Patents
Literature
2279 results about "Hollow fibre" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
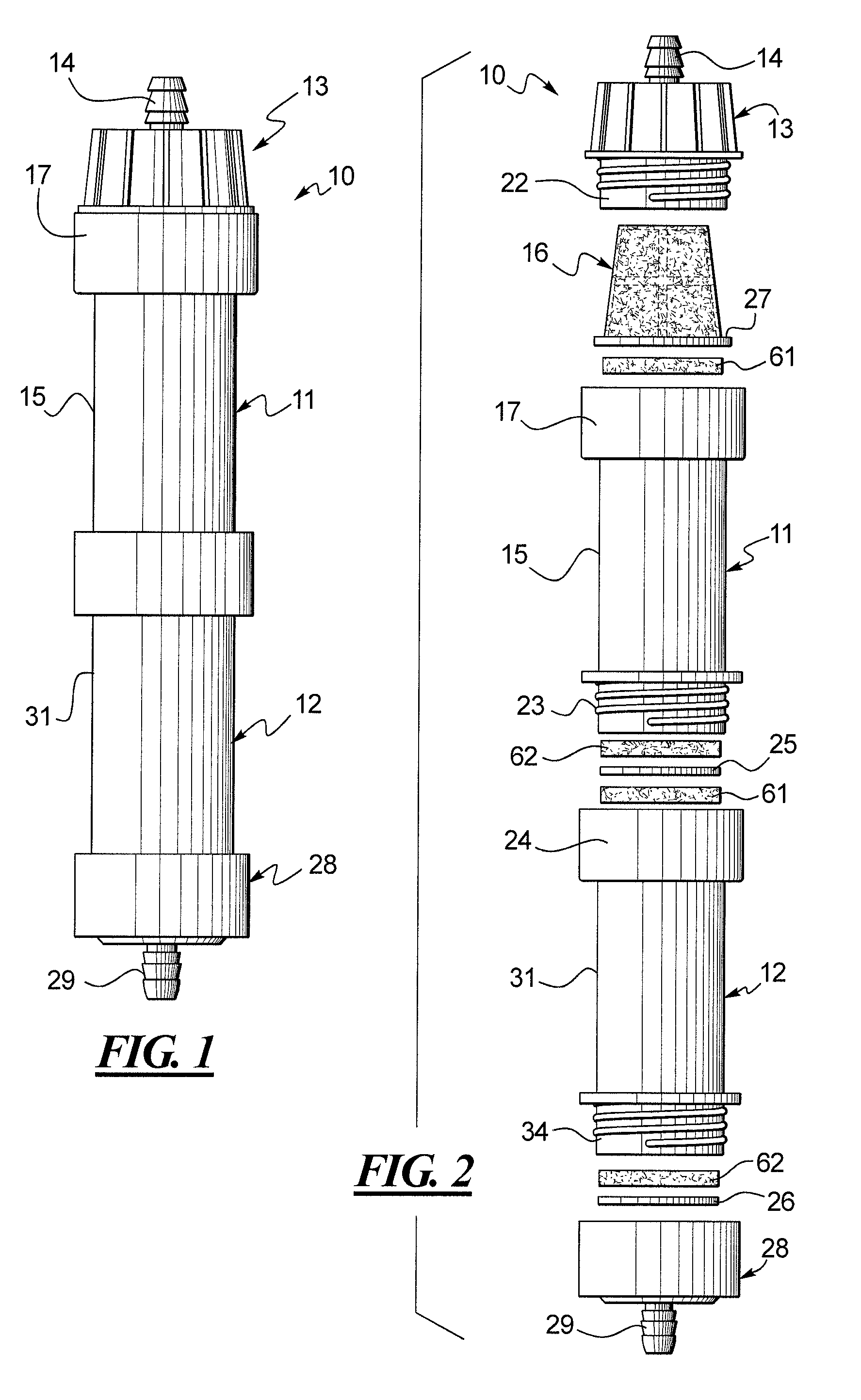
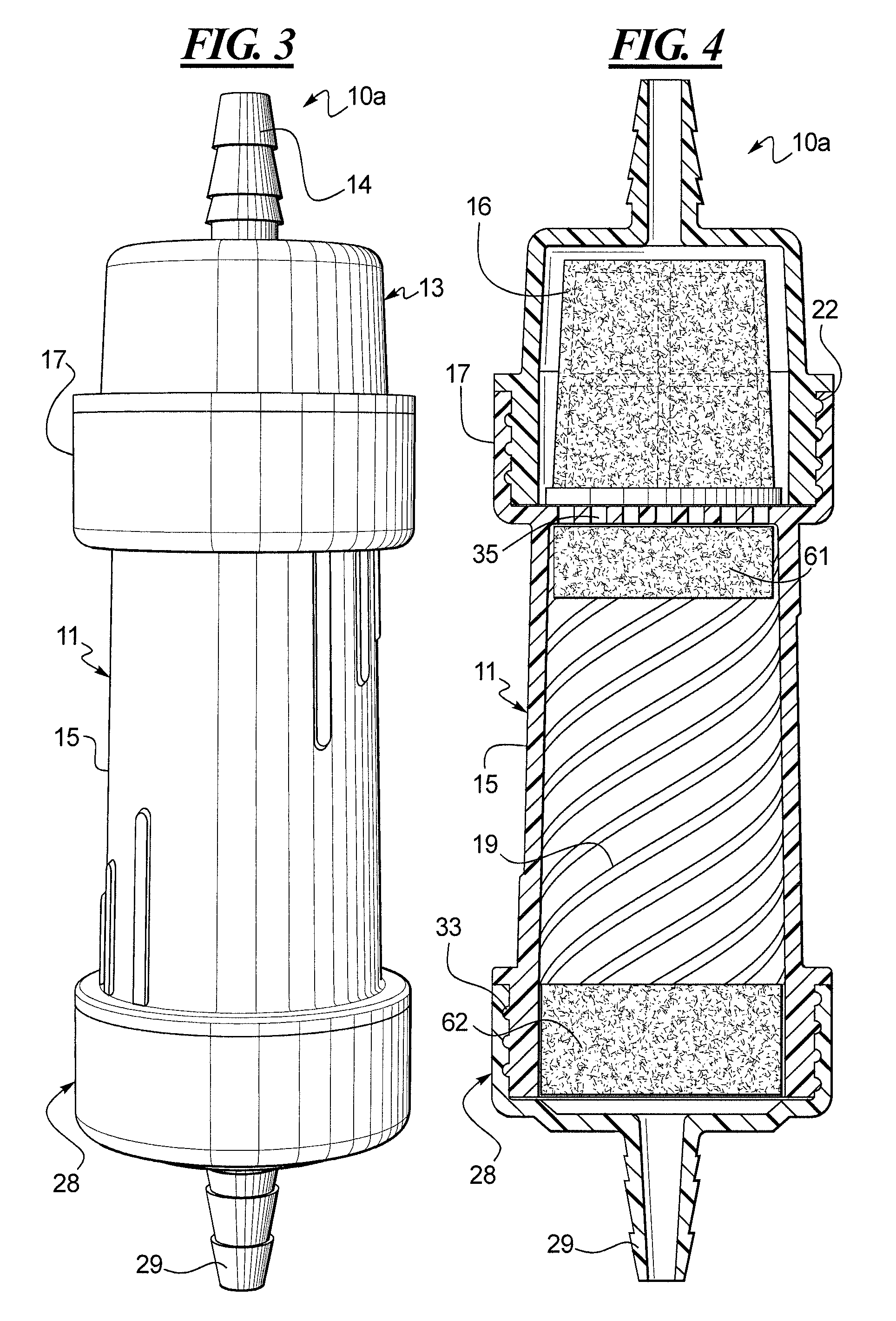
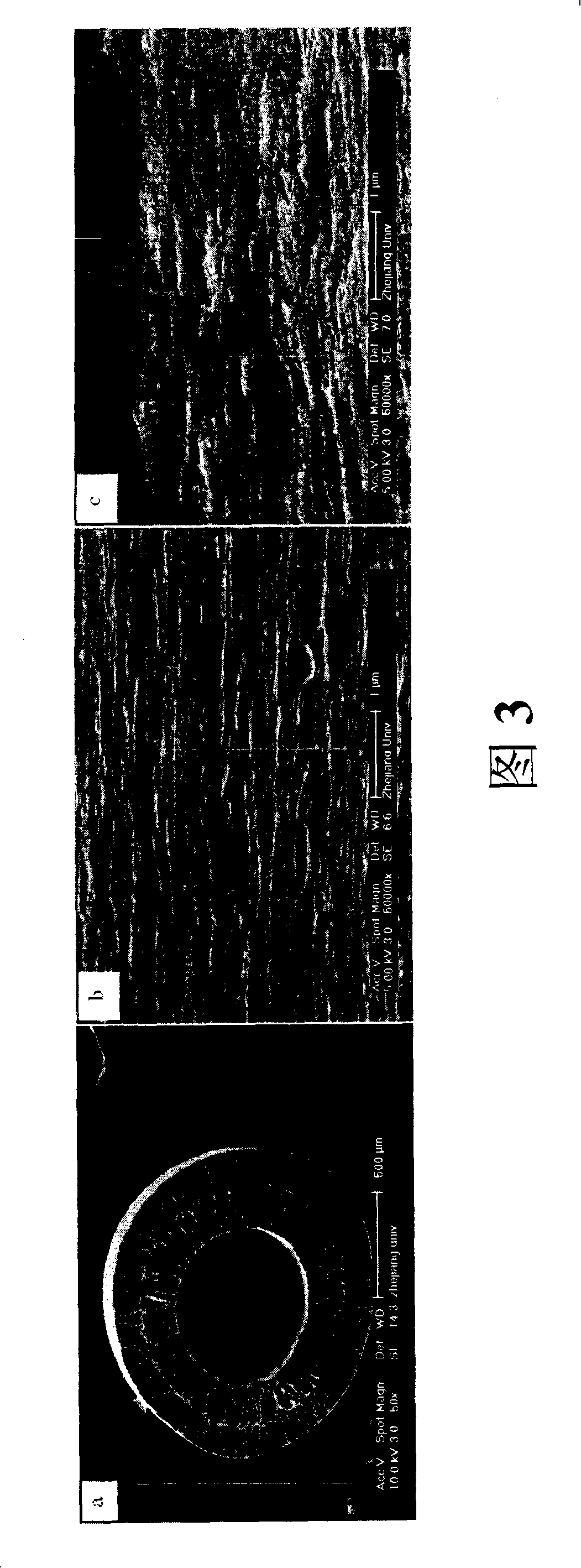
Method of selectively shaping hollow fibers of heat exchange catheter
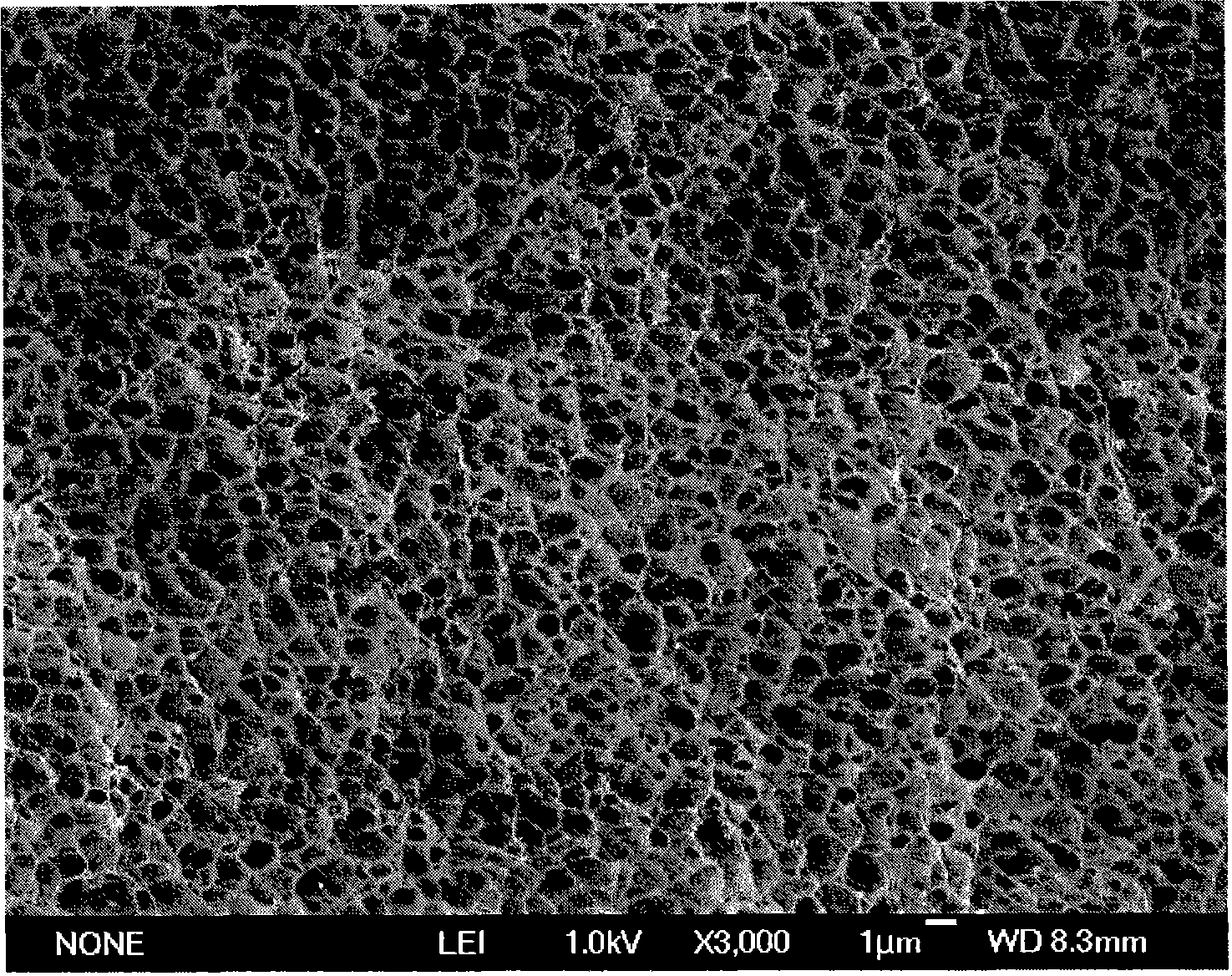
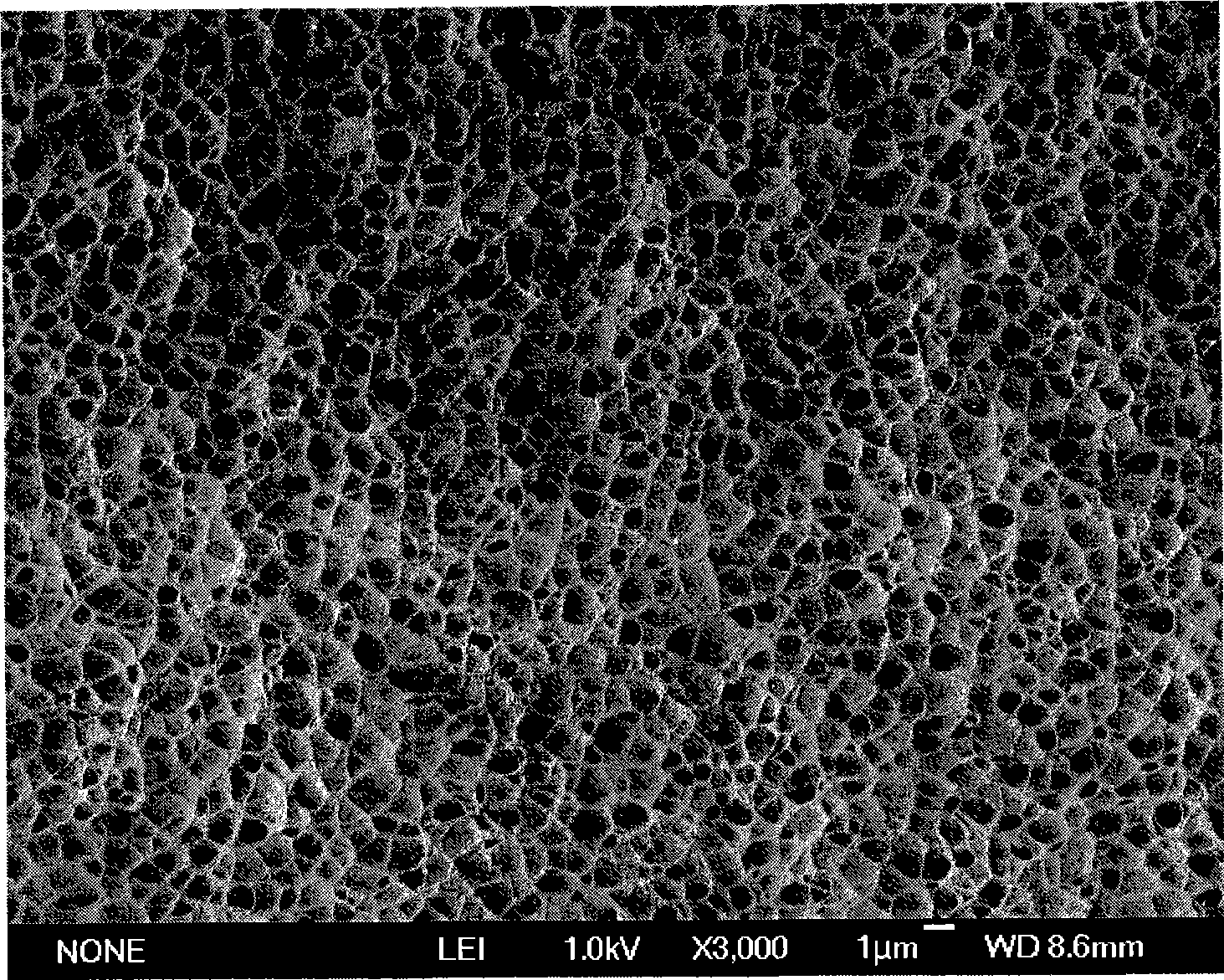
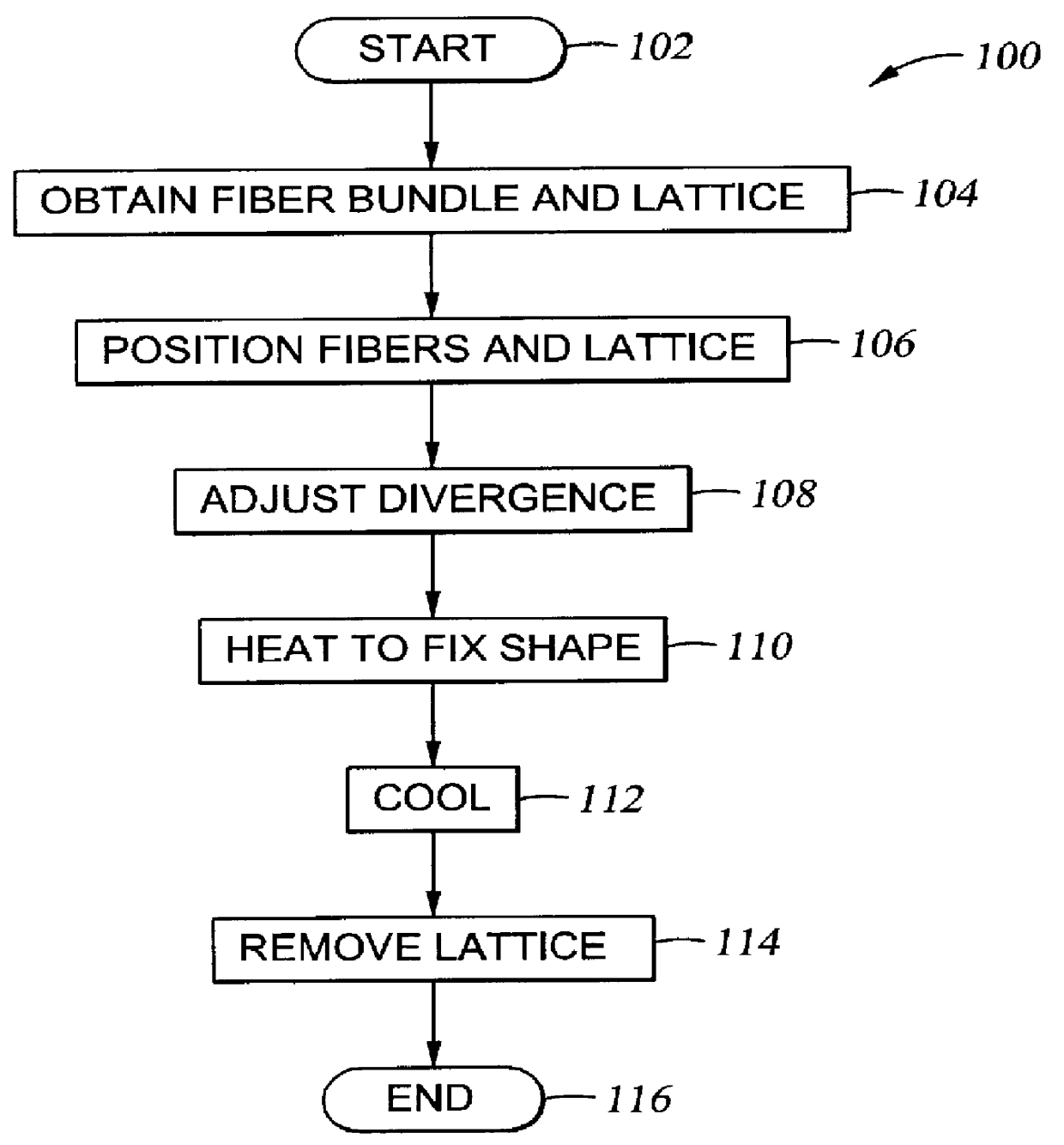
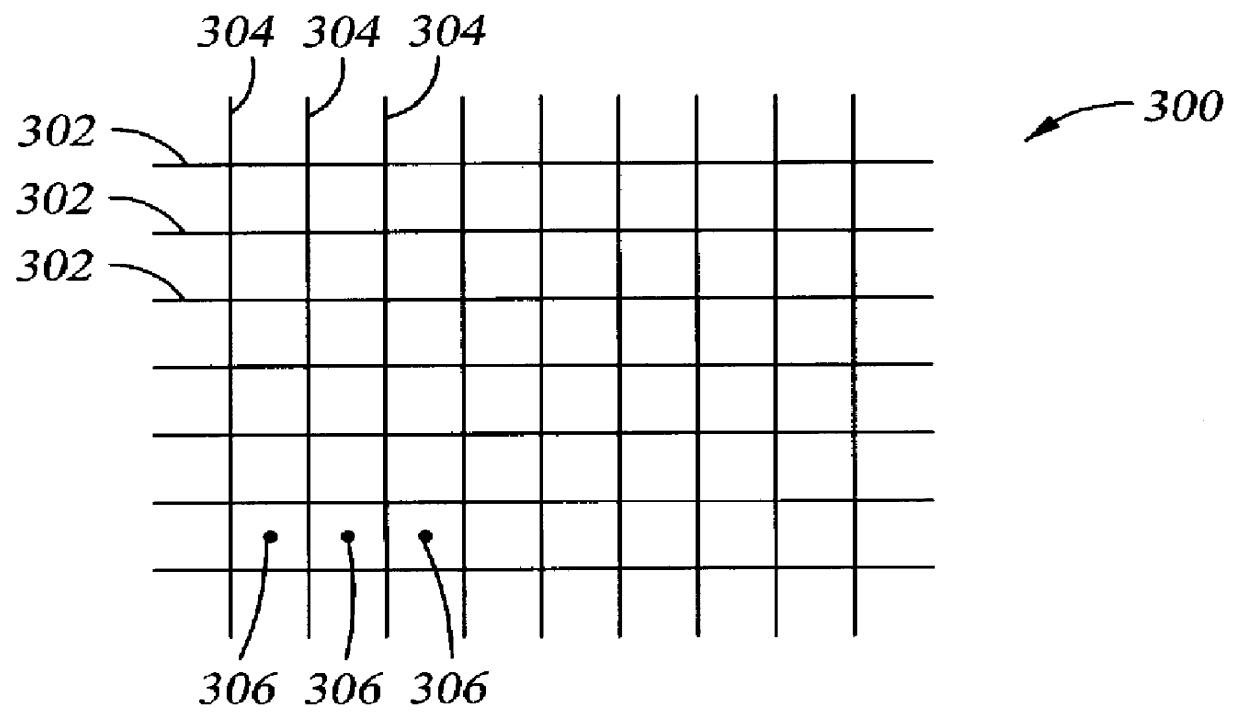
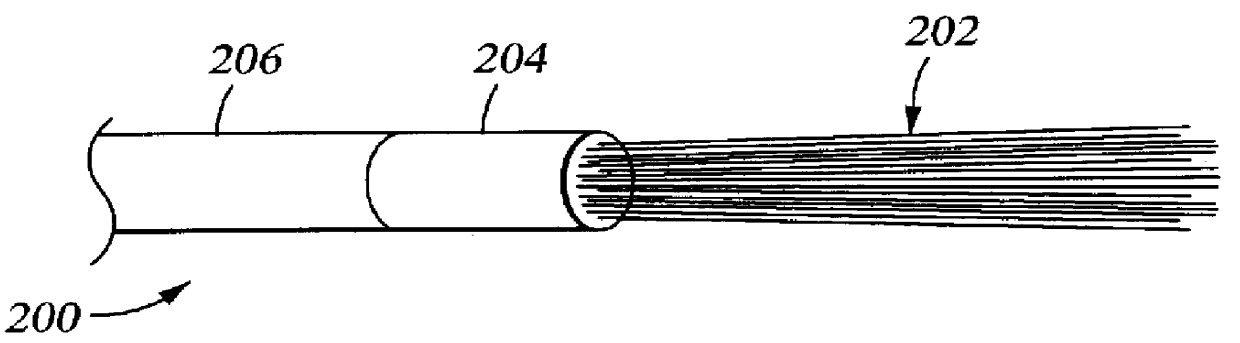
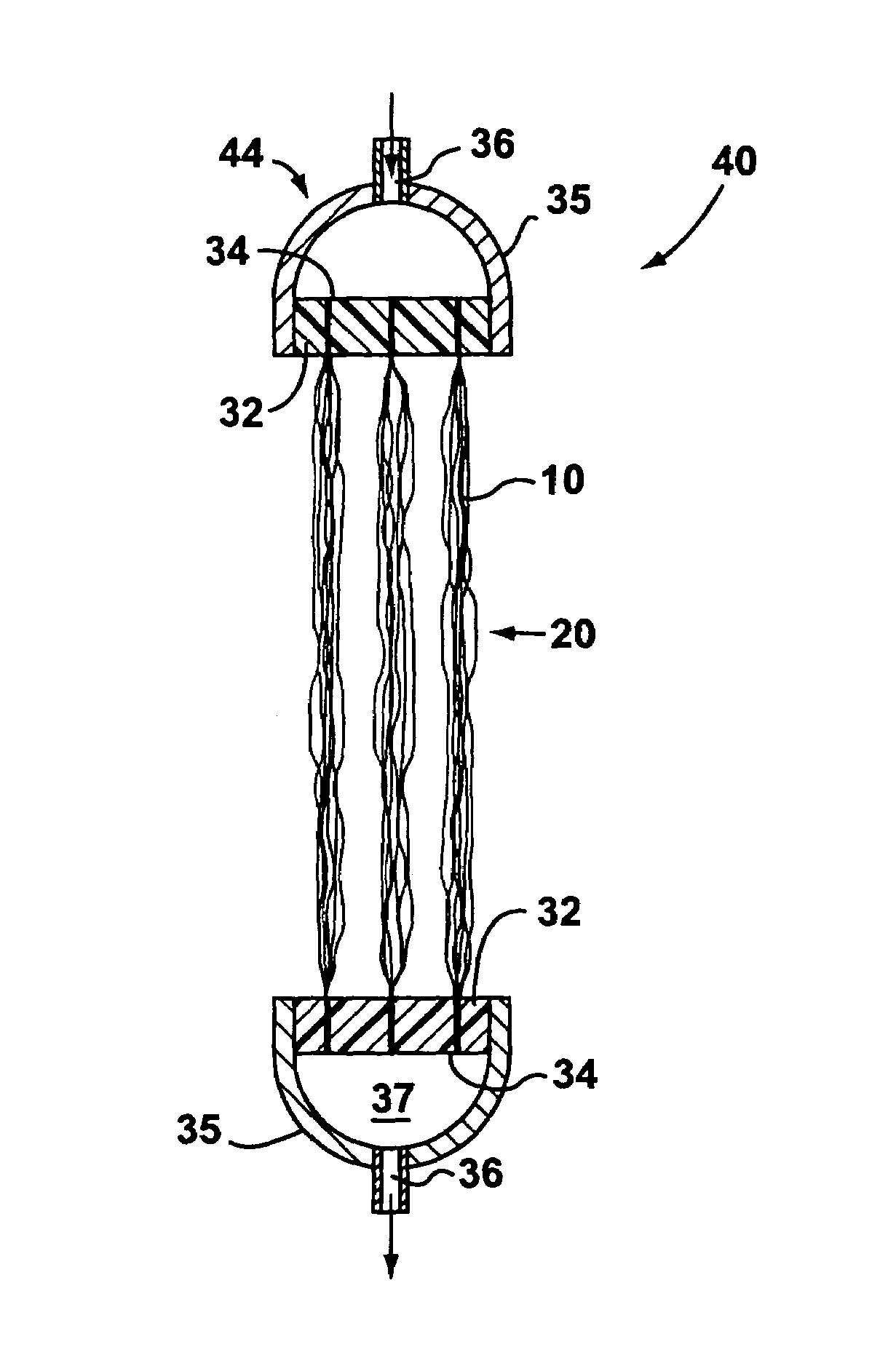
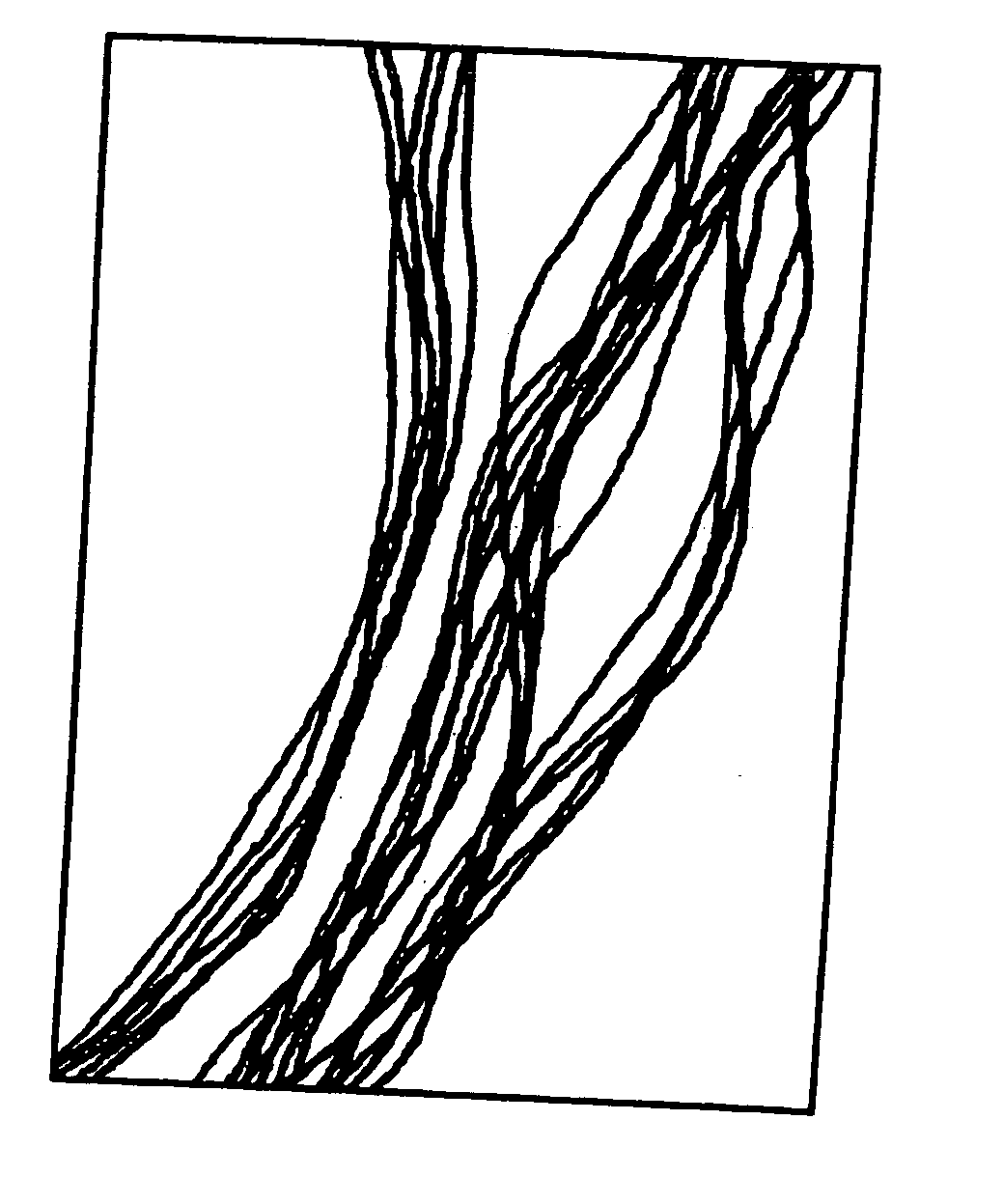
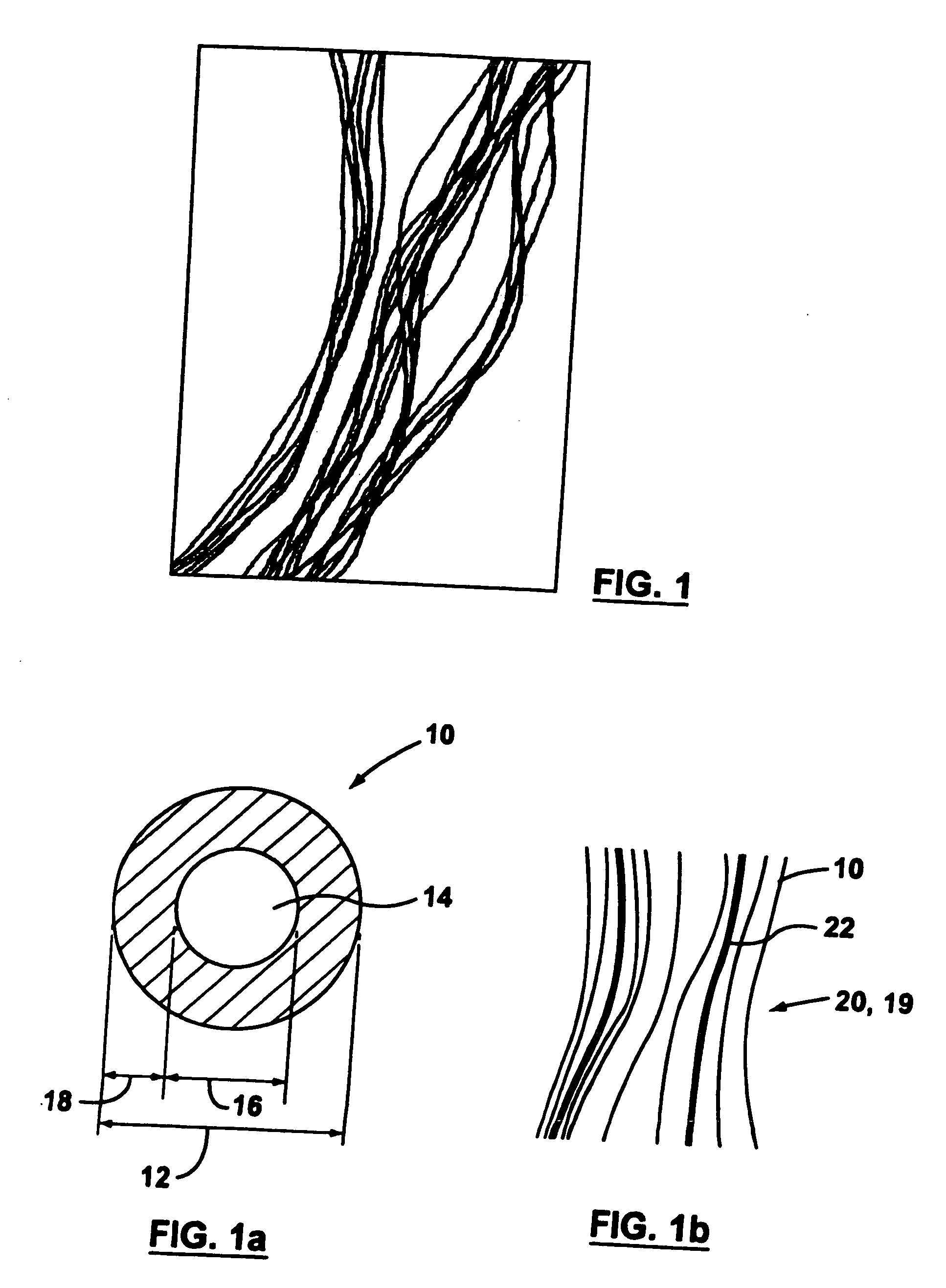
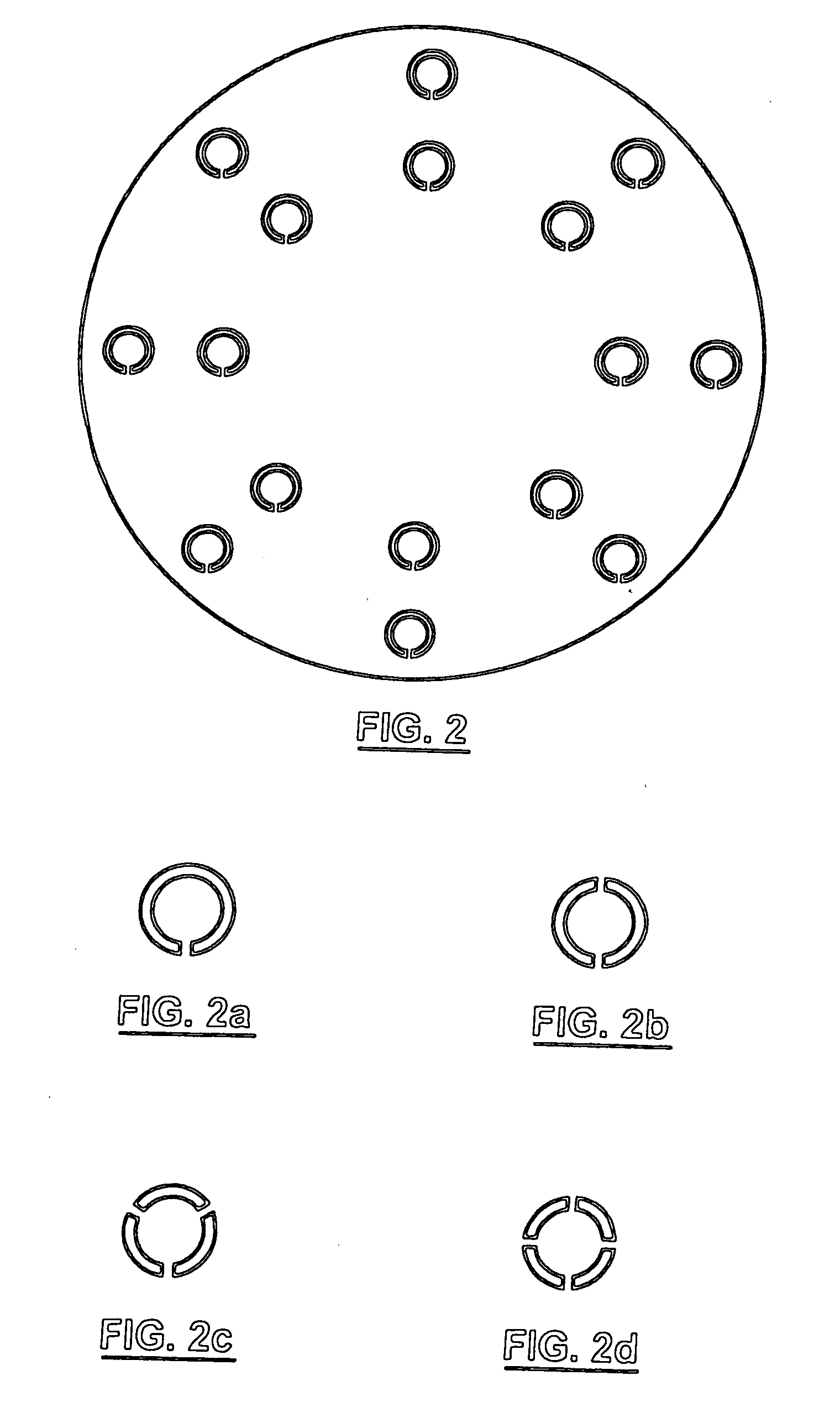
A group of multiple hollow fibers may be shaped to introduce angular divergence among the fibers, or to introduce a selected longitudinal oscillation into the fibers. In one shaping technique, the fibers are held in parallel while upper and lower crimping assemblies of parallel crimping bars are drawn together on opposite sides of the parallel fibers. When bars of the opposing assemblies draw sufficiently close, they sandwich the fibers in between them, causing each fiber to assume a shape that oscillates as the fiber repeatedly goes over and then under successive bars. Since the crimping bars are aligned at oblique angles to the fibers, the peaks and troughs of successive fibers are offset. While in this position, the fibers are heated and then cooled to permanently retain their shapes. A different shaping technique utilizes a lattice of crisscrossing tines defining multiple apertures. In this technique, the lattice and fibers are positioned so that each fiber passes through one of the apertures. Then, the lattice and / or the fibers are slid apart or together until the lattice holds the fibers in a desired configuration, where the fibers have a prescribed outward divergence relative to each other. While in this position, the fibers are heated and then cooled to permanently retain this angular divergence.
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Metal-organic framework supported on porous polymer
ActiveUS20130313193A1Degrade polymer structureDegrade pore structureSemi-permeable membranesGas treatmentHollow fibreMetal-organic framework
The growth of continuous MOF membranes on porous polymeric supports is reported, wherein a dip-coating procedure is used to deposit a layer of seed MOF nanocrystals on the surfaces of porous polymers, preferably in the form of hollow fibers, and polycrystalline MOF membranes are subsequently grown at temperatures as low as 65° C. from precursor solutions. The present work opens the road to inexpensive and scalable fabrication of MOF membranes for large-scale separation applications.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Mixed matrix membranes
InactiveUS7109140B2Enhanced interactionEffectively incorporated into polymer structureSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre
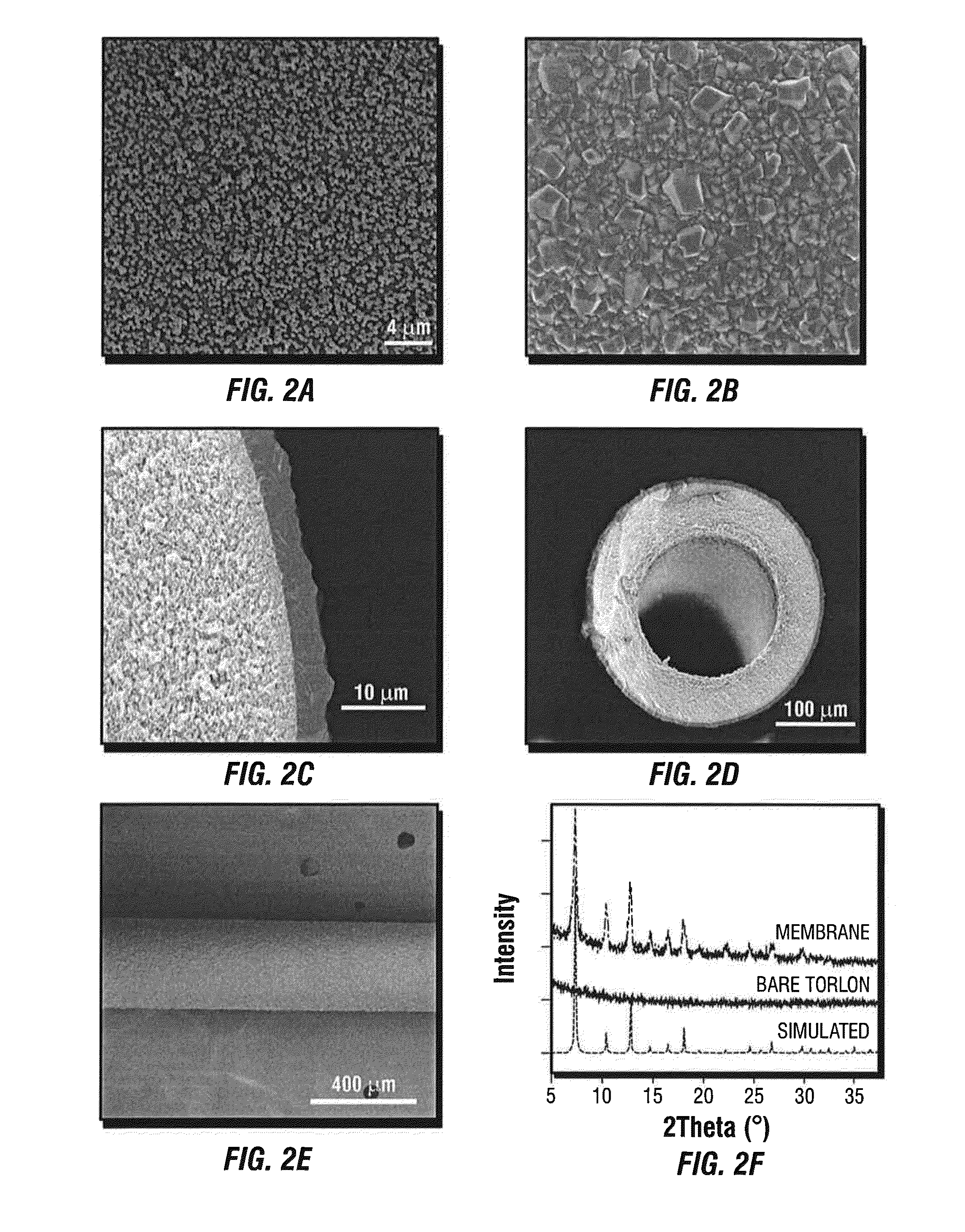
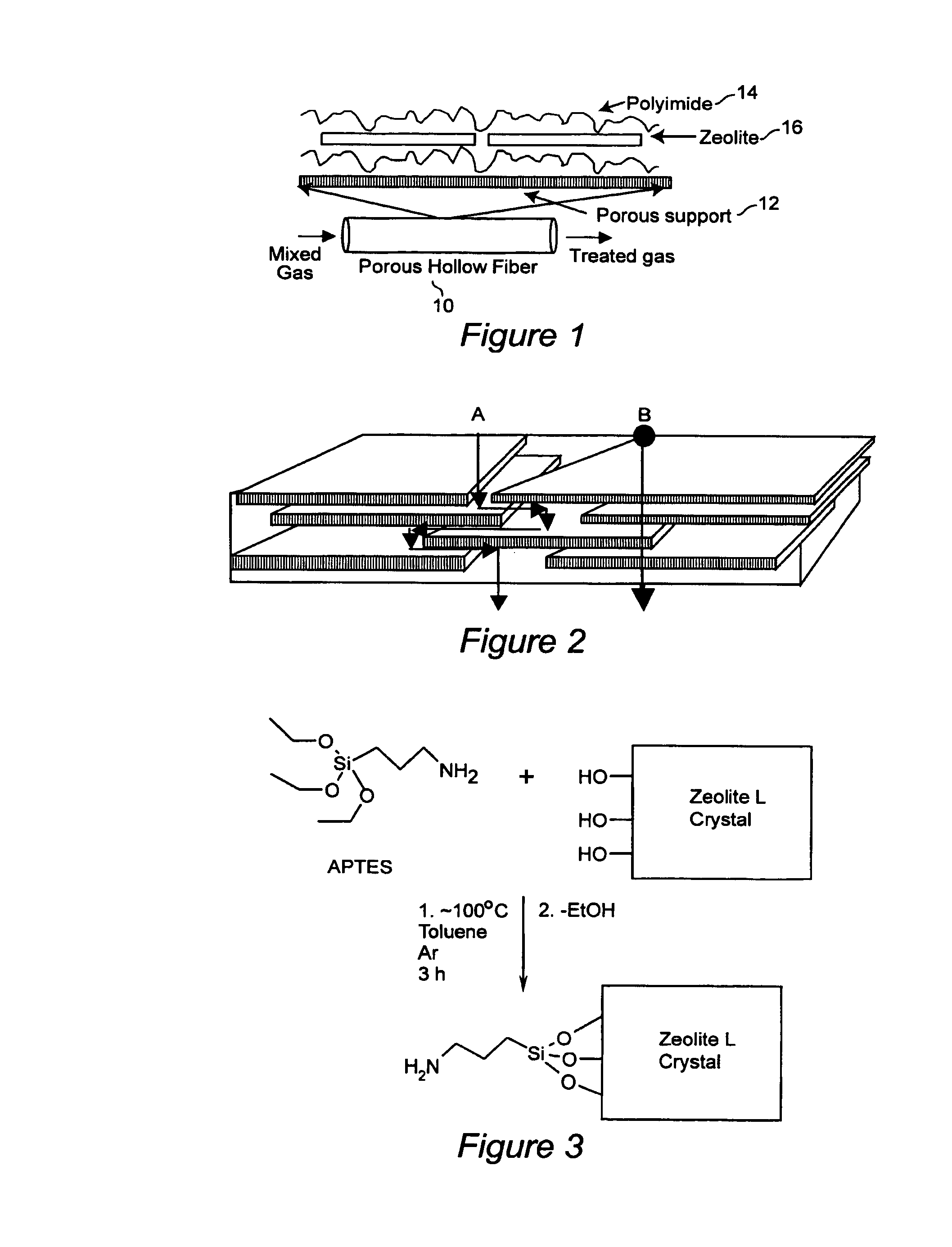
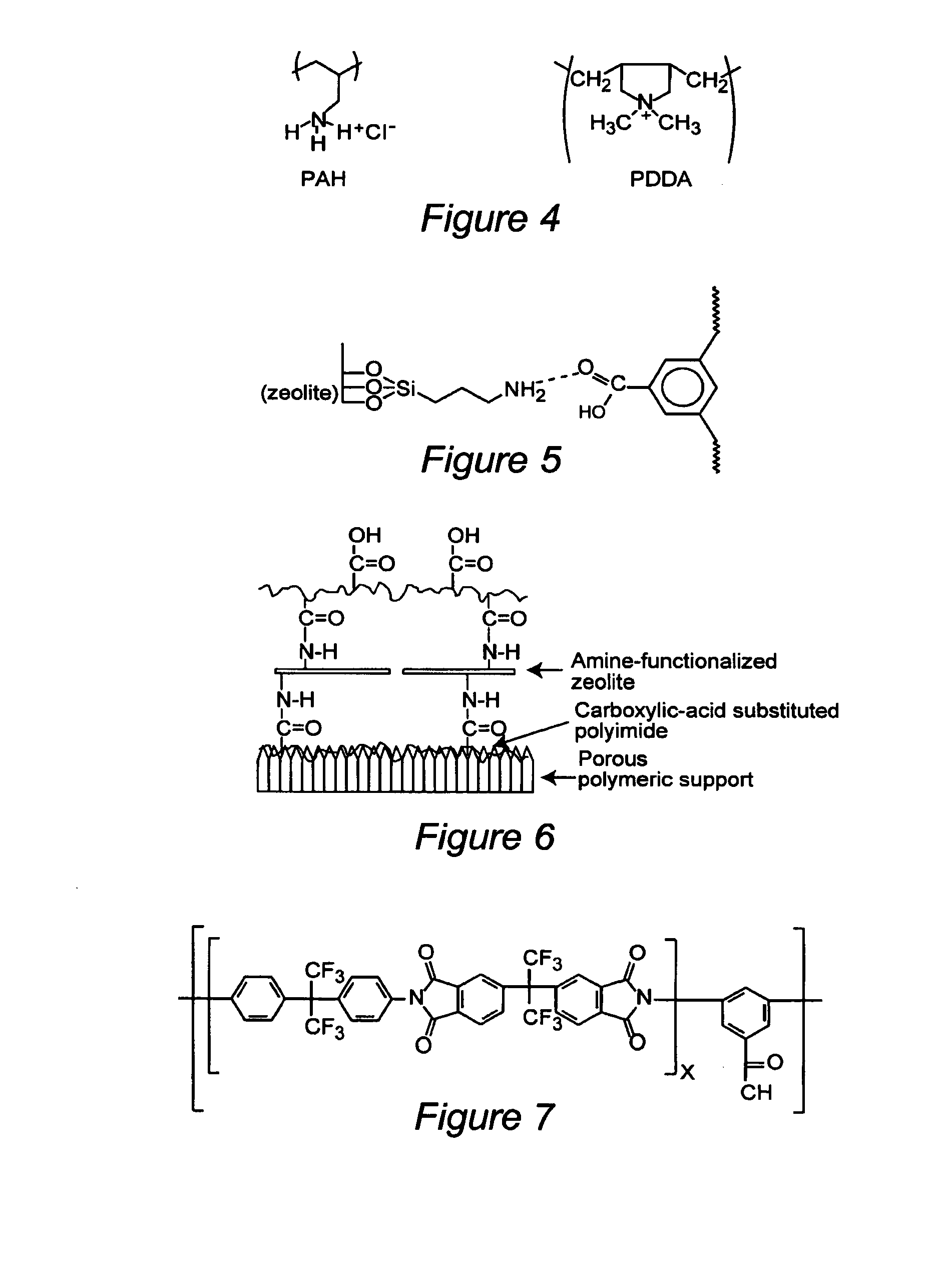
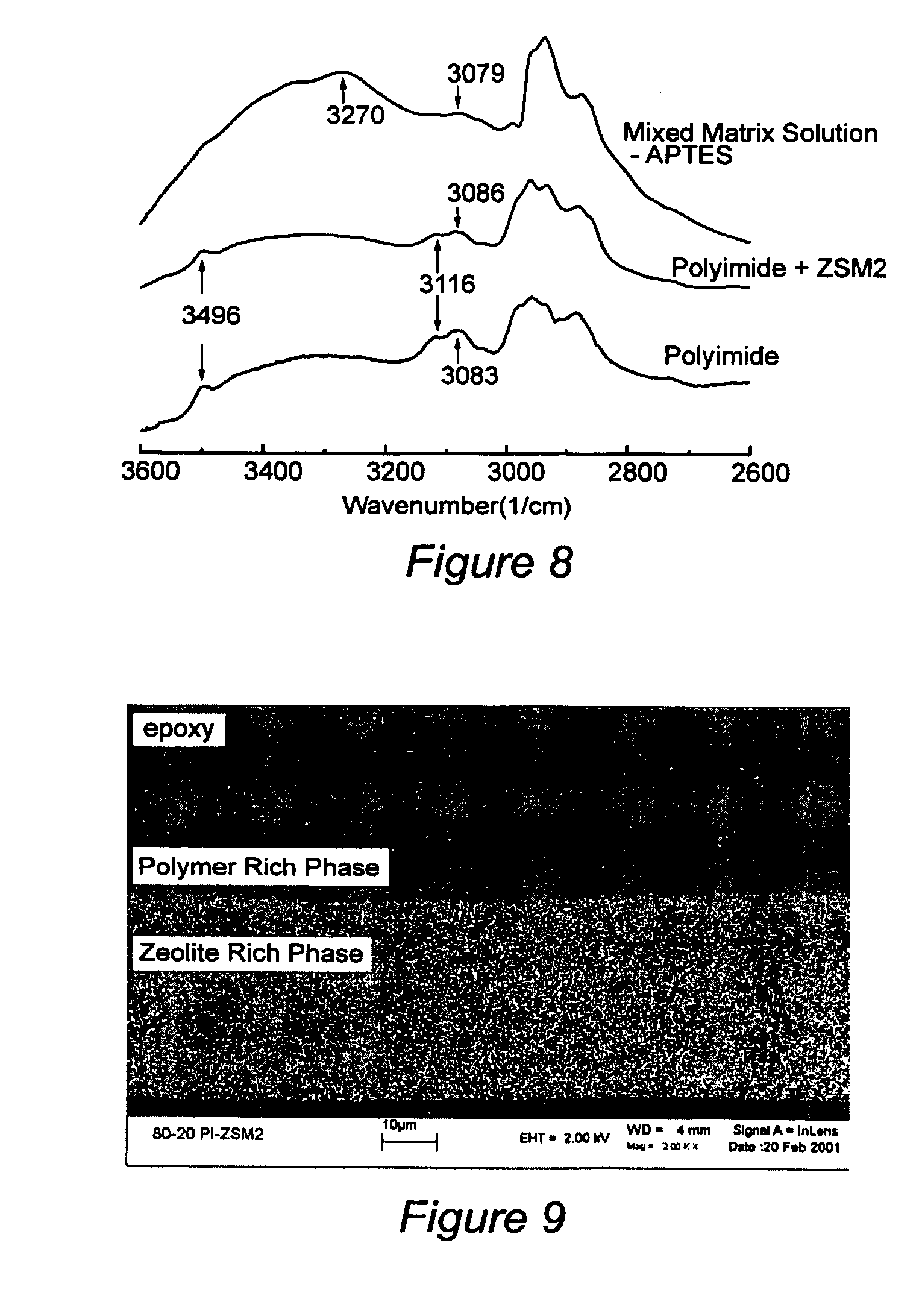
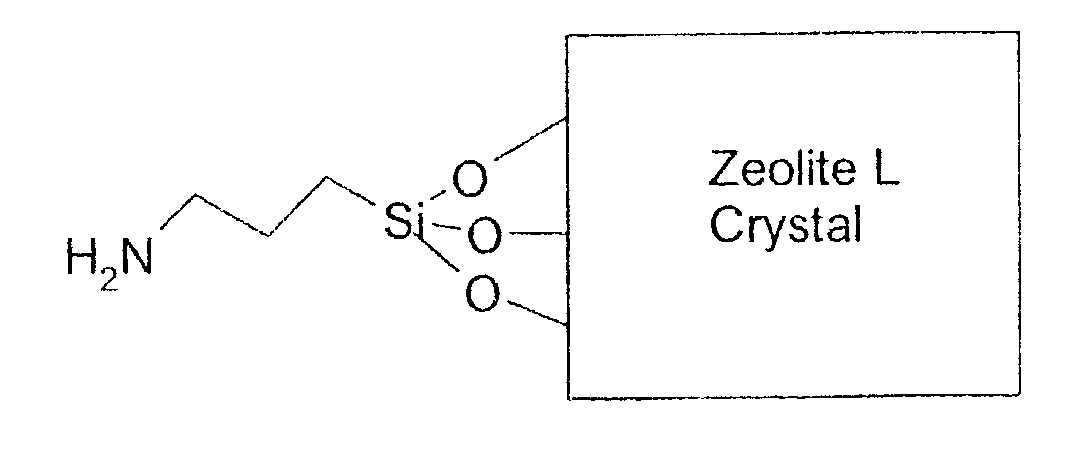
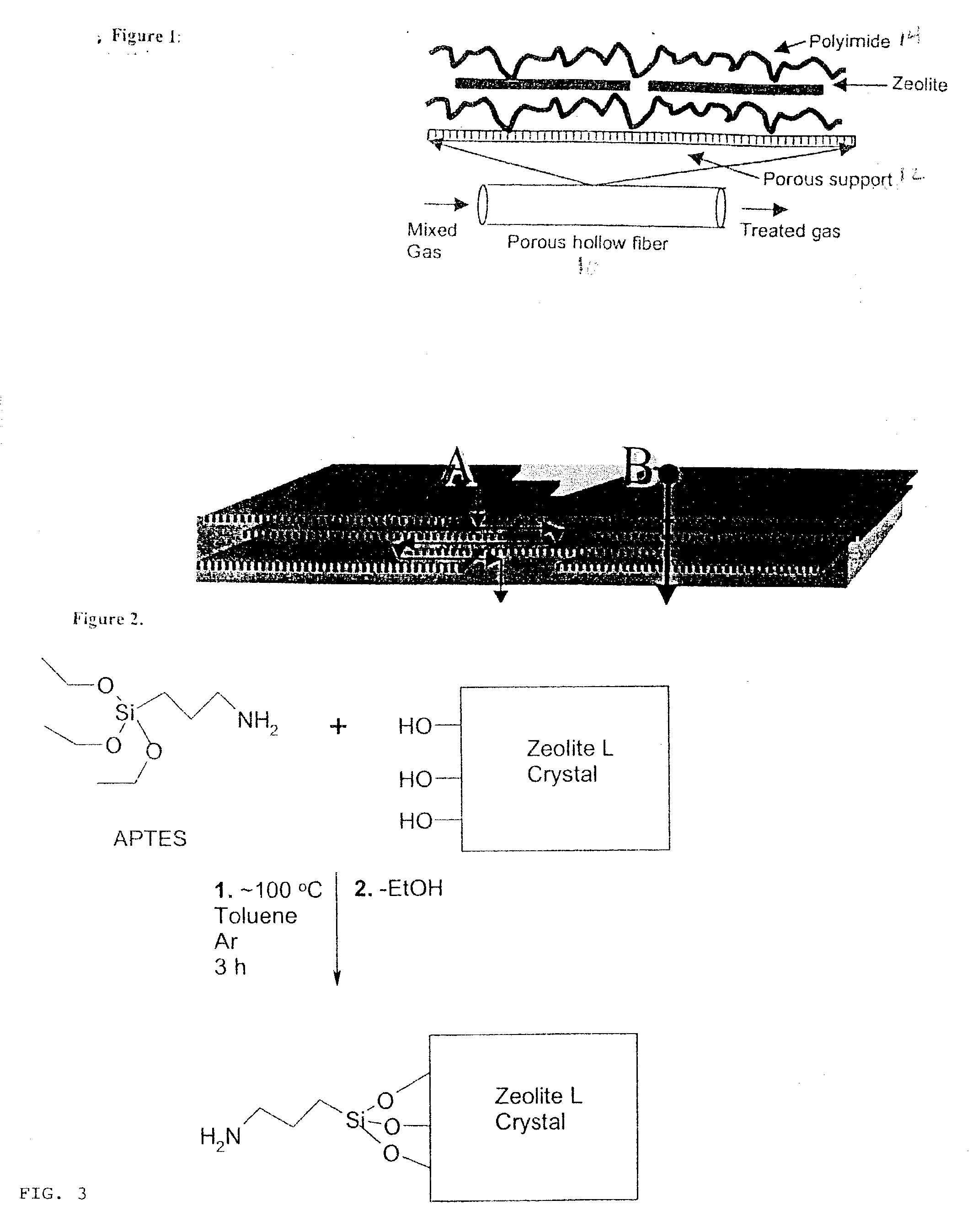
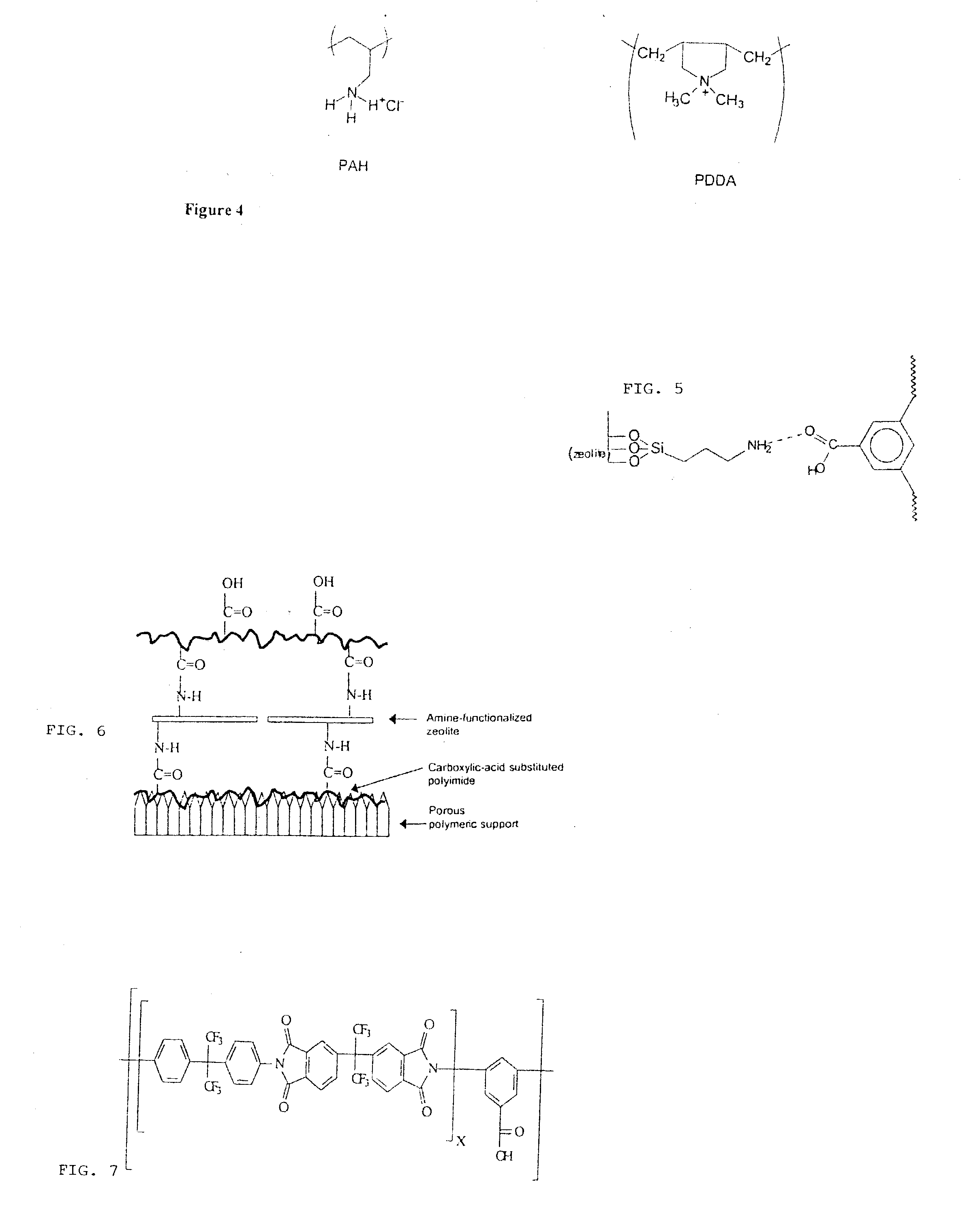
Mixed matrix membranes are prepared from zeolites and polymers, such as polyimides, in a void free fashion where either no voids or voids of less than several Angstroms are present at the interface of the polymer and the zeolite by bonding (hydrogen, ionic, or covalent) functional groups on the zeolite with functional groups on the polymer. The mixed matrix membranes may be cast or formed by ISAM processes, and may be present on a variety of supports including hollow fibers.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Mixed matrix membranes
InactiveUS20030220188A1High selectivityIncrease productivitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre
Mixed matrix membranes are prepared from zeolites and polymers, such as polyimides, in a void free fashion where either no voids or voids of less than several Angstroms are present at the interface of the polymer and the zeolite by bonding (hydrogen, ionic, or covalent) functional groups on the zeolite with functional groups on the polymer. The mixed matrix membranes may be cast or formed by ISAM processes, and may be present on a variety of supports including hollow fibers.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Modular Water Purification and Delivery System
InactiveUS20090008318A1Maximize capacityFlattening or eliminating the parabolic fluid flow profileUltrafiltrationWater/sewage treatment by ion-exchangeFiberHollow fibre
A modular filter system is provided with one or more modules that can be interchangeable, depending upon the specific application or specific health or environmental issue presented. Disclosed combinations can include one or more of any of the following modules in any relative position to one another: (a) a microbiological contaminant mitigation module, preferably in the form of an inverted u-shaped hollow fiber filter module wherein the fibers have ends potted on the downstream side and that consists essentially of hydrophilic fibers for water filtration with a small amount of hydrophobic fibers for venting of entrapped air; (b) a first chemical mitigation module, preferably in the form of an adsorption module comprising carbon or the combination of carbon and a deionization resin; and (c) a second chemical mitigation module, preferably in the form of a deionization resin module. Modules including a carbon bed or a resin bed may be equipped with a pair of hydrophobic foam bed restraints that apply opposing axial pressure to the bed in all operating conditions.
Owner:PRISMEDICAL CORP
Production of submicron diameter fibers by two-fluid electrospinning process
InactiveUS20060213829A1Conjugated cellulose/protein artificial filamentsElectro-spinningHollow fibreNanowire
Electrospinning of materials that are difficult or impossible to process into nanofibers by conventional fiber-forming techniques or by electrospinning are prepared by an electrospinning procedure which uses an electrospinnable outer “shell” fluid around an inner “core” fluid, which may or may not be electrospinnable, to form nanofibers of the inner core fluid having a core / shell morphology. The resulting shell around the nanofiber can remain in place or be removed during post-processing with the core of the fiber remaining intact. The dual-fluid electrospinning process can produce core fibers having diameters less than 100 nm, insulated nanowires, as well as tough, bio-compatible silk fibers. Alternatively, the core can be removed leaving a hollow fiber of the shell fluid.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
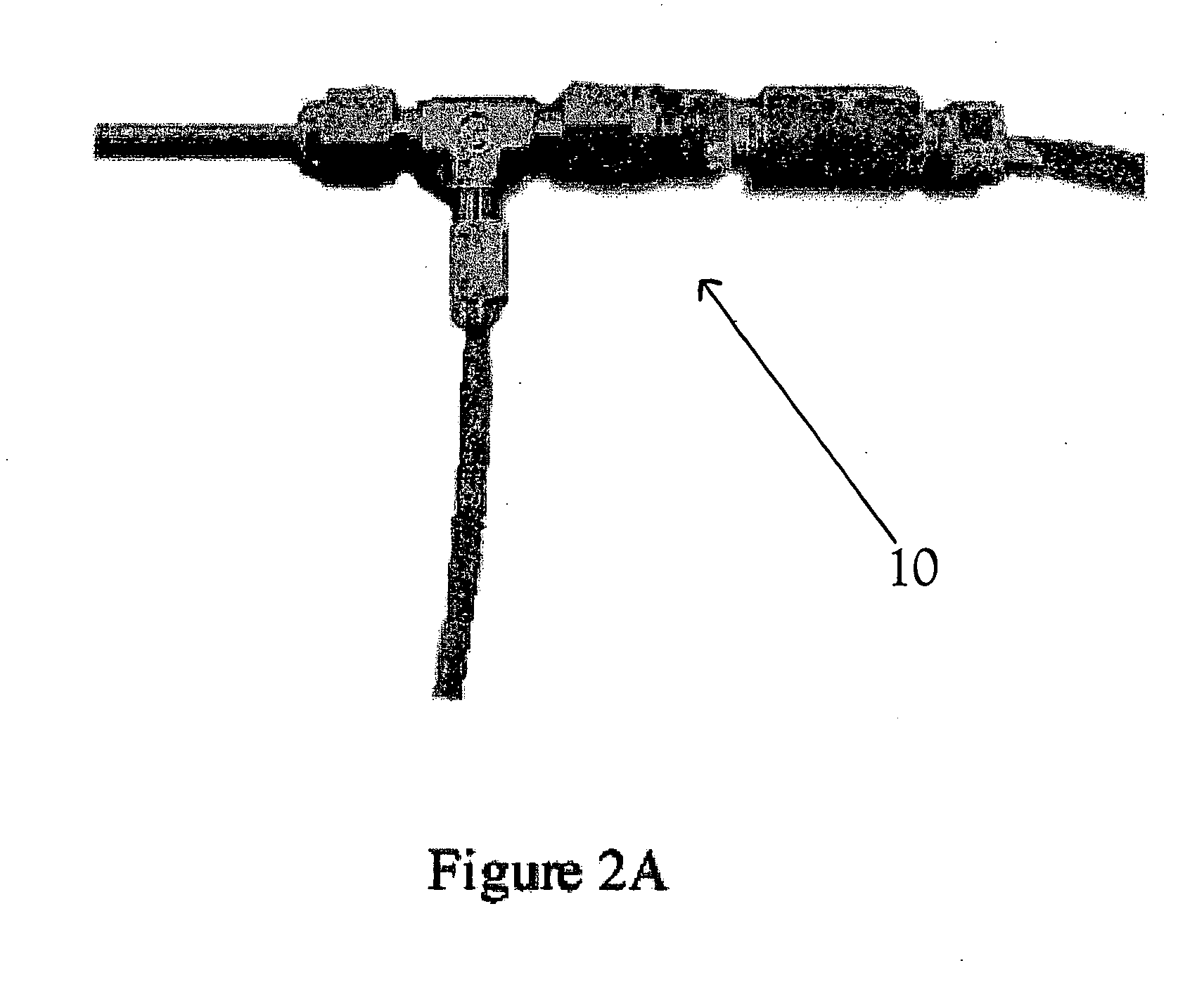
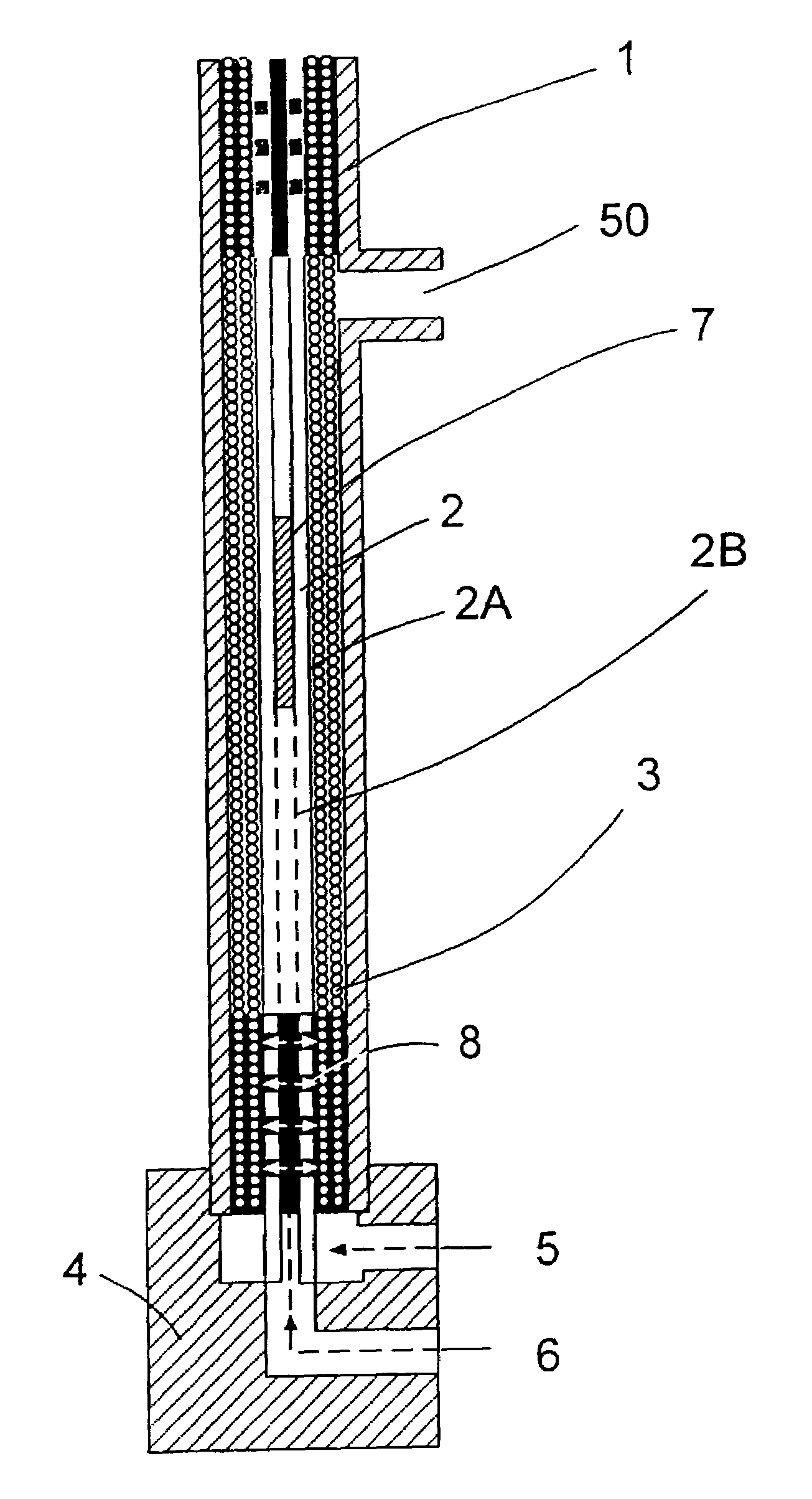
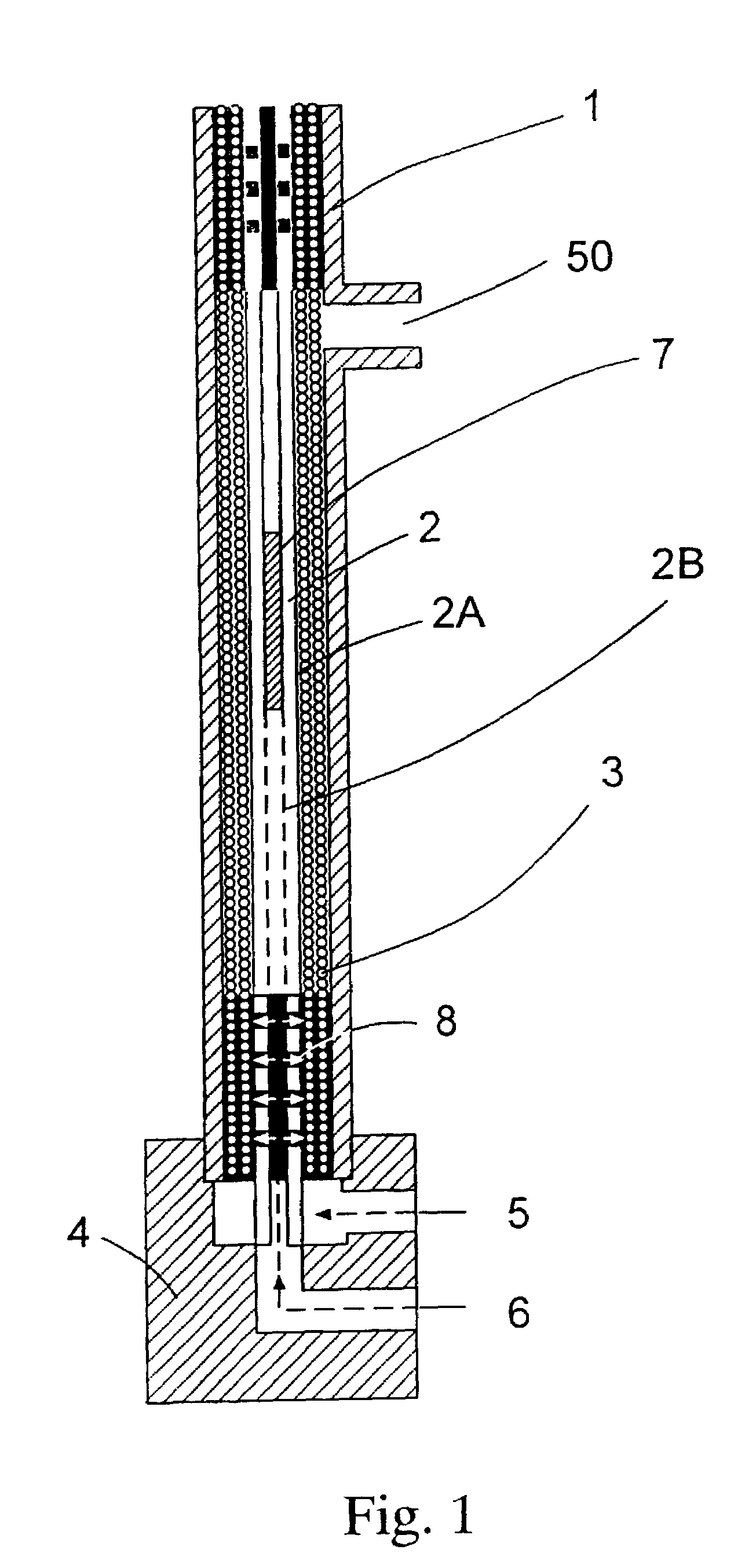
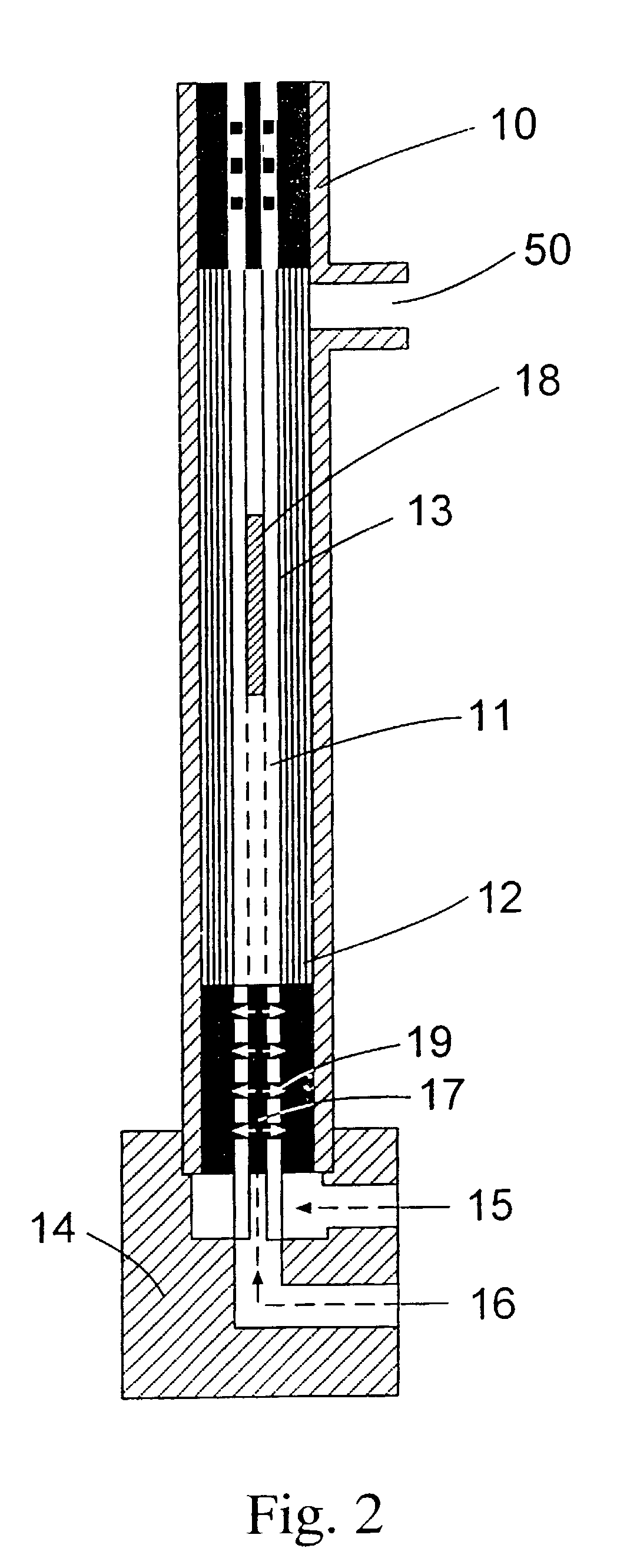
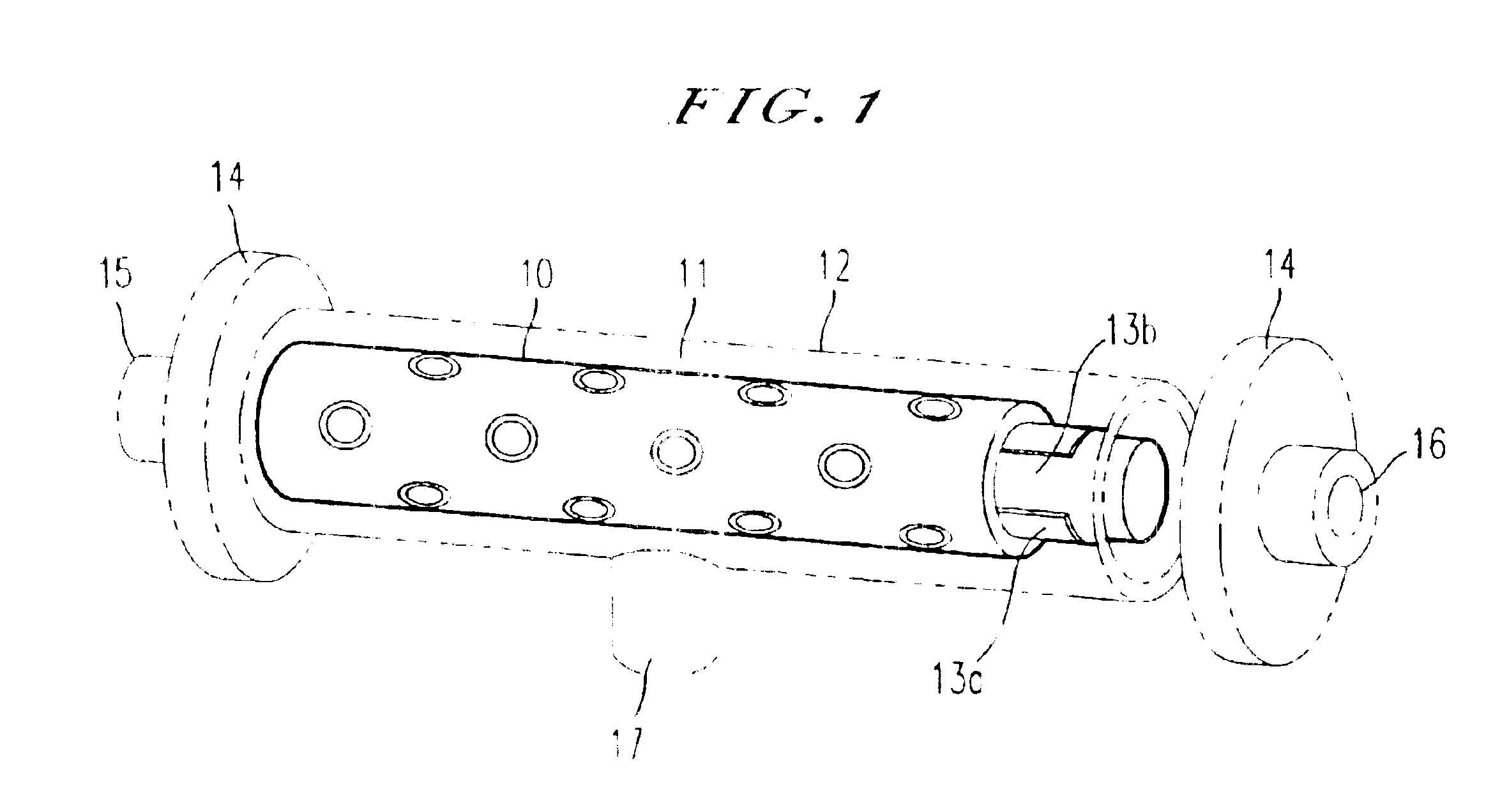
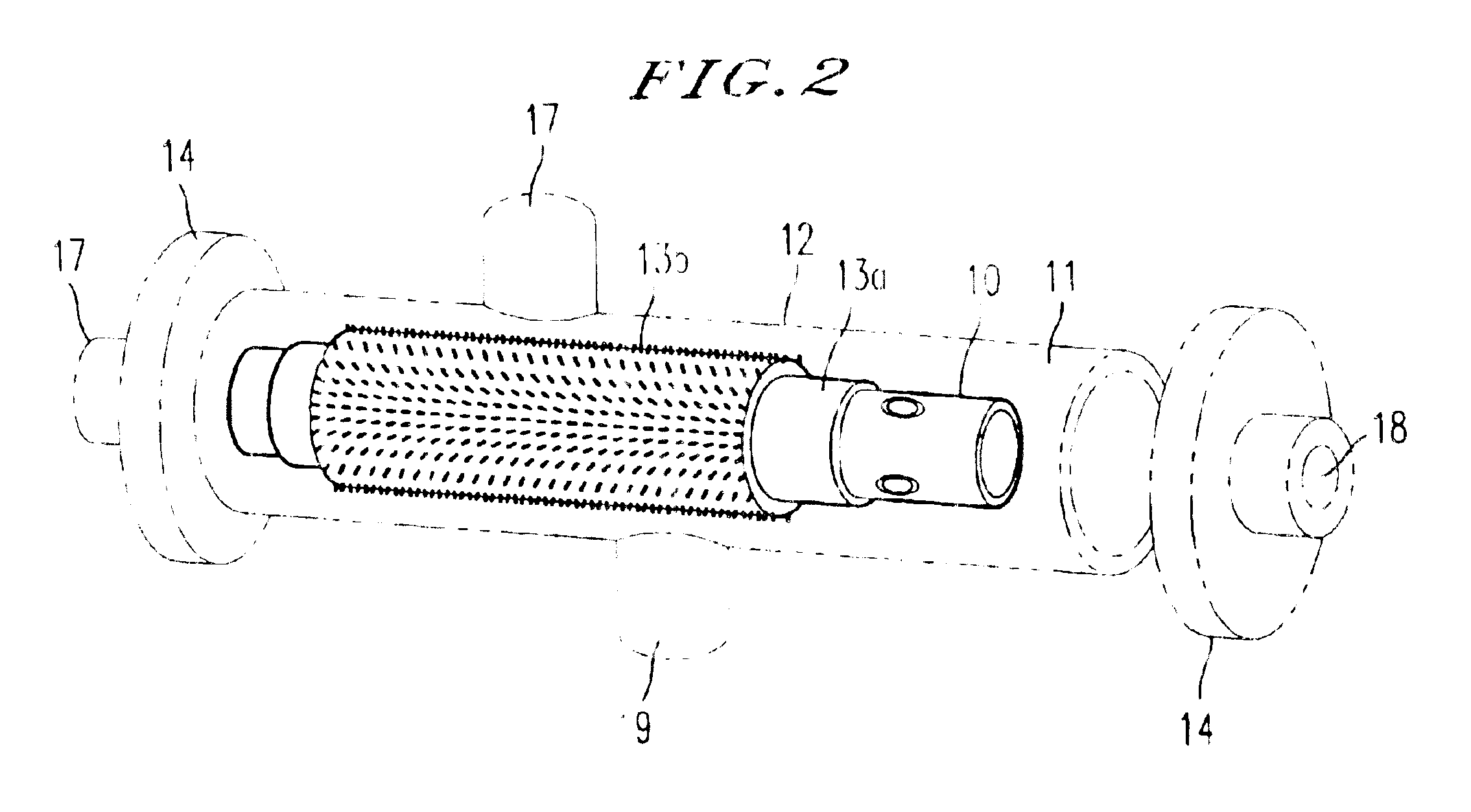
Method for manufacturing a potted bundle of hollow fibers
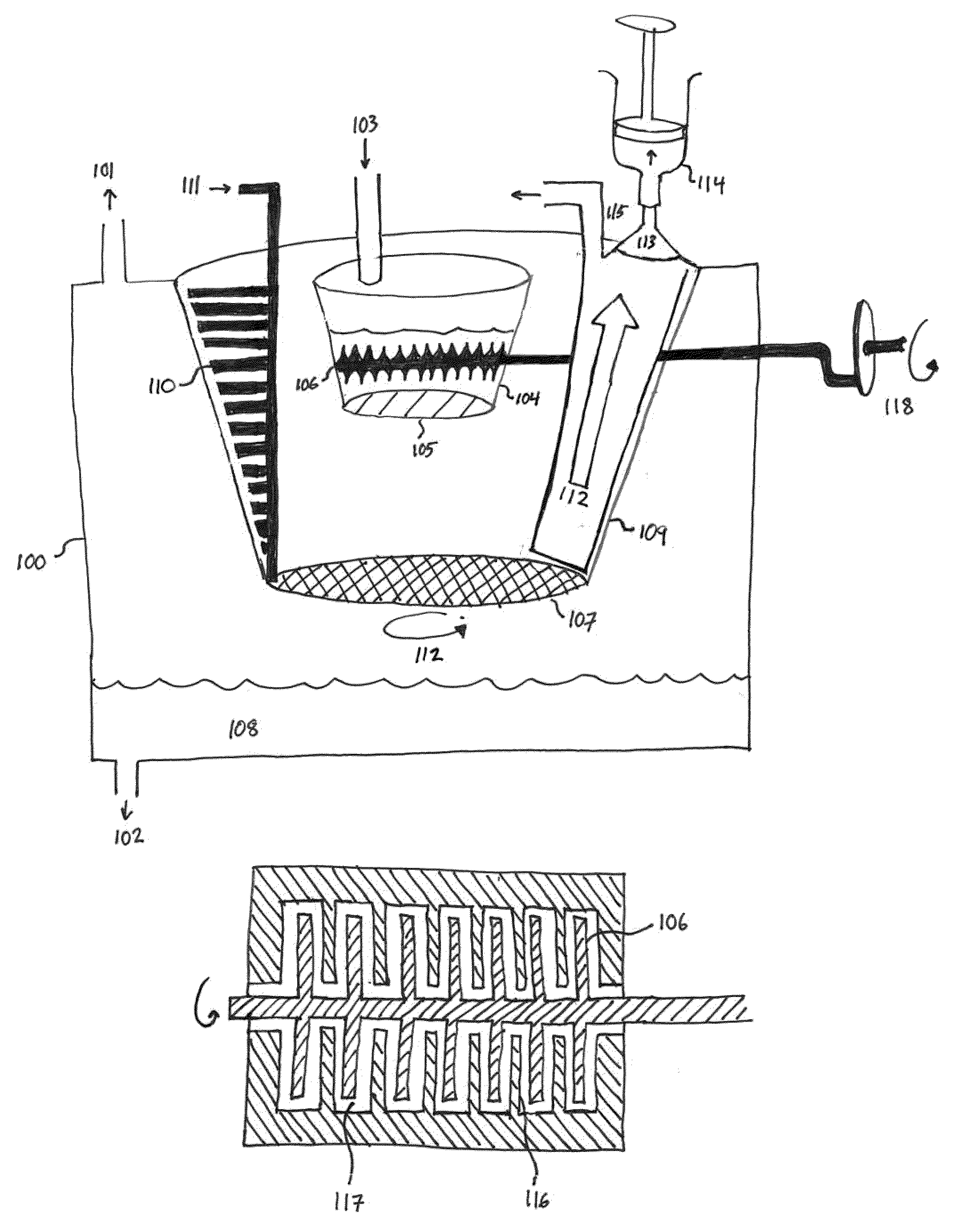
The present invention involves a process that includes injecting a potting compound such as an epoxy through a hollow portion (2B) of the central mandrel (2) and onto the inner layer(s) of a multi-layered fiber bundle (3) and through the outside of the bundle and onto the outer layer(s) of the bundle. By potting through the central mandrel (2), the potting compound distributes evenly throughout the inner fibers of the bundle (3). The steps may be sequentially or simultaneously. Preferably it is done as a two-step process, with the first step being to apply the potting compound through the central mandrel (2) and onto the inner fibers first. The second step is to pot around the outer layer of the fiber bundle (3) to finish the process. The resultant product is also disclosed.
Owner:MILLIPORE CORP
Method and apparatus for culturing cells
InactiveUS20070122904A1Reduce consumptionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHollow fibreCellulose
A method for culturing cells, the method comprising: providing a plurality of cellulose hollow fibre capillaries having cells and at least one protein required for proliferation, differentiation and / or genetic modification of the cells therein and optionally at least one metabolite; and providing on the extracapillary side of the semi-permeable substrate at least one metabolite required for proliferation of the cells.
Owner:UNISEARCH LTD
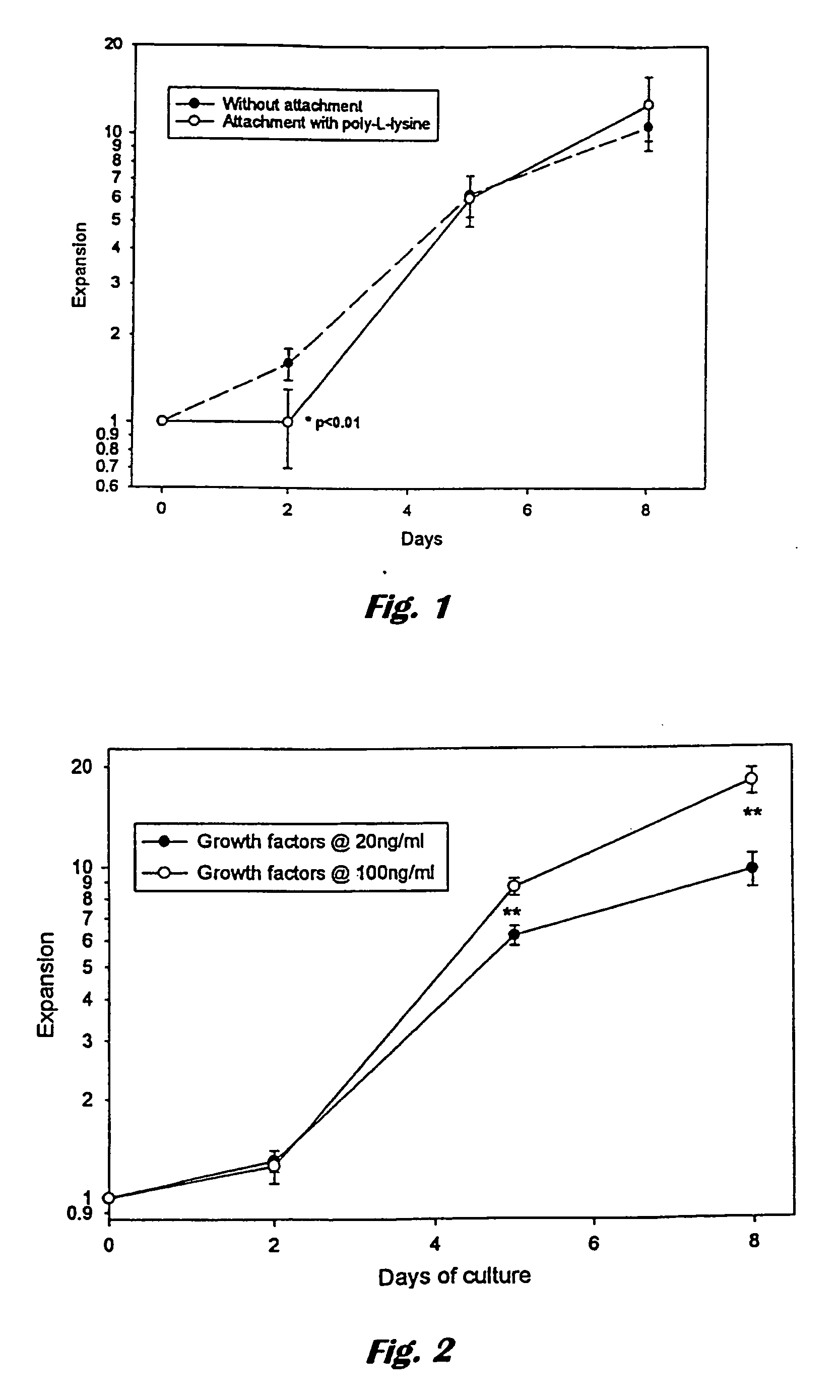
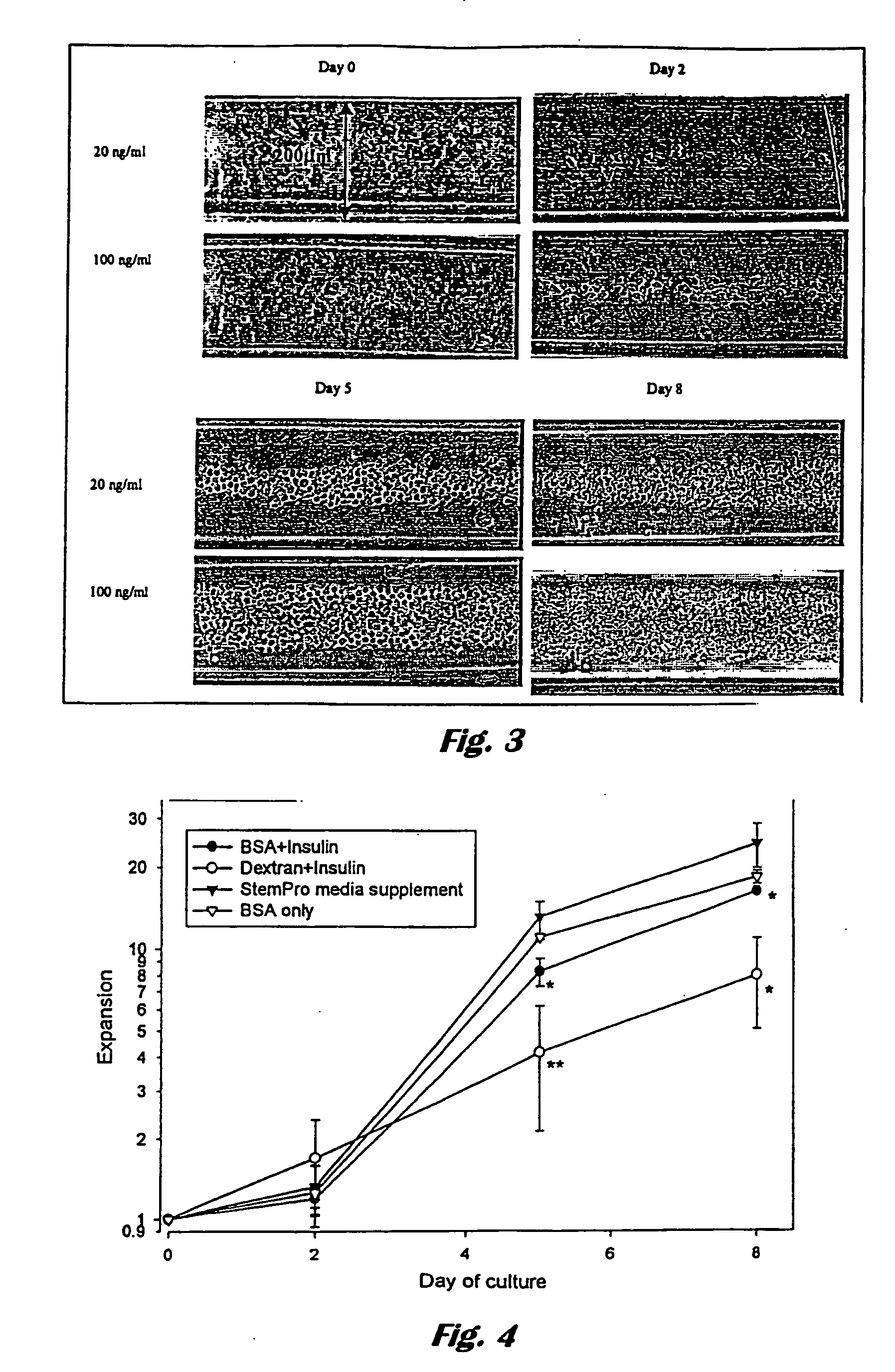
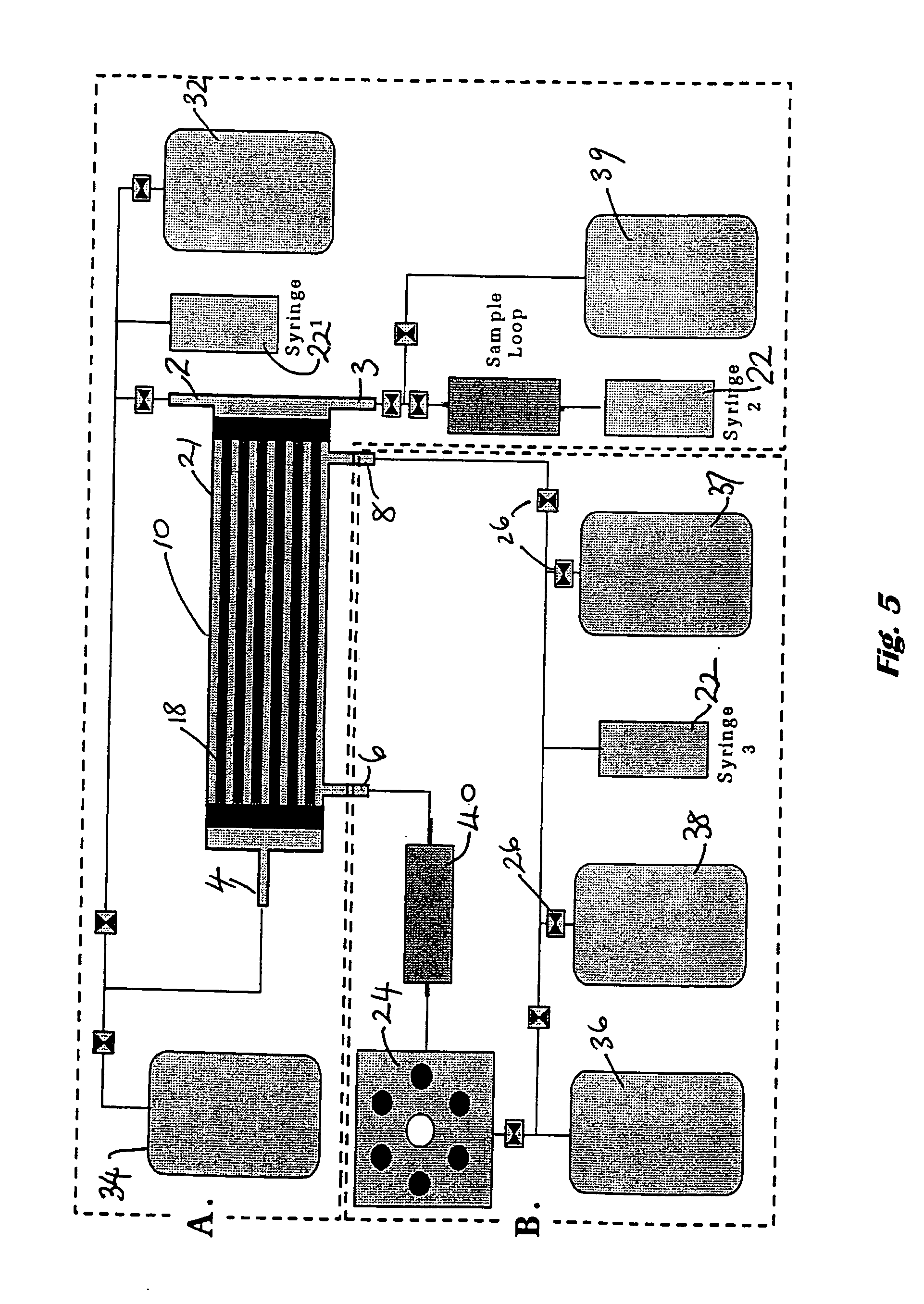
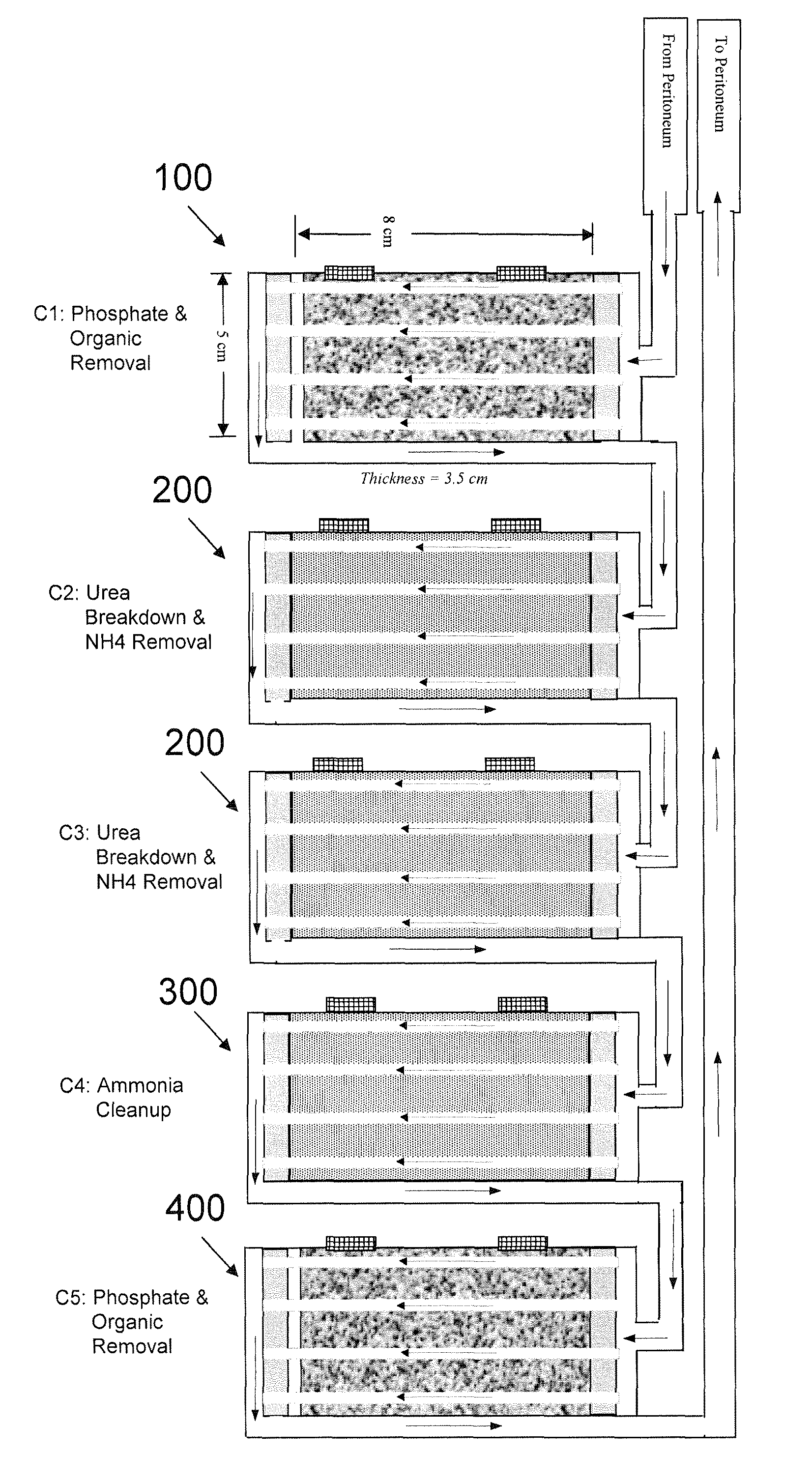
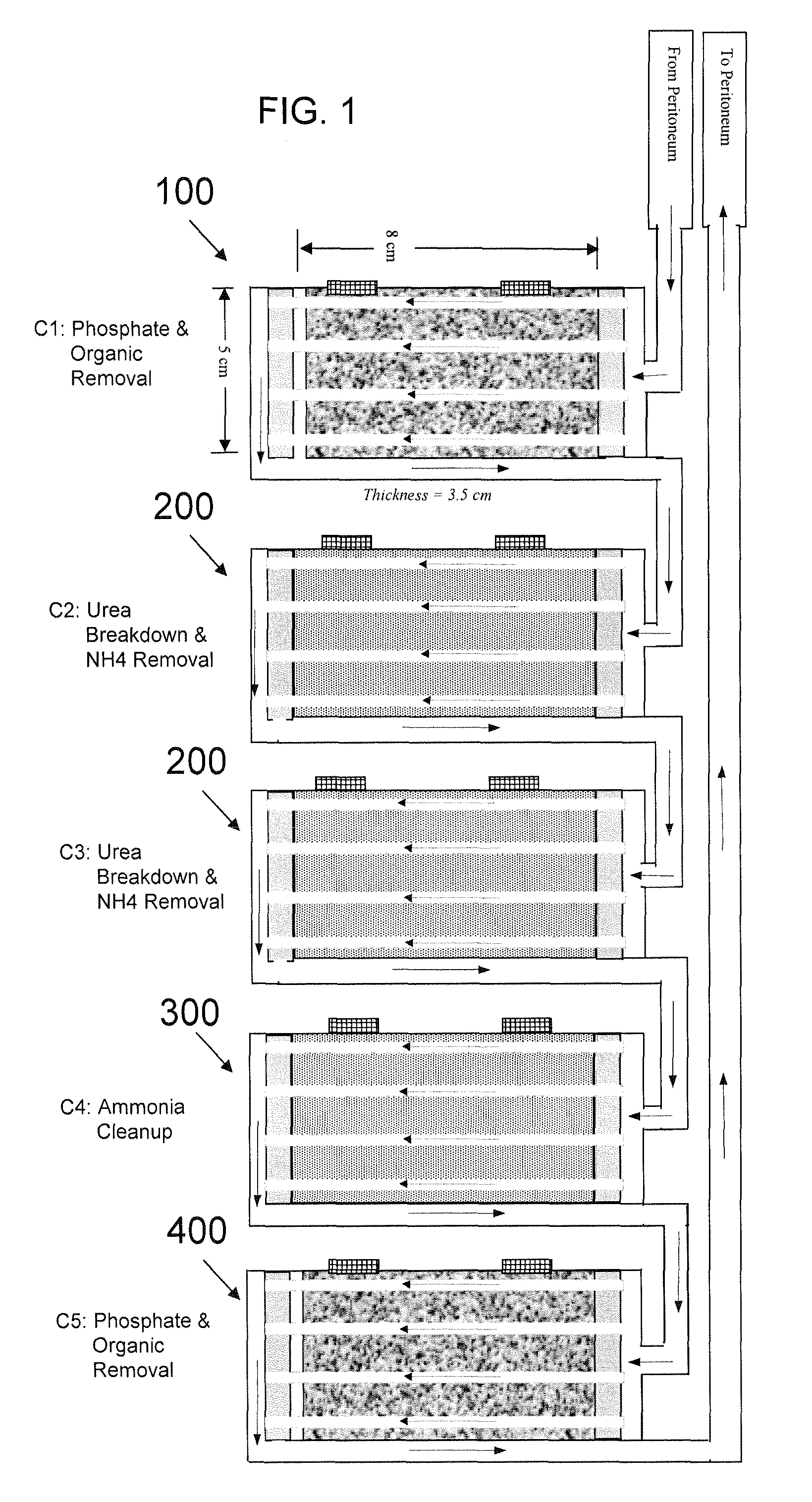
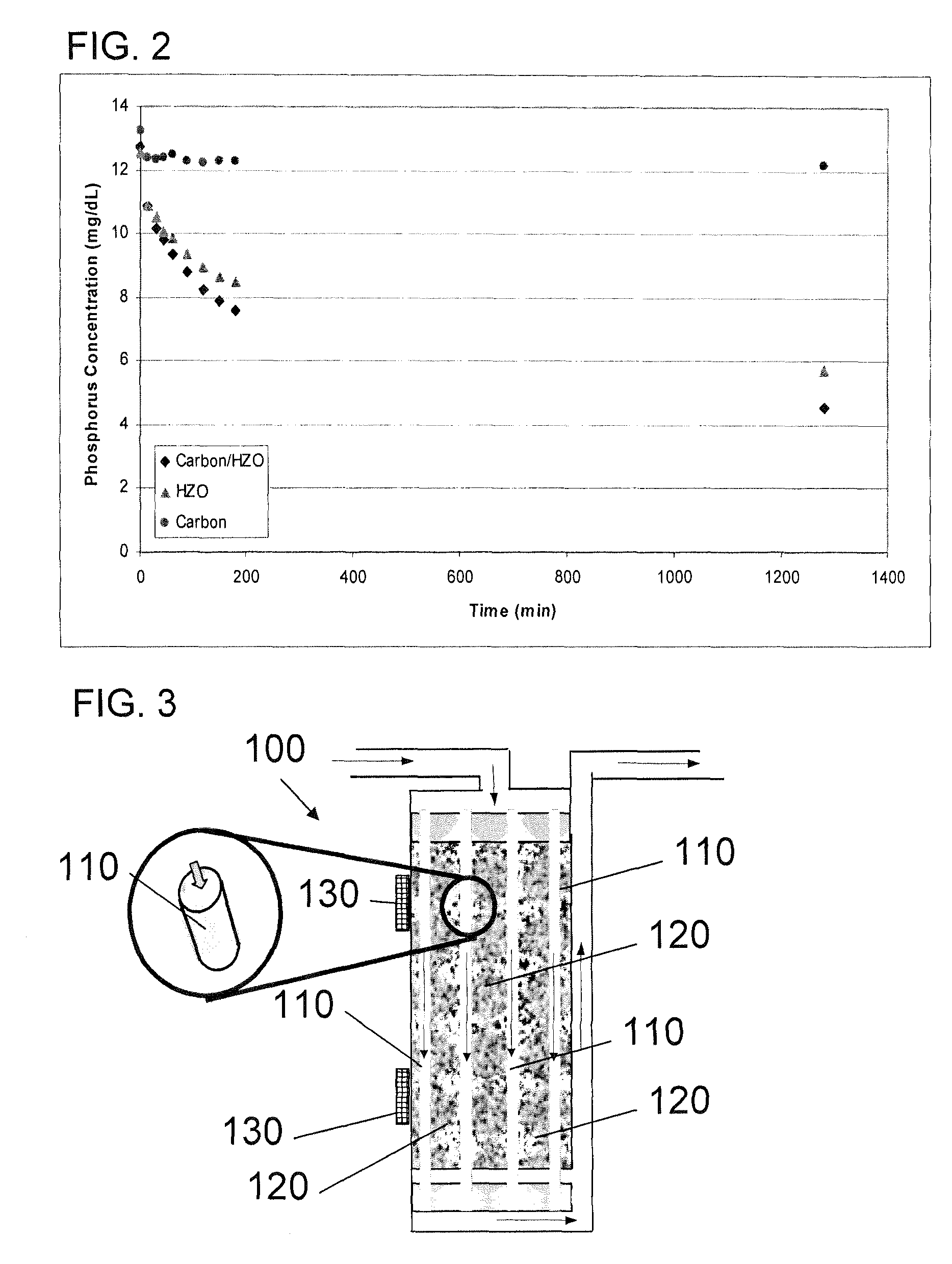
Portable peritoneal dialysis system
ActiveUS8777892B2Comfortably wornComfortable to carrySolvent extractionMedical devicesHollow fibreFiber
A portable peritoneal dialysis system for a patient includes an inlet port for providing inflow to the patient's peritoneal cavity, an outlet port for providing outflow from the patient's peritoneal cavity, and a volume of dialysate for flow into and out of the patient's peritoneal cavity, thereby removing from the dialysate uremic waste metabolites that have diffused into the dialysate. The portable peritoneal dialysis system also includes a closed liquid flow loop, including a pump, for flowing the dialysate into and out of the patient's peritoneal cavity, and an organic- and phosphate-removing stage, including at least one replaceable cartridge in the closed liquid flow loop, the cartridge containing material for removing organic compounds and phosphate from dialysate removed from the patient's peritoneal cavity. The portable peritoneal dialysis system further includes a urea- and ammonia-removing stage, including at least one replaceable cartridge in the closed liquid flow loop, the cartridge containing material for removing urea and ammonia from dialysate removed from the patient's peritoneal cavity, the material being packed around semi-permeable hollow fibers with interior fiber walls that reject cations, thereby retaining cations in the dialysate.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE HLDG INC
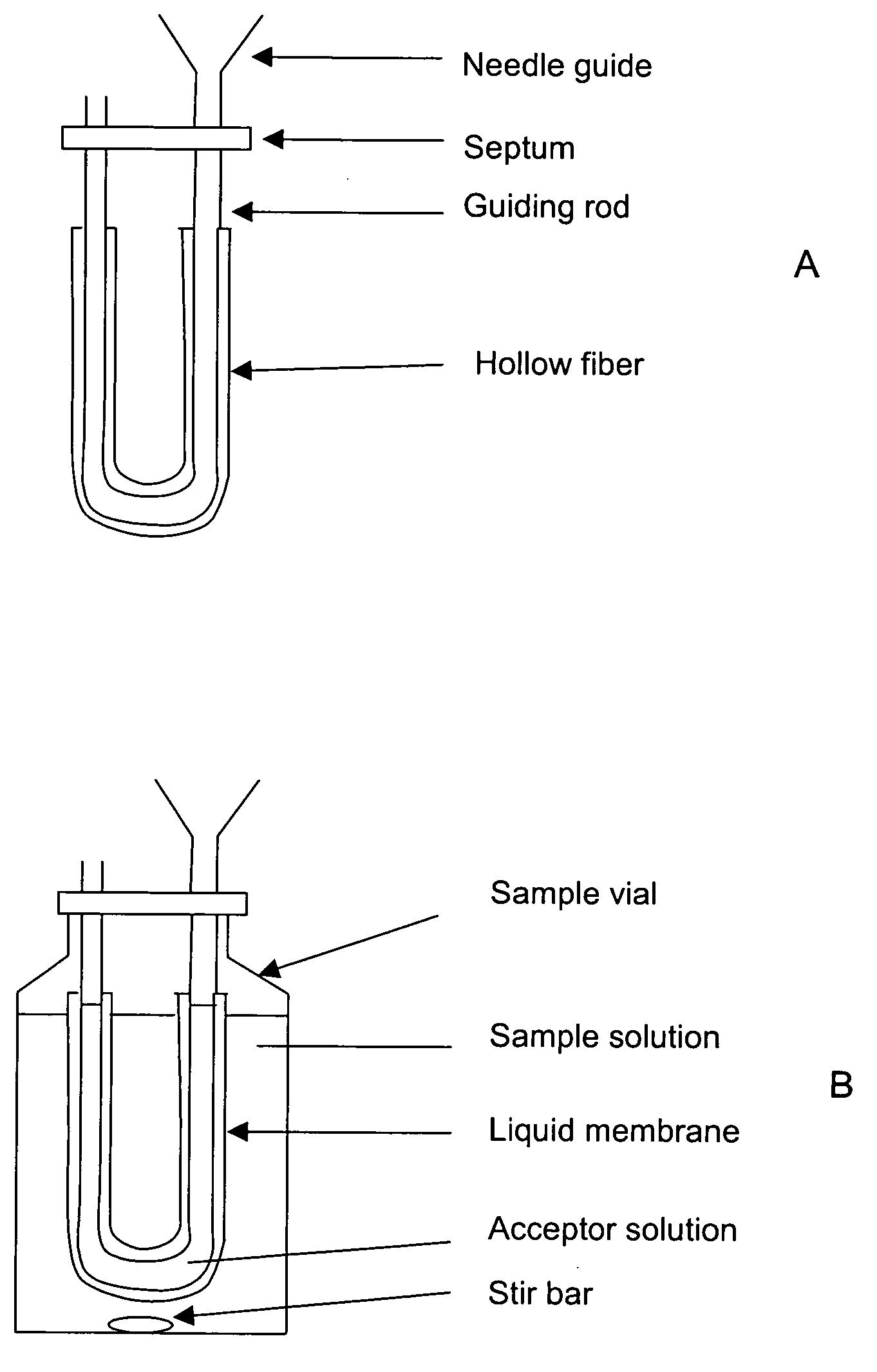
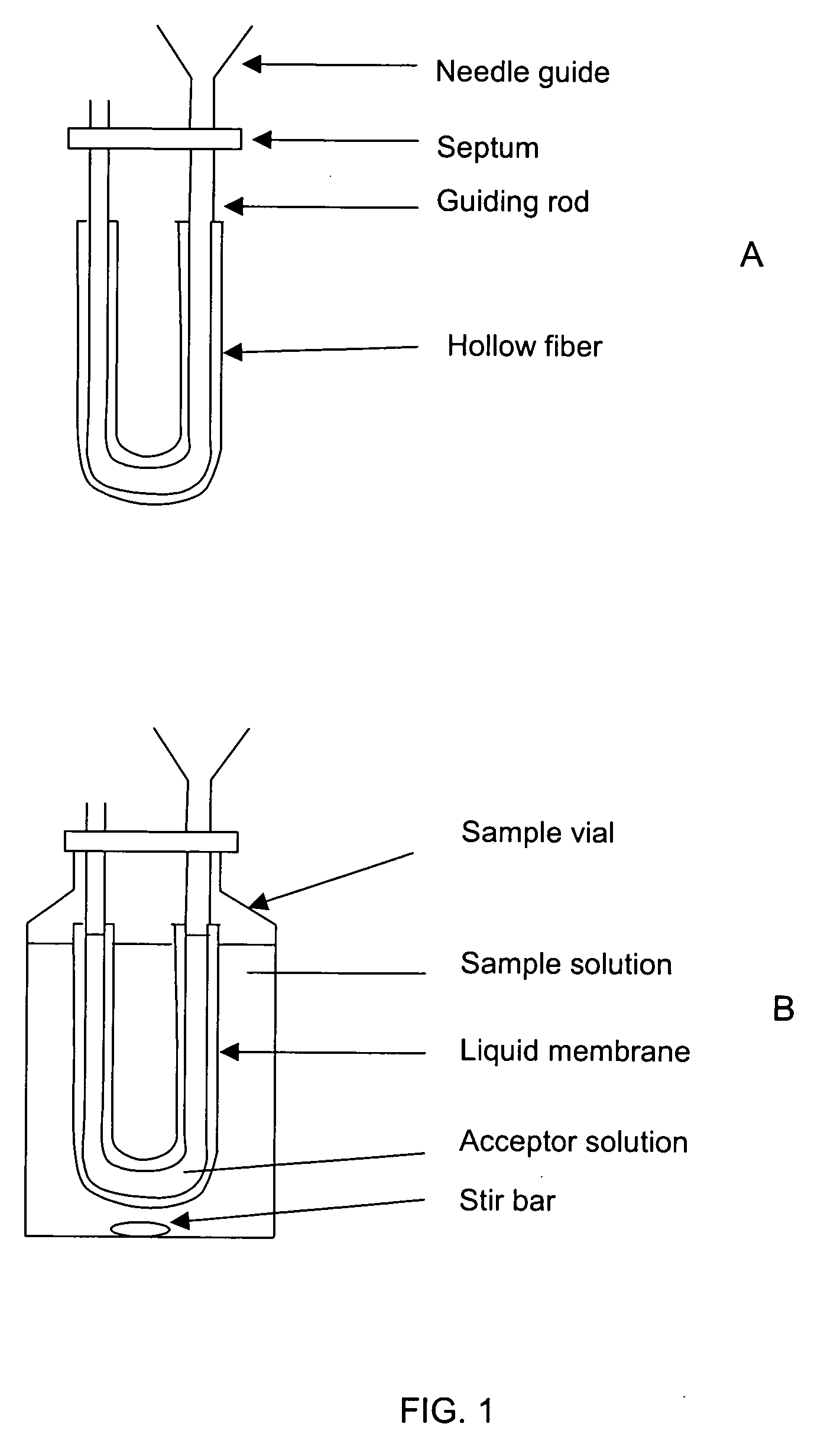
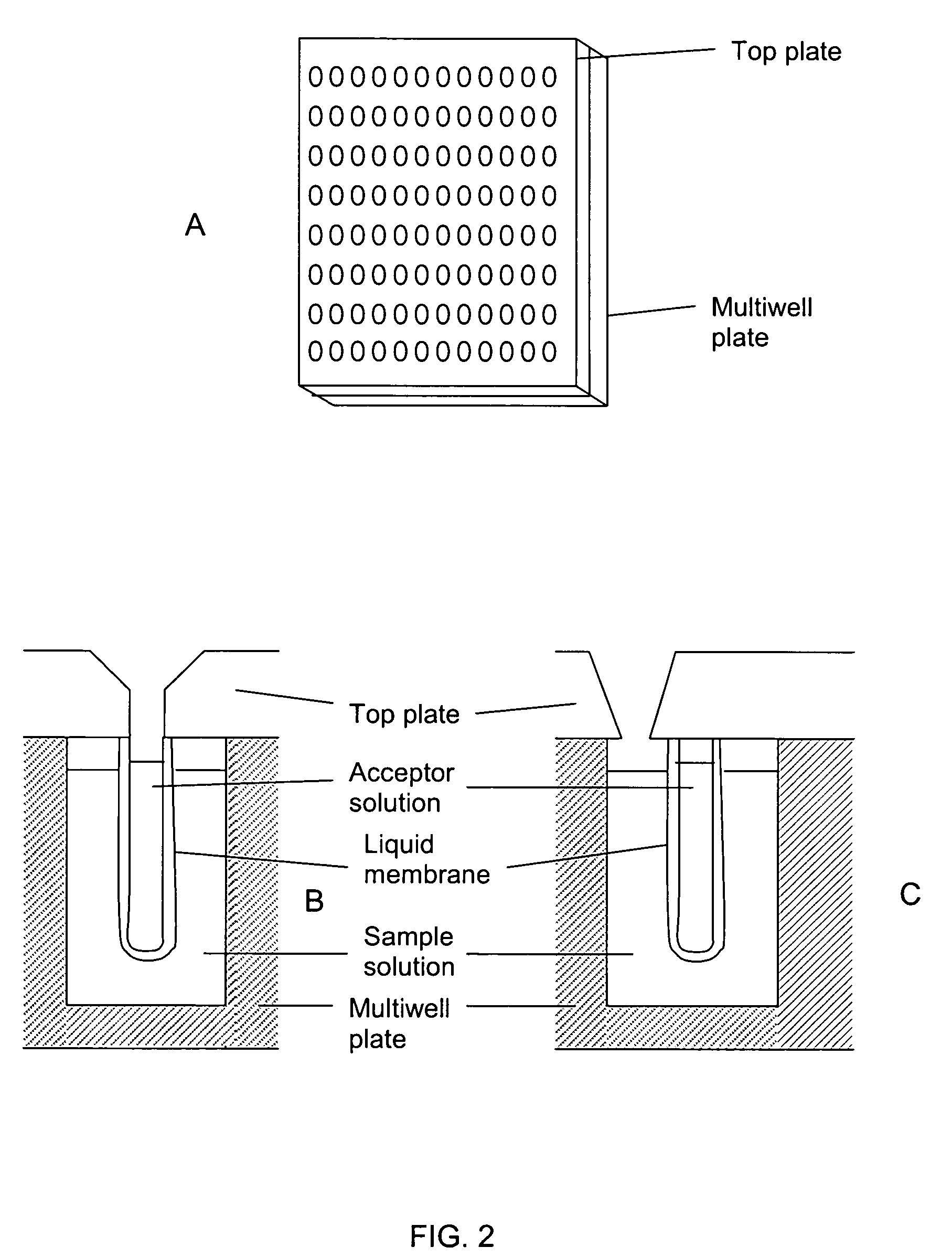
Stable liquid membranes for liquid phase microextraction
The invention provides devices and methods for performing liquid phase microextraction of at least one analyte from an aqueous sample, wherein the device comprises a liquid membrane comprising a fatty acid ester, a vegetable oil, a silicone oil, a nitroarylalkylether, or mixtures thereof, and an optional carrier, supported on a porous polymeric substrate. In a preferred embodiment, the porous polymeric substrate is a hollow fiber. The devices and methods for preparing them provide stable liquid membranes for performing liquid phase microextraction, where the membranes can be stored for 30, 60 or 90 days prior to use.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Antimicrobial semi-permeable membranes
Cast semi-permeable membranes made from synthetic polymer used in reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and microfiltration are treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent to prevent its bio-fouling and bacterial breakthrough. The semi-permeable membranes include a polymeric material and a non-leaching antimicrobial agent that is incorporated into and homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric material. The polymeric material, in the case of one membrane, may be cellulose acetate. In the case of thin film composite polyamide membranes, the antimicrobial agent is incorporated in a microporous polysulfone layer that is sandwiched between a reinforcing fabric and an ultrathin polyamide material. The invention also includes a treatment of flat and hollow fiber semipermeable membranes made with polysulfones and polyvinylidene fluoride.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
Supported biofilm apparatus and process
ActiveUS7169295B2Good curative effectSpeed up biological digestion reactionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHollow fibreEngineering
A membrane supported biofilm reactor uses modules having fine, hollow fibres, for example, made from dense wall Poly methylpentene (PMP) used in tows or formed into a fabric. In one module, one or more sheets of the fabric are potted into a module to enable oxygen containing gas to be supplied to the lumens of the hollow fibres. Various reactors and processes, for example to treat wastewater, using such modules are described. Mechanical, chemical and biological methods are used to control the thickness of the biofilm.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Method for preparing polyvinylidene fluoride porous membrane
ActiveCN101362057AGuaranteed StrengthGuaranteed high water fluxSemi-permeable membranesMembranesHollow fibreFiber
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Enhanced graphene oxide hollow fiber composite membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102600734AImprove hydrophilic abilityImprove hydrophilicitySemi-permeable membranesFiberPolymer science
The invention relates to an enhanced graphene oxide hollow fiber composite membrane and a preparation method of the composite membrane. The composite membrane is characterized in that a supporting layer is a hollow pipe woven by polymer fibers, and a membrane separation layer on a surface is graphene oxide or a mixture of the graphene oxide and polymer resin; and the outer diameter of the hollow pipe woven by the polymer fibers is 1-4mm, and the inner diameter of the hollow pipe woven by the polymer fibers is 0.5-1mm; the thickness of the membrane separation layer is 0.01-1mm; and the membrane pore diameter of the enhanced graphene oxide hollow fiber composite membrane is 1-500nm. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving the polymer resin, an organic additive, an inorganic additive and the graphene oxide into a organic solvent to prepare a membrane preparing solution; coating the membrane preparing solution onto the surface of the hollow pipe woven by the polymer fibers to obtain a blank body of a pre-fabricated composite membrane; and carrying out solidification and formation, rinsing and drying in the air to obtain the enhanced graphene oxide hollow fiber composite membrane. The prepared composite membrane is strong in hydrophilicity, and the water permeability of the composite membrane is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bioartificial filtration device for filtering blood to mimic kidney function
InactiveUS6942879B2Long life-timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBioartificial liver deviceUltrafiltration
A novel cell seeded hollow fiber bioreactor is described as a potential bioartificial kidney. Endothelial cells along with pericyte, vascular smooth muscle, and / or mesangial cells or any mesenchymally derived support cells are seeded along a hollow fiber in a perfused bioreactor to reproduce the ultrafiltration function and transport function of the kidney. Maintenance of tissue specific function and ultrastructure suggest that this bioreactor provides an economical device for treating renal failure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
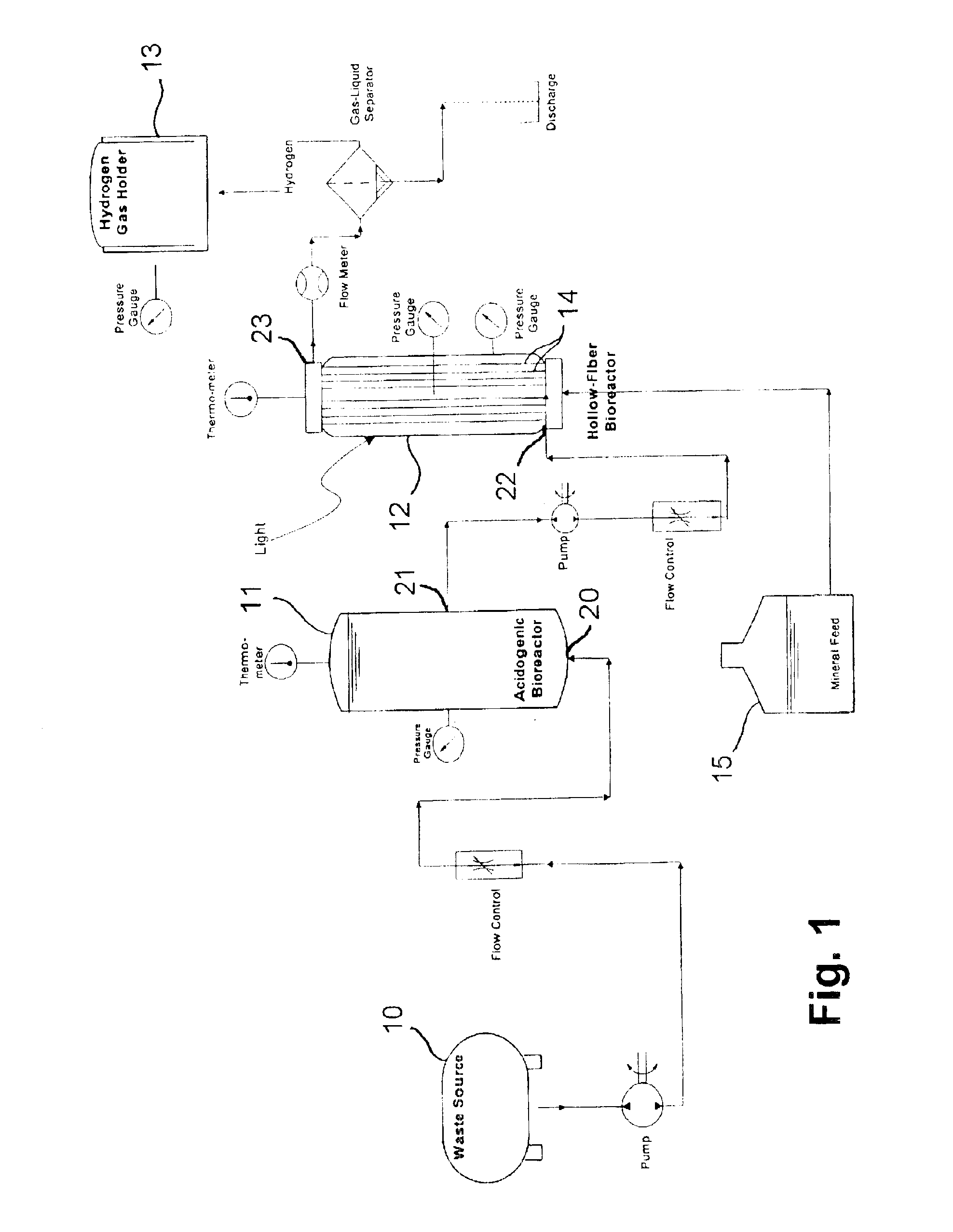
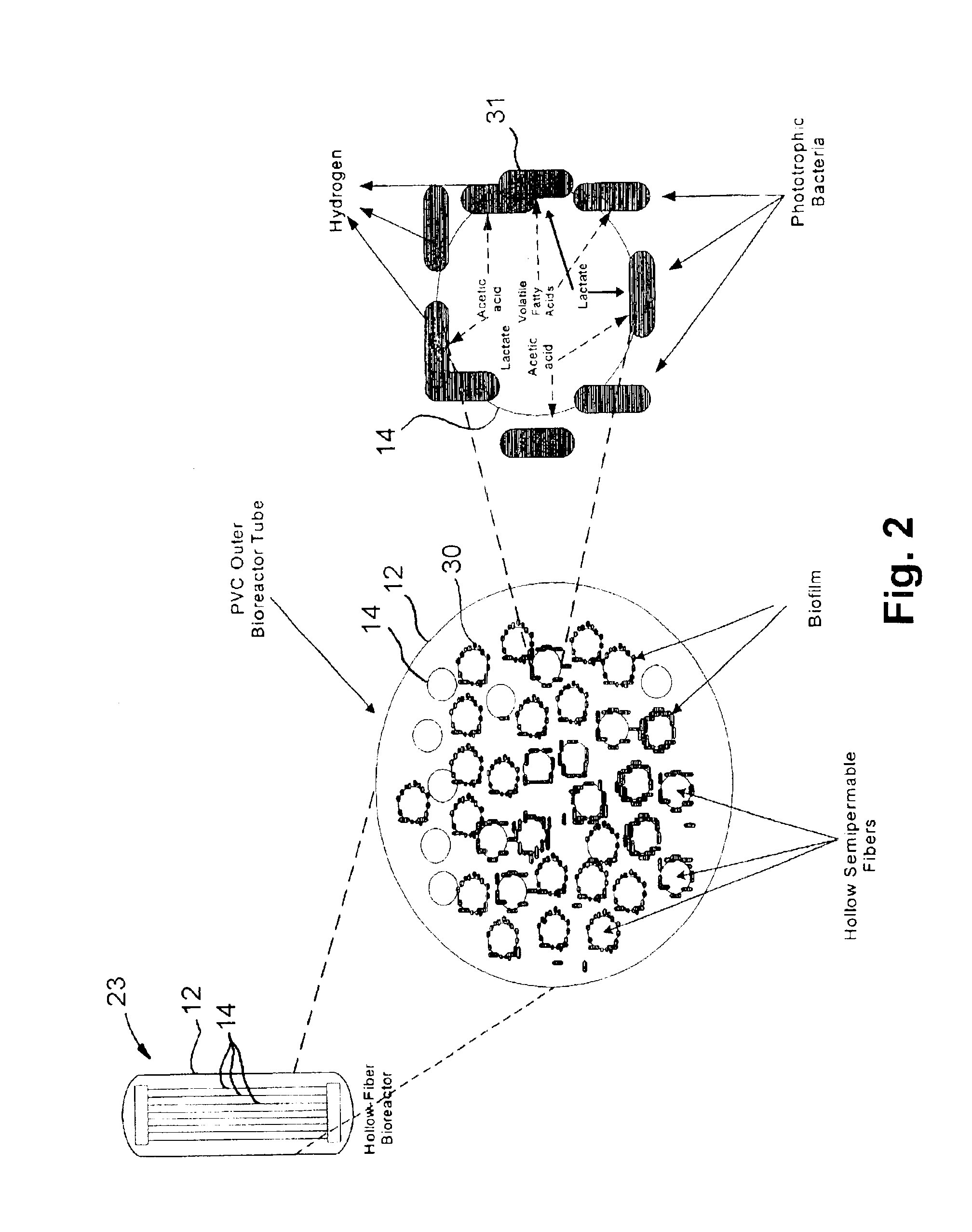
Method and apparatus for hydrogen production from organic wastes and manure
InactiveUS6887692B2Good characterBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiberHollow fibre
Owner:GAS TECH INST
Supported biofilm apparatus and process
ActiveUS20060037896A1High gas transfer rateIncrease the areaSemi-permeable membranesTransportation and packagingBiofilmFiber
A membrane supported biofilm reactor uses modules having fine, hollow fibres, for example, made from melt spun thermoplastic polymers treated after spinning to increase their permeability to oxygen, used, for example, in tows or formed into a fabric. In one module, one or more sheets of the fabric are potted into a module to enable oxygen containing gas to be supplied to the lumens of the hollow fibres. Various reactors and processes, for example to treat wastewater, using such modules are described. In one process, oxygen travels through fibers, optionally through an attached biofilm, to oxygenate surrounding water. Mechanical, chemical and biological methods, for example endogenous respiration, are used to control the thickness of the biofilm.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Adipose tissue collection and pre-processing devices for use in liposuction procedure
InactiveUS20100285521A1Obstruct passageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHollow fibreFiber
Devices and methods are described for pre-processing tissue samples containing cells of interest for various therapeutic procedures. Fibrous material may be extracted from the tissue sample through a shredding and separating device, resulting in a non-fibrous sample containing the cells of interest, which may then be washed and centrifuged to remove fluids, oil, and contaminants. The sample may then be digested in a large-volume container, and a piston within the container may push the resulting liberated cell suspension through a cell concentrator such as a hollow-fiber separation module.
Owner:TISSUE GENESIS
Membrane filter cleansing process
InactiveUS20060065596A1Reduce accumulationLower the liquid levelMembranesSemi-permeable membranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
Immersed hollow-fiber membrane filtration systems sometimes encounter process problems as a result of solids accumulation in and around the hollow fibers. The solids can accumulate to the point where they begin to dewater and form a mud like substance known as sludge. In some embodiments of the invention there is provided a process for substantially preventing the accumulation of sludge build-up on membrane fibers and / or cleansing membrane fibers that have been fouled by a substantial sludge build-up. Many of these embodiments involve aerating a membrane tank in which the membrane fibers are immersed after the water level has been reduced to near the level of solids accumulation. In some embodiments of the invention, the energy released by bursting bubbles at the liquid-air interface is employed to prevent fouling of membrane fibers and / or cleanse fouled membrane fibers.
Owner:ZENON TECH PARTNERSHIP
Method for electro-permeabilization of individual cellular and organellar structures and use thereof
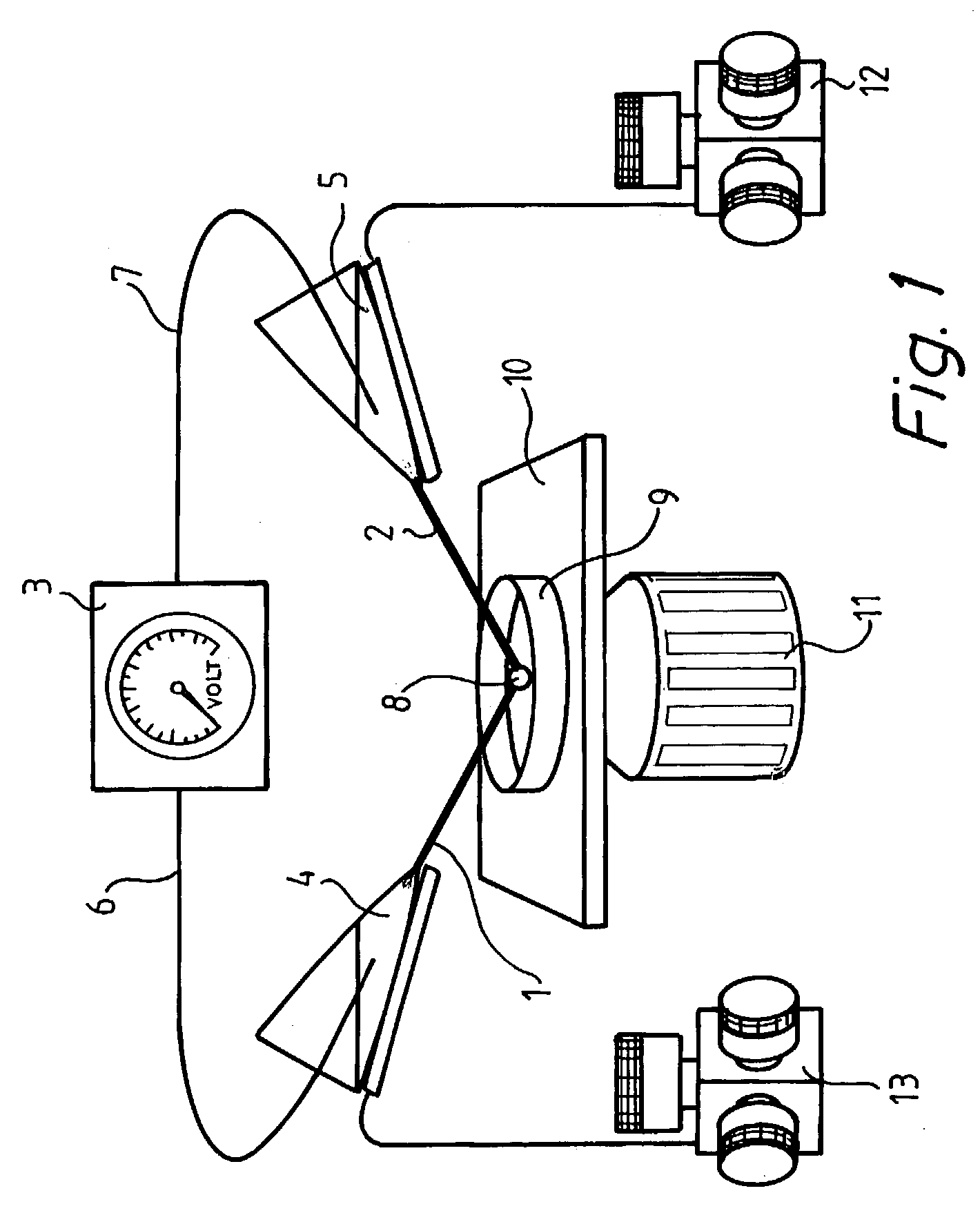
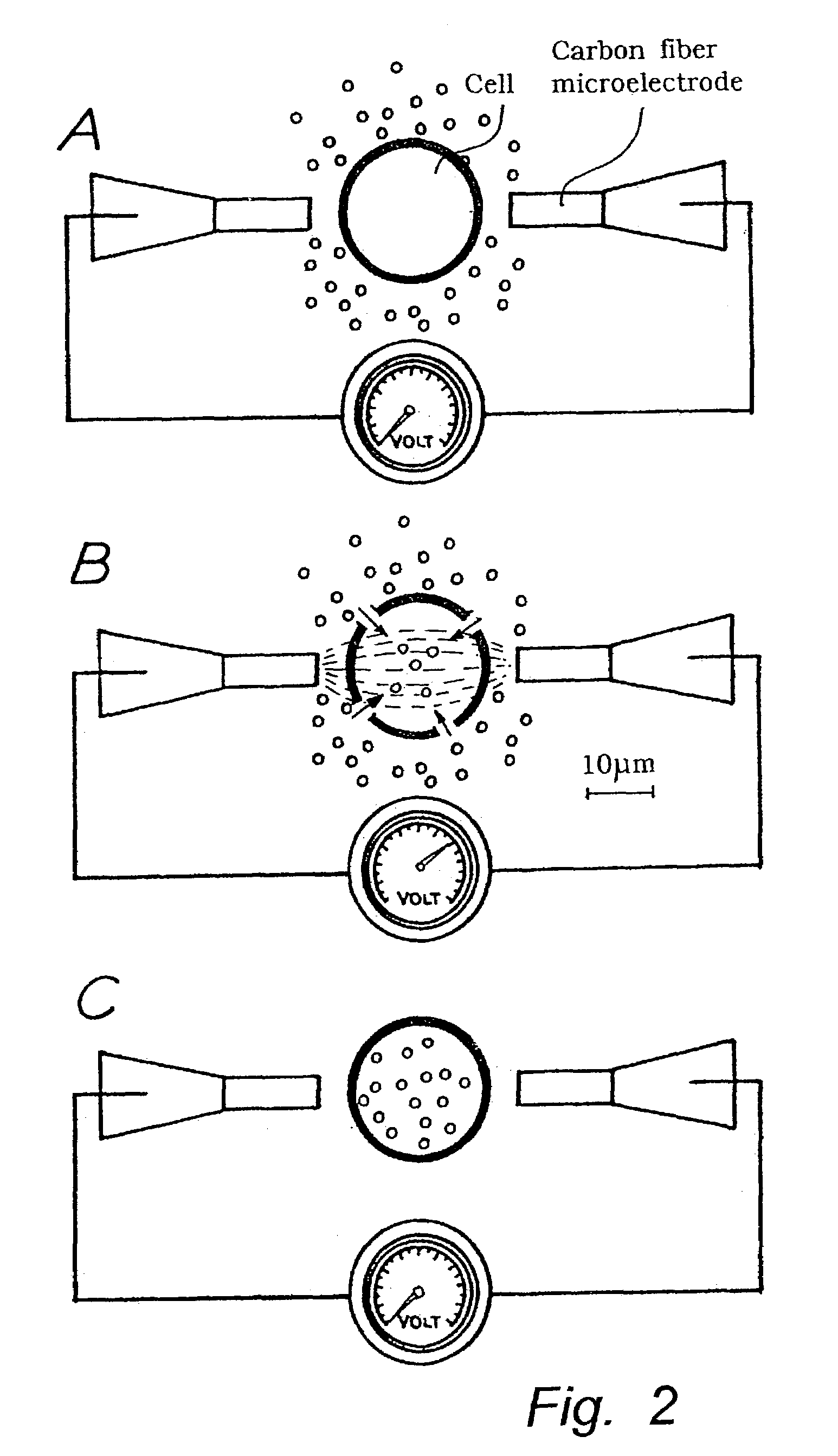
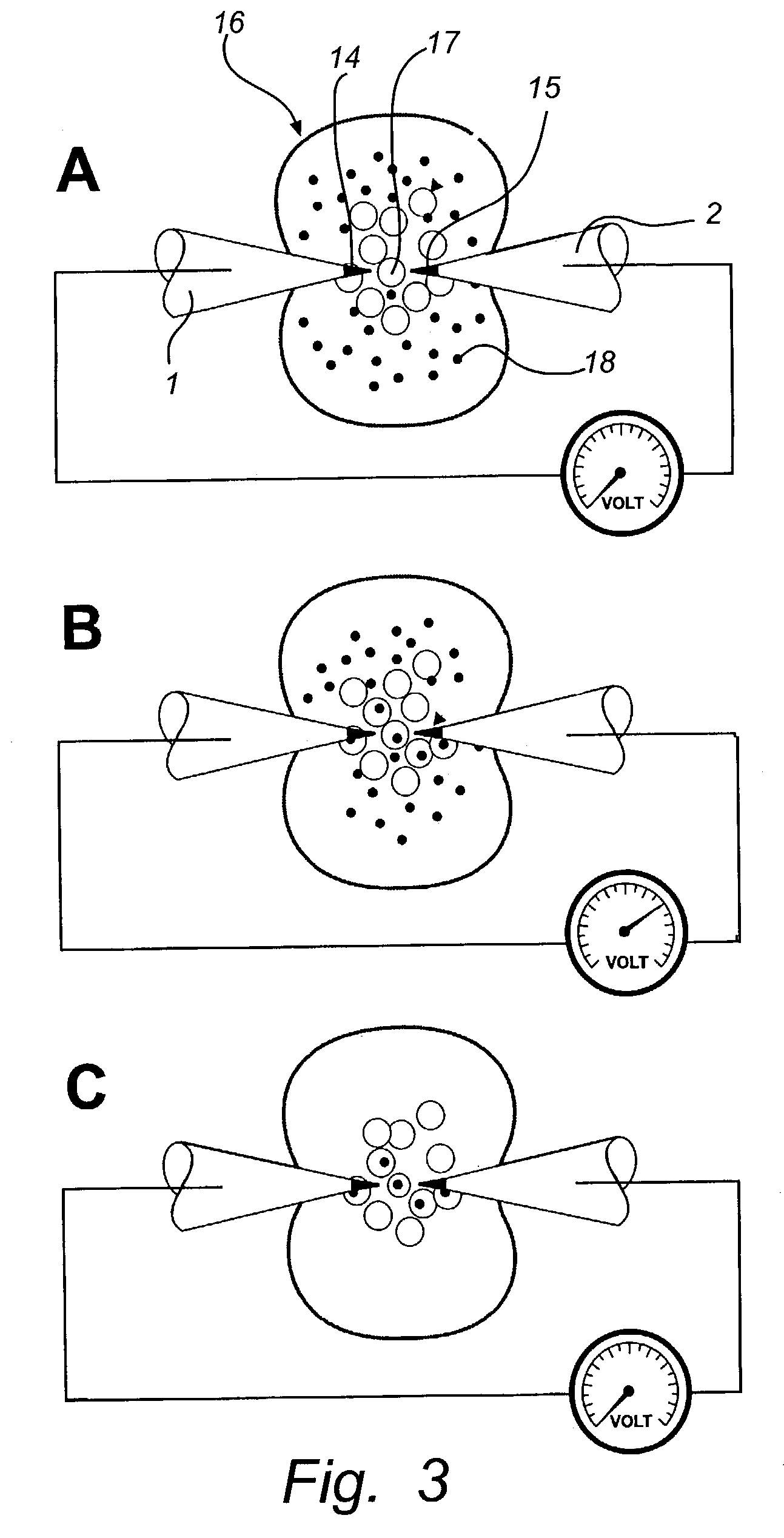
InactiveUS7109034B2Accurate focusImprove spatial resolutionBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrotherapyFiberDisease
The invention relates to a method for permeabilization of a cell structure consisting of a single cell, an intracellular structure or an organelle comprising the following steps: (a) microelectrodes, preferably two carbon fiber electrodes or hollow fiber electrodes, are provided, (b) the microelectrodes are connected to a power supply, (c) the electrodes, individually controlled by high-graduation micromanipulators, are placed close to the cell structure at an appropriate inter-electrode distance, and (d) a highly focused electric field of a strength sufficient to obtain electroporation is applied between the electrodes. The method may be used in order to transfer cell impermeant solutes, such as drugs or genes, into the cell structure or out of the cell structure, in biosensors, in the treatment of tumours and neurodegenerative diseases and in the study of biophysical processes.
Owner:CELLECTRICON
Hollow fiber, dope composition for forming hollow fiber, and method of making hollow fiber using the same
InactiveUS20090297850A1Improve permeabilityHigh selectivitySuture equipmentsCosmetic preparationsHollow fibreFiber
Owner:IUCF HYU (IND UNIV COOP FOUND HANYANG UNIV)
Preparation of hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride microporous membrane
InactiveCN1704152AImprove hydrophilicitySimple processSemi-permeable membranesPhysical chemistryFiber type
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydrophilic PVDF microporous barrier. The principal raw material is polyvinylidene fluoride with the range of molecular weight: 5000 to 50000. It prepares hydrophilic PVDF microporous barrier by the method of separating solution and compounding dip-coating modification. It especially suits the occasion of effluent treatment, medicine separation and biochemy. The technology can prepare microporous barriers with plate type and hollow fiber type.
Owner:杨虎
Hydrophilicity kynoar hollow fiber microporous membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101190401AImprove anti-pollution performanceAvoid adsorptionSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibrePorosity
The invention discloses a hydrophilic polyvinylidene fluoride hollow fiber microporous membrane and the preparation method thereof. The main composition and the mass content of the membrane are 70% to 90% of polyvinylidene fluoride, amphiphilic poly-(propylene oxide-oxirane), 5% to 29% of poly-(methacrylic acid- acrylic acid) or poly-(methacrylic acid methyl ester-vinyl alcohol) copolymer and 1% to 5% of nano-silicon dioxide. The membrane preparation method is that all the components are mixed and dissolved with aperture regulator, thickener and solvent to obtain the membrane preparation liquid; after that, the hollow fiber forming is carried out through a dry-wet spinning technique, and finally cleaning and drying are implemented. The obtained membrane has adjustable internal diameter and external diameter, 60% to 80% of porosity and the aperture ranging from 0.01micron to 0.2micron. As a water disposal separating membrane material with excellent performance, the invention has the advantages of being able to be fully humid, organic adsorption resistance and great water flux, etc.
Owner:HAINAN LITREE PURIFYING TECH CO LTD
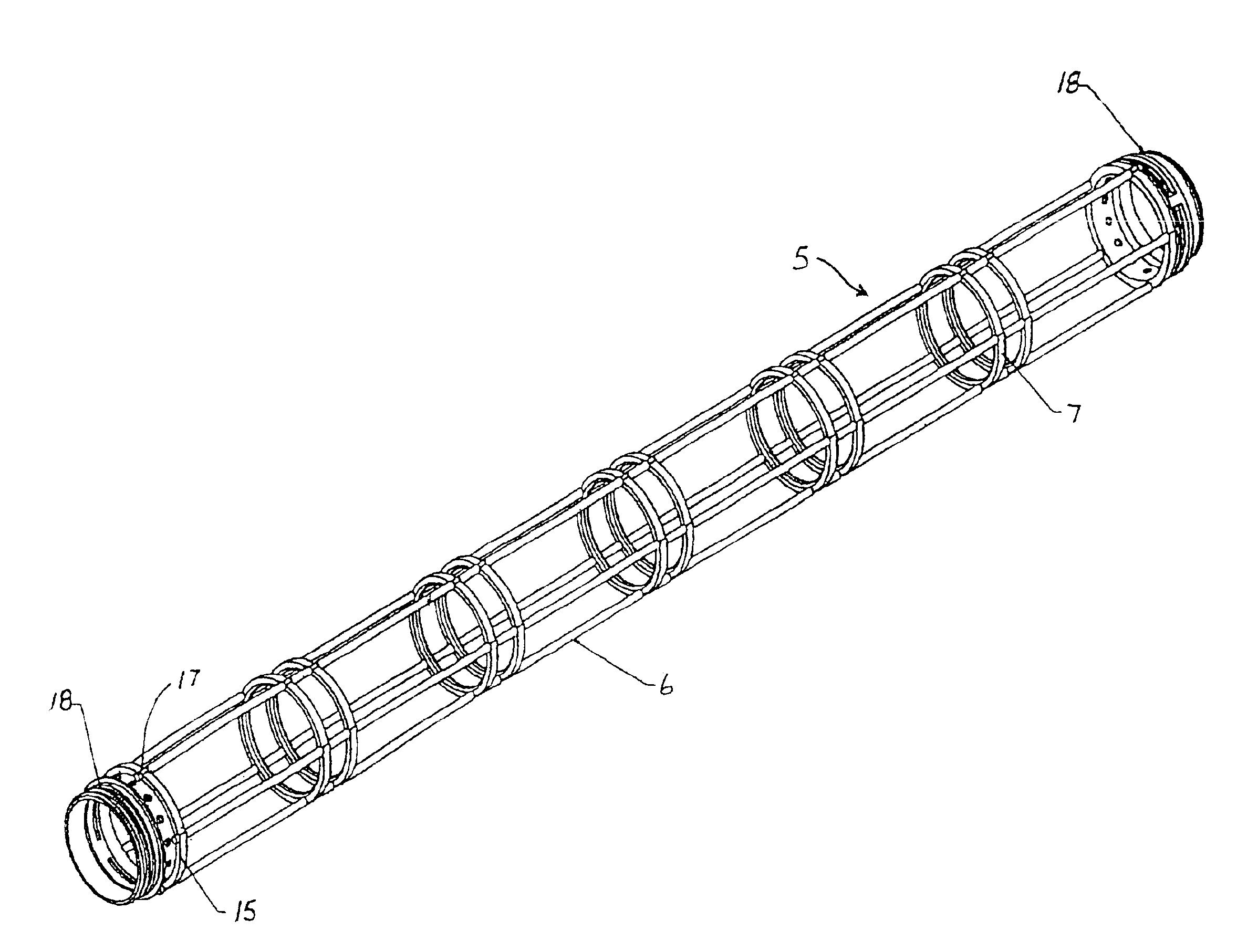
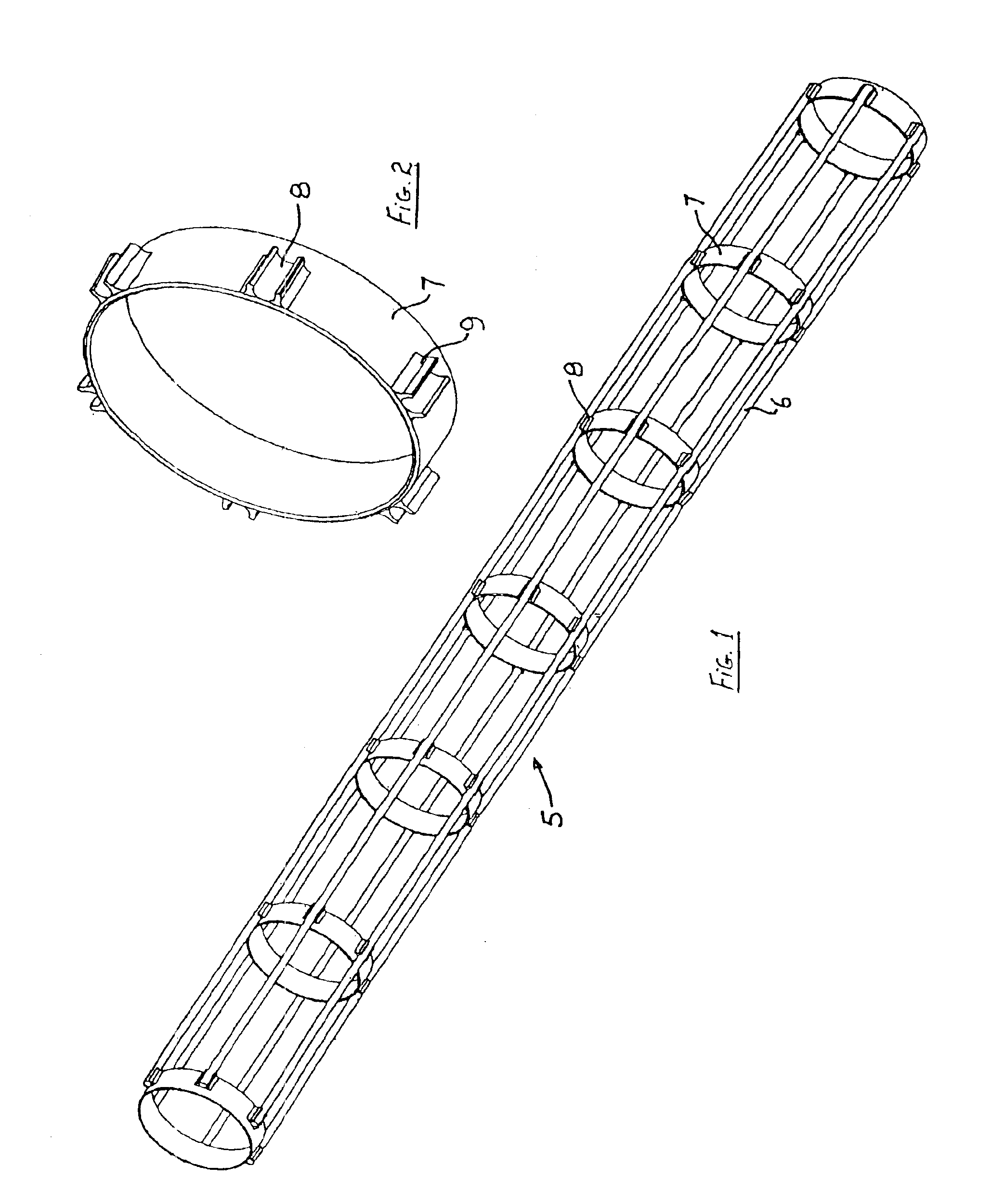
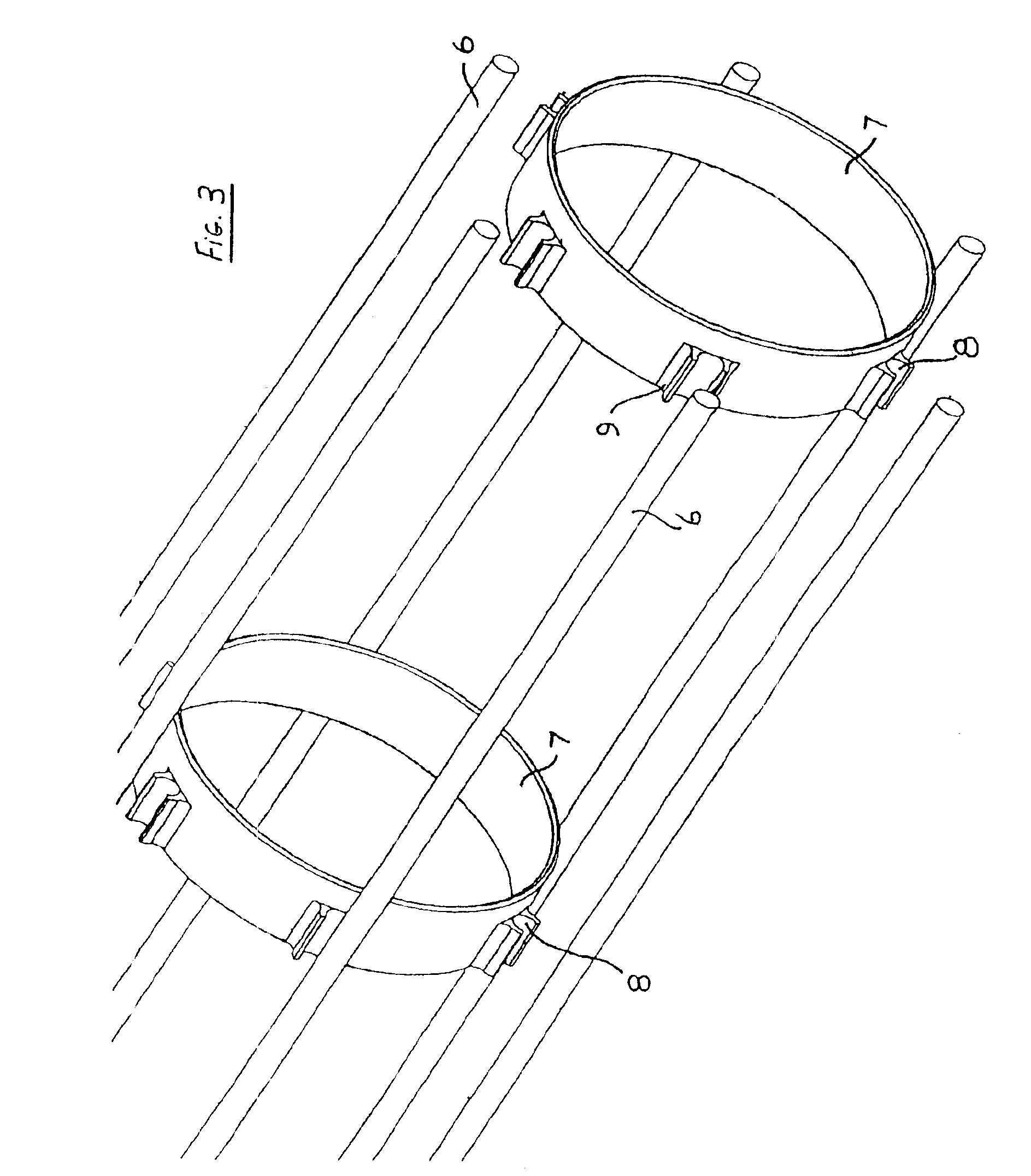
Hollow fiber restraining system
A restraining system for hollow fibers is provided. The restraining system includes a plurality of longitudinally extending elements spaced from one another and supported by a number of discrete spacer elements, each spacer element extending generally transverse of said longitudinal elements, such that in combination with said longitudinal elements they define a cage-like structure.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
Method for fabricating fiber reinforcement type microporous filter membranes of hollow fiber made from polyvinylidene fluoride
InactiveCN1695777AHigh tensile strengthTightly boundSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibrePolymer science
A fibre reinforced millipore filter membrane of hollow polyvinylidene fluoride fibre is prepared through preparing solution from polyvinylidene fluoride, solvent and additive, pretreating the reinforcing fibres, spinning, gelatinizing and post-treating. Said solvent, additive and reinforcing fibre are also disclosed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Preparation method for organic and inorganic hollow fiber composite membrane
ActiveCN102350226AImprove high temperature resistanceInhibit swellingSemi-permeable membranesHollow fibreFiber
The invention relates to a preparation method for an organic and inorganic hollow fiber composite membrane. An inorganic ceramic hollow fiber serves as a support body on which one layer of organic high molecular polymer membrane is coated; the layer of the polymer membrane can be hydrophilic polymer, hydrophobic polymer or amphipathy polymer, and is mainly used for separating close-boiling or constant-boiling organic solvent in a pervaporation mode and removing tract components in the solution. The average aperture of the inorganic ceramics hollow fiber support is 0.2-0.8 microns, and the inorganic ceramics hollow fiber support has higher mechanical strength. The composite membrane is prepared on the macropore inorganic ceramics support by the bridging effect and solvent prewetting, and the problems that the organic membrane layer is easily stripped from the inorganic support with larger curvature, hole leakage is serious to cause the organic matter to excessively block the duct of the inorganic support can be solved. Compared with a micropore support of 0.02-0.2 microns, the method is more convenient, and a technical support is provided for the large-scale application of the organic and inorganic hollow fiber composite membrane.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Ceramic hollow fibers made from nanomscale powder particles
The invention relates to a method for producing ceramic hollow fibers from nanoscale particles and to hollow fibers produced in such a manner. The inventive method is characterized in that the ceramic material has a solids content of >25% by volume, preferably >30% by volume and is processed by means of extrusion and spinning. The hollow fiber is sintered according to conventional sintering methods. A hollow fiber produced in this manner is used for metal, polymer and ceramic matrix reinforcements, for artificial organs, for microsystems technology components, for fiber optical waveguides, for ceramic membranes, for solid electrolyte in fuel cells (SOFC), for tissue engineering and for producing extremely light ceramic parts, such as heat shields or brake systems, that are subjected to temperature stresses. The inventive ceramic batch can also be processed by means of silk screening whereby resulting in the production of filigree structures over the ceramic silk screening.
Owner:ITN NANOVATION AG
Cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane and preparing method thereof
The invention discloses a cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane and a preparing method thereof. The preparing method of the cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane includes the steps that cellulose acetate serves as a raw material, an organic metal framework compound and a small molecule pore-forming agent serve as a mixed additive, the raw material and the mixed additive are dissolved through a solvent to prepare a cellulose acetate membrane casting solution, a dry and clean glass plate with a supporting layer is coated with the prepared membrane casting solution to form a plate nascent-state membrane or the prepared membrane casting solution and a medium with an inner fiber cavity are extruded through a spinneret plate to obtain a hollow fiber nascent-state membrane, the hollow fiber nascent-state membrane is solidified and subjected to heat treatment, and the cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane is prepared. As the cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane is prepared through the organic metal framework compound, the porosity factor of the cellulose acetate nanofiltration membrane is increased, and the water flux is improved; the amine-modified organic metal framework compound is introduced into the formula of the membrane casting solution of the cellulose acetate, the nanofiltration membrane can show charged positive electricity after cross-linking, separation of amino acid with positive charges and protein with positive charges can be promoted, and the reject rate of the nanofiltration membrane is increased.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing hollow yarn film
InactiveUS20030107150A1Effect of shaking is smallHigh in resistance against marringWrappers shrinkageFilament/thread formingYarnFiltration
In a method for producing hollow fiber membranes which comprises melt kneading a mixture comprising polyvinylidene fluoride and an organic liquid or a mixture comprising polyvinylidene fluoride, an organic liquid and an inorganic fine powder, extruding the kneaded mixture to form hollow fibers, and extracting the organic liquid or the organic liquid and the inorganic fine powder from the hollow fibers, which includes the steps of drawing the hollow fibers before or after termination of the extraction and then shrinking the fibers. According to this method, it is possible to stably produce hollow fiber membranes having dense pores and having a high water permeation performance, excellent endurance and stain resistance, and which are suitable for filtration uses such as removal of turbidity of water.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI KK
Hollow fiber filter for extracorporeal blood circuit
A filter for an extracorporeal blood circuit including a bundle of hollow fibers having an end section encased in a potting material, wherein the end section of potting material has an end surface with open ends of the fibers distributed throughout the end surface, and a filter header cap having an inlet connectable to a blood line and an open end sealed around a side surface of the end section of the bundle of hollow fibers.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com