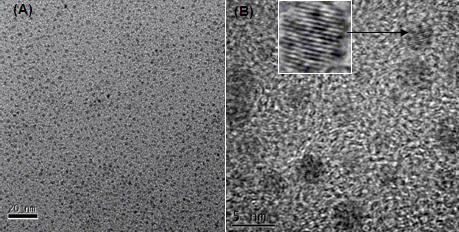
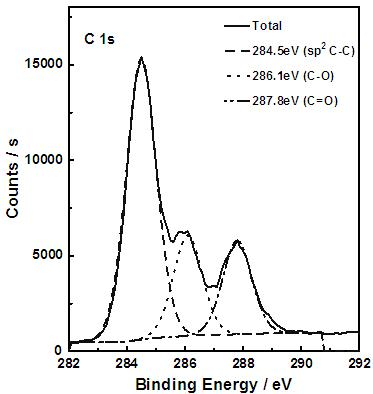
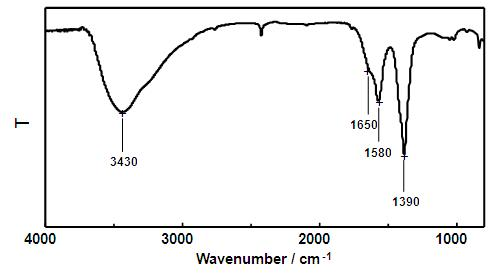
Method for extracting carbon quantum dots from activated carbon
A technology for carbon quantum dots and activated carbon, which is applied in the field of extracting carbon quantum dots, can solve the problems of low yield, expensive instruments, complicated processes, etc., and achieves the effects of uniform particle size, easy purification, and simple preparation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Add 1 g of dry activated carbon powder to 100 ml of 4 mol L -1 Reflux in nitric acid for 24 h. After naturally cooling to room temperature, take out the suspension and evaporate the resulting suspension to dryness by distillation under reduced pressure. The black solid (about 1.105 g) obtained by evaporation to dryness was dispersed in water and washed with 0.5 mol L -1 Neutralize with NaOH solution, and then centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 15 min to remove non-fluorescent precipitates. Collect the supernatant, and use four ultrafiltration centrifuge tubes with different molecular weight cut-offs of 3 kDa, 5 kDa, 10 kDa, and 30 kDa for step-by-step centrifugation. Five products with molecular weights 30 KDa were obtained by ultrafiltration and centrifugation, except for the product of >30 KDa, the other products showed good fluorescence activity. By weighing the mass of non-fluorescent active components, it can be estimated that the yield of carbon quantum dots is about 30...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 50 g of dry activated carbon powder to 100 ml of 12 mol L -1 Reflux in nitric acid for 30 h. After cooling down to room temperature naturally, take out the suspension and evaporate the resulting suspension to dryness by distillation under reduced pressure. Disperse the black solid obtained by evaporating to dryness with 0.5 mol L -1 Neutralize with NaOH solution, and then centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 30 min to remove non-fluorescent precipitates. The supernatant was collected, centrifuged with an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 30 kDa, and the filtrate was collected and dried at 80°C to obtain <30 kDa carbon quantum dots.
Embodiment 3
[0030] Add 25 g of dry activated carbon powder to 100 ml of 8 mol L -1 Reflux in nitric acid for 30 h. After cooling down to room temperature naturally, take out the suspension and evaporate the resulting suspension to dryness by distillation under reduced pressure. Disperse the black solid obtained by evaporating to dryness with 0.5 mol L -1 Neutralize with NaOH solution, and then centrifuge at 4000 rpm for 30 min to remove non-fluorescent precipitates. The supernatant was collected, centrifuged with an ultrafiltration centrifuge tube with a molecular weight cut-off of 10 kDa, and the filtrate was collected and dried at 100°C to obtain <10 kDa carbon quantum dots.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com