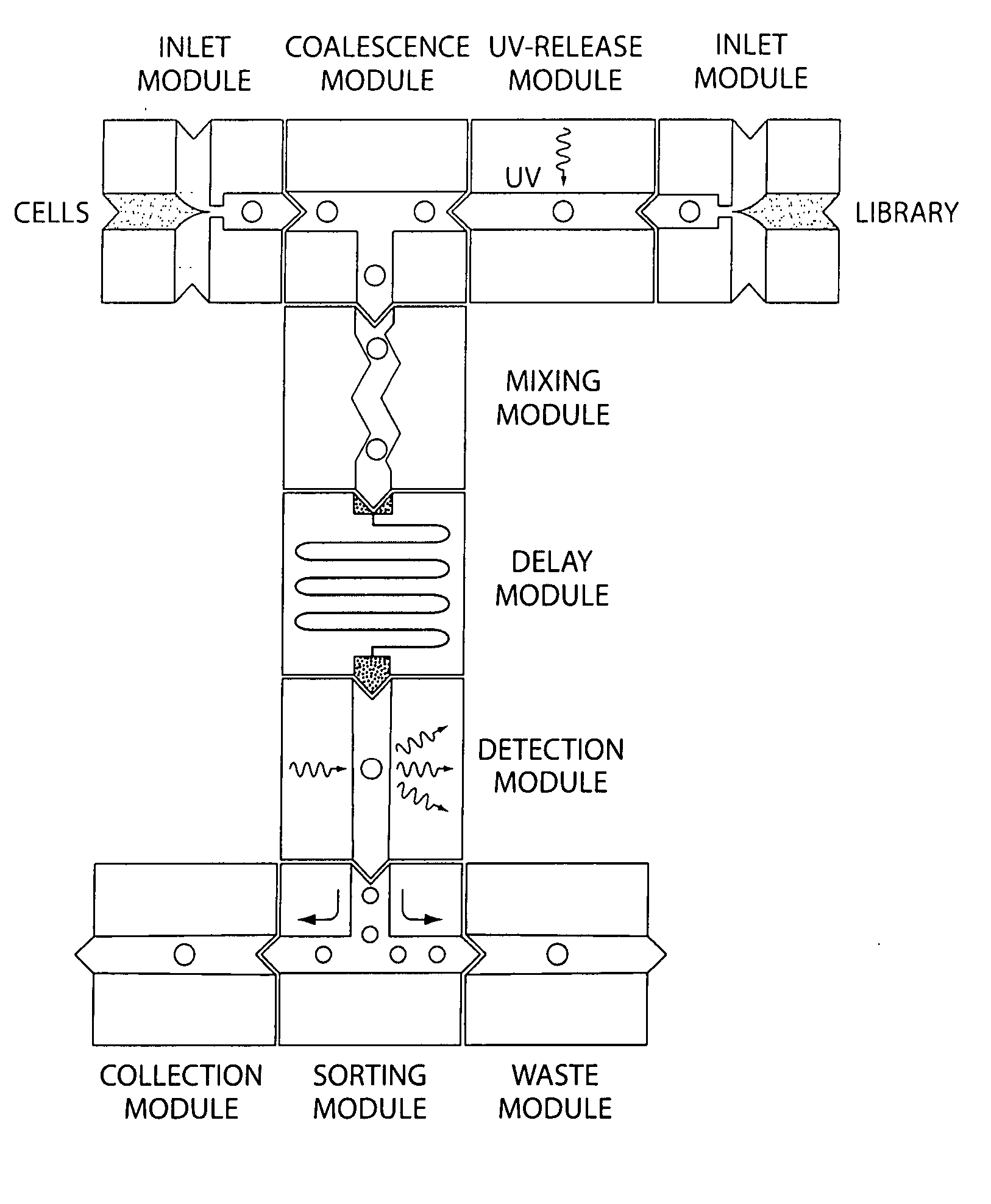
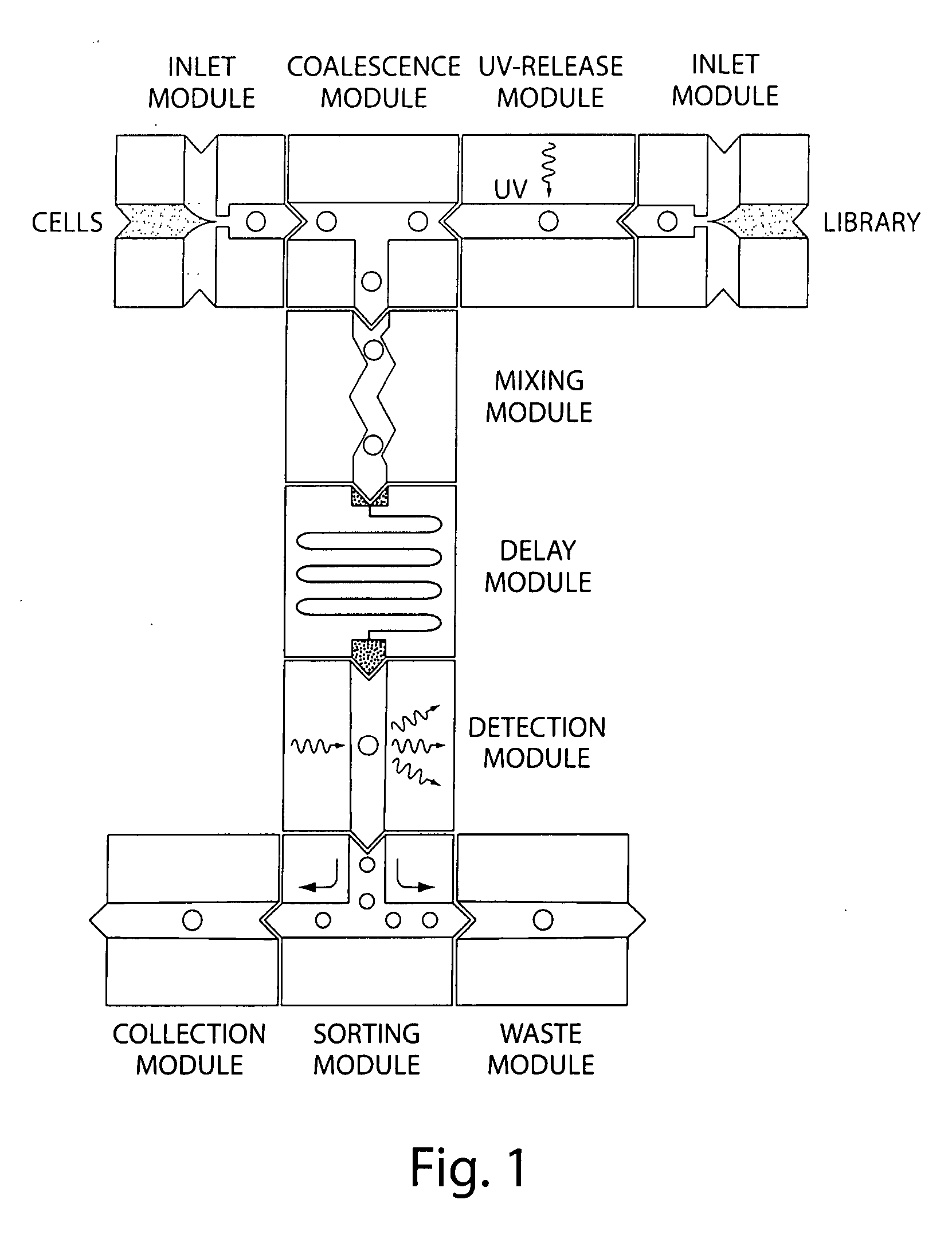
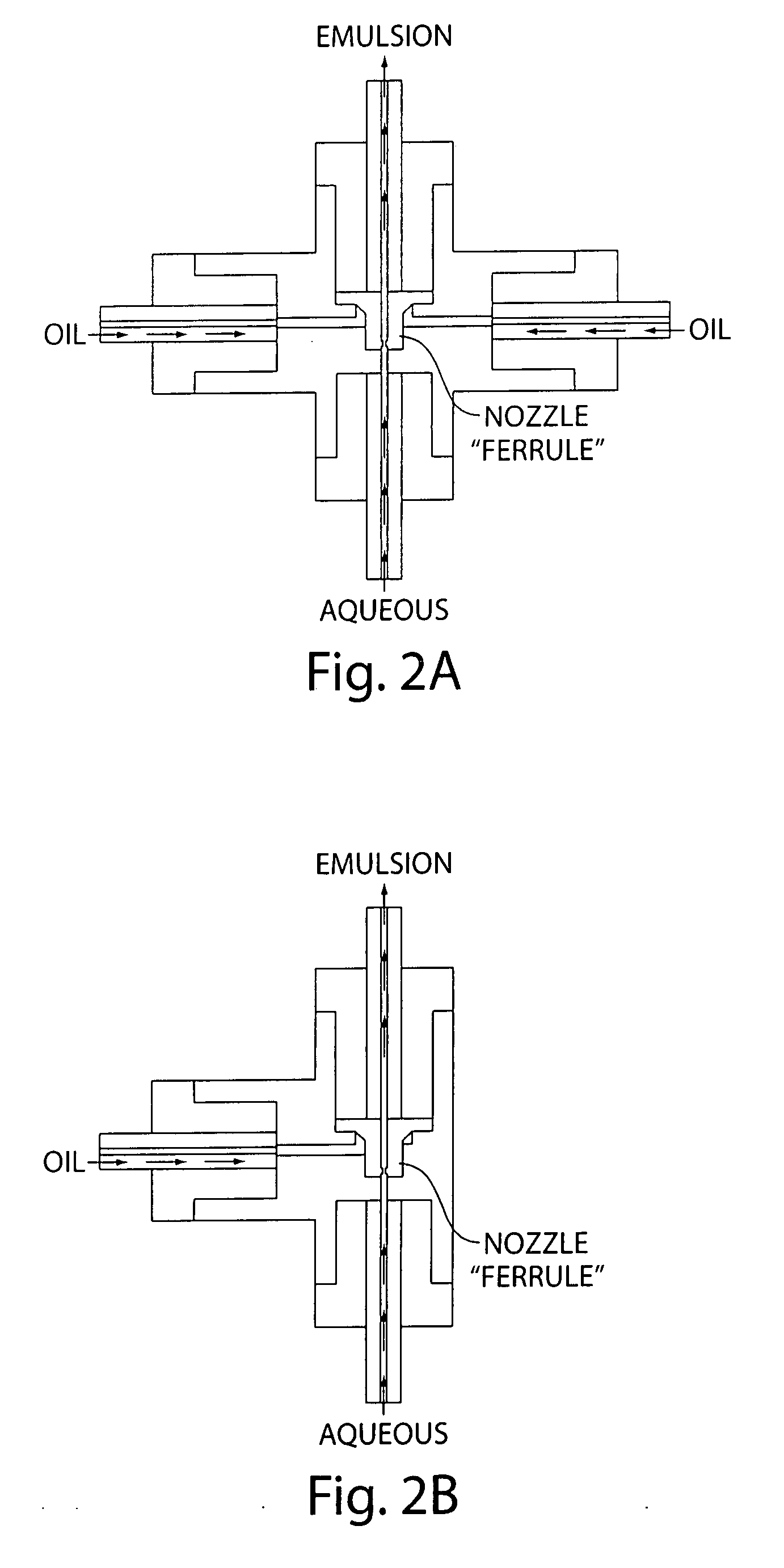
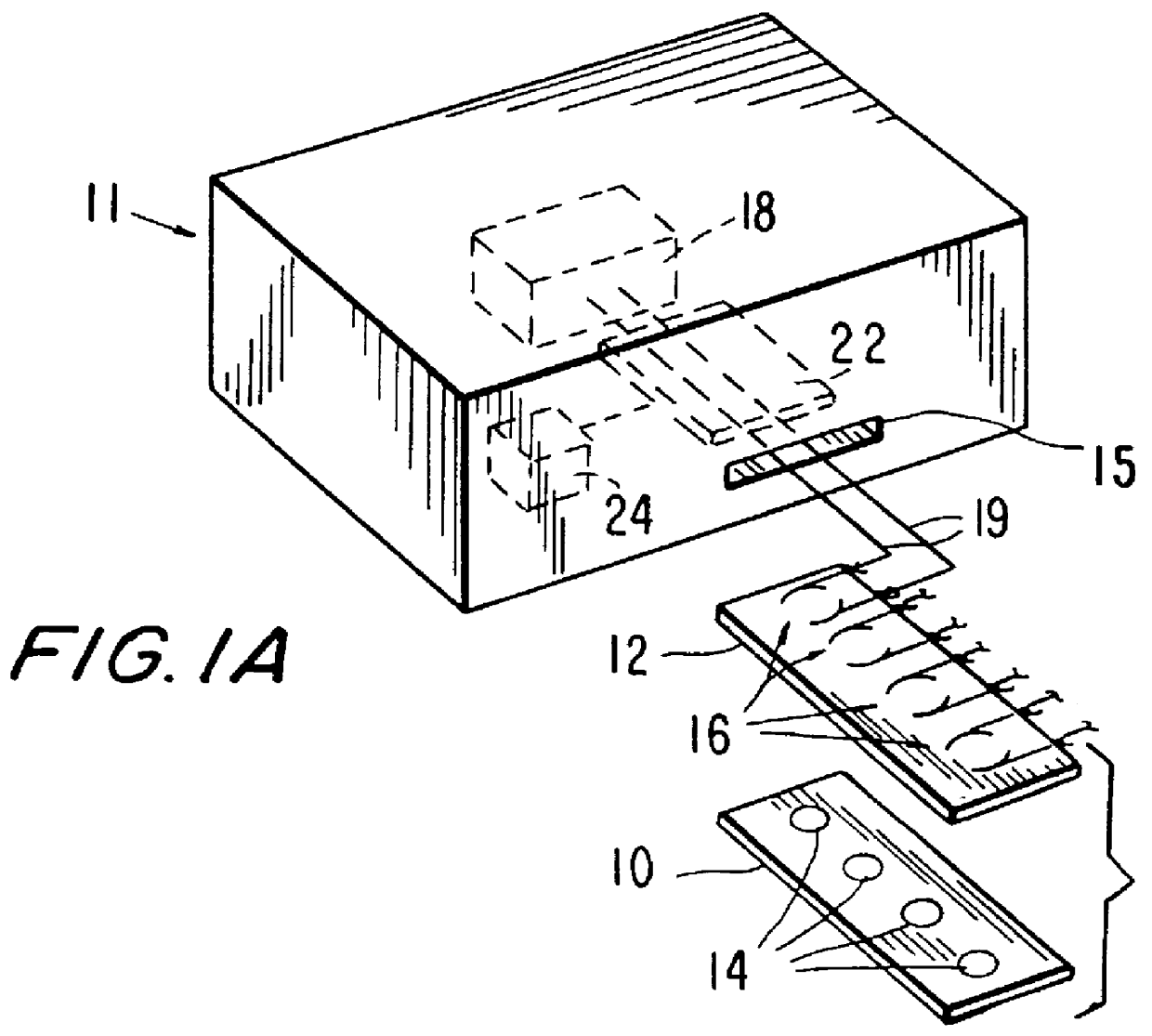
Patents
Literature
1679results about "Analysis by electrical excitation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfluidic devices
InactiveUS20080003142A1Quickly and effectively and inexpensivelyDielectrophoresisHeating or cooling apparatusEngineering
Owner:BIO RAD LAB INC
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6066448AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Systems and devices for sequence by synthesis analysis
ActiveUS20100111768A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsDNAComputational biology
The present invention comprises systems and devices for sequencing of nucleic acid, such as short DNA sequences from clonally amplified single-molecule arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
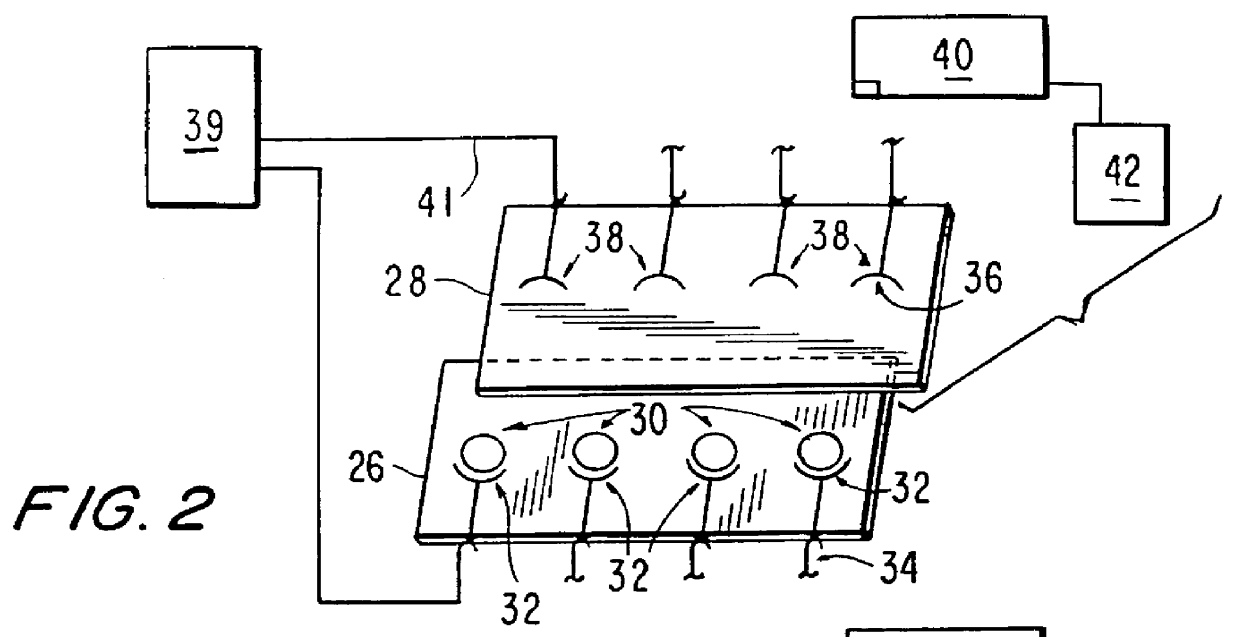
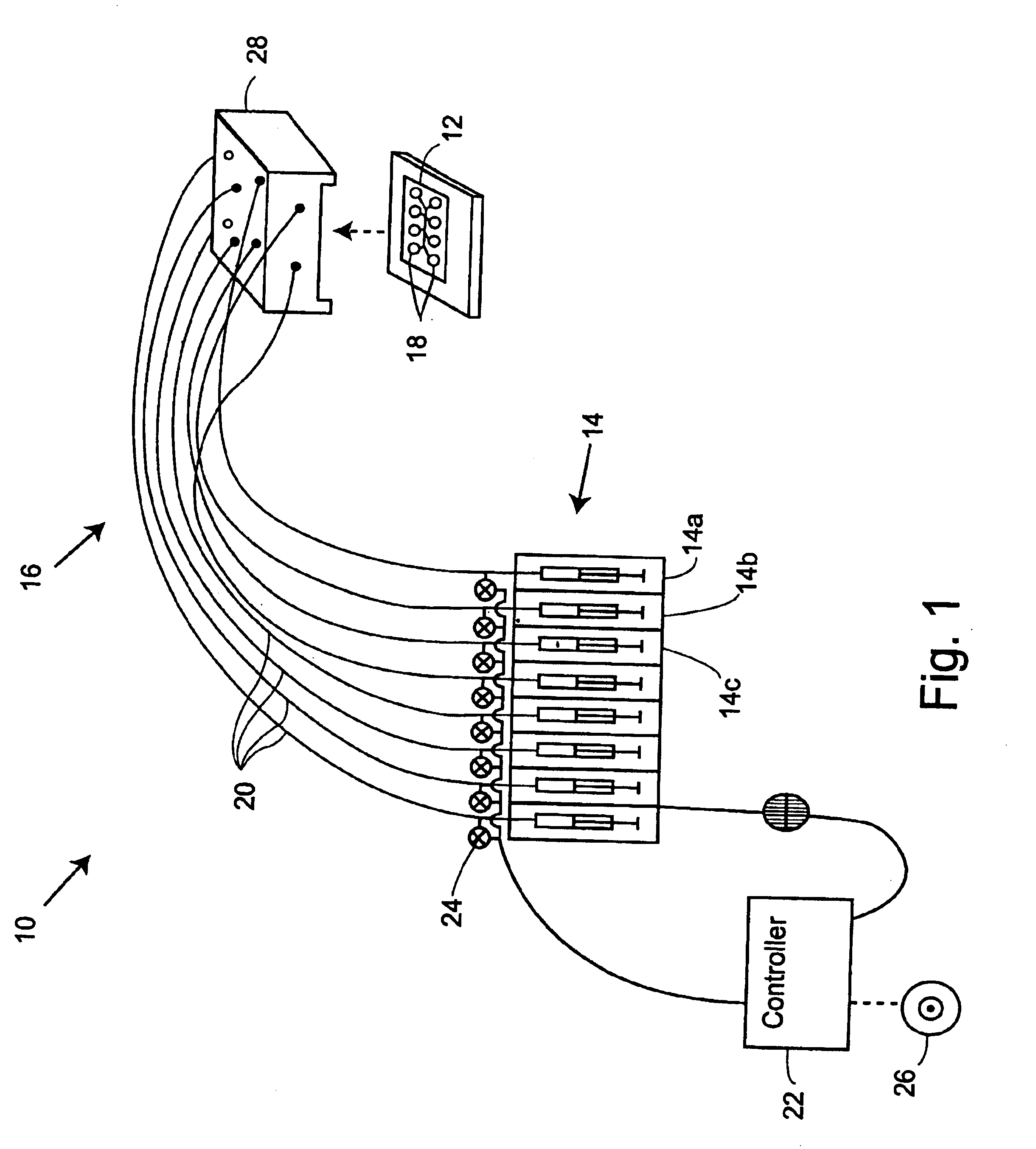
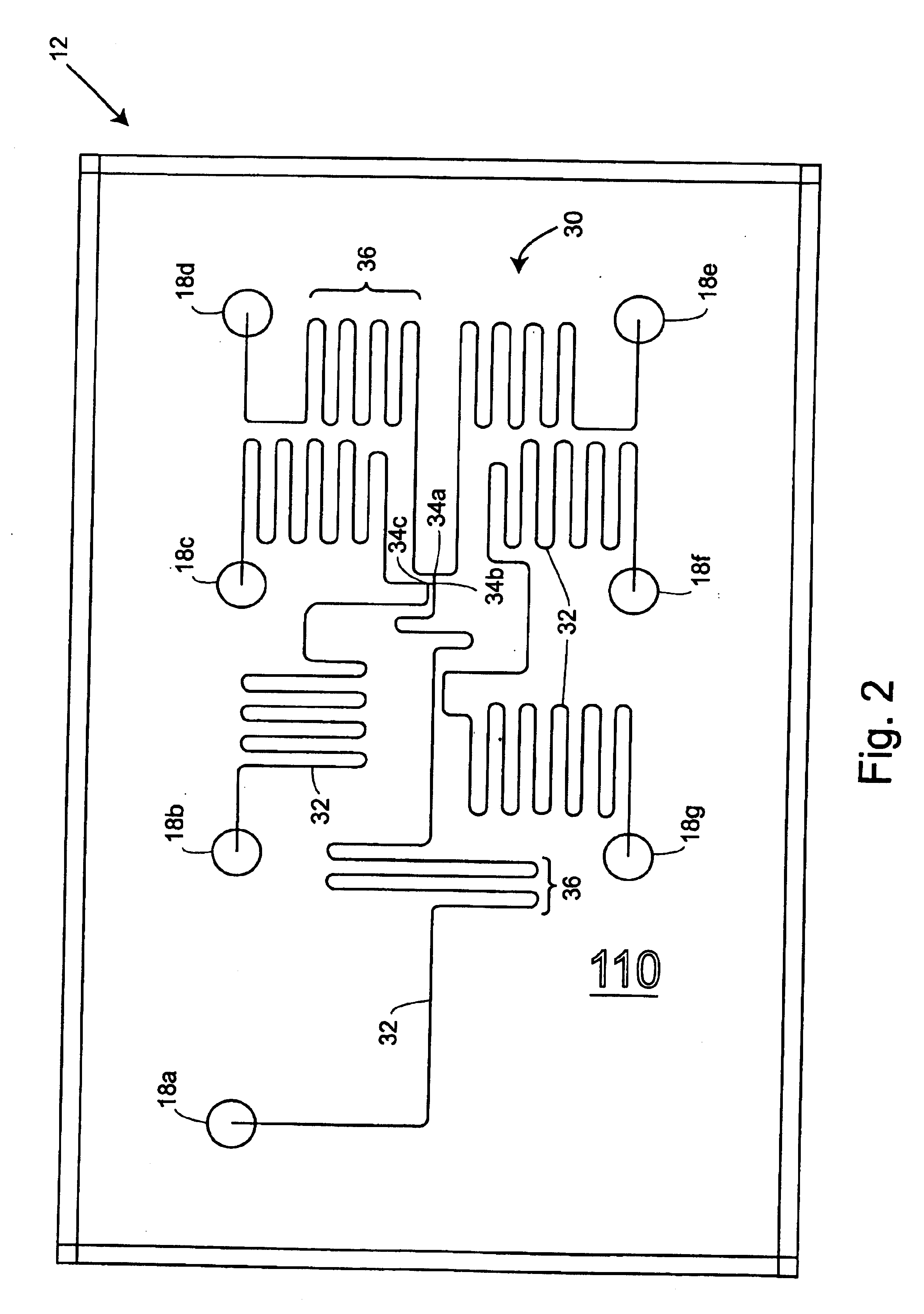
Assay plates, reader systems and methods for luminescence test measurements
ActiveUS20040022677A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease assayBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Optical determination of ph and glucose
InactiveUS20080188722A1Biological material analysisAnalysis by electrical excitationAnalyteSingle indicator
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to an optical sensor capable of measuring two analytes simultaneously with a single indicator system. In preferred embodiments, the sensor comprises a fluorescent dye having acid and base forms that facilitate ratiometric pH sensing, wherein the dye is further associated with a glucose binding moiety and configured to generate a signal that varies in intensity with the concentration of glucose.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Modular assay plates, reader systems and methods for test measurements
ActiveUS20050142033A1Improve collection efficiencyIncrease assayAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6090545AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
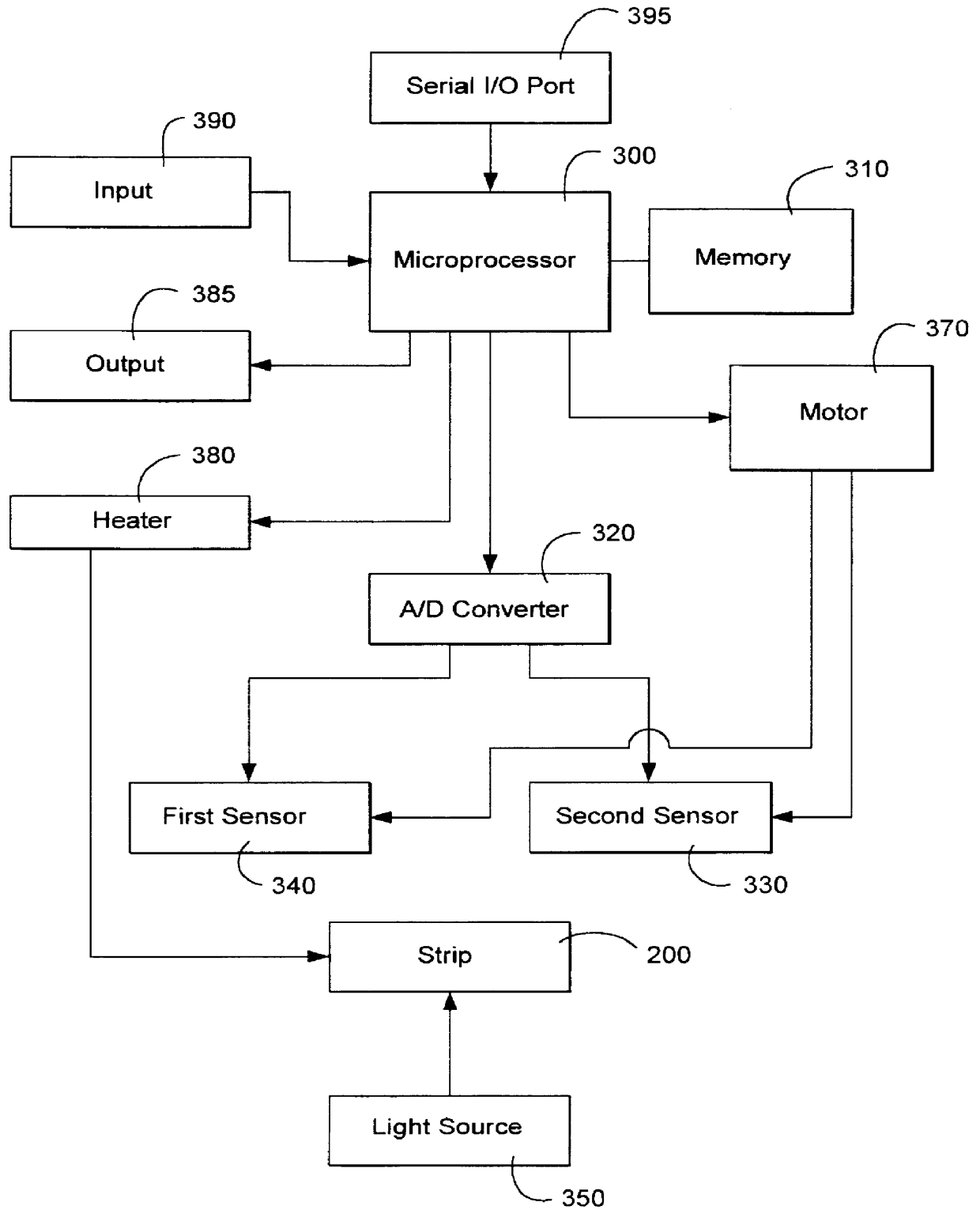
Method and apparatus for performing a lateral flow assay
InactiveUS6136610AThe result is accurateEasy to controlBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringTest strips
An embodiment of the present invention provides a method for performing a lateral flow assay. The method includes depositing a sample on a test strip at an application region, detecting a first detection signal arising from the test strip in the first detection zone, and generating a baseline for the first measurement zone by interpolating between values of the detection signal outside of the first measurement zone and inside of the first detection zone. The method may include locating a beginning boundary and an ending boundary for the first measurement zone on the test strip. Additional detection zones having measurement zones may also be incorporated with the embodiment.
Owner:RELIA BIOTECH SHENZHEN LTD
Systems and devices for sequence by synthesis analysis
ActiveUS8241573B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid sequencingDNA
The present invention comprises systems and devices for sequencing of nucleic acid, such as short DNA sequences from clonally amplified single-molecule arrays.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Multi-reservoir pressure control system
InactiveUS6915679B2Sufficient oscillationAccurate and stable and reliable assayAnalysis by electrical excitationLaboratory glasswaresFluid transportFlow resistivity
Improved microfluidic devices, systems, and methods allow selective transportation of fluids within microfluidic channels of a microfluidic network by applying, controlling, and varying pressures at a plurality of reservoirs. Modeling the microfluidic network as a series of nodes connected together by channel segments and determining the flow resistance characteristics of the channel segments may allow calculation of fluid flows through the channel segments resulting from a given pressure configuration at the reservoirs. To effect a desired flow within a particular channel or series of channels, reservoir pressures may be identified using the network model. Viscometers or other flow sensors may measure flow characteristics within the channels, and the measured flow characteristics can be used to calculate pressures to generate a desired flow. Multi-reservoir pressure modulator and pressure controller systems can optionally be used in conjunction with electrokinetic or other fluid transport mechanisms.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
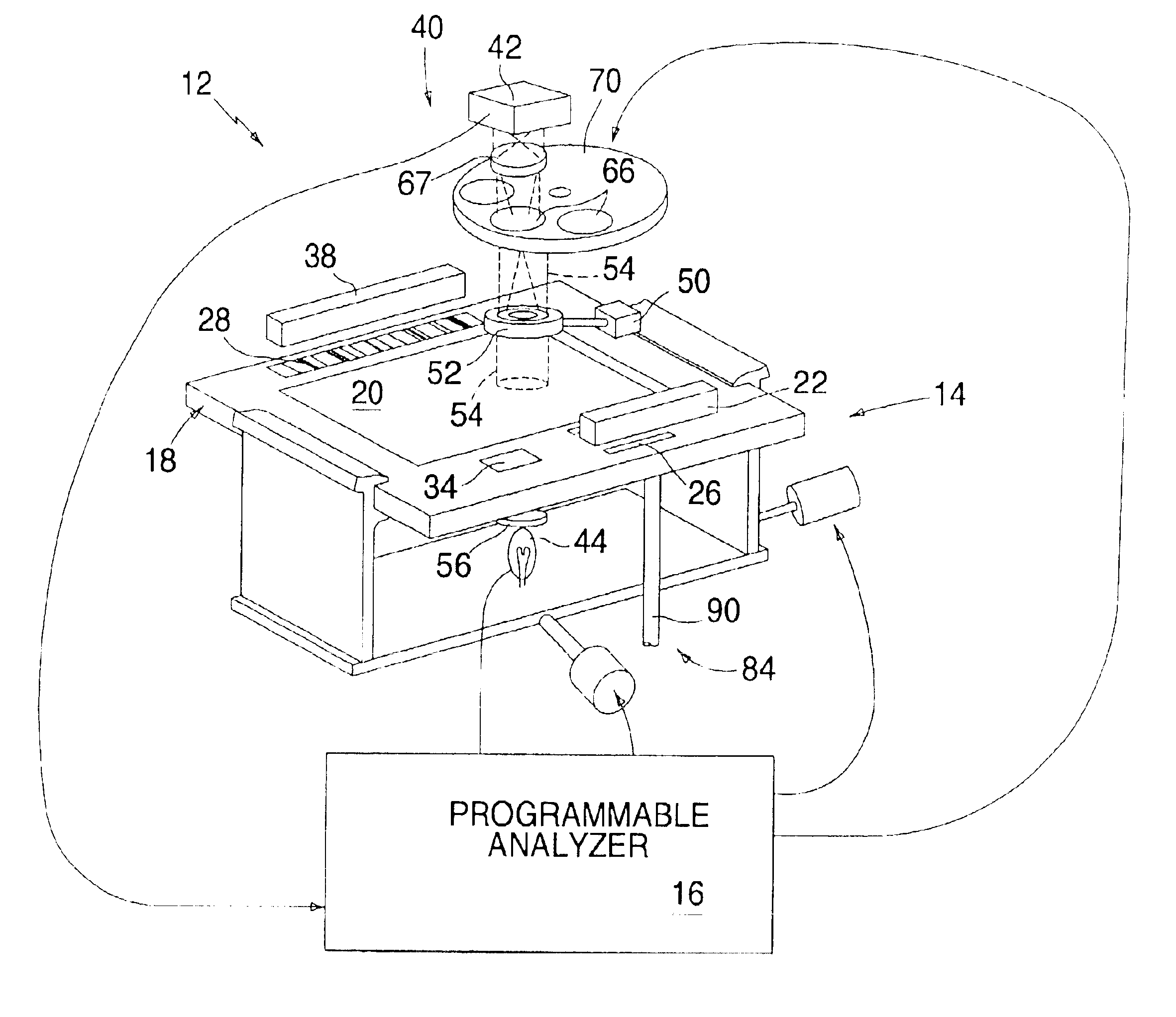
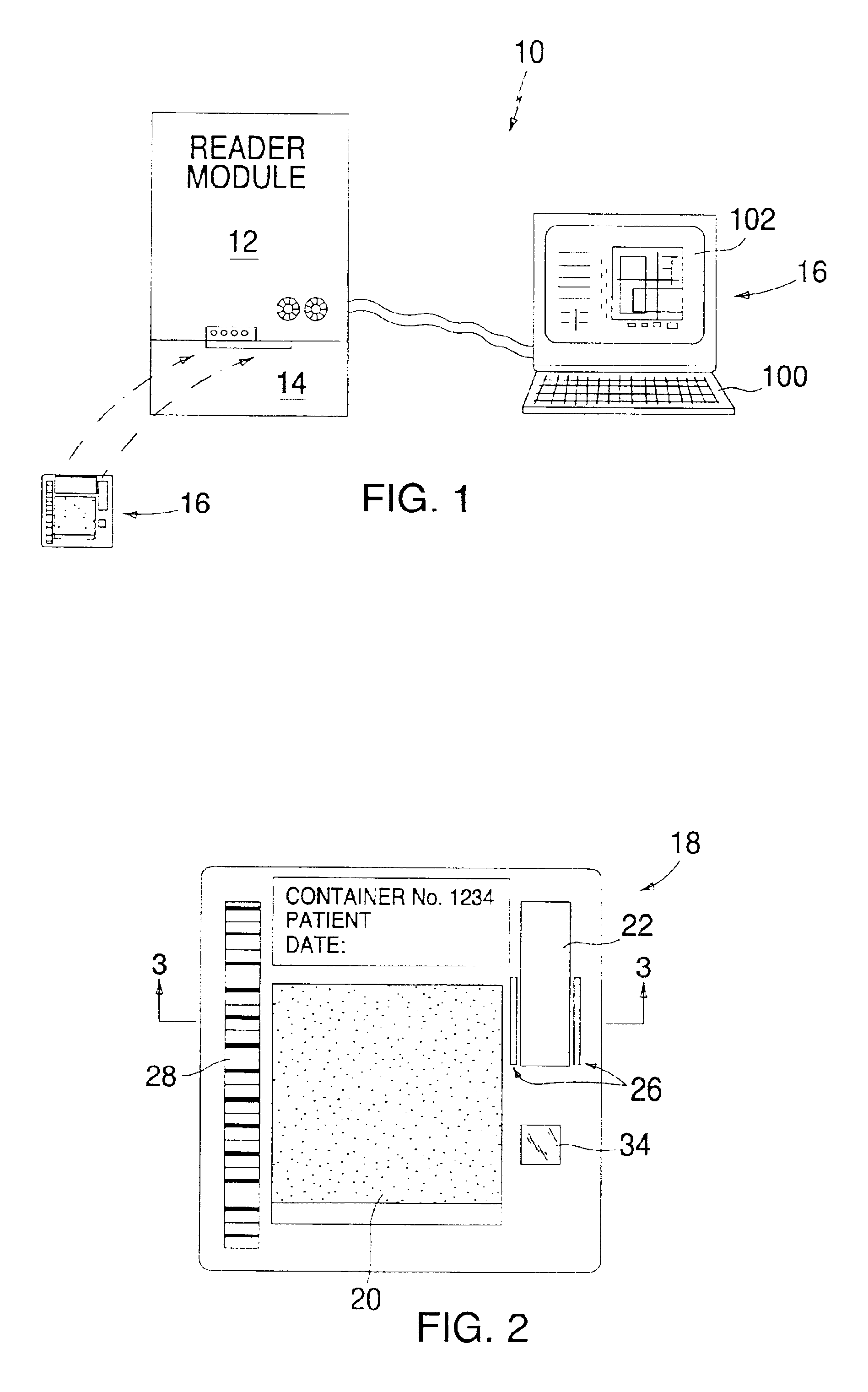
Apparatus for analyzing biologic fluids
InactiveUS6866823B2Low costReduce spacingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImage dissectorImage conversion
An apparatus for analyzing a sample of biologic fluid quiescently residing within a chamber is provided. The apparatus includes a light source, a positioner, a mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field, and an image dissector. The light source is operable to illuminate a sample field of known, or ascertainable, area. The positioner is operable to selectively change the position of one of the chamber or the light source relative to the other, thereby permitting selective illumination of all regions of the sample. The mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field can determine the volume of a sample field illuminated by the light source. The image dissector is operable to convert an image of light passing through or emanating from the sample field into an electronic data format.
Owner:WARDLAW PARTNERS +2
Automated microfabrication-based biodetector
InactiveUS6878755B2Reduce riskHeating or cooling apparatusMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation processingChannel coupling
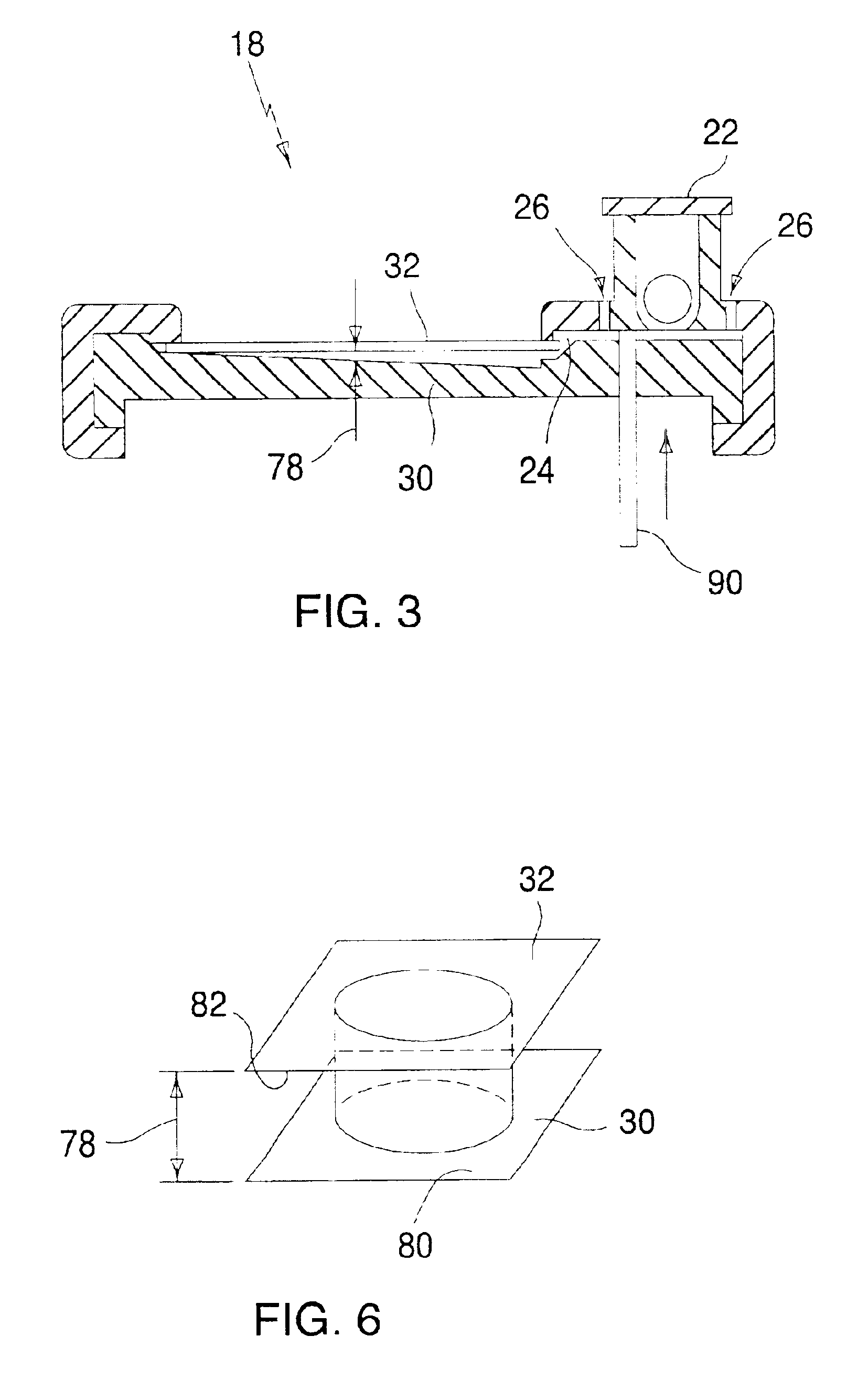
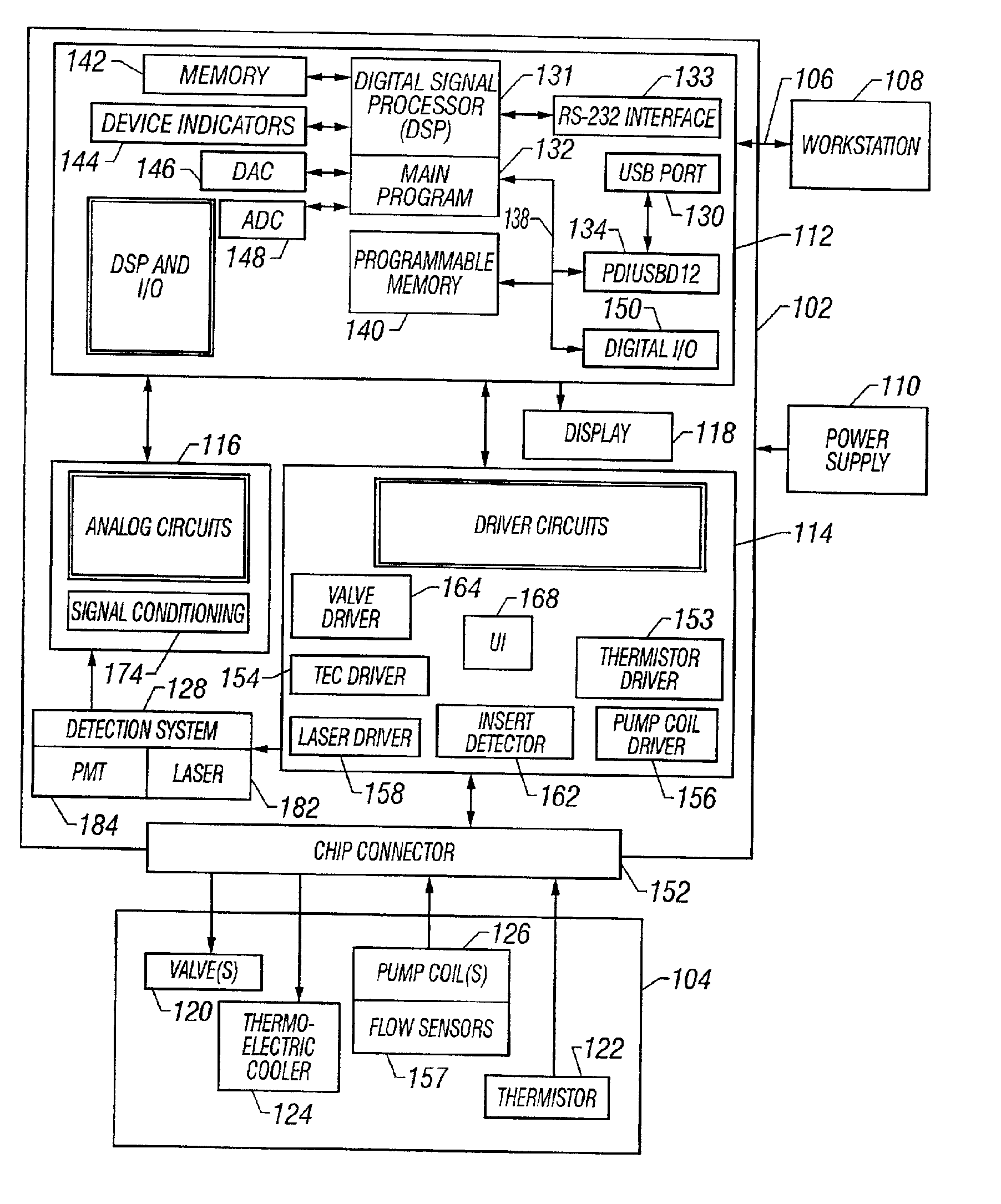
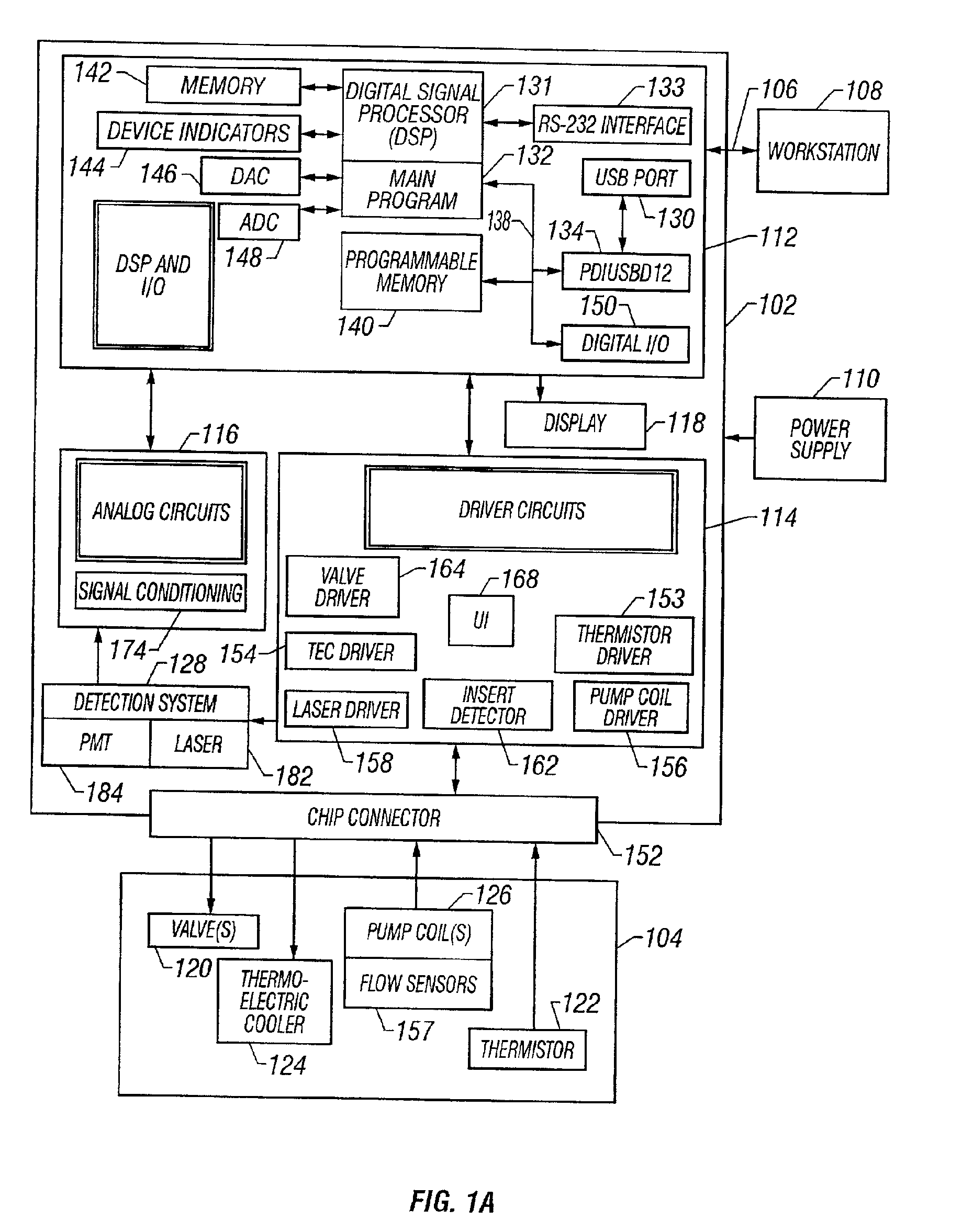
A system, apparatus, and method for processing a sample for chemical and / or biological analysis, and detecting one or more target substances. A first system of microfabricated components includes at least a reservoir and a channel, and a second system of detection components including at least a lens. The lens is focused on a sensing platform of the first system. The sensing platform is coupled to the reservoir by the channel. Various types of detection systems can be utilized with the present invention including fluorescence detection systems with a laser that is positioned to illuminate a sample in the sensing platform. The microfabricated components include one or more pumps, valves, mixers, and filters. A thermoelectric cooler can be positioned to control the temperature of at least one of the microfabricated components. A variety of component configurations can be implemented, and a variety of different processes can be performed, depending on the configuration of components. The device can also be networked with other information processing devices and share data regarding substances detected from the sample.
Owner:MICROGEN SYST
Assay plates, reader systems and methods for luminescence test measurements
InactiveUS20050052646A1Improve collection efficiencyEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryTest measurementBiology
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
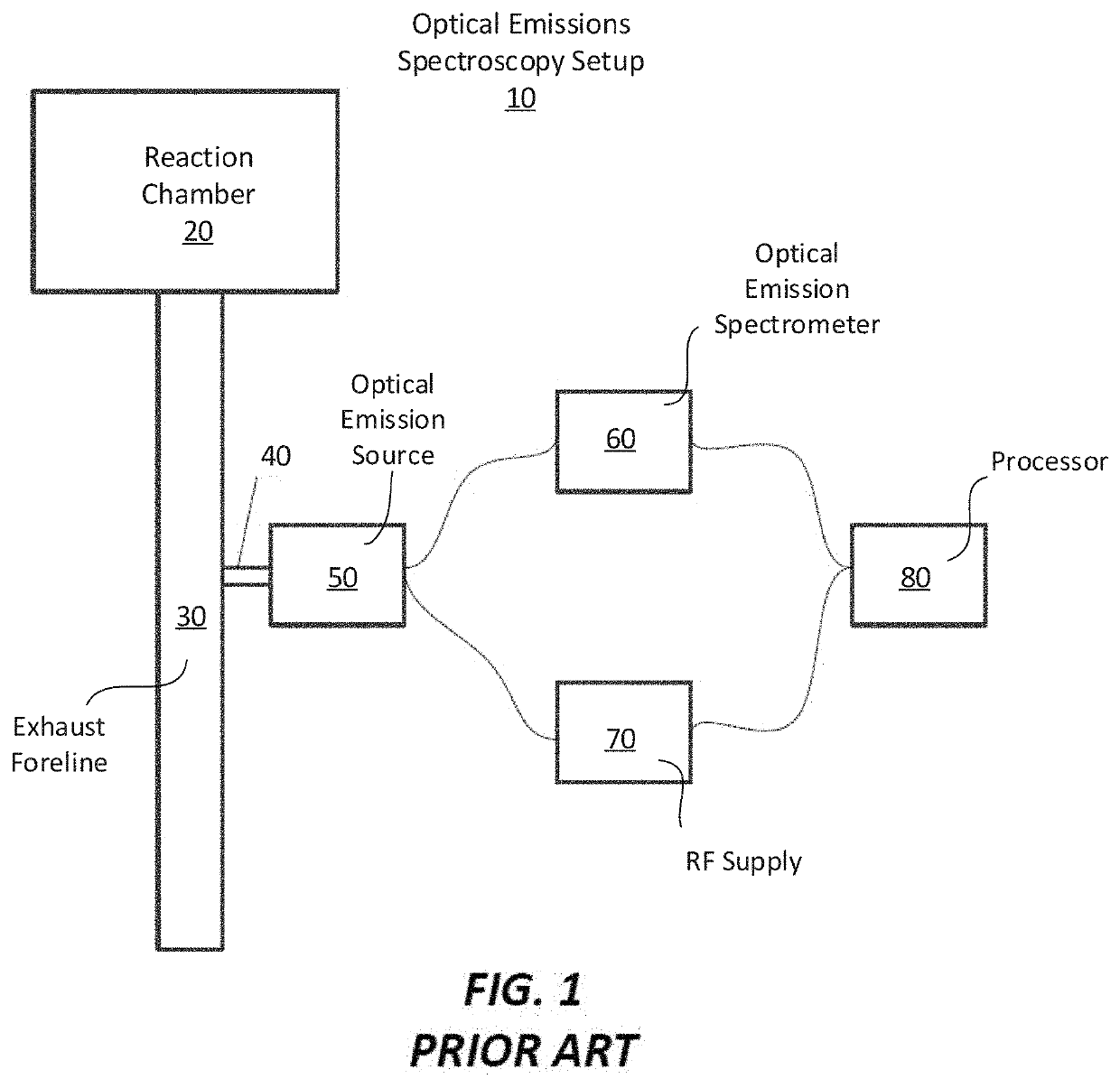
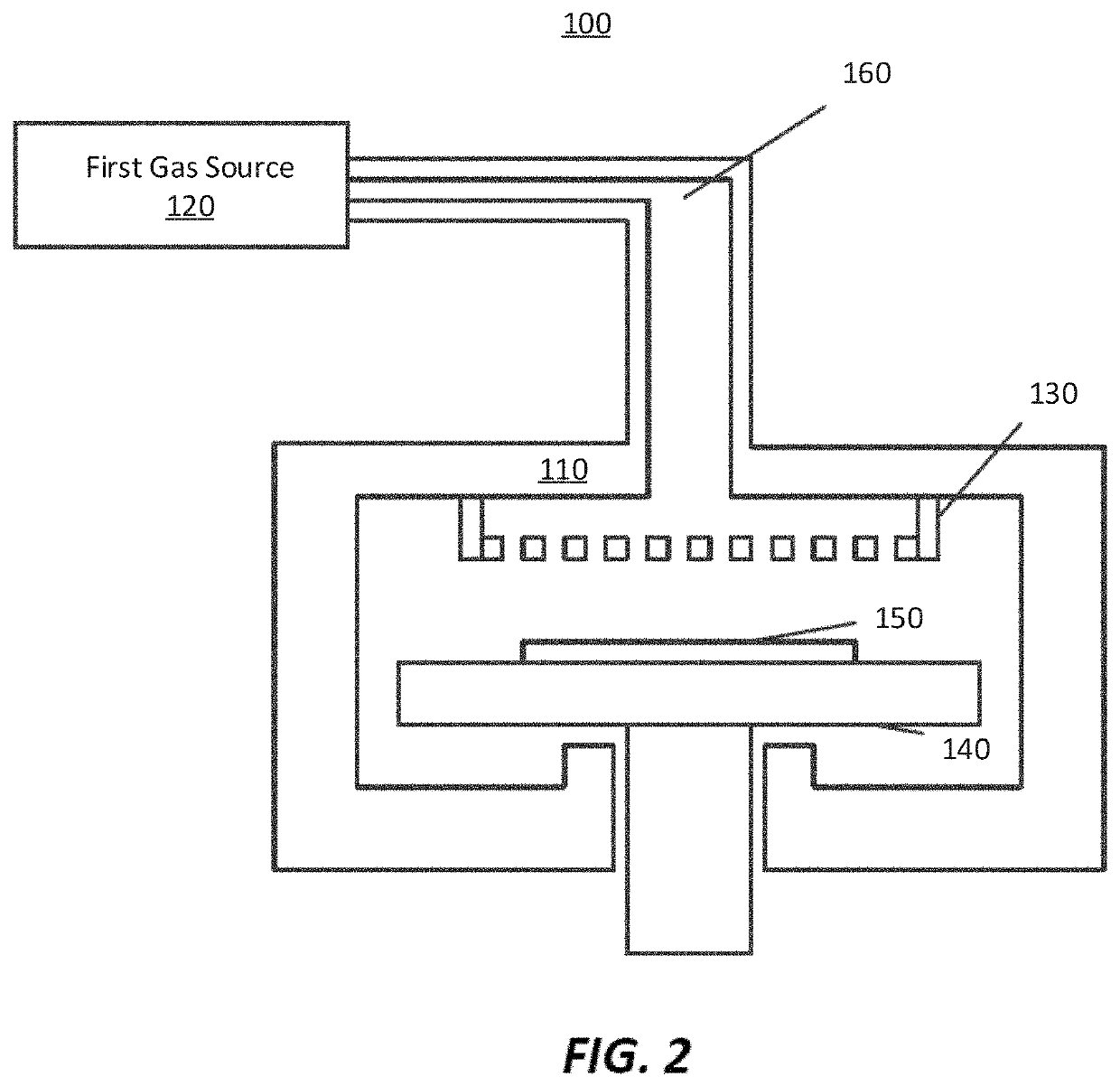
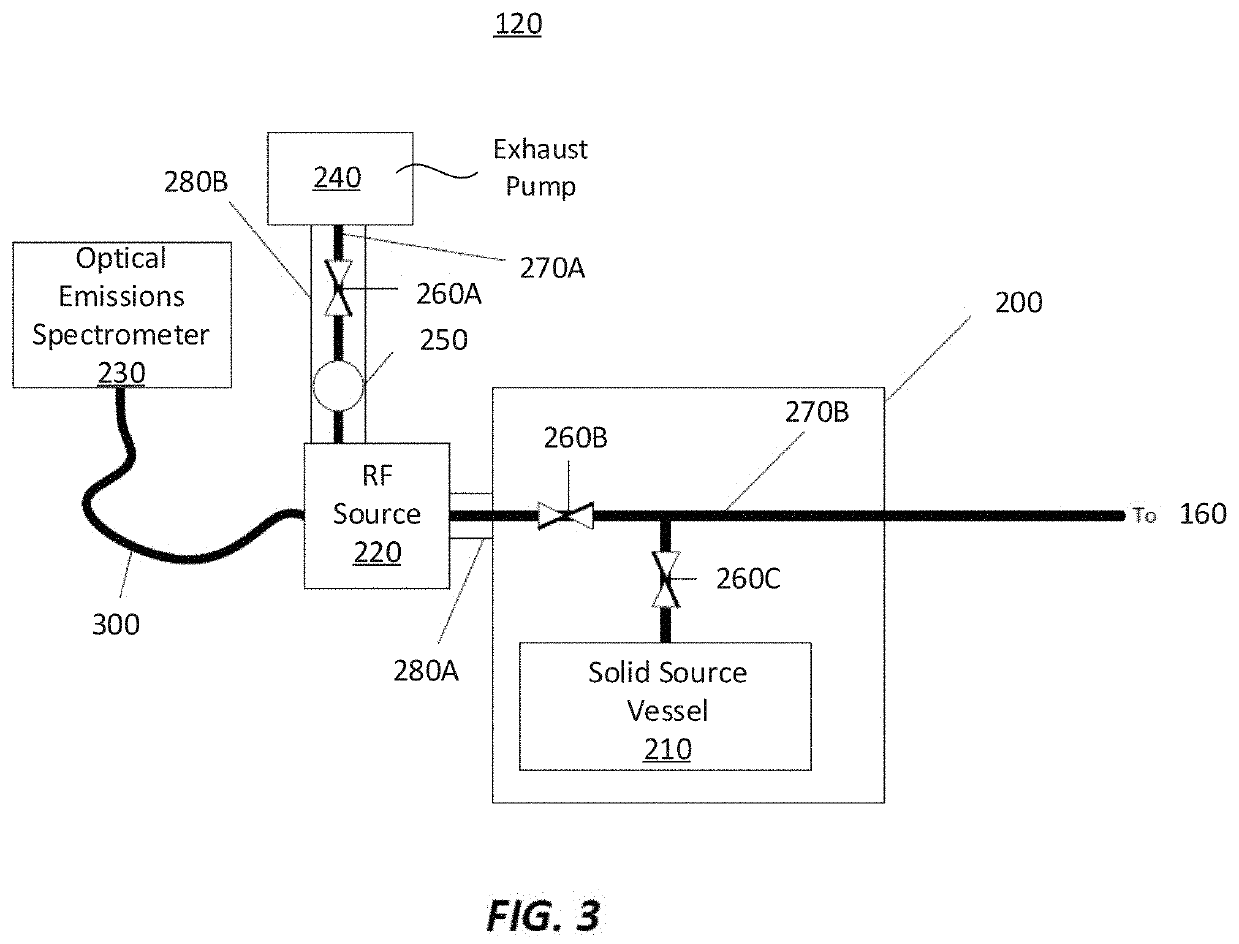
Apparatus for detecting or monitoring for a chemical precursor in a high temperature environment
ActiveUS20190264324A1Emission spectroscopyElectric discharge tubesOptical Emission SpectrometerSmall sample
An apparatus and method are disclosed for monitoring and / or detecting concentrations of a chemical precursor in a reaction chamber. The apparatus and method have an advantage of operating in a high temperature environment. An optical emissions spectrometer (OES) is coupled to a gas source, such as a solid source vessel, in order to monitor or detect an output of the chemical precursor to the reaction chamber. Alternatively, a small sample of precursor can be periodically monitored flowing into the OES and into a vacuum pump, thus bypassing the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Immunoassay fluorometer
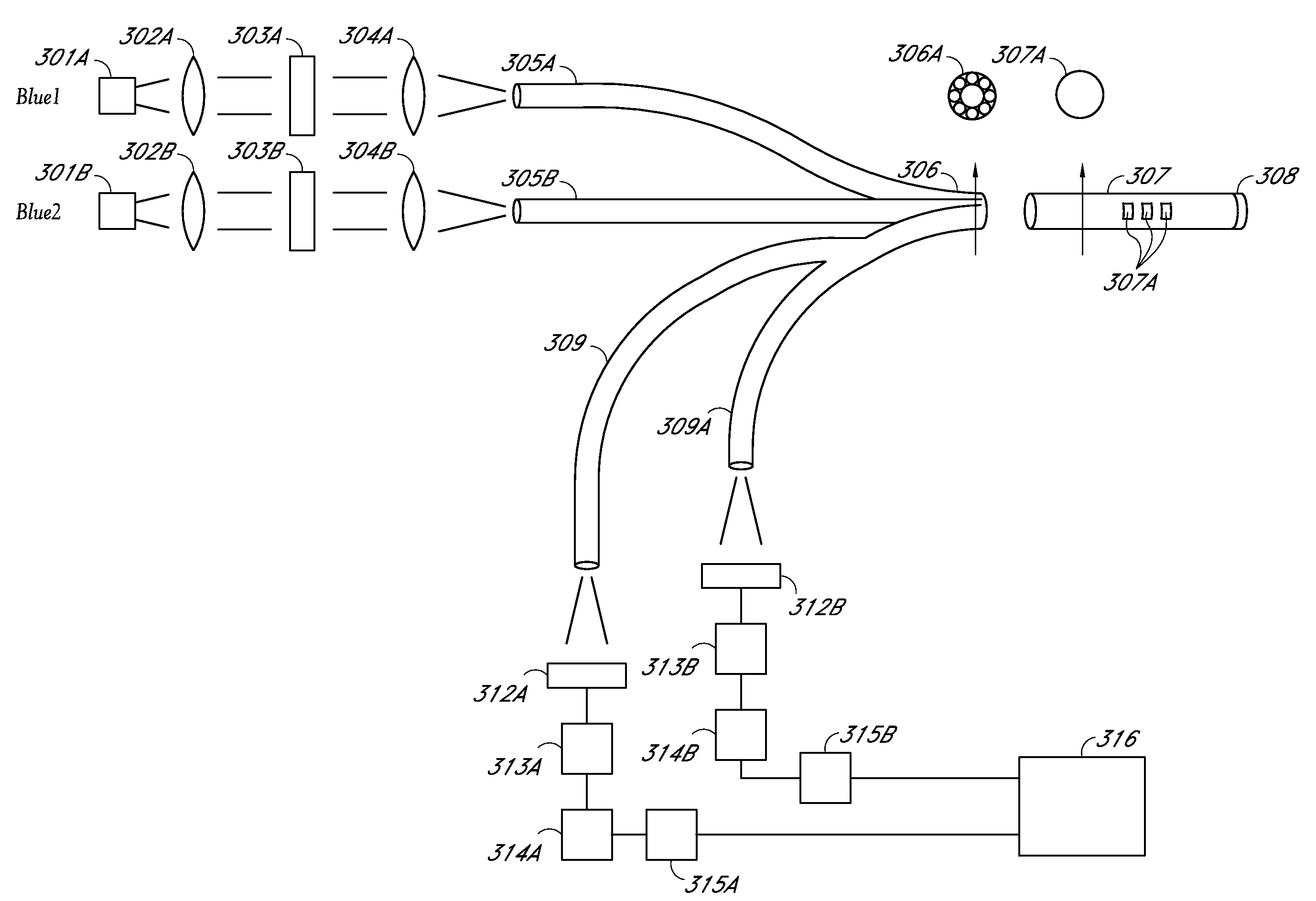
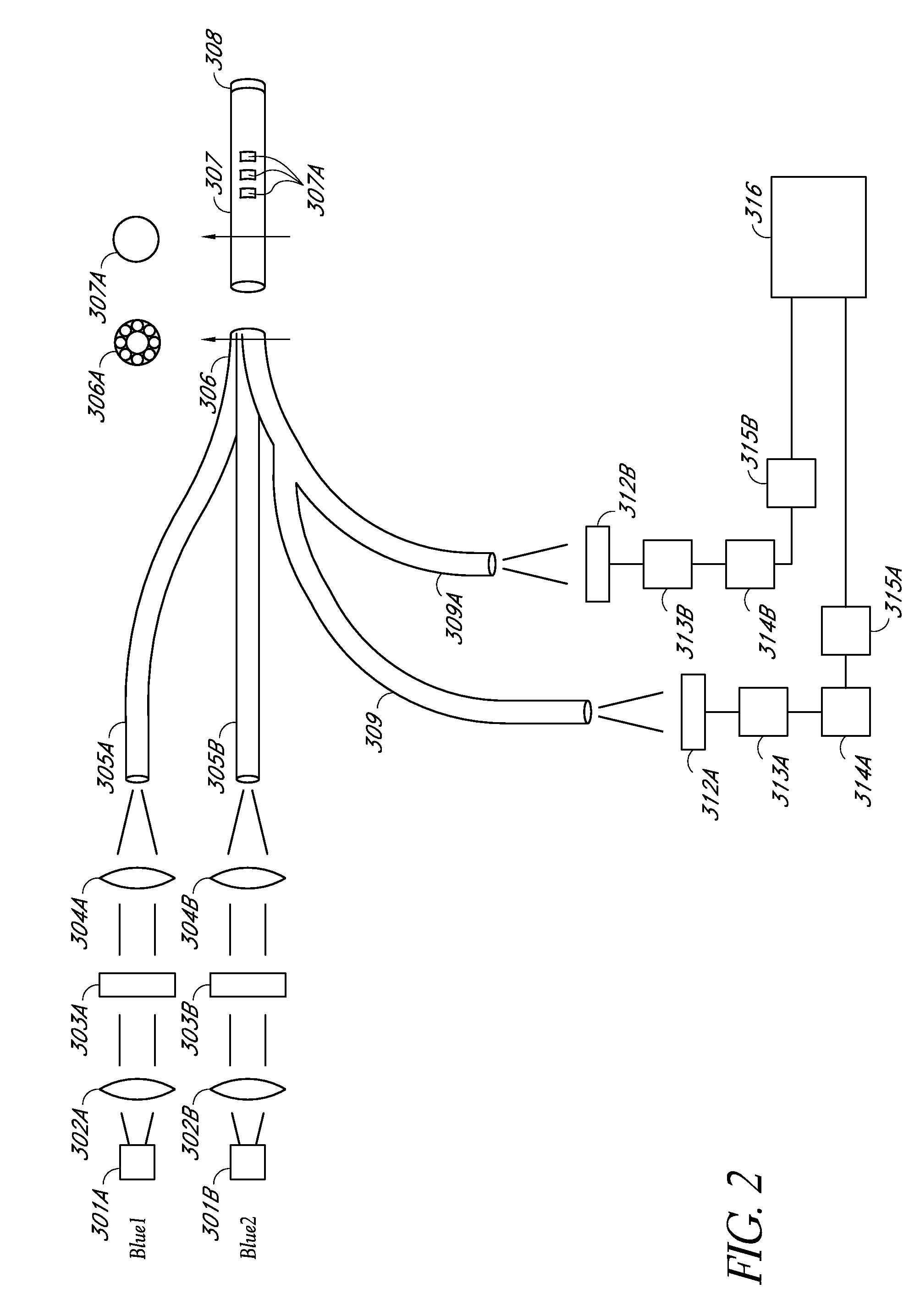
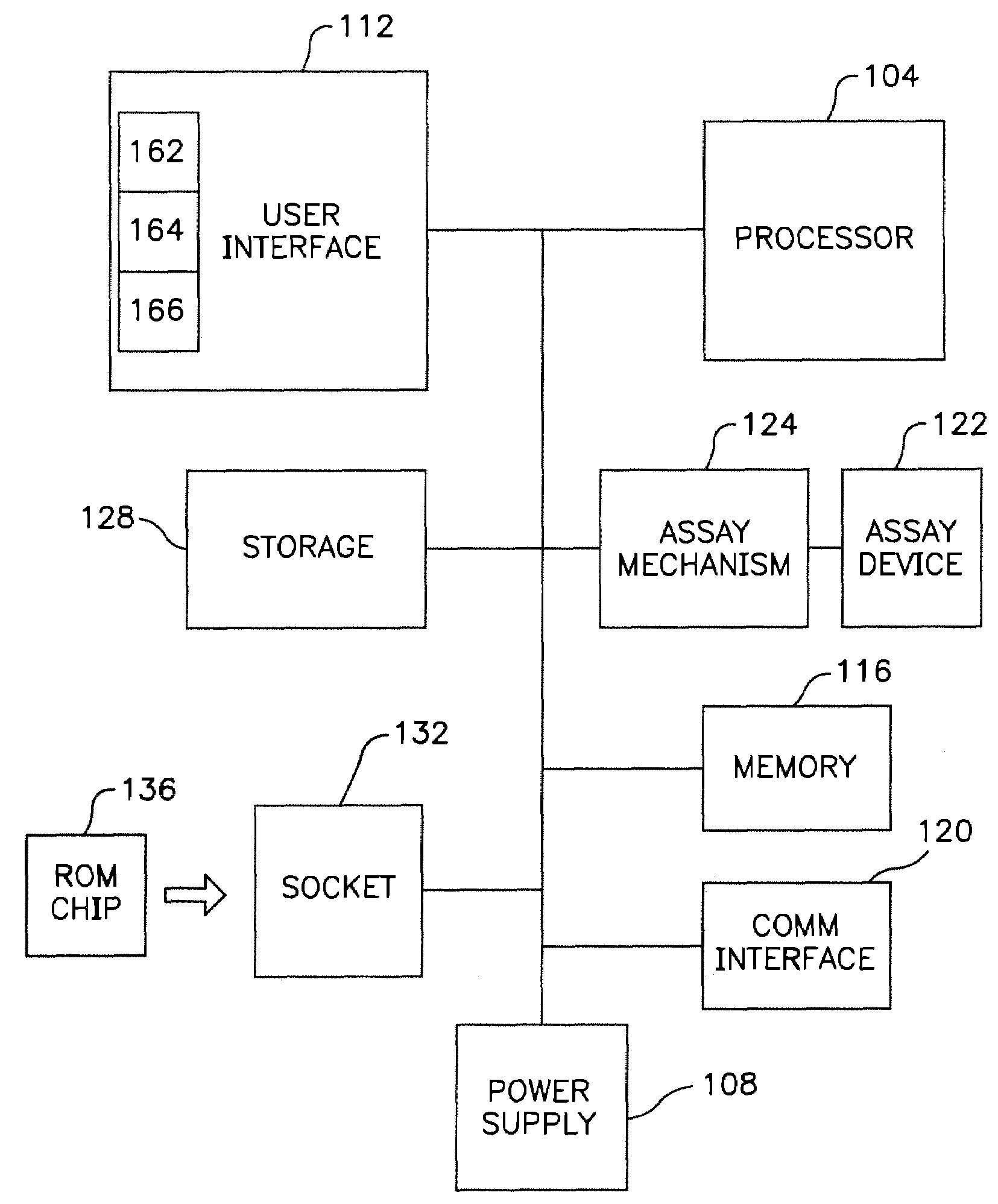
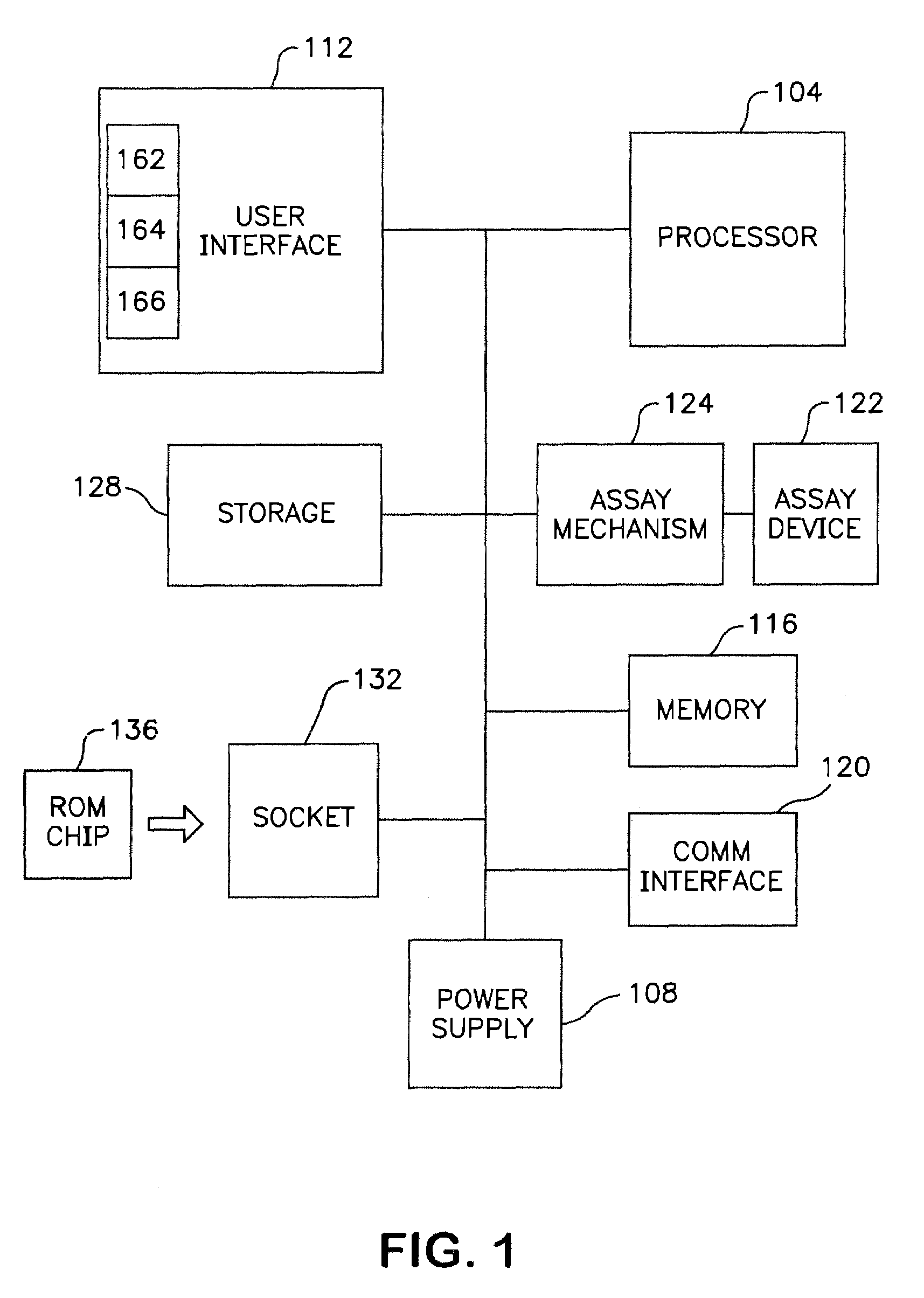
InactiveUS7416700B2Easy accessChance for errorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationCommunication interfaceData set
A fluorometer for sensing the fluorescence of a sample utilizes an optical energy source for exciting a sample to be tested and an optical energy detector for detecting the emitted energy from the excited sample. Drive electronics are used for positioning the sample with respect to the optical components allowing a plurality of sample regions to be tested. A processor is utilized to control the operation of the test in accordance with test instructions and for processing the emitted energy detected from the sample to determine test results. A ROM chip socket accepts a plurality of ROM chips, wherein each ROM chip stores test data sets for one or more test types to be performed. ROM chips can be swapped to allow the fluorometer to be configured and reconfigured to perform a plurality of different tests. A communications interface facilitates the sharing of test information between the fluorometer and external entities.
Owner:BIOSITE INC
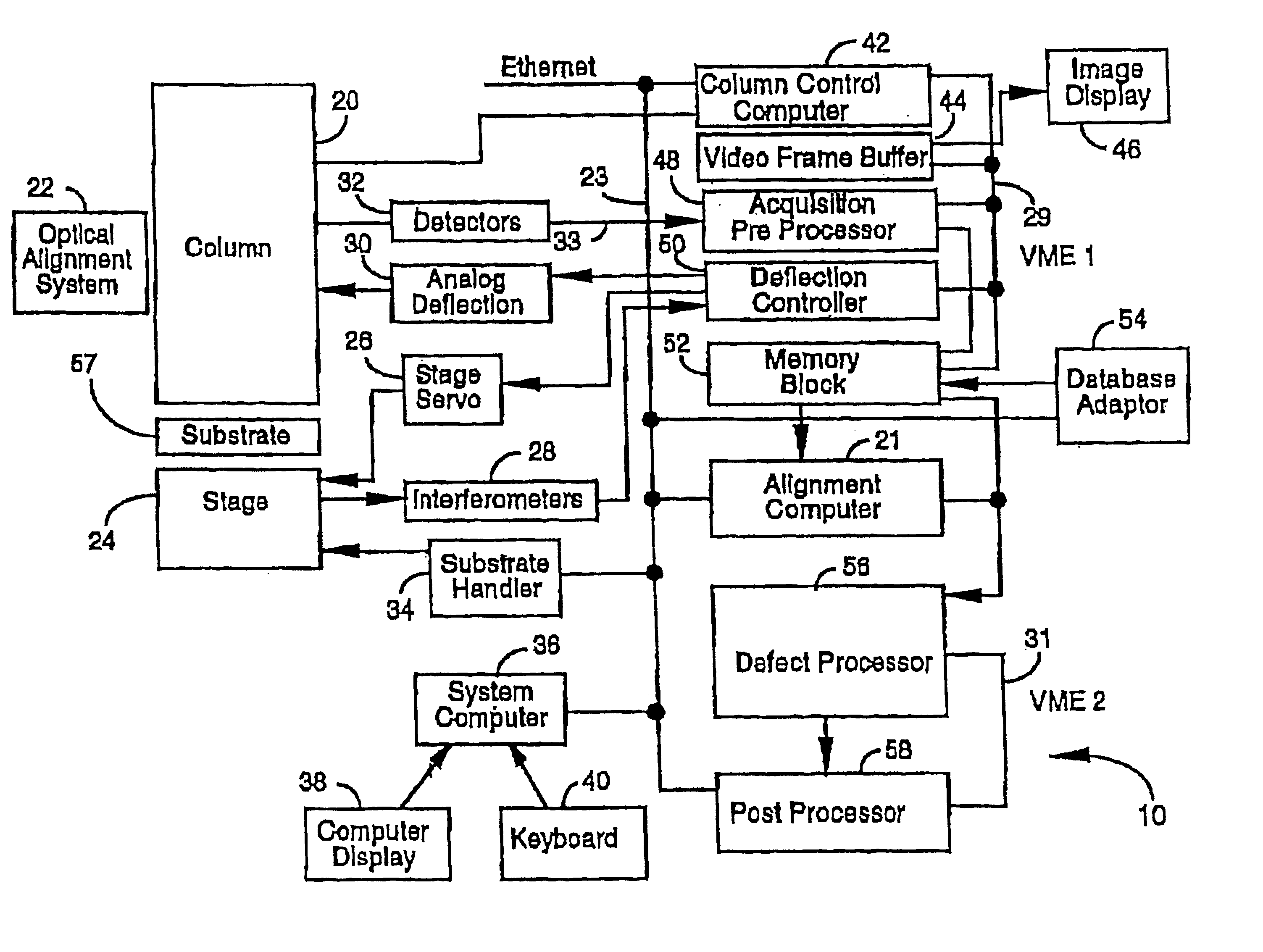
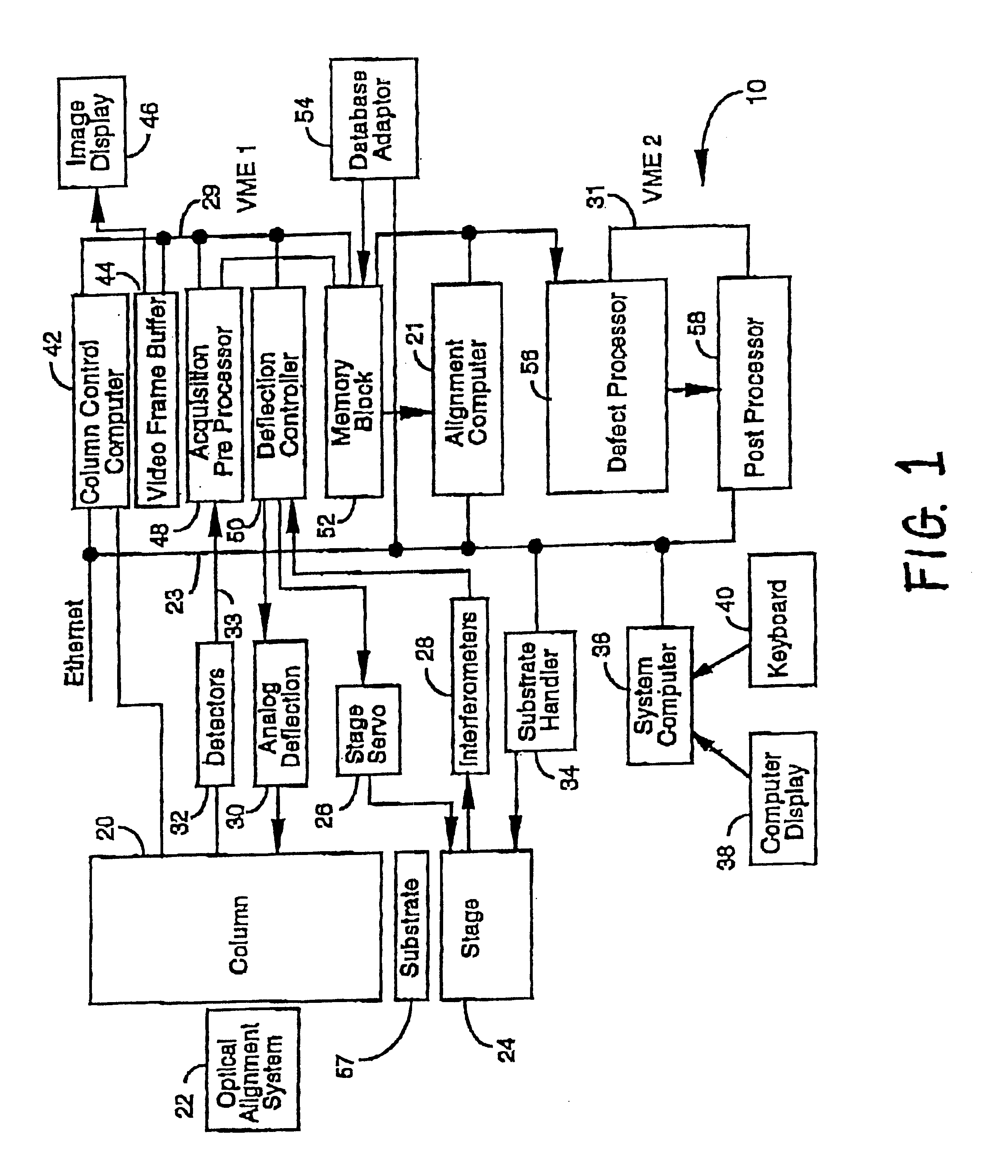
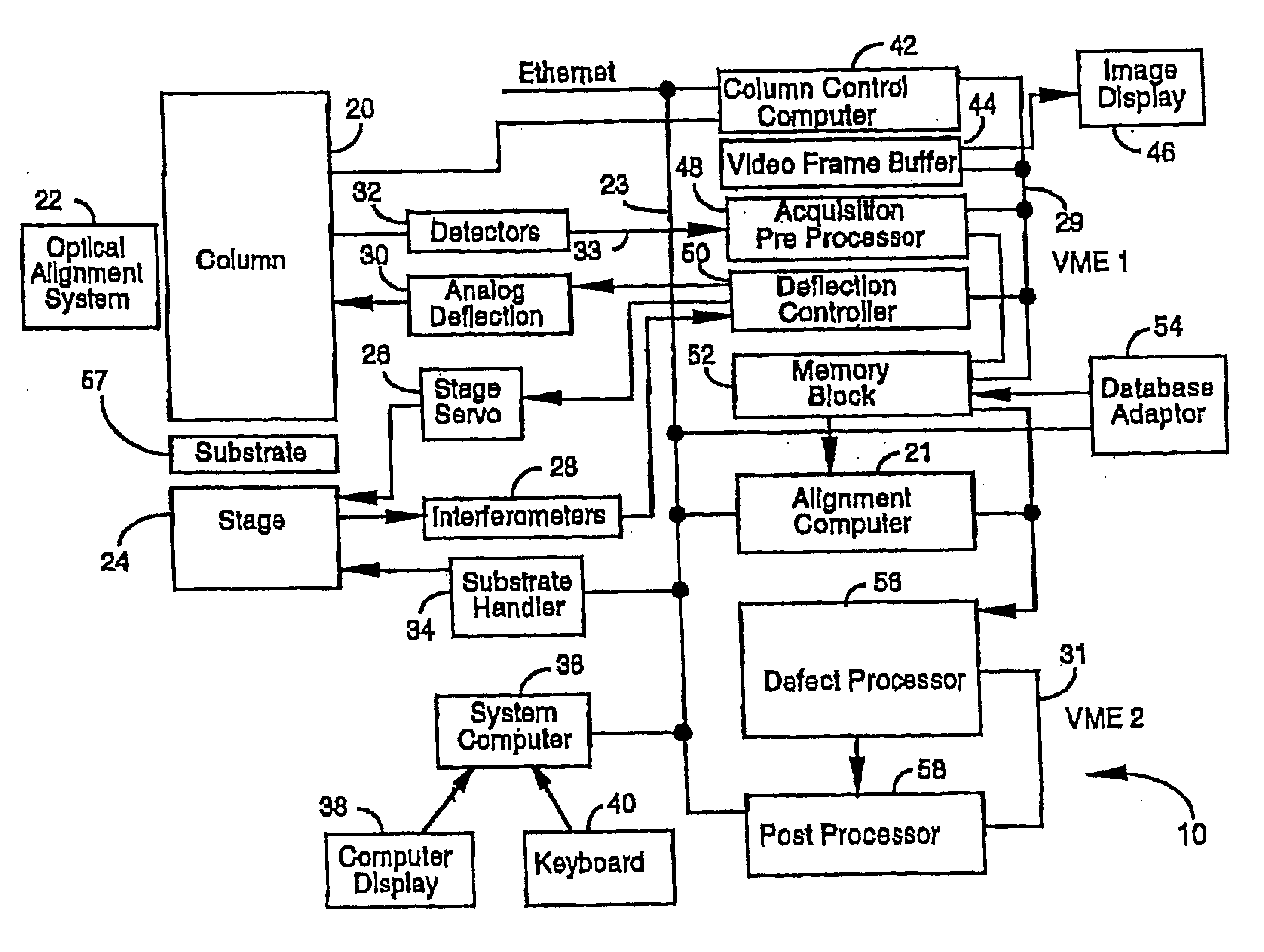
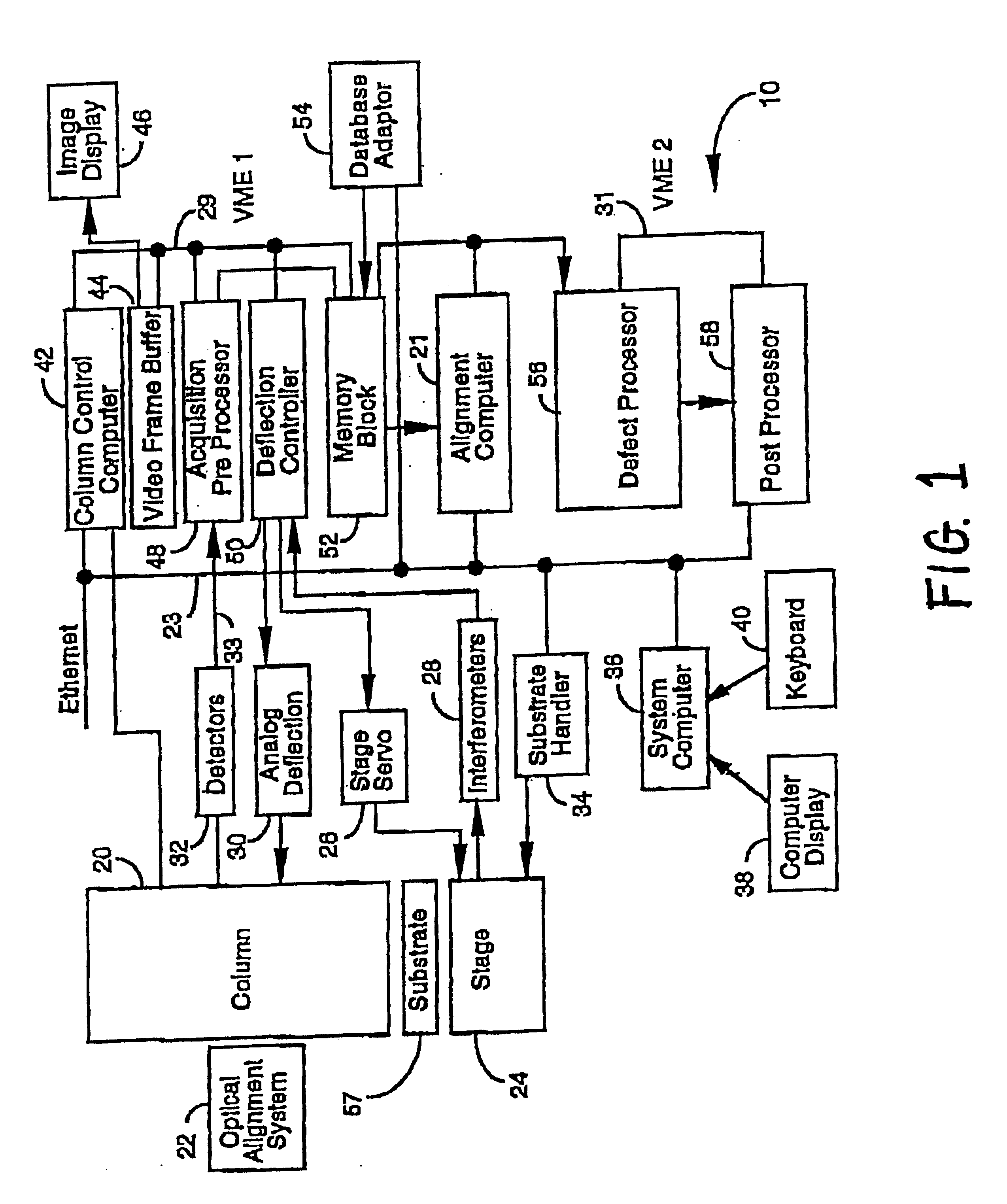
Stepper type test structures and methods for inspection of semiconductor integrated circuits
InactiveUS6633174B1Reduce pressureNanotechSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementEngineeringSemiconductor
Disclosed is a method of inspecting a sample. The method includes moving to a first field associated with a first group of test structures. The first group of test structures are partially within the first field. The method further includes scanning the first field to determine whether there are any defects present within the first group of test structures. When it is determined that there are defects within the first group of test structures, the method further includes repeatedly stepping to areas and scanning such areas so as to determine a specific defect location within the first group of test structures. A suitable test structure for performing this method is also disclosed.< / PTEXT>
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Apparatus for detecting or monitoring for a chemical precursor in a high temperature environment
ActiveUS20210180189A1Emission spectroscopyElectric discharge tubesOptical Emission SpectrometerOptical spectrometer
An apparatus and method are disclosed for monitoring and / or detecting concentrations of a chemical precursor in a reaction chamber. The apparatus and method have an advantage of operating in a high temperature environment. An optical emissions spectrometer (OES) is coupled to a gas source, such as a solid source vessel, in order to monitor or detect an output of the chemical precursor to the reaction chamber. Alternatively, a small sample of precursor can be periodically monitored flowing into the OES and into a vacuum pump, thus bypassing the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
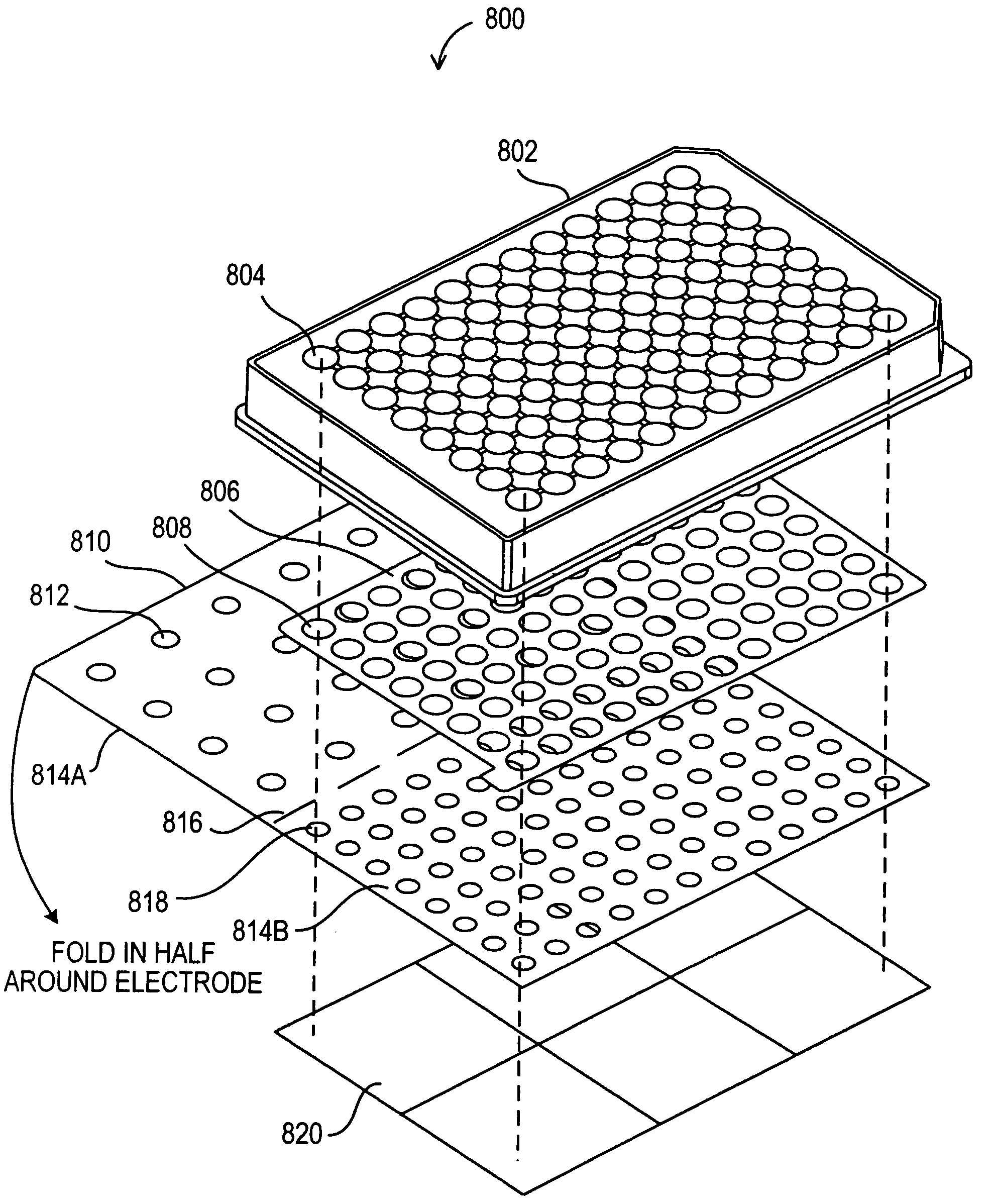
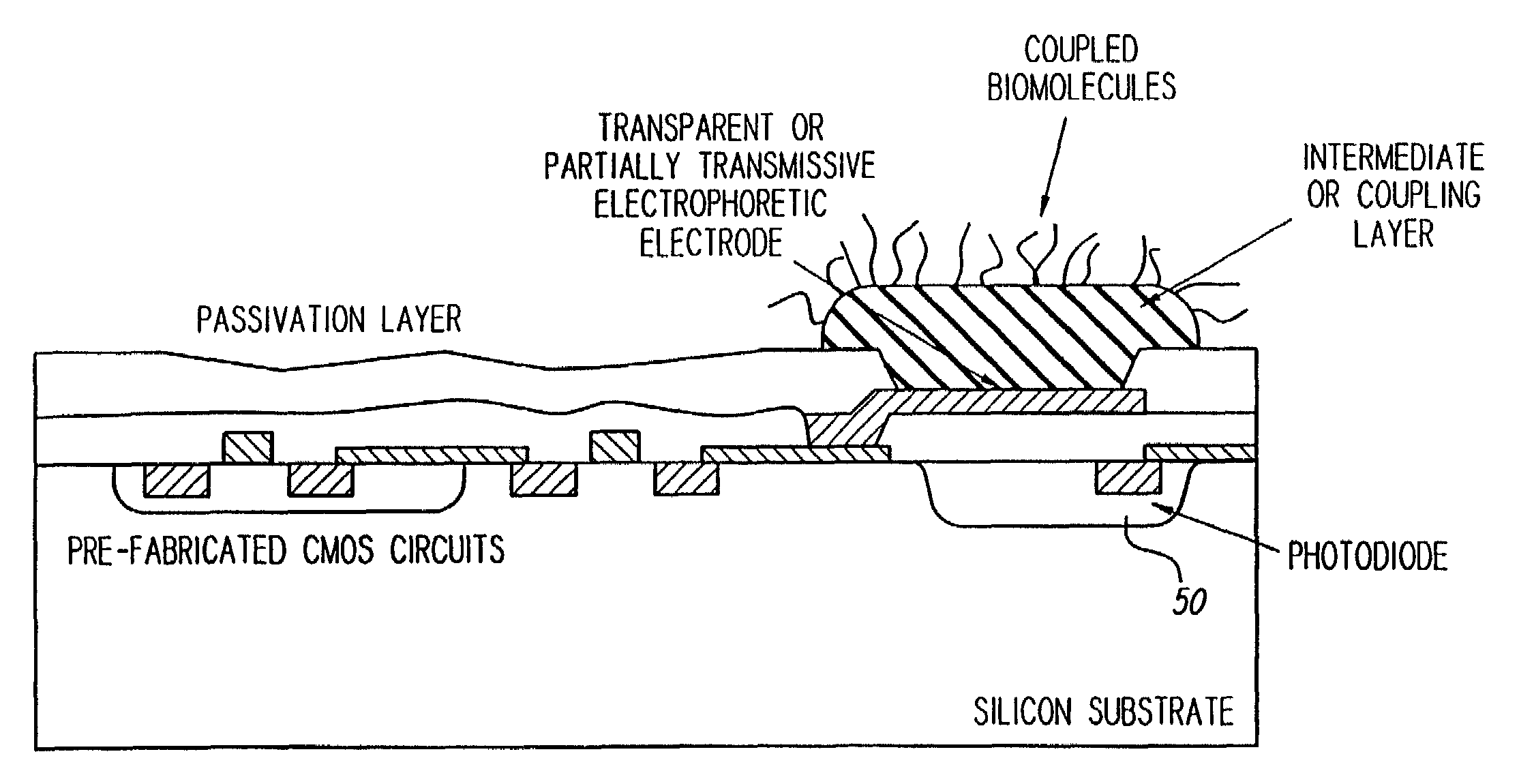
Biologic electrode array with integrated optical detector
InactiveUS7045097B2Easy to controlLow costSequential/parallel process reactionsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceElectrode arraySemiconductor
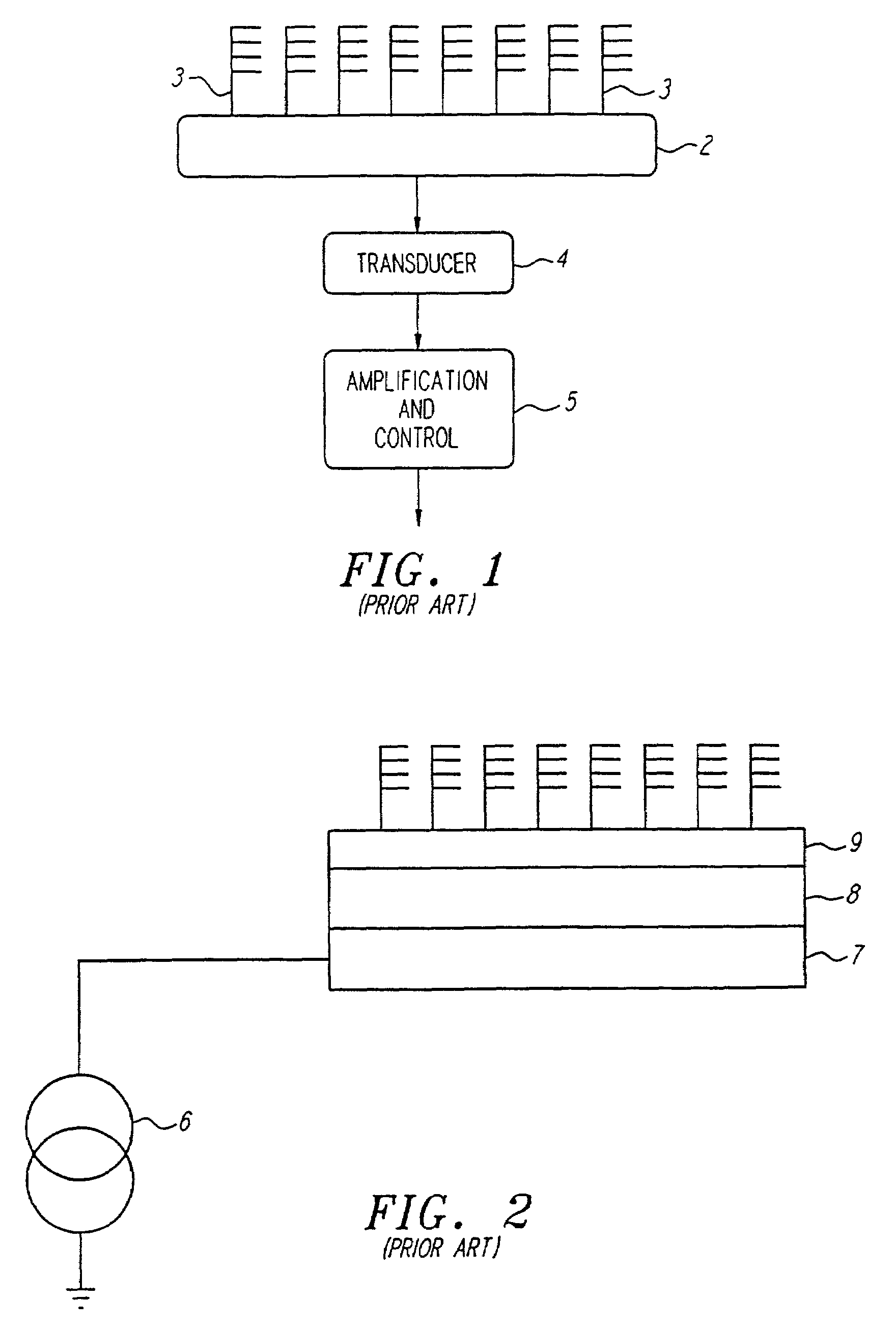
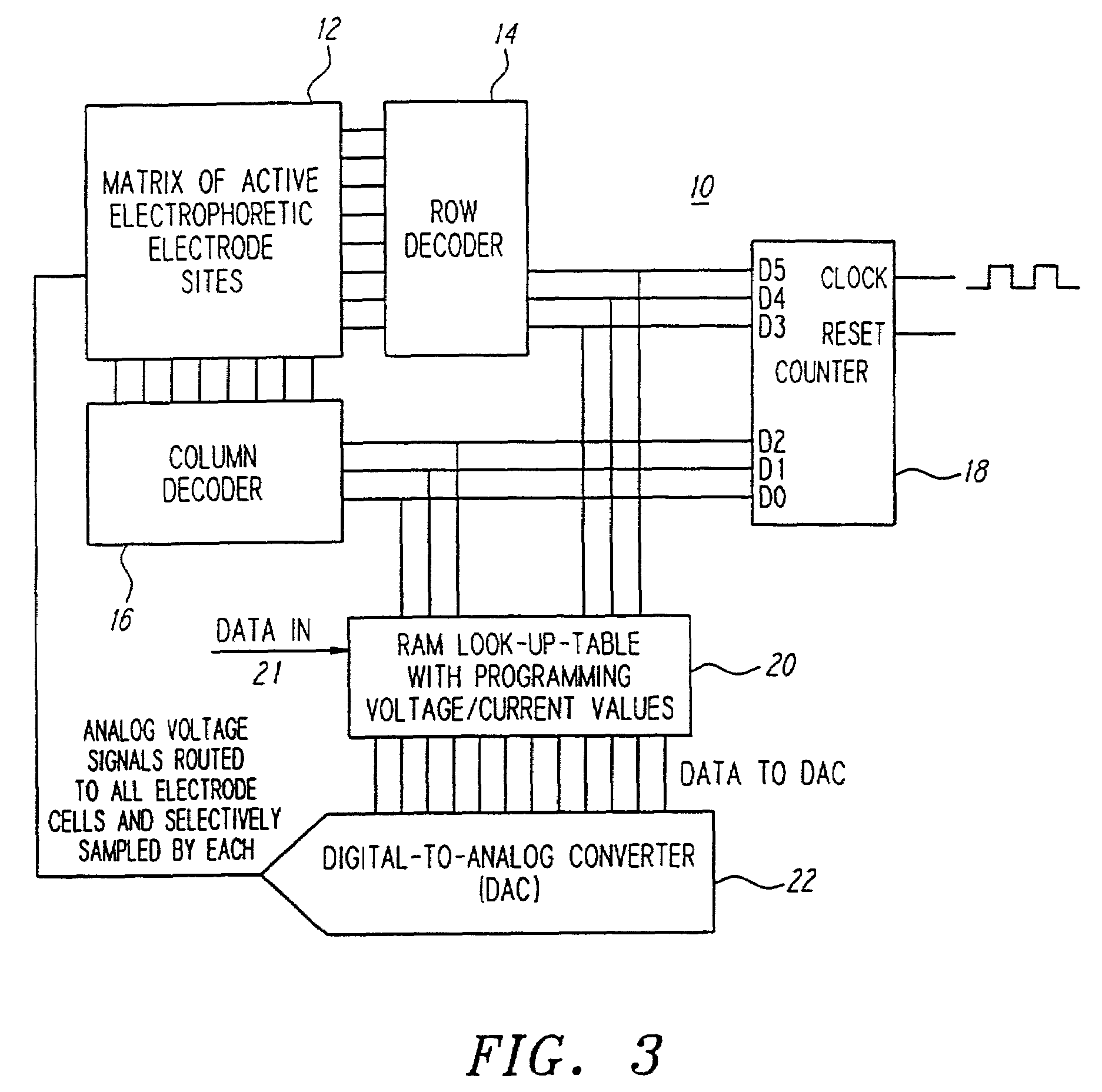
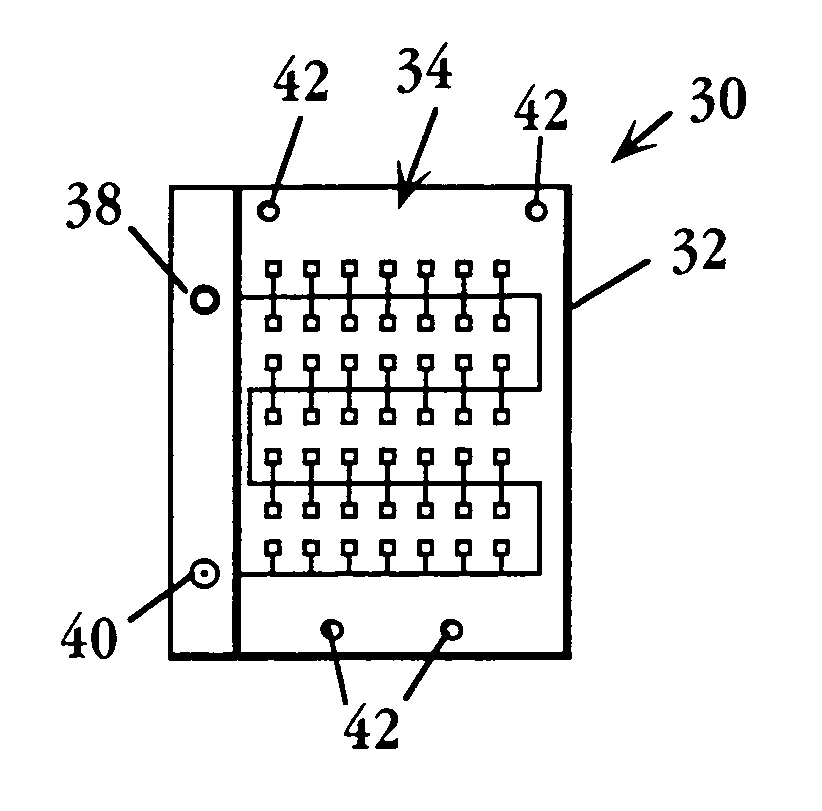
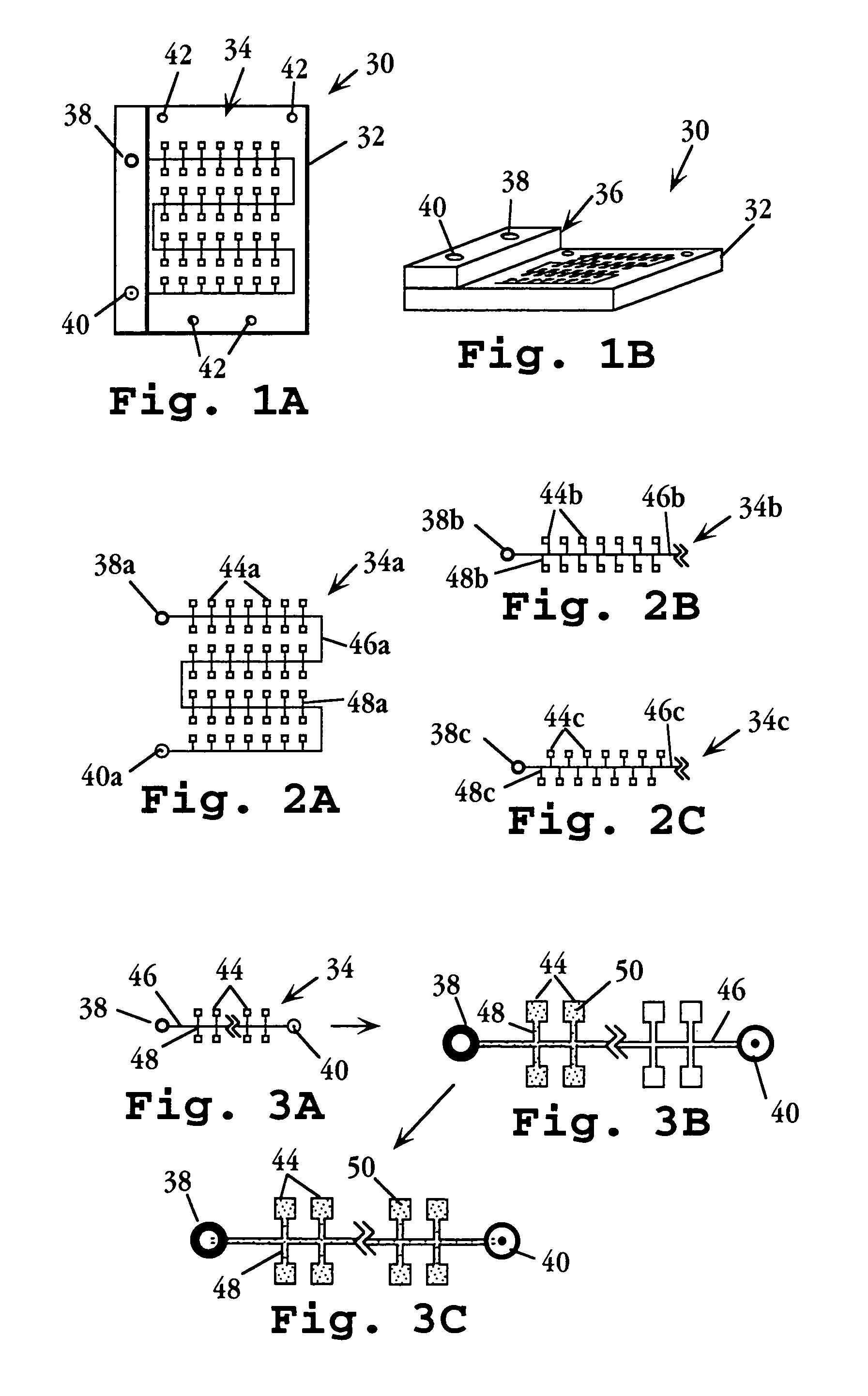
A biologic electrode array is formed on a semiconductor substrate. A matrix of electrode sites is disposed on the semiconductor substrate. A matrix of optical detectors is disposed beneath the electrode sites in the semiconductor substrate, wherein each electrode site is associated with a corresponding optical detector. The optical detectors are coupled to detection circuitry formed on the semiconductor substrate. The electrode sites may include slitted electrodes, punctuated electrodes, or optically transparent electrodes.
Owner:GAMIDA FOR LIFE
Nucleic acid analysis device
InactiveUS7235406B1Avoid accumulationEnough timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteAnalyte-specific reagent
The invention is directed to a method and device for simultaneously testing a sample for the presence, absence, and / or amounts of one or more a plurality of selected analytes. The invention includes, in one aspect, a device for detecting or quantitating a plurality of different analytes in a liquid sample. The device includes a substrate which defines a sample-distribution network having (i) a sample inlet, (ii) one or more detection chambers, and (iii) channel means providing a dead-end fluid connection between each of the chambers and the inlet. Each chamber may include an analyte-specific reagent effective to react with a selected analyte that may be present in the sample, and detection means for detecting the signal. Also disclosed are methods utilizing the device.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Modular assay plates, reader systems and methods for test measurements
ActiveUS7981362B2Improve collection efficiencyAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyLuminescence
Luminescence test measurements are conducted using an assay module having integrated electrodes with a reader apparatus adapted to receive assay modules, induce luminescence, preferably electrode induced luminescence, in the wells or assay regions of the assay modules and measure the induced luminescence.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Methods and apparatus for optimizing semiconductor inspection tools
InactiveUS6433561B1Reduce pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesEngineeringVoltage contrast
Disclosed is a method of inspecting a sample. At least a portion of the sample is illuminated. Signals received from the illuminated portion are detected, and the detected signals are processed to find defects present on the sample. The processing of the detected signals is optimized, at least in part, based upon results obtained from voltage contrast testing. In one implementation, the illumination is an optical illumination. In another embodiment, the processing comprises automated defect classification, and setup of the automated classification is optimized using the results obtained from voltage contrast testing. In another implementation, the results relate to a probability that a feature present on the sample represents an electrical defect.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
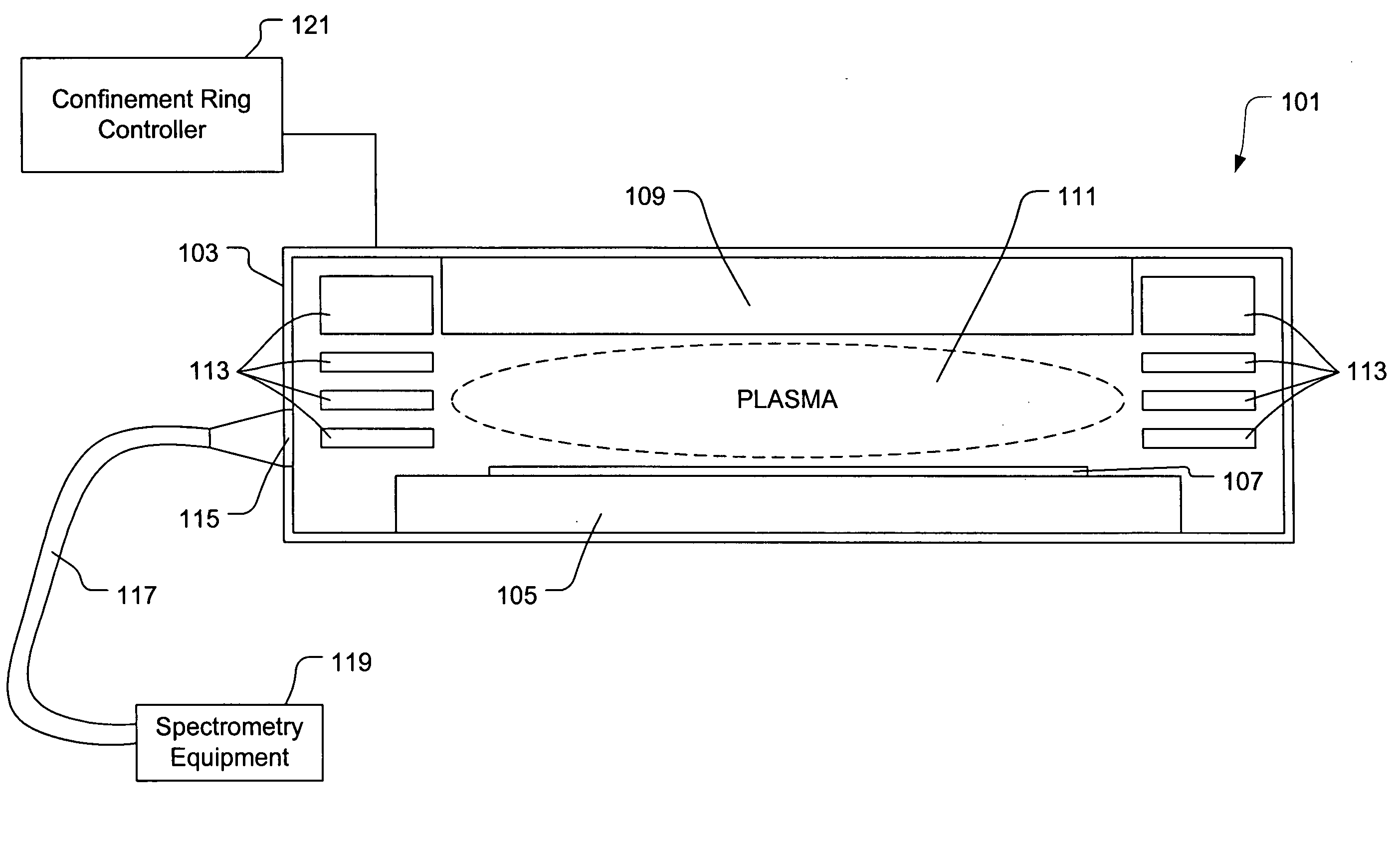
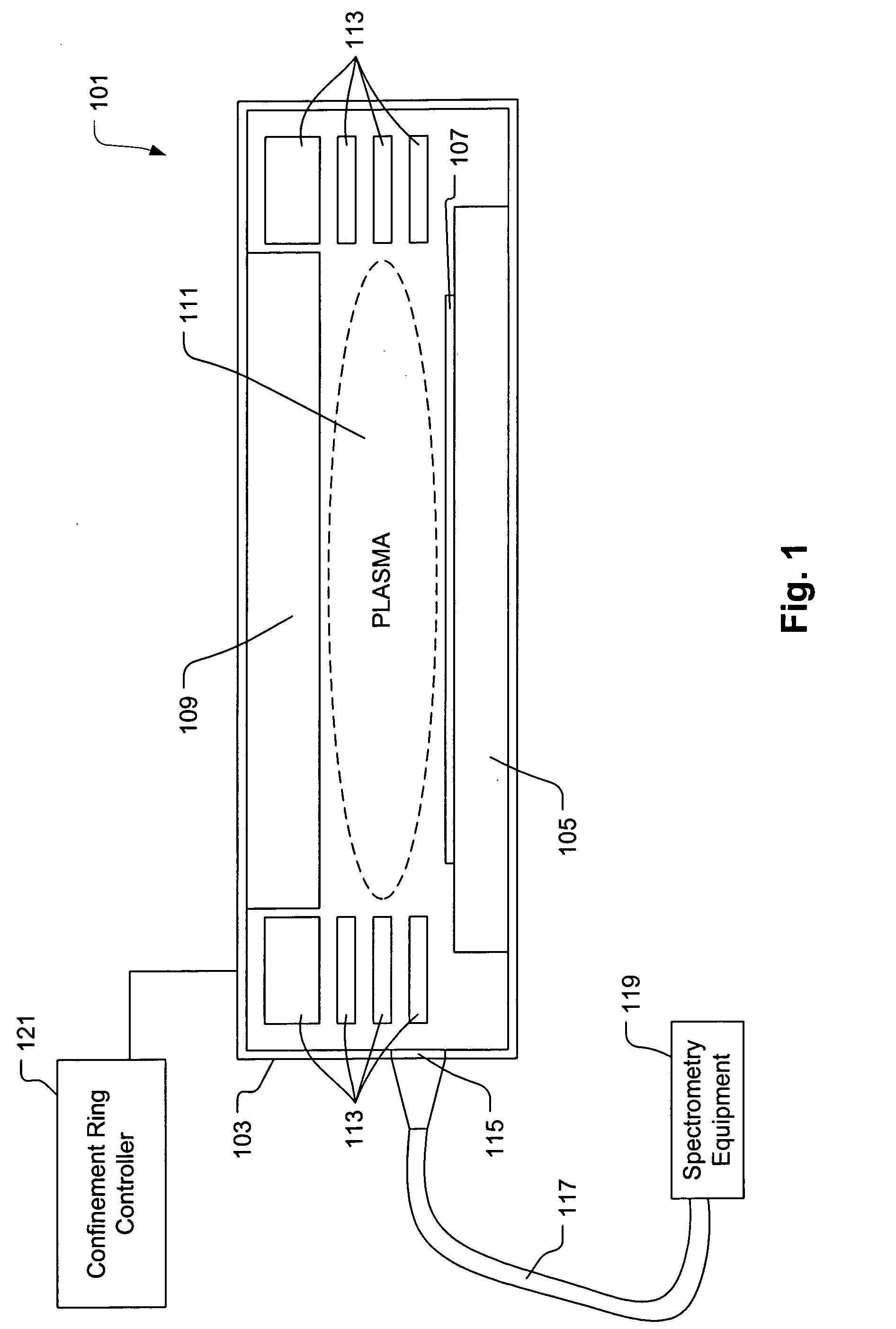
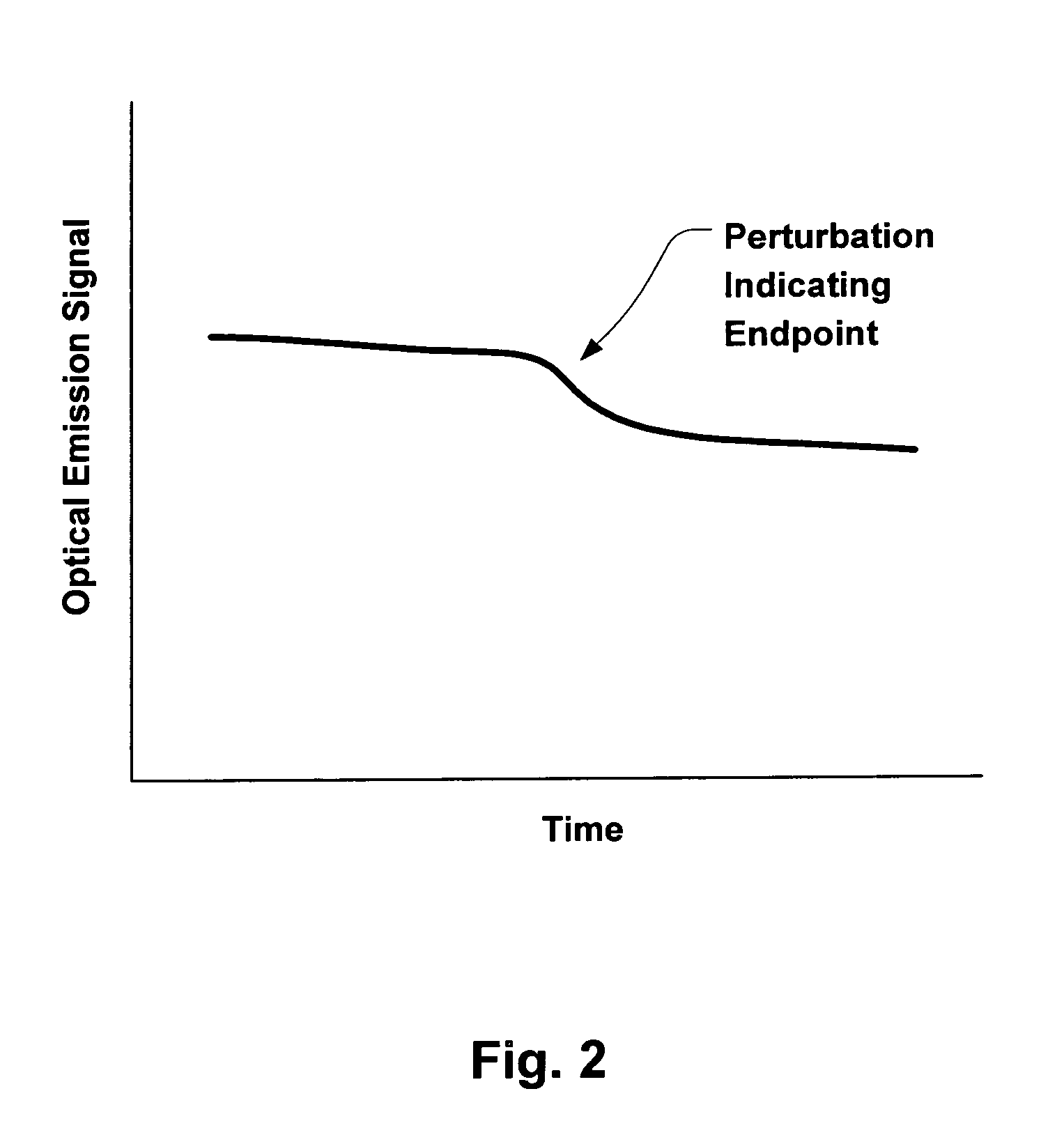
Method and apparatus for etch endpoint detection
ActiveUS20060087644A1Preventing any perturbationEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryEngineeringSpecific time
Broadly speaking, an invention is provided for monitoring a plasma optical emission. More specifically, the present invention provides a method for monitoring the plasma optical emission through a variable aperture to detect an endpoint of a plasma etching process without interferences that could lead to false endpoint calls. The method includes collecting optical emission data from a plasma through an aperture defined by moveable members. The moveable members are capable of varying a configuration of the aperture. The method also includes holding the moveable members at a particular time to cause the aperture to maintain a fixed configuration. The method further includes detecting a specific perturbation in the plasma optical emission while holding the moveable members.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Apparatus for analyzing biologic fluids
InactiveUS6869570B2Low costReduce spacingMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceImage dissectorImage conversion
An apparatus and method for analyzing a sample of biologic fluid quiescently residing within a chamber is provided. The apparatus includes a light source, a positioner, a mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field, and an image dissector. The light source is operable to illuminate a sample field of known, or ascertainable, area. The positioner is operable to selectively change the position of any or any or all of the chamber, the light source, or the image dissector, thereby enabling selective illumination of all regions of the sample. The mechanism for determining the volume of a sample field can determine the volume of a sample field illuminated by the light source. The image dissector is operable to convert an image of light passing through or emanating from the sample field into an electronic data format.
Owner:ABBOTT LAB INC +2
Method and apparatus using optical techniques to measure analyte levels
ActiveUS20060204399A1High density designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteFluorescence
A device is provided for use with a tissue penetrating system and / or a metering device for measuring analyte levels. The device comprises a cartridge and a plurality of analyte detecting members mounted on the cartridge. The cartridge may have a radial disc shape. The cartridge may also be sized to fit within the metering device. The analyte detecting members may be optical system using fluorescence lifetime to determine analyte levels. In one embodiment, the device may also include a fluid spreader positioned over at least a portion of the analyte detecting member to urge fluid toward one of the detecting members. A plurality of analyte detecting members may be used. Each analyte detecting member may be a low volume device.
Owner:SANOFI AVENTIS DEUT GMBH
Inspectable buried test structures and methods for inspecting the same
InactiveUS6509197B1Easily dry-etchedEasy to processSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesVoltage contrastSemiconductor
Disclosed is a semiconductor die having a lower test structure formed in a lower metal layer of the semiconductor die. The lower conductive test structure has a first end and a second end. The first end is coupled to a predetermined voltage level. The semiconductor die also includes an insulating layer formed over the lower metal layer. The die further includes an upper test structure formed in an upper metal layer of the semiconductor die. The upper conductive test structure is coupled with the second end of the lower conductive test structure. The upper metal layer is formed over the insulating layer. In a specific implementation, the first end of the lower test structure is coupled to ground. In another embodiment, the semiconductor die also includes a substrate and a first via coupled between the first end of the lower test structure and the substrate. In yet another aspect, the lower test structure is an extended metal line, and the upper test structure is a voltage contrast element. Methods for inspecting and fabricating such semiconductor die are also disclosed.
Owner:KLA TENCOR CORP
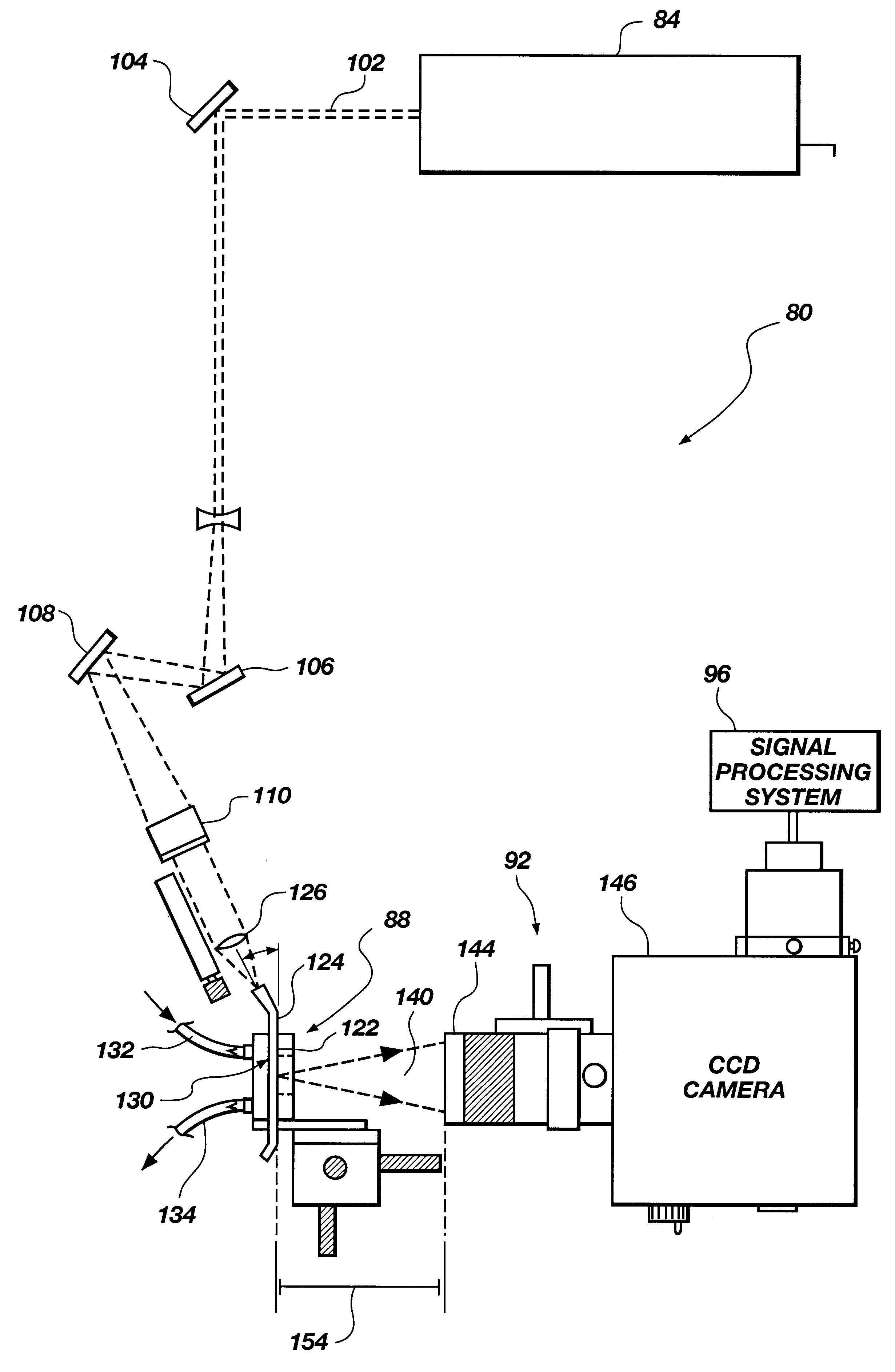
System for determining analyte concentration
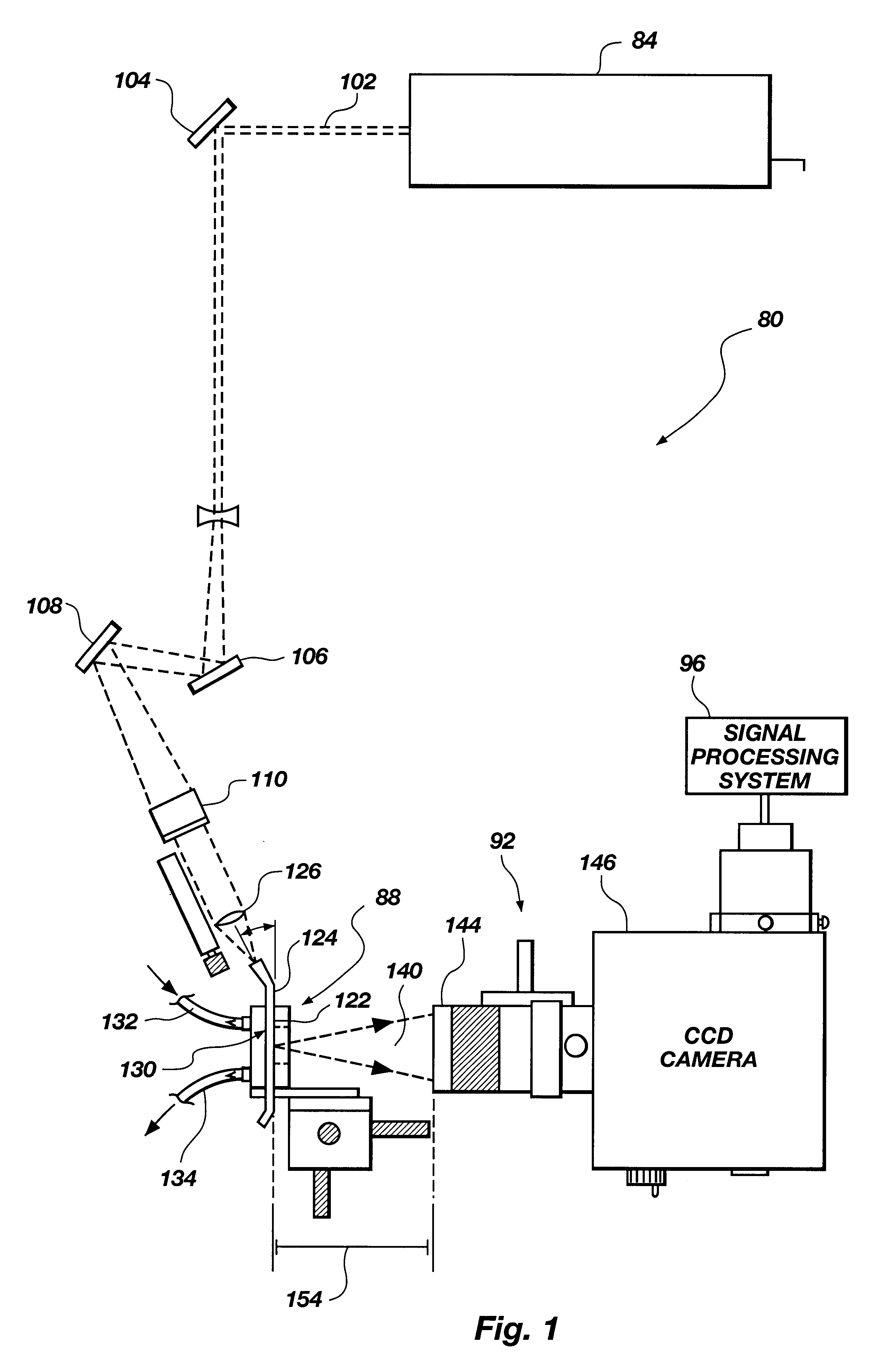
InactiveUS6287871B1Chemiluminescene/bioluminescenceAnalysis by electrical excitationPhotovoltaic detectorsAnalyte
The present invention relates to a system (80) for determining analyte concentration. The system (80) includes an optical detection system (92) that detects fluorescence from fluorescent binding assays in a biosensor (88). A processing system (96) may be used to determine analyte concentration from the fluorescence detected by the optical detection system (92). The optical detection system (92) may include photodetectors with or without in series lenses. Alternatively, a CCD camera (146) may be used.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Systems and methods of conducting multiplexed experiments
A method for multiplexed detection and quantification of analytes by reacting them with probe molecules attached to specific and identifiable carriers. These carriers can be of different size, shape, color, and composition. Different probe molecules are attached to different types of carriers prior to analysis. After the reaction takes place, the carriers can be automatically analyzed. This invention obviates cumbersome instruments used for the deposition of probe molecules in geometrically defined arrays. In the present invention, the analytes are identified by their association with the defined carrier, and not (or not only) by their position. Moreover, the use of carriers provides a more homogenous and reproducible representation for probe molecules and reaction products than two-dimensional imprinted arrays or DNA chips.
Owner:VITRA BIOSCIENCES ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS LLC +1
Smart hydrogel particles for biomarker harvesting
ActiveUS20090148961A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteSmart hydrogels
Capture particles for harvesting analytes from solution and methods for using them are described. The capture particles are made up of a polymeric matrix having pore size that allows for the analytes to enter the capture particles. The pore size of the capture particles may be changeable upon application of a stimulus to the particles, allowing the pore size of the particles to be changed so that analytes of interest remain sequestered inside the particles. The polymeric matrix of the capture particles may be made of co-polymeric materials having a structural monomer and an affinity monomer, the affinity monomer having properties that attract the analyte to the capture particle. The capture particles may be used to isolate and identify analytes present in a mixture. They may also be used to protect analytes which are typically subject to degradation upon harvesting and to concentrate low an analyte in low abundance in a fluid.
Owner:INST SUPERIORE DI SANITA +1
Apparatus for DNA sequencing
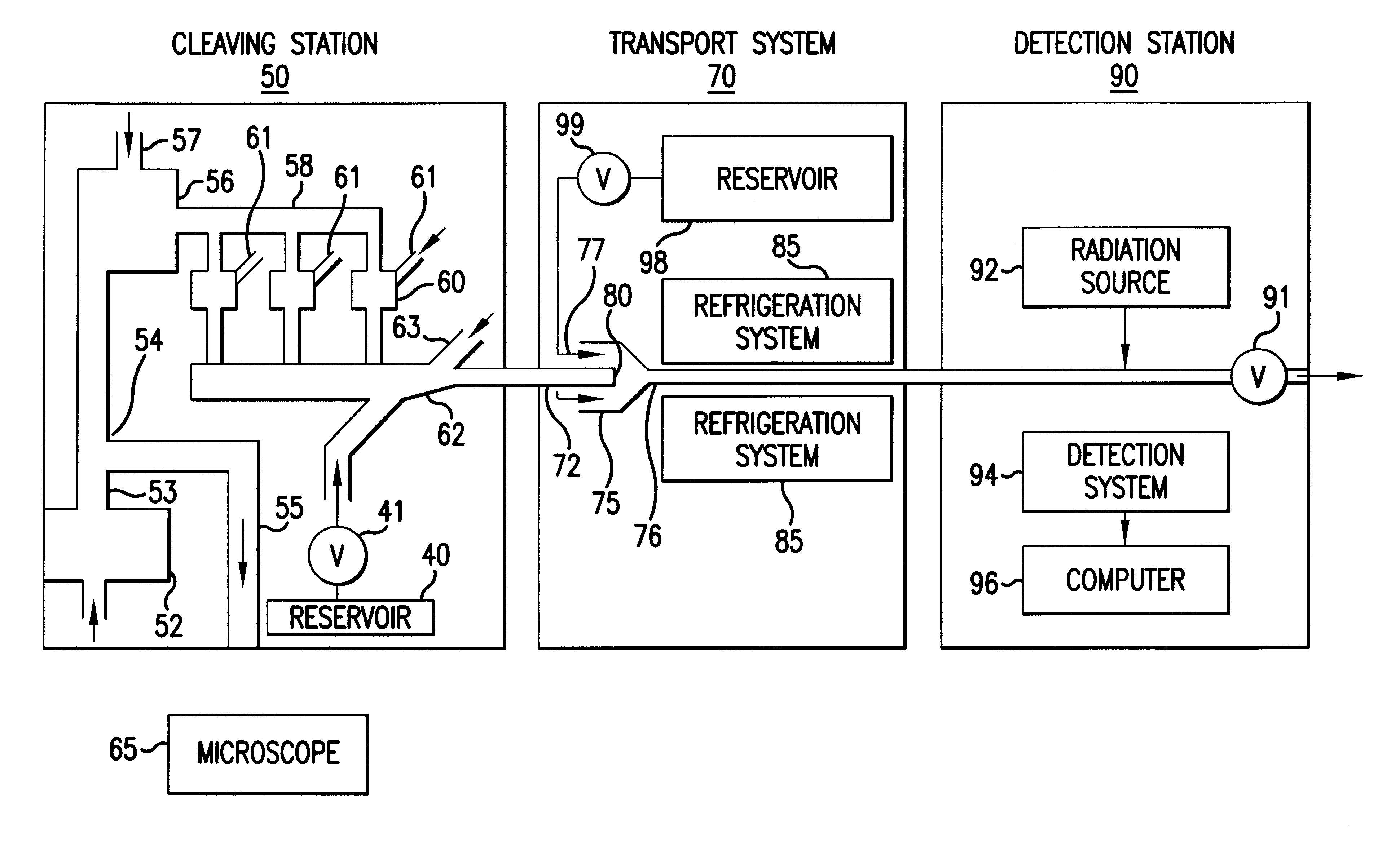
InactiveUS6296810B1Enhances natural fluorescent activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsTransport systemNucleotide
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for automated DNA sequencing. The method of the invention includes the steps of: a) using a processive exonuclease to cleave from a single DNA strand the next available single nucleotide on the strand; b) transporting the single nucleotide away from the DNA strand; c) incorporating the single nucleotide in a fluorescence-enhancing matrix; d) irradiating the single nucleotide to cause it to fluoresce; e) detecting the fluorescence; f) identifying the single nucleotide by its fluorescence; and g) repeating steps a) to f) indefinitely (e.g., until the DNA strand is fully cleaved or until a desired length of the DNA is sequenced). The apparatus of the invention includes a cleaving station for the extraction of DNA from cells and the separation of single nucleotides from the DNA; a transport system to separate the single nucleotide from the DNA and incorporate the single nucleotide in a fluorescence-enhancing matrix; and a detection station for the irradiation, detection and identification of the single nucleotides. The nucleotides are advantageously detected by irradiating the nucleotides with a laser to stimulate their natural fluorescence, detecting the fluorescence spectrum and matching the detected spectrum with that previously recorded for the four nucleotides in order to identify the specific nucleotide.
Owner:AMERSHAM BIOSCIENCES KK
Method and apparatus for sorting biological cells with a MEMS device
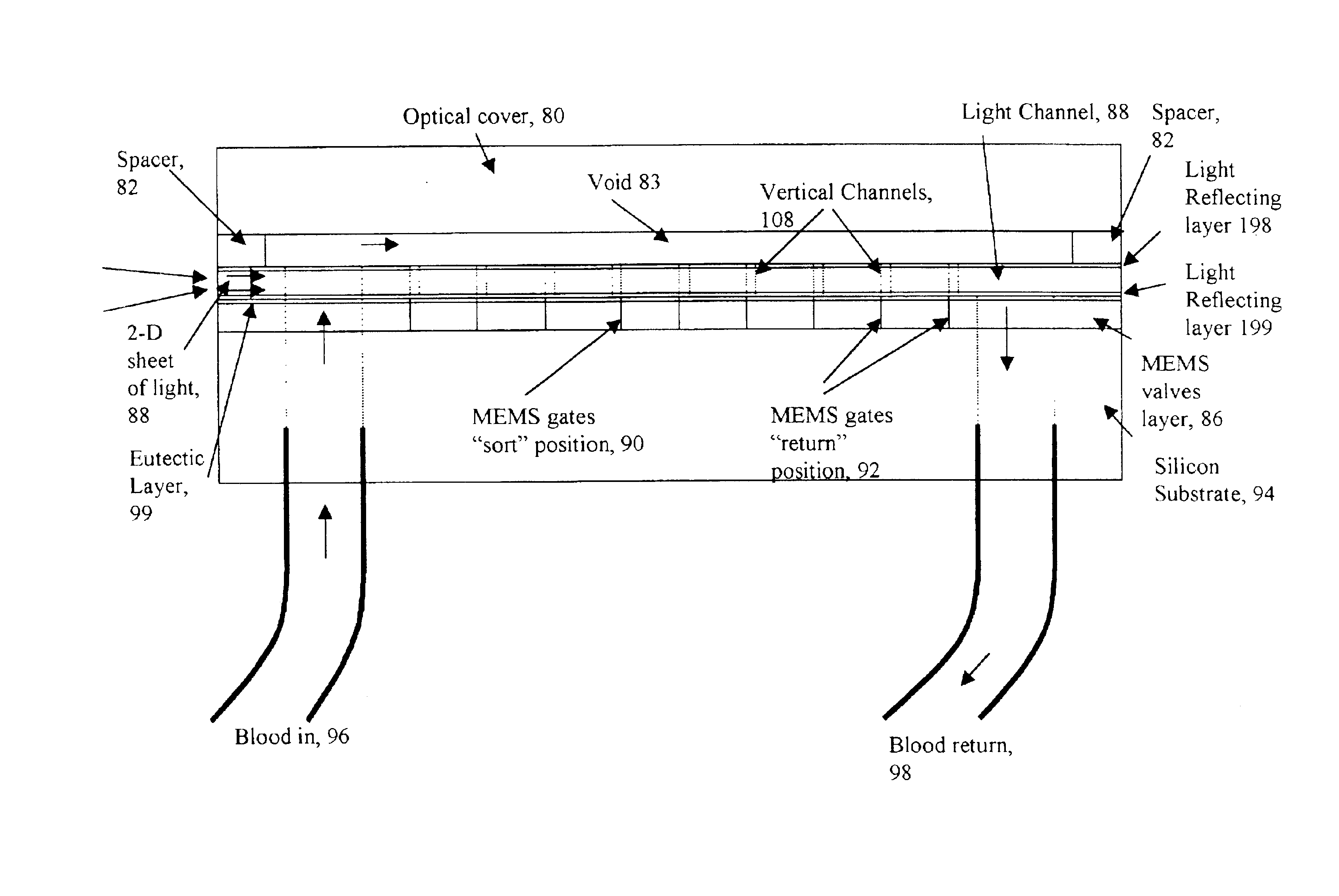
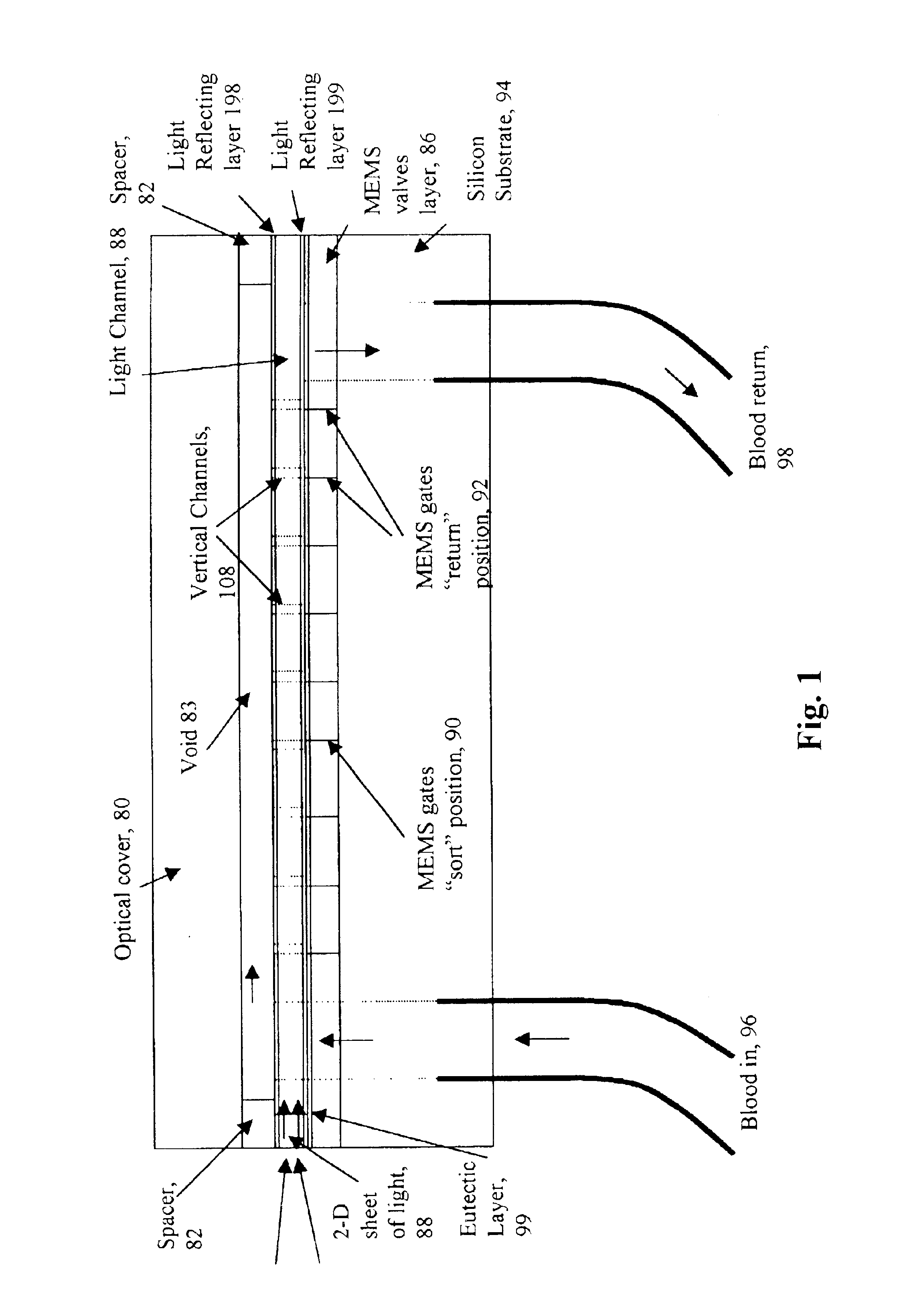
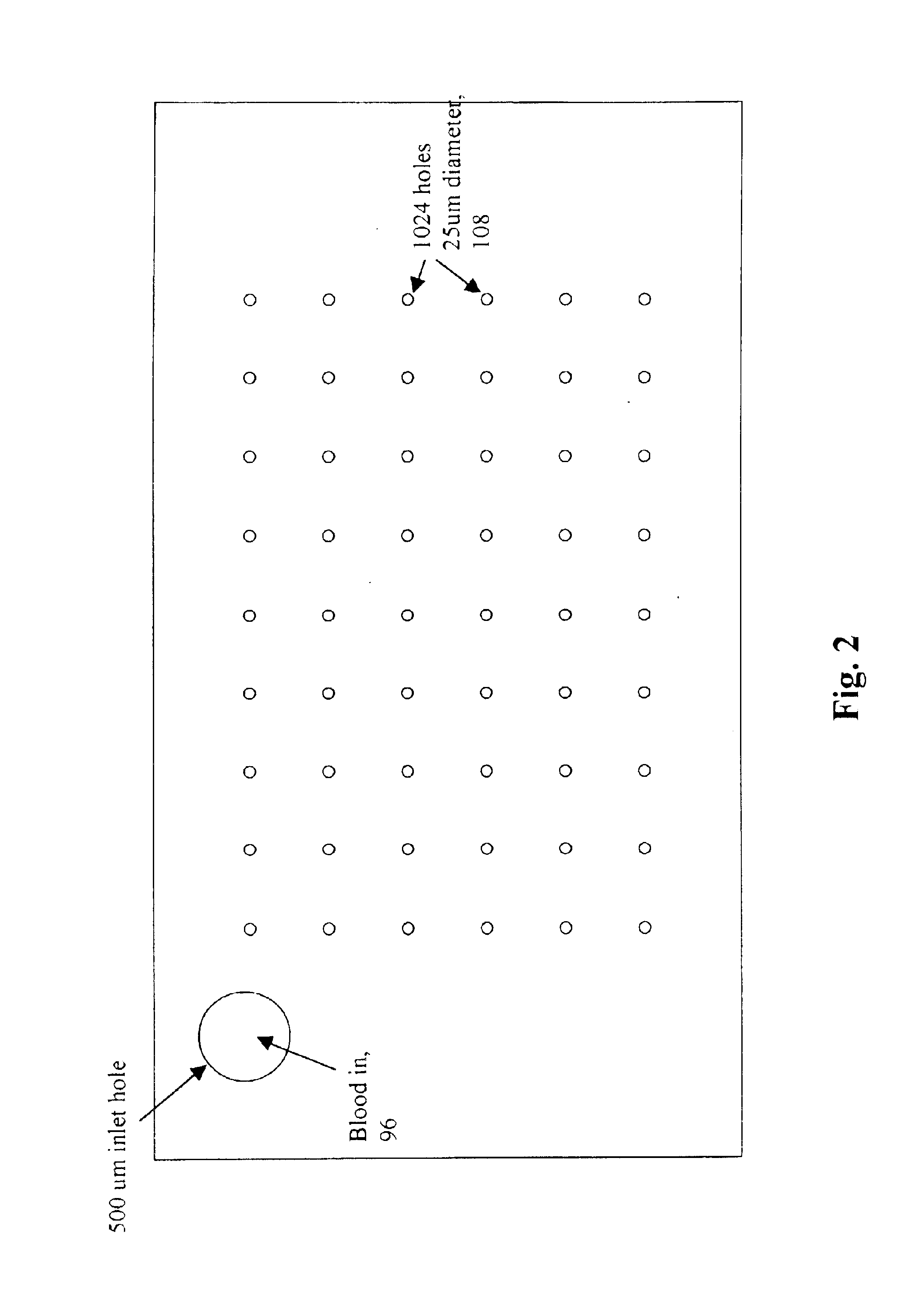
InactiveUS6838056B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological cellLaser light
A micromechanical actuator for sorting hematopoietic stem cells for use in cancer therapies. The actuator operates by diverting cells into one of a number of possible pathways fabricated in the fabrication substrate of the micromechanical actuator, when fluorescence is detected emanating from the cells. The fluorescence results from irradiating the cells with laser light, which excites a fluorescent tag attached to the cell. The micromechanical actuator thereby sorts the cells individually, with an operation rate of 3.3 kHz, however with the massively parallel 1024-fold device described herein, a throughput of 3.3 million events / second is achievable.
Owner:OWL BIOMEDICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com