Patents
Literature
5144results about "Ear treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
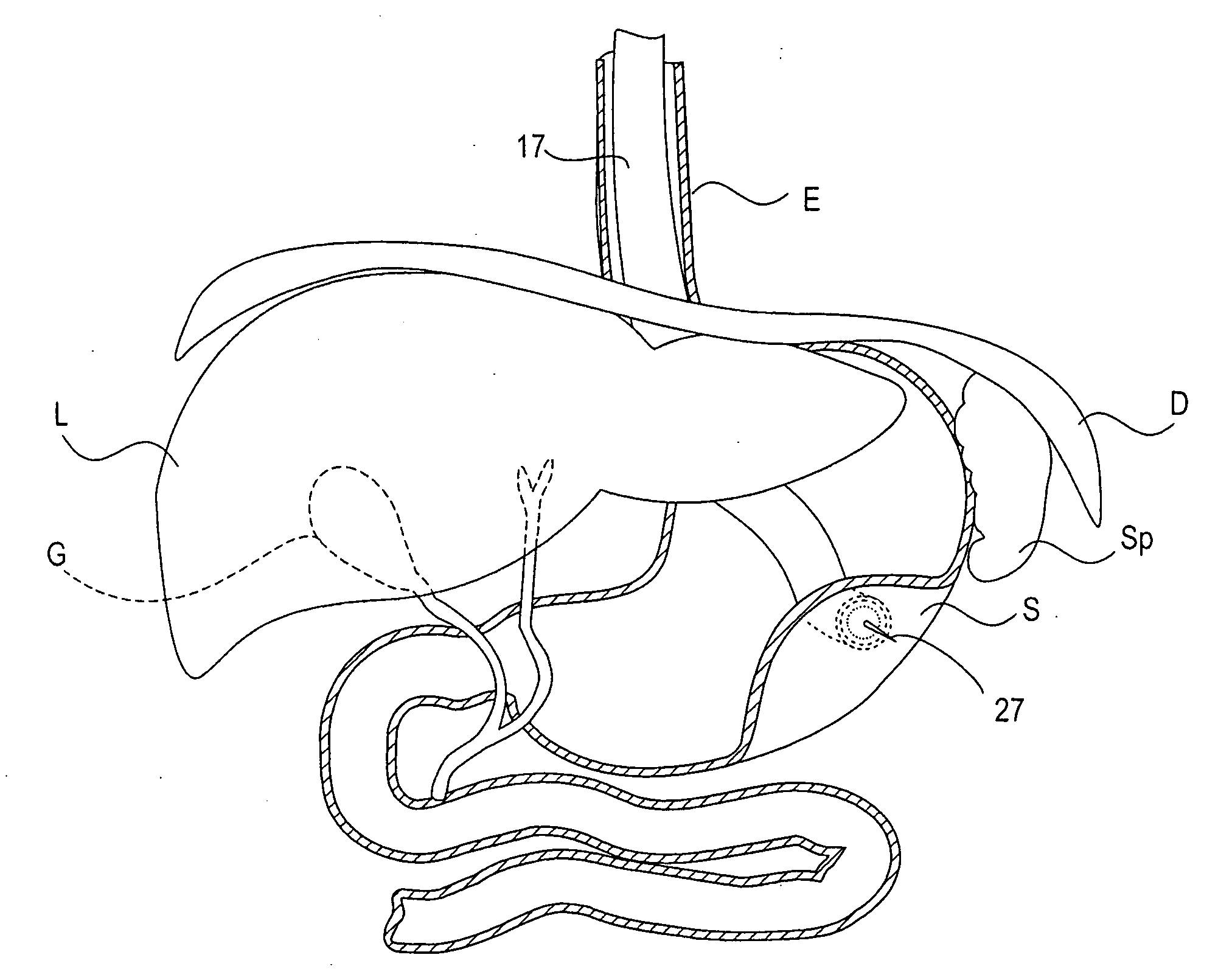
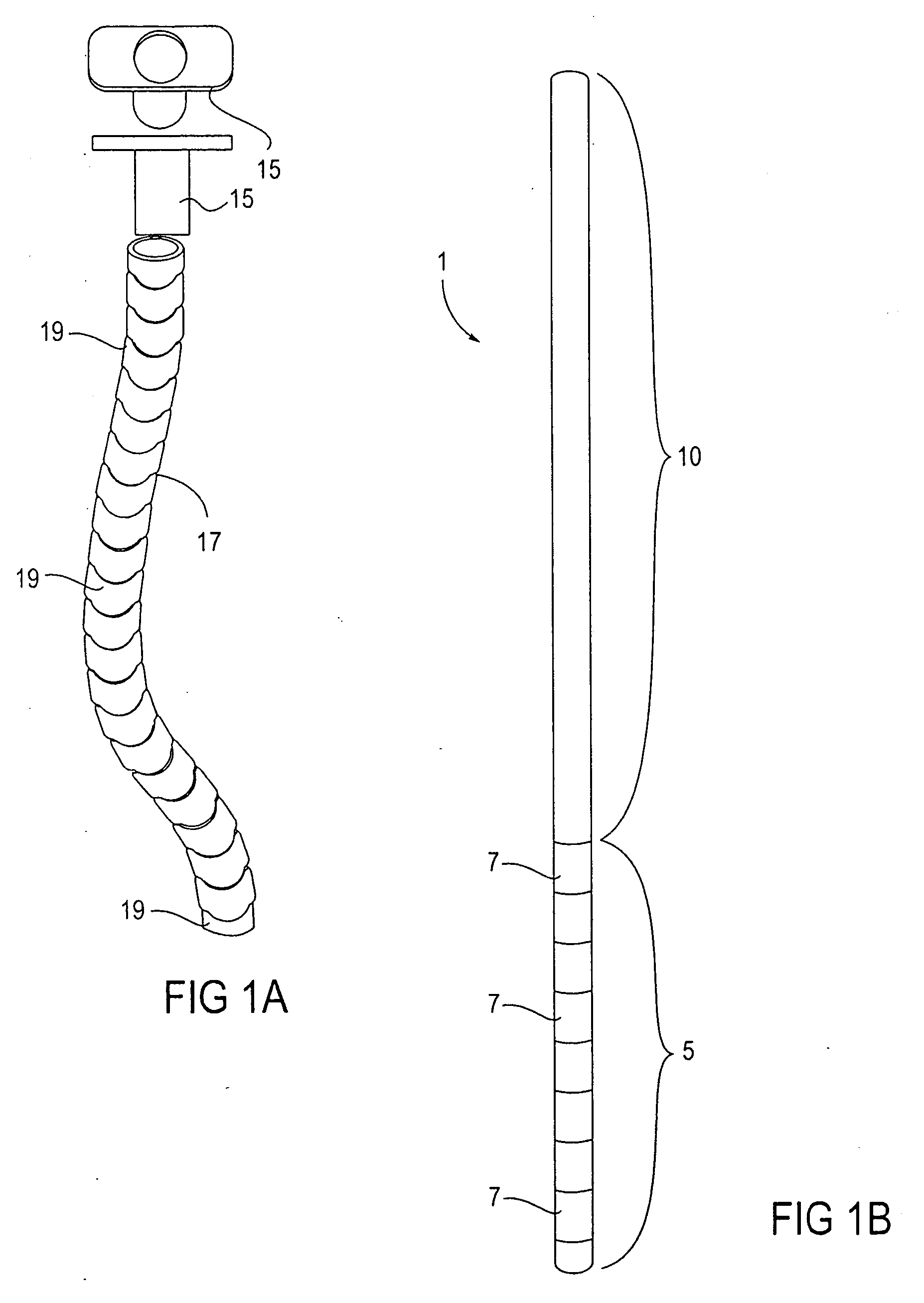
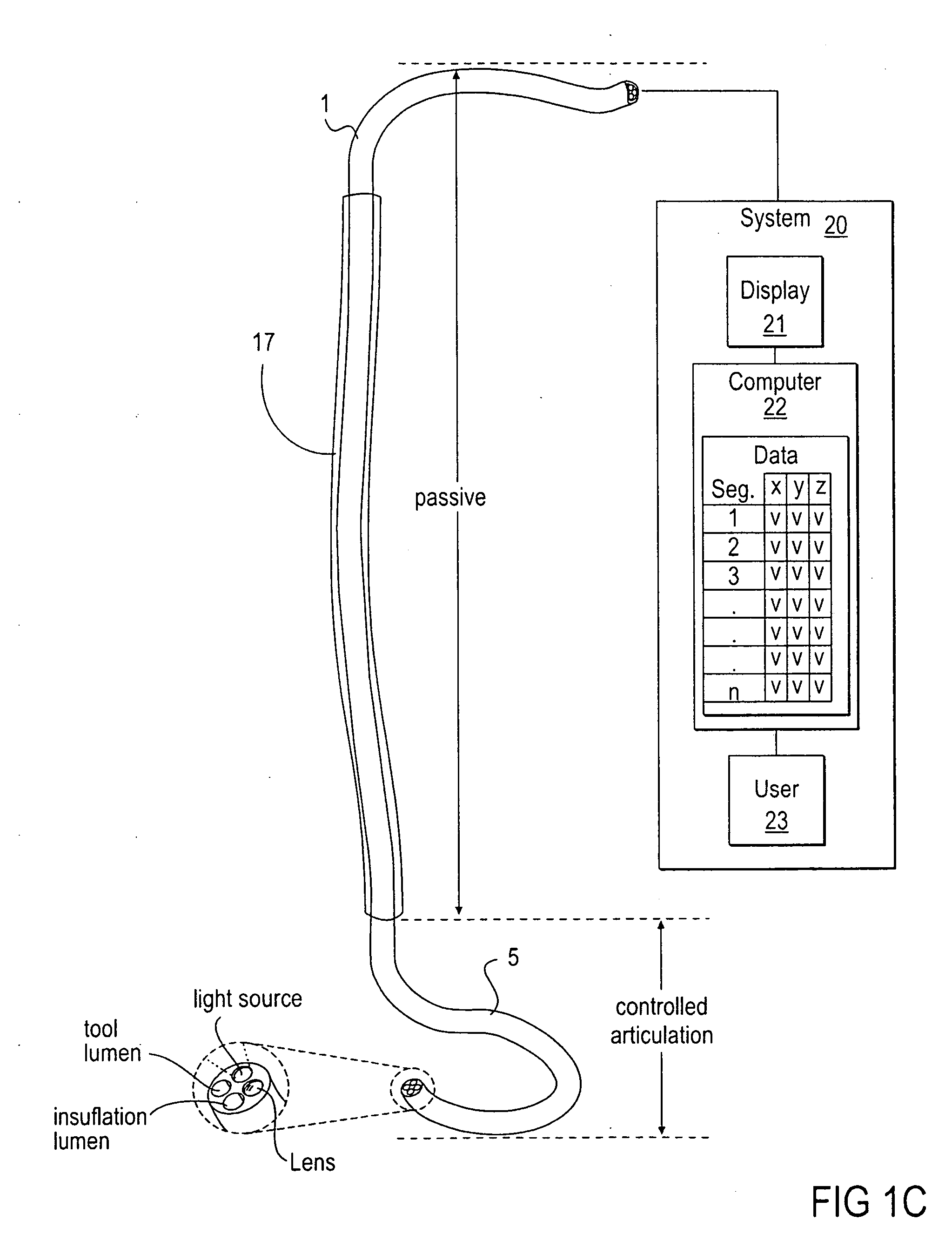
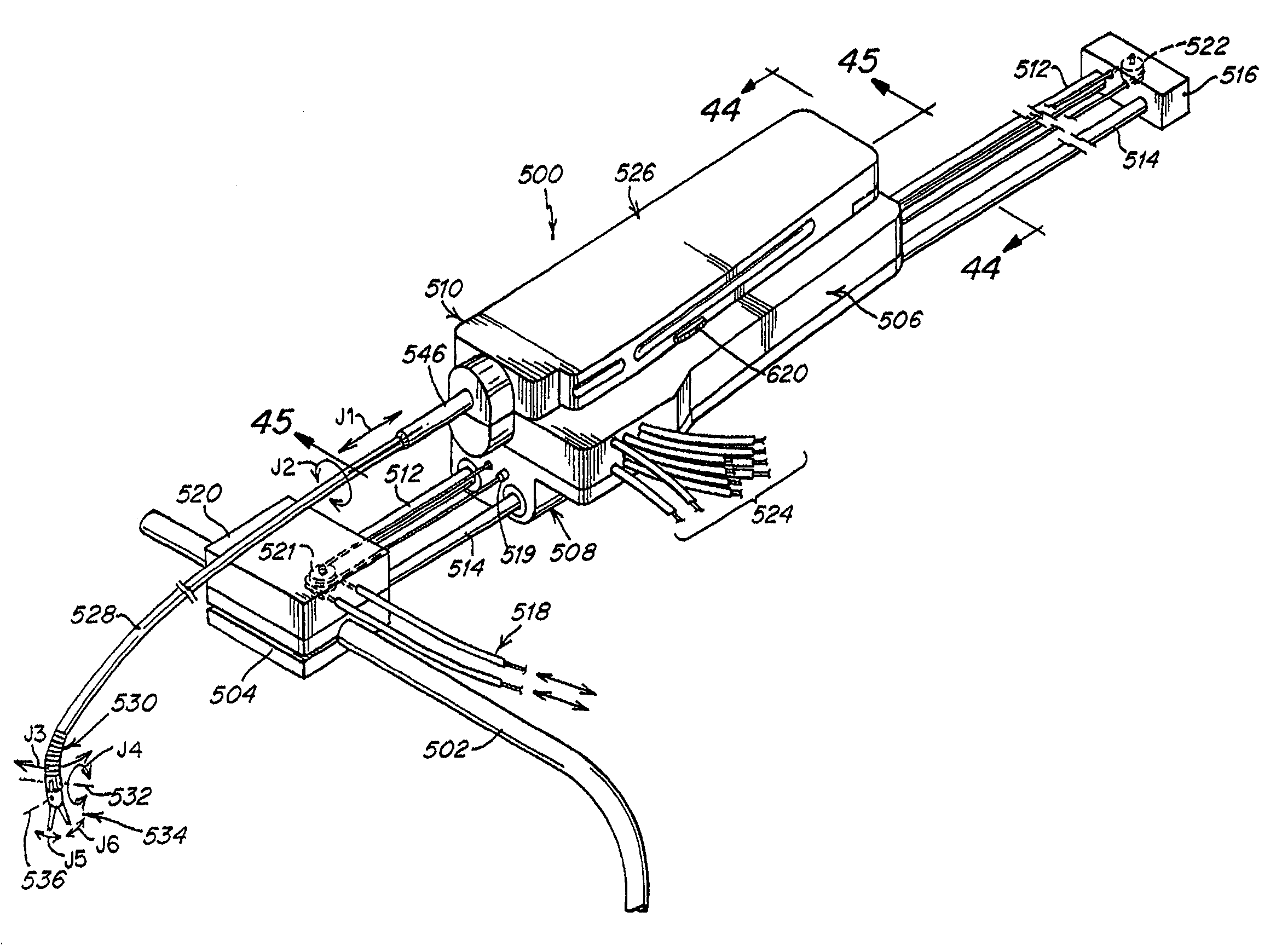
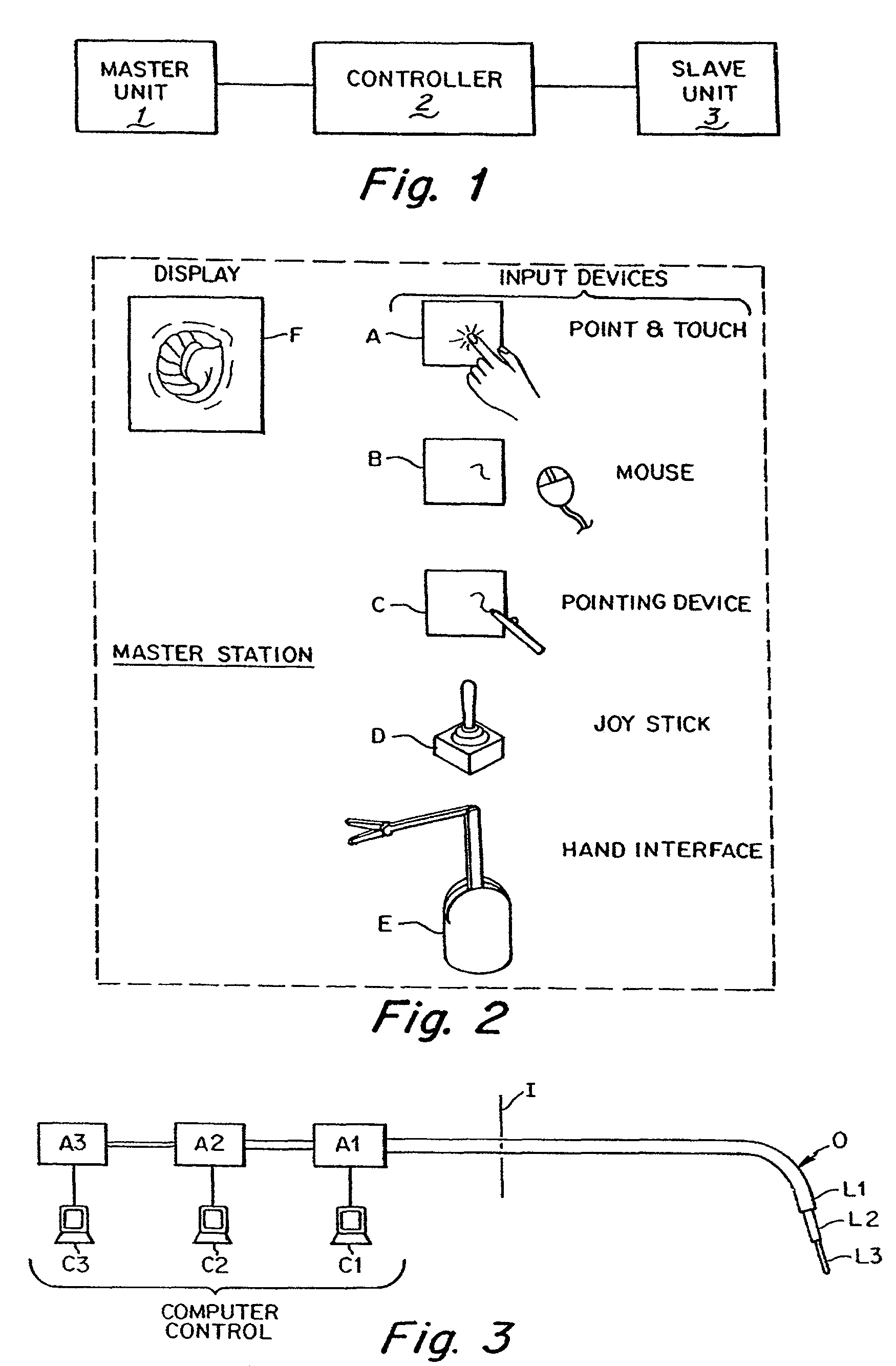
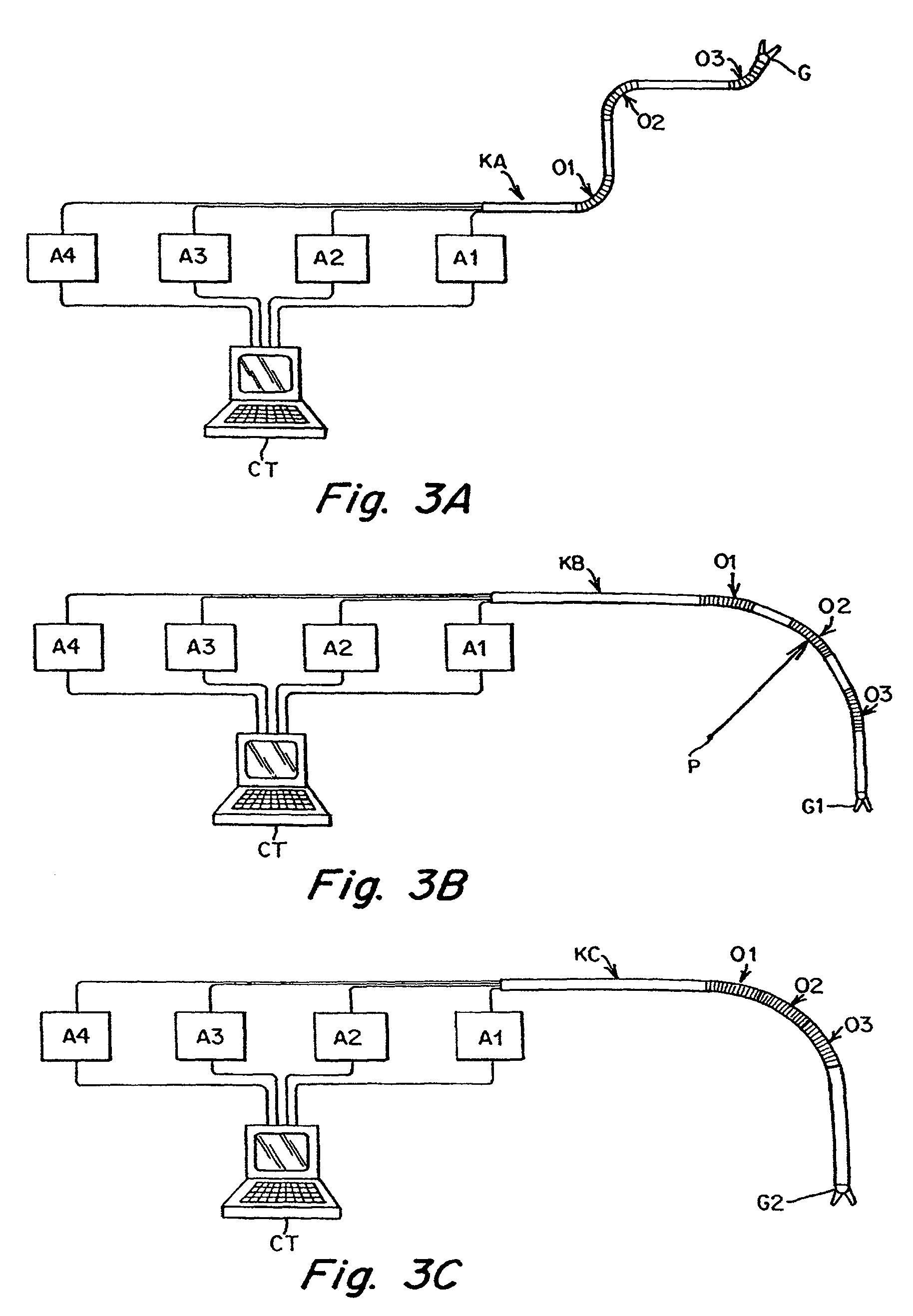
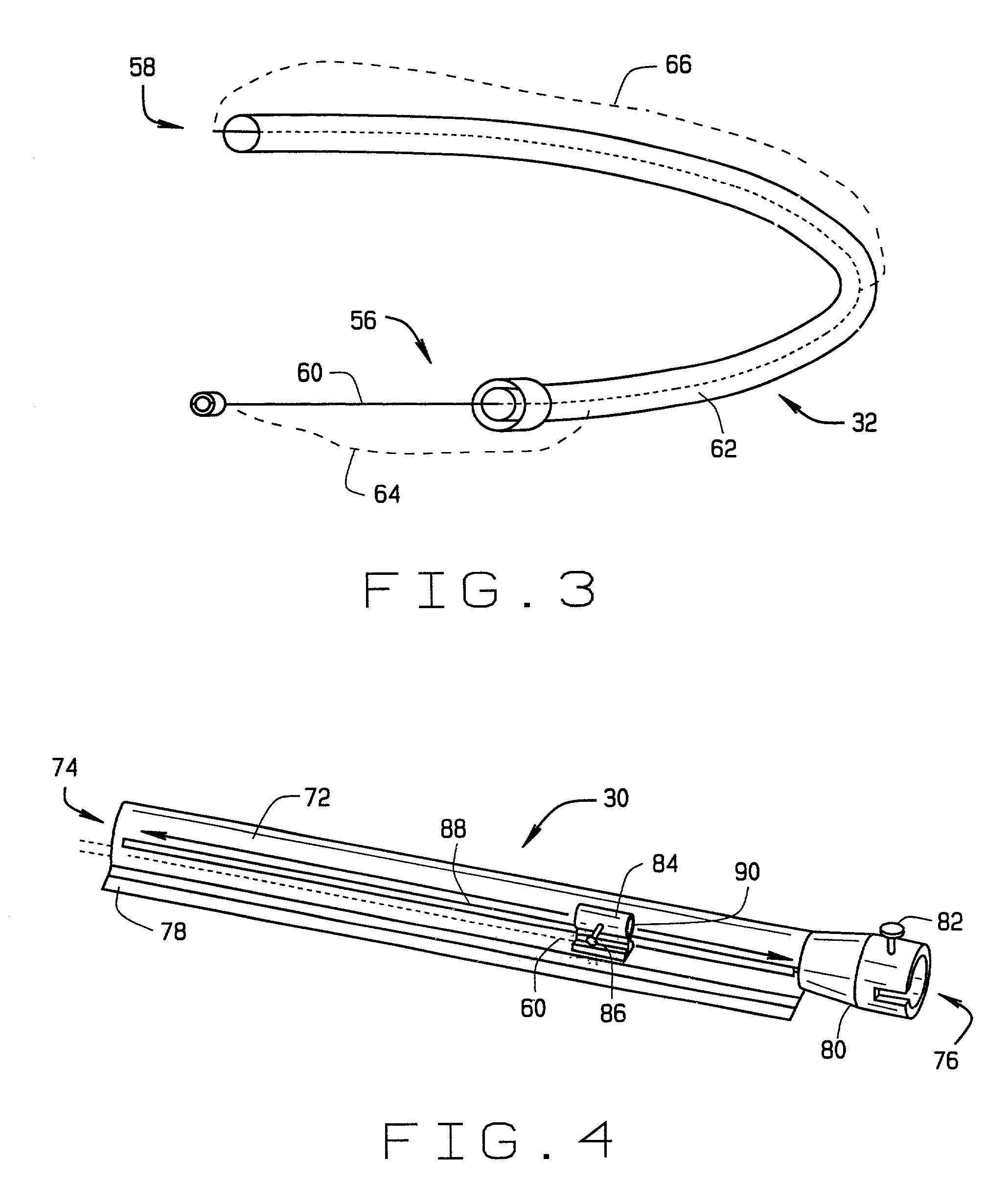
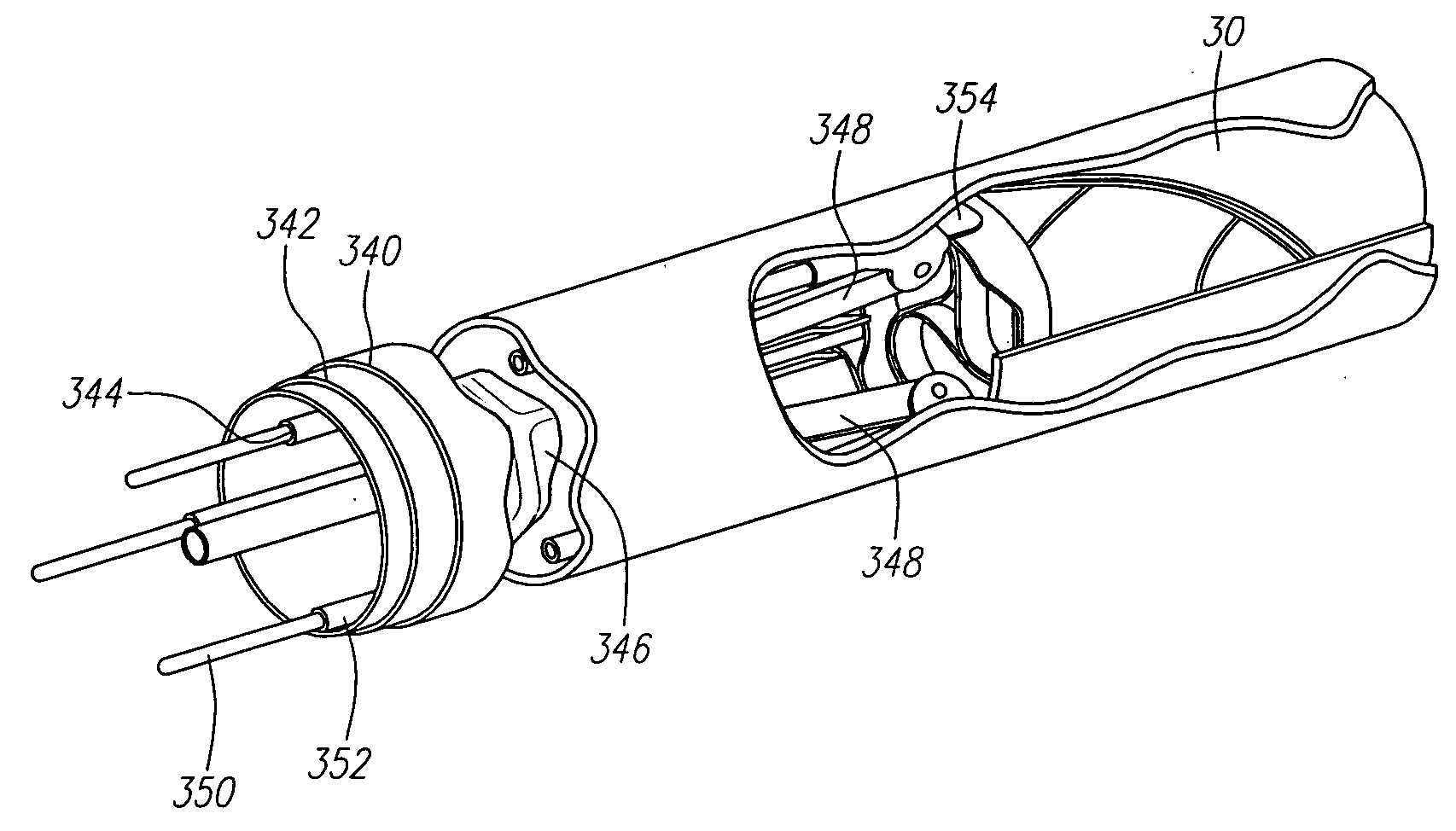
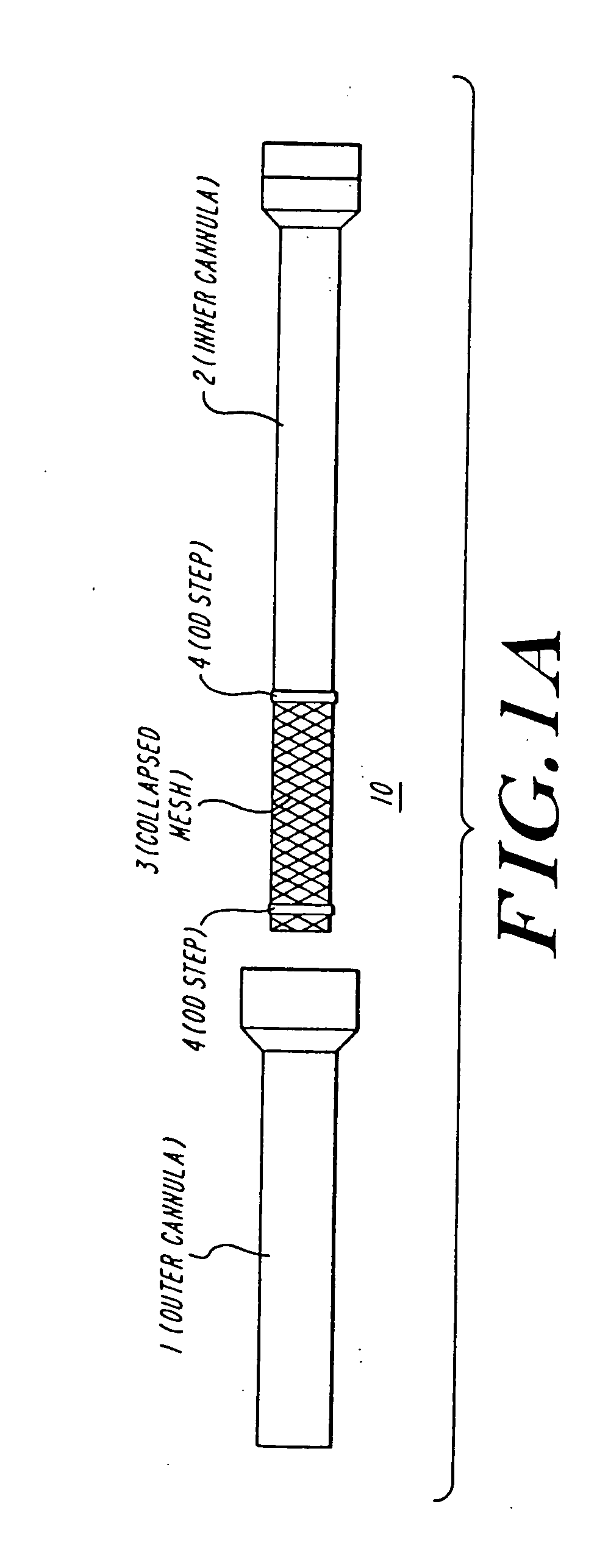
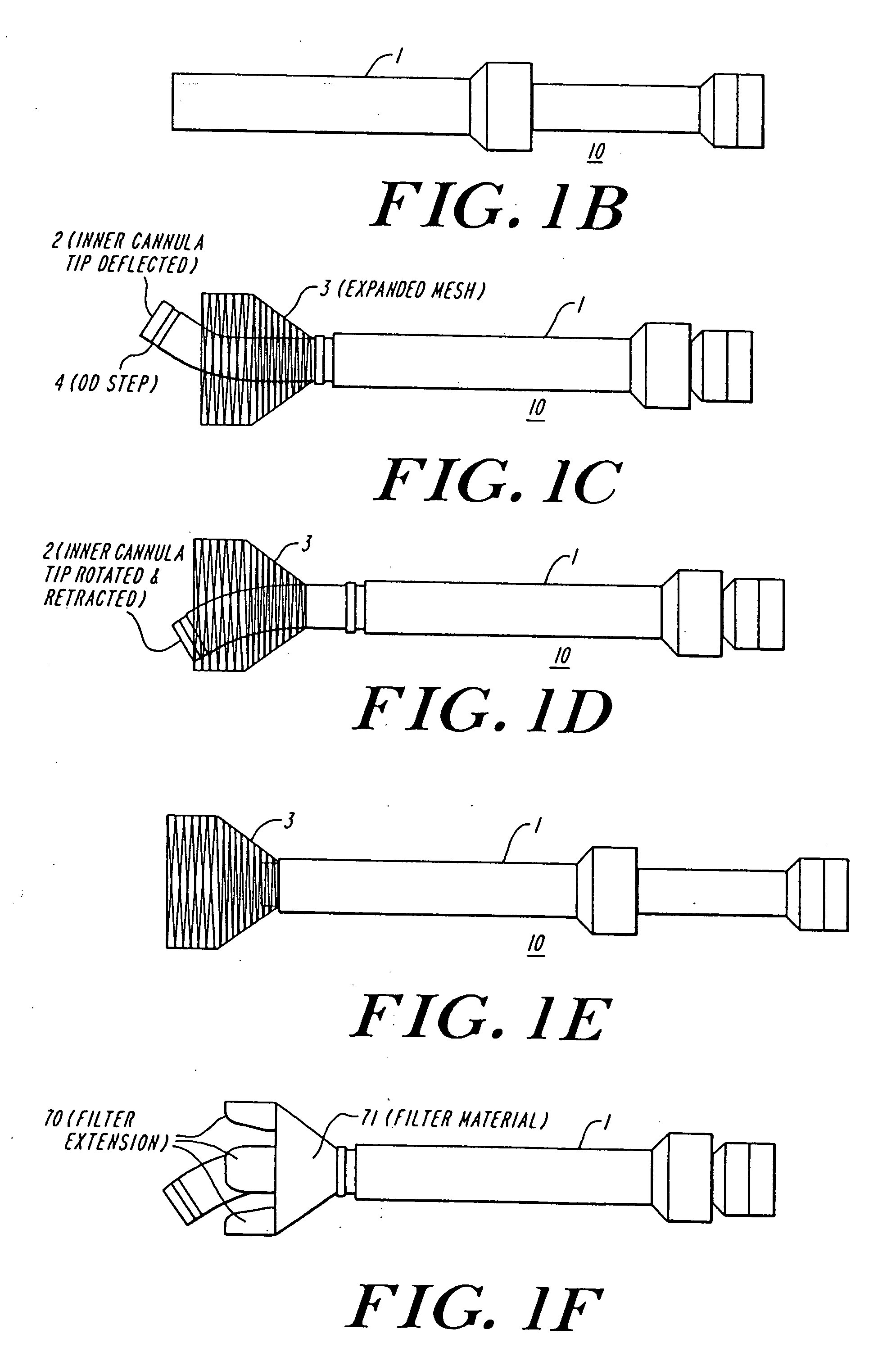
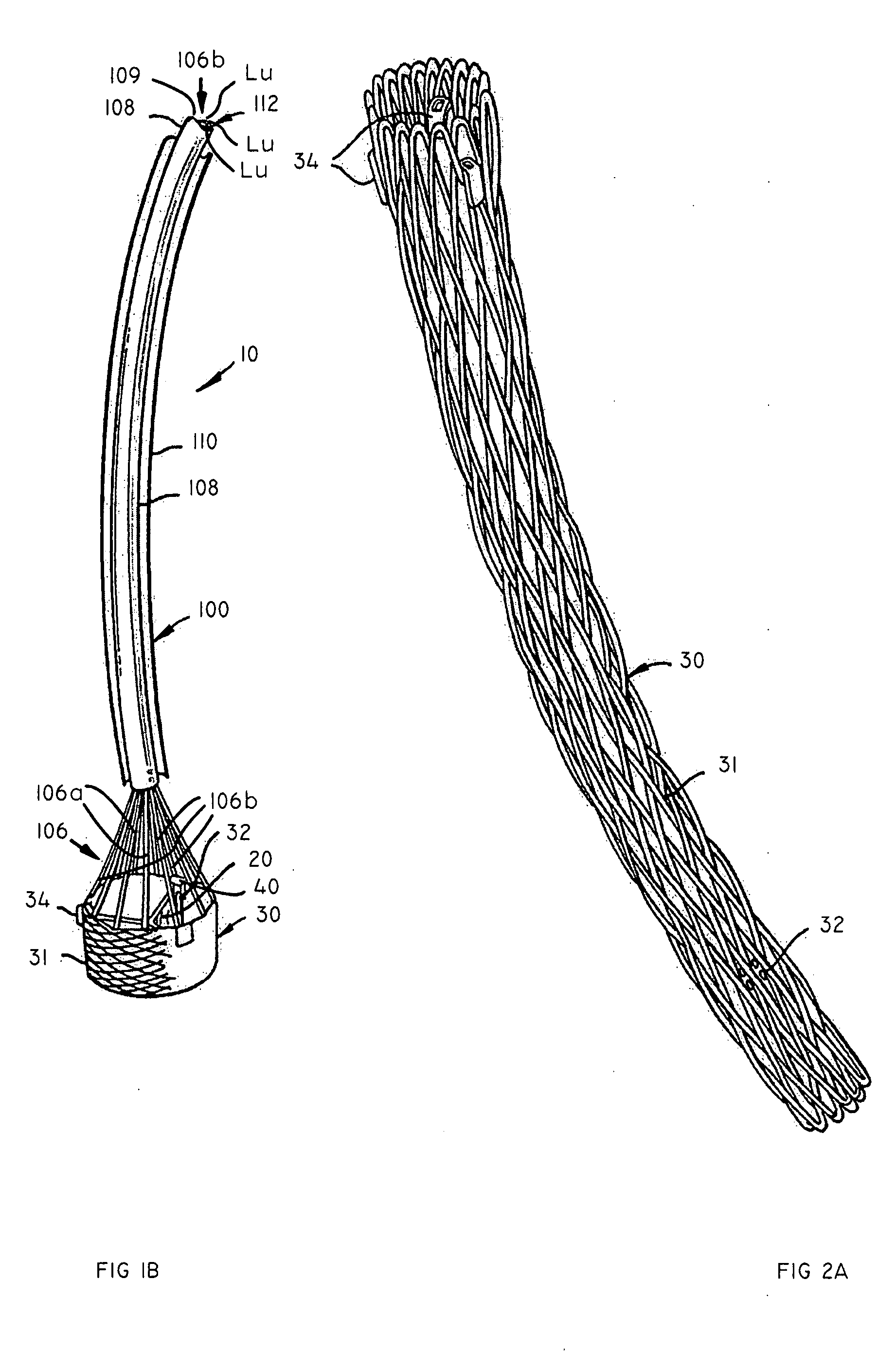
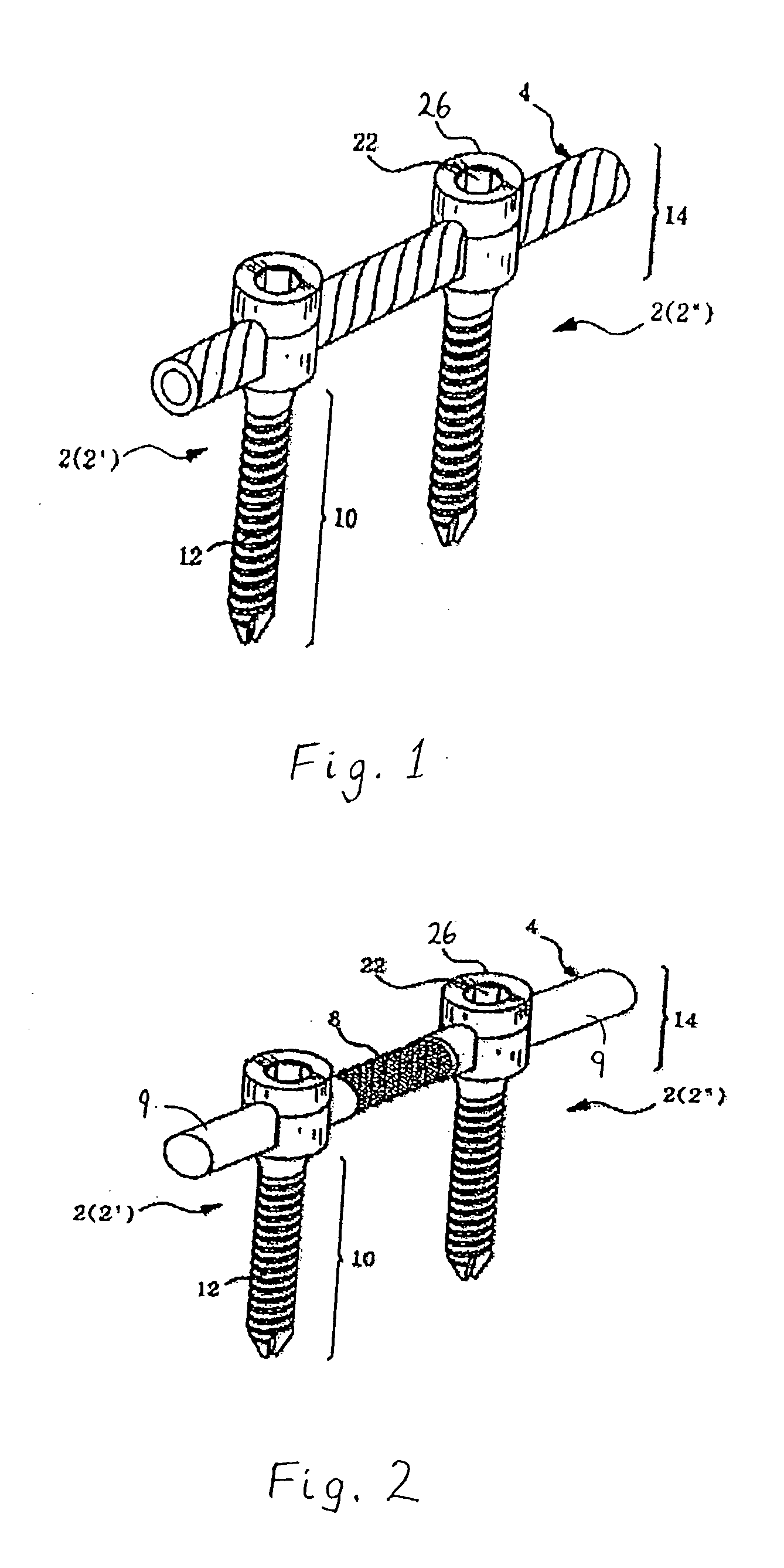
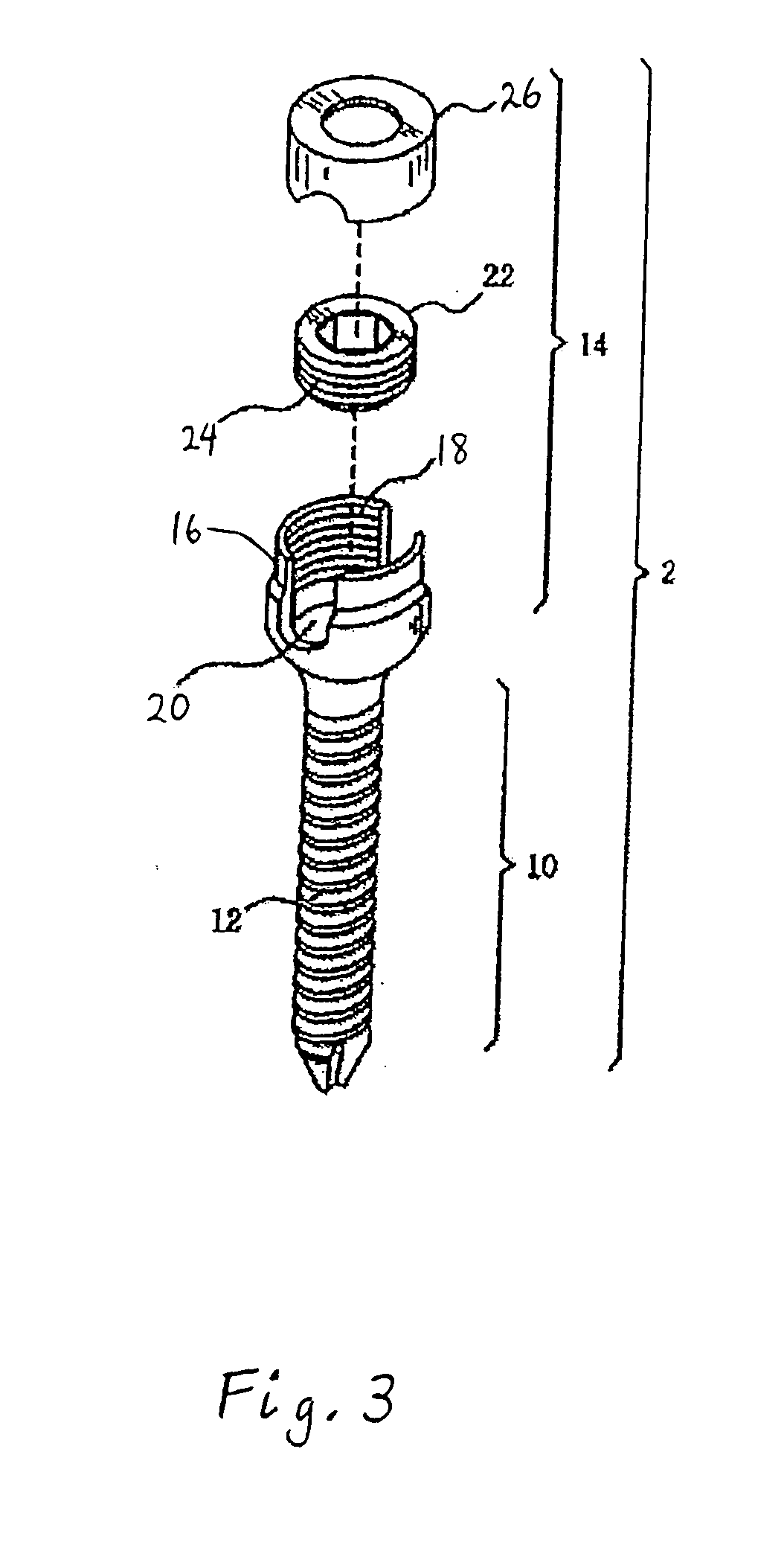
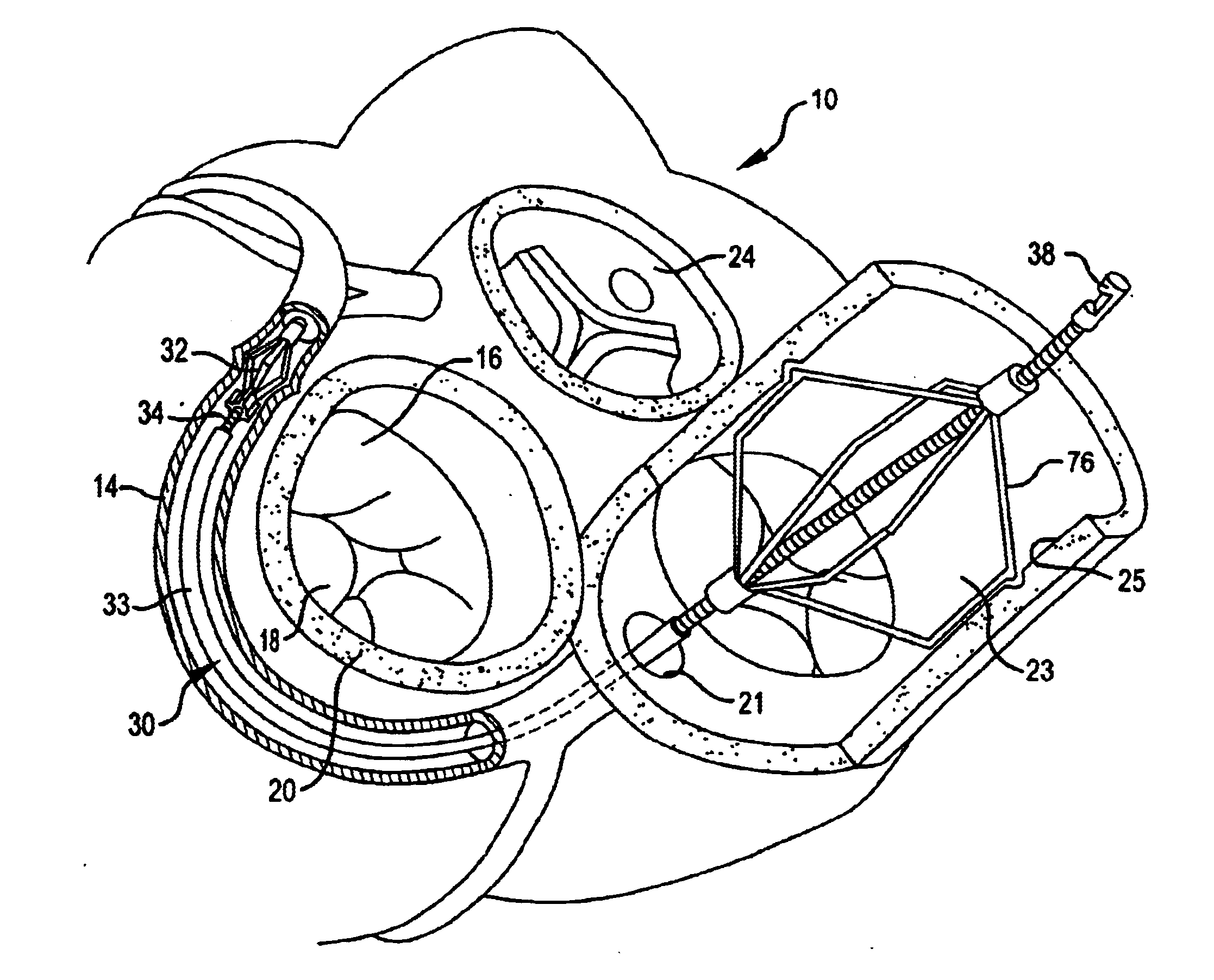
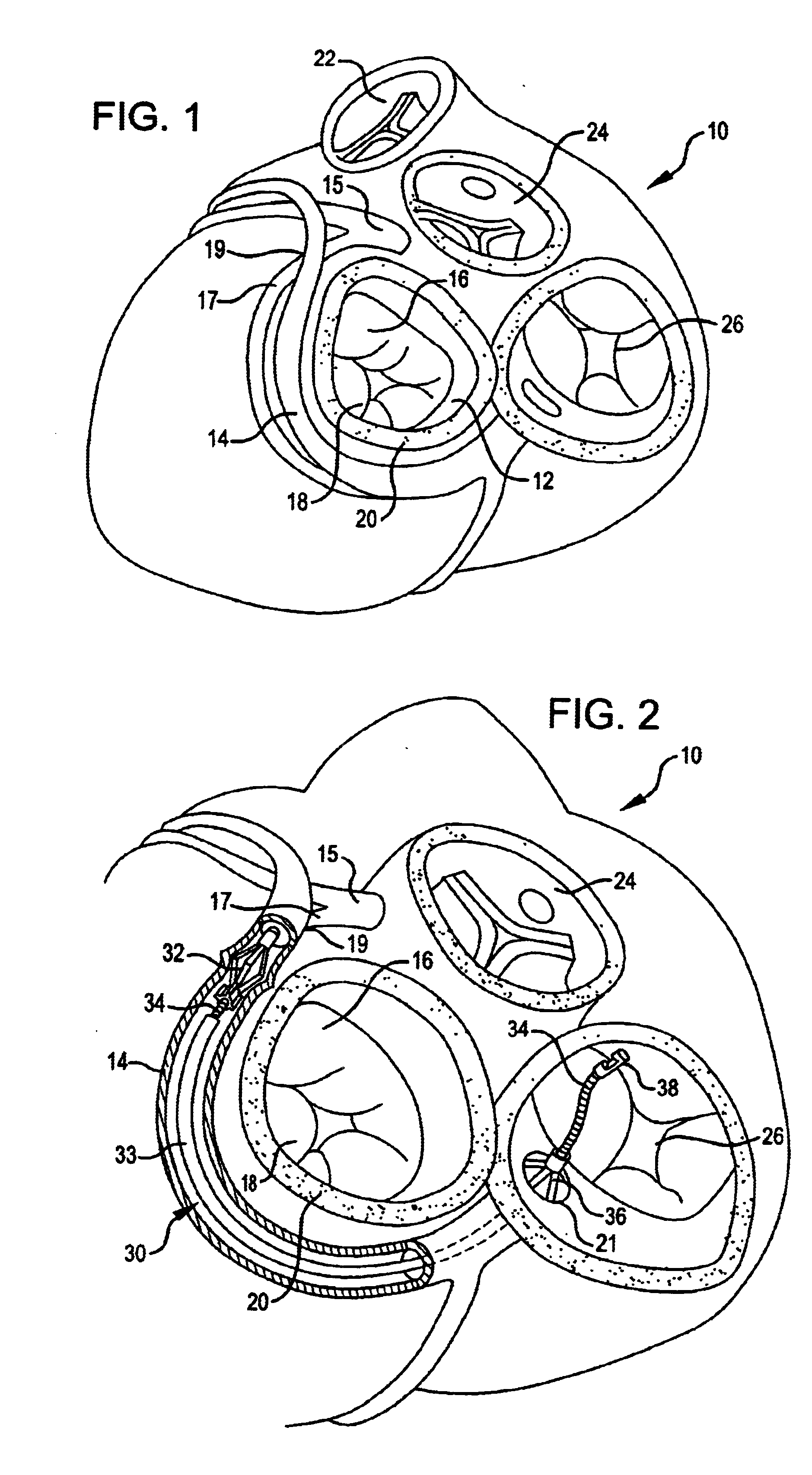
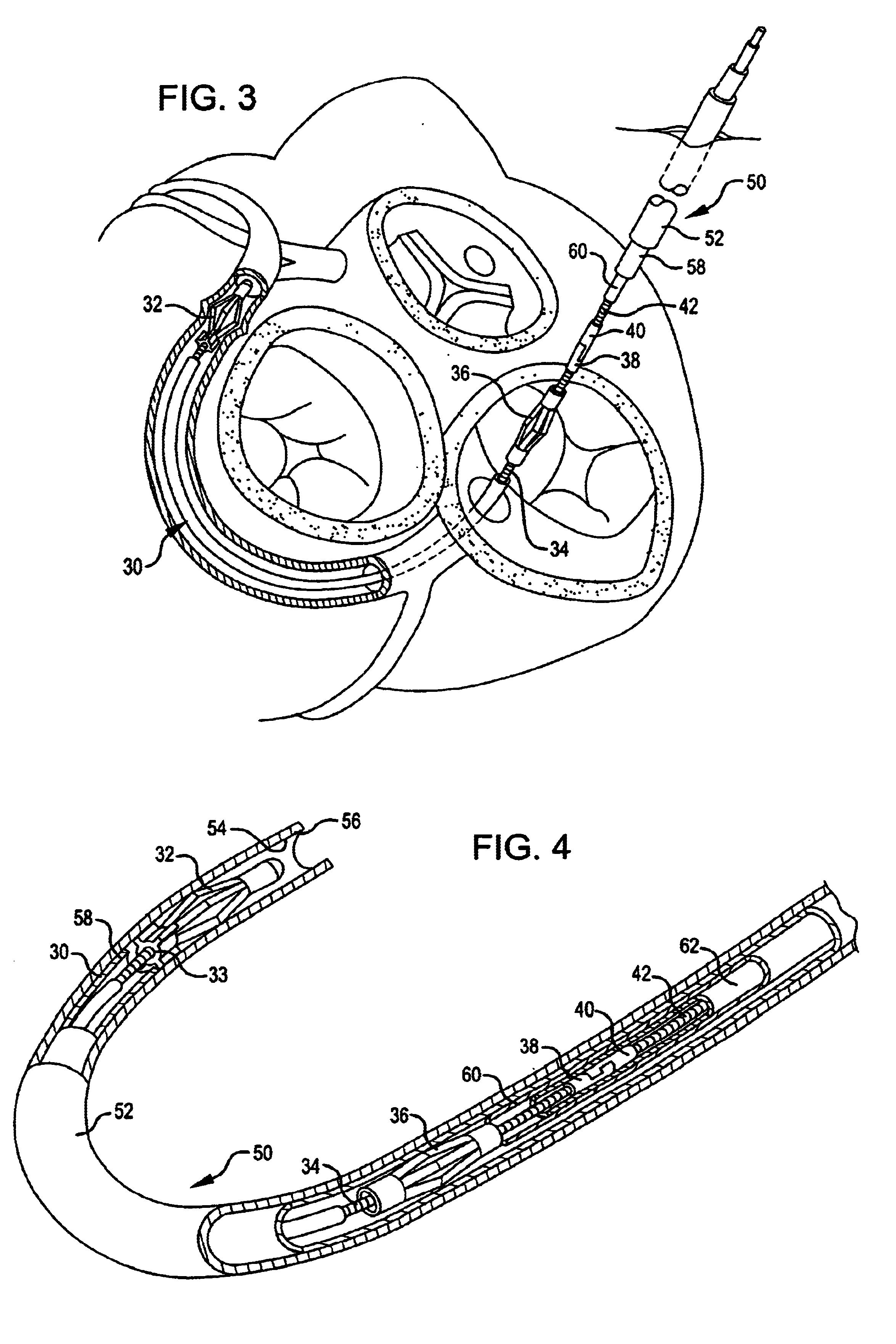
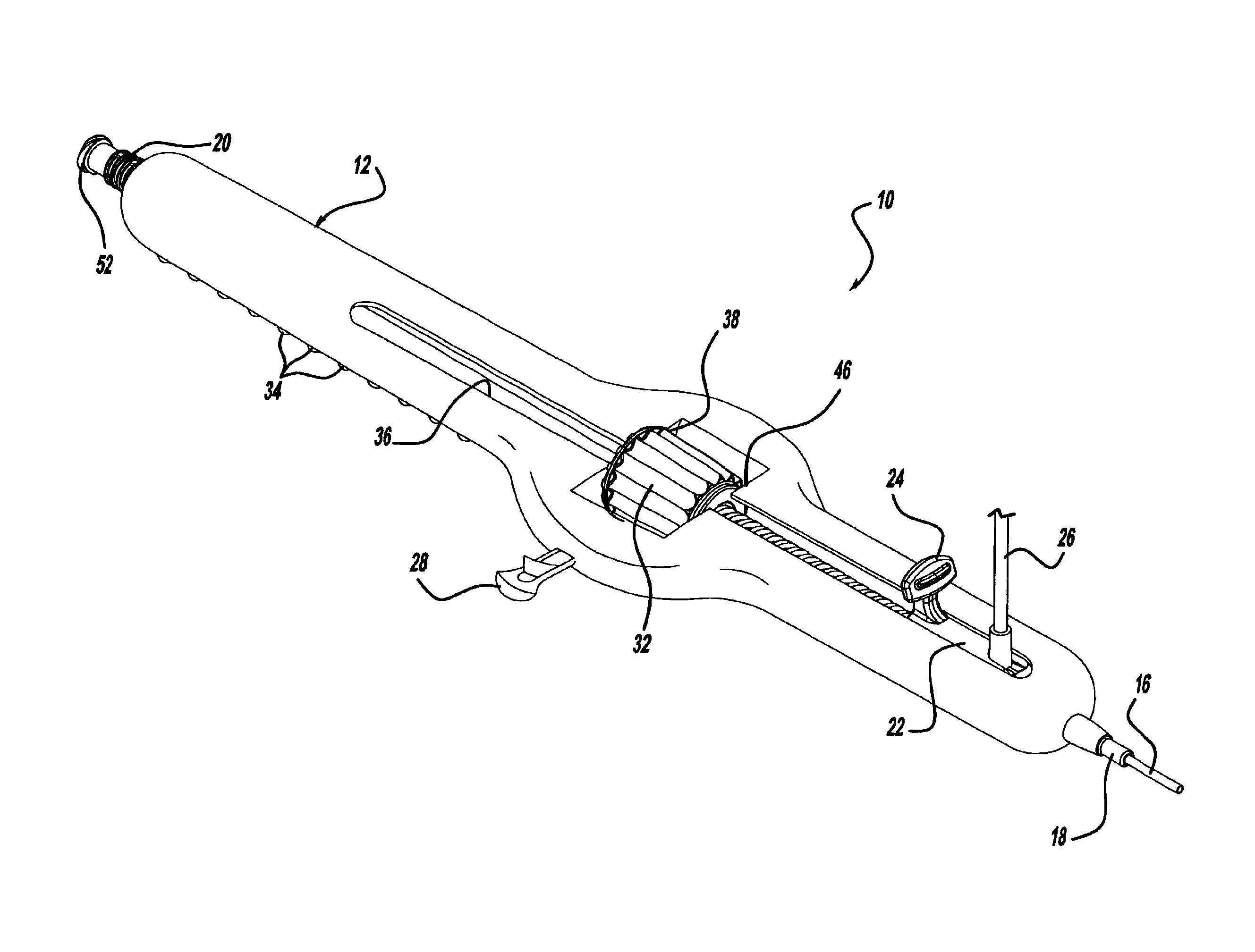
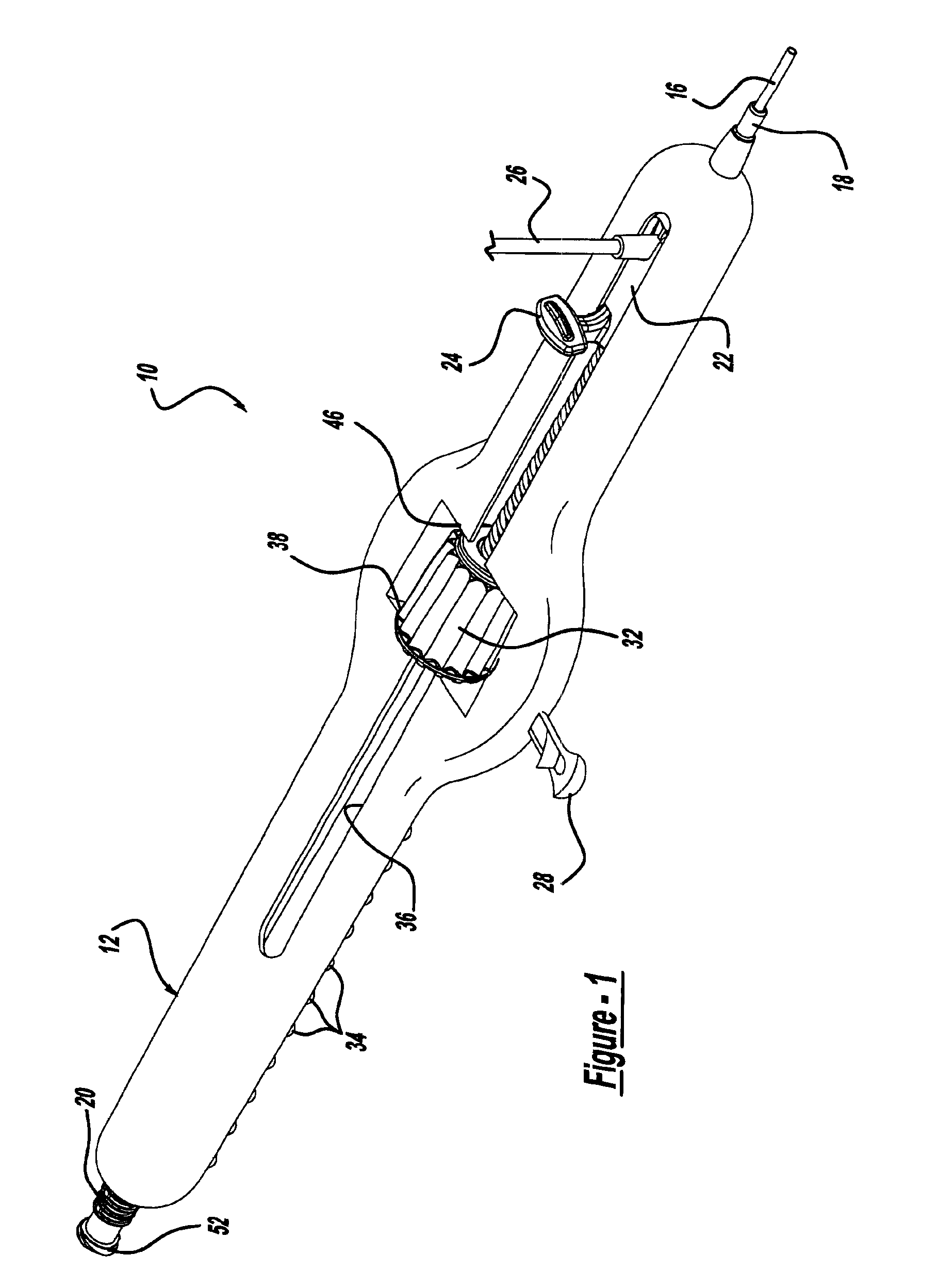
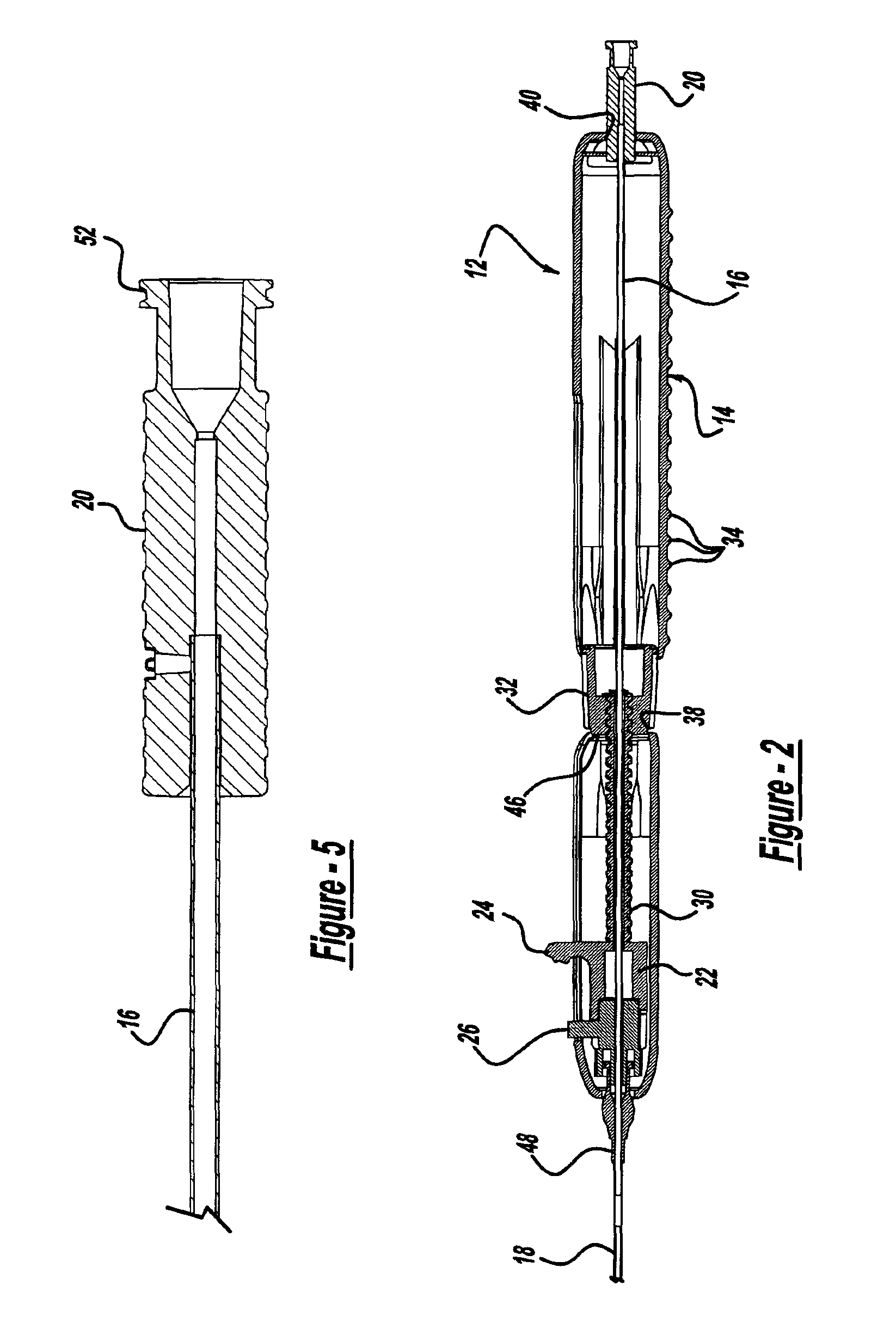
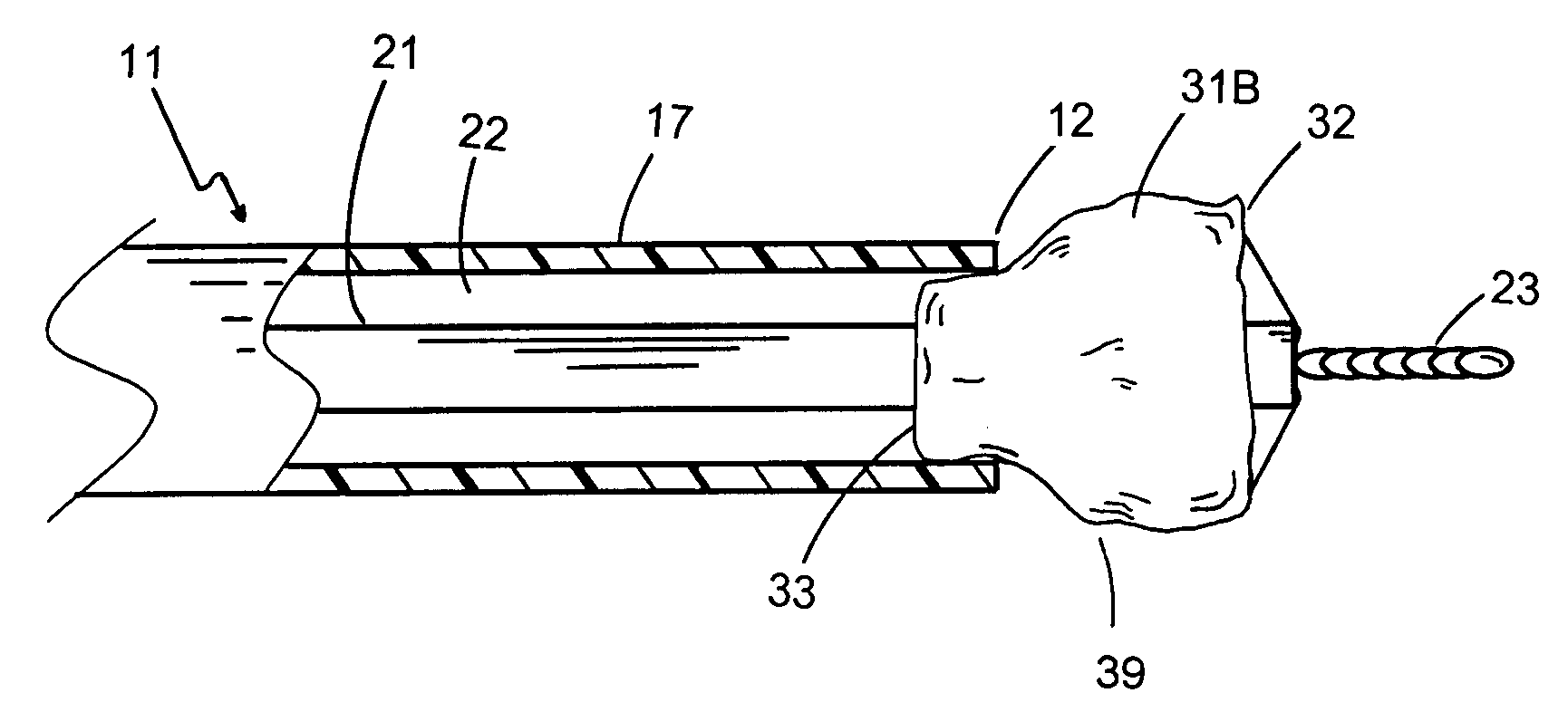
Methods and apparatus for performing transluminal and other procedures
InactiveUS20070135803A1Prevent overflowPrevent leakageSuture equipmentsEar treatmentSurgeryInstrumentation
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
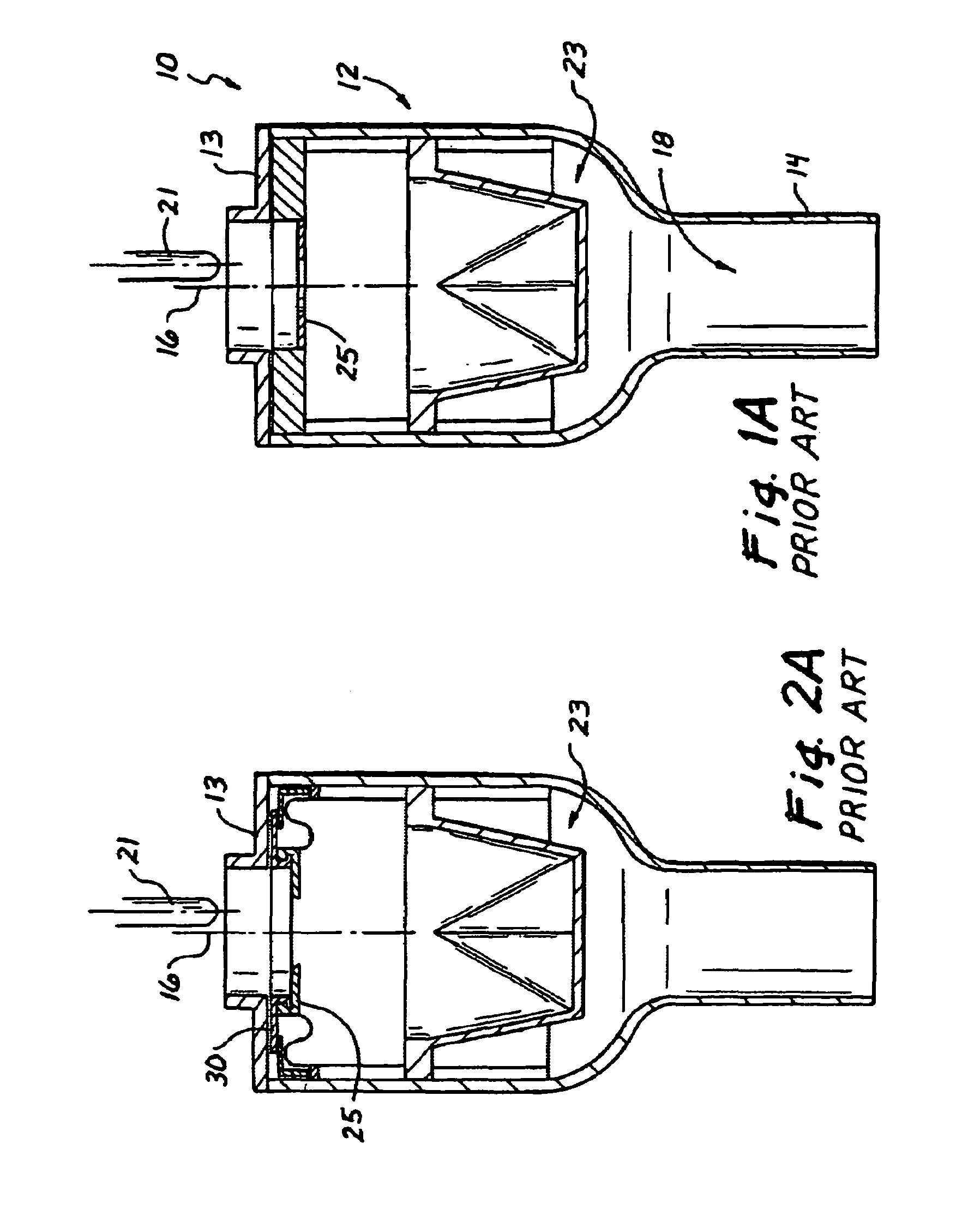
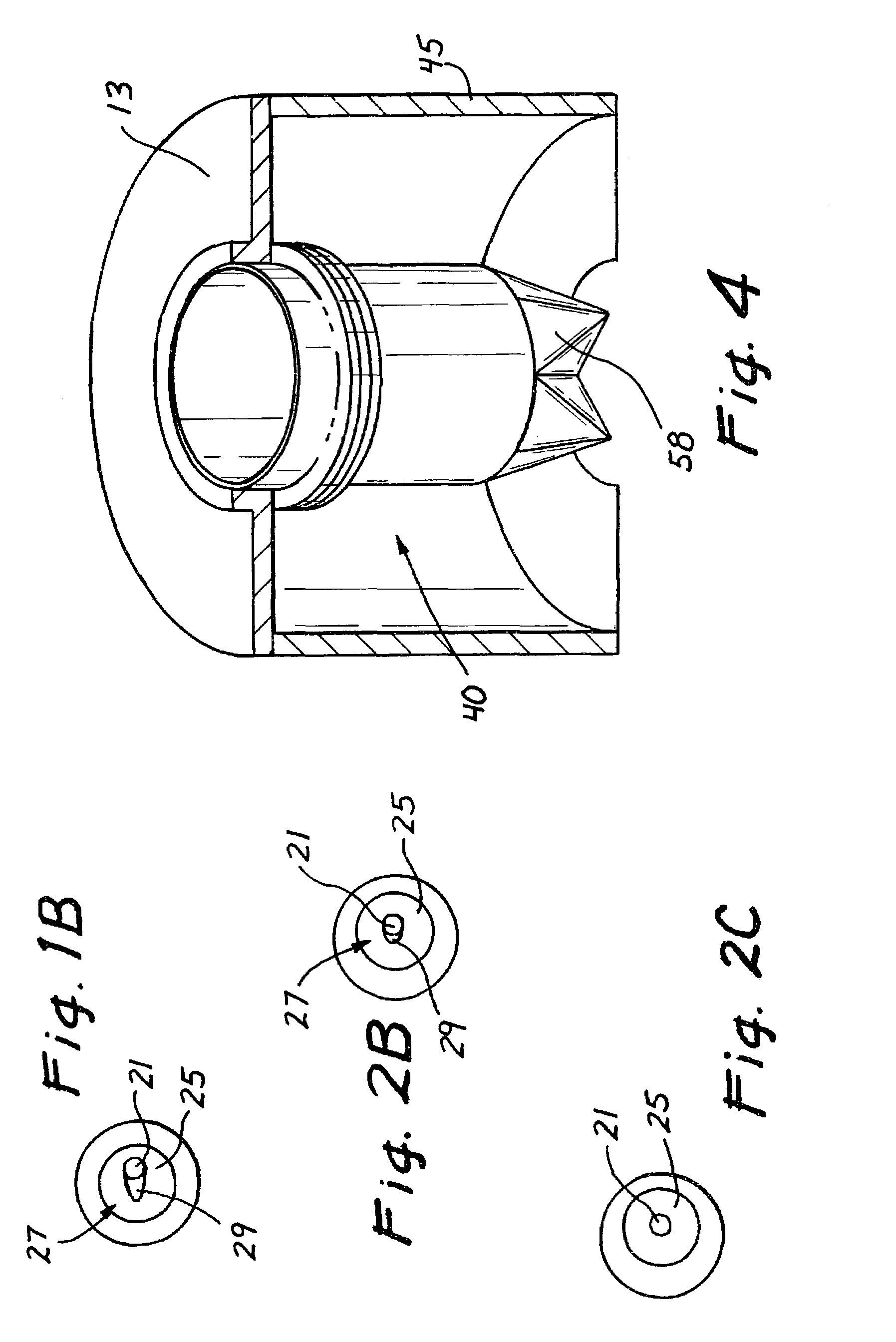
Sealed surgical access device
InactiveUS7052454B2” laparoscopy is greatly facilitatedFulfil requirementsEar treatmentCannulasCouplingEngineering
A surgical access device is adapted to facilitate access through an incision in a body wall having an inner surface and an outer surface, and into a body cavity of a patient. The device includes first and second retention members adapted to be disposed in proximity to the outer surface and the inner surface of the body wall, respectively. A membrane extending between the two retention members forms a throat which is adapted to extend through the incision and form a first funnel extending from the first retention member into the throat, and a second funnel extending from the second retention member into the throat. The throat of the membrane has characteristics for forming an instrument seal in the presence of an instrument and a zero seal in the absence of an instrument. The first retention member may include a ring with either a fixed or variable diameter. The ring can be formed in first and second sections, each having two ends. Couplings can be disposed between the ends to accommodate variations in the size of the first retention member. The first retention member can also be formed as an inflatable toroid, a self-expanding foam, or a circumferential spring. A plurality of inflatable chambers can also provide the surgical access device with a working channel adapted for disposition across the body wall. A first retention member with a plurality of retention stations functions with a plurality of tethers connected to the membrane to change the shape of the membrane and the working channel. A stabilizing platform can be used to support the access device generally independent of any movement of the body wall.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Tissue access guidewire system and method
A method and system for guiding at least a portion of a surgical device to a desired position between two tissues in a patient's body involves coupling a guidewire to the device and pulling the distal end of the guidewire to guide at least a portion of the surgical device to a desired position between the two tissues. The surgical device generally includes one or more guidewire coupling members and may comprise a tissue access device. A system may include a guidewire and a surgical device. In some embodiments, a guidewire, a tissue access device, and one or more additional devices to use with the access device may be provided. Methods, devices and systems may be used in open, less-invasive or percutaneous surgical procedures, in various embodiments.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC +1
Flexible delivery device
InactiveUS6921397B2Improved torque and flexure characteristicYielding couplingEar treatmentEngineeringDelivery system
This invention relates to catheter delivery systems, and more specifically, to a tubular device with improved torque and flexure characteristics. The present invention is a tubular device having improved torque and flexure characteristics which uses a series of permanently interlocking independent segments to provide the necessary torque and flexure characteristics.
Owner:ATRIAL SOLUTIONS INC
Surgical access device with pendent valve
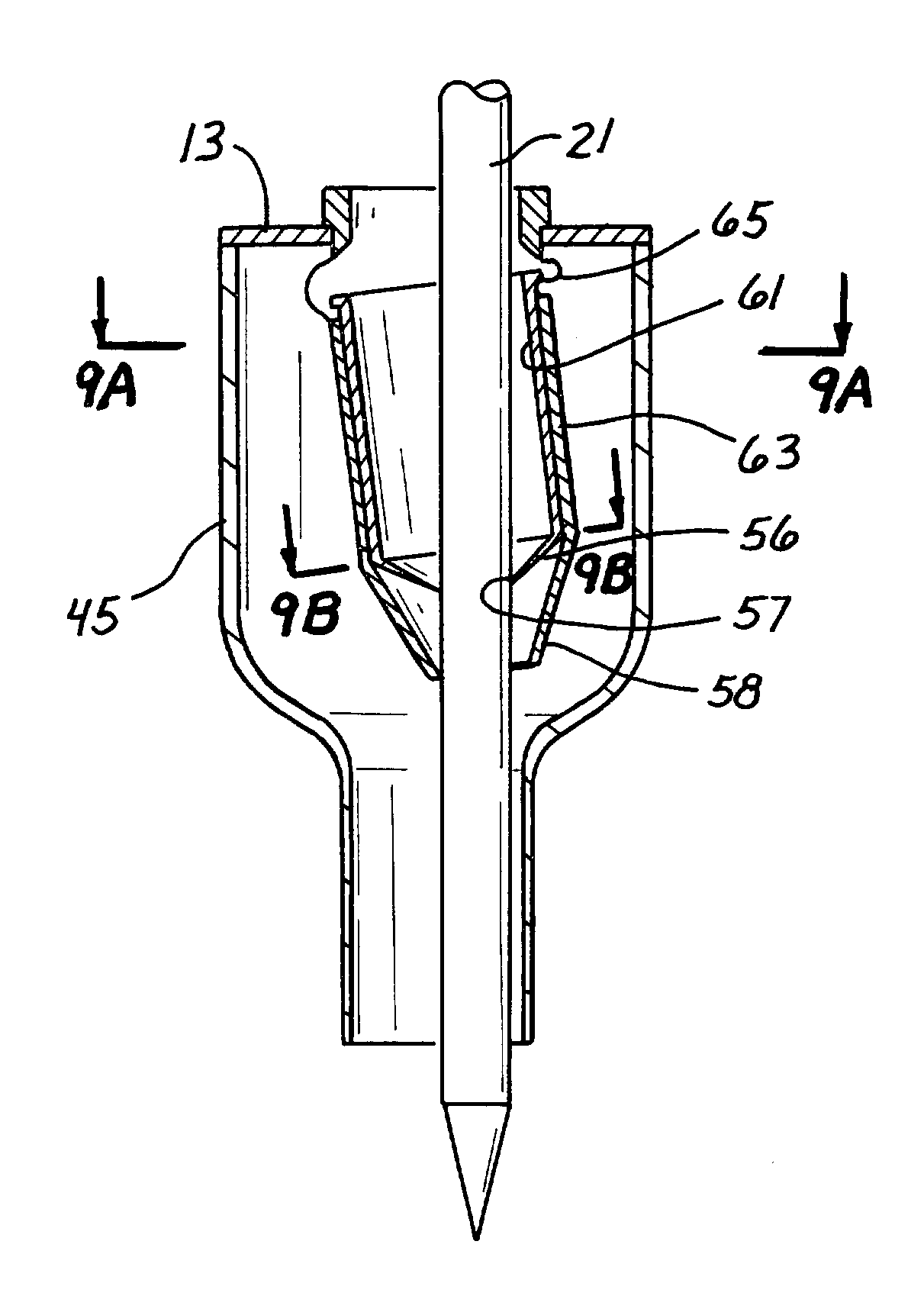
InactiveUS7083626B2Precise positioningMaximize ease and safetyEar treatmentCannulasSurgical departmentVALVE PORT
A surgical access device, such as a trocar, includes a pendent valve having an elongate structure extending from a proximal end to a septum valve disposed at a distal end. In operation, the elongate structure follows the angle of the instrument to pre-position the septum valve into the path of the instrument where it is not significantly challenged during instrument insertion or manipulation. The pendant valve can be made to float at both the proximal end and the distal end of the elongate structure, to further reduce the vulnerability of the septum valve. Since the valve is less vulnerable to instrument insertion, it can be formed to minimize friction and maximize the functional range of the access device.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
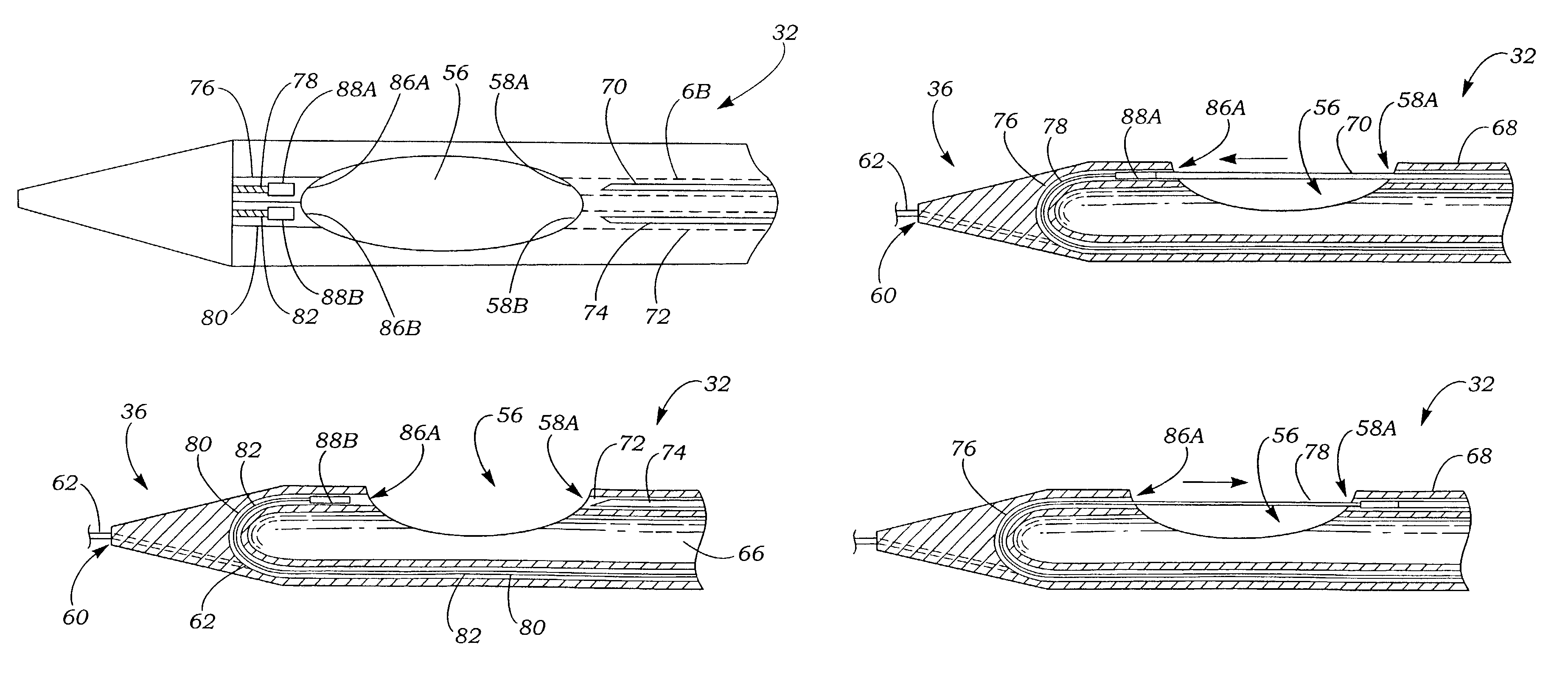
Flexible instrument
InactiveUS7775972B2Suture equipmentsProgramme-controlled manipulatorElement spaceBiomedical engineering
A medical probe and medical system are provided. The medical probe comprises an elongated shaft, a plurality of electromagnetic elements spaced along the elongated shaft, and a plurality of wires extending through the elongated shaft and configured for energizing the electromagnetic elements that actuate a controlled bending of the elongated shaft. The medical system may comprise the medical probe and a controller configured for energizing the electromagnetic elements via the wires to actuate the controlled bending of the elongated shaft. The medical system may optionally comprise a user interface configured for conveying commands to the controller, in which case, the controller will be configured for energizing the electromagnetic elements via the wires to actuate a controlled bending of the elongated shaft in response to the commands.
Owner:HANSEN MEDICAL INC
System and methods for advancing a catheter
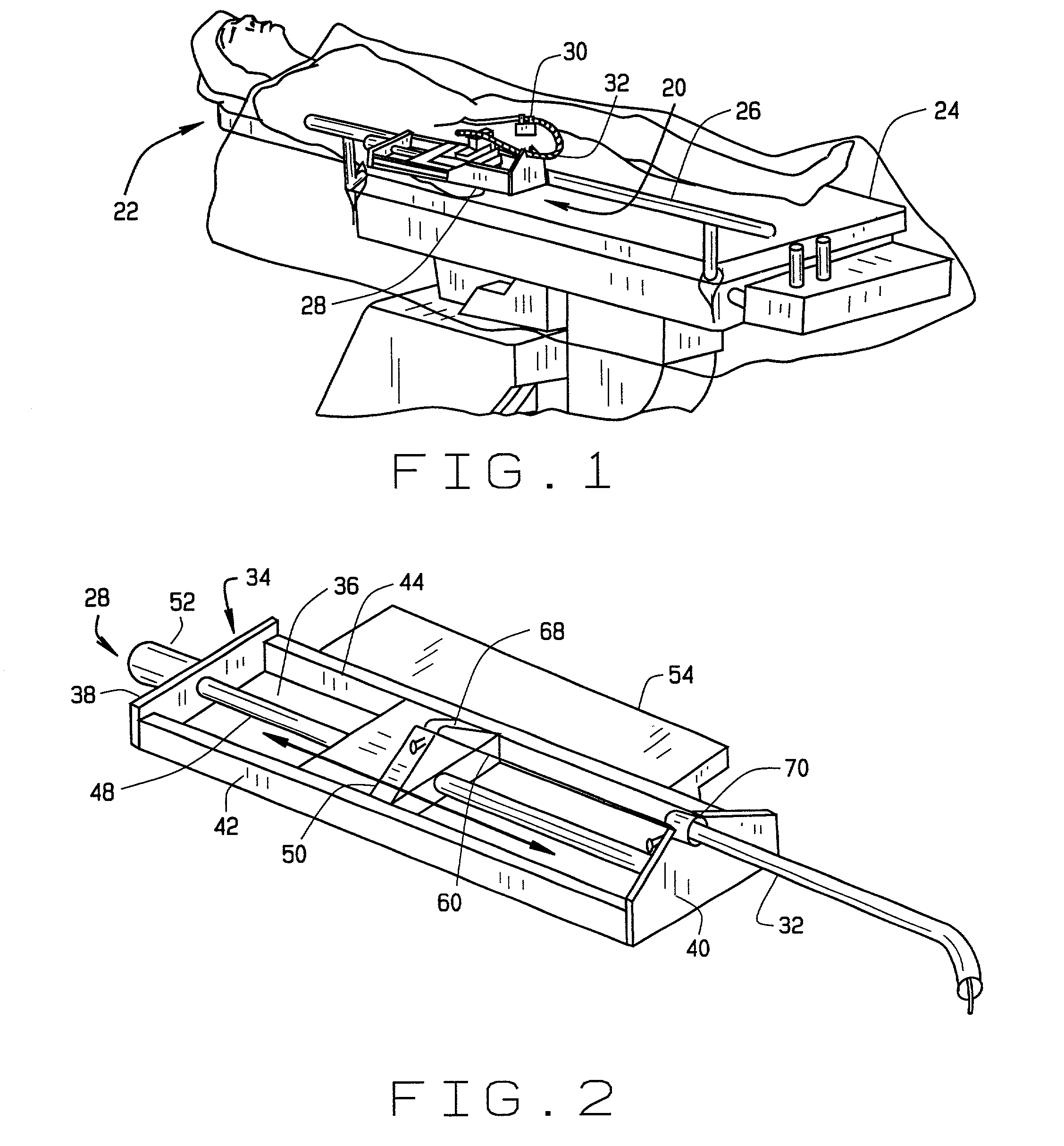
InactiveUS7276044B2Reduce repeated x-ray exposureReduce X-ray exposureEar treatmentSurgical needlesControl systemEngineering
An advancer system is described for moving an elongate medical device within a body. The system includes a drive unit having a motor. The drive unit is configured to translate movement of the motor to the device so as to alternately advance and retract the device relative to the body. The advancer system also includes a user-operable control system configured to control the drive unit. The control system can interface with a magnetic navigation system. The above-described system allows an operating physician to control catheter advancement and retraction while remaining outside an x-ray imaging field. Thus the physician is freed from repeated x-ray exposure.
Owner:STEREOTAXIS
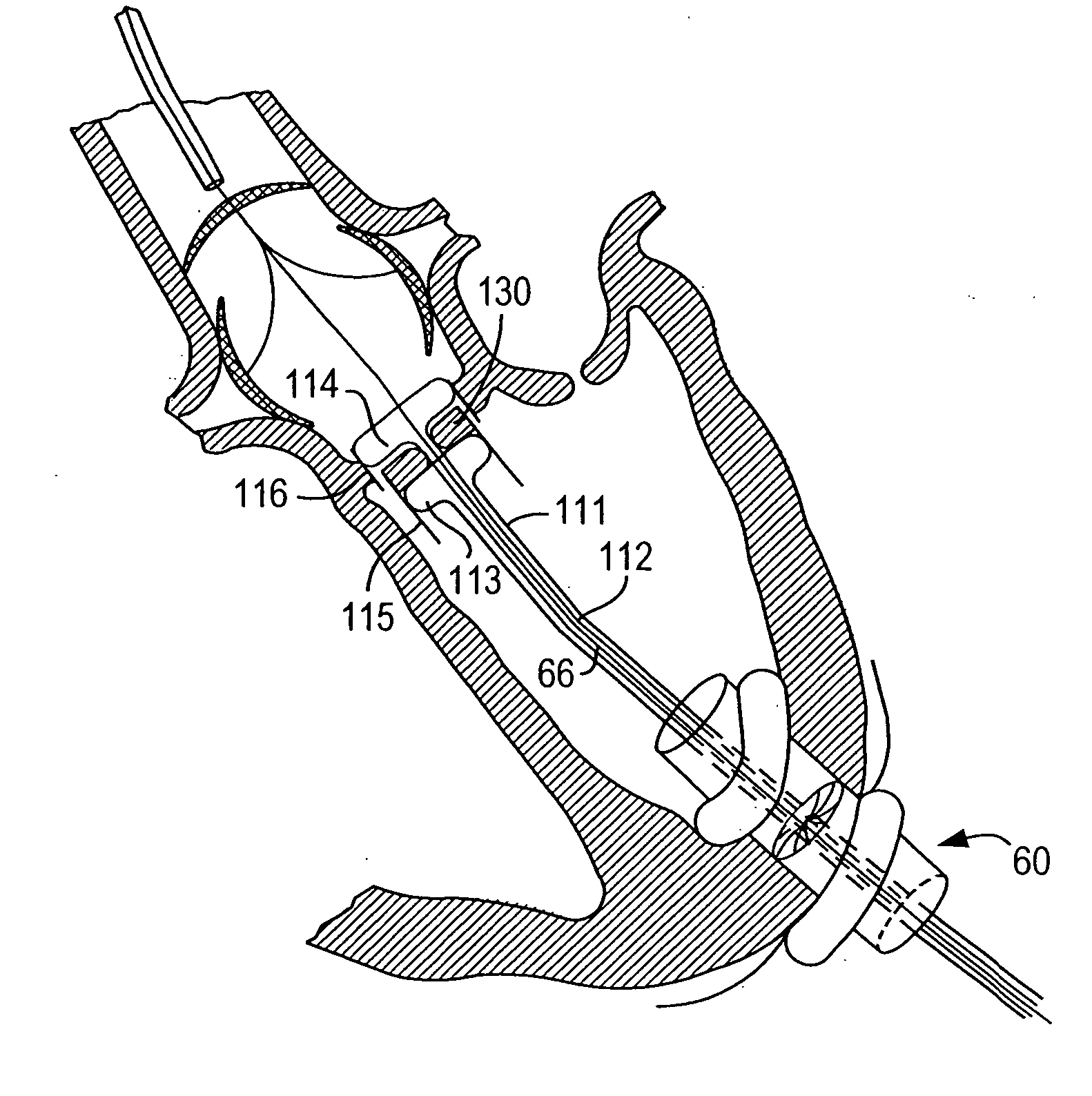
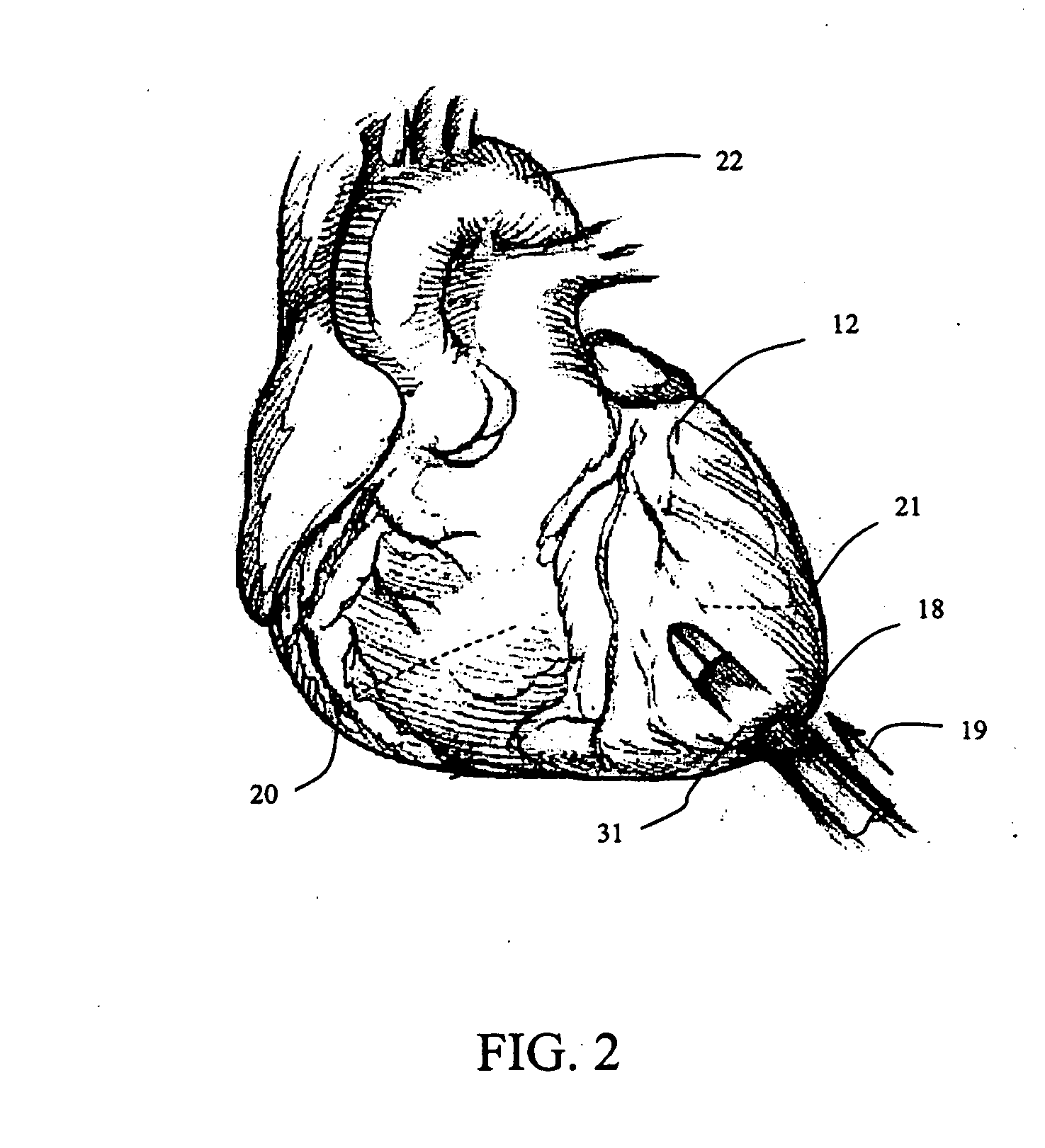
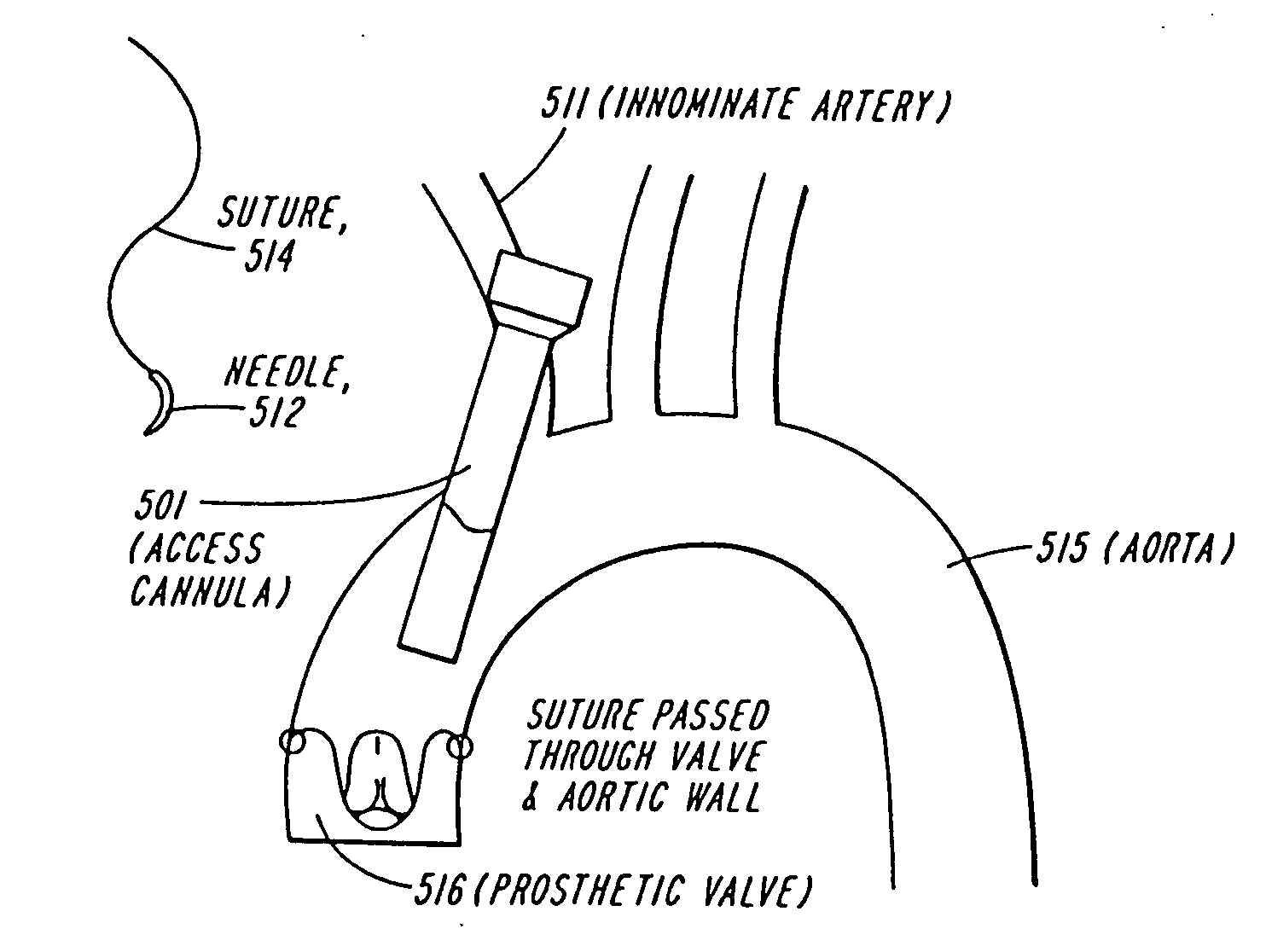
Methods and devices for repair or replacement of heart valves or adjacent tissue without the need for full cardiopulmonary support
ActiveUS20060074484A1Reduce in quantityEliminate needEar treatmentCannulasAortic dissectionVentricular aneurysm
Methods and systems for endovascular, endocardiac, or endoluminal approaches to a patient's heart to perform surgical procedures that may be performed or used without requiring extracorporeal cardiopulmonary bypass. Furthermore, these procedures can be performed through a relatively small number of small incisions. These procedures may illustratively include heart valve implantation, heart valve repair, resection of a diseased heart valve, replacement of a heart valve, repair of a ventricular aneurysm, repair of an arrhythmia, repair of an aortic dissection, etc. Such minimally invasive procedures are preferably performed transapically (i.e., through the heart muscle at its left or right ventricular apex).
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCI CARDIAQ
Method and apparatus for tissue connection
InactiveUS7101395B2Minimize traumaFunction increaseSuture equipmentsEar treatmentBiomedical engineering
A tissue connecting device is provided. The device comprise an elongate delivery device having a lumen, a proximal end, and a distal end. The distal end is configured to engage tissue and advance said device into tissue. At least one anchor deliverable through a lumen of the elongate delivery device. The distal end of the device may be designed to engage tissue upon rotation of the device about its longitudinal axis.
Owner:MITRAL INTERVENTIONS INC
Modified delivery device for coated medical devices
InactiveUS7527632B2Minimize potential risk of damageReduce frictionStentsEar treatmentBiological bodyMedical device
Medical devices, and in particular implantable medical devices, including self-expanding stents, may be coated to minimize or substantially eliminate a biological organism's reaction to the introduction of the medical device to the organism. The devices utilized to deliver the implantable medical devices may be modified to reduce the potential for damaging the implantable medical device during deployment.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Method and system for cardiac valve delivery
The invention provides methods and systems for introducing a delivery device in the heart at or near the apex of the heart, wherein the delivery device includes a prosthesis, advancing the prosthesis to the target site, and disengaging the prosthesis from the delivery device at the target site for implantation. Specifically, the present invention provides valve replacement systems for delivering a replacement heart valve to a target site in or near a heart. The valve replacement system comprises a trocar or other suitable device to penetrate the heart at or near the apex of the heart, a delivery member that is movably disposed within the trocar, and a replacement cardiac valve disposed on the delivery member. The delivery member may further comprise mechanical or inflatable expanding members to facilitate implantation of the prosthetic valve at the target site.
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
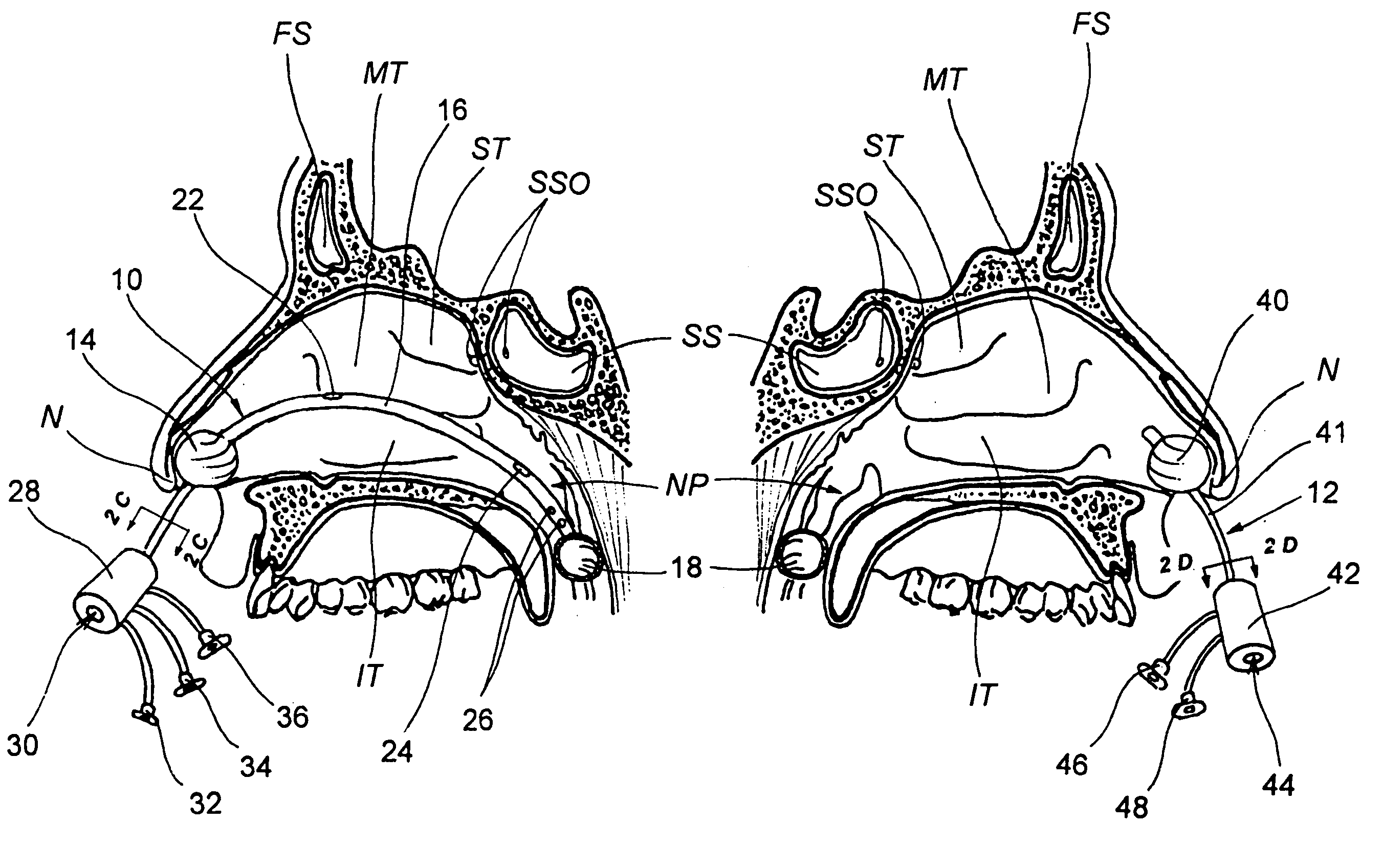
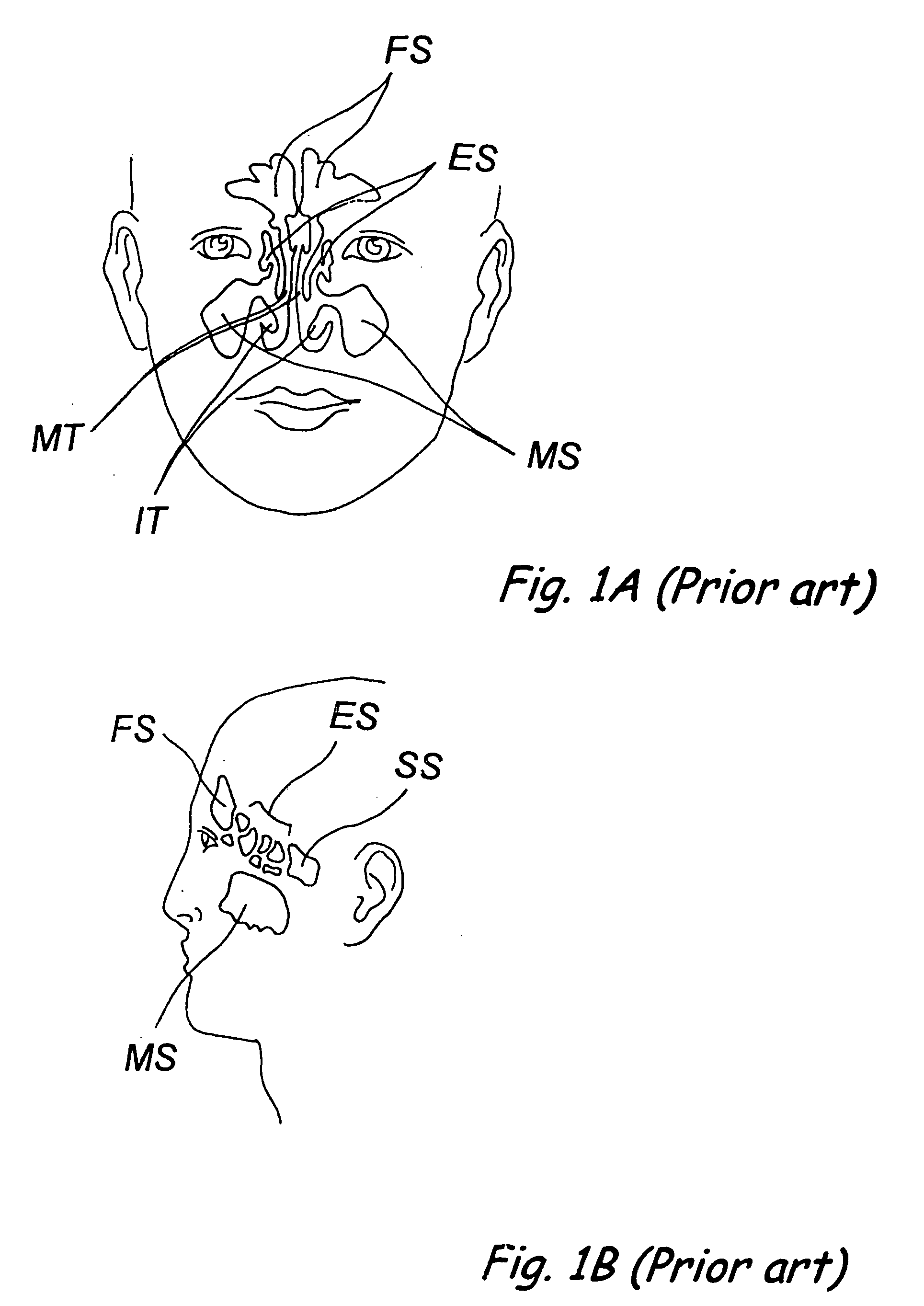
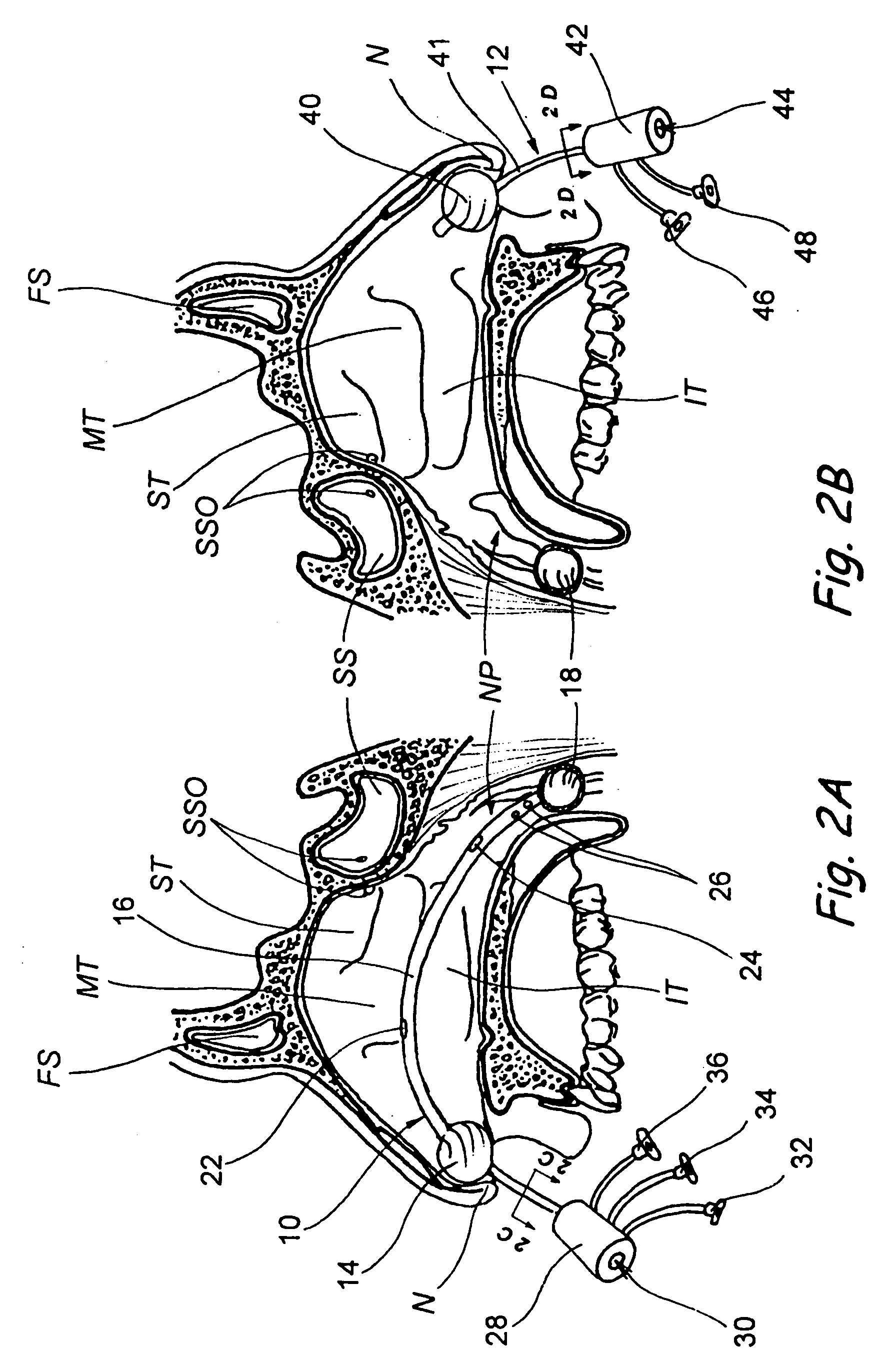
Devices, systems and methods for diagnosing and treating sinusitus and other disorders of the ears, nose and/or throat
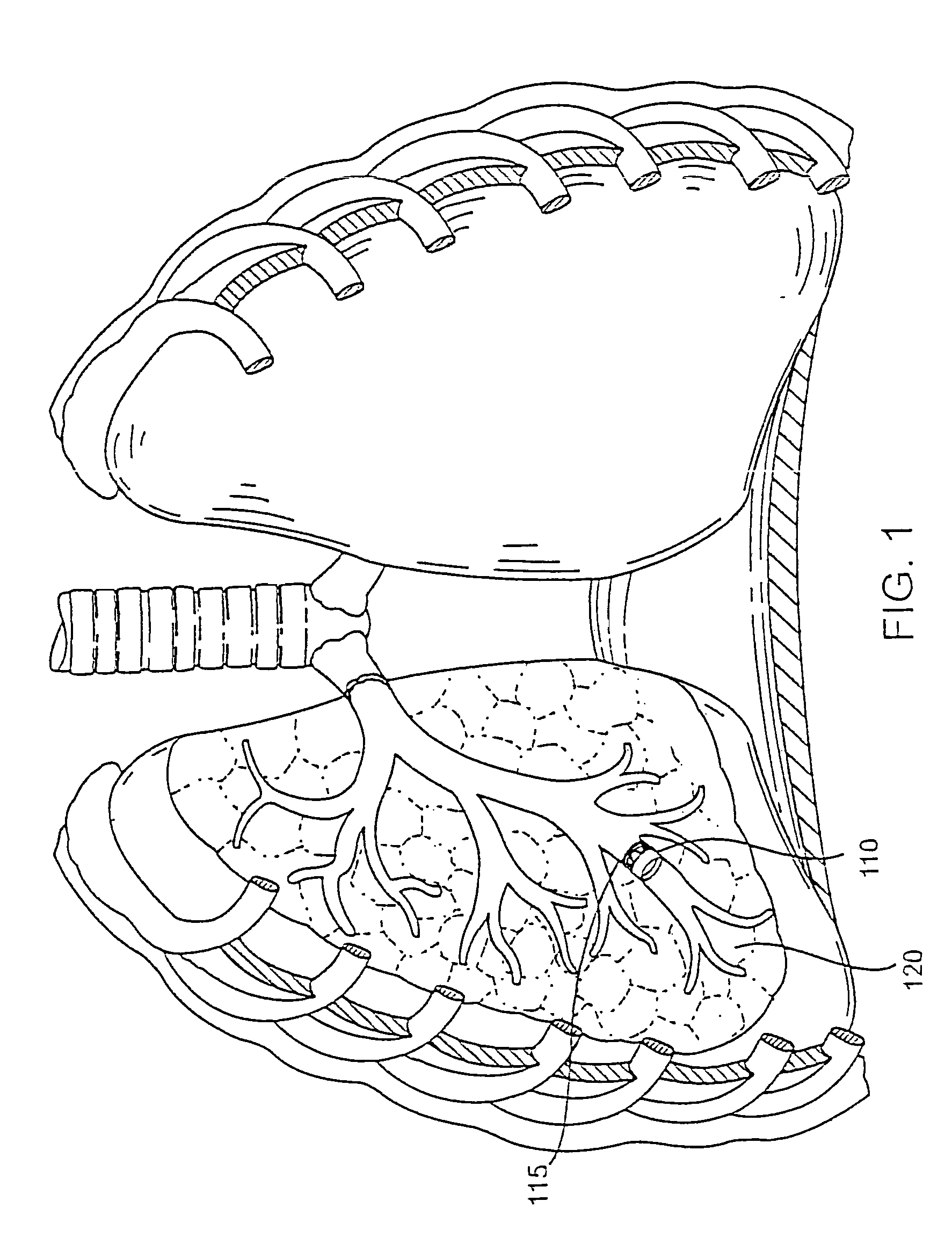
Sinusitis, enlarged nasal turbinates, tumors, infections, hearing disorders, allergic conditions, facial fractures and other disorders of the ear, nose and throat are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches and, in many cases, flexible catheters as opposed to instruments having rigid shafts. Various diagnostic procedures and devices are used to perform imaging studies, mucus flow studies, air / gas flow studies, anatomic dimension studies, endoscopic studies and transillumination studies. Access and occluder devices may be used to establish fluid tight seals in the anterior or posterior nasal cavities / nasopharynx and to facilitate insertion of working devices (e.g., scopes, guidewires, catheters, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for injecting diagnostic or therapeutic agents, devices for implanting devices such as stents, substance eluting devices, substance delivery implants, etc.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
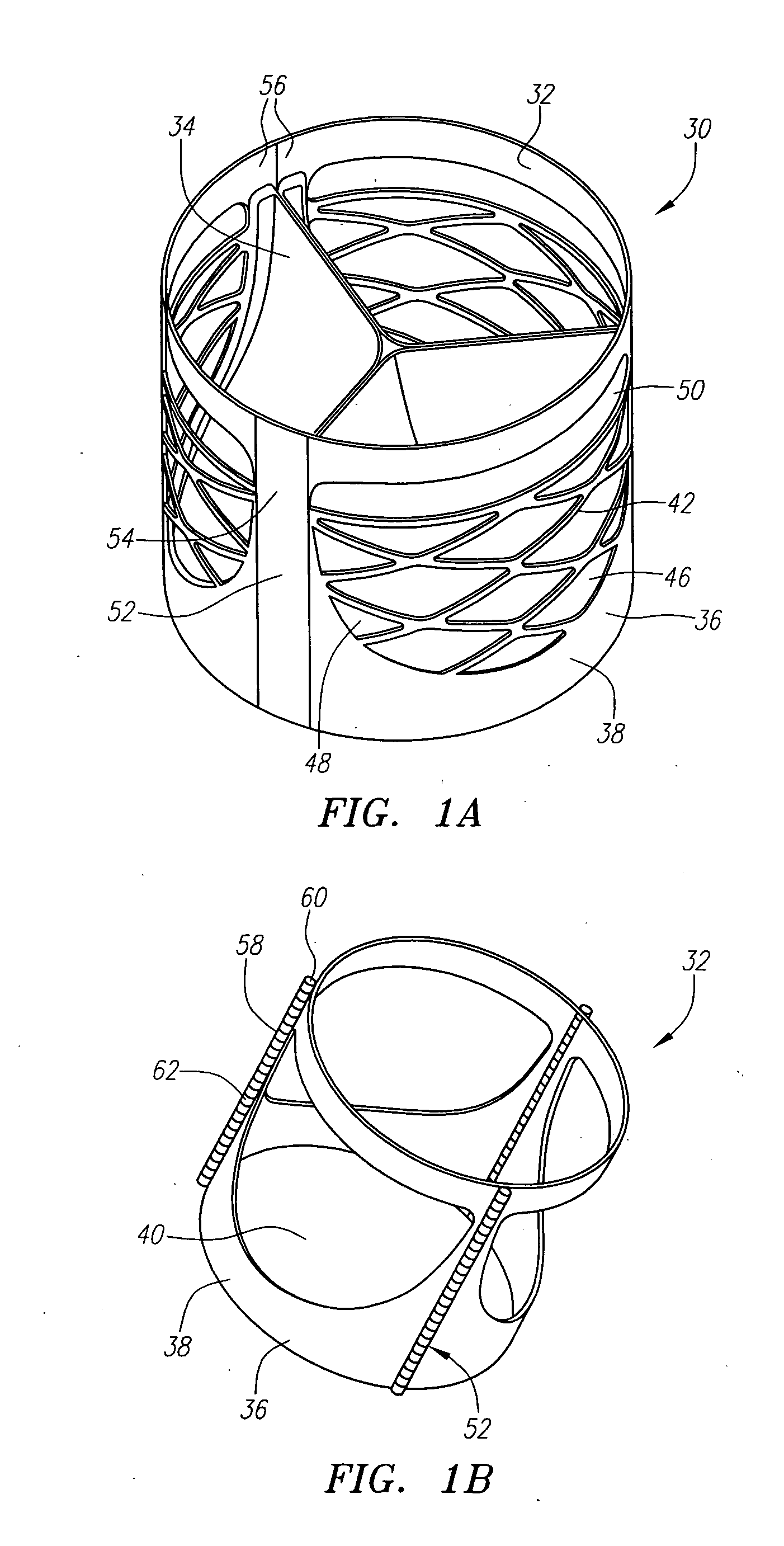
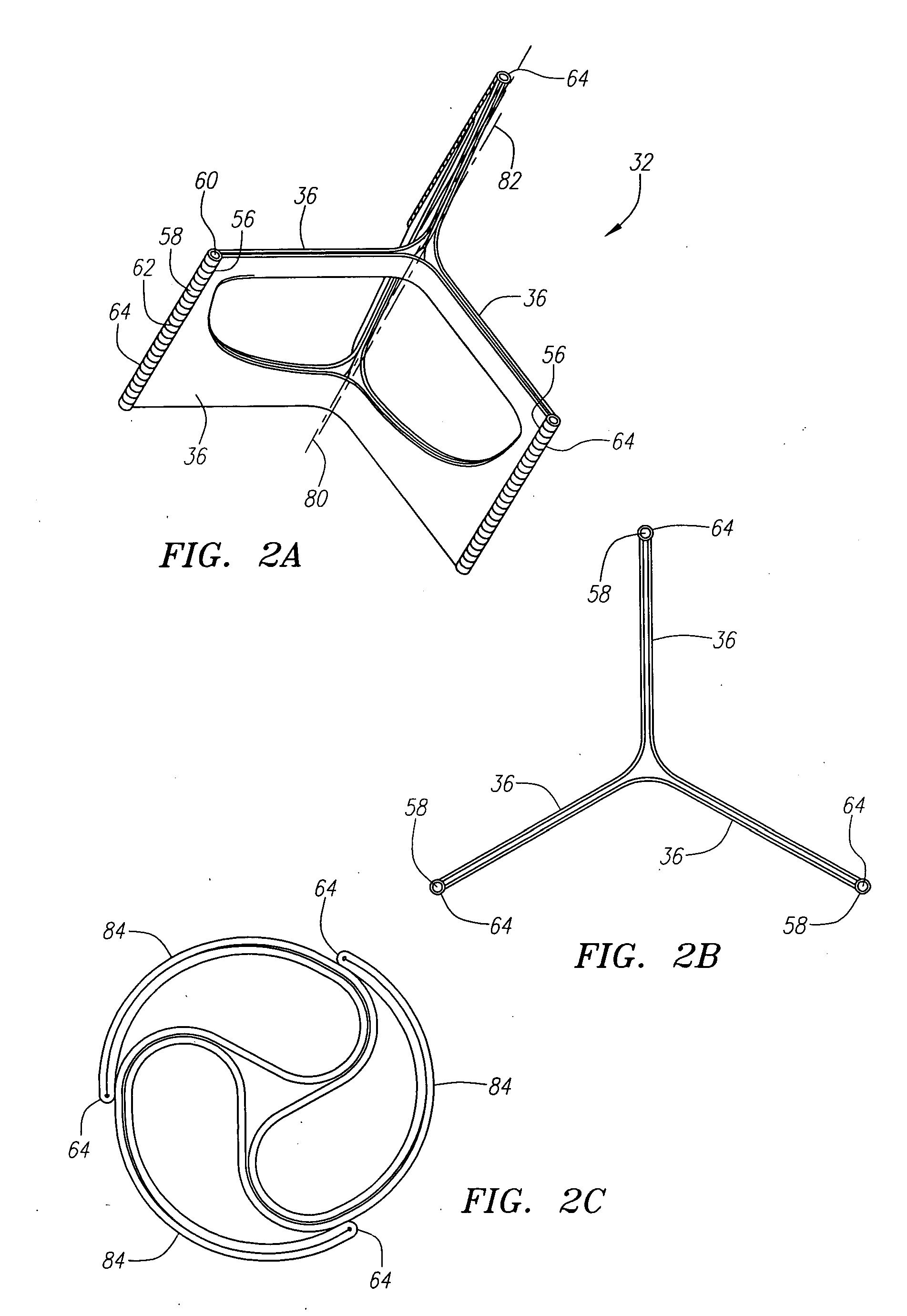
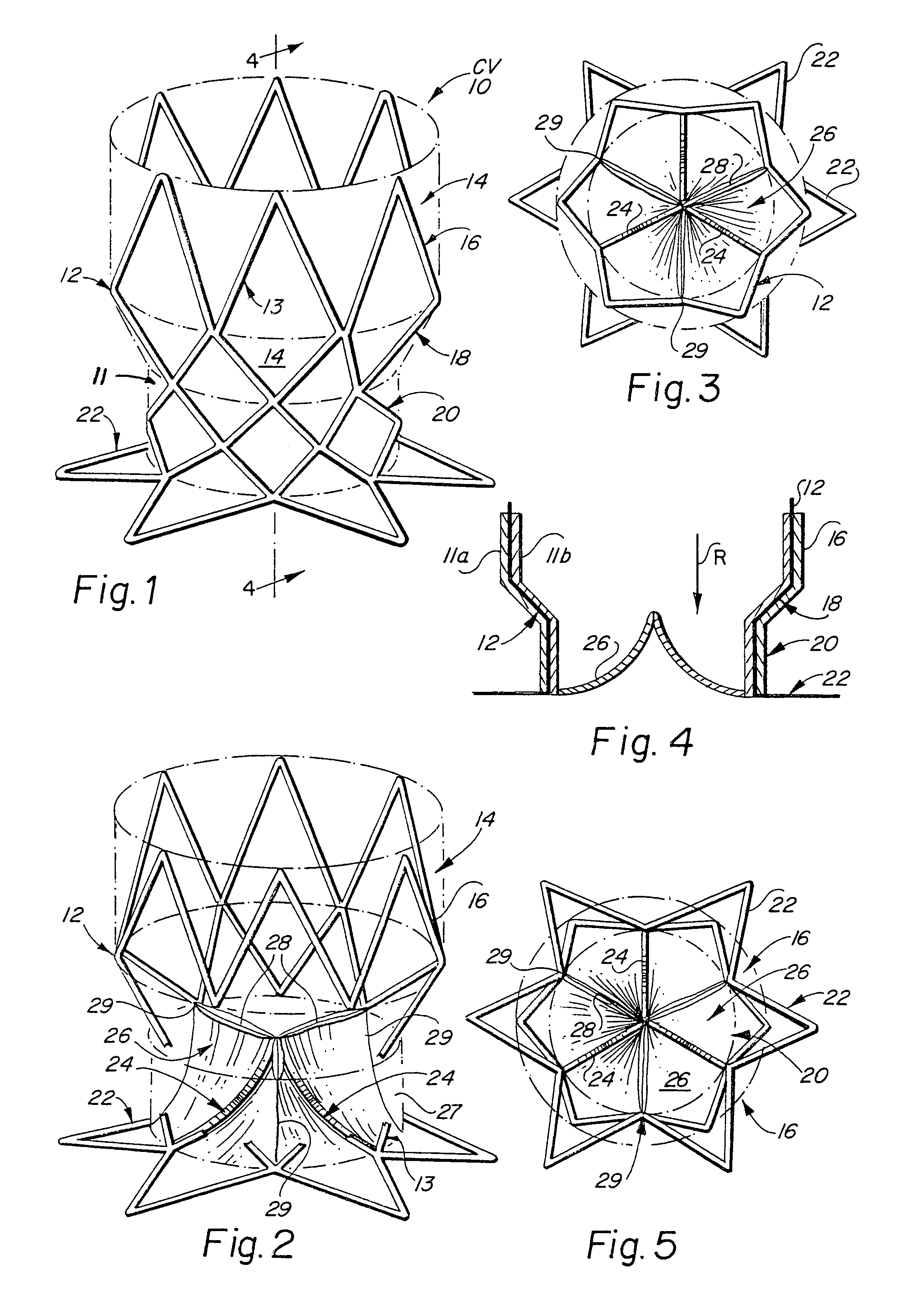
Prosthetic heart valves, scaffolding structures, and systems and methods for implantation of same
InactiveUS20050203614A1Inhibit migrationGood tissue adhesionBalloon catheterEar treatmentProsthesisBiomedical engineering
Prosthetic valves and their component parts are described, as are prosthetic valve delivery devices and methods for their use. The prosthetic valves are particularly adapted for use in percutaneous aortic valve replacement procedures. The delivery devices are particularly adapted for use in minimally invasive surgical procedures.
Owner:AORTX
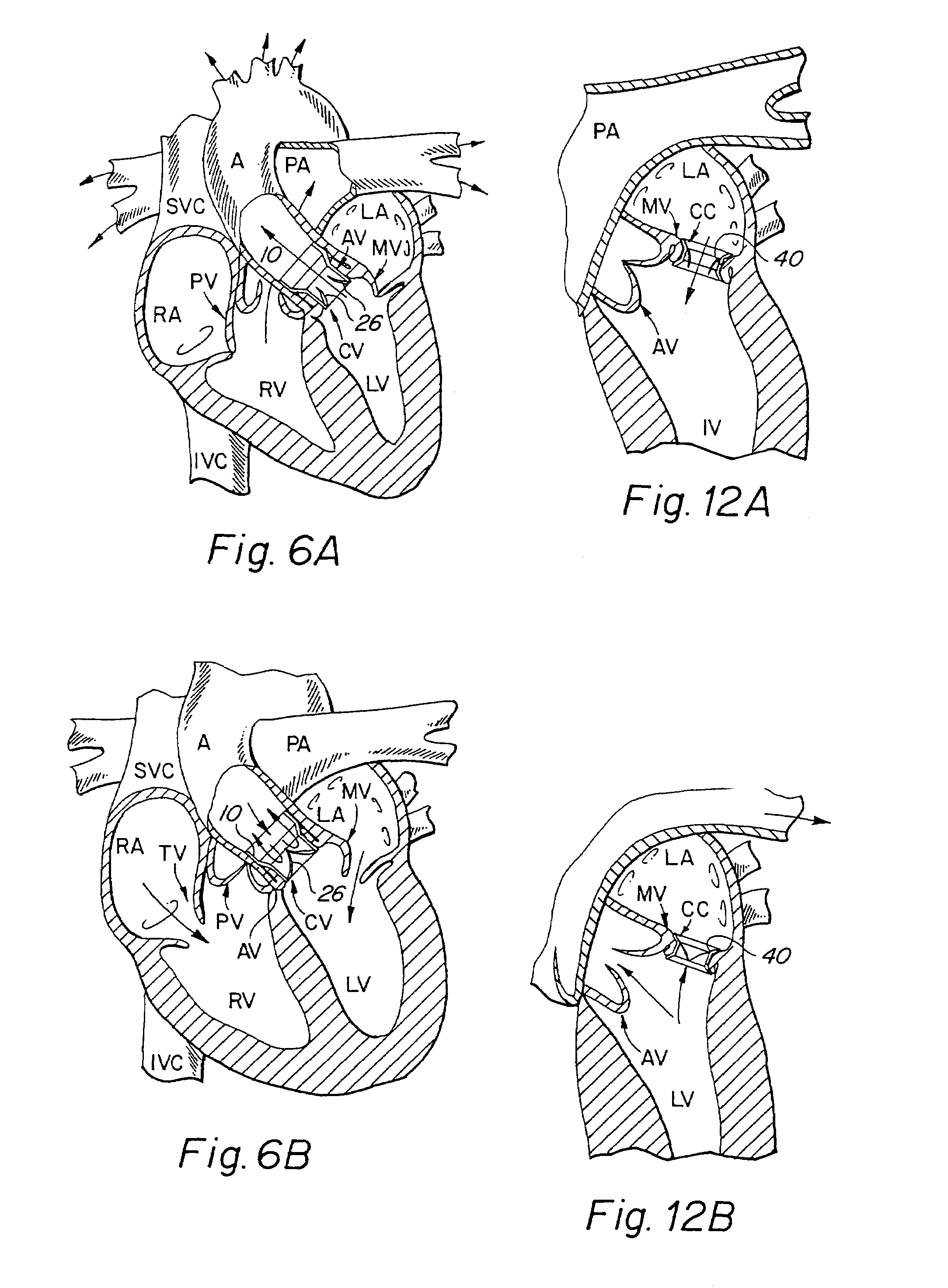
Cardiac valve procedure methods and devices
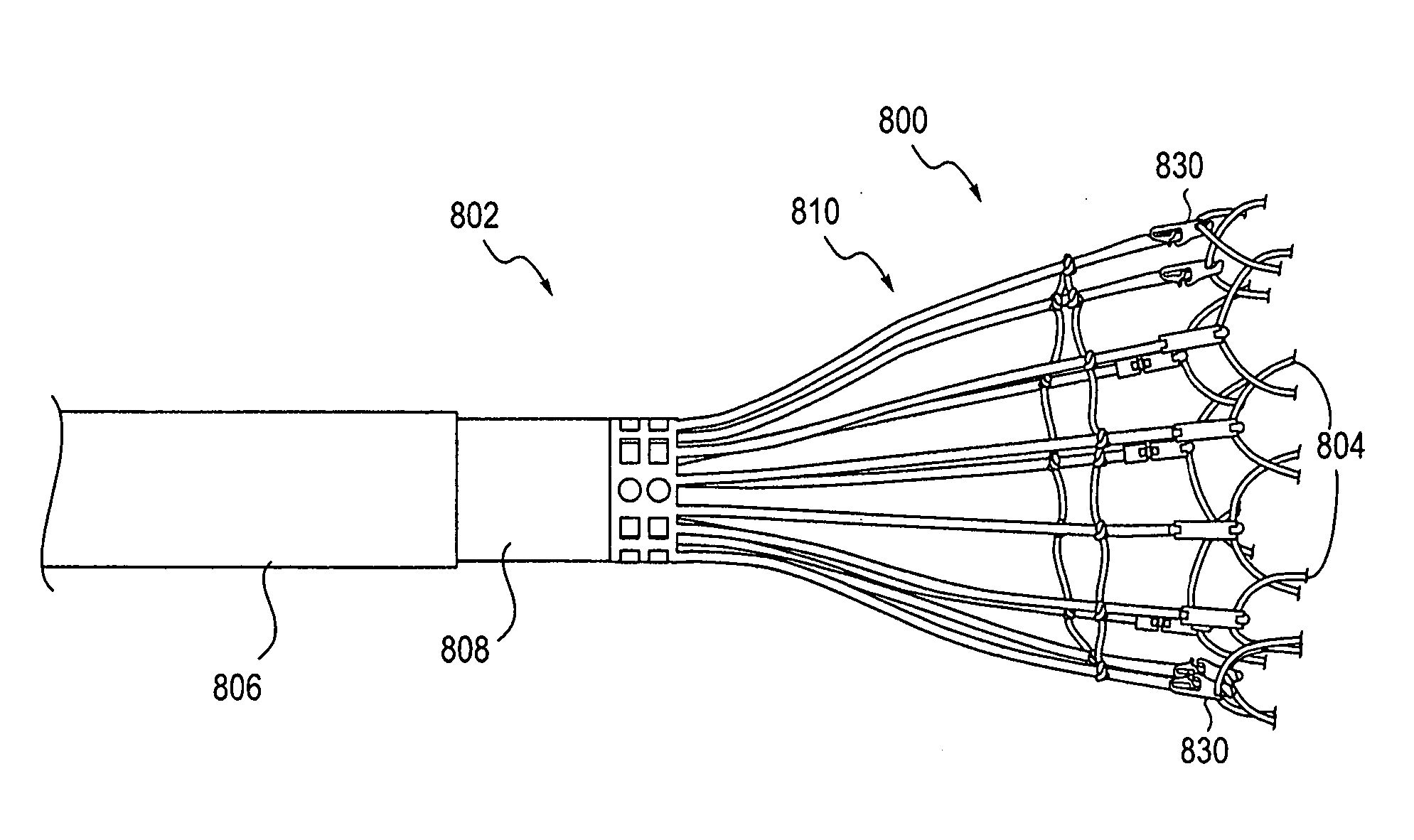
The present invention discloses devices and methods for performing intravascular procedures with out: cardiac bypass. The devices include various embodiments of temporary filter devices, temporary valves, and prosthetic valves. The temporary filter devices have one or more cannulae which provide access for surgical tools for effecting repair of the cardiac valves. A cannula may have filters of various configurations encircling the distal region of the cannula, which prevent embolitic material from entering the coronary arteries and aorta. The temporary valve devices may also have one or more cannulae which guide the insertion of the valve into the aorta. The valve devices expand in the aorta to occupy the entire flow path of the vessel. In one embodiment, the temporary valve is a disc of flexible, porous, material that acts to filter blood passing therethrough. A set of valve leaflets extend peripherally from the disc. These leaflets can alternately collapse to prevent blood flow through the valve and extend to permit flow. The prosthetic valves include valve fixation devices which secure the prosthetic valve to the wall of the vessel. In one embodiment, the prosthetic valves have at least one substantially rigid strut, at least two expandable fixation rings located about the circumference of the base of the apex of the valve, and one or more commissures and leaflets. The prosthetic valves are introduced into the vascular system a compressed state, advanced to the site of implantation, expanded and secured to the vessel wall.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Systems and methods for delivering a medical implant
The present invention relates to apparatus and methods for endovascularly delivering and releasing a prosthesis, e.g., an aortic prosthesis, within and / or across a patient's native heart valve, referred to hereinafter as replacing the patient's heart valve. In some embodiments the delivery system comprises a plurality of first actuatable element adapted to engage a plurality of second elements in a first configuration to capture the implant within the delivery system, and wherein the plurality of first actuatable element are adapted to engage the plurality of second elements in a second configuration and to release the implant from the delivery system.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Endoluminal cardiac and venous valve prostheses and methods of manufacture and delivery thereof
This invention relates to prosthetic cardiac and venous valves and a single catheter device and minimally invasive techniques for percutaneous and transluminal valvuloplasty and prosthetic valve implantation.
Owner:VACTRONIX SCI LLC
Bioprosthetic cardiovascular valve system
InactiveUS7011681B2Ensure correct executionSafe and convenient removal and replacementEar treatmentHeart valvesProsthesisEngineering
A cardiovascular valve system including a permanent base unit that is affixed to the patient using conventional sutures or staples, and a collapsible valve having a collapsible frame that mates with the permanent base unit, and supports valve leaflets. An installed collapsible frame may be re-collapsed and disengaged from the permanent housing. A new collapsible valve is then installed, to resume the function of the prosthesis.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Bronchial flow control devices and methods of use
Owner:PULMONX
Devices, systems and methods for treating disorders of the ear, nose and throat
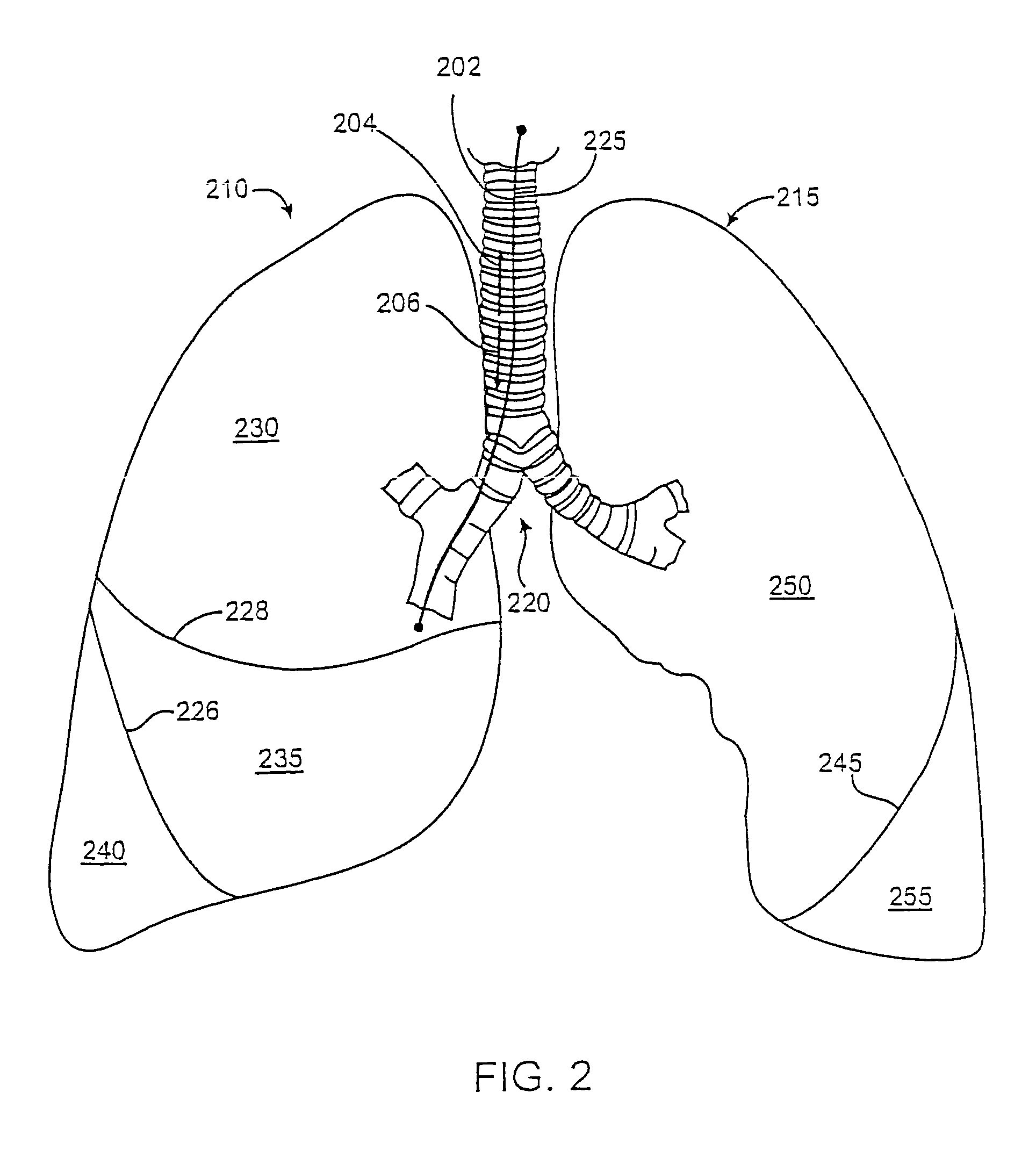
Sinusitis, mucocysts, tumors, infections, hearing disorders, choanal atresia, fractures and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, Eustachian tubes, Lachrymal ducts and other ear, nose, throat and mouth structures are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches and, in many cases, flexible catheters as opposed to instruments having rigid shafts. Various diagnostic procedures and devices are used to perform imaging studies, mucus flow studies, air / gas flow studies, anatomic dimension studies and endoscopic studies. Access and occluding devices may be used to facilitate insertion of working devices such asendoscopes, wires, probes, needles, catheters, balloon catheters, dilation catheters, dilators, balloons, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, suction or irrigation devices, imaging devices, sizing devices, biopsy devices, image-guided devices containing sensors or transmitters, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for injecting diagnostic or therapeutic agents, devices for implanting devices such as stents, substance eluting or delivering devices and implants, etc.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Expandable sheath for delivering instruments and agents into a body lumen and methods for use
Apparatus and methods are provided for delivering a guidewire, agents, and the like through an occlusion in a body vessel or other body lumen. The apparatus includes a flexible catheter or other elongate member including a proximal end, a distal end sized for insertion into a body lumen, and a first lumen extending from the proximal end to a distal region of the tubular member. An expandable sheath is provided on the distal region of the catheter that is expandable from a contracted condition to minimize a profile of the sheath to allow insertion along with the tubular member into a body lumen, to an enlarged condition wherein the sheath at least partially defines a lumen communicating with and extending distally from the first lumen of the tubular member.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
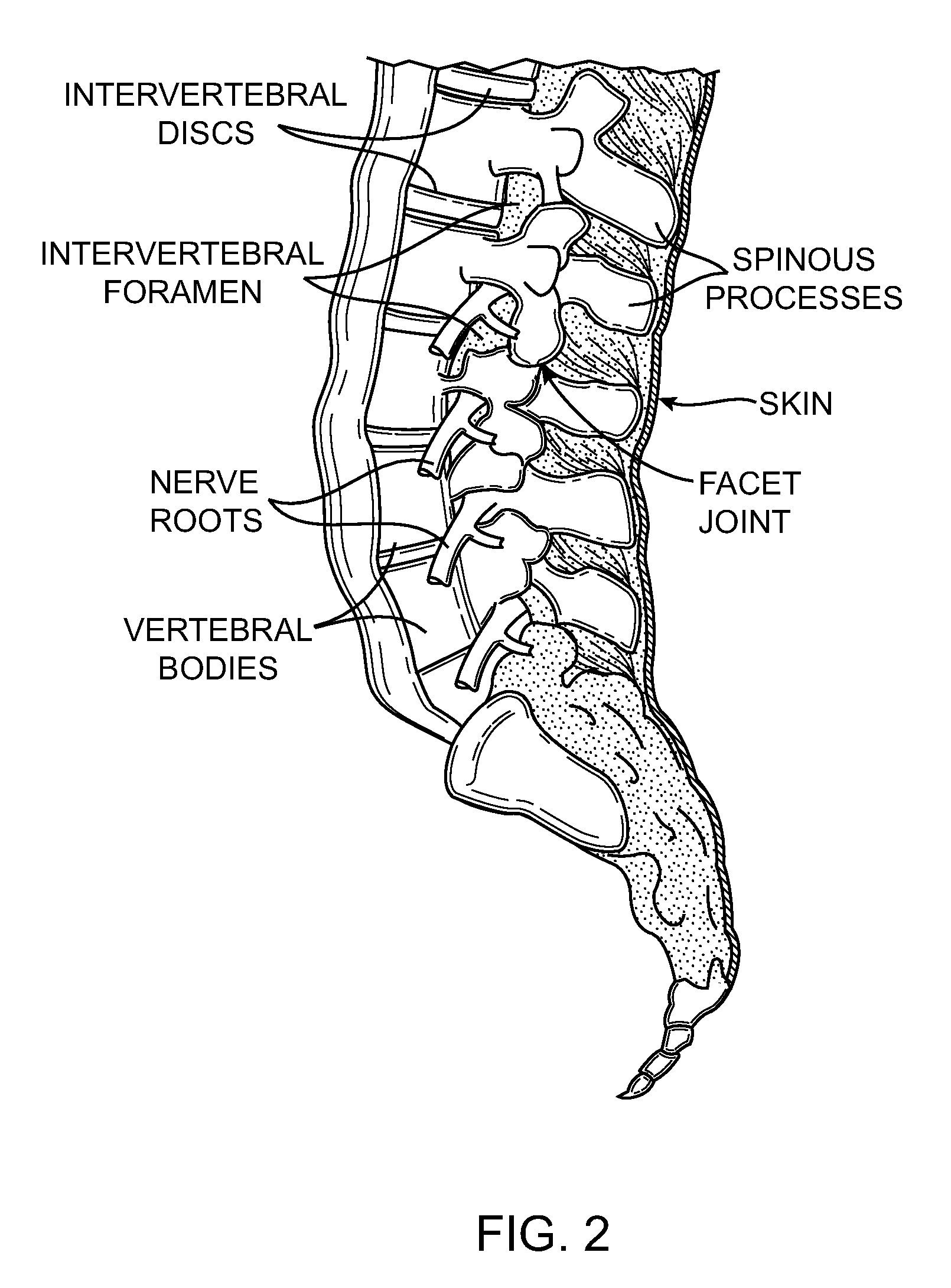
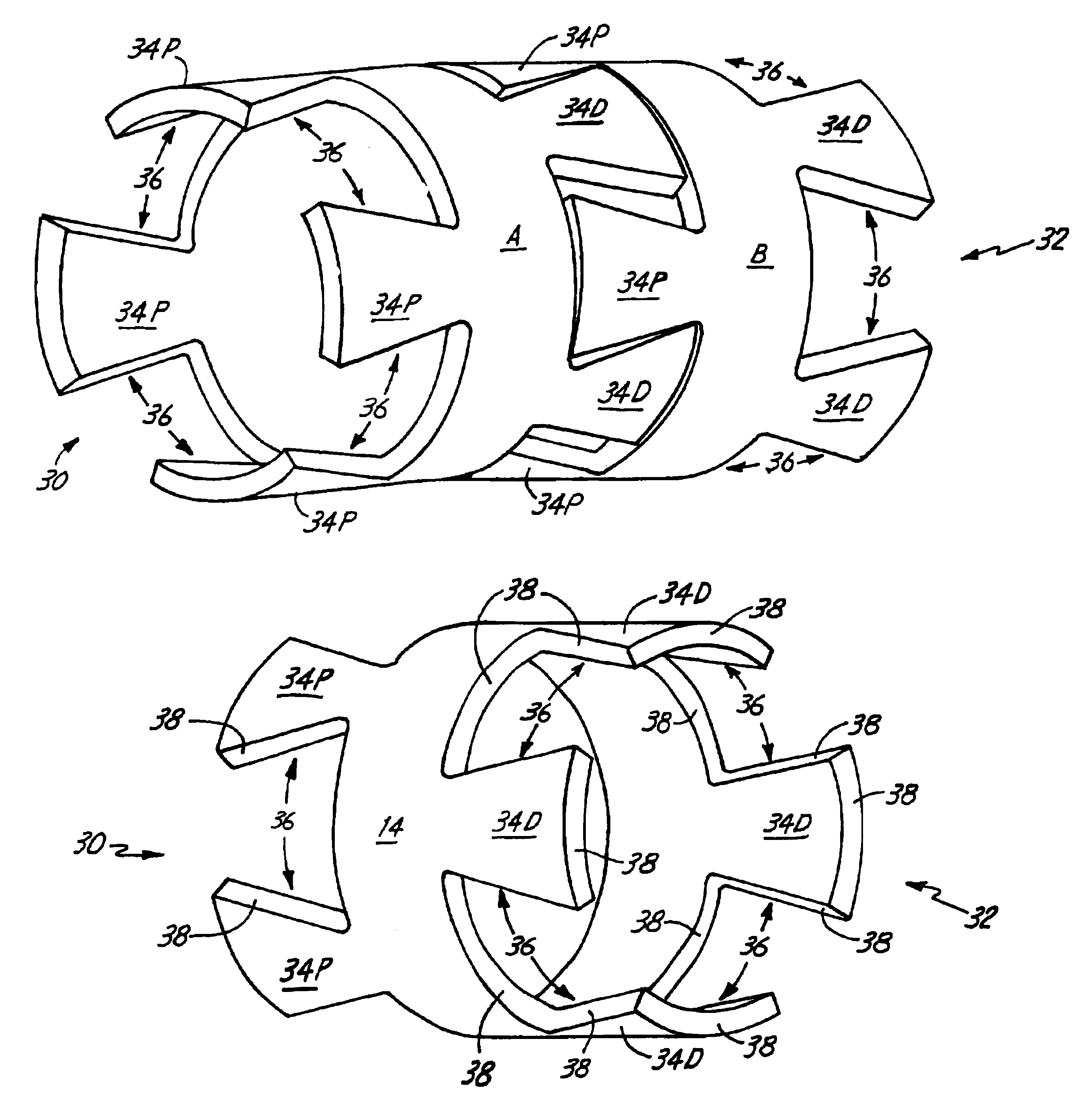
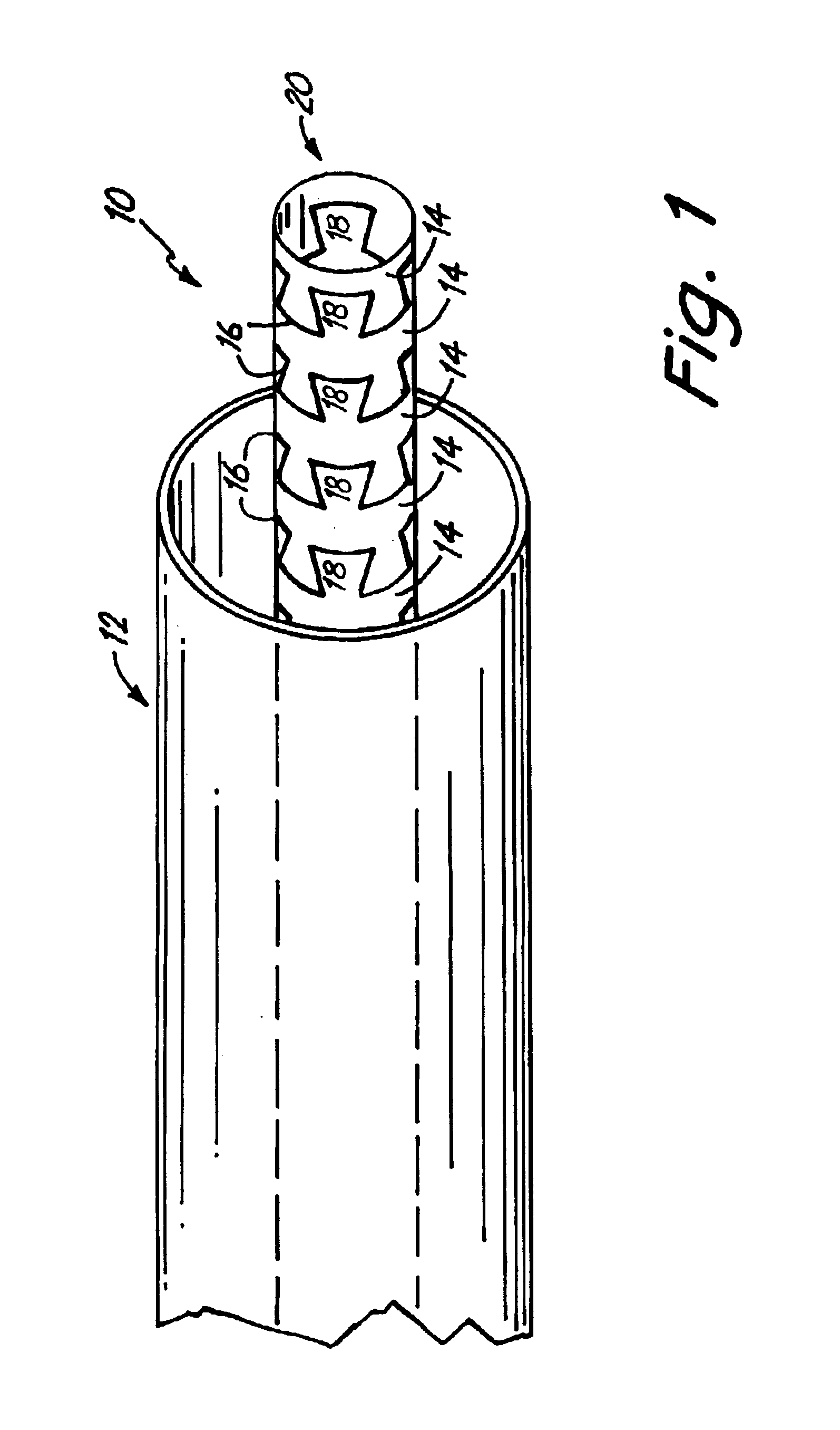
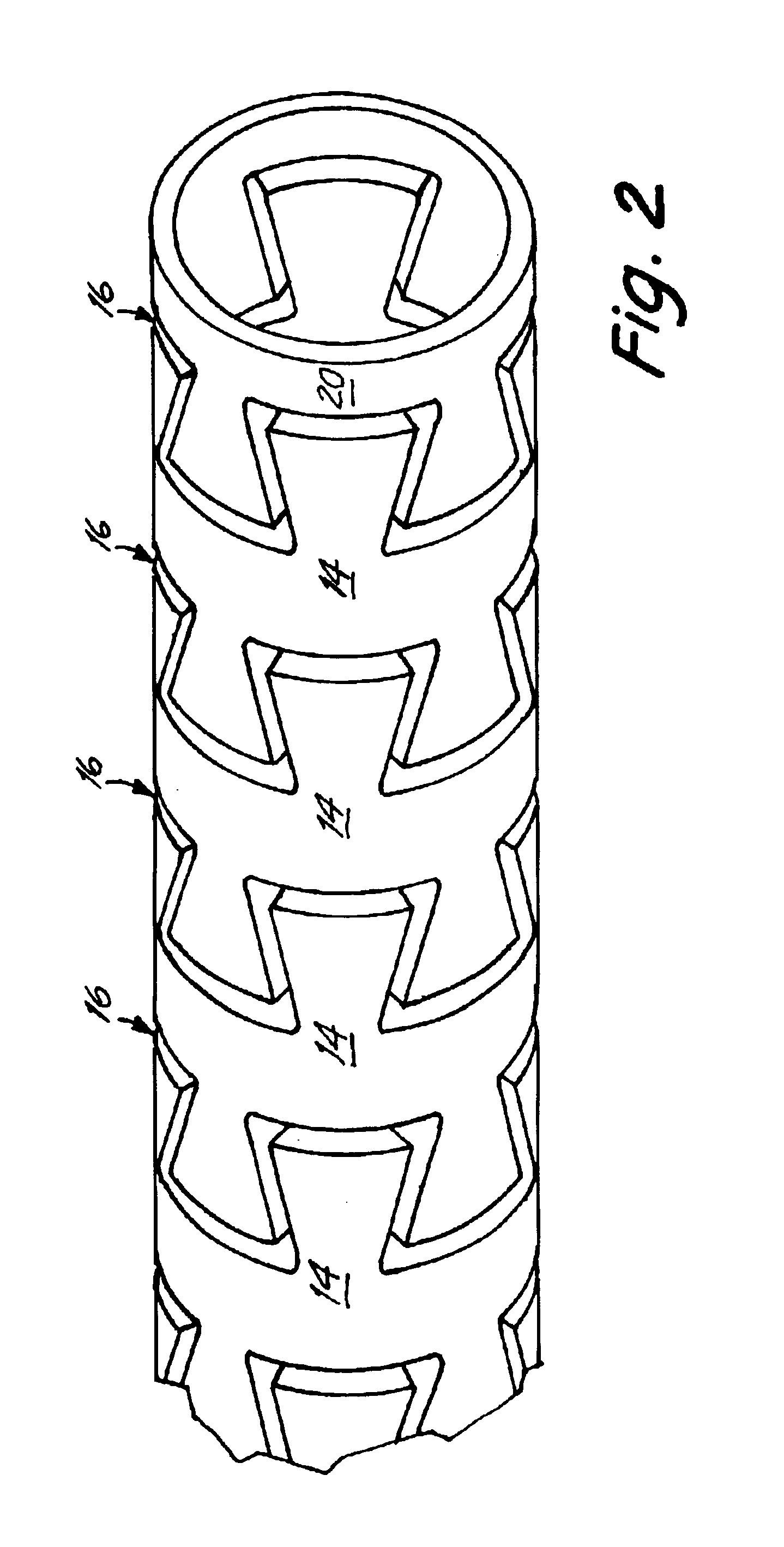
Spinal stabilization device
ActiveUS20050203517A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
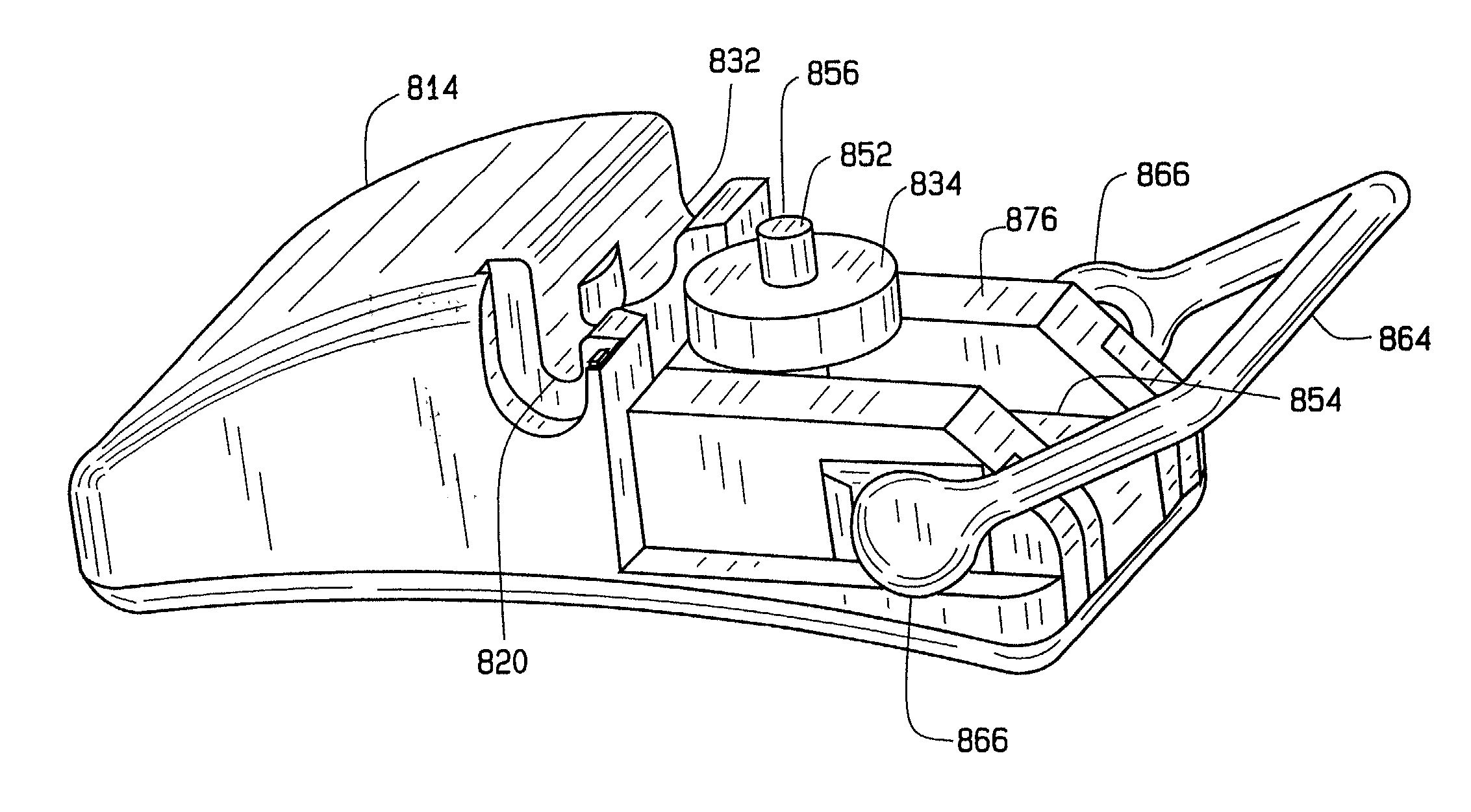
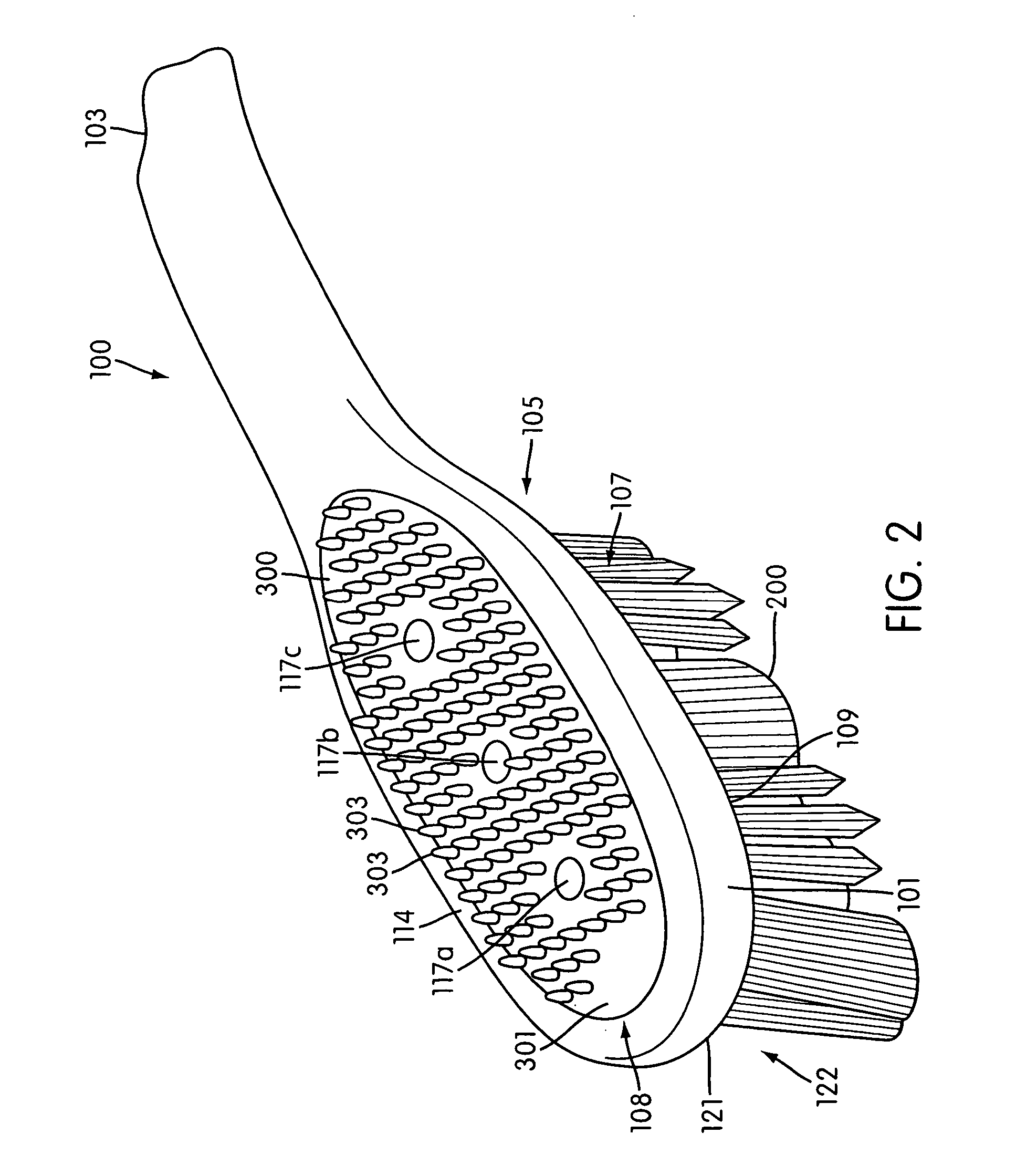
Oral care implement
An oral care implement with a handle includes a head with a tissue cleanser. The tissue cleanser may be a pad composed of an elastomeric material. The pad is disposed on the head on a surface opposite the tooth cleaning elements. The tissue cleanser may include a plurality of nubs extending for cleaning between the papillae of the tongue. The tissue cleanser may include a plurality of conically shaped nubs. A tissue cleanser can be used to reduce oral malodor problems and remove oral epithelial cells.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Method and apparatus for flexible fixation of a spine
InactiveUS20050065516A1Easy constructionSimple designInternal osteosythesisEar treatmentSpinal columnCoupling
A flexible spinal fixation device having a flexible metallic connection unit for non-rigid stabilization of the spinal column. In one embodiment, the fixation device includes at least two securing members configured to be inserted into respective adjacent spinal pedicles, each securing member each including a coupling assembly. The fixation device further includes a flexible metal connection unit configured to be received and secured within the coupling assemblies of each securing member so as to flexibly stabilize the affected area of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Mitral valve repair system and method for use
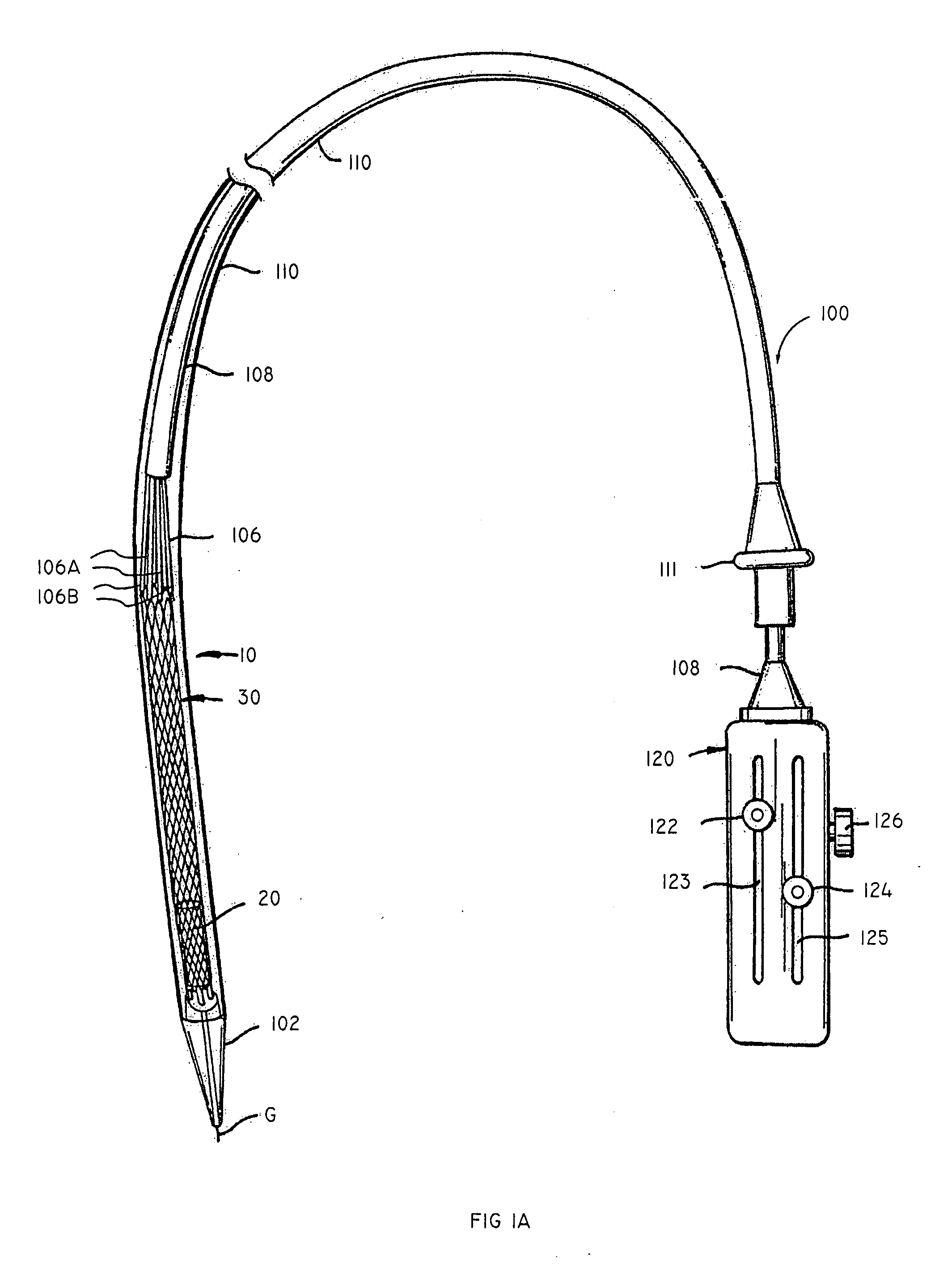
ActiveUS7381210B2Effective and stableEffectively stabilizing at least one tissue portionSuture equipmentsEar treatmentRepair tissueMitral valve operation
The present invention is directed to various systems for repairing tissue within the heart of a patient. The mitral valve repair system of the present invention comprises a guide catheter having a proximal end, a distal end, and at least one internal lumen formed therein, a therapy catheter capable of applying a suture to the tissue, and a fastener catheter capable of attaching a fastener to the suture. The therapy catheter and the fastener catheter are capable of traversing the internal lumen of the guide catheter. In addition, the present invention discloses various methods for repairing tissue within the heart of a patient.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Anchor and pull mitral valve device and method
A device, system, and method effects mitral valve annulus geometry of a heart. The device includes a first anchor configured to be positioned within and fixed to the coronary sinus of the heart adjacent the mitral valve annulus within the heart. A cable is fixed to the first anchor and extends proximately therefrom and slidingly through a second anchor which is positioned and fixed in the heart proximal to the first anchor. A lock locks the cable to the second anchor when tension is applied to the cable for effecting the mitral valve annulus geometry.
Owner:CARDIAC DIMENSIONS
Device for the implantation and fixation of prosthetic valves
ActiveUS20070100440A1High positioning accuracyImprove mobilityStentsBalloon catheterProsthetic valveProsthetic heart
A device for the transvascular implantation and fixation of prosthetic heart valves having a self-expanding heart valve stent (10) with a prosthetic heart valve (11) at its proximal end is introducible into a patient's main artery. With the objective of optimizing such a device to the extent that the prosthetic heart valve (11) can be implanted into a patient in a minimally-invasive procedure, to ensure optimal positioning accuracy of the prosthesis (11) in the patient's ventricle, the device includes a self-expanding positioning stent (20) introducible into an aortic valve positioned within a patient. The positioning stent is configured separately from the heart valve stent (10) so that the two stents respectively interact in their expanded states such that the heart valve stent (10) is held by the positioning stent (20) in a position in the patient's aorta relative the heart valve predefinable by the positioning stent (20).
Owner:JENAVALVE TECH INC
Stent delivery system for prevention of kinking, and method of loading and using same
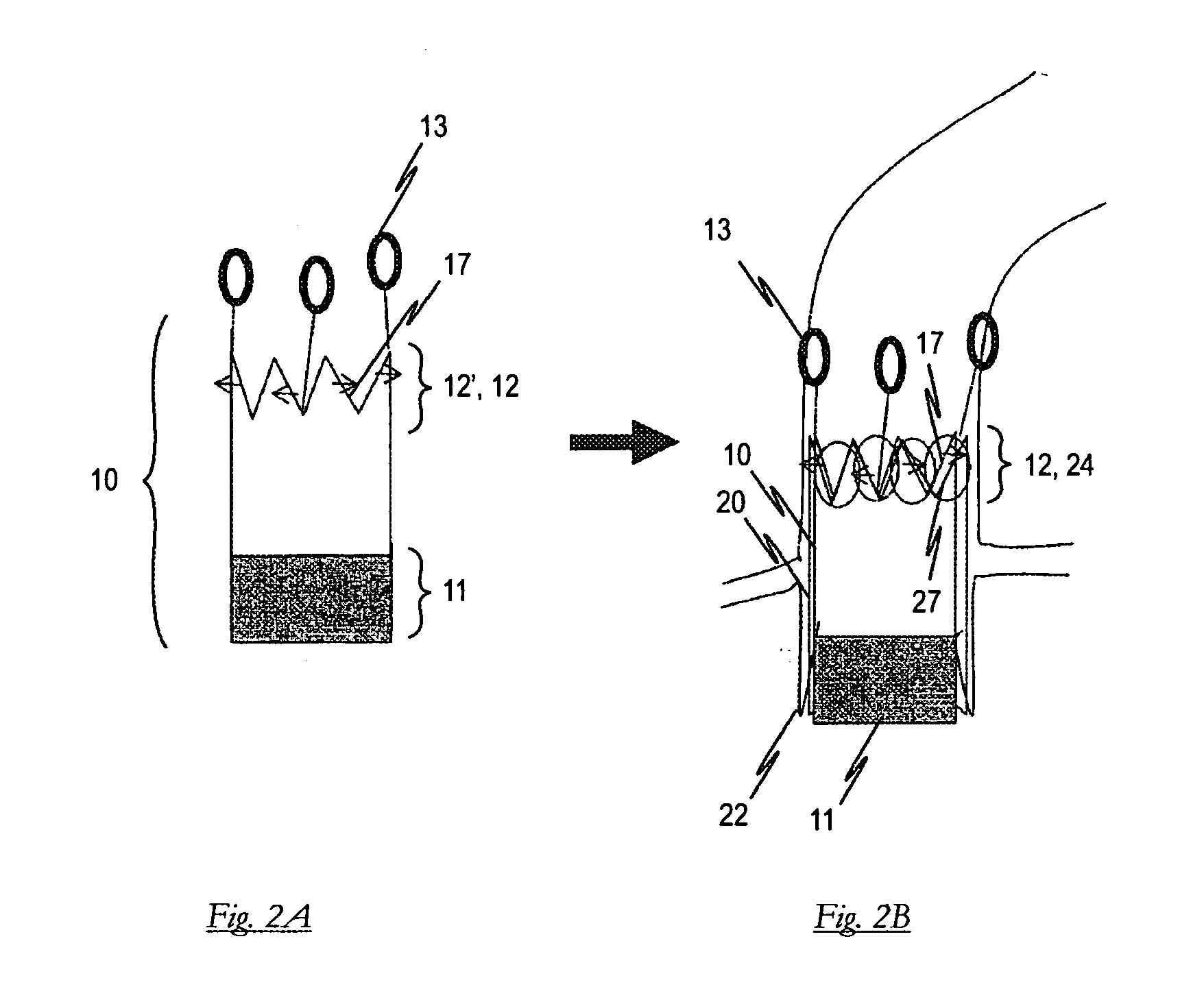
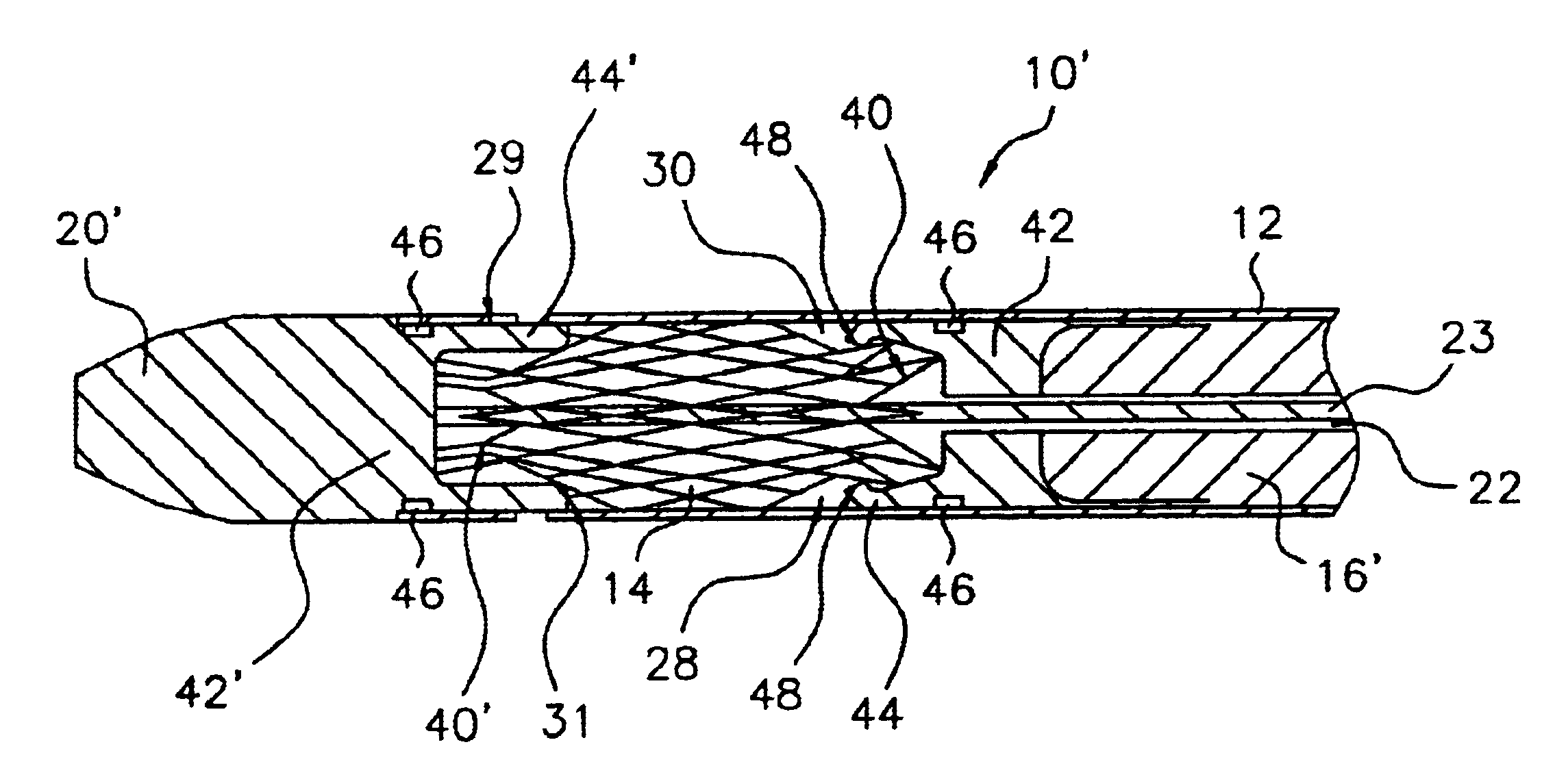
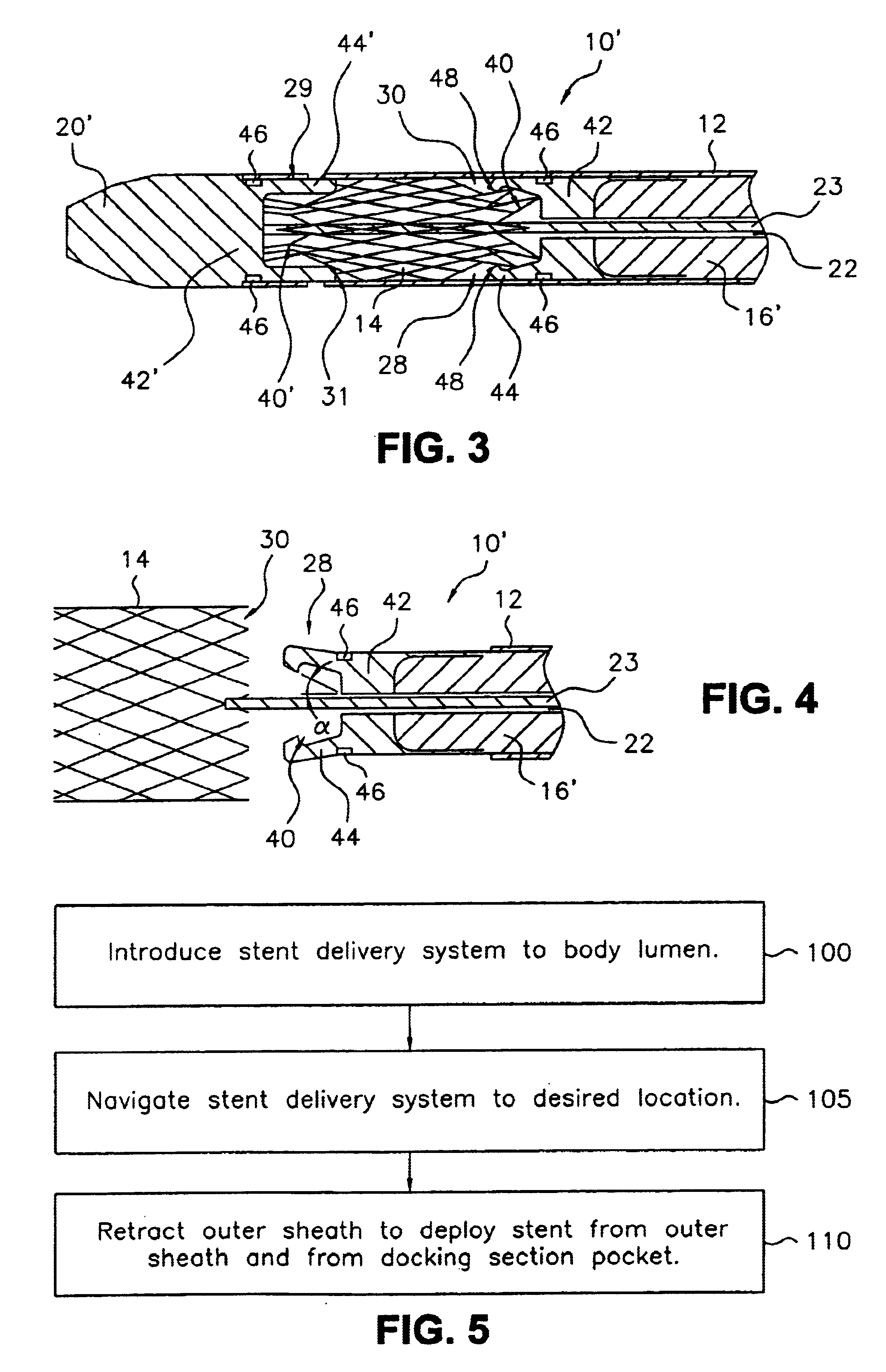
A stent delivery system adapted to deliver a compressed stent to a distal deployment location inside a body lumen from a proximal access location outside the body lumen. The system houses a compressed stent and includes a pusher and a catheter tip attached to a central core slideably disposed within the pusher. At least one of the pusher distal end and catheter tip proximal end comprises a docking section adapted to releasably engage a limited length of one end of the compressed stent. The docking section may comprise a pocket having a flared end rim that is radially biased outward and adapted to be inwardly compressed to grip the stent end when the docking section is loaded in an outer sheath. Other docking section configurations are also disclosed, such as an insert within the stent, an annular pocket, and / or a set of fingers that grip the stent. A docking pusher and a docking catheter tip having such docking sections are disclosed, as are methods for loading and deploying a stent with a stent delivery system as described herein.
Owner:LIFEPORT SCI
Locking handle deployment mechanism for medical device and method
InactiveUS6866669B2Easy and accurate deployment and positioningEasy to operateStentsEar treatmentLocking mechanismMedical device
A system for delivering at least one medical device to a desired location for treatment, and then selectively deploy it in position, includes an improved handle. One of the possible features of the handle may be to selectively hold the delivery system components at any desired configuration during deployment and positioning of the medical device. Another possible feature of the handle may be more than one mode of operation, in which the deployment of the medical device can selectively proceed at more than one speed. Yet another possible feature of the handle may be a locking mechanism that resists inadvertent or accidental movement or retraction of the stent delivery system components during packaging, sterilization, shipping, storage, handling and preparation of the stent delivery system.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
Delivery system for a stentless valve bioprosthesis
InactiveUS20040111096A1Easy to fixReduce the patient's hospital stayEar treatmentTubular organ implantsProsthesisGuide tube
The current invention discloses a catheter and a method for delivering a stentless bloprosthesis in a body channel, the method comprising percutaneously introducing a catheter into the body channel, wherein the catheter contains said stentless bloprosthesis at a retracted state; and disengaging said stentless bioprosthesis out of a distal opening of the catheter by a pulling mechanism associated with the catheter structure.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com