Patents
Literature
153 results about "Liver failure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Liver (hepatic) failure is a loss of liver function because of the death of many hepatocytes. The damage can occur suddenly, as with a viral infection, or slowly over time, as with cirrhosis. Acute liver failure refers to both fulminant hepatic failure (FHF) and subfulminant hepatic failure.
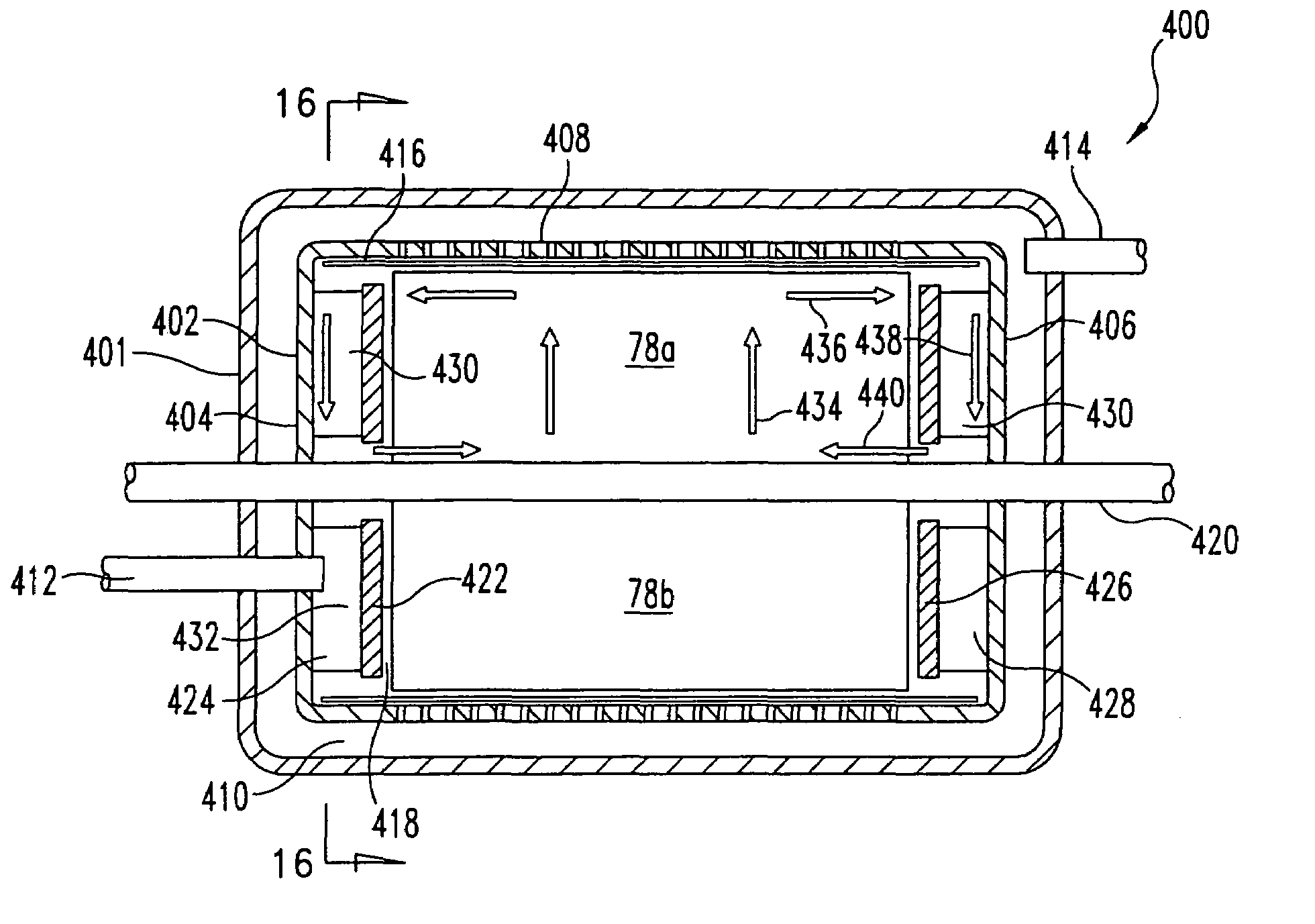
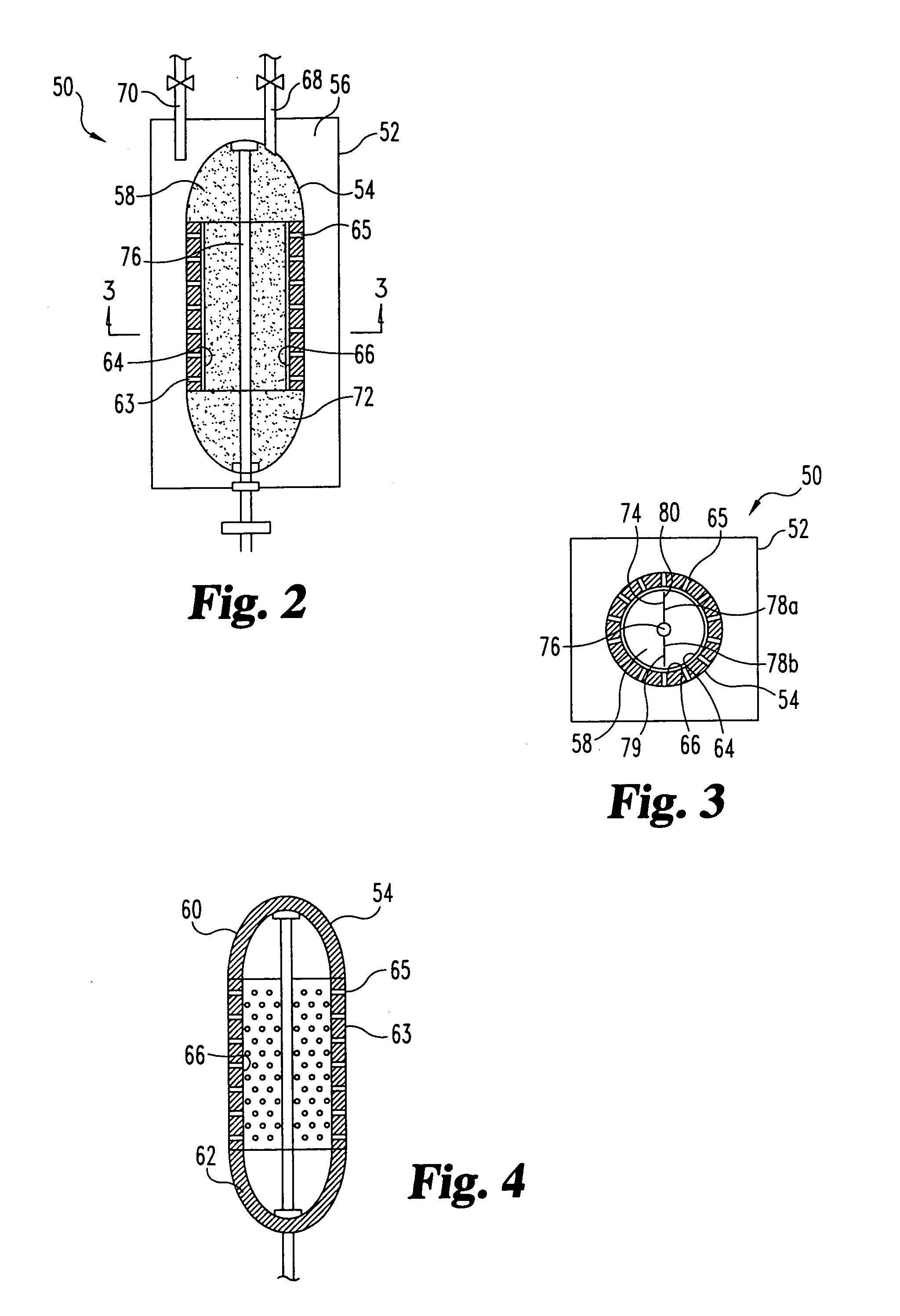
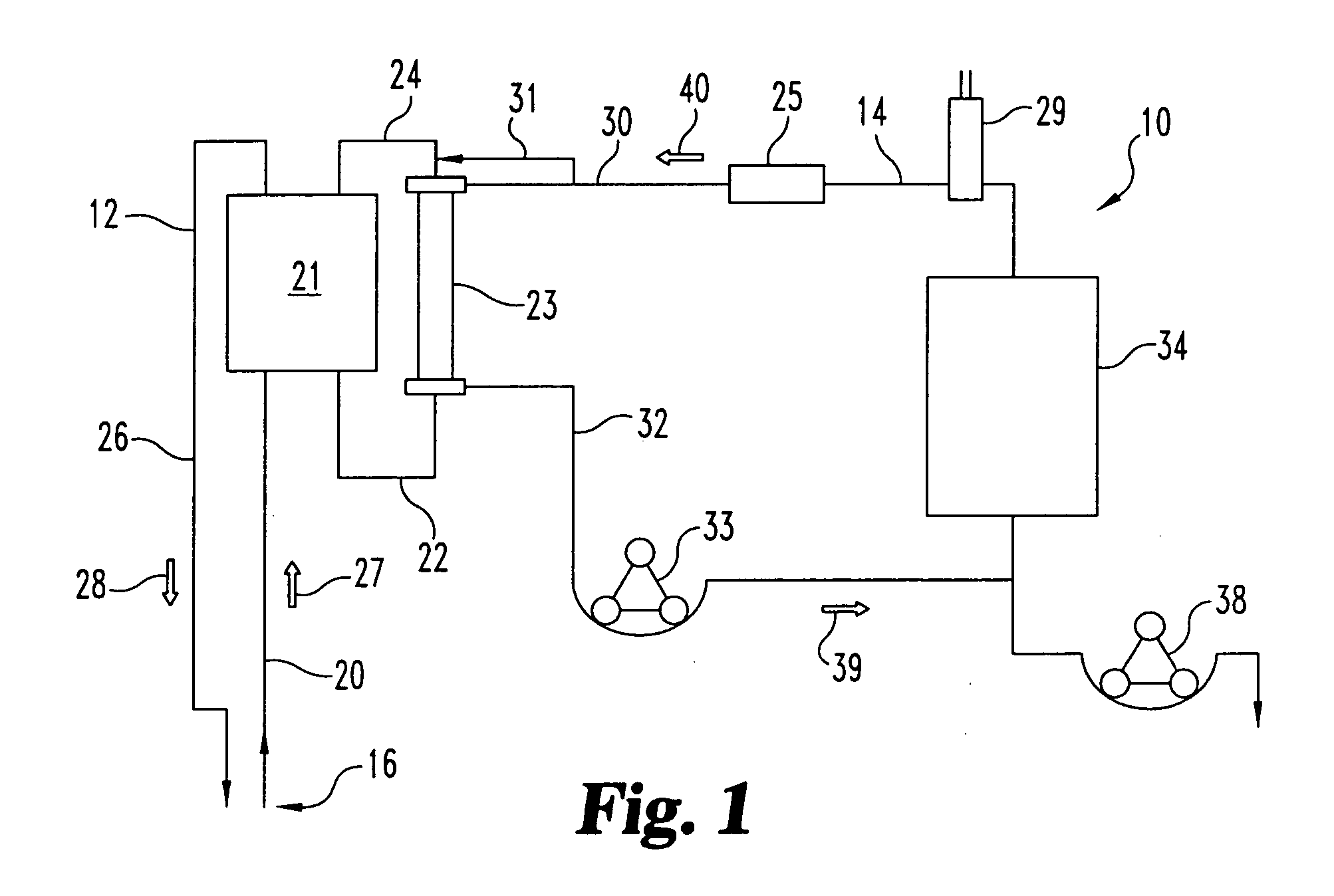
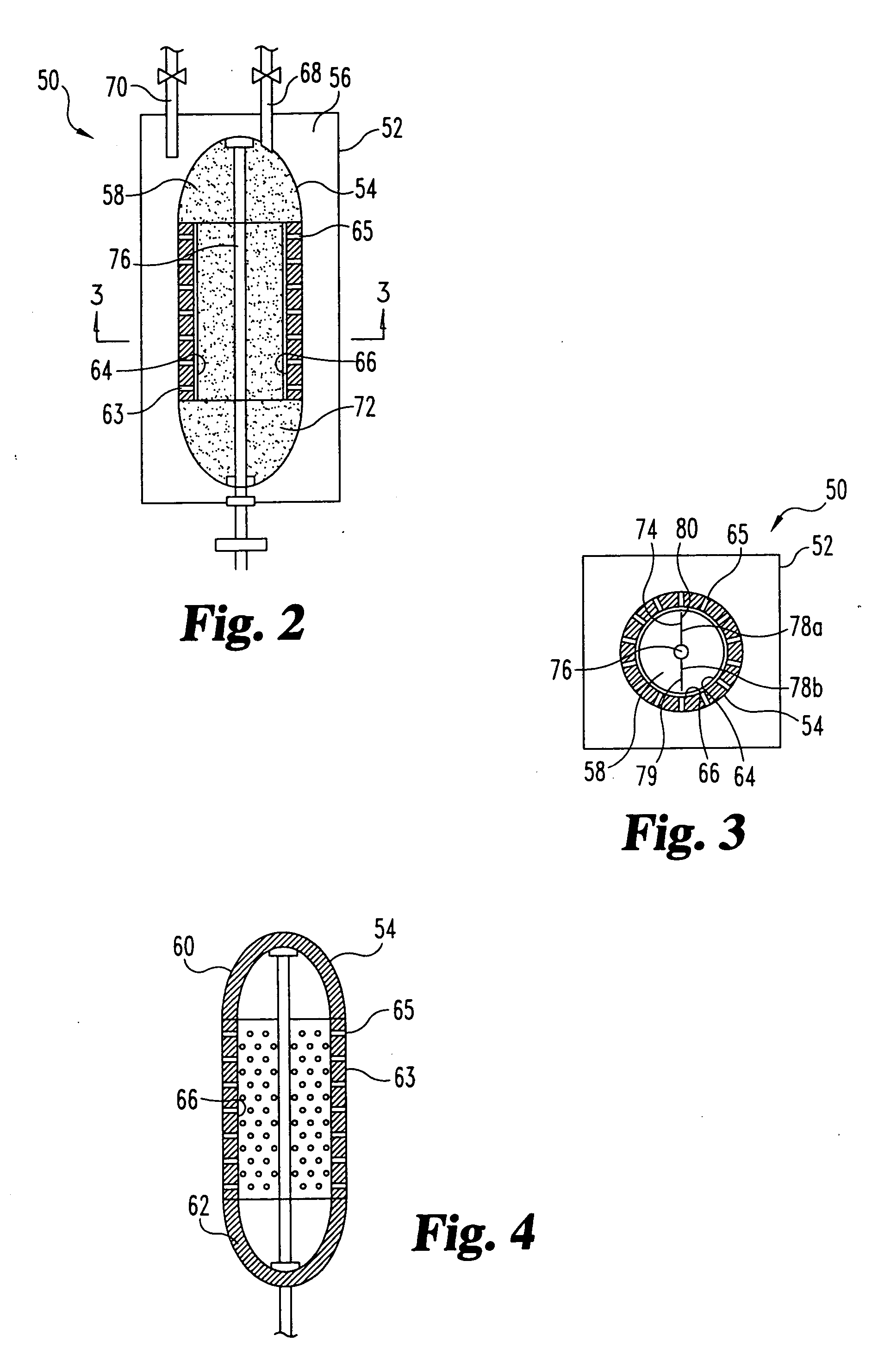
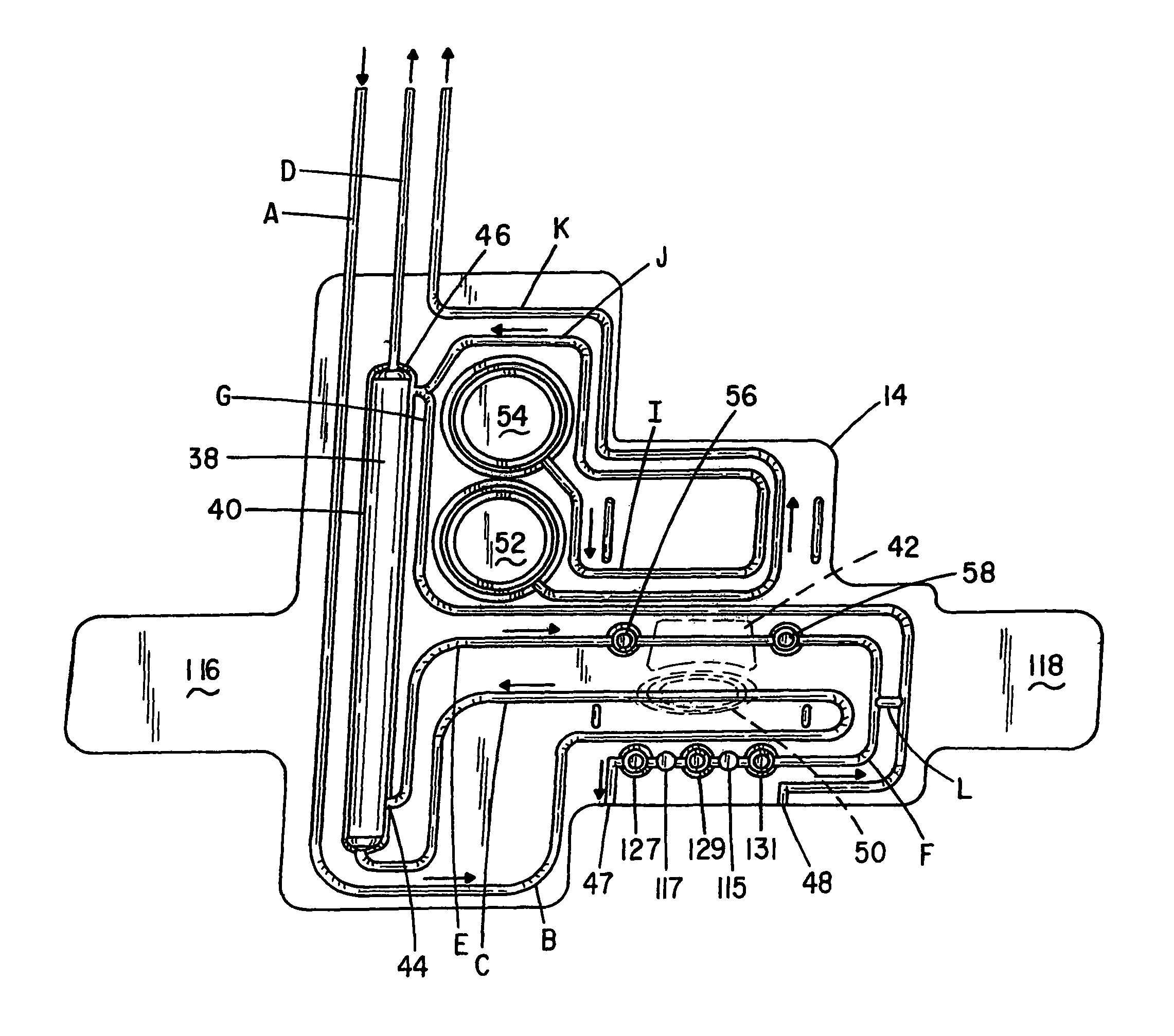
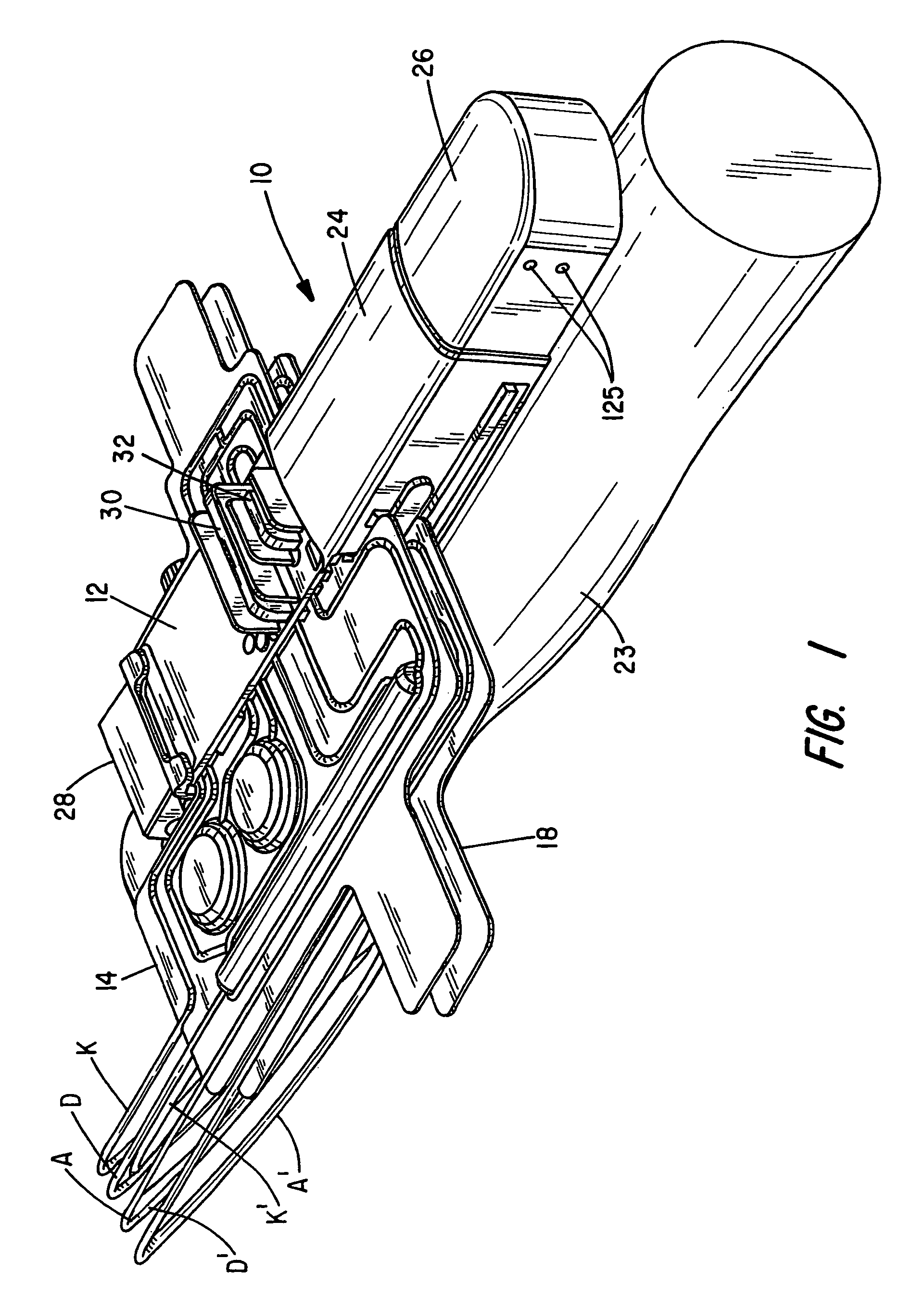
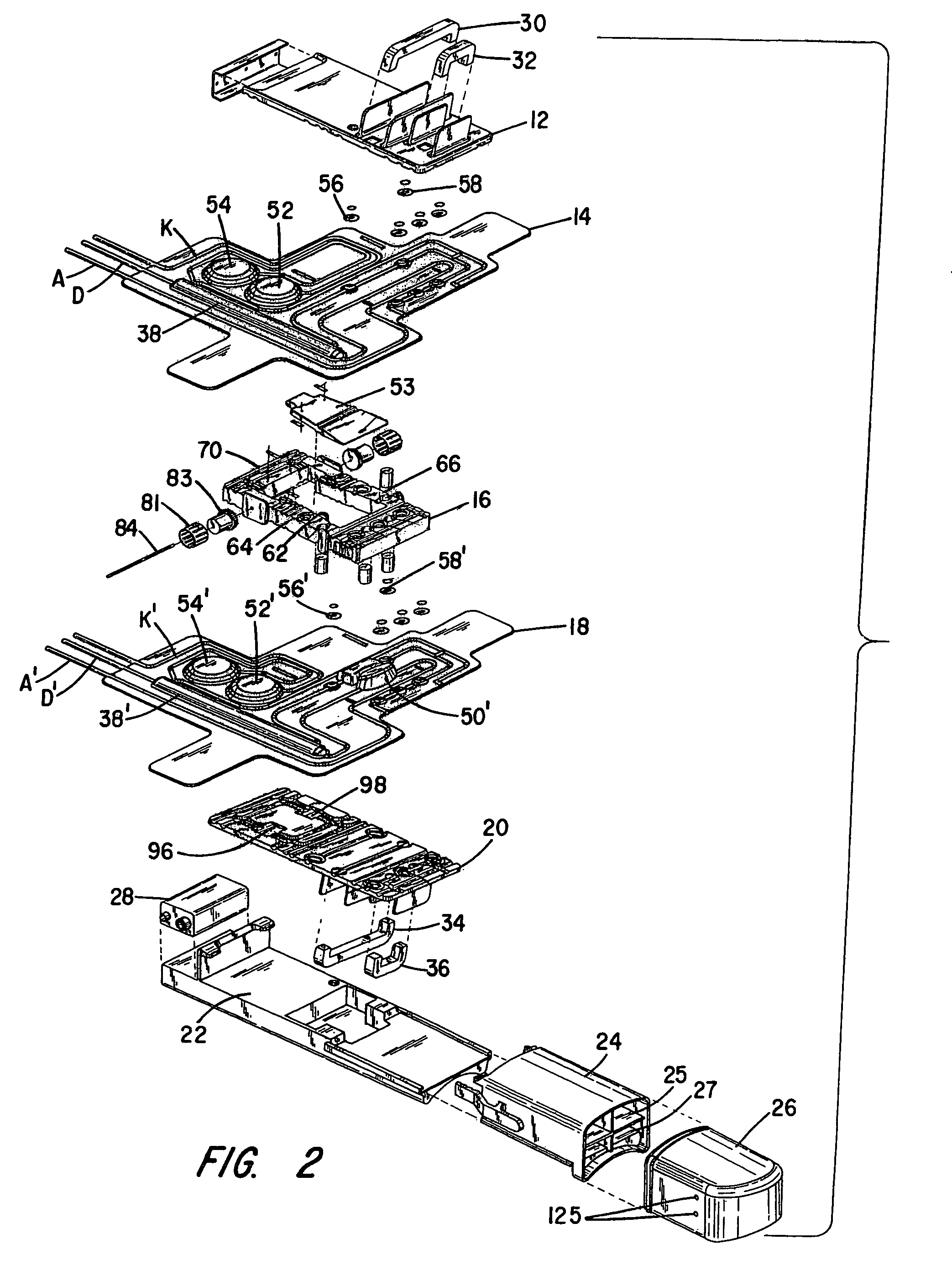
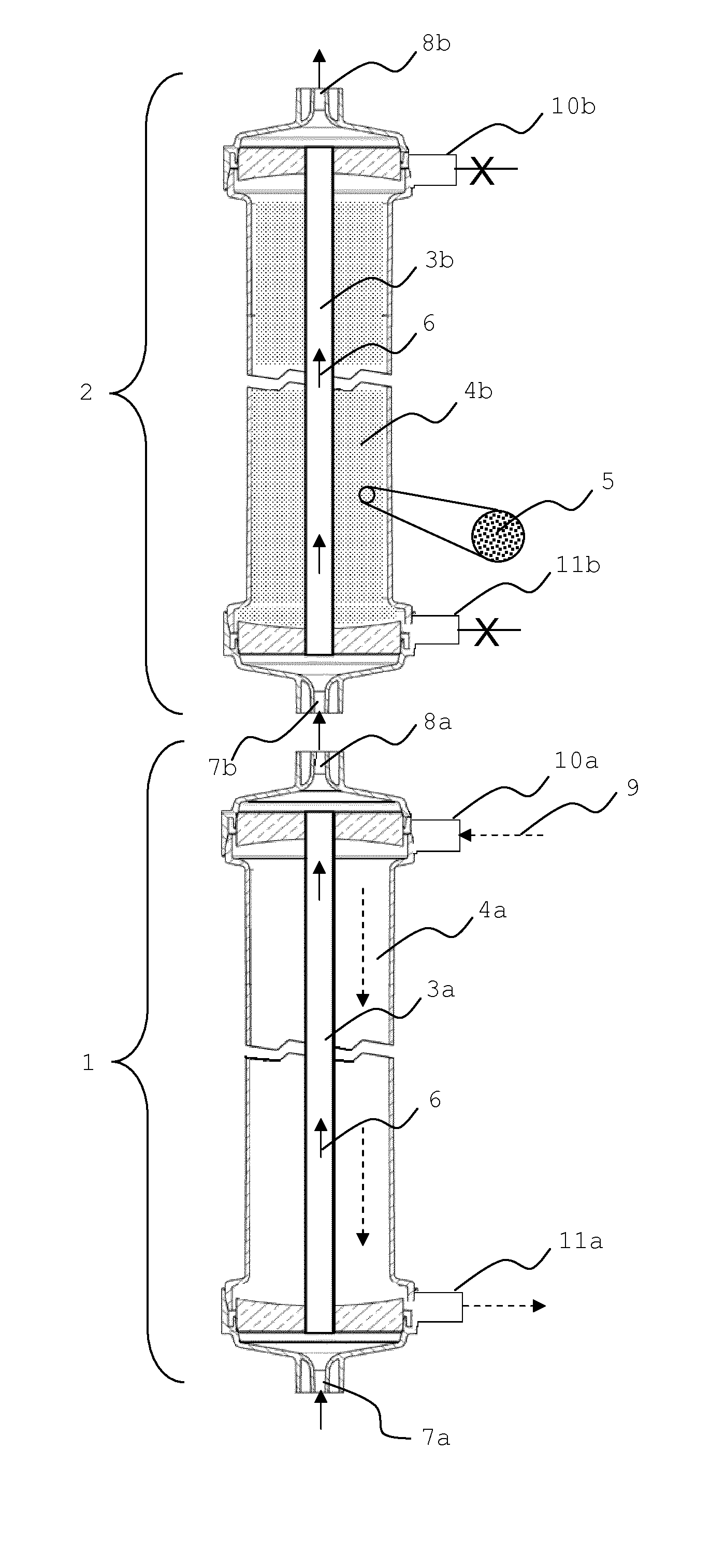
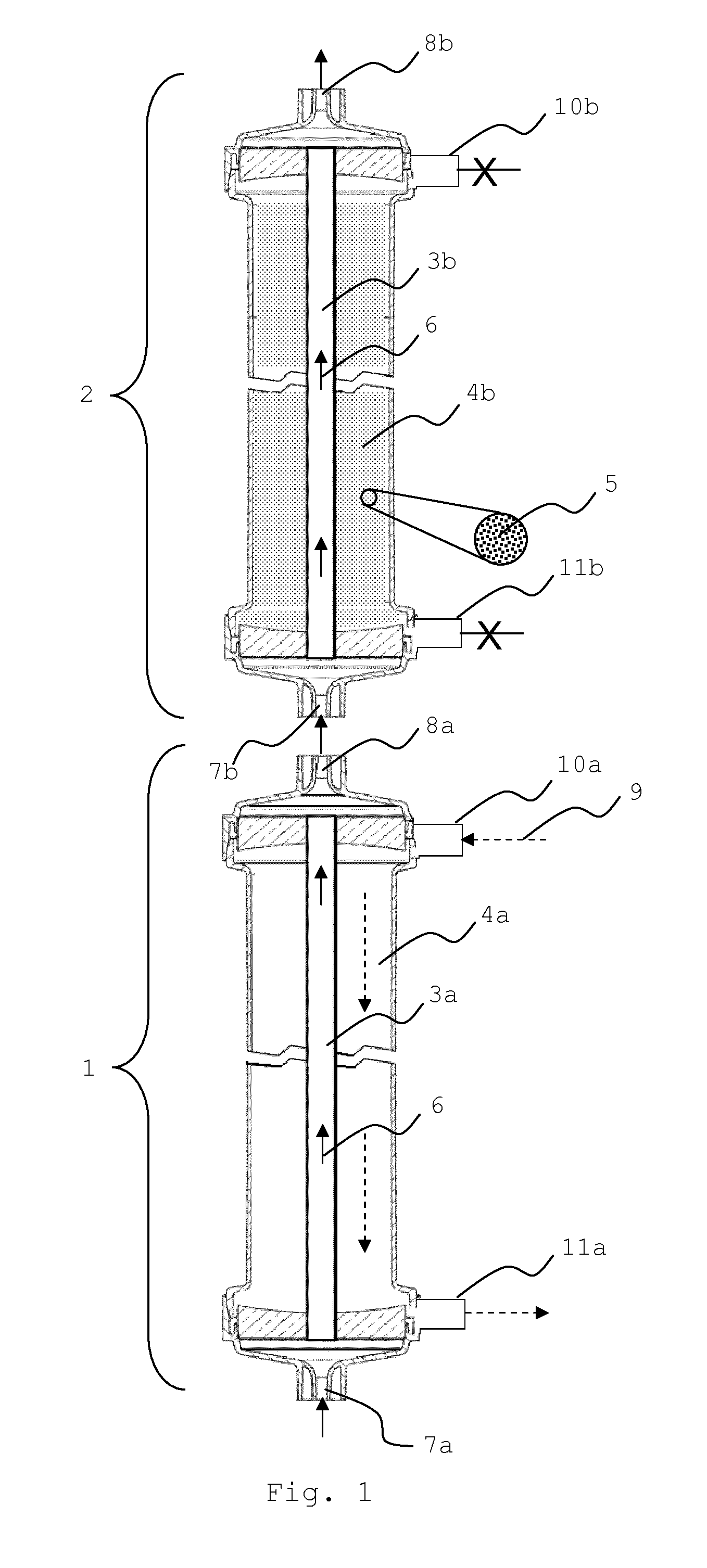
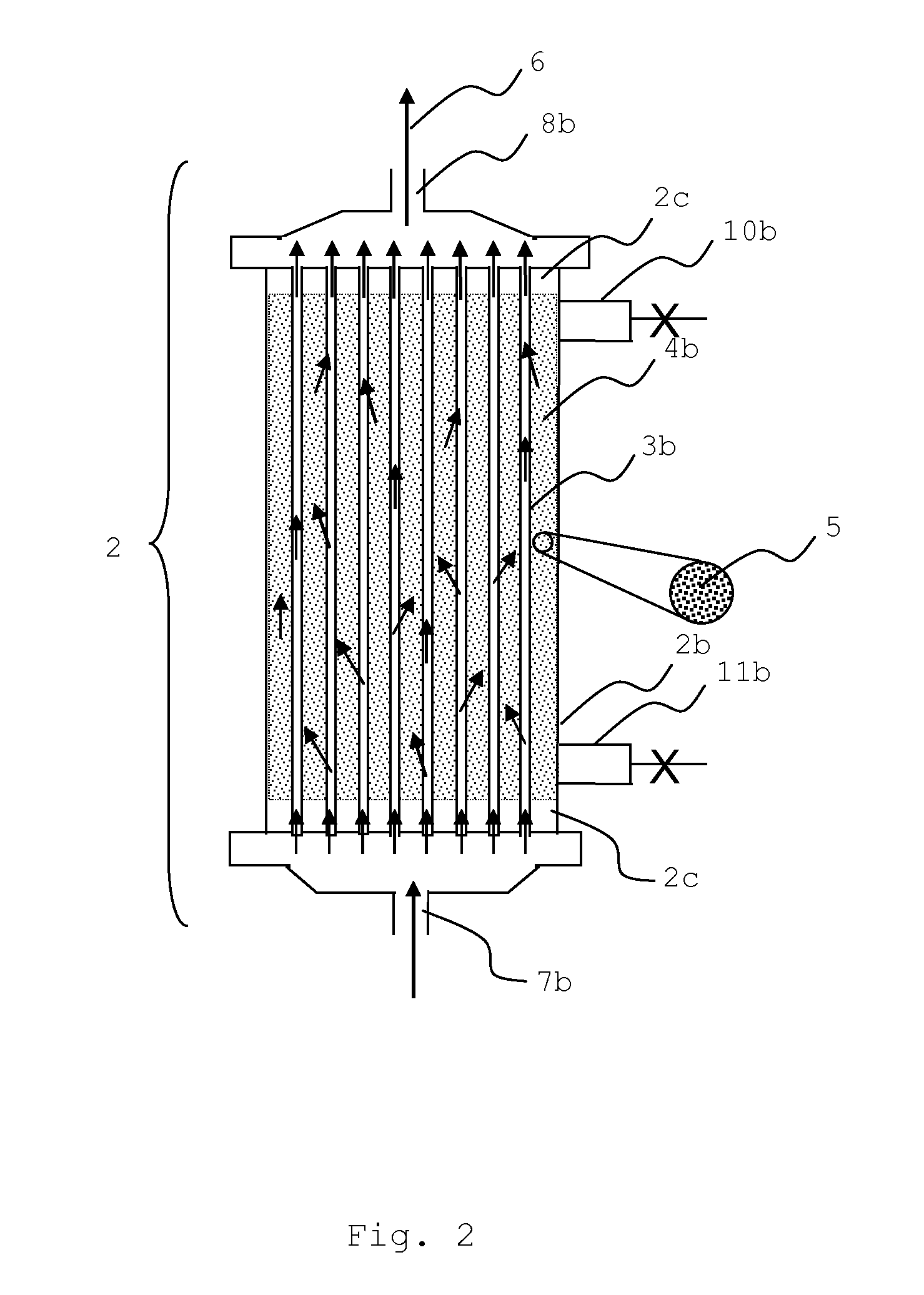
Sorbent reactor for extracorporeal blood treatment systems, peritoneal dialysis systems, and other body fluid treatment systems
InactiveUS7169303B2Facilitate homogeneous suspensionReduce probabilitySolvent extractionHaemofiltrationFluid balancePeritoneal dialysis
Systems and methods for extracorporeal processing of blood or other body fluid for the treatment of conditions, such as sepsis, autoimmune disease, or toxemia related to kidney failure, liver failure, or drug overdose are provided. In an extracorporeal treatment system, a fraction of a body fluid is passed into a treatment fluid, at least a portion of which is then passed through a sorbent suspension reactor for treatment by a sorbent suspension. The treatment fluid circuit can be maintained at a fixed volume, which enables accurate fluid balance between the patient and the extracorporeal circuit. Some or all of the treatment fluid, optionally also containing nutrients and / or therapeutic agents, is returned to the patient. In a peritoneal dialysis system, dialysate is passed into a patient's peritoneal cavity, recovered from the cavity, passed through a sorbent suspension reactor in accordance with the invention, and returned to the cavity.
Owner:HEMOCLEANSE TECH
Sorbent reactor for extracorporeal blood treatment systems, peritoneal dialysis systems, and other body fluid treatment systems
InactiveUS20050006296A1Facilitate homogeneous suspensionReduce probabilityWater treatment parameter controlSemi-permeable membranesFluid balancePeritoneal dialysis
Systems and methods for extracorporeal processing of blood or other body fluid for the treatment of conditions, such as sepsis, autoimmune disease, or toxemia related to kidney failure, liver failure, or drug overdose are provided. In an extracorporeal treatment system, a fraction of a body fluid is passed into a treatment fluid, at least a portion of which is then passed through a sorbent suspension reactor for treatment by a sorbent suspension. The treatment fluid circuit can be maintained at a fixed volume, which enables accurate fluid balance between the patient and the extracorporeal circuit. Some or all of the treatment fluid, optionally also containing nutrients and / or therapeutic agents, is returned to the patient. In a peritoneal dialysis system, dialysate is passed into a patient's peritoneal cavity, recovered from the cavity, passed through a sorbent suspension reactor in accordance with the invention, and returned to the cavity.
Owner:HEMOCLEANSE TECH
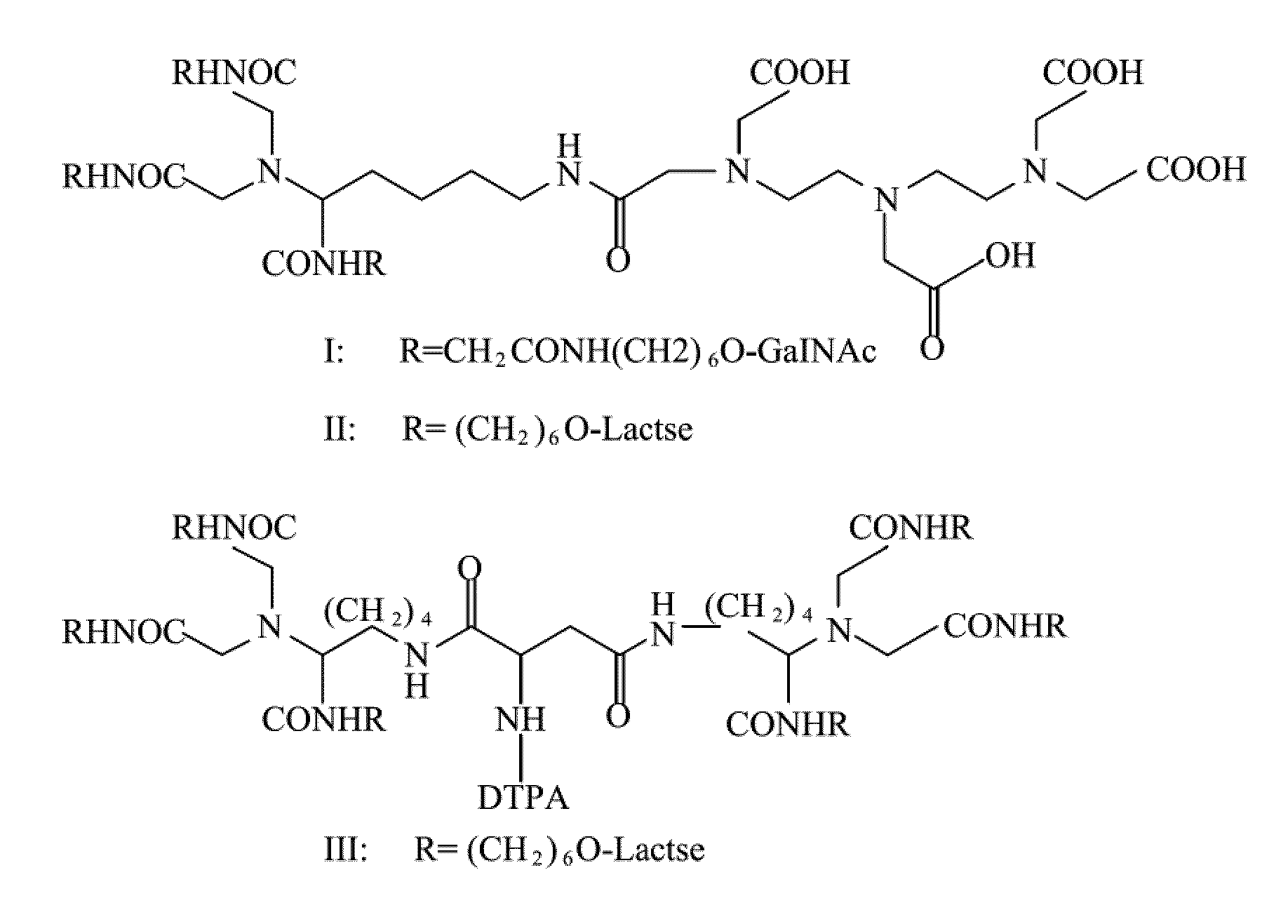
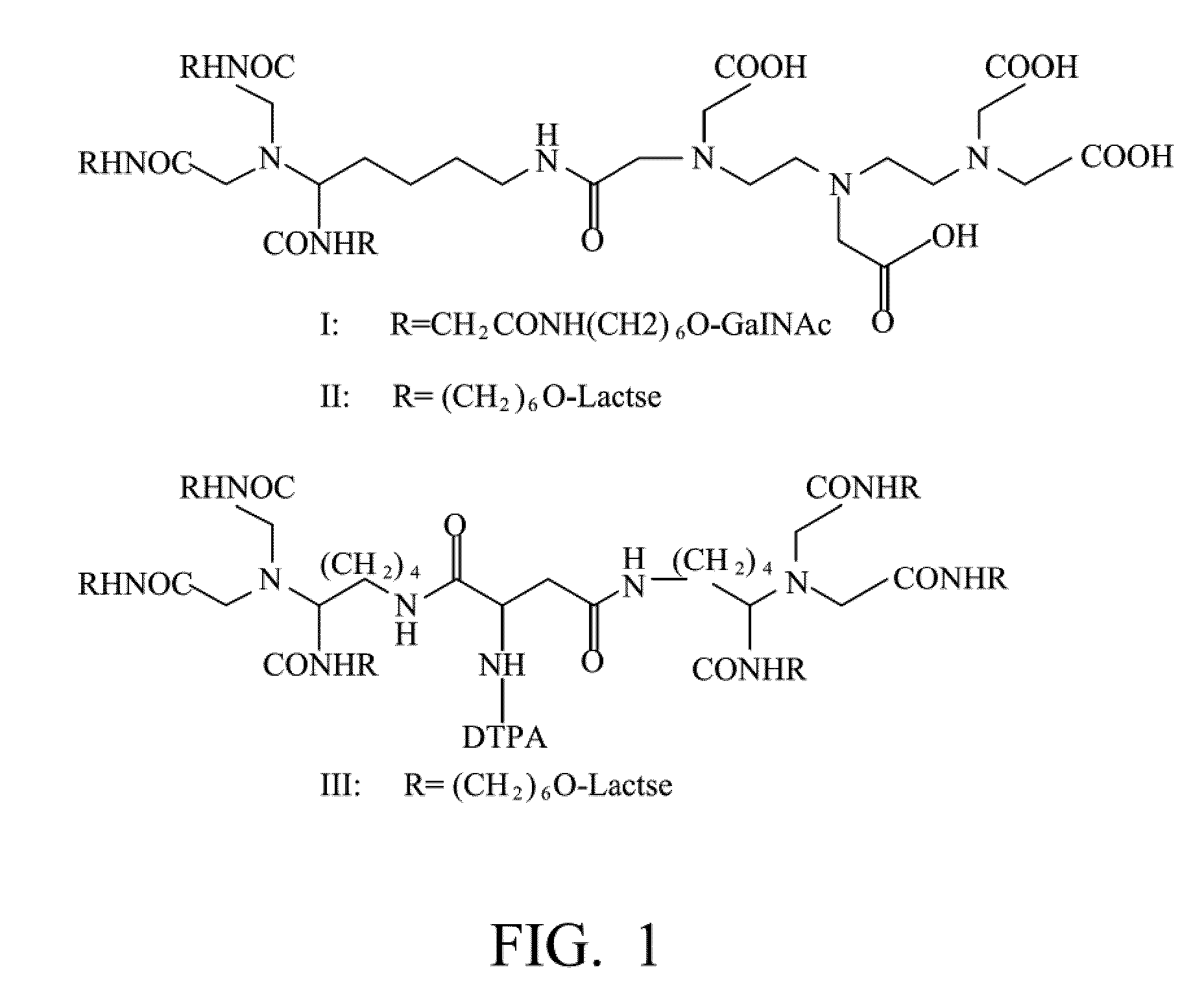
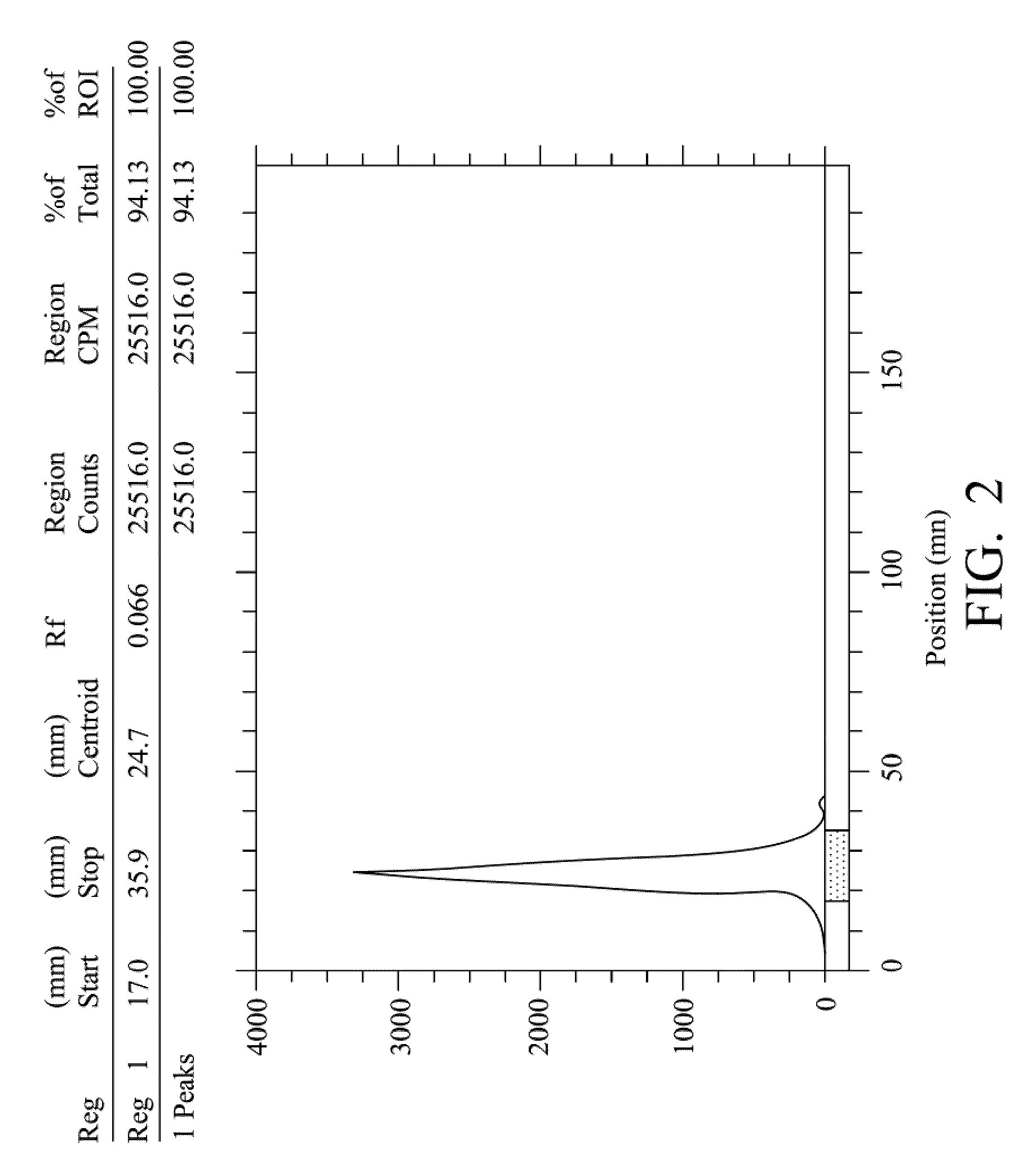
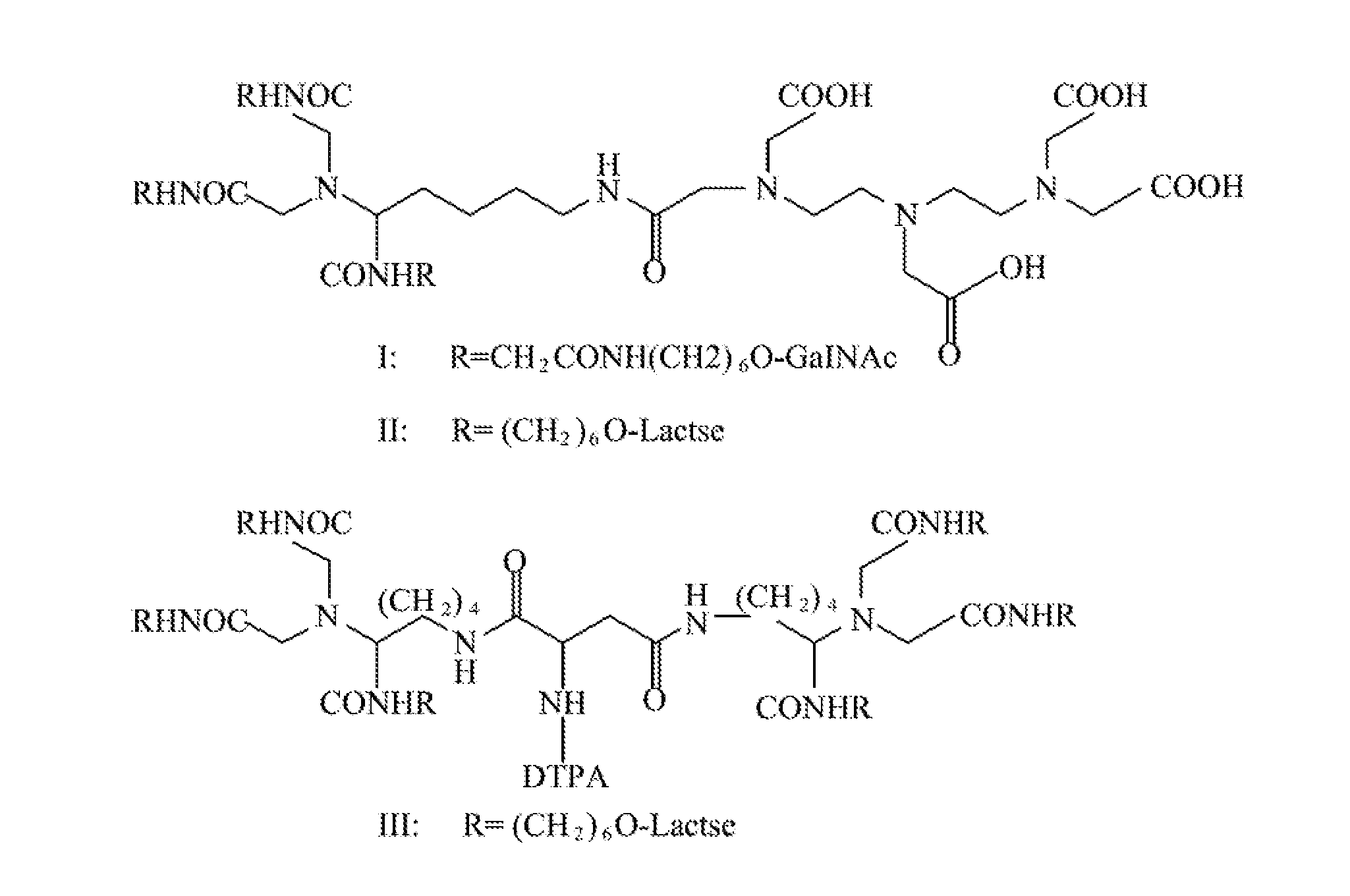
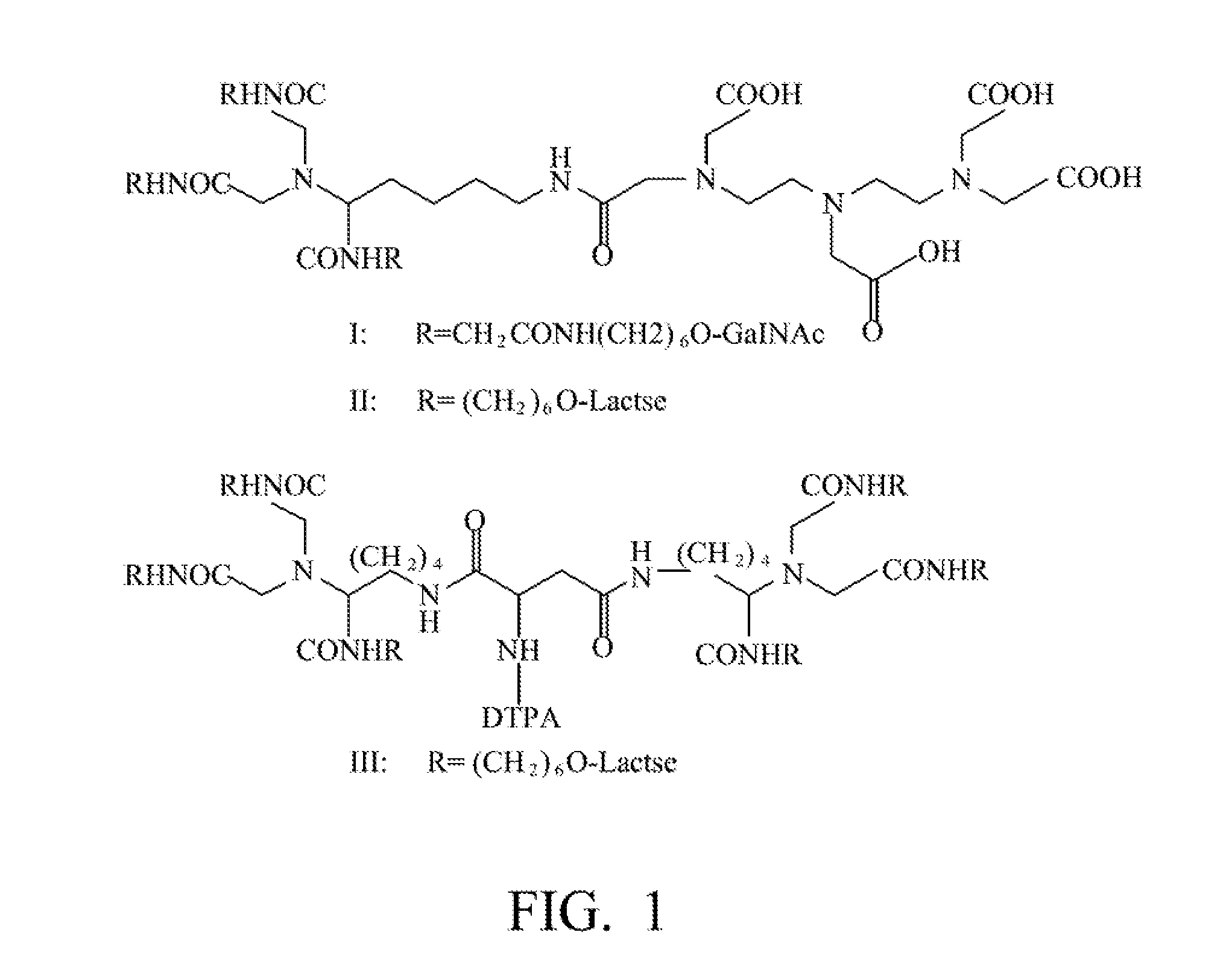
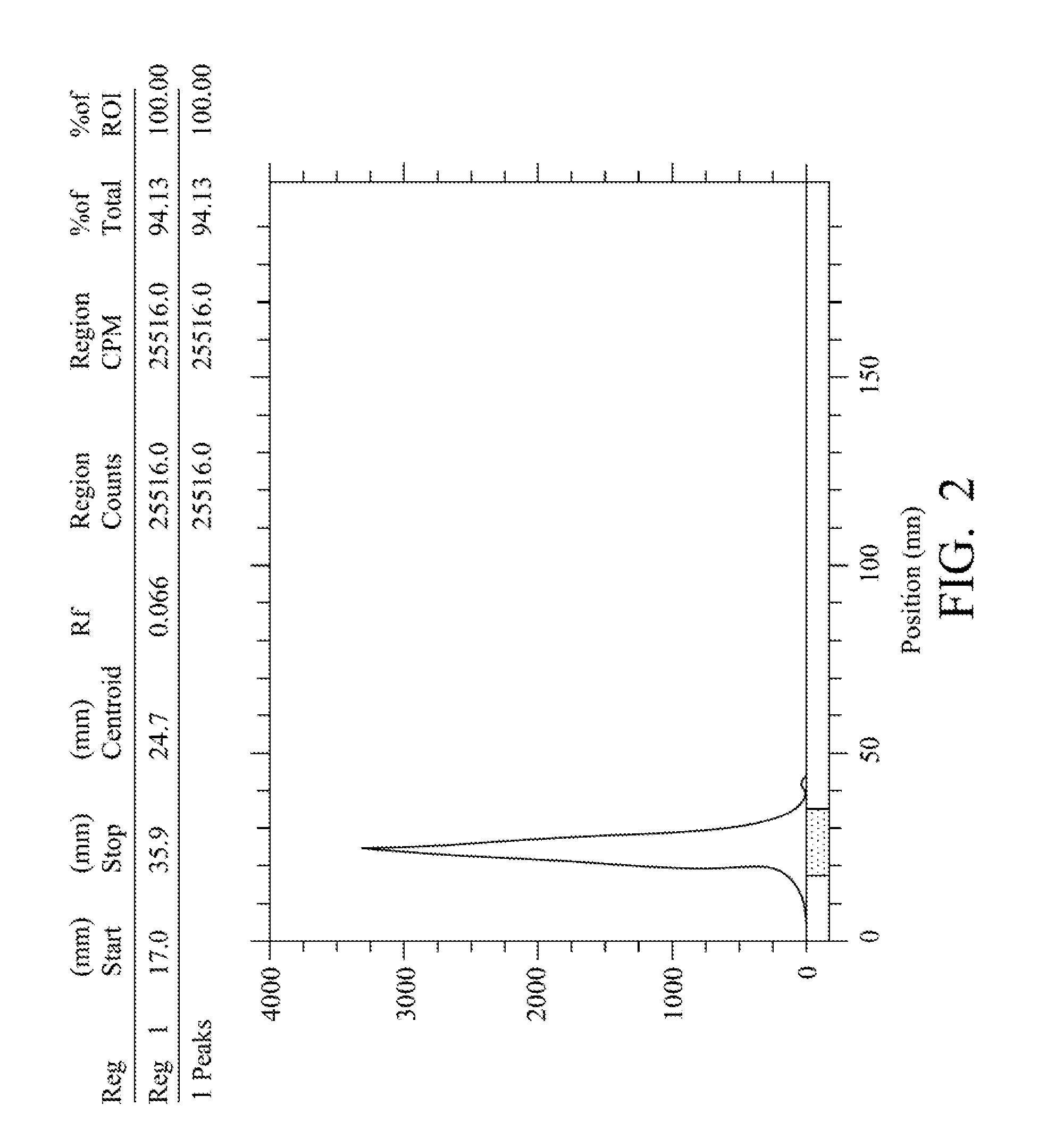
Quantification method for remaining liver function and novel liver receptor imaging agent
ActiveUS20110097265A1High measurement accuracyImprove accuracySugar derivativesSaccharide peptide ingredientsDiseaseReceptor
A test indicator for quantifying remaining liver function is provided. A novel liver receptor imaging agent with liver targeting property is utilized to develop a method for quantifying remaining liver function to serve as test indicator for judging the liver failure outcome in clinic, particularly for judging the necessity of liver transplantation for patients with liver failure or liver disease. The radioactivity uptake of the test indicator was negatively correlated with the extent of liver reserve. The cutoff value of liver reserve for liver transplantation is also disclosed.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
Treatment of fatty liver
InactiveUS20070265340A1Shorten the progressIncreased riskBiocideDigestive systemFatty liverBeta oxidation
Methods and compositions comprising peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents to reverse or resolve, slow the progression of, treat or prevent the development of fatty liver and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure. An active agent that by itself is associated with an increased risk of fatty liver development and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure, may be administered in combination with peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents. A combination regimen involving such agents, as simultaneous or concomitant therapy, or as a fixed dosage form, is also provided.
Owner:RELIANT PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Quantification method for remaining liver function and novel liver receptor imaging agent
ActiveUS8435491B2High measurement accuracyImprove accuracySugar derivativesRadioactive preparation carriersDiseaseLiver function
A test indicator for quantifying remaining liver function is provided. A novel liver receptor imaging agent with liver targeting property is utilized to develop a method for quantifying remaining liver function to serve as test indicator for judging the liver failure outcome in clinic, particularly for judging the necessity of liver transplantation for patients with liver failure or liver disease. The radioactivity uptake of the test indicator was negatively correlated with the extent of liver reserve. The cutoff value of liver reserve for liver transplantation is also disclosed.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
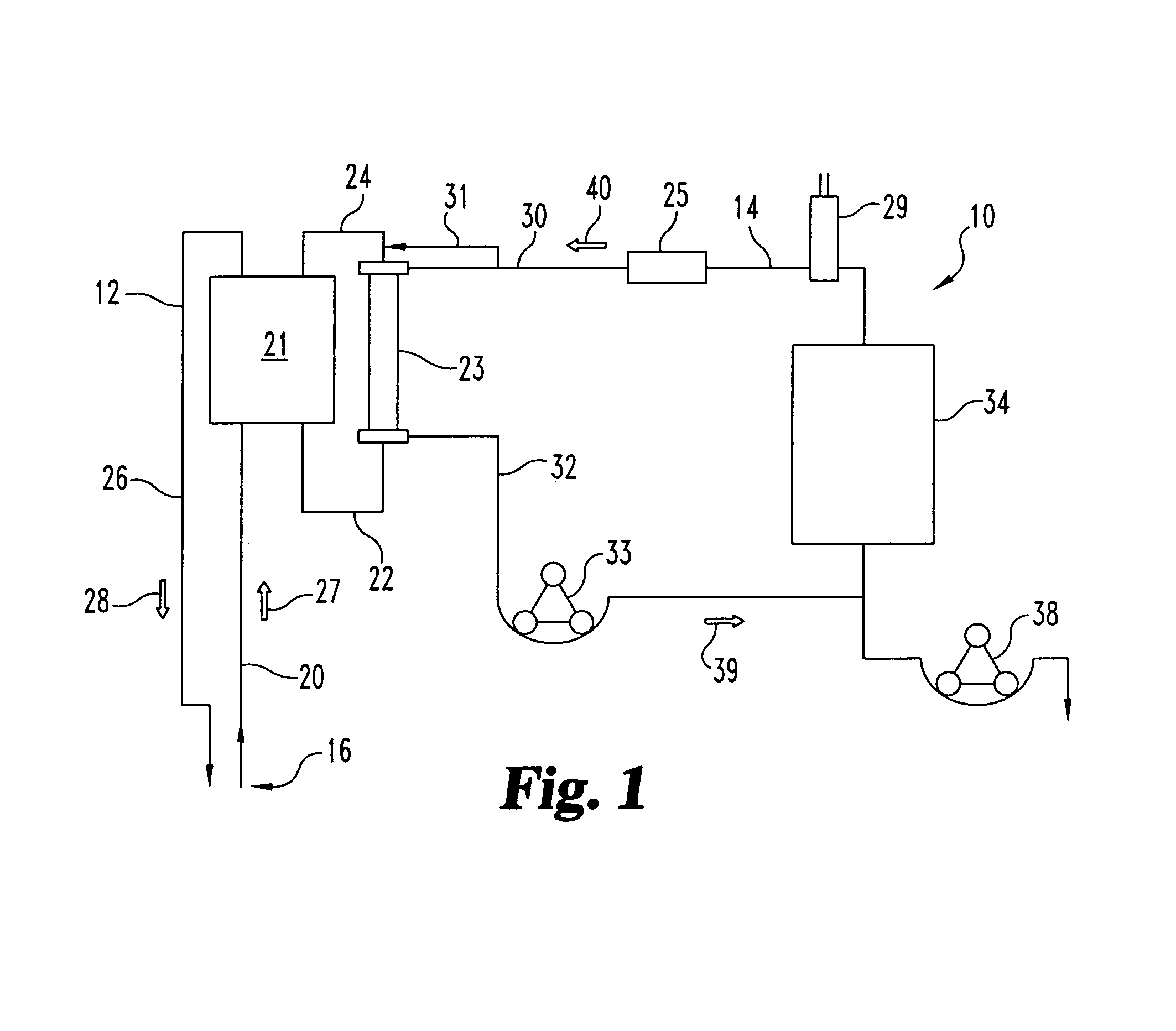
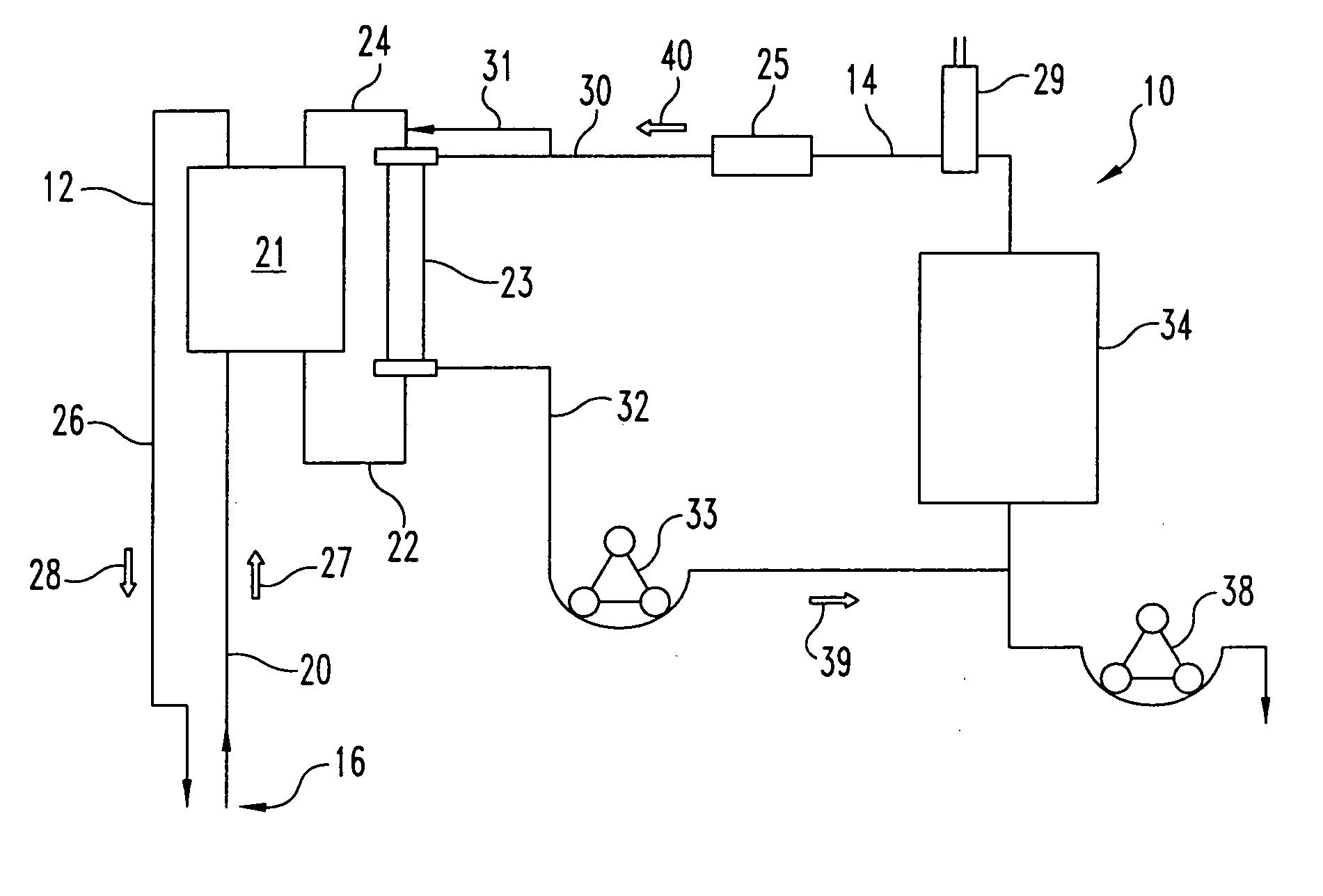
Chronic access system for extracorporeal treatment of blood including a continously wearable hemodialyzer
ActiveUS8109893B2More convenientEliminates the need for time-consuming, sedentary, hospital or clinic dialysisSemi-permeable membranesSolvent extractionIntravenous cannulaHaemodialysis machine
Owner:LANDE ARNOLD J
Carbon and its use in blood cleansing applications
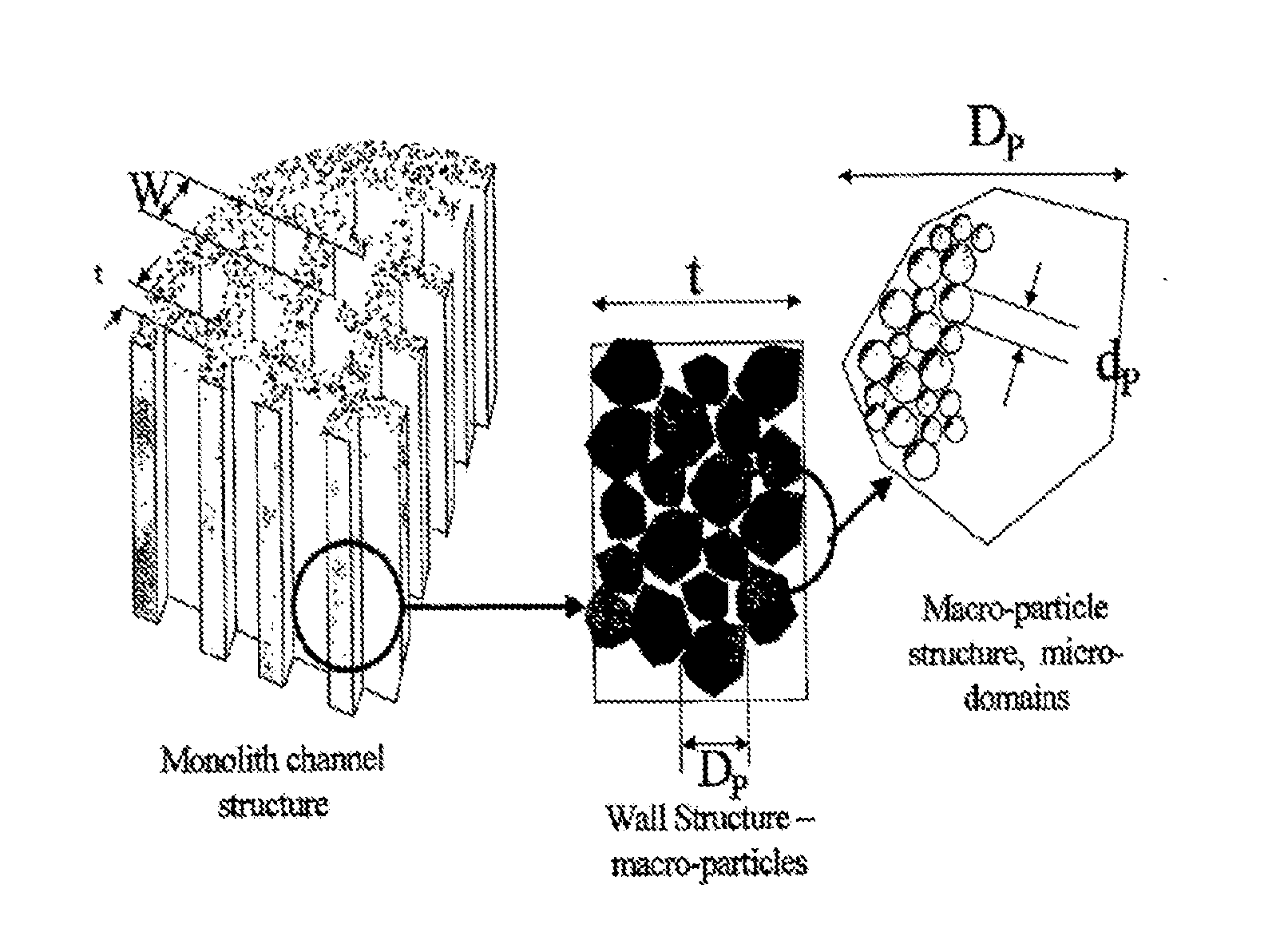
ActiveUS20130072845A1Improve the level ofEffective sorbentHaemofiltrationMedical devicesCardiopulmonary bypassWhole body
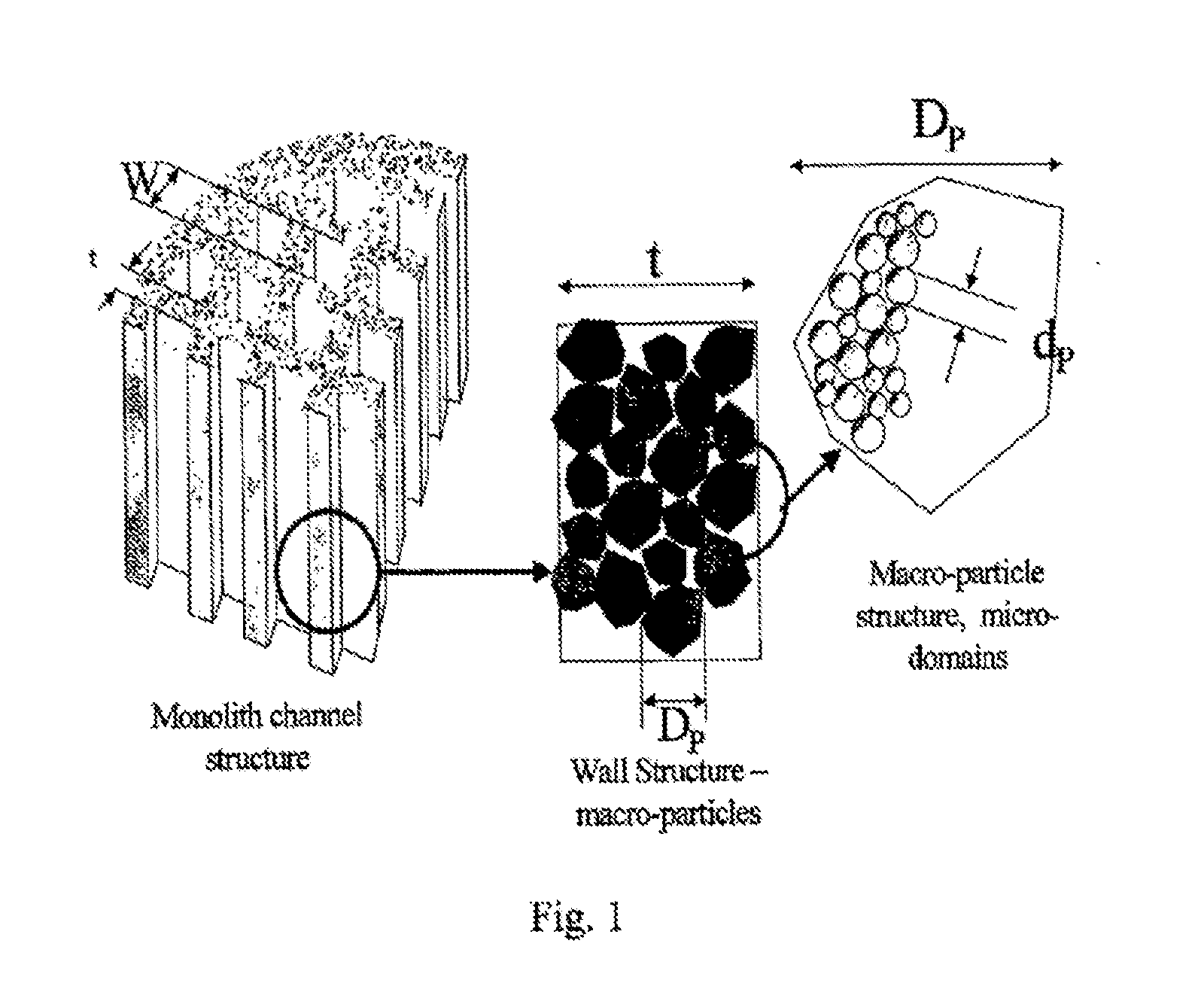
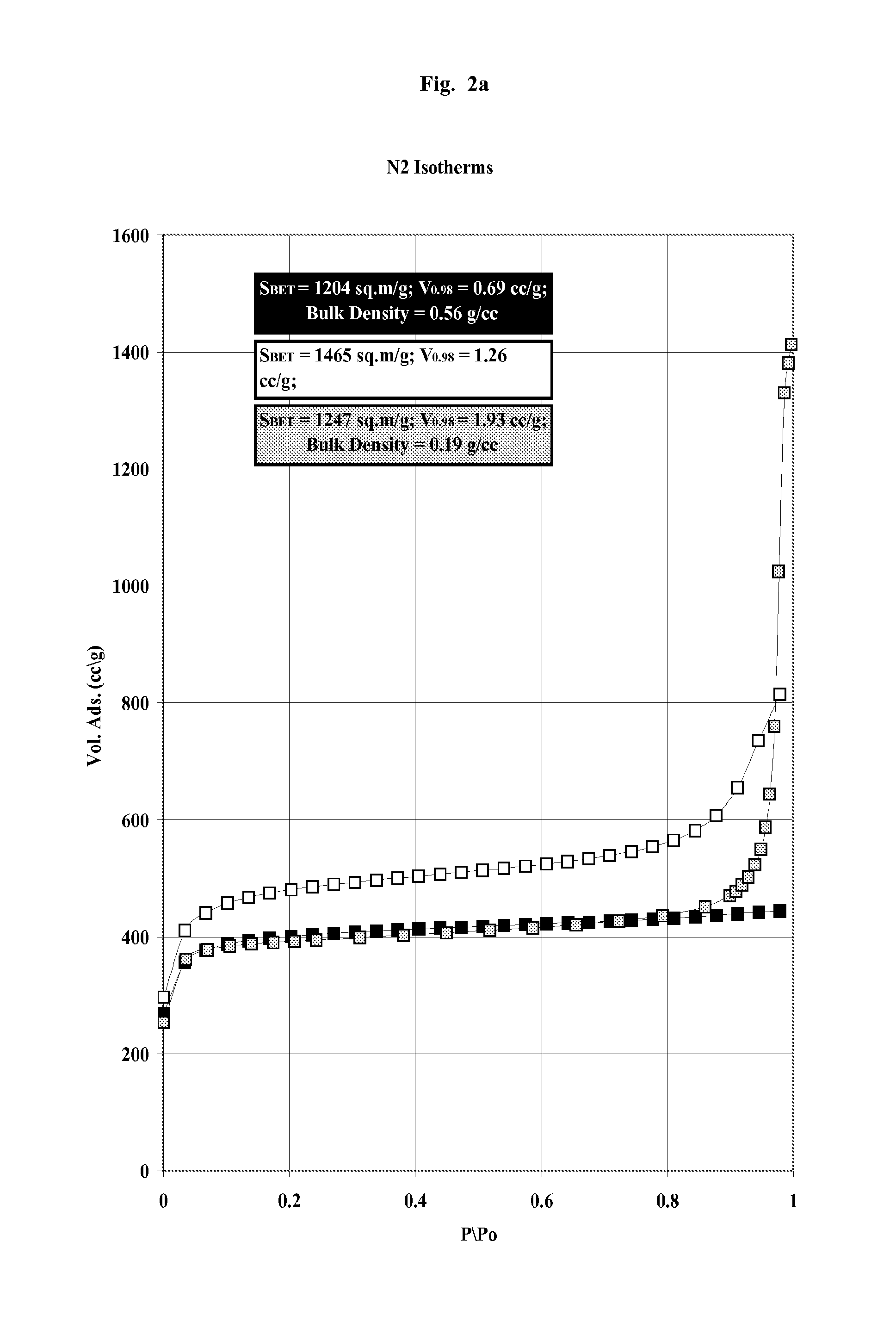
Whole blood is treated extracorporeally to remove substances contrary to health using mesoporous / microporous or macroporopus / microporous carbon in the form of beads or a channel monolith. The carbon may be the result of carbonising a mesoporous or macroporous phenolic resin. Substances contrary to health include externally introduced toxins such as bacterially derived staphylococcus enterotoxins A, B, TSST-1 or autologous, biologically active molecules with harmful, systemic effects when their activity is excessive or unregulated. Examples include the removal of inappropriate amounts of pro- or anti-inflammatory molecules and toxic mediators of systemic inflammatory response syndrome related to sepsis, cardio-pulmonary by-pass surgery, ischaemic reperfusioninjury; the removal of larger molecular weight and protein bound uremic toxins related to kidney and hepatic toxins related to liver failure and the removal of toxins relevant to biological and chemical warfare.
Owner:UNVIERSITY OF BRIGHTON +1
Treatment of Fatty Liver
InactiveUS20090182022A1Shorten the progressAvoid developmentBiocideDigestive systemBeta oxidationActive agent
Methods and compositions comprising peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents to reverse or resolve, slow the progression of, treat or prevent the development of fatty liver and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure. An active agent that by itself is associated with an increased risk of fatty liver development and conditions stemming from fatty liver, such as NASH, liver inflammation, cirrhosis and liver failure, may be administered in combination with peroxisomal and / or mitochondrial beta oxidation stimulating agents. A combination regimen involving such agents, as simultaneous or concomitant therapy, or as a fixed dosage form, is also provided.
Owner:RELIANT PHARMACEUTICALS INC
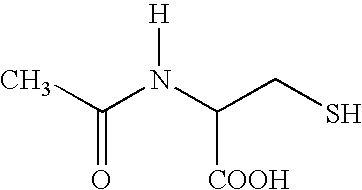
Acetylcysteine composition and uses therefor
This invention relates to novel acetylcysteine compositions in solution, comprising acetylcysteine and which are substantially free of metal chelating agents, such as EDTA. Further, this invention relates to methods of making and using the acetylcysteine compositions. The present compositions and methods are designed to improve patient tolerance and compliance, while at the same time maintaining the stability of the pharmaceutical formulation. The compositions and methods of this invention are useful in the treatment of acetaminophen overdose, acute liver failure, various cancers, methacrylonitrile poisoning, reperfusion injury during cardio bypass surgery, and radiocontrast-induced nephropathy, and can also be used as a mucolytic agent.
Owner:CUMBERLAND PHARM INC
Application of fructus forsythiae aglycone in preparing medicament for preventing or treating liver injury or liver failure
InactiveCN103989668ASignificant preventionGood treatment effectDigestive systemHeterocyclic compound active ingredientsSide effectAglycone
The invention discloses application of fructus forsythiae aglycone in preparing a medicament for preventing or treating liver injury or liver failure, and belongs to the medical field. The fructus forsythiae aglycone is a traditional Chinese medicine monomer obtained by extracting from the conventional fructus forsythiae, and is shown to have better treatment effect for the liver injury caused by acetaminopben, the livery injury caused by anti-tumor drug cis-platinum, acute or chronic livery injury caused by carbon tetrachloride, the livery injury caused by D-galactosamine and the liver failure caused by the D-galactosamine and lipopolysaccharide according to an animal test, has effect, which is better than that of fructus forsythiae and fructus forsythiae aglycone, in treating liver injury or liver failure. The fructus forsythiae aglycone is exact in curative effect and low in side effect for treating the liver injury and the liver failure, and has wide medical application prospect.
Owner:LUNAN PHARMA GROUP CORPORATION
Pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof
ActiveCN103540545AImprove acid resistanceGood resistance to bile saltsAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyStaining
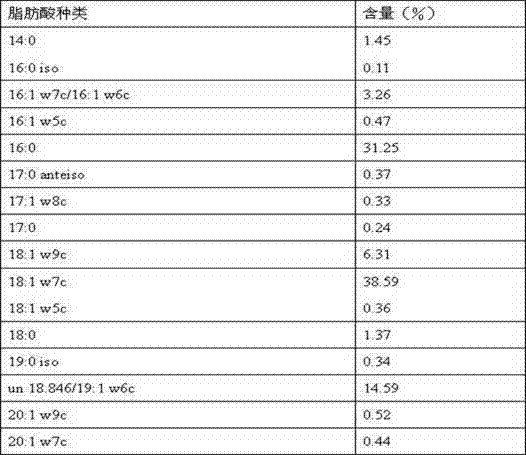
The invention discloses pediococcus pentosaceus and application thereof. The Latin name of the pediococcus pentosaceus is Pediococcus pentosaceus LI05, and the pediococcus pentosaceus is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.7049. The pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention has the morphological characteristics that the thallus is rod-shaped, dose not generate spores, does not have motility, and has masculine Gram staining. The whole-cell fatty acid of the pediococcus pentosaceus disclosed by the invention comprises the following main components in percentage by weight: about 1.45% of 14:0, about 3.26% of 16:1w7c / 16:1w6c, about 31.25% of 16:0, about 6.31% of 18:1w9c, about 38.59% of 18:1w7c, about 1.37% of 18:0 and about 14.59% of un18.846 / 19:1w6c. The invention also discloses a complete sequence of 16S ribosome DNA (16SrDNA) of the pediococcus pentosaceus. The pediococcus pentosaceus and a preparation thereof disclosed by the invention can be used for adjusting the micro-ecological balance of intestinal tracts of human or animals, promoting digestive absorption and slowing down the happening and development of liver failure of experimental animals.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Multiple organ dysfunction and support system
ActiveCN101041092ARemove inflammatory mediatorsEliminate endotoxinOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsOrgan dysfunctionOxygen
The invention discloses a multiple organ function support system, formed by a body, an external blood circuit, a plasma separating-adsorbing circuit, an albumin circuit, a dialysate circuit, a feeding circuit and an operating system. The invention can eliminate the inflammation medium, toxin and lots of middle and small molecule materials in the body of multiple organ function obstacle complex symptom (MODS) patient, and uses a lung membrane oxygen generator to replace the air exchange function of lung, to be used in reversal breath exhaustion, and uses albumin circulate purification treatment to completely eliminate the protein combine toxin and soluble small molecule toxin (as blood ammonia) of lung exhaustion patient, and accurately release water slowly. The invention can combine the support functions of lung, heart, kidney and liver, based on present clinic test and technique, with wide application.
Owner:SWS HEMODIALYSIS CARE CO LTD
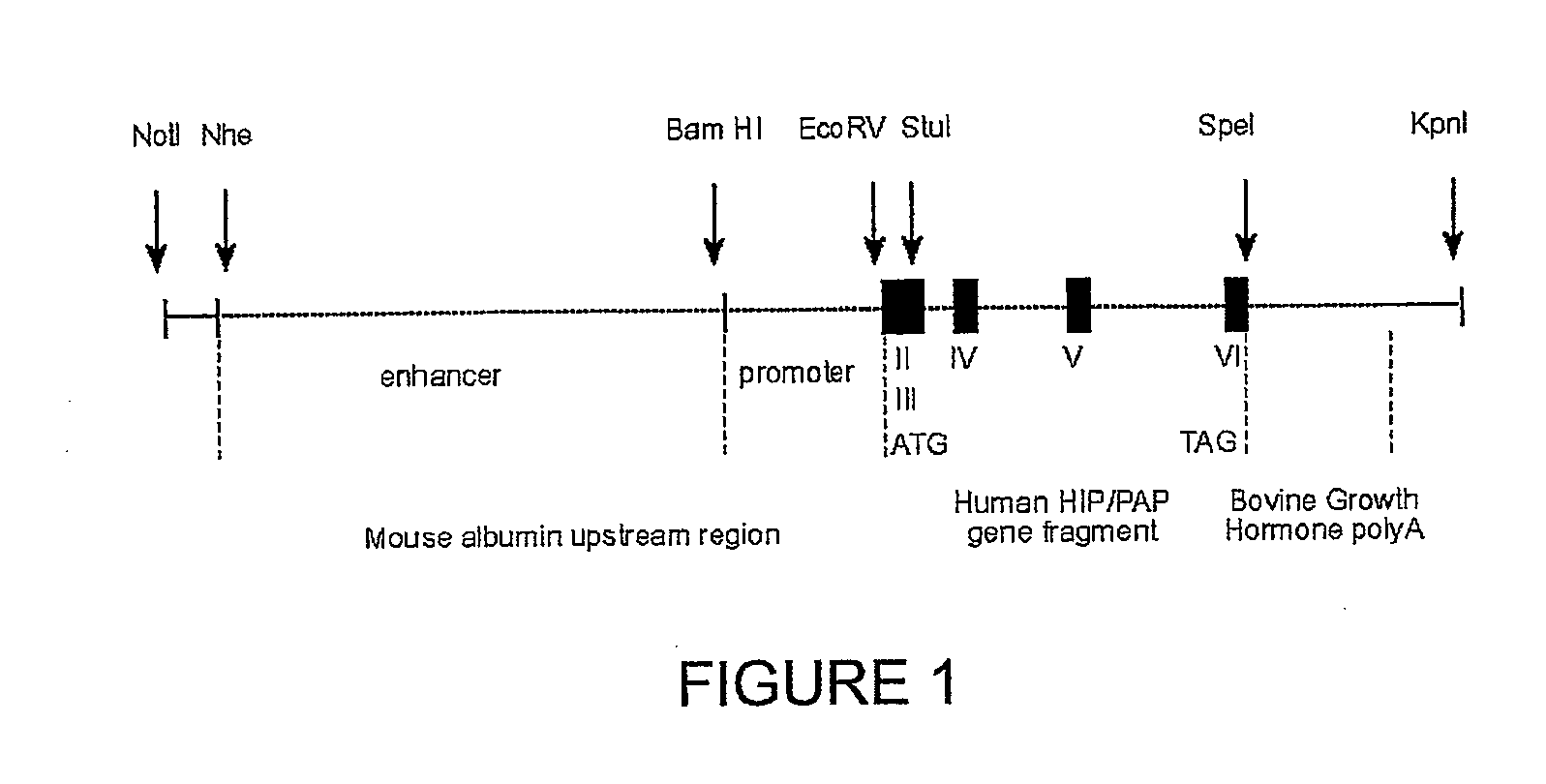
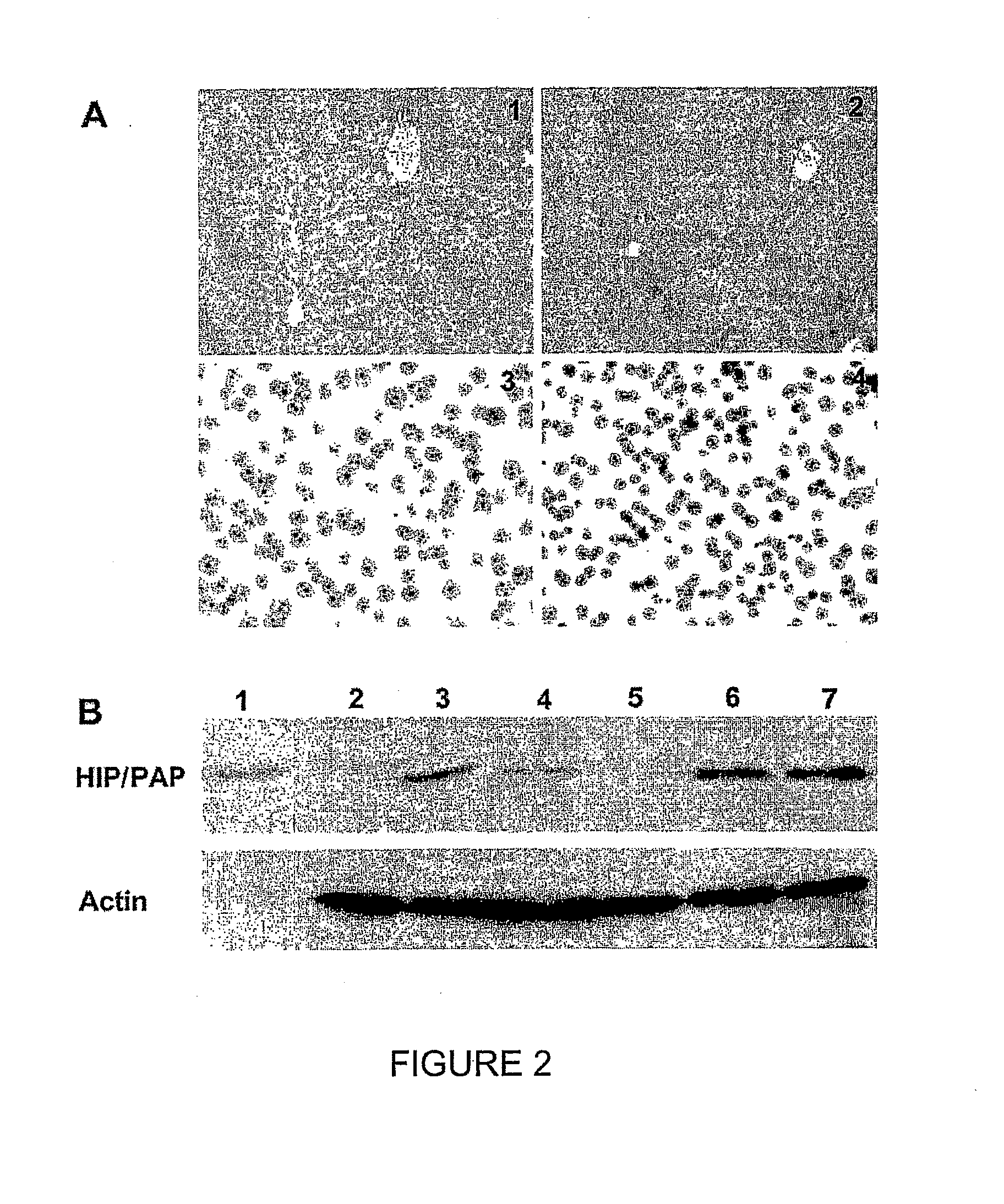
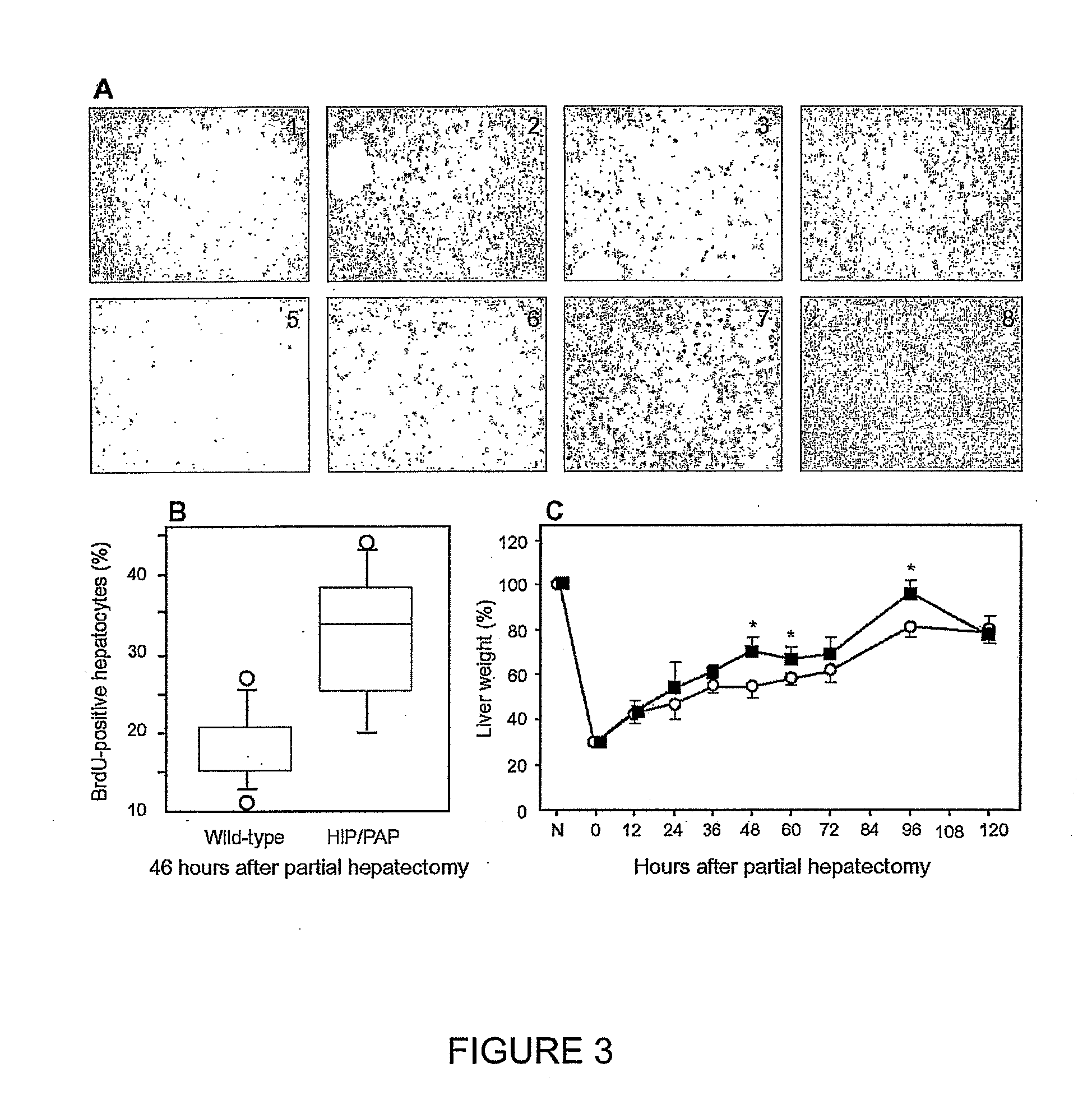
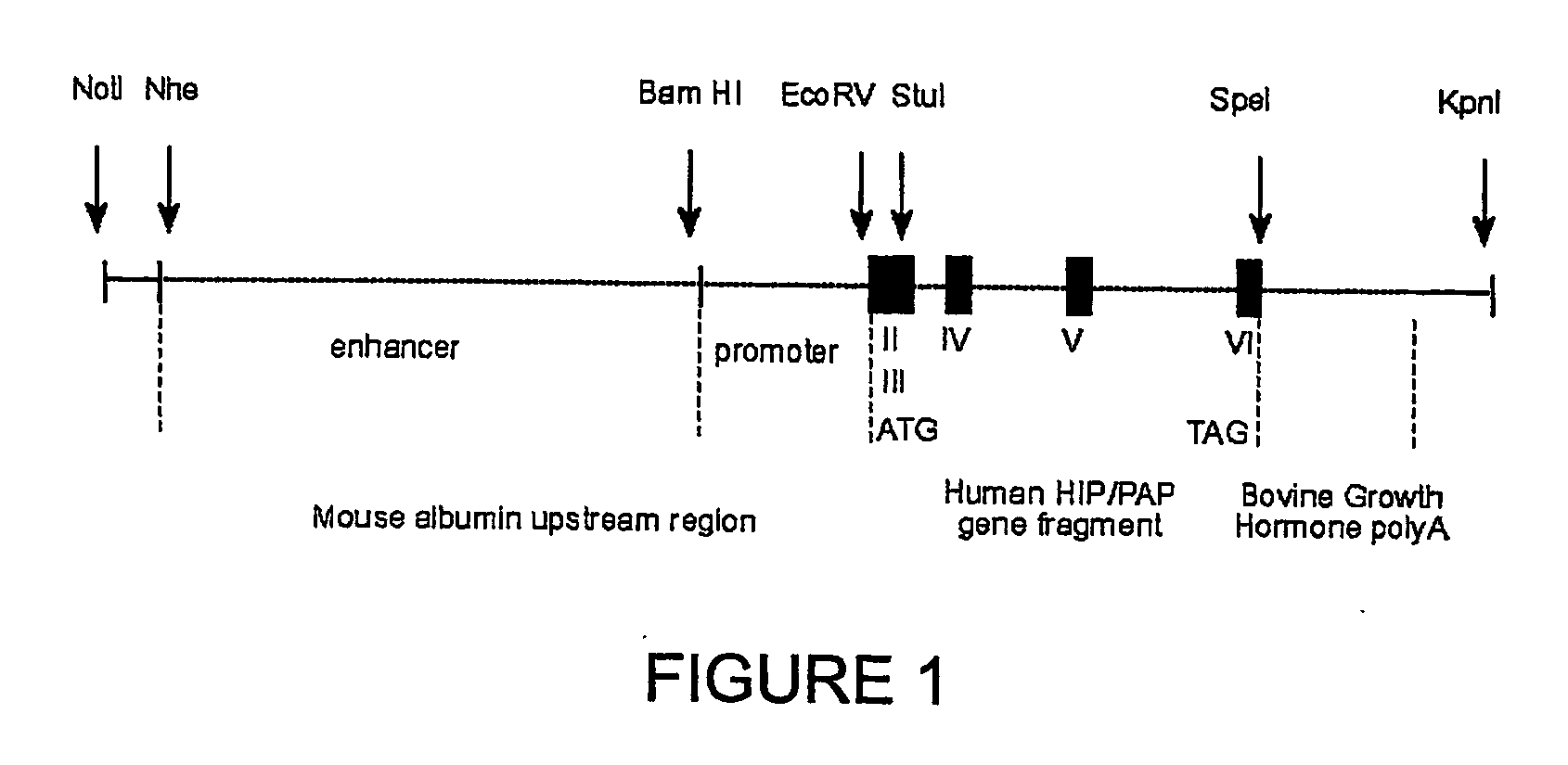
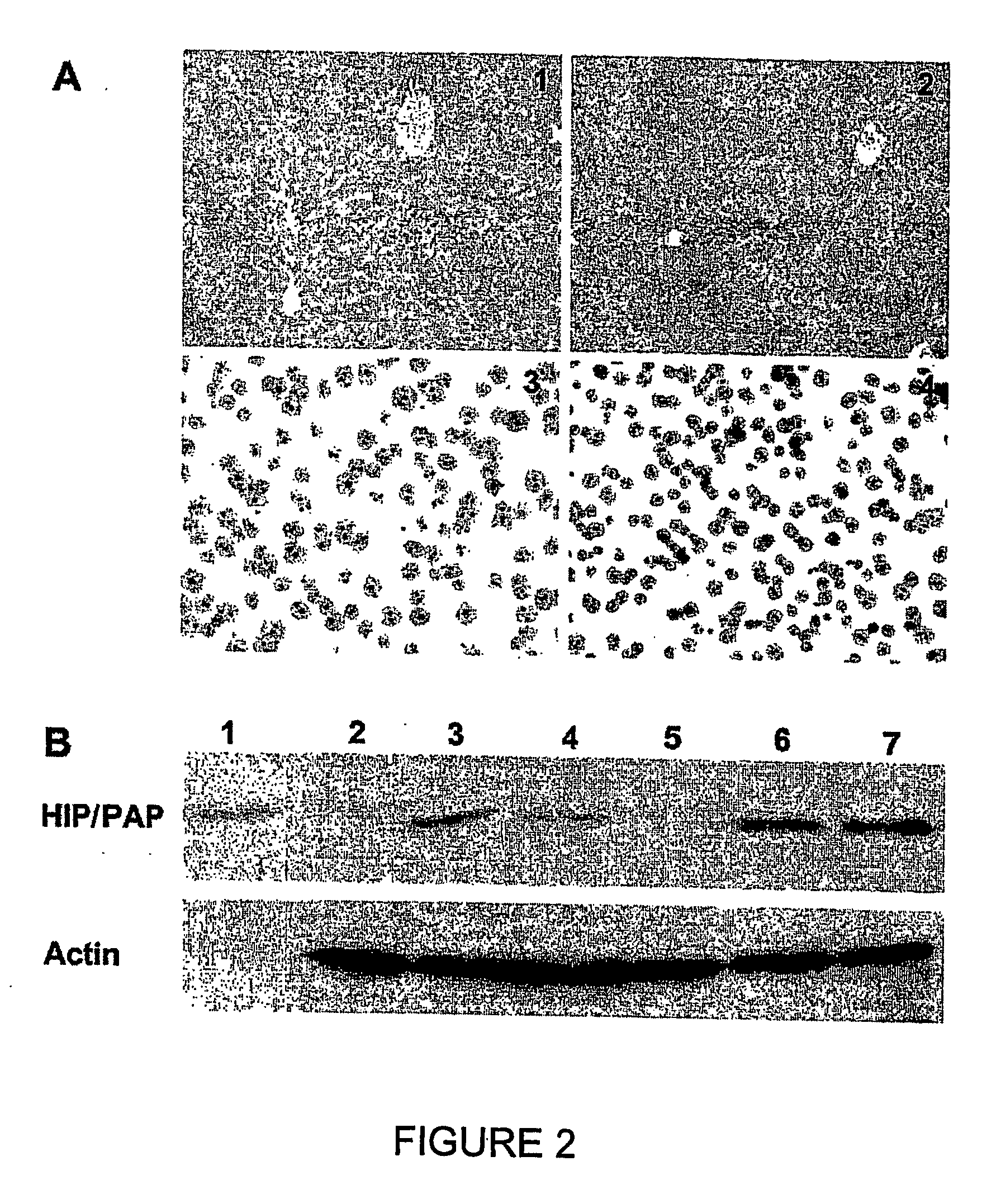
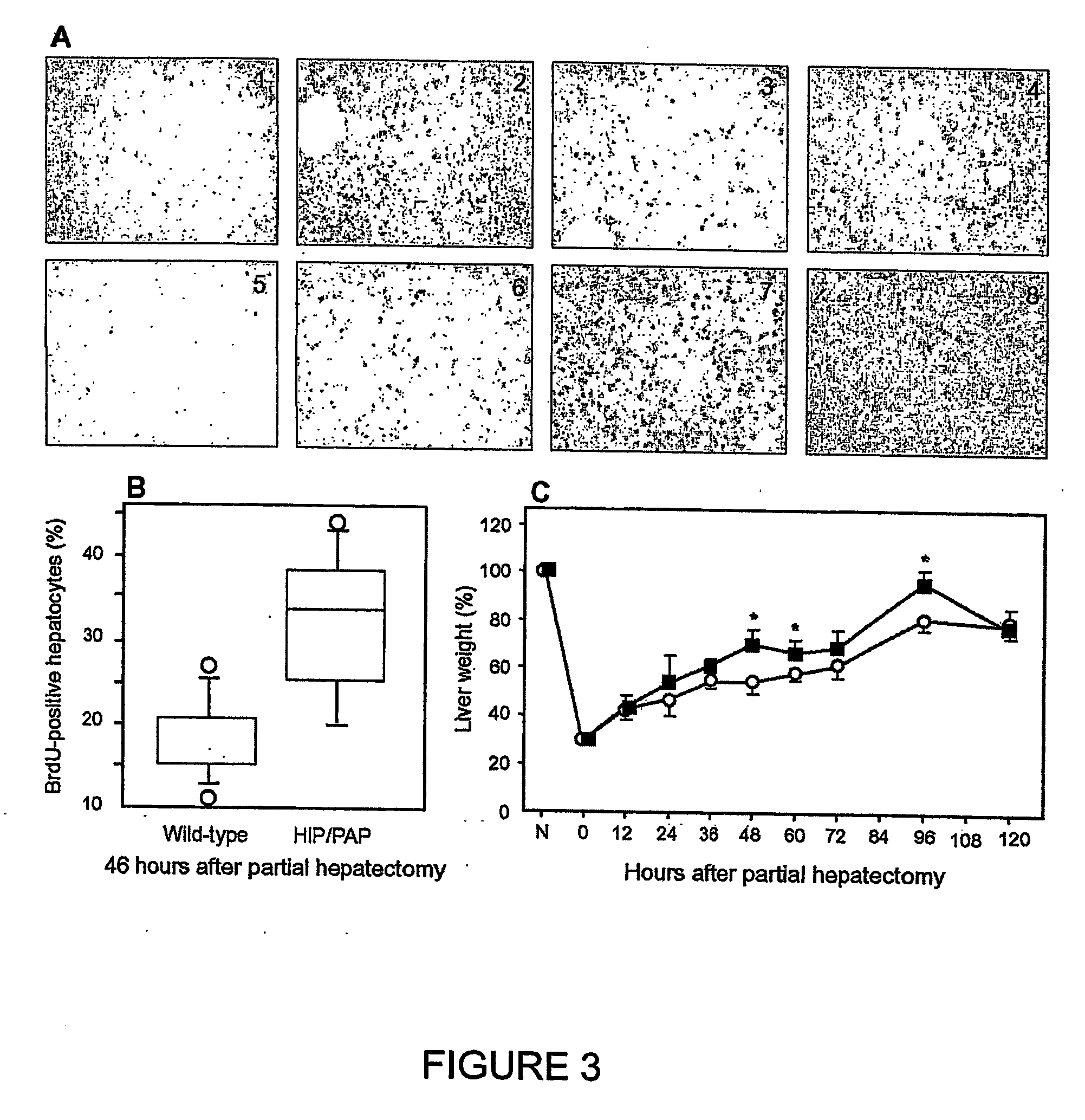
HIP/PAP Polypeptide Composition for Use in Liver Regeneration and for the Prevention of Liver Failure
Owner:VIVO BIOSCI CO LTD
GSTM3 (Glutathione S-Transferase M3) gene methylation quantitative detection method for hepatic failure prognosis and kit
InactiveCN103525907ASimple and fast operationHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementReference genesDeoxyribose
The invention provides a GSTM3 (Glutathione S-Transferase M3) gene methylation quantitative detection method for hepatic failure prognosis and a kit, and provides a method and a device for quantitatively detecting the methylation degree of a glutathione S-transferase M3 promoter. The kit is internally provided with a reagent for extracting peripheral blood genome DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid), a reagent for modifying the genome DNA, a 5*premixing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system, a methylation specific primer pair and a Taqman fluorescence probe aiming at a target gene GSTM3 promoter, and a specific primer pair and a Taqman fluorescence probe of reference genes ALU-C4. According to the GSTM3 gene methylation quantitative detection method for the hepatic failure prognosis and the kit, the methylation specific primer pair and the probe of the target gene GSTM3 promoter and the specific primer pair and the probe of the reference genes can be used for carrying out a real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on the peripheral blood genome DNA; a quantitative methylation specific PCR method is used for detecting a threshold value circulation value of the target gene GSTM3 and the reference genes ALU-C4 and calculating a gene GSTM3 methylation quantitative value, so as to be good for evaluating illness states, judging the prognosis and guiding the treatment.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Isolated liver stem cells
The present invention relates to isolated liver progenitor stem cells, and cell population thereof, wherein said progenitor stem cells originate from adult liver, esp. of human. The present invention also relates to the use of said isolated progenitor stem cells in medicine, hepatology, inborn errors of liver metabolism, transplantation, infectious diseases, liver failure. The present invention also relates to methods of isolating these cells, their culture, characterization before and after differentiation, and their use for transplantation, animal models of human disease, toxicology and pharmacology.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
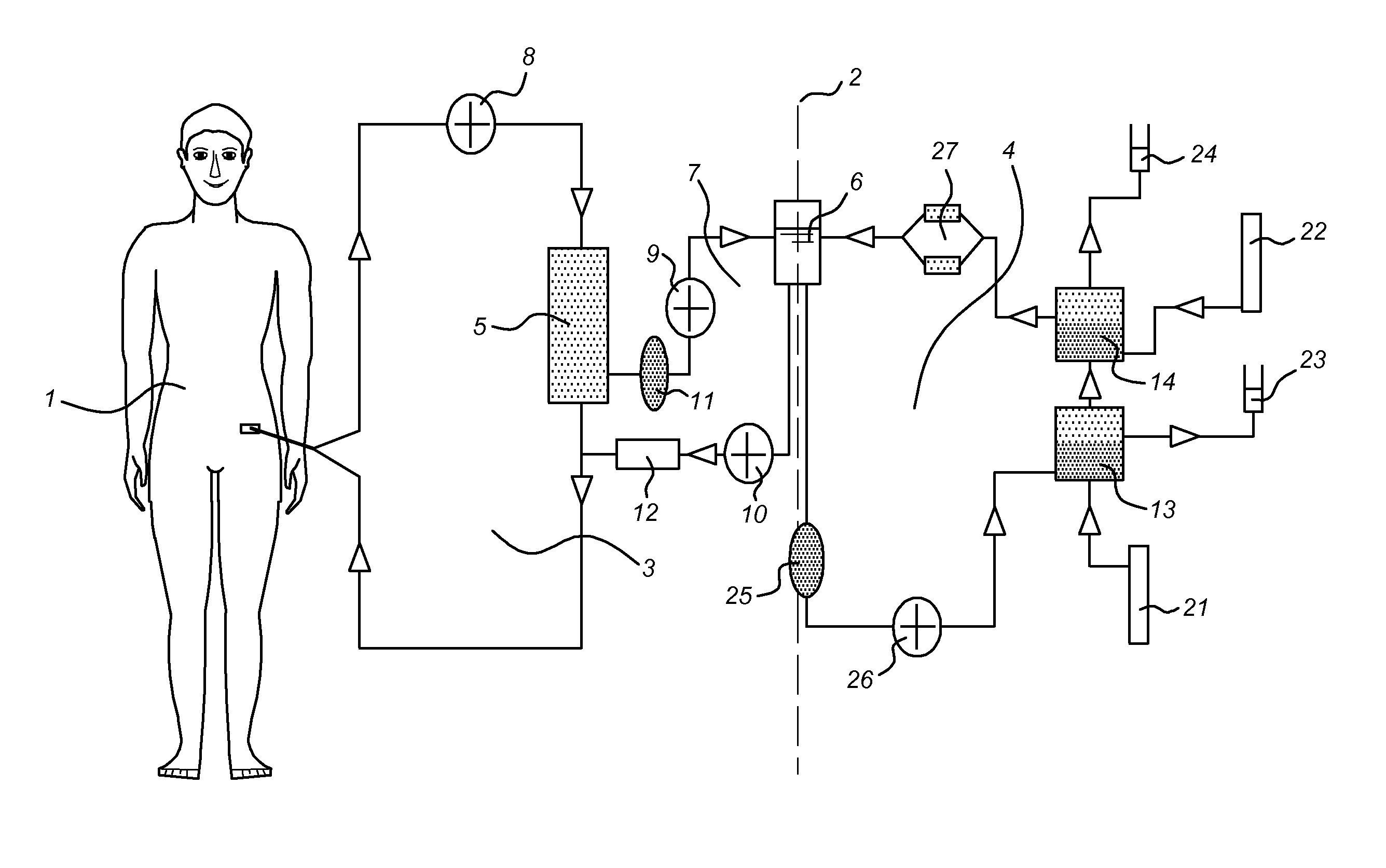
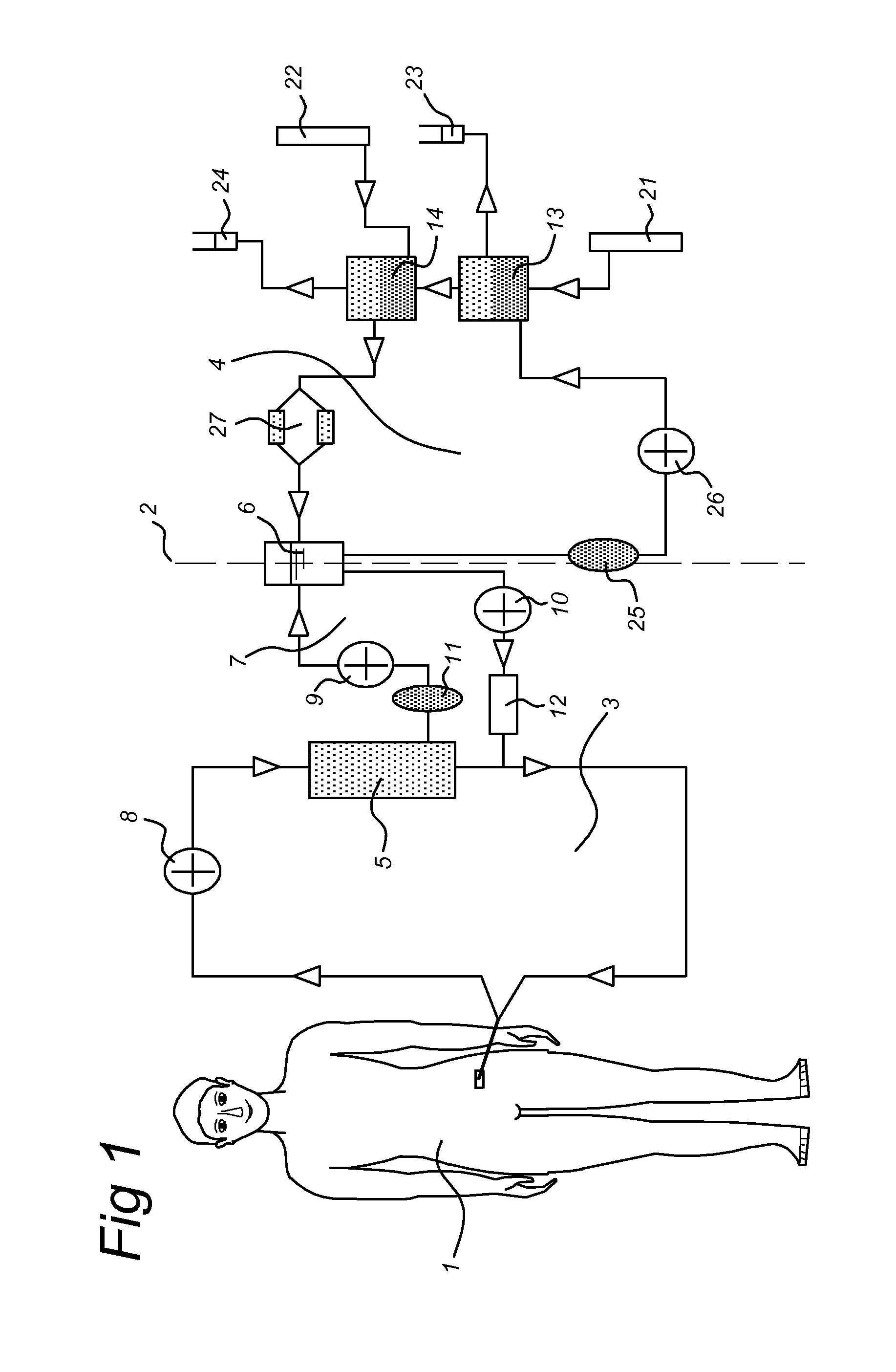
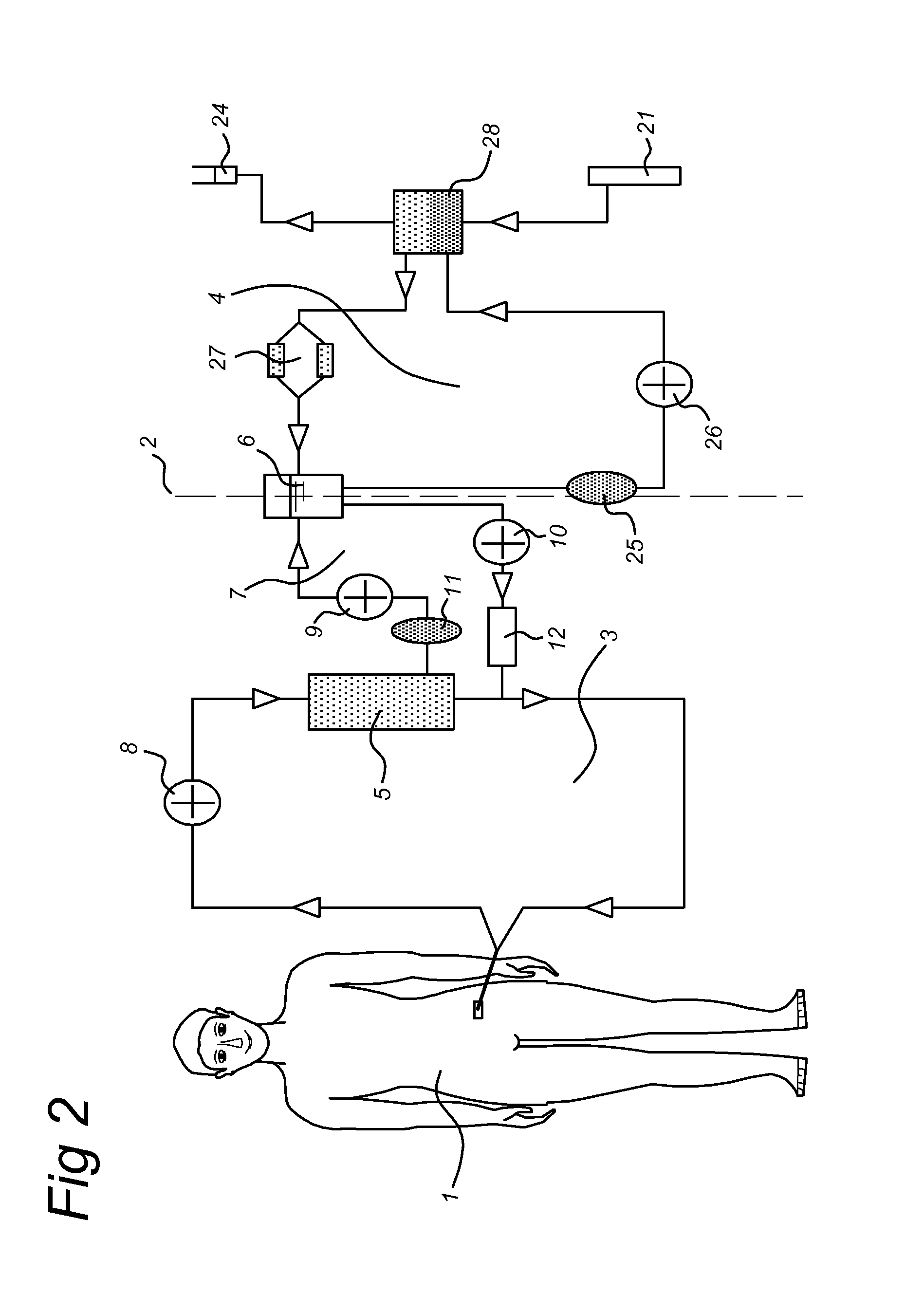
Liver support system
ActiveUS20150273127A1Easy to eliminateSufficient amountIon-exchange process apparatusMembranesLiver dialysisHemodialysis
An artificial, extracorporeal system for liver replacement and / or assistance, comprises a liver dialysis device for conducting hemodialysis on a patient suffering from liver failure. The liver dialysis device comprises a first standard hollow fiber membrane dialyzer which does not allow passage of an essential amount of albumin over the membrane wall and which is perfused with the patient's blood, and a second hollow fiber membrane dialyzer which allows the passage of essential but defined amounts of albumin over the membrane wall and which receives the blood of the first standard hemodialyzer. The filtrate space is closed off from the lumen space of the hollow fibers and is populated by adsorbent material which may comprise one or more different adsorbents.
Owner:GAMBRO LUNDIA AB
Differentiated human liver cell cultures and their use in bioartificial liver systems
InactiveUS20120111795A1Function increaseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsLiver failureOrganism
The present invention concerns human hepatocyte cell line cultures and their use in bioartificial liver (BAL) systems. These systems are used to treat subjects suffering from liver failure to temporarily compensate for loss of hepatocellular function and generally comprise a bioreactor loaded with functional liver cells. Until now, it has been problematic to acquire cells with a broad spectrum metabolic functionality, resembling that of freshly isolated human hepatocytes, to the extent that they are in fact suitable for successful clinical BAL application The present inventors have managed to develop human hepatocyte cell line cultures that display broad-spectrum metabolic functionality such as to render them particularly suitable for effective clinical BAL application.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
Hip/pap polypeptide compositions for use in liver regeneration and for the prevention of liver failure
This invention is based on the experimental finding that HIP / PAP has mitogenic and antiapoptotic effects in vitro on hepatocytes in primary culture. Moreover, HIP / PAP is a mitogenic and anti-apoptotic molecule for hepatocytes, in vivo, during liver failure and liver regeneration. The present invention is also based on the experimental finding that HIP / PAP administration has no adverse effects in mammals. This invention concerns a pharmaceutical composition for stimulating liver regeneration in vivo including after chronic / acute liver failure, comprising an effective amount of a polypeptide comprising an amino acid sequence having 90% amino acid identity with the polypeptide consisting of the amino acid sequence starting at the amino acid residue (36) and ending at the amino acid residue (175) of sequence SEQ ID No. 1, in combination with at least one physiologically acceptable excipient.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +1
Humanized adipose-derived stem cell exosome and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN109749990ADigestive systemSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHigh concentrationHepatic Diseases
The invention provides an exosome from adipose-derived stem cells and a preparation method thereof. The exosome from the adipose-derived stem cells can be used for treating an acute hepatic failure, liver fibrosis, liver cirrhosis and other liver diseases. The exosome from the adipose-derived stem cells can remarkably increase the survival rate of a patient with the acute hepatic failure and evencan realize the 100% survival rate of the patient with the acute hepatic failure under high concentration.
Owner:博品(上海)生物医药科技有限公司
Isolated Liver Stem Cells
ActiveUS20080311094A1Improve propertiesSimple methodAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticProgenitorAdult liver
Isolated liver progenitor stem cells and cell populations of isolated liver progenitor stem cells are disclosed. The progenitor stem cells originate from adult liver, especially human adult liver. The isolated progenitor stem cells have uses in medicine, hepatology, inborn errors of liver metabolism transplantation, infectious diseases and liver failure. Methods of isolating these cells and their culture is described. The isolated cells are characterized before and after differentiation. Their use for transplantation and as animal models of human disease, toxicology and pharmacology is disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Whole blood perfusion bioartificial liver system
ActiveCN104958795AAchieve continuous treatmentImprove the efficiency of material exchangeDialysis systemsPerfusionKidney
The invention relates to a whole blood perfusion bioartificial liver system which comprises a blood circulation part and a bioartificial liver circulation part. The blood circulation part comprises a blood input port, a blood pump, a hollow fiber column and a blood feedback port which are sequentially connected. The bioartificial liver circulation part comprises a circulation pump, a constant temperature heater, an oxygenator and a bioreactor which are sequentially connected. An inlet of the circulation pump is connected with an outlet of an outer cavity of the hollow fiber column. A liquid outlet of the bioreactor is connected with an inlet of the outer cavity of the hollow fiber column. The bioartificial liver circulation part is further provided with two bypass pipelines. The whole blood perfusion bioartificial liver system further comprises a liquid input part and a dialyzate drainage part. The whole blood perfusion bioartificial liver system is safe, reliable and efficient, achieves continuous treatment, combines the venous transfusion and part kidney dialysis functions, is comprehensive, and provides effective support for hepatic failure patients.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Drug for treating end-stage liver diseases caused by chronic hepatitis B and preparation method of drug
InactiveCN104383055AEasy to prepareAbundant raw materialsDigestive systemPlant ingredientsAngelica Sinensis RootRadix Astragali seu Hedysari
The invention discloses a drug for treating end-stage liver diseases caused by chronic hepatitis B. The drug is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 30-60 parts of astragalus, 20-30 parts of radix pseudostellariae, 20-30 parts of fried rhizoma atractylodis macrocephalae, 10-15 parts of tangerine peel, 10-20 parts of angelica sinensis, 10-15 parts of tuckahoe, 3-6 parts of honey-fried licorice roots, 10-20 parts of scutellaria baicalensis and 10-20 parts of ligusticum wallichii. The traditional Chinese medicine composition is prepared by using a conventional traditional Chinese medicine preparation method and comprises the dosage forms such as a decoction, a capsule or powder. The drug for effectively treating end-stage liver diseases including chronic and acute liver failure, chronic liver failure and decompensated cirrhosis caused by chronic hepatitis B is created on the basis of multi-year clinical experience and is remarkable in curative effect.
Owner:THE SECOND HOSPITAL OF NANJING
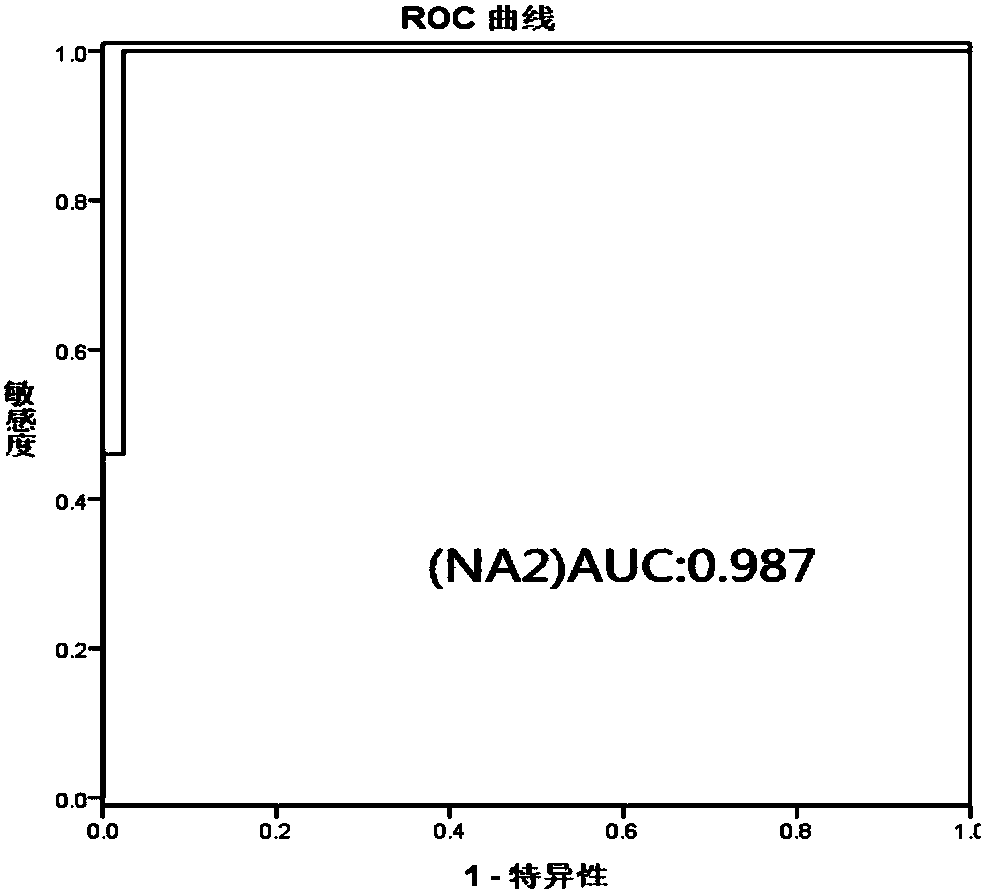
Hepatic failure serum glycoprotein N-glycome map model establishing method
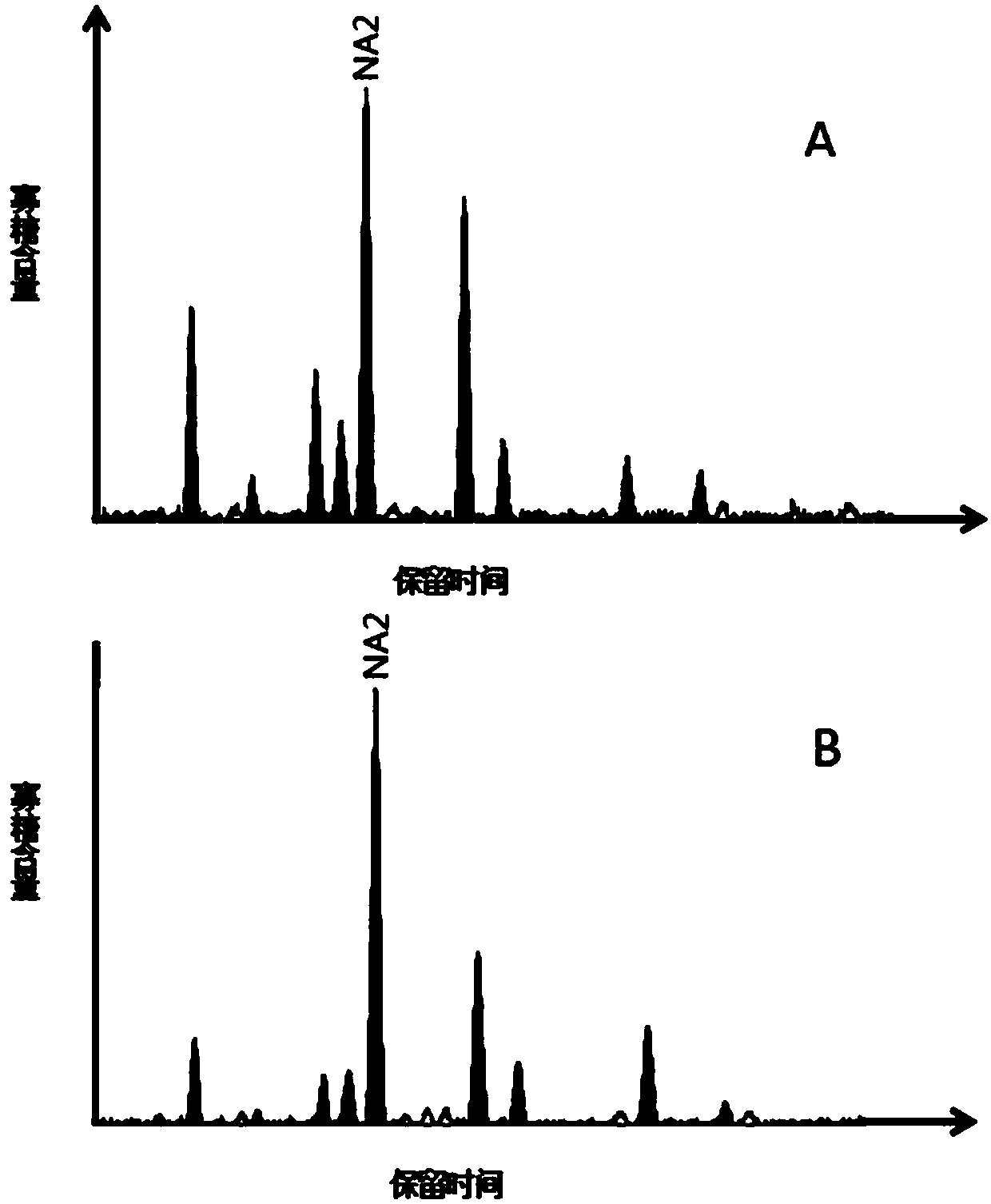
The invention discloses a hepatic failure serum glycoprotein N-glycome map model establishing method, wherein a serum glycoprotein N-glycome map is detected by using a G-Test detection method, the N-glycome map model having significant difference between hepatic failure patients and normal control people is established, and the NA2 having significant expression difference between the hepatic failure group and the normal control group is screened. According to the present invention, the hepatic failure detection sensitivity and the hepatic failure detection specificity of the N-glycome map model constructed based on the method of the present invention respectively are 100.0% and 97.6%; in the subsequent applications, by comparing the peak value of the single-peak NA2 in the serum glycoprotein N-glycome map of the person to be detected and in the map model established by the method of the present invention, the hepatic failure degree of the person to be detected can be detected; and baseon the method of the present invention, a large number of hepatic failure patients can be subjected to conventional and non-invasive detection so as to help doctors and patients timely monitor the occurrence and the progression of hepatic failure, such that the method is expected to be popularized in clinical practice.
Owner:JIANGSU XIANSIDA BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Quantitative detection method and reagent kit of GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis
InactiveCN103805699AGuaranteed specificityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceReference genesGenomic DNA
The invention provides a quantitative detection method and a reagent kit GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis. The invention relates to quantitative detection for gene methylation, and in particular relates to a quantitative detection method and a reagent kit f GSTP1 (Glutathione S-Transferase P1) methylation for predicting hepatic failure prognosis. The reagent kit contains a reagent for extracting genomic DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid), a reagent for modifying the genomic DNA, a 5x premixing PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) system, a standard substance, positive and negative control, a methylation-specific primer pair aiming at a target gene GSTP1 promoter, a specific primer pair of a reference gene ALU-C4, and a corresponding Taqman fluorescent probe. By extracting peripheral blood genomic DNA and carrying out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR, a quantitative value of the gene GSTP1 methylation is obtained through calculation. The reagent kit provided by the invention can help doctors to determine the pathogenetic condition and prognosis of hepatic failure patients so as to make effective treatment plans.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV QILU HOSPITAL
Tissue engineering microencapsulated hepatocyte and preparation and application thereof
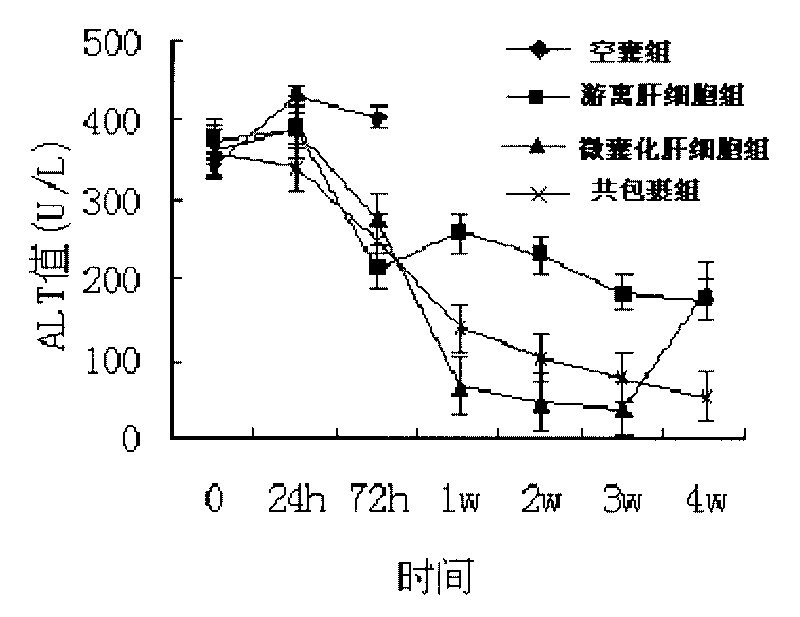
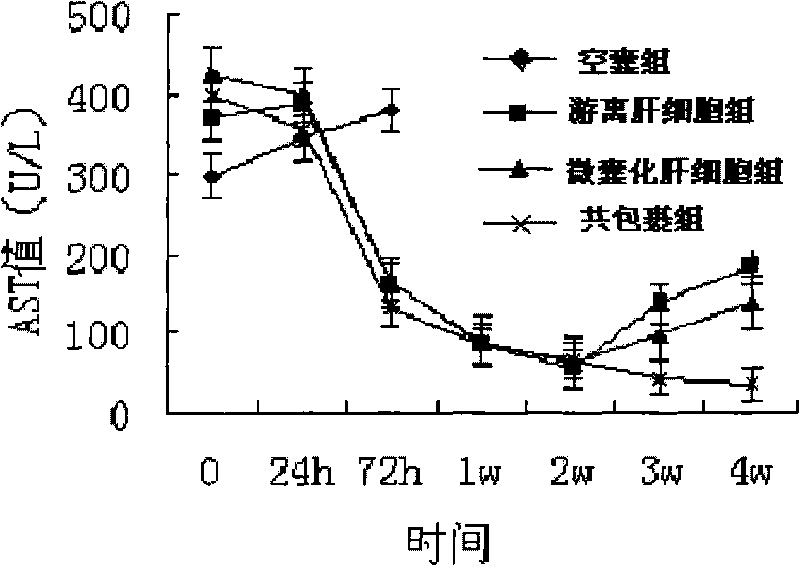
InactiveCN101717767AReduce volumeGood biocompatibilityDigestive systemMammal material medical ingredientsSide effectBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a tissue engineering microencapsulated hepatocyte and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of animal cell tissue engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: adding hepatocytes and vascular endothelial cells in the quantity ratio of 1: (0.5-1) into water solution of sodium alginate for mixing to prepare a cell suspension, wherein the mass percentage concentration of the water solution of sodium alginate is 1.5-2; and then preparing sodium alginate-polylysine-sodium alginate microencapsulated hepatocyte by adopting a high-voltage static microcapsule generator. The invention also discloses the application of the tissue engineering microencapsulated hepatocyte in preparing hepatic failure medicaments; the prepared microencapsulated hepatocyte has the characteristics of small volume, high biocompatibility and favorable permeability, is suitably used as a vector for cell transplantation, and can exert in a host body for a long term so as to avoid the side effects caused by repeatedly using chemical medicaments; in addition, the microencapsulated hepatocyte has simple preparation process, thereby being suitable for large-batch production.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Isolated liver stem cells
Isolated liver progenitor stem cells and cell populations of isolated liver progenitor stem cells are disclosed. The progenitor stem cells originate from adult liver, especially human adult liver. The isolated progenitor stem cells have uses in medicine, hepatology, inborn errors of liver metabolism transplantation, infectious diseases and liver failure. Methods of isolating these cells and their culture is described. The isolated cells are characterized before and after differentiation. Their use for transplantation and as animal models of human disease, toxicology and pharmacology is disclosed.
Owner:UNIVERSITE CATHOLIQUE DE LOUVAIN
Traditional Chinese medicine for regulating liver regeneration and prevention and treatment method by using same
The invention discloses a compound composition of traditional Chinese medicine granules for regulating liver regeneration and prevention and treatment methods for chronic liver diseases by using the compound alone or in combination with antiviral medicine. The medicine is composed of: 5-30 parts of prepared Chinese foxglove root, 5-30 parts of virgate wormwood, 3-9 parts of turmeric, 3-12 parts of licorice, 3-15 parts of schisandra fruit, 5-15 parts of underleaf pearl, 5-30 parts of diffusa , 5-30 parts of poria, 5-30 parts of coix seed, 5-30 parts of salvia fruit, 1-10 parts of curcuma rhizome, 3-12 parts of dodder, and 5-15 parts of mistletoe For people suffering from chronic liver diseases (drug-induced liver disease, alcoholic or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, autoimmune liver disease, viral hepatitis, etc.) which have high risk of liver failure, liver cirrhosis, and liver cancer, and people suffering from liver cancer or people after liver cancer surgery, clinical and experimental evidences show that the traditional Chinese medicine granules have synergies of regulation of liver regeneration and anti-virus, anti-liver injury, anti-liver fibrosis, and liver cancer prevention, and a relatively high level of clinical evidence based medicine evidences are obtained.
Owner:李瀚旻
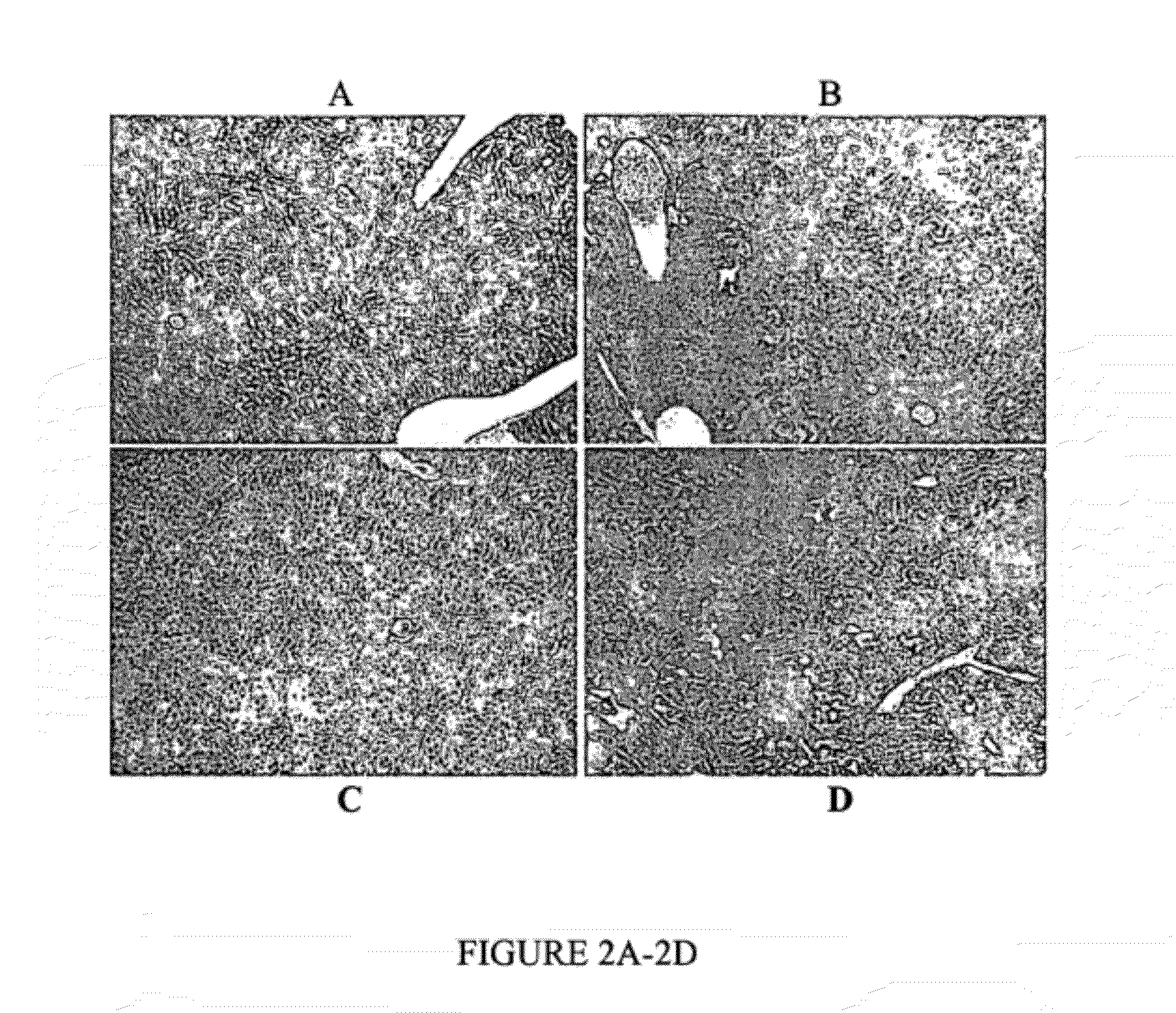
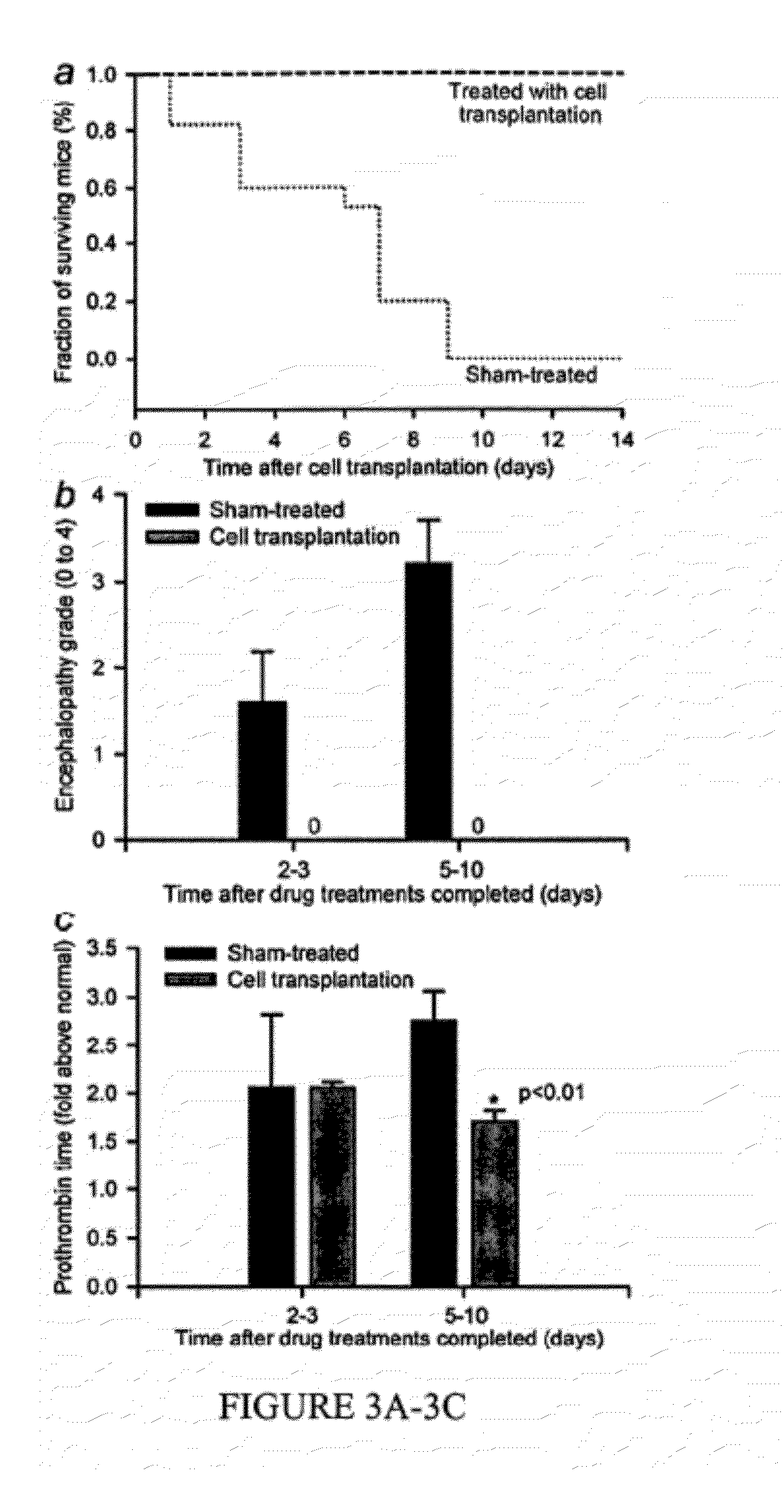
Cell therapy for treatment of liver failure
Disclosed are methods for treating liver failure in a subject comprising transplanting hepatocytes or stem or progenitor cells in an extrahepatic site in the subject in an amount sufficient to provide liver support and / or induce liver regeneration, where the transplanted hepatocytes or stem or progenitor cells are used along with extracellular matrix-coated microcarriers.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
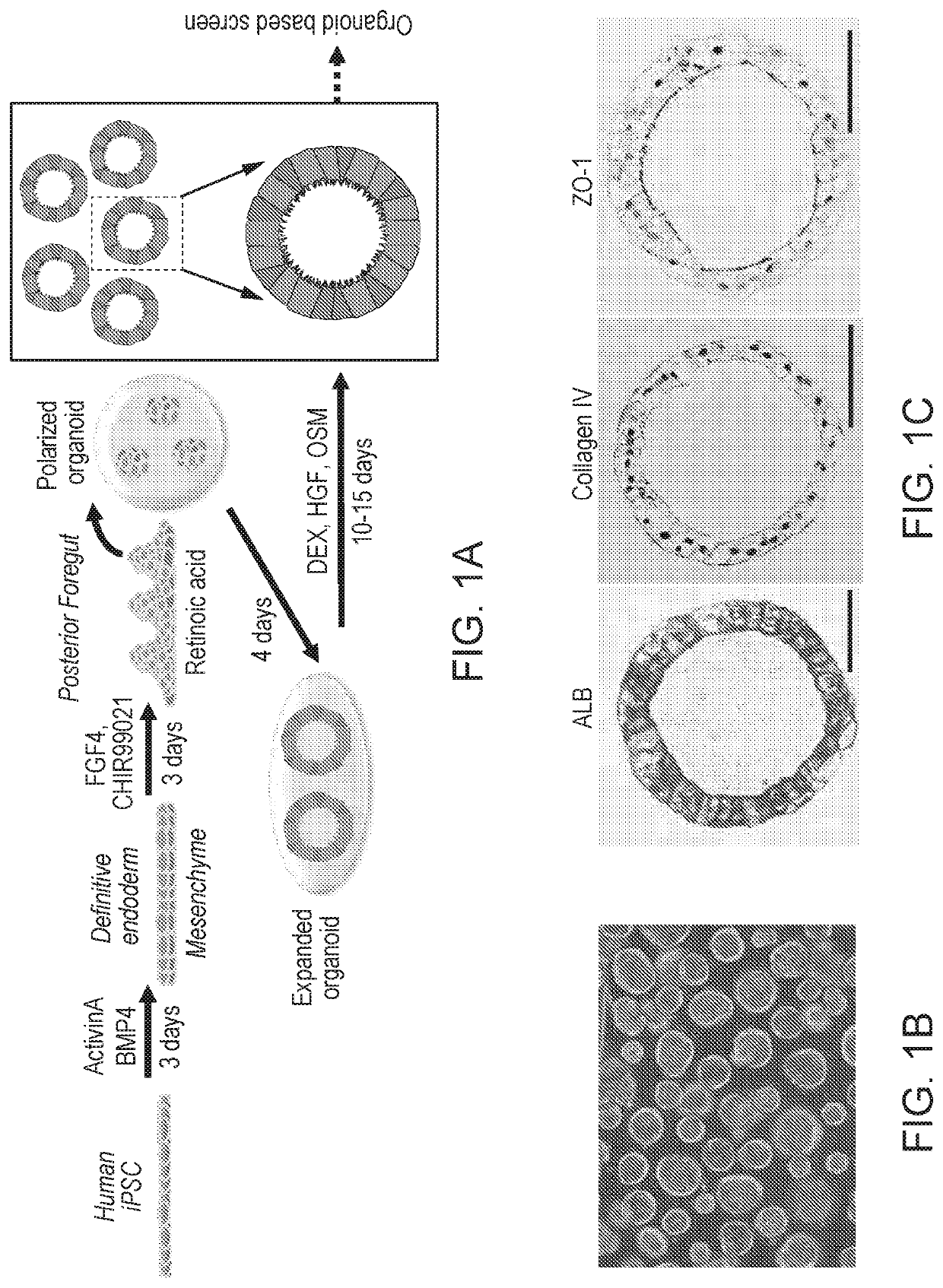
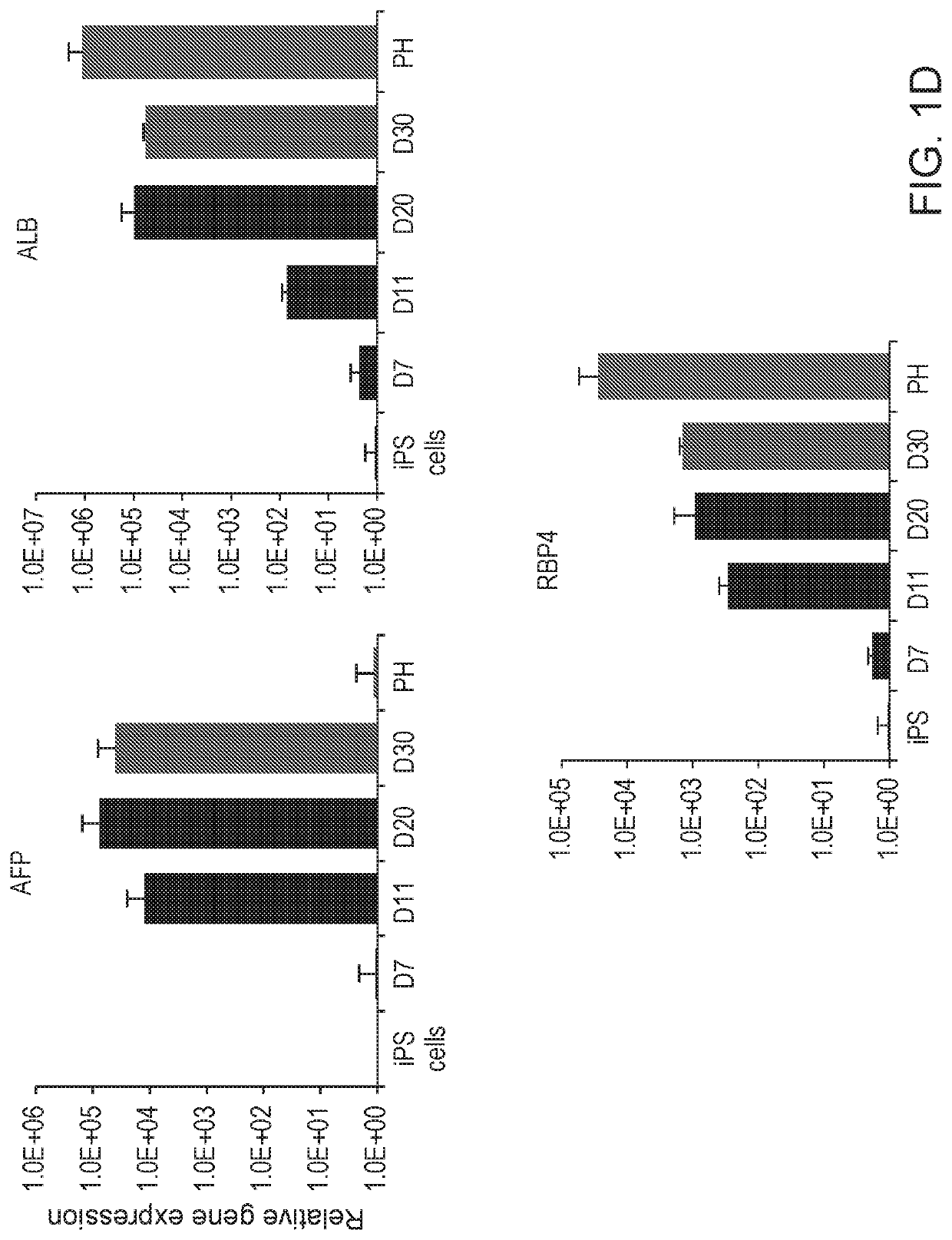
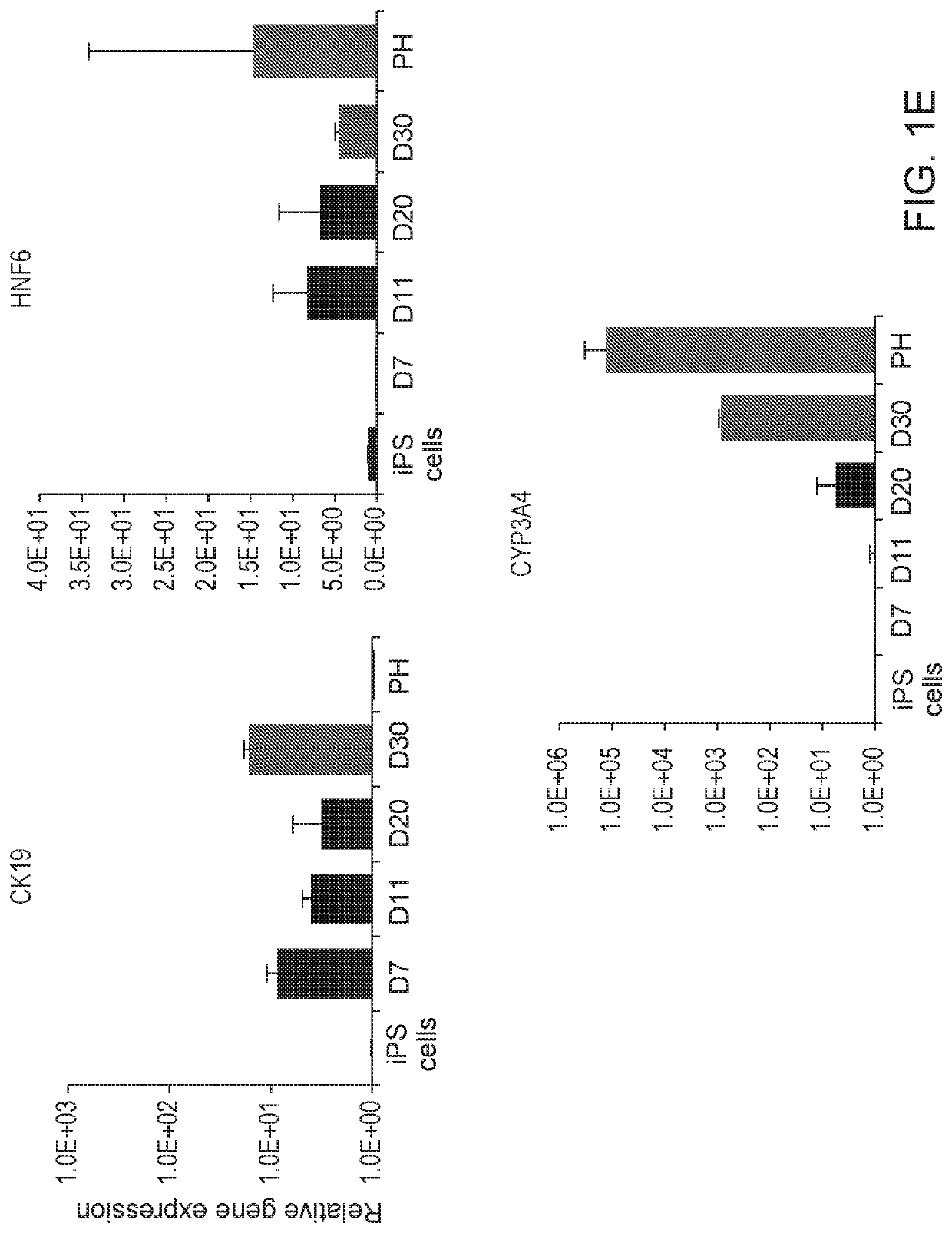
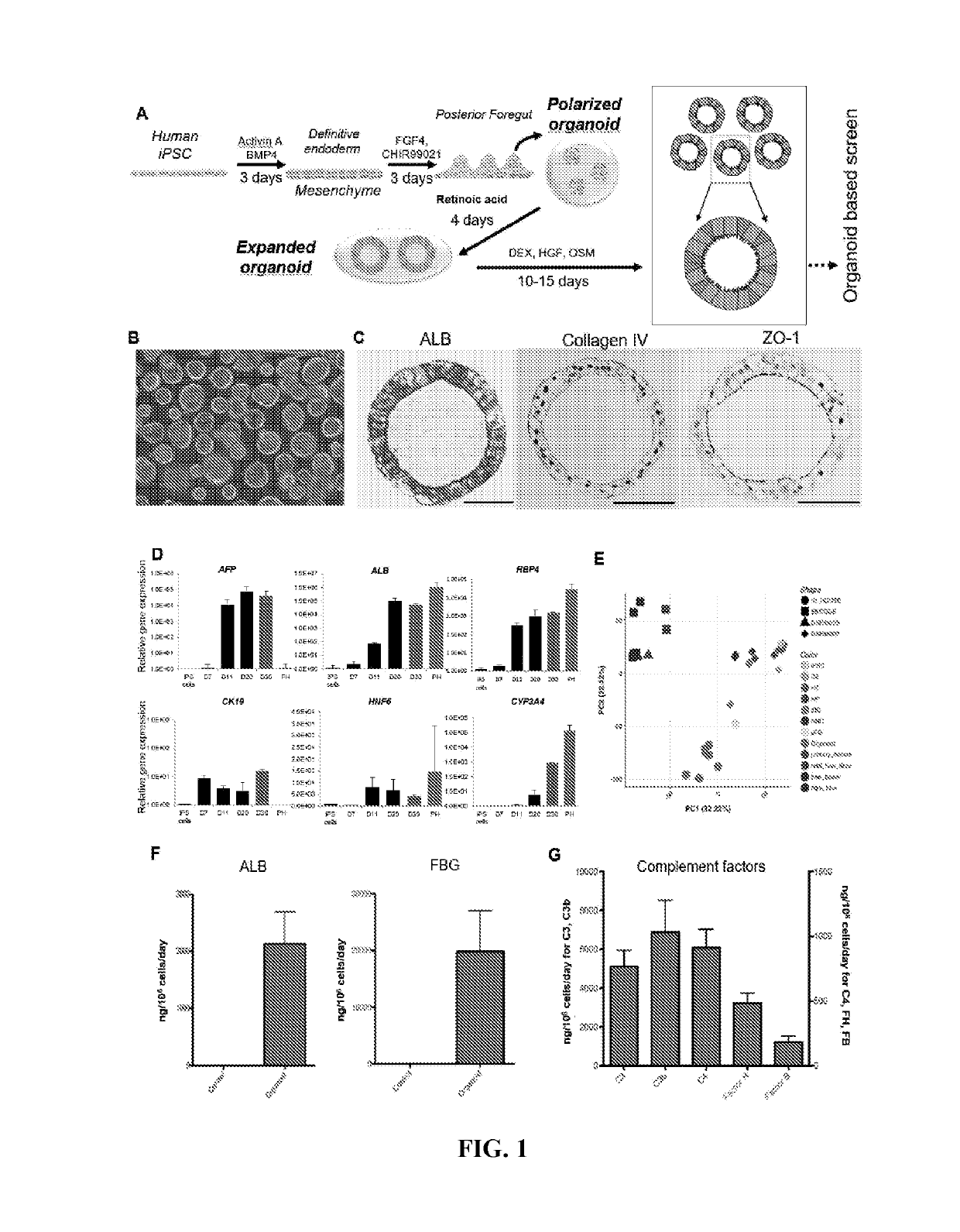
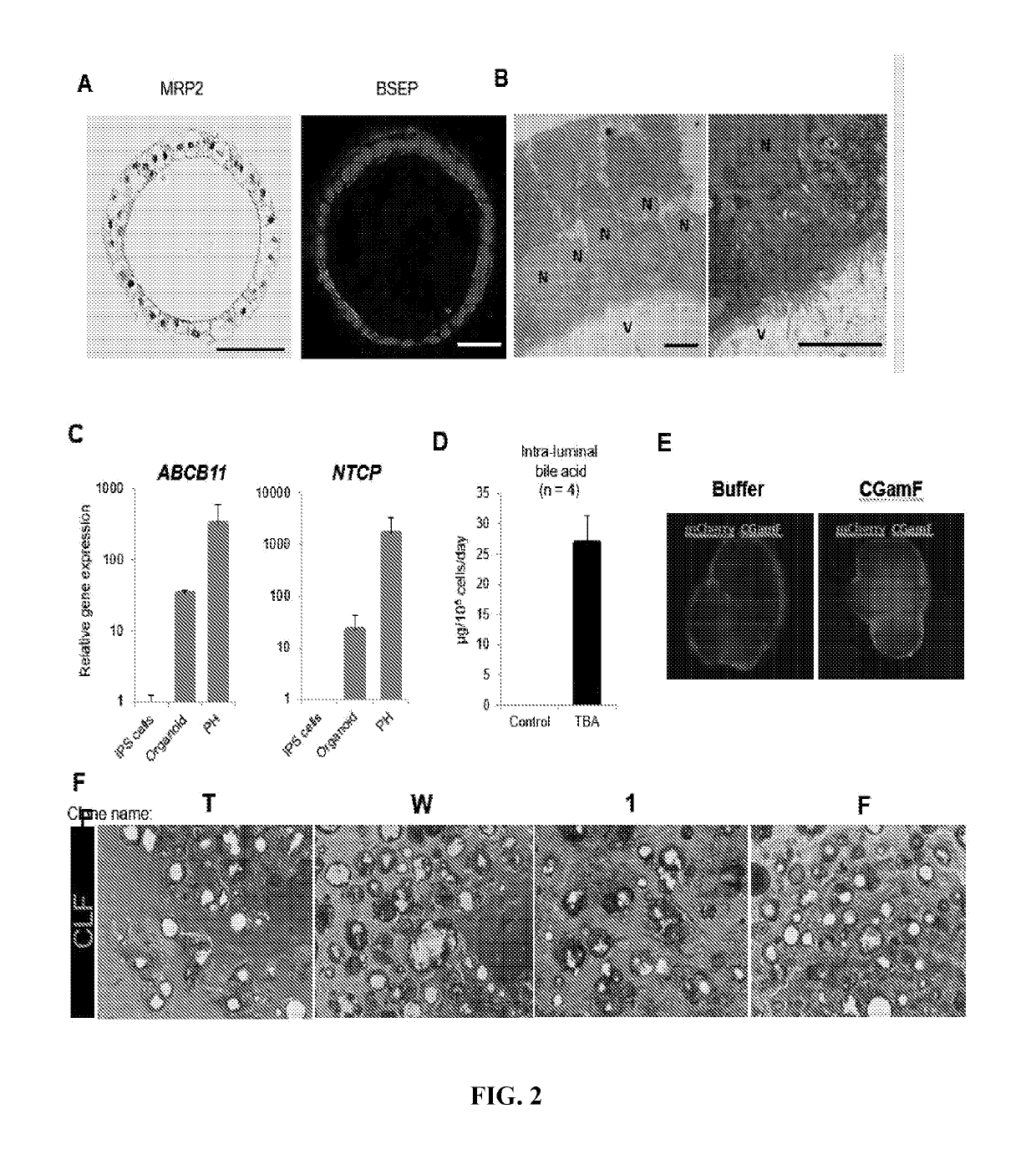
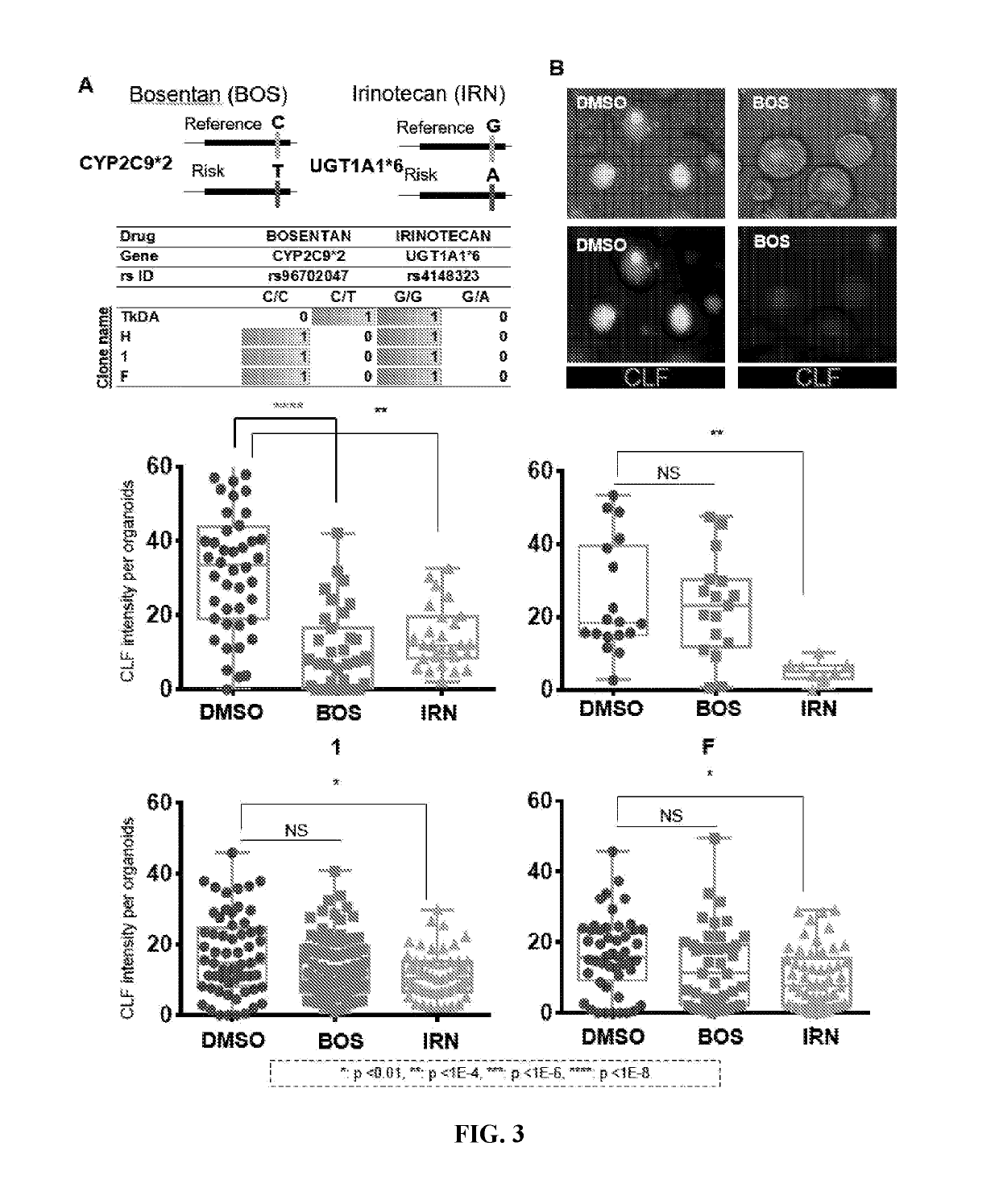
Liver organoid compositions and methods of making and using same
Disclosed are methods of inducing formation of a liver organoid from precursor cells, such as iPSC cells. The disclosed liver organoids may be used for screening for a serious adverse event (SAE), such as liver failure and / or drug induced liver injury (DILI), and / or drug toxicity. The disclosed liver organoids may also be used to treat an individual having liver damage, or for identifying a preferred therapeutic agent.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Liver organoid compositions and methods of making and using same
Disclosed are methods of inducing formation of a liver organoid from precursor cells, such as iPSC cells. The disclosed liver organoids may be used for screening for a serious adverse event (SAE), such as liver failure and / or drug induced liver injury (DILL), and / or drug toxicity. The disclosed liver organoids may also be used to treat an individual having liver damage, or for identifying a preferred therapeutic agent.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com