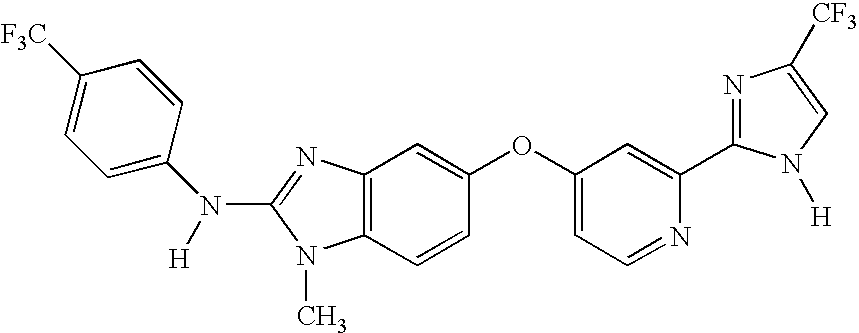
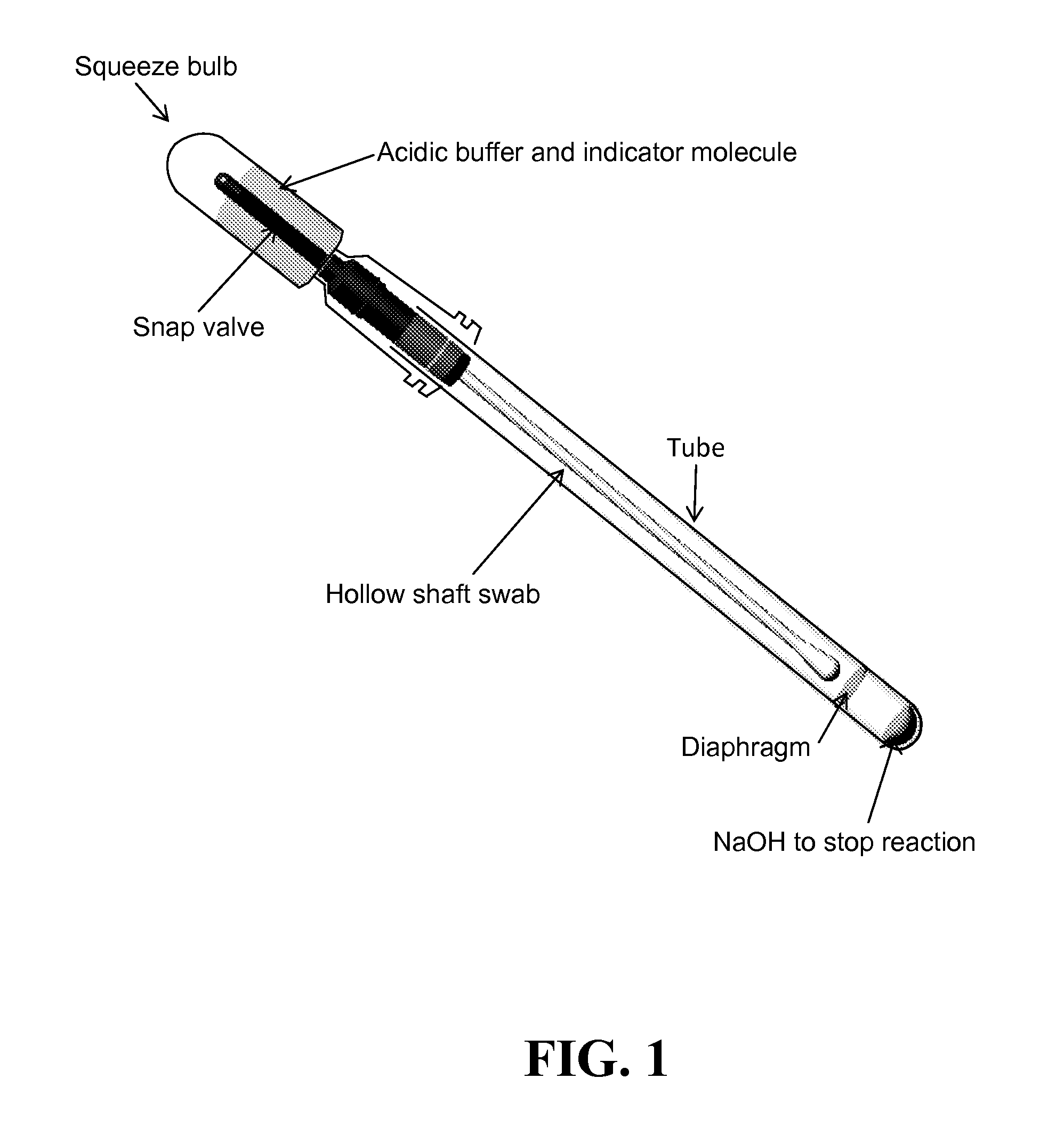
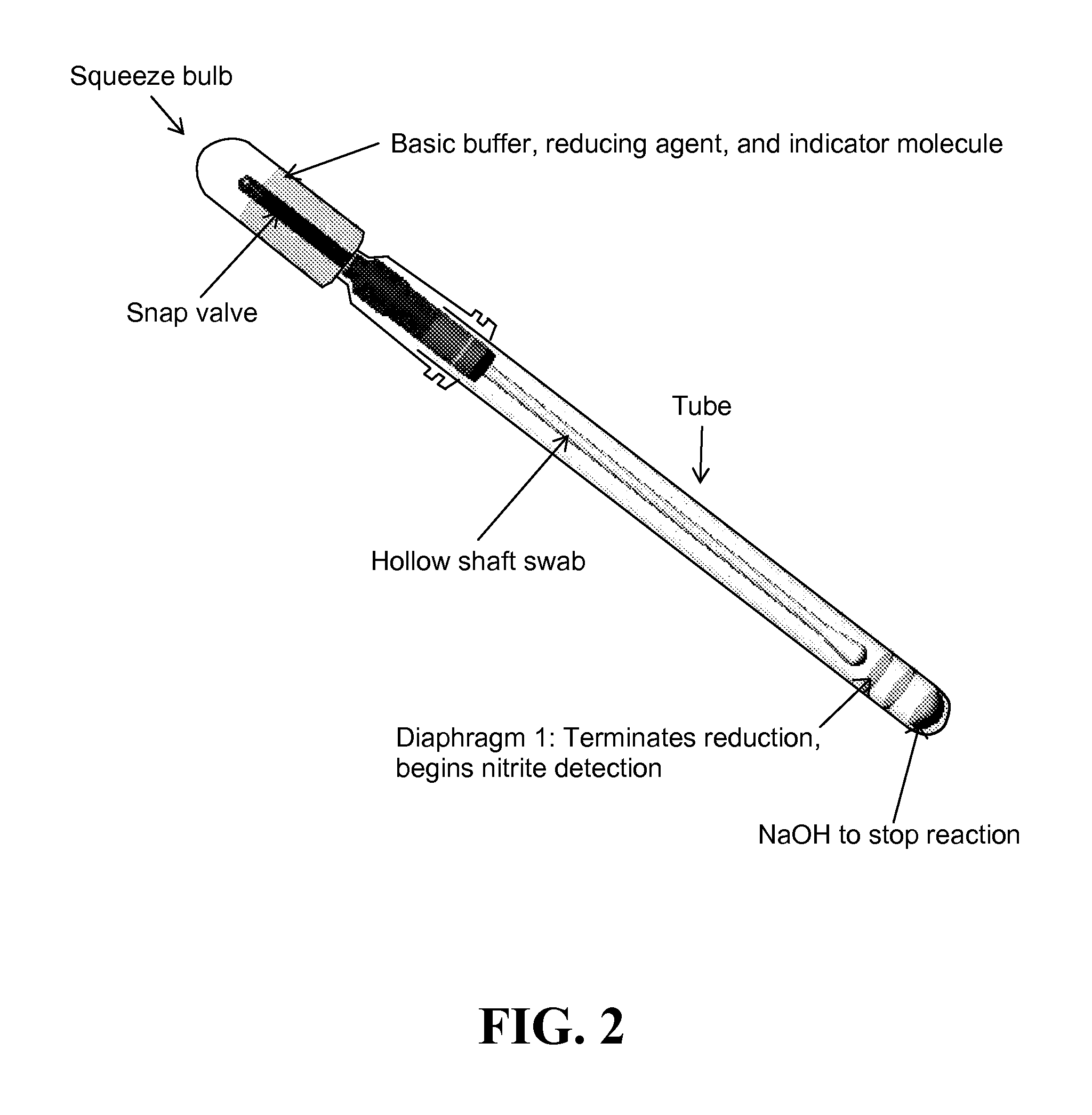
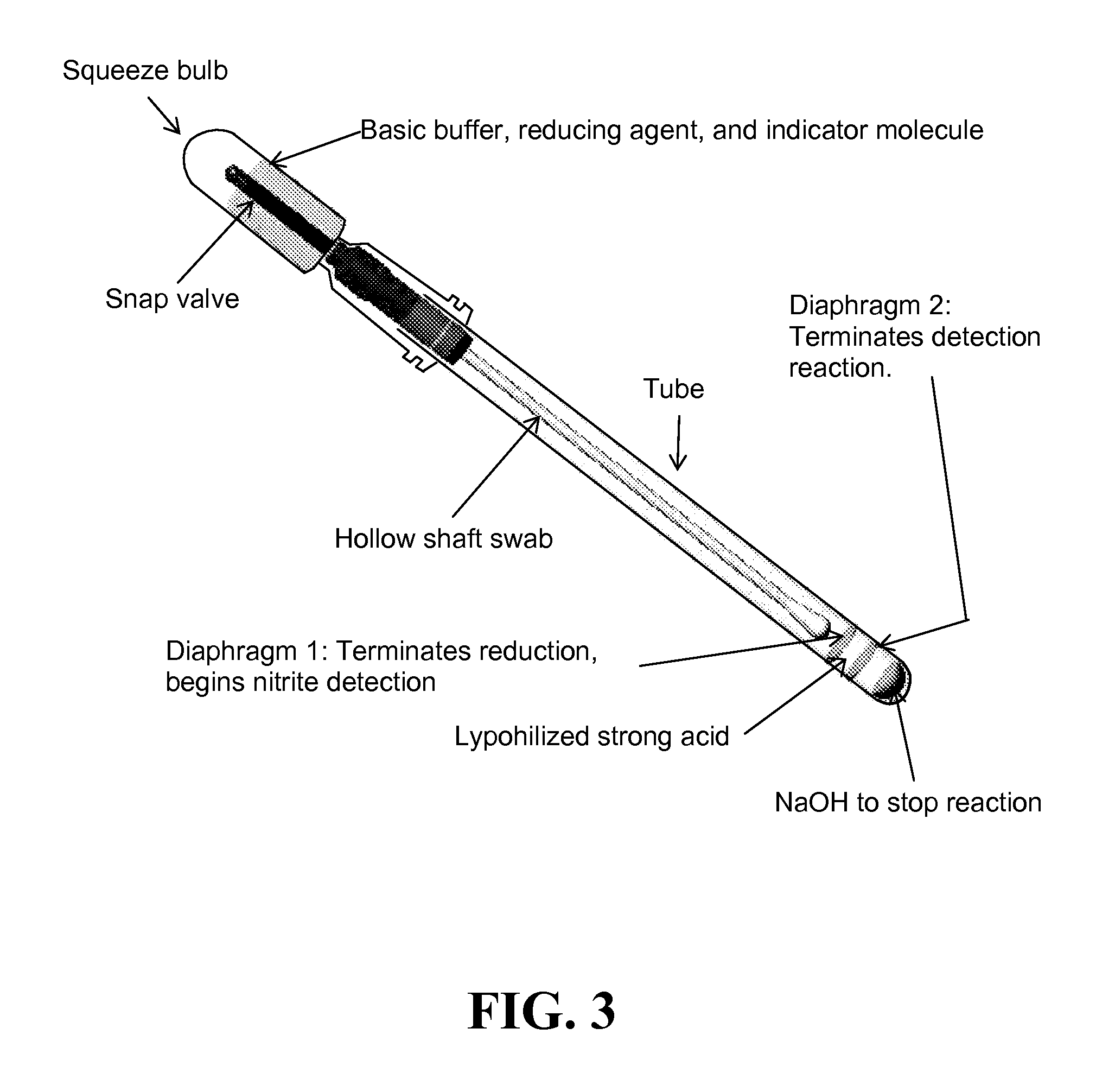
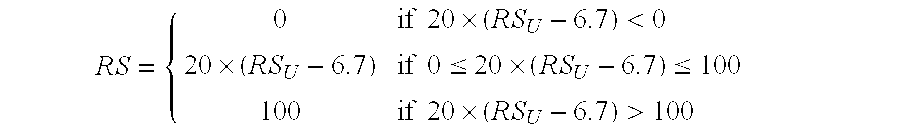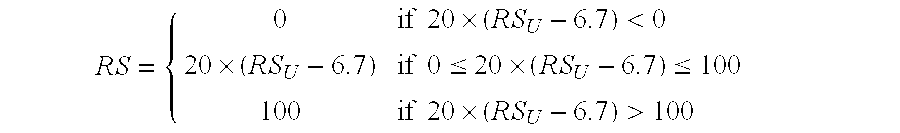Patents
Literature
189 results about "Response to treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Treatment of hypertension
InactiveUS7155284B1Sufficient amountAvoid the needPharmaceutical delivery mechanismImplantable neurostimulatorsCarotid bodyElectrical stimulations
Treatment of hypertension includes implantation of the discharge portion(s) of a catheter and / or electrical stimulation electrode(s) adjacent the tissue(s) to be stimulated. Stimulation pulses, i.e., drug infusion pulses and / or electrical pulses, are supplied by one or more implanted stimulators, through the catheter and possibly also a lead, tunneled subcutaneously between the stimulator and stimulation site. A microstimulator(s) may also / instead deliver electrical stimulation pulses. Stimulation sites include the carotid sinus and carotid body, among other locations. Treatments include drugs used for acute and / or chronic treatment of hypertension. In a number of embodiments, a need for or response to treatment is sensed, and the electrical and / or infusion pulses adjusted accordingly.
Owner:BOSTON SCI NEUROMODULATION CORP
System and method of measuring disease severity of a patient before, during and after treatment
ActiveUS20050065421A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisData setImaging data
A system and method of obtaining serial biochemical, anatomical or physiological in vivo measurements of disease from one or more medical images of a patient before, during and after treatment, and measuring extent and severity of the disease is provided. First anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a first co-registered composite image data set. At least a volume of interest (ROI) within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. The first co-registered composite image data set including the ROI is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine extent and severity of the disease. Second anatomical and functional image data sets are acquired, and form a second co-registered composite image data set. A global, rigid registration is performed on the first and second anatomical image data sets, such that the first and second functional image data sets are also globally registered. At least a ROI within the globally registered image data set using the identified ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set is identified. A local, non-rigid registration is performed on the ROI within the first co-registered composite image data set and the ROI within the globally registered image data set, thereby producing a first co-registered serial image data set. The first co-registered serial image data set including the ROIs is qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed to determine severity of the disease and / or response to treatment of the patient.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
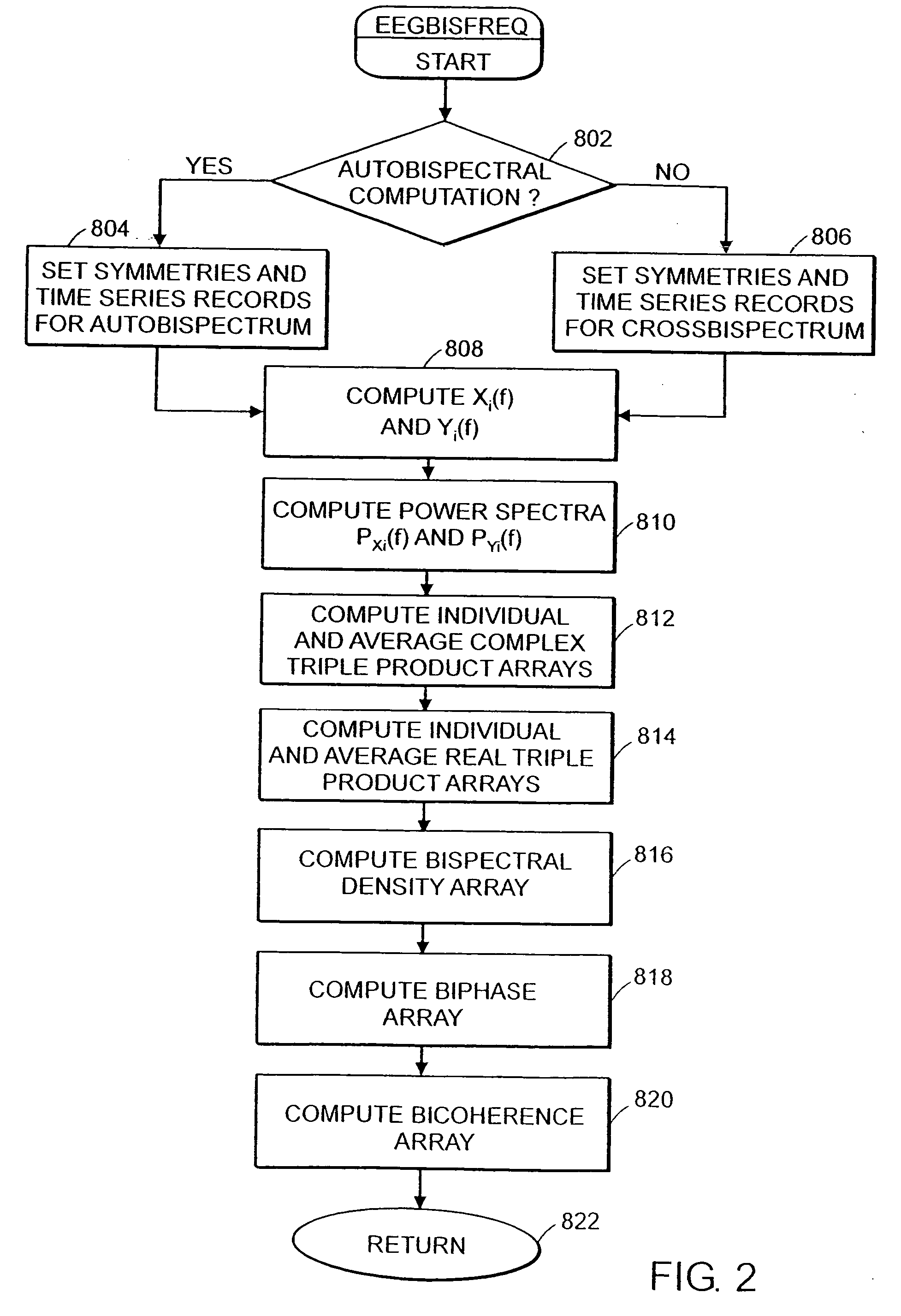
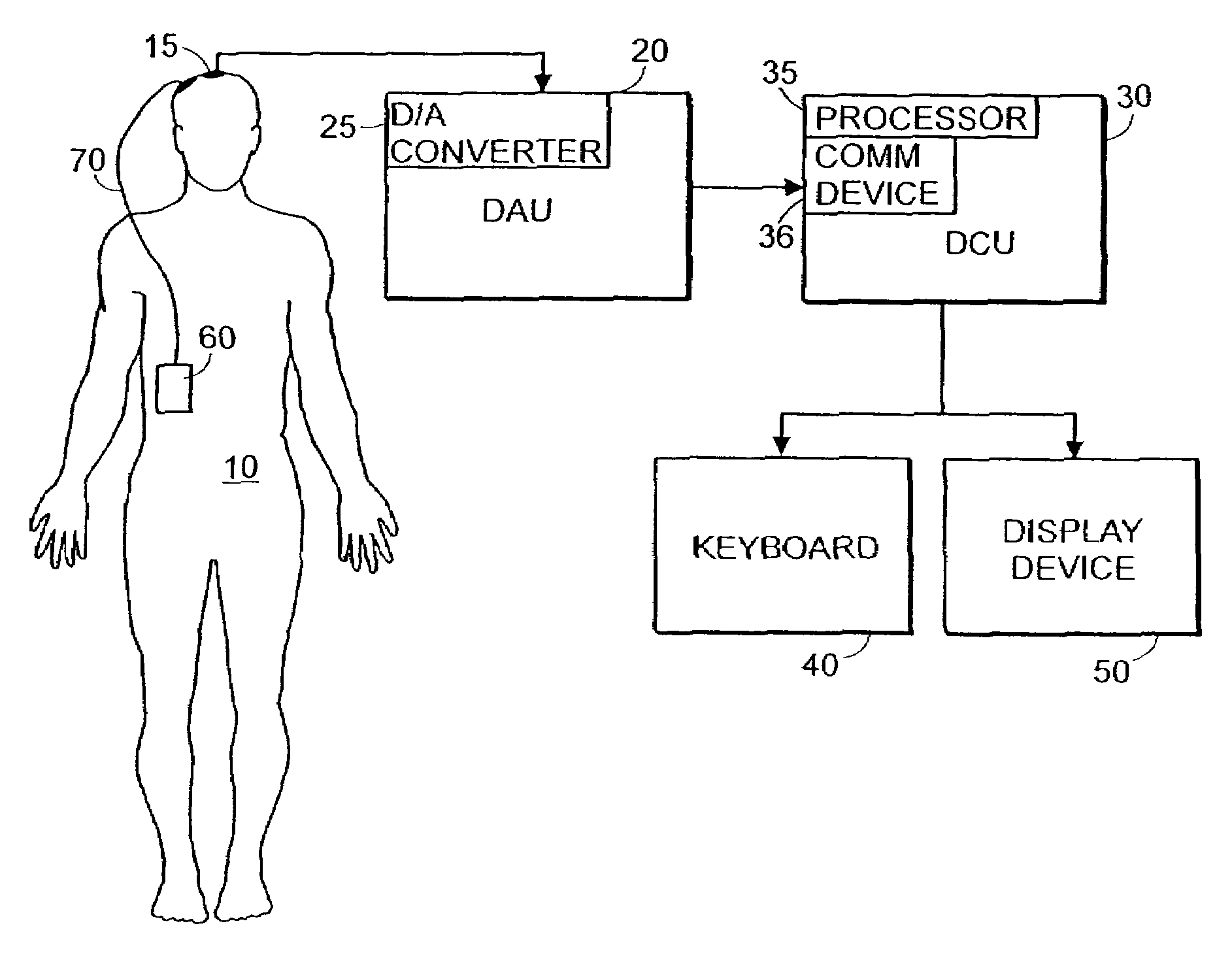
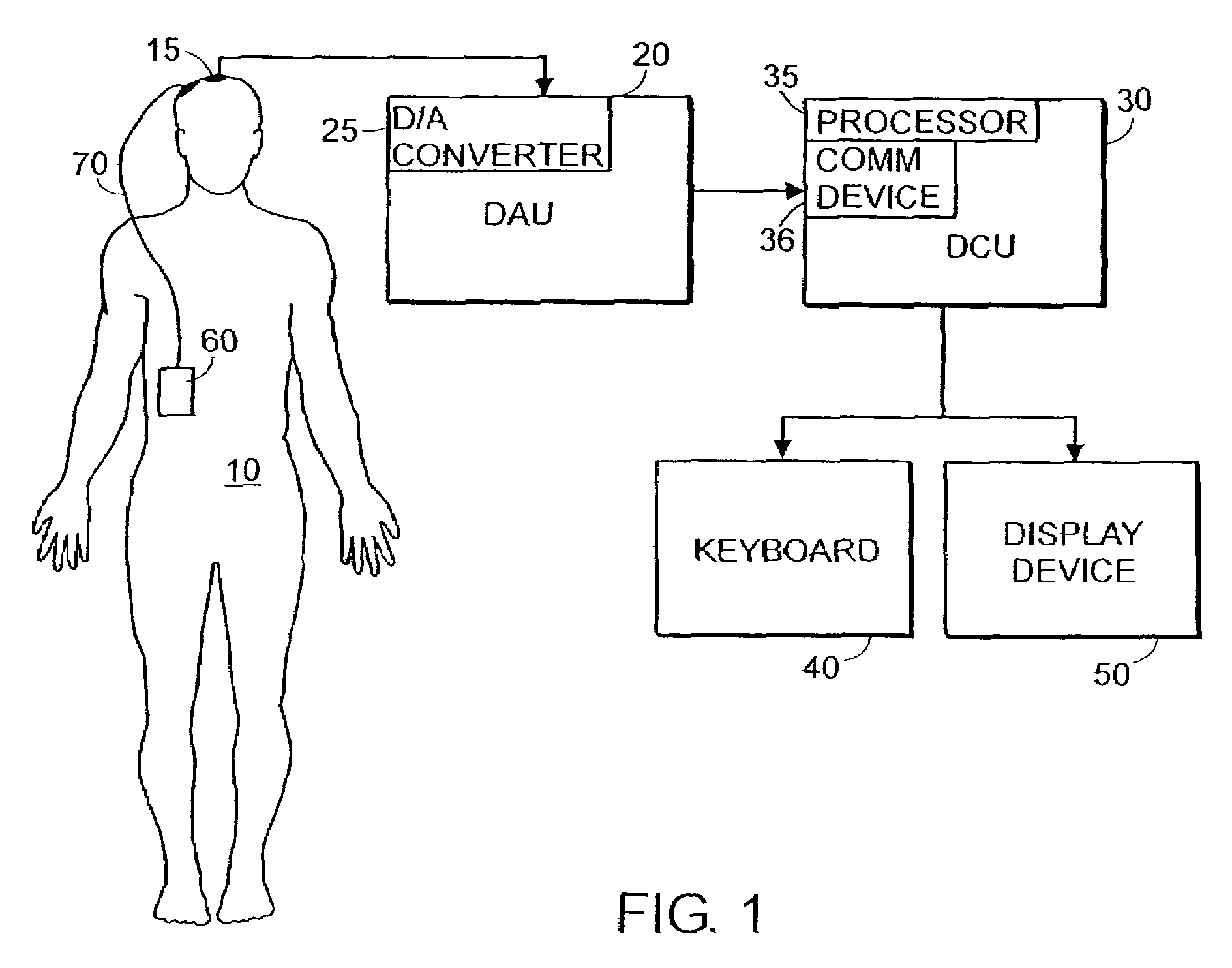
System and method of prediction of response to neurological treatment using the electroencephalogram
Disclosed is a system and method of assessing the efficacy of and predicting response to treatment of neurological or psychological disorders. The preferred embodiment uses at least two surface electrodes to acquire EEG signals from the surface of a patient's body, a processor for computing from the EEG signals various features and indices that are representative of the patient's neurological or psychological state. Pretreatment indices represent a patient's neurological or psychological state and therefore may be used to predict the response to treatment. Changes in these parameters may be used to assess the efficacy of treatment and to modify the treatment to optimize the resultant patient state.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
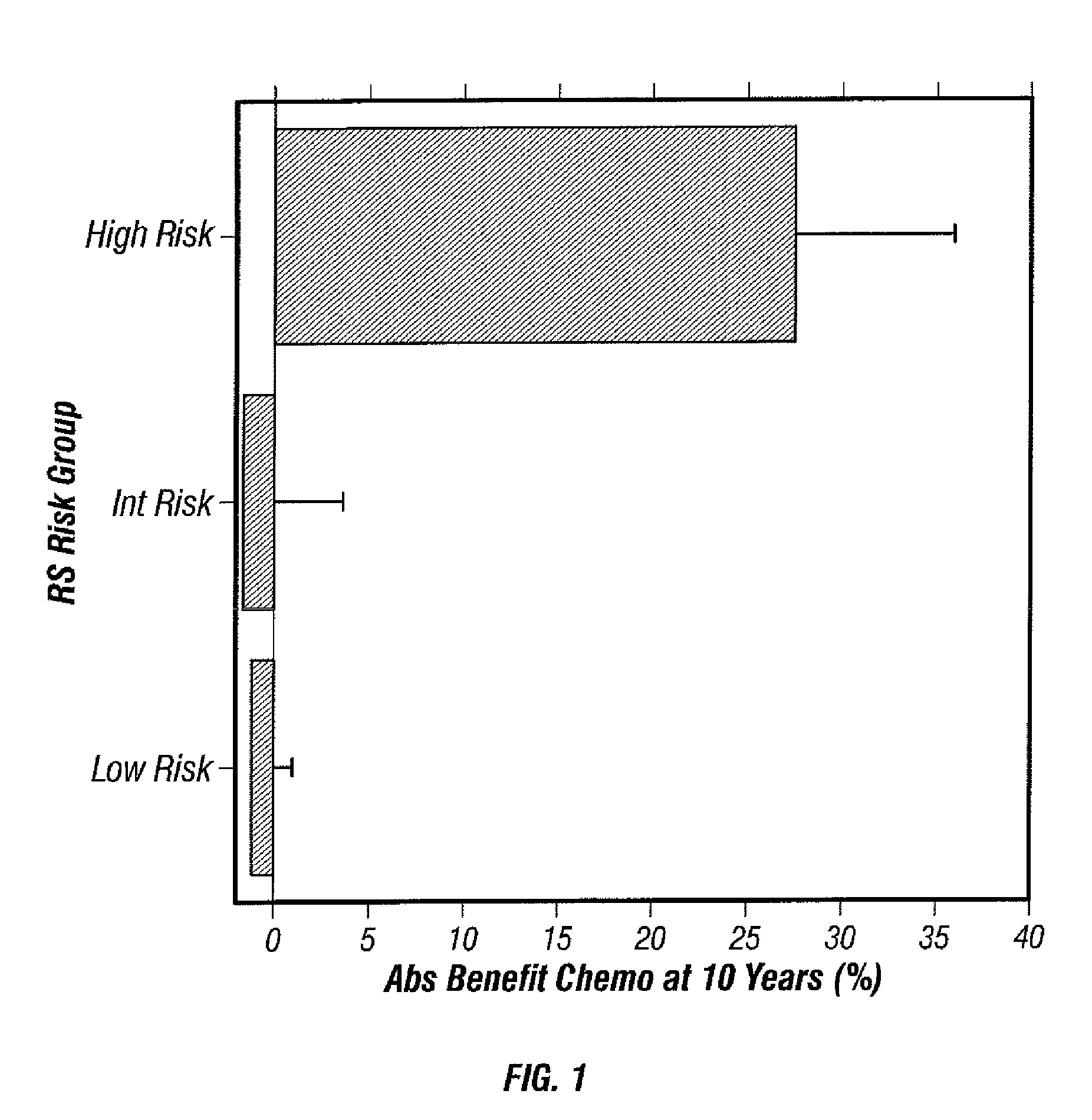
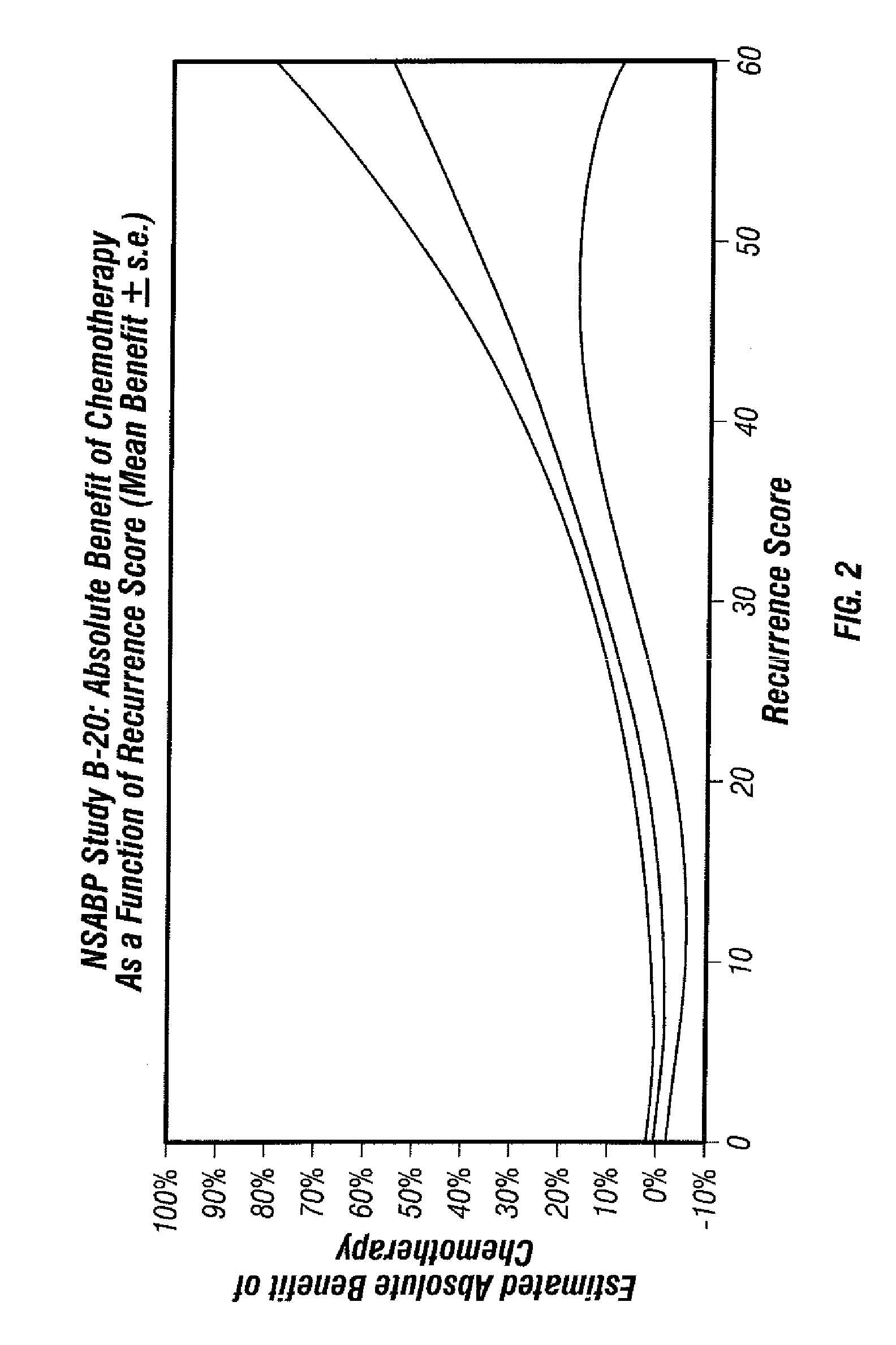
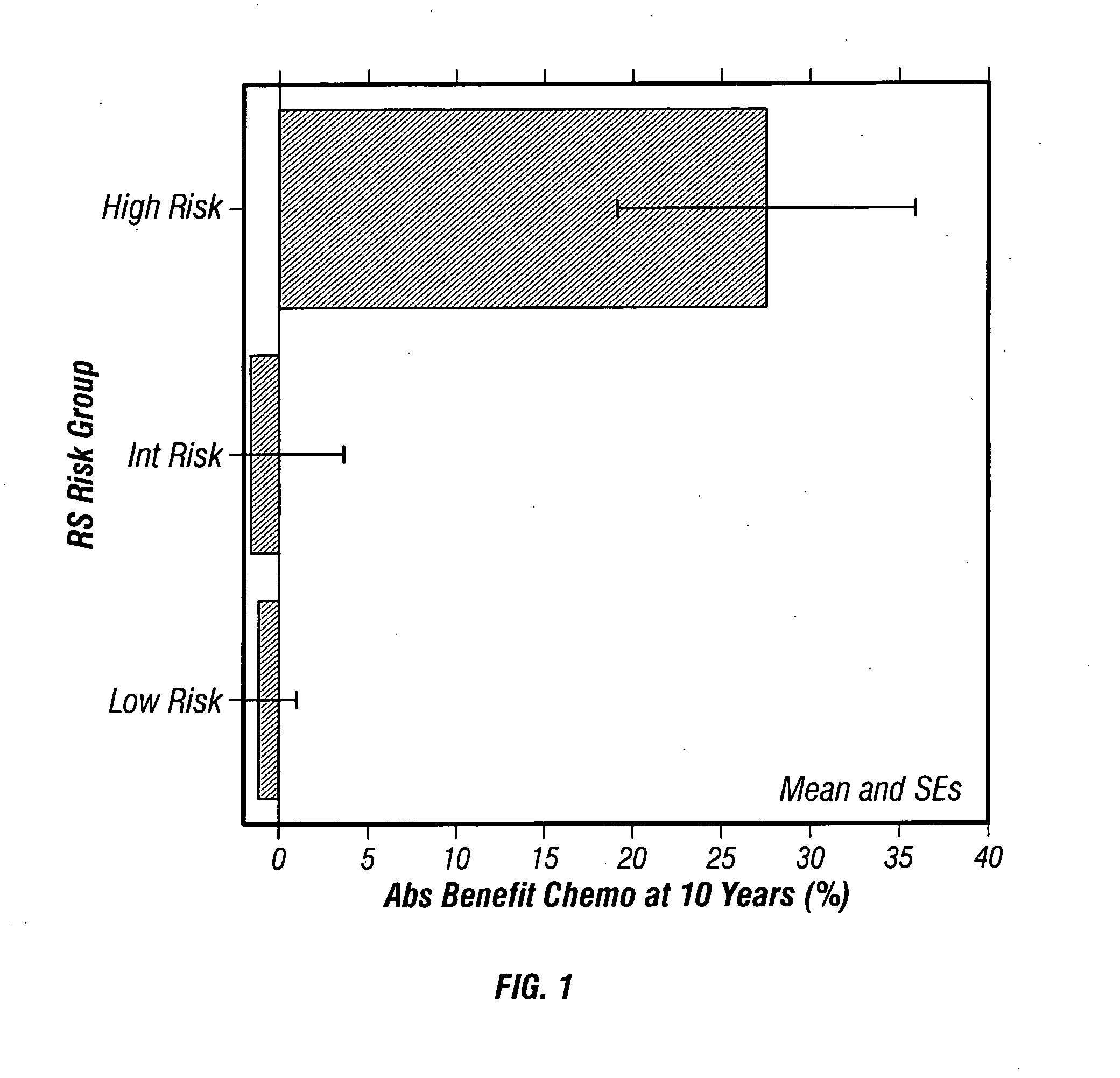
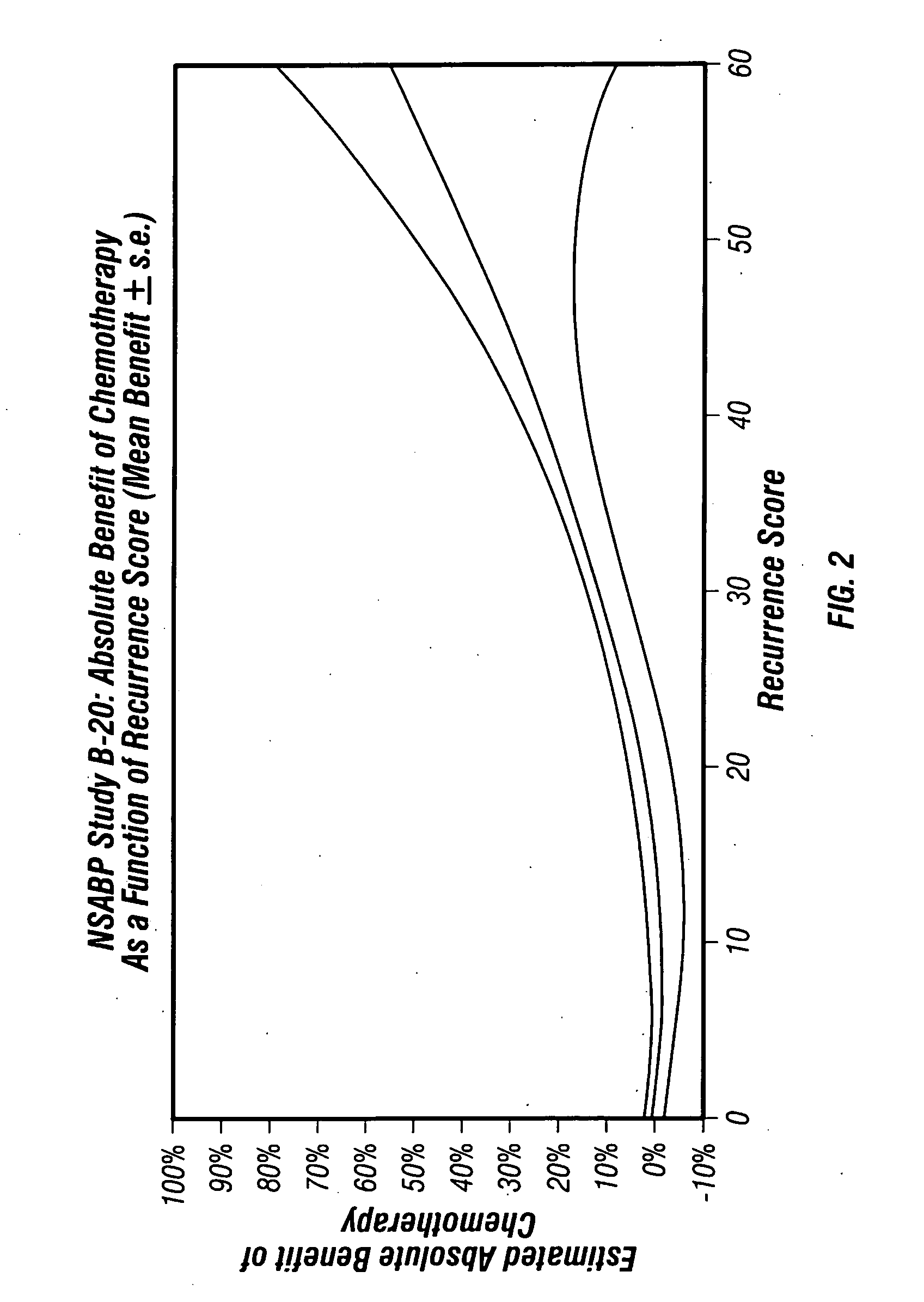
Predicting response to chemotherapy using gene expression markers
ActiveUS7930104B2Raise the possibilityReduce riskMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalogue computers for chemical processesRecurrence scoreOncology
The present invention provides gene expression information useful for predicting whether a cancer patient is likely to have a beneficial response to treatment with chemotherapy, comprising measuring, in a biological sample comprising a breast tumor sample obtained from the patient, the expression levels of gene subsets to obtain a risk score associated with a likelihood of a beneficial response to chemotherapy, wherein the score comprises at least one of the following variables: (i) Recurrence Score, (ii) ESRI Group Score; (iii) Invasion Group Score; (iv) Proliferation Group Score; and (v) the expression level of the RNA transcript of at least one of MYBL2 and SCUBE2, or the corresponding expression product. The invention further comprises a molecular assay-based algorithm to calculate the likelihood that the patient will have a beneficial response to chemotherapy based on the risk score.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Physiologic Database And System For Population Modeling And Method of Population Modeling
InactiveUS20110054289A1Improve care deliveryReduce deliveryPhysical therapies and activitiesMedical simulationPatient characteristicsExercise performance
The present invention provides apparatuses and methods for creating a physiologic database or library that can be indexed to at least health, disease, patient characteristics, and acute medical crises or other dangerous condition. The present invention also provides apparatuses and methods for creating an athletic performance database or library. The database can be structured and continuous / pseudo-continuous modeling statistics applied to provide novel insight into performance and progress of an athlete or group of athletes, as well as standing relative to other athletes, or to provide novel insight into the natural history of disease and the response to treatment, and ultimately to improve care delivery.
Owner:ADIDAS
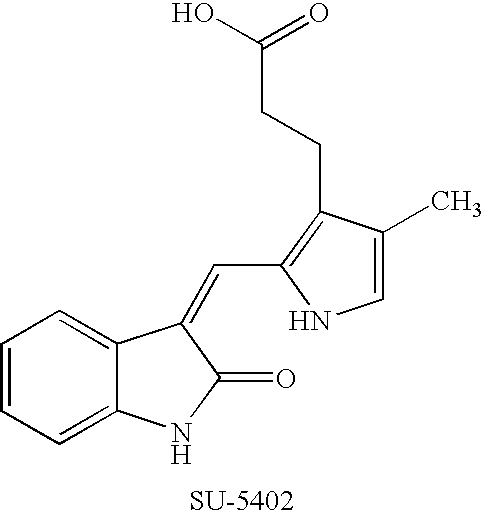
Effects of inhibitors of FGFR3 on gene transcription
InactiveUS8158360B2Improve responseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMedicineBiomarker identification
Methods of utilizing biomarkers to identify patients for treatment or to monitor response to treatment are taught herein. Alterations in levels of gene expression of the biomarkers, particularly in response to FGFR3 inhibition, are measured and identifications or adjustments may be made accordingly.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
System and method for diagnosis and treatment
ActiveUS8658128B2Good curative effectPromote resultsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsPhysiologyHydrocortisone
This invention relates to a low cost rapid response diagnostic system to determine cortisol levels in patients selected as potential candidates for GCR (glucocorticoid receptor) antagonist therapy utilizing a GCR antagonist, such as ORG 34517. The rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive test can be used to determine patients who have non-normal cortisol production or disordered circadian rhythms as a method for selecting subjects for GCR antagonist therapy for whom it is likely to have beneficial and / or therapeutic effects, and can also be used to monitor changes in cortisol levels in response to treatment.
Owner:POP TEST ONCOLOGY LIMITED LIABILITY
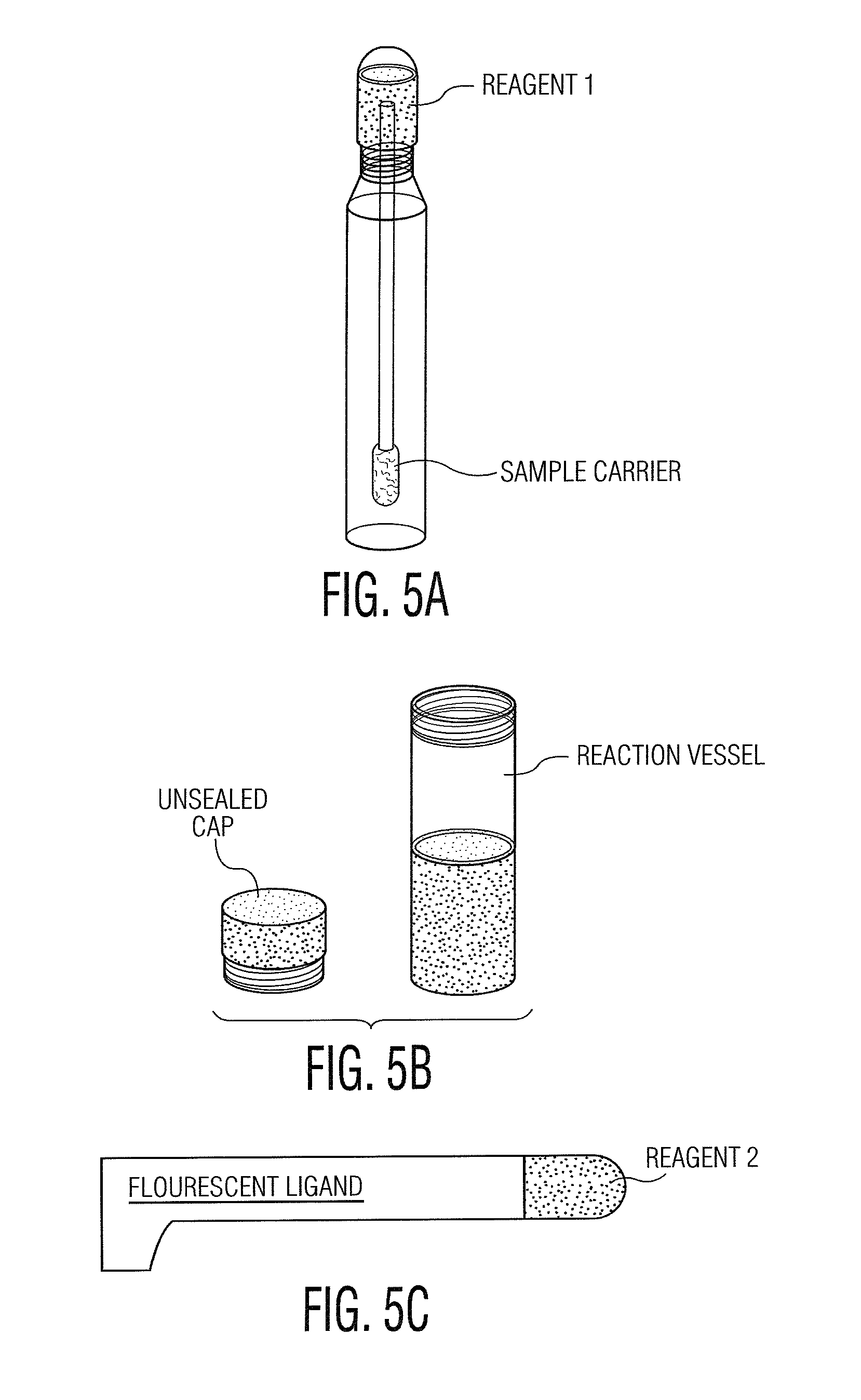
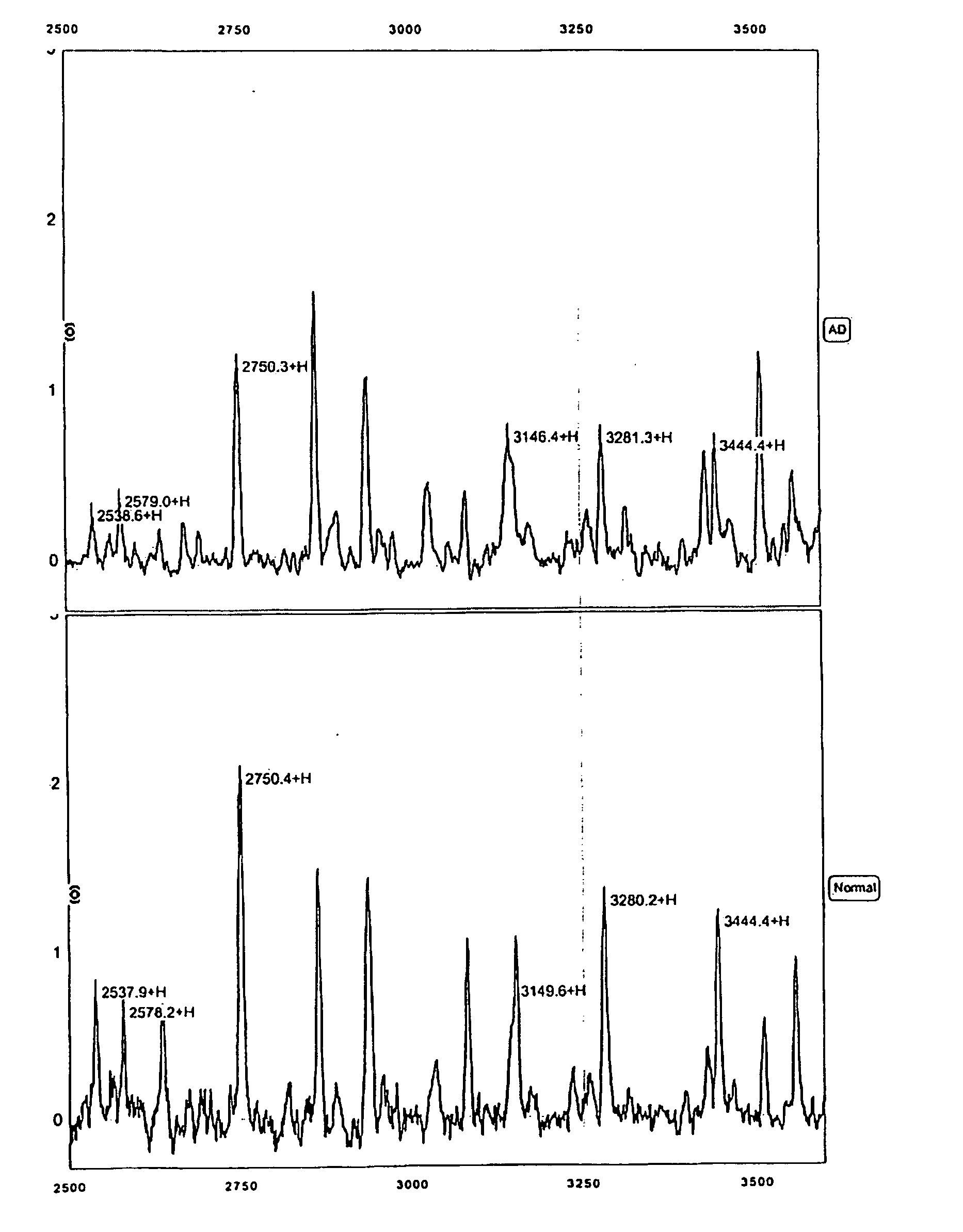
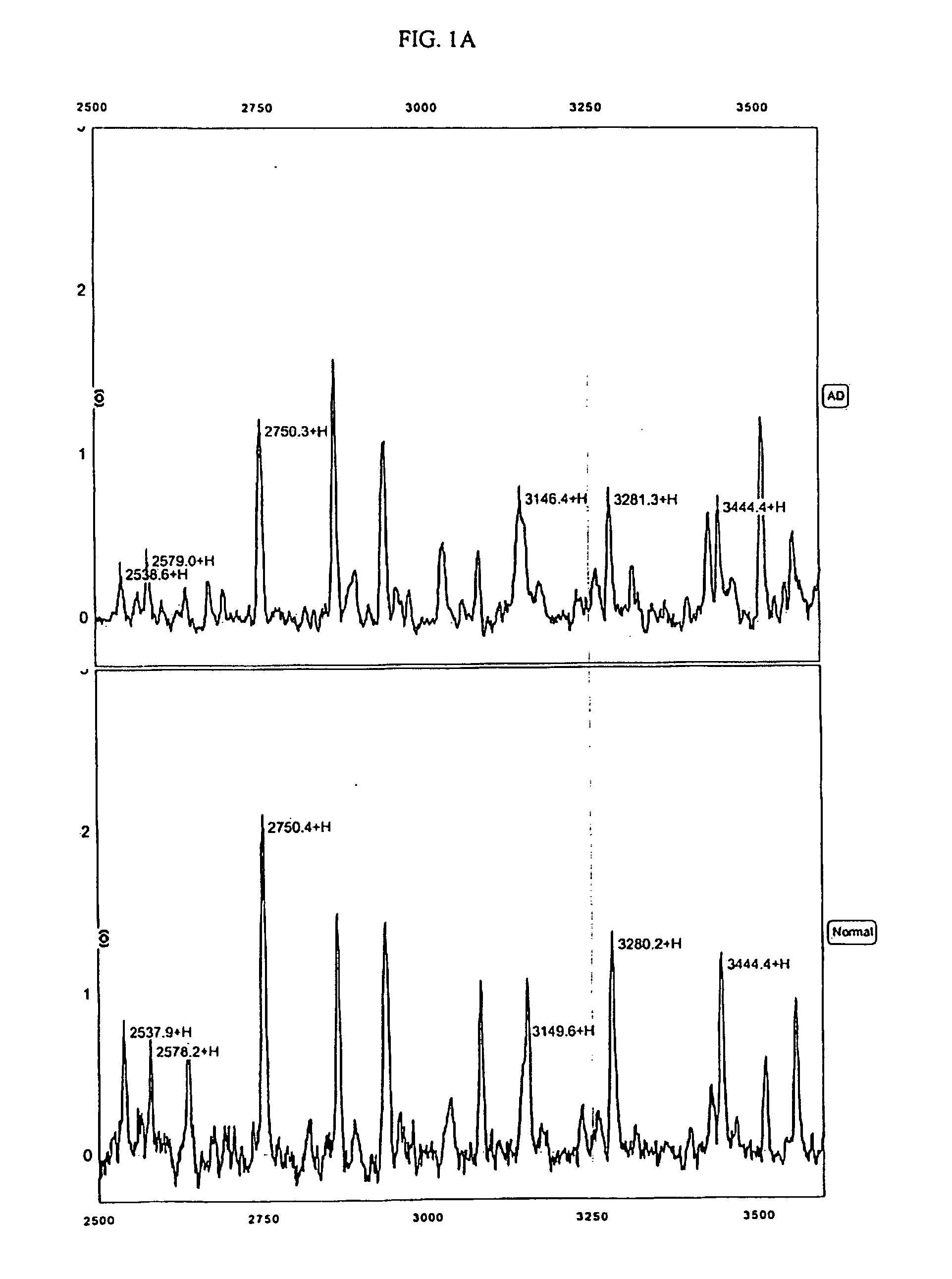
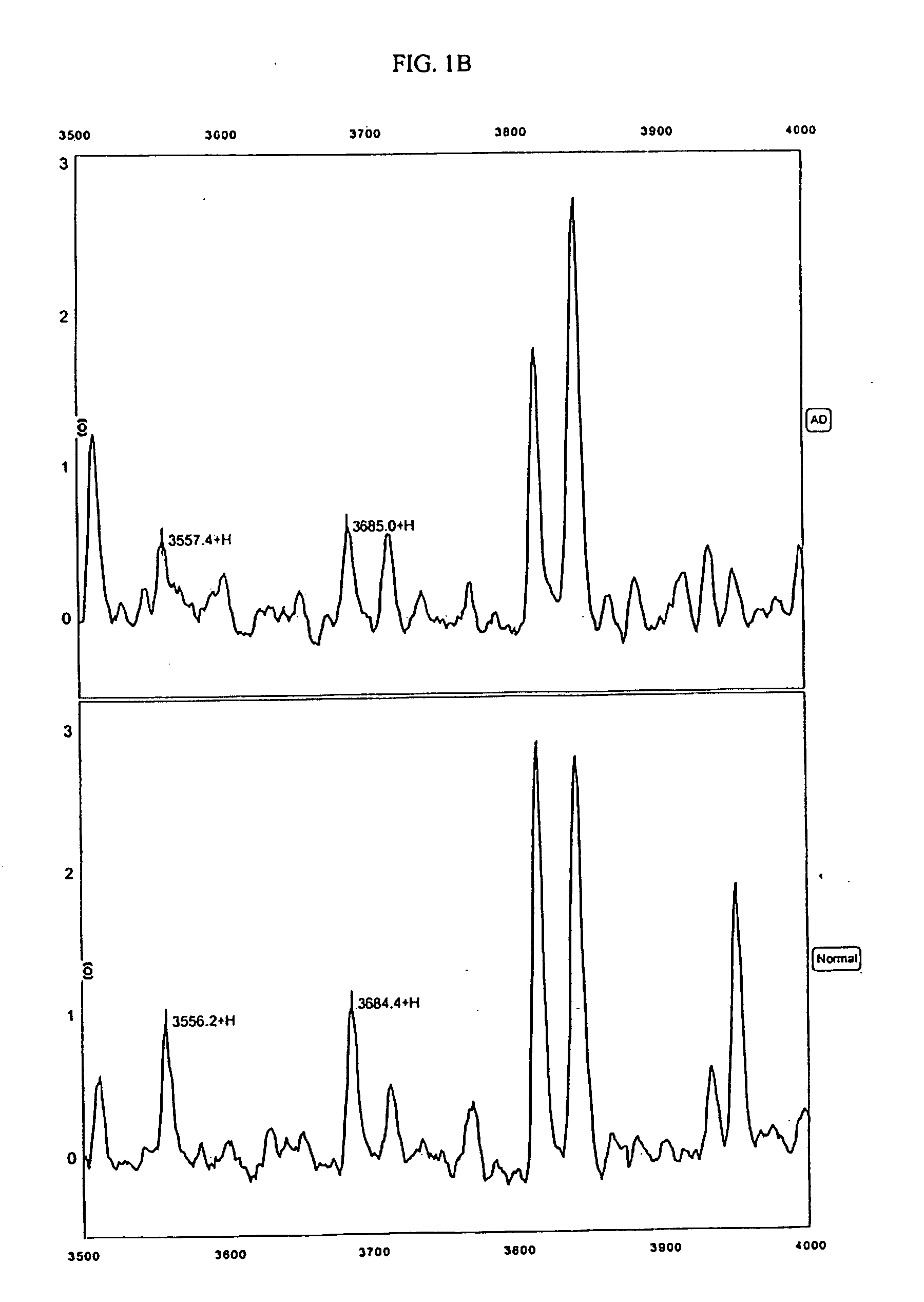
Biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease
The present invention provides protein-based biomarkers and biomarker combinations that are useful in qualifying Alzheimer's disease status in a patient. In particular, the biomarkers of this invention are useful to classify a subject sample as Alzheimer's or non-Alzheimer's dementia or normal. The biomarkers can be detected by SELDI mass spectrometry. In addition, the invention provides appropriate treatment interventions and methods for measuring response to treatment. Certain biomarkers of the invention may also be suitable for employment as radio-labeled ligands in non-invasive imaging techniques such as Positron Emission Tomography (PET).
Owner:VERMILLION INC
Improved Method And System For Predicting Outcomes Based On Spatio/Spectro-Temporal Data
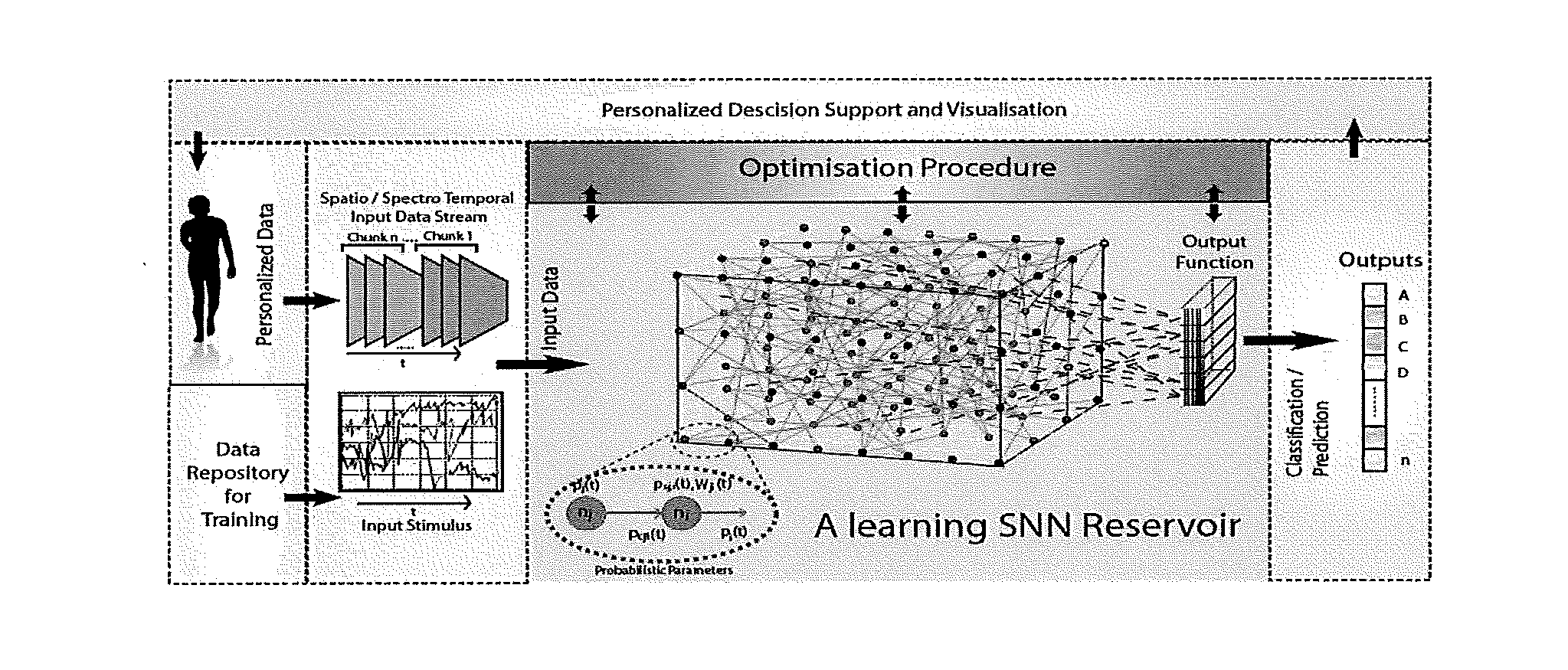
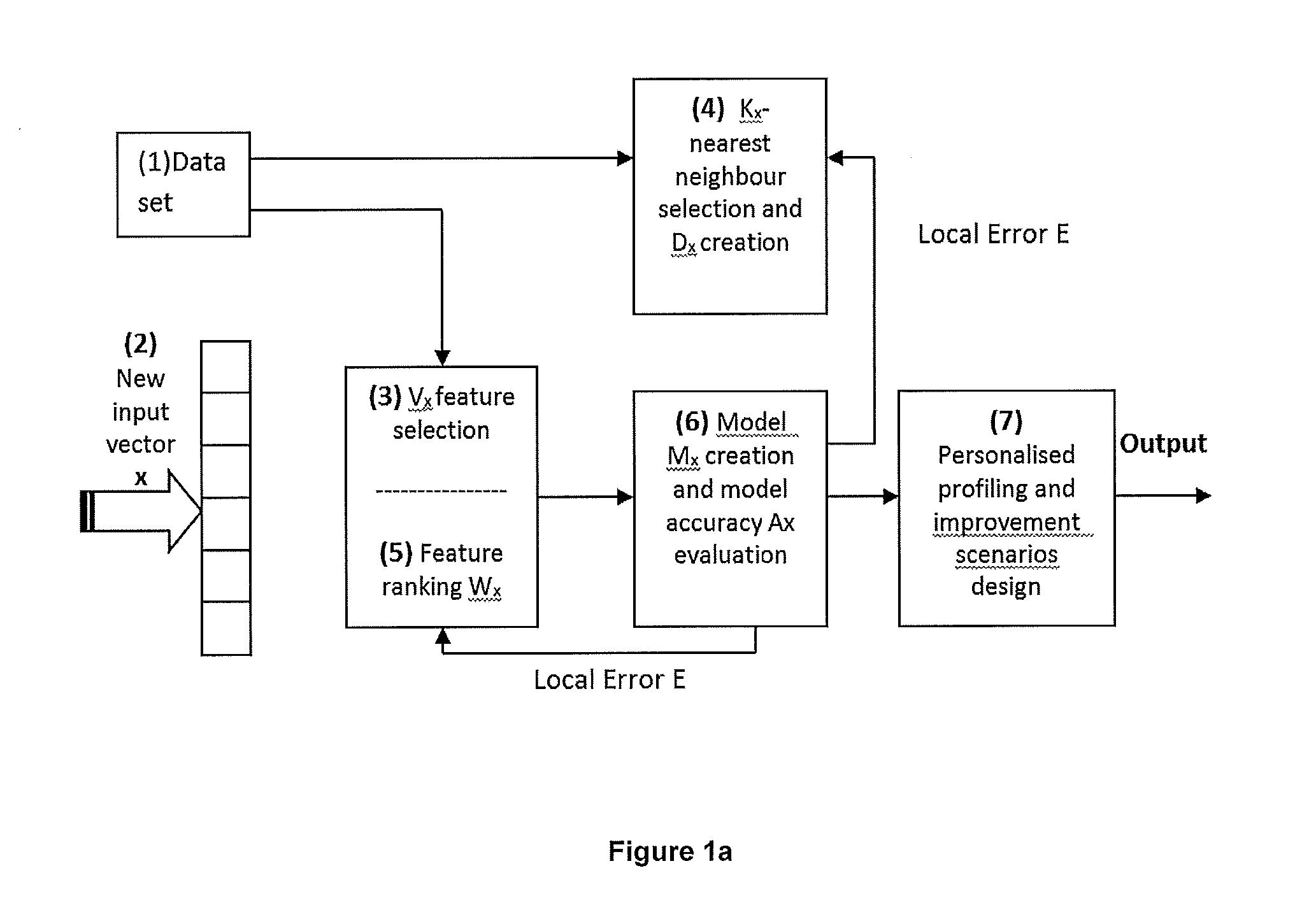
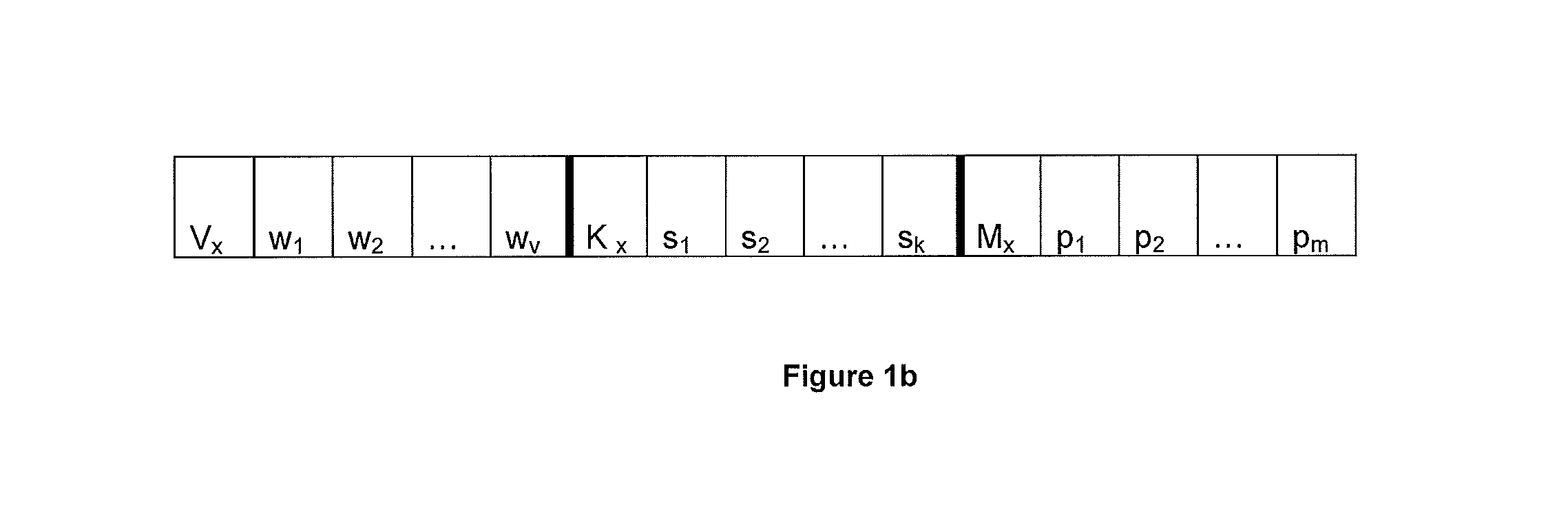
ActiveUS20160210552A1Improve accuracyShorten the timeDigital computer detailsDigital dataSpike trainSpatiotemporal pattern
This invention involves use of temporal or spatio / spector-temporal data (SSTD) for early classification of outputs that are results of spatio-temporal patterns of data. Classification models are based on spiking neural networks (SNN) suitable to learn and classify SSTD. The invention may predict early events in many applications, i.e. engineering, bioinformatics, neuroinformatics, predicting response to treatment of neurological and brain disease, ecology, environment, medicine, and economics, among others. The invention involves a method and system for personalized modelling of SSTD and early prediction of events based on evolving spiking neural network reservoir architecture (eSNNr). The system includes a spike-time encoding module to encode continuous value input information into spike trains, a recurrent 3D SNNr and an eSSN as an output classification module.
Owner:AUT VENTURES LTD
Method for Vaginal Skin Biomechanical Evaluation
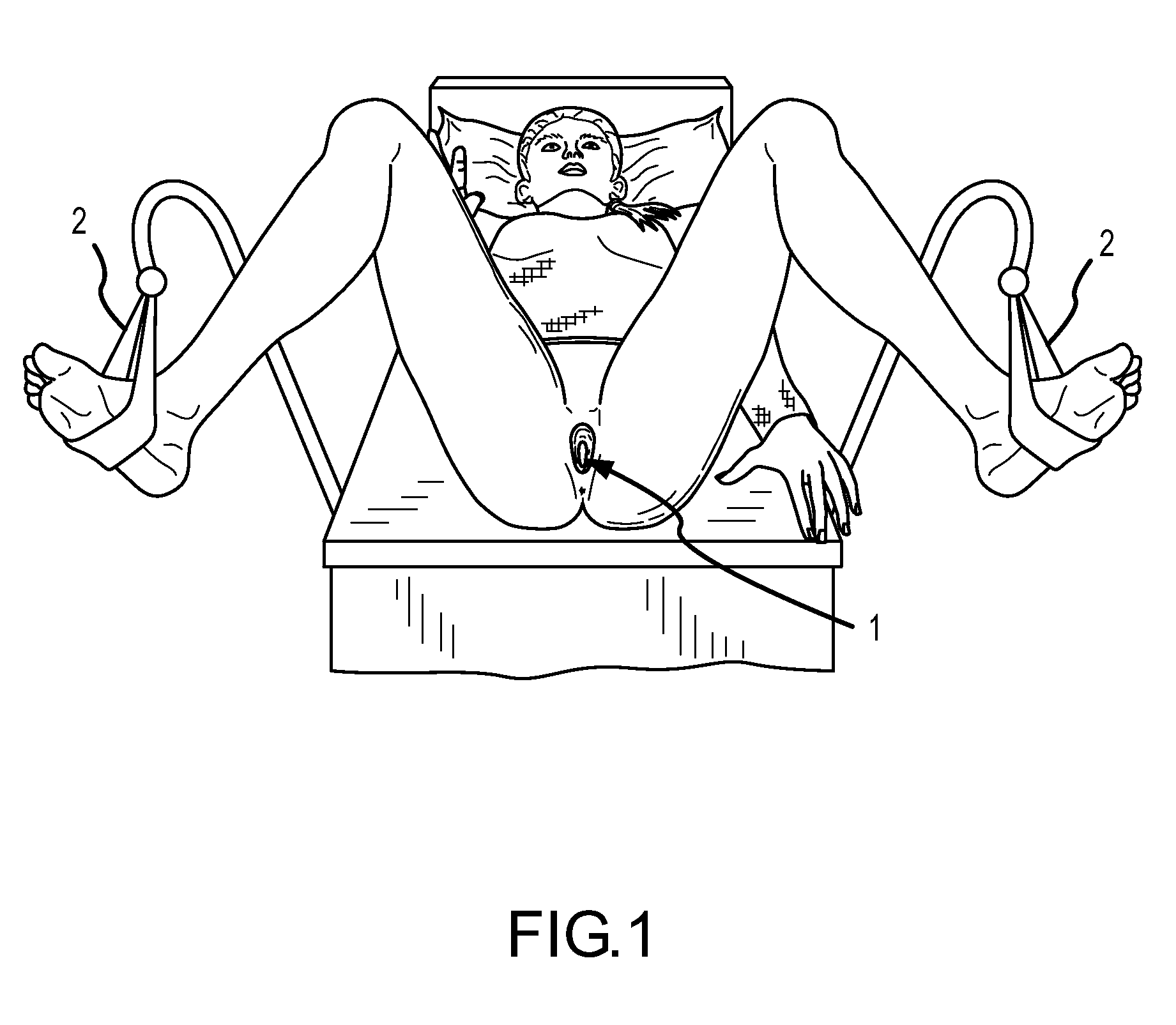
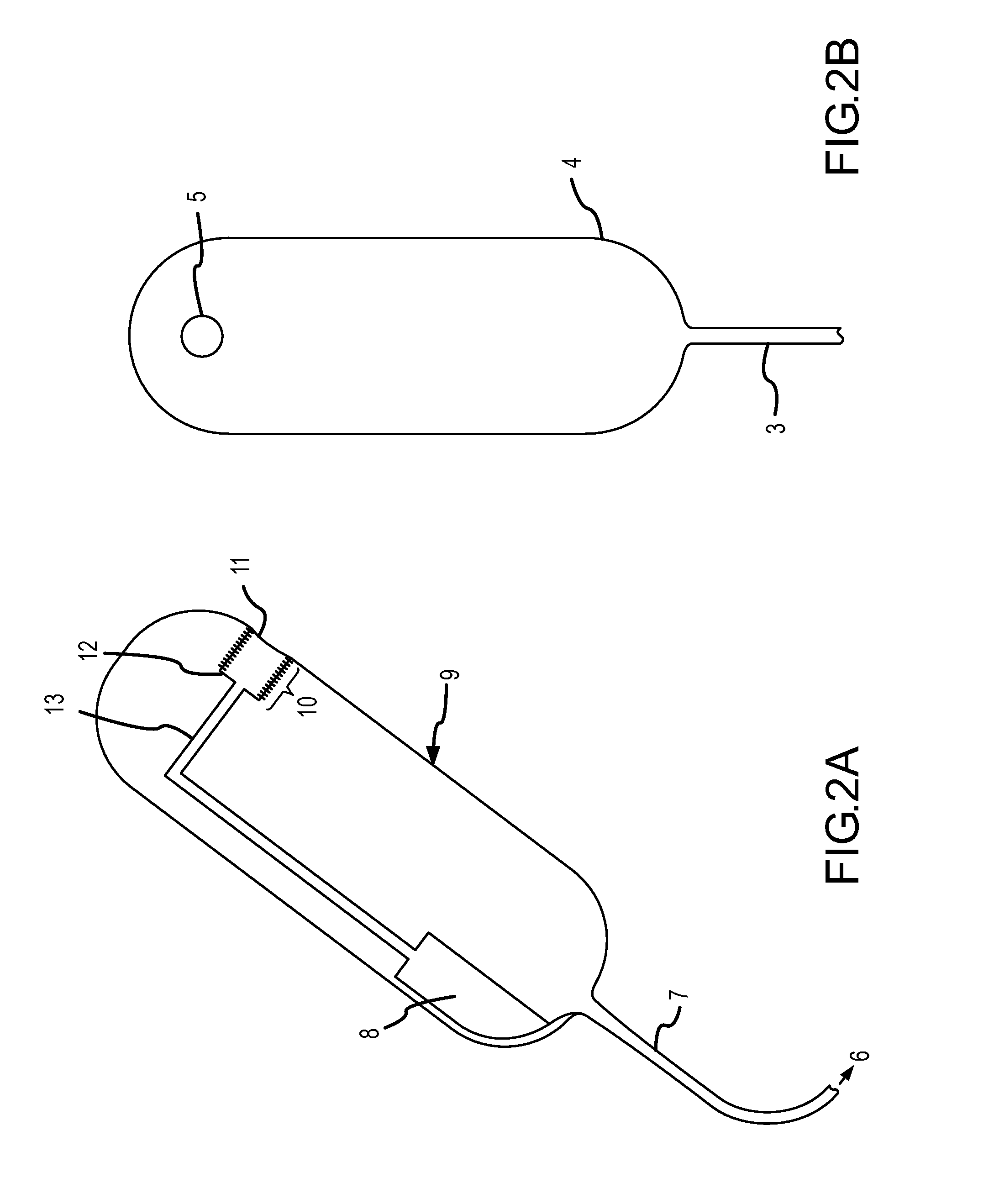
A method and technique to measure vaginal skin biomechanical properties in vivo by applying a temporary deforming force to the vaginal skin while using sensors to monitor and record the vaginal skins response to the deforming force as well as how it responds after the deforming force is removed. By placing a female participant in the correct anatomical position and employing a vaginal biomechanical evaluation tool to temporarily distort and measure the vaginal skin an examiner is able to obtain measurements for biomechanical properties of the vaginal skin. These measurements may allow clinicians and medical researchers to understand a woman's vaginal tissue quality, response to treatment, and risk for future pelvic floor disorders more completely in order to take appropriate prophylactic or corrective action.
Owner:EPSTEIN LEE BRANDON +2
Methods of determining acute myeloid leukemia response to treatment with farnesyltransferase
InactiveUS7932036B1Improve accuracyHigh response rateSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNewly diagnosedClinical study
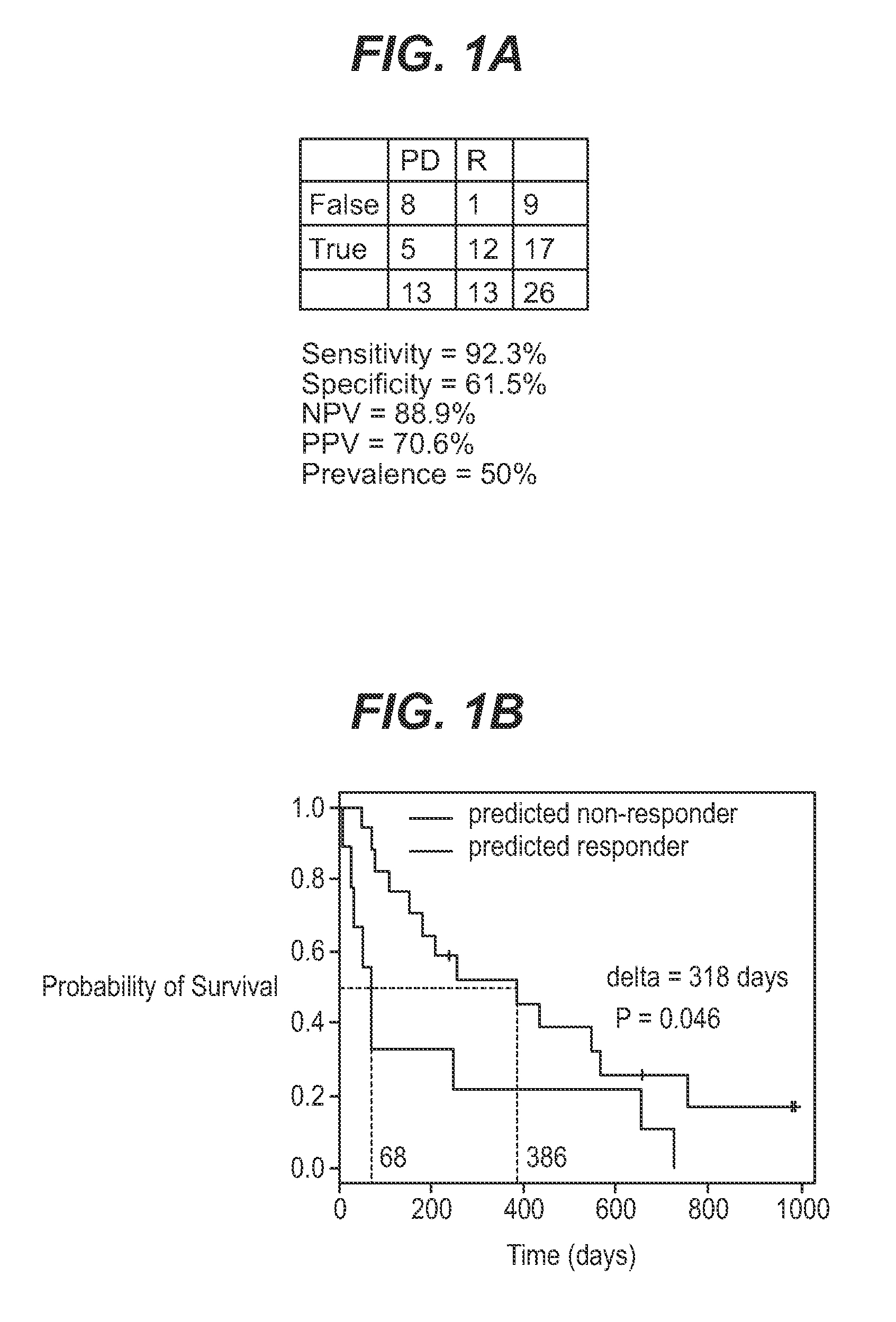
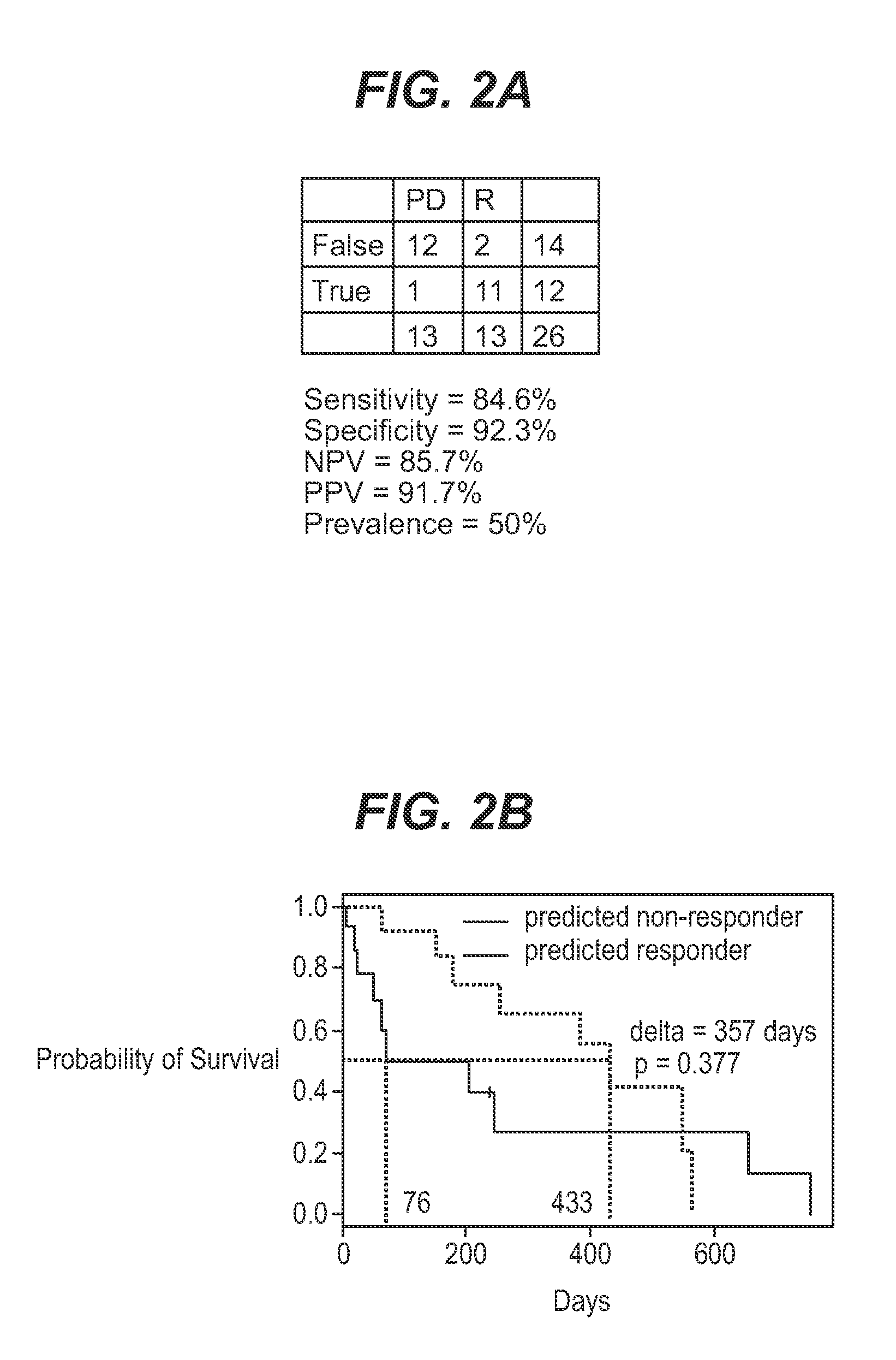
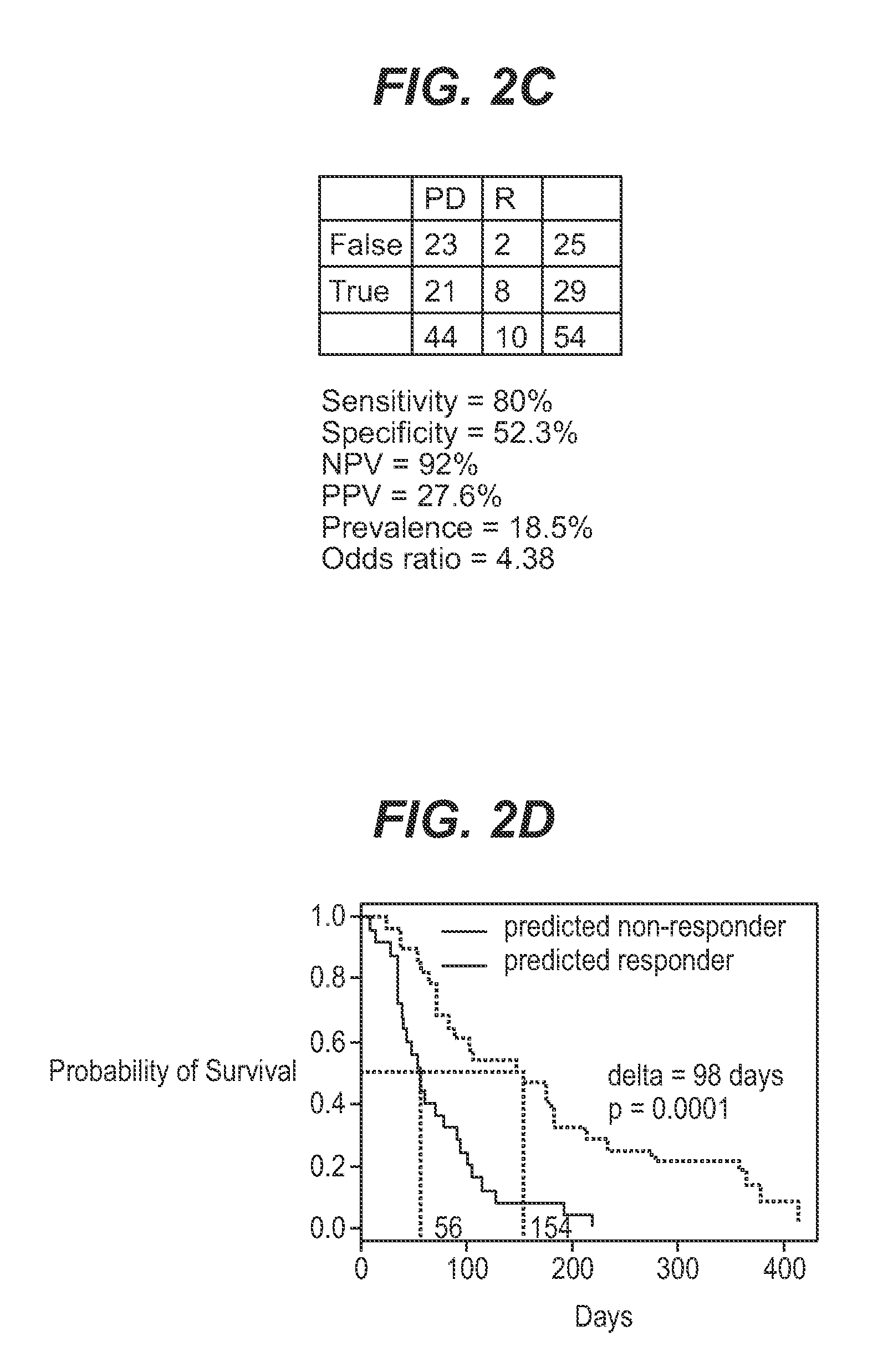
We analyzed bone marrow from 67 patients from a phase 2 study of farnesyltransferase inhibition with tipifarnib (R115777, ZARNESTRA®), in older adults with previously untreated, poor-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML) for N-Ras mutations, global gene expression, and / or quantitative PCR (qPCR) of specific genes. Microarray profiling identified a two-gene expression ratio (RASGRP1:APTX) which provided the greatest accuracy for predicting response to tipifarnib. We demonstrated that this classifier could predict response to tipifarnib in an independent set of 54 samples from relapsed or refractory AML, with a NPV and PPV of 92% and 28%, respectively (odds ratio of 4.4). Therefore, in both newly diagnosed and relapsed or refractory AML, this classifier improves the overall response rate by approximately 50% while maintaining a high NPV, and significantly improves patient overall survival. The two-gene classifier was also validated by qPCR in thirty AML samples from the same clinical study demonstrating a negative predictive value (NPV) and positive predictive value (PPV) of 81% and 50%, respectively (odds ratio of 4.3). These data indicate that a simple two-gene expression assay may have utility in diagnosing a population of AML patients who are more likely to respond to tipifarnib.
Owner:JANSSEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Method and system to predict response to treatments for mental disorders
The present inventions relates to methods and assays to predict the response of an individual to a psychiatric treatment and to a method to improve medical treatment of a disorder, which is responsive to treatment with a psychiatric treatment.
Owner:PATHWAY GENOMICS
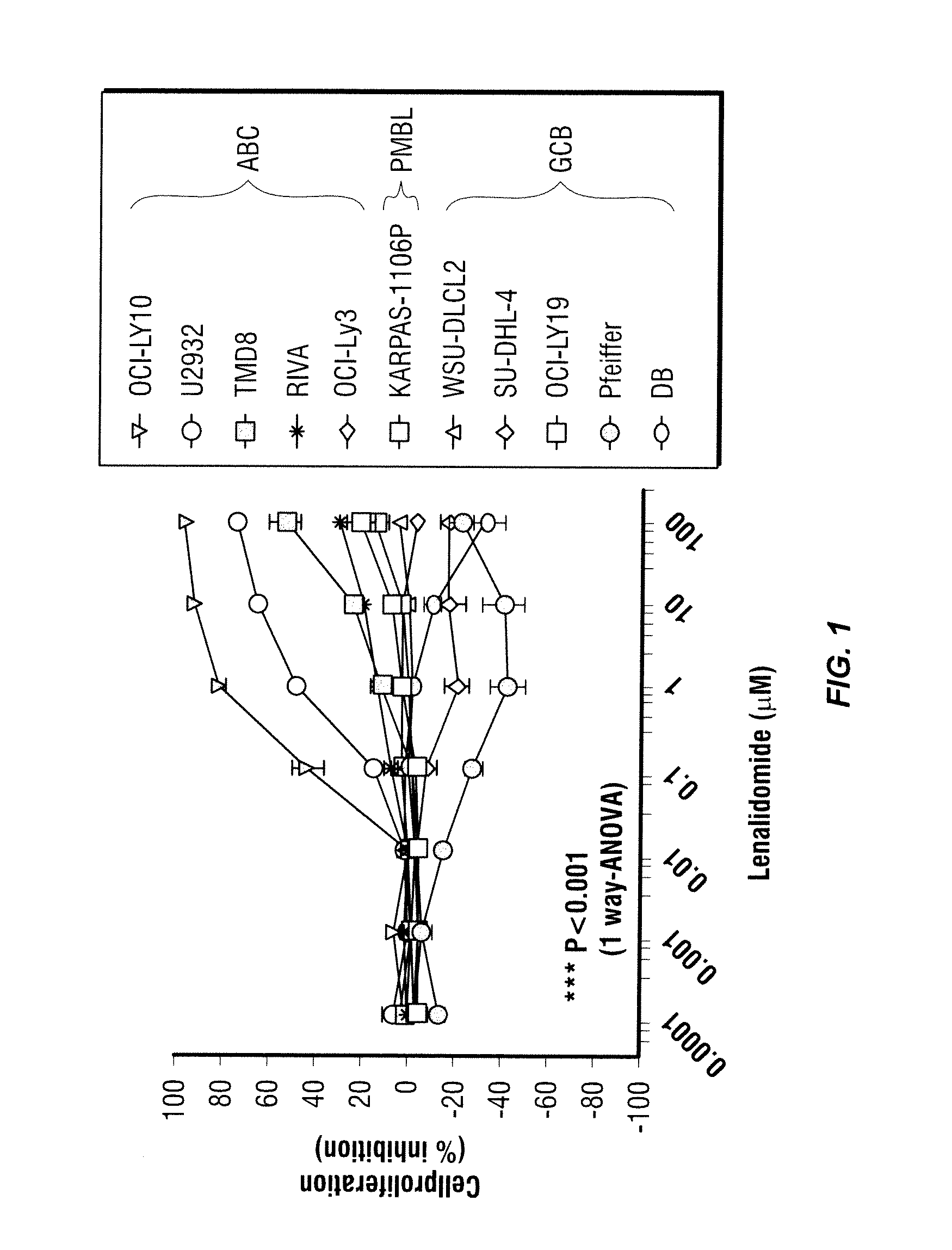
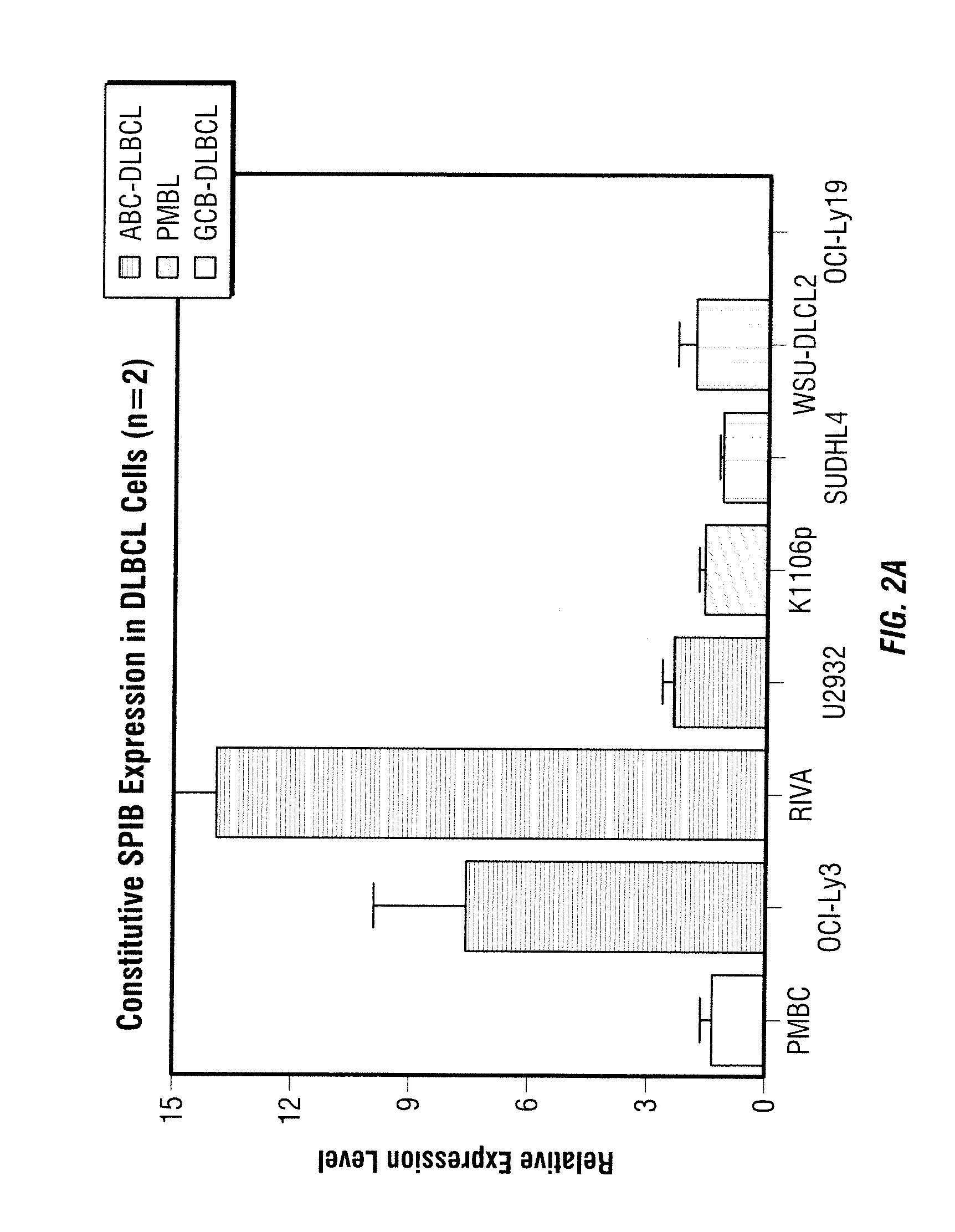
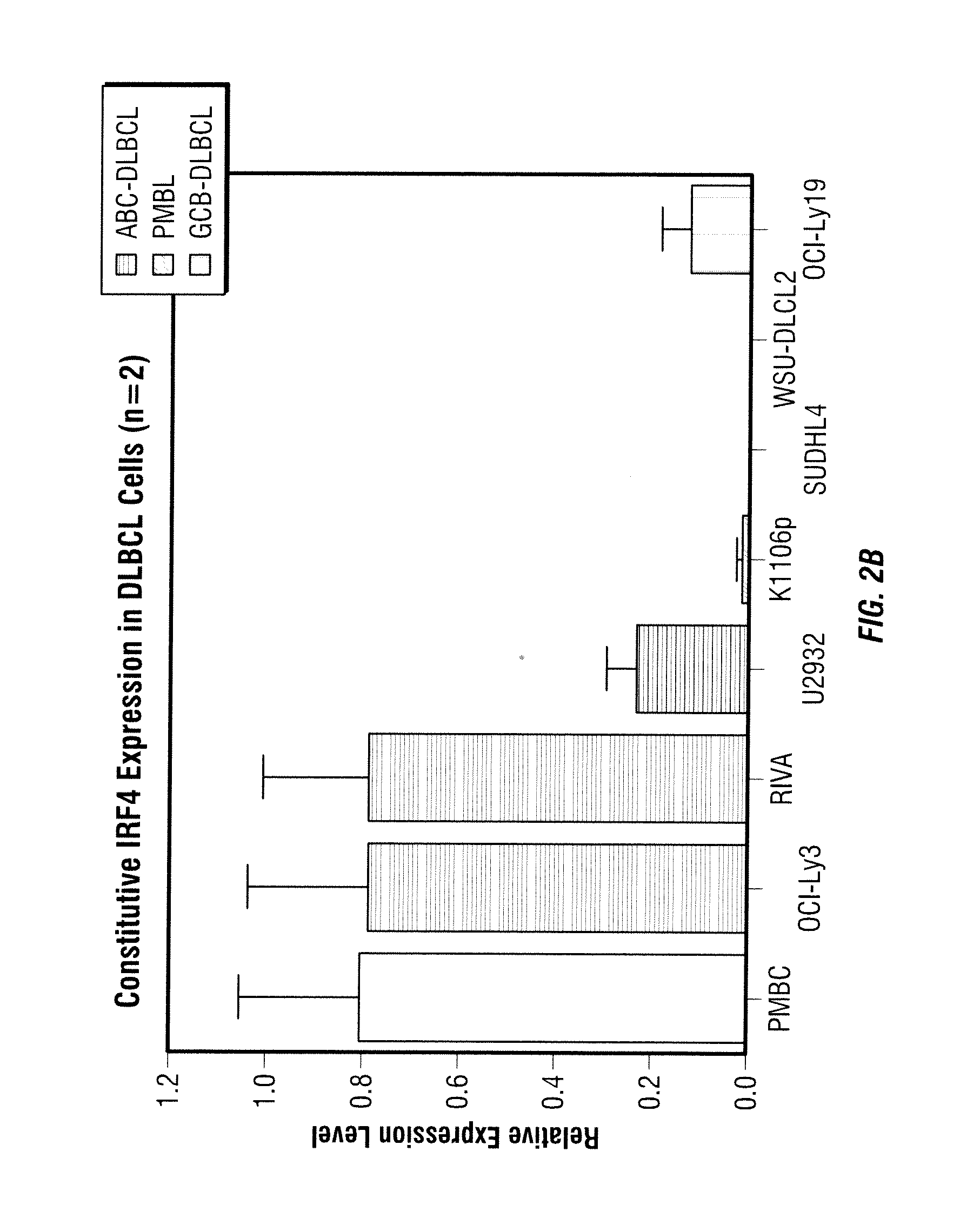
Methods for the treatment of non-hodgkin's lymphomas using lenalidomide, and gene and protein biomarkers as a predictor
InactiveUS20110223157A1Monitoring effectiveness of treatmentBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementADAMTS ProteinsFhit gene
Methods of treating or managing specific cancers, including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, by the administration of 3-(4-amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-isoindol-2-yl)-piperidine-2,6-dione are disclosed. Methods of using gene and protein biomarkers as a predictor of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma response to treatment with 3-(4-amino-1-oxo-1,3-dihydro-isoindol-2-yl)-piperidine-2,6-dione are also disclosed.
Owner:SCHAFER PETER H +3
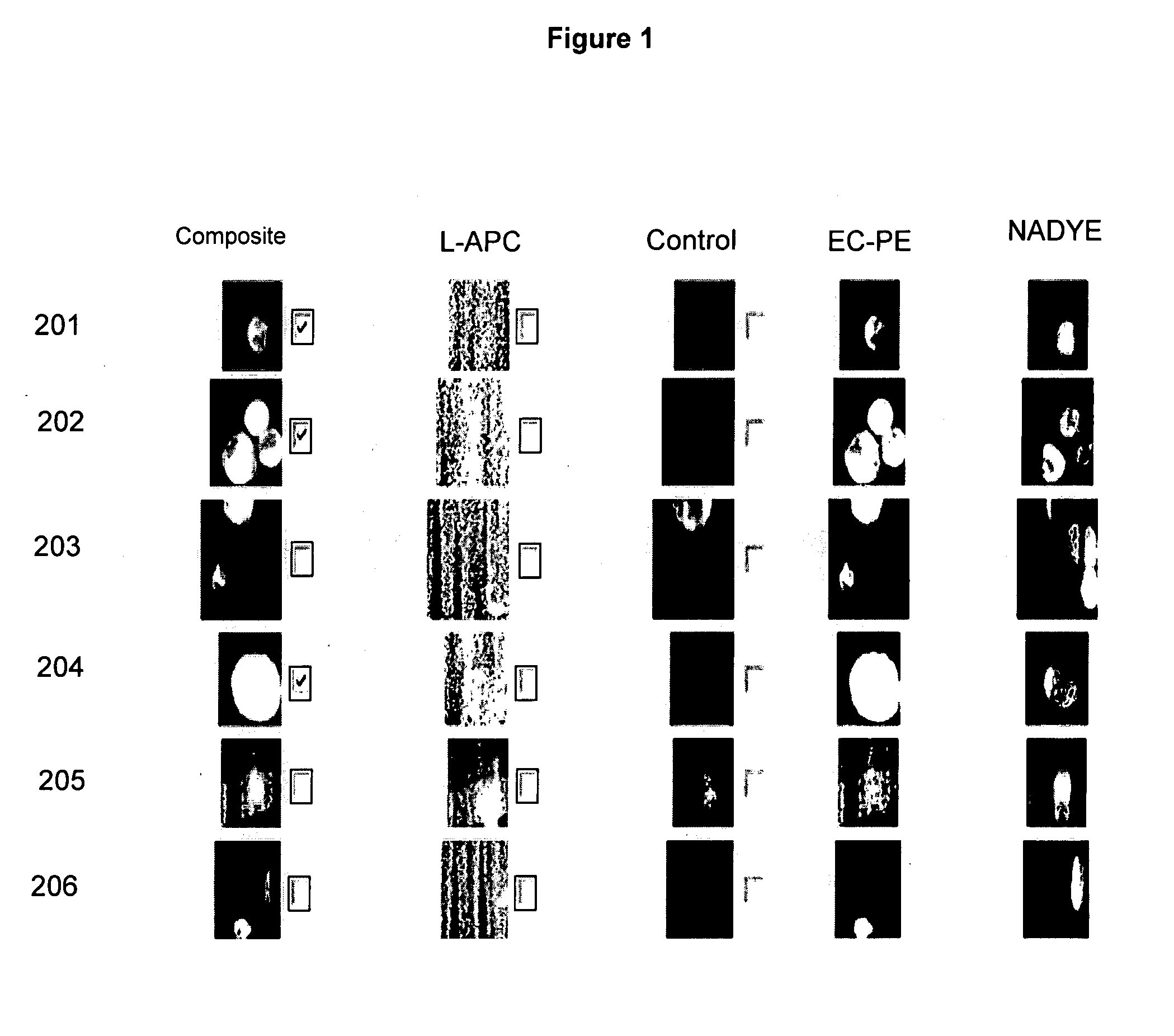
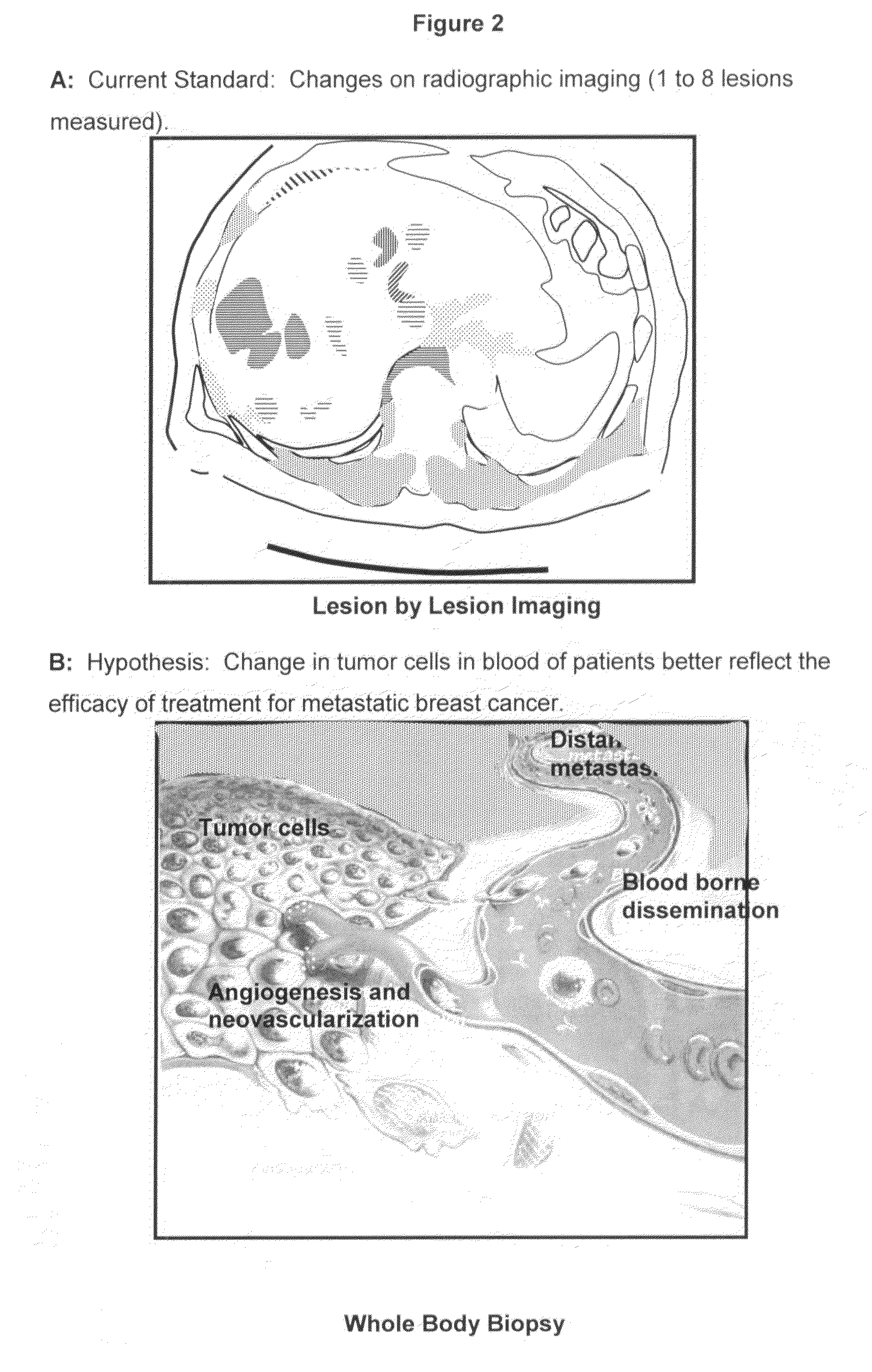
Method for predicting progression free and overall survival at each follow-up time point during therapy of metastatic breast cancer patients using circulating tumor cells
InactiveUS20090061456A1Less side effectsImprove the quality of lifeDisease diagnosisBiological testingOncologyDisease progression
A cancer test having prognostic utility in predicting time to disease progression, overall survival, and response to therapy in patients with MBC based upon the presence and number of CTC's. The Cell Spotter® System is used to enumerate CTC's in blood. The system immunomagnetically concentrates epithelial cells, fluorescently labels the cells and identifies and quantifies CTC's. The absolute number of CTC's detected in the peripheral blood tumor load is, in part, a factor in prediction of survival, time to progression, and response to therapy. The mean time to survival of patients depended upon a threshold number of 5 CTC's per 7.5 ml of blood. Detection of CTC's in metastatic cancer represents a novel prognostic factor in patients with metastatic cancers, suggests a biological role for the presence of tumor cells in the blood, and indicates that the detection of CTC's could be considered an appropriate surrogate marker for prospective therapeutic clinical trials.
Owner:VERIDEX LCC
Polymorphism markers for predicting response to interleukin-6 receptor-inhibiting monoclonal antibody drug treatment
InactiveUS20110262462A1Raise the possibilityNucleotide librariesAntipyreticMonoclonal antibodyTocilizumab therapy
The present invention provides single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with clinical responsiveness of rheumatoid arthritis patients to treatment with an interleukin-6 receptor antibody such as tocilizumab, and methods of using such SNPs for predicting clinical response to treatment with the antibody.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
System and method of prediction of response to neurological treatment using the electroencephalogram
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
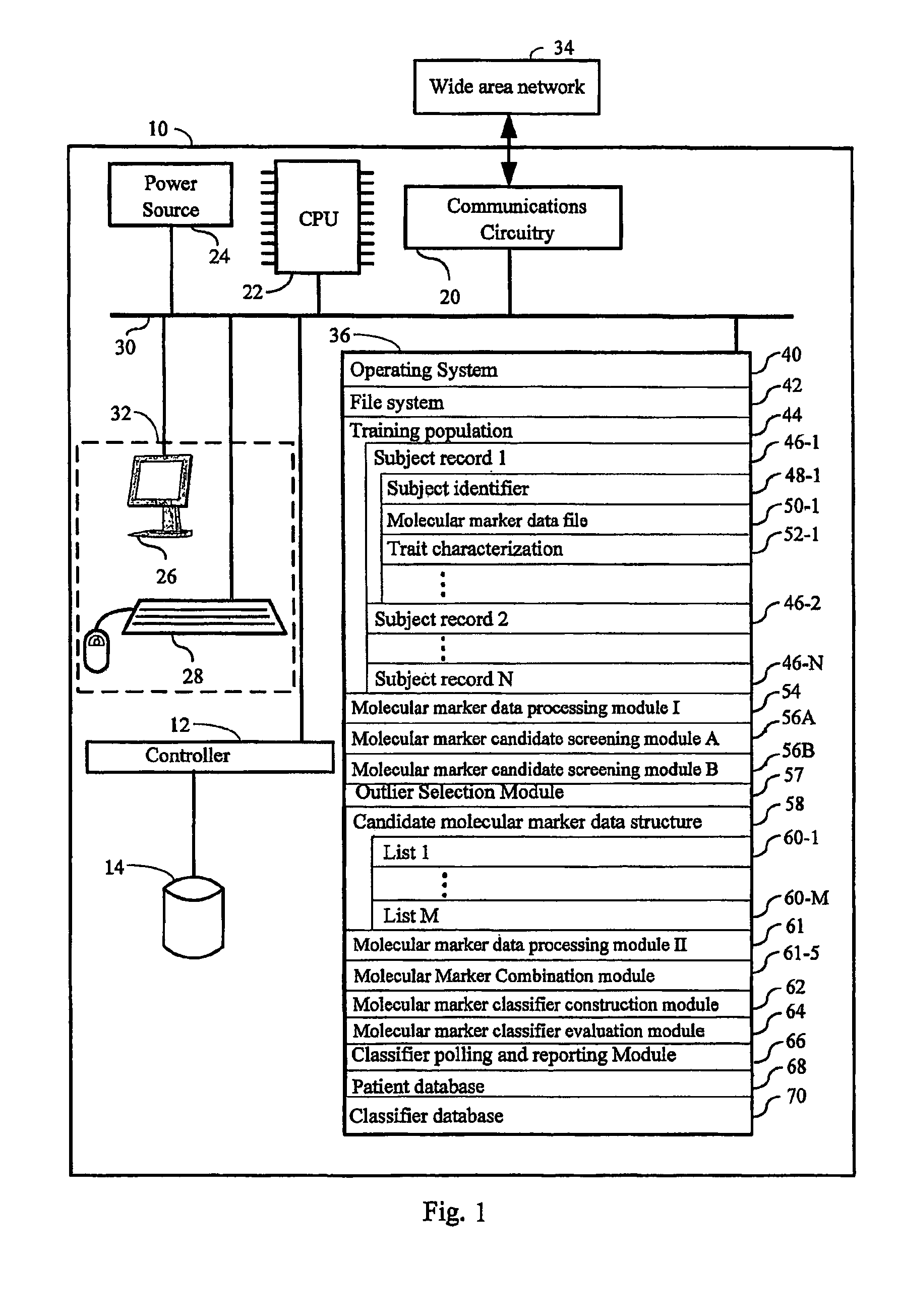
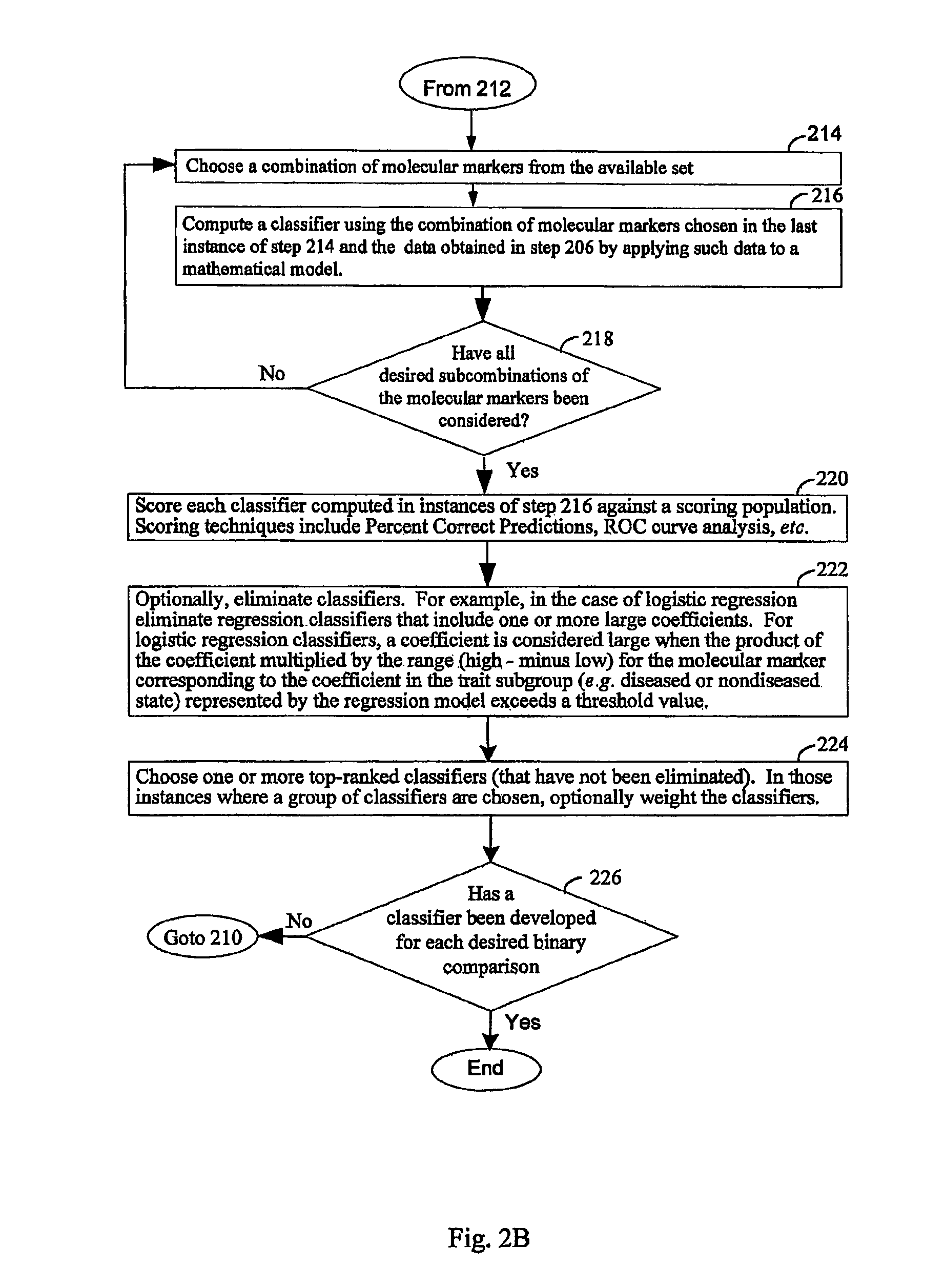
Computer system and methods for constructing biological classifiers and uses thereof
The present invention provides systems and method for constructing classifiers that distinguish between trait subgroups using molecular marker data from blood samples. The invention further encompasses the use of the classifiers and combinations of molecular markers identified by the classifiers in a wide variety of applications including: diagnosis; prognosis; prediction of disease, stage of disease or disease risk; monitoring disease progression and / or regression; monitoring disease reoccurrence and identifying risk of disease reoccurrence; determining and / or predicting response to treatment and / or treatment outcomes; monitoring and / or predicting treatment compliance or non compliance and the like. The invention further provides a variety of selected molecular markers and a means to identify combinations of the selected molecular markers useful for diagnosing particular traits of interest.
Owner:GENENEWS
System and Method for Diagnosis and Treatment
ActiveUS20120201747A1Good curative effectPromote resultsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsTreatment effectPhysiology
This invention relates to a low cost rapid response diagnostic system to determine cortisol levels in patients selected as potential candidates for GCR (glucocorticoid receptor) antagonist therapy utilizing a GCR antagonist, such as ORG 34517. The rapid, sensitive, and inexpensive test can be used to determine patients who have non-normal cortisol production or disordered circadian rhythms as a method for selecting subjects for GCR antagonist therapy for whom it is likely to have beneficial and / or therapeutic effects, and can also be used to monitor changes in cortisol levels in response to treatment.
Owner:POP TEST ONCOLOGY LIMITED LIABILITY
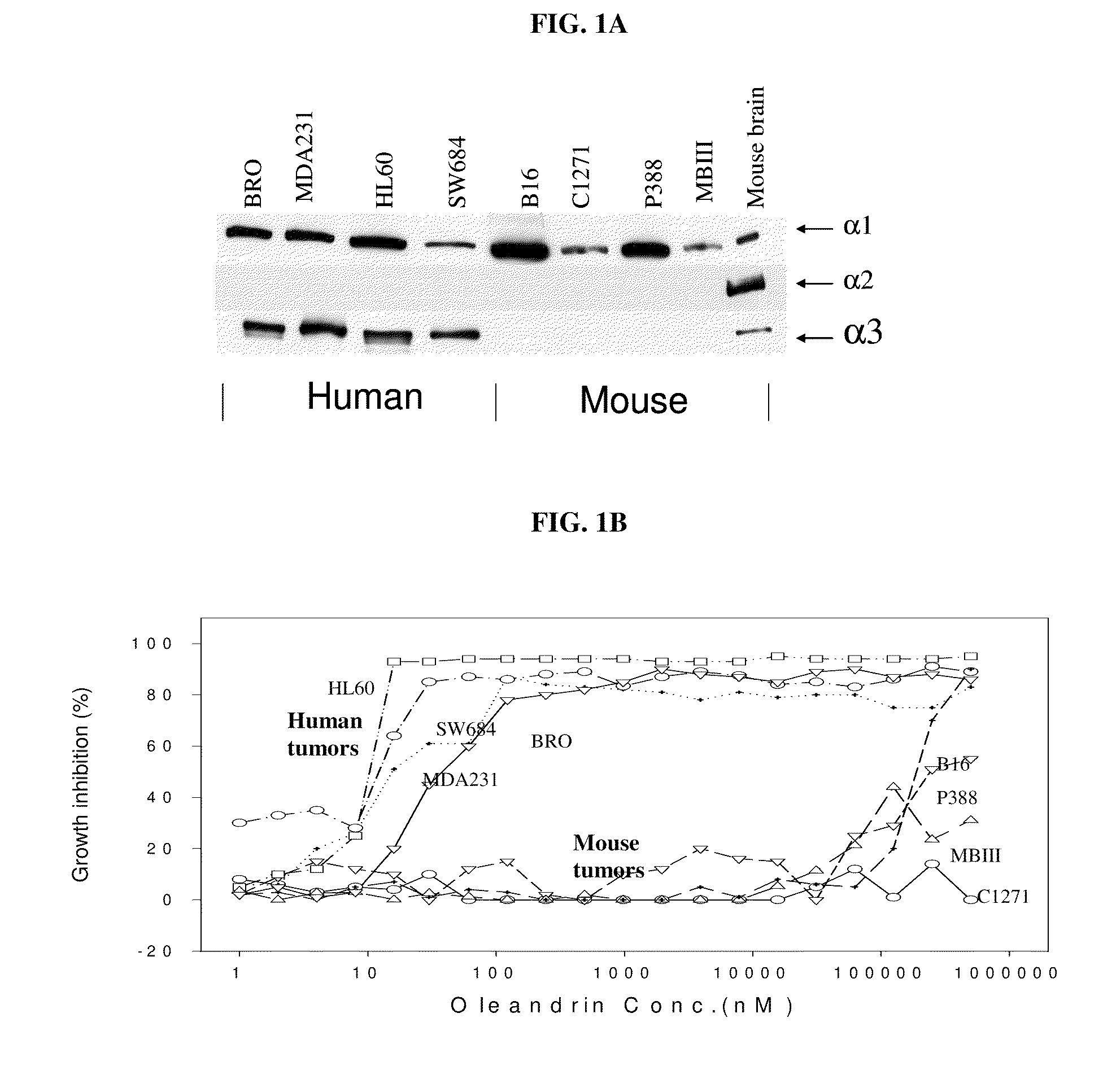
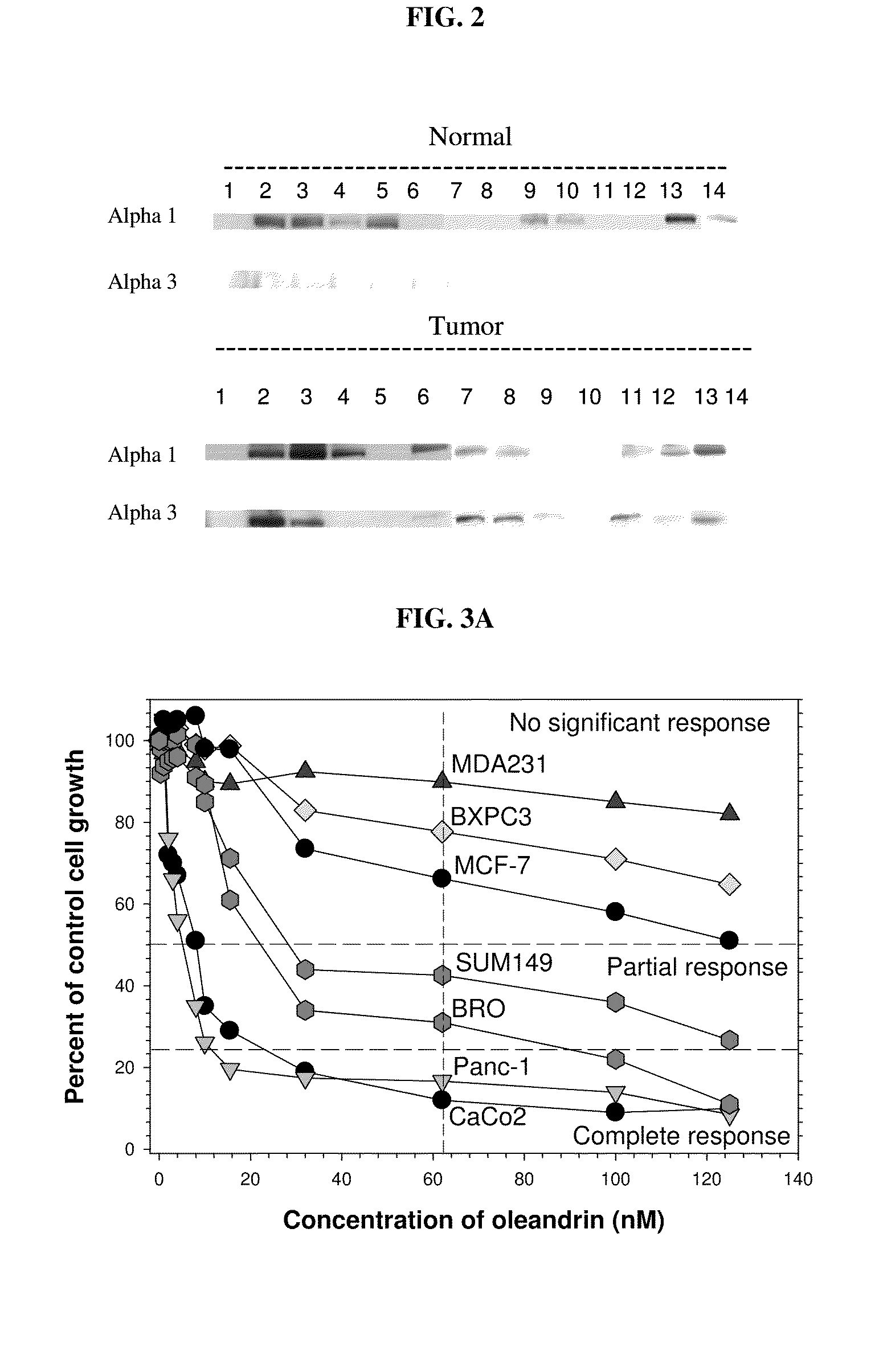
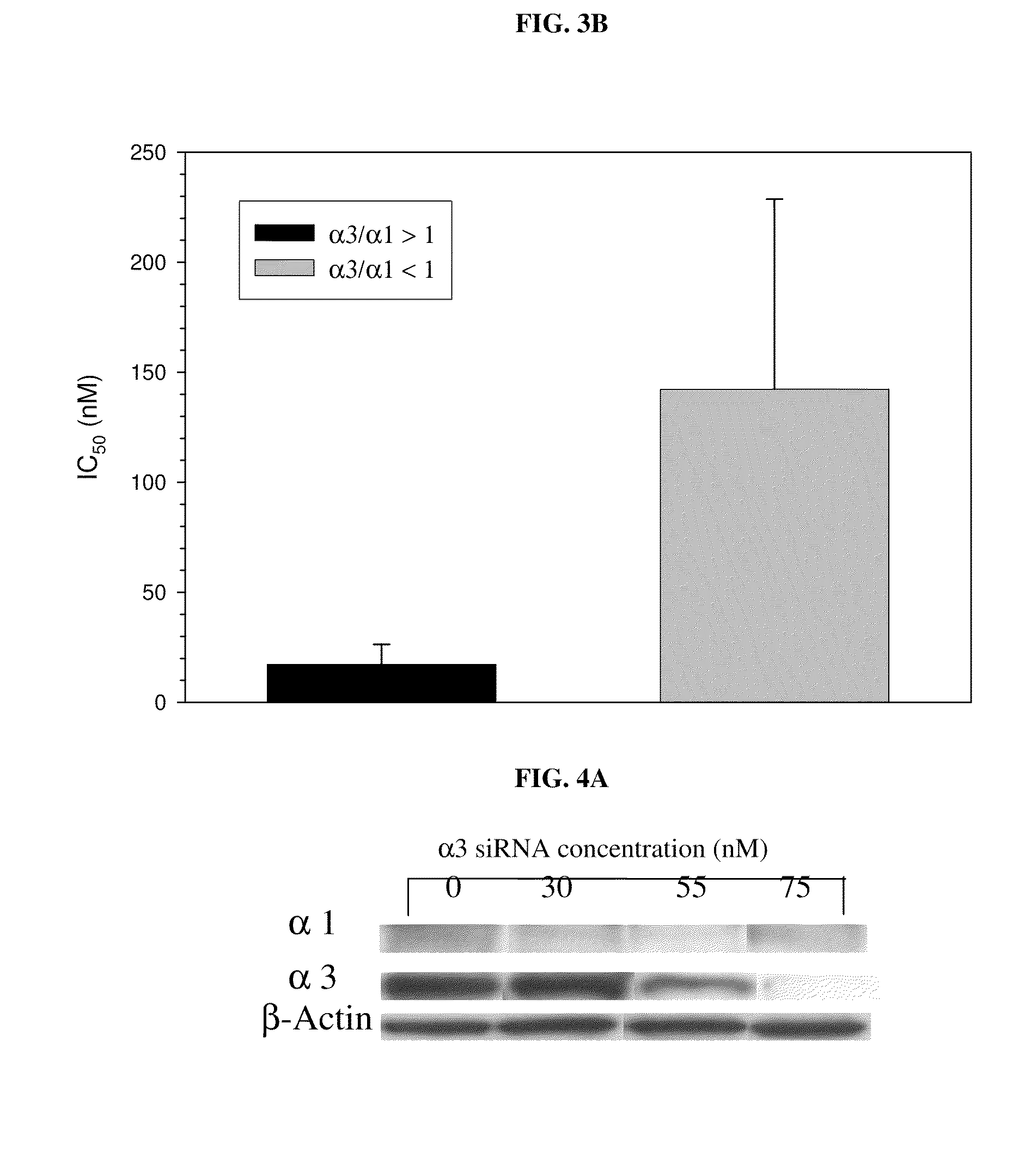
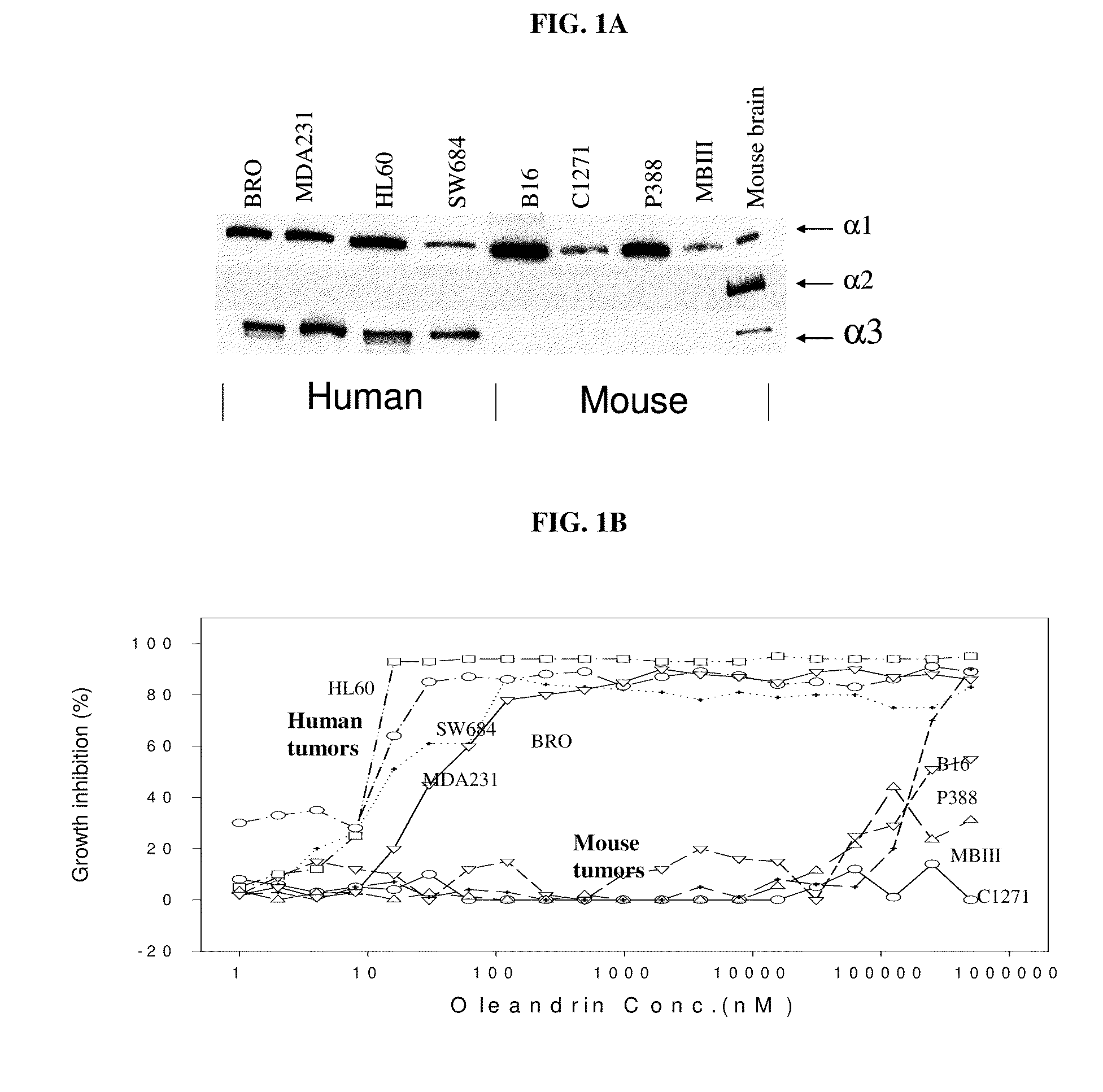
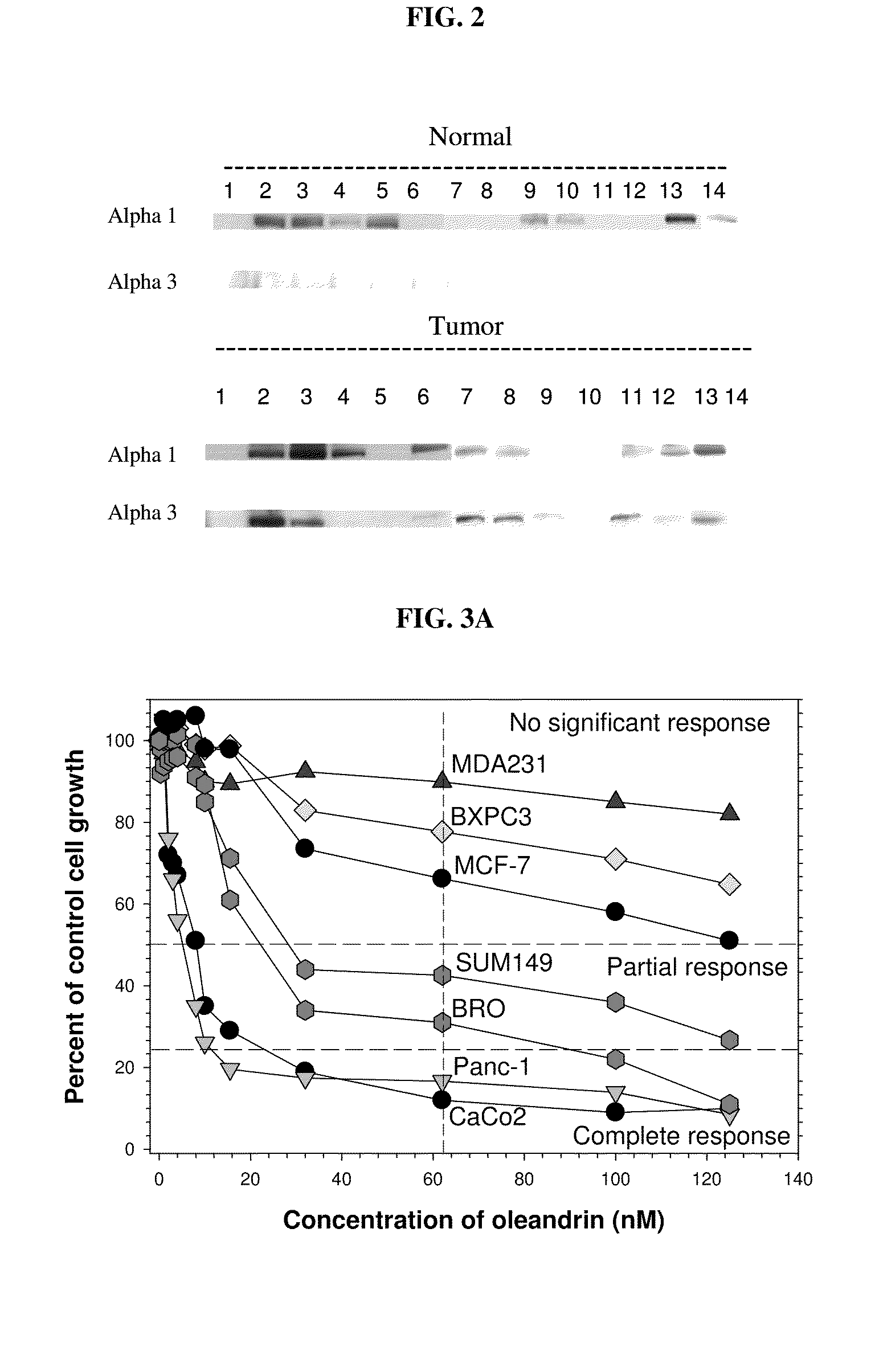
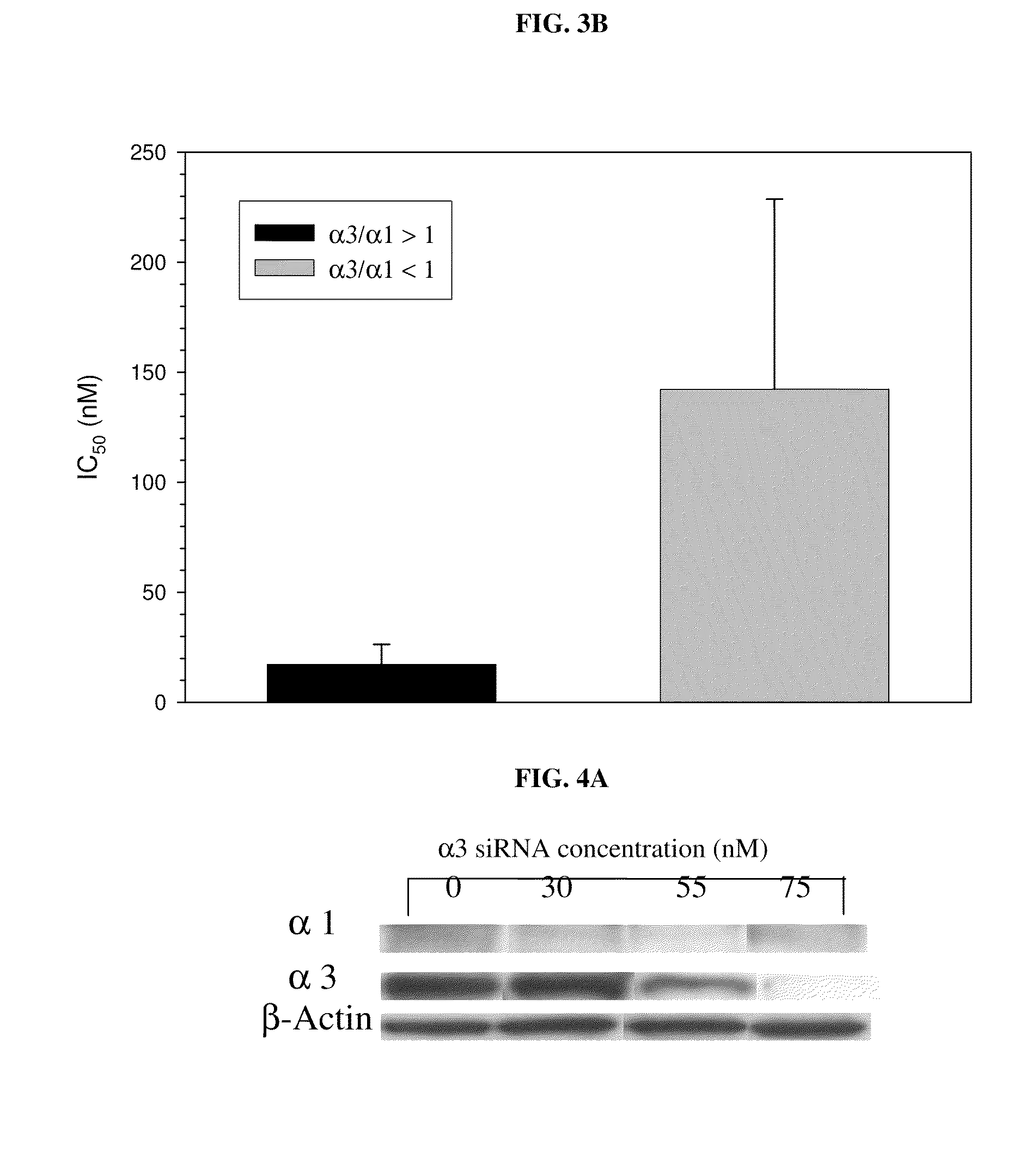
Method of determining the probability of a therapeutic response in cancer chemotherapy with cardiac glycoside
A prognostic assay and kit and method of use thereof are provided. The kit and assay are used to determine the likelihood of a diseased cell or tissue having a therapeutic response to treatment with a cardiac glycoside in a disease having an etiology associated with excessive cell proliferation. The kit and assay are used to determine the ratio of isoforms of the α subunit of Na, K-ATPase obtained from the diseased cell or tissue. The kit can be used to predict the therapeutic responsiveness of cancer or tumor in a subject to treatment with a cardiac glycoside. The kit and assay can be incorporated in a method of treating a disease or disorder having an etiology associated with excessive cell proliferation with a composition comprising a cardiac glycoside.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOTECH INC
Method for diagnosis and monitoring of disease activity and response to treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and other autoimmune diseases
InactiveUS20100233752A1Sensitive methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAutoimmune thyroid diseaseWhite blood cell
The present invention provides methods of diagnosing and monitoring systemic lupus erythematosus and drug-induced lupus erythematosus by measuring cell-based complement activation products in a subject's blood. In particular, the invention describes a diagnostic method employing the measurement of multiple complement activation products, such as C3d and C4d, on the surfaces of red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Kits and automated systems for performing the methods of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:EXAGEN DIAGNOSTICS +1
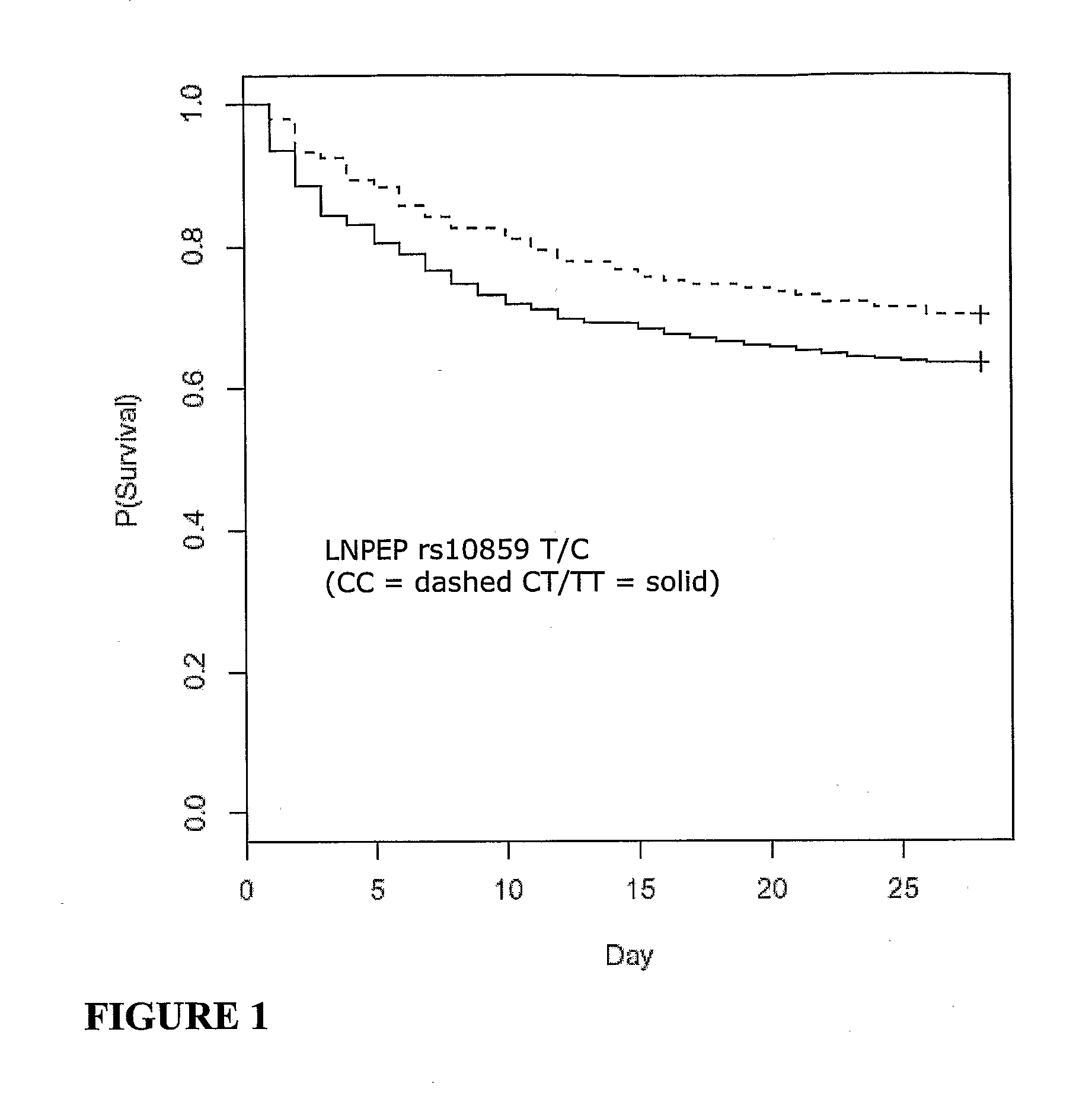
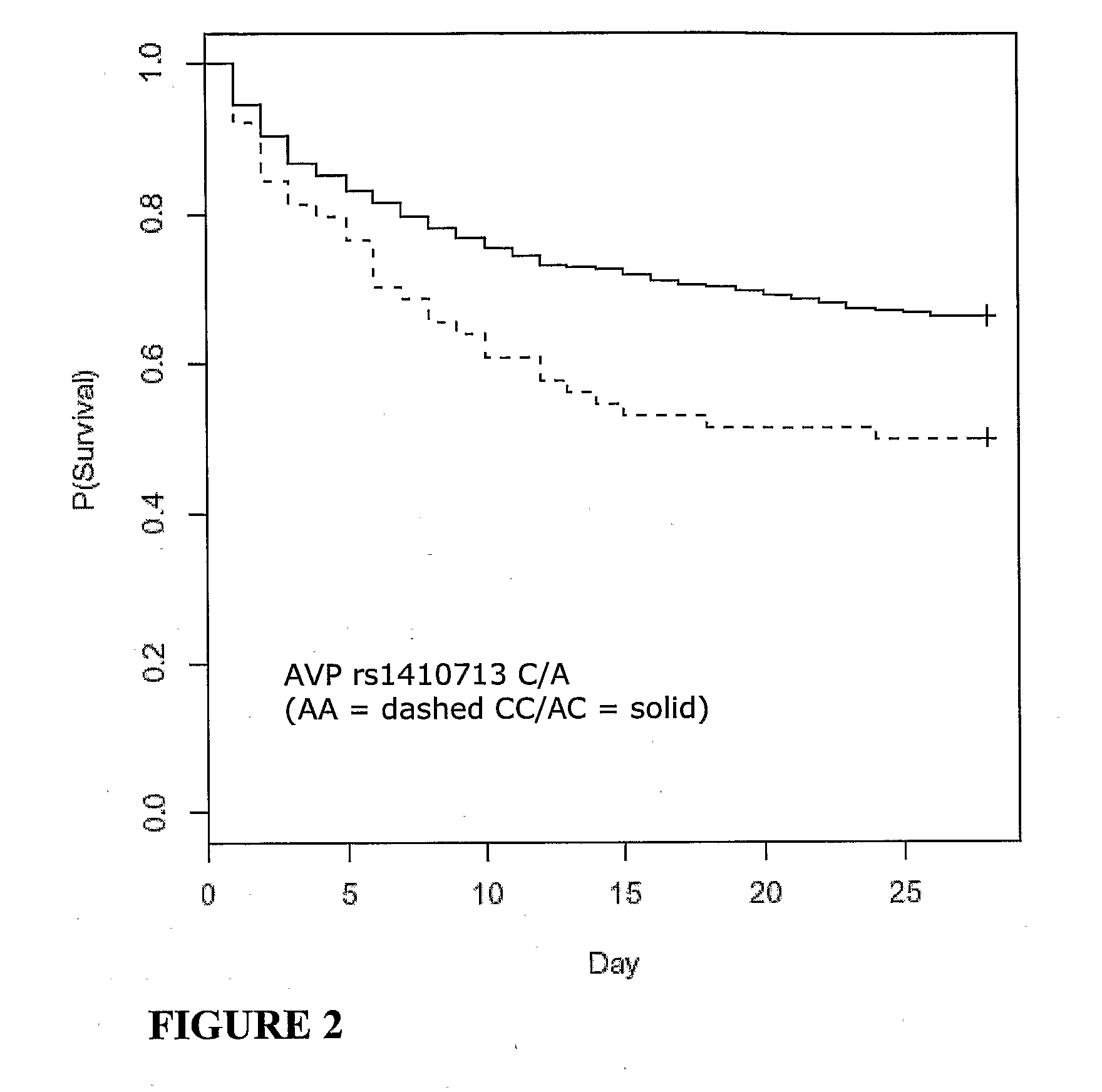
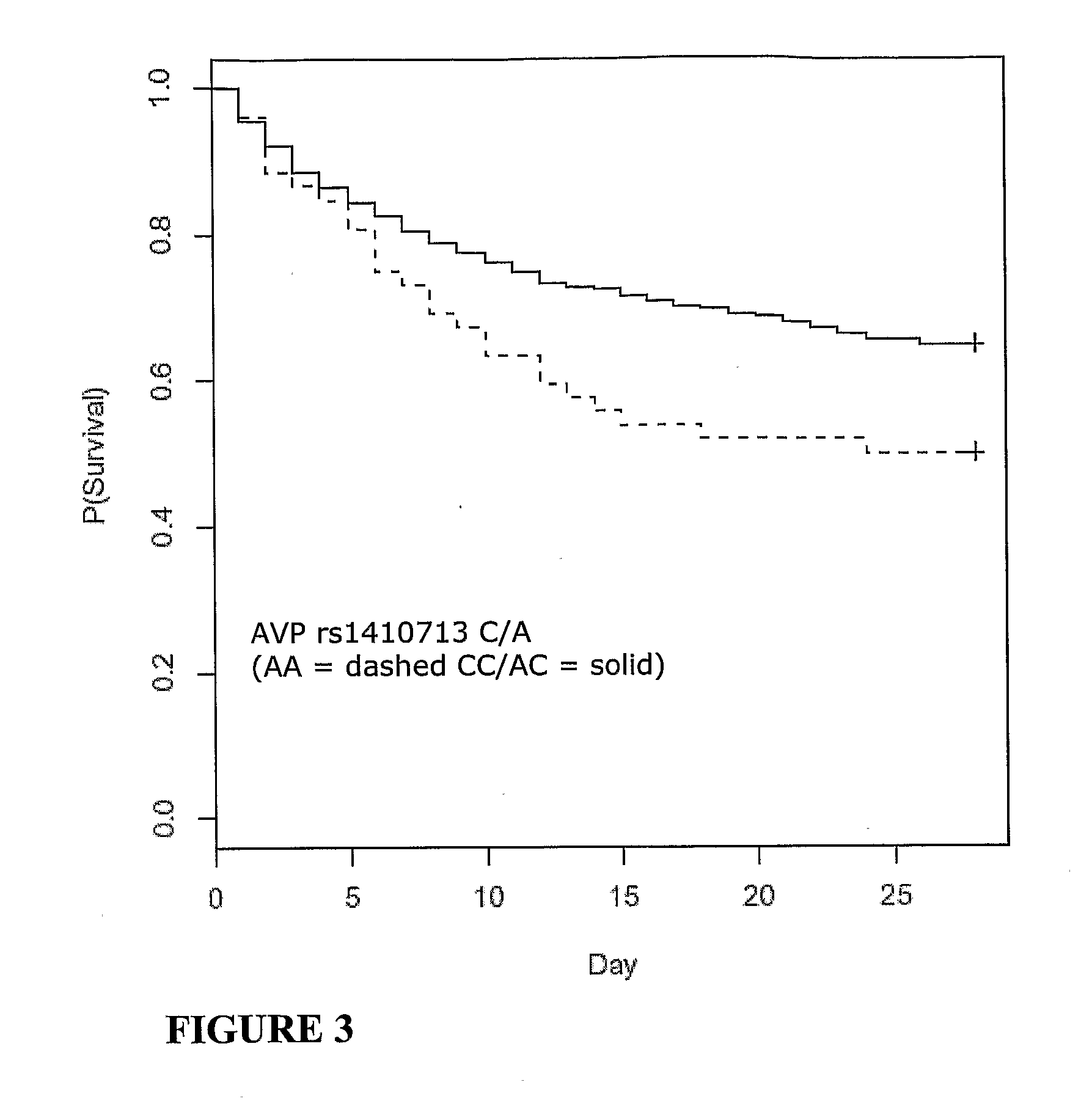
Vasopressin pathway polymorphisms as indicators of subject outcome in critically ill subjects
InactiveUS20090298711A1Decreased of organ dysfunctionNucleotide librariesPeptide/protein ingredientsCritically illVasopressin receptor
The invention provides methods, nucleic acids, compositions and kits for predicting a subject's response to treatment with one or more vasopressin receptor agonists to identify subjects having a greater benefit from treatment with vasopressin receptor agonist(s). The method generally comprises determining a vasopressin pathway associated gene polymorphism genotype(s) of a subject for one or more polymorphisms in the these genes, comparing the determined genotype with known genotypes for the polymorphism that correspond with an improved response genotype to identify potential subjects having an inflammatory condition who are more likely to benefit from treatment with a vasopressin receptor agonist and subsequent to treatment recover from the inflammatory condition. The invention also provides for methods of treating such subjects with vasopressin receptor agonists based on the subject's genotype.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA +1
Predicting response to chemotherapy using gene expression markers
ActiveUS20060166230A1Raise the possibilityReduce the possibilityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsCancer researchGene expression
The present invention provides gene expression information useful for predicting whether cancer patients are likely to have a beneficial response to treatment response with chemotherapy.
Owner:GENOMIC HEALTH INC
Markers and Methods for Assessing and Treating Ulcerative Colitis and Related Disorders Using a 43 Gene Panel
InactiveUS20080293582A1Avoid actionInhibit productionMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMedicineUlcerative colitis
A method for prognostic or diagnostic assessment of a gastrointestinal-related disorder, such as ulcerative colitis, in a subject correlates the presence, absence, and / or magnitude of a gene in a sample with a reference standard to determine the presence and / or severity of the disorder, and / or the response to treatment for the disorder. The method enables identification of the effectiveness of candidate therapies.
Owner:CENTOCOR ORTHO BIOTECH
Method of Determining the Probability of a Therapeutic Response in Cancer Chemotherapy With Cardiac Glycoside
ActiveUS20100317541A1Sensitivity and therapeutic responsivenessRaise the ratioOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderAssayIV Chemotherapy
A prognostic assay and kit and method of use thereof are provided. The kit and assay are used to determine the likelihood of a diseased cell or tissue having a therapeutic response to treatment with a cardiac glycoside in a disease having an etiology associated with excessive cell proliferation. The kit and assay are used to determine the ratio of isoforms of the α subunit of Na, K-ATPase obtained from the diseased cell or tissue. The kit can be used to predict the therapeutic responsiveness of cancer or tumor in a subject to treatment with a cardiac glycoside. The kit and assay can be incorporated in a method of treating a disease or disorder having an etiology associated with excessive cell proliferation with a composition comprising a cardiac glycoside.
Owner:PHOENIX BIOTECH INC
Biomarkers of target modulation, efficacy, diagnosis and/or prognosis for raf inhibitors
InactiveUS20100004253A1Improving patient careBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiomarker identificationGene expression level
Methods of utilizing biomarkers to identify patients for treatment or to monitor response to treatment are taught herein. Alterations in levels of gene expression of the biomarkers, particularly in response to Raf kinase inhibition, are measured and identifications or adjustments may be made accordingly.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
System for assessing drug efficacy and response of a patient to therapy
A system for identifying, monitoring and matching patients with appropriate treatments using a systemic mediator-associated physiologic test profile are provided. The system of the present invention increases the likelihood of demonstrating clinical efficacy in clinical trial datasets.
Owner:SLOTMAN GUS J
Materials and methods for measuring nitric oxide levels in biological fluids
ActiveUS8906693B2Improve treatmentAdministration of appropriateBiocideAnalysis by electrical excitationIntensive care medicineNitric oxide metabolism
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Methods and compositions of treating cancer
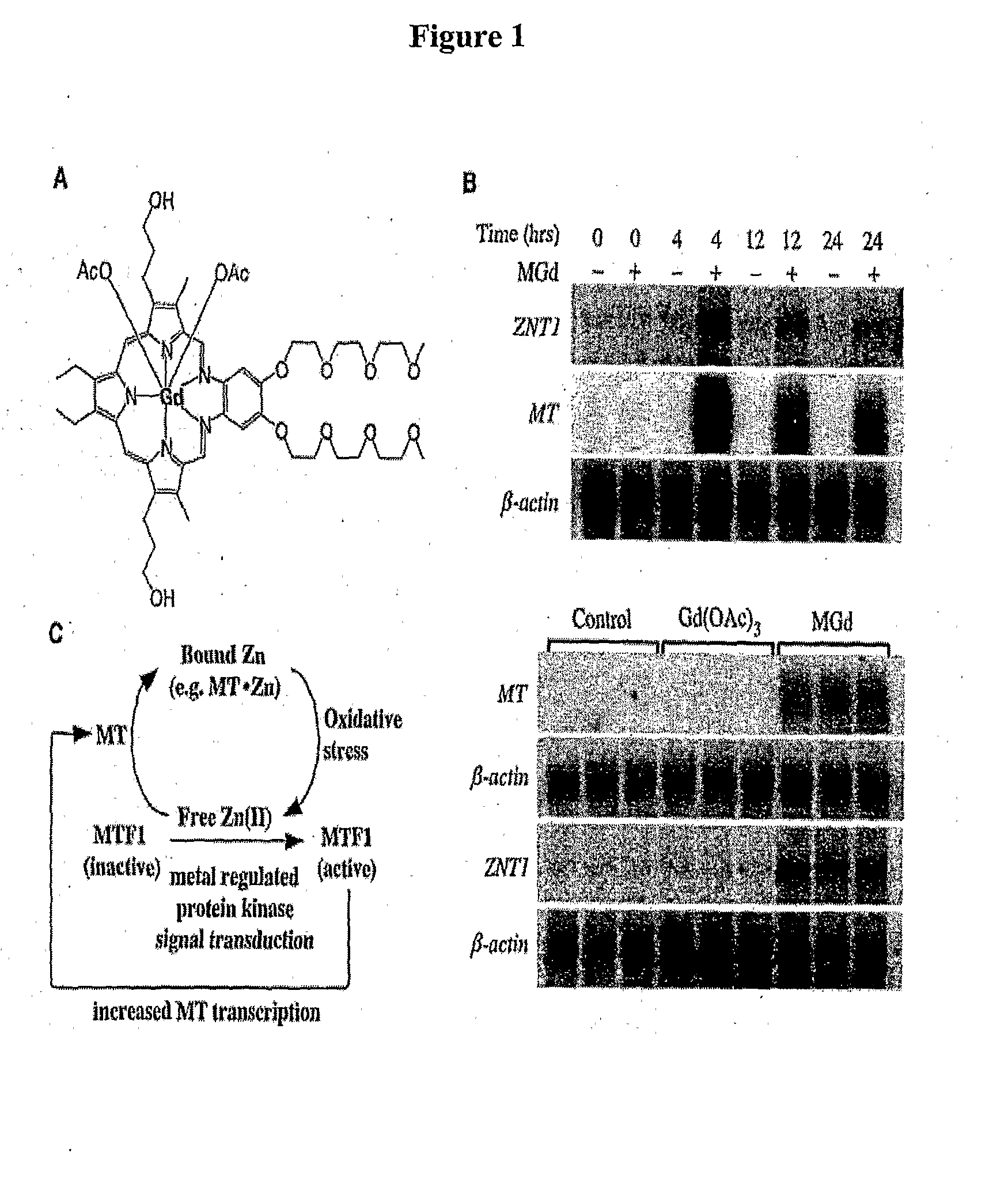
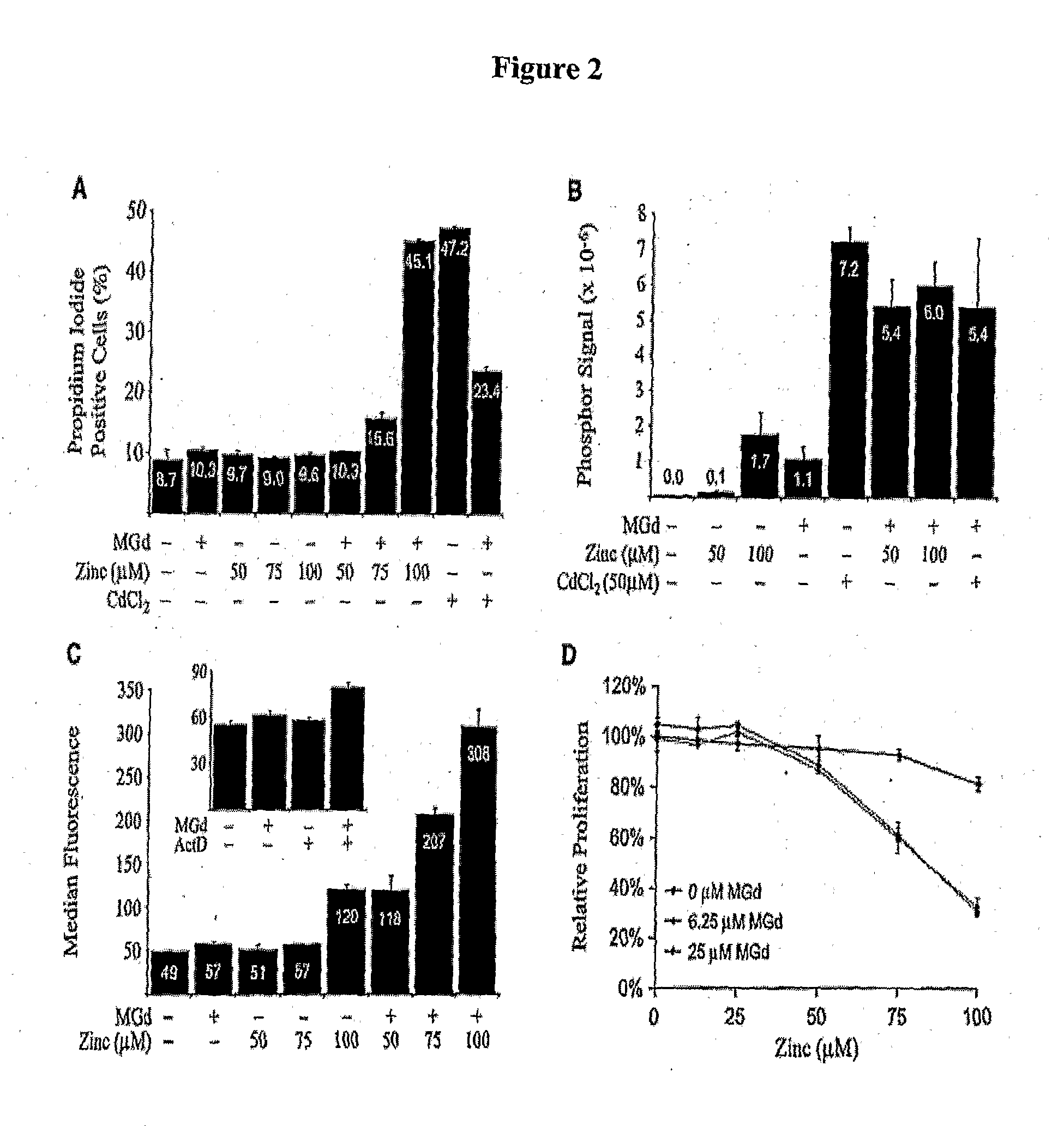
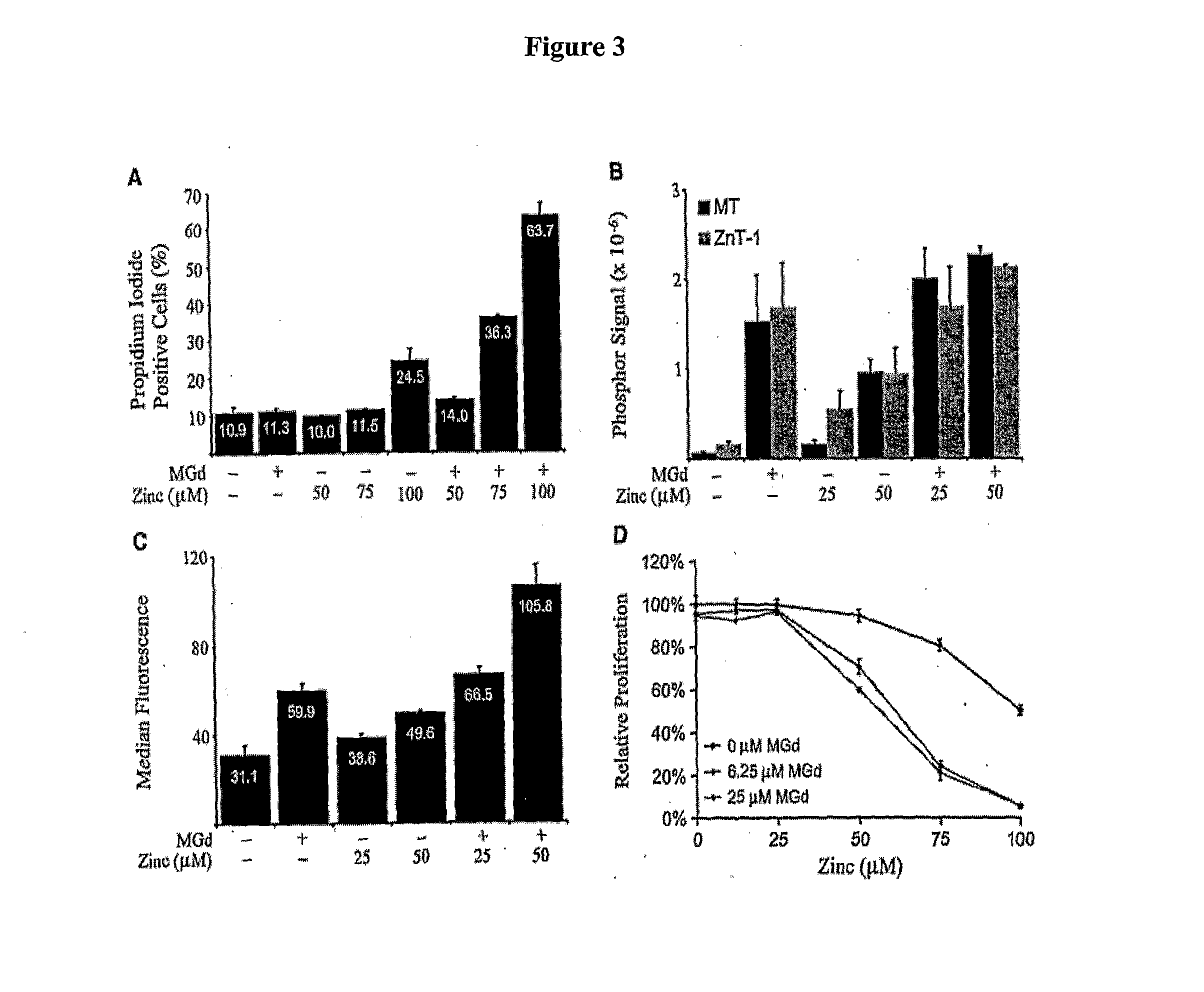
The present disclosure involves the use of metal-containing texaphyrins and zinc (II) reagents for the treatment of tumors, atheromas and other neoplastic tissue. The present application demonstrates increased oxidative stress, alterations in zinc homeostasis, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis of cancer cells in the presence of texaphyrins and / or zinc. One aspect is to monitor oxidative stress and / or alterations in zinc homeostasis in target cells prior to and / or after treatment with metal-containing texaphyrins and / or zinc (II) reagents as a predictor for treatment efficacy. The present disclosure provides molecular basis for the cell cycle arrest and apoptosis on cancer cells in the presence of texaphyrins and zinc. Another aspect is to monitor different genes involved in response to treatment with texaphyrins and zinc prior to and / or after treatment as predictors for treatment efficacy.
Owner:PHARMACYCLICS
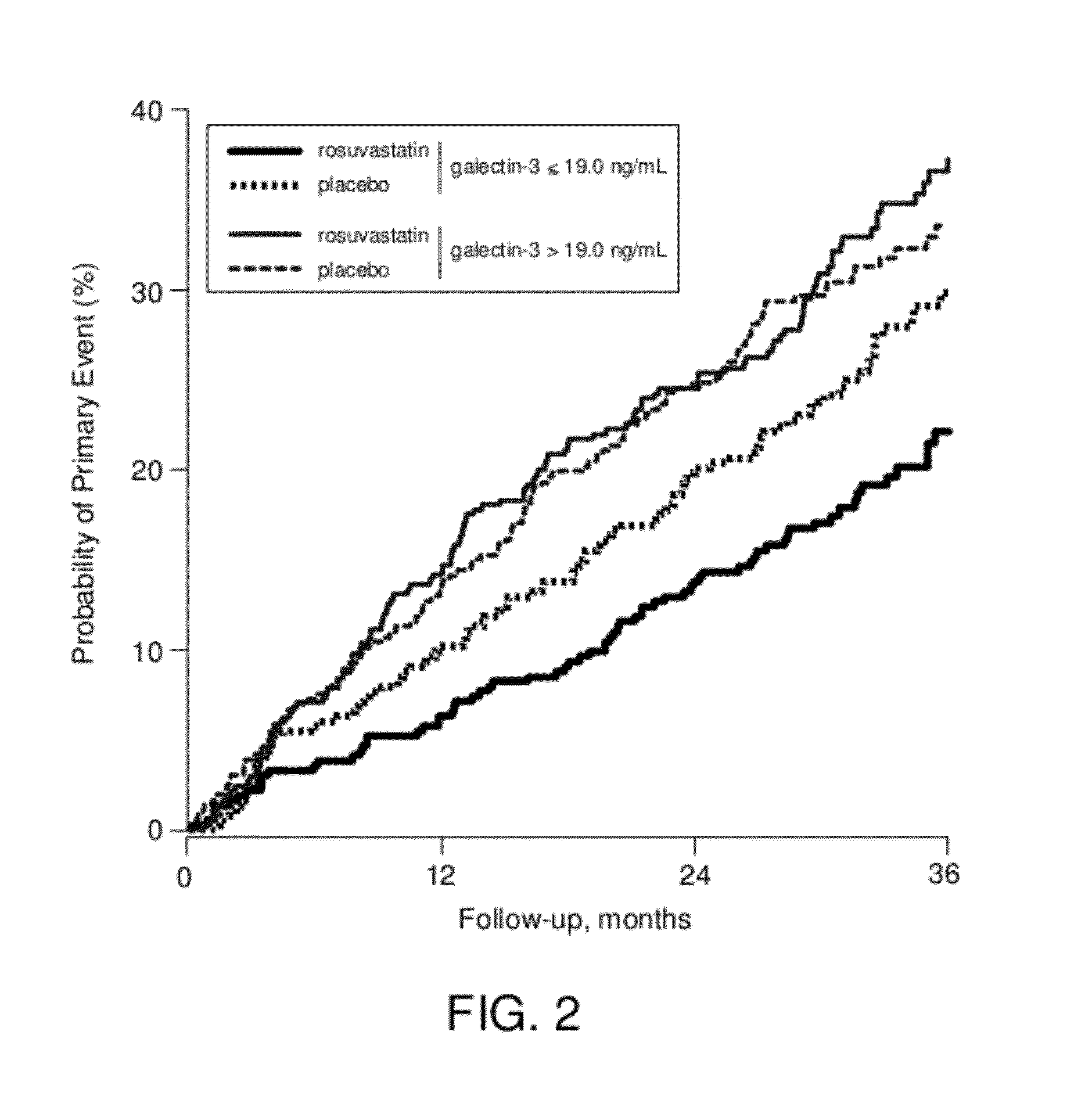
Galectin-3 and statin therapy
InactiveUS20120029003A1Improve survivalReduce developmentBiocideNervous disorderEnzyme inhibitor3 hydroxy 3 methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase
Described herein are materials and methods for predicting and monitoring a heart failure patient's physiological response to treatment with a statin. More specifically, the present invention relates to the endogenous protein galectin-3 and its use as a predictor of response to treatment with 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A reductase inhibitors, or statins.
Owner:BG MEDICINE
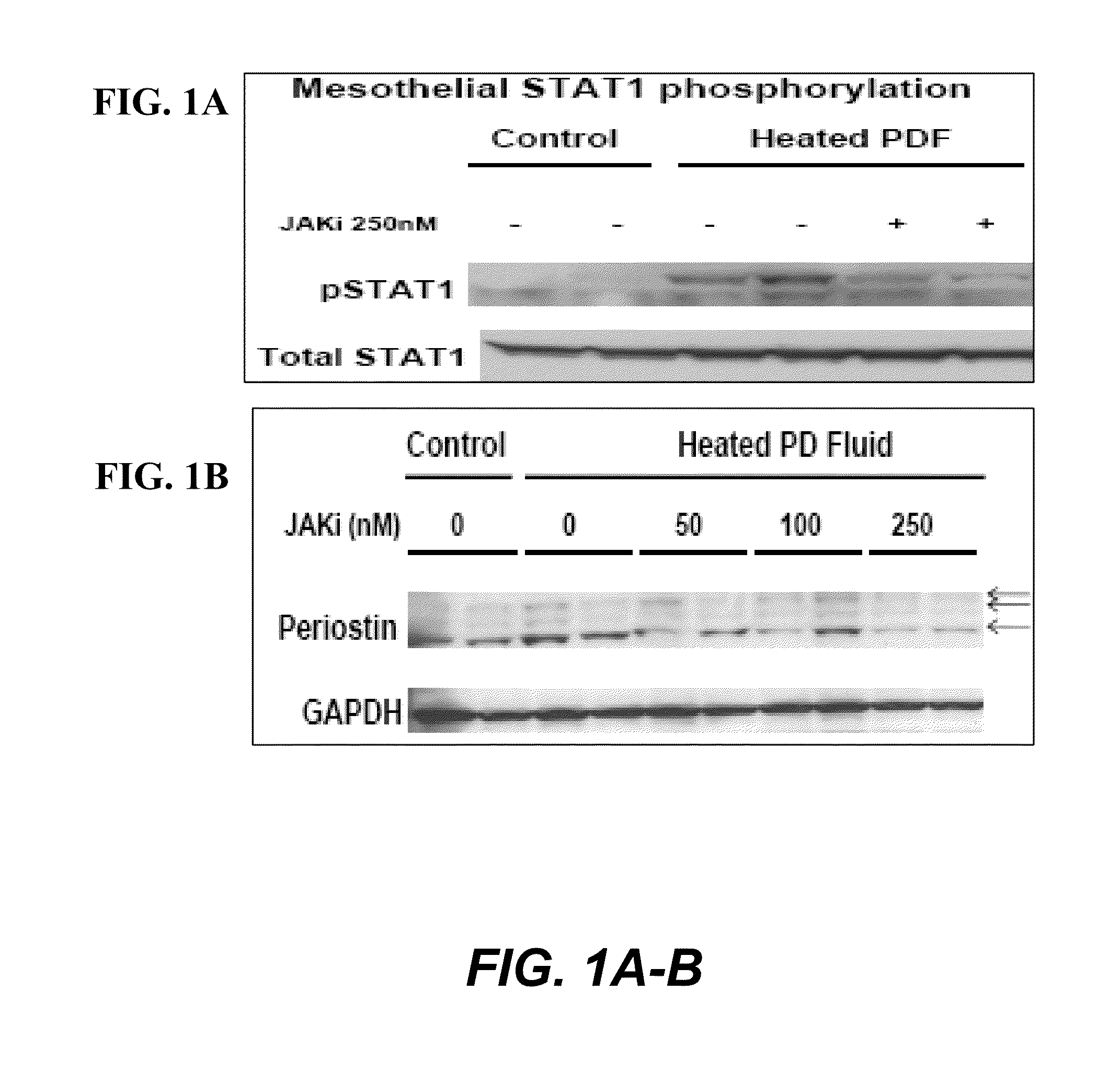
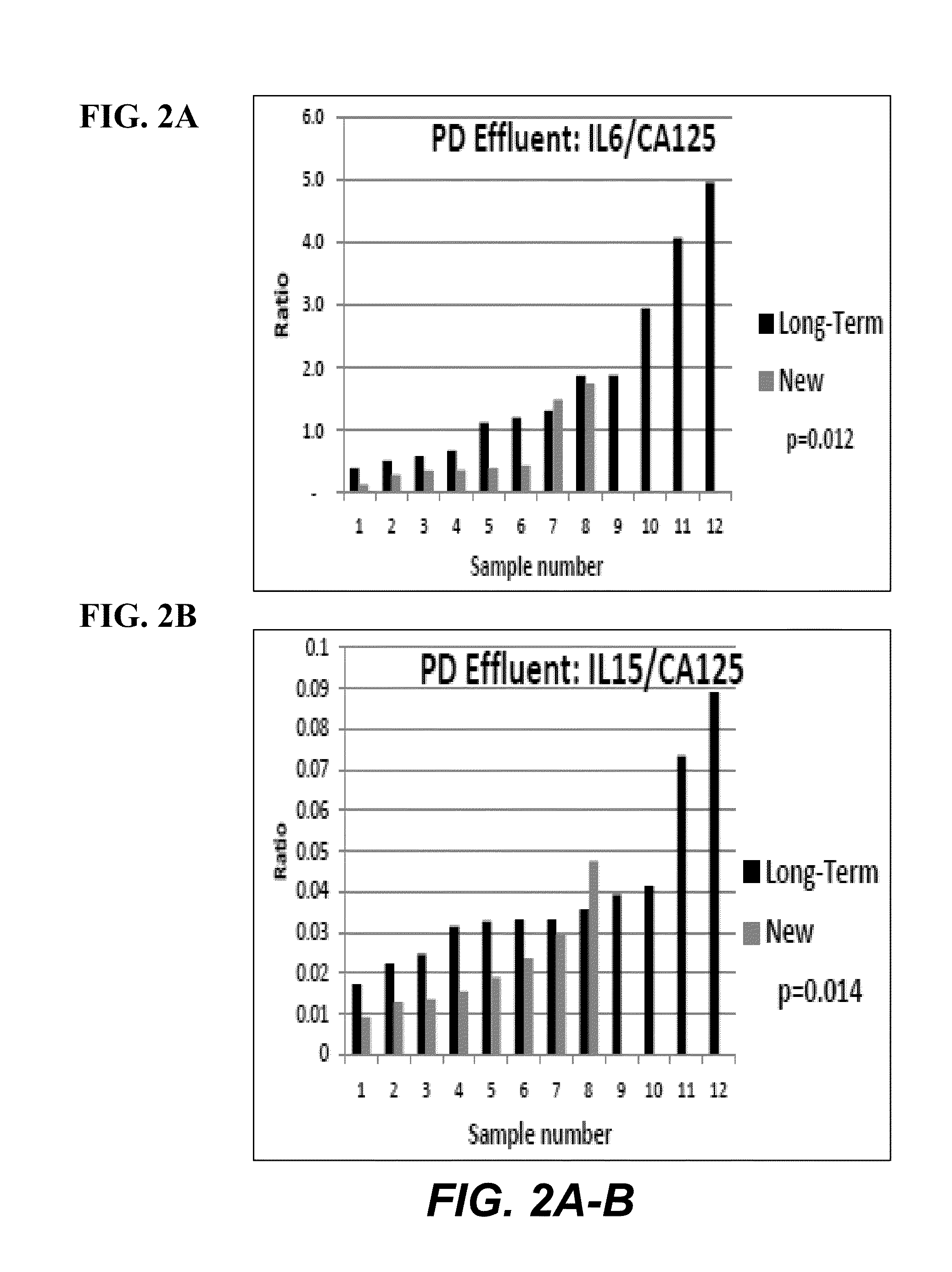
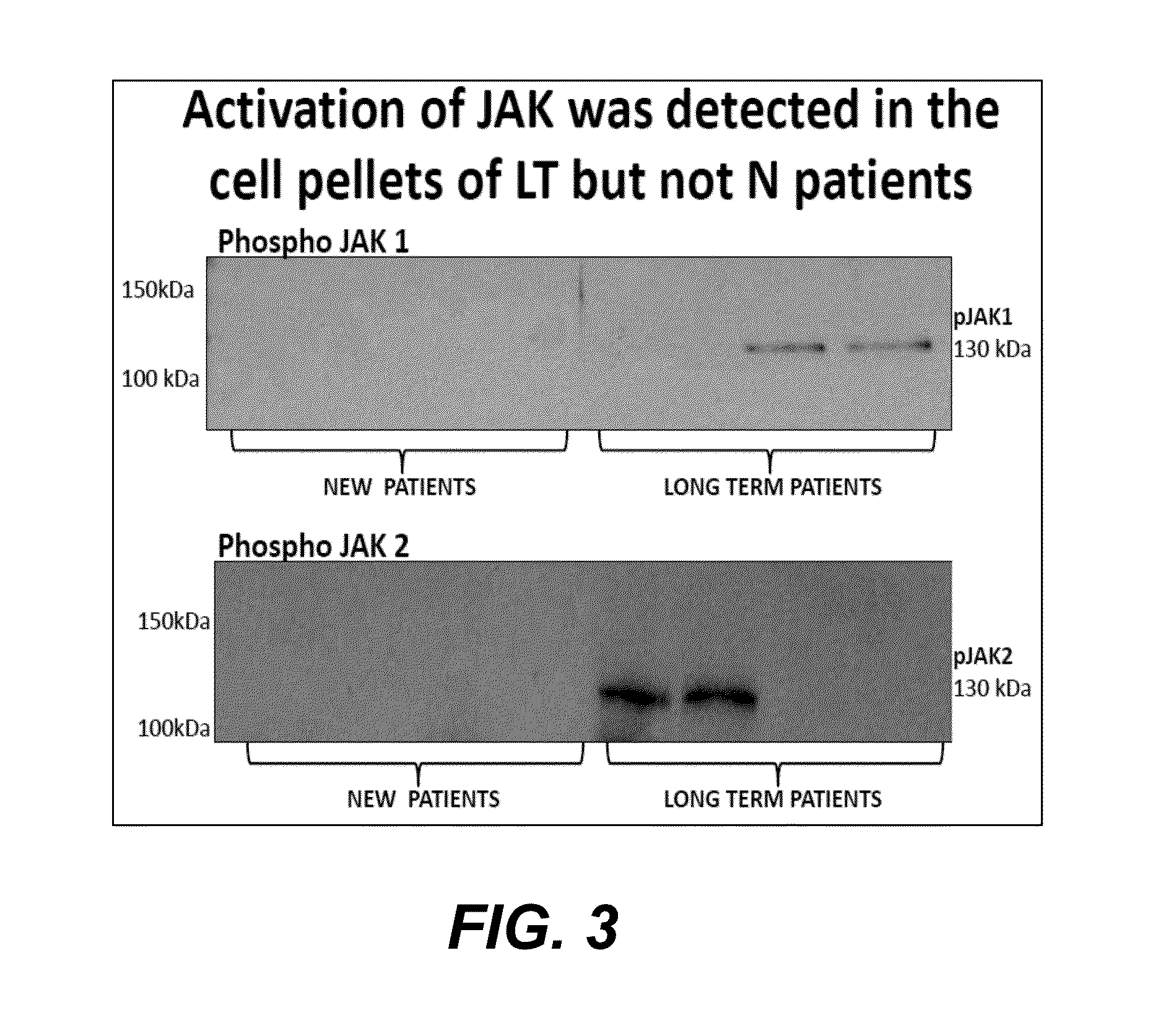
Treatment of peritoneal injury using jak inhibitors
The invention provides, in certain embodiments, a method of preventing and / or treating peritoneal injury and / or diminished function by administering an effective amount of one or more inhibitors of JAK. The invention also provides a pharmaceutical composition including a JAK inhibitor for the treatment of peritoneal injury and / or diminished function. In another aspect, the invention provides a method of detecting an indicator of peritoneal injury. The method entails assaying a biological sample for periostin, wherein the presence of periostin at an elevated level indicates the presence and / or degree of peritoneal injury. Also provided, are methods of identifying subject for treatment of peritoneal injury and / or diminished function, methods of determining progression of these conditions, as well as methods of determining subjects' response to treatment.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com