Patents
Literature
704results about How to "Efficient heat transfer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
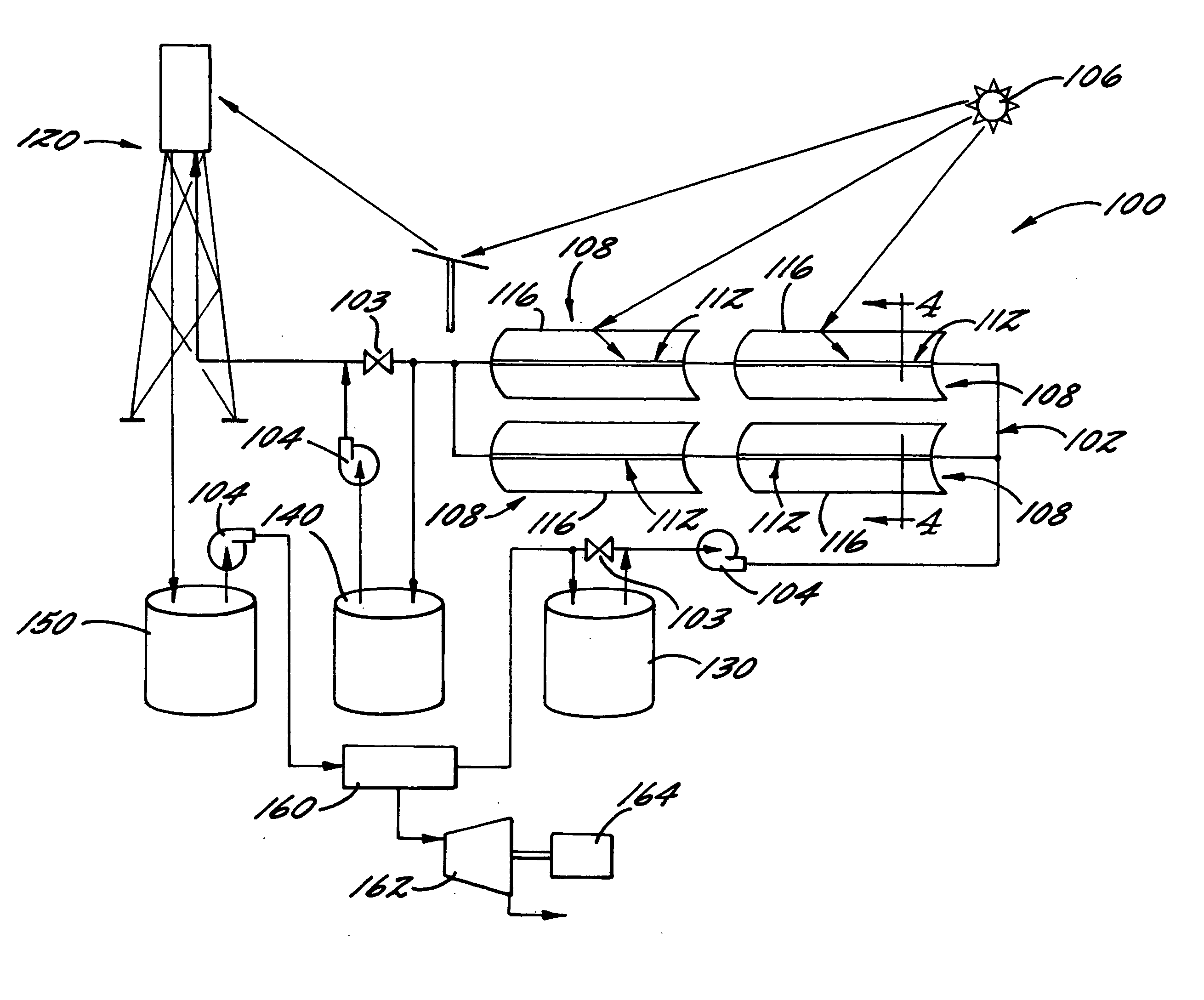
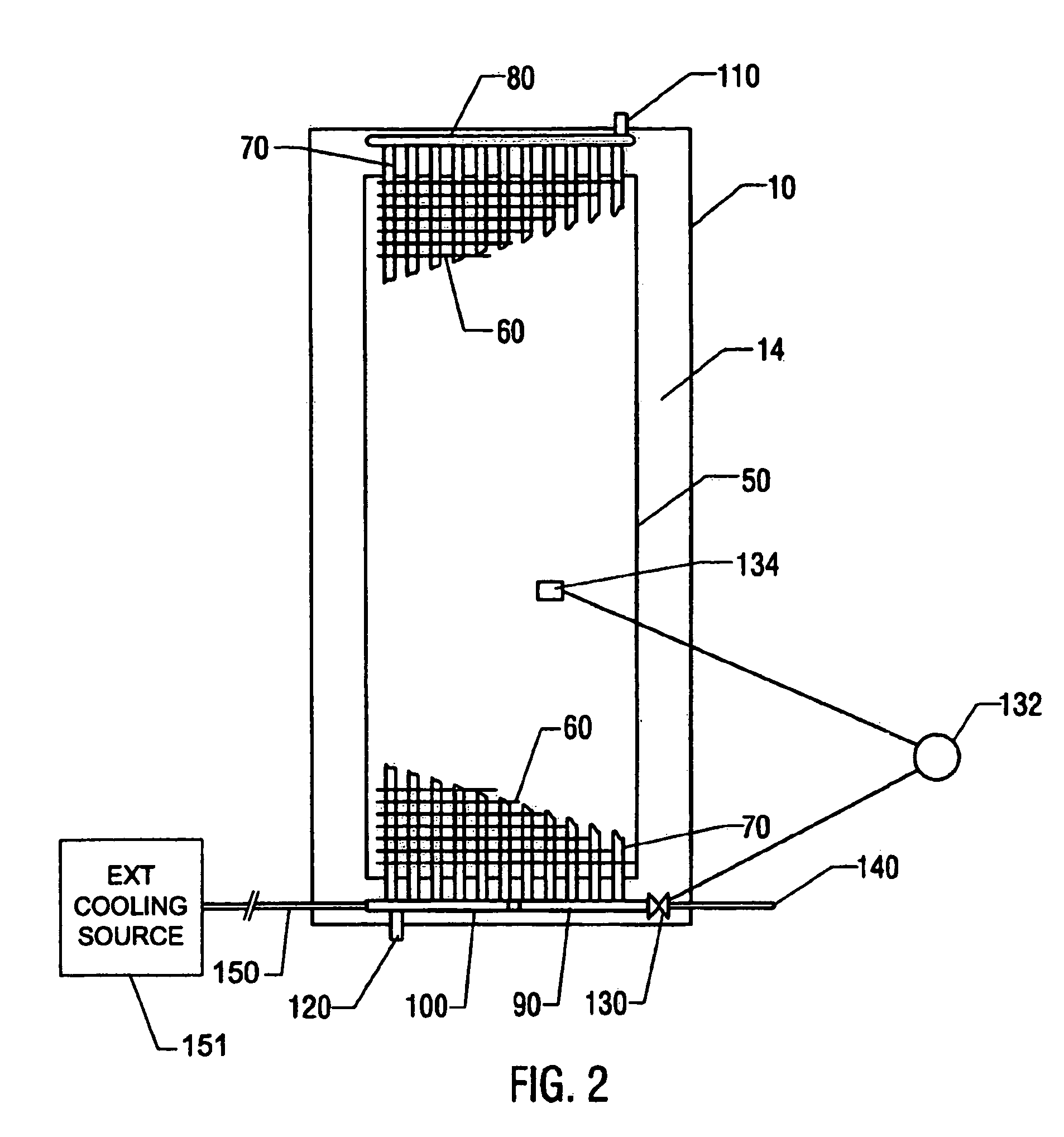
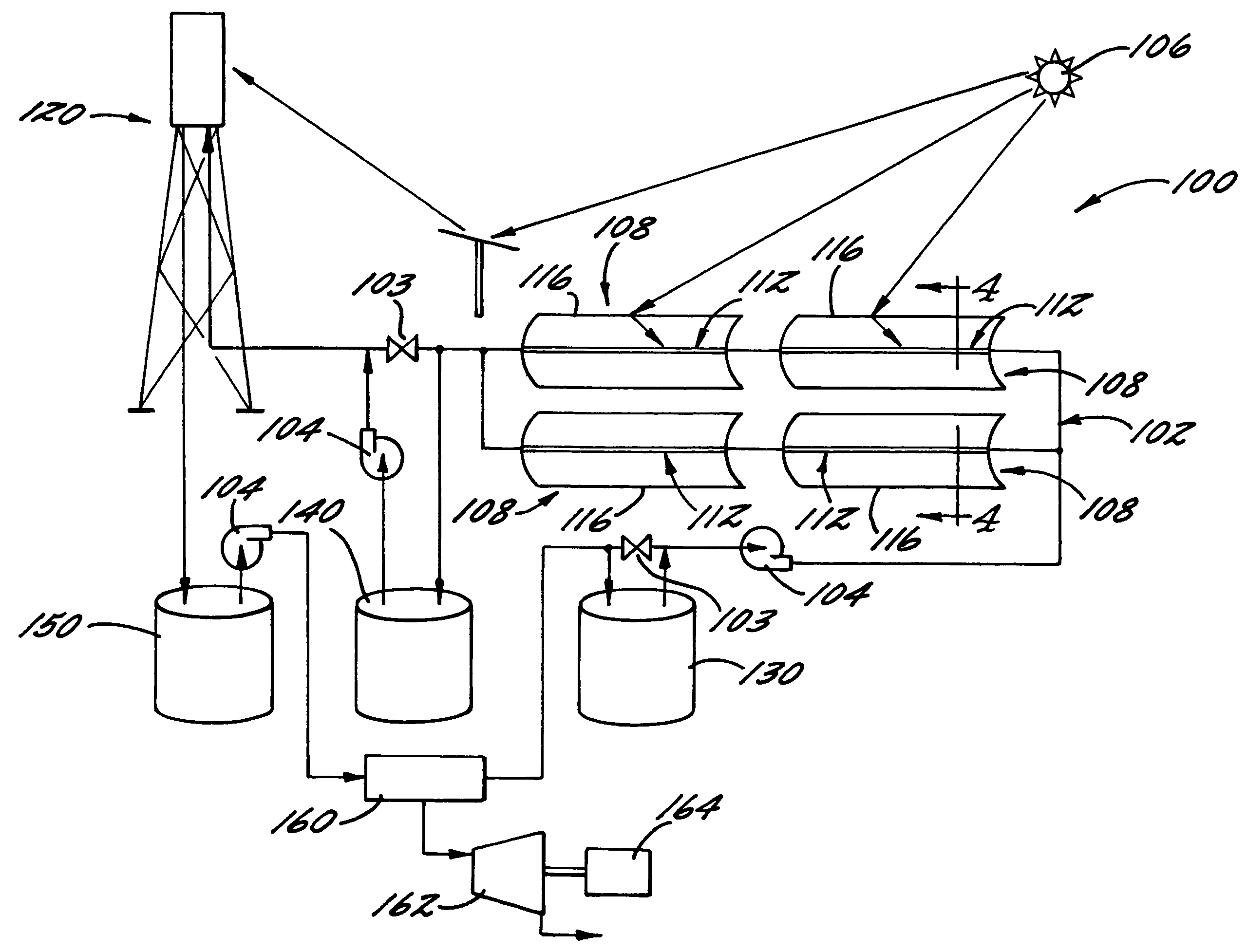
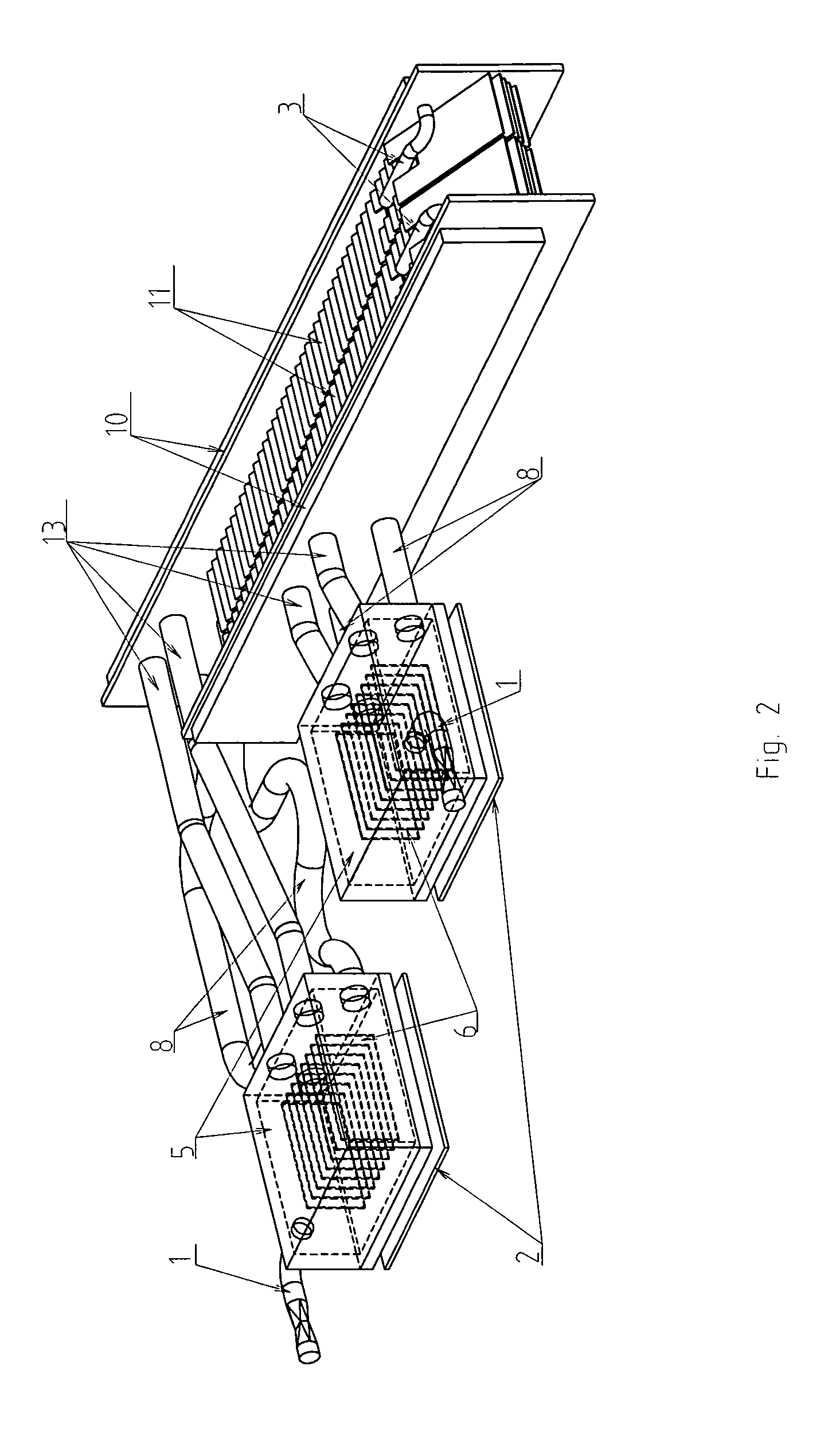
Solar power system and method for power generation
InactiveUS20050126170A1Efficient heat transferEfficient heatingSolar heating energyAuxillary drivesElectricityEngineering
A solar-powered power generation system and an associated method are provided. The system includes at least one trough solar absorption device for heating a heat transfer fluid to a first temperature, and at least one tower solar absorption device for further heating the transfer fluid to a second temperature. Thus, the generation system can efficiently heat the transfer fluid to high temperatures. Subsequently, the heated fluid can be used, e.g., to generate steam and / or electricity.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP +2
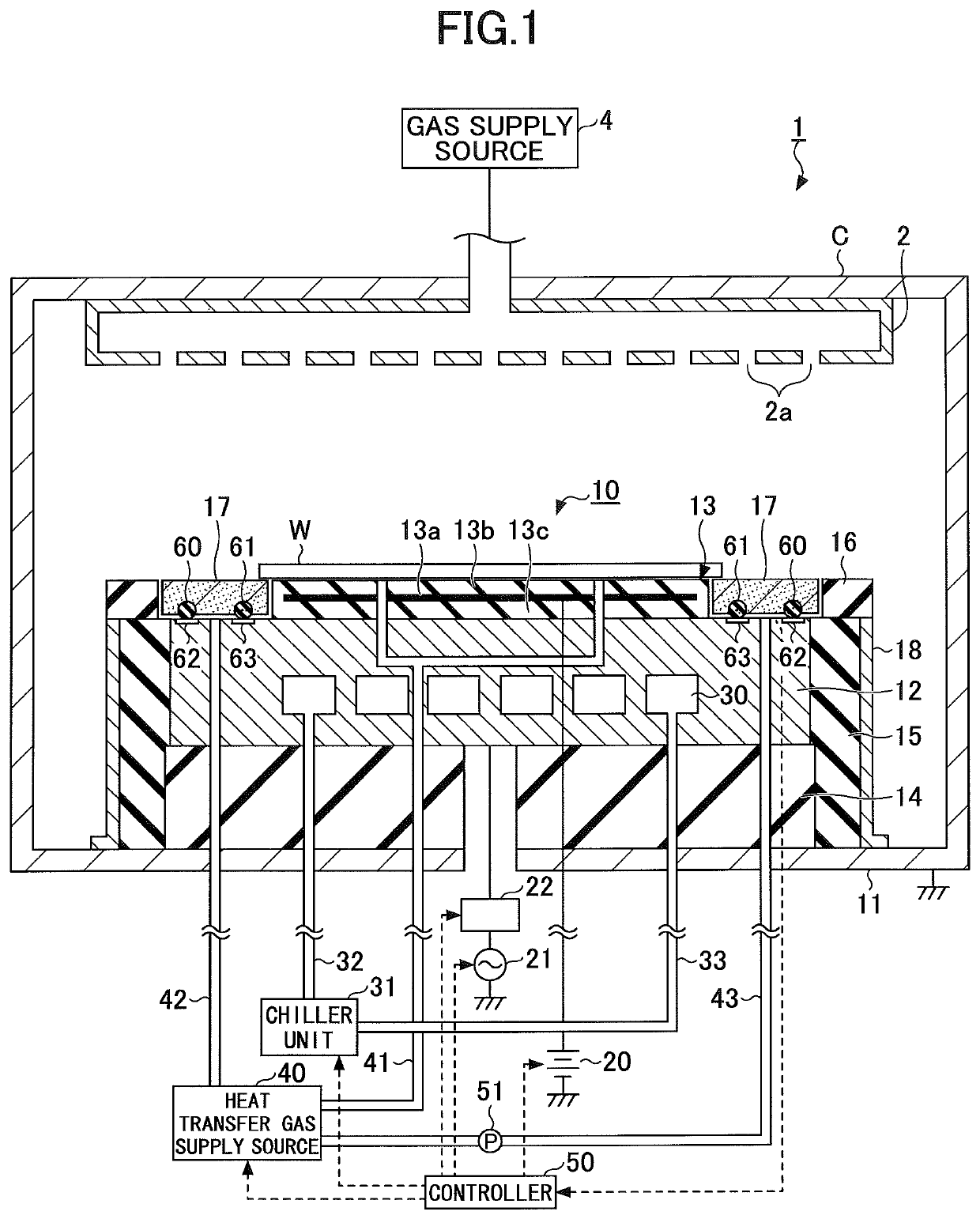
Plasma processing apparatus
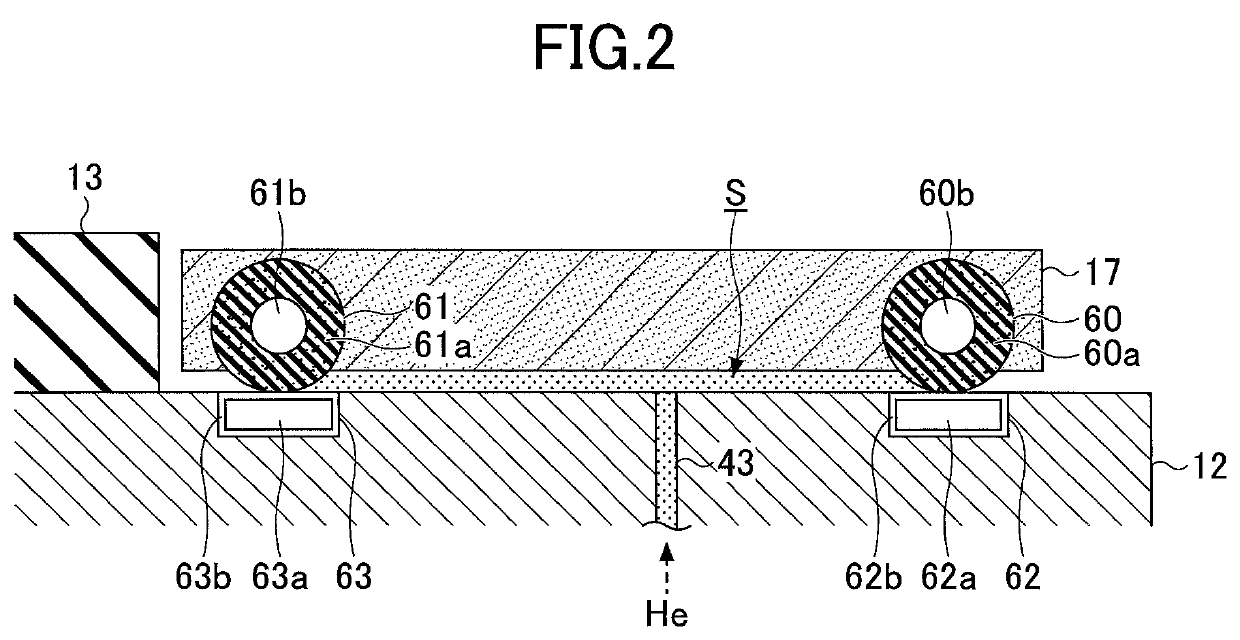
ActiveUS10622196B2Efficient heat transferTemperature controlElectric discharge tubesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A plasma processing apparatus includes a mounting stage on which a substrate is mounted, a focus ring arranged around a periphery of the mounting stage, a plurality of magnetic members arranged at a surface of the focus ring and a surface of the mounting stage facing opposite each other, and a temperature adjustment unit configured to adjust a temperature of the focus ring by introducing a heat transfer gas between the surface of the focus ring and the surface of the mounting stage facing opposite each other.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method and apparatus for cooling electronic enclosures
InactiveUS7051802B2Reduce and eliminate heat loadSupplement cool capacityShow cabinetsDomestic cooling apparatusIndoor airMoisture condensation
A cooling apparatus and method, and more particularly, an apparatus and method for cooling the air exiting an electronics enclosure, are disclosed. Air is taken into the enclosure and heated by the electronic equipment. The air is then expelled through a heat exchanger, which cools the exiting air. The exiting air is cooled using an external source of cooling liquid, which absorbs the heat from the exiting air. This absorbed heat is then expelled from the liquid outside of the environment containing the enclosure. Cooling the air exiting the enclosure causes the enclosure to present a neutral heat load to a room containing such an enclosure. Cooling the exiting air obviates the necessity of increasing the room air conditioning capacity to account for the heat added to the room by the electronics within the enclosure. Further, the disclosed apparatus and method decrease the possibility of moisture condensation within the enclosure and also provide more efficient cooling than is available from prior art devices and techniques.
Owner:VERTIV CORP
Solar power system and method for power generation
InactiveUS7296410B2Efficient heat transferEfficient heatingAuxillary drivesSolar heating energyElectricityEngineering
A solar-powered power generation system and an associated method are provided. The system includes at least one trough solar absorption device for heating a heat transfer fluid to a first temperature, and at least one tower solar absorption device for further heating the transfer fluid to a second temperature. Thus, the generation system can efficiently heat the transfer fluid to high temperatures. Subsequently, the heated fluid can be used, e.g., to generate steam and / or electricity.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP +2
Water heater
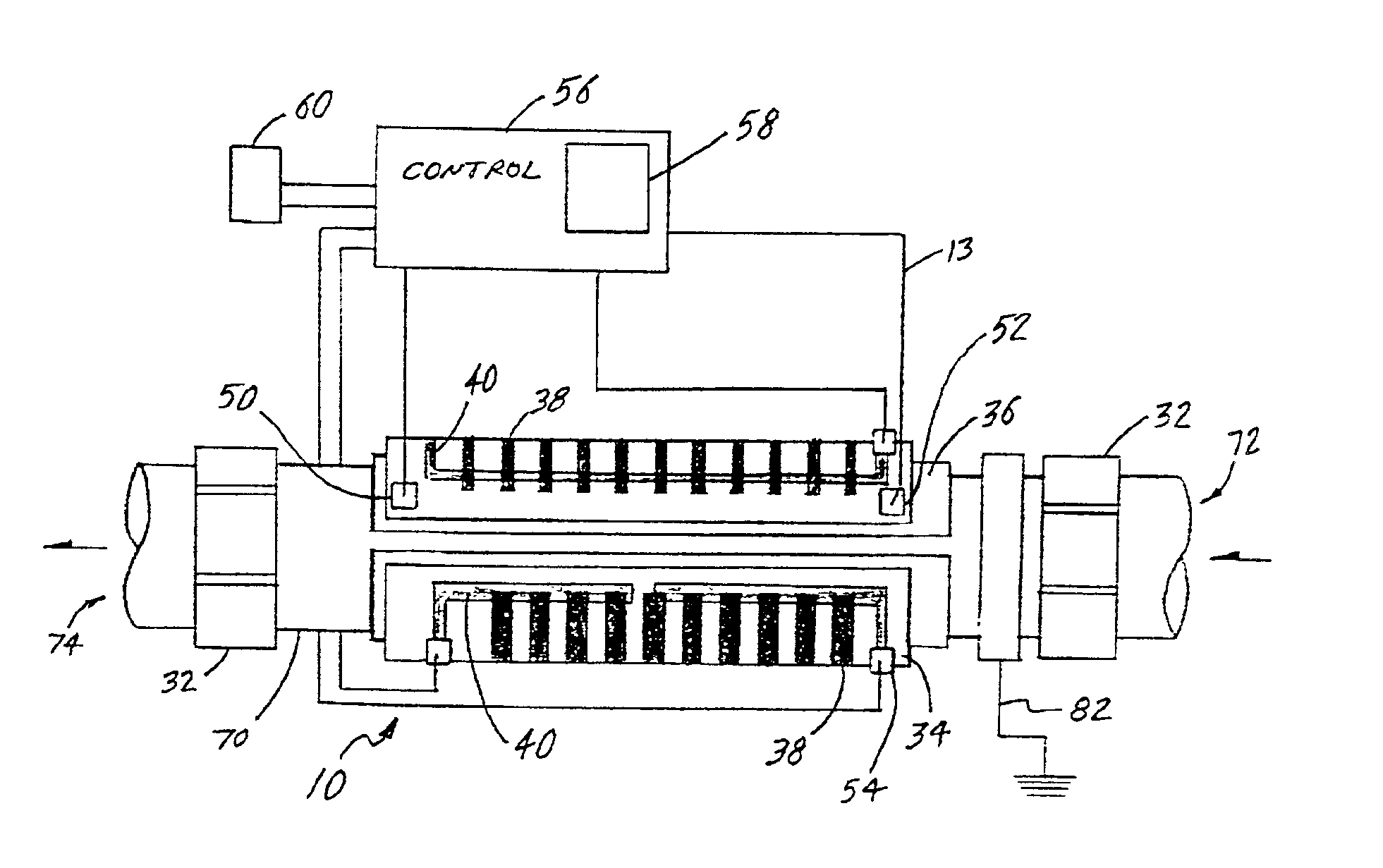
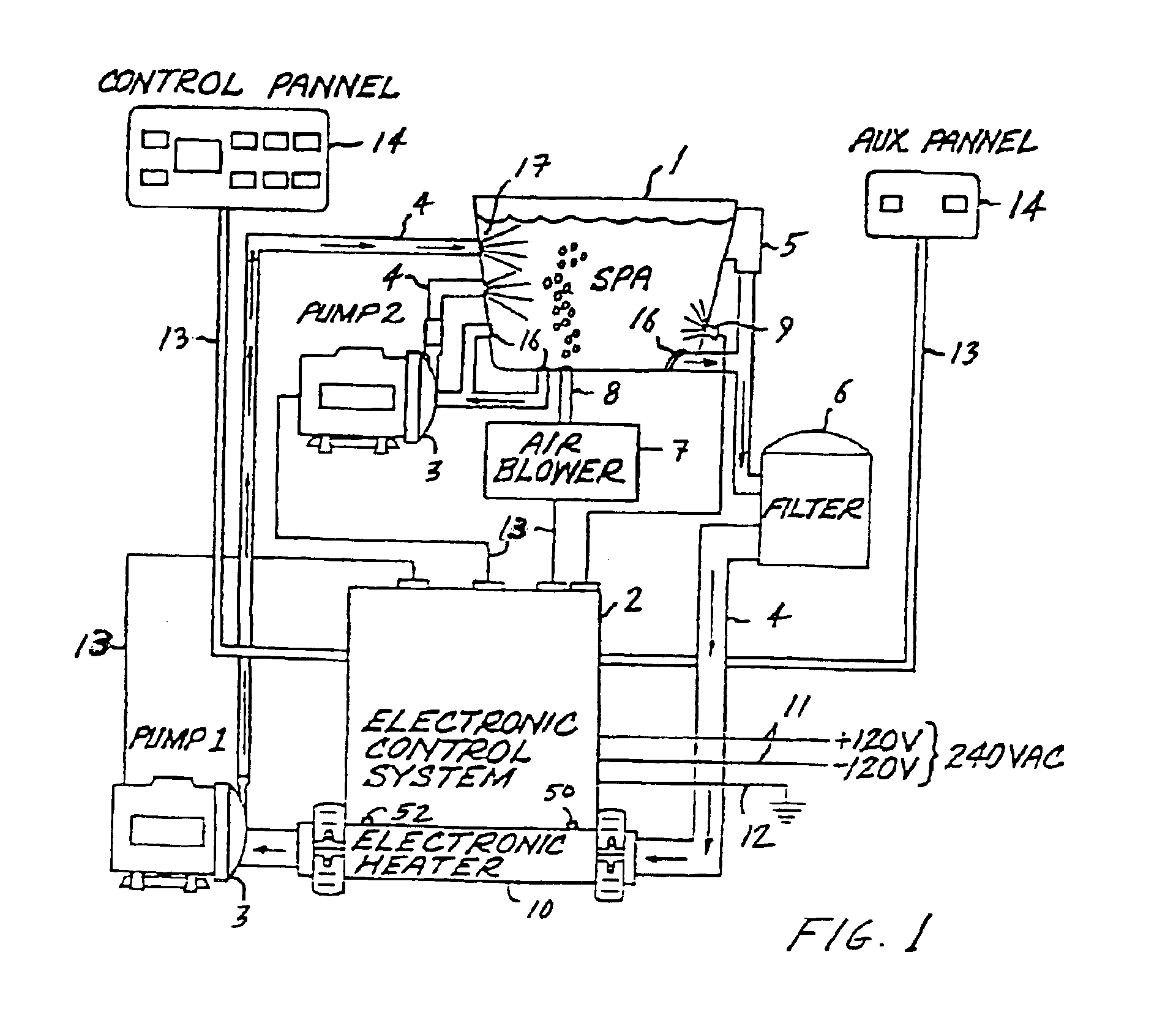
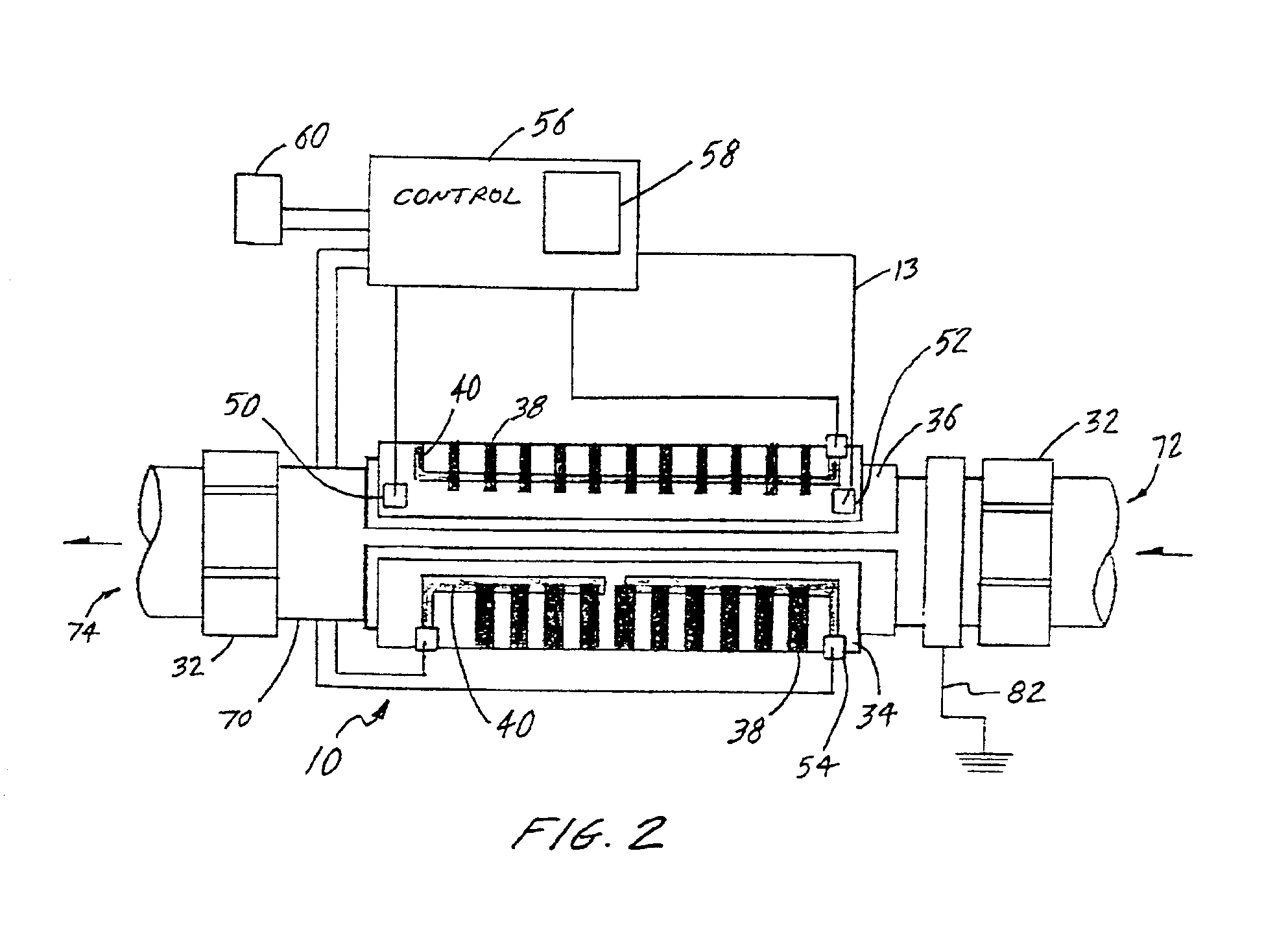
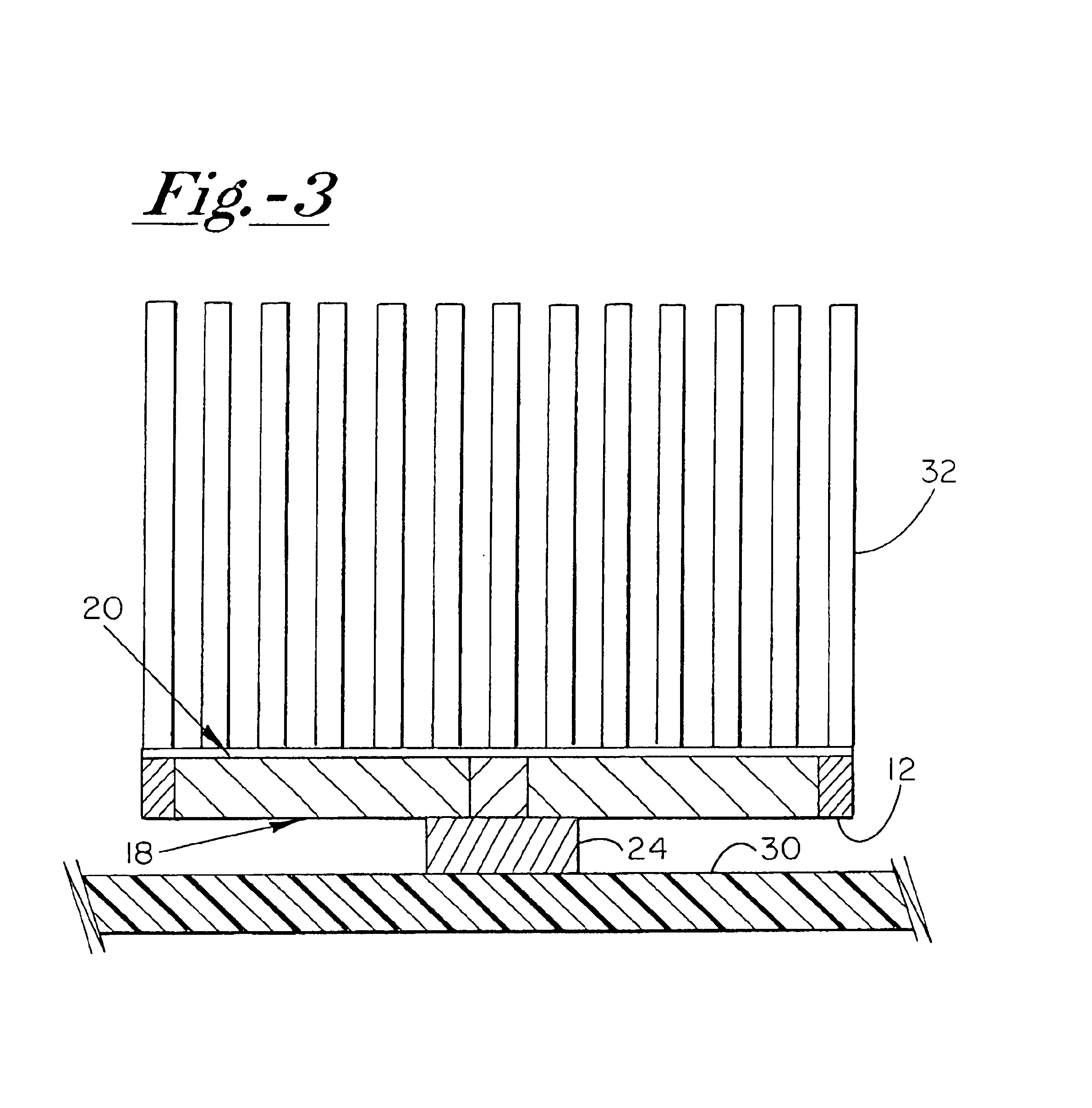
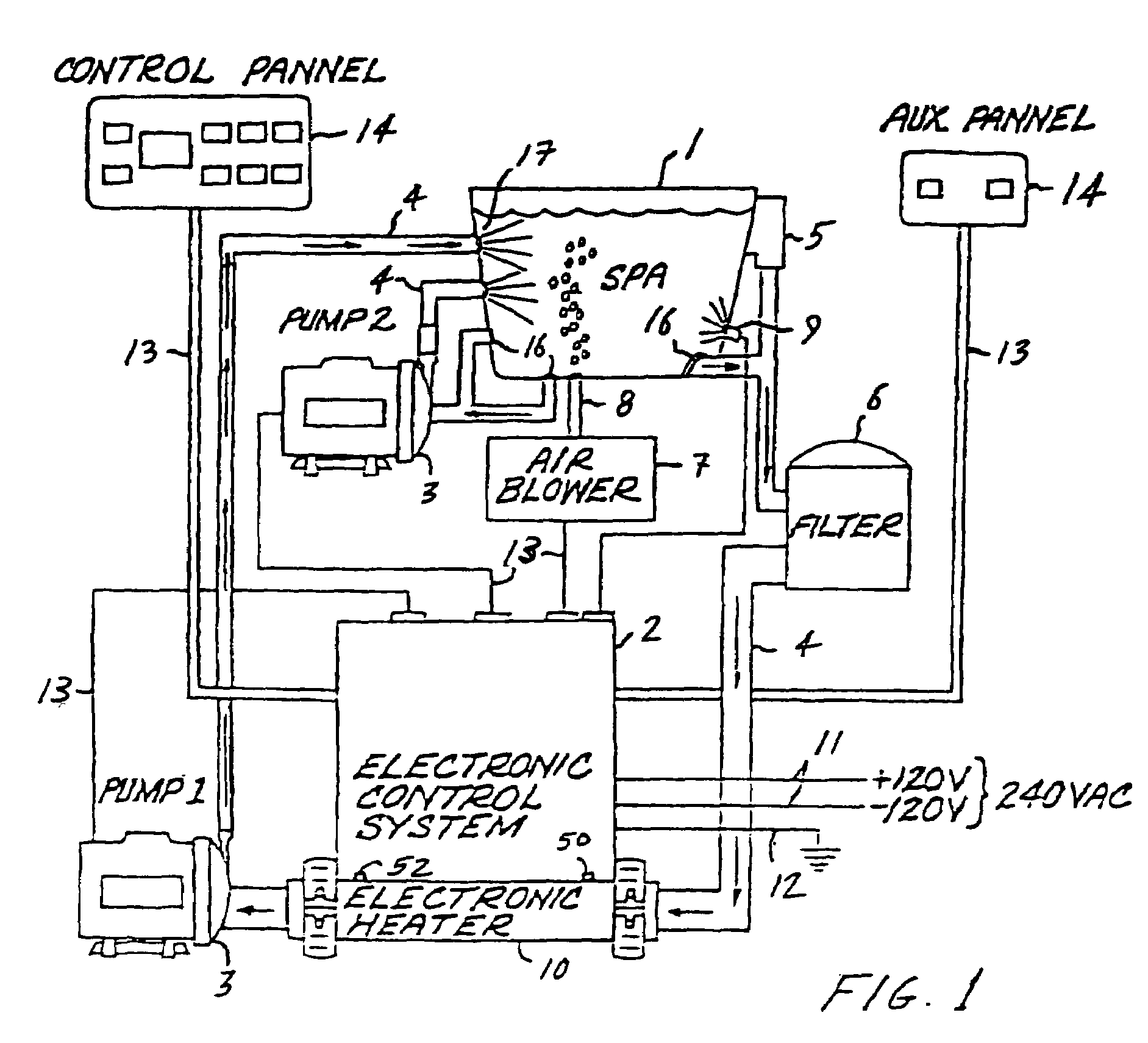
InactiveUS6943325B2Eliminate riskEliminate the risk of corrosionBathsDouchesWater useElectronic controller
An improved water heater for use in spas, hot tubs, pools, hydrotherapy pools, bath tubs, and similar bodies of water used indoors, outdoors, or both indoors and outdoors are used for both therapeutic and recreational purposes. The water heater uses heating element technology know as thick film on substrate comprising resistive elements bonded to the outer dry surface of a pipe to heat the pipe which in turn heats the water flowing therethrough. The heater is highly efficient due to the direct contact of the wet heating surface with the water and provides a smooth seamless inner heating surface by eliminating the need to pass electrical leads into the wet region of the heater. This virtually eliminates the risk of leaks in the water heater due to bulkhead fittings. The invention further eliminates the need for a heating element to be contained in the inner wet region of a spa heater, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion. The water heater is used in combination with an electronic controller having a microprocessor to control and regulate the operation of the water heater. The water heater can be used with electrical, electro-mechanical, and mechanical control systems for spas and can be retrofitted into existing spa applications.
Owner:DYMAS FUNDING COMPANY
Apparatuses for dissipating heat from semiconductor devices
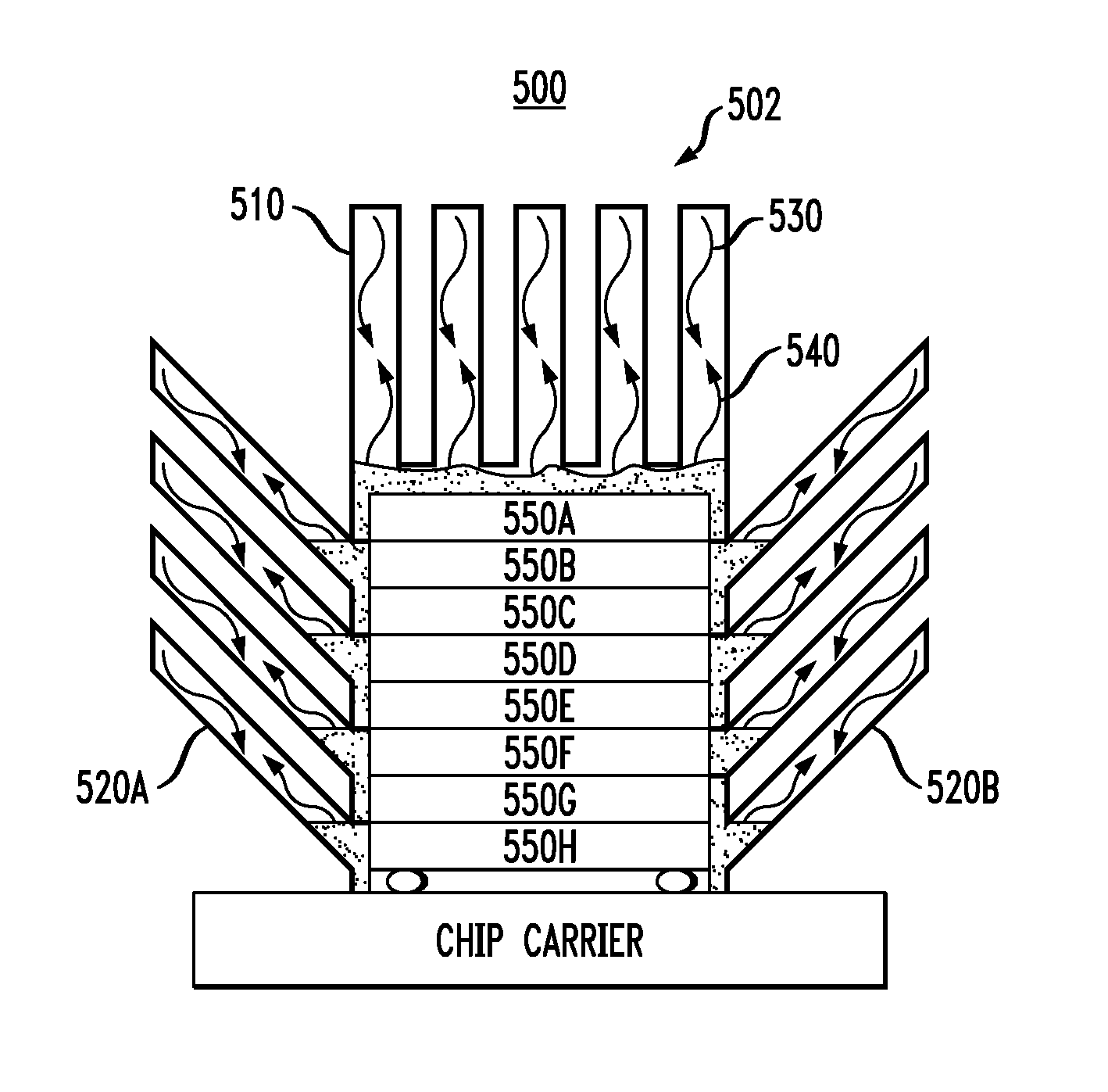
ActiveUS7369410B2Increase surface areaImprove cooling efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devices3d shapesEngineering
An apparatus for providing two-phase heat transfer for semiconductor devices includes a vapor chamber configured to carry a cooling liquid, the vapor chamber having base section, and a plurality of three-dimensional (3D) shaped members. The plurality of 3D-shaped members have interior and exterior sidewalls, the 3D-shaped members being connected to the base section so that vapor carrying latent heat can reach the respective interior sidewalls and get transferred to the respective exterior sidewalls configured to be in contact with an external coolant. The vapor chamber is configured to be in contact with a semiconductor device in order to remove heat therefrom.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Low-profile thermosyphon-based cooling system for computers and other electronic devices
ActiveUS20050217829A1Increase surface areaEfficient heat transferDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityElectron
This invention provides a cooling system comprising a thermosyphon for computer and electronic devices. The thermosyphon comprises an evaporator placed on top of a heat source, such as CPU. Heat from the heat source causes liquid coolant inside the evaporator to evaporate or boil. The resulting vapor enters a condenser and returns to a liquid phase. Cooling fins are attached to the condenser to facilitate heat transfer with the surrounding airflow. The cooling system and computer or electronic device fit within standard computer cases and high density server rack-mountable cases.
Owner:BELITS COMP SYST
Convection blood warming system with disposable flattened tube envelope incorporating paperboard "needle" for inserting envelope between heating plates and employing active and passive insulation of outlet flow path to provide normothermic fluid at zero to 600 milliliters per minute
InactiveUS6608968B2Closer spacingEconomical and simpleWater heating stoves/rangesMedical devicesBlood warmersDistal portion
A thin, flat paperboard inserter or "needle" which is longer than the blood warmer heating plates is attached to the edge of the flattened tube envelope to enter the very narrow gap between the heating plates. The inserter is fed between the heating plates and advanced to emerge from the other end of the blood warmer where it is grasped and used to pull the envelope into operational position. A high air flow hydrophobic vent with check valve to prevent reverse flow is incorporated into the drip chamber to allow automatic priming and venting of air bubbles. A conductively heated and externally insulated drip chamber holder and a patient intravenous line that is passively insulated by a small annular air space extruded as part of the tube preserve heat in the warmed fluid, improving low flow rate performance. A reusable external heater may optionally be applied to the distal portion of the patient line to provide normothermic fluid to the patient down to essentially zero flow rate.
Owner:BAKKE ALLAN P
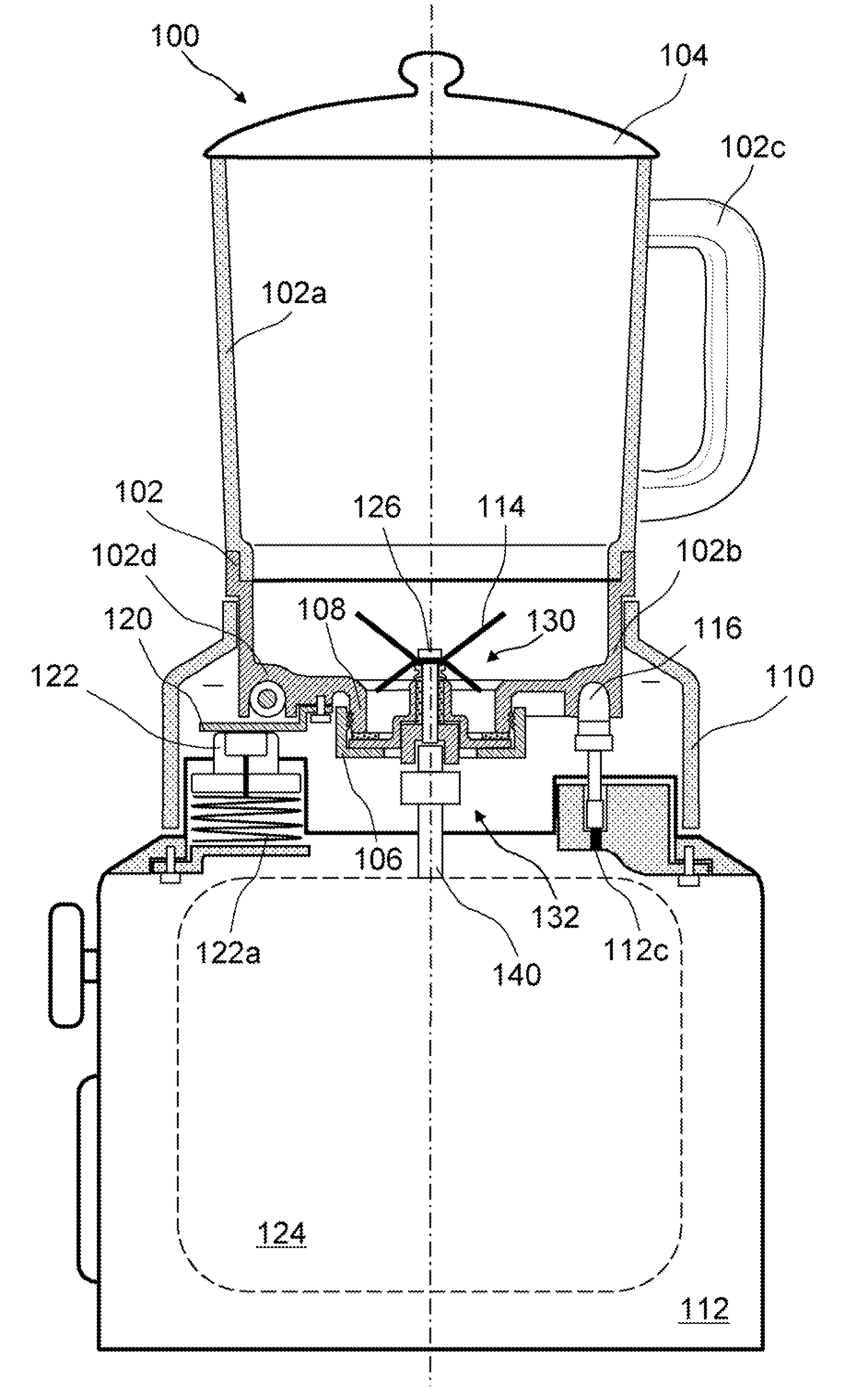
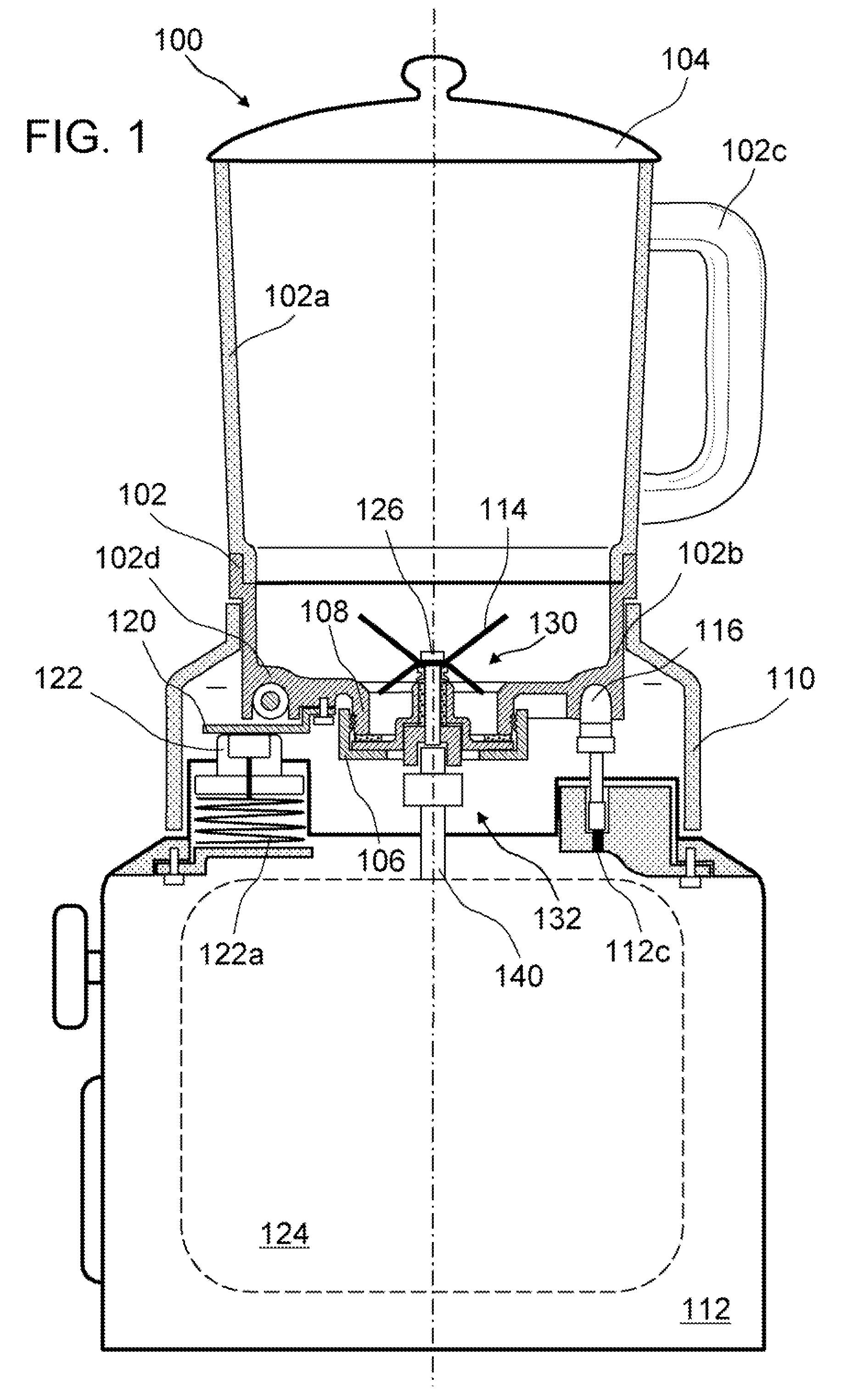
Blend soup maker
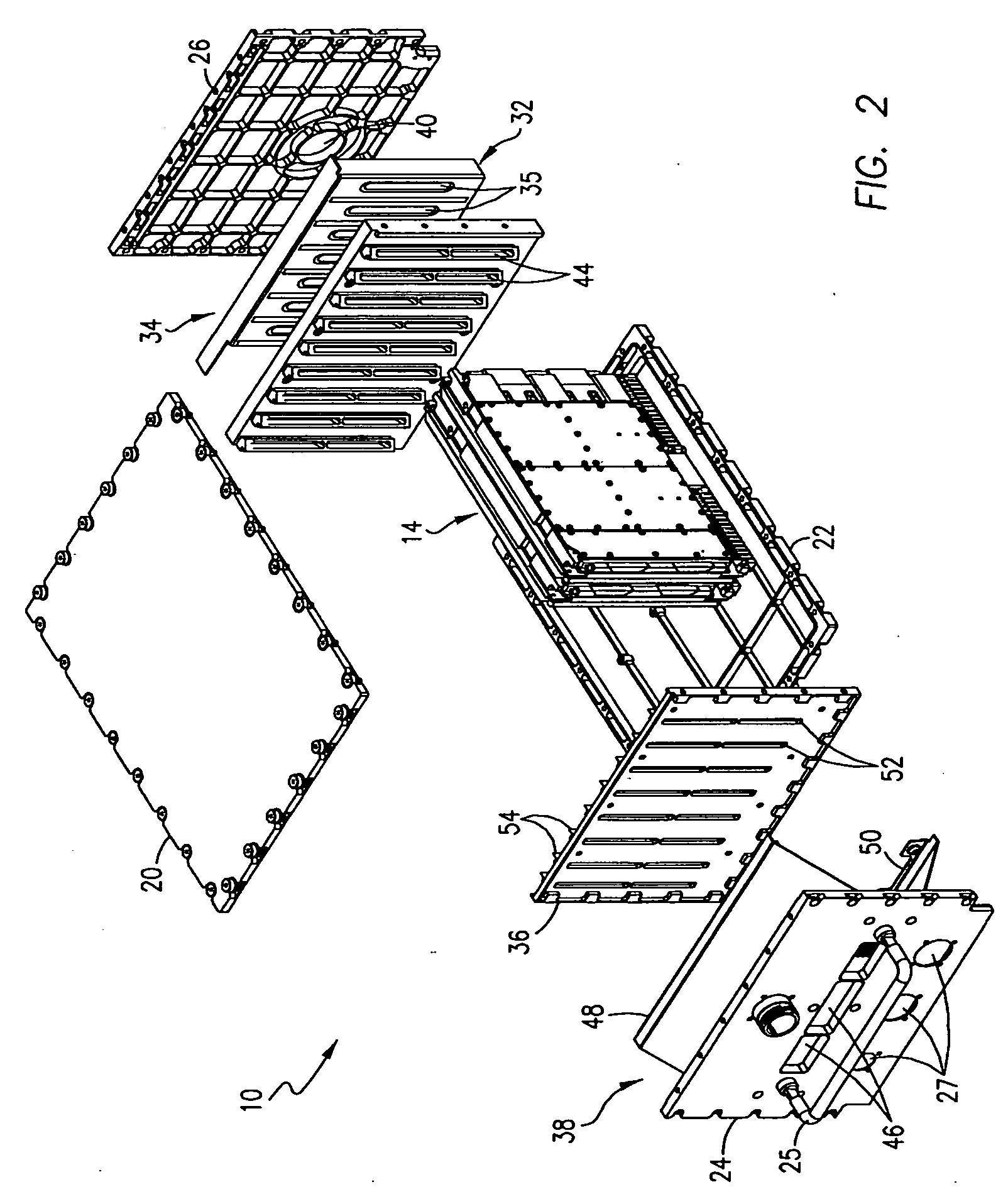
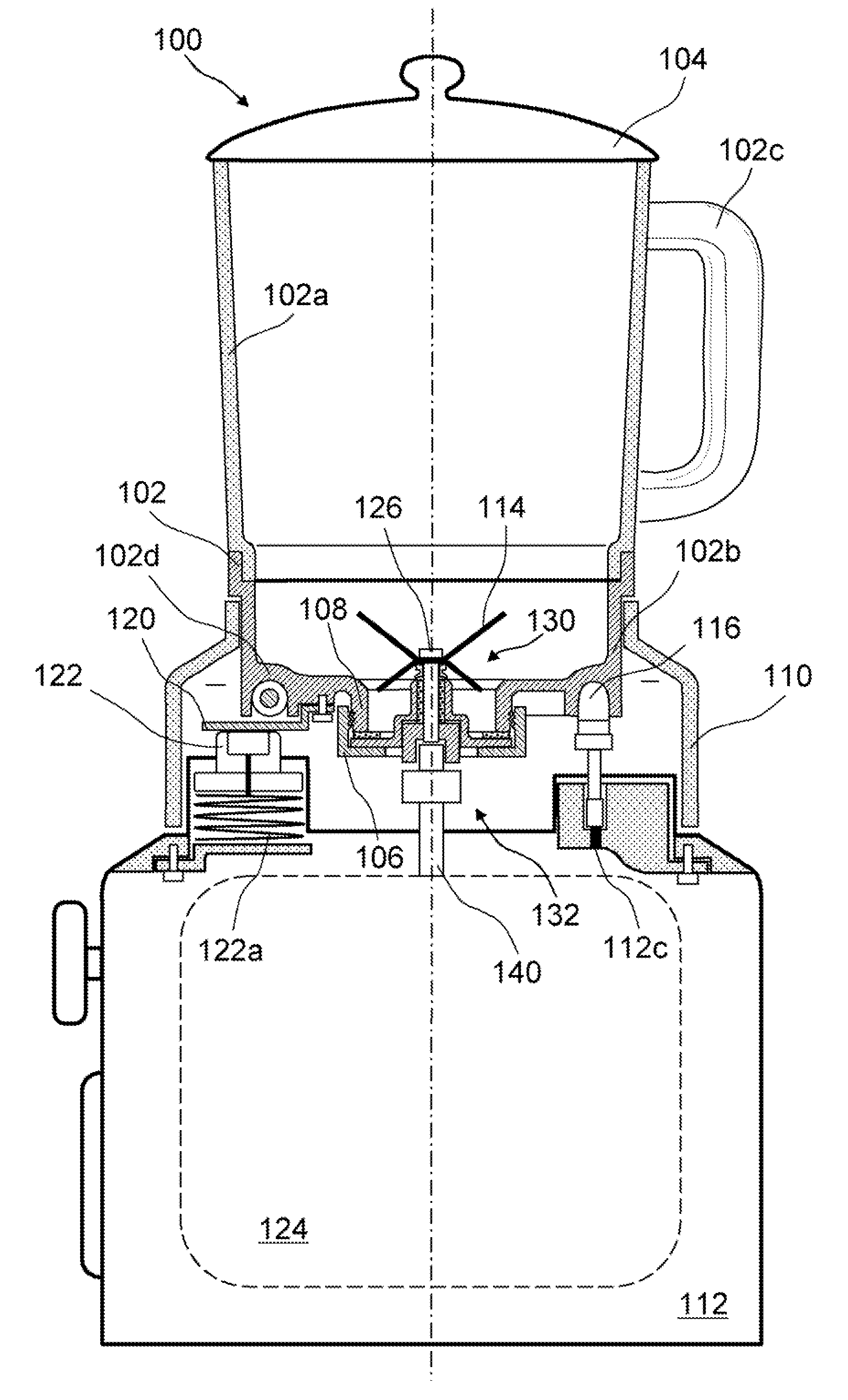
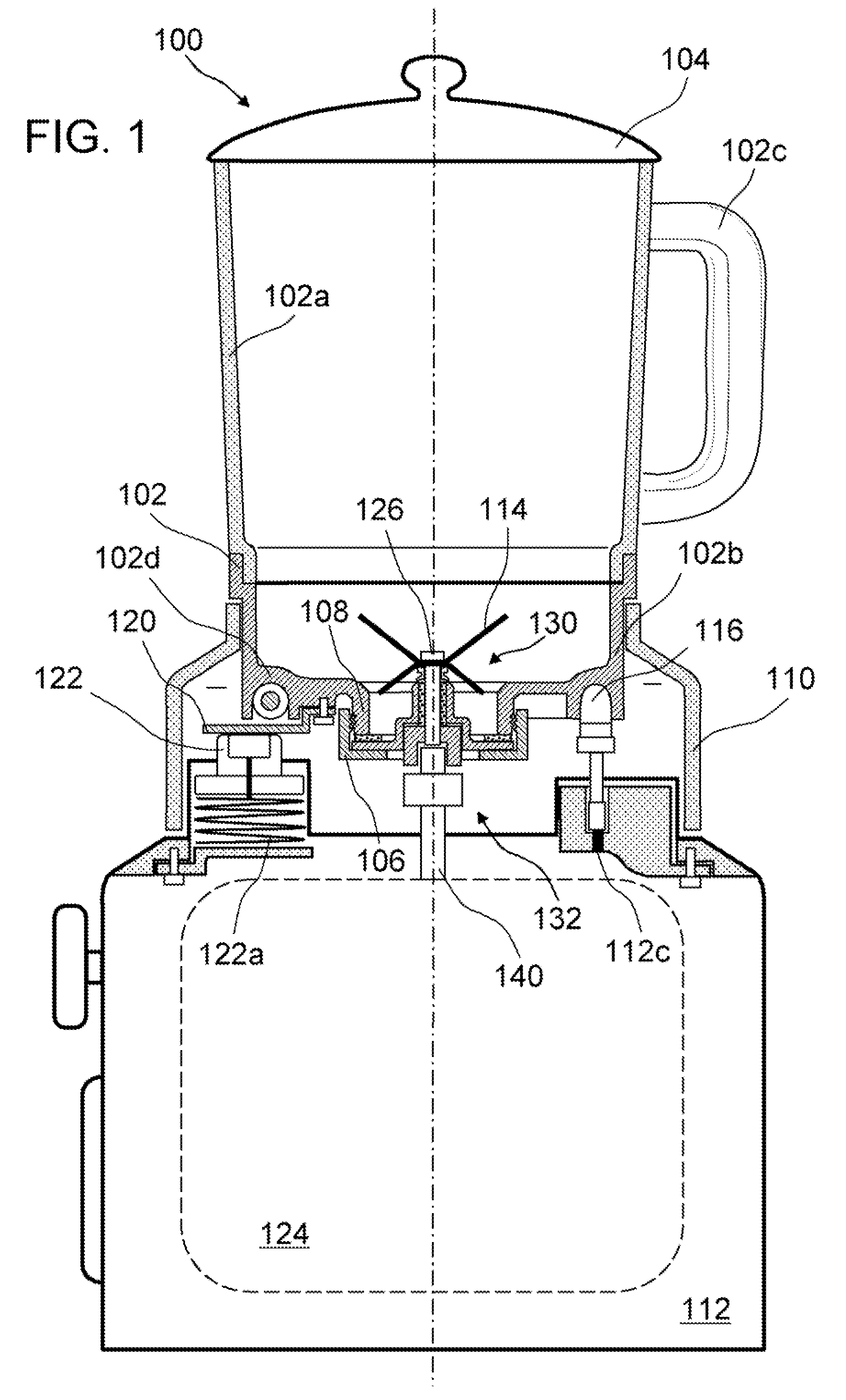
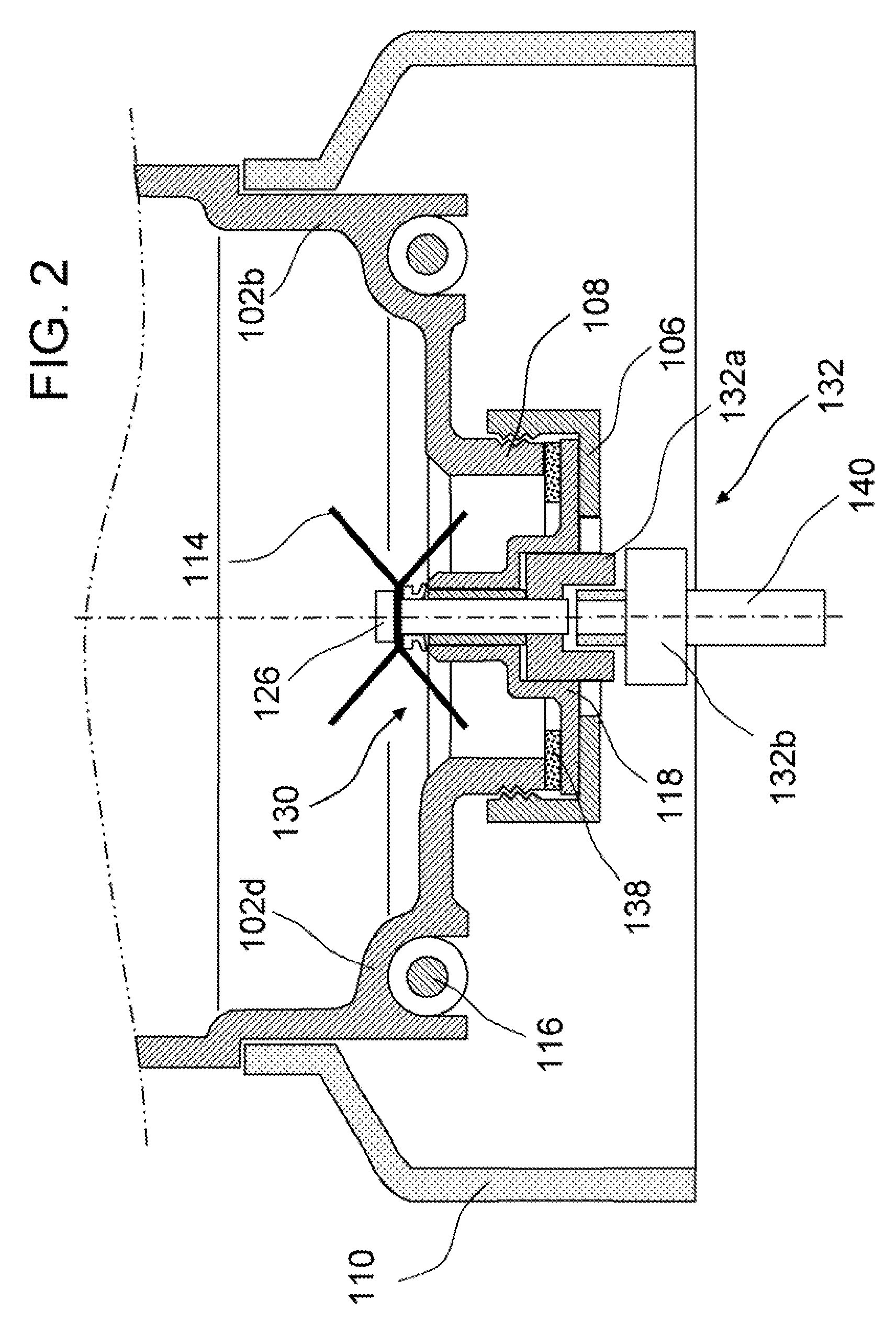
InactiveUS20080198688A1Efficient heat transferSave energyTransportation and packagingMixing methodsMechanical engineeringEngineering
A blend soup maker (100). Soup maker (100) comprises a jar (102) having an open top and an open bottom for holding food, a lid (104) for closing the open top of jar (102), a bottom cap (106) for closing the open bottom of jar (102), a blending blade (114) installed inside jar (102) for blending food, an electrical heating tube (116) fixedly installed on the bottom of jar (102) for heating food, a base support (112) disposed underneath jar (102) for supporting jar (102), a blending motor (124) installed inside support base (112) and removably coupled with blade (114) for driving blade (114) to blend food, and a support member (110) engaged with the lower portion of jar (102) for adapting jar (102) to stand on base support (112).
Owner:PENG ZHENG
Thermoelectric Conversion Module
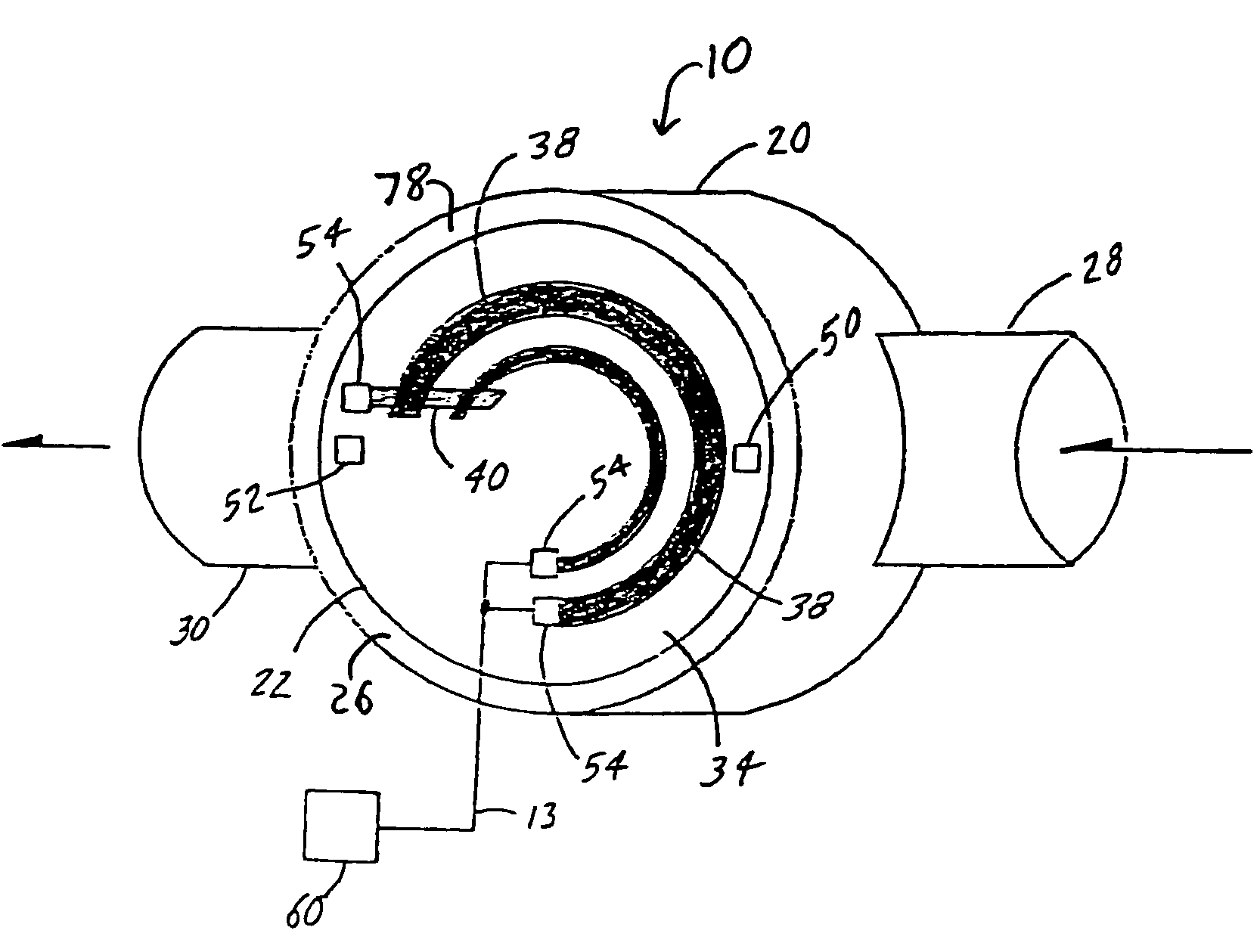
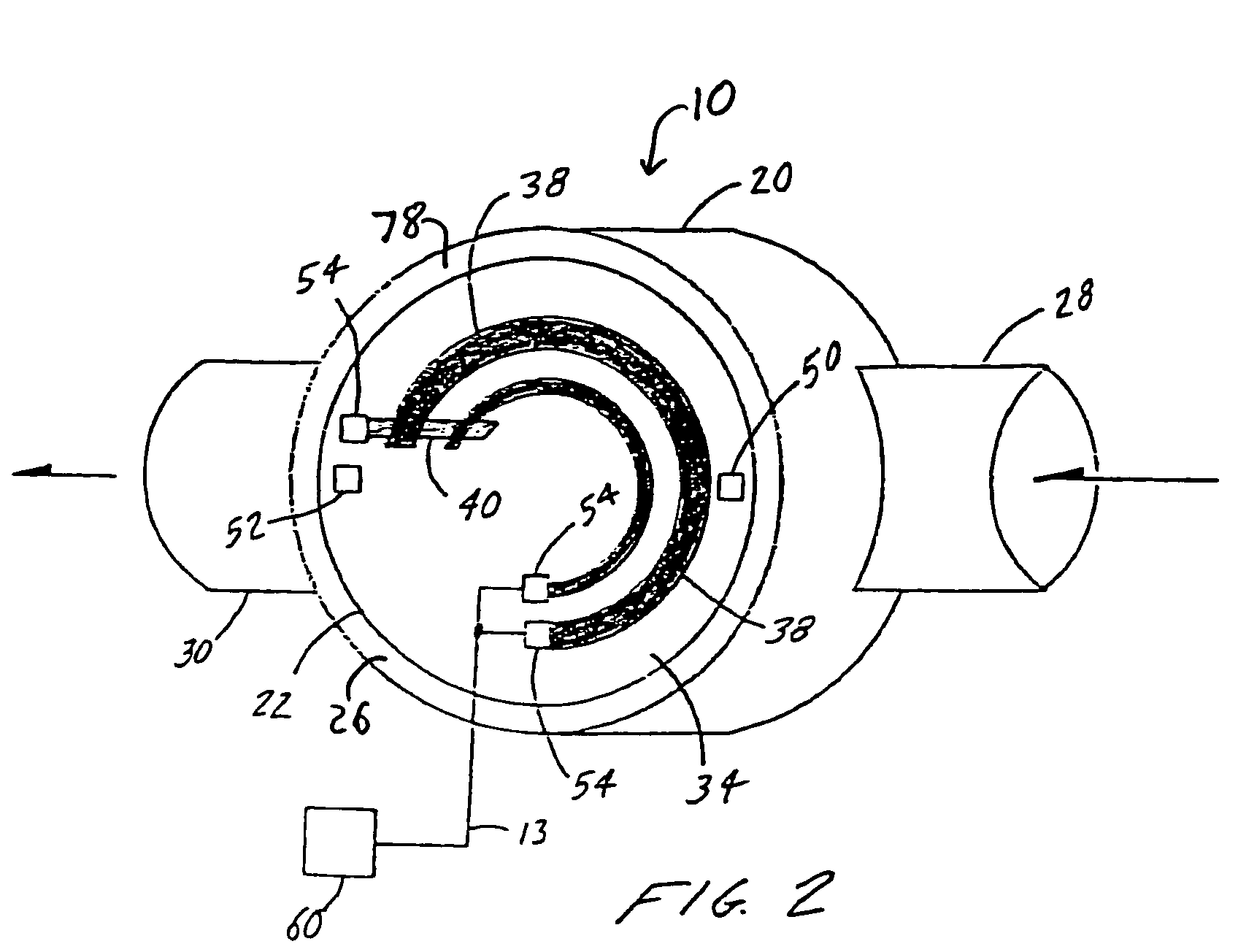
InactiveUS20090133734A1Simple structureShorten the timeThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectGenerators/motorsTemperature differenceEngineering
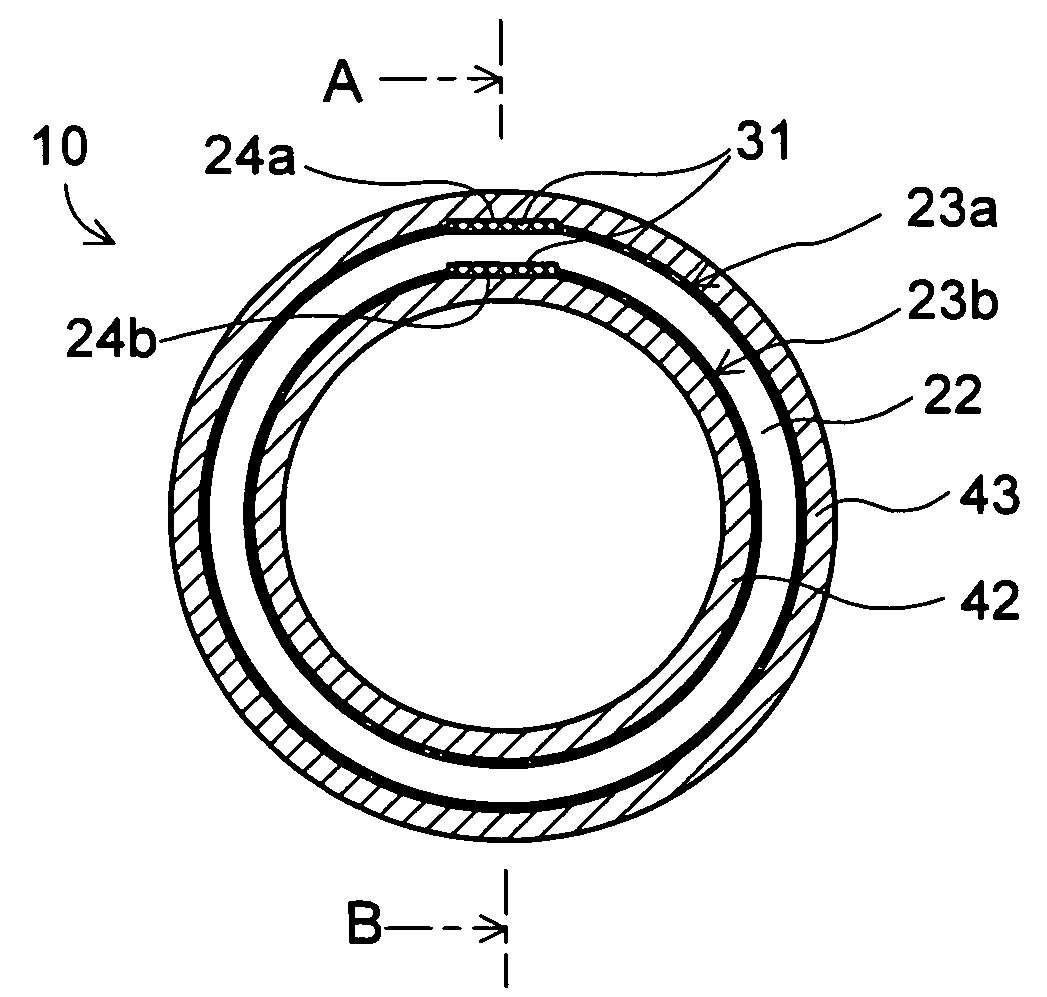
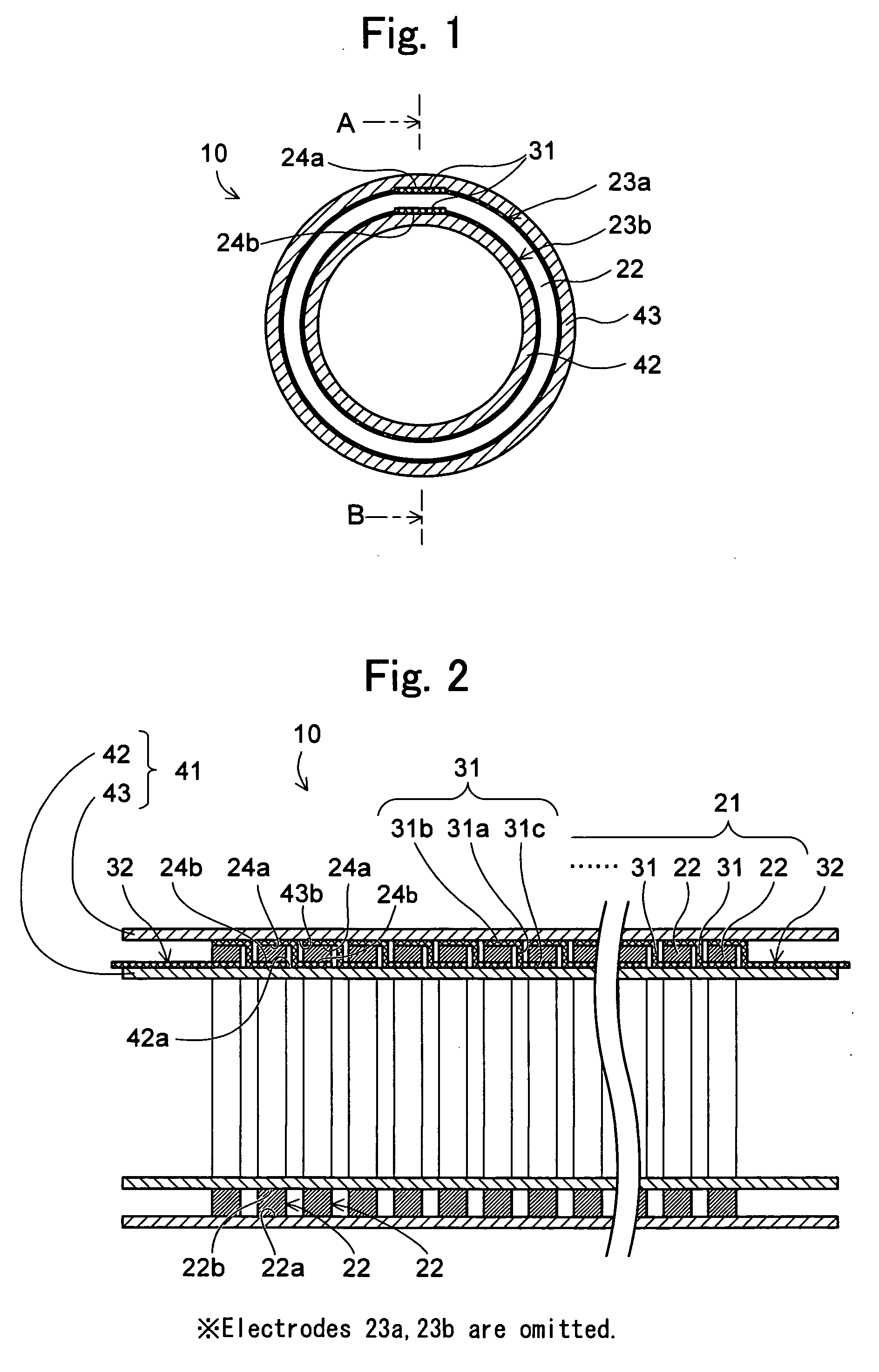
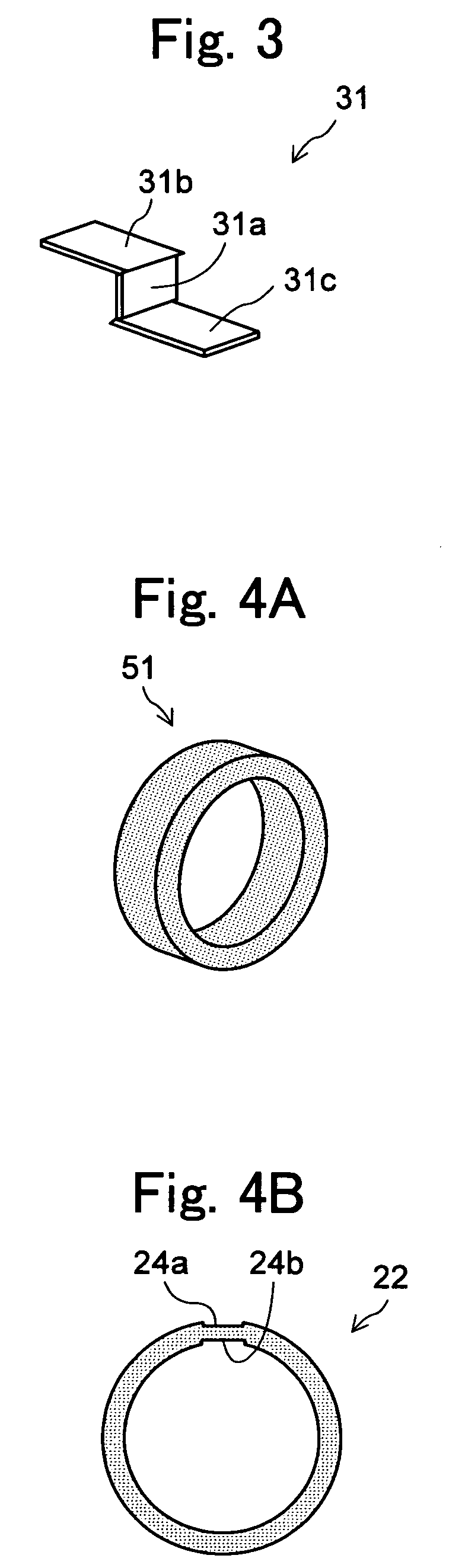
To provide a thermoelectric conversion module enabling cost reduction by reducing time and work required for assembly, and so on. A thermoelectric conversion module 10 comprises a tubular element unit 21 having a plurality of ring-like thermoelectric elements 22 coaxially arranged with air as an insulator sandwiched inbetween, wherein the ring-like thermoelectric element 22 is covered approximately entirely with electrodes 23a, 23b at its outer circumference surface 22a and inner circumference surface 22b, respectively, and generates electricity by temperature difference between the outer circumference surface 22a and the inner circumference surface 22b, a lead wire 31 electrically connecting the electrode 23a covered on the outer circumference surface 22a of one ring-like thermoelectric element 22 among the plurality of ring-like thermoelectric elements 22 to the electrode 23b covered on the inner circumference surface 22b of another ring-like thermoelectric element 22 adjacent to this one ring-like thermoelectric element 22, and a doubled cylindrical support unit 41 consisting of a SUS tube 42 whose outer circumference surface 42a supports the tubular element unit 21 and a SUS tube 43 whose inner circumference surface 43b supports the tubular element unit 21.
Owner:UNIVERSAL ENTERTAINMENT CORP
Interconnection element for electric circuits
ActiveUS8299368B2Efficient heat transferImprove installation strengthLine/current collector detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical conductorInterconnection
Owner:INVENSAS CORP
Air conditioning apparatus
InactiveUS20060032623A1Efficient heat transferImprove heat transfer efficiencyHeat storage plantsDesuperheatersEngineeringHeat exchanger
An air conditioning system for cooling or heating an air, and for feeding the heated or cooled air to predetermined portions is characterized by comprising: a first circulating circuit for circulating a first heating medium; a second circulating circuit for circulating a second heating medium; a control unit for controlling the heat for executing heat exchange between the first heating medium and the second heating medium to flow through either the heat exchanger or the first heat storing device. Moreover, an air temperature is controlled by heat of the second heating medium.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Thermal diffusion apparatus
InactiveUS6898084B2Improve heat transfer performanceEffectively distributes thermal energyMechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMechanical engineeringThermal conductivity
An apparatus for operably conveying heat away from a heat source includes a thermally conductive substrate having a thickness defining a planar boundary thereof, and an insert portion disposed in the substrate and being positioned so as not to extend beyond the planar boundary. The insert portion is a material having a thermal conductivity value of at least 1.5 times that of the substrate material along at least two axial directions, with one of such axial directions extending substantially perpendicularly to first and second opposed sides of the substrate.
Owner:TCLAD INC
Water heater
InactiveUS7057140B2Eliminate riskEliminate the risk of corrosionBathing devicesImmersion heating arrangementsWater useEngineering
An improved water heater for use in spas, hot tubs, pools, hydrotherapy pools, bath tubs, and similar bodies of water used indoors, outdoors, or both indoors and outdoors are used for both therapeutic and recreational purposes. The water heater uses heating element technology know as thick film on substrate comprising resistive elements bonded to the outer dry surface of a substrate to heat the substrate which in turn heats the water flowing through the heating chamber. The heater is highly efficient due to the direct contact of the wet heating surface with the water and provides a smooth seamless inner heating surface by eliminating the need to pass electrical leads into the wet region of the heater. This virtually eliminates the risk of leaks in the water heater due to bulkhead fittings. The invention further eliminates the need for a heating element to be contained in the inner wet region of a spa heater, thereby reducing the risk of corrosion. The water heater can be used with electrical, electro-mechanical, and mechanical control systems for spas and can be retrofitted into existing spa applications.
Owner:DYMAS FUNDING COMPANY
Cooling plate for lithium-ion battery pack
InactiveUS20110162820A1Efficient heat transferEvenly distributedFinal product manufactureCell temperature controlMechanical engineeringBattery cell
A cooling plate for a battery pack with a plurality of battery cells is provided. The cooling plate includes a cooling fin with a substantially planar surface and a perimeter. The cooling plate includes a frame abutting the cooling fin and forming a seal with the cooling fin adjacent the perimeter of the same. The frame and the cooling fin define at least one fluid inlet, at least one fluid outlet, and a flow channel therebetween. The at least one fluid inlet and the at least one fluid outlet are disposed through the seal and are in fluid communication with the flow channel. The flow channel is disposed adjacent the perimeter and in heat transfer communication with the substantially planar surface of the cooling fin. A battery pack with the cooling plate, and a method for controlling a temperature of the battery pack, are also provided.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Liner and liquid heating container
InactiveCN108926249AEasy to passReduce deliveryWater-boiling vesselsWarming devicesEngineeringPower density
The invention provides a liner and a liquid heating container. The liner comprises a body, a heat conduction plate and a heating part, wherein the body comprises a barrel body and a barrel bottom connected with the bottom of the barrel body; the heat conduction plate fits to the outer wall face of the barrel bottom, and the heat conduction coefficient of the heat conduction plate is greater than that of the barrel bottom; the heating part is ring-shaped and fits to the lower surface of the heat conduction plate, and the projection of the heating part is positioned in the heat conduction plate;the thickness of the heat conduction plate is greater than or equal to 2mm; and / or, a spacing between the outer periphery of the contact part of the heating part and the heat conduction plate and theouter periphery of the heat conduction plate is greater than or equal to 3mm. For the liner provided by the invention, by increasing the spacing between the outer periphery of the contact part of theheating part and the heat conduction plate and the outer periphery of the heat conduction plate, heat generated by the heating part becomes bidirectional heat conduction from unidirectional heat conduction, so that the local thermal power density is greatly reduced, and the noises caused by heating water are reduced; and / or, the heat conduction plate is thickened, so that the local thermal shockis prevented, heat is uniformly transmitted as far as possible, and further, the noises caused by heating water are reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG MIDEA CONSUMER ELECTRICS MFG CO LTD
Low-Profile Thermosyphon-Based Cooling System for Computers and Other Electronic Devices
ActiveUS20070242438A1Increase surface areaEfficient heat transferDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHigh densityEngineering
This invention provides a cooling system comprising a thermosyphon for computer and electronic devices. The thermosyphon comprises an evaporator placed on top of a heat source, such as CPU. Heat from the heat source causes liquid coolant inside the evaporator to evaporate or boil. The resulting vapor enters a condenser and returns to a liquid phase. Cooling fins are attached to the condenser to facilitate heat transfer with the surrounding airflow. The cooling system and computer or electronic device fit within standard computer cases and high density server rack-mountable cases.
Owner:BELITS COMP SYST
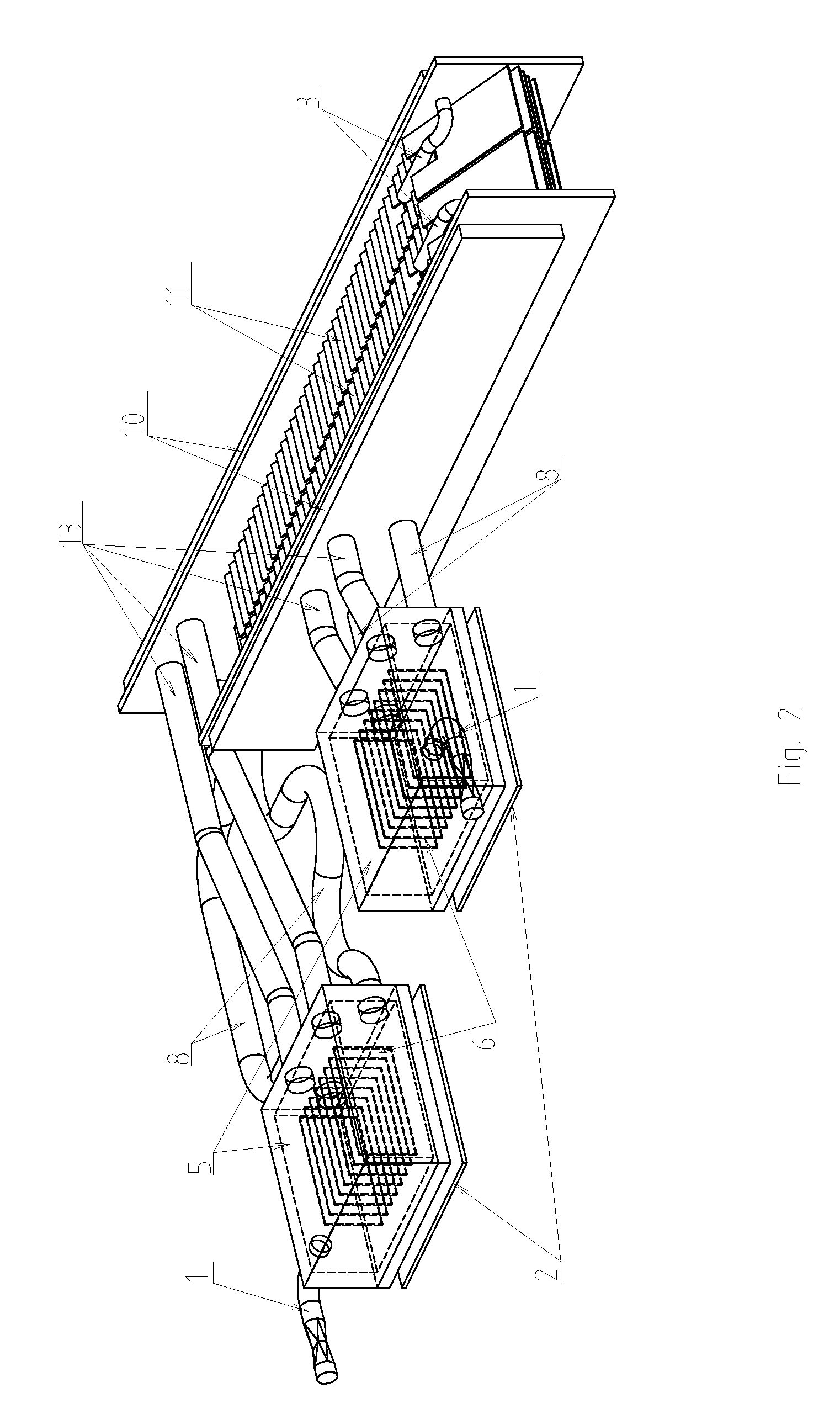
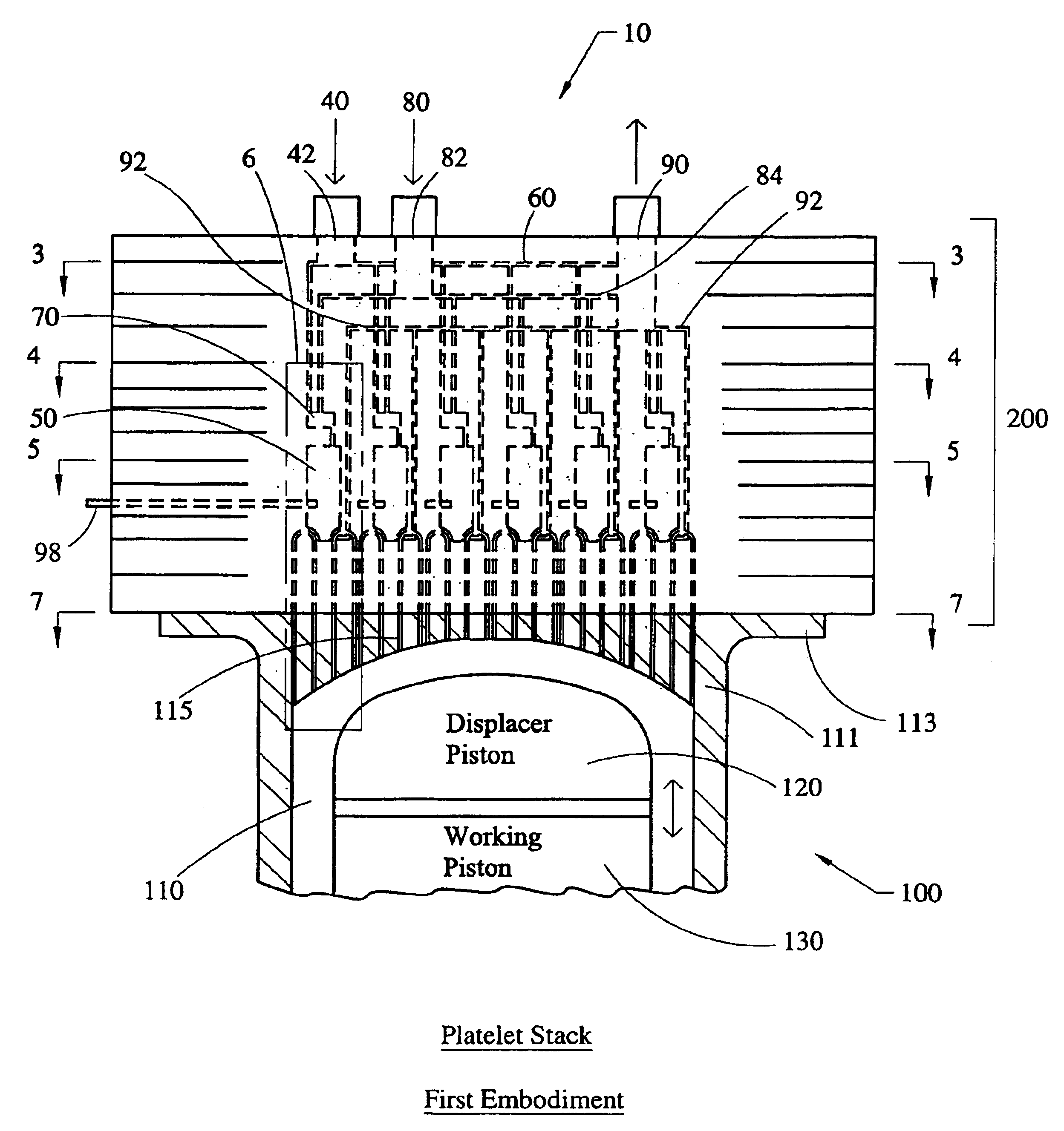
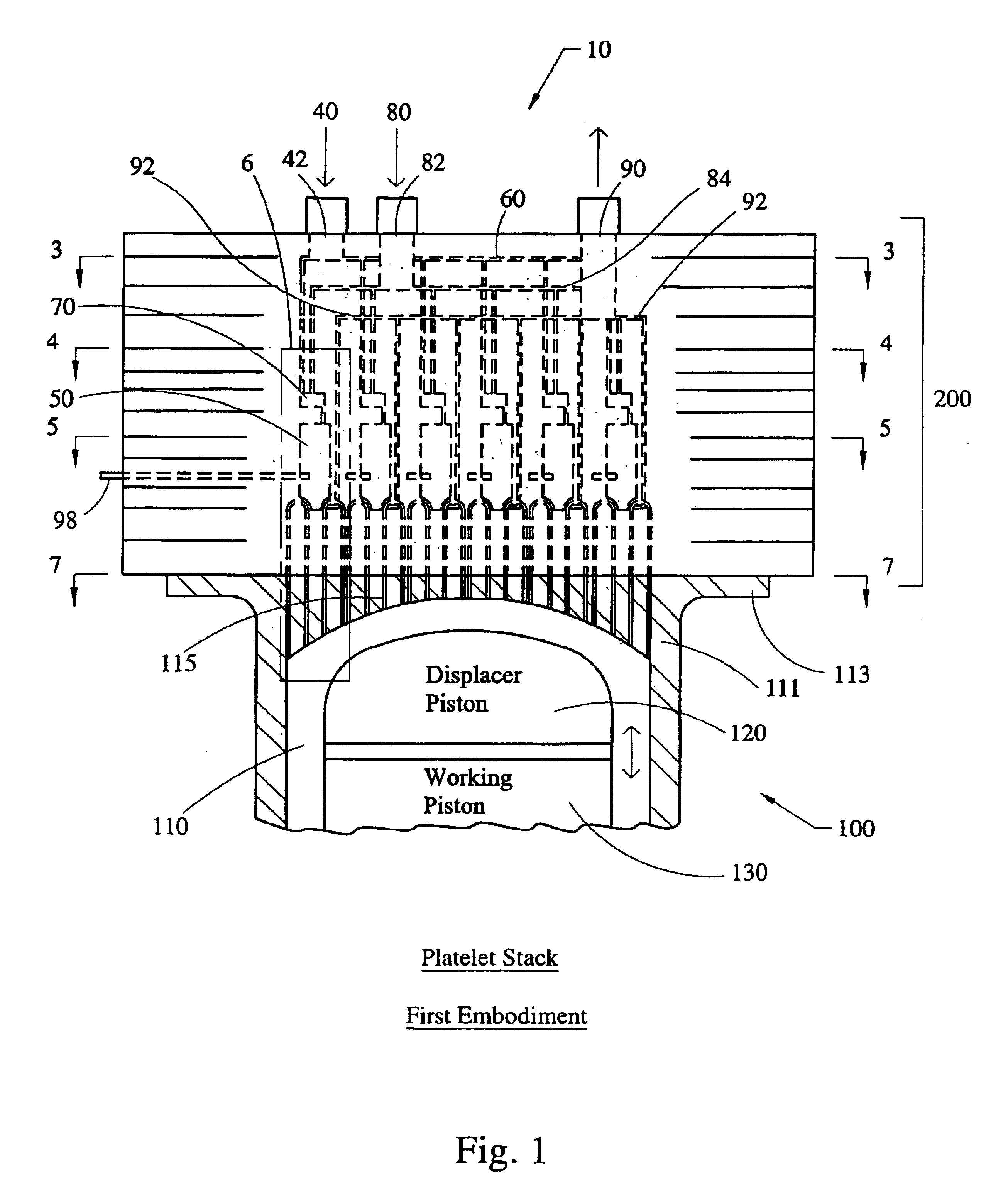
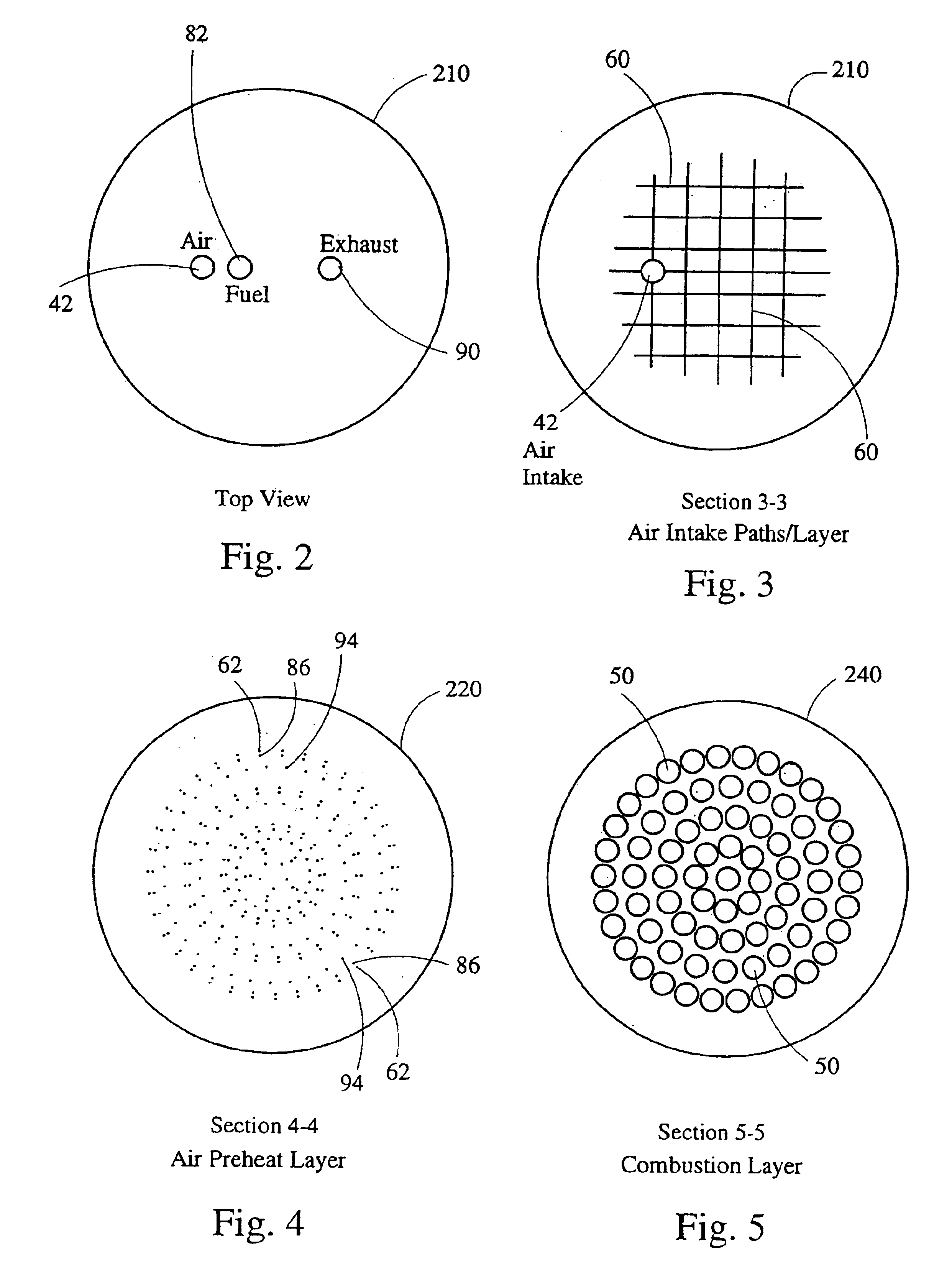
Stirling engine having platelet heat exchanging elements
InactiveUS6931848B2Guaranteed uptimeEfficient heat transferSolar heating energySolar heat devicesEngineeringStaged combustion
The present invention provides heat exchanging elements for use in Stirling engines. According to the present invention, the heat exchanging elements are made from muliple platelets that are stacked and joined together. The use of platelets to make heat exchanging elements permits Stirling engines to run more effiecient because the heat transfer and combustion processes are improved. In one embodiment, multi-stage combustion can be introduced with platlets, along with the flexibility to use different types of fuels. In another embodiment, a single component constructed from platelets can provide the heat transfer rquirements betweeen the combustion gas / working gas, working gas in the regenerator and the working gas / coolant fluid of a Stirling engine. In another embodiment, the platelet heat exchanging element can recieve solar energy to heat the Stirling engine's working gas. Also, this invention provides a heat exchanging method that allows for multiple fluids to flow in opposing or same direction.
Owner:DISENCO +1
Clamp for holding and efficiently removing heat from workpieces
InactiveUS20050036267A1Effectively safely clampIncrease resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEmergency protective arrangement detailsEtchingCelsius Degree
The invention described in this disclosure is an apparatus and method for clamping semiconductor wafers or other substrates or workpieces during etching, CVD, or surface modification processes. The purpose of the invention is to achieve improved heat transfer during processing between the wafer / substrate and a temperature controlled pedestal used for supporting it in the process chamber. The typical level of process heat put into the wafer during plasma-based etching or deposition processes will be up to about 10 Watts per centimeter squared while the maximum acceptable temperature differential between wafer / substrate and pedestal is less than about 100 Celsius. In such low gas pressure environments typical for plasma-based processes, the heat removal from the wafer / substrate by gaseous conduction may be inadequate to meet requirements. This invention achieves excellent heat transfer to the pedestal from the wafer / substrate when there is a thin, resilient, electrically insulating layer (tape) bonded to the wafer / substrate or the pedestal. Wafer / substrate clamping for improved process heat removal is achieved by a combination of vacuum clamping of the wafer / substrate beginning prior to evacuation of the processing chamber, along with or followed by electrostatic clamping of the wafer / substrate which continues during processing. The invention also permits the wafer / substrate to be rapidly and safely released from the electrostatic clamping when the chamber is returned to atmospheric pressure by a providing a slight pressure increase, above atmospheric pressure, between wafer and pedestal. The pedestal may have some roughening or narrow grooves on the wafer clamping surface, and some small holes from its surface leading to an evacuated plenum or channel within the pedestal. Alternatively, the pedestal may have a layer of a porous metal extending from its surface down to the evacuated channel or plenum which permits gas to be evacuated. These structures allow vacuum pumping of gas that might otherwise be trapped between the insulating layer and the pedestal. When a wafer / substrate is placed on the pedestal by loading at atmospheric pressure, vacuum pumping through the pedestal is commenced. This causes the workpiece to be pressed to the pedestal clamping surface with approximately atmospheric pressure compressing the soft layer against its clamping surface. This provides sufficient contact of the soft layer with the pedestal to greatly improve heat transfer from the wafer / substrate to the pedestal. A voltage is applied to the pedestal, beginning any time after the wafer is on the pedestal, to further clamp the wafer electrostatically. As the processing chamber is then pumped down to operating pressure for processing the electrostatic clamping voltage maintains sufficient pressure of the wafer / substrate against the pedestal to maintain the heat conductive contact between the soft layer and the pedestal. This permits good heat conduction to be maintained during the low pressure plasma-based etching or CVD processing. Following processing when the wafer / substrate is to be removed it may be rapidly de-clamped from the electrostatic clamping by application of a slight over-atmospheric pressure in the reservoir or pumping channels within the pedestal.
Owner:SAVAS STEPHEN EDWARD +1
Thermal diffusion apparatus
InactiveUS20050013119A1Improve heat transfer performanceEffectively distributes thermal energyMechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for operably conveying heat away from a heat source includes a thermally conductive substrate having a thickness defining a planar boundary thereof, and an insert portion disposed in the substrate and being positioned so as not to extend beyond the planar boundary. The insert portion is a material having a thermal conductivity value of at least 1.5 times that of the substrate material along at least two axial directions, with one of such axial directions extending substantially perpendicularly to first and second opposed sides of the substrate.
Owner:TCLAD INC
Battery pack
ActiveUS20090191452A1Efficient thermal managementImprove performanceCell temperature controlSecondary cells manufactureEngineeringElectrochemical cell
Disclosed herein is a multi-cell battery pack having optimal temperature distribution throughout the battery pack and optimal air flow through the battery pack. Disclosed herein is a battery pack which provides optimal temperature distribution throughout the battery pack, wherein maximum cell temperature (Tmax) and temperature differential amongst all cells in the battery pack (ΔTcell) are optimized for efficient thermal management providing safety, improved performance and extended life of the battery pack and electrochemical cells. Also disclosed herein is a battery pack which provides optimal flow through the battery pack and minimal pressure drop (ΔP) throughout the battery pack.
Owner:COBASYS LLC
Controllable bi-circulating hot-pipe system
This invention relates to a double- cycle high efficient heat pipe heat exchanging system that can control the heat exchanging quantity. There are evaporator and condenser two types of heat exchangers. The number of each type is one or several that formed by connected in parallel. This system includes: condensate supplying and distributing system; gas-liquid two phases flowing and separating system; gaseous phase transmitting and distributing system, liquid phase collecting and storing system; heat exchanging quantity controlling system. The evaporator of heat pipe, condenser, gas-liquid separator, liquid storage, solution circulating pump, liquid distributor, the connecting pipeline and related controlling parts are connected together to form the double cycles controllable heat pipe system. The solution pump, liquid distributor, evaporator and gas-liquid separator are connected together to form independent working fluid cycle, which settle the problems that working fluid carrying capacity is not enough and liquid distribution is uneven.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Thermal control system and method
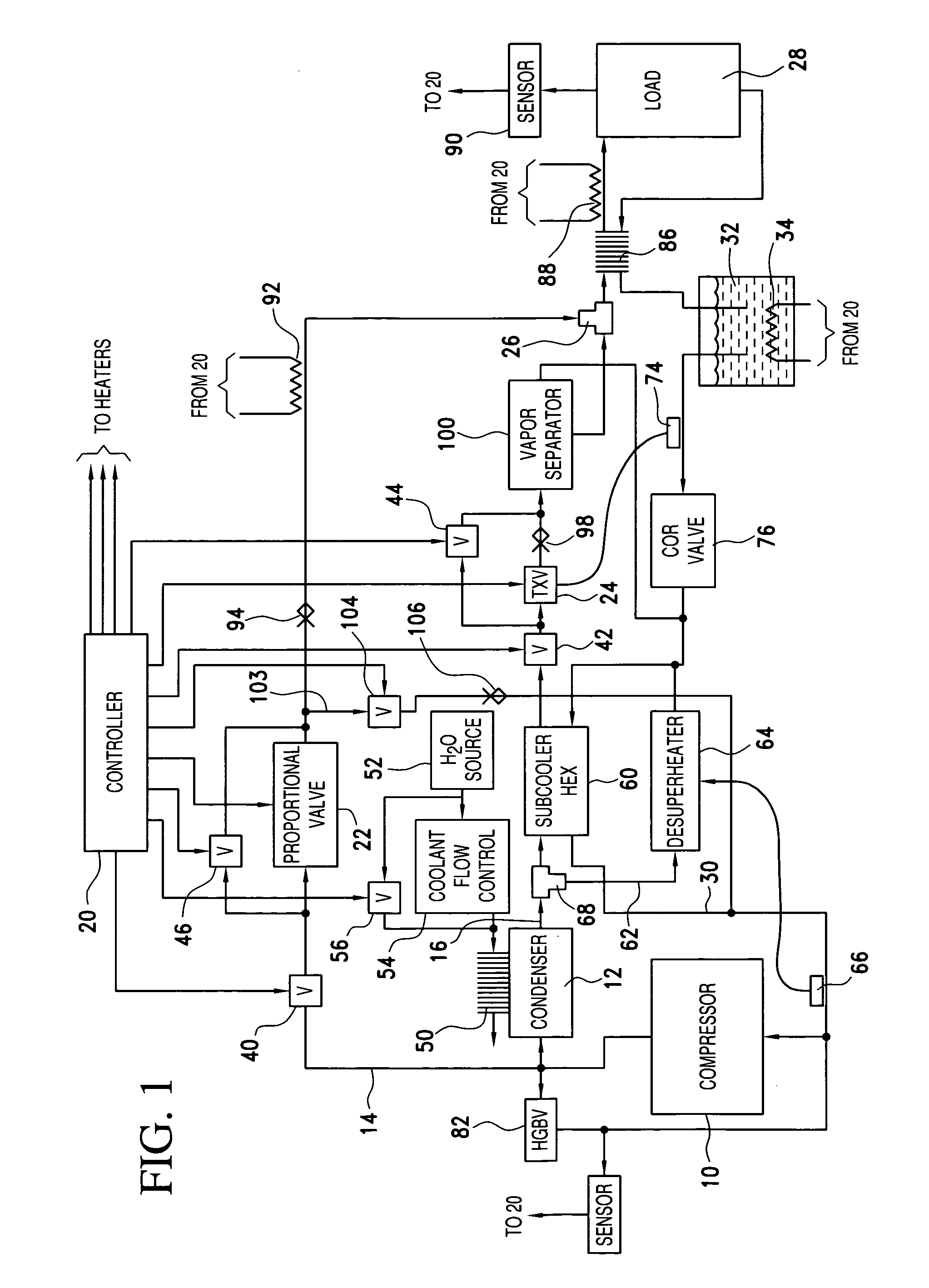
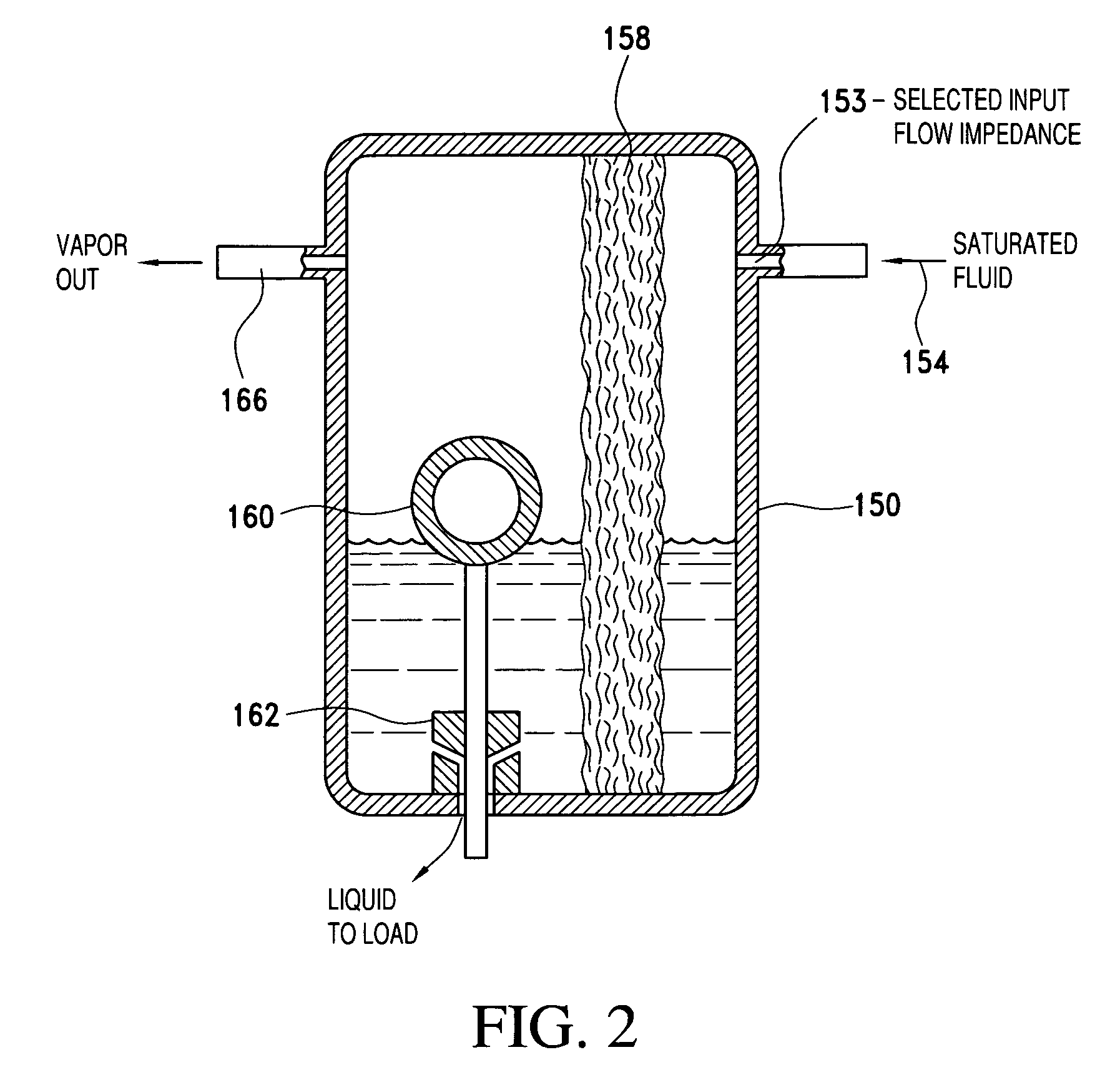
InactiveUS20070095097A1Lower overall pressure dropImprove efficiencyFluid circulation arrangementHigh rateThermal control system
Improvements in systems and methods which employ a two-phase fluid, such as a refrigerant, as a saturable fluid in direct heat transfer relation to a thermal load, are realized by extraction of vapor from the saturated fluid before heat exchange. Moreover, automatic changing of the paths under command of a controller enables charges to be effected between different modes at higher rates than in other systems by employing the variety of modes available in the direct transfer system.
Owner:ADVANCED THERMAL SCI
Multi-purpose stovetop grilling and cooking device
InactiveUS7059318B2Reduce needFacilitate releaseDomestic stoves or rangesLiquid heating fuelEngineeringSupport surface
Owner:3844374 CANADA
Thermosyphon and method for producing it
InactiveUS20050056403A1Suitable for mass productionEfficient heat transferSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectronic componentFriction stir welding
The present invention relates to thermosyphons, in particular for use in the cooling of electronic components. In a first embodiment a thermosyphon is manufactured by extruding a base (1) and milling a channel structure in the base to produce a plurality of fins (5) extending vertically from the base. A lid (3) comprising a number of fins (4) extending vertically from the lid is placed over the heat sink channel structure so that a thermosyphon of an expanding channel system is formed. In a second embodiment the evaporator and condenser sections are separated and connected by pipes. To form a leak proof seal between the lid and the base, joining is preferably done by friction stir welding. By providing an extruded thermosyphon, heat transfer is made more efficient than when junctions are used. The present invention provides a new way of efficiently manufacturing an integrated structure, while keeping the heat transfer of the structure high.
Owner:SAPA
Plasma display panel and plasma display device having the same
InactiveUS20050077822A1Improve heat transfer efficiencySimple structureAlternating current plasma display panelsDischarge tube main electrodesEngineeringHeat transfer efficiency
A plasma display panel having improved heat transfer efficiency and temperature distribution, and a plasma display device including the same are disclosed. The plasma display device includes a plasma display module that includes a plasma display panel on which an image is displayed, a chassis base facing the plasma display panel, a circuit unit disposed at a back side of the chassis base for driving the plasma display panel, a front cover and a back cover that house the plasma display module, and at least a heat radiation coating layer formed between the front cover and the back cover. The heat radiation layer reduces a conventional heat dissipation sheet unnecessary, and thus reduces process times and manufacturing costs.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
Stator for an electric motor having a temperature monitor
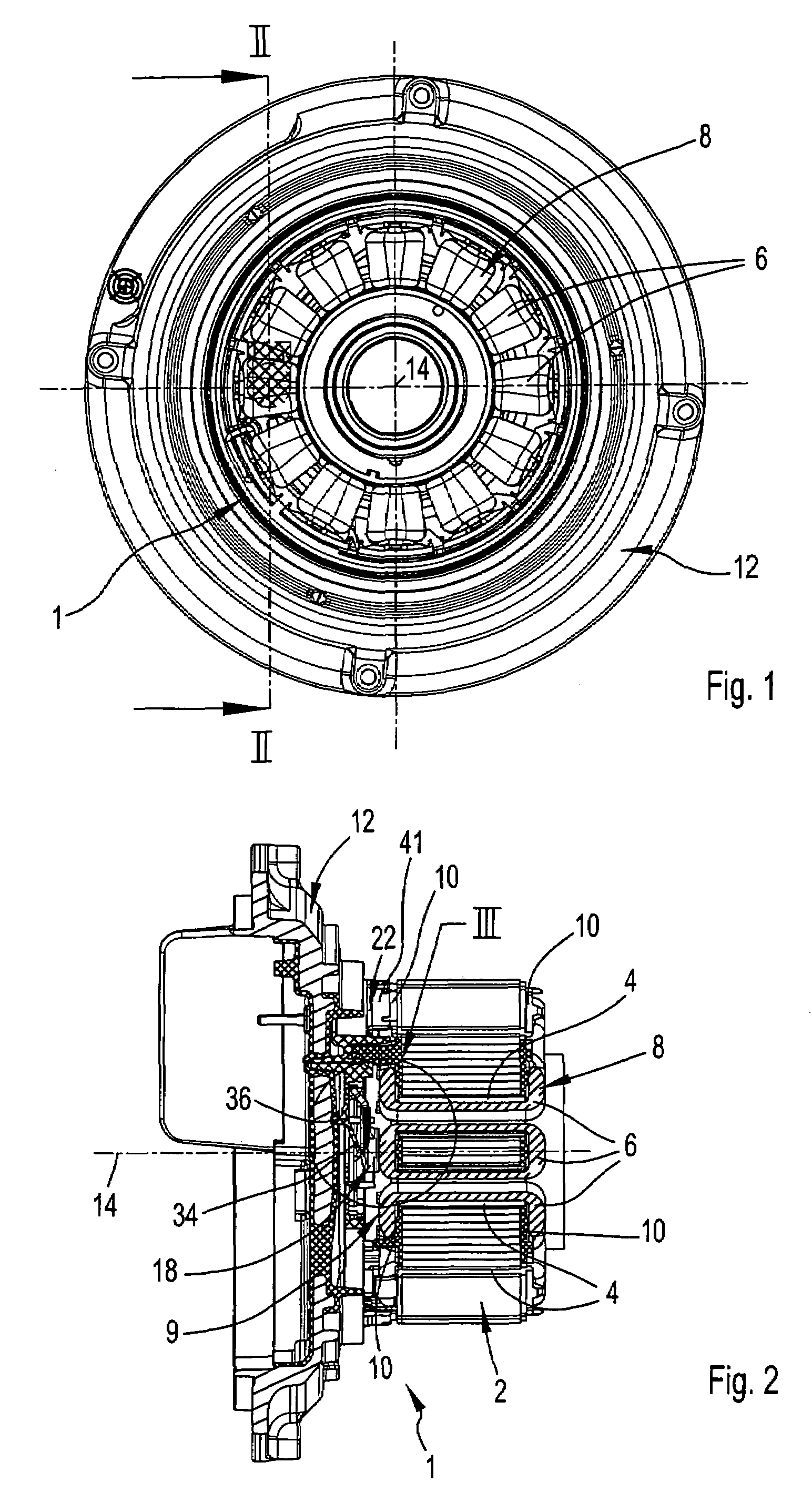
ActiveUS7402925B2Efficient heat transferImprove reliabilityWindingsStructural associationTemperature monitoringConductor Coil
A stator for an electric motor, in particular for an external rotor motor, includes a laminated stator core which is provided with a stator winding and having a connecting arrangement, which is arranged on one end side in the region of an end winding of the stator winding, for the purpose of electrically connecting winding wire ends of the stator winding and connecting wires of a temperature monitor connected upstream of the stator winding. The connecting arrangement has an insulating switching disk which covers the region of the end winding, in particular in the form of a cap. The temperature monitor is held in the switching disk in an integrated manner such that, on the end-winding side, it rests between the Mater winding and the switching disk such that it is in thermally conductive bearing contact with said stator winding.
Owner:EBM PAPST MULFINGEN GMBH & CO KG
Heat exchanger system for circuit card assemblies
ActiveUS20060133033A1Raise transfer toEfficient heat transferAir heatersInsulated cablesEngineeringConductive materials
An apparatus for housing and cooling circuit card assemblies employed in communication and other systems is disclosed including a chassis having opposed end walls which are formed with a series of spaced inlet card guides and correspondingly spaced outlet card guides, respectively. A straight-pass heat exchanger is directly mounted to each circuit card assembly via thermally conductive material, and opposed ends of the heat exchanger are mounted by a wedge lock to respective inlet and outlet card guides. The heat exchanger employs unique angled interface geometry that creates a gasketless airtight joint with complimentary inlet and outlet card guide geometry through which cooling air passes.
Owner:HARRIS CORP
Blend soup maker
InactiveUS7780337B2Efficient heat transferSave energyRotary stirring mixersTransportation and packagingEngineeringMechanical engineering
A blend soup maker (100). Soup maker (100) comprises a jar (102) having an open top and an open bottom for holding food, a lid (104) for closing the open top of jar (102), a bottom cap (106) for closing the open bottom of jar (102), a blending blade (114) installed inside jar (102) for blending food, an electrical heating tube (116) fixedly installed on the bottom of jar (102) for heating food, a base support (112) disposed underneath jar (102) for supporting jar (102), a blending motor (124) installed inside support base (112) and removably coupled with blade (114) for driving blade (114) to blend food, and a support member (110) engaged with the lower portion of jar (102) for adapting jar (102) to stand on base support (112).
Owner:PENG ZHENG
Low-cost solar energy tracking and condensing power generation method
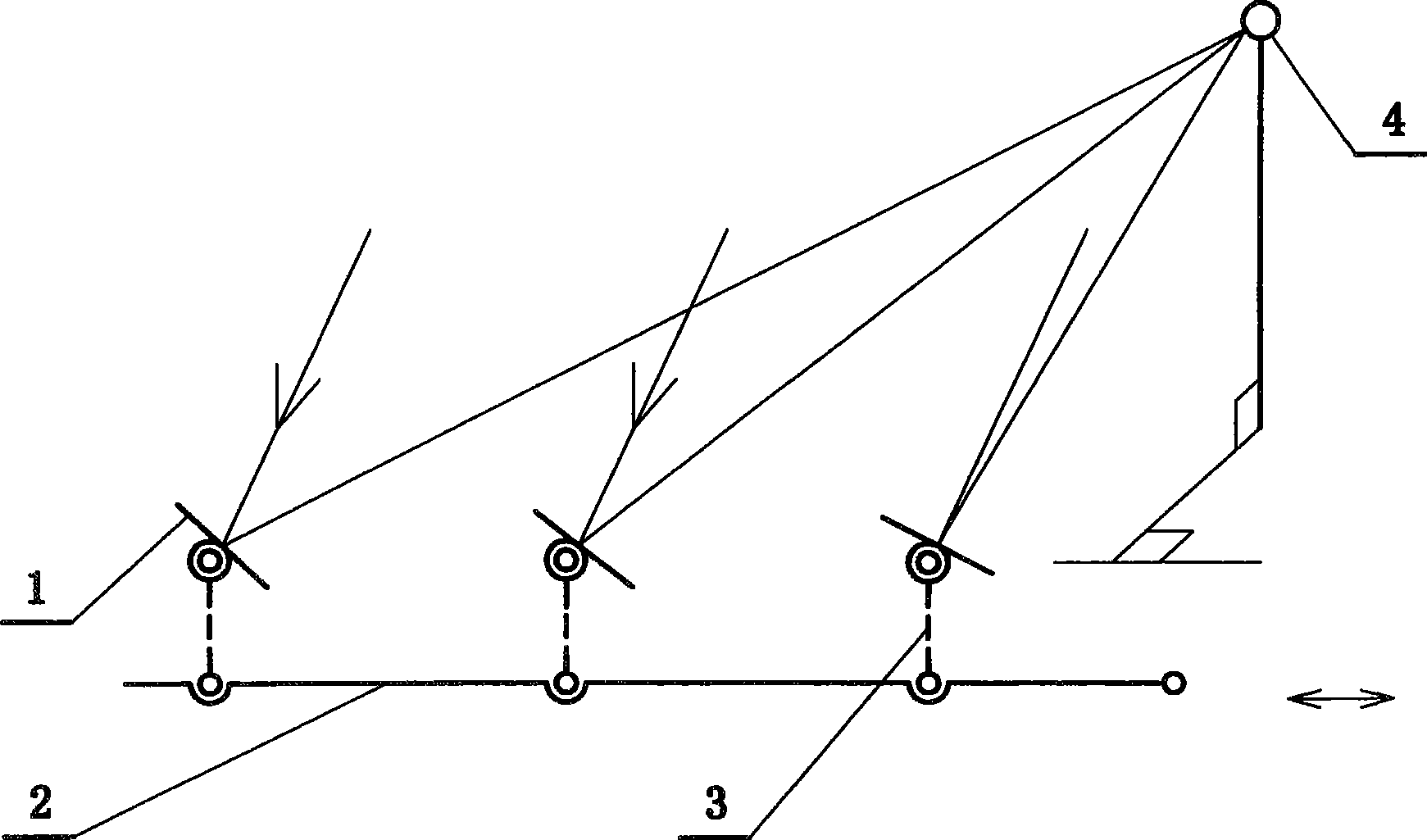
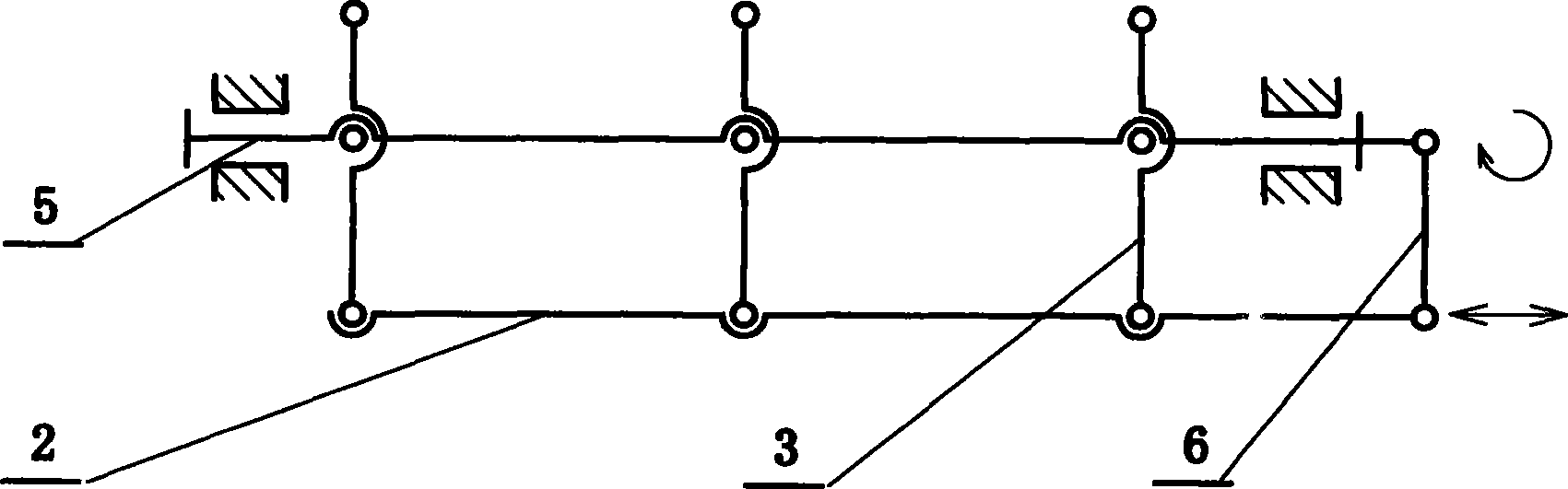
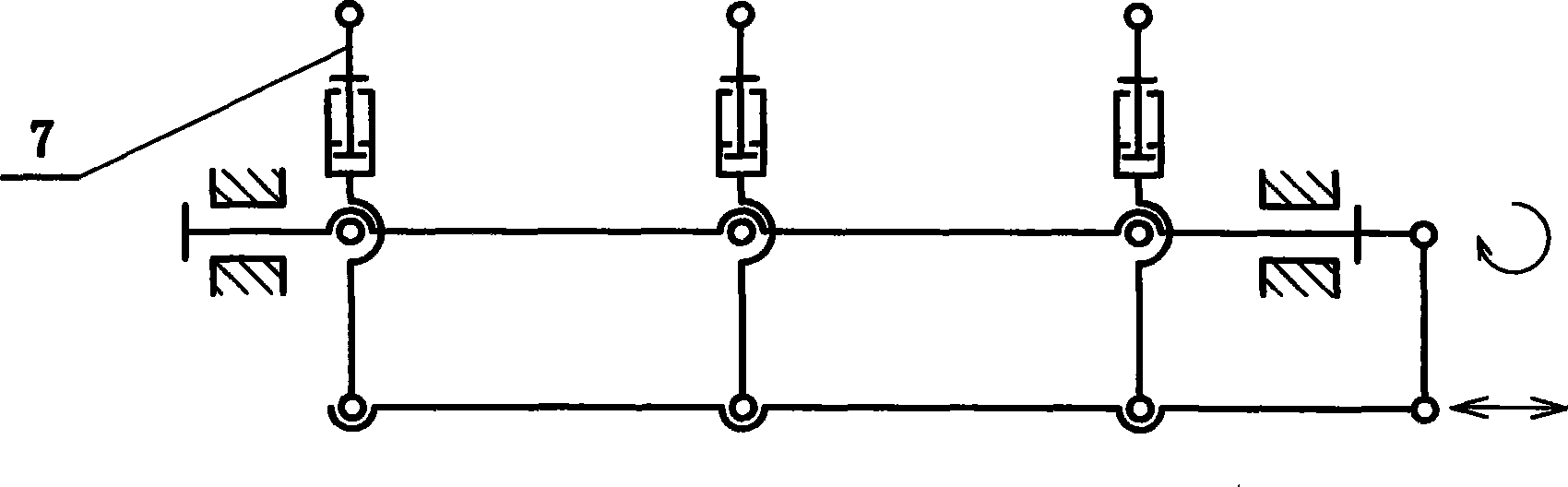
InactiveCN101521477ALow costLow wind resistancePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heat devicesHeating powerSolar power
The invention provides a low-cost solar energy tracking and condensing power generation method, belongs to the field of solar utilization, relates to solar energy condensing light and heat power generation and condensing photovoltaic power generation and solar energy condensing light and heat utilization, and realizes a whole low-cost proposal for solar energy power generation through technical breakthroughs in various links. The method comprises that: a parallel linkage and a compensation mechanism control a reflecting mirror array to trace and condense light in low cost; heat induction of a power thermotube of an inverted valve is added to a thermotube cycle for evaporation and condensation; container type heat evaporation and pressurization replaces a feed pump to make a heat power generation cycle freely select working media for high-efficiency fully-enclosed operation; and a simple linear motor type hydrothermomagnetic power generation method can make the heat pressurization power generation cycle have higher efficiency and lower cost, make thermotubes on solar cell backboards radiate heat, condense light, generate power and the like. The low-cost whole resolution proposal can promote wide use of solar energy, and the technical breakthroughs in the various links can play important roles in saving energy in respective fields.
Owner:张玉良
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com