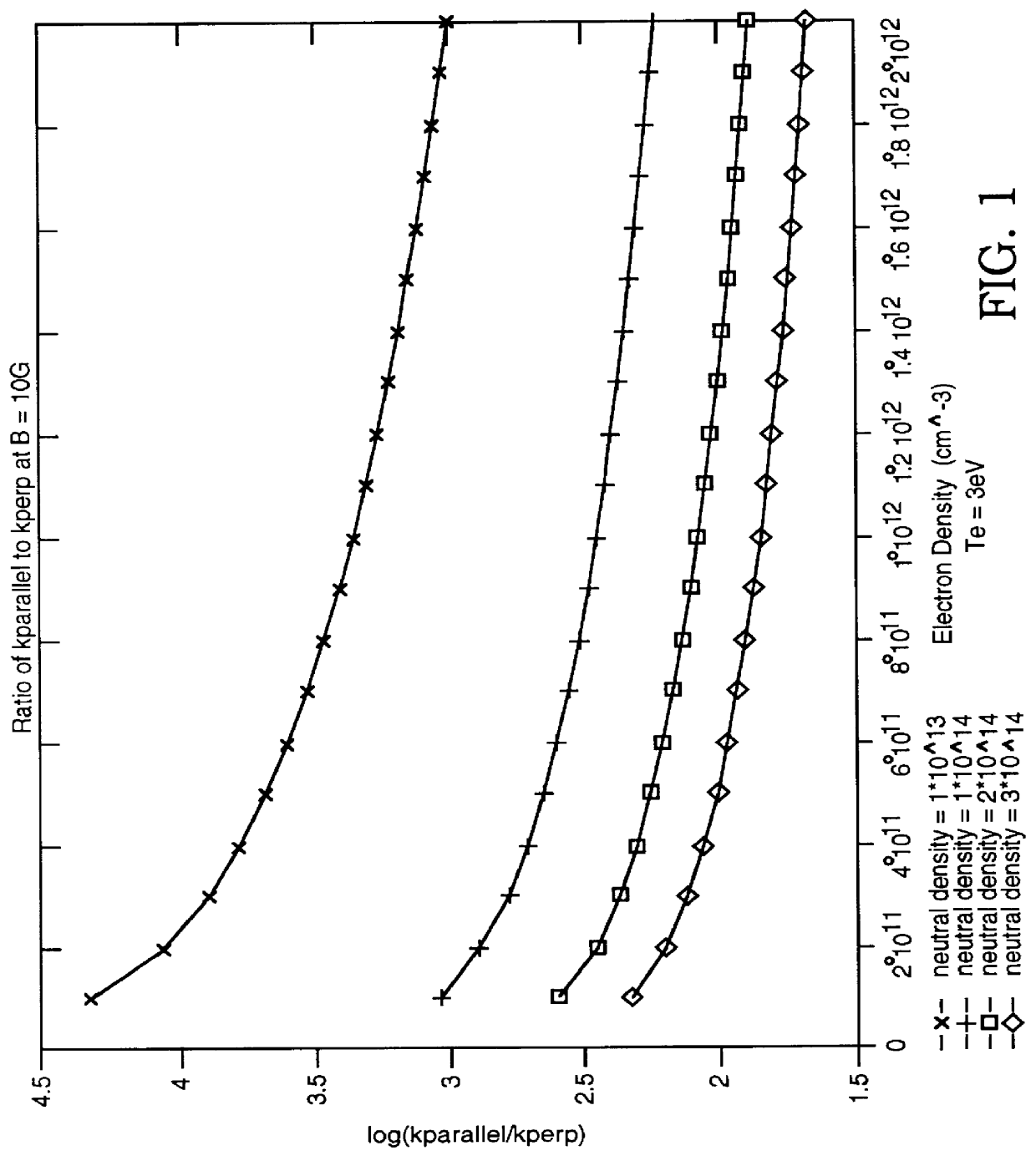
The present invention relates to a method and structure for controlling plasma uniformity in plasma processing applications. Electron thermal conductivity parallel and perpendicular to magnetic field lines differs by orders of magnitude for low magnetic fields (on the order of 10 gauss). This property allows the directing of heat flux by controlling the magnetic field configuration independent of ions since the effect of modest magnetic fields upon the transport of ions themselves is minimal. Heat is preferentially conducted along magnetic field lines with electron temperatures on the order of 0.1 to 1 eV / cm being sufficient to drive kilowatt-level heat fluxes across areas typical of plasma processing source dimensions.
Owner:SPTS TECH LTD
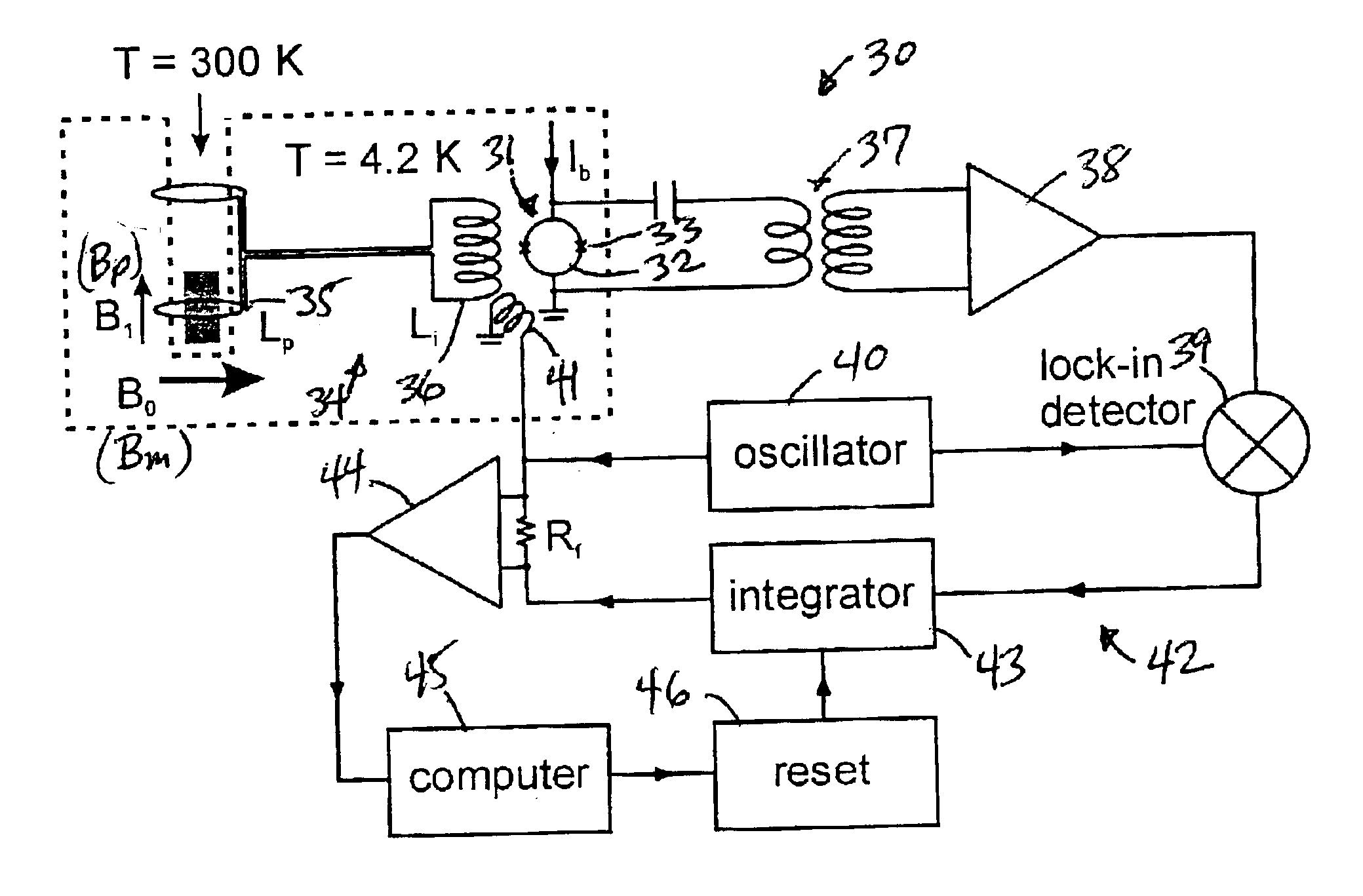
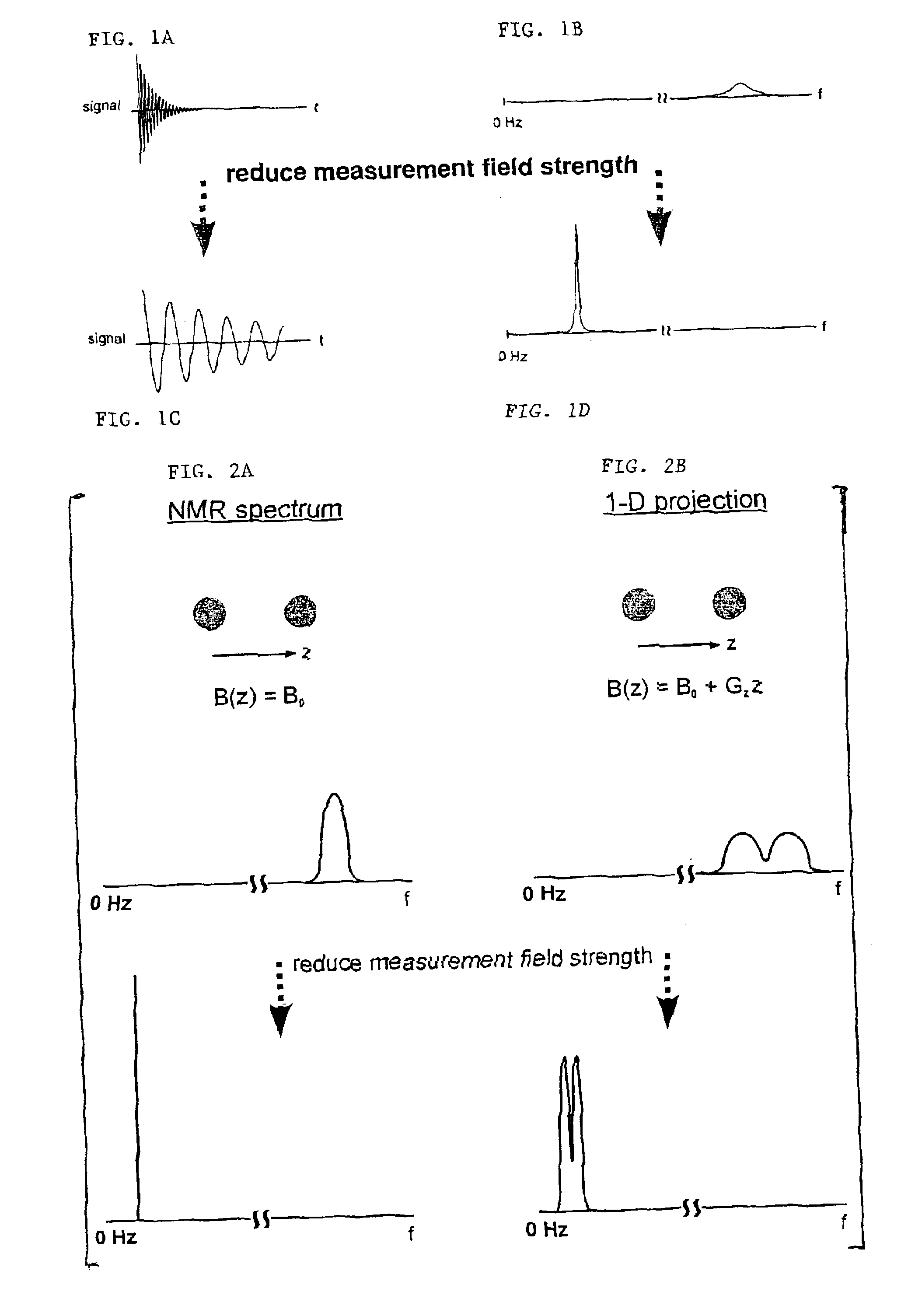
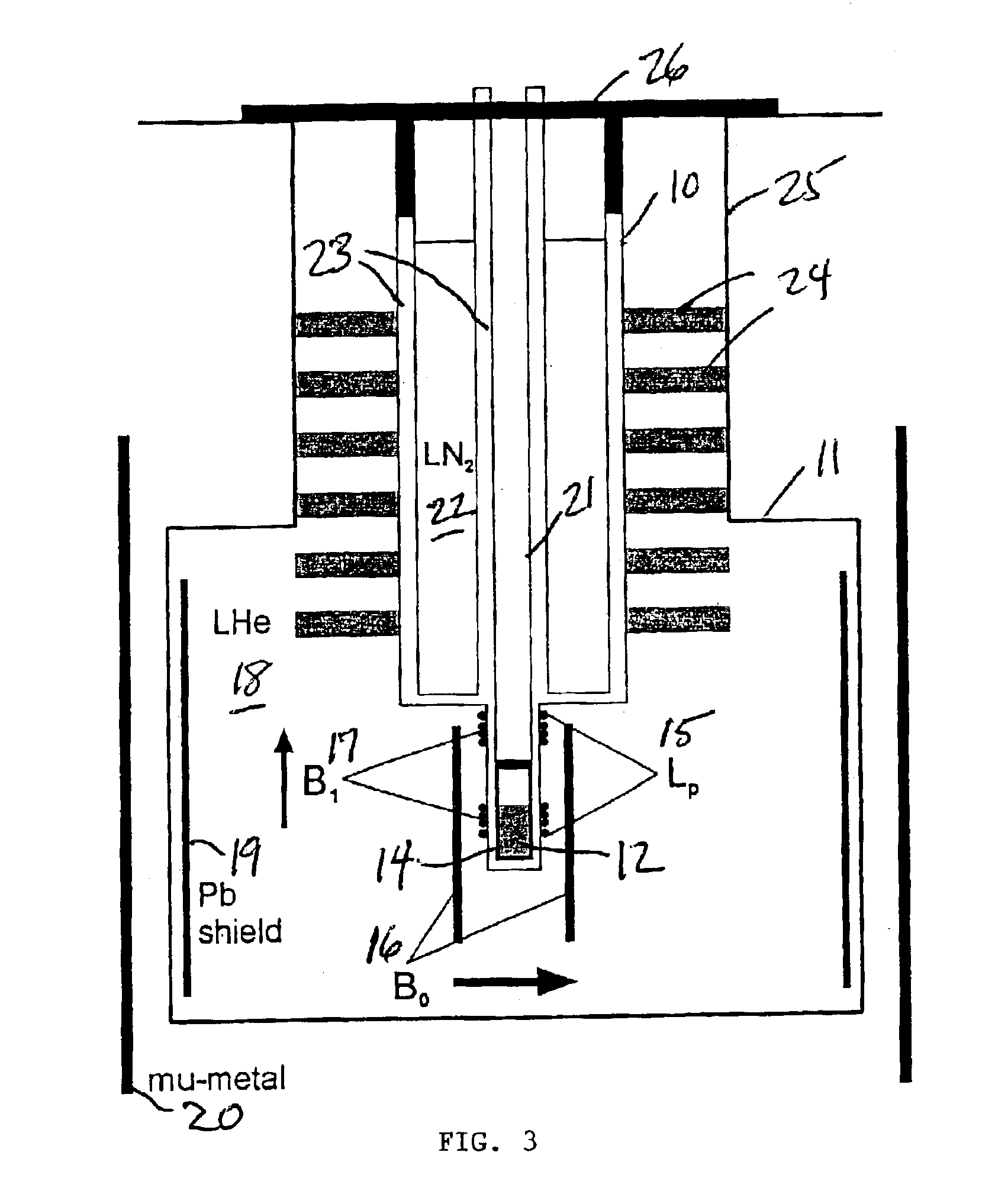
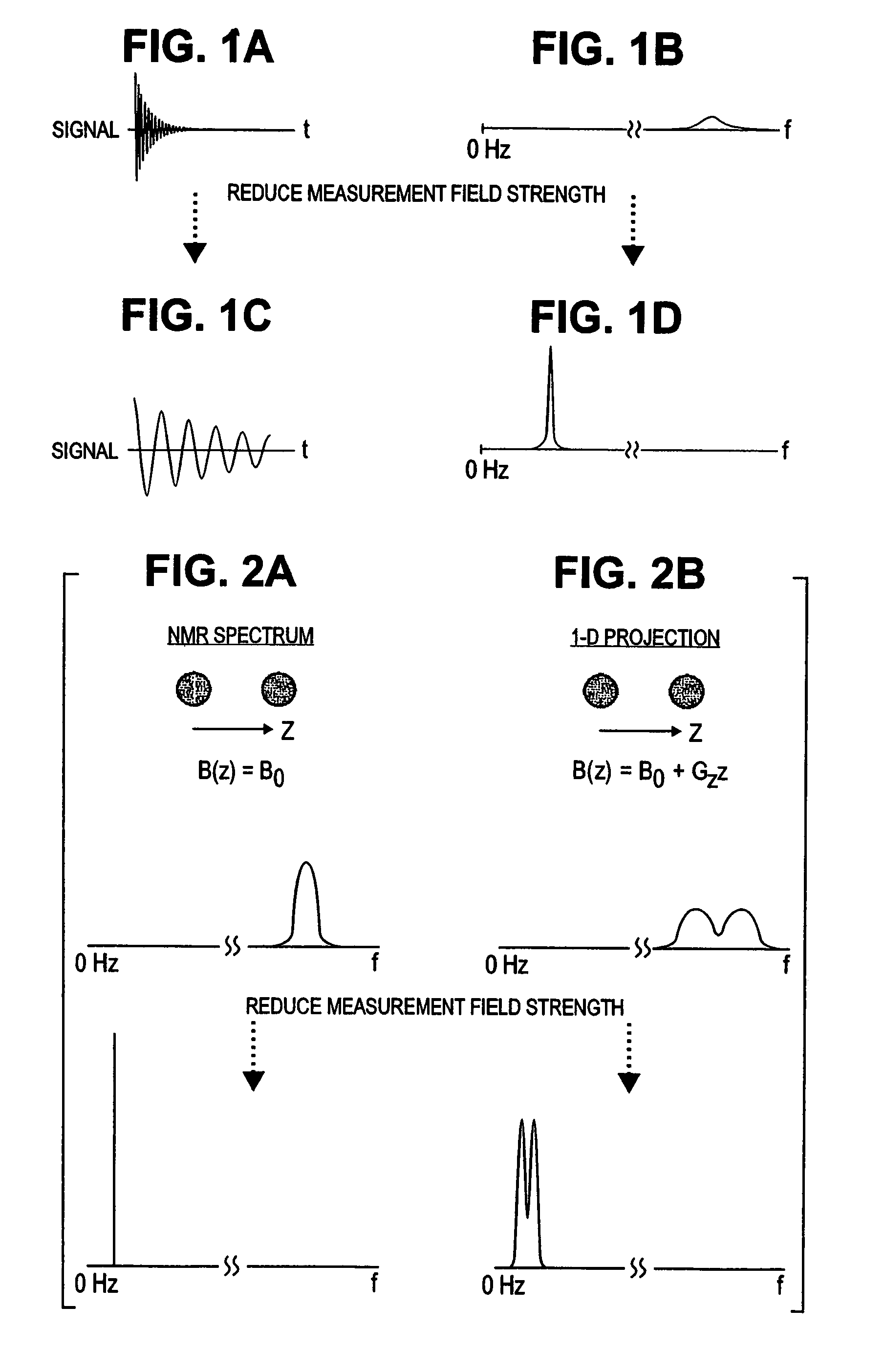
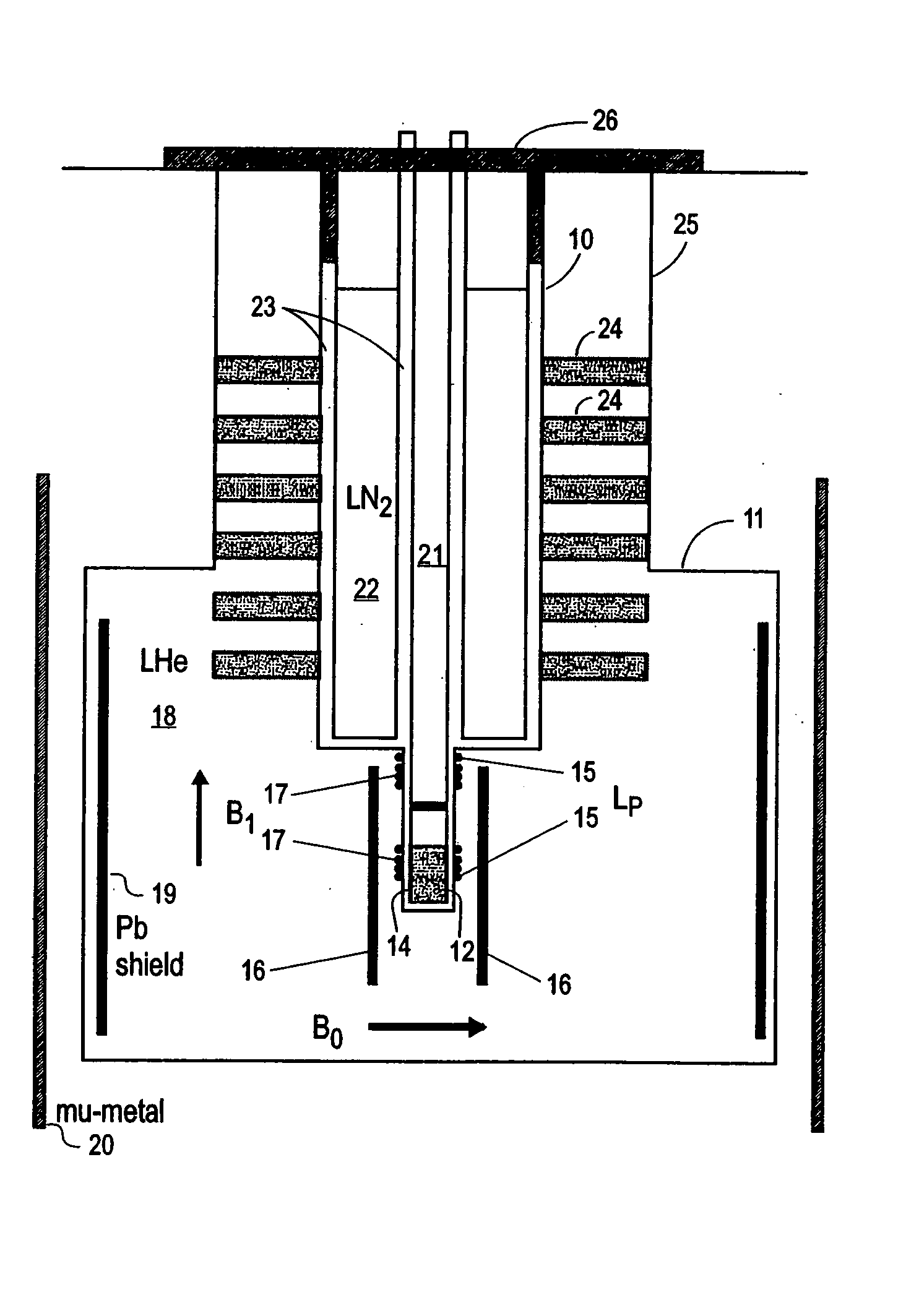
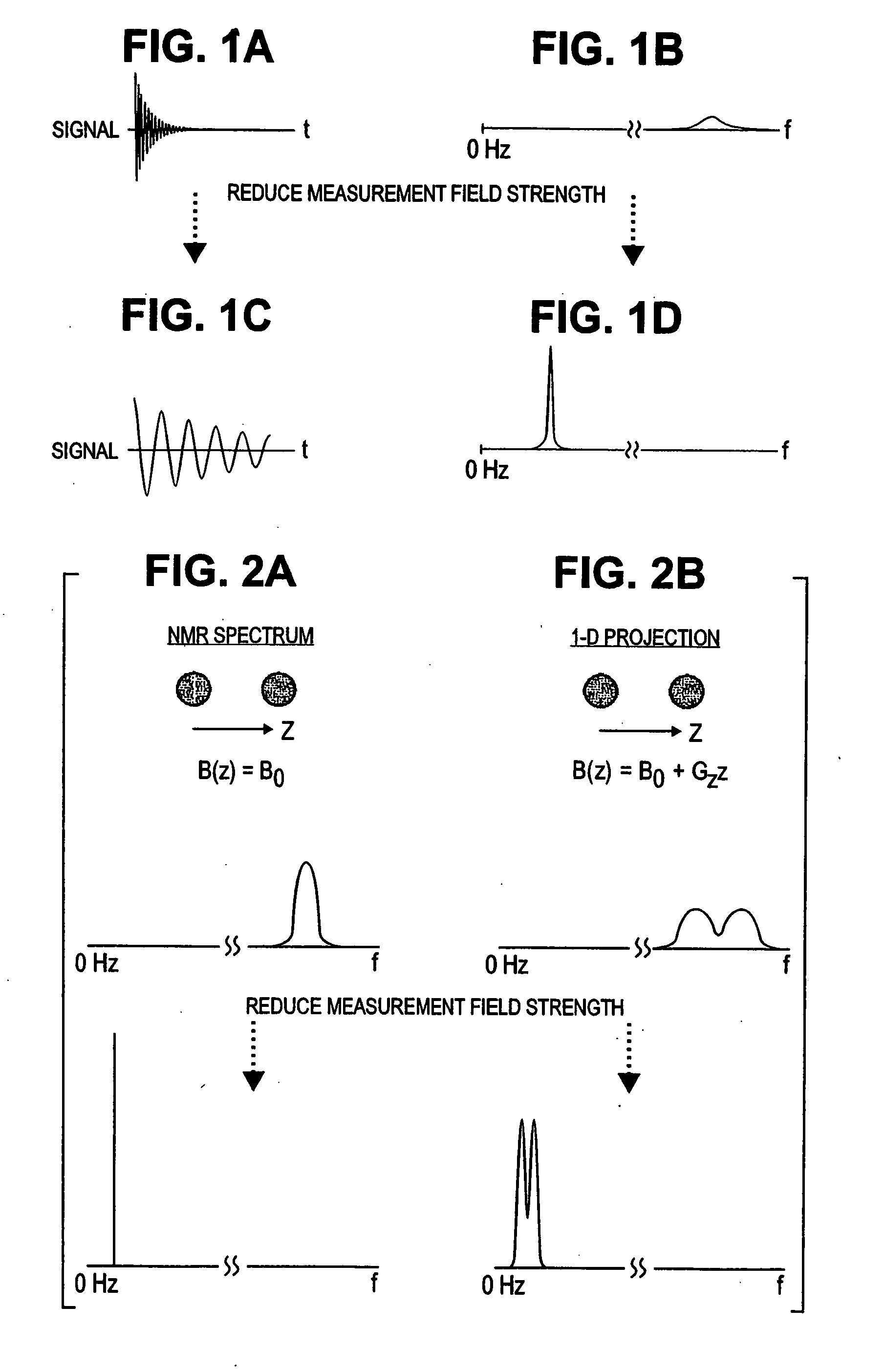
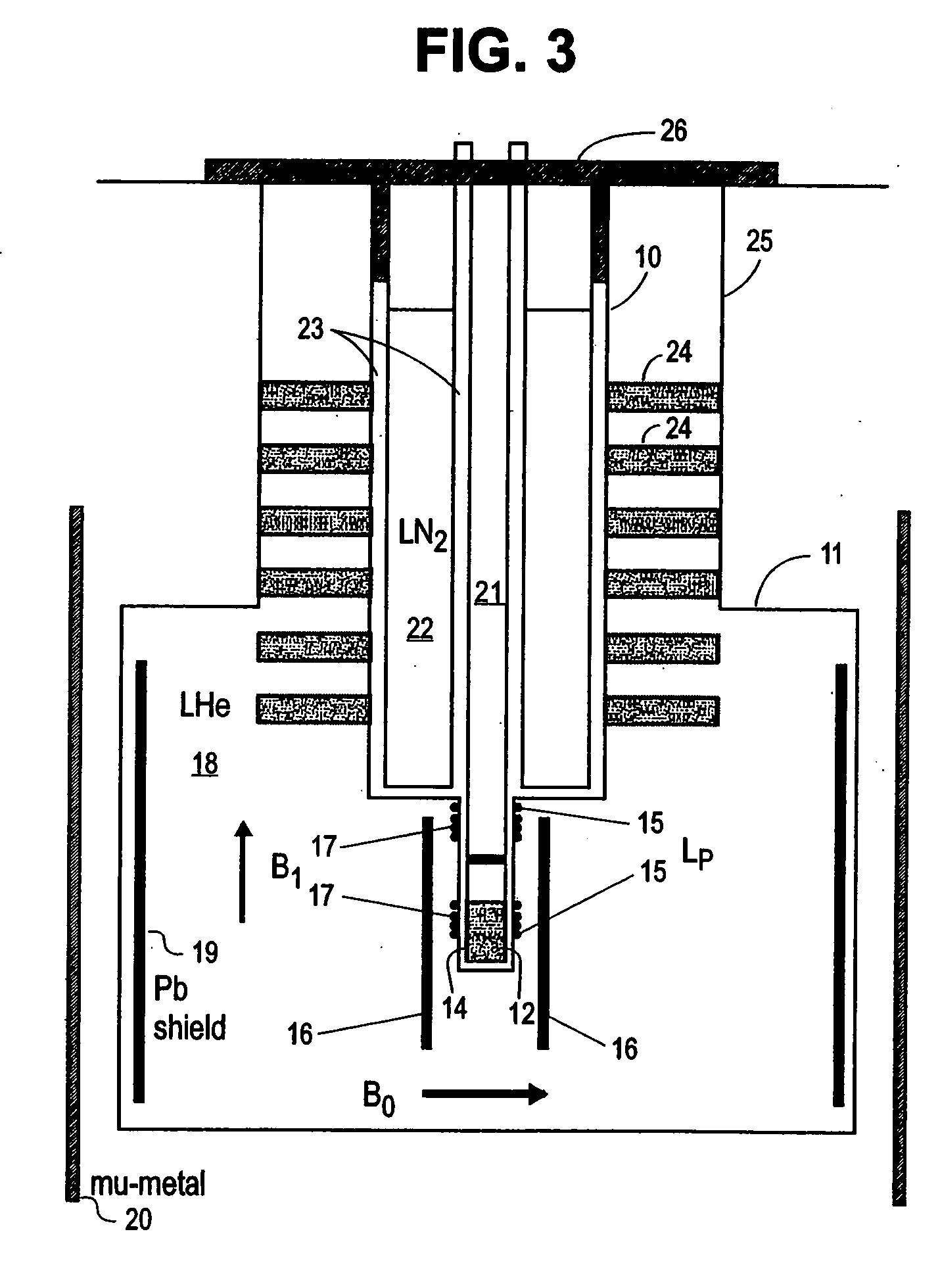
SQUID detected NMR and MRI at ultralow fields
InactiveUS6885192B2Accurate couplingReduce signal bandwidthUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceSignal-to-noise ratio
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signals are detected in microtesla fields. Prepolarization in millitesla fields is followed by detection with an untuned de superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer. Because the sensitivity of the SQUID is frequency independent, both signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and spectral resolution are enhanced by detecting the NMR signal in extremely low magnetic fields, where the NMR lines become very narrow even for grossly inhomogeneous measurement fields. MRI in ultralow magnetic field is based on the NMR at ultralow fields. Gradient magnetic fields are applied, and images are constructed from the detected NMR signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
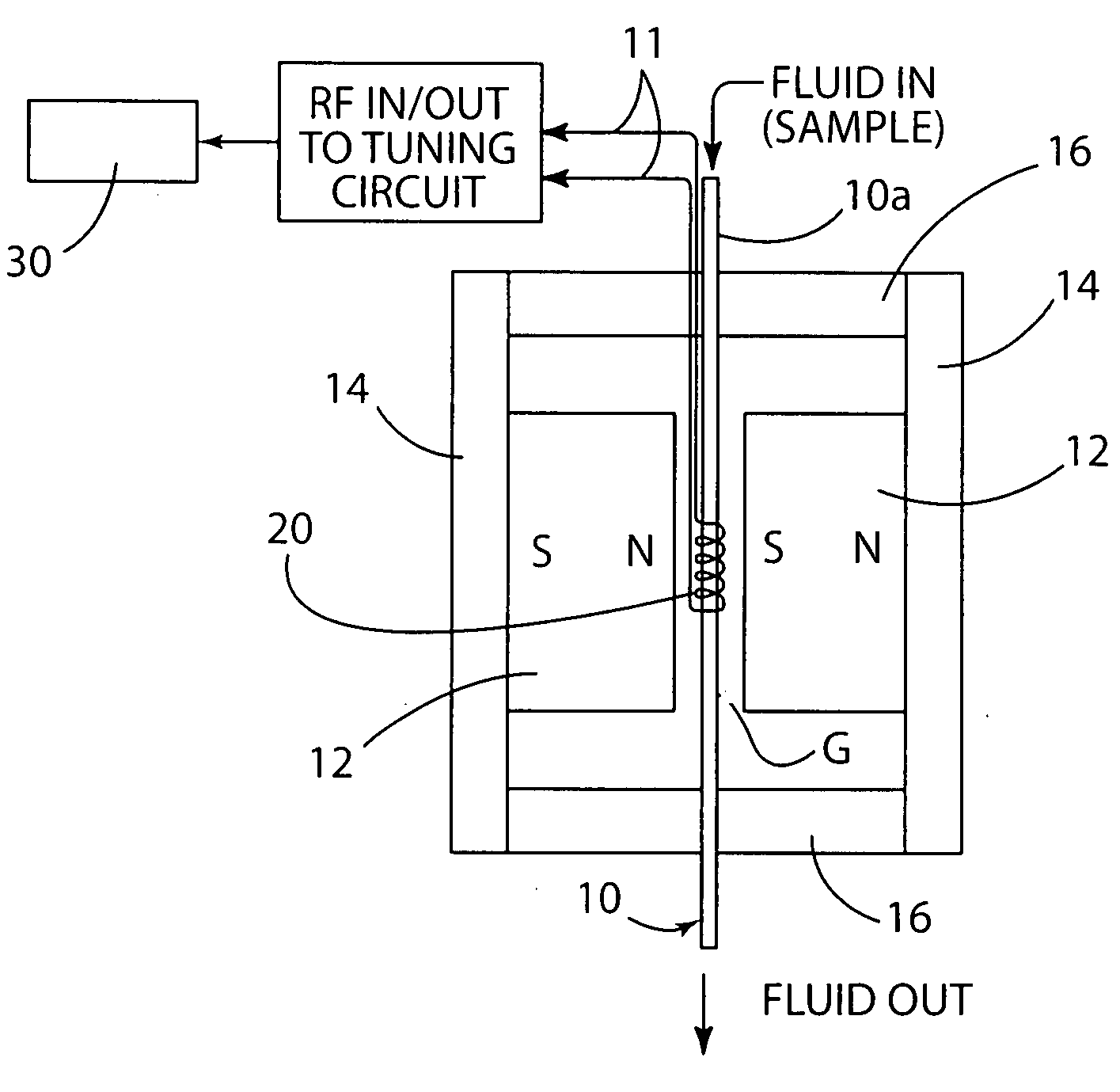
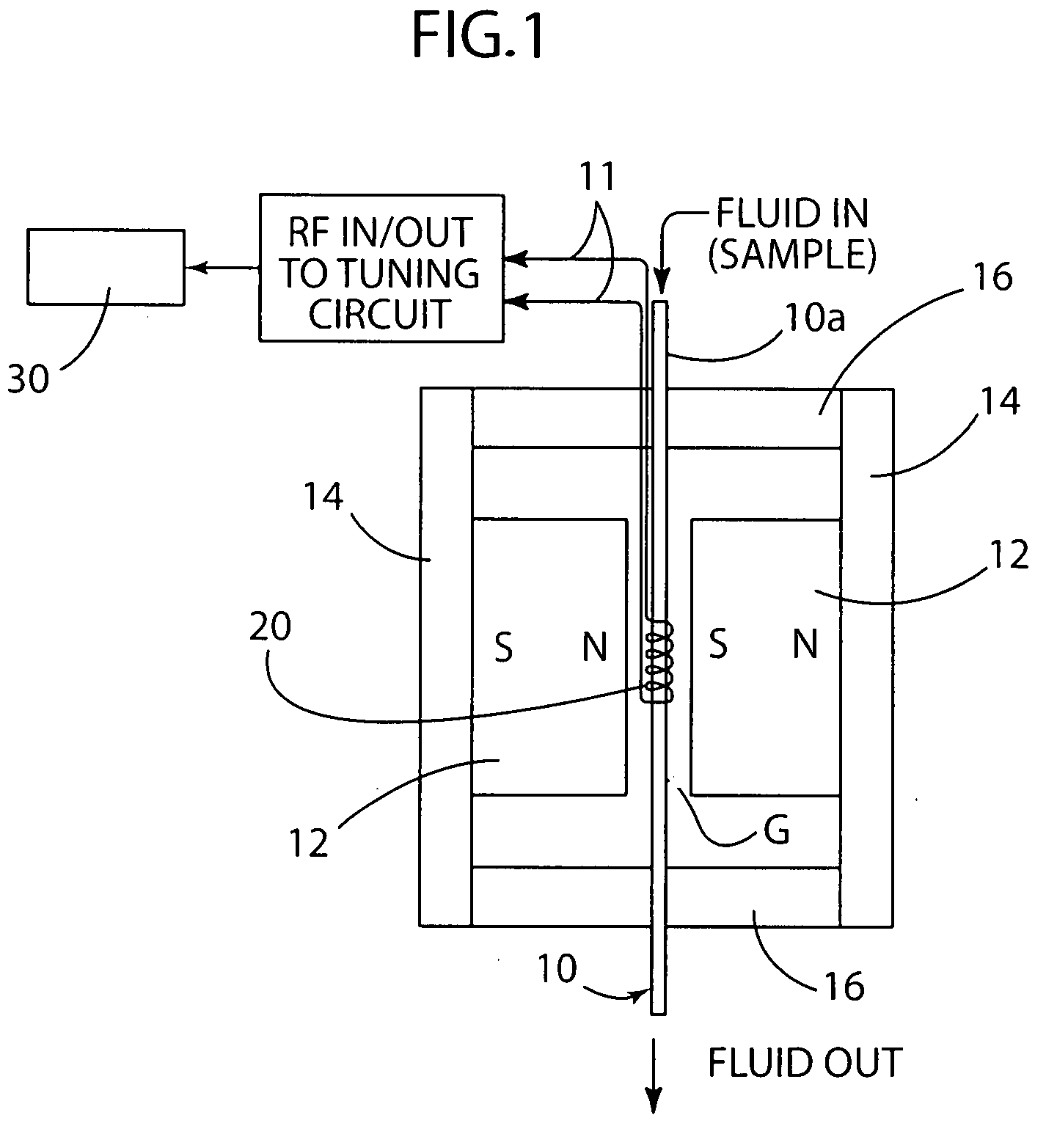
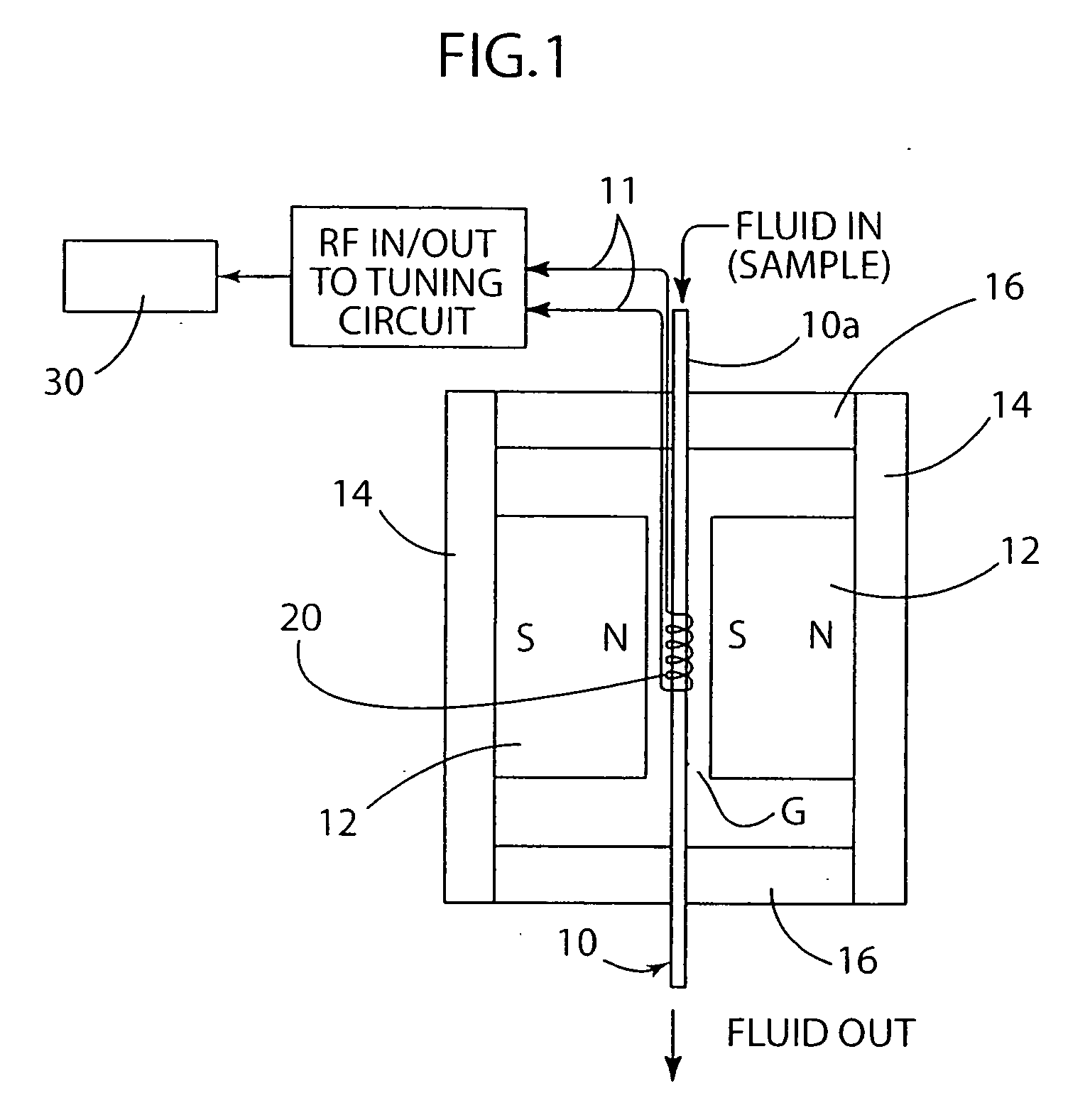
Biological detector and method
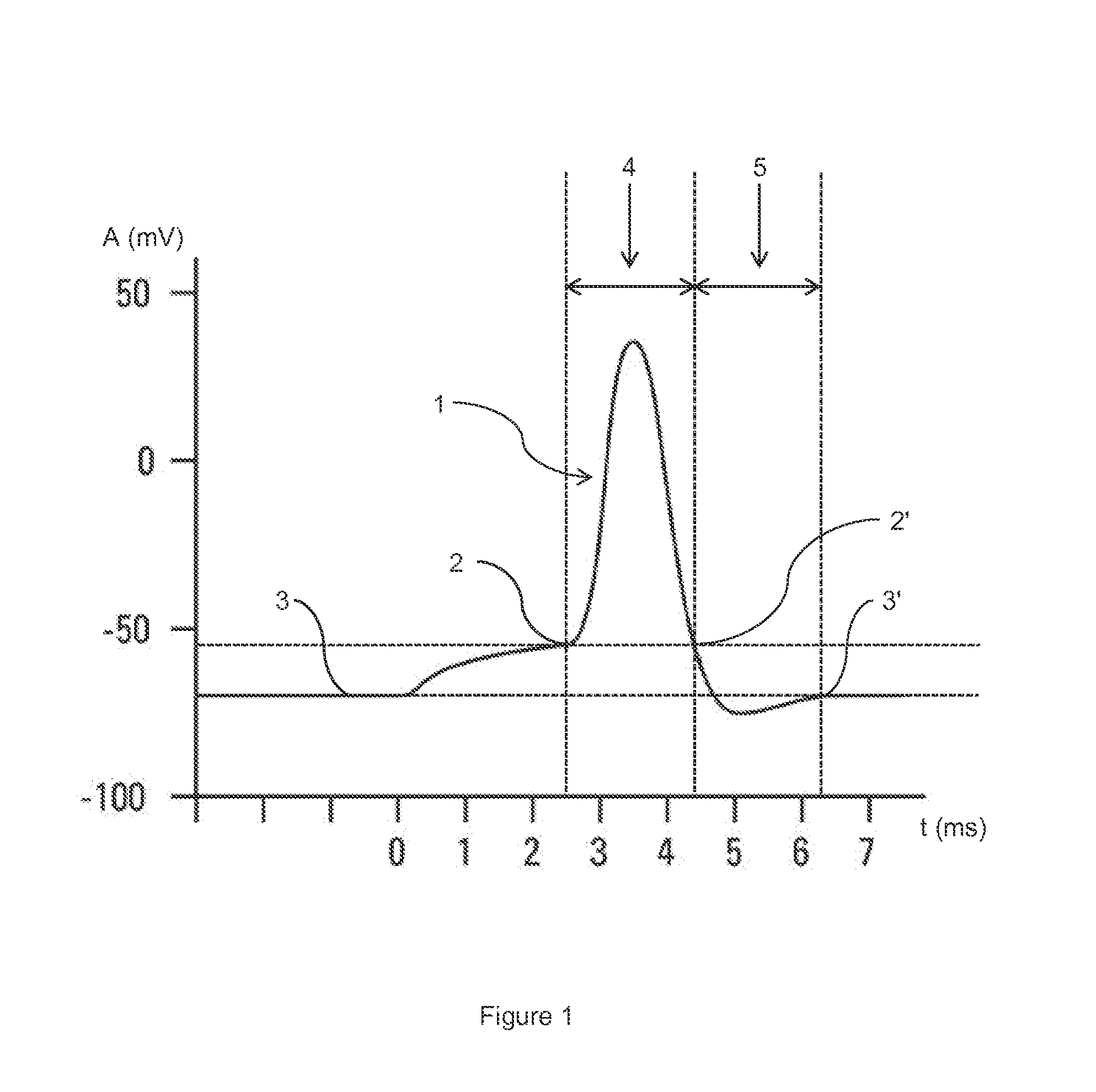
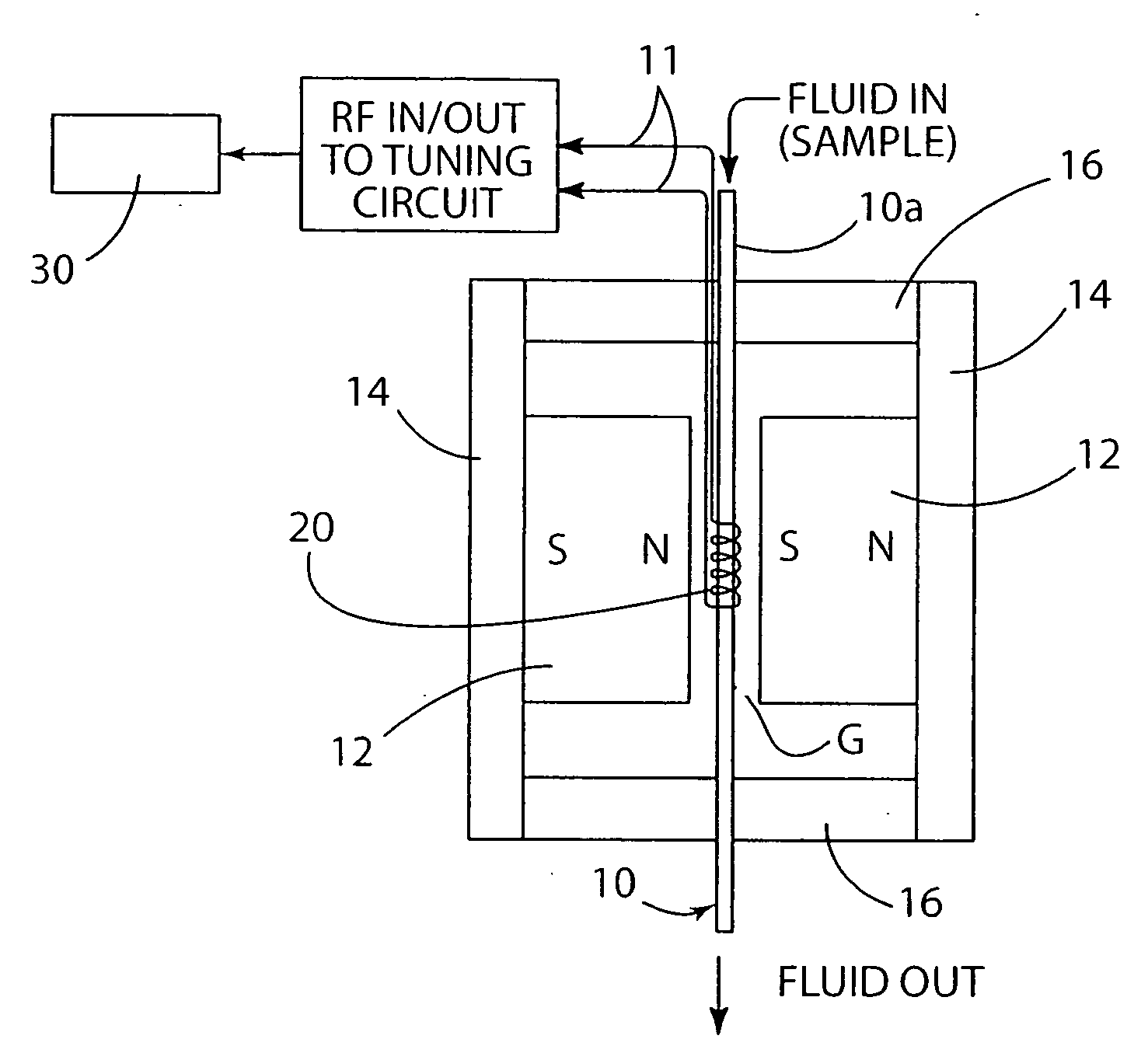
ActiveUS20080204022A1Low costCompact assemblyNanosensorsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceProximateSpectroscopy
A biological detector includes a conduit for receiving a fluid containing one or more magnetic nanoparticle-labeled, biological objects to be detected and one or more permanent magnets or electromagnet for establishing a low magnetic field in which the conduit is disposed. A microcoil is disposed proximate the conduit for energization at a frequency that permits detection by NMR spectroscopy of whether the one or more magnetically-labeled biological objects is / are present in the fluid.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC +2
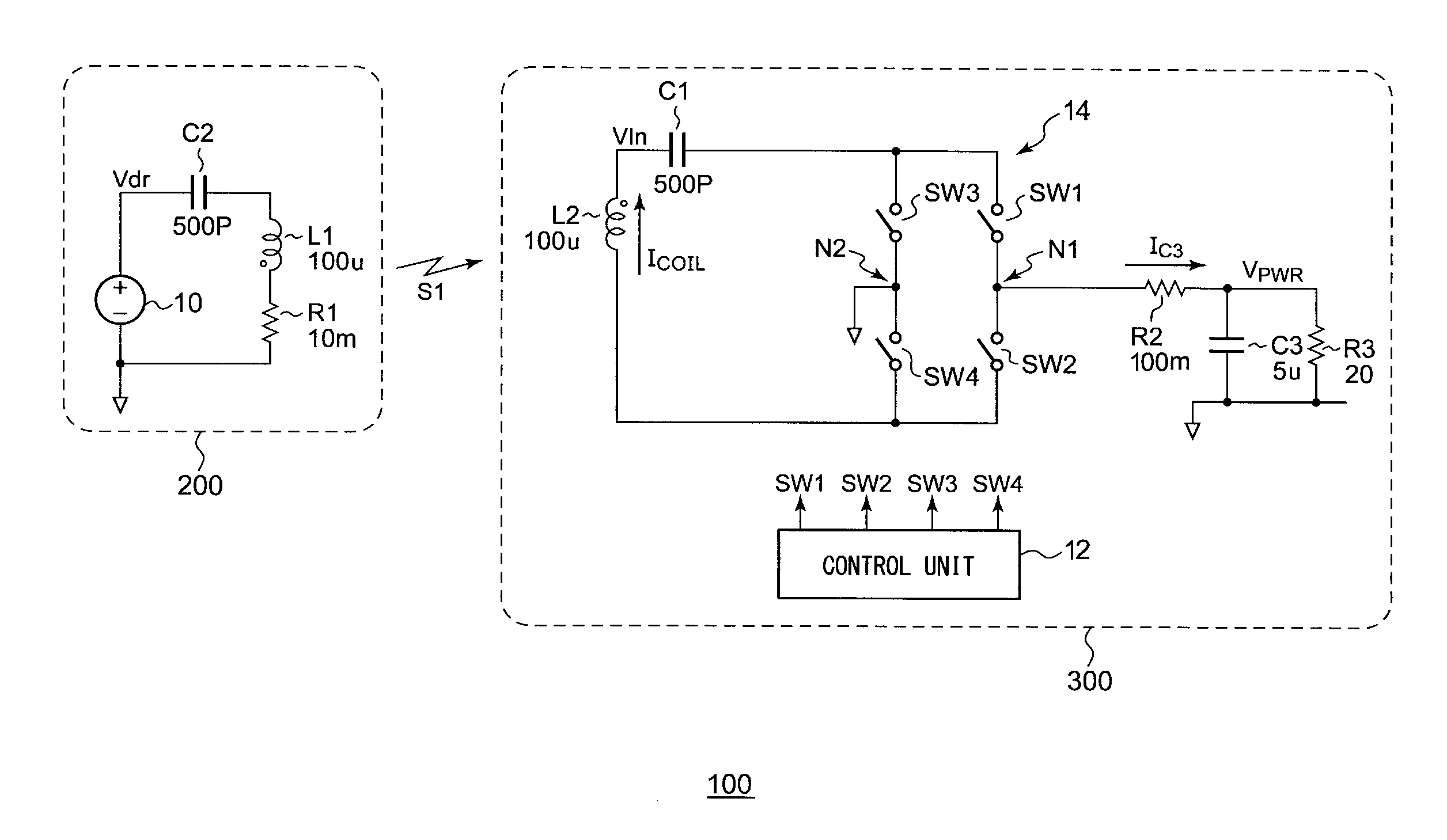
Wireless power supply apparatus
InactiveUS20120068548A1Increase the number ofReduce in quantityNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectromagnetic fieldElectric power
A wireless power supply apparatus transmits an electric power signal including any one of an electric field, a magnetic field, and an electromagnetic field. A bridge circuit includes multiple switches. A control unit performs switching control of the multiple switches of the bridge circuit at a first frequency configured as a transmission frequency. A transmission coil and a resonance capacitor form a resonance antenna, which is connected to the bridge circuit. The resonance frequency of the resonance antenna thus formed is a second frequency that is equal to or higher than the first frequency. A control unit is configured to be capable of adjusting the length of the dead time during which the multiple switches are all turned off at the same time.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
NMR and MRI apparatus and method
InactiveUS7187169B2Avoid interferenceRaise the ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionLow noiseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer
InactiveCN106443520APromote formationSimple structureMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesNon magneticQuenching
The invention discloses a biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer. The biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer comprises an alkali metal gas chamber, non-magnetic electric heating equipment, a three-dimensional magnetic coil, a magnetic shielding layer, a pumping laser module and a detecting laser module. The alkali metal gas chamber is filled with alkali metal atoms, a quenching gas and a buffering gas; the non-magnetic electric heating equipment and the magnetic shielding layer enable the alkali metal atoms to work in a high-temperature and low-magnetic field environment, and ensure the alkali metal atoms in a non-spinning exchange relaxation state; the pumping laser module is used for polarizing the alkali metal atoms; the detecting laser module comprises two beams of independent detecting laser which are perpendicular to each other, and are used for sensing the magnetic field intensity in two directions which are perpendicular to each other simultaneously; measurement results are demodulated through a phase-locked amplifier. The biaxial atomic spinning magnetometer can acquire biaxial magnetic field information simultaneously through one alkali metal gas chamber, has the characteristics of high sensitivity, high integration degree and low cost, and has a wide application prospect in the fields of brain magnetic measurement, magnetocardiographic measurement and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
NMR and MRI apparatus and method
InactiveUS20060091881A1Avoid interferenceRaise the ratioMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionLow noiseNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signals are detected in microtesla fields. Prepolarization in millitesla fields is followed by detection with an untuned dc superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID) magnetometer. Because the sensitivity of the SQUID is frequency independent, both signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and spectral resolution are enhanced by detecting the NMR signal in extremely low magnetic fields, where the NMR lines become very narrow even for grossly inhomogeneous measurement fields. Additional signal to noise benefits are obtained by use of a low noise polarization coil, comprising litz wire or superconducting materials. MRI in ultralow magnetic field is based on the NMR at ultralow fields. Gradient magnetic fields are applied, and images are constructed from the detected NMR signals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High power time varying magnetic field therapy
InactiveUS20170001024A1High repetition rateIncrease muscle strengthElectrotherapyMagnetotherapy using coils/electromagnetsBiological structureLow magnetic field
In a method for stimulation and treatment, a biological structure is stimulated by a high power time-varying magnetic field. The stimulation is followed by at least a partial muscle contraction. The methods can be used e.g. in physiotherapy, urology or urogynecology.
Owner:BTL MEDICAL SOLUTIONS AS
Biological detector and method
InactiveUS20080315875A1Low costReduced cost and maintenance and space requirementMagnetic property measurementsNanosensorsMagnetite NanoparticlesSpectroscopy
Owner:SILLERUD LAUREL O
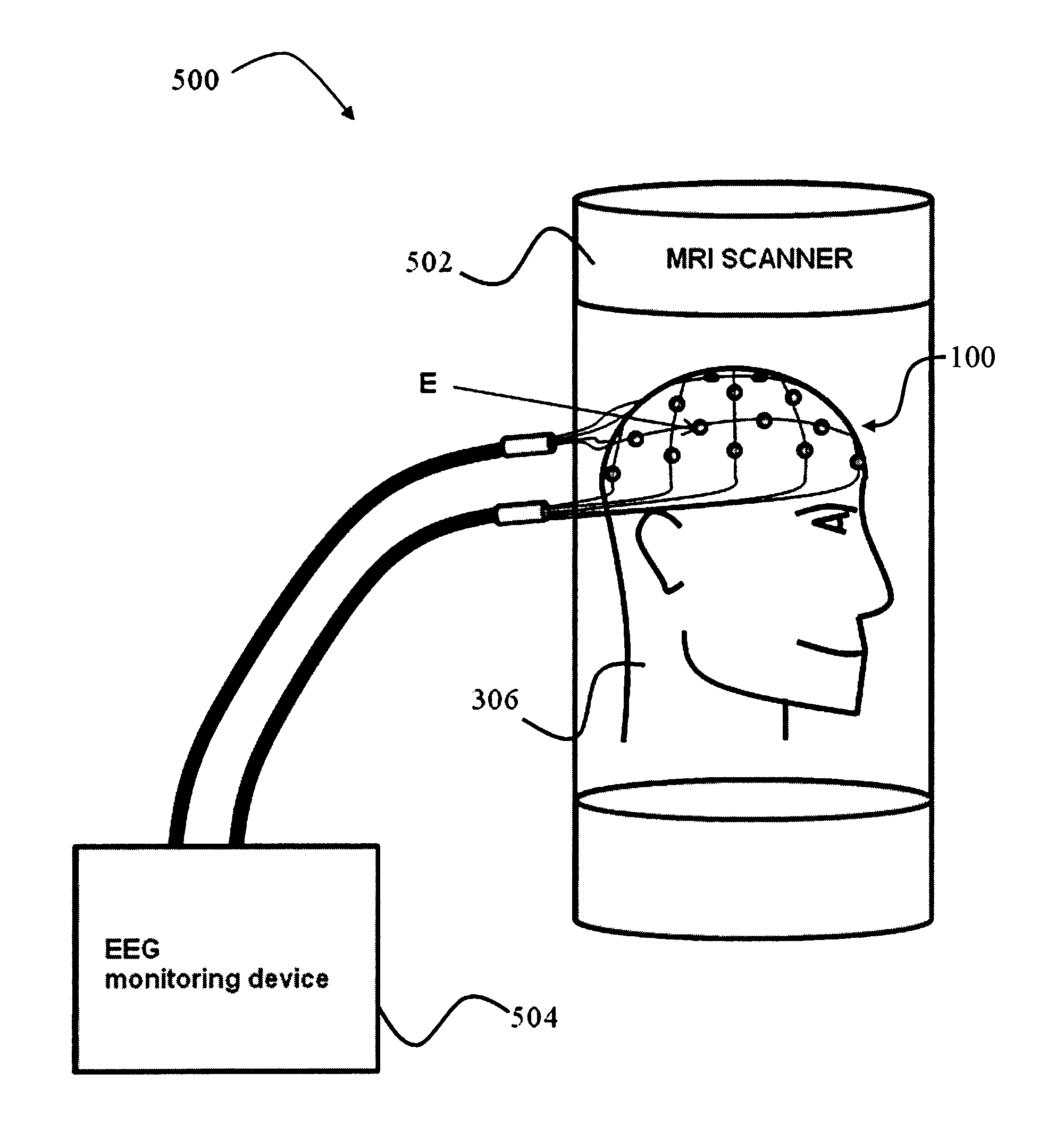
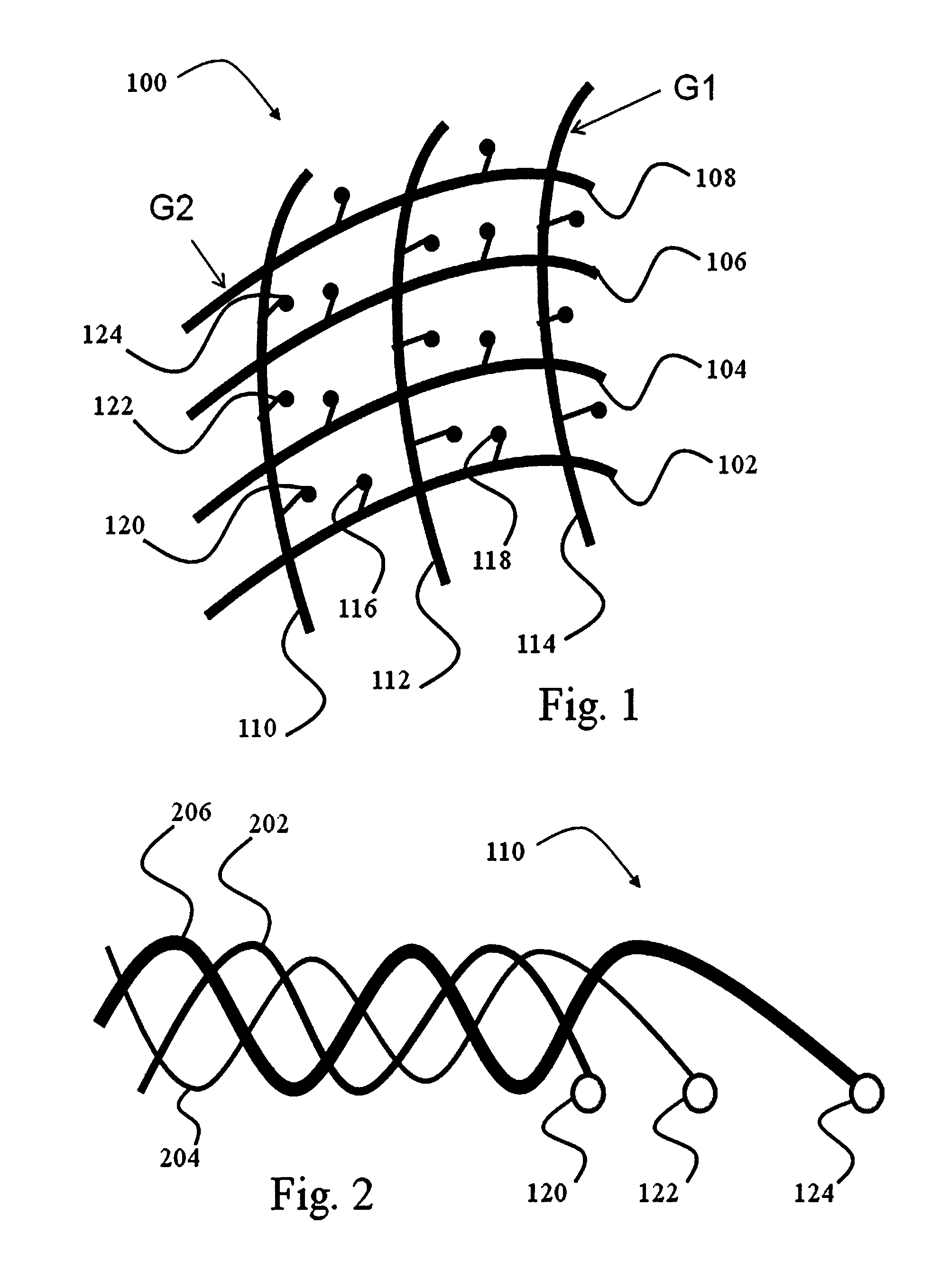
Device for use in electro-biological signal measurement in the presence of a magnetic field
ActiveUS20130204122A1Electrical size reductionReduce Motion ArtifactsElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using suctionEeg dataMeasurement device
A measurement device is presented for use in an EEG measurement performed in the presence of a magnetic field. The device comprises a wiring array for connecting an electrodes arrangement to an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring device. The wiring array comprises a plurality of sampling lines arranged to form a first group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a first axis, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said first group comprising a plurality of first wires for connecting to a corresponding first plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes arrangement; and a second group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a second axis, intersecting with said first axis, such that said second group of bundles crosses said first group of bundles to form a net structure, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said second group comprising a plurality of second wires for connecting to a corresponding second plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes' arrangement. The wiring array is configured and operable for transmitting a signal measured by the respective electrodes to the EEG monitoring device, enabling generation of EEG data indicative of the neural signal profile along tow directions and characterized by reduced motion artifact and / or reduced gradient artifact associated with the presence of the magnetic field during the EEG measurement.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
Rubidium atomic magnetometer and magnetic field measuring method thereof
ActiveCN107015172ALarge measuring rangeMagnetic field sampling rate adjustableMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesData acquisitionWork flow
The invention discloses a rubidium atomic magnetometer and a magnetic field measuring method. Based on the principle of nonlinear magneto-optic rotation, and through combination of timing control and tracking type frequency locking control, the atomic magnetometer achieves a large dynamic measurement range, high magnetic field sampling rate and high sensitivity. A DSP timing control module controls on-off of an acousto-optic modulator and a radio-frequency signal source in the physical part of the rubidium atomic magnetometer according to timing combination to adjust the magnetic field sampling rate N. The DSP timing control module further controls acquisition triggering of a data acquisition card. A calculation unit gets the Larmor precession frequency (f) through fast Fourier transform with use of a received rubidium atom Larmor precession free relaxation signal, and further calculates the value of an external magnetic field. The calculation unit selects a high magnetic field sampling rate module or a low magnetic field sampling rate module before measurement according to the pre-judged dynamic range of a to-be-measured magnetic field, and sets whether a tracking type frequency locking work mode is used when the low magnetic field sampling rate module is selected. In the working process, data is acquired and processed, and the value of the magnetic field is output.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Spin-injection device and magnetic device using spin-injection device
InactiveUS20060022220A1Large output resistanceLarge signal voltageNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsElectrical conductorCharge-carrier density
A first and a second tunnel junctions (2 and 3) which have a common electrode composed of a nonmagnetic conductor (4) and each of which has a counterelectrode composed of a ferromagnet (6, 8) are disposed spaced apart from each other by a distance that is shorter than a spin diffusion length of the nonmagnetic conductor (4) wherein the first tunnel junction (2) acts to inject spins from the ferromagnet (6) into the nonmagnetic conductor (4) and the second tunnel junction (3) serves to detect, between the ferromagnetic metal (8) and the nonmagnetic conductor (4), a voltage that accompanies spin injection of the first tunnel junction (2) and wherein the nonmagnetic conductor (4) is a nonmagnetic conductor, such as a semiconductor or a semimetal, that is lower in carrier density than a metal. The common electrode alternatively may be composed of a superconductor (4′). A spin injection device thus provided can exhibit a large signal voltage with low current and under low magnetic field and can be miniaturized in device size. Magnetic apparatuses utilizing such a spin injection device are also provided.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
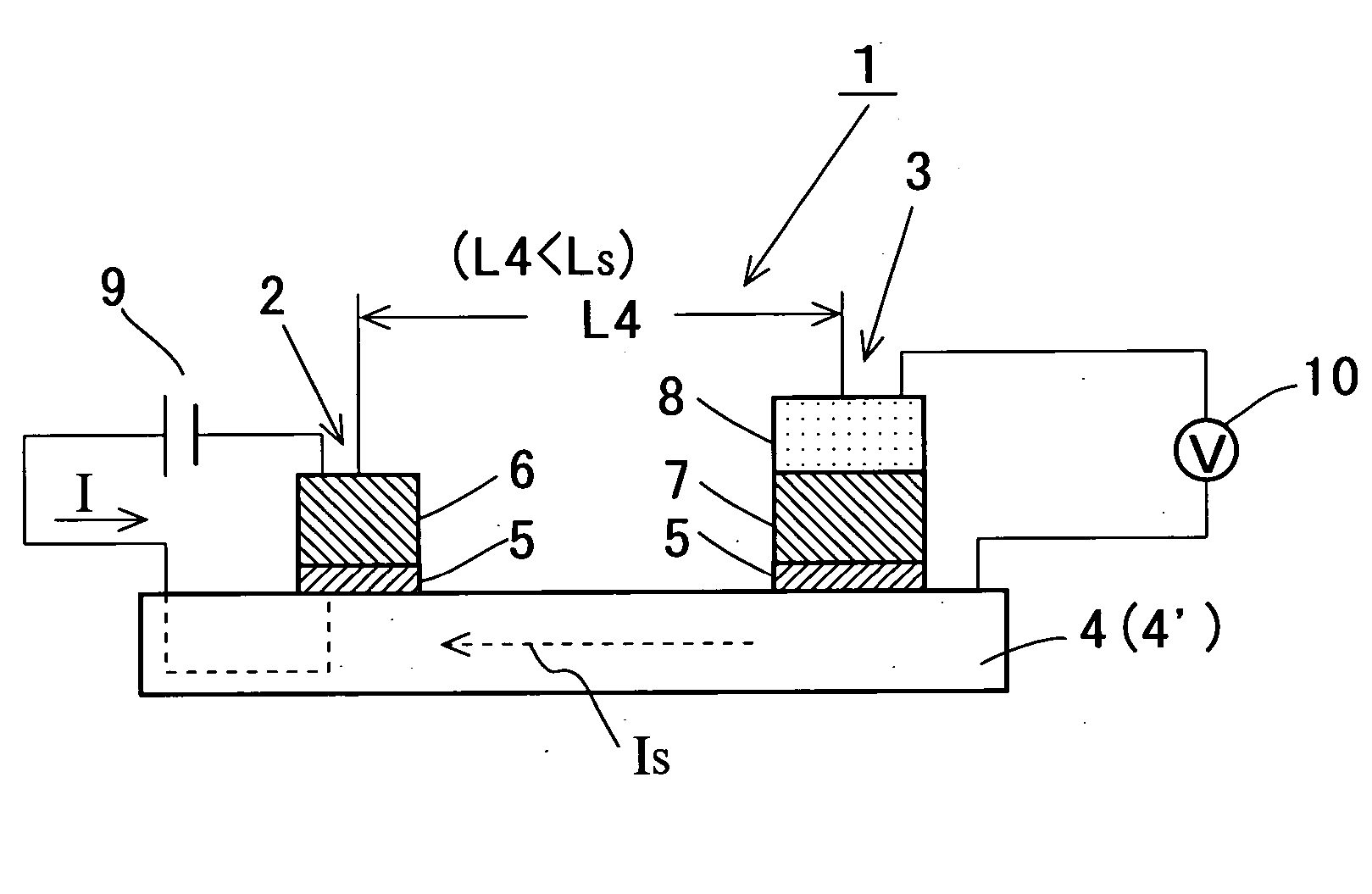
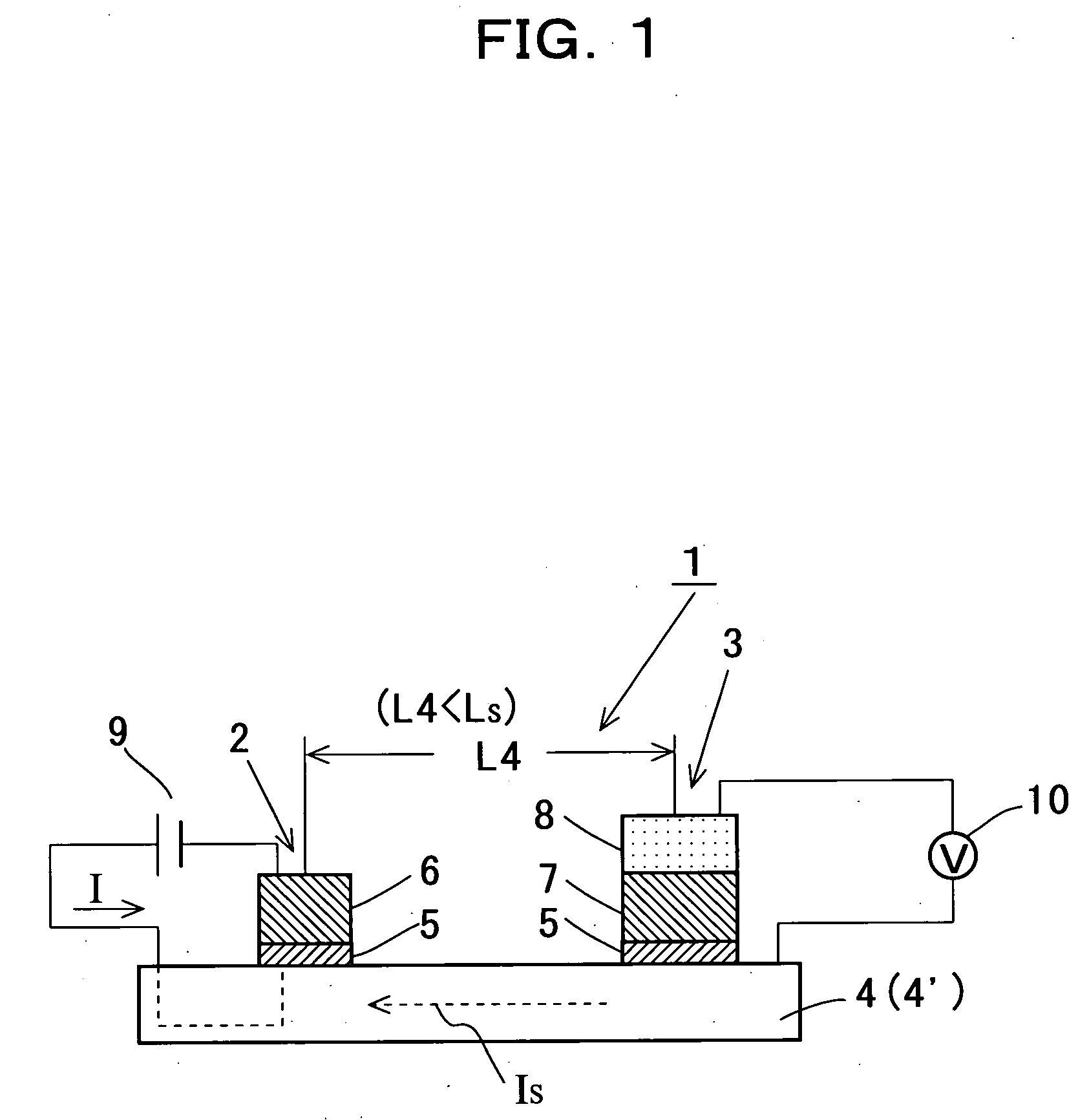
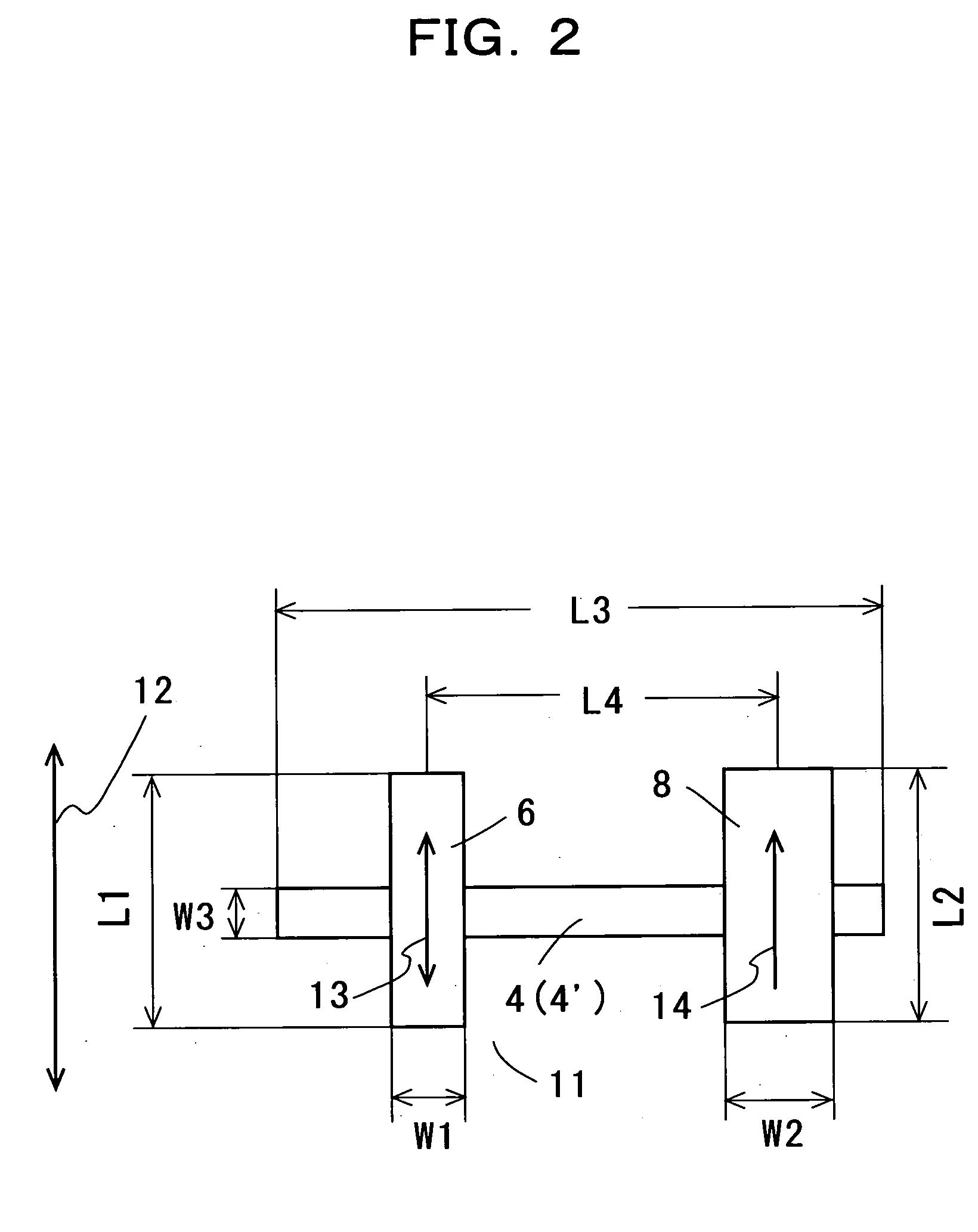
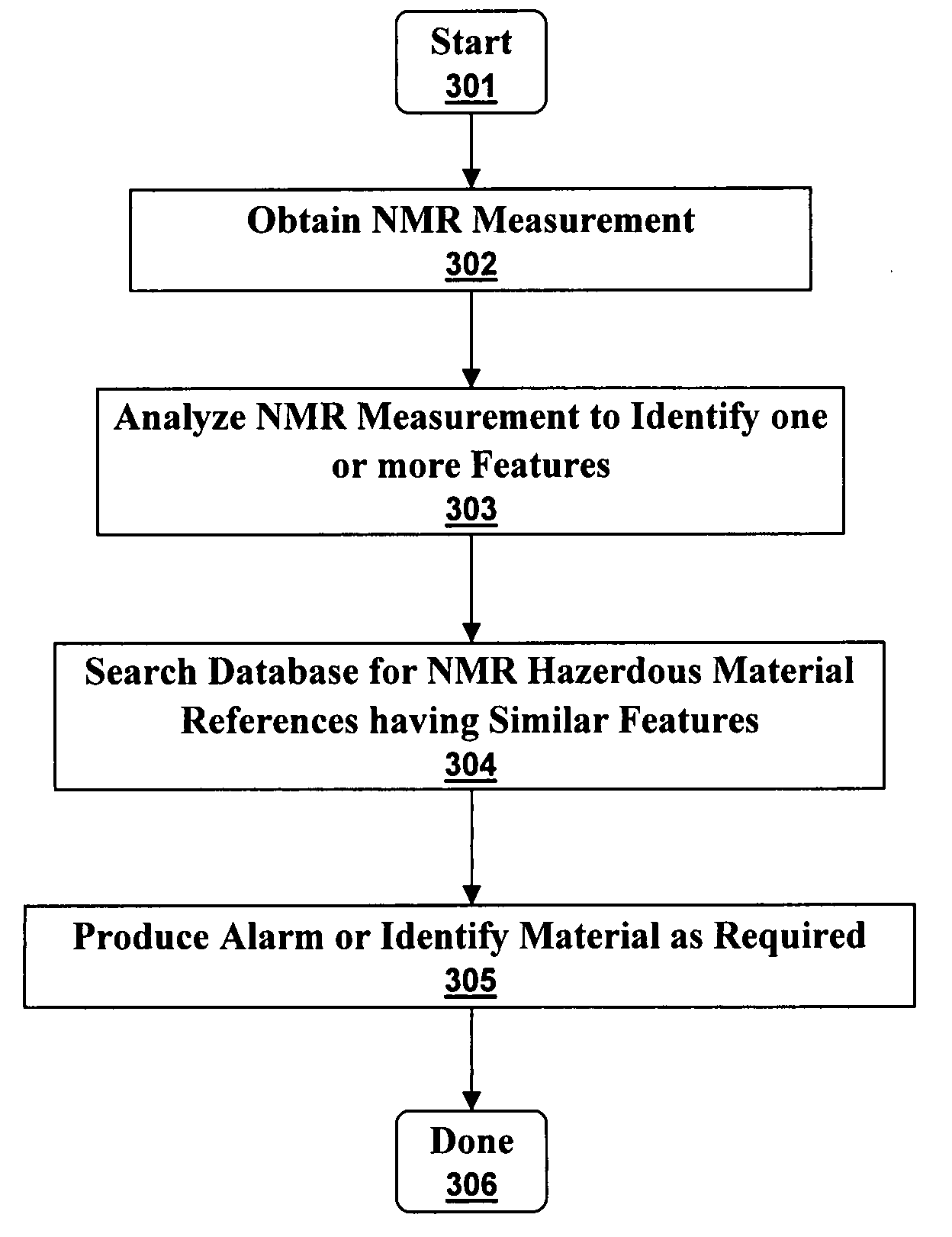
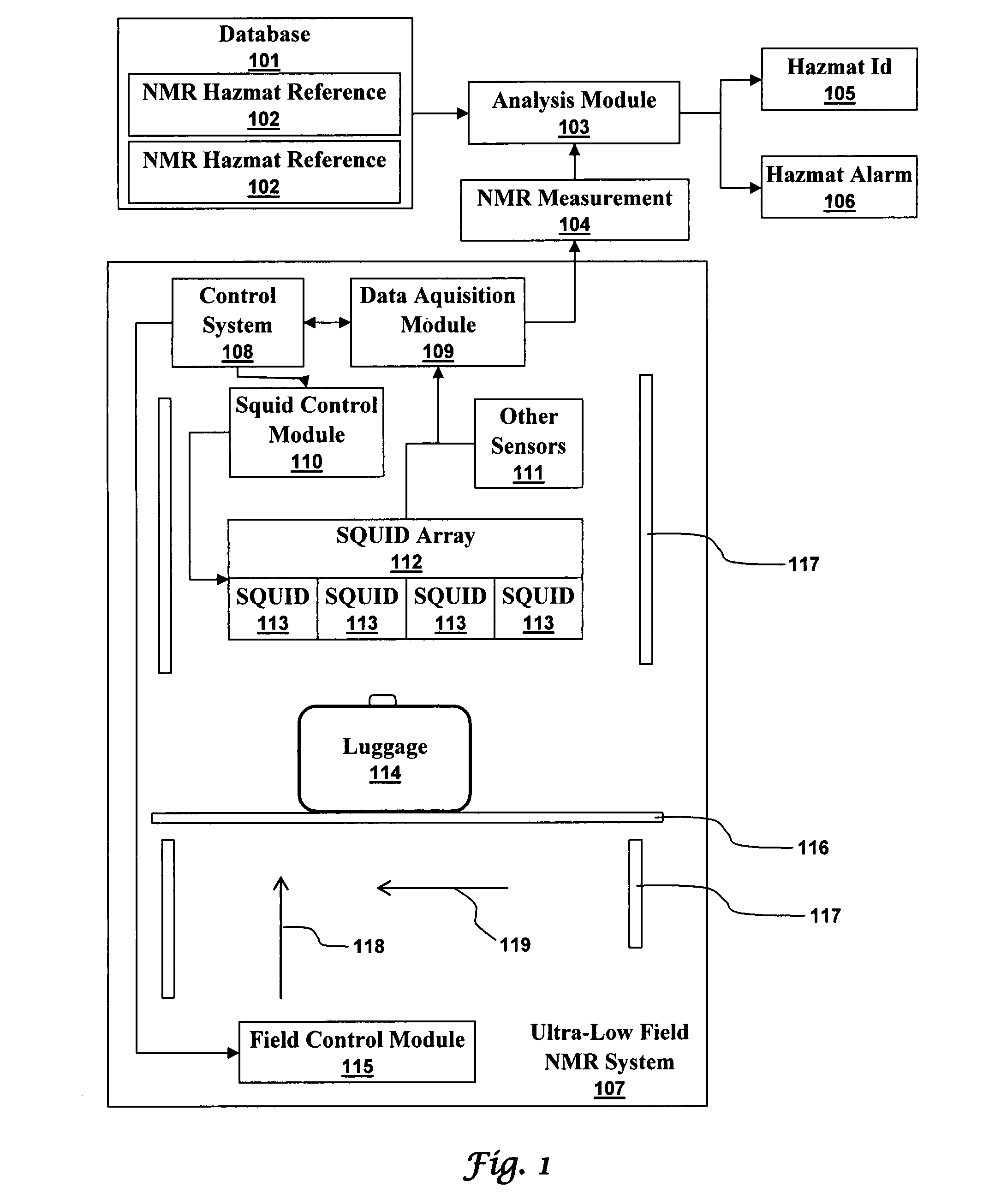
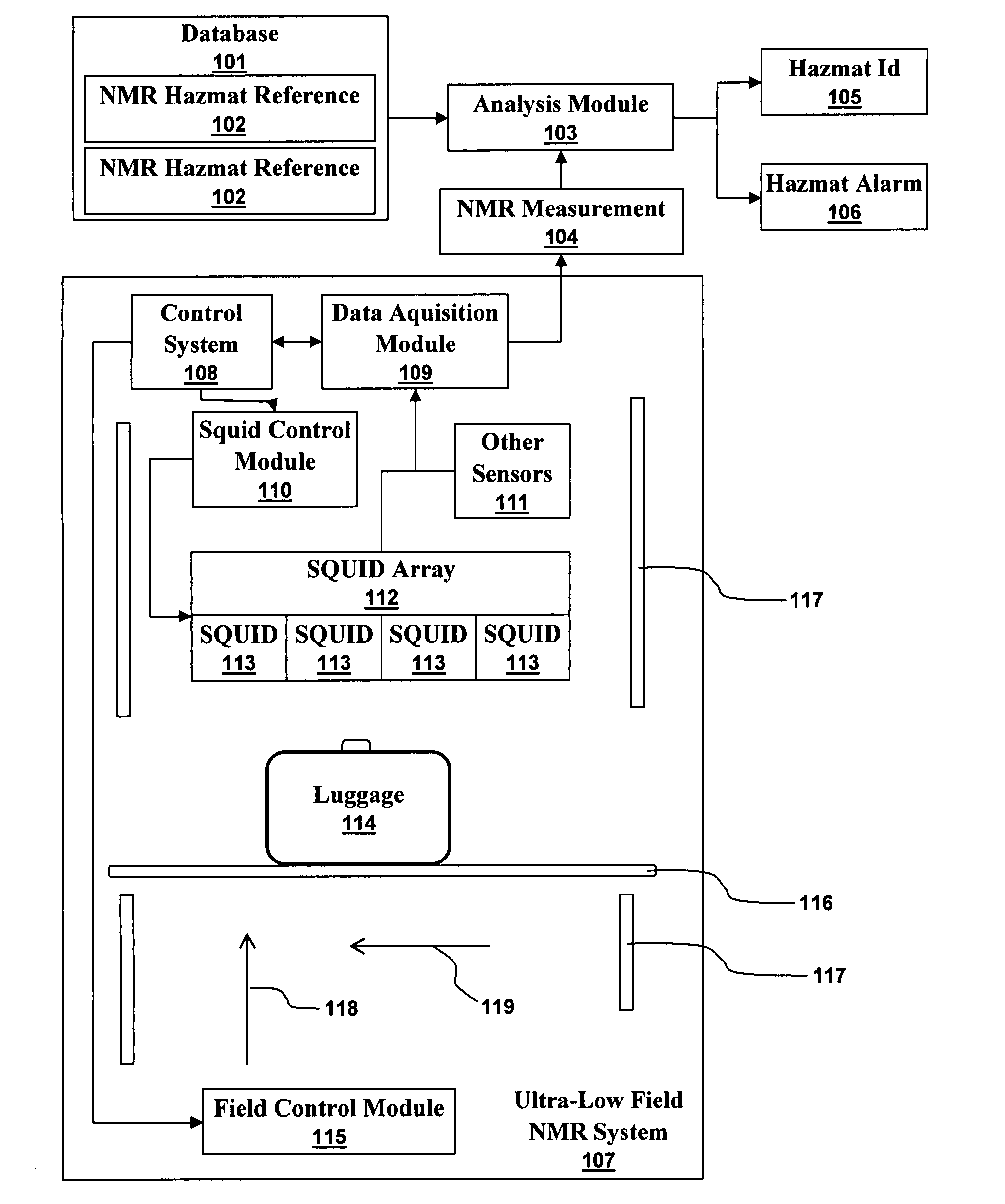
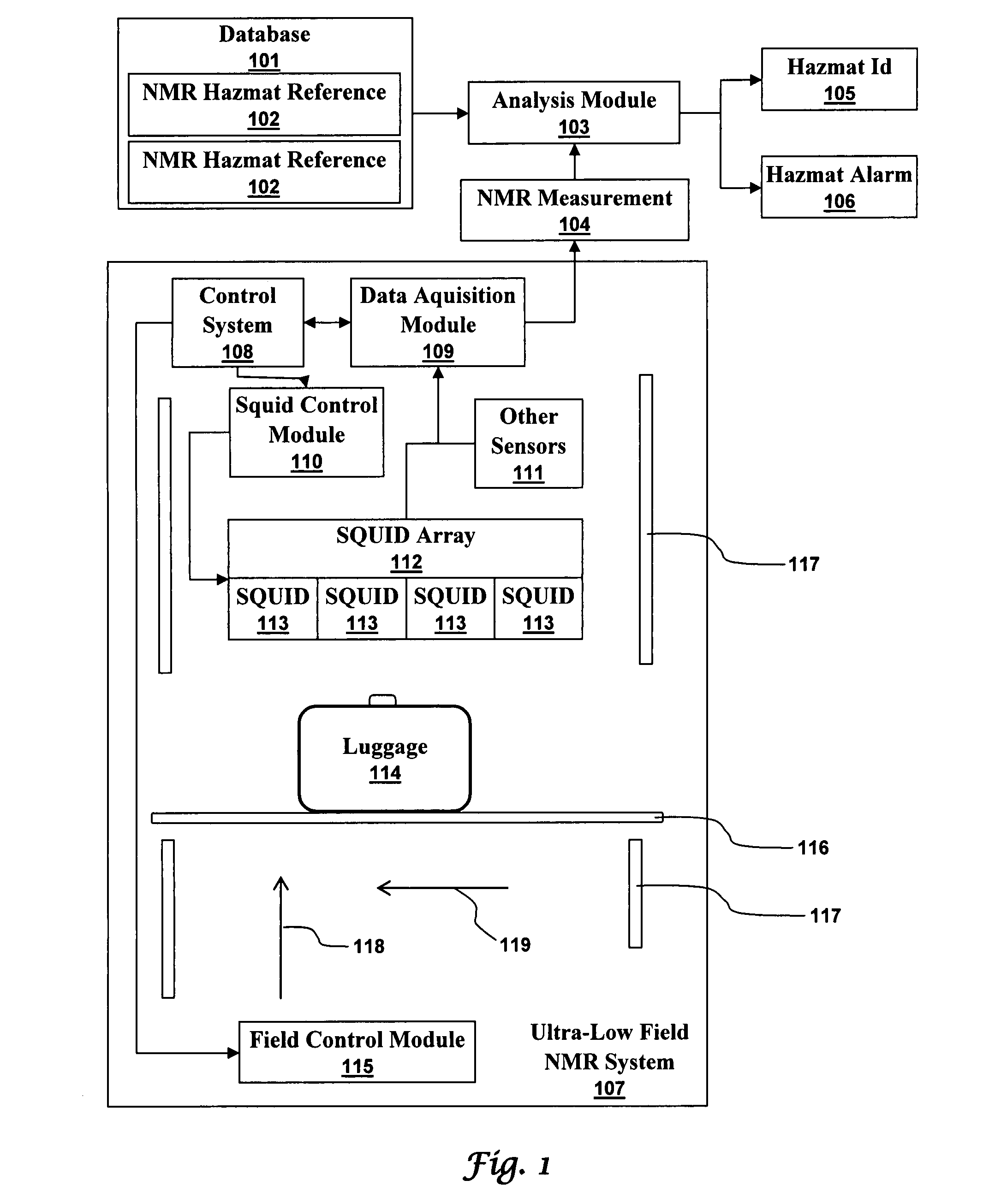
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS20080284433A1Increased signal noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonanceProton NMR
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
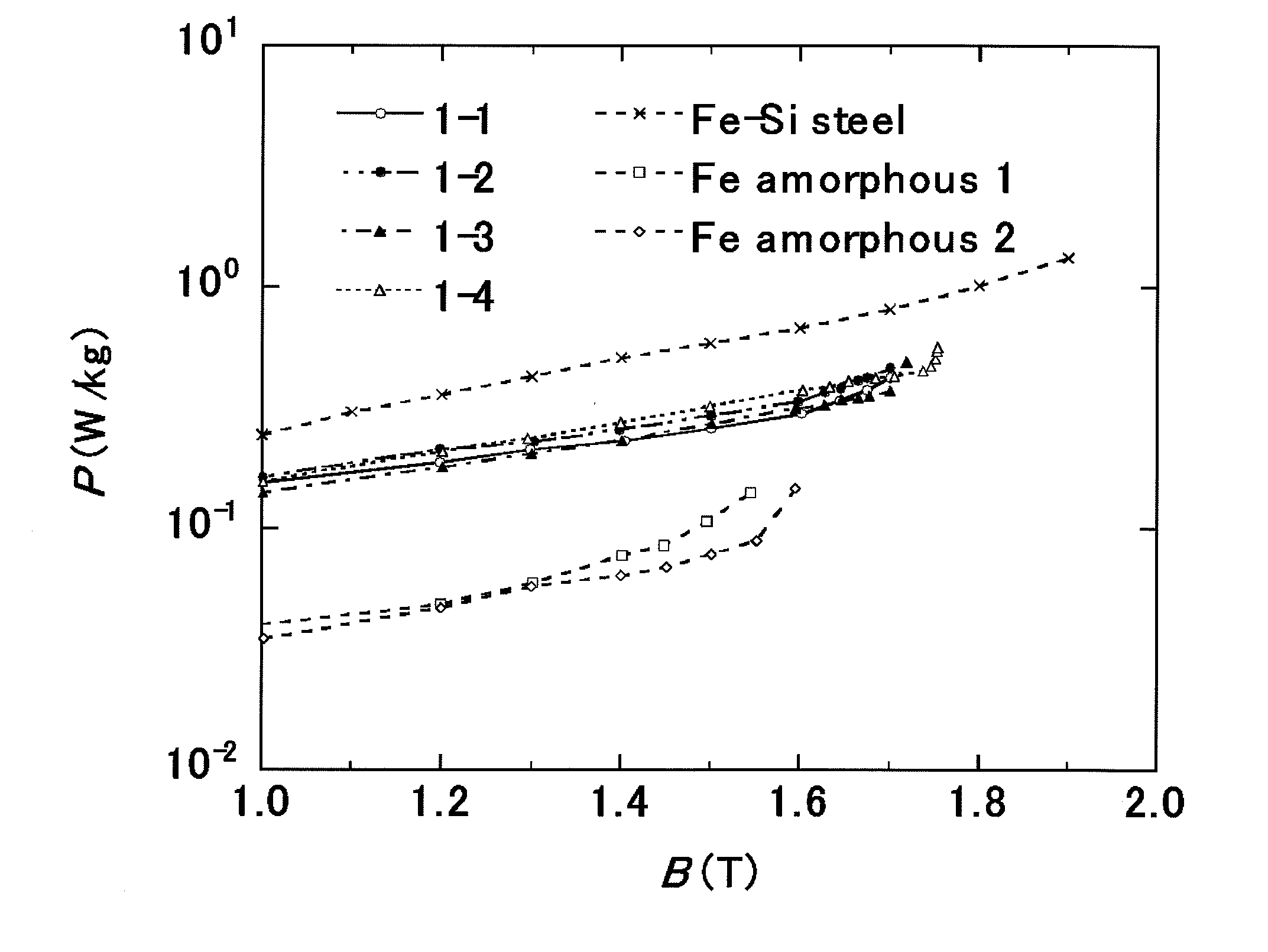
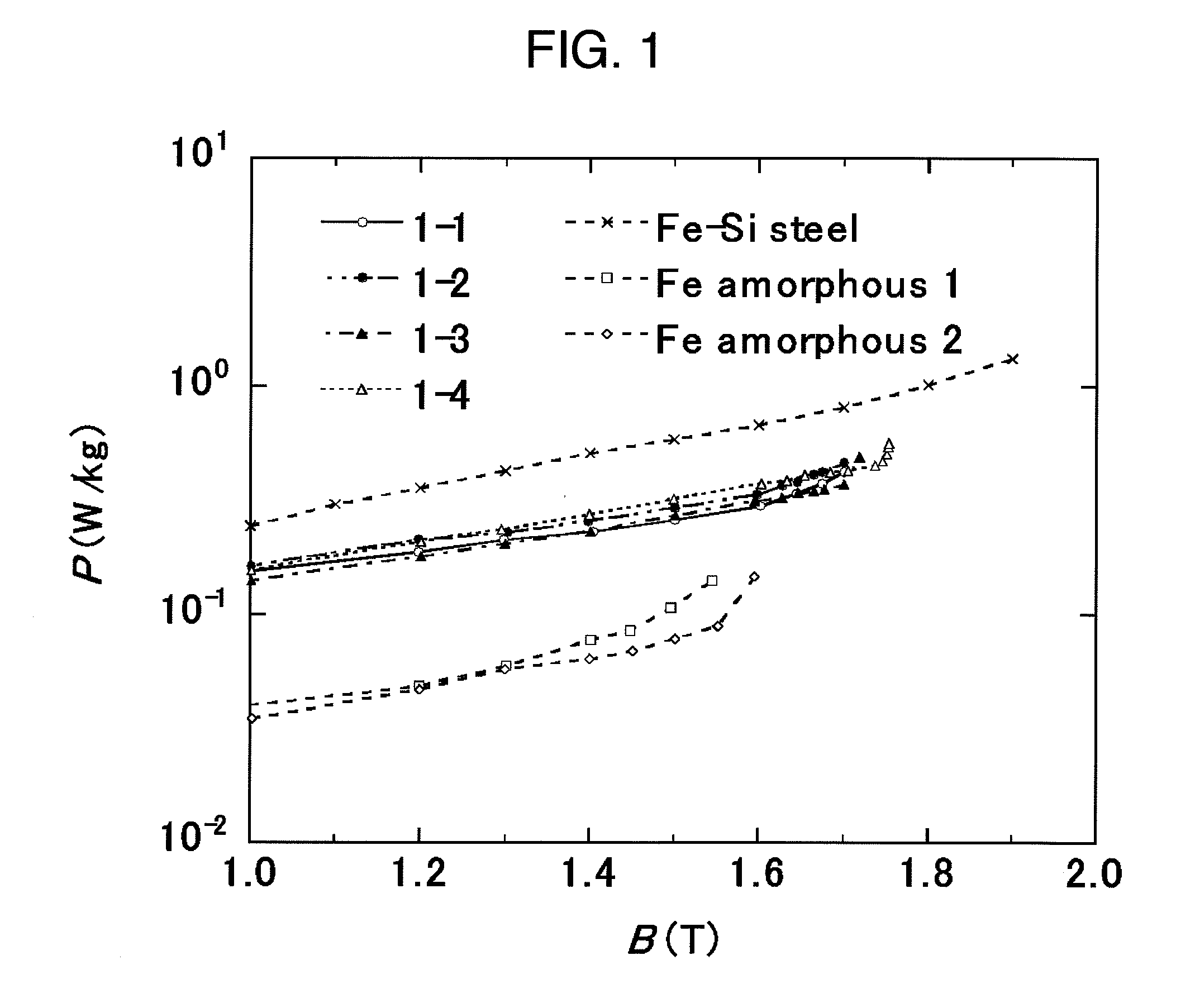
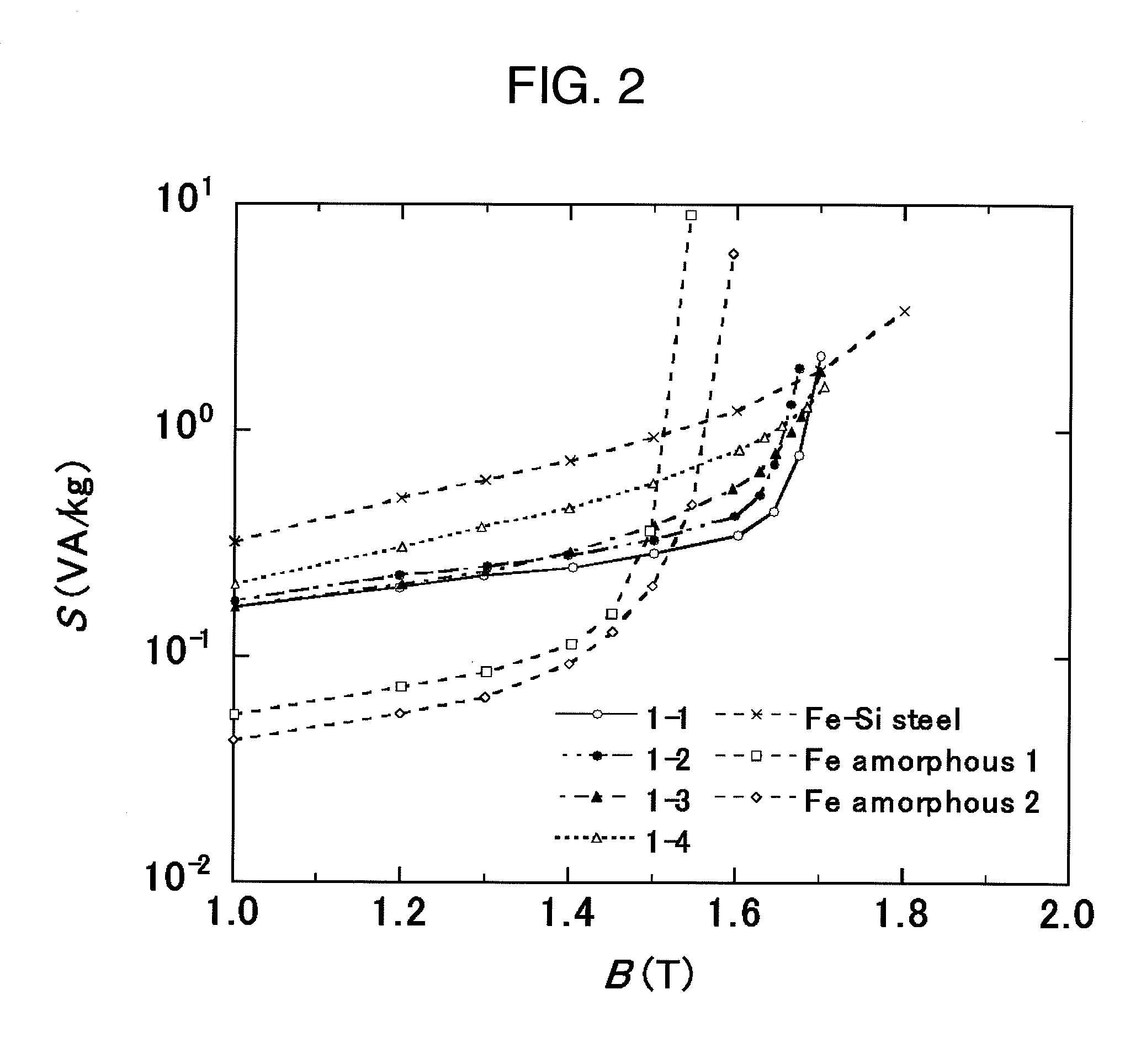
Soft magnetic ribbon, magnetic core, magnetic part and process for producing soft magnetic ribbon
ActiveUS20100108196A1High magnetic flux densityInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsMagnetic tapeMagnetization curve
A soft magnetic ribbon that especially in a relatively low magnetic field region of 500 A / m or less, is high in the squareness of magnetic flux density-magnetization curve. There is disclosed a soft magnetic ribbon of 100 μm or less thickness comprising a parent phase structure in which by volume ratio, 30% or more of crystal grains of 60 nm or less (not including 0) crystal grain diameter are dispersed in an amorphous phase and comprising an amorphous layer disposed on the surface side of the parent phase structure. Preferably, the soft magnetic ribbon is represented by the composition formula Fe100-x-yCuxXy (wherein X is at least one element selected from among B, Si, S, C, P, Al, Ge, Ga and Be), in which the atomic percents (%) satisfy the relationships 0<x≦5 and 10≦y≦24.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
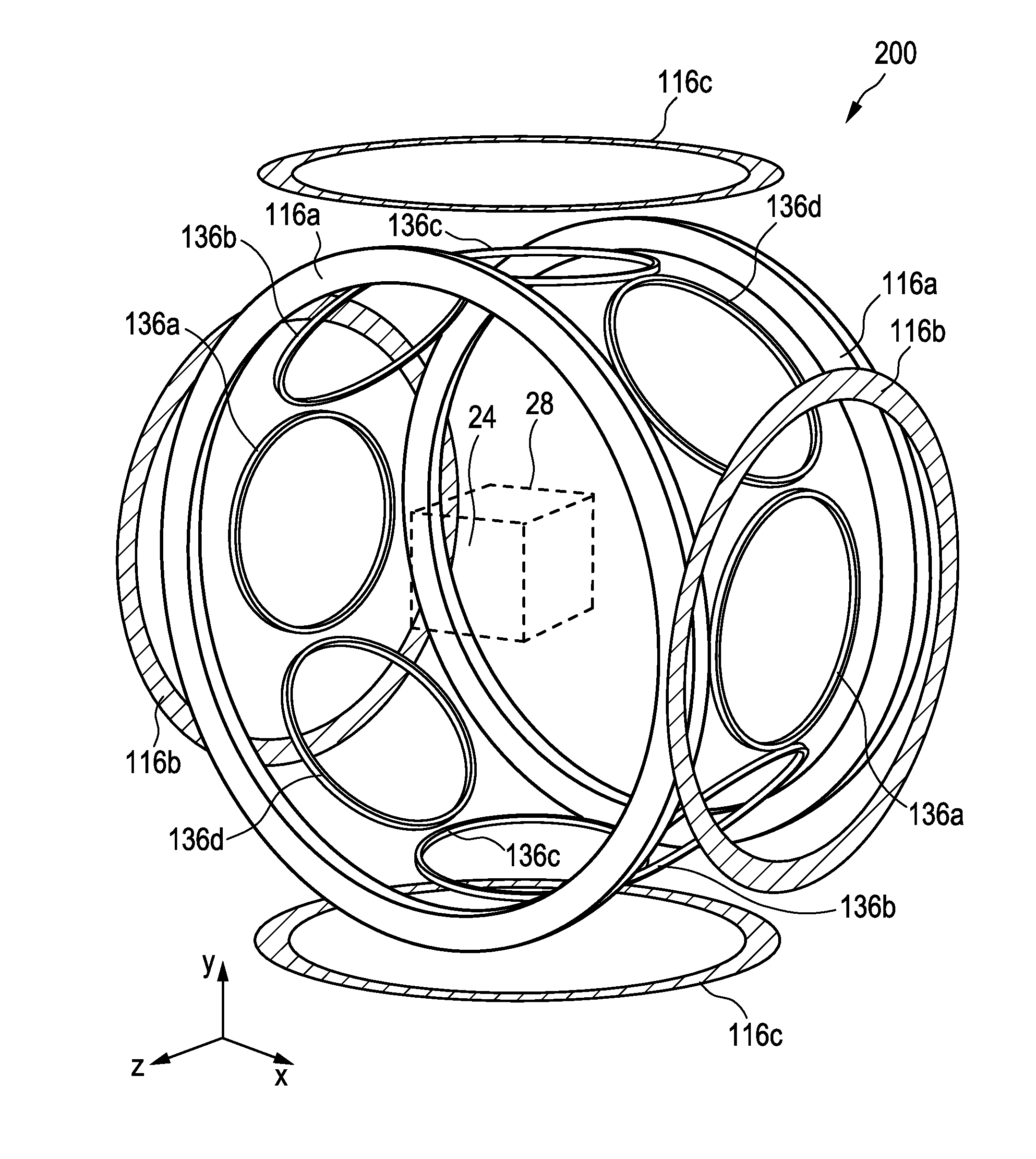
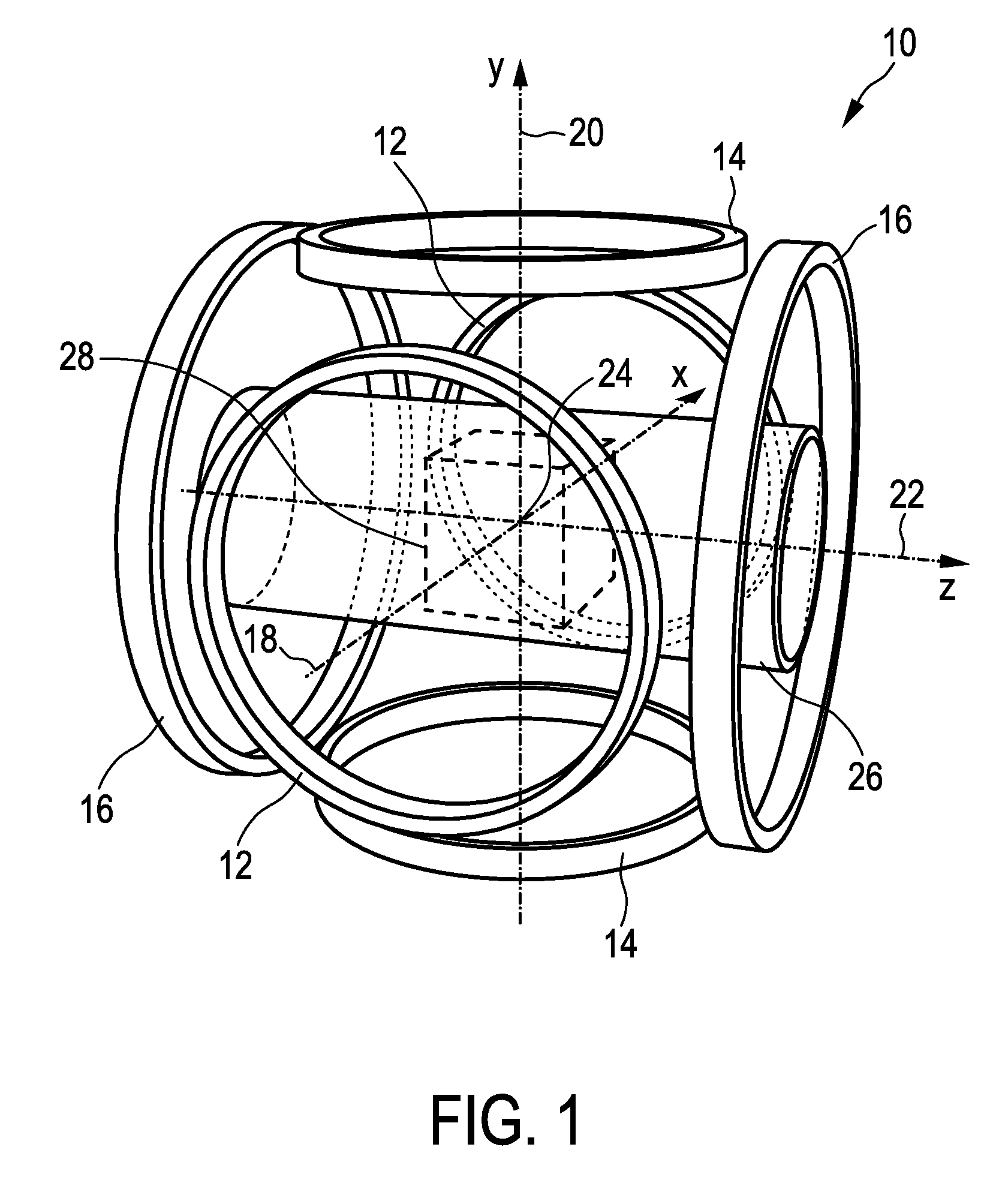
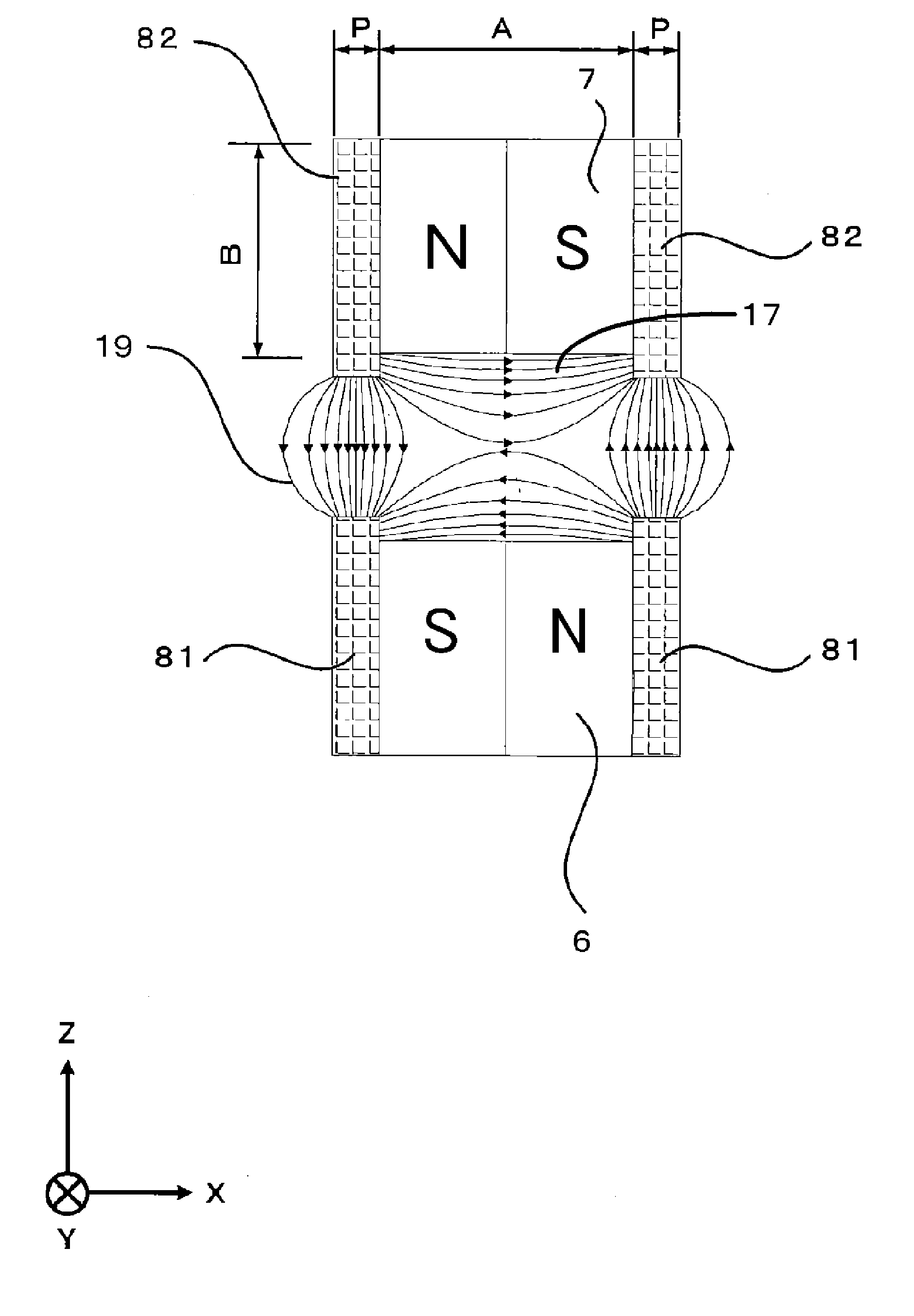
Apparatus and method for generating and moving a magnetic field having a field free line
InactiveUS20120126808A1Reduce power lossHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHigh magnetic field strengthGenerators (Apparatus)
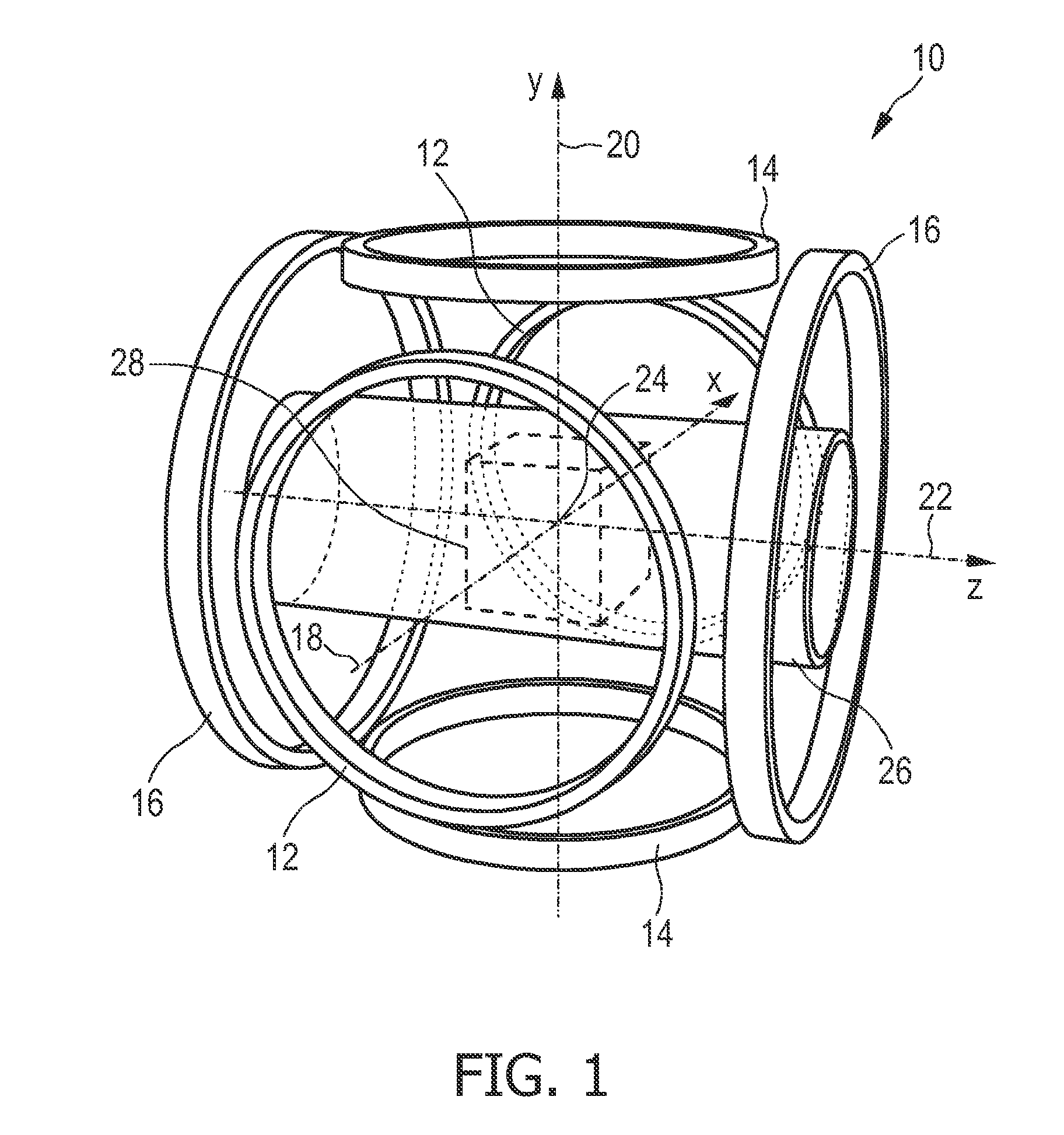
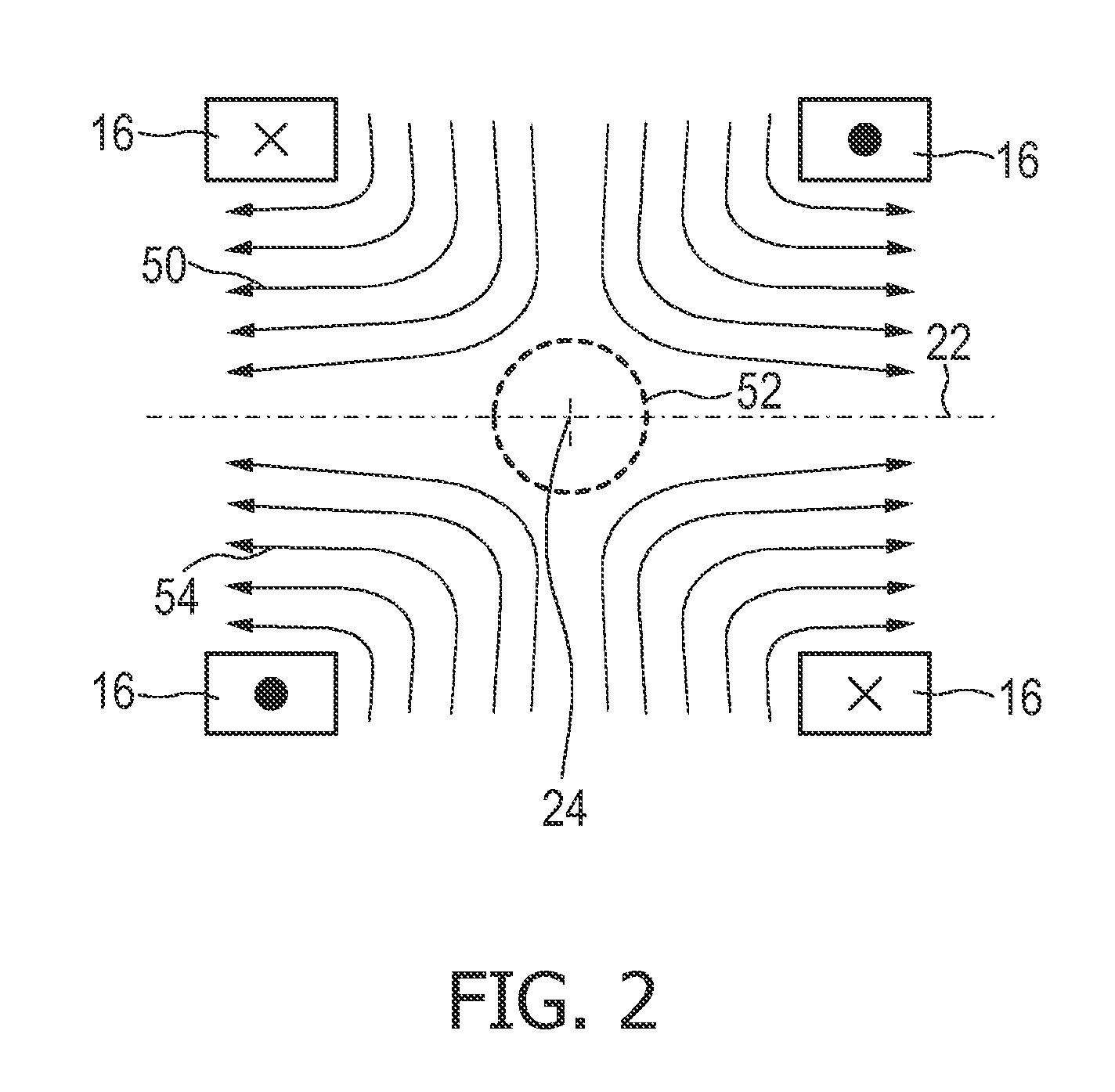
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for generating and changing a magnetic field in a field of view (28), said magnetic field having a, in particular ball-shaped or line-shaped, first sub-zone (62) having a low magnetic field strength and a second sub-zone (64) having a higher magnetic field strength. The proposed apparatus comprises at least three pairs of first coils (136a-136d), wherein the coils are arranged along a ring around the field of view and wherein the two coils of each pair are opposingly arranged on opposite sides of the field of view, at least one pair of second coils (116) opposingly arranged on opposite sides of the field of view at the open sides of said ring, generator means (110, 130) for generating current signals for provision to said first and second coils for generating the desired magnetic fields by said first and second coils, and control means (150) for controlling said generator means.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Remote NMR/MRI detection of laser polarized gases
InactiveUS7061237B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh spin densityDispersion deliveryMeasurements using NMR spectroscopySpectroscopyPulse sequence
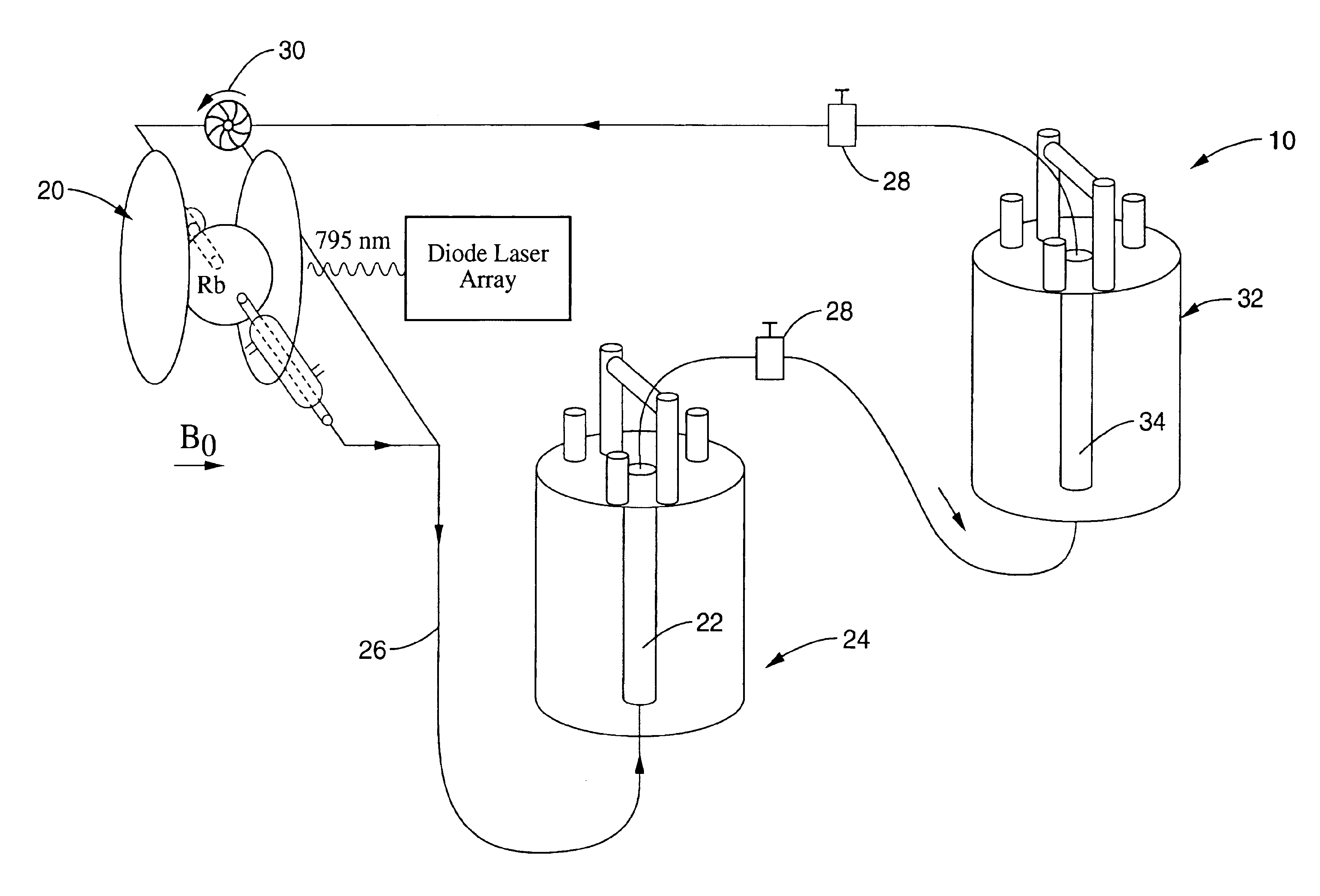
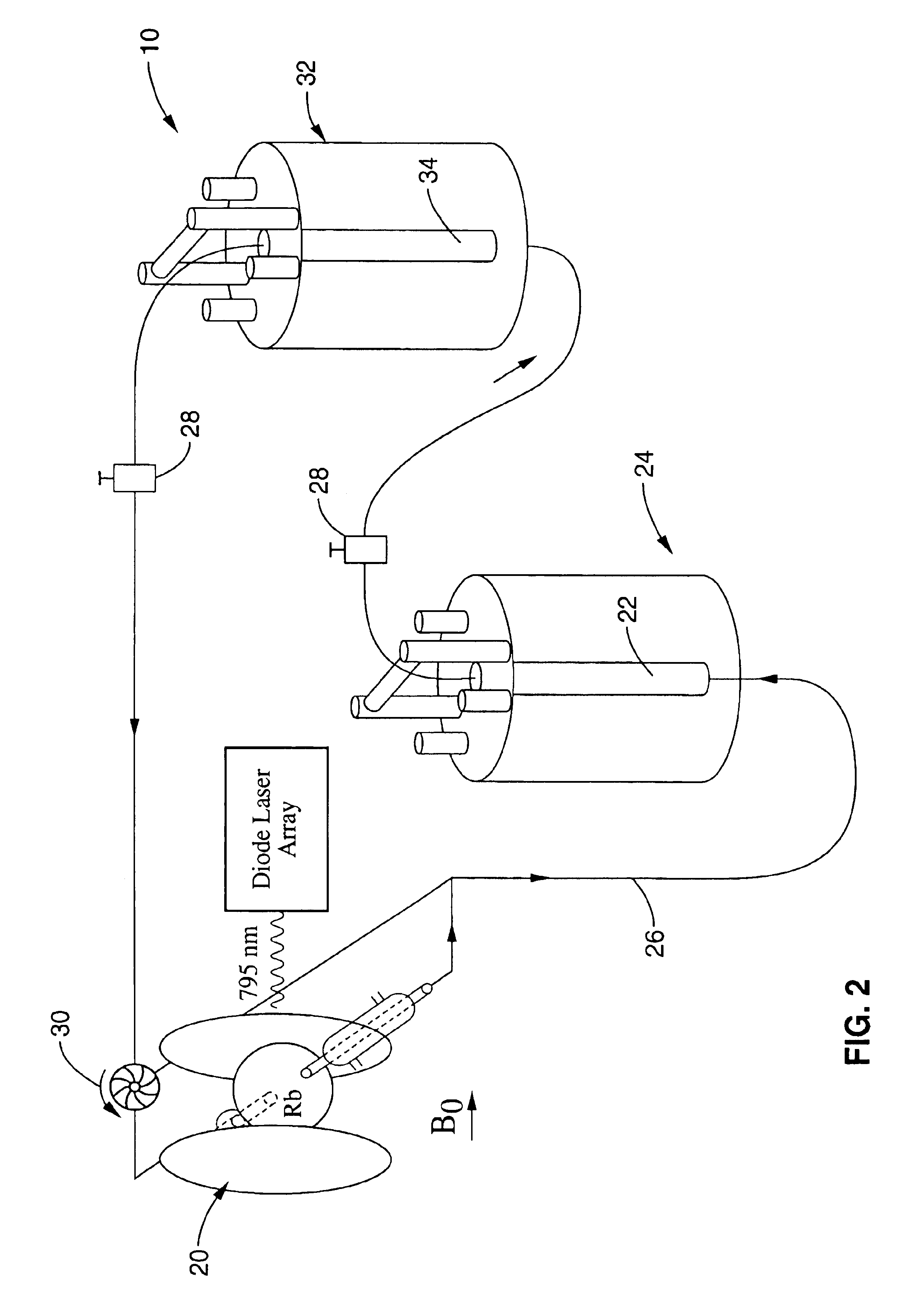
An apparatus and method for remote NMR / MRI spectroscopy having an encoding coil with a sample chamber, a supply of signal carriers, preferably hyperpolarized xenon and a detector allowing the spatial and temporal separation of signal preparation and signal detection steps. This separation allows the physical conditions and methods of the encoding and detection steps to be optimized independently. The encoding of the carrier molecules may take place in a high or a low magnetic field and conventional NMR pulse sequences can be split between encoding and detection steps. In one embodiment, the detector is a high magnetic field NMR apparatus. In another embodiment, the detector is a superconducting quantum interference device. A further embodiment uses optical detection of Rb—Xe spin exchange. Another embodiment uses an optical magnetometer using non-linear Faraday rotation. Concentration of the signal carriers in the detector can greatly improve the signal to noise ratio.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
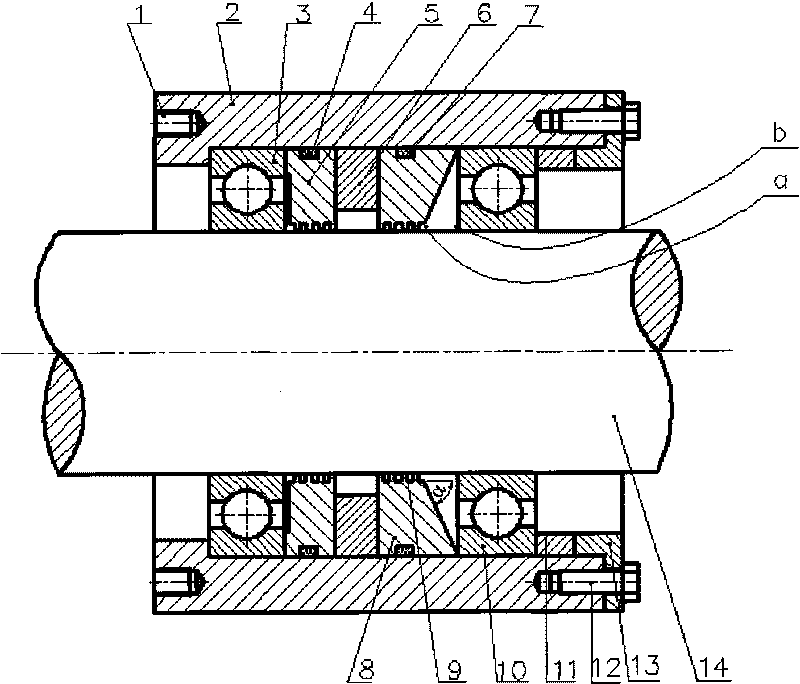
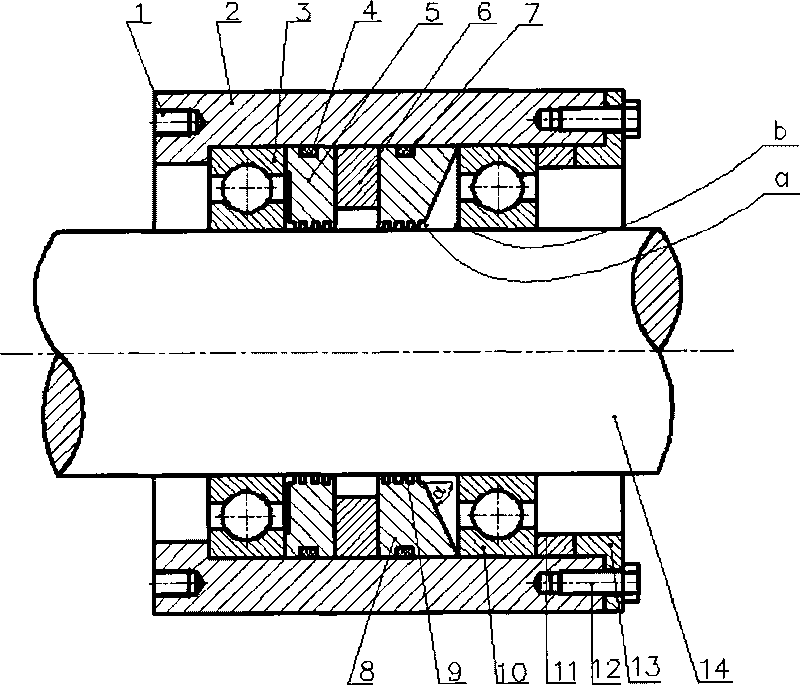
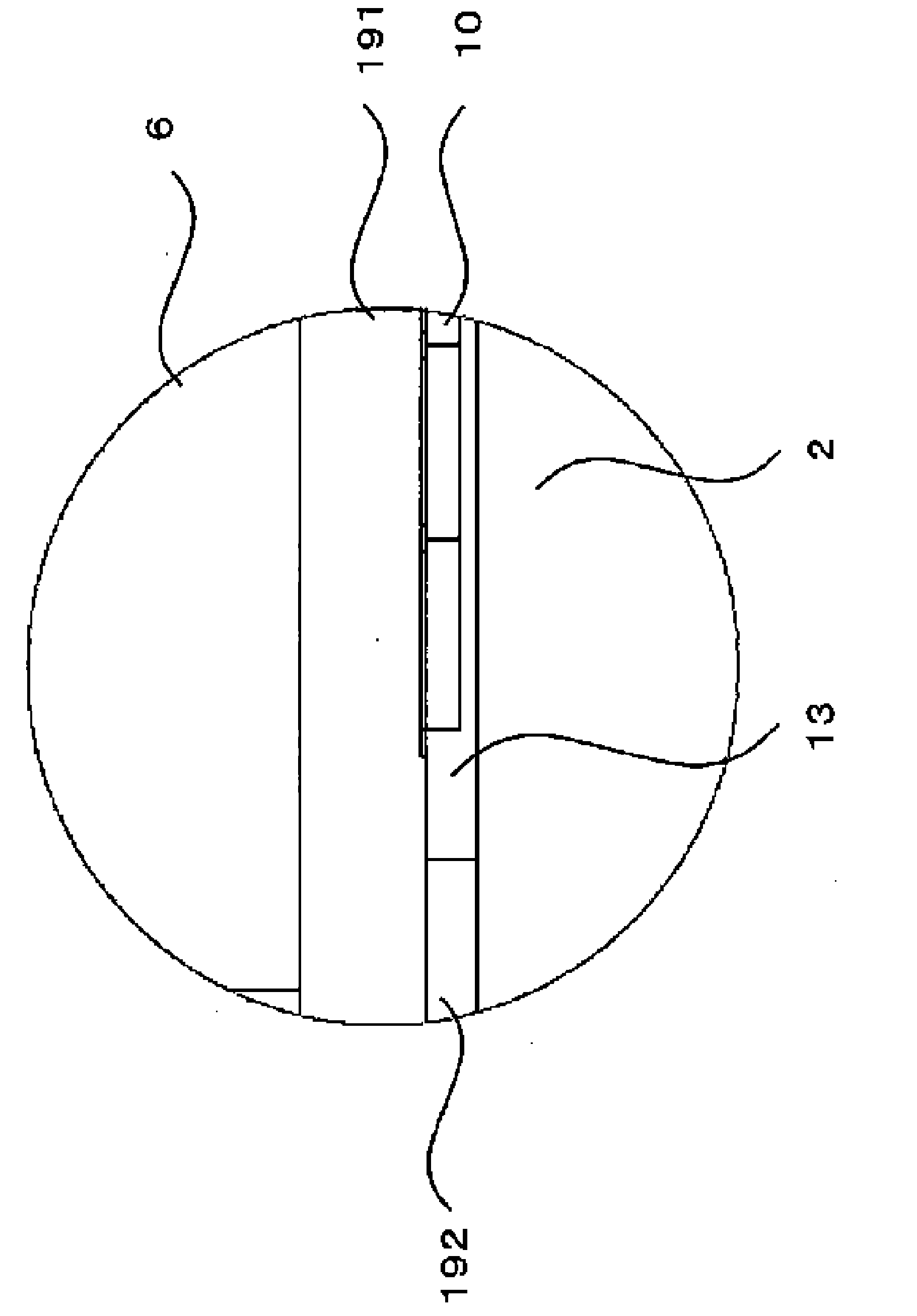
Magnetic liquid sealing device with self-cleaning function
InactiveCN101737499AImprove sealingSeal applicableEngine sealsForeign matterHigh magnetic field strength
The invention discloses a magnetic liquid sealing device with a self-cleaning function, which belongs to the technical field of mechanical engineering sealing and comprises a shell (2), a left bearing (3), a left pole shoe (5) with a rubber seal ring, a permanent magnet (6), a right pole shoe (8) with a rubber seal ring, a right bearing (10), an adjusting gasket (11), a flange disk (13) and a shaft (14). The right end face of the right pole shoe and an axle line form an angle alpha of 10 to 80 degrees to change the shape of the right pole shoe and the magnetic field strength, so that the magnetic field strength on the side a of the right pole shoe is higher than that on the side b. According to Bernoullis equation, the pressure of the granules entering a magnetic liquid from outside on the side with high magnetic field strength is higher that on the side with low magnetic field strength, namely the pressure on the side a is more than that on the side b. The system generates a repulsive force to outside foreign materials so as to fulfil the aim of self cleaning.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Therapeutic equipment for physical therapy using dense multi-point fine magnetic field
InactiveCN101327358AHigh precisionReduce lossElectrotherapyDevices for locating reflex pointsTransformerFloating point
The present invention discloses therapeutic equipment that adopts the concentrated multi-point fine magnetic field to perform the physical therapy, and comprises a hardware part and a software part, wherein, the hardware part is mainly composed of a magnetic therapeutic head, a host machine and a circuit that is arranged inside the host machine; an electromagnetic skeleton is arranged inside the magnetic therapeutic head; coil is wounded on the electromagnetic skeleton; the magnetic field that is generated inside the coil is outputted after being led and collected by a plurality of high magnetic-conducting material iron pins, and is characterized in that the software part is solidified in an main-controlled CPU circuit that is arranged inside the host machine; the software part contains a dual-precision floating-point calculation device that can directly calculate the conversion between the Julian calendar and the lunar calendar; an IGBT protective controlling circuit and a transformer circuit are arranged inside the host machine; the transformer circuit outputs direct-current electricity, so that the therapeutic head outputs a constant N-polar magnetic field. The therapeutic equipment is applied to magnetic therapeutic equipment, and has wide application range and good therapeutic effect, and can reasonably use the energy and reduce the loss and consumption, and has favorable popularization value.
Owner:李久峰
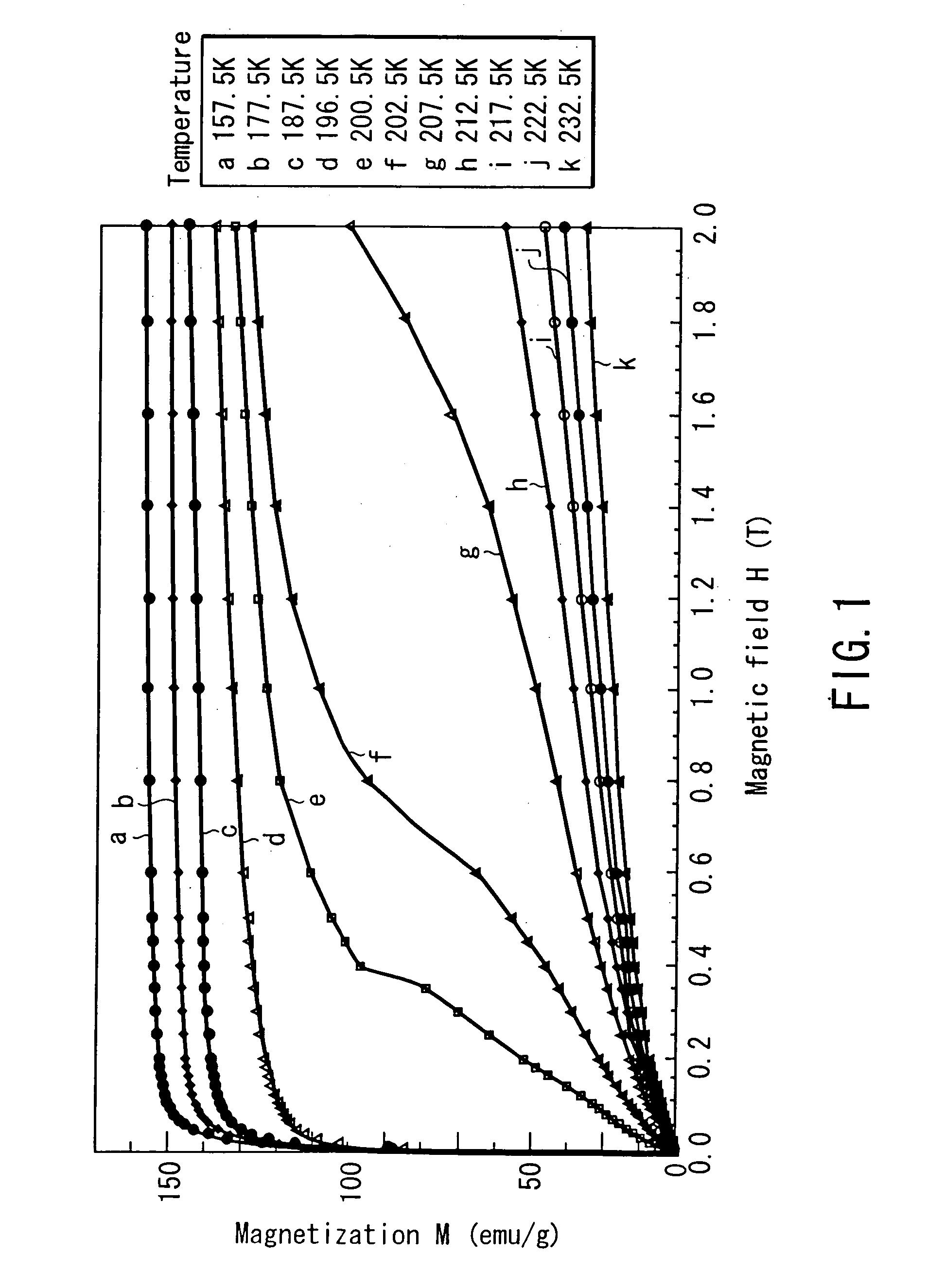
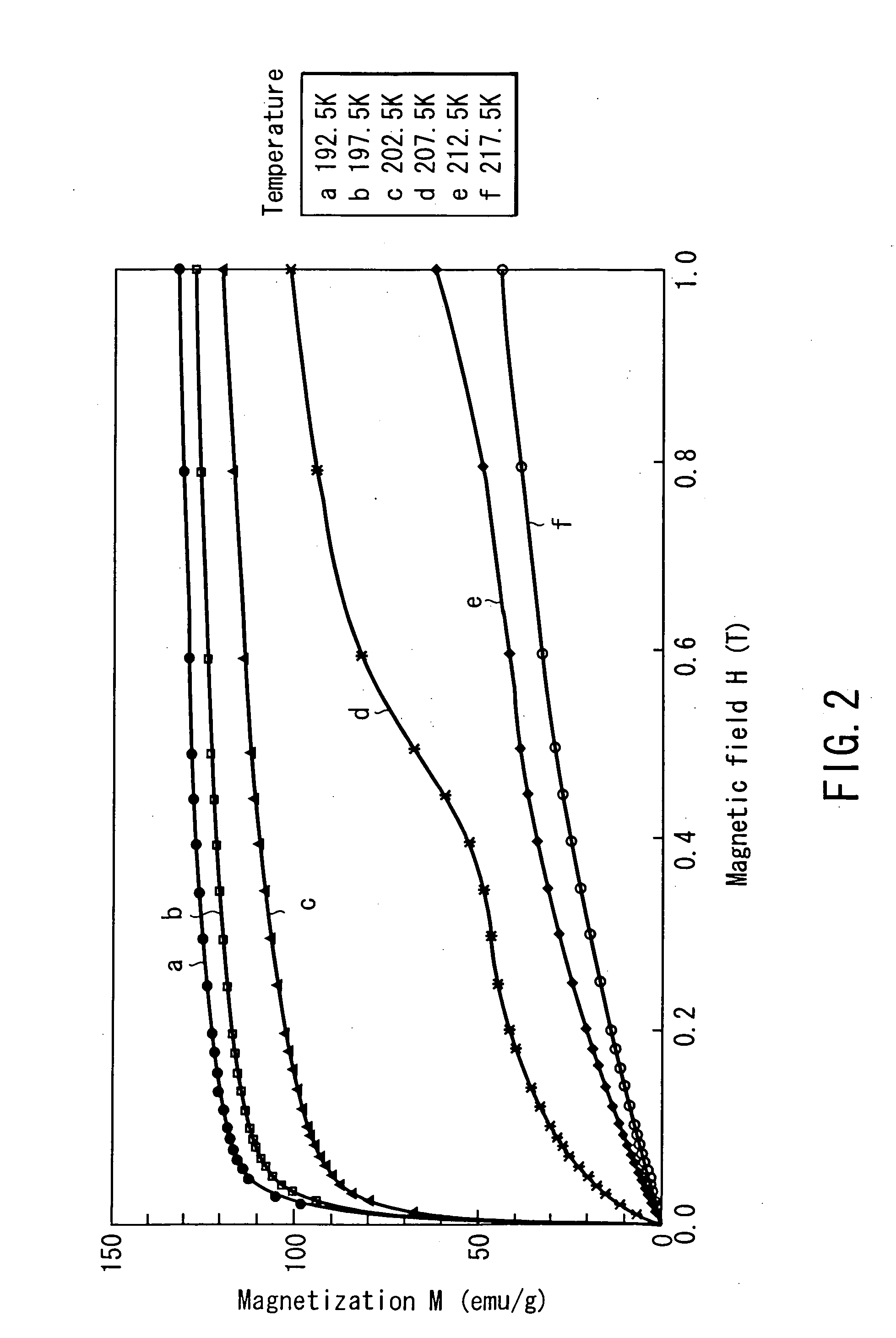
Magnetic material
InactiveUS20050000230A1Change level balanceIncreased overall peak widthEnergy efficient heating/coolingInorganic material magnetismDifferential coefficientMagnetization curve
The magnetic material for magnetic refrigeration of the present invention is characterized by exhibiting, in a certain temperature region, preferably, only in part of a temperature region from 200 K to 350 K, an inflection point at which a second order differential coefficient of a magnetization curve changes from positive to negative with respect to a magnetic field, within the range of this magnetic field formed using a permanent magnet unit. This magnetic material of the present invention can generate a low temperature by using a relatively low magnetic field, by transferring the entropy between the electron spin system and the lattice system near the temperature at which an inflection point appears on the magnetization curve. Examples of the magnetic material meeting this condition are La(Fe,Si)13, (Hf,Ta)Fe2, (Ti,Sc)Fe2, and (Nb,Mo)Fe2, each containing 50 to 60 atomic % of transition metals such as Fe.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
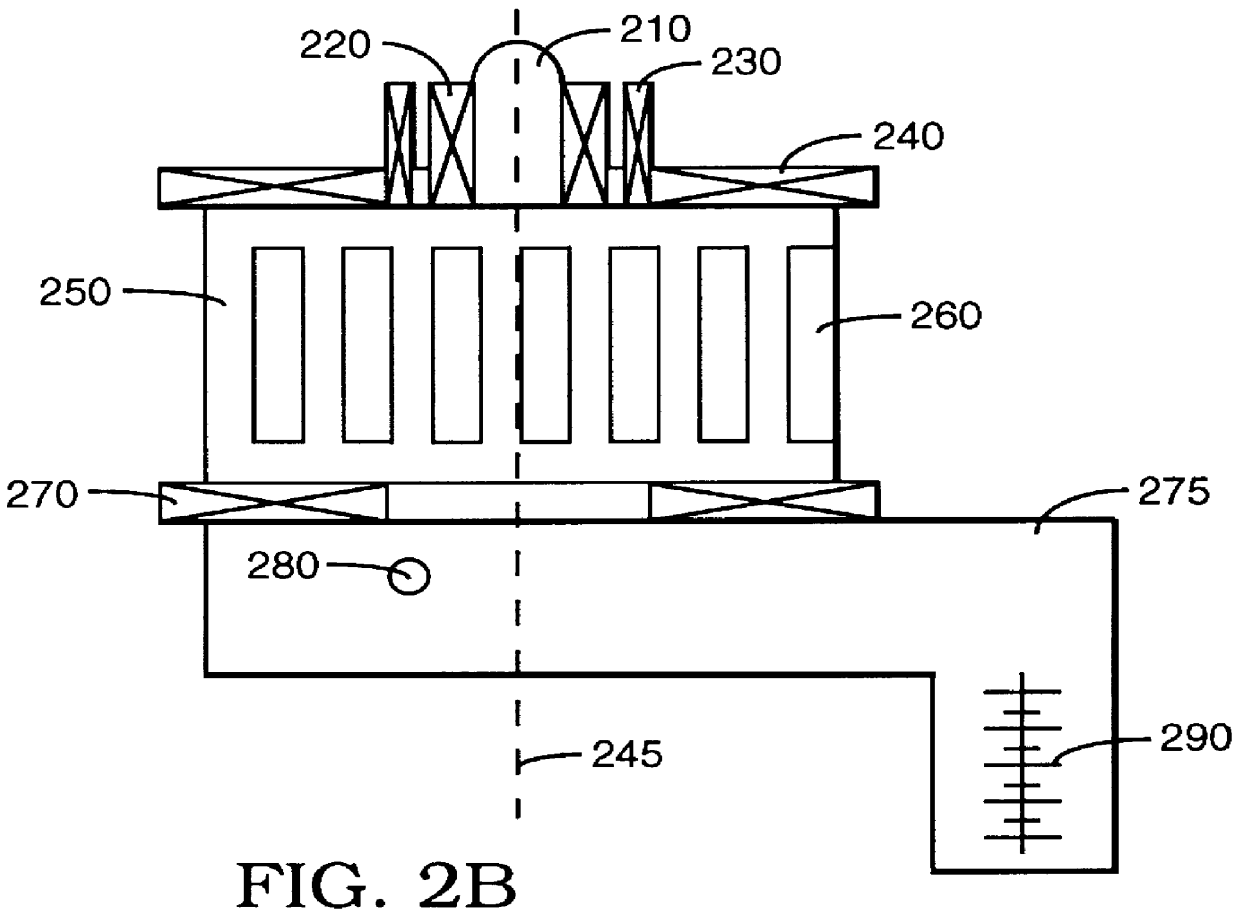
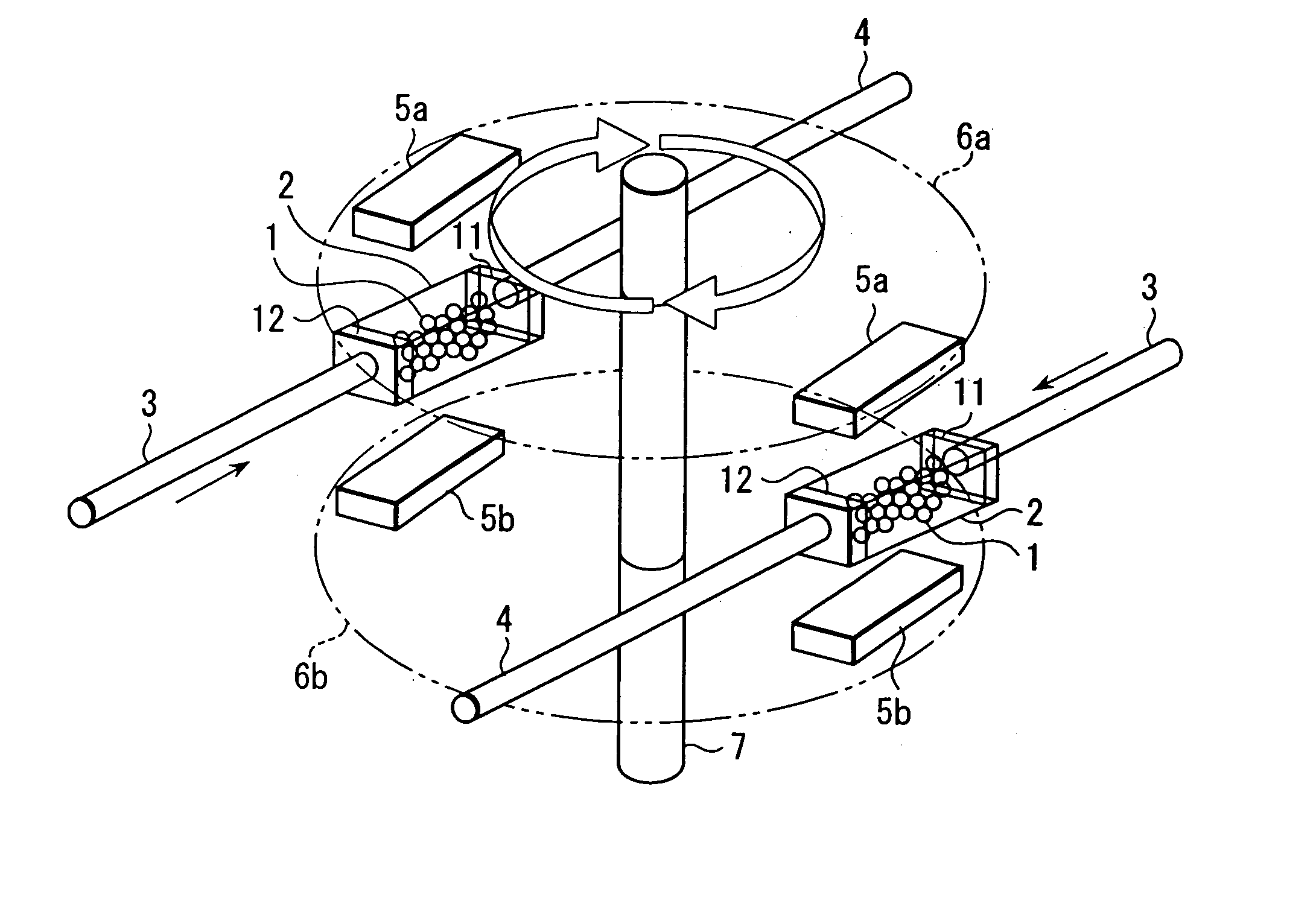
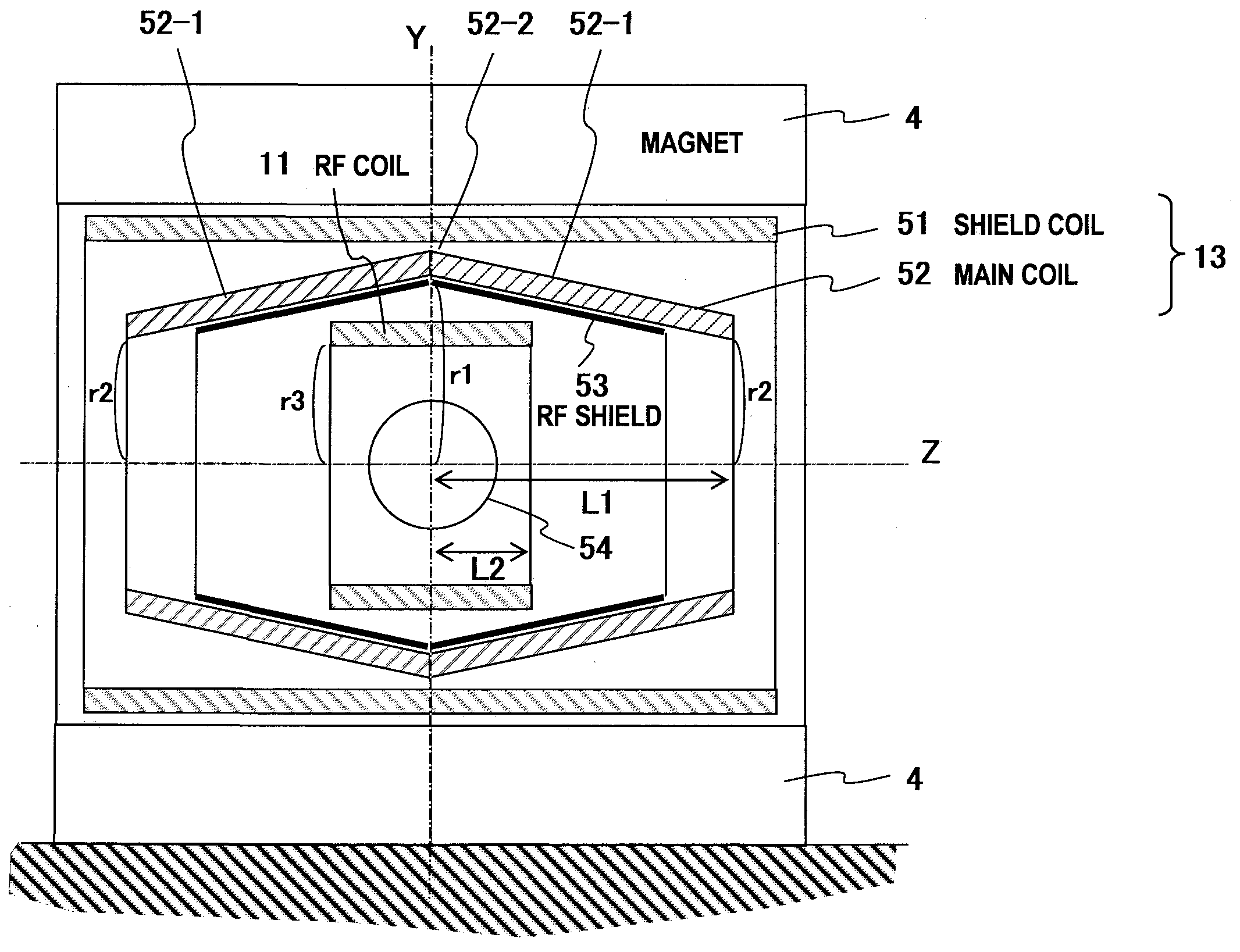
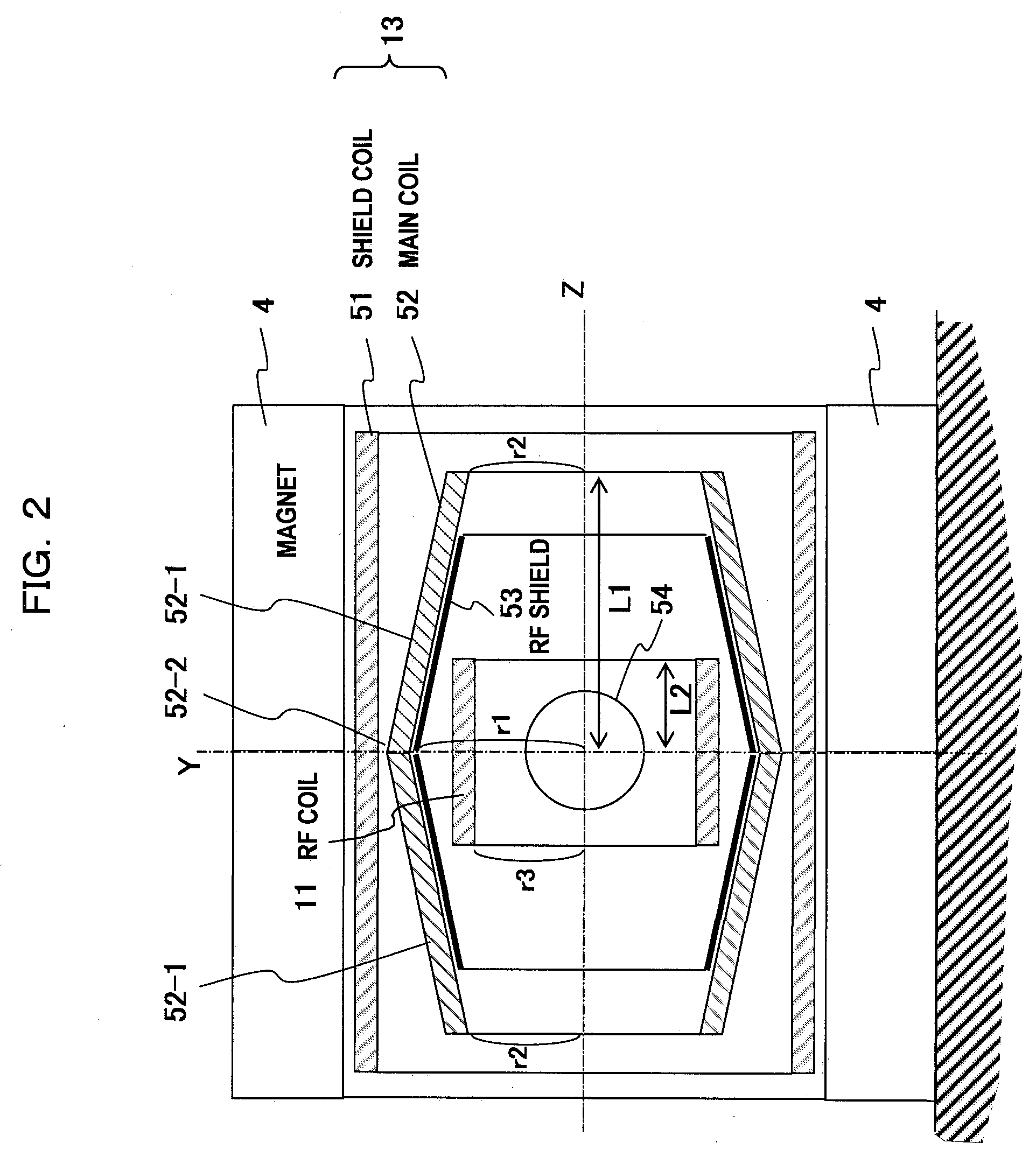
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and gradient magnetic field coil
InactiveUS20090066332A1Easy to manufactureMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceTotal thickness
An MRI apparatus excellent in magnetic field generation efficiency is provided. According to this invention, a main coil (52) of a gradient magnetic field coil (13) is partially recessed to reduce the total thickness of a radio-frequency coil (11) and a gradient magnetic field coil (13). That is, the main coil (52) is designed in a tubular shape, and the diameter r1 at the center portion of the imaging space is larger than the diameter r2 of the main coil end portion. Accordingly, the RF coil (11) can be disposed to be near to the gradient magnetic field coil (13) side without lowering the magnetic field generation efficiency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device
The invention discloses a repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device. The device comprises an anode, a cathode, a guiding magnetic field generator, slow wave structures and a coaxial internal conductor, the anode is internally provided with an emission area and a beam wave interaction area, the cathode is arranged in the emission area, the slow wave structures and the coaxial internal conductor are arranged in the beam wave interaction area of the anode, the cathode is coaxial with the coaxial internal conductor, the slow wave structures are fixed to the inner side of the anode and arranged in the periphery of the coaxial internal conductor, a vacuum cavity is formed by vacuum pumping in the repetition-frequency low-magnetic-field axial C-waveband high-power microwave device, and the vacuum degree of the vacuum cavity does not exceed 10mPa. A baffle plate is arranged between the emission area and the beam wave interaction area. The baffle plate is provided with an annular inlet for guiding high-current electron beams generated by the cathode into the beam wave interaction area, and the diameter of the annular inlet is consistent with that of the cathode. The device is characterized by being capable of generating C-waveband high-power microwaves in repetition frequency and high in the beam wave conversion efficiency.
Owner:INST OF APPLIED ELECTRONICS CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
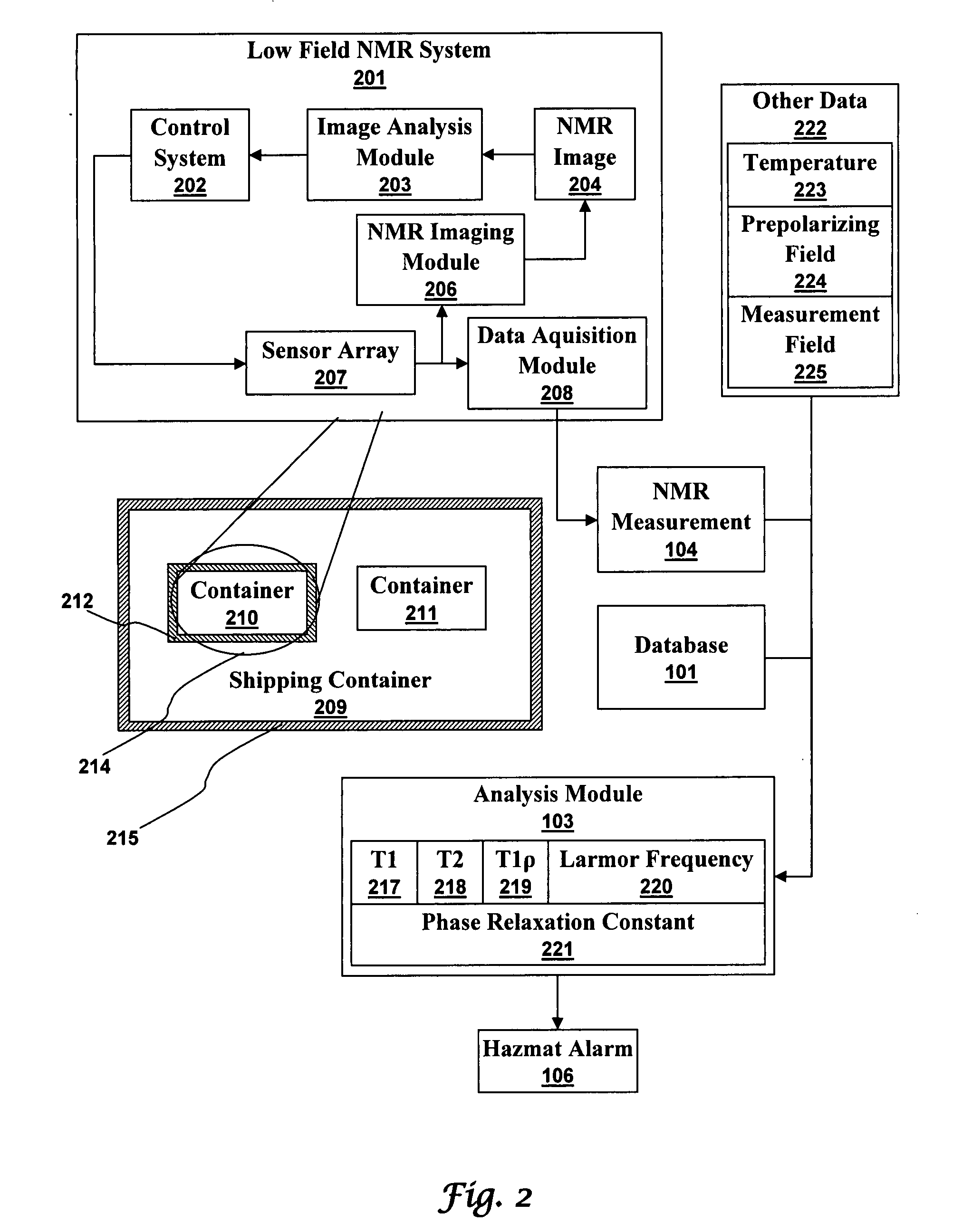
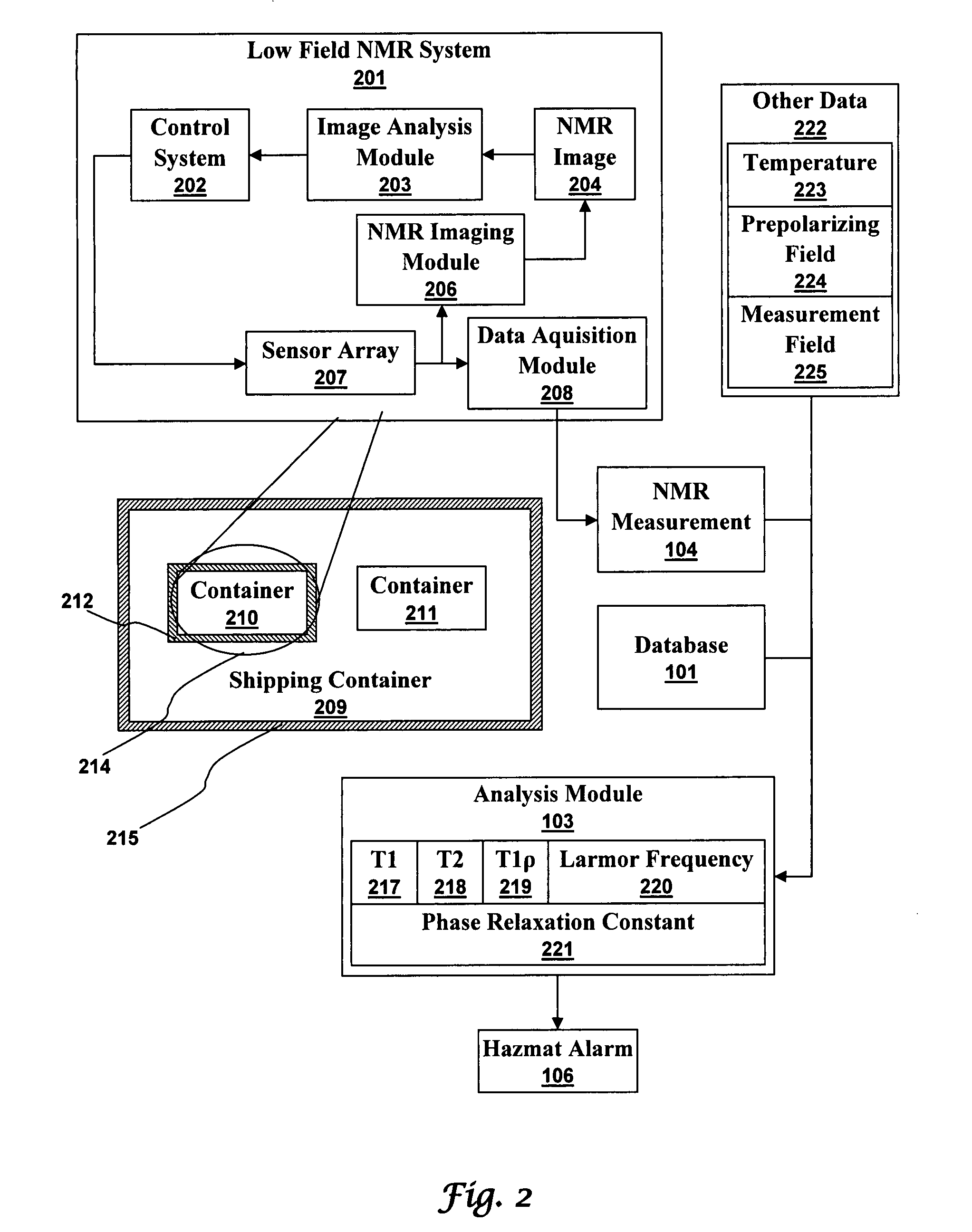
Ultra-low field nuclear magnetic resonance and magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate and identify materials
InactiveUS7688069B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsMaterial analysis by using resonanceHazardous substanceLow field nuclear magnetic resonance
An ultra-low magnetic field NMR system can non-invasively examine containers. Database matching techniques can then identify hazardous materials within the containers. Ultra-low field NMR systems are ideal for this purpose because they do not require large powerful magnets and because they can examine materials enclosed in conductive shells such as lead shells. The NMR examination technique can be combined with ultra-low field NMR imaging, where an NMR image is obtained and analyzed to identify target volumes. Spatial sensitivity encoding can also be used to identify target volumes. After the target volumes are identified the NMR measurement technique can be used to identify their contents.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Magnetic sensor device
InactiveCN103003711AEfficient detectionPaper-money testing devicesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsHigh magnetic field strengthEngineering
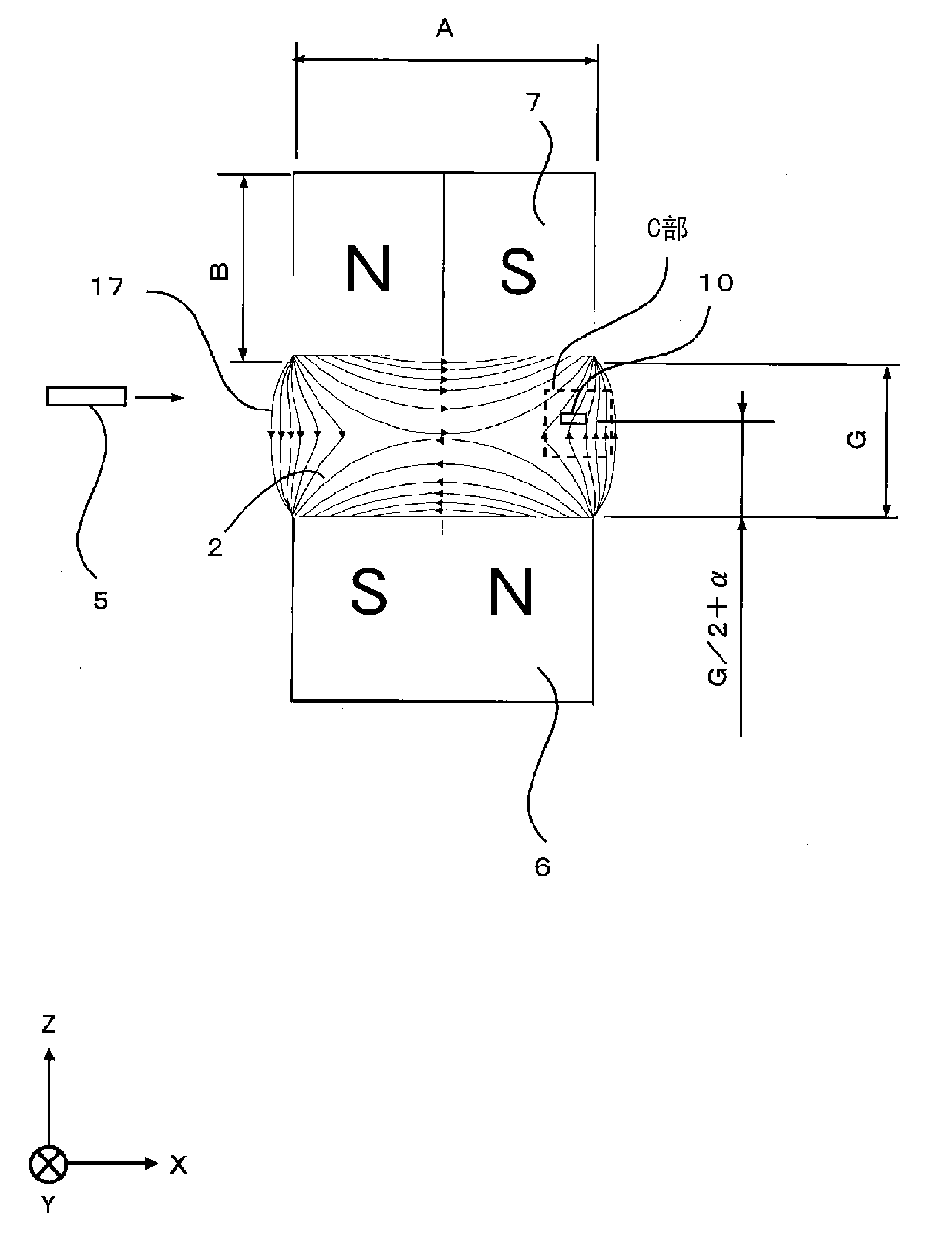
A first magnet (6) and a second magnet (7) arranged so that the opposite poles thereof face one another are provided in a wall surface of a hollow section (2) through which paper currency (5) is transported, and thereby form a gradient magnetic field including a zero point both in a magnetic field component in the direction in which the poles face one another between the magnets, and in a magnetic field component in the direction of transport of the paper currency (5) within the hollow section (2). An AMR element (10) is provided between the paper currency (5) and the first magnet (6). The AMR element (10) is enclosed in a multilayer substrate and is clad with a resin. The AMR element (10) is provided in a region of low magnetic field strength near where the magnetic field strength of the gradient magnetic field reaches the zero point in the transport direction. The paper currency (5) passes through a region of high magnetic field strength in the gradient magnetic field.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Automatic magnetic field compensation device and method
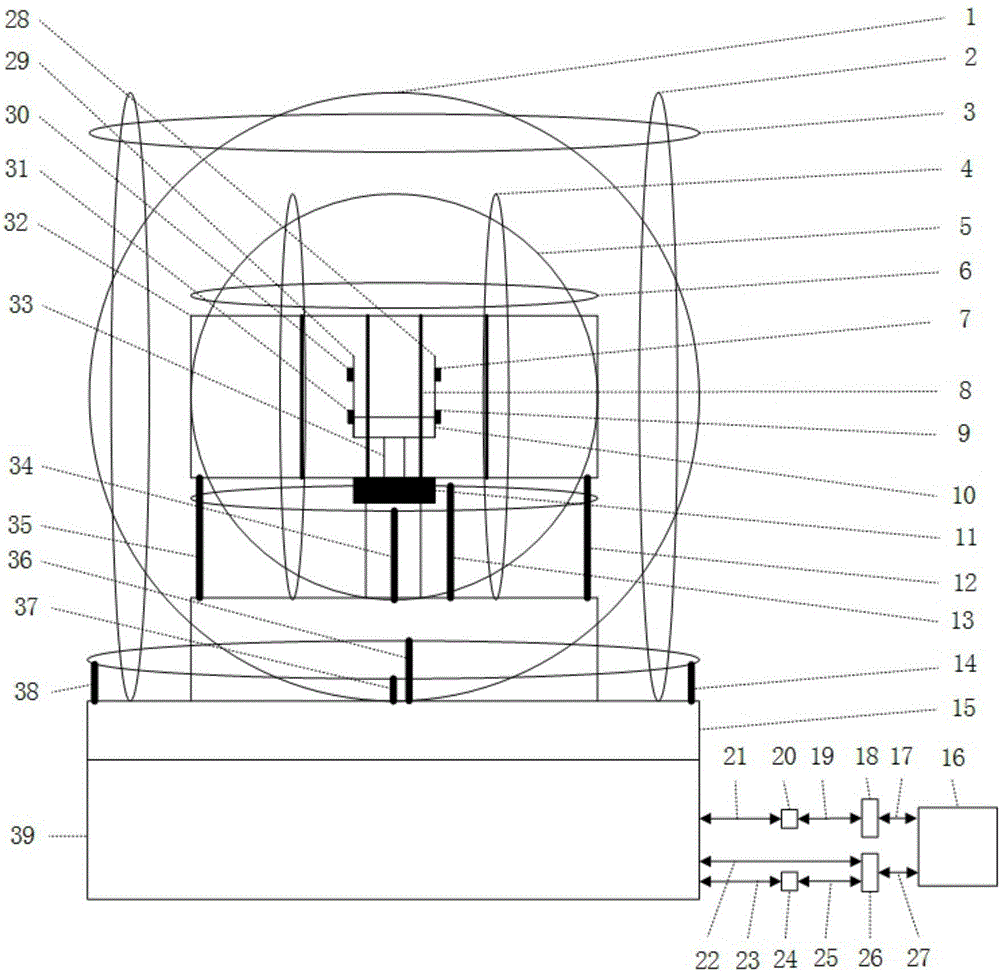
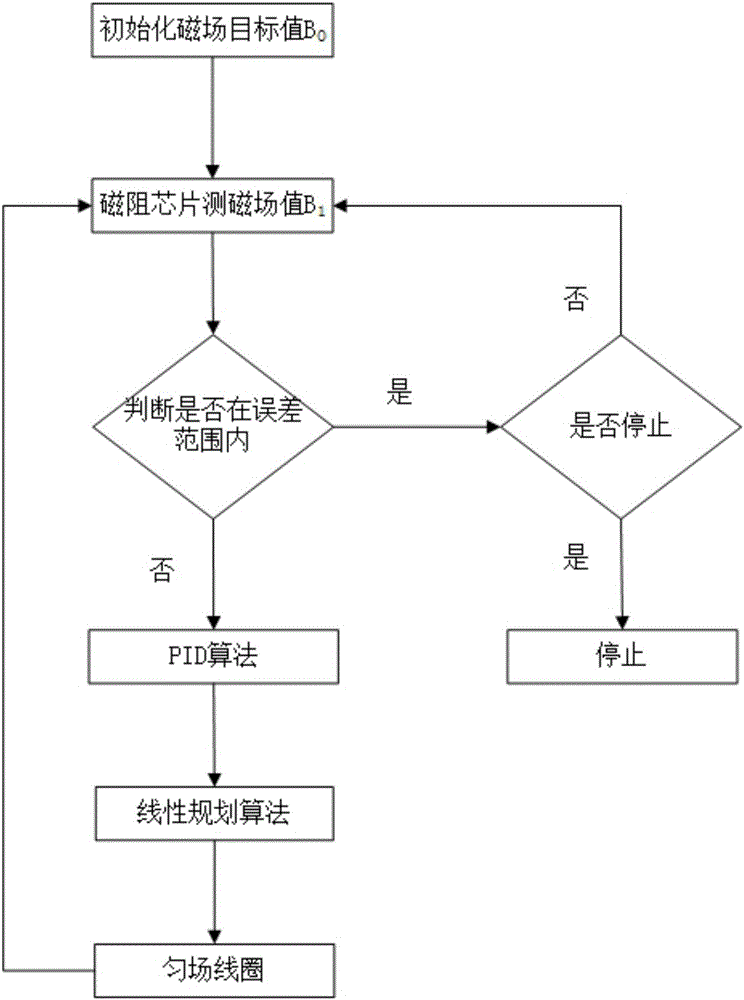
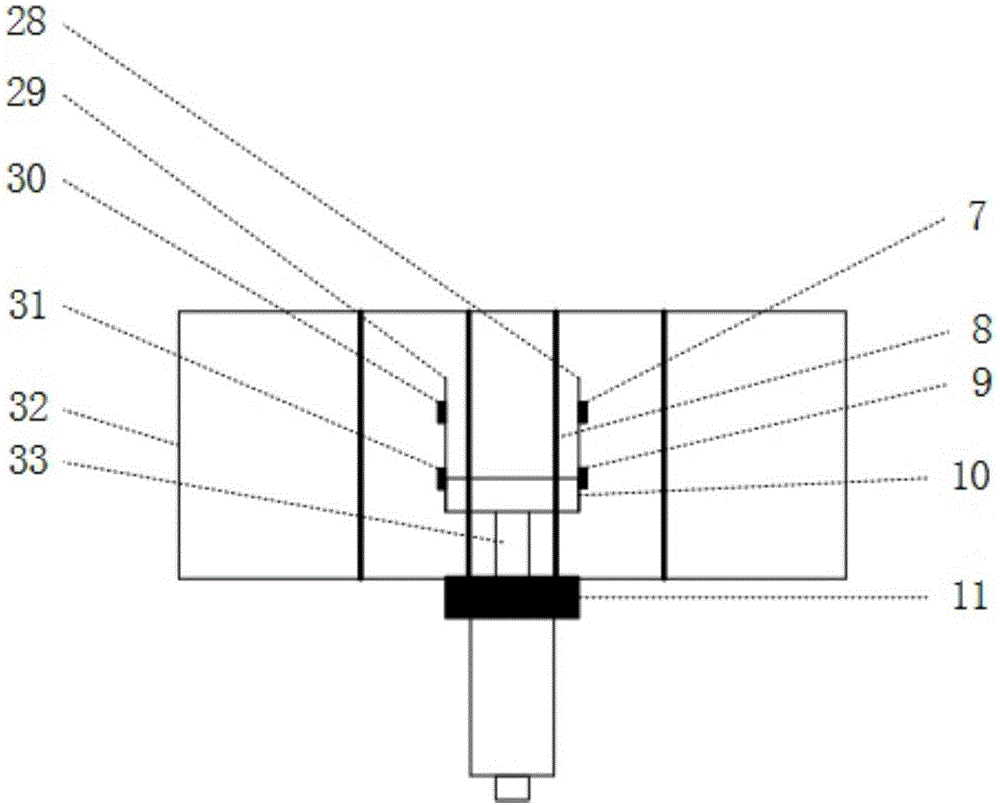
ActiveCN106772134ALarge magnetic field compensation rangeSimple structureMagnetic field offset compensationHelmholtz coilPhysical field
The invention discloses an automatic magnetic field compensation device. The automatic magnetic field compensation device comprises a first magnetic reluctance chip, a second magnetic reluctance chip, a third magnetic reluctance chip and a fourth magnetic reluctance chip which are used for measuring the magnetic field value in an outside environment and further comprises a fixing unit, a support unit, a collection unit, a feedback unit and a rotation unit as well as three-dimensional Helmholtz coils, three-dimensional one-order gradient coil and a two-order gradient coil unit which are used for shimming. The invention further discloses an automatic magnetic field compensation method. The magnetic field compensation range is large, the device is simple in structure and convenient to operate, and the device and method are applicable to physical field research based on low-magnetic-field environment signal detection and atom magnetometer and have great significance.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Fe-Ga based magnetostrictive wire and preparation method thereof
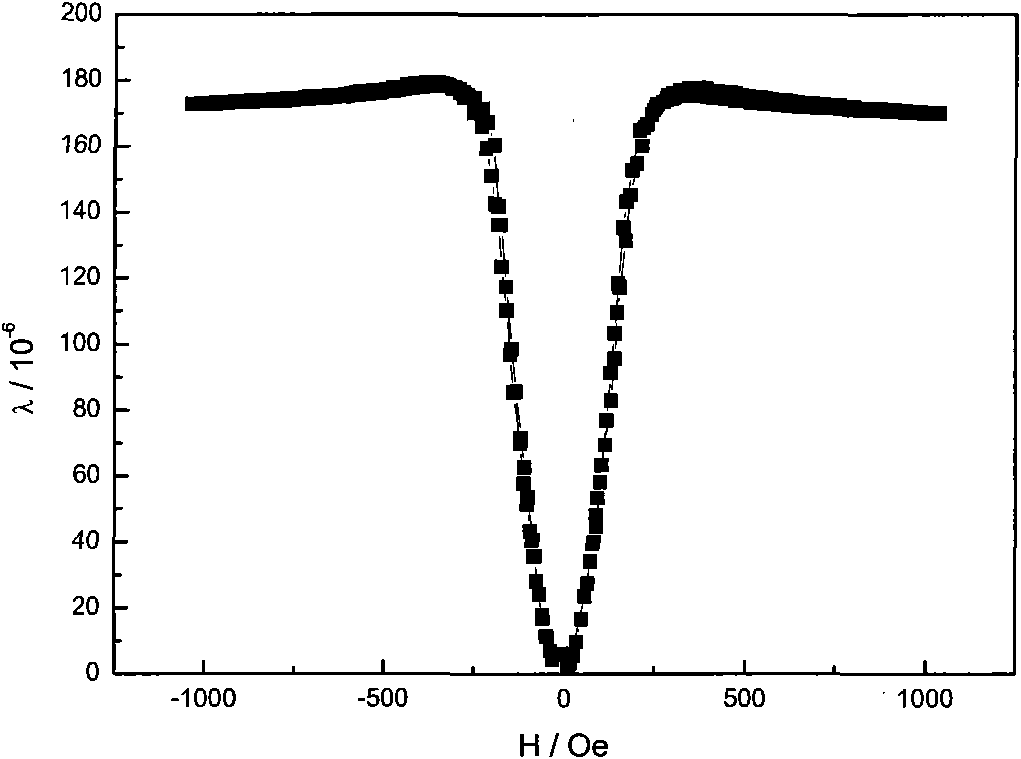
ActiveCN101812628AImprove surface qualityExcellent low-field magnetostrictive performanceMagnetostrictive material selectionAlloyProcessing cost
The invention relates to an Fe-Ga based magnetostrictive wire and a preparation method thereof. The raw material component used by the method is (Fel-x-yGaxMy)l-z(NC)z, wherein M is selected from one or more types of all transition elements other than Fe, B, Be, Al, In, Ge, Sn, Sb, Bi, Pb, S and Se, and N is Nb, Ti, Si, Zr, Mo and the like, x is equal to 0.10 to 0.30, y is equal to 0.00 to 0.05, z is equal to 0.00 to 0.02, and the balance Fe. The method processes an Fe-Ga alloy into a finished wire through cold- or warm-hydrostatic extrusion. The invention solves the problems of poor plasticity, larger flow friction resistance and high processing cost when in Fe-Ga alloy plastic processing. The diameter of the prepared Fe-Ga based magnetostrictive wire is between 0.01mm and 2mm, the surface finishment is high, and the magnetostrictive properties under the low-magnetic field environment can reach 180*10-6.
Owner:BEIJING MAGORIENTAL MATERIALS TECH CO LTD
Novel fiber optic gyro interference light path based on photonic crystal fiber
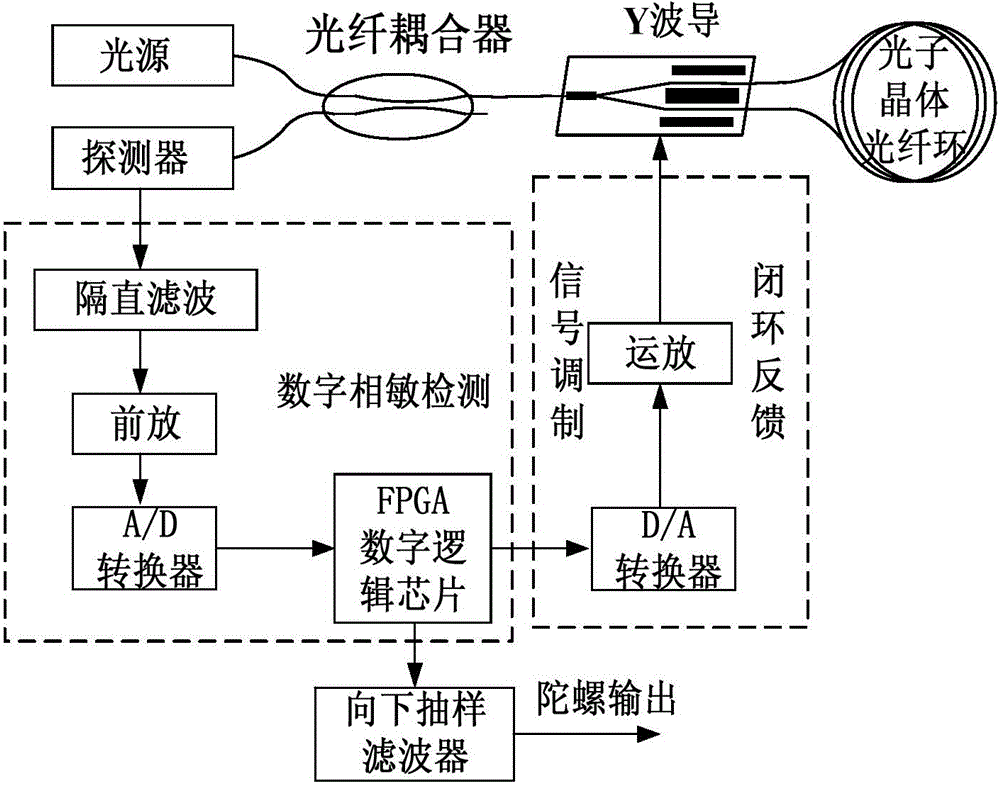
ActiveCN104316040AAvoid lossPrevent mode field distortioSagnac effect gyrometersGyroscopeRefractive index
A novel fiber optic gyro interference light path based on photonic crystal fiber includes a photonic crystal fiber ring and a Y waveguide integrated optical device. The optical fiber ring adopts an refractive index guided photonic crystal fiber; for winding of the fiber ring, a mode of solidifying one layer after winding is employed; and the Y waveguide tail fiber employs the same type of fiber as the optical fiber ring. The design of photonic crystal fiber meets the requirements of birefringence of gyro and at the same time has the mode field as Y waveguide chip, and a shrinkage cavity method is used for further expansion of the field mode of the optical fiber, so as to reduce additional loss caused by optical fiber splicing. The designed interference optical path has the characteristics of good polarization stability, low magnetic field polarization sensitivity and radiation resistance; the fiber optic gyro using the interference light path has the characteristics of radiation resistance, good temperature stability and low magnetic field sensitivity, and is especially can be used as high precision fiber optic gyroscope for satellite and other space vehicles.
Owner:BEIJING AEROSPACE TIMES OPTICAL ELECTRONICS TECH
Head-mountable adjustable devices for generating magnetic fields
ActiveUS9962555B1Easy to tuneFlexible adjustmentElectroencephalographyElectrotherapyEngineeringMagnet
Helmets for applying a magnetic field to the head of a subject, comprising: a housing comprising a concave surface configured to receive a portion of the head of the subject; a motor coupled to one or more of: a first permanent magnet via a first axle along a first axis of rotation, wherein the first axle drives movement of the first magnet; a second magnet via a second axle along a second axis of rotation wherein the second axle drives movement of the second magnet; and a third magnet via a third axle along the third axis of rotation wherein the third axle drives movement of the third magnet, wherein the axes are parallel; and a fit mechanism comprising a adjuster coupled to the first magnet, wherein movement of the adjustor moves the first magnet independently of the second or the third magnet.
Owner:WAVE NEUROSCI INC
Superconducting wire rod, persistent current switch, and superconducting magnet
InactiveUS20100245005A1Increase probabilityImprove reliabilitySuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor detailsElectrical conductorMetal filament
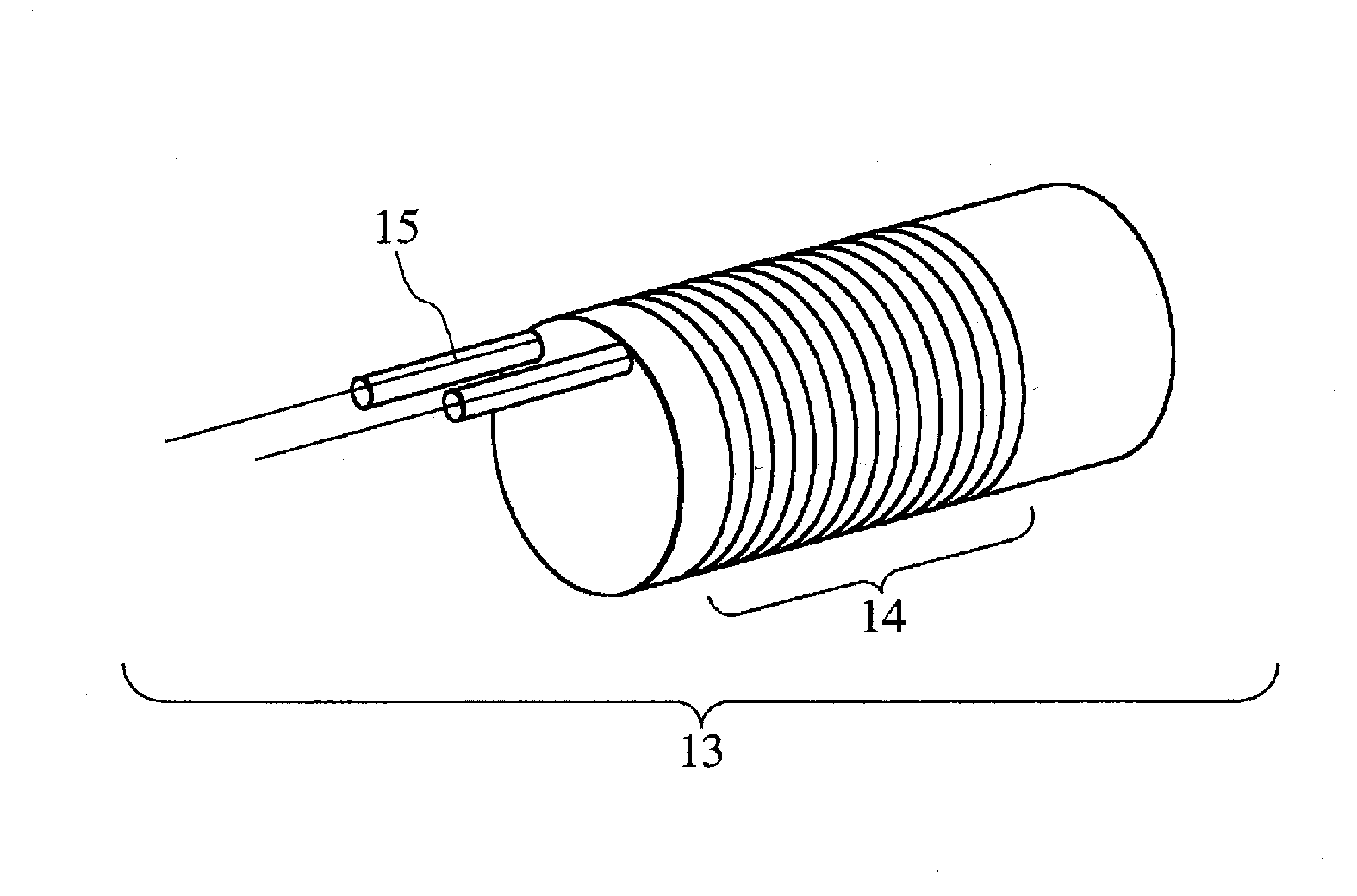
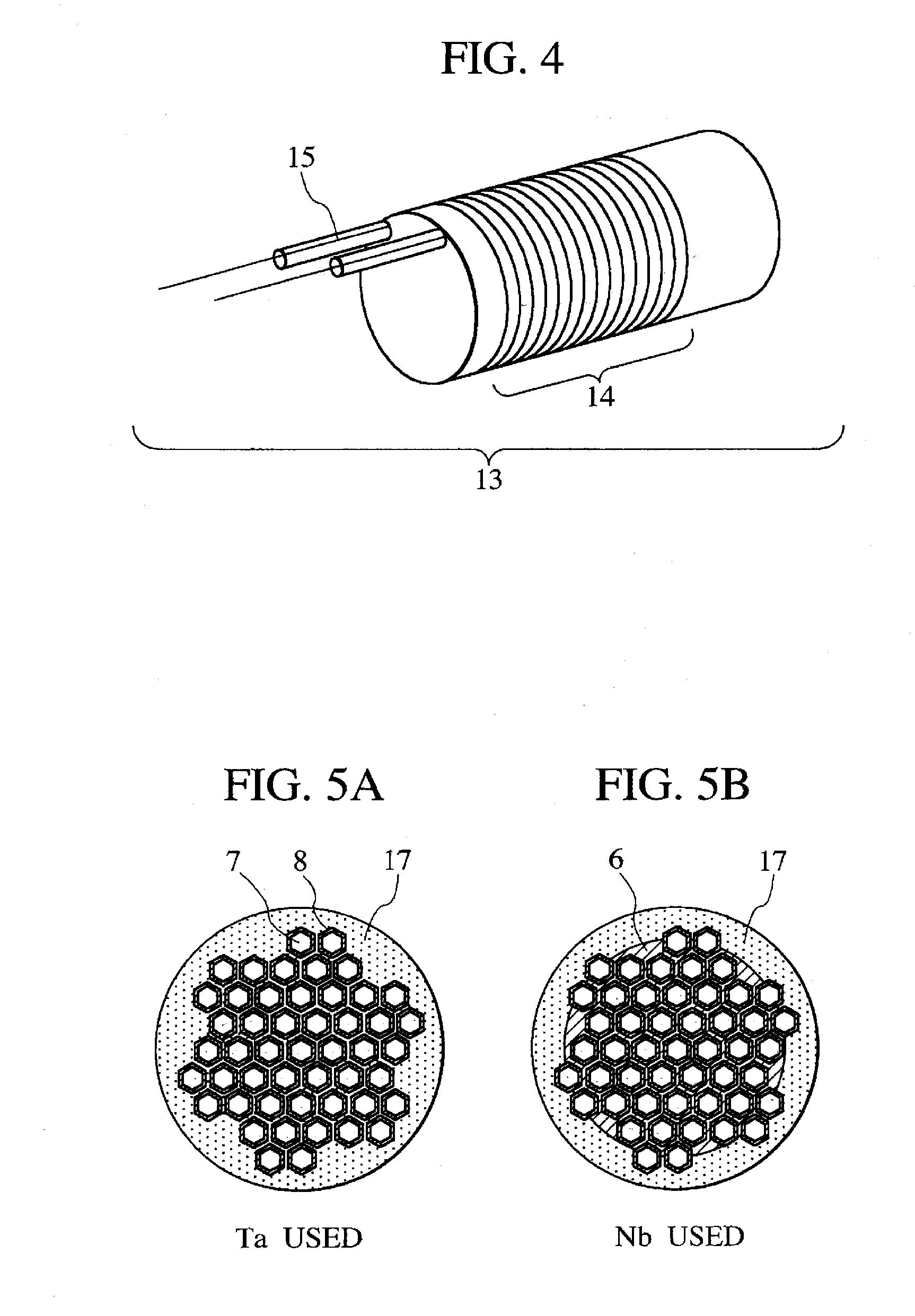
The present invention provides a superconducting wire usable in a low magnetic field region of 2 T or lower and at a temperature of 4.2 K or lower and a connection structure and a connection method for permitting such a superconducting wire use. The present invention also provides a highly reliable device that uses a superconducting wire. A superconducting wire rod according to an embodiment of the present invention includes a plurality of superconducting metal filaments, which are embedded in a metallic matrix of a normal conductor. Each superconducting metal filament is provided with a barrier layer made of a metal that does not react with Sn at a temperature between 250° C. and 500° C. The barrier layer is preferably made of Ta, Mo, or Ta- or Mo-based alloy and 0.01 μm to 1 μm in thickness.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
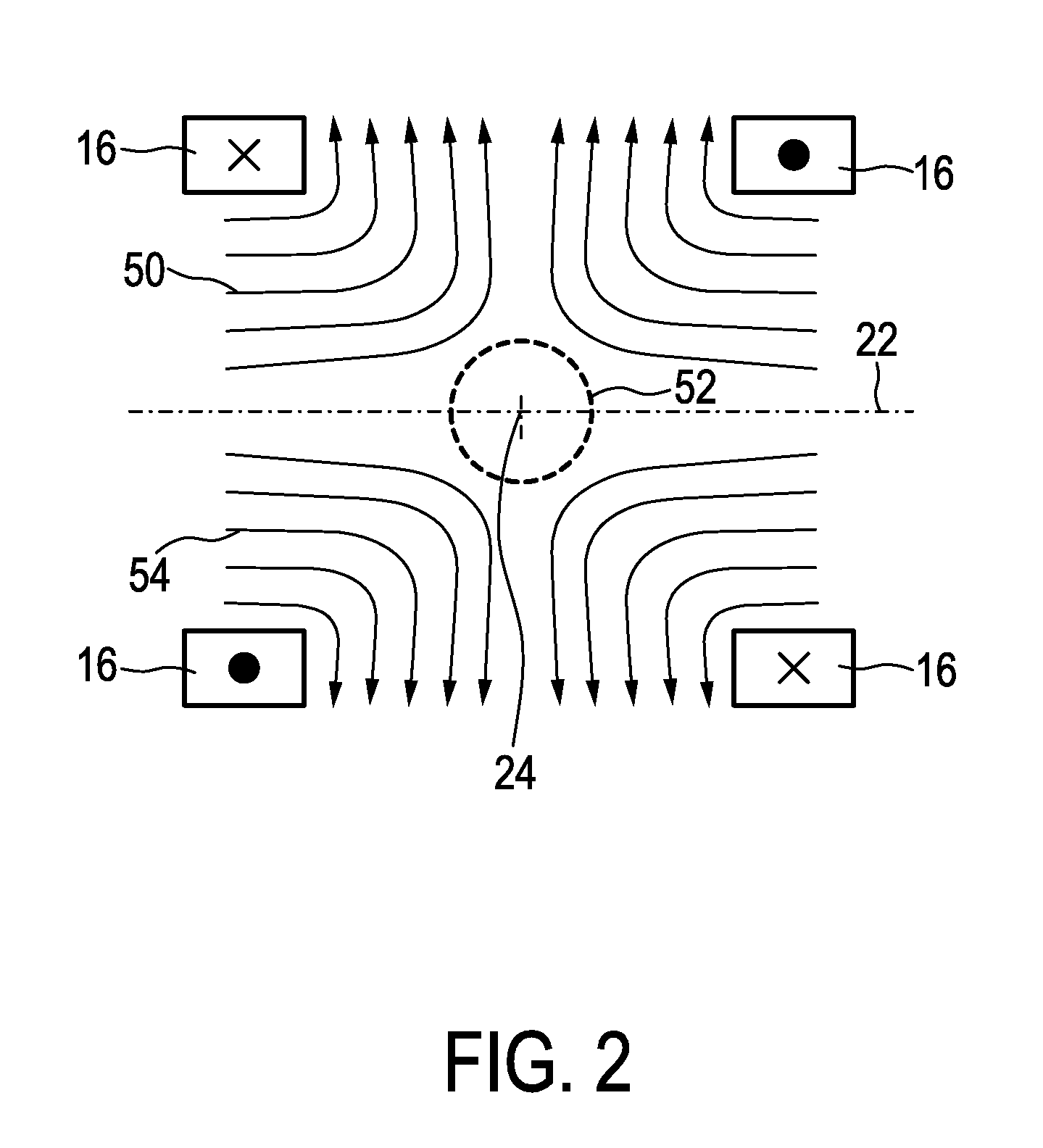
Apparatus and method for influencing and/or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view having an array of single-sided transmit coil sets
InactiveUS20120310076A1Improve image qualityExpand field of viewDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHigh magnetic field strengthMagnetization
The present invention relates to an apparatus and a method for influencing and / or detecting magnetic particles in a field of view. To increase the field of view and, at the same time, allow access to the patient during imaging, the apparatus comprises two or more transmit coil sets (200) wherein neighboring coil sets are partially overlapping, a transmit coil set comprising: a pair (210) of concentrically arranged selection field coils (211, 212) for generating a magnetic selection field (50) having a pattern in space of its magnetic field strength such that a first sub-zone (52) having a low magnetic field strength and a second sub-zone (54) having a higher magnetic field strength are formed in the field of view (28), and at least one pair (220, 230) of drive field coils (221, 222; 231, 232) for changing the position in space of the two sub-zones (52, 54) in the field of view (28) by means of a magnetic drive field so that the magnetization of the magnetic particles changes locally, said at least one pair (220, 230) of drive field coils being arranged parallel to said pair (210) of selection field coils (211, 212) and being formed by two neighboring coil loops.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com