Patents
Literature
1320results about "Tubular organ implants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Apparatus and methods for treatment of morbid obesity
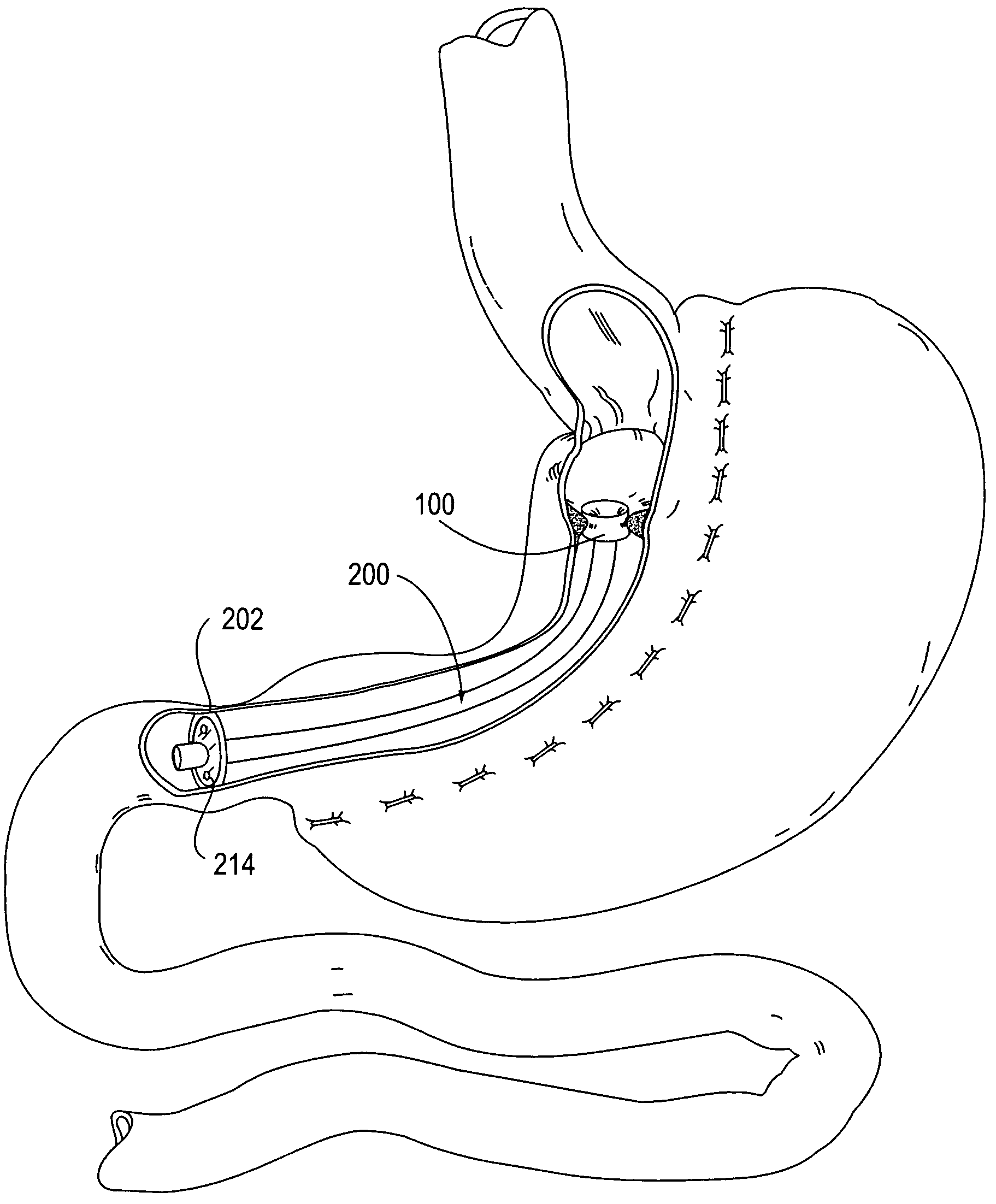
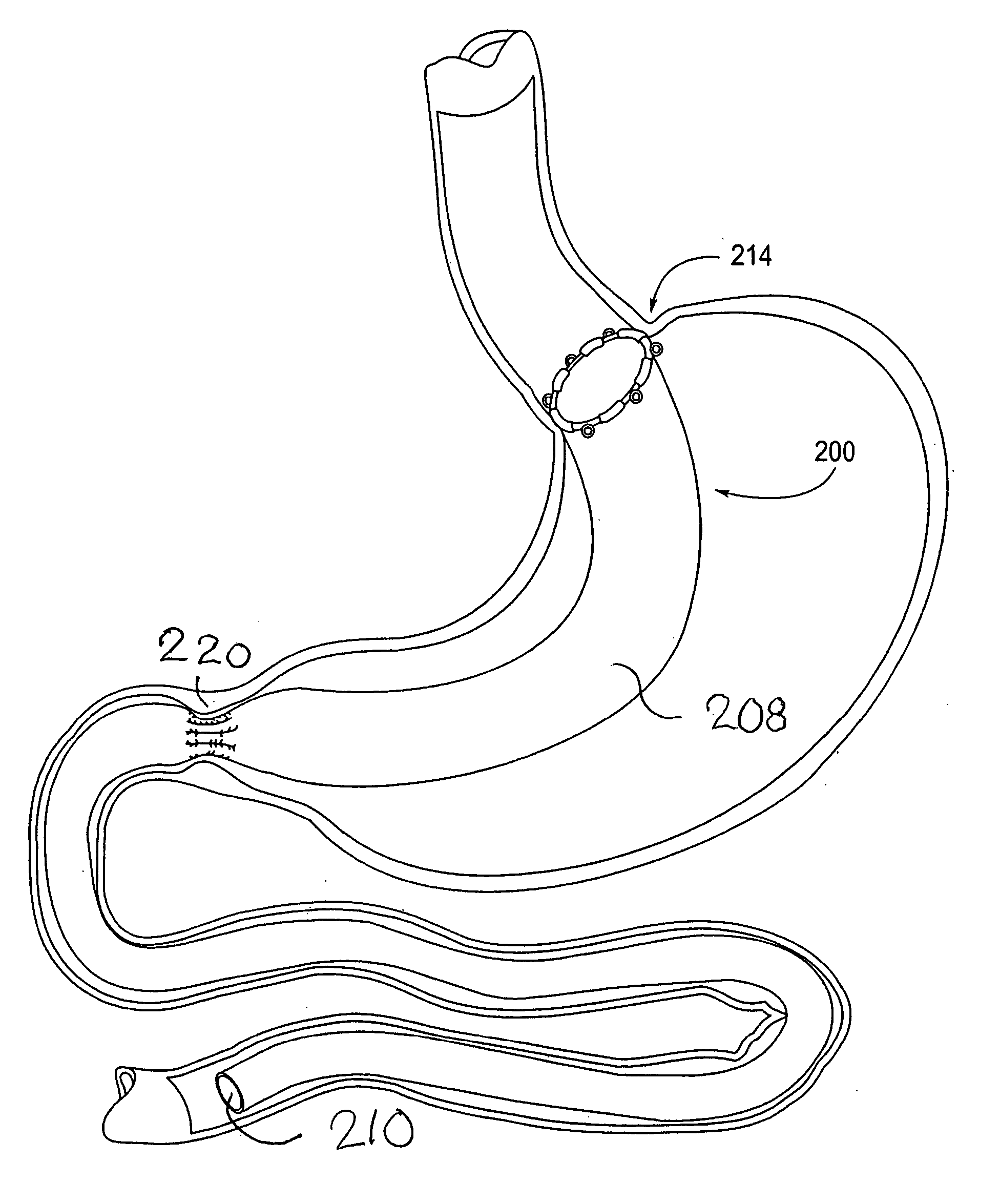
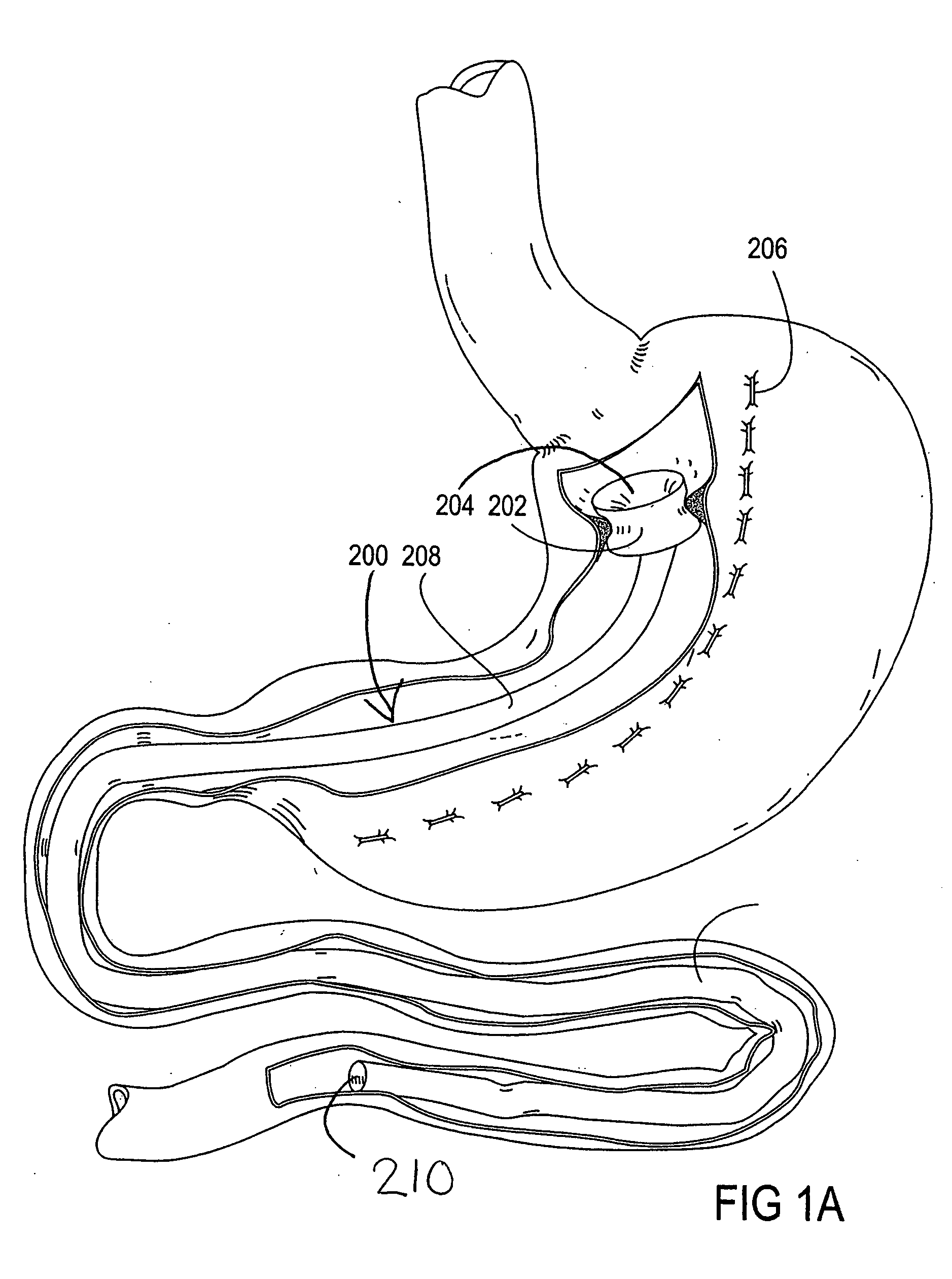
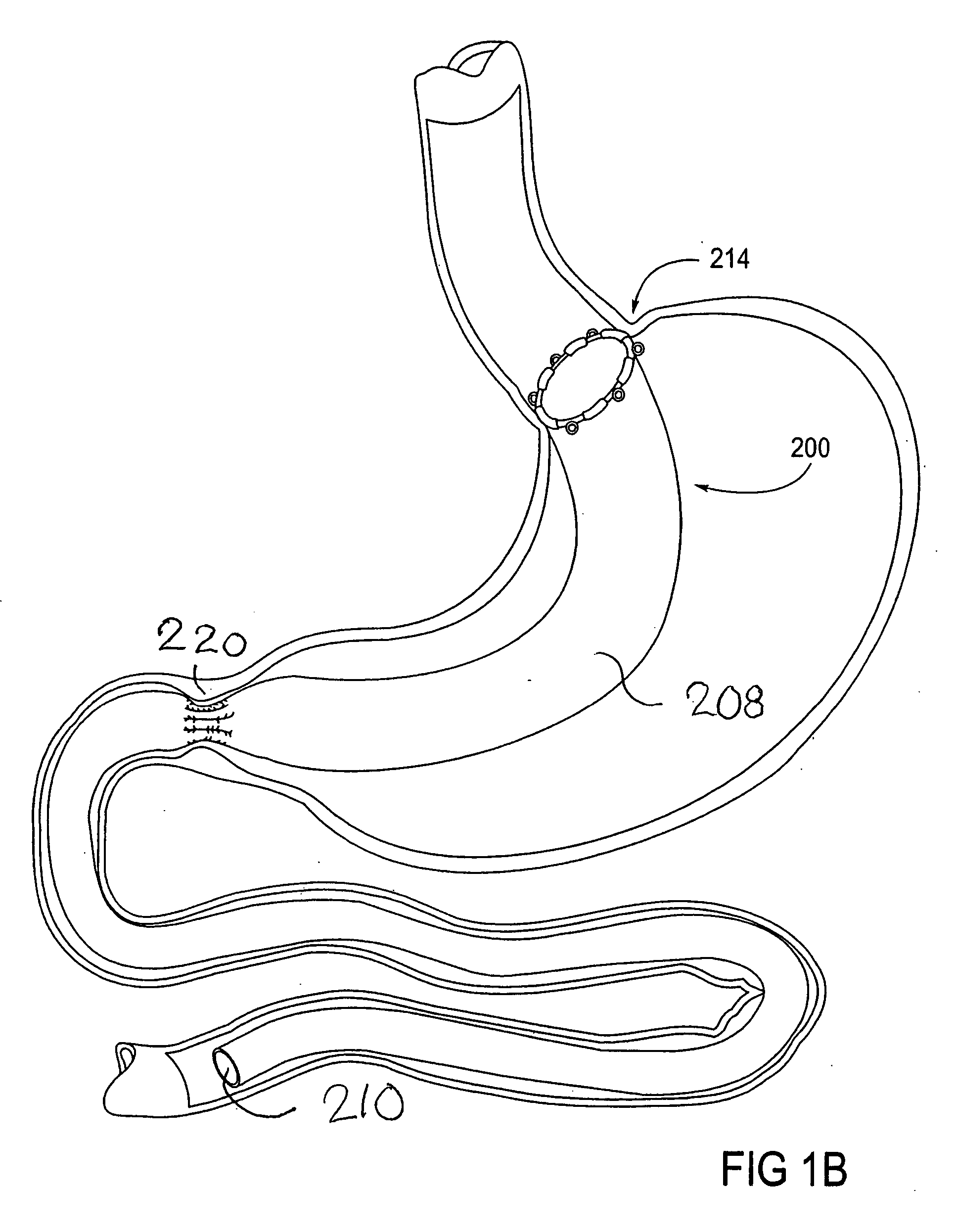
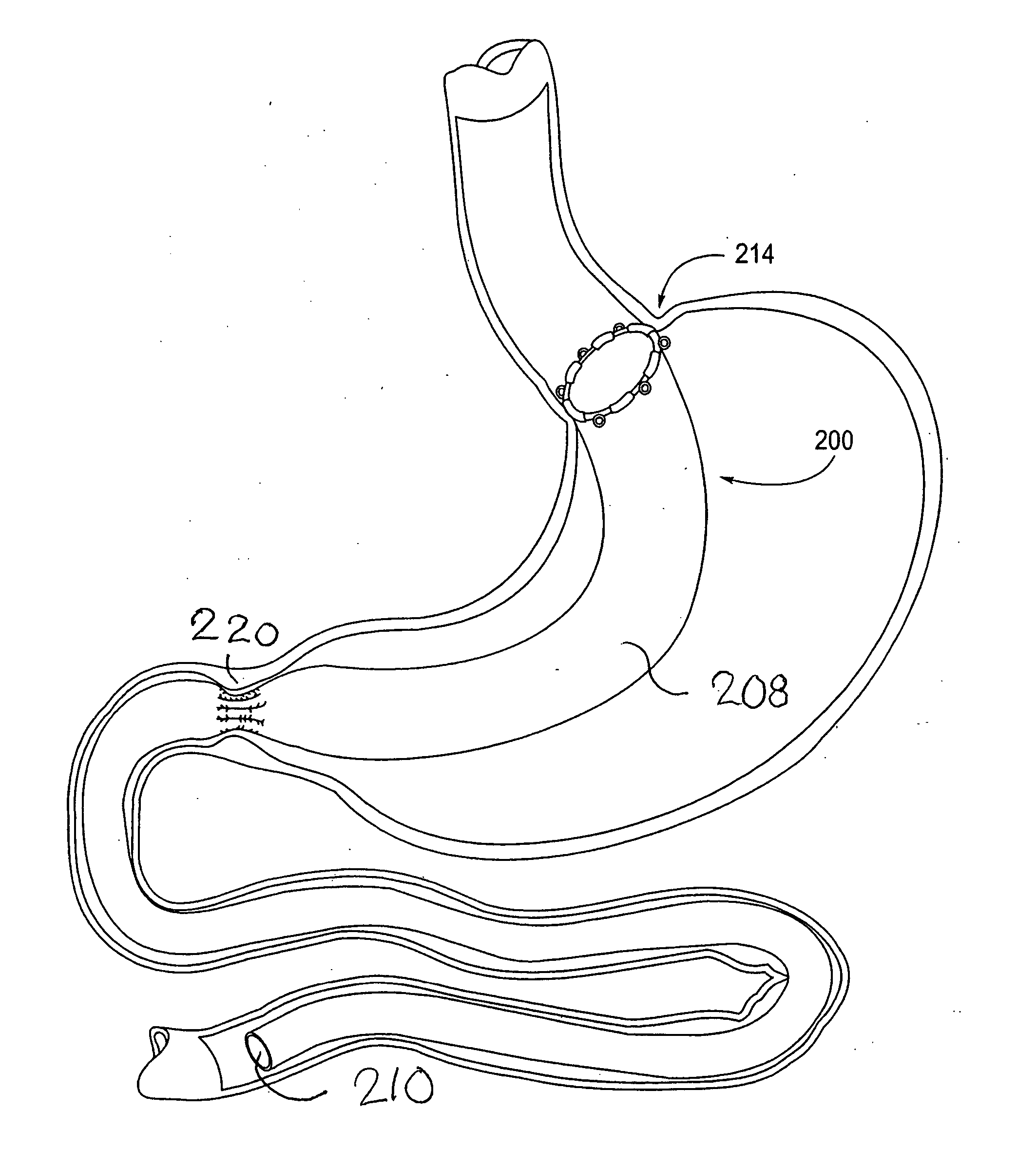
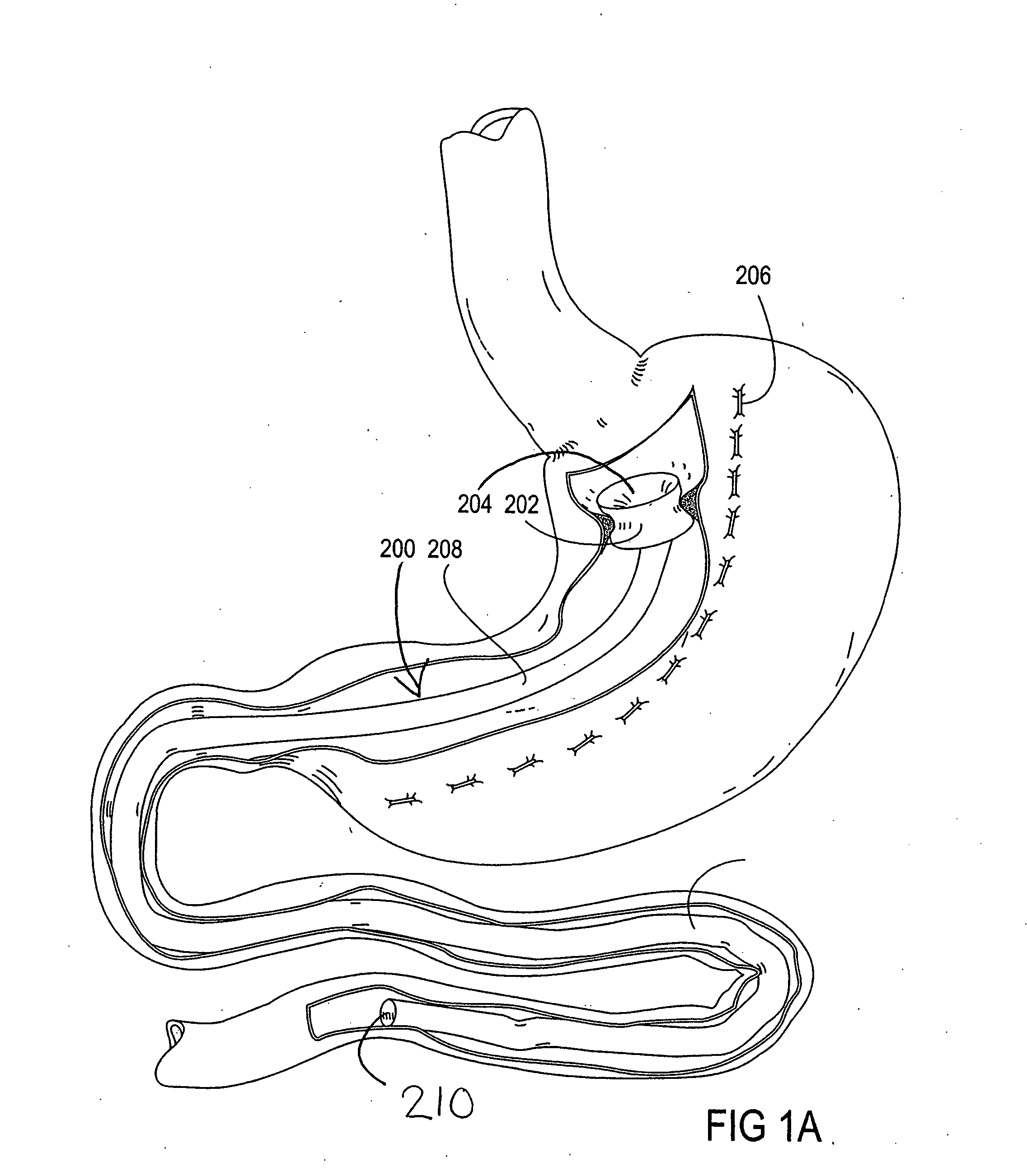
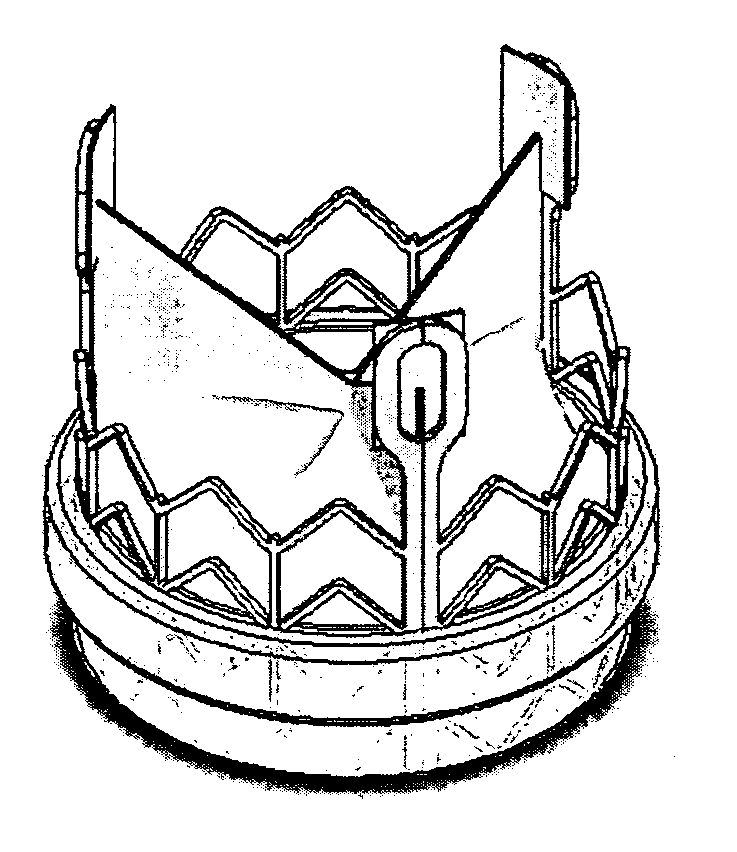
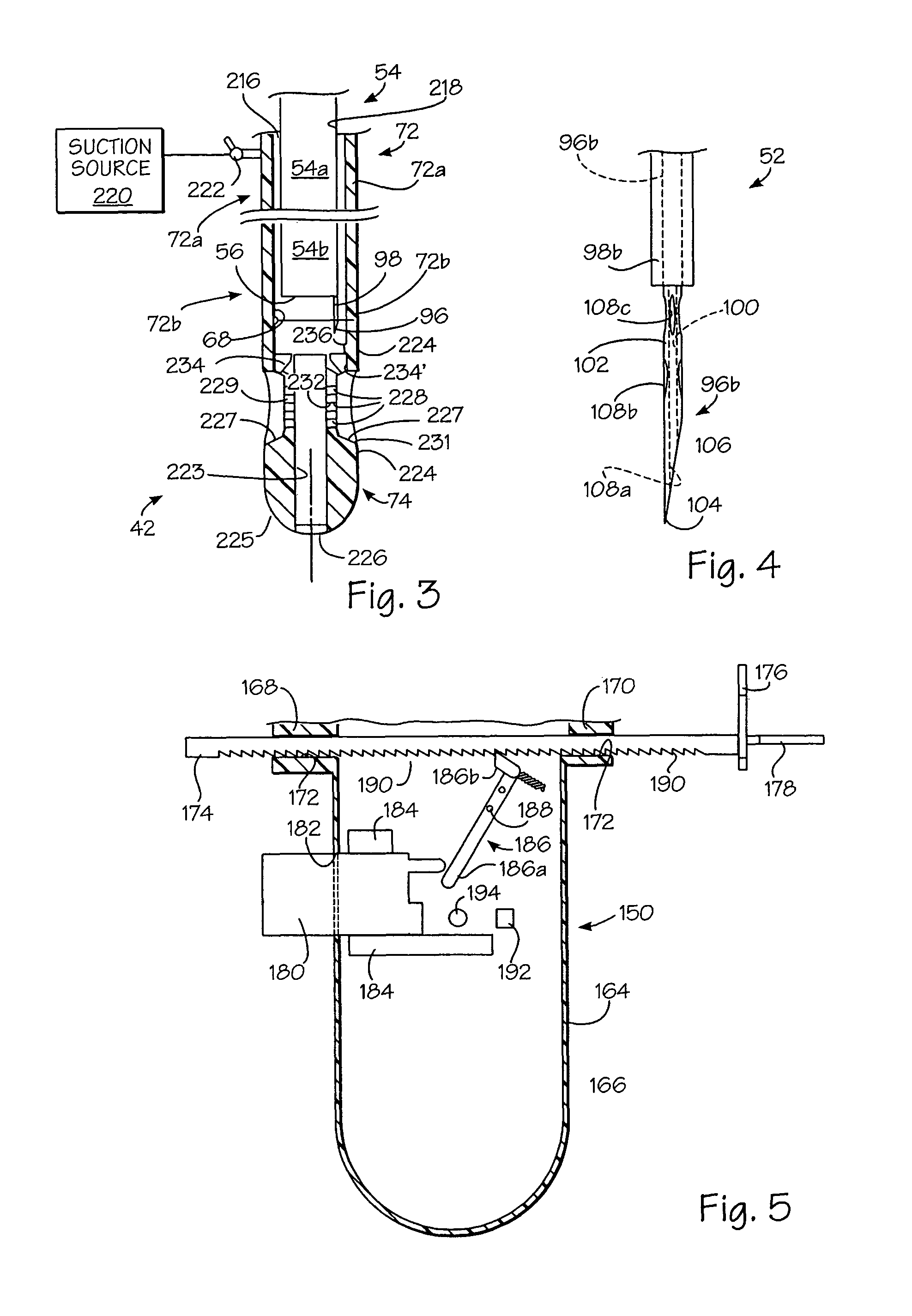
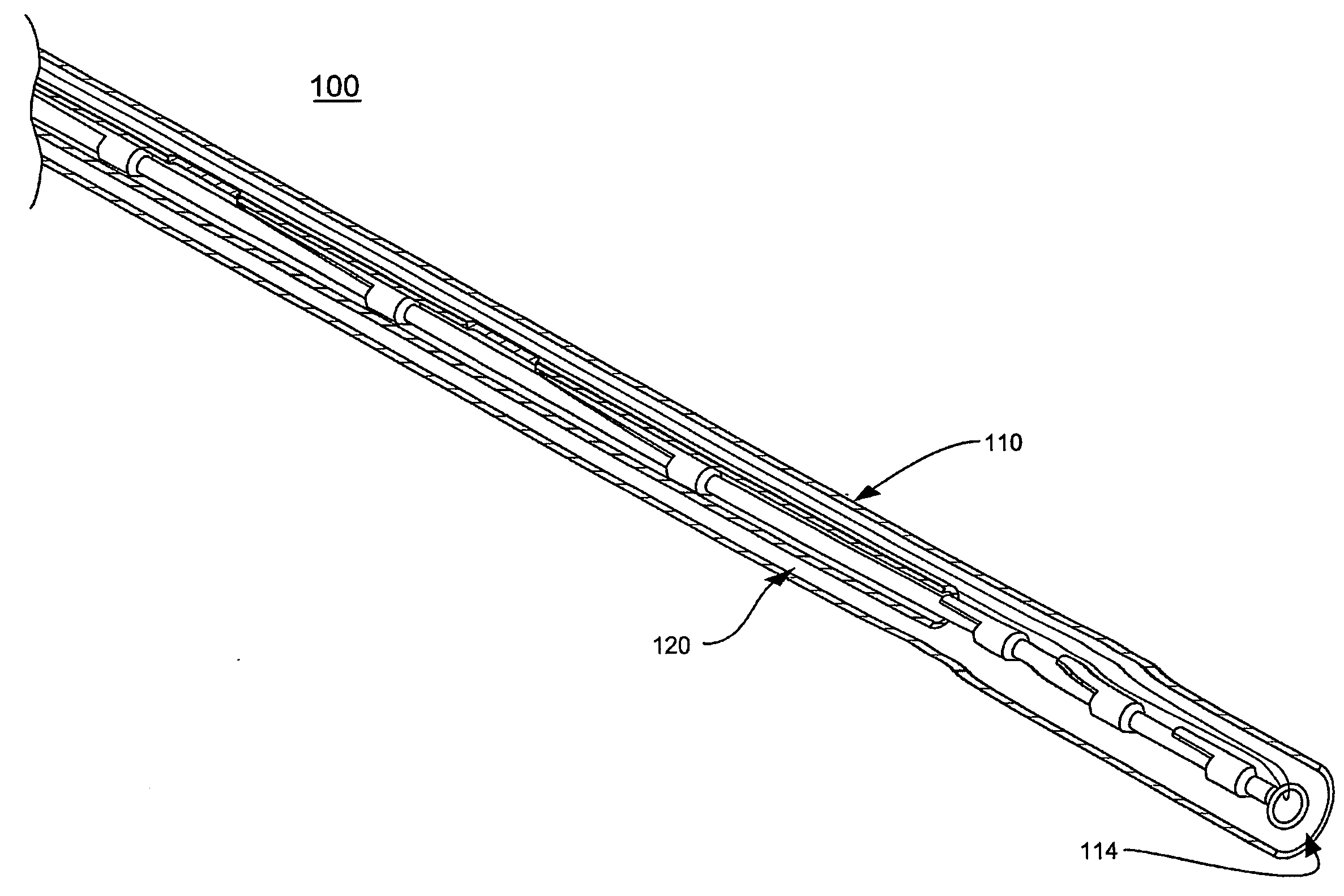
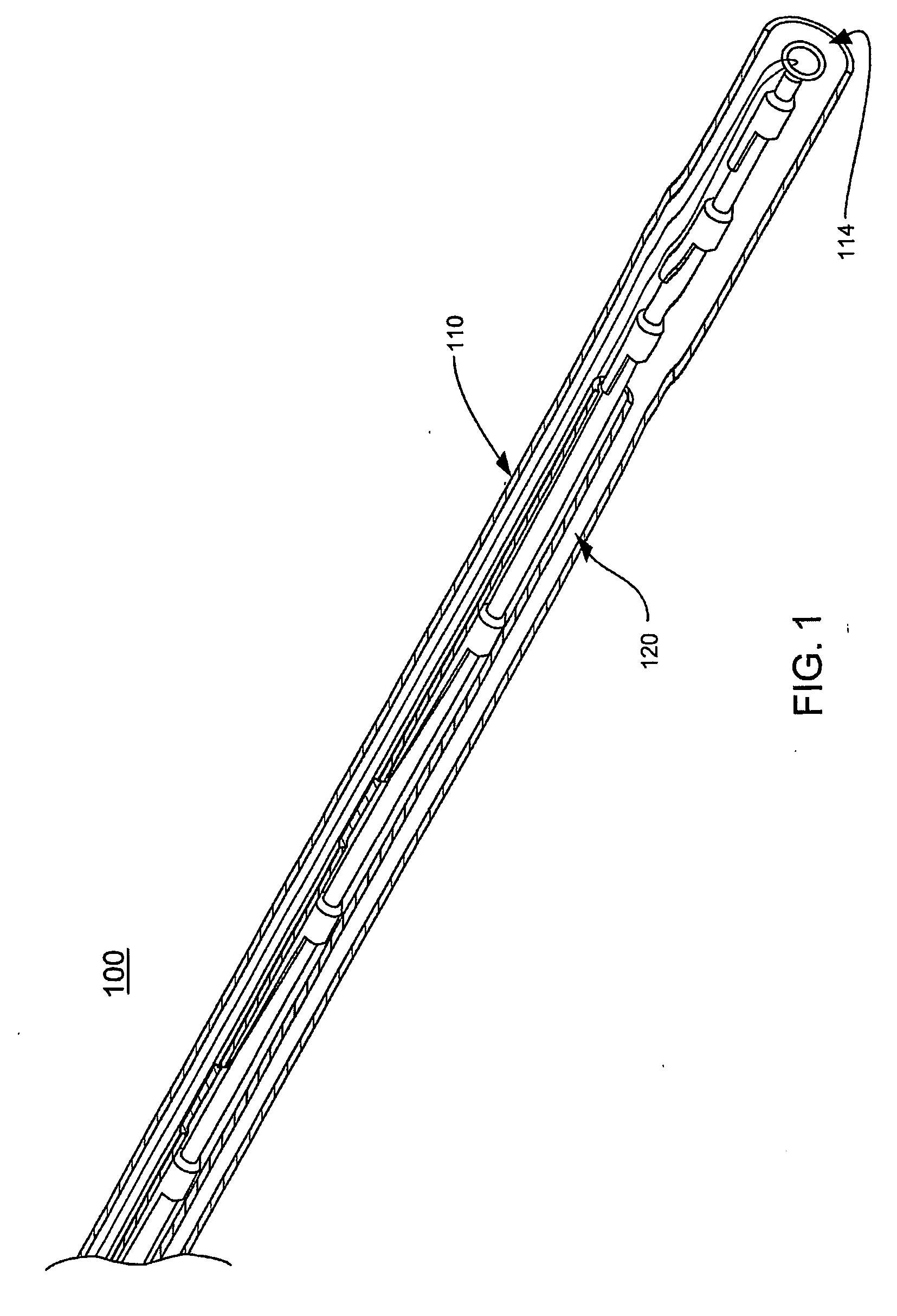
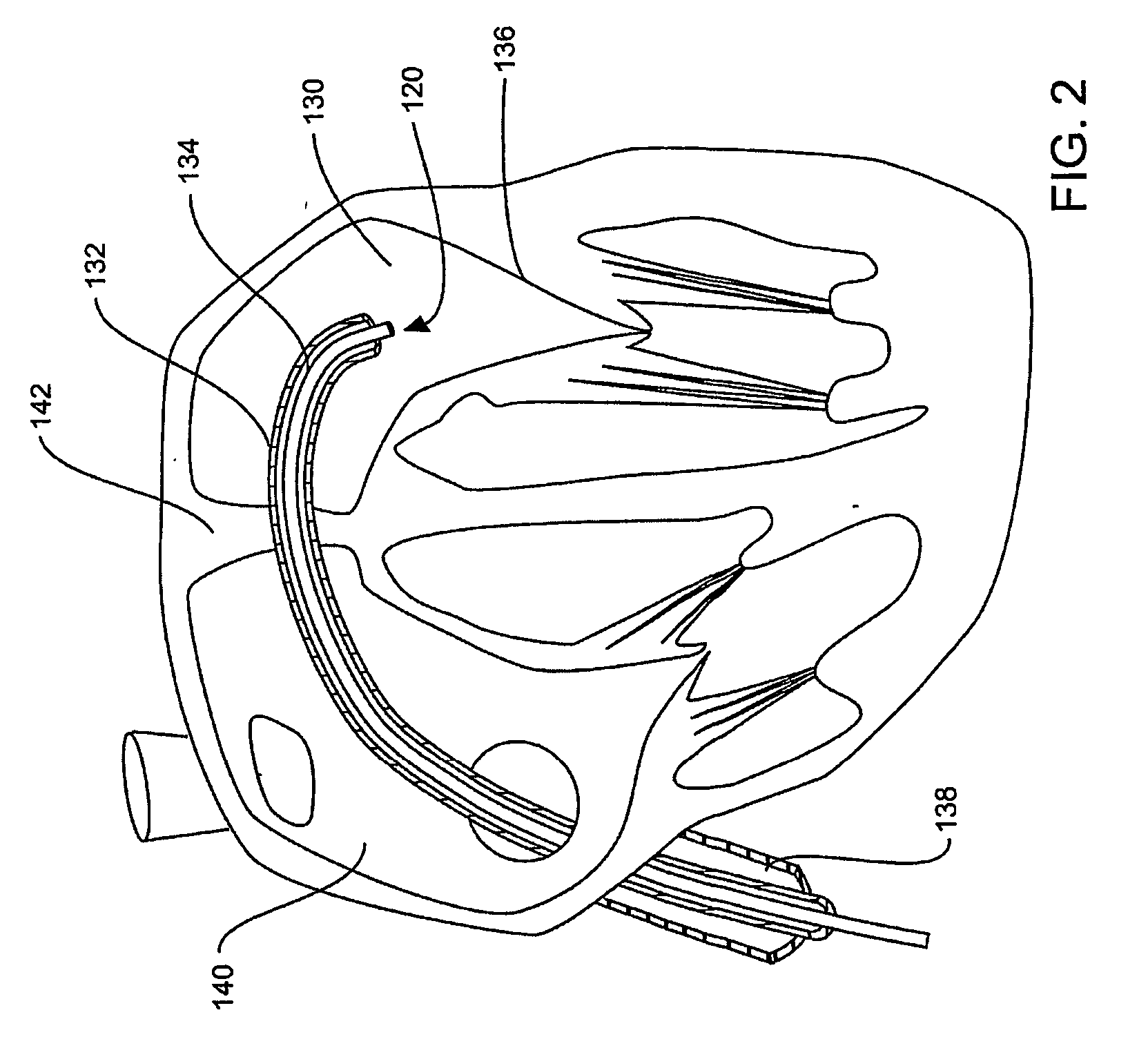
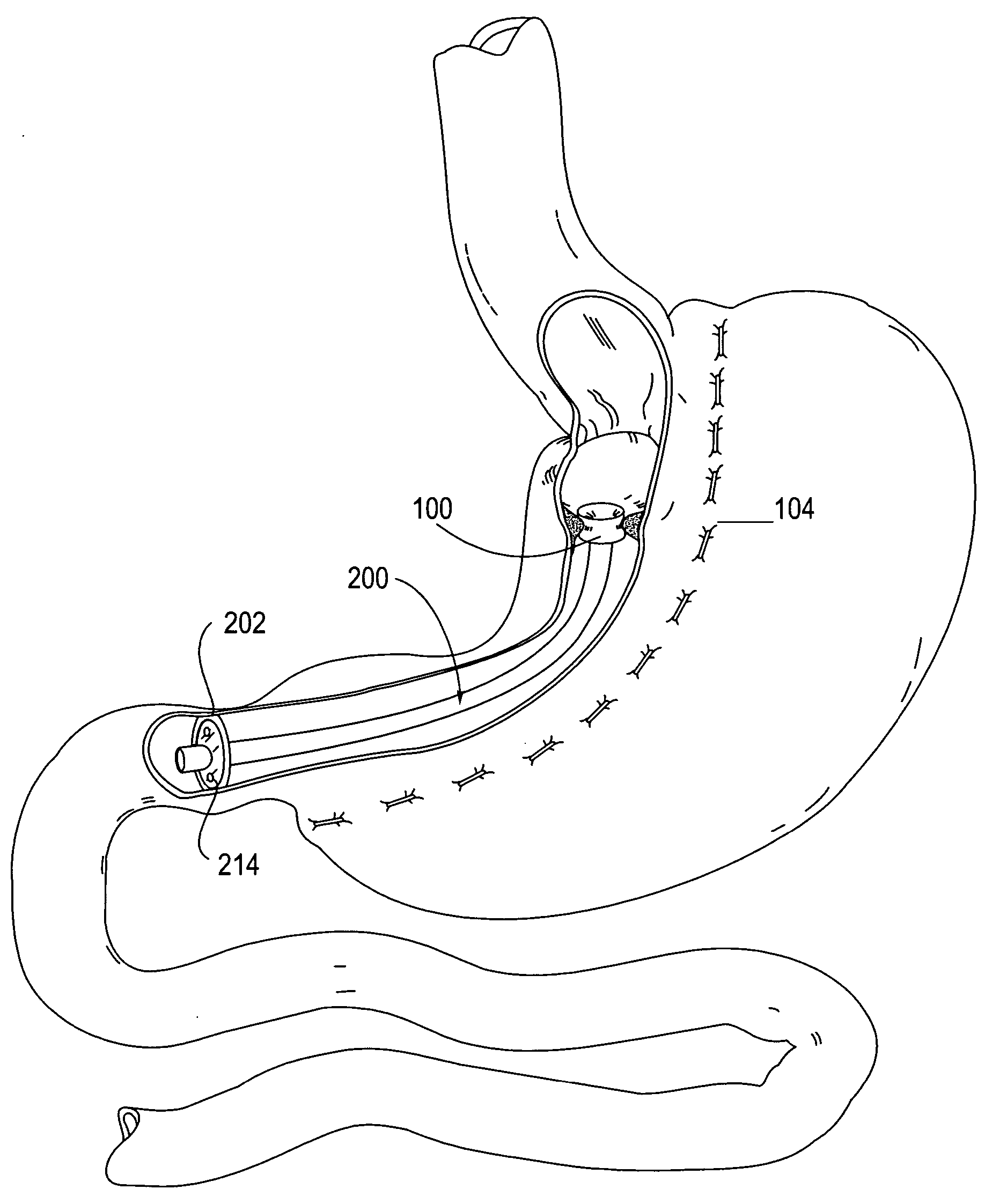
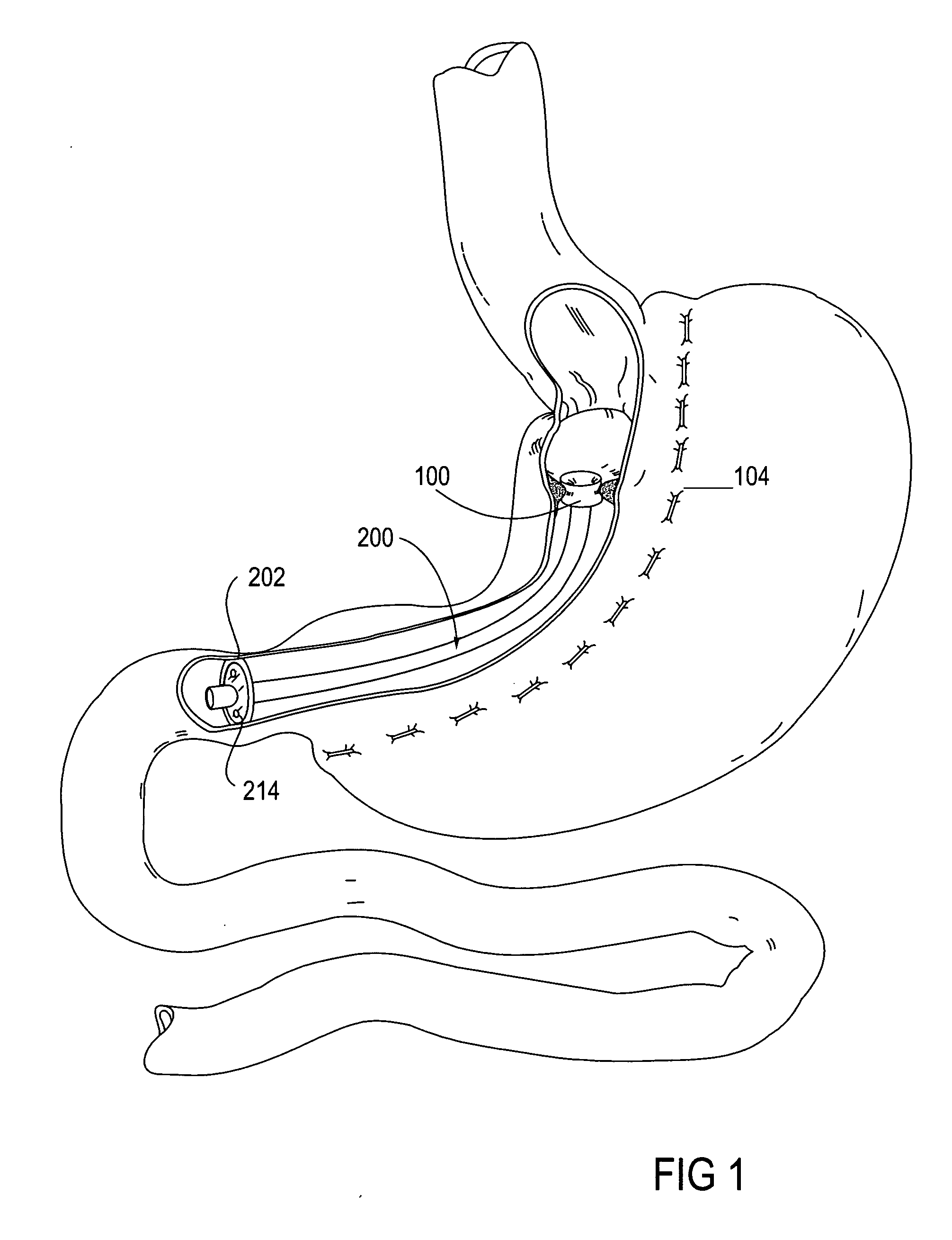
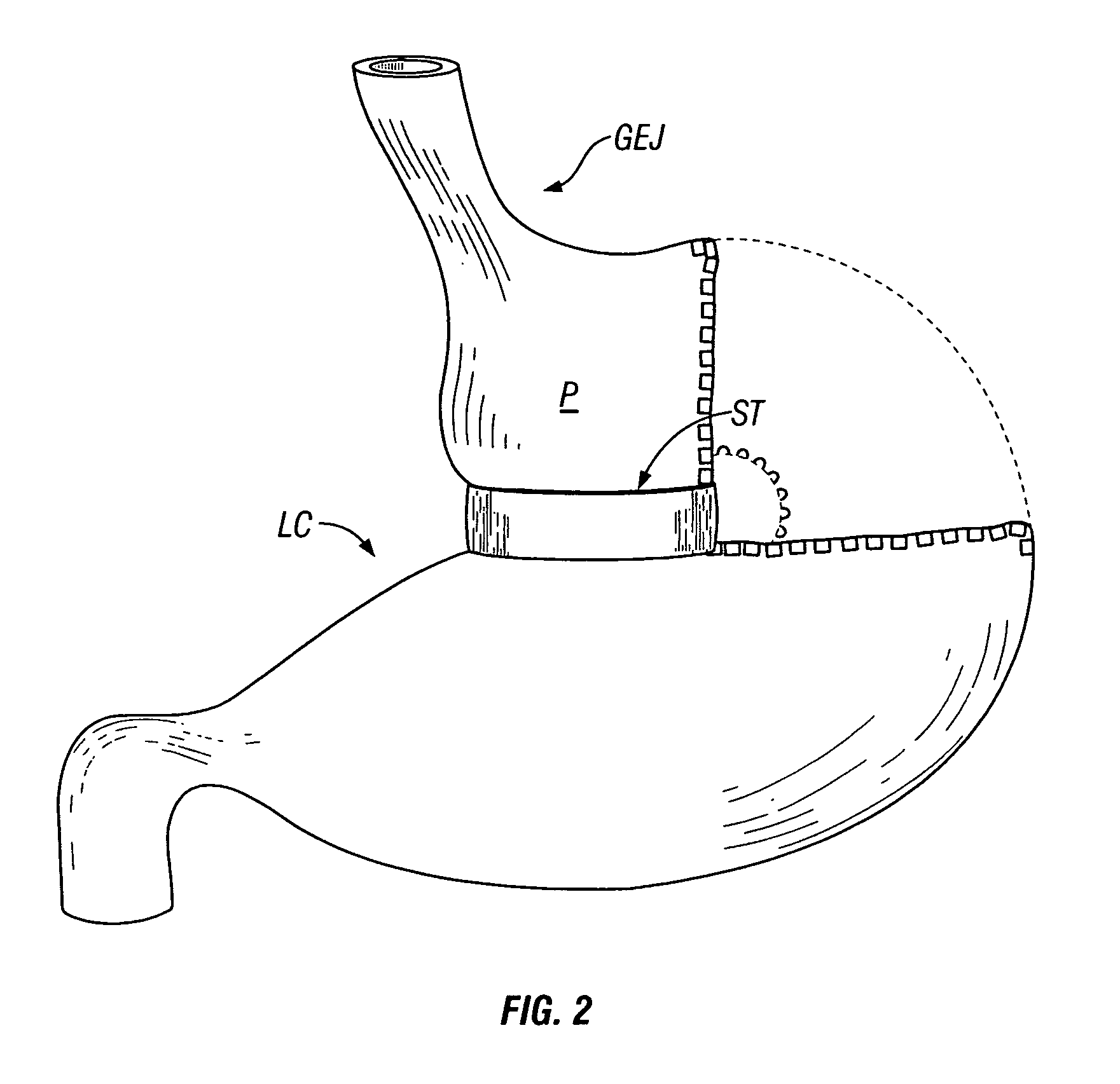
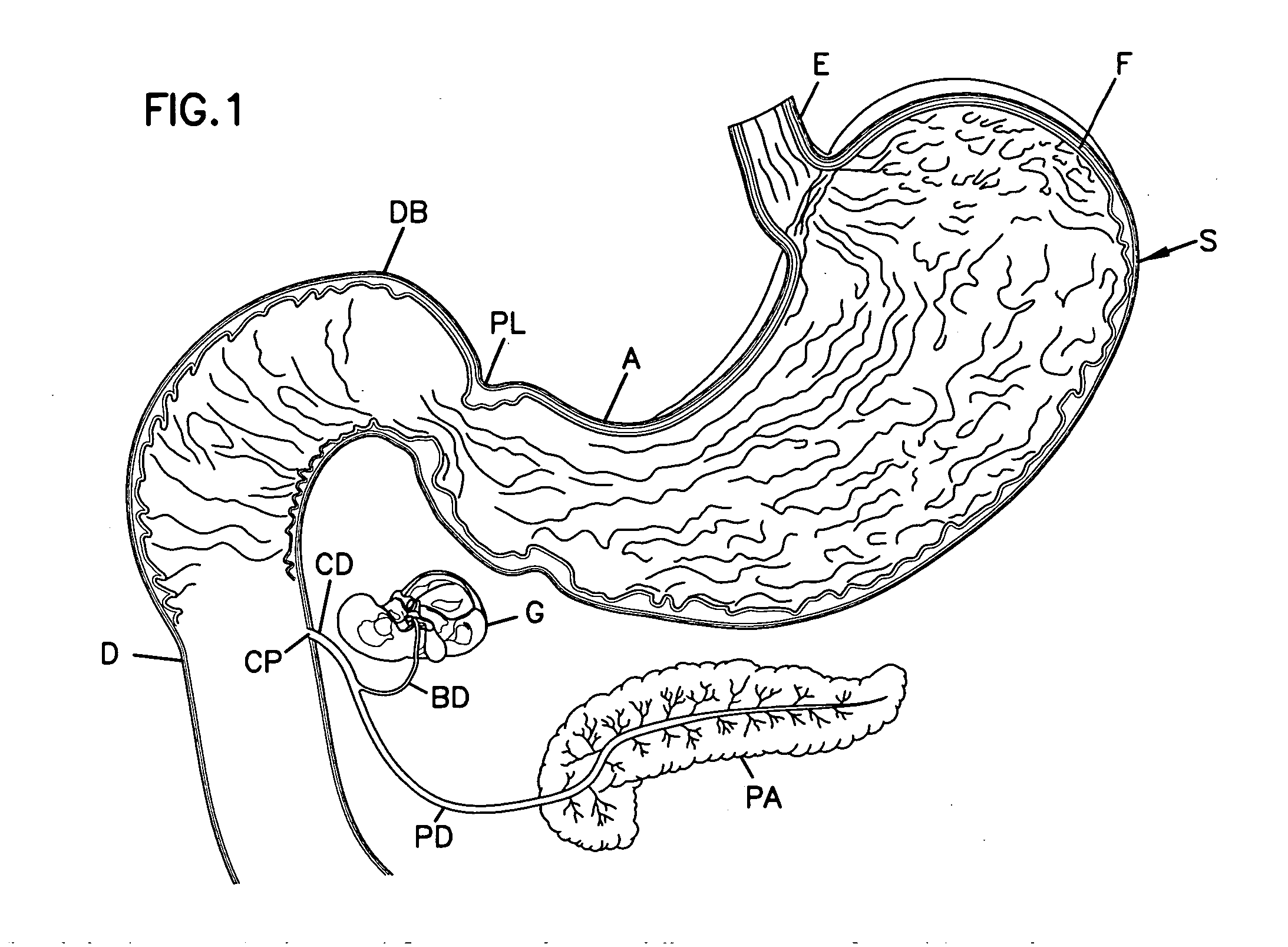
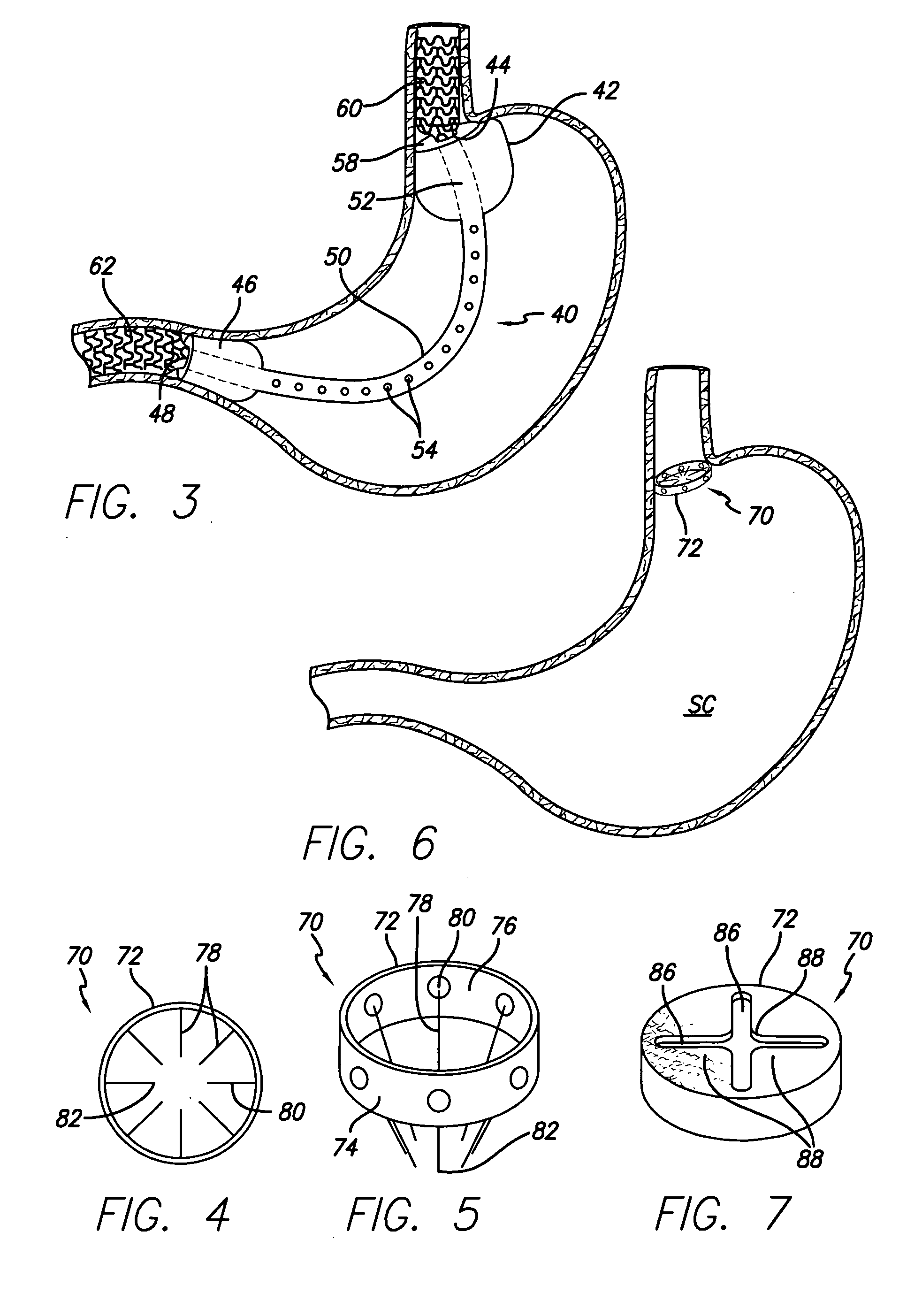
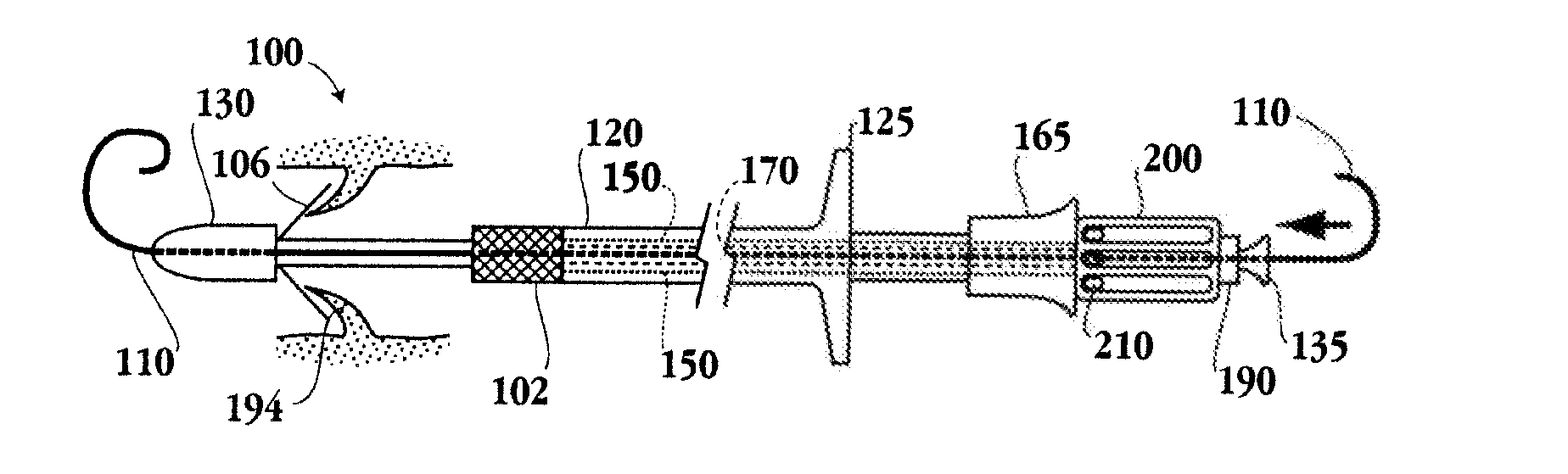
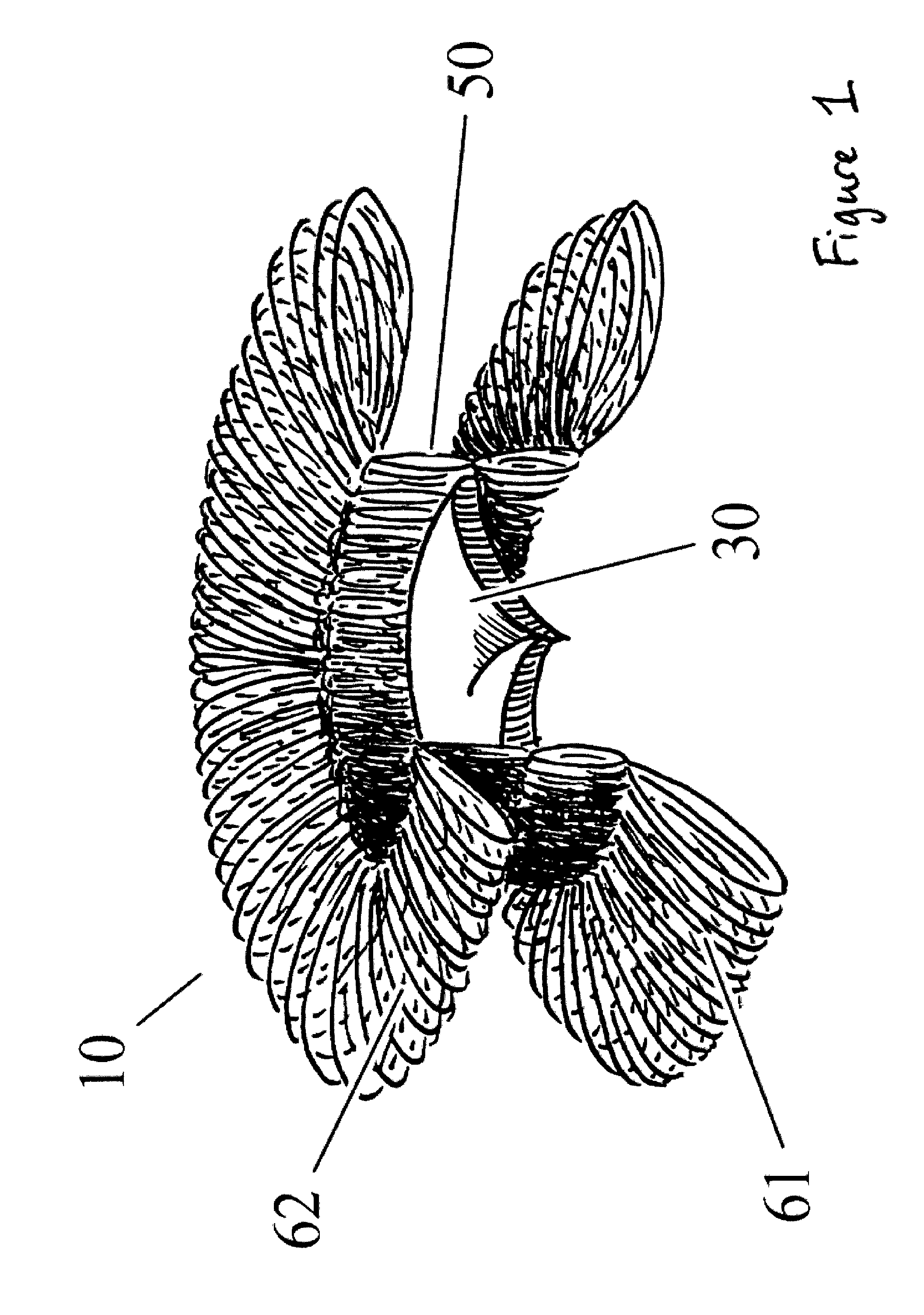
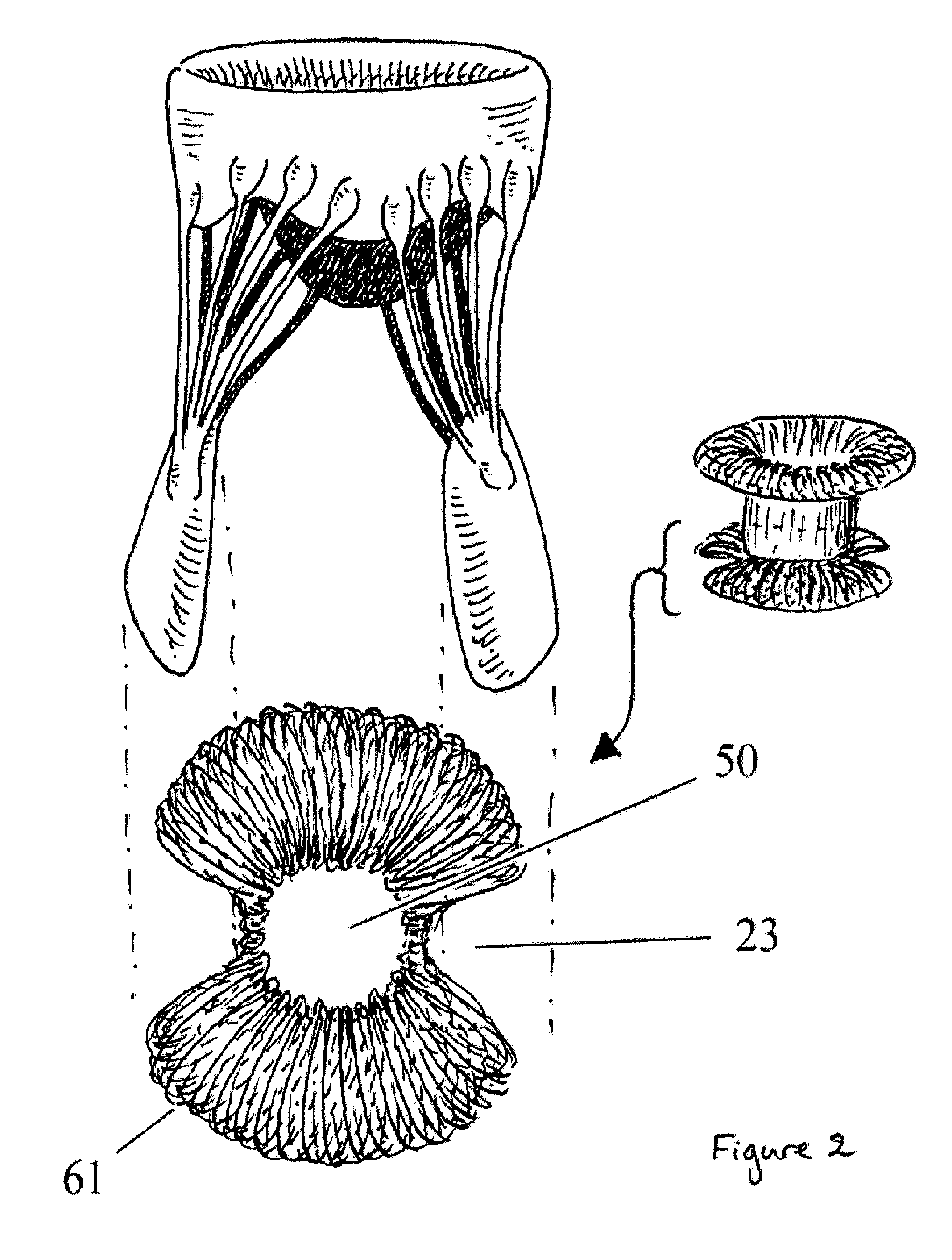
Apparatus and methods are described for treatment of morbid obesity using minimally invasive techniques. The apparatus includes a system of components that may be used separately or in combination for effectively reducing stomach volume, bypassing a portion of the stomach and / or small intestines, reducing nutrient absorption in the stomach and / or small intestines and / or depositing minimally or undigested food farther than normal into the intestines, thereby stimulating intestinal responses. The components described include an artificial stoma device, a gastric sleeve device, an intestinal sleeve device and a combined gastrointestinal sleeve device.
Owner:VALENTX
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
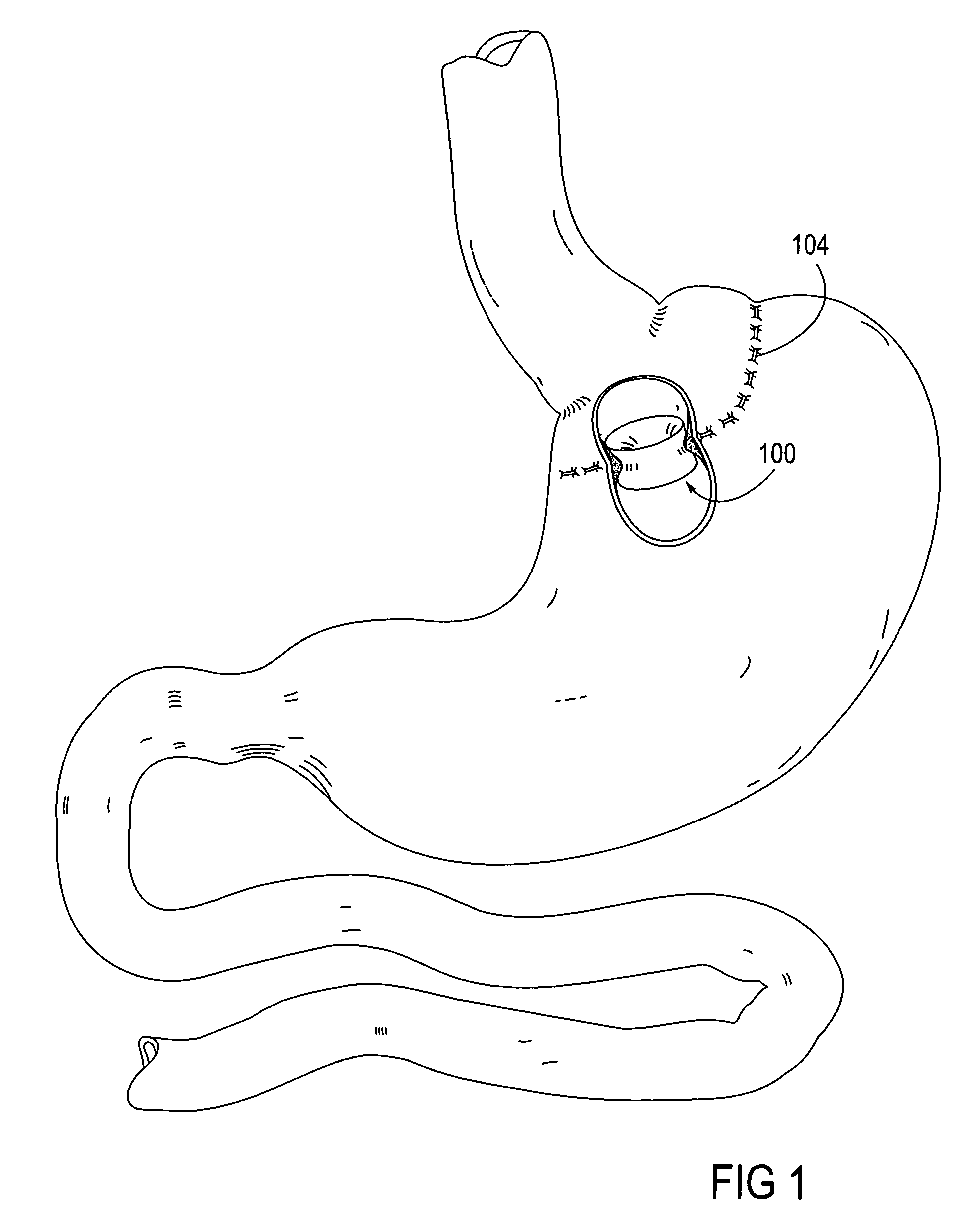
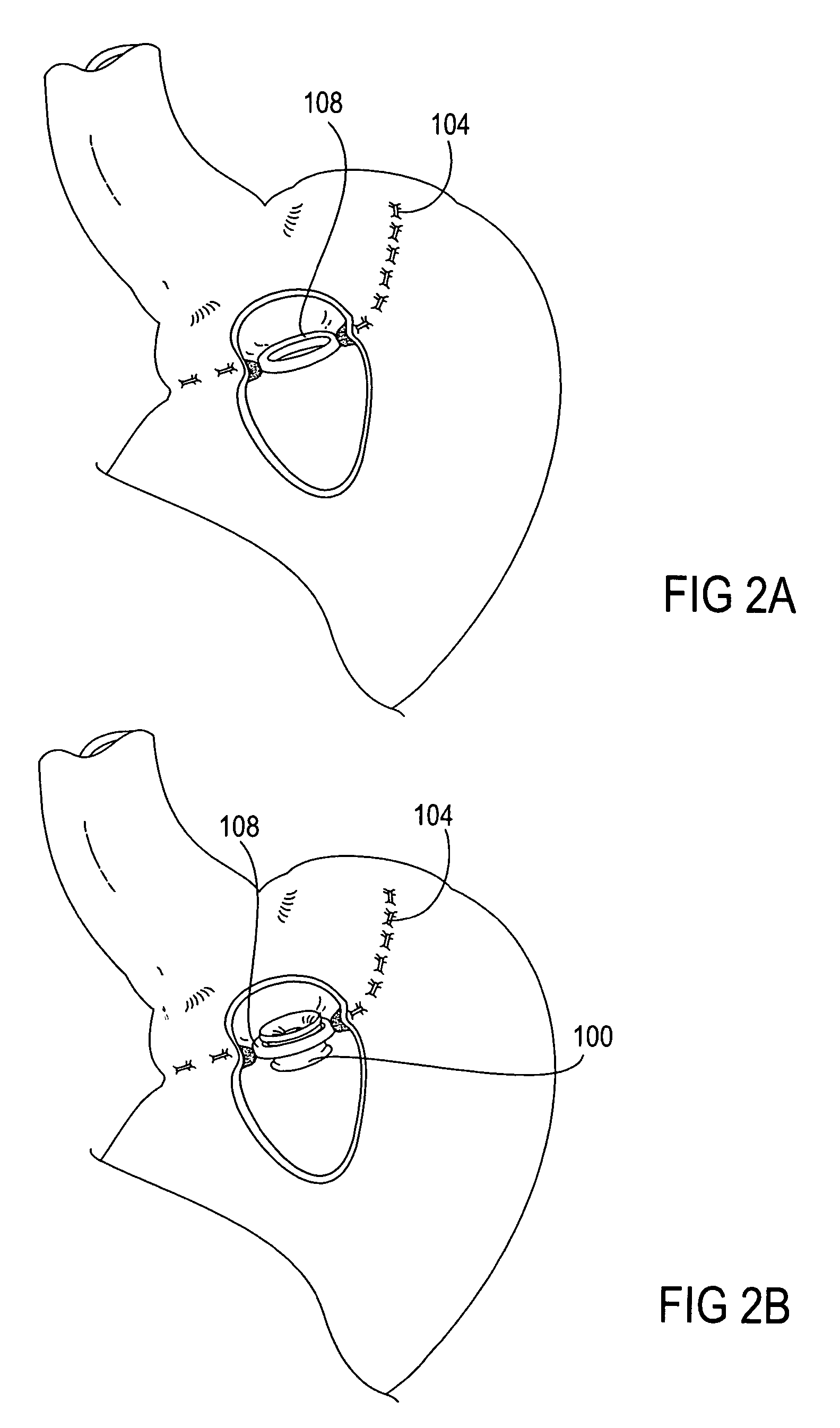
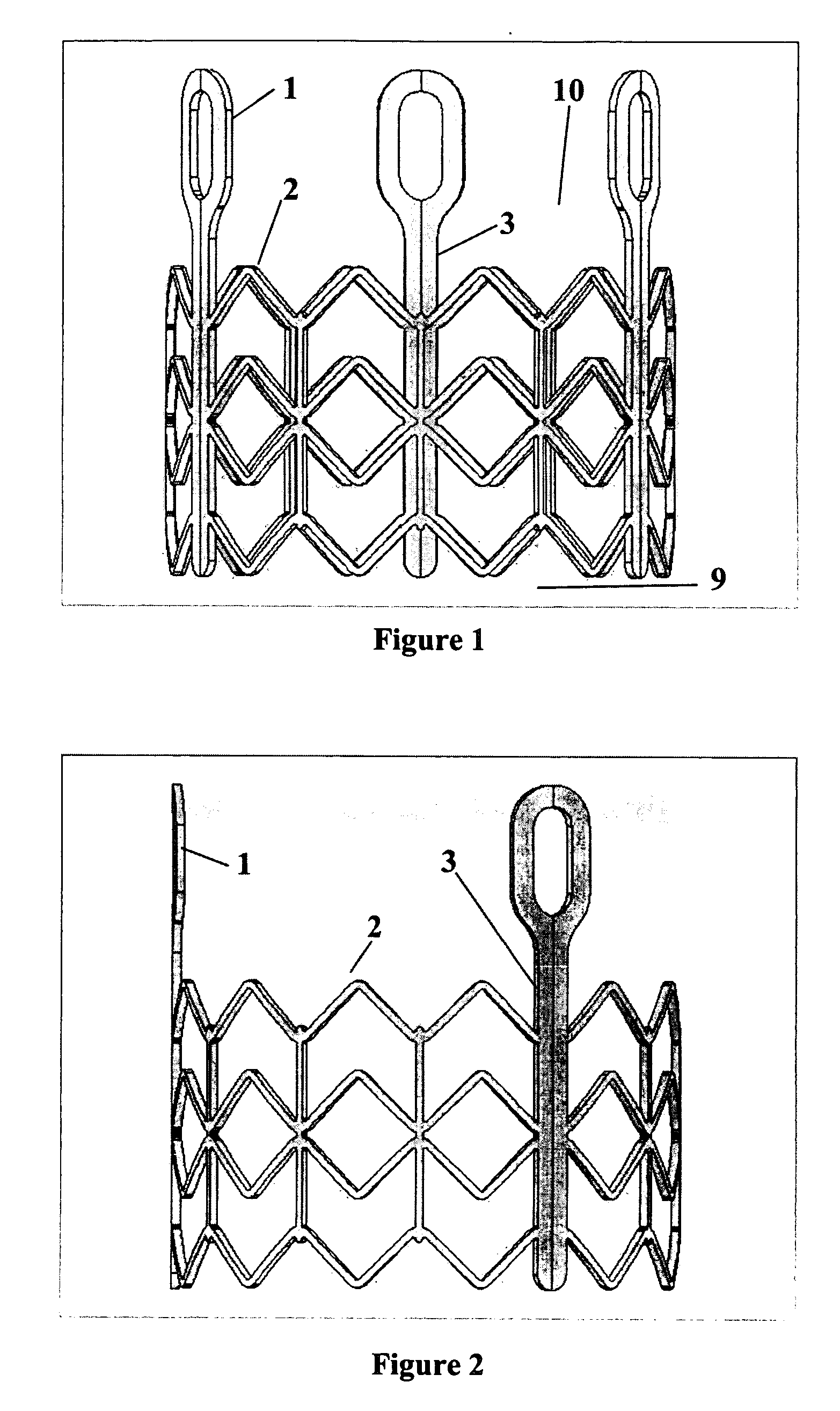
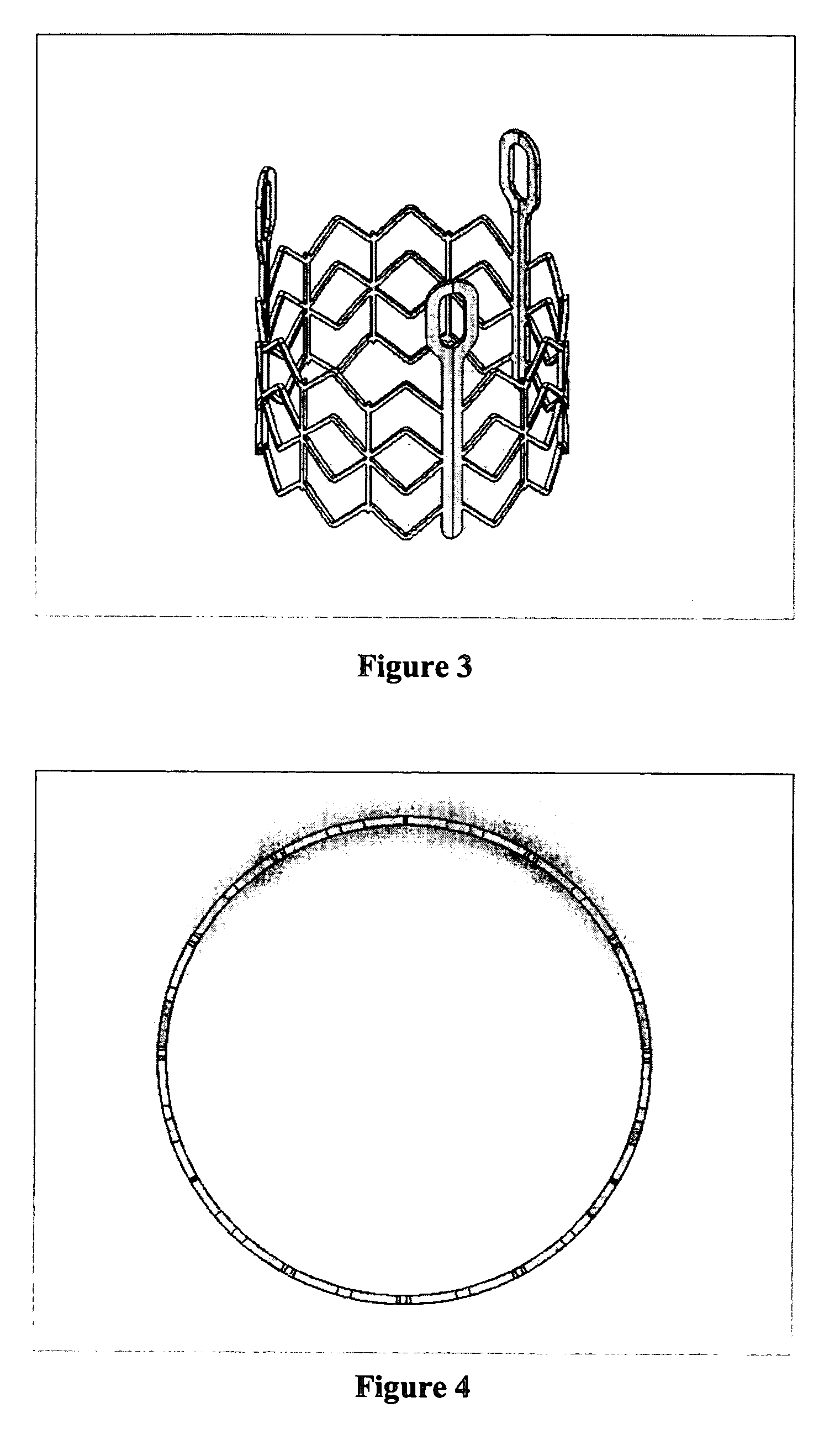
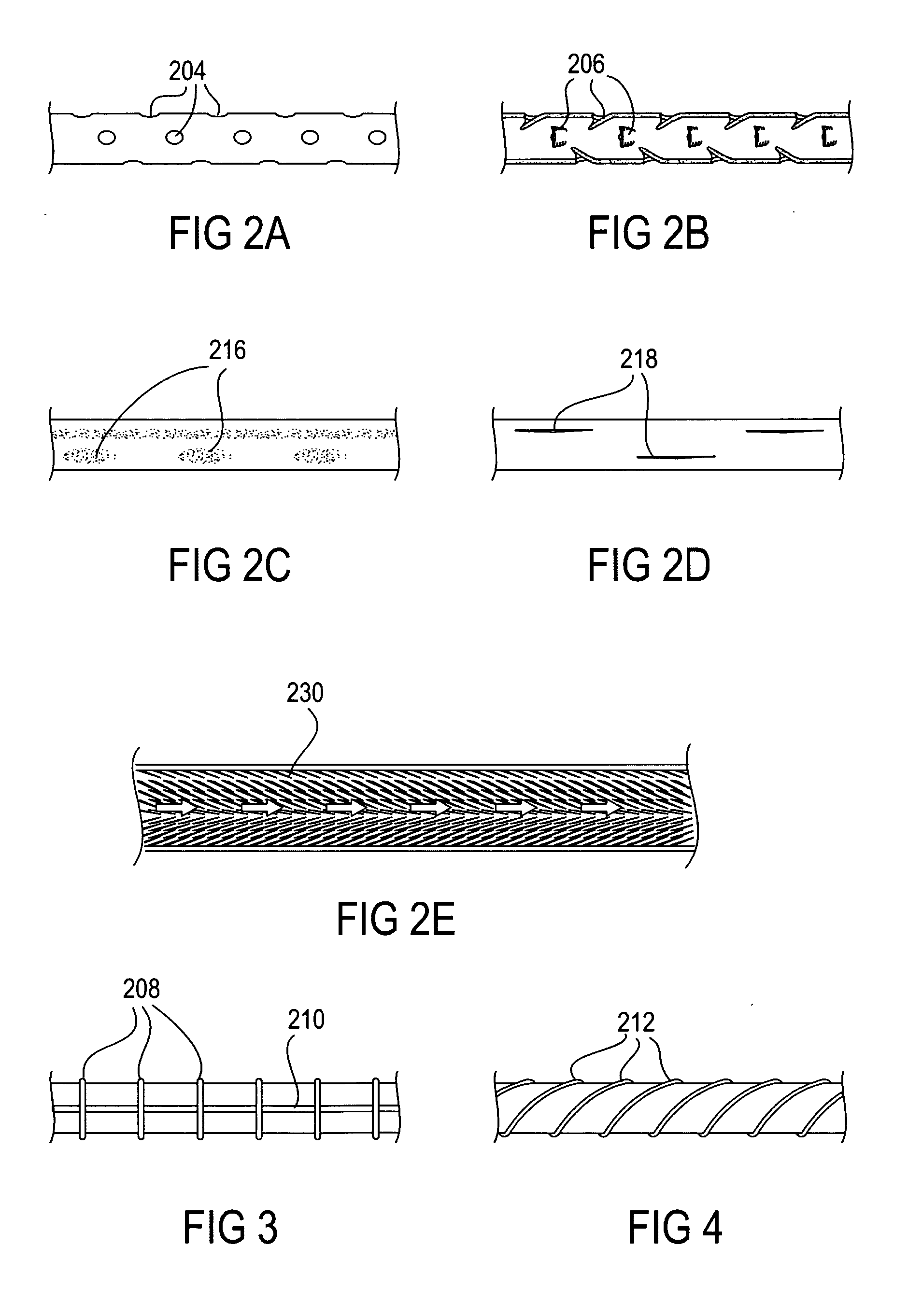
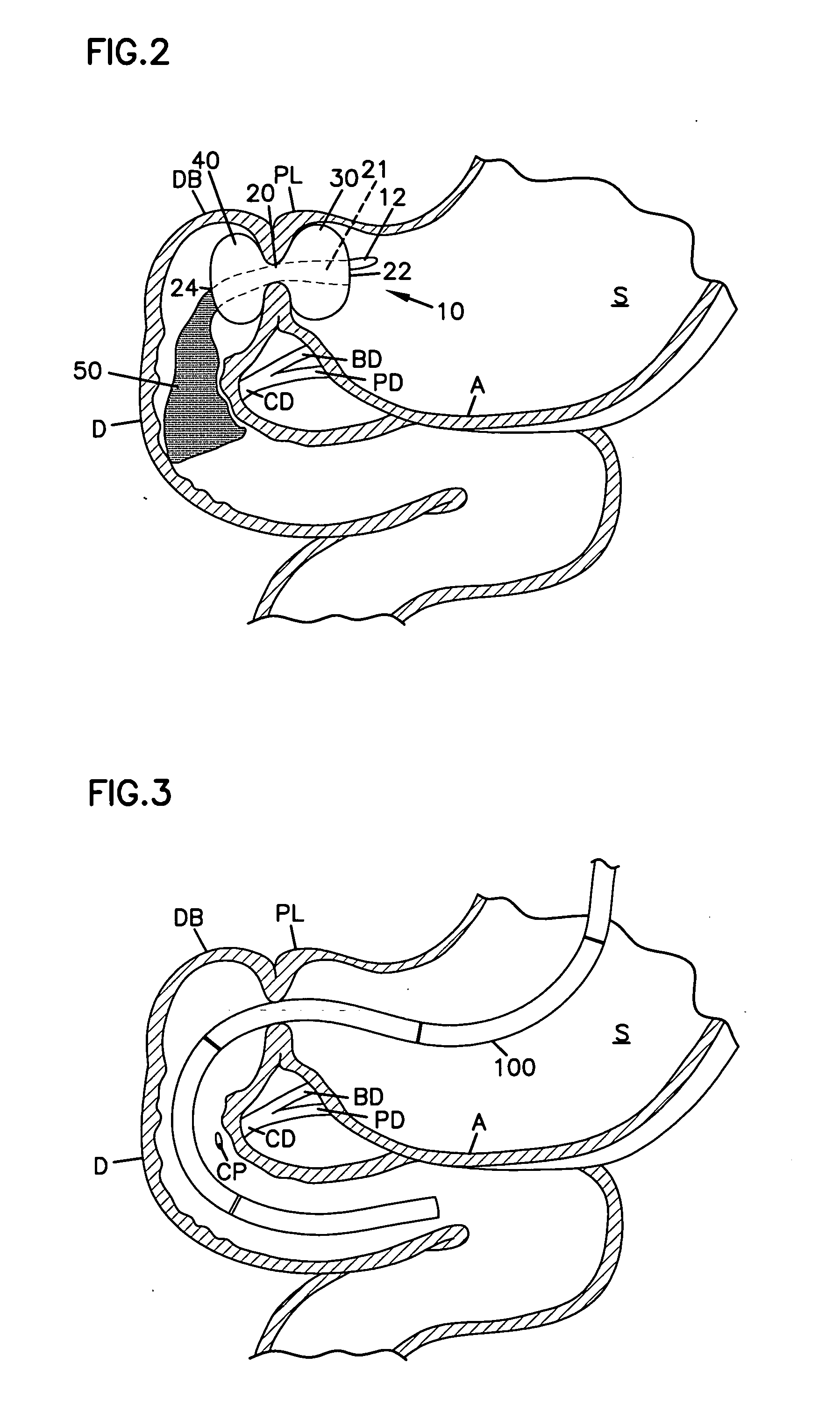
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Devices and methods for treating morbid obesity
The present invention provides devices and methods for attachment of an implanted device, such as an artificial stoma device, a gastrointestinal sleeve device or an attachment cuff, within a patient's digestive tract for treatment of obesity. Special surgical fasteners provide a lasting and durable attachment to the gastrointestinal tissue without causing excessive pressure that could result in tissue erosion and detachment of the implanted device. Fastener delivery devices that facilitate peroral placement and deployment of fasteners and secondary devices are also provided. Also described are implantable devices and attachment means that avoid causing excessive pressure within the tissue by having compliance that is compatible with the gastrointestinal tissues where it is attached.
Owner:VALENTX
Method of repairing inguinal hernias
A universal, surgical prosthesis for hernia repair is provided in the form of a foldable sheet. The prosthesis includes a barrier layer formed of a material adapted to prevent biological adherence thereto, such as polytetrafluoroethylene, and a second surface layer formed of a material adapted to promote biological tissue adherence thereto, such as polypropylene. The second surface may be formed of a series of spaced projections. The prosthesis is adapted to be manipulated into an operative position to exhibit an appropriate exterior when in the operative position. In this manner, the universal, surgical prosthesis can be utilized for a wide range of surgical procedures.
Owner:DAVOL
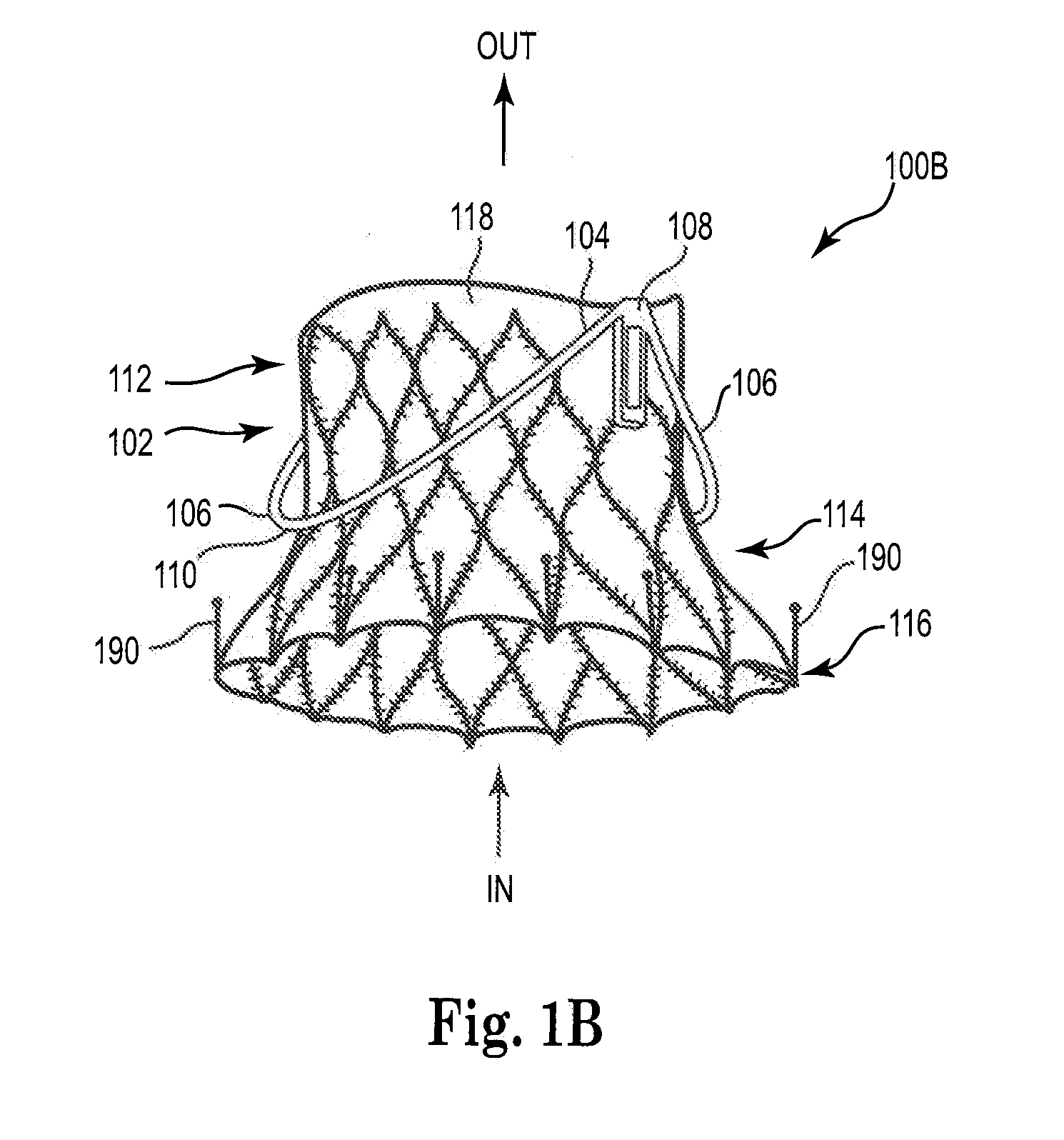
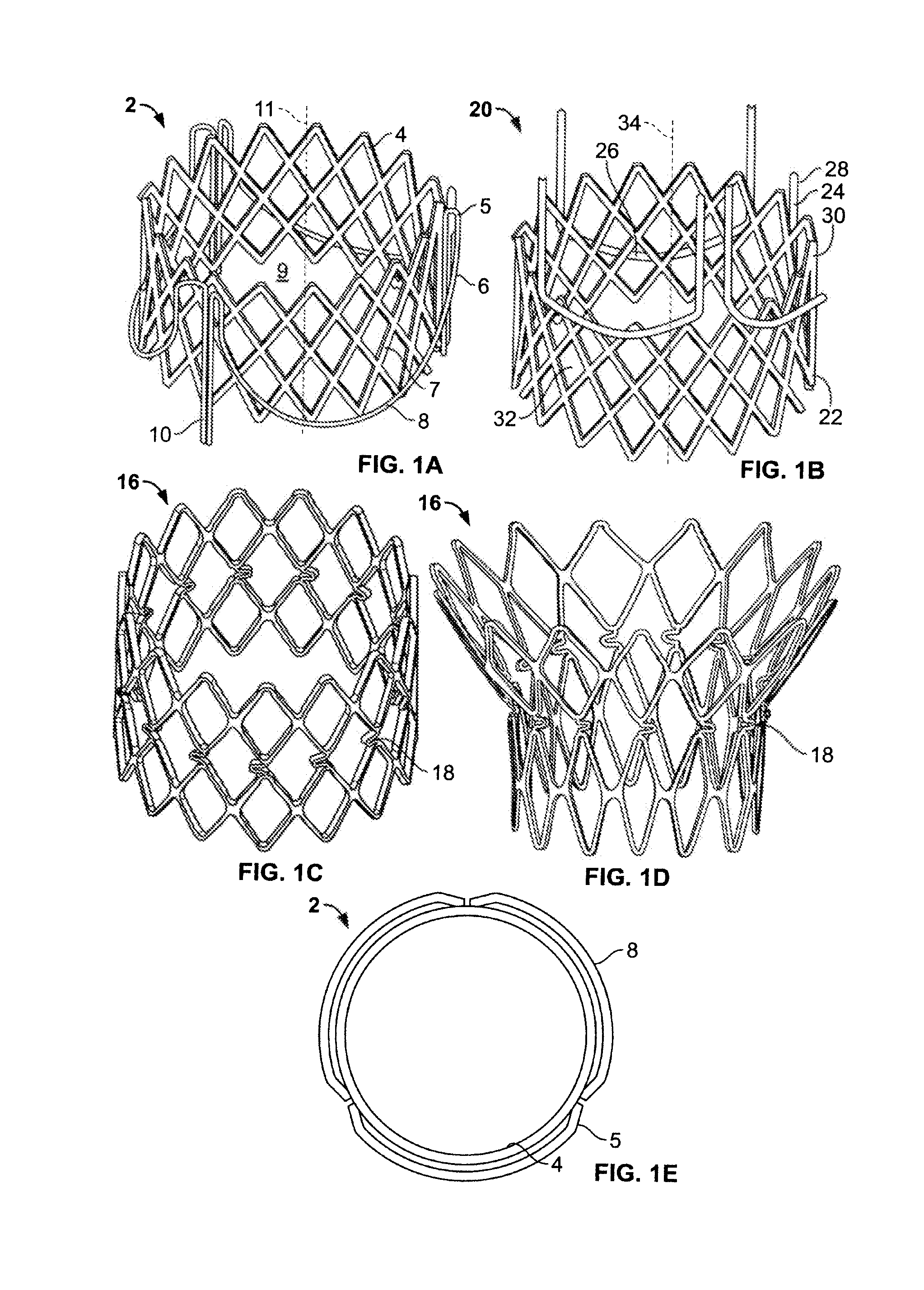
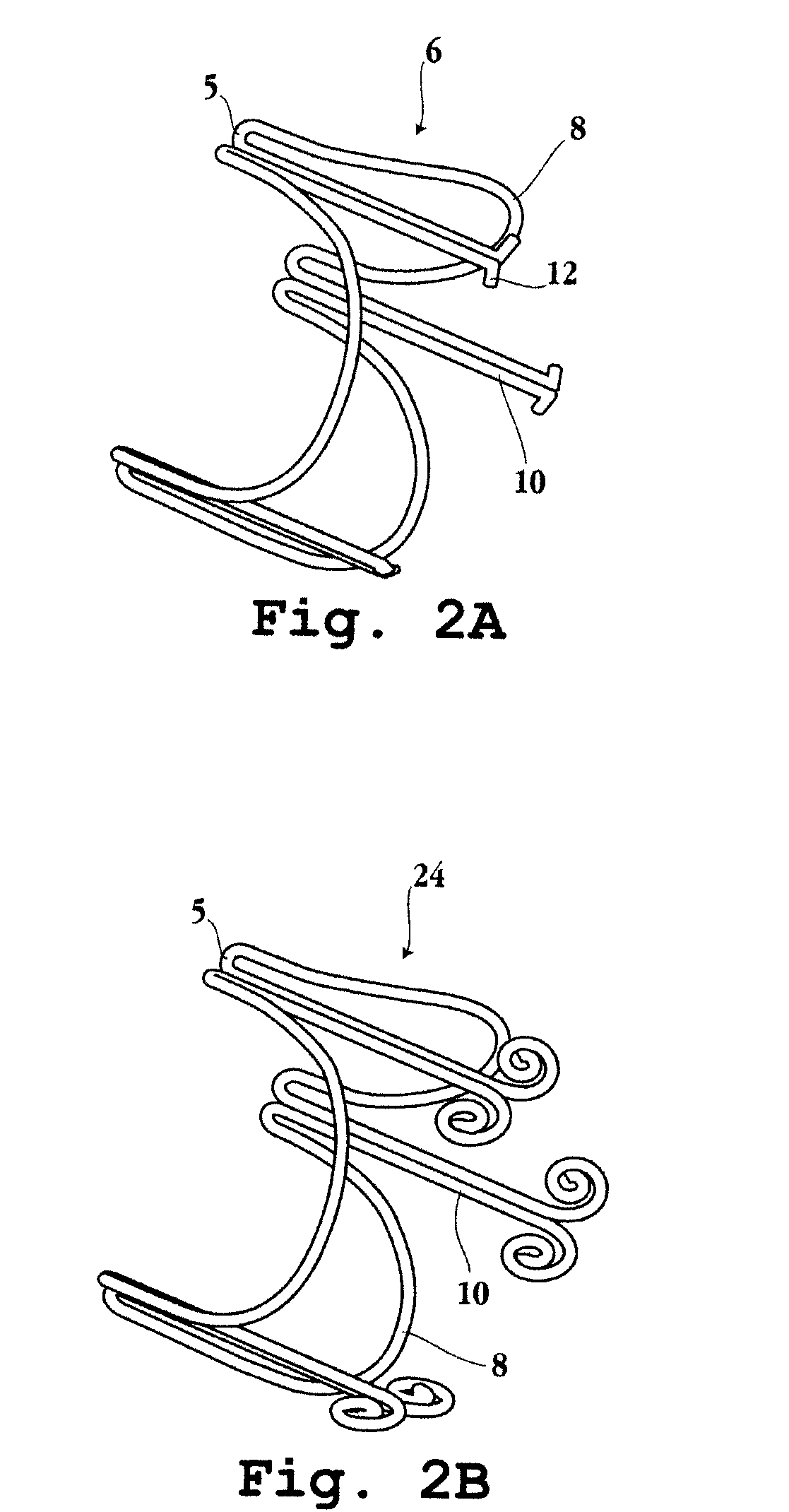
Implantable prosthetic valve
InactiveUS20060025857A1Minimize contactFirmly attachedHeart valvesTubular organ implantsEngineeringCatheter
Owner:MEDTRONIC 3F THERAPEUTICS
Method of preparation of bioabsorbable porous reinforced tissue implants and implants thereof
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Kit for forming implants in wall of gastrointestinal tract
InactiveUS7846085B2Inhibit injectionAvoid the needSurgical needlesMedical devicesGastrointestinal tractGeneral surgery
A kit for treating a gastrointestinal tract of a mammal and including a package and a tubular needle, an end piece and a container of an implant-forming material carried within the package. The end piece has an outer surface provided with at least one recess and an internal passageway communicating with the recess. The end piece is mounted on the distal extremity of an elongate probe member and introduced into the upper portion of the gastrointestinal tract. A portion of the wall of the gastrointestinal tract is drawn into the recess and the tubular needle is extended through the elongate probe member and the internal passageway into the portion of the wall in the recess. Material from the container is loaded into the tubular needle and injected into the portion of the wall to form an implant in the wall.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
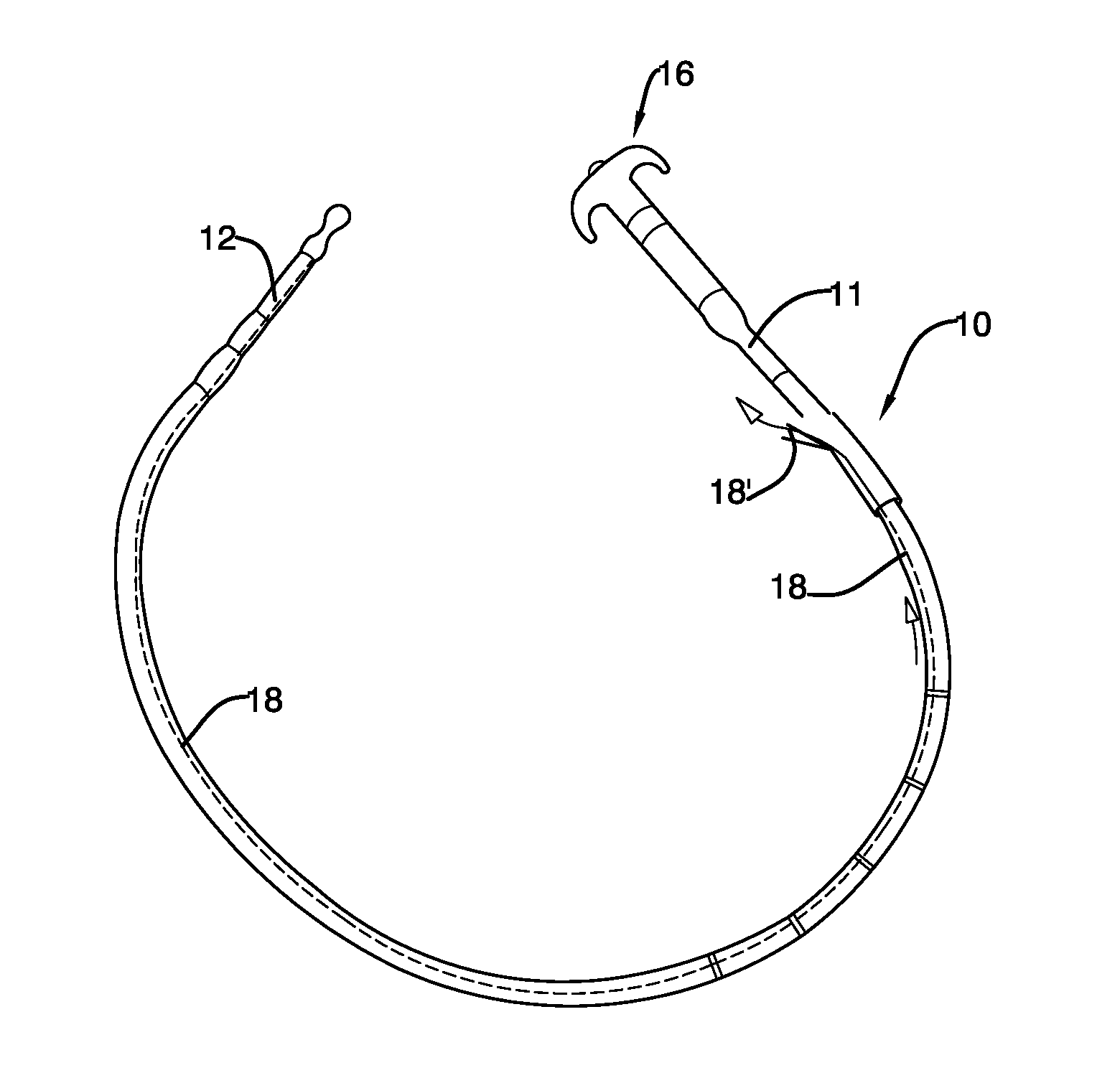
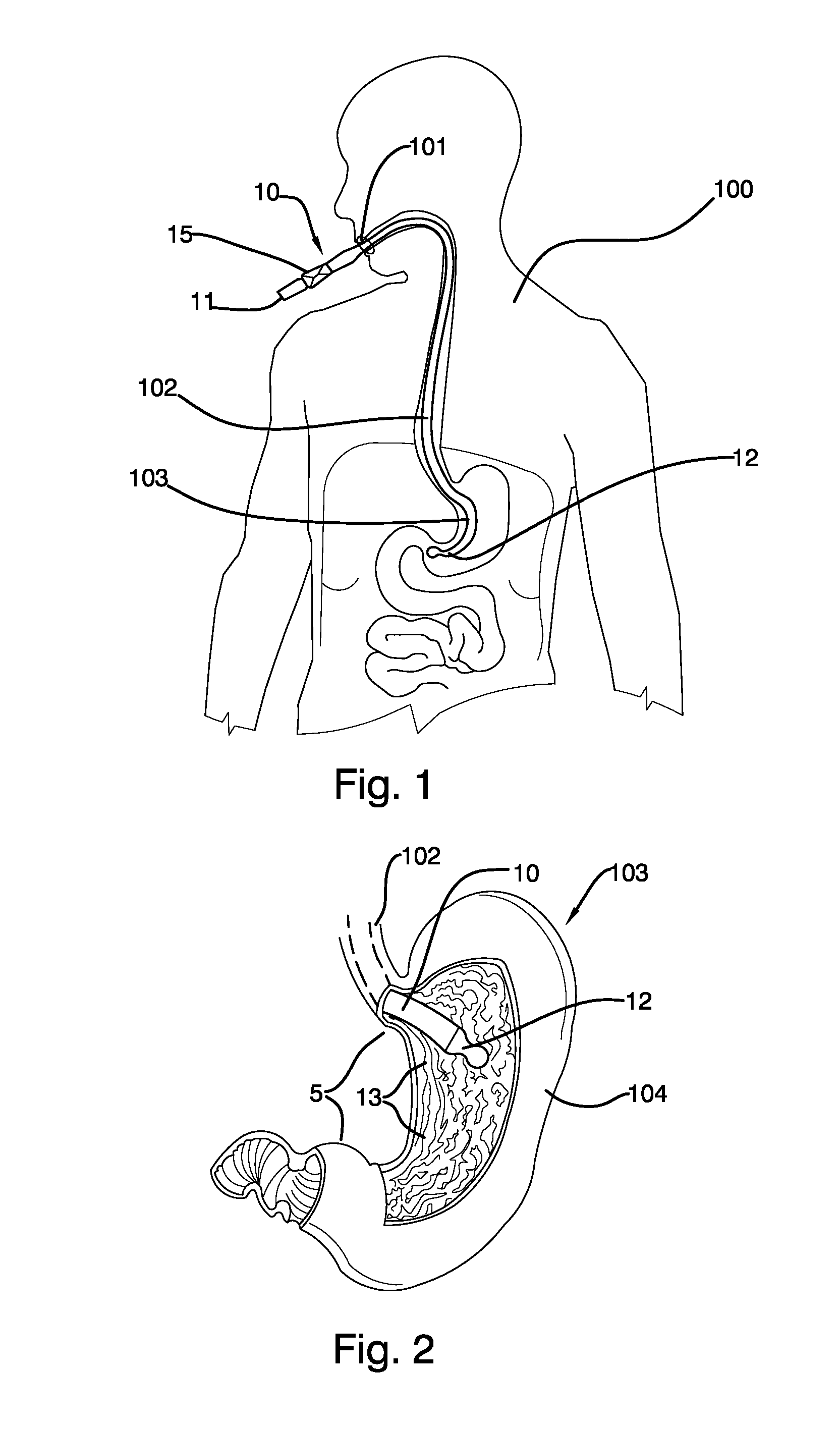
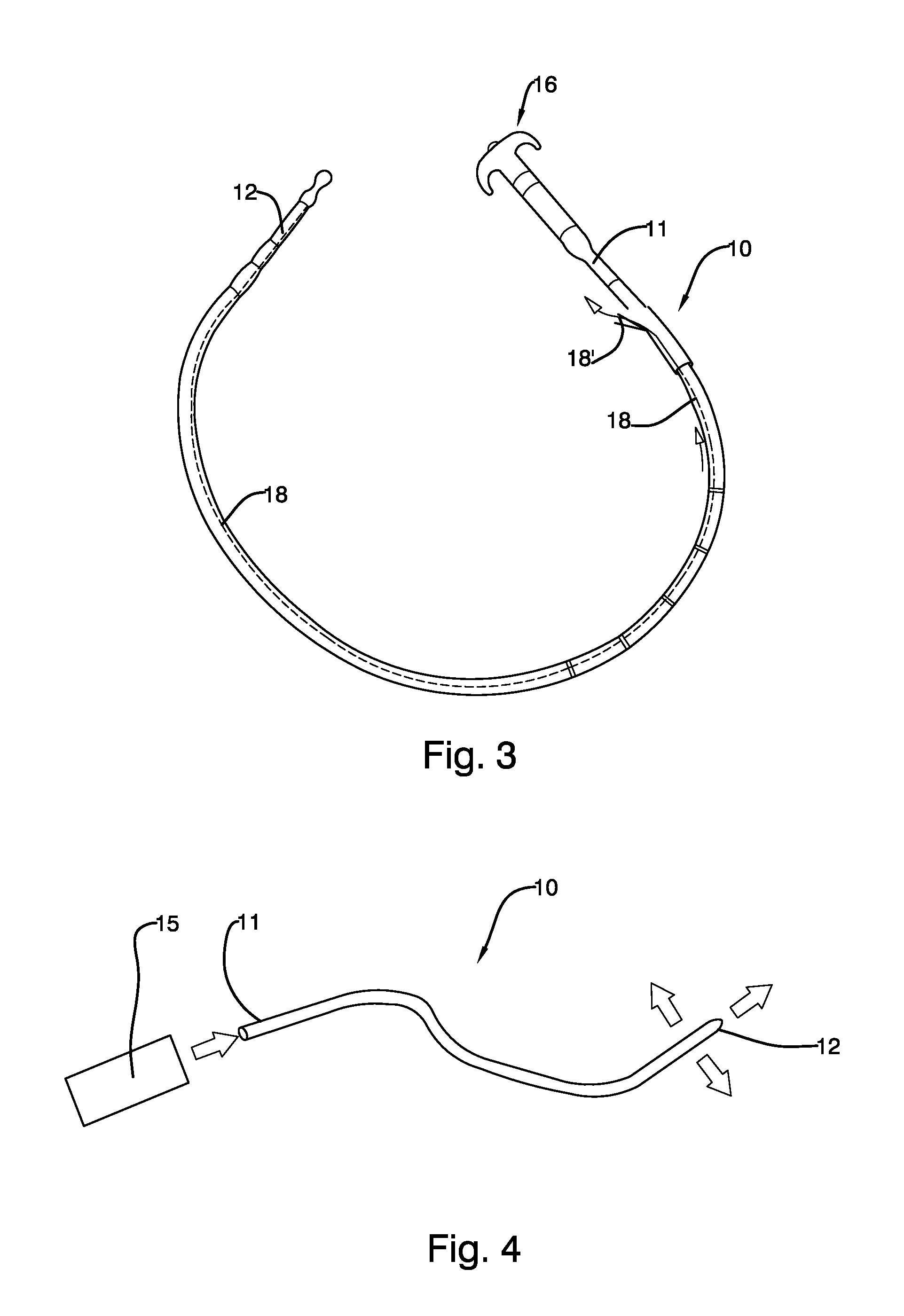
Mechanically-guided transoral bougie
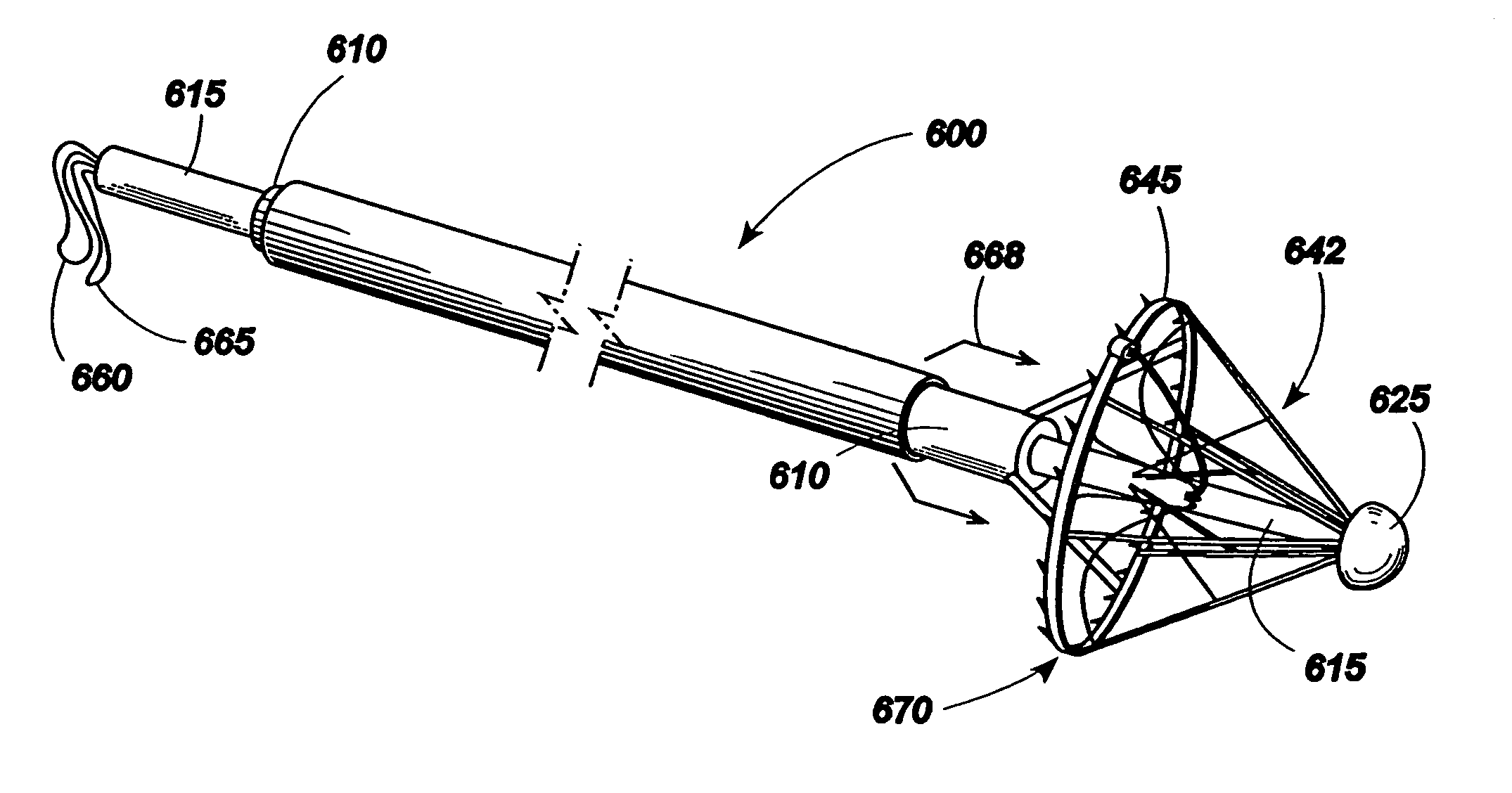
The present invention is referred to a mechanically-guided transoral bougie, comprising an elongated body with an external end and a distal end; said external end includes a guiding mechanism mechanically connected to said distal end to allow the surgeon to move said distal end in any direction once the bougie is inserted into the stomach. Said guiding mechanism includes a manually operated guiding control.
Owner:JACOBS MOISES
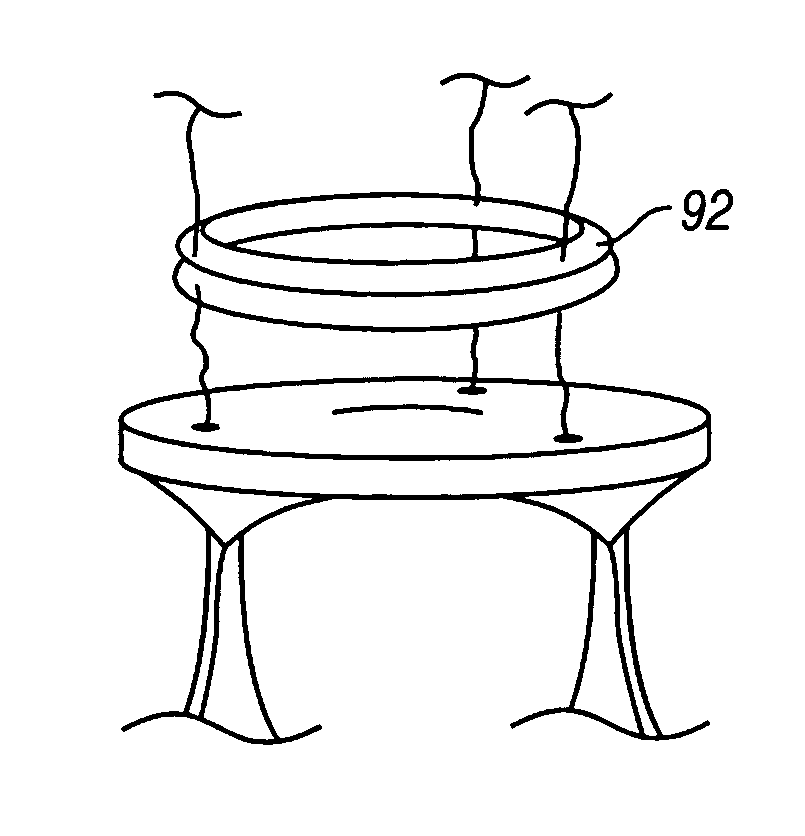
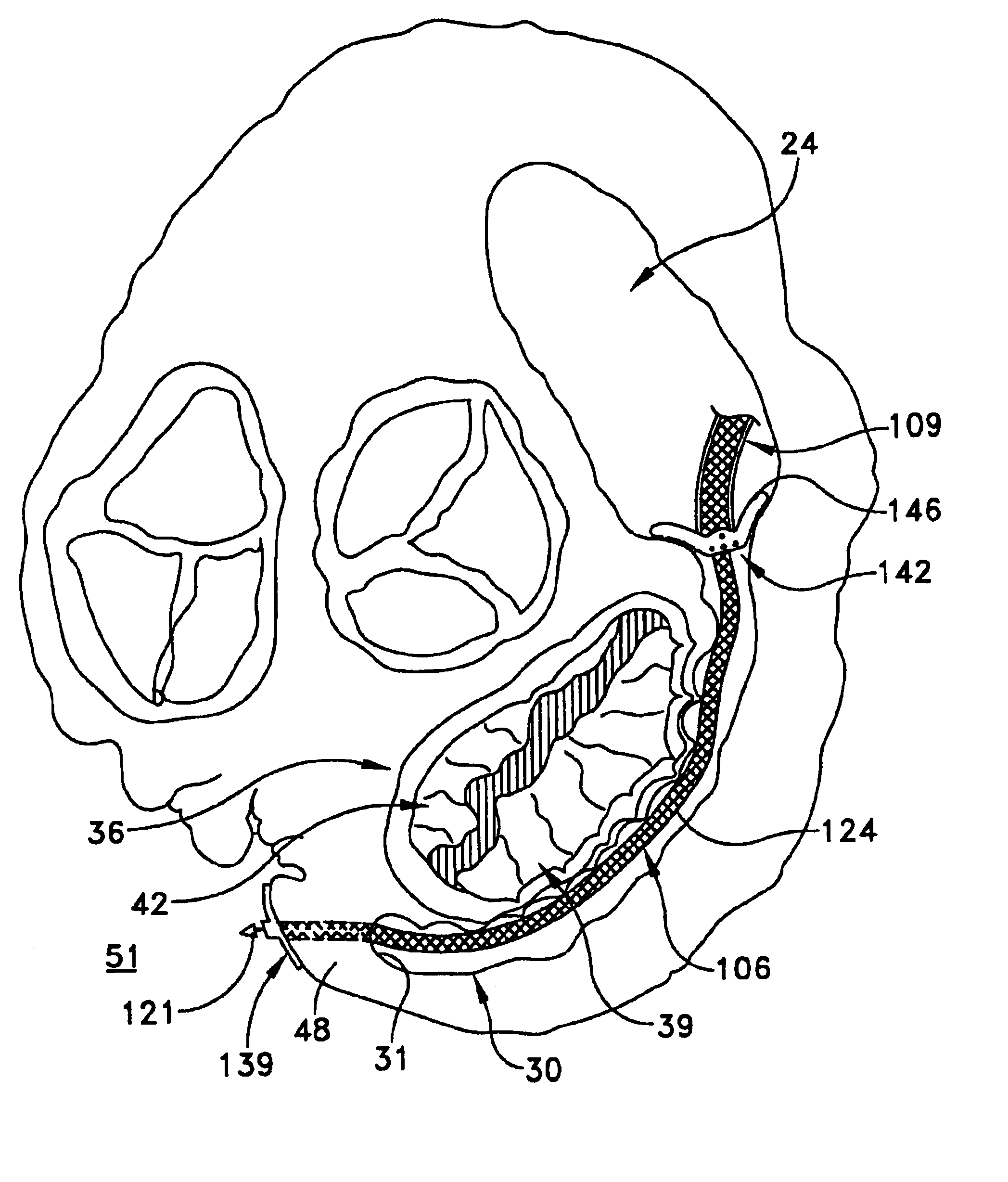
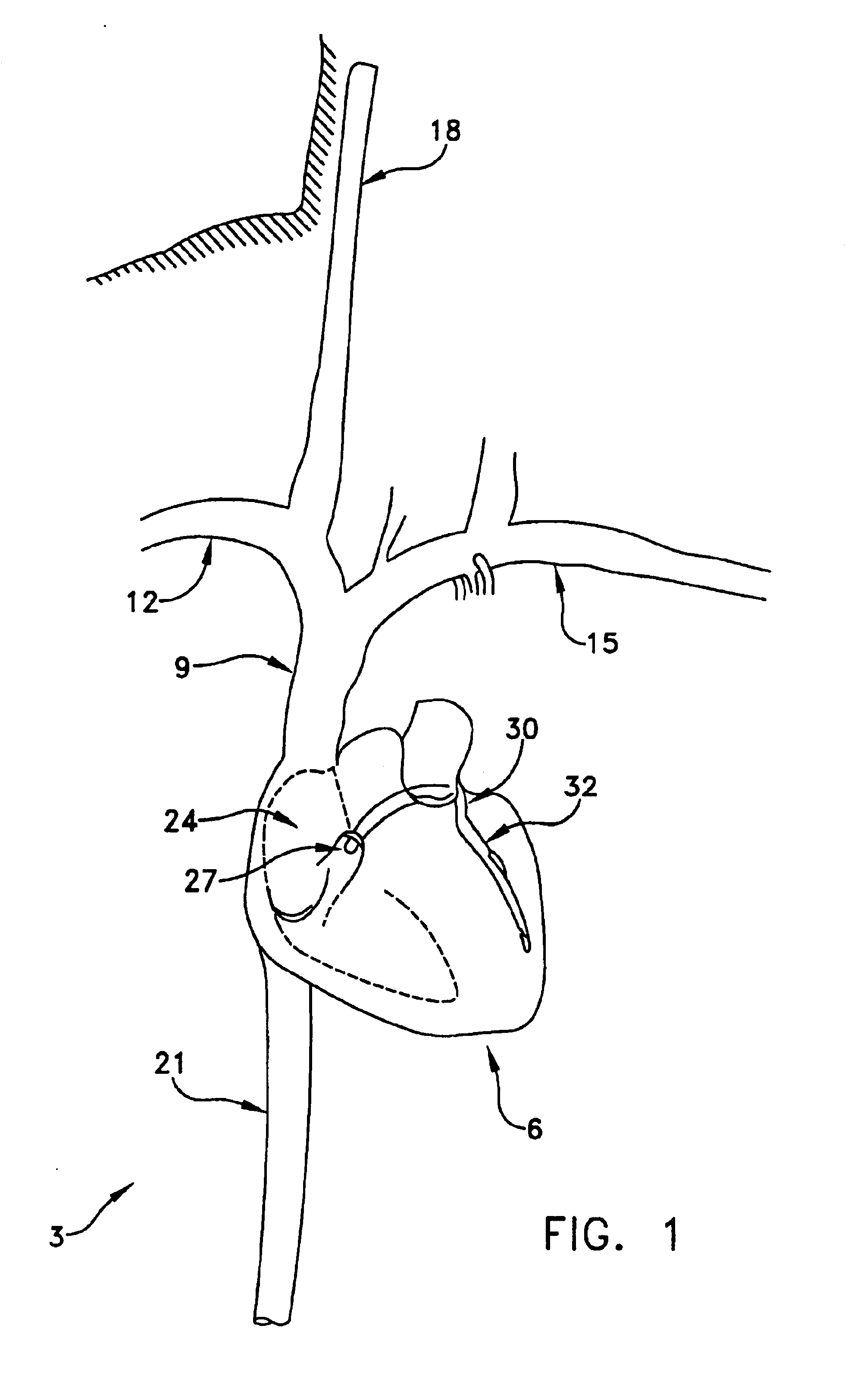
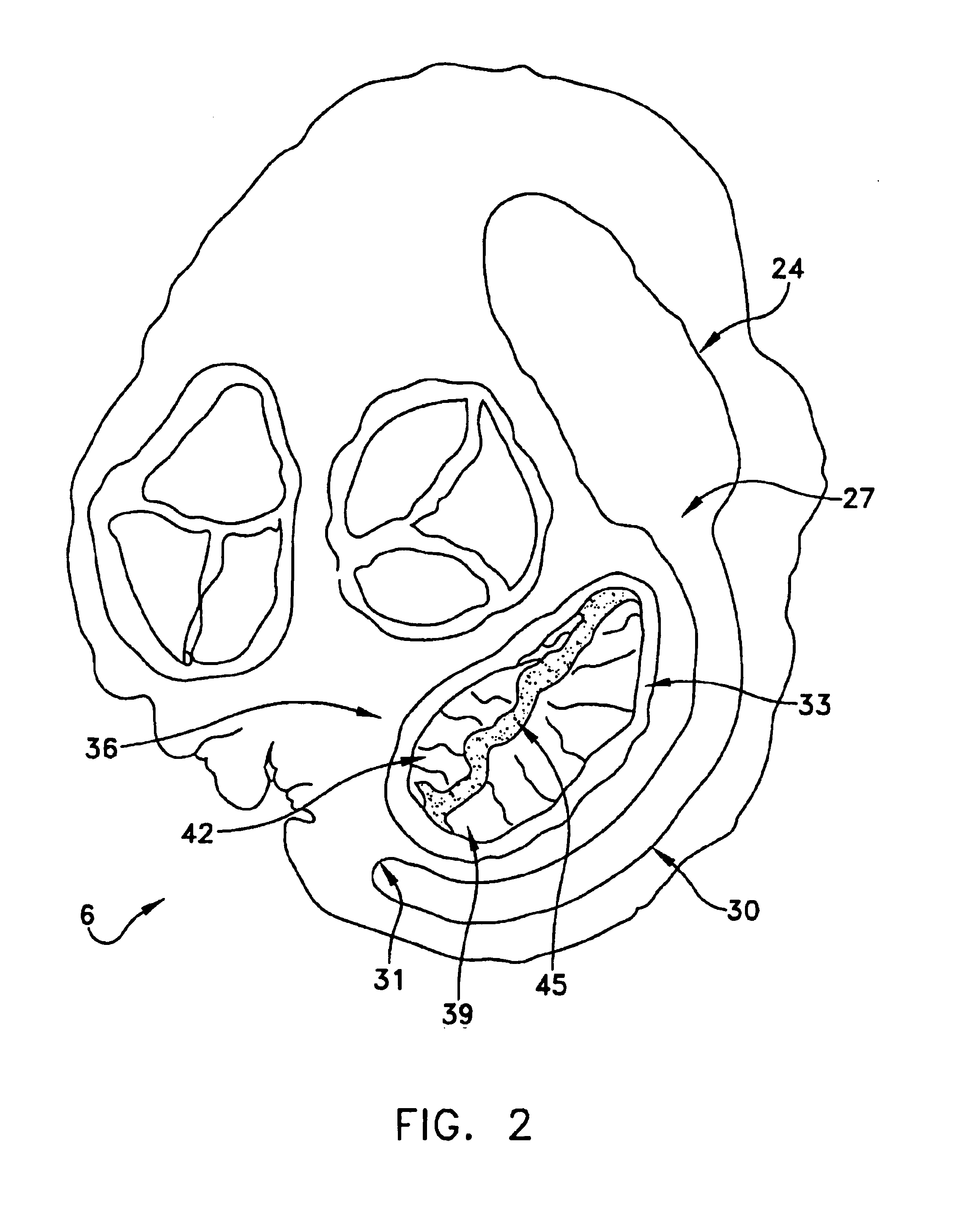
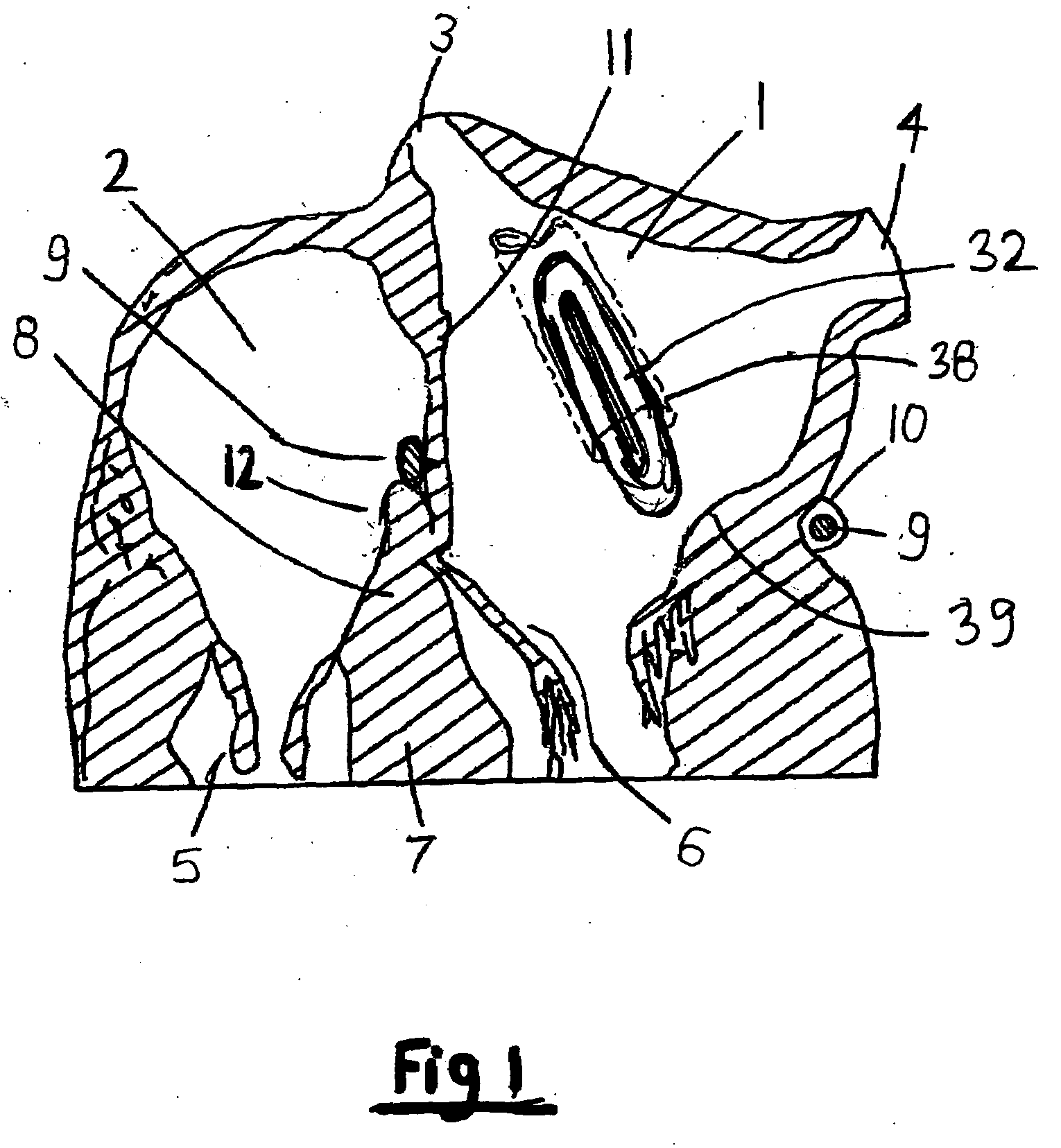
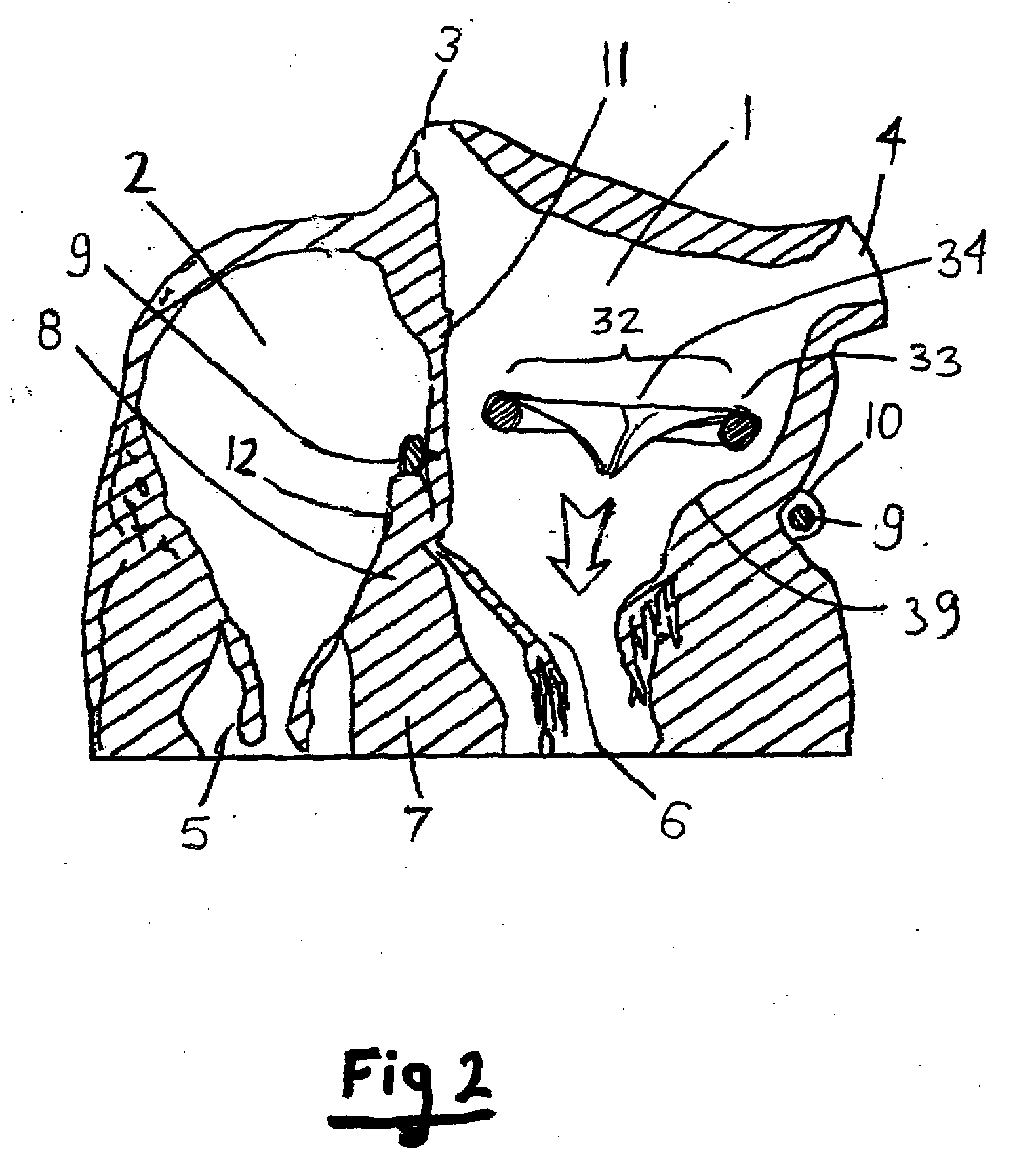
Method and apparatus for valve repair
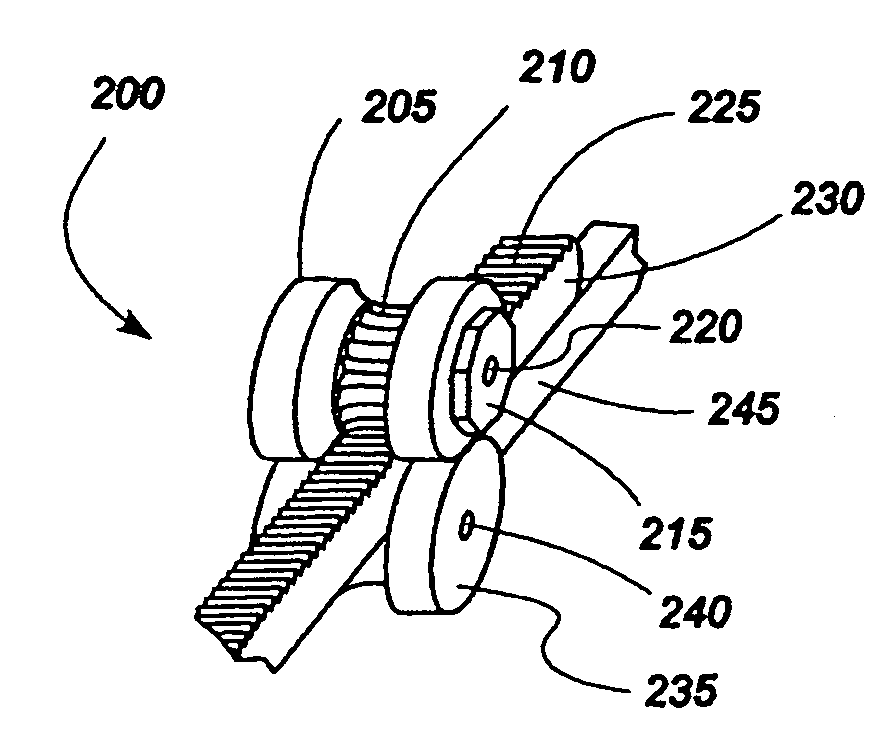
InactiveUS7125421B2Minimize traumaLow costAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsLinear configurationBiomedical engineering
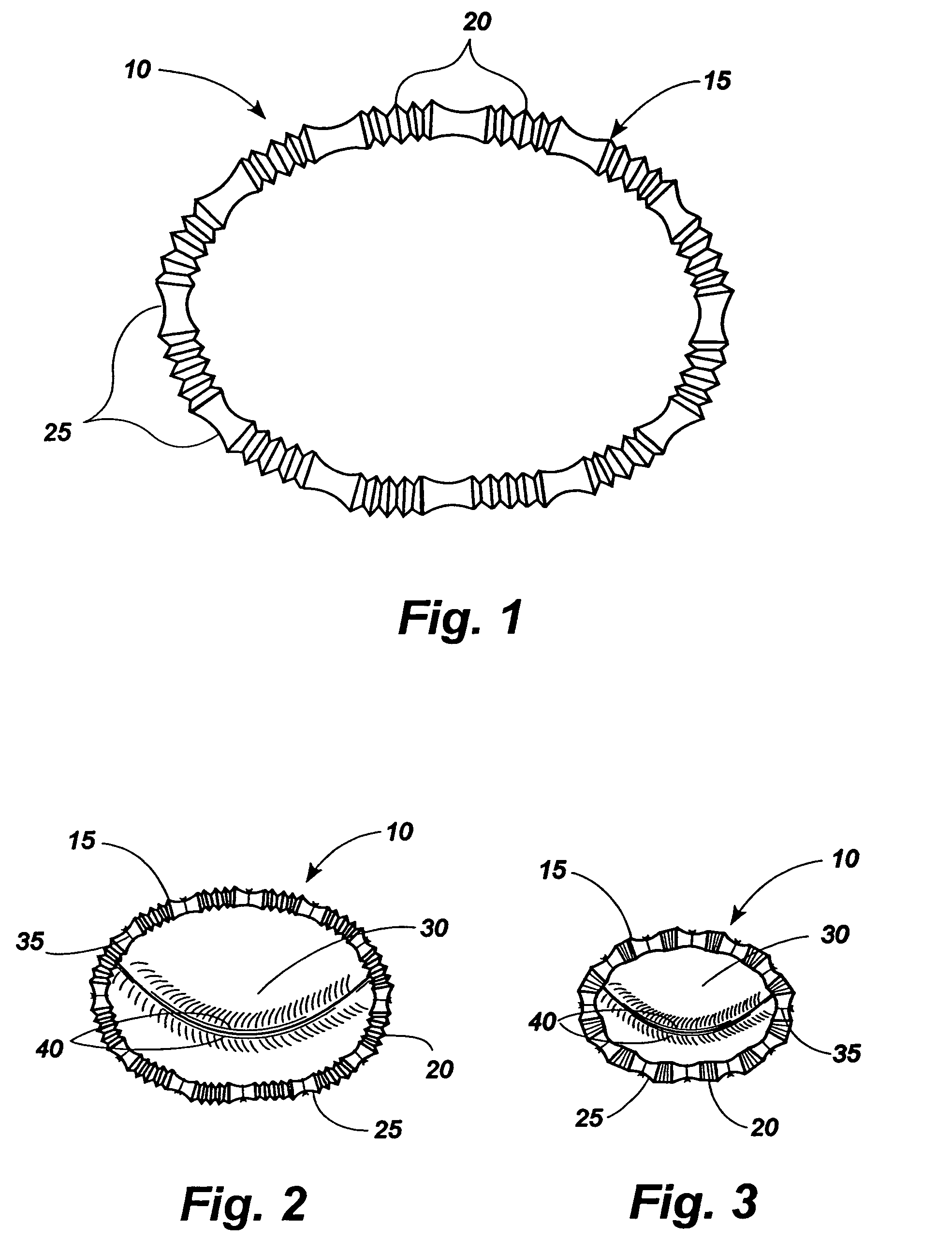
A tissue connection device is provided for use on a patient at a treatment site. The device comprises an elongate member having a distal end and a proximal end. The elongate member has a first, substantially linear configuration during delivery through an elongate delivery device, wherein the first configuration is sufficient to allow said member to be delivered percutaneously into the patient to the treatment site. The elongate member has a second, substantially circular configuration when said member disengages from the delivery device, wherein the second configuration is sufficient to support tissue at the treatment site. The elongate member in the second configuration defines a single ring.
Owner:MITRAL INTERVENTIONS INC
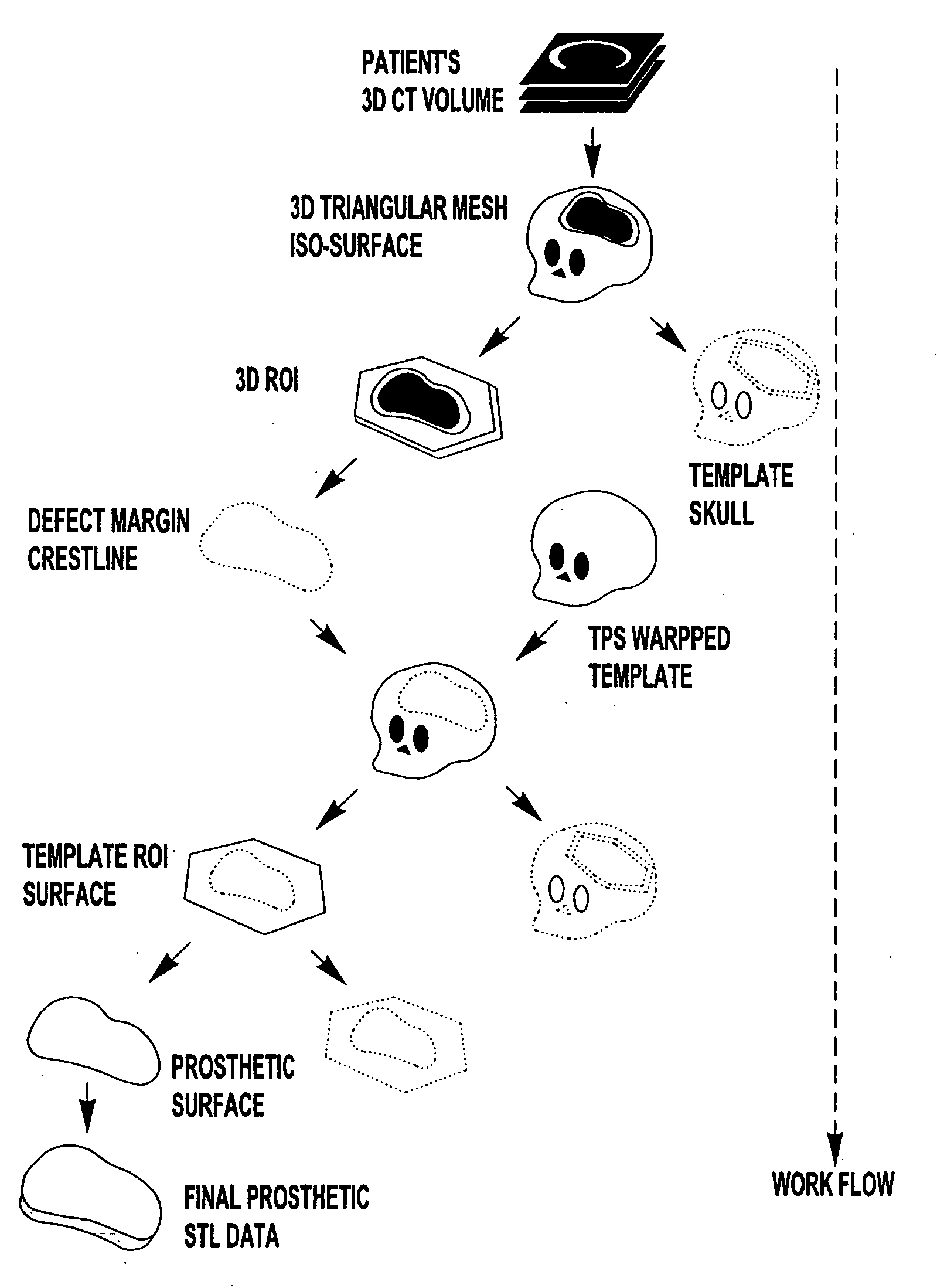
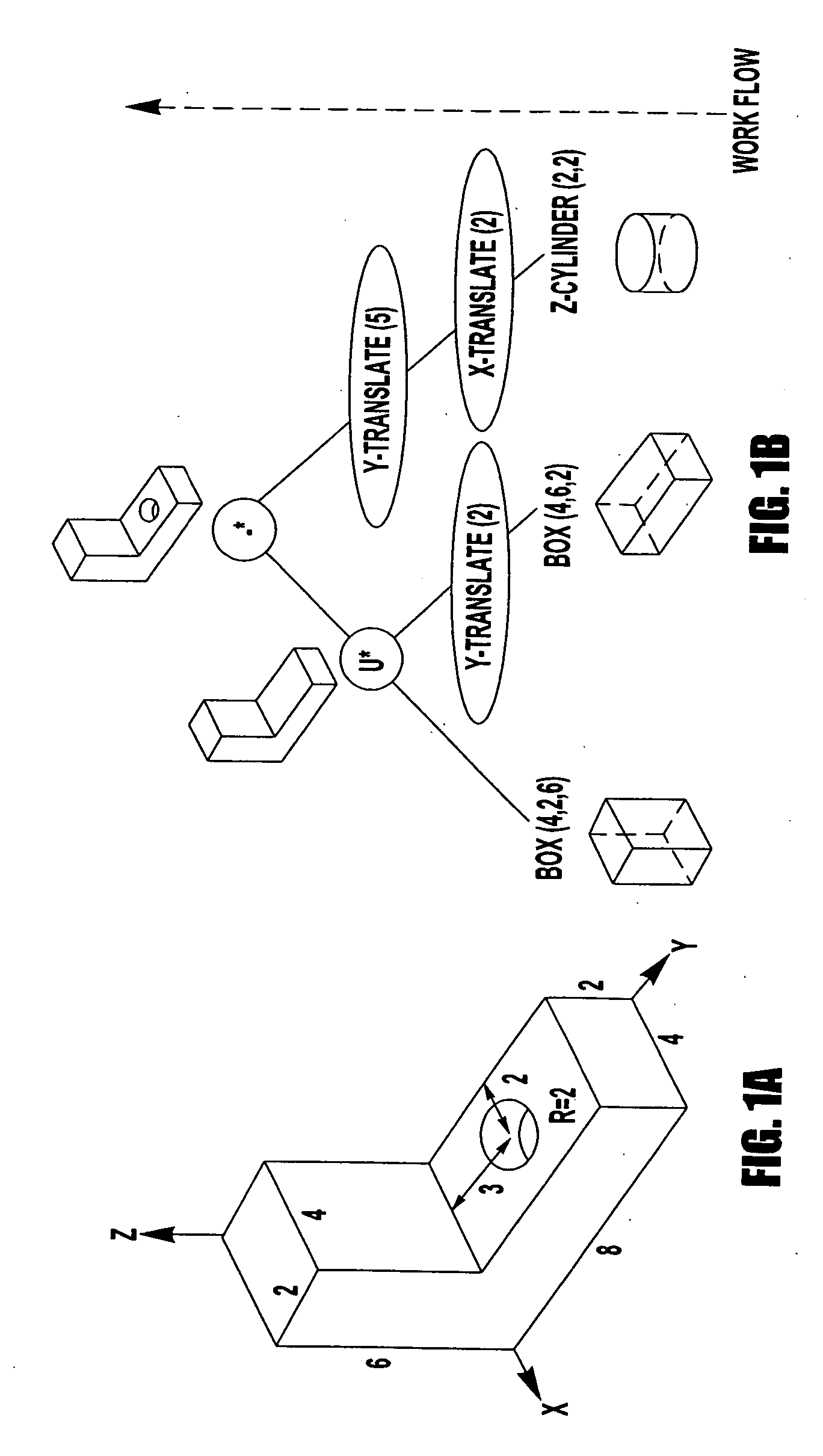
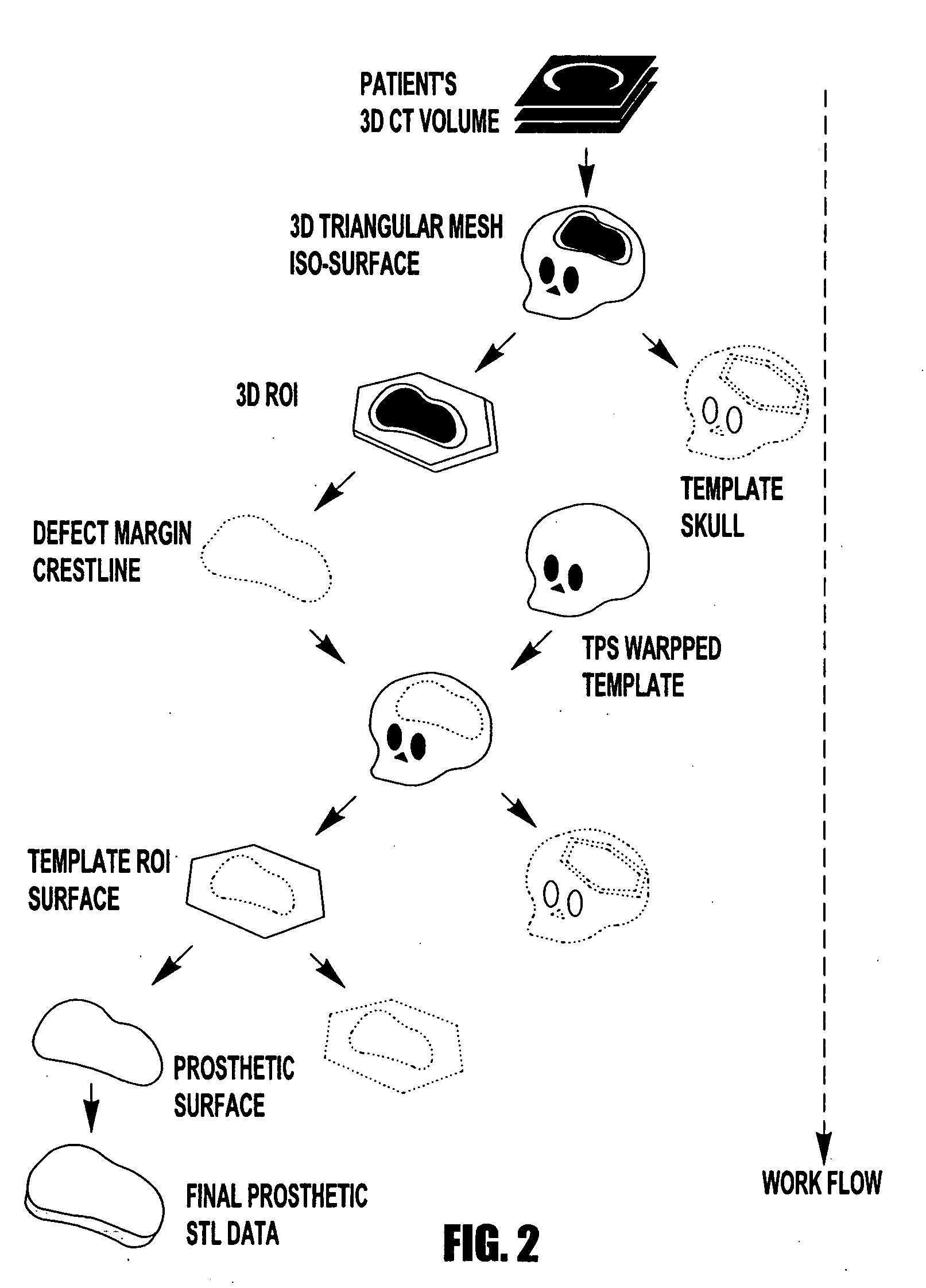
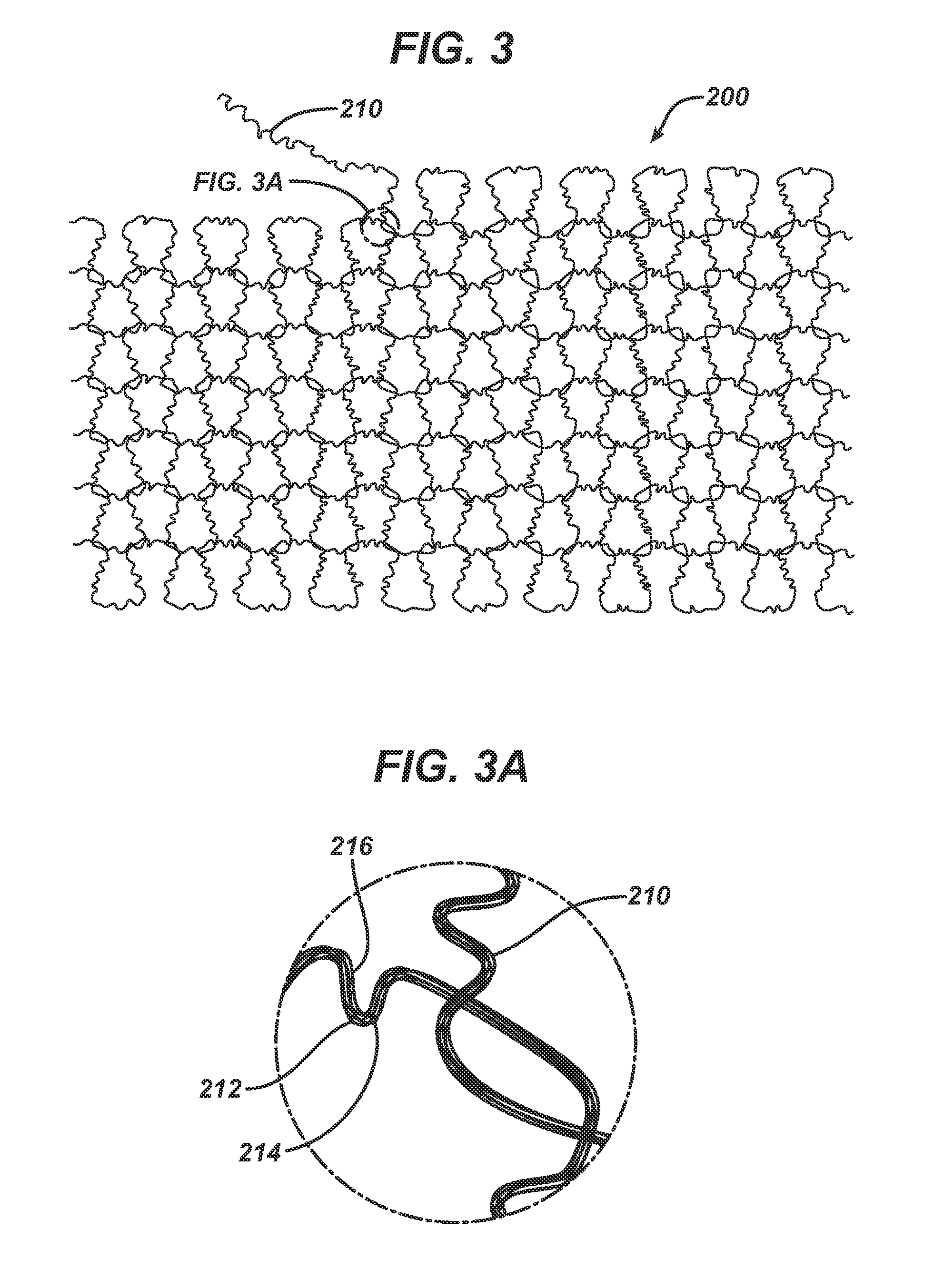
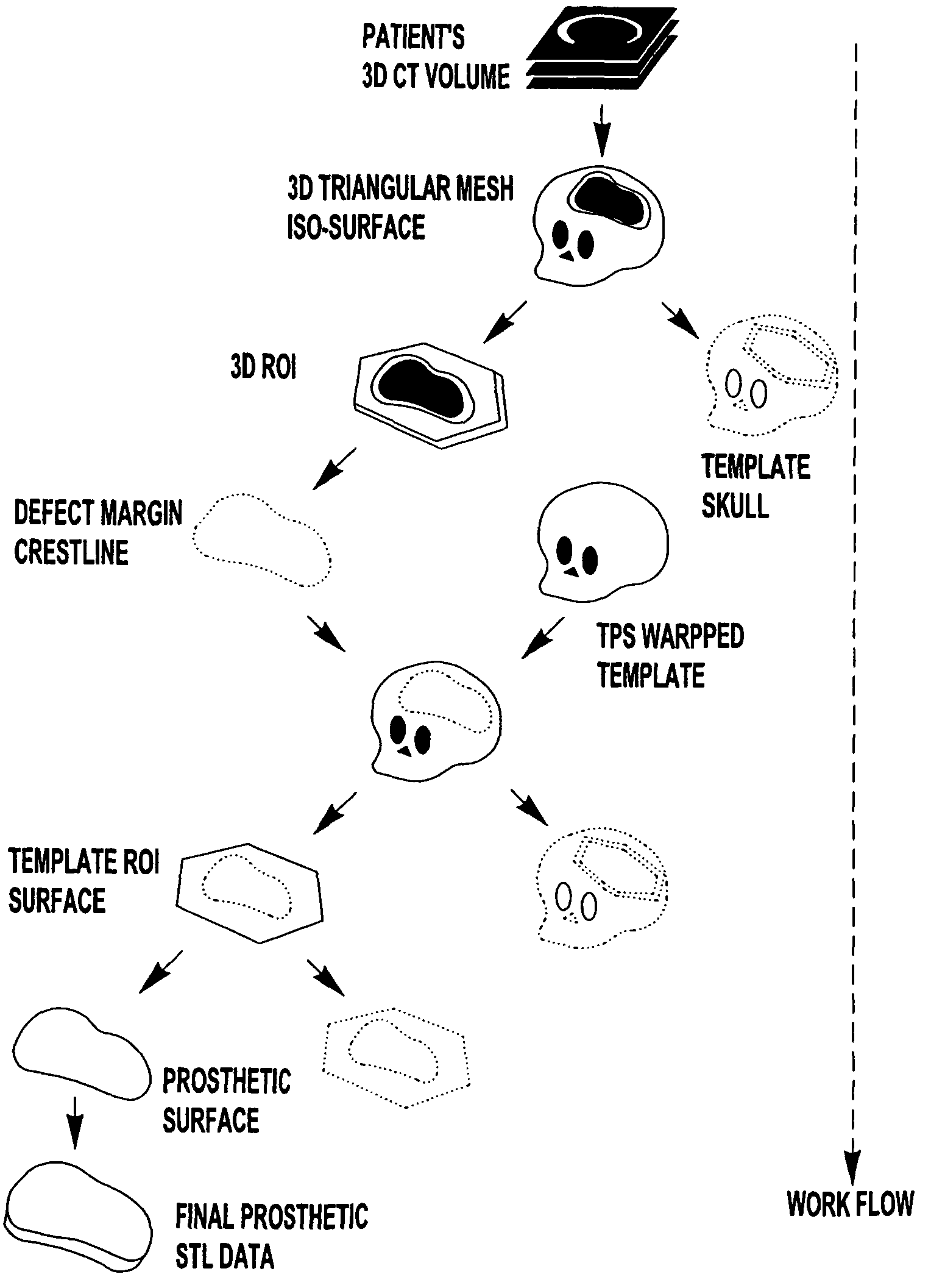
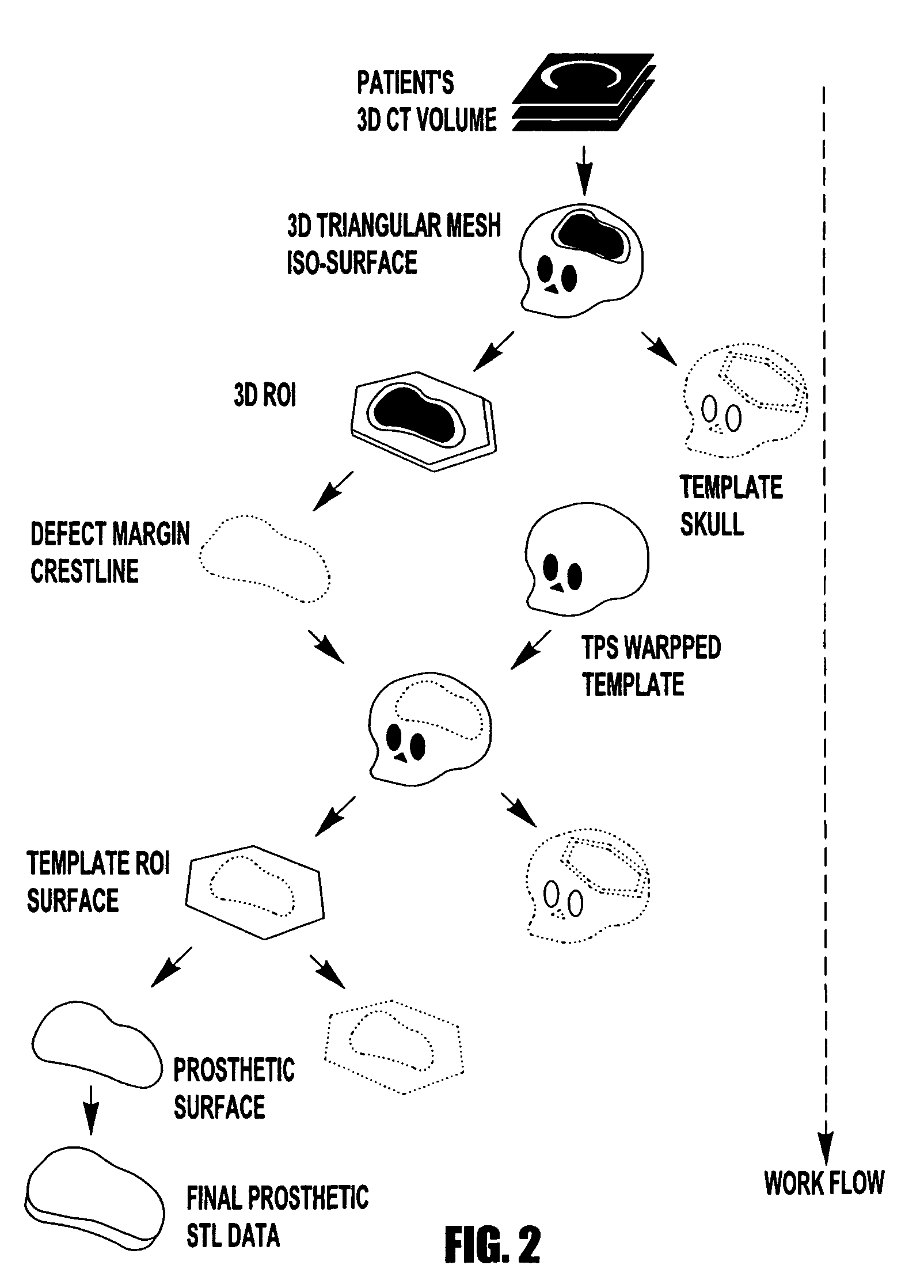
Computer-aided-design of skeletal implants
InactiveUS20060094951A1ContrastMaintain continuityProgramme controlMedical simulationComputer Aided DesignDigital data
The present invention is directed to a computer aided design method for producing an implant for a patient prior to operation comprising the steps of: generating data with a non-invasive 3D (3-dimensional) scan of the patient's defect site that digitally represents the area that will receive the implant; designing and validating an implant on a computer based on digital data generated from a volume image of the patient; and fabricating the implant based solely on the implant design data generated on computer.
Owner:OSTEOPLASTICS
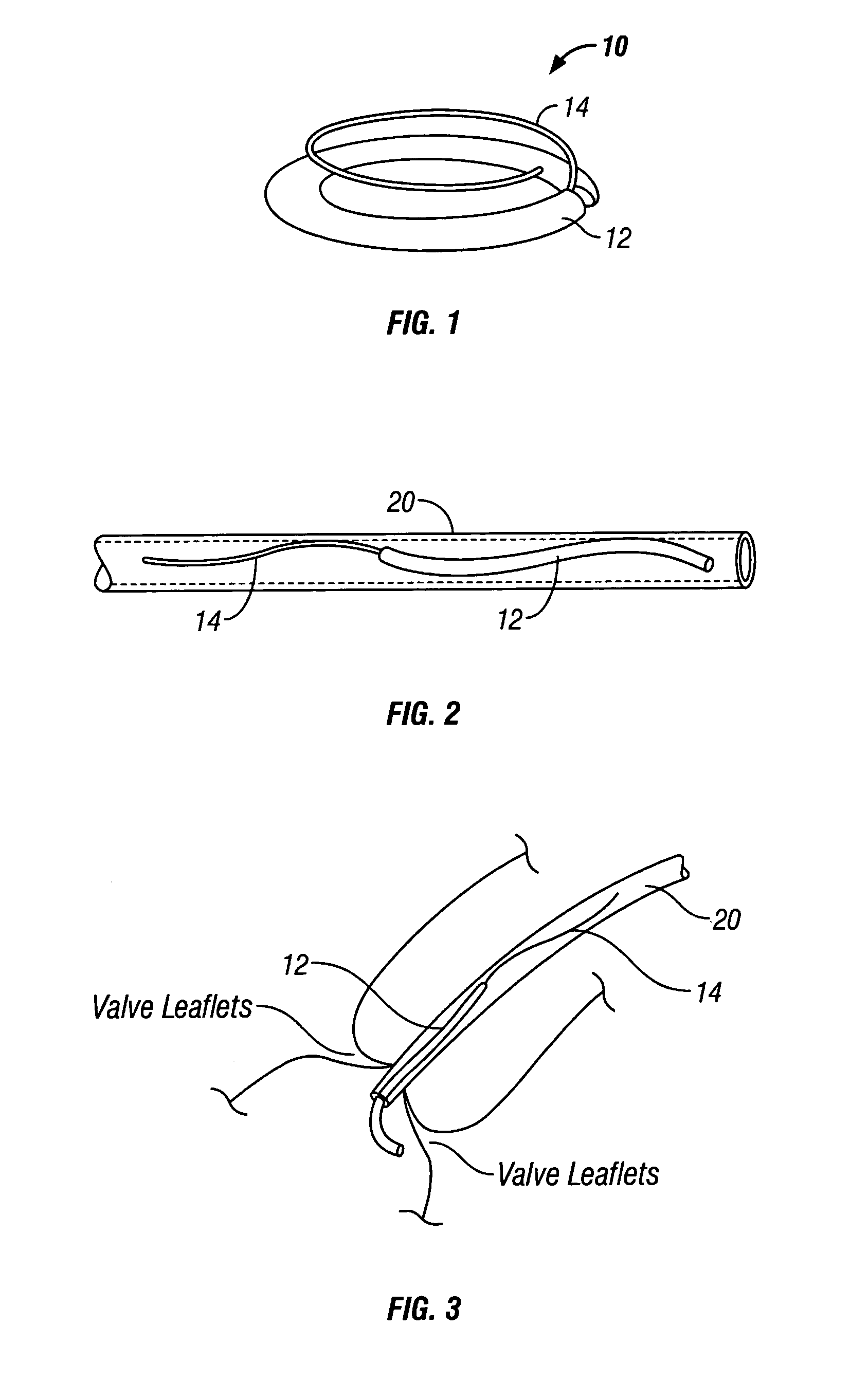
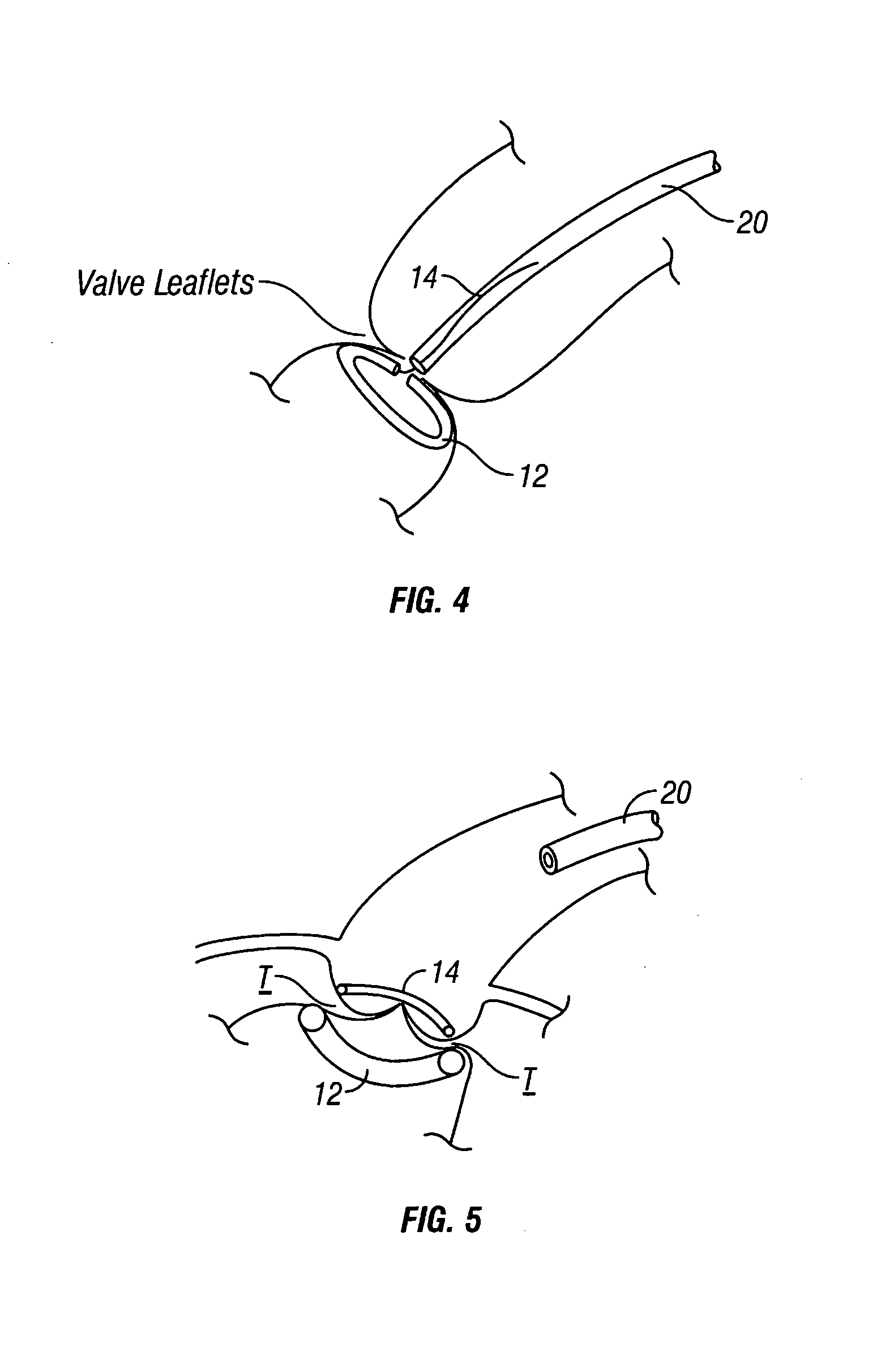
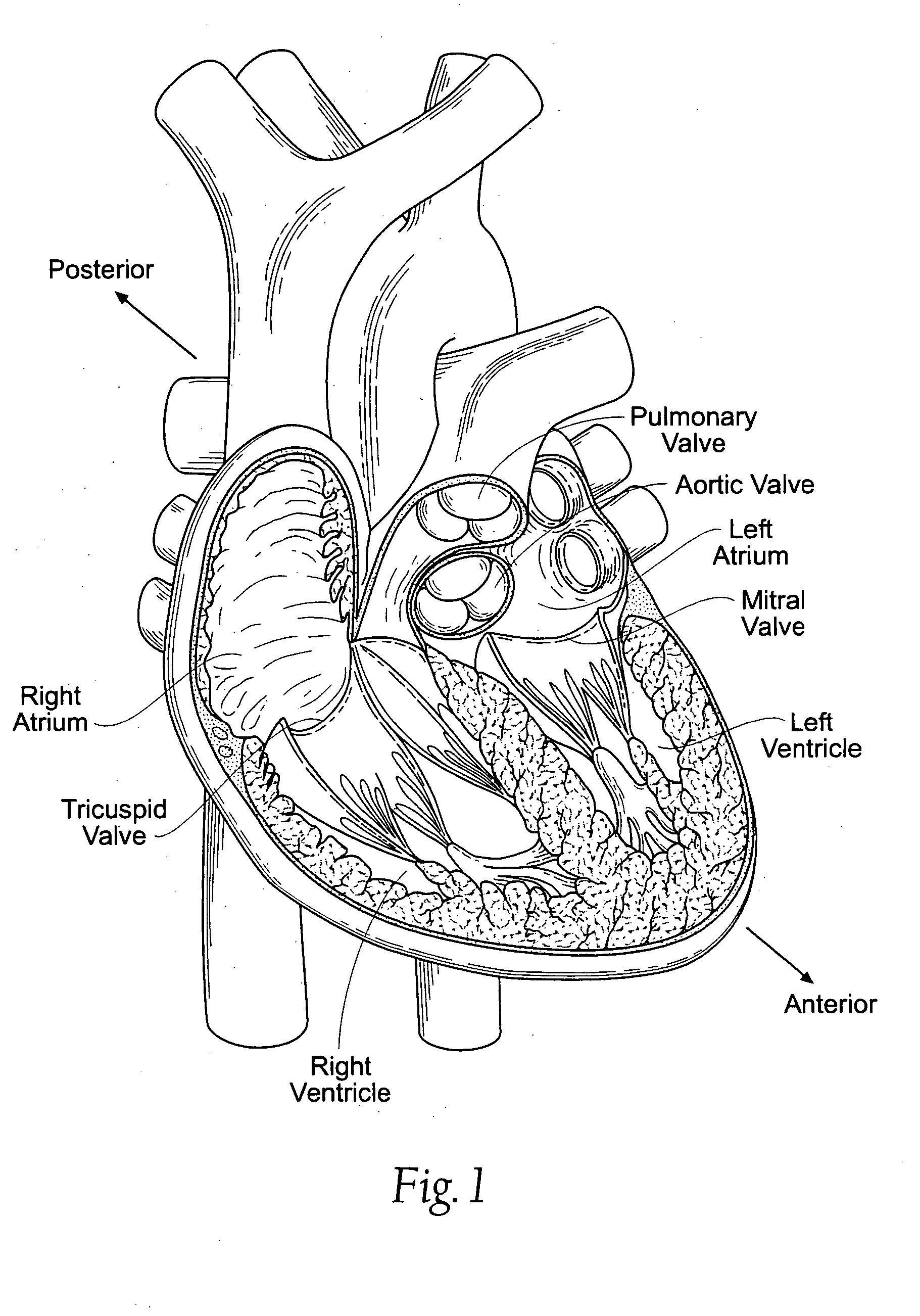
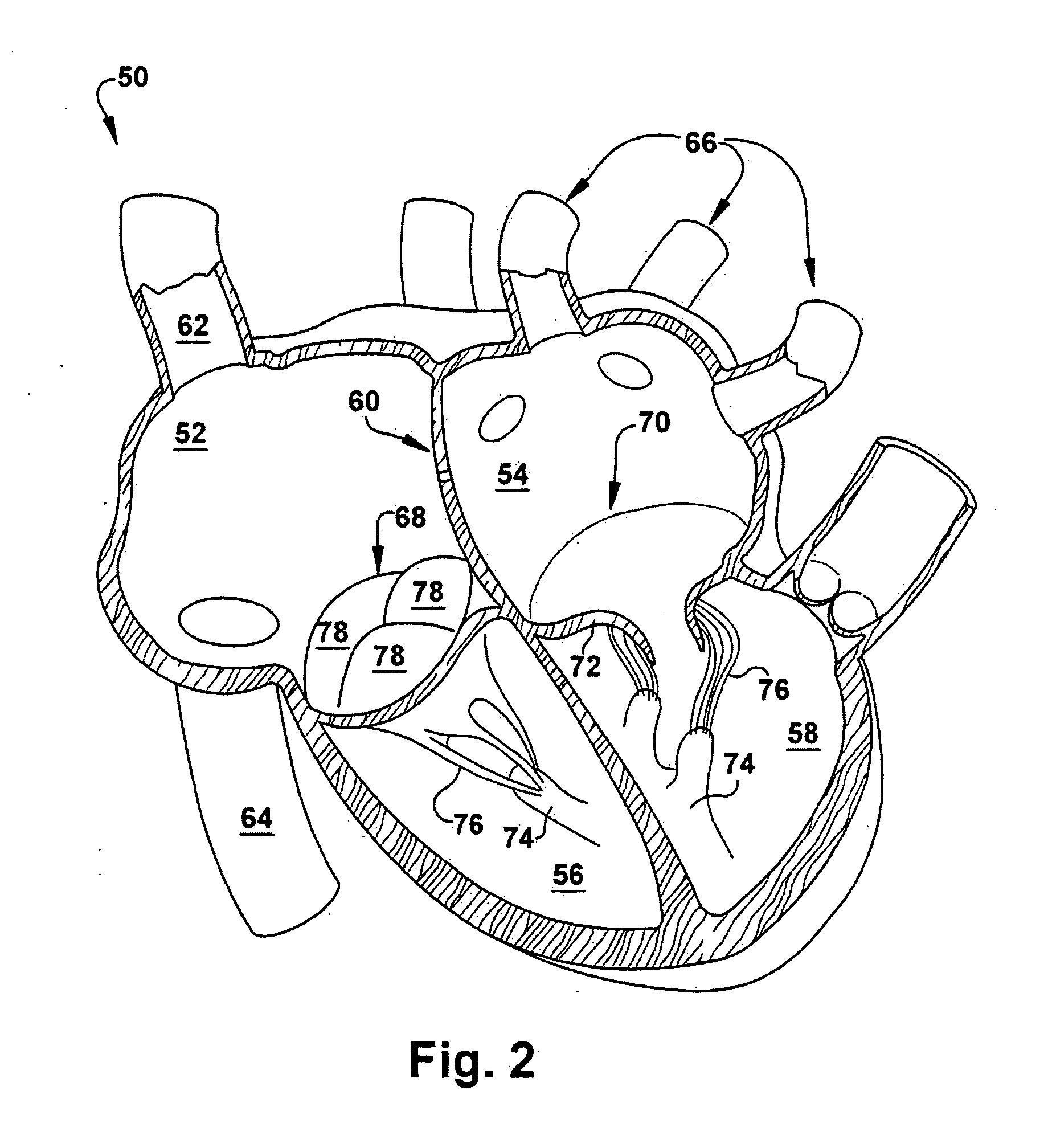
Device and method for treatment of heart valve regurgitation
In one embodiment, the present invention provides a prosthesis that can be implanted within a heart to at least partially block gaps that may be present between the two mitral valve leaflets. In one preferred embodiment, the prosthesis includes an anchoring ring that expands within the left atrium to anchor the prosthesis and a pocket member fixed to the anchoring ring. The pocket member is positioned within the mitral valve, between the leaflets so that an open end of the pocket member is positioned within the left ventricle. When the mitral valve is open, blood flows past the pocket member, maintaining the pocket member in a collapsed state. When the mitral valve closes, the backpressure of the blood pushes into the pocket member, expanding the pocket member to an inflated shape. The mitral valve leaflets contact the expanded pocket member, allowing the prosthesis to block at least a portion of the openings between the leaflets, thereby minimizing regurgitated blood flow into the left atrium.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES AG
Tissue fastening systems and methods utilizing magnetic guidance
ActiveUS7166127B2Reducing circumferenceReduce distanceSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve leafletImage guidance
Catheter based systems and methods for securing tissue including the annulus of a mitral valve. The systems and methods employ catheter based techniques and devices to plicate tissue and perform an annuloplasty.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES CORP
Cardiac valve annulus reduction system
A catheter-based, annulus reduction device and system for cardiac valve repair and method of using the same. The system is usable for treating mitral valve regurgitation and comprises a catheter, a reduction ring carried within the catheter, the reduction ring including a plurality of exit ports formed in a side wall of the reduction ring and filament received in the reduction ring. The filament includes a plurality of radially extendible barbs corresponding to the sidewall openings. The reduction ring carrying the filament is deployed adjacent a mitral valve annulus and the filament is translated relative to the reduction ring to deploy the barbs through the exit ports and into the annulus and to further translate the reduction ring with deployed barbs to reshape the annulus.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
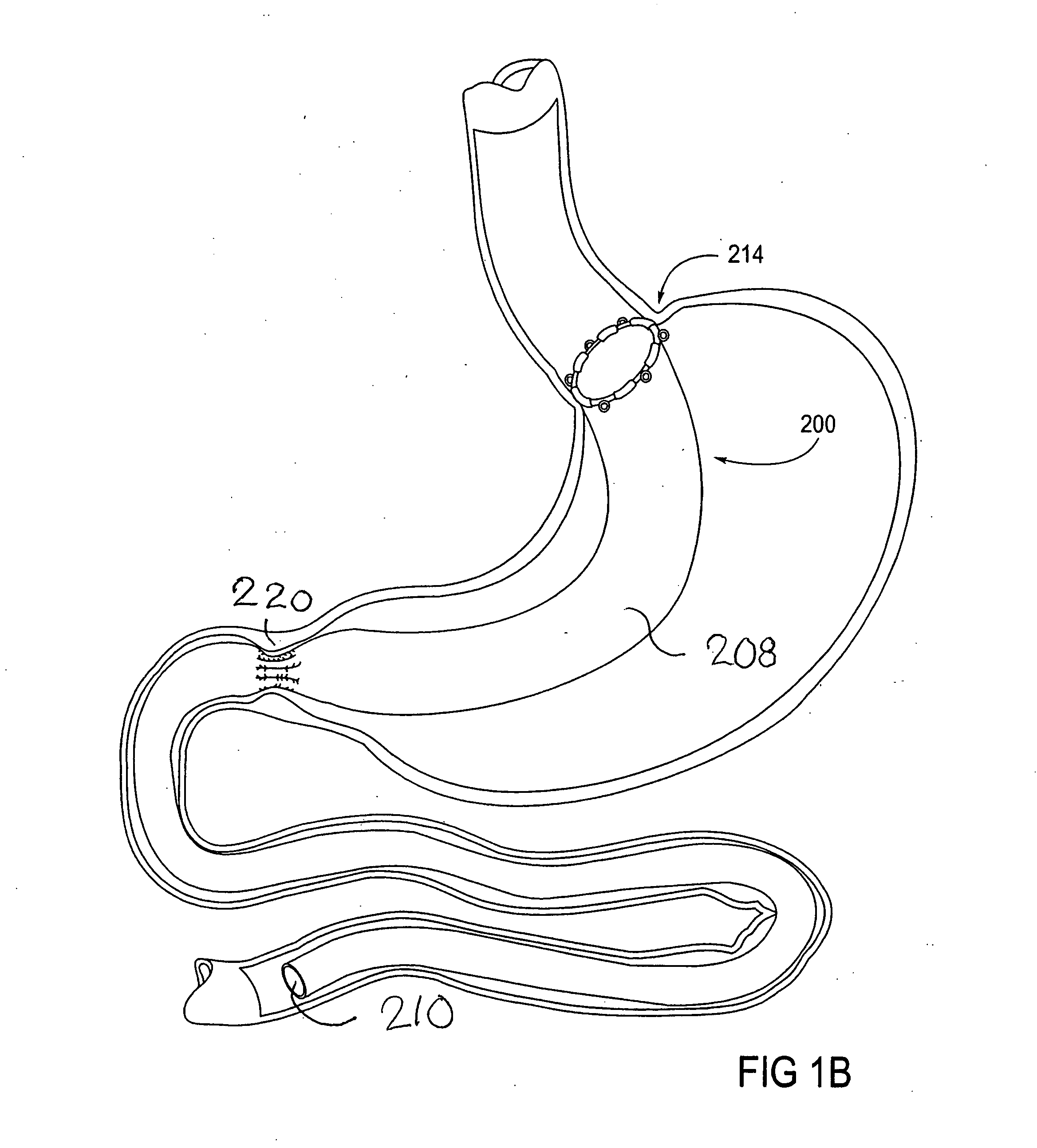
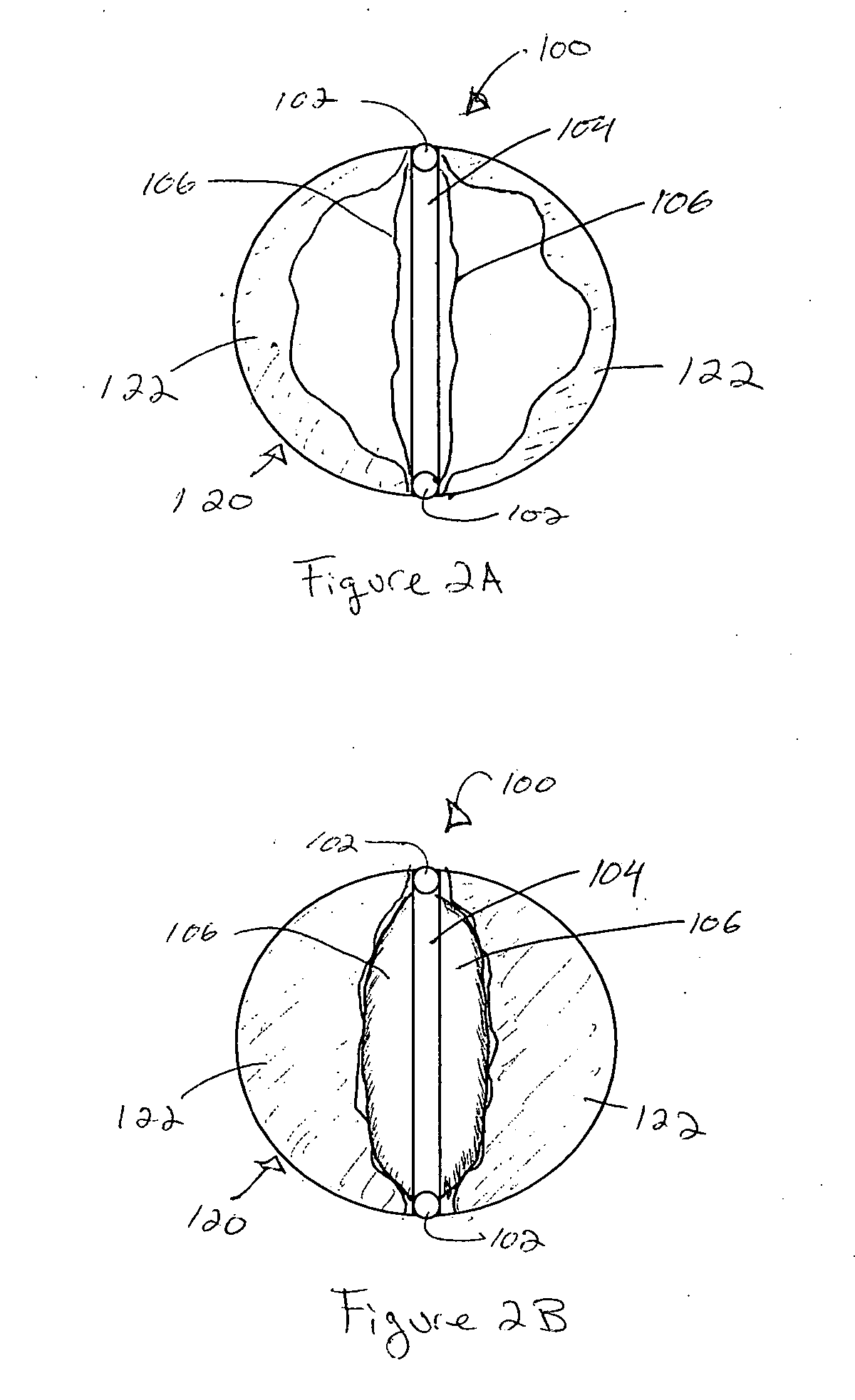
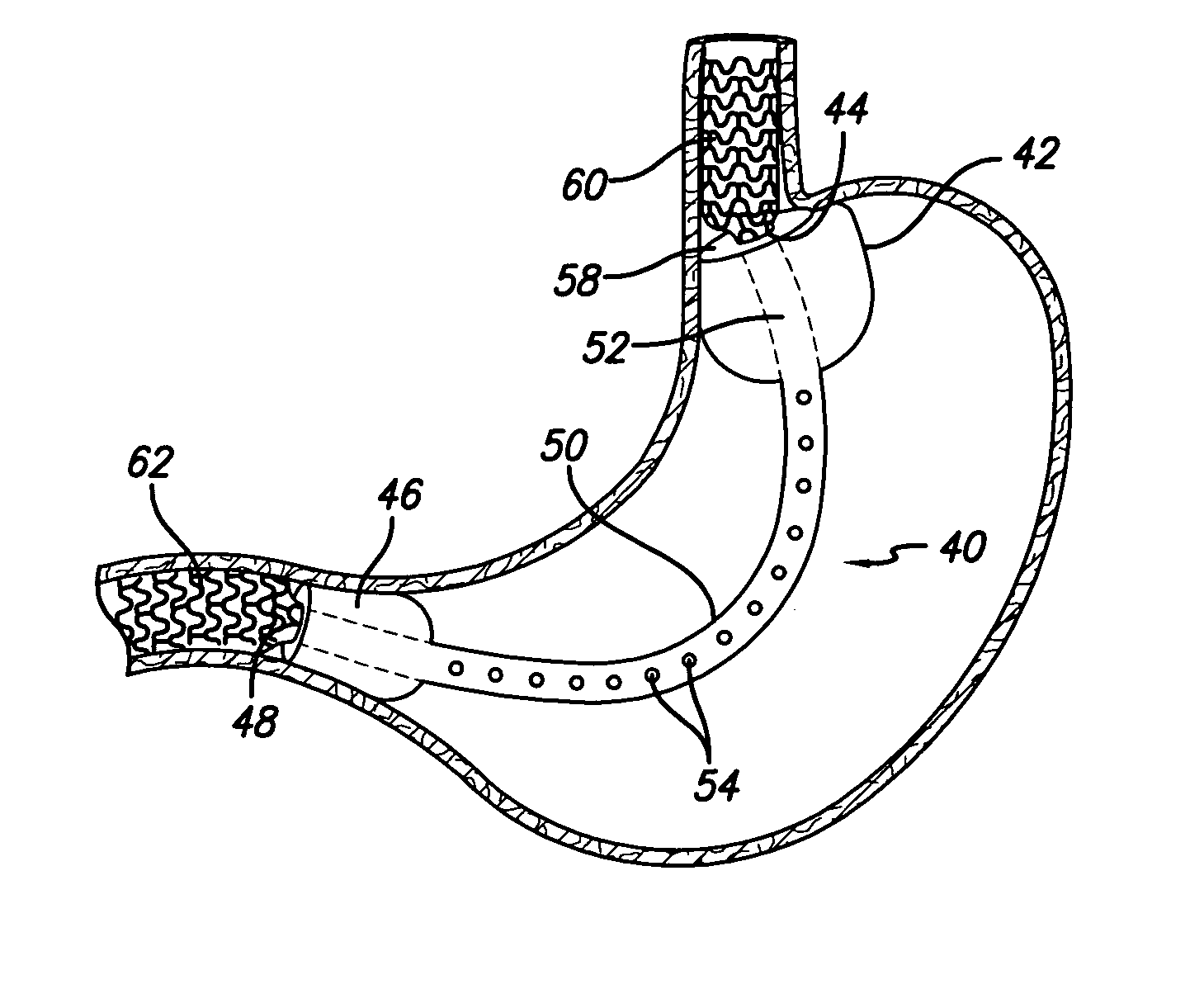
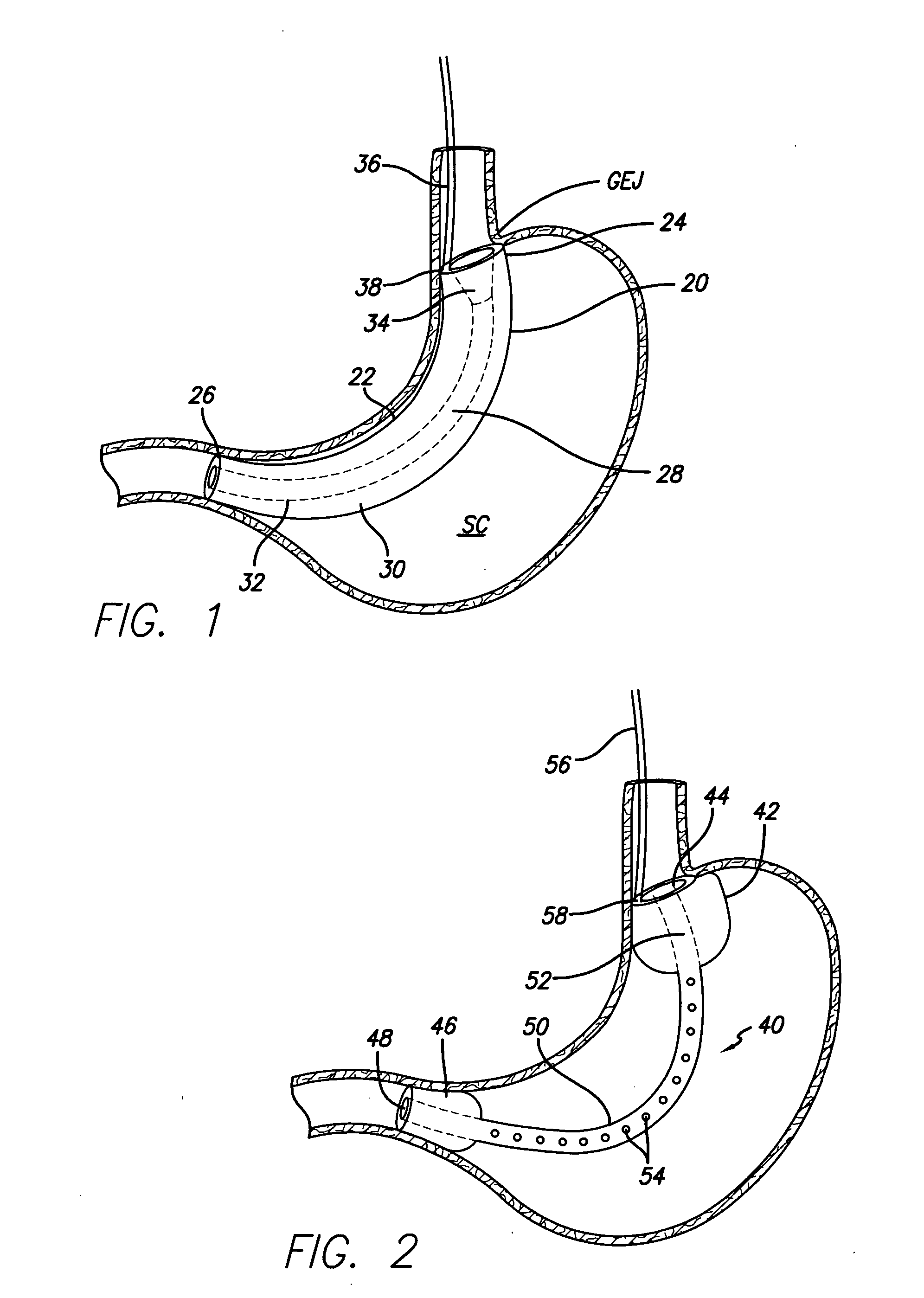
Gastrointestinal sleeve device and methods for treatment of morbid obesity
InactiveUS20050049718A1Effectively reducing stomach volumeStimulating intestinal responseMedical devicesTubular organ implantsIntestinal structureMorbid obesity
Apparatus and methods are described for treatment of morbid obesity using minimally invasive techniques. The apparatus includes a system of components that may be used separately or in combination for effectively reducing stomach volume, bypassing a portion of the stomach and / or small intestines, reducing nutrient absorption in the stomach and / or small intestines and / or depositing minimally or undigested food farther than normal into the intestines, thereby stimulating intestinal responses. The components described include a gastric sleeve device, an intestinal sleeve device, and a combined gastrointestinal sleeve device.
Owner:VALENTX
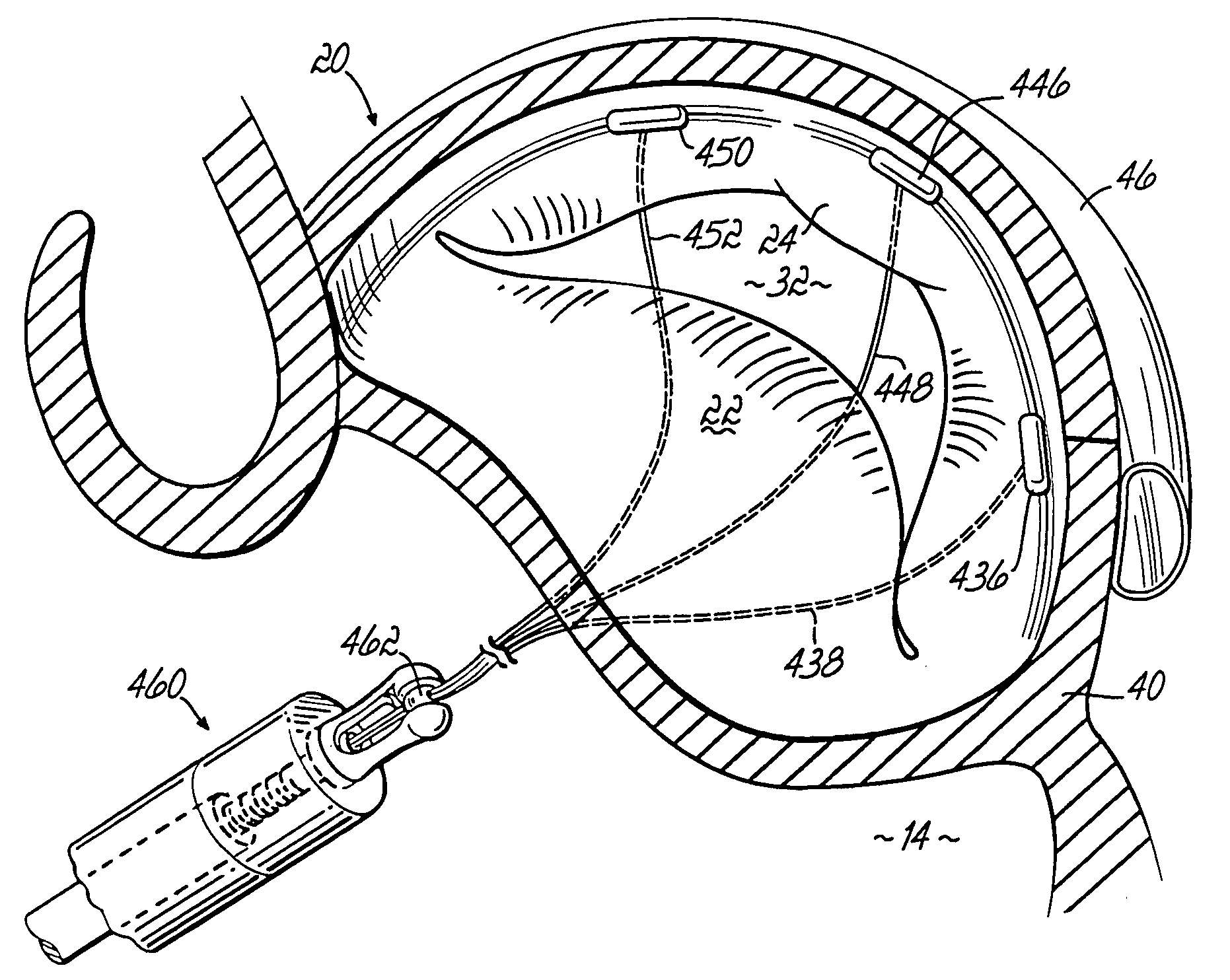
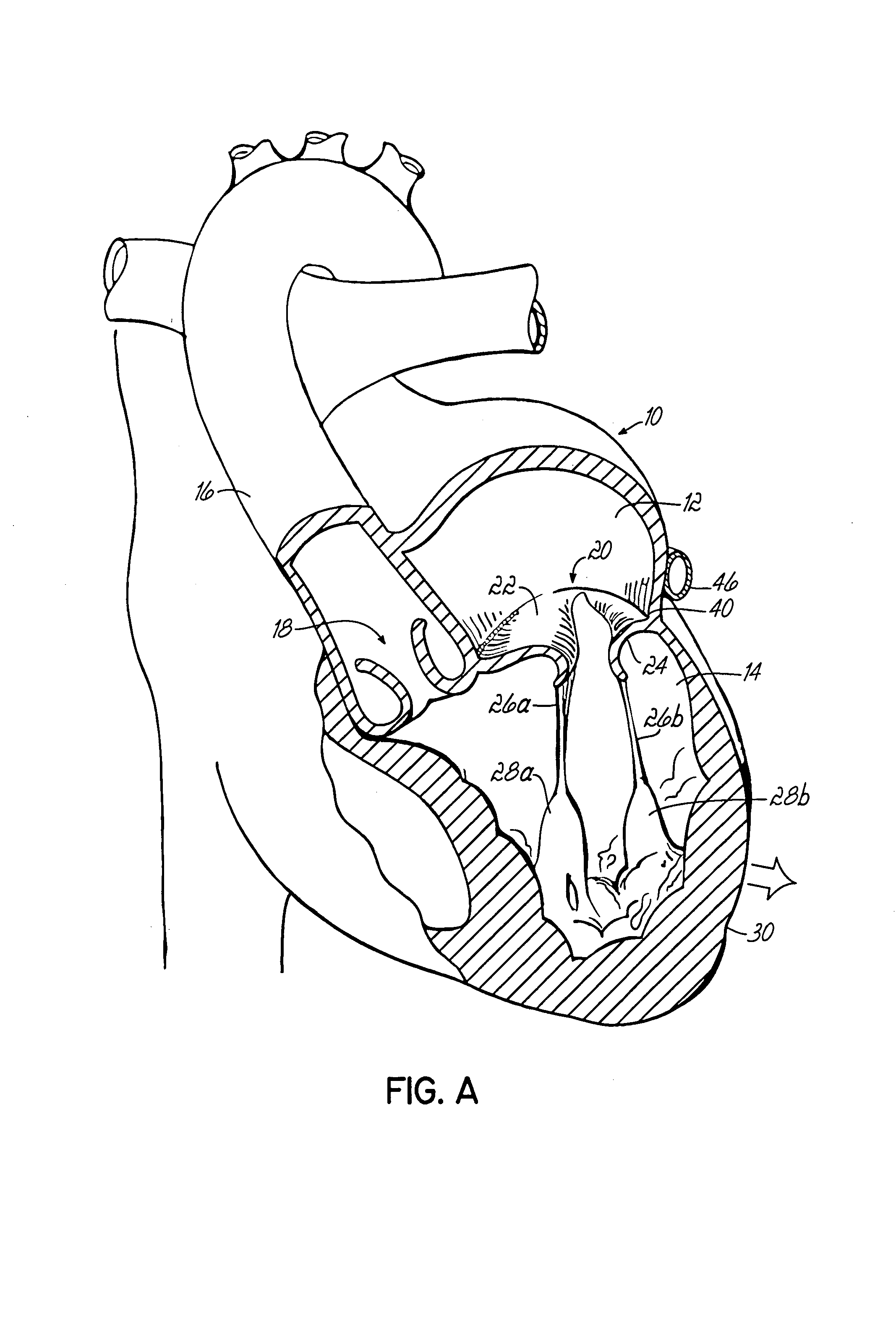
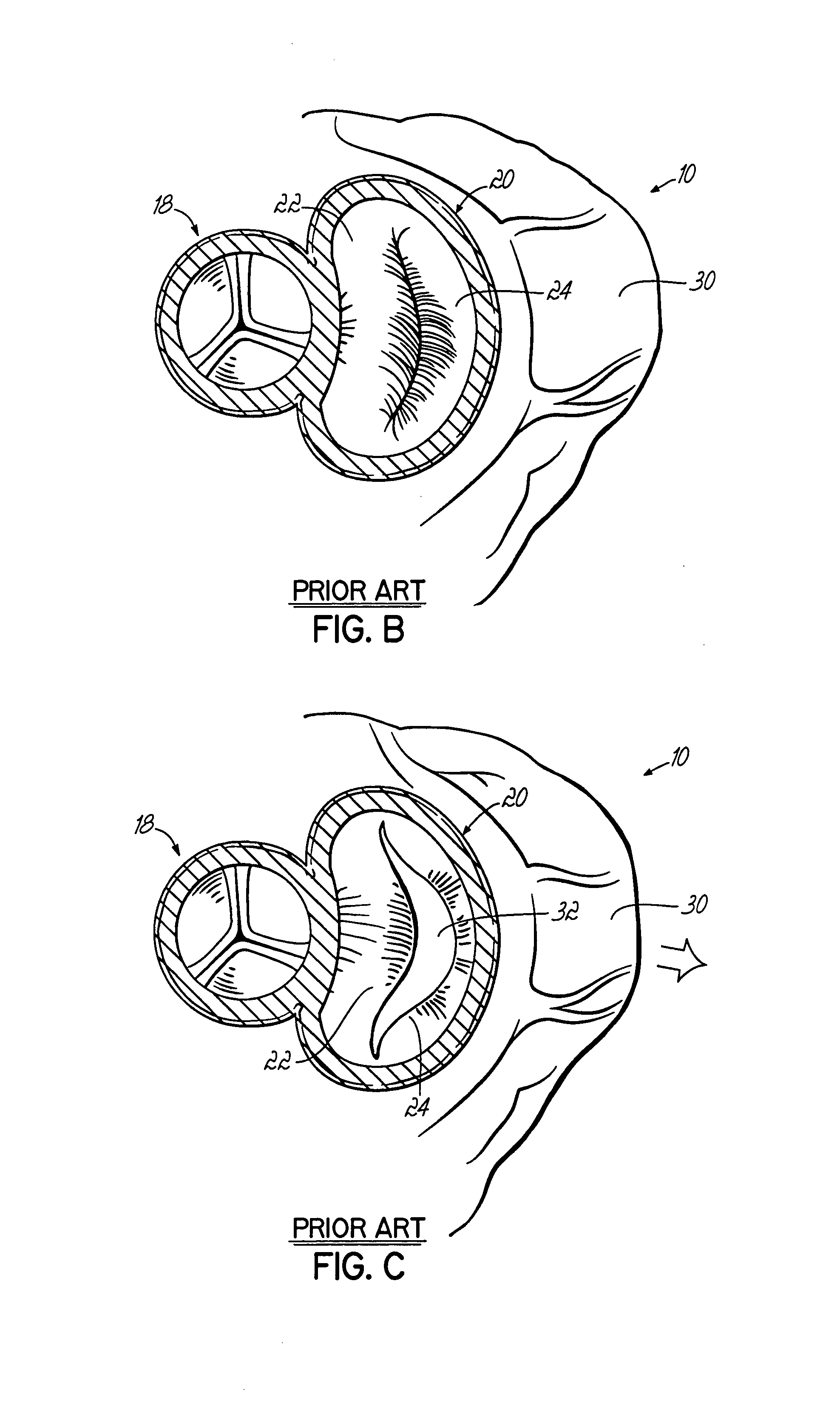
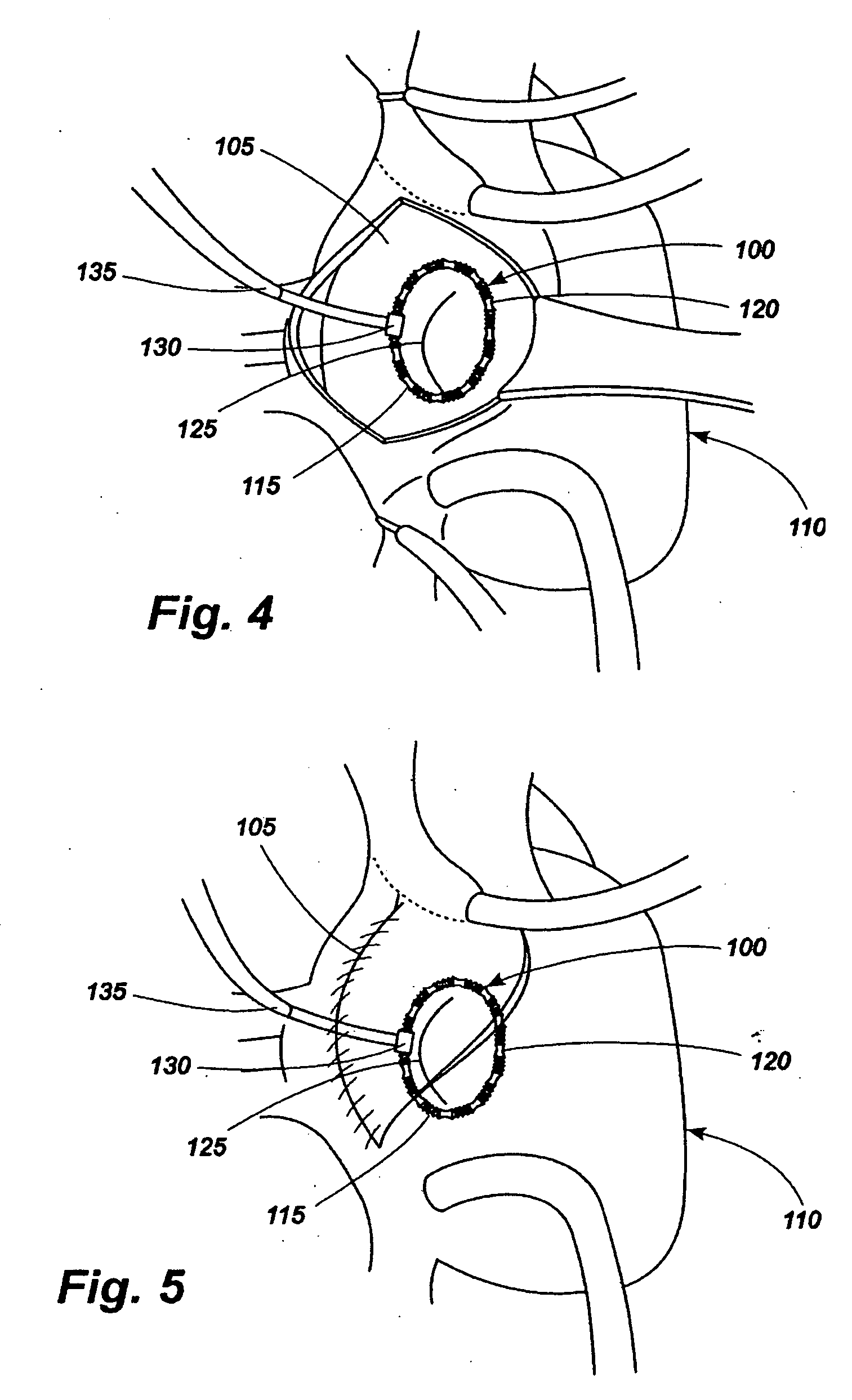
Method and device for use in endoscopic organ procedures
InactiveUS7220237B2Maintain alimentary flowImprove adhesionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsStomaBody organs
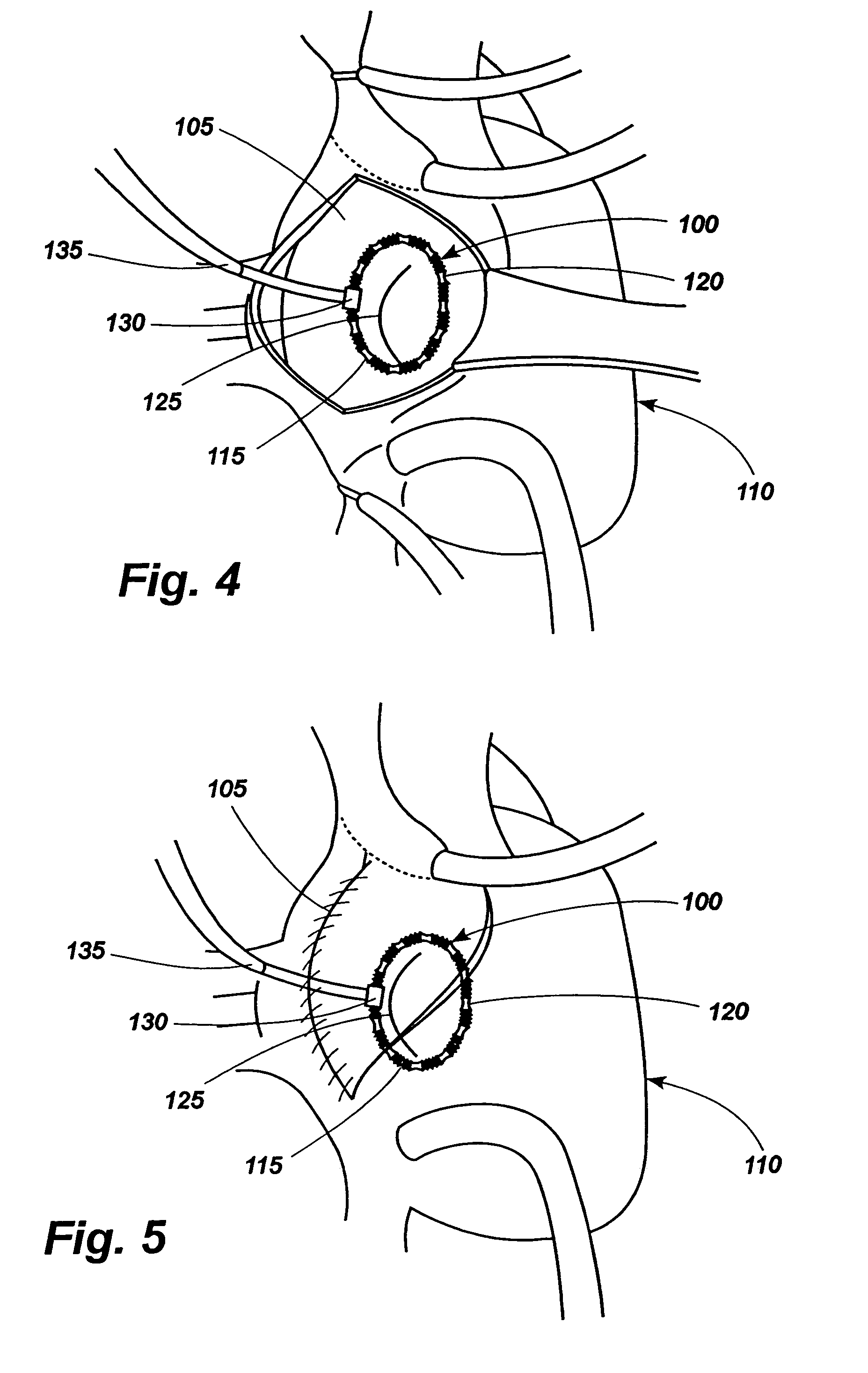
Methods and devices for use in tissue approximation and fixation are described herein. The present invention provides, in part, methods and devices for acquiring tissue folds in a circumferential configuration within a hollow body organ, e.g., a stomach, positioning the tissue folds for affixing within a fixation zone of the stomach, preferably to create a pouch or partition below the esophagus, and fastening the tissue folds such that a tissue ring, or stomas, forms excluding the pouch from the greater stomach cavity. The present invention further provides for a liner or bypass conduit which is affixed at a proximal end either to the tissue ring or through some other fastening mechanism. The distal end of the conduit is left either unanchored or anchored within the intestinal tract. This bypass conduit also includes a fluid bypass conduit which allows the stomach and a portion of the intestinal tract to communicate.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
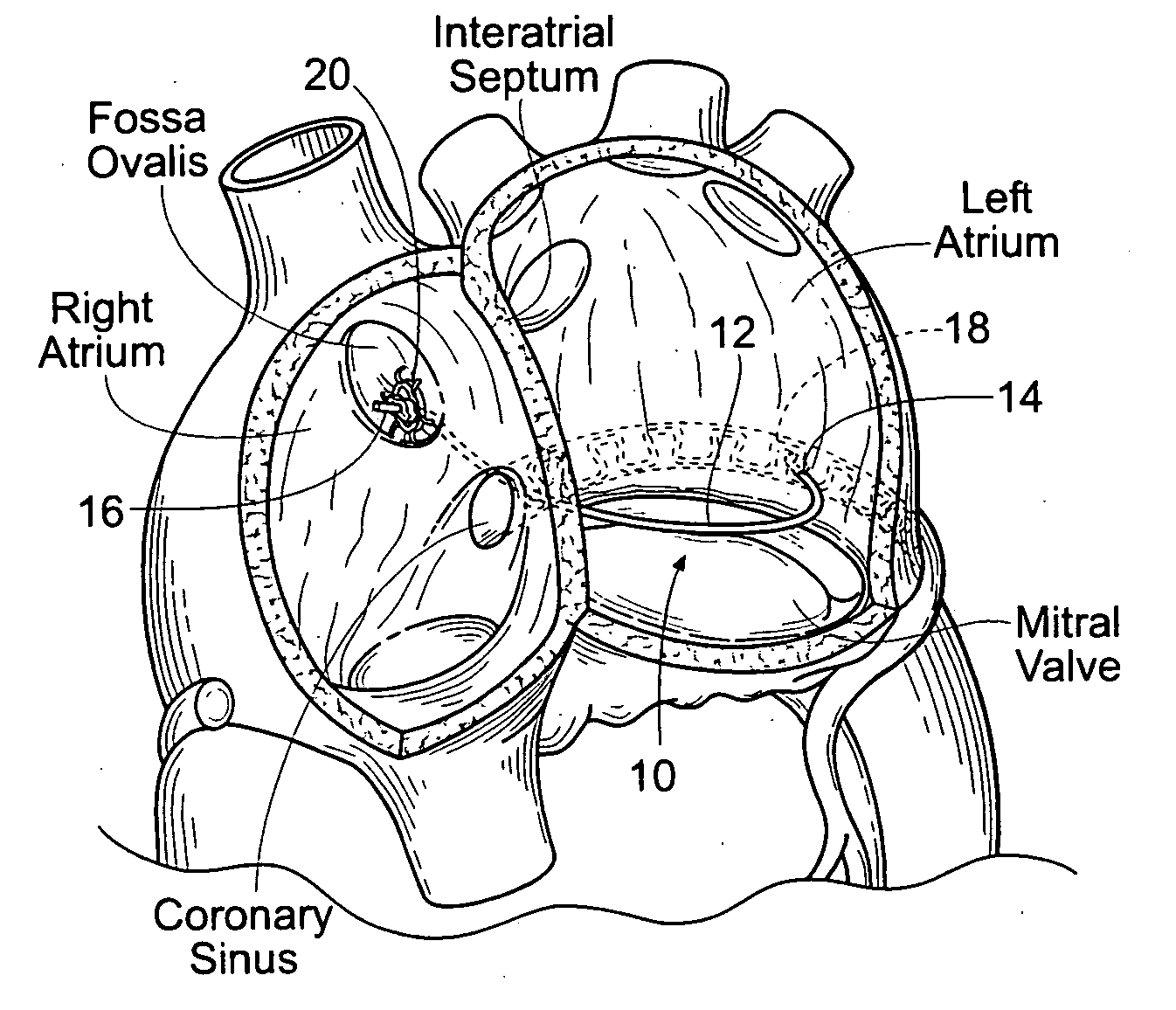
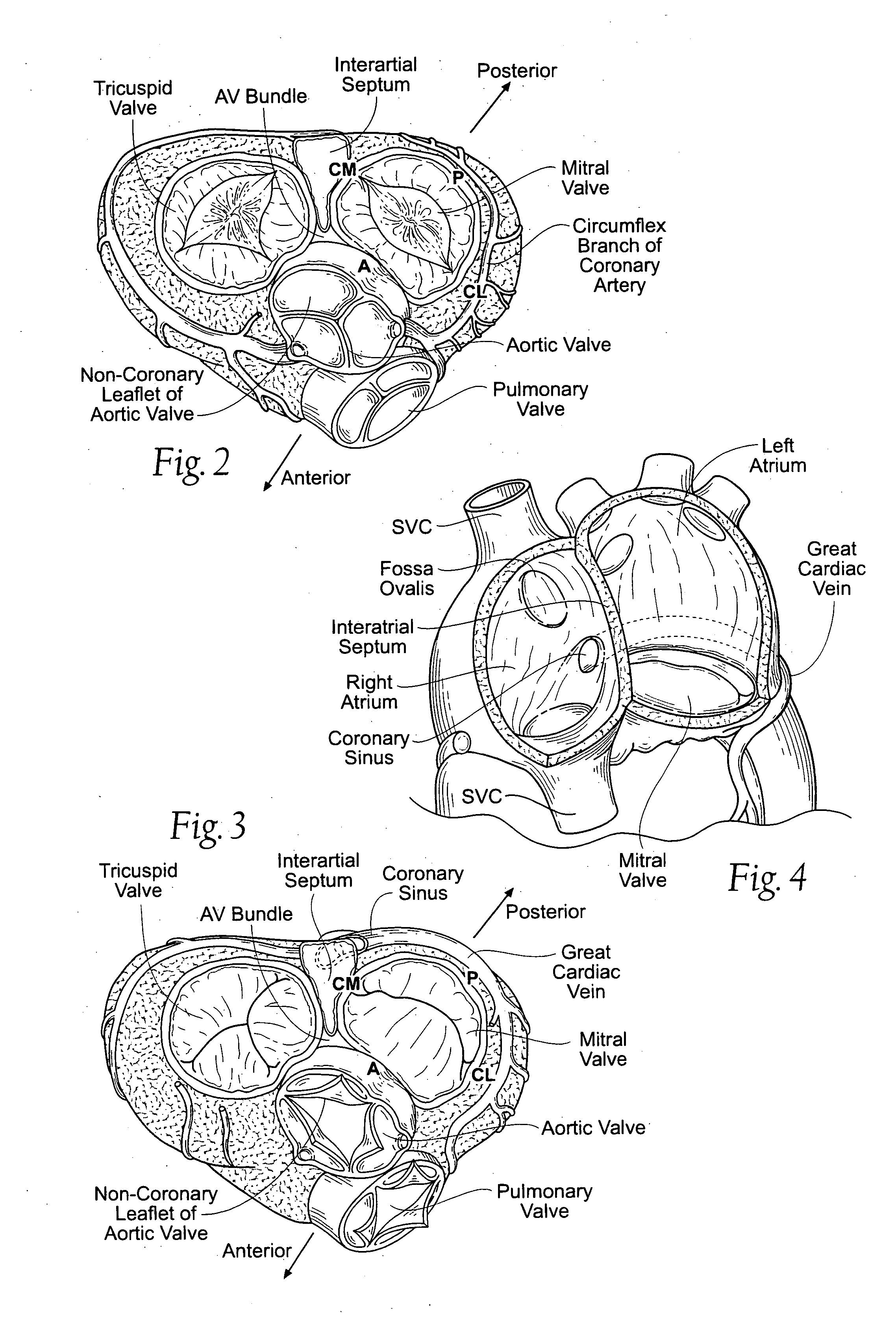
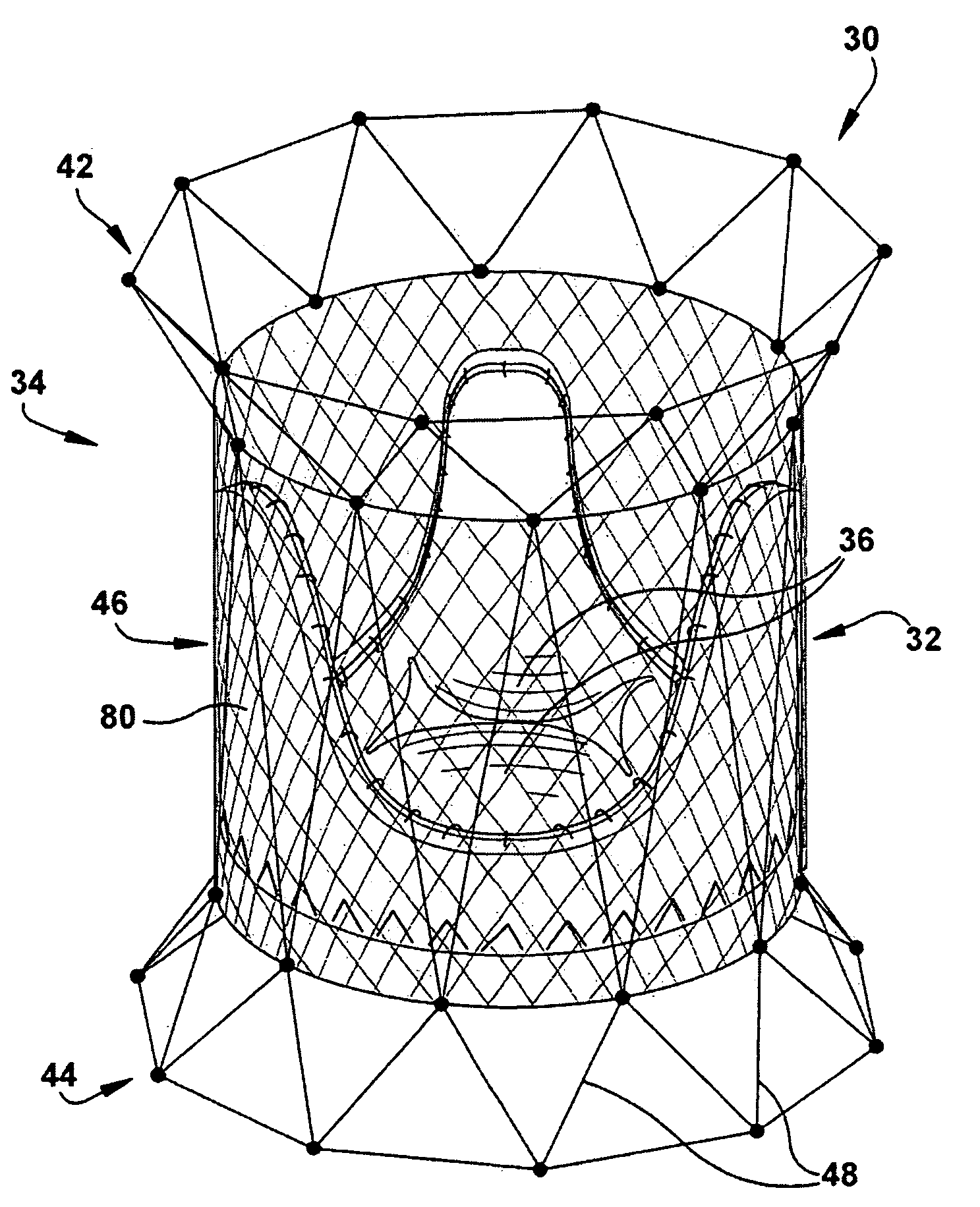
Devices, systems, and methods for reshaping a heart valve annulus
ActiveUS20050055089A1Improve septal-to-lateral dimensionImproved leaflet coaptionSuture equipmentsAnnuloplasty ringsMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
Implants or systems of implants apply a selected force vector or a selected combination of force vectors within or across the left atrium, which allow mitral valve leaflets to better coapt. The implants or systems of implants make possible rapid deployment, facile endovascular delivery, and full intra-atrial retrievability. The implants or systems of implants also make use of strong fluoroscopic landmarks.
Owner:VENTURE LENDING & LEASING IV
Method and apparatus for reducing mitral regurgitation
Apparatus for reducing mitral regurgitation, by applying a force to the wall of the coronary sinus so as to force the posterior leaflet anteriorly and thereby reduce mitral regurgitation.
Owner:ANCORA HEART INC
Method for anchoring a mitral valve
An artificial mitral valve is anchored in the left atrium by placing the valve between the annulus of the natural mitral valve and an artificial annulus. The artificial annulus is formed by inserting a tool into the coronary sinus, and adjusting the tool to force the wall of the left atrium to form an annulus above the artificial valve, this locking it in place and forming a hemostatic seal.
Owner:KARDIUM
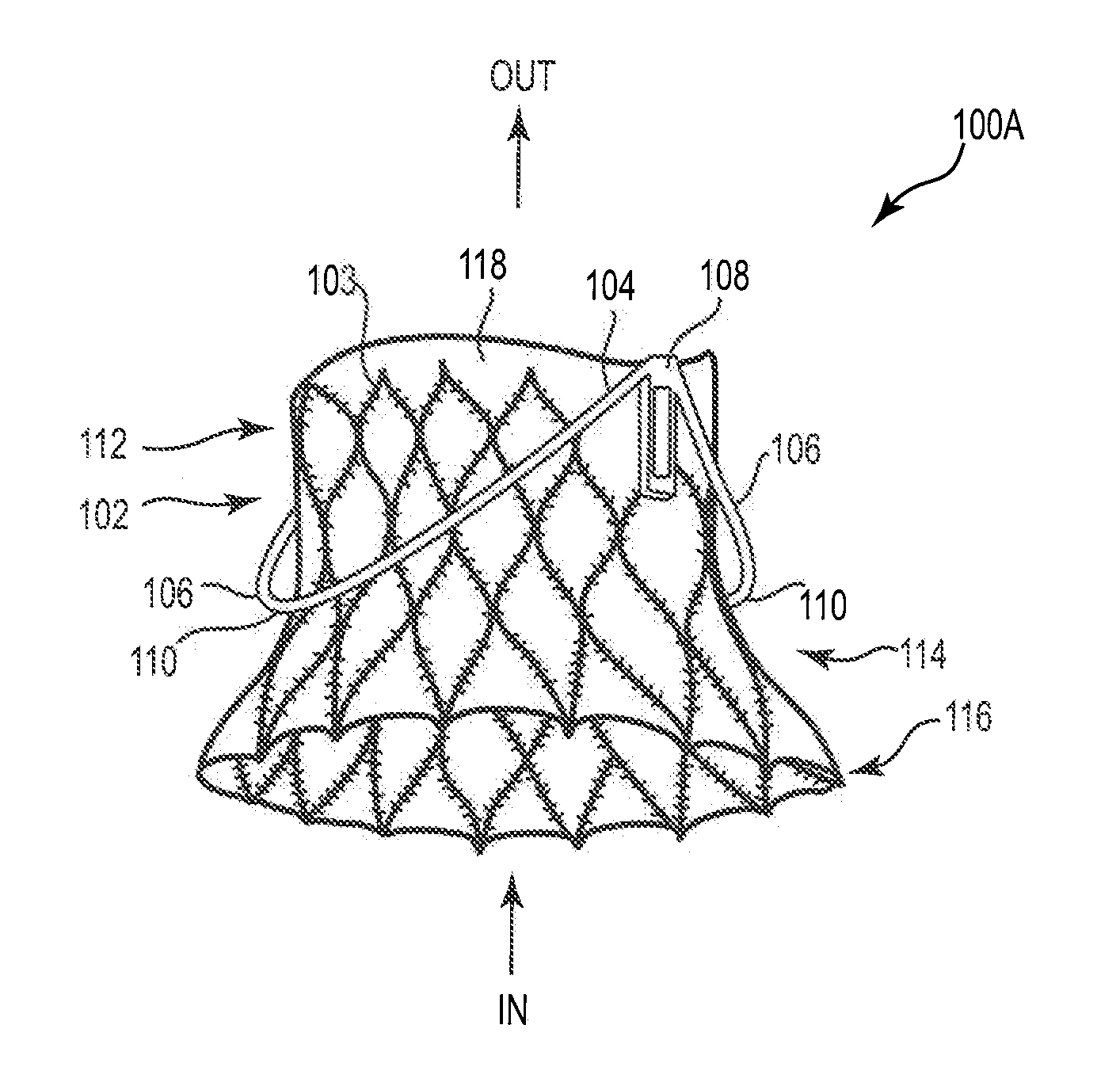
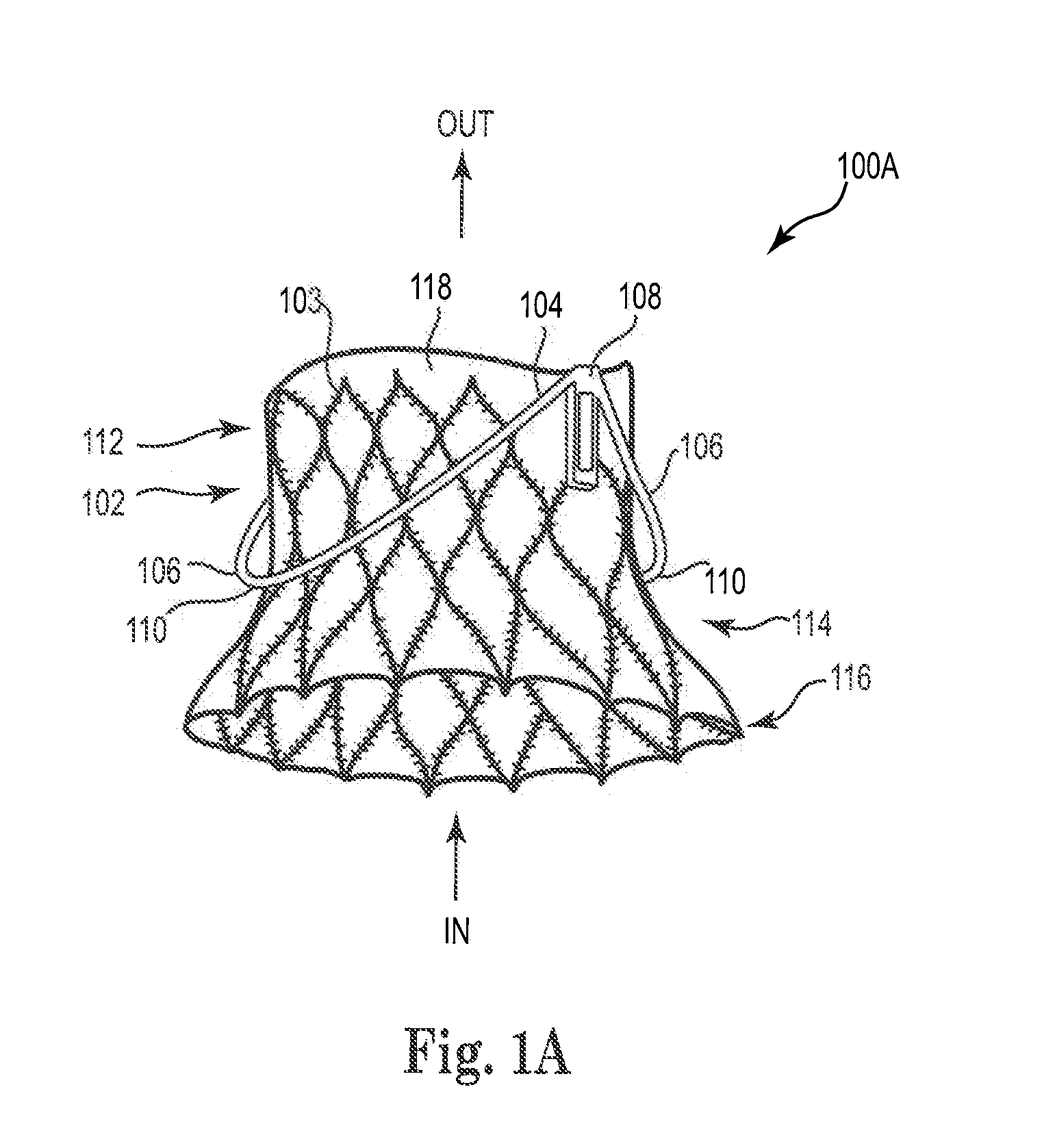
Mitral Prosthesis and Methods for Implantation
ActiveUS20120035722A1Minimizing peri-valvular leaksMaintain stabilityStentsHeart valvesMitral valve leafletLeft atrium
A mitral valve prosthesis and methods for implanting the prosthesis transapically (i.e., through the apex of the heart), transatrially (i.e., through the left atrium of the heart), and transseptally (i.e., through the septum of the heart). The prosthesis generally includes a self-expanding frame and two or more support arms. A valve prosthesis is sutured to the self-expanding frame. Each support arm corresponds to a native mitral valve leaflet. At least one support arm immobilizes the native leaflets, and holds the native leaflets close to the main frame.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VENTOR TECH
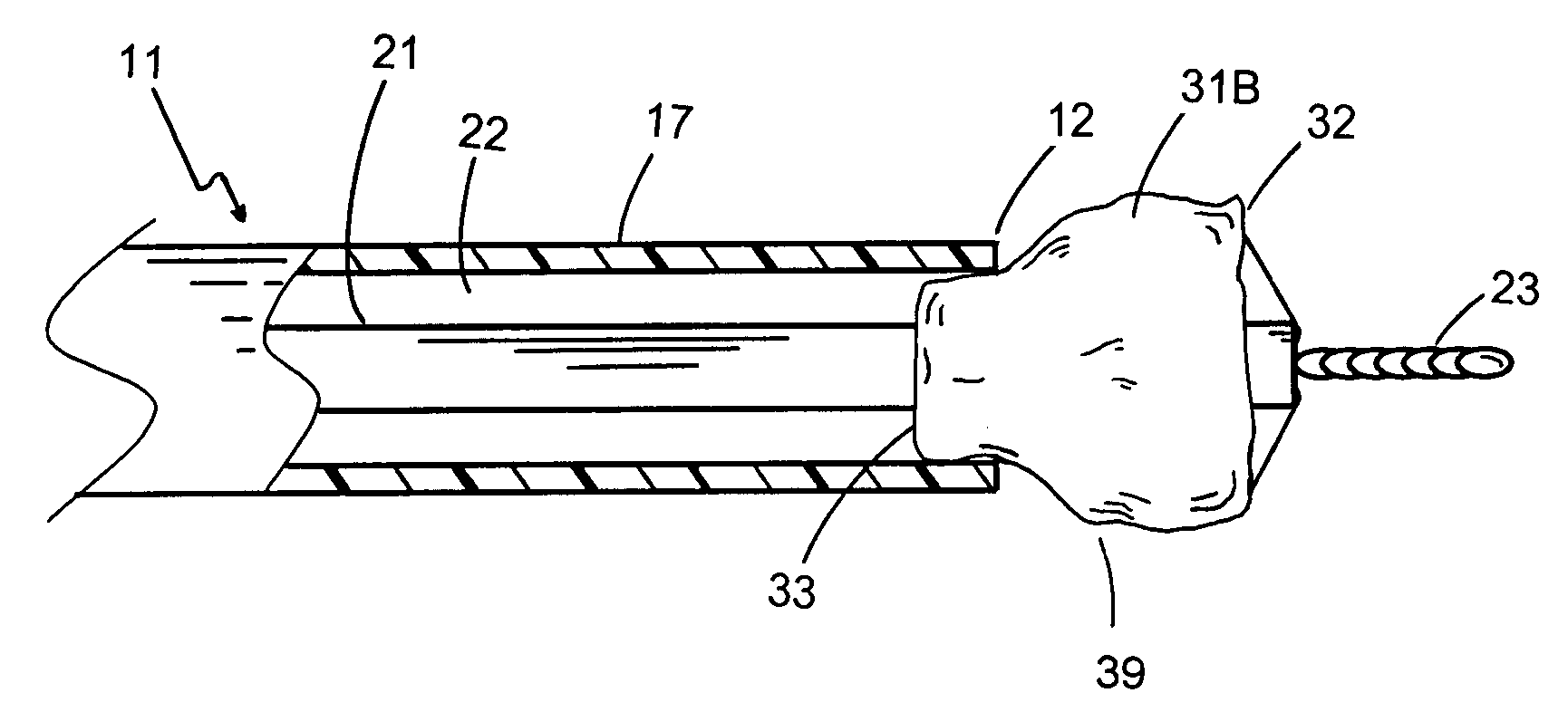
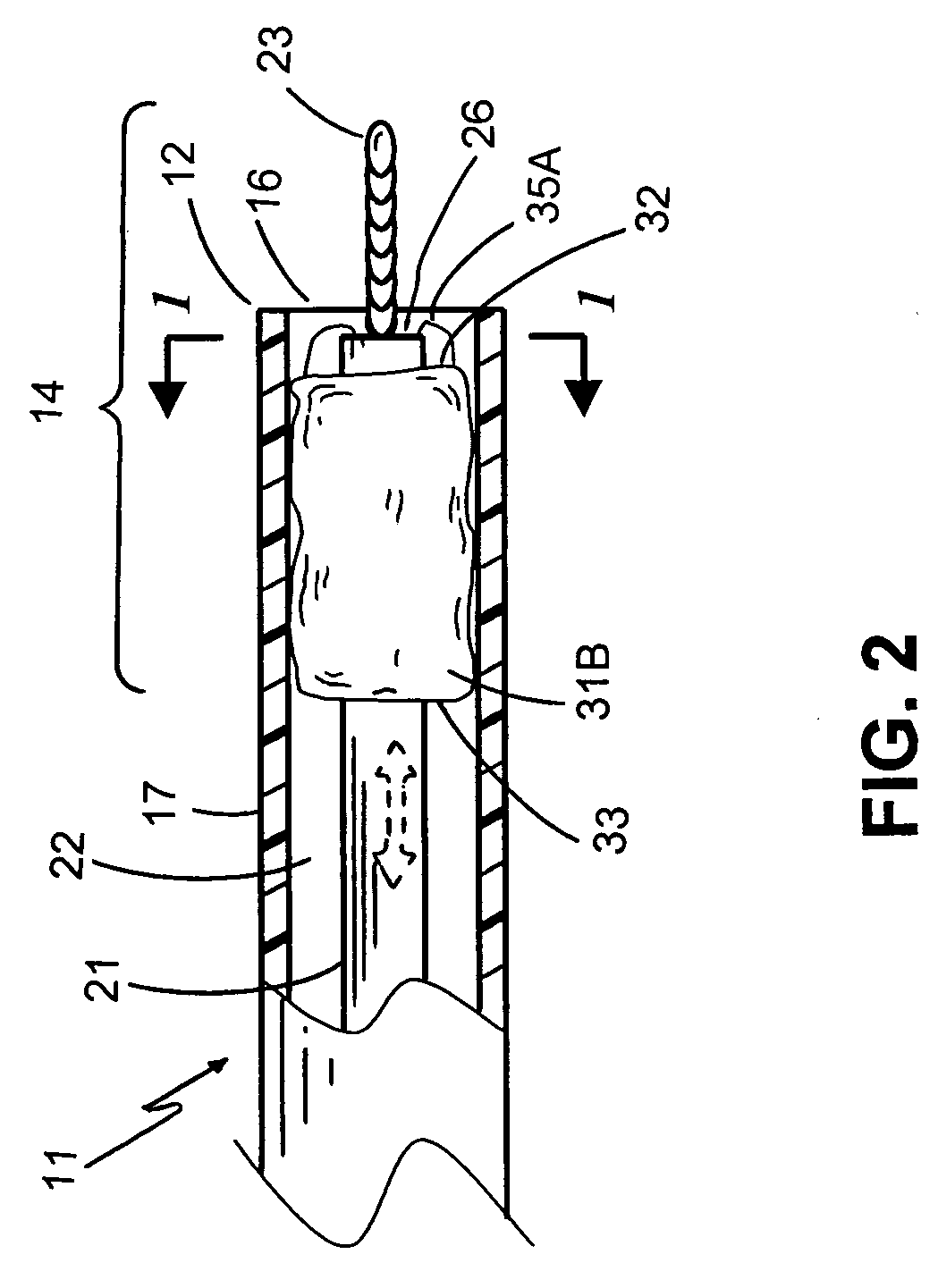
Delivery system for a stentless valve bioprosthesis
InactiveUS20040111096A1Easy to fixReduce the patient's hospital stayEar treatmentTubular organ implantsProsthesisGuide tube
The current invention discloses a catheter and a method for delivering a stentless bloprosthesis in a body channel, the method comprising percutaneously introducing a catheter into the body channel, wherein the catheter contains said stentless bloprosthesis at a retracted state; and disengaging said stentless bioprosthesis out of a distal opening of the catheter by a pulling mechanism associated with the catheter structure.
Owner:3F THERAPEUTICS
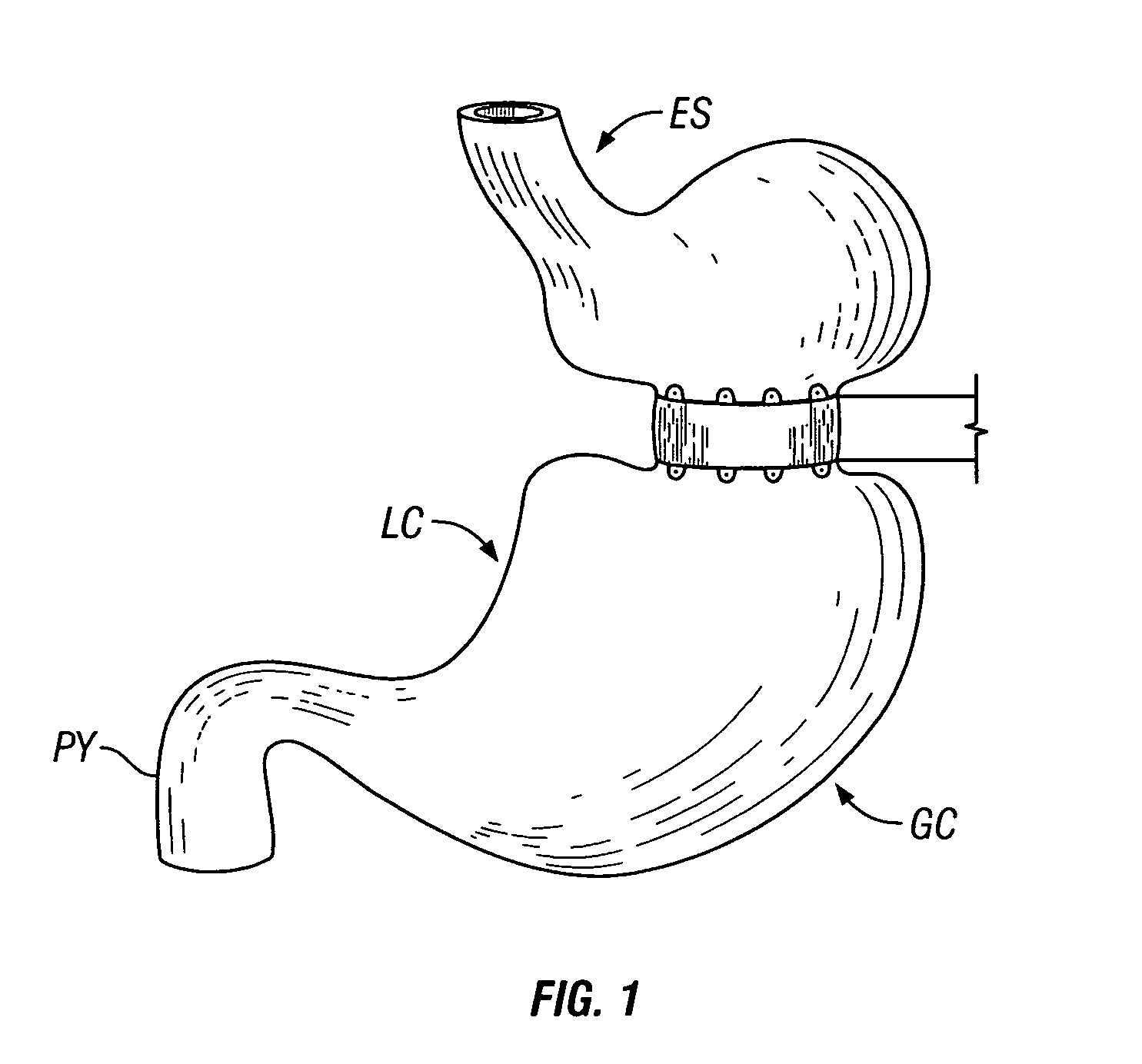
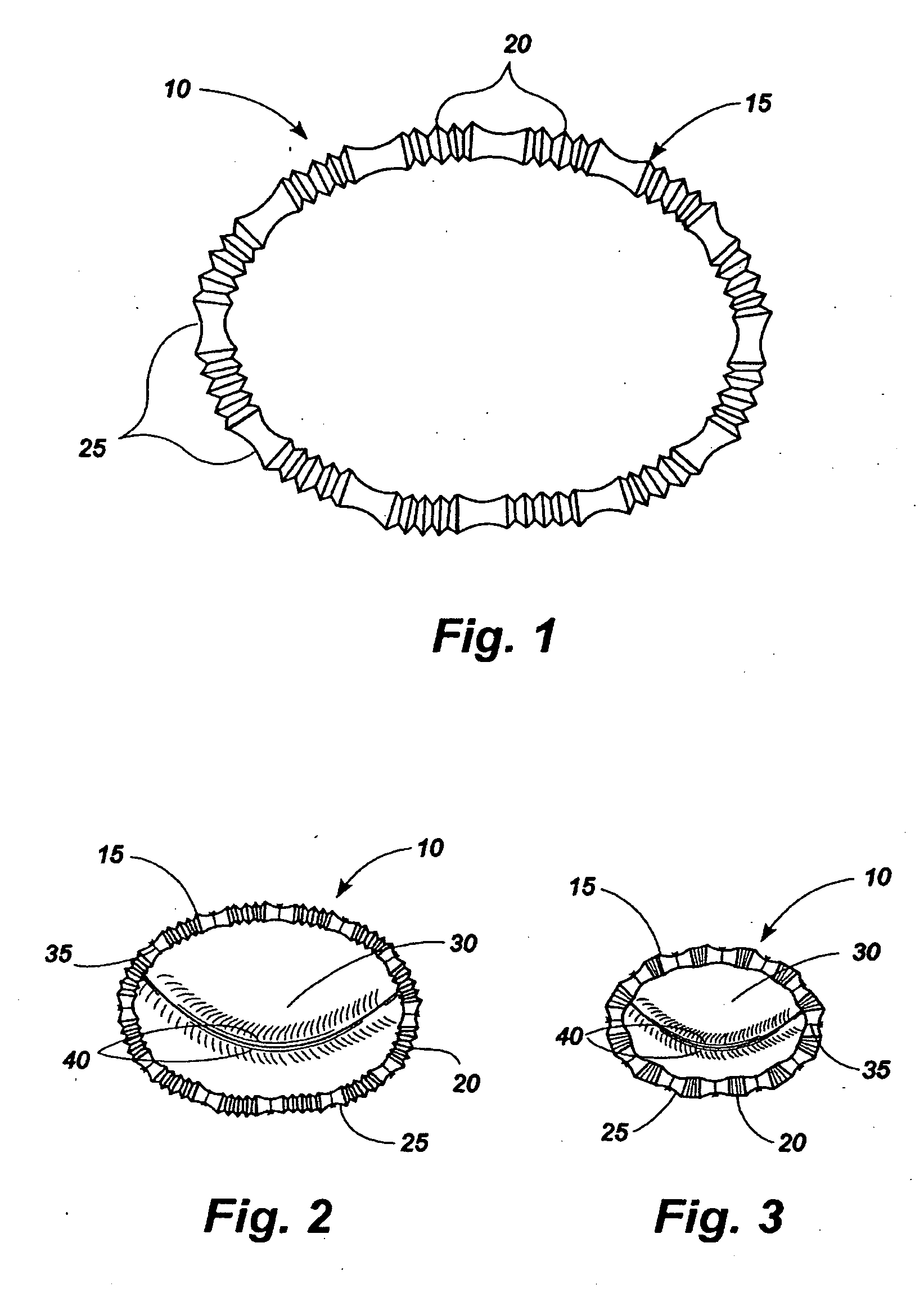
Apparatus for implanting surgical devices for controlling the internal circumference of an anatomic orifice or lumen
A system for implanting a surgical device to control the circumference of internal anatomic passages corrects physiologic dysfunctions resulting from a structural lumen which is either too large or too small. Implants are disclosed which employ various means for adjusting and maintaining the size of an orifice to which they are attached. Systems permit the implants to be implanted using minimally invasive procedures and permit final adjustments to the circumference of the implants after the resumption of normal flow of anatomic fluids in situ. Methods are disclosed for using the implants to treat heart valve abnormalities, gastroesophageal abnormalities, anal incontinence, and the like.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Obesity treatment and device
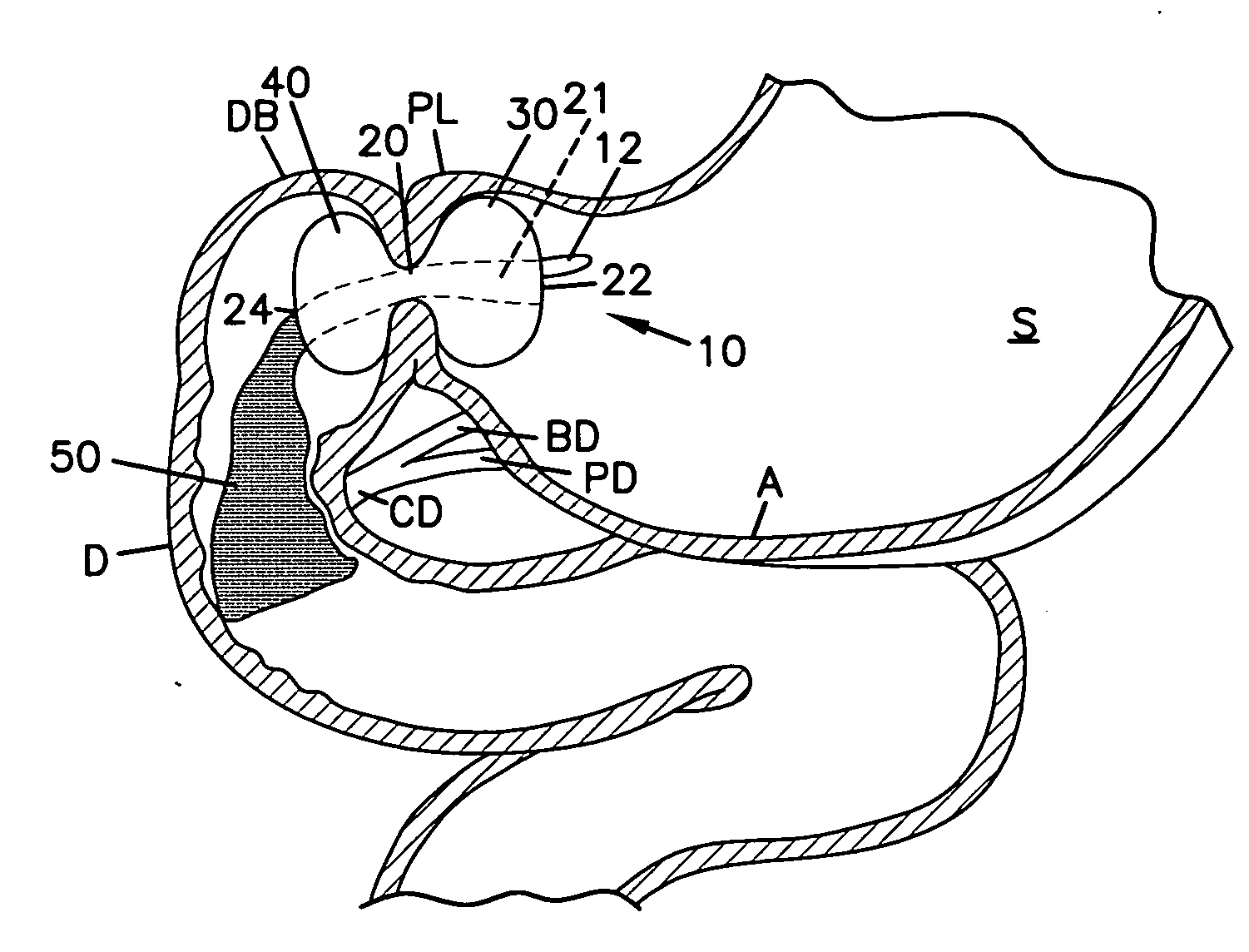
A method and apparatus are disclosed for treating obesity includes an artificial fistula created between gastrointestinal organs such as between the stomach and the colon. The method includes selecting an implant comprising a passageway having an internal lumen with an inlet end and an outlet end. The passageway is positioned passing through a first wall of first gastrointestinal organ (for example, passing through the wall of the stomach) and a second wall of a second gastrointestinal organ (for example, passing through the wall of the large intestine) with the inlet end disposed within an interior of the first gastrointestinal organ and with the outlet disposed within an interior of the second gastrointestinal organ.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Method of forming an implantable device
ActiveUS9352071B2Greater and beneficial tissue ingrowthLow melting pointWeft knittingMedical devicesImplanted devicePliability
Owner:ETHICON INC
Computer-aided-design of skeletal implants
InactiveUS7747305B2ContrastMaintain continuityMedical simulationProgramme controlDigital dataComputer Aided Design
The present invention is directed to a computer aided design method for producing an implant for a patient prior to operation comprising the steps of: generating data with a non-invasive 3D (3-dimensional) scan of the patient's defect site that digitally represents the area that will receive the implant; designing and validating an implant on a computer based on digital data generated from a volume image of the patient; and fabricating the implant based solely on the implant design data generated on computer.
Owner:OSTEOPLASTICS
Methods and apparatus for controlling the internal circumference of an anatomic orifice or lumen
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
Method for implanting a cardiovascular valve
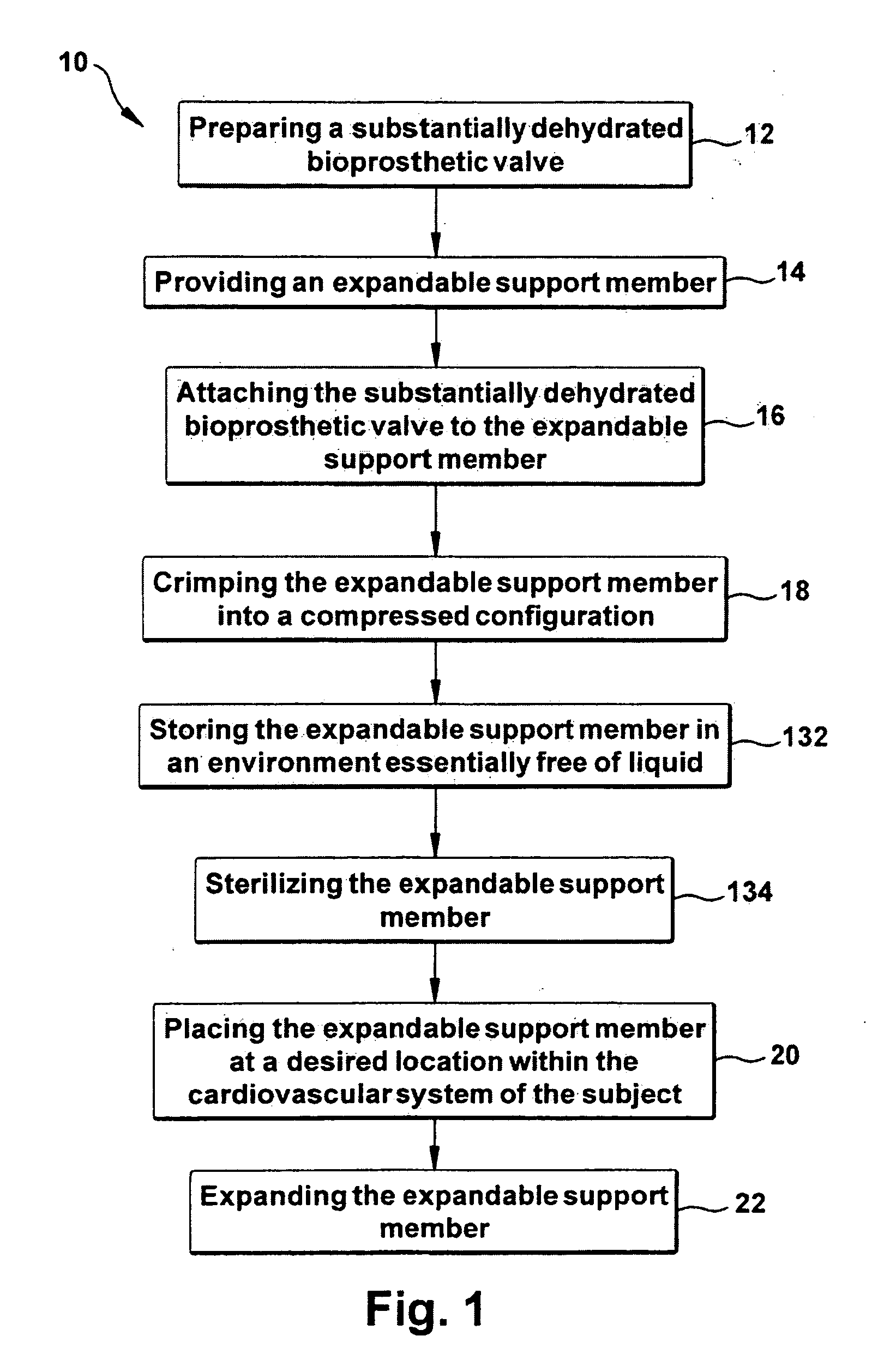
A method is provided for implanting a valve having at least one valve leaflet within the cardiovascular system of a subject. One step of the method includes preparing a substantially dehydrated bioprosthetic valve and then providing an expandable support member having oppositely disposed first and second ends and a main body portion extending between the ends. Next, the substantially dehydrated bioprosthetic valve is attached to the expandable support member so that the substantially dehydrated bioprosthetic valve is operably secured within the main body portion of the expandable support member. The expandable support member is then crimped into a compressed configuration and placed at a desired location within the cardiovascular system of the subject. Either before or after placement at the desired location, fluid or blood re-hydrates the substantially dehydrated bioprosthetic valve.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
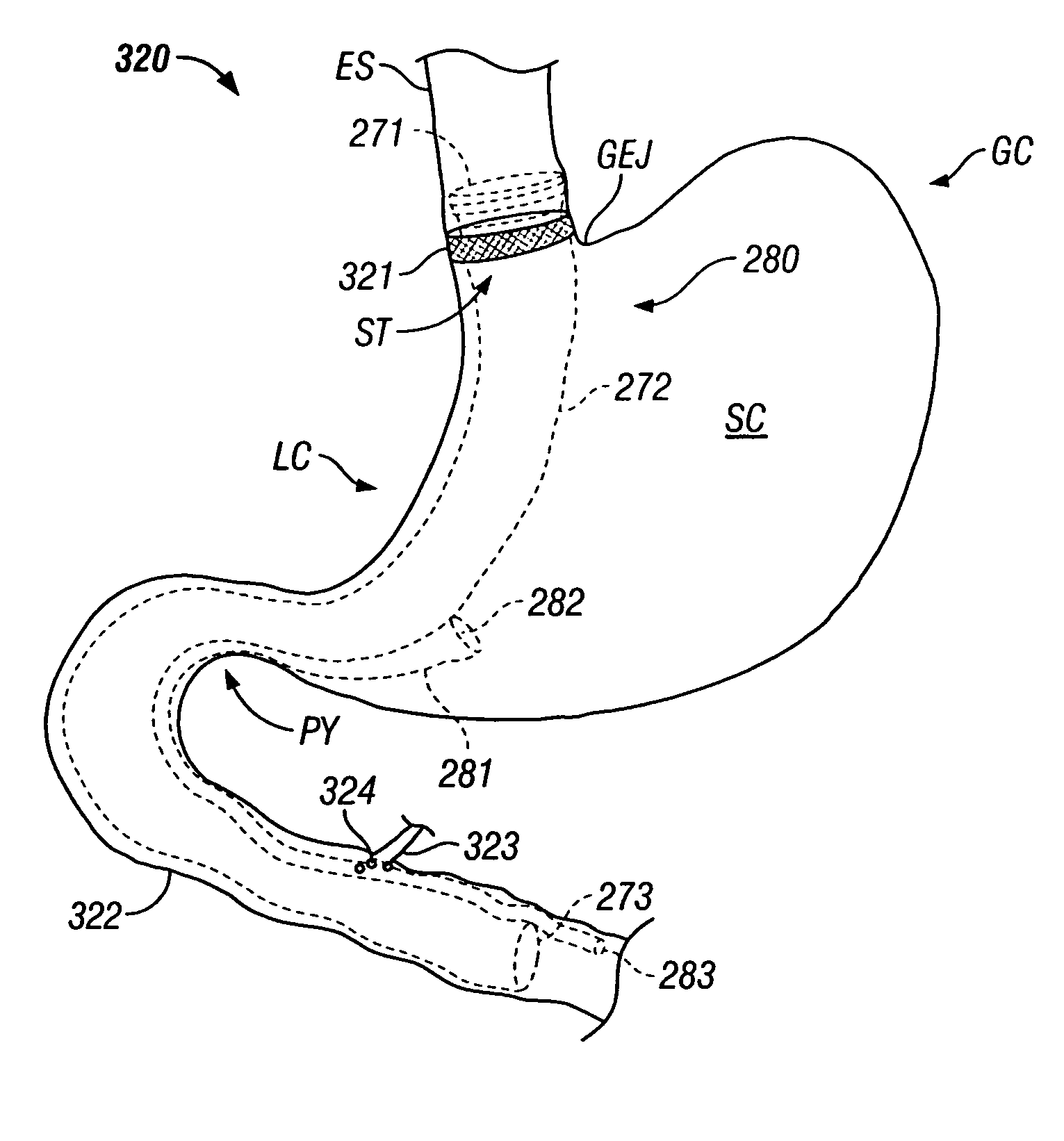
Systems and methods for treating obesity
ActiveUS20050228504A1Good for weight lossStimulatesIntravenous devicesTubular organ implantsPylorusGastric emptying
Methods and devices for simulating a gastric bypass and reducing the volume of the stomach involve placing a tubular liner along the lesser curve of the stomach cavity. Also, methods and devices for slowing gastric emptying involve placing valves within the stomach cavity near the gastrointestinal junction and / or the pylorus. These methods and devices may prevent a patient from drinking and eating large volumes at one time and from eating slowly all day.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
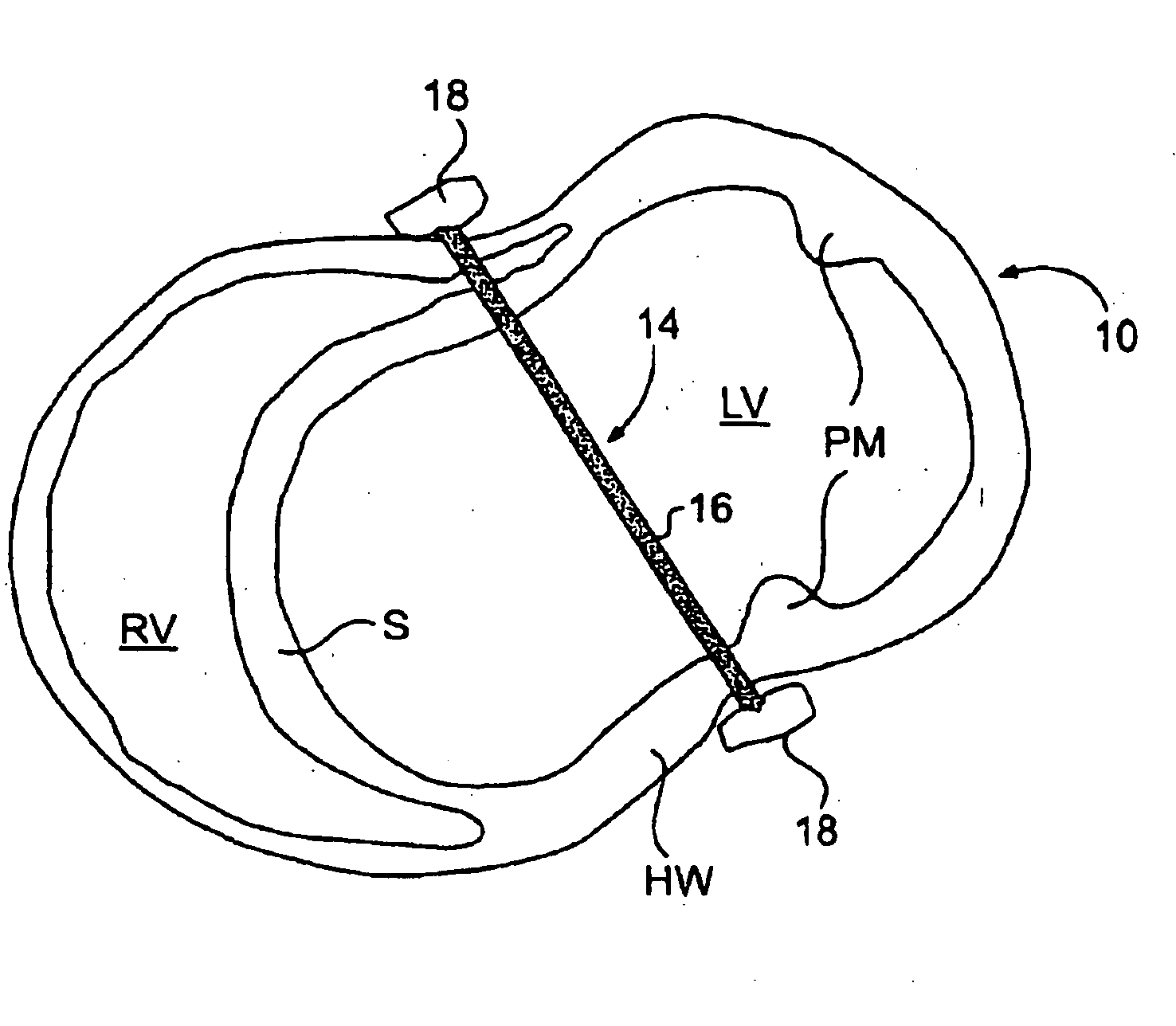
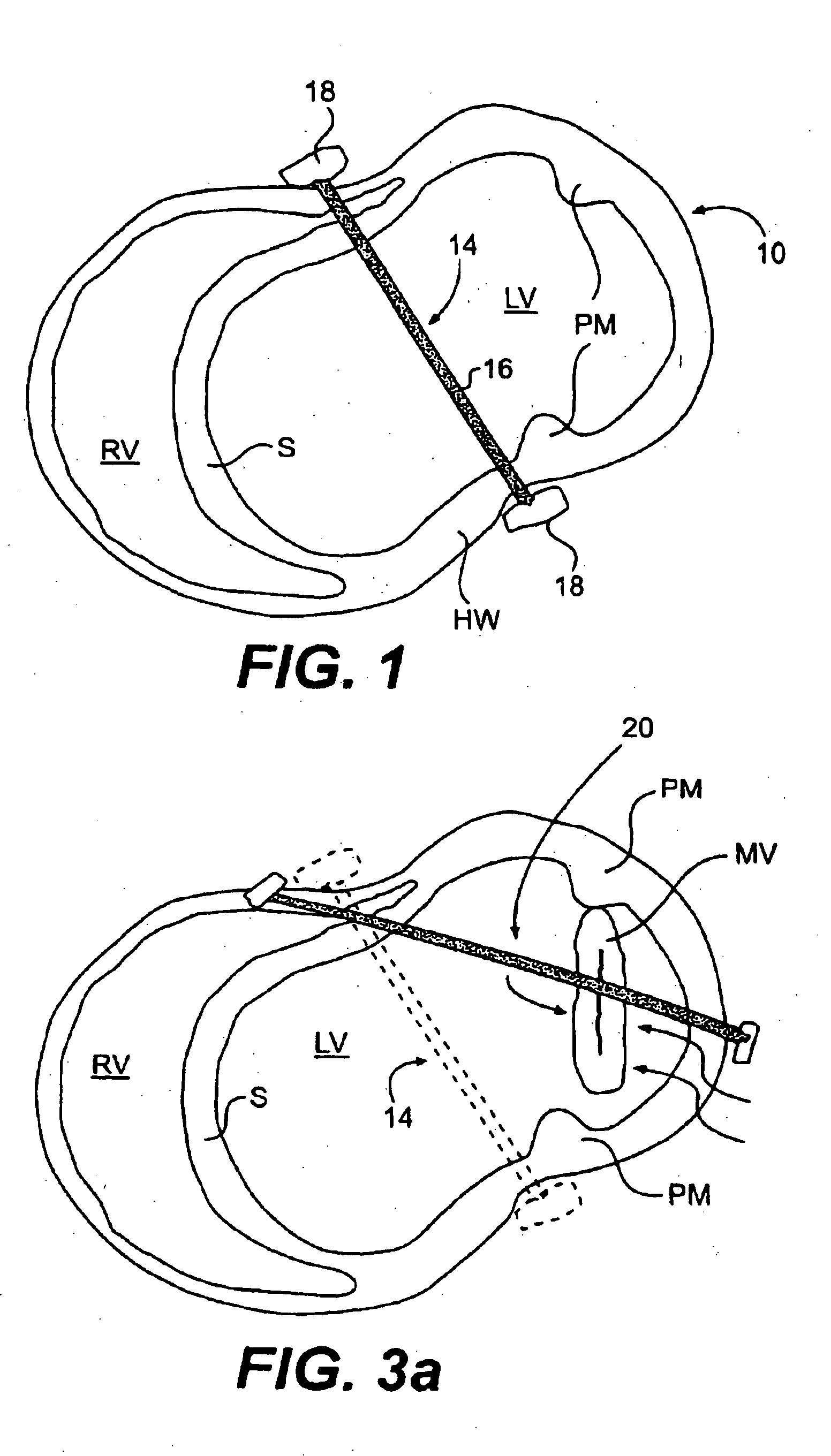
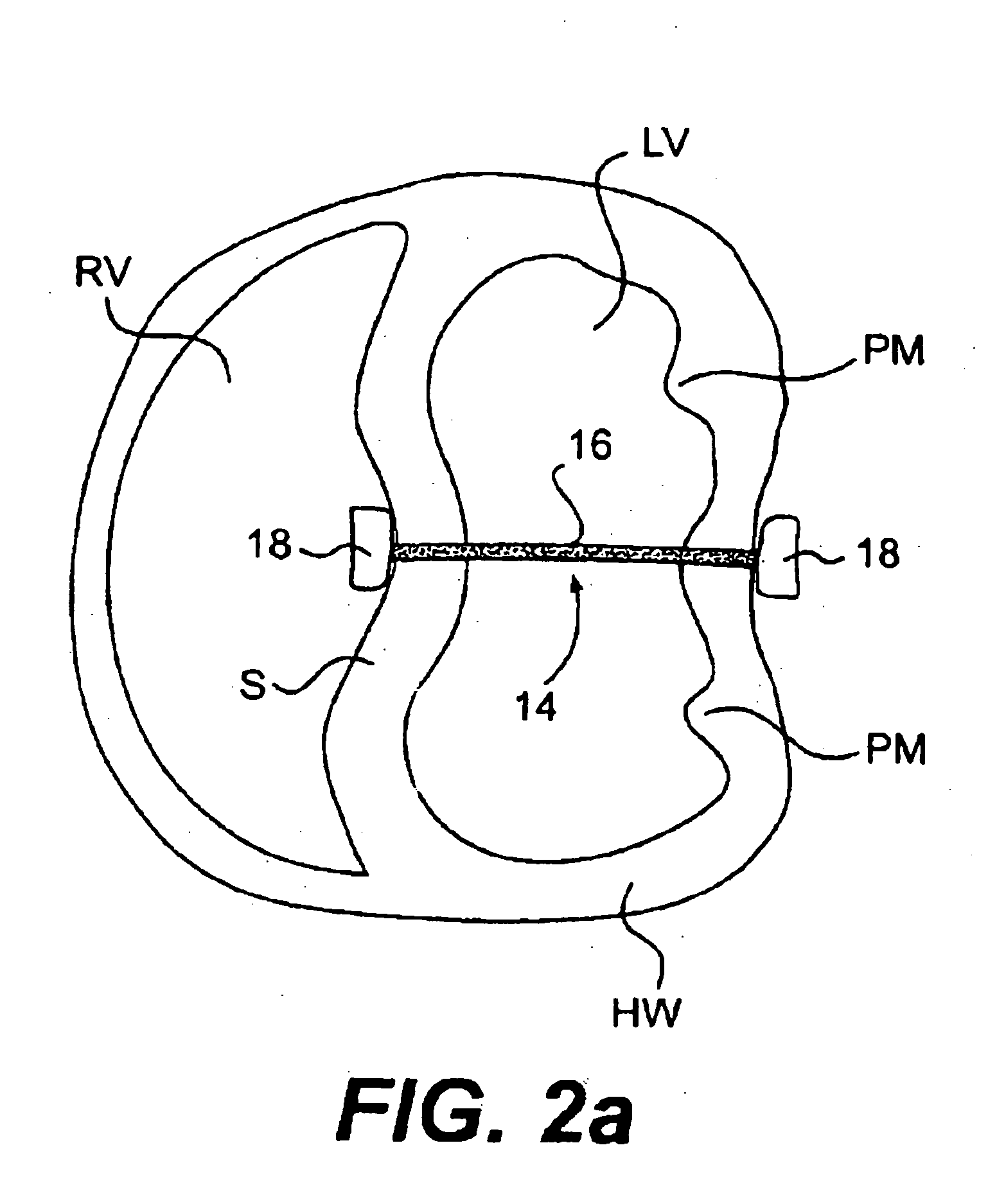
Methods and devices for improving mitral valve function
InactiveUS20050075723A1Less riskMinimally invasiveSuture equipmentsHeart valvesMitral valve functionCardiac wall
The various aspects of the invention pertain to devices and related methods for treating heart conditions, including, for example, dilatation, valve incompetencies, including mitral valve leakage, and other similar heart failure conditions. The devices and related methods of the present invention operate to assist in the apposition of heart valve leaflets to improve valve function. According to one aspect of the invention, a method improves the function of a valve of a heart by placing an elongate member transverse a heart chamber so that each end of the elongate member extends through a wall of the heart, and placing first and second anchoring members external the chamber. The first and second anchoring members are attached to first and second ends of the elongate member to fix the elongate member in a position across the chamber so as to reposition papillary muscles within the chamber. Also described herein is a method for placing a splint assembly transverse a heart chamber by advancing an elongate member through vasculature structure and into the heart chamber.
Owner:EDWARDS LIFESCIENCES LLC
Valve prosthesis with movably attached claspers with apex
A valve prosthesis, implantation device, and methods for use are provided. The implantation device utilizes movable claspers for both positioning and anchoring the valve prosthesis. Alternative designs of the devices allow different methods for minimally invasive implantation of a sutureless valve prosthesis, including transapical and transcatheter approaches. Also provided is a delivery device for delivery of a medical prosthesis though minimally invasive means.
Owner:JC MEDICAL INC
Disk-based valve apparatus and method for the treatment of valve dysfunction
ActiveUS8728155B2Safer mechanism of deploymentAnnuloplasty ringsTubular organ implantsSelf positioningSelf anchoring
Owner:CEPHEA VALVE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com