Patents
Literature
1864 results about "Microfiltration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Microfiltration is a type of physical filtration process where a contaminated fluid is passed through a special pore-sized membrane to separate microorganisms and suspended particles from process liquid. It is commonly used in conjunction with various other separation processes such as ultrafiltration and reverse osmosis to provide a product stream which is free of undesired contaminants.
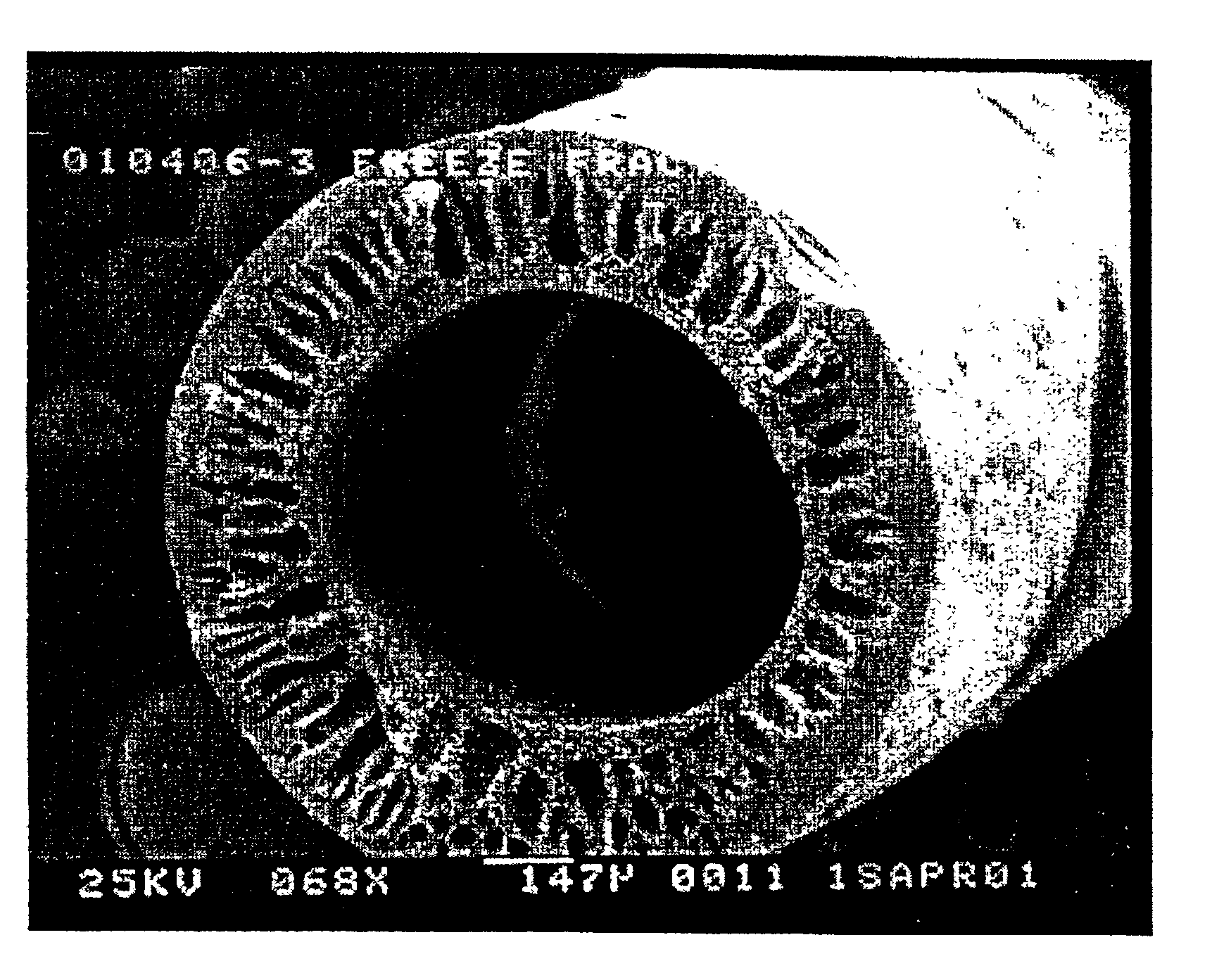
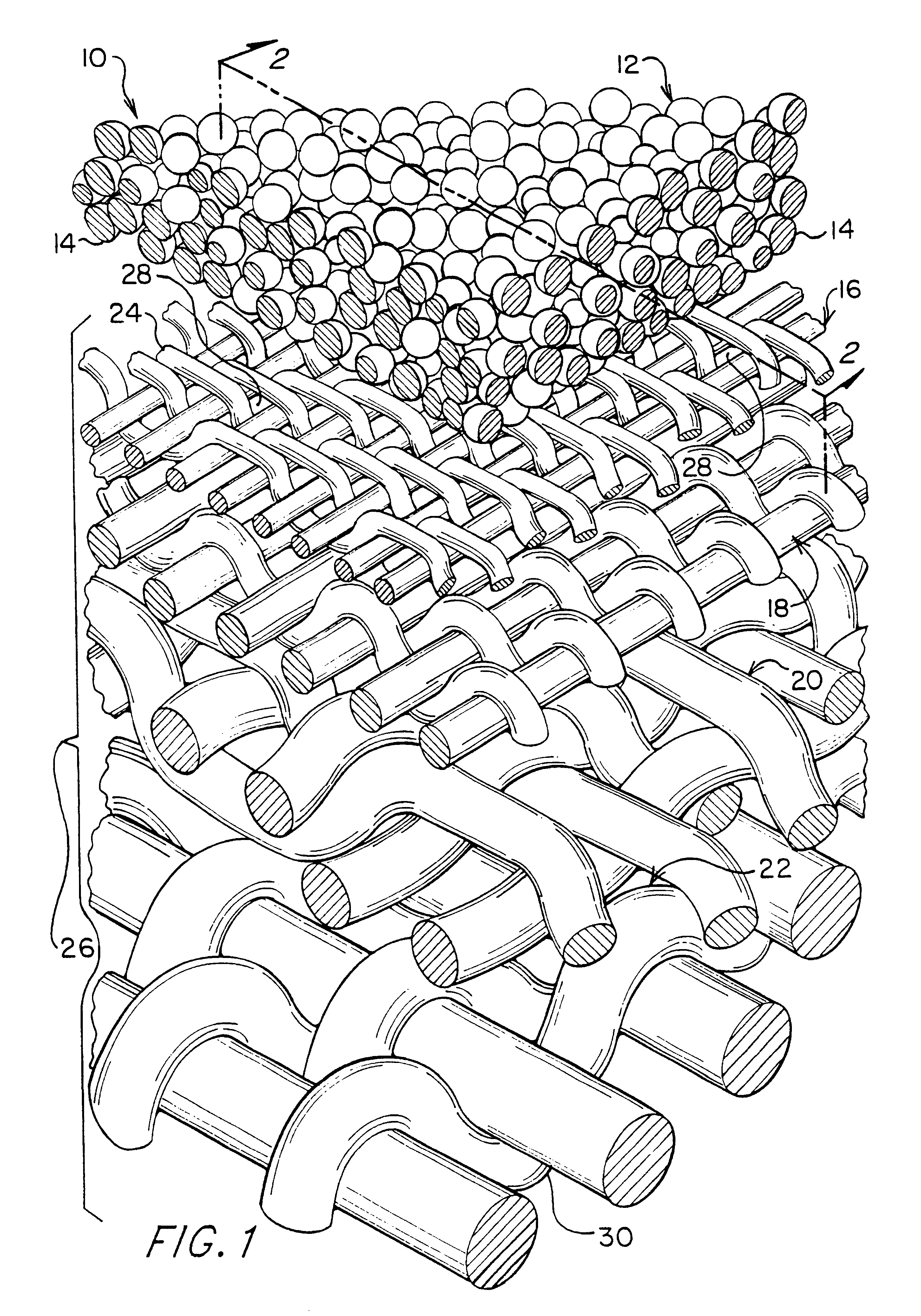
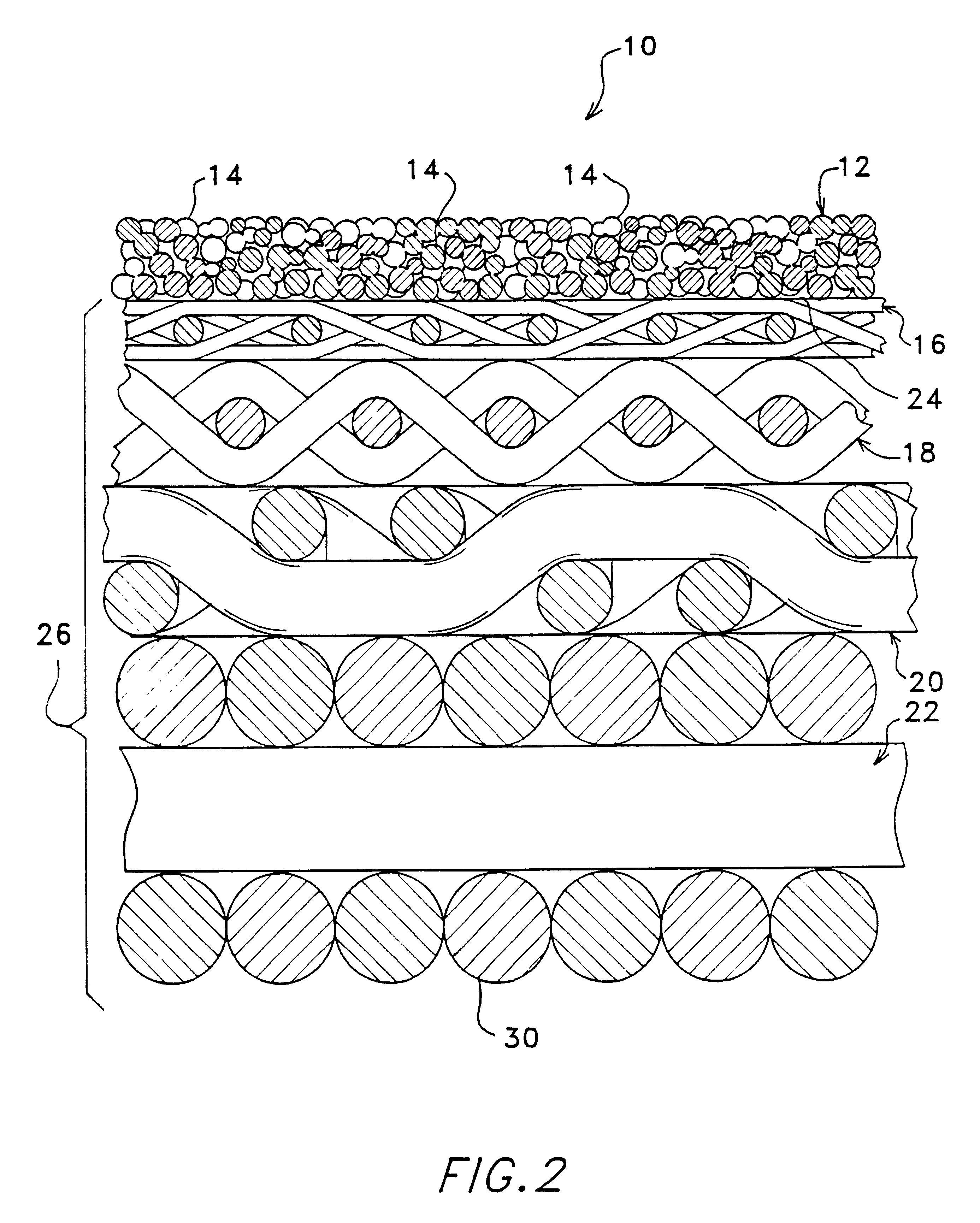
Hollow fiber microfiltration membranes and a method of making these membranes
InactiveUS6890435B2Narrow pore size distributionHigh mechanical strengthSemi-permeable membranesMembranesFiberHollow fibre membrane
A hollow fiber microfiltration (MF) membrane is provided. The casting solution used to make this membrane includes a fiber-forming polymer having a degree of polymerization greater than about 1000, a water-soluble polymer, an anhydride with about 2 to 12 carbon atoms, and a solvent. The membrane is formed by mixing and heating these components to form a viscous dope and then extruding the dope through an annular orifice to form a hollow fiber MF membrane. The hollow fiber membrane is then fed through a coagulation bath and two leaching baths. The membrane is especially useful for filtering liquids, such as wine and juice, so as to remove bacteria, gel, and solid particles from the liquids.
Owner:KOCH MEMBRANE SYST
Micro and ultrafilters with controlled pore sizes and pore size distribution and methods for making
InactiveUS6309546B1High permeabilityMinimal pressure dropSemi-permeable membranesMembranesMicrometerPore diameter
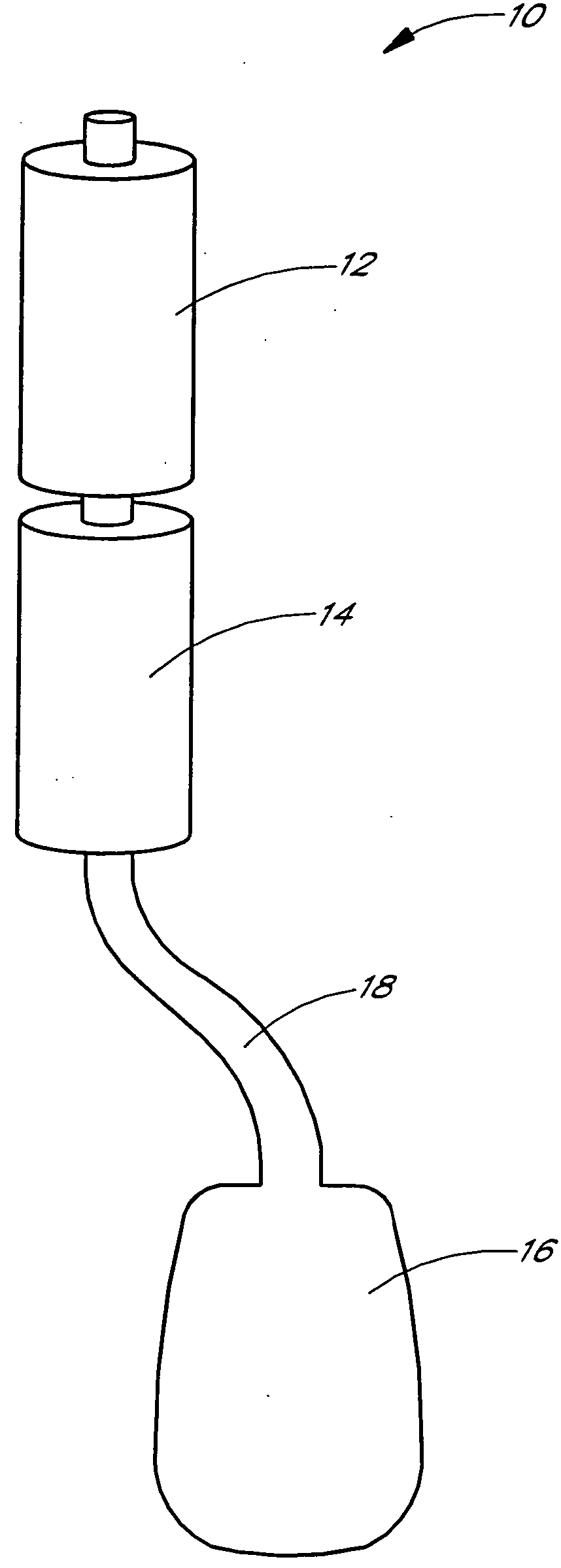
A micro / ultrafiltering element (10) and method for making a filter element are provided. The filtering element comprises a multi-level support (26) having a filtering membrane layer (12) formed thereon comprising sintered particles (14) of uniform diameter. The filtering membrane preferably has an average pore size of from about 0.005-10 micrometers. The filter element is capable of being formed in a variety of geometrical shapes based on the shape of the porous support,
Owner:ELLIPSIS CORP
Process and apparatus for purifying impure water using microfiltration or ultrafiltration in combination with reverse osmosis
InactiveUS20070181496A1Avoid Particulate ContaminationReduces and eliminates amountGeneral water supply conservationUltrafiltrationWater usePotable water
A method of purifying impure water contaminated with a filterable impurity and a dissolved impurity, such as sea-water, comprising the steps of: providing impure water to a primary microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit to remove the filterable impurity and produce impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity; providing the impure filtered water contaminated with a dissolved impurity to a reverse osmosis unit to produce a potable water stream and a residual reverse osmosis stream; and treating the residual reverse osmosis stream prior to reuse. The treatment may be in the form of passing through a secondary filter (such as another microfiltration or ultrafiltration membrane or a cartridge filter, and the subsequently treated reverse osmosis reject may be used to backwash the microfiltration or ultrafiltration unit.
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
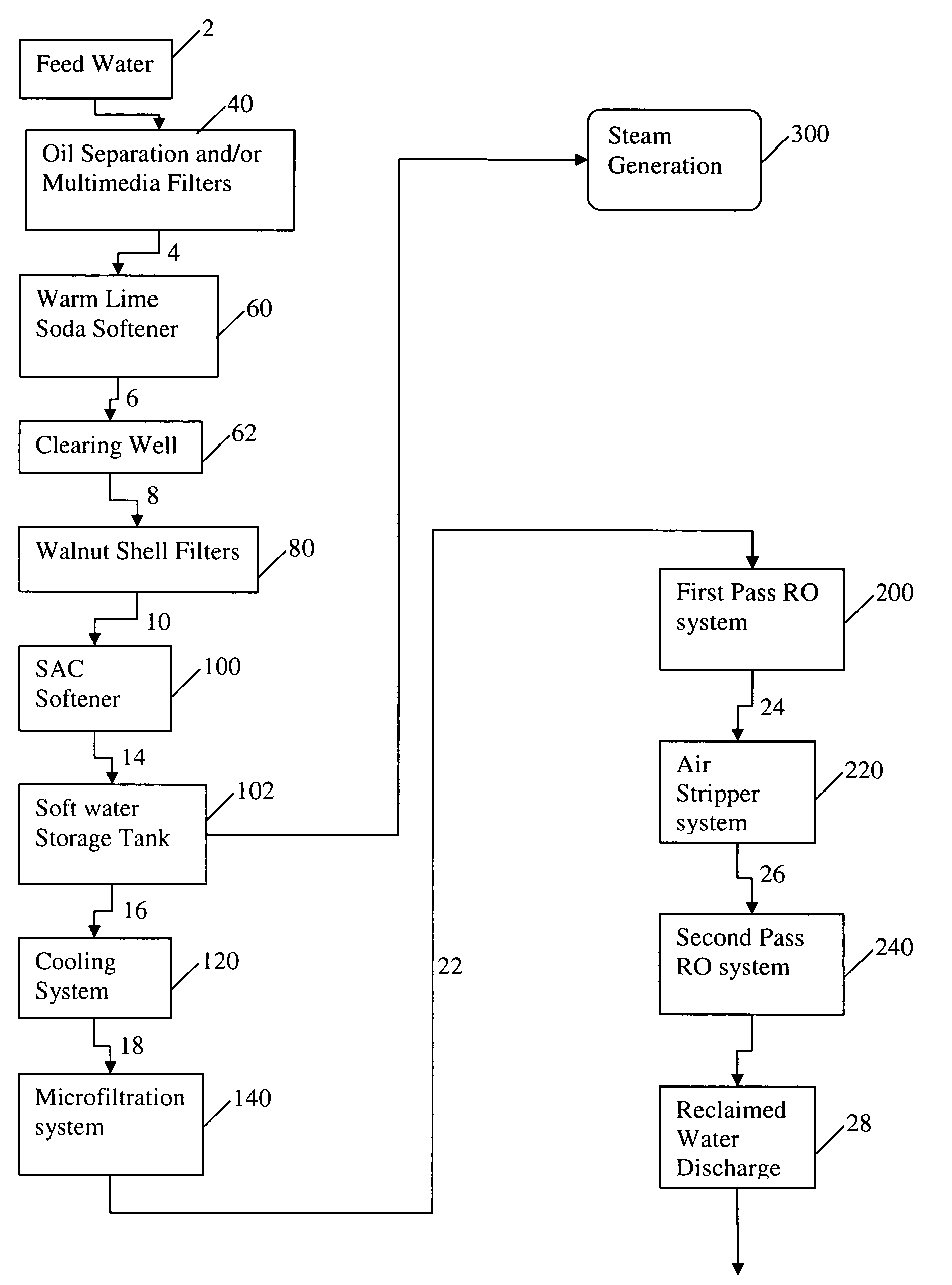
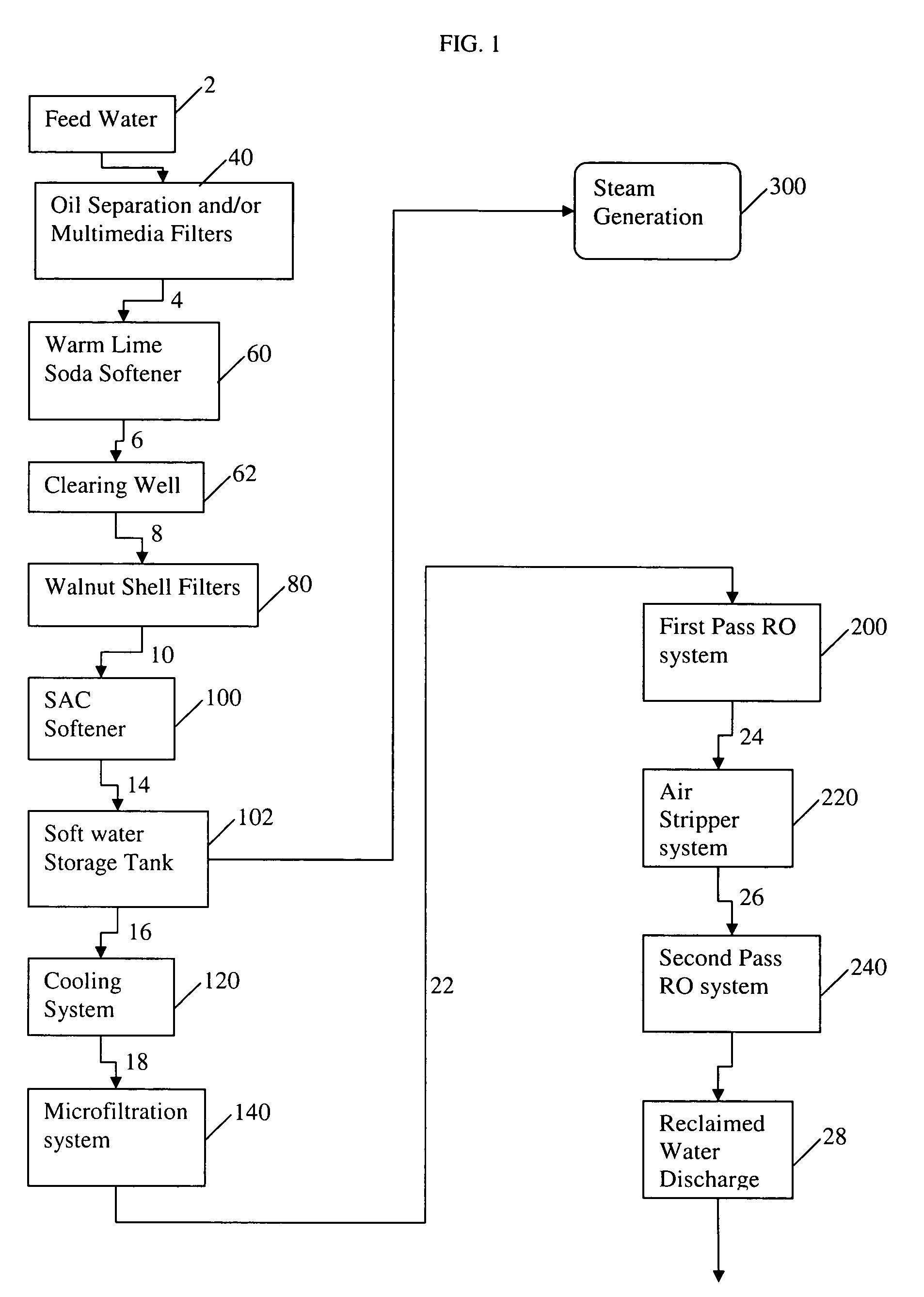
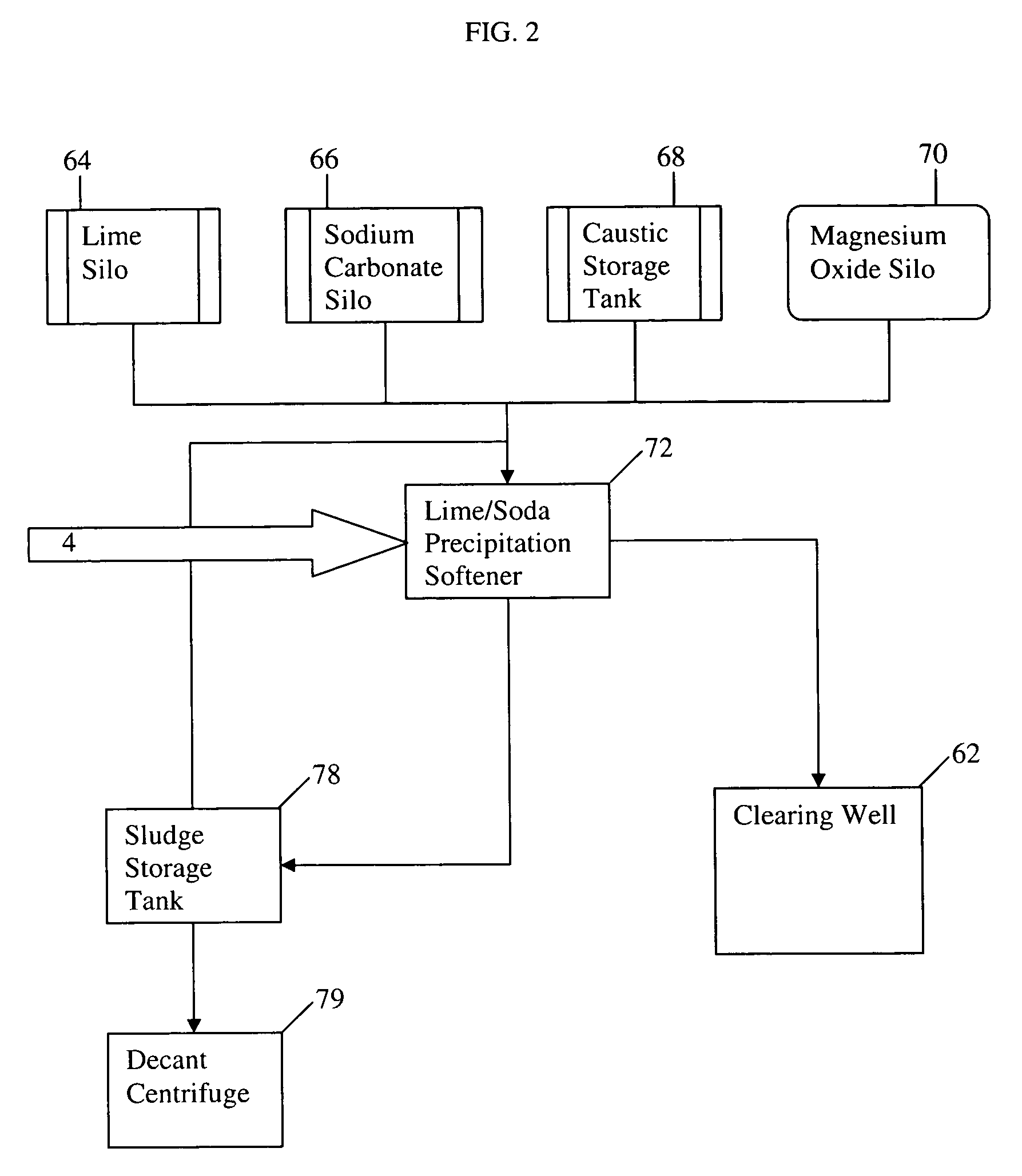
Water treatment process for oilfield produced water
ActiveUS7520993B1Minimize continued precipitationLiquid separation auxillary apparatusUsing liquid separation agentSludgeTreatments water
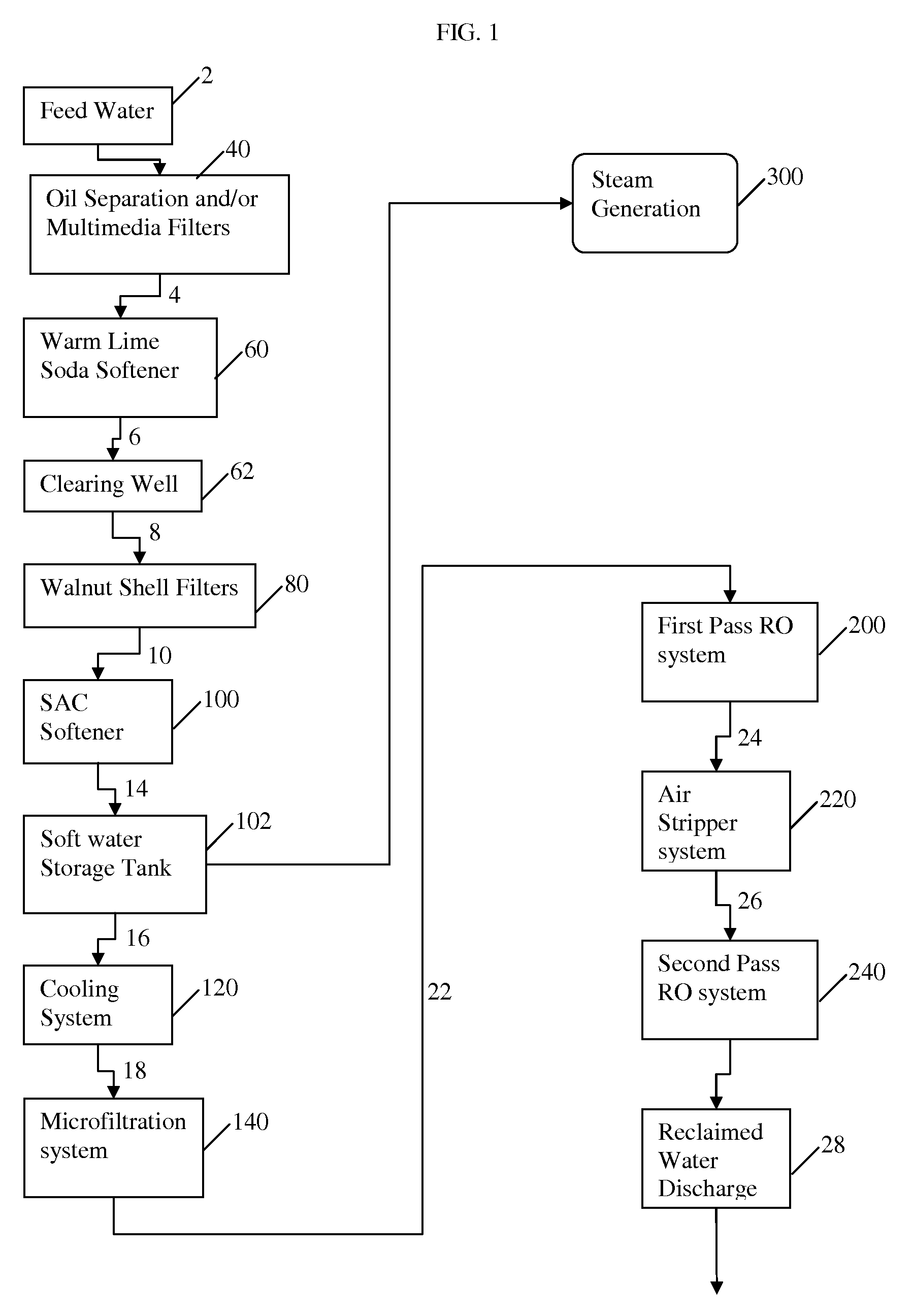
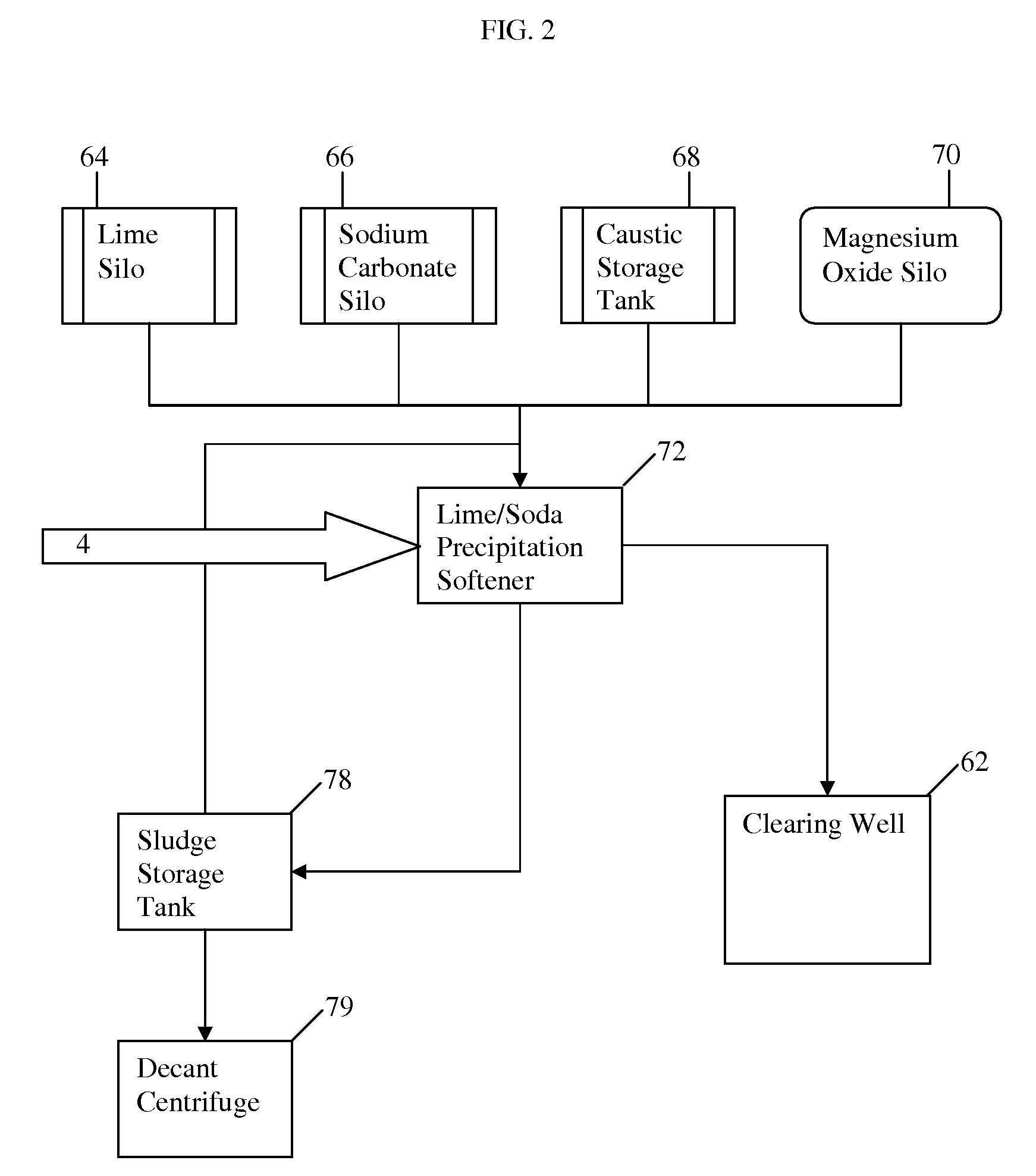
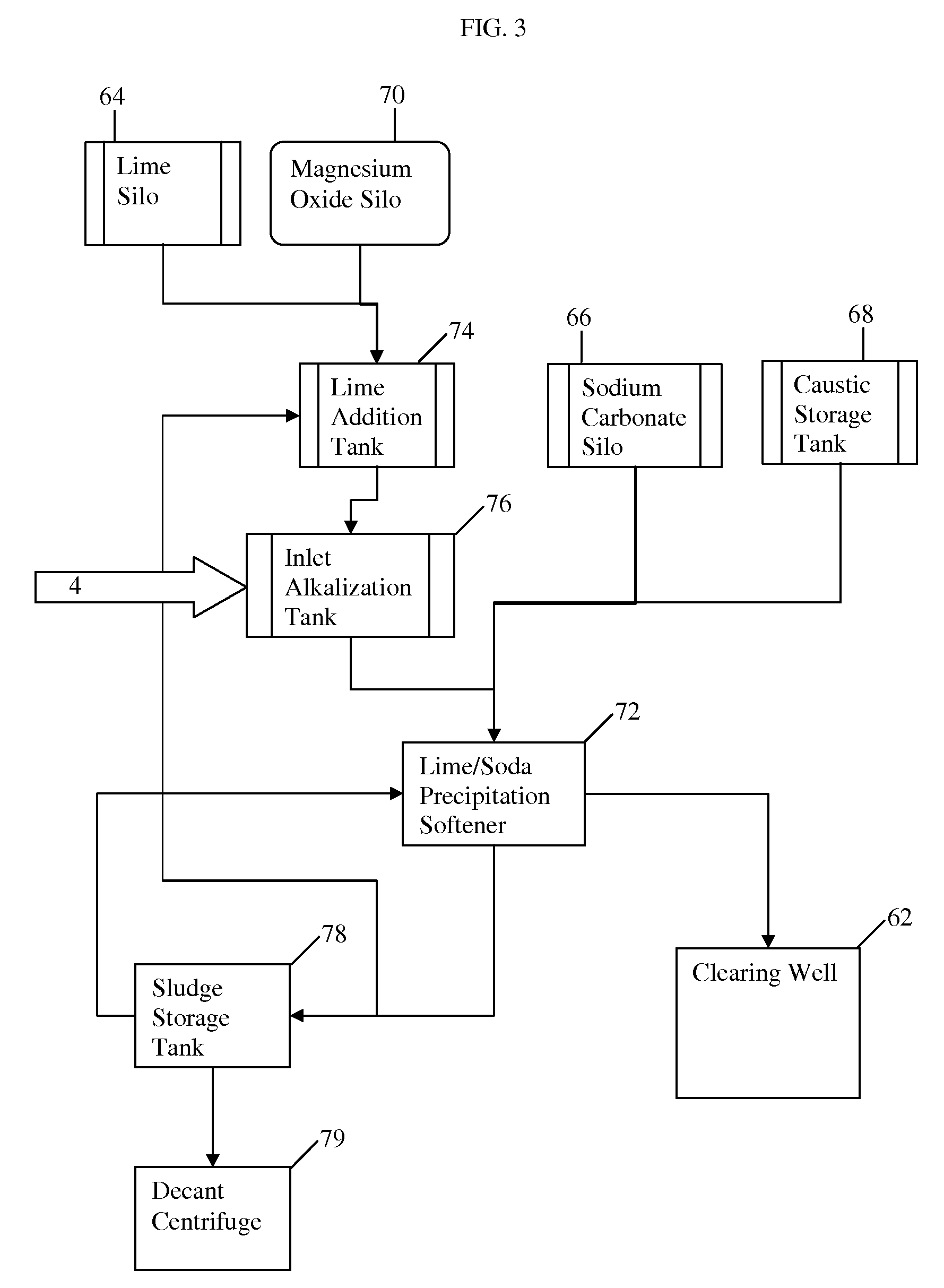
The invention relates to a method and system for treating an aqueous liquid containing dissolved minerals and dissolved hydrocarbons. Method steps and apparatus for treating a waste water feed stream are disclosed which utilize a warm lime softening system in fluid communication with the waste water feed stream, wherein sludge from the warm lime softening system is recycled to improve lime utilization and enhance silica and boron removal without the addition of an external source of magnesium. In addition, a microfiltration system and / or an air stripper system may be used in fluid communication with at least one reverse osmosis system to produce a treatment water that meets state and federal guidelines for surface discharge.
Owner:WATER & POWER TECH
Water purification pack
InactiveUS20050113796A1General water supply conservationTransportation and packagingHuman bodyQuality level
An apparatus and methods are disclosed for purifying fluid, such as potable water, to quality levels suitable for medical application, particularly to applications involving injection of the fluid into a human body. The apparatus comprises a portable purification pack constructed for a single use. The pack houses depth filtration, activated carbon, mixed bed ion exchange resins and terminal filtration stages in series. The terminal filter comprises a fine (microfiltration or ultrafiltration), permeable membrane, treated with an endotoxin-binding chemistry. In contrast with semi-permeable osmotic membranes, the permeable membrane produces high flow rates at relatively low pressures, while still safely purifying fluid to injection quality.
Owner:TAYLOR MICHAEL A
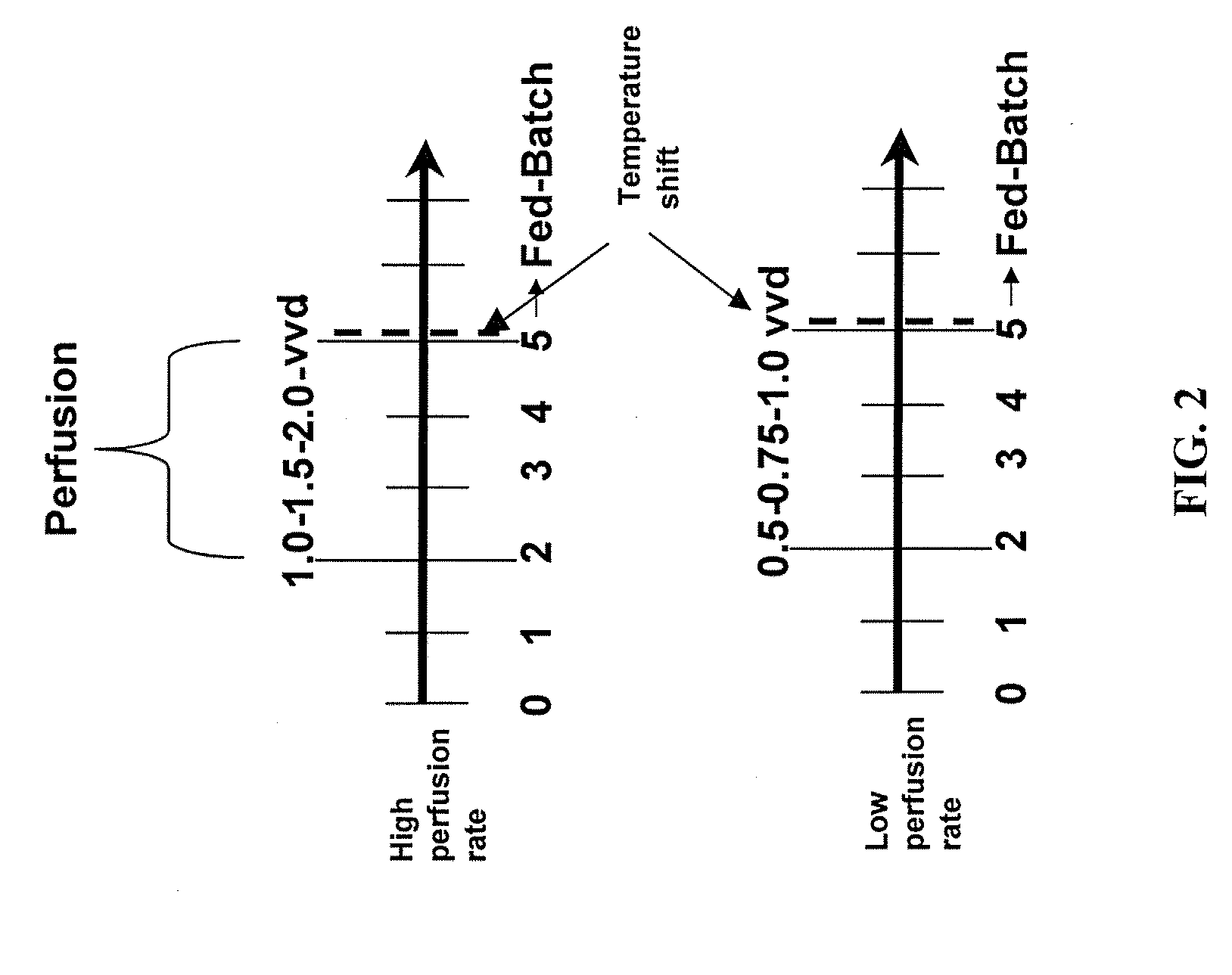
Use of perfusion to enhance production of fed-batch cell culture in bioreactors
InactiveUS20090042253A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationFeed pump
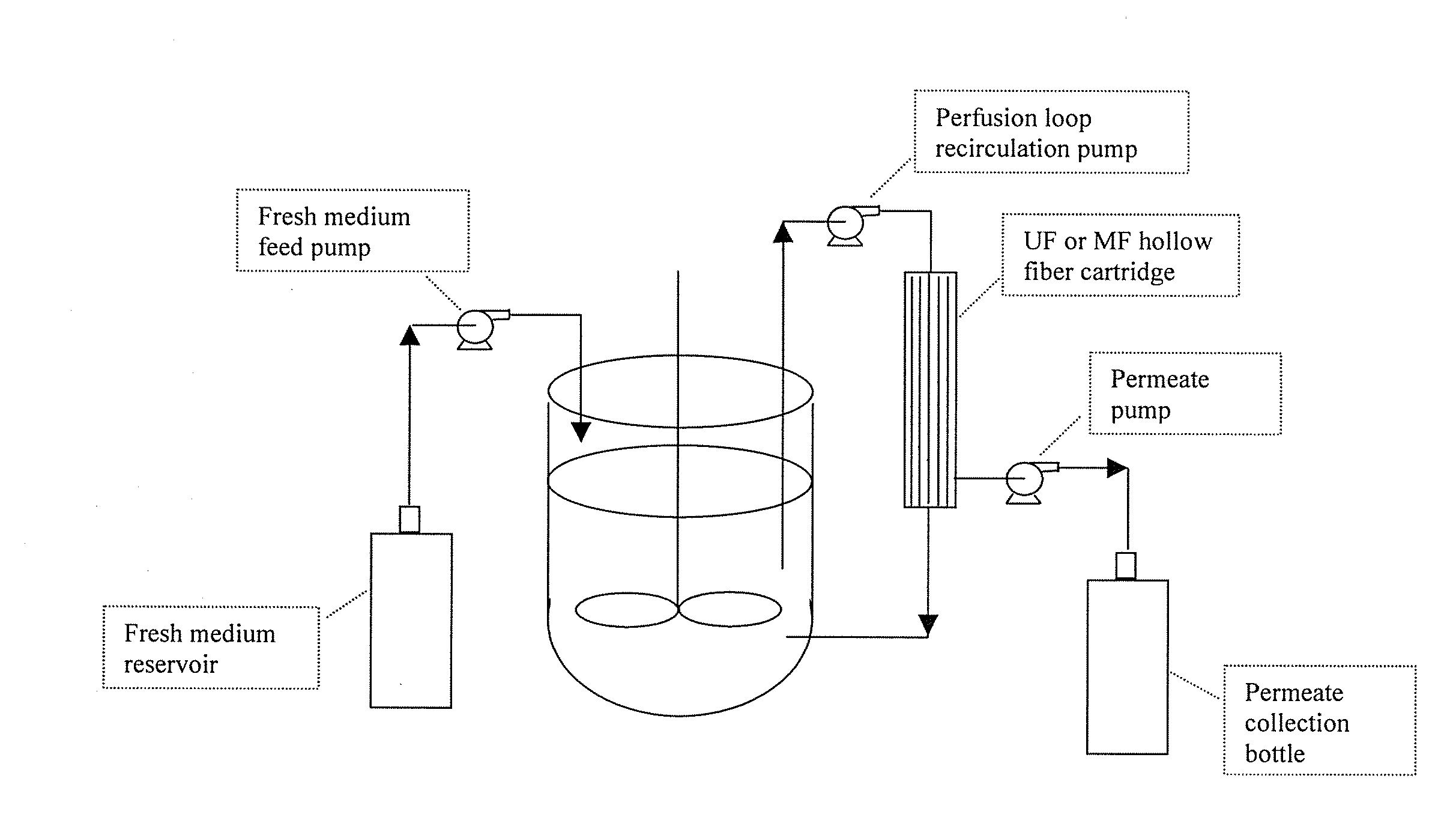
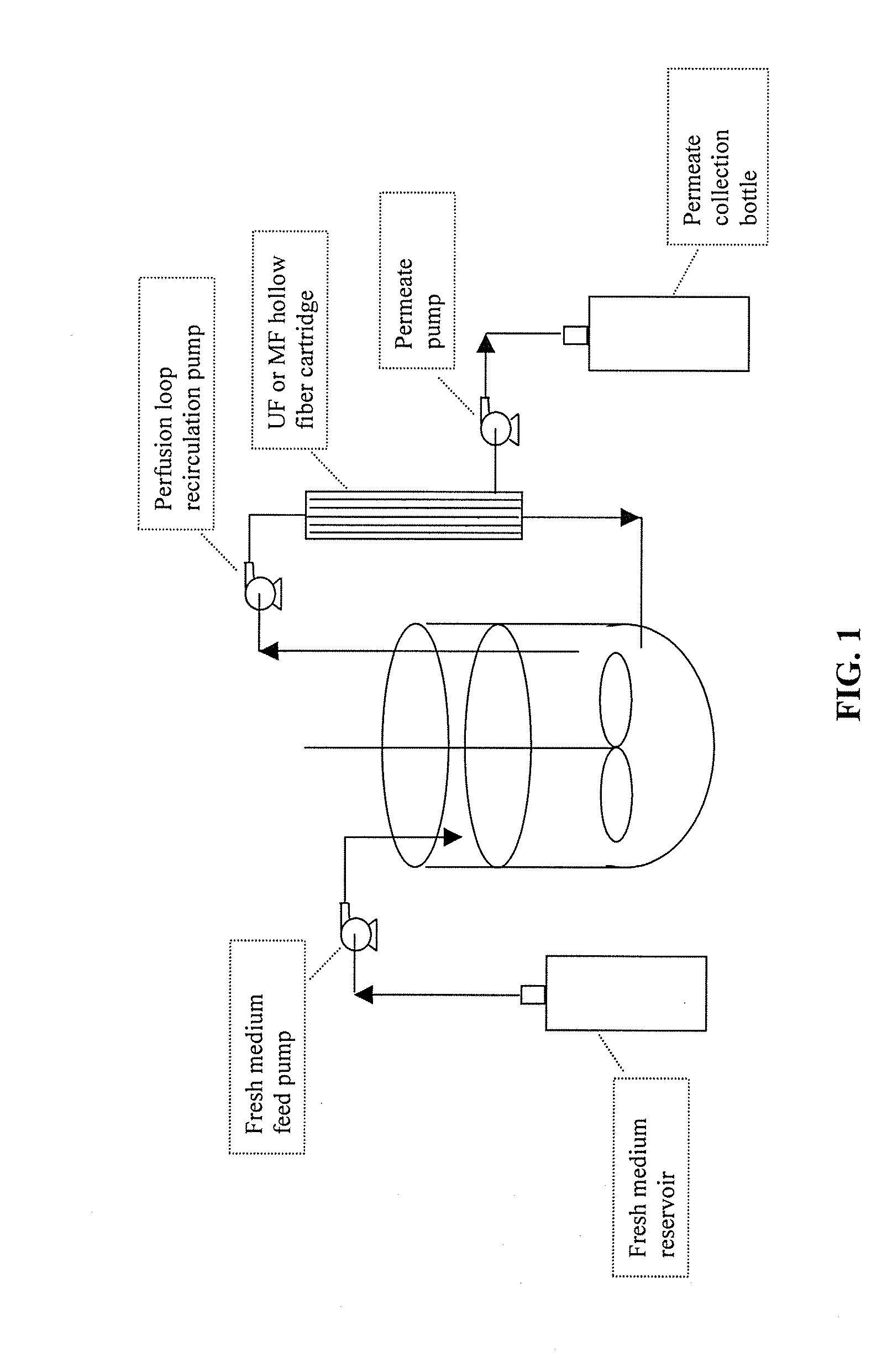
The invention relates to methods of improving protein production, e.g., large-scale commercial protein production, e.g., antibody production, utilizing a modified fed-batch cell culture method comprising a cell growth phase and a polypeptide production phase. The modified fed-batch cell culture method combines both cell culture perfusion and fed-batch methods to achieve higher titers of polypeptide products. Because the modified fed-batch cell culture method of the invention produces higher polypeptide product titers than fed-batch culture alone, it will substantially improve commercial-scale protein production. The invention also relates to a perfusion bioreactor apparatus comprising a fresh medium reservoir connected to a bioreactor by a feed pump, a recirculation loop connected to the bioreactor, wherein the recirculation loop comprises a filtration device, e.g., ultrafiltration or microfiltration, and a permeate pump connecting the filtration device to a permeate collection container.
Owner:WYETH LLC
Method and apparatus for microfiltration to perform cell separation
ActiveUS20090188864A1Laborious and expensiveMembranesDecorative surface effectsParyleneMicrofabrication
A microfiltration apparatus and method for separating cells, such as circulating tumor cells, from a sample using a microfiltration device having a top porous membrane and a bottom porous membrane. The porous membranes are formed from parylene and assembled using microfabrication techniques. The porous membranes are arranged so that the pores in the top membrane are offset from the pores in the bottom membrane.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA +1
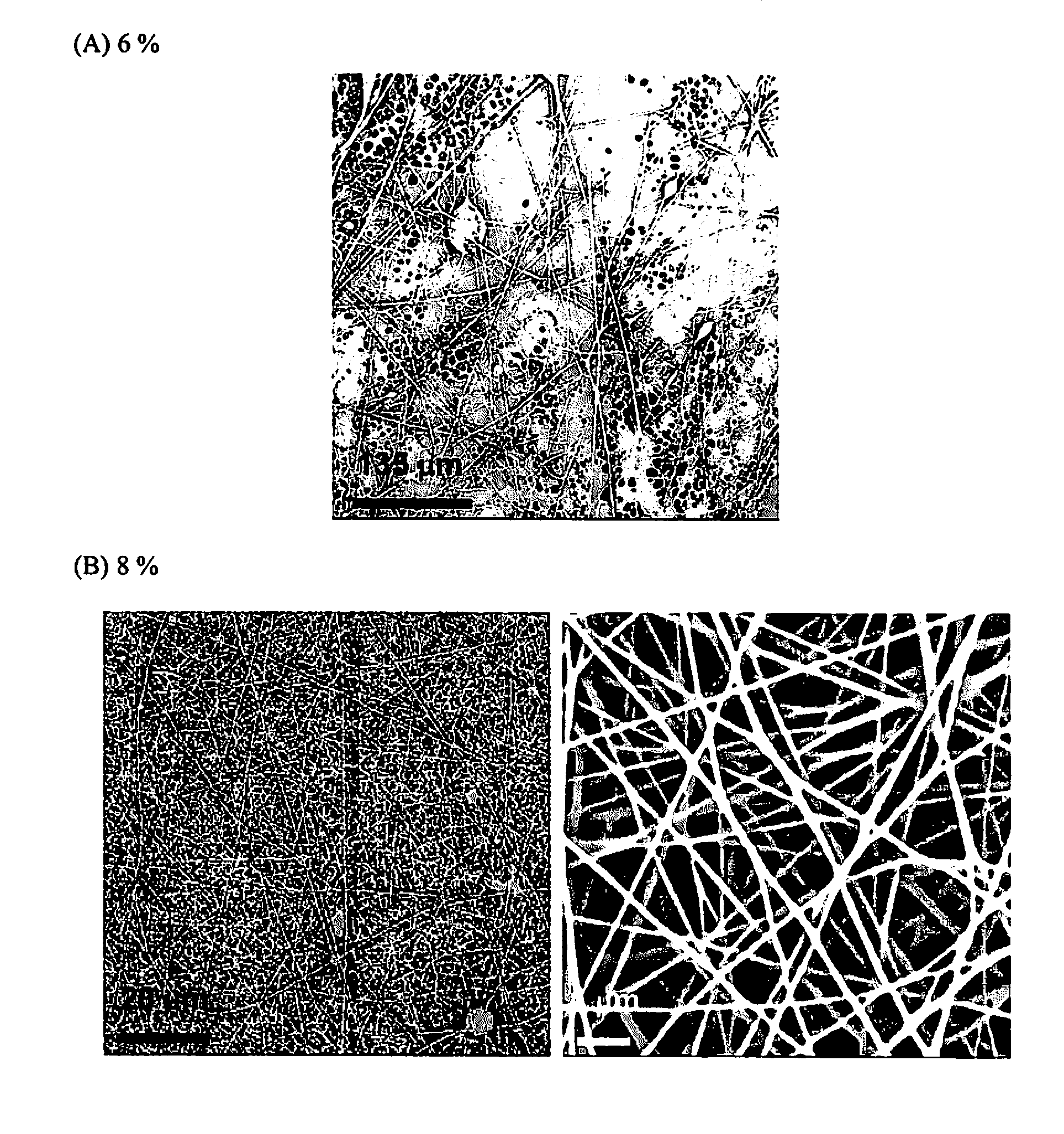
Combination of electrostatic spinning and electrostatic spraying for preparing nanofibre base composite separation membrane
InactiveCN101947415AControl thicknessControl UniformitySemi-permeable membranesFilament/thread formingChemical treatmentPolymer science
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
High flux high efficiency nanofiber membranes and methods of production thereof
A membrane is provided including a coating layer having cellulose nanofibers produced from oxidized cellulose microfibers and an electrospun substrate upon which the coating layer is applied. The nanofibers of the electrospun substrate have a diameter greater than that of the cellulose nanofibers. The membrane also has non-woven support upon which the electrospun substrate is disposed. Microfibers of the non-woven support have a diameter greater than that of the nanofibers of the electrospun substrate. Application of electrospun membrane is in microfiltration area, while the cellulose nanofiber membrane serves in ultra-filtration, nanofiltration, and reverse osmosis after chemical modification.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Membrane polymer compositions
InactiveUS7226541B2Good chemical stabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHexafluoropropylenePolyvinylidene difluoride
Owner:EVOQUA WATER TECH LLC
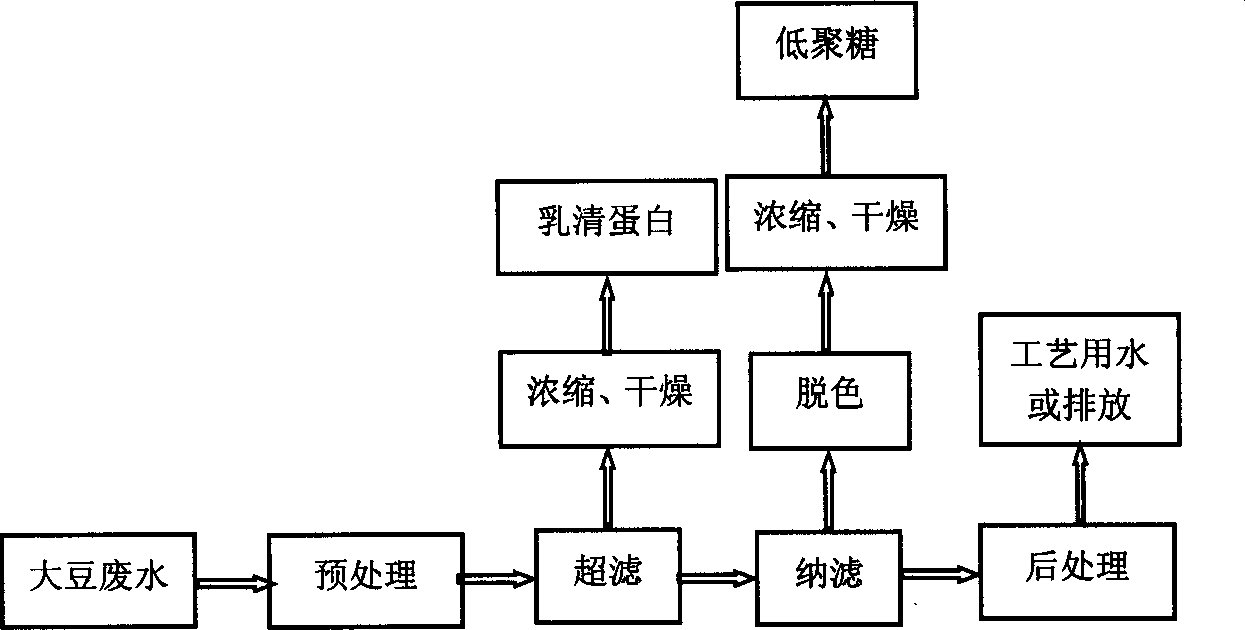
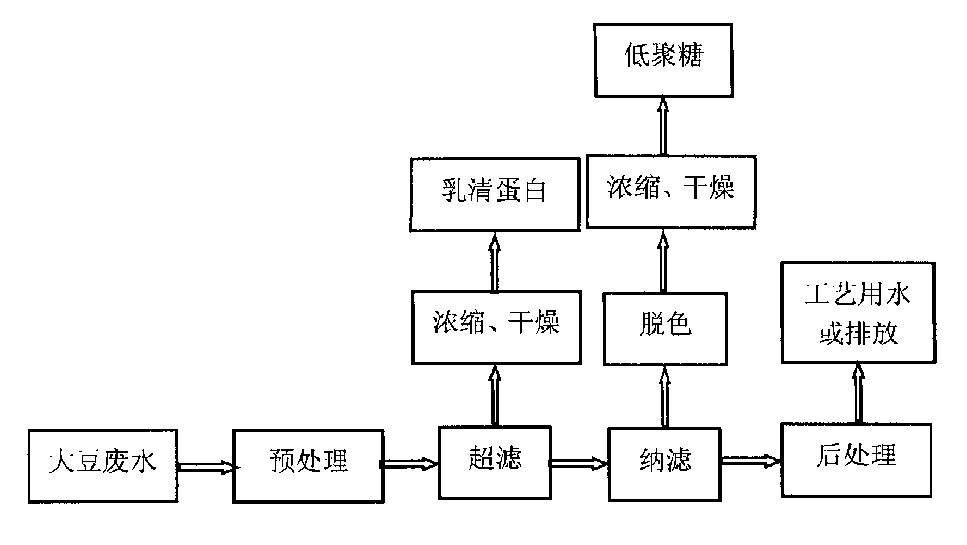
Membrane separation process of treating soybean processing waste water
InactiveCN1336333AAchieve separationAchieve enrichmentUltrafiltrationWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisFiltration membraneWastewater
The present invention relates to method of treating soybean processing waste water by using membrane filtration technique, the soybean processing waste water is pretreated through pH value regulation, centrifuge, prefiltration, microfiltration, and temp regulation etc; then the pretreated soybean processing waste water is passed through ultrafiltration membrane system under pressure to extract soybean lactoalbumin; then the filtrate from ultrafiltration membrane is passed through nm filtration membrane system under pressure to extract soybean oligosaccharide which is further decolorized; the filtrate from nm filtration membrane system is post treated to obtain water suitable for use in production or water conformed with state discharge standard. Advantages: low cost, high purity of soybean lactoalbumin and oligosaccharide.
Owner:TSINGHUA TONGFANG CO LTD
Antimicrobial semi-permeable membranes
Cast semi-permeable membranes made from synthetic polymer used in reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and microfiltration are treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent to prevent its bio-fouling and bacterial breakthrough. The semi-permeable membranes include a polymeric material and a non-leaching antimicrobial agent that is incorporated into and homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric material. The polymeric material, in the case of one membrane, may be cellulose acetate. In the case of thin film composite polyamide membranes, the antimicrobial agent is incorporated in a microporous polysulfone layer that is sandwiched between a reinforcing fabric and an ultrathin polyamide material. The invention also includes a treatment of flat and hollow fiber semipermeable membranes made with polysulfones and polyvinylidene fluoride.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
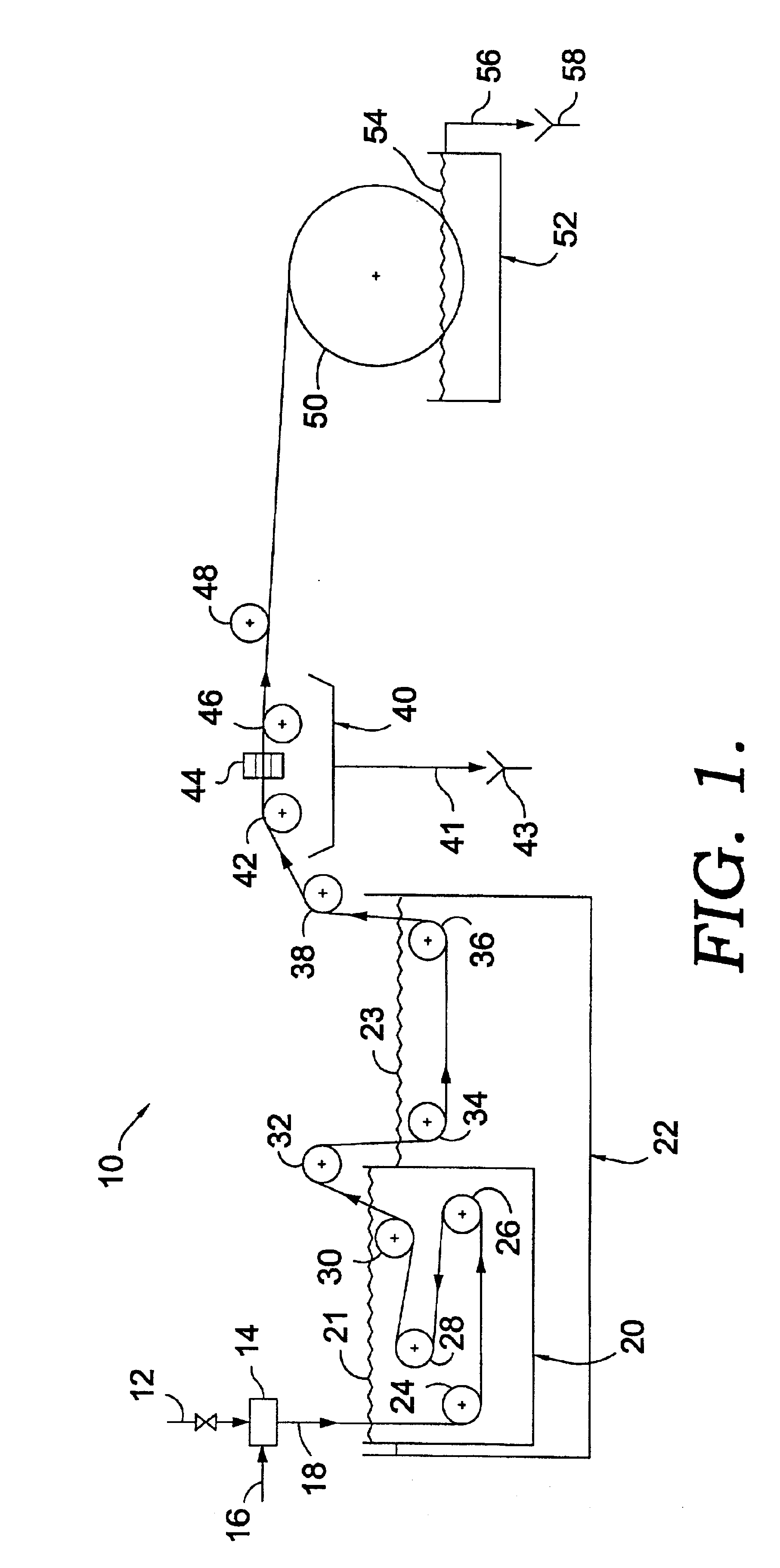
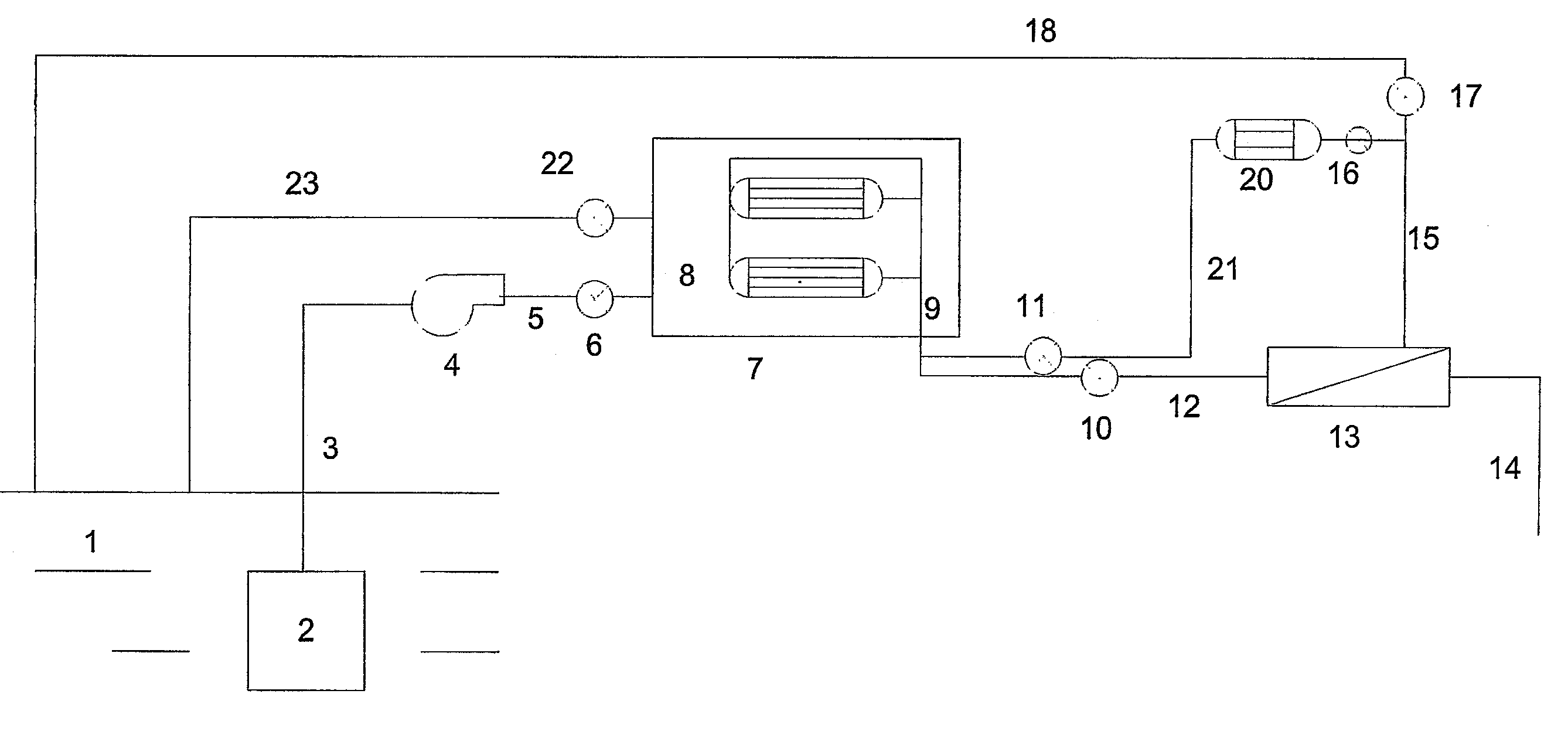
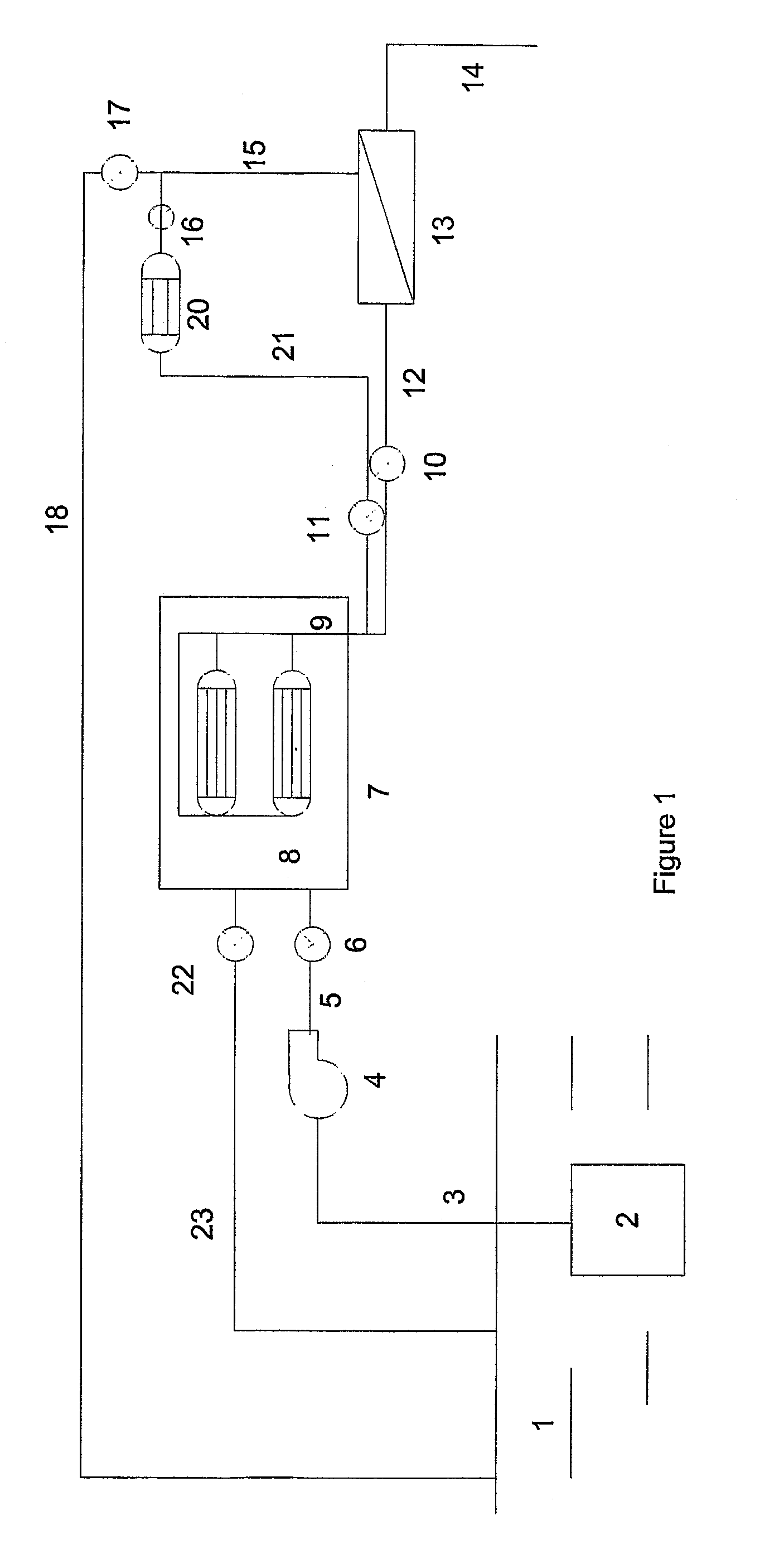
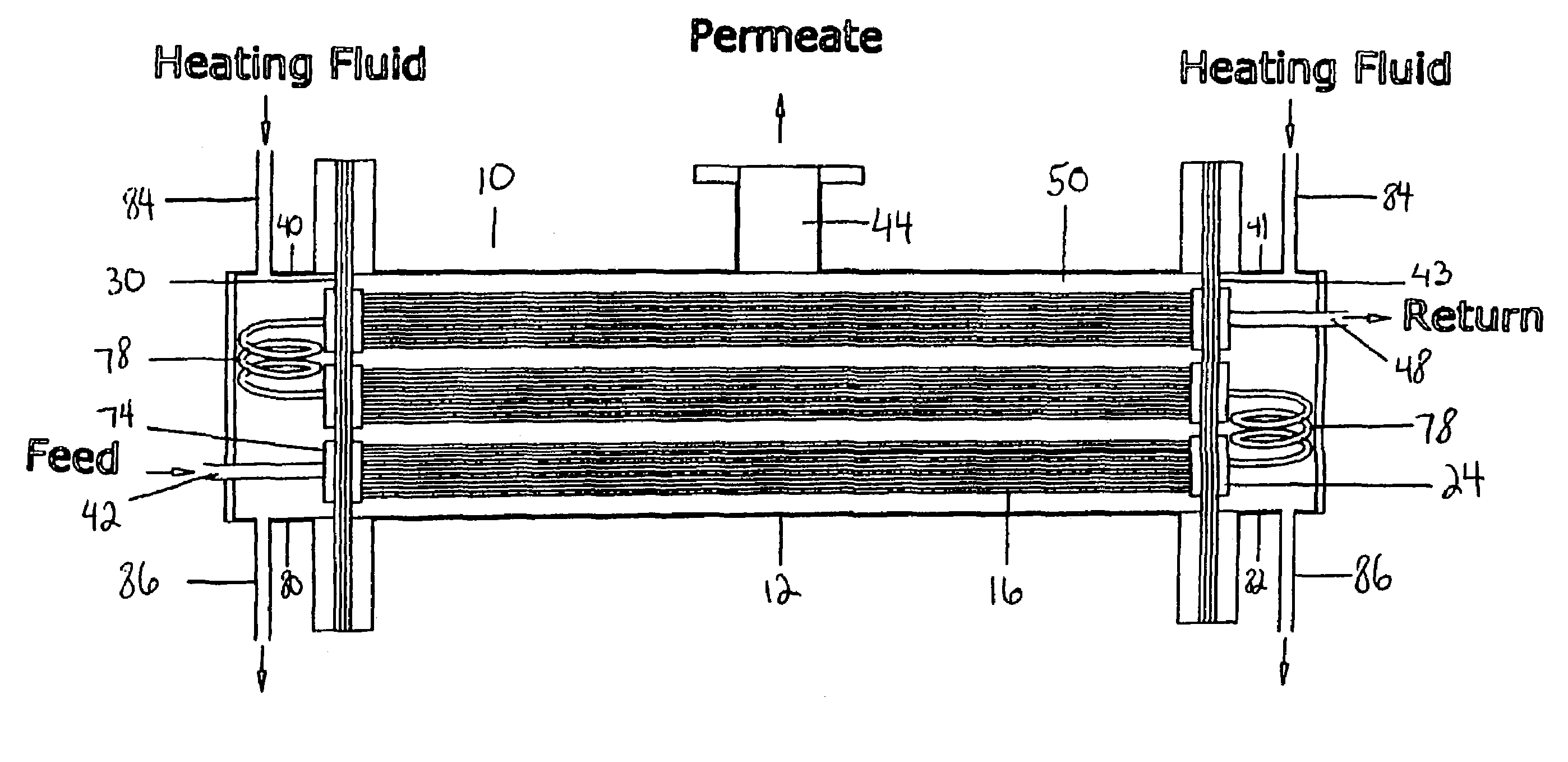
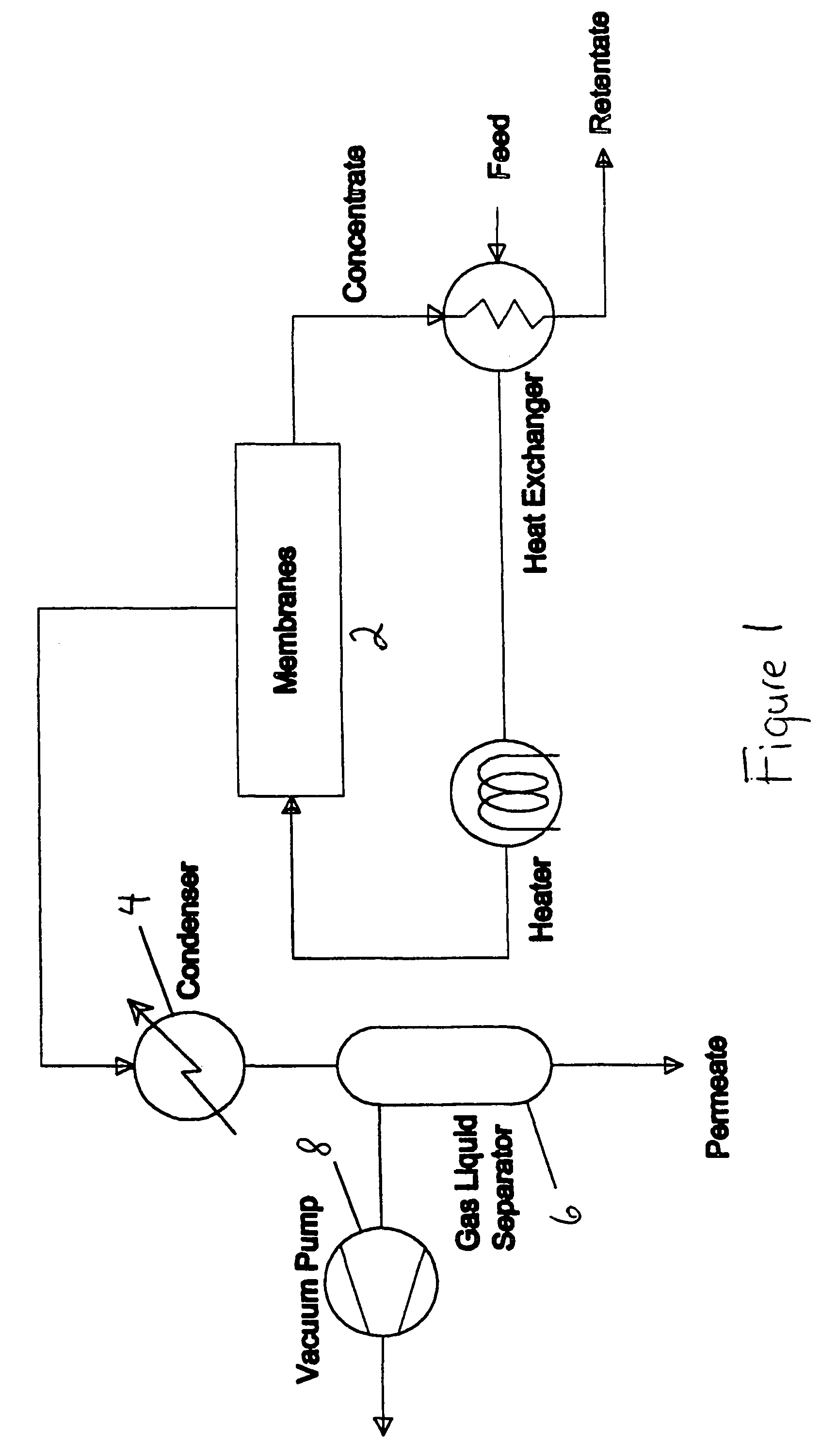
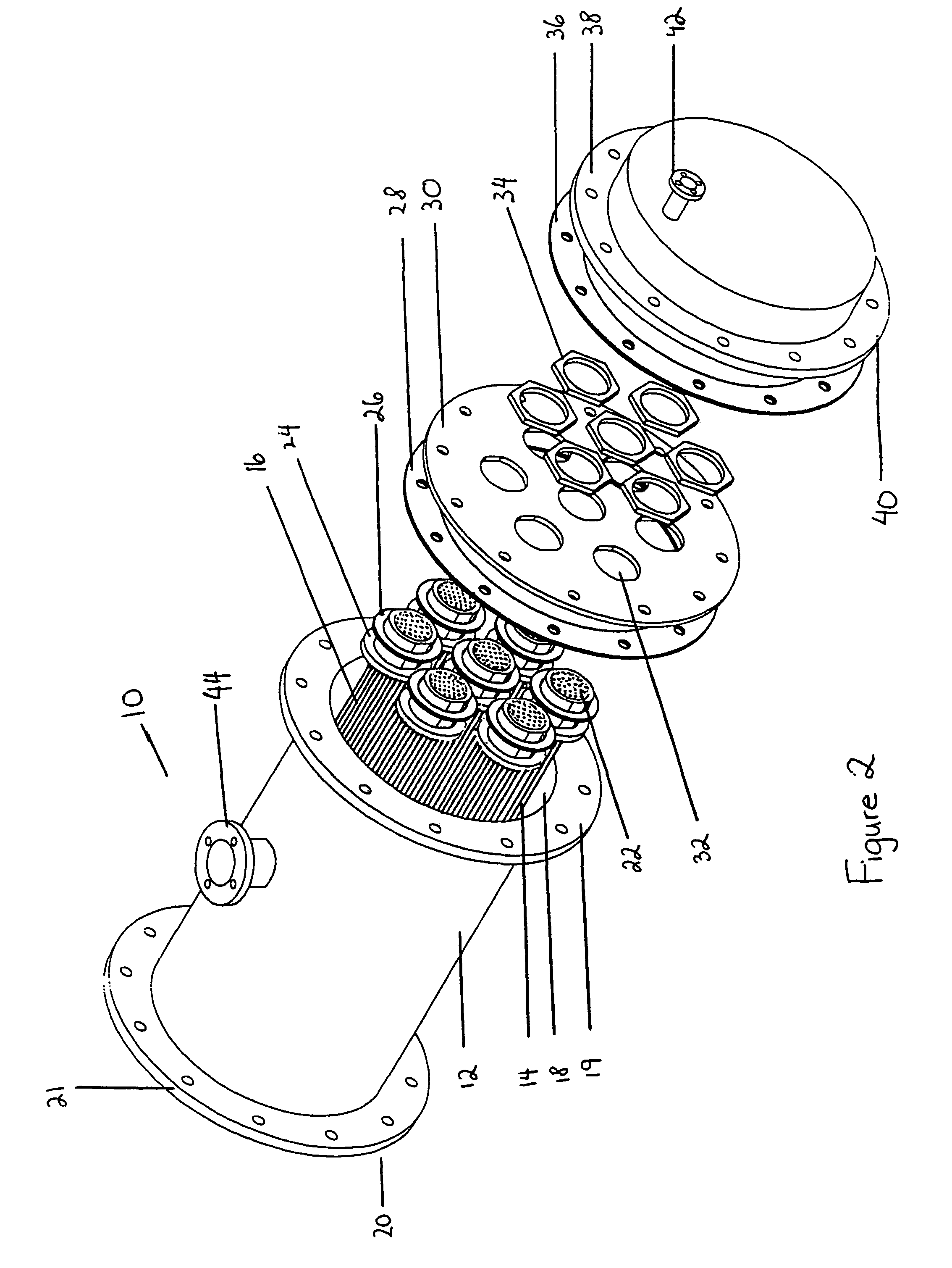
Membrane-assisted fluid separation apparatus and method
InactiveUS7459084B2Easy to disassembleReduce complexityMembranesGeneral water supply conservationFiberHigh concentration
This present invention relates to a fluid separation module adapted to separate a given fluid mixture into permeate and retentate portions using bundles of hollow fiber membranes. The membranes may be composed of different kinds of membranes depending on the application being used to separate the fluid mixture. The fluid separation module may be used to separate fluid mixtures by a number of different processes, including but not limited to, pervaporation, vapour permeation, membrane distillation (both vacuum membrane distillation and direct contact membrane distillation), ultra filtration, microfiltration, nanofiltration, reverse osmosis, membrane stripping and gas separation. The present invention also provides an internal heat recovery process applied in association with those fluid separation applications where separation takes place by evaporation through the membrane of a large portion of the feed into permeate. Desalination and contaminated water purification by means of vacuum membrane distillation are just two examples where the internal heat recovery process may be applied. In these two examples, large portions of the feed are separated by membranes into a high purity water permeate stream by evaporation through the membranes and into a retentate stream containing a higher concentration of dissolved components than present in the feed. In this process the permeate vapour that is extracted from the fluid separation module is compressed by an external compressor to increase the temperature of the vapour higher than the temperature of the feed entering the separation module. Heat from the permeate vapour at the elevated temperature is transferred back to the incoming feed fluid mixture entering the fluid separation module in a condenser / heat exchange.
Owner:LOEB INVESTORS CO 166 LP +1
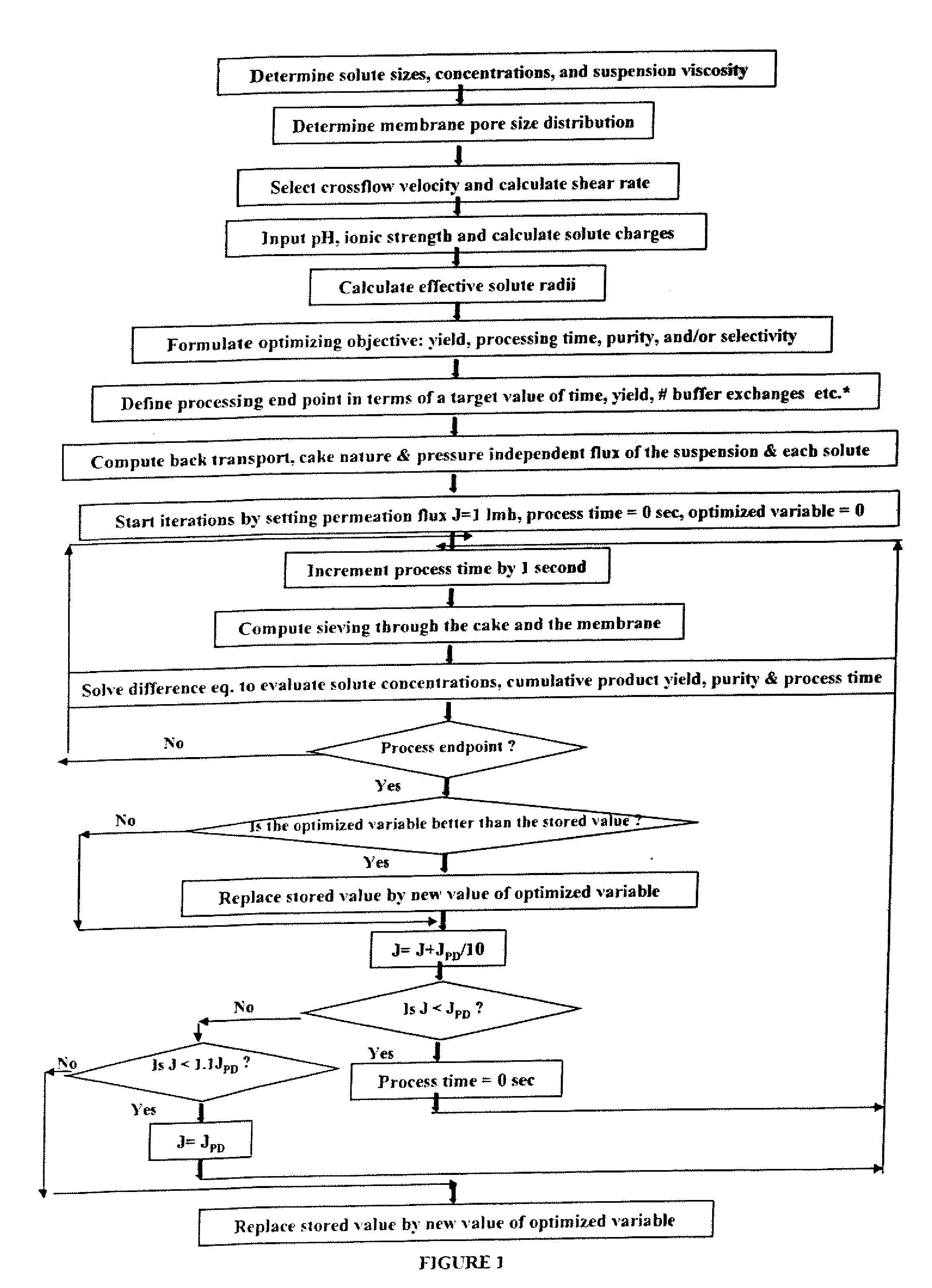
Global model for optimizing crossflow microfiltration and ultrafiltration processes
InactiveUS20080017576A1Realistic and rapid in silico MF/UF optimizationFill in the blanksMembranesUltrafiltrationChemical physicsSieving coefficient
The present invention is a method for optimizing operating conditions for yield, purity, or selectivity of target species, and / or processing time for crossflow membrane filtration of target species in feed suspensions. This involves providing as input parameters: size distribution and concentration of particles and solutes in the suspension; suspension pH and temperature; physical and operating properties of membranes, and number and volume of reservoirs. The method also involves determining effective membrane pore size distribution; suspension viscosity, hydrodynamics, and electrostatics; pressure-independent permeation flux of the suspension and cake composition; pressure-independent permeation flux for each particle and overall observed sieving coefficient of each target species through cake deposit and pores; solving mass balance equations for all solutes; and iterating the mass balance equation for each solute at all possible permeation fluxes, thereby optimizing operating conditions. The invention also provides a computer readable medium for carrying out the method of the present invention.
Owner:RENESSELAER POLYTECHNIC INST
Preparation of continuous hole graded ceramic tube
The invention relates to a preparation method of a gradient ceramic tube with continuous holes, which combines with the advantages of a centrifugal shaping method and gel-casting. Evenly distributed gel-casting suspension is poured into a pattern to carry out centrifugation and gelatinization occurs to the suspended slurry under the effect of centrifugal force and heating to realize solidification and shaping. A wet blank is demoulded, dried and sintered and the gradient ceramic tube with the continuous holes is prepared. The pore diameters of pattern tubes are distributed continuously along the radial direction of the pattern tubes, the pore diameter of an inner surface is the smallest while the bore diameter of an outer surface is the largest; besides, the inner surface is quite flat and smooth without defect, therefore, the ceramic tube can be used both in the process of microfiltration and ultrafiltration and as a good support to further paint film on the inner surface. The preparation method is simple, thus saving the vacuum degassing procedure in traditional gel-casting; the gradient ceramic tube with the continuous holes can be shaped by one step; the pattern tubes with different pore diameters can be prepared by controlling the initial grain sizes of ceramic powders; the blank has high strength and is easy to operate with high efficiency and the yield of pattern tubes is high.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Polyimide membranes
InactiveUS20040177753A1Improve performanceStable membranes for gas/vapourMembranesIsotope separationDendrimerHydrocarbon mixtures
The present invention deals with a process for treating a polyimide comprising exposing said polyimide to a compound selected from the group consisting of dendrimers, hyperbranched polymers and mixtures thereof. The polyimide may be in the form of a membrane and the membrane, after treatment according to the process of the invention, may be suitable for use in a membrane-based separation technique, for example gas separation, filtration, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis or pervaporation. The membrane may for example be suitable for separation of gas and hydrocarbon mixtures including mixtures of H2 / N2, H2 / CO2, He / N2, CO2 / CH4, and C2-C4 hydrocarbon mixtures.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Porous poly(aryl ether ketone) membranes, processes for their preparation and use thereof
ActiveUS6887408B2Simple and cost-effective and industrially feasibleIncreased porous structureMembranesSemi-permeable membranesArylPorous medium
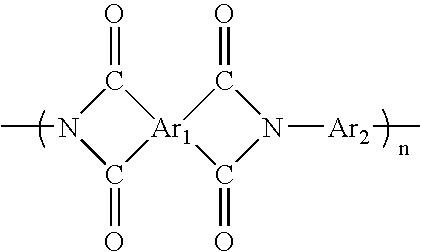
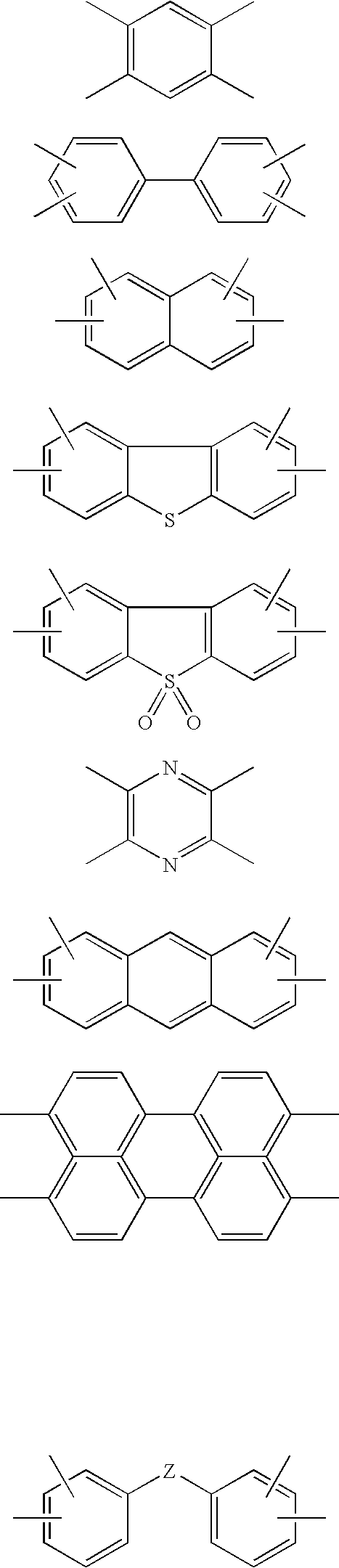
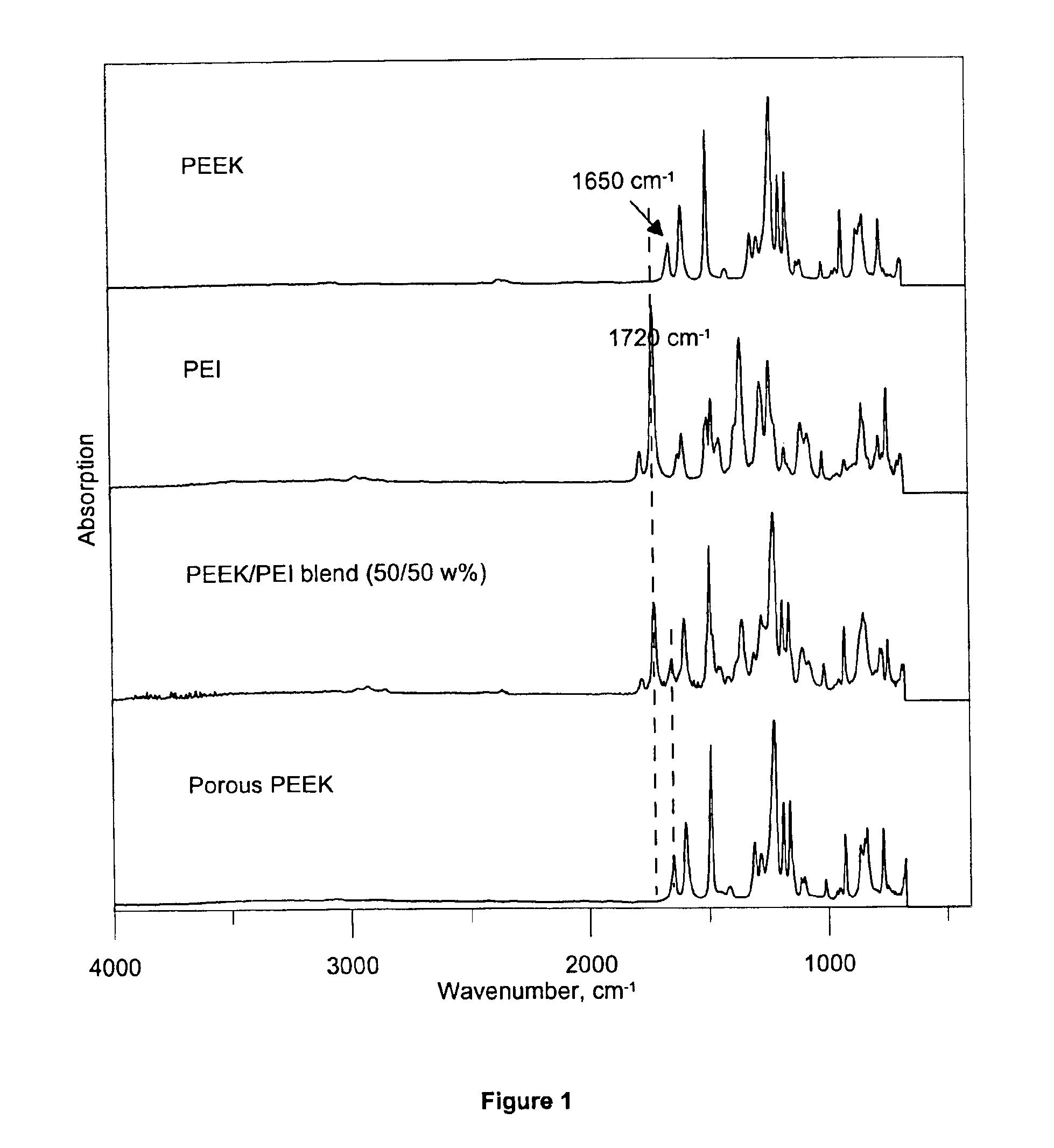
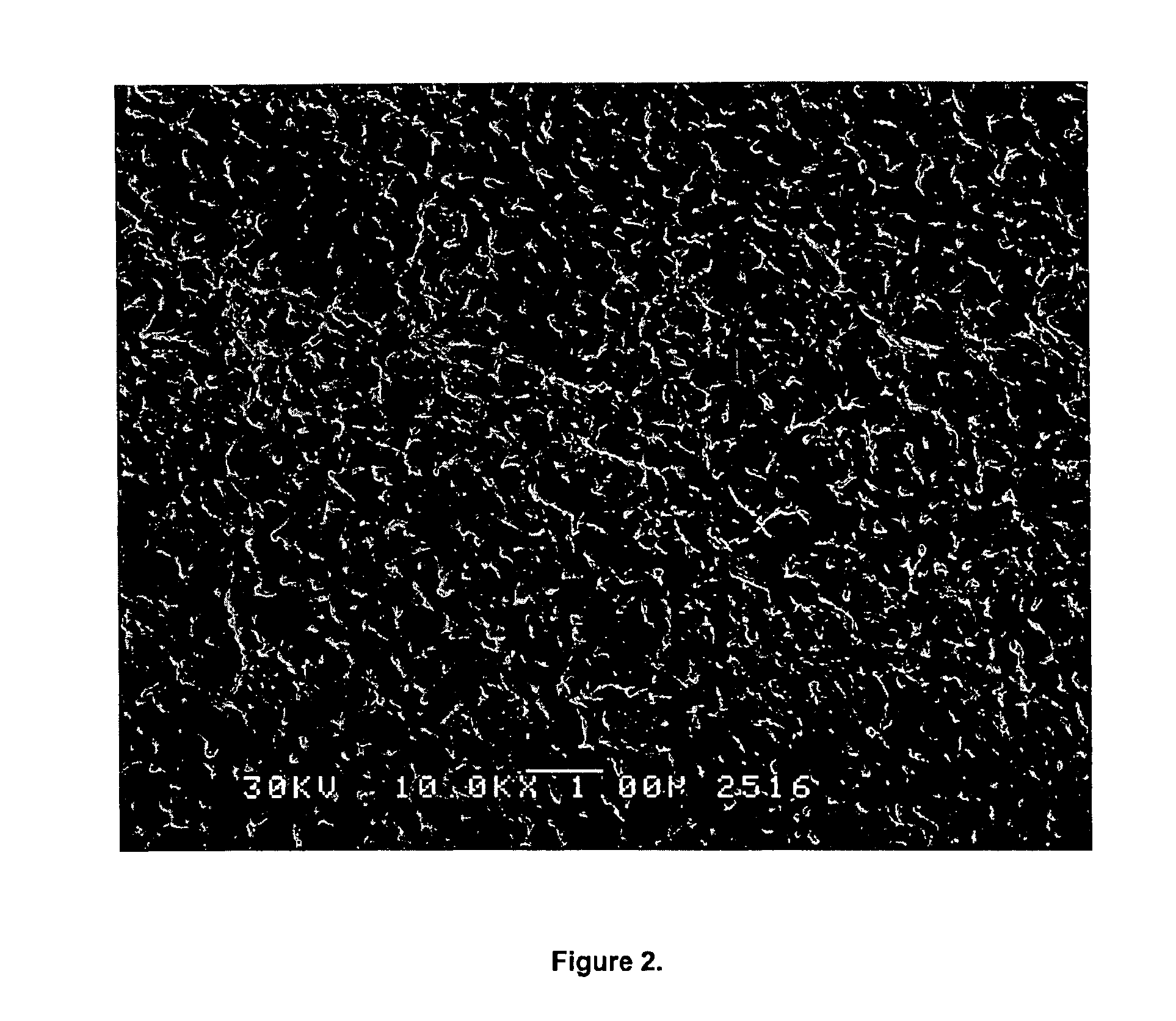
Porous poly(aryl ether ketone) (PAEK) articles are prepared from PAEK / polyimide blends by selective chemical decomposition and subsequent removal of the polyimide phase. Porous PAEK articles exhibit highly interconnected pore structure and a narrow pore size distribution. The porous PAEK articles of the present invention can be utilized as a porous media for a broad range of applications, including membranes for fluid separations, such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and as a sorption media.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS DEV FINANCE AGENCY
High flux and low fouling filtration media
Membranes suitable for microfiltration, ultrafiltration (UF) and nanofiltration (NF) filters are provided. Such membranes may include a nanofibrous scaffold, optionally in combination with a non-woven substrate and / or a coating of a polymer and a functionalized nanofiller. Suitable membranes may also include a coating of a polymer and a functionalized nanofiller on a substrate, which can include a non-woven membrane, a nanofibrous scaffold, or both.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
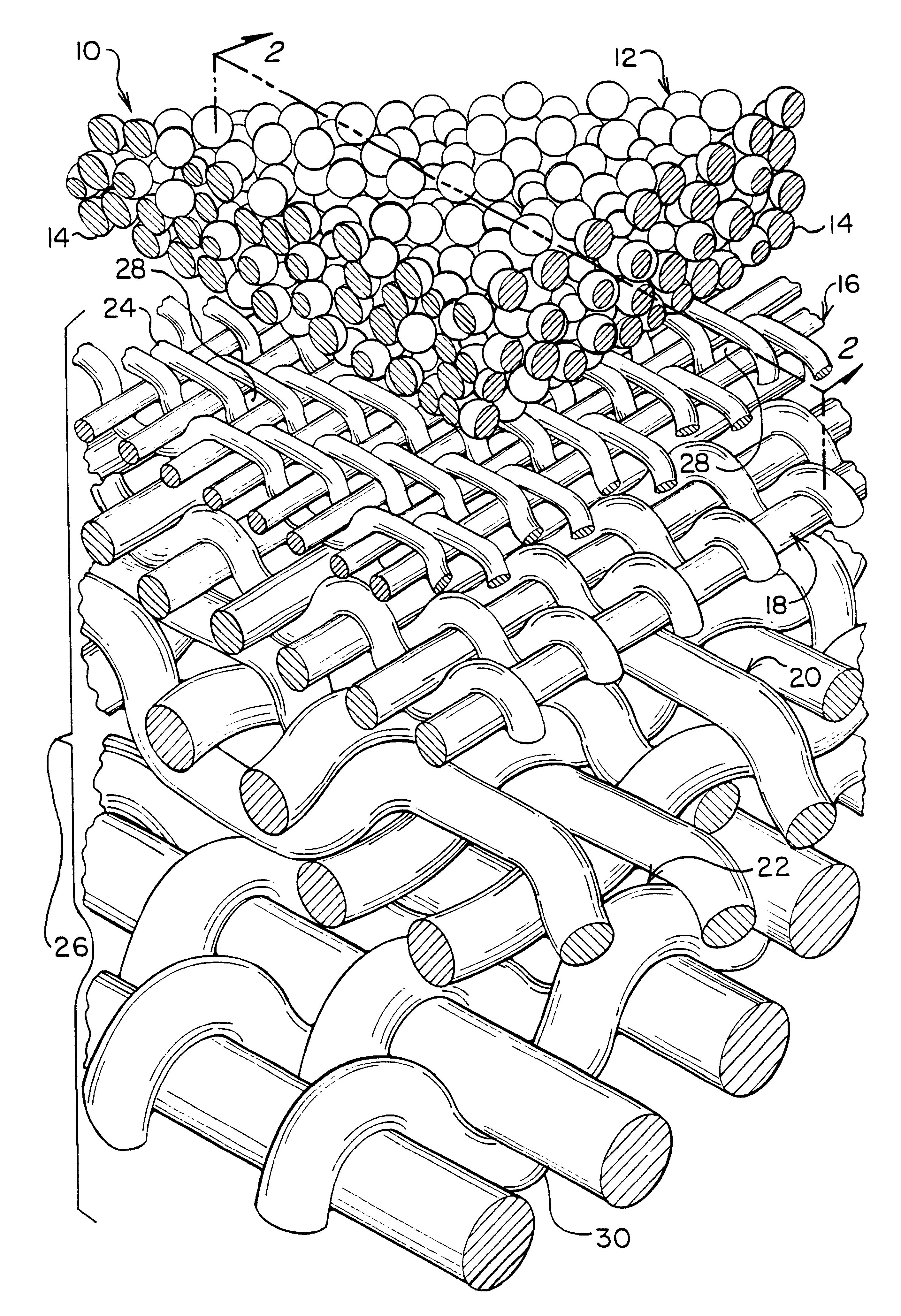
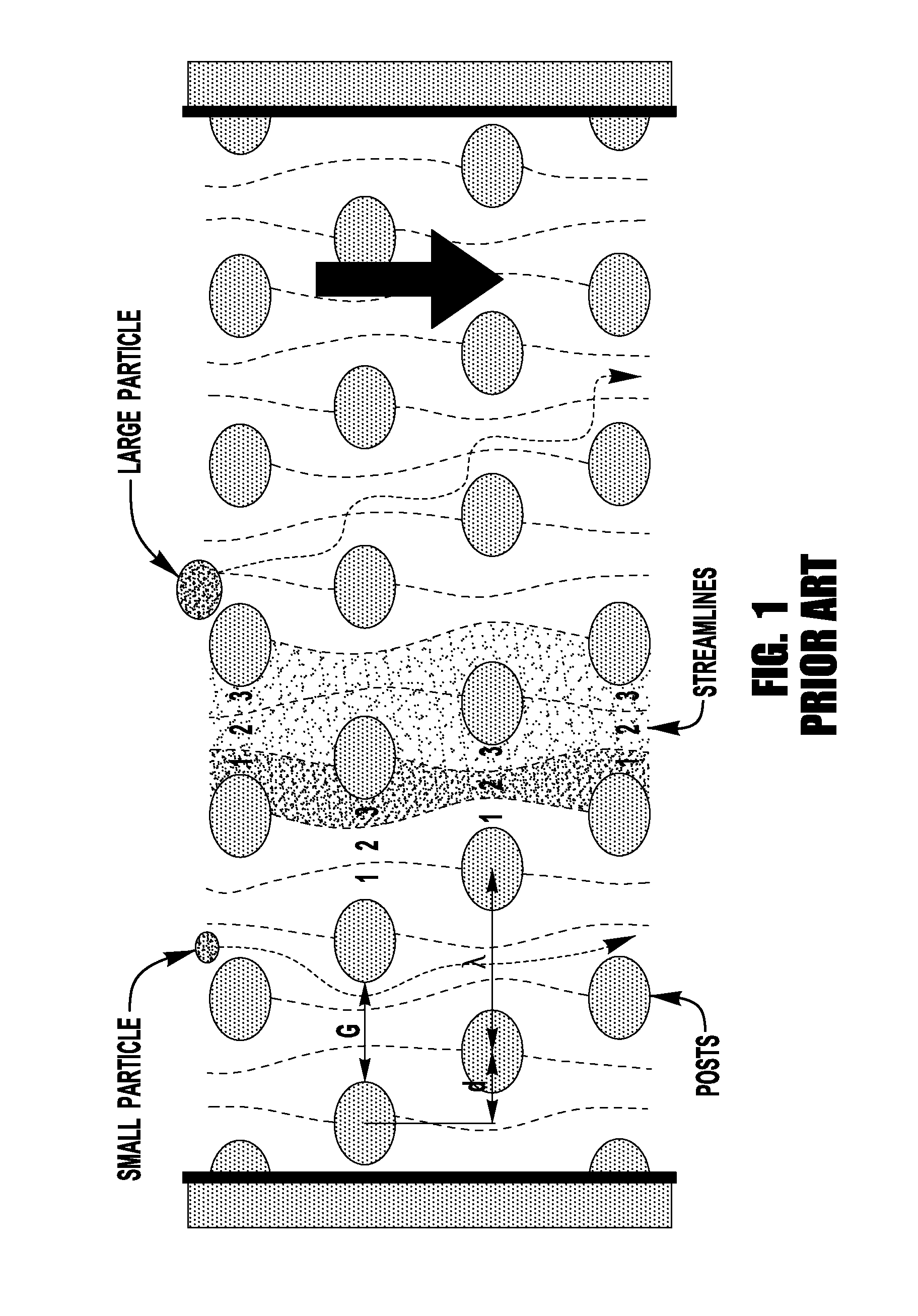
Lateral displacement array for microfiltration
InactiveUS20120037544A1Easy to manufactureEasy to assembleGas current separationLaboratory glasswaresVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
A lateral displacement array that includes a conduit in which there is an array that includes a number of vertically asymmetrical posts that are positioned in an ordered fashion that is asymmetric with respect to the direction of liquid flow within the array such that particles of at least a critical size will be laterally displaced as they flow through the array is described. Methods for separating particles having at least a critical diameter from 16 a liquid using a lateral displacement array and a microfiltration system including a number of lateral displacement arrays are also described. Array subunits suitable for the assembly of the lateral displacement array are also described that include posts on either side of a floor that are arranged on each side with half the usual density so that when the subunits are combined a lateral displacement array with the desired array of posts is formed.
Owner:LOGOS ENERGY INC
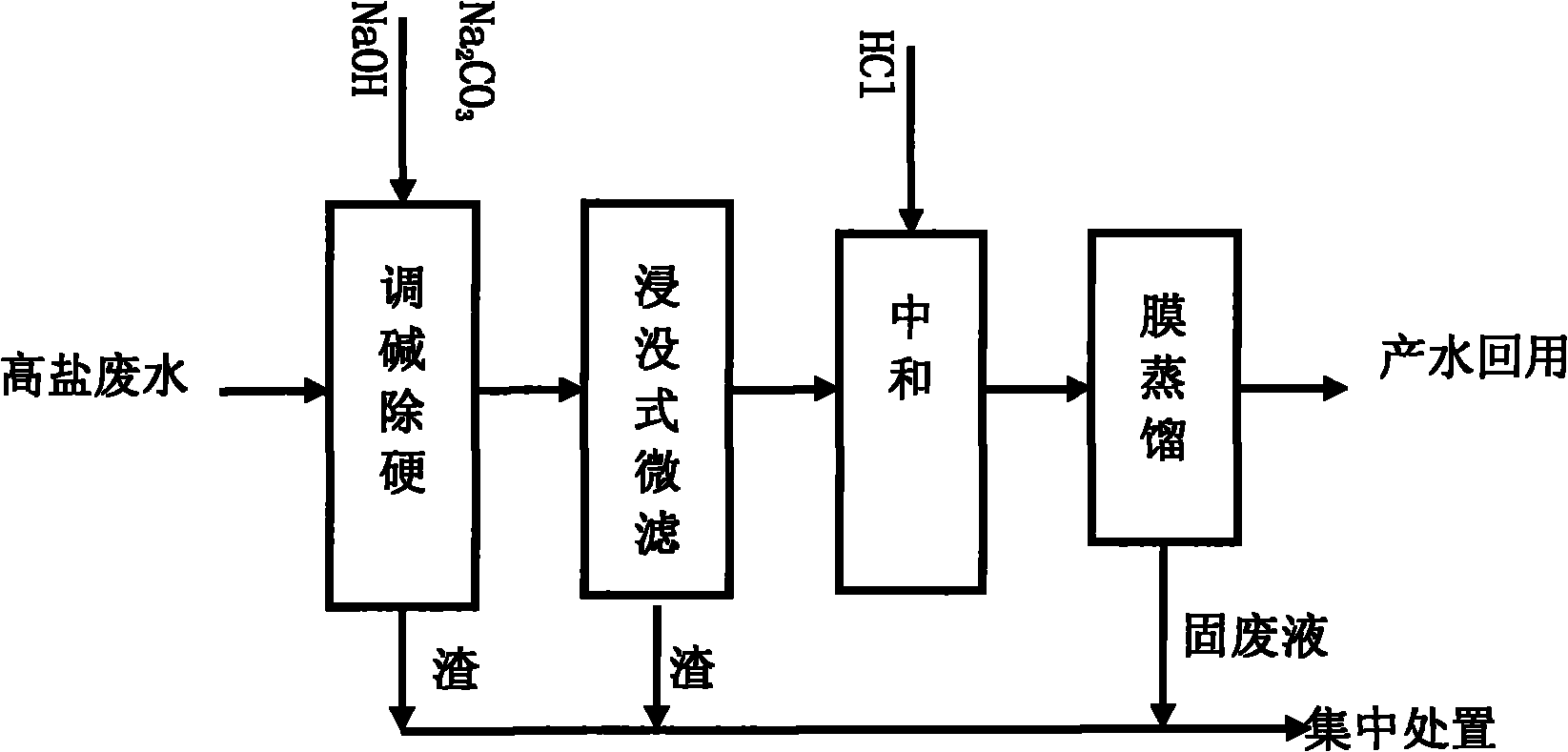
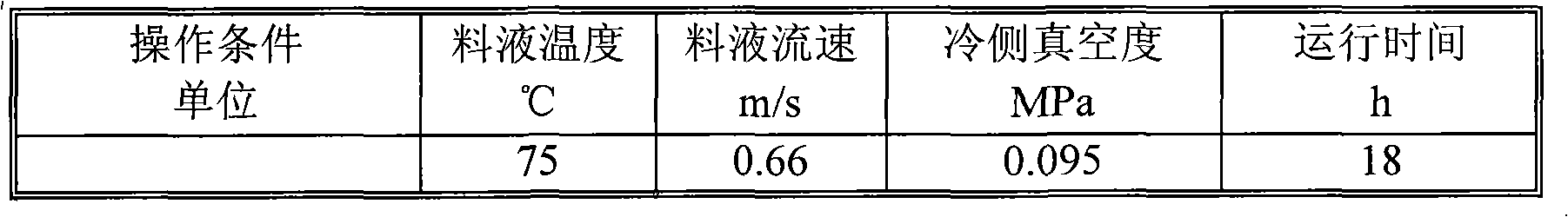
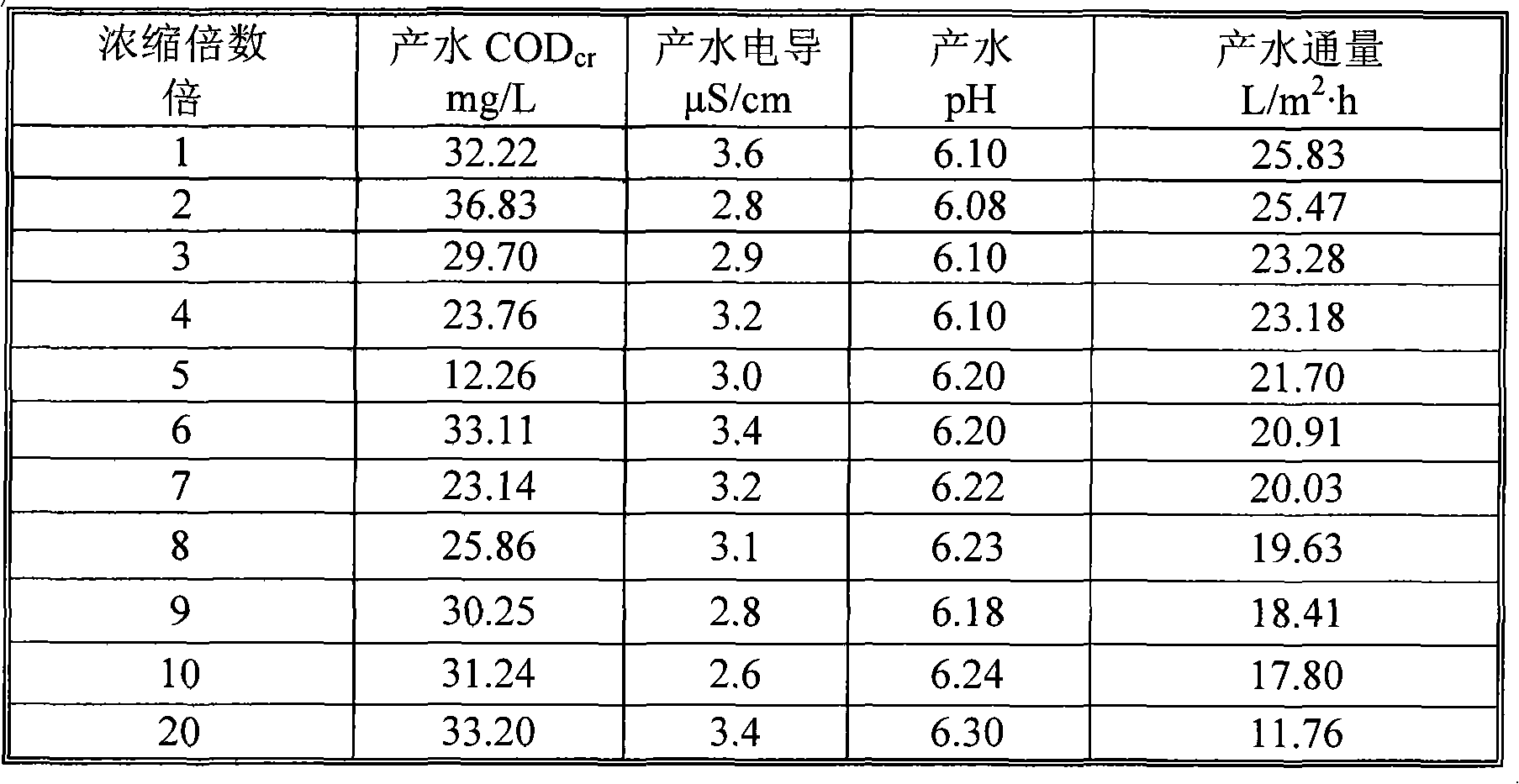
Method for treating high salinity wastewater
ActiveCN101928087AHigh hardnessHardness removalWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisMultistage water/sewage treatmentWastewaterWater quality
The invention relates to a method for treating high salinity wastewater. The invention uses treatment processes of alkali regulation and hardness removal, immersed microfiltration, neutralization and membrane distillation, aiming at the high salinity wastewater in petrifaction enterprises. The immersed microfiltration solves the problems of easy blocking, rapid flux decline rate and the like of a membrane; and the alkali regulation and hardness removal effectively removes the hardness in wastewater, reduces membrane pollution, improves the concentration multiple of the membrane distillation, lowers the load of evaporation and improves the processing effect and the operation stability of the membrane distillation. The method of the invention has wide applicability, simple device, convenient operation, stable operation and the like, and water produced by membrane distillation is good in water quality and can be directly reused for production.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Water flux polymer membranes
The invention relates to a polymer membrane composition having improved water flux and stable pore size. The water flux is improved by increasing the hydrophilicity of the membrane using a matrix polymer blended with controlled architecture amphiphilic block copolymers. Preferred membranes are those having a fluoropolymer matrix and acrylic amphiphilic block copolymers. The addition of the amphiphilic block copolymers are especially useful in microfiltration and ultra filtration membranes when used in water filtration.
Owner:ARKEMA INC
Antimicrobial semi-permeable membranes
Cast semi-permeable membranes made from synthetic polymer used in reverse osmosis, ultrafiltration and microfiltration are treated with a non-leaching antimicrobial agent to prevent its bio-fouling and bacterial breakthrough. The semi-permeable membranes include a polymeric material and a non-leaching antimicrobial agent that is incorporated into and homogeneously distributed throughout the polymeric material. The polymeric material, in the case of one membrane, may be cellulose acetate. In the case of thin film composite polyamide membranes, the antimicrobial agent is incorporated in a microporous polysulfone layer that is sandwiched between a reinforcing fabric and an ultrathin polyamide material. The invention also includes a treatment of flat and hollow fiber semipermeable membranes made with polysulfones and polyvinylidene fluoride.
Owner:MICROBAN PROD CO INC
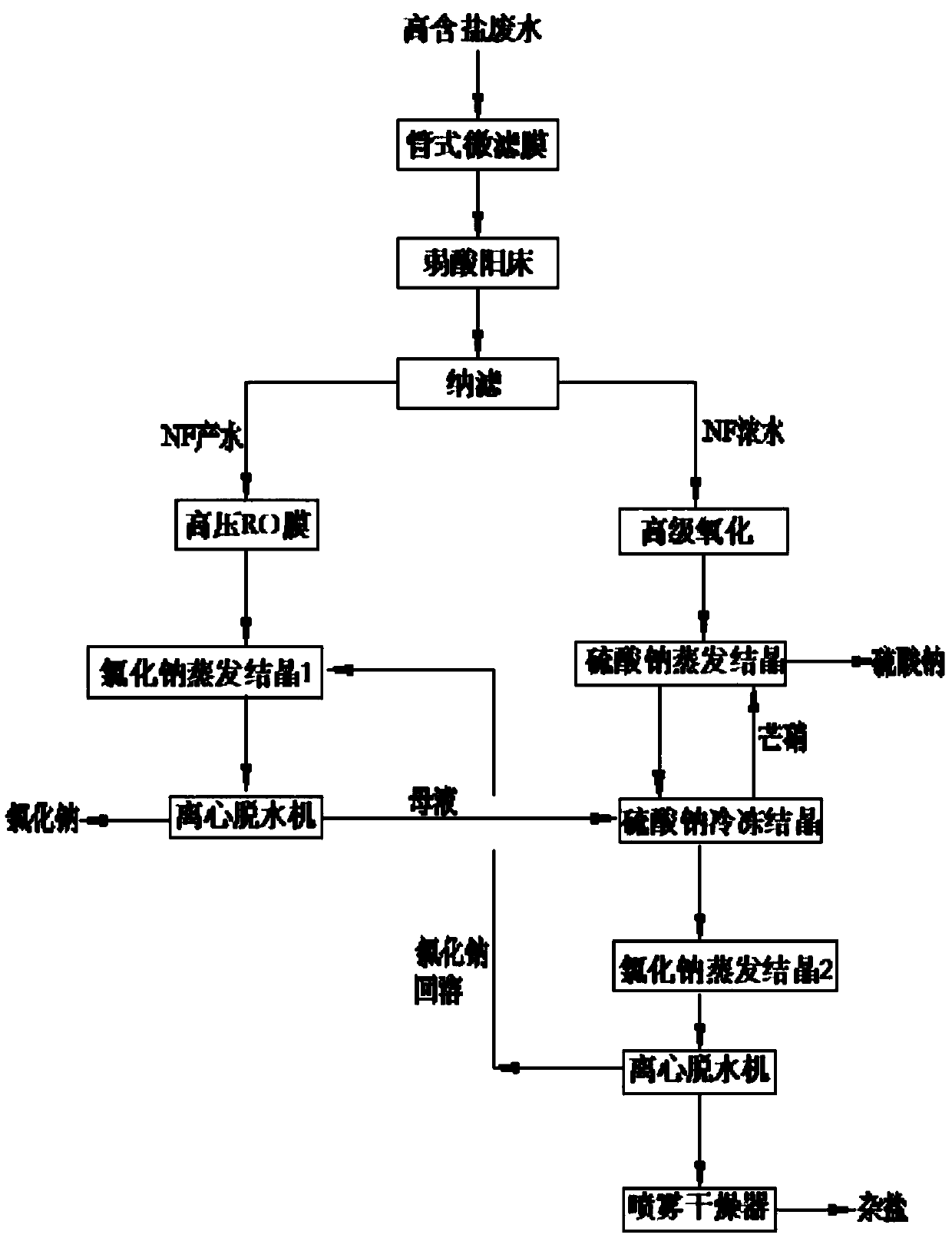
Resource technology and system for separating salt from high-salinity wastewater
InactiveCN107619144ASolve the problem of pipe blockageReduce energy consumptionMultistage water/sewage treatmentAlkali metal chloridesMirabiliteProduced water
The invention discloses a zero-drainage technology for recycling crystallizing salt from high-salinity wastewater and a treatment system thereof. The treatment system comprises a tubular microfiltration system, a weak acid resin hardness removal system, a nanofiltration membrane salt separating system, a nanofiltration concentrated water oxidizing system, a nanofiltration concentrated water sodiumsulfate evaporating and crystallizing system, a sodium sulfate freezing and crystallizing system and the like. The zero-drainage technology has the advantages that the pretreated wastewater is subject to nanofiltration primary salt separating, the salt component in the produced water is mainly sodium chloride, the sodium chloride with purity no lower than 98.5% is obtained by membrane concentration, evaporating and crystallizing, and the sodium sulfate with purity 99.1% or more is produced by MVR (mechanical vapor recompression) crystallizing after concentrated water oxidizing; a mother liquid after evaporating and crystallizing of sodium sulfate and a mother liquid after nanofiltration evaporating and crystallizing are mixed and frozen, so as to obtain mirabilite, and the mirabilite is converted into anhydrous sodium sulfate after sodium sulfate evaporating and crystallizing; at the premises of ensuring quality, the whole recycling rate of salt reaches 90% or above; finally, a smallamount of mother liquid is sprayed, dried and cured, and the zero-drainage effect of wastewater is realized.
Owner:侯新春 +1
Low pressure filtration
ActiveUS20070131614A1Produced economicallyReduce energy consumptionMembranesUltrafiltrationFiltrationStreamflow
High flow, low-pressure ultrafiltration or microfiltration spiral wound membrane cartridges are used in filtration of liquid feedstocks having high suspended solids. Applications may utilize either vacuum or pumping for transmembrane drive pressure (TMP), and gas may optionally be bubbled up through the cartridges with certain feedstocks. Water permeate flux rates as high as 90 gallons per square foot per day (gfd) can be obtained at TMPs below 5 pounds per square inch. By locating each spiral wound cartridge in its own casing and supplying liquid feedstock to an open lower end of the casing, as opposed to submerging such cartridges in a tank filled with feedstock, overall low pressure performance is greatly improved. High permeate flow can be maintained for long periods of time between shutdowns for intensive cleaning. TMP is gradually increased to maintain a substantially constant rate of permeate discharge until a target is reached, indicative of solids accumulation on the membrane surface to an undesirable extent; then backflushing is effected for a short time. Discarding the hold-up volume of feedstock in the cartridge, the backflushing fluid and dislodged solids, allows production to be promptly resumed with fresh feedstock at performance at near original levels.
Owner:MANNHUMMEL WATER & FLUID SOLUTIONS GMBH
Method for one-time separation and extraction of dendrobe polysaccharide, dendrobine and erianin from dendrobium candidum
InactiveCN102786604AHigh purityAvoid lostEther separation/purificationEnzymatic hydrolysisDendrobium candidum
The invention discloses a method for one-time separation and extraction of dendrobe polysaccharide, dendrobine and erianin from dendrobium candidum. The method for extraction of dendrobe polysaccharide, dendrobine and erianin from dendrobium candidum comprises the steps of crushing of dendrobe, enzymatic hydrolysis, ultrasonic extraction, microfiltration, ultrafiltration and nano-membrane concentration, solid-liquid separation, vacuum cryogenic distillation, solvent extraction, solvent recovery, recrystallization, vacuum low-temperature drying and purification in the carbon dioxide supercritical fluid, thereby obtaining the dendrobe polysaccharide, dendrobine and erianin. The prepared product has good color, good solubility and high active ingredients.
Owner:HHUANGSHAN LVJIUYUAN BIOLOHICAL TECH
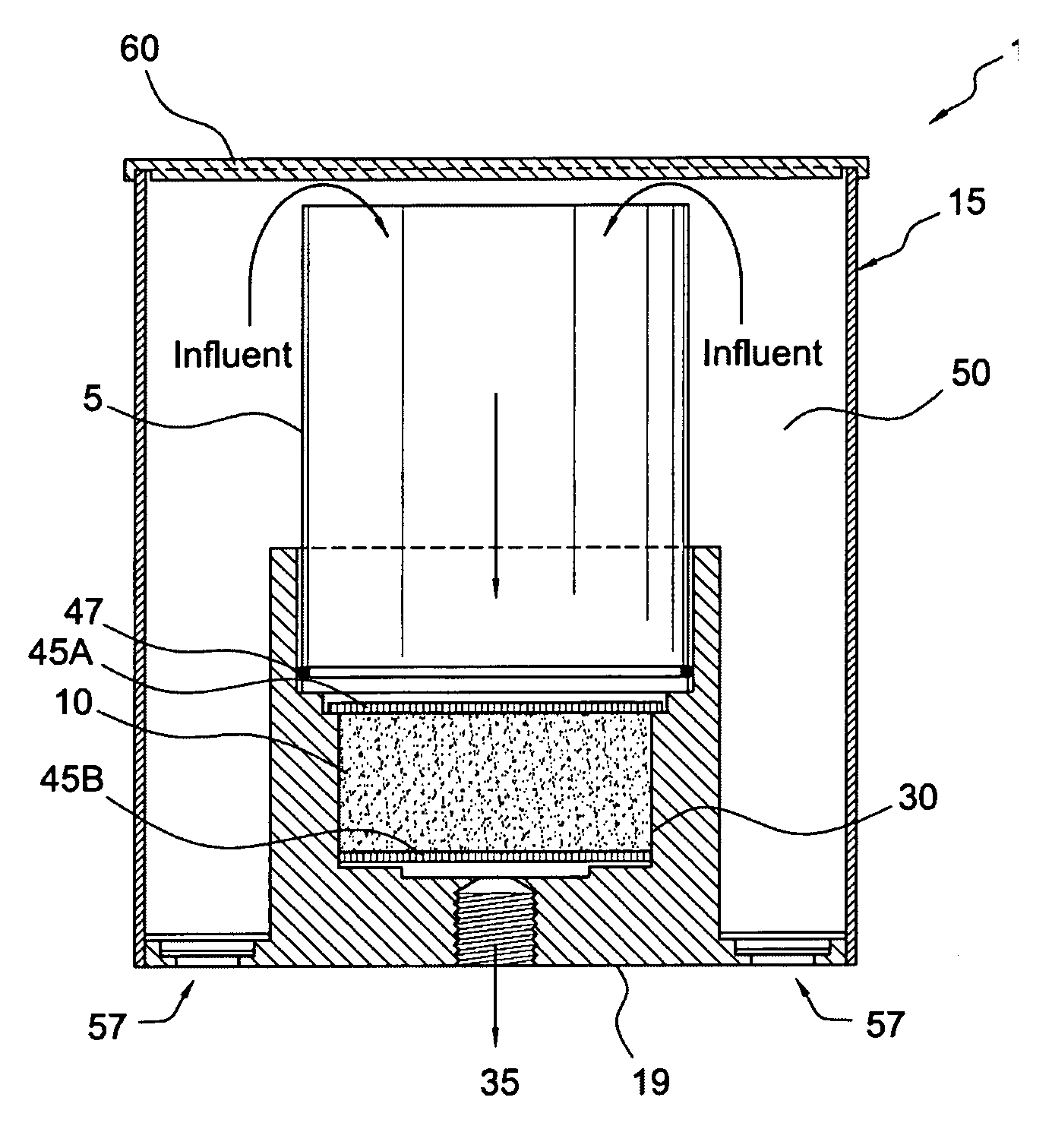
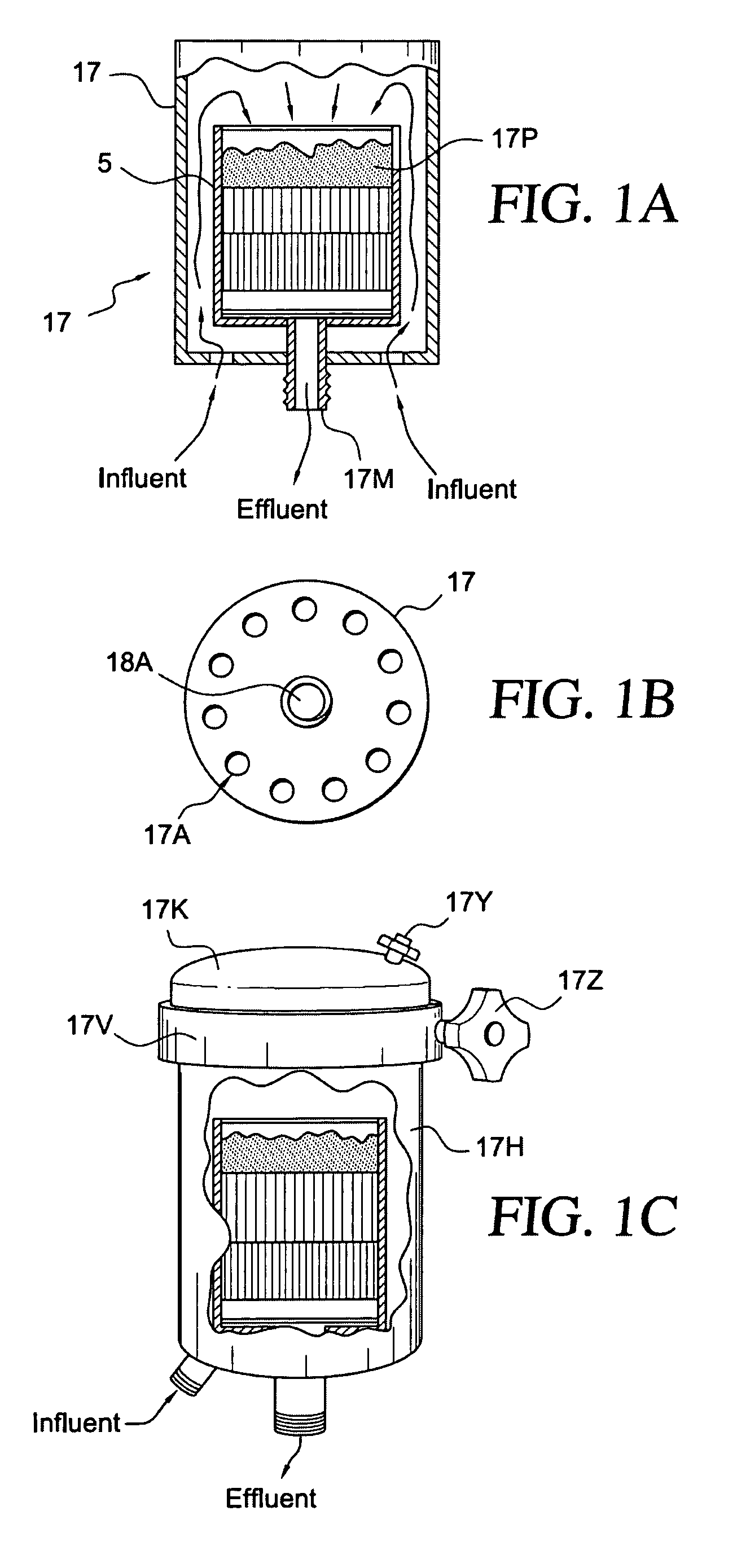
Microfiltration devices
ActiveUS20070062870A1Improve filtering effectImprove performanceSemi-permeable membranesMembranesHollow fibre membraneFiber
A method of treating a hollow fiber membrane microfiltration filter having an influent side and an effluent side to improve performance of the filter is disclosed. The method entails sealing imperfections in surfaces of the filter by flushing the filter with a liquid aqueous suspension of particulates. Filter cartridge devices also are disclosed. The devices may include a bactericidal chamber. A radial flow filter may be included in the devices. The filter cartridges may include a drain tube positioned within the filter for removing of effluent generated by the filter. A plurality of filter cartridges may be positioned on the drain tube.
Owner:STREAMLINE CAPITAL
Nanometre-sized fibre liquid separation composite film and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101559327AEasy to controlSimple manufacturing methodUltrafiltrationChemical treatmentComposite film
The invention discloses a nanometre-sized fibre liquid separation composite film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of (1) performing electrostatic spinning for a macromolecular spinning solution A to obtain a non-woven fabric as a supporting layer of the composite film; (2) coating a macromolecular spinning solution B on the surface of the non-woven fabric obtained in the step (1) in a spray coating manner as a selection layer of the composite film; and (3) suffocating the surface of a second nanometre-sized fibre layer by solvent steam; and (4) thermally treating or chemically treating the product obtained in the step (3) to obtain the finished product. The method of the invention has a manufacturing process that is simple and easily controlled,is capable of conveniently and precisely controlling the thickness and uniformity of the surface selection layer, and easily realizes operations of mass production. The obtained nanometre-sized fibreliquid separation composite film can be widely applied to the fields such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration and reverse osmosis, etc.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Water treatment process for oilfield produced water
ActiveUS20090173692A1Minimize continued precipitationSolid sorbent liquid separationWater softeningSludgeTreatments water
The invention relates to a method and system for treating an aqueous liquid containing dissolved minerals and dissolved hydrocarbons. Method steps and apparatus for treating a waste water feed stream are disclosed which utilize a warm lime softening system in fluid communication with the waste water feed stream, wherein sludge from the warm lime softening system is recycled to improve lime utilization and enhance silica and boron removal without the addition of an external source of magnesium. In addition, a microfiltration system and / or an air stripper system may be used in fluid communication with at least one reverse osmosis system to produce a treatment water that meets state and federal guidelines for surface discharge.
Owner:WATER & POWER TECH
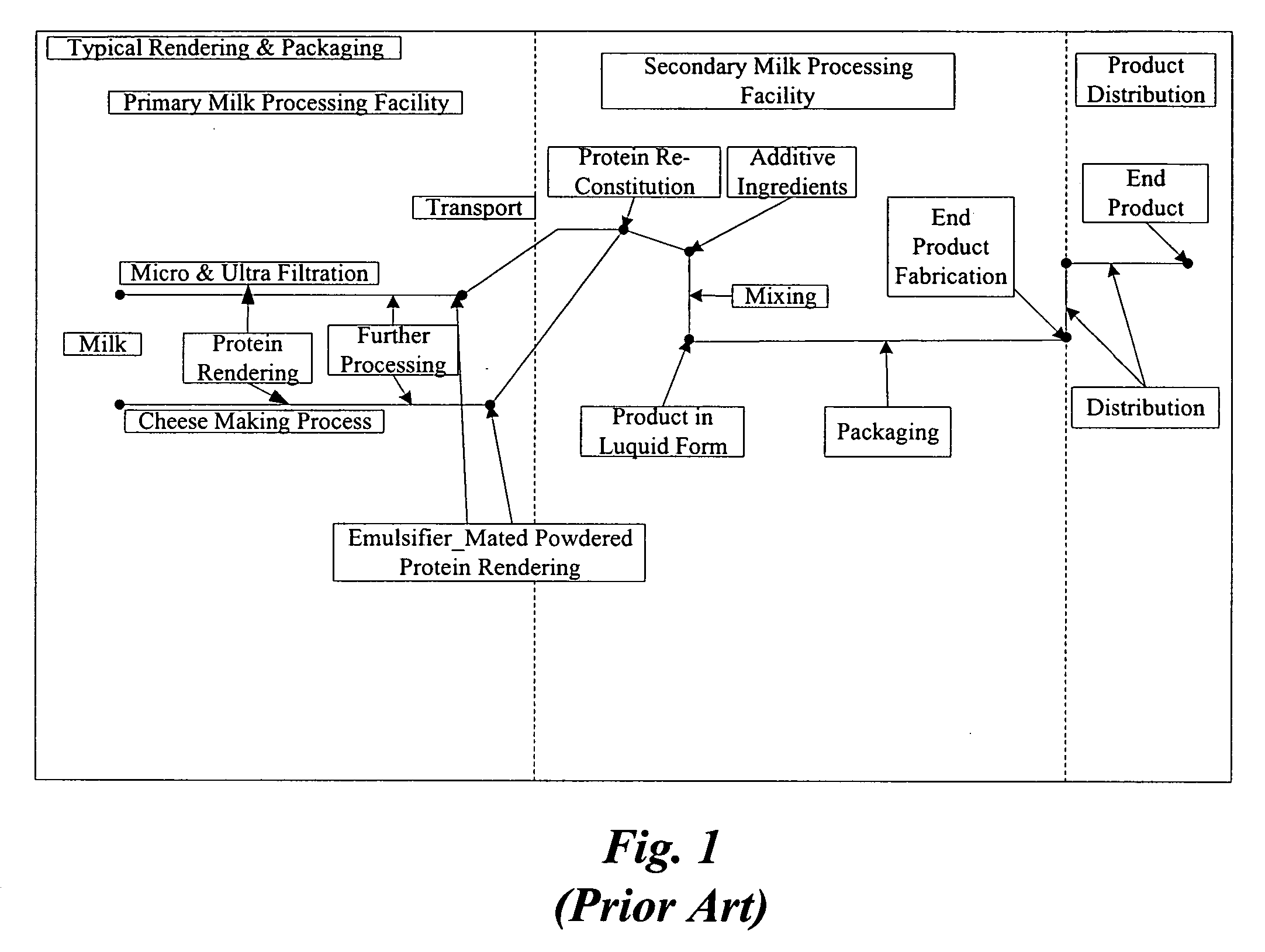
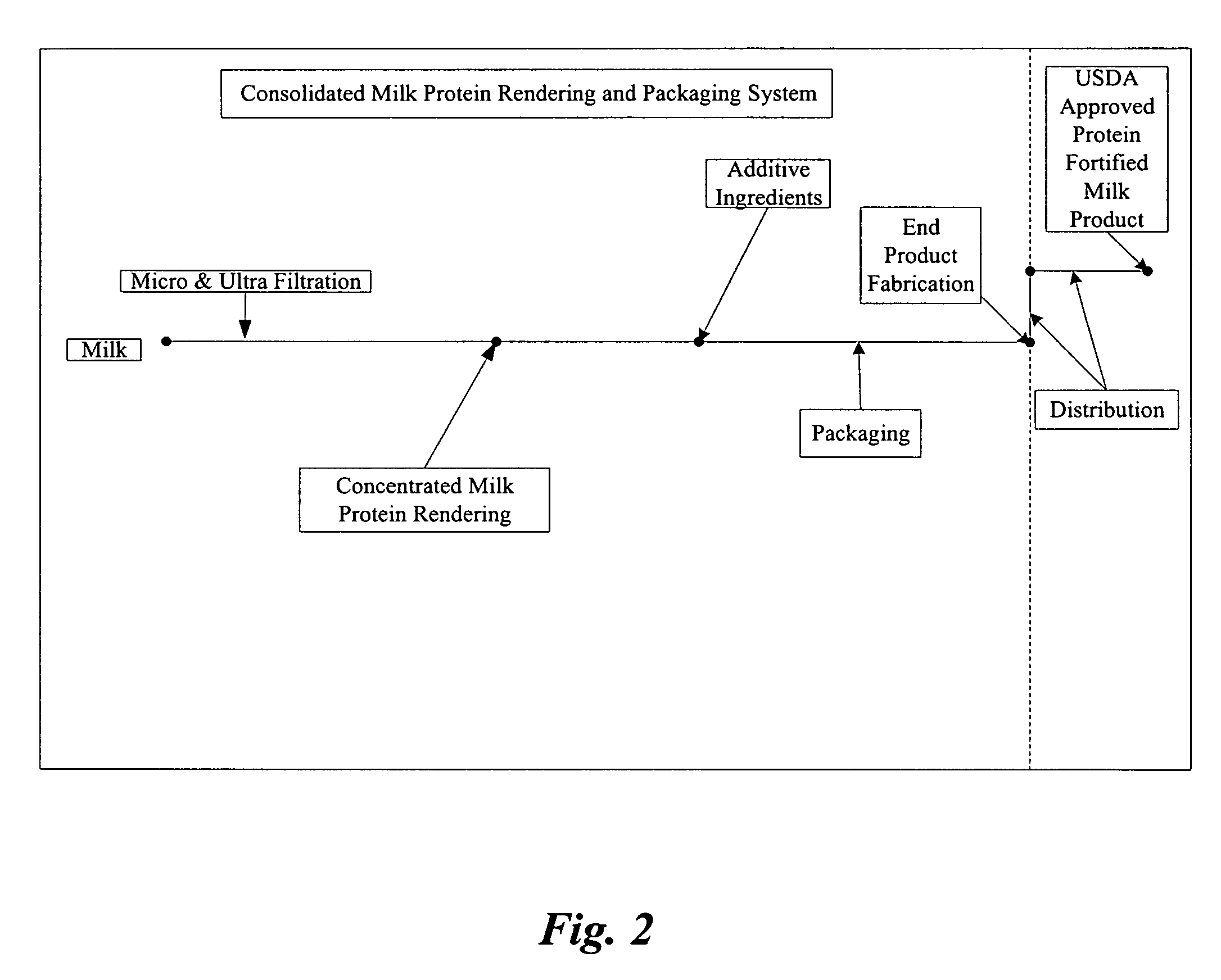
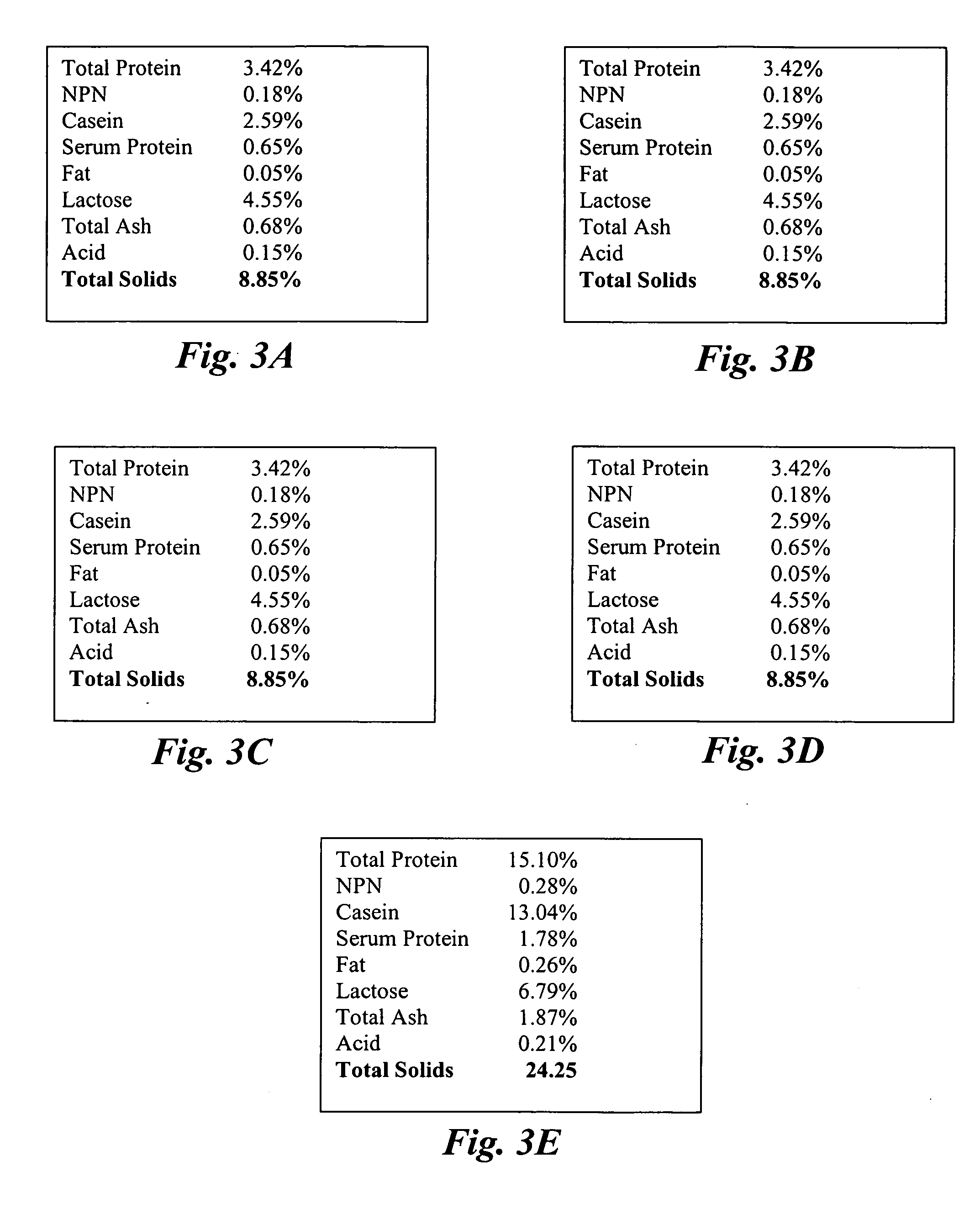
Concentrated-protein food product and process
InactiveUS20050181095A1Ultra-low fatHigh in proteinMilk preparationProtein composition from milkConcentration proteinMicrofiltration
A system, processes, and milk-based food products made from the system and processes, in which cream is separated from milk to produce an ultra-low fat milk product. The milk product is microfiltered to produce a retentate that is ready to drink and is high in protein and has no or substantially no fat. The permeate from the microfiltration process is ultrafiltered to produce a retentate that is high in protein with few other solids. The permeate may be used to provide protein fortification to other food and beverage products, and is especially useful in its liquid form for such fortification.
Owner:DOMINION NUTRITION
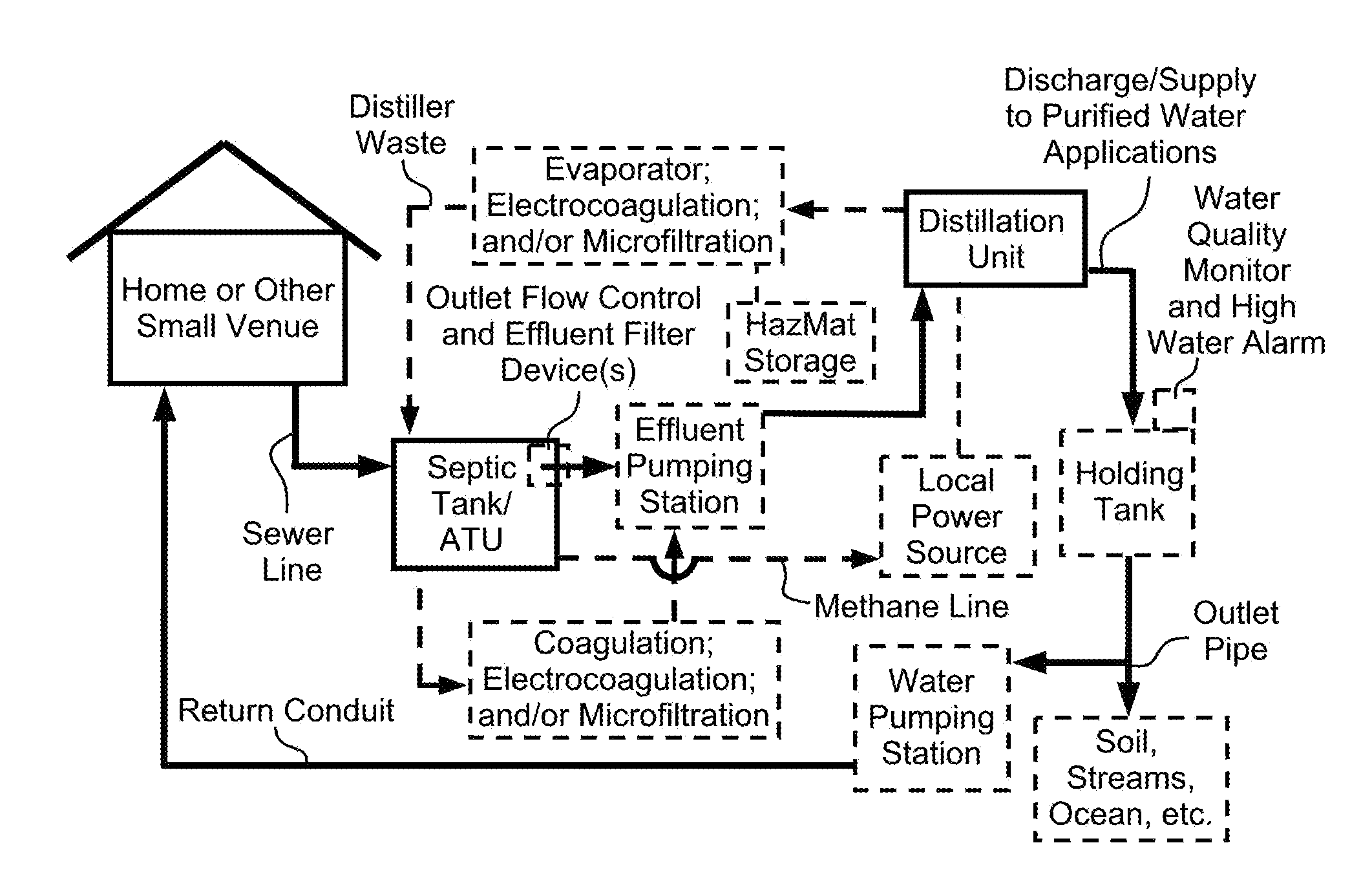
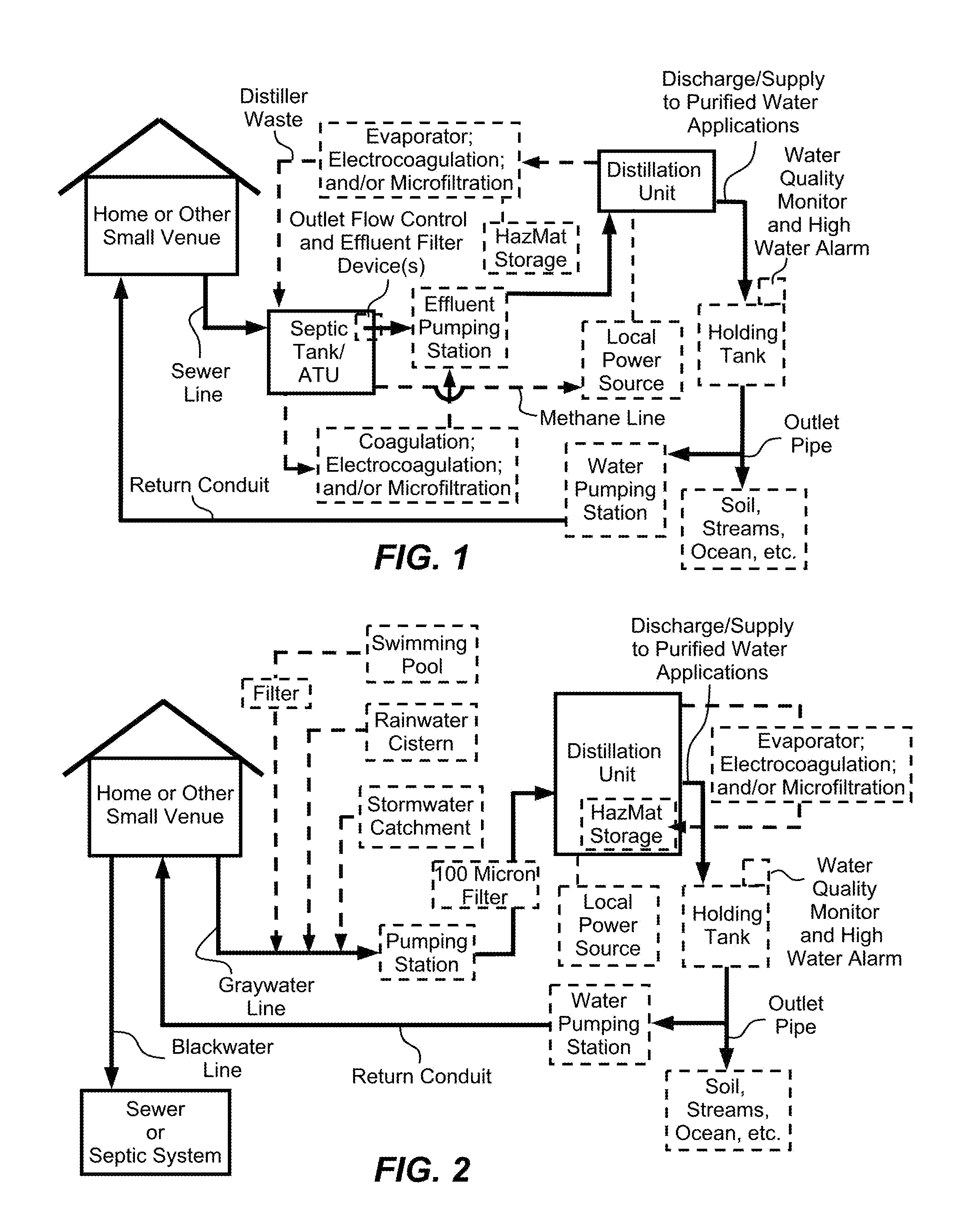
System and method of purifying and recycling or discharging septic tank effluent, graywater, rainwater and stormwater
InactiveUS20120228117A1Eliminate needEfficient trappingAuxillariesEnergy based wastewater treatmentDistillationWater quality
Methods and systems are disclosed which provide for the purification of effluent from a septic system or natural water from rainwater or stormwater collection devices for the storage and reuse of water. The purified water may be supplied to water applications, such as a return conduit to a home for potable or graywater usage. The distillation unit may be powered by a local power independent of a municipal power grid and which may employ sustainable energy mechanisms. The distiller residue may undergo a volume reduction process, such as evaporation, coagulation, electrocoagulation or microfiltration. The purified water may be stored in a holding tank with sensors to monitor the water quality and water level within the tank. Alarms, release valves or relief valves may be activated in response to such monitoring.
Owner:PANUNZIO MINDY S
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com