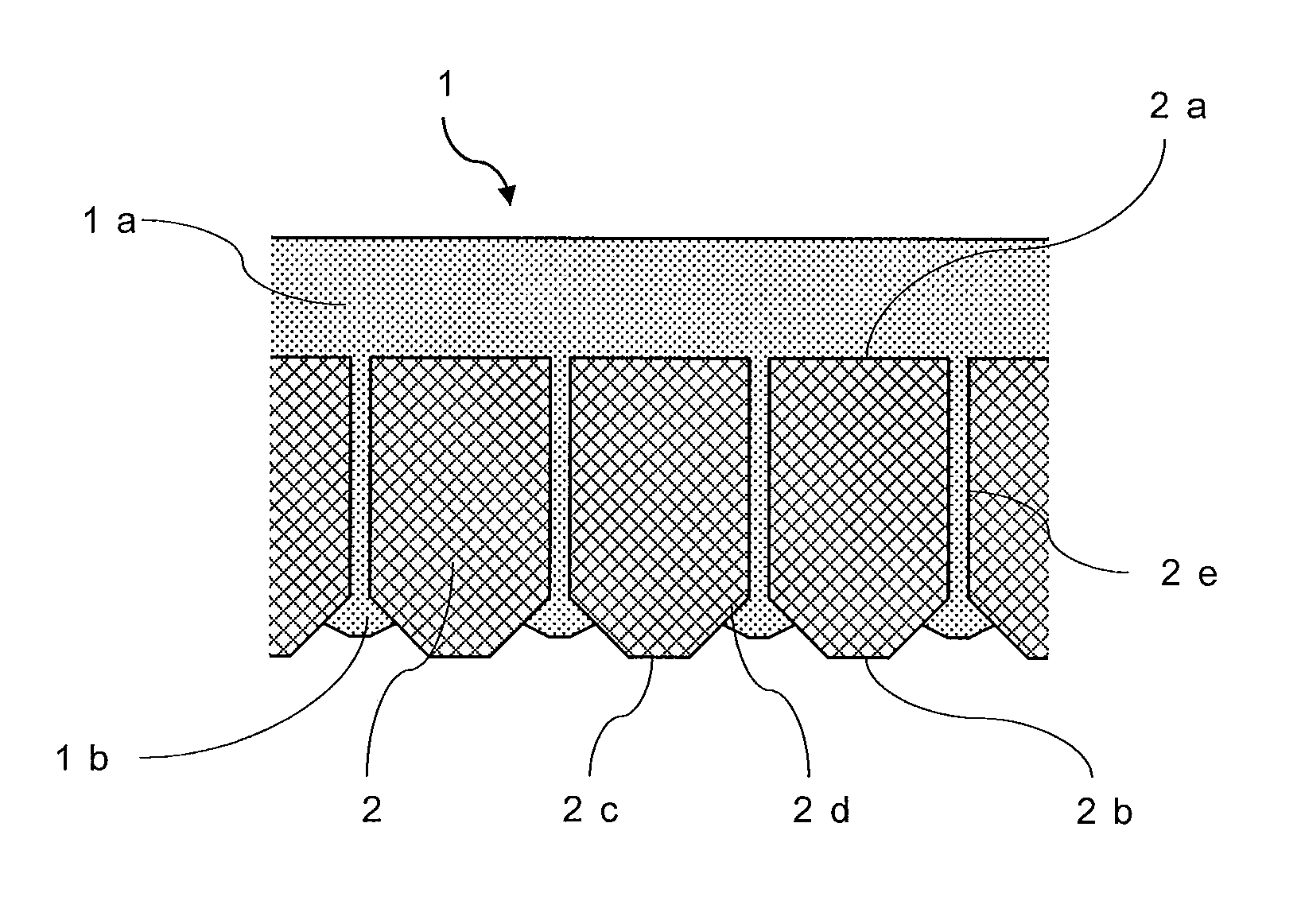
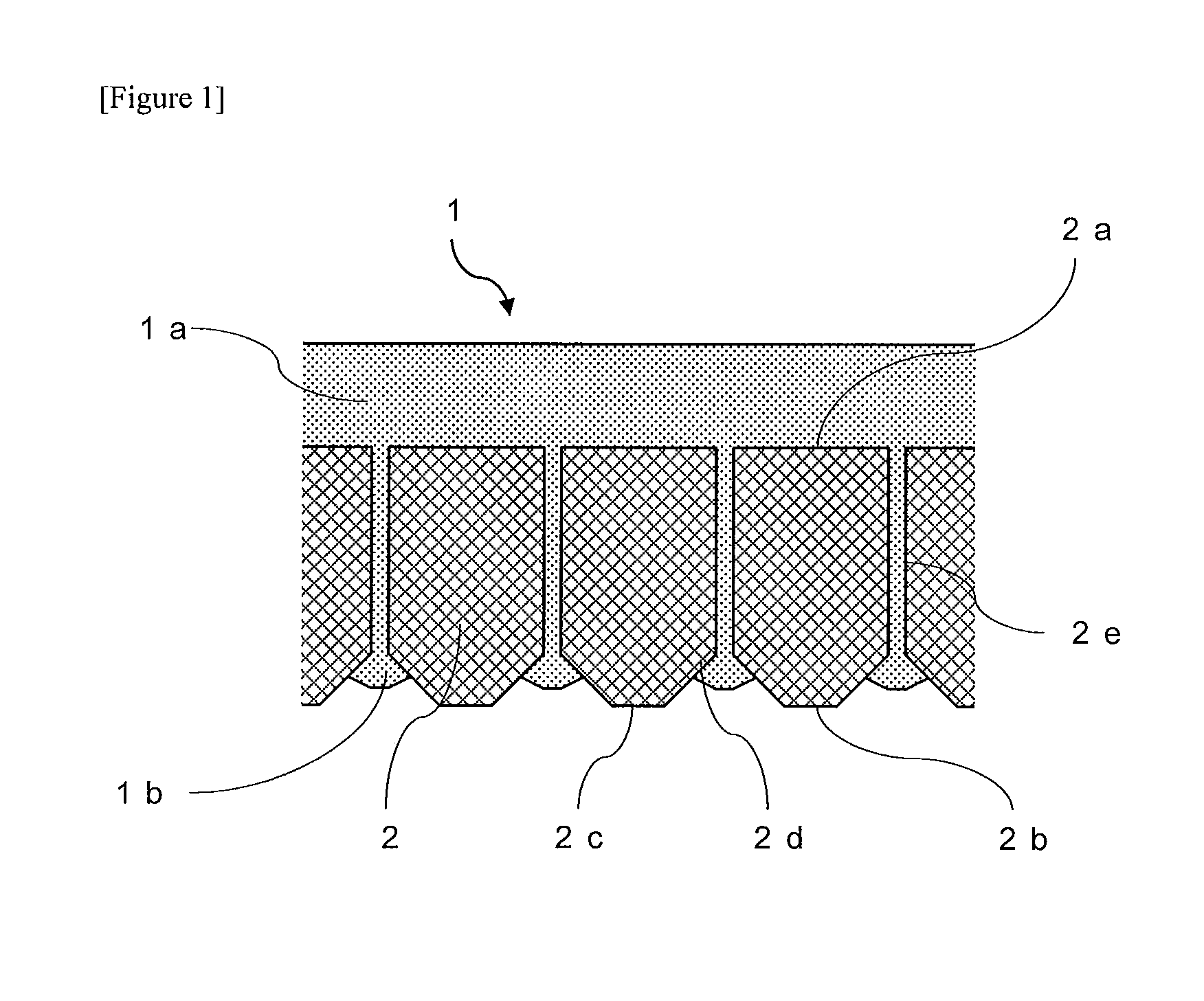
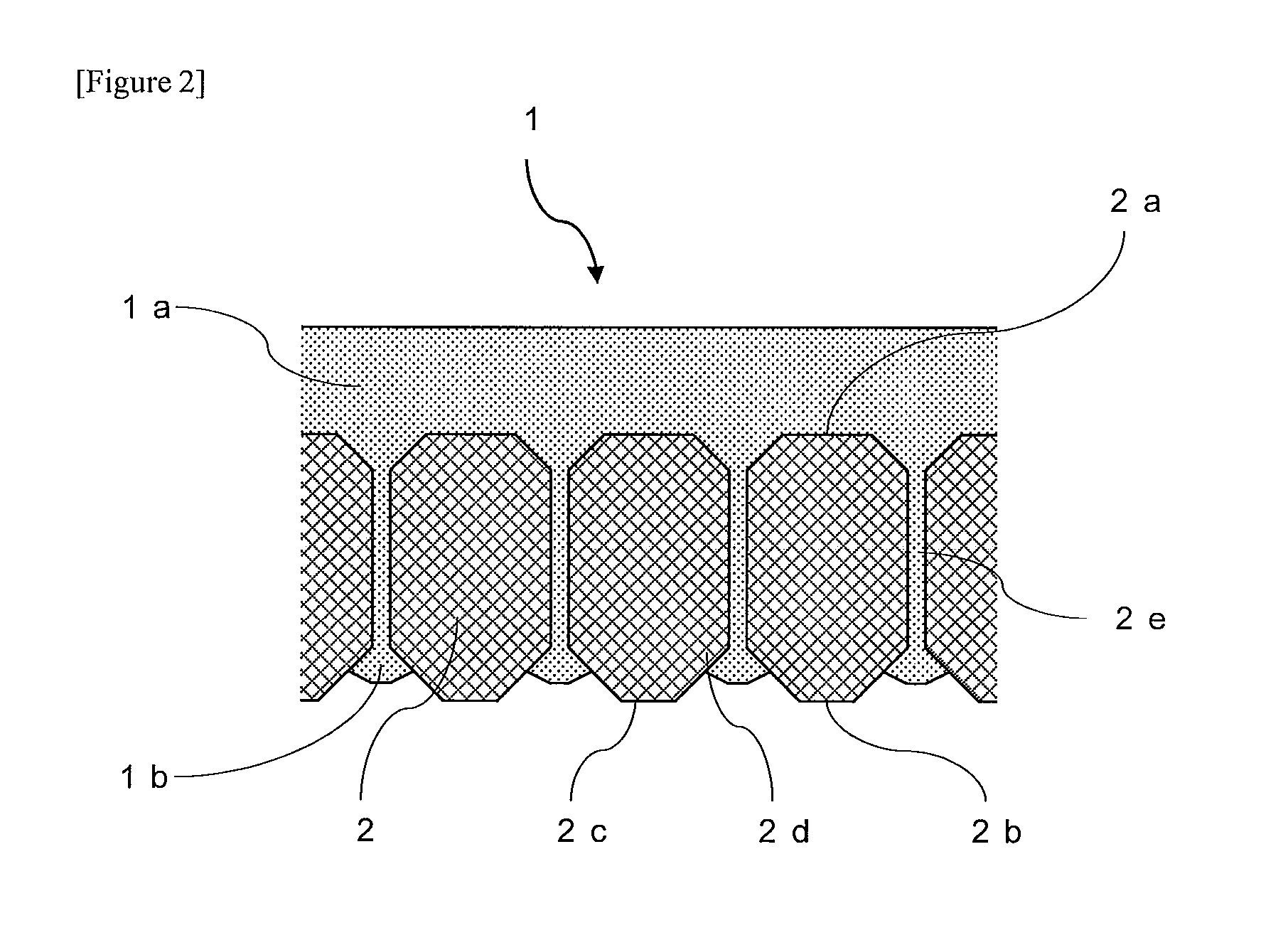
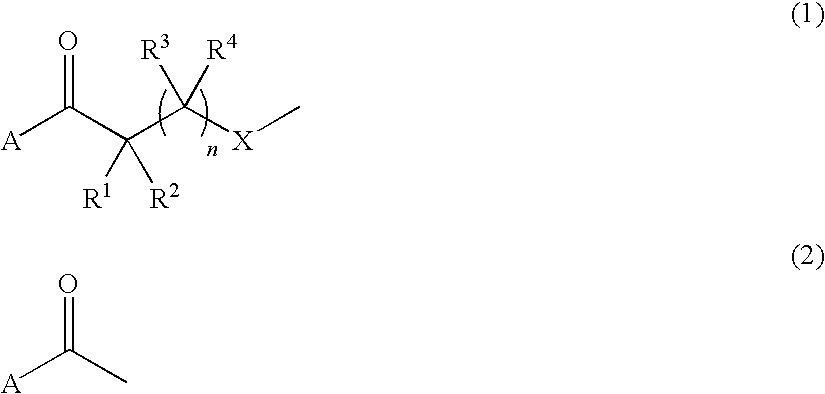Patents
Literature
782 results about "Semipermeable membranes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Semipermeable Membrane Definition. A semipermeable membrane is a layer that only certain molecules can pass through. Semipermeable membranes can be both biological and artificial.
Perorally removeable anti-reflux valve implantation
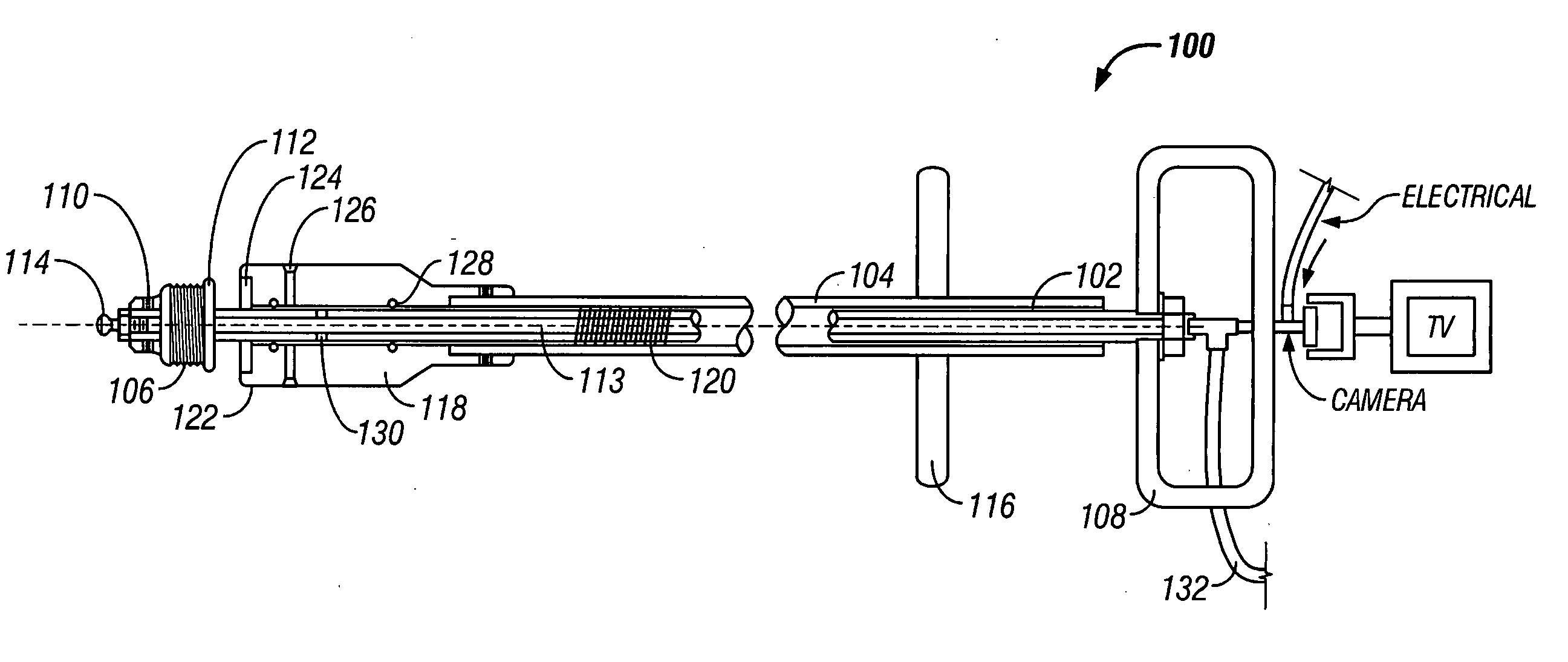
InactiveUS20060041319A1Easy to closeEasy to bendEar treatmentHeart valvesReflux valveVacuum assisted
Disclosed are esophageal anti-reflux valve prostheses, and tools and procedures for peroral implantation and extraction of the prostheses. The prostheses disclosed have a semipermeable membrane to allow retrograde passage of gas, magnets disposed at a distal end of the sleeve to facilitate closure, and an outwardly bendable array of spikes that are longitudinally aligned for peroral insertion and lockable into a radially outwardly deployed configuration to keep the prosthesis from dislocating after implantation. The implantation tool has inner and outer concentric tubes, the inner tube releasably threadably connected to the prosthesis, the outer tube reverse threaded with the inner tube to advance a distal headpiece to engage, deploy and lock the spikes into the deployed configuration. A vacuum assist can be used to help impact the lumen wall on the spikes. The extraction tool is similar to the implantation tool with an inner tube for threadably engaging the prosthesis, an outer tube with a distal crown with a plurality of shoes to unseat and unlock the spikes, and an overtube shield to receive the spikes and facilitate extraction of the prosthesis.
Owner:REFLUX CORP
Haemodialysis device
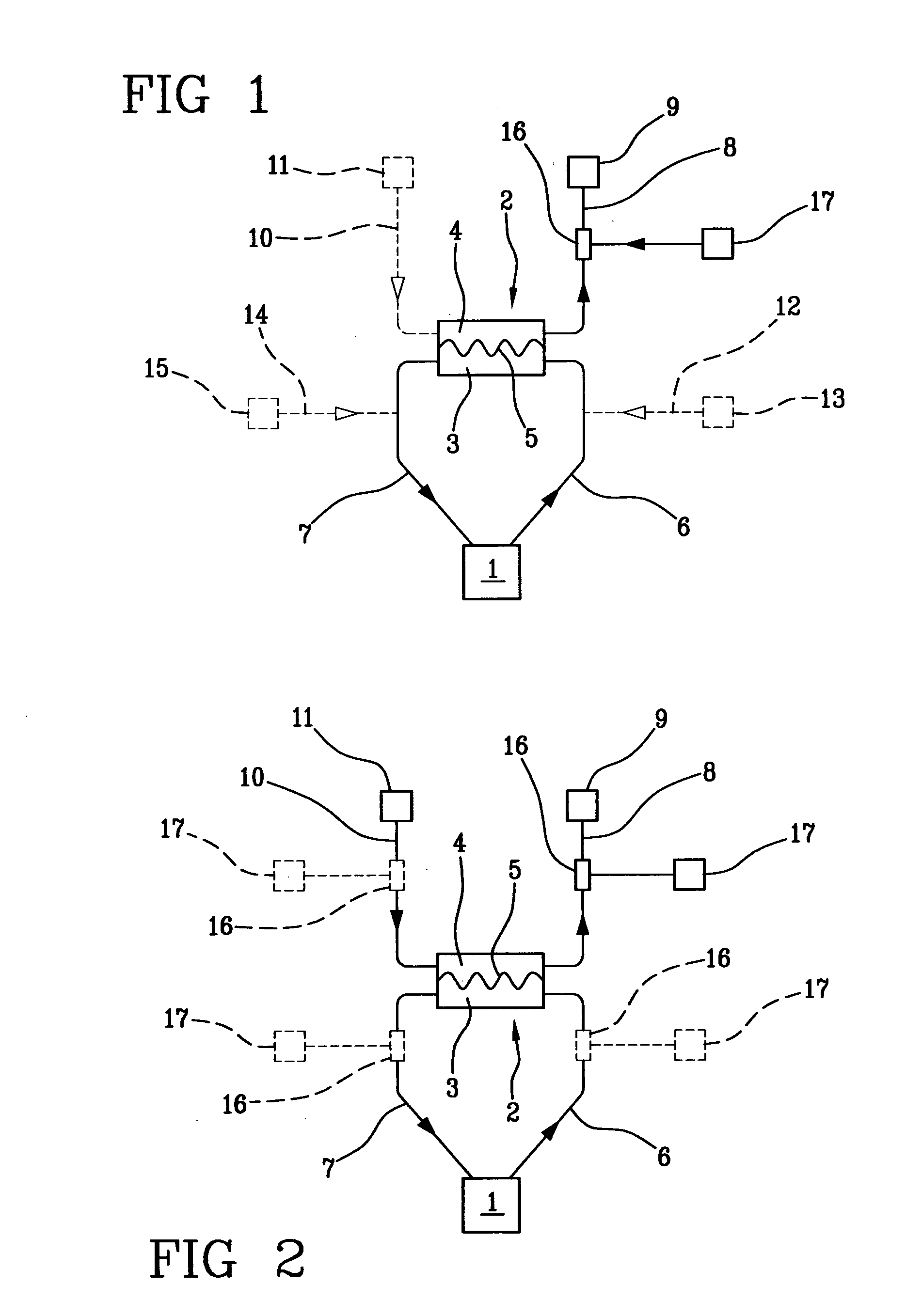
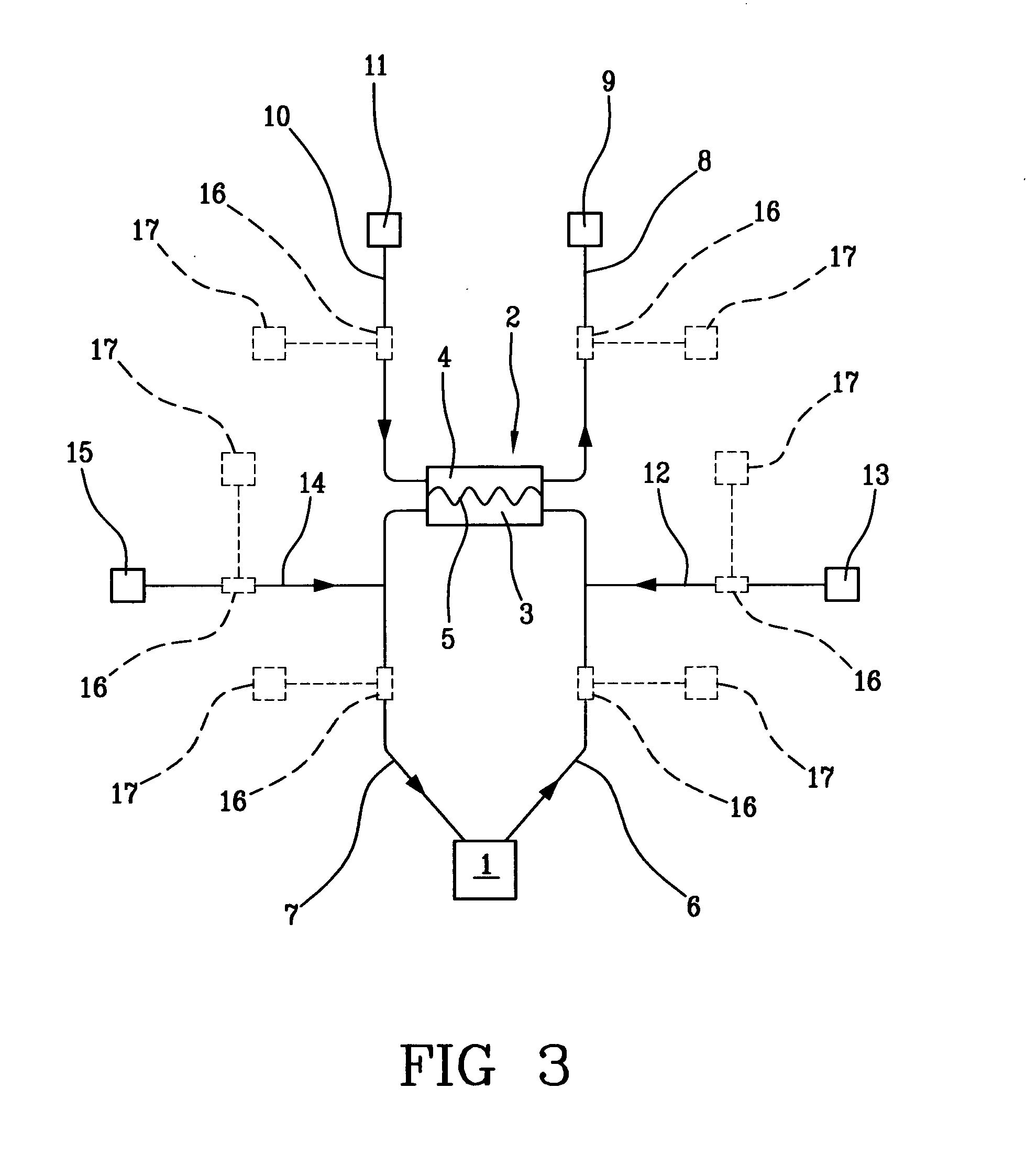
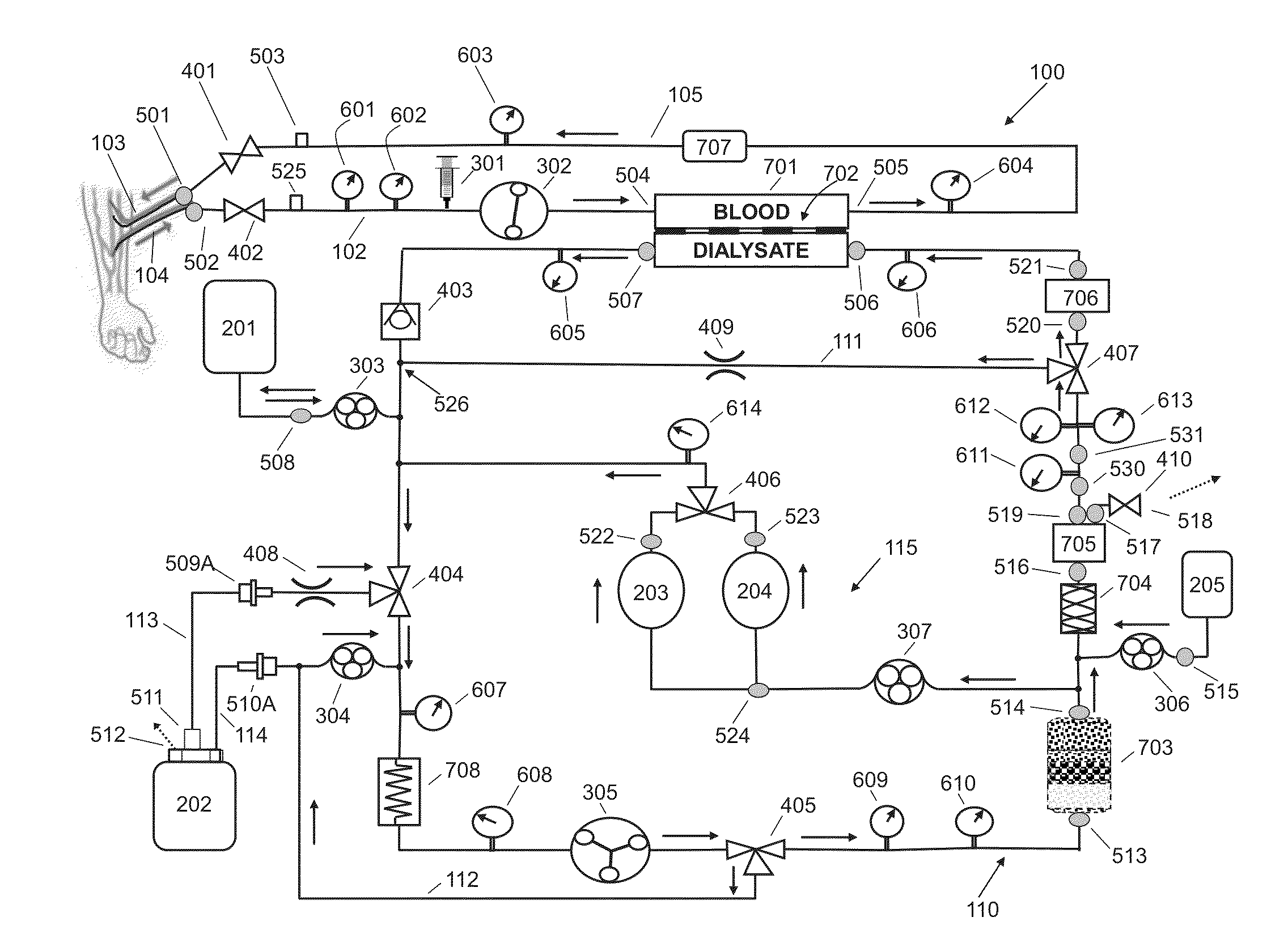
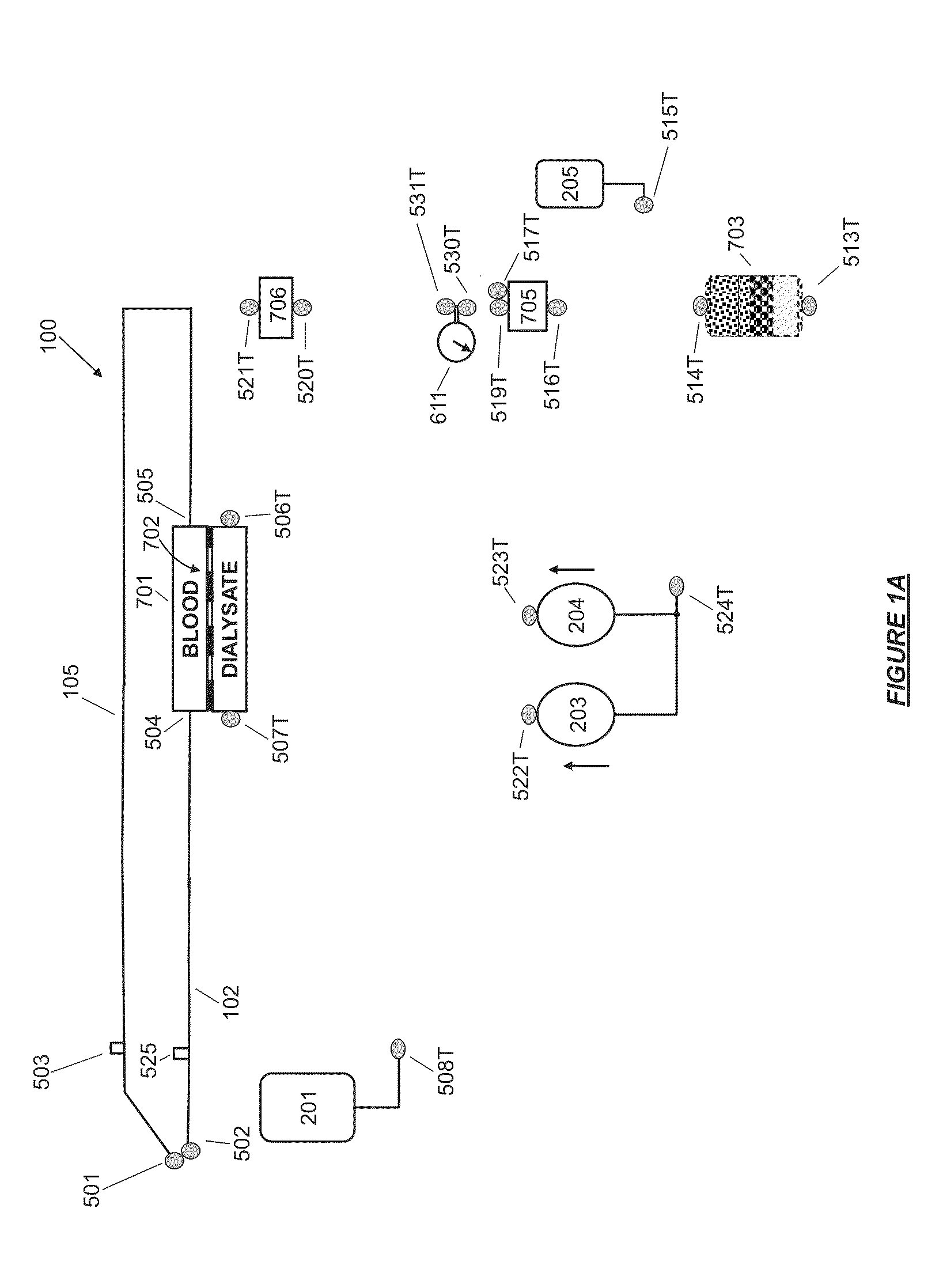
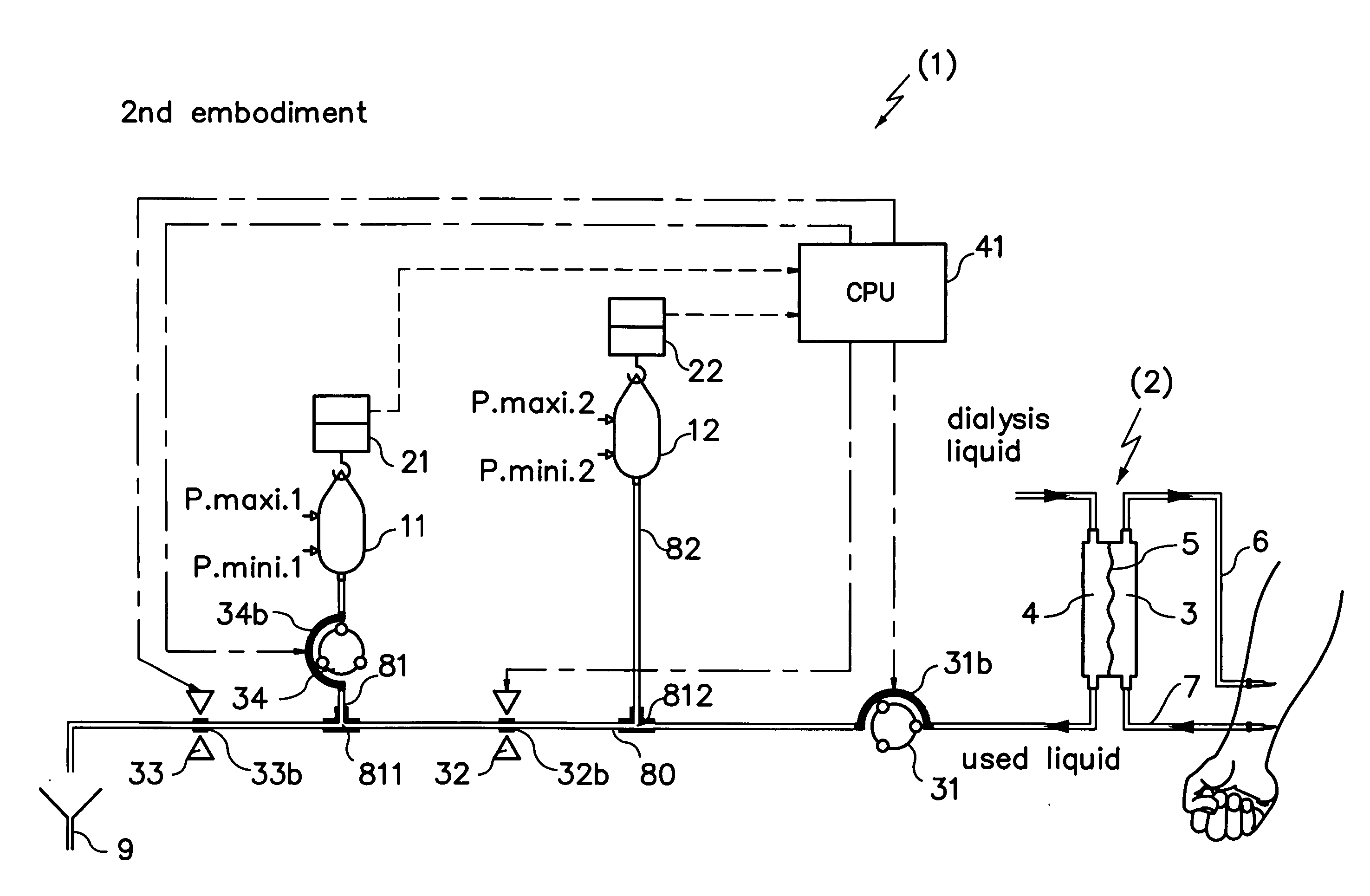
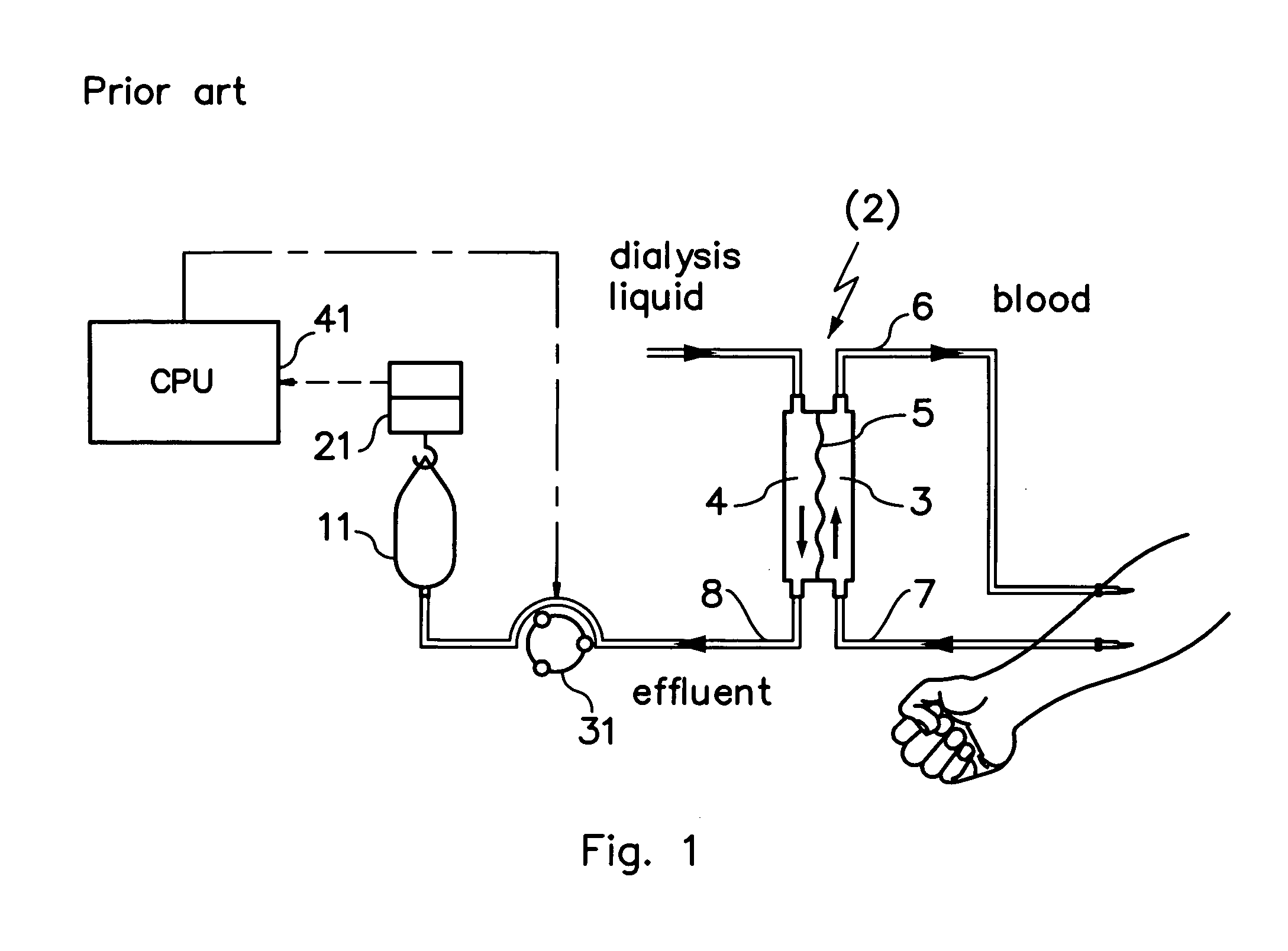
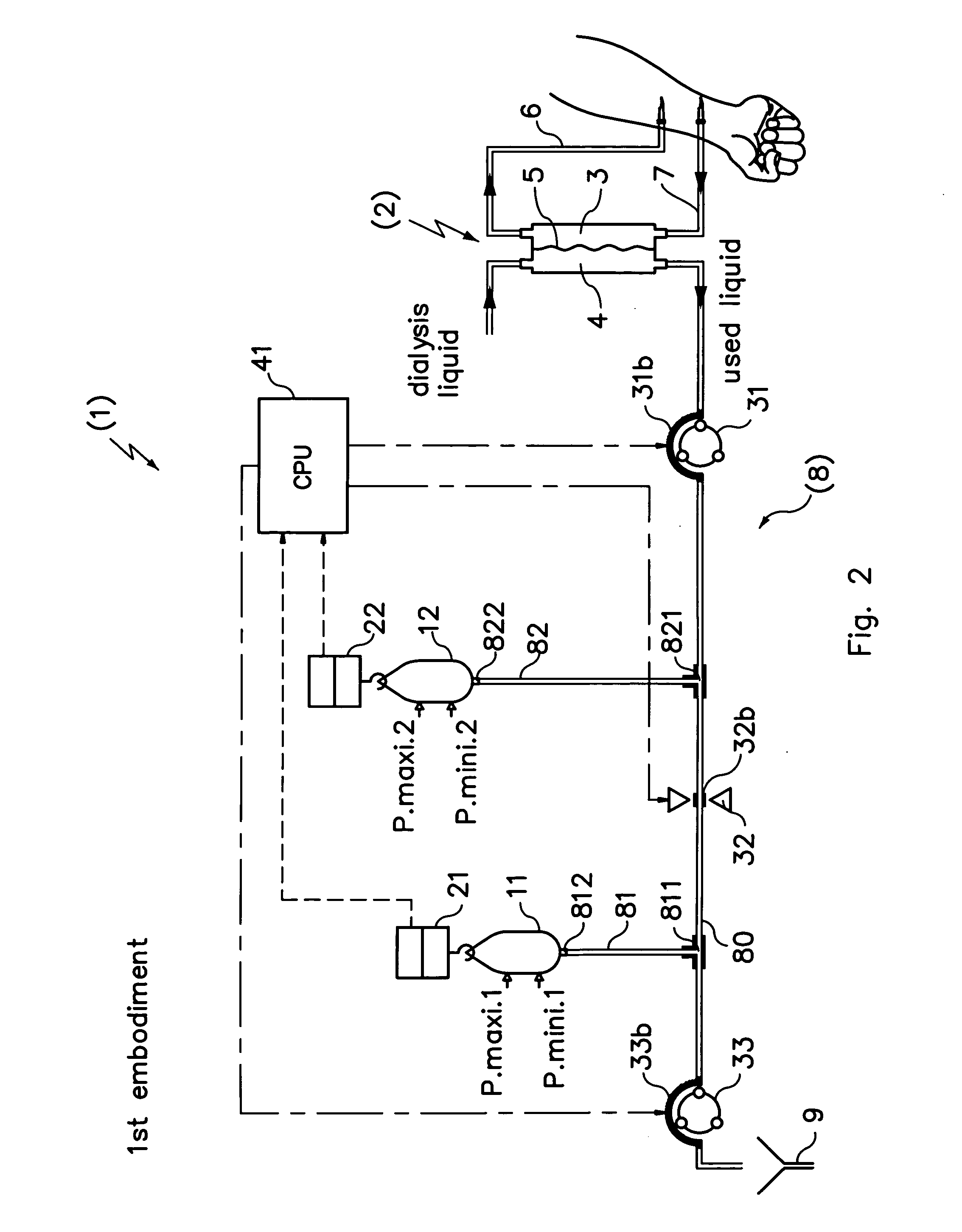
A blood purification device has a blood purification element divided into two chambers by a semipermeable membrane, with a first chamber as part of a dialysis fluid loop and a second chamber as part of an extracorporeal blood loop. By virtue of an analysis unit operatively connected to a sensor in the dialysis fluid loop, the device provides simple and uncomplicated determination of the blood purification performance of the blood purification element for a second material by derivation from a previously established blood purification performance for a first material. In this way, the device also determines the blood concentration of the second material during the blood treatment through measurements in the dialysis fluid without intervention in the treatment sequence.
Owner:FRESENIUS MEDICAL CARE DEUTSCHLAND GMBH
Process for producing composite semipermeable membrane
InactiveUS6521130B1Increase volumePromote hydrolysis reactionReverse osmosisWater/sewage treatment bu osmosis/dialysisPolymer sciencePolyamide
When forming a separating functional layer containing crosslinked polyamide, by carrying this out in the presence of 1) carboxylic acid ester with a total of 8 or more carbons, or 2) carboxylic acid, it is possible to provide a composite semipermeable membrane which, while still maintaining a high rejection rate, is more outstanding in its water permeability than hitherto.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Polymeric membranes incorporating nanotubes
InactiveUS20100206811A1Inhibition formationMaterial nanotechnologyMembranesSemipermeable membraneNanotube
The present invention relates to semipermeable membranes with nanotubes dispersed therein, and the methods of preparing the same.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Medical apparatus
ActiveUS20100312161A1Economical and simpleHigh level of electrical safetyOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationPlastic materialsBiomedical engineering
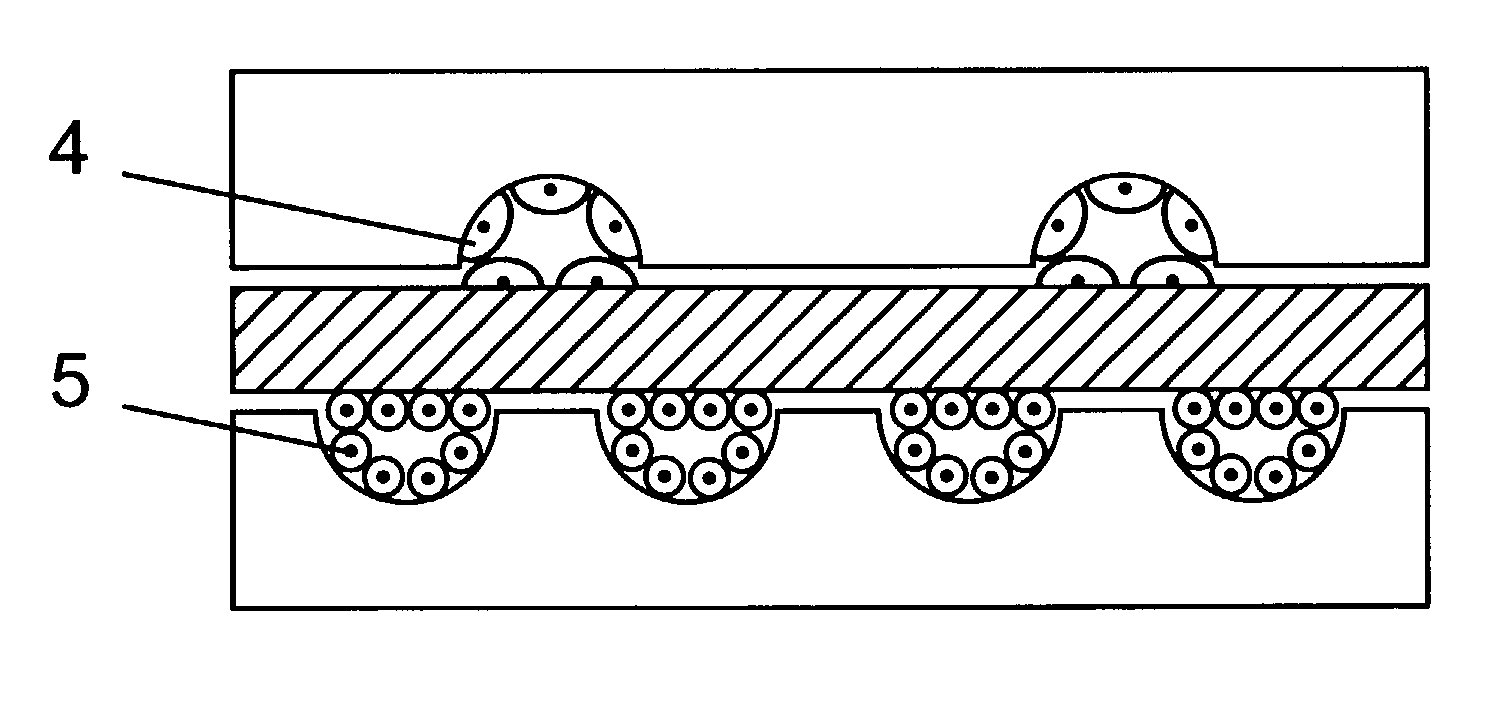
In a hemodiafiltration apparatus, a membrane device (2) comprises a blood chamber (3) and a fluid chamber (4) separated by a semipermeable membrane (5). A grounding device (17) is connected to the discharge line by means of a tubular connector (16) made of an electrically-conductive plastic material. The grounding device can disconnect the grounding connection if the leakage current measured on a patient (1) connected to the apparatus exceeds a predetermined value. The apparatus can be classified as Cardiac Floating and, at the same time, causes no disturbances to an electrocardiograph connected to the patient.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Systems and methods for multifunctional volumetric fluid control
Systems and methods for controlling fluid movement and volumes of fluid between a subject and a controlled compliant flow path. The controlled compliant flow path has a means for selectively metering in and metering out fluid from the controlled compliant flow path. An extracorporeal flow path is in fluid communication with the controlled compliant flow path across a semi-permeable membrane where the extracorporeal flow path has a first terminal end and a second terminal end.
Owner:MOZARC MEDICAL US LLC
Semimanufactured Waterproofed Products, Particularly Shoes, Clothing Items and Accessories
InactiveUS20080127426A1Improve adhesionPhysical treatmentInsolesWork in processBiomedical engineering
Owner:OUTDRY TECH
Composite semipermeable membrane and method for producing same
ActiveUS20120248027A1Improve performanceGood removal effectSemi-permeable membranesMembranesOrganic solventPolyamide
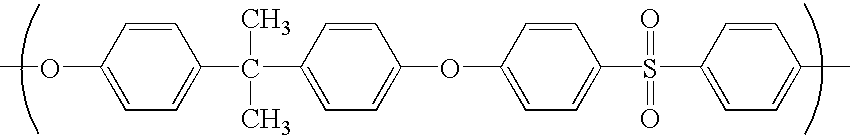
A composite semipermeable membrane comprising a porous support membrane on which a separating functional polyamide layer resulting from the polycondensation reaction of polyfunctional aromatic amines with polyfunctional acid halides is formed, wherein the separating functional polyamide layer has carboxy groups, amino groups, phenolic hydroxyl groups, and azo groups, wherein XA, the ratio of the amino groups (molar equivalent of the amino groups / (molar equivalent of the azo groups+molar equivalent of the phenolic hydroxyl groups+molar equivalent of the amino groups)) on a feed water contact surface of the separating functional polyamide layer (an A surface), is in the range 0.5 or less, and XB, the ratio of the amino groups (molar equivalent of the amino groups / (molar equivalent of the azo groups+molar equivalent of the phenolic hydroxyl groups+molar equivalent of the amino groups)) on a permeate-side surface of the separating functional polyamide layer (a B surface), i.e., the opposite side to the A surface, is in the range of 0.5 to 1. The present invention provides a composite semipermeable membrane that achieves a balance between high solute removal properties and a high permeate flow rate and has high organic-solvent resistance, and a method for producing same.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
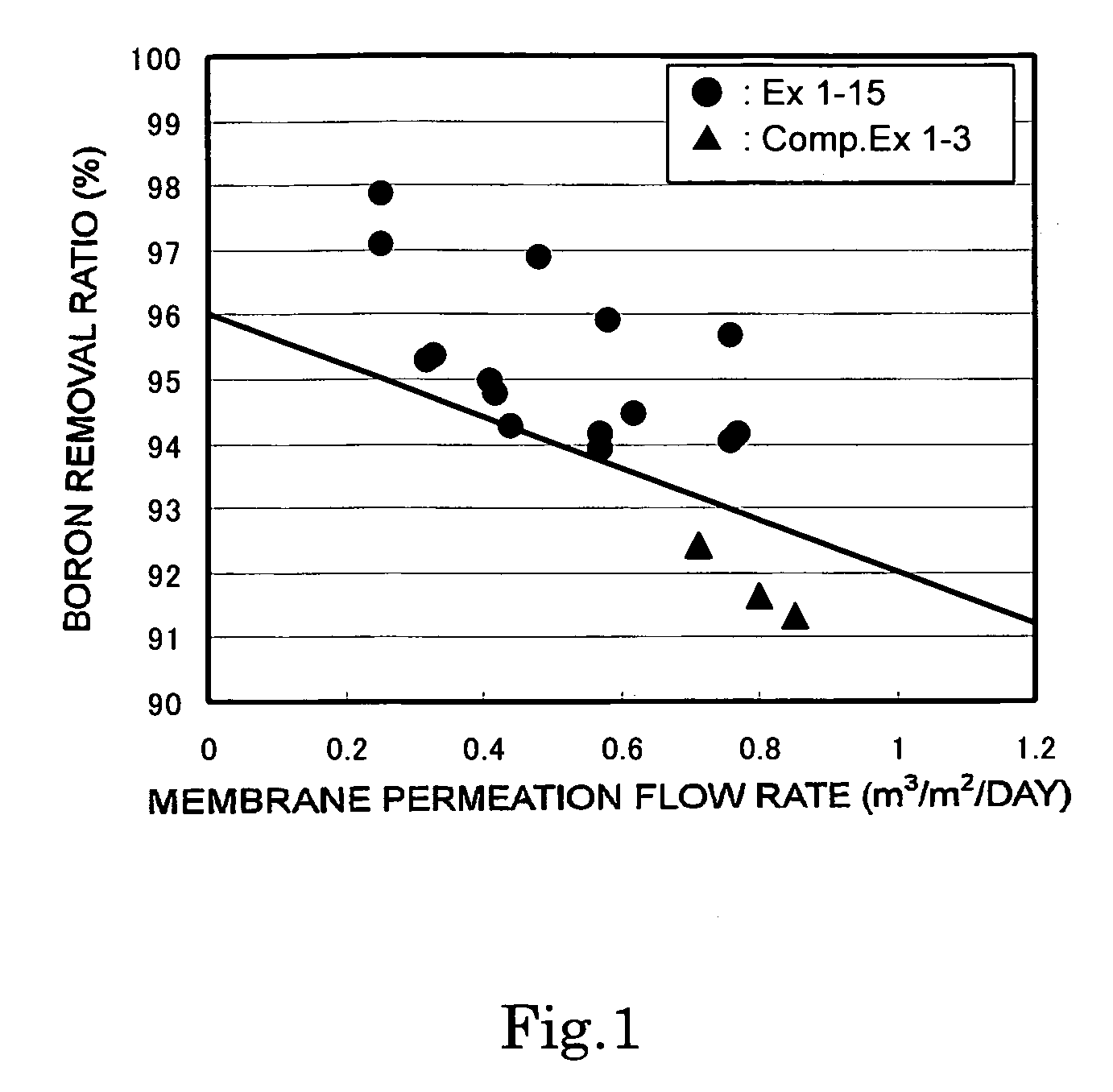
Composite semipermeable membrane, and production process thereof
InactiveUS7279097B2High desalination rateImprove performanceMembranesGeneral water supply conservationSemipermeable membranePermeation
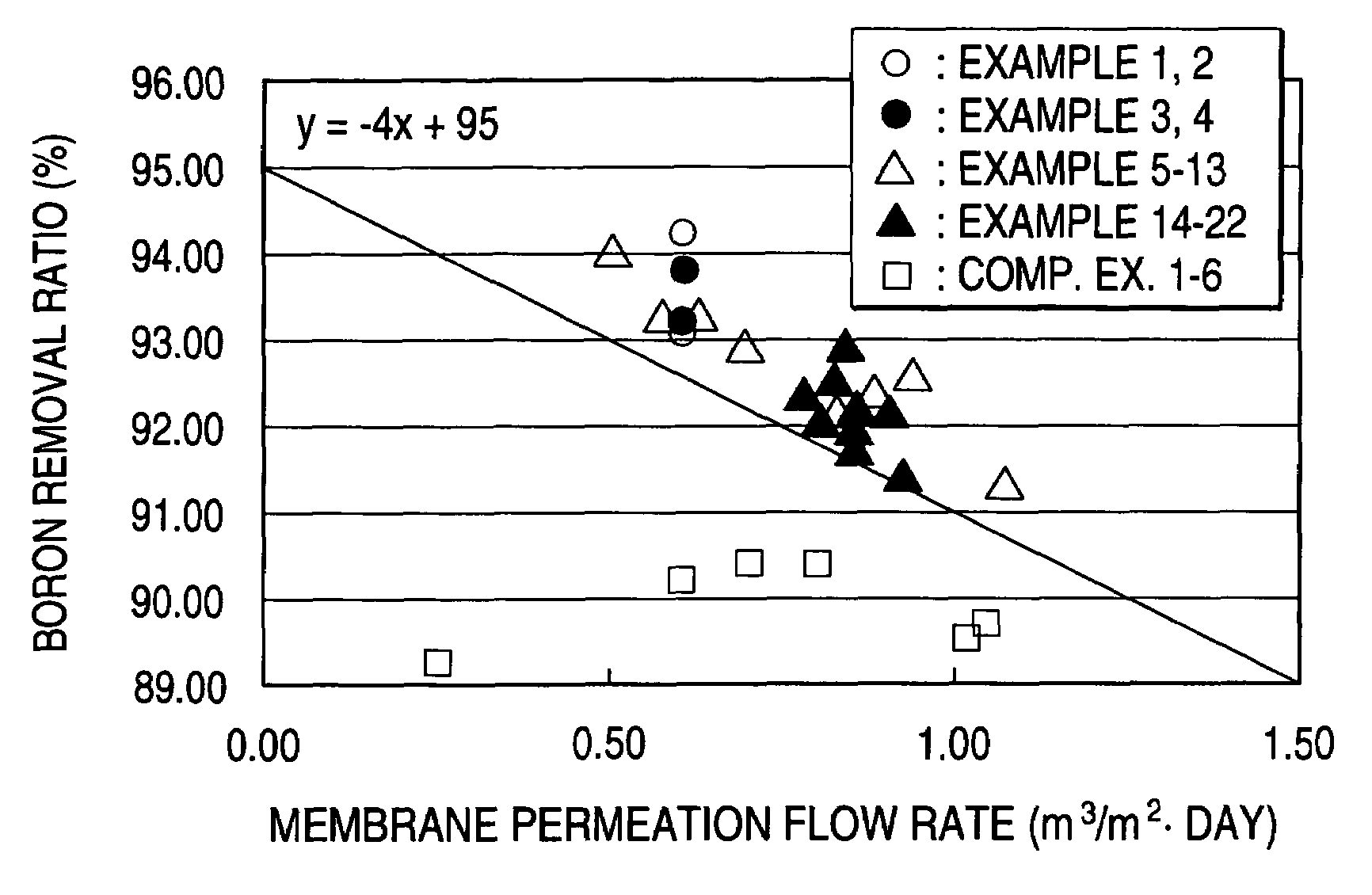
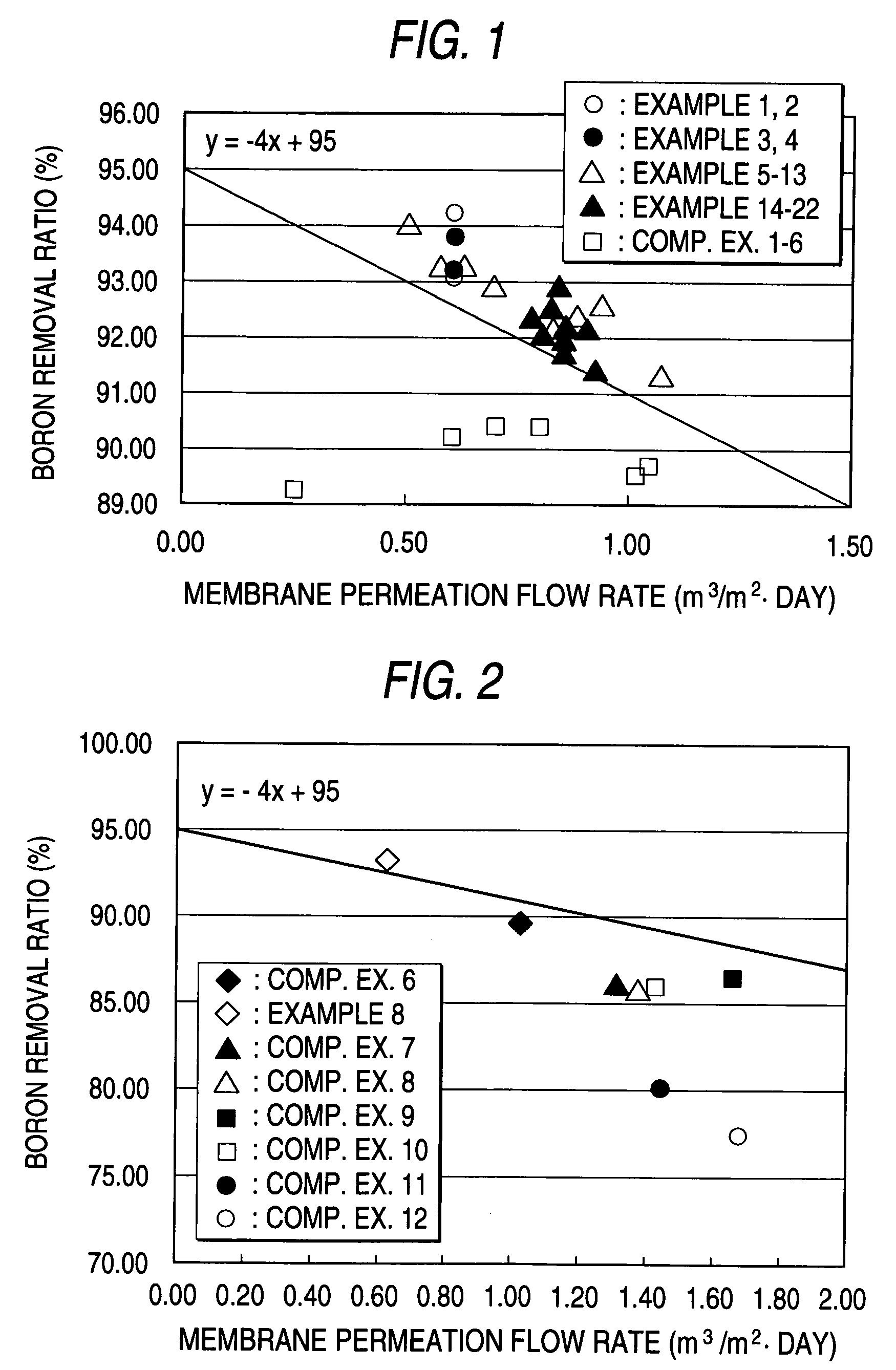
A composite semipermeable membrane which satisfies the following relationship when seawater at 25° C. having a pH of 6.5, a boron concentration of 5 ppm and a TDS concentration of 3.5% by weight is permeated under an operation pressure of 5.5 MPa: Boron removal ratio (%)≧95−4×membrane permeation flow rate (m3 / m2·day).
Owner:TORAY IND INC
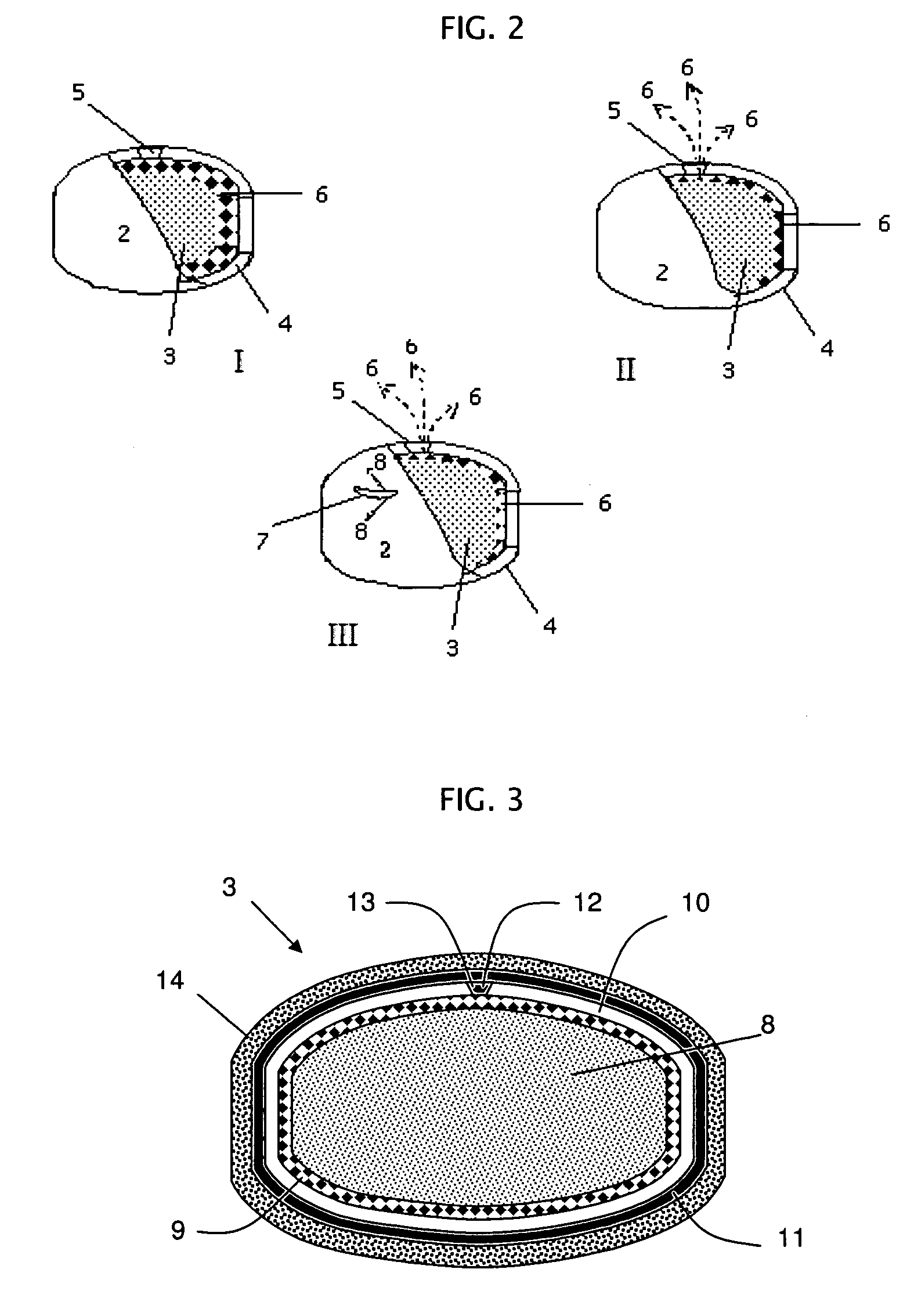
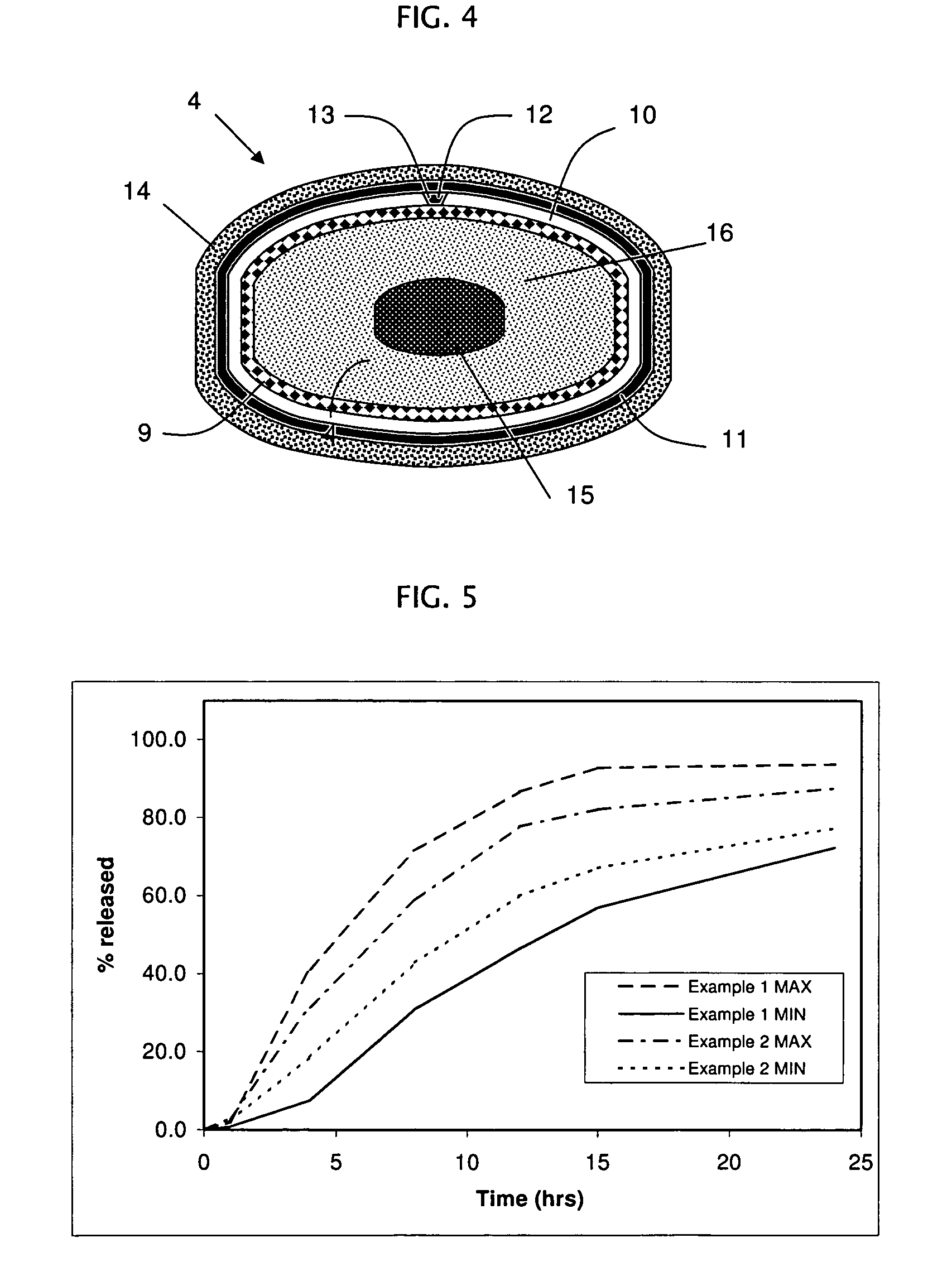
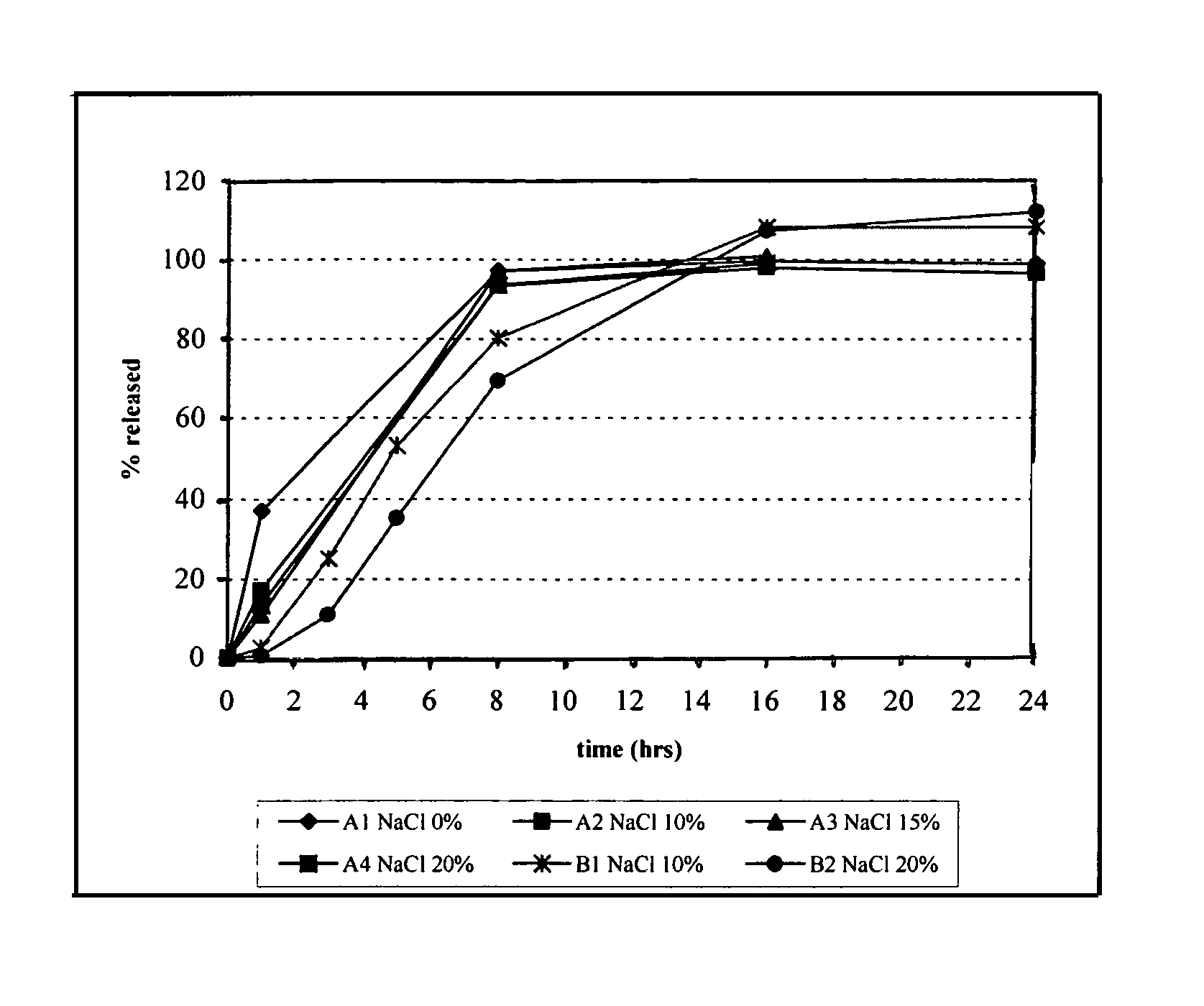
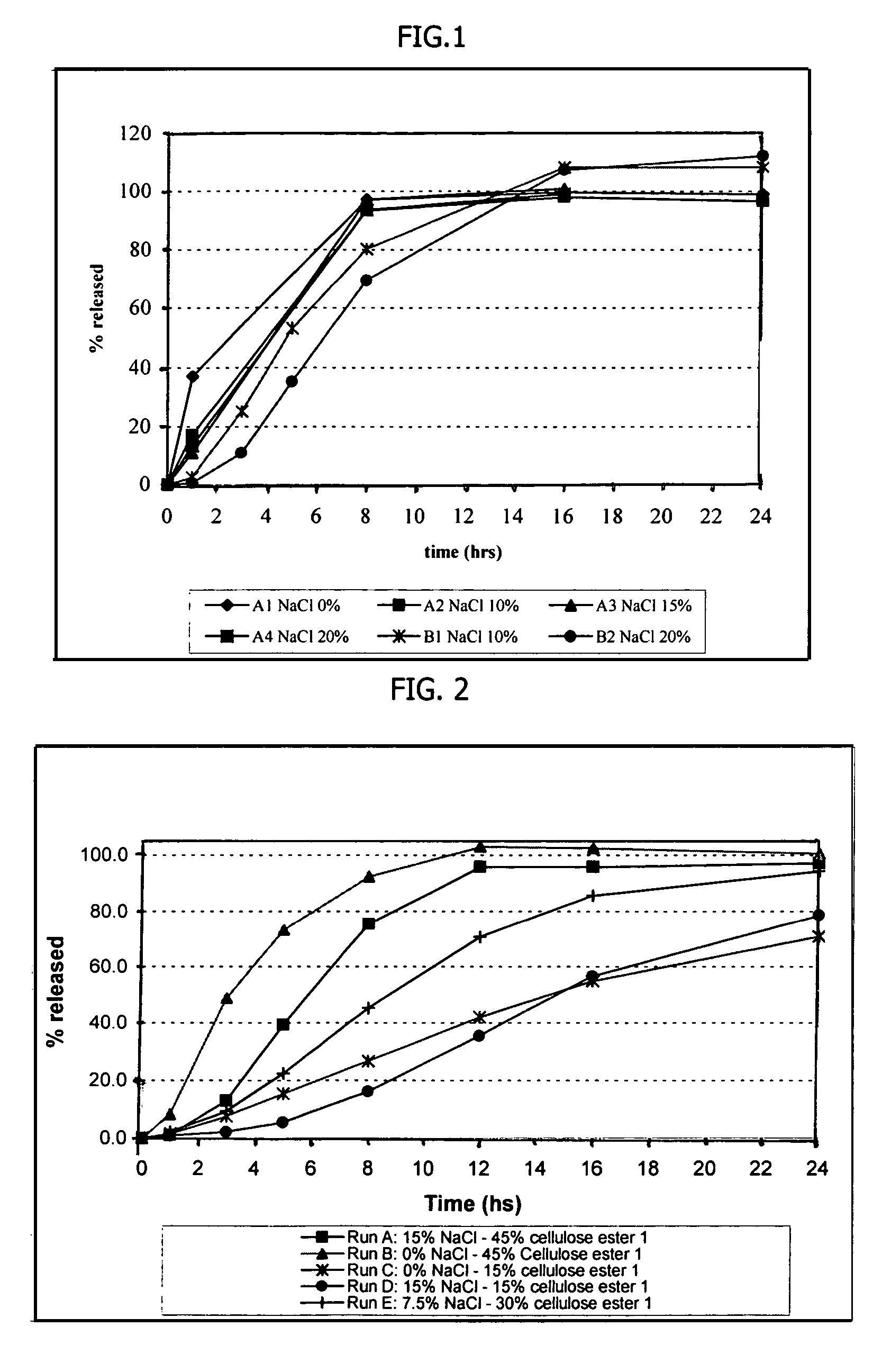
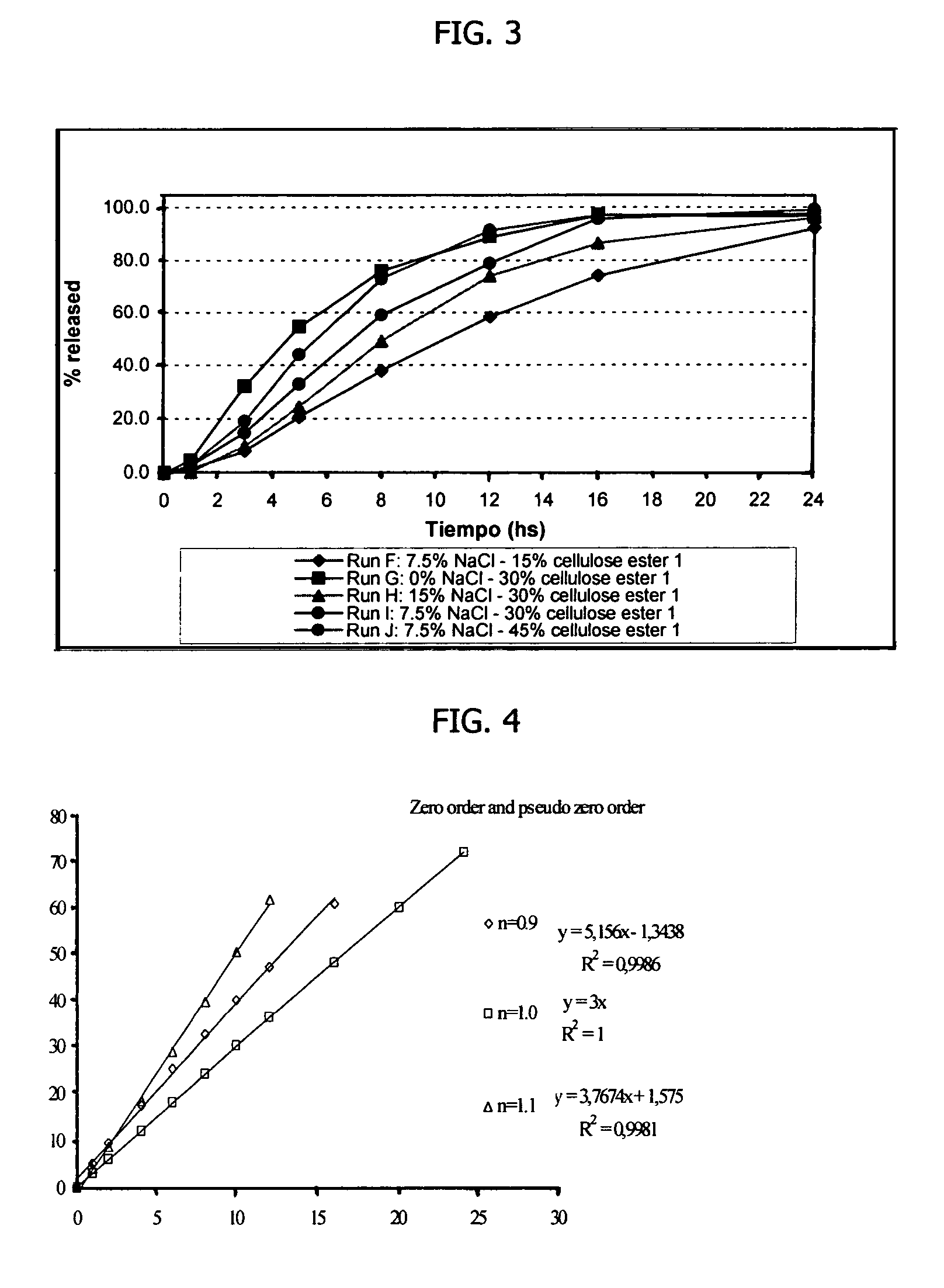
Rupturing controlled release device comprising a subcoat
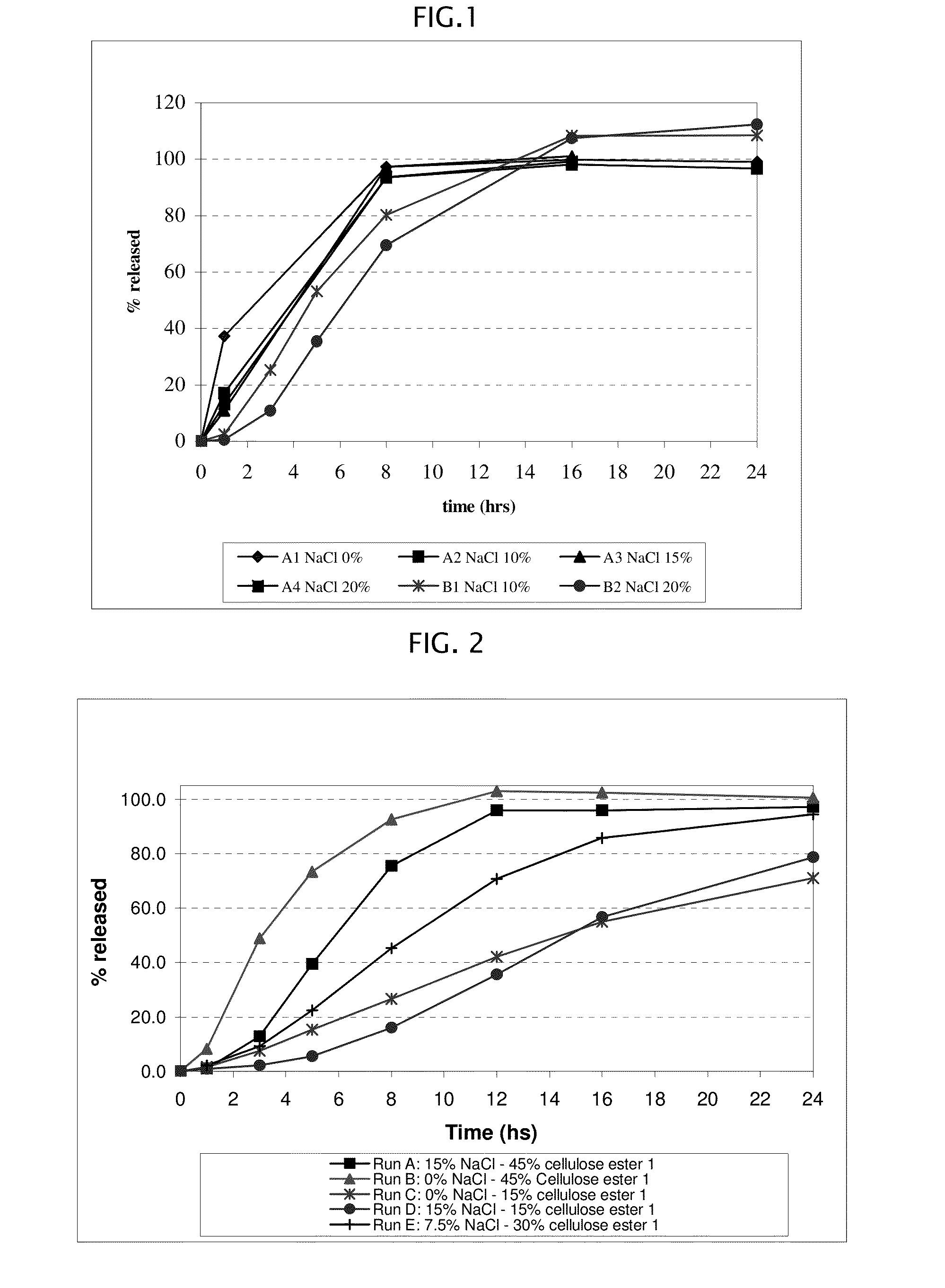
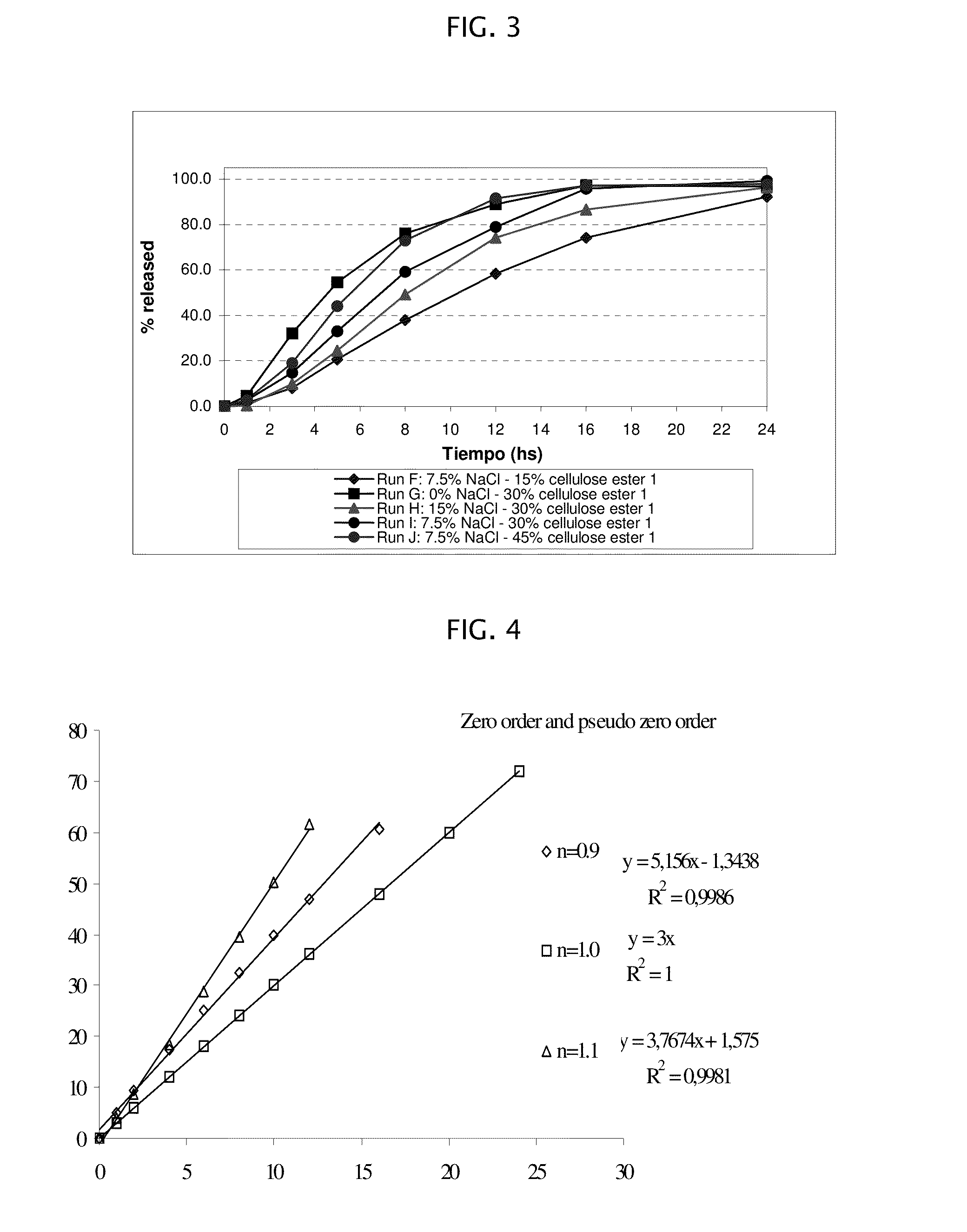
ActiveUS20090004229A1Low variabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsControlled releaseActive agent
The present invention provides a simple and improved rupturing controlled release device that is capable of providing a controlled release of active agent contained in the core first through a preformed passageway and then through an in situ formed second passageway into an environment of use in a standardized release profile manner. The rupturing controlled release device comprises a core comprising at least one drug and at least one osmopolymer, a semipermeable membrane enclosing the core and having at least one preformed passageway there through, wherein the semipermeable membrane ruptures during use to form a second passageway in the semipermeable membrane at a location spaced away from the preformed passageway, and a release-controlling subcoat between the core and the semipermeable membrane.
Owner:OSMOTICA KERESKEDELMI & SZOLGALTATO +1
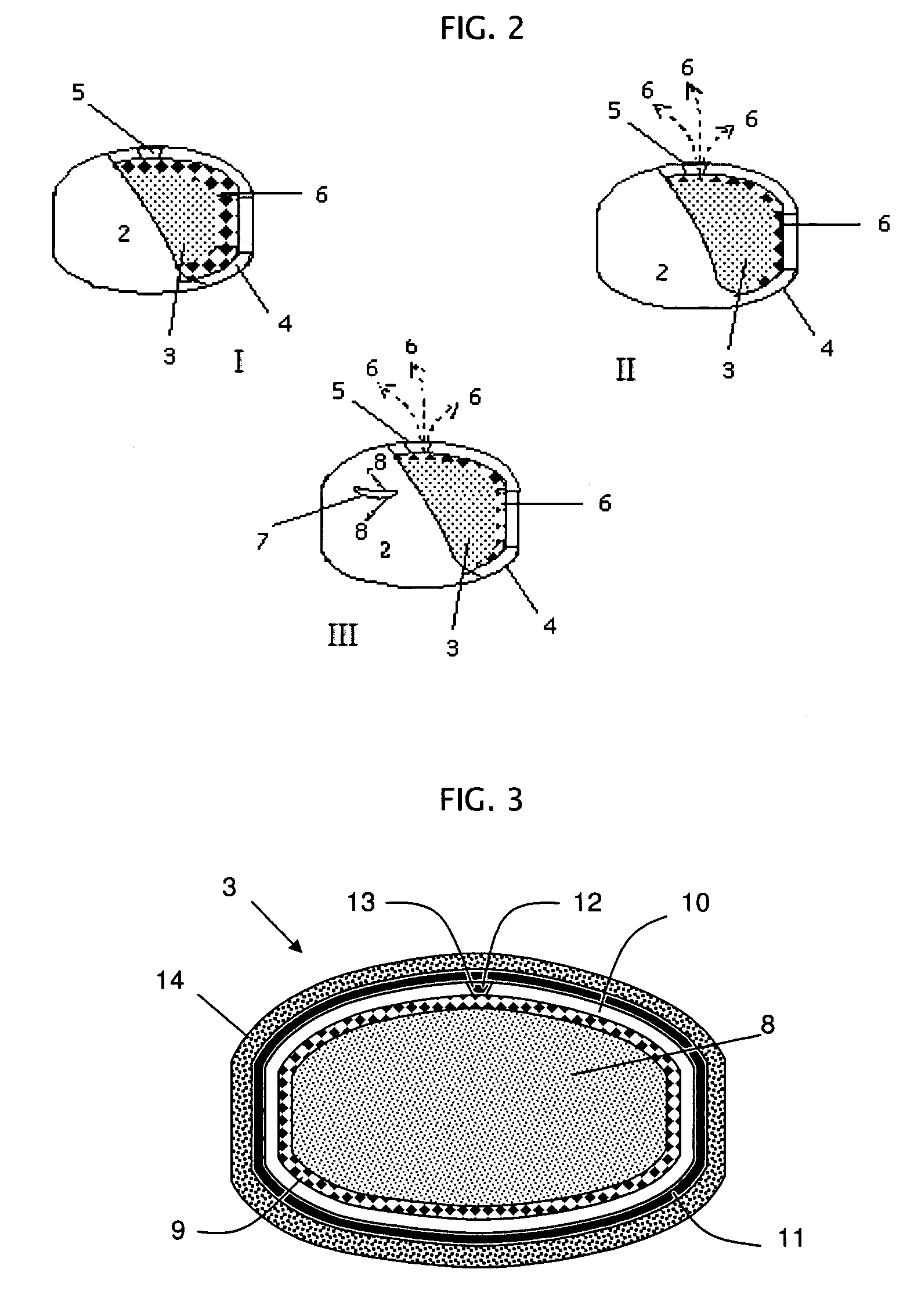
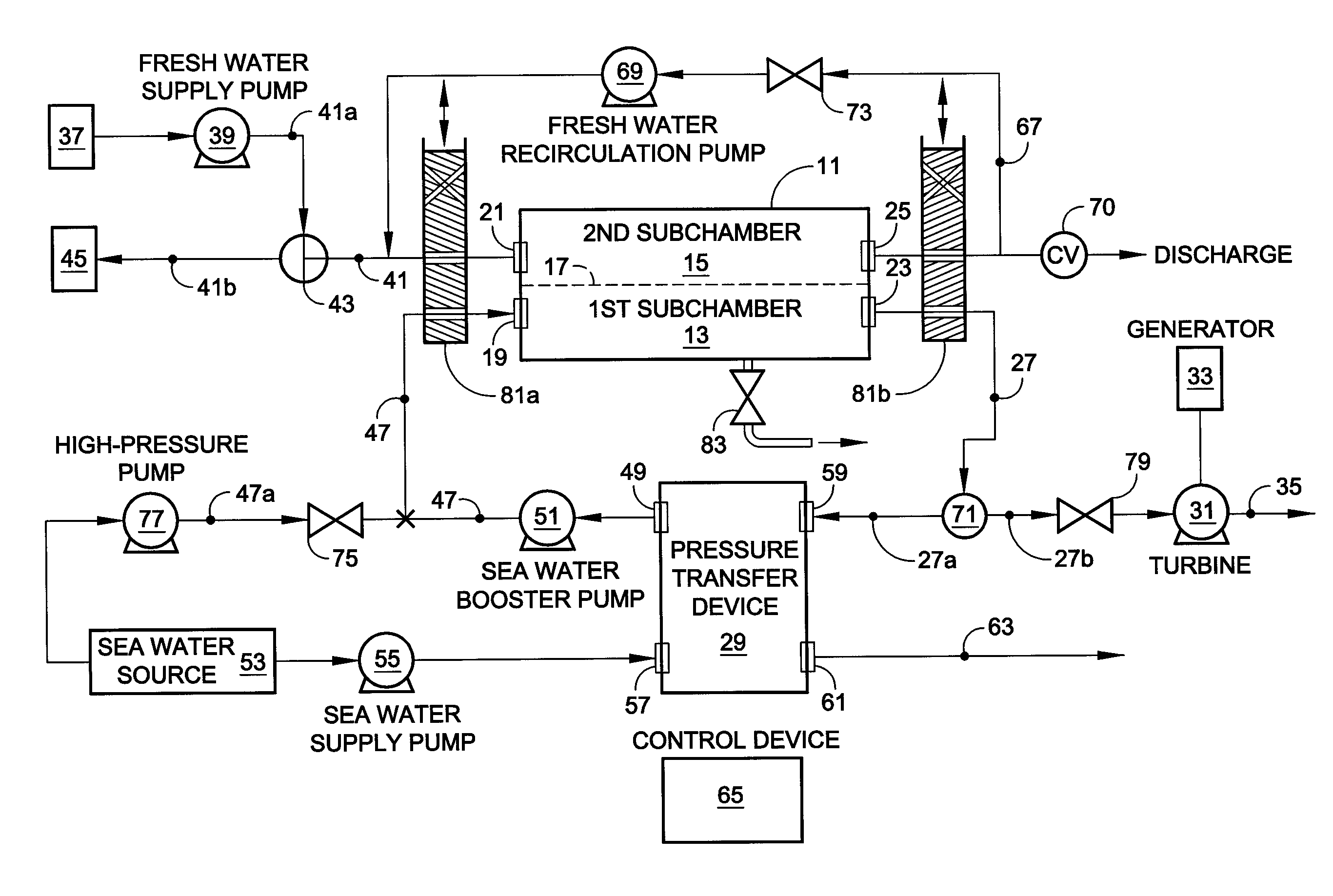
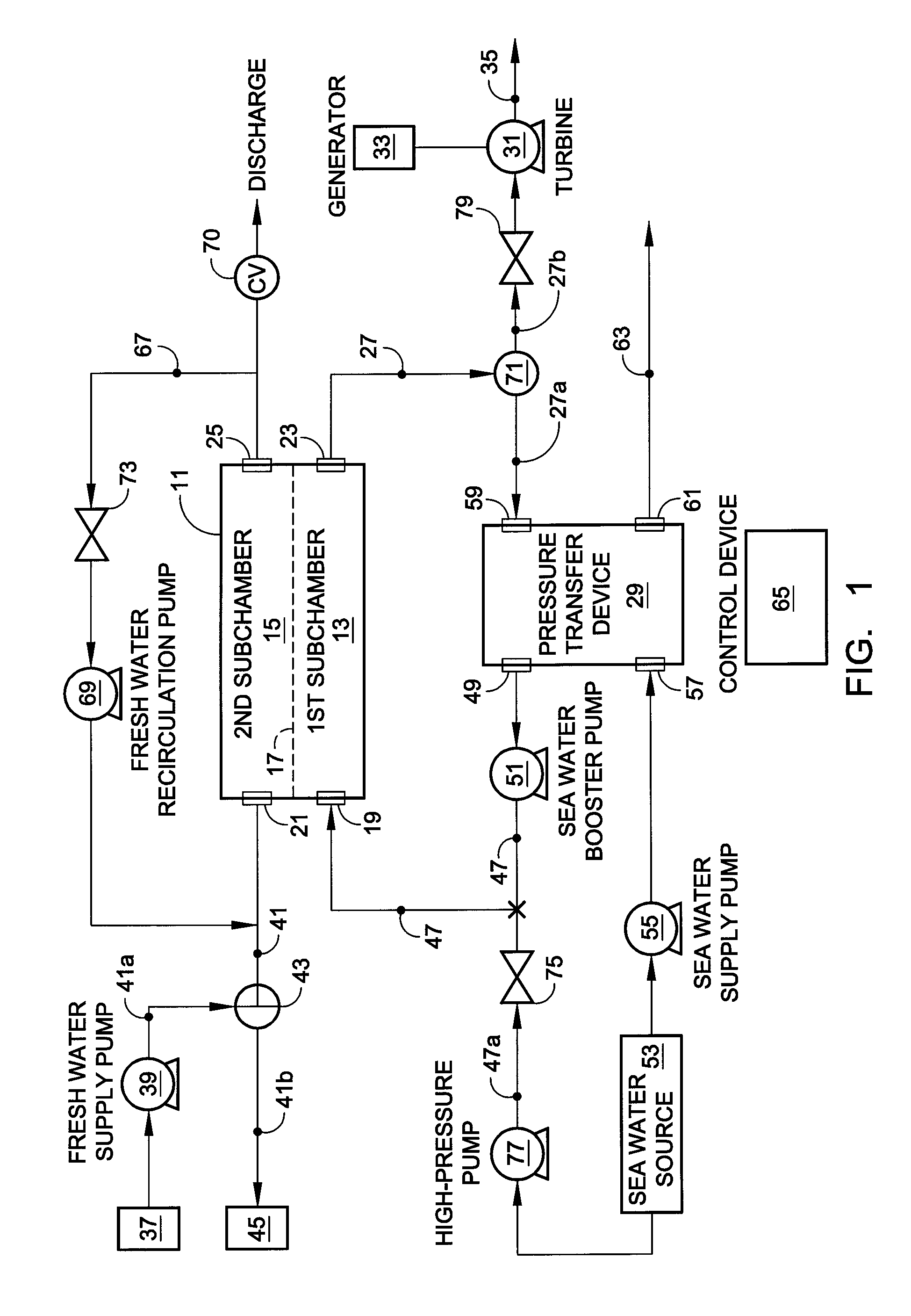
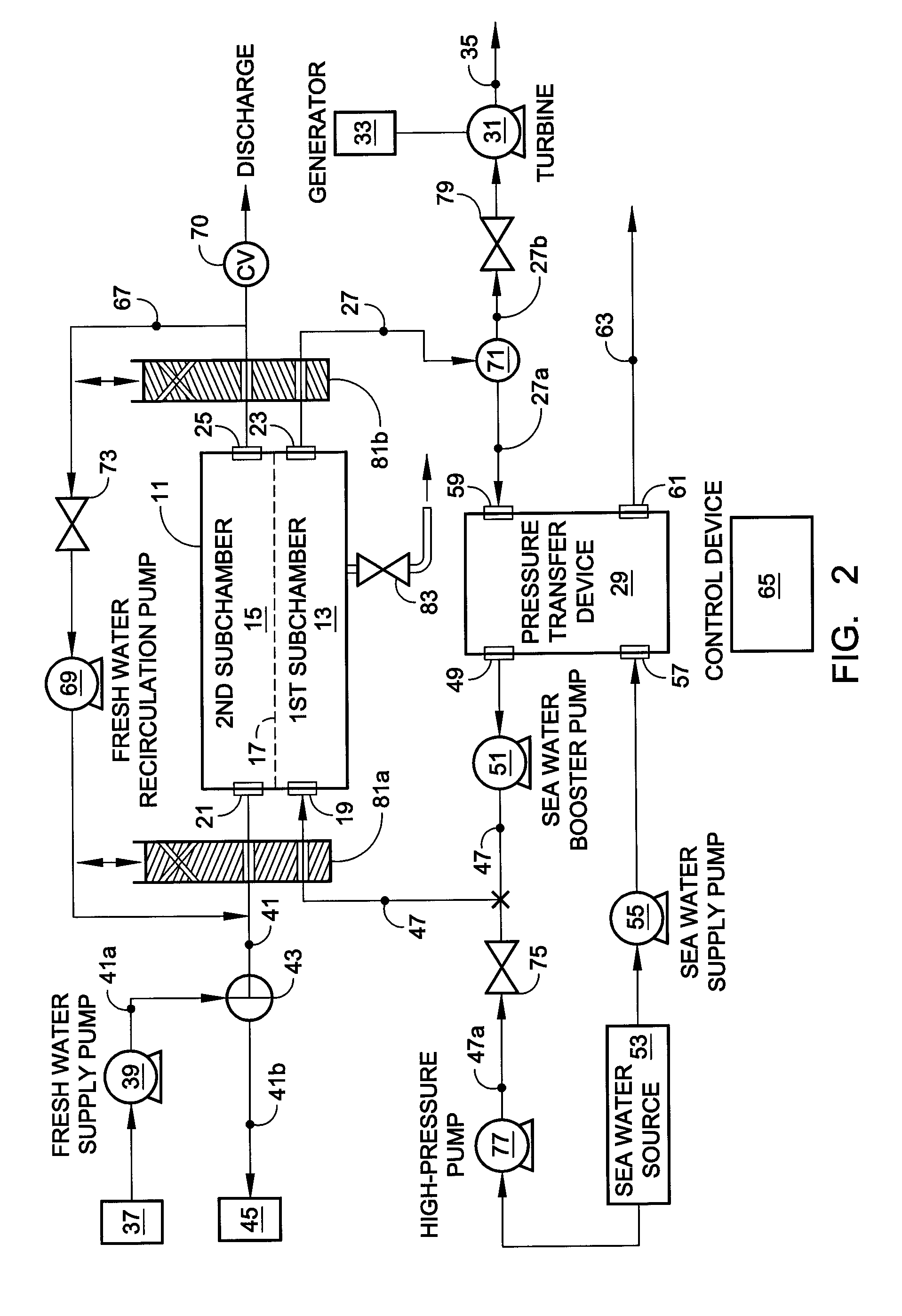
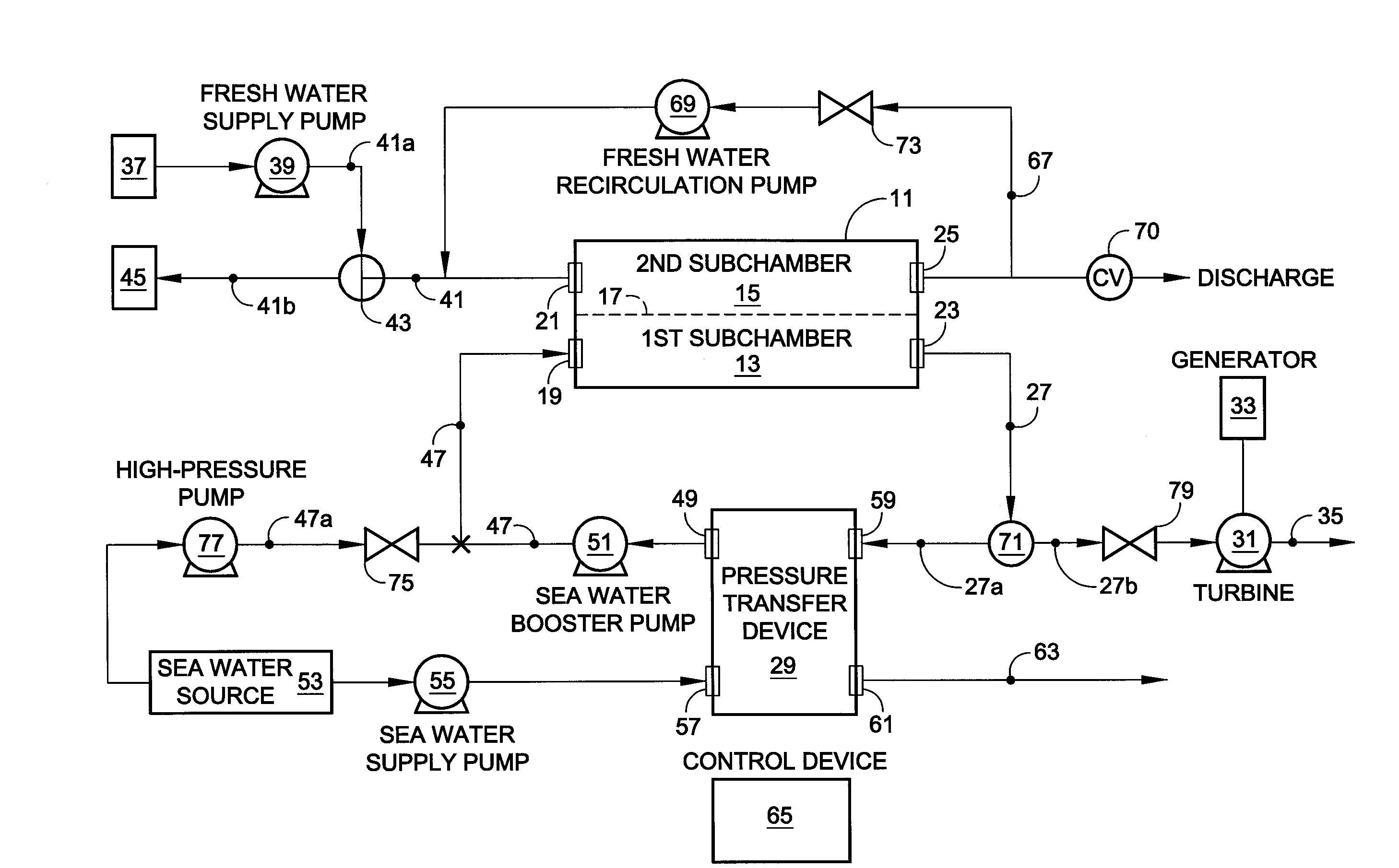
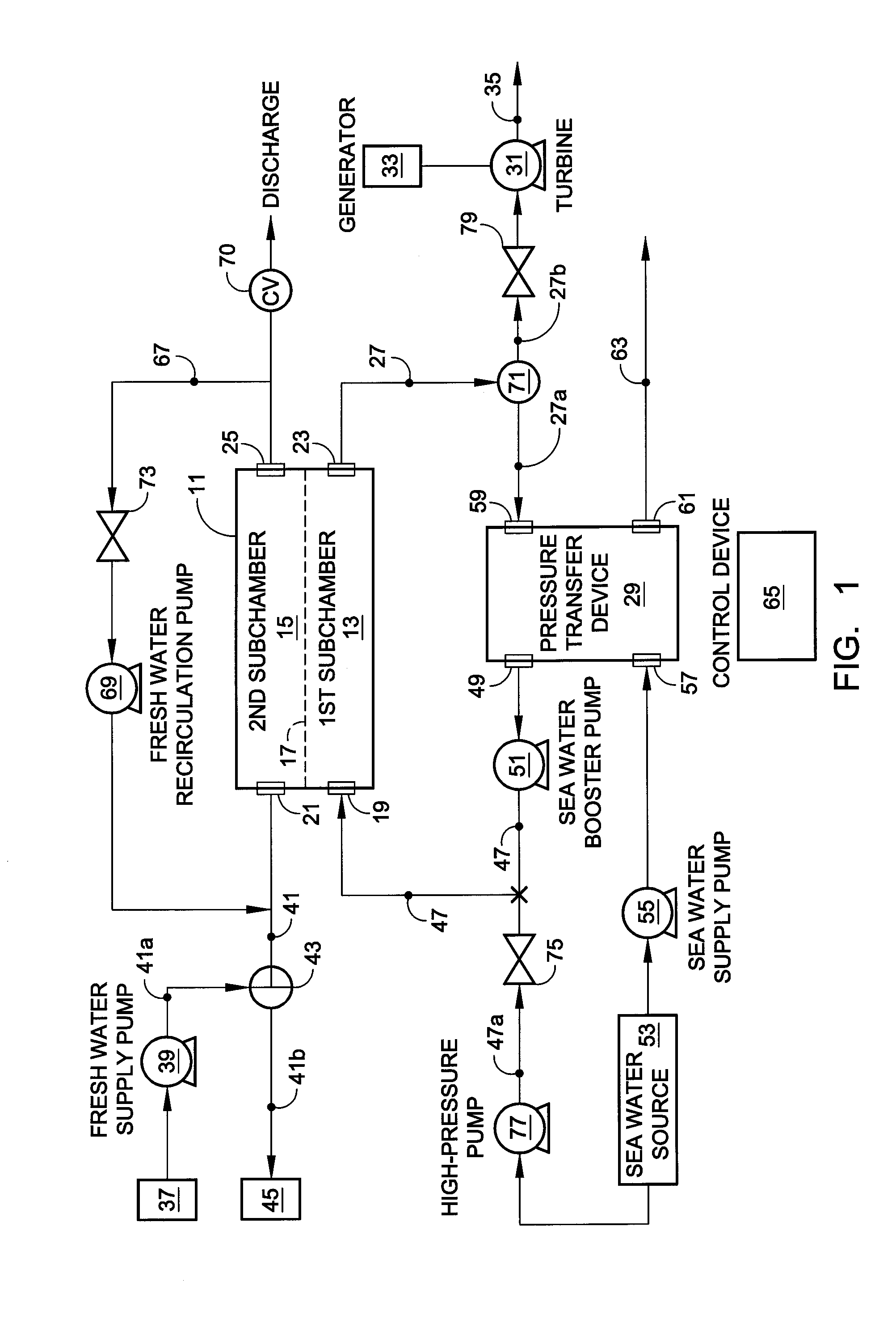
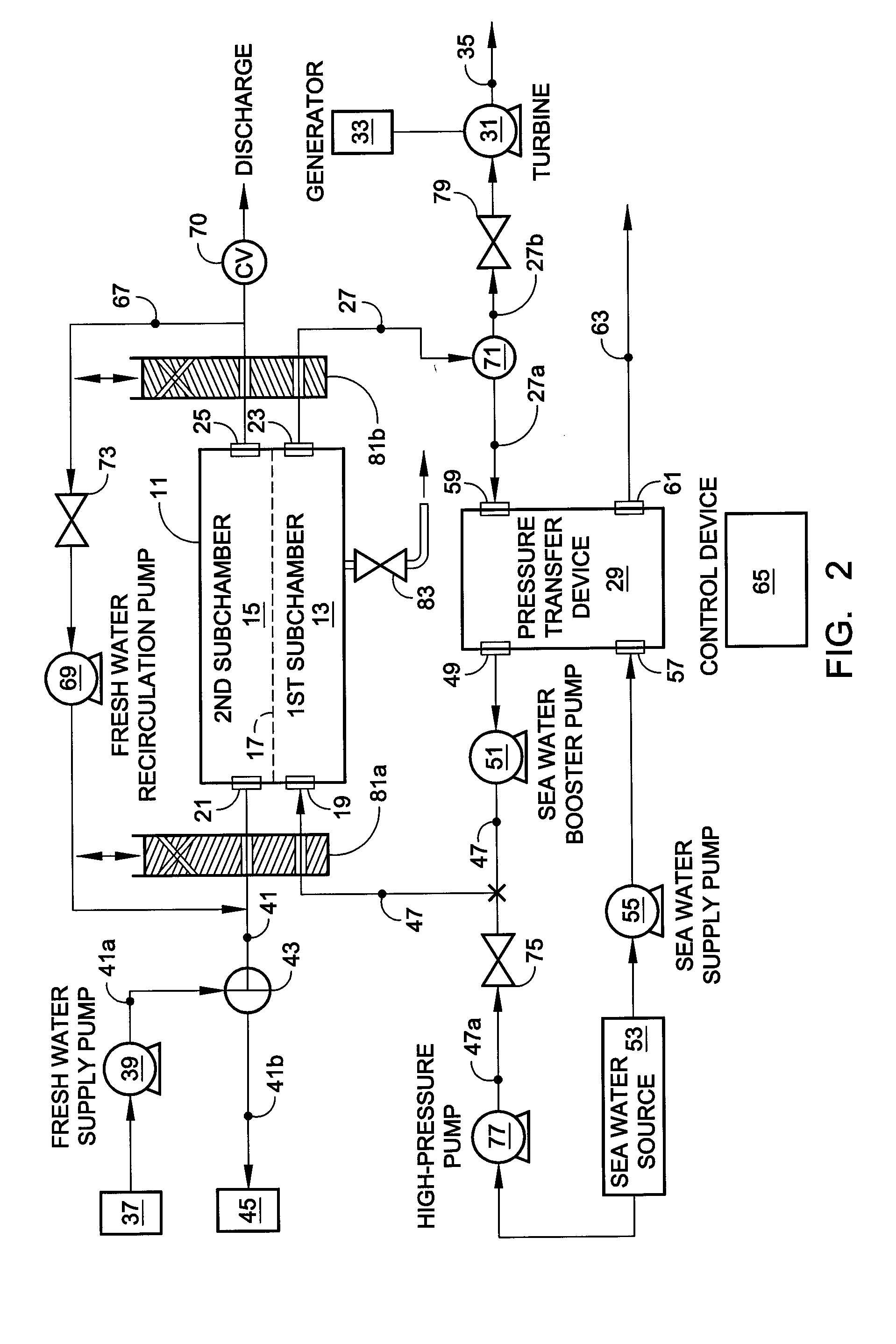
Hybrid RO/PRO system
ActiveUS7871522B2Easy to controlEfficientlyGeneral water supply conservationSolvent extractionSystems designAqueous solution
A system which includes a separation element (11) employing semipermeable membrane material (17), which system is designed so that it can operate either in an RO mode to produce high quality water or in a PRO mode to generate power from two aqueous solutions of different salt concentrations. In a preferred embodiment, a rotary pressure transfer device (29) is included to transfer pressure from an outlet stream exiting the separation element to an inlet stream being supplied to the separation element.
Owner:ENERGY RECOVERY INC
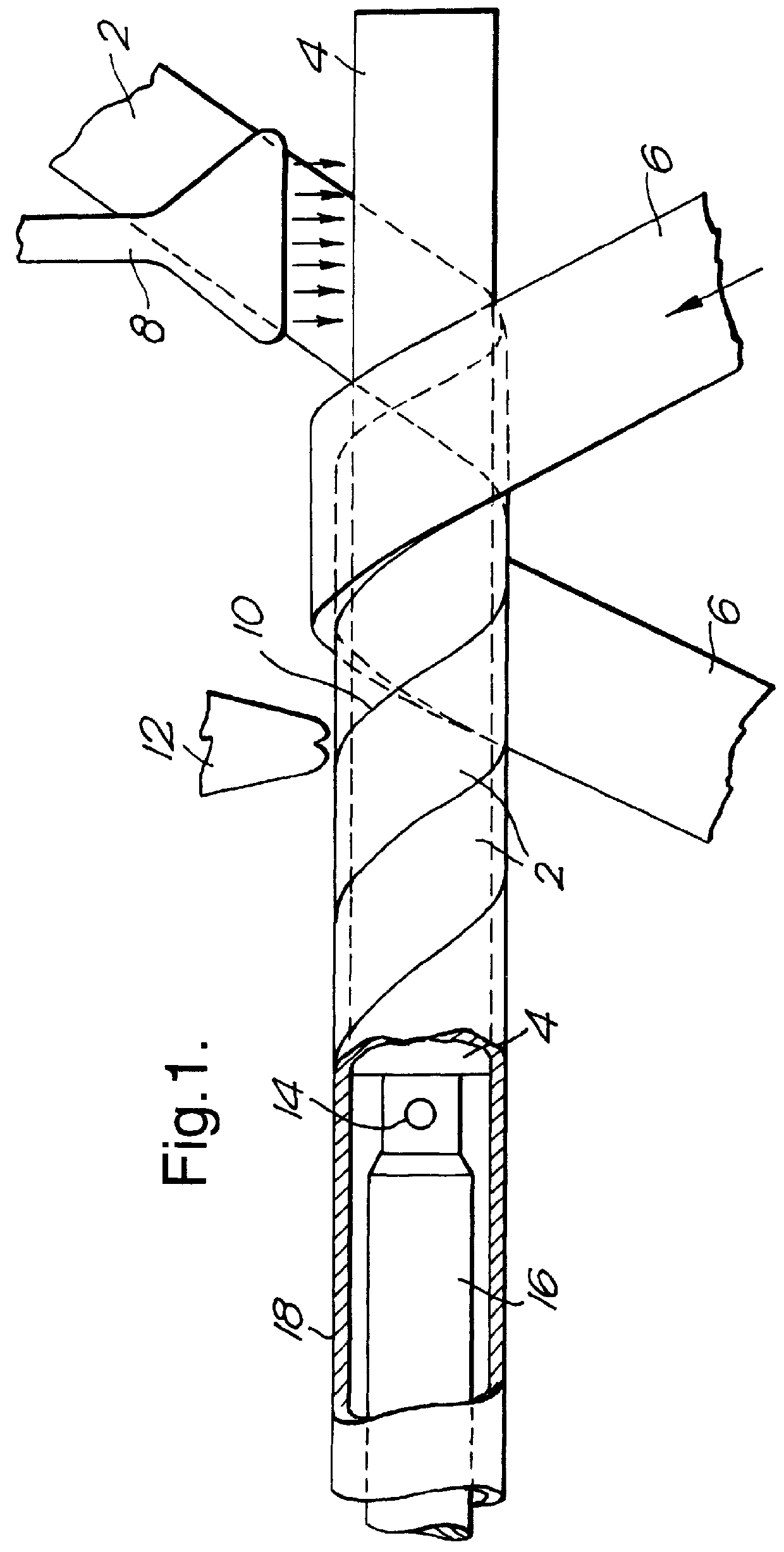
Process for producing a tubular membrane assembly
InactiveUS6077376ALow selectivityMinimizes problemSemi-permeable membranesPaper/cardboard wound articlesFiberSemipermeable membrane
The invention provides a process for producing a tubular membrane assembly comprising helically winding at least one strip of fibrous material on a mandrel to produce at least a single ply tubular support member for a semi-permeable membrane, characterized by passing the strip through a heated section of the mandrel during the helical winding thereof to flatten and smooth fibers protruding along the cross-sectional width of the strip, whereby a tube with a smooth inner bore along its entire length is formed.
Owner:MEMBRANE PRODS KIRYAT WEIZMANN
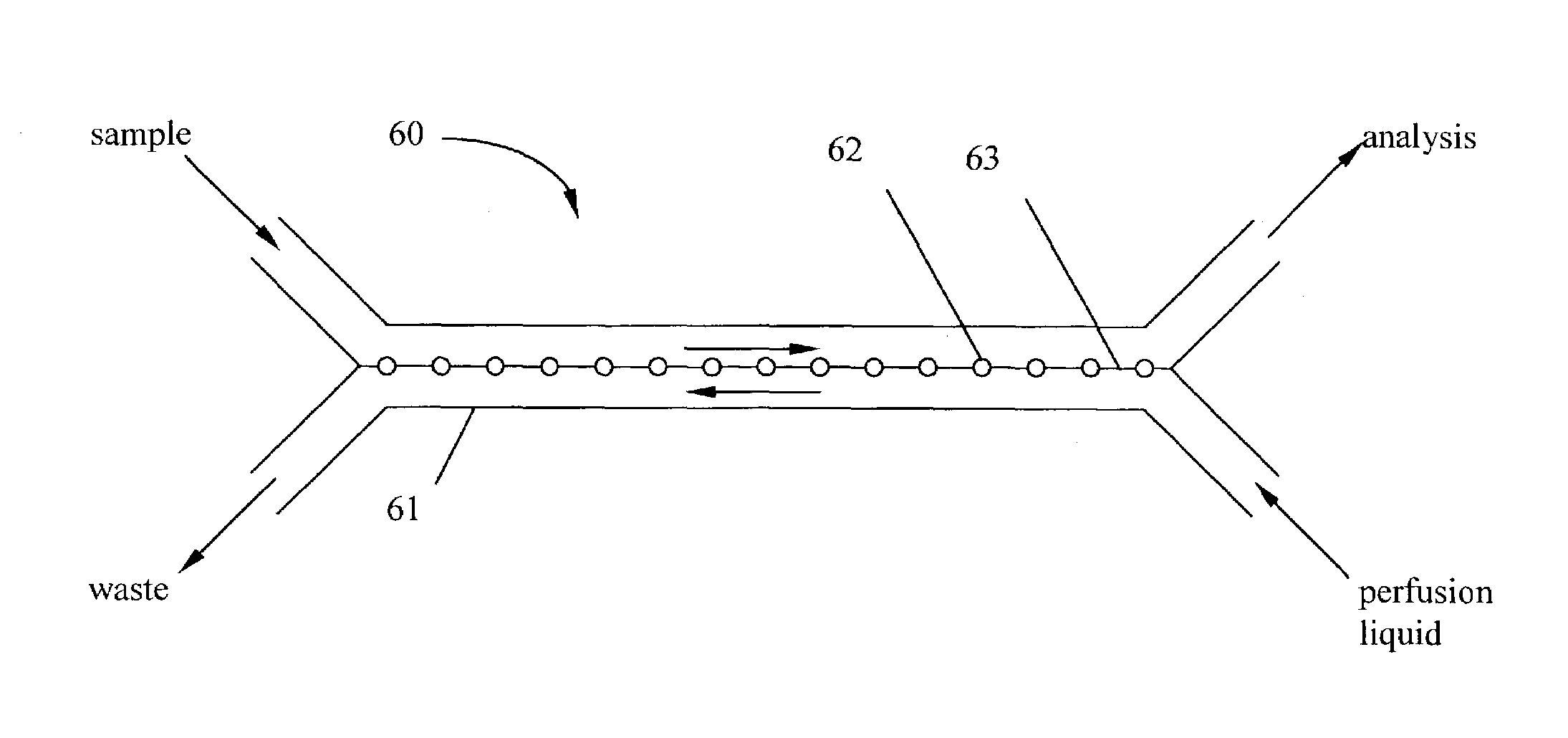
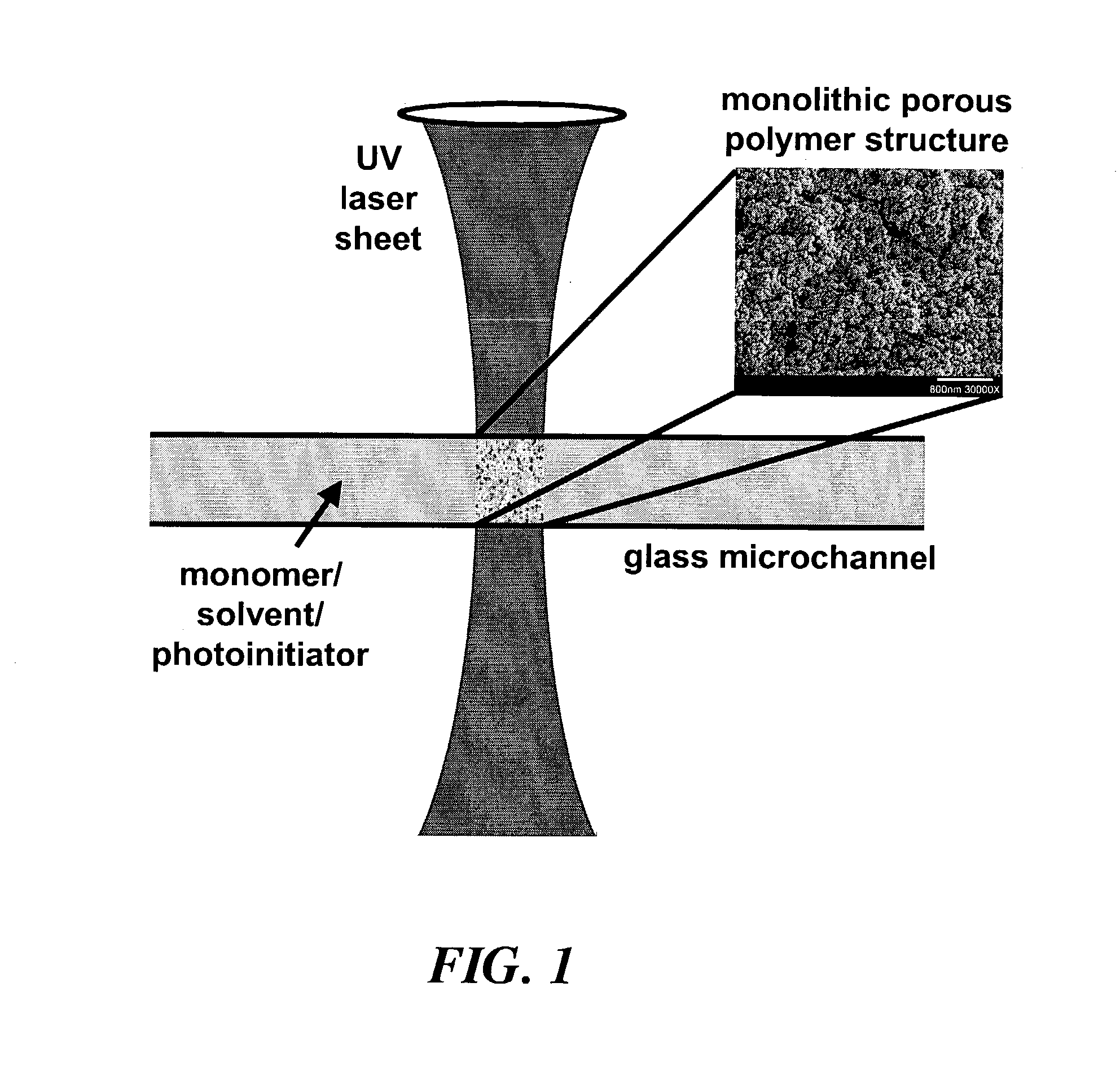
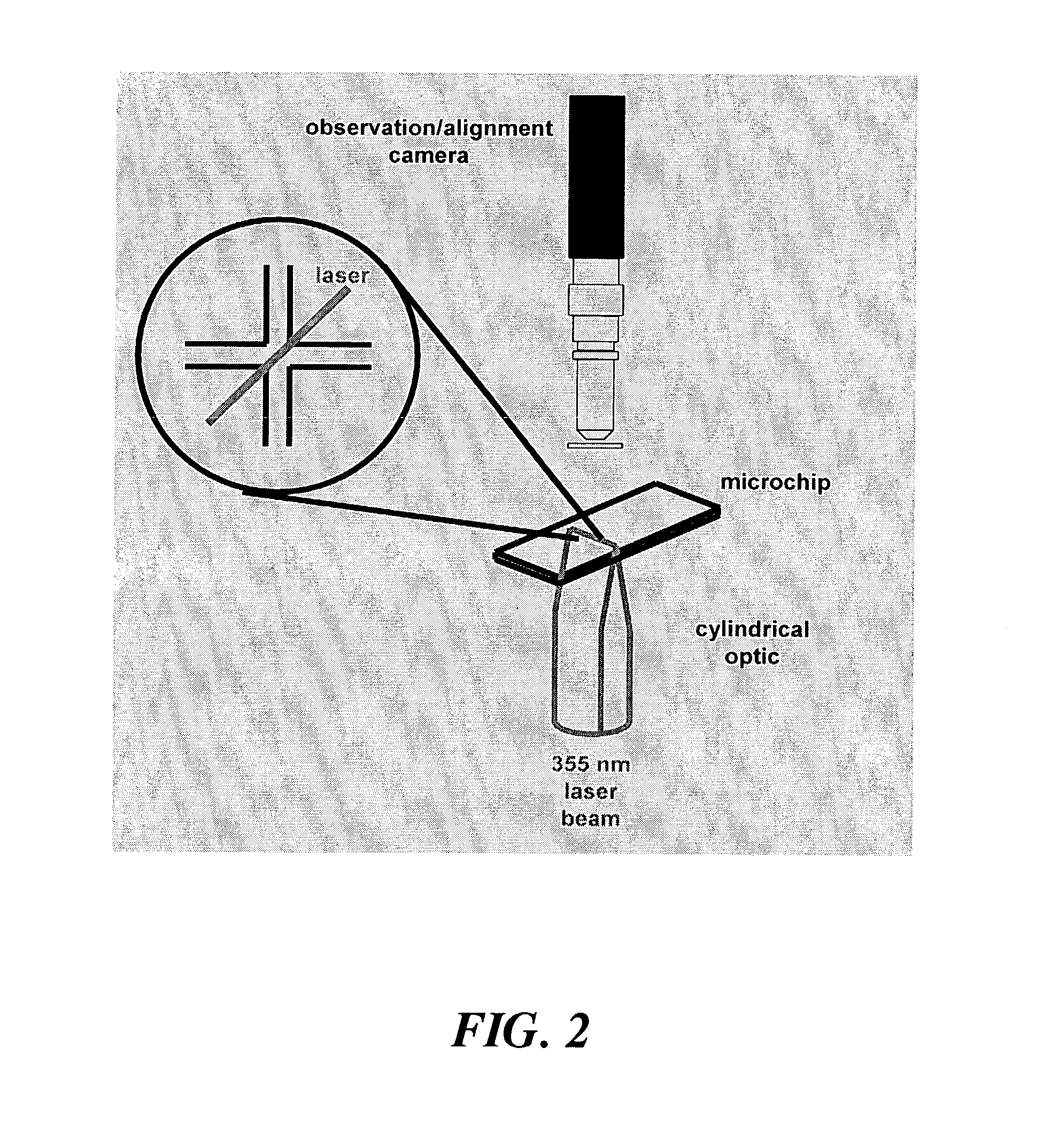
Dialysis on microchips using thin porous polymer membranes
ActiveUS7264723B2Minimize handlingComplicated operationSolvent extractionTransportation and packagingDialysis membranesMeth-
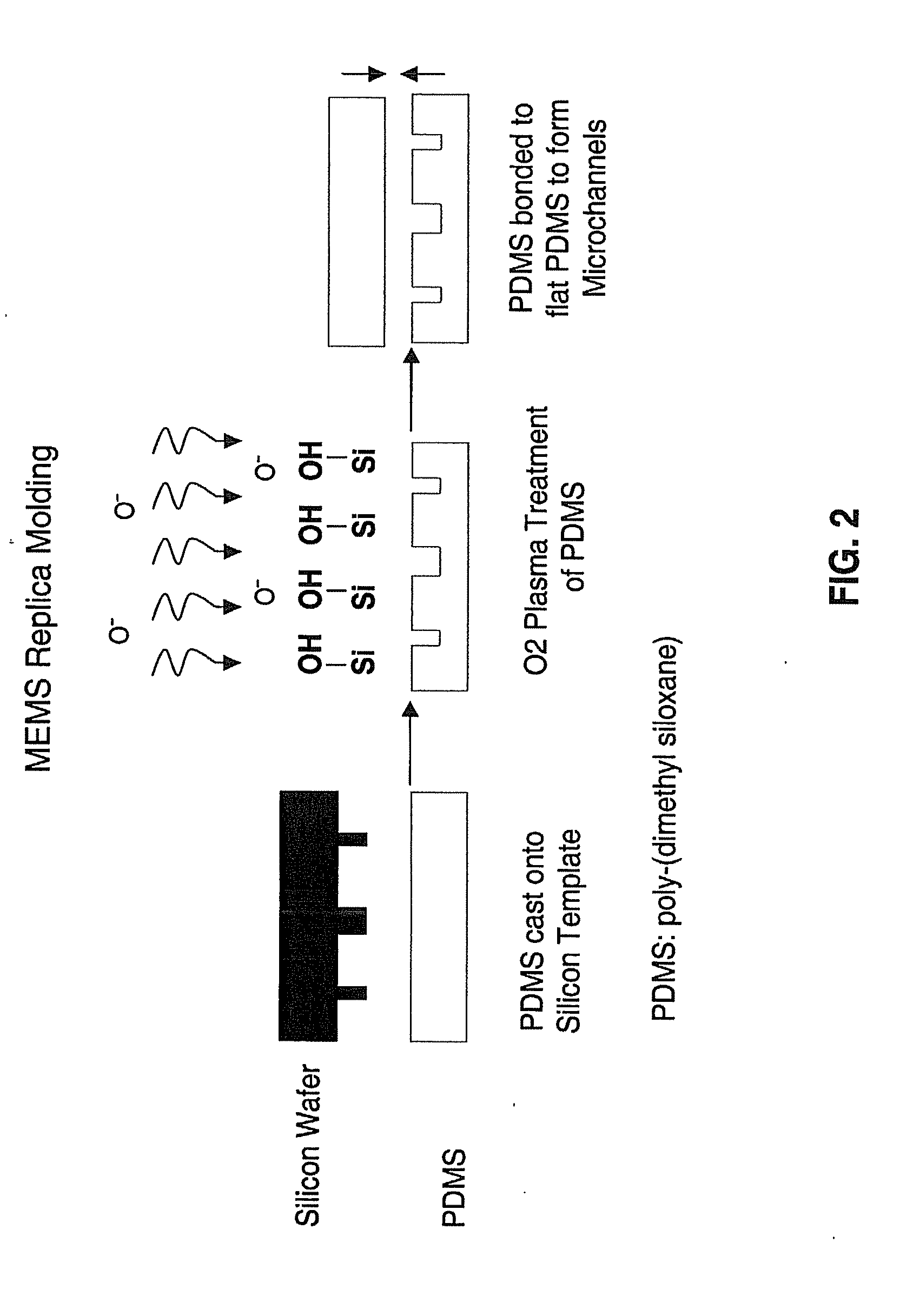
Laser-induced phase-separation polymerization of a porous acrylate polymer is used for in-situ fabrication of dialysis membranes inside glass microchannels. A shaped 355 nm laser beam is used to produce a porous polymer membrane with a thickness of about 15 μm, which bonds to the glass microchannel and form a semi-permeable membrane. Differential permeation through a membrane formed with pentaerythritol triacrylate was observed and quantified by comparing the response of the membrane to fluorescein and fluorescently tagging 200 nm latex microspheres. Differential permeation was observed and quantified by comparing the response to rhodamine 560 and lactalbumin protein in a membrane formed with SPE-methylene bisacrylamide. The porous membranes illustrate the capability for the present technique to integrate sample cleanup into chip-based analysis systems.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
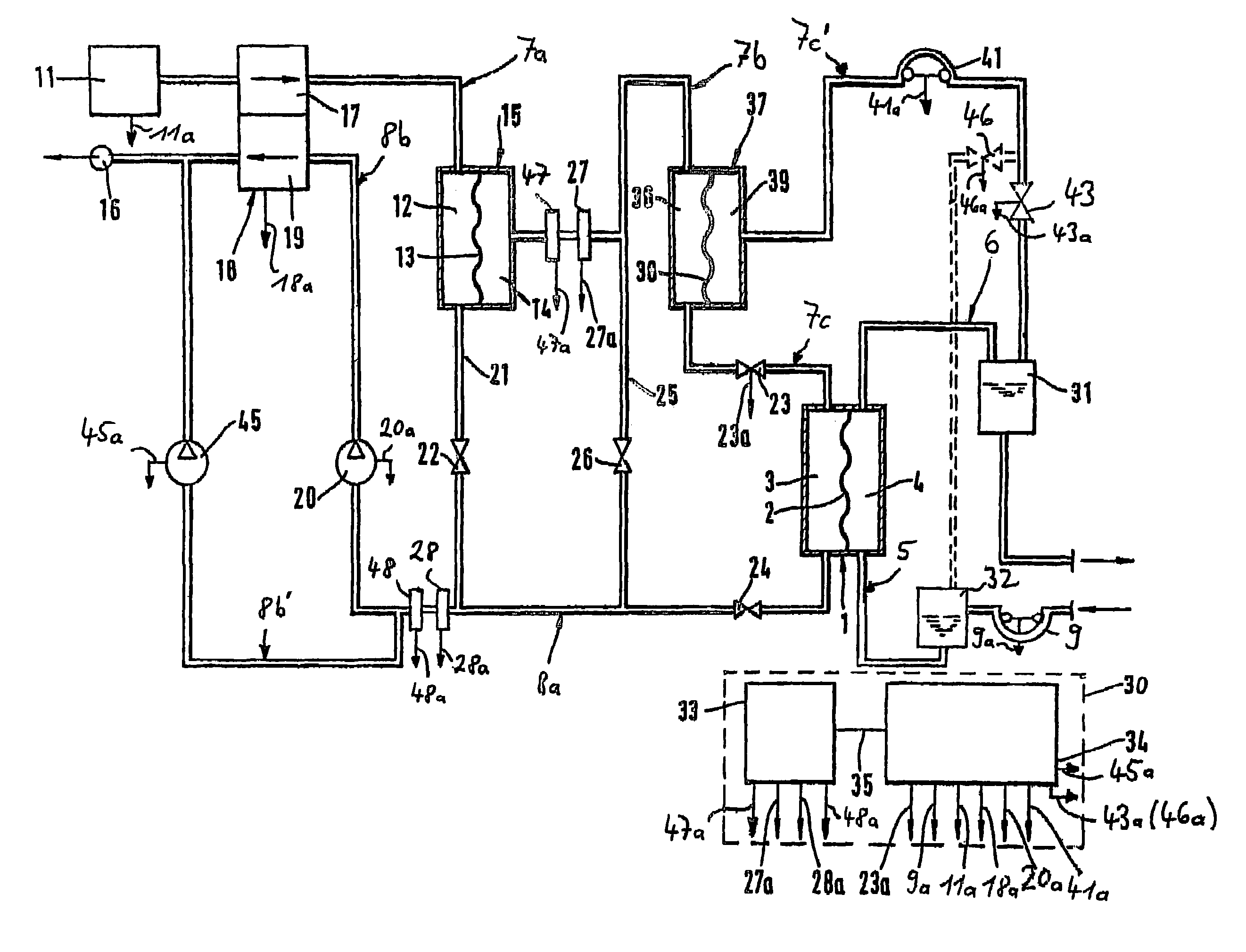
Extracorporeal treatment device with automatic emptying of waste bag
ActiveUS20040267183A1Semi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionExtracorporeal circulationBlood treatments
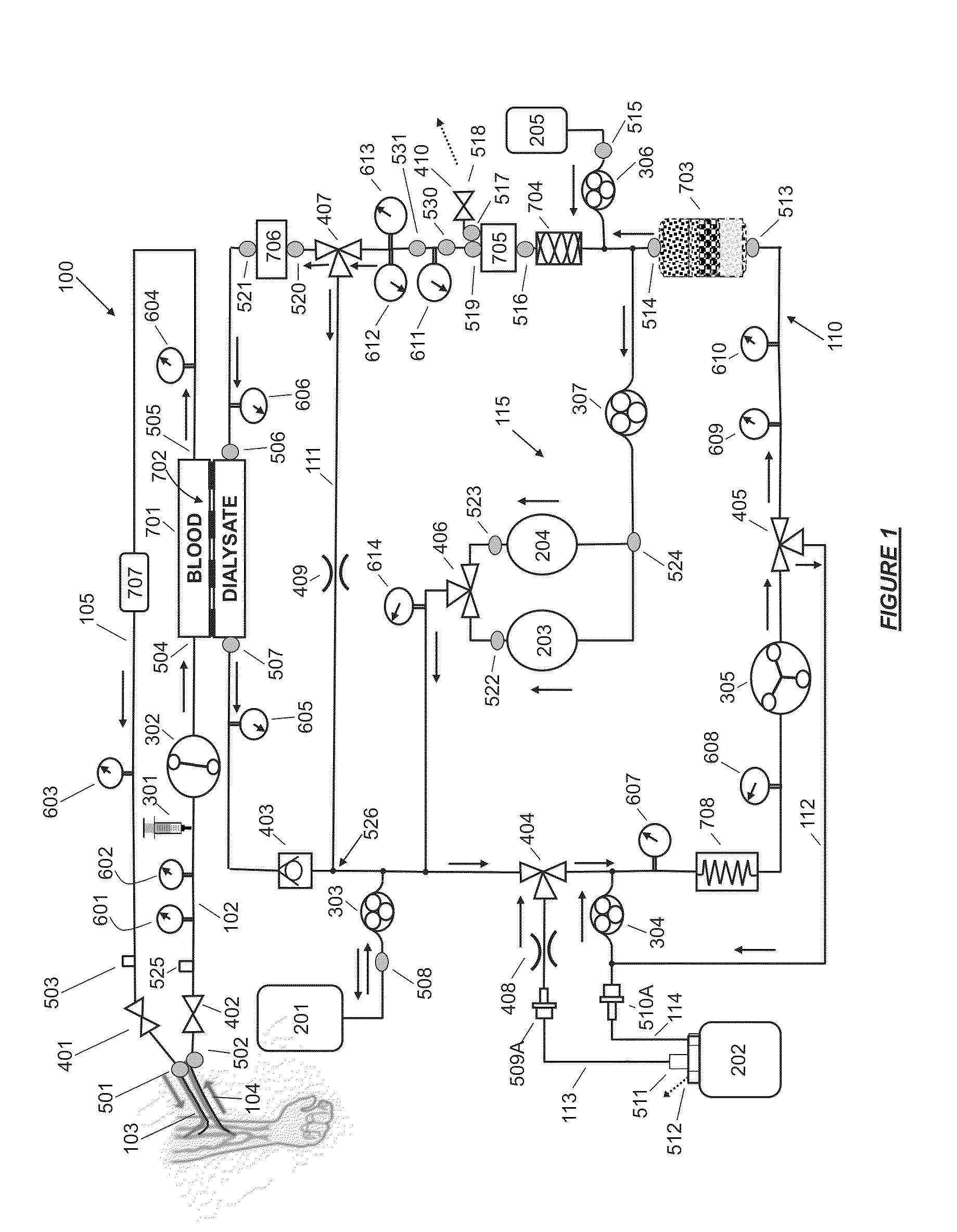
The invention relates to a blood treatment device by extracorporeal circulation comprising a filter having a primary chamber and a secondary chamber separated by a semi-permeable membrane; a blood circuit comprising an arterial line intended to come from the patient, the filter's primary chamber and the venous line intended to return to the patient; a dialysate circuit comprising the filter's secondary chamber and at least a drain line for circulating the waste intended to come from the filter and intended to go to a drain; a first bag in fluid communication with the drain line; at least a first gravimetric weighing means linked to the first bag, fluid flow rate adjustment means acting on the drain line; a control unit linked to the first gravimetric weighing means and with the fluid flow rate adjustment means; a second bag in fluid communication with the drain line, the control unit being capable of receiving weight signals from the first gravimetric weighing means and of controlling the fluid flow rate adjustment means to load one of the bags with liquid while the other bag unloads liquid, and vice-versa. The invention also relates to a single-use drain line for use in a treatment device according to the invention.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
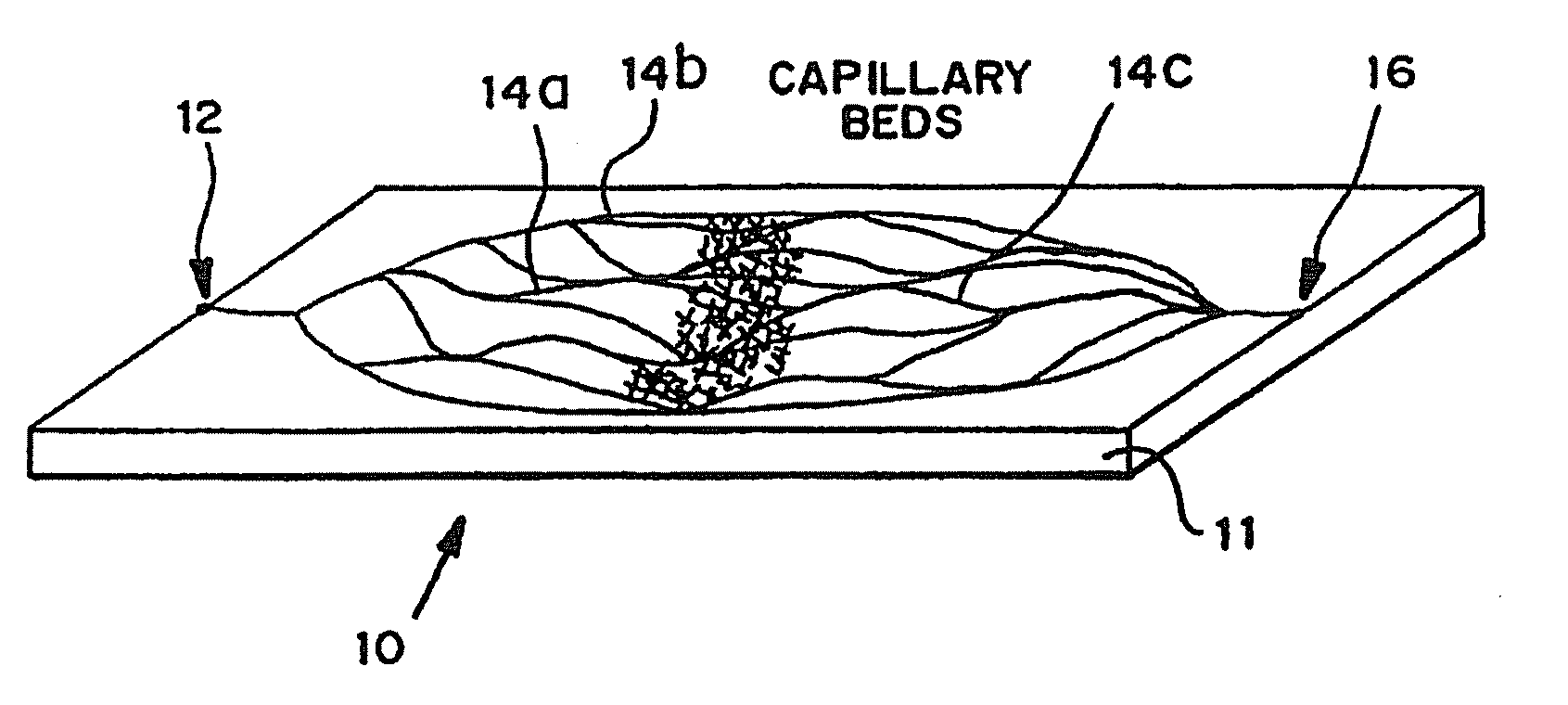
Fabrication of vascularized tissue using microfabricated two-dimensional molds
InactiveUS20100267136A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVascularizesLiver tissue
Methods and materials for making complex, living, vascularized tissues for organ and tissue replacement, especially complex and / or thick structures, such as liver tissue is provided. Tissue lamina is made in a system comprising an apparatus having (a) a first mold or polymer scaffold, a semi-permeable membrane, and a second mold or polymer scaffold, wherein the semi-permeable membrane is disposed between the first and second molds or polymer scaffolds, wherein the first and second molds or polymer scaffolds have means defining microchannels positioned toward the semi-permeable membrane, wherein the first and second molds or polymer scaffolds are fastened together; and (b) animal cells. Methods for producing complex, three-dimensional tissues or organs from tissue lamina are also provided.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Osmotic device containing amantadine and an osmotic salt
Owner:OSMOTICA KERESKEDELMI & SZOLGALTATO
Device for Determining Fat Expenditure from Levels of Ketone Bodies That Have Passed Through the Skin and Methods for Determining the Same
A sensing device having a first and second opening, a first semipermeable membrane having a first surface and a second surface, and a second semipermeable membrane having a third and fourth surface, a ketone body sensor, and a void. The first opening is juxtaposed to the first surface and the second opening is juxtaposed to the third surface. The space between the first and second openings is the void and wherein the ketone body sensor is positioned within the void. Gasses may permeate through the first opening and into the void to contact the sensor and exit the void through the second opening.
Owner:DETURK STEPHEN
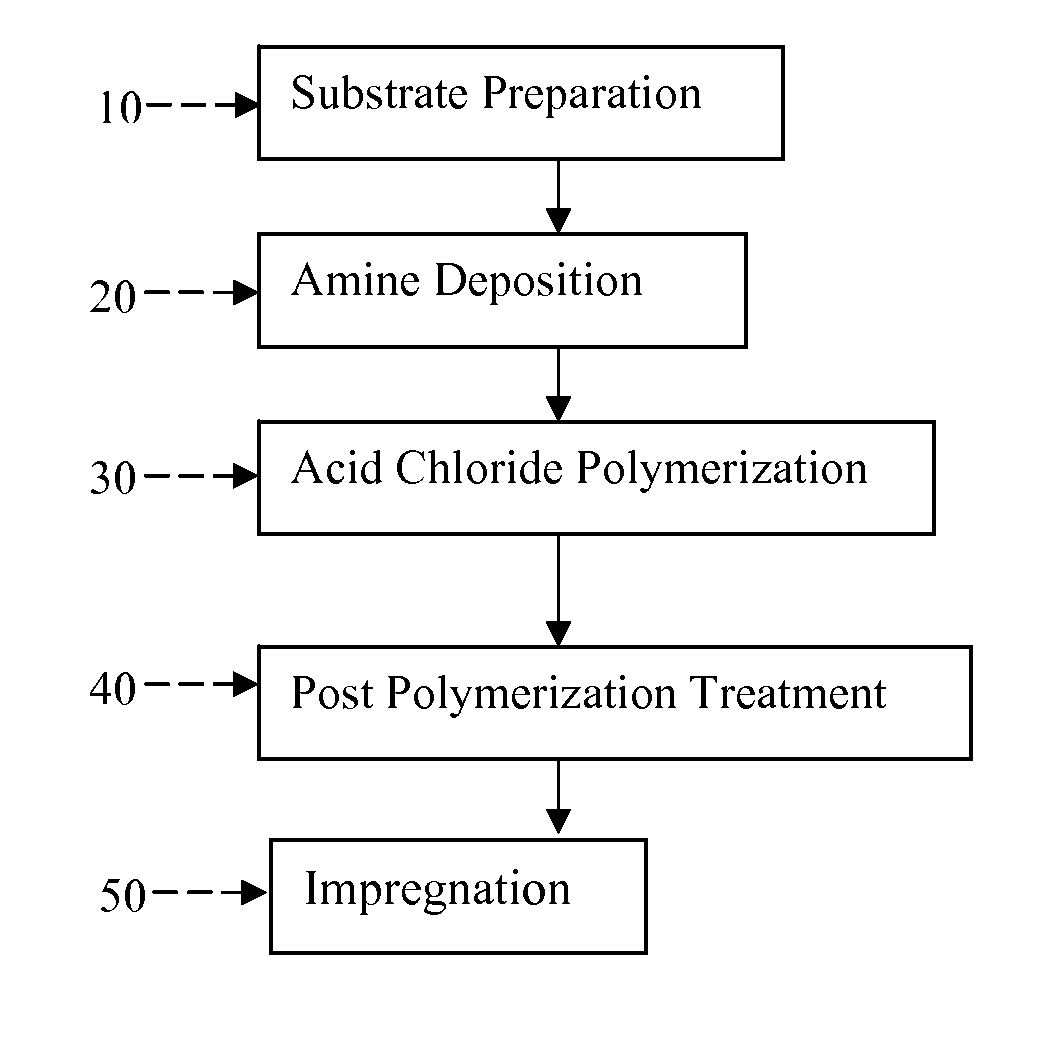
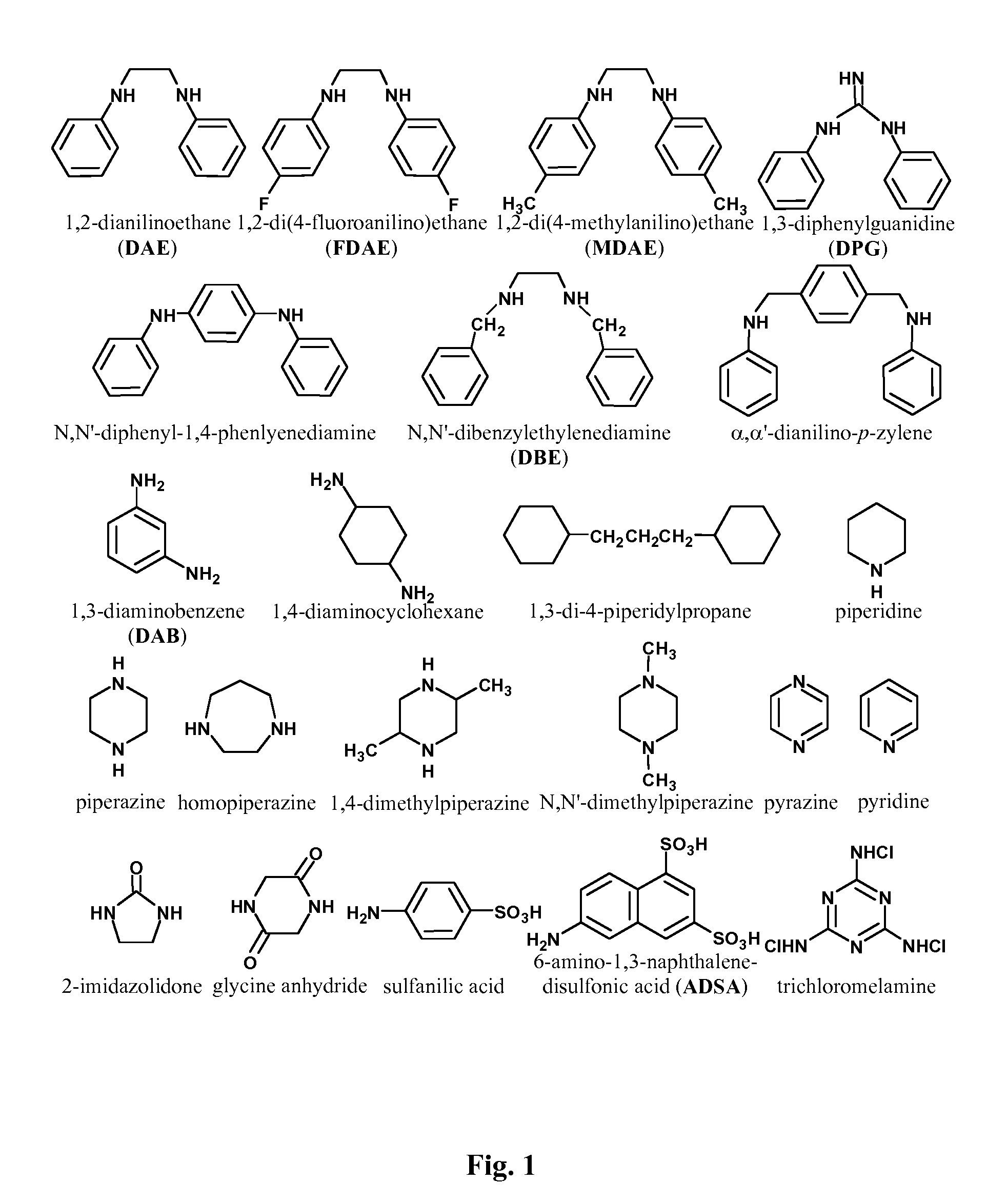
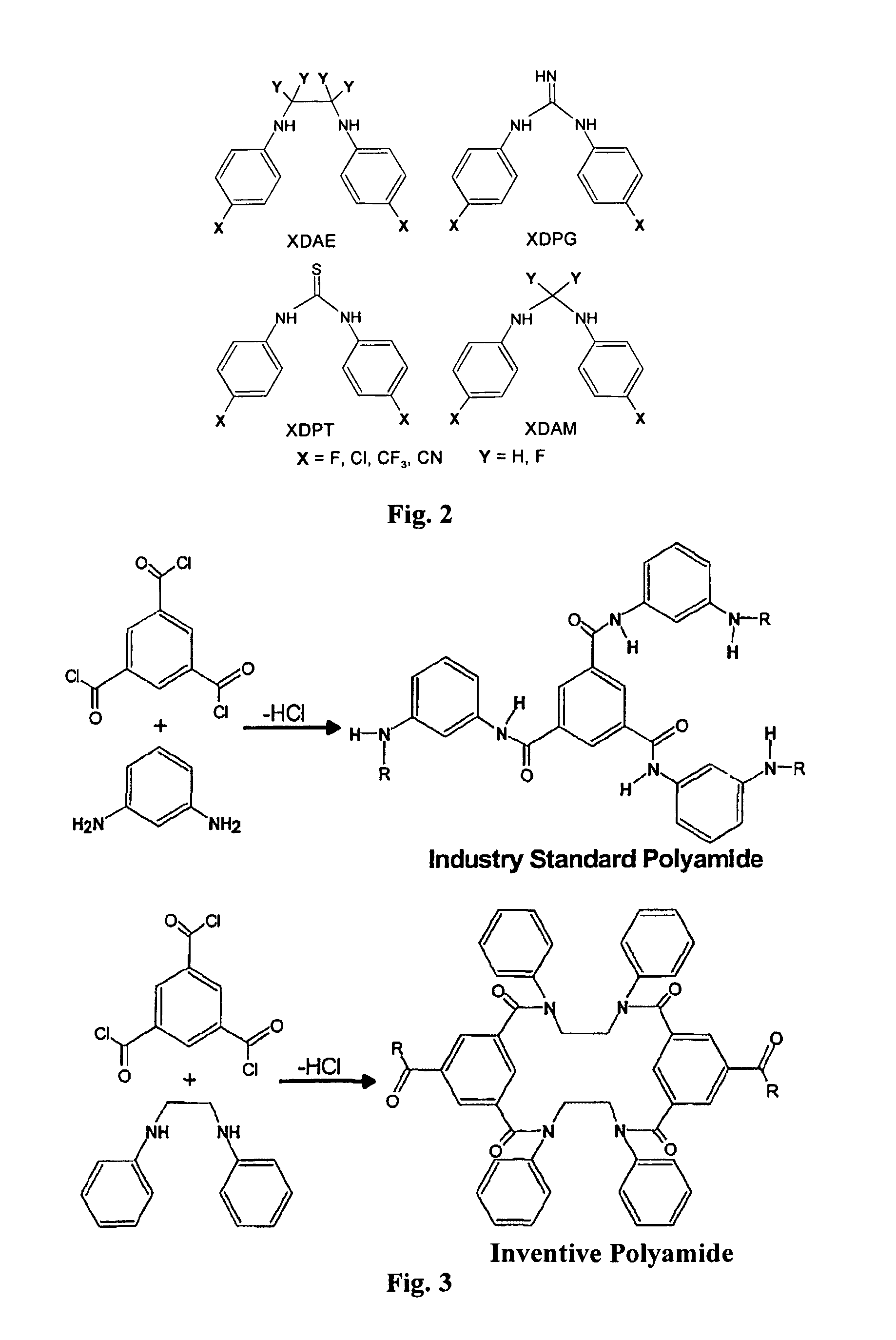
Semipermeable polymers and method for producing same
A polyamide membrane comprising reaction product of an anhydrous solution comprising an anhydrous solvent, at least one polyfunctional secondary amine and a pre-polymer deposition catalyst; and an anhydrous, organic solvent solution comprising a polyfunctional aromatic amine-reactive reactant comprising one ring. A composite semipermeable membrane comprising the polyamide membrane on a porous support. A method of making a composite semipermeable membrane by coating a porous support with an anhydrous solution comprising an anhydrous solvent, a polyfunctional secondary amine and a pre-polymer deposition catalyst, to form an activated pre-polymer layer on the porous support and contacting the activated pre-polymer layer with an anhydrous, organic solvent solution comprising a polyfunctional amine-reactive reactant to interfacially condense the amine-reactive reactant with the polyfunctional secondary amine, thereby forming a cross-linked, interfacial polyamide layer on the porous support. A method of impregnating a composite semipermeable membrane with nanoparticles selected from heavy metals and / or oxides of heavy metals.
Owner:ELTRON RES
Fabrication of tissue lamina using microfabricated two-dimensional molds
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
Secretion of neublastin
InactiveUS20050089960A1Reduce the possibilityObstruct passageSenses disorderNervous disorderNervous systemPro region
The present invention concerns improved methods and compositions for producing a Neublastin polypeptide as well as local delivery of Neublastin to specific regions of the nervous system including the central nervous system and the eye for example by gene therapy. The invention also concerns Neublastin expression constructs which do not encode a pro-region of a Neublastin polypeptide, which expression construct result in increased secretion of bioactive Neublastin. The invention includes the delivery of Neublastin from transduced or transfected cells encapsulated into a macrocapsule with a semipermeable membrane. The invention further concerns mammalian cells capable of producing Neublastin in increased amounts.
Owner:NSGENE AS
Rupturing controlled release device comprising a subcoat
The present invention provides a simple and improved rupturing controlled release device that is capable of providing a controlled release of active agent contained in the core first through a preformed passageway and then through an in situ formed second passageway into an environment of use in a standardized release profile manner. The rupturing controlled release device comprises a core comprising at least one drug and at least one osmopolymer, a semipermeable membrane enclosing the core and having at least one preformed passageway there through, wherein the semipermeable membrane ruptures during use to form a second passageway in the semipermeable membrane at a location spaced away from the preformed passageway, and a release-controlling subcoat between the core and the semipermeable membrane.
Owner:OSMOTICA KERESKEDELMI & SZOLGALTATO +1
Hybrid ro/pro system
ActiveUS20090071902A1Impairing amountEasy to controlGeneral water supply conservationSolvent extractionEnvironmental engineeringAqueous solution
A system which includes a separation element (11) employing semipermeable membrane material (17), which system is designed so that it can operate either in an RO mode to produce high quality water or in a PRO mode to generate power from two aqueous solutions of different salt concentrations. In a preferred embodiment, a rotary pressure transfer device (29) is included to transfer pressure from an outlet stream exiting the separation element to an inlet stream being supplied to the separation element.
Owner:ENERGY RECOVERY INC
Perorally insertable/removable anti-reflux valve
Disclosed are esophageal anti-reflux valve prostheses, and tools and procedures for peroral implantation and extraction of the prostheses. The prostheses disclosed have a semipermeable membrane to allow retrograde passage of gas, magnets disposed at a distal end of the sleeve to facilitate closure, and an outwardly bendable array of spikes that are longitudinally aligned for peroral insertion and lockable into a radially outwardly deployed configuration to keep the prosthesis from dislocating implantation. The implantation tool has inner and outer concentric tubes, the inner tube releasably threadably connected to the prosthesis, the outer tube reverse threaded with the inner tube to advance a distal headpiece to engage, deploy and lock the spikes into the deployed configuration. A vacuum assist can be used to help impact the lumen wall on the spikes. The extraction tool is similar to the implantation tool with an inner tube for threadably engaging the prosthesis, an outer tube with a distal crown with a plurality of shoes to unseat and unlock the spikes, and an overtube shield to receive the spikes and facilitate extraction of the prosthesis.
Owner:REFLUX CORP
Composite semipermeable membrane and manufacturing method therefor
Owner:TORAY IND INC
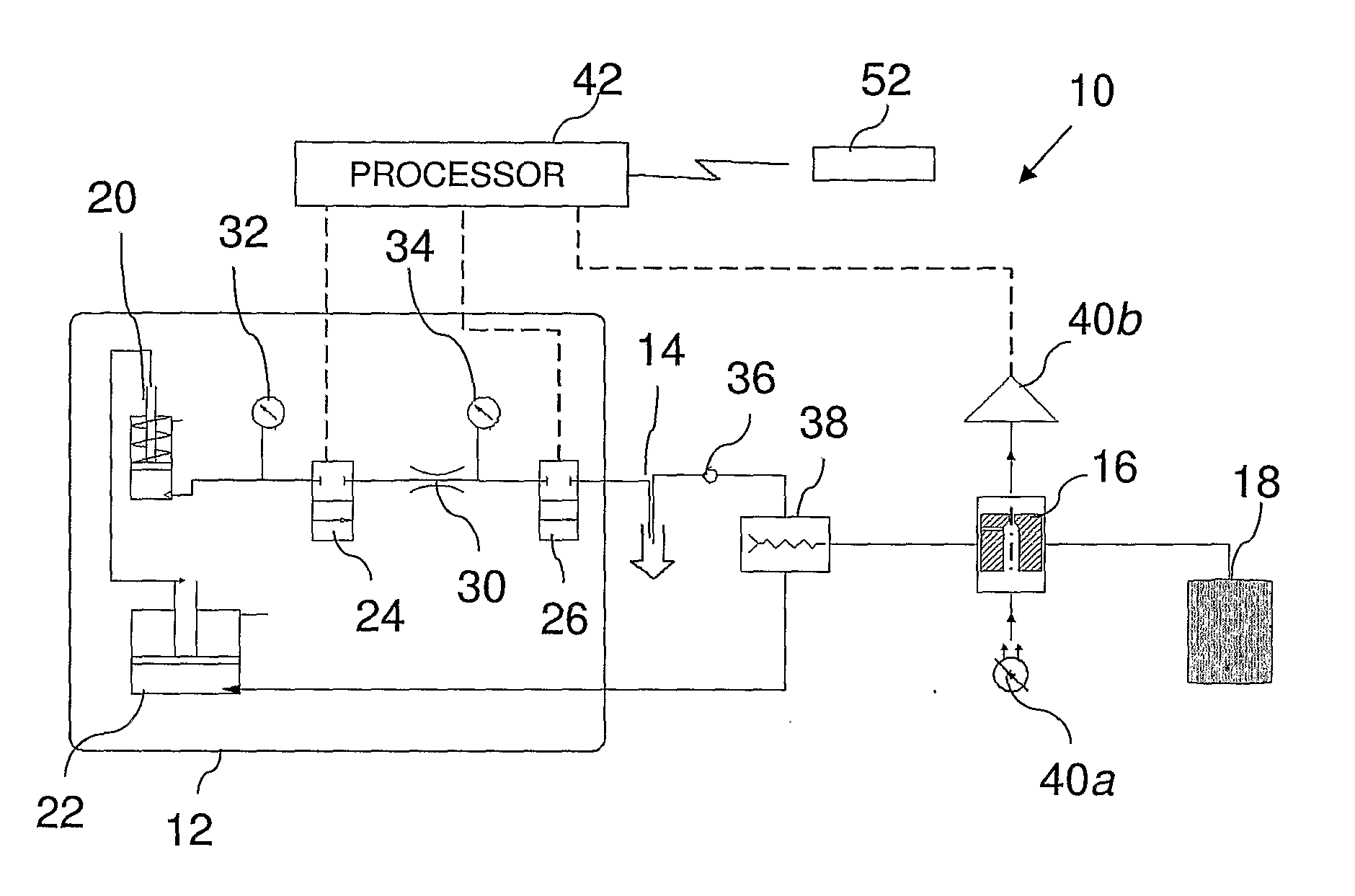
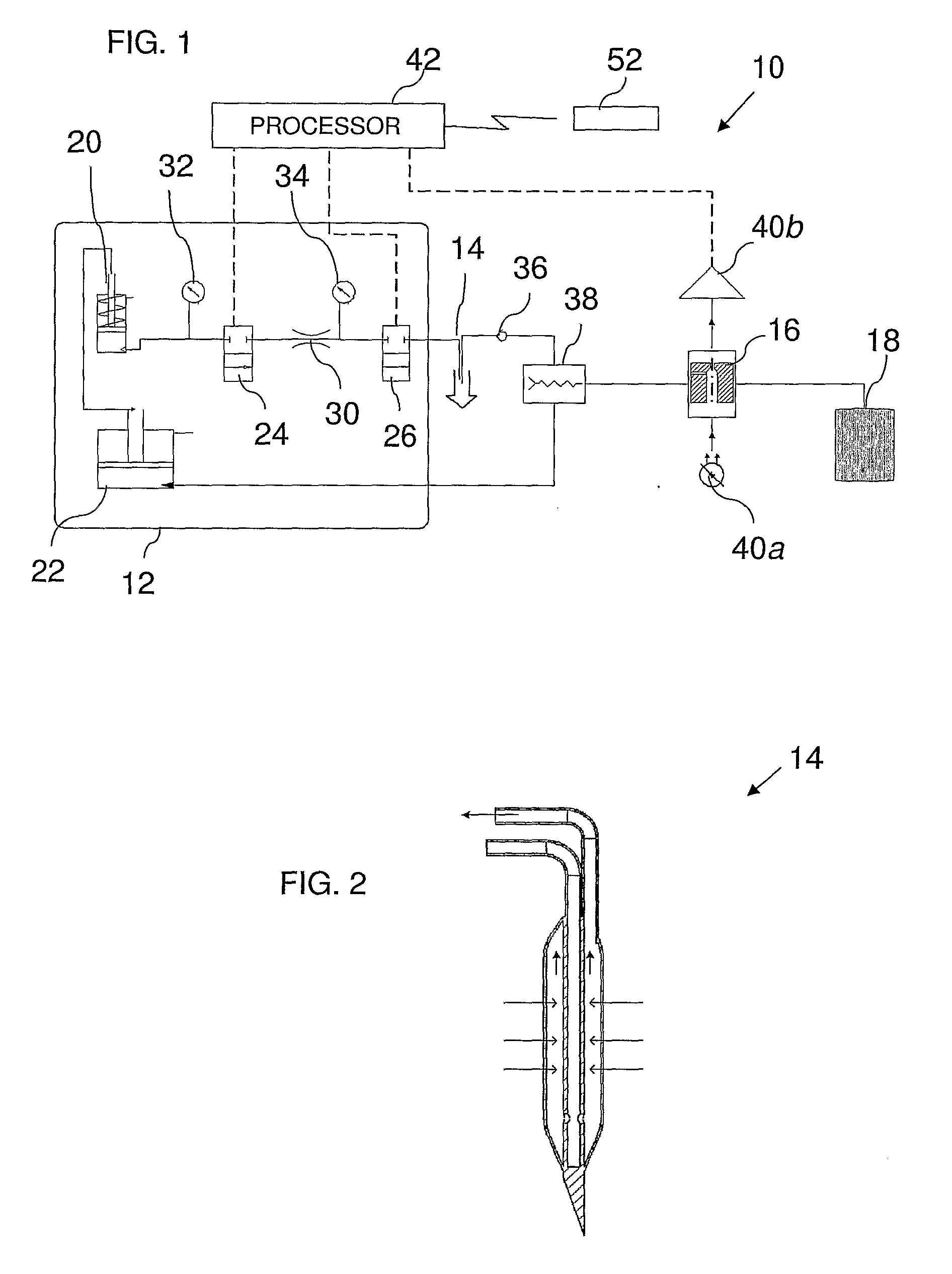
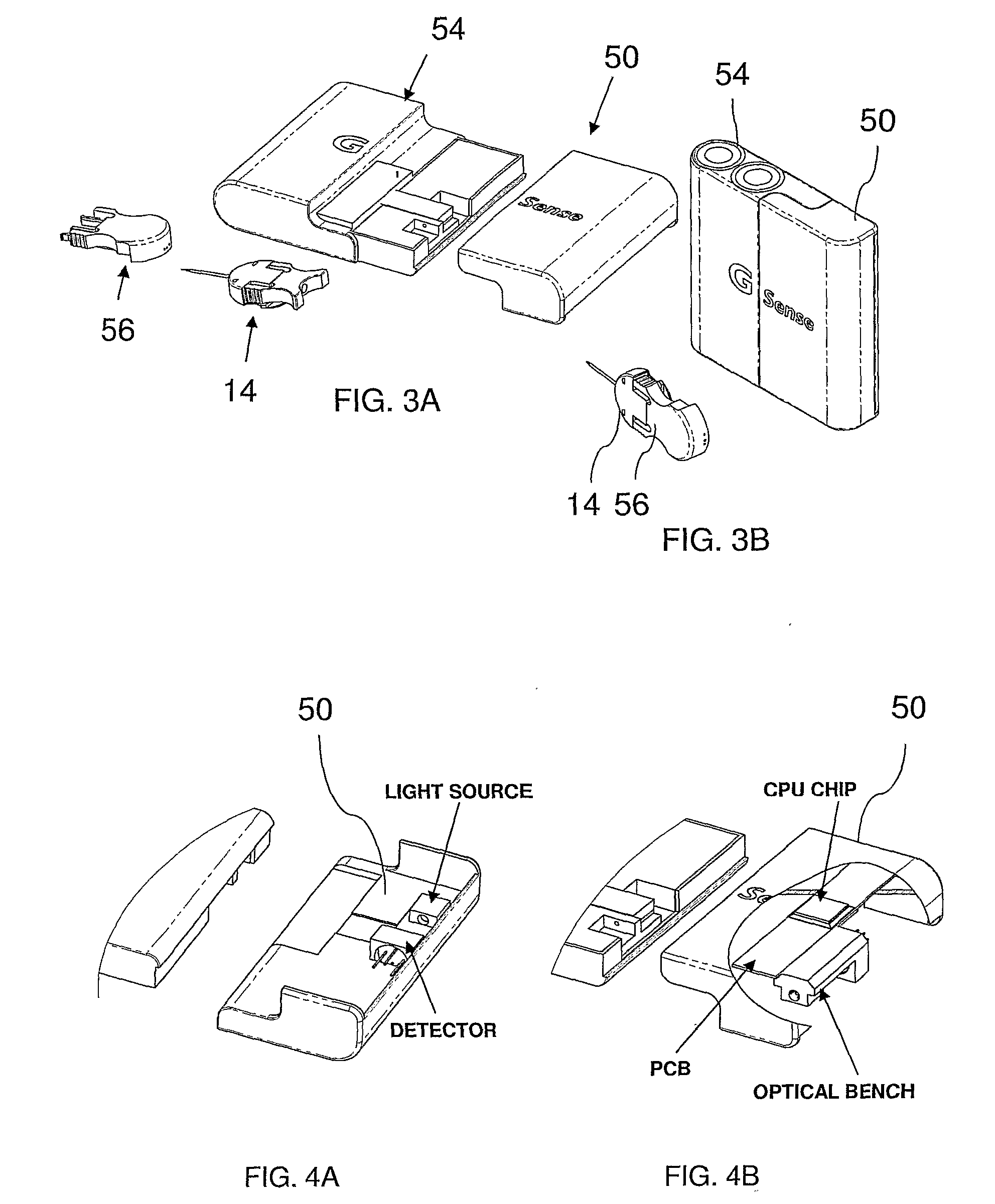
System and Method for Pseudo-Continuous Measurement of Metabolite Concentrations in a Mammalian Body
A metabolite monitoring system comprising a microdialysis probe including a semi-permeable membrane and a probe flow path passing from an inlet through a sensing volume adjacent to said semi-permeable membrane to an outlet, a fluid delivery device for delivering dialysate to said inlet; and a metabolite monitoring system associated with said outlet for monitoring a concentration of at least one metabolite in said dialysate from said microdialysis probe, wherein said fluid delivery device is configured to deliver a pulsed flow of said dialysate to said inlet.
Owner:G SENSE LTD
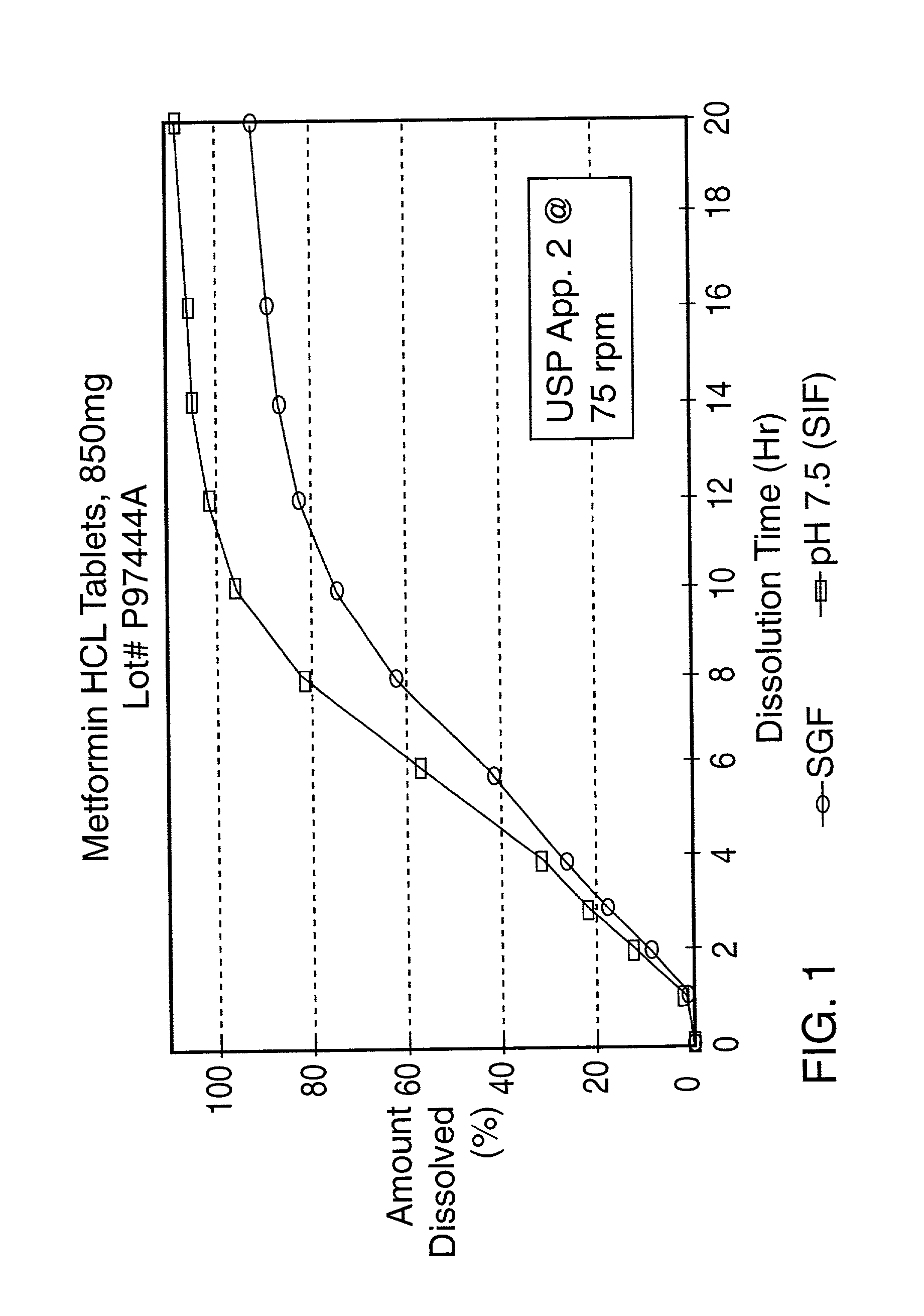
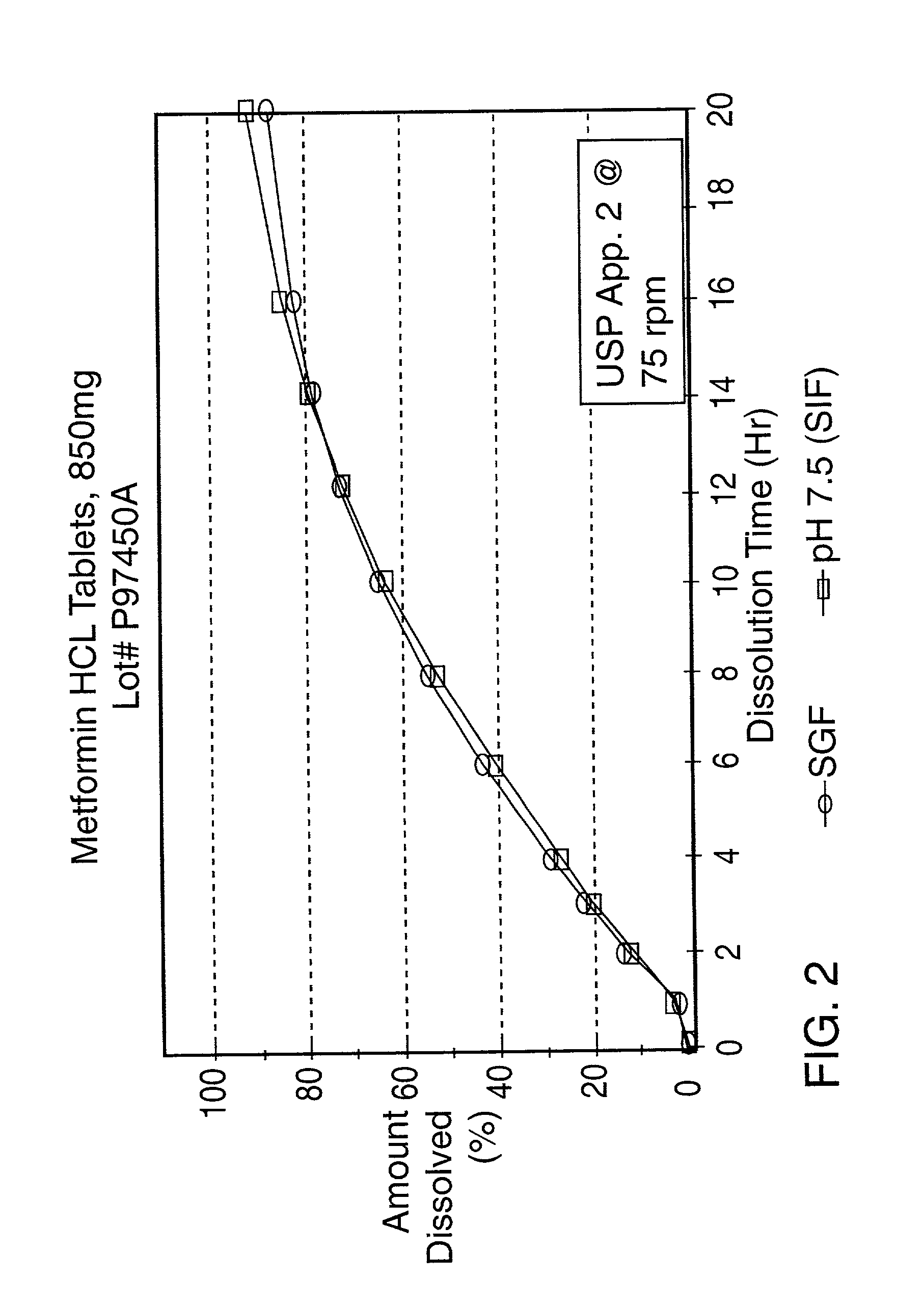
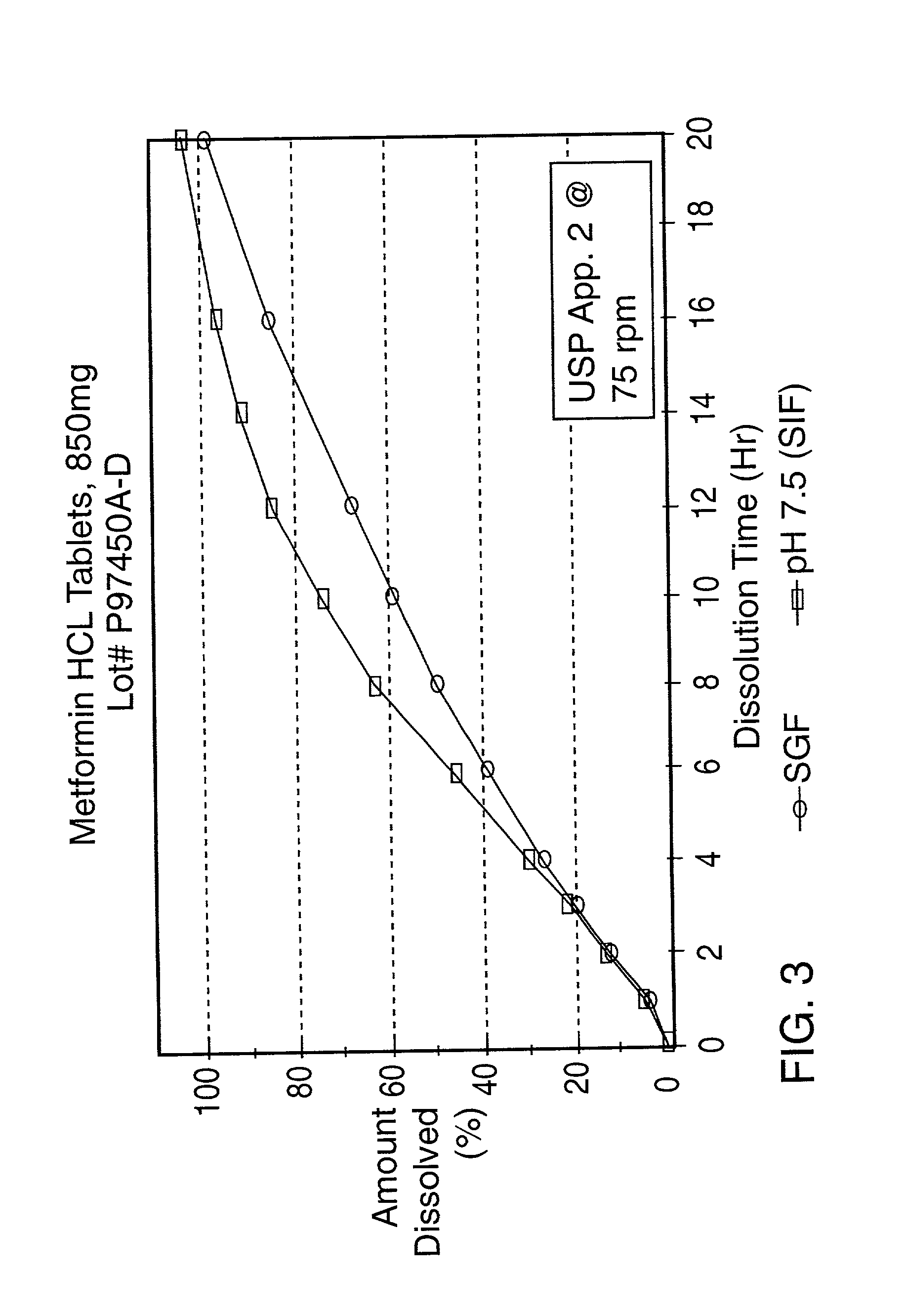
Controlled release oral tablet having a unitary core
A controlled release antihyperglycemic tablet that does not contain an expanding polymer and comprising a core containing the antihyperglycemic drug, a semipermeable membrane coating the core and at least one passageway in the membrane.
Owner:ANDRX LABS
Osmotic device containing amantadine and an osmotic salt
Owner:OSMOTICA KERESKEDELMI & SZOLGALTATO
Semipermeable Composite Membrane and Process for Producing the Same
InactiveUS20080257818A1Good water permeabilityReduce contentSemi-permeable membranesCoatingsSemipermeable membraneHalide
The present invention aims at providing a composite semipermeable membrane having outstanding water permeability and salt-blocking rate, and extremely small amount of unreacted polyfunctional amine components in the porous support, and at providing a process for producing the composite semipermeable membrane. A composite semipermeable membrane having a skin layer formed on the surface of a porous support, the skin layer comprising a polyamide resin obtained by interfacial polymerization of a polyfunctional amine component and a polyfunctional acid halide component, wherein the porous support has a microporous layer on a base material, and the content of an unreacted polyfunctional amine component in the base material after a membrane washing treatment is 0.5 mg / m2 or less.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Composite Semipermeable Membranes, Methods for Production Thereof and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090071903A1Improve desalination performanceHigh removal rateGeneral water supply conservationSeawater treatmentPorous substratePolymer science
There is provided a composite semipermeable membrane that shows a high salt removal ratio and high performance in rejecting boron that is not dissociated in the neutral region. The composite semipermeable membrane is produced by a process that includes forming a separating functional polyamide layer on a porous substrate film, while using an organic solvent solution containing a specific cyclic aliphatic compound or a specific aromatic compound such that a polyamide molecule that forms the separating functional polyamide layer has a partial structure composed of “a cyclic aliphatic group or an aromatic group having at least two specific substituents, at least one of which contains a heteroatom bond and a carbonyl group at the β or γ position”.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method for producing a wet-laid nonwoven fabric
ActiveUS10443167B2Occurrence can be suppressedEasy to confirmSemi-permeable membranesPaper/cardboardPapermakingSlurry
A method for producing a wet-laid nonwoven fabric for a semipermeable membrane supporting body, the method comprising: performing papermaking according to a wet papermaking method by using a fiber slurry containing a synthetic fiber as a main constituent fiber; drying the fiber slurry; subsequently subjecting the dried sheet to hot press processing two times by using a heat calender apparatus, wherein the hot press process temperature in the second treatments is adjusted to be higher by 10° C. or more than the hot press processing temperature in the first treatment, while treating the dried sheet by using a hard nip heat calender apparatus equipped with a combination of a metal roll and a metal roll for at least one time of the hot press processing; and thereby obtaining a wet-laid nonwoven fabric for a semipermeable membrane supporting body.
Owner:HOKUETSU KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com