Patents
Literature
45results about "Diagnostics using suction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
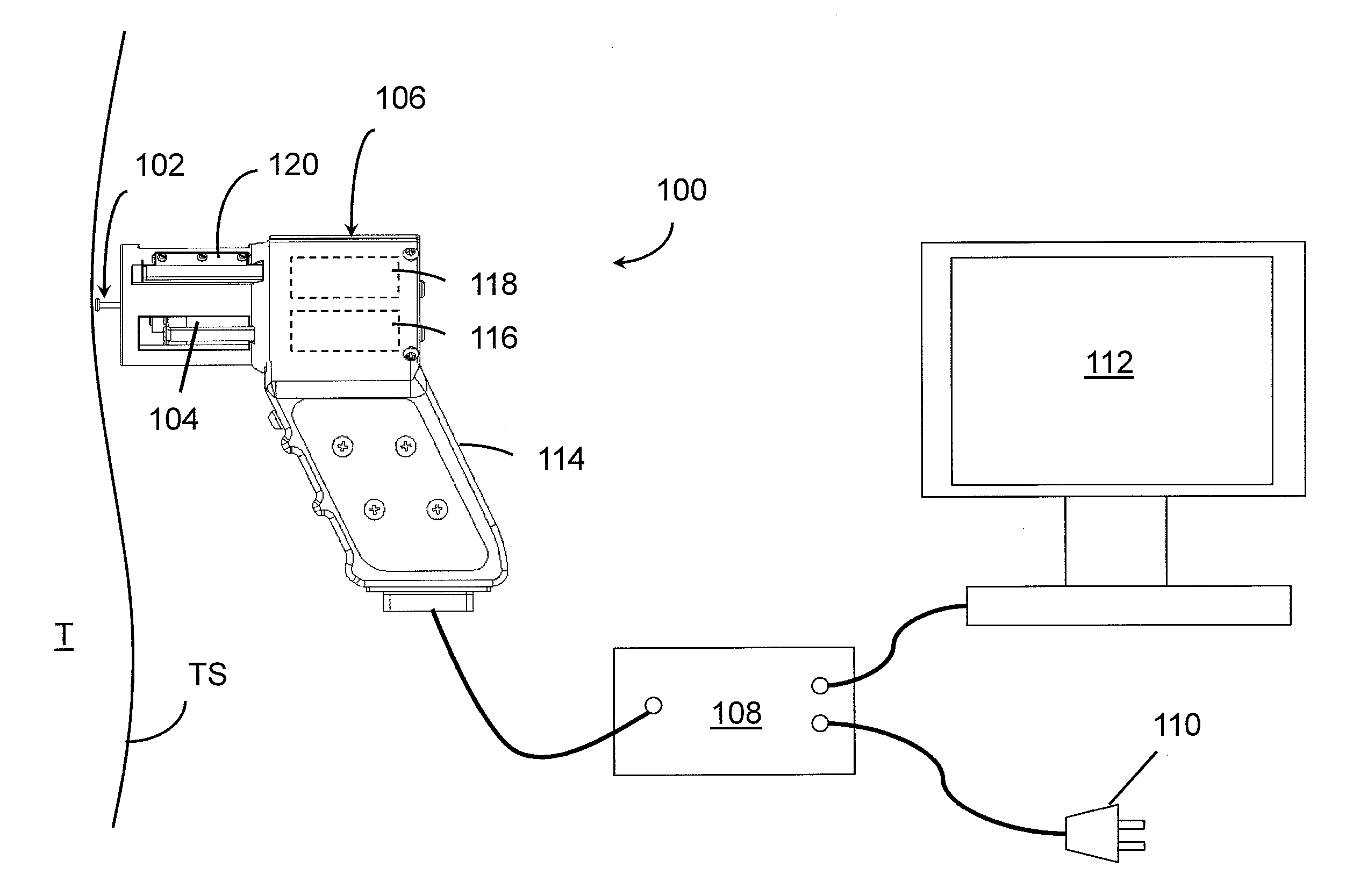
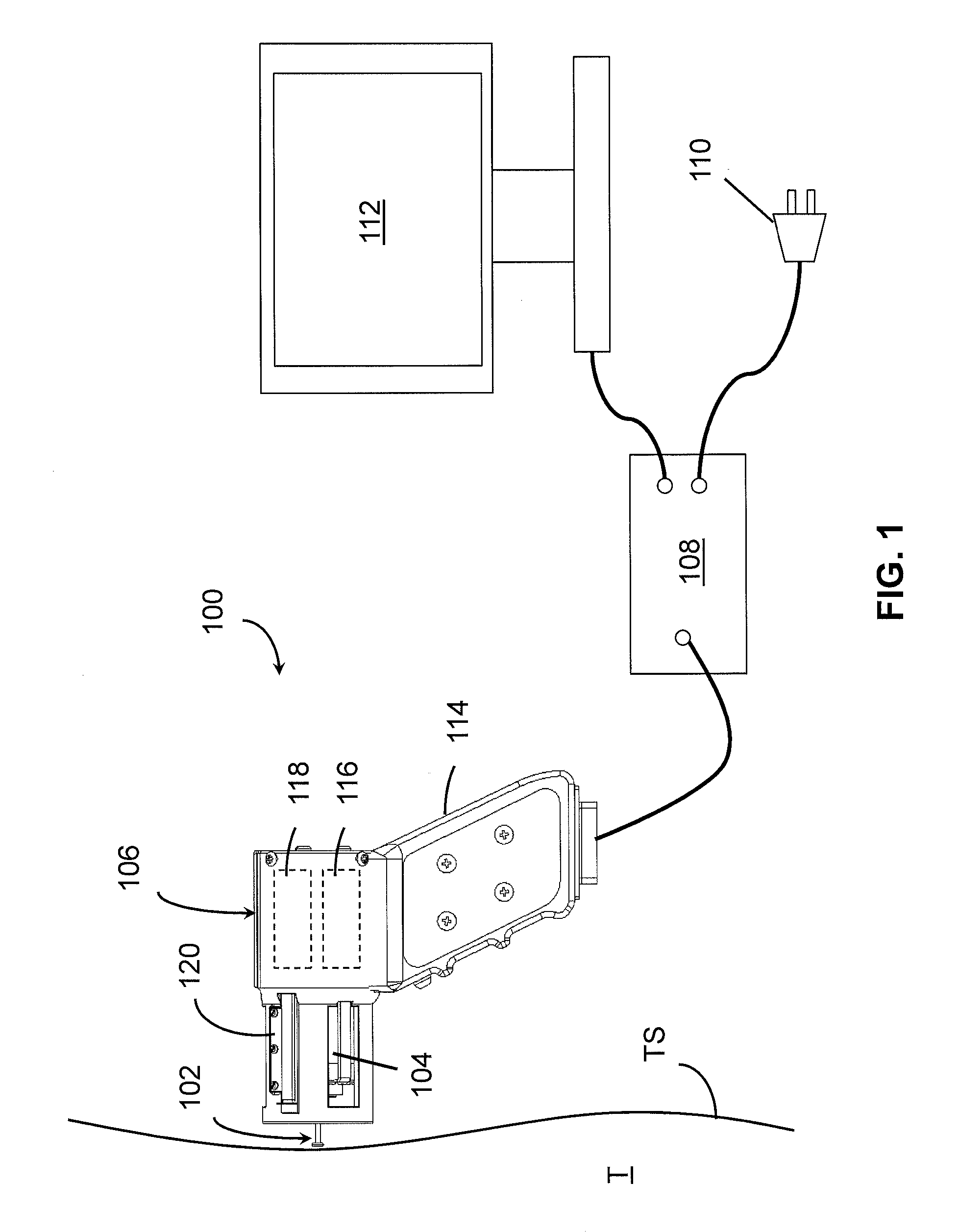
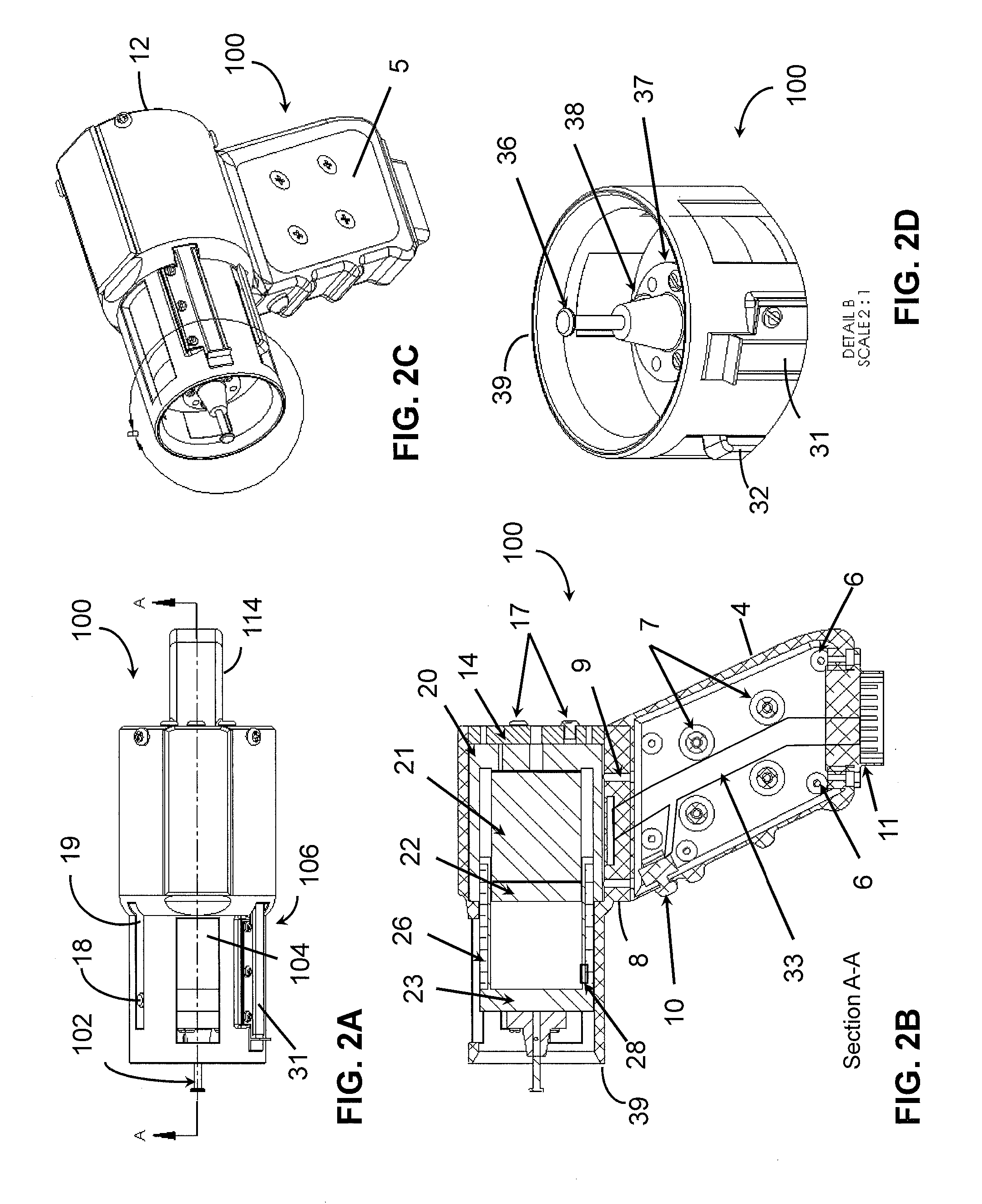
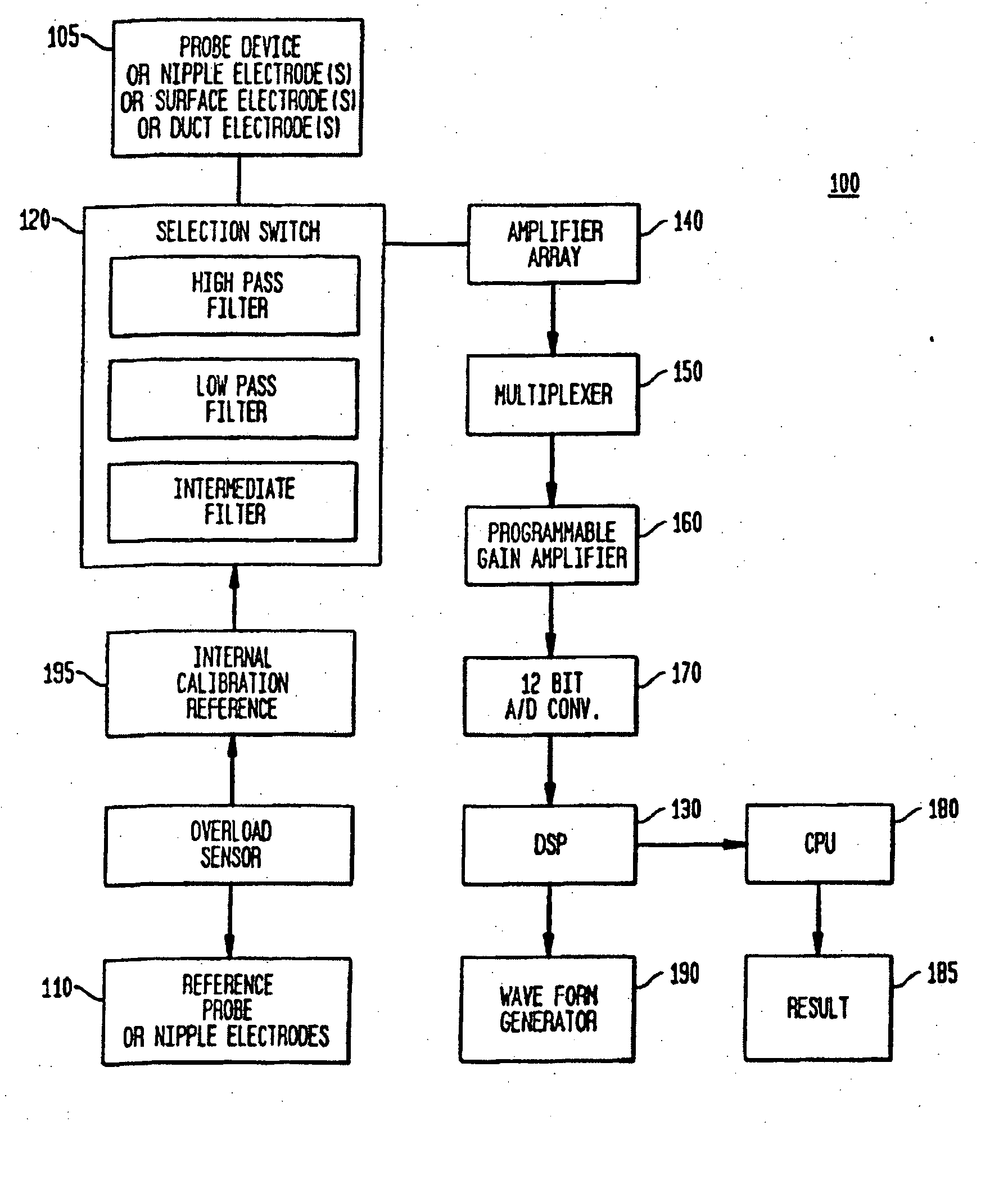
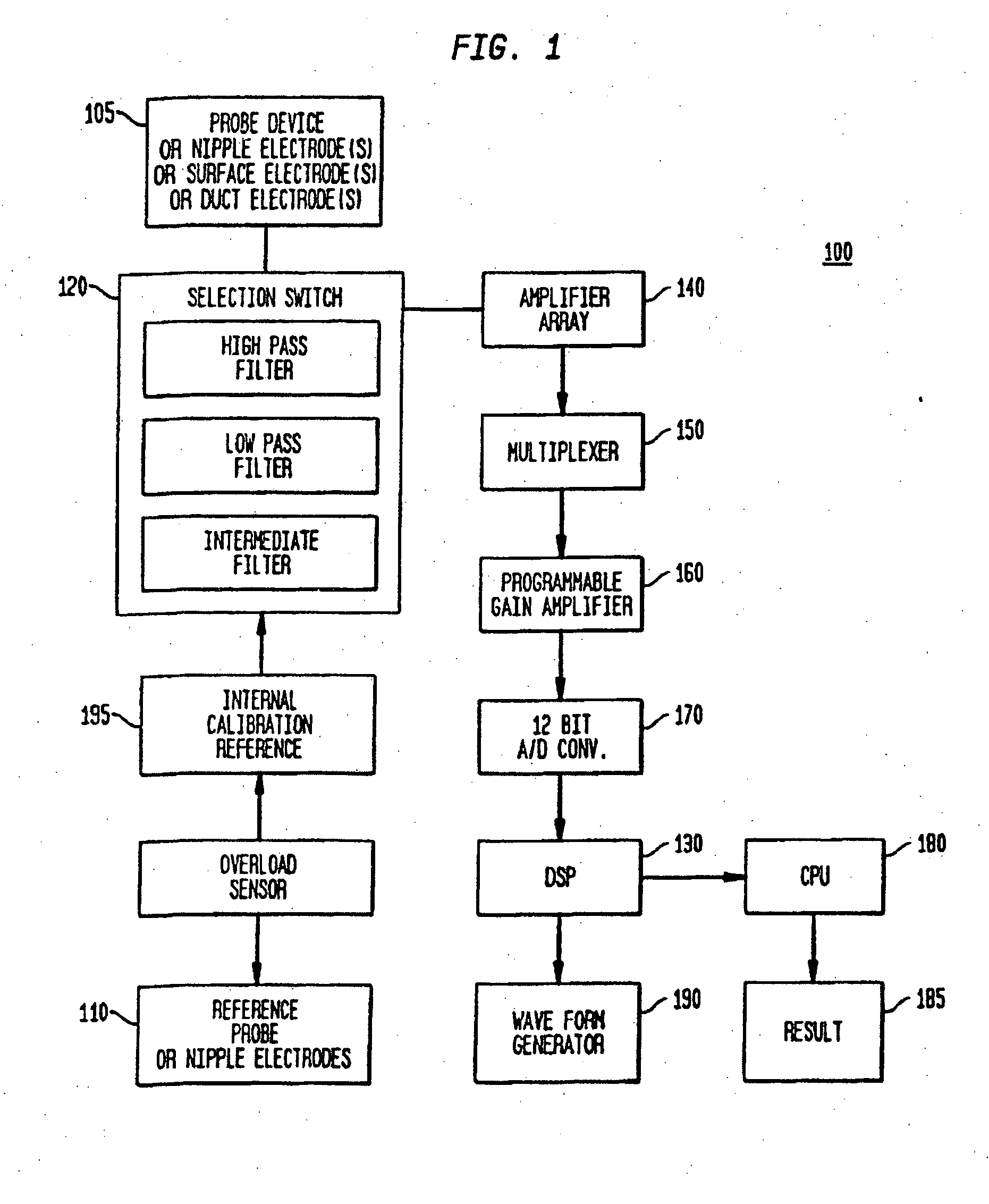
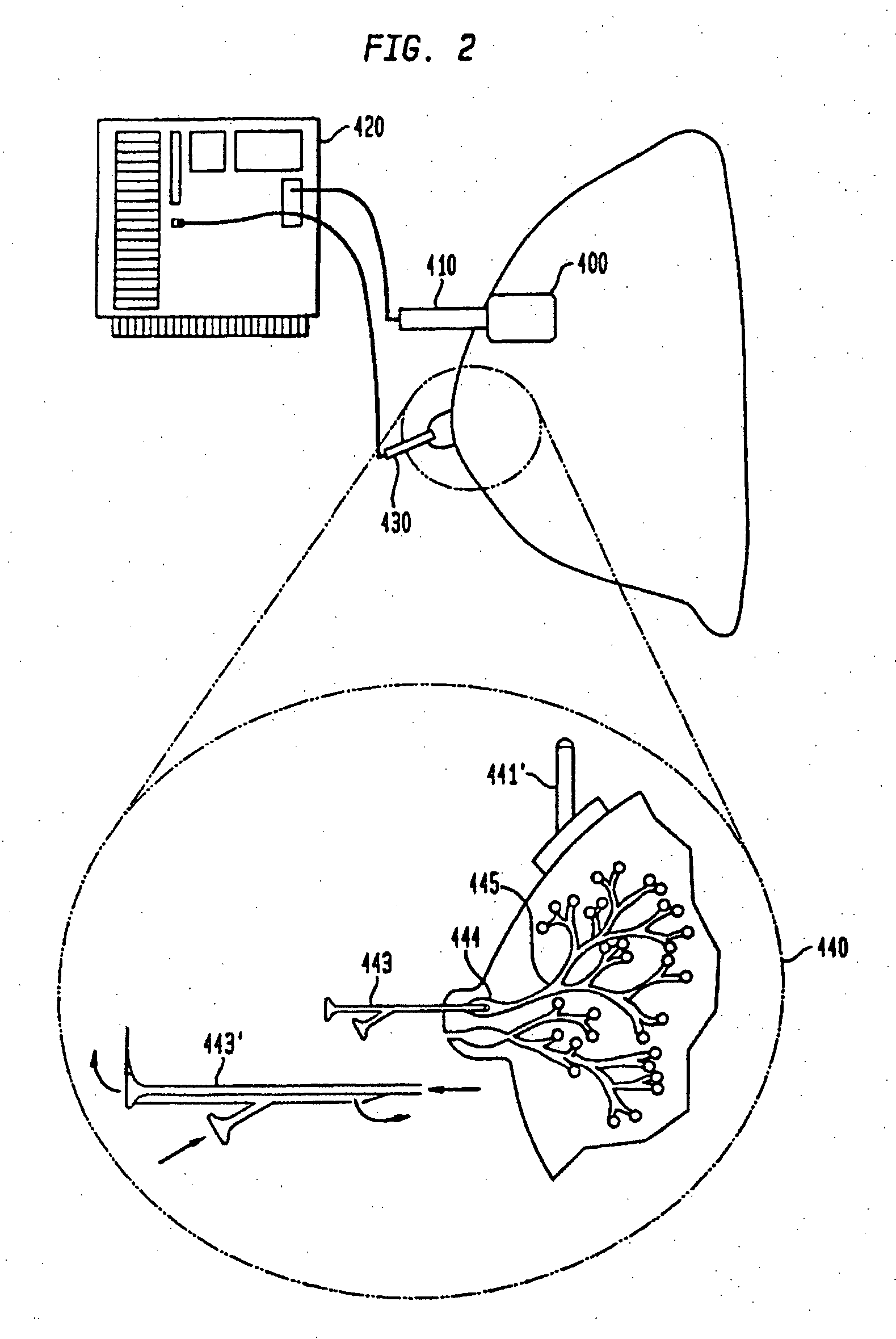
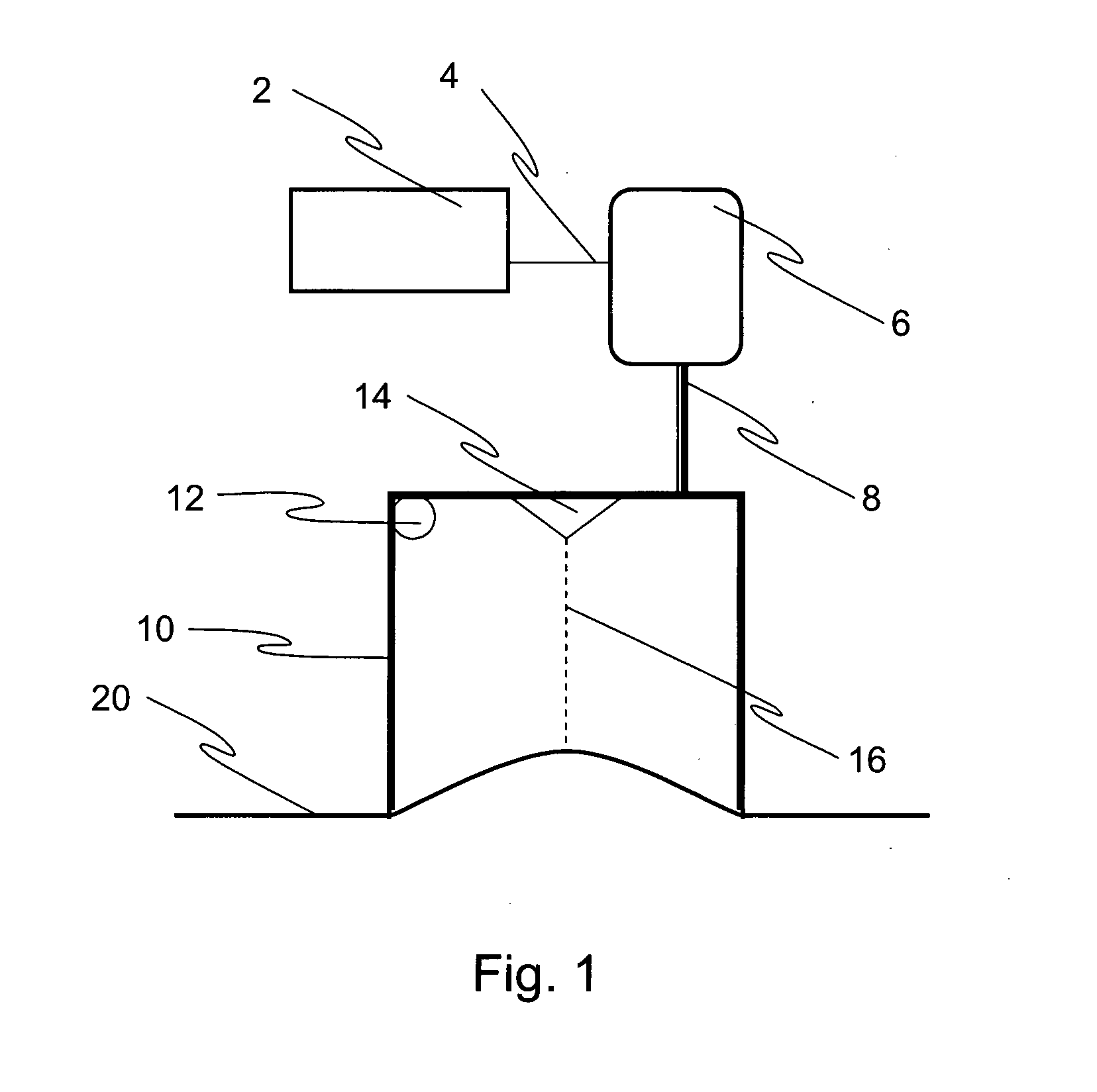
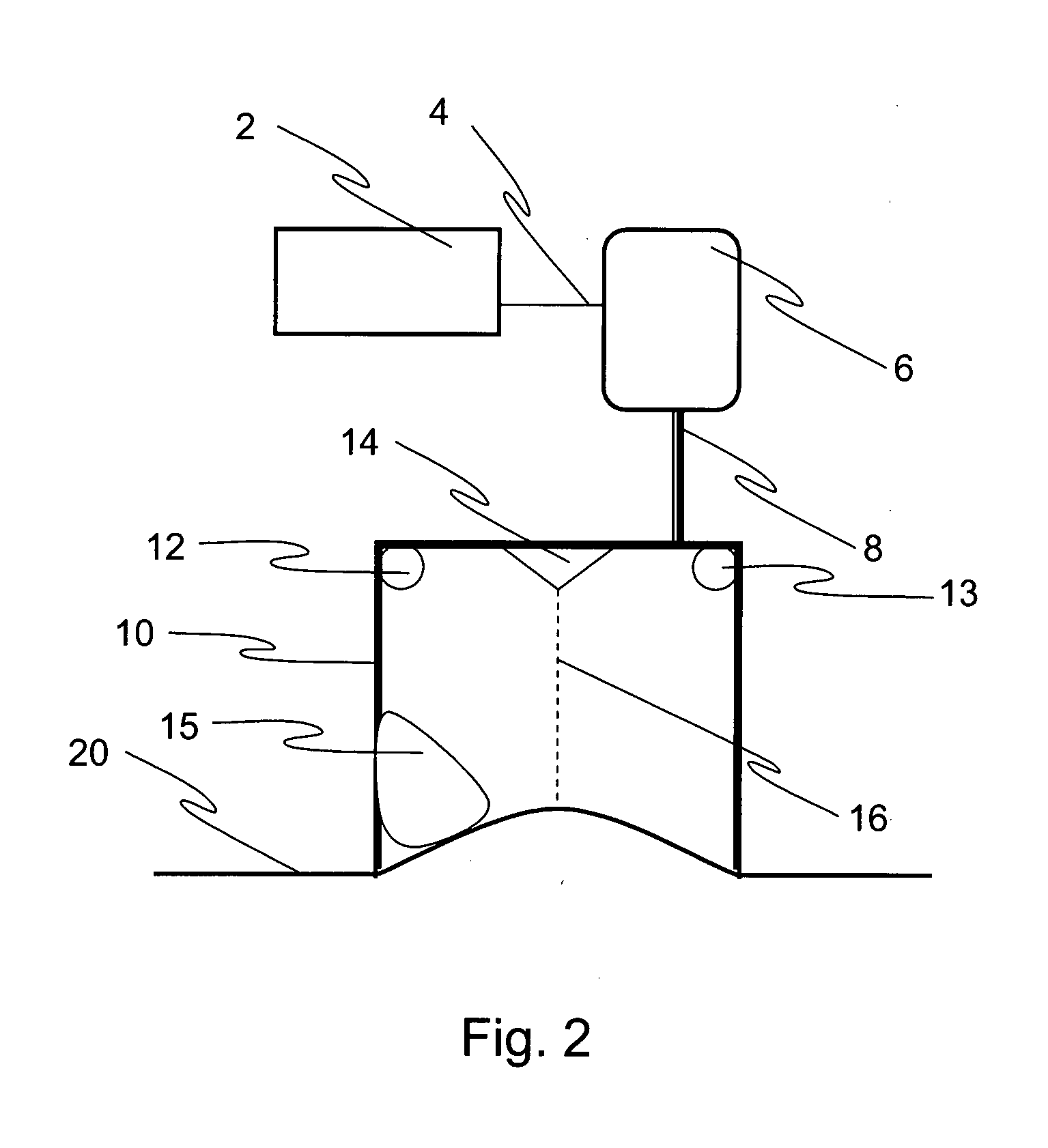
Nonlinear System Identification Techniques and Devices for Discovering Dynamic and Static Tissue Properties
ActiveUS20110054354A1Quickly mechanical propertyLow costDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureAccelerometerEngineering
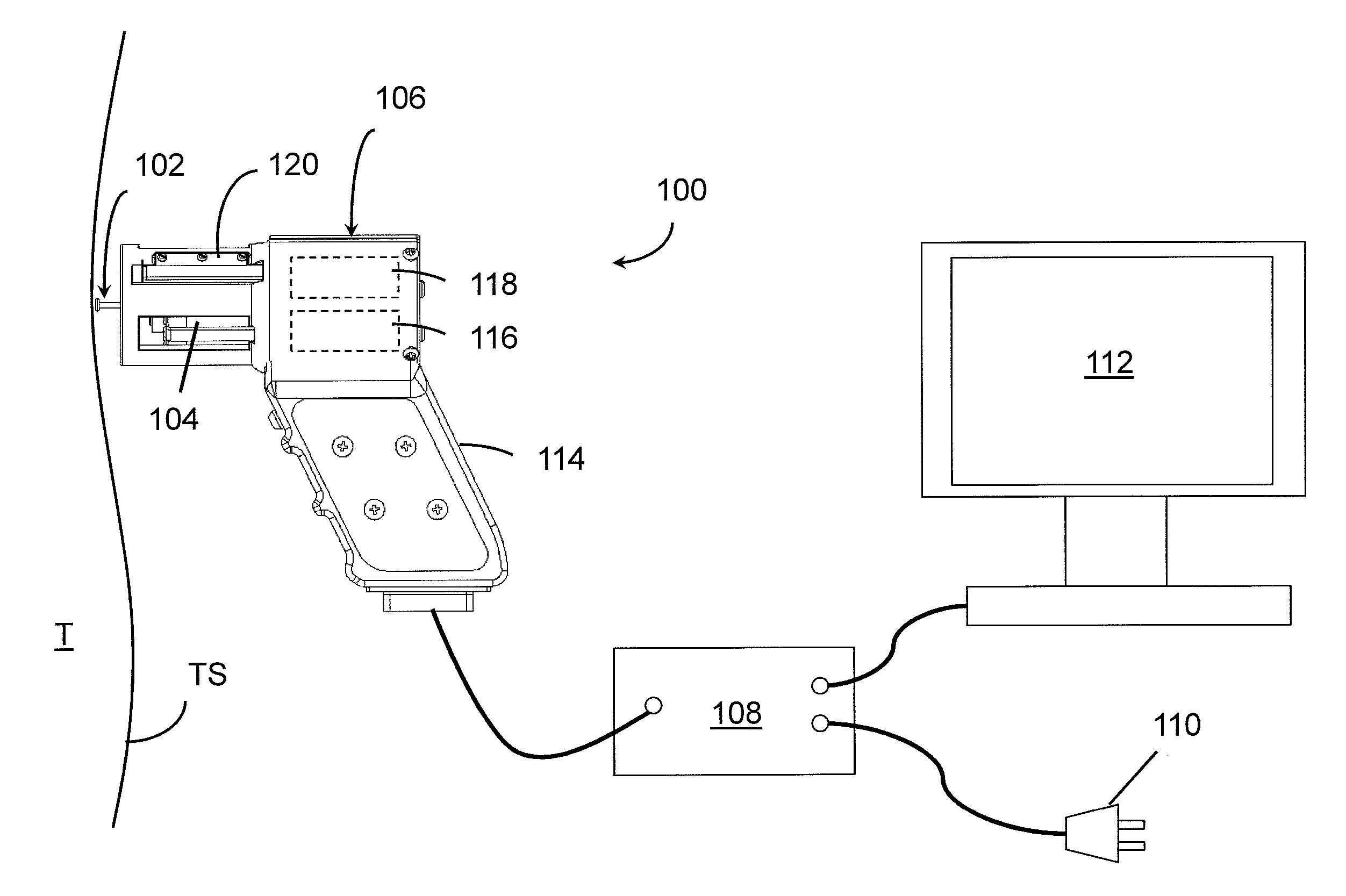
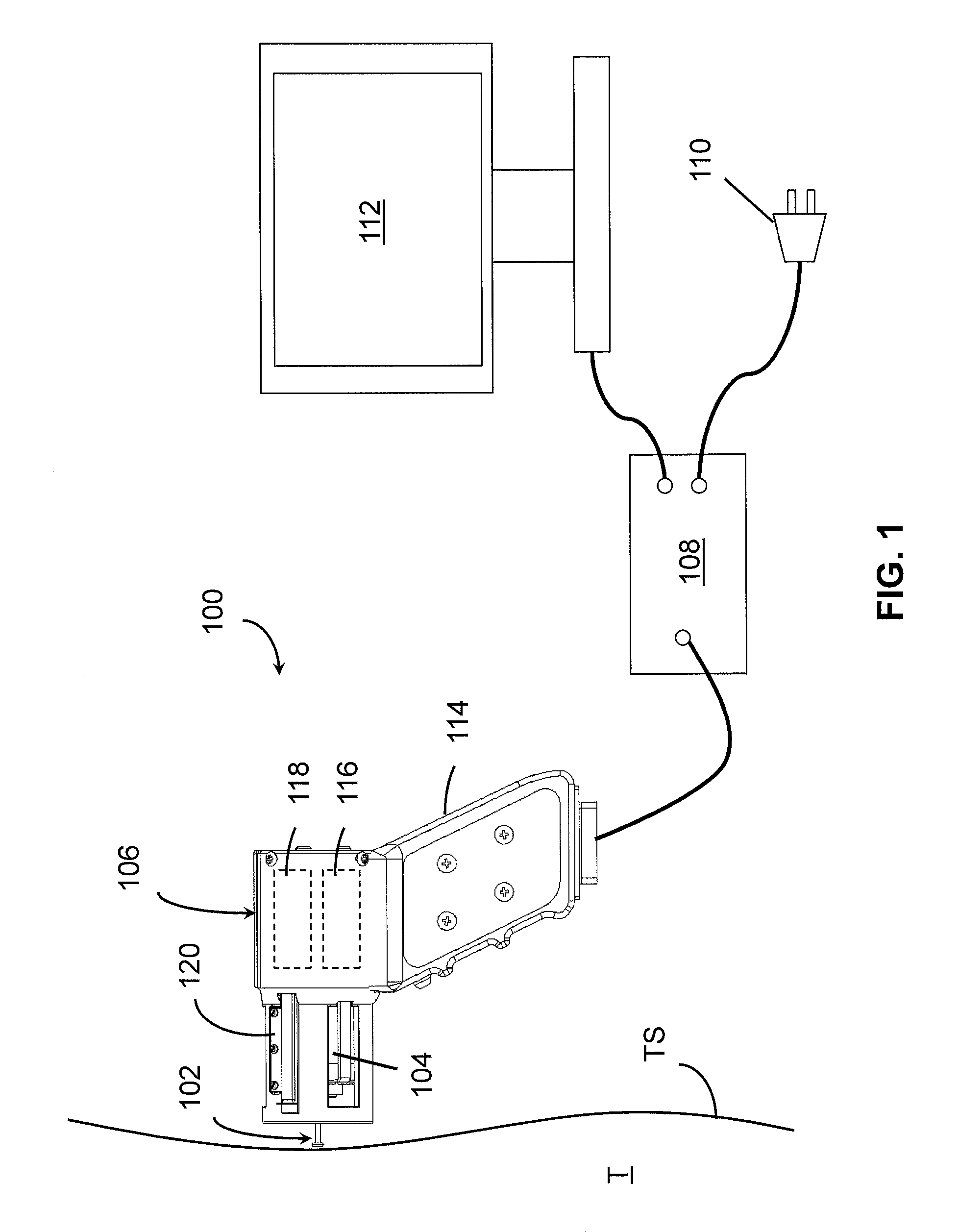
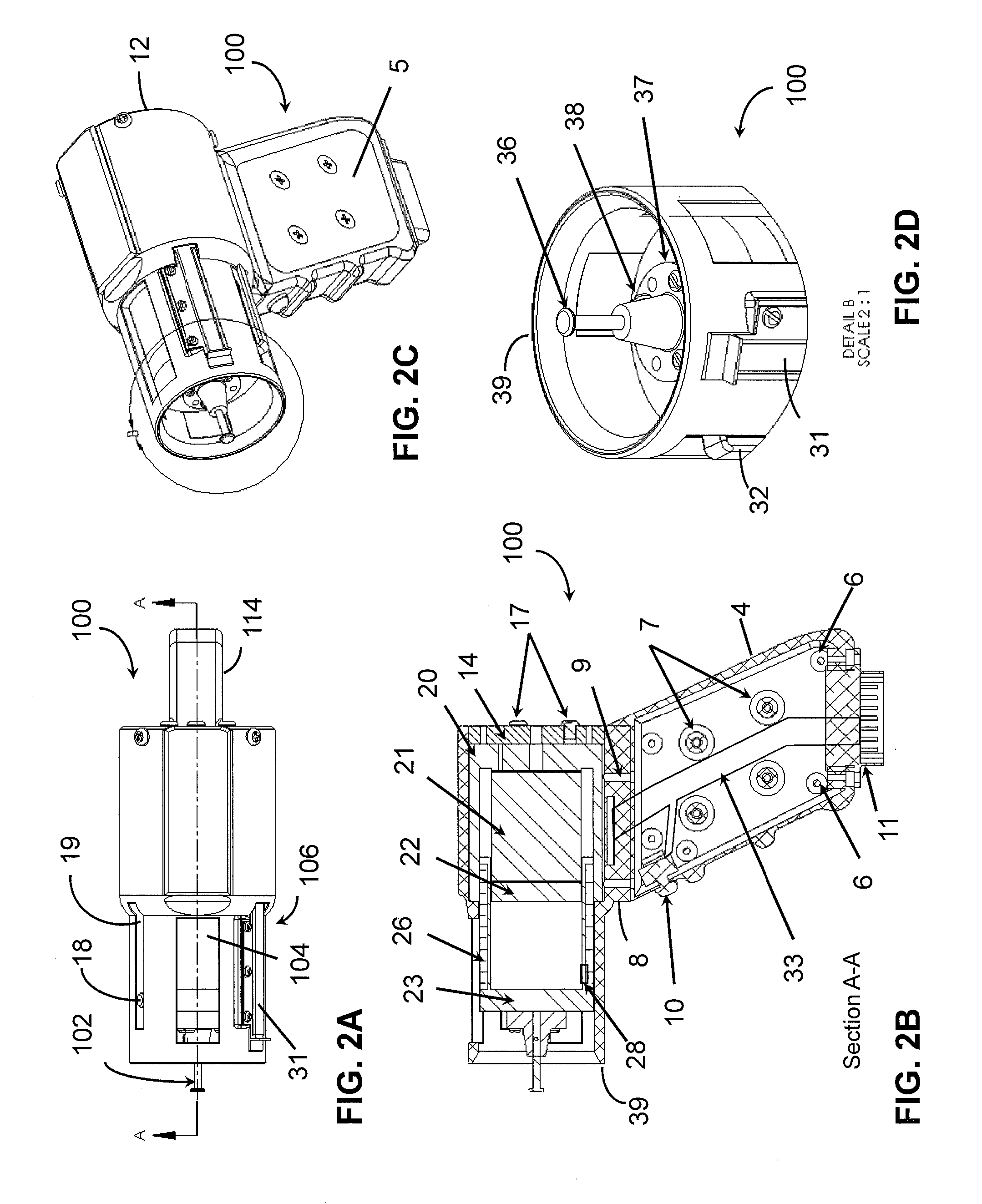
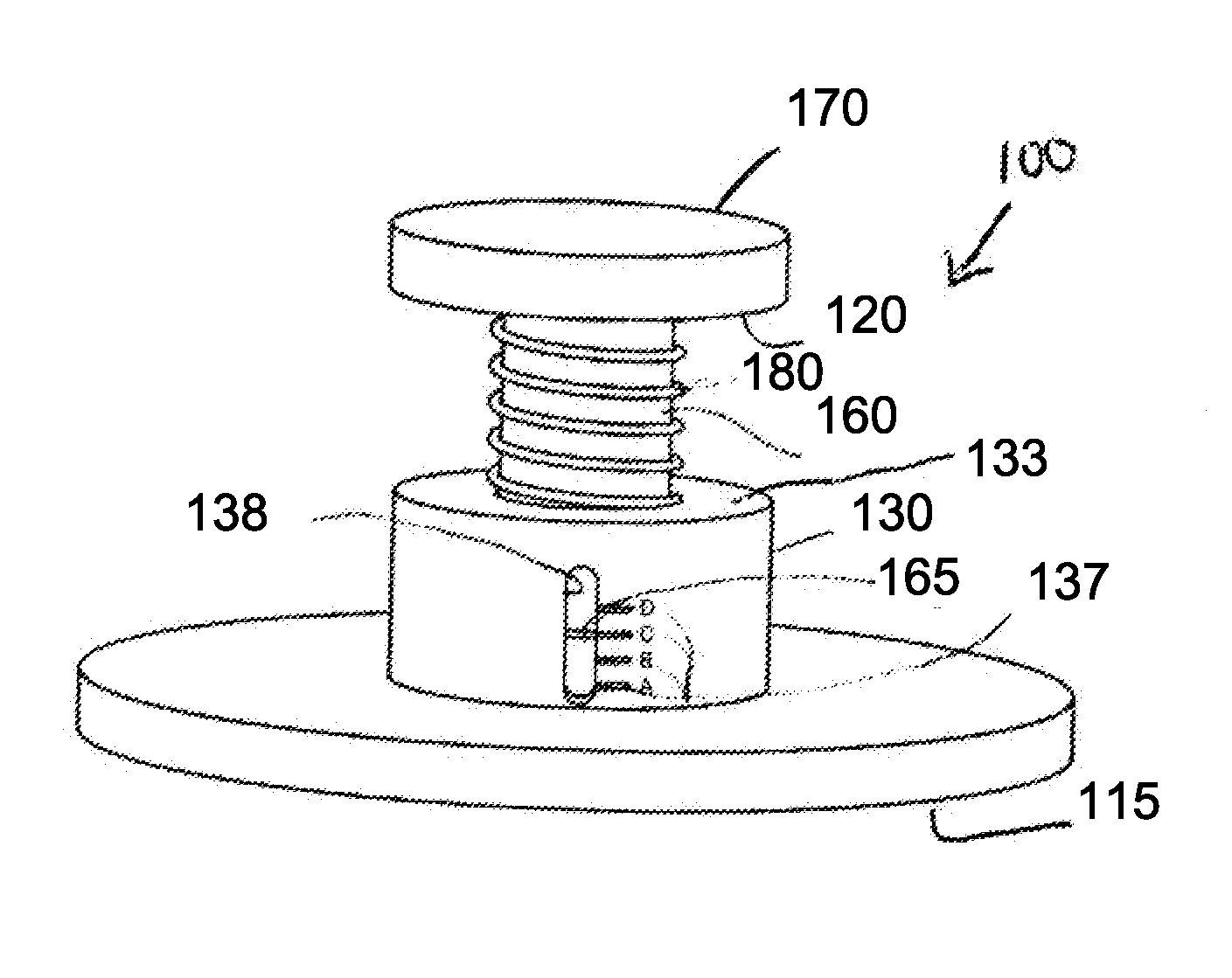
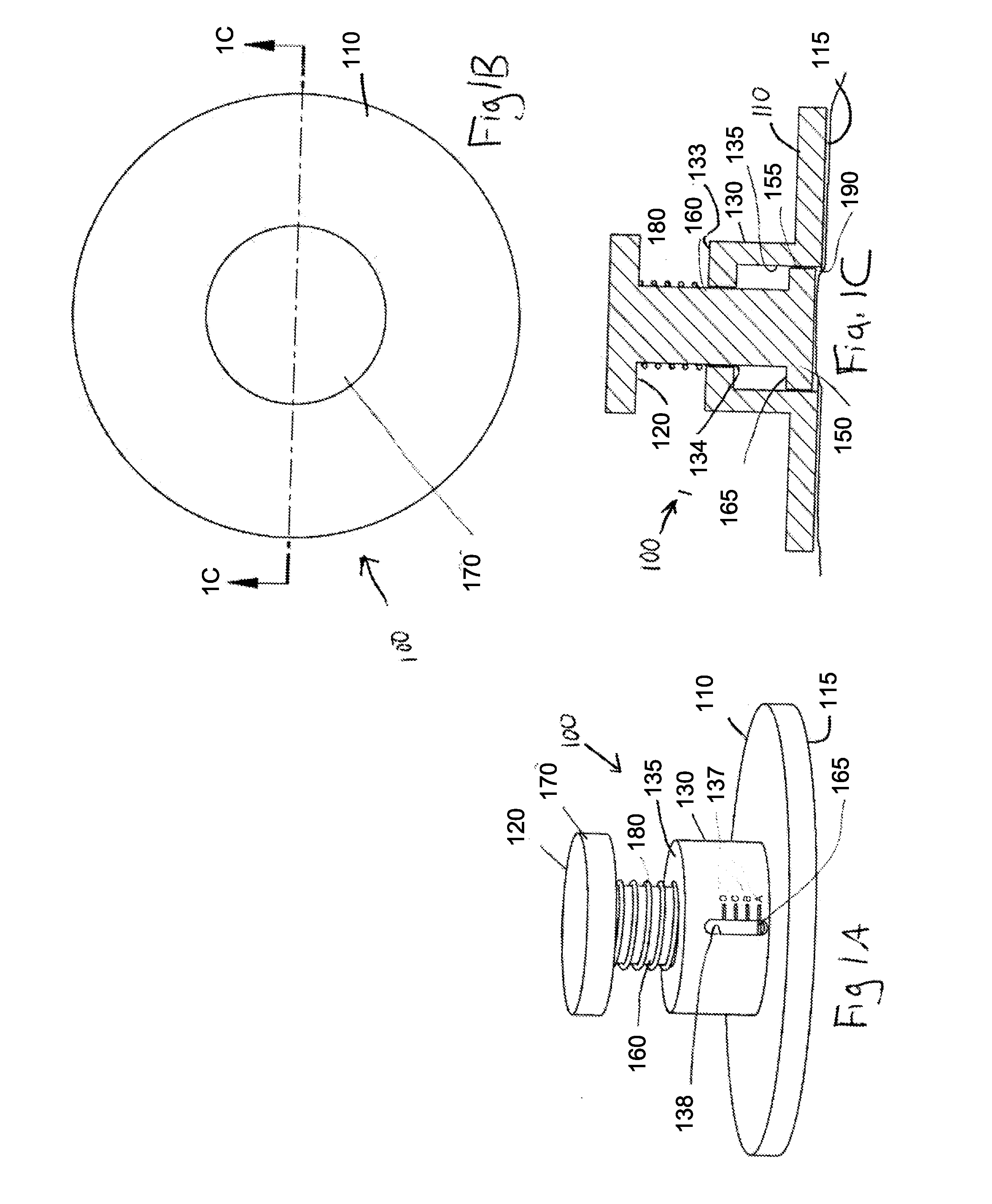
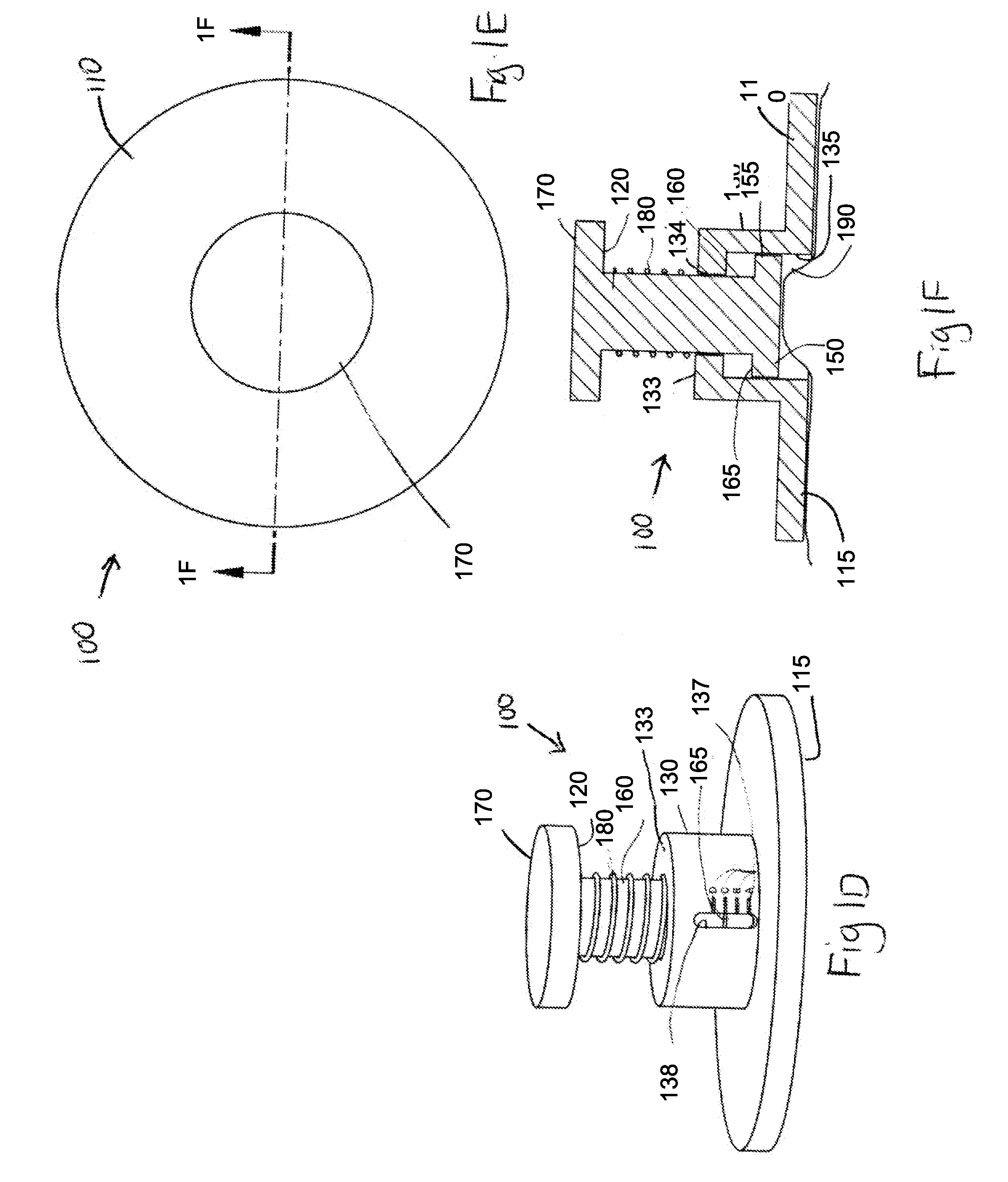
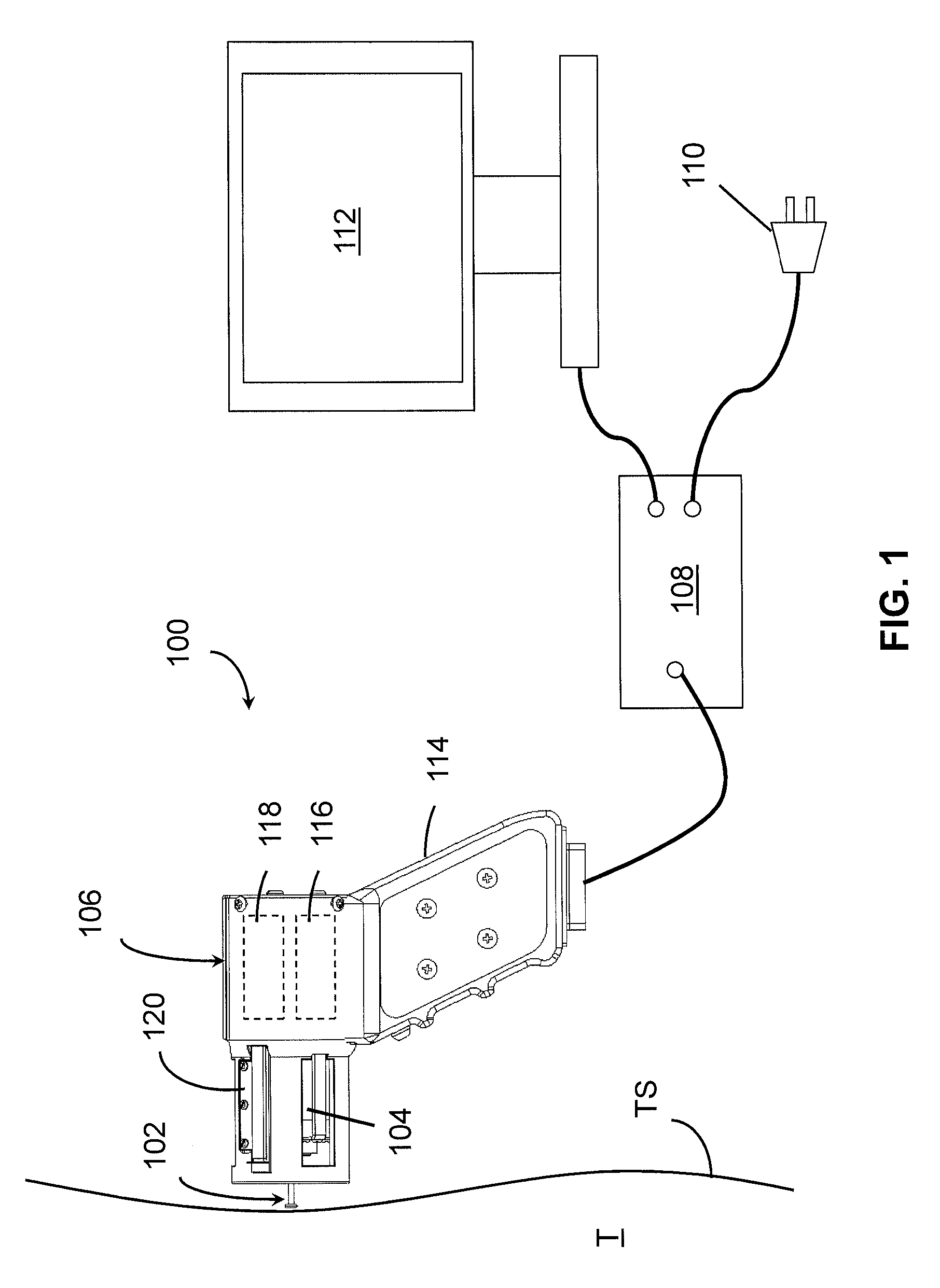
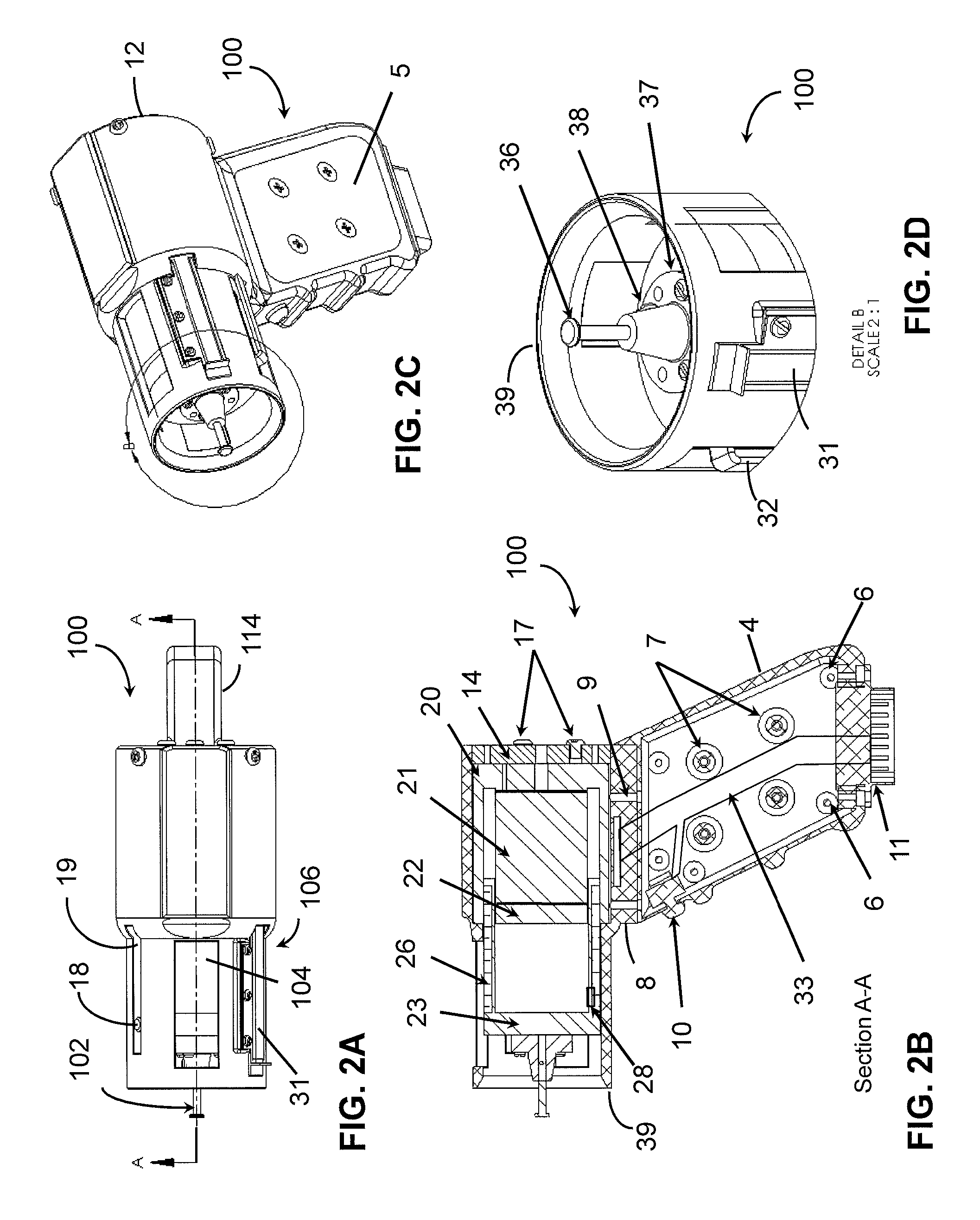
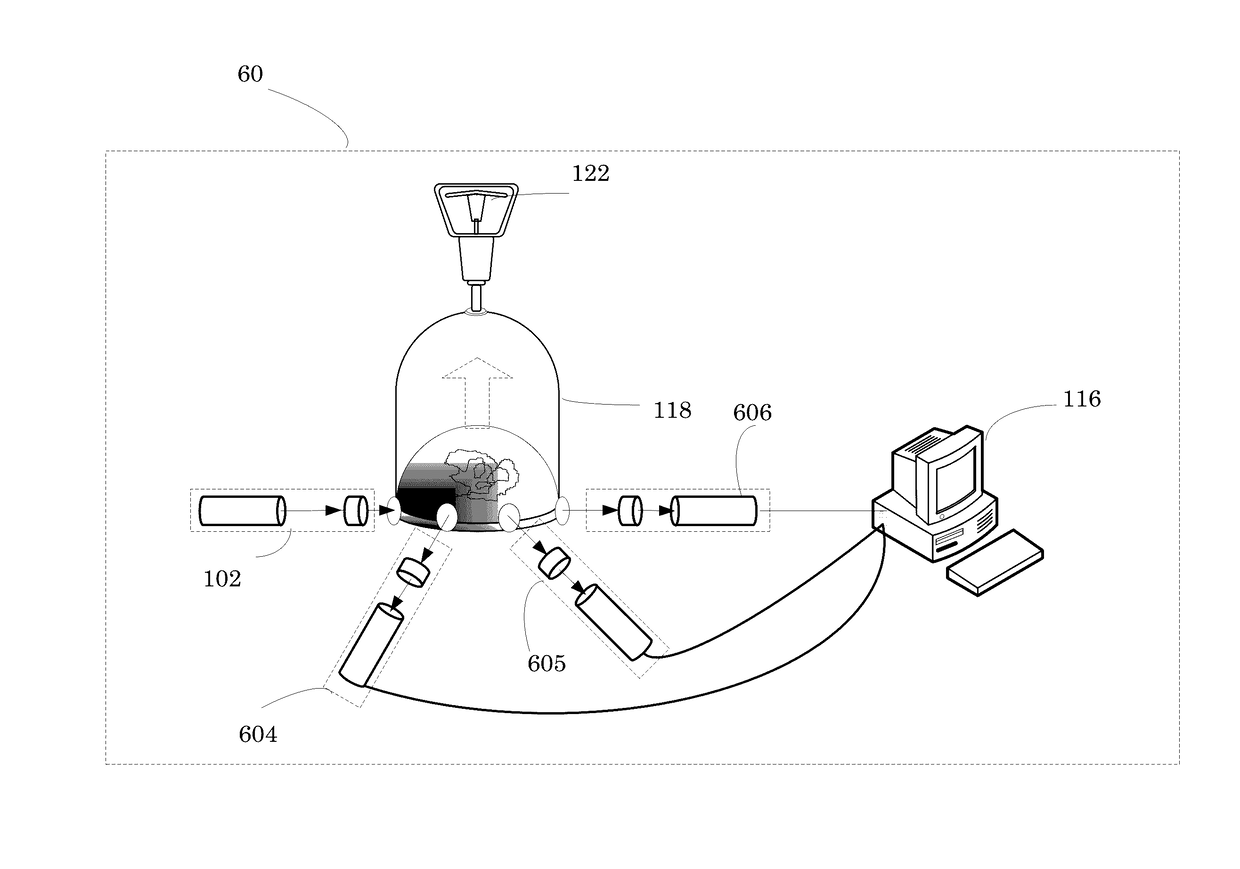
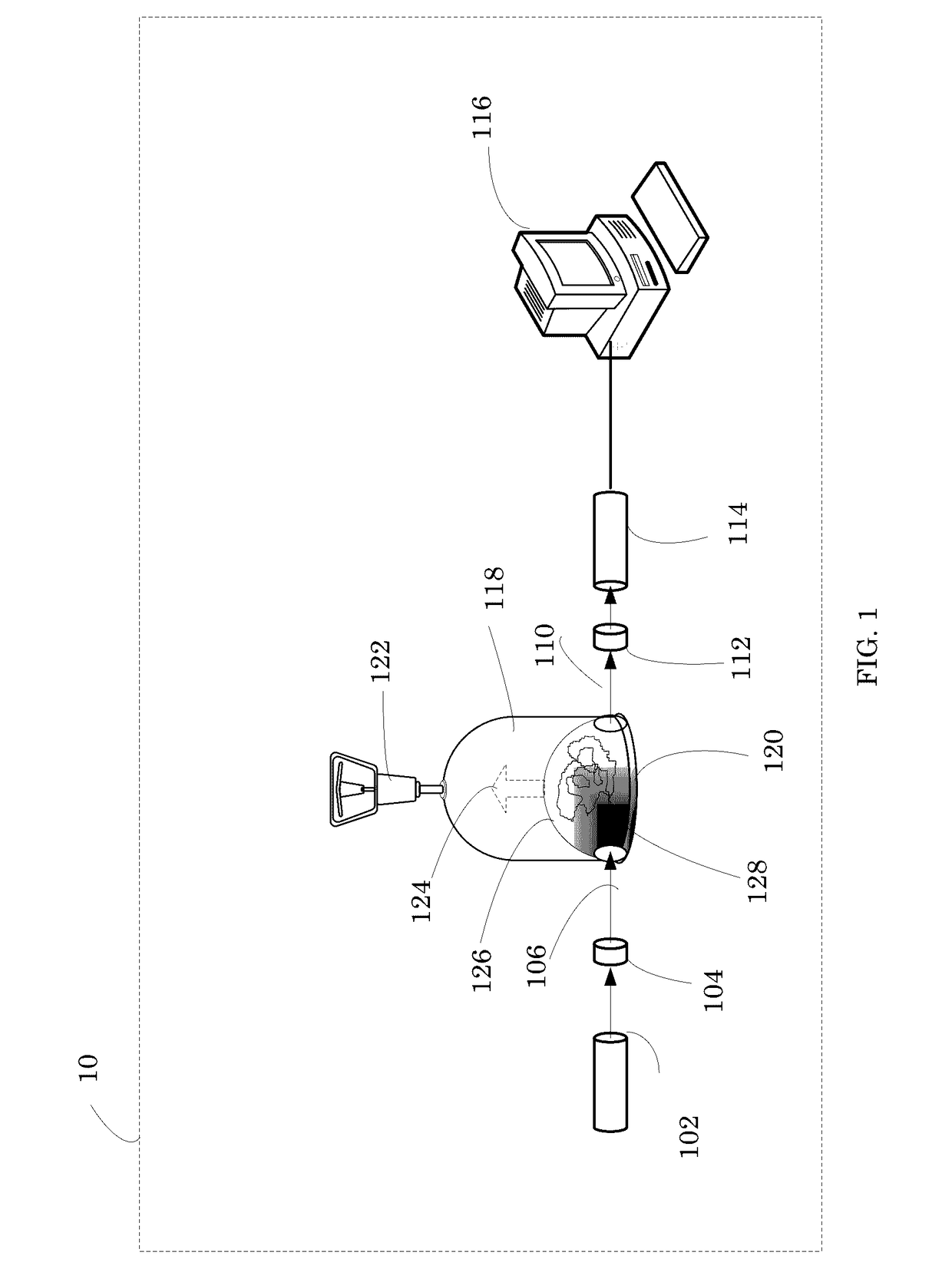
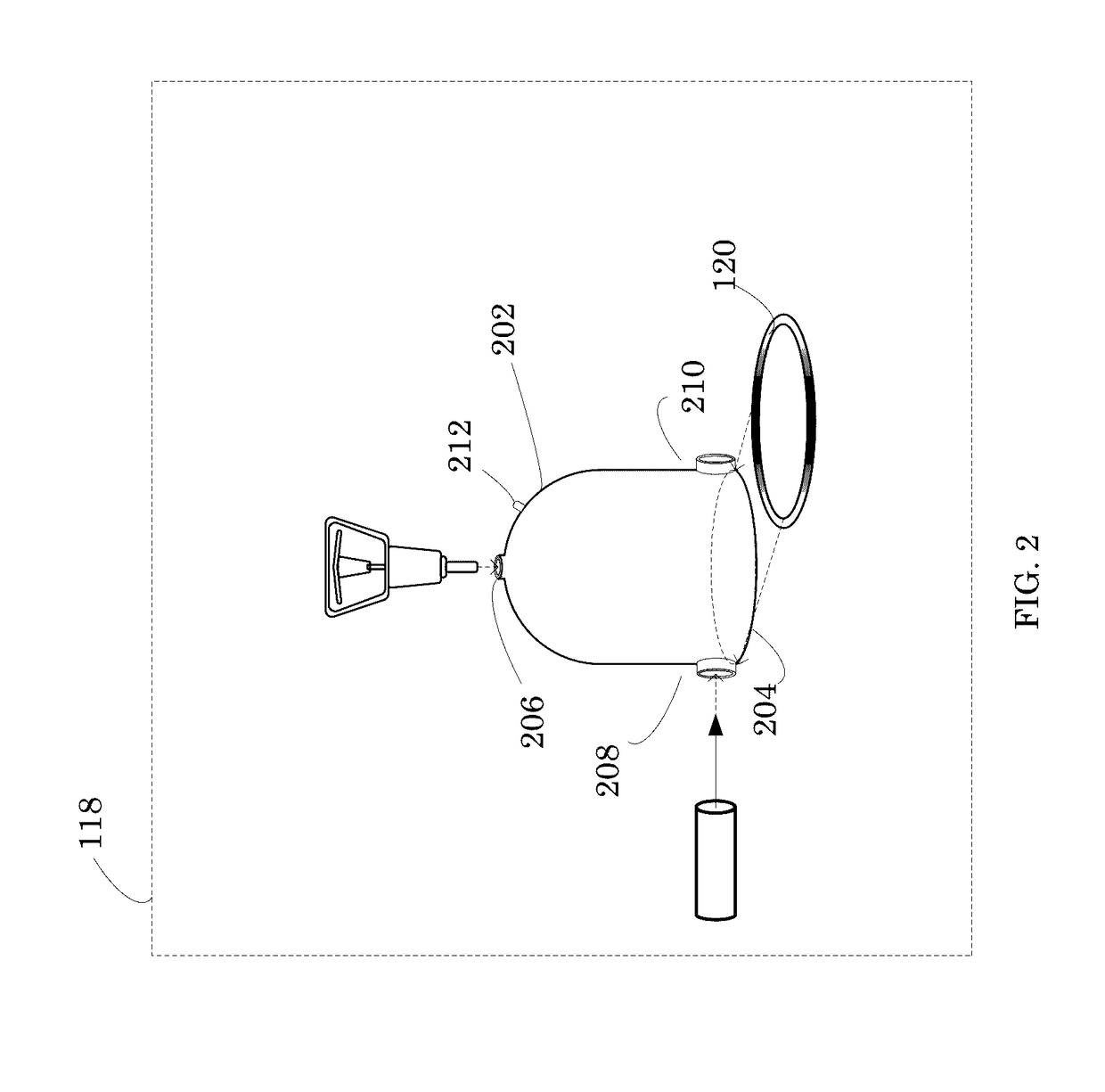
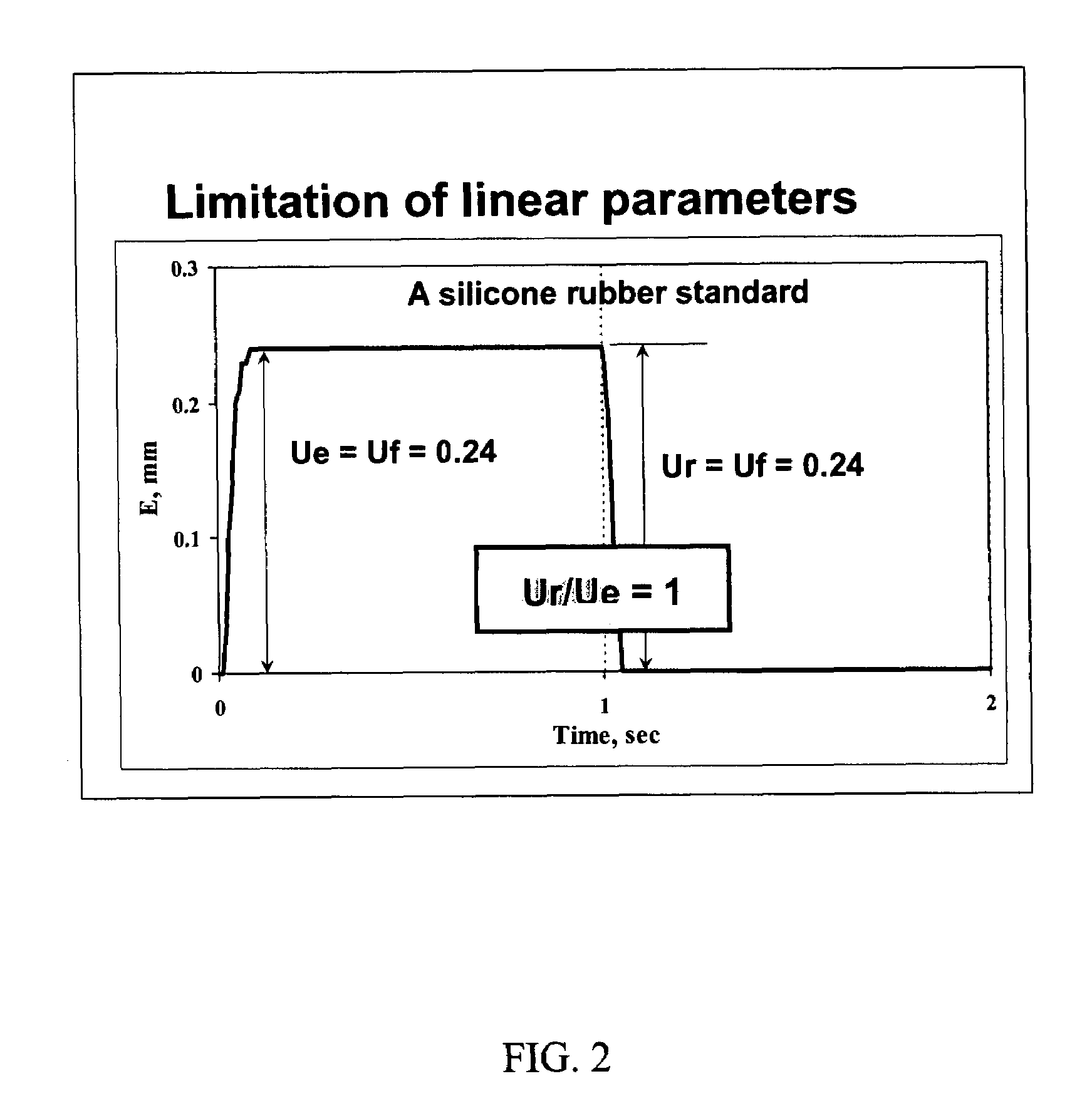
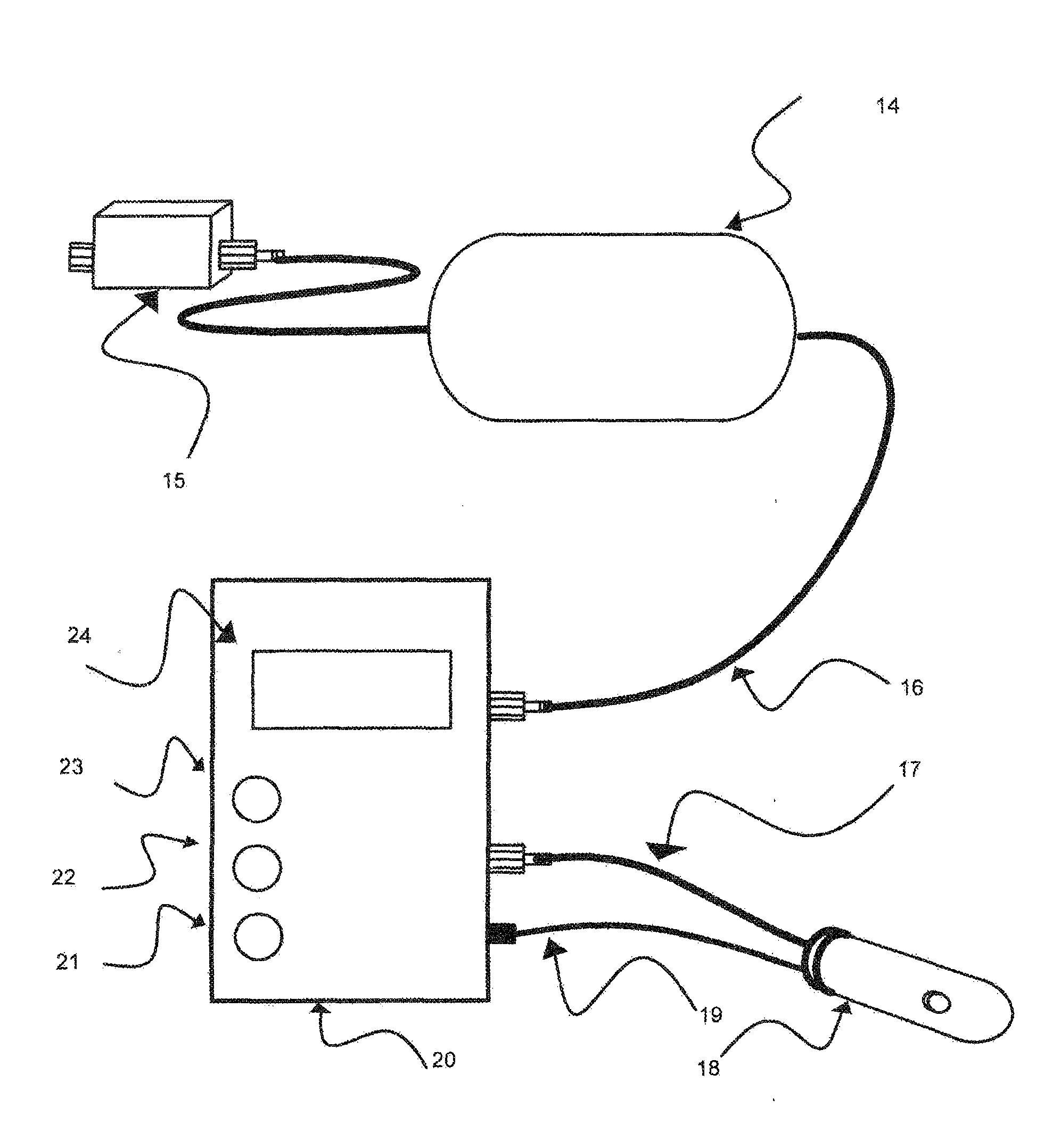
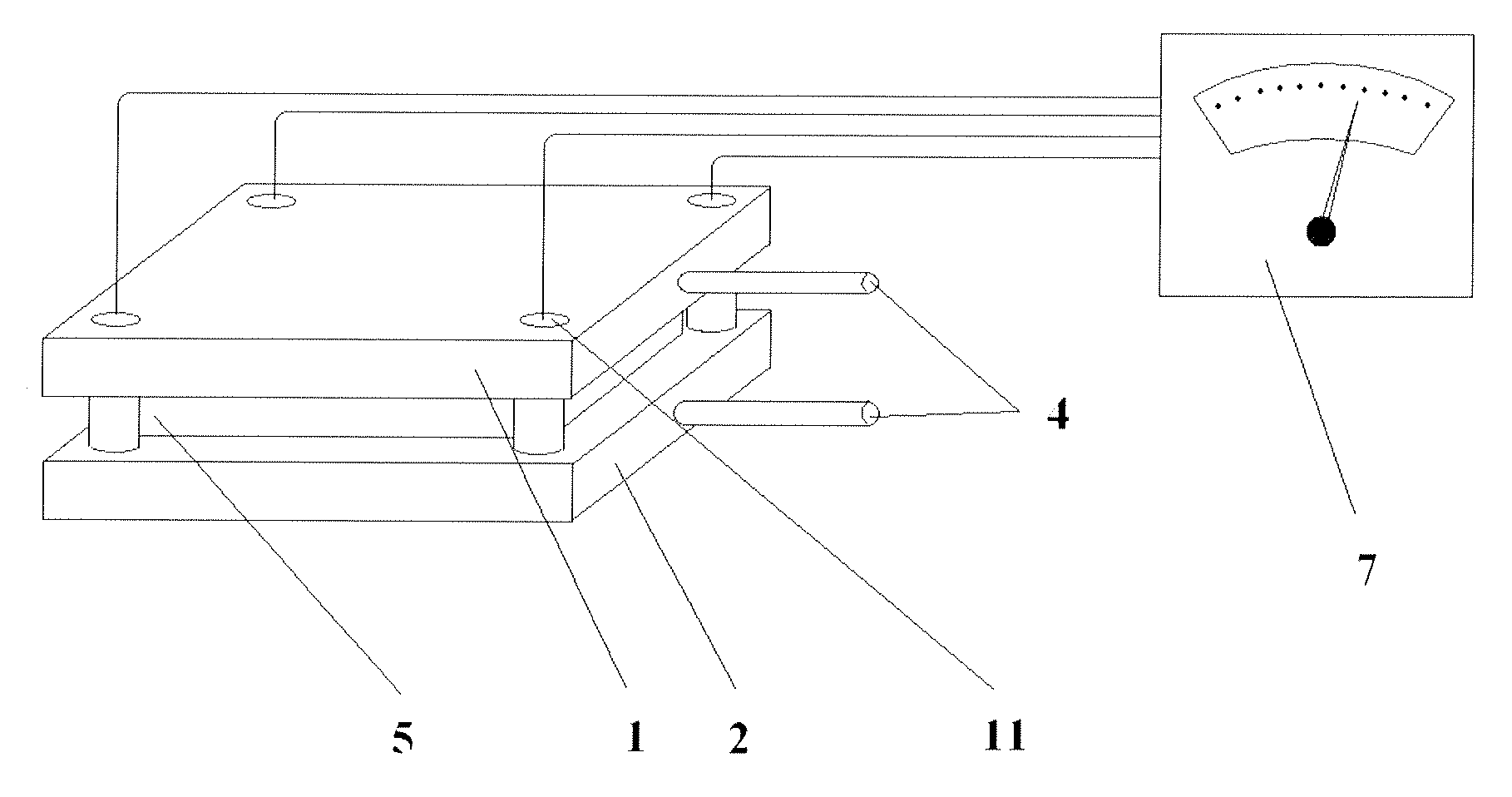
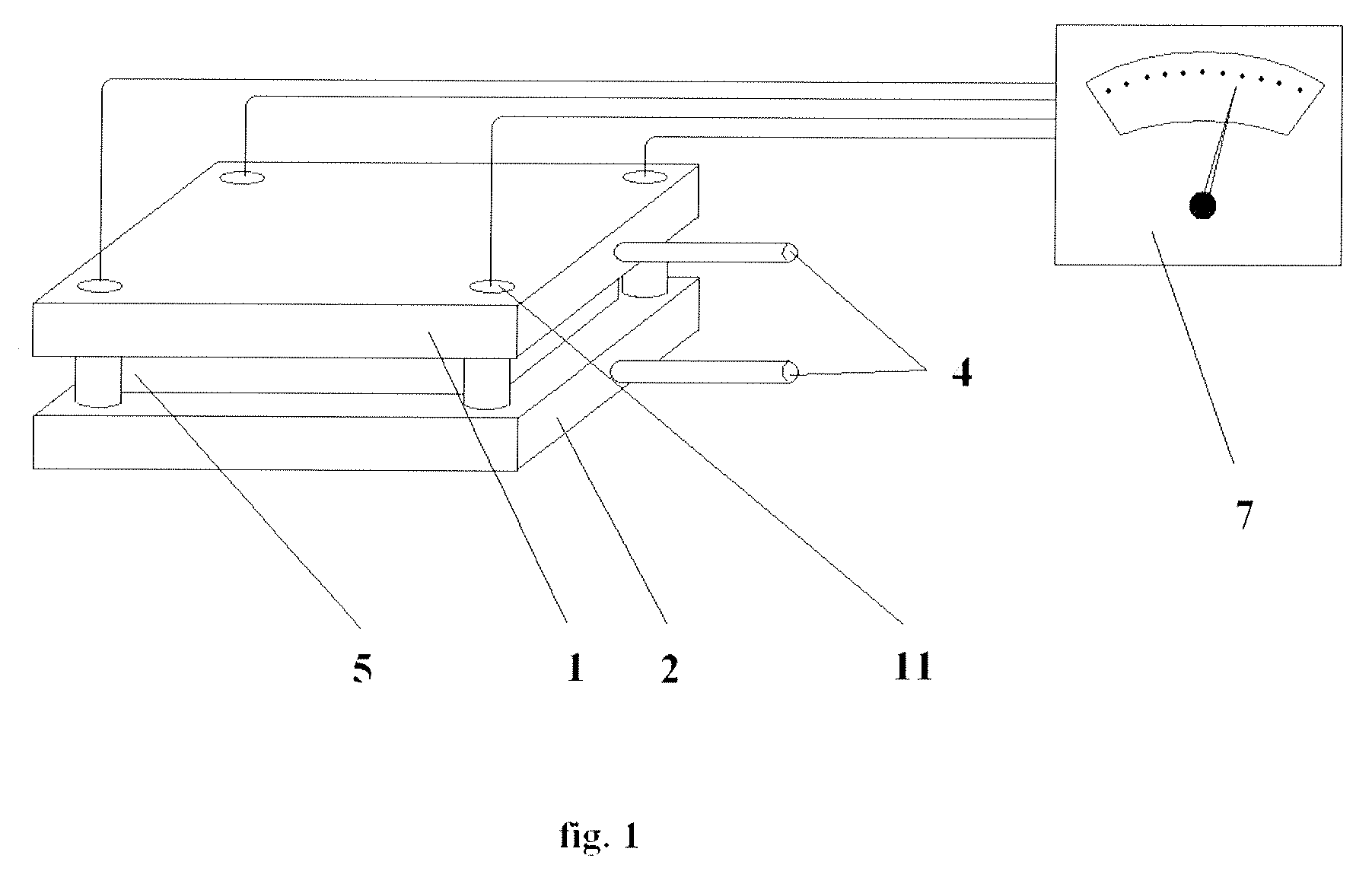
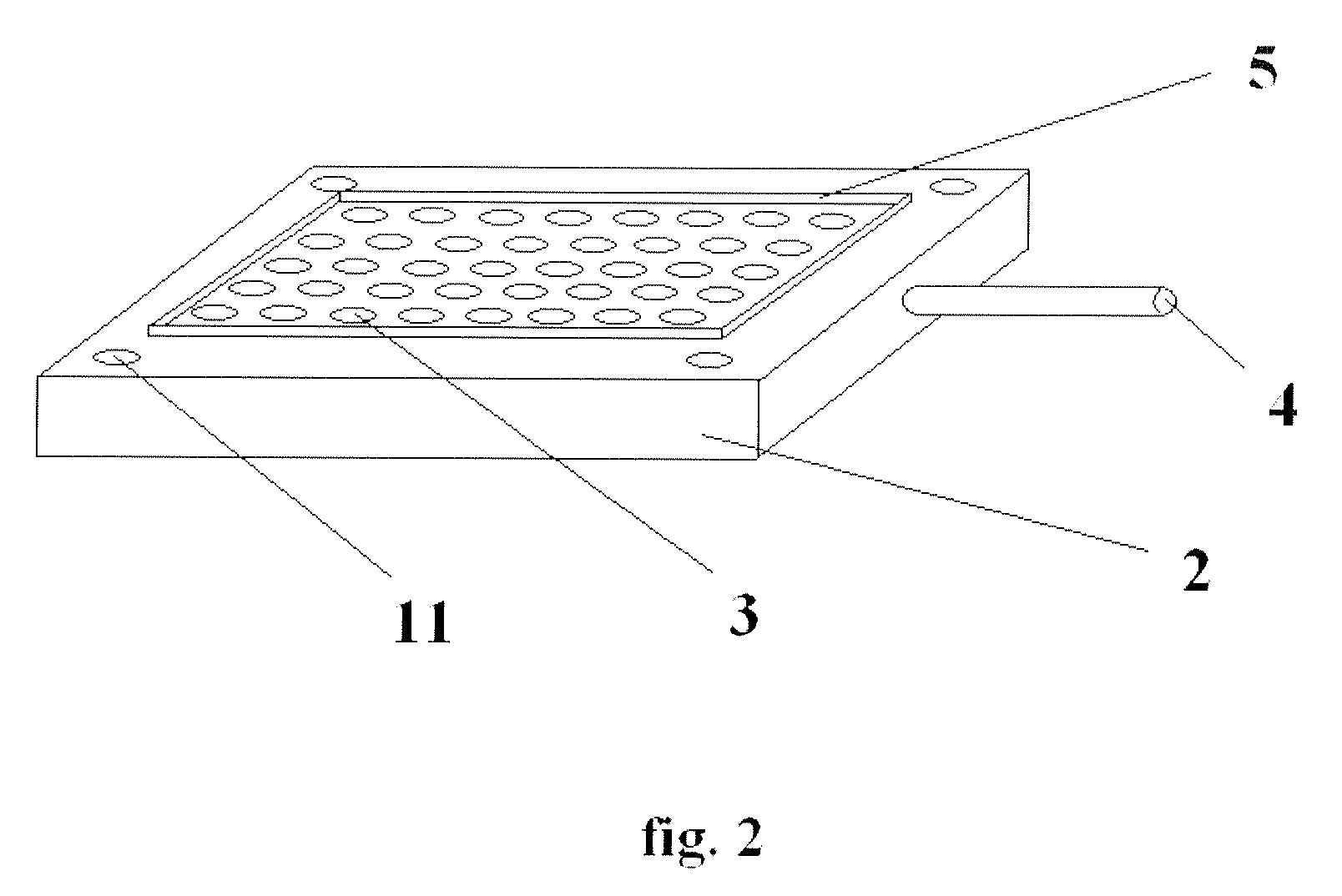
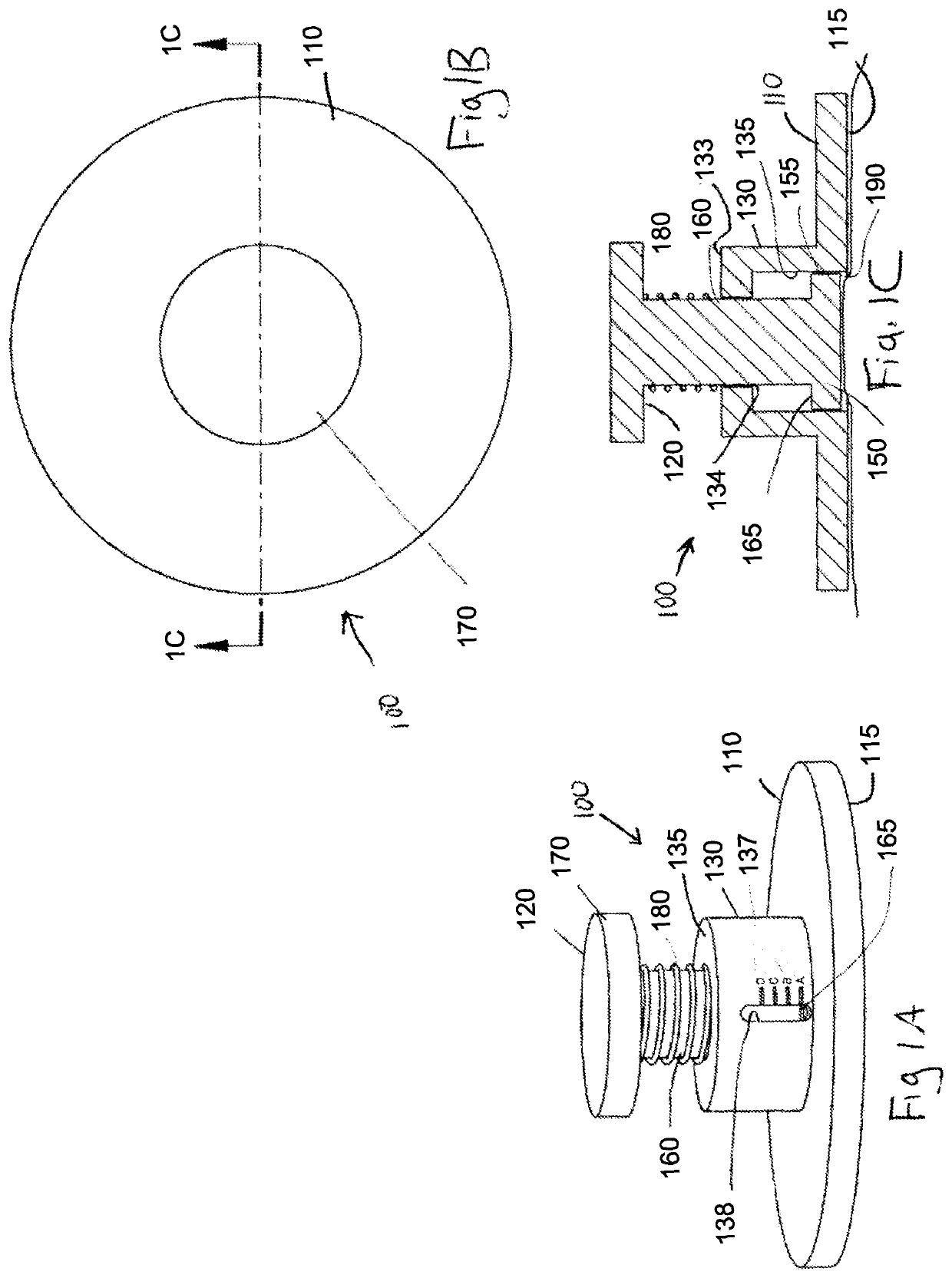
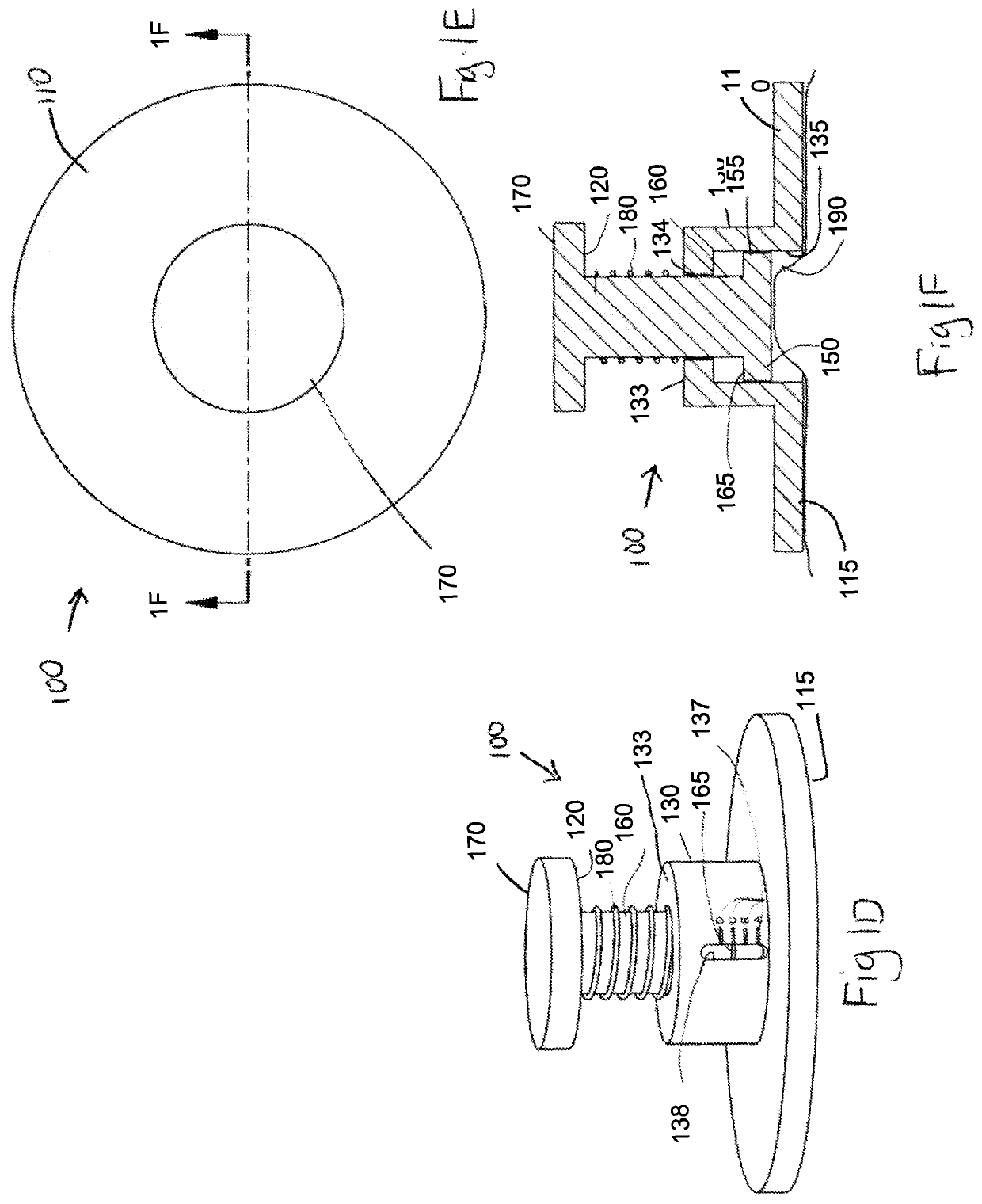
A device for measuring a mechanical property of a tissue includes a probe configured to perturb the tissue with movement relative to a surface of the tissue, an actuator coupled to the probe to move the probe, a detector configured to measure a response of the tissue to the perturbation, and a controller coupled to the actuator and the detector. The controller drives the actuator using a stochastic sequence and determines the mechanical property of the tissue using the measured response received from the detector. The probe can be coupled to the tissue surface. The device can include a reference surface configured to contact the tissue surface. The probe may include a set of interchangeable heads, the set including a head for lateral movement of the probe and a head for perpendicular movement of the probe. The perturbation can include extension of the tissue with the probe or sliding the probe across the tissue surface and may also include indentation of the tissue with the probe. In some embodiments, the actuator includes a Lorentz force linear actuator. The mechanical property may be determined using non-linear stochastic system identification. The mechanical property may be indicative of, for example, tissue compliance and tissue elasticity. The device can further include a handle for manual application of the probe to the surface of the tissue and may include an accelerometer detecting an orientation of the probe. The device can be used to test skin tissue of an animal, plant tissue, such as fruit and vegetables, or any other biological tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system for detecting electrophysiological changes in pre-cancerous and cancerous tissue and epithelium
InactiveUS20080009764A1Diagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureEpitheliumFunctional change
Methods and systems are provided for determining a condition of an organ, or epithelial or stromal tissue, for example in the human breast. The methods incorporate sonophoresis, the application of ultrasonic energy, in order to condition tissue for testing and enhance test measurements. A plurality of electrodes are used to measure surface and transepithelial electropotential and impedance of breast tissue at one or more locations and at several frequencies, particularly very low frequencies. An agent may be introduced into the region of tissue to enhance electrophysiological characteristics. Pressure, drugs and other agents can optionally be applied for enhanced diagnosis. Tissue condition is determined based on the electropotential and impedance profile at different depths of the epithelium, stroma, tissue, or organ, together with an estimate of the functional changes in the epithelium due to altered ion transport and electrophysiological properties of the tissue. Devices for practicing the disclosed methods are also provided.
Owner:EPI SCI LLC
Identification Techniques and Device for Testing the Efficacy of Beauty Care Products and Cosmetics
ActiveUS20110054355A1Low costProcedure can be fast and accurateDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using vibrationsMedicineSkin surface
A method for testing the effect of a skin care product includes measuring a mechanical property of skin tissue using nonlinear stochastic system identification, applying the product to the skin, repeating the measurement of the mechanical property after the application of the product, and comparing the before and after measurements to quantify the effect of the product.Measuring the mechanical property of the skin can include placing a probe against a surface of the skin, perturbing the skin with the probe using a stochastic sequence, and measuring the response of the skin to the perturbation. Perturbing the skin can include indenting the skin with the probe, extending the skin with the probe, and sliding the probe across the skin surface. The mechanical property may be indicative of skin compliance, skin elasticity, skin stiffness, or skin damping. The mechanical property can be dependent on perturbation depth and may be measured at a plurality of anatomical locations.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method for Vaginal Skin Biomechanical Evaluation
A method and technique to measure vaginal skin biomechanical properties in vivo by applying a temporary deforming force to the vaginal skin while using sensors to monitor and record the vaginal skins response to the deforming force as well as how it responds after the deforming force is removed. By placing a female participant in the correct anatomical position and employing a vaginal biomechanical evaluation tool to temporarily distort and measure the vaginal skin an examiner is able to obtain measurements for biomechanical properties of the vaginal skin. These measurements may allow clinicians and medical researchers to understand a woman's vaginal tissue quality, response to treatment, and risk for future pelvic floor disorders more completely in order to take appropriate prophylactic or corrective action.
Owner:EPSTEIN LEE BRANDON +2
Device for use in electro-biological signal measurement in the presence of a magnetic field
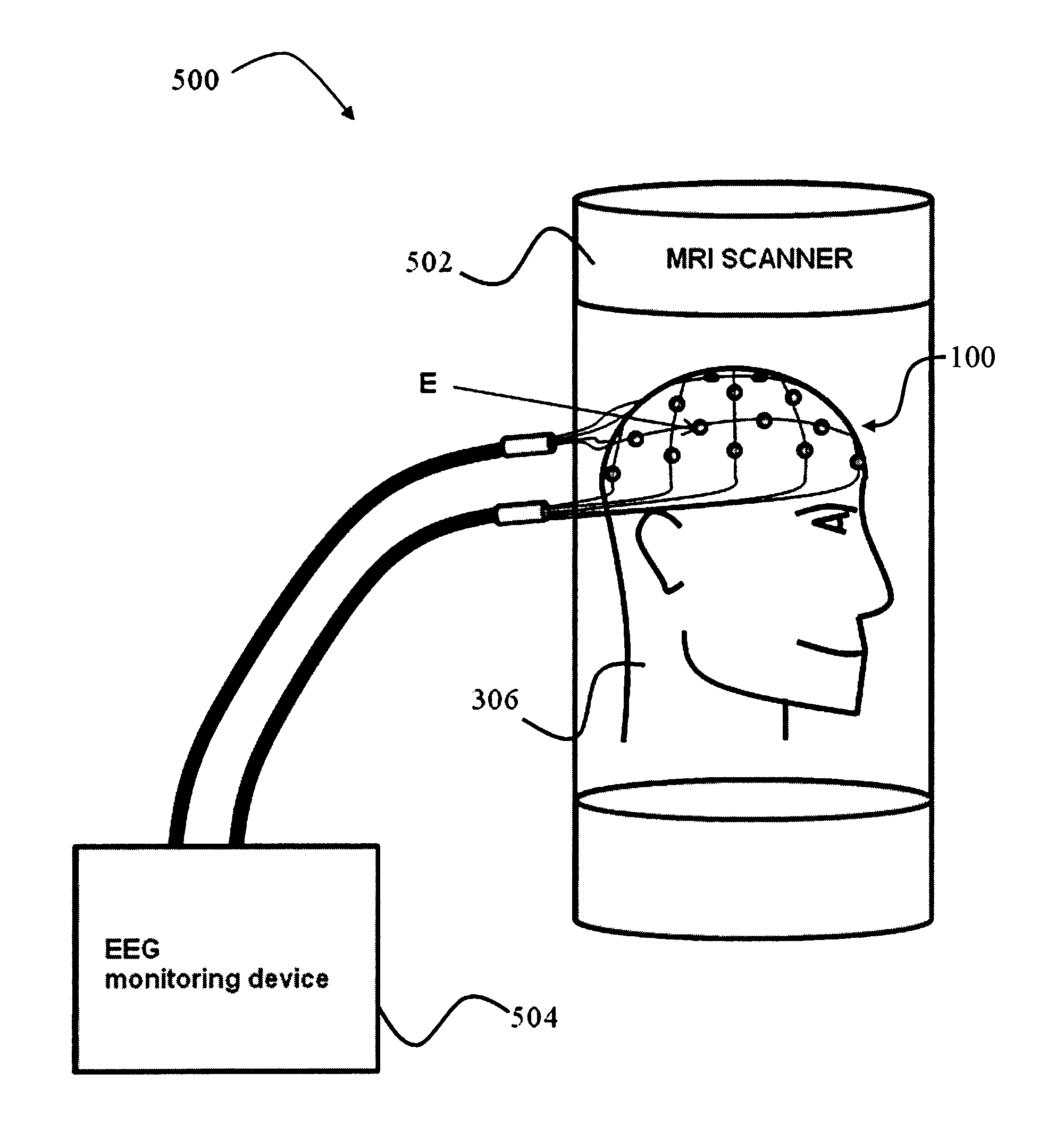
ActiveUS20130204122A1Electrical size reductionReduce Motion ArtifactsElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using suctionEeg dataMeasurement device
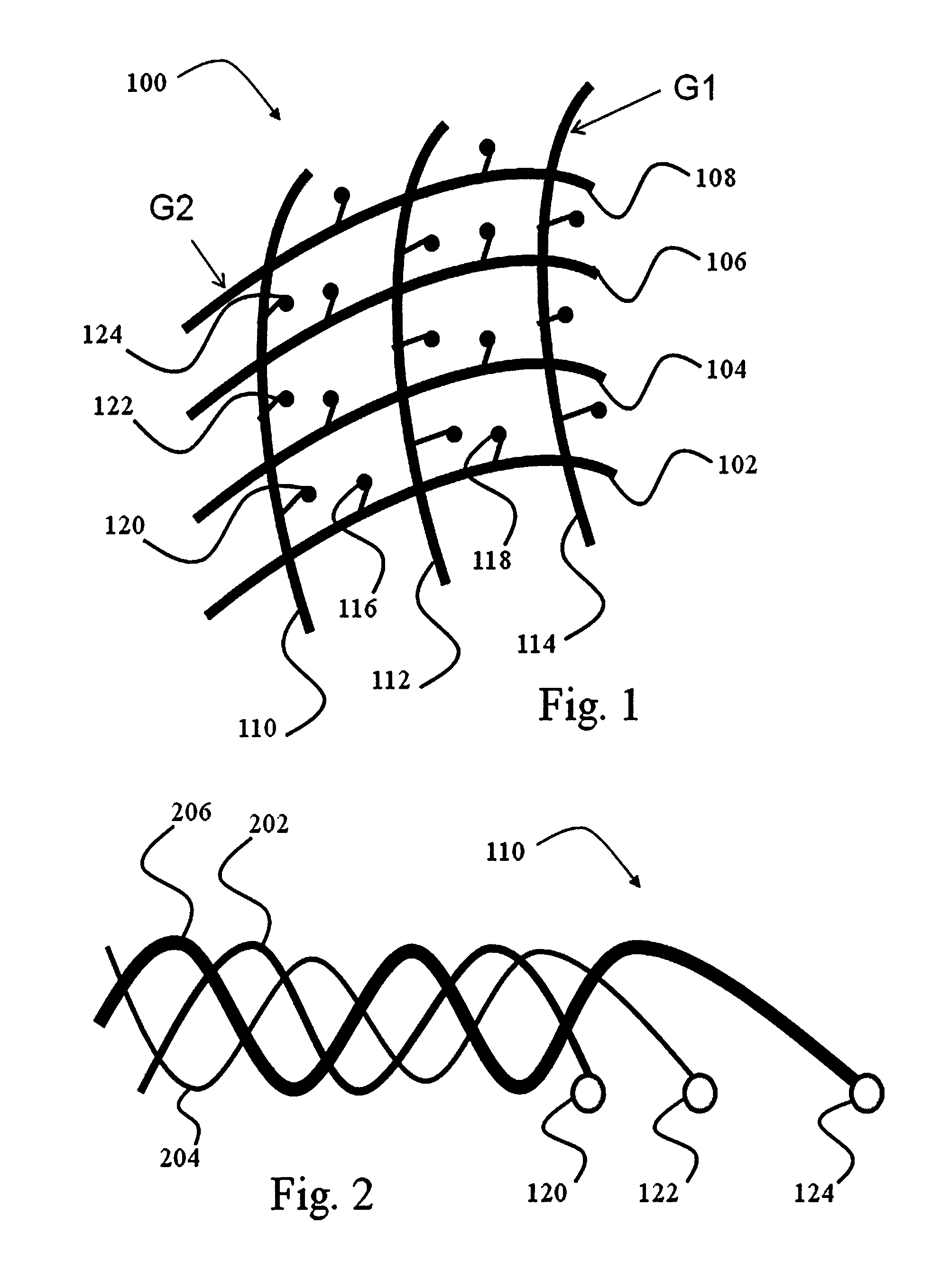
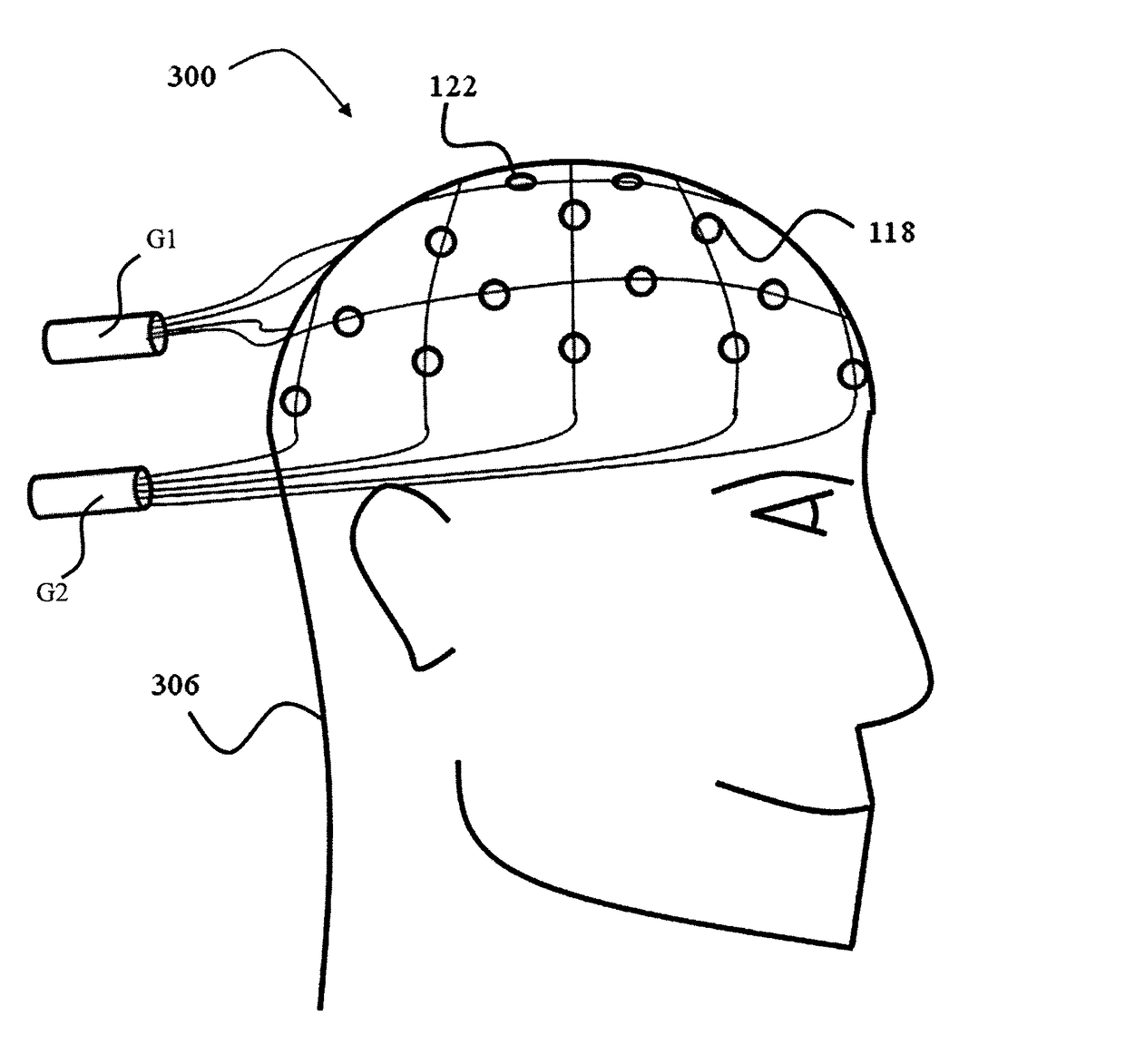
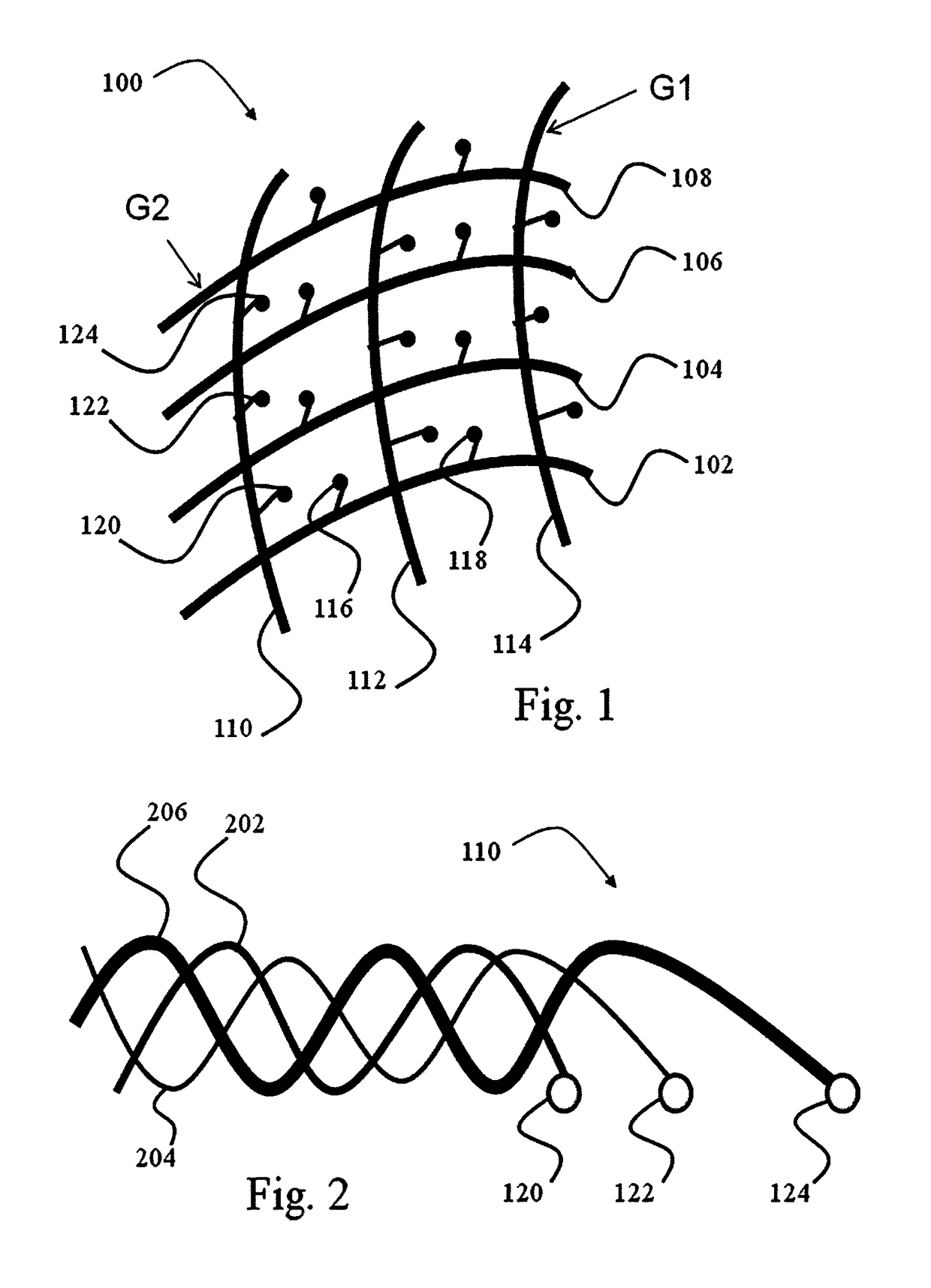
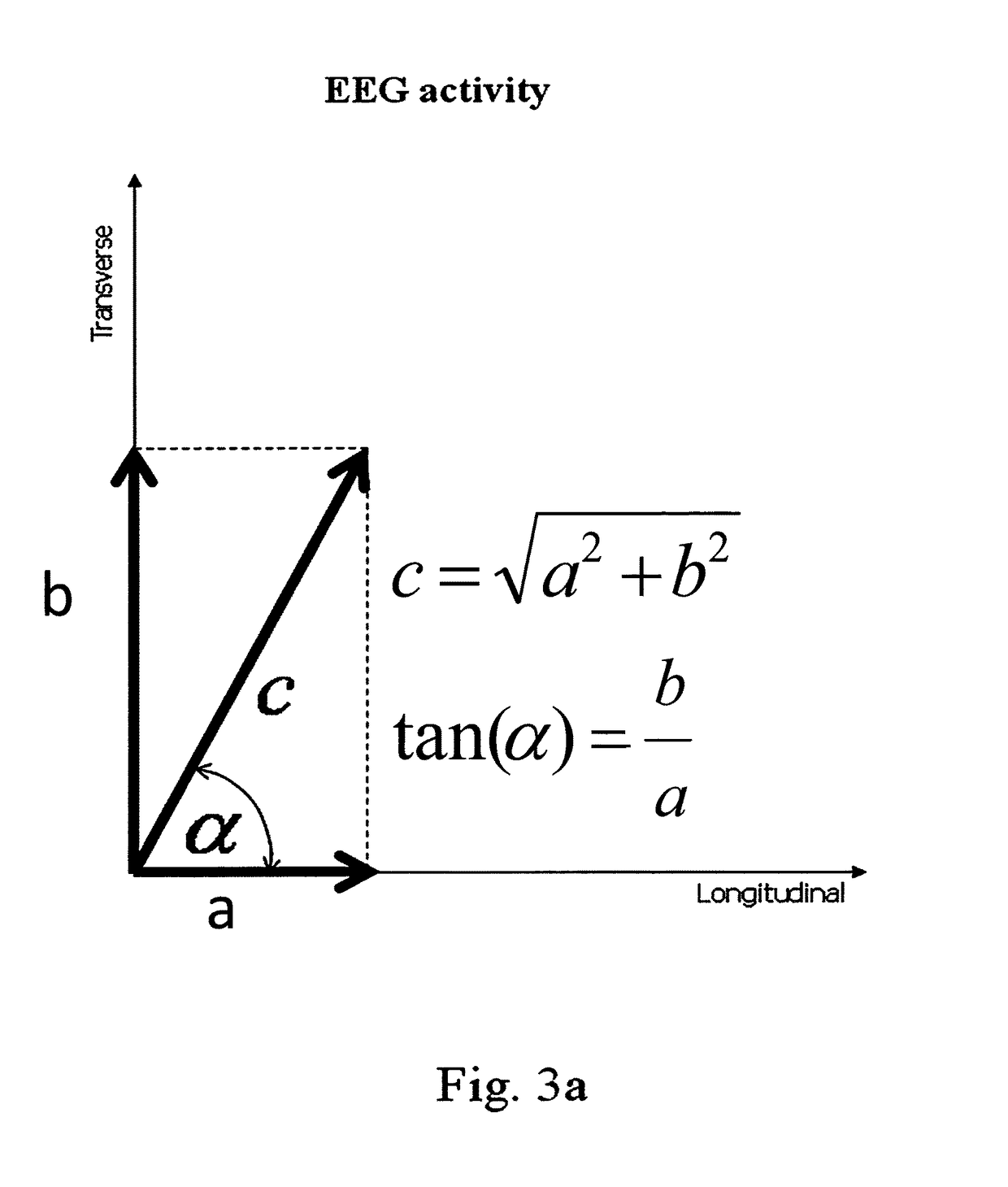
A measurement device is presented for use in an EEG measurement performed in the presence of a magnetic field. The device comprises a wiring array for connecting an electrodes arrangement to an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring device. The wiring array comprises a plurality of sampling lines arranged to form a first group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a first axis, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said first group comprising a plurality of first wires for connecting to a corresponding first plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes arrangement; and a second group of sampling lines arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along a second axis, intersecting with said first axis, such that said second group of bundles crosses said first group of bundles to form a net structure, at least some of said sampling lines being wire bundles of said second group comprising a plurality of second wires for connecting to a corresponding second plurality of electrodes of said EEG electrodes' arrangement. The wiring array is configured and operable for transmitting a signal measured by the respective electrodes to the EEG monitoring device, enabling generation of EEG data indicative of the neural signal profile along tow directions and characterized by reduced motion artifact and / or reduced gradient artifact associated with the presence of the magnetic field during the EEG measurement.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
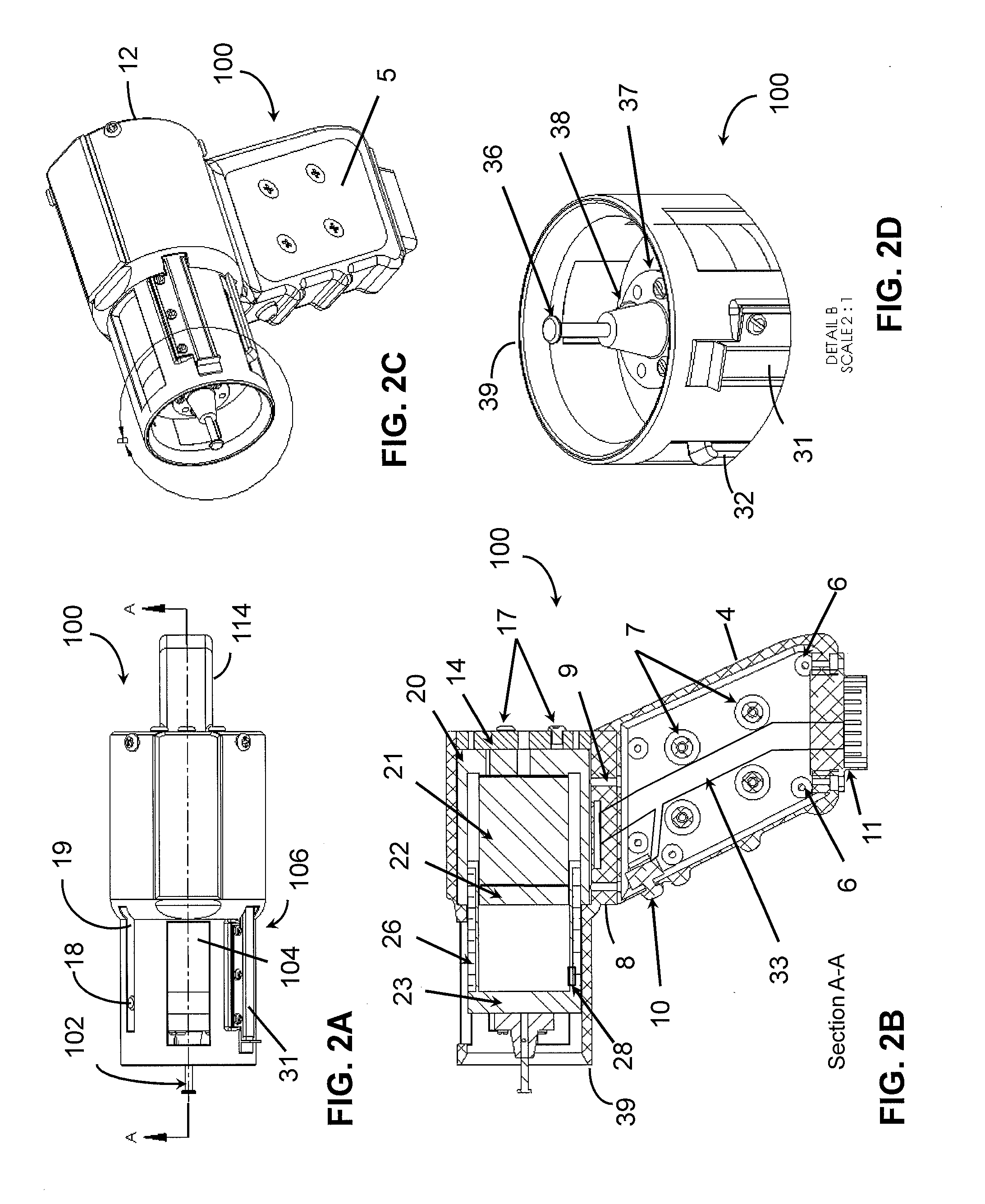
Aspiration methods and devices for assessment of viscoelastic properties of soft tissues
Owner:ARTANN LAB
Aspiration methods and devices for assessment of viscoelastic properties of soft tissues
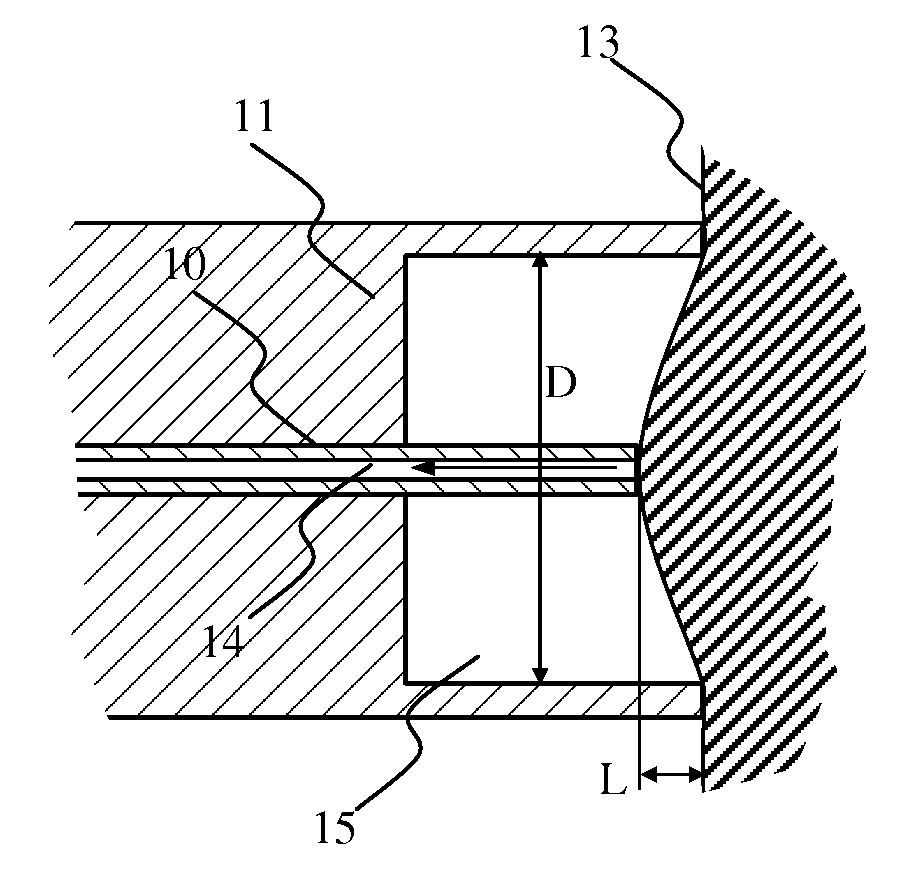
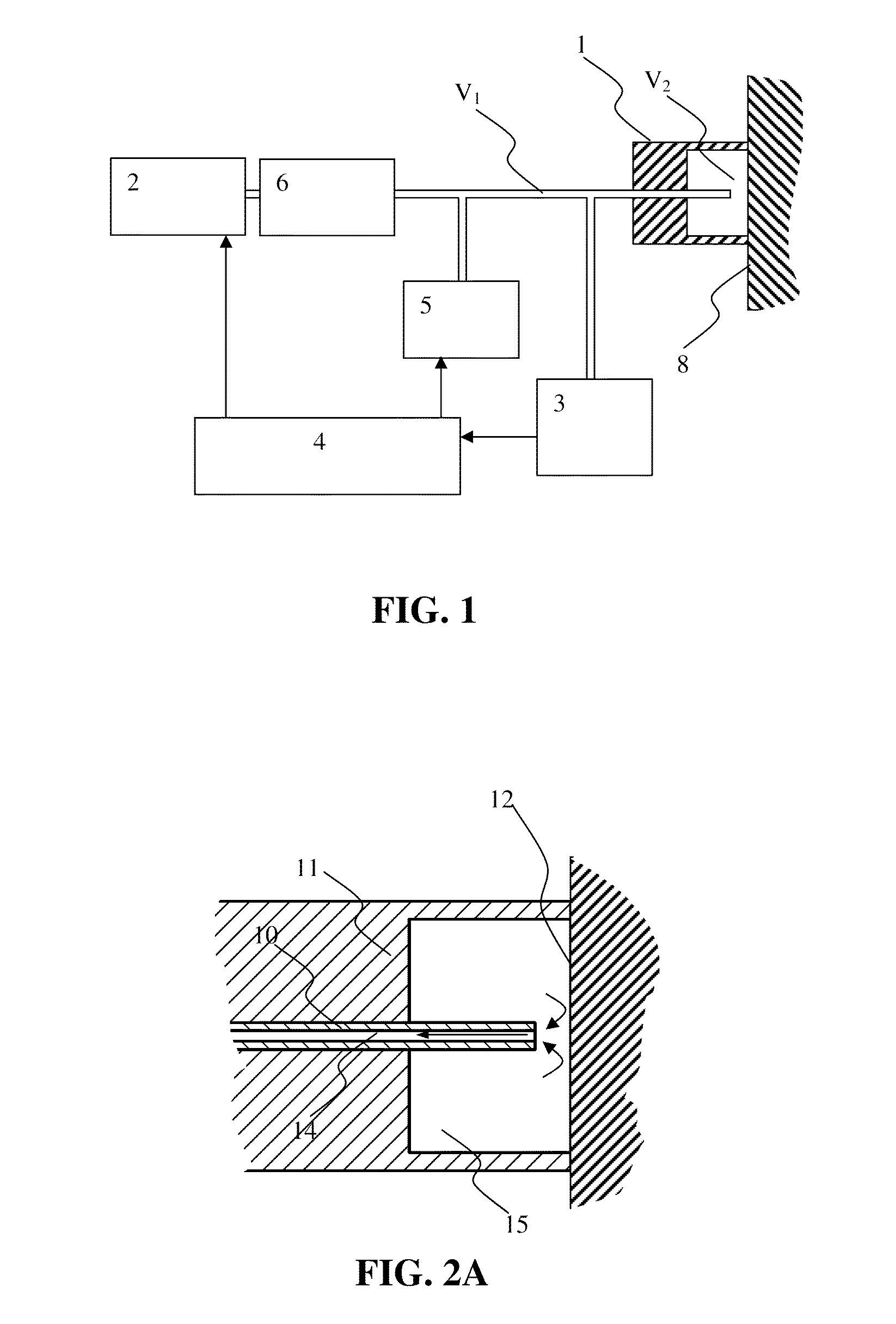
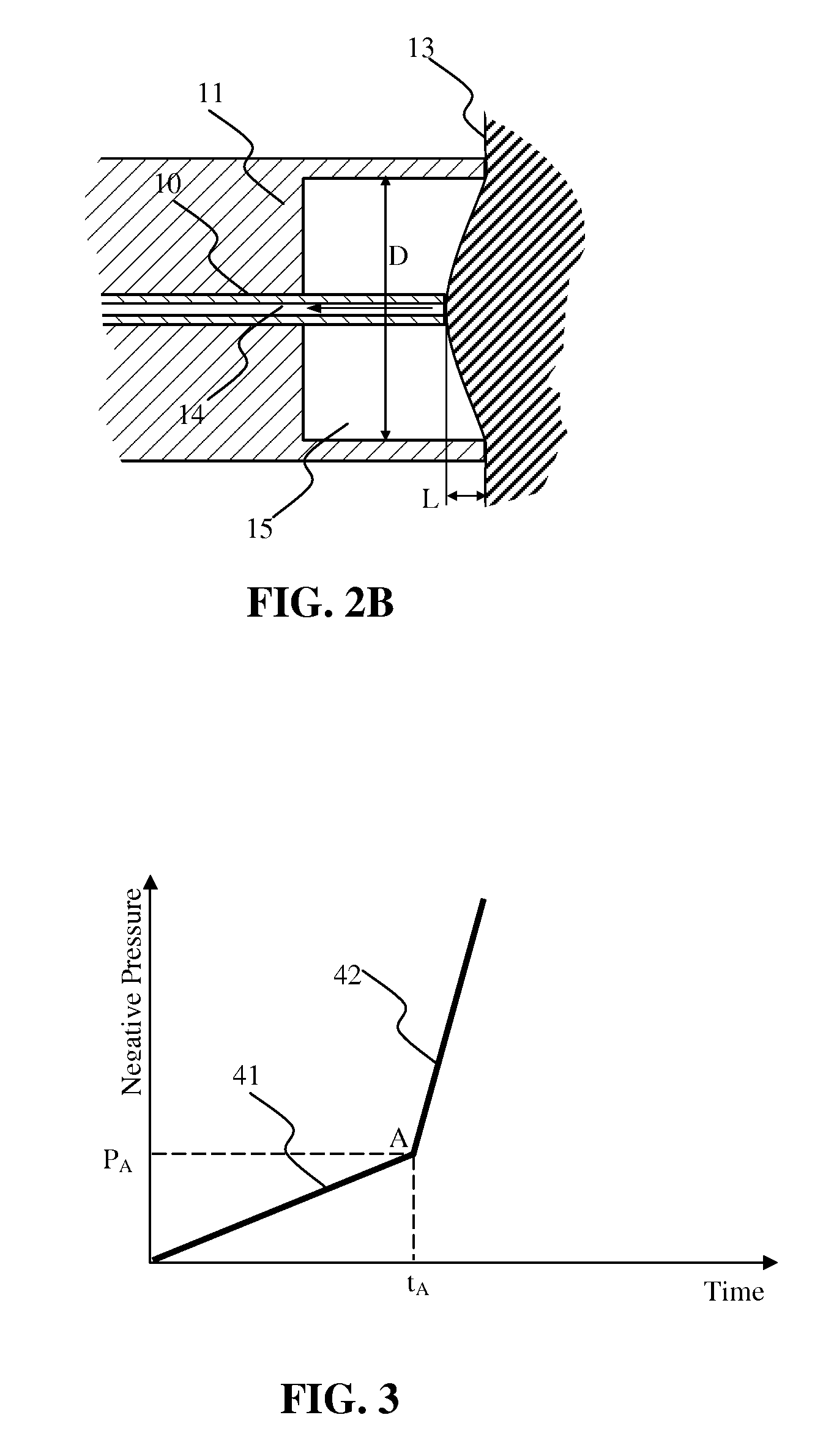
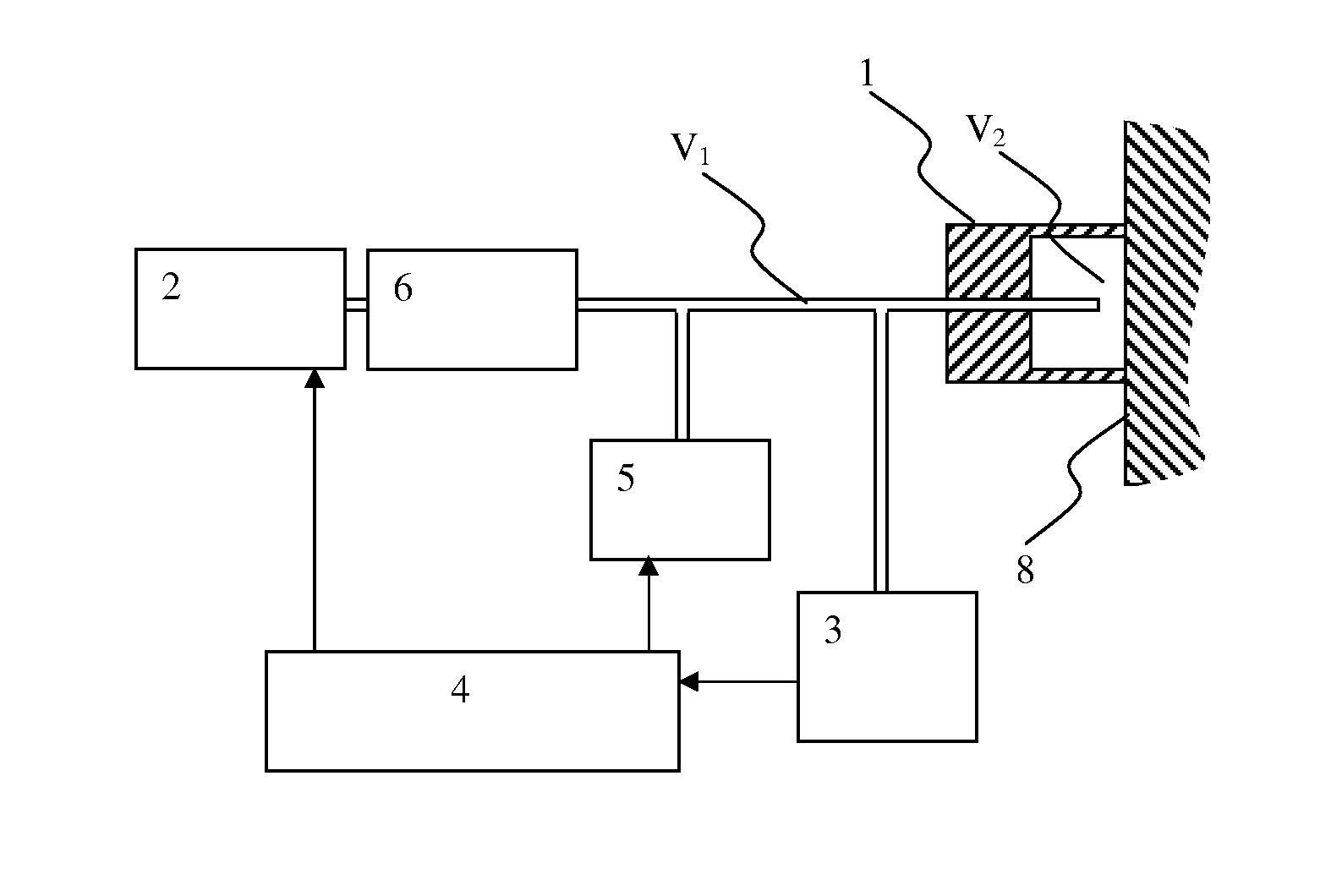
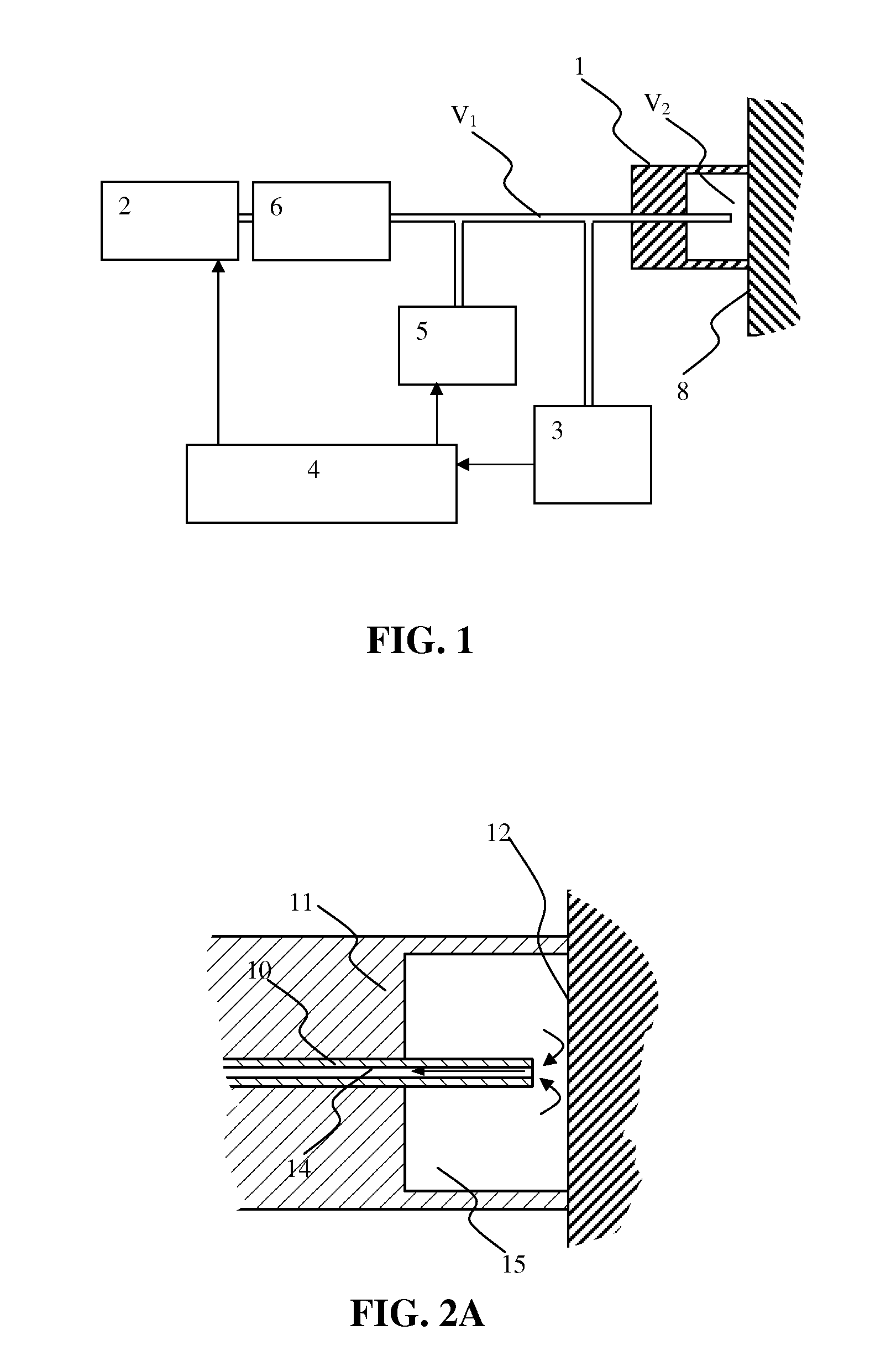
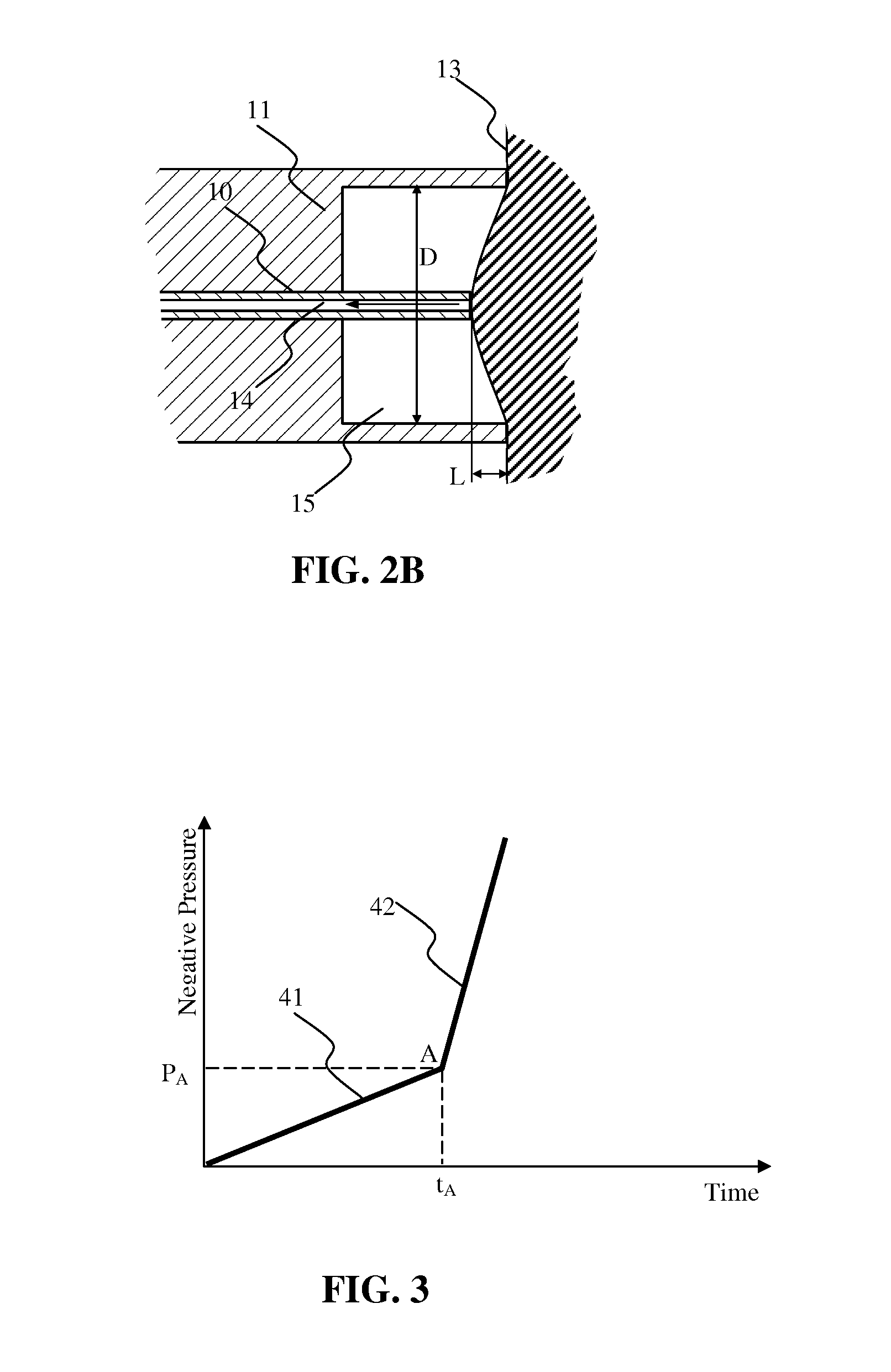
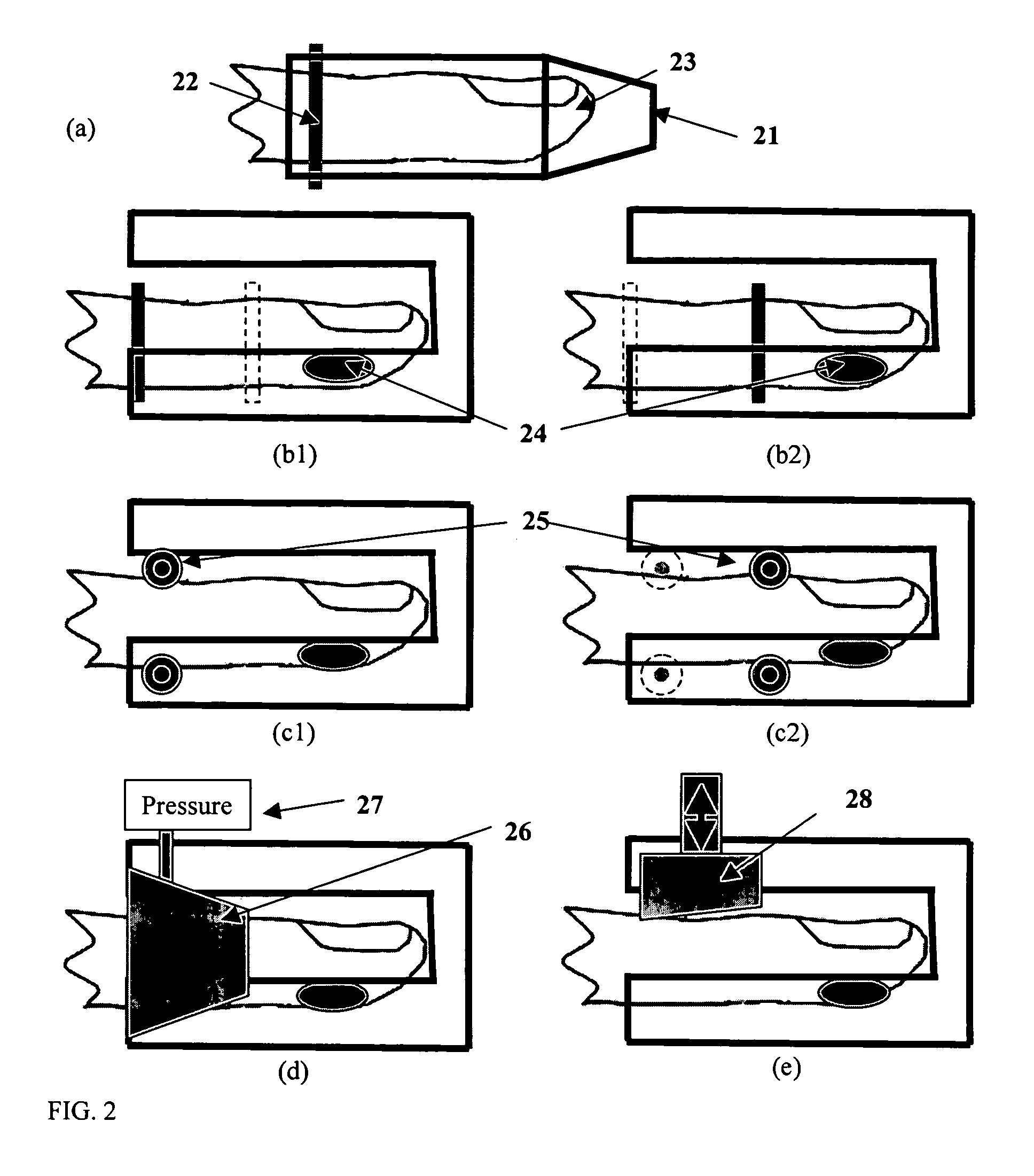
Methods for assessing viscoelastic properties of soft tissues are based on detecting an inflection point on a pressure-time plot when air is aspirated from a cavity placed over the tissue sample. A small diameter tube through which air aspiration is conducted is ultimately closed off by tissue being drawn into the cavity causing an abrupt change in pressure slope. First or second derivatives of the pressure-time plot can be used to detect the inflection point. Repeating the test with a different aspiration rates or after a predetermined relaxation time allows determining tissue viscosity and tissue creep in addition to tissue elasticity expressed as Young's modulus.
Owner:ARTANN LAB
Nonlinear system identification techniques and devices for discovering dynamic and static tissue properties
ActiveUS8758271B2Low costProcedure can be fast and accurateDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureAccelerometerMechanical property
A device for measuring a mechanical property of a tissue includes a probe configured to perturb the tissue with movement relative to a surface of the tissue, an actuator coupled to the probe to move the probe, a detector configured to measure a response of the tissue to the perturbation, and a controller coupled to the actuator and the detector. The controller drives the actuator using a stochastic sequence and determines the mechanical property of the tissue using the measured response received from the detector. The probe can be coupled to the tissue surface. The device can include a reference surface configured to contact the tissue surface. The probe may include a set of interchangeable heads, the set including a head for lateral movement of the probe and a head for perpendicular movement of the probe. The perturbation can include extension of the tissue with the probe or sliding the probe across the tissue surface and may also include indentation of the tissue with the probe. In some embodiments, the actuator includes a Lorentz force linear actuator. The mechanical property may be determined using non-linear stochastic system identification. The mechanical property may be indicative of, for example, tissue compliance and tissue elasticity. The device can further include a handle for manual application of the probe to the surface of the tissue and may include an accelerometer detecting an orientation of the probe. The device can be used to test skin tissue of an animal, plant tissue, such as fruit and vegetables, or any other biological tissue.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Apparatus and methods for compensation of blood volume effects on NIR spectroscopic measurements of blood analytes
ActiveUS7613488B1Error minimizationDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using pressureAnalyteMedicine
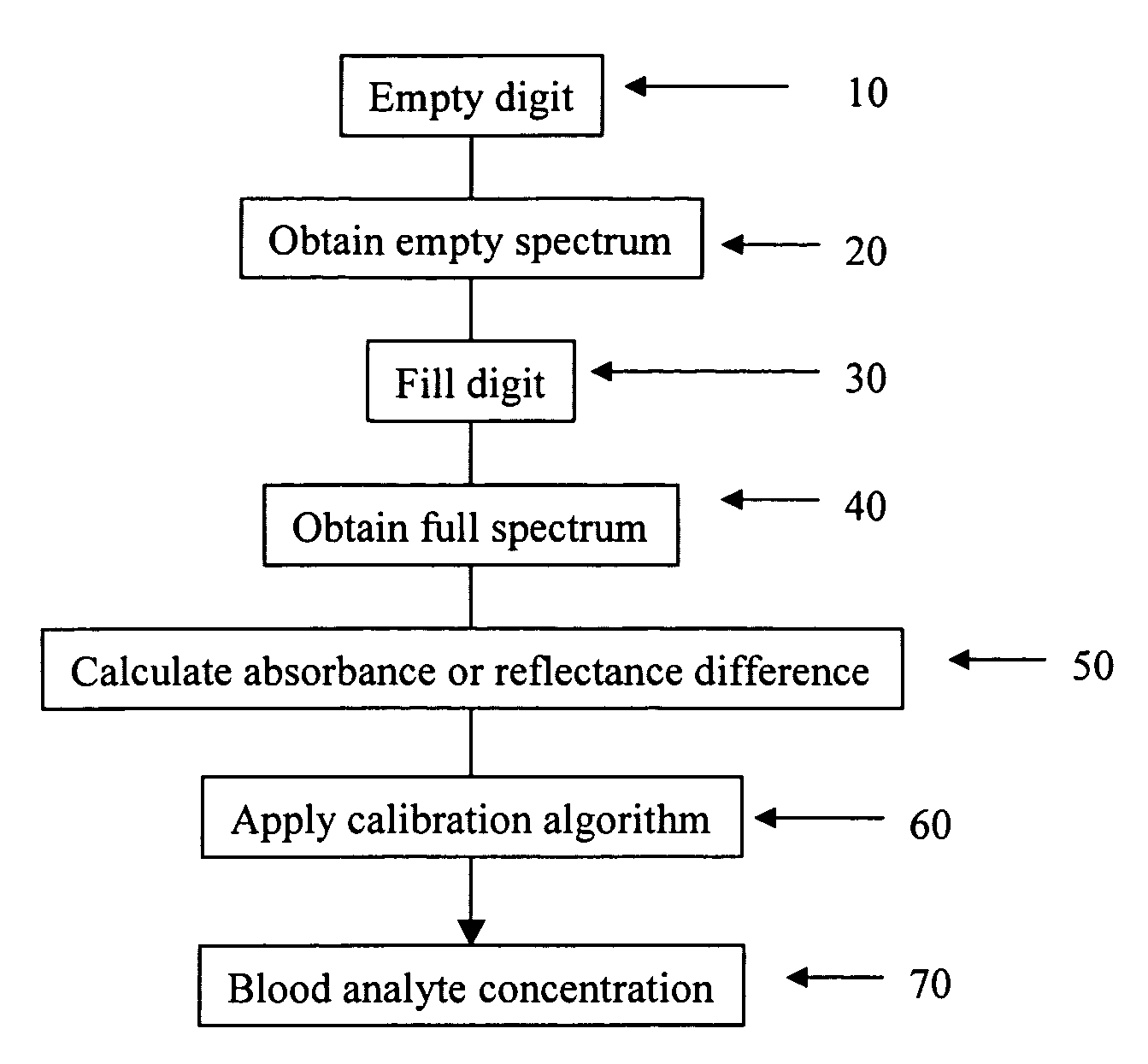
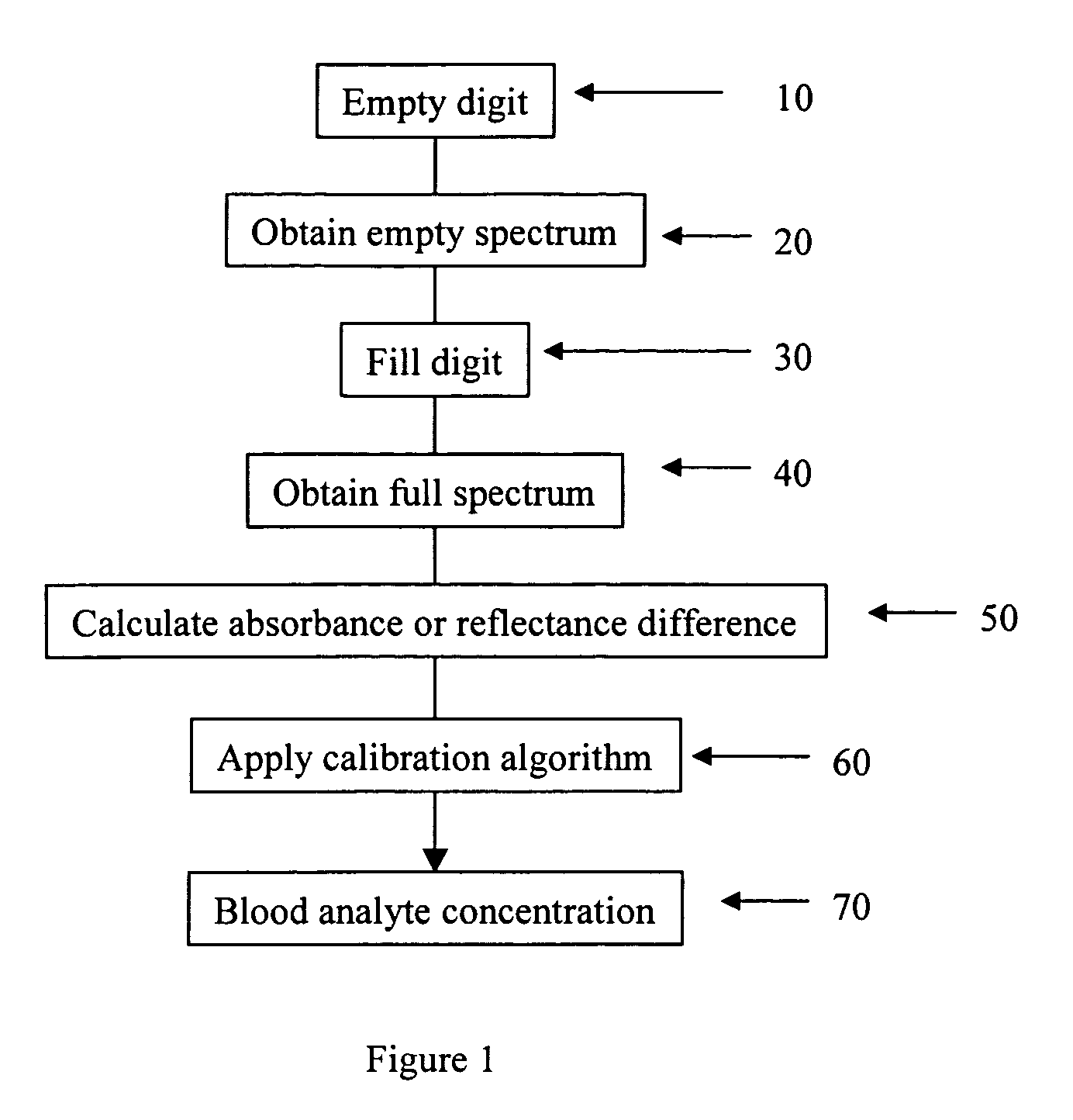
The present invention provides a method for measuring a blood analyte concentration of a body part comprising removing a portion or all of the blood from the body part to produce a modified body part, and recording a first absorbance value of the modified body part. This is followed by filling the body part with blood to produce a filled body part, and recording a second absorbance value of the filled body part. A difference spectrum is obtained by subtracting the first absorbance values from the second absorbance values, and a calibration algorithm for the blood analyte is applied to the difference spectrum, thereby measuring the concentration of the blood analyte. Also provided is an apparatus for determining the concentration of a blood analyte of a body part. The apparatus comprising a chamber of a size and shape to receive the body part, where the chamber comprises an element for withdrawing and reintroducing blood from the body part, when the body part is inserted within the chamber. The chamber also comprising one or more than one port for introducing electromagnetic radiation into the chamber and onto that body part, and collecting remaining electromagnetic radiation following interaction with the body part.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP +1
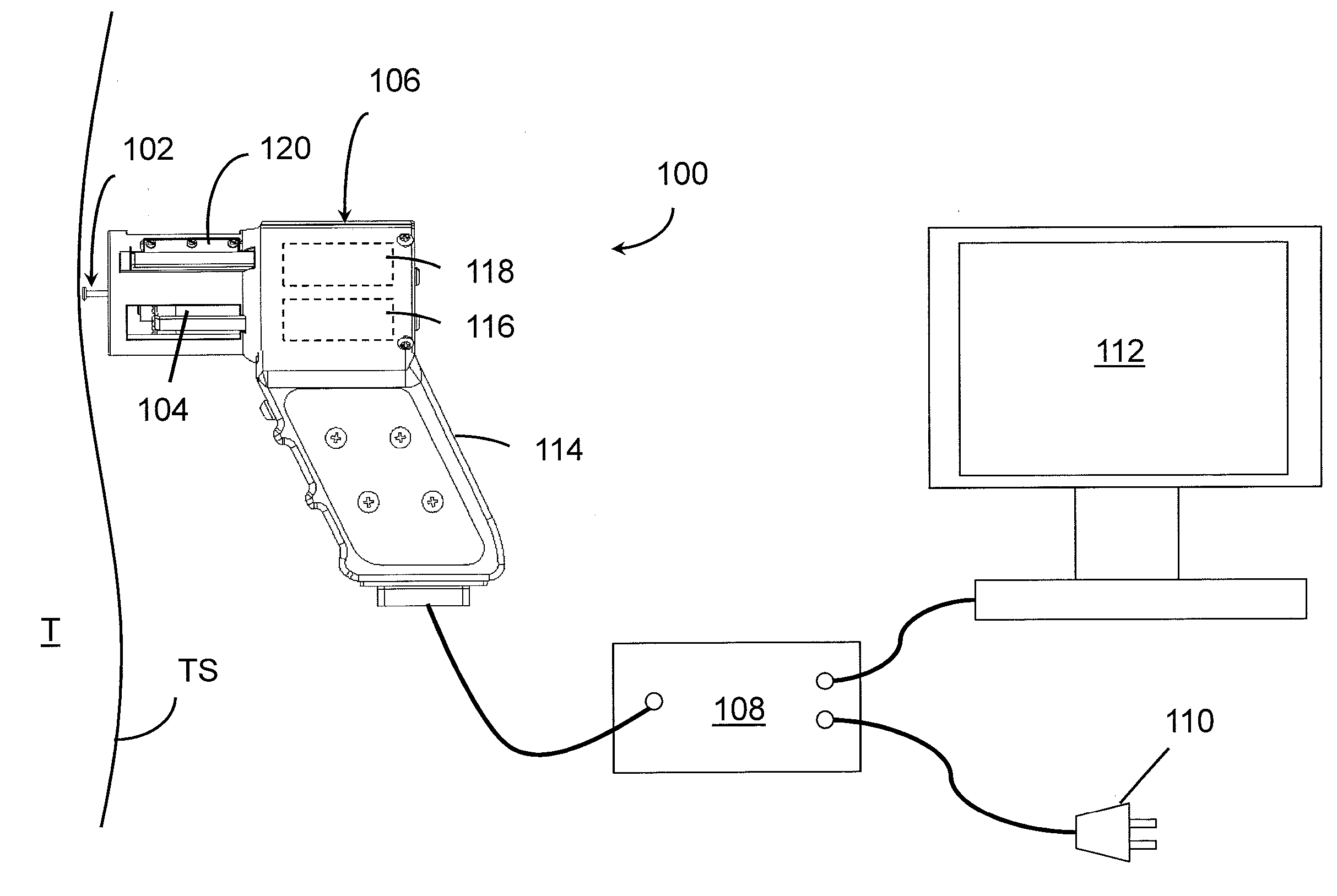
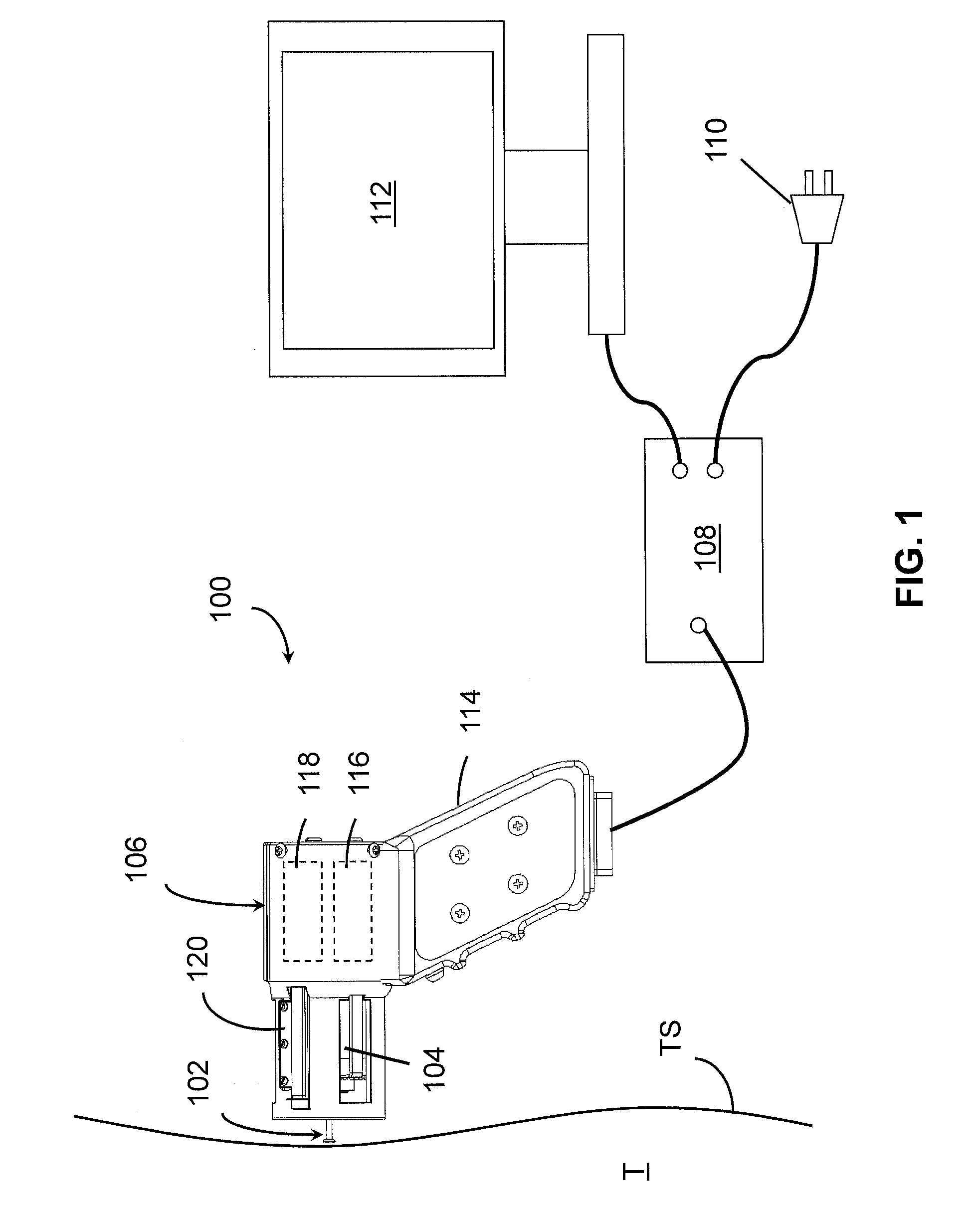
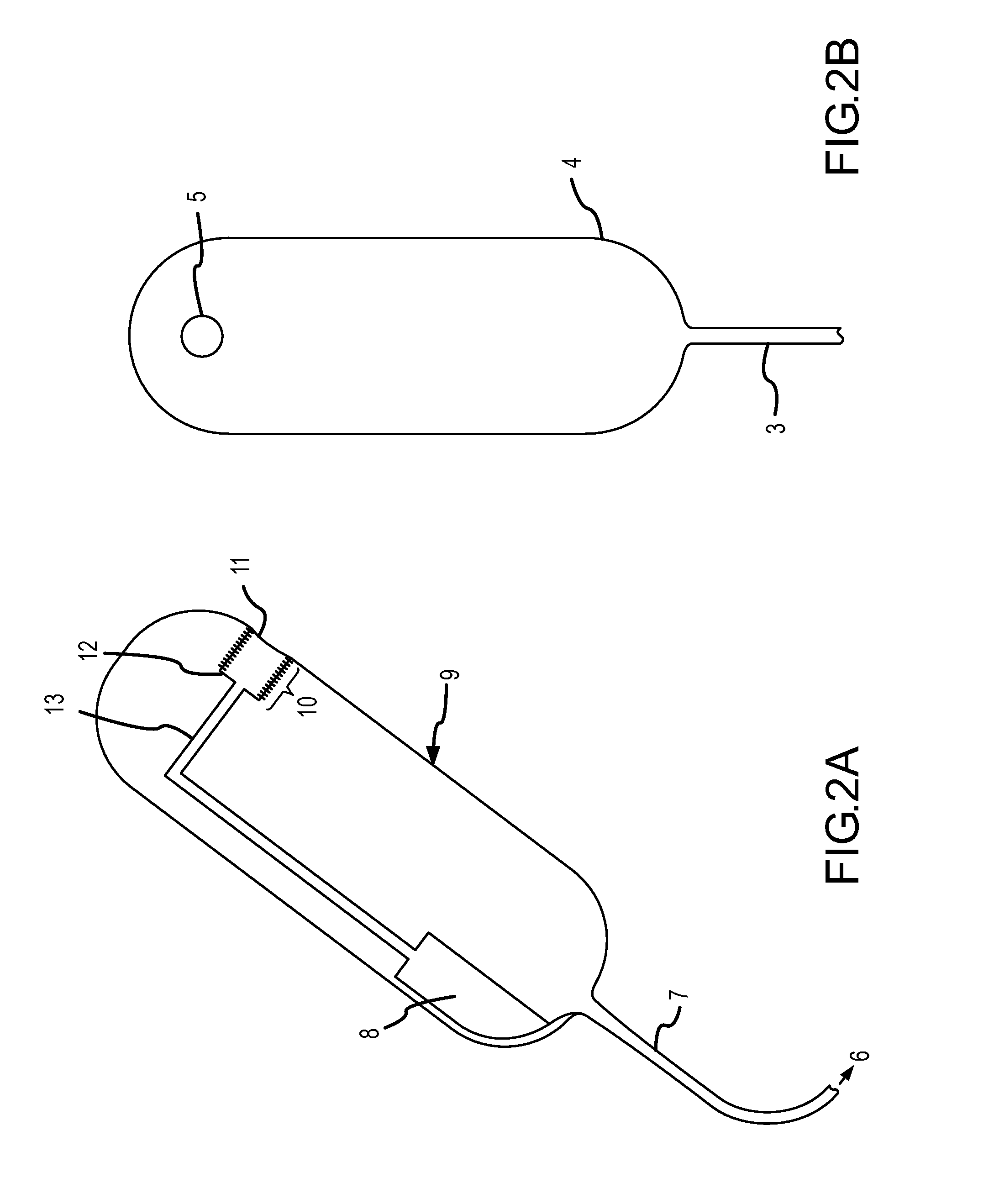
Vaginal Bio-mechanics Analyzer
InactiveUS20130035611A1Diagnostics using suctionPerson identificationProximity sensorVacuum pressure
The present invention relates to a method for measuring the elasticity of the anterior walls of the human vagina. The elasticity of the vagina walls degrade as women age. When a condition occurs called pelvic organ prolapse, the vaginal walls have lost much of the visco-elastic properties. The ability to measure the elasticity in healthy women at an early age and track the changes over time will give researchers the chance to develop new therapies to manage this growing problem. The present invention makes multiple data measurements of vacuum pressures and proximity measurement, by the use of a small insertable, user friendly and quickly sterilizable vaginal device. The proximity sensor not only measures the deformation of the skin pulled into a small hole of the vaginal probe but also measures the skin deformation after the skin has retracted out of the probe hole.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Methods for determining elastic and viscoelastic properties of skin
ActiveUS20080087098A1Promotes skin healthDiagnostics using suctionFlow propertiesRelaxation curveOral treatment
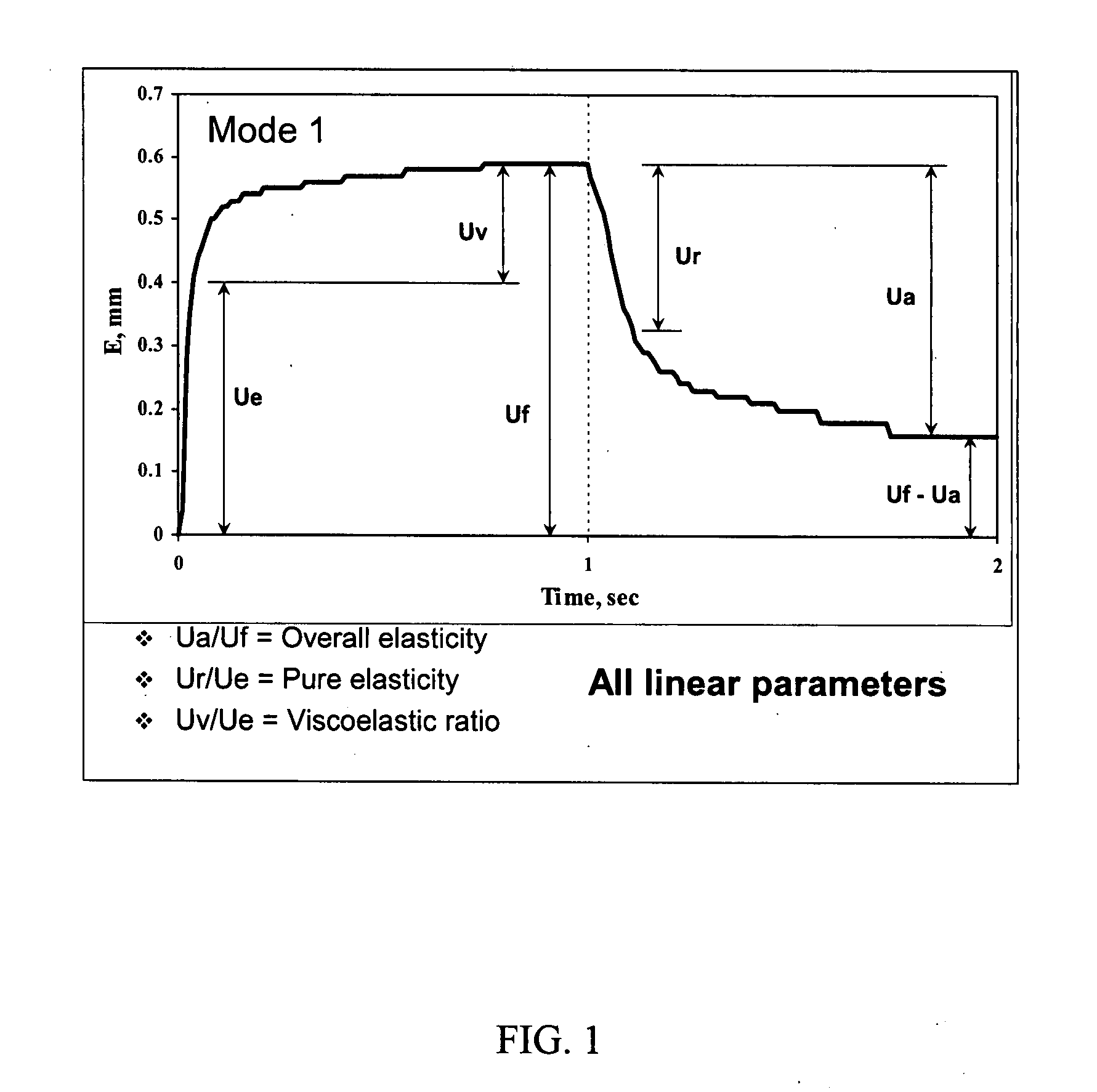
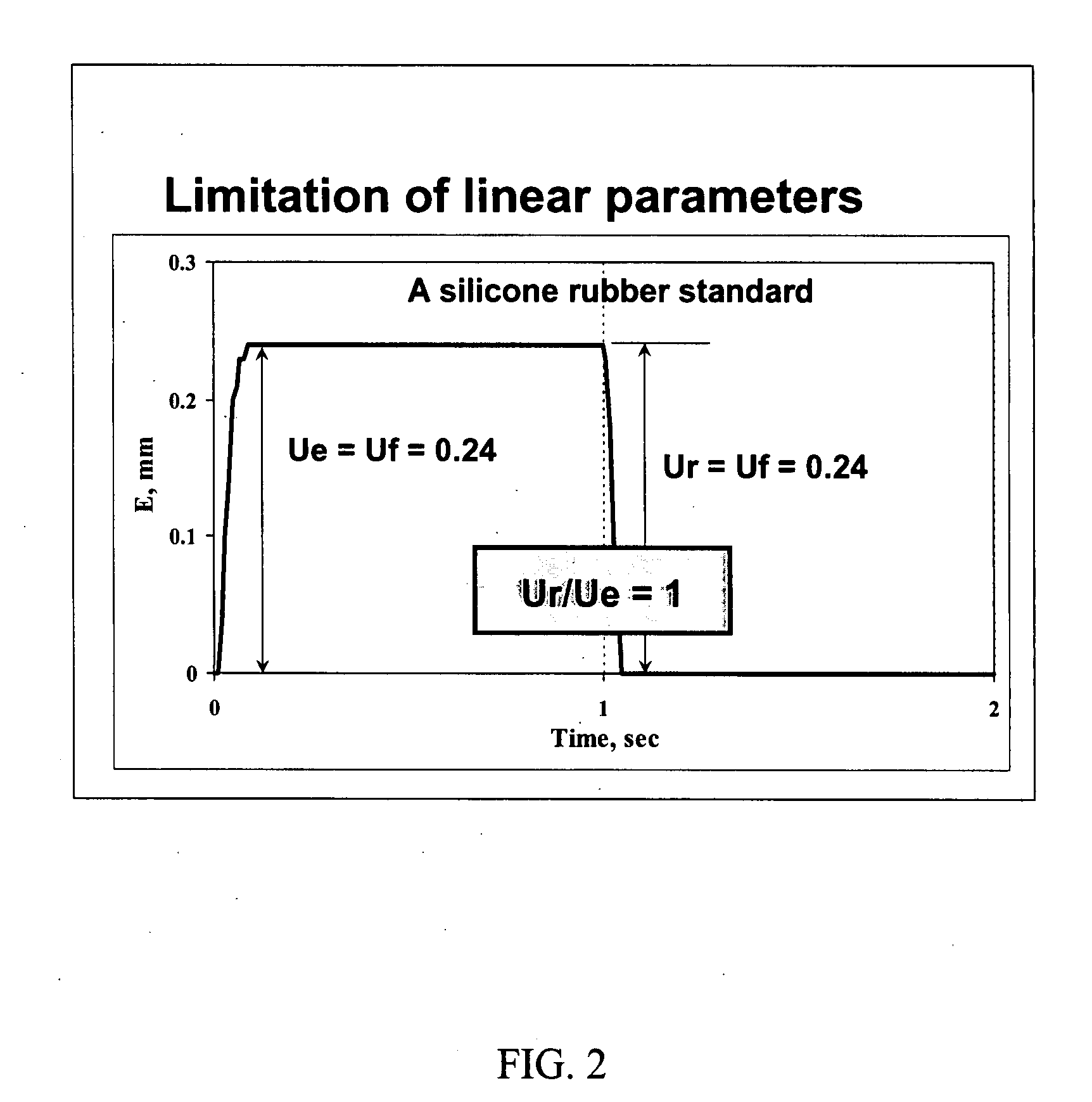
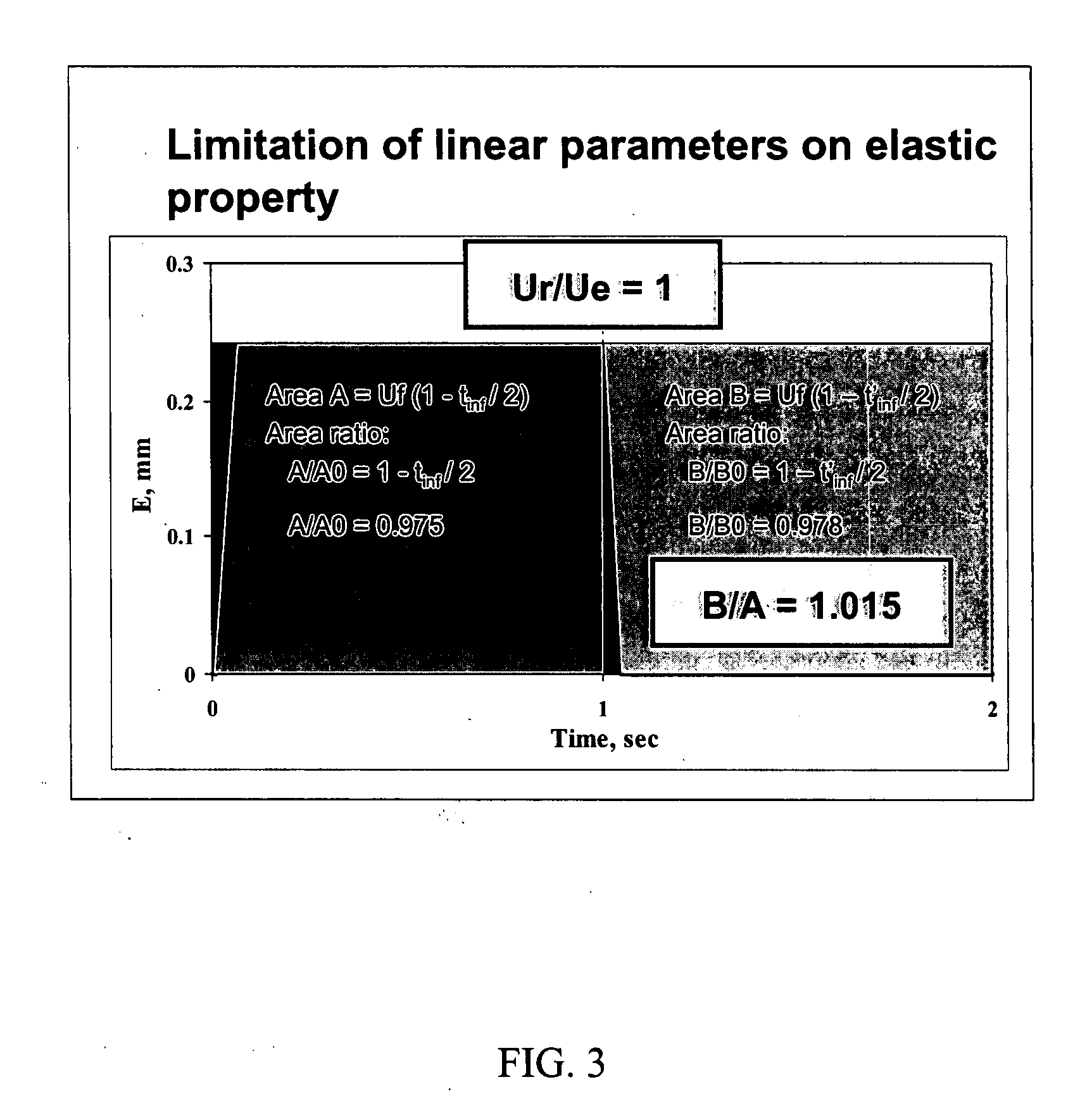
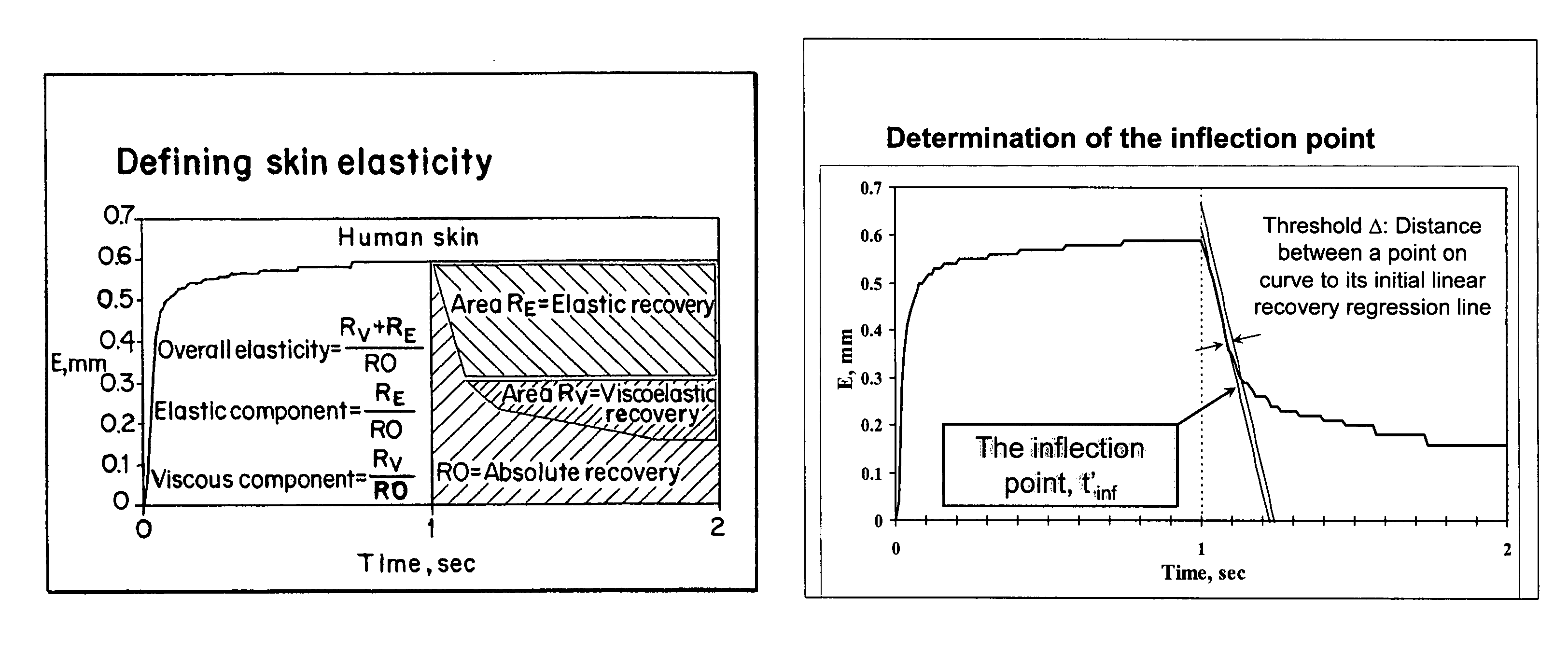
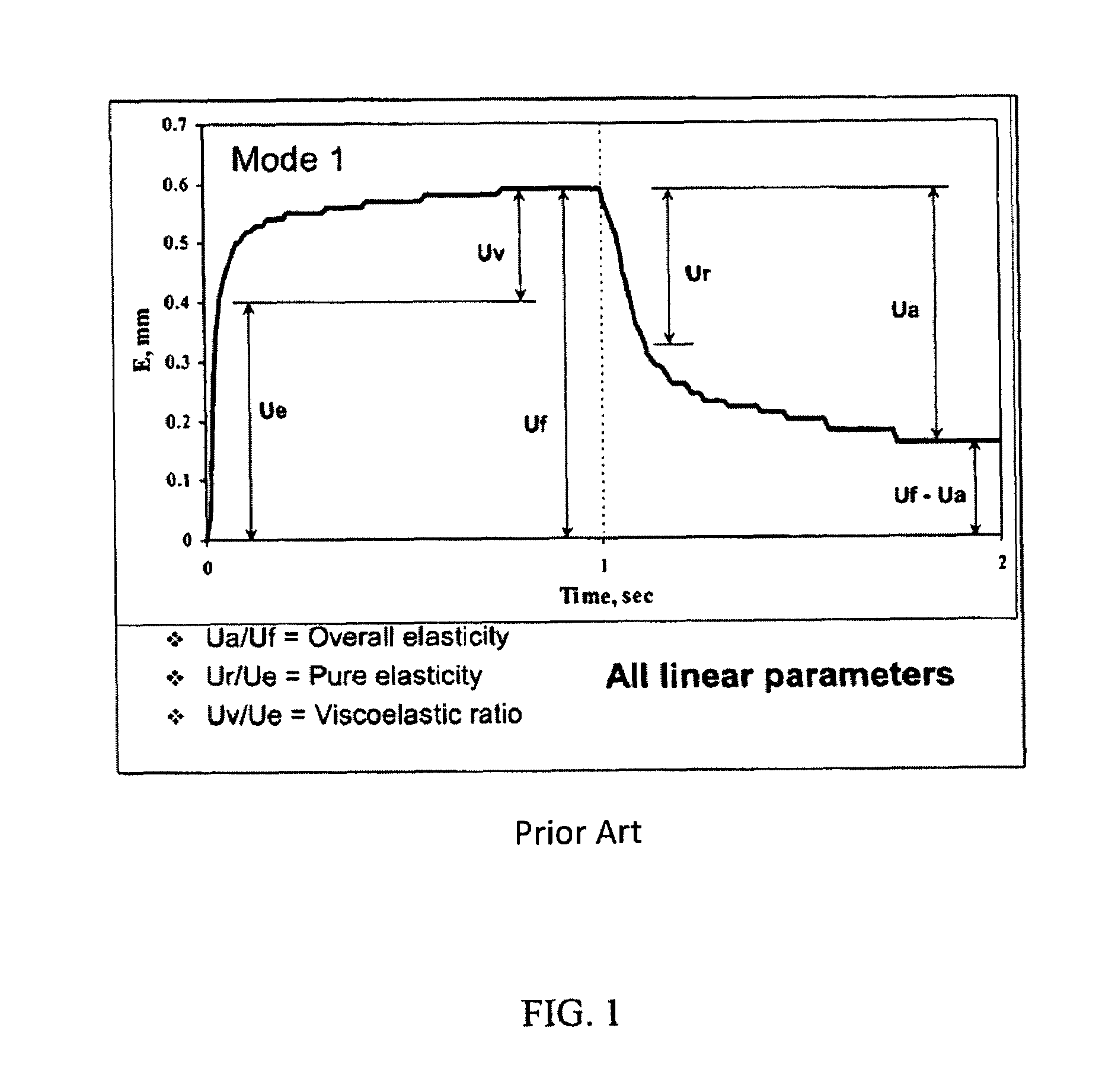
The invention relates to methods of measuring the overall elasticity of skin and determining the portion of the overall elasticity that is due to elastic properties and the portion of overall elasticity that is due to viscoelastic properties of the skin and correlating the results of the measurement to an individual's chronological age. The invention also relates to methods of measuring improvements in a person's skin health by measuring elasticity before, during and after human clinical trials of topical and / or oral treatment compositions. The parameters for determining elasticity are based on areas that are defined on a deformation / relaxation curve and require that an inflection point be determined for each skin sample analyzed.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Systems and methods for automated detection in magnetic resonance images
Some aspects include a method of detecting change in degree of midline shift in a brain of a patient. While the patient remains positioned within the low-field magnetic resonance imaging device, acquiring first magnetic resonance (MR) image data and second MR image data of the patient's brain; providing the first and second MR data as input to a trained statistical classifier to obtain corresponding first and second output, identifying, from the first output, at least one initial location of at least one landmark associated with at least one midline structure of the patient's brain; identifying, from the second output, at least one updated location of the at least one landmark; and determining a degree of change in the midline shift using the at least one initial location of the at least one landmark and the at least one updated location of the at least one landmark.
Owner:HYPERFINE
Elastic devices, methods, systems and kits for selecting skin treatment devices
ActiveUS20130190655A1Great inherent skin tensionReduce tensionDiagnostics using suctionPerson identificationWound healingSkin treatments
Devices, kits, systems and methods are described herein for treatment to skin, including but not limited to wound healing, the treatment, amelioration, and / or prevention of scars or keloids. Certain devices kits, systems and methods are used to select treatment parameters, devices or methods for treating skin in a location, zone, or region of skin having particular mechanical or other properties.
Owner:NEODYNE BIOSCI INC
Identification techniques and device for testing the efficacy of beauty care products and cosmetics
ActiveUS9265461B2Low costProcedure can be fast and accurateDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using vibrationsSkin surfaceSkin elasticity
A method for testing the effect of a skin care product includes measuring a mechanical property of skin tissue using nonlinear stochastic system identification, applying the product to the skin, repeating the measurement of the mechanical property after the application of the product, and comparing the before and after measurements to quantify the effect of the product.Measuring the mechanical property of the skin can include placing a probe against a surface of the skin, perturbing the skin with the probe using a stochastic sequence, and measuring the response of the skin to the perturbation. Perturbing the skin can include indenting the skin with the probe, extending the skin with the probe, and sliding the probe across the skin surface. The mechanical property may be indicative of skin compliance, skin elasticity, skin stiffness, or skin damping. The mechanical property can be dependent on perturbation depth and may be measured at a plurality of anatomical locations.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Device for use in electro-biological signal measurement in the presence of a magnetic field
ActiveUS9636019B2Electrical size reductionReduce Motion ArtifactsElectroencephalographyDiagnostics using suctionEeg dataEngineering
A device is presented for use in an EEG measurement performed in the presence of a magnetic field. The device includes a wiring array for connecting an electrodes arrangement to an electroencephalogram (EEG) monitoring device. The wiring array includes sampling lines arranged to form first and second groups of sampling lines, arranged in a spaced-apart substantially parallel relationship extending along first and second axes respectively, at least some of the sampling lines being wire bundles including a plurality of wires for connecting to a corresponding plurality of electrodes of the EEG electrodes arrangement; the first and second groups of sampling lines intersect with each other to form a net structure when placed on area of measurement. The wiring array thereby enable generation of EEG data characterized by reduced motion artifact and / or reduced gradient artifact associated with the presence of the magnetic field during the EEG measurement.
Owner:THE MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & HEALTH SERVICES FUND OF THE TEL AVIV MEDICAL CENT
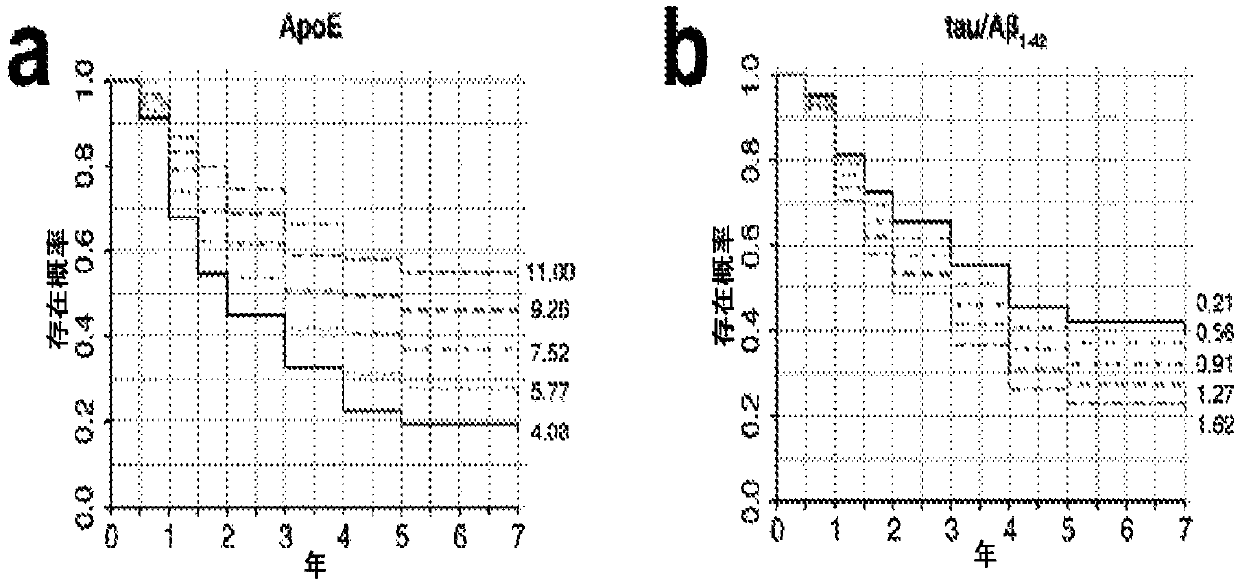
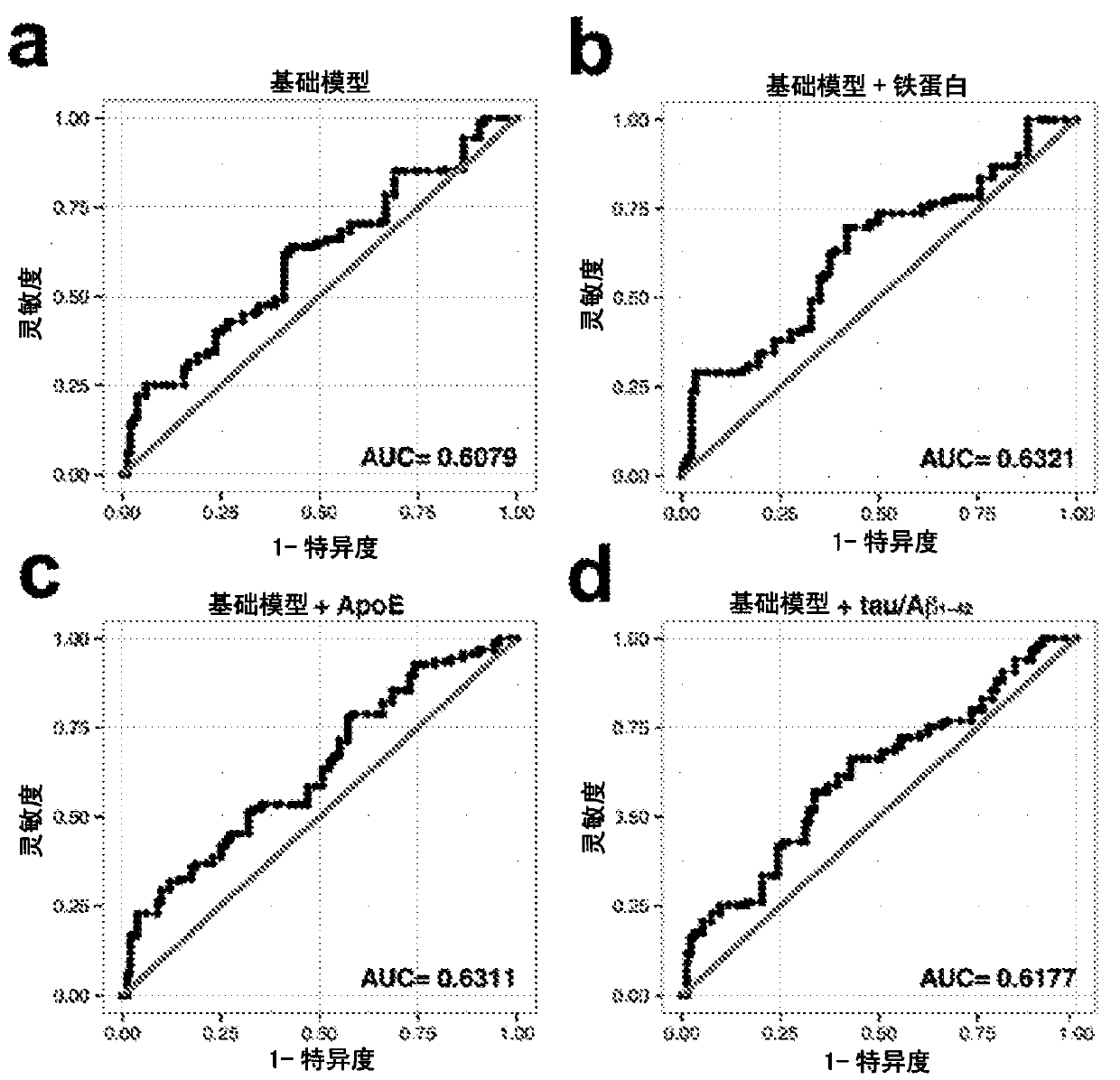
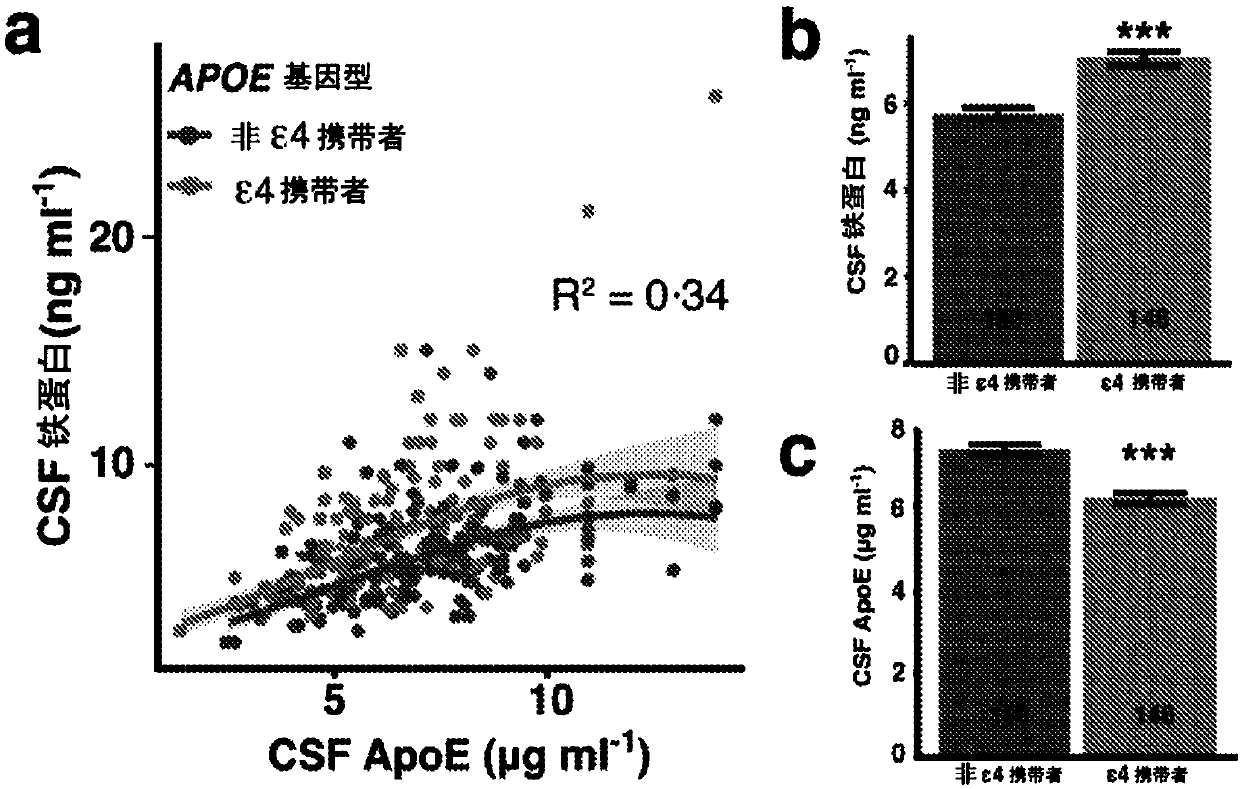
Method for predicting risk of cognitive deterioration
InactiveUS20180284141A1Improve accuracyAssess cognitive deteriorationOrganic active ingredientsDiagnostics using suctionIron levelsCvd risk
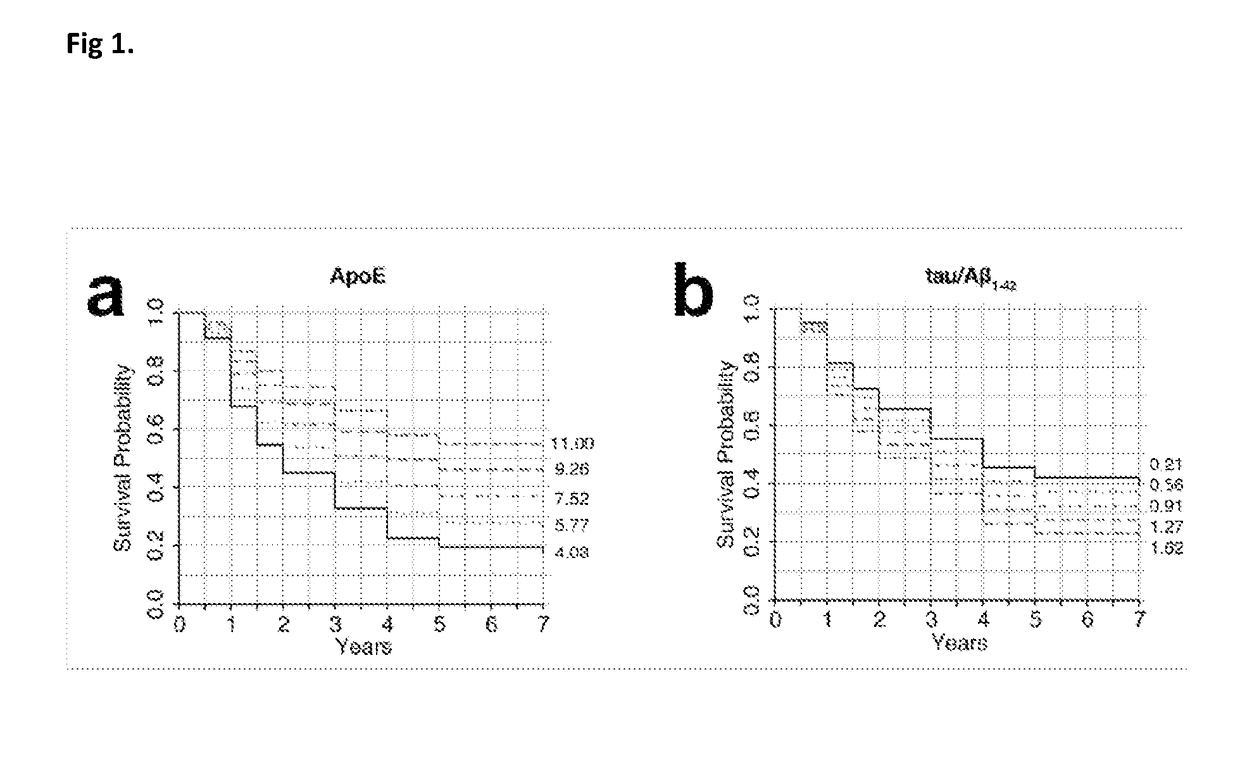
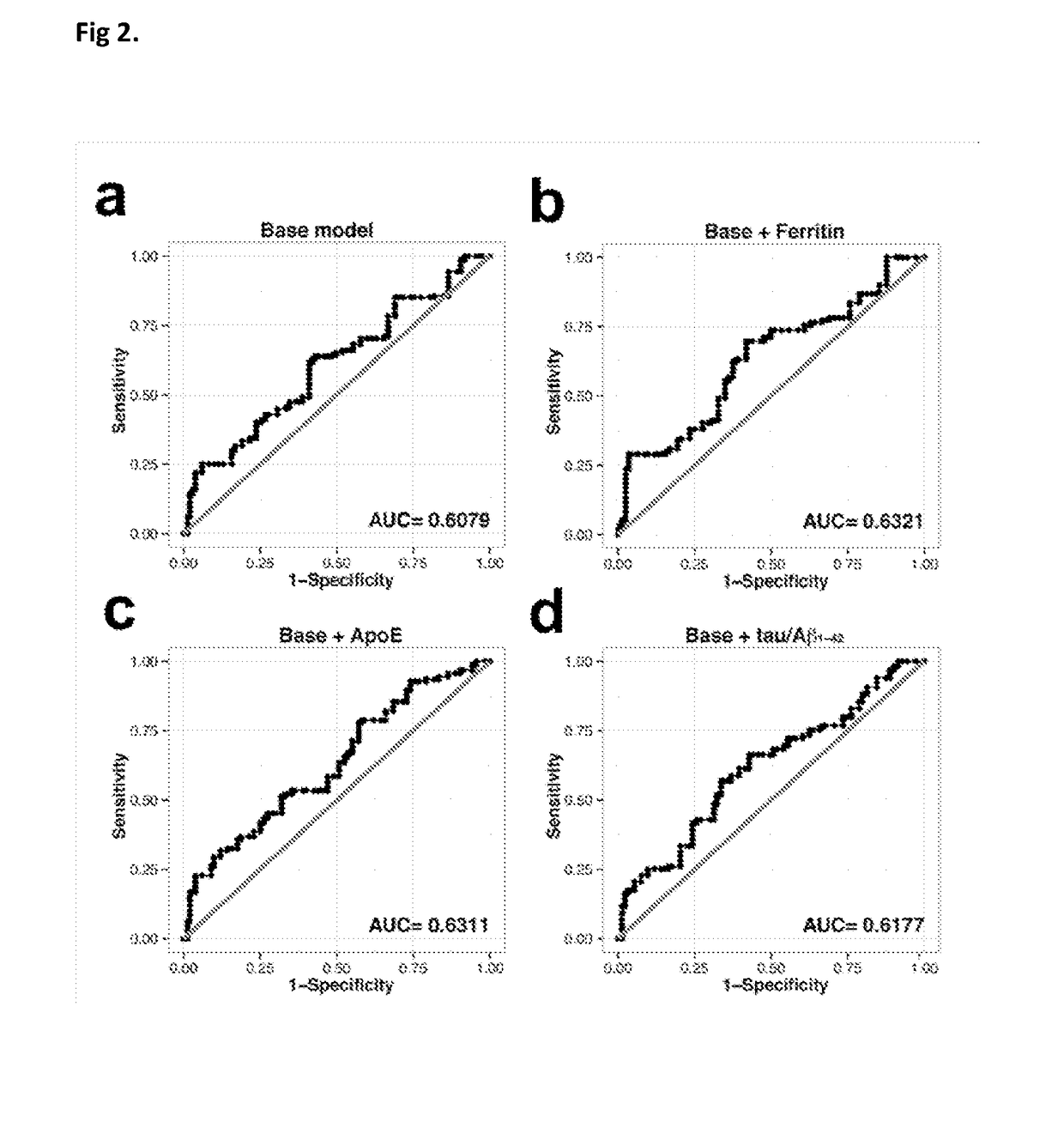
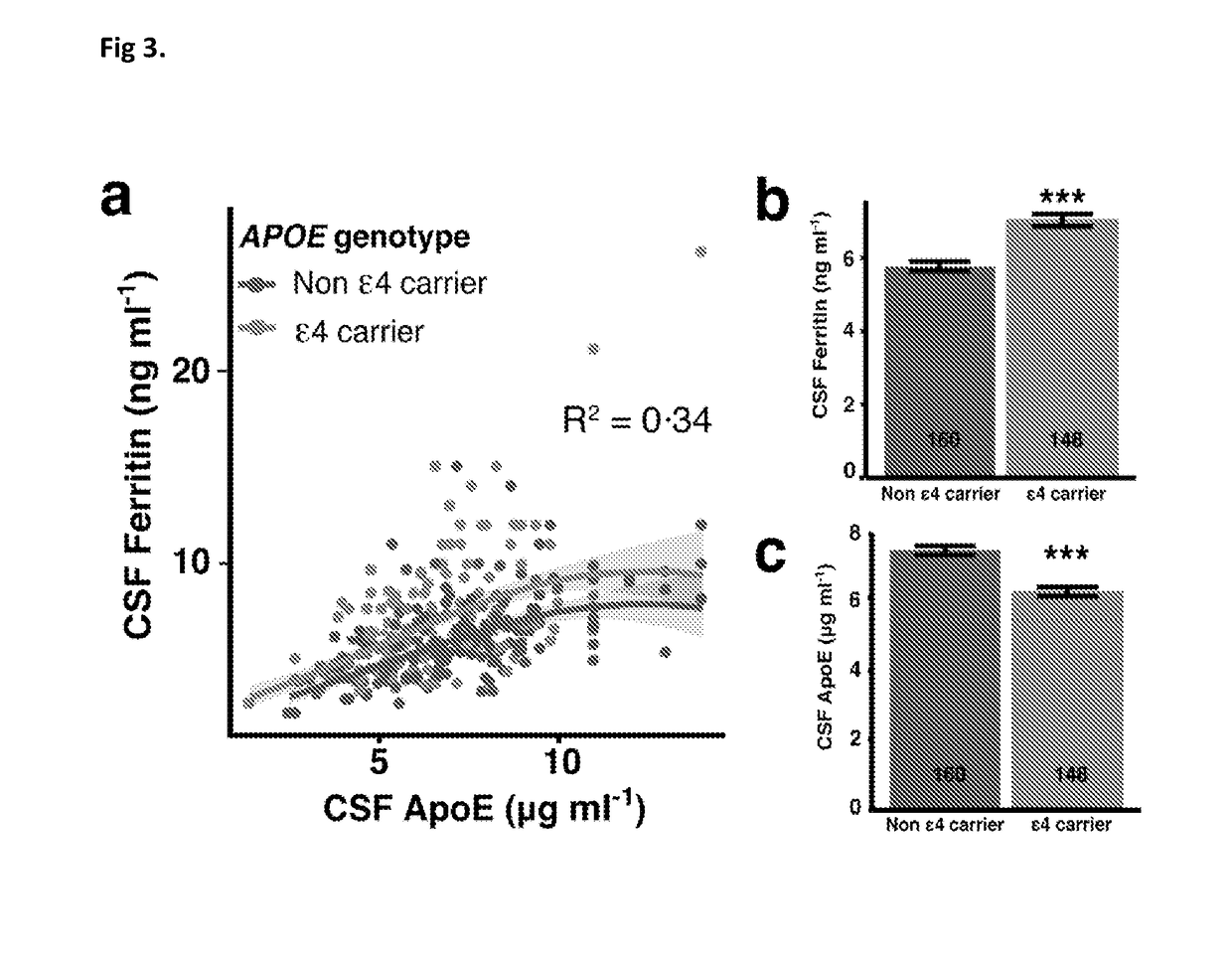
The present invention relates to methods for predicting a risk of cognitive deterioration, monitoring progression of cognitive deterioration and diagnosing cognitive deterioration in a patient. The present invention further relates to methods for diminishing progression rate of cognitive deterioration in a patient by lowering brain iron levels in the patient or lowering CSF ferritin levels in the patient.
Owner:CRC FOR MENTAL HEALTH
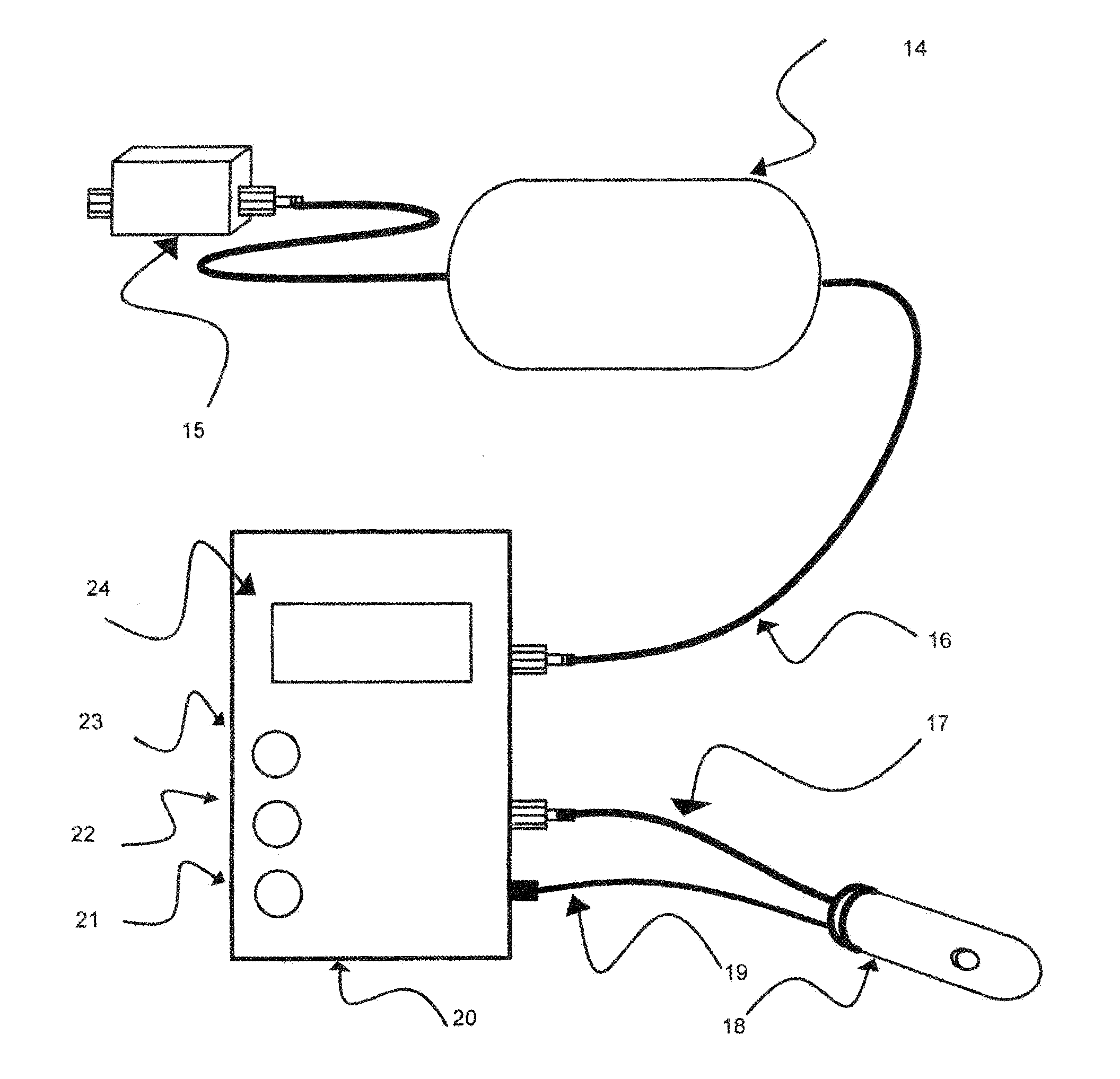
Method and apparatus of non-invasive biological sensing using controlled suction device
InactiveUS20170119290A1Accurate detectionAccurate measurementDiagnostics using suctionDiagnostics using spectroscopyElectricitySuction stress
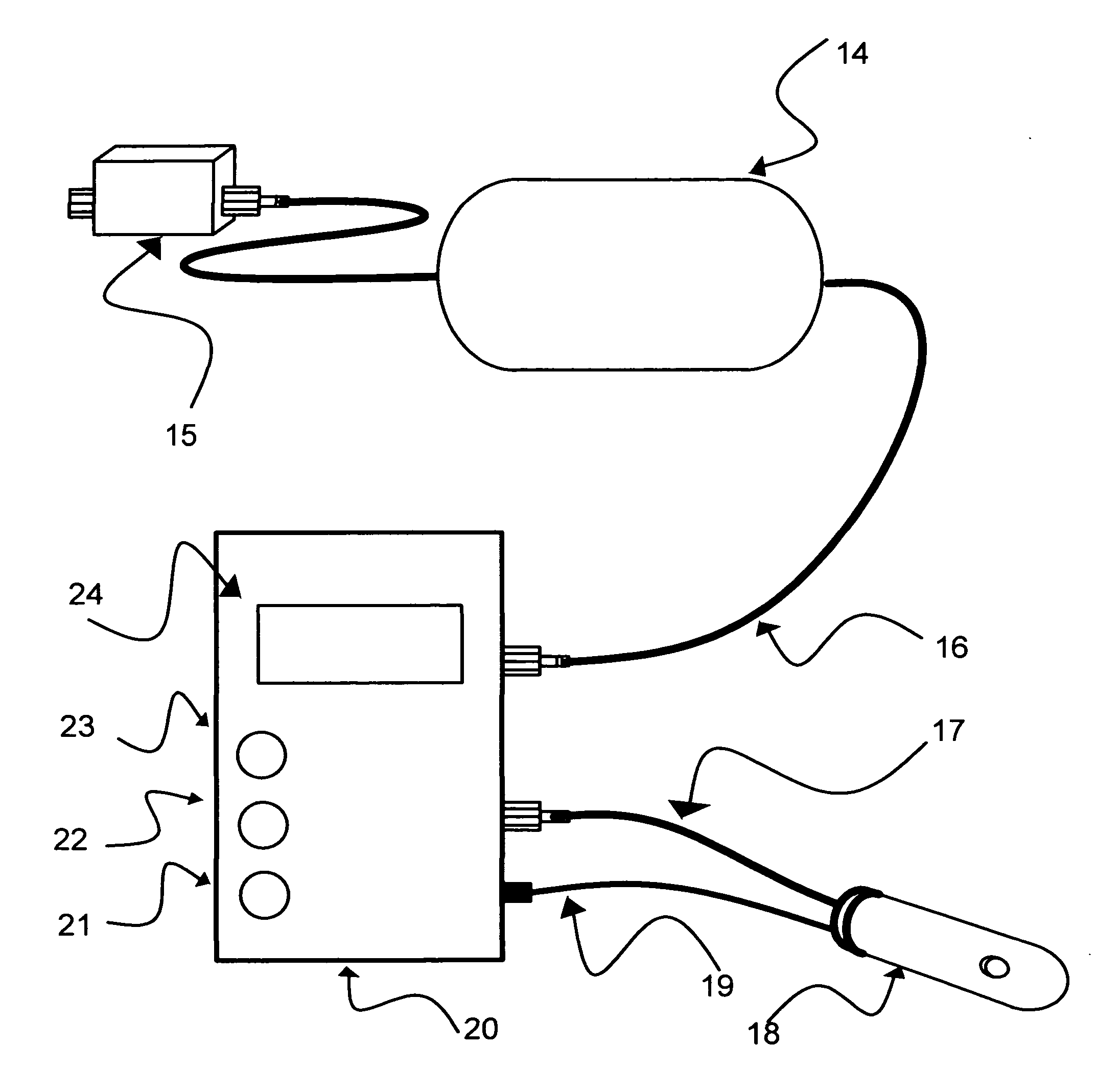
The present invention relates to systems and methods using optical or electrical spectroscopy for accurate detection and monitoring of biological tissue properties in a noninvasive manner. To perform in vivo diagnose with more accurate and repeatable measurements, an air-tight micro suction cup is placed against biological tissue under test (such as skin of a patient), around which an electrical or optical sensing system comprising excitation and detection sensors is integrated. Applying a high power suction pump over the micro cup, a negative pressure is generated to reshape the skin covered by the cup to a contour suitable for better measurement results. Most important, as the suction power increases, certain amount of blood flow or body fluid is brought to skin layer, providing great potential of improving those diagnoses that require direct analysis over these biological components.
Owner:CAI LUJING +1
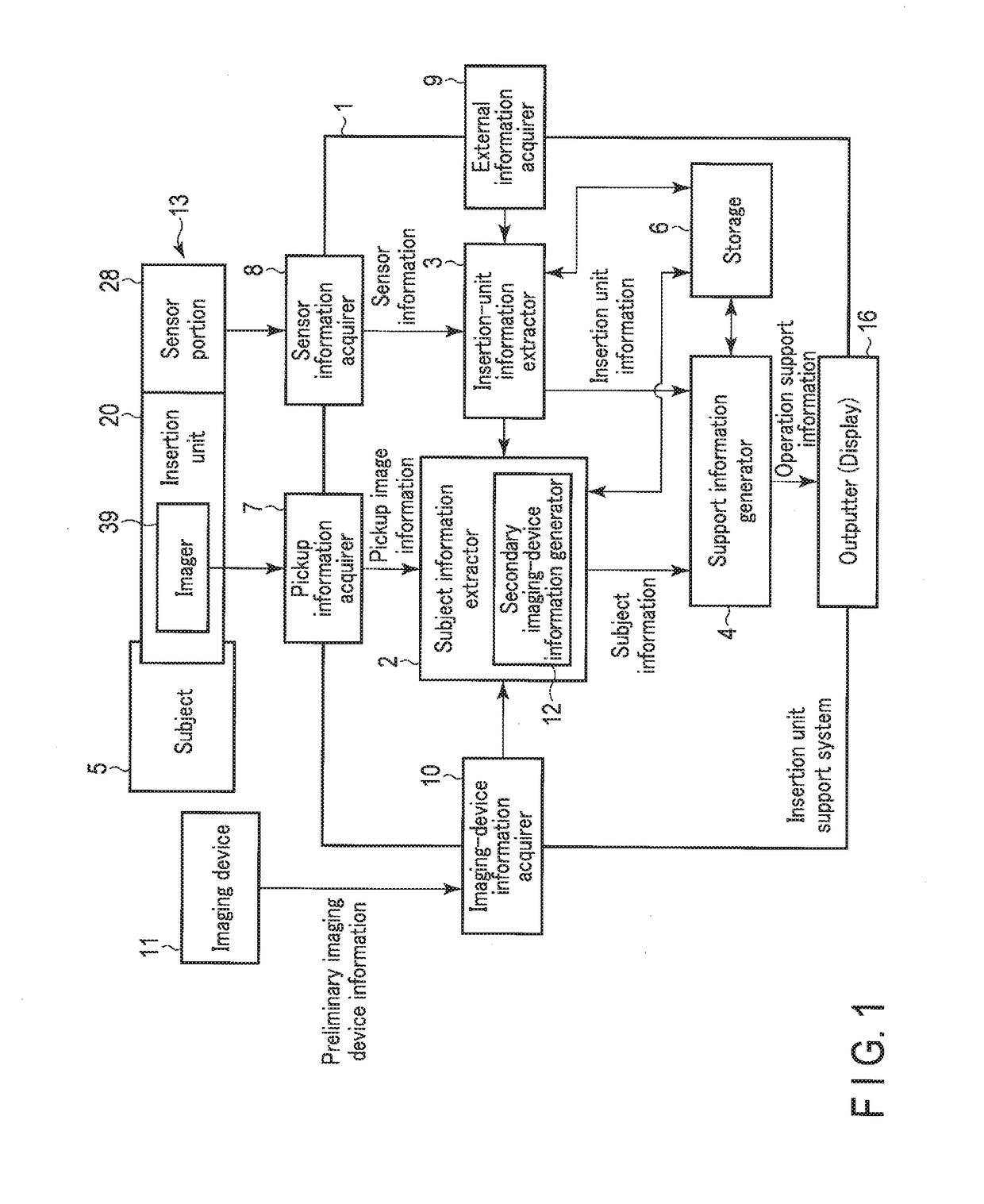
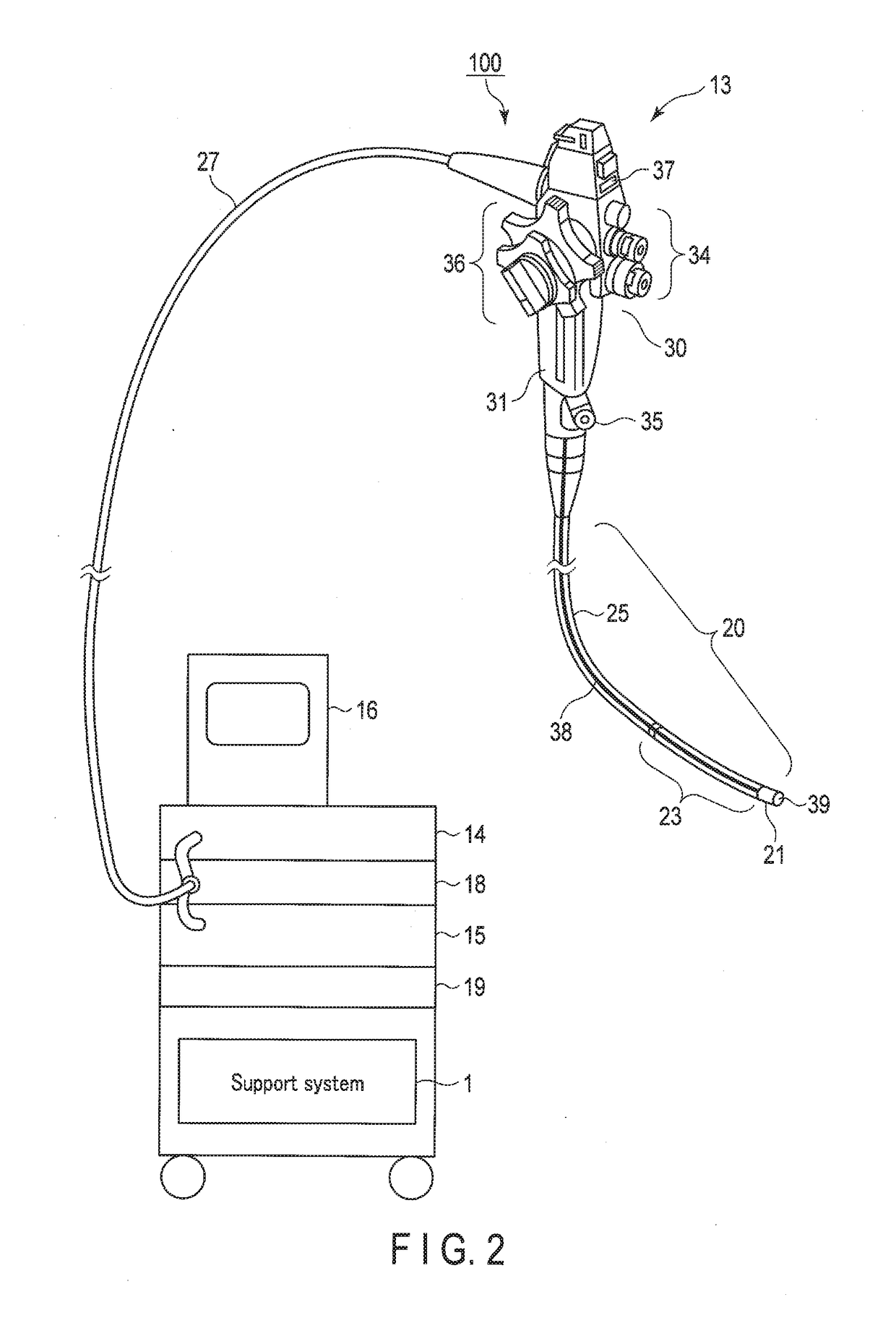
Insertion unit support system
The insertion unit support system is provided for a tubular insertion system, and generates lumen information including the shape and location of a lumen based on the pre-acquired information about the lumen of a subject as an observation target that includes image information of two- or higher dimensional images, i.e., three-dimensional images or three-dimensional tomograms, so that the lumen information is used as support information for inserting the insertion unit of an endoscope. The lumens of the subjects targeted for the support of the insertion unit support system may vary in shape and location, and are deformed according to the shape of an inserted insertion unit. Thus, the support information is corrected and updated based on the deformation.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Methods for determining elastic and viscoelastic properties of skin
ActiveUS7556605B2Promotes skin healthDiagnostics using suctionFlow propertiesOral treatmentRelaxation curve
The invention relates to methods of measuring the overall elasticity of skin and determining the portion of the overall elasticity that is due to elastic properties and the portion of overall elasticity that is due to viscoelastic properties of the skin and correlating the results of the measurement to an individual's chronological age. The invention also relates to methods of measuring improvements in a person's skin health by measuring elasticity before, during and after human clinical trials of topical and / or oral treatment compositions. The parameters for determining elasticity are based on areas that are defined on a deformation / relaxation curve and require that an inflection point be determined for each skin sample analyzed.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
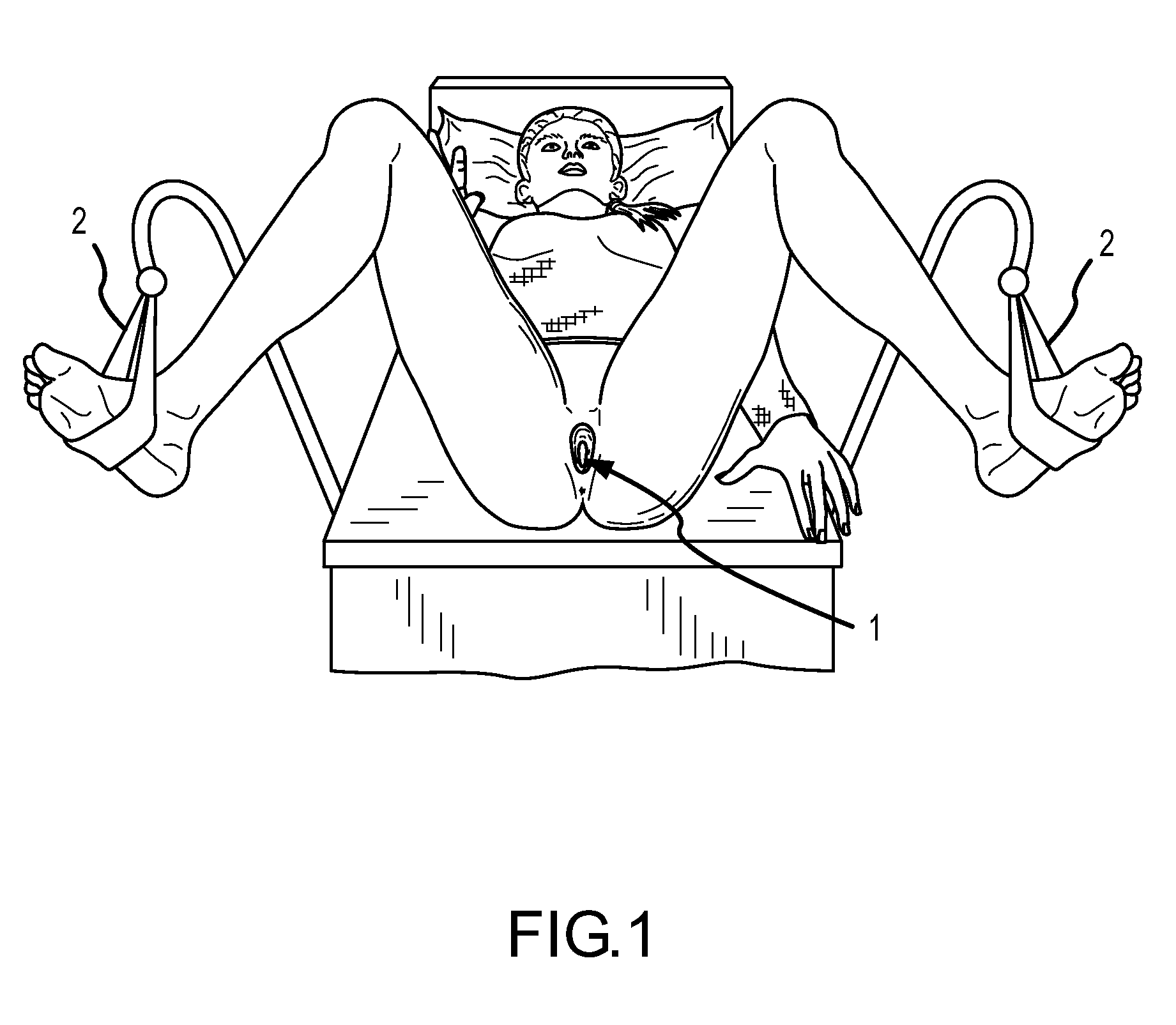
Vaginal biomechanics analyzer
ActiveUS20150133750A1Easy to useEasily insertableDiagnostics using suctionPerson identificationMicrocontrollerProximity sensor
The present invention includes a device and method for measuring skin elasticity that comprises: a probe, wherein the probe comprises one or more holes, a vacuum source, a pressure sensor, and one or more proximity sensors aligned about the one or more holes; and a processor for recording the deformation of the skin using a control unit comprising a microcontroller connected to the proximity and the pressure sensors, wherein the proximity sensor and the processor is adapted to automatically initiate a test when the sensor is positioned at a pre-determined distance from the skin, wherein a vacuum in the probe is capable of pulling skin into the one or more holes and the proximity sensor is capable of measuring an amount of skin drawn into the one or more holes to determine an elasticity of the skin.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method for predicting risk of cognitive deterioration
InactiveCN107636468ADiagnostics using suctionOrganic active ingredientsIron levelsCognitive deterioration
The present invention relates to methods for predicting a risk of cognitive deterioration, monitoring progression of cognitive deterioration and diagnosing cognitive deterioration in a patient. The present invention further relates to methods for diminishing progression rate of cognitive deterioration in a patient by lowering brain iron levels in the patient or lowering CSF ferritin levels in thepatient.
Owner:CRC FOR MENTAL HEALTH
Vaginal biomechanics analyzer
ActiveUS20160317078A1Easily insertableEasily user-friendlyDiagnostics using suctionAnti-incontinence devicesMicrocontrollerProximity sensor
The present invention includes a device and method for measuring skin elasticity that comprises: a probe with one or more holes, a vacuum source, a pressure sensor, and one or more infrared or optical proximity sensors aligned about the one or more holes, wherein the probe further comprises a raised area surrounding the one or more holes; and a processor for recording the deformation of the skin using a control unit comprising a microcontroller connected to the one or more infrared or optical proximity sensors and the one or more pressure sensors, to measure an amount of skin drawn into and out of the one or more holes to determine the distance between the one or more proximity sensors and the skin both inside and outside the probe.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Integration of T2-preparation and motion tracking in magnetic resonance imaging
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides concurrent measurement of motion during T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. The present invention combines T2 preparation, a module used to impart T2 contrast, and motion measurement, tracking, and / or correction. The present invention provides for the expedition of more efficient motion compensation during T2-weighted imaging. The proposed invention can be used to provide a variety of measurements of motion, with no overhead in imaging time. The proposed invention also enables T2 contrast imaging to be executed while a subject is breathing freely, without the additional time cost associated with the standard motion tracking methodologies.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Integration of t2-preparation and motion tracking in magnetic resonance imaging
An embodiment in accordance with the present invention provides concurrent measurement of motion during T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. The present invention combines T2 preparation, a module used to impart T2 contrast, and motion measurement, tracking, and / or correction. The present invention provides for the expedition of more efficient motion compensation during T2-weighted imaging. The proposed invention can be used to provide a variety of measurements of motion, with no overhead in imaging time. The proposed invention also enables T2 contrast imaging to be executed while a subject is breathing freely, without the additional time cost associated with the standard motion tracking methodologies.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Device for determining the quality and solidness of the vascular wall
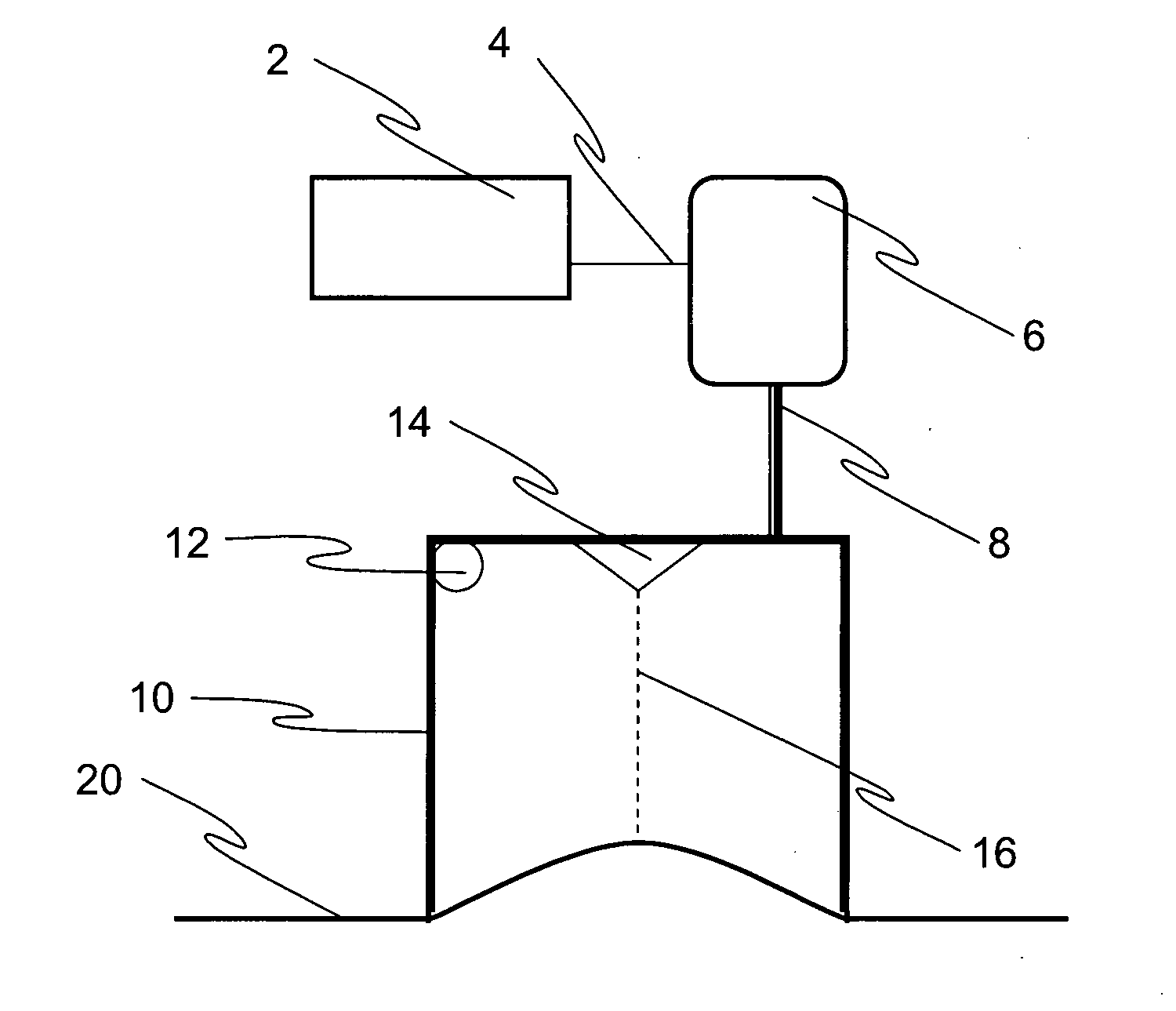
InactiveUS20090191615A1Quality is determinedEasy to useBioreactor/fermenter combinationsDiagnostics using suctionTissue sampleAir pump
A device for determining the quality and solidness of the vascular wall is provided for testing tissue samples and includes opposed first and second fixation plates. The fixation plates are connectable to an air pump or other source of vacuum for fixing the tissue sample in position. The device is connectable to a detector such as a meter, gauge, or printing device capable of displaying or producing an image or display corresponding to the value of a force required to disrupt or break the internal links between individual layers of the vascular wall. The fixation plates are movable relative to one another and may be abducted by abductors connecting the plates or by rotational movement of one fixation plate relative to the other by a shaft or other rotational mechanism.
Owner:BENEDIK JAROSLAV
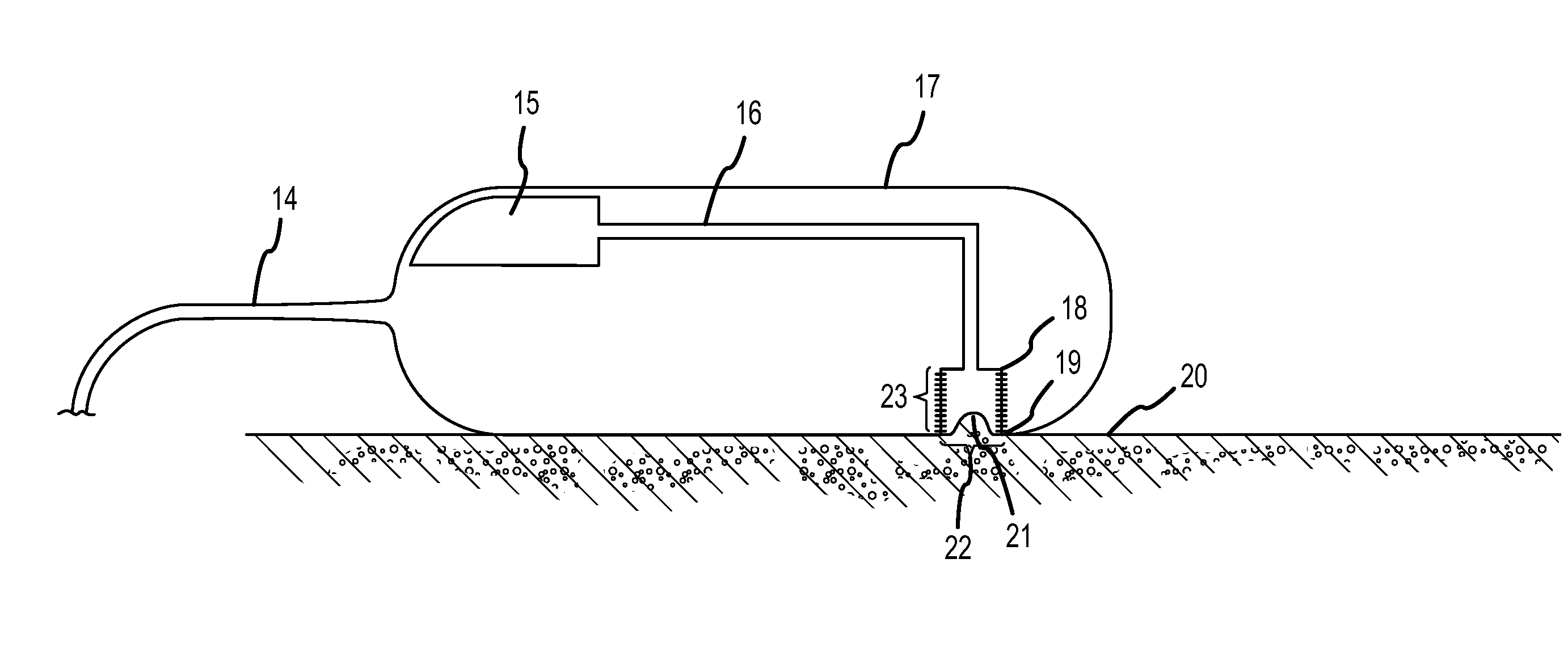
Method and device for measuring tissue pressure
The method facilitates measuring of a tissue pressure non-invasively utilizing a negative pressure. The device has a pressure chamber, pressure sensor for measuring the pressure in the pressure chamber and a range sensor for measuring the skin tissue rising caused by the negative pressure.
Owner:HLD HEALTHY LIFE DEVICES
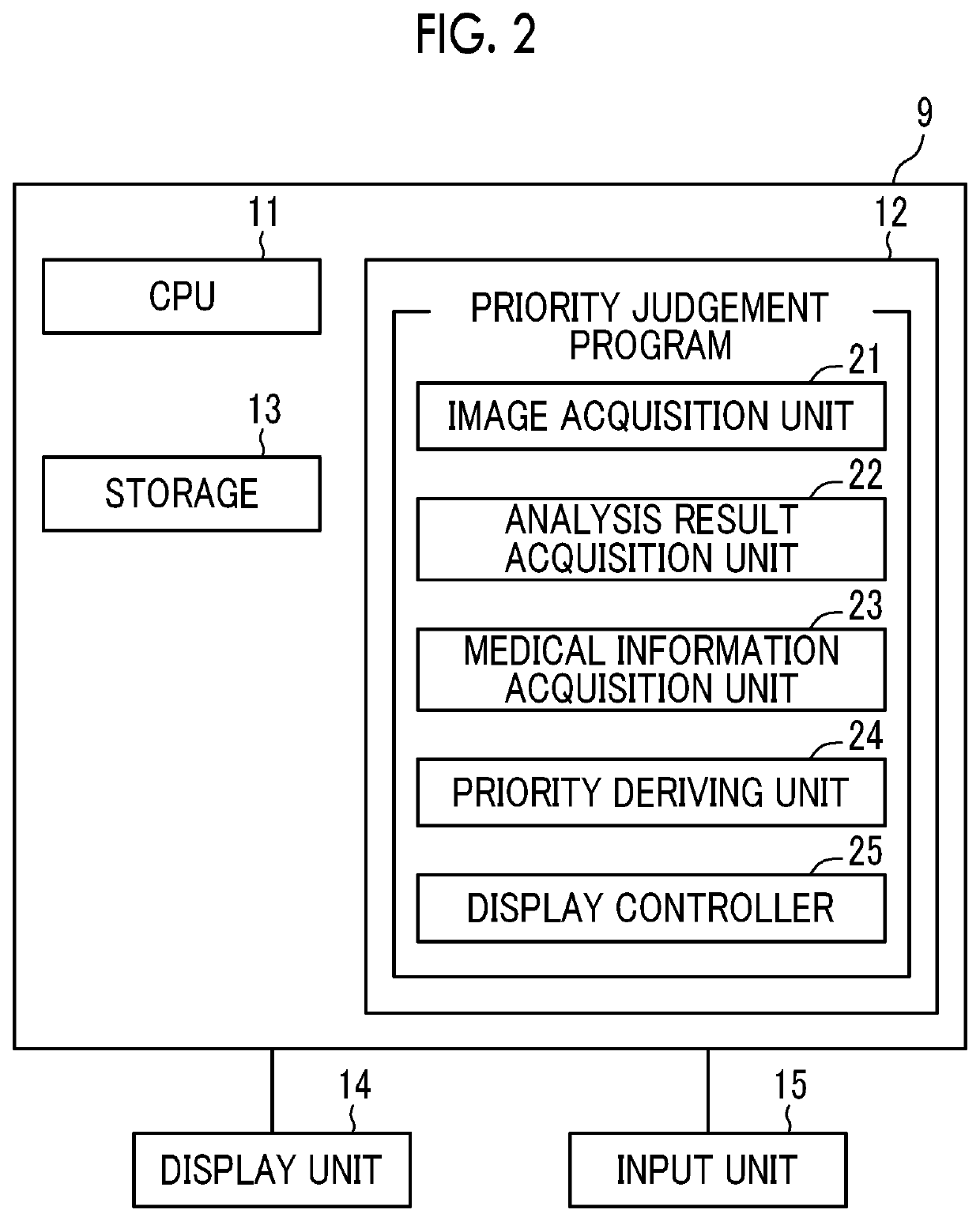
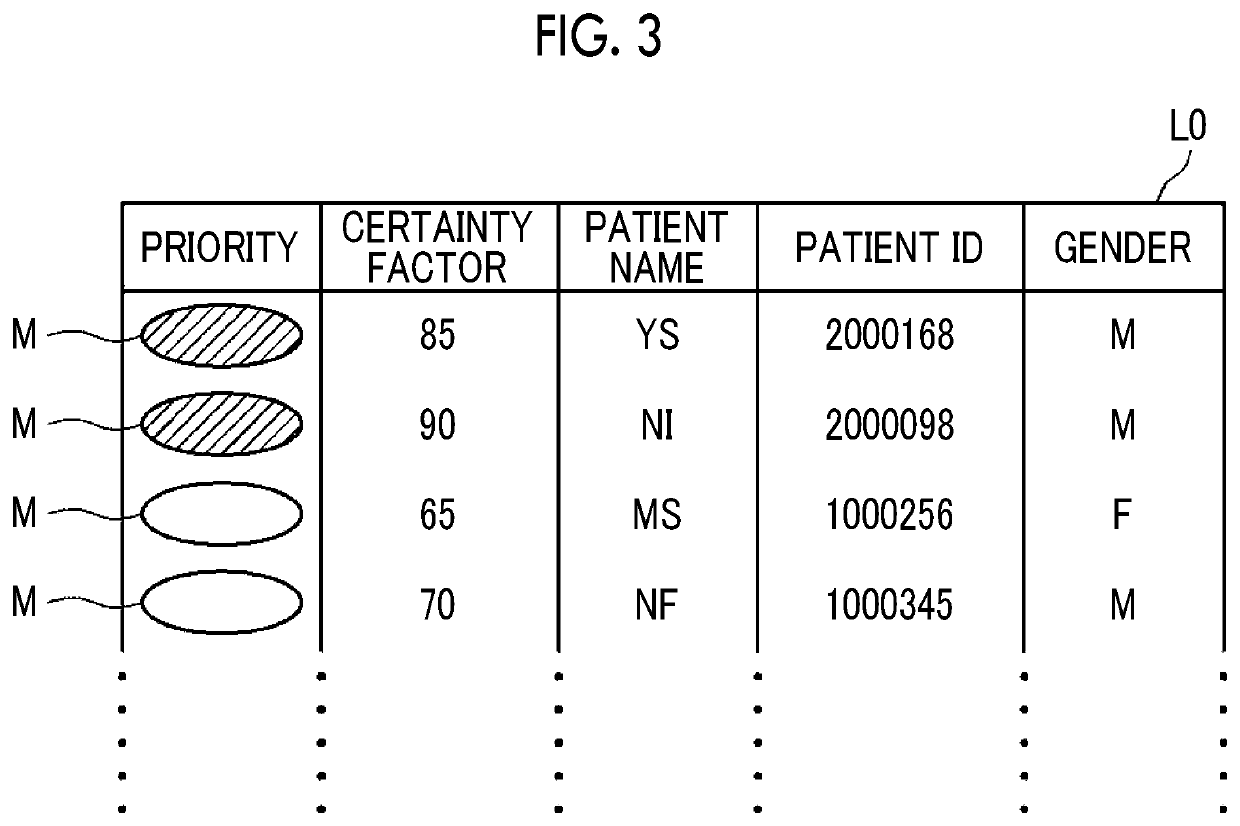
Priority judgement device, method, and program
An analysis result acquisition unit acquires an analysis result of a medical image. A medical information acquisition unit acquires medical information different from the medical image. A priority deriving unit derives a priority of the medical image based on the analysis result and the medical information.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
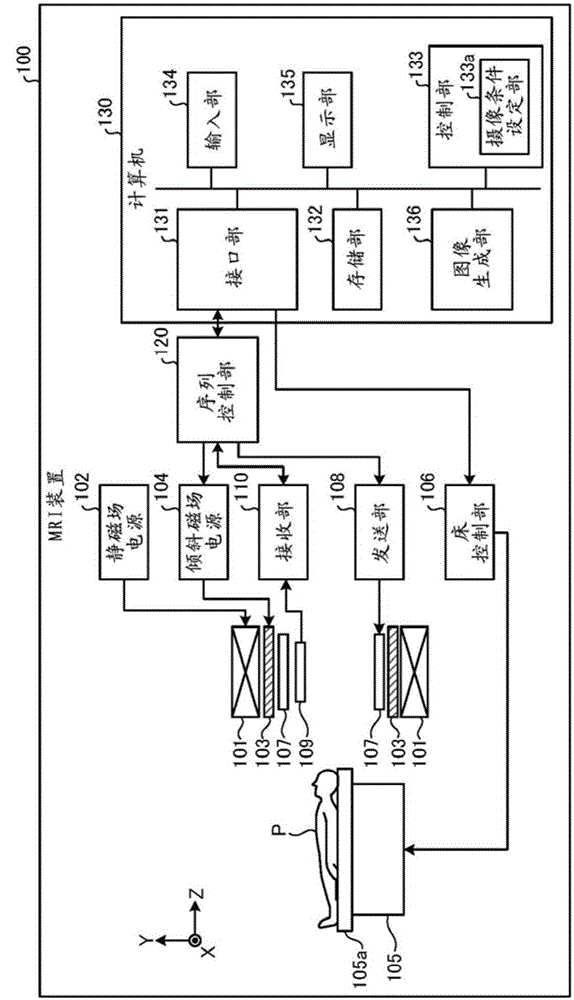
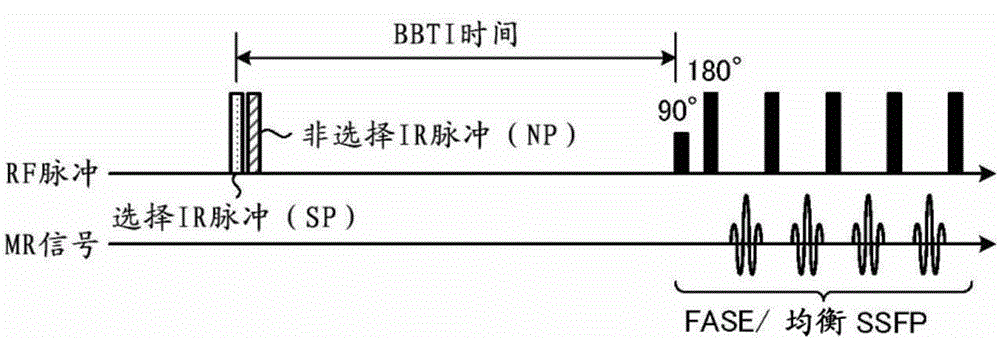
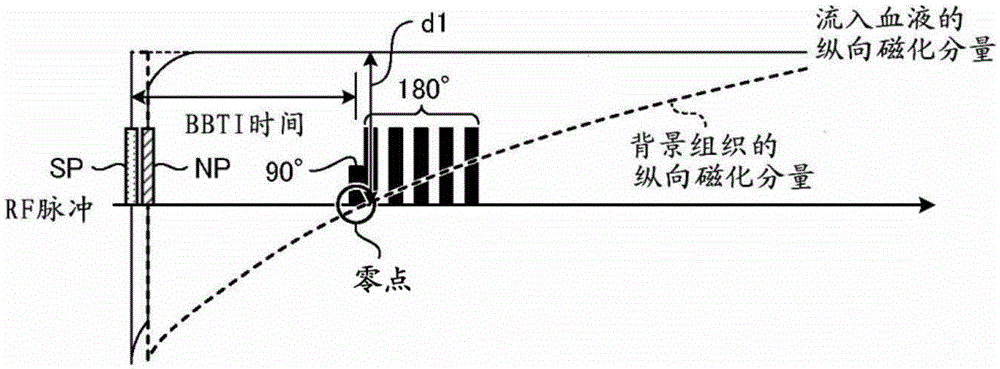
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveCN105007814AImprove drawing abilityDiagnostics using suctionSensorsSequence controlRadio frequency
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus (100) according to one embodiment of the present invention is provided with a sequence control unit (120) and an image generation unit (136). The sequence control unit (120) collects magnetic resonance signals within an imaging region from the time a radio frequency (RF) pulse is applied to a labeling region until a prescribed amount of time has elapsed. The image generation unit (136) generates an image using the magnetic resonance signals. Also, the sequence control unit (120) sets the application timing of the RF pulse such that a first amount of time, from the time when the first RF pulse is applied without selecting a region until the collection of the magnetic resonance signals starts, differs from a second amount of time, from the time when the labeling region is selected and the second RF pulse is applied until the collection of magnetic resonance signals starts.
Owner:KYOTO UNIV +1
Elastic devices, methods, systems and kits for selecting skin treatment devices
Devices, kits, systems and methods are described herein for treatment to skin, including but not limited to wound healing, the treatment, amelioration, and / or prevention of scars or keloids. Certain devices kits, systems and methods are used to select treatment parameters, devices or methods for treating skin in a location, zone, or region of skin having particular mechanical or other properties.
Owner:NEODYNE BIOSCI INC
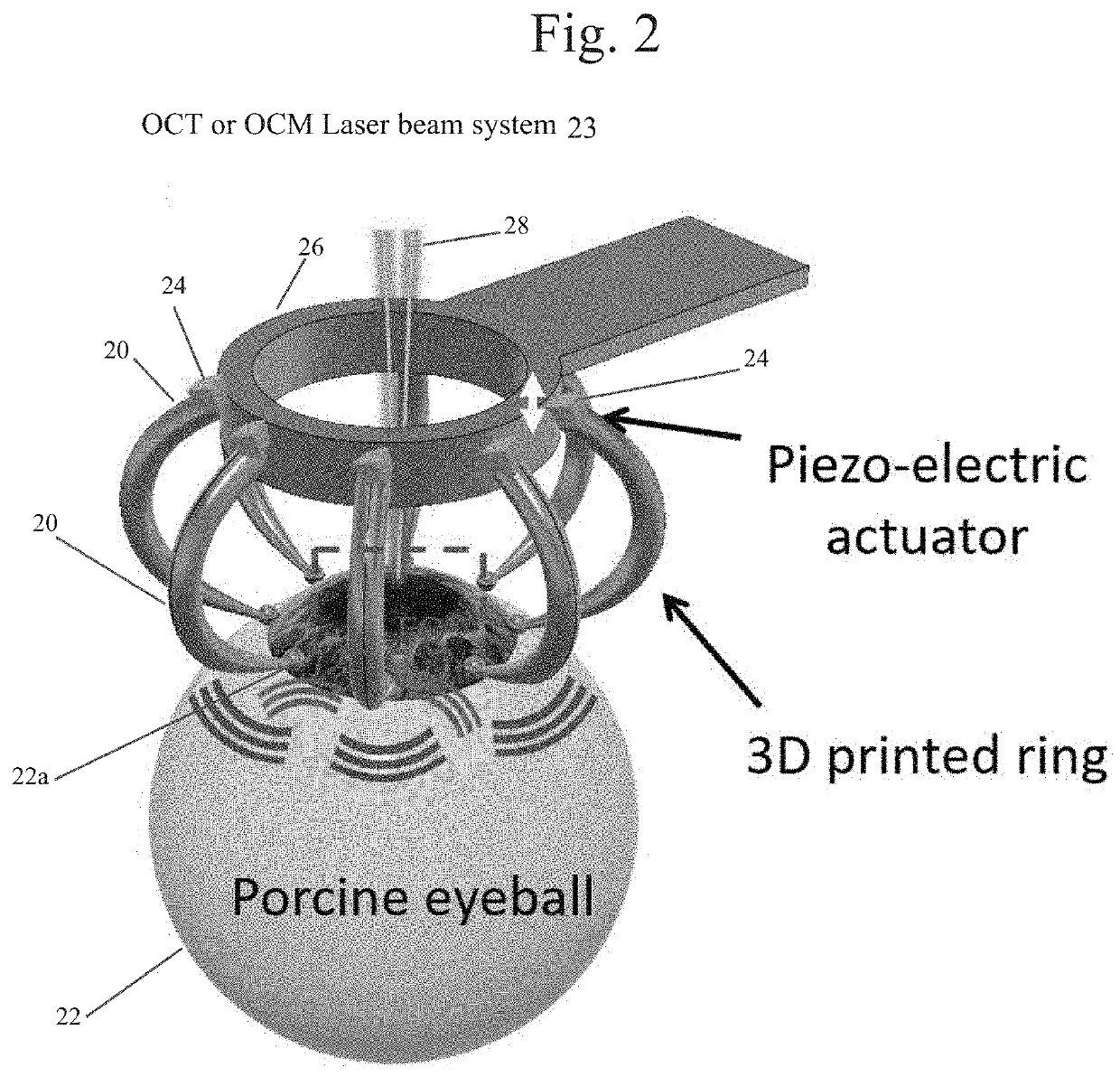
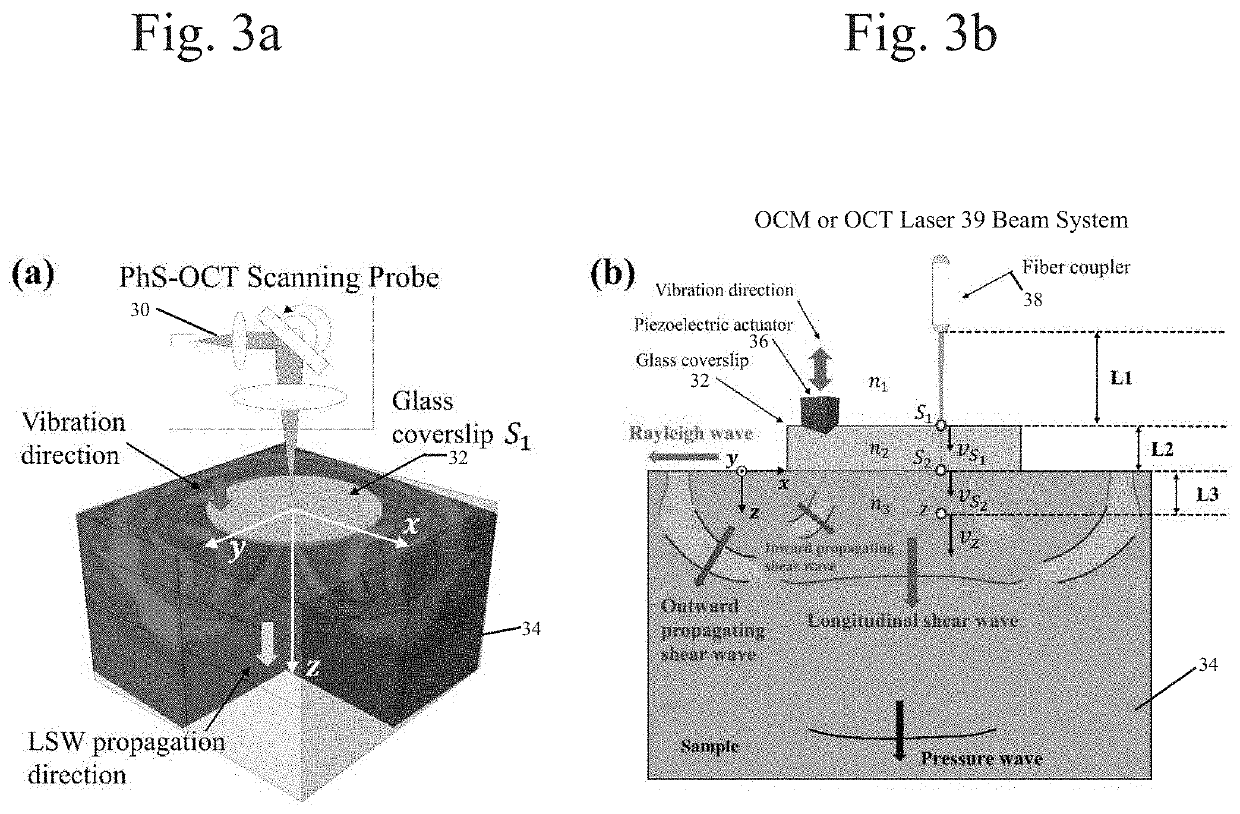
Gabor Domain Optical Coherence Elastography
ActiveUS20210307611A1Shear speed can be easily converted into shear and Young 's modulusSharp contrastDiagnostics using suctionImage enhancementWave fieldComputational physics
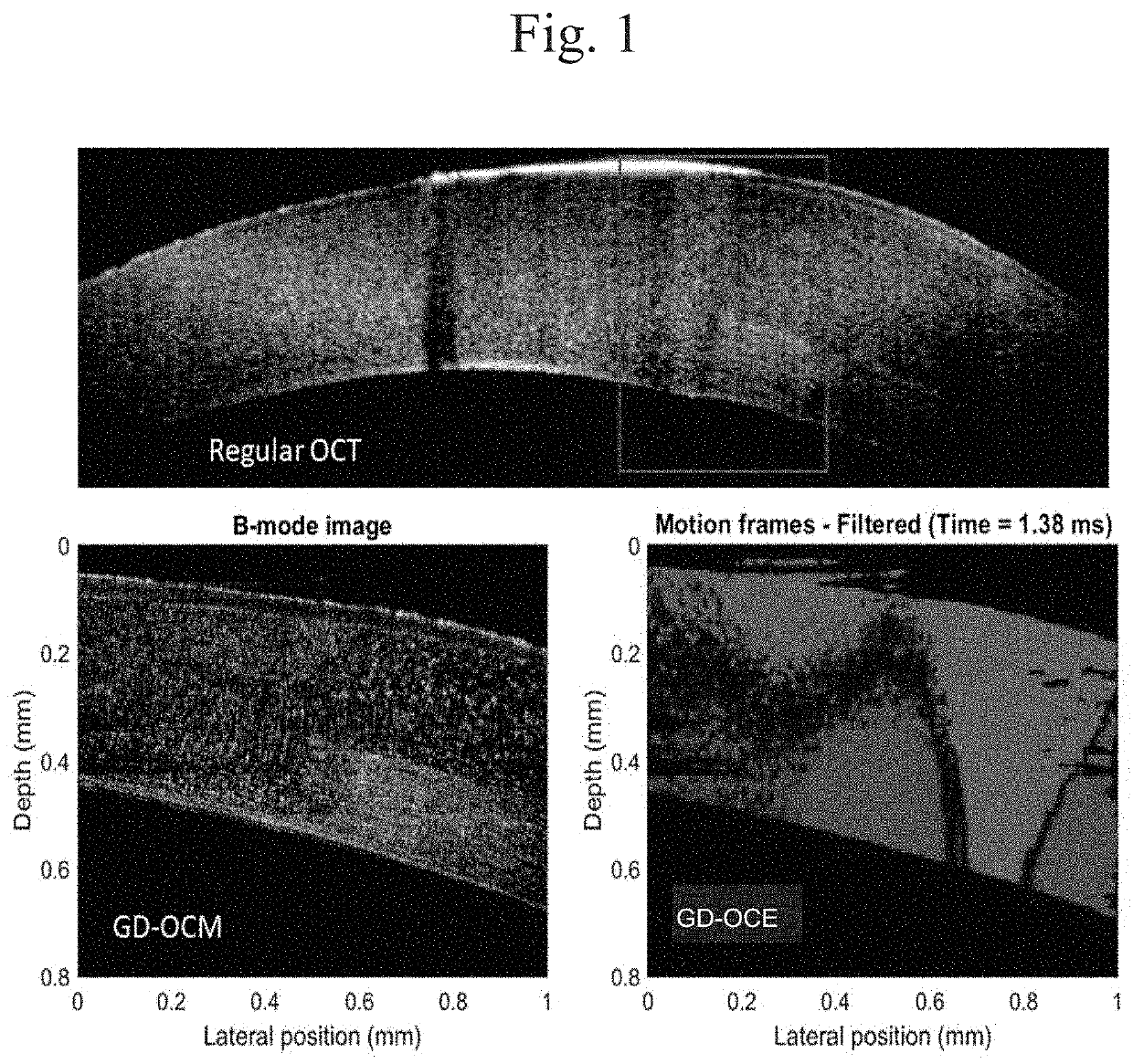
a) A Gabor domain optical coherence microscopy (GD-OCM) system providing high resolution of structural and motion imaging of objects such as tissues is combined with the use of reverberant shear wave fields (RevSW) or longitudinal shear waves (LSW) and two novel mechanical excitation sources: a coaxial coverslip excitation (CCE) and a multiple pronged excitation (MPE) sources providing structured and controlled mechanical excitation in tissues and leading to accurate derivation of elastographic properties. Alternatively, general optical computed tomography (OCT) is combined with RevSW or LWC in the object to derive elastographic properties. The embodiments include (a) GD-OCM with RevSW; (b) GD-OCM with LSW; (c) General OCT with RevSW; and General OCT with LSW.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ROCHESTER +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com