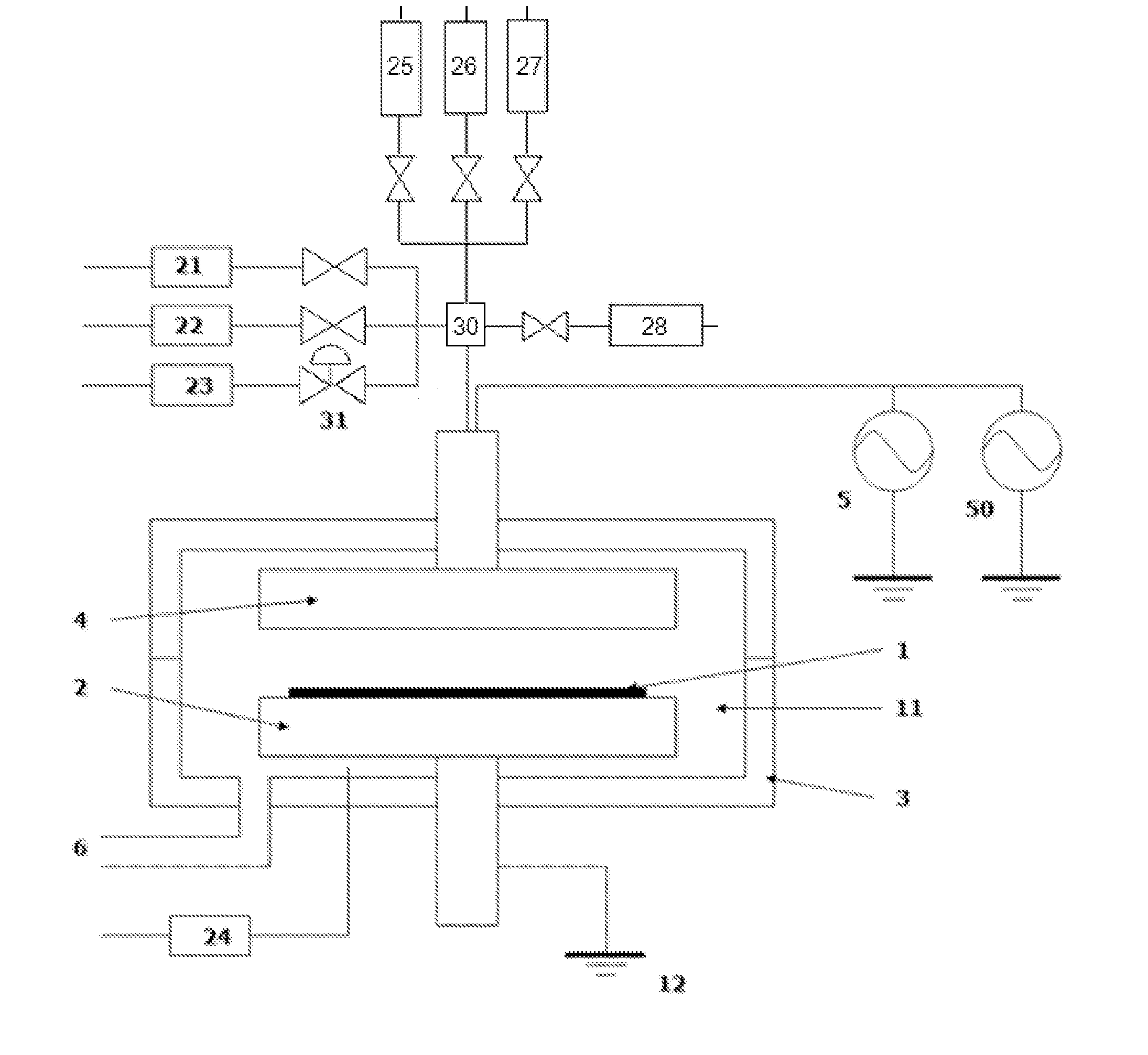Patents
Literature
14242 results about "Etching" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types of material. As a method of printmaking, it is, along with engraving, the most important technique for old master prints, and remains in wide use today. In a number of modern variants such as microfabrication etching and photochemical milling it is a crucial technique in much modern technology, including circuit boards.
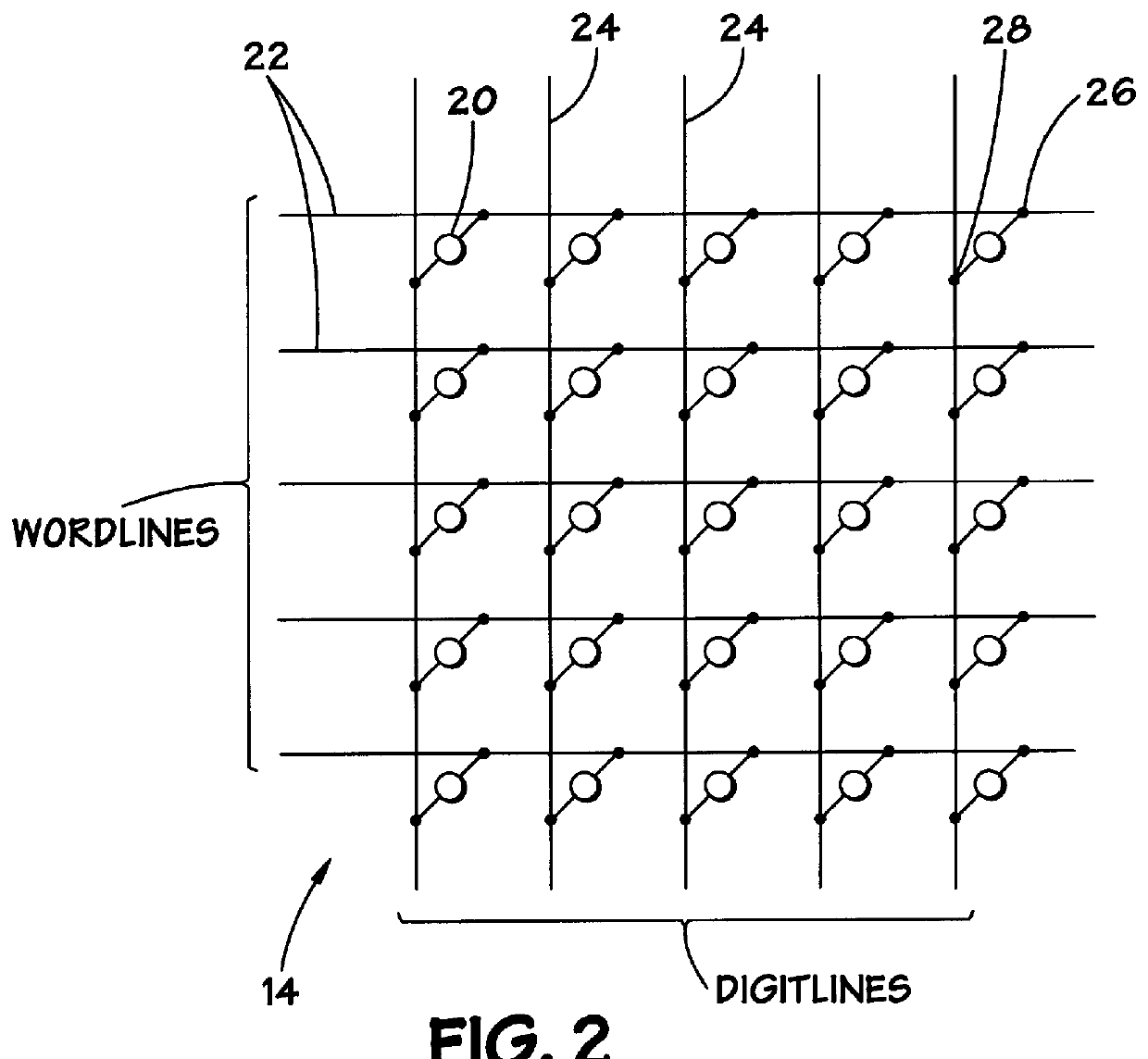
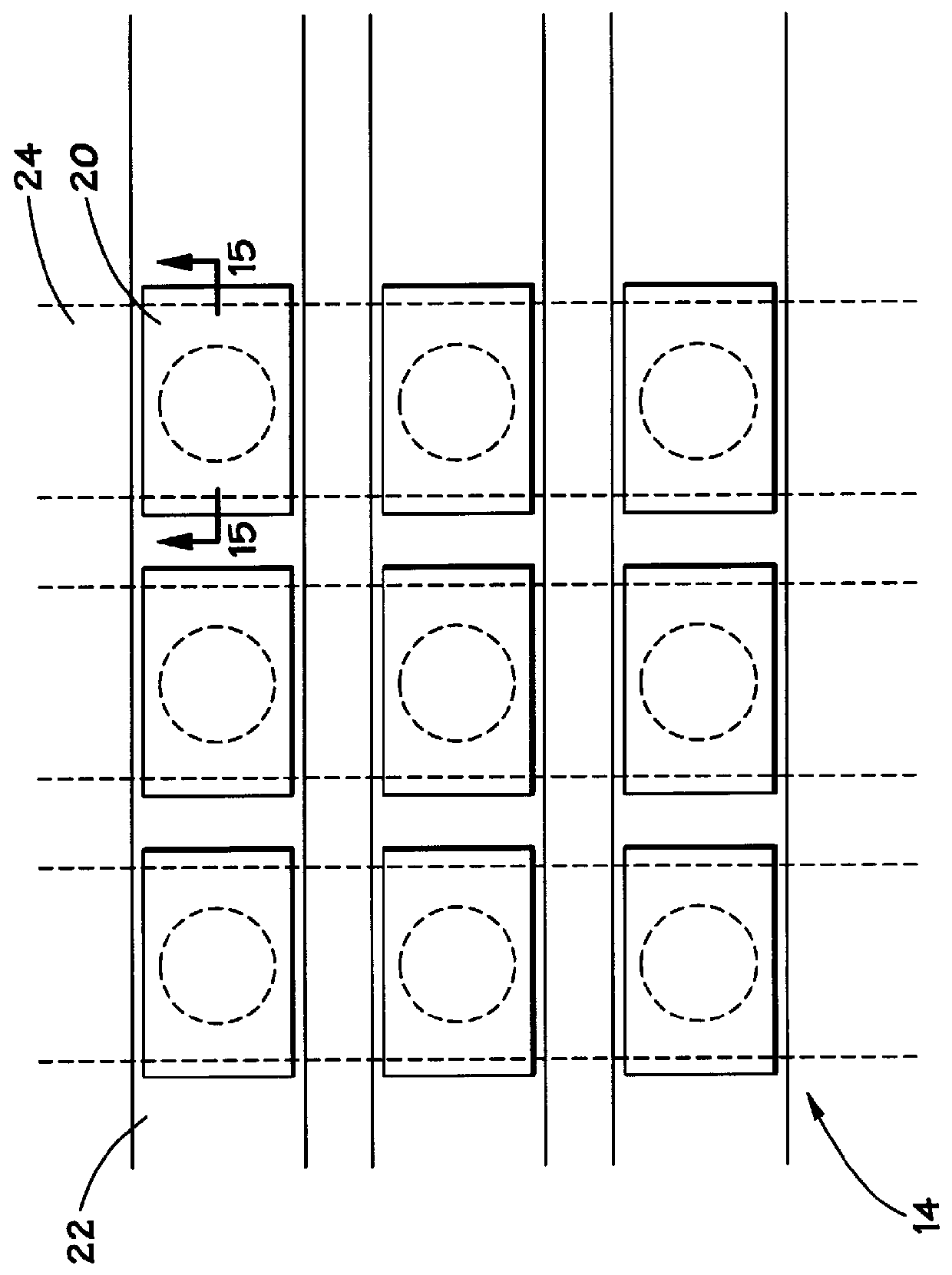
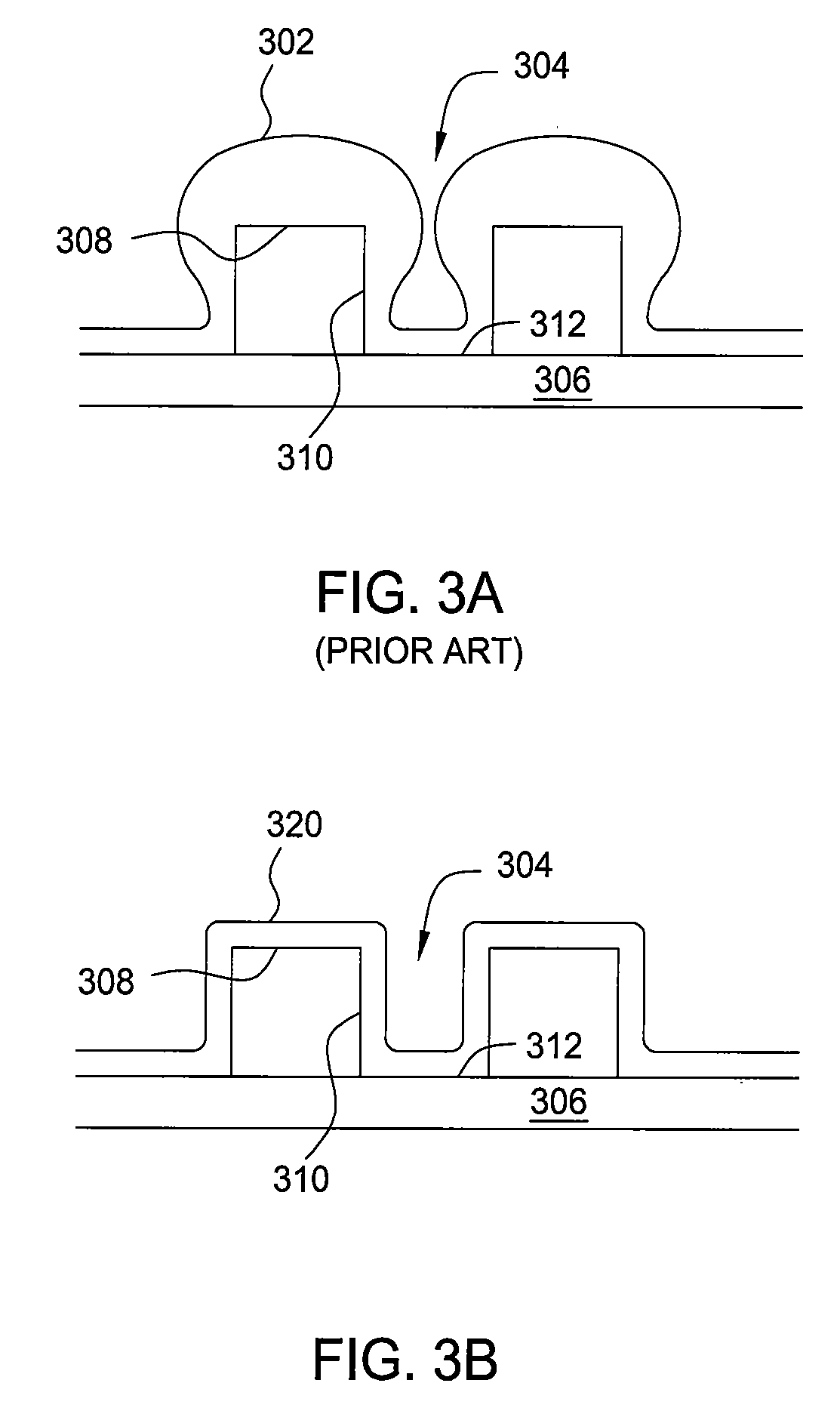
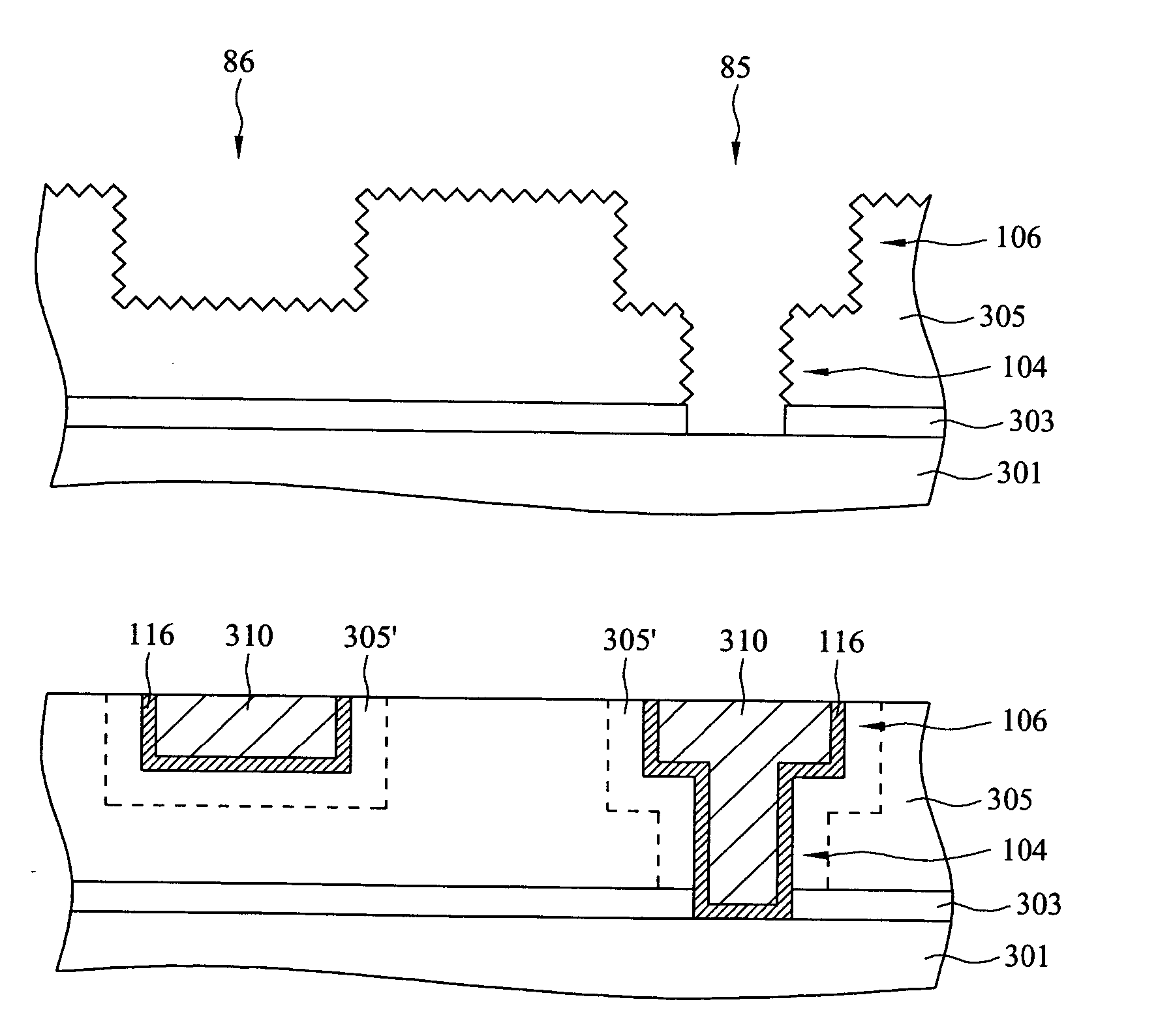
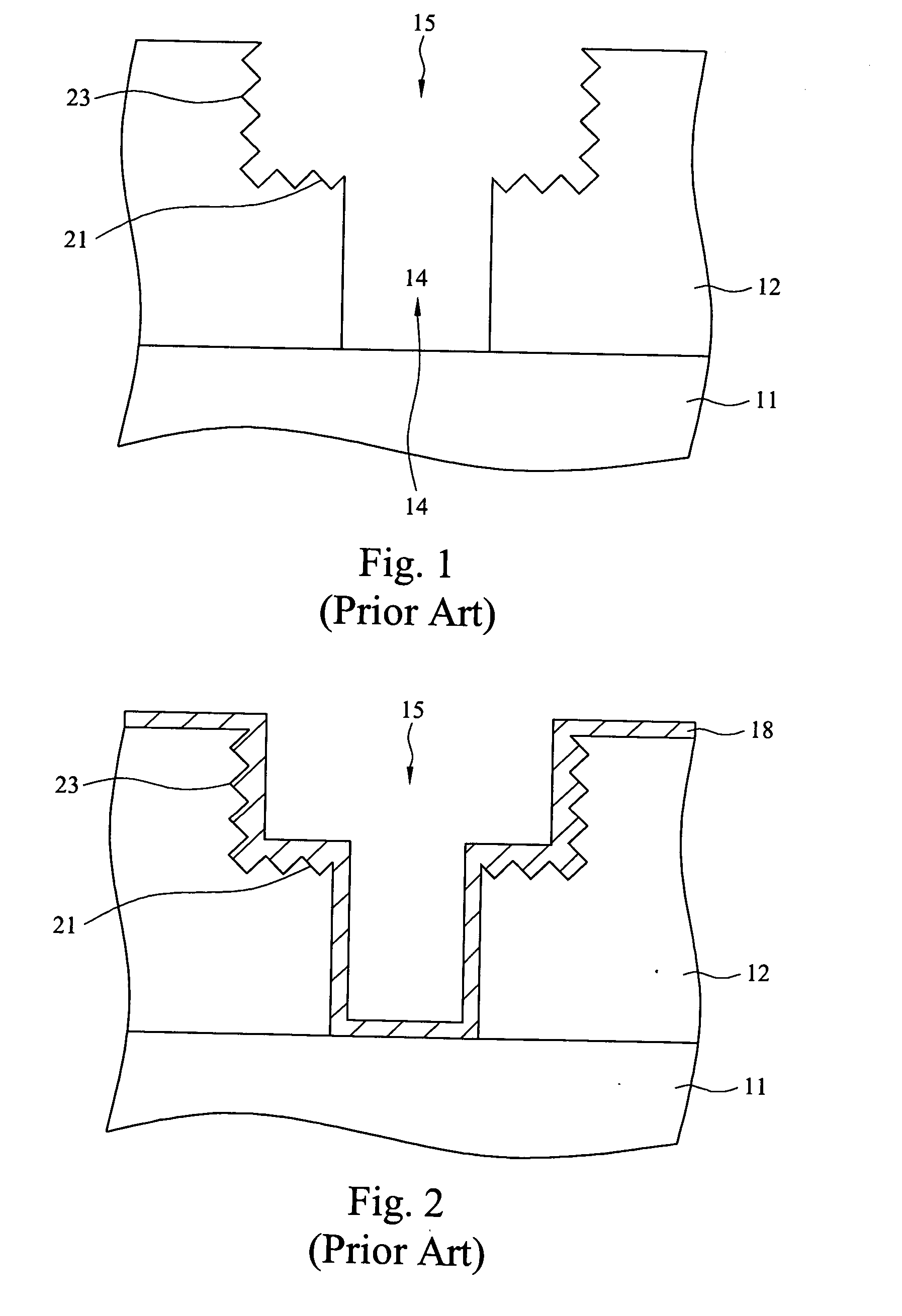
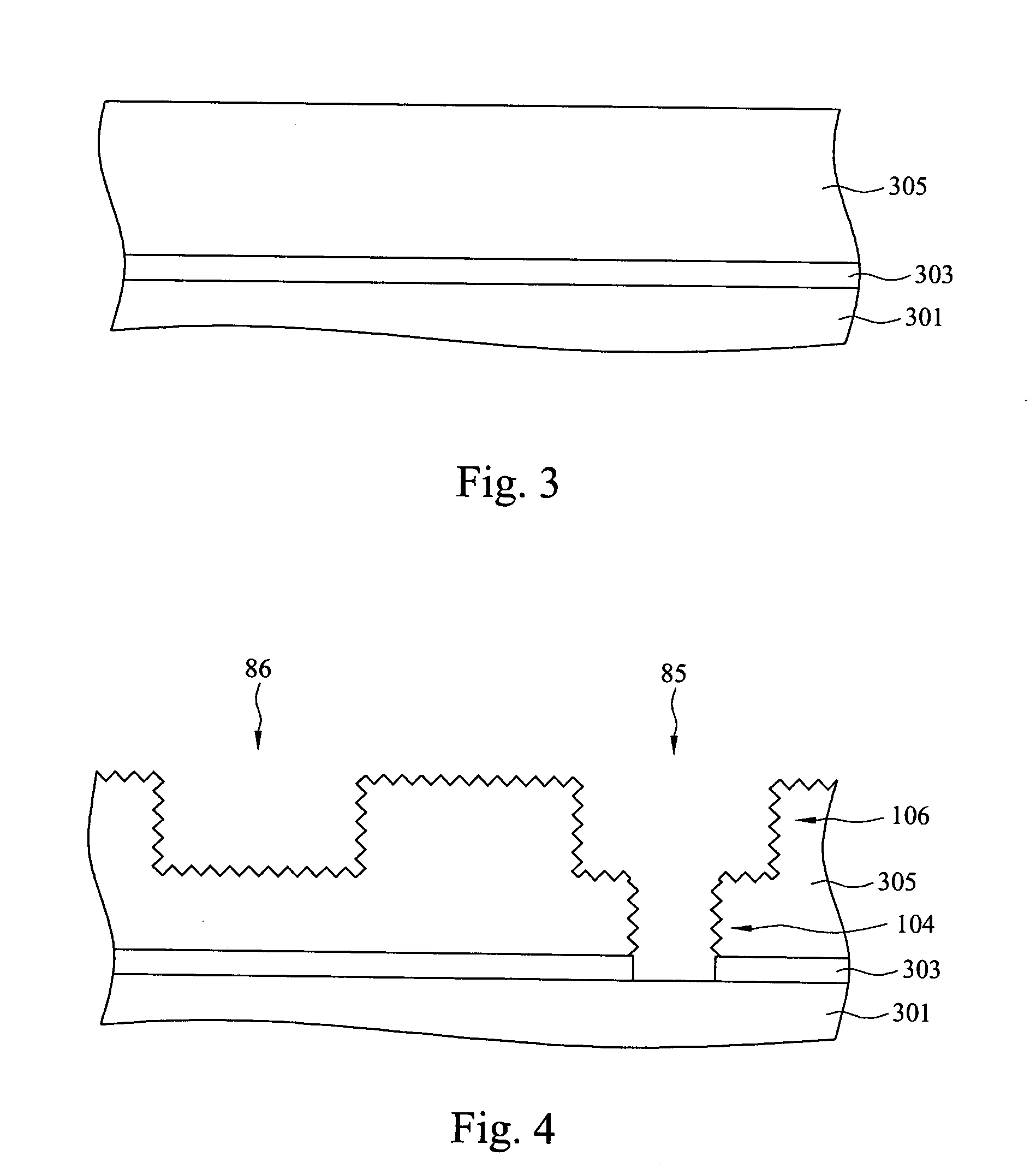
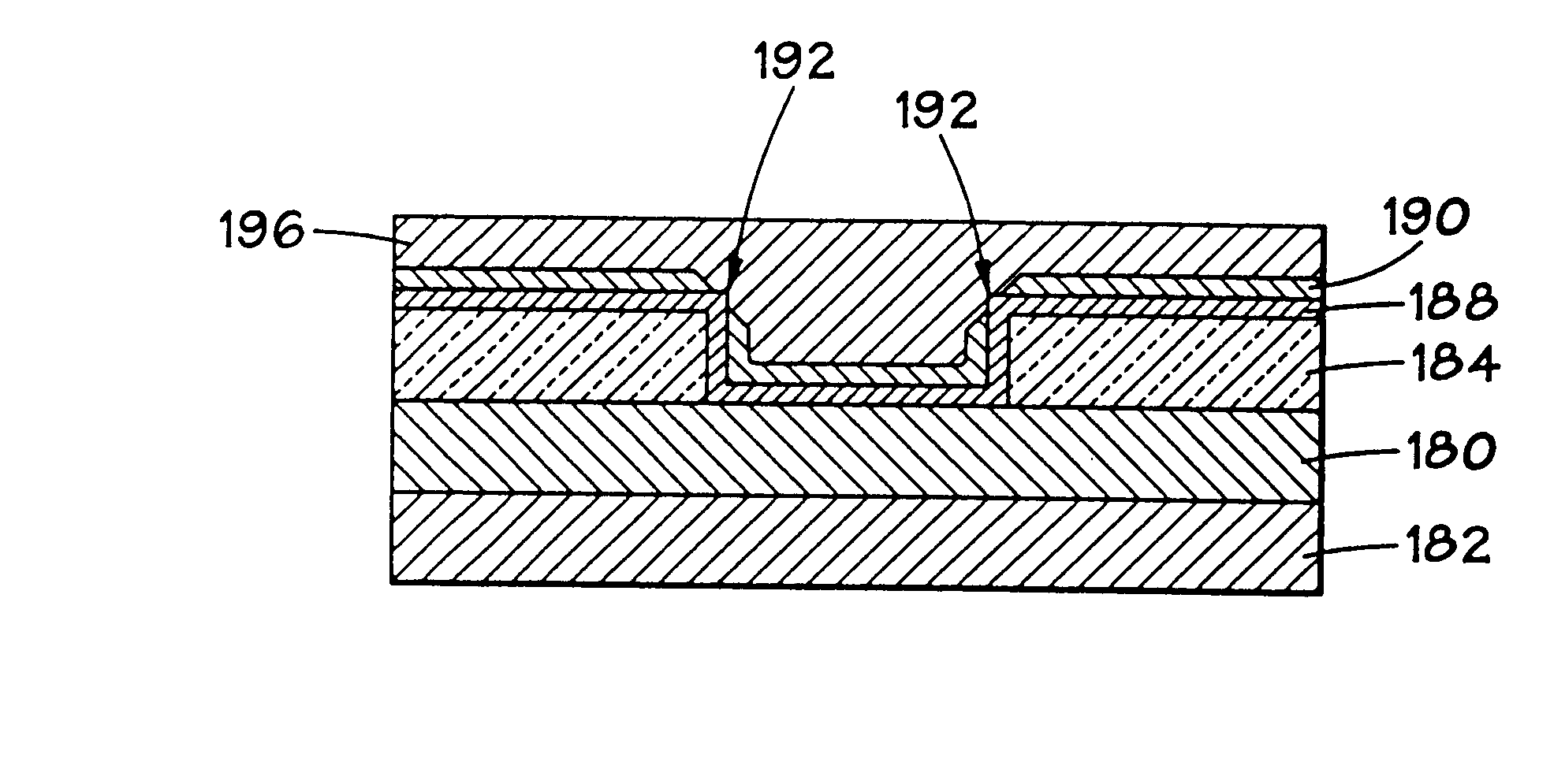
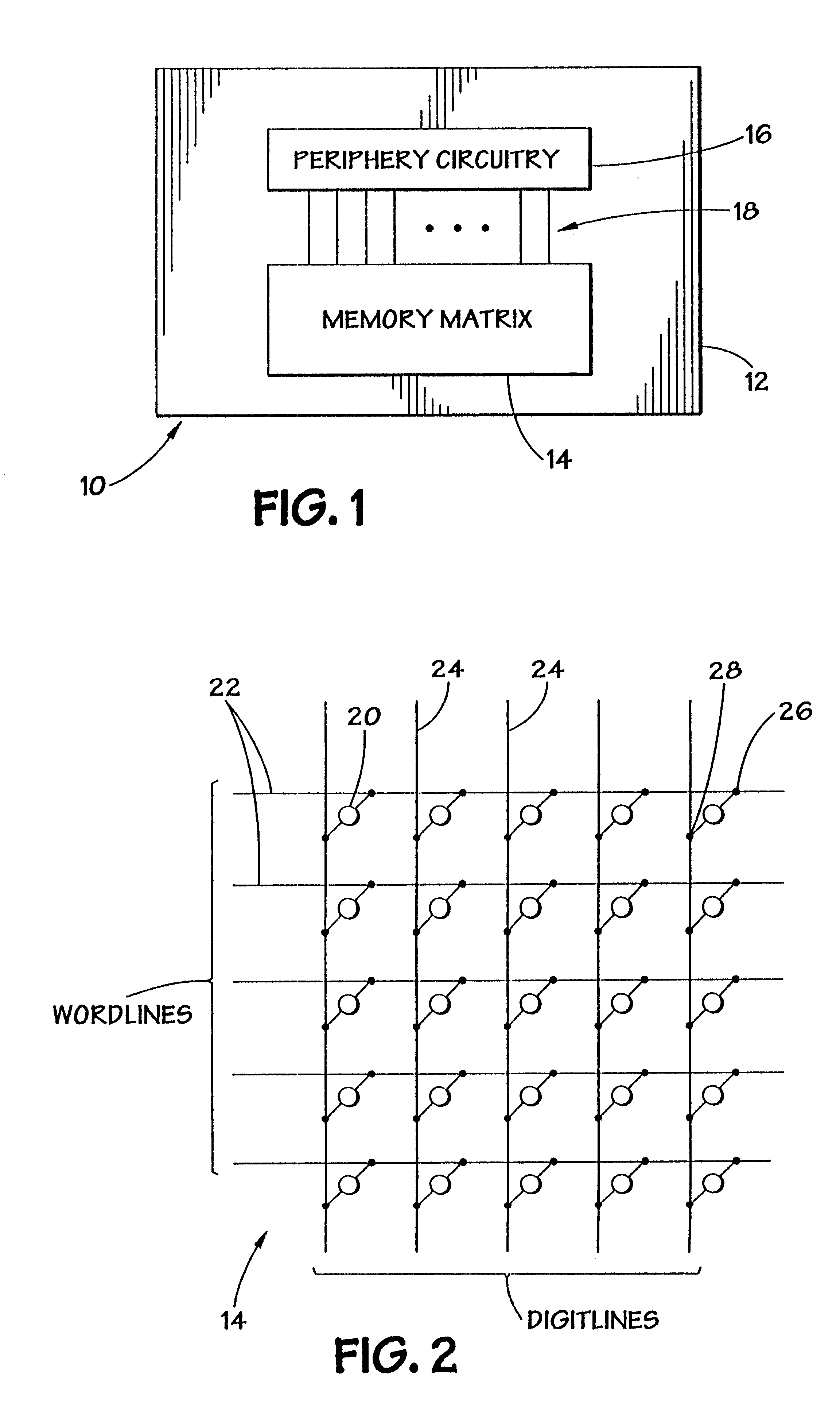
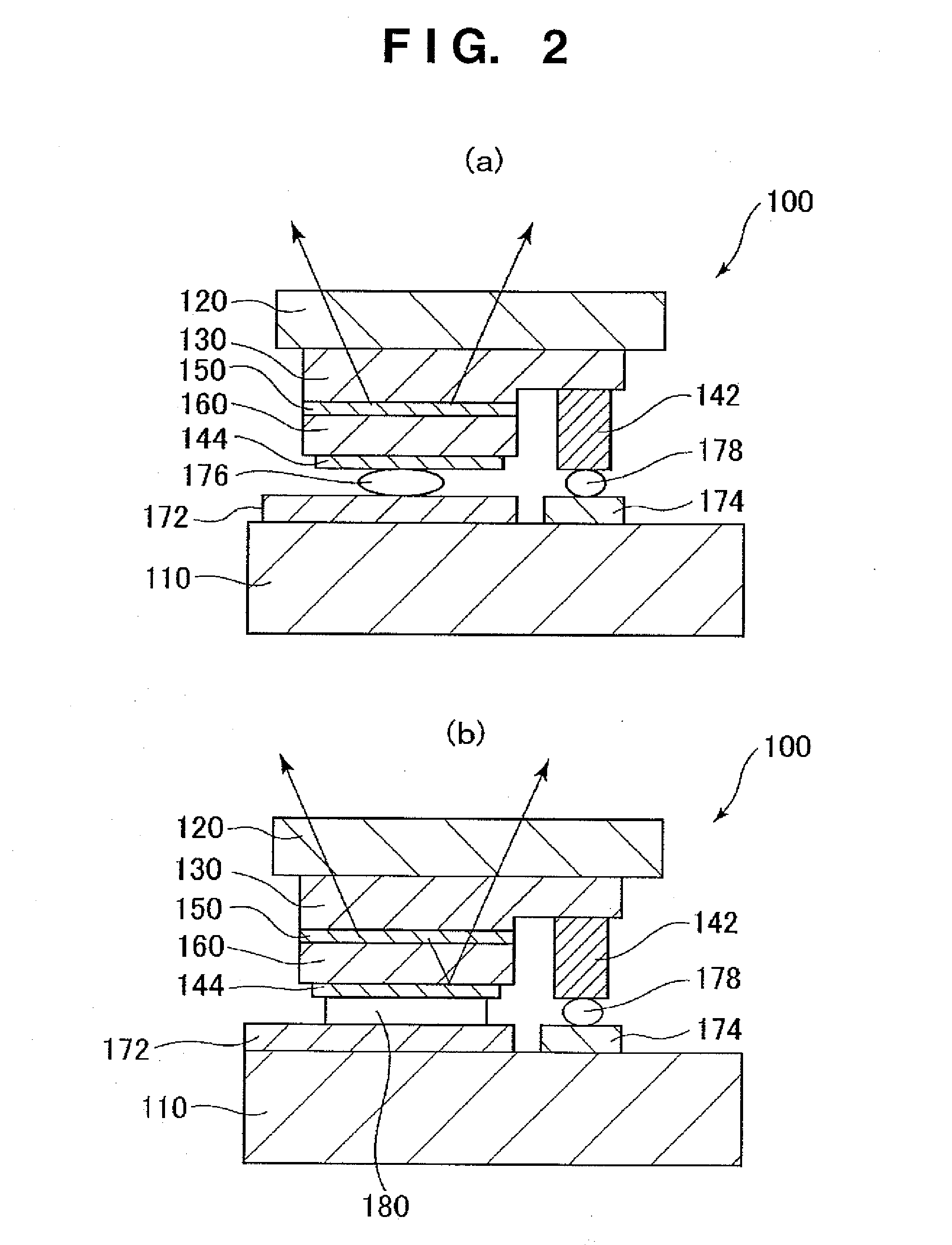
Contact structure and memory element incorporating the same
InactiveUS6031287ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesChemical-mechanical planarizationEtching
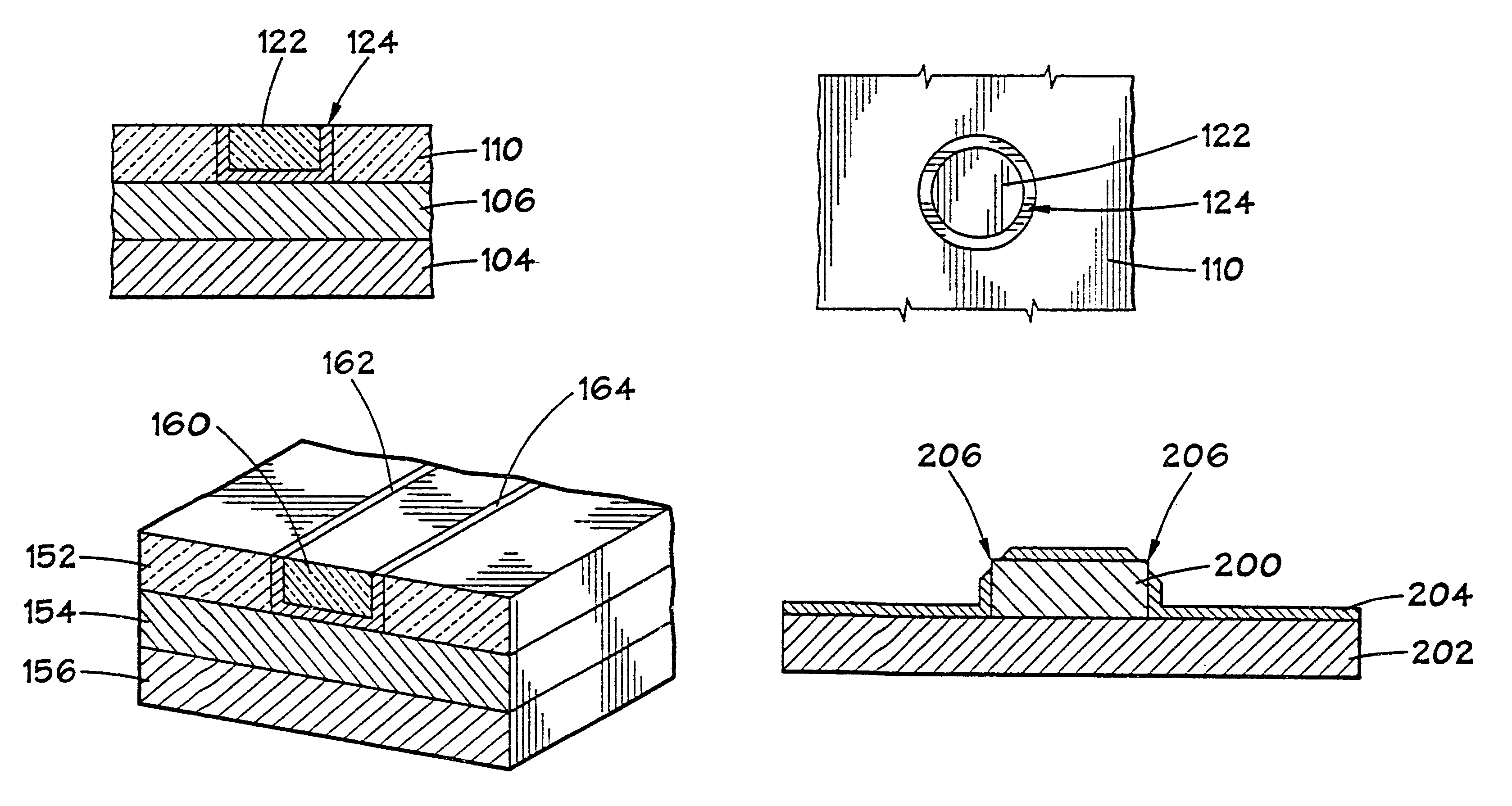
Annular and linear contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
Wound closure material
Articles are provided having no orientation or a multi-directional orientation. Such articles may be in the form of films, ribbons, sheets, and / or tapes and may be utilized as buttresses with a surgical stapling apparatus or as reinforcing means for suture lines. The articles may be produced with etchings on at least a part of a surface of the article.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method to improve the step coverage and pattern loading for dielectric films
InactiveUS20070232071A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingSilicon oxide
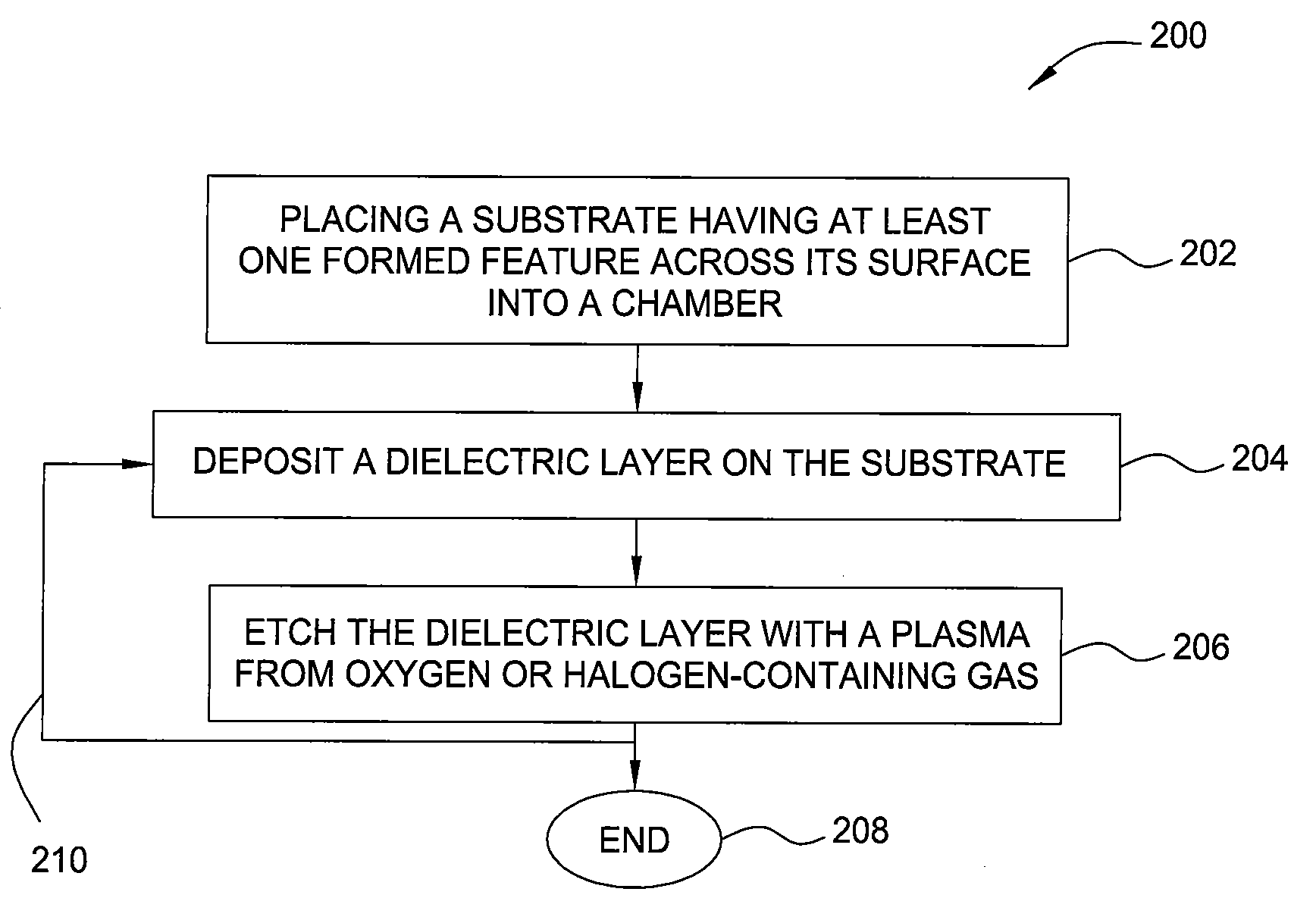
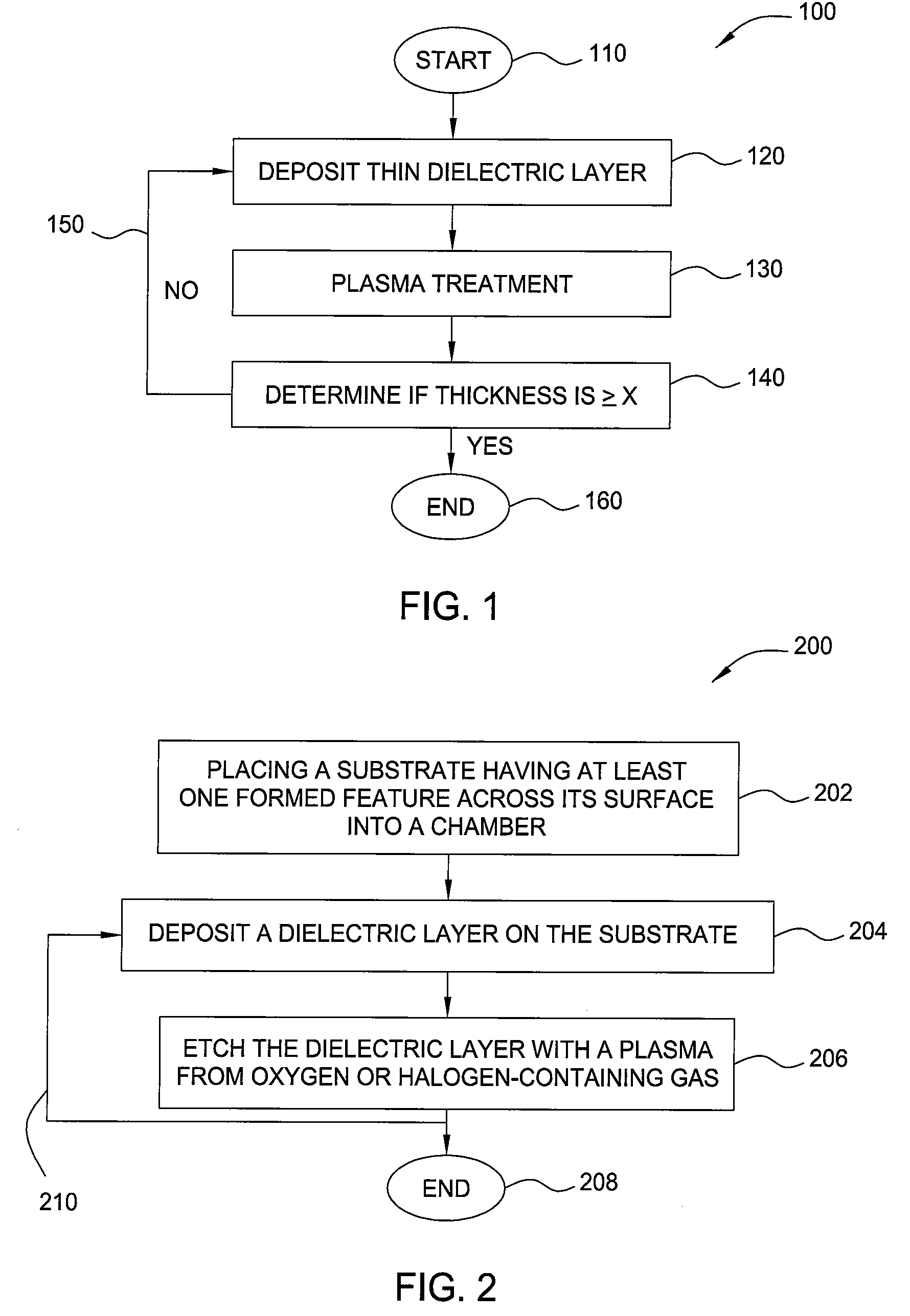
Methods of controlling the step coverage and pattern loading of a layer on a substrate are provided. The dielectric layer may be a silicon nitride, silicon oxide, or silicon oxynitride layer. The method comprises depositing a dielectric layer on a substrate having at least one formed feature across a surface of the substrate and etching the dielectric layer with a plasma from oxygen or a halogen-containing gas to provide a desired profile of the dielectric layer on the at least one formed feature. The deposition of the dielectric layer and the etching of the dielectric layer may be repeated for multiple cycles to provide the desired profile of the dielectric layer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Sealing pores of low-k dielectrics using CxHy
A semiconductor method of manufacturing involving porous and / or carbon containing, low-k dielectrics is provided. The method includes forming a hydrocarbon of the general composition CxHy on the surface of the low-k dielectric. The hydrocarbon layer includes depositing a precursor material, preferably C2H4 or (CH3)2CHC6H6CH3. In accordance with embodiments of this invention, carbon diffuses into the low-k dielectric, thereby reducing carbon depletion damage caused by plasma processing or etching. Surface dielectric pores damaged by plasma processing are also repaired by sealing them with the CXHY layer. Embodiments include semiconductor devices, such as devices having damascene interconnect structures, manufacturing using methods provided.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
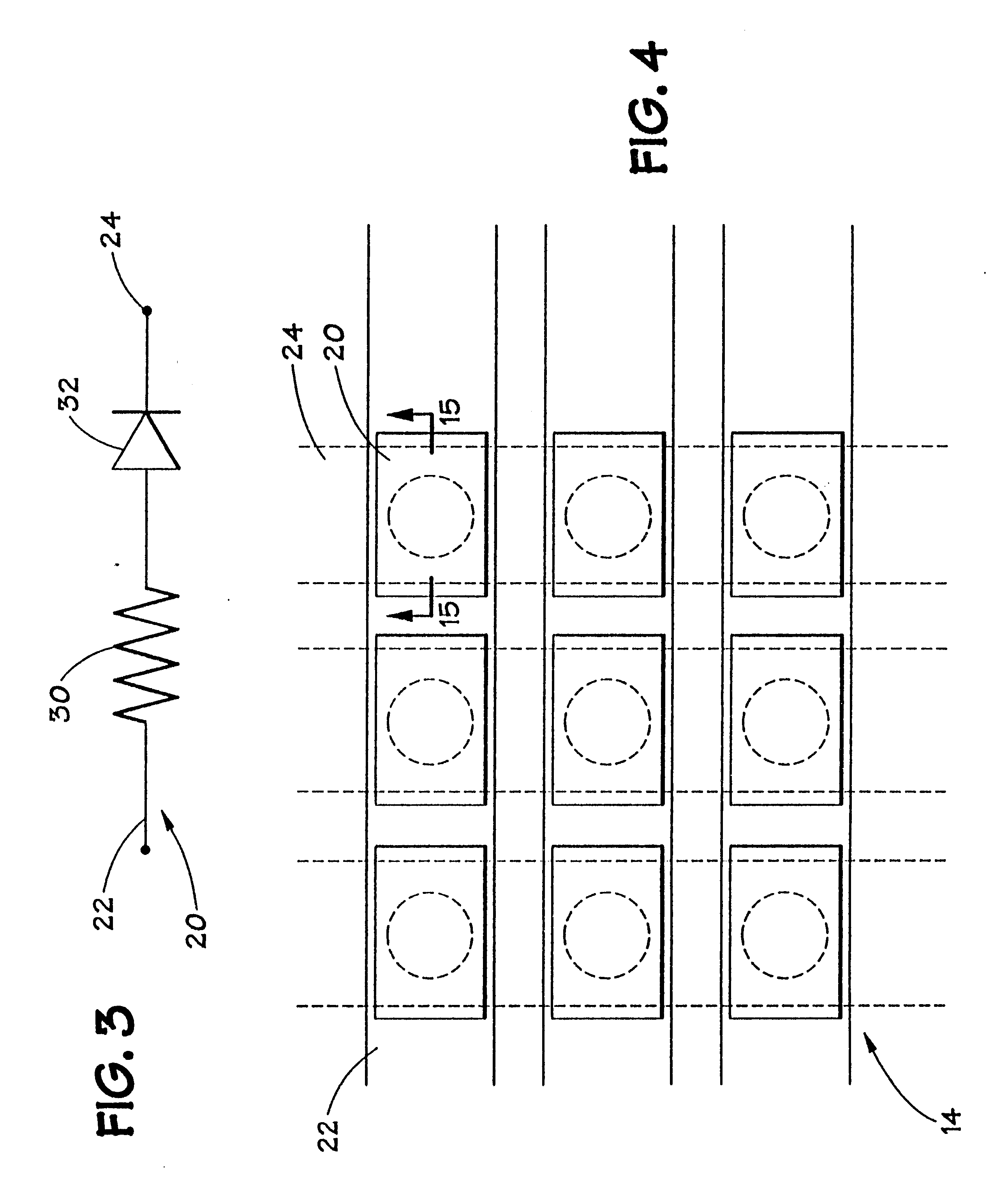
Memory elements and methods for making same
Annular, linear, and point contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
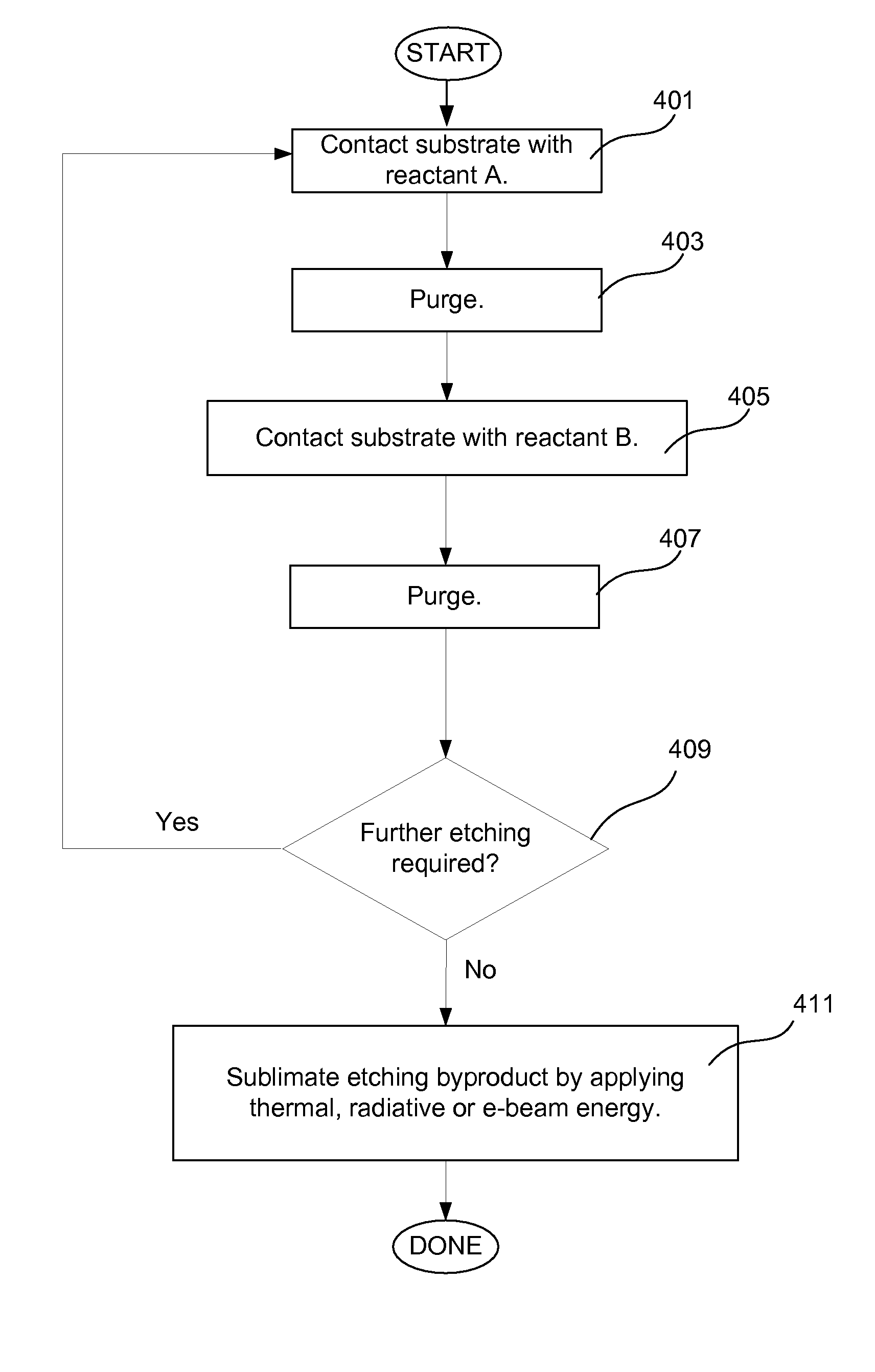
Adsorption based material removal process
InactiveUS8043972B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSelf limitingEtching
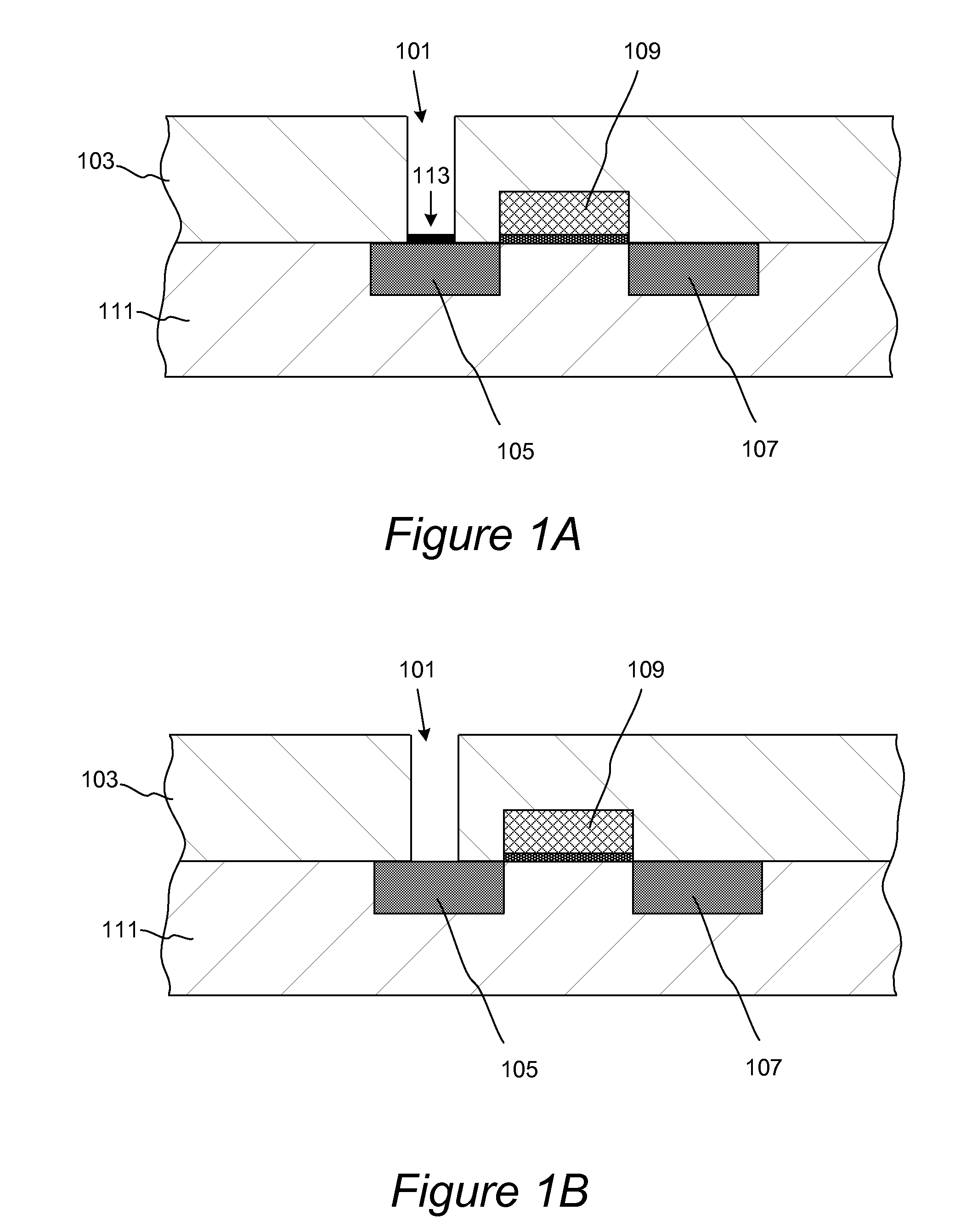
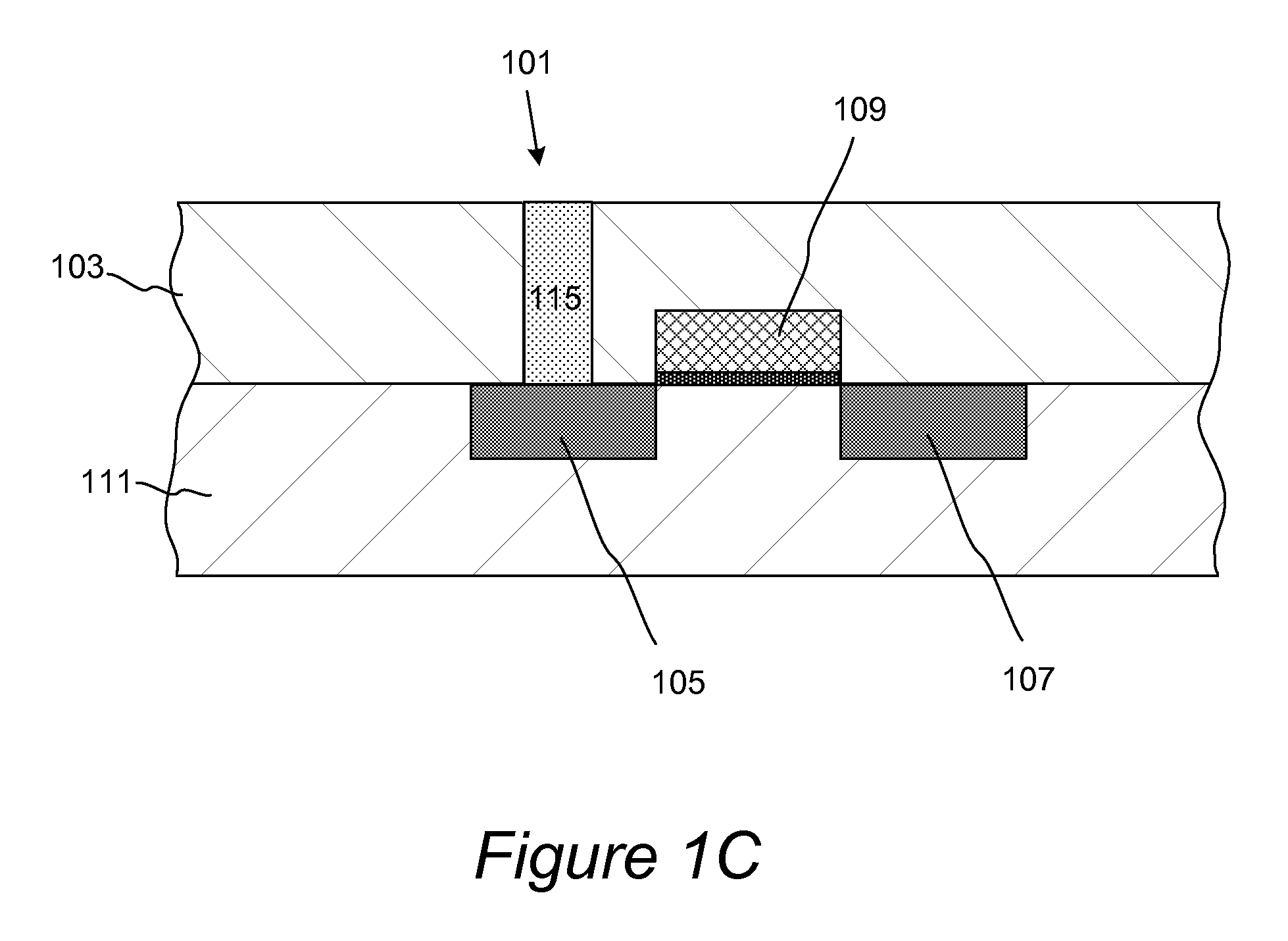
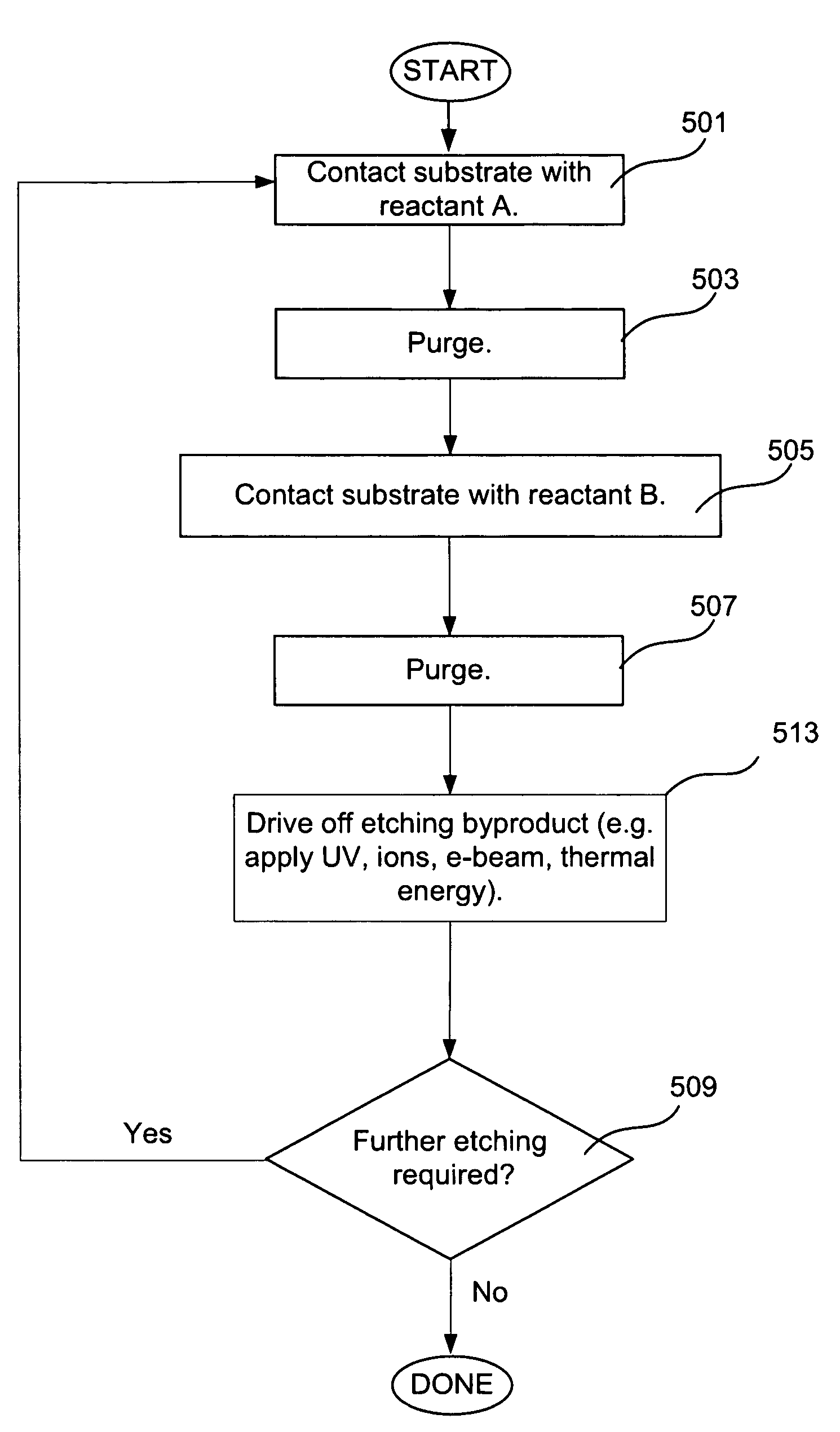
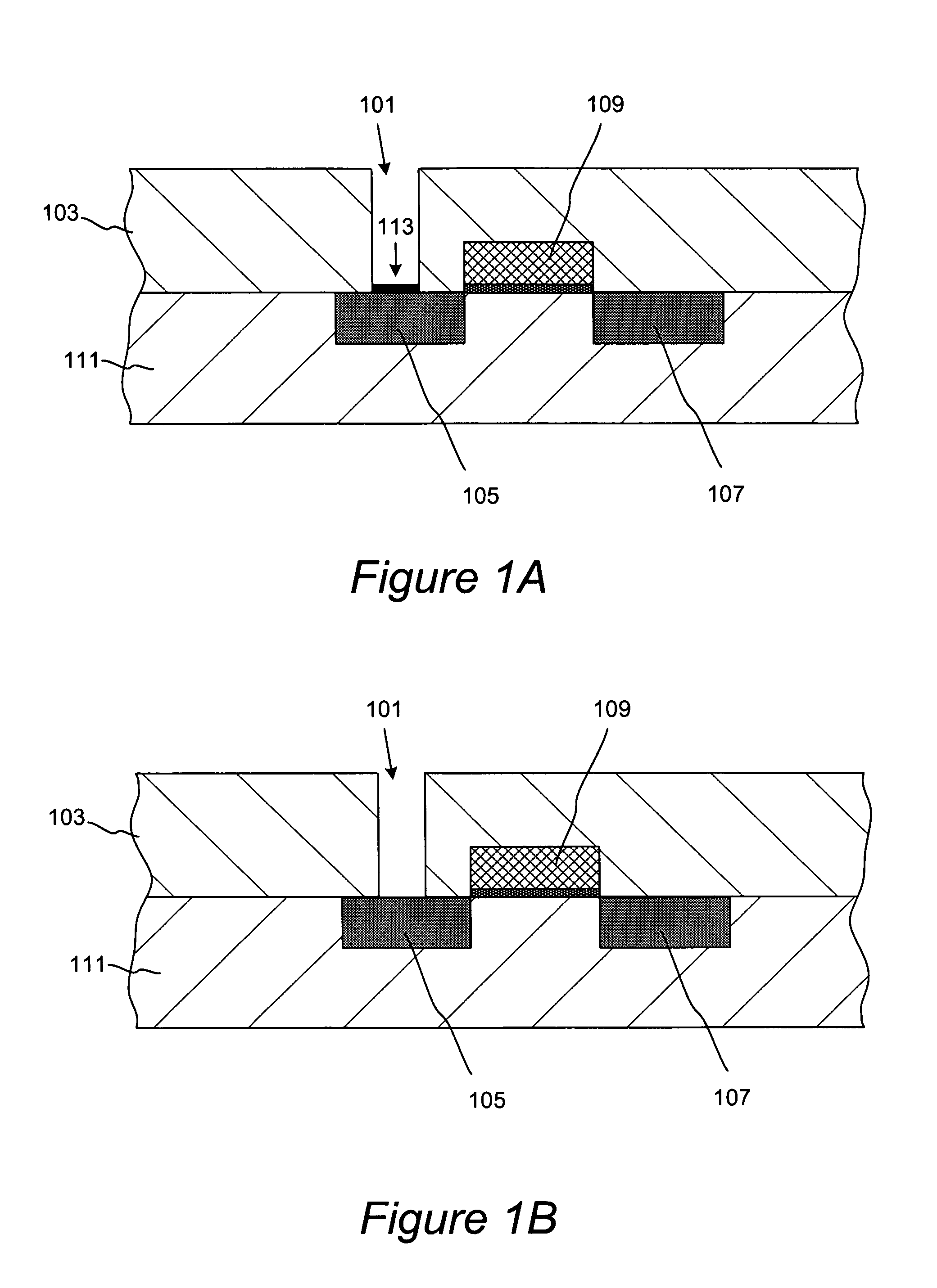
Methods for accurate and conformal removal of atomic layers of materials make use of the self-limiting nature of adsorption of at least one reactant on the substrate surface. In certain embodiments, a first reactant is introduced to the substrate in step (a) and is adsorbed on the substrate surface until the surface is partially or fully saturated. A second reactant is then added in step (b), reacting with the adsorbed layer of the first reactant to form an etchant. The amount of an etchant, and, consequently, the amount of etched material is limited by the amount of adsorbed first reactant. By repeating steps (a) and (b), controlled atomic-scale etching of material is achieved. These methods may be used in interconnect pre-clean applications, gate dielectric processing, manufacturing of memory devices, or any other applications where removal of one or multiple atomic layers of material is desired.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Adsorption based material removal process
Methods for accurate and conformal removal of atomic layers of materials make use of the self-limiting nature of adsorption of at least one reactant on the substrate surface. In certain embodiments, a first reactant is introduced to the substrate in step (a) and is adsorbed on the substrate surface until the surface is partially or fully saturated. A second reactant is then added in step (b), reacting with the adsorbed layer of the first reactant to form an etchant. The amount of an etchant, and, consequently, the amount of etched material is limited by the amount of adsorbed first reactant. By repeating steps (a) and (b), controlled atomic-scale etching of material is achieved. These methods may be used in interconnect pre-clean applications, gate dielectric processing, manufacturing of memory devices, or any other applications where removal of one or multiple atomic layers of material is desired.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
Chip interconnect wiring structure with low dielectric constant insulator and methods for fabricating the same
A method to achieve a very low effective dielectric constant in high performance back end of the line chip interconnect wiring and the resulting multilayer structure are disclosed. The process involves fabricating the multilayer interconnect wiring structure by methods and materials currently known in the state of the art of semiconductor processing; removing the intralevel dielectric between the adjacent metal features by a suitable etching process; applying a thin passivation coating over the exposed etched structure; annealing the etched structure to remove plasma damage; laminating an insulating cover layer to the top surface of the passivated metal features; optionally depositing an insulating environmental barrier layer on top of the cover layer; etching vias in the environmental barrier layer, cover layer and the thin passivation layer for terminal pad contacts; and completing the device by fabricating terminal input / output pads. The method obviates issues such as processability and thermal stability associated with low dielectric constant materials by avoiding their use. Since air, which has the lowest dielectric constant, is used as the intralevel dielectric the structure created by this method would possess a very low capacitance and hence fast propagation speeds. Such structure is ideally suitable for high density interconnects required in high performance microelectronic device chips.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
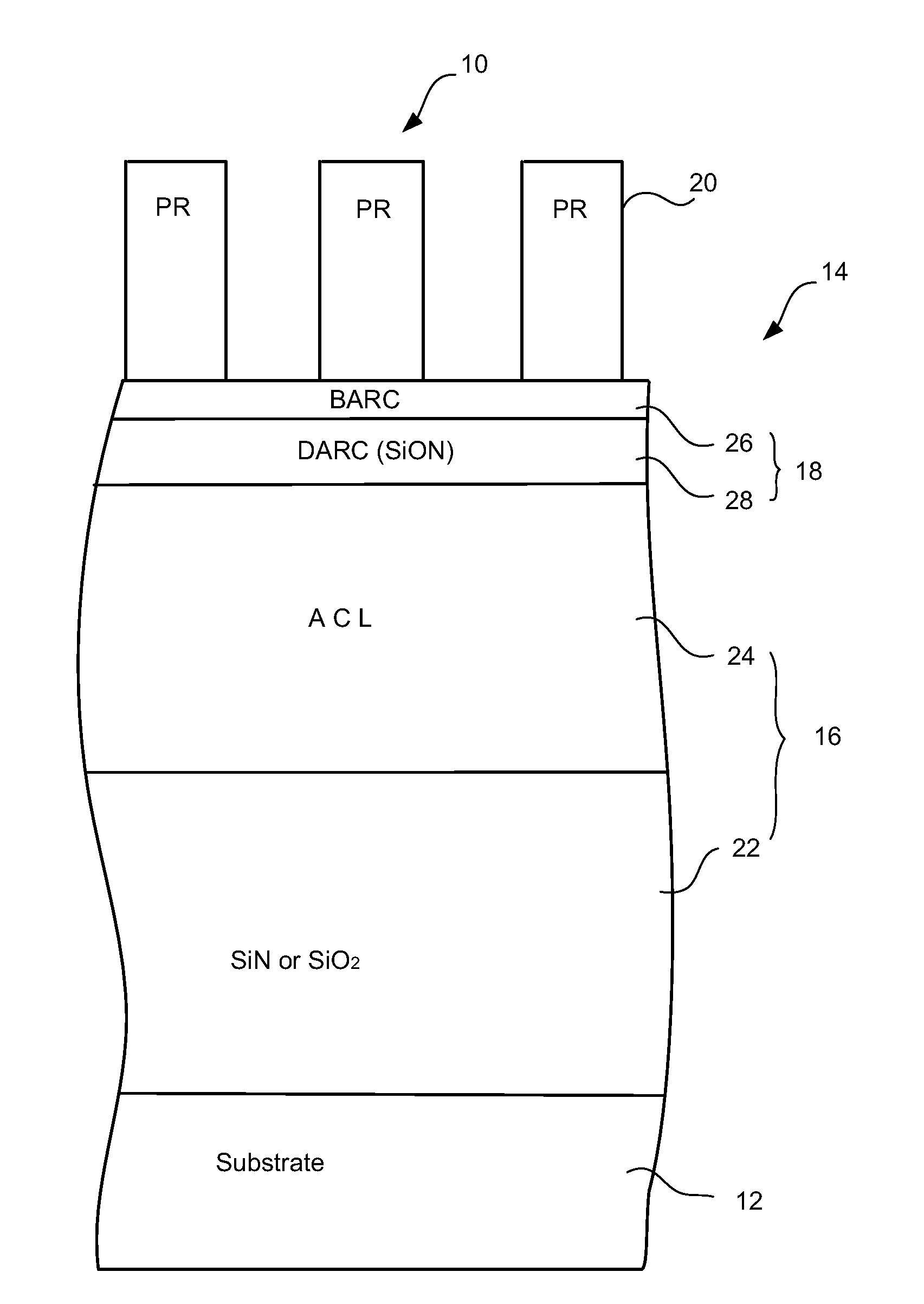
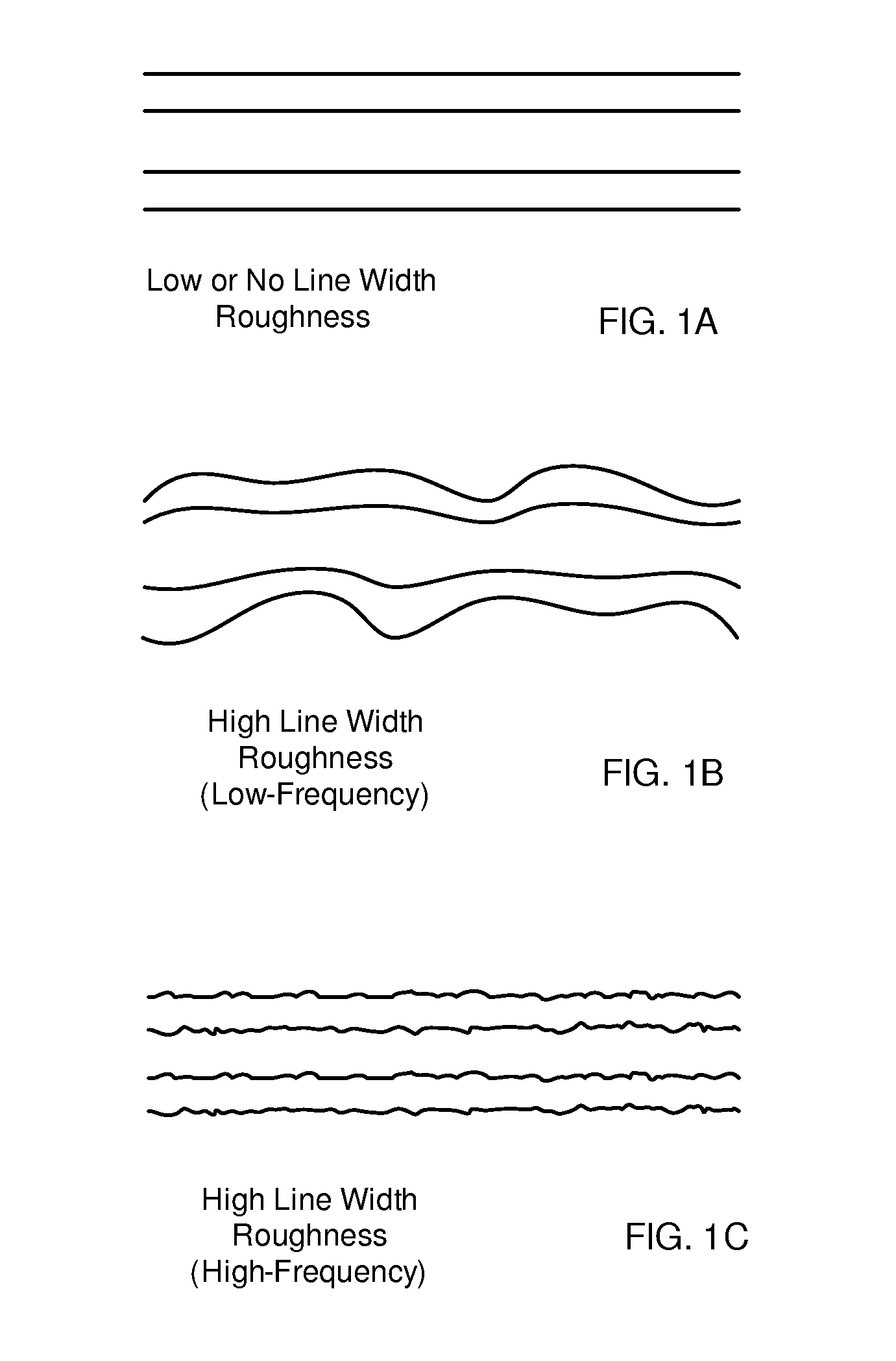
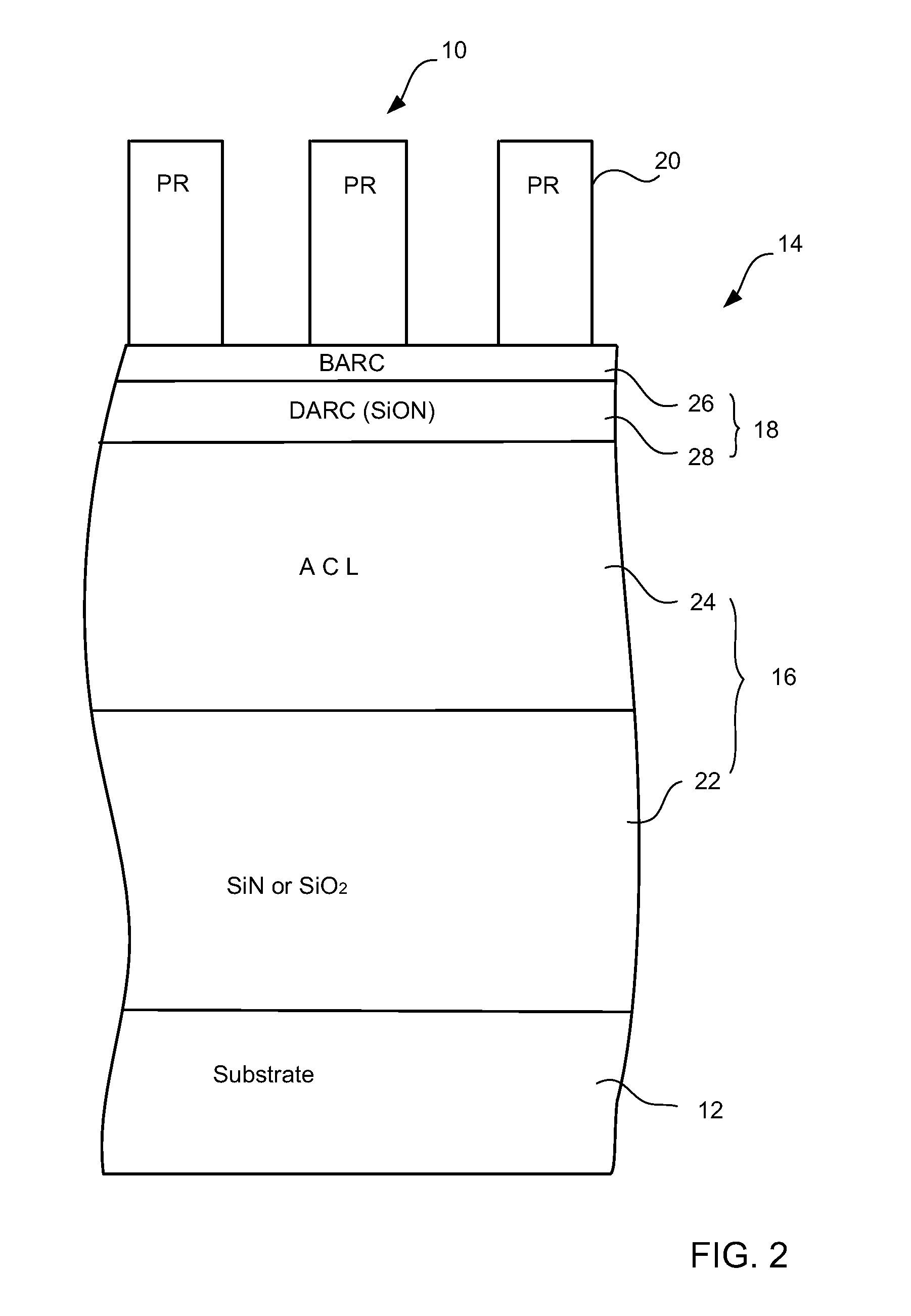
Method for reducing line width roughness with plasma pre-etch treatment on photoresist
InactiveUS20110117749A1Reduce line width roughnessElectric discharge tubesDecorative surface effectsEtchingLine width
A method for reducing line width roughness (LWR) of a feature in an etch layer below a patterned photoresist mask having mask features is provided. The method includes (a) non-etching plasma pre-etch treatment of the photoresist mask, and (b) etching of a feature in the etch layer through the pre-treated photoresist mask using an etching gas. The non-etching plasma pre-etch treatment includes (a1) providing a treatment gas containing H2 and COS, (a2) forming a plasma from the treatment gas, and (a3) stopping the treatment gas.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
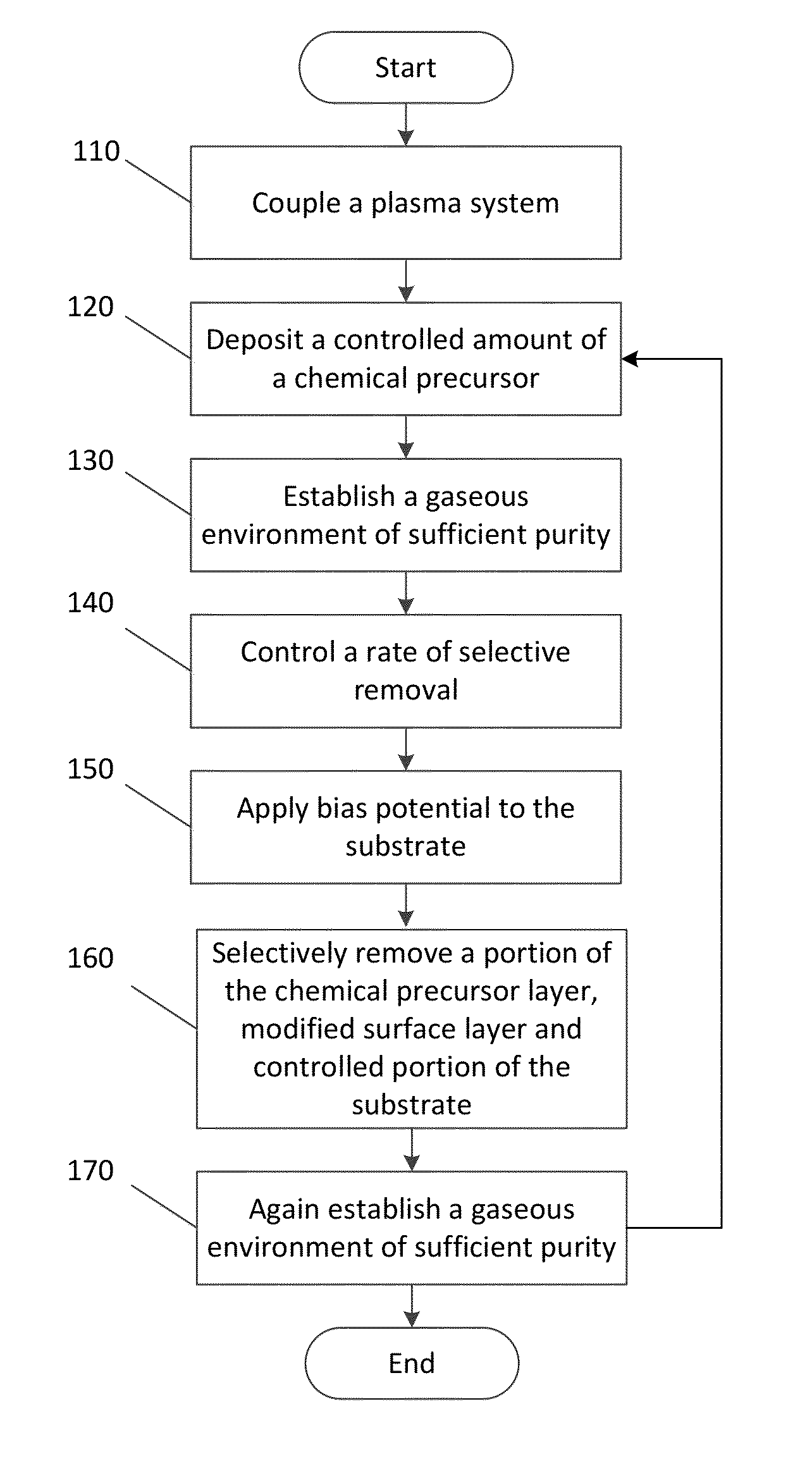
Reactor for plasma-based atomic layer etching of materials
ActiveUS20150162168A1Liquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge tubesSurface engineeringSurface layer
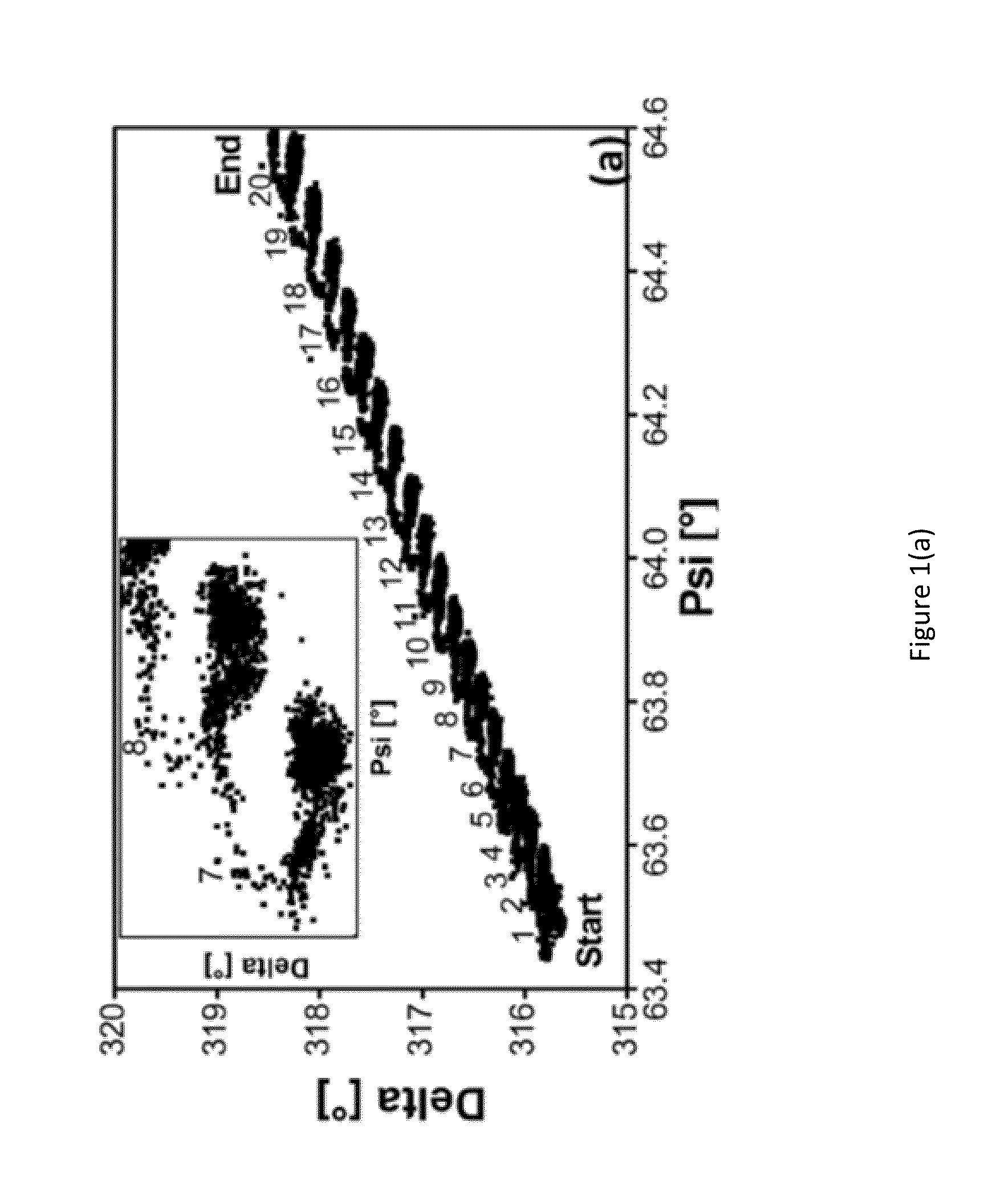
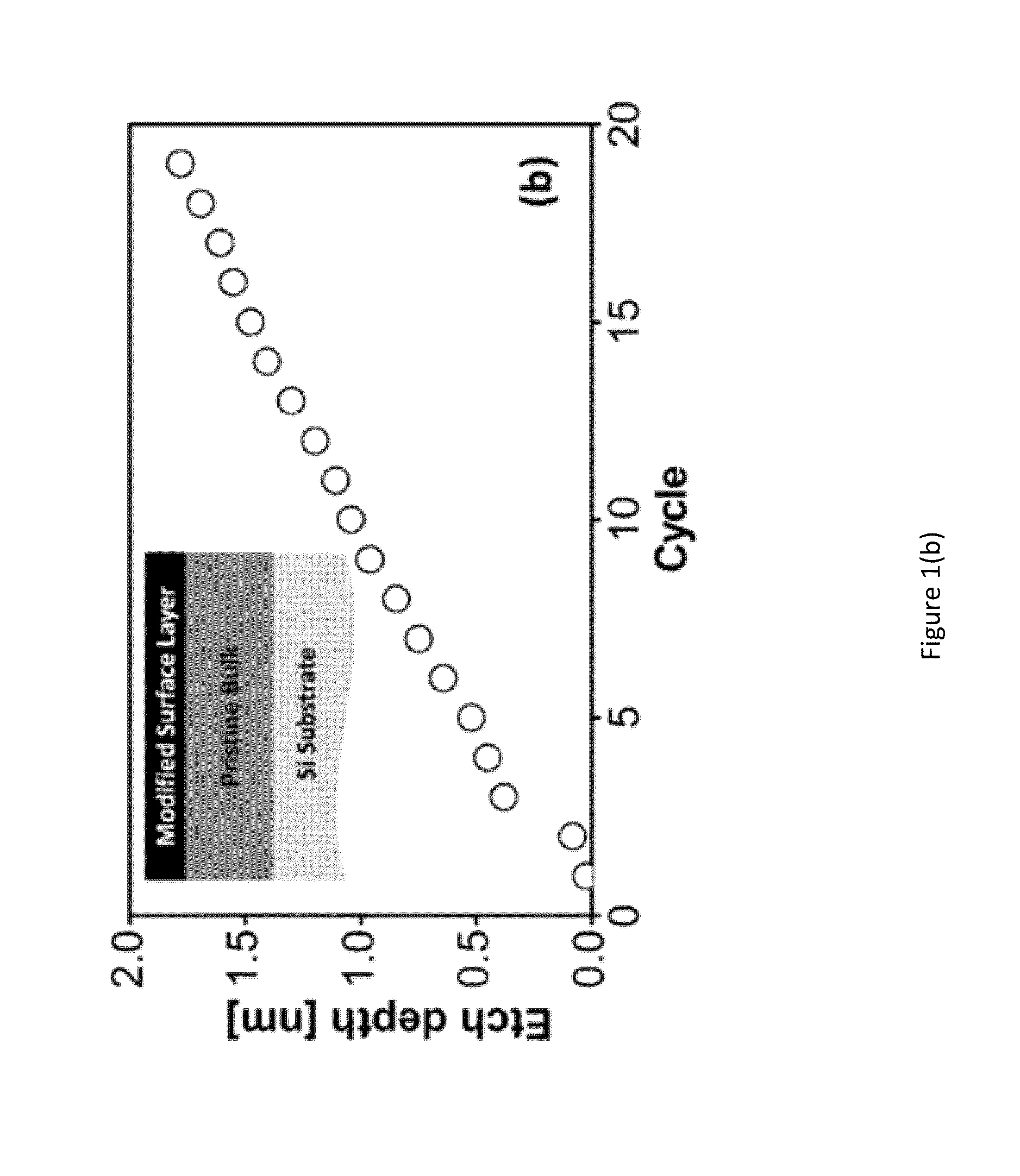
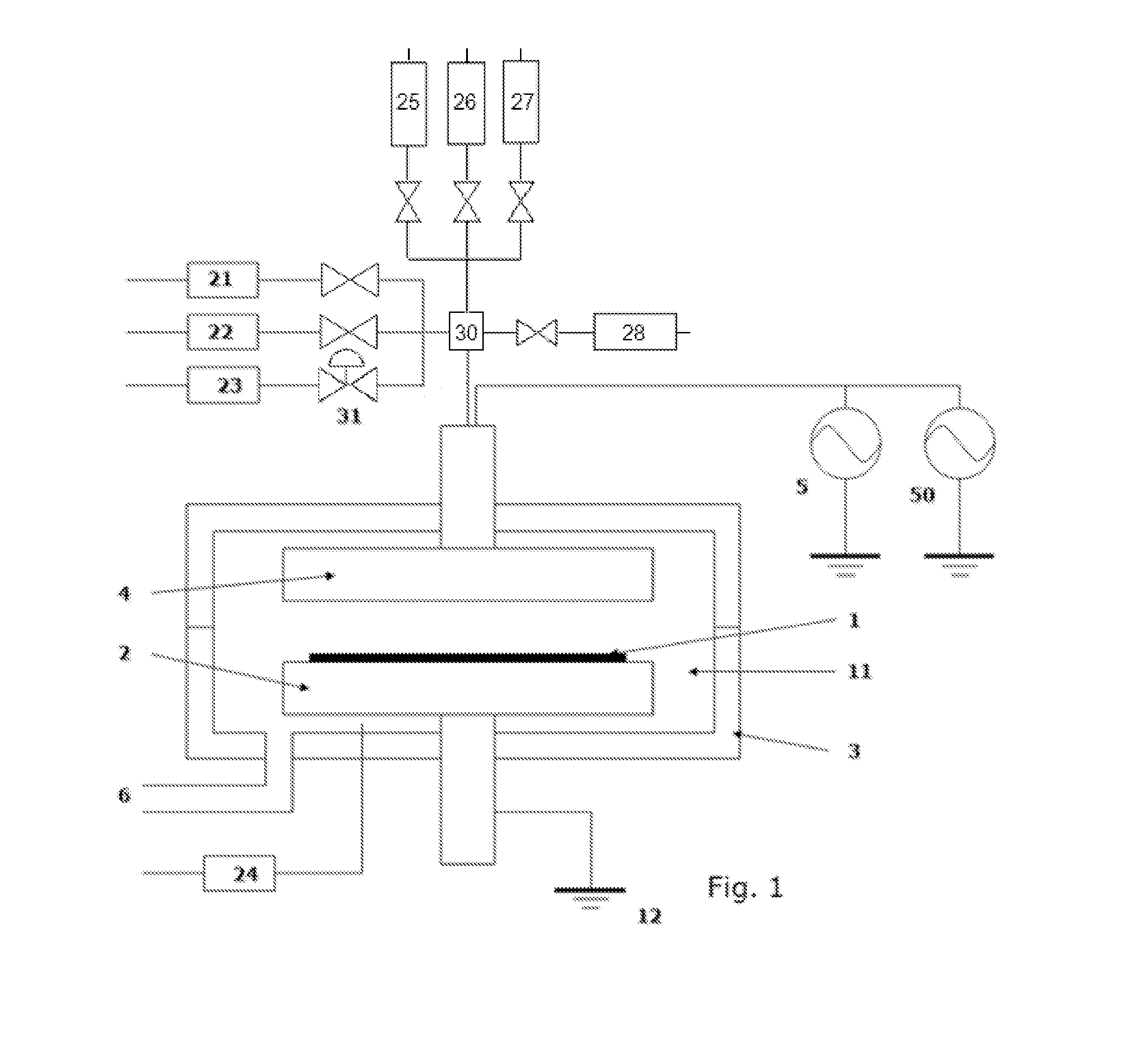
Plasma-based atomic layer etching of materials may be of benefit to various semiconductor manufacturing and related technologies. For example, plasma-based atomic layer etching of materials may be beneficial for adding and / or removing angstrom thick layers from a surface in advanced semiconductor manufacturing and related technologies that increasingly demand atomistic surface engineering. A method may include depositing a controlled amount of a chemical precursor on an unmodified surface layer of a substrate to create a chemical precursor layer and a modified surface layer. The method may also include selectively removing a portion of the chemical precursor layer, a portion of the modified surface layer and a controlled portion of the substrate. Further, the controlled portion may be removed to a depth ranging from about 1 / 10 of an angstrom to about 1 nm. Additionally, the deposition and selective removal may be performed under a plasma environment.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Method of plasma-enhanced atomic layer etching
ActiveUS20160211147A1Improve efficiencyElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingAnalytical chemistry
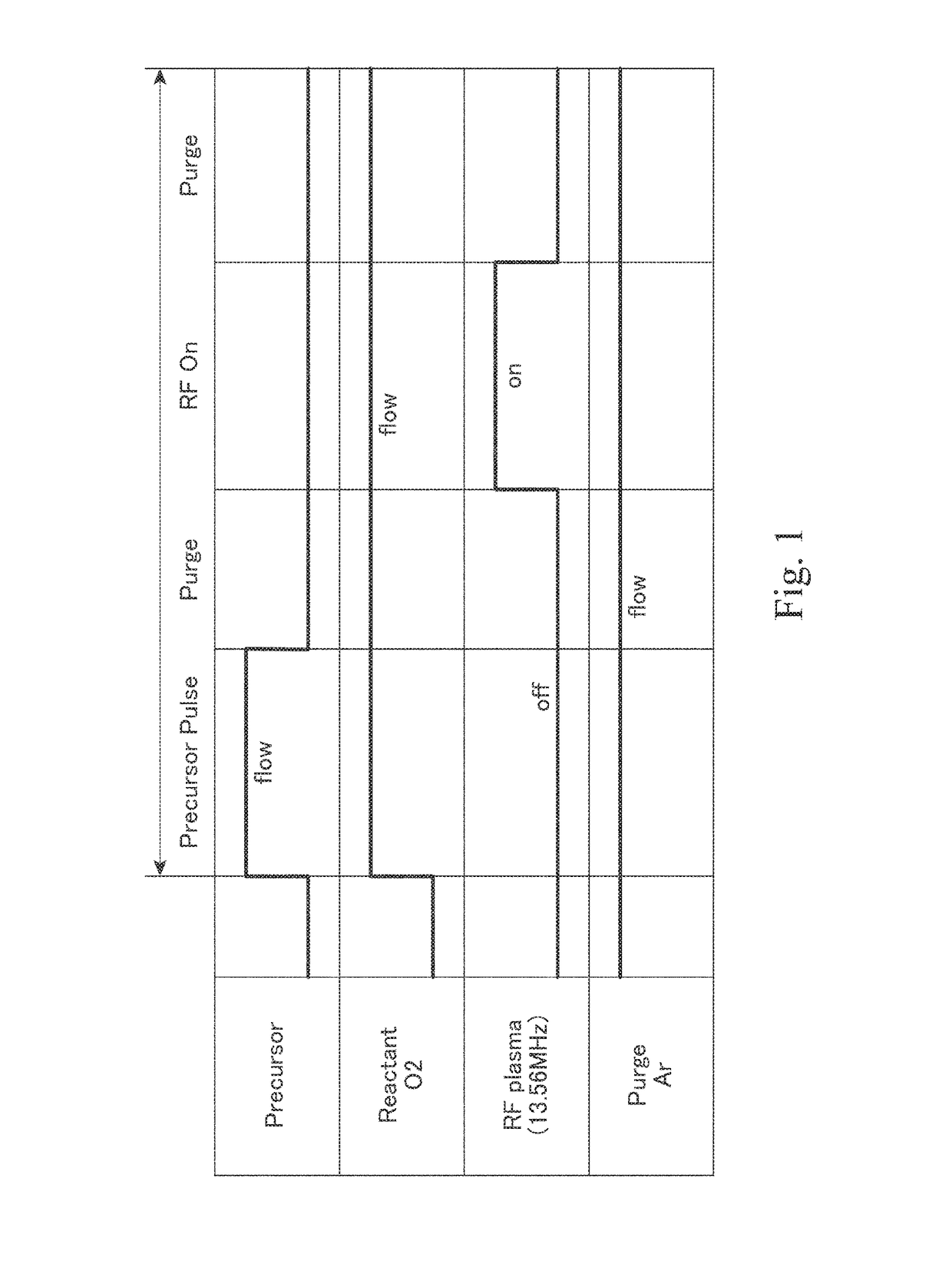
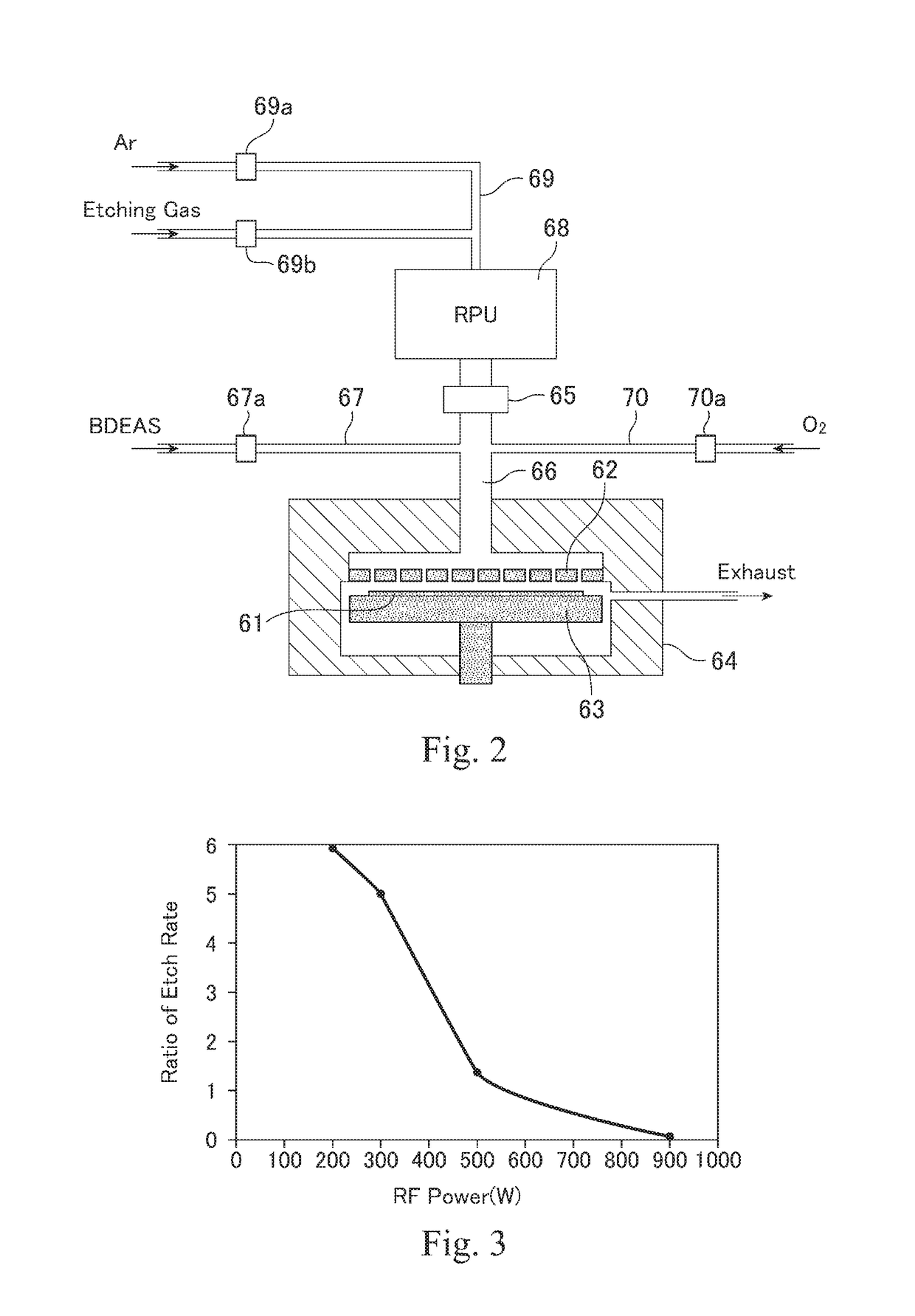
A method for etching a layer on a substrate includes at least one etching cycle, wherein an etching cycle includes: continuously providing an inert gas into the reaction space; providing a pulse of an etching gas into the continuous inert gas flow upstream of the reaction space to chemisorb the etching gas in an unexcited state on a surface of the substrate; and providing a pulse of RF power discharge between electrodes to generate a reactive species of the inert gas in the reaction space so that the layer on the substrate is etched.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
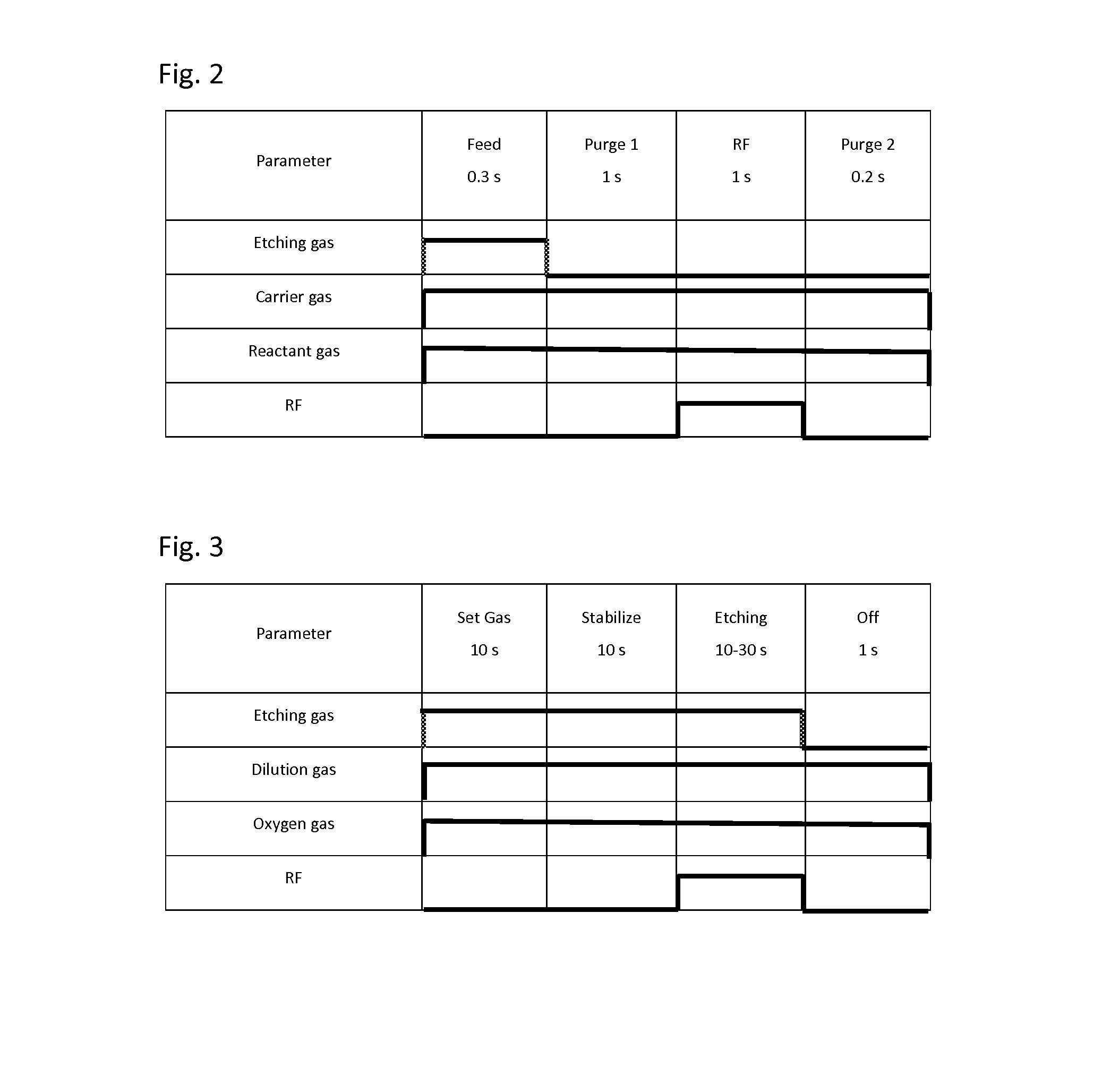
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
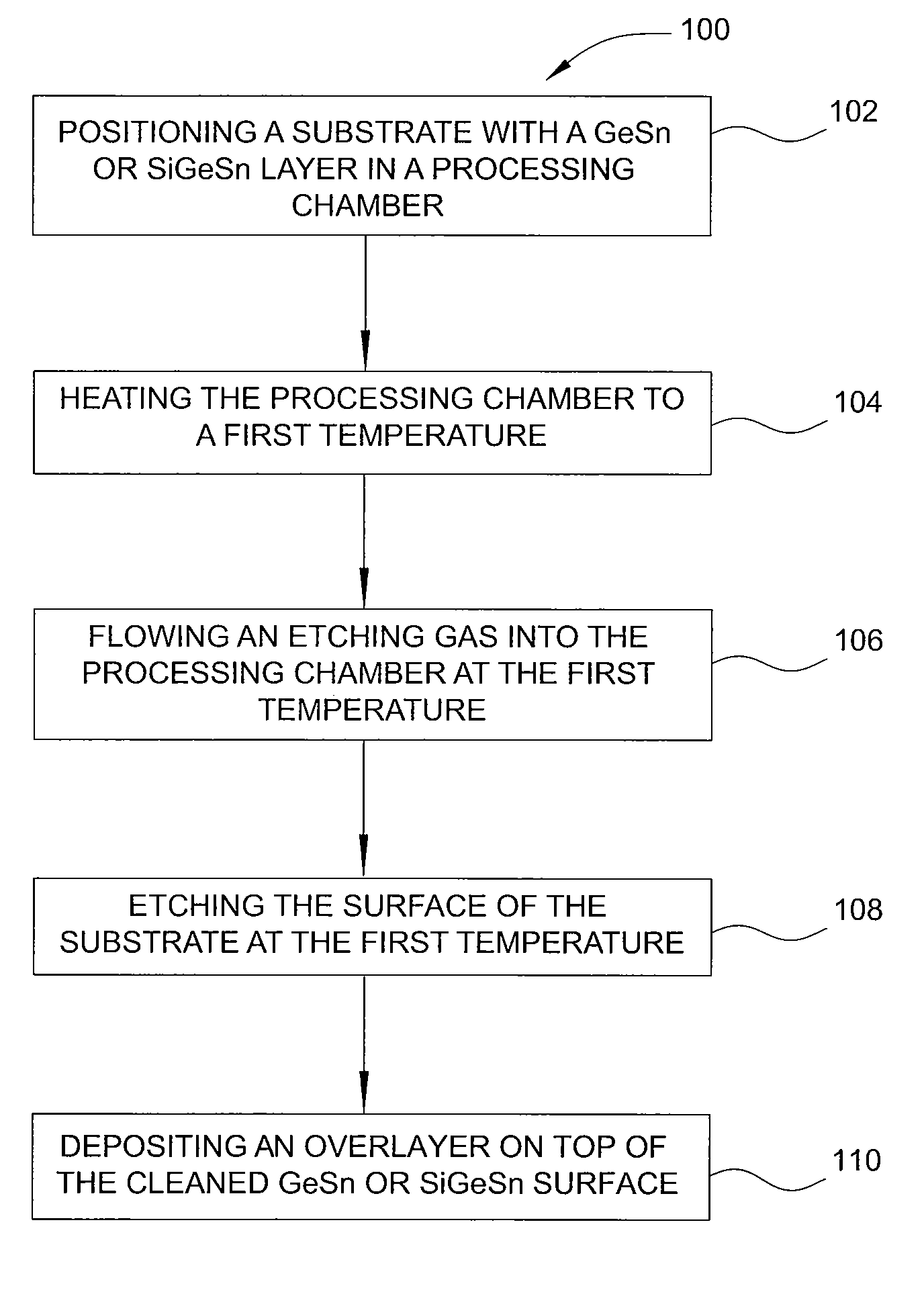
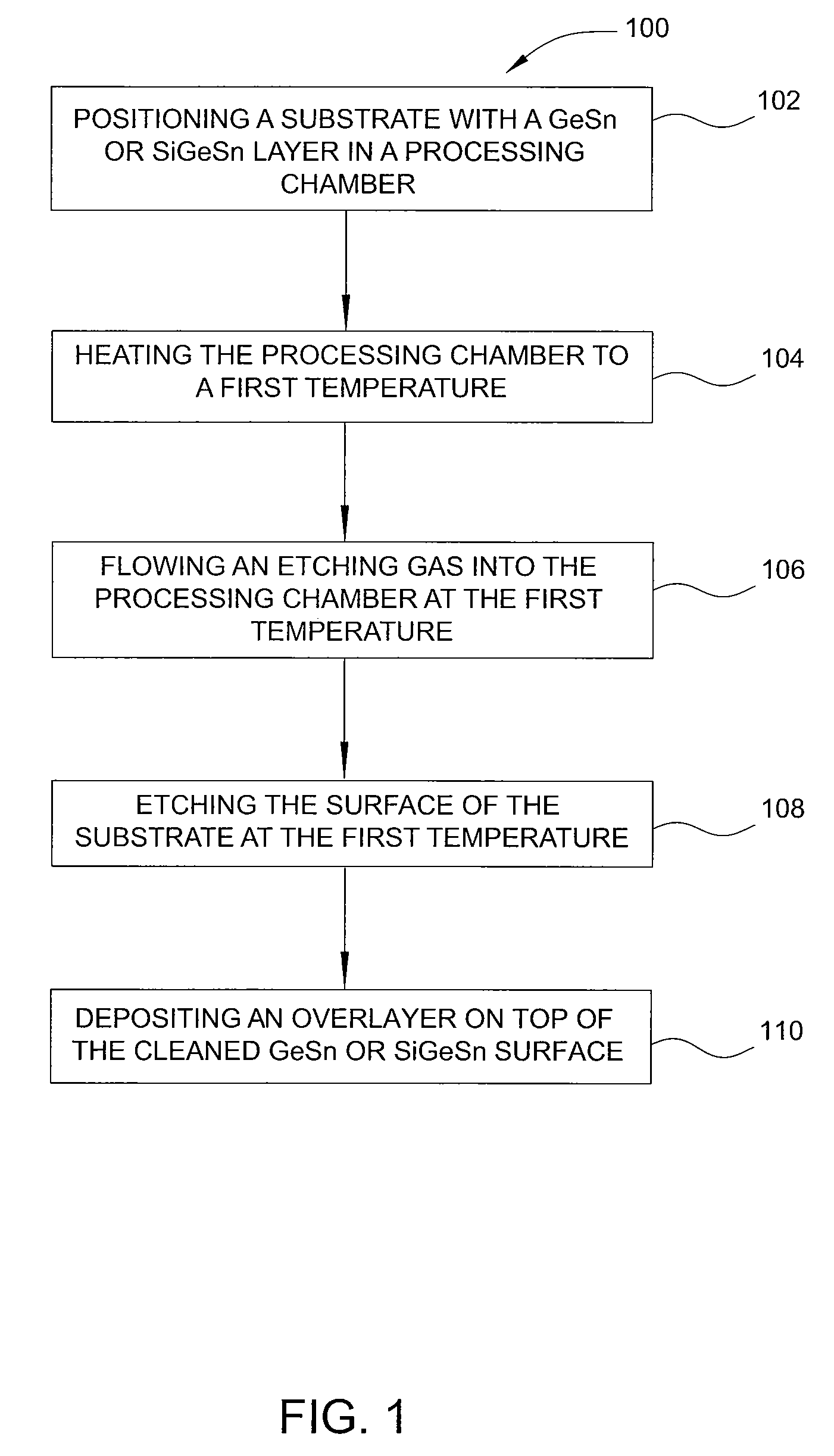
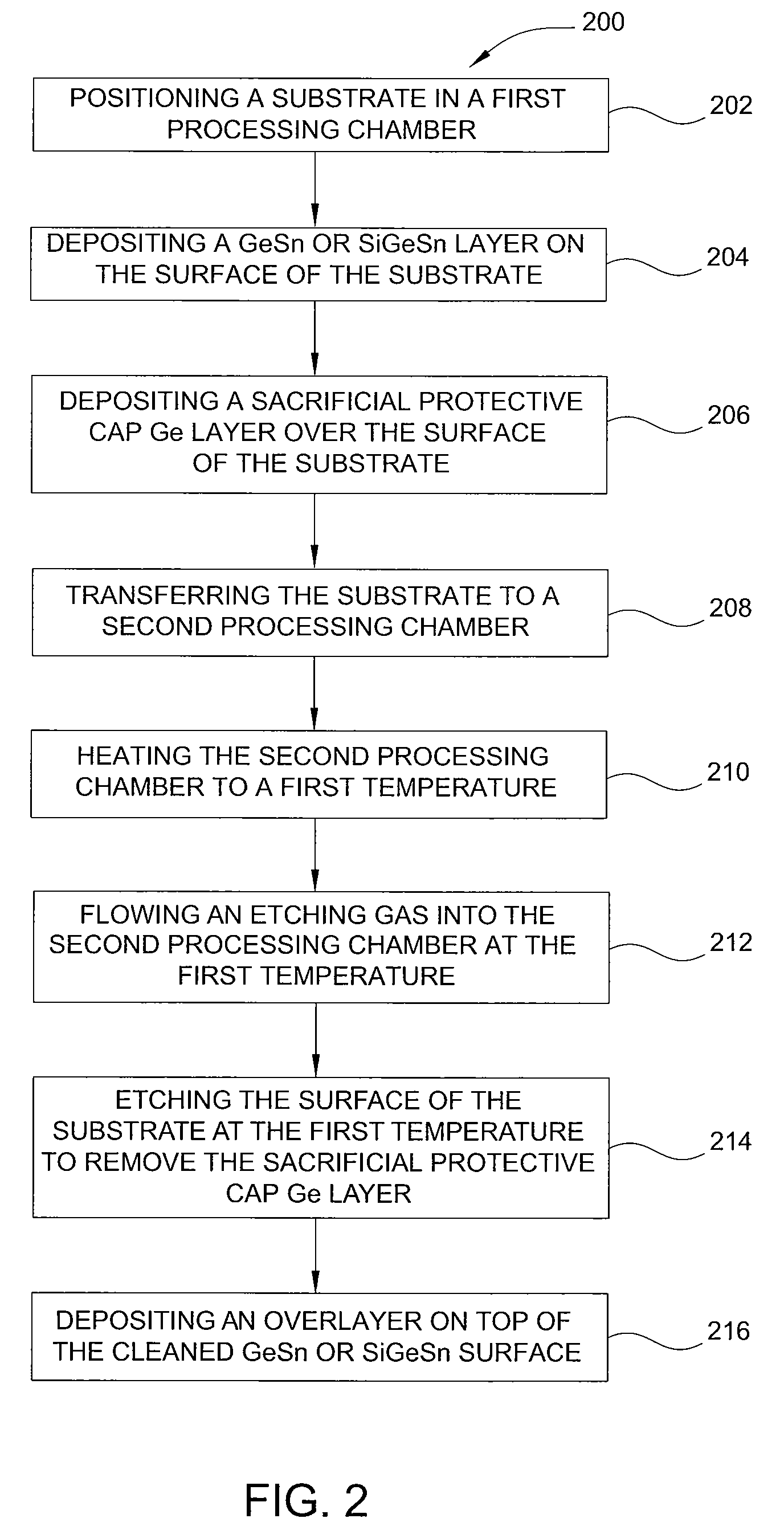
ActiveUS20130288480A1Increase temperatureStop the flowSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationEtchingRapid thermal annealing
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
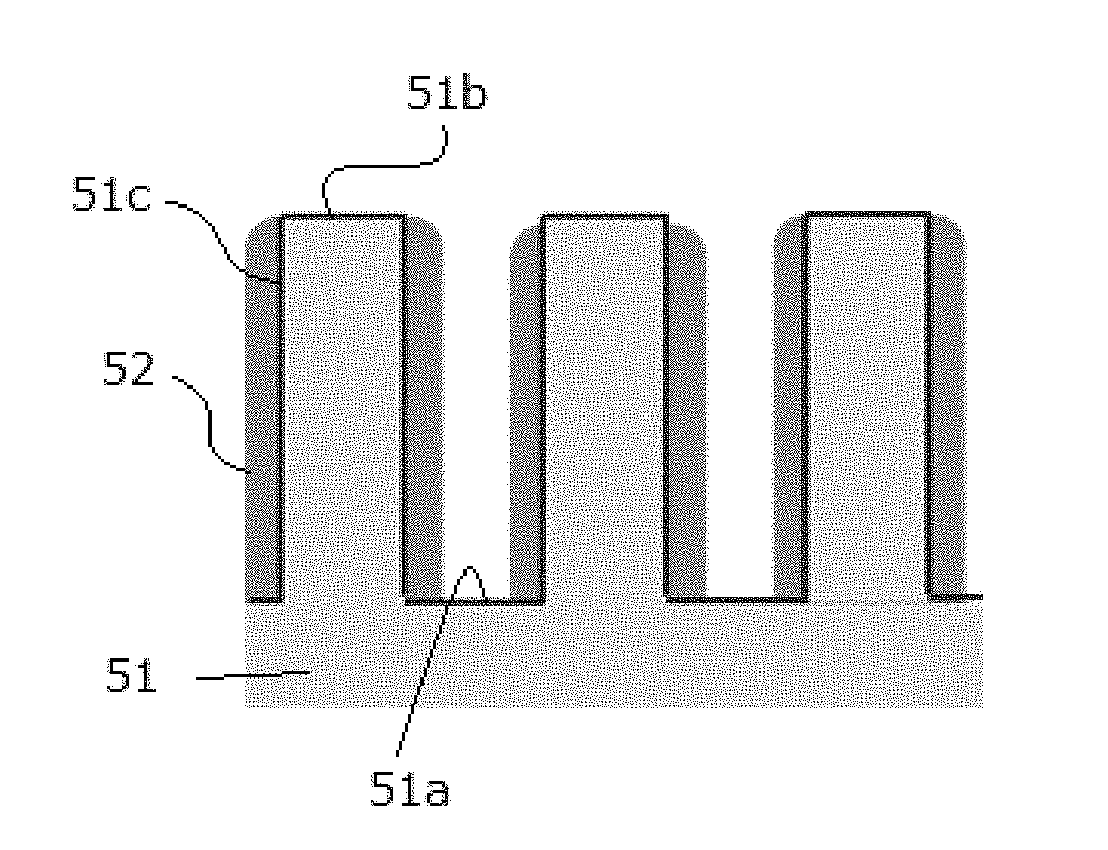
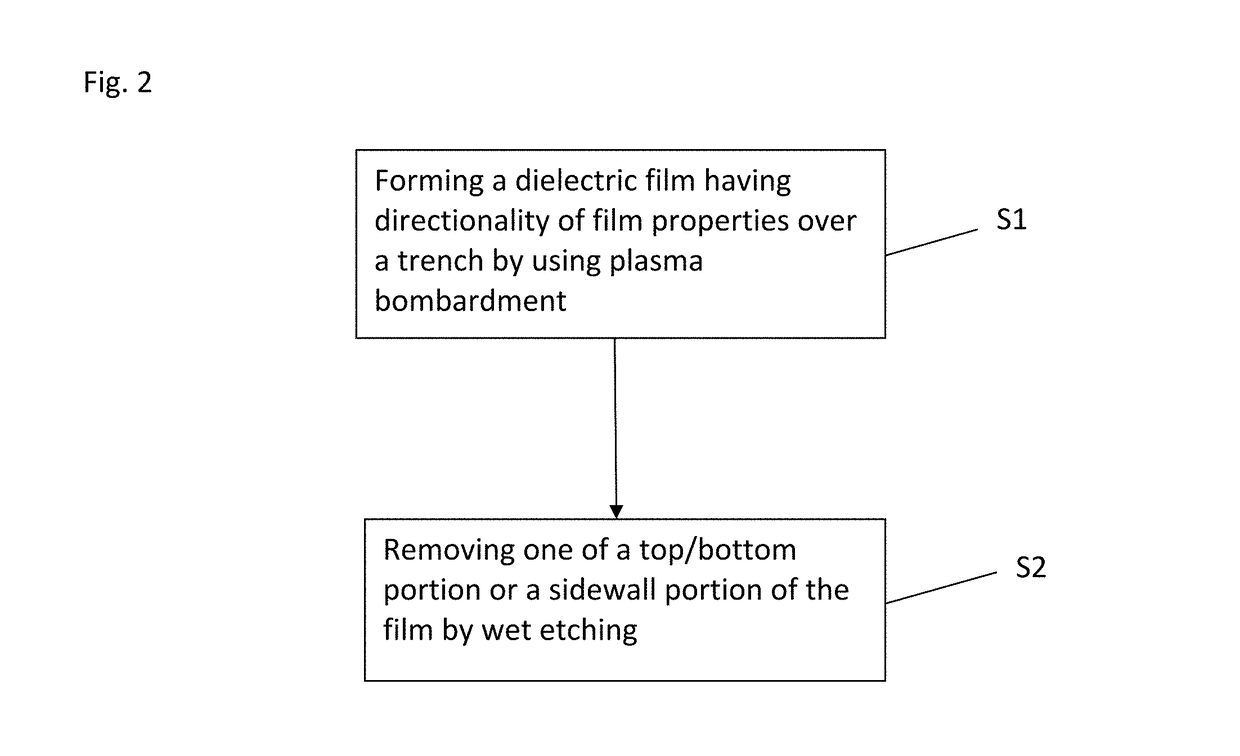
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS9754779B1Low densityPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
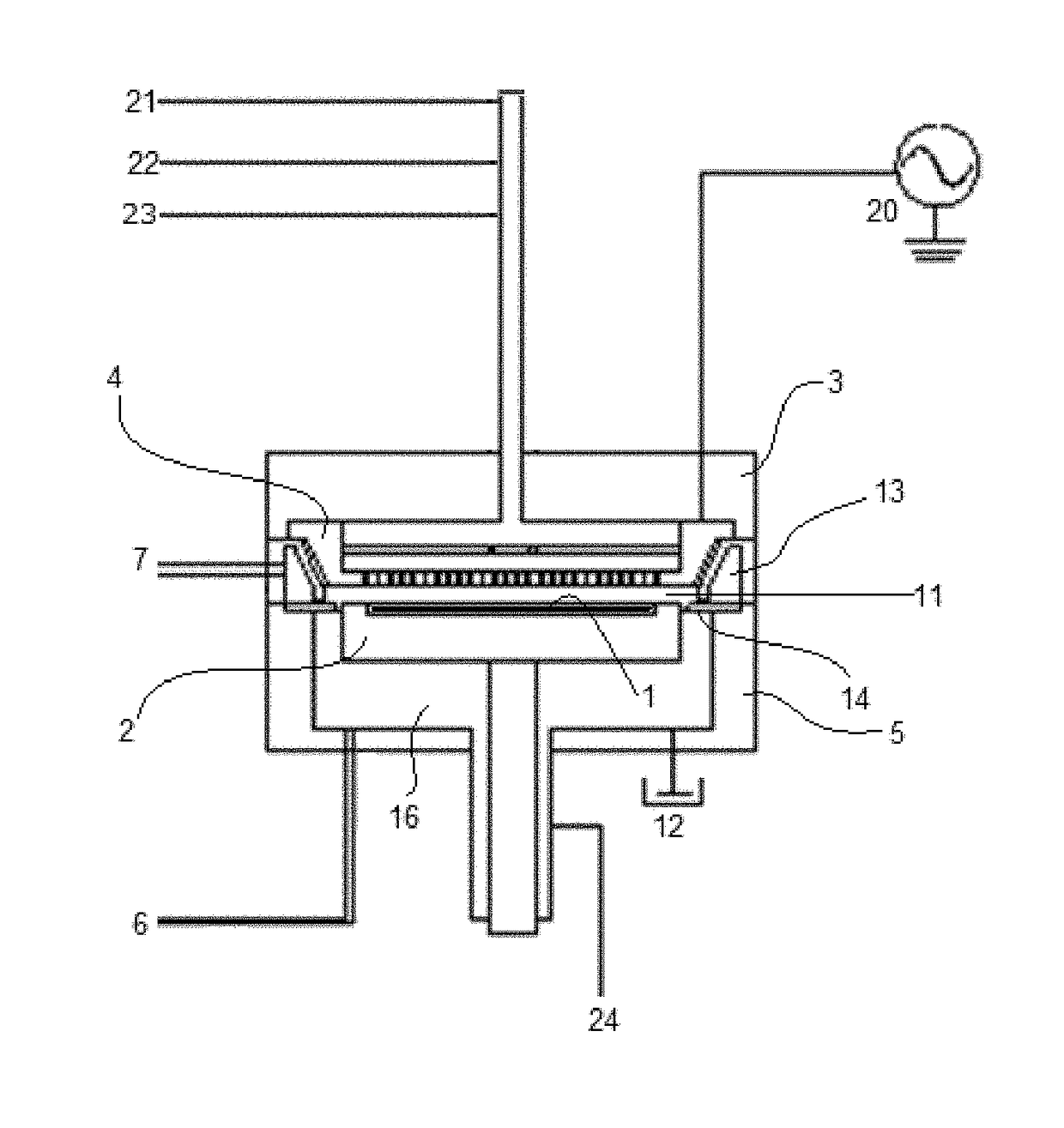
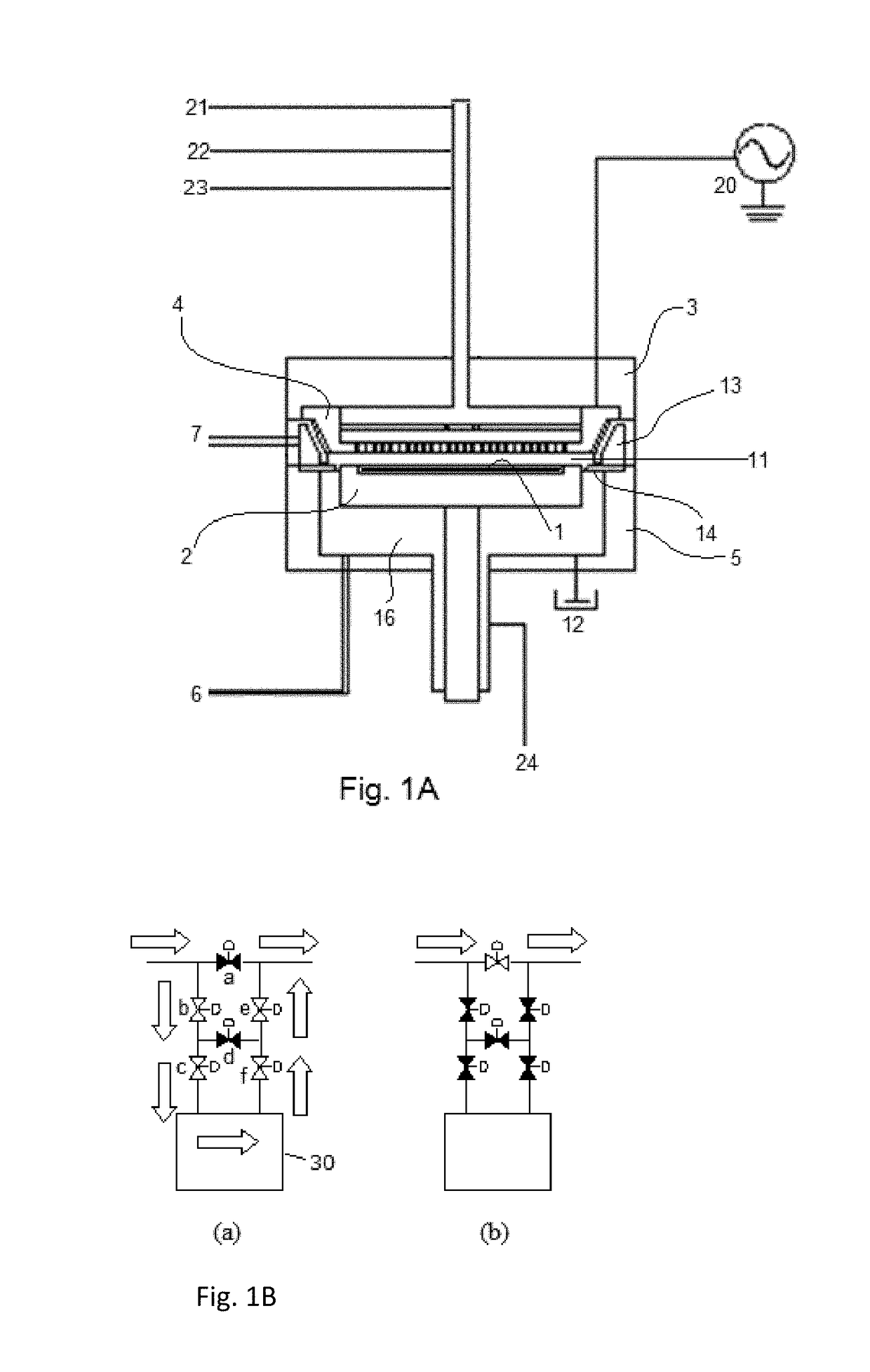
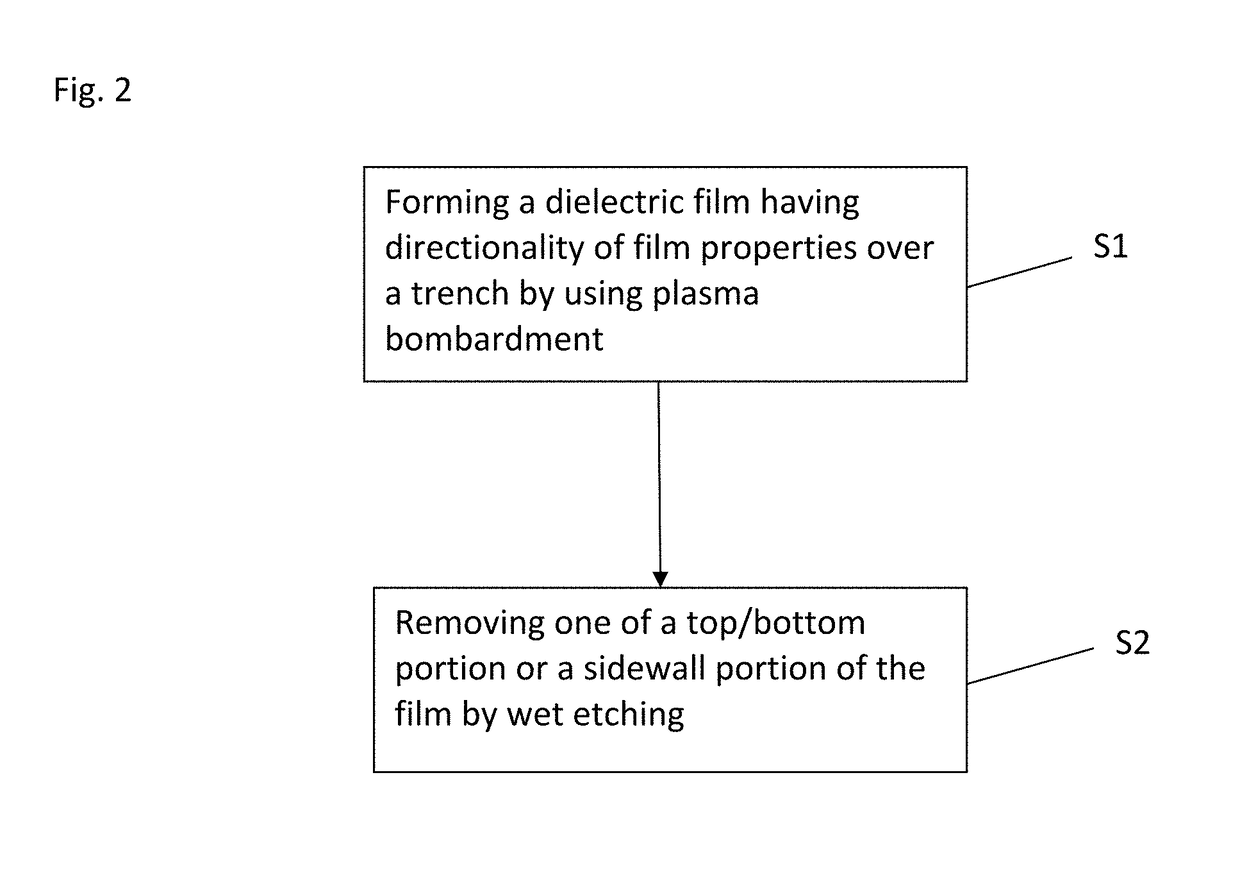
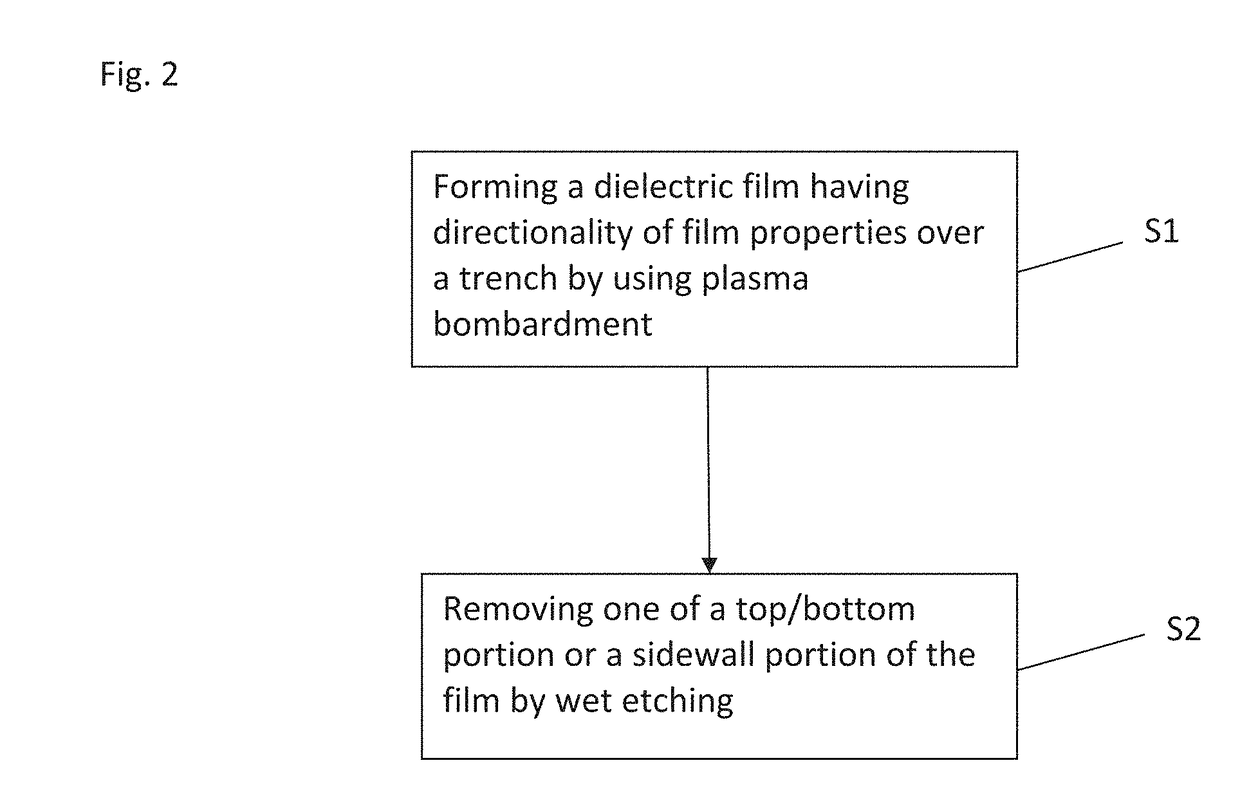
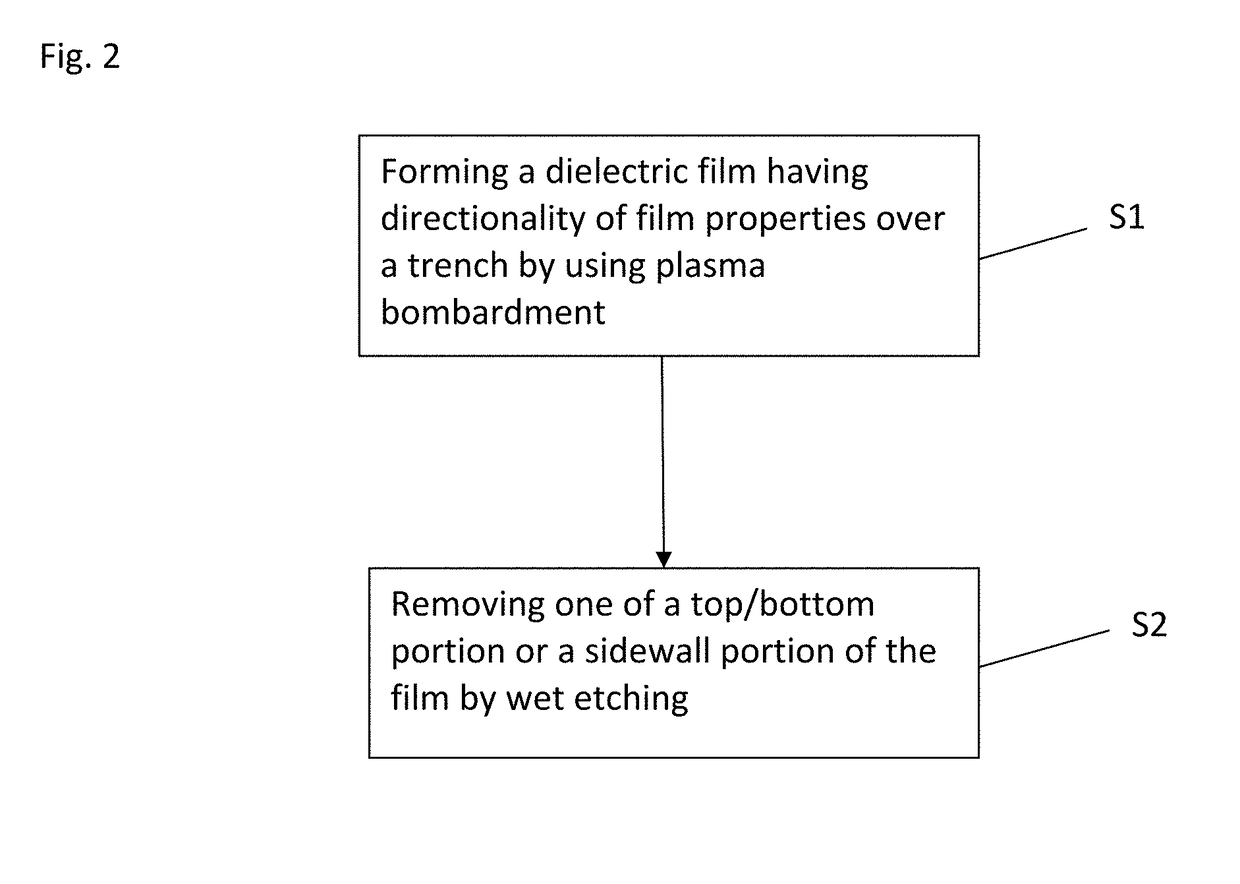
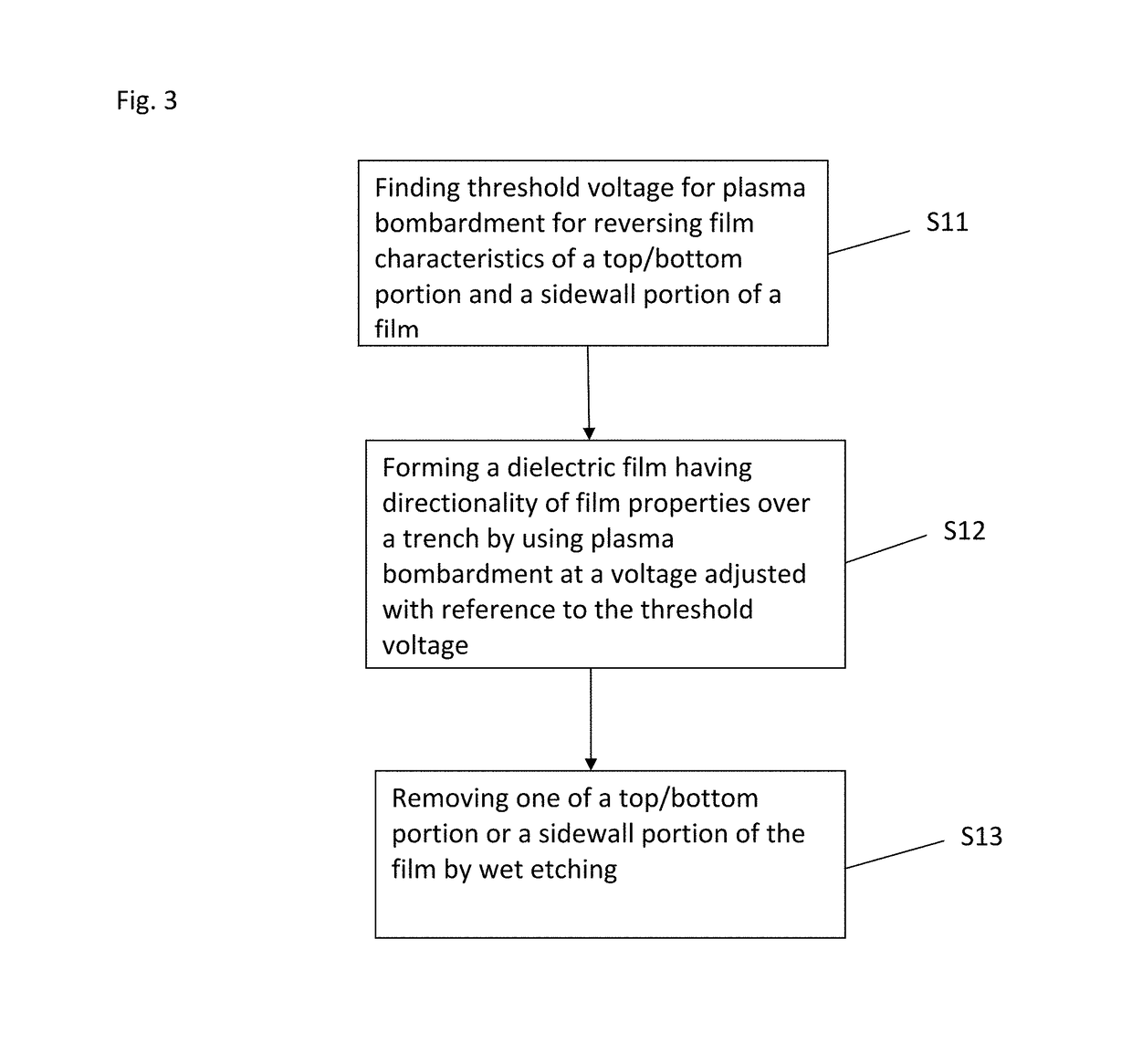
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method of forming a contact structure in a semiconductor device
InactiveUS6440837B1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingProcess deviationsEtching
Annular and linear contact structures are described which exhibit a greatly reduced susceptibility to process deviations caused by lithographic and deposition variations than does a conventional circular contact plug. In one embodiment, a standard conductive material such as carbon or titanium nitride is used to form the contact. In an alternative embodiment, a memory material itself is used to form the contact. These contact structures may be made by various processes, including chemical mechanical planarization and facet etching.
Owner:ROUND ROCK RES LLC
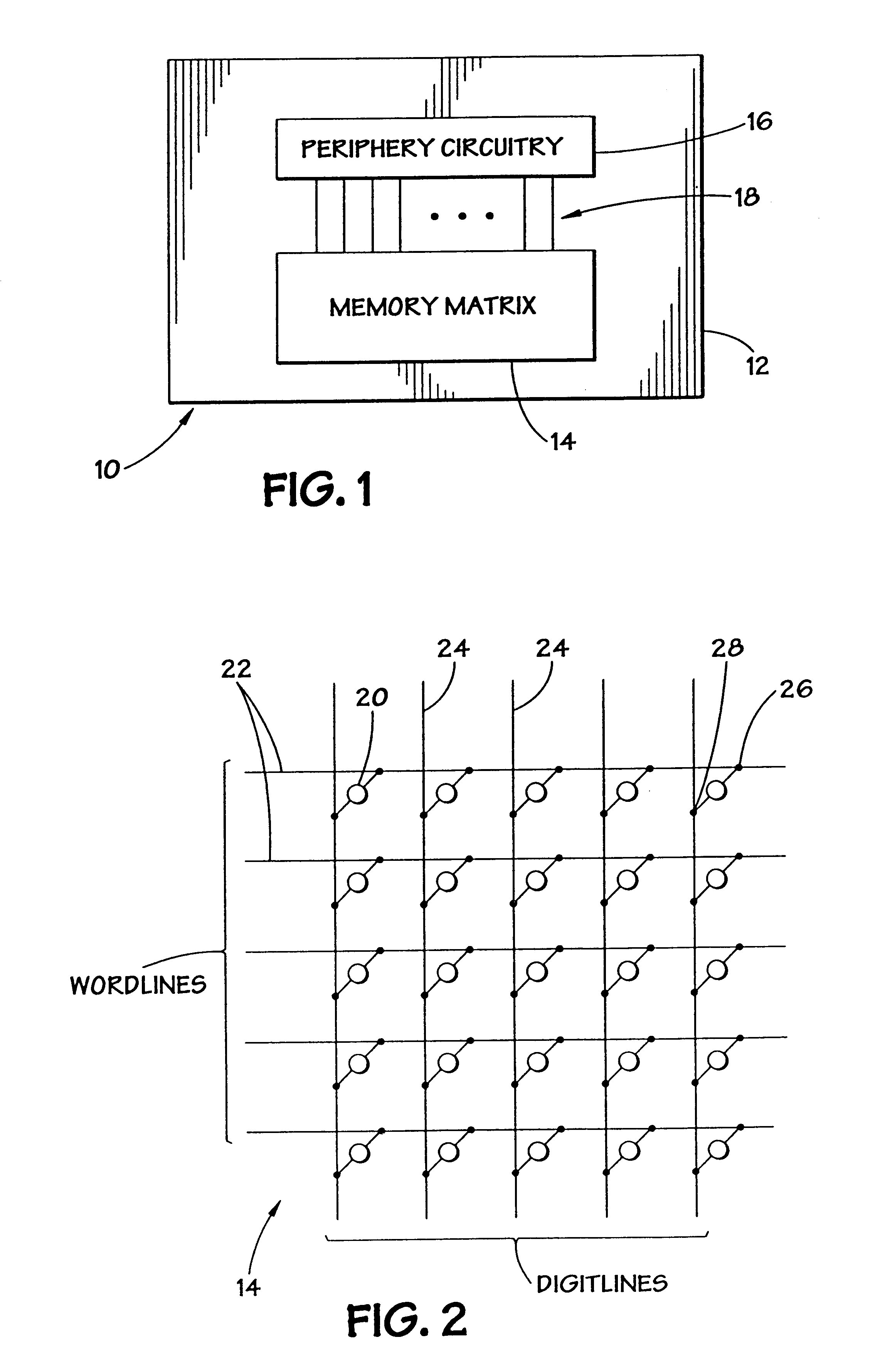
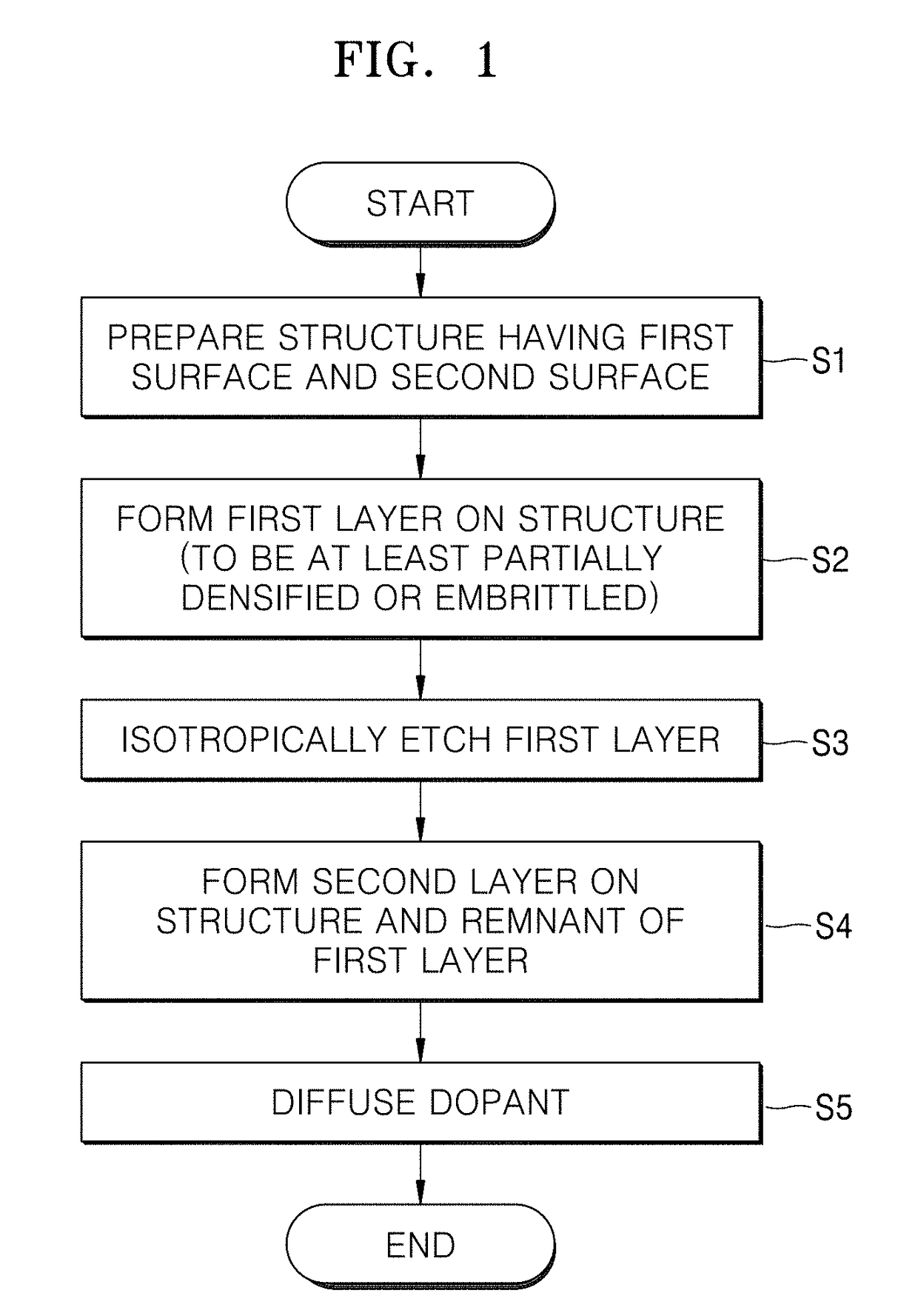
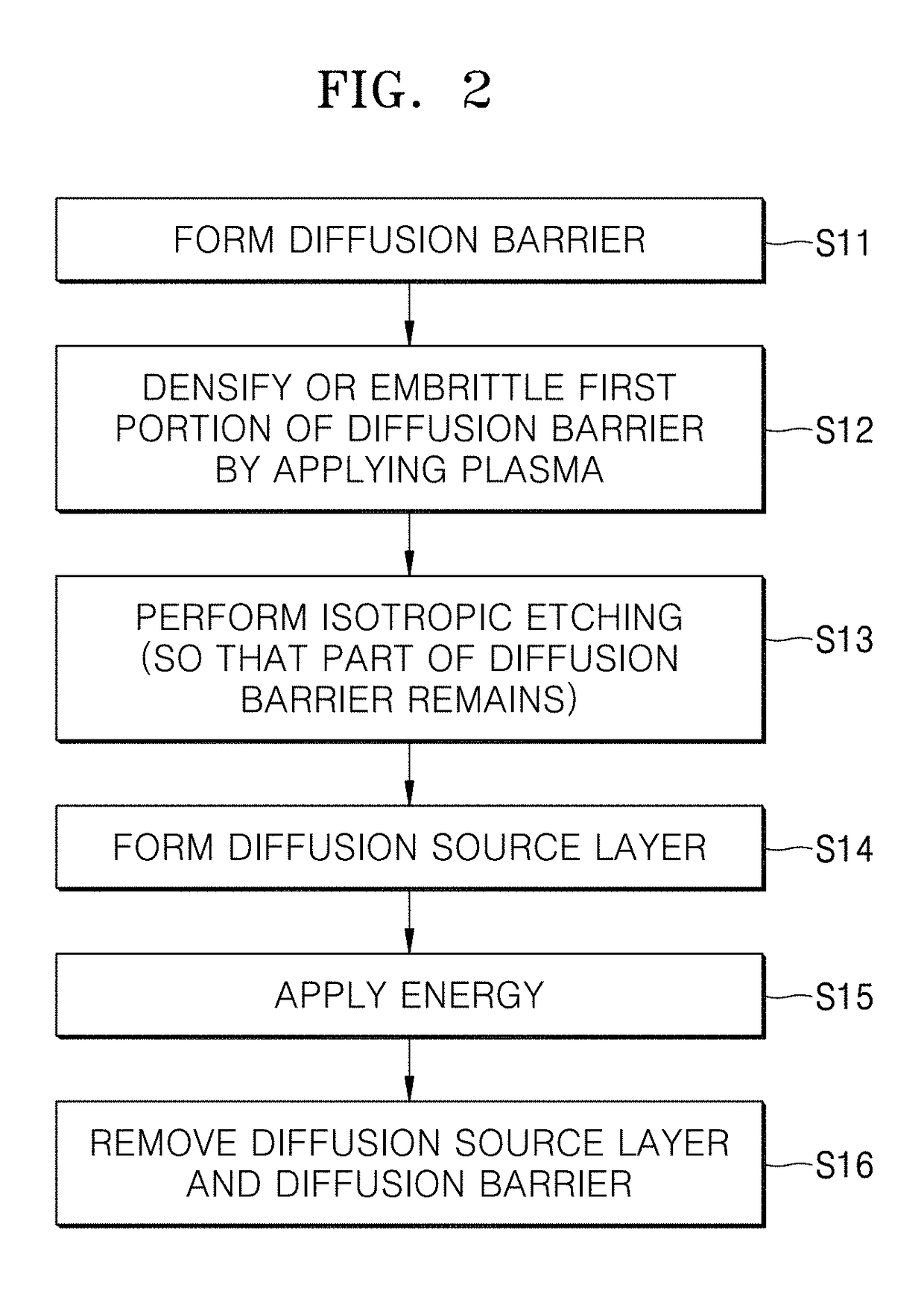
Method of processing substrate
A method of processing a substrate to enable selective doping without a photolithography process is provided. The method includes forming a diffusion barrier on the substrate having a patterned structure using plasma deposition method, removing the diffusion barrier except for part of the diffusion barrier using wet etching, forming a diffusion source layer on the patterned structure and the part of the diffusion barrier, and applying energy to the diffusion source layer.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS20170243734A1Improve film qualityDecreasing density of filmElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Reactor system and method to reduce residue buildup during a film deposition process
ActiveUS20180195174A1Mitigate formation of residueSubstrate throughput can be increasedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingReactor system
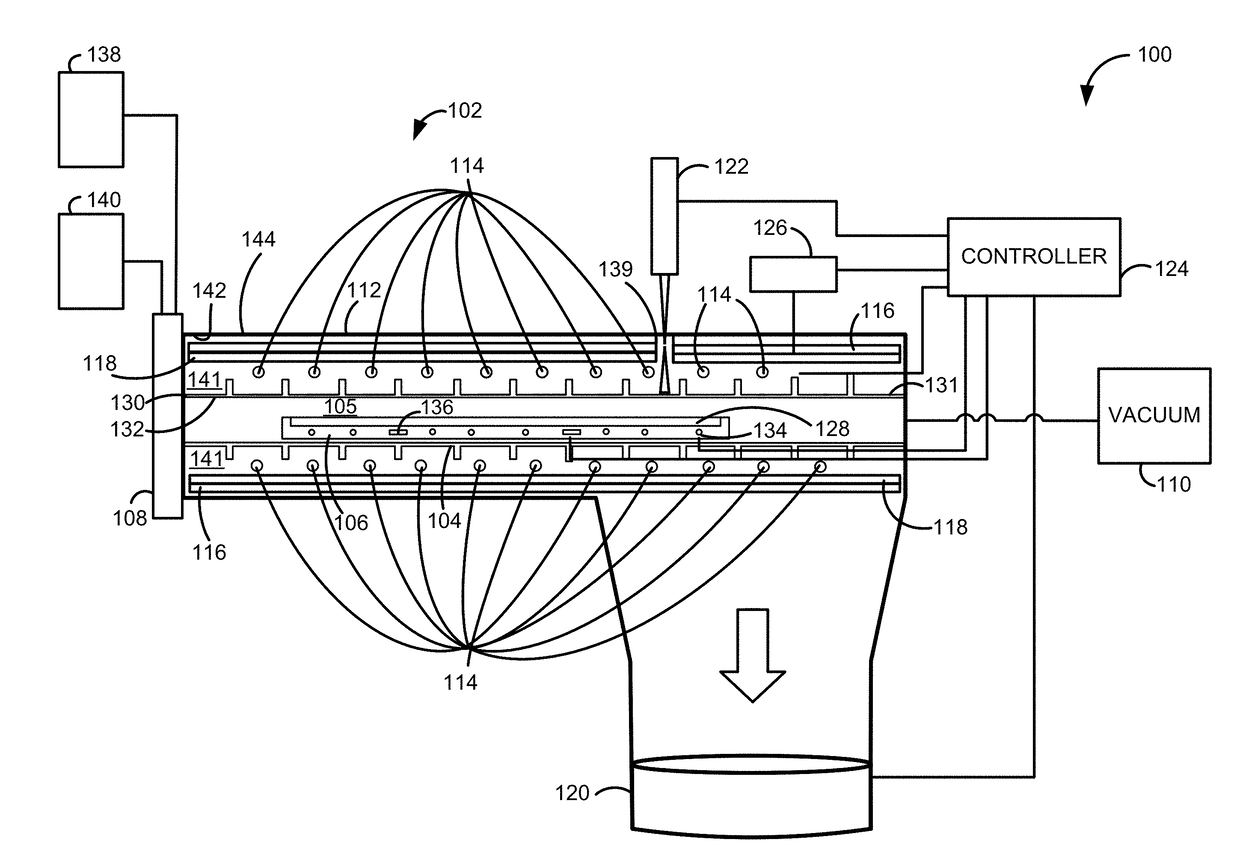
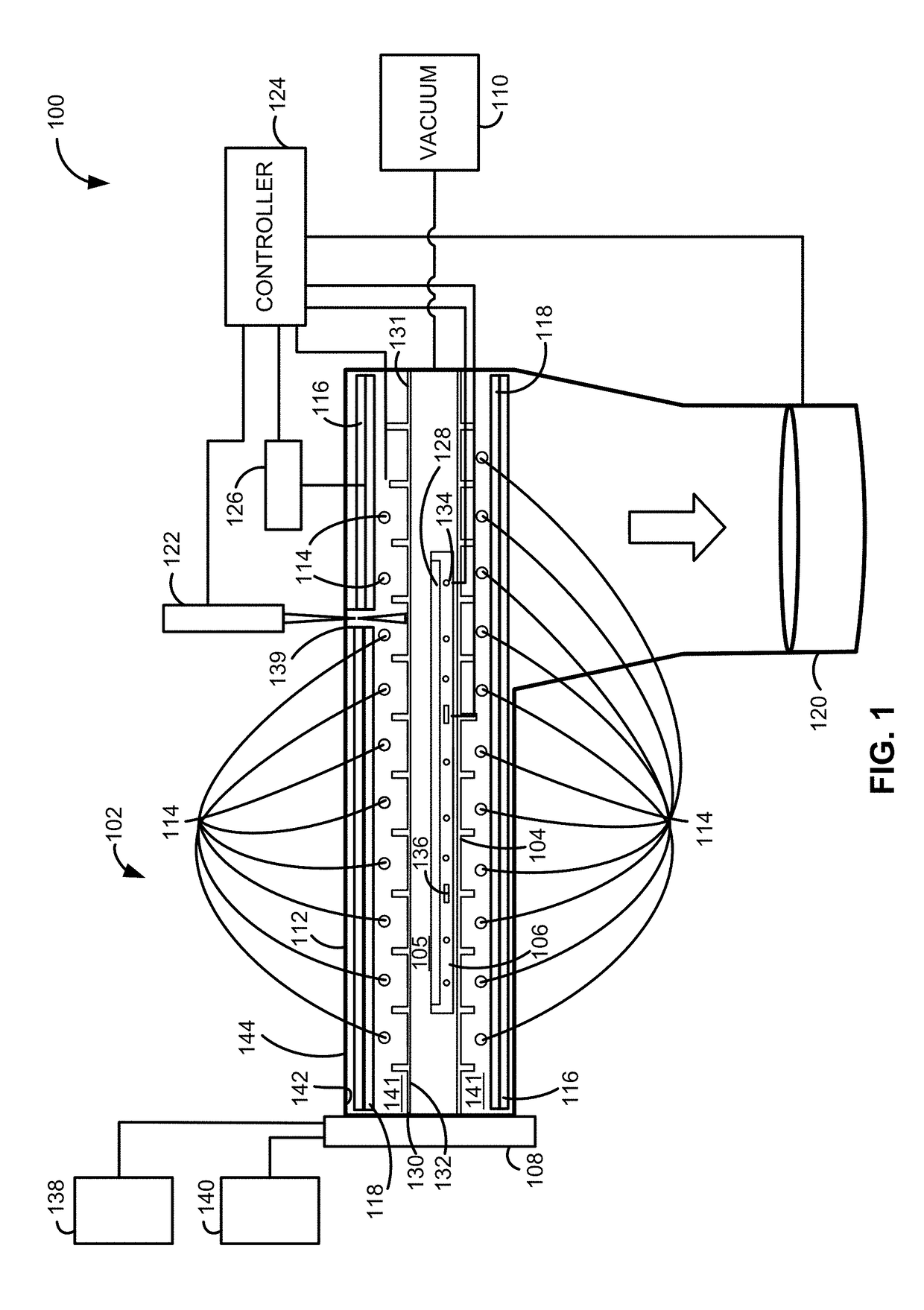
A system and method for depositing a film within a reaction chamber are disclosed. An exemplary system includes a temperature measurement device, such as a pyrometer, to measure an exterior wall surface of the reaction chamber. A temperature of the exterior wall surface can be controlled to mitigate cleaning or etching of an interior wall surface of the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
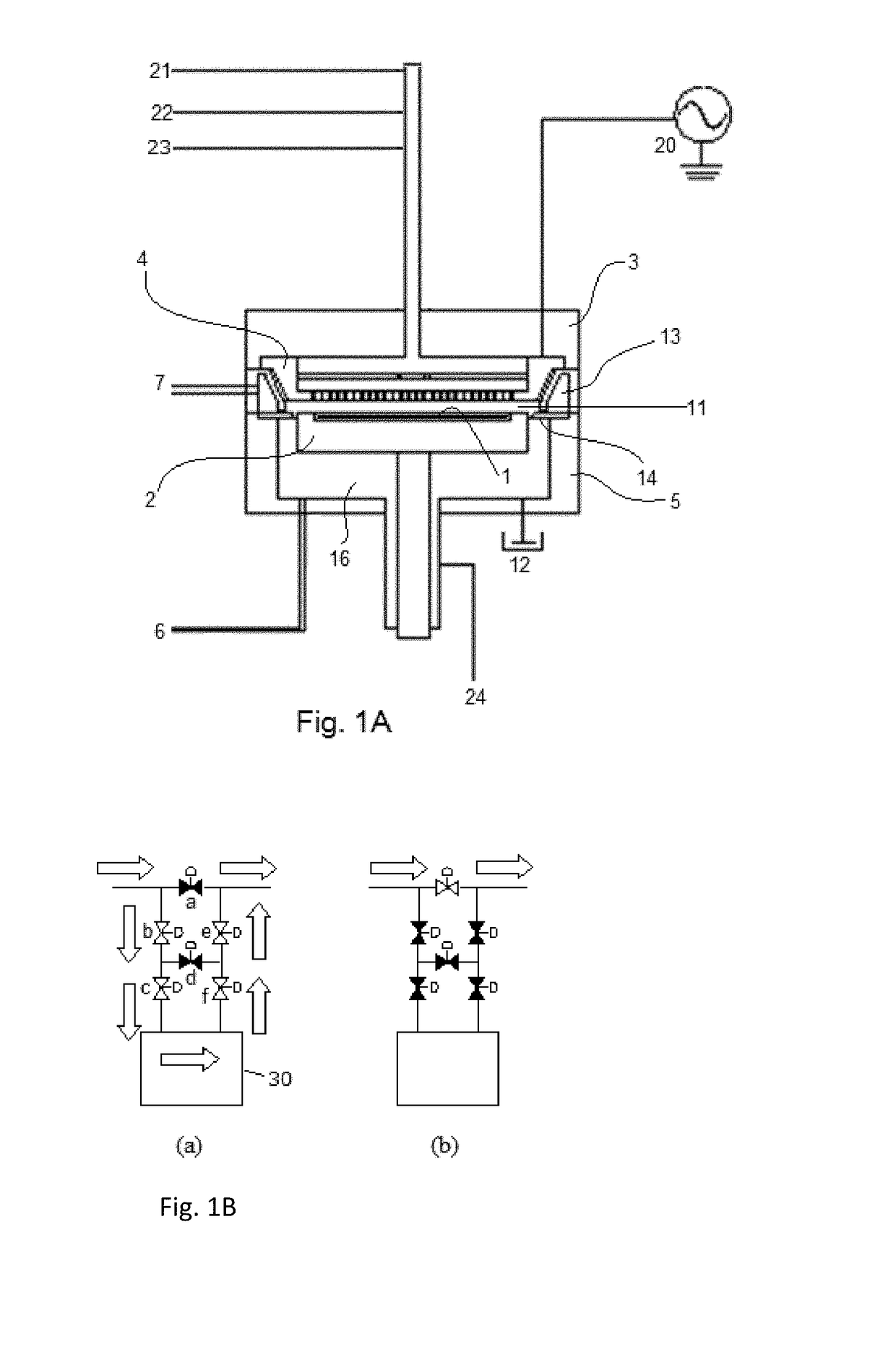
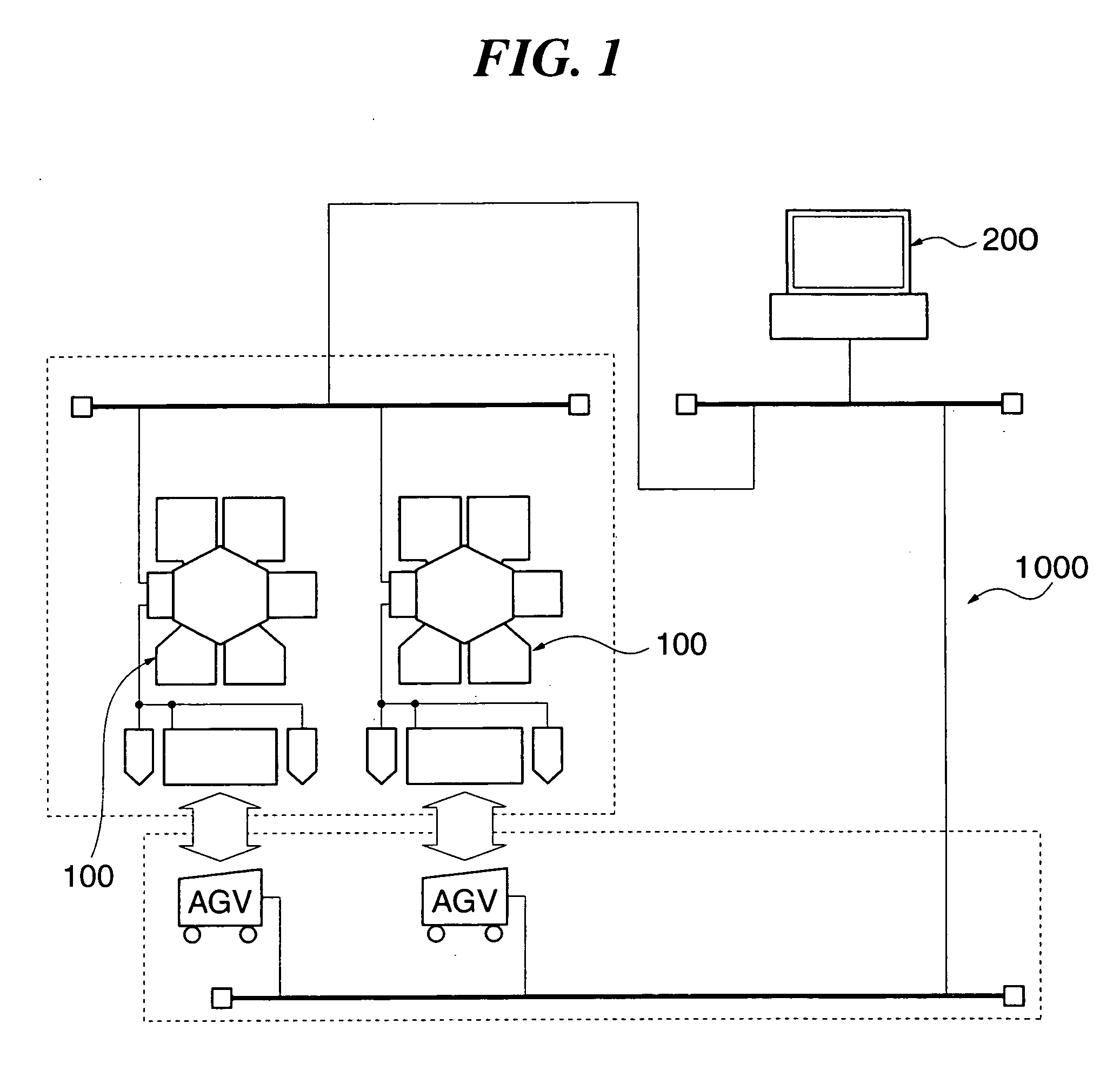
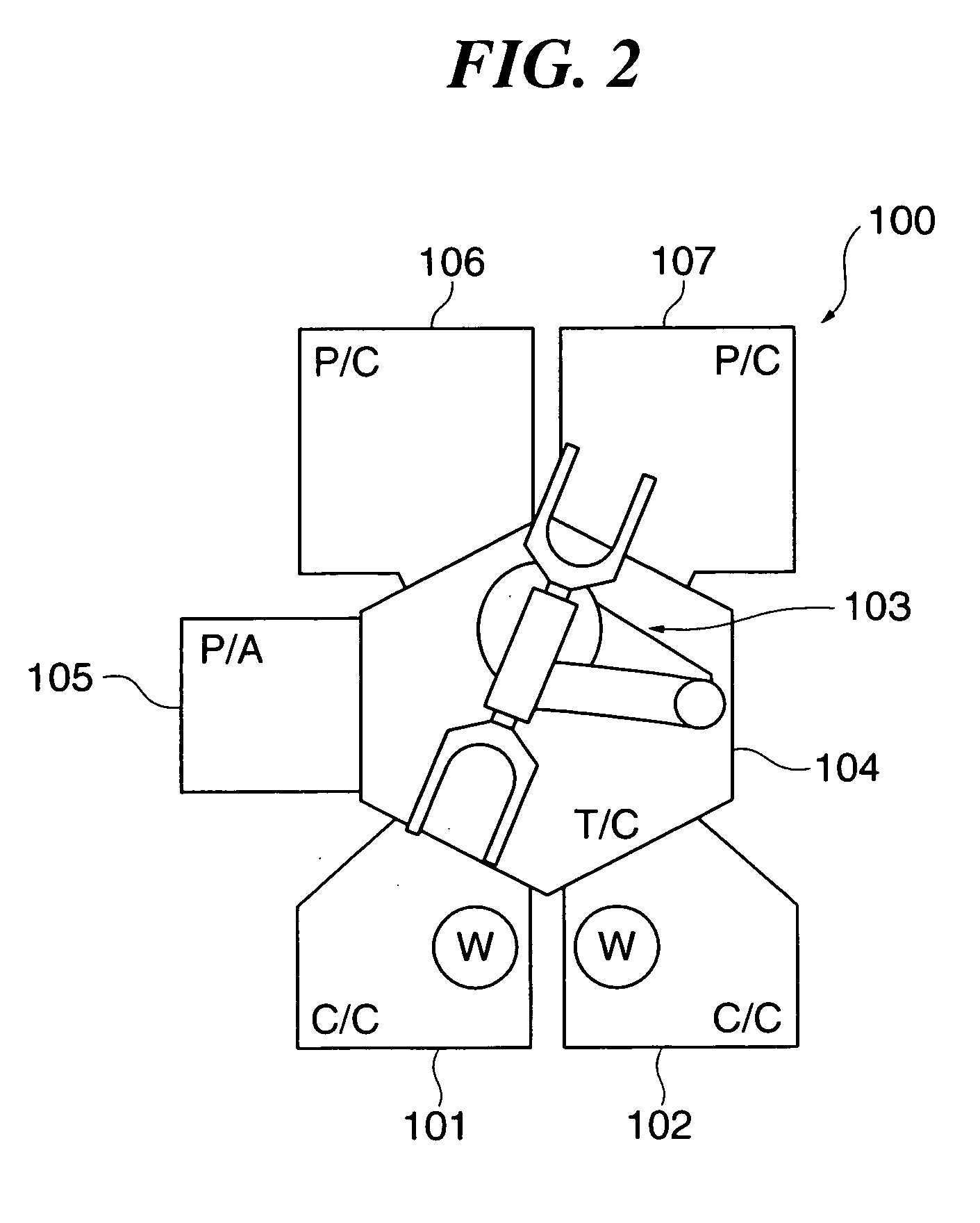
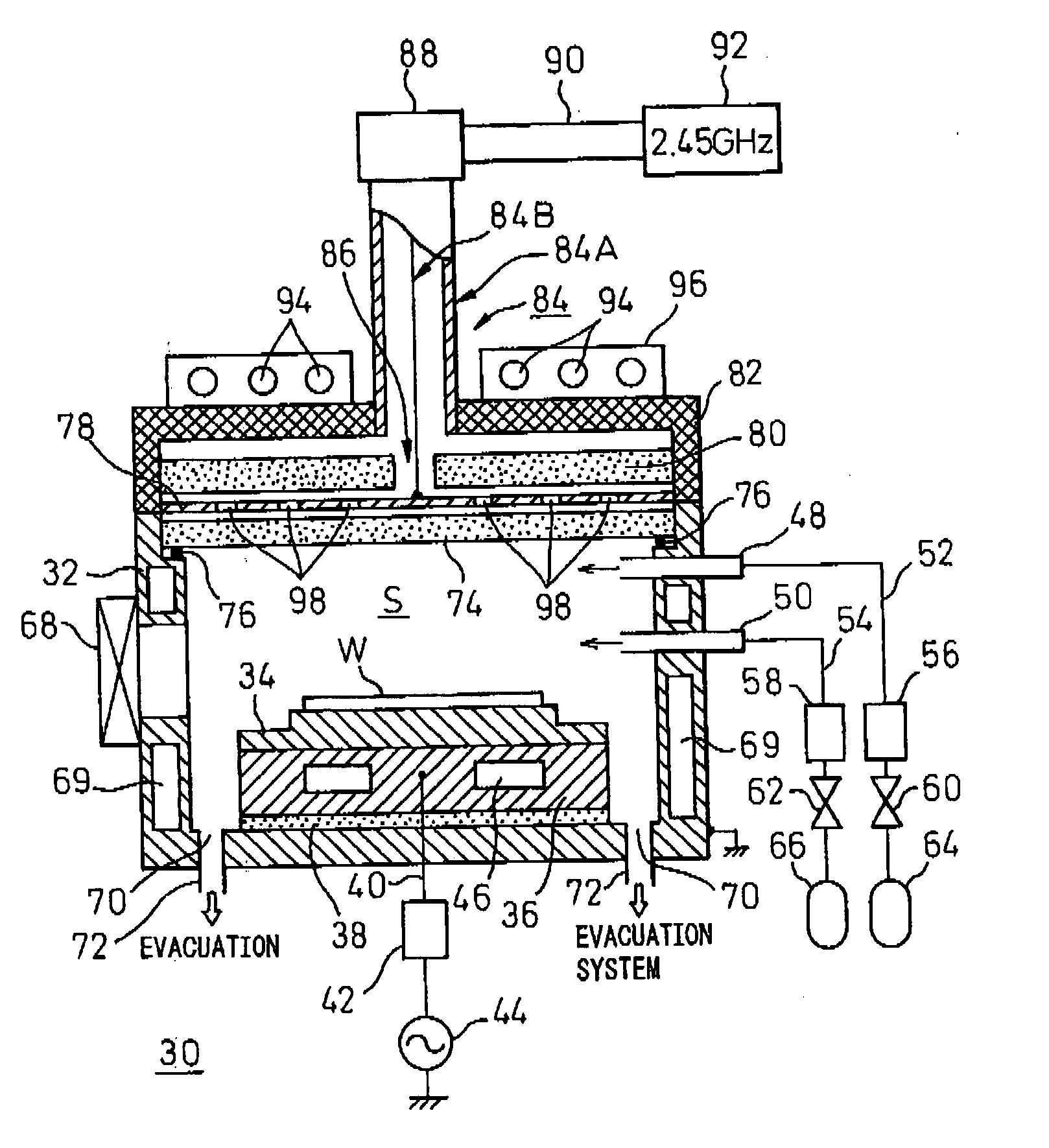
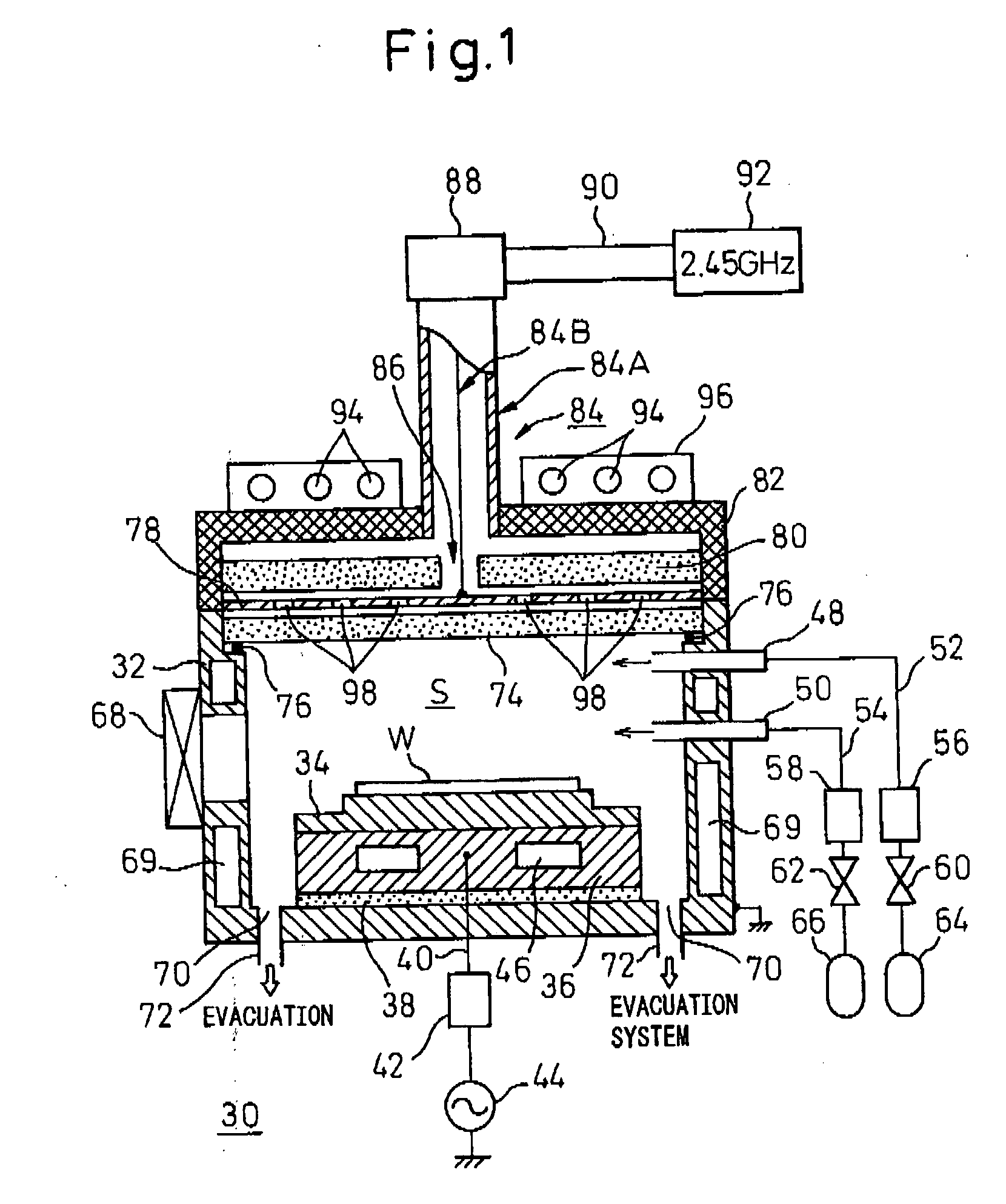
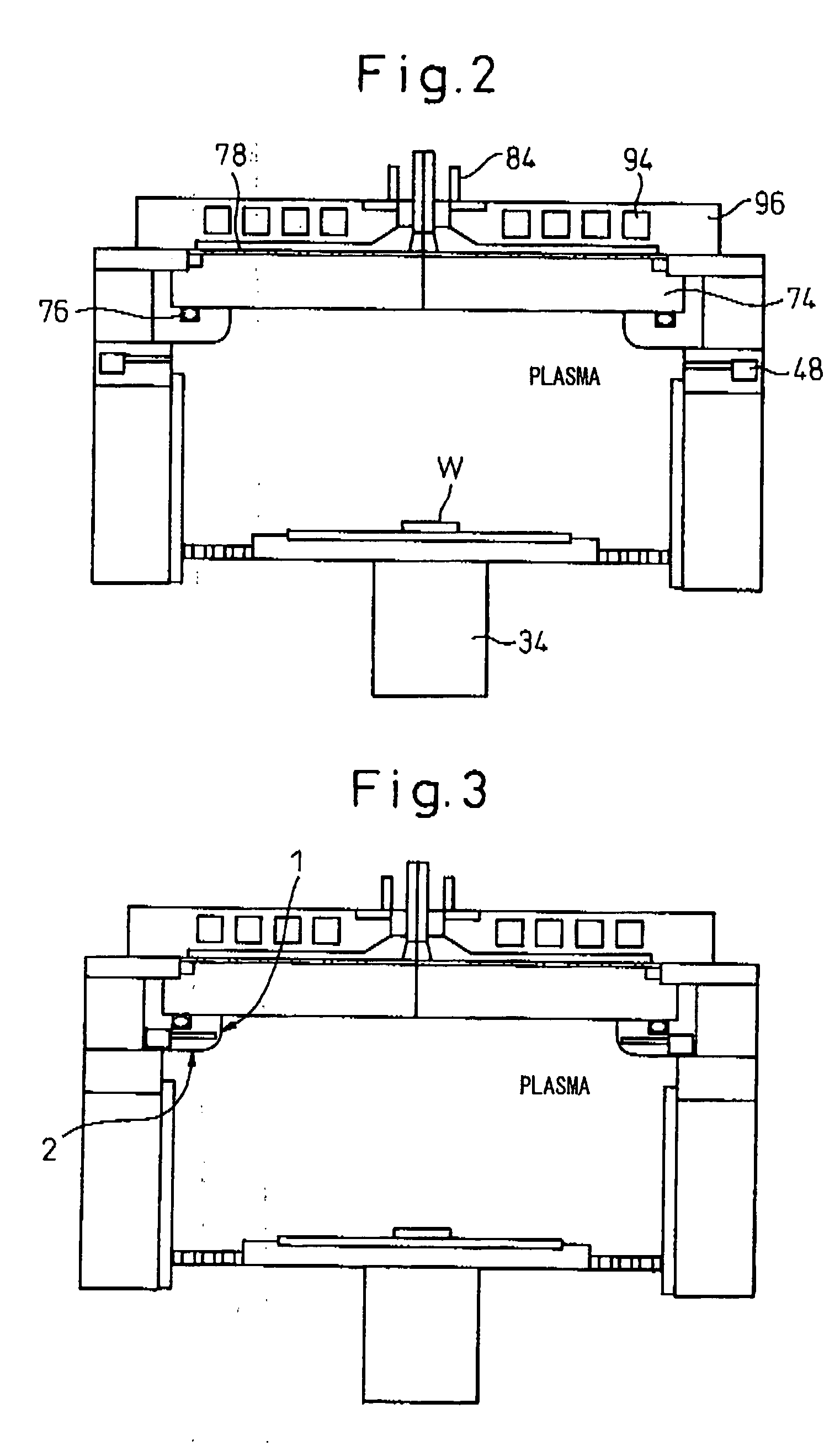
Substrate processing apparatus, substrate processing method, and program for implementing the method
InactiveUS20050233477A1Improve productivityLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementProduction rateEtching
A substrate processing apparatus which is capable of enhancing productivity in manufacturing product substrates. In process chambers 106 and 107 of an etching apparatus 100, etching is carried out on a substrate as an object to be processed, and dummy processing is carried out on at least one non-product substrate before execution of the etching. A host computer 200 determines whether or not the dummy processing is to be executed. The host computer 200 determines whether or not the interior of each of the process chambers 106 and 107 is in a stable state, and omits the execution of the dummy processing when it is determined that it is in the stable state.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls or flat surfaces of trenches
ActiveUS20170250068A1Improve film qualityDecreasing density of filmElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon nitrideEtching
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing either one of but not both of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the one of the top / bottom portion and the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the other according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Method for forming silicon nitride film selectively on sidewalls of trenches
ActiveUS20190057857A1Low densityPlasma-enhanced chemical vapor depositionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingChemical resistance
A method for fabricating a layer structure in a trench includes: simultaneously forming a dielectric film containing a Si—N bond on an upper surface, and a bottom surface and sidewalls of the trench, wherein a top / bottom portion of the film formed on the upper surface and the bottom surface and a sidewall portion of the film formed on the sidewalls are given different chemical resistance properties by bombardment of a plasma excited by applying voltage between two electrodes between which the substrate is place in parallel to the two electrodes; and substantially removing the sidewall portion of the film by wet etching which removes the sidewall portion of the film more predominantly than the top / bottom portion according to the different chemical resistance properties.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
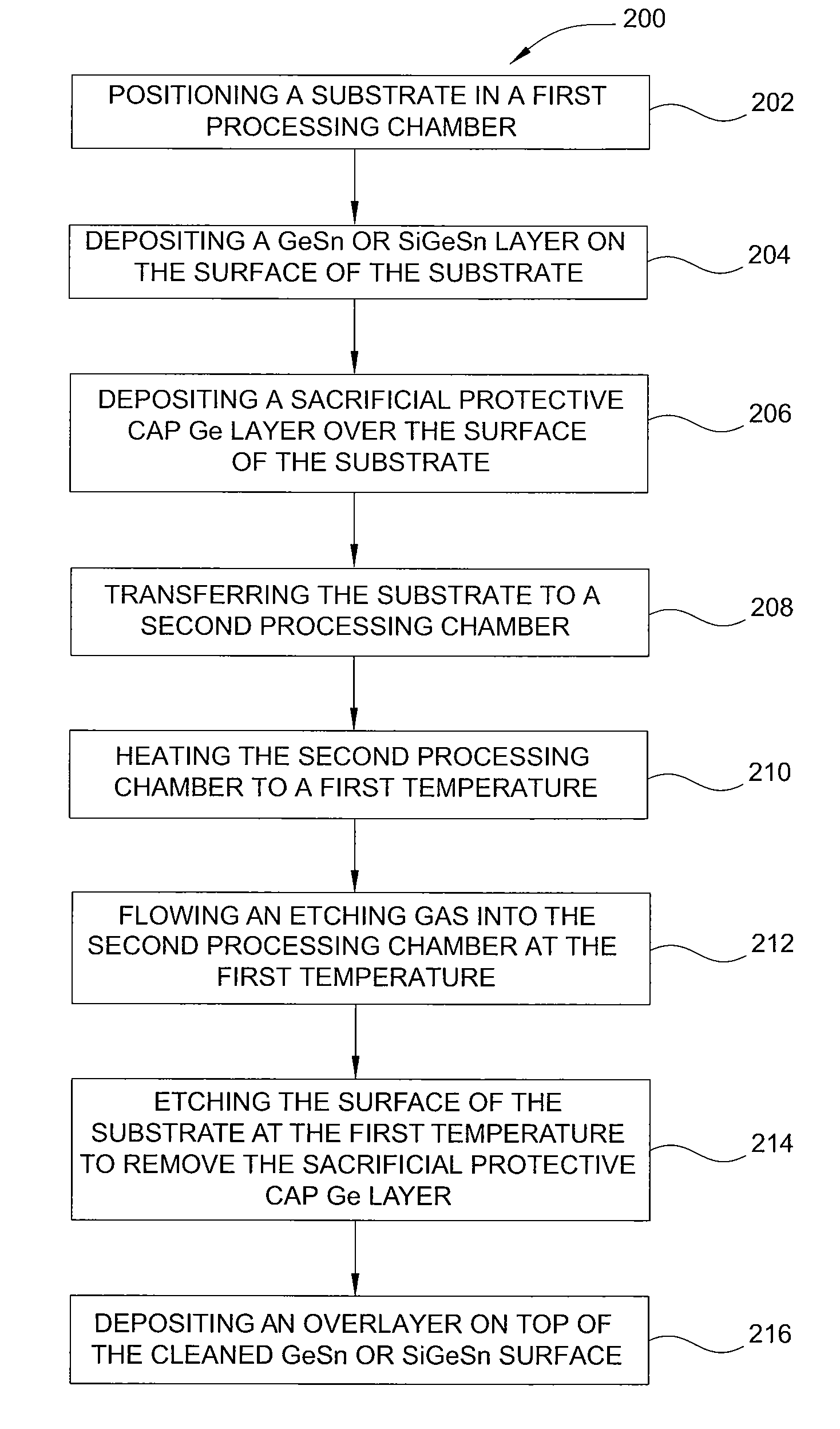
Method of epitaxial germanium tin alloy surface preparation
Methods of preparing a clean surface of germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layers for subsequent deposition are provided. An overlayer of Ge, doped Ge, another GeSn or SiGeSn layer, a doped GeSn or SiGeSn layer, an insulator, or a metal can be deposited on a prepared GeSn or SiGeSn layer by positioning a substrate with an exposed germanium tin or silicon germanium tin layer in a processing chamber, heating the processing chamber and flowing a halide gas into the processing chamber to etch the surface of the substrate using either thermal or plasma assisted etching followed by depositing an overlayer on the substantially oxide free and contaminant free surface. Methods can also include the placement and etching of a sacrificial layer, a thermal clean using rapid thermal annealing, or a process in a plasma of nitrogen trifluoride and ammonia gas.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
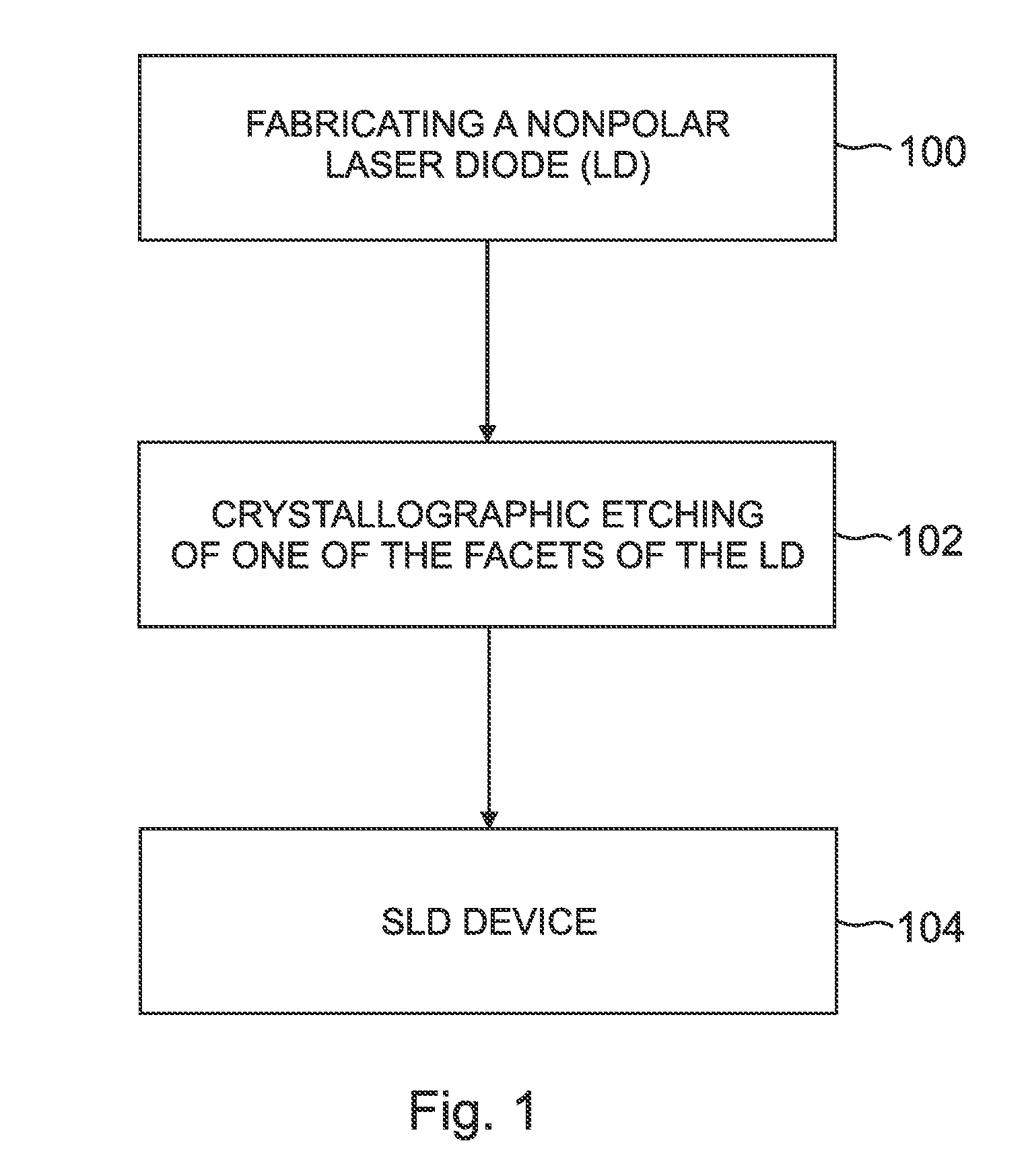
Superluminescent diodes by crystallographic etching
InactiveUS20110103418A1Reduce internal lossSignificant contributionOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsSuperluminescent diodeEtching
An optoelectronic device, comprising an active region and a waveguide structure to provide optical confinement of light emitted from the active region; a pair of facets on opposite ends of the device, having opposite surface polarity; and one of the facets which has been roughened by a crystallographic chemical etching process, wherein the device is a nonpolar or semipolar (Ga,In,Al,B)N based device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for Growth of Gan Single Crystal, Method for Preparation of Gan Substrate, Process for Producing Gan-Based Element, and Gan-Based Element
InactiveUS20080261378A1Reduce defectsEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingGas phase
A GaN-based thin film (thick film) is grown using a metal buffer layer grown on a substrate. (a) A metal buffer layer (210) made of, for example, Cr or Cu is vapor-deposited on a sapphire substrate (120). (b) A substrate obtained by vapor-depositing the metal buffer layer (210) on the sapphire substrate (120) is nitrided in an ammonia gas ambient, thereby forming a metal nitride layer (212). (c) A GaN buffer layer (222) is grown on the nitrided metal buffer layers (210, 212). (d) Finally, a GaN single-crystal layer (220) is grown. This GaN single-crystal layer (220) can be grown to have various thicknesses depending on the objects. A freestanding substrate can be fabricated by selective chemical etching of the substrate fabricated by the above steps. It is also possible to use the substrate fabricated by the above steps as a GaN template substrate for fabricating a GaN-based light emitting diode or laser diode.
Owner:FURUKAWA COMPANY +4
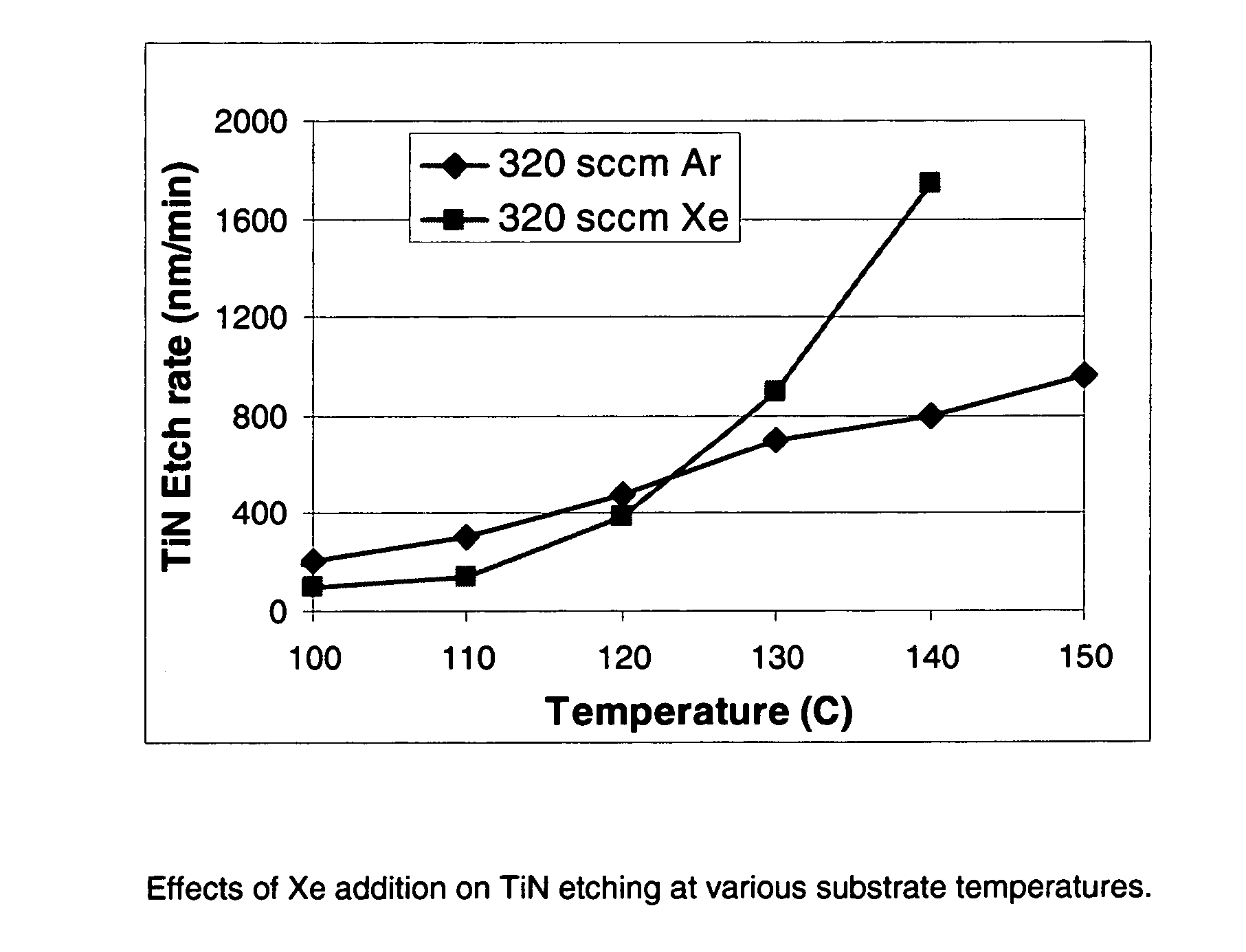
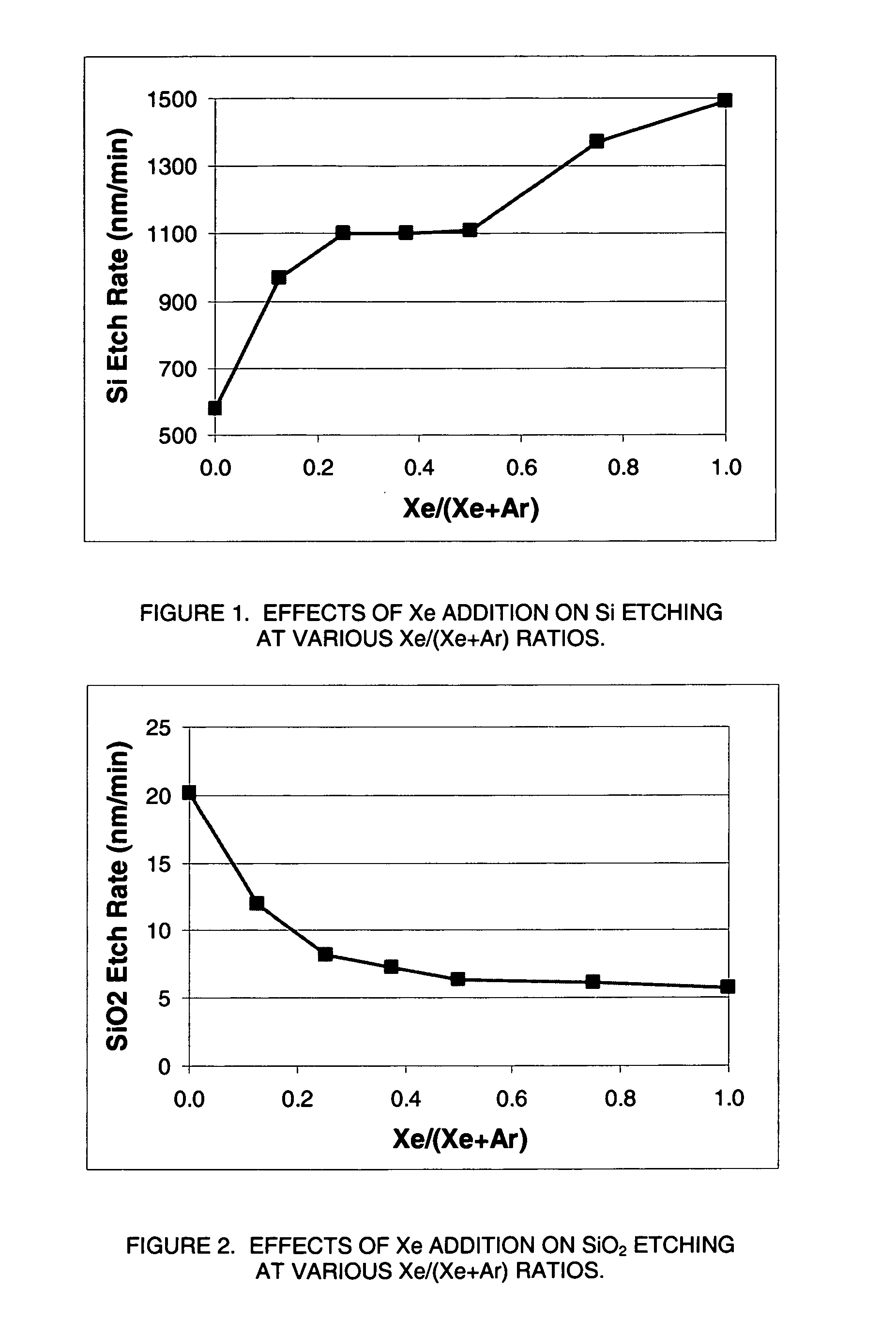
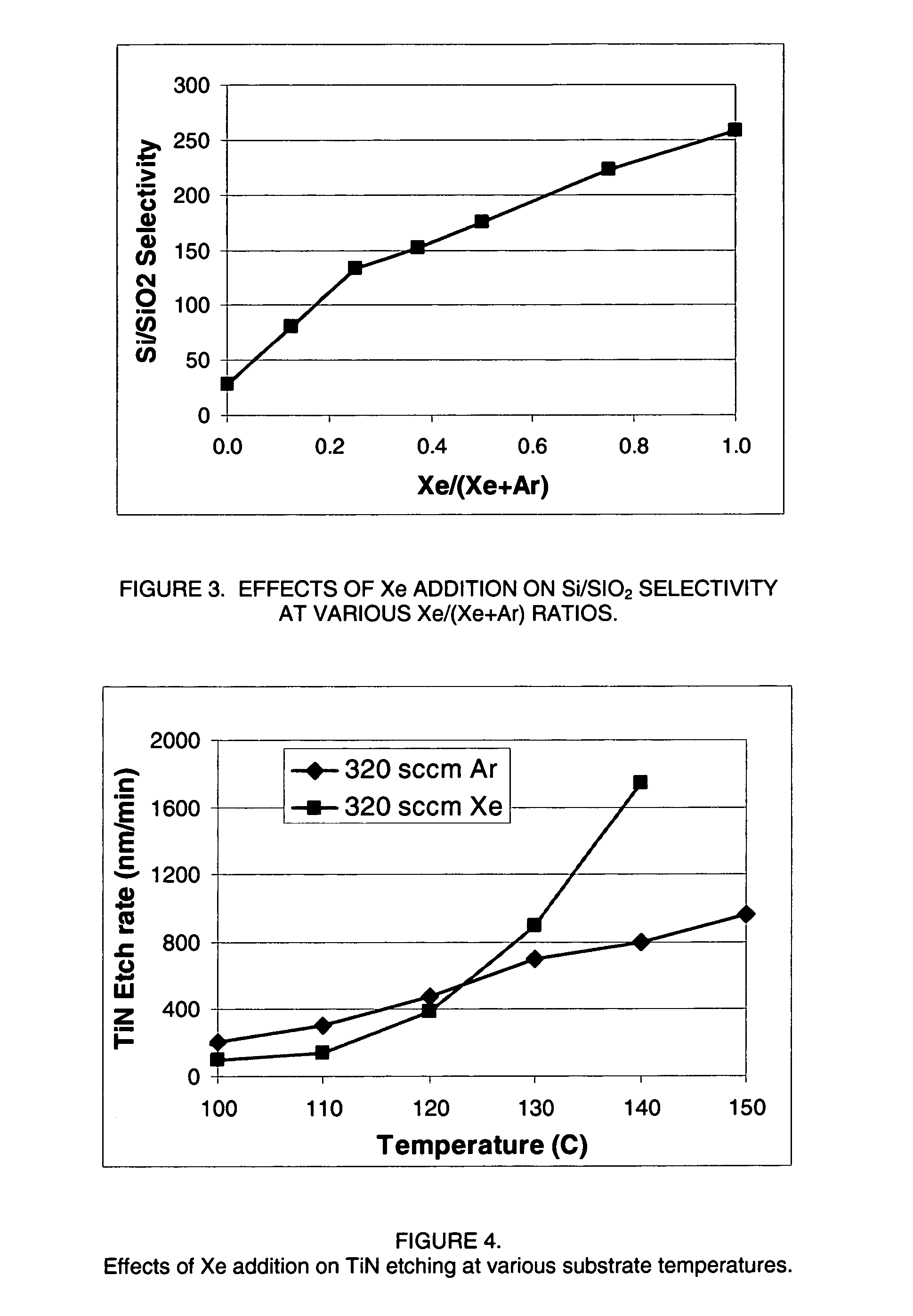
Selective etching of titanium nitride with xenon difluoride
InactiveUS20070117396A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingEtchingTitanium nitride
This invention relates to an improved process for the selective etching of TiN from silicon dioxide (quartz) and SiN surfaces commonly found in semiconductor deposition chambers equipment and tools. In the process, an SiO2 or SiN surface having TiN thereon is contacted with XeF2 in a contact zone to selectively convert the TiN to a volatile species and then the volatile species is removed from the contact zone. XeF2 can be preformed or formed in situ by reaction between Xe and a fluorine compound.
Owner:VERSUM MATERIALS US LLC
Laminated semiconductor substrate process for producing the same
InactiveUS20060118935A1Simple processReduce surface roughnessDecorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEtchingSurface roughness
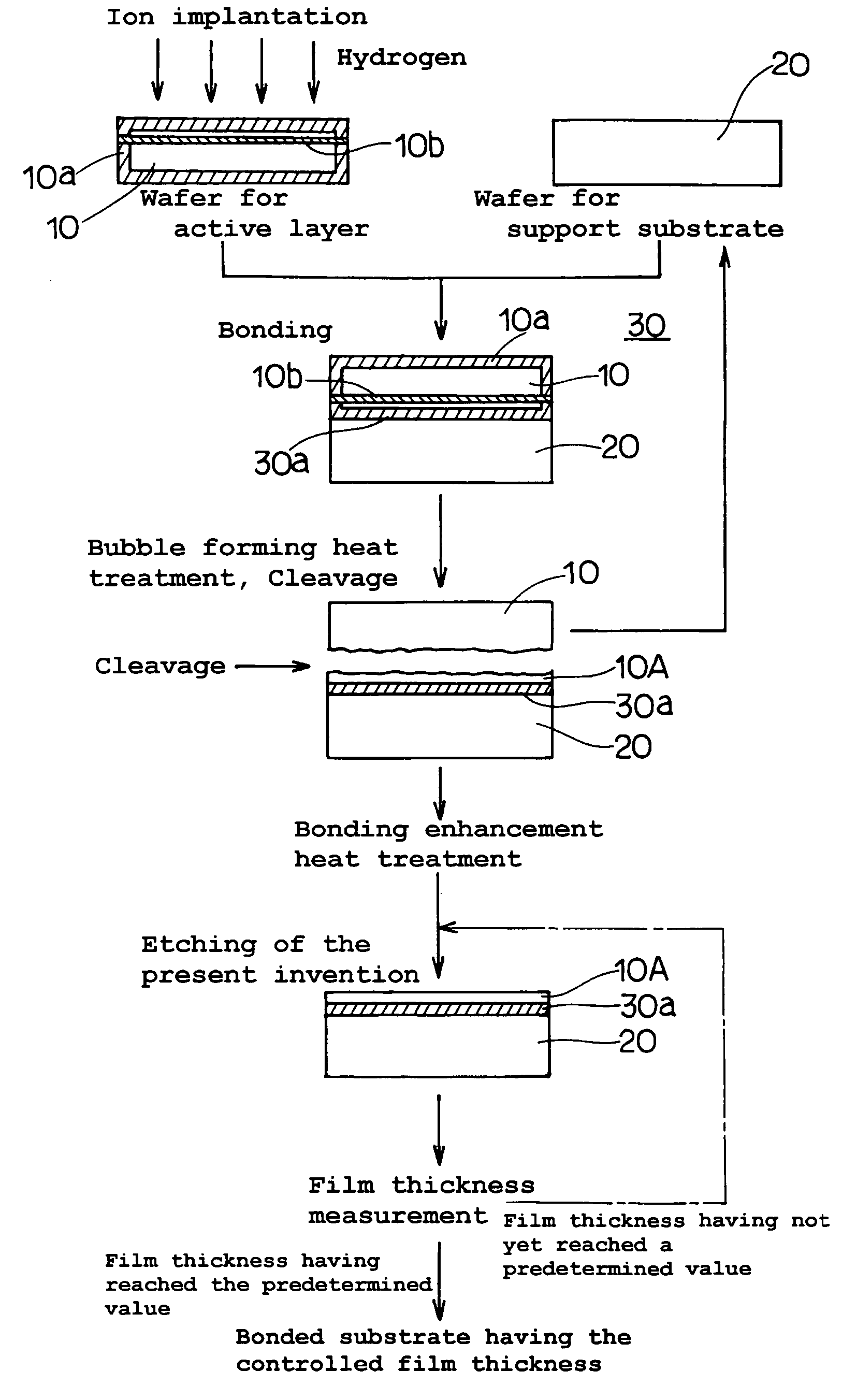
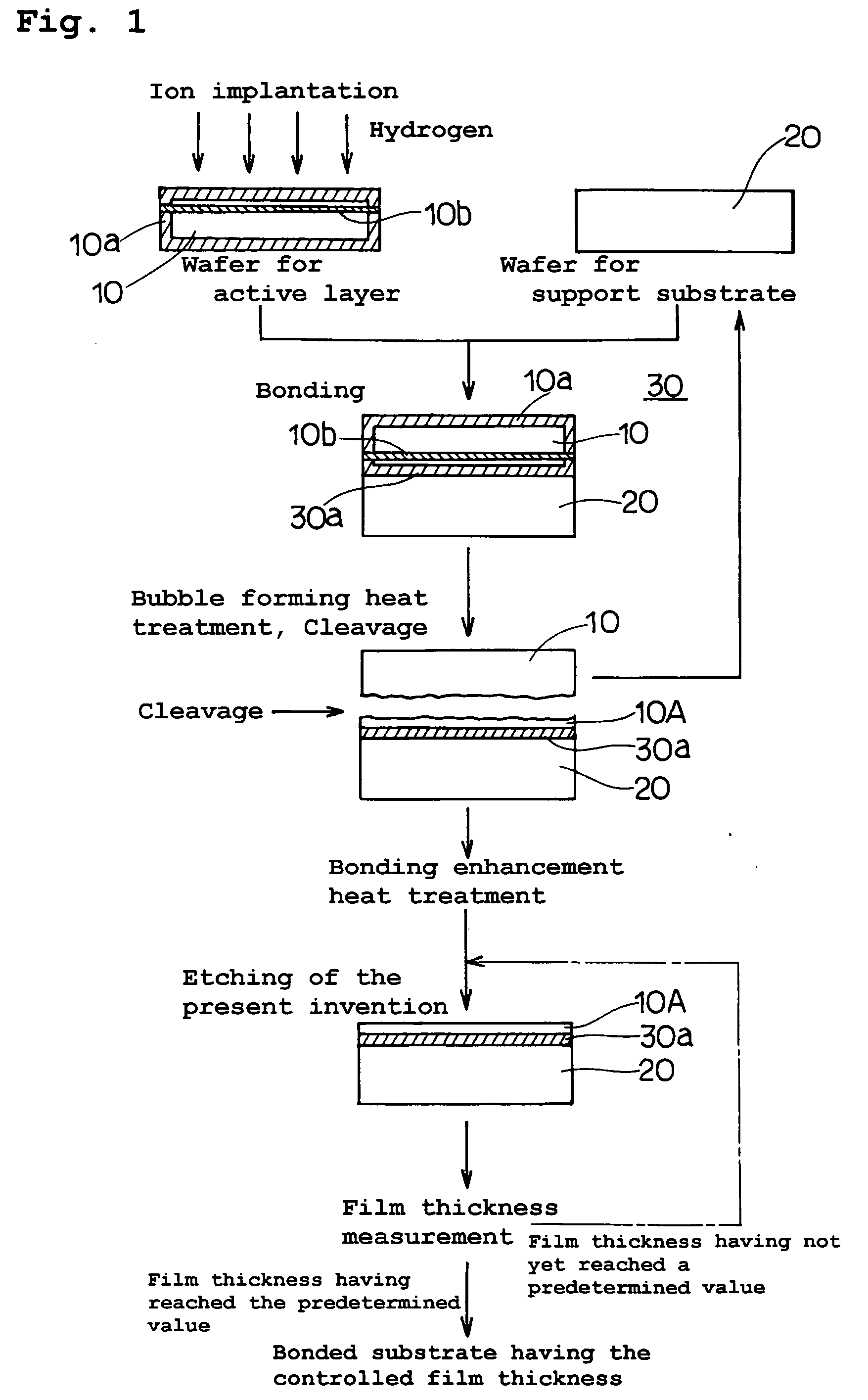
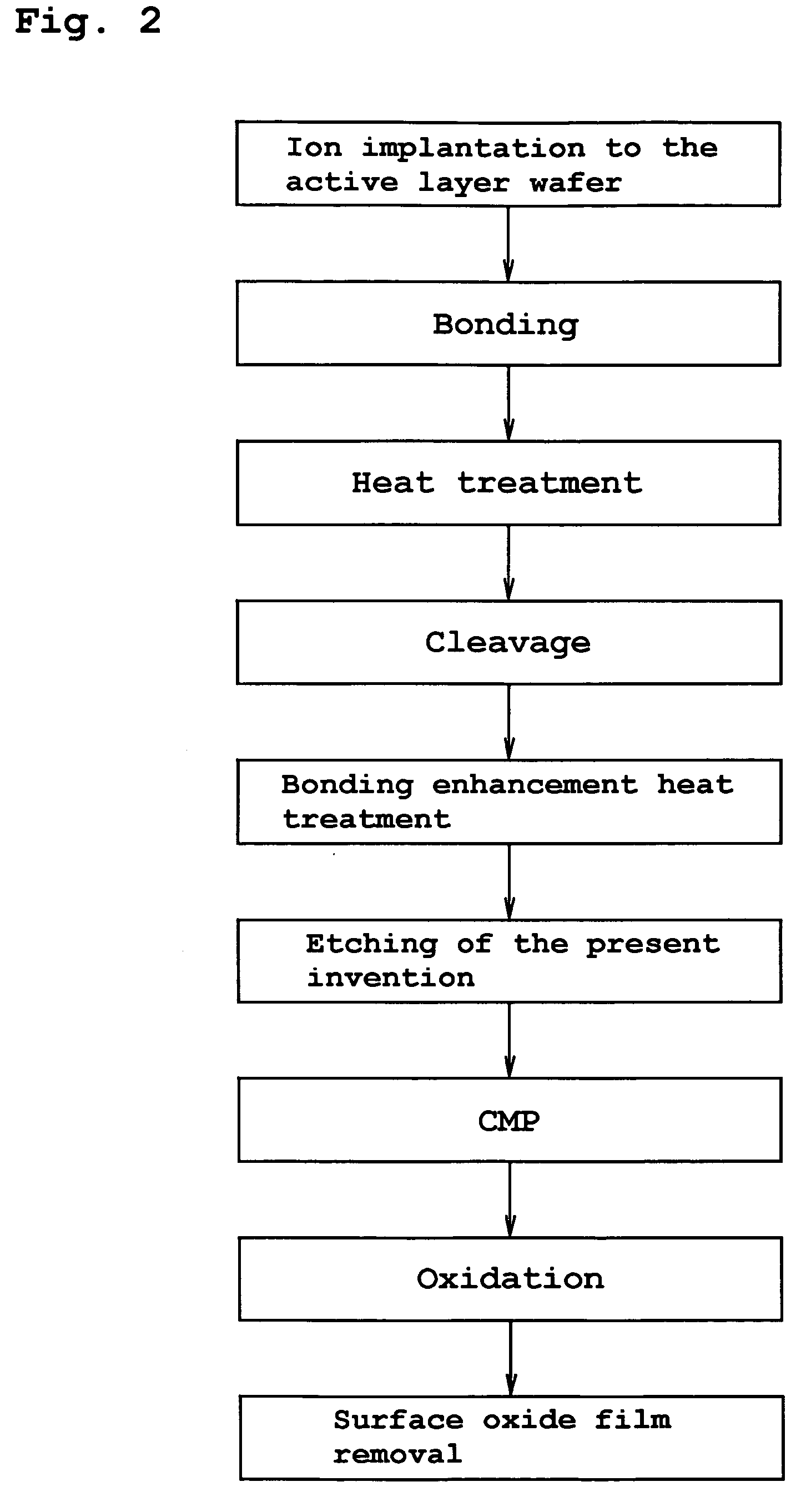
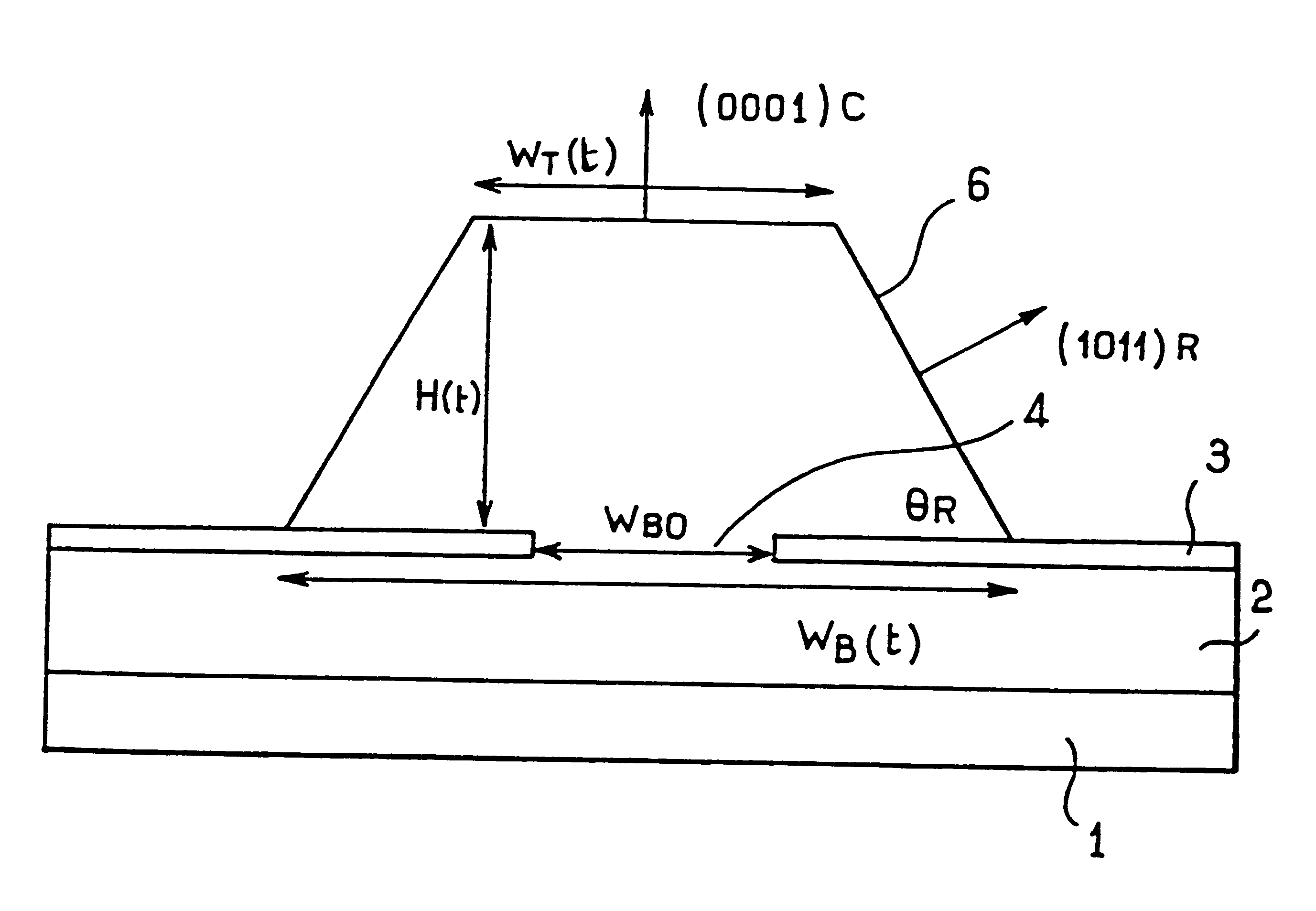
The present invention provides a bonded substrate fabricated to have its final active layer thickness of 200 nm or lower by performing the etching by only 1 nm to 1 μm with a solution having an etching effect on a surface of an active layer of a bonded substrate which has been prepared by bonding two substrates after one of them having been ion-implanted and then cleaving off a portion thereof by heat treatment. SC-1 solution is used for performing the etching. A polishing, a hydrogen annealing and a sacrificial oxidation may be respectively applied to the active layer before and / or after the etching. The film thickness of this active layer can be made uniform over the entire surface area and the surface roughness of the active layer can be reduced as well.
Owner:SUMCO CORP +1
Method for producing a gallium nitride epitaxial layer
InactiveUS6325850B1GaN crystal qualityImprove crystal qualityPolycrystalline material growthLaser detailsEtchingGallium nitride
The invention concerns a method for producing a gallium nitride (GaN) epitaxial layer characterised in that it consists in depositing on a substrate a dielectric layer acting as a mask and depositing on the masked gallium nitride, by epitaxial deposit, so as to induce the deposit of gallium nitride patterns and the anisotropic lateral growth of said patterns, the lateral growth being pursued until the different patterns coalesce. The deposit of the gallium nitride patterns can be carried out ex-situ by dielectric etching or in-situ by treating the substrate for coating it with a dielectric film whereof the thickness is of the order of one angstrom. The invention also concerns the gallium nitride layers obtained by said method.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CRISTAUX & DETECTEURS
Plasma processing apparatus and plasma processing method
InactiveUS20060108331A1Reduce defectsPollution suppressionElectric discharge tubesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingPre treatment
A plasma processing apparatus comprising at least a plasma processing chamber for plasma-processing an object; object-holding means for disposing the object in the plasma processing chamber; and plasma-generating means for generating a plasma in the plasma processing chamber. The inner wall of the plasma processing chamber is at least partially covered with an oxide film based on a pre-treating plasma. A plasma processing apparatus and a plasma processing method effectively prevent the spluttering and the etching of the inner wall of the plasma processing chamber while suppressing contamination to the object.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
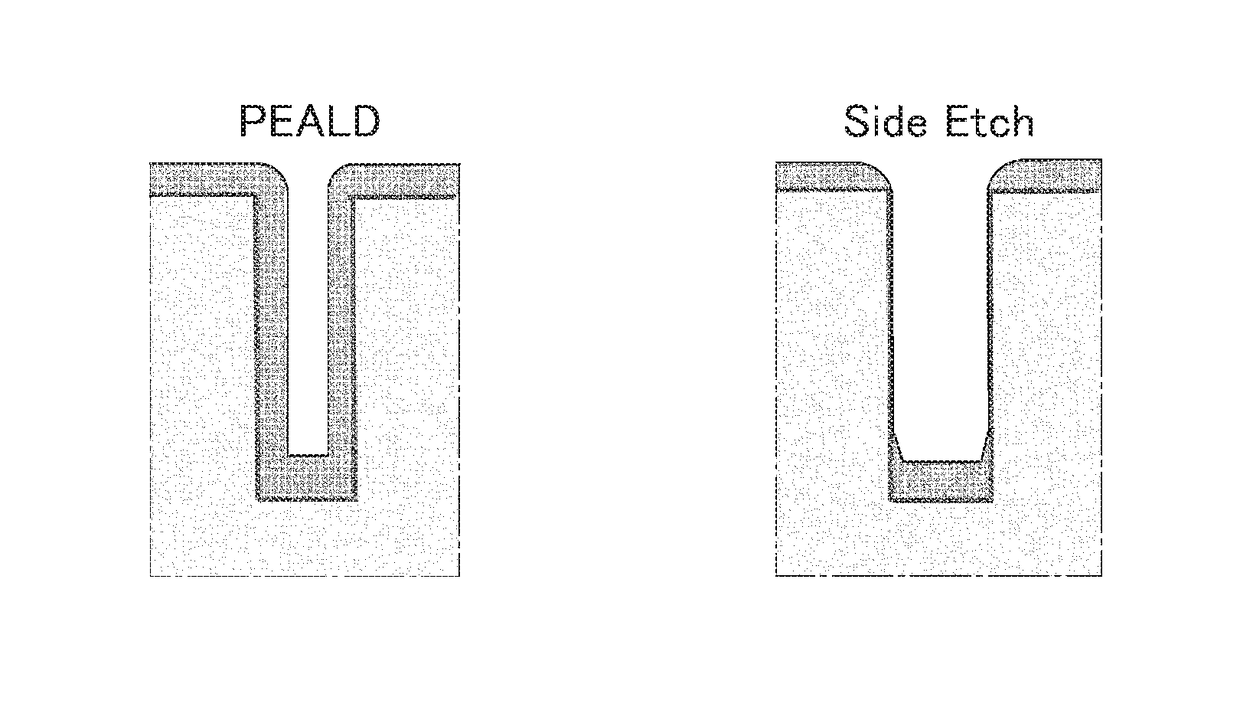
Method of depositing and etching Si-containing film
ActiveUS9960033B1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingElectrical and Electronics engineering
A method of filling recesses or grooves on a patterned surface with a layer of film, by combining depositing a film by PEALD / PPECVD on the patterned surface and etching the film, wherein the deposition and the etching are separately controlled, and wherein the conditions for deposition can be controlled by controlling RF power.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Leadless plastic chip carrier with standoff contacts and die attach pad
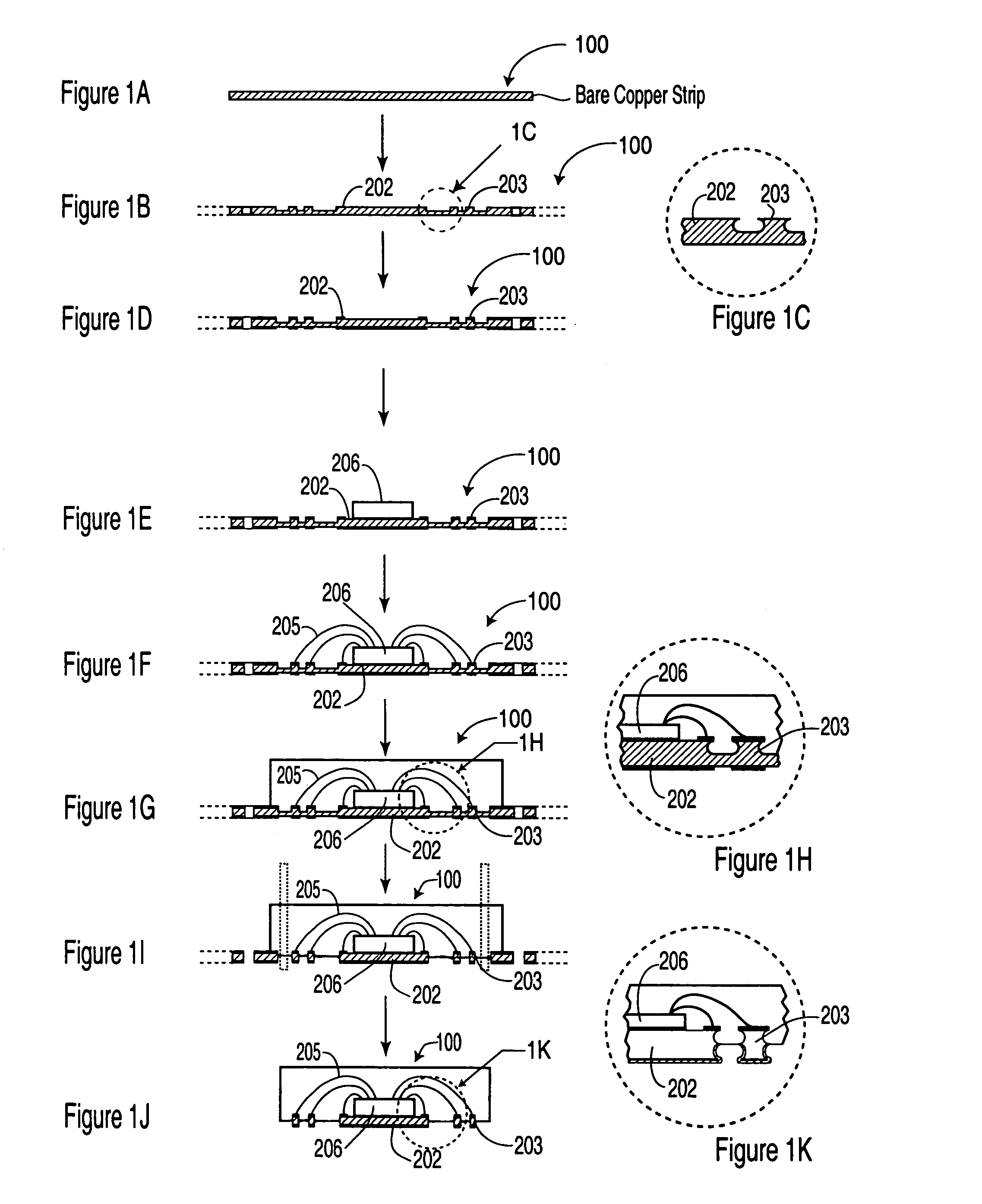
ActiveUS7049177B1Improve motherboard assemblyRelieve pressureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEtchingContact pad
A process for fabricating a leadless plastic chip carrier includes selectively etching at least a first surface of a leadframe strip to partially define at least a plurality of contact pads and a die attach pad; selectively plating at least one layer of metal on a second surface of the leadframe strip, on an undersurface of at least the plurality of contact pads and the die attach pad; mounting a semiconductor die on the first surface, on the partially defined die attach pad; wire bonding the semiconductor die to ones of the contact pads; encapsulating the wire bonds and the semiconductor die in a molding material such that the molding material covers a first portion of the die attach pad and first portions of the contact pads; selectively etching a second surface of the leadframe strip to define a second portion of the contact pads and a second portion of the die attach pad by etching the second surface with the at least one layer of metal resisting etching; and singulating the leadless plastic chip carrier from the leadframe strip.
Owner:UTAC HEADQUARTERS PTE LTD
MTJ MRAM with stud patterning
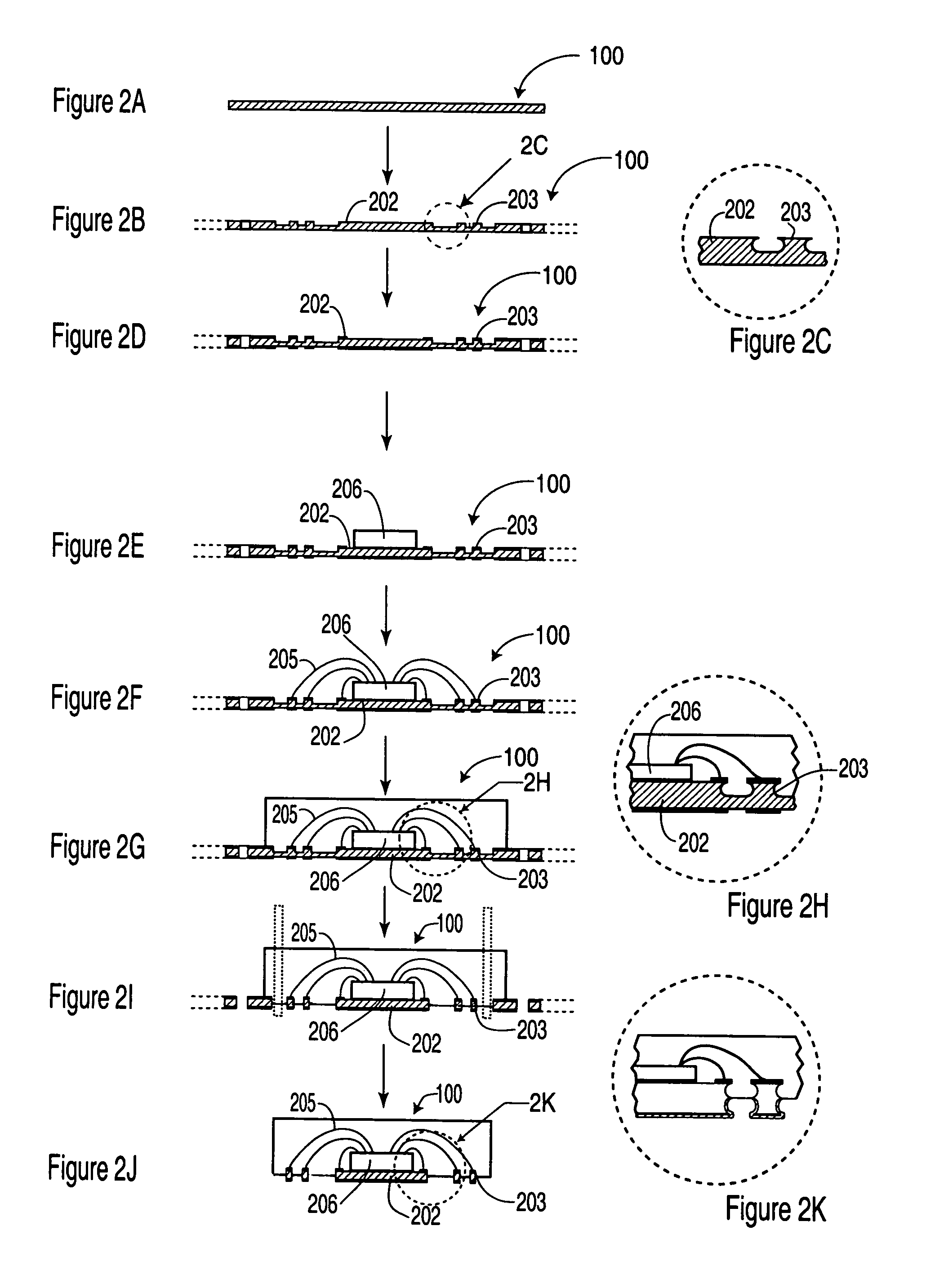
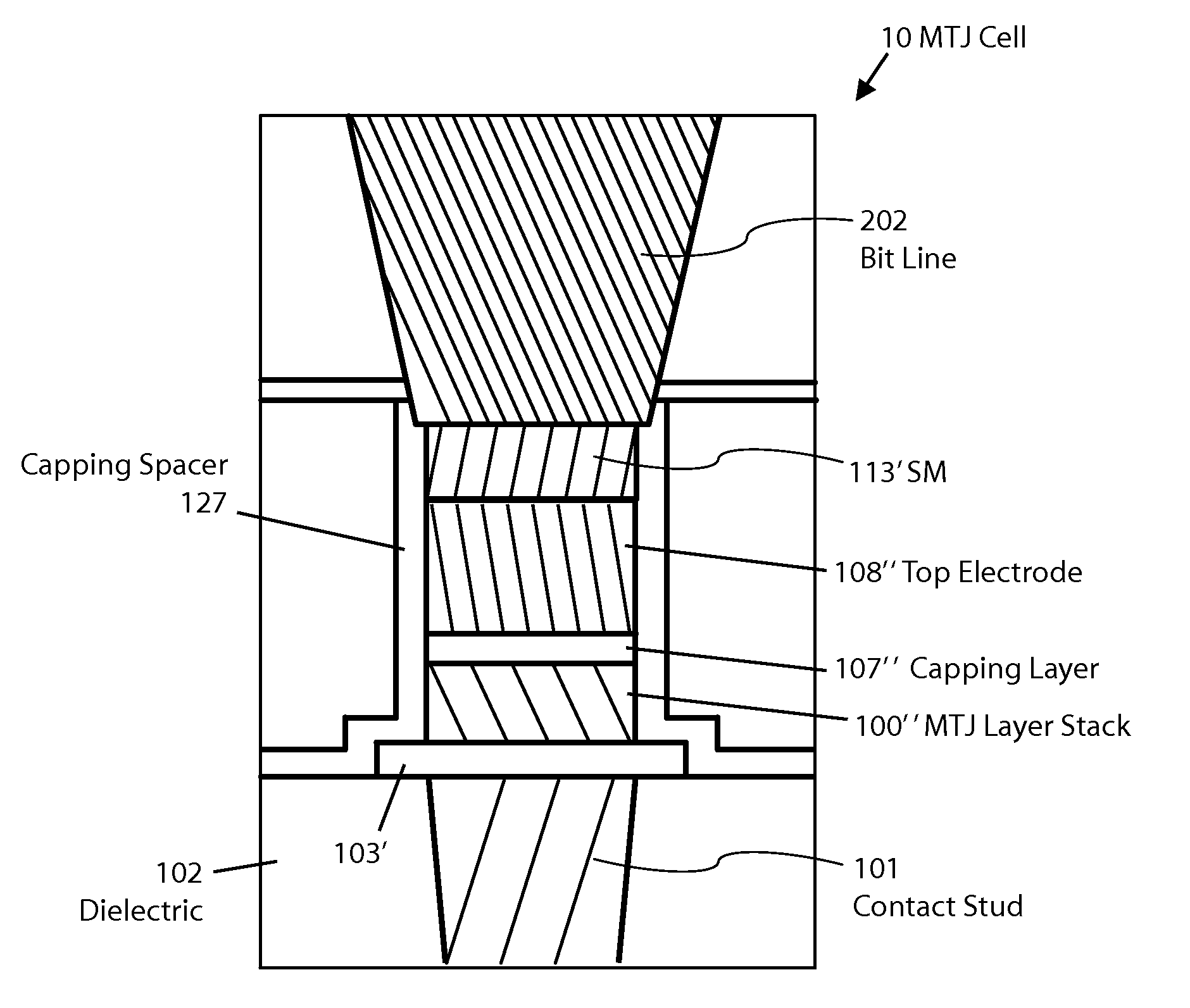
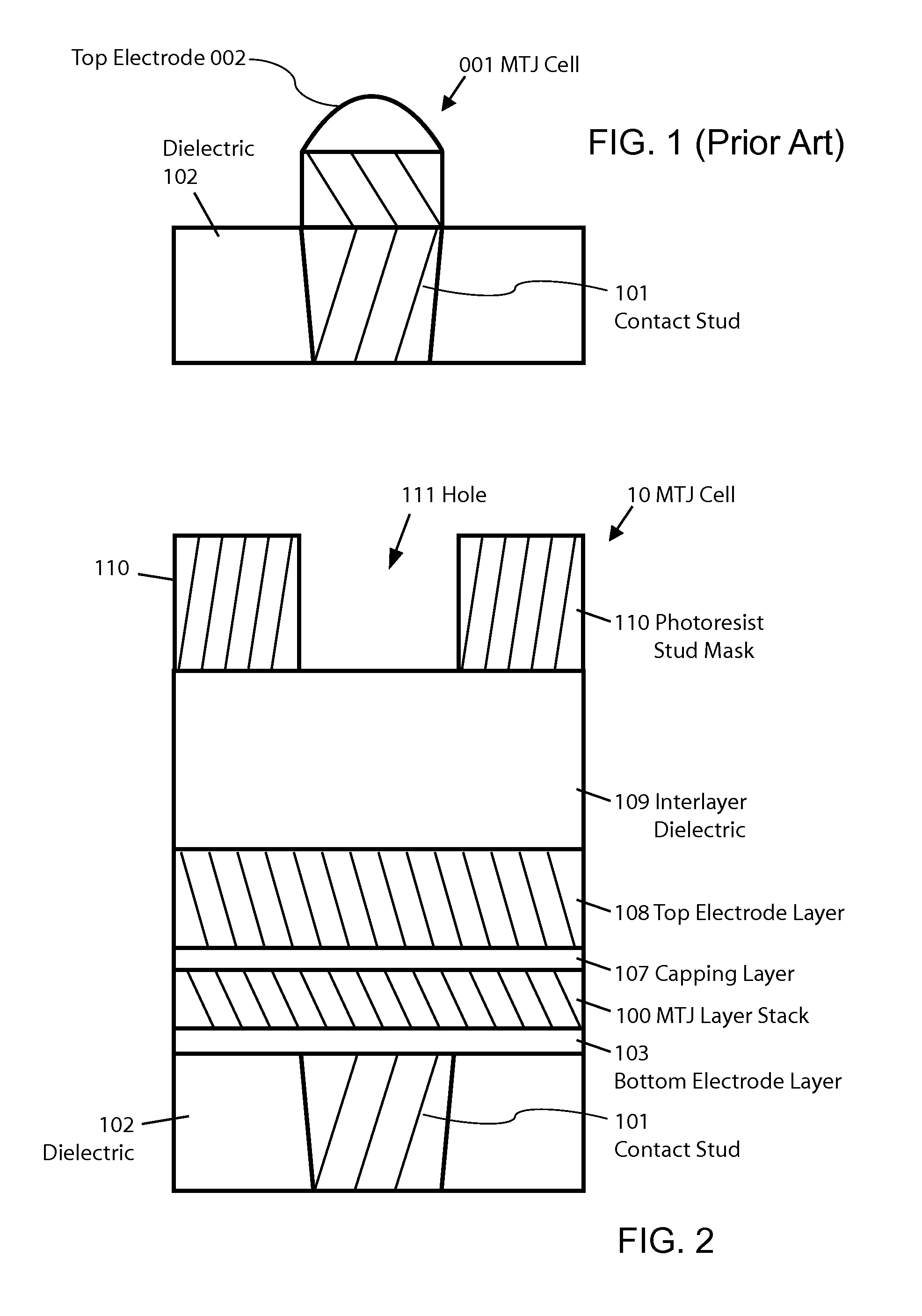
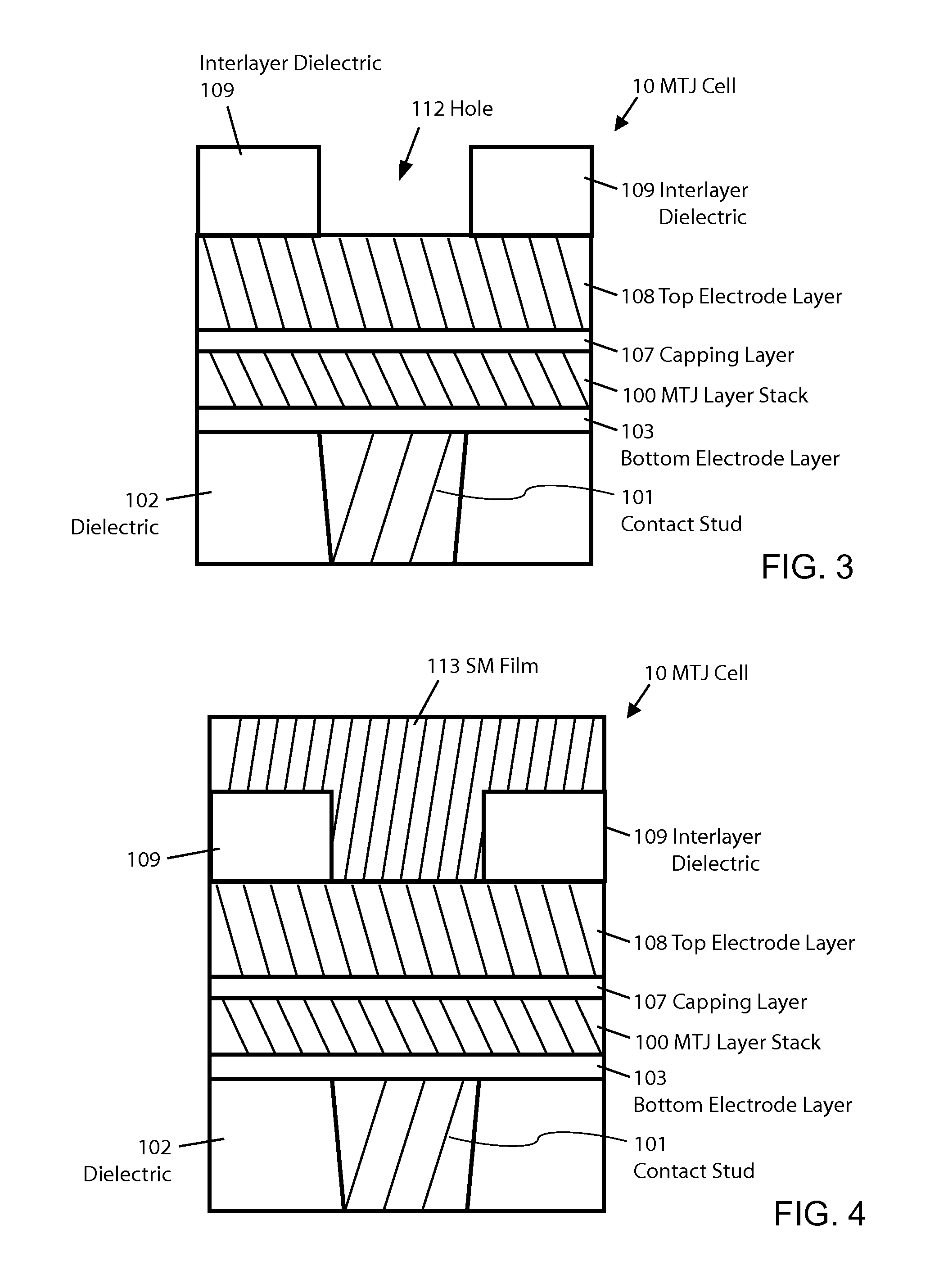
ActiveUS8772888B2Reduce widthImprove errorMagnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesEtchingConductive materials
Owner:AVALANCHE TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com