Patents
Literature
5997results about How to "Temperature control" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
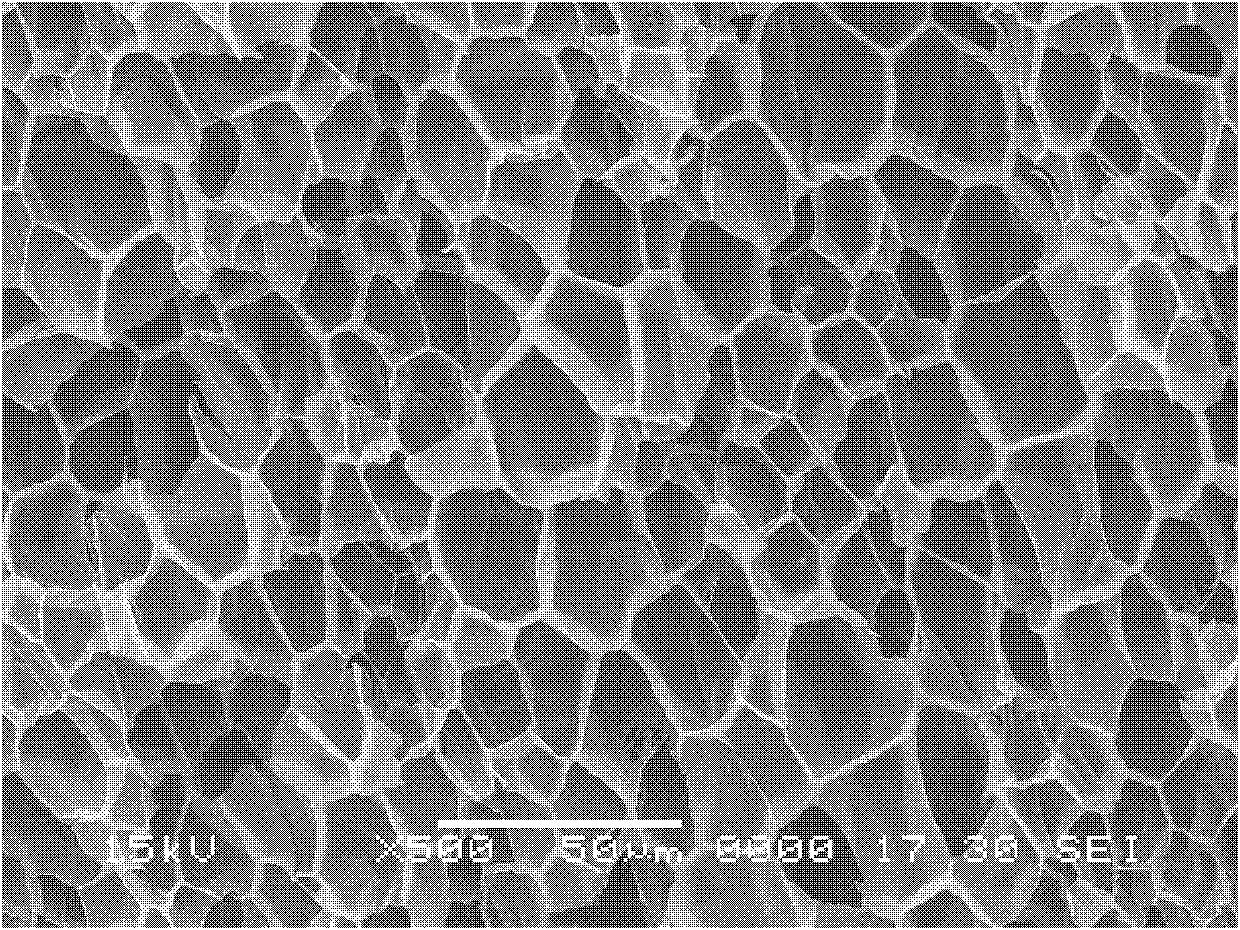
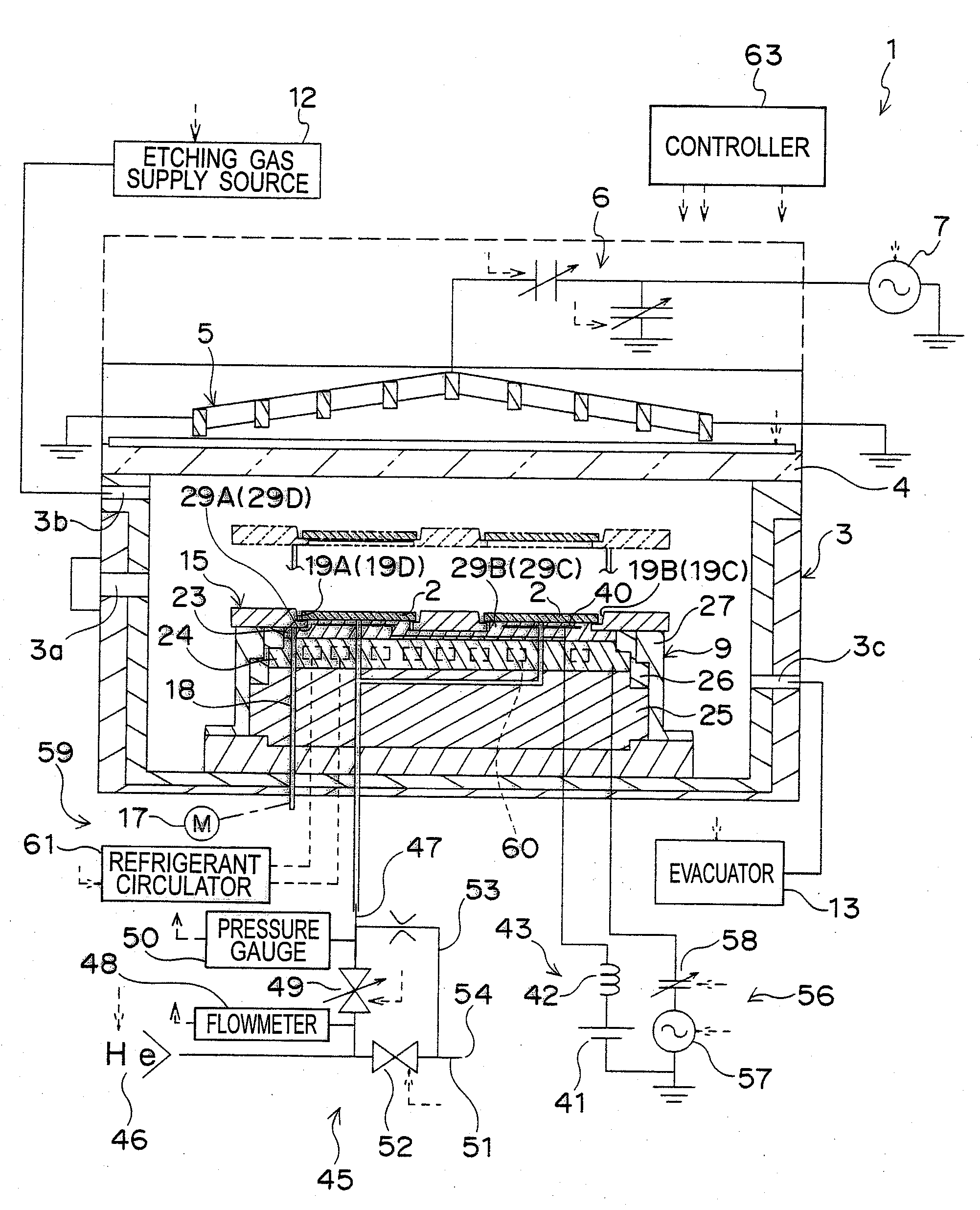
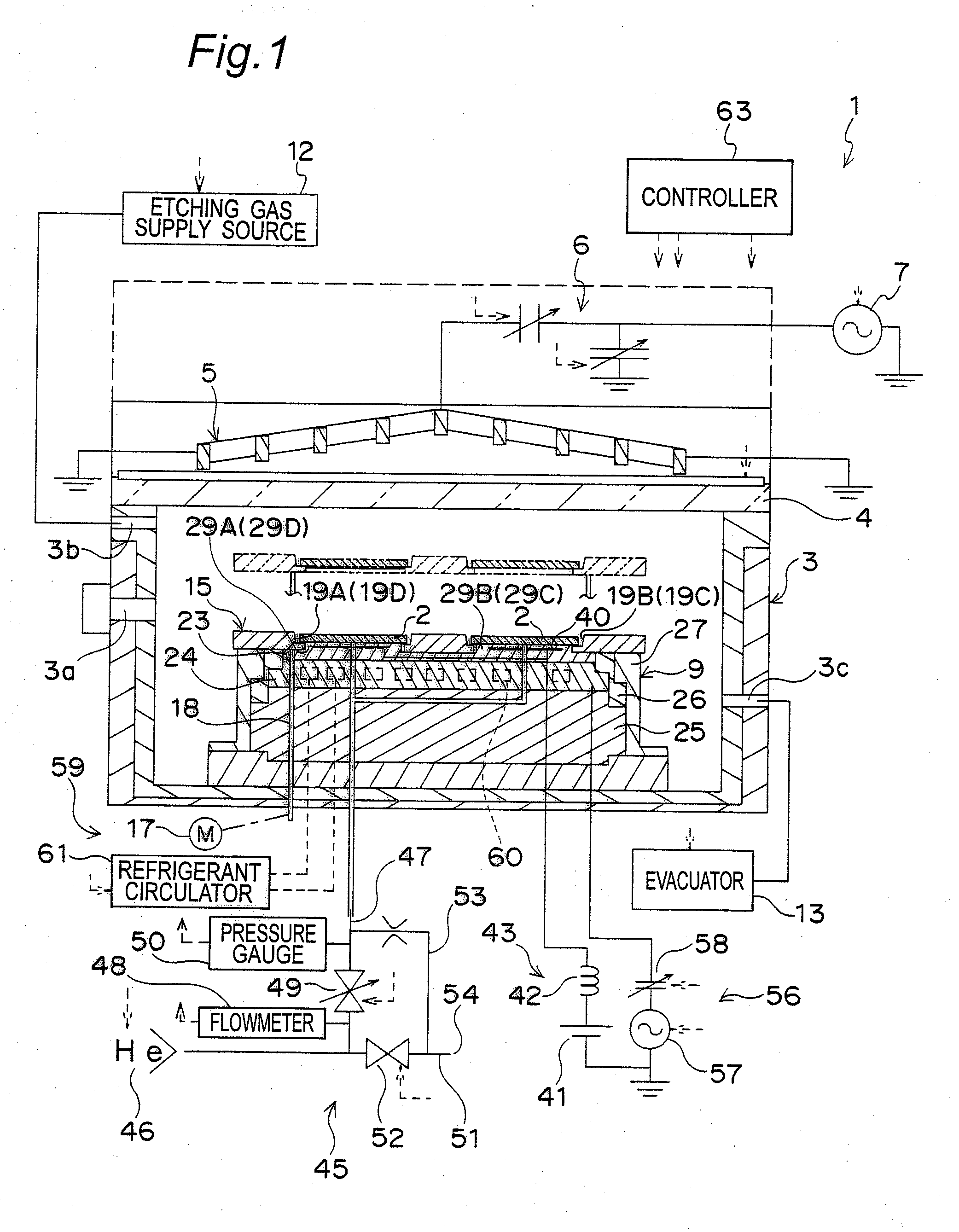
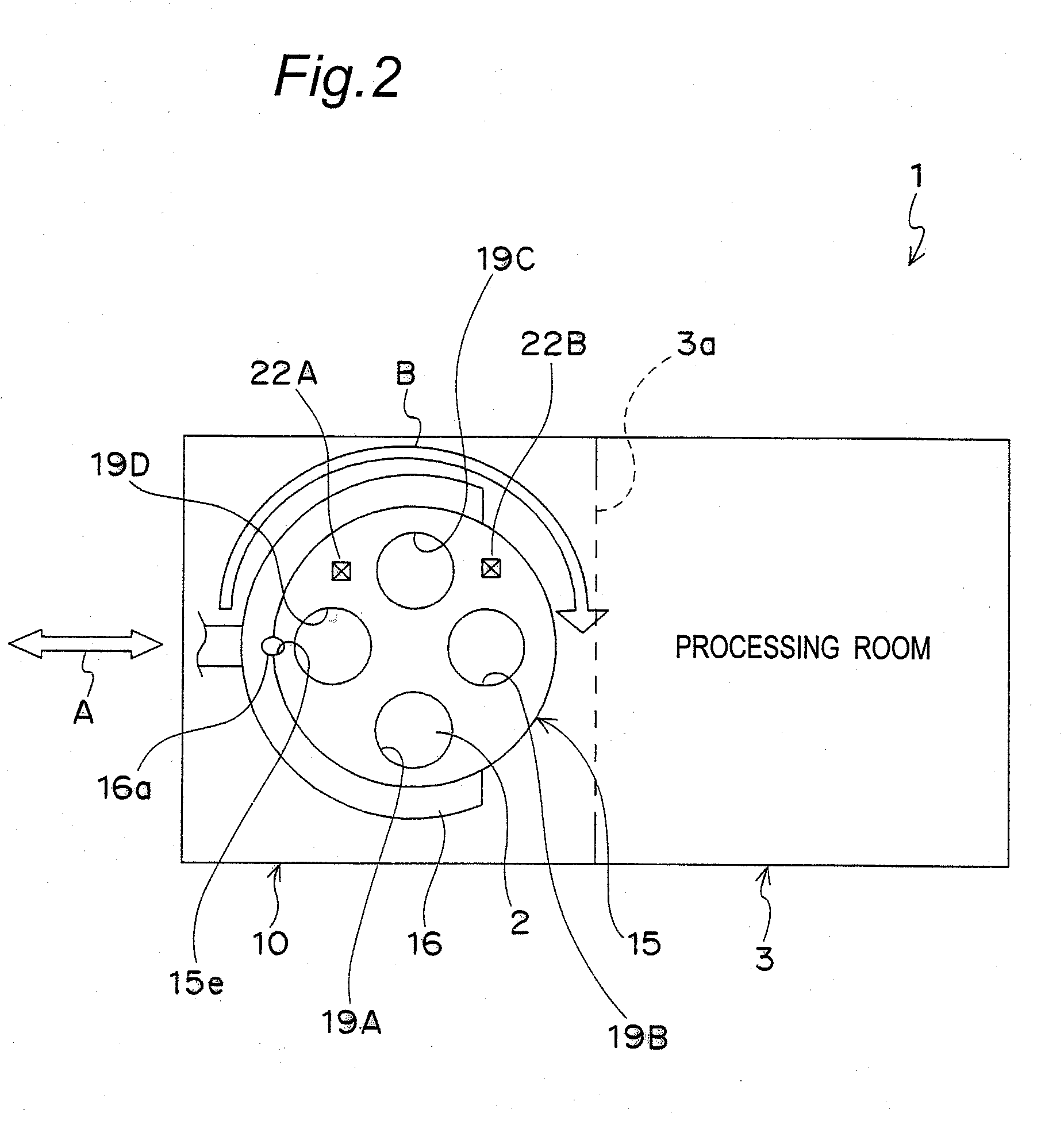
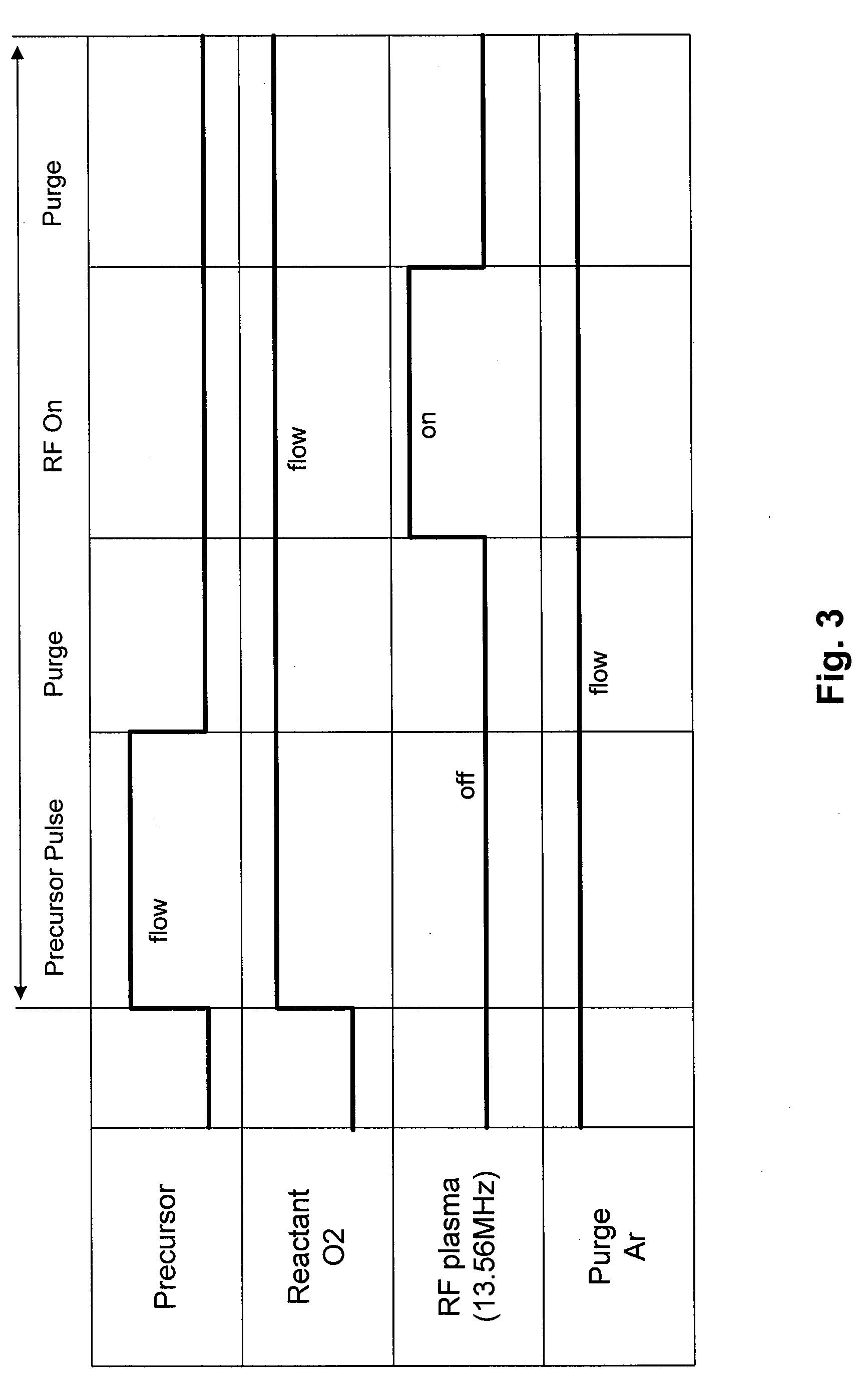
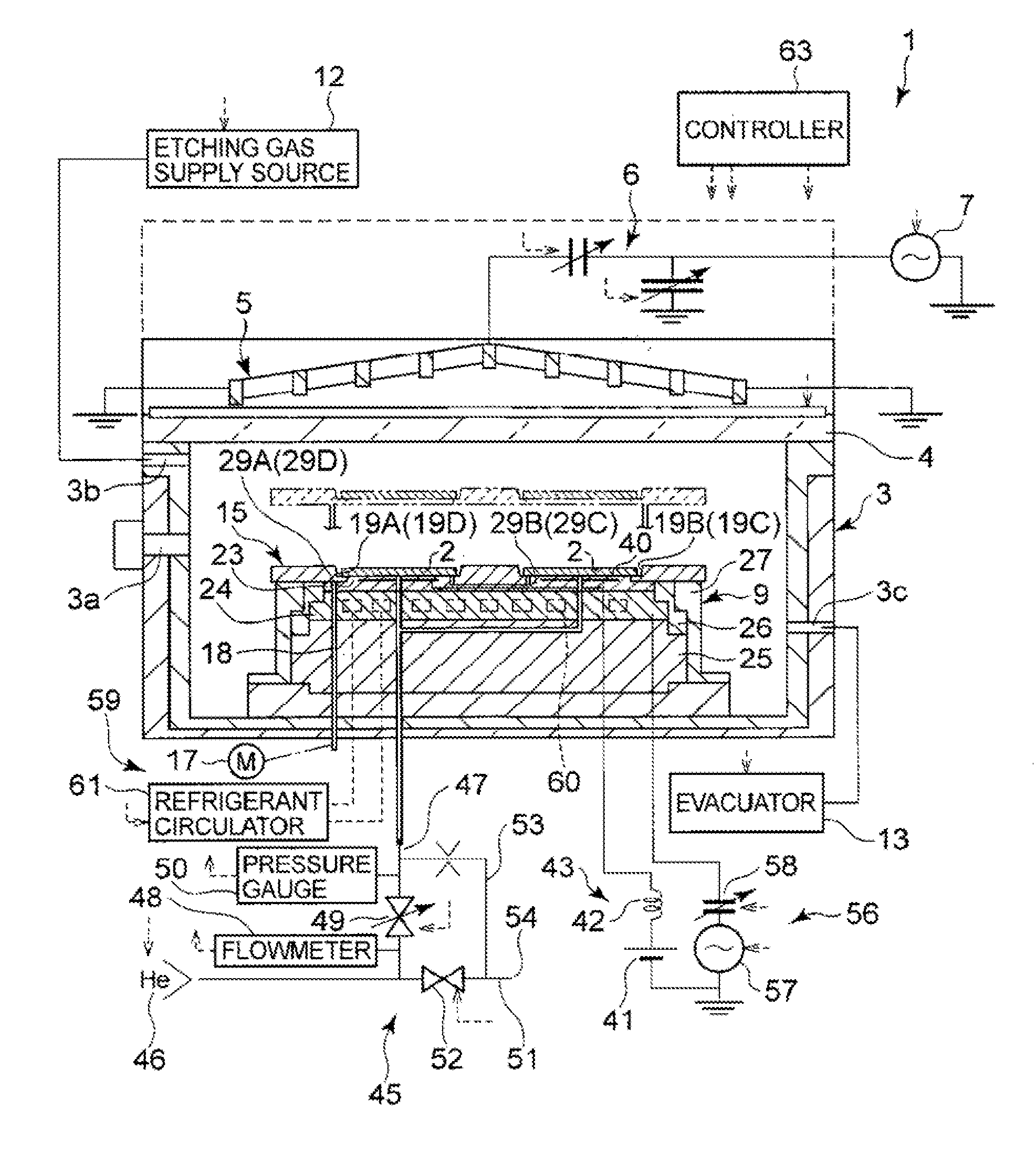
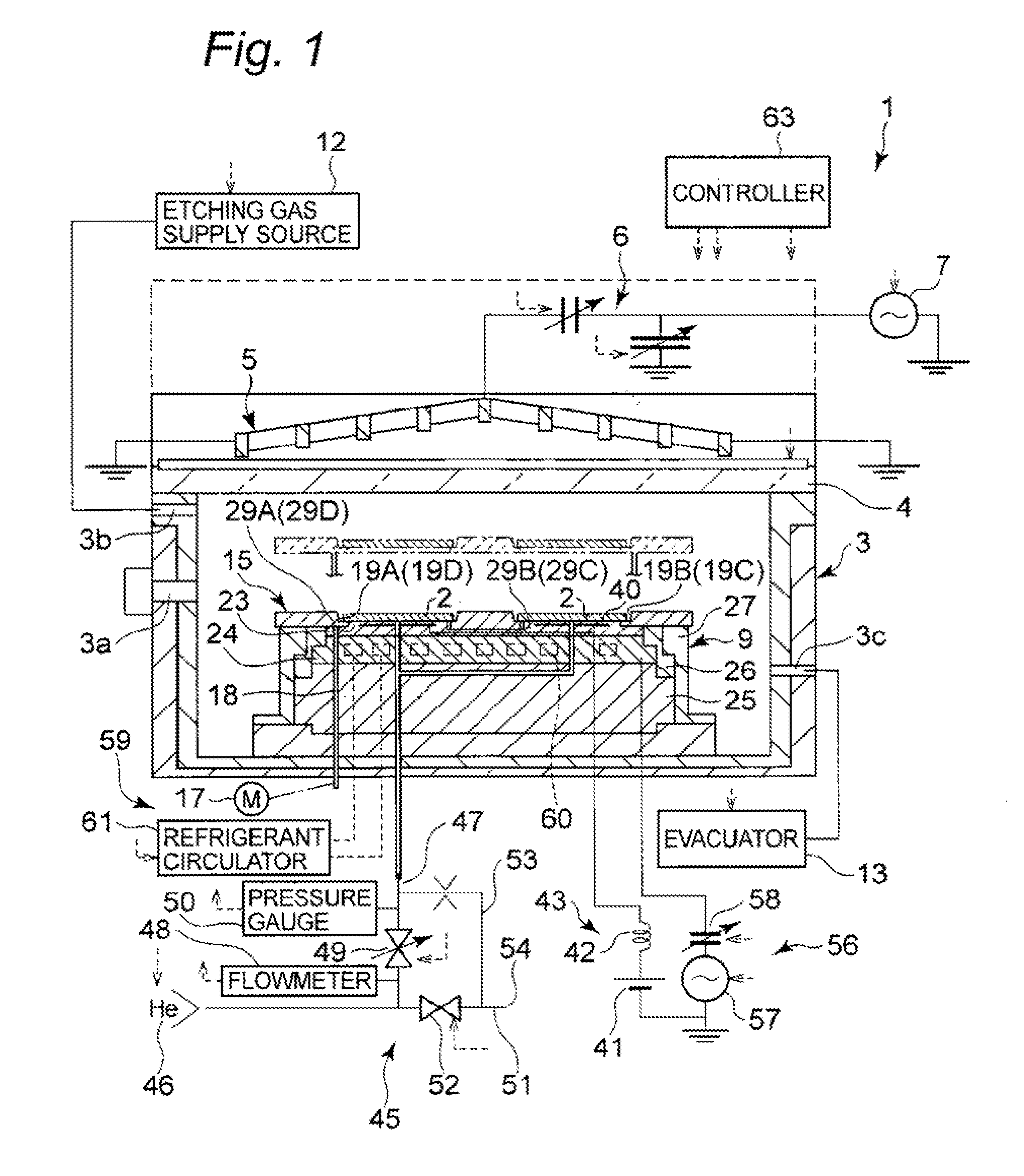
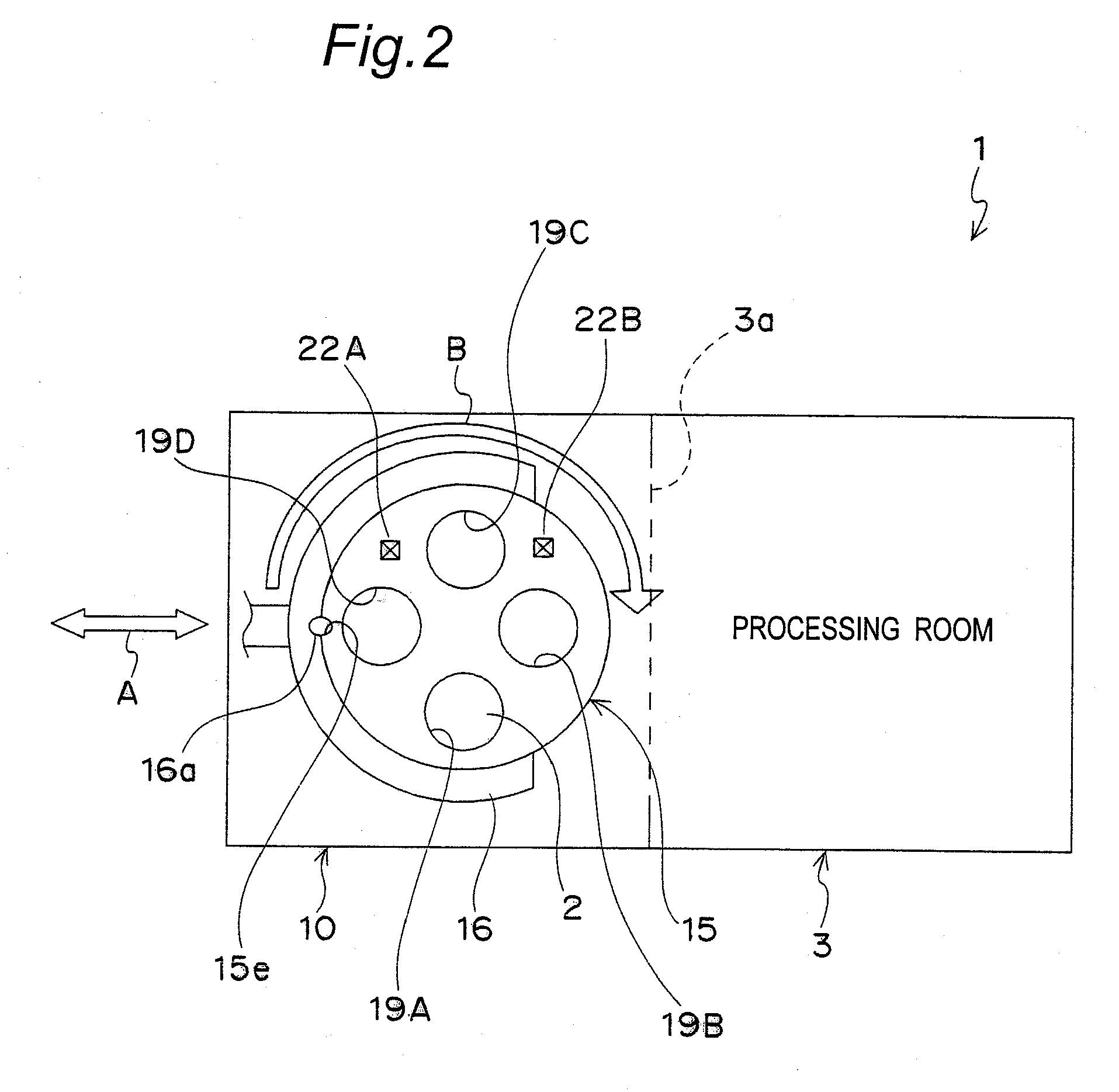
Plasma processing apparatus, plasma processing method, and tray
ActiveUS20090255901A1Uniform plasma treatmentImprove adhesionElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectric plateEngineering
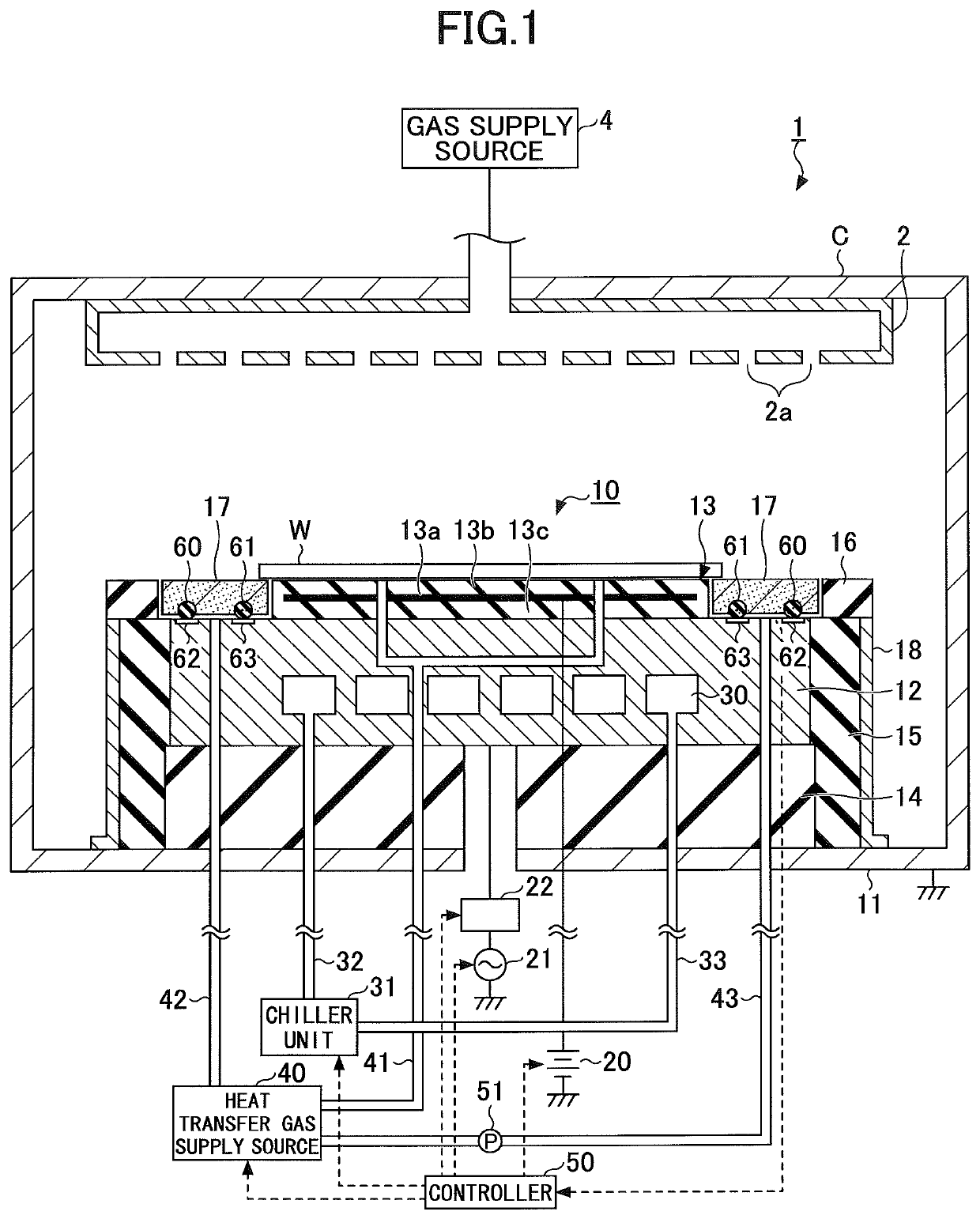
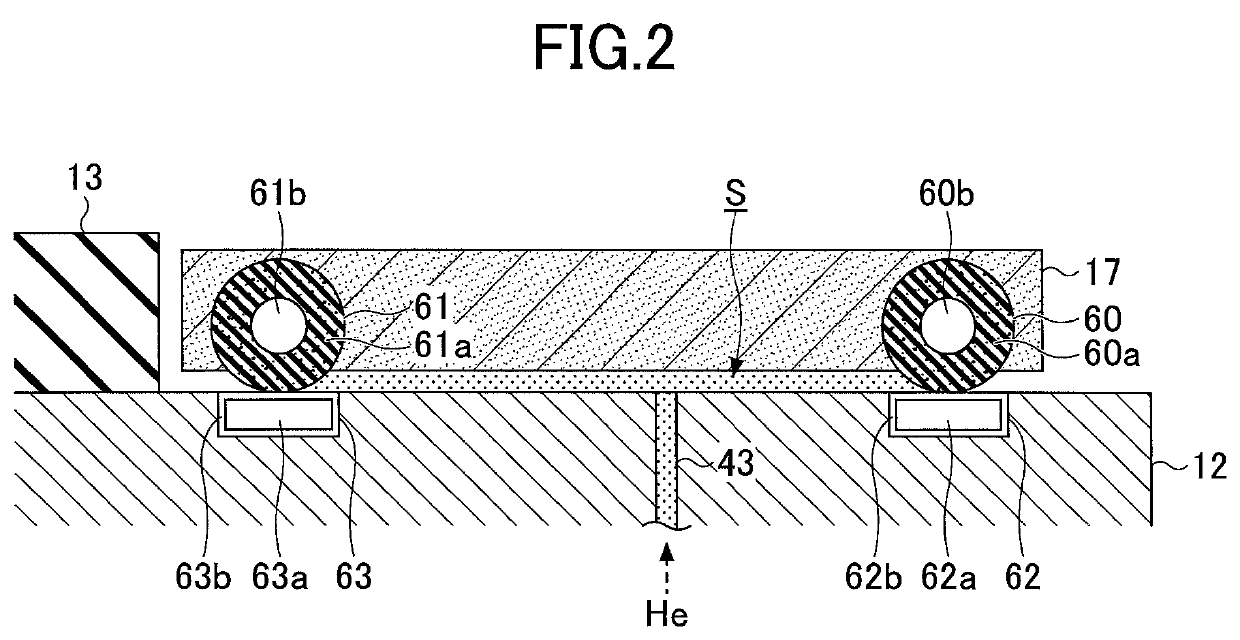
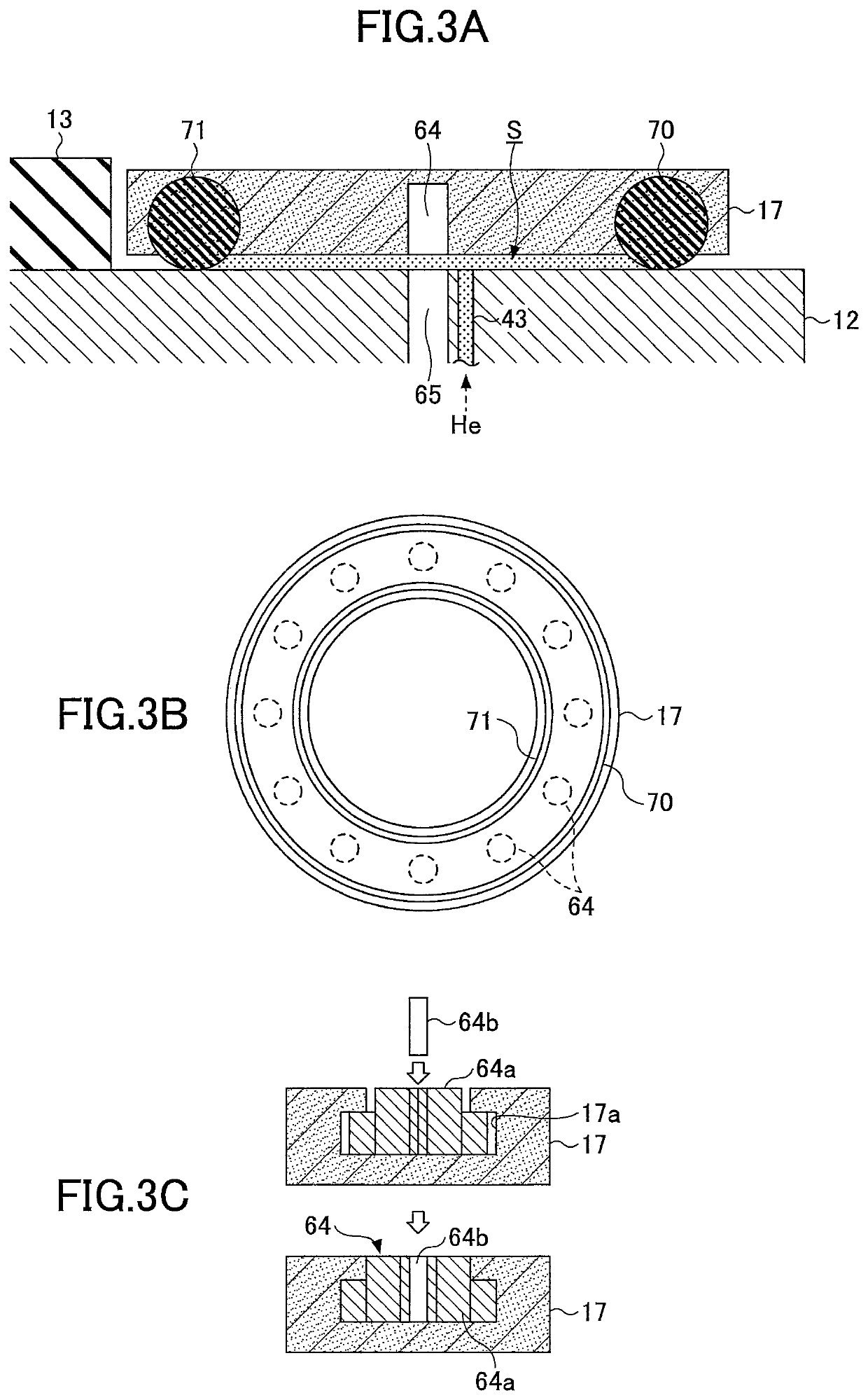
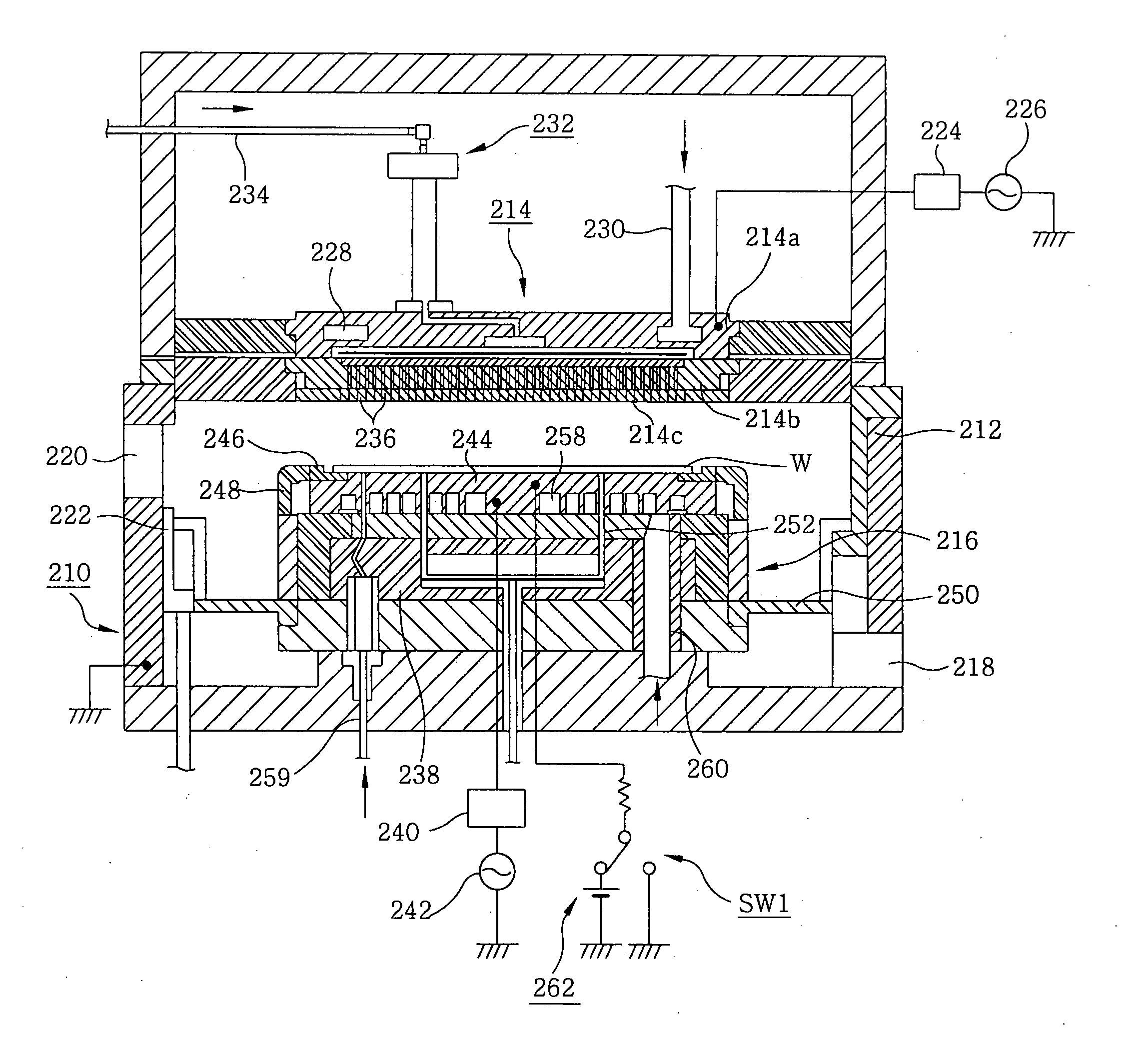
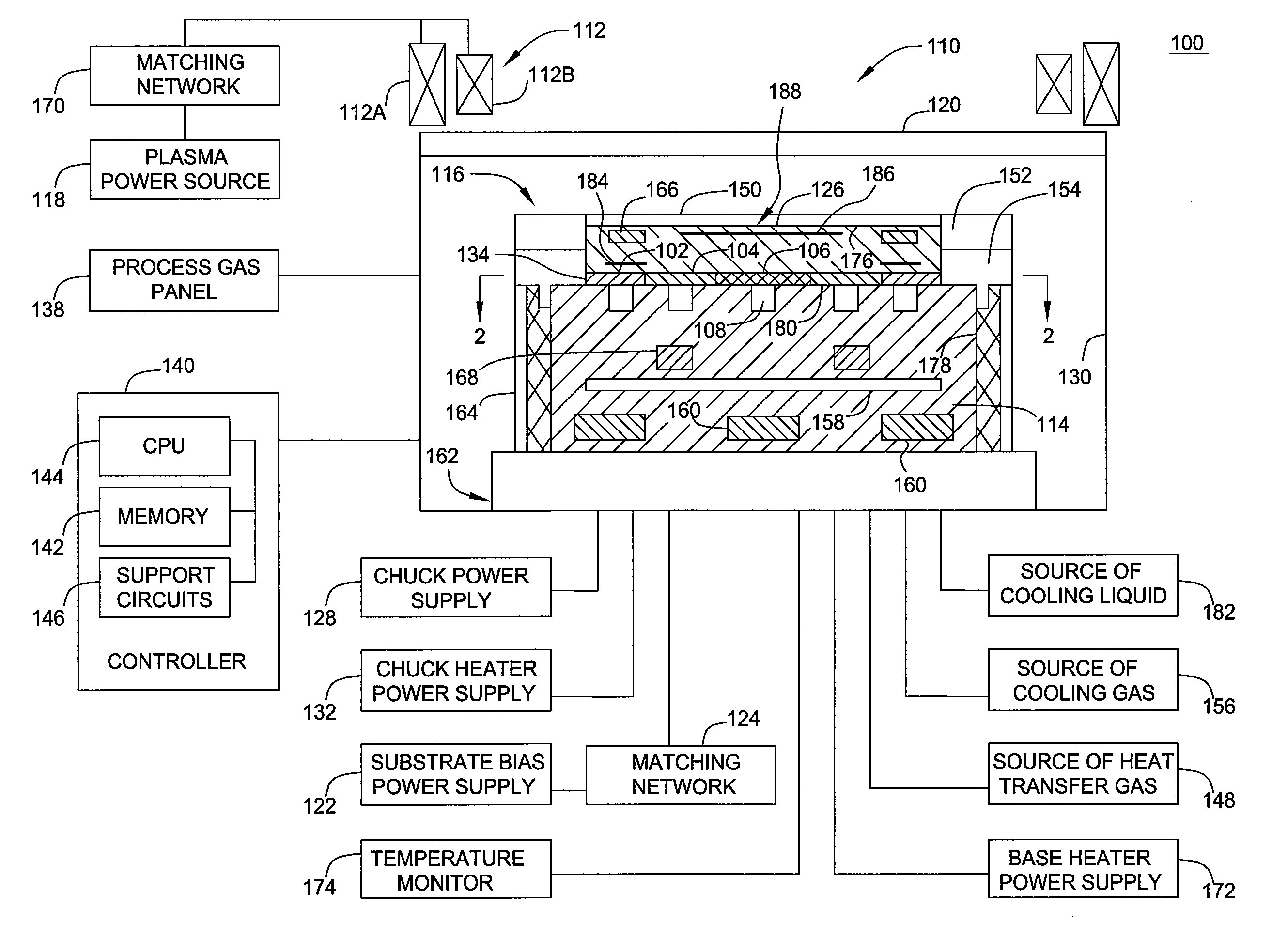
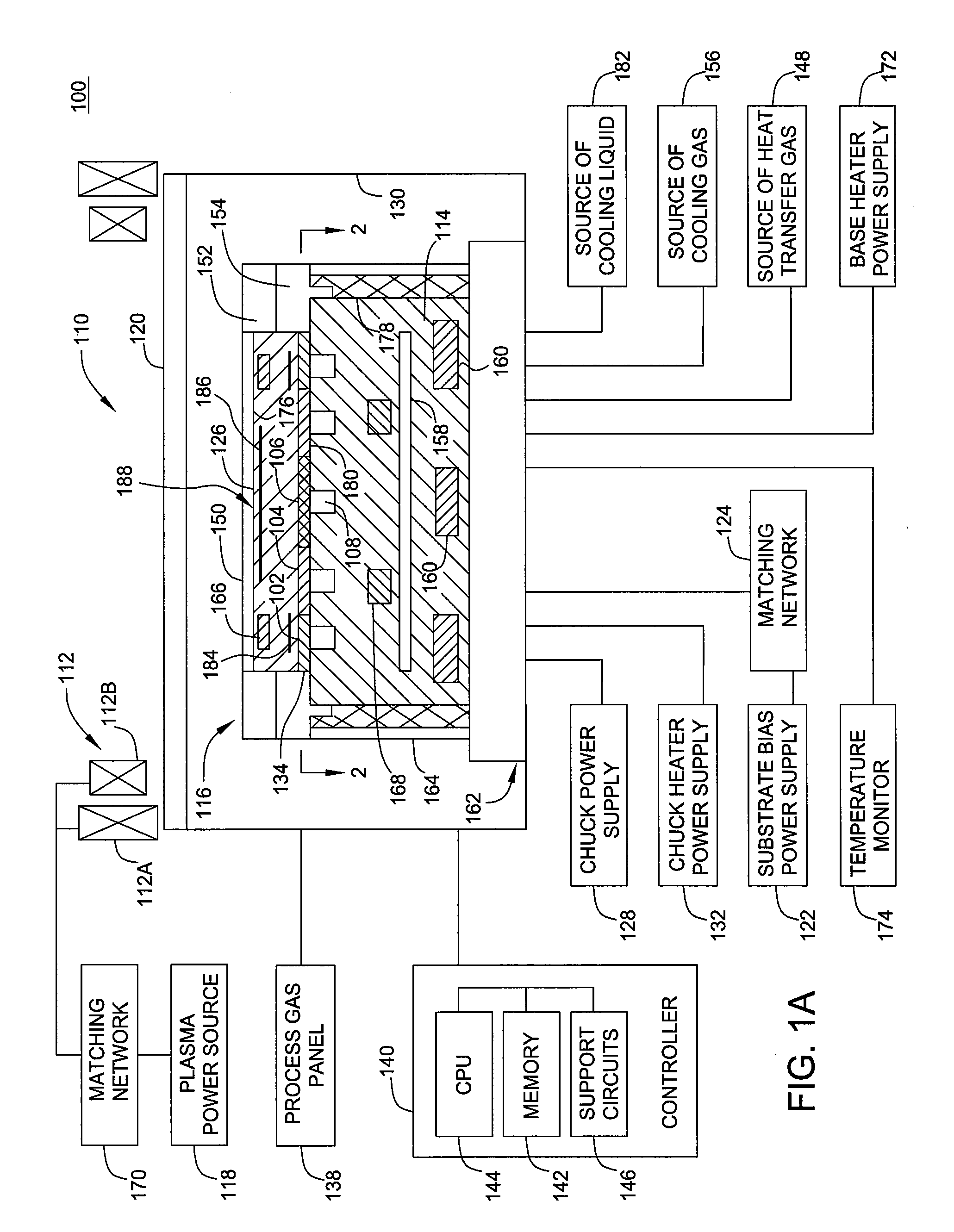
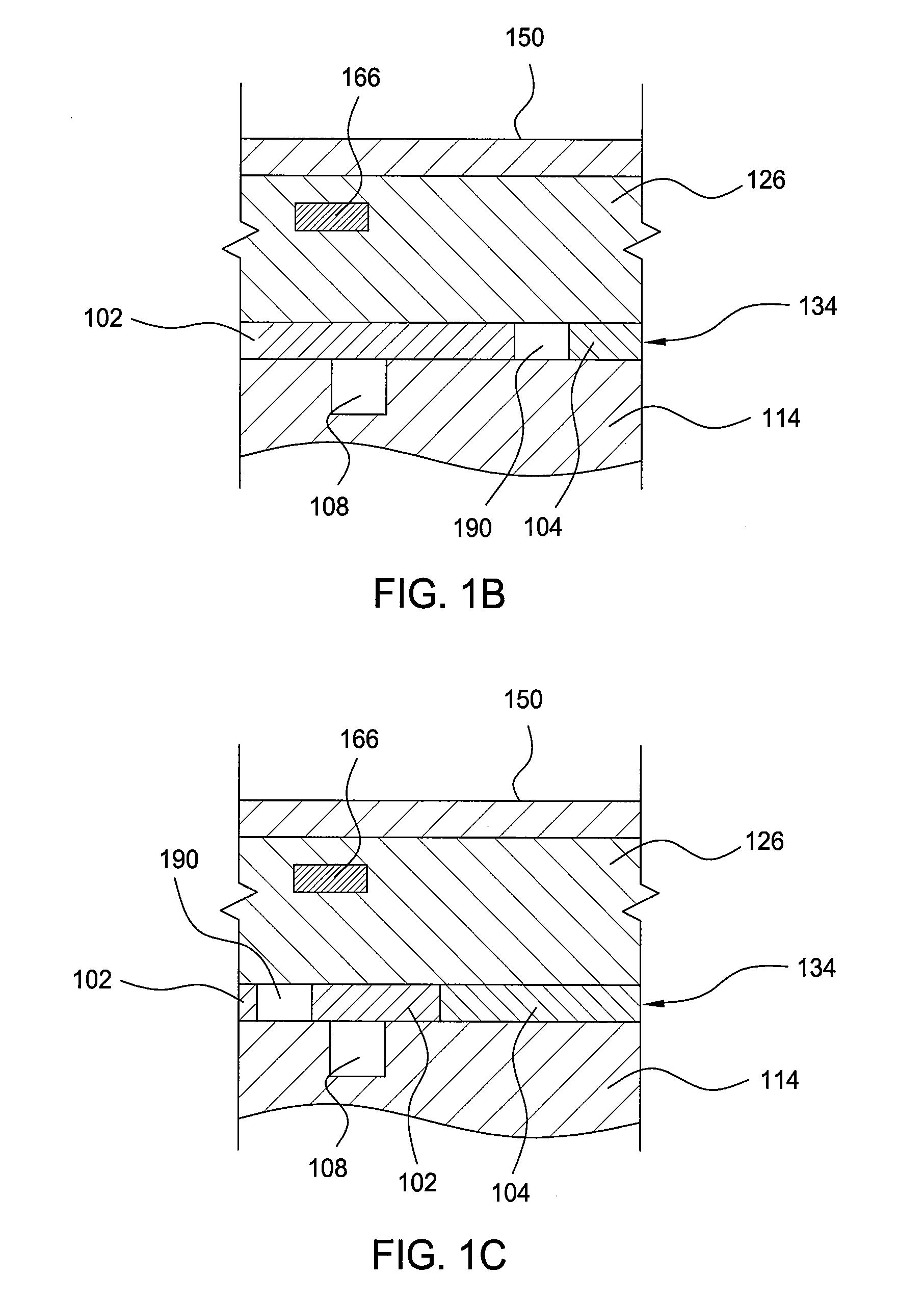
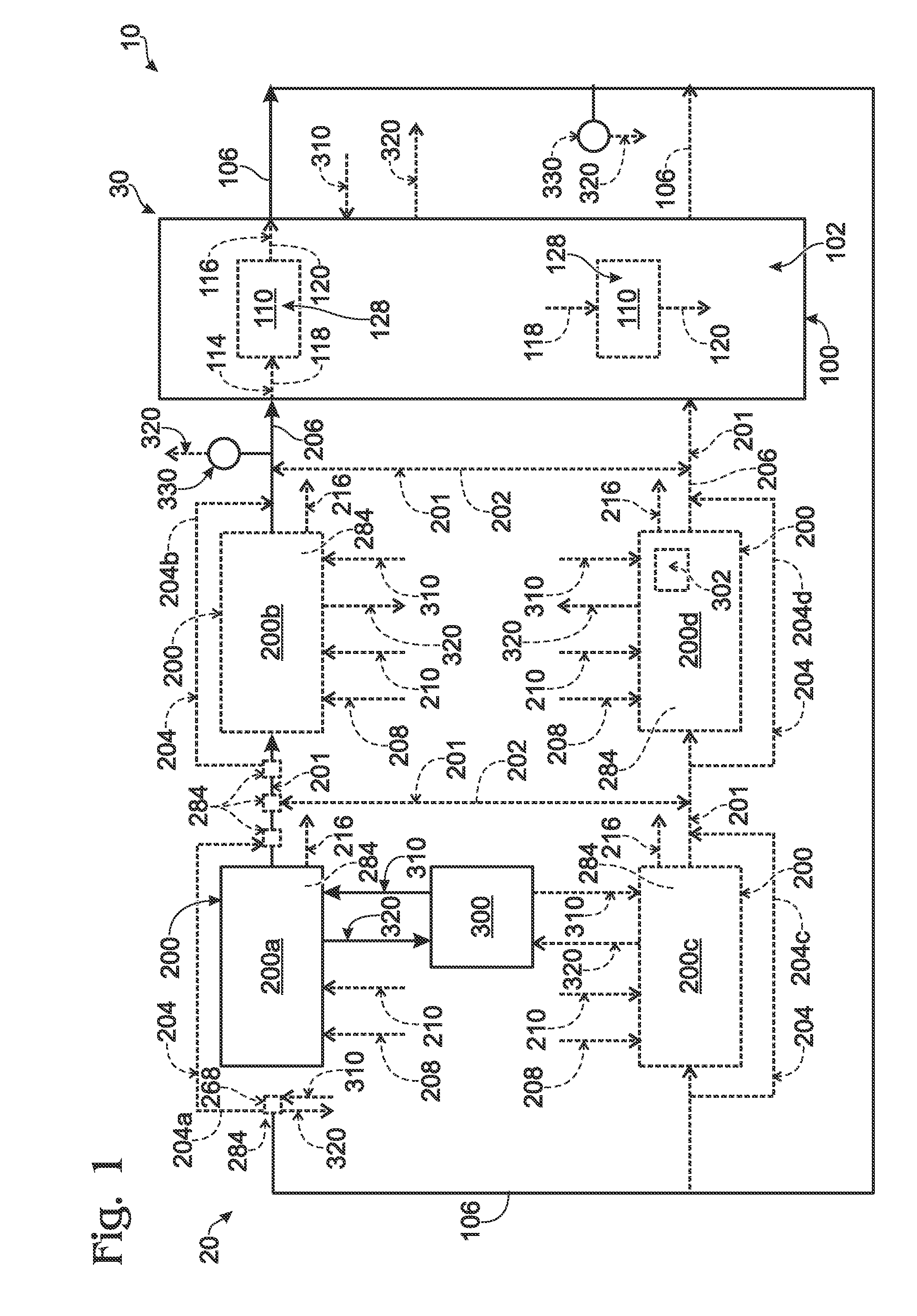
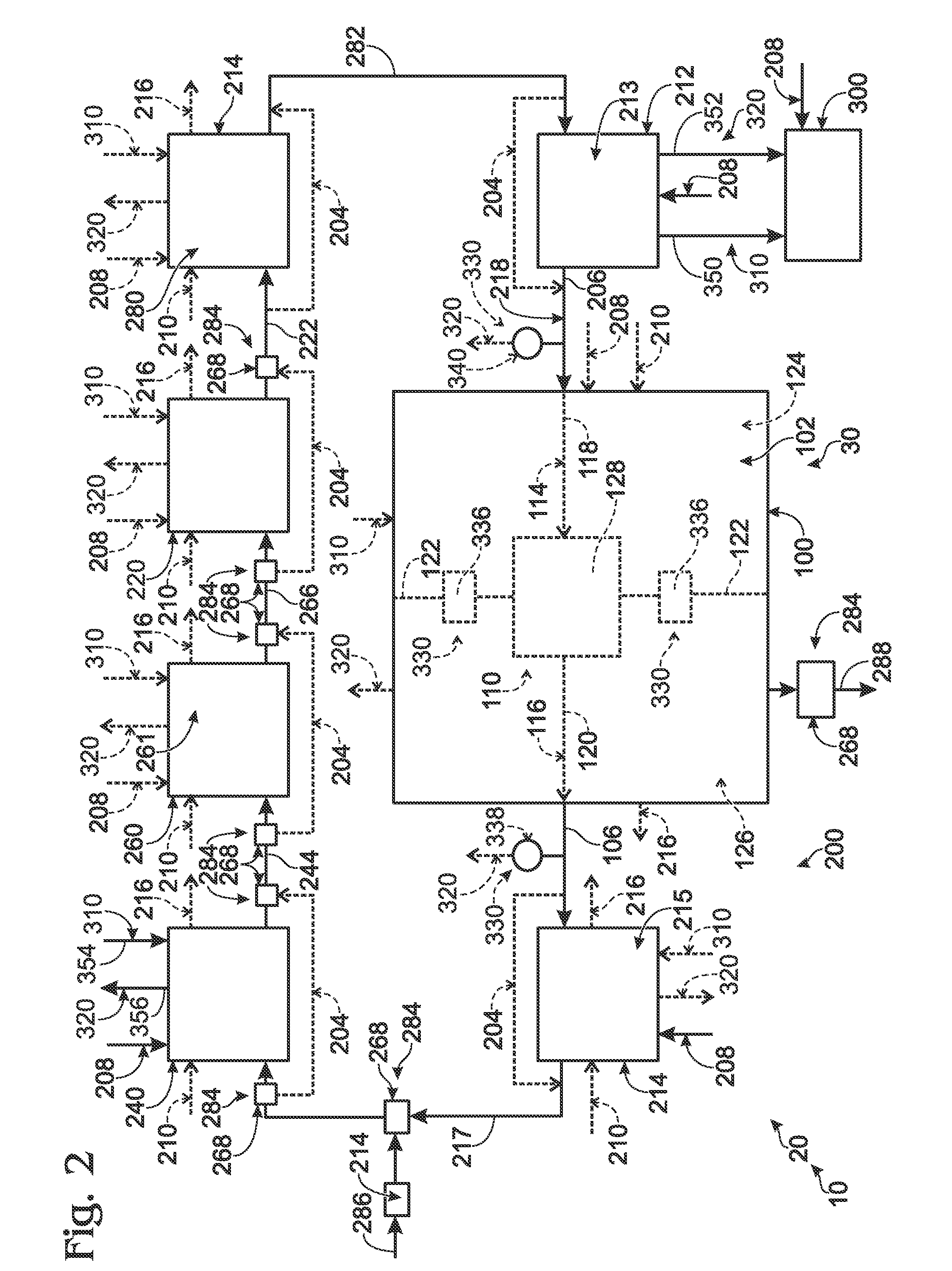
A tray 15 for a dry etching apparatus 1 has substrate accommodation holes 19A to 19D penetrating thickness direction and a substrate support portion 21 supporting an outer peripheral edge portion of a lower surface 2a of a substrate 2. A dielectric plate 23 has a tray support surface 28 supporting a lower surface of the tray 15, substrate placement portions 29A through 29D inserted from a lower surface side of the tray 15 into the substrate accommodation holes 19A through 19D and having a substrate placement surface 31 at its upper end surface for placing the substrate 2. A dc voltage applying mechanism 43 applies a dc voltage to an electrostatic attraction electrode 40. A heat conduction gas supply mechanism 45 supplies a heat conduction gas between the substrate 2 and substrate placement surface 31. The substrate 2 can be retained on the substrate placement surface 31 with high degree of adhesion. This results in that the cooling efficiency of the substrate 2 is improved and processing is uniformed at the entire region of the substrate surface including the vicinity of the outer peripheral edge.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
Method of depositing silicon oxide film by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition at low temperature
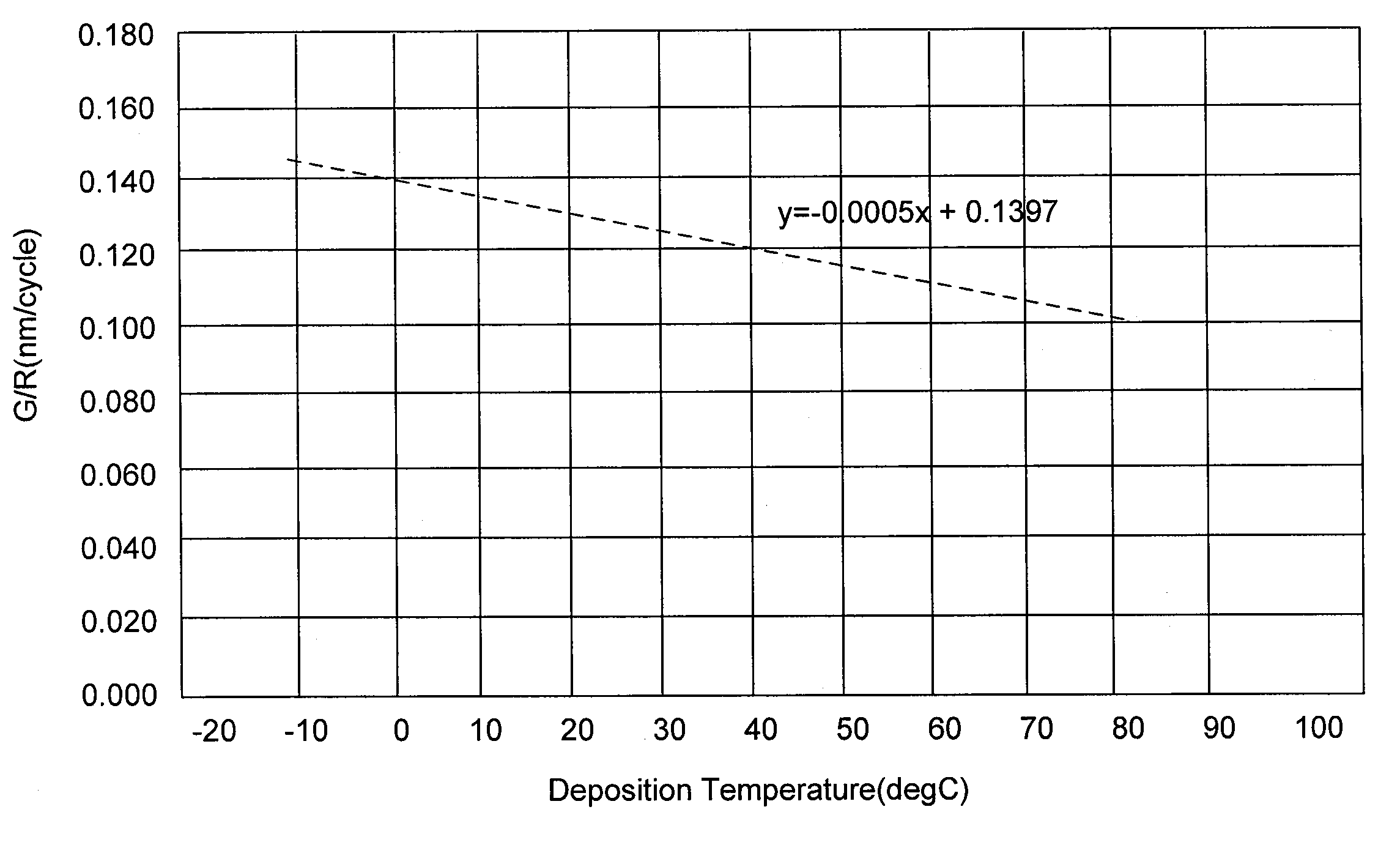
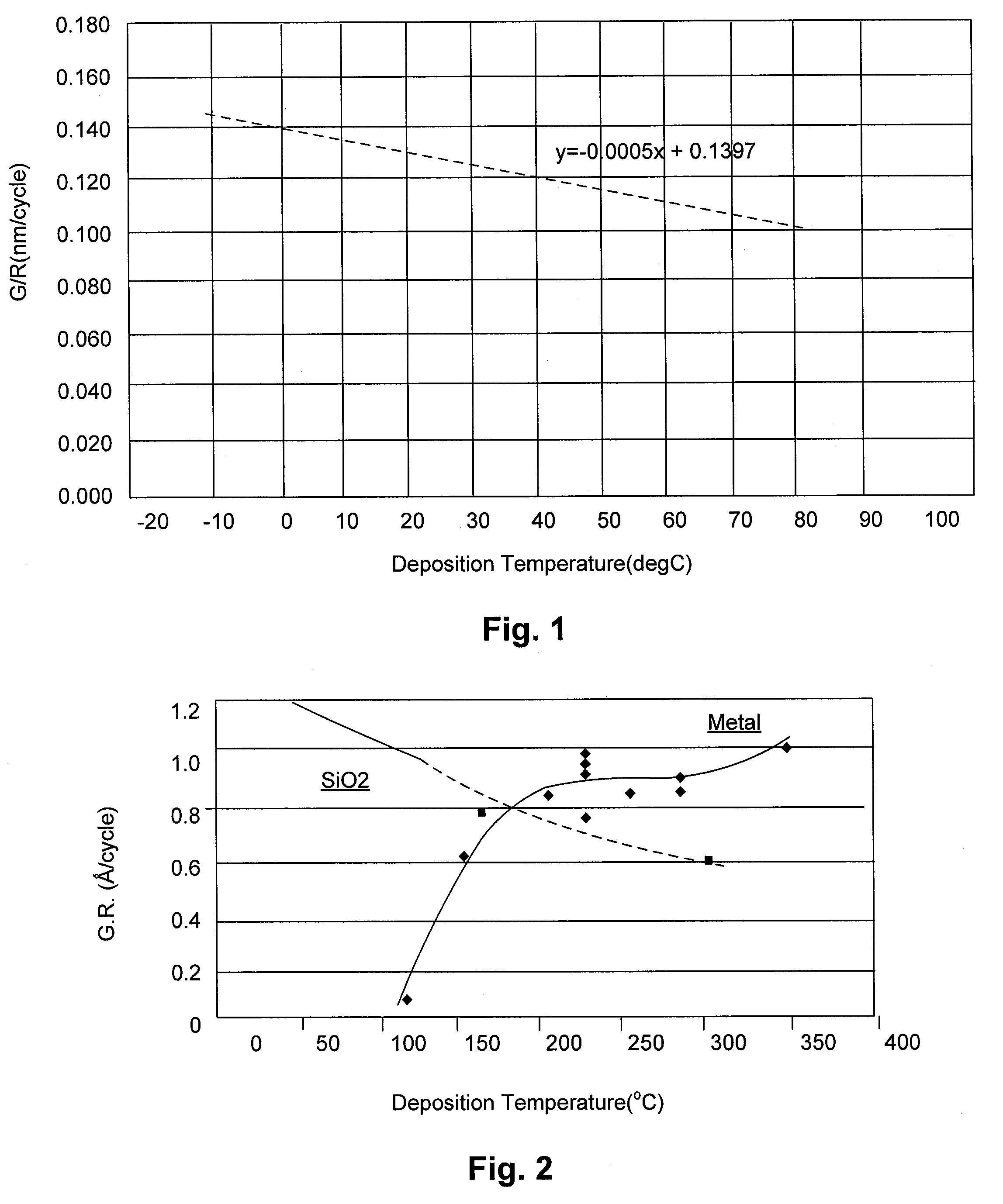
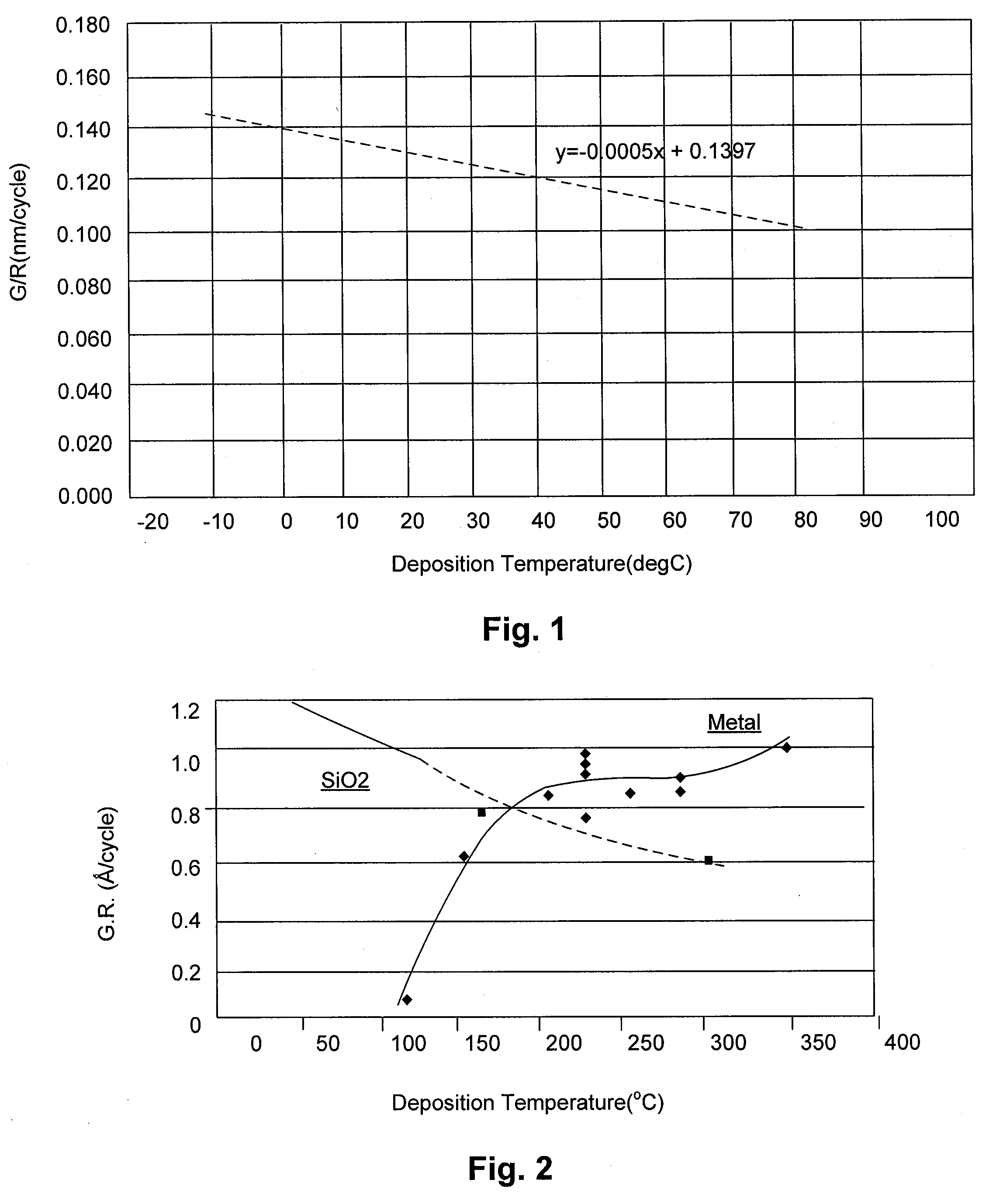
ActiveUS8197915B2Increase deposition rateInhibition is effectiveSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistDeposition temperature
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Method of Depositing Silicon Oxide Film by Plasma Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition at Low Temperature
ActiveUS20100255218A1Increase deposition rateInhibition is effectiveLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistDeposition temperature
A method of depositing a silicon oxide film on a resist pattern or etched lines formed on a substrate by plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) includes: providing a substrate on which a resist pattern or etched lines are formed in a PEALD reactor; controlling a temperature of a susceptor on which the substrate is placed at less than 50° C. as a deposition temperature; introducing a silicon-containing precursor and an oxygen-supplying reactant to the PEALD reactor and applying RF power therein in a cycle, while the deposition temperature is controlled substantially or nearly at a constant temperature of less than 50° C., thereby depositing a silicon oxide atomic layer on the resist pattern or etched lines; and repeating the cycle multiple times substantially or nearly at the constant temperature to deposit a silicon oxide atomic film on the resist pattern or etched lines.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
ActiveUS20100051584A1Improve adhesionImprove cooling efficiencyElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsDielectric plateEngineering
A tray 15 for a dry etching apparatus 1 has substrate accommodation holes 19A to 19D penetrating thickness direction and a substrate support portion 21 supporting an outer peripheral edge portion of a lower surface 2a of a substrate 2. A dielectric plate 23 has a tray support surface 28 supporting a lower surface of the tray 15, substrate placement portions 29A through 29D inserted from a lower surface side of the tray 15 into the substrate accommodation holes 19A through 19D and having a substrate placement surface 31 at its upper end surface for placing the substrate 2. A dc voltage applying mechanism 43 applies a dc voltage to an electrostatic attraction electrode 40. A heat conduction gas supply mechanism 45 supplies a heat conduction gas between the substrate 2 and substrate placement surface 31. The substrate 2 can be retained on the substrate placement surface 31 with high degree of adhesion. This results in that the cooling efficiency of the substrate 2 is improved and processing is uniformed at the entire region of the substrate surface including the vicinity of the outer peripheral edge.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
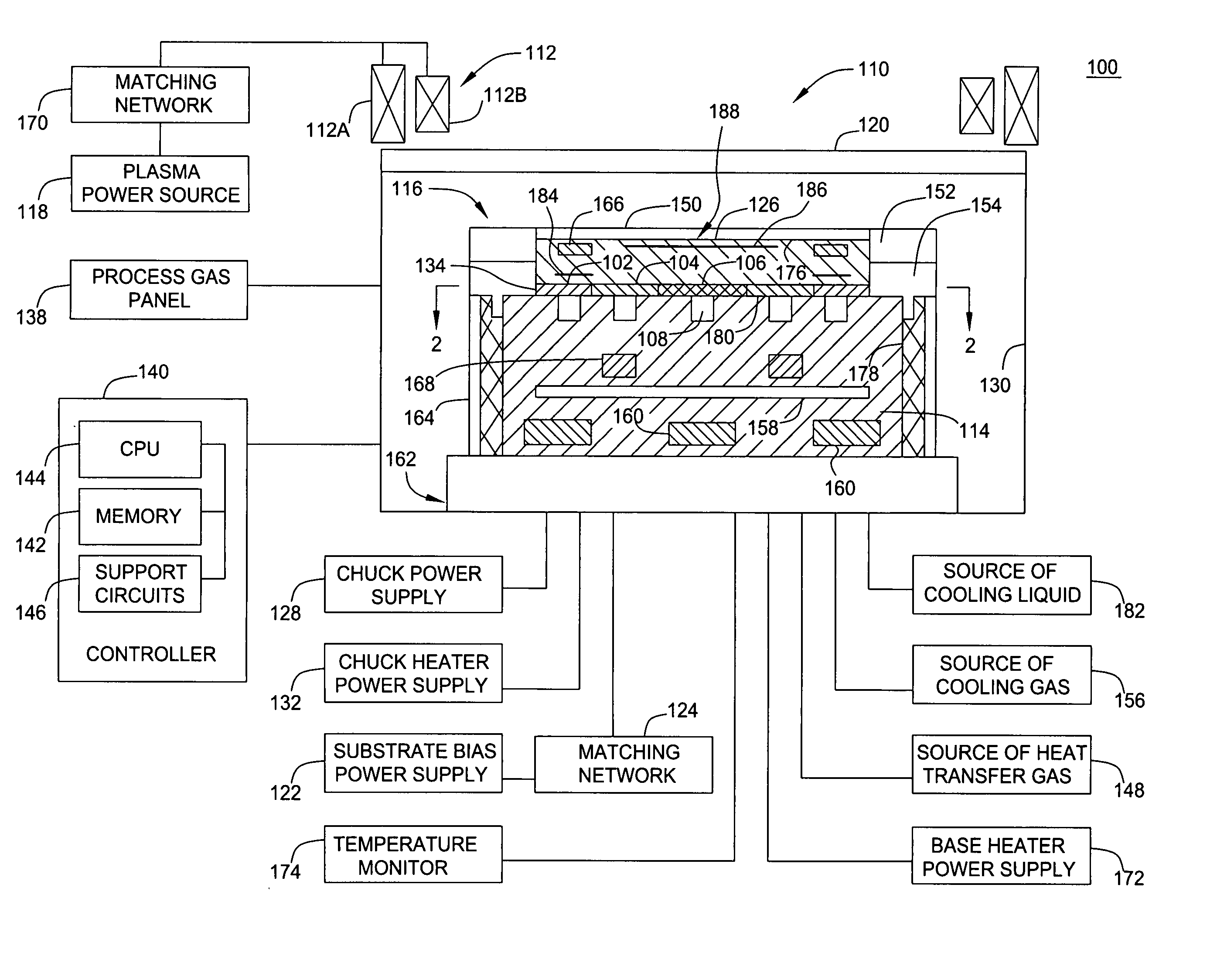
Plasma processing apparatus
InactiveUS20100126666A1Uniform processingUnified controlElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingIn planeEngineering
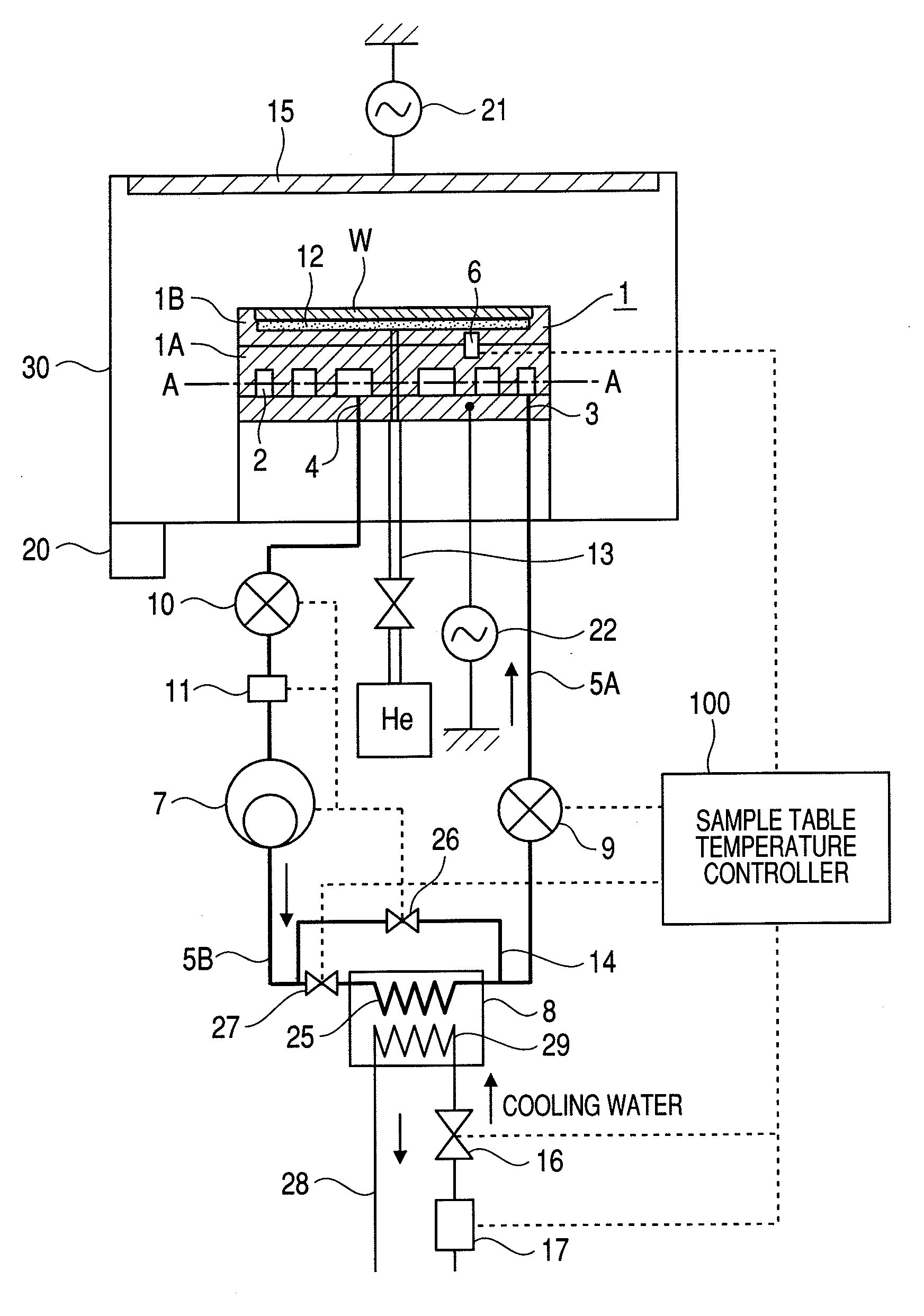
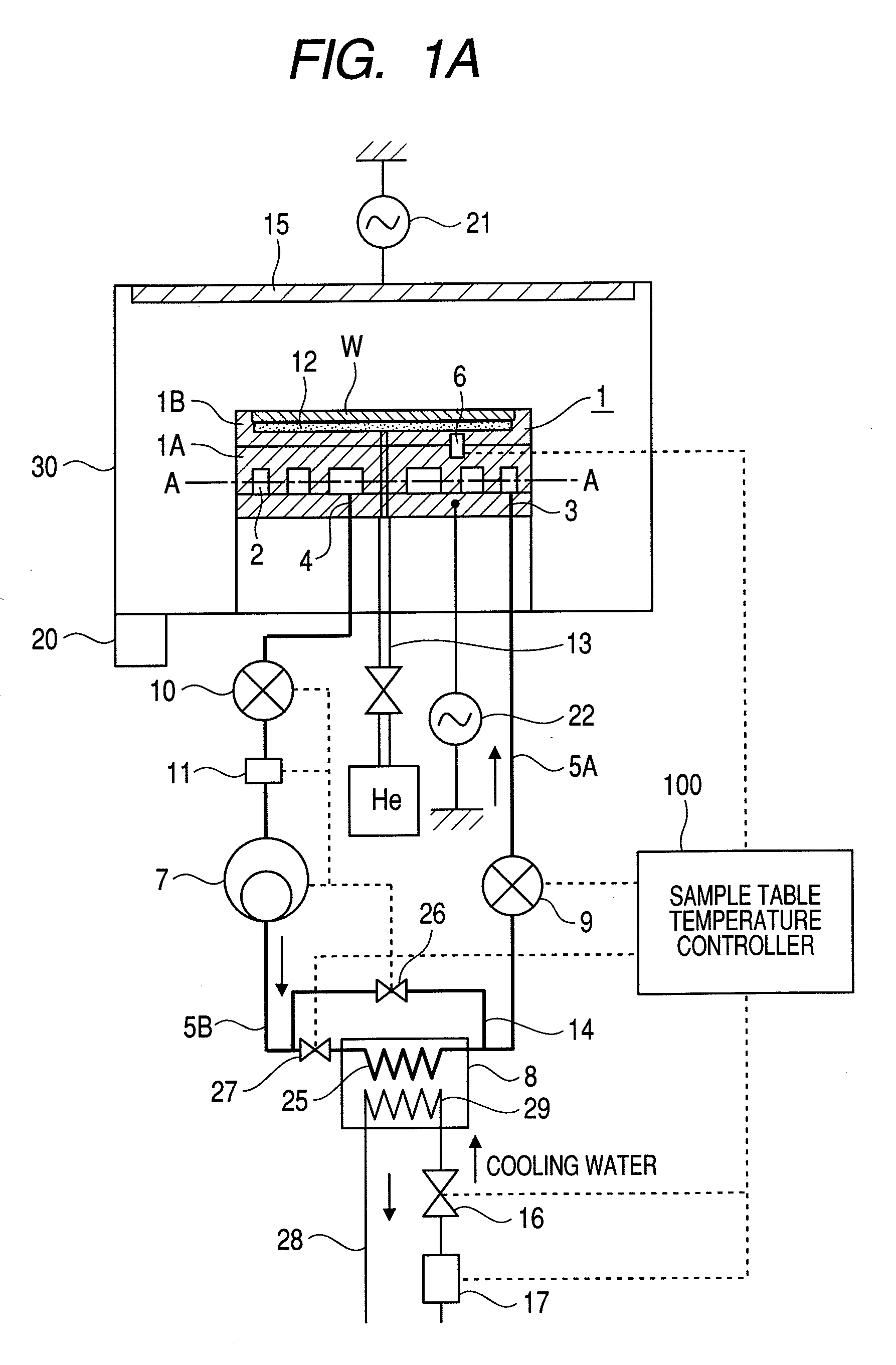
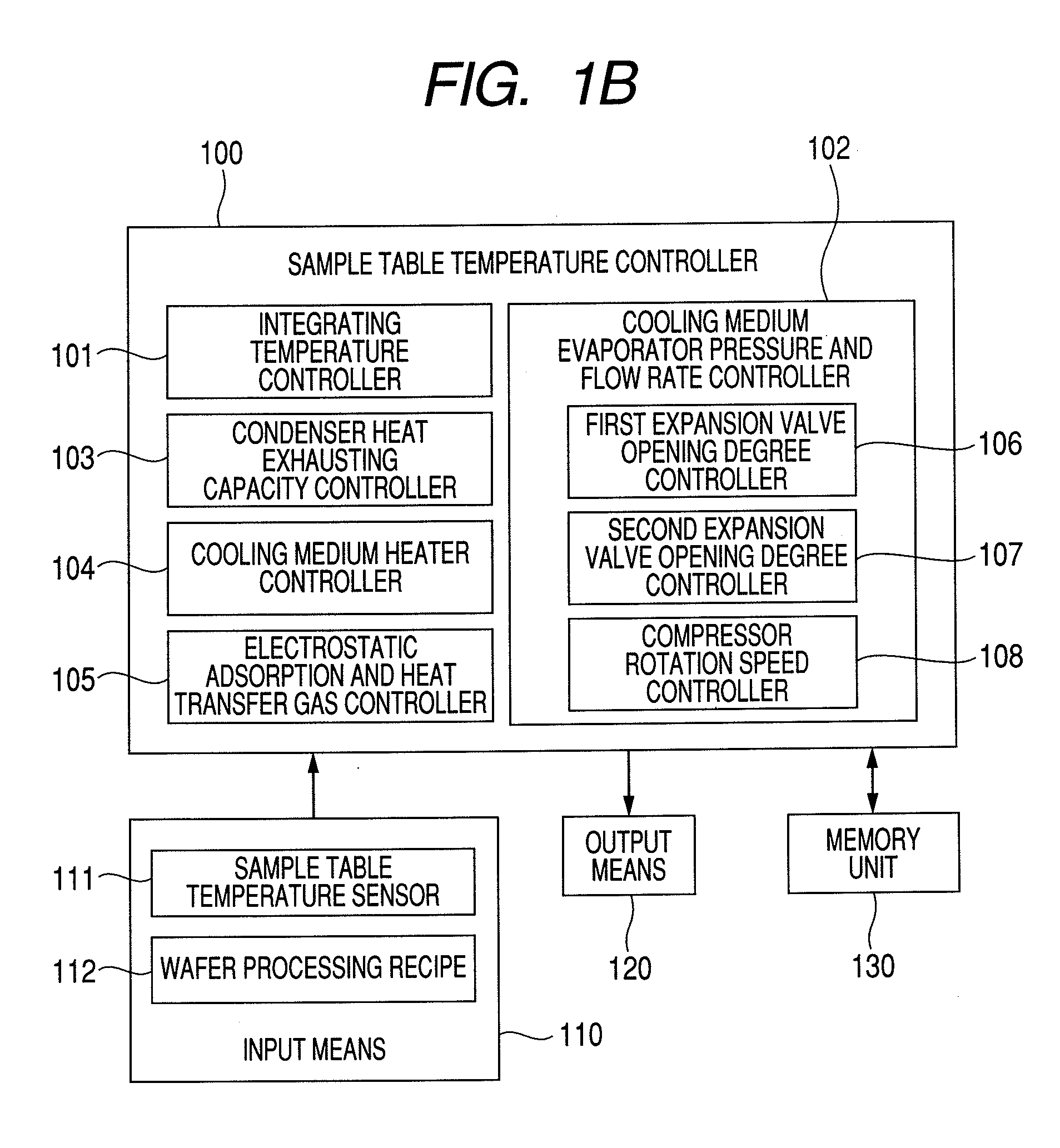
In a plasma processing apparatus; a refrigerant flow passage being formed in the sample table and constituting an evaporator of a cooling cycle and the in-plane temperature of the sample to be processed is controlled uniformly by controlling the enthalpy of the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage and thereby keeping the flow mode in the refrigerant flow passage, namely in the sample table, in the state of a gas-liquid two-phase. If by any chance dry out of the refrigerant occurs in the refrigerant flow passage because the heat input of plasma increases with time or by another reason, it is possible to increase speed of a compressor and inhibit the dry out from occurring in the refrigerant flow passage. Further, if the refrigerant supplied to the refrigerant flow passage is liquefied, it is kept in the gas-liquid two-phase state.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
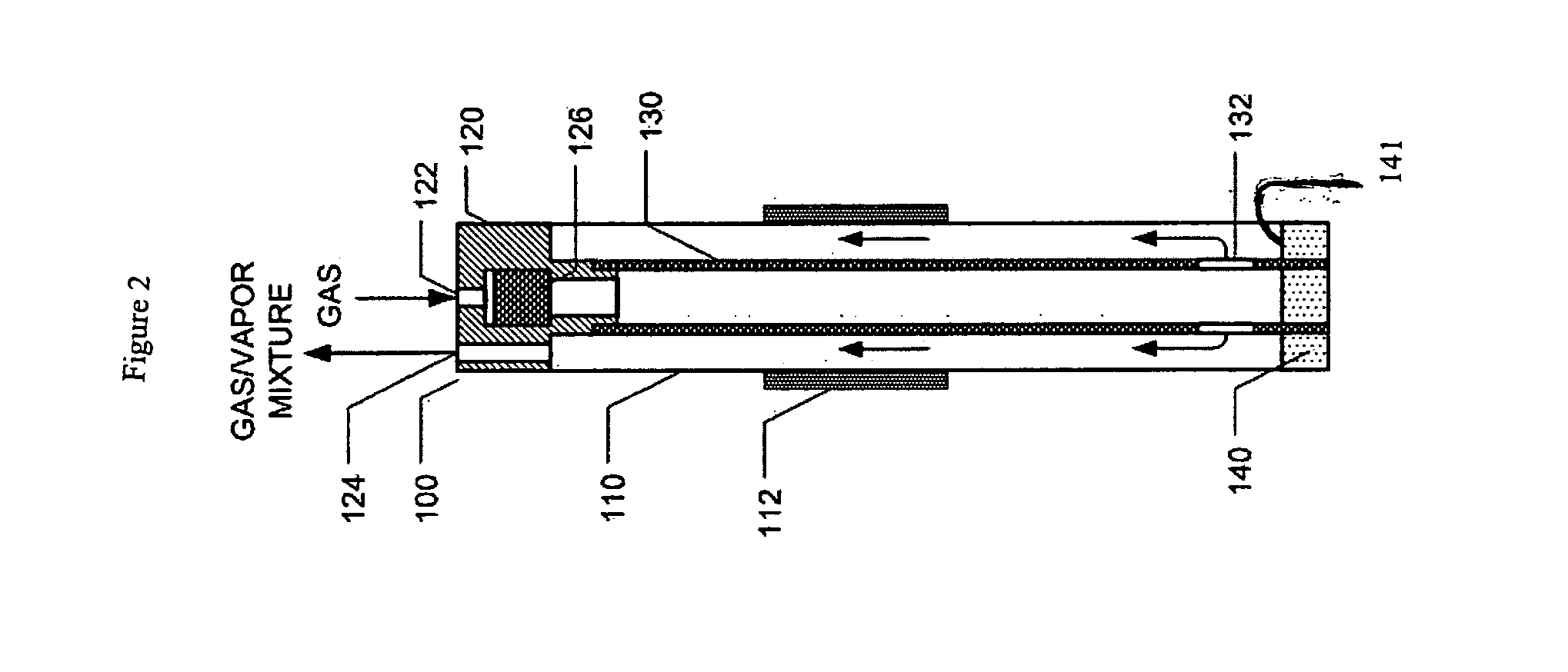
High stability and high capacity precursor vapor generation for thin film deposition
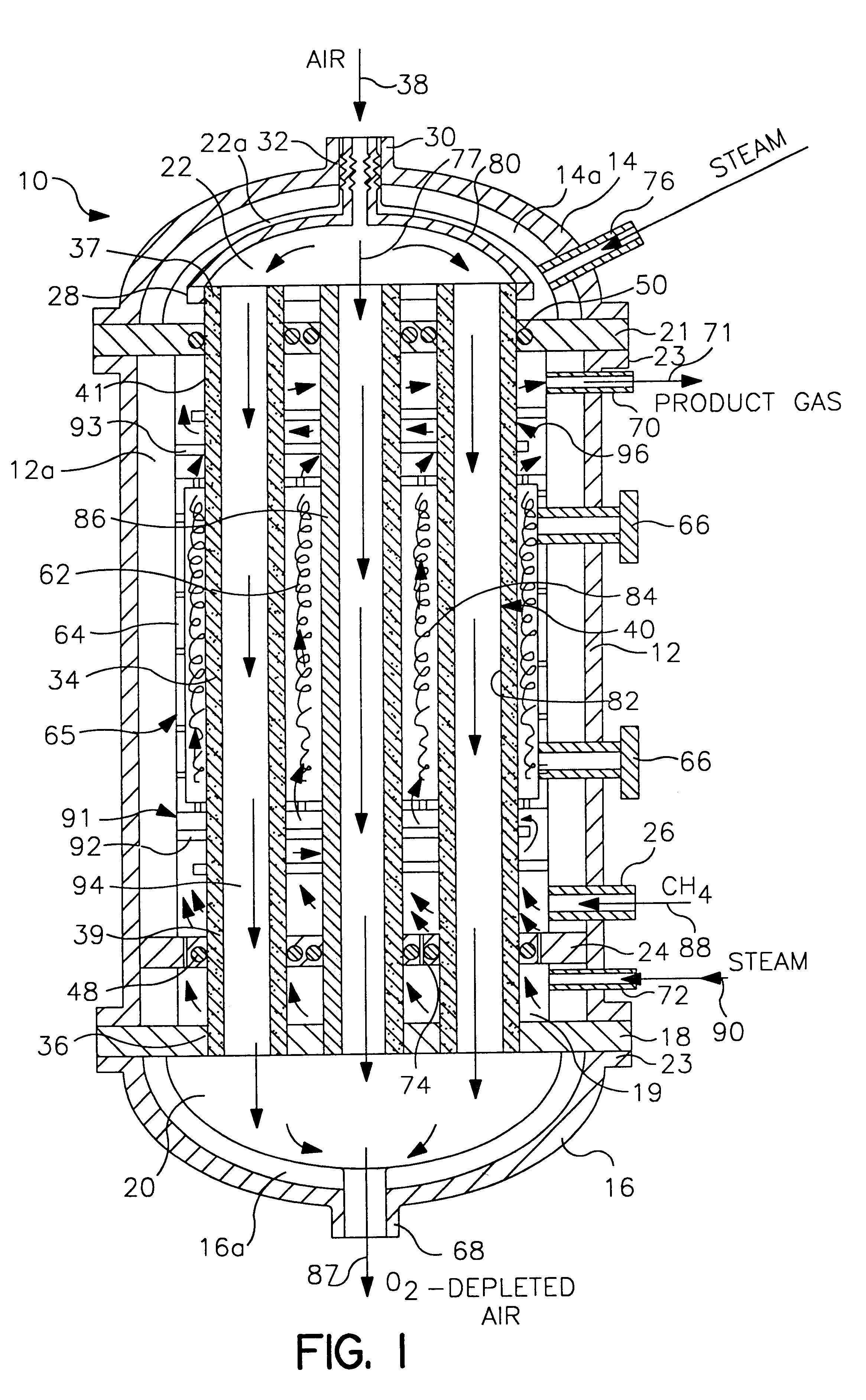
ActiveUS20070120275A1Temperature controlUsing liquid separation agentMachines/enginesAirflowProduct gas
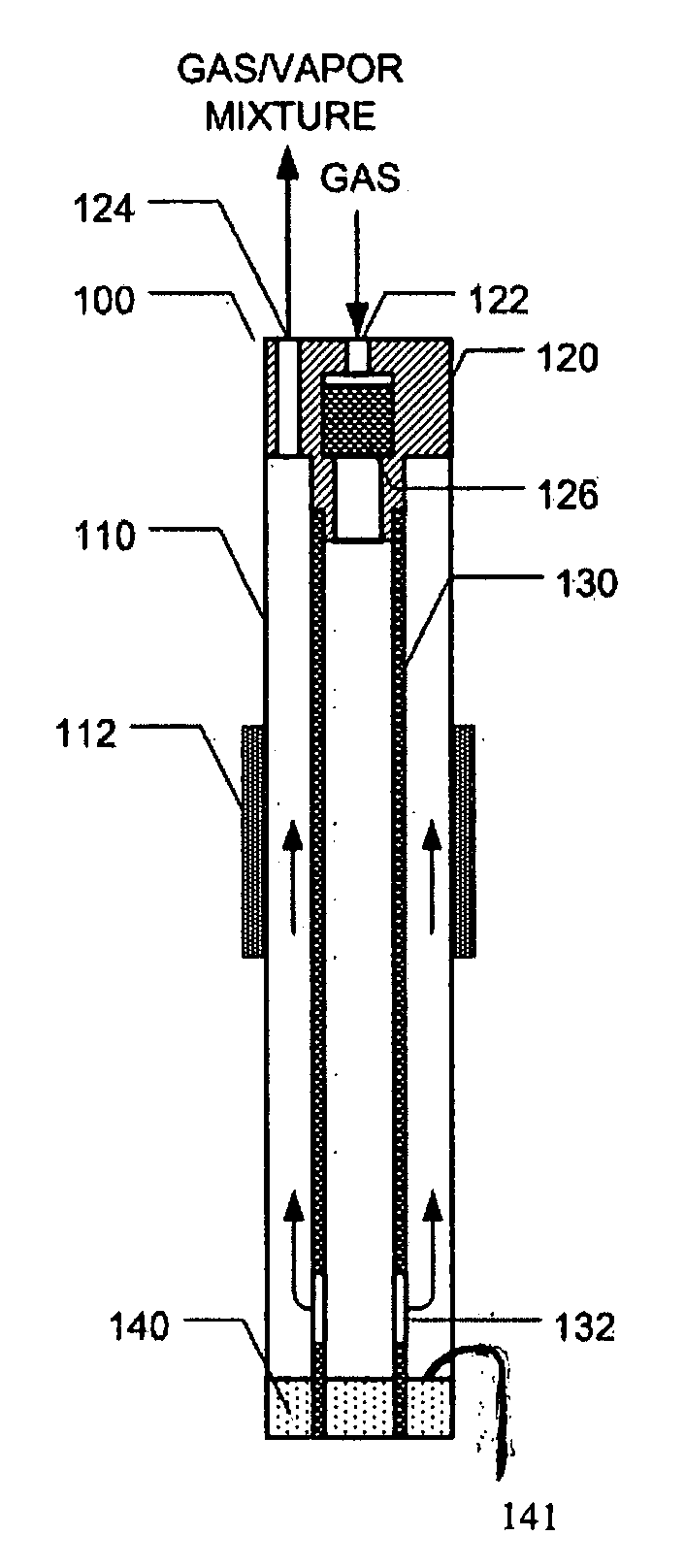
An apparatus for vaporizing a liquid for subsequent thin film deposition on a substrate. The apparatus comprises a housing with an inlet and an outlet and a liquid reservoir. A mechanism controls the liquid level in the reservoir to a substantially constant level. A gas flow passageway extends along side a porous metal wall with interstitial spaces for containing liquid from the reservoir and with a package for a carrier gas to flow along side the porous metal wall, forming a gas / vapor mixture suitable for thin film deposition.
Owner:MSP
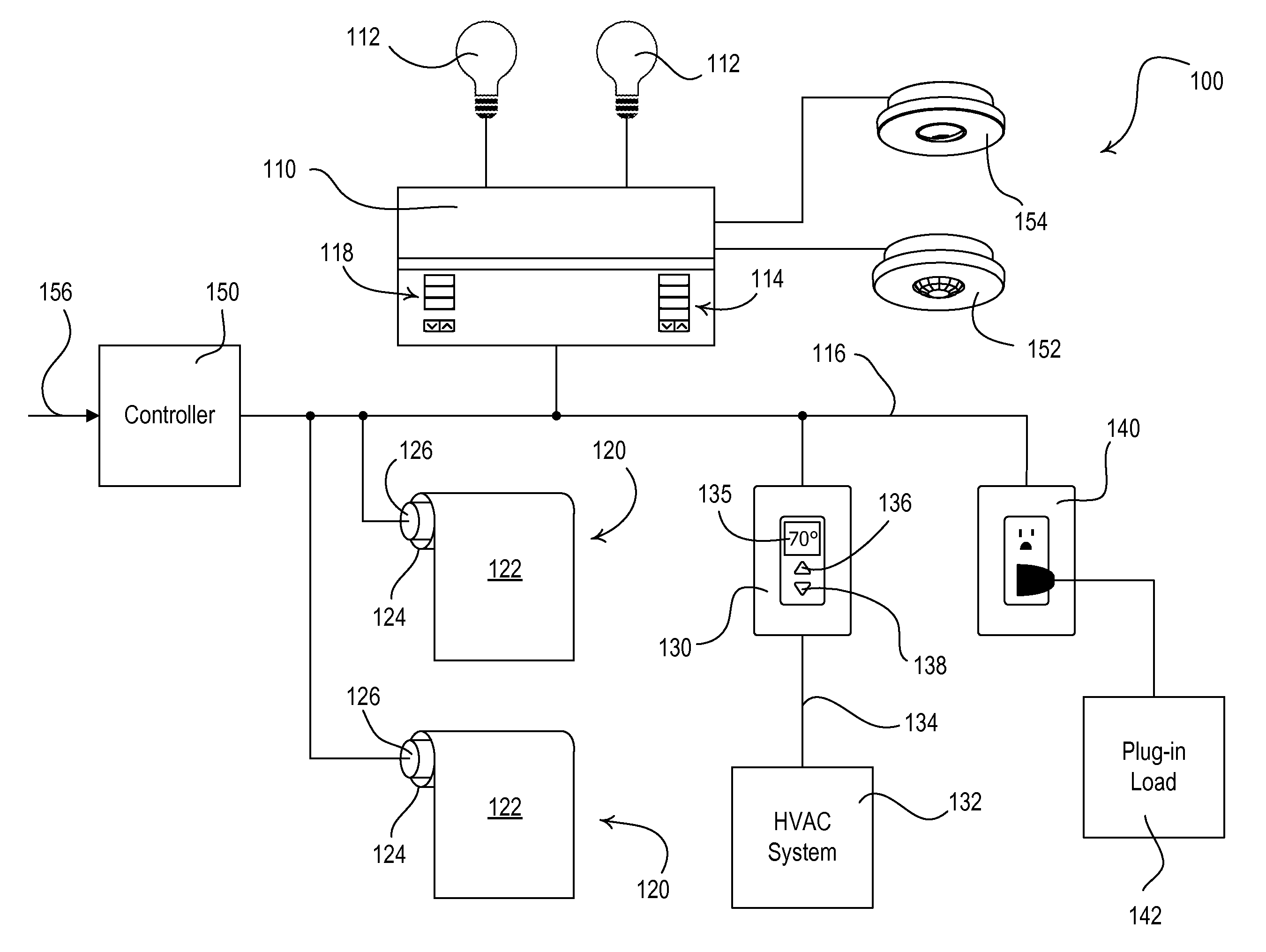
Dynamic Keypad for Controlling Energy-Savings Modes of a Load Control System
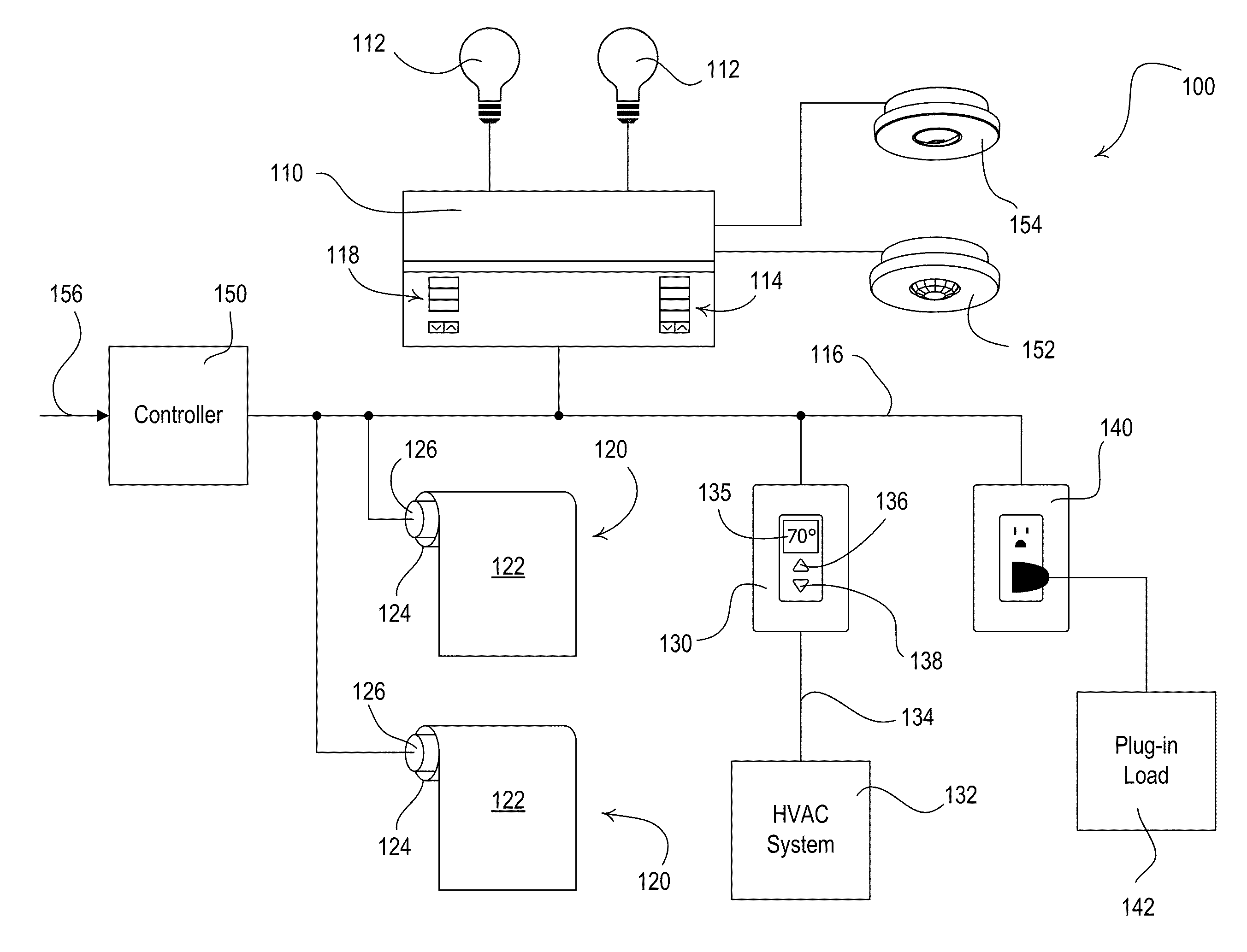
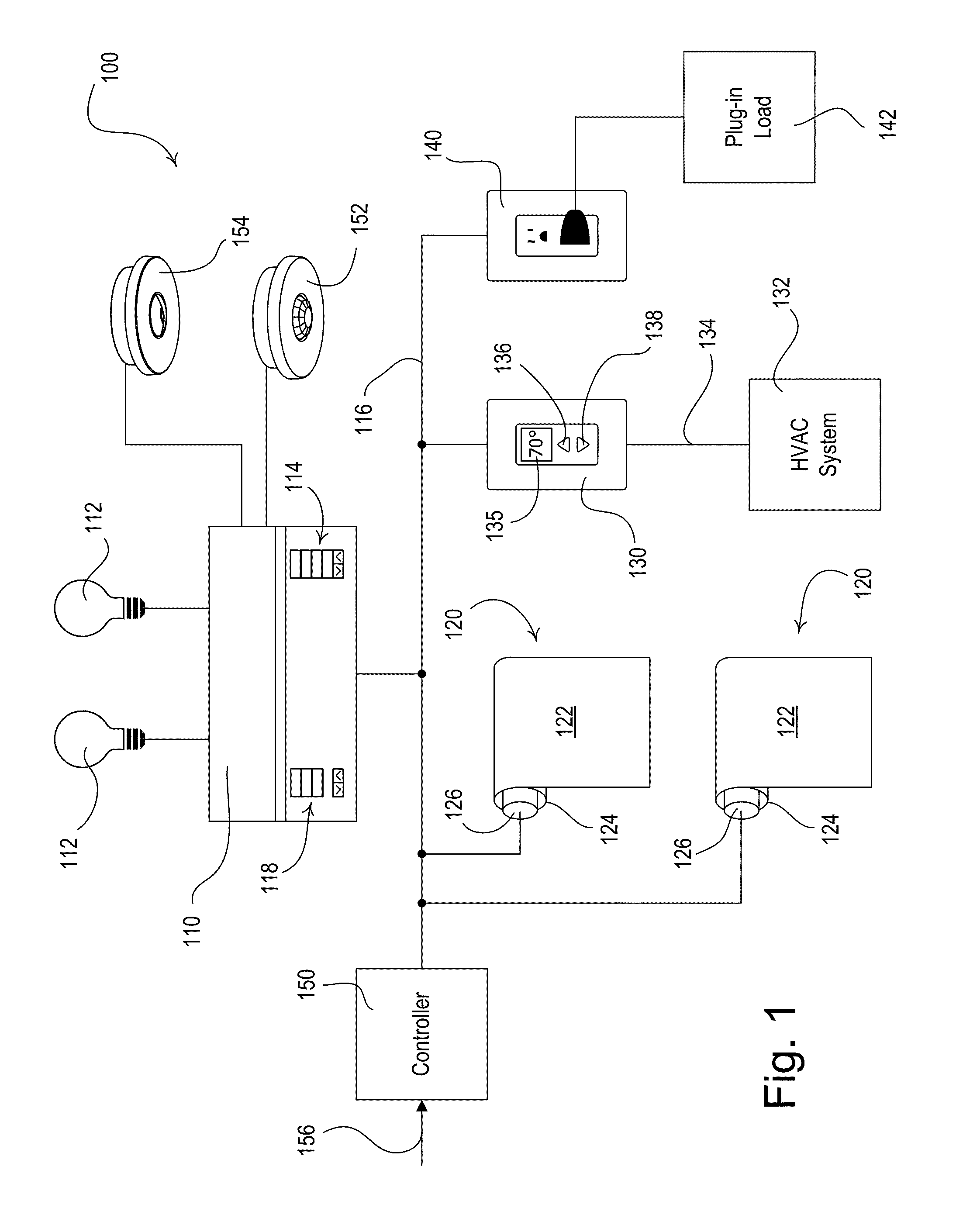
ActiveUS20120095601A1Reduce the amount of powerIncrease setpoint temperatureSampled-variable control systemsMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsTemperature controlOperating energy
A load control system for a building having a lighting load, a window, and a heating and cooling system comprises a lighting control device for controlling the amount of power delivered to the lighting load, a motorized window treatment comprising a window treatment fabric for covering the window, a temperature control device for controlling a setpoint temperature of the heating and cooling system to thus control a present temperature in the building, and a dynamic keypad comprising a visual display and operable to receive a user input. The dynamic keypad allows a user to select, adjust, and monitor a plurality of energy-savings modes of the load control system. For example, the dynamic keypad allows the user to enable and adjust a setback temperature of the temperature control device on-the-fly.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Plasma processing apparatus
ActiveUS10622196B2Efficient heat transferTemperature controlElectric discharge tubesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A plasma processing apparatus includes a mounting stage on which a substrate is mounted, a focus ring arranged around a periphery of the mounting stage, a plurality of magnetic members arranged at a surface of the focus ring and a surface of the mounting stage facing opposite each other, and a temperature adjustment unit configured to adjust a temperature of the focus ring by introducing a heat transfer gas between the surface of the focus ring and the surface of the mounting stage facing opposite each other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling temperature of a substrate
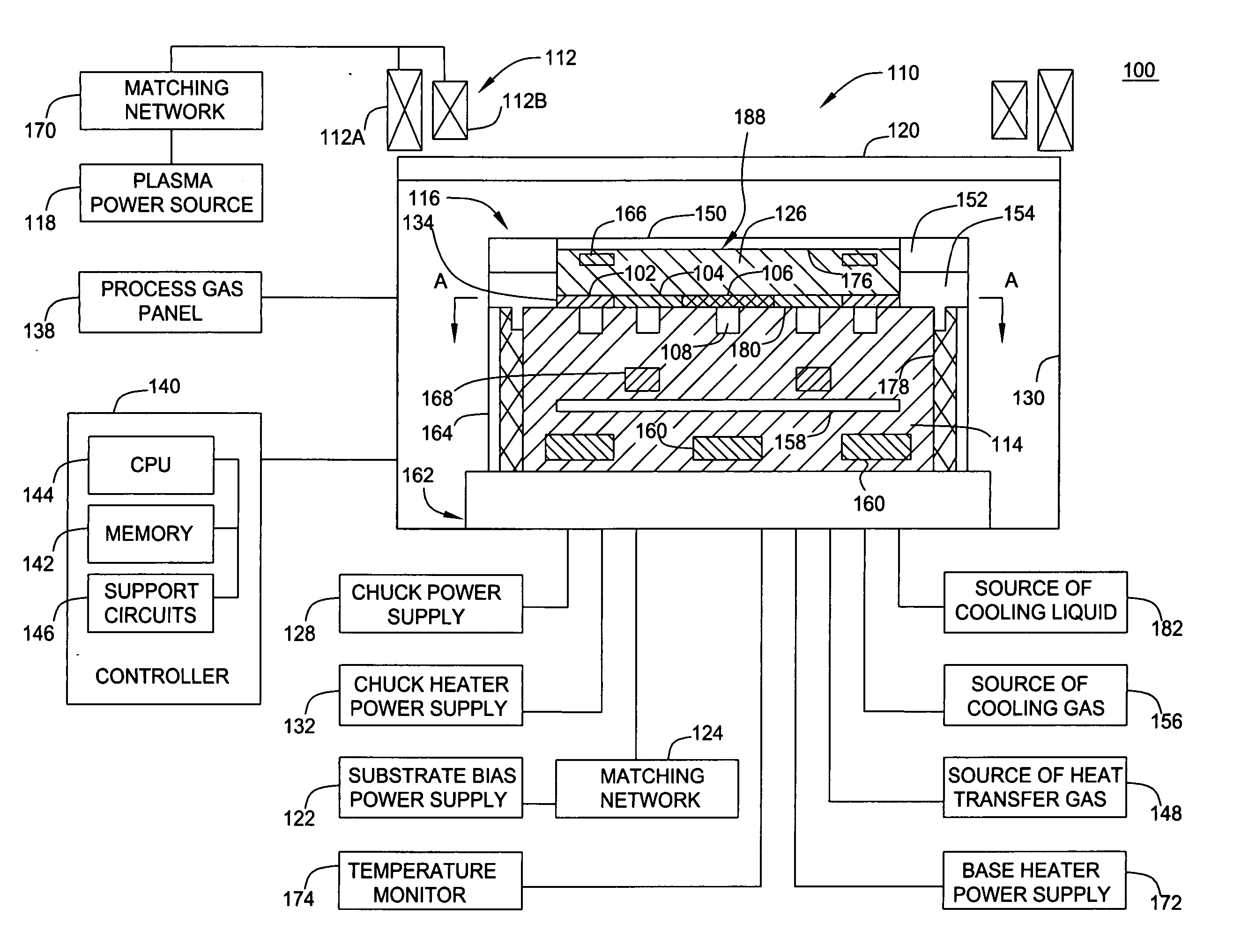
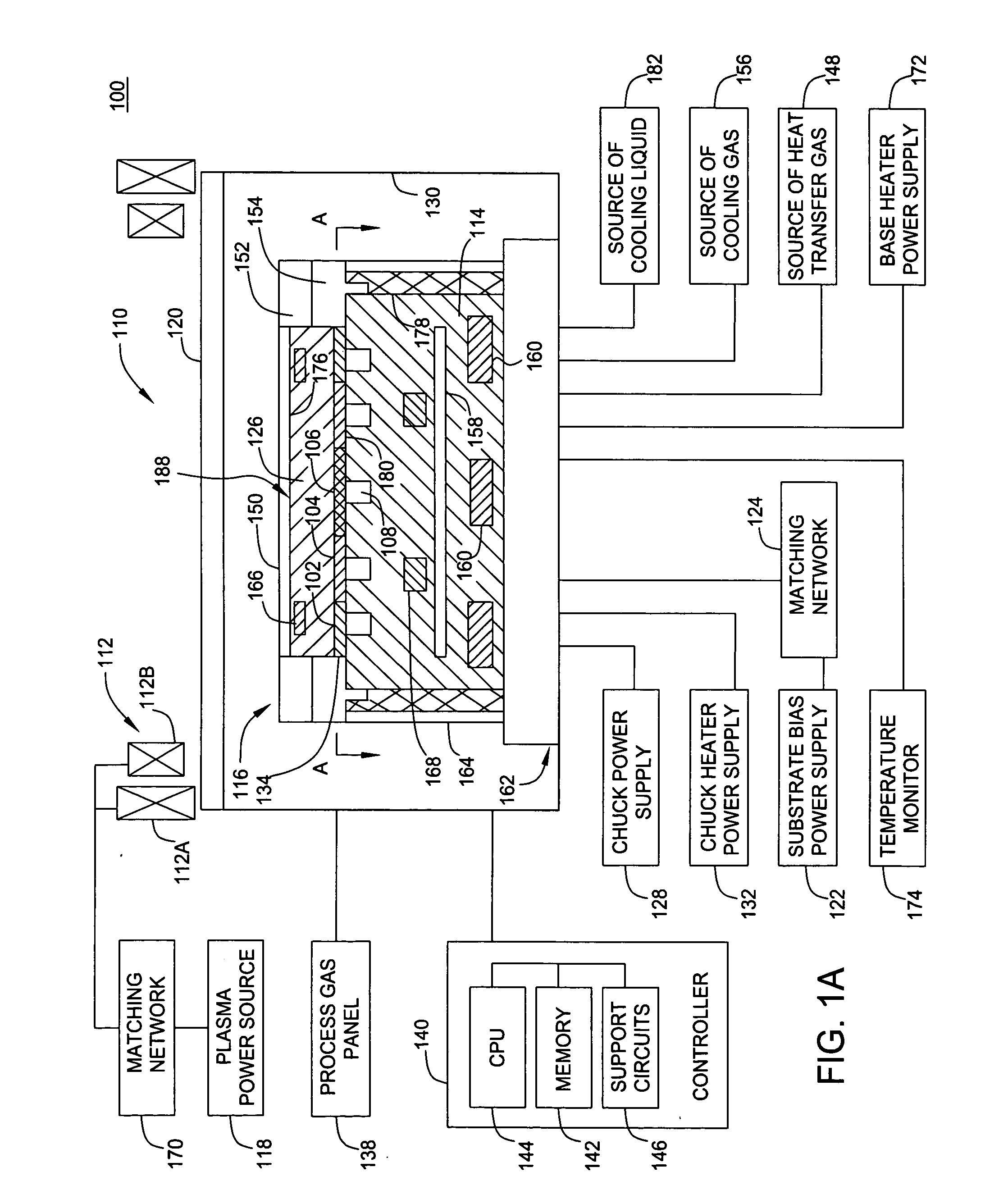
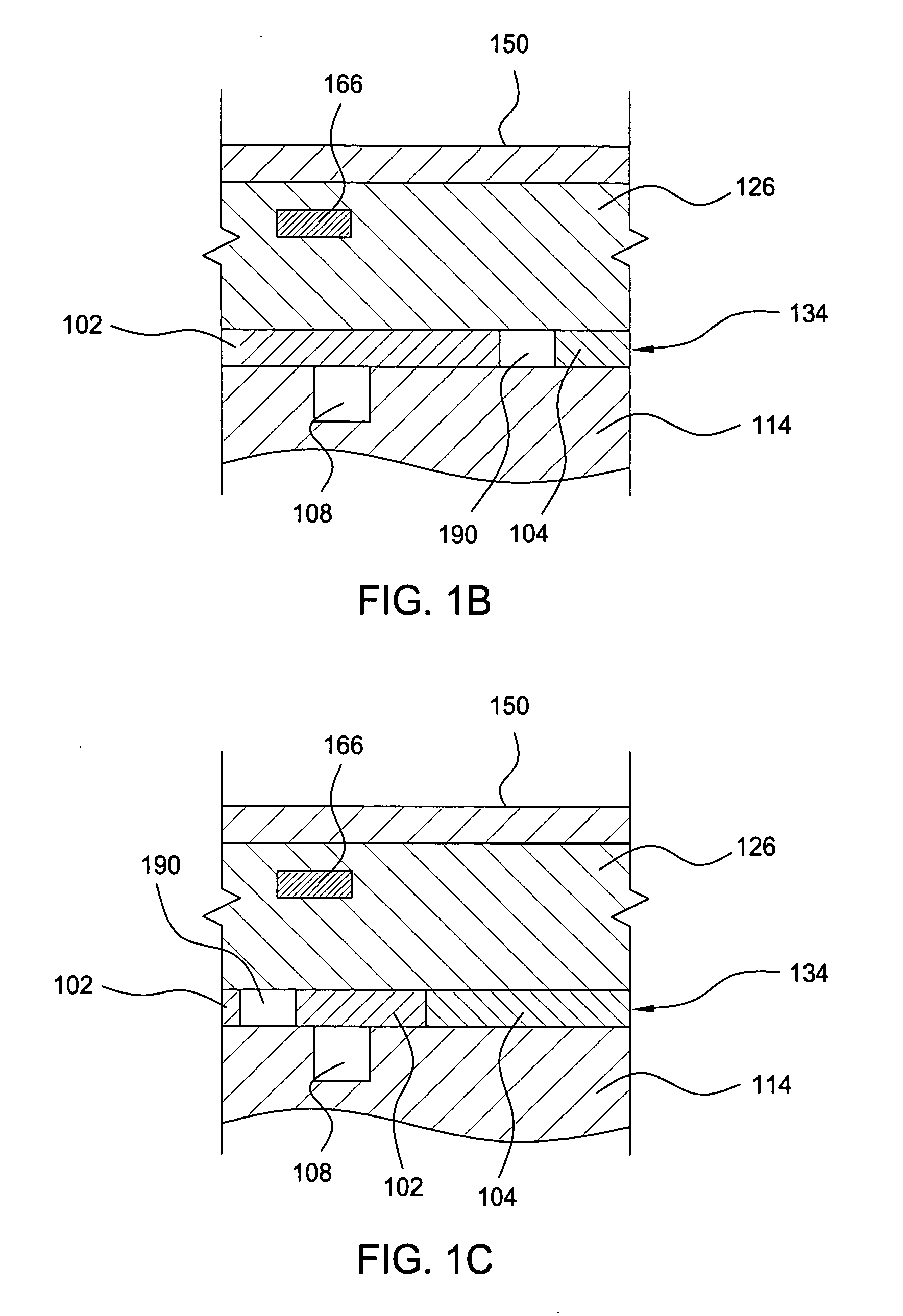
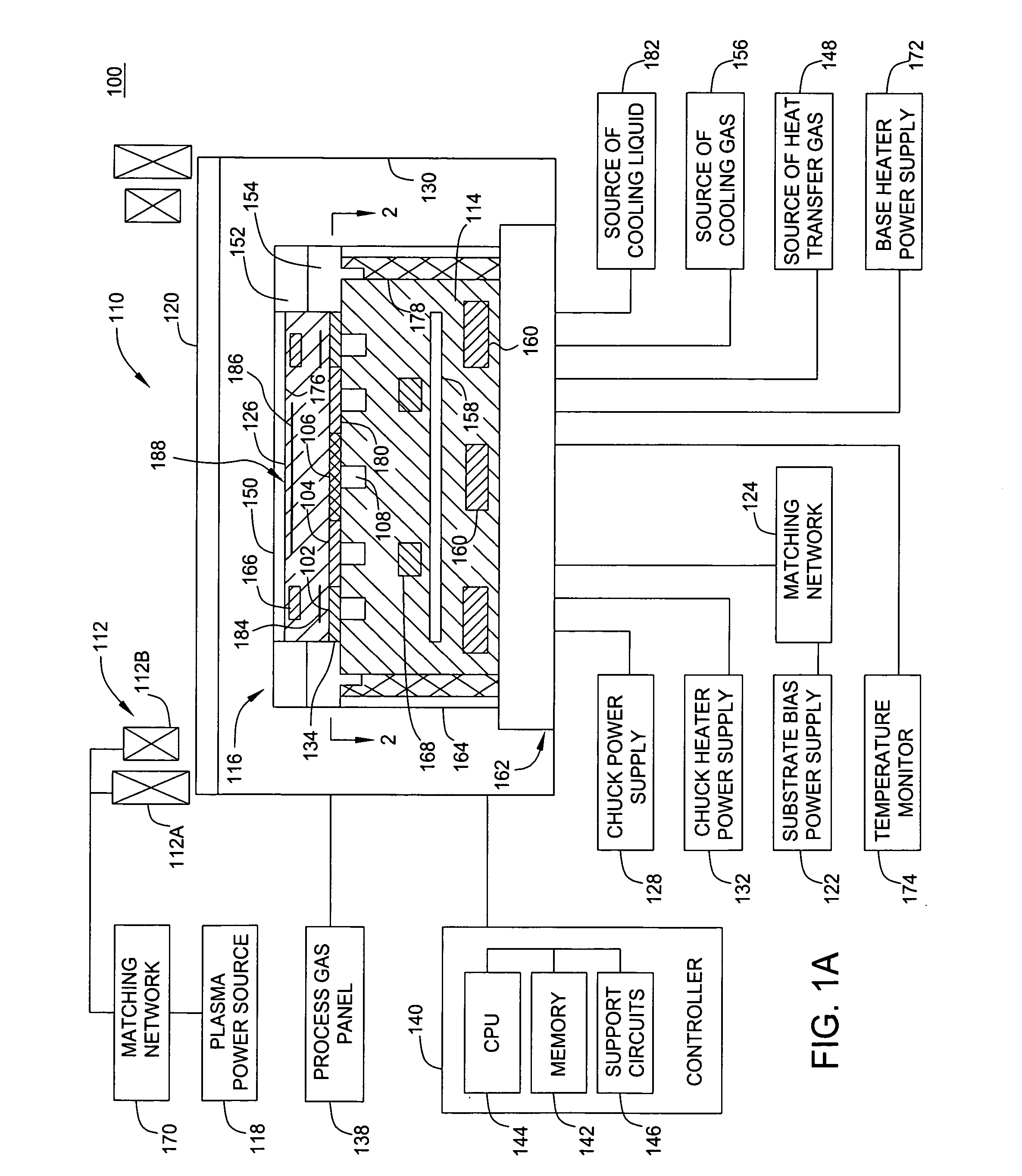
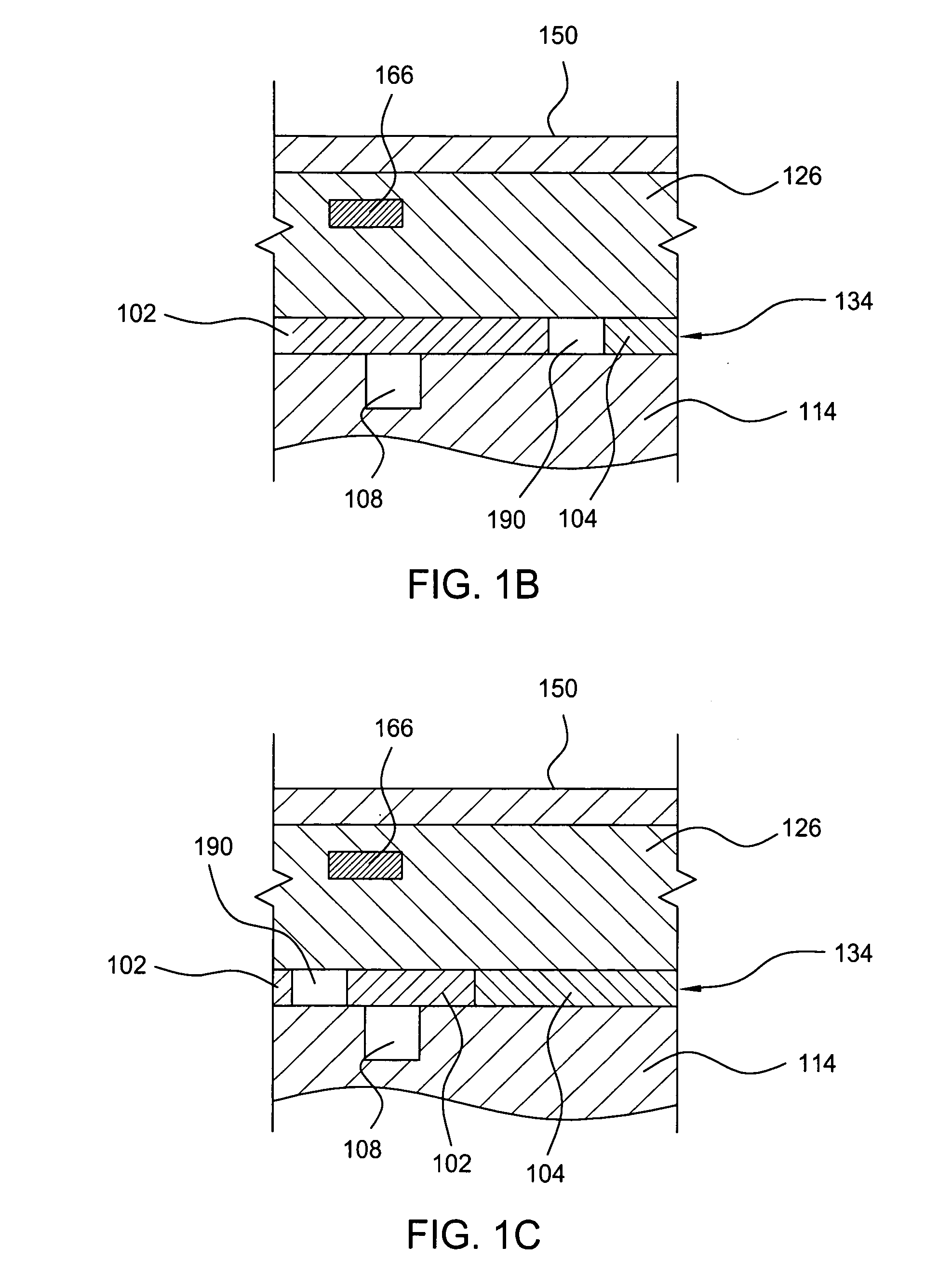
InactiveUS20060076108A1Easy temperature controlTemperature controlSleeve/socket jointsDecorative surface effectsEngineeringMechanical engineering
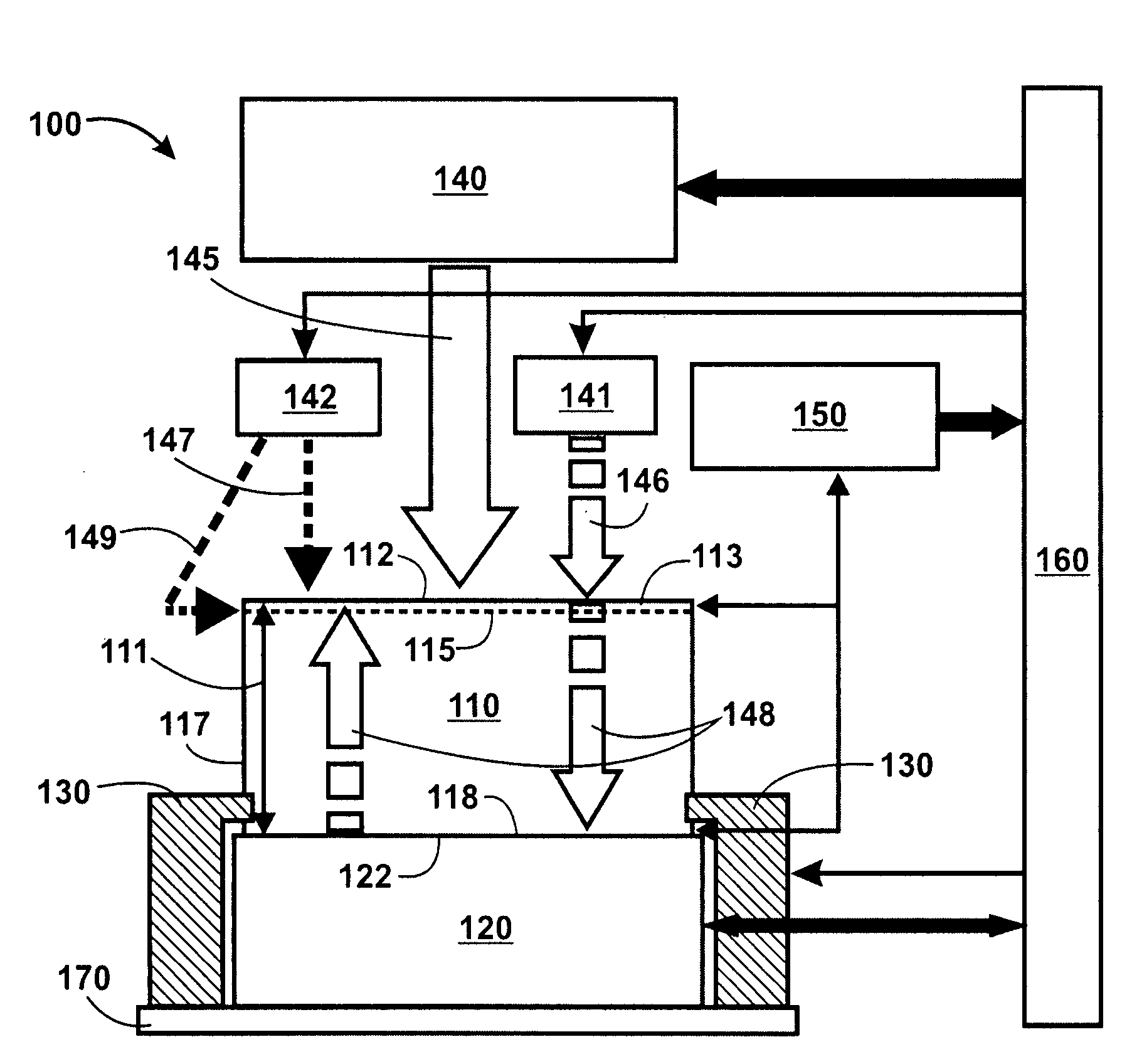
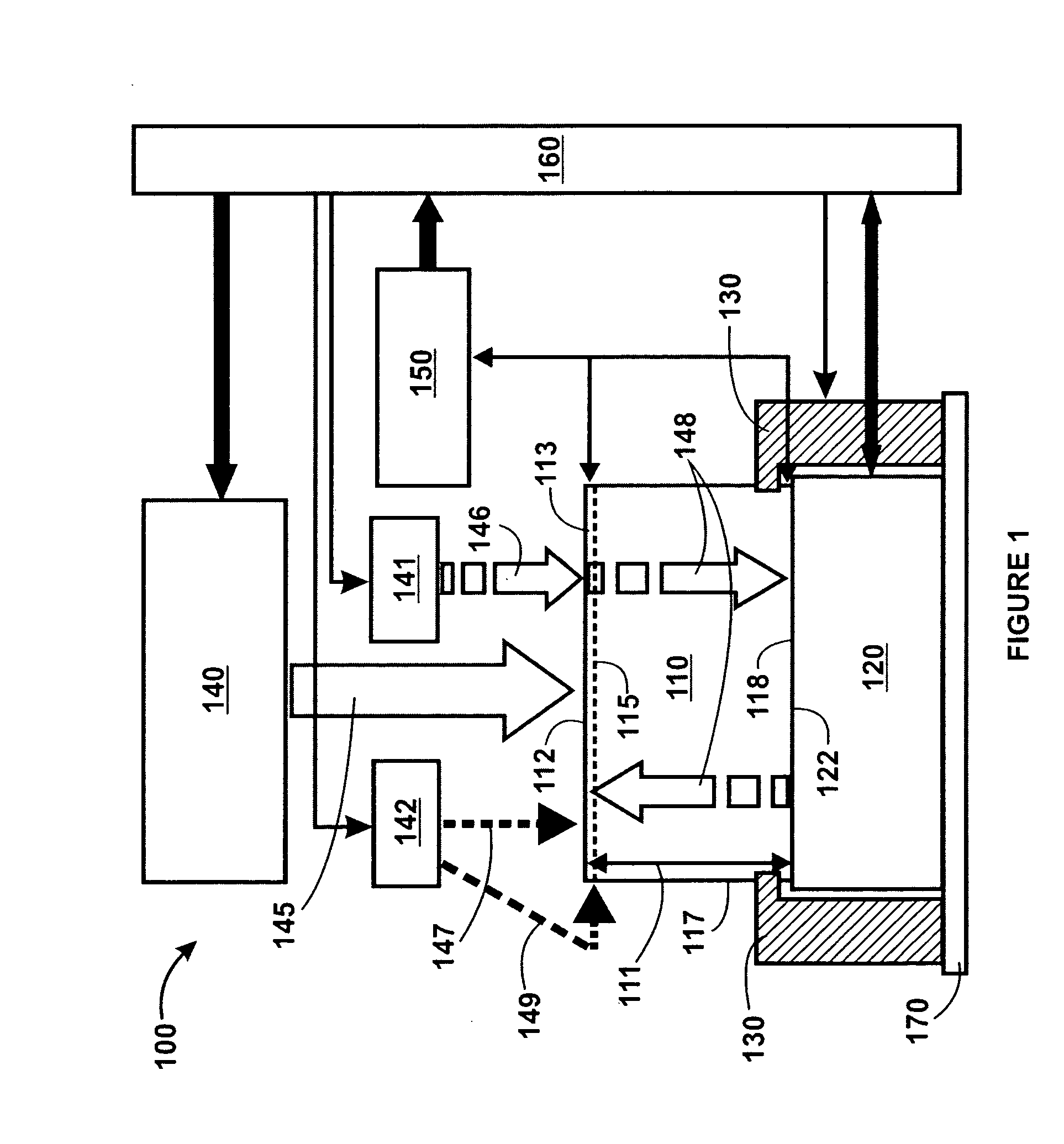
A pedestal assembly and method for controlling temperature of a substrate during processing is provided. In one embodiment, the pedestal assembly includes a support member that is coupled to a base by a material layer. The material layer has at least two regions having different coefficients of thermal conductivity. In another embodiment, the support member is an electrostatic chuck. In further embodiments, a pedestal assembly has channels formed between the base and support member for providing cooling gas in proximity to the material layer to further control heat transfer between the support member and the base, thereby controlling the temperature profile of a substrate disposed on the support member.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and system for controlled thermal injury of human superficial tissue
InactiveUS20060116671A1Produce lesionRestricted in mannerUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionThermal injuryControl system
A method and system for controlled thermal injury of human superficial tissue based on the ability to controllably create thermal lesions of variable shape, size, and depth via precise spatial and temporal control of acoustic energy deposition. The apparatus includes a control system and probes that facilitate treatment planning, control and delivery of energy, and monitoring of treatment conditions.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
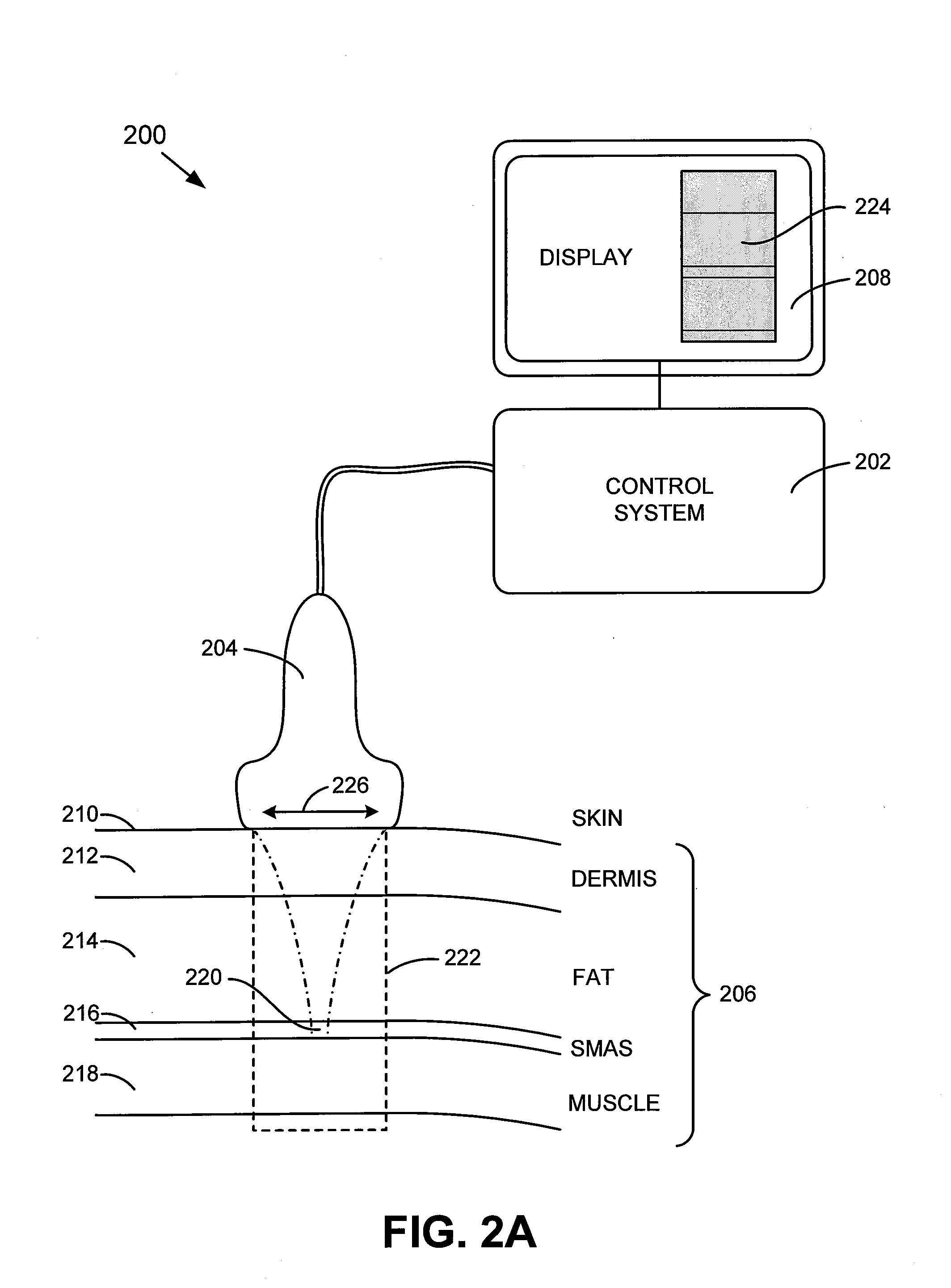
Method and system for noninvasive face lifts and deep tissue tightening
ActiveUS20080214966A1Precise and temporal controlProduce lesionUltrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionThermal injuryTherapeutic effect
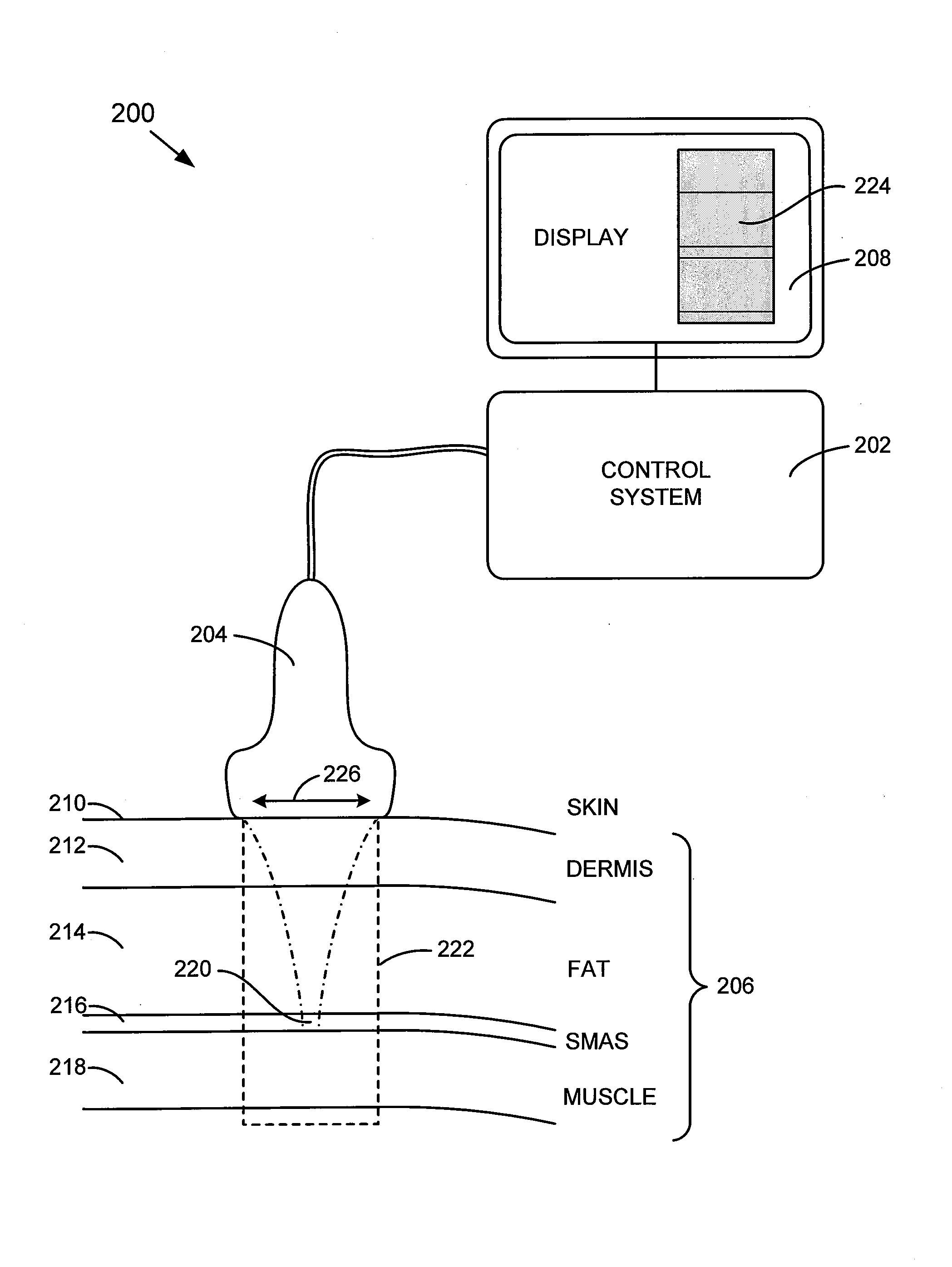
A method and system for noninvasive face lifts and deep tissue tightening are disclosed. An exemplary method and treatment system are configured for the imaging, monitoring, and thermal injury to treat the SMAS region. In accordance with an exemplary embodiment, the exemplary method and system are configured for treating the SMAS region by first, imaging of the region of interest for localization of the treatment area and surrounding structures, second, delivery of ultrasound energy at a depth, distribution, timing, and energy level to achieve the desired therapeutic effect, and third to monitor the treatment area before, during, and after therapy to plan and assess the results and / or provide feedback.
Owner:GUIDED THERAPY SYSTEMS LLC
Methods and apparatus for adjusting blood circulation
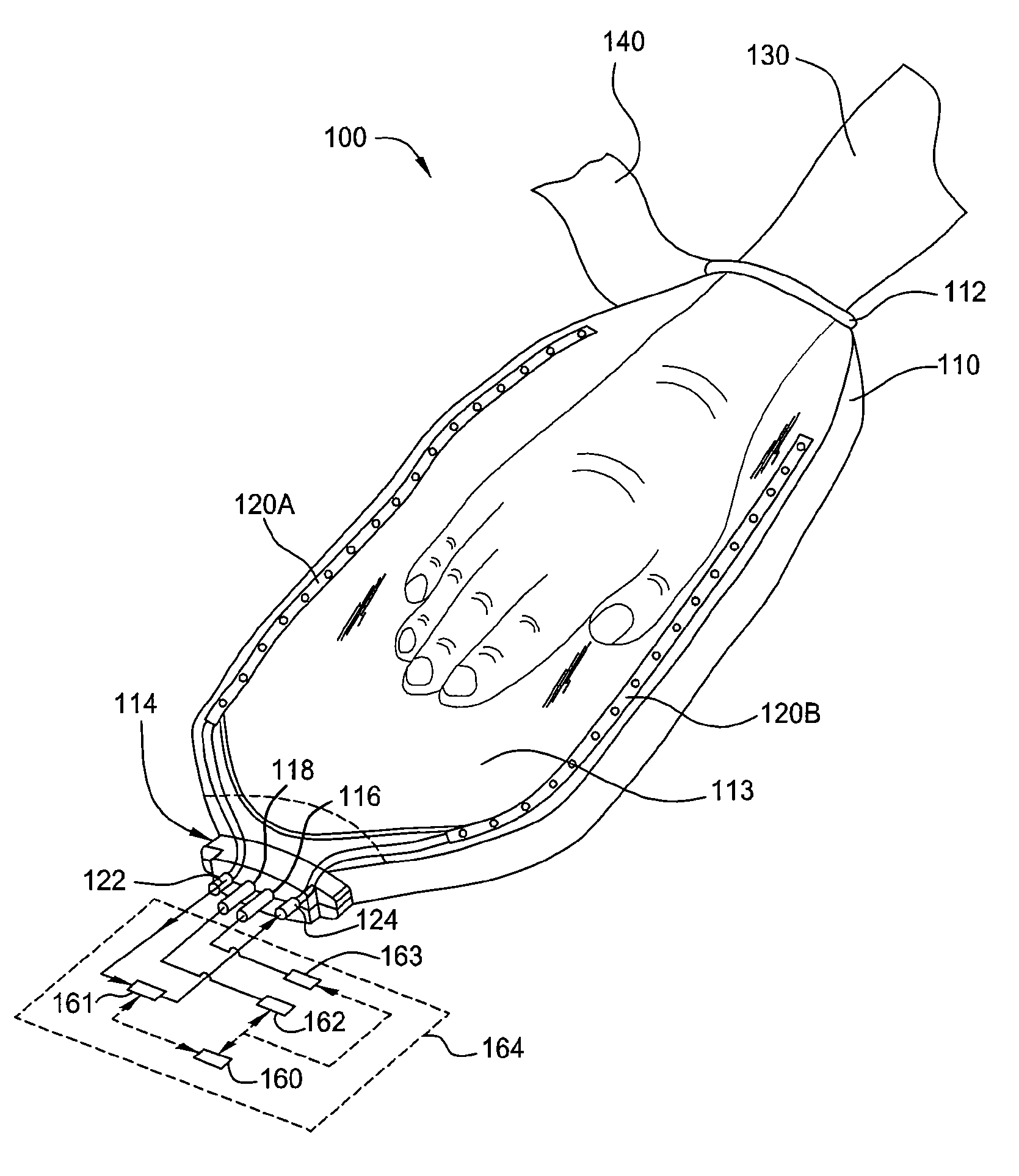
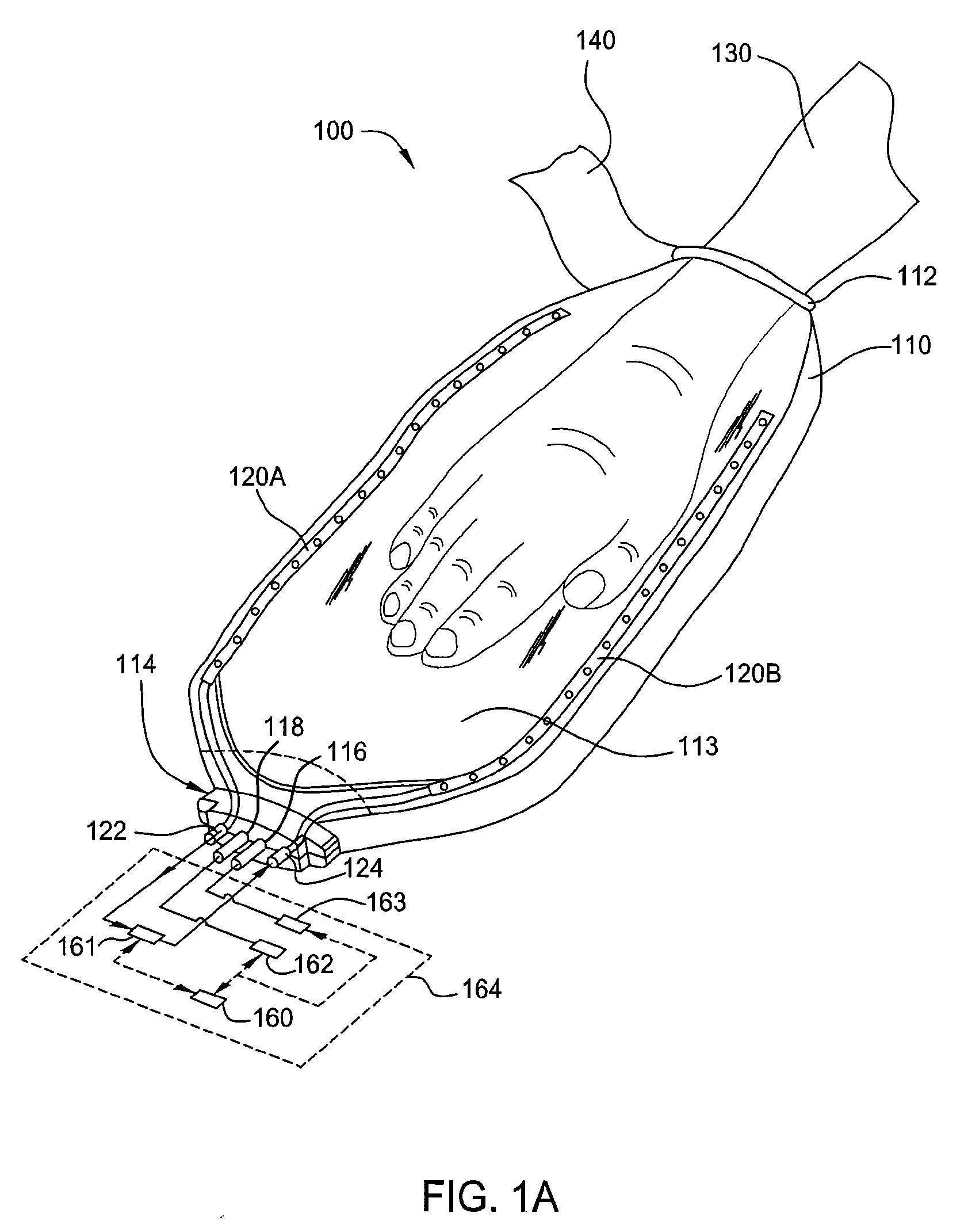
ActiveUS20080132976A1Good thermal contactIncrease blood flowBlood stagnation preventionElectrotherapyThermal energyEngineering
Embodiments of the invention include a method and a device for increasing blood flow and controlling the temperature of a mammal by applying a desired pressure to extremities of a mammal. The device generally includes one or more collapsible and pliant body elements, capable of expanding from a first volume into an expanded second volume so the device can receive a portion of an extremity of the mammal therein and then be reduced from the expanded second volume into a pressurized third volume to conformably enclose the portion of the extremity. One or more thermal exchange units can be positioned in the one or more collapsible and pliant body elements. Accordingly, the temperature of the extremity of a mammal can be regulated by providing a heated or cooled fluid medium or electric thermal energy to the one or more thermal exchange units. Next, by evacuating the region in which the extremity is enclosed the contact surface area between the extremity of a mammal and the one or more thermal exchange units is increased, due to the external atmospheric pressure acting on the pliant body elements against the skin of the extremity of the mammal. The application of pressure assures that sufficient contact and thermal heat transfer (heating or cooling) is provided to the extremity of the mammal.
Owner:AVACORE TECH
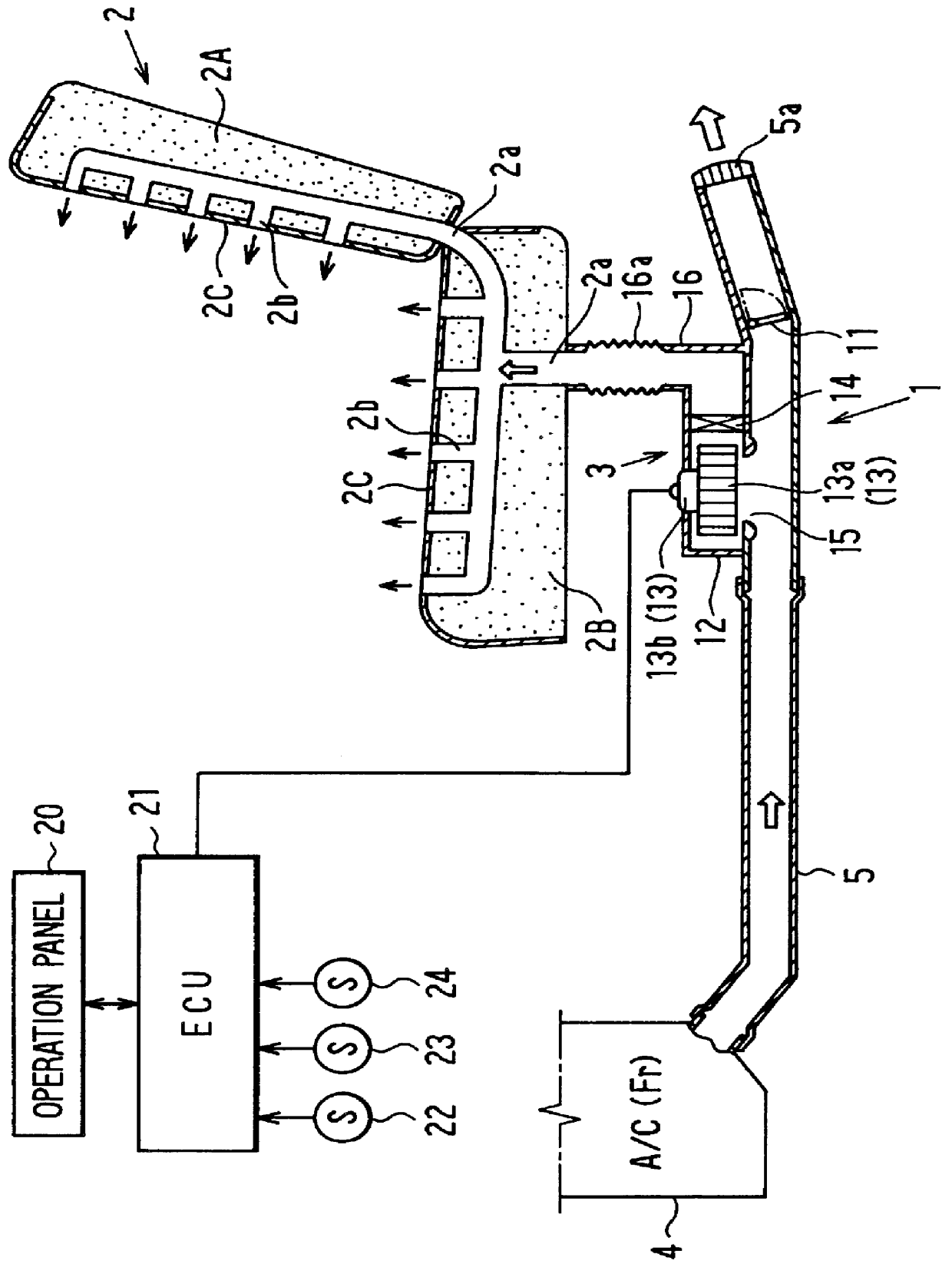
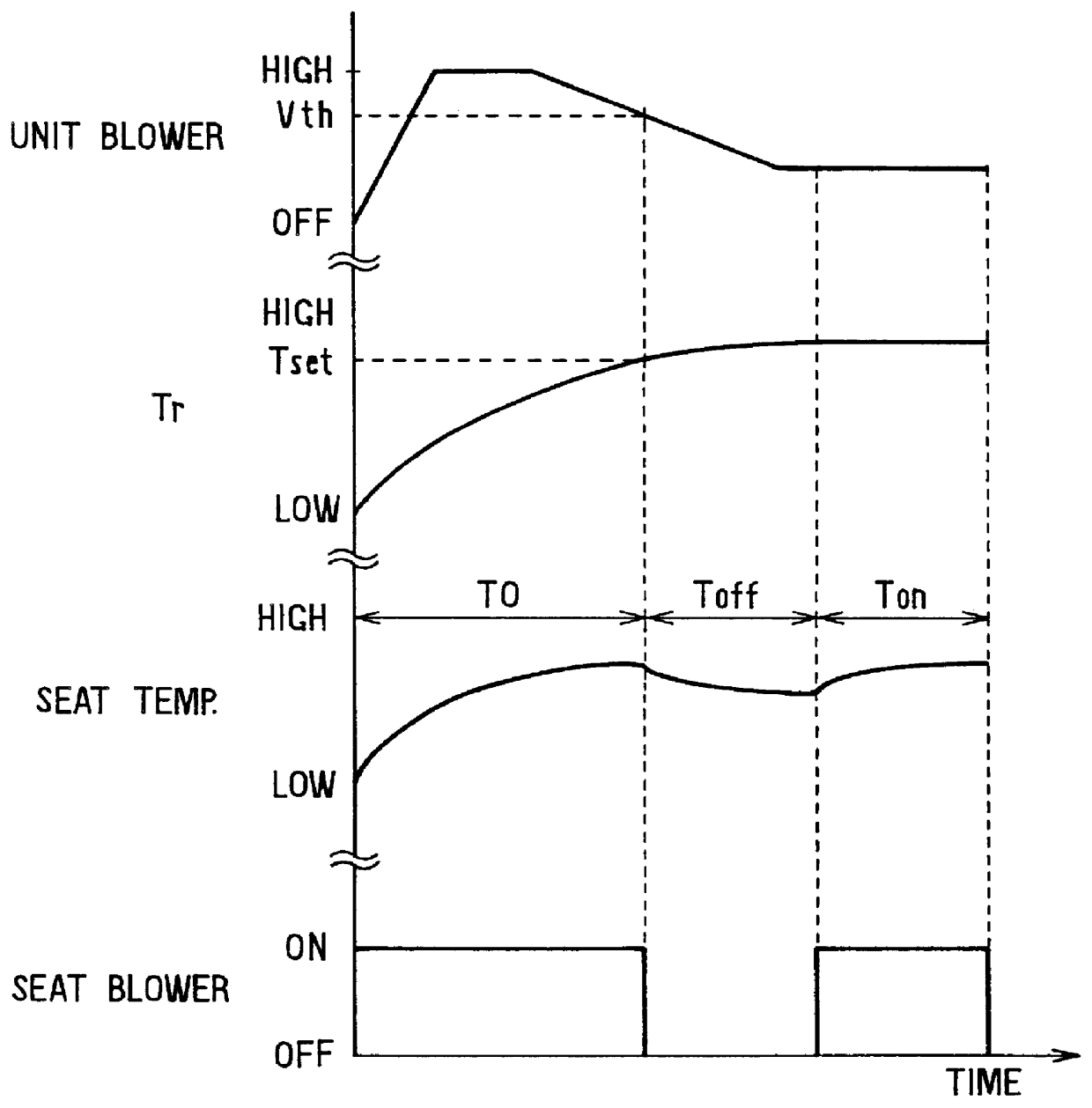
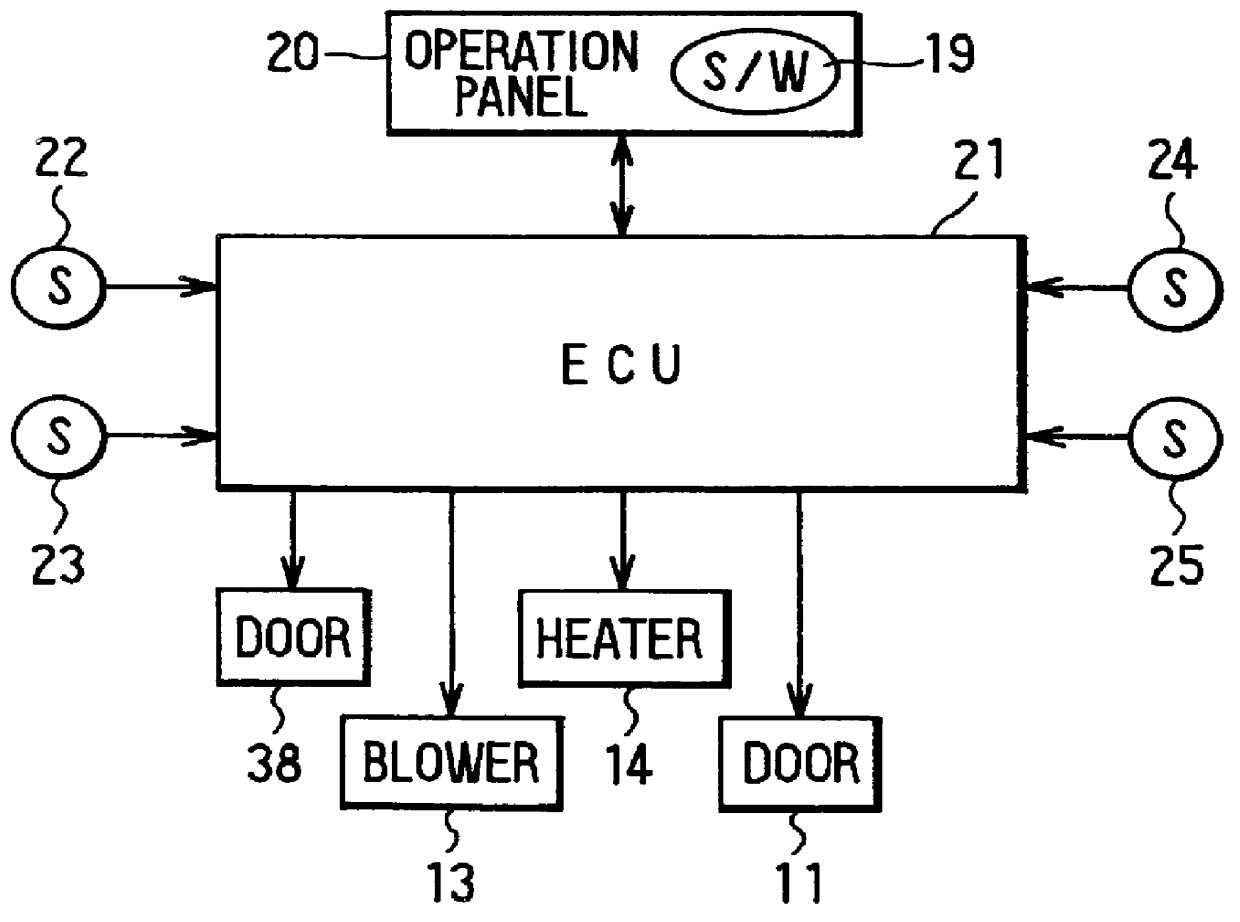
Air conditioning apparatus for vehicle seat
InactiveUS6105667ATemperature controlAuxillariesOther heat production devicesTemperature controlEngineering
An air conditioning apparatus for a vehicle seat includes a seat blower unit disposed in a lower side of the seat, and a seat duct for leading air from an air conditioning unit to the seat through the seat blower unit. In the air conditioning apparatus, it can be determined that heat load of a passenger compartment is decreased to a predetermined value based on an operation state of a unit blower of the air conditioning unit, and the seat blower is stopped when the heat load is decreased to the predetermined value. Further, the seat blower is turned on or off according to the heat load of the passenger compartment, so that temperature of the seat can be controlled within a predetermined range. On the other hand, even when the unit blower is stopped when a water temperature of a heating unit of the air conditioning unit is lower than a set temperature, the seat blower unit and an electrical heater disposed in the seat duct are operated so that air passing through the heating unit is heated by the electrical unit and is blown into the seat by the seat blower unit.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Method and apparatus for controlling temperature of a substrate
InactiveUS20060076109A1Easy to controlEasy temperature controlSleeve/socket jointsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A pedestal assembly and method for controlling temperature of a substrate during processing is provided. In one embodiment, the pedestal assembly includes an electrostatic chuck coupled to a metallic base. The electrostatic chuck includes at least one chucking electrode and metallic base includes at least two fluidly isolated conduit loops disposed therein. In another embodiment, the pedestal assembly includes a support member that is coupled to a base by a material layer. The material layer has at least two regions having different coefficients of thermal conductivity. In another embodiment, the support member is an electrostatic chuck. In further embodiments, a pedestal assembly has channels formed between the base and support member for providing cooling gas in proximity to the material layer to further control heat transfer between the support member and the base, thereby controlling the temperature profile of a substrate disposed on the support member.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
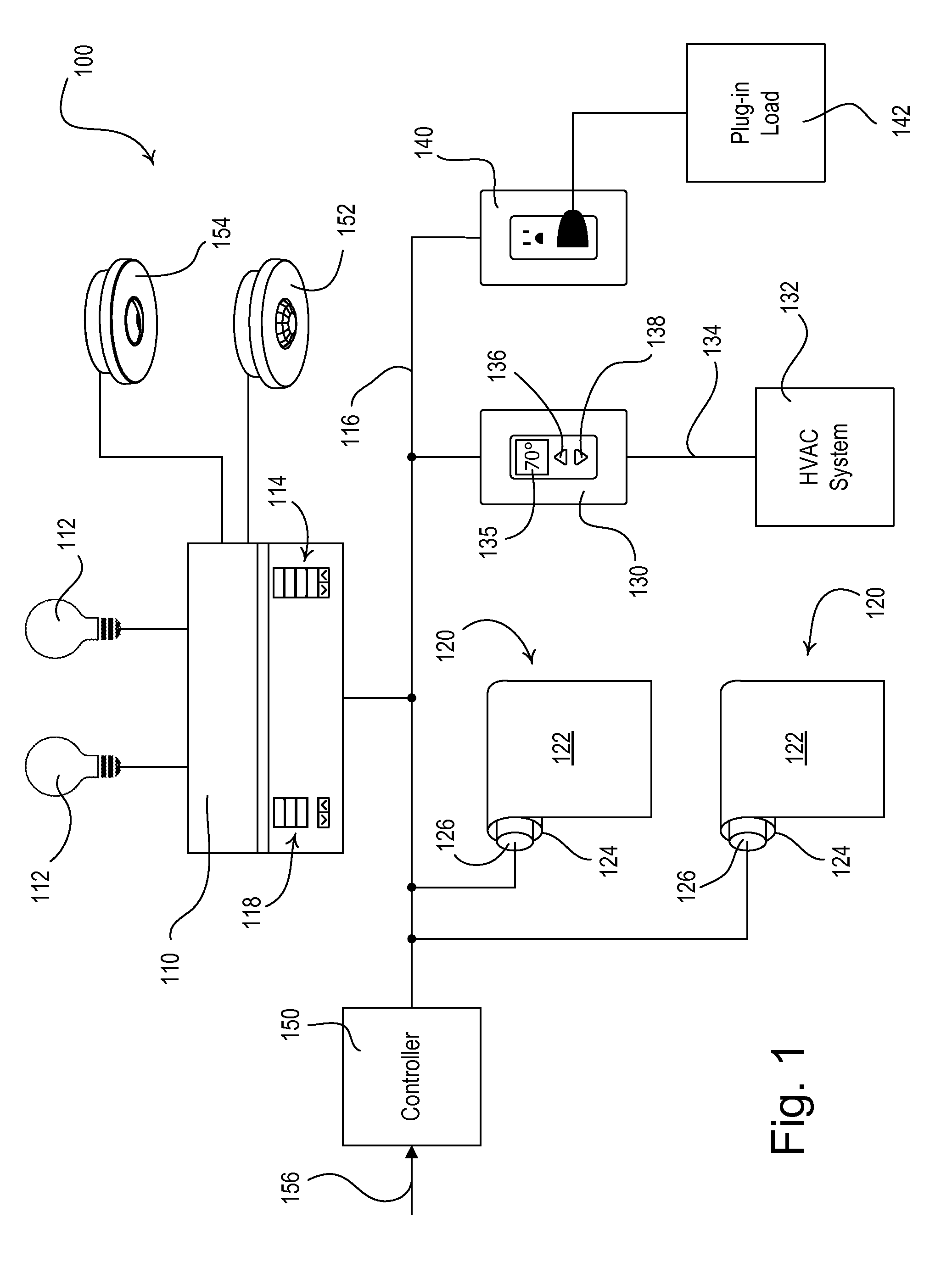
Dynamic keypad for controlling energy-savings modes of a load control system
ActiveUS8866343B2Reduce the amount requiredReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsTemperature controlUser input
A load control system for a building having a lighting load, a window, and a heating and cooling system comprises a lighting control device for controlling the amount of power delivered to the lighting load, a motorized window treatment comprising a window treatment fabric for covering the window, a temperature control device for controlling a setpoint temperature of the heating and cooling system to thus control a present temperature in the building, and a dynamic keypad comprising a visual display and operable to receive a user input. The dynamic keypad allows a user to select, adjust, and monitor a plurality of energy-savings modes of the load control system. For example, the dynamic keypad allows the user to enable and adjust a setback temperature of the temperature control device on-the-fly.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
Processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050042881A1Improve thermal conductivityShorten the timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermal conductivityTungsten
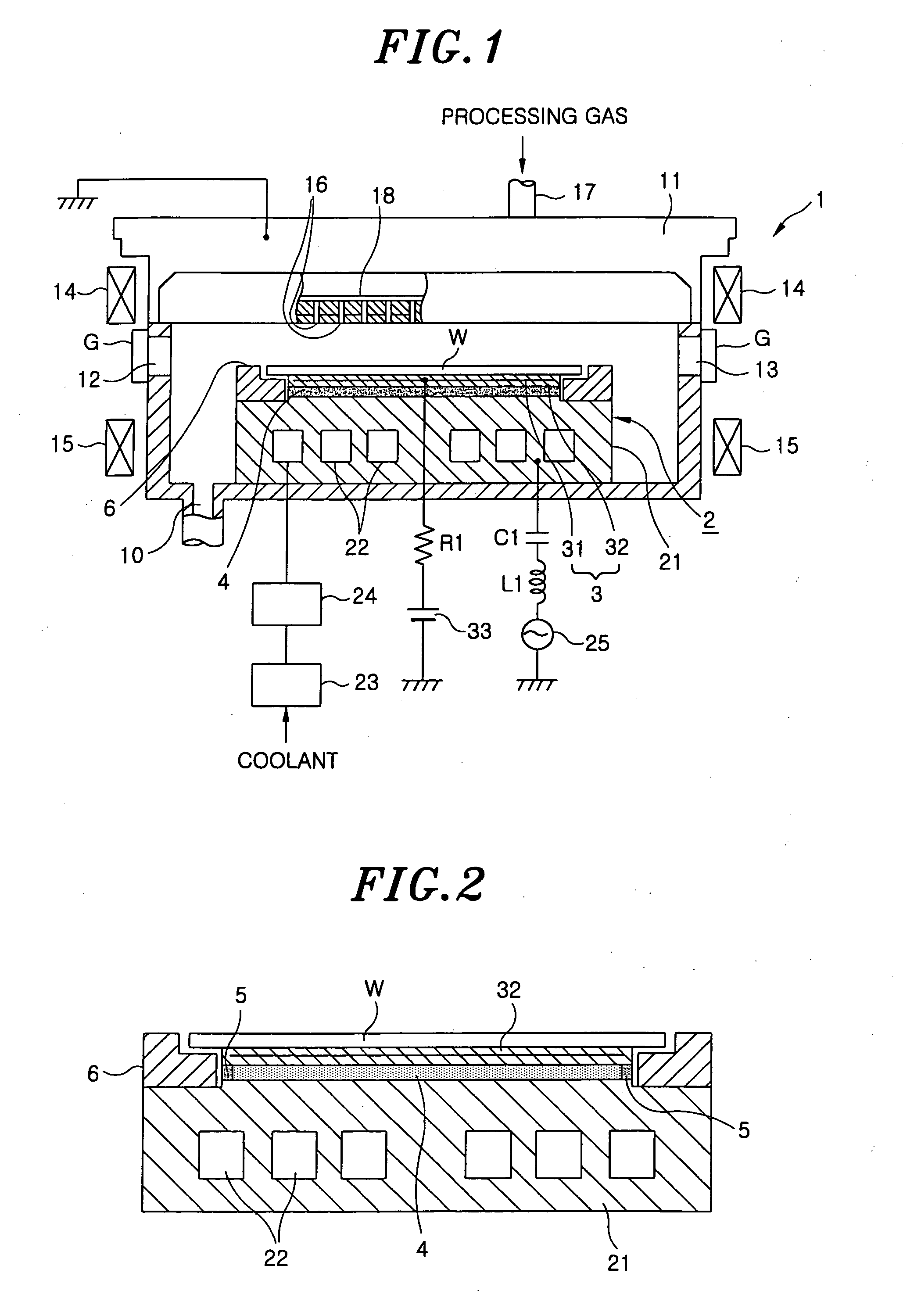
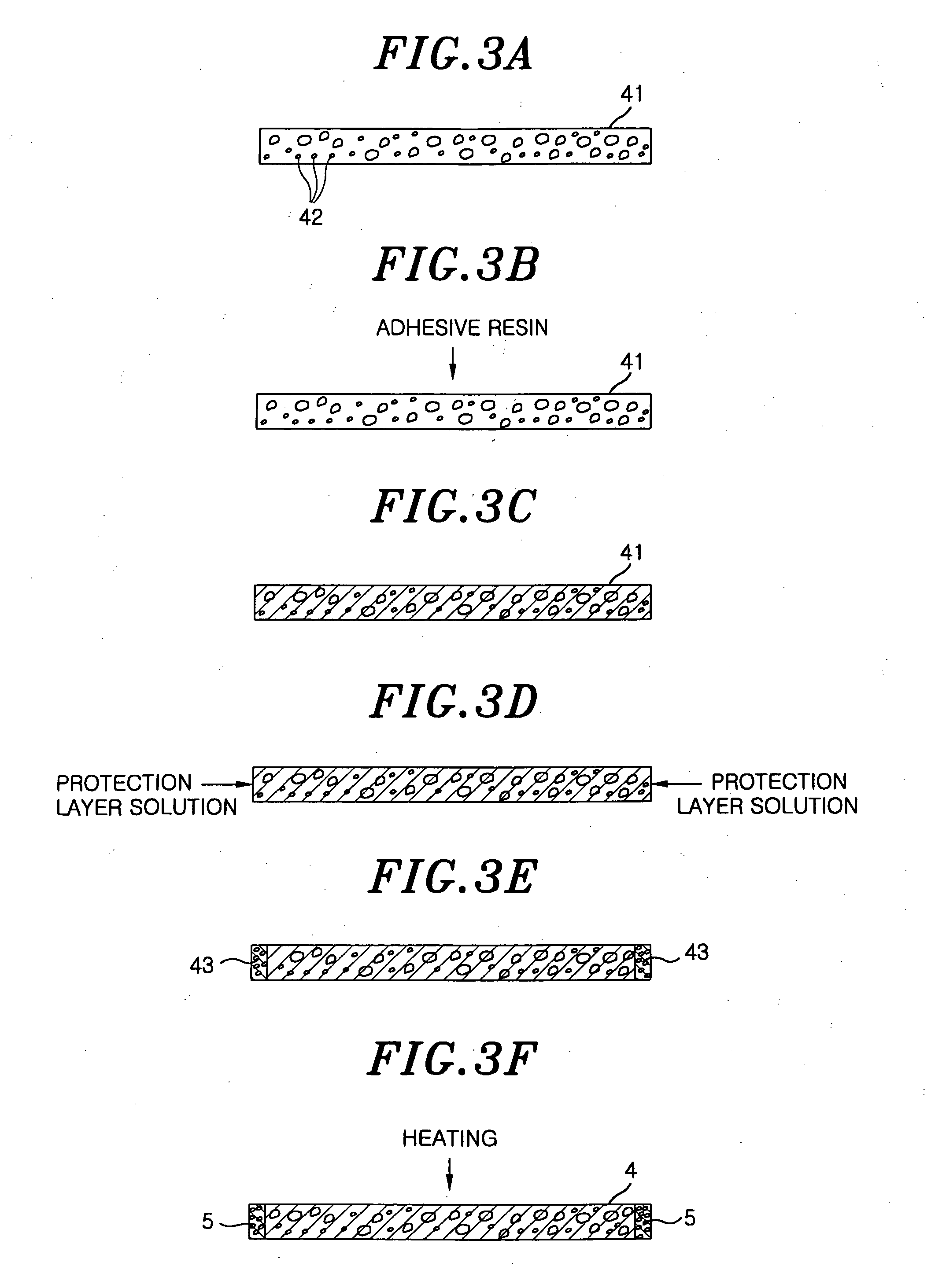
The time period during which a wafer is stabilized to a predetermined temperature by increasing a thermal conductivity of a junction layer for bonding an electrostatic chuck layer and a support together, and the deterioration of the junction layer that is caused by active species generated by plasma is suppressed. Between the electrostatic chuck layer formed by sintering together a chuck electrode made of tungsten and an insulating layer made of alumina and the support, made of aluminum, for supporting the electrostatic chuck layer, the junction layer is provided to bond the electrostatic chuck layer and the support together. The junction layer is formed by impregnating a porous ceramic with a silicone-based adhesive resin. Further, rubber or a heat shrink tube made of a fluoric resin such as PFA is provided as a soft coating member so as to coat a side circumferential surface of the junction layer and the side circumferential surfaces of the electrostatic chuck layer and the support come into a tight contact with the heat shrink tube or rubber.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for preparing polymer microporous foaming material by supercritical mould foaming
The invention provides a method for preparing a polymer microporous foaming material by supercritical mould foaming. The method comprises the following steps of: heating a foaming mould on a mould press to the foaming temperature; placing a polymer into the mould; closing the mould by using the mould press; sealing the mould; introducing supercritical fluid, which swells and diffuses to the polymer, into the mould; and opening the mould by using the mould press to release pressure and foam to obtain the polymer microporous foaming material. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that: the high-temperature and high-pressure supercritical fluid is used for swelling the polymer, so the moulding cycle is greatly shortened; the limit that only microporous foaming sheet material with lesser thickness can be manufactured in the prior art is broken through, so a polymer microporous foaming plate with greater thickness can be manufactured; when the mould is opened, the pressure-releasing speed is high and the foaming pore core-forming speed is high, so the formed microporous foaming material has smaller foaming pores, higher pore density and more excellent performance; and multiple layers of moulds can be placed on one mould press, so the method is suitable for industrialized scale production.
Owner:常州福源科技新材料有限公司
Devices and methods for the performance of miniaturized in vitro amplification assays
InactiveUS20040259237A1Temperature controlEfficient use ofBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAssayBiomedical engineering
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. The invention specifically provides devices and methods for performing miniaturized in vitro amplification assays such as the polymerase chain reaction. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing PCR are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
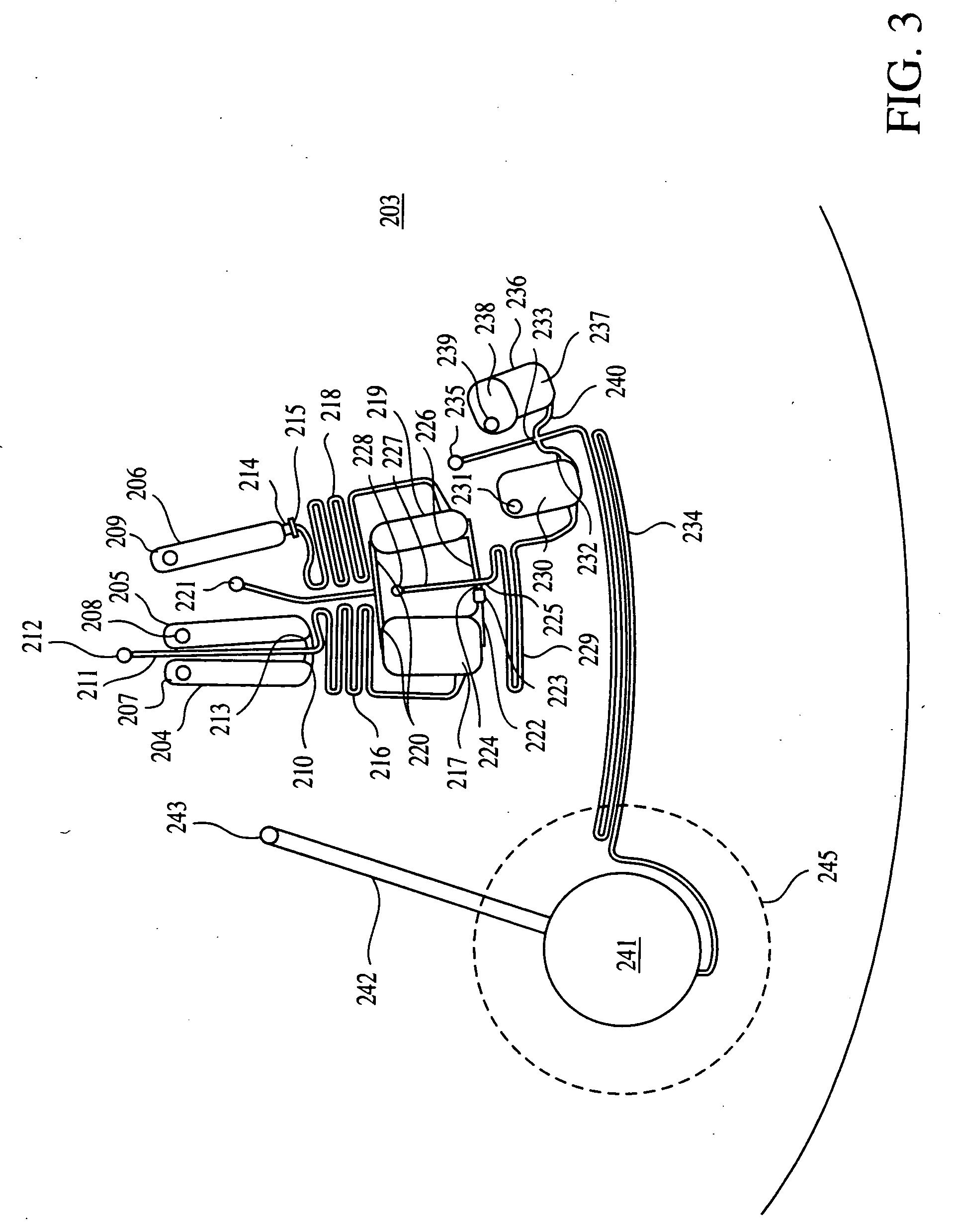
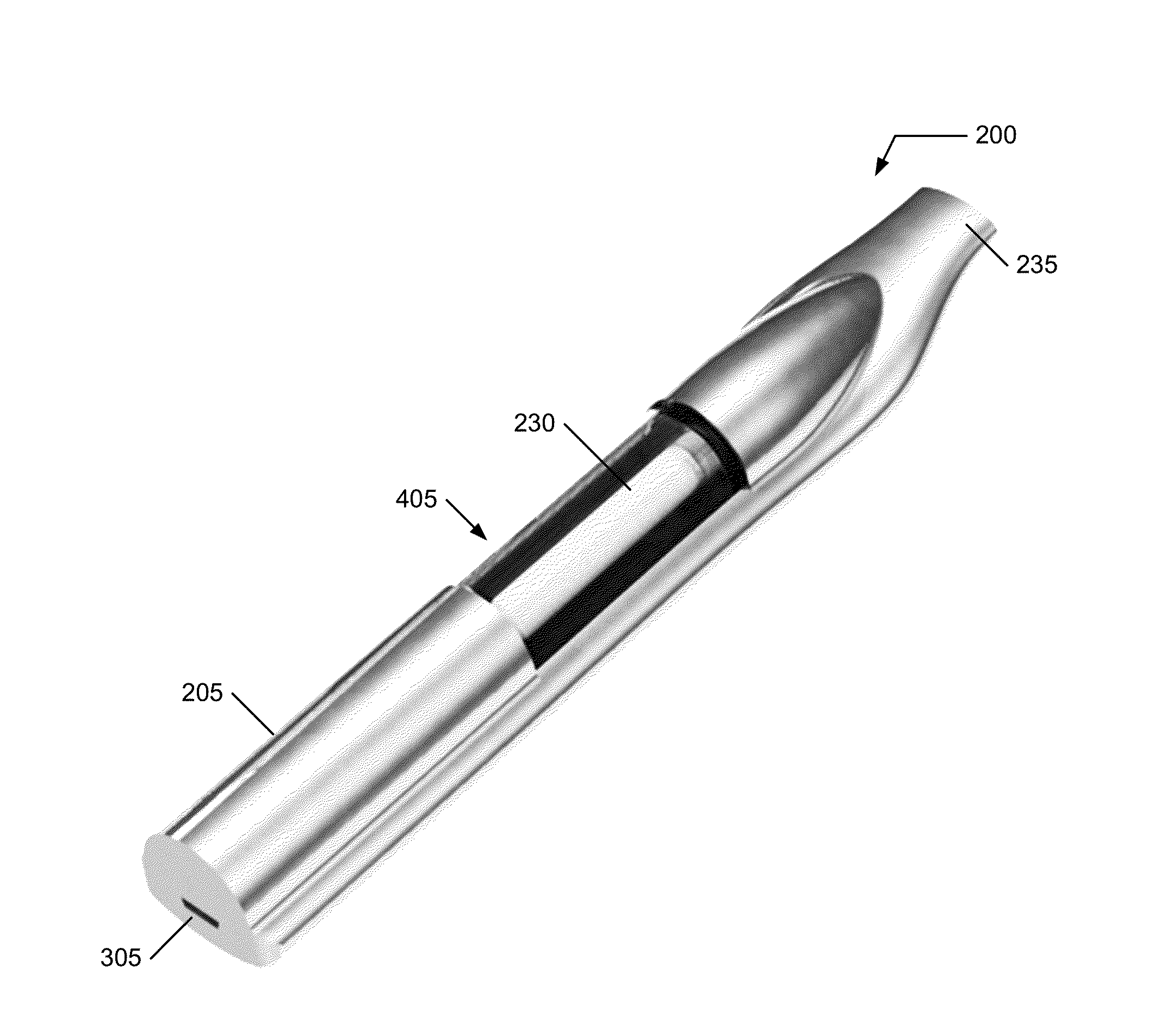
Vaporizing reservoir
InactiveUS20160150828A1Less-prone to leakingEasy to change out flavorSpace heating and ventilationTobacco devicesElectricityEngineering
A vaporizing reservoir including a containment vessel having a first shaft port exposed to ambient and one or more sidewalls defining a body portion having an interior cavity and a vaporizing portion communicated to the interior cavity; an inductive coil disposed within the vaporizing portion, the inductive coil electrically disconnected outside of the containment vessel and configured for inductive heating; and an air shaft communicated to the vaporizing portion and extending to the first shaft port. Fluid or solid material may be present in the interior cavity for vaporization. For fluid material, a wick may be included with the inductive coil to facilitate communication of the material to the inductive coil. An exterior inductive coil heats the inductive coil within the vaporizing portion and vaporizes the material communicated to the interior inductive coil. Vapor from the heated interior inductive coil is extracted through the air shaft.
Owner:GOLDSTEIN GABRIEL MARC
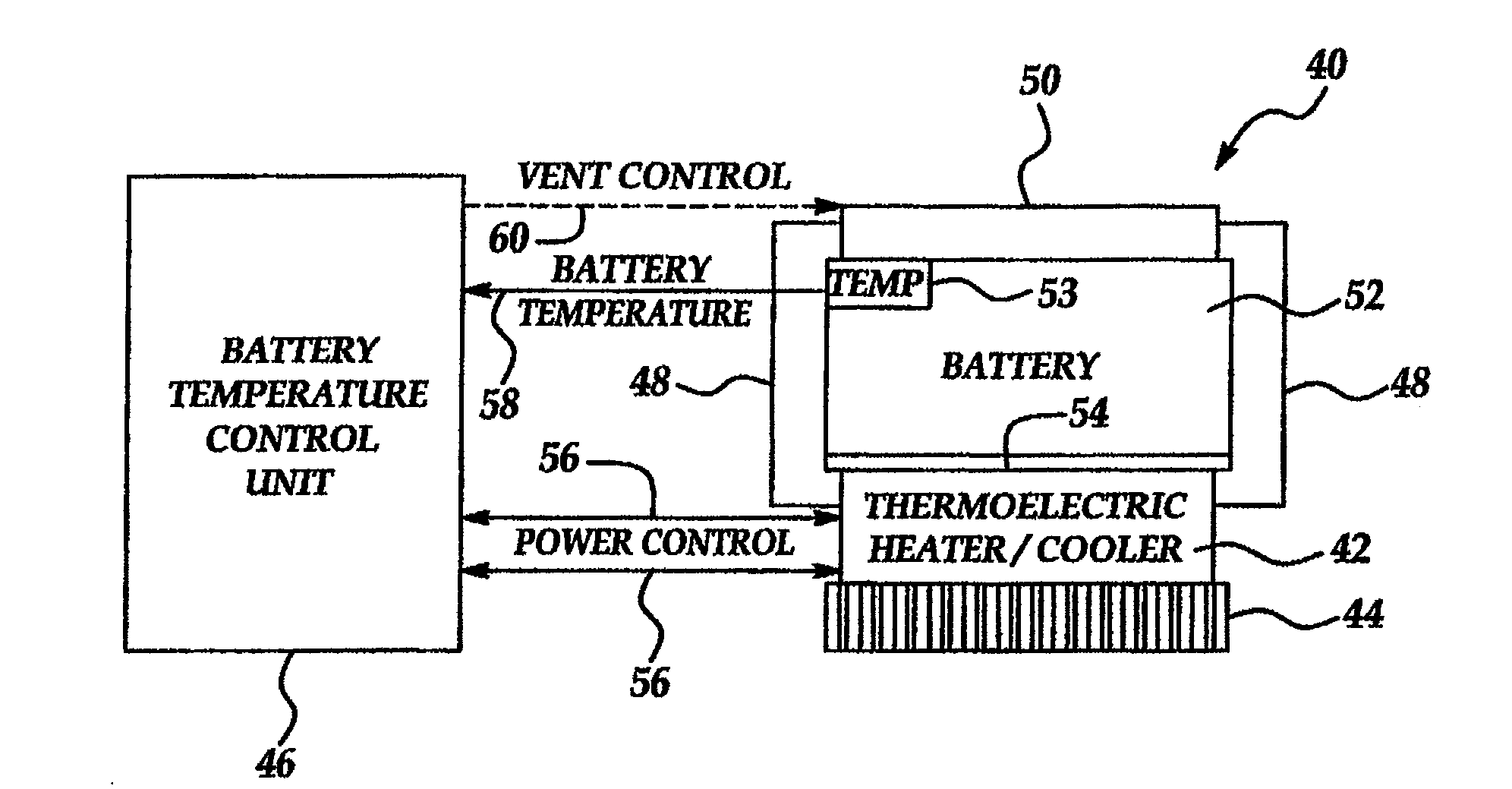
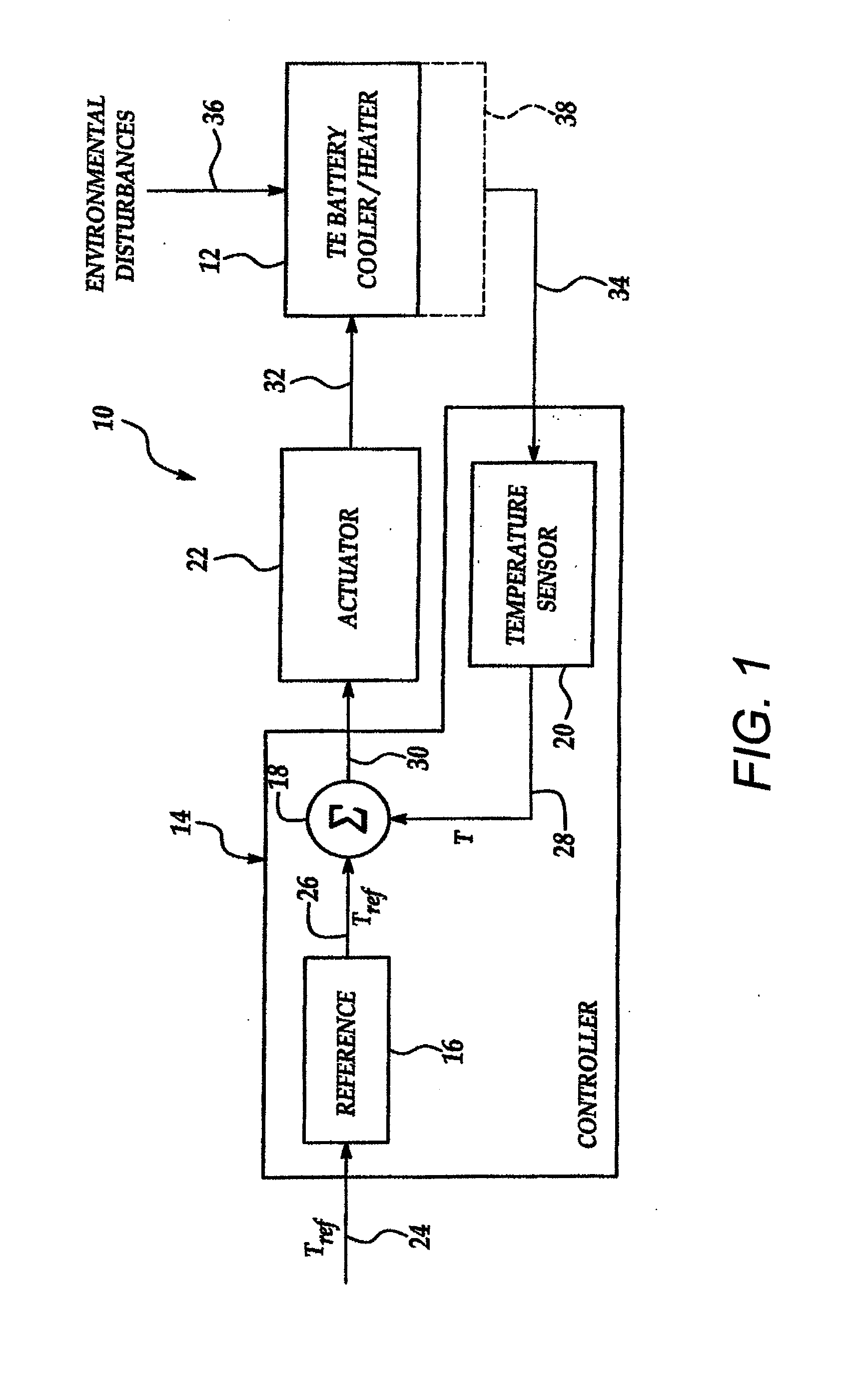
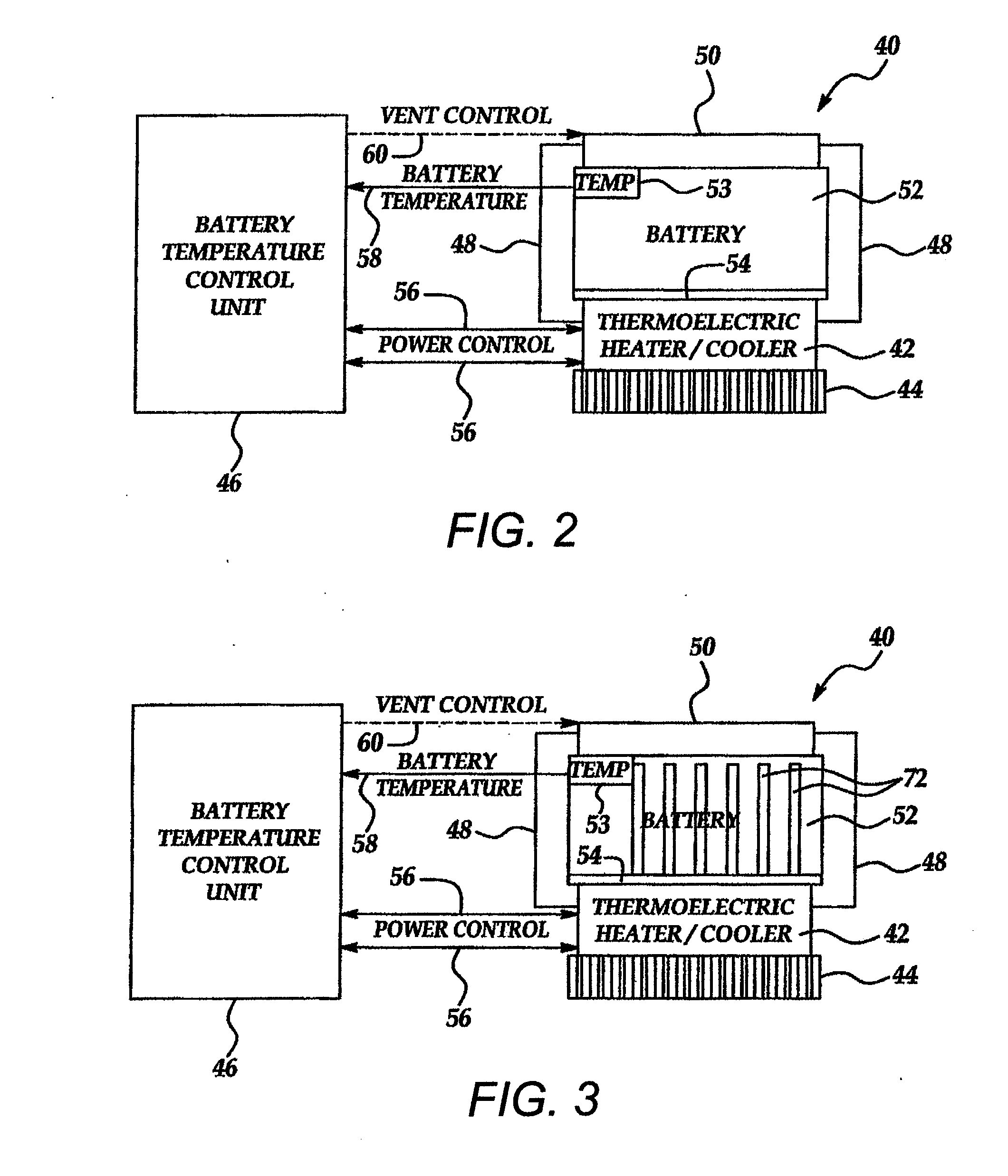
Thermoelectric methods to control temperature of batteries
ActiveUS20080311466A1Temperature controlCell temperature controlElectrical and Electronics engineeringThermoelectric generator
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Process for producing a syngas
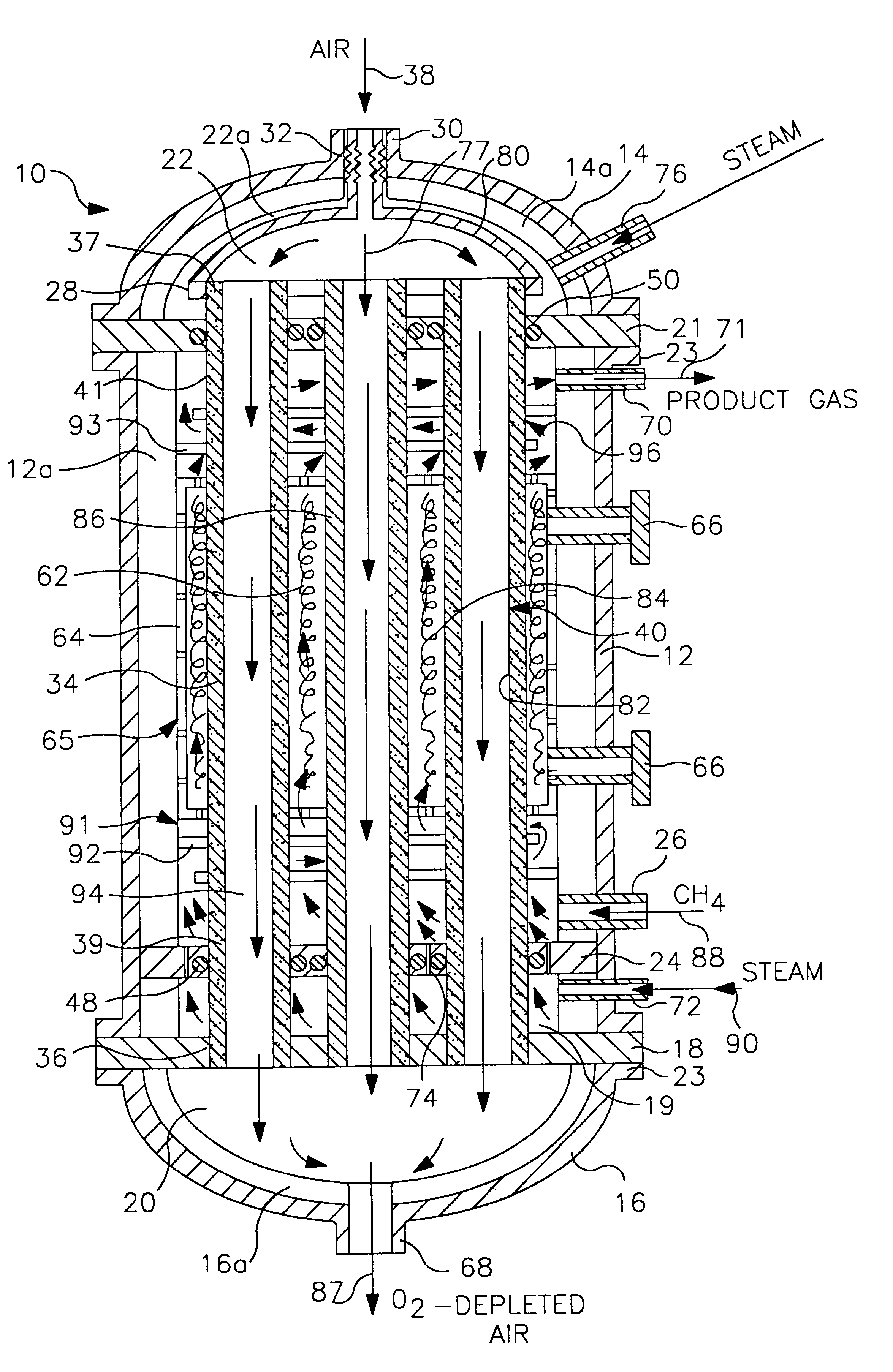
InactiveUS6402988B1Minimize the temperatures experienced by sealsMinimize pressure differenceCatalytic gas-gas reactionHydrogenSyngasReactor design
An exothermic reaction and an endothermic reaction are thermally combined in a reactor having at least one oxygen selective ion transport membrane that provides the exothermic reaction with oxygen from an oxygen-containing gas such as air. The thermal requirements of the endothermic reaction are satisfied by the exothermic reaction. Dependent on the reactor design employed, the exothermic and endothermic reactions may be gaseously combined.
Owner:PRAXAIR TECH INC +1
Methods and Apparatus for Adjusting Blood Circulation
ActiveUS20080132816A1Increase blood flowSpeed up the flowDiagnosticsChiropractic devicesPositive pressureCombined use
A method and device for increasing blood flow by applying positive pressure to extremities of a mammal and / or controlling the temperature of the mammal. The device includes one or more collapsible and pliant body elements capable of expanding and flexibly applying pressurized compression forces to the extremity of the mammal by attaching one or more pressure-applying gas plenums as close to the extremity as possibly. The flexible extremity device can be used independently or can be used in conjunction with thermal pads disposed to the one or more collapsible and pliant body elements. Alternatively, the one or more collapsible and pliant body elements can be manufactured into thermal pads.
Owner:AVACORE TECH
Shipping box system with multiple insulation layers
InactiveUS9429350B2Constant temperature range during shipmentTemperature controlLighting and heating apparatusCooling fluid circulationTemperature controlInsulation layer
The present invention relates to a box system for keeping medicine and other payloads at a desired temperature for prolonged periods of time. The system generally includes three or more insulating materials between a refrigerant and the payload so that the payload is not cold-shocked by the refrigerant but instead maintains a desired temperature range during shipment. An advantage of the box system of certain embodiments of the present disclosure is that the system allows a shipper to use a temperature controlled system that is effective in controlling temperature without the need for any expensive phase change materials. A box having foldable tabs for securing the materials to each other is also disclosed herein.
Owner:EFP
Method and apparatus for controlling temperature of a substrate
InactiveUS20070139856A1Easy temperature controlTemperature controlSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMechanical engineeringMetal
A pedestal assembly and method for controlling temperature of a substrate during processing is provided. In one embodiment, the pedestal assembly includes an electrostatic chuck coupled to a metallic base. The electrostatic chuck includes at least one chucking electrode and metallic base includes at least two fluidly isolated conduit loops disposed therein. In another embodiment, the pedestal assembly includes a support member that is coupled to a base by a material layer. The material layer has at least two regions having different coefficients of thermal conductivity. In another embodiment, the support member is an electrostatic chuck. In further embodiments, a pedestal assembly has channels formed between the base and support member for providing cooling gas in proximity to the material layer to further control heat transfer between the support member and the base, thereby controlling the temperature profile of a substrate disposed on the support member.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Automated retail facility
ActiveUS10181113B2Improved storage and safety featureTemperature controlDigital data processing detailsCoin-freed apparatus detailsPaymentHand held
An automated retail facility and system with accompanying methods comprising customer interfacing modules, payment receiving modules, product storage and distribution modules, and computer components in communication with device actors that automate connected components of the facility and system in an Internet of Things configuration. The configuration advantageously allows for remote operation of that facility, while maintaining required levels of customer service and supervisory actions within the facility, as needed. To service the system remotely or on location, a handheld inventory management device and inventory management vehicle are provided. To enhance available services, an automatic package receiver / distributor service module is integrated in some embodiments.
Owner:SMARTMART INC
Load Control System That Operates in an Energy-Savings Mode When an Electric Vehicle Charger is Charging a Vehicle
ActiveUS20120001487A1Decrease power consumptionDecrease amount of powerMechanical apparatusMetering/charging/biilling arrangementsElectric vehicleOperating energy
A load control system for a building having a lighting load, a window, a heating and cooling system, and an electric vehicle charger for charging a vehicle (e.g., an electric or hybrid vehicle) operates in an energy-savings mode to reduce the total power consumption of the load control system when the vehicle charger is presently charging the vehicle. The load control system may comprise a lighting control device for controlling the intensity of the lighting load, a daylight control device for adjusting the amount of natural light admitted through the window, and a temperature control device for controlling a setpoint temperature of the heating and cooling system to thus control a present temperature in the building. When the vehicle charger is presently charging the vehicle, the load control system automatically controls the lighting control device, the daylight control device, and the temperature control device to decrease the total power consumption of the load control system.
Owner:LUTRON TECH CO LLC
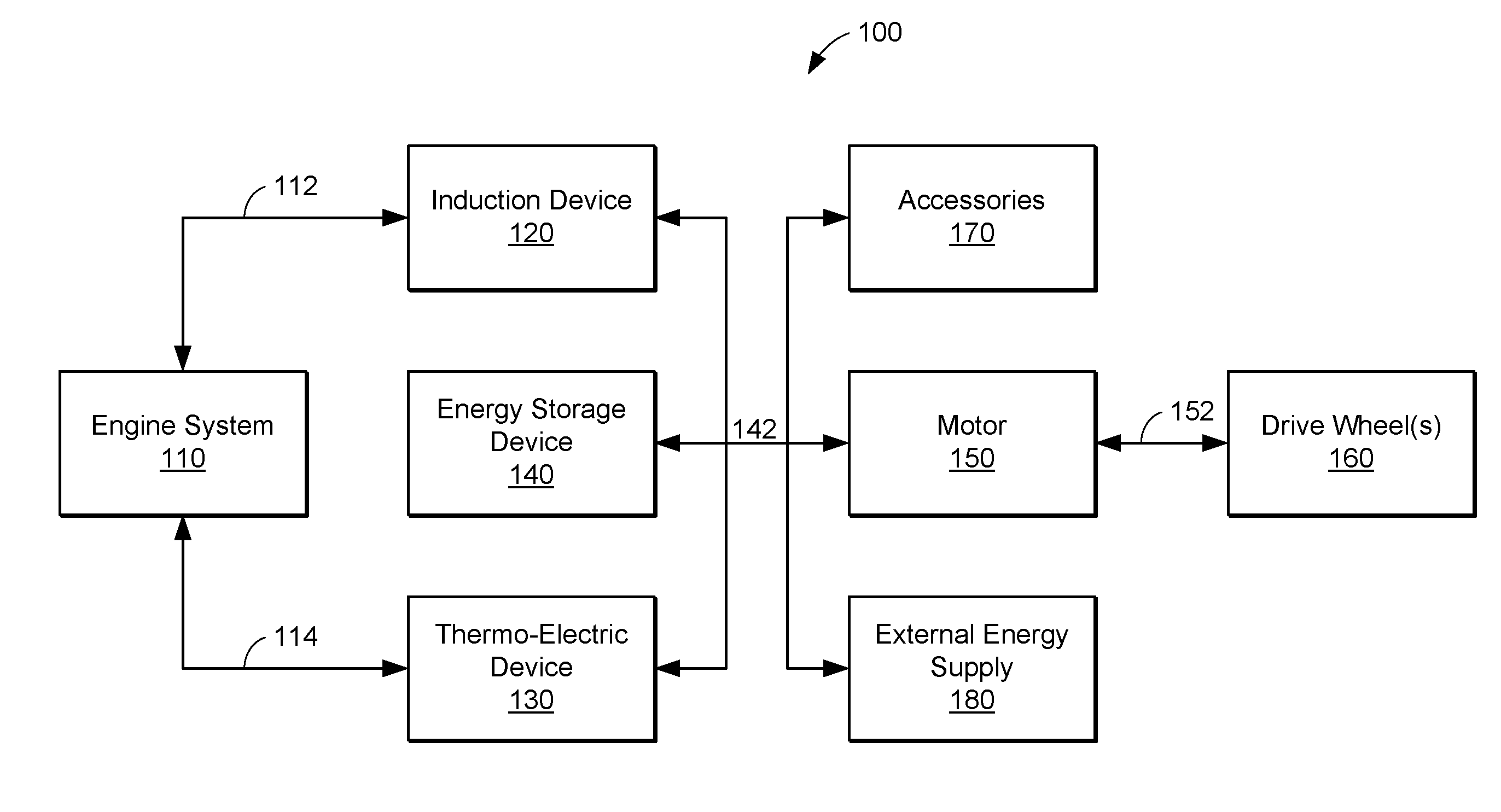
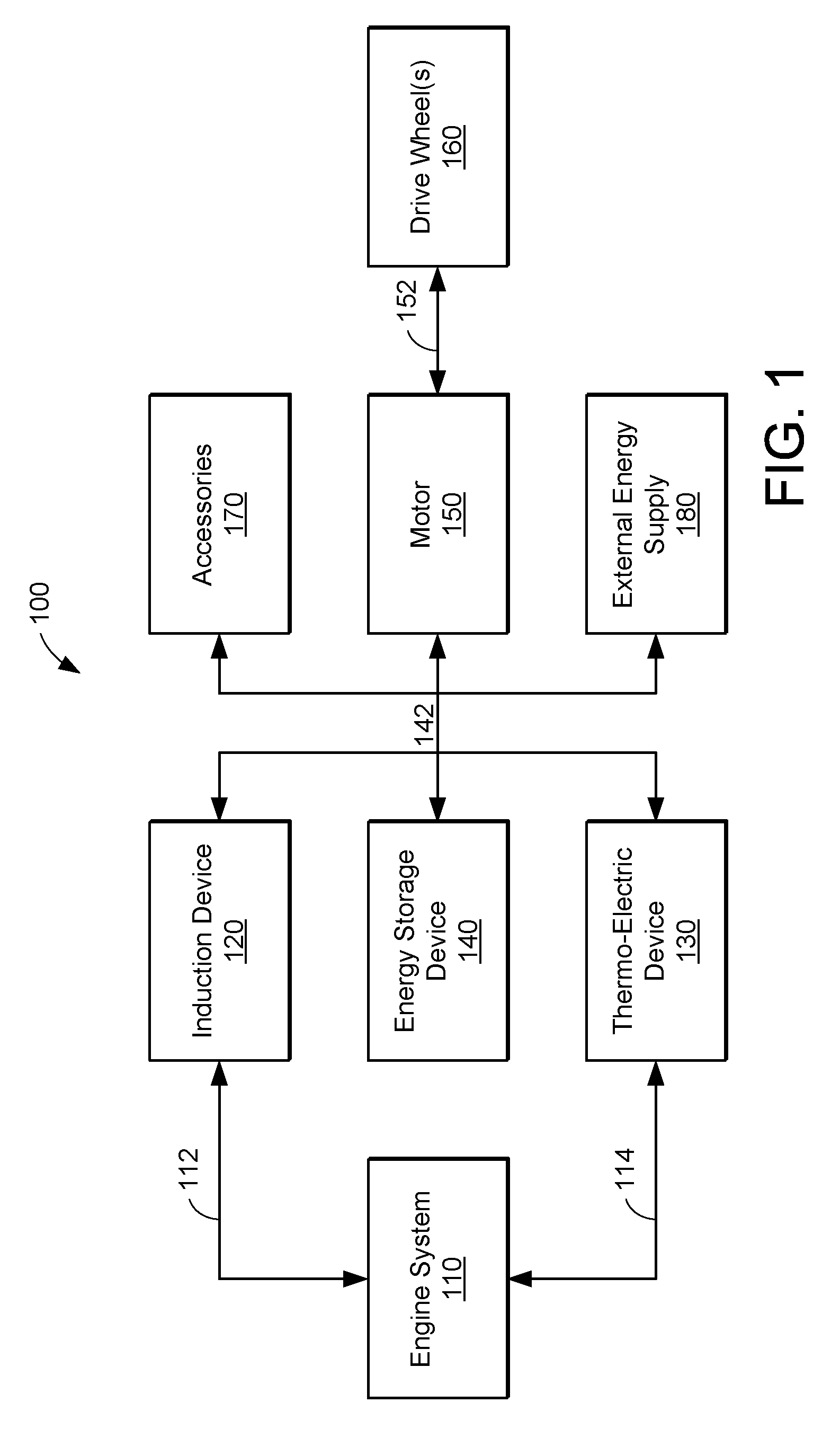
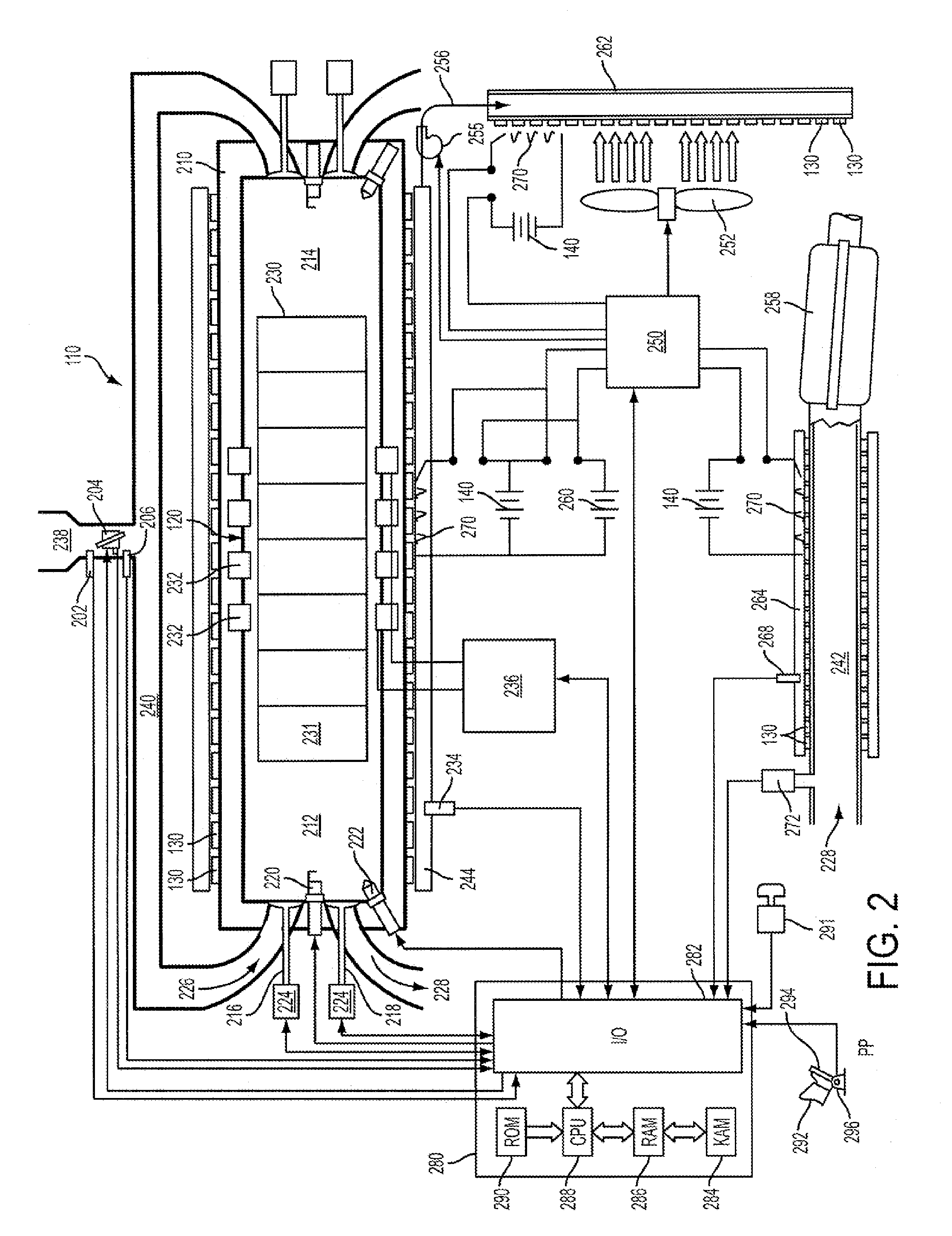
Engine system having improved efficiency
InactiveUS7426910B2Low efficiencyReduce weightInternal combustion piston enginesThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectControl systemInternal combustion engine
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Radiating and cooling device for power battery
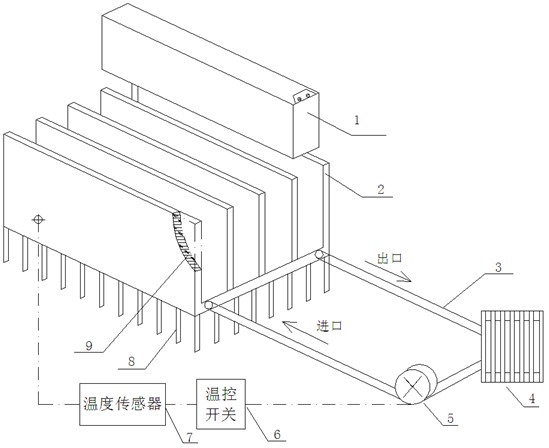
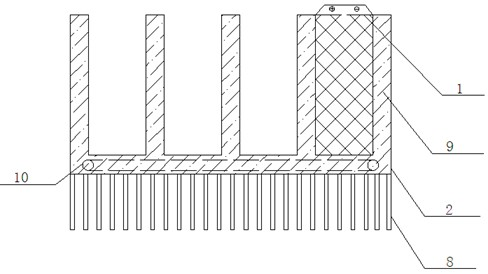
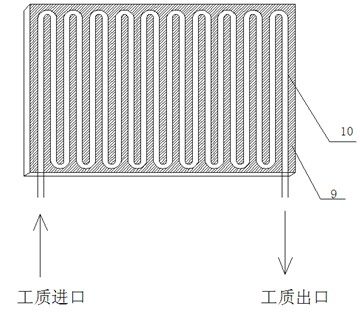
InactiveCN102664292ATemperature controlImprove energy efficiencySecondary cellsTemperature controlPower battery
The invention relates to a radiating and cooling device for a power battery. An aluminum hollow cold plate shell is in the form of a radiating fin; the inside of the shell is hollow; a plurality of groove spaces are formed on the aluminum shell; power batteries can be embedded into grooves; the aluminum hollow cold plate shell is filled with a phase change material; radiating fins are arranged on an aluminum hollow cold plate shell bottom plate; a snakelike copper tube is arranged at the bottom of an aluminum shell cavity, and is contacted with the phase change material; a liquid cooling working medium is introduced into the snakelike copper tube; the snakelike copper tube, a pump and an external heat exchanger are connected in series, so that an active liquid cooling system is formed; a temperature sensor is arranged on the surface of the power battery; and a temperature switch is connected in series with a pump body power supply. The flow of the cooling working medium can be adjusted according to different requirements of battery temperature control; the using amount of a metal is reduced by adding the phase change material on the premise of ensuring the battery radiating effect, so that the cost of a battery radiating device is reduced effectively; and the requirements of different power batteries are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Systems and methods for cooling data centers and other electronic equipment
InactiveUS20110195652A1Control humidityTemperature controlDucting arrangementsLighting and heating apparatusControl systemElectronic equipment
Temperature, humidity, and pressure control systems and methods for enclosed spaces, including data centers. In some embodiments, the rotational frequency of the air supply fans is controlled based on a pressure associated with the enclosed space. In some embodiments, the rotational frequency of the air supply fans is controlled based on a pressure differential between an inlet region and an exhaust region within the enclosed space. In some embodiments, air within the inlet region is segregated from air within the exhaust region. In some embodiments, the cooling capacity of the cooling equipment is controlled responsive to a temperature associated with the enclosed space. In some embodiments, the cooling capacity is controlled based on a temperature associated with the inlet region of the enclosed space. In some embodiments, the humidity within the enclosed space is controlled.
Owner:IT AIRE +2
Apparatus and method of temperature conrol during cleaving processes of thick film materials
InactiveUS20080188011A1Improve utilityCost reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectric discharge tubesFilm materialEngineering
An apparatus for temperature control of manufacture of thick film materials includes a stage comprising a planar surface for supporting a bulk material to be implanted and subsequently cleaved. The bulk material has a surface region, a side region, and a bottom region which provides a volume of material and defines a length between the bottom region and the surface region. The apparatus further includes a mechanical clamp device adapted to engage the bottom region to the planar surface of the stage such that the bulk material is in physical contact with the planar surface for thermal energy to transfer through an interface region between the bulk material and the stage while the surface region is substantially exposed. Additionally, the apparatus includes a sensor device configured to measure a temperature value of the surface region and generate an input data. The apparatus further includes an implant device configured to perform implantation of a plurality of particles through one or more portions of the surface region of the bulk material and a controller configured to receive and process the input data to increase and / or decrease the temperature value of the surface region through at least the interface region between the planar surface of the stage and the bottom region of the bulk material.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com