Patents
Literature
71154 results about "Nutrient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
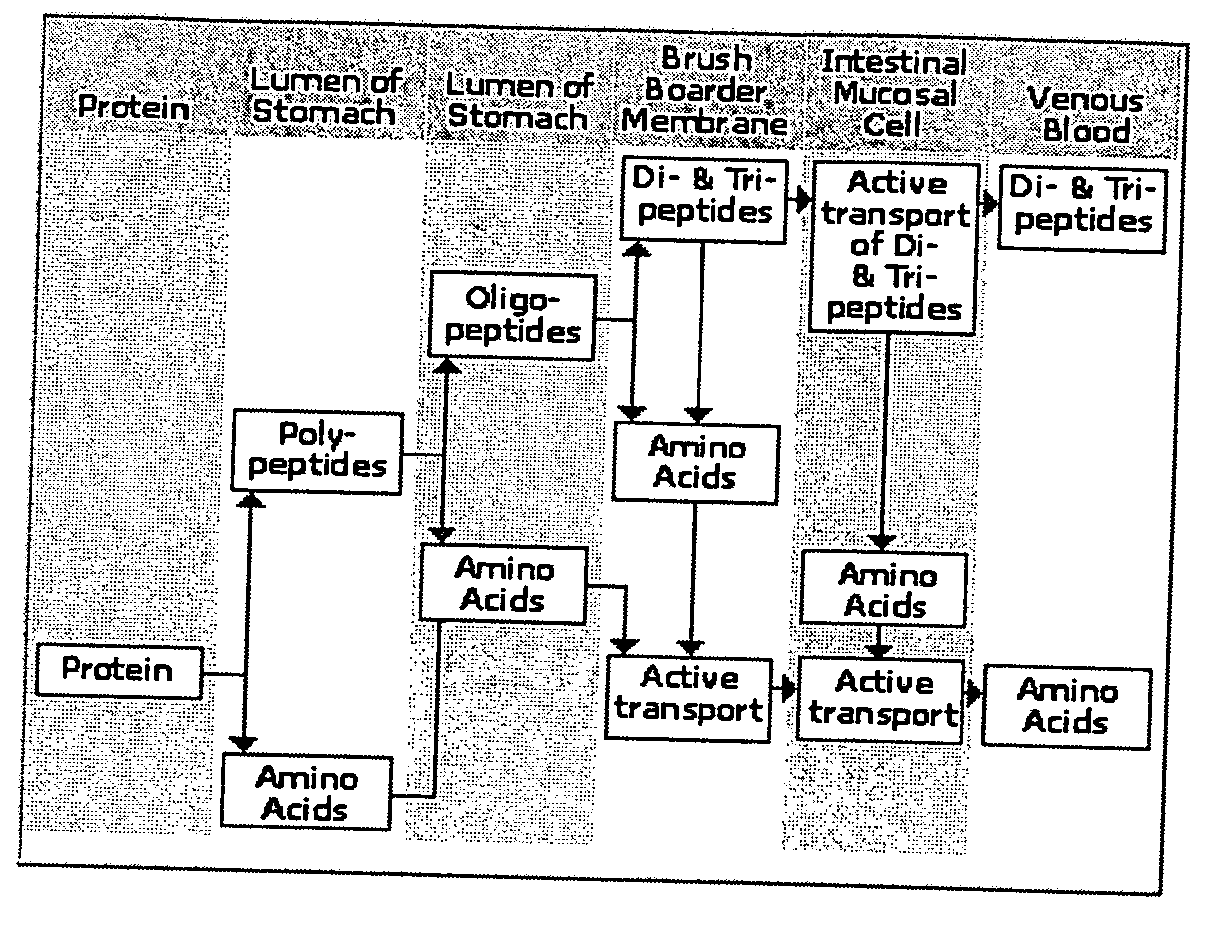
A nutrient is a substance used by an organism to survive, grow, and reproduce. The requirement for dietary nutrient intake applies to animals, plants, fungi, and protists. Nutrients can be incorporated into cells for metabolic purposes or excreted by cells to create non-cellular structures, such as hair, scales, feathers, or exoskeletons. Some nutrients can be metabolically converted to smaller molecules in the process of releasing energy, such as for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and fermentation products (ethanol or vinegar), leading to end-products of water and carbon dioxide. All organisms require water. Essential nutrients for animals are the energy sources, some of the amino acids that are combined to create proteins, a subset of fatty acids, vitamins and certain minerals. Plants require more diverse minerals absorbed through roots, plus carbon dioxide and oxygen absorbed through leaves. Fungi live on dead or living organic matter and meet nutrient needs from their host.
Methods and materials for the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells in feeder-free culture
Methods and materials for culturing primate-derived primordial stem cells are described. In one embodiment, a cell culture medium for growing primate-derived primordial stem cells in a substantially undifferentiated state is provided which includes a low osmotic pressure, low endotoxin basic medium that is effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells. The basic medium is combined with a nutrient serum effective to support the growth of primate-derived primordial stem cells and a substrate selected from the group consisting of feeder cells and an extracellular matrix component derived from feeder cells. The medium further includes non-essential amino acids, an anti-oxidant, and a first growth factor selected from the group consisting of nucleosides and a pyruvate salt.
Owner:ASTERIAS BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
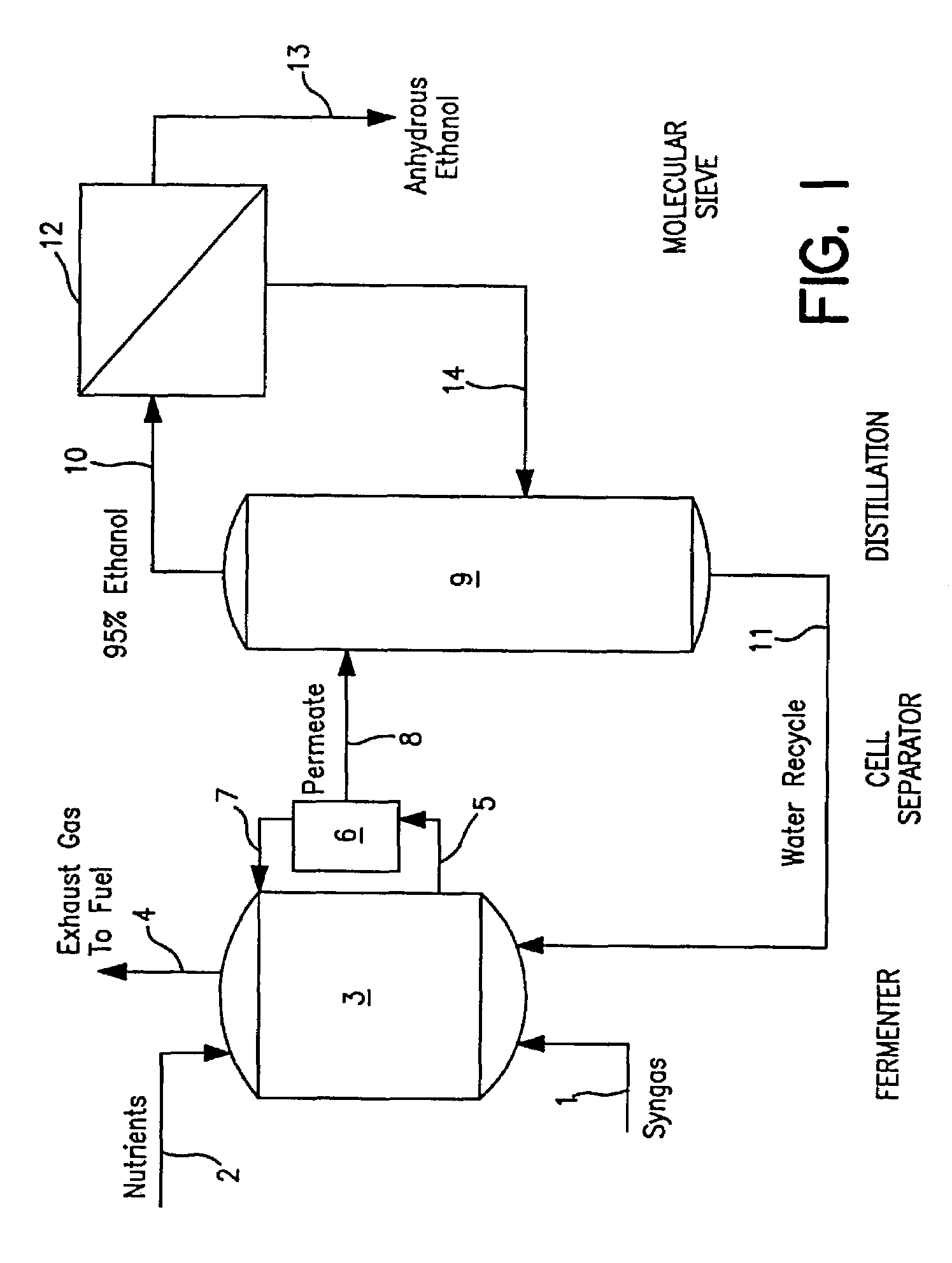
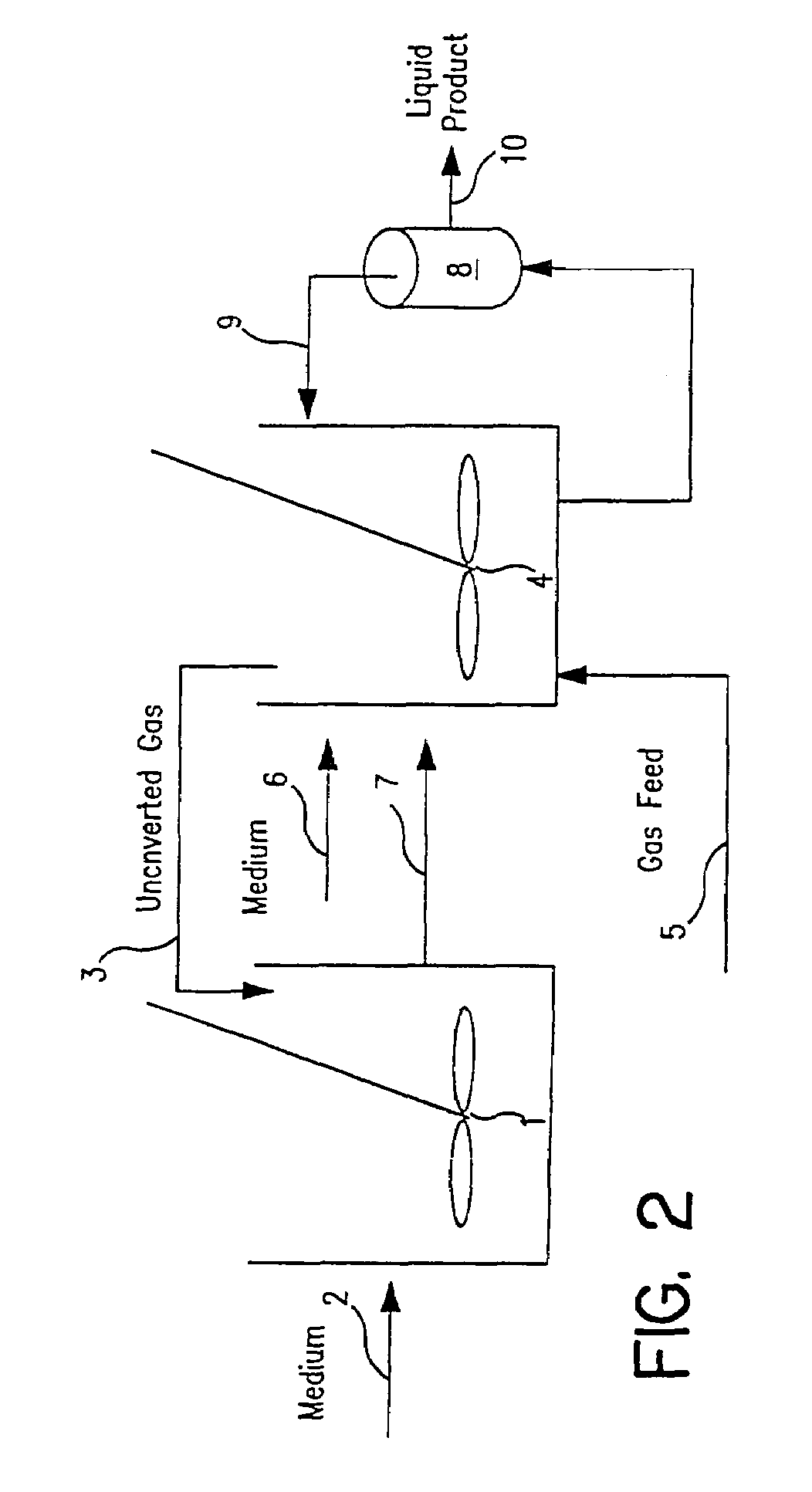
Methods for increasing the production of ethanol from microbial fermentation
InactiveUS7285402B2Good culture stabilityPermit growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsSolid waste disposalBioreactorNutrient
A stable continuous method for producing ethanol from the anaerobic bacterial fermentation of a gaseous substrate containing at least one reducing gas involves culturing a fermentation bioreactor anaerobic, acetogenic bacteria in a liquid nutrient medium; supplying the gaseous substrate to the bioreactor; and manipulating the bacteria in the bioreactor by reducing the redox potential, or increasing the NAD(P)H TO NAD(P) ratio, in the fermentation broth after the bacteria achieves a steady state and stable cell concentration in the bioreactor. The free acetic acid concentration in the bioreactor is maintained at less than 5 g / L free acid. This method allows ethanol to be produced in the fermentation broth in the bioreactor at a productivity greater than 10 g / L per day. Both ethanol and acetate are produced in a ratio of ethanol to acetate ranging from 1:1 to 20:1.
Owner:JUPENG BIO HK LTD
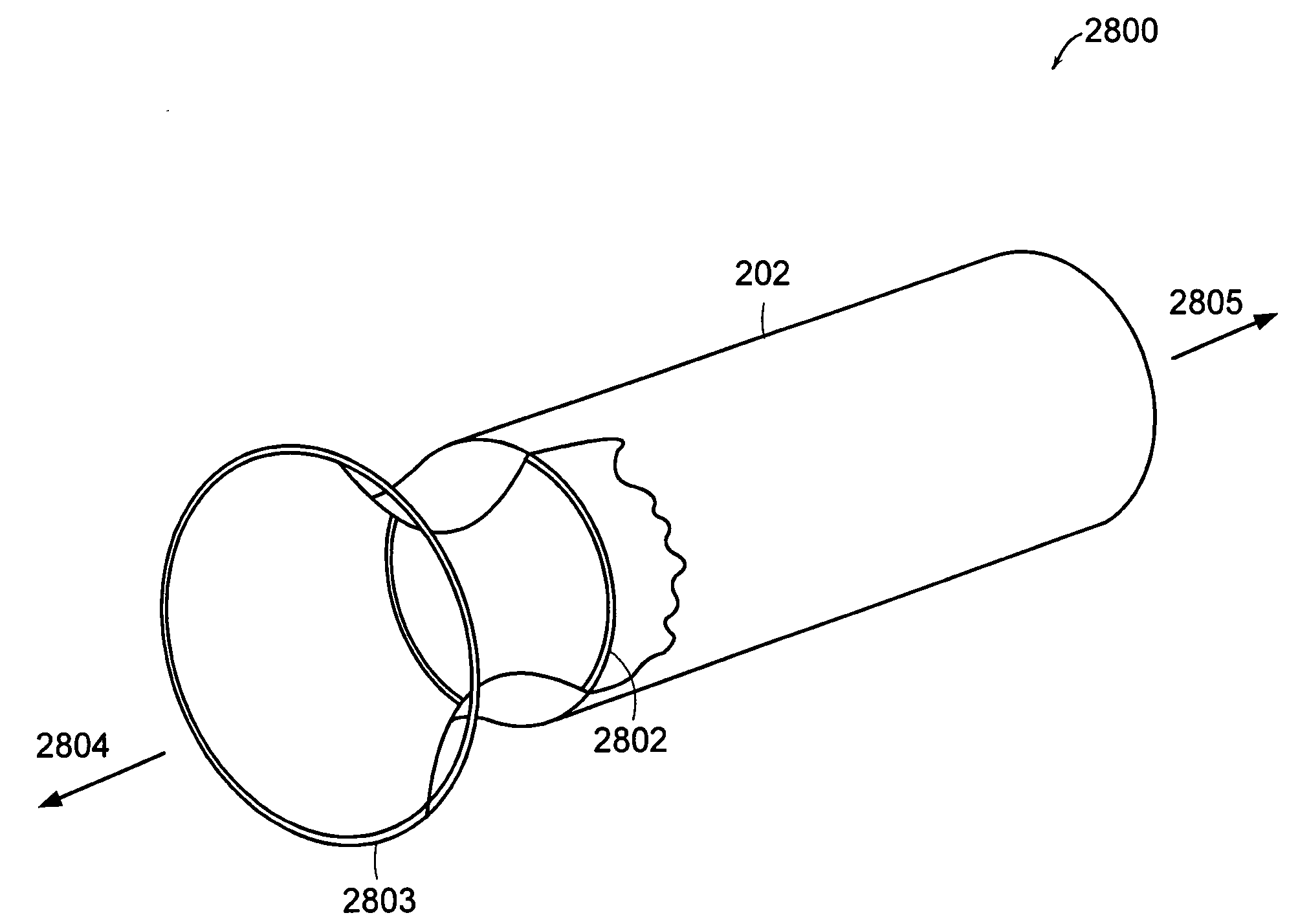
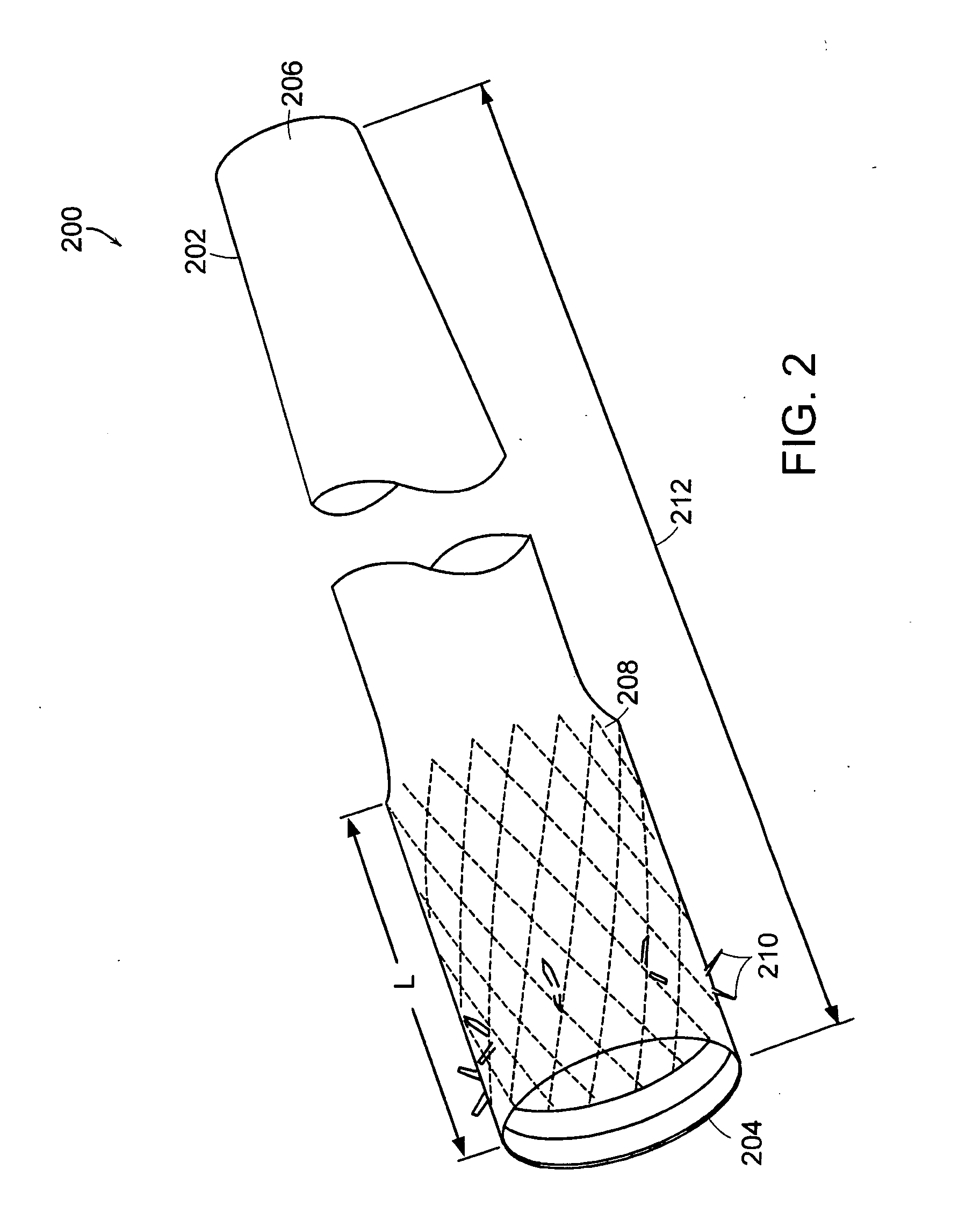
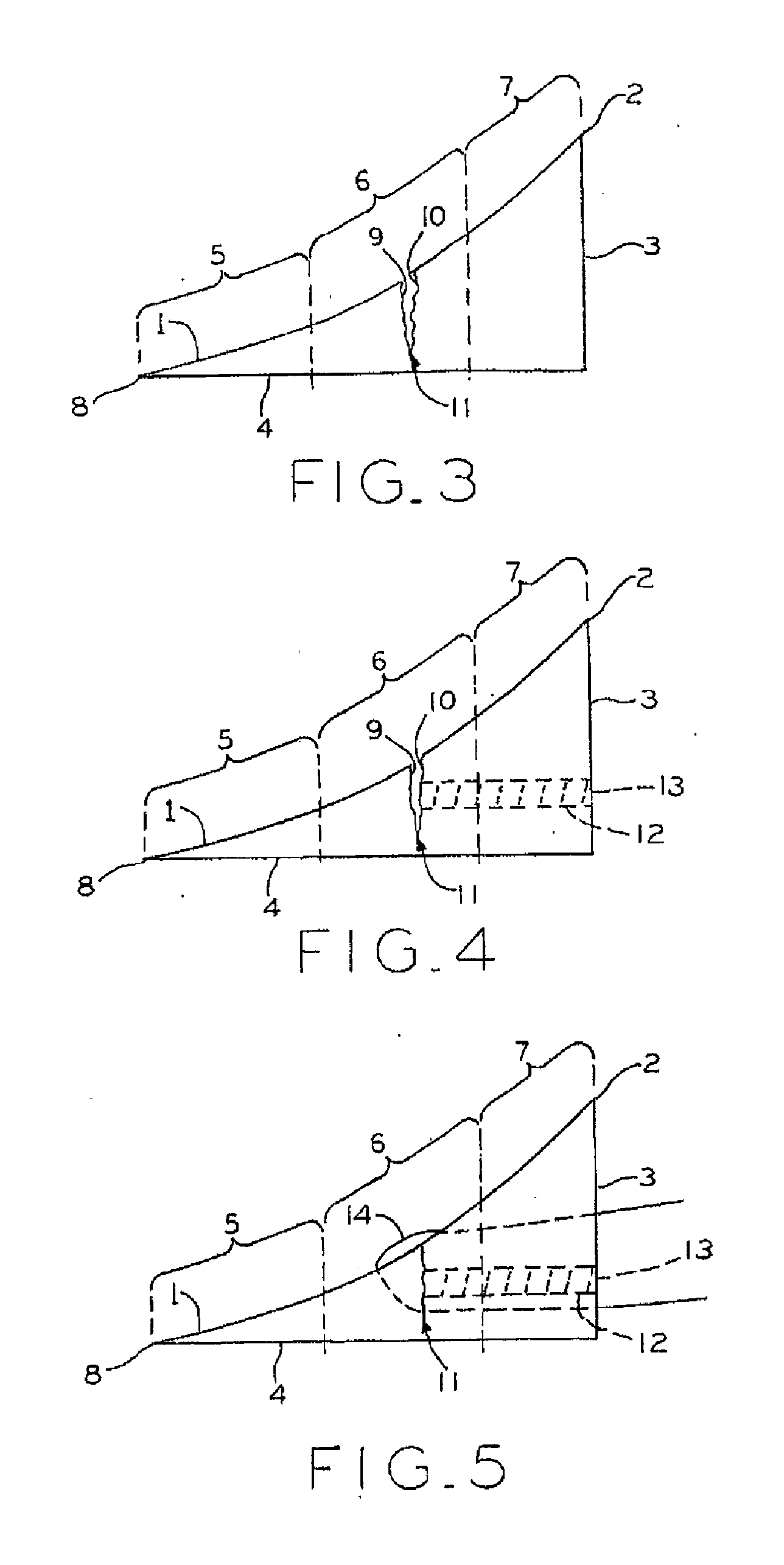
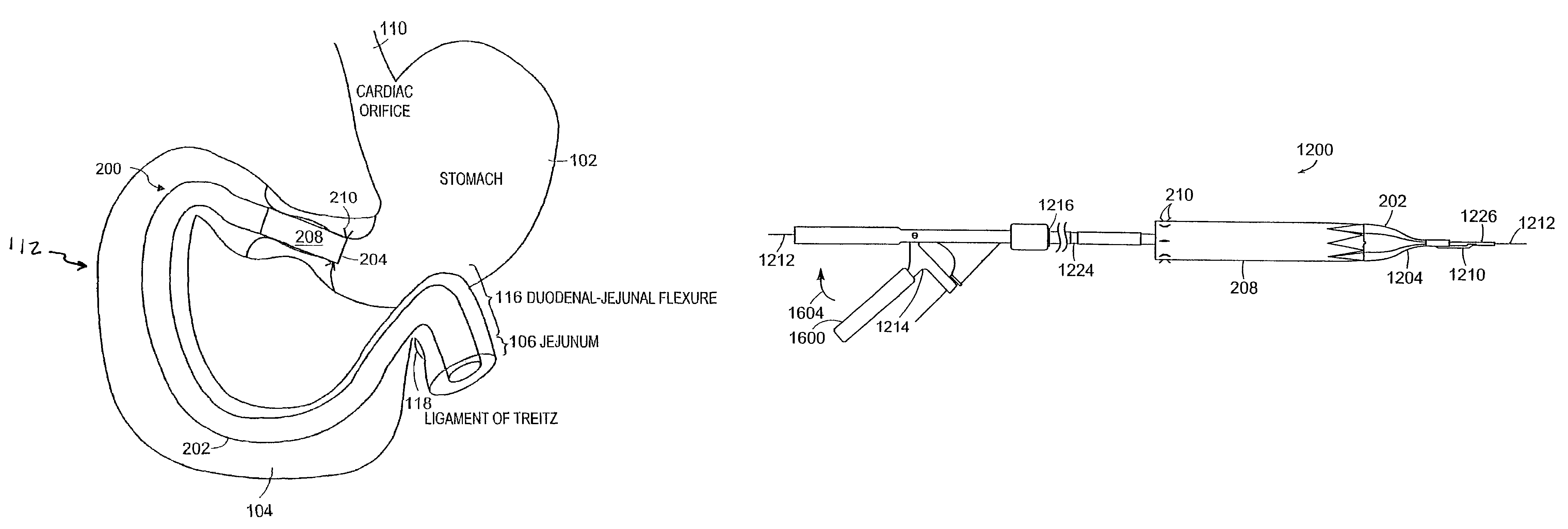
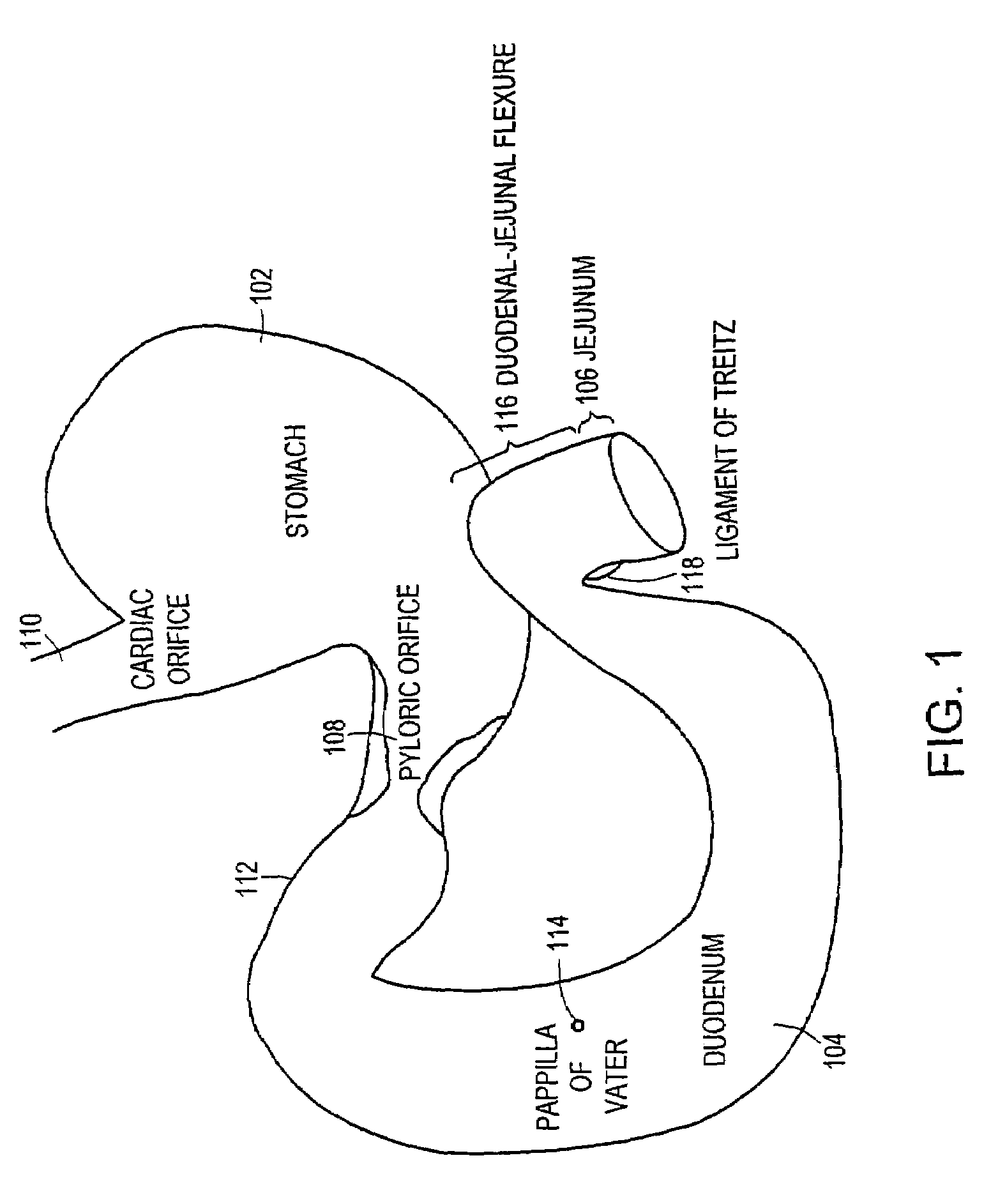
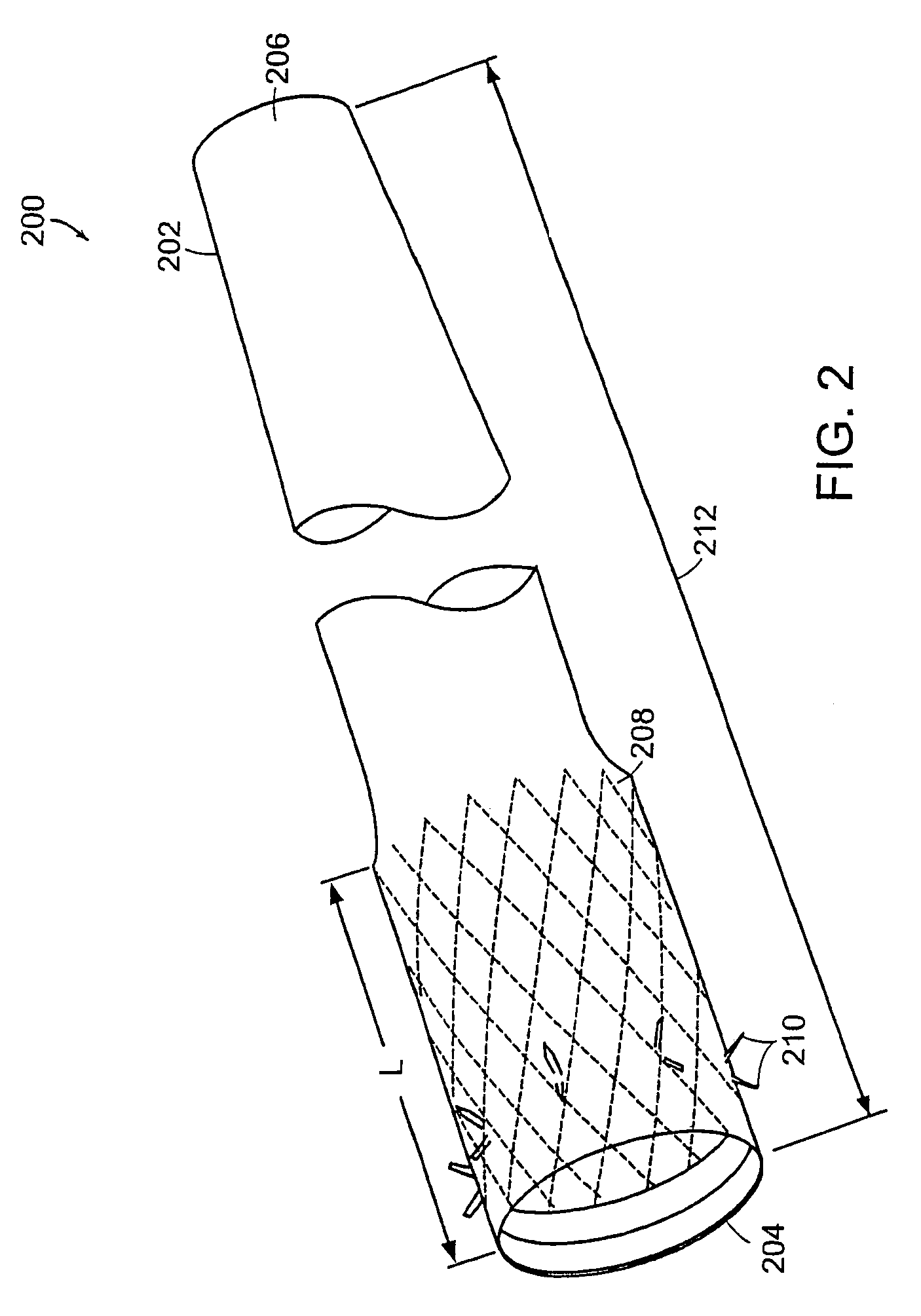
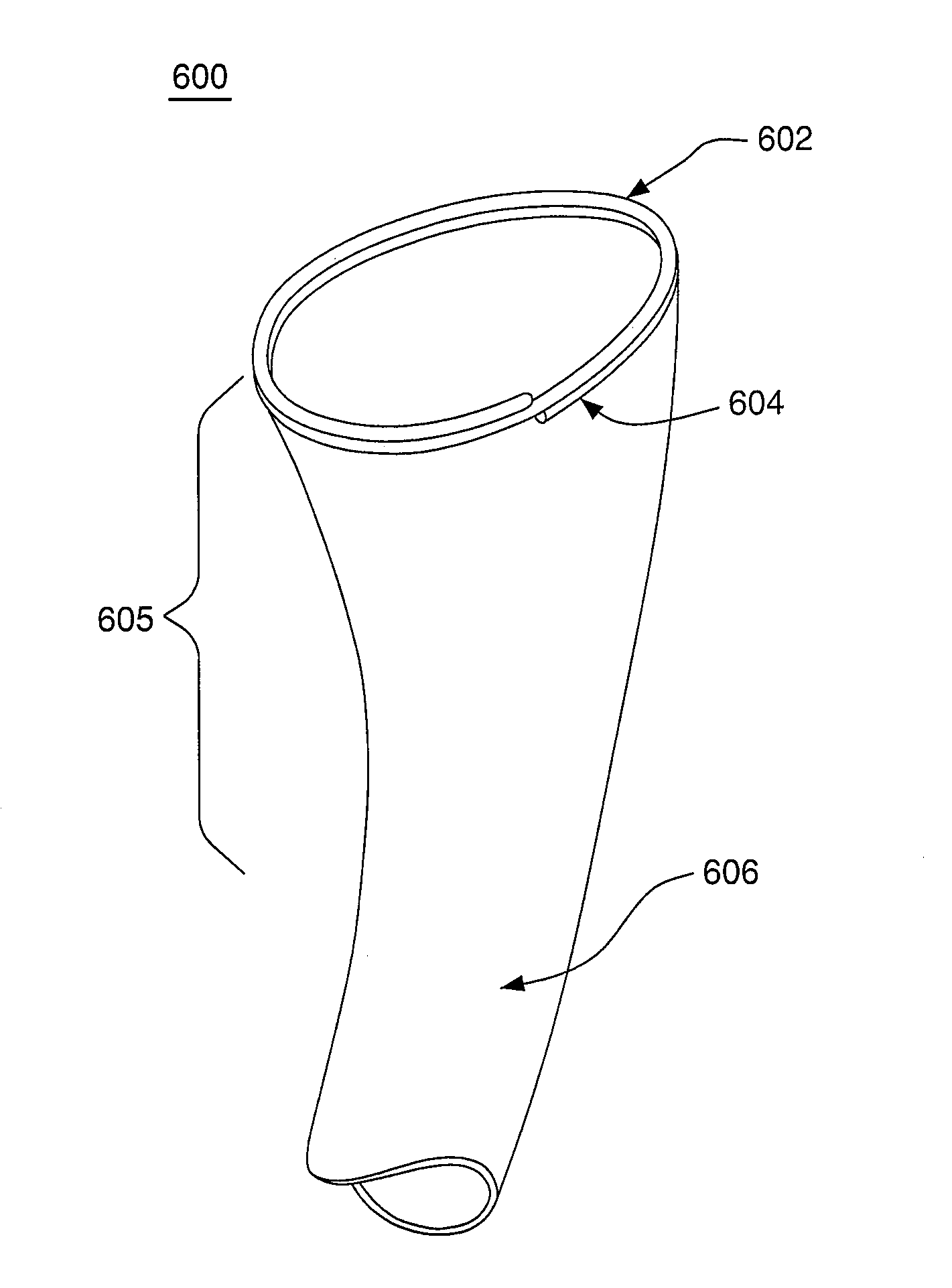
Bariatric sleeve
InactiveUS20060161265A1Increased axial stabilityLess movementSuture equipmentsStentsIntestinal structureGastrointestinal device
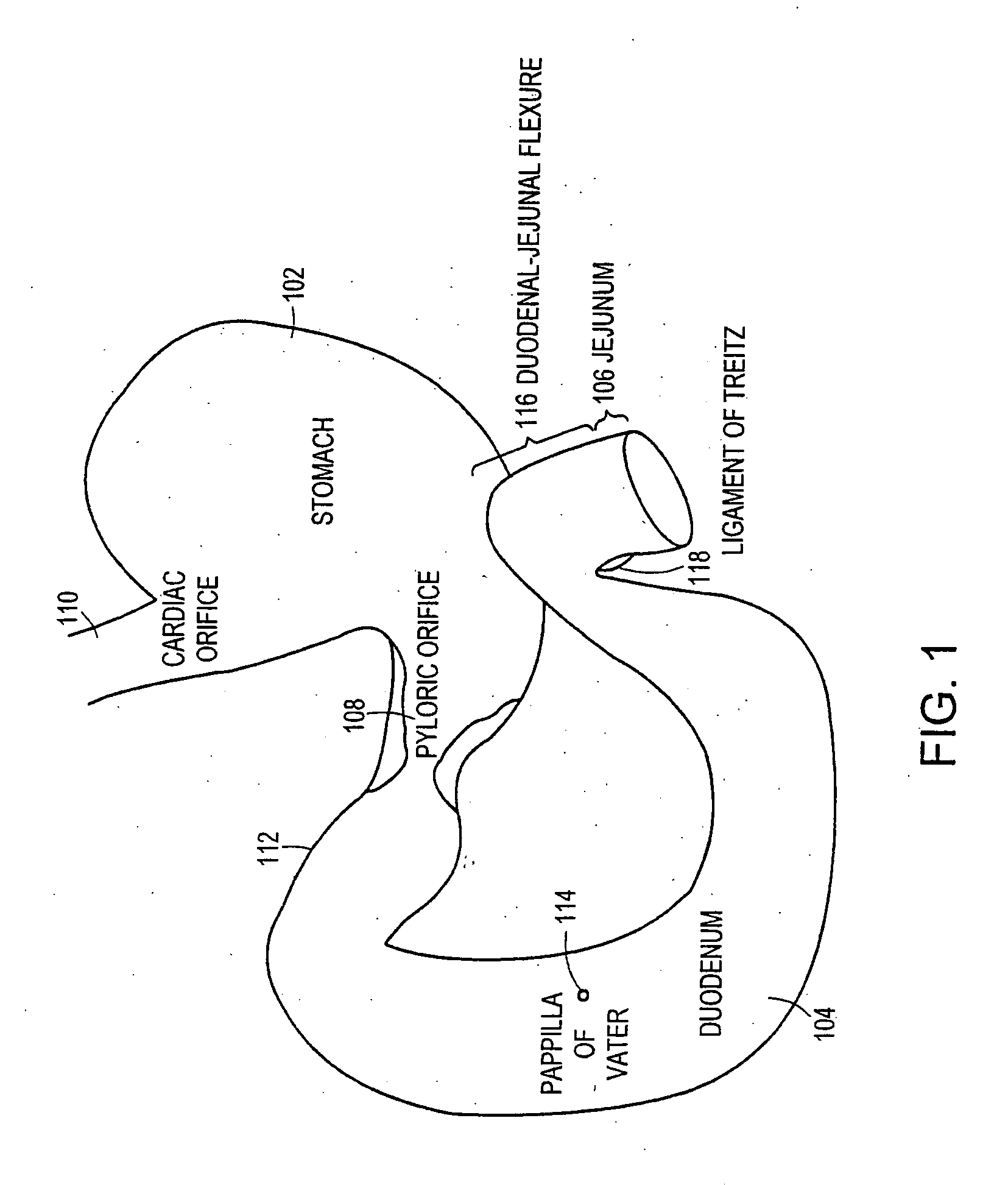
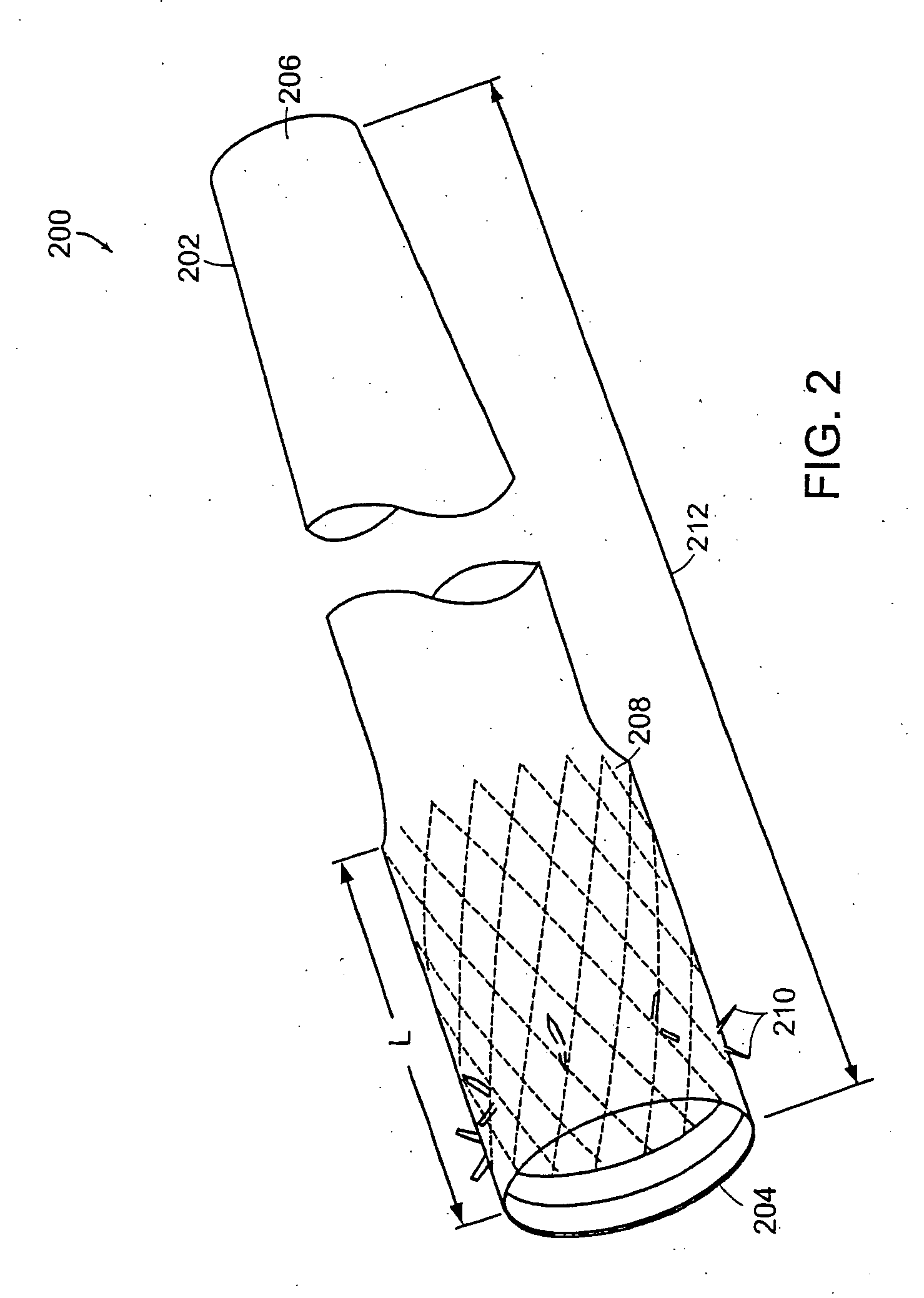
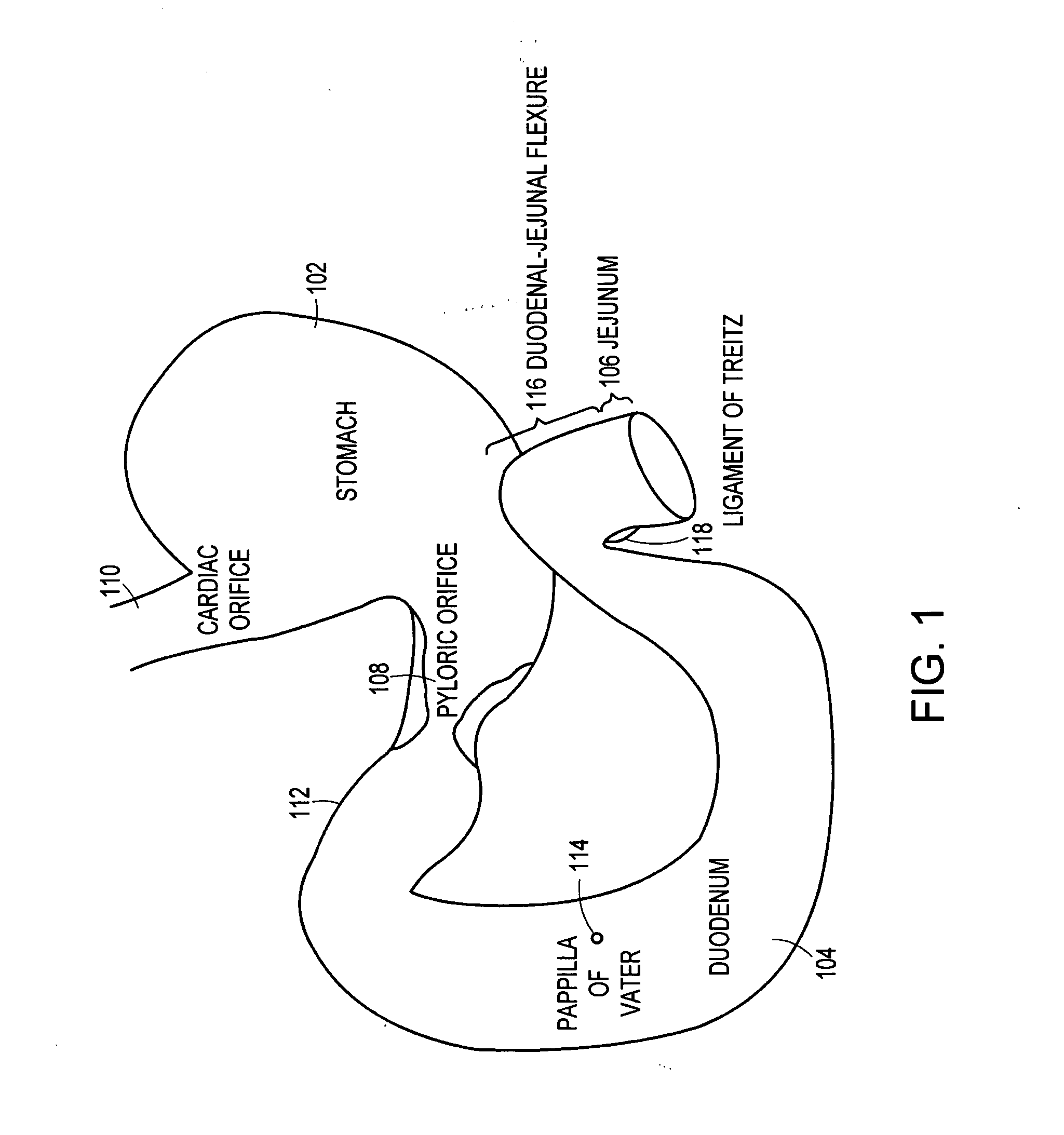
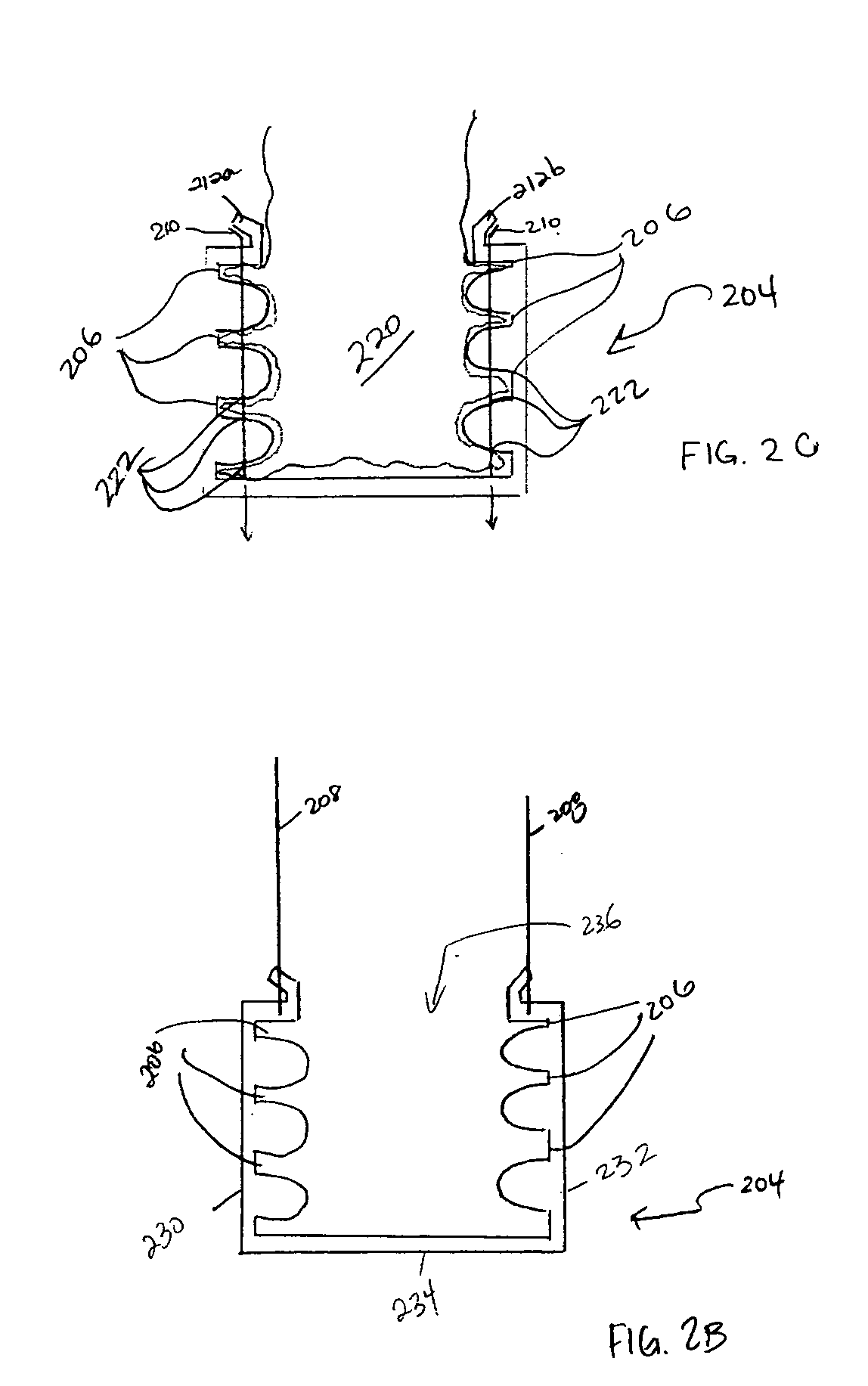
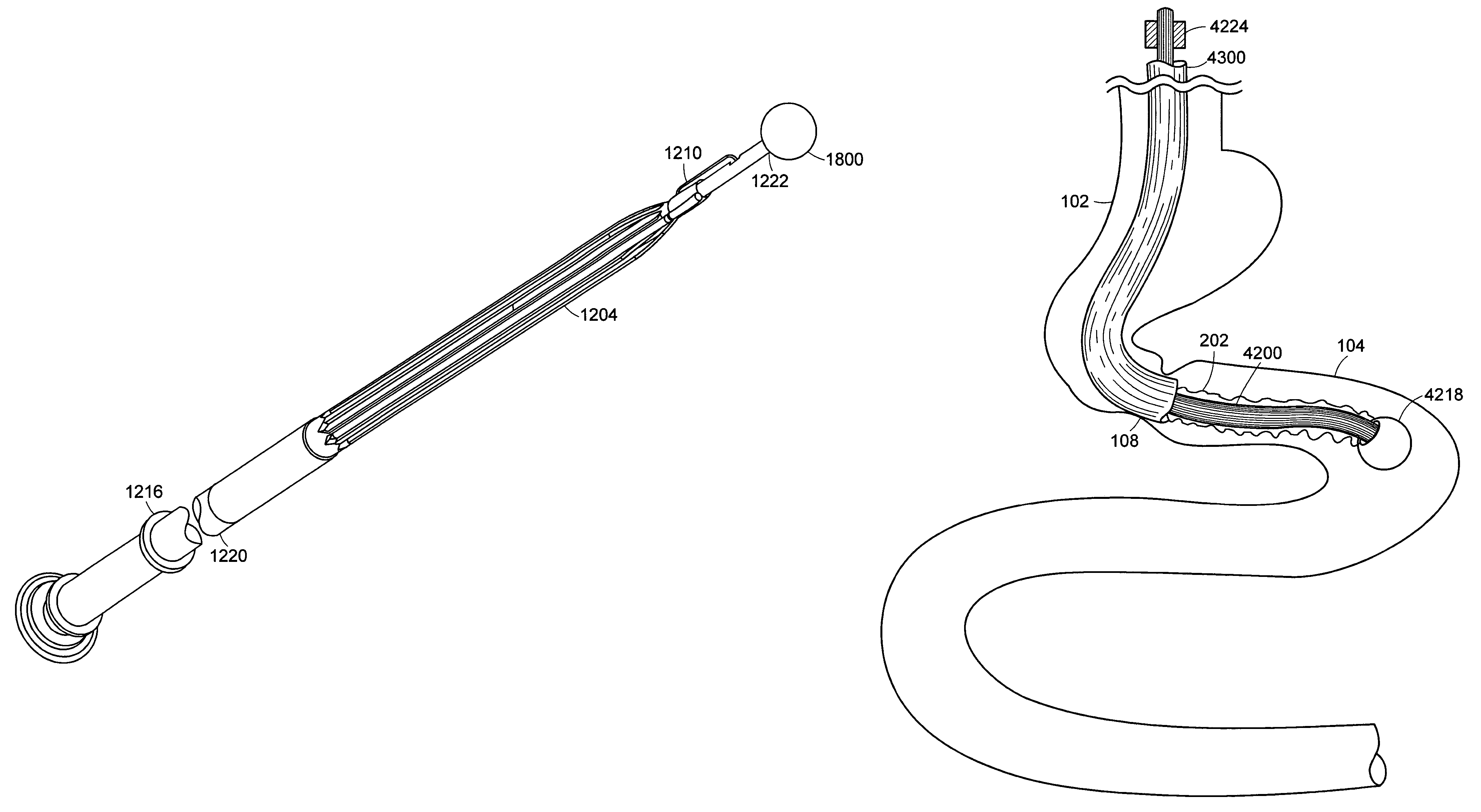
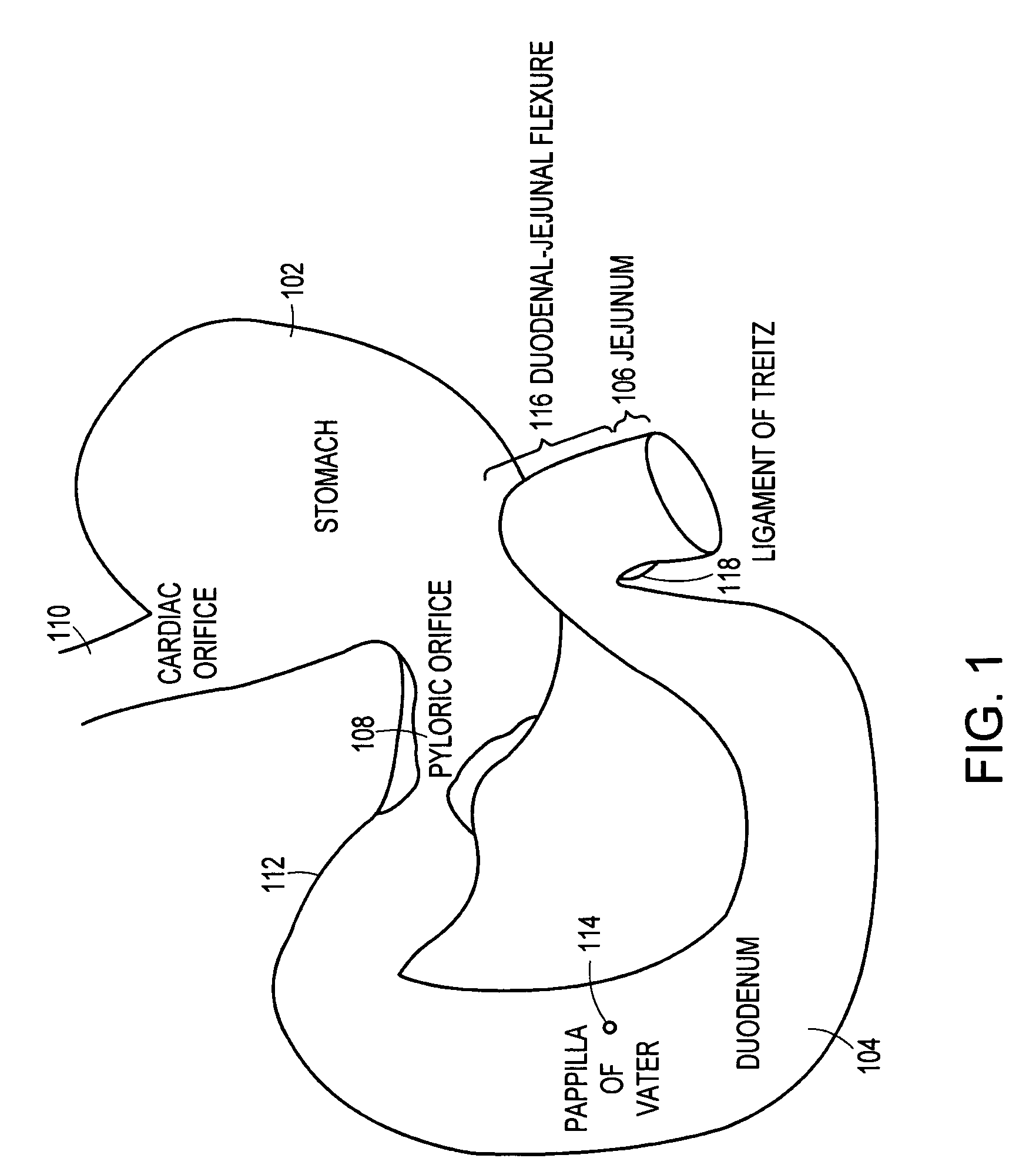
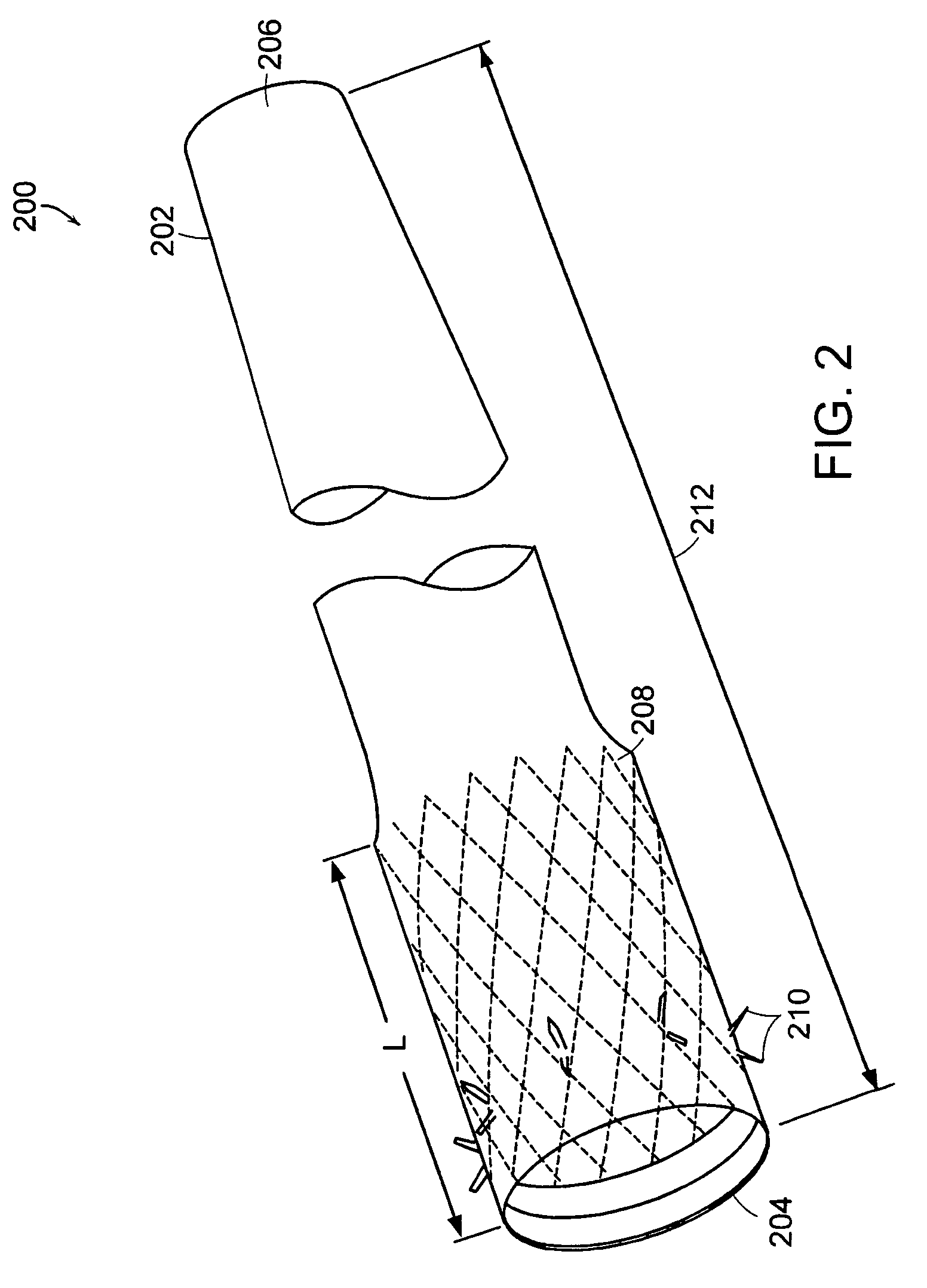
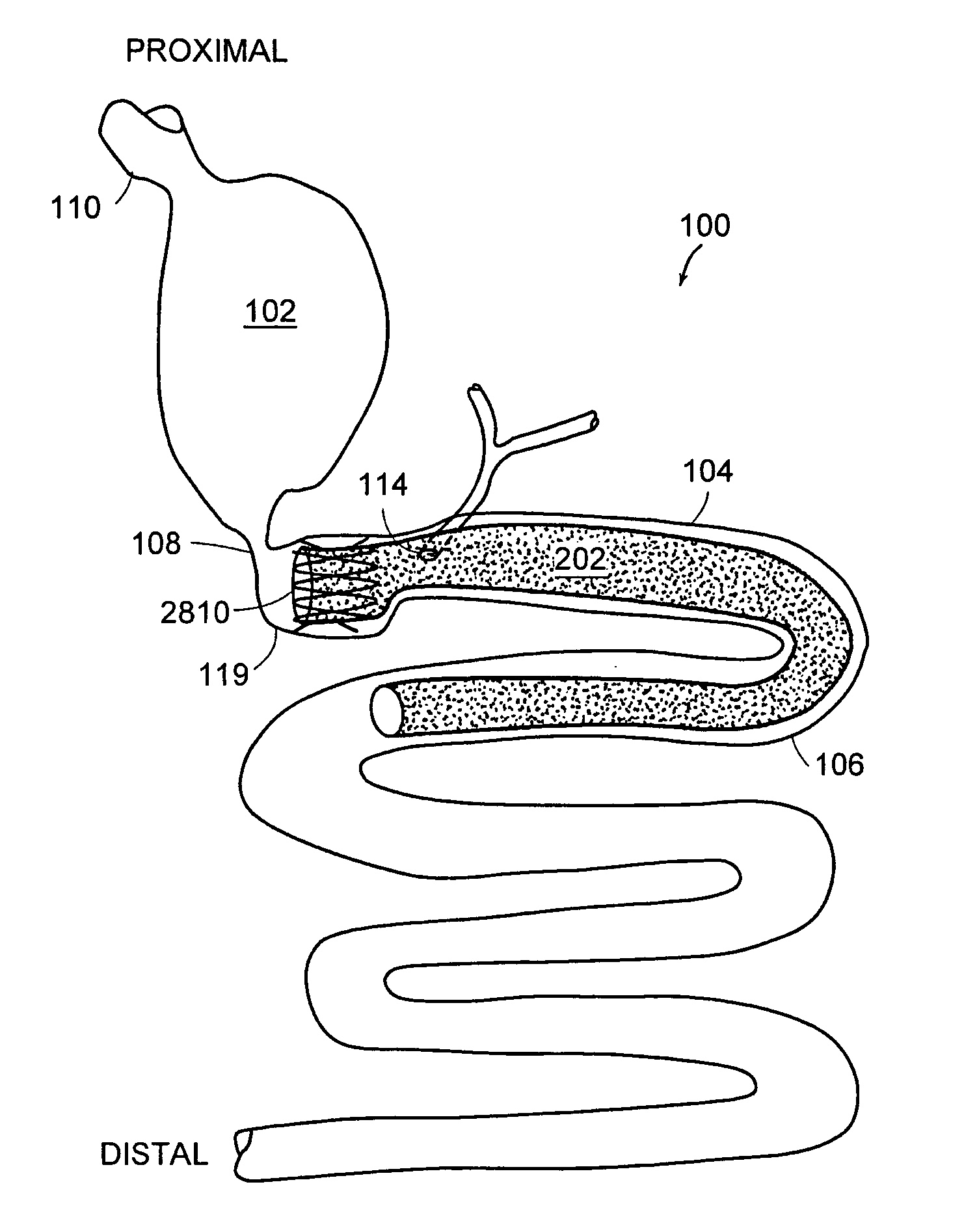
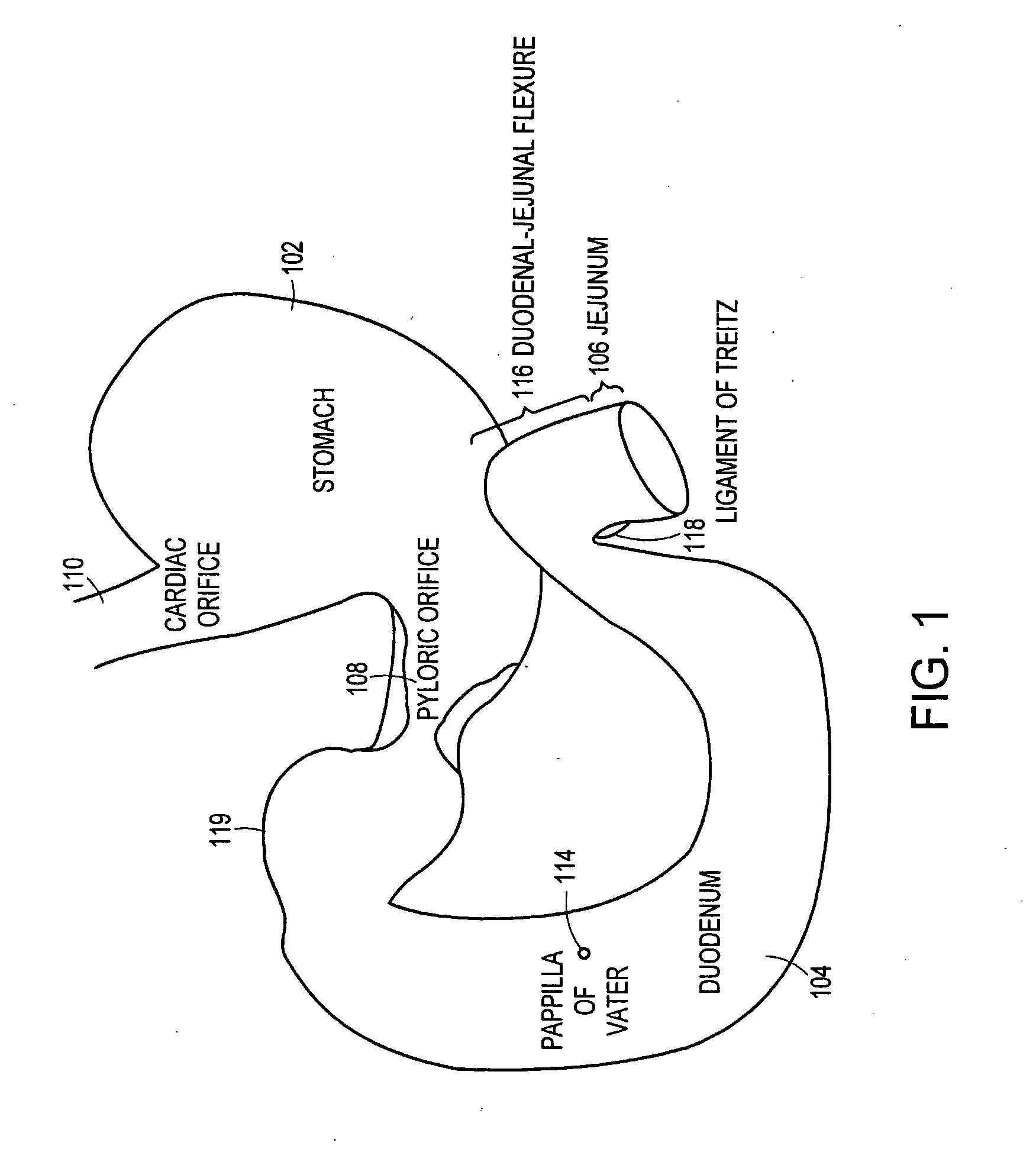
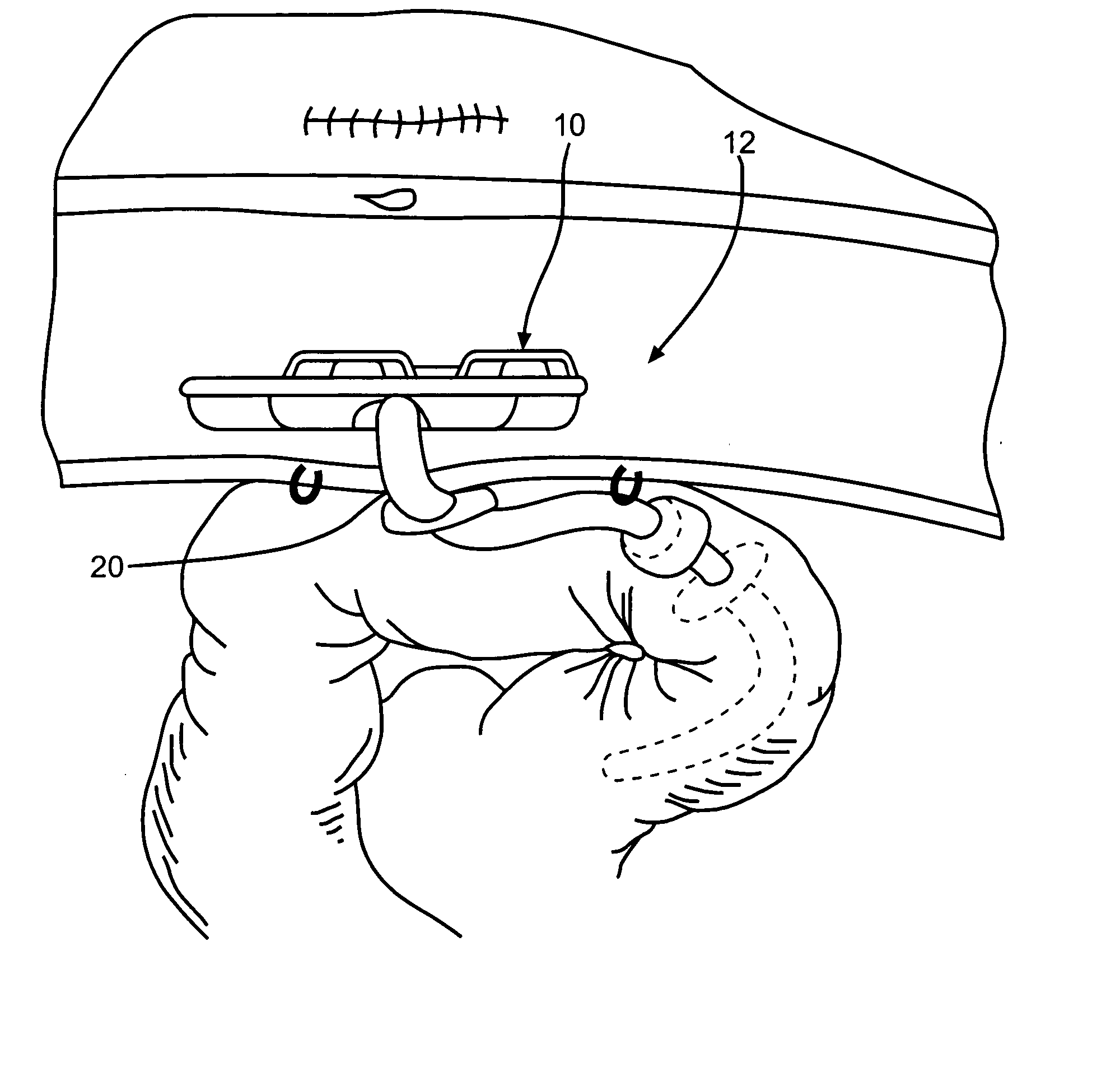
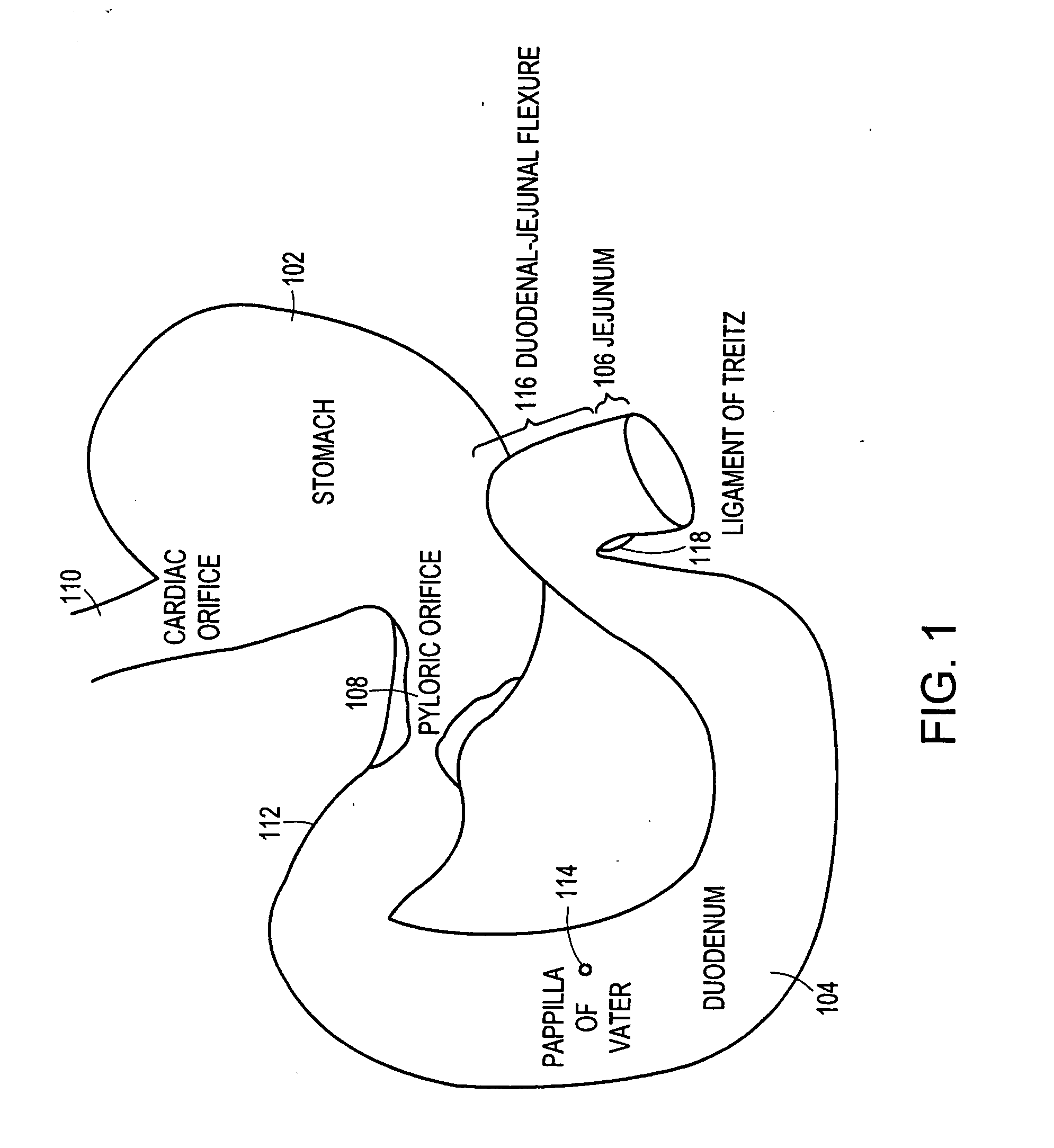
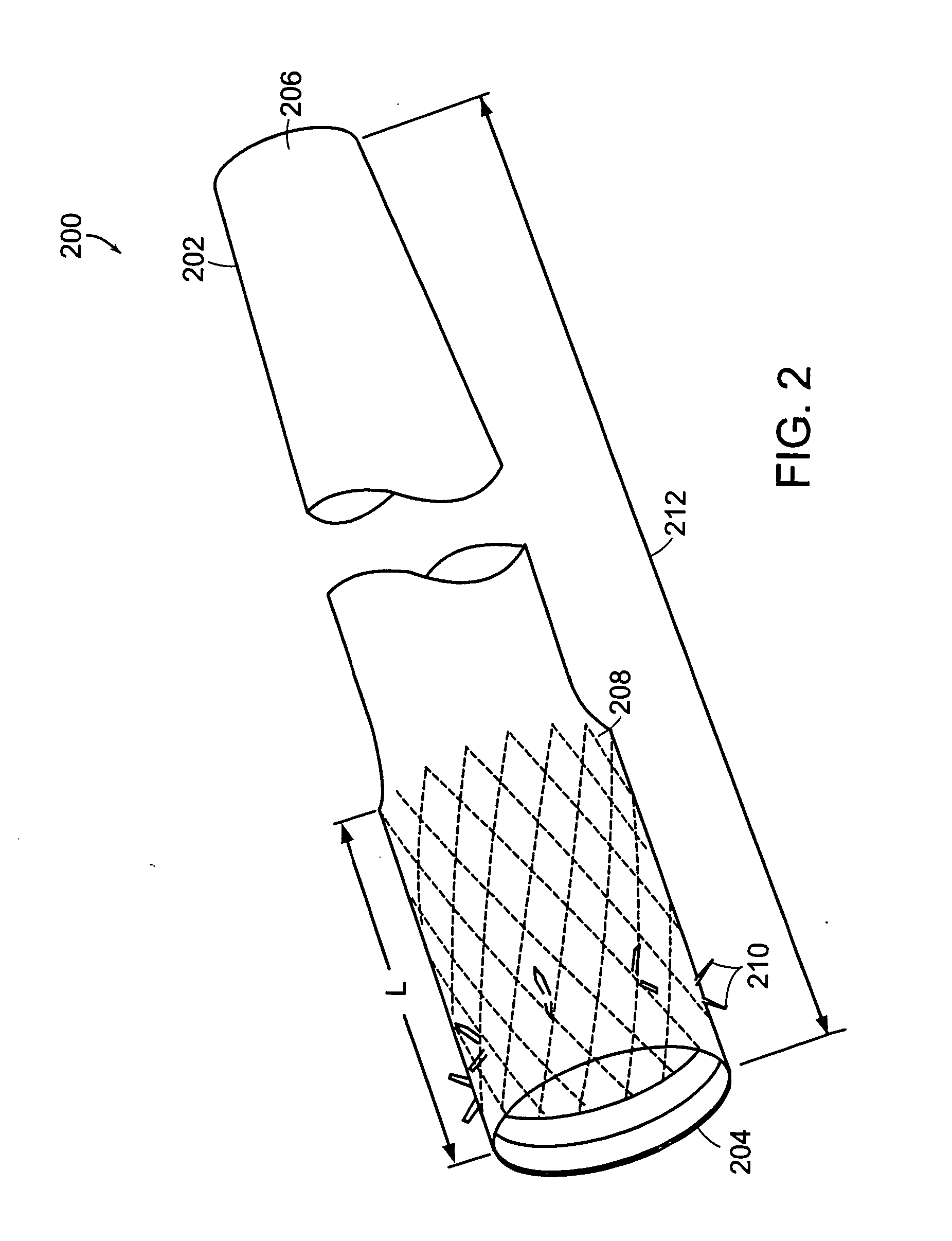
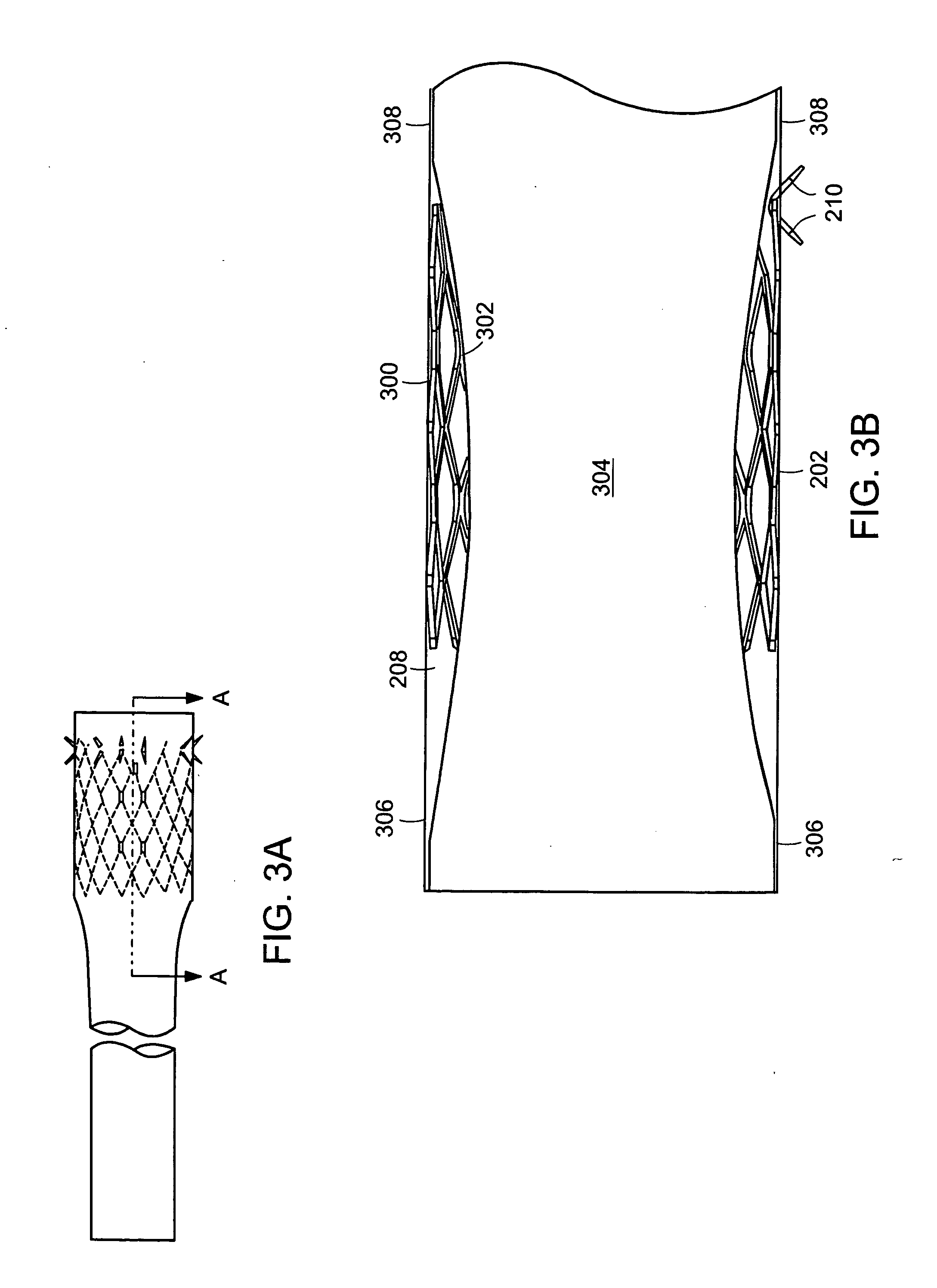
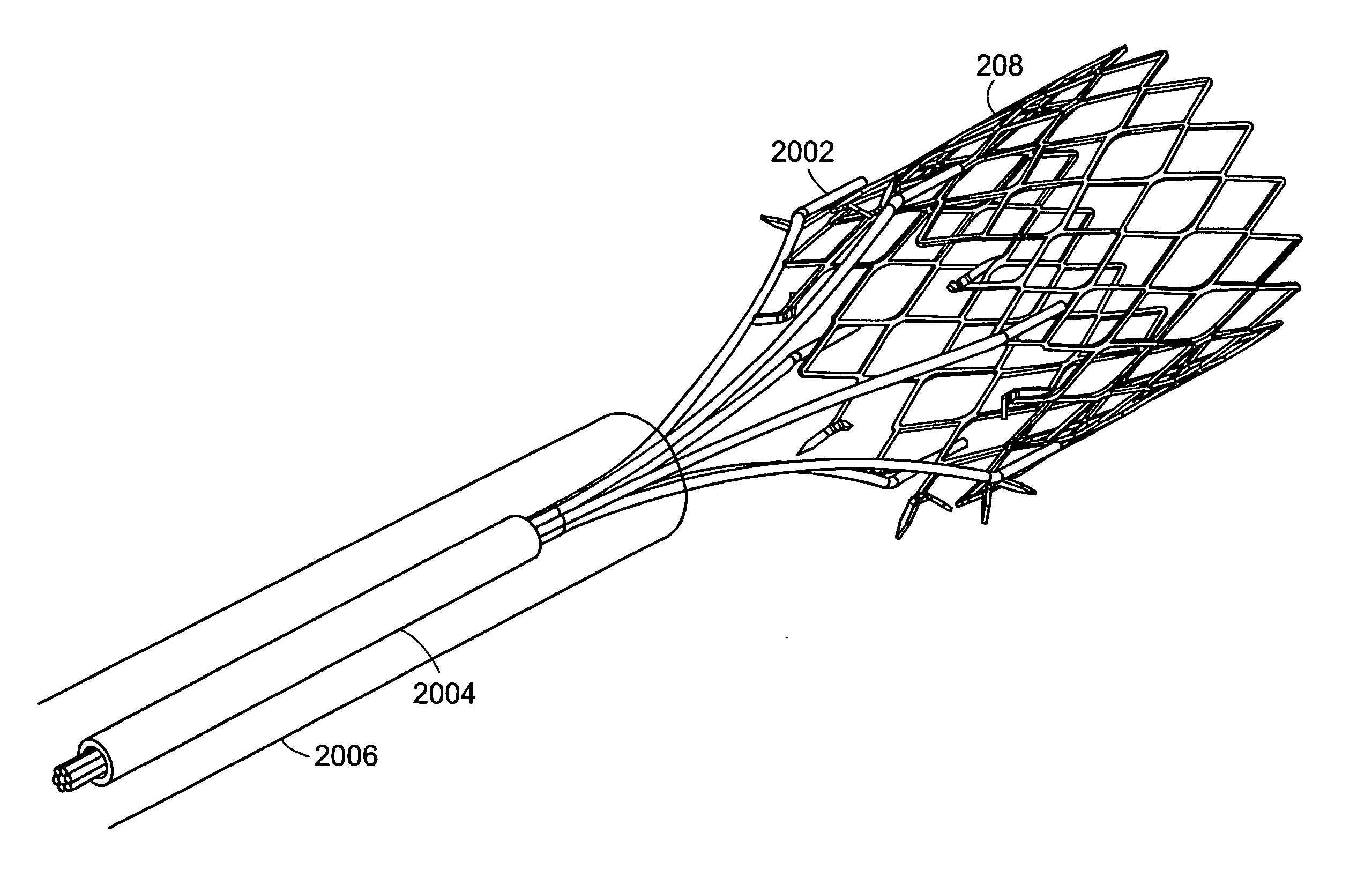
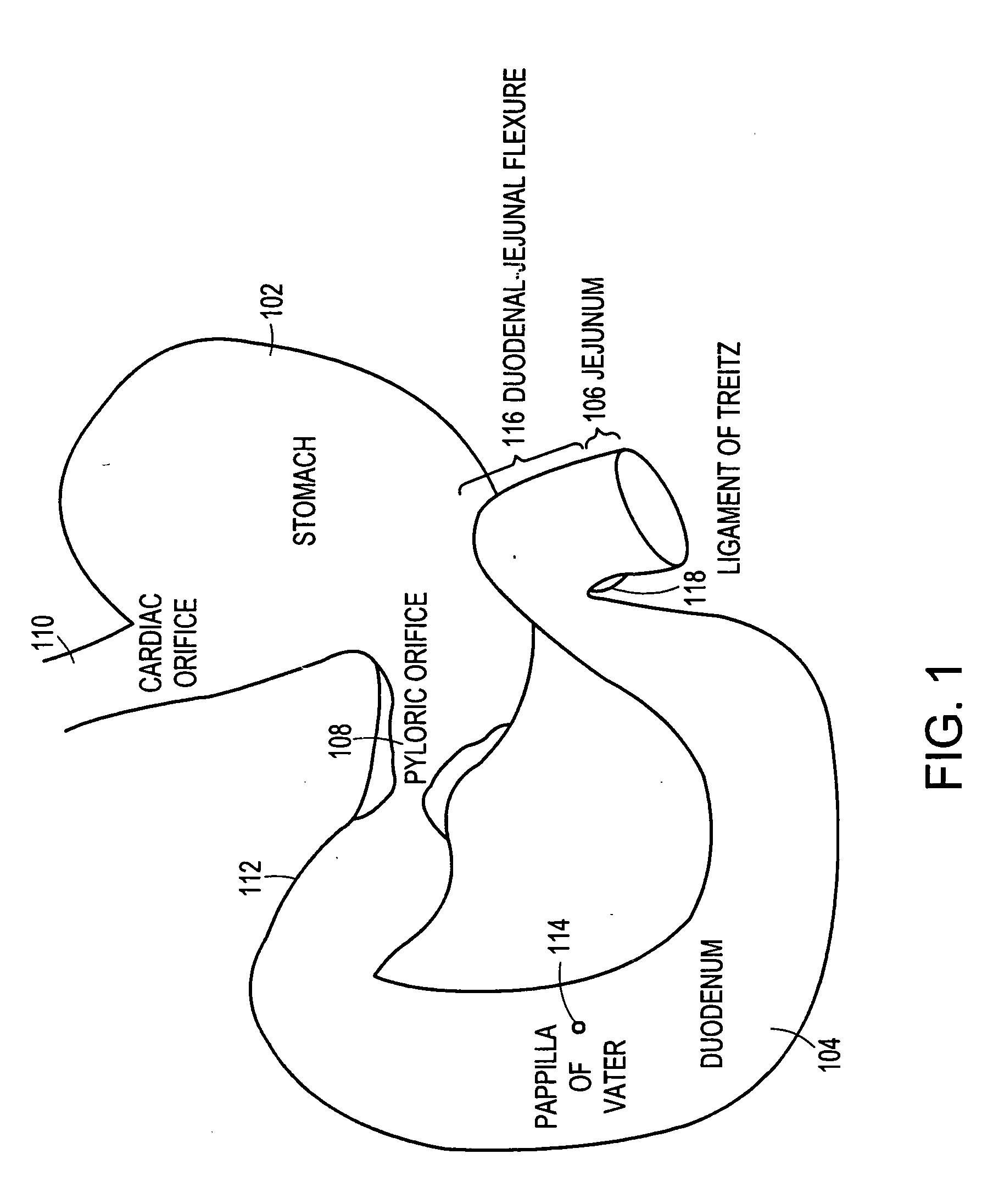
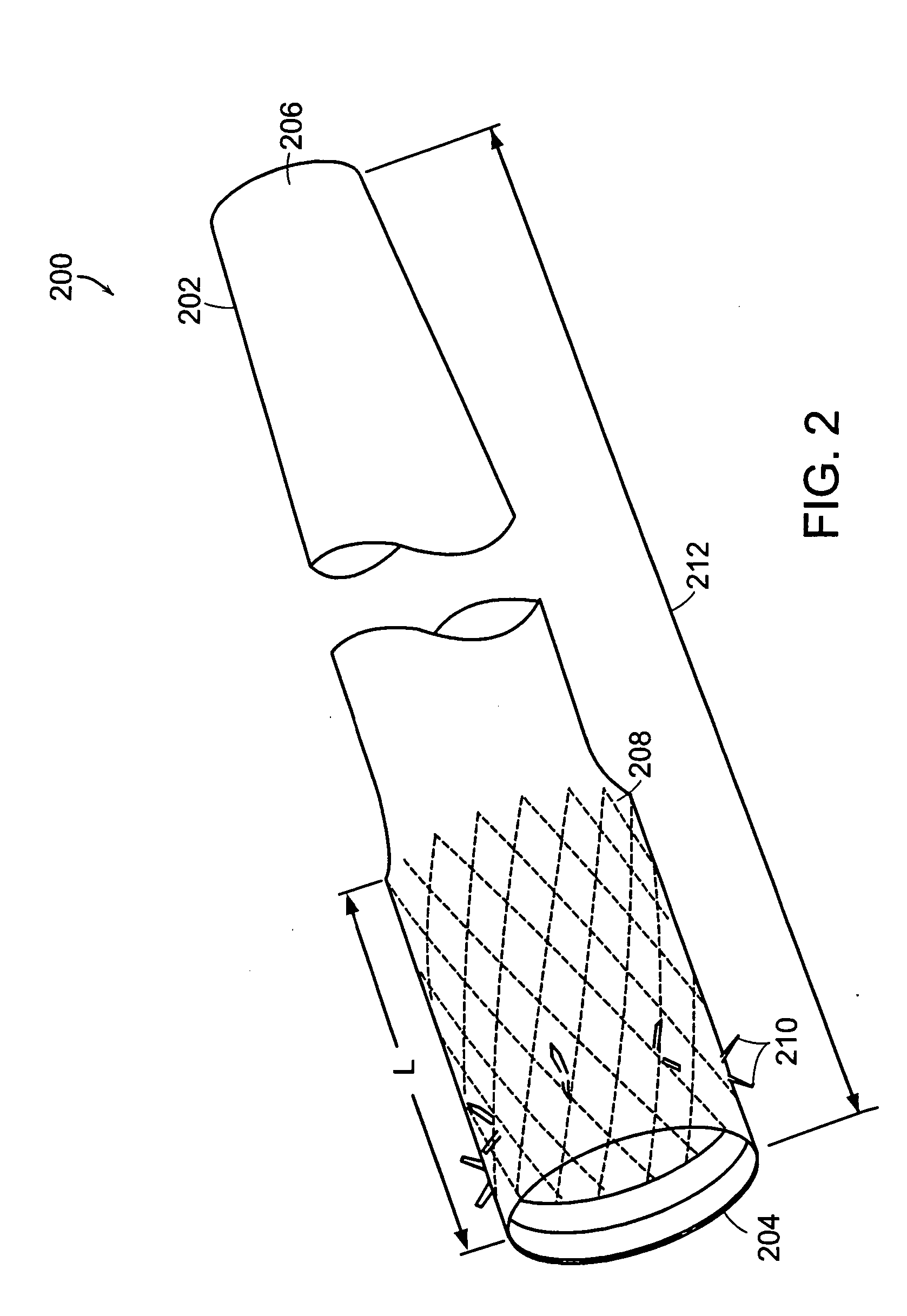
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve. When implanted within the intestine, the sleeve can limit the absorption of nutrients, delay the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes, altering hormonal triggers, providing negative feedback, and combinations thereof. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
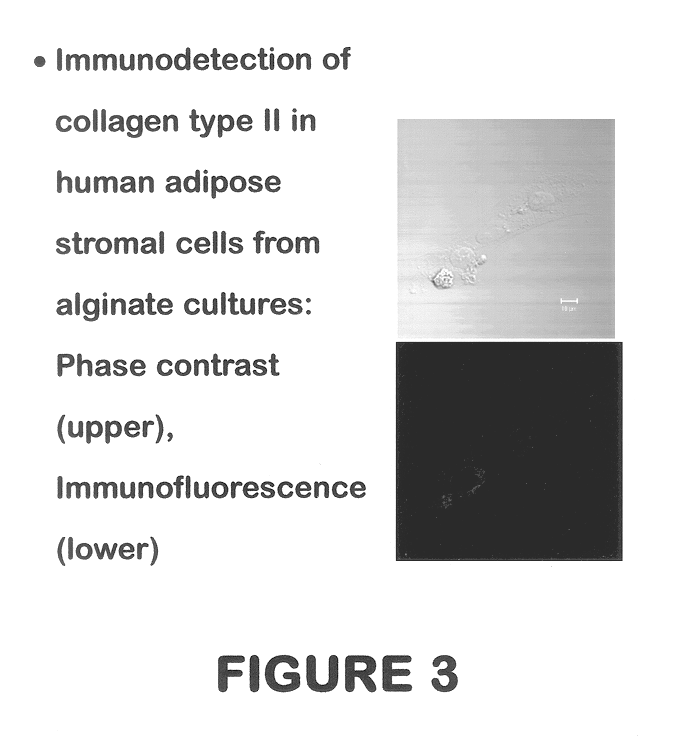
Use of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells for chondrocyte differentiation and cartilage repair
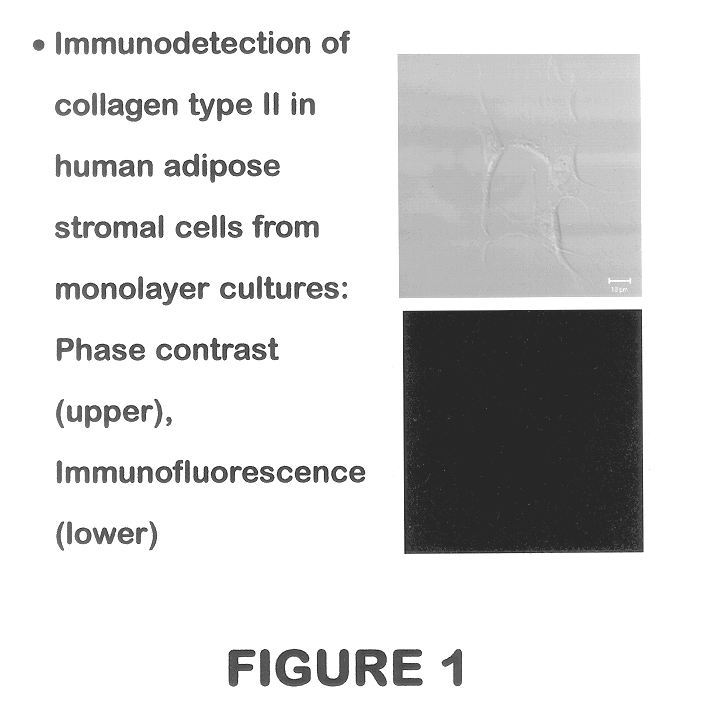
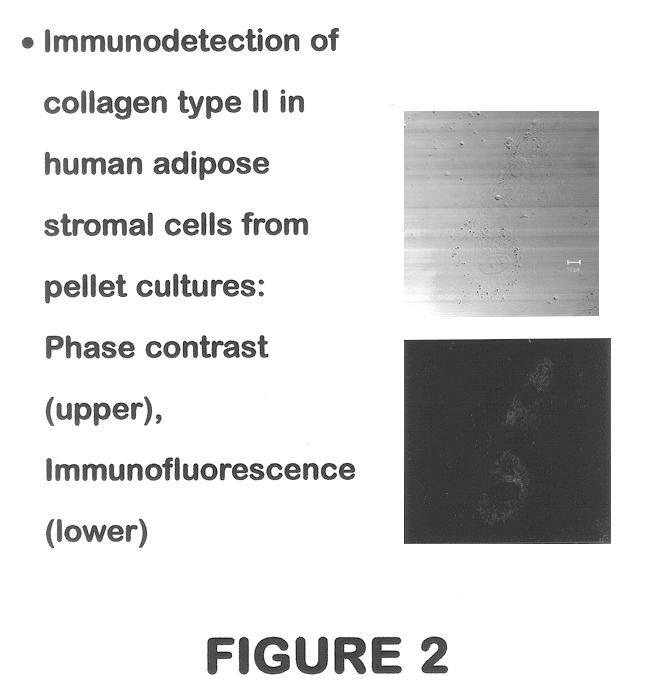
Methods and compositions for directing adipose-derived stromal cells cultivated in vitro to differentiate into cells of the chondrocyte lineage are disclosed. The invention further provides a variety of chondroinductive agents which can be used singly or in combination with other nutrient components to induce chondrogenesis in adipose-derived stromal cells either in cultivating monolayers or in a biocompatible lattice or matrix in a three-dimensional configuration. Use of the differentiated chondrocytes for the therapeutic treatment of a number of human conditions and diseases including repair of cartilage in vivo is disclosed.
Owner:COGNATE BIOSERVICES
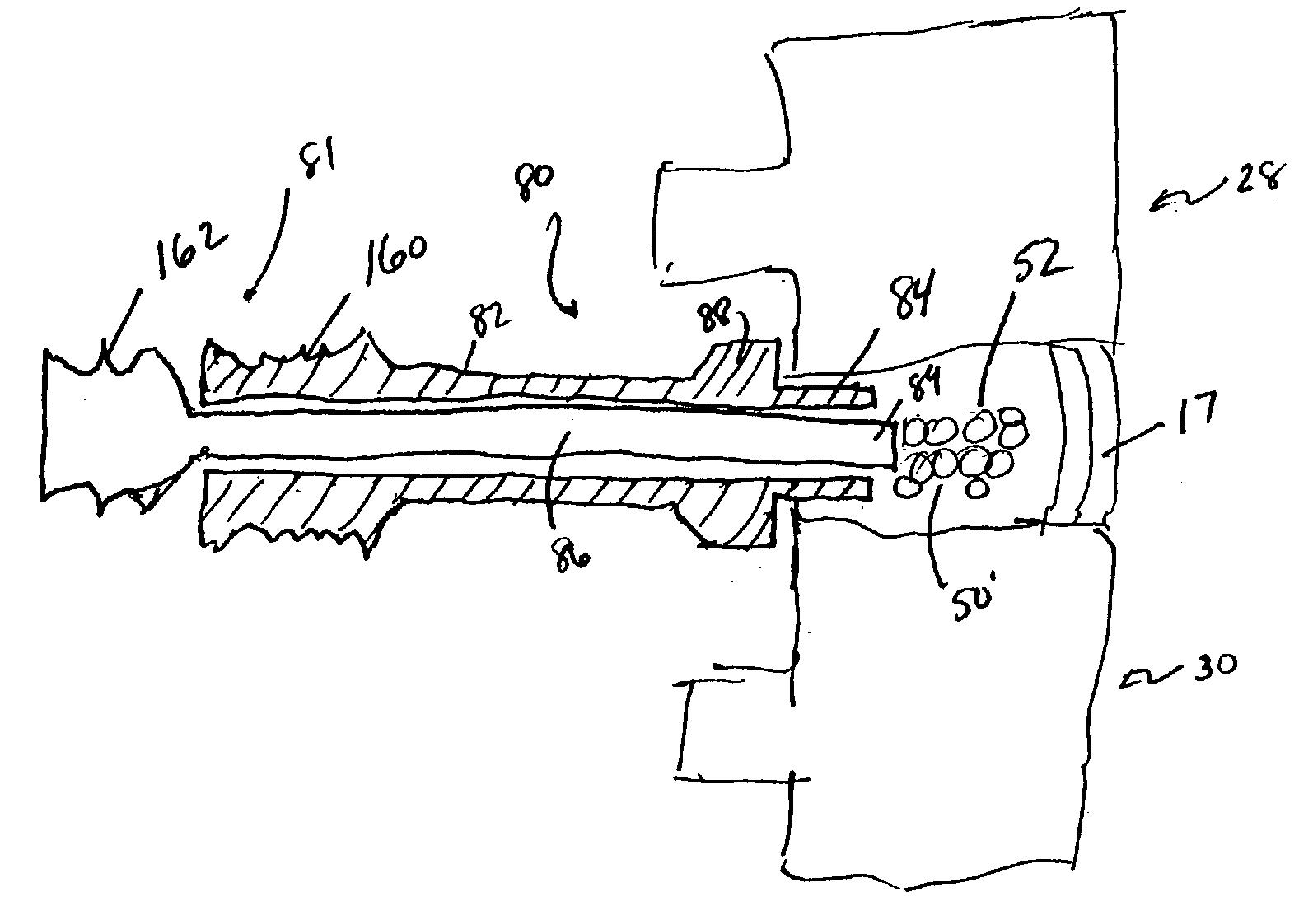
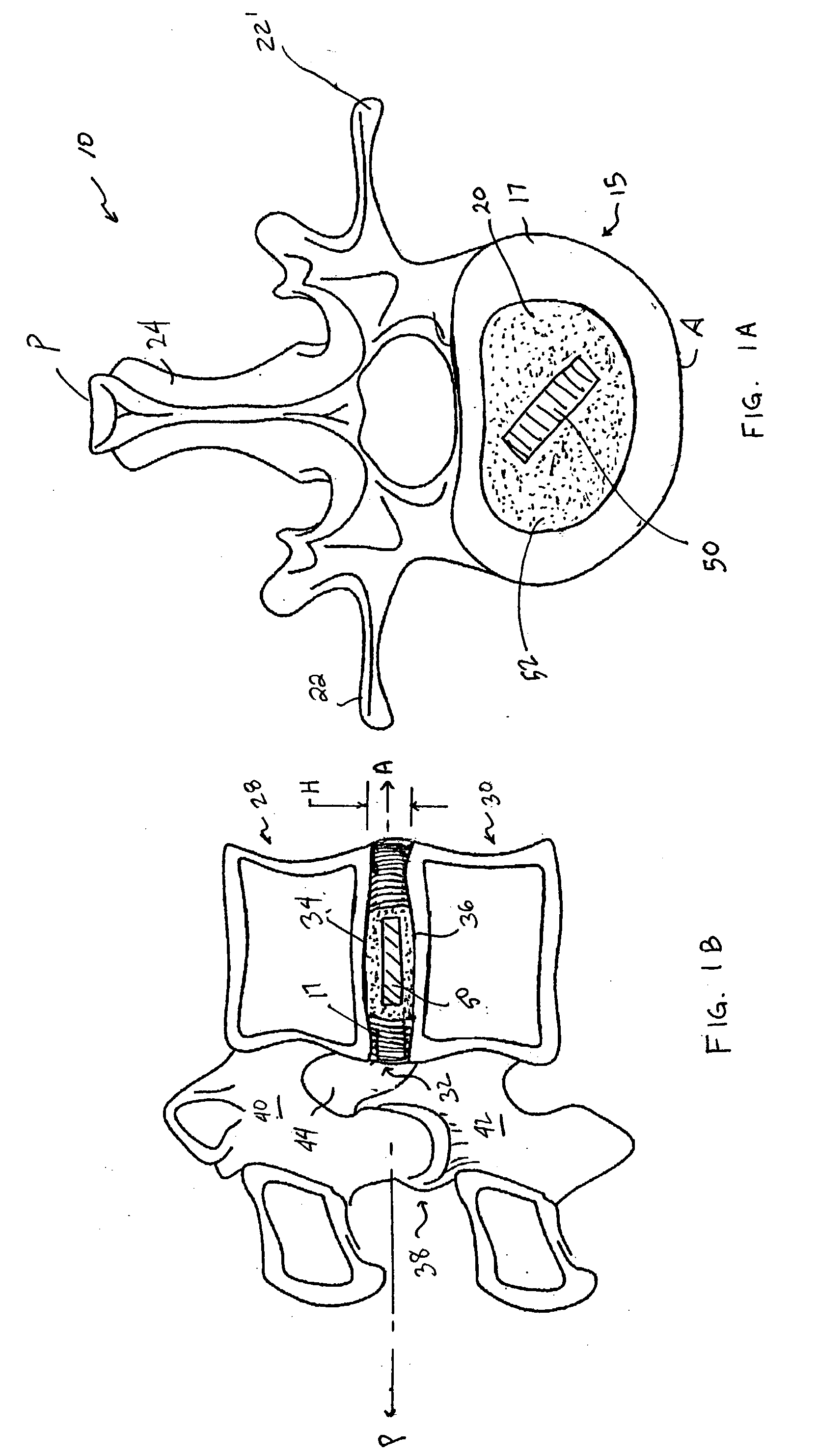
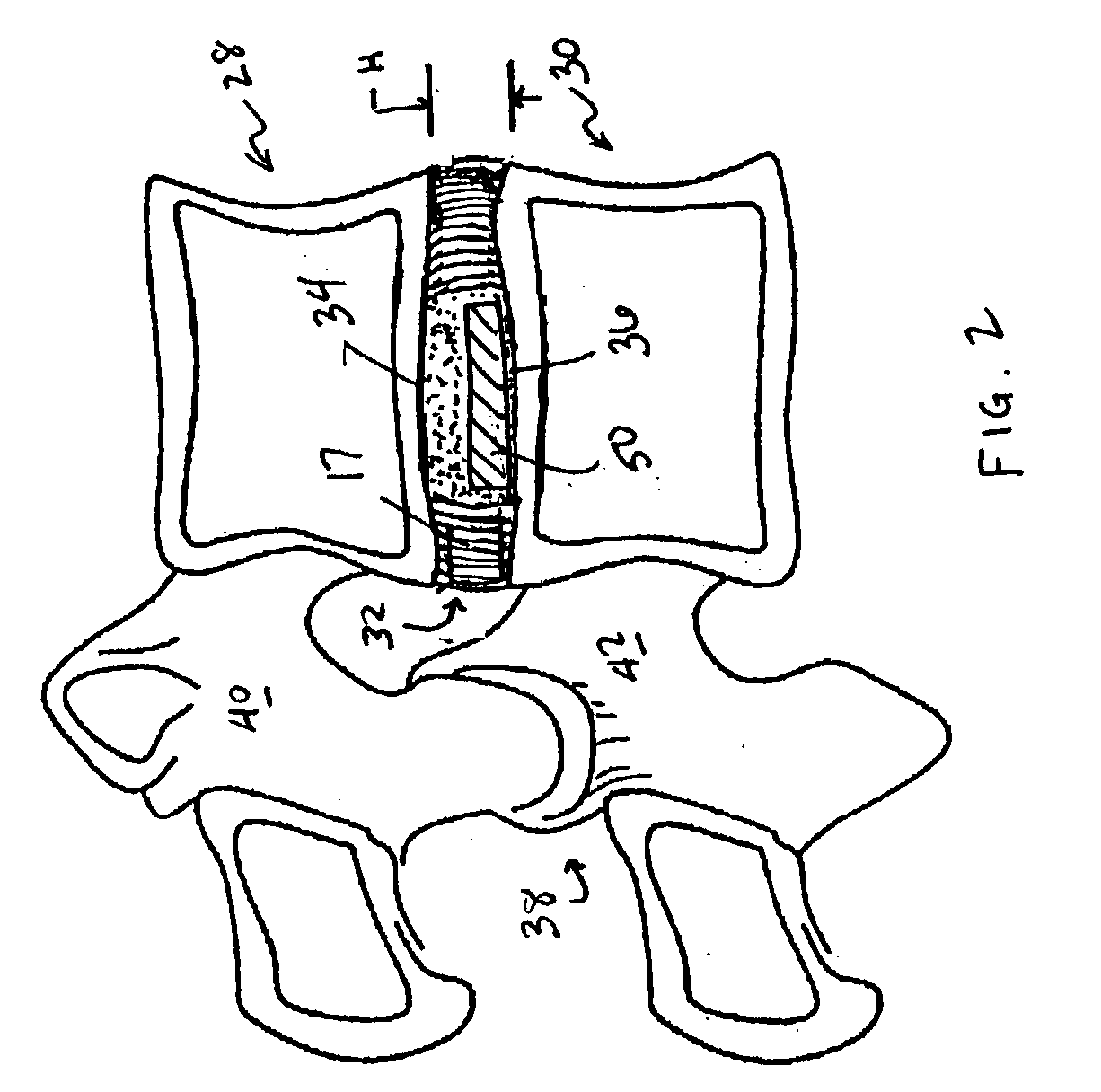
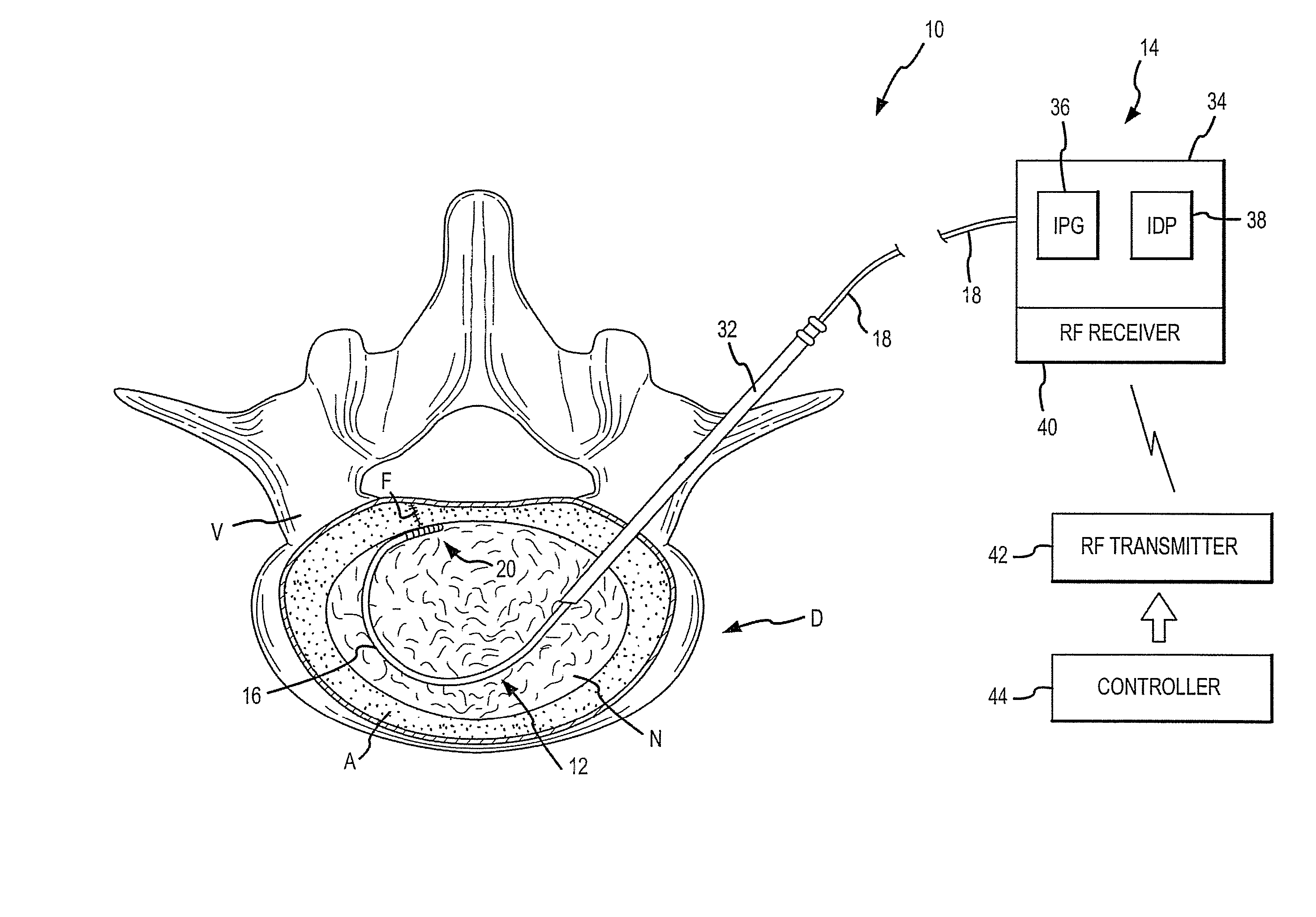
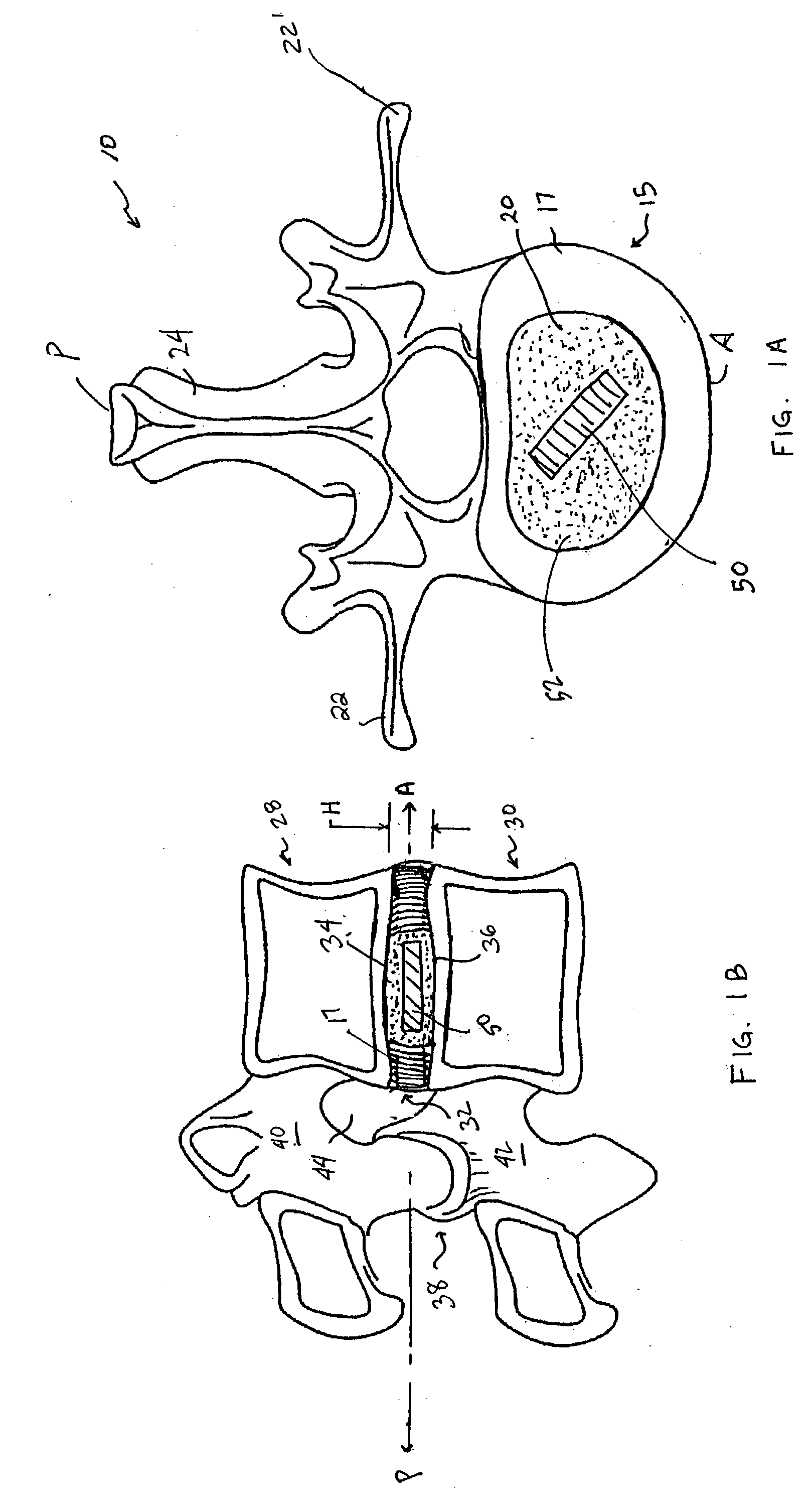
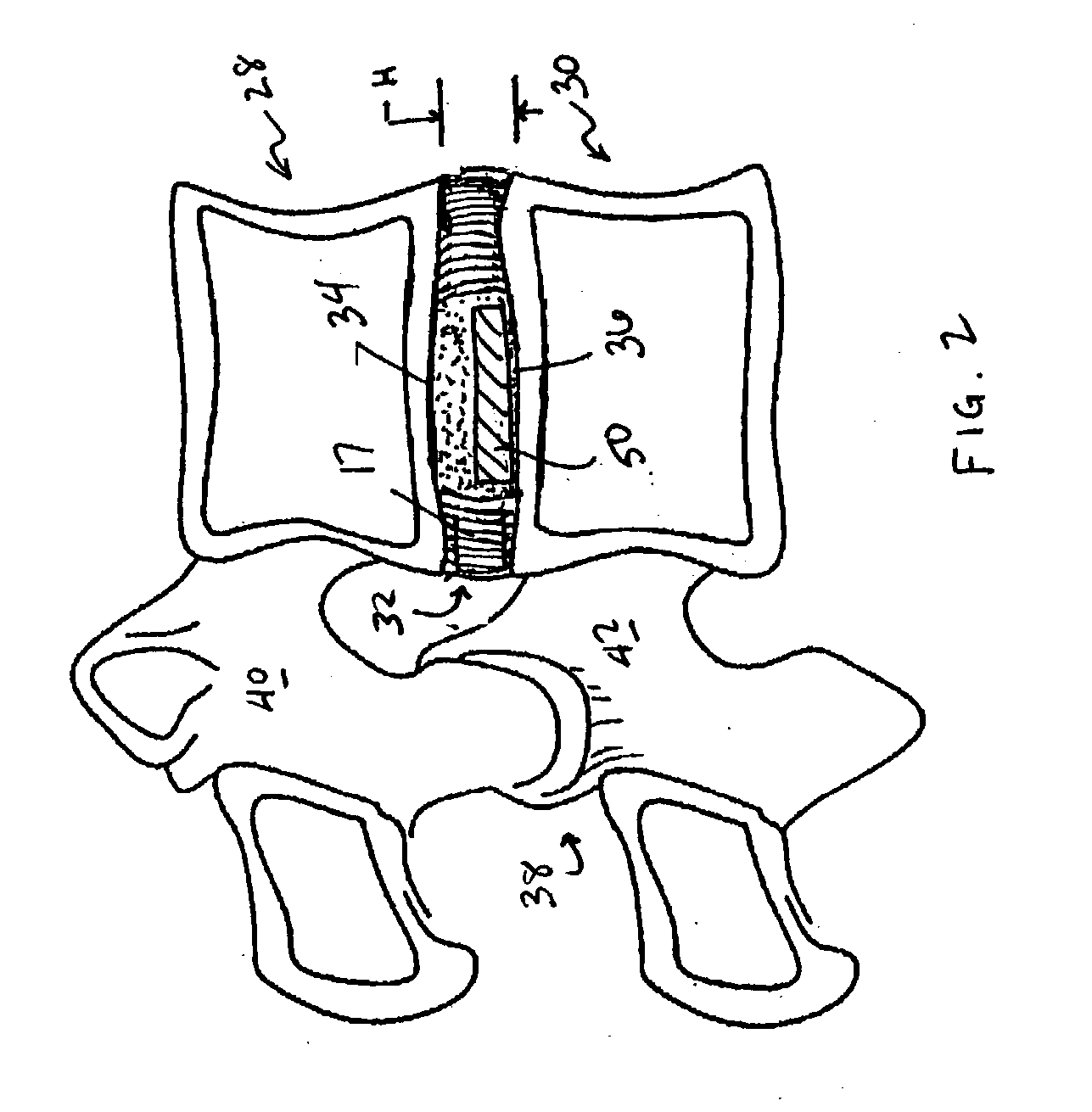
Devices and method for augmenting a vertebral disc
A vertebral disc prosthesis, a method of implanting a prosthesis and a deployment device is provided. The prosthesis may be implanted into the interior region of the vertebral disc so as to displace existing vertebral tissue, such as NP. The size or amount of the prosthesis inserted into the interior region of the vertebral disc may be a characteristic of the disc or the prosthesis. For example, the amount or size of prosthesis inserted into the disc may be dependent upon restoring the functionality of the disc (e.g., the ability of the disc to transfer nutrients or otherwise survive, the ability of the disc to carry the required loads and absorb stress or the reduction of pain). Restoring disc function may be determined by the resulting disc height desired, the resulting disc pressure desired or the resulting disc volume desired. The prosthesis may be sized or positioned within the interior of the vertebral disc such that it is spaced from at least one of the end plates of the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may be formed of a material having a compression strength that is less than 4 mn / m<2>. A deployment device may be used to facilitate placement of the prosthesis within the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may include a grouping of multiple components that can be deployed as group.
Owner:LAMBRECHT GREGORY +3
Anti-obesity devices
InactiveUS20050085923A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Solid solution perforator for drug delivery and other applications
InactiveUS6945952B2Fast biodegradationBarrier property can be diminished and controlledSurgeryMicroneedlesDrug reservoirDrugs solution
A solid drug solution perforator (SSP) system and an associated drug reservoir are provided for delivering therapeutic, prophylactic and / or cosmetic compounds, for nutrient delivery and for drug targeting. For drug delivery, the SSP system includes an active drug ingredient and a matrix of perforator material that biodegrades or dissolves quickly upon contact with a patient's body. The SSP system provides a skin barrier perforator and a controller for prompt initiation and cut-off drug delivery. In a preferred method of transdermal drug delivery, an SSP system containing a selected drug penetrates into an epidermis or dermis, and the drug is promptly released from the (dissolving) SSP system perforator. An additional drug is optionally delivered from a patch reservoir through skin pores created by insertion of the perforator. Formulation and fabrication procedures for the SSP and associated reservoir are also provided. An SSP system can be fabricated with variety of shapes and dimensions.
Owner:THERAJECT INC.
Minimally invasive gastrointestinal bypass
A solution is provided for modifying the location at which bodily fluids interact with nutrients in a gastrointestinal tract having a conduit with a first end and a second end. The first end is configured to divert bodily fluids from an entrance within a gastrointestinal tract to a location downstream from the entrance. The solution also provides for a means for attaching the second end to the entrance.
Owner:LAUFER MICHAEL D
Anti-obesity devices
InactiveUS7122058B2Limit absorptionModify their heating habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceImplanted device
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Intestinal sleeve
ActiveUS20050125075A1Controlled absorptionChange habitsSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceInsertion stent
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the duodenum and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for attaching the device to the duodenum and an unsupported flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor can include a stent and / or a wave anchor and is collapsible for catheter-based delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
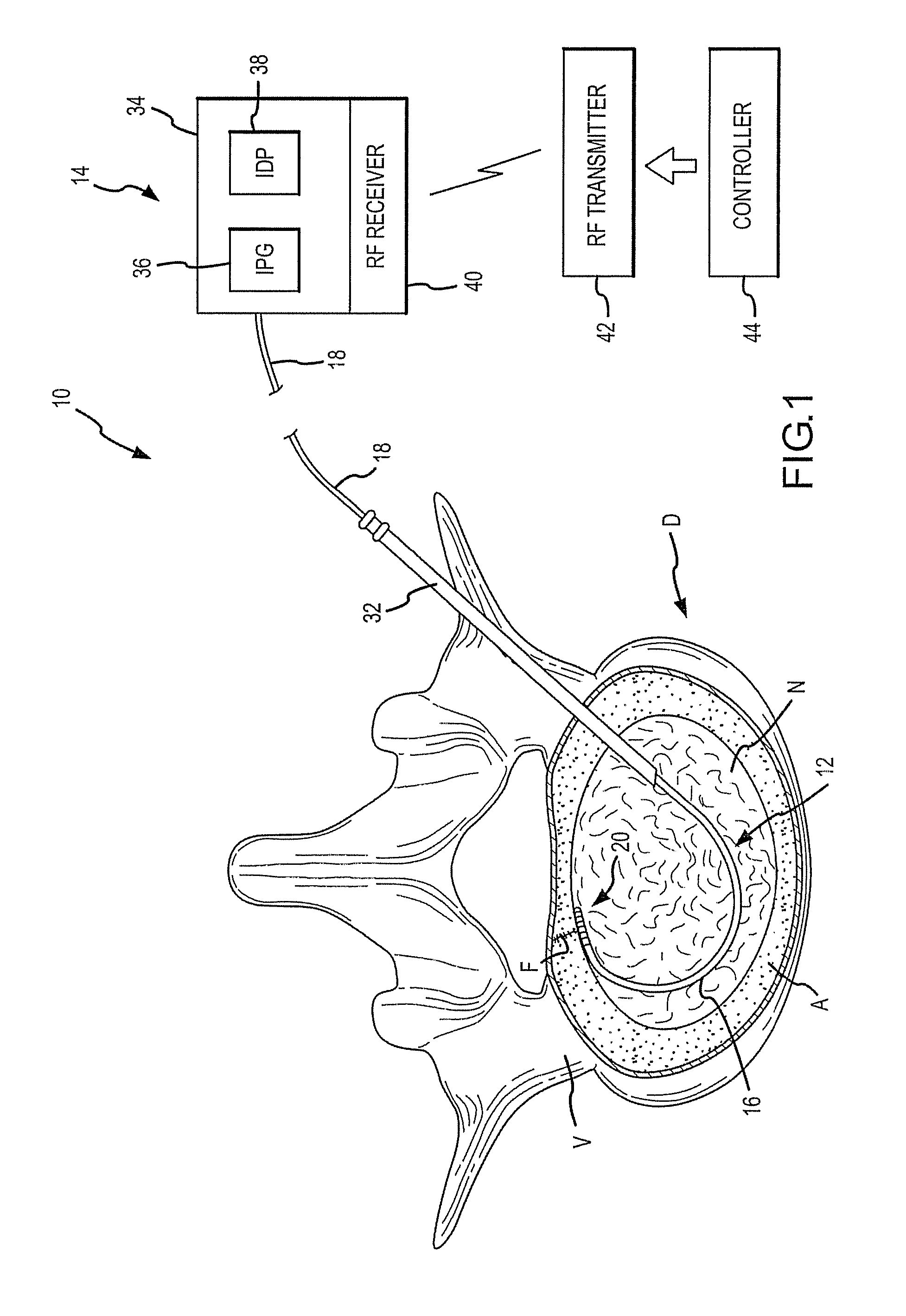
Combination Electrical Stimulating and Infusion Medical Device and Method
InactiveUS20080009927A1Prevent inadvertent bucklingAvoid displacementSpinal electrodesSurgical needlesElectricityChemical stimuli
A combined electrical and chemical stimulation lead is especially adapted for providing treatment to the spine and nervous system. The stimulation lead includes electrodes that may be selectively positioned along various portions of the stimulation lead in order to precisely direct electrical energy to ablate or electrically stimulate the target tissue. Embodiments of the stimulation lead include single or multiple lead elements. The multiple lead element embodiments can be selectively deployed to cover a targeted area. The lead may also includes central infusion passageway(s) or lumen(s) that communicates with various infusion ports spaced at selected locations along the lead to thereby direct the infusion of nutrients / chemicals to the target tissue. Some embodiments utilize a disposable sheath in combination with a reusable stimulation lead.
Owner:VILIMS BRADLEY D
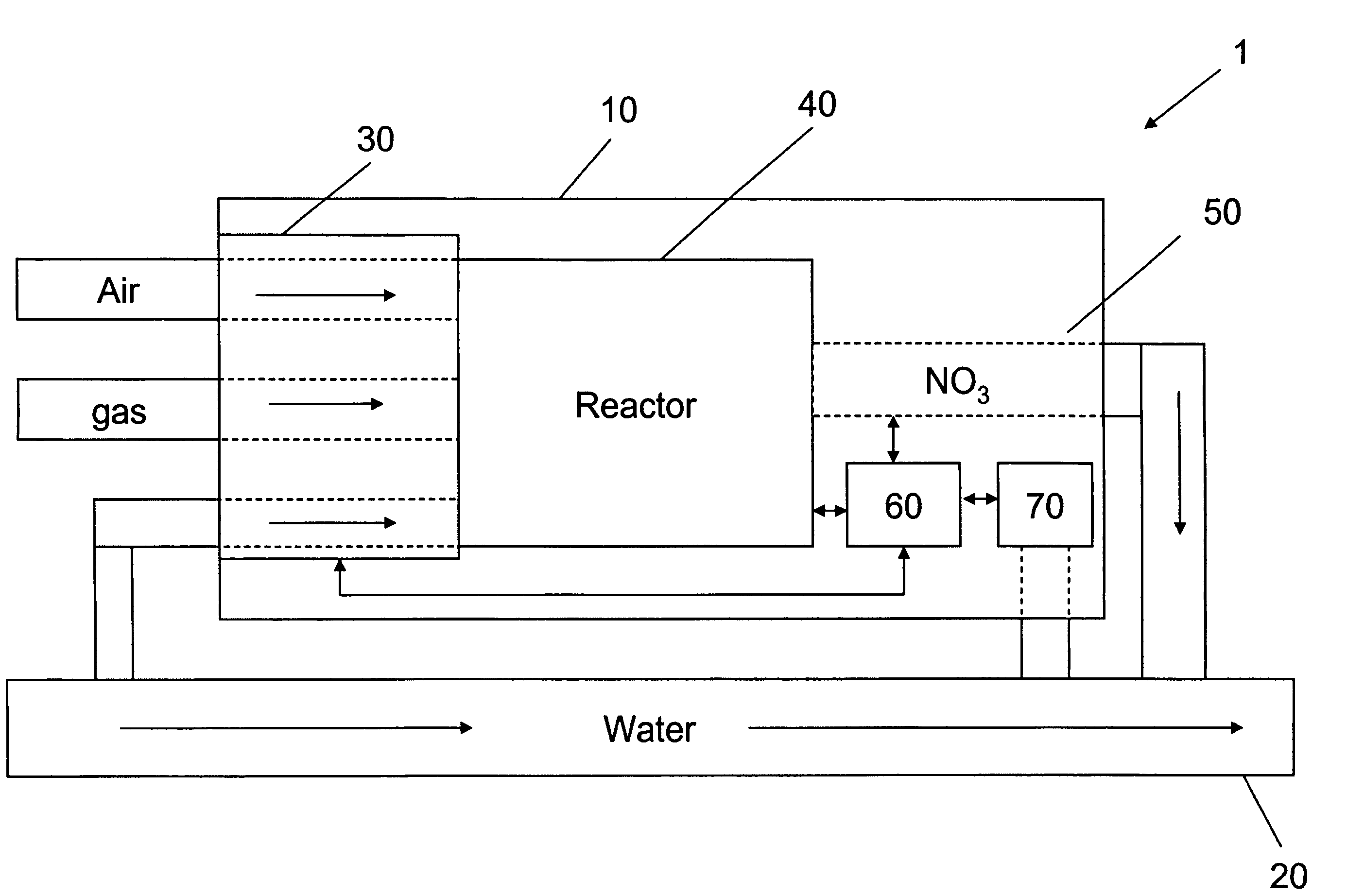
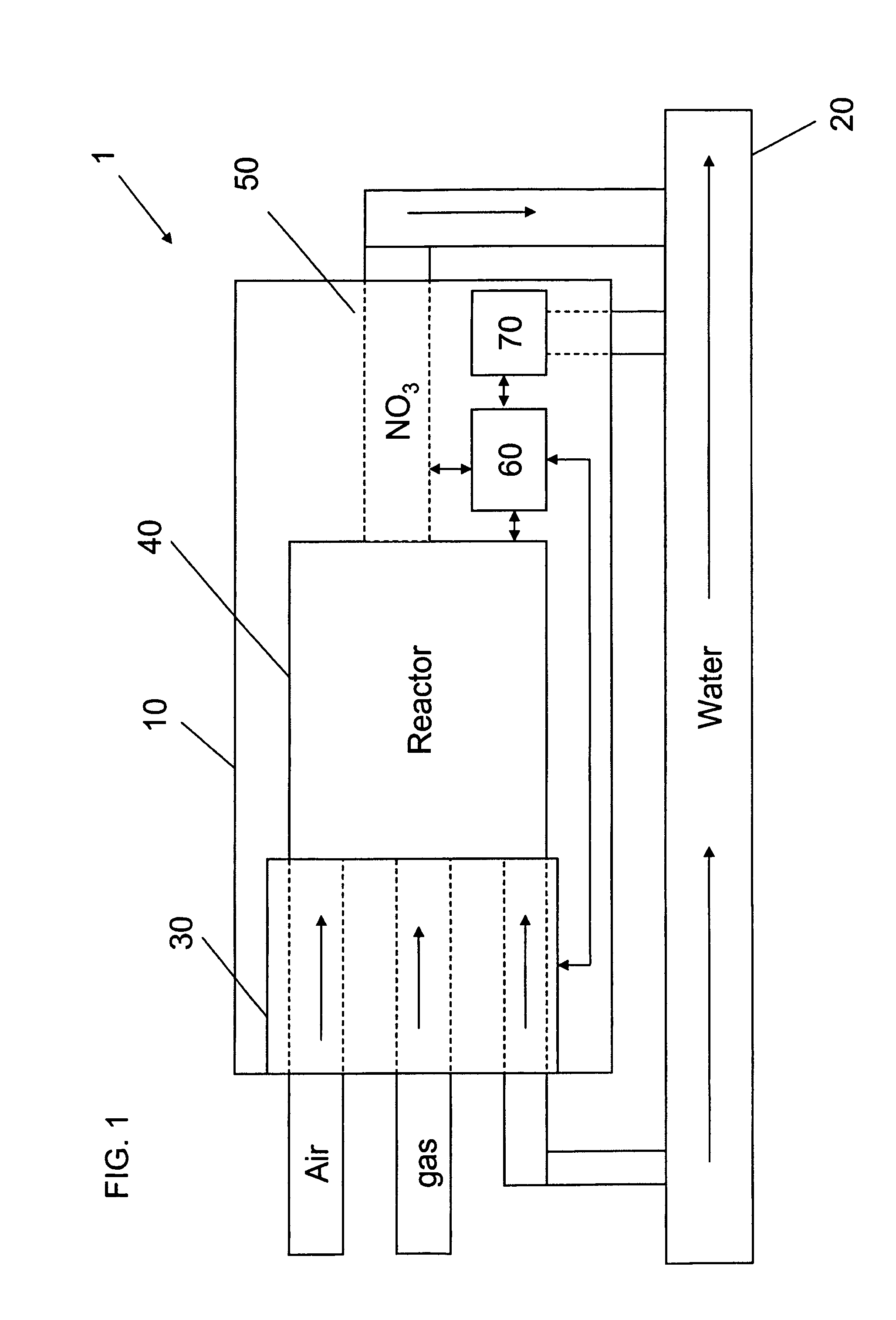
Apparatus for on-site production of nitrate ions
InactiveUS7514058B1Enhanced overall recoveryWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsMicrobial enhanced oil recoverySulfate-reducing bacteria
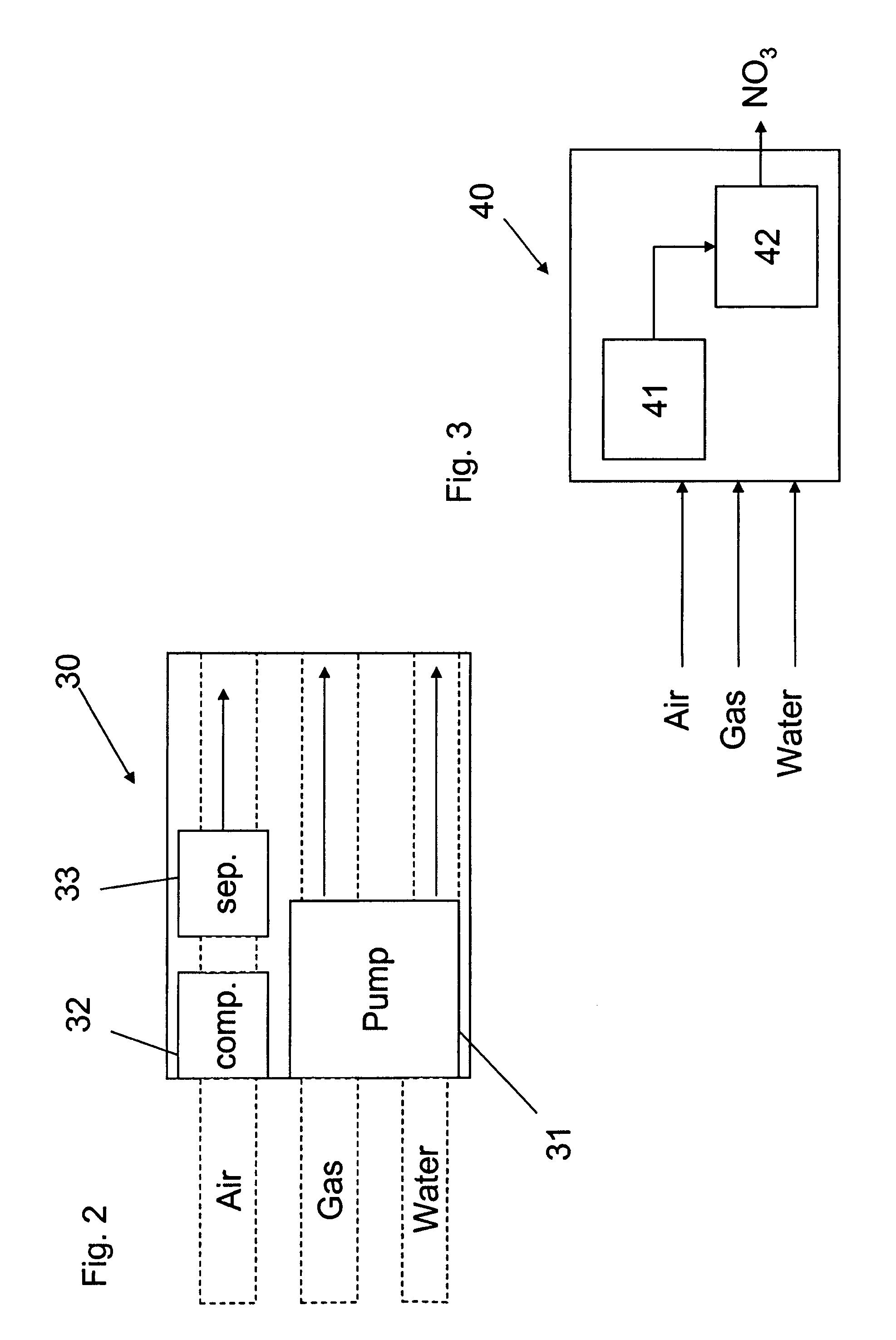
An apparatus and method produces nitrate ions on-site from water, natural gas and air extracted in proximity to the apparatus. The apparatus generates nitrate ions and brings the nitrate ions into contact with an aqueous system. Hydrogen sulfide present in the aqueous system is removed and the production of hydrogen sulfide by sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) is eliminated by introducing into the system nitrate ions, whereby denitrifying microorganisms, using nitrate, outcompete the sulfate-reducing bacteria for the available carbon nutrients, thus preventing the SRB from producing hydrogen sulfide. Nitrate ions generated by the apparatus and added to the aqueous system which contains the denitrifying microorganisms can enhance oil recovery by means of microbial enhanced oil recovery mechanisms.
Owner:NITRA GEN LLC
Method and apparatus for the treatment of obesity
InactiveUS20050038415A1Improve effectivenessImprove solubilityMetabolism disorderDigestive systemDrug compoundGastrointestinal transit
The present invention includes methods and materials for manipulating the sense of satiety developed from the gastrointestinal transit of a substance in a mammal, whether the substance be a food or drug compound. The method involves administering a therapeutically effective amount, by a direct delivery route, of a pharmaceutically acceptable formulation comprising nutrients and pharmacological agents to the mammal's gastrointestinal tract. The present system is designed to maximize satiety feedback from normal intestinal sensors by small amounts of nutrients or nutrient derivatives, in essence, to “fool” body sensors that are not usually in contact with nutrients unless very large amounts are ingested.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Compositions used in human treatment
A composition for treatment of a human body comprises a combination of at least one hormone, at least one amino acid, at least one enzyme and / or vitamin, and least one mineral. The relative proportions of the hormone, amino acid, enzyme and mineral in the combination are balanced with respect to each other so as to be present in effective amounts to substantially restore to optimal levels in the body the hormone, amino acid, enzyme and mineral The hormone, amino acid, enzyme and mineral in the combination further operate synergistically to provide both nutrients and command components to enable the body to effectively utilize the nutrients. The invention is also a method of forming a composition for the treatment of a human body.
Owner:COCHRAN TIMOTHY M
Devices and method for augmenting a vertebral disc
A vertebral disc prosthesis, a method of implanting a prosthesis and a deployment device is provided. The prosthesis may be implanted into the interior region of the vertebral disc so as to displace existing vertebral tissue, such as NP. The size or amount of the prosthesis inserted into the interior region of the vertebral disc may be a characteristic of the disc or the prosthesis. For example, the amount or size of prosthesis inserted into the disc may be dependent upon restoring the functionality of the disc (e.g., the ability of the disc to transfer nutrients or otherwise survive, the ability of the disc to carry the required loads and absorb stress or the reduction of pain). Restoring disc function may be determined by the resulting disc height desired, the resulting disc pressure desired or the resulting disc volume desired. The prosthesis may be sized or positioned within the interior of the vertebral disc such that it is spaced from at least one of the end plates of the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may be formed of a material having a compression strength that is less than 4 mn / m<2>. A deployment device may be used to facilitate placement of the prosthesis within the vertebral disc. The prosthesis may include a grouping of multiple components that can be deployed as group.
Owner:LAMBRECHT GREGORY +3
Parenteral delivery systems
Hypertonic sugar compositions administered by other than ingestion and swallowing or intravascular injection, such as by intranasal spray or drops, intraocular drops or ointment, oral spray, intraotic spray or drops, lozenges, chewable tablet, chewing gum, or gargle, pulmonary inhalation, vaginal or rectal suppositories, or transdermal creams, ointments, lotions, or patches, are effective to open the blood-brain barrier to permit entry into the central nervous system of a co-administered chemical compound, such as a nutrient or a therapeutic or diagnostic agent. In this way, the compositions and methods of the invention increase the therapeutic or diagnostic efficacy of such chemical compounds.
Owner:NAITO ALBERT T
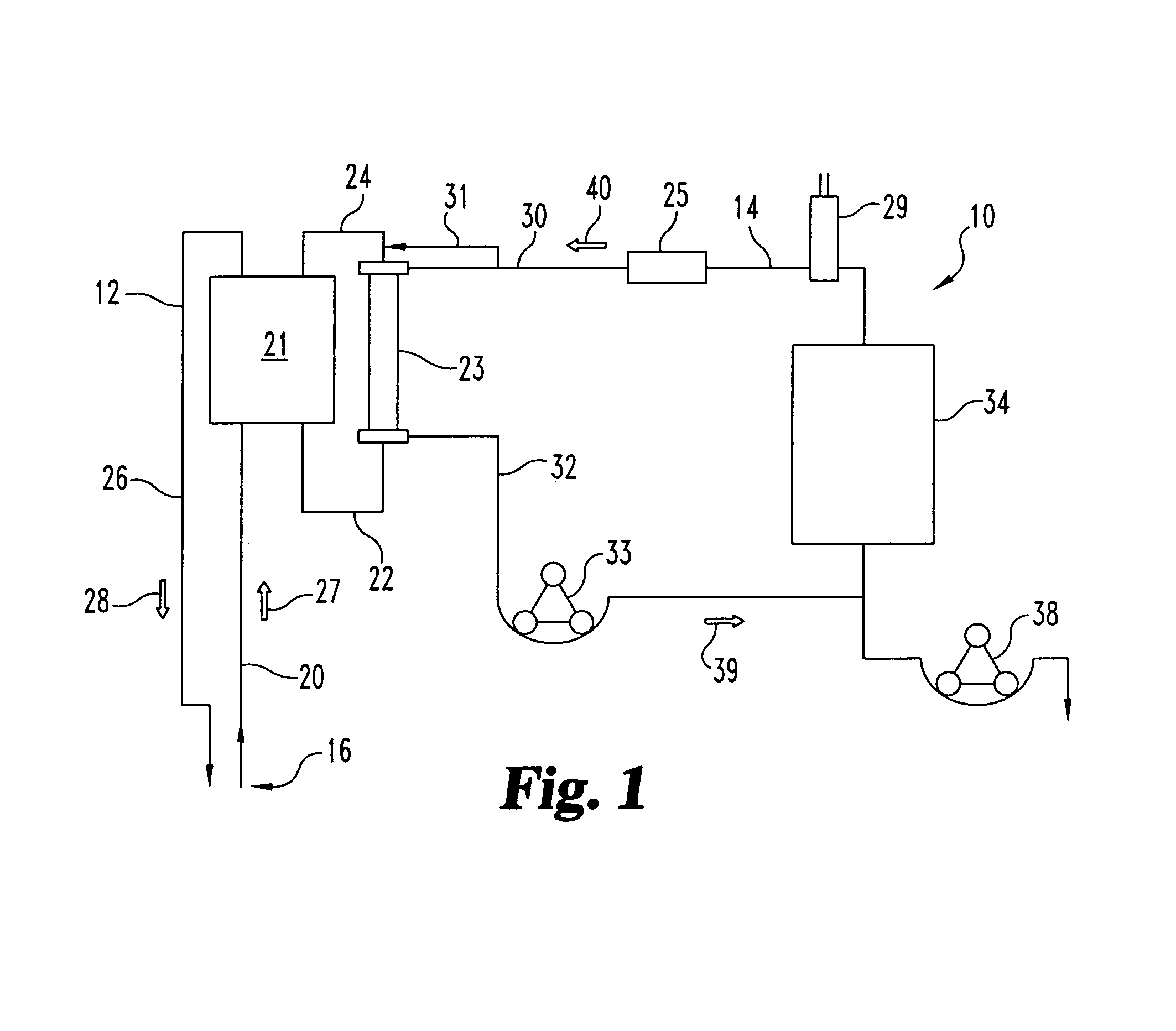
Sorbent reactor for extracorporeal blood treatment systems, peritoneal dialysis systems, and other body fluid treatment systems
InactiveUS7169303B2Facilitate homogeneous suspensionReduce probabilitySolvent extractionHaemofiltrationFluid balancePeritoneal dialysis
Systems and methods for extracorporeal processing of blood or other body fluid for the treatment of conditions, such as sepsis, autoimmune disease, or toxemia related to kidney failure, liver failure, or drug overdose are provided. In an extracorporeal treatment system, a fraction of a body fluid is passed into a treatment fluid, at least a portion of which is then passed through a sorbent suspension reactor for treatment by a sorbent suspension. The treatment fluid circuit can be maintained at a fixed volume, which enables accurate fluid balance between the patient and the extracorporeal circuit. Some or all of the treatment fluid, optionally also containing nutrients and / or therapeutic agents, is returned to the patient. In a peritoneal dialysis system, dialysate is passed into a patient's peritoneal cavity, recovered from the cavity, passed through a sorbent suspension reactor in accordance with the invention, and returned to the cavity.
Owner:HEMOCLEANSE TECH
Analysis of metabolic activity in cells using extracellular flux rate measurements
InactiveUS20070087401A1To promote metabolismEliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGeneration rateOxygen
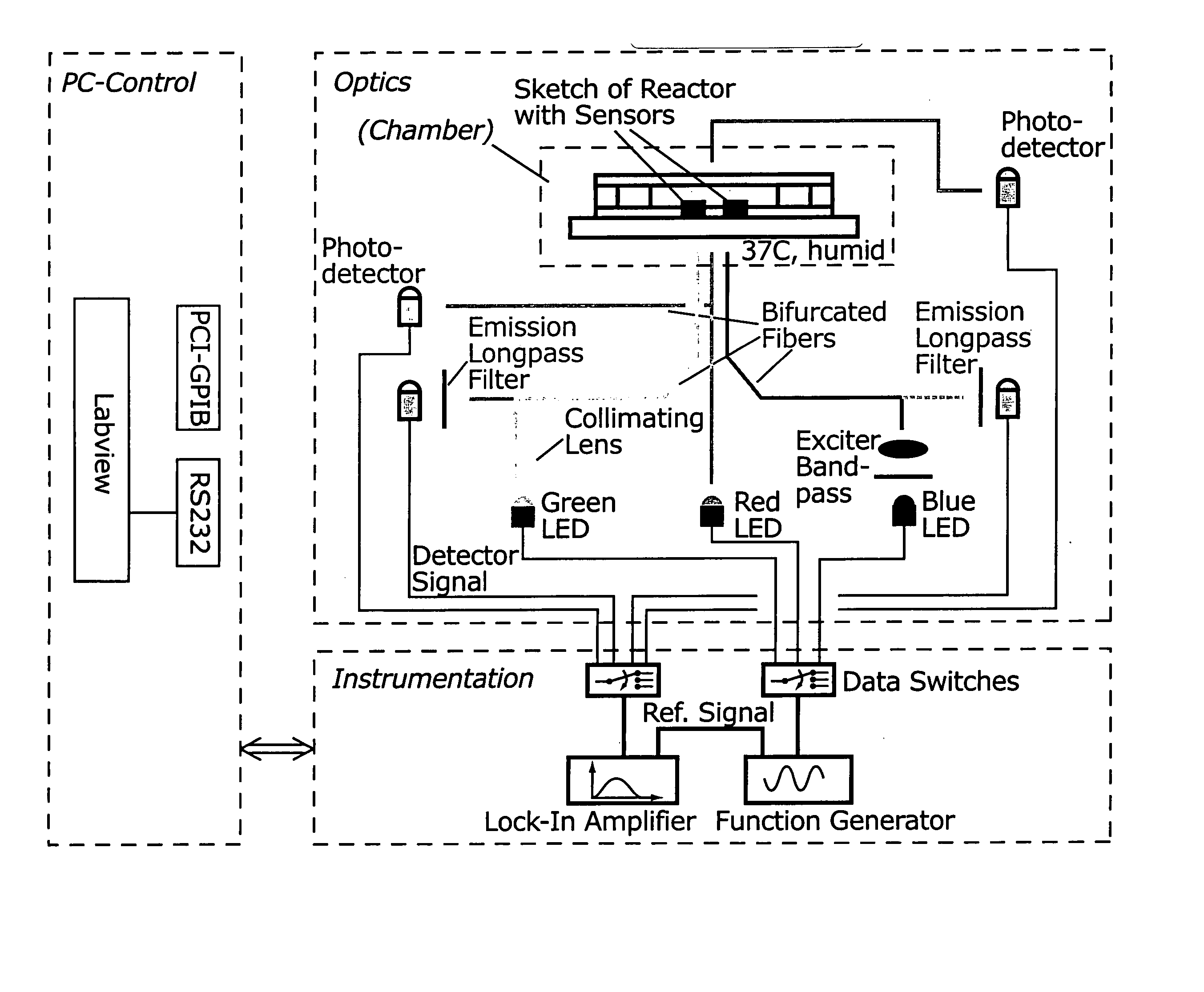
Disclosed are methods for non-destructively measuring in vitro the effect on cellular metabolism of the addition to animal cells in culture of a soluble molecule potentially capable of perturbing the biological state of the cells, such as a drug or drug candidate, a toxin, a ligand known or suspected to bind to a cell surface receptor, a nutrient, a cytokine, a growth factor, a chemokine, a metabolism inhibitor or stimulator. Also disclosed are methods for measuring cell viability, vitality, or quality, e.g., in anticipation of the execution of an experiment on the cells. The measurements are done by observing alteration in the rates of consumption or production of extracellular solutes related to aerobic and anaerobic cellular metabolism, such as oxygen, protons, nutrients, carbon dioxide, lactate, or lactic acid. The methods are particularly useful in drug discovery efforts, such as cancer drug discovery and searches for modulators of cellular metabolism.
Owner:SEAHORSEBIOSCIENCE INC
Bariatric sleeve
InactiveUS20050075622A1Reduce twistDelayed bucklingSuture equipmentsStentsGastrointestinal deviceLigament structure
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Bariatric sleeve removal devices
Method and apparatus for limiting absorption of food products in specific parts of the digestive system is presented. A gastrointestinal implant device is anchored in the stomach and extends beyond the ligament of Treitz. All food exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. The gastrointestinal device includes an anchor for anchoring the device to the stomach and a flexible sleeve to limit absorption of nutrients in the duodenum. The anchor is collapsible for endoscopic delivery and removal.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS
Non-destructive tissue repair and regeneration
ActiveUS20070185568A1Facilitate healing and regenerationEasy to fixStentsAdditive manufacturing apparatusNon destructiveTissue repair
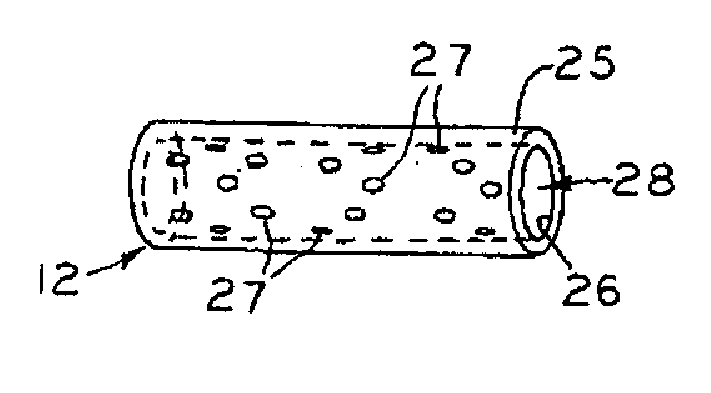
A surgical stent made of biocompatible material for implantation in human tissue to enable blood and nutrients to flow from an area of vascular tissue to an area of tissue with little or no vasculature.
Owner:HOWMEDICA OSTEONICS CORP
Autogenic living scaffolds and living tissue matrices: methods and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050226856A1Preventing host rejectionThicker and strongBiocideSkin implantsTransdifferentiationOrganism
A 3-dimensional structure comprising suitable cells (or entities) and the ECM (or matrix) that has been completely produced and arranged by these cells (or entities) that promotes the differentiation, dedifferentiation and / or transdifferentiation of cells and / or formation of tissue in vitro and in vivo, while at the same time promoting cell growth, proliferation, migration, acquisition of in vivo-like morphology, or combinations thereof, and that 1. provides structural and / or nutritional support to cells, tissue, organs, or combinations thereof, termed an “Autogenic Living Scaffold” (ALS); or 2. is capable of being transformed into a more complex tissue (or matrix) or a completely different type of tissue (or matrix), termed a “Living Tissue Matrix” (LTM). Autogenic means it is self-produced. The living cells that produce the LTM or ALS, or are added to Autogenic Living Scaffolds, may be genetically engineered or otherwise modified. The matrix component of the ALS or LTM provides a structural framework for cells that guide their direction of growth, enables them to be correctly spaced, prevents overcrowding, enables cells to communicate between each other, transmit subtle biological signals, receive signals from their environment, form bonds and contacts that are required for proper functioning of all cells within a unit such as a tissue, or combinations thereof. The ALS or LTM may thus provide proper or supporting mechanical and chemical environments, signals, or stimuli to other cells, to the cells that produce the ALS, to surrounding tissue at an implantation site, to a wound, for in vitro and ex vivo generation and regeneration of cells, tissue and organs, or combinations thereof. They may also provide other cells with nutrients, growth factors, and / or other necessary or useful components. They may also take in or serve as buffers for certain substances in the environment, and have also some potential at adapting to new environments.
Owner:GENESIS TECH LTD
Methods of treatment using a bariatric sleeve
ActiveUS7695446B2Promote healingControlled absorptionSuture equipmentsStentsDiseaseIntestinal structure
Methods of treatment using a gastrointestinal implant device removably anchored within an animal's gastrointestinal tract. For example, the implant device includes a collapsible anchor for anchoring the device coupled to a proximal end of a flexible sleeve. The implant device can be anchored within the stomach, within the pyloric orifice, and / or distal to the pylorus and extended into the duodenum. All partially-digested food, or chyme, exiting the stomach is funneled through the device. Methods of treatment include treating obesity by one or more of: limiting the absorption of nutrients within the duodenum; delaying the mixing of chyme with digestive enzymes; alter hormonal triggers; and providing negative feedback. Alternatively or in addition, the desired result includes treating a diseases, such as diabetes, or temporarily shielding a portion of the intestine to promote healing within the intestine.
Owner:GI DYNAMICS INC
Universal protein formulation meeting multiple dietary needs for optimal health and enhancing the human immune system
InactiveUS20060280840A1Weight controlGood for healthVitamin food ingredientsInorganic compound food ingredientsWeight gainingAdditive ingredient
The invention includes a protein rich, dry dietary supplement comprising a blend of legume protein, whey protein, egg white, calcium caseinate and powdered skim milk that is specifically formulated for weight control without the use of artificial appetite suppressants, but instead provides beneficial nutrients and supplements that naturally curb the appetite for specified periods of time. A preferred set of ingredients includes a protein blend combined with additional nutrients, vitamins, minerals and flavorings to enhance taste and further control the need for caloric intake. Various other preferred forms of the invention provide for implementation to allow for weight gain or weight maintenance of individuals desirous of the use of the beverage as a dietary supplement for those purposes.
Owner:ROBERTSON MARION G
Medical apparatus and method of making the same
InactiveUS20080255678A1Minimize complicationsLess invasiveEar treatmentSurgeryMedical deviceEndoscope
The invention relates to a medical apparatus including a device used in the treatment of weight loss, obesity and potentially other associated health problems, e.g., type II diabetes. The device is used to impede absorption of nutrients within the gastrointestinal tract, i.e., bypassing a portion of the gastrointestinal tract. The medical apparatus enables implantation of the device using minimally invasive techniques, such a transesophageal approach under visualization. The device may be implanted via a working channel of a medical scope, e.g., an endoscope or in combination with a medical scope.
Owner:WL GORE & ASSOC INC
Apparatus for processing materials in supercritical fluids and methods thereof
ActiveUS20060177362A1After-treatment apparatusUltra-high pressure processesHigh intensityPressure difference
An apparatus and method for processing materials in supercritical fluids is disclosed. The apparatus includes a capsule configured to contain a supercritical fluid, a high strength enclosure disposed about the capsule and a sensor configured to sense pressure difference between an interior and an exterior of the capsule. The apparatus also includes a pressure control device configured to adjust pressure difference of the capsule in response to the pressure difference sensed by the sensor. The apparatus further includes at least one dividing structure disposed within the capsule that divides the capsule into a seed growing chamber and a nutrient chamber.
Owner:SLT TECH
Apparatus and methods for simultaneous operation of miniaturized reactors
InactiveUS20050089993A1Big advantageBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNutrientSupporting cell
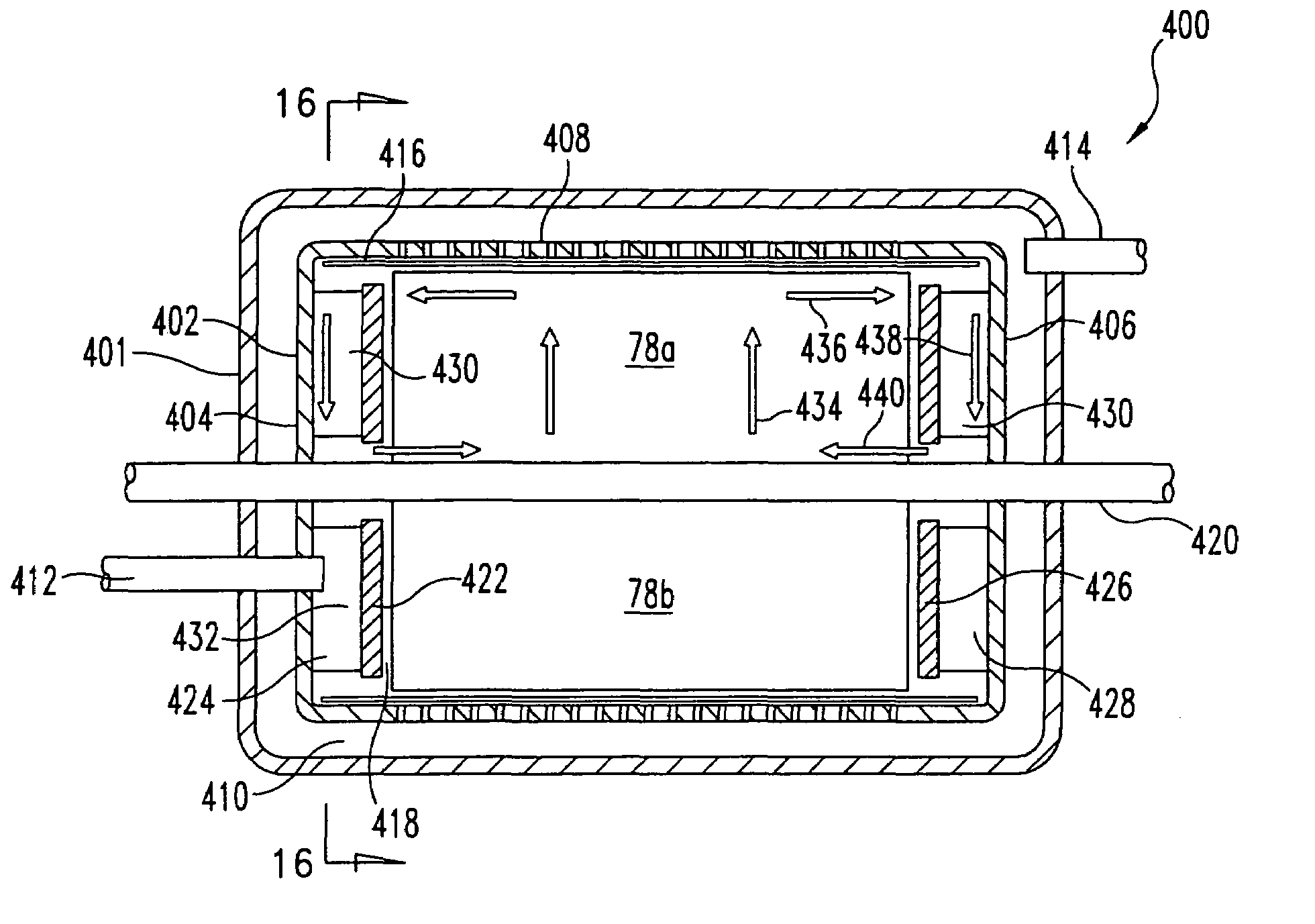
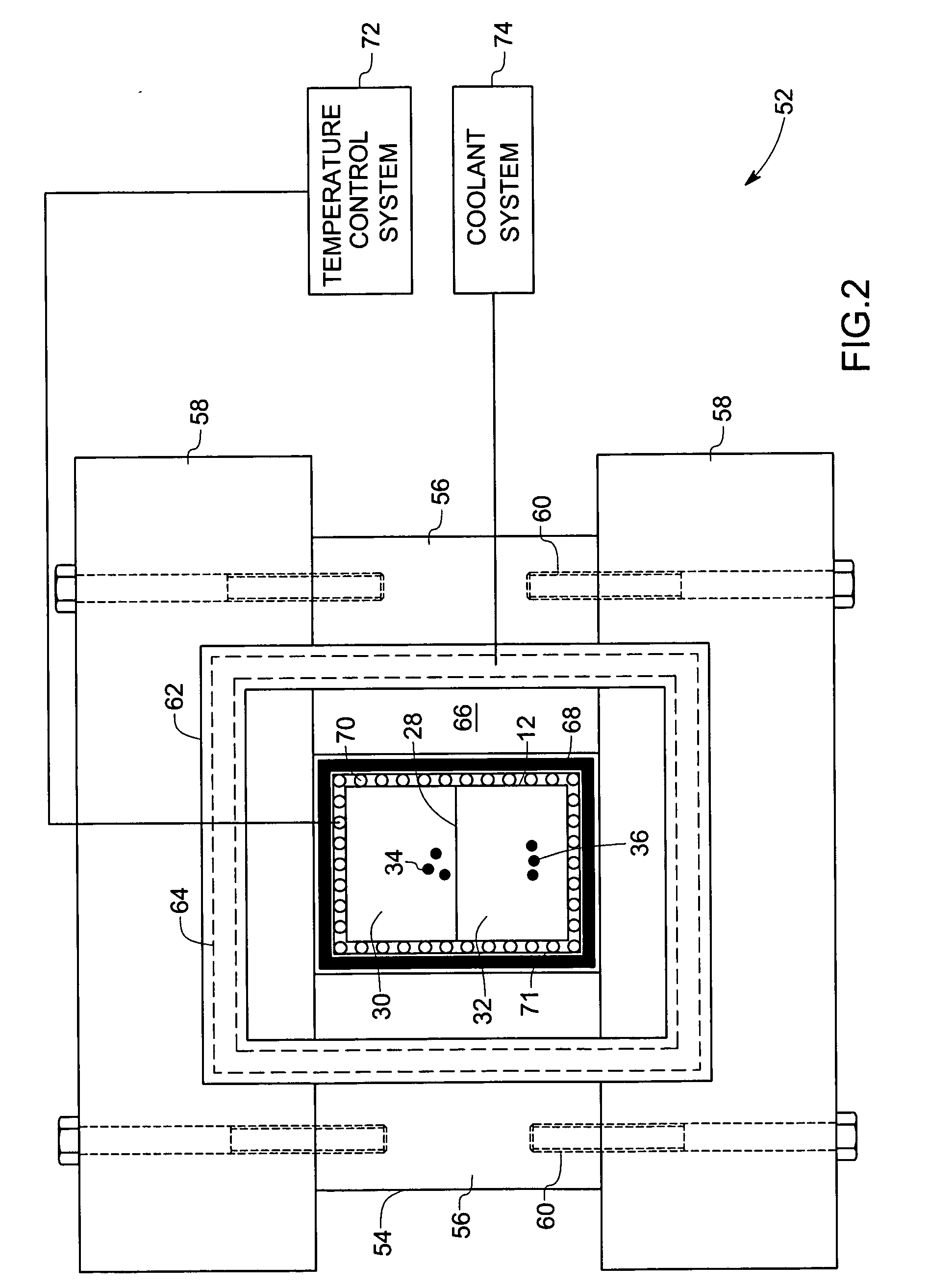
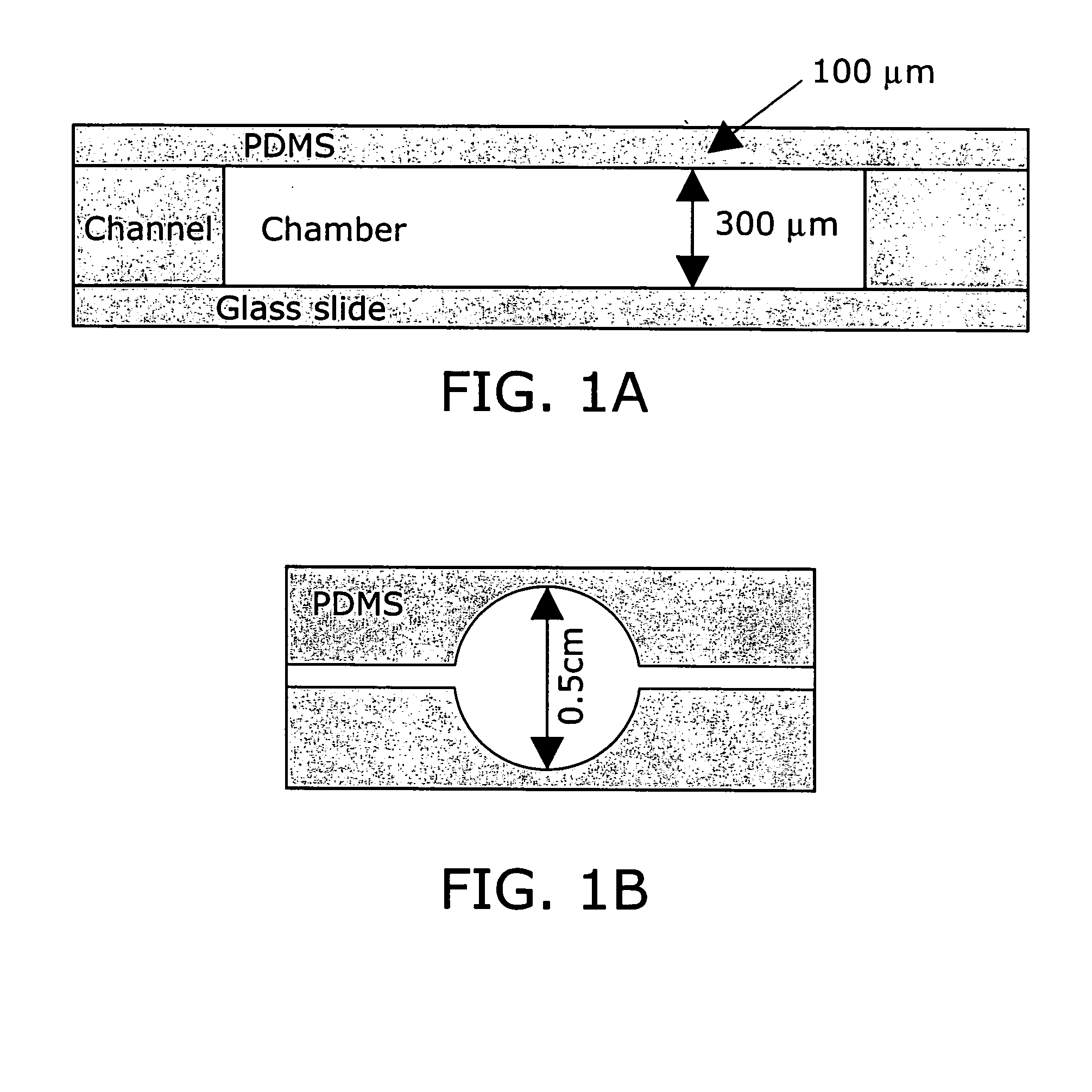
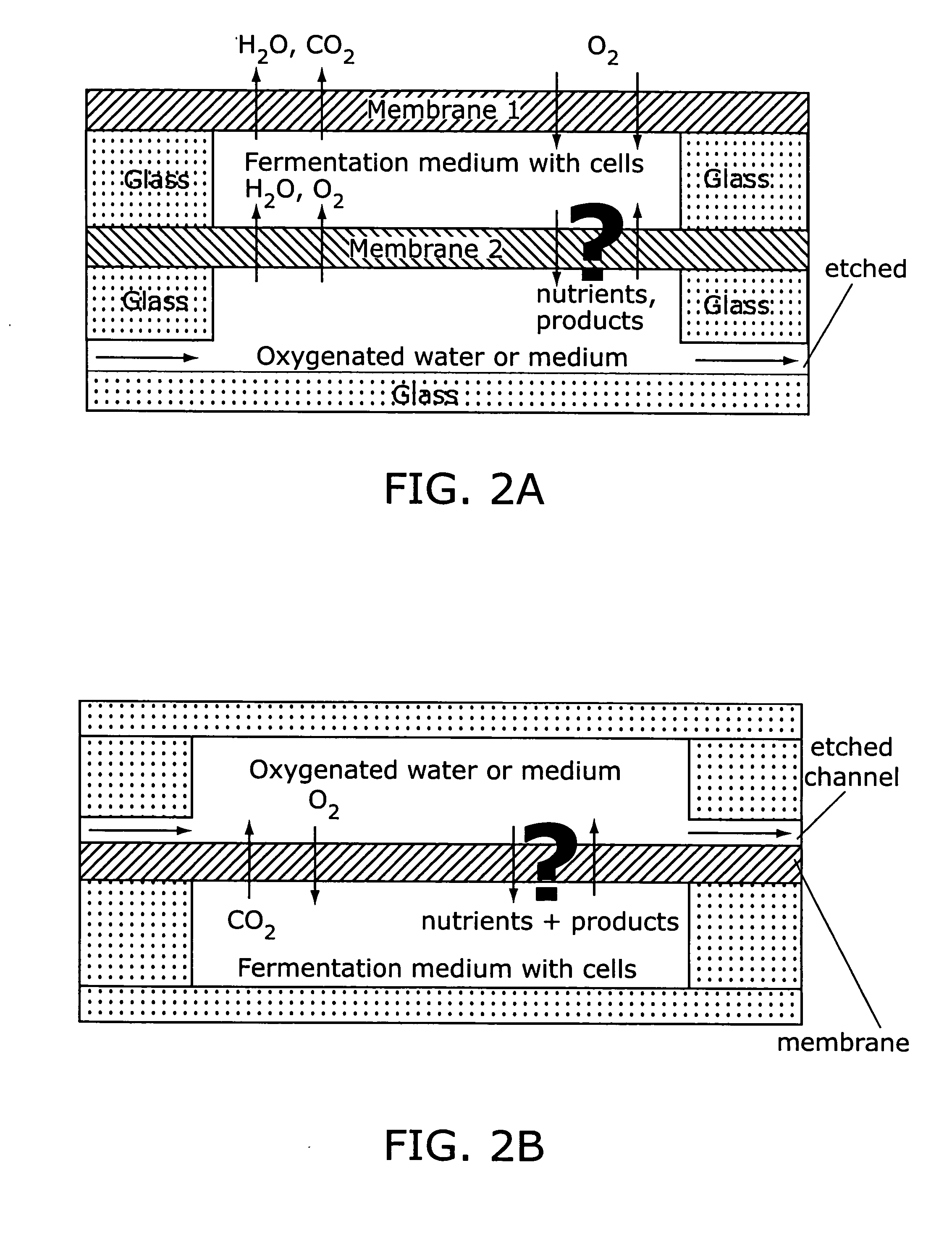
The present invention provides a variety of microscale bioreactors (microfermentors) and microscale bioreactor arrays for use in culturing cells. The microfermentors include a vessel for culturing cells and means for providing oxygen to the interior of the vessel at a concentration sufficient to support cell growth, e.g., growth of bacterial cells. Depending on the embodiment, the microfermentor vessel may have various interior volumes less than approximately 1 ml. The microfermentors may include an aeration membrane and optionally a variety of sensing devices. The invention further provides a chamber to contain the microfermentors and microfermentor arrays and to provide environmental control. Certain of the microfermentors include a second chamber that may be used, e.g., to provide oxygen, nutrients, pH control, etc., to the culture vessel and / or to remove metabolites, etc. Various methods of using the microfermentors, e.g., to select optimum cell strains or bioprocess parameters are provided. The invention provides microreactors having a variety of different designs, some of which incorporate active stirring and / or have the capability to operate in batch or fed-batch mode. The invention further provides an apparatus and methods for simultaneous operation of a plurality of microreactors, with monitoring of the individual microreactors during a run. The invention further provides methods of performing gene expression analysis on cells cultured in microreactors.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Materials, methods, and devices for treatment of arthropathies and spondylopathies
Novel modalities are introduced to treat joint and cartilage ischemia and related pathologies to improve outcome in the treatment of arthropathies and spondylopathies. The invention includes compositions, materials or devices which will improve oxygen, substrate and nutrient delivery to joint tissues and modalities to decrease the degradation of joint tissues by inflammatory and other destructive processes.
Owner:LEVIN BRUCE
Sorbent reactor for extracorporeal blood treatment systems, peritoneal dialysis systems, and other body fluid treatment systems
InactiveUS20050006296A1Facilitate homogeneous suspensionReduce probabilityWater treatment parameter controlSemi-permeable membranesFluid balancePeritoneal dialysis
Systems and methods for extracorporeal processing of blood or other body fluid for the treatment of conditions, such as sepsis, autoimmune disease, or toxemia related to kidney failure, liver failure, or drug overdose are provided. In an extracorporeal treatment system, a fraction of a body fluid is passed into a treatment fluid, at least a portion of which is then passed through a sorbent suspension reactor for treatment by a sorbent suspension. The treatment fluid circuit can be maintained at a fixed volume, which enables accurate fluid balance between the patient and the extracorporeal circuit. Some or all of the treatment fluid, optionally also containing nutrients and / or therapeutic agents, is returned to the patient. In a peritoneal dialysis system, dialysate is passed into a patient's peritoneal cavity, recovered from the cavity, passed through a sorbent suspension reactor in accordance with the invention, and returned to the cavity.
Owner:HEMOCLEANSE TECH
Super-enhanced aquatic floating island plant habitat
InactiveUS20050183331A1Increase plantingEnhance animal lifeWater cleaningClimate change adaptationThermoplastic elastomerCompound (substance)
A super-enhanced aquatic floating island plant habitat that is adjustably buoyant and optionally biodegradable. The first embodiment is comprised of a thermoplastic elastomer, a mat, soil / flotation chambers, apertures, nutrient channels, buoyant waterscape options, and a tethering system. The floating island can include monitors that measure water and atmospheric conditions, dispensers for fish food or chemicals, and a water agitation / oxygenation device. Another embodiment comprises a positively buoyant soil matrix contained within a water-permeable bag. Another embodiment comprises a flotation collar, an outrigger, and one or more water-permeable bladders containing negatively or neutrally buoyant bedding soil. The present invention also covers an aquarium-scale floating island and submersible planter, a plant containment bag made out of thermoplastic elastomer, and several methods of adjusting the buoyancy of a floating island. A method of manufacturing a floating island comprising molded thermoplastic elastomer.
Owner:FOUNTAINHEAD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com