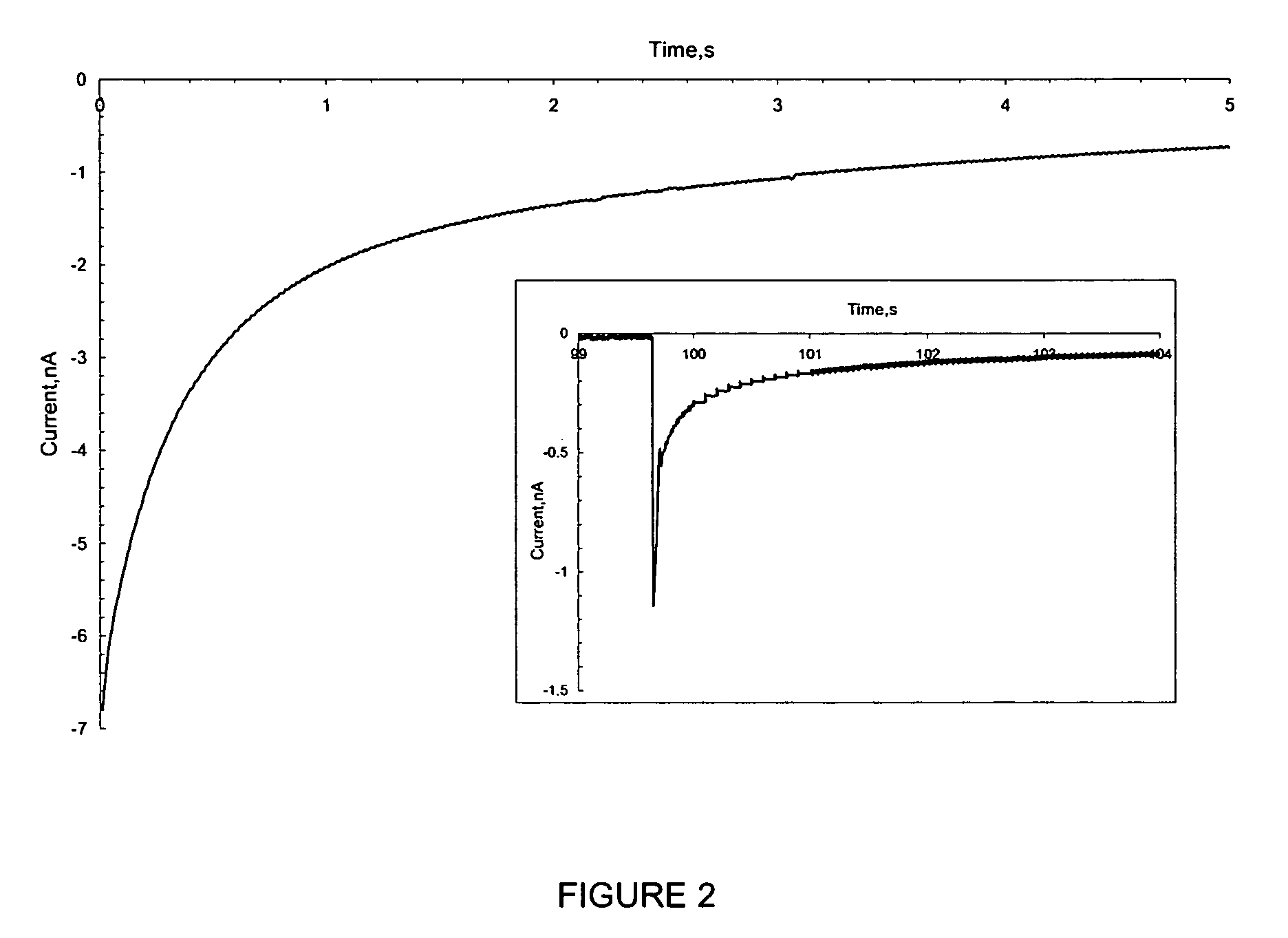
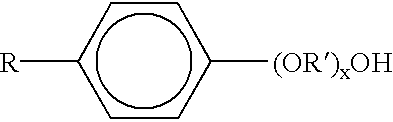
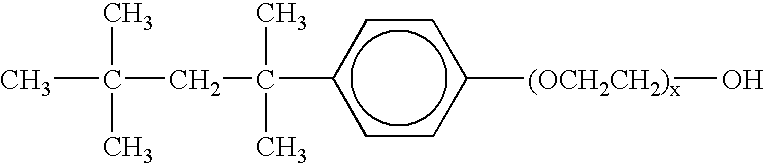
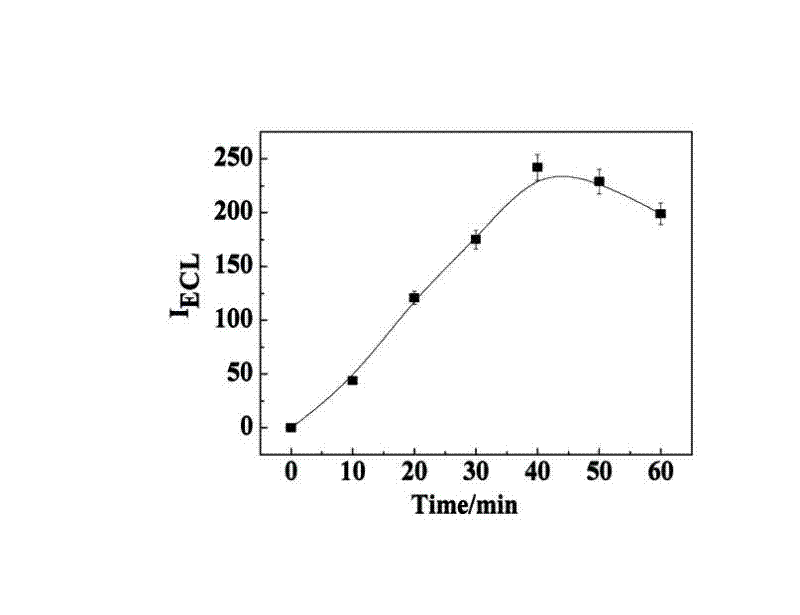
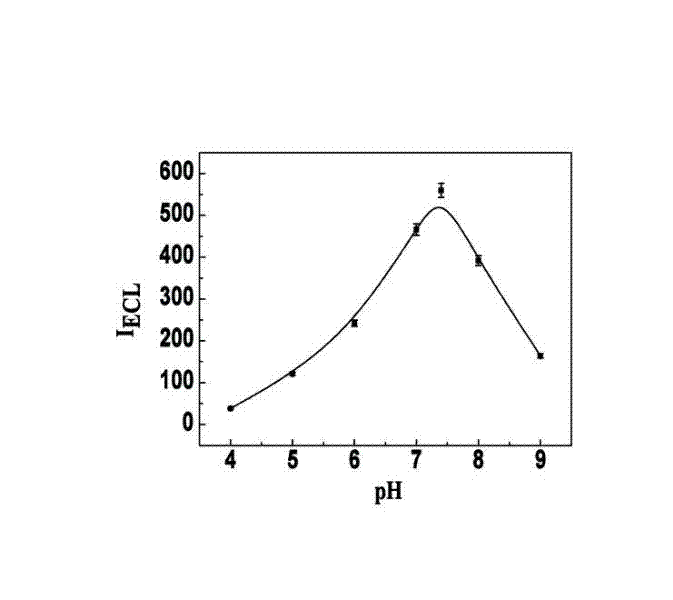
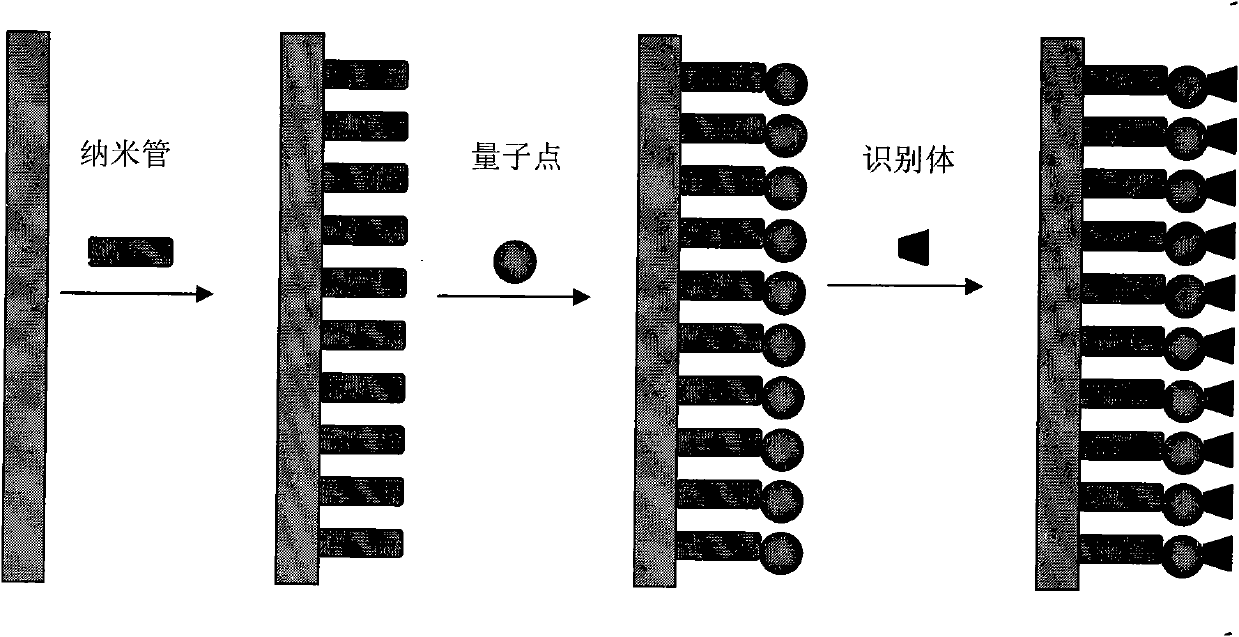
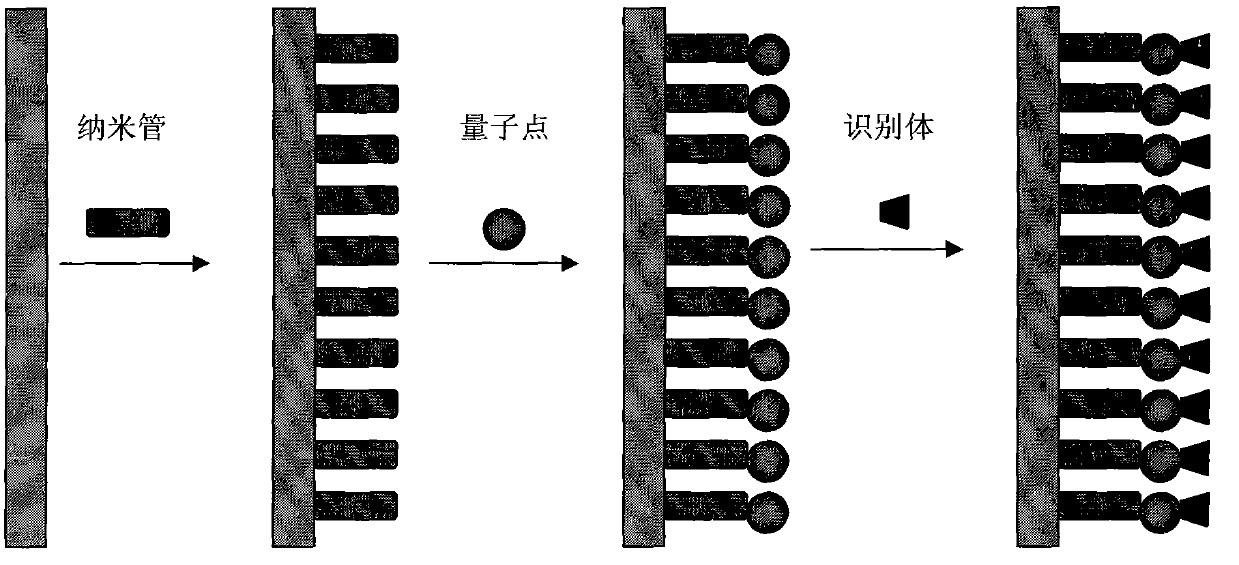
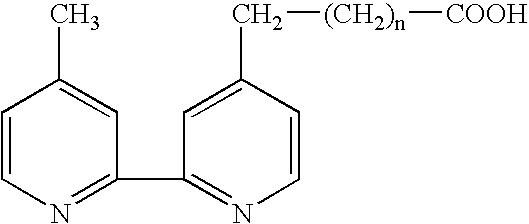
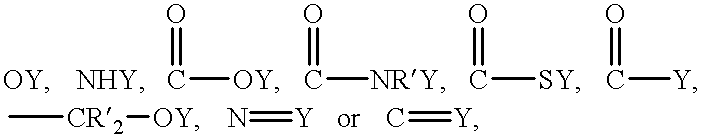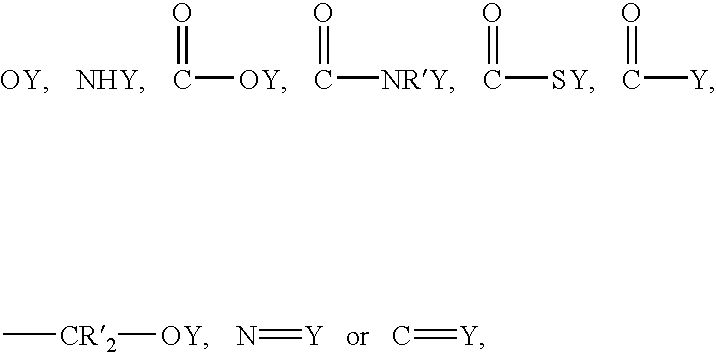Patents
Literature
1066 results about "Electrochemiluminescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
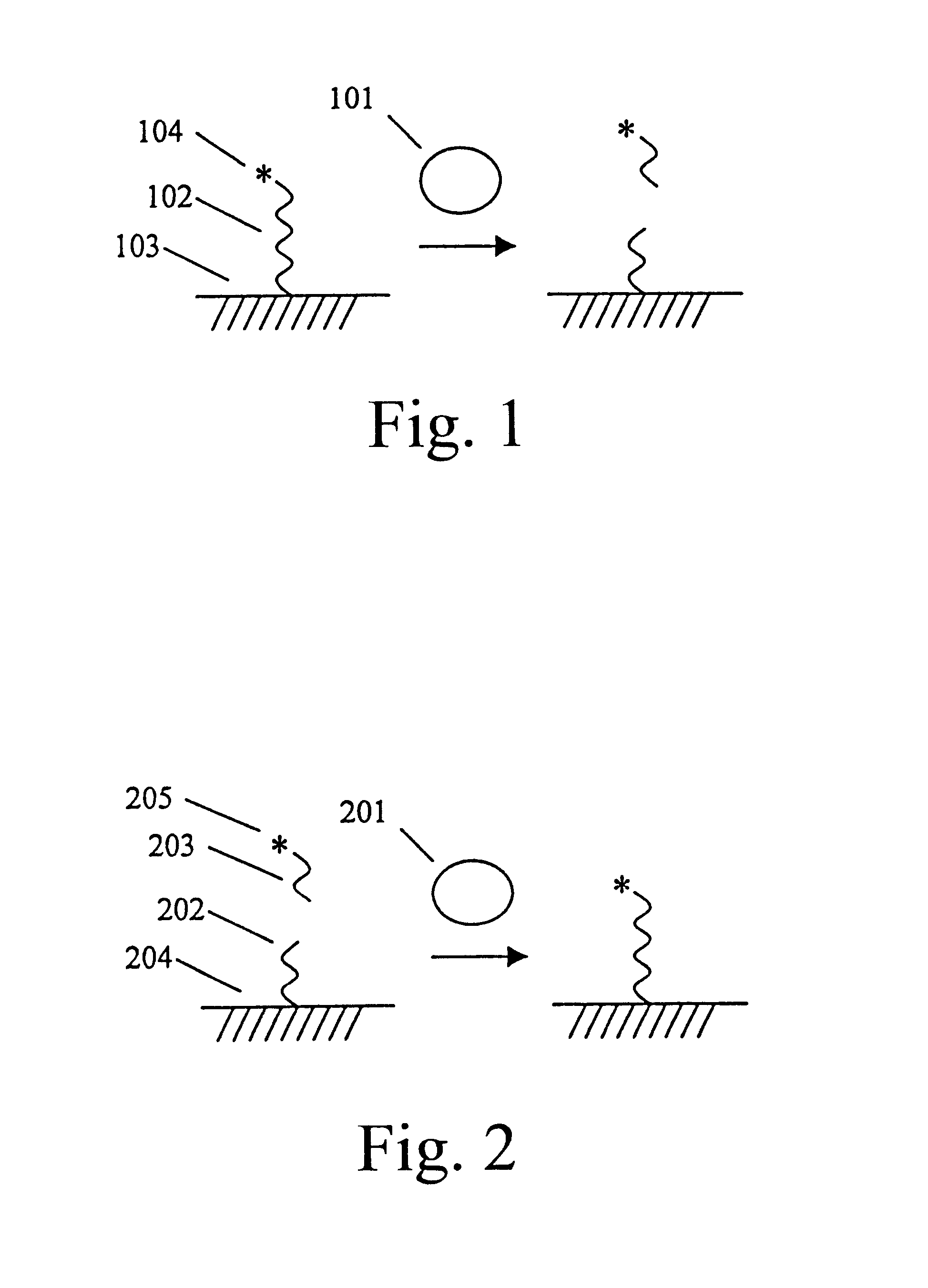
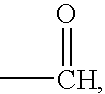
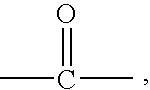
Electrochemiluminescence or electrogenerated chemiluminescence (ECL) is a kind of luminescence produced during electrochemical reactions in solutions. In electrogenerated chemiluminescence, electrochemically generated intermediates undergo a highly exergonic reaction to produce an electronically excited state that then emits light upon relaxation to a lower-level state. This wavelength of the emitted photon of light corresponds to the energy gap between these two states. ECL excitation can be caused by energetic electron transfer (redox) reactions of electrogenerated species. Such luminescence excitation is a form of chemiluminescence where one/all reactants are produced electrochemically on the electrodes.
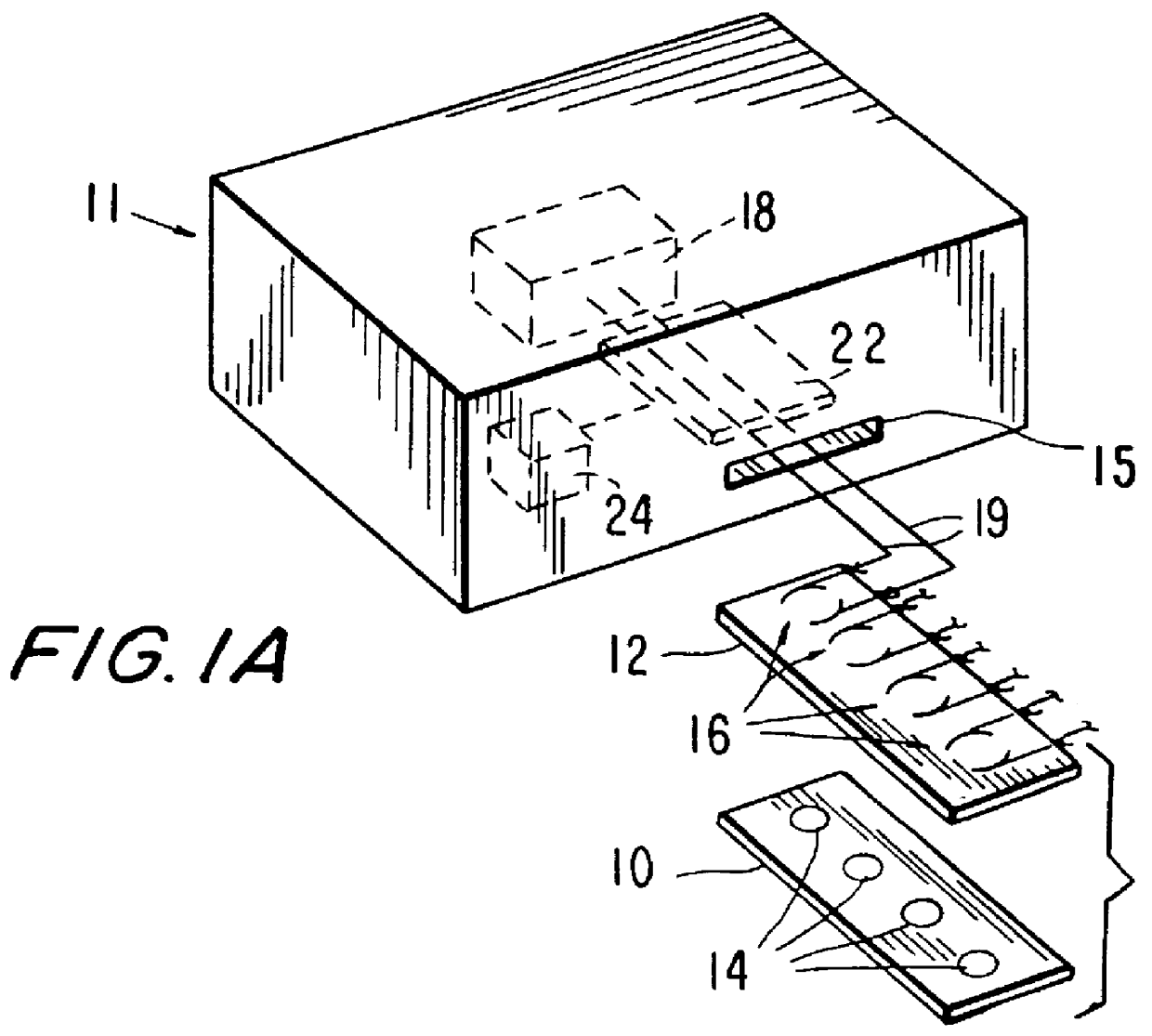
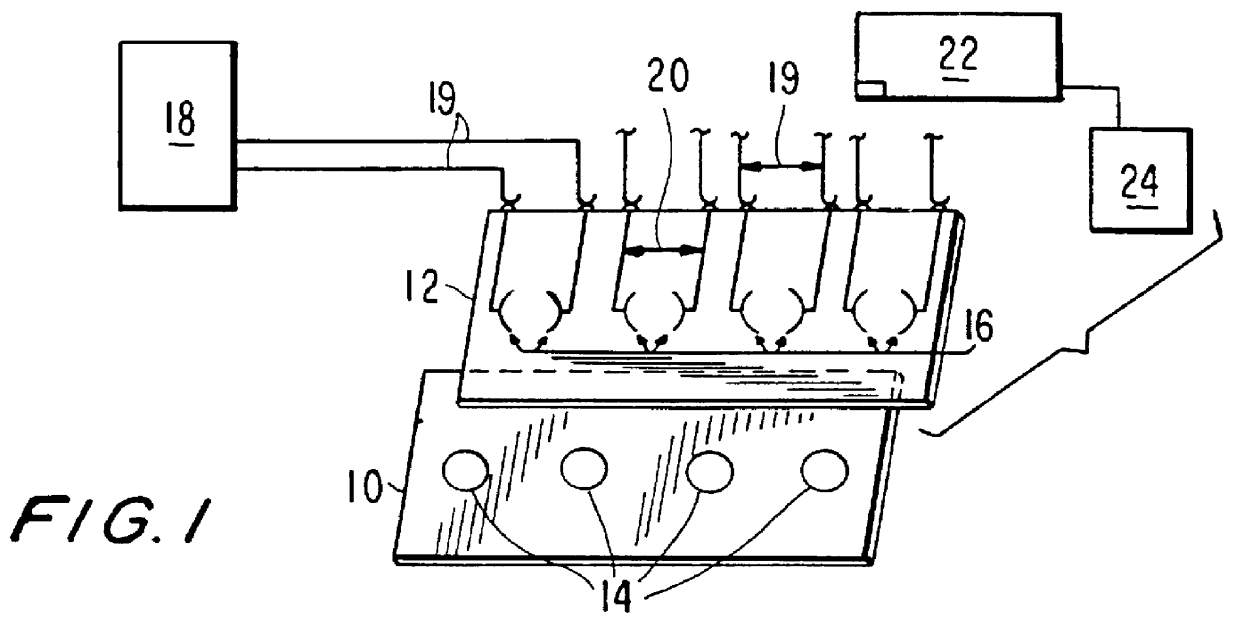
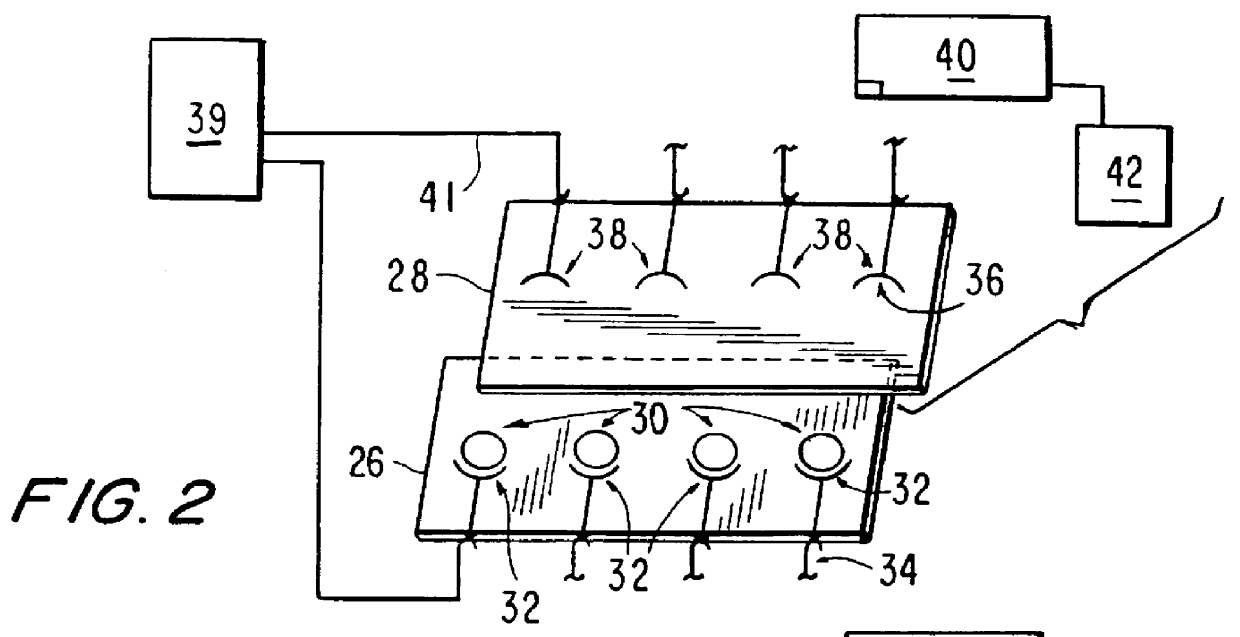
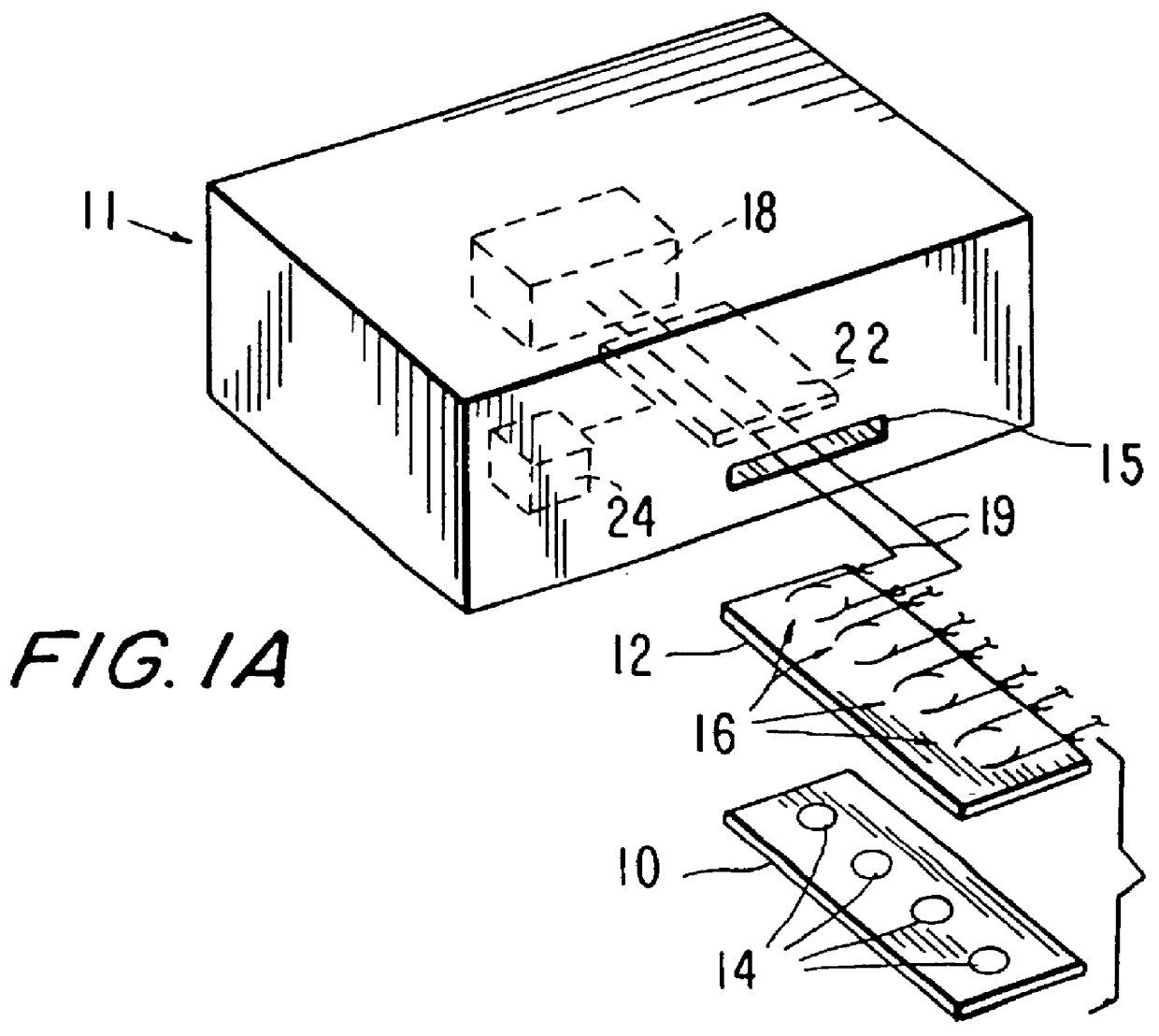
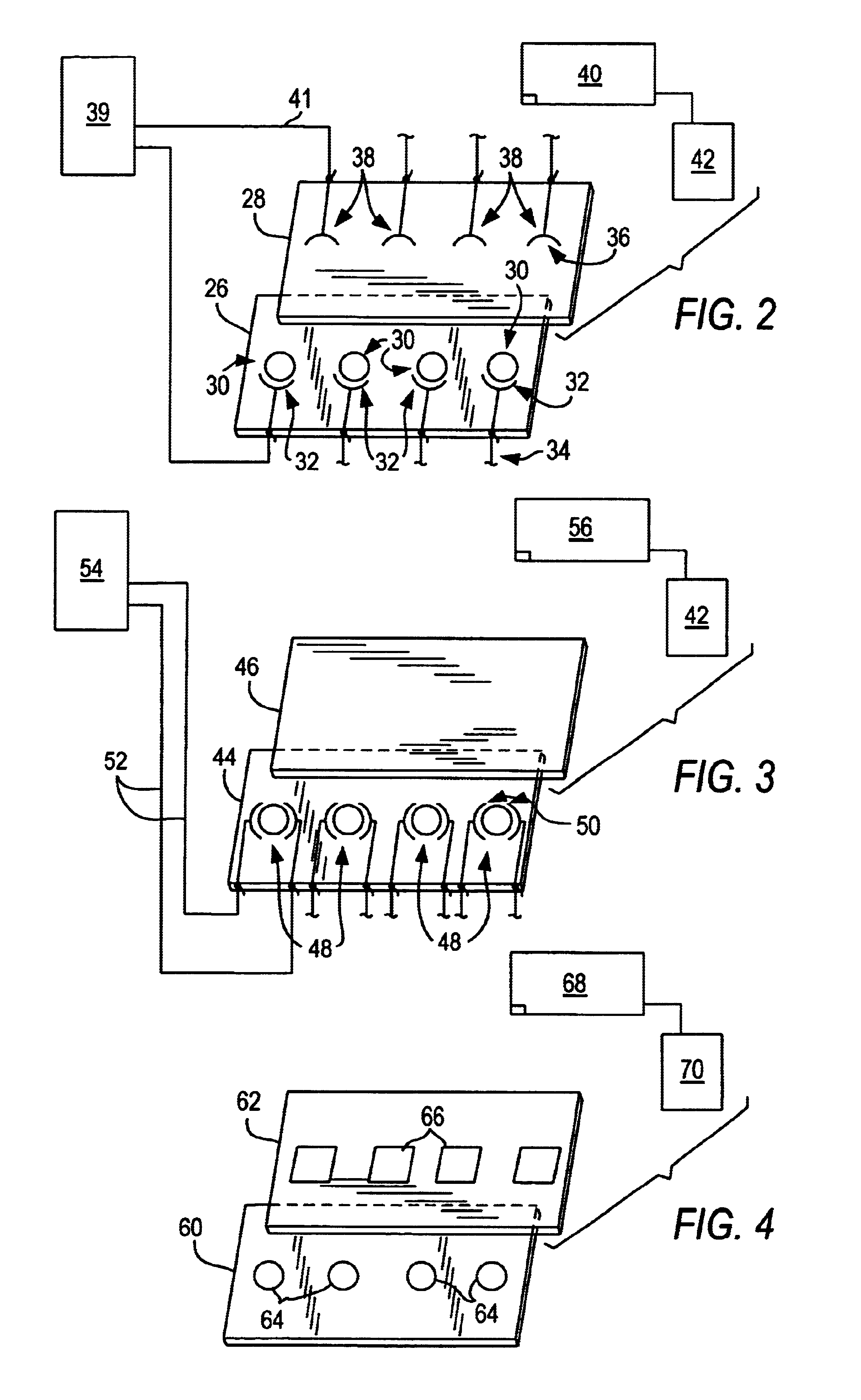
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
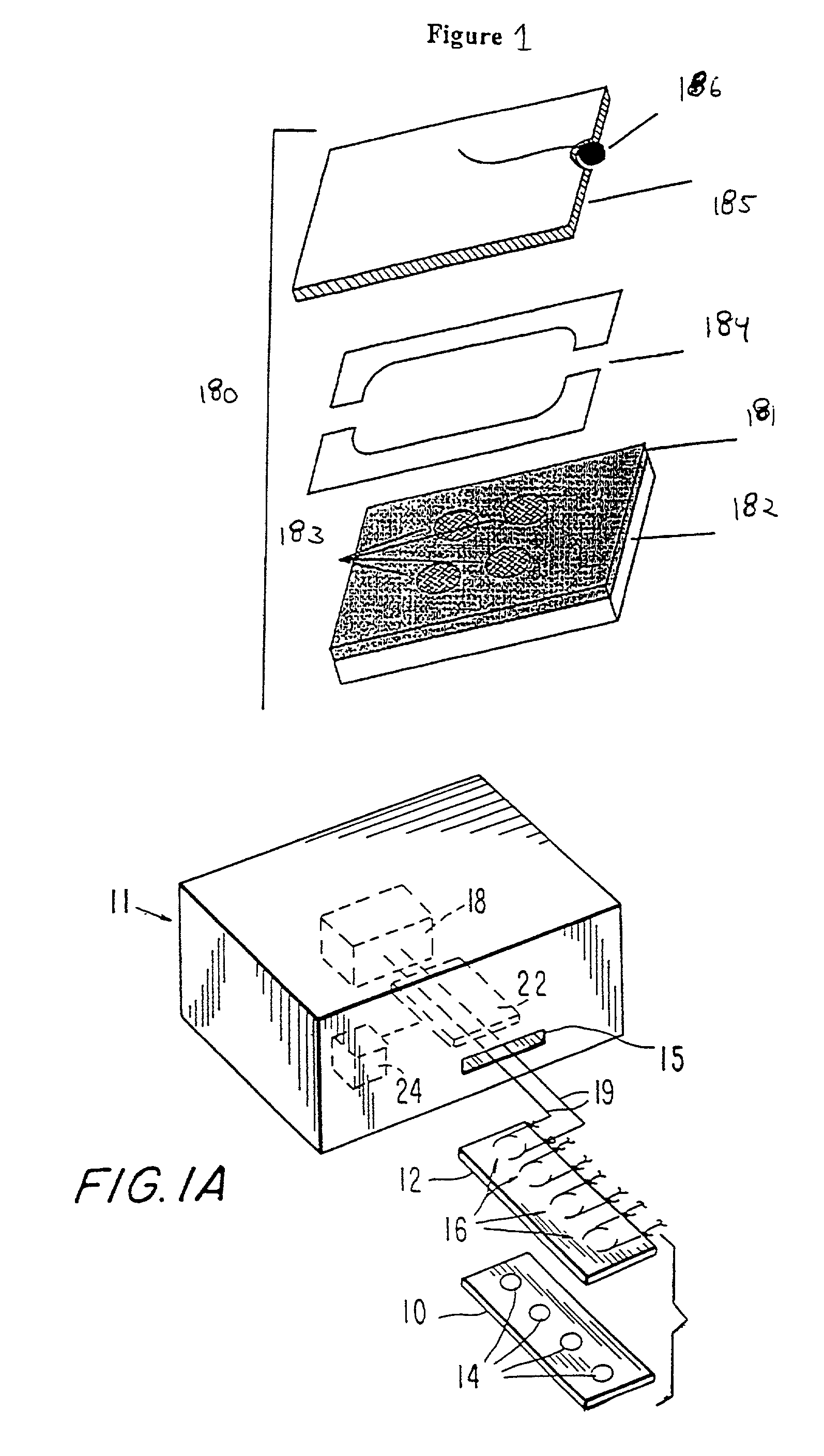
InactiveUS6066448AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
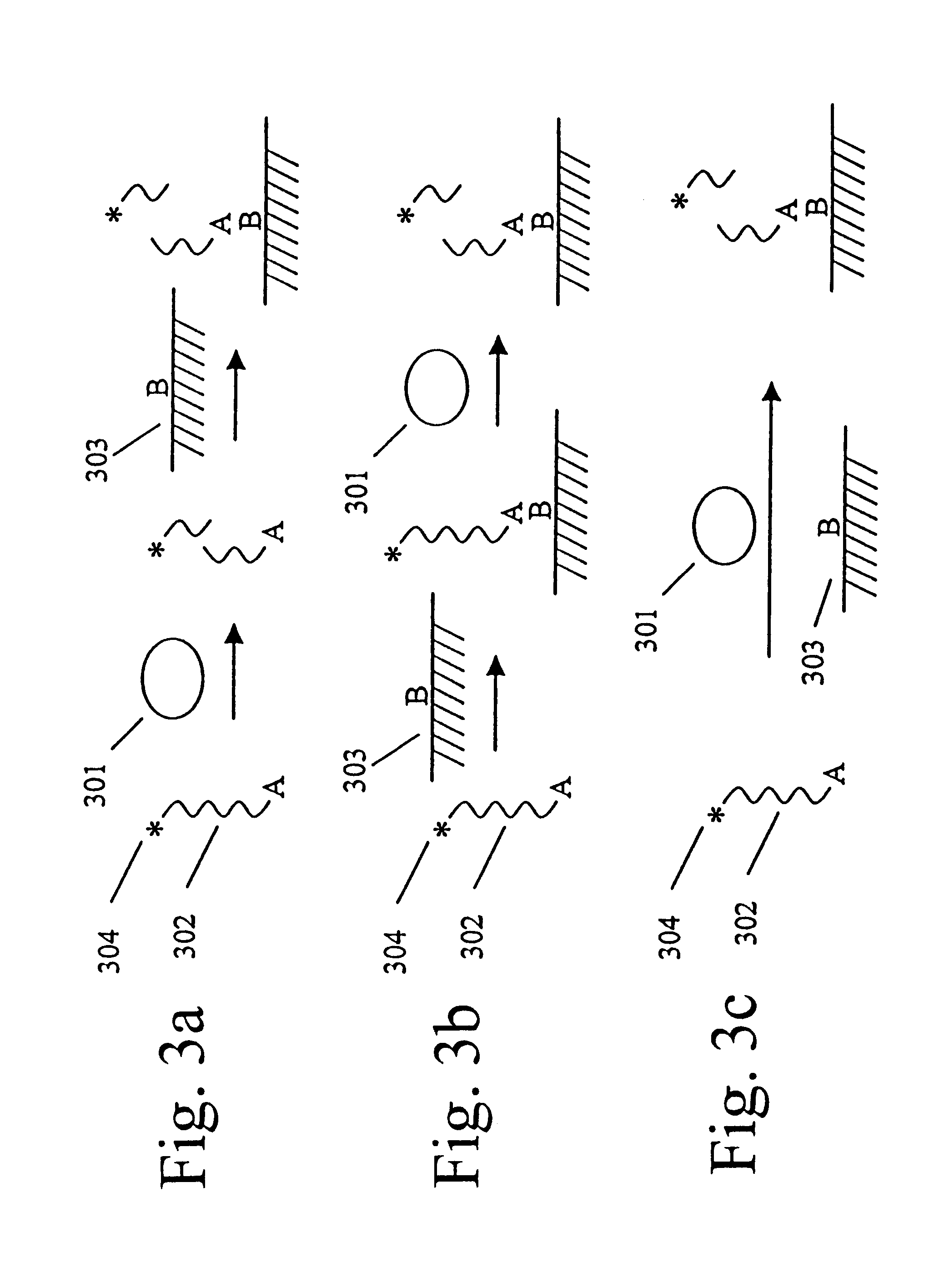
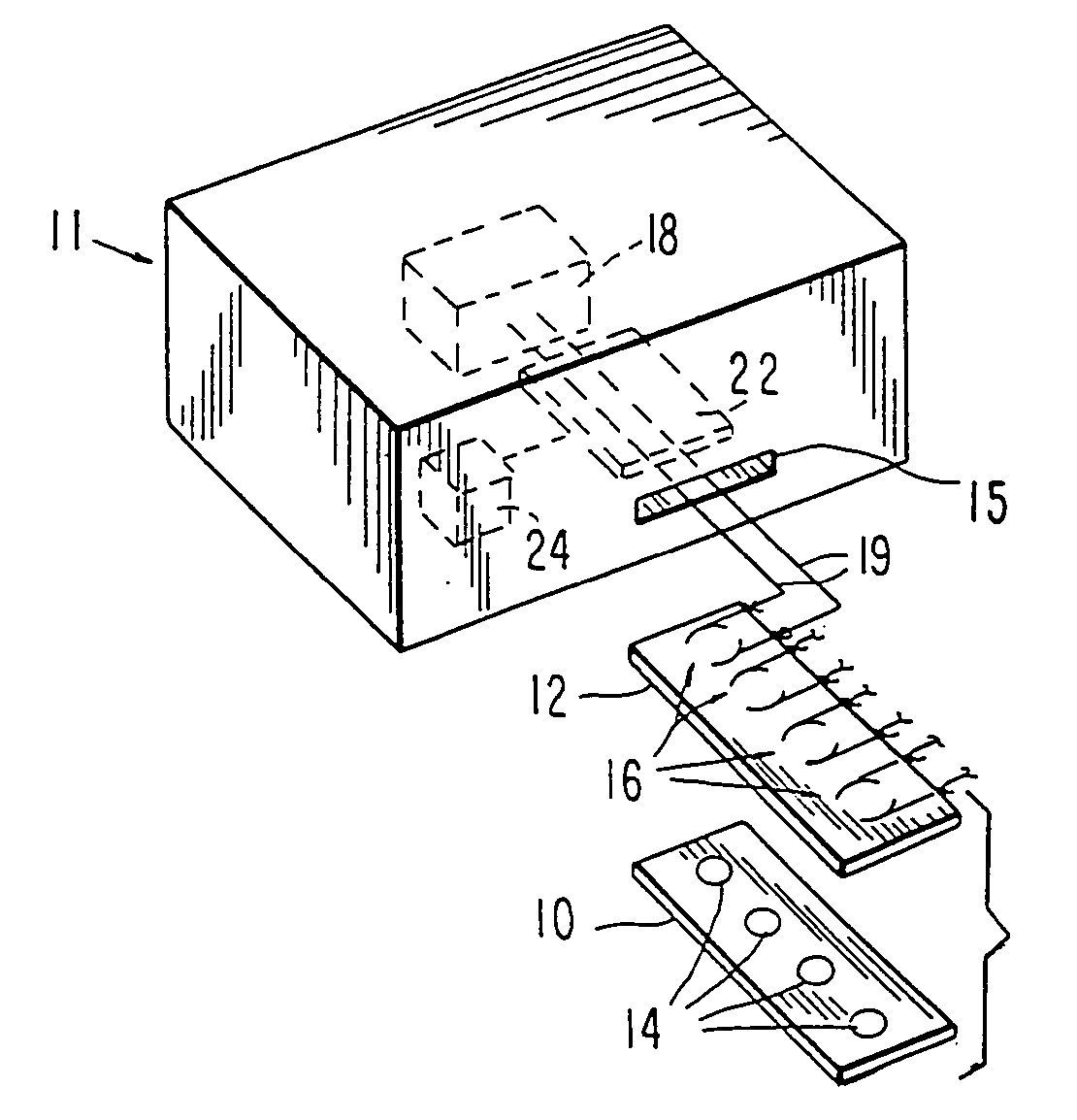
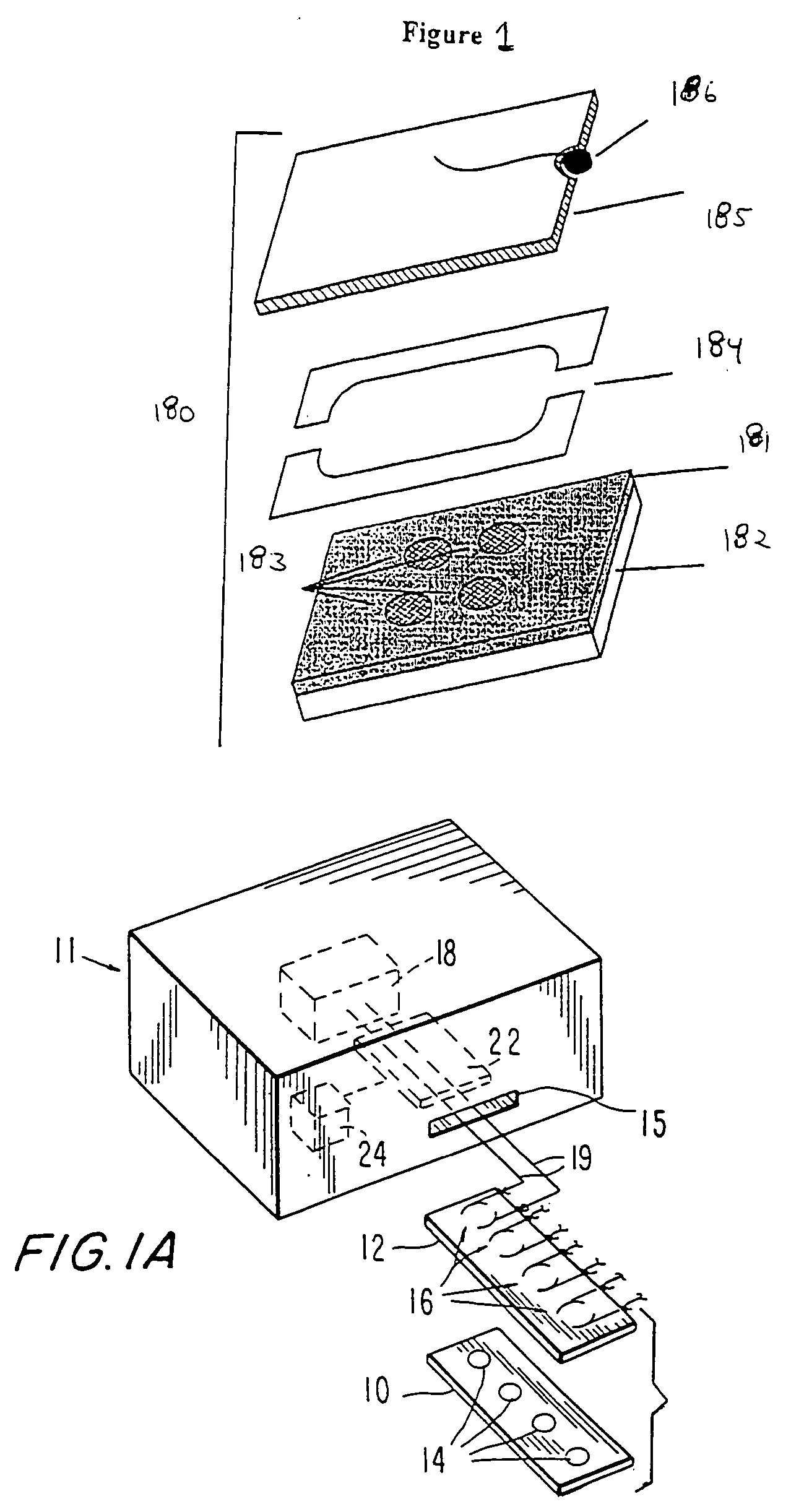
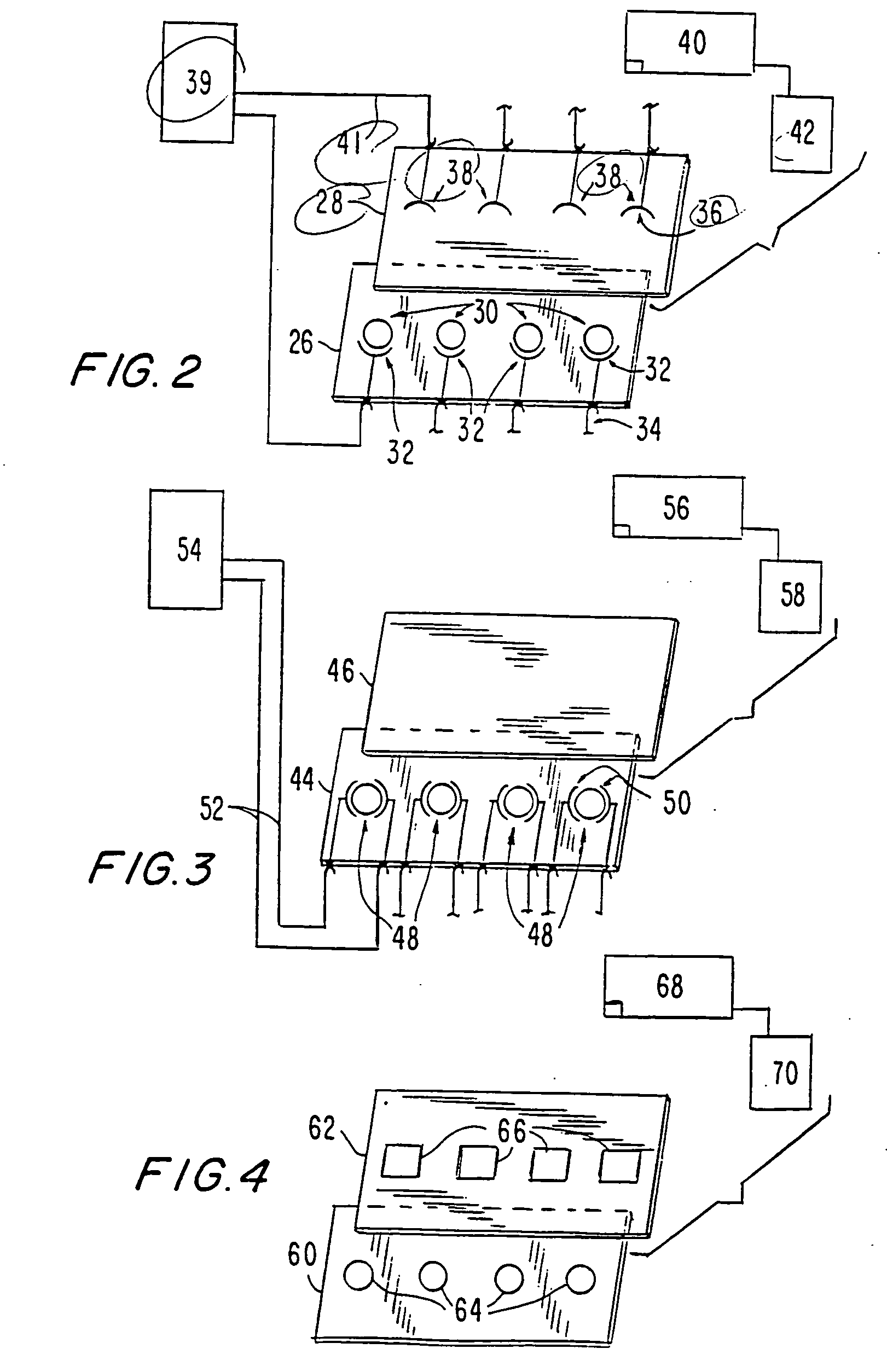
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6090545AMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsProviding materialElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces which are electronically excited for use in electrochemiluminescence based tests. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use in flat panel displays and multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Multi-array multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS6673533B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyAnalyteElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Graphitic nanotubes in luminescence assays
Graphitic nanotubes, which include tubular fullerenes (commonly called "buckytubes") and fibrils, which are functionalized by chemical substitution, are used as solid supports in electrogenerated chemiluminescence assays. The graphitic nanotubes are chemically modified with functional group biomolecules prior to use in an assay. Association of electrochemiluminescent ruthenium complexes with the functional group biomolecule-modified nanotubes permits detection of molecules including nucleic acids, antigens, enzymes, and enzyme substrates by multiple formats.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Assays for measuring nucleic acid damaging activities
InactiveUS6214552B1Simple and accurate and reliable assayEfficient transferSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrochemiluminescenceDouble strand
A method for assaying a sample for a nucleic acid damaging activity using at least one singular double-stranded nucleic acid with at least one electrochemiluminescent label, and a method for measuring an inhibitor of a nucleic acid damaging activity with at least one singular double-stranded nucleic acid using at least one electrochemiluminescent label, are disclosed.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS20040086423A1Volume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsAnalyteProviding material
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
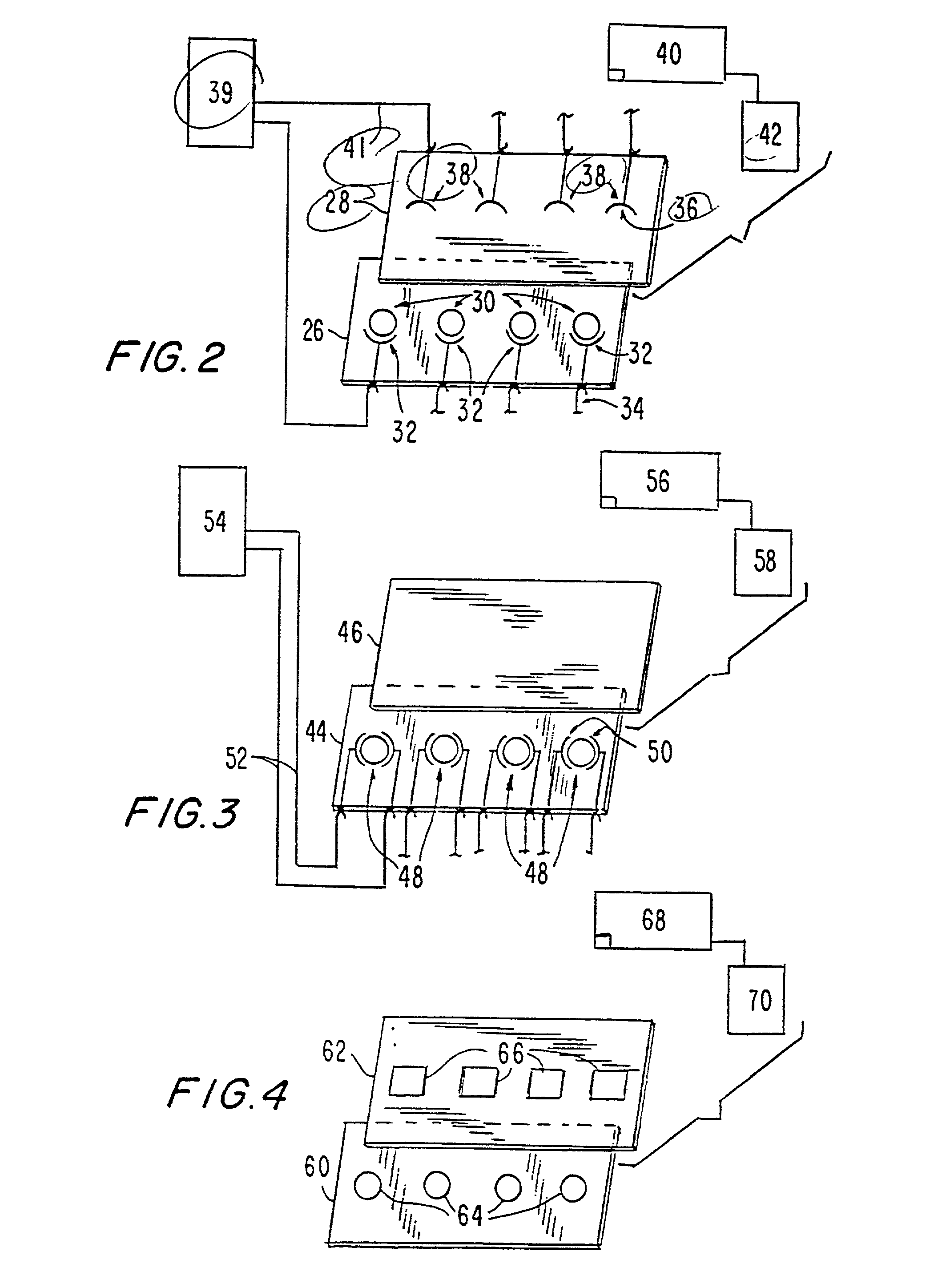
Methods and apparatus for improved luminescence assays
InactiveUS6325973B1High sensitivityFaster assay timeImmobilised enzymesCombination devicesAnalyteElectrochemiluminescence
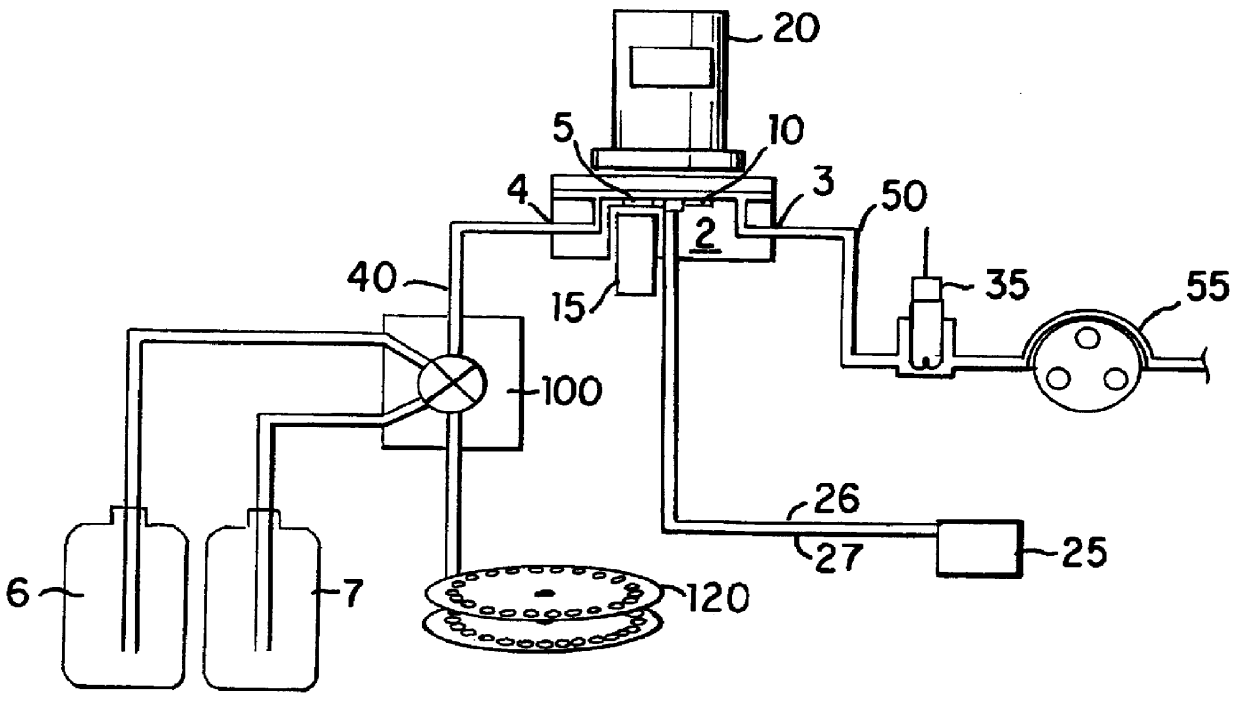
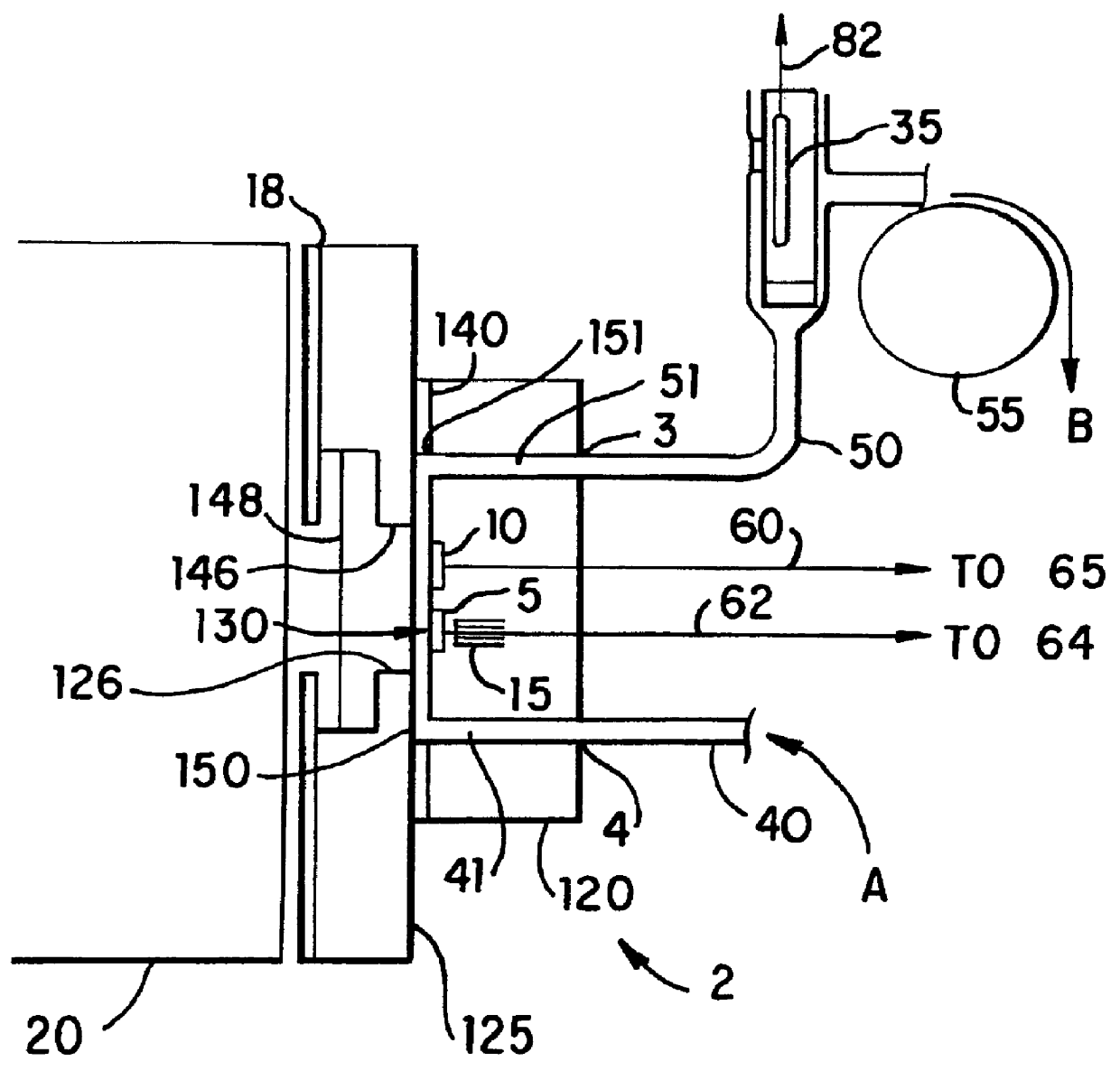
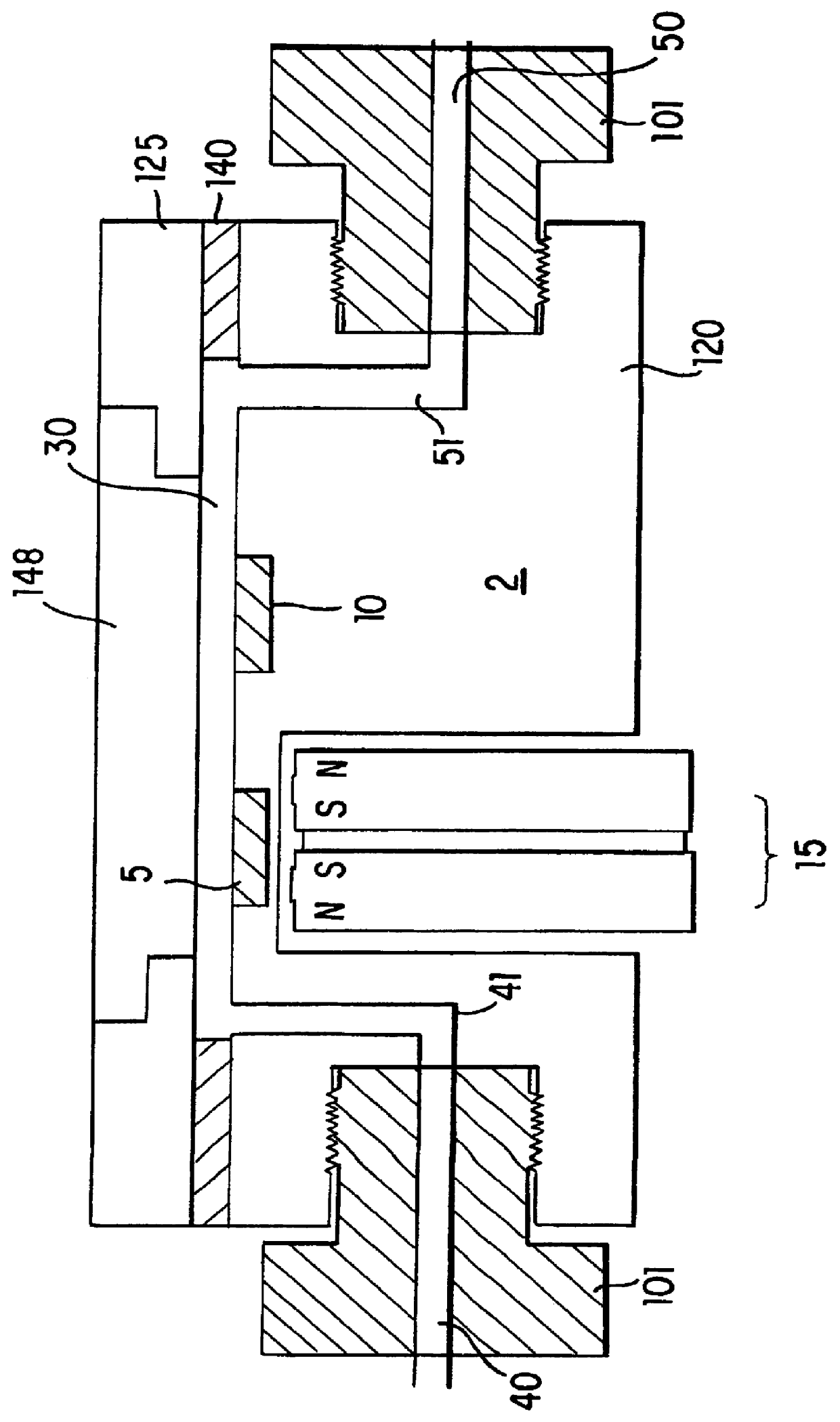
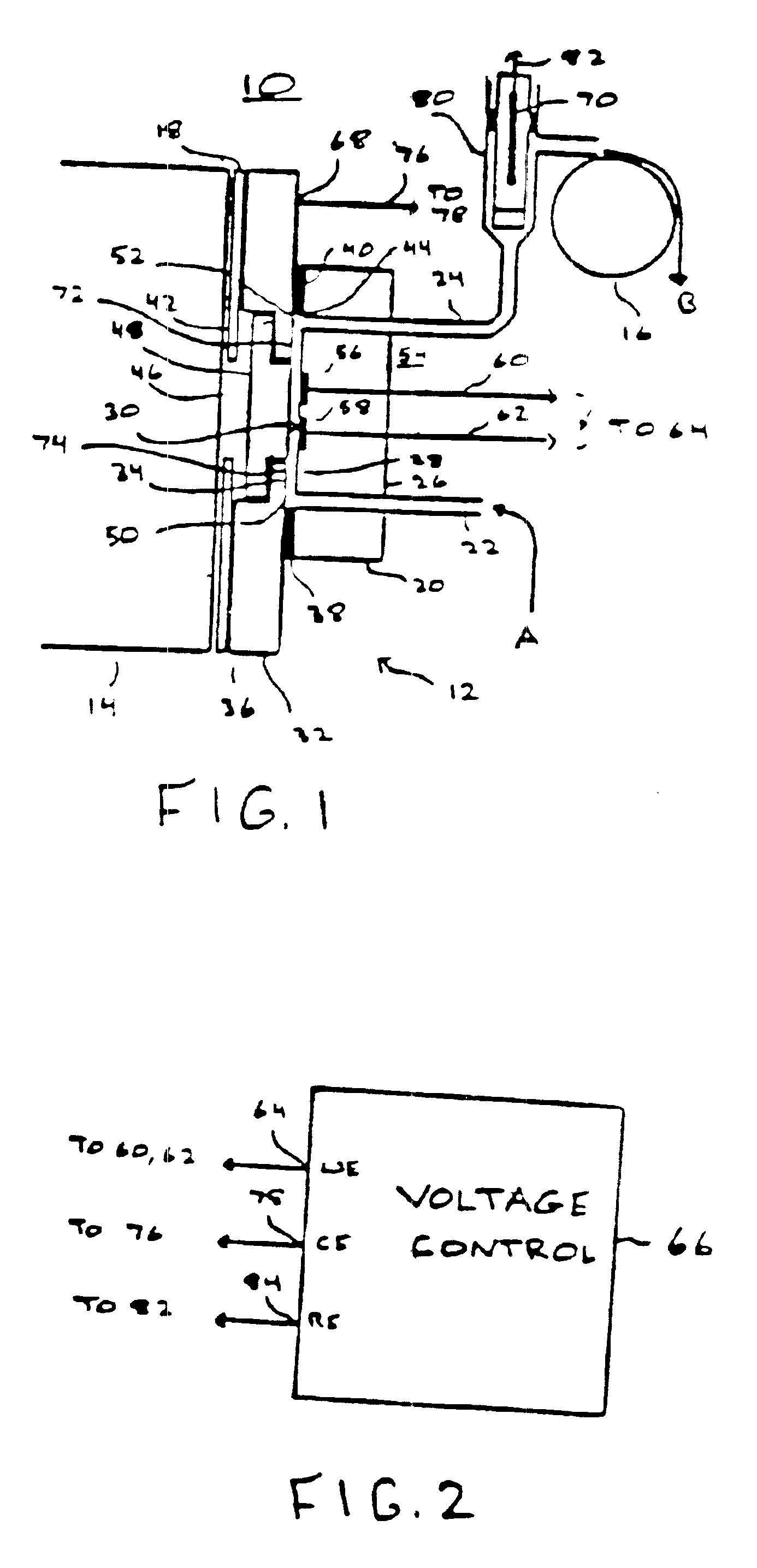
An apparatus for performing a binding assay for an analyte of interest in a sample based upon measurement of clectrochemiluminescence at an electrode surface comprising: (a) a cell defining a sample; (b) an electrode adjacent a portion of the sample containing volume; (c) a voltage control device for impressing electrochemical energy upon the electrode sufficient to generate luminescence; (d) means for magnetically collecting particles along the electrode surface; and (e) a light detection device for measuring the luminescence.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Magnetic particle based electrochemiluminescent detection apparatus and method
InactiveUS6133043AHigh sensitivityFaster assay timeMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMagnetic field gradientElectrochemiluminescence
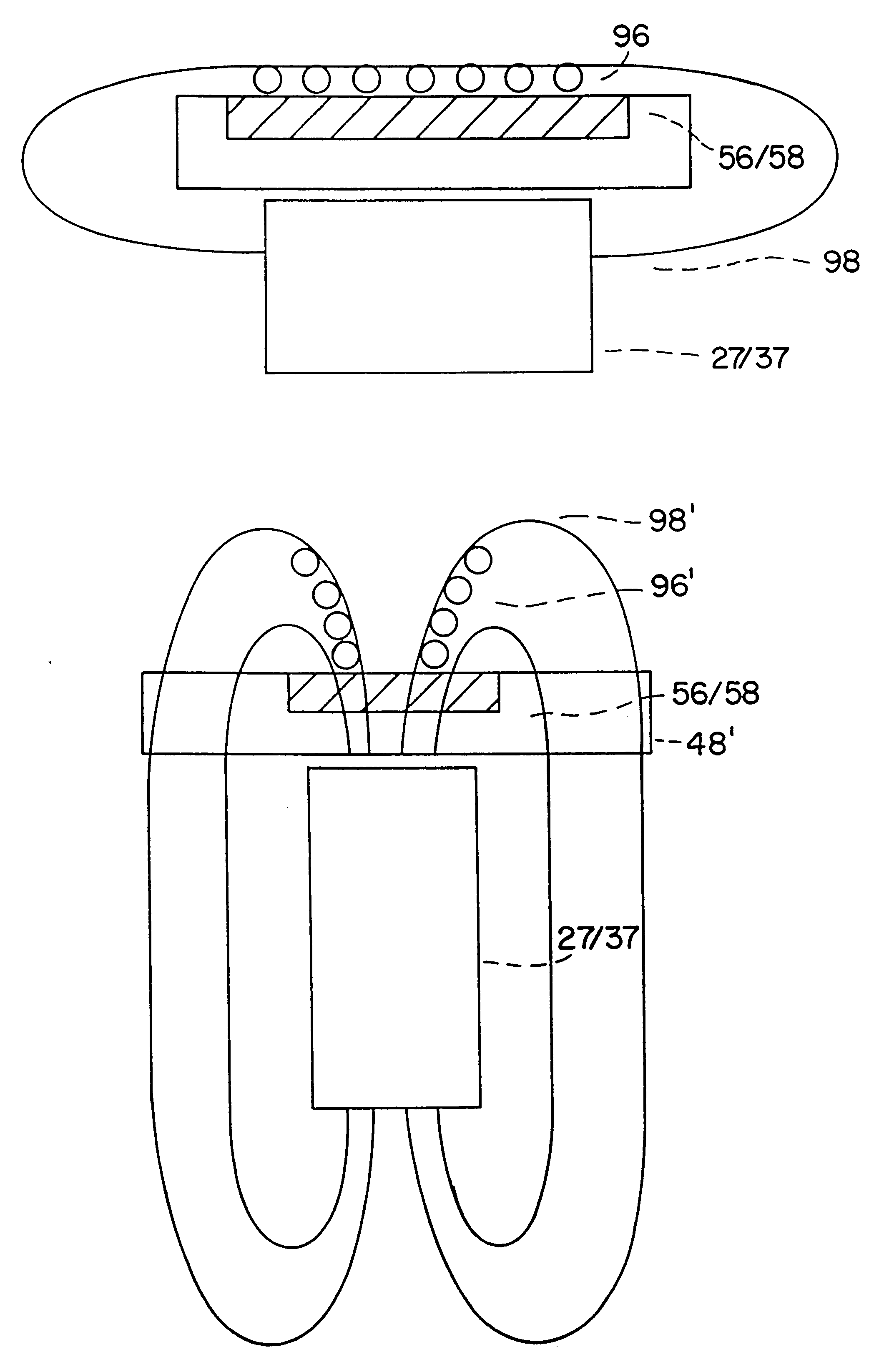
A method and apparatus for measuring electrochemiluminescence from a sample composition are described wherein magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species are captured on the electrode with the aid of a capture magnet having a configuration such that the magnetic flux lines (or the magnetic field gradient) of at least one magnetic field source therein are compressed and / or dispersed. This capture magnet improves the distribution of the magnetically responsive electrochemiluminescent active species on the electrode surface and reduces interference with the photomultiplier tube, thereby enhancing the ECL signal and improving sensitivity. The improved capture and distribution also allows for shorter assay times.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Particle based electrochemiluminescent assays
InactiveUS6881536B1Improve performanceFaster assay timeRuthenium organic compoundsSugar derivativesChemical MoietyAnalyte
A method for the detection of an analyte of interest in a sample, which method comprises the steps of:(1) forming a composition comprising(a) a sample,(b) at least one substance selected from the group consisting of(i) added analyte of interest or an analog of the analyte of interest,(ii) a binding partner of the analyte of interest or its said analog, and(iii) a reactive component capable of binding with (i) or (ii),wherein one of said substances is linked to a label compound having a chemical moiety capable of being induced to luminesce, and(c) a plurality of particles capable of specifically binding with the analyte and / or a substance defined in (b) (i), (b) (ii), or (b) (iii);(2) inducing the label compound to luminesce; and(3) measuring luminescence emitted by the composition to determine the presence of the analyte of interest in the sample.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence with a single faradaic electrode
ActiveUS20070034529A1Photography auxillary processesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceCapacitanceOxidation-Reduction Agent
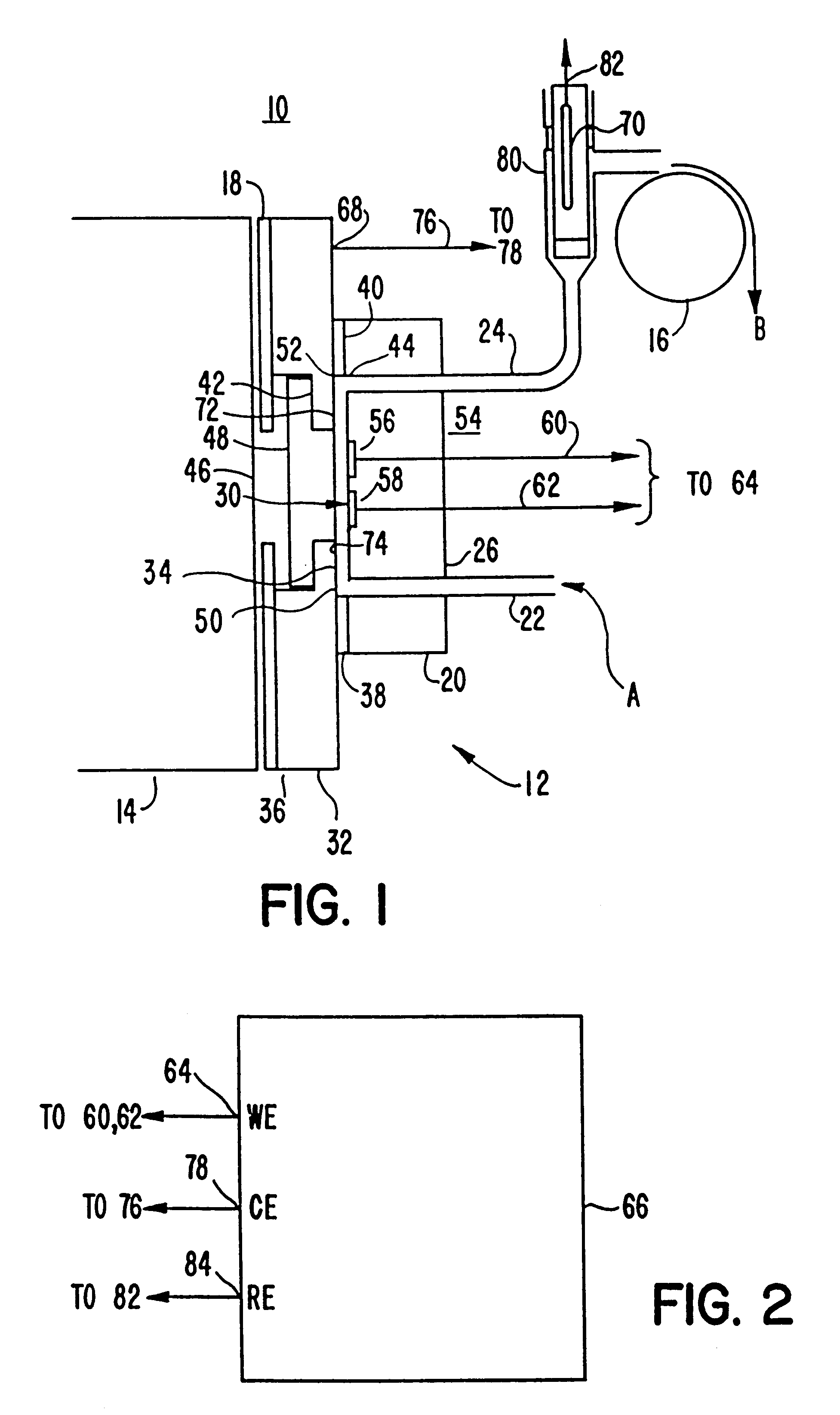
Described herein is an apparatus comprising an electrochemical cell that employs a capacitive counter electrode and a faradaic working electrode. The capacitive counter electrode reduces the amount of redox products generated at the counter electrode while enabling the working electrode to generate redox products. The electrochemical cell is useful for controlling the redox products generated and / or the timing of the redox product generation. The electrochemical cell is useful in assay methods, including those using electrochemiluminescence. The electrochemical cell can be combined with additional hardware to form instrumentation for assay methods.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Graphitic nanotubes in luminescence assays
Graphitic nanotubes, which include tubular fullerenes (commonly called "buckytubes") and fibrils, which are functionalized by chemical substitution, are used as solid supports in electrogenerated chemiluminescence assays. The graphitic nanotubes are chemically modified with functional group biomolecules prior to use in an assay. Association of electrochemiluminescent ruthenium complexes with the functional group biomolecule-modified nanotubes permits detection of molecules including nucleic acids, antigens, enzymes, and enzyme substrates by multiple formats.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
Detecting water-borne parasites using electrochemiluminescence
InactiveUS6146838AFast and sensitive and preciseChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWithdrawing sample devicesAntigenSludge
A method for the detection or quantitation of a water-borne parasite, such as Cryptosporidia. The detection or quantitation is accomplished by an electrochemiluminescence assay comprising the steps of filtering water to obtain a sludge thought to contain the parasite or a fragment thereof; extracting a sample of said sludge in a extraction medium to form antigenic derivatives of said parasite; forming an assay mixture comprising a sample of said extracted sludge and an antibody specific to said antigenic derivative; incubating said assay mixture to permit binding of said antibody and said antigenic derivative; and conducting an electrochemiluminescence assay for the bound complex of antibody and antigenic derivative, thereby detecting or quantitating the Cryptosporidia in said water.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Method for extracting carbon quantum dots from activated carbon
ActiveCN101973541AUniform particle sizeImprove photoelectric performanceNanostructure manufactureLuminescent compositionsActivated charcoal powderCarboxyl radical
The invention provides a method for extracting carbon quantum dots from activated carbon, which comprises the following steps of: adding dry activated carbon powder to salpeter solution and stirring for backflow; performing reduced pressure distillation for evaporating suspension obtained by backflow to dryness; dispersing obtained black solids in water, and neutralizing obtained solution with sodium hydroxide; and finally, centrifugating neutralized black suspension for removing precipitation, separating supernatant fluid by using an ultrafiltration centrifugal tube or an ultrafiltration membrane, collecting filtrate, and drying the filtrate to obtain carbon quantum dots. The method uses cheap and available activated carbon as carbon sources, and can obtain a large number of carbon quantum dots by simple chemical oxidation process and simple subsequent processes of evaporation, saturation, centrifugation and ultrafiltration. The carbon quantum dots are graphite structure nanocrystals with the grain diameter of 3 to 5 nm, the surfaces of which have a large amount of hydroxide radicals. The carbon quantum dots have good fluorescence and electrochemiluminescence.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Manufacturing method and application of electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin
ActiveCN102507689AHigh sensitivityHigh luminous intensityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansSingle strandElectrochemiluminescence
The invention relates to a manufacturing method and application of an electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting thrombin. Ruthenium bipyridine with active group is modified to the gold nanoparticle surface to form an electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probe, which plays the role of amplifying electrochemiluminescence, and the upper part DNA single strand is modified on the working electrode surface to constitute an electrochemiluminescence sensor. The target analyte of thrombin is subjected to reaction with partial DNA double strands and then with DNA polymerase, Nb.BbvCI nicking enzyme and partial DNA single strand to obtain DNA hybrid solution which is added into the sensor, so as to increase electrochemiluminescence nanoparticle probes on the electrode surface and further lead to an enhanced electrochemiluminescence signal, and accordingly thrombin determination is realized. The inventive sensor has high selectivity and detection sensitivity.
Owner:武汉菲思特医学检验实验室有限公司
Preparation and application of electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting trace pesticide residue
InactiveCN101995402AIncreased sensitivityExpand the scope of detectionChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesPesticide residueElectrochemiluminescence
The invention discloses an electrochemiluminescence sensor for detecting trace pesticide residue and a method for detecting pesticide residue. An electrode preparation method (figure attached) comprises the following steps: selecting an identifier of the pesticide residue; preparing quantum dots and graphene nano material according to documents; and modifying the nano material, the quantum dots and the identifier onto the electrode surface of the sensor by the electrode surface modification technology. The method for detecting the trace pesticide residue comprises the following steps: connecting the modified electrode to an electrochemiluminescence instrument and detecting the pesticide residue in the sample extract. The electrode in the invention has high specificity and sensitivity capable of reaching ng level, a basic detection process is finished only within 3-5 min, and the cost is low. The method for detecting the pesticide residue by utilizing the electrode is fast and simple to operate, and the reaction is automatically finished and the result is automatically recorded by an apparatus.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Methods for improved particle electrochemiluminescence assays
InactiveUS6078782AHigh sensitivityFaster assay timeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTarget analysisAnalyte
The invention relates to methods of performing a binding assay for an analyte of interest present in a sample based upon electrochemiluminescence at an electrode of interest. Particles are employed in the method, which are then collected in a zone at which electrochemiluminescence can be induced, wherein the amount of induced electrochemiluminescence is related to the amount of analyte in the sample.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Display apparatus and display element driving method
InactiveUS20070109218A1High voltageMaintain voltageStatic indicating devicesElectrochemiluminescenceLuminescent material
A display apparatus includes a display element that includes an electrolyte solution layer containing an electrochemical luminescent material; and a voltage applying unit that applies a voltage with a waveform having a gradient for a first period and a flat top for a second period following the first period, to the electrolyte solution layer, so that the electrochemical luminescent material emits light.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
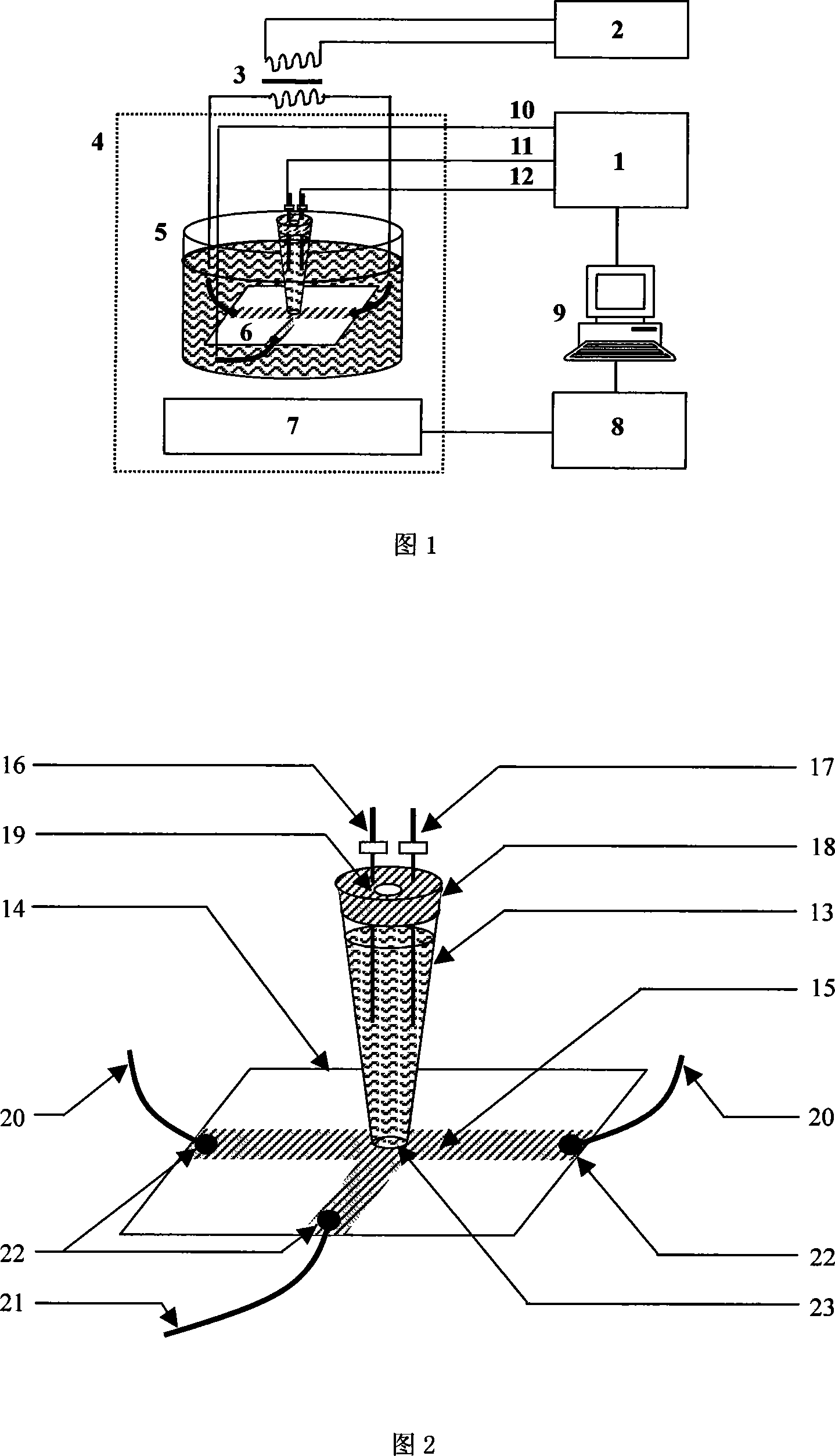
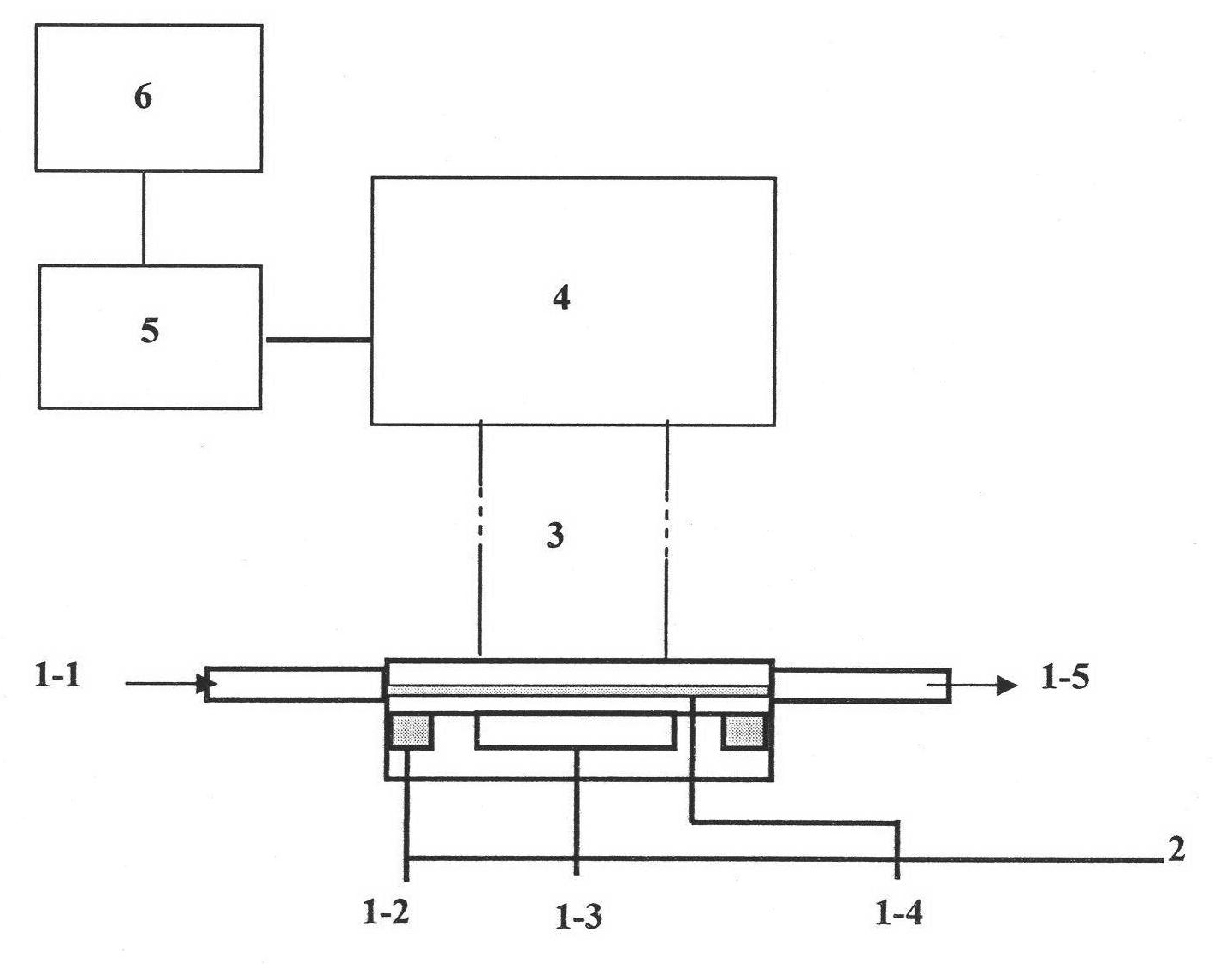
Heat controlled electric pole electrogenerated chemiluminescence testing apparatus and testing-pool preparation method
InactiveCN101162199AReduce dosageImprove collection efficiencyAnalysis by electrical excitationMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemiluminescenceEngineering
The invention provides a detection device of thermal control electrode electrochemiluminescence, which is characterized in that the detection device comprises a detection cell and an electrical heating system. The electrical heating system is connected with working electrodes of the detection cell, the working electrodes are conducting glass electrodes with indium-tin oxide (ITO) coating; the detection cell is a three-electrode system, the three electrodes are respectively connected with an electrochemical workstation which is connected with a computer; the detection cell is provided with a photomultiplier at the lower part; the photomultiplier is connected to a feeble light detector which is connected to the computer; the photomultiplier and the detection cell are both arranged in a dark box. The invention is simple to manufacture and convenient to use. The system is stable and is of low cost, which can facilitate in heating the working electrodes. The integrated thermal control ITO electrode electrochemiluminescence detection system has good sensitivity and repeatability on the detection of amines.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Multi-array, multi-specific electrochemiluminescence testing
InactiveUS20060172340A1Cost effectiveImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteElectrochemiluminescence
Materials and methods are provided for producing patterned multi-array, multi-specific surfaces for use in diagnostics. The invention provides for electrochemiluminescence methods for detecting or measuring an analyte of interest. It also provides for novel electrodes for ECL assays. Materials and methods are provided for the chemical and / or physical control of conducting domains and reagent deposition for use multiply specific testing procedures.
Owner:MESO SCALE TECH LLC
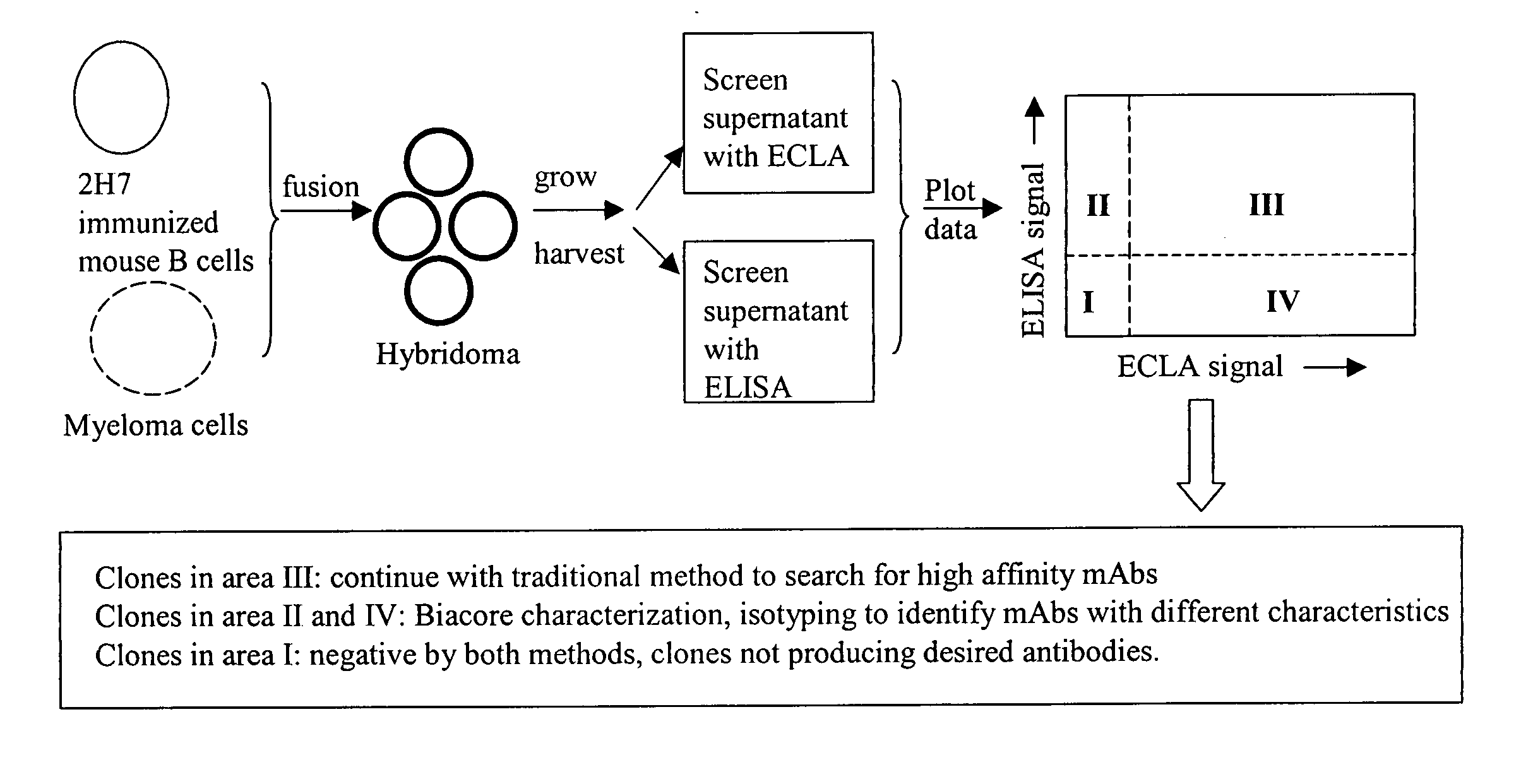
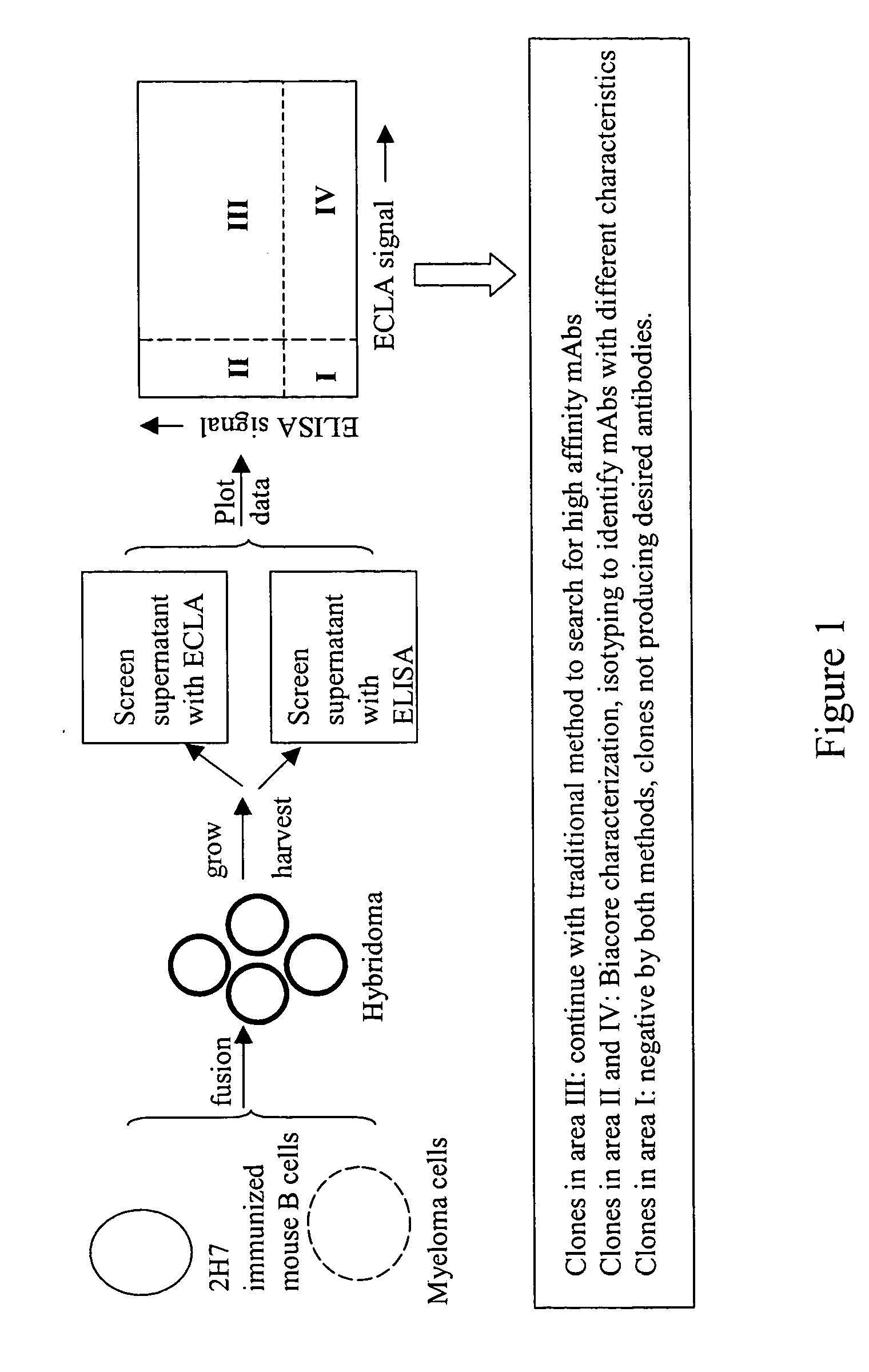
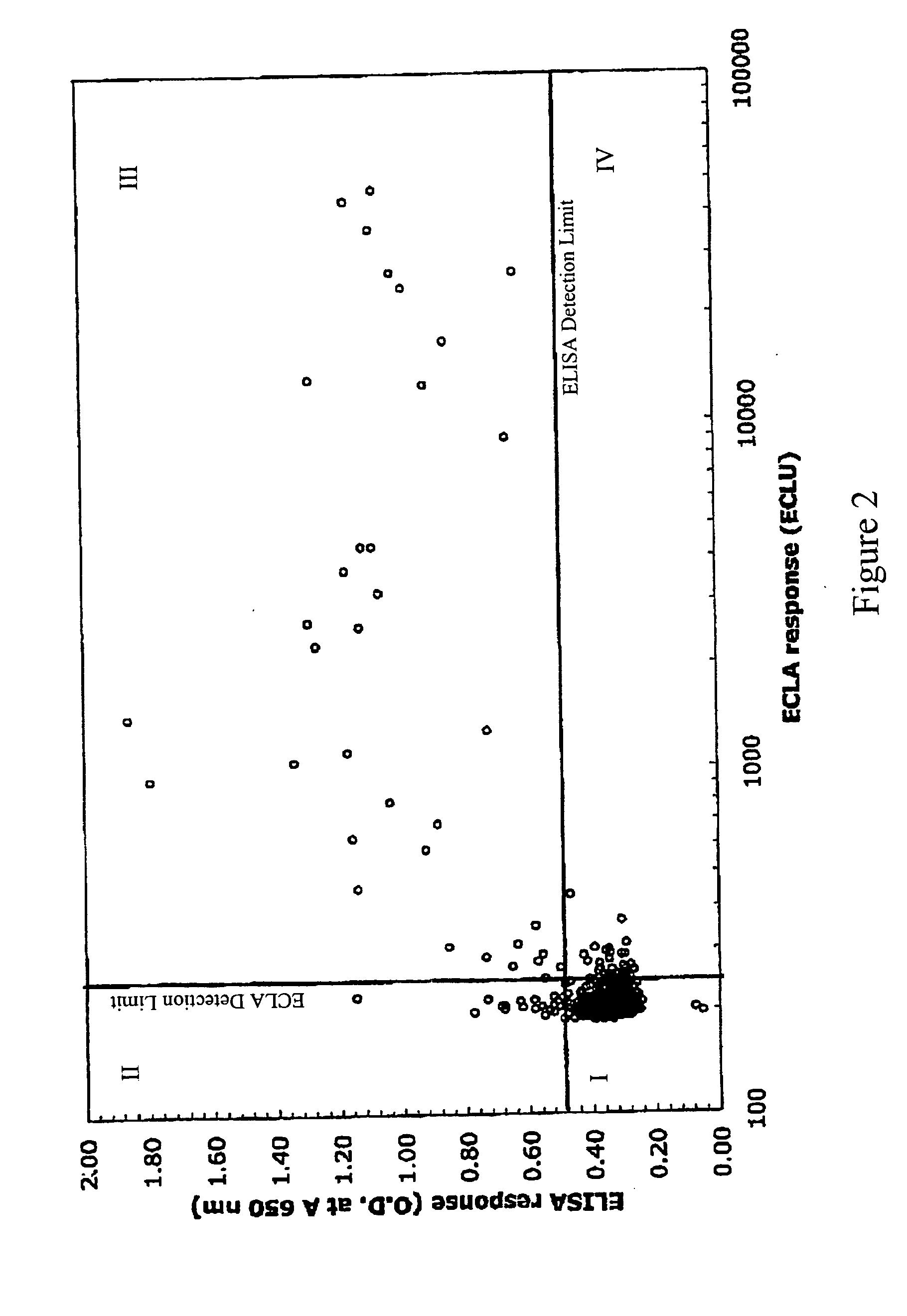
Cross-screening system and methods for detecting a molecule having binding affinity for a target molecule
ActiveUS20050255527A1Reduce concentrationSafety and efficacyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLow affinityElectrochemiluminescence
The invention is directed to a cross-screening system and methods of the invention utilizing a combination of an immunoassay (IA) and electrochemiluminescence assay (ECLA) to identify molecules that have binding affinities for a target molecule. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention can detect molecules that have binding affinities for the target molecule below the detection limits of the individual immunoassay or ECLA. The cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful for generating a pool of candidate analyte molecules enriched in a desired characteristic, such as low binding affinity for a target molecule. Low affinity antibodies identified by the cross-screening system and methods of the invention are useful, for example, in assessing the safety and efficacy of biological therapeutics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Preparation of electrochemical luminescence paper chip and application of chip in hydrogen sulfide detection
InactiveCN104819976ASpeed up the flowReduce volatilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceWaxSignalling molecules
The invention discloses a method for preparing an electrochemical luminescence paper chip and a method for measuring content of signal molecule hydrogen sulfide in MCF-7 by using an electrochemical luminescence sensor. The method is characterized by preparing a hydrophobic region, a semi-hydrophobic region, a hydrophilic region and a hollow channel on paper by utilizing a wax printing technology, cutting the hollow channel by virtue of a laser cutting machine, preparing proper printing ink, printing a corresponding reference electrode and a working electrode on the paper, functionalizing the working area, dripping stock solution in a pretreatment region, and fixing cancer cells; and folding the prepared paper chip, forming a three-electrode system, dropwise adding electrolyte solution in a reaction region, connecting an electrochemical workstation, thus realizing high-sensitivity detection of the low-content signal molecules in the cancer cells.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
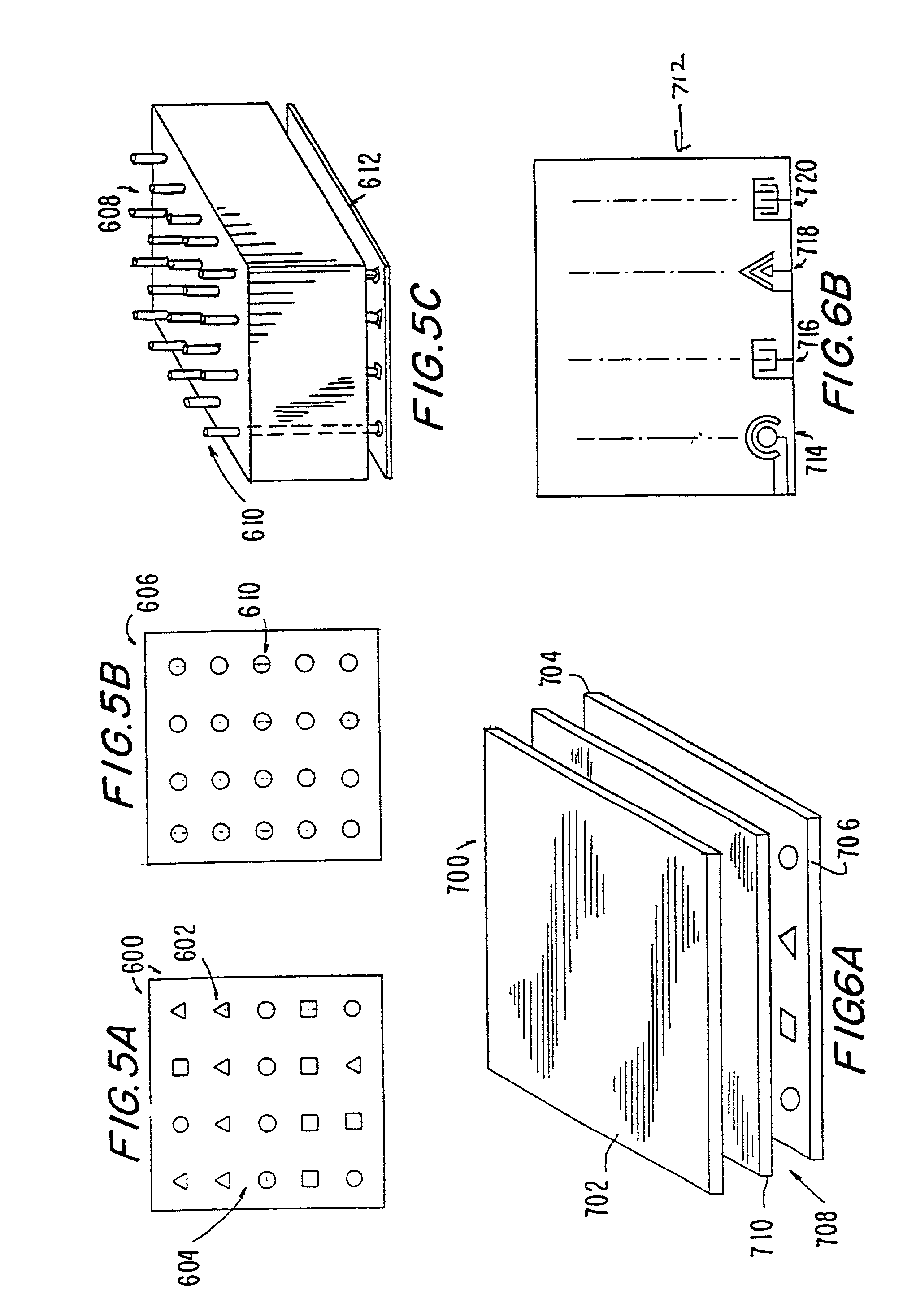
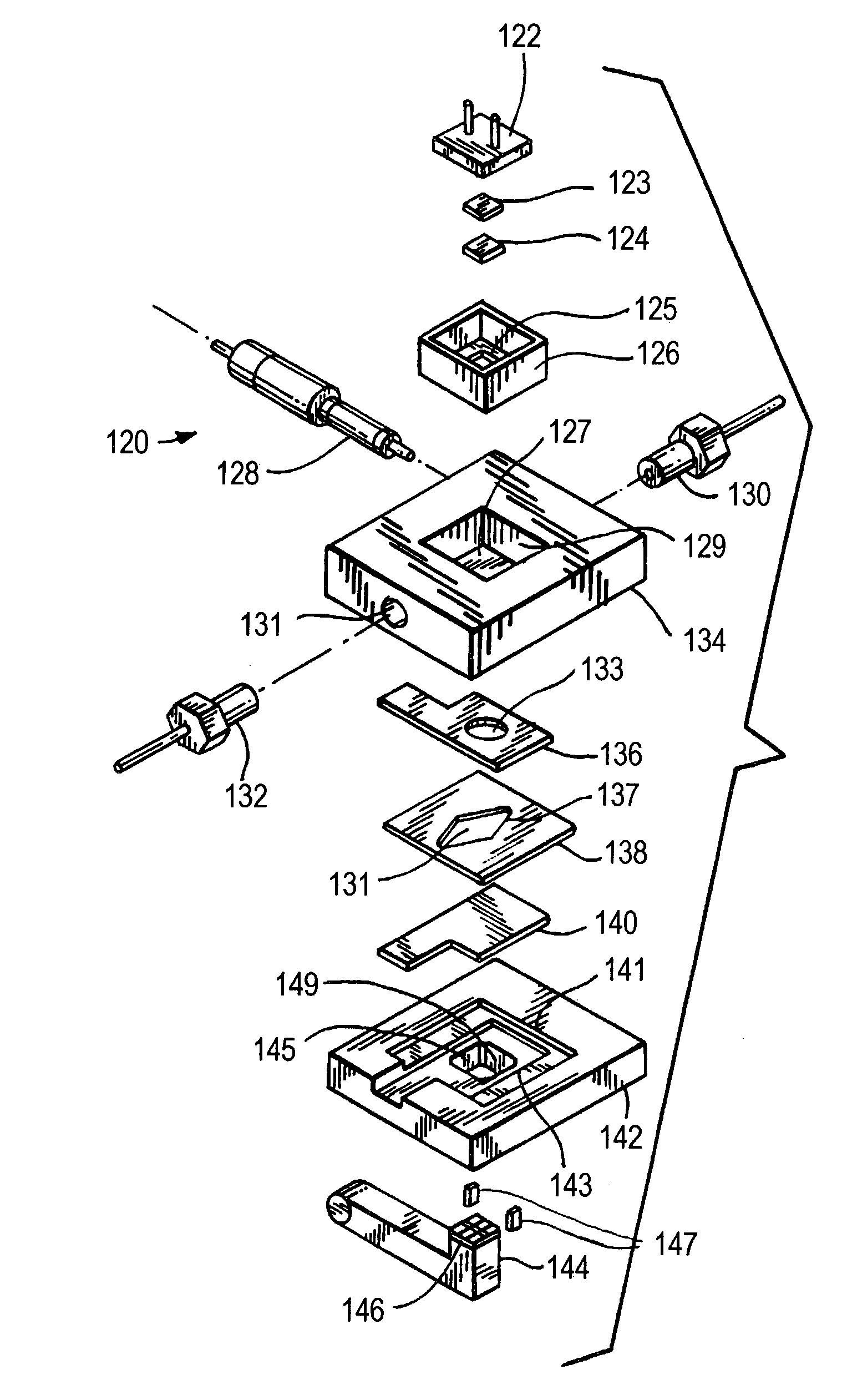
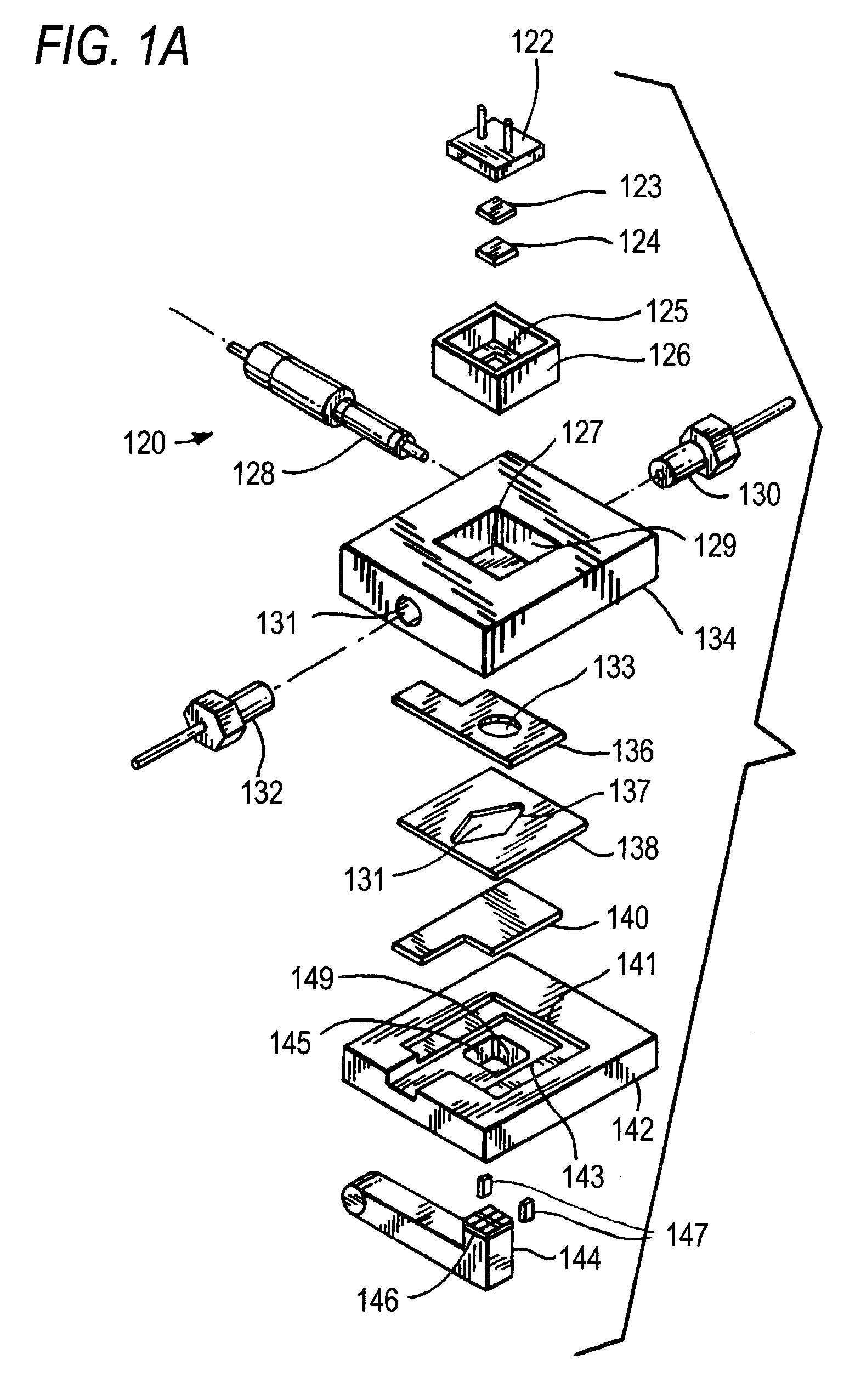
Electrochemiluminescence flow cell and flow cell components
InactiveUS7553448B2Improve propertiesIncrease apparatus operational lifetimeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsIridiumFlow cell
An electrochemiluminescence cell comprising an electrode capable of inducing an electrochemiluminescence-active species to electrochemiluminesce. The electrode is preferably made of rhodium, iridium or an alloy of platinum, rhodium or iridium alloyed with an alloy material comprising a transition element. The electrode may be used as counter electrode and / or as a working electrode in the electrochemiluminescence cell. The cell preferably includes a counter electrode and a support attached to the counter electrode. The support comprises a transparent portion in optical registration with the working electrode. The counter electrode may include one or more field extending elements interposed between the transparent portion and the working electrode. The field extending element is preferably a ladder or a grid.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
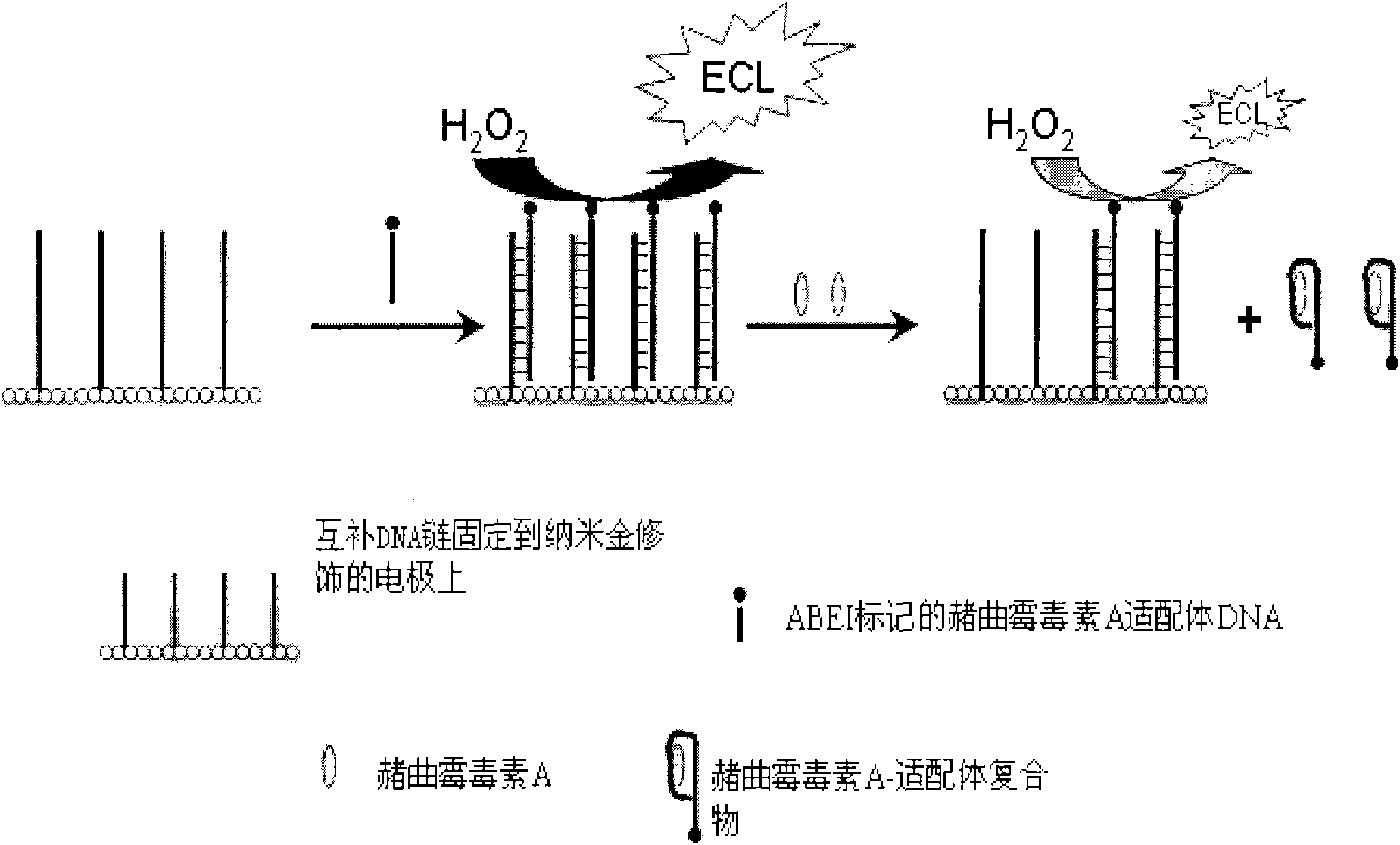
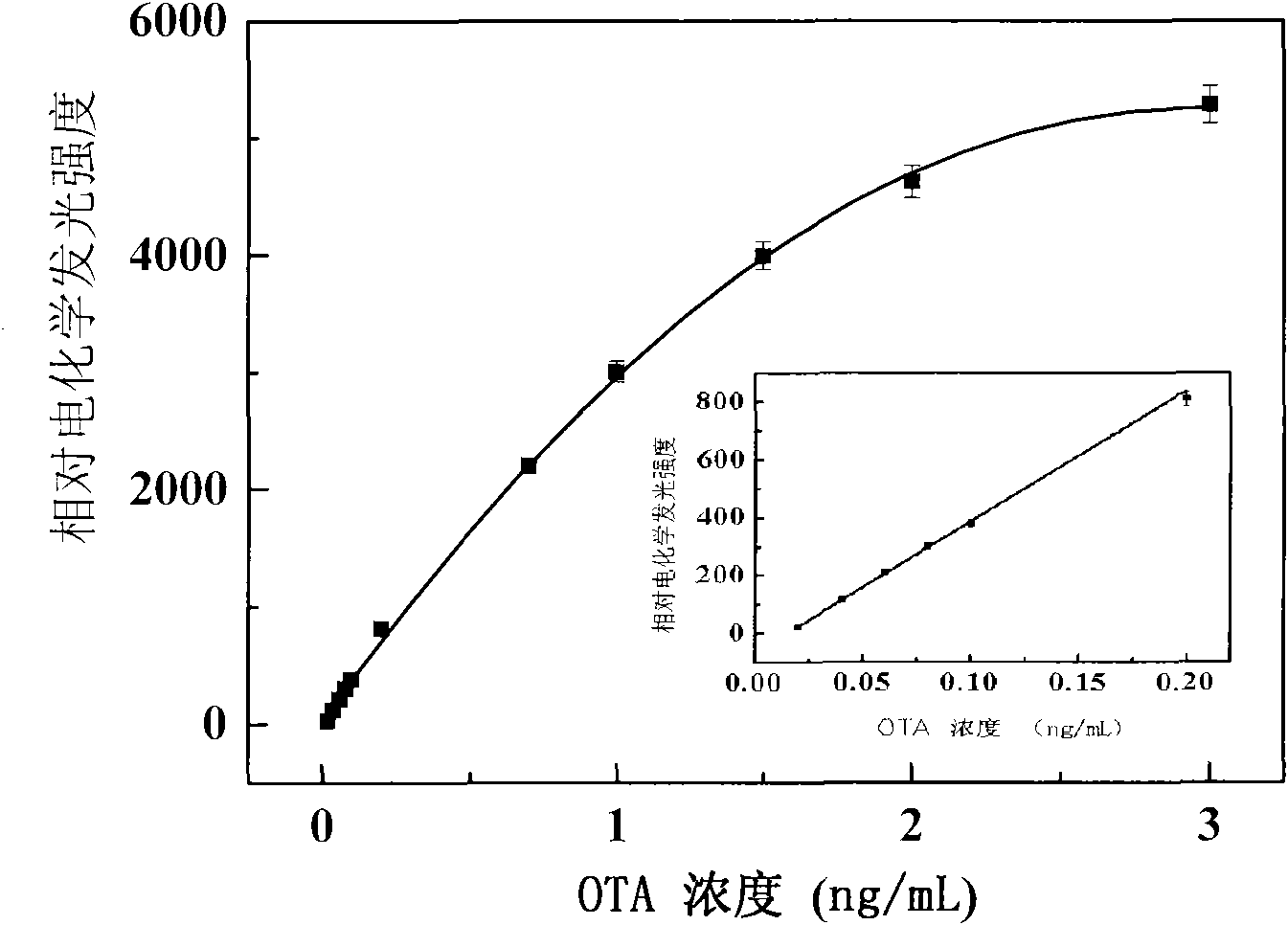
Method for detecting ochratoxin A by using electrochemical luminous adaptor sensor
InactiveCN101936940AStrong electrochemical working signalHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoparticleOperability
The invention discloses a method for detecting ochratoxin A by using an electrochemical luminous adaptor sensor, which belongs to the technical field of electrochemical luminous sensors and is used for detecting the ochratoxin A content of wheat, grains, feeds and products thereof. The method is based on the ochratoxin A specificity identification by an adaptor and an electrochemical luminous reaction of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and isoluminol (ABEI) under an alkaline condition. The method comprises the following steps of: modifying the surface of a naked gold electrode by using gold nanoparticles to amplify an electrochemical luminous signal; modifying the surface of a working electrode by using single stranded DNA, and modifying the electrode surface with the adaptor marked with the isoluminol (ABEI) by base pairing; adding the hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) to detect the electric luminous signal; and establishing a quantitative detection standard curve of the ochratoxin A according to the ratio of the strength of the electrochemical luminous signal to the concentration of the ochratoxin A. The invention aims to provide a high-sensitivity and high-operability ochratoxin A quantitative detection method.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
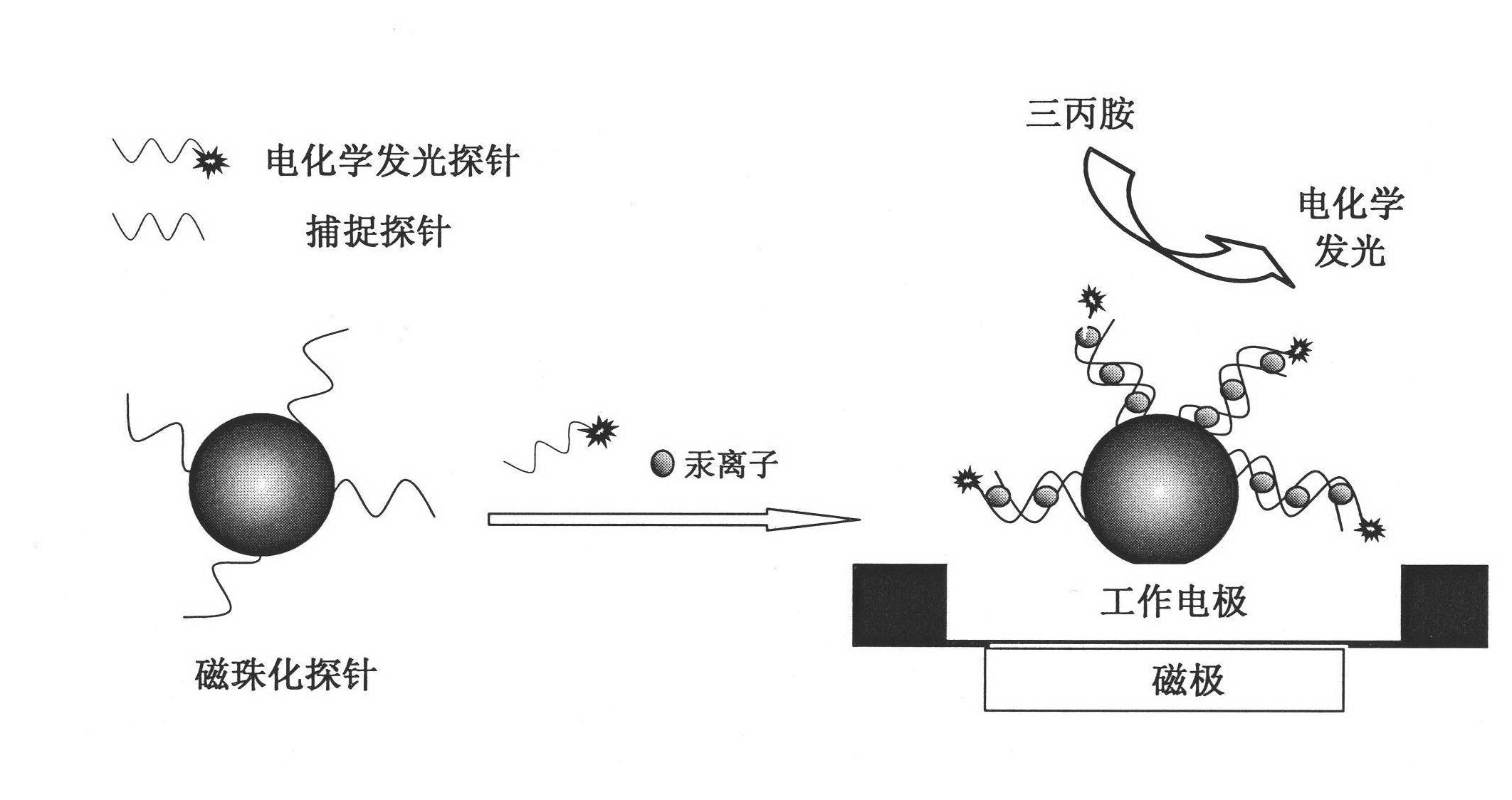
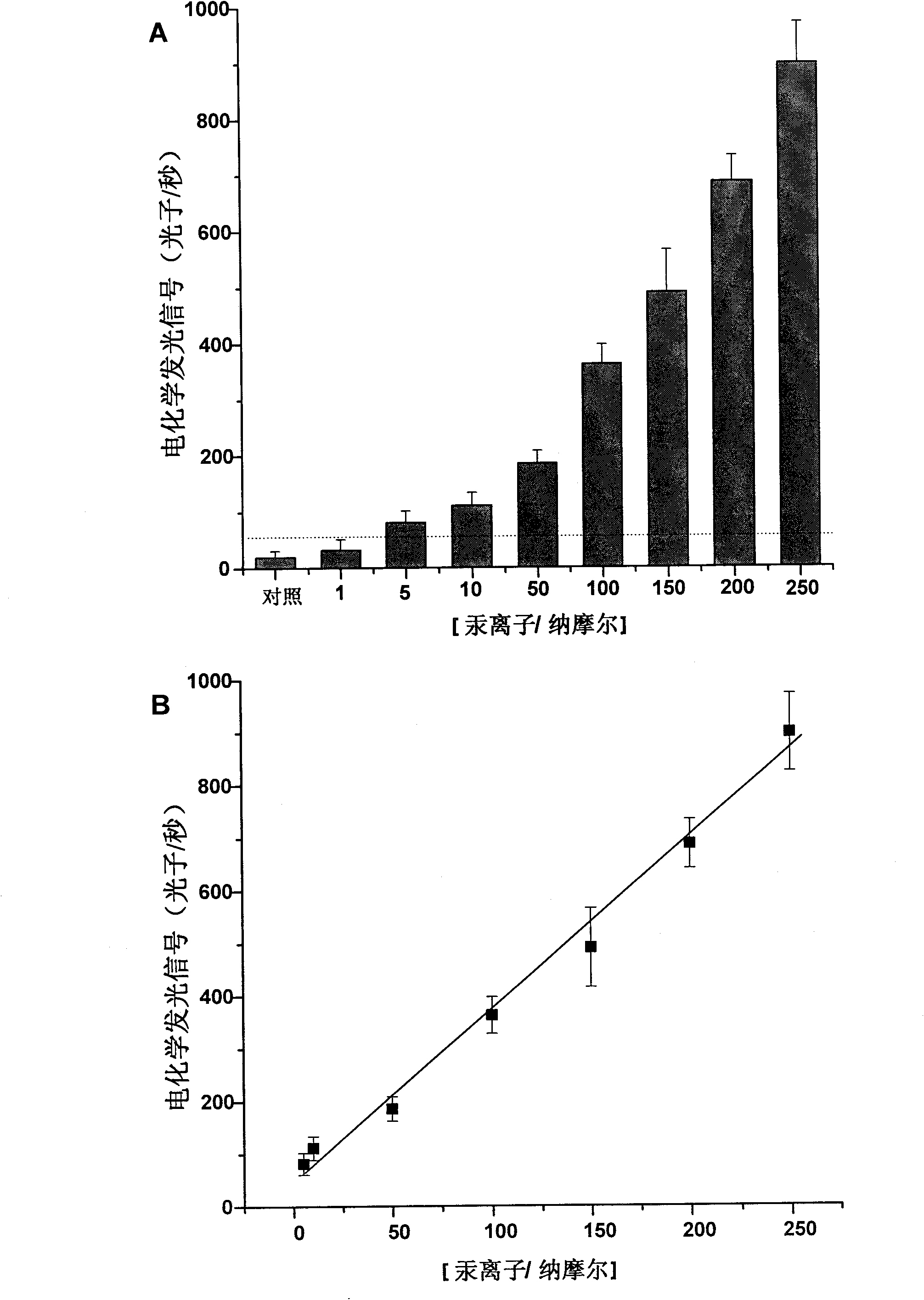
Magnetic bead electrochemiluminescence gene sensor-based method for detecting mercury ions and application thereof
InactiveCN101892294AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMagnetic beadElectrochemiluminescence
The invention discloses a magnetic bead electrochemiluminescence gene sensor-based method for detecting mercury ions and an application thereof. In the method, two probes are designed, one is a capture probe to be labelled on the surface of magnetic beads and form a magnetic bead probe; and the other probe is labelled with tris(2,2'-bipyridyl)ruthenium(II) to form an electrochemiluminescence probe. As the two probes have T:T mismatch structures, the two probes can not form a matched double helix structure at room temperature in the absence of mercury ions. When mercury ions exist, the mismatched T:T can form a stable T-Hg2 +-T coordination-complex structure with mercury ions according to the specificity of mercury ions so that mercury ions can mediate the two probes to form the double helix structure. Therefore, the magnetic bead probe can capture the electrochemiluminescence probe on the surface in the presence of mercury ions and then mercury ions can be detected through magnetic bead separation and electrochemiluminescence detection. The method of the invention has high specificity and sensitivity and facilitates the qualitative measurement and quantitative measurement of mercury ions.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
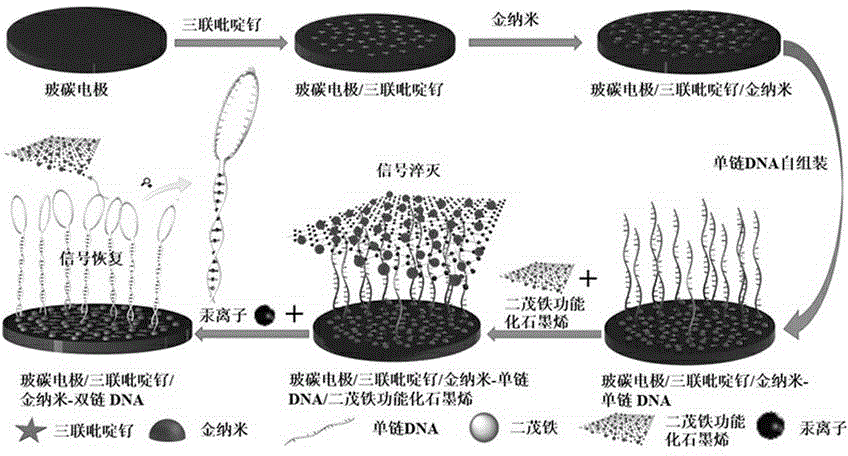
Preparation method and application of modified glassy carbon electrode
ActiveCN103913496ARealize visual detectionImprove stabilityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansMercuric ionSample water
The invention discloses a preparation method for a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA-ferrocene functionalized graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. The method comprises the following concrete steps: polishing of a glassy carbon electrode; coating of Ru(bpy)3<2+> to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+> modified glassy carbon electrode; coating of gold nanoparticles to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode; coating of single-stranded DNA to prepare a Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA modified glassy carbon electrode, wherein the sequence of the single-stranded DNA is rich in T bases, a stable double-stranded DNA structure can be formed after bonding with Hg2+, and the 5' end of the sequence of the single-stranded DNA is connected with an SH-(CH2)6 group; and coating pf ferrocene functionalized graphene so as to prepare the Ru(bpy)3<2+>-gold nanoparticle-DNA-ferrocene functionalized graphene modified glassy carbon electrode. The modified glassy carbon electrode prepared in the invention can be used for detecting the content of mercury ions in a water sample and has good electrochemiluminescence performance, excellent stability and reproducibility and high sensitivity; and operation of the method is easy and convenient.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
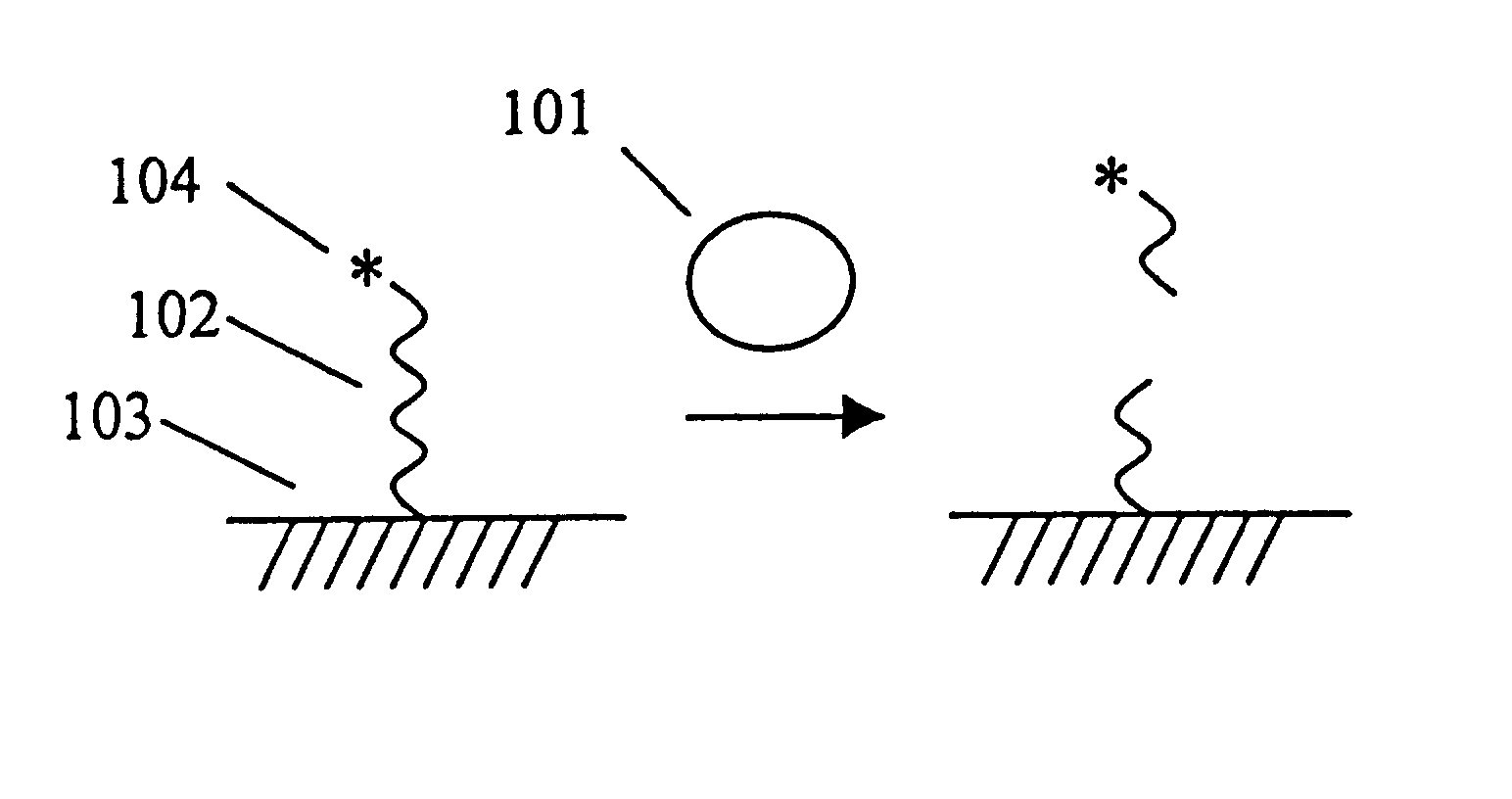
Electrochemiluminescent assays
Qualitative and quantitative electrochemiluminescent assays for analytes of interest present in multicomponent liquids are provided. These methods comprise contacting a sample with a reagent labeled with an electrochemiluminescent chemical moiety and capable of combining with the analyte of interest, exposing the resulting sample to electrochemical energy and detecting electromagnetic radiation emitted by the electrochemiluminescent chemical moiety. Further provided are methods for detecting and identifying the presence of a multiplicity of analytes in a liquid food or food homogenate. These methods comprise immersing a diagnostic reagent holder, provided with a multiplicity of reagents, into the food or food homogenate, removing the diagnostic reagent holder from the liquid food or food homogenate, and detecting and identifying the presence of a multiplicity of analytes of interest bound to the diagnostic reagent holder, thereby detecting and identifying the presence of a multiplicity of analytes of interest in the food or food homogenate. The invention further provides an enzyme immunoassay for coliform bacteria. This assay comprises inoculating a sample into a suitable medium for coliform reproduction, immobilizing coliforms present in the medium to a suitable surface, treating the surface with an antibody directed to the immobilized coliforms and detecting the presence of the immobilized coliforms immobilized to a suitable surface.
Owner:BIOVERIS CORP
Conductor/Insulator/Porous Film-Device and Its Use With the Electrochemiluminescence-Based Analytical Methods
ActiveUS20090178924A1High densityPractical to useImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsAnalyteElectrical conductor
A conductor / insulator / porous film device is provided which is used in electrochemiluminescence methods and instrumentation based on the chemical excitation of label molecules with subsequent measurement of the luminescence in order to quantitate analyte concentrations especially in bioaffinity assays.
Owner:BIOMETRO CO LTD
Bipolar electrode electrochemiluminescent detection method for microfluidic droplet array
InactiveCN102749322ASimple structureEasy to manufactureChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceLiquid storage tankIndium tin oxide
The invention discloses a bipolar electrode electrochemiluminescent detection device for a microfluidic droplet array and a detection method thereof. According to the invention, a bipolar electrode and a drive electrode are processed on an indium tin oxide conductive glass substrate, a sample micro droplet micro liquid storage tank array and a reagent micro droplet micro liquid storage tank are processed on a polydimethylsiloxane cover plate, so a polydimethylsiloxane-conductive glass microfluidic chip is prepared by sealing the substrate and the cover plate; sample micro droplets and reagent micro droplets with a micro upgrading volume are respectively added into micro liquid storage tanks at the two ends of the bipolar electrode, and a constant potential is applied onto the drive electrode so as to allow the two ends of the bipolar electrode to undergo a redox reaction; and detection of the microfluidic droplet array is realized by observing an electrochemiluminescent signal emitted by an anode terminal of the bipolar electrode. The method provided in the invention has the advantages of simple operation, a small consumption amount of a sample and a reagent, high sensitivity, a short analysis time and capacity of realizing multi-point detection at the same time.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
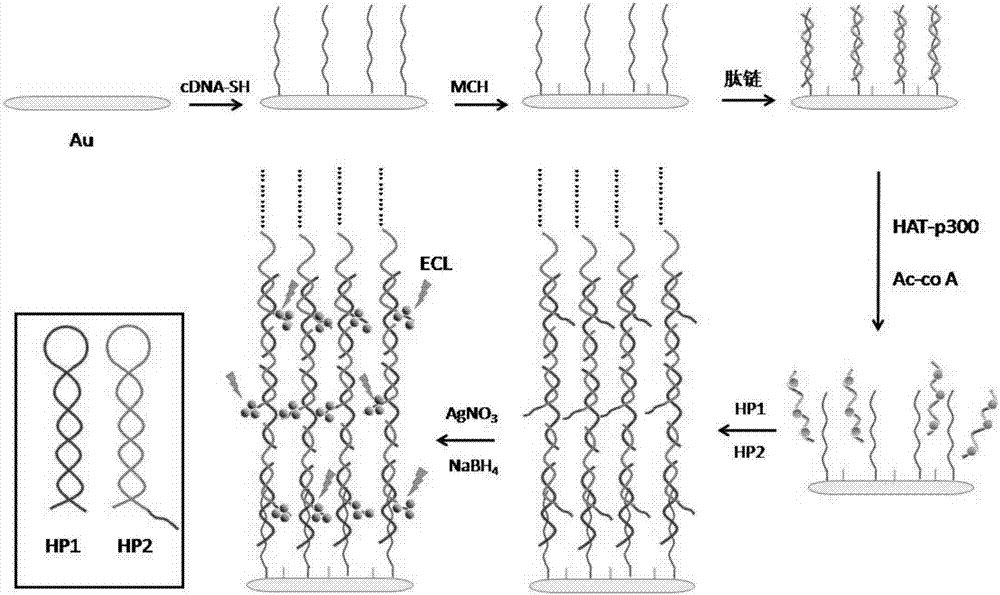
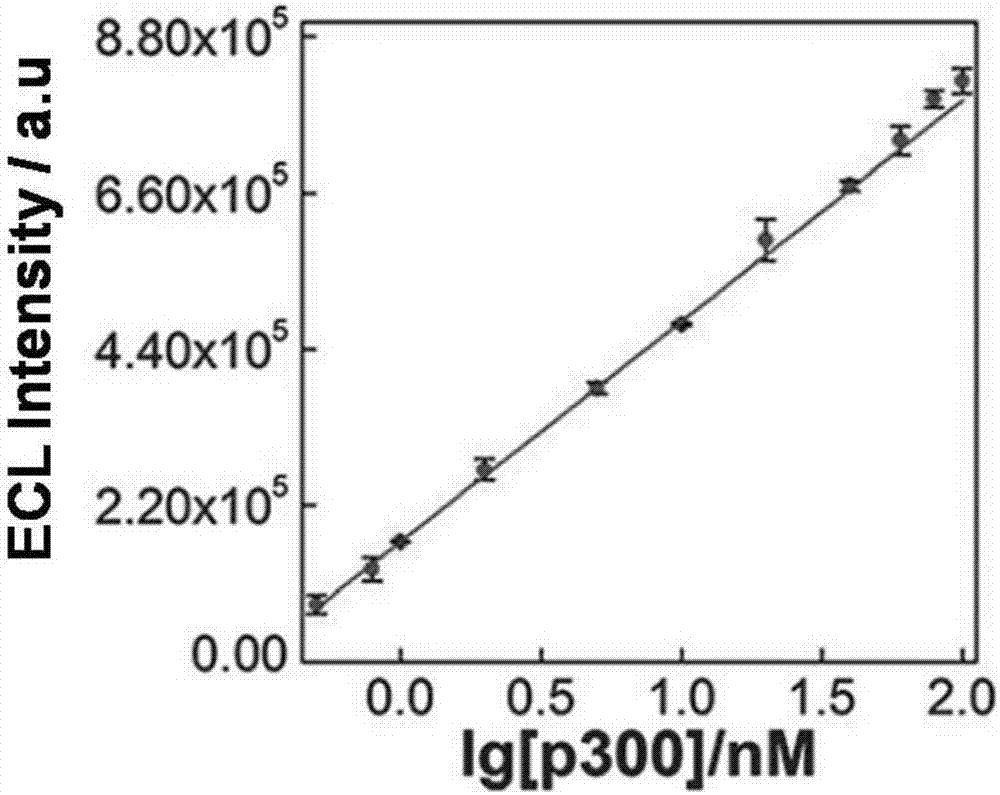
Construction of electrochemical luminescence sensor for detecting acetyltransferase activity
ActiveCN107101997AEasy to prepareEasy to operateChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPhysical chemistryAcetyltransferase activity
The invention relates to a construction of an electrochemical luminescence sensor for detecting acetyltransferase activity. The construction comprises the following steps: firstly, polishing, cleaning and activating a gold electrode, assembling captured DNA on the surface of the electrode through action of gold-sulfur bond, and enclosing non-specific binding sites on the surface of the electrode with MCH; then adsorbing a polypeptide chains through electrostatic action, performing acetylation treatment on the polypeptide chains under the action of HATp300, so as to separate from the surface of the electrode; secondly, performing hybrid chain reaction on the electrode in a hybrid chain solution containing two hairpin DNA, and reducing a silver cluster; and finally, detecting electrochemical luminescence signal of the assembled electrochemical luminescence sensor in the solution. The ECL biosensor has remarkable advantages on the quantitative analysis of HAT p300 and the activity analysis on HAT p300 in complicated cell lysis buffering solution.
Owner:青岛卓越海特信息技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com