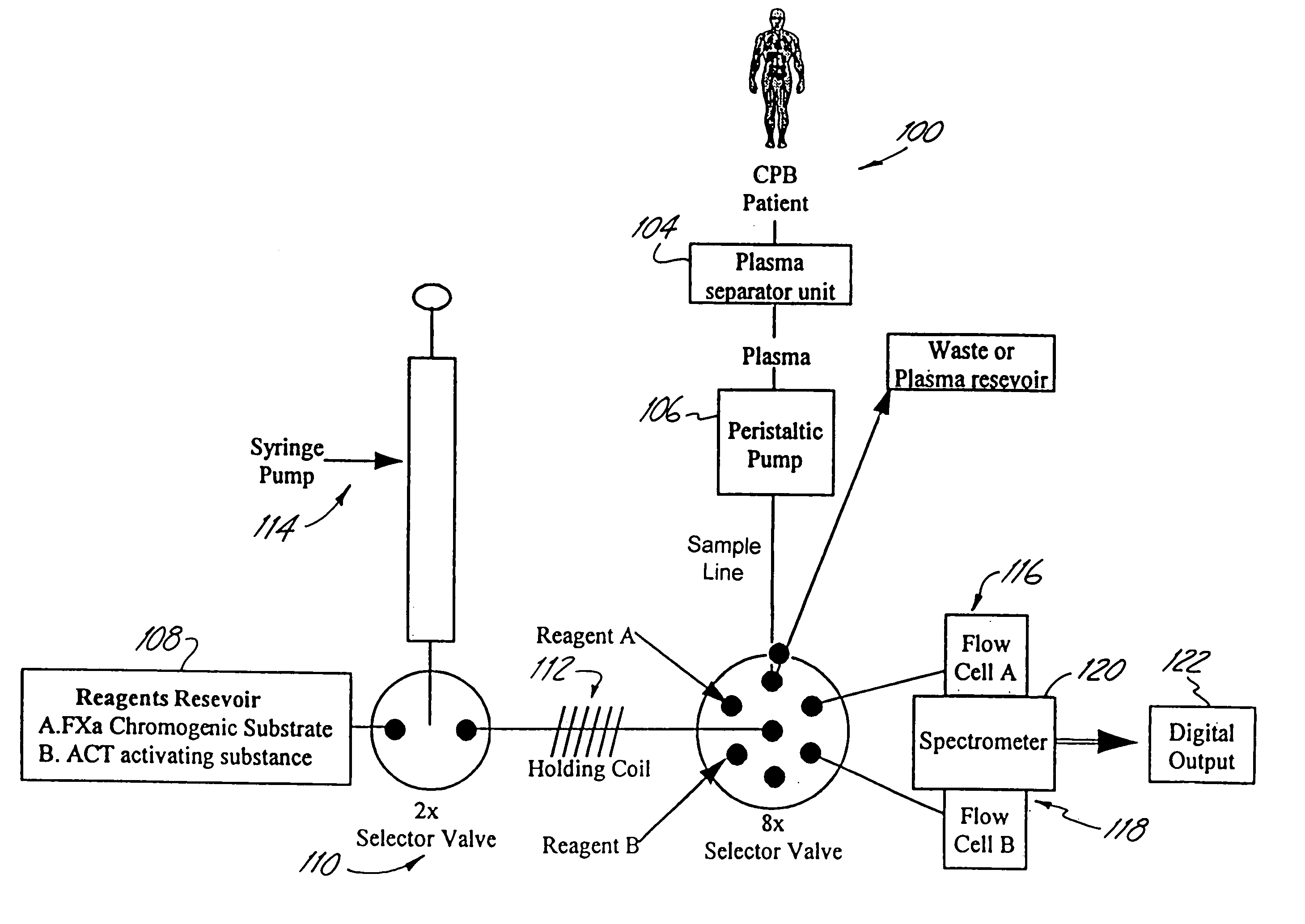
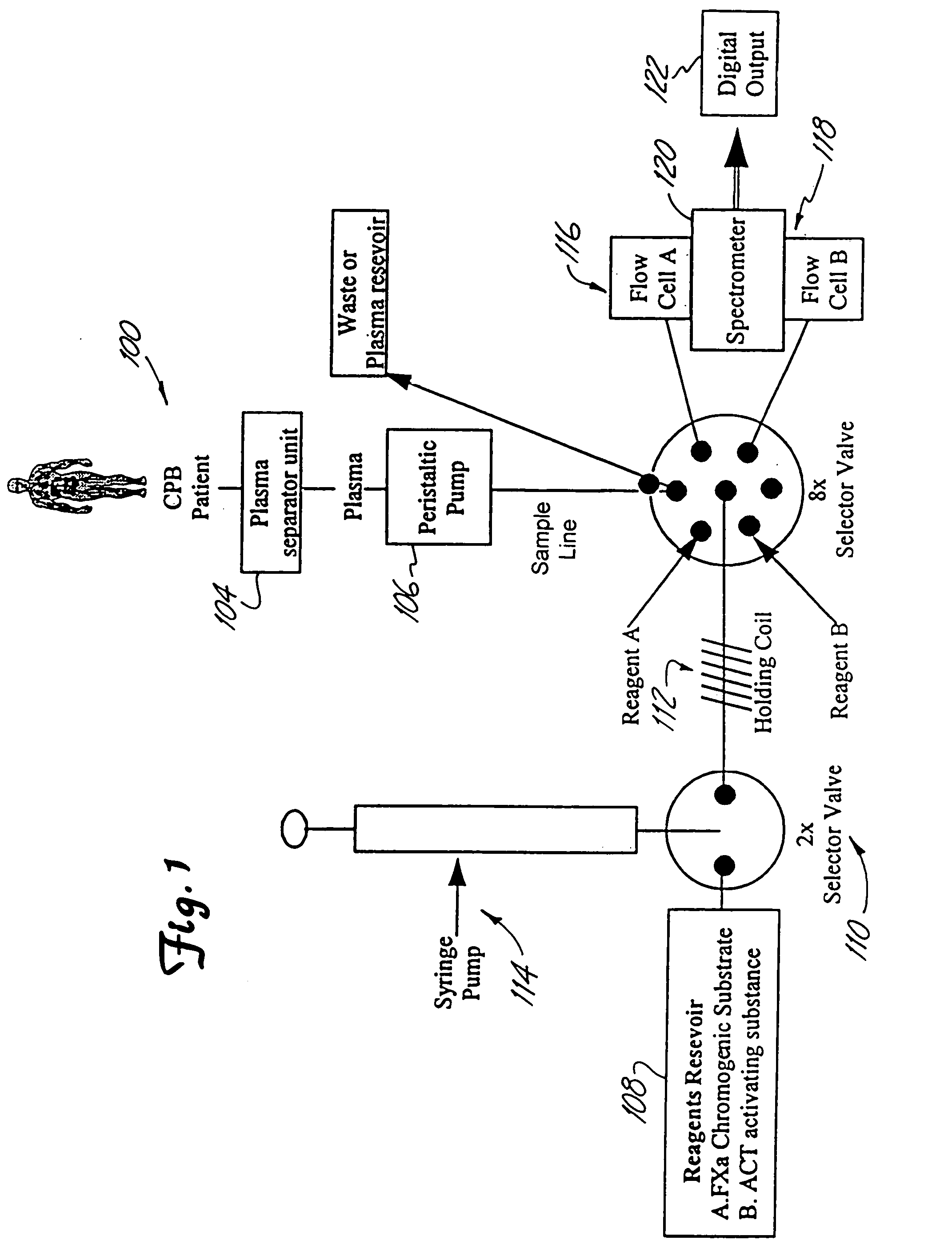
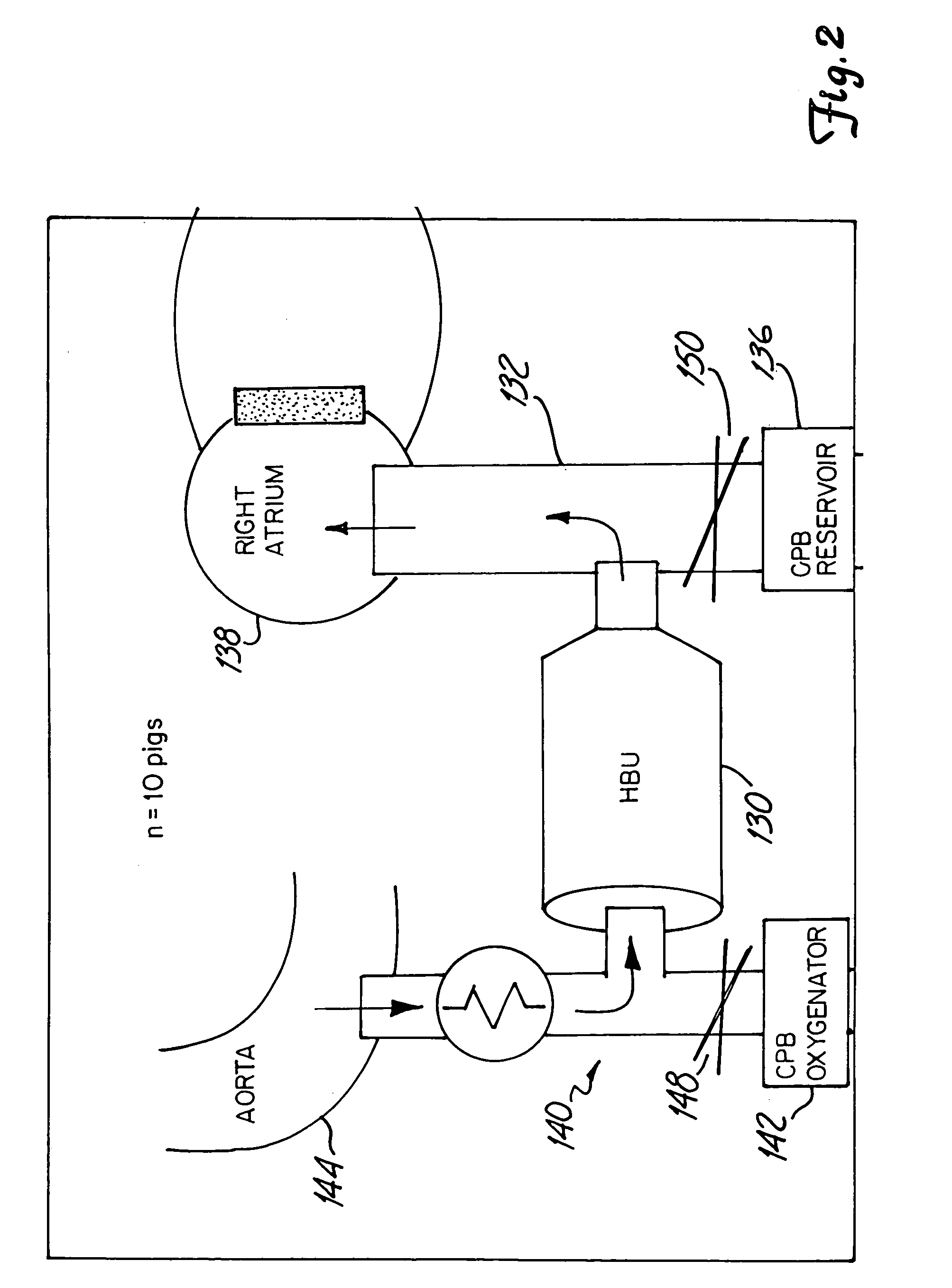
Patents
Literature
43 results about "Cardiopulmonary bypass" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) is a technique in which a machine temporarily takes over the function of the heart and lungs during surgery, maintaining the circulation of blood and the oxygen content of the patient's body. The CPB pump itself is often referred to as a heart–lung machine or "the pump". Cardiopulmonary bypass pumps are operated by perfusionists. CPB is a form of extracorporeal circulation. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation is generally used for longer-term treatment.
Vascular filter system for cardiopulmonary bypass
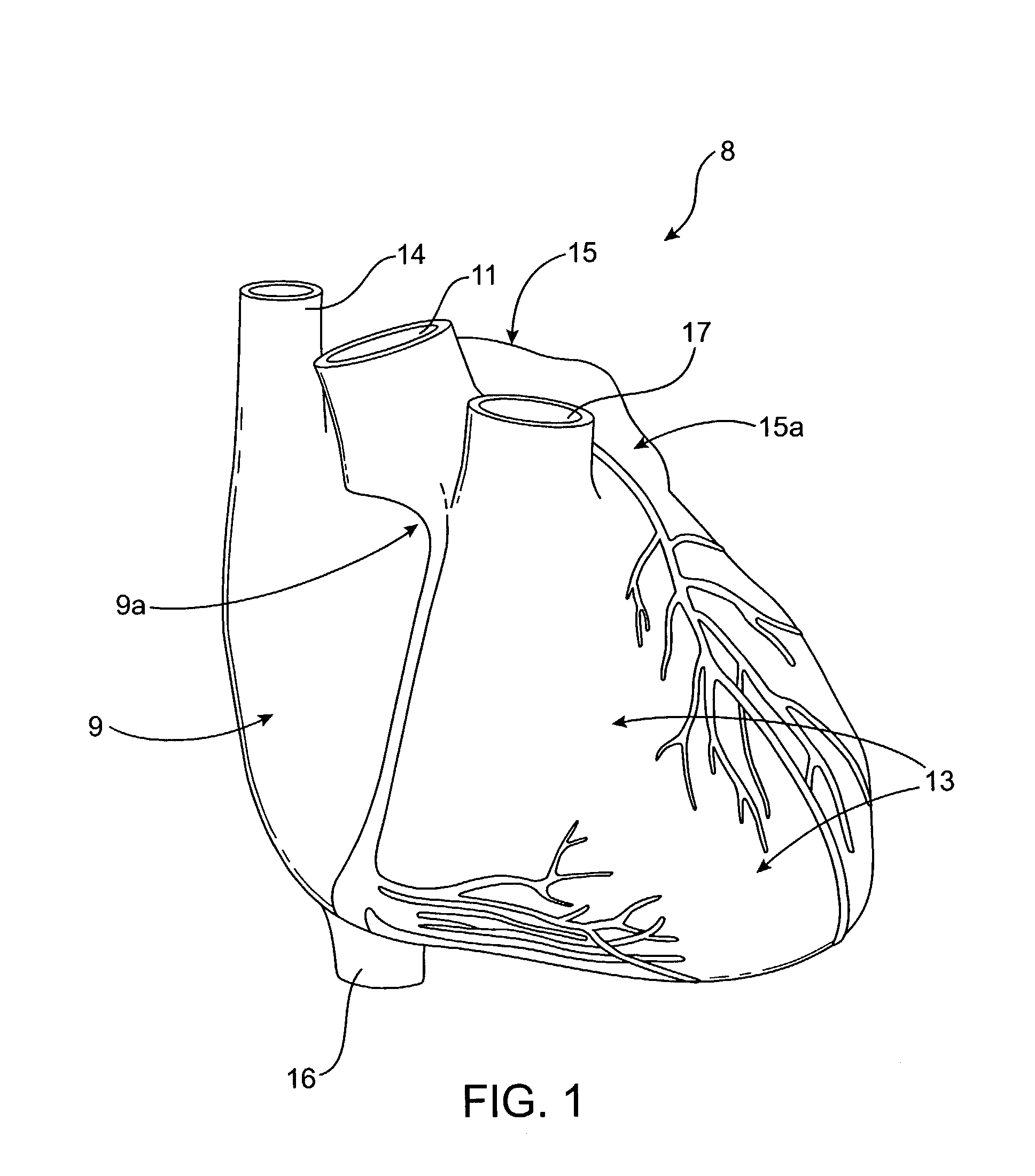
InactiveUS7229463B2Other blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A removable vascular filter system for capture and retrieval of emboli while allowing continuous perfusion of blood during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure, comprising a porous filter membrane with variable diameter holes, and a filter membrane support structure. The system may minimize the incidence of stroke, myocardial infarction or other clinical complications that may be associated with cardiopulmonary bypass procedures.
Owner:CARDINAL HEALTH SWITZERLAND 515 GMBH
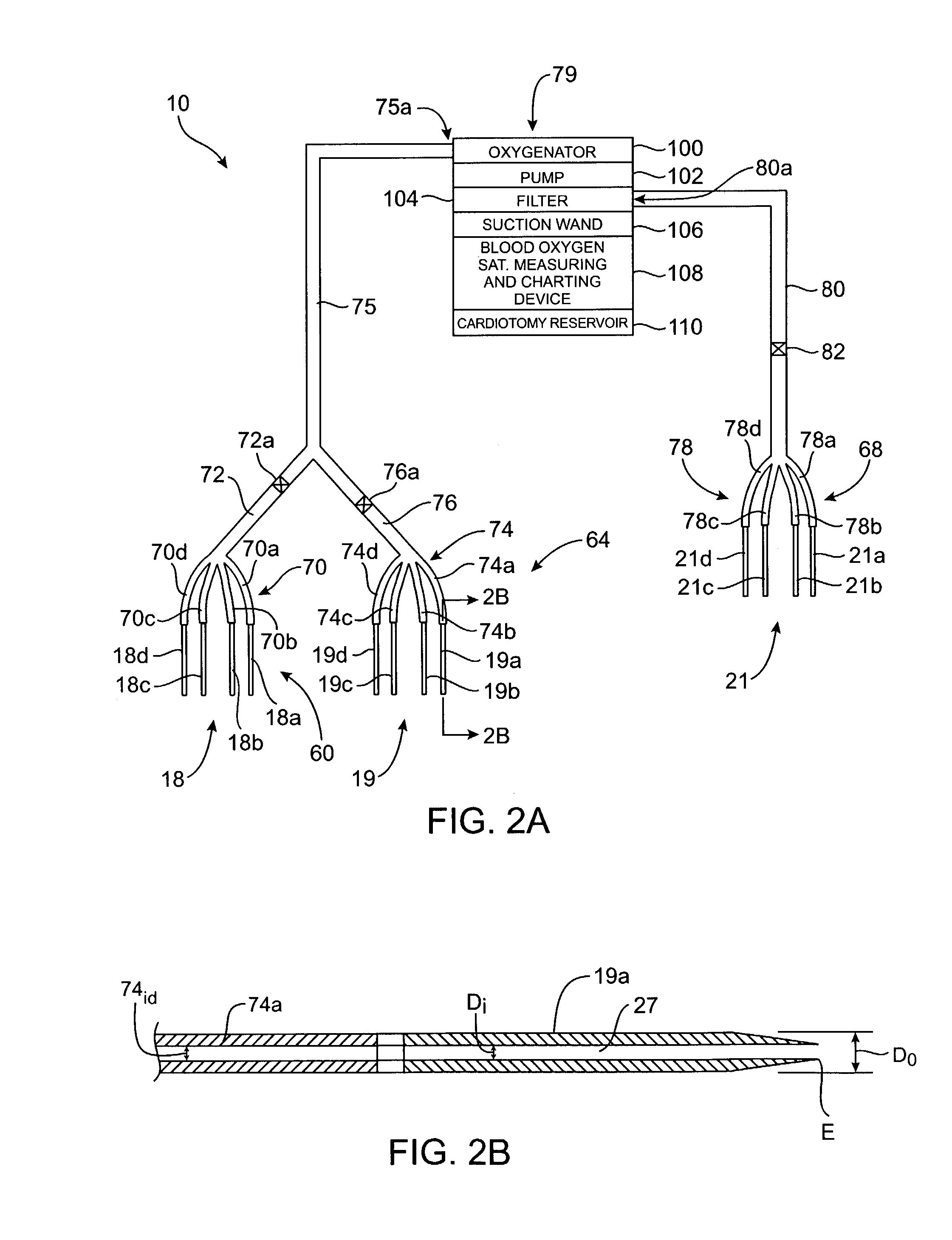
Cardiopulmonary bypass device and method
InactiveUS6979423B2Other blood circulation devicesSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A method and system for performing a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure are provided. The method includes accessing a source of blood in a patient body from which source the blood is to be passed through a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, drawing blood from the source through the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and introducing the blood into an aortic artery of the patient body through a plurality of separate passages, after the blood has been passed through the cardiopulmonary bypass machine. The system includes a cardiopulmonary bypass machine, a tubular member coupled to an outlet port of the cardiopulmonary bypass machine and a plurality of separate needle members connected in fluid flow communication with the tubular member, the needle members being arranged to be connected in fluid flow communication with an aortic artery, during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
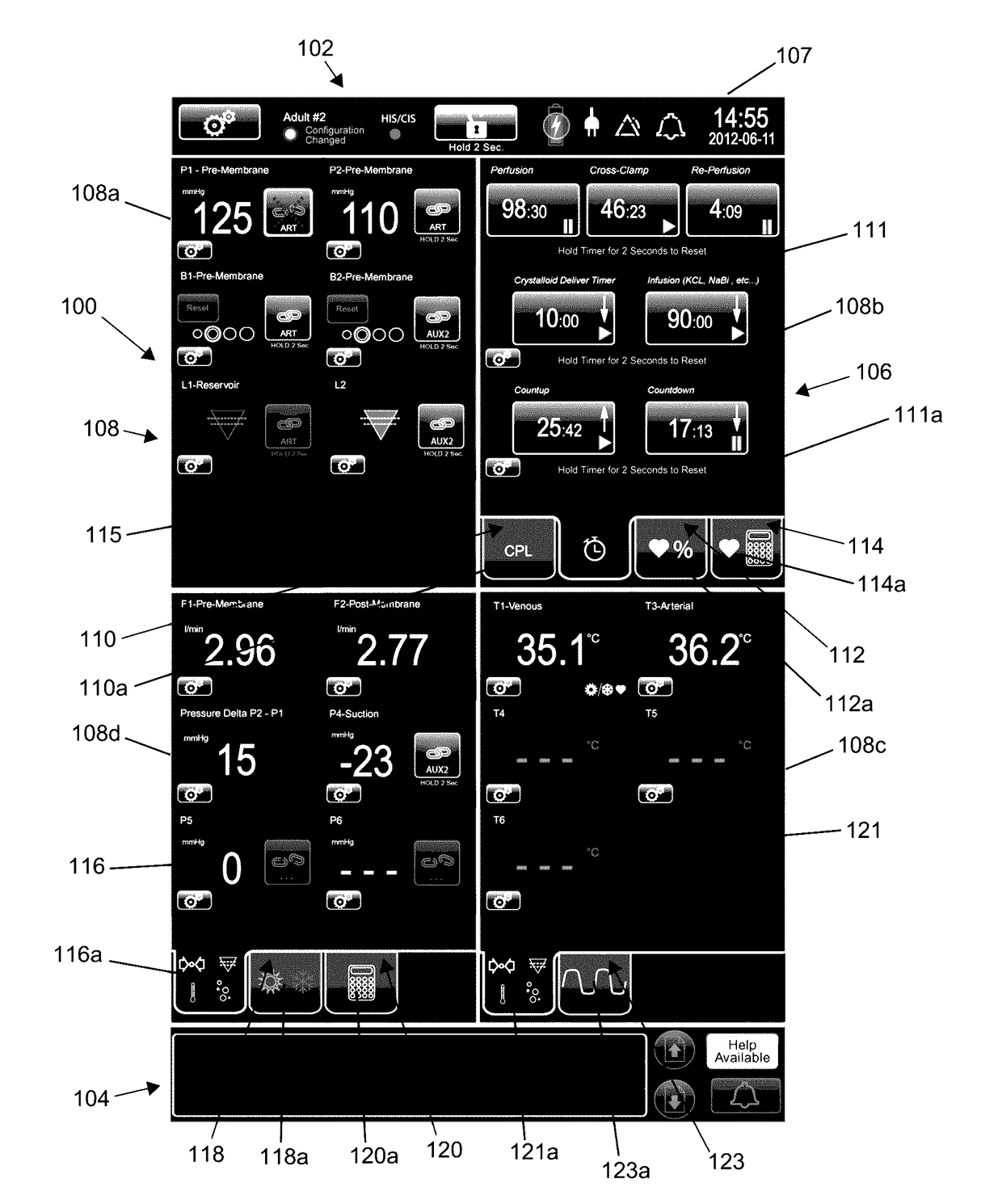
User interface system for a medical device
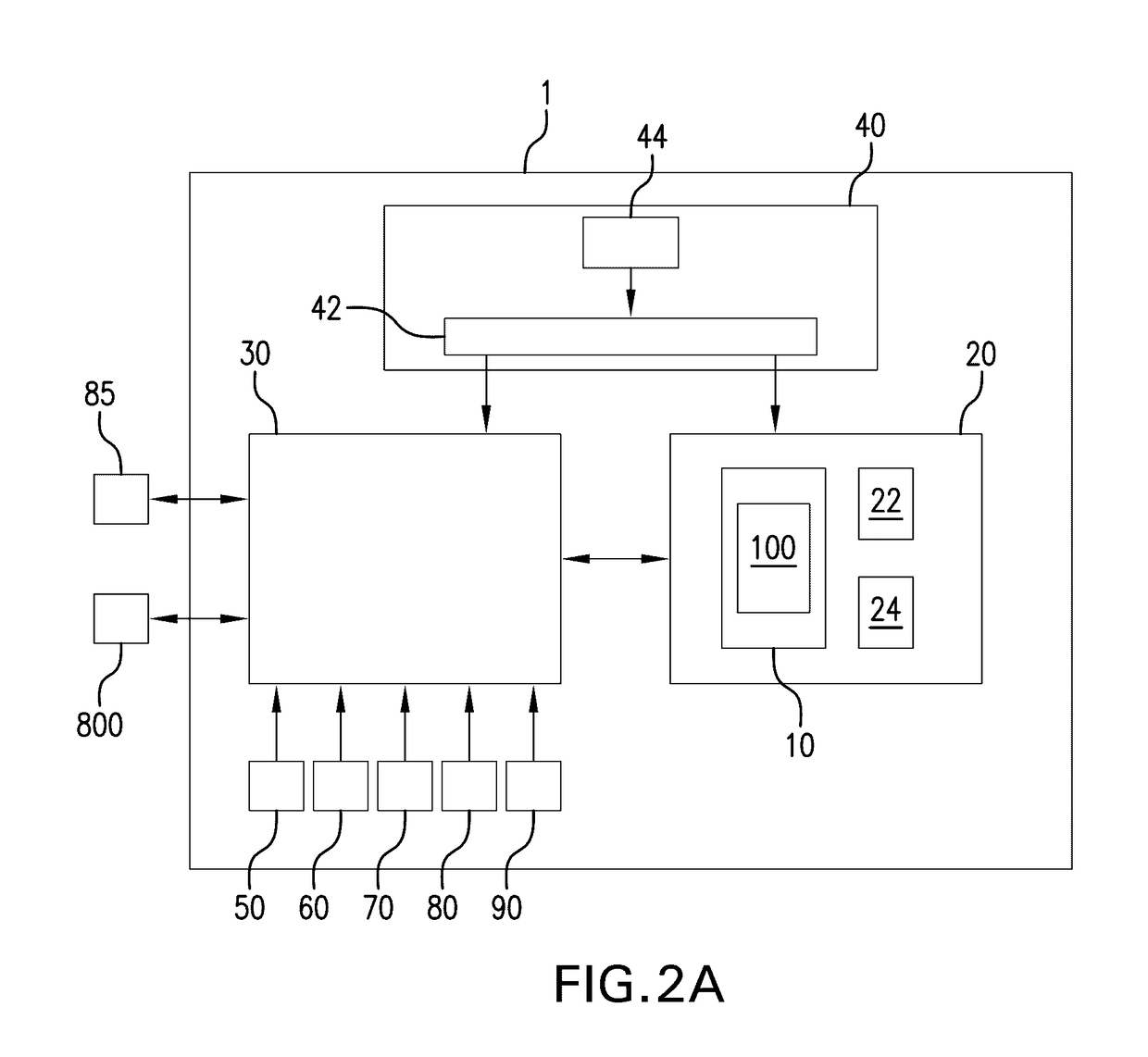
PendingUS20170102846A1Easy to modularizeEasy to useMechanical/radiation/invasive therapiesOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
A customizable and intuitive user interface for medical systems and devices, such as cardiopulmonary bypass systems, perfusion systems, extracorporeal circulation apparatuses, and heart-lung machines, is provided, which allows for ease of access to critical patient data to facilitate blood perfusion and to monitor and regulate various physiological parameters of a patient and an extracorporeal blood flow circuit during surgical procedures, such as cardiopulmonary bypass and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO).
Owner:MAQUET CARDIOPULMONARY GMBH
Carbon and its use in blood cleansing applications
ActiveUS20130072845A1Improve the level ofEffective sorbentHaemofiltrationMedical devicesCardiopulmonary bypassWhole body
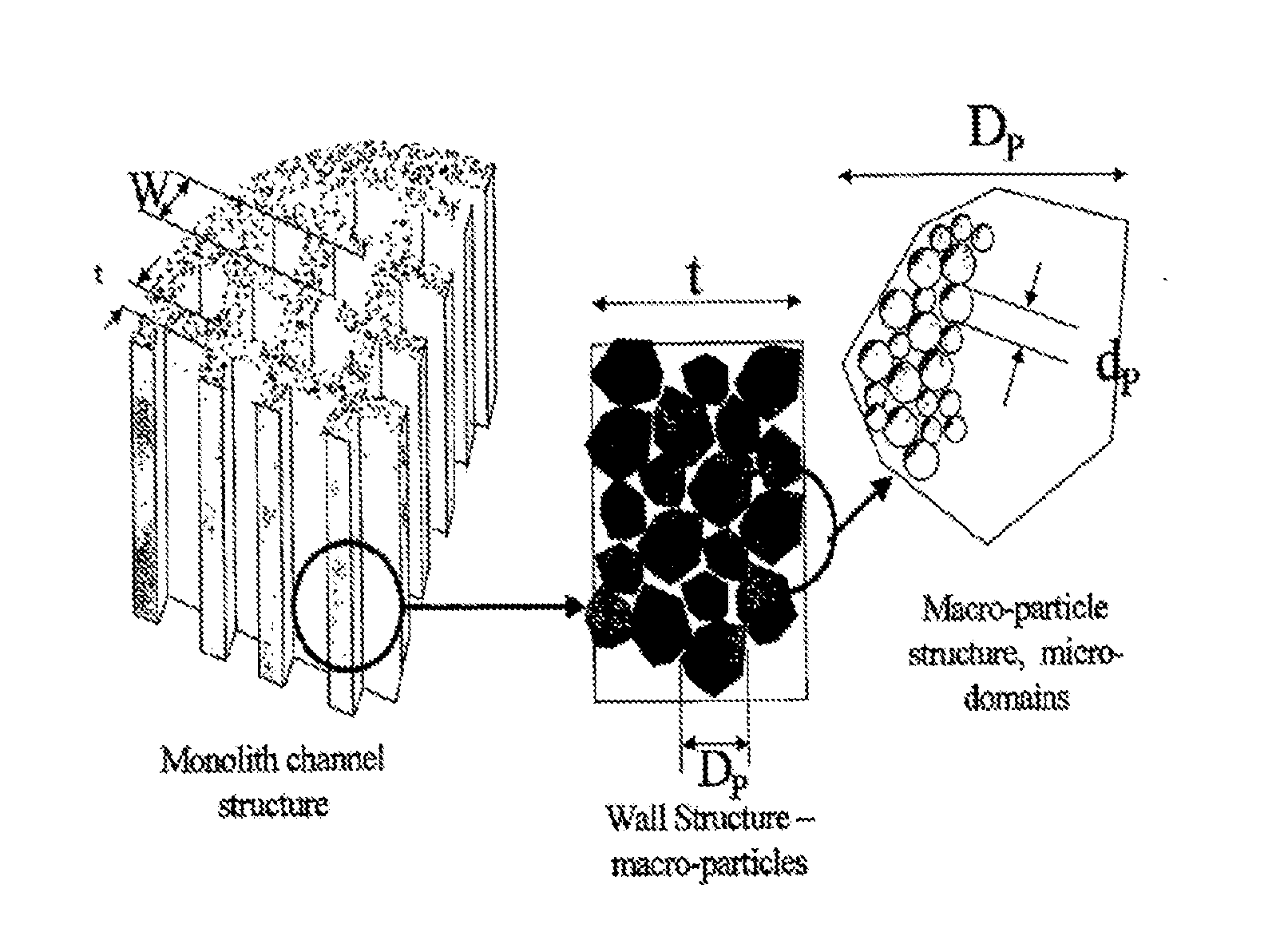
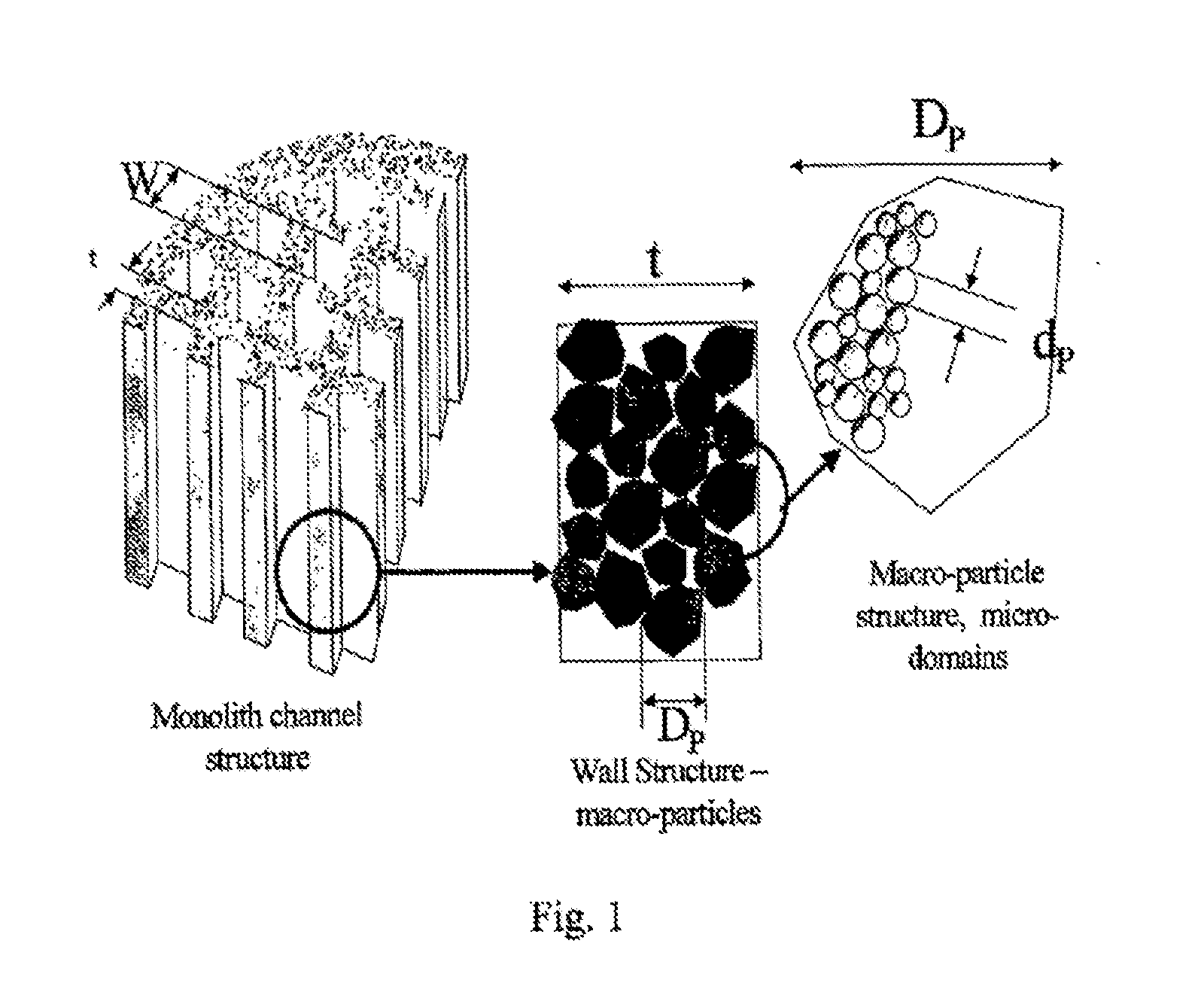
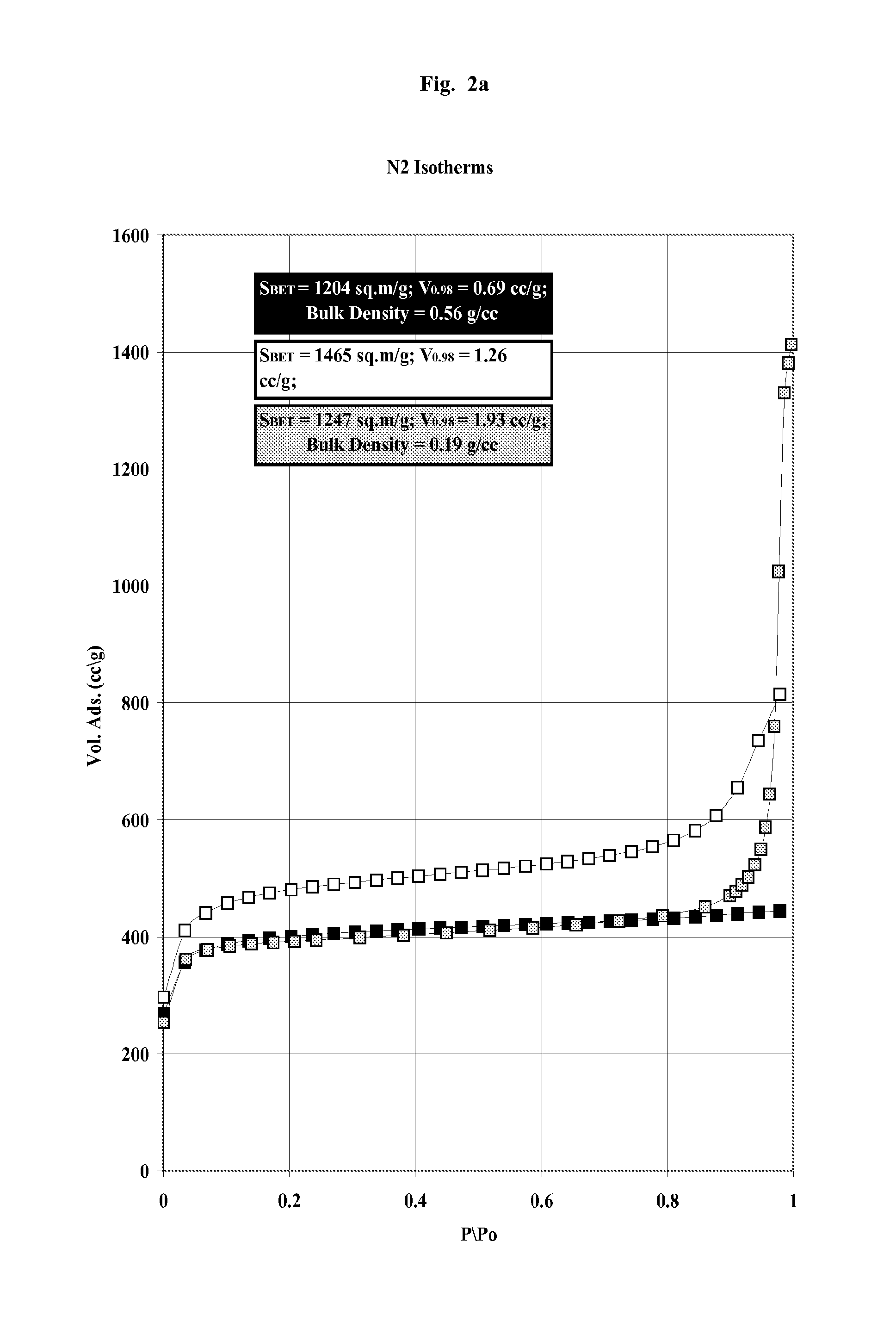
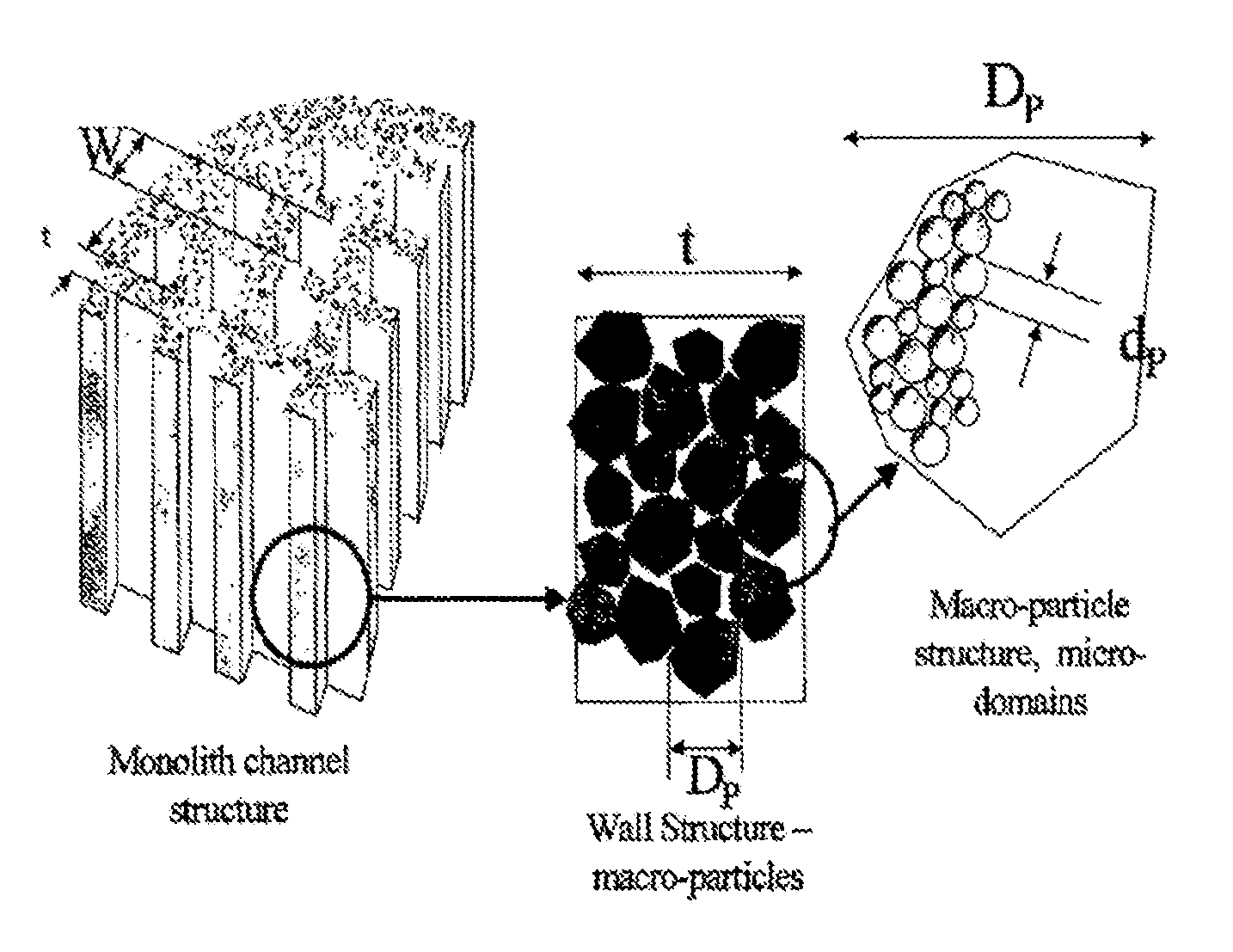
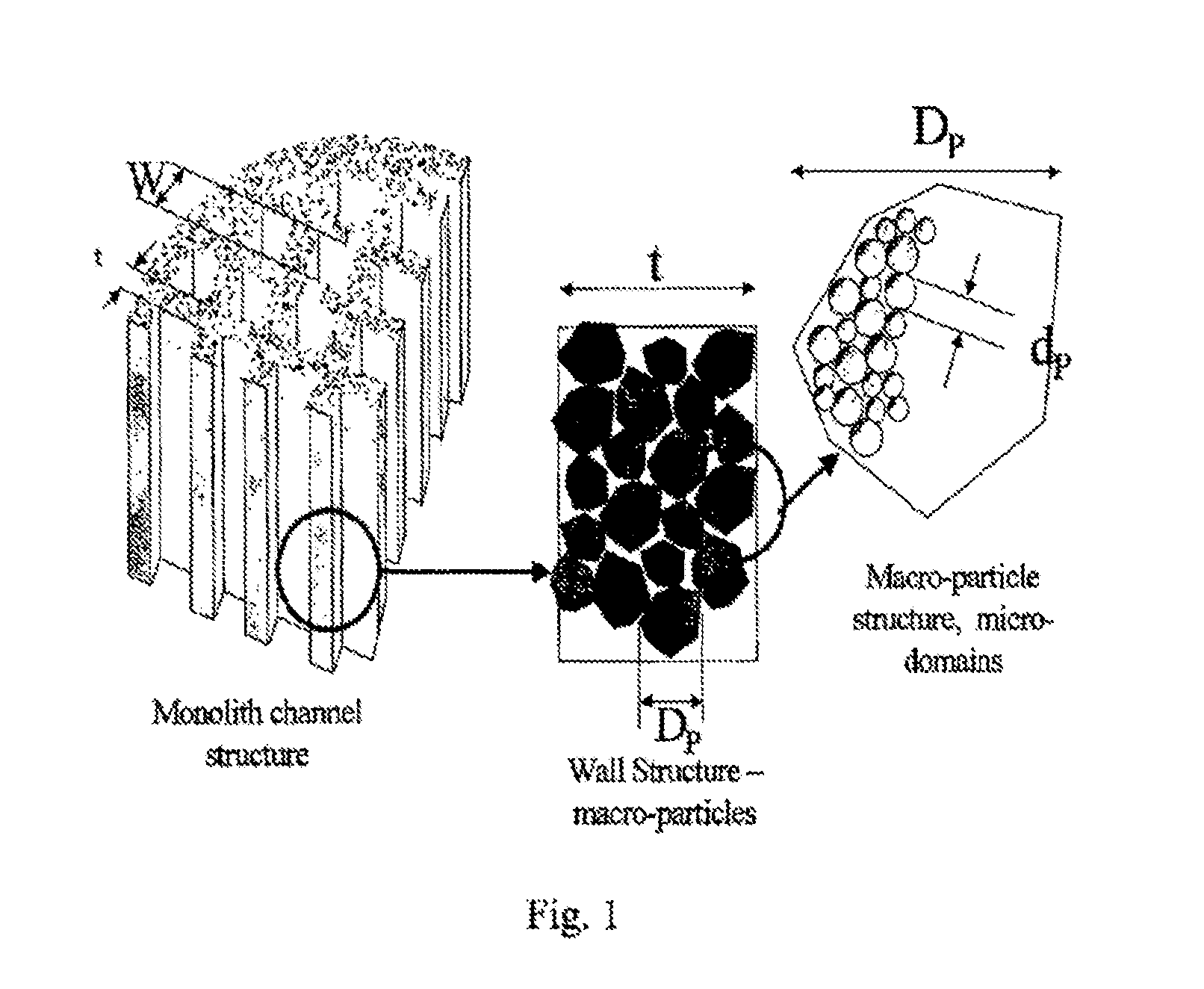
Whole blood is treated extracorporeally to remove substances contrary to health using mesoporous / microporous or macroporopus / microporous carbon in the form of beads or a channel monolith. The carbon may be the result of carbonising a mesoporous or macroporous phenolic resin. Substances contrary to health include externally introduced toxins such as bacterially derived staphylococcus enterotoxins A, B, TSST-1 or autologous, biologically active molecules with harmful, systemic effects when their activity is excessive or unregulated. Examples include the removal of inappropriate amounts of pro- or anti-inflammatory molecules and toxic mediators of systemic inflammatory response syndrome related to sepsis, cardio-pulmonary by-pass surgery, ischaemic reperfusioninjury; the removal of larger molecular weight and protein bound uremic toxins related to kidney and hepatic toxins related to liver failure and the removal of toxins relevant to biological and chemical warfare.
Owner:UNVIERSITY OF BRIGHTON +1
Medical oscillating compliance devices and uses thereof
ActiveUS20090177279A1Improve efficiencyStentsBalloon catheterExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
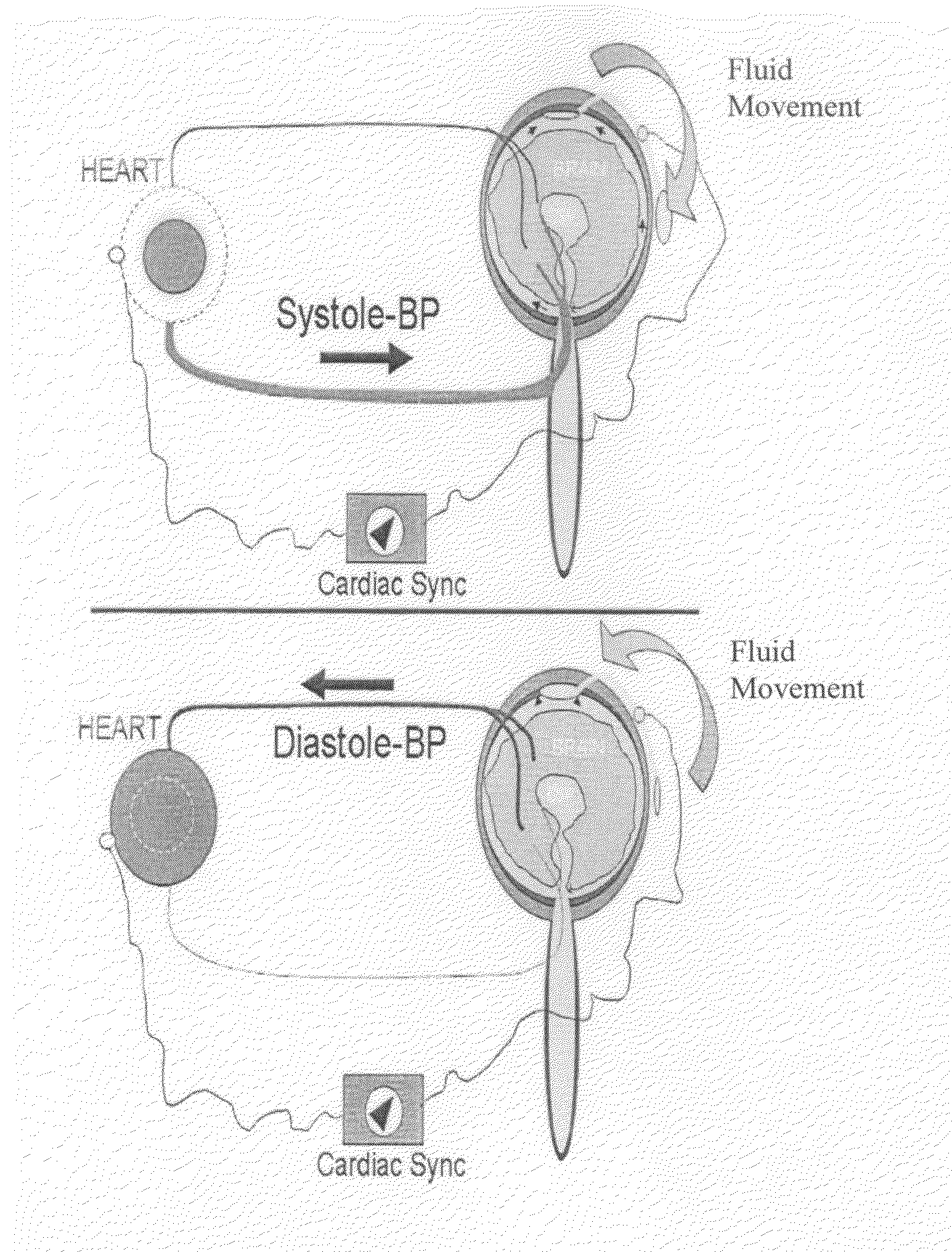
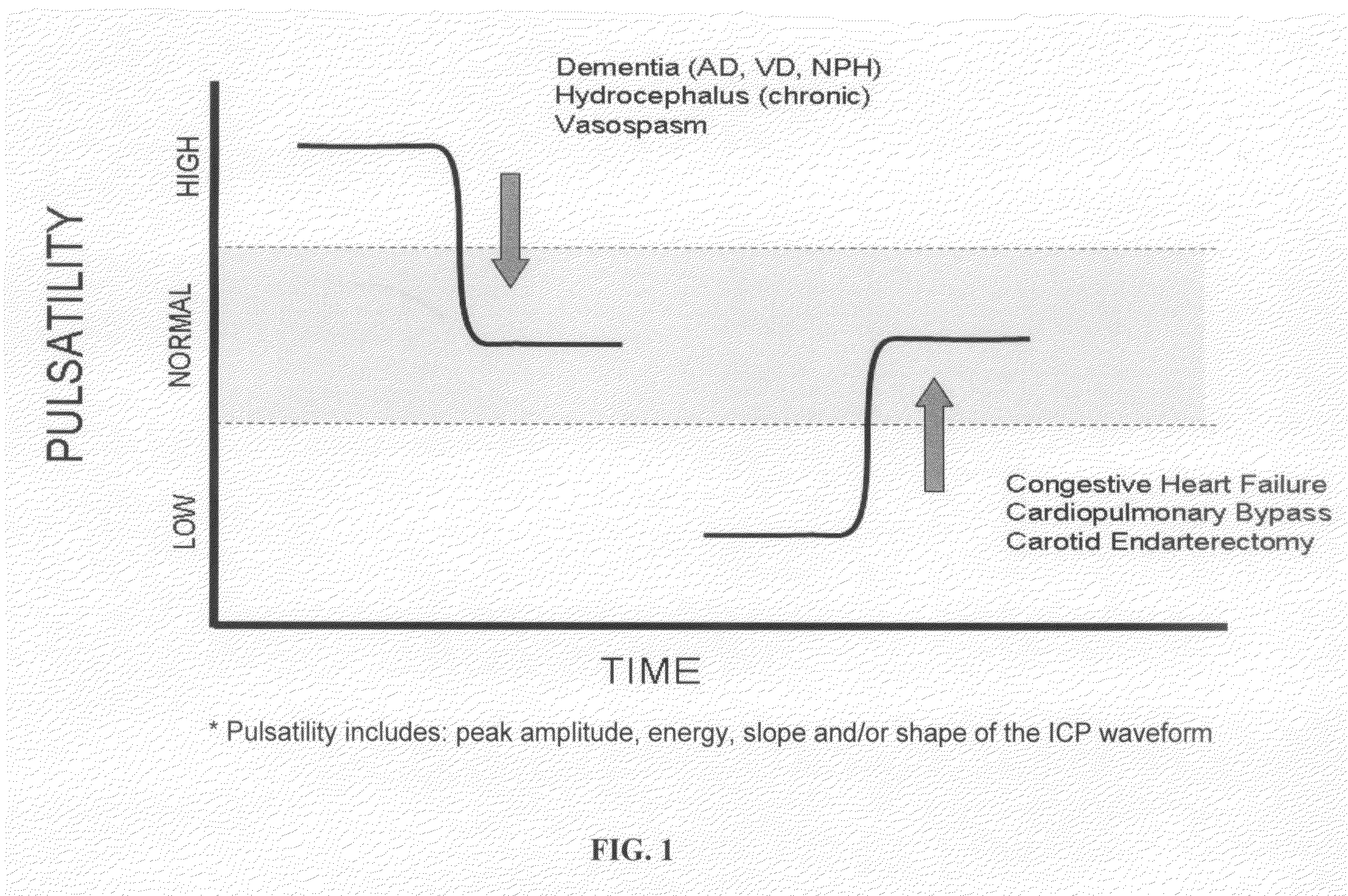
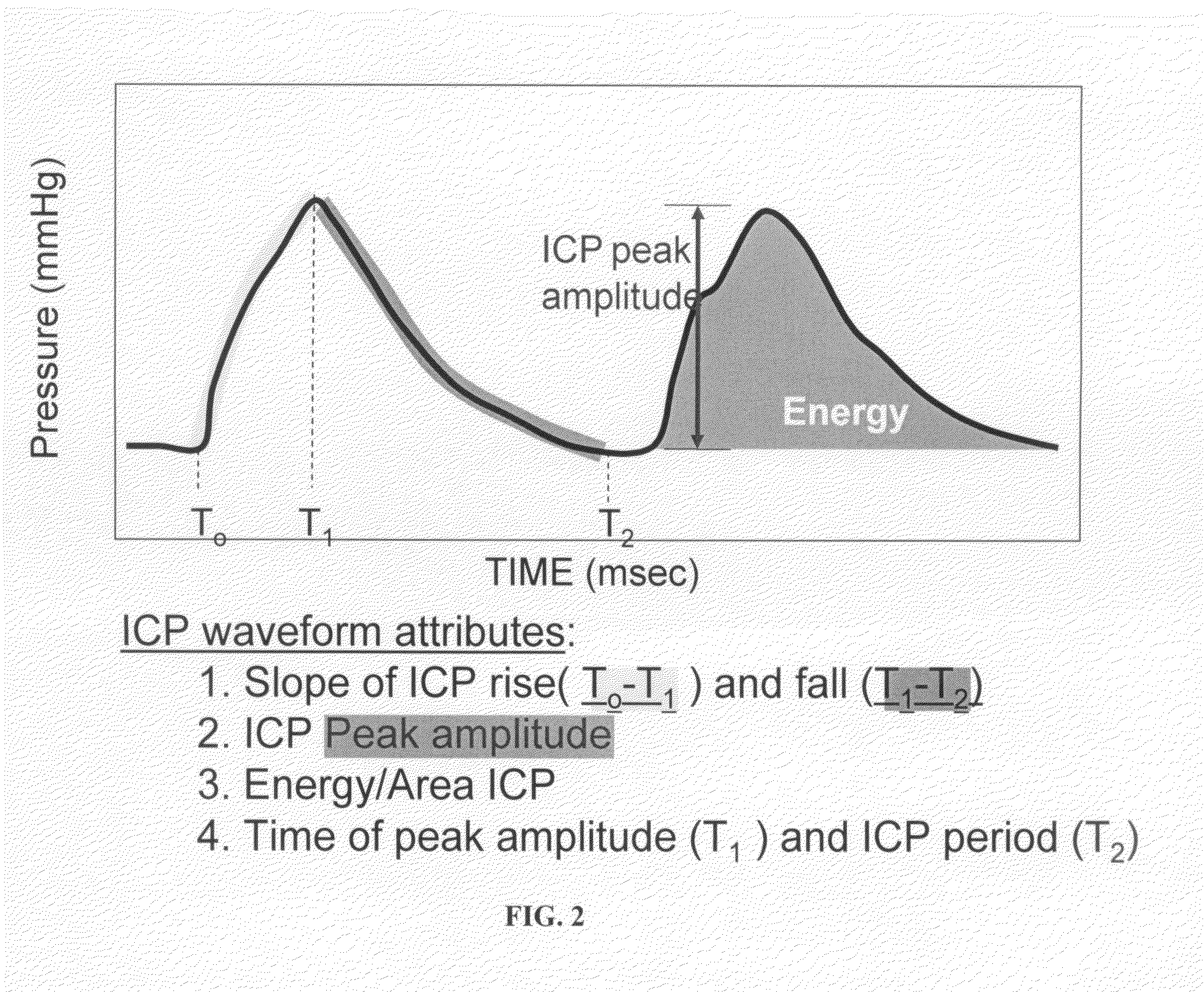
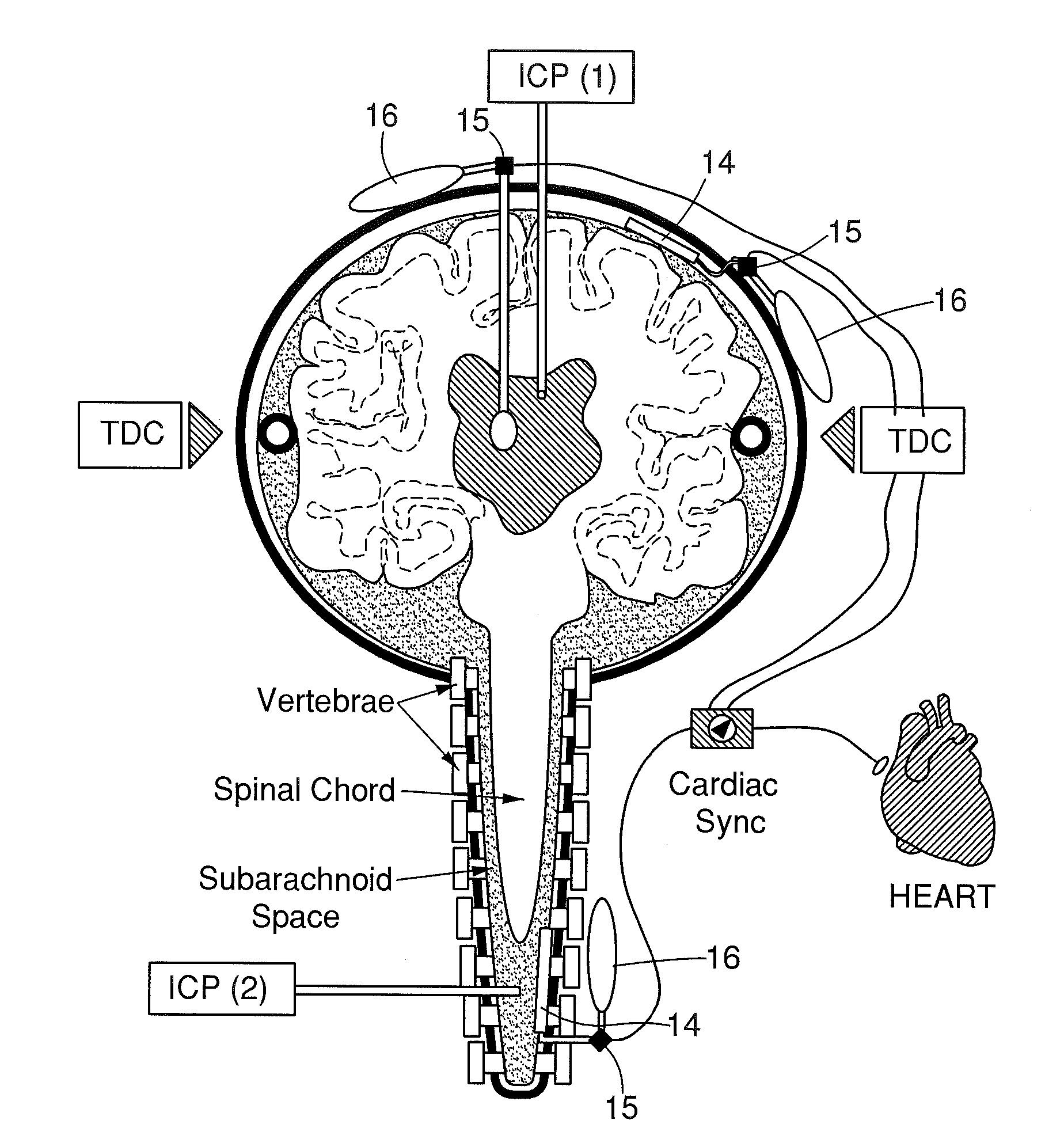
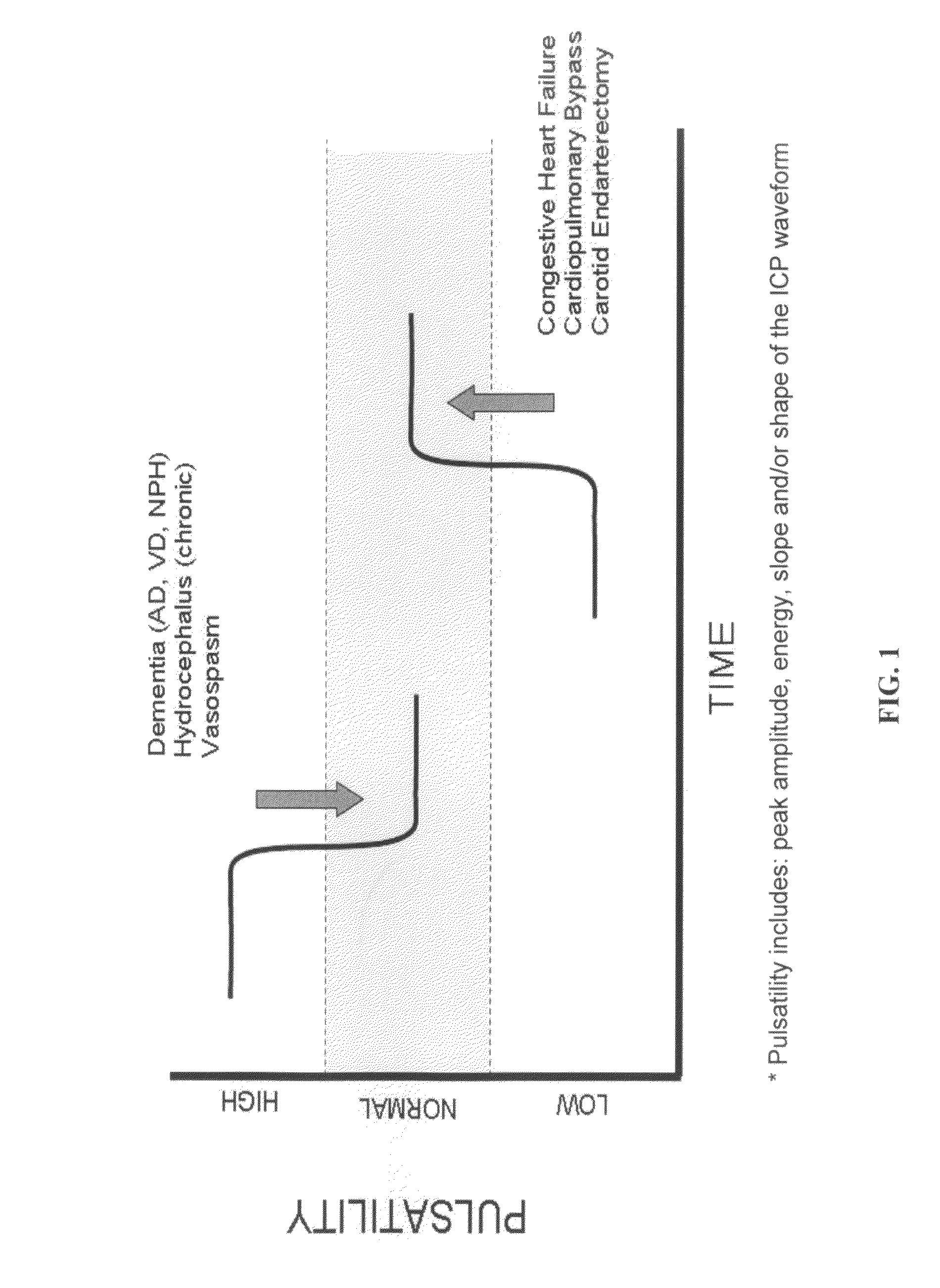
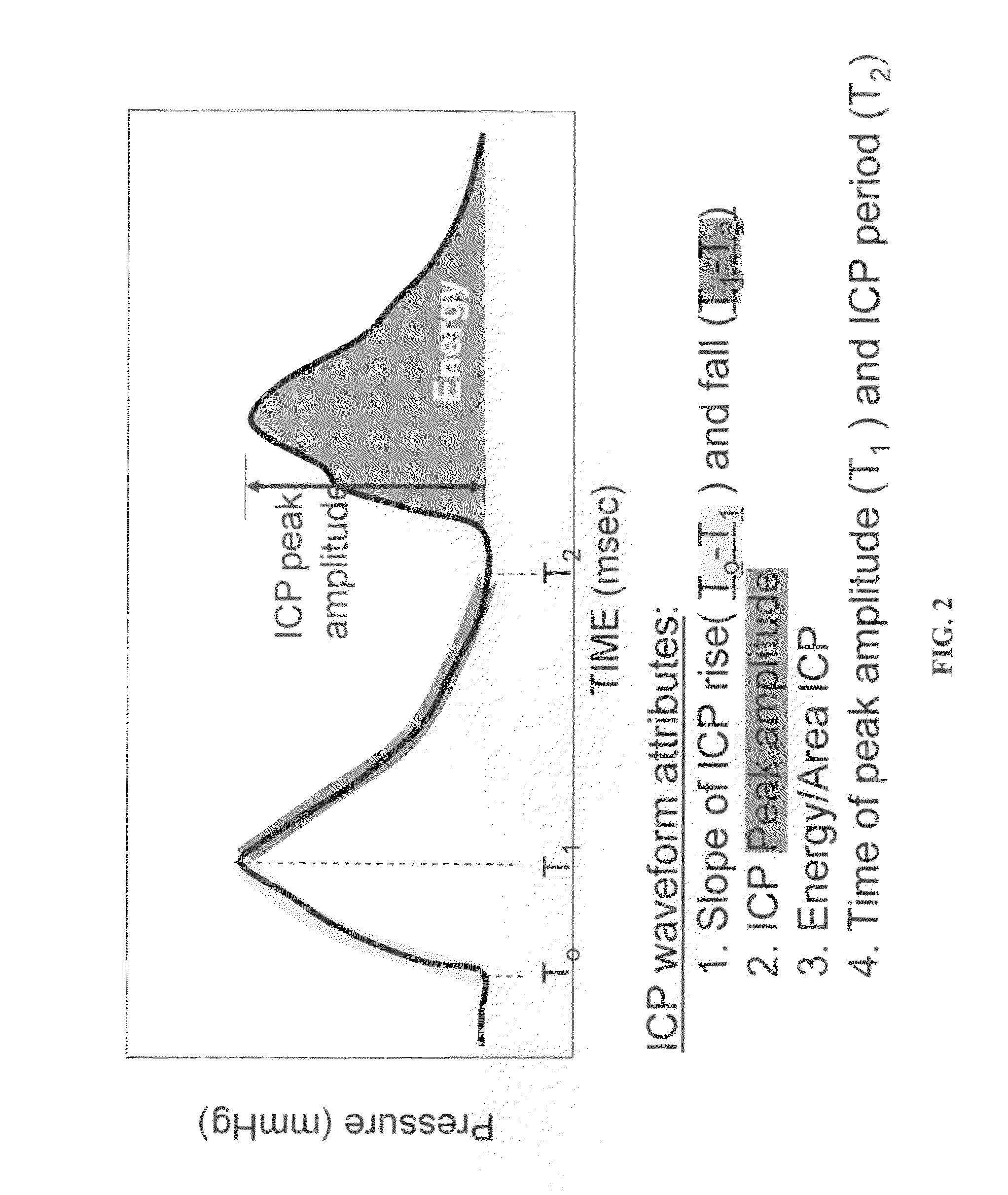
The present invention relates to devices and systems that alter intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform by oscillating the contraction and expansion of a compressible composition within the cranial or spinal cavities such that they increase intracranial capacity. The contraction and expansion of the compressible composition in the oscillating compliance devices can be due to an individual's intracranial pressure, the result of the expansion and compression of a reservoir which is mediated by the contractility of the heart or driven by a pump gaited to a biorhythm. The invention also relates to methods for protecting an individual's brain from abnormal arterial pulsations and for altering an individual's cerebral blood flow using the devices and systems of the invention. The oscillating compliance devices can be used to treat several diseases and / or conditions characterized by altered / abnormal intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform, including hydrocephalus, stroke, dementia and migraine headaches, vasospasms, congestive heart failure, cardiopulmonary bypass or carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
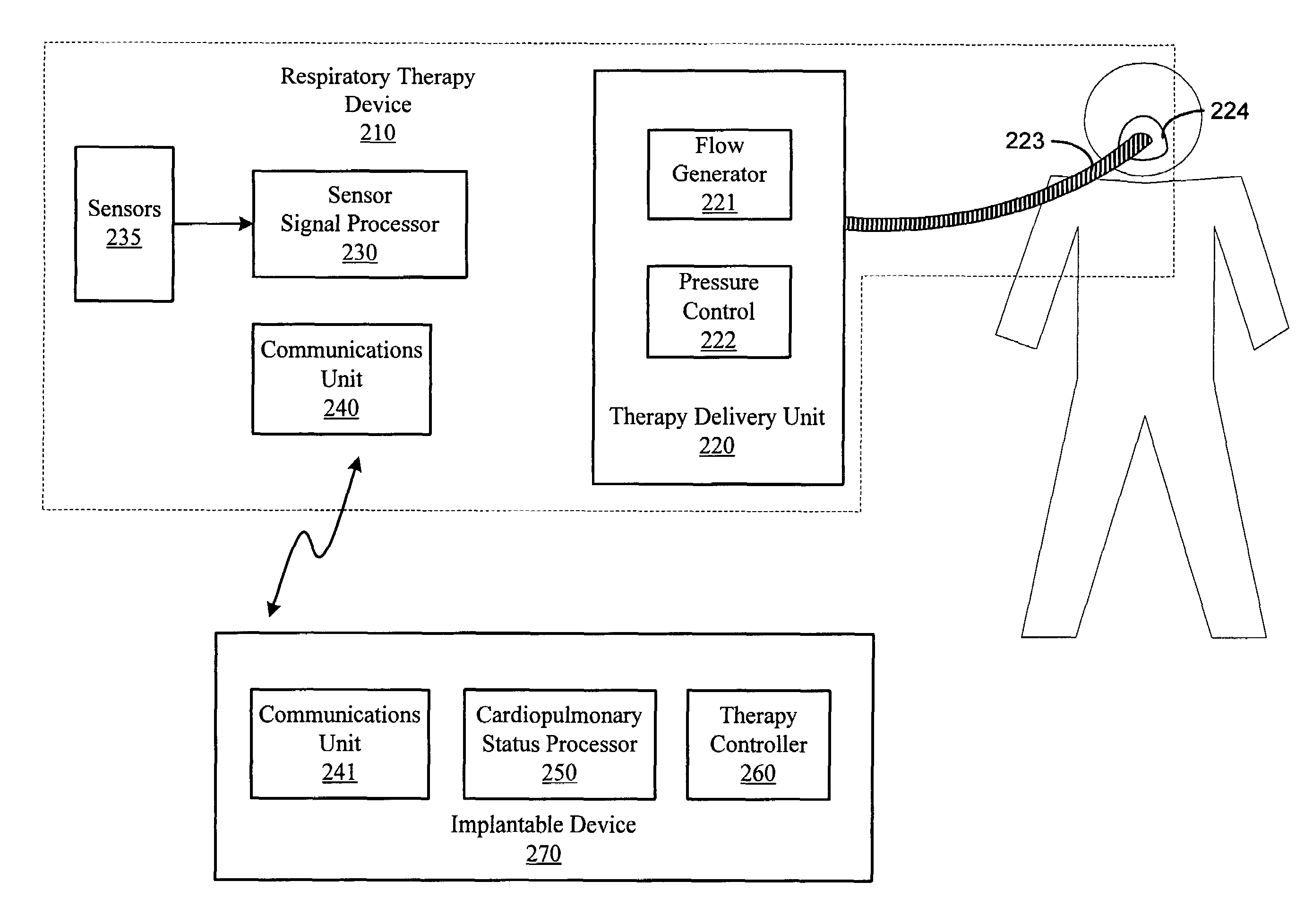
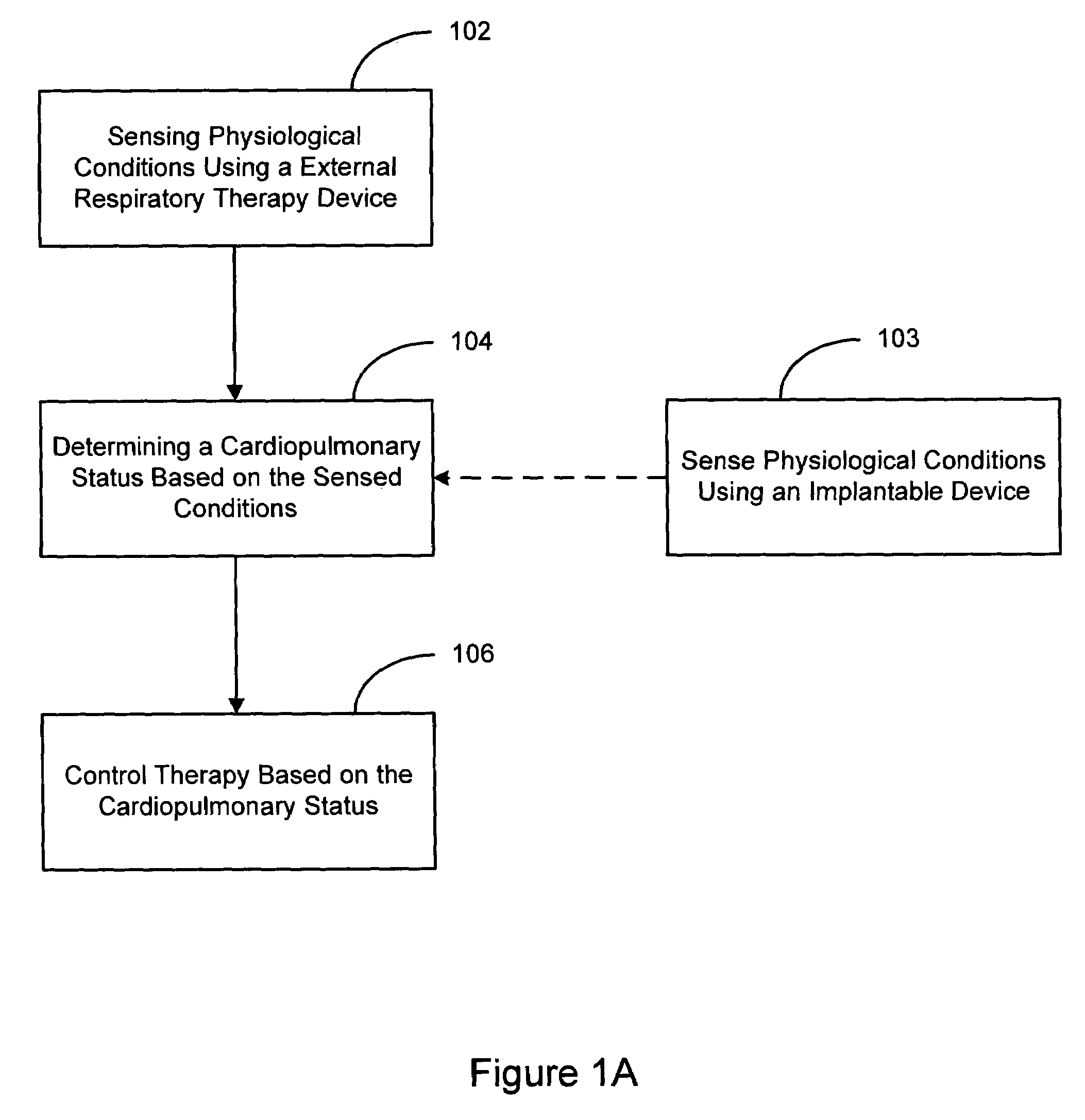
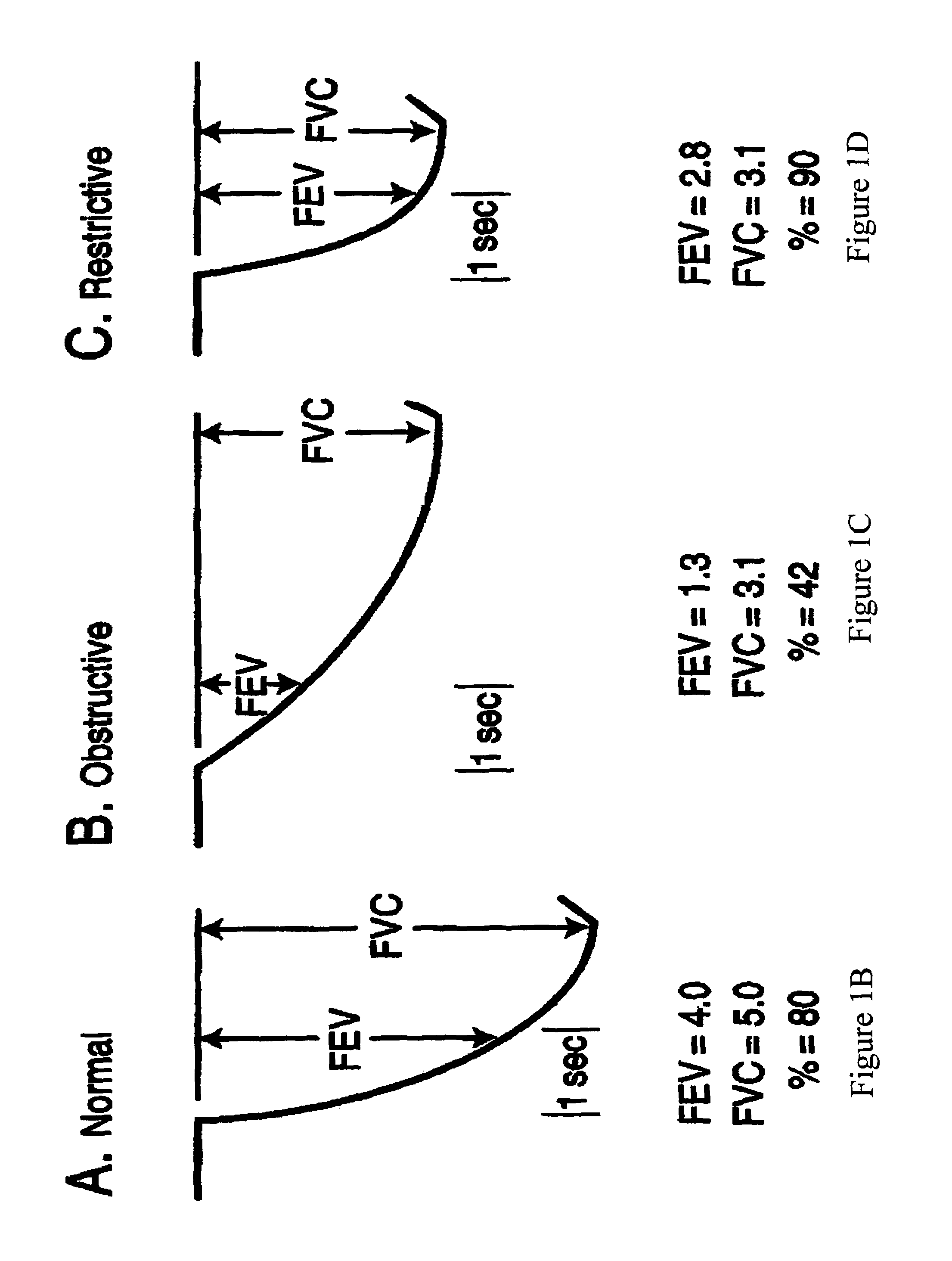
Therapy control based on cardiopulmonary status
InactiveUS7662101B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCardiopulmonary bypassImplanted device
Methods and systems provide an approach to therapy control based on assessment of a patient's cardiopulmonary status. Conditions sensed via sensors of an external respiratory therapy device are used to assess a patient's cardiopulmonary status. The respiratory therapy device sensors may be utilized alone or in combination with other sensors to determine cardiopulmonary status of a patient. Therapy delivered to the patient is controlled based on the cardiopulmonary status assessment. For example, therapy delivered to the patient may be initiated, terminated, and / or modified based on the assessed cardiopulmonary status of the patient. Cardiopulmonary status assessment, therapy control, or both, are performed by an implantable device.
Owner:CARDIAC PACEMAKERS INC
Systems, Devices and Methods for Cardiopulmonary Treatment and Procedures
ActiveUS20120130298A1Reduce shear forceVolume measurement apparatus/methodsOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassBlood pump
A cardiopulmonary bypass system utilizing membrane-based reciprocating positive displacement blood pumps (“pod pumps”). In one aspect, the pod pumps are constructed to provide reduced shear forces on the blood being pumped. In another aspect blood flow through the pod pumps can he controlled by a controller using information from pressure sensors in the control chamber of the pod pumps. In another aspect, the pod pumps are included on a disposable unit that can be received and held by a receptacle means on a base unit, the base unit also providing pressurized control fluid to the pod pumps on the disposable unit through the receptacle means.
Owner:DEKA PROD LLP
Medical oscillating compliance devices and uses thereof
ActiveUS8956379B2Improve efficiencyServomotor componentsSurgeryExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
The present invention relates to devices and systems that alter intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform by oscillating the contraction and expansion of a compressible composition within the cranial or spinal cavities such that they increase intracranial capacity. The contraction and expansion of the compressible composition in the oscillating compliance devices can be due to an individual's intracranial pressure, the result of the expansion and compression of a reservoir which is mediated by the contractility of the heart or driven by a pump gaited to a biorhythm. The invention also relates to methods for protecting an individual's brain from abnormal arterial pulsations and for altering an individual's cerebral blood flow using the devices and systems of the invention. The oscillating compliance devices can be used to treat several diseases and / or conditions characterized by altered / abnormal intracranial compliance, cerebral blood flow and / or intracranial pressure pulsatility / waveform, including hydrocephalus, stroke, dementia and migraine headaches, vasospasms, congestive heart failure, cardiopulmonary bypass or carotid endarterectomy.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND
Hemostatic system and components for extracorporeal circuit
InactiveUS7153473B2Reduce or minimize inflammation, excessive bleedingEasy to adaptSolvent extractionOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
A method and system for use in the course of extracorporeal blood flow, e.g., cardiopulmonary bypass, dialysis, and angioplasty procedures, in order to reduce or minimize inflammation, excessive bleeding, and other undesirable side effects. The system can include one or more automated blood parameter sensor modules and one or more blood parameter regulating modules. The system is particularly well suited to monitor and / or regulate blood parameters that include blood analytes (e.g., biomolecules, drugs or metabolites) as well as blood functions (e.g., clotting time, fibrinolytic activity, immune response). The system is particularly well suited for use in the management of clotting (e.g., heparing / protamine) and bleeding (e.g., aprotinin).
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
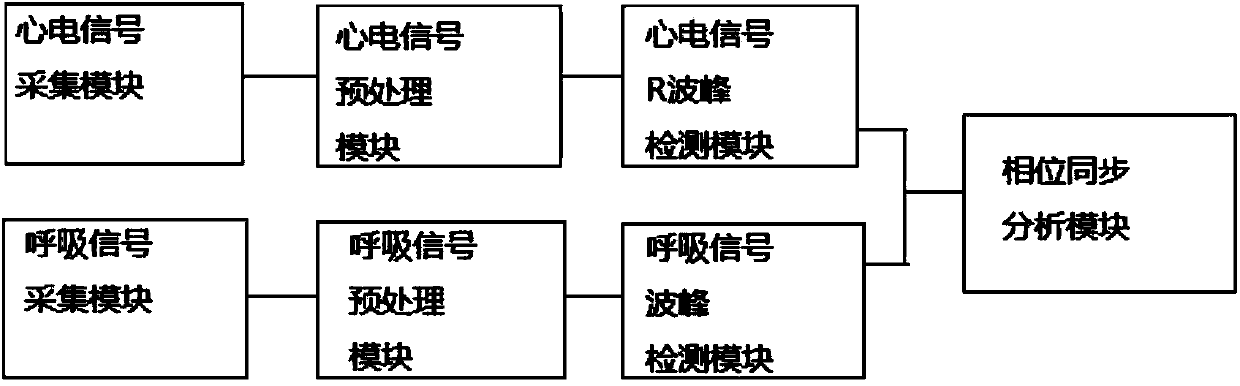
System and method for phase synchronization analysis of cardiopulmonary system
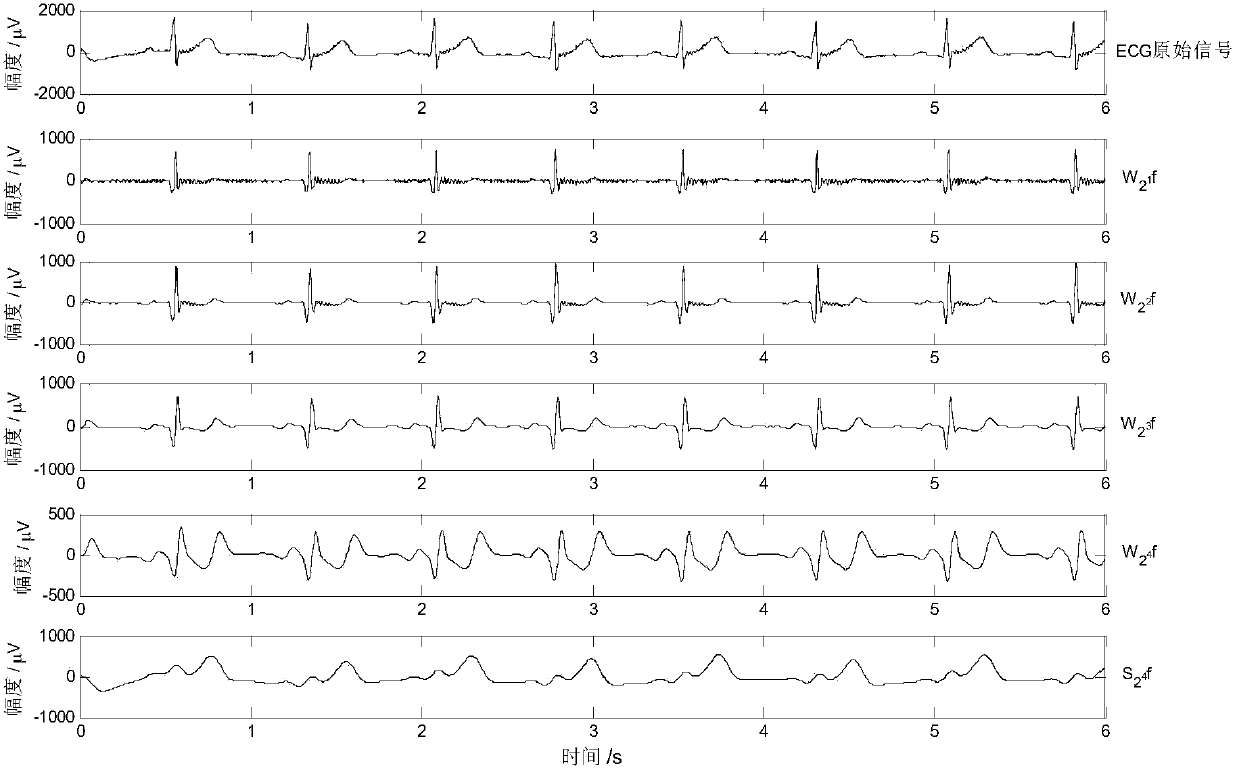
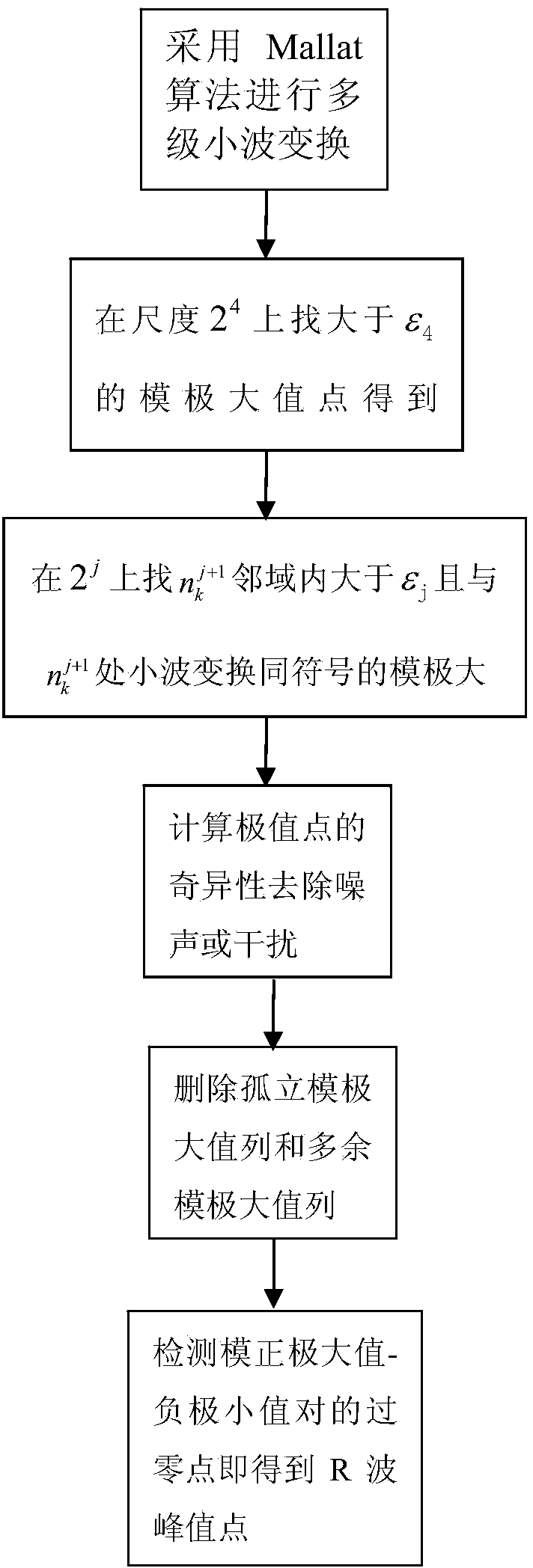
The invention provides a system and method for phase synchronization analysis of a cardiopulmonary system. The system and method are used for evaluating the synchronization degree of the heart rate and respiration, namely cardiopulmonary coupling strength. The system comprises an electrocardio signal collecting module, an electrocardio signal preprocessing module, an electrocardio R wave crest detection module, a respiration signal collecting module, a respiration signal preprocessing module, a respiration signal wave crest detection module and a phase synchronization analyzing module. The electrocardio signal collecting module is used for collecting electrocardio signals, the electrocardio R wave crest detection module detects an R wave crest by the adoption of an R wave detection algorithm based on wavelet transform, the respiration signal collecting module is used for collecting respiration signals, the respiration signal wave crest detection module is used for detecting a respiration wave crest point by the adoption of a threshold method, and the phase synchronization analyzing module is used for calculating cardiopulmonary synchronization time on the basis of a phase synchronization graph to serve as a quantitative index of the cardiopulmonary coupling strength.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of reducing pulmonary hypertension and atrial fibrillation after surgery using cardiopulmonary bypass
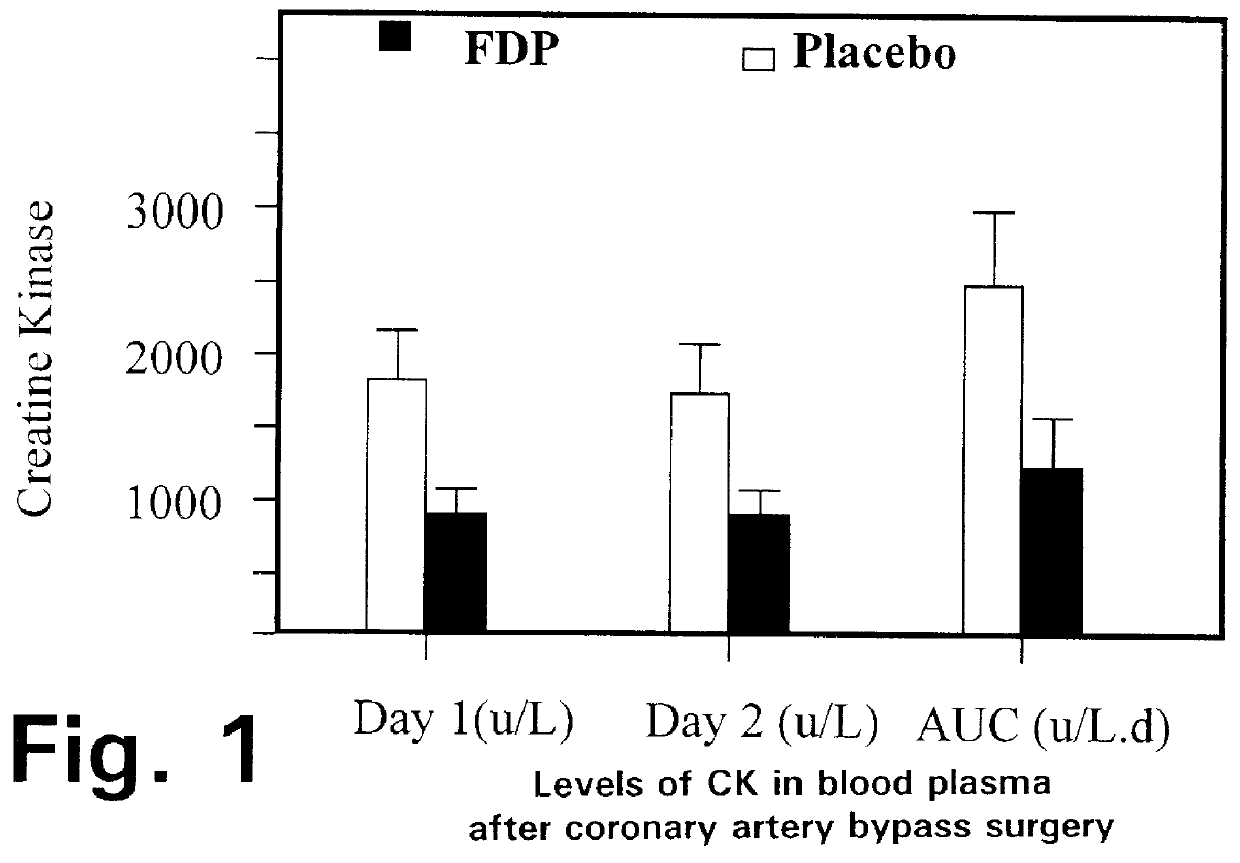
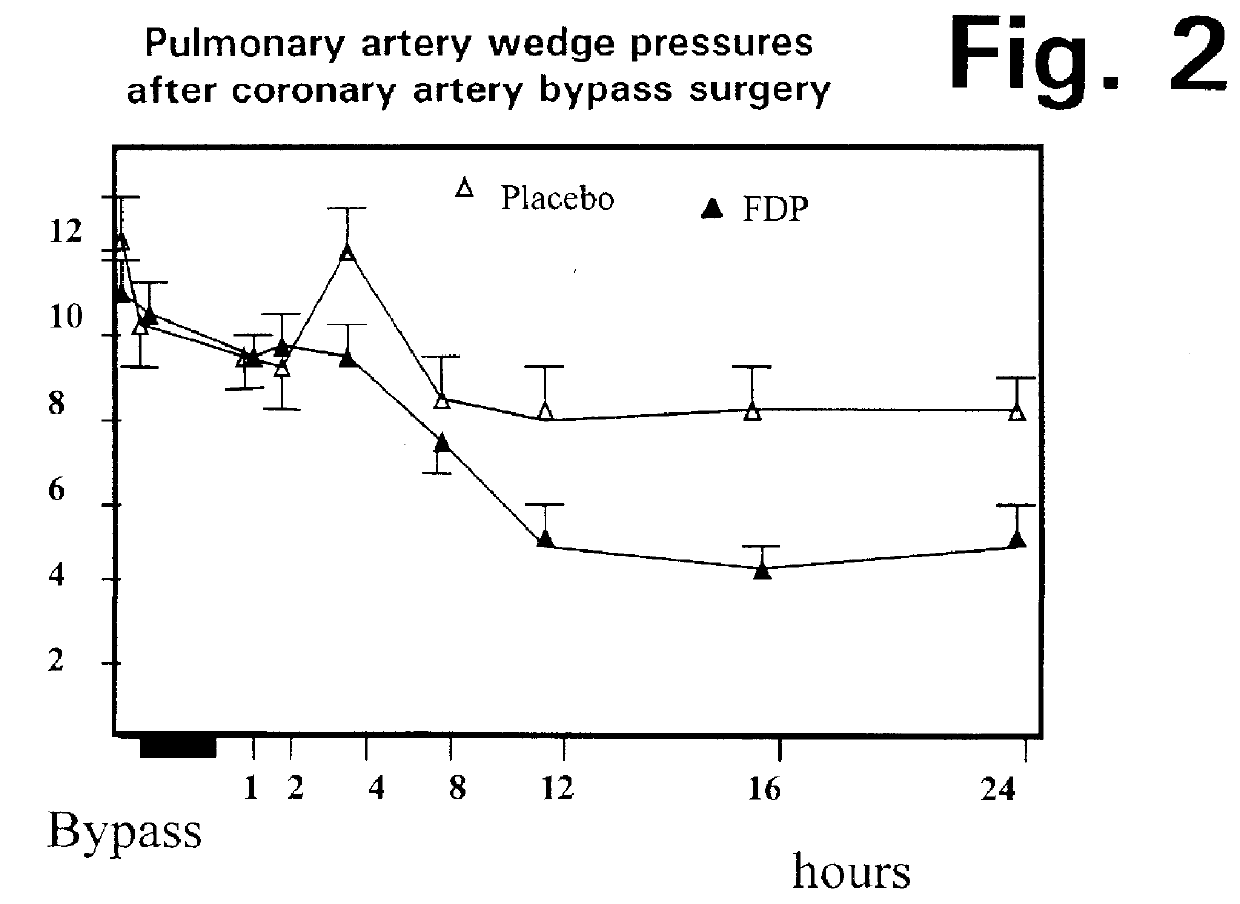
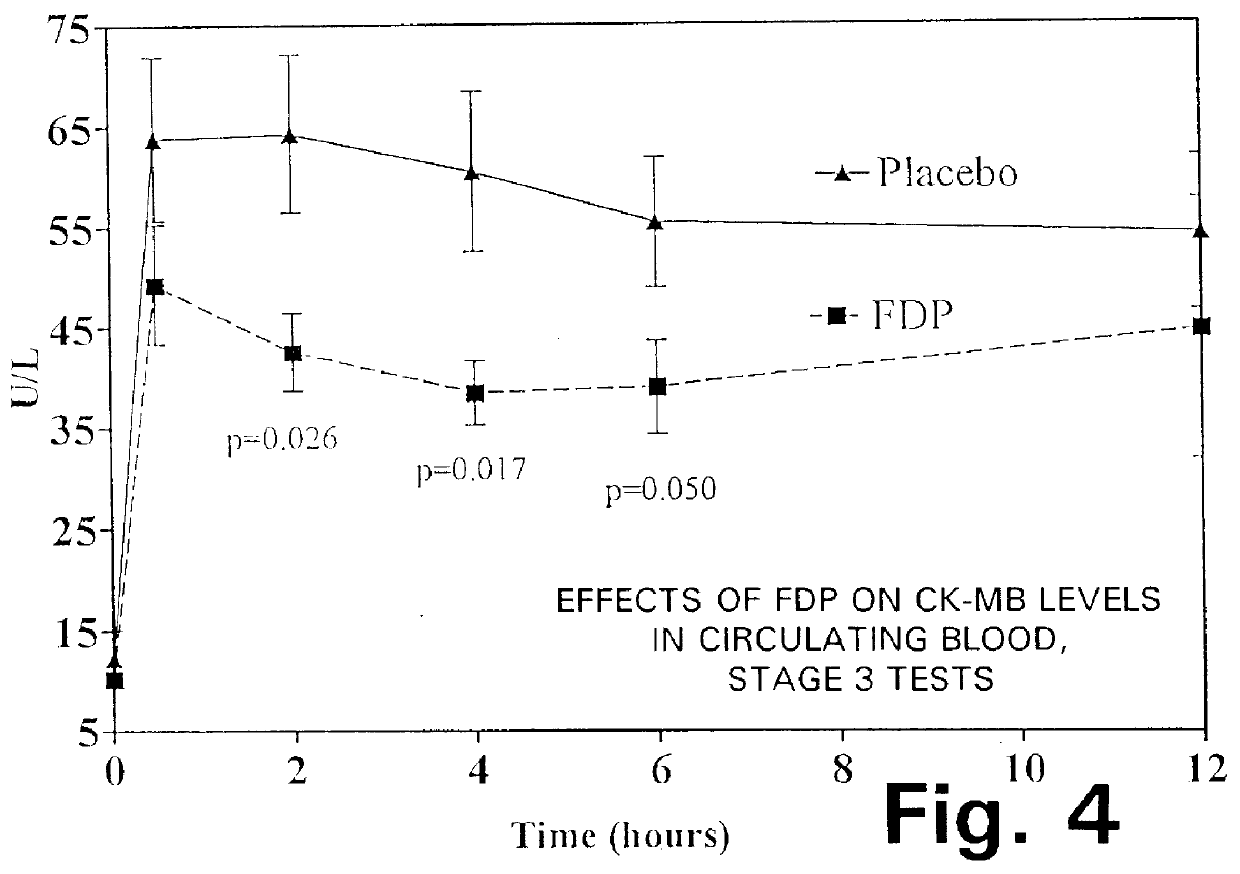
A method is disclosed for using fructose-1,6-diphosphate (FDP) to reduce and prevent two very serious problems caused by surgery that requires cardiopulmonary bypass. Before bypass begins, a liquid that contains FDP is intravenously injected into the patient, preferably over a period such as about 10 to 30 minutes, to allow the FDP to permeate in significant quantity into the heart and lungs while the heart is still beating. FDP can be added to the cardioplegia solution that is pumped through the heart to stop the heartbeat, and / or during bypass. This treatment was found to reduce two very important and serious problems that have unavoidably plagued CPB surgery in the past, which are: (1) elevated levels of pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR), which includes pulmonary hypertension; and (2) high occurrence rates for atrial fibrillation. Prior to this discovery, there has never been any satisfactory treatment which could reduce the severity and occurrence rates for these two major problems. FDP also can be co-administered in this manner, along with (1) a buffering or alkalizing agent that counteracts acidosis, such as sodium bicarbonate or THAM, and / or (2) a drug that reduces the formation of lactic acid, such as dichloroacetate.
Owner:QUESTCOR PHARMA
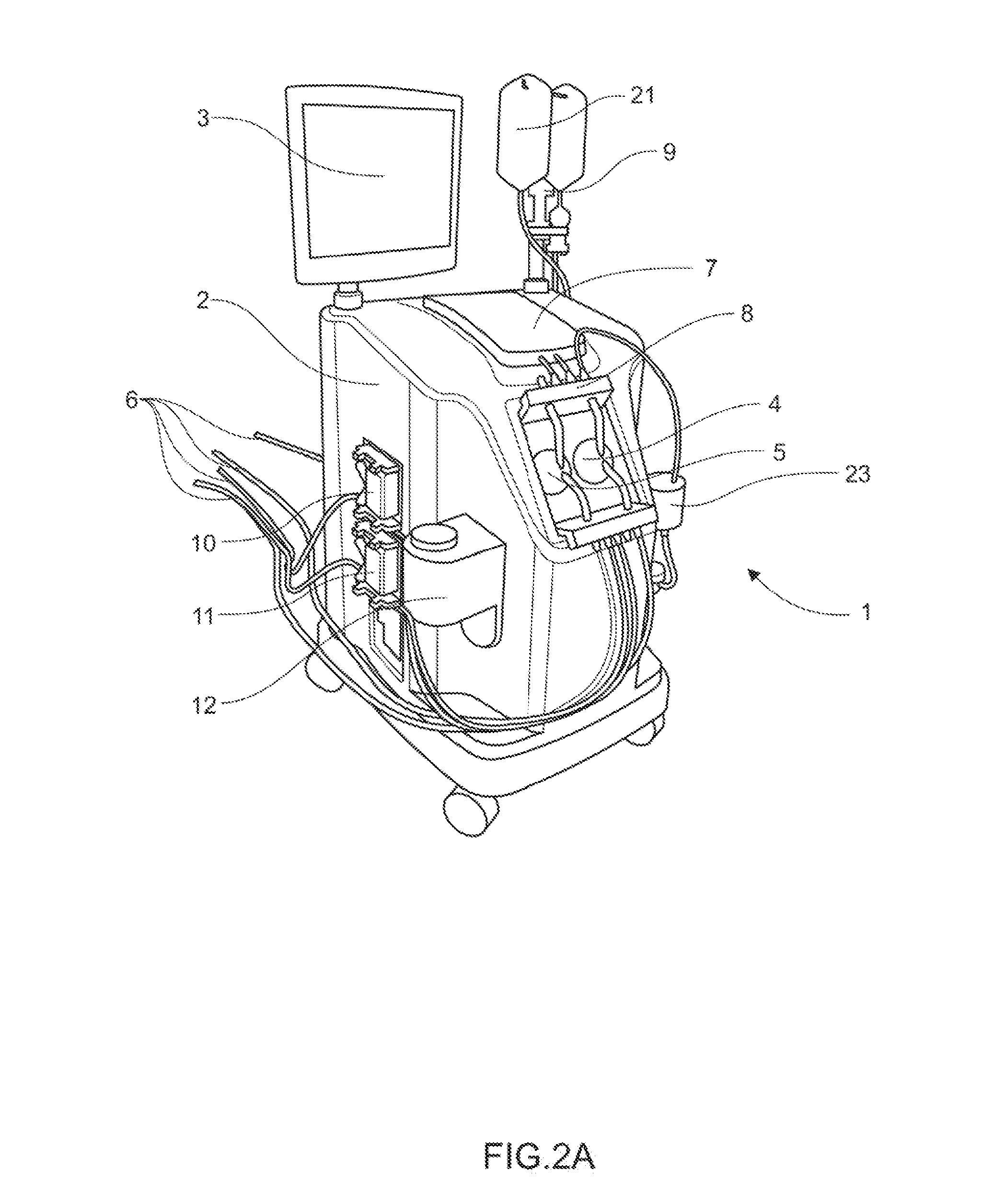
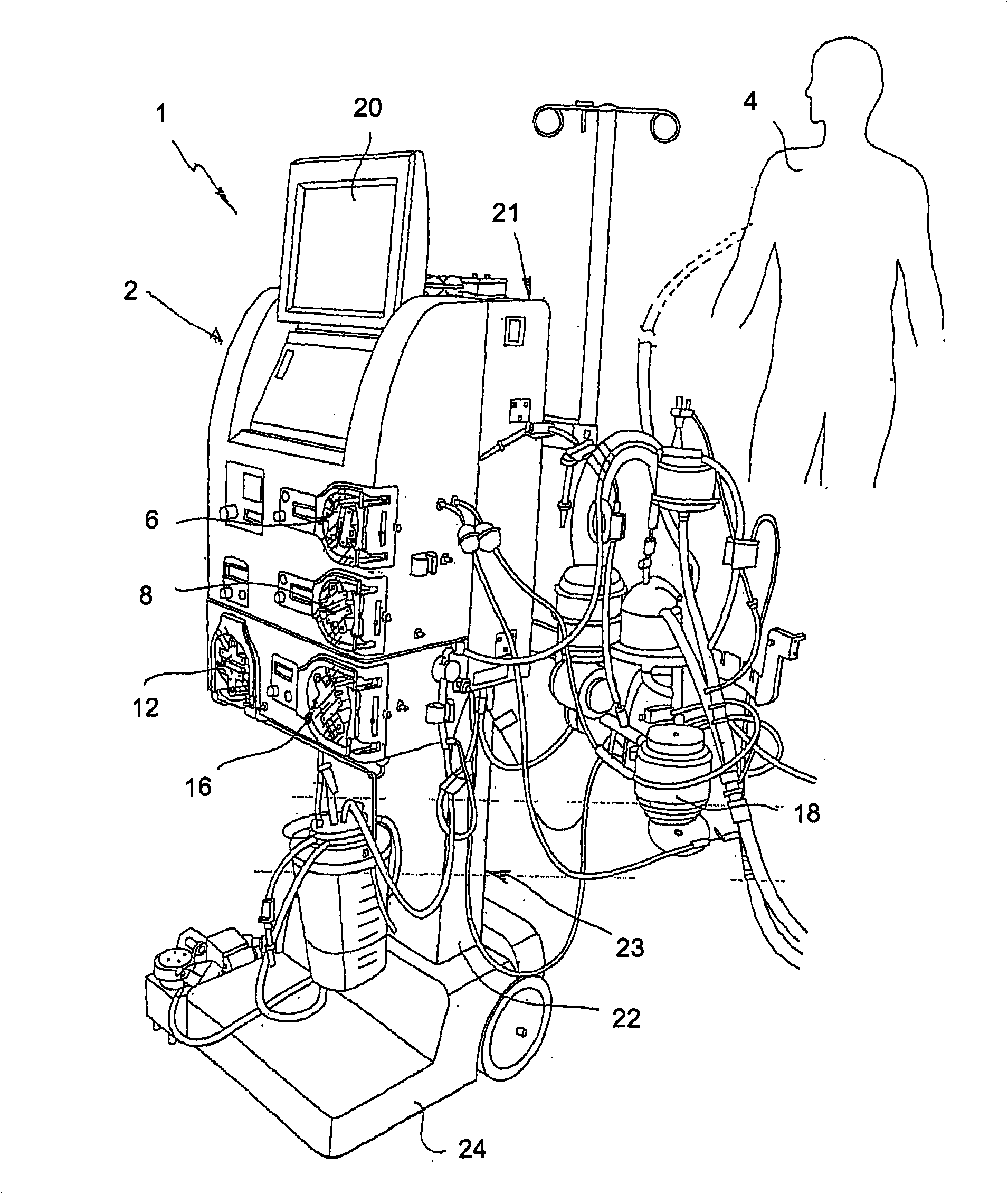
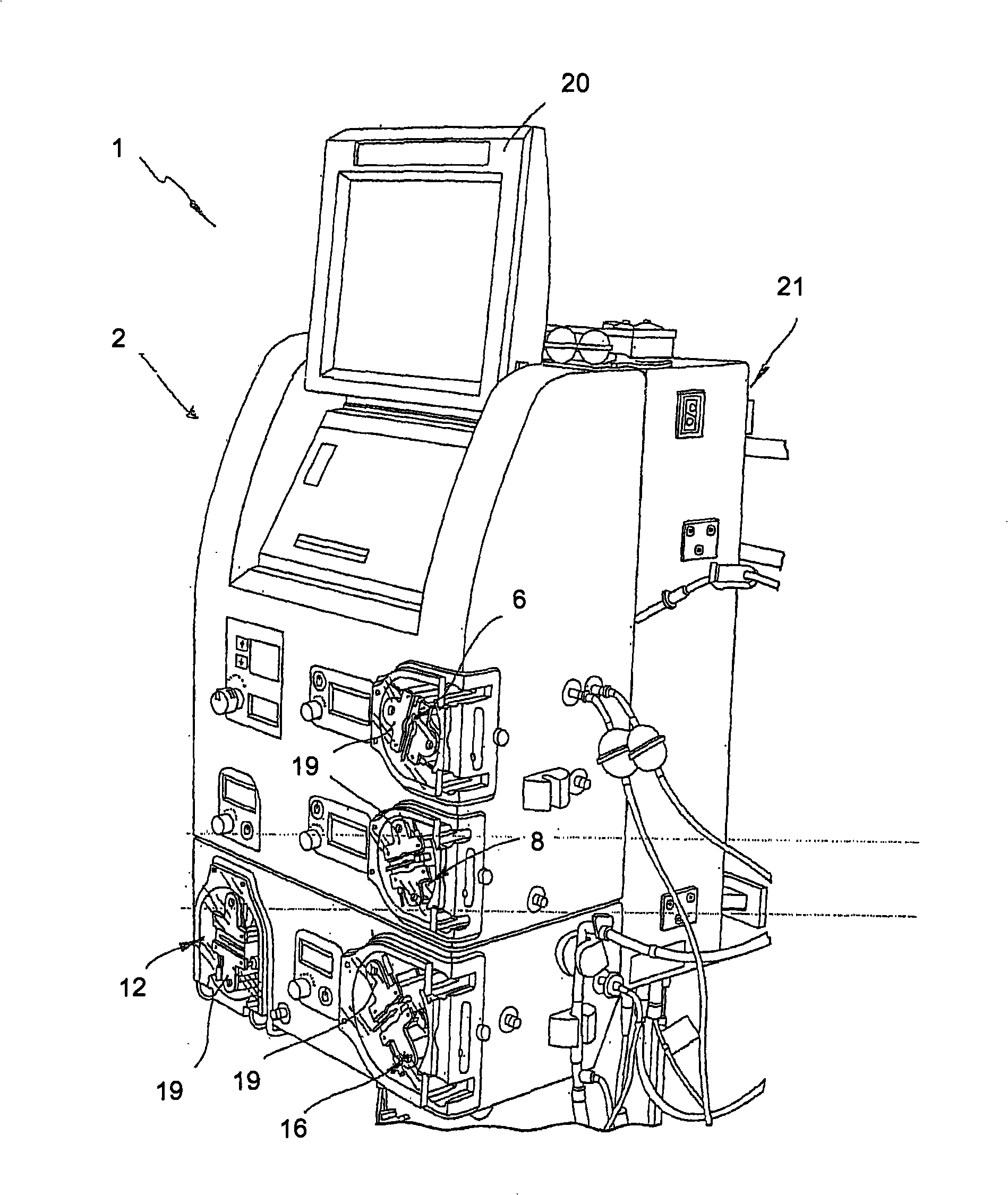
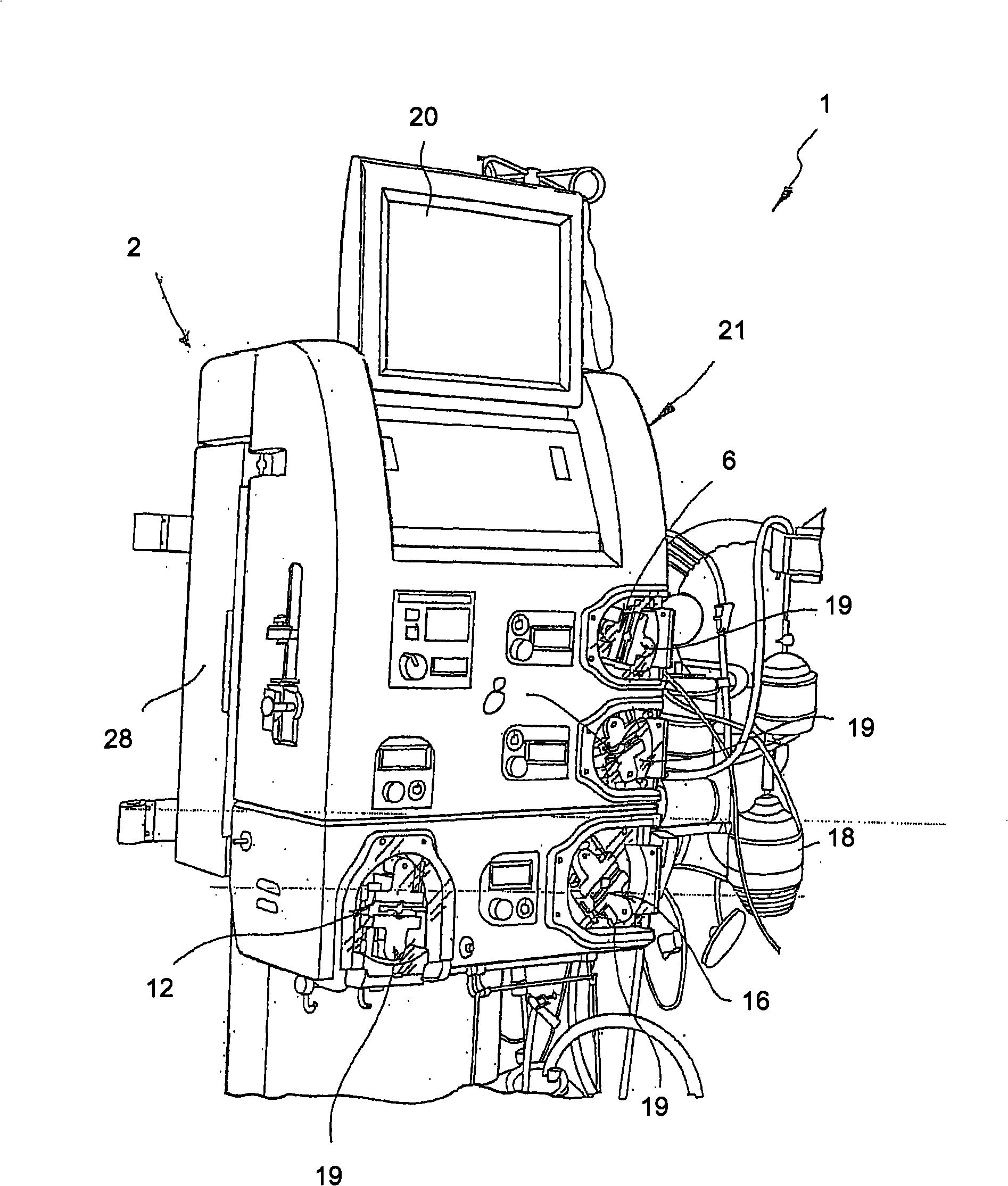
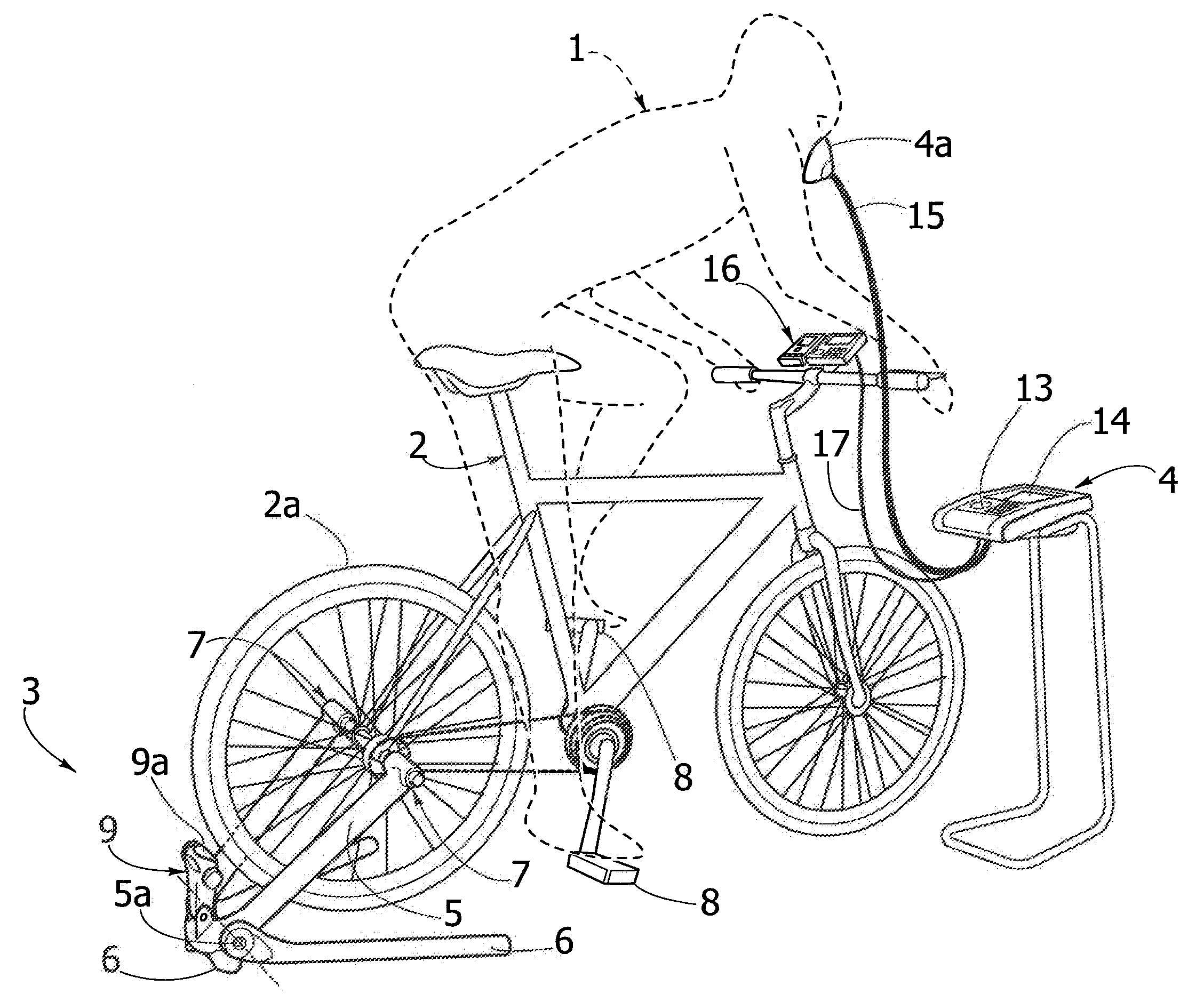
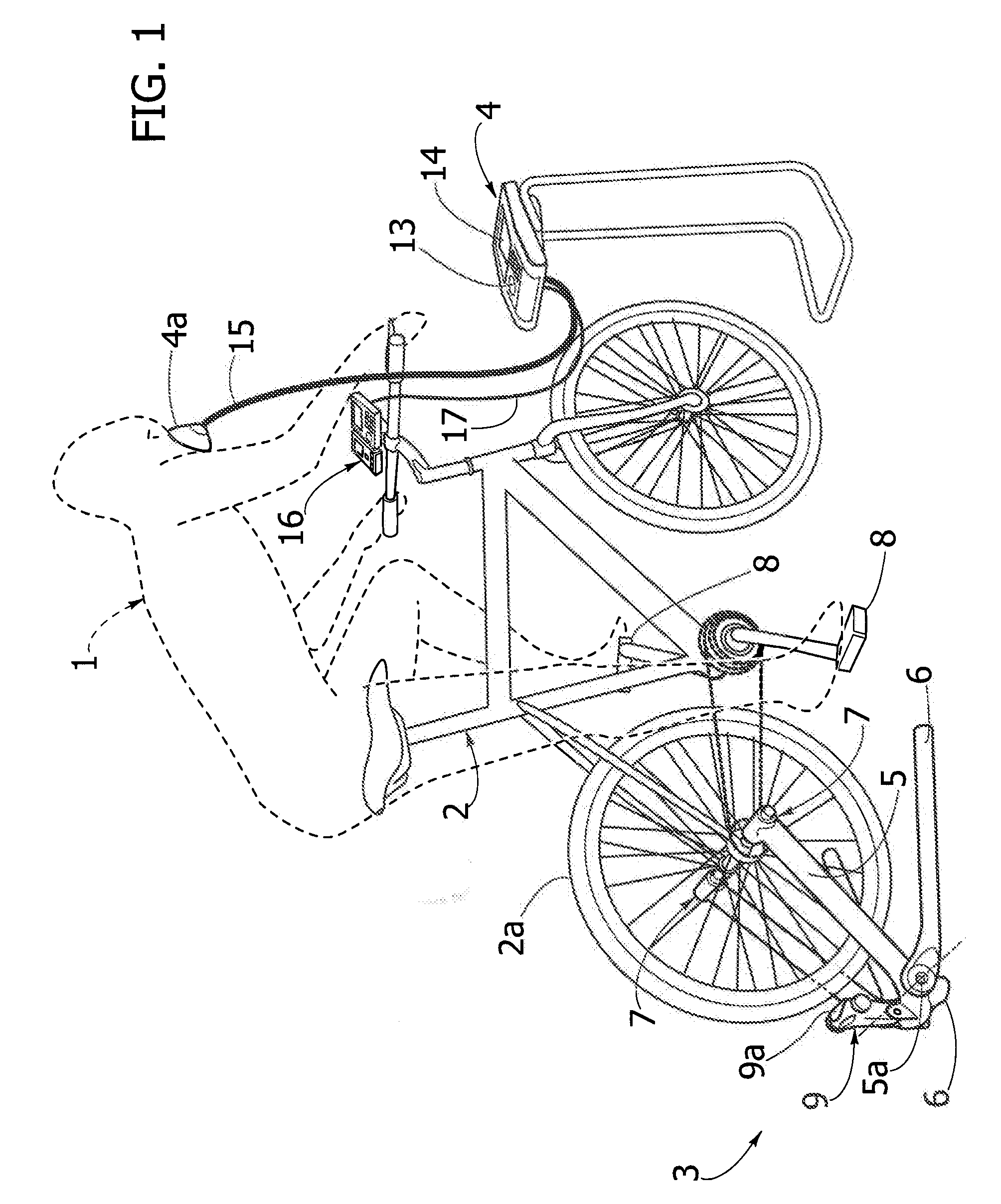
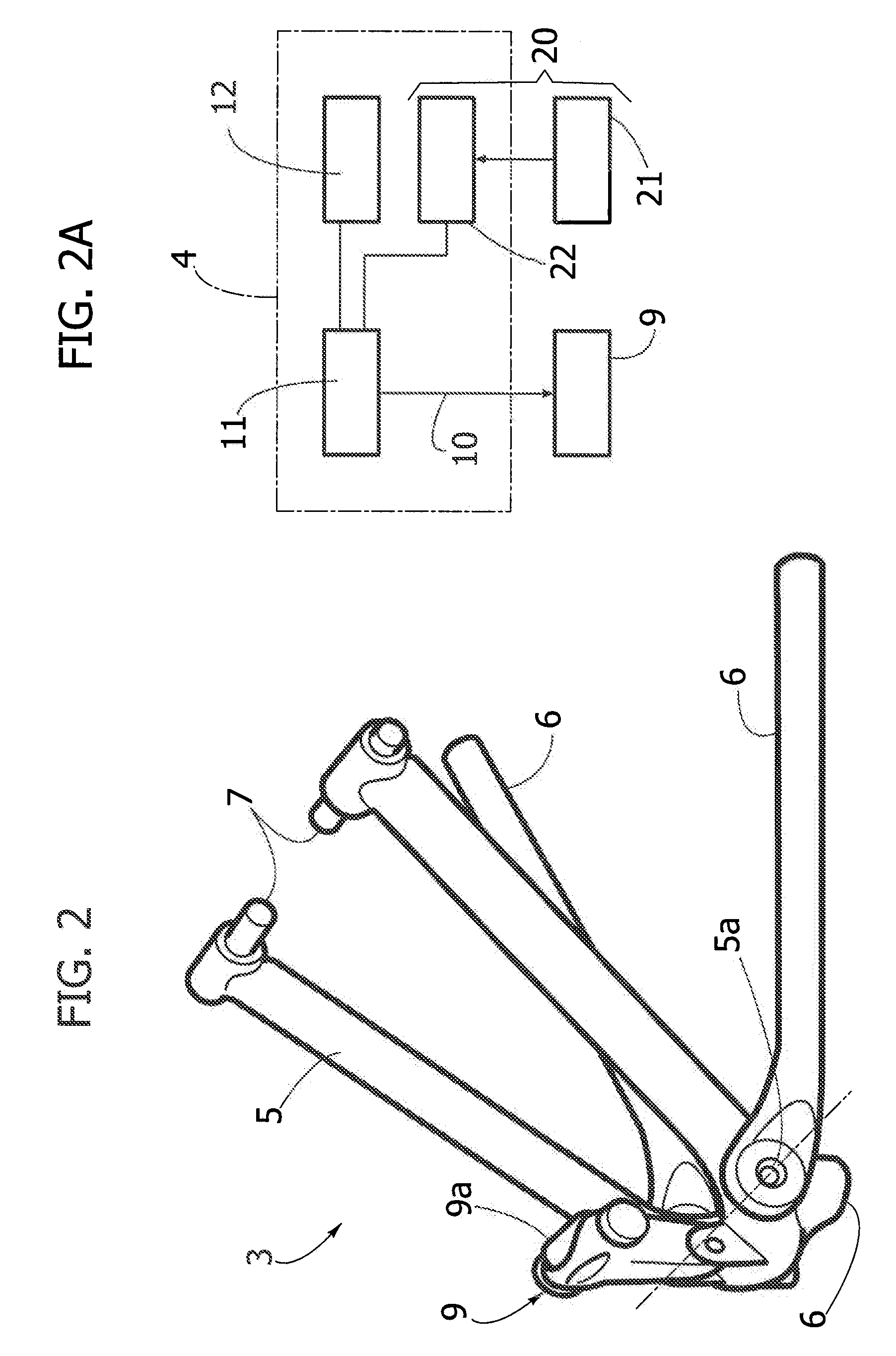
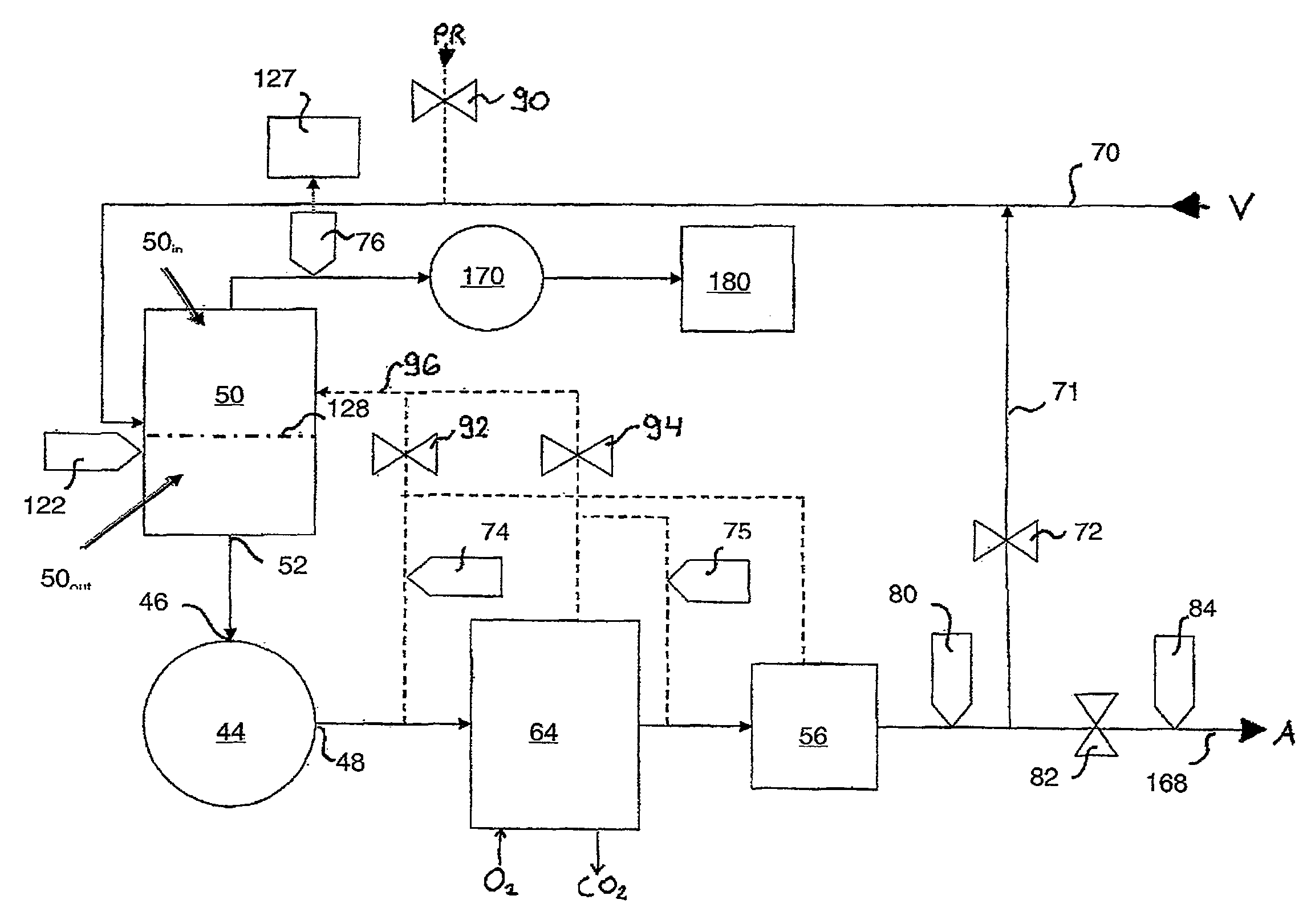
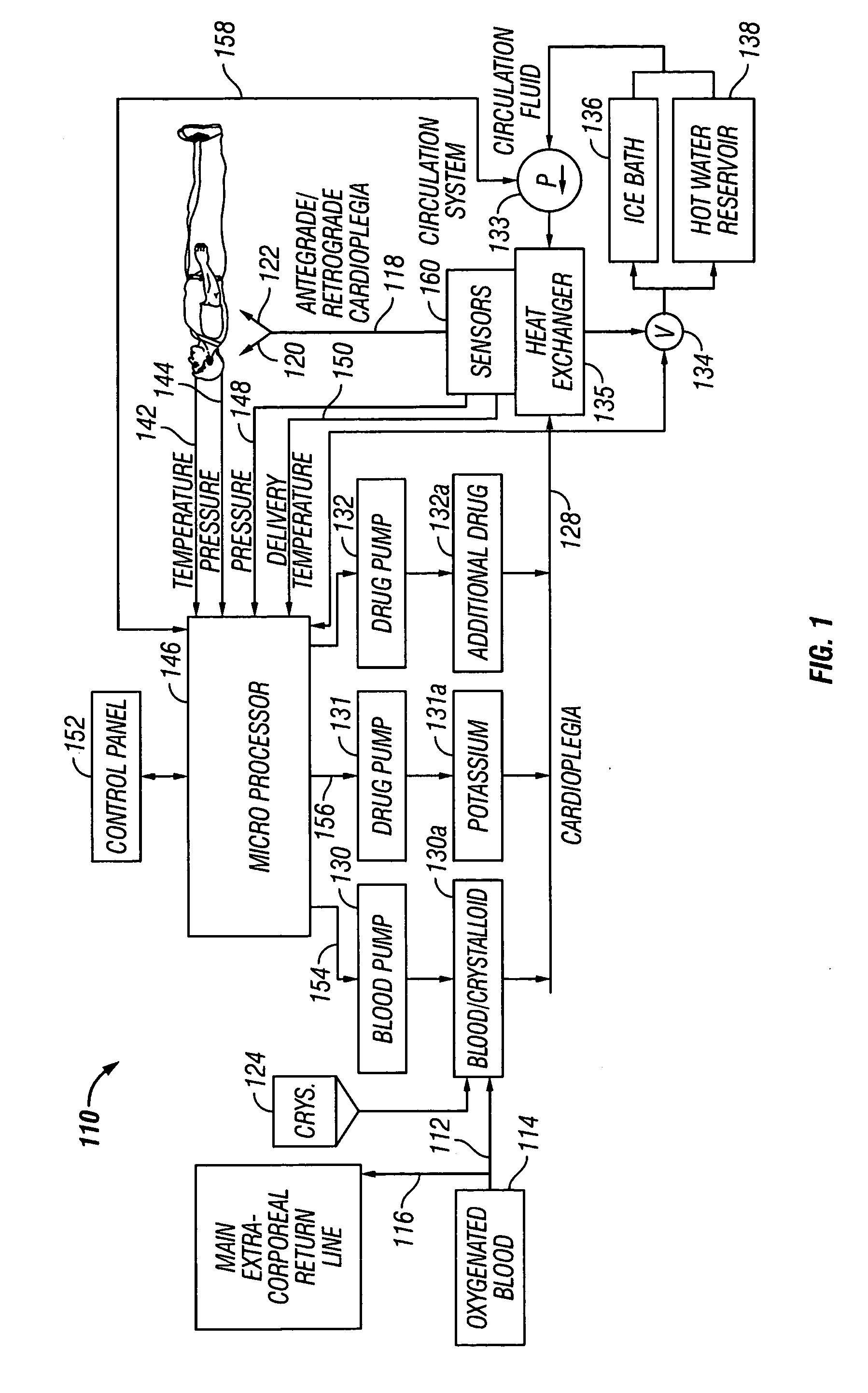
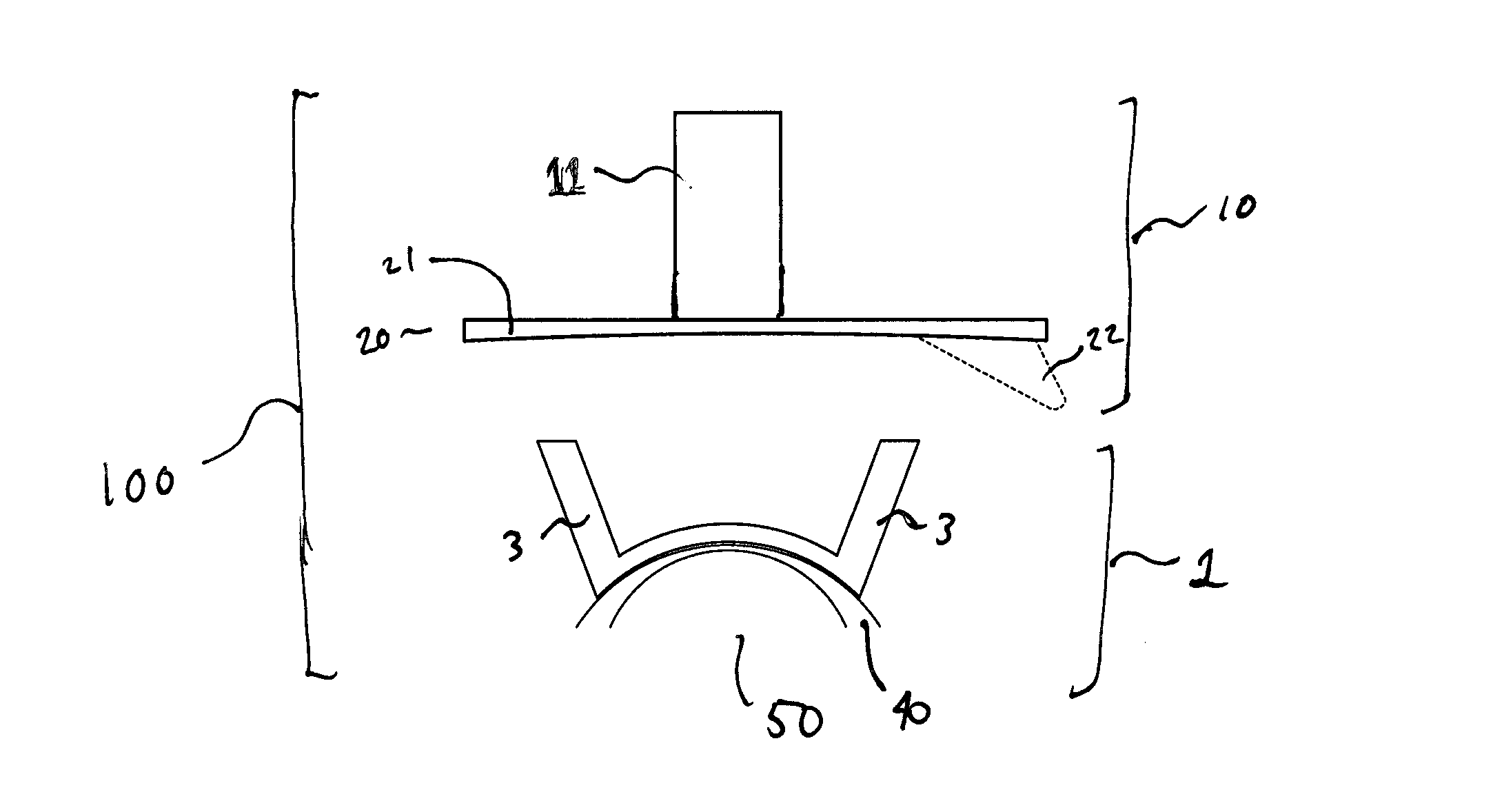
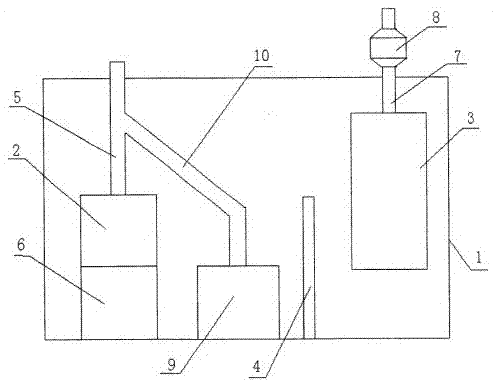
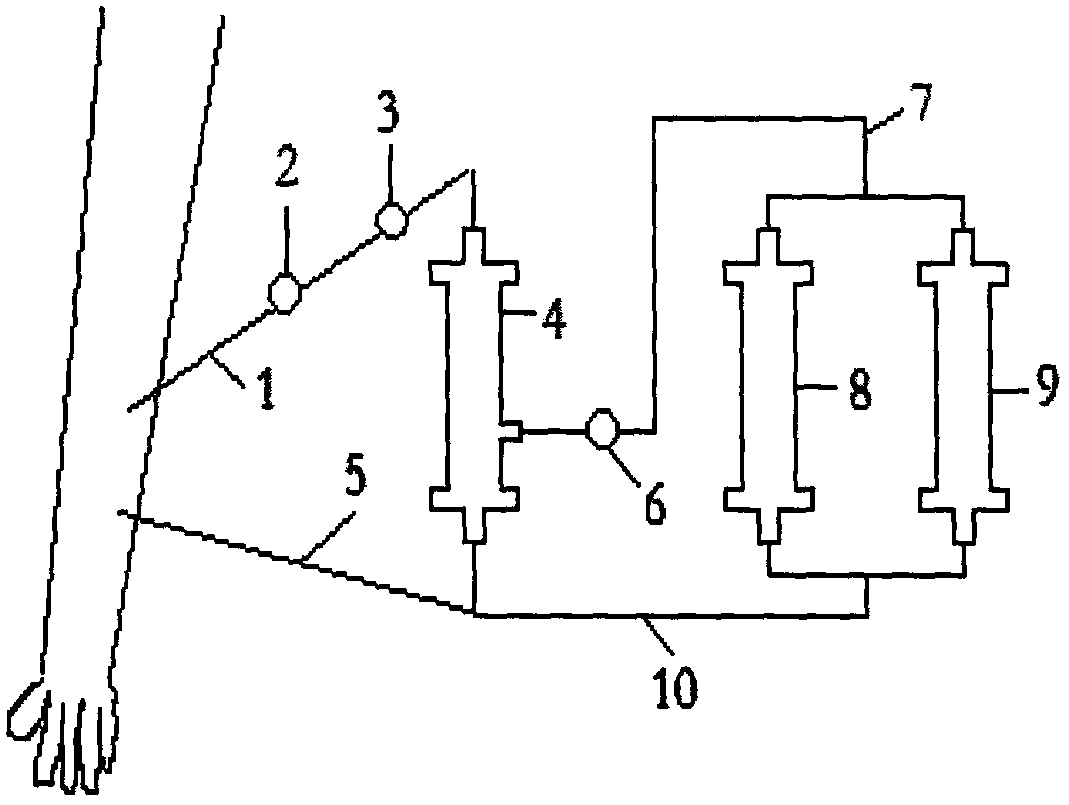
System for monitoring extracorporeal circulation and perfusion of medical fluid in heart lung bypass process
The invention relates to an extracorporeal circulation and infusion system (1) applied to medical fluid in the cardiopulmonary bypass. The system of the invention comprises basically-vertical supporting structures (2, 21, 22, 23, 24) which can be correlated with at least a blood induced circulation loop (3) of a patient (4) and at least provided with one integrated pump (6,8) which is used for infusing the medical fluid into at least one infusion loop (5) of the patient (4) and designed to be applied together with a device(20) monitoring and controlling the induced circulation loop (3) and the infusion loop (5).
Owner:兰德公司
Portable kit, device and method for the execution of cardiopulmonary tests under strain, with the use of a normal bicycle
InactiveUS20080200308A1Reduced dimensionLow costRespiratory organ evaluationSpace saving gamesCardiopulmonary bypassEngineering
A device for the execution of cardiopulmonary tests under strain includes a device for measuring the respiratory activity of a user and physical exercise equipment to be used in combination with the measuring device. The physical exercise equipment is a portable training tool, to be used in combination with a normal bicycle in stationary position.
Owner:PEDRINI +1
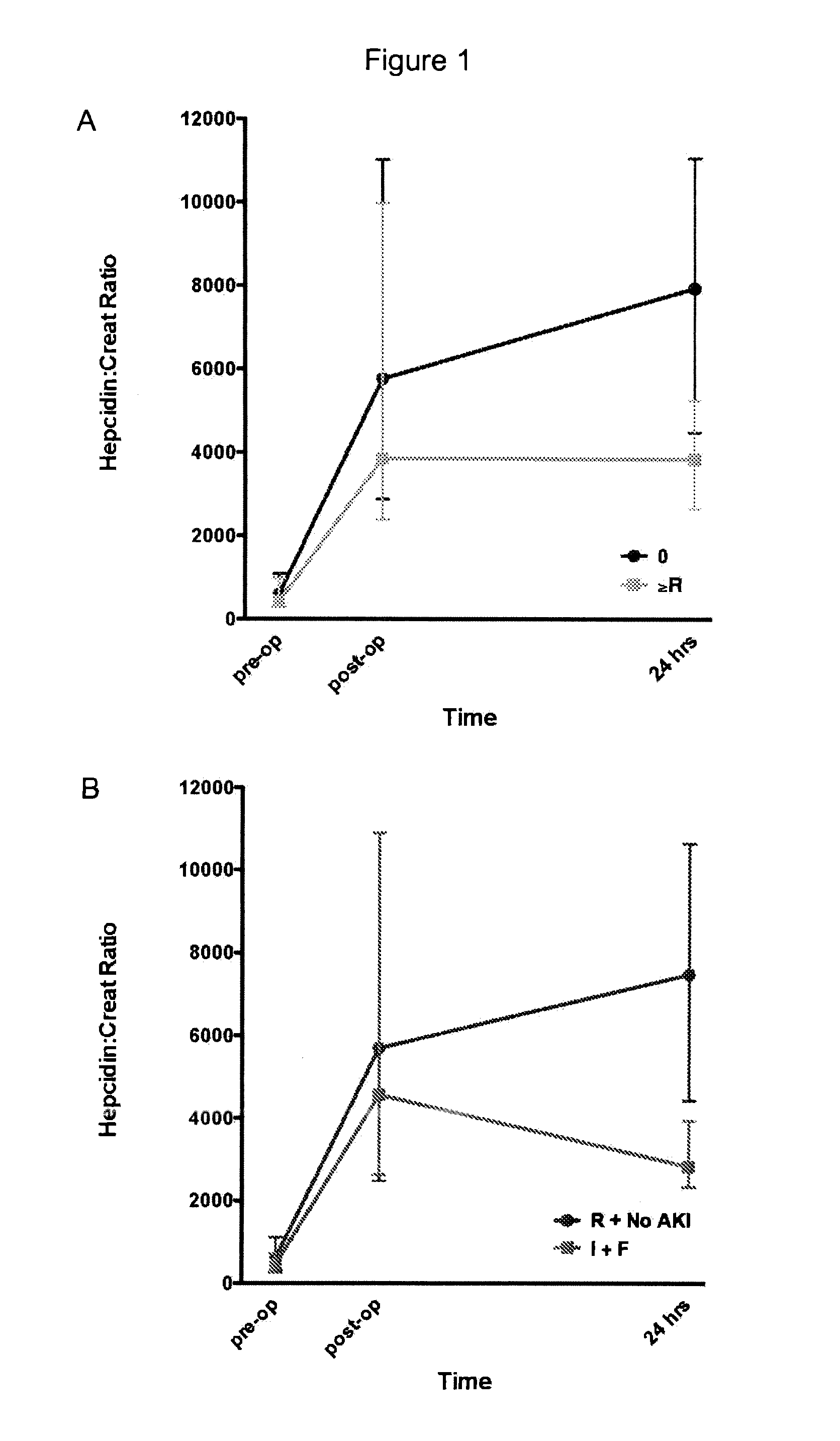
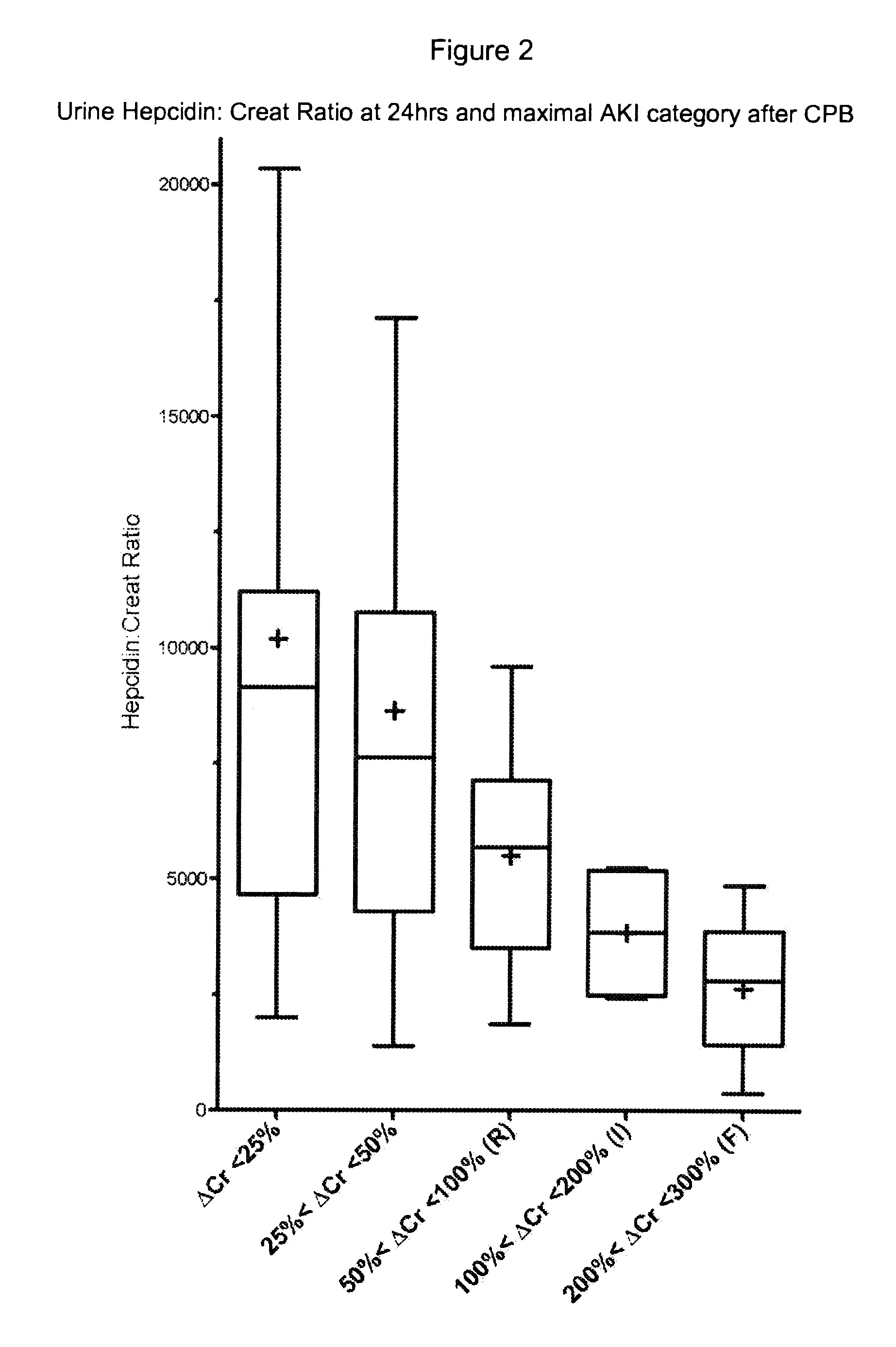
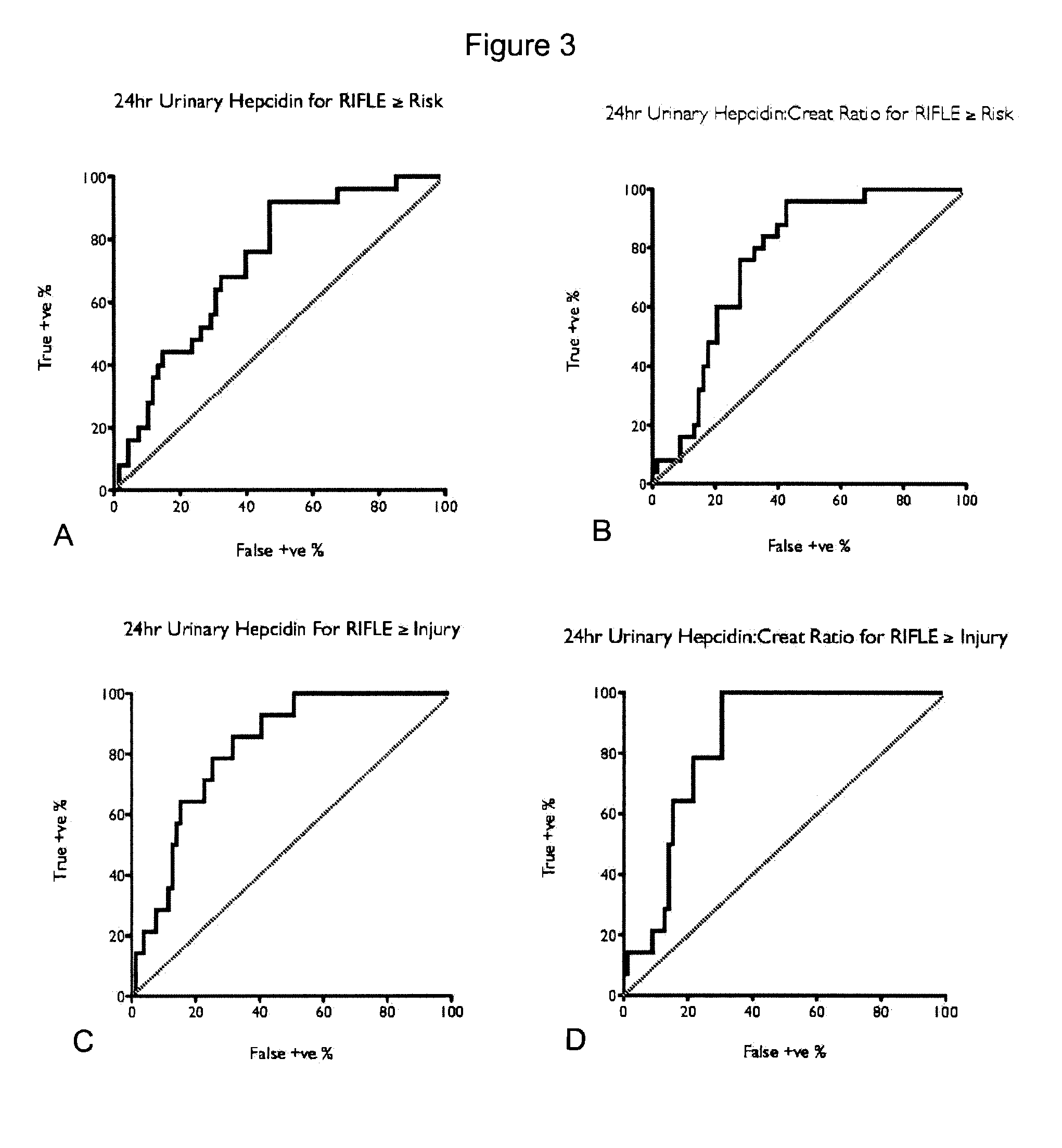
Markers for acute kidney injury
Provided are methods and compositions for predicting the development of kidney disease, including acute kidney injury. In certain aspects and embodiments the provided methods and compositions are particularly useful for predicting kidney injury following an event likely to cause kidney injury and / or kidney failure in a patient, such as a cardiac surgery, e.g., a surgery involving a cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB), such as a coronary artery bypass graft surgery. In some embodiments, the higher the urinary hepcidin-to-urinary creatinine ratio (uHep / uCr) at 6-24 hours following initiation of CPB, the lower is the risk for development of AKI determined by RIFLE criteria in the ensuing four to five days. Conversely, the higher the urinary NGAL to urinary creatinine ratio (uNGAL / uCr) at 6-24 hours following initiation of CPB, the higher is the risk of developing CPB-mediated AKI over the same time period.
Owner:INTRINSIC LIFESCIENCES LLC +1
Apparatus to treat cardiopulmonary disease
InactiveUS20190343579A1Suppressing nerve signal transmissionReduce deliverySurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesCardiopulmonary bypassTherapeutic Devices
A treatment apparatus including: a bronchoscope including a flexible shaft having working channel; a transbronchial ablation probe configured to extend from a distal end of the working channel and extend thru a wall of a trachea and into tissue outside of the trachea; and a stabilization element mounted to a distal portion of the flexible shaft, wherein the stabilization element is configured to brace the distal portion against the wall of the trachea while the transbronchial ablation probe is extended through the wall of the trachea.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
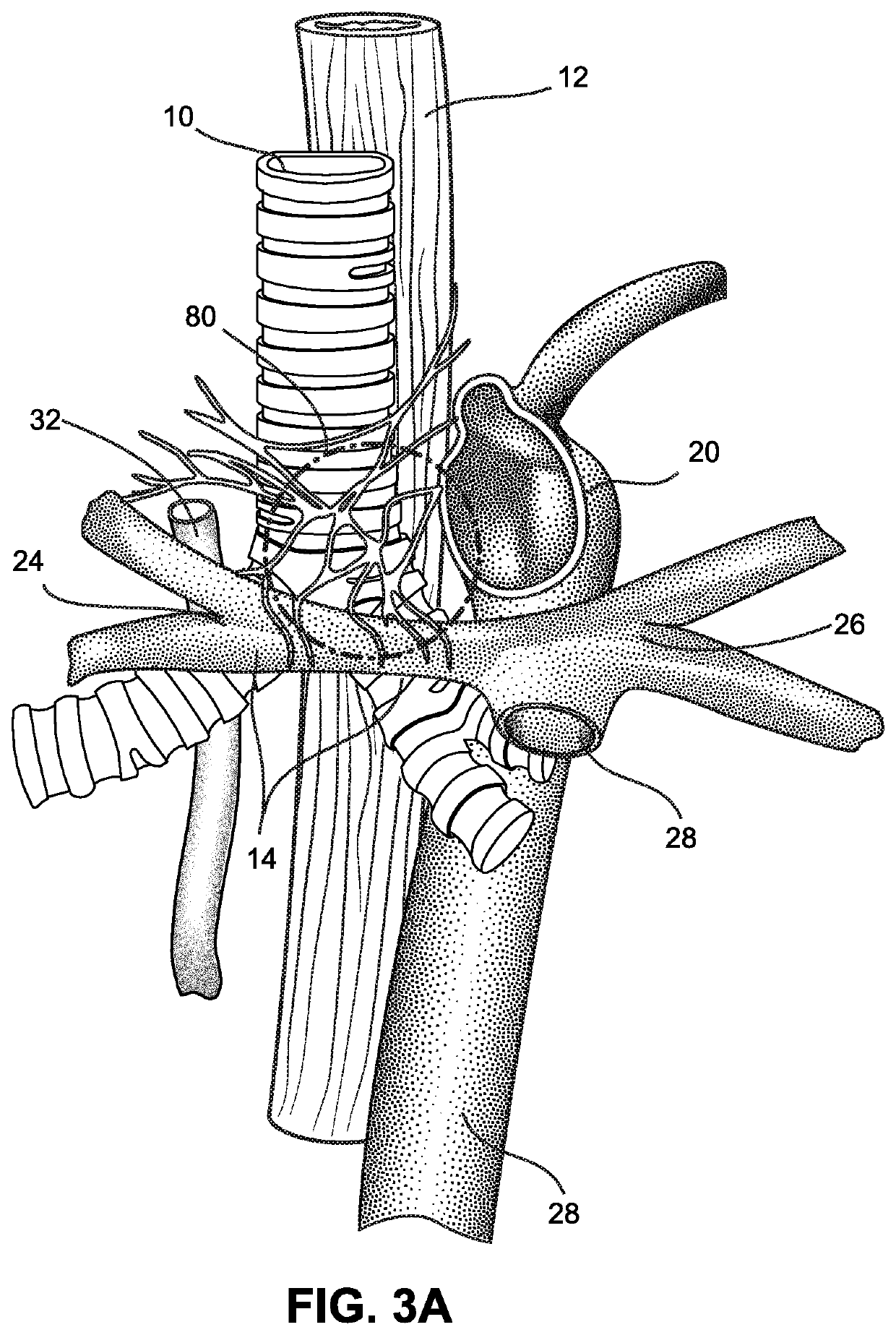
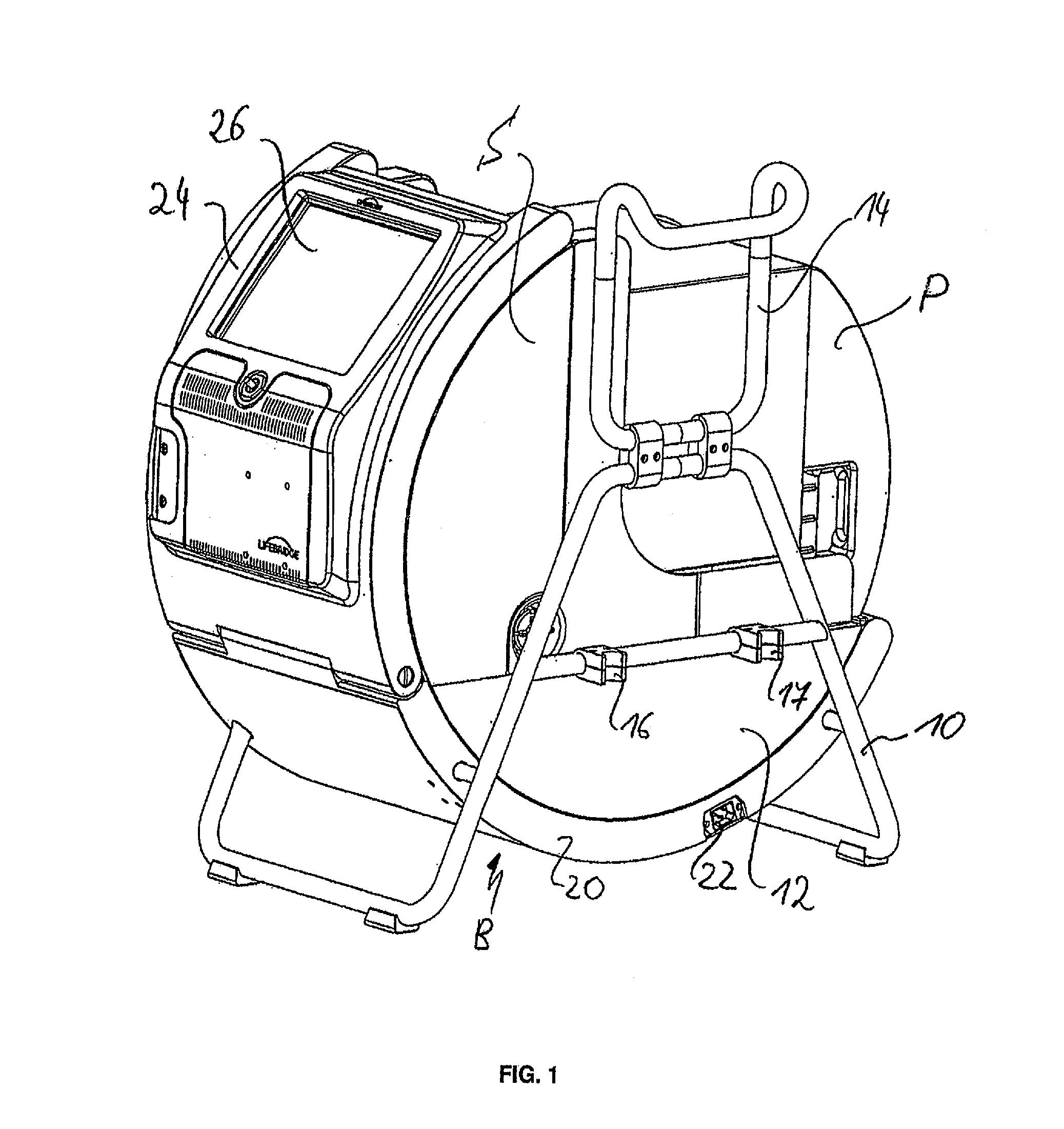
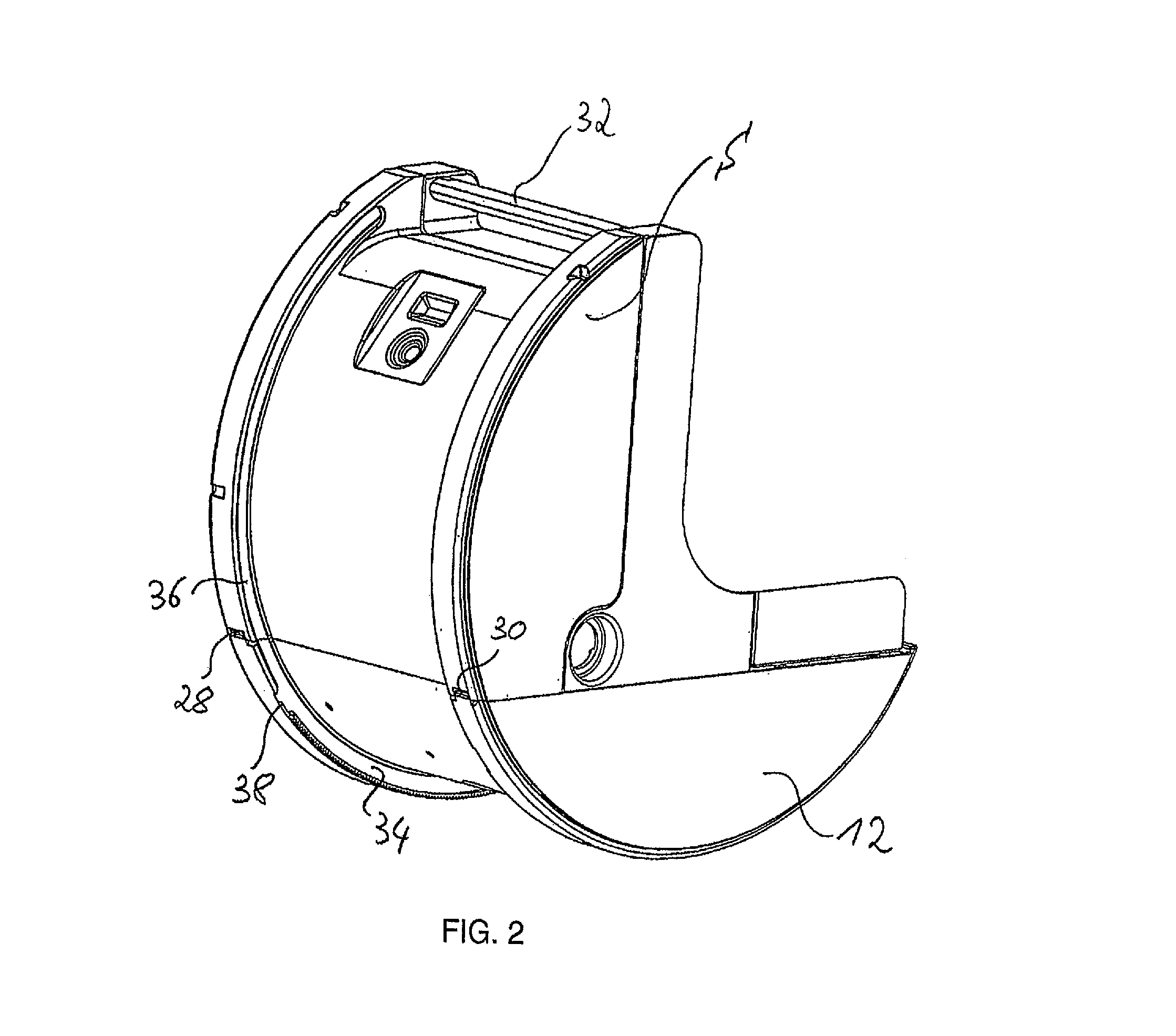
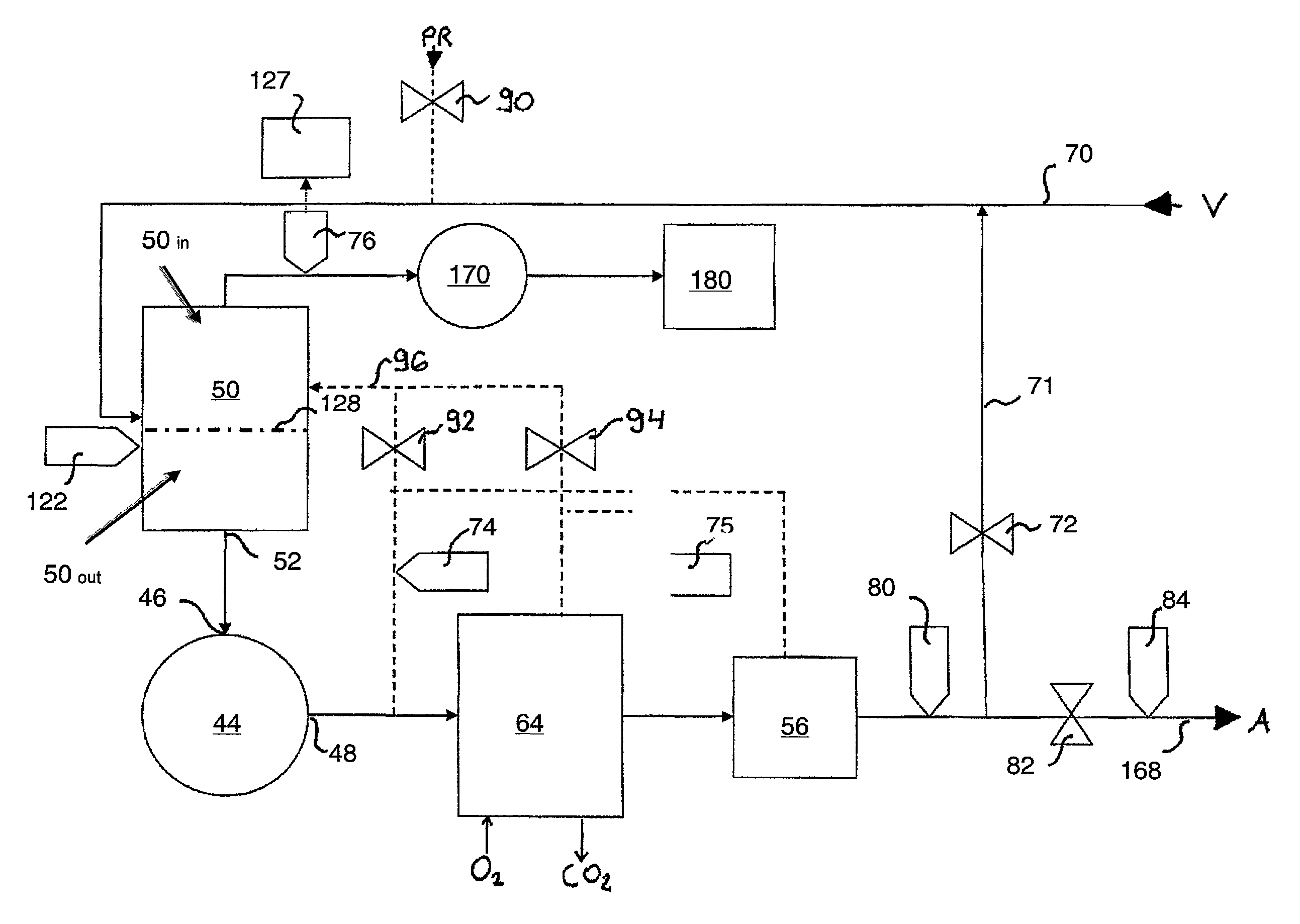
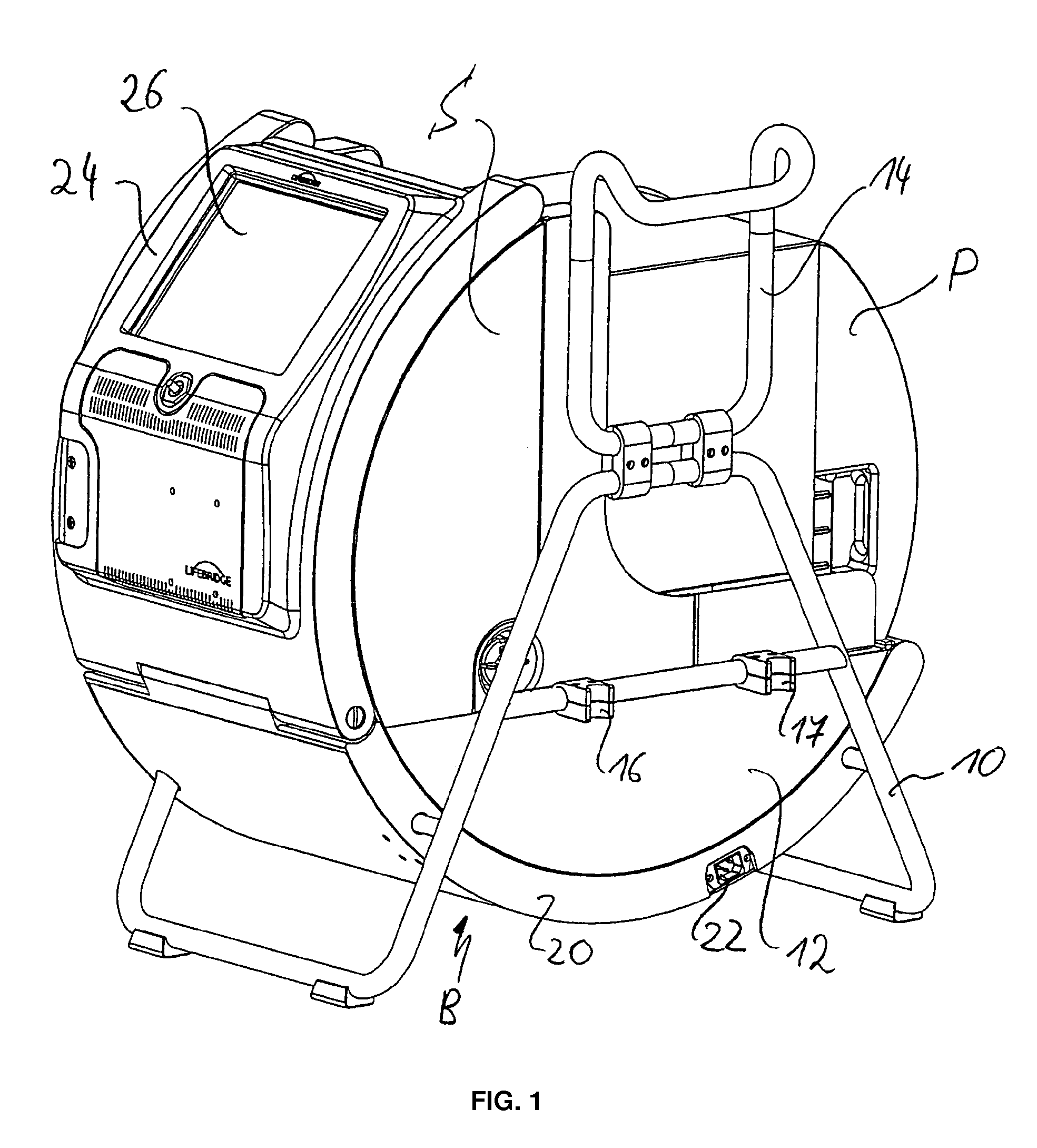
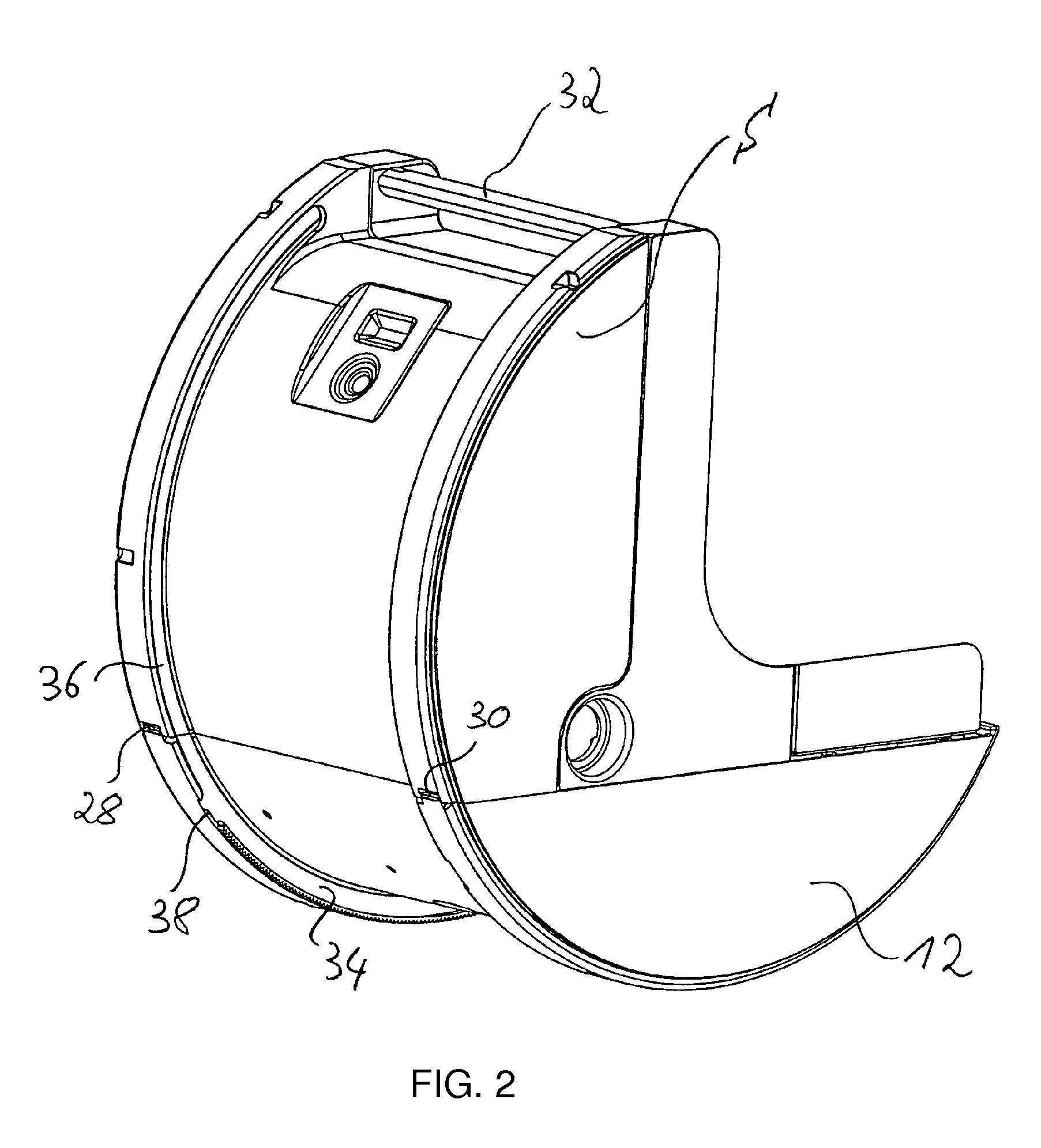
Cardiopulmonary apparatus and methods for preserving organ viability
InactiveUS8834399B2Maintain their viabilityImprove securityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassOrgan Viability
Owner:ZOLL LIFEBRIDGE
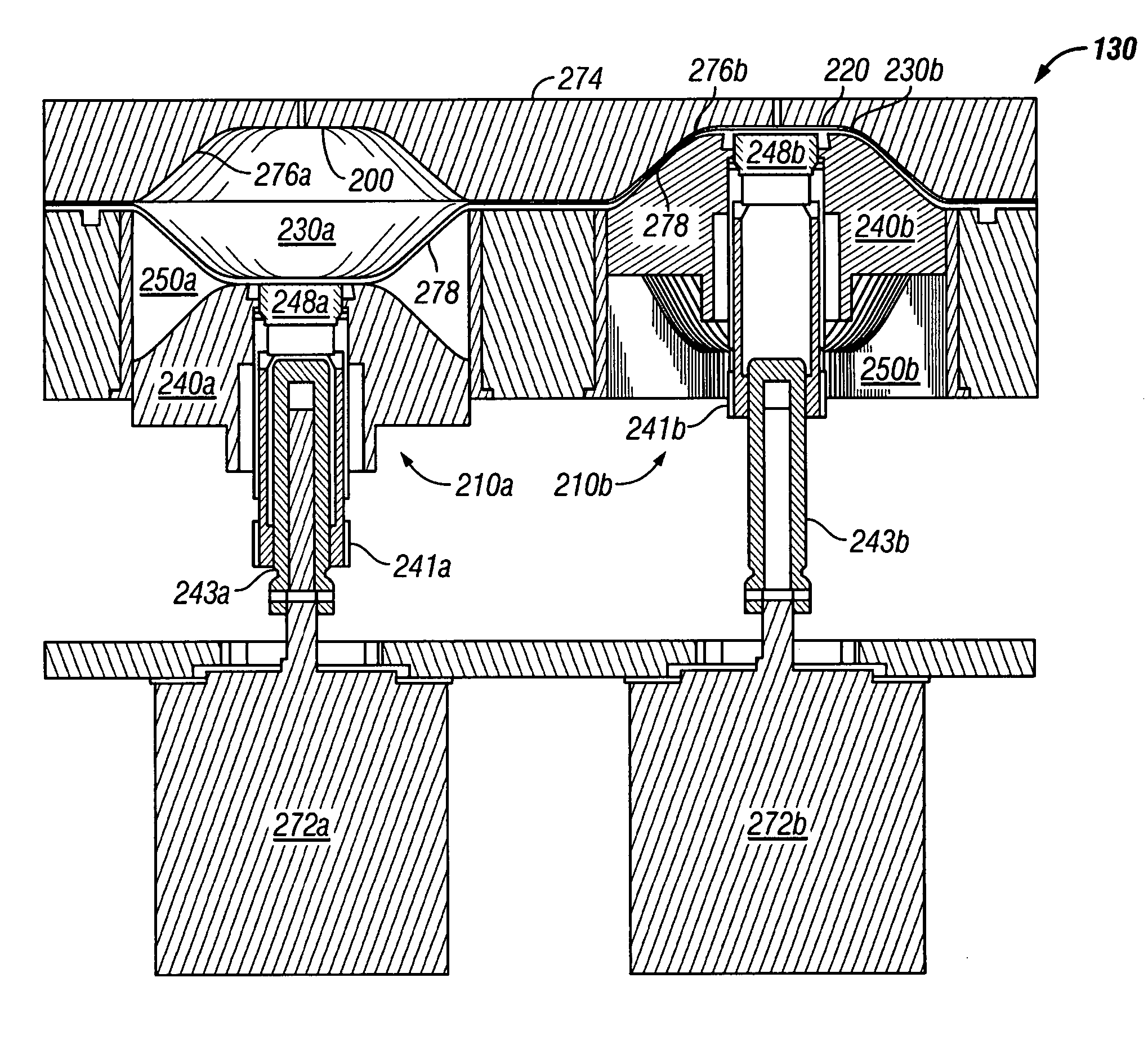
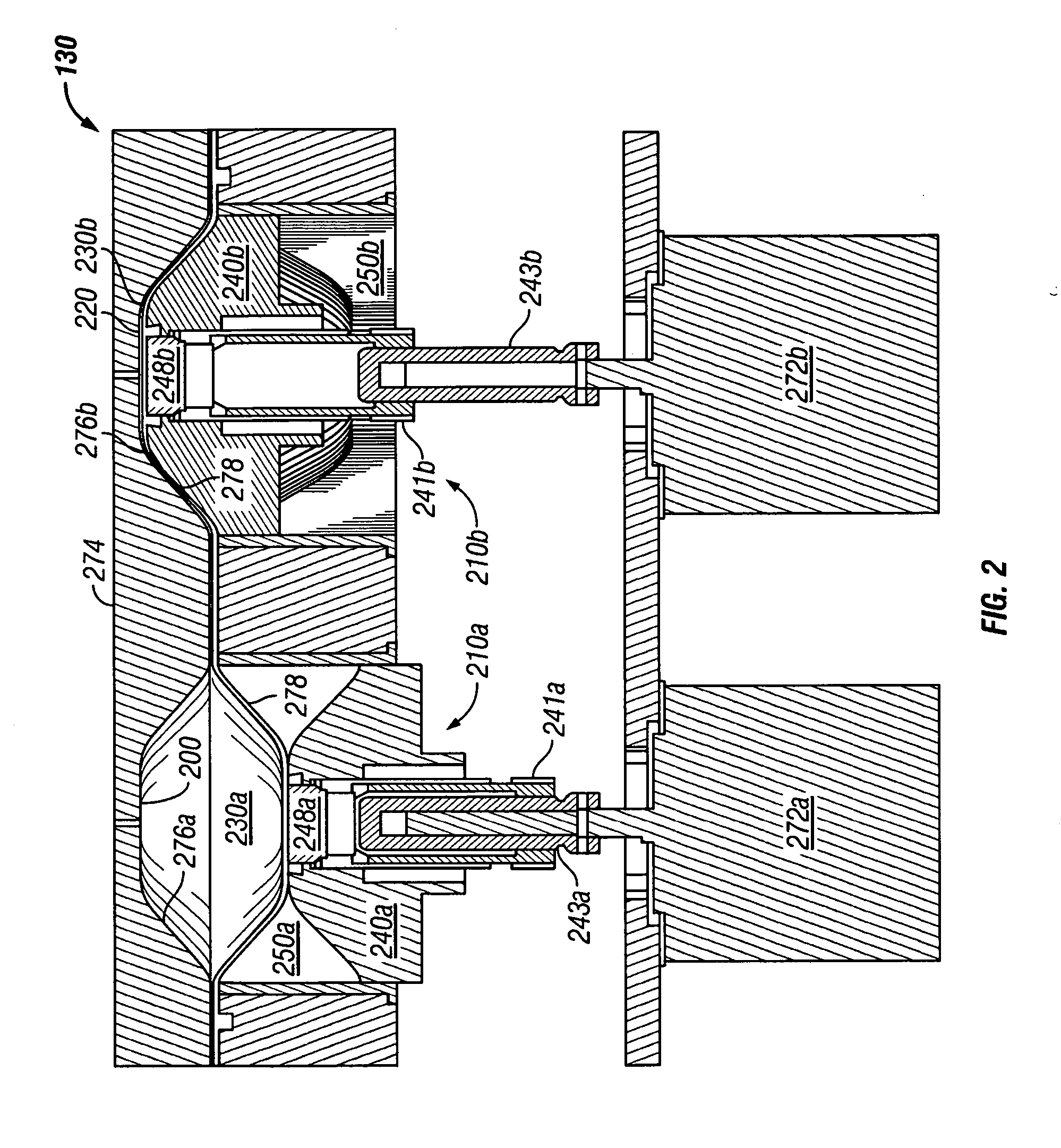
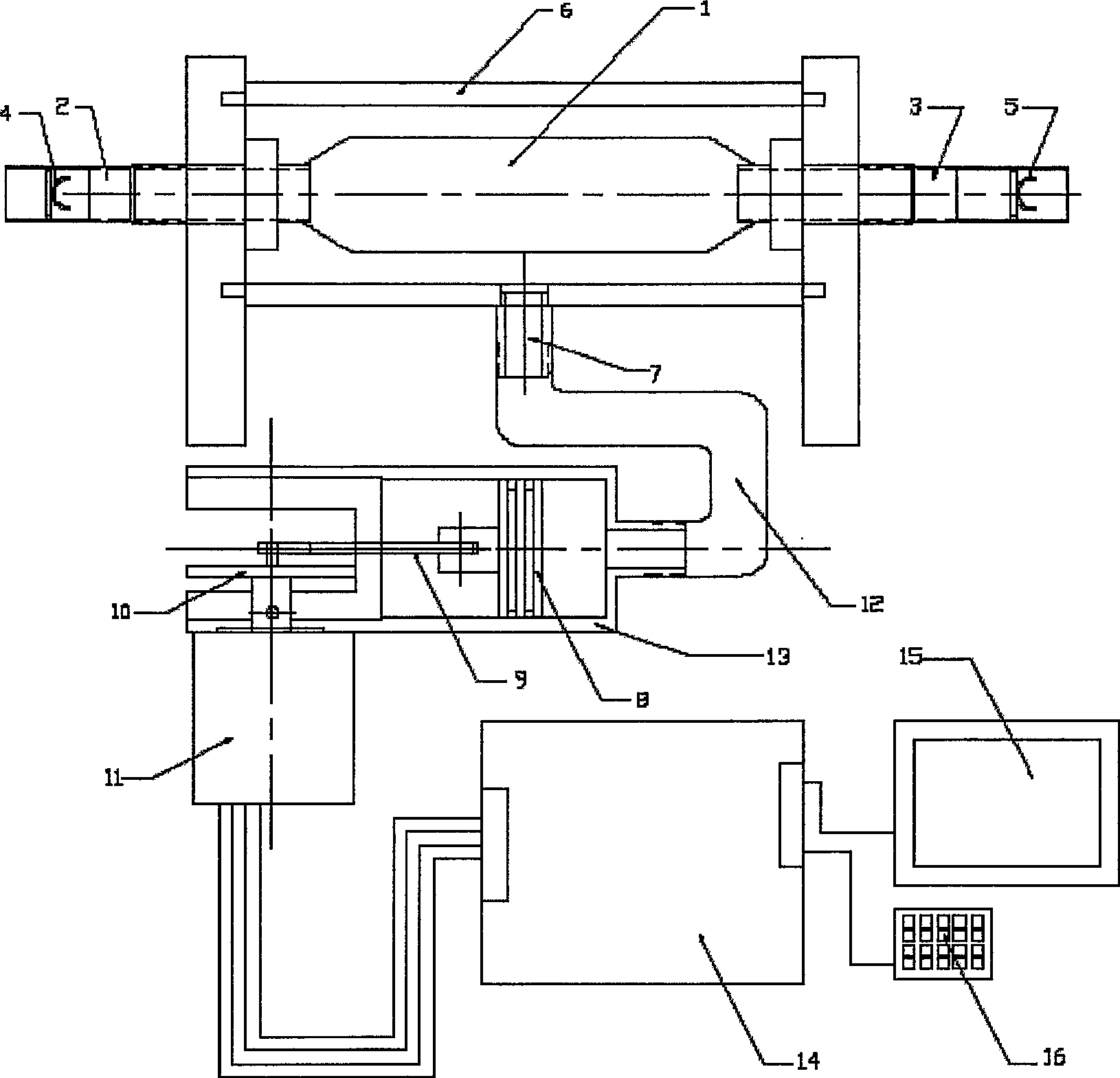
Pulsatile fluid delivery system
ActiveUS20070134101A1Flexible member pumpsMedical devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
A system for delivering blood, cardioplegia solution, and other medications or fluids in a pulsatile flow pattern to a patient during cardiopulmonary bypass is disclosed. In a preferred embodiment, a pumping apparatus having at least one chamber is utilized in which a pumping action is achieved by compressing one of the chambers with a piston mechanism, while allowing the other chamber to fill with fluid via retracting its respective piston. The instantaneous flow rate of either of the chambers is determined by the speed of the piston. In a preferred embodiment, a pulsatile flow of fluid is achieved by cyclically alternating the velocity of the piston between two different speeds. A desired average flow rate and / or delivery pressure and / or constant pulse pressure is maintained by adjusting the alternating velocities at the desired frequency and duty cycle. The calculations necessary to obtain a desired average flow rate are performed by a microprocessor, which also controls the movement of the pistons.
Owner:QUEST MEDICAL
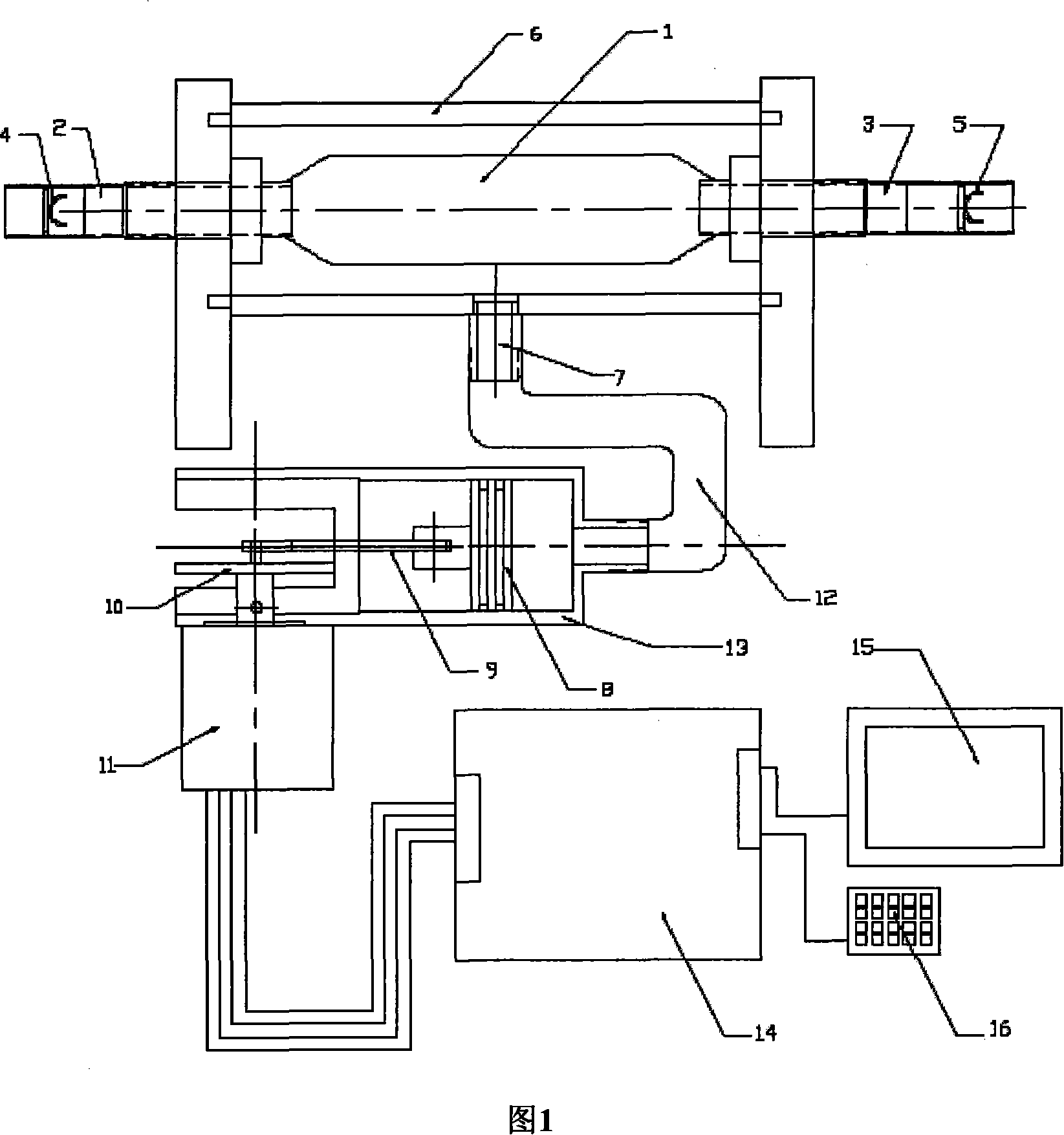
Electric-liquid type heart extracorporeal circulation pulsatory blood pump
InactiveCN101138658AAvoid cross infectionAchieve therapeutic effectProsthesisExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
The present invention relates to an electro hydraulic-typed blood pulsation pump for the heart cardiopulmonary bypass. The shell of the blood pump is provided with a blood package, which is arranged in the inlet and out blood vessels at the two ends of the blood pump shell. The liquid is pumping in or pumping out of the pump by a piston mechanism, therefore the blood package in the pump can shrink and expand and the blood can pump in and pump out of the blood package. A butterfly-typed valve with single direction is arranged in two ends of his inlet and out blood vessels. The blood can flow in and flow out of the blood package in single direction; therefore the blood supply function of the heart is formed. The circuit, the pulse and the blood flow are controlled by the industrial control computer. By adjusting the rotating speed of the motor, the treatment effect is guaranteed according to the settled moving parameter.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
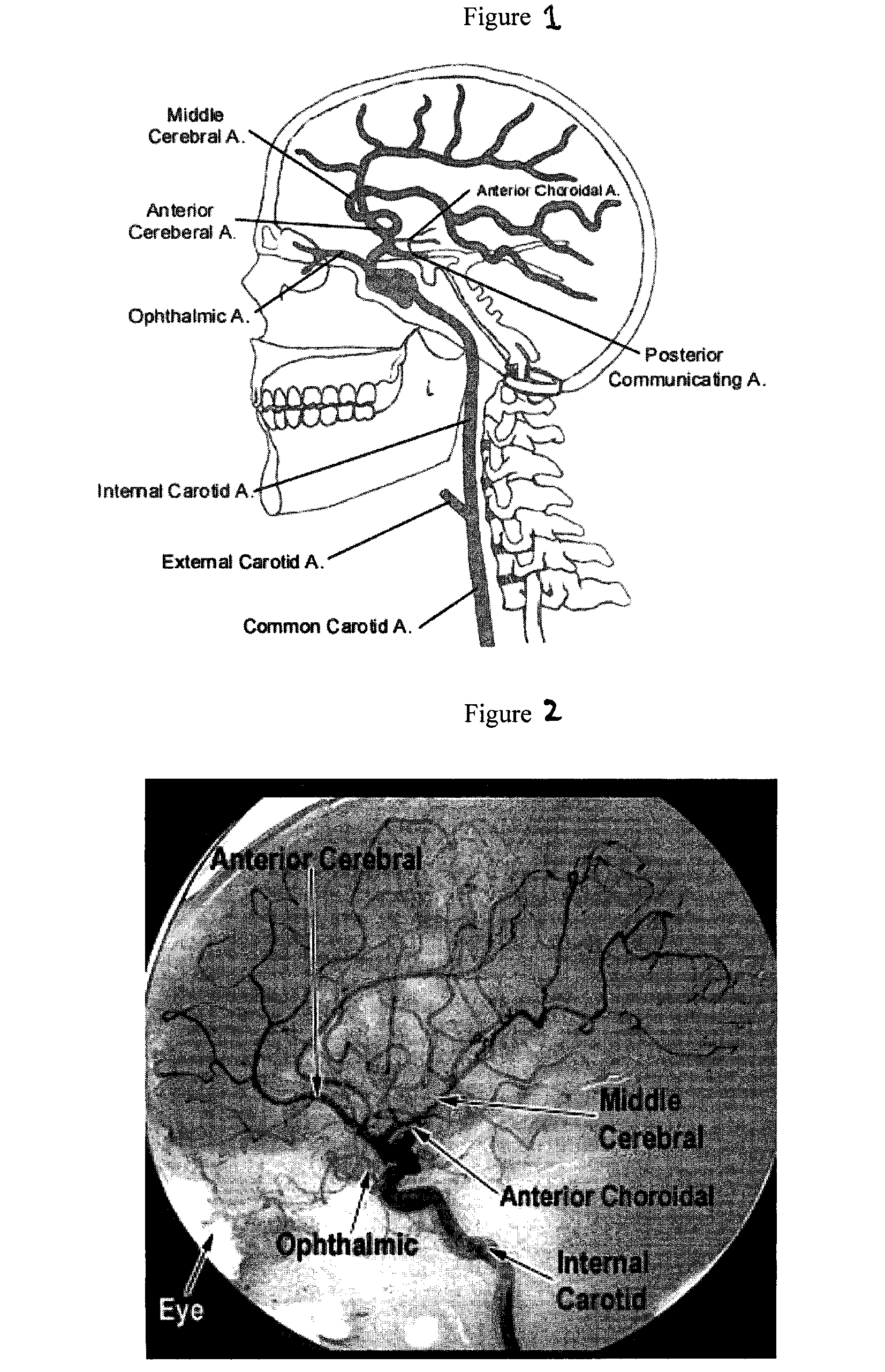
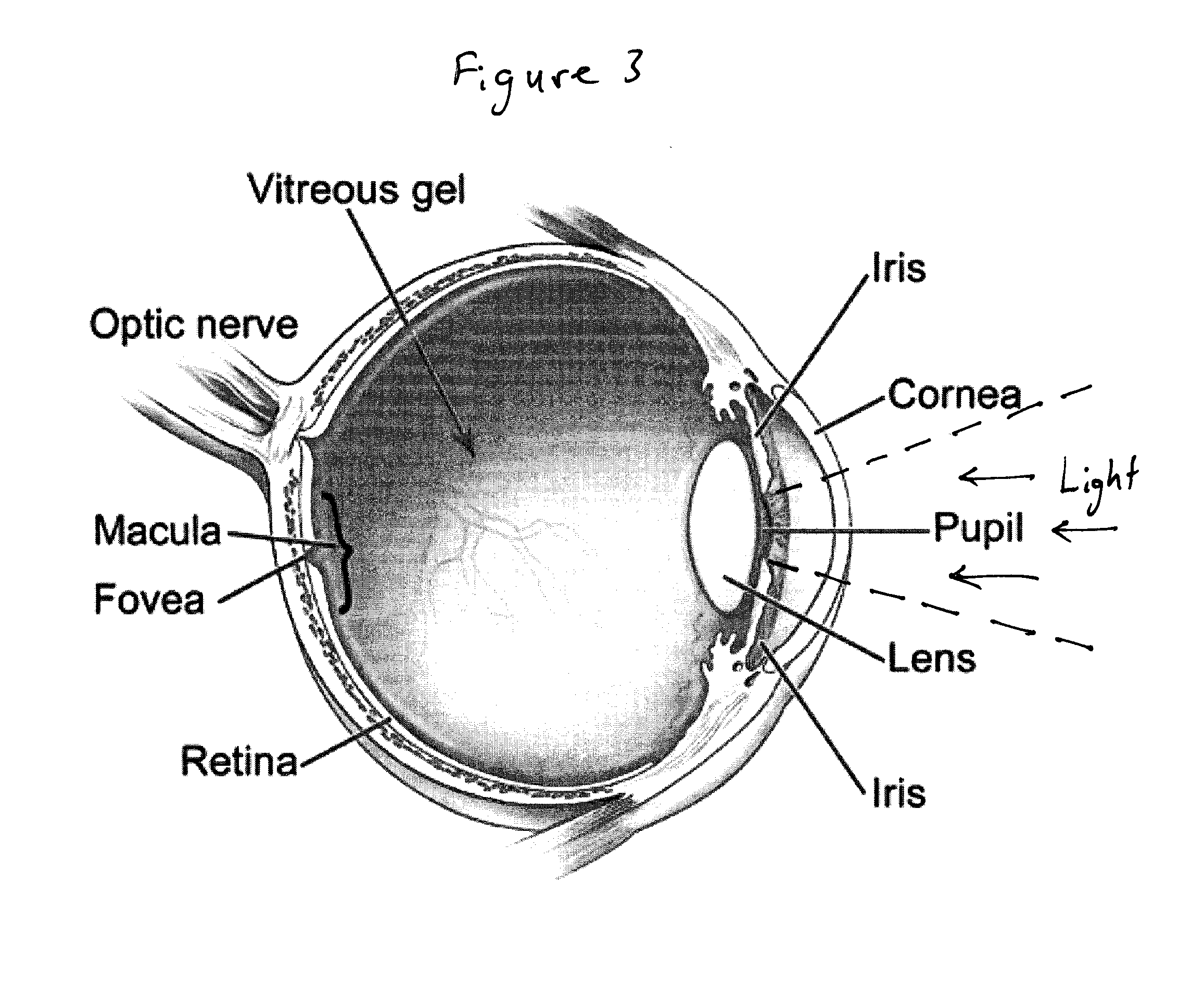
Cerebral and Retinal Perfusion Monitoring Systems and Devices
Cerebral and retinal perfusion monitoring devices, systems, and methods, are described. Such devices, systems, and methods can be used during surgical procedures, including cardiac surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass and spine surgery in prone position, to monitor a patient's brain perfusion in real time. In some embodiments, such monitoring allows trends in perfusion over time to be assessed. Such monitoring allows appropriate medical interventions to be undertaken in the event a state of hypoperfusion is detected, thereby reducing risks of brain hypoperfusion and stroke for patients undergoing heart surgery with cardiopulmonary bypass, as well as minimizing risk of retinal artery thrombosis with resulting blindness for patients undergoing prolonged procedures in the prone position.
Owner:GELLAND YURI
Electric-liquid type heart extracorporeal circulation pulsatory blood pump
InactiveCN100509066CAvoid cross infectionAchieve therapeutic effectProsthesisCardiopulmonary bypassMotor speed
The invention relates to an electro-hydraulic cardiac extracorporeal circulation pulsating blood pump. A blood bag is arranged in the blood pump casing. The blood bag is installed on the blood-inlet and bleeding pipes at both ends of the blood pump casing. The blood sac in the pump body contracts and expands, so that blood can be pumped into and pressed out of the hemorrhage sac, and butterfly-shaped one-way valves are installed in the inflow and outflow pipelines at both ends, so that blood can flow in and out of the pump sac in one direction, forming the blood supply function of the heart, controlled by industrial control The computer controls the beating frequency and the extruded blood flow through the control circuit respectively, so as to ensure the blood supply balance required by the human body. The industrial control computer can interact with the screen and keyboard to accept the selection of the number of beats and the flow rate of extruded blood. By adjusting the speed of the control motor, it is guaranteed to achieve the therapeutic effect according to the predetermined value of the set exercise parameters.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
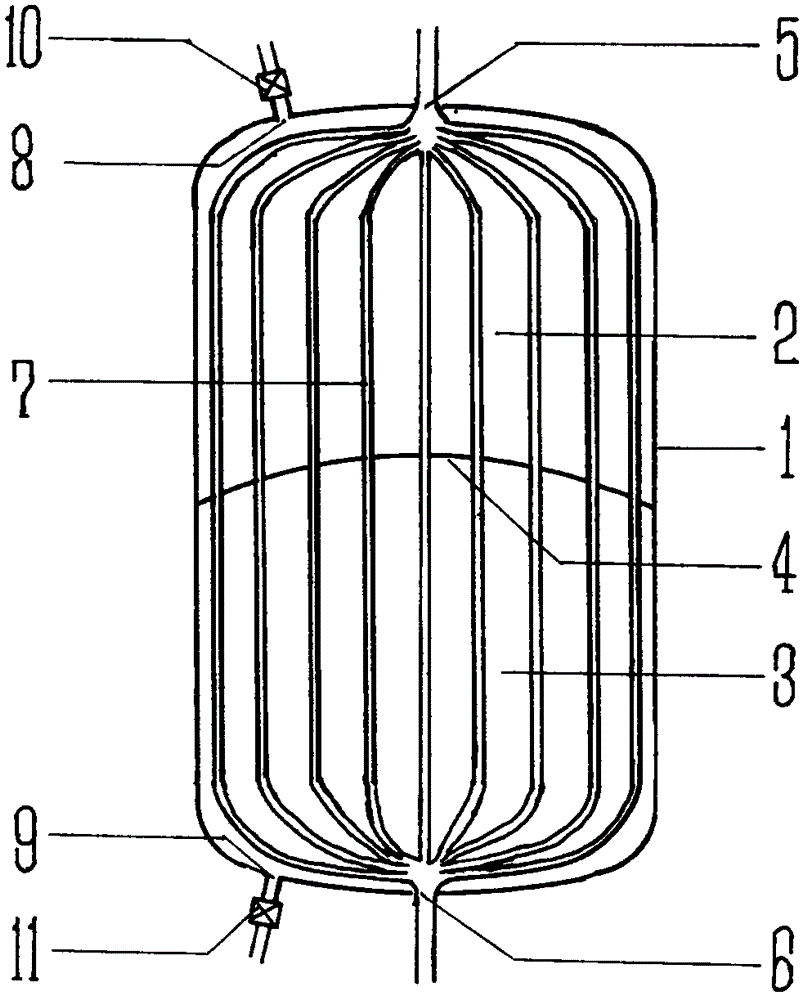
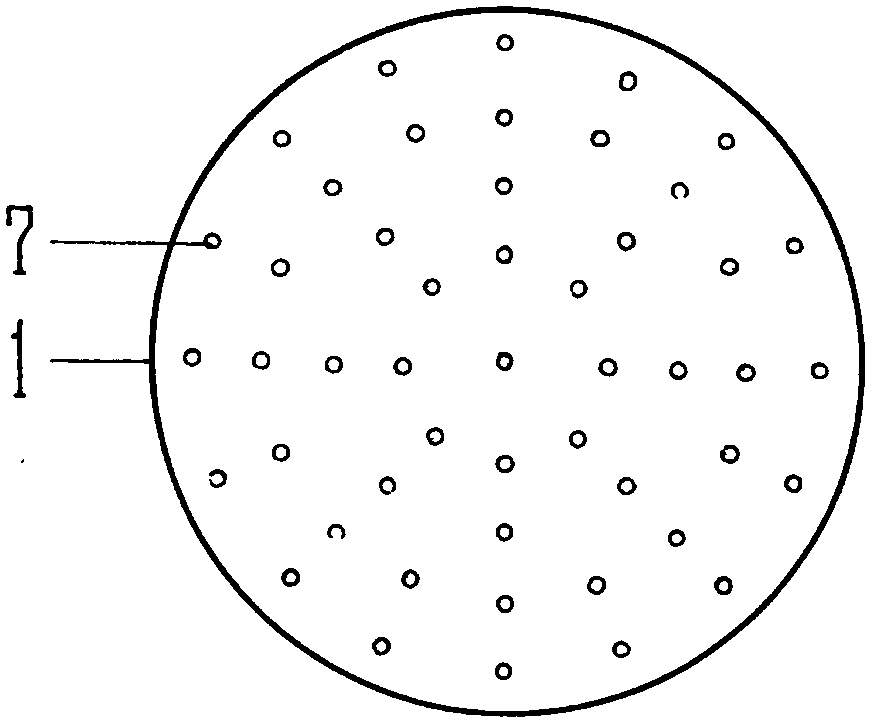
Cardiopulmonary bypass artificial lung
ActiveCN106620914AHighlight substantiveSignificant progressOther blood circulation devicesDialysis systemsExtracorporeal circulationHuman body
Owner:北京米道斯医疗器械有限公司
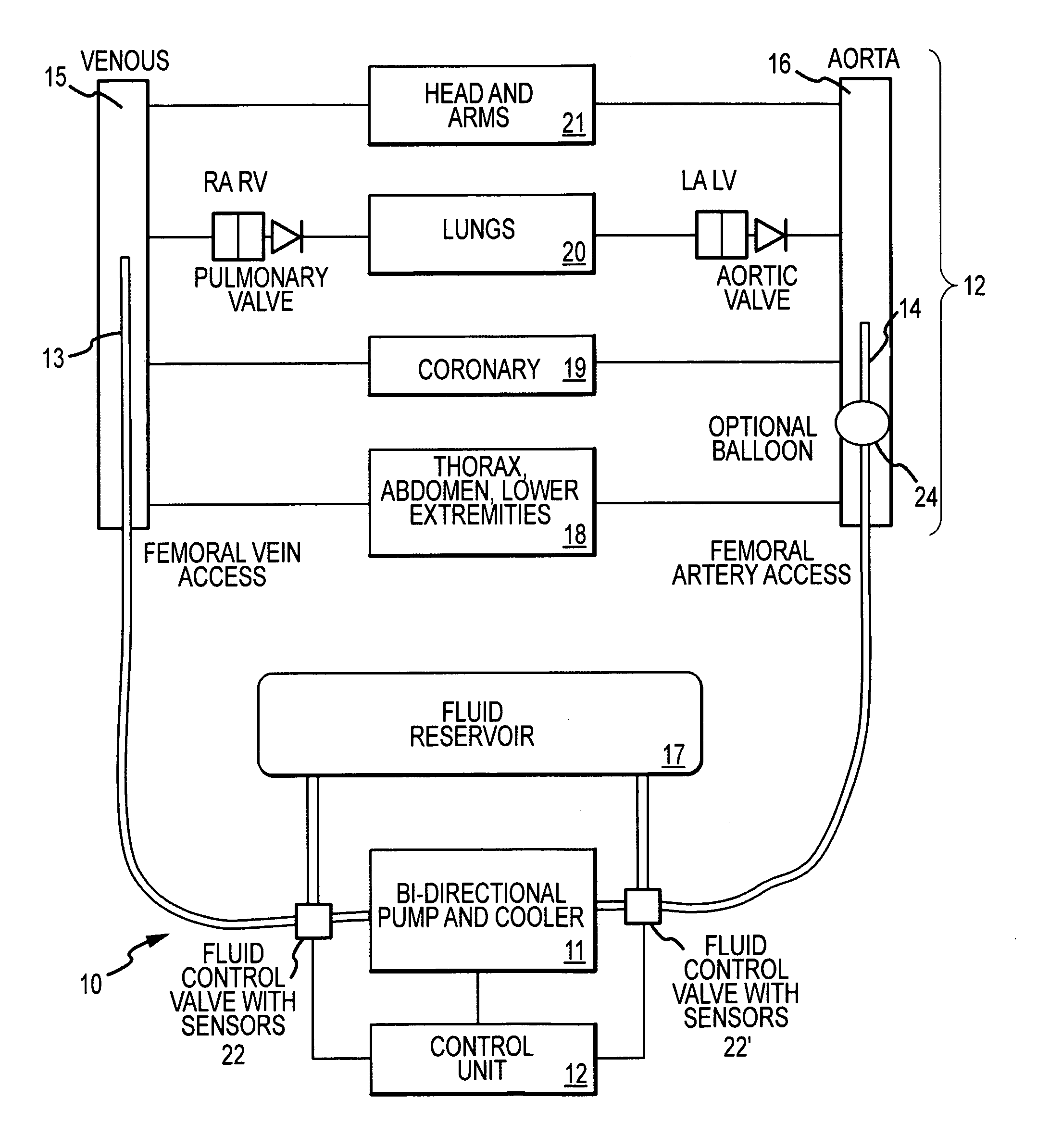
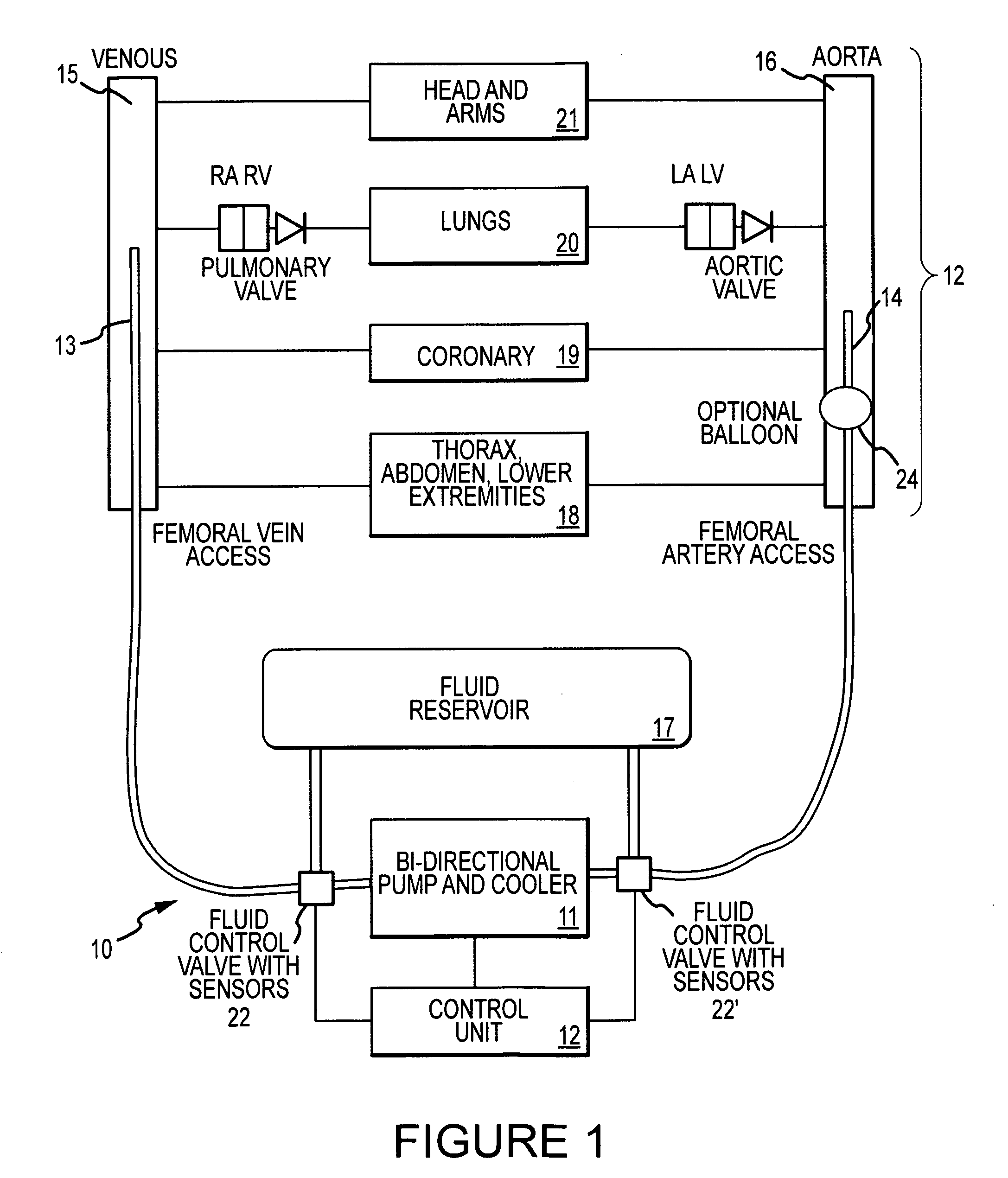
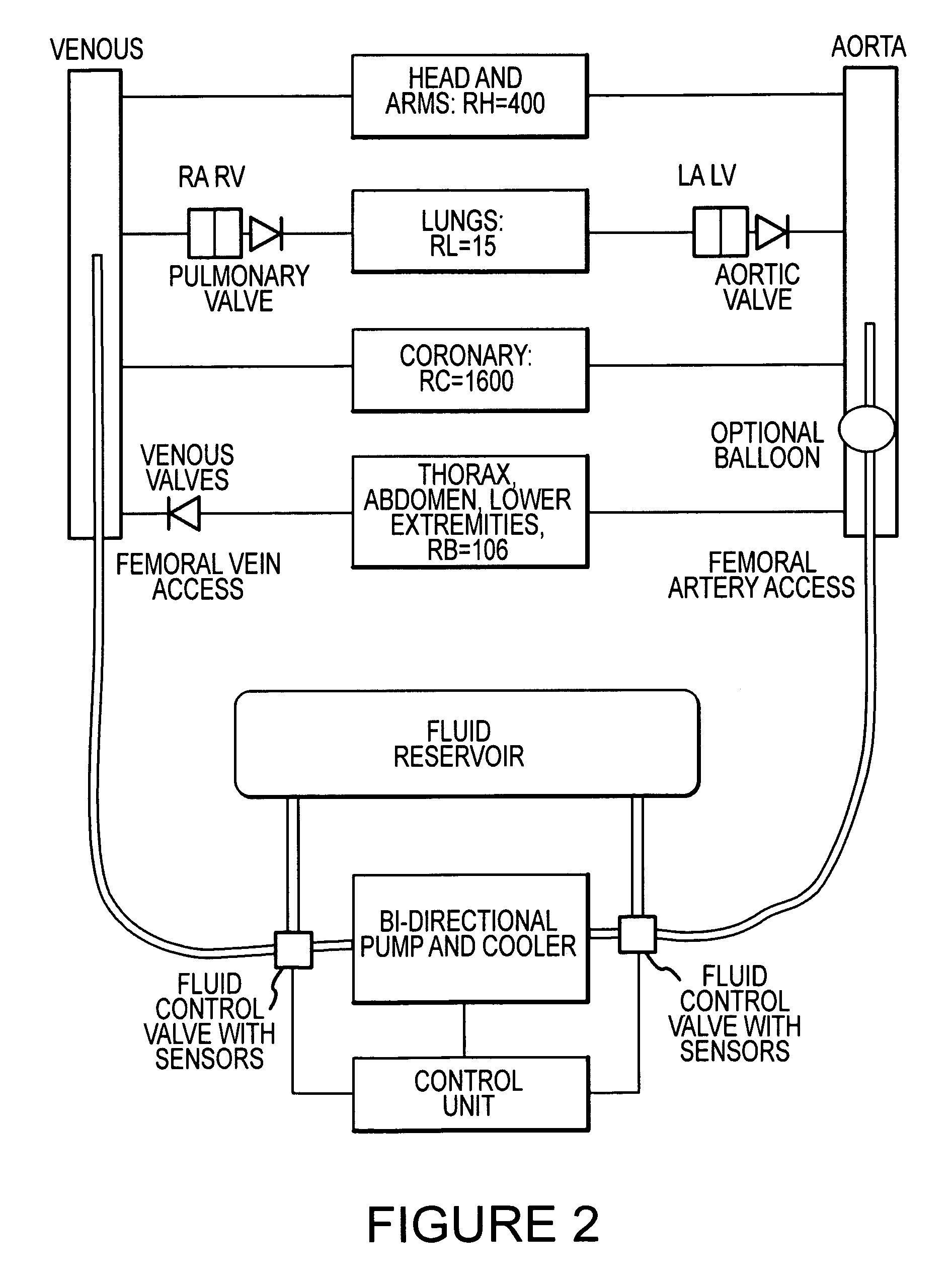
Cardiopulmonary bypass devices and methods
InactiveUS8672867B2RespiratorsOther blood circulation devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
A cardiopulmonary bypass device may include a first tube configured for connection to a vein and a second tube configured for connection to an artery. The device may further include a pump connected between the first and second tubes. In a first mode, the pump may pump fluid in one direction and in a second mode, the pump may pump fluid in the opposite direction. A control unit may be coupled to the pump to control its operation. Lungs may functions as the oxygenator of the cardiopulmonary bypass device.
Owner:LAERDAL MEDICAL AS
Extracorporeal blood circuit for cardiopulmonary bypass
InactiveUS9044555B2Reduce exposureLess spaceOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
The subject invention provides an improved bypass circuit for use in adult and especially pediatric cardiac surgery. The auto regulating capability of this circuit design simplifies its operation and combines the benefits of both VAVD and KAVD systems while eliminating the need for multiple blood pumps. Advantageously, this system occupies less space than existing systems, requires the use of less blood, reduces the contact between blood and tubing, reduces damage to blood cells, eliminates the need for multiple blood pumps and also reduces the incidence of gaseous emboli.
Owner:MIAMI CHILDRENS HOSPITAL RES INST
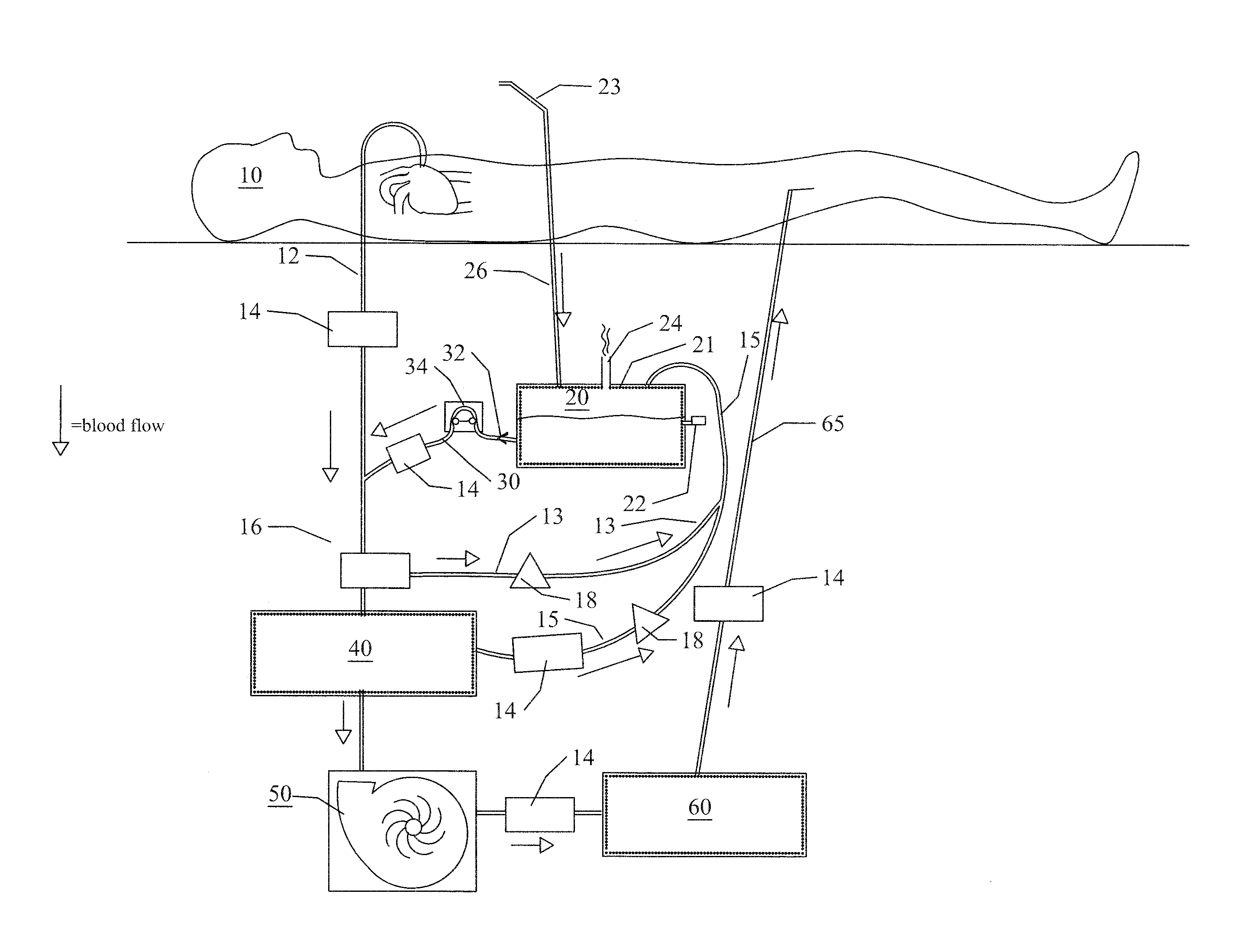
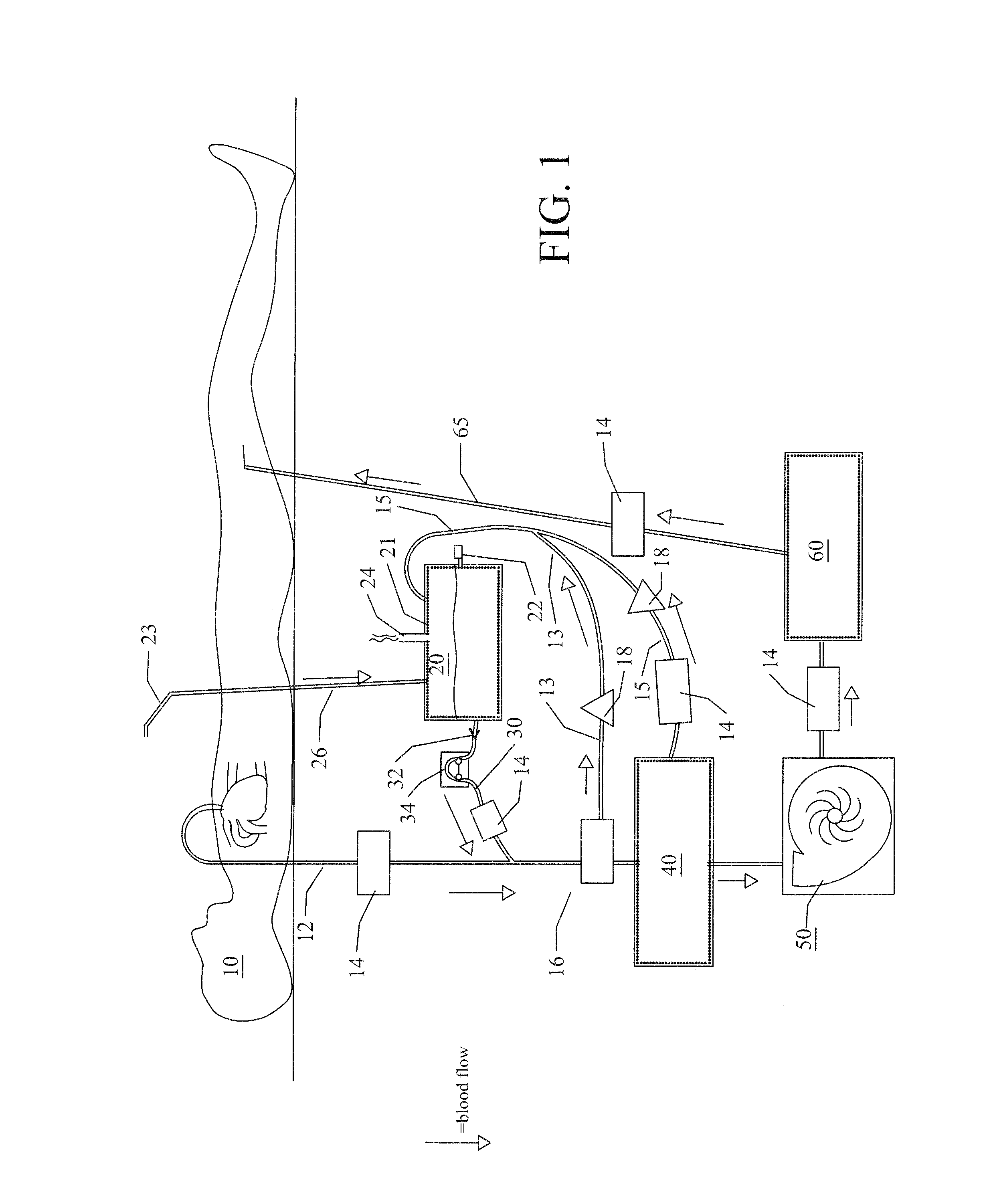
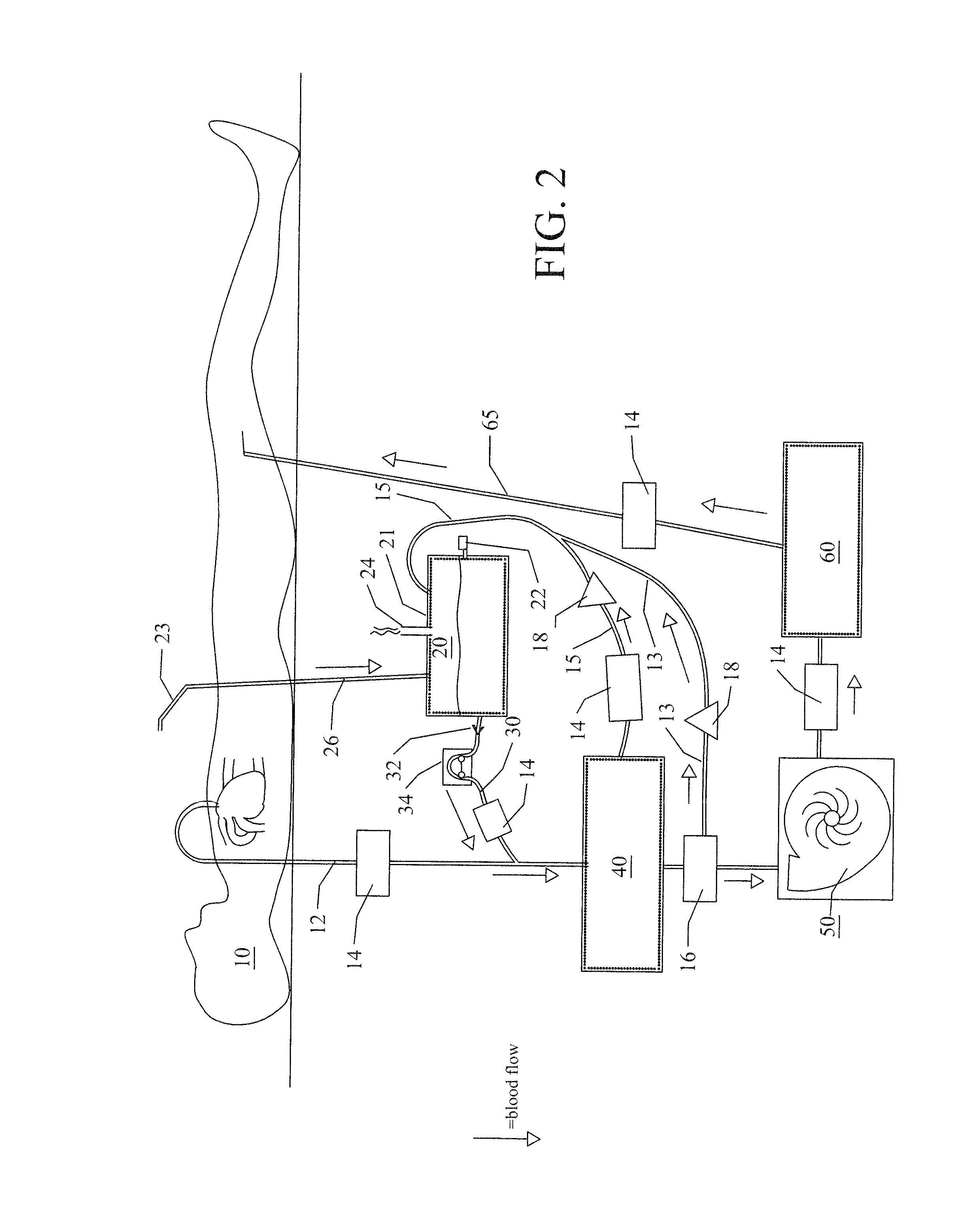
Cardiopulmonary apparatus and methods for preserving life
InactiveUS8882693B2Rapid and safe transitionMaintaining the life of a patientRespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCardiopulmonary bypassIntensive care medicine
Apparatus and methods for providing extracorporeal blood circulation and oxygenation control include seven-stage de-airing of blood to provide automated cardiopulmonary replacement to sustain patient life during a medical procedure comprising repairing or replacing the heart valve in a patient.
Owner:ZOLL LIFEBRIDGE
Multifunctional medical instrument internal structure sterilizer
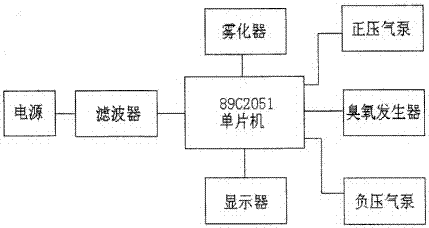
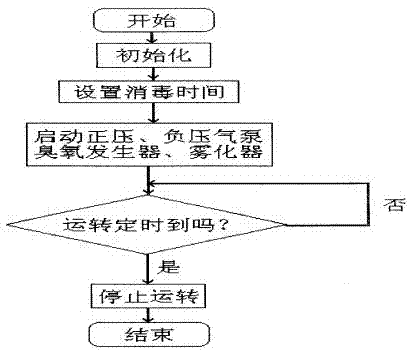
InactiveCN107875424ANot corrodedSo as not to damageChemicalsCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
The invention discloses a multi-purpose medical instrument internal structure disinfection machine, which includes a box body, an ozone generator connected with a positive pressure air pump, a negative pressure air pump and a control circuit are arranged in the box body, the ozone generator is connected with the first The negative pressure air pump is connected to the filter through the second conduit, the atomizer is arranged in the box, the atomizer is connected to the first conduit through the third conduit, and the control circuit controls the positive Compression pump, ozone generator, atomizer and negative pressure air pump are opened or closed, and described atomizer is provided with the hydrogen peroxide aqueous solution that volume percent concentration is 8%~12%, and the present invention is applied to various Disinfection of the inside of pipeline medical equipment, such as ventilator, anesthesia machine, lung function tester, extracorporeal circulation machine, artificial kidney dialysis machine, it can completely disinfect the inside of the contaminated instrument without being corroded or damaged.
Owner:常州市郝思琳医用仪器有限公司
Carbon and its use in blood cleansing applications
ActiveUS9278170B2Tailored porosity of the carbonsIncrease surface areaOther blood circulation devicesHaemofiltrationCardiopulmonary bypassWhole body
Whole blood is treated extracorporeally to remove substances contrary to health using mesoporous / microporous or macroporopus / microporous carbon in the form of beads or a channel monolith. The carbon may be the result of carbonizing a mesoporous or macroporous phenolic resin. Substances contrary to health include externally introduced toxins such as bacterially derived staphylococcus enterotoxins A, B, TSST-1 or autologous, biologically active molecules with harmful, systemic effects when their activity is excessive or unregulated. Examples include the removal of inappropriate amounts of pro- or anti-inflammatory molecules and toxic mediators of systemic inflammatory response syndrome related to sepsis, cardio-pulmonary by-pass surgery, ischaemic reperfusion injury; the removal of larger molecular weight and protein bound uremic toxins related to kidney and hepatic toxins related to liver failure and the removal of toxins relevant to biological and chemical warfare.
Owner:UNVIERSITY OF BRIGHTON +1
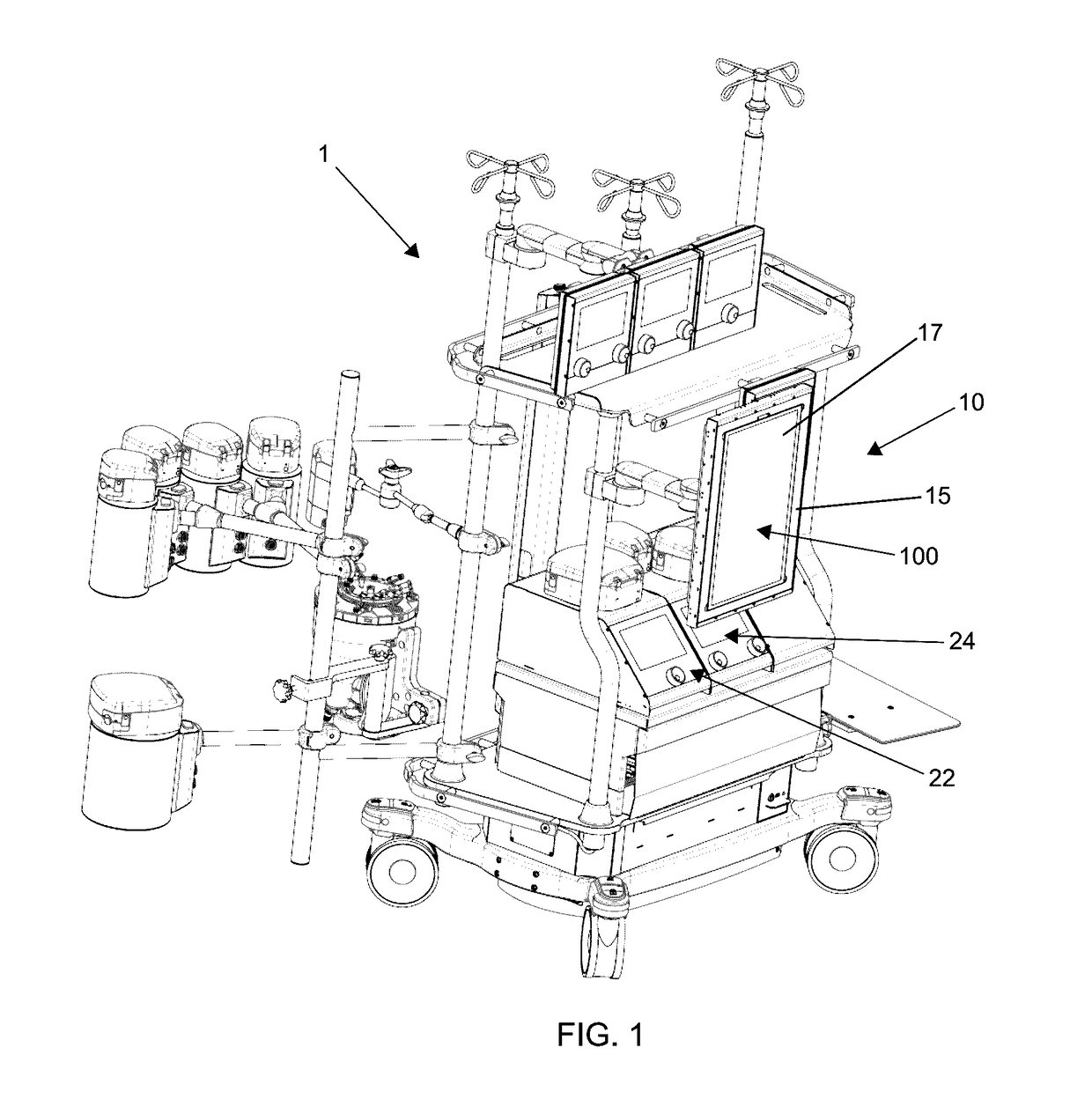
Integrated perfusion device
ActiveUS9408959B2Eliminate the risk of contaminationTemperature controlOther blood circulation devicesControl devicesCardiopulmonary bypassExtracorporeal circulation
An integrated perfusion apparatus or device for use in e.g. extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, cardiopulmonary bypass, or isolated organ or limb perfusion, comprises a blood pump for circulating blood through the device; a blood oxygenator for oxygenating blood, and at least one heat control unit capable of controlling and / or regulating blood temperature within the device, wherein the at least one heat control unit comprises at least one solid state heating and / or cooling source, such as at least one Peltier device. The invention also relates to a method of performing perfusion on a patient, limb or organ, comprising using the perfusion device.
Owner:UNIV OF STRATHCLYDE
A maternal and fetal blood group incompatibility immunosorbent therapeutic apparatus
InactiveCN109157694ASpeed can be adjustedEasy to transportOther blood circulation devicesMedical devicesExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
A maternal-fetal blood group incompatibility immunosorbent therapy apparatus used in the medical field is characterized in that a blood separator and a plasma adsorber are connected through a circulation line to form a cardiopulmonary bypass adsorption device, wherein the blood separator is used for separating blood cells and plasma, as the separated plasma flows through and filters through the plasma adsorber, wherein the pathogenic antibody is adsorbed, the filtered plasma is combined with the separated blood cells and then re-enters a cardiopulmonary bypass adsorption device for circulatingadsorption to achieve the purpose of cleaning the pathogenic antibody, and the plasma adsorber is filled with a solid-phase carrier coated with blood group antigen or anti-blood group antibody with high to low gradient titer from an inlet to an outlet in a layered manner.
Owner:翁炳焕
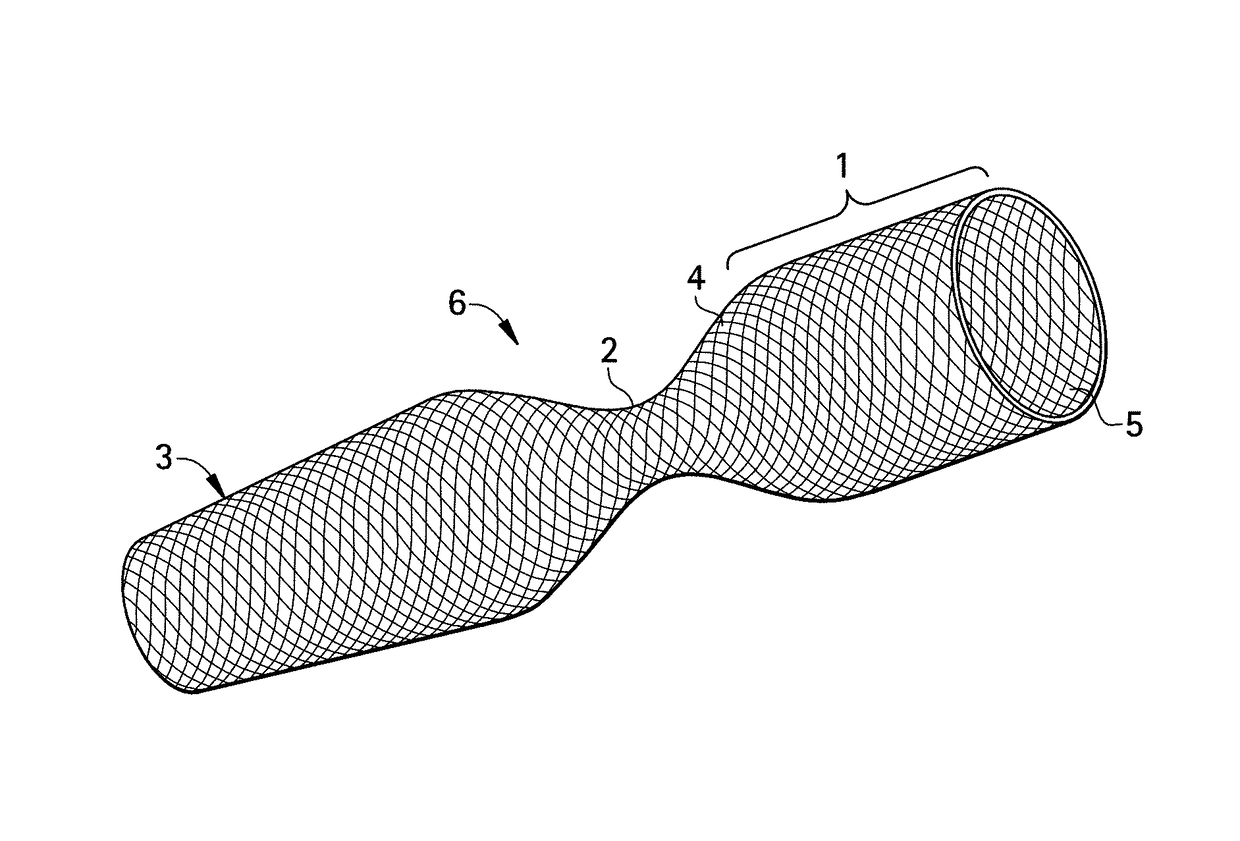
Methods, apparatuses and systems for drainage
ActiveUS10022528B2Easy to drainDrainage is enhancedStentsCannulasCardiopulmonary bypassGeneral surgery
A self expanding cannula with improved drainage properties based upon its greater length is provided, along with methods of using the cannula in cardiopulmonary bypass.
Owner:CORAFLO
Priming solutions for cardiopulmonary bypass
ActiveUS20130316977A1Low mean arterial pressureLow systemic vascular resistanceOrganic active ingredientsBiocideExtracorporeal circulationCardiopulmonary bypass
The present invention relates to priming solutions used during cardiopulmonary bypass procedures. In particular, the present invention relates to a cardiopulmonary bypass priming solution comprising a balanced salt solution and a combination of oncotic and non-oncotic dextran molecules. The present invention also relates to the use of the priming solution in a cardiopulmonary bypass method, a method of maintaining oncotic pressure in a patient during a cardiopulmonary bypass procedure, and a combination of cardiopulmonary bypass priming solution and cardiopulmonary bypass apparatus.
Owner:XVIVO PERFUSION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com