Patents
Literature
338 results about "Pyrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A pyrometer is a type of remote-sensing thermometer used to measure the temperature of a surface. Various forms of pyrometers have historically existed. In the modern usage, it is a device that from a distance determines the temperature of a surface from the amount of the thermal radiation it emits, a process known as pyrometry and sometimes radiometry.
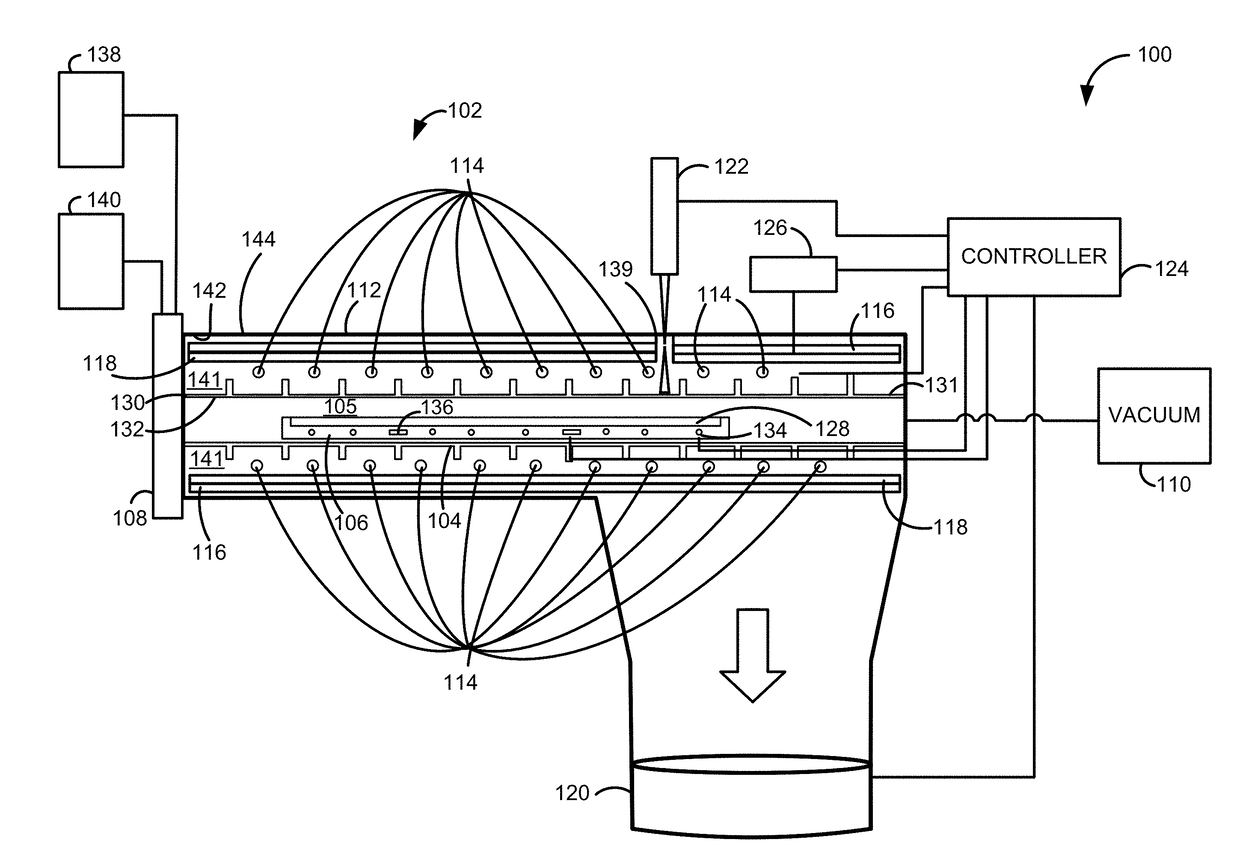
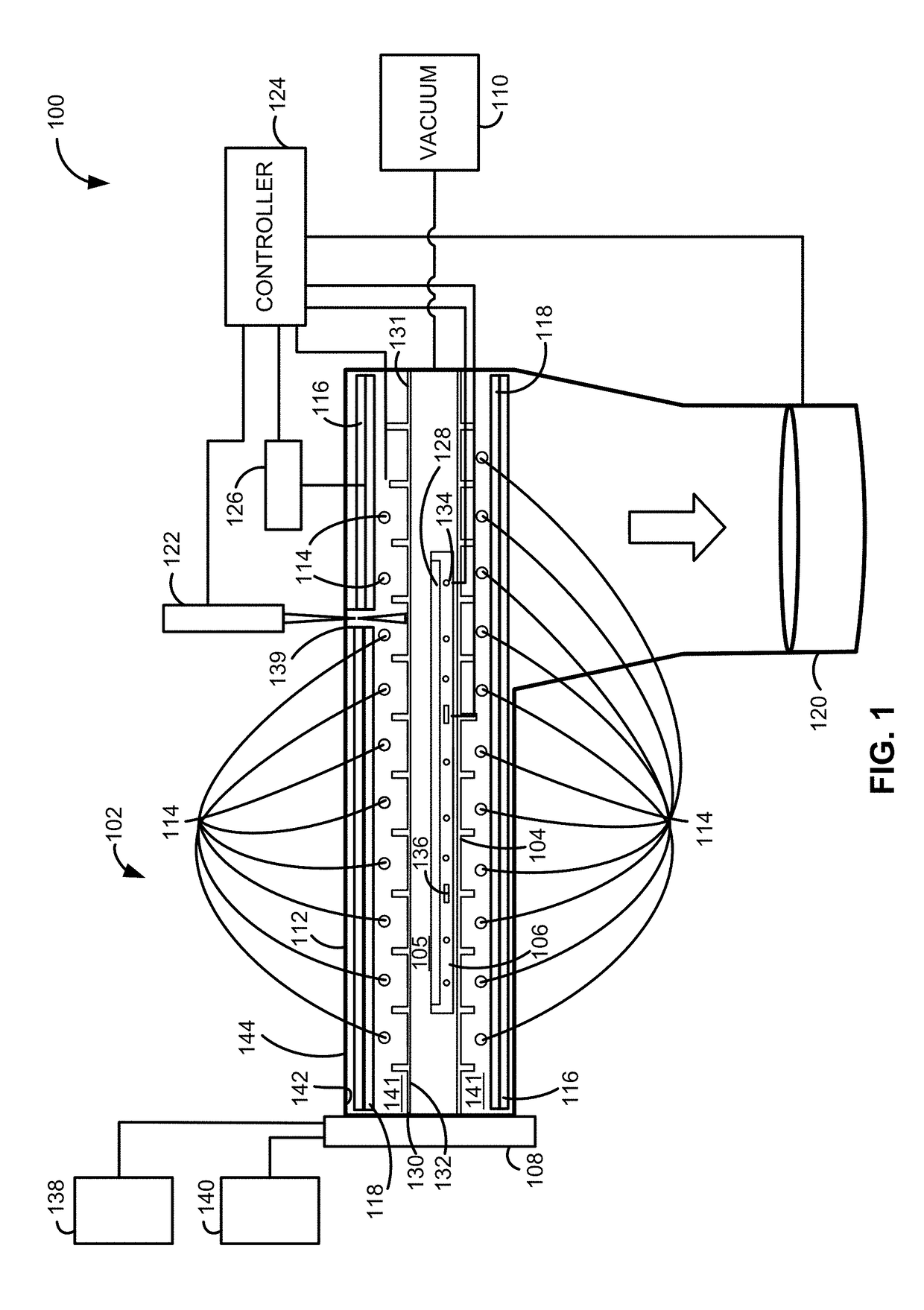
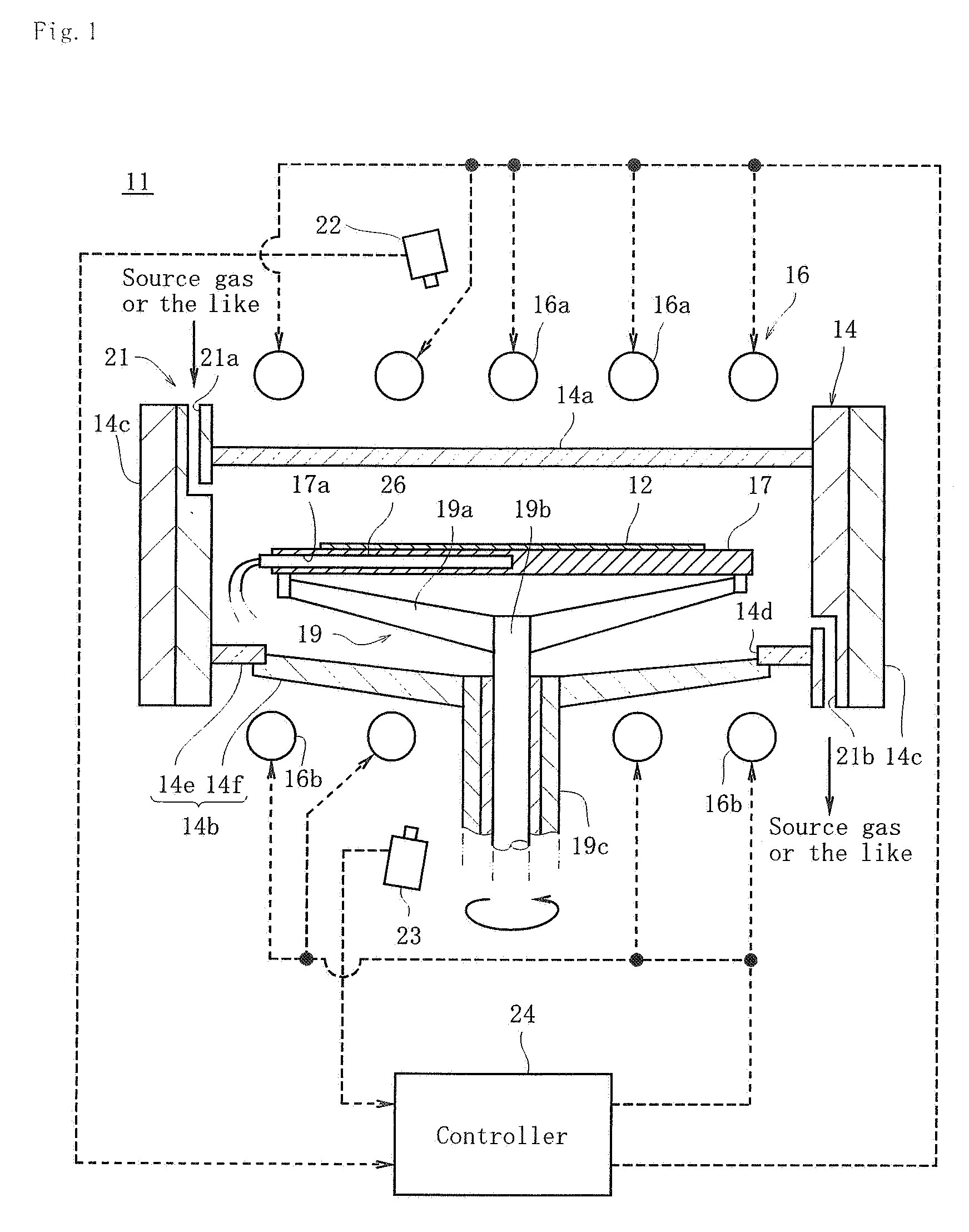
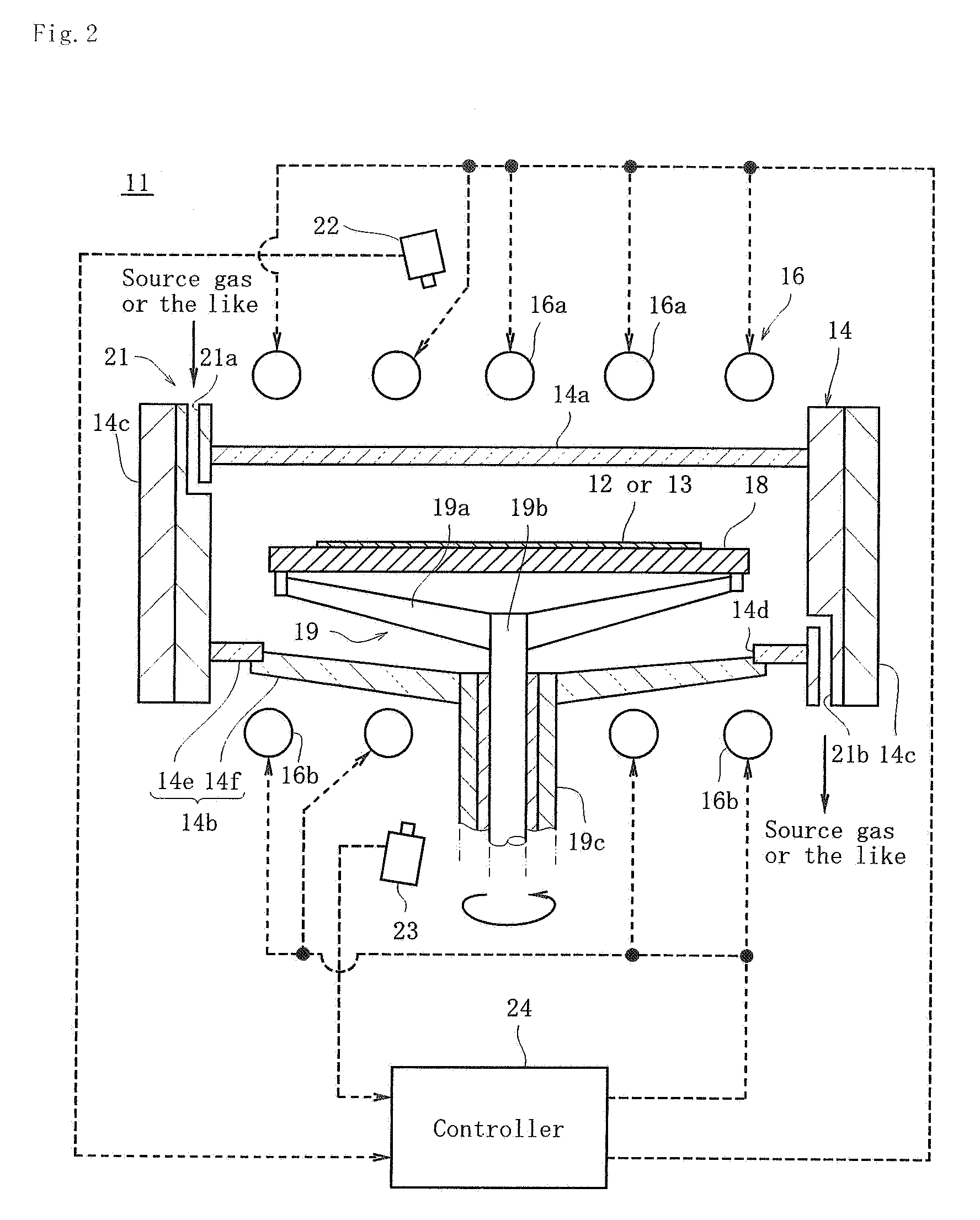
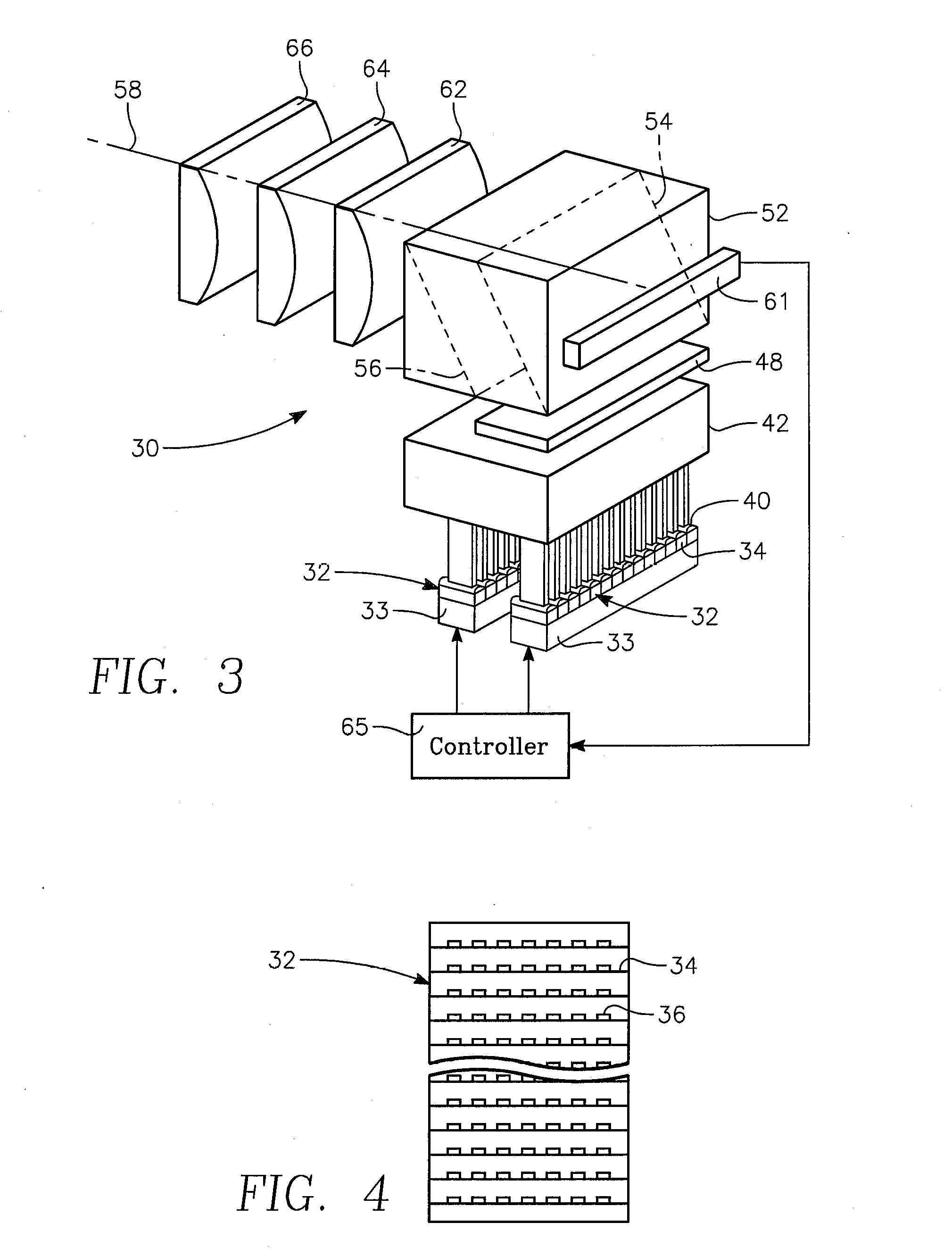
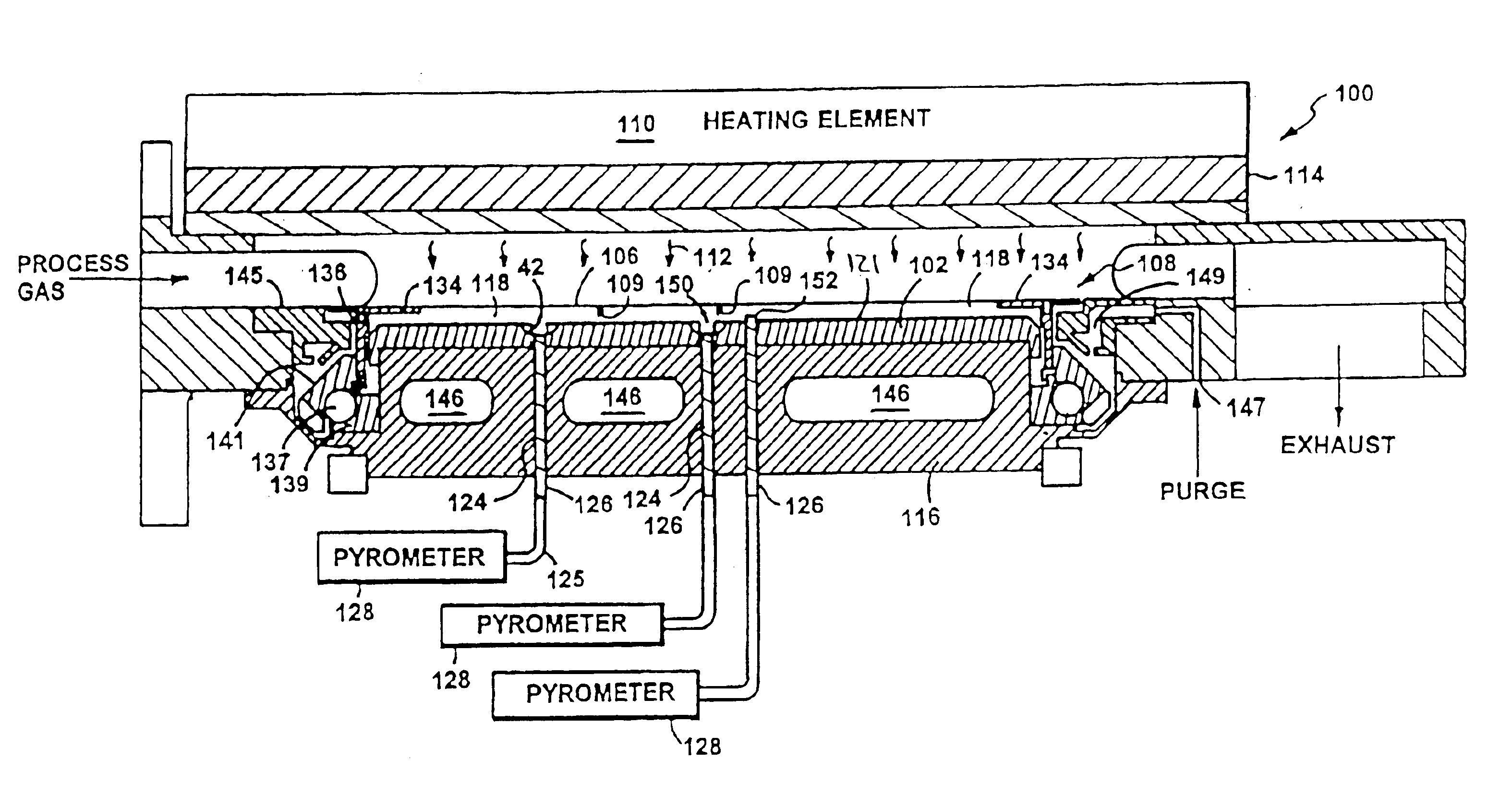
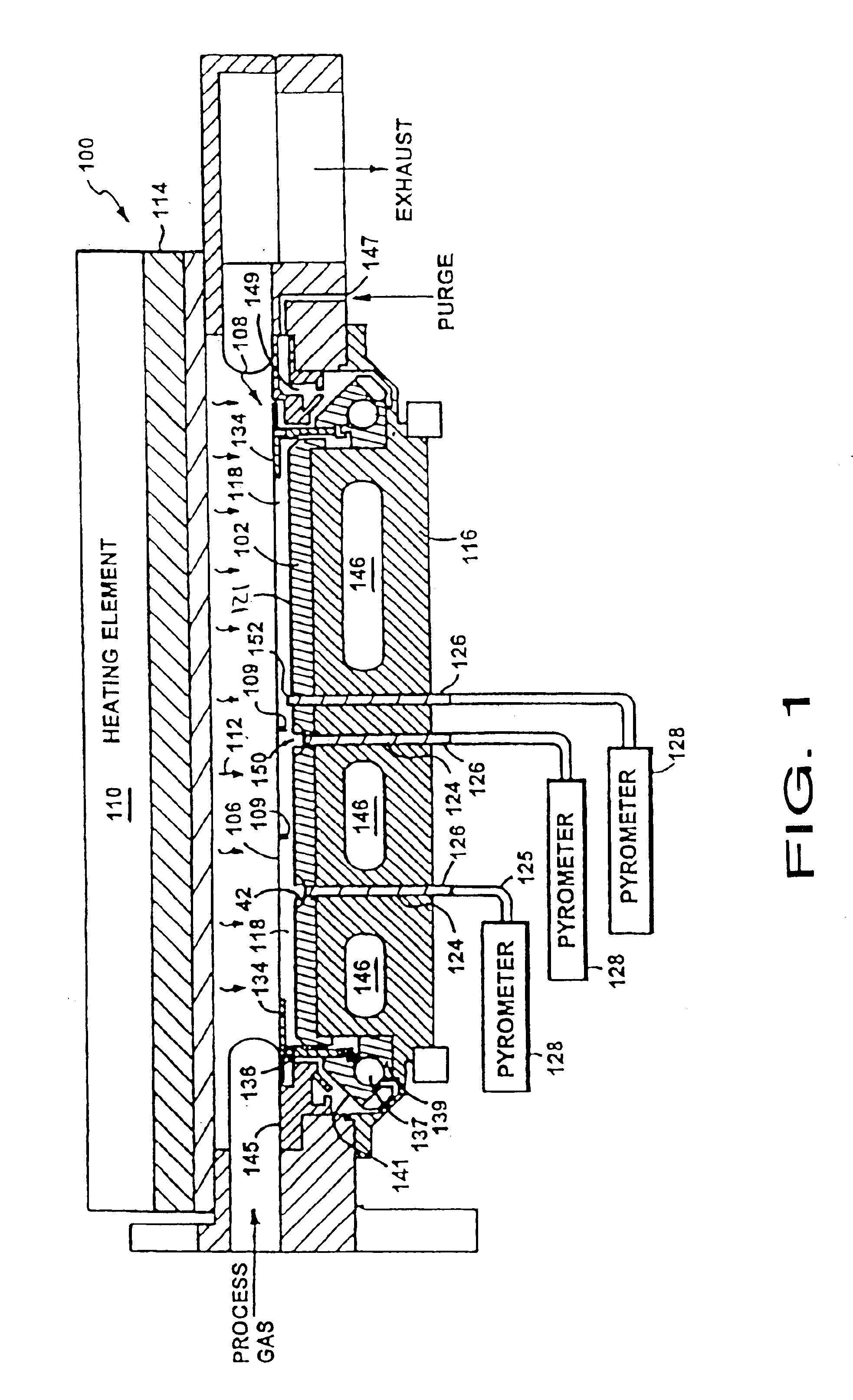
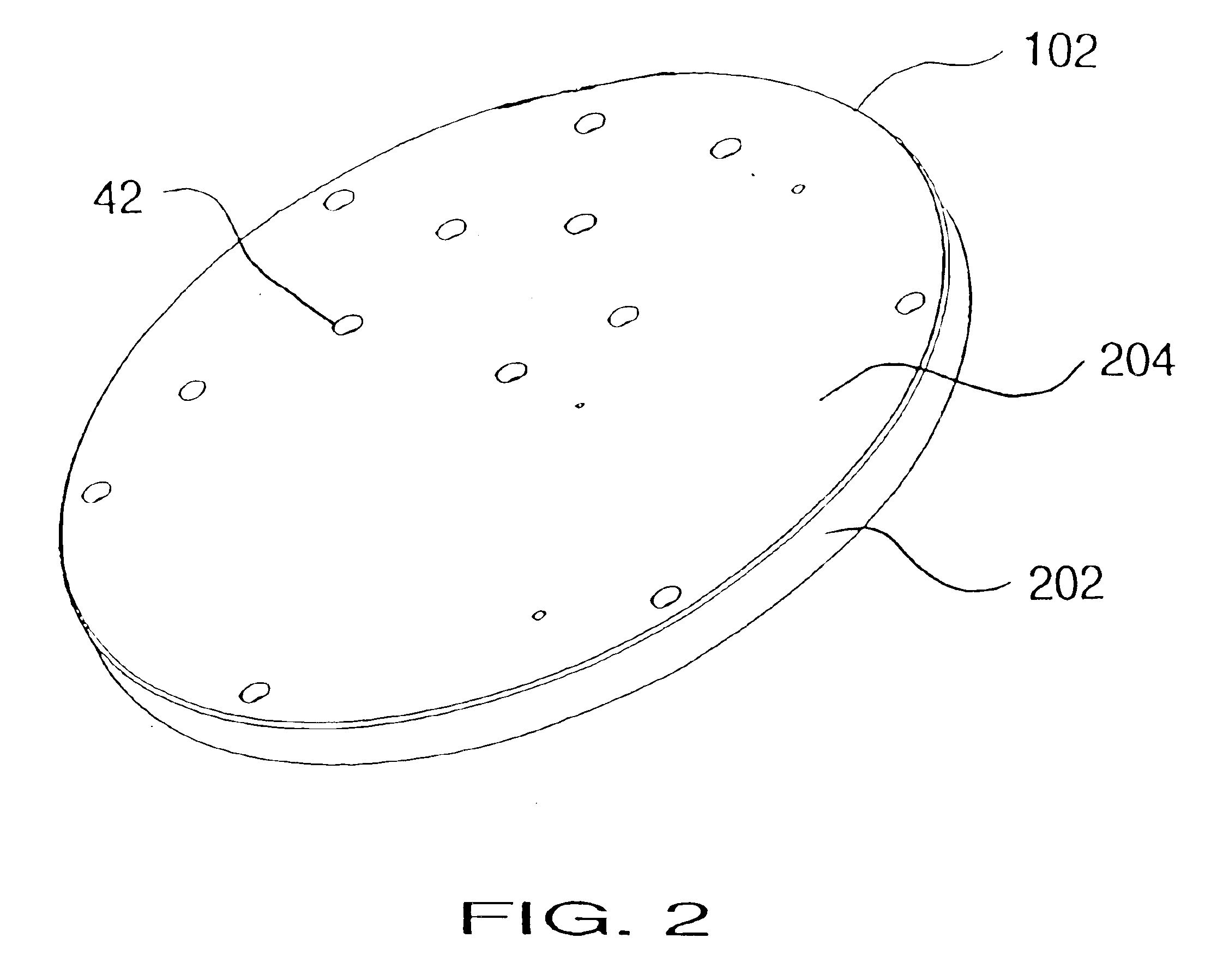
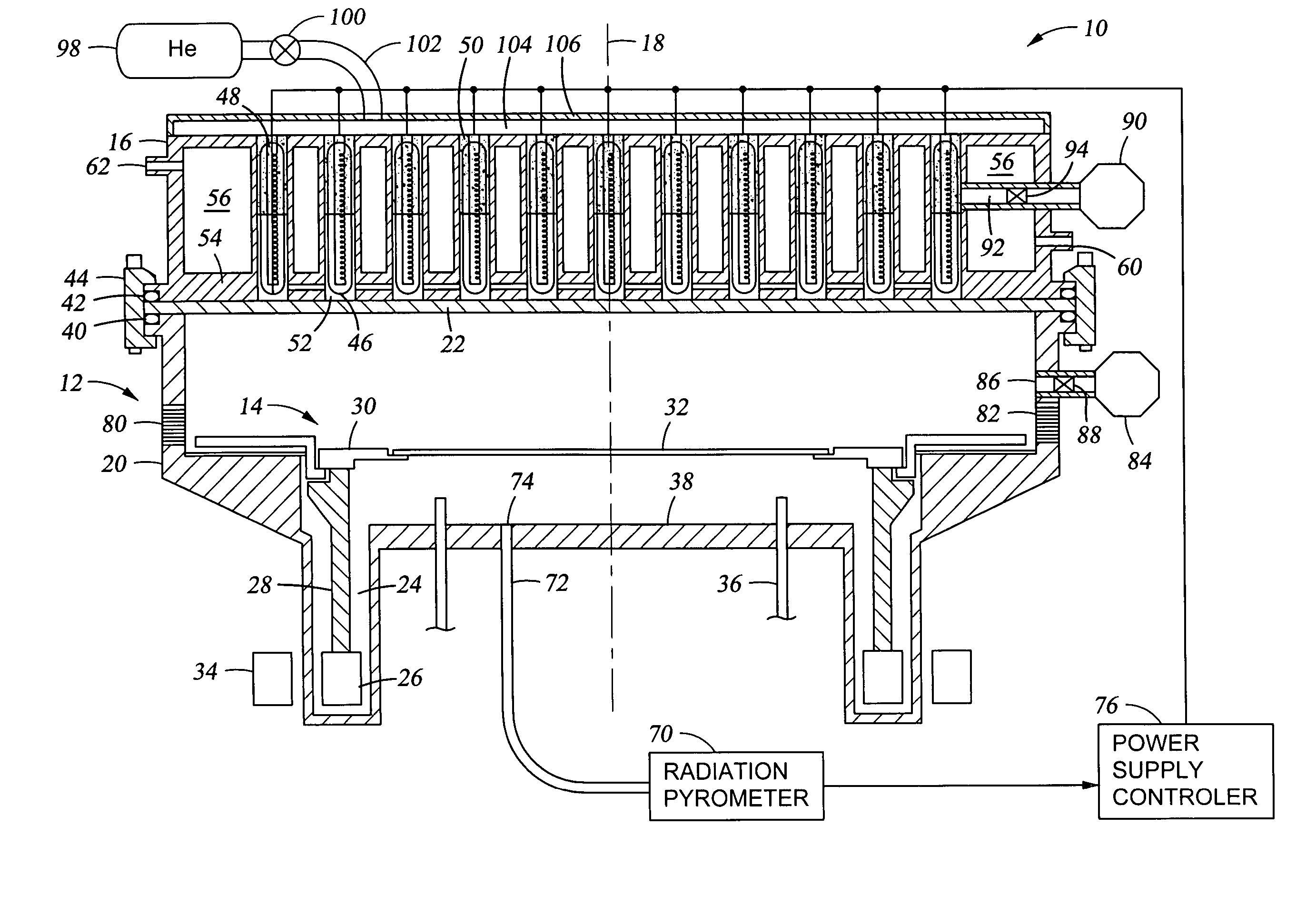
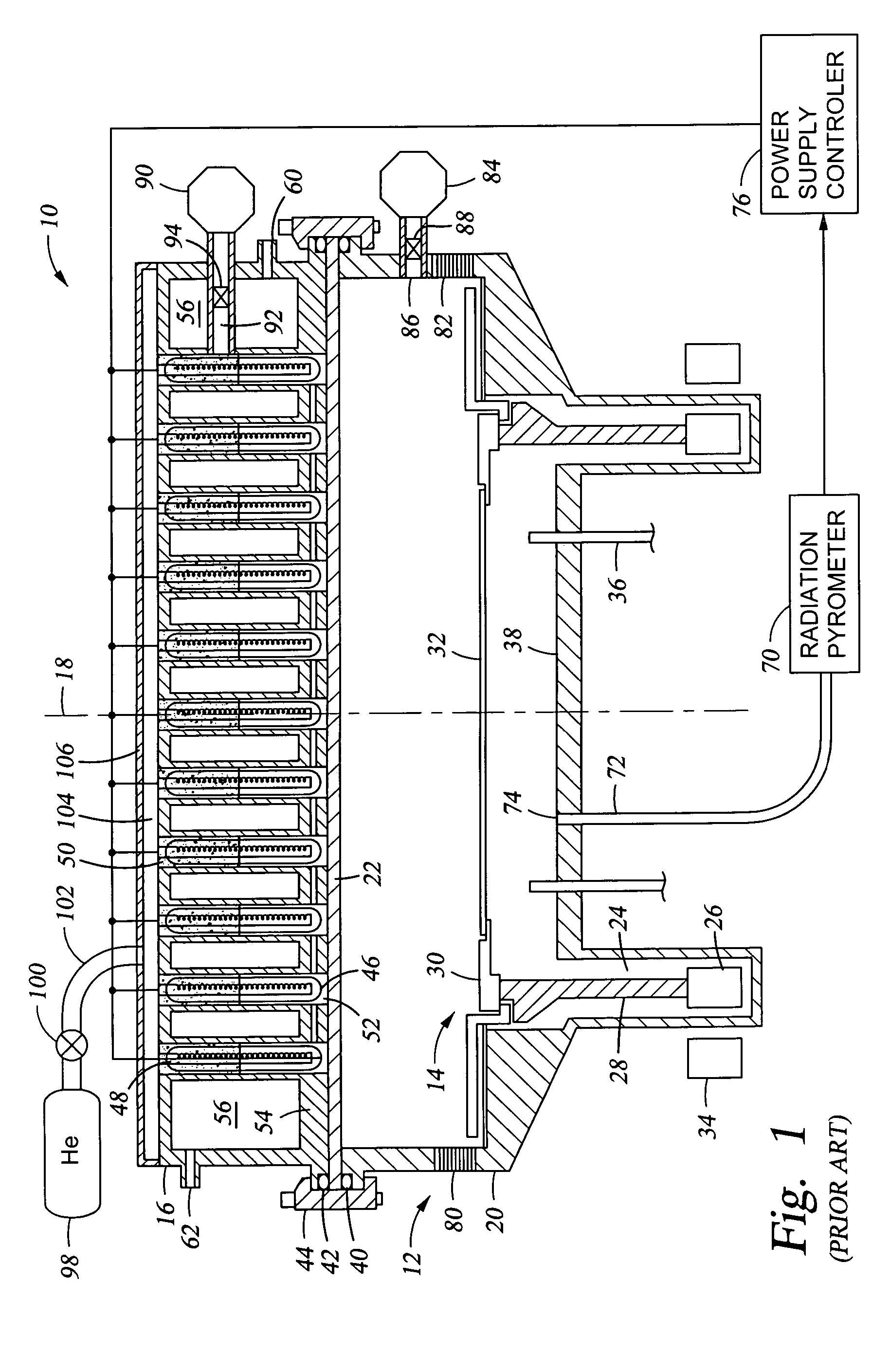
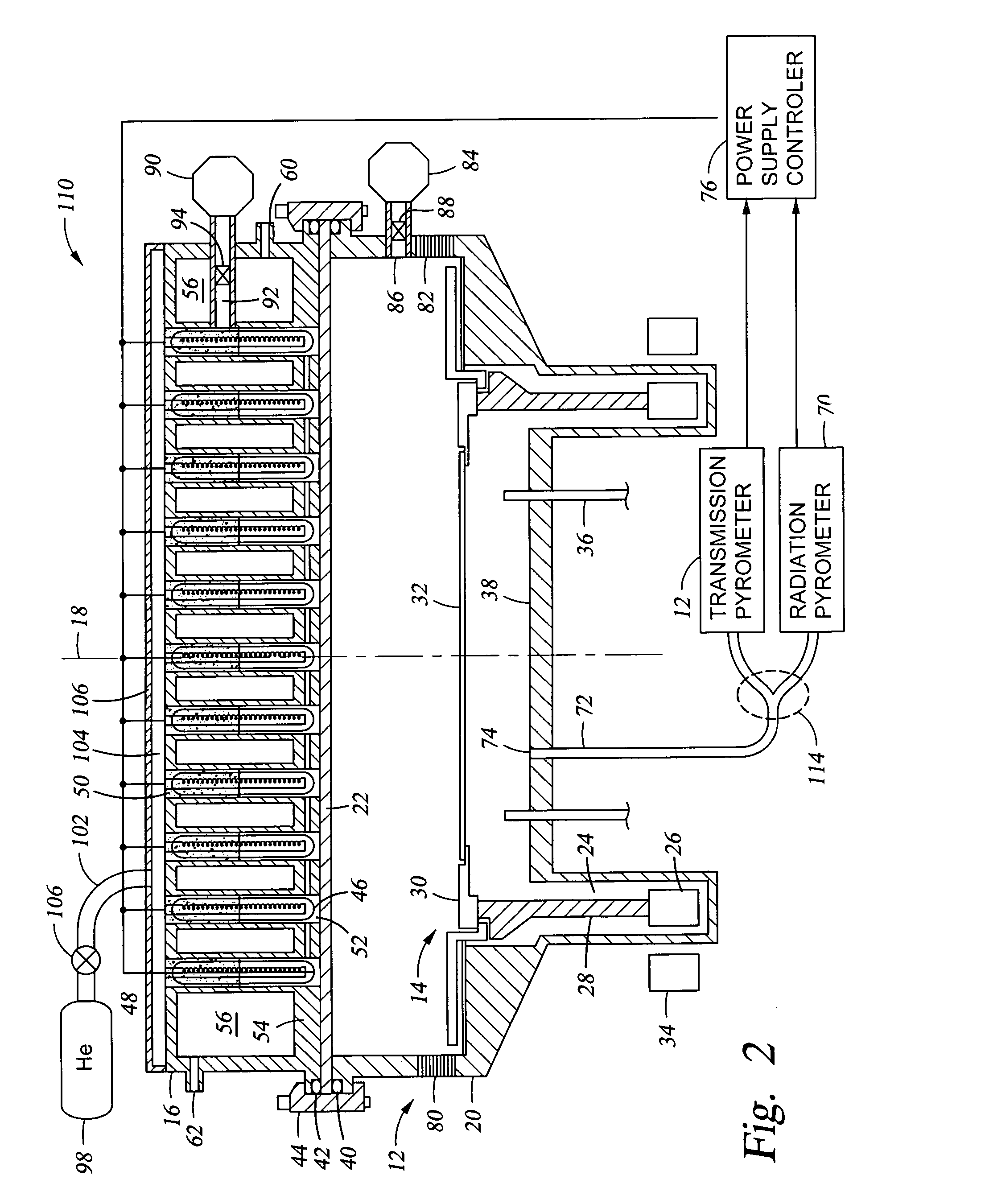
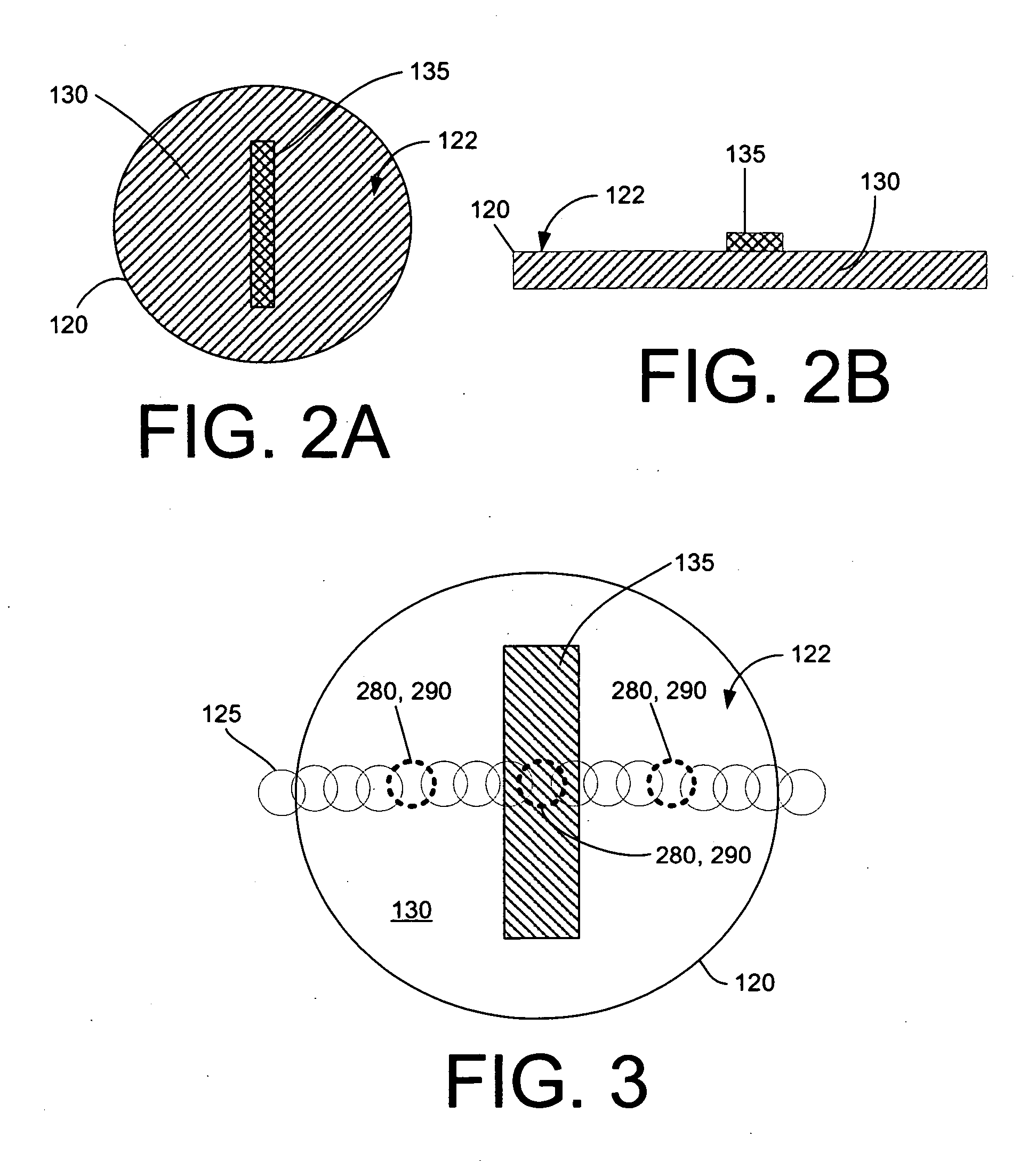
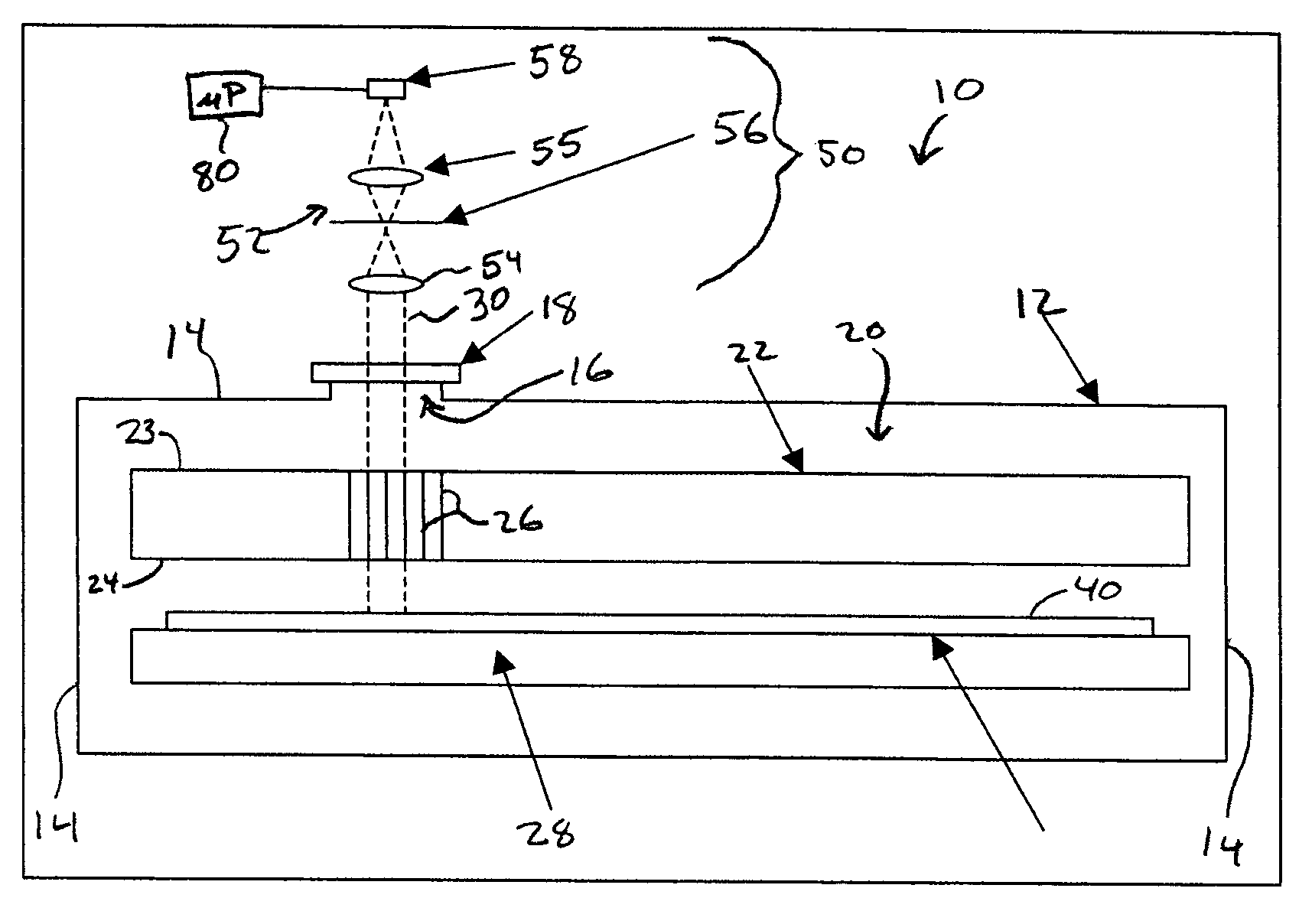
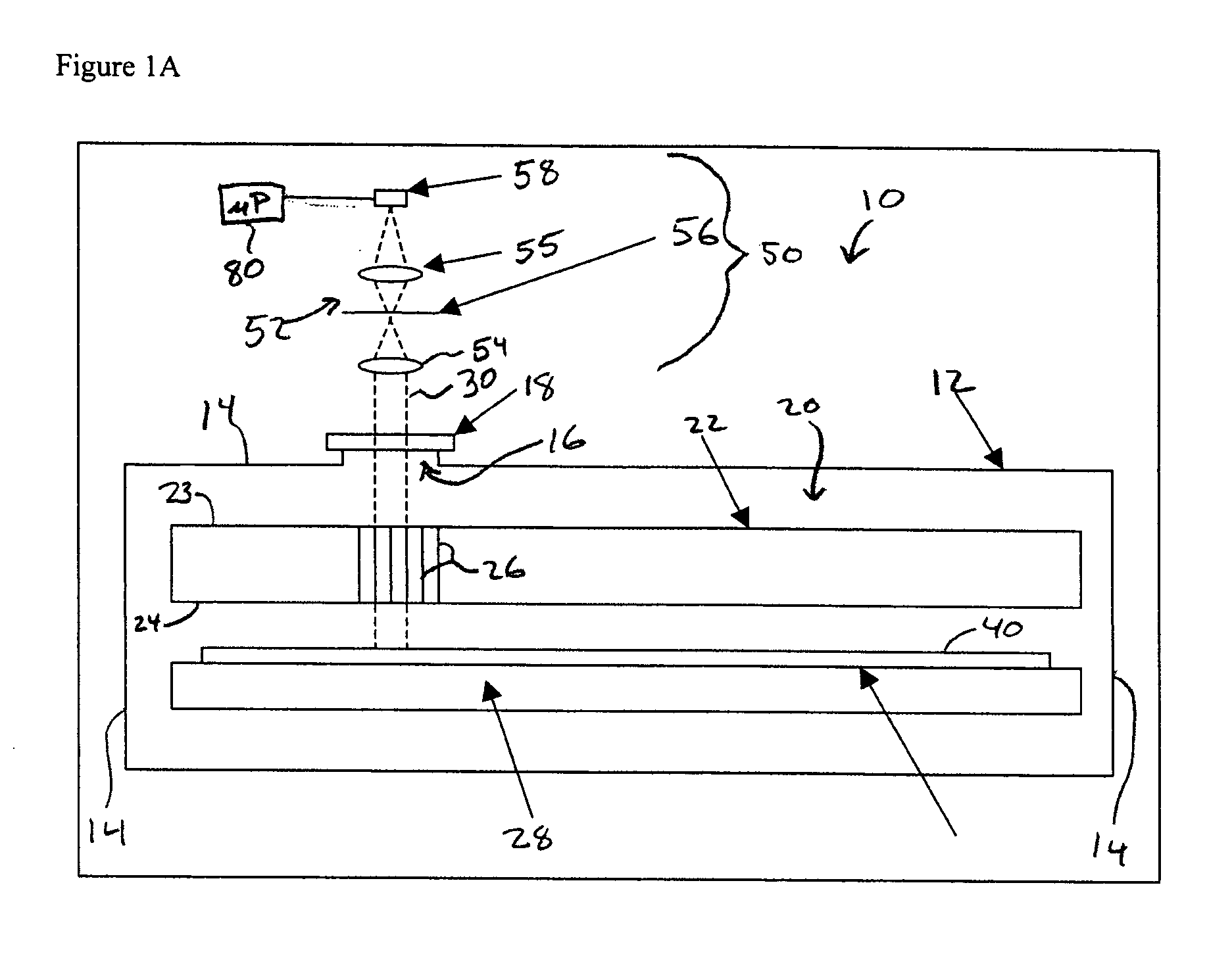
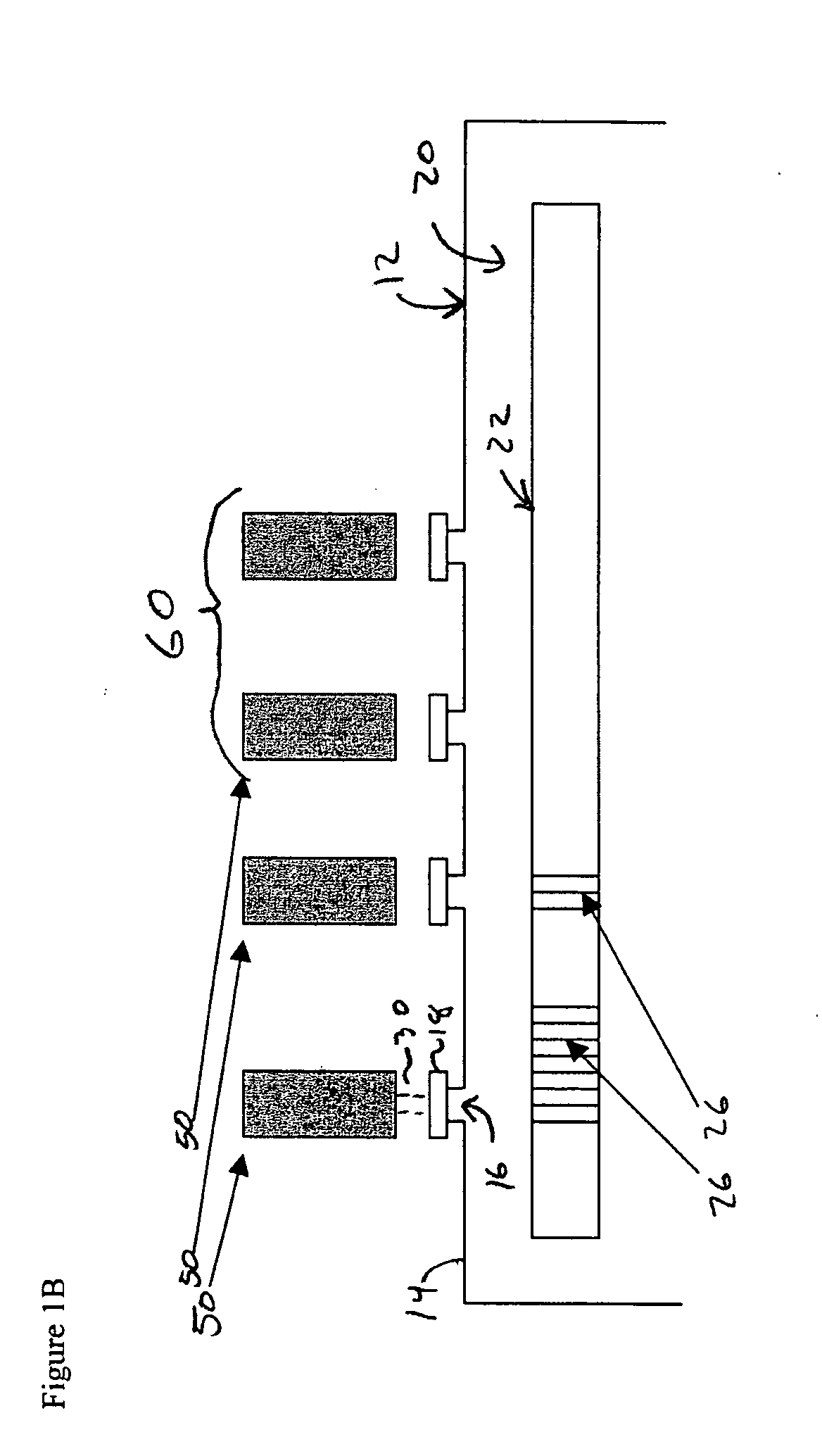
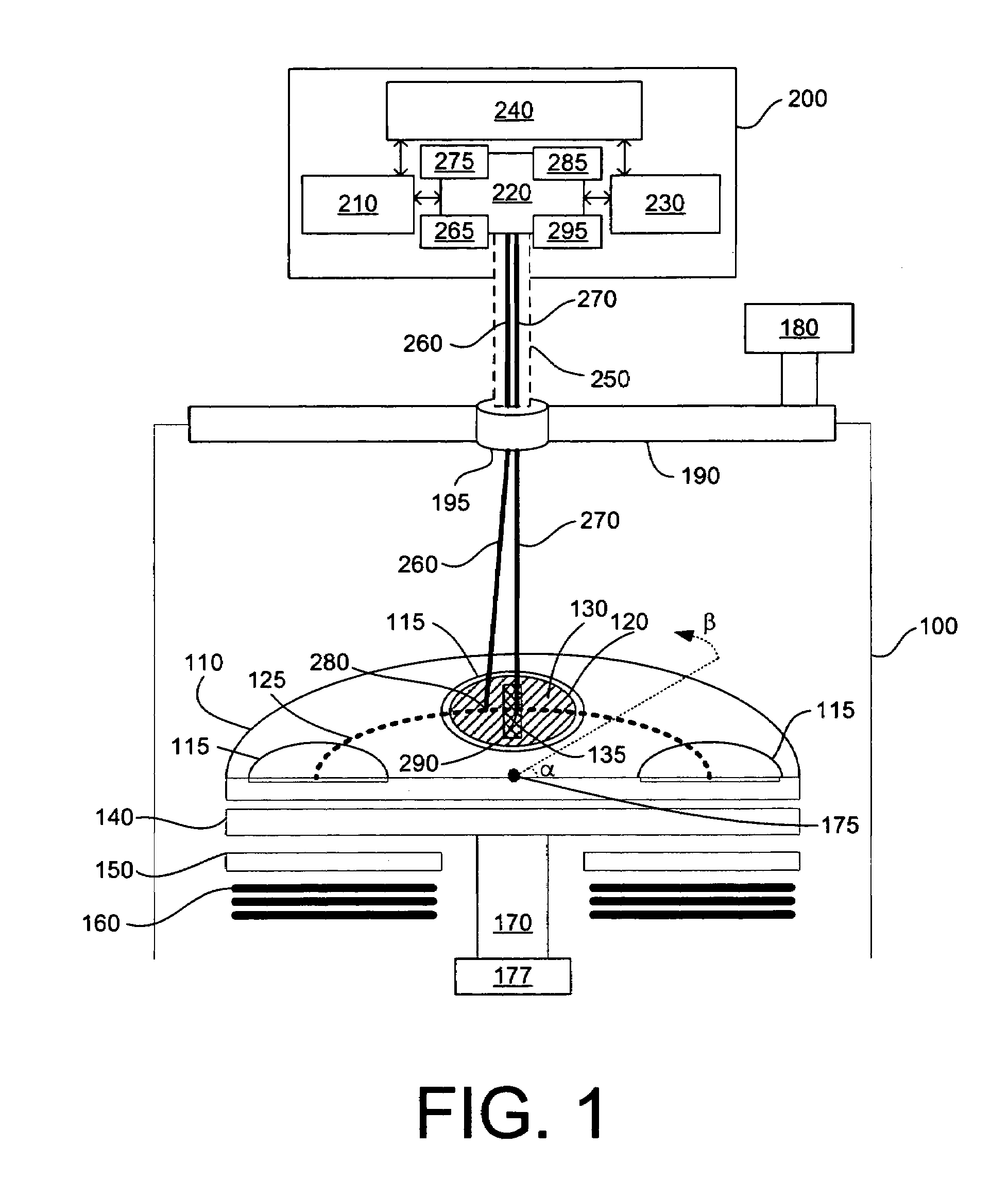
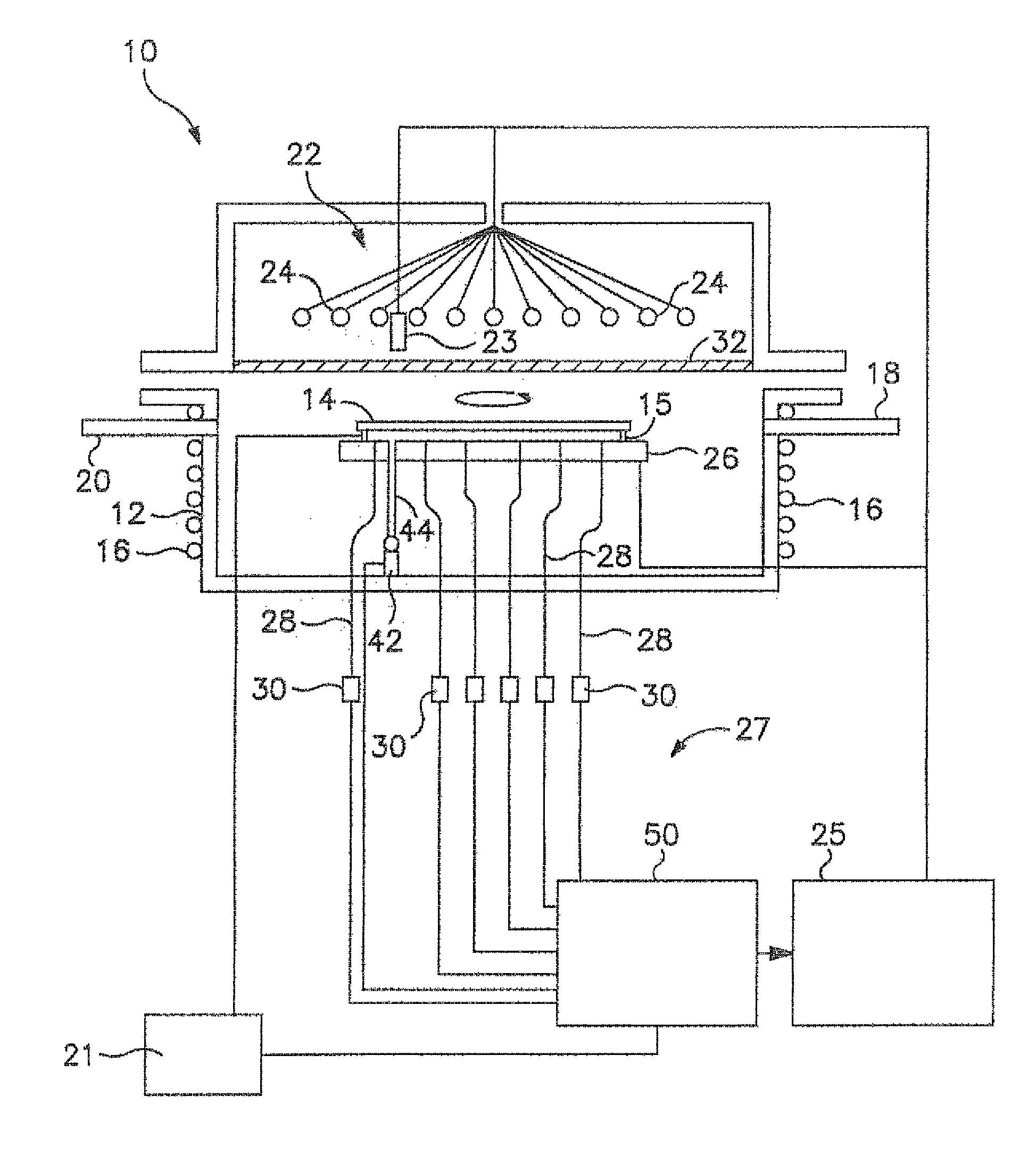
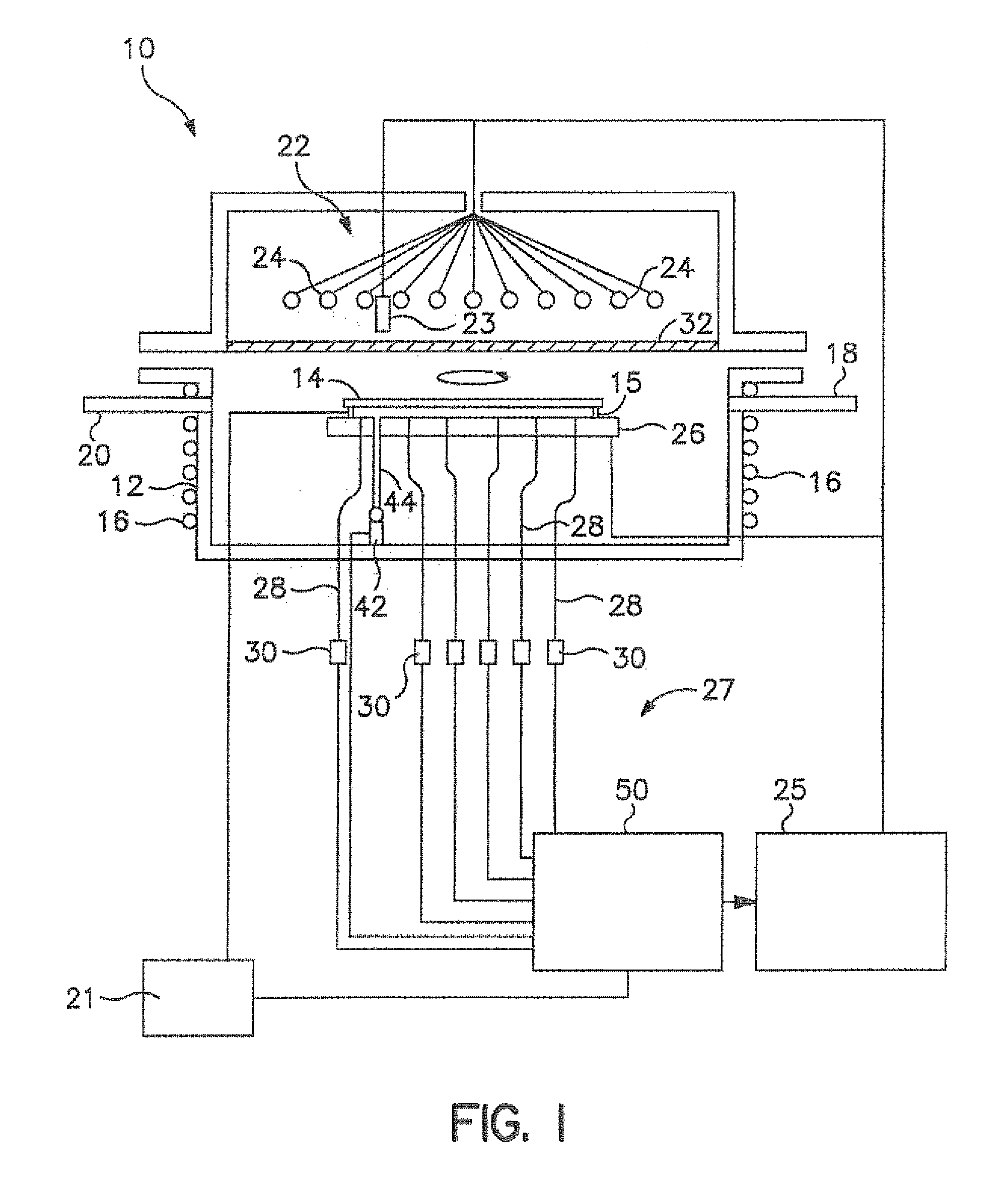
Reactor system and method to reduce residue buildup during a film deposition process
ActiveUS20180195174A1Mitigate formation of residueSubstrate throughput can be increasedSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEtchingReactor system
A system and method for depositing a film within a reaction chamber are disclosed. An exemplary system includes a temperature measurement device, such as a pyrometer, to measure an exterior wall surface of the reaction chamber. A temperature of the exterior wall surface can be controlled to mitigate cleaning or etching of an interior wall surface of the reaction chamber.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Temperature Control Method of Epitaxial Growth Apparatus
ActiveUS20070062439A1Quality improvementPrevent slippingPolycrystalline material growthThermometer testing/calibrationTemperature controlSusceptor
An object of the invention is to calibrate an upper pyrometer for indirectly measuring a substrate temperature at the time of epitaxial growth in a comparatively short time and with accuracy to thereby improve the quality of an epitaxial substrate. After calibrating an upper pyrometer by a thermocouple mounted to a temperature calibrating susceptor, a measured value of a lower pyrometer is adjusted to a calibrated value of the upper pyrometer. Then, a correlation line between substrate temperature indirectly measured by the upper pyrometer at the time of epitaxial growth onto a sample substrate and haze of a sample substrate measured immediately after epitaxial growth is set to indirectly measure a substrate temperature by the upper pyrometer at the time of epitaxial growth onto a mass-production substrate. Moreover, substrate temperature at the time of epitaxial growth onto the mass-production substrate is estimated by applying the haze of the mass-production substrate measured immediately after epitaxial growth to the correlation line and then a measured temperature of the upper pyrometer is adjusted to the estimated temperature.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
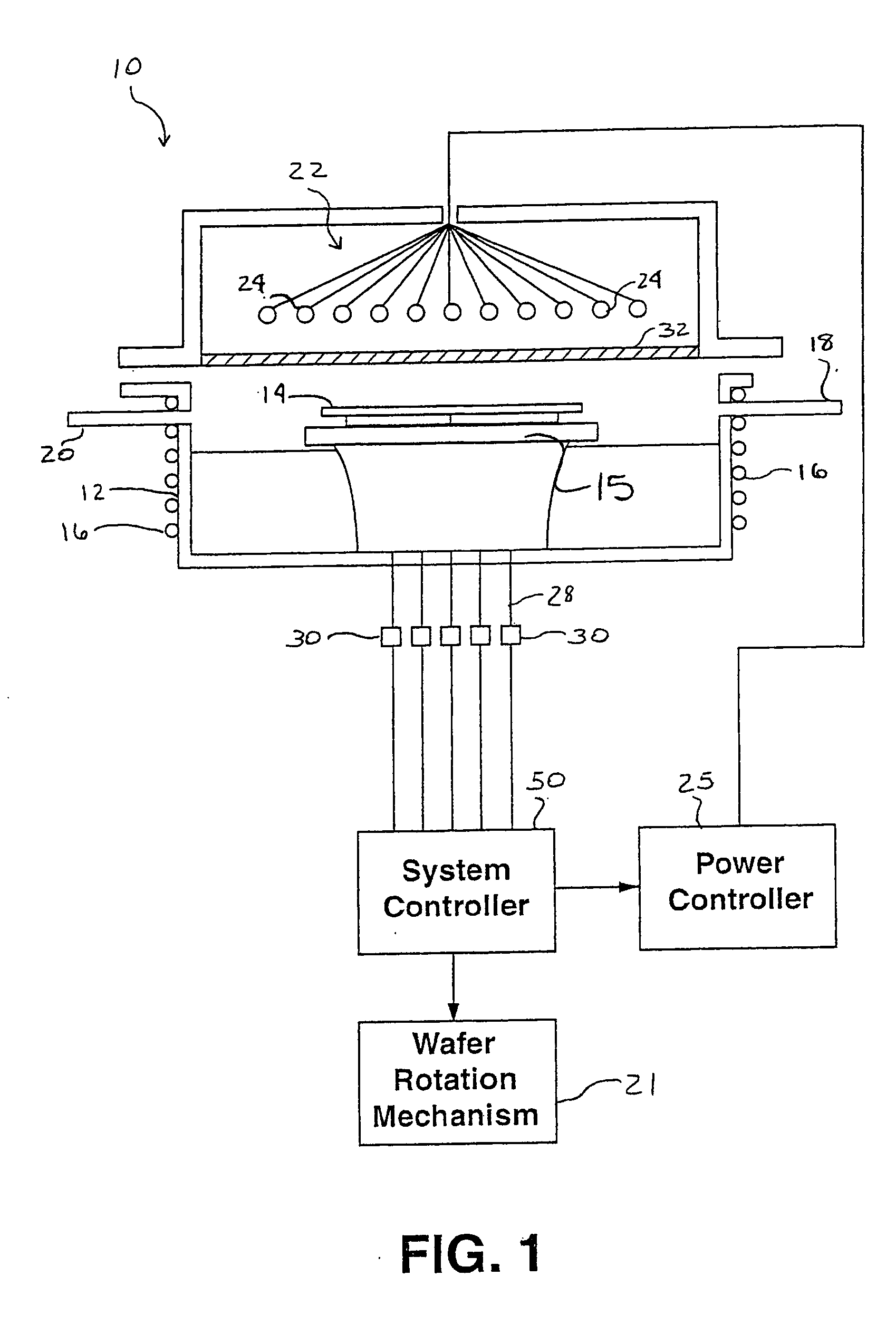
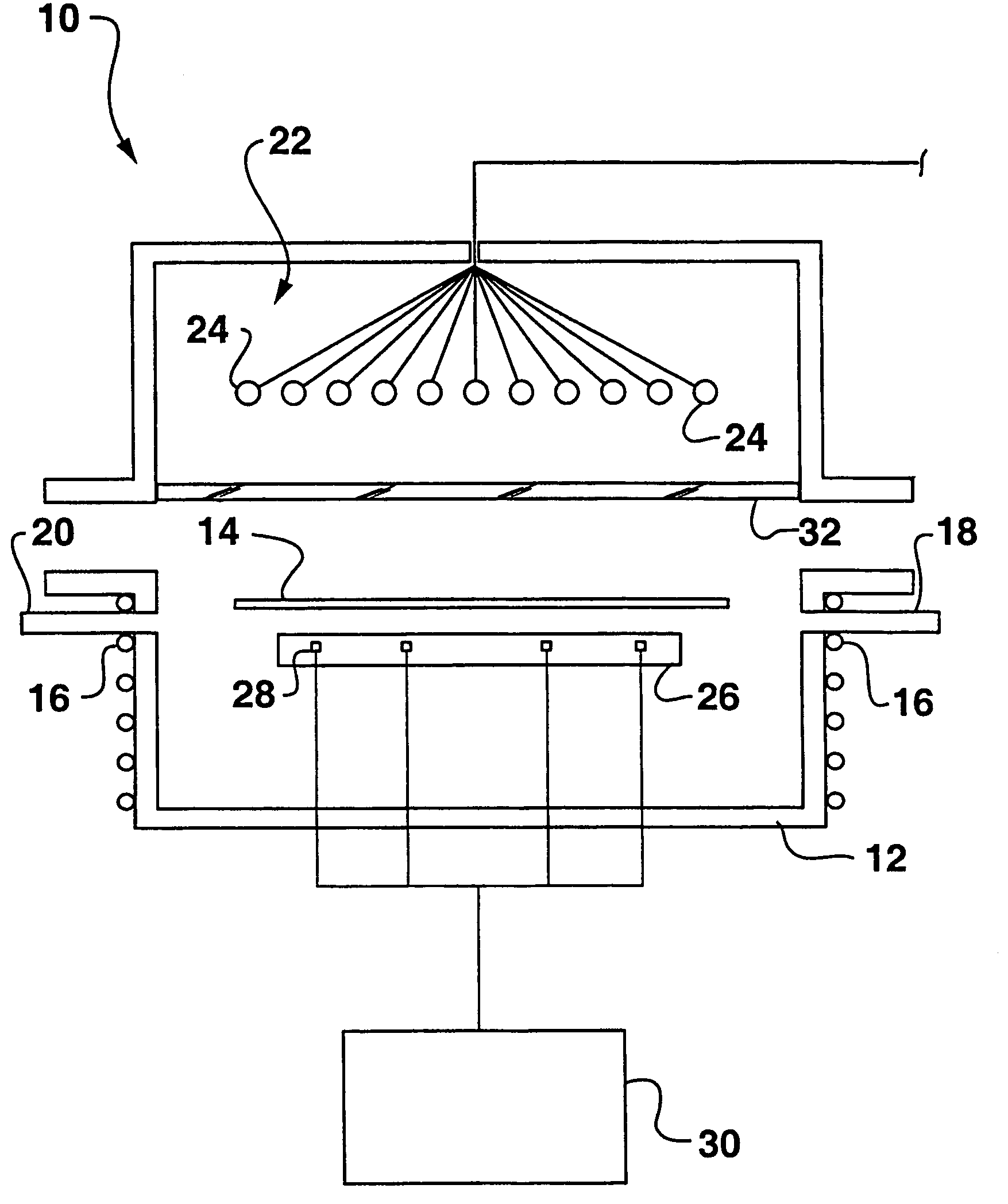
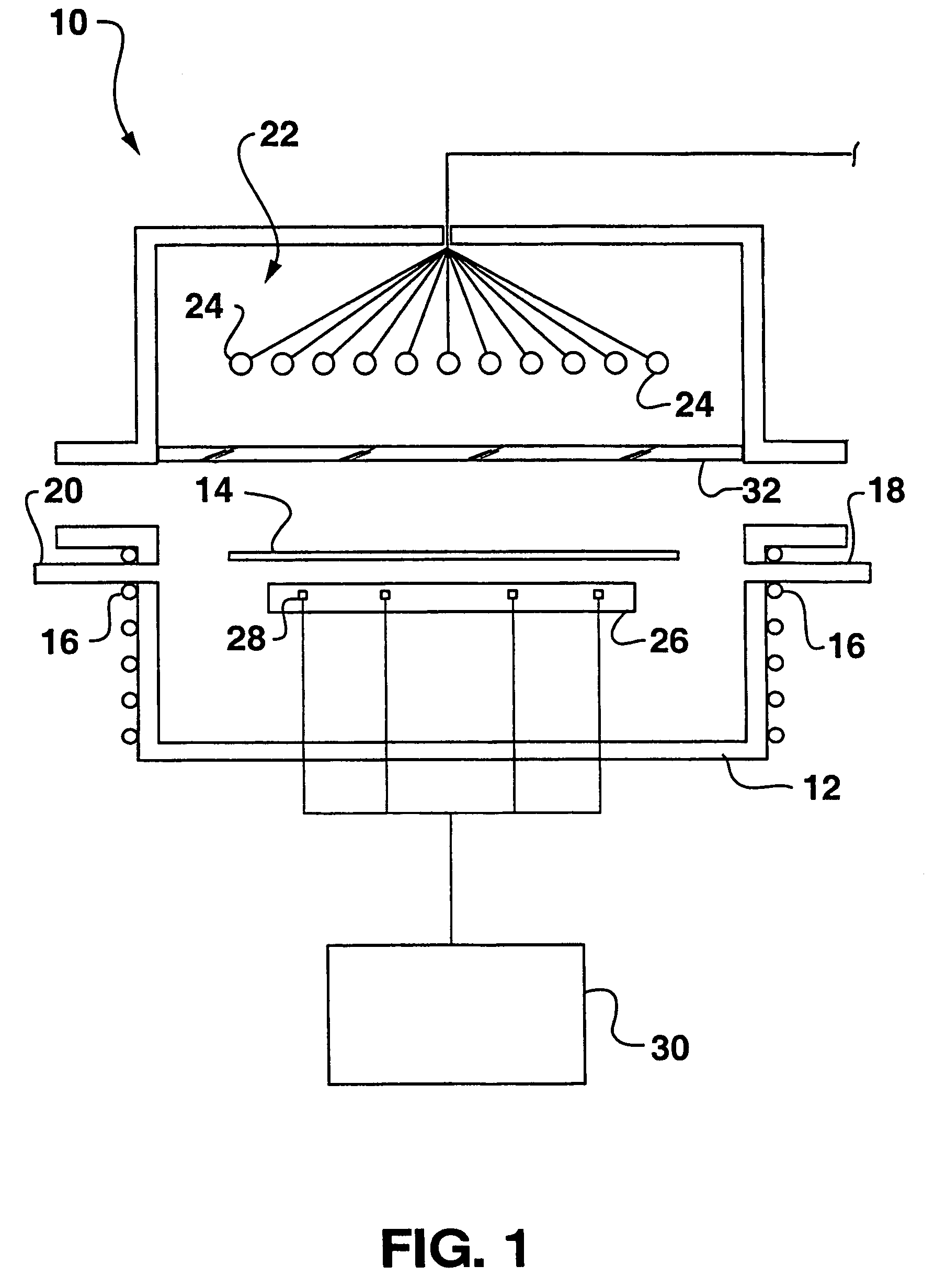
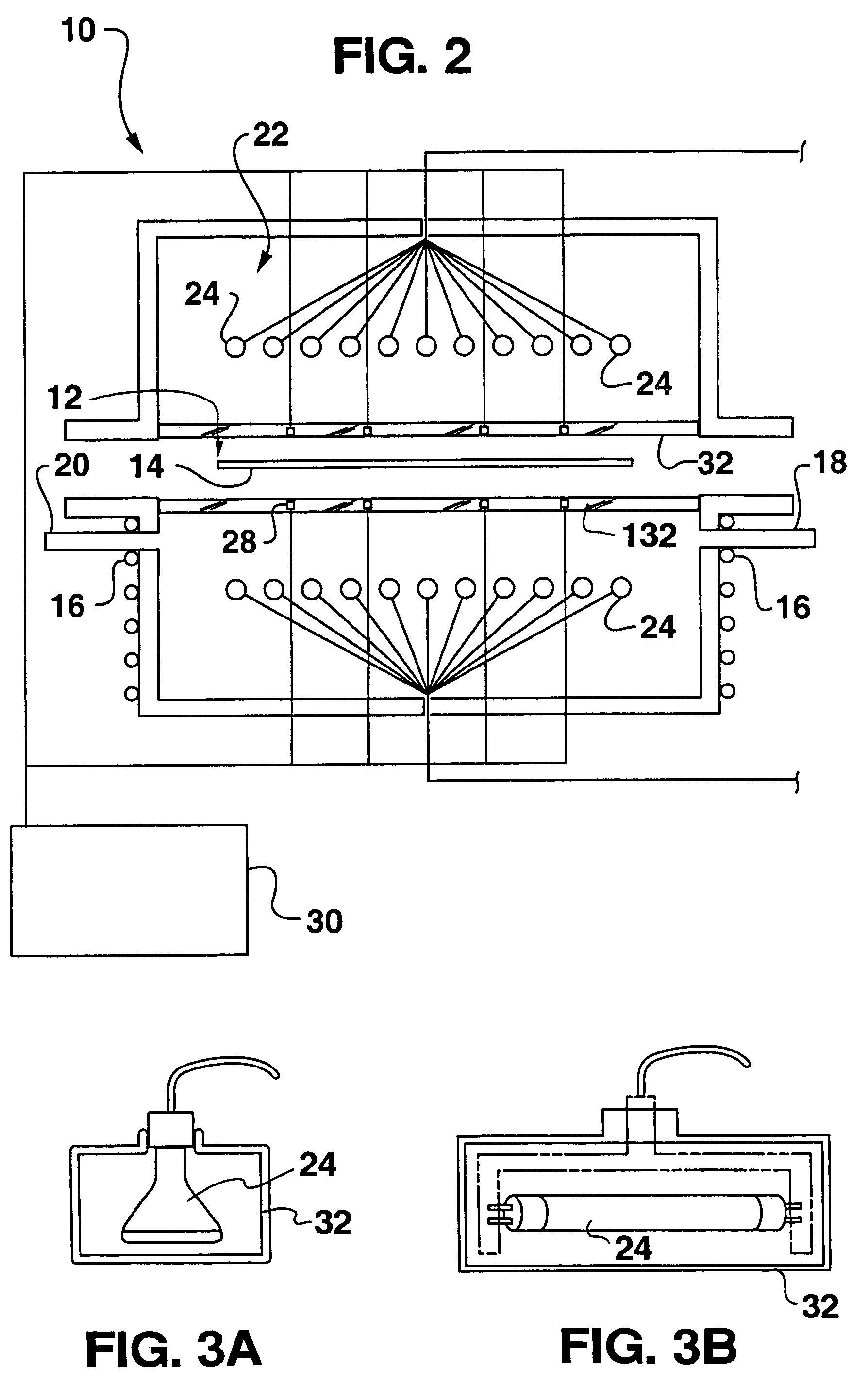
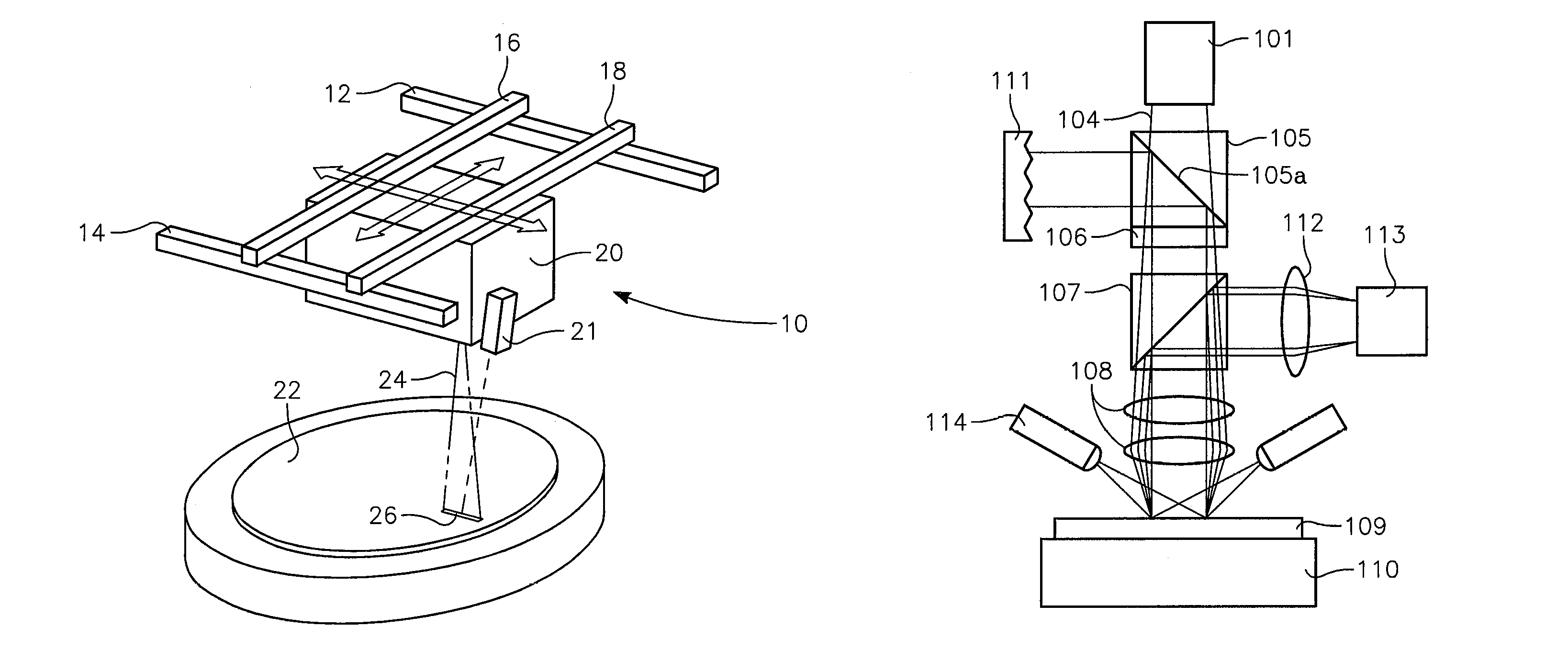
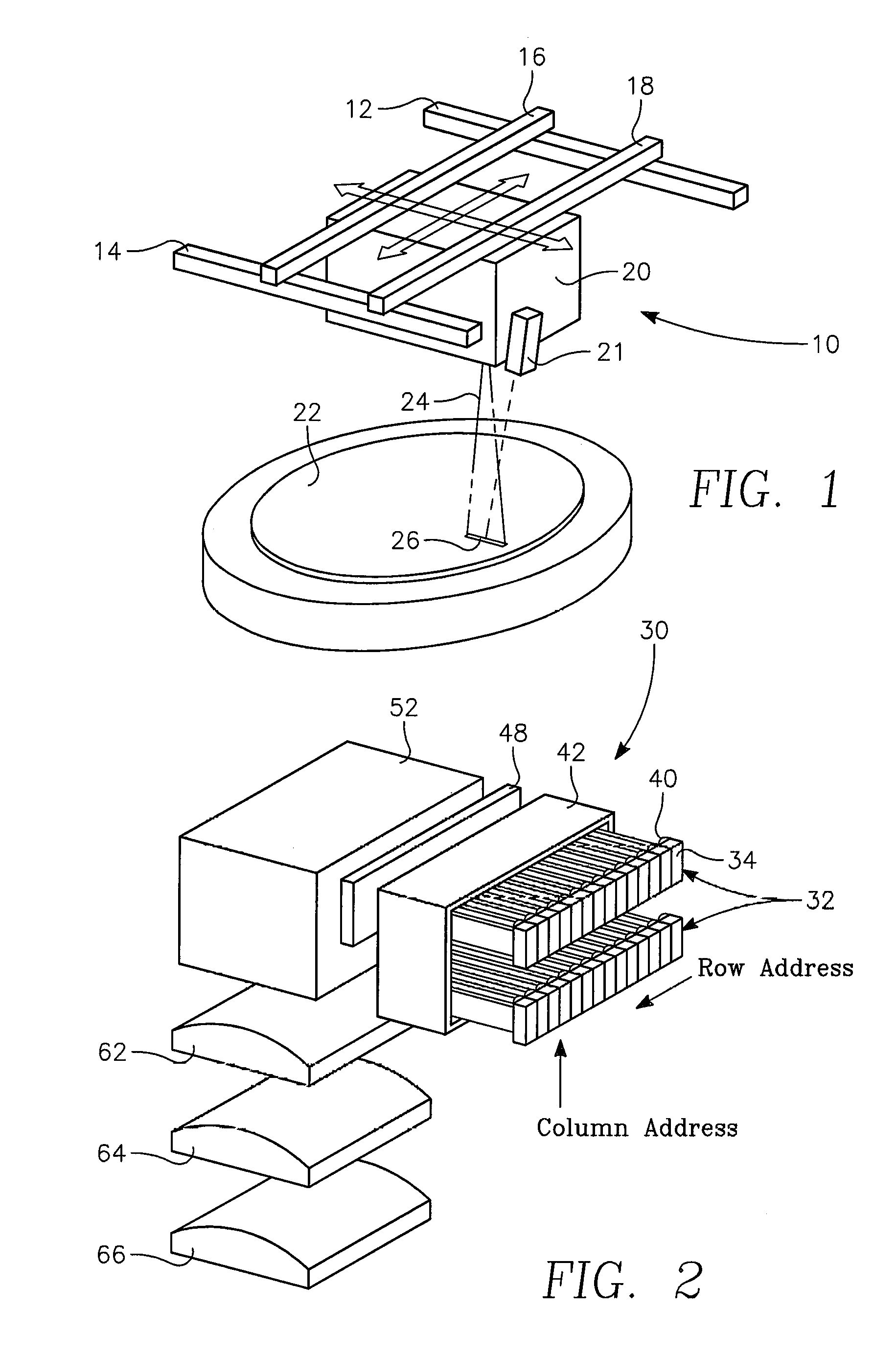
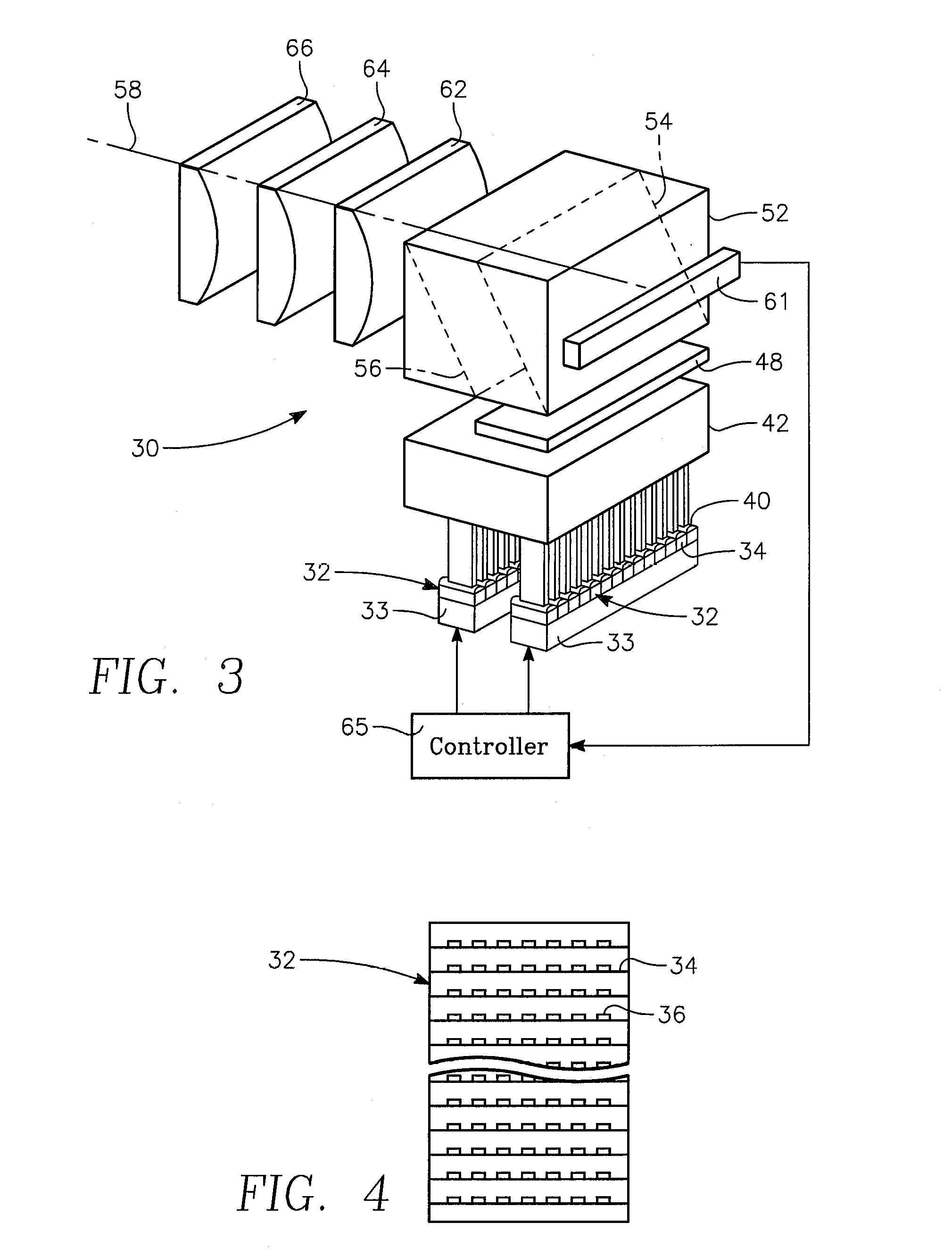
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Temperature control method of epitaxial growth apparatus
ActiveUS7833348B2Accurate CalibrationQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthThermometer testing/calibrationTemperature controlSusceptor
An object of the invention is to calibrate an upper pyrometer for indirectly measuring a substrate temperature at the time of epitaxial growth in a comparatively short time and with accuracy to thereby improve the quality of an epitaxial substrate.After calibrating an upper pyrometer by a thermocouple mounted to a temperature calibrating susceptor, a measured value of a lower pyrometer is adjusted to a calibrated value of the upper pyrometer. Then, a correlation line between substrate temperature indirectly measured by the upper pyrometer at the time of epitaxial growth onto a sample substrate and haze of a sample substrate measured immediately after epitaxial growth is set to indirectly measure a substrate temperature by the upper pyrometer at the time of epitaxial growth onto a mass-production substrate. Moreover, substrate temperature at the time of epitaxial growth onto the mass-production substrate is estimated by applying the haze of the mass-production substrate measured immediately after epitaxial growth to the correlation line and then a measured temperature of the upper pyrometer is adjusted to the estimated temperature.
Owner:SUMCO CORP
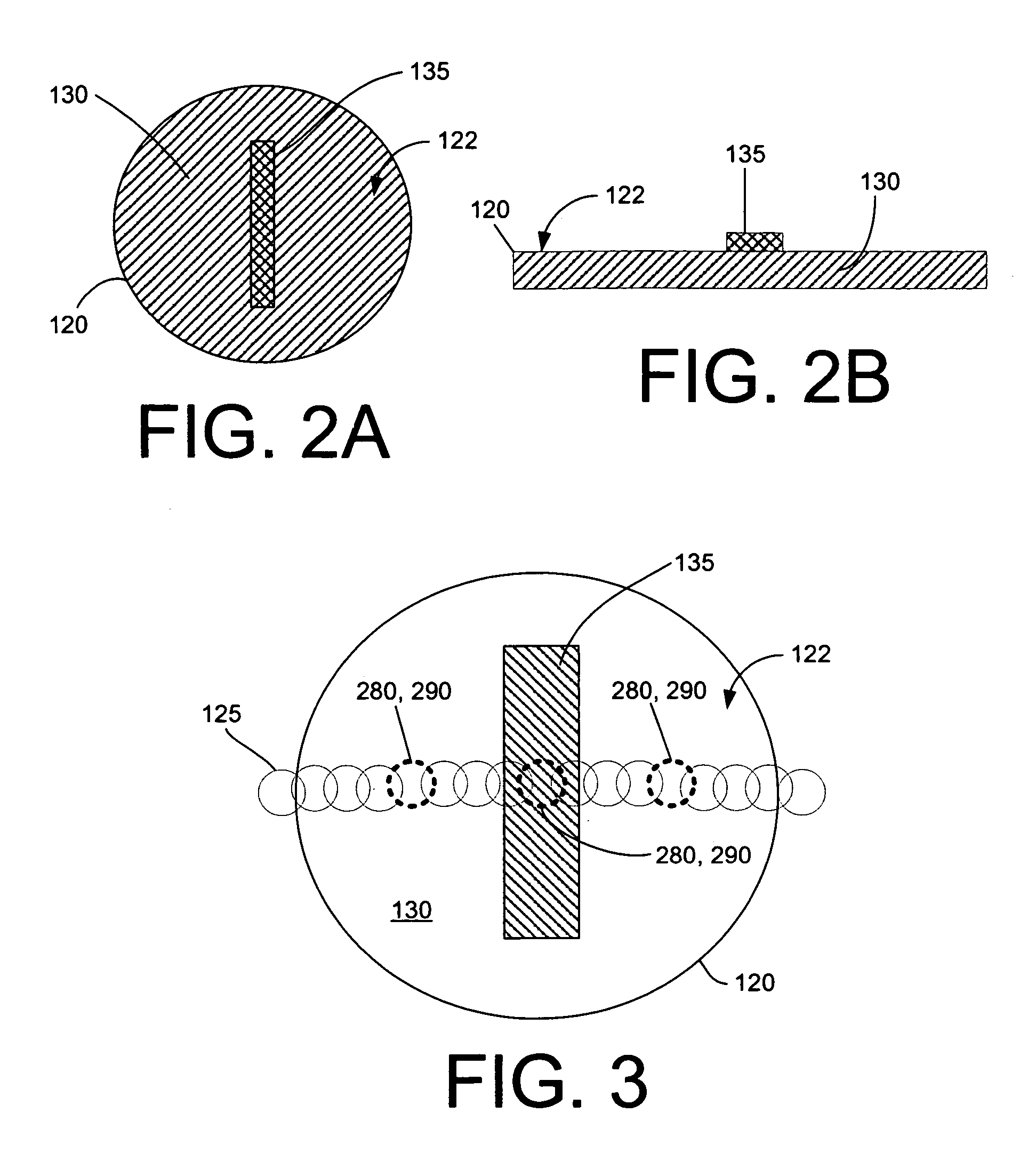
Black reflector plate
InactiveUS6839507B2Improve temperature measurement accuracyImprove cooling effectThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometrySemiconductorWavelength range
In a system for thermal processing of a semiconductor substrate, an RTP system employs a reflector plate which is highly reflective of radiation in a target wavelength range, and less reflective of radiation outside that target wavelength range. In one embodiment, the reflector plate has a highly reflective portion overlying a less reflective portion, wherein the highly reflective portion is highly reflective of radiation in the target wavelength range. As radiation emitted by the substrate is received on the reflector, the radiation in the target wavelength range is reflected, thereby facilitating measurement of the substrate temperature by the pyrometer(s), while radiation outside the target wavelength range is absorbed, thereby facilitating cooling of the substrate.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
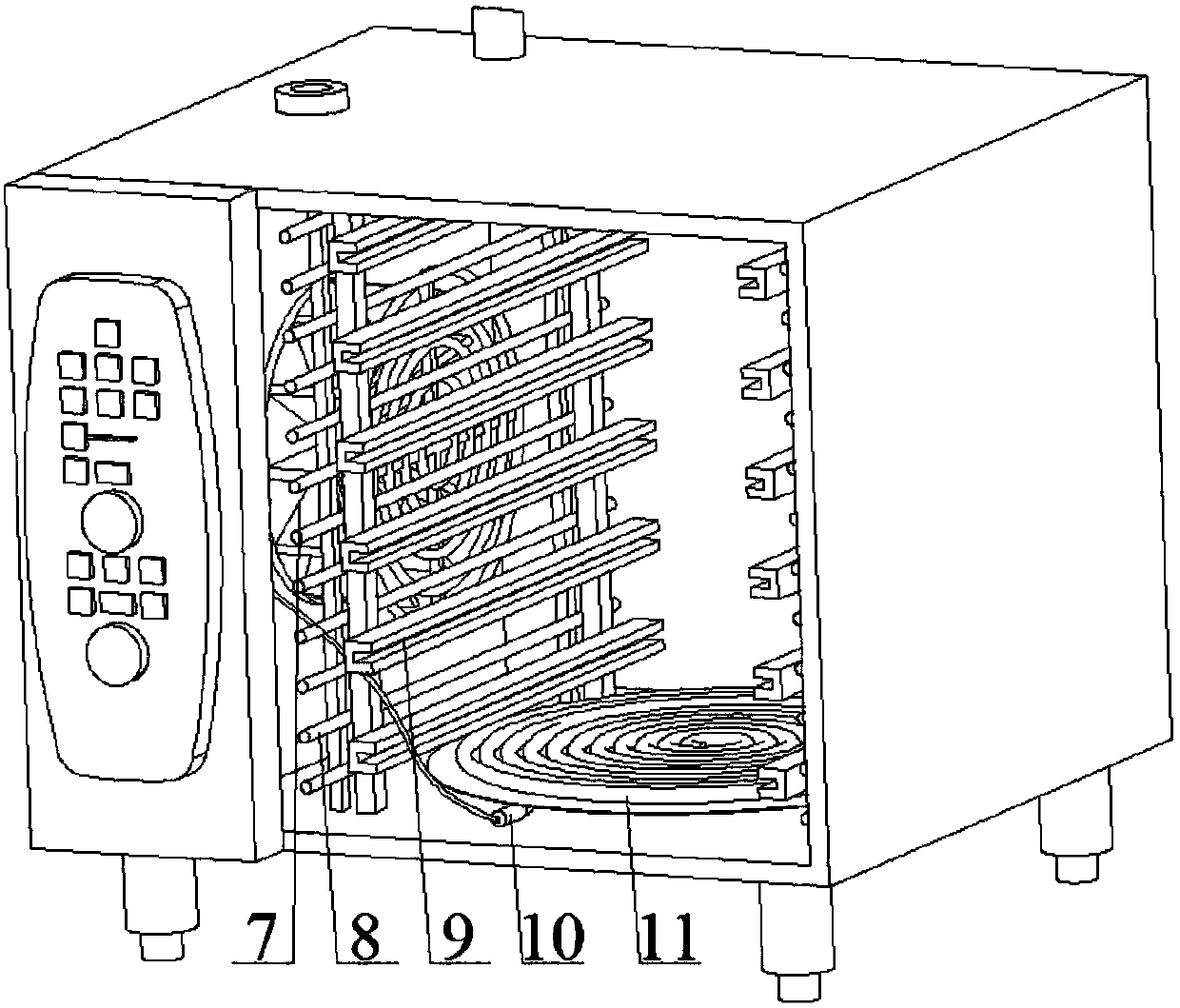
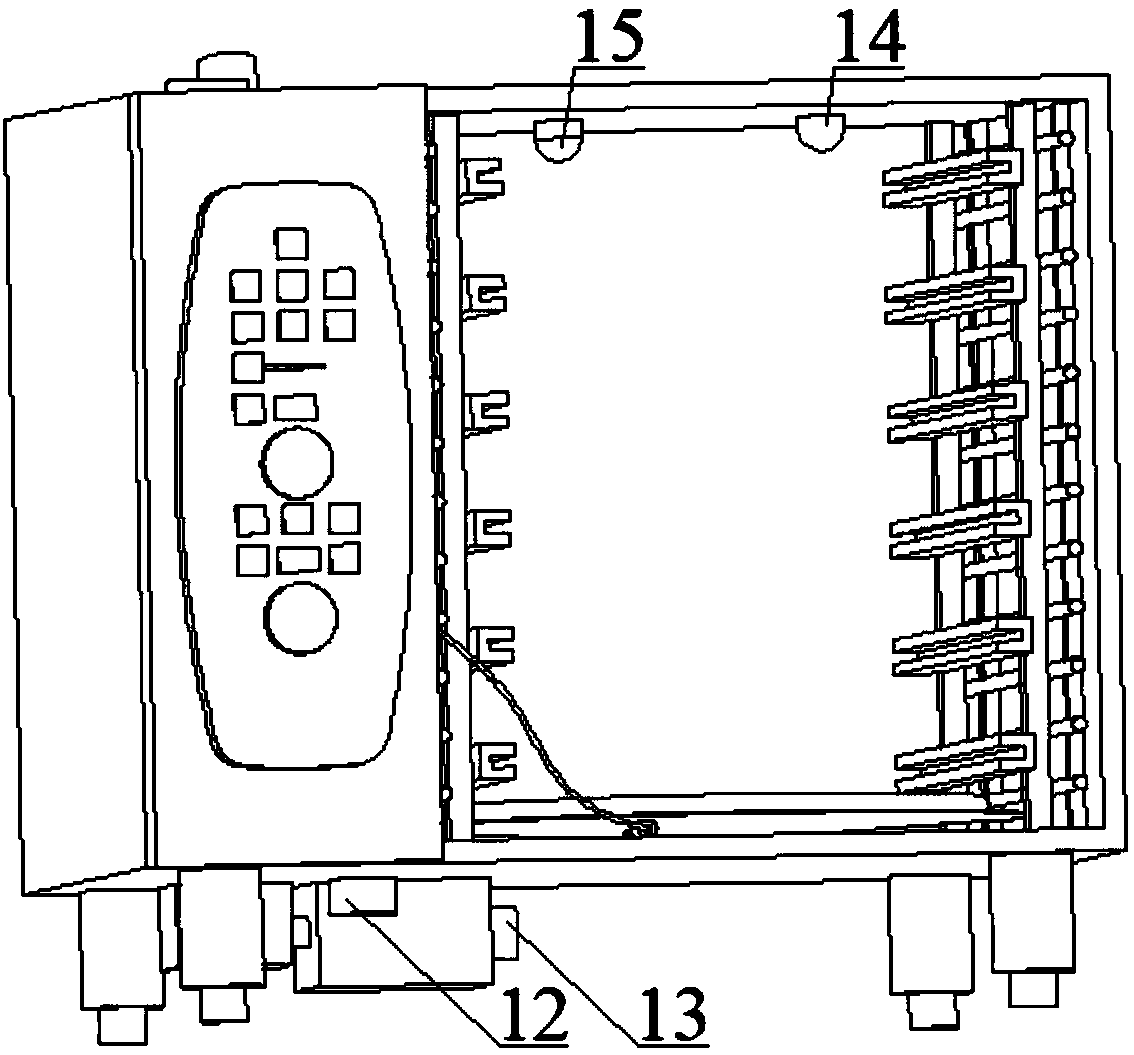
Steaming oven having multiple operating modes
PendingCN107898351AMeet the diverse needs of processingRapid coolingRoasters/grillsWarming devicesComputer moduleEngineering
The invention provides a steaming oven having multiple operating modes. The steaming oven is characterized by comprising an oven body, a steaming-baking module, a humidity regulating and detecting module, a menu editing and storing module, a central temperature detecting module and a control module, wherein the oven body comprises a steaming-baking chamber and a control chamber, the steaming-baking module comprises heating tubes, a steam generator, a turbo fan and an infrared thermodetector, the humidity regulating and detecting module comprises a dryer, a humidifier and a humidity detecting gauge, the menu editing and storing module comprises a menu memorizer and a USB flash disk reading port, the central temperature detecting module is used for food internal-temperature detection, and the control module comprises a photographing camera, a timer, an alarm apparatus, a controller and a central processing unit and is used for providing operation control. The steaming oven has multiple operation modes by arranging the modules, can meet the diversified food processing demands and is high in processing efficiency.
Owner:珠海家宝德科技有限公司
Tunnel for conditioning of products, especially for sterilization of food in prepackaged containers
ActiveUS20090283517A1Reduce maintenanceIncreases useful treatment capacityDough treatmentDisinfectionControl systemClosed loop
Tunnel is provided for conditioning of food products, especially for sterilization of food in containers or vessels of the heat-sealed type, in which the conditioning unit has: 1) an active temperature and pressure control system provided in at least one magnetron supported heating stage, which provides for balancing of the pressure within the heat-sealed vessels or containers; 2) a conveyor which conveys the heat-sealed vessels or containers through the stages along the conditioning unit which contains mechanisms that move the conveyor outside of the conditioning tunnel, and 3) doors operating like check valves that separate the conditioning stages, but still provide for continuous linear feed of products through conditioning tunnel. In preferred embodiment, the conditioning tunnel in includes a plurality temperature sensors, such as linear pyrometers for measuring the temperature of for mapping the temperature of products within the tunnel Moreover, preferably the conveyor is adjustable to move forward and rearward, and the magnetrons, which preferably operate at approximately 915 Mhz and 2400 Mhz, are adjustable to provide a controllable movement and amplitude. A controller is connected to the temperature sensors, conveyor and magnetrons to cause the conveyor to move products forward or rearward, or cause the magnetrons to move the magnetic field relative to the food products to more thoroughly and evenly cook the food products. Movement of the magnetron electromagnetic field and / or conveyor is controlled by software which utilizes the temperature and / or density measurements in a closed loop process to ensure uniform heating of the products.
Owner:MACKAY JEFFREY H +3
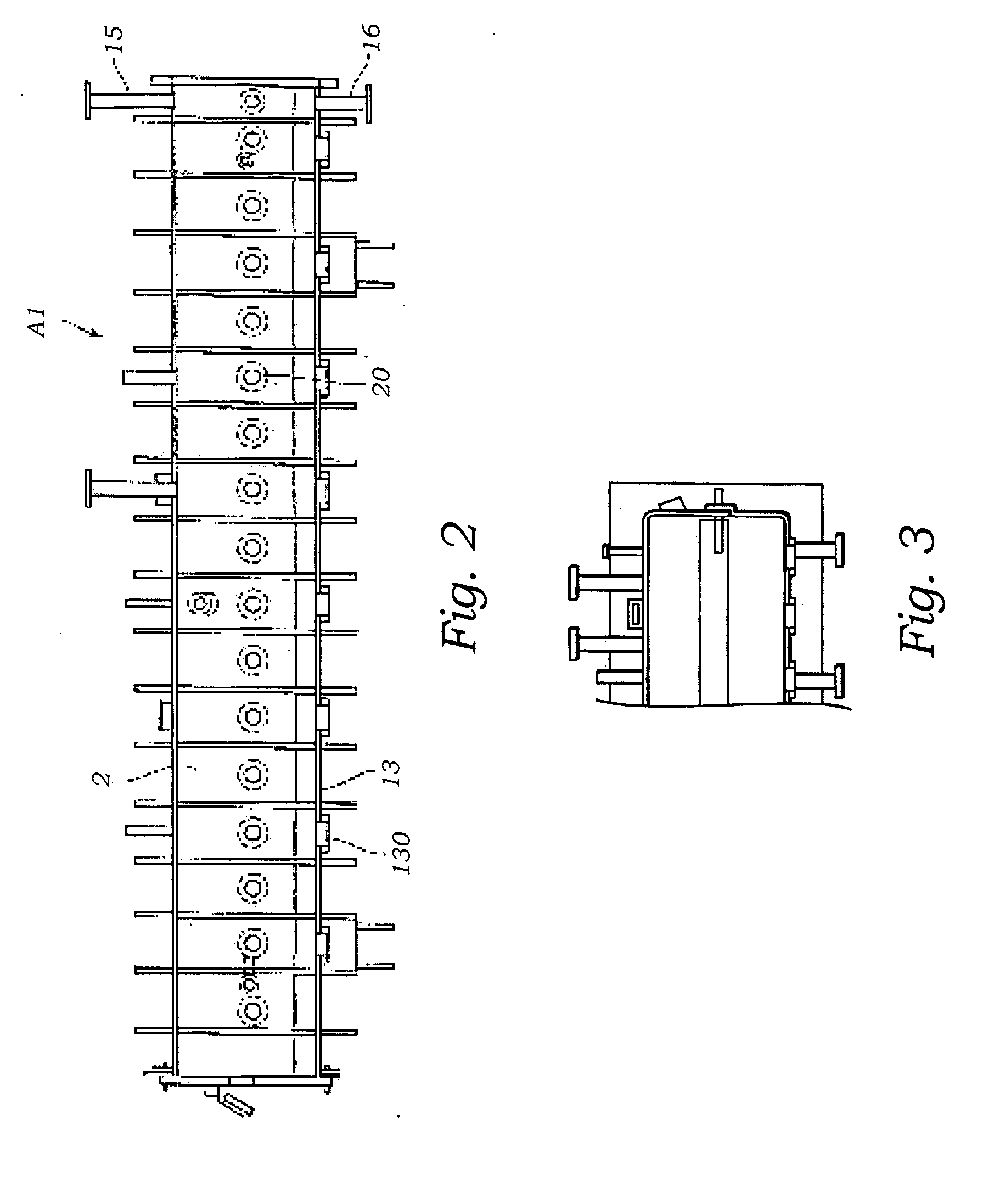
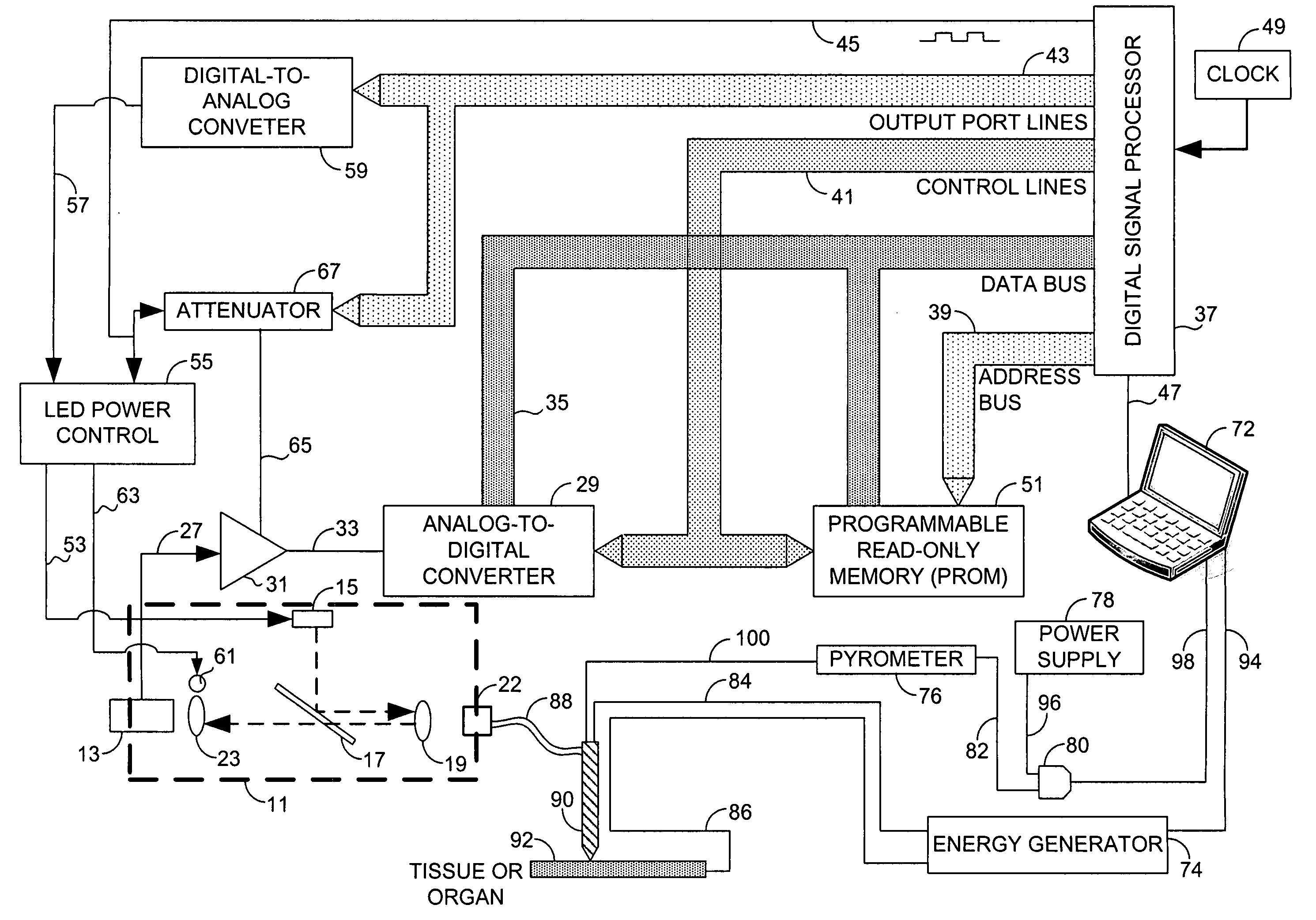
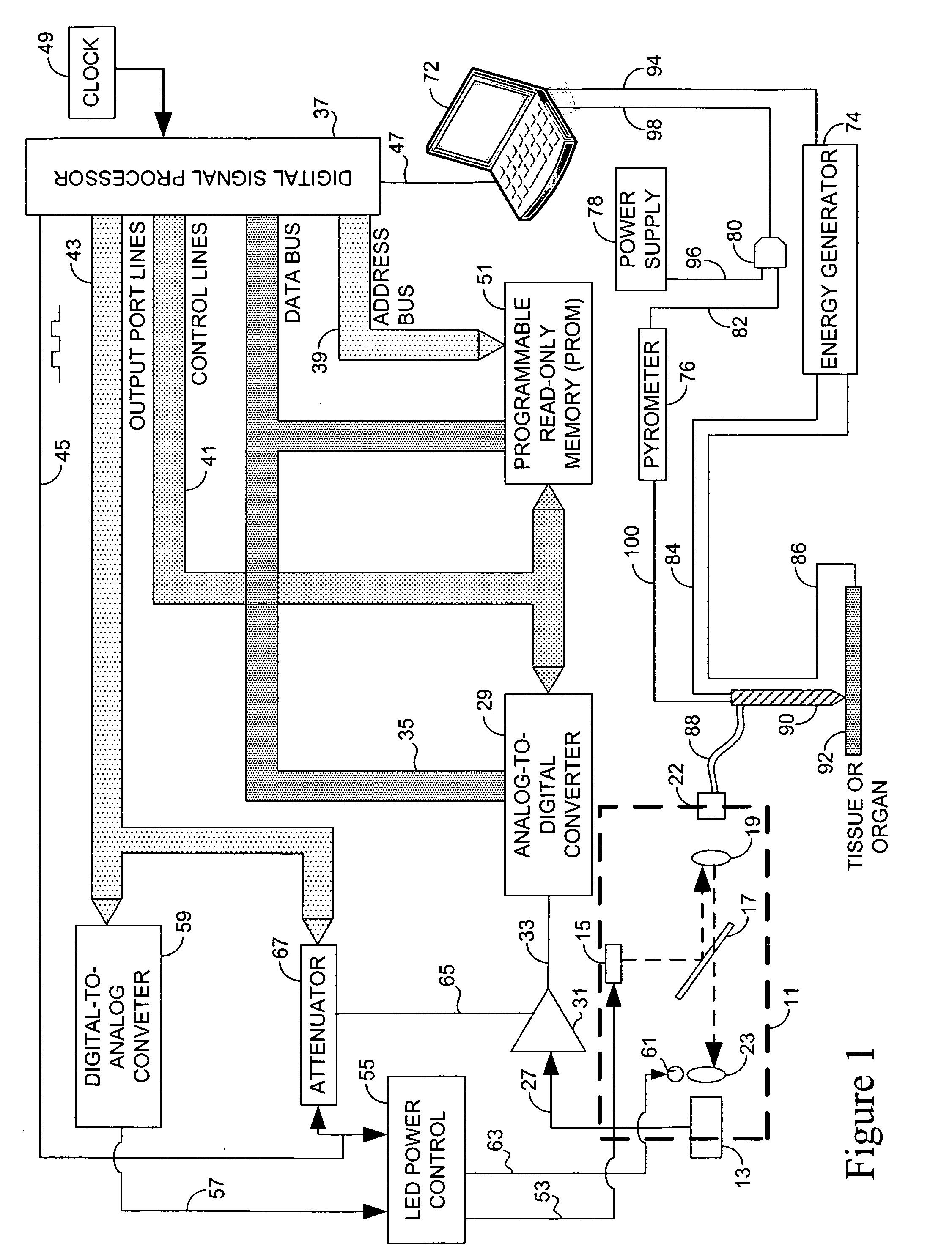
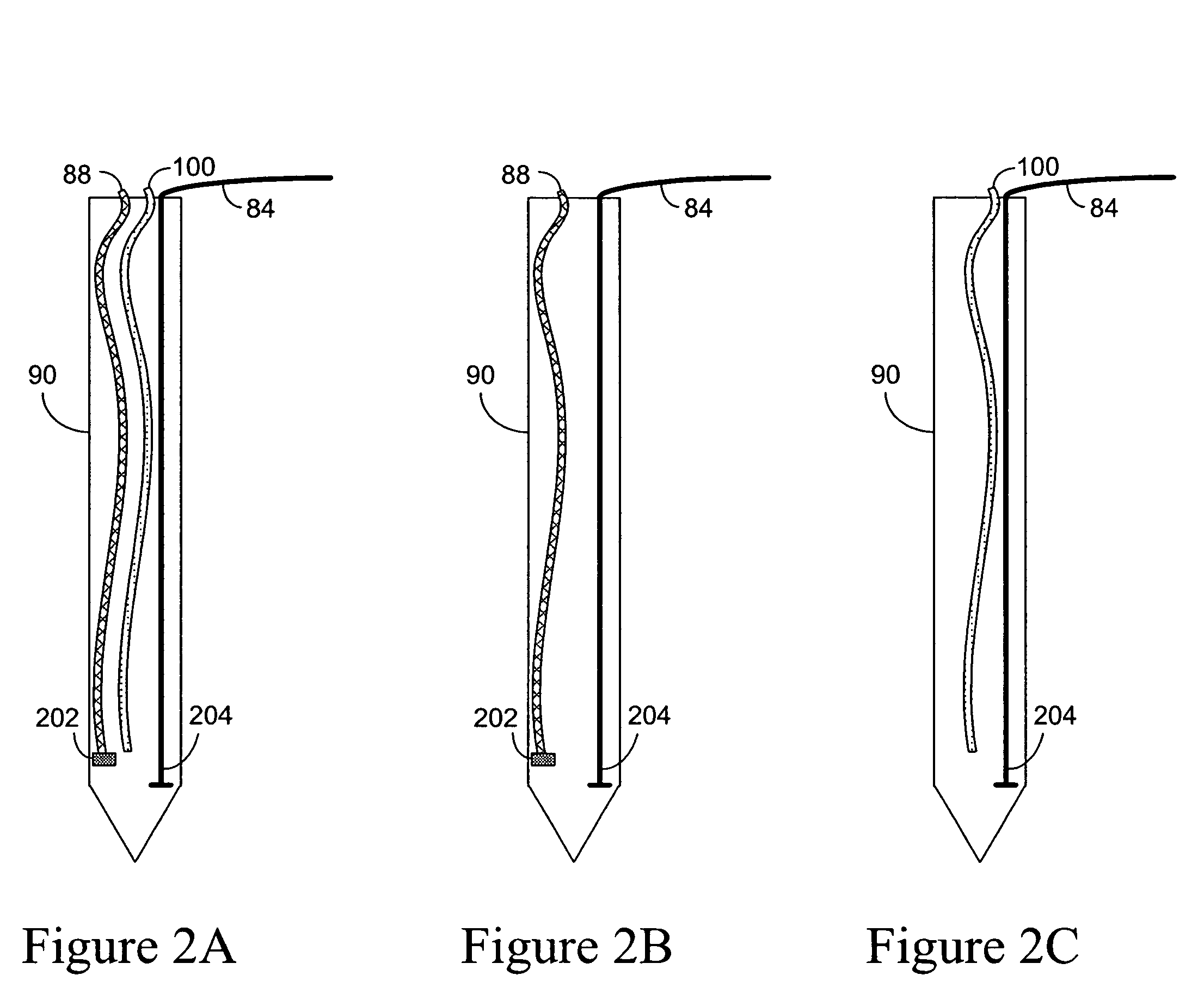
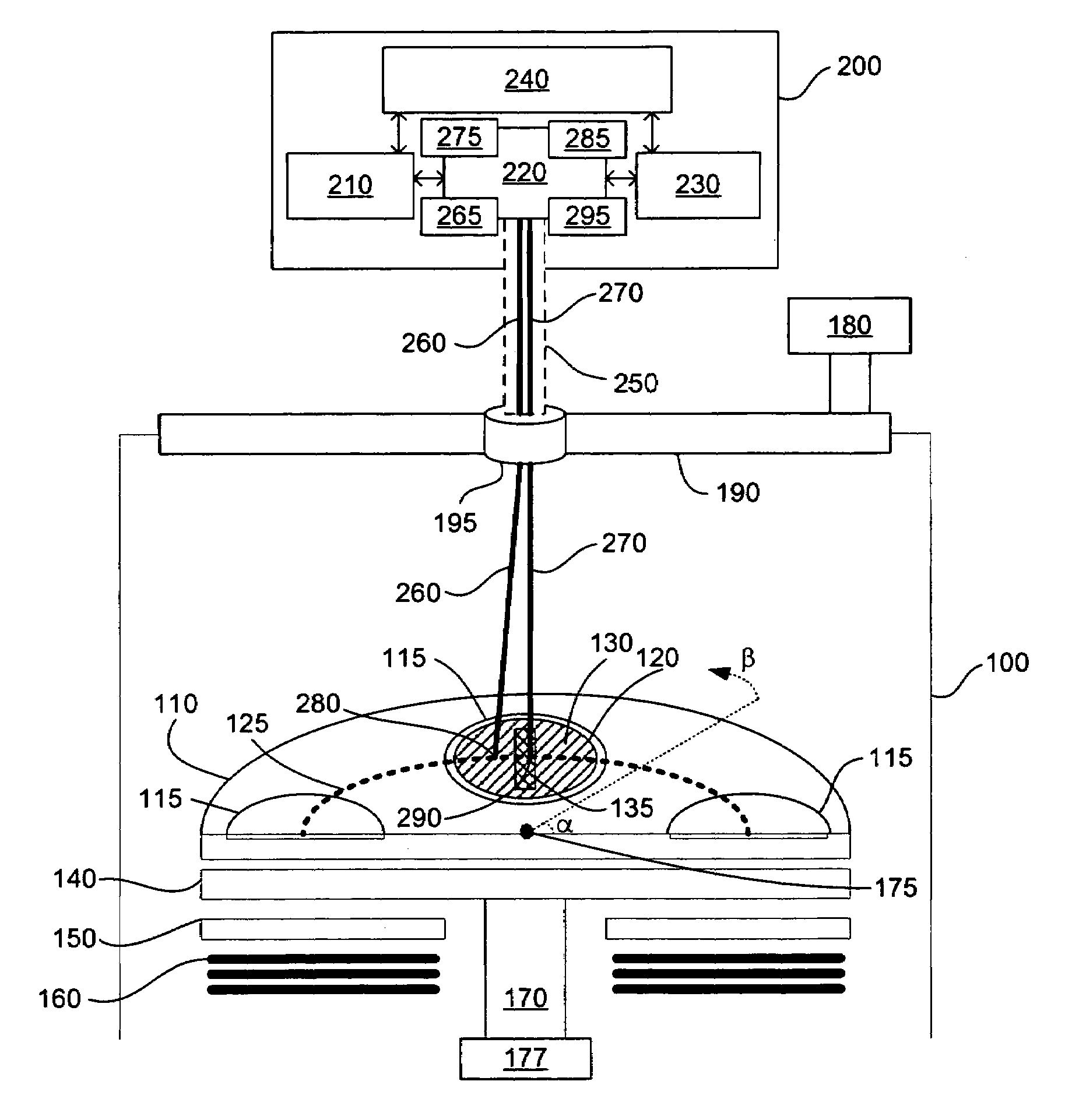
Systems and methods for monitoring temperature during electrosurgery or laser therapy
InactiveUS20080033300A1Diagnostic recording/measuringSurgical instruments for heatingLaser probeHigh heat
Systems that measure temperatures of tissue during electrosurgery or laser therapy of the tissue or organs is provided. One system provides a pyrometer that measures infrared electromagnetic energy emitted by a surface of a tissue or organ thereby determining a sub-surface temperature of the tissue or organ. The system further has an energy generator and an ablation electrode or laser probe that delivers energy from the energy generator to a tissue or organ, responsive to a sub-surface temperature determined by the pyrometer. The pyrometer can be calibrated using a luminescent material having known optical properties as a function of temperature. The luminescent material can be positioned on the surface of the tissue or organ or inserted directly into the tissue or organ using a catheter. Methods in which the surface or sub-surface temperature of the tissue is measured during therapy are also provided.
Owner:LUMASENSE TECH HLDG
Method for preparing silicon thin film heterojunction solar cell
InactiveCN1588649AAvoid damageReduce hydrogen contentFinal product manufacturePhotovoltaic energy generationHeterojunctionSilicon thin film
A prepn. method of silicon thin film heterojunction solar cell includes following steps: cleaning substrate, semiconductor cleaning technology is used to do primary cleaing to substrate surface, then do ultrasonic cleaning in deionized water several times; nitrogen blow drying; prepare nitrinsic amorphous silicon layer by heater chemical vapour phase depositing technology, tungsten filament temp. is measured by pyrometer, temp of heater and sample are determined separately by two electric thermo-couples, temp. is controlled by electric temp. controller; to react and grow thin film on substrate surface; to redeposit a transmitting layer on intrinsic amorphous silicon thin film; front and back electrodes forming, sputtering technology is used to form front and back electrodes; finally to proceed vacuum heat annealing process. The thin film produced by the invention has illumination stability, the photoconduction gain can reach to 10 to the power 6 on Am1.5 100mW / cm2 standard illumination.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
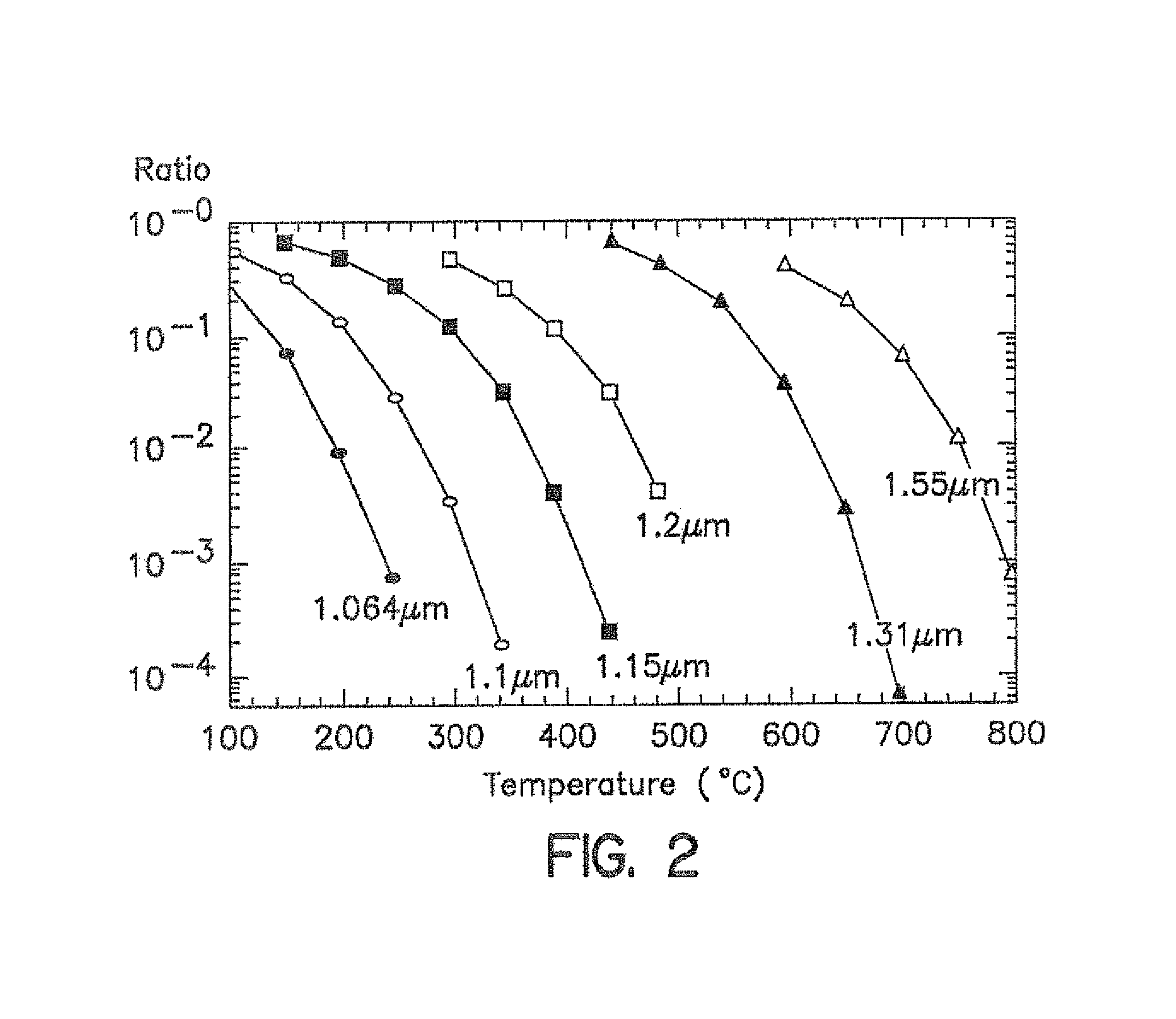
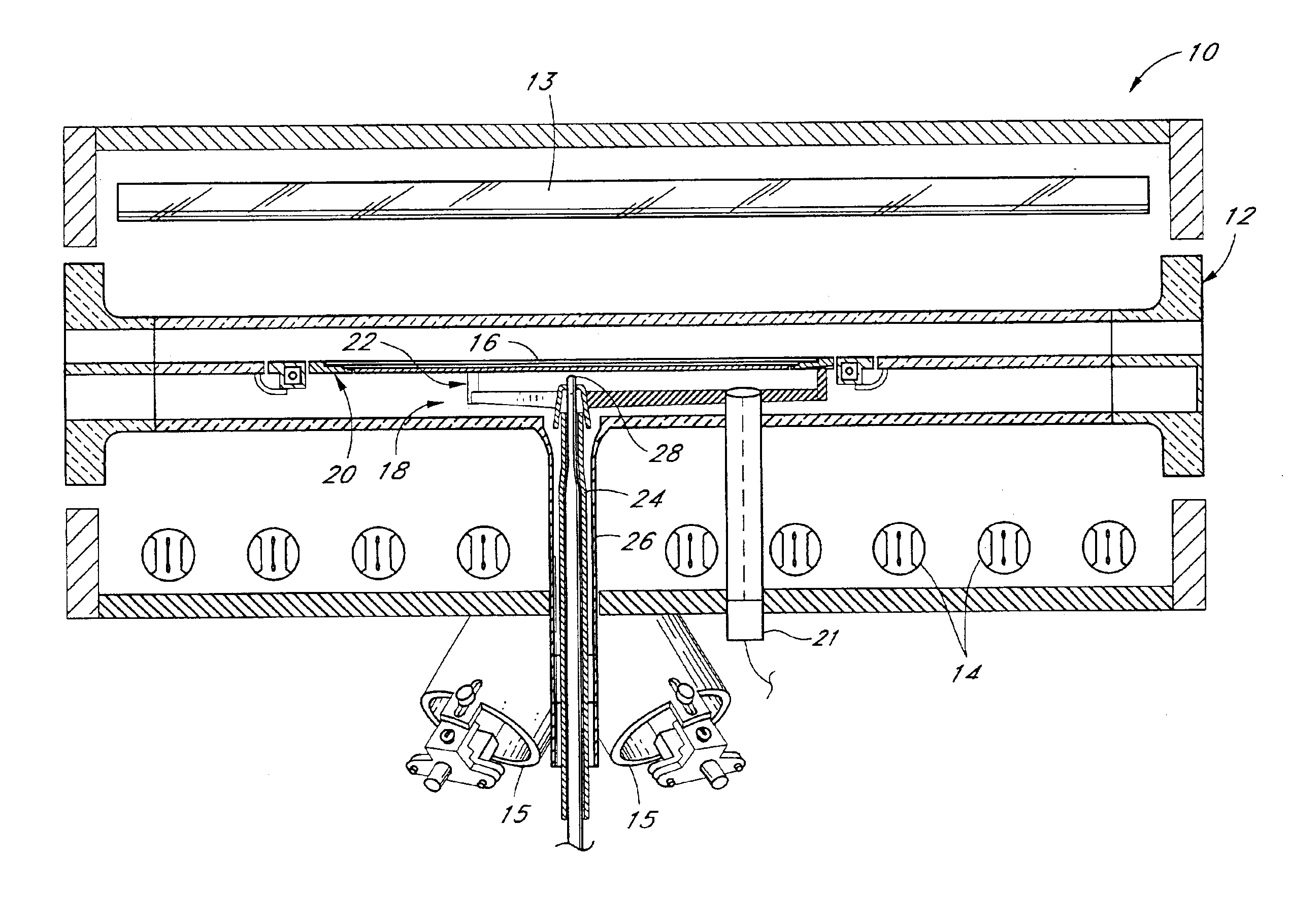
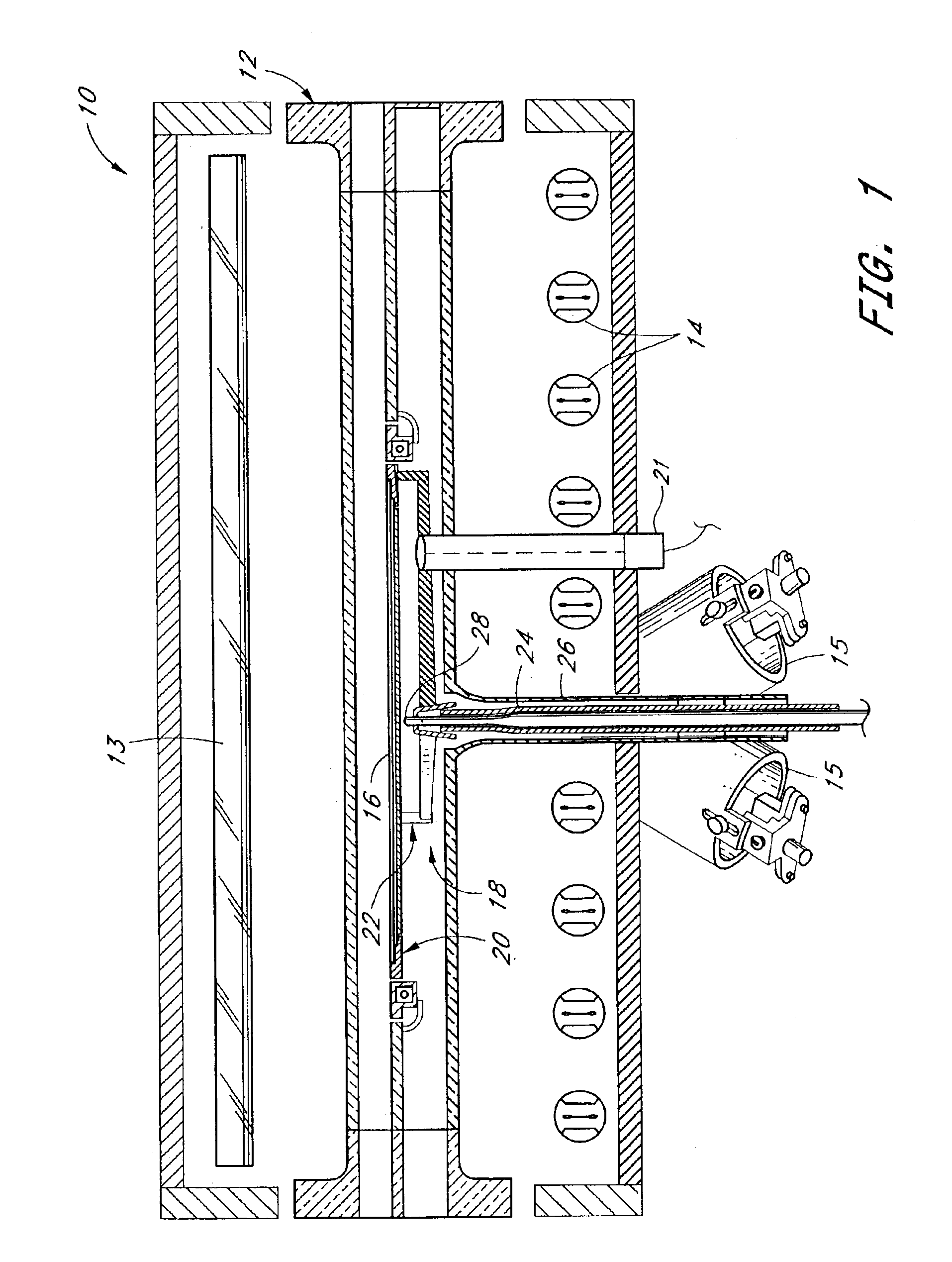
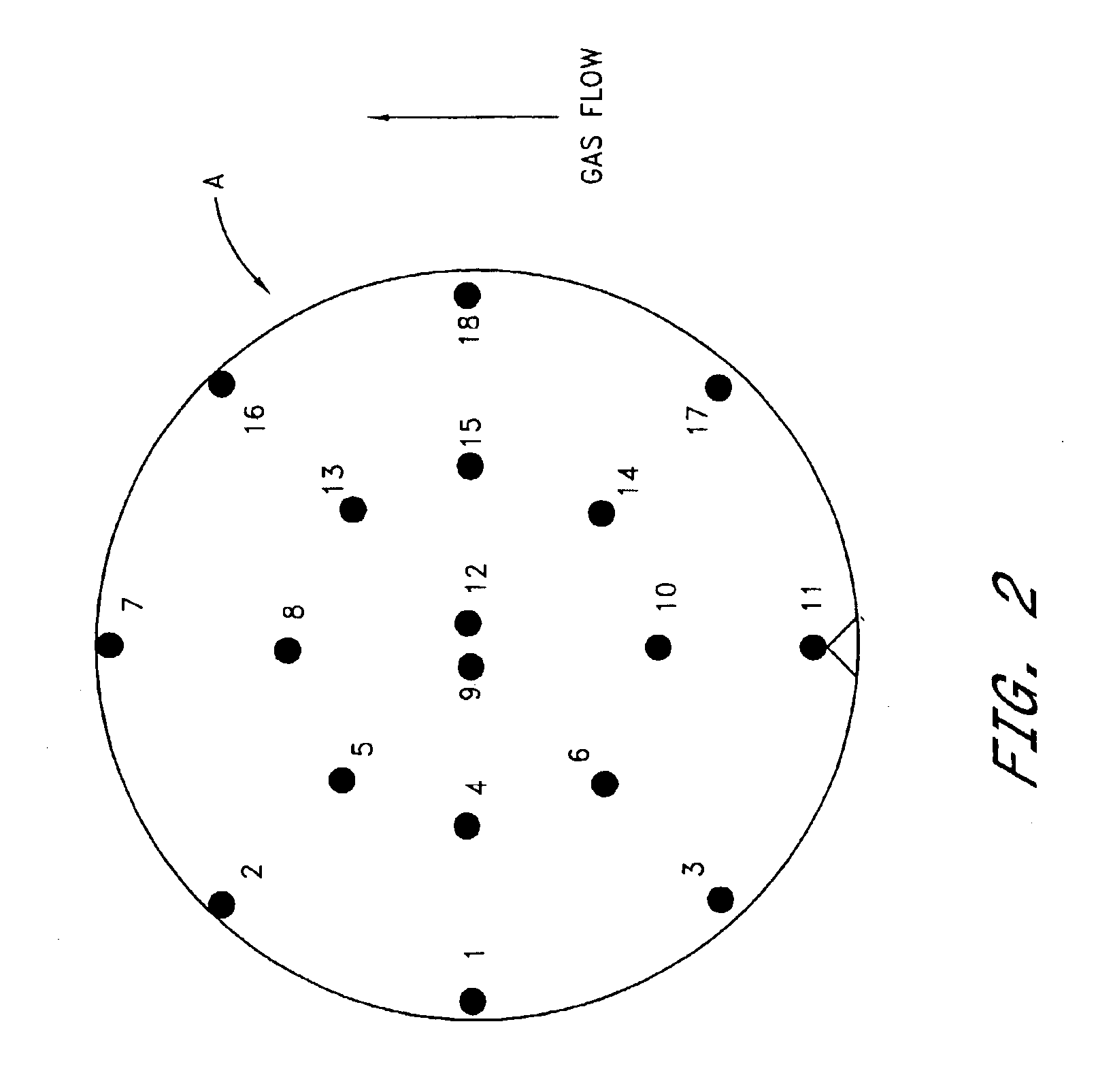
Method and apparatus for low temperature pyrometry useful for thermally processing silicon wafers
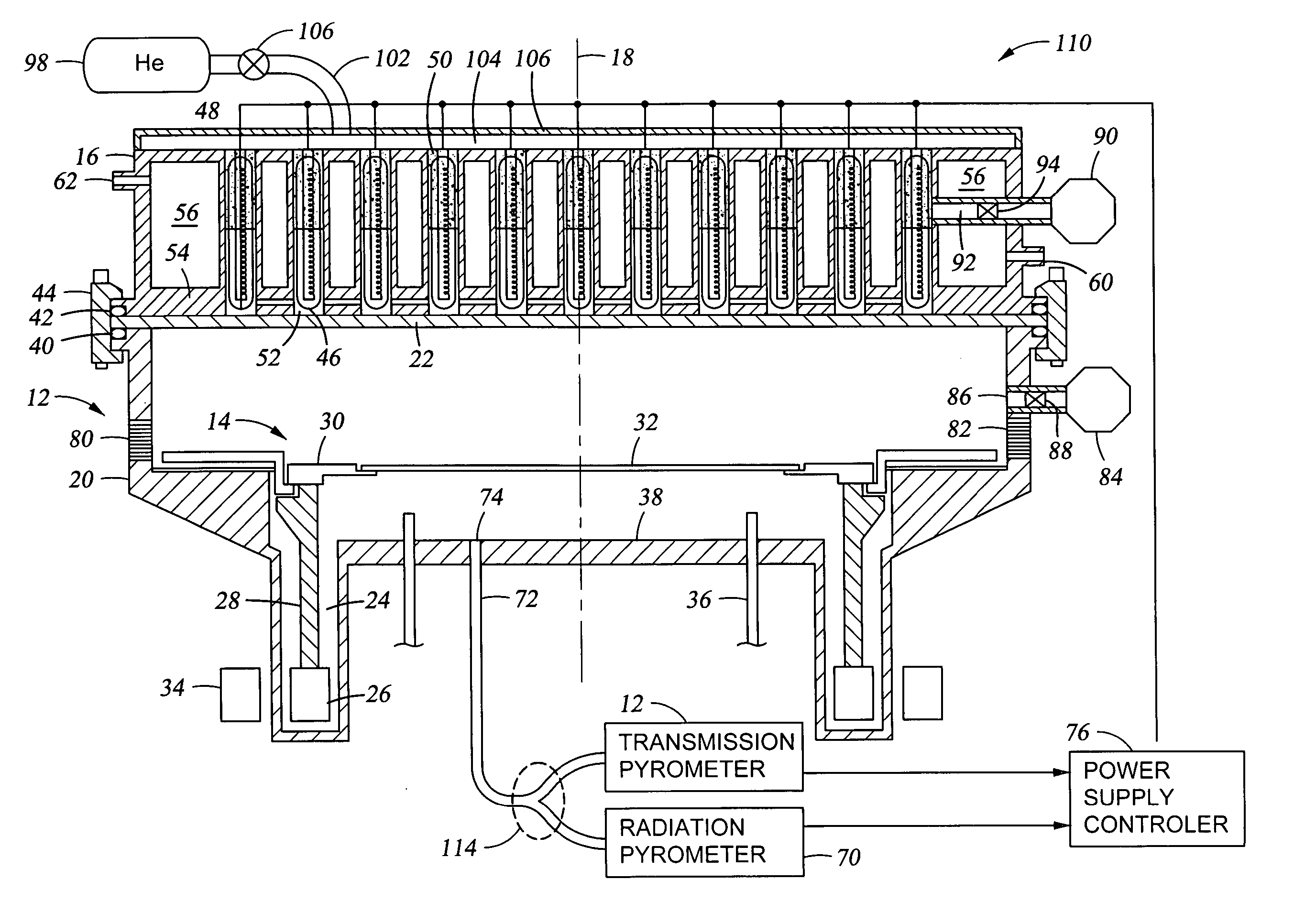
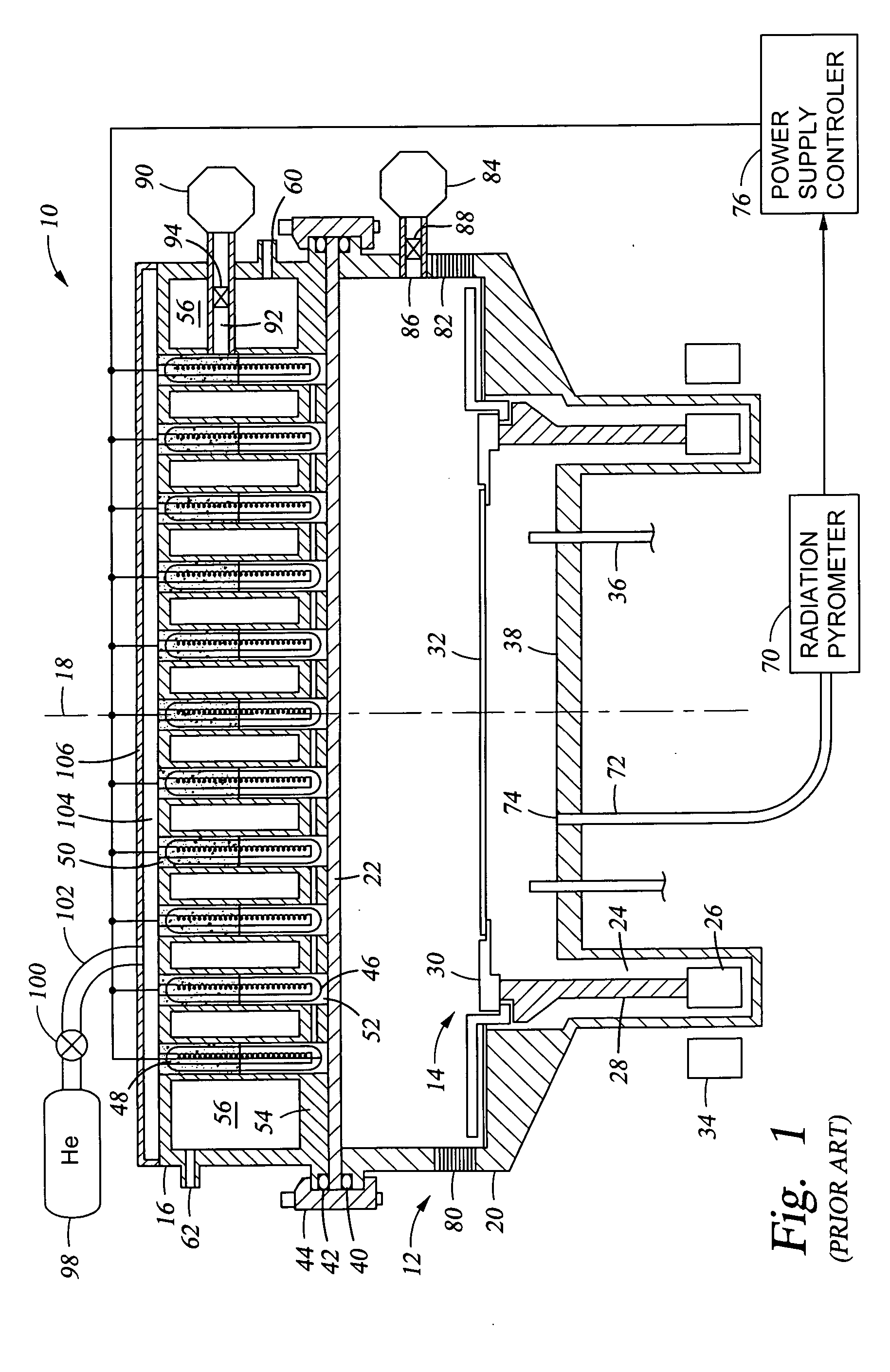
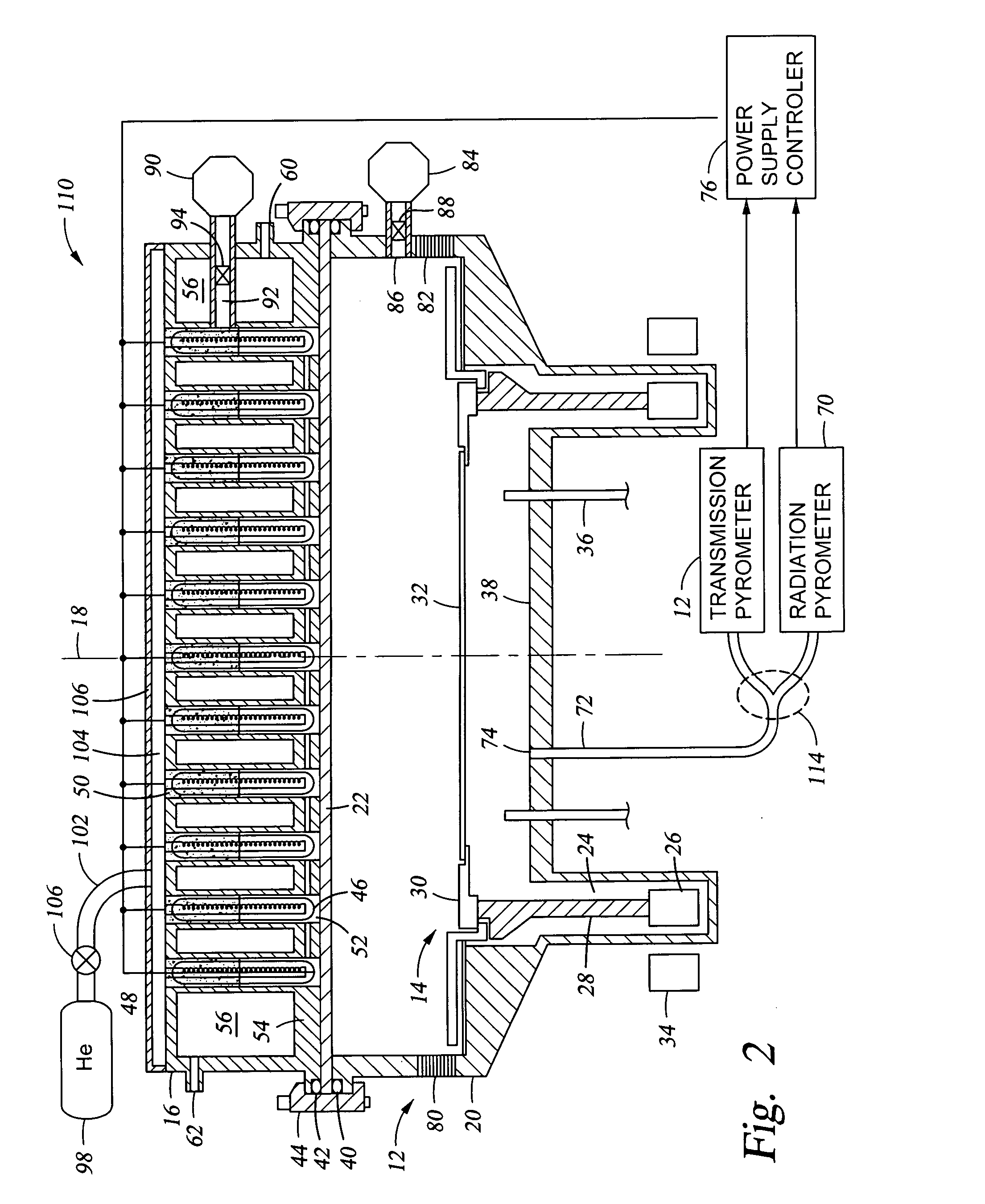
A rapid thermal processing (RTP) system including a transmission pyrometer monitoring the temperature dependent absorption of the silicon wafer for radiation from the RTP lamps at a reduced power level. A look-up table is created relating unnormalized values of photodetector photocurrents with wafer and radiant lamp temperatures. A calibrating step measures the photocurrent with known wafer and lamp temperatures and all photocurrents measured thereafter are accordingly normalized. The transmission pyrometer may be used for closed loop control for thermal treatments below 500° C. or used in the pre-heating phase for a higher temperature process including radiation pyrometry in closed loop control. The pre-heating temperature ramp rate may be controlled by measuring the initial ramp rate and readjusting the lamp power accordingly. Radiation and transmission pyrometers may be included in an integrated structure with a beam splitter dividing radiation from the wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Method and system for determining optical properties of semiconductor wafers
ActiveUS20070020784A1Precise heatingImprove accuracyRadiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementOptical propertyEmissivity
A method and system are disclosed for determining at least one optical characteristic of a substrate, such as a semiconductor wafer. Once the optical characteristic is determined, at least one parameter in a processing chamber may be controlled for improving the process. For example, in one embodiment, the reflectivity of one surface of the substrate may first be determined at or near ambient temperature. From this information, the reflectance and / or emittance of the wafer during high temperature processing may be accurately estimated. The emittance can be used to correct temperature measurements using a pyrometer during wafer processing. In addition to making more accurate temperature measurements, the optical characteristics of the substrate can also be used to better optimize the heating cycle.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
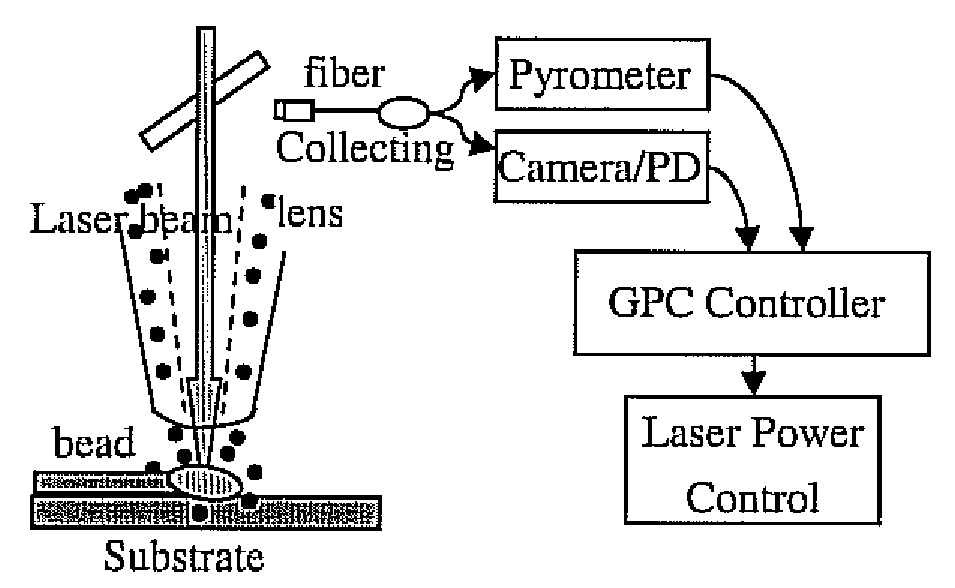
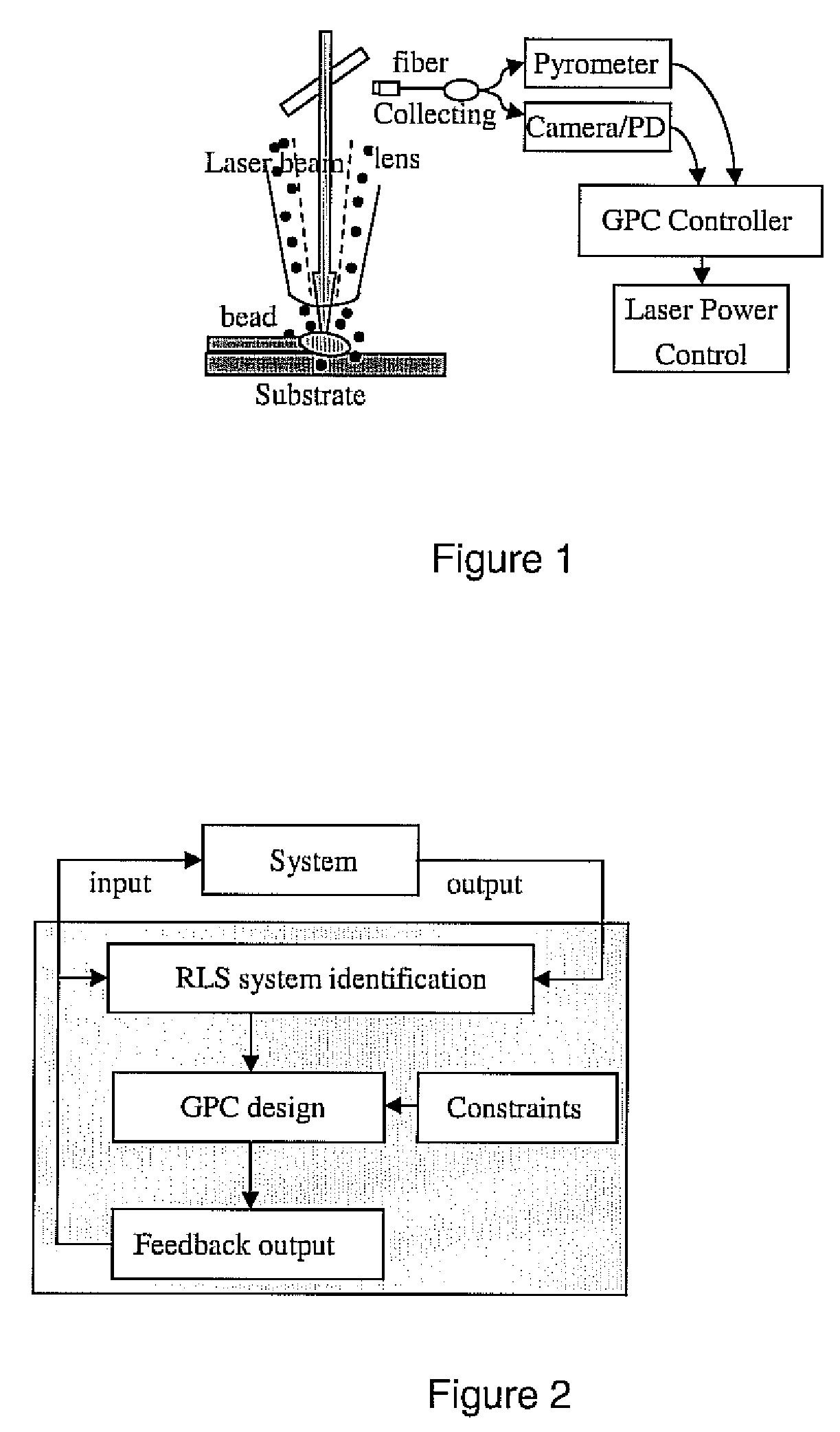
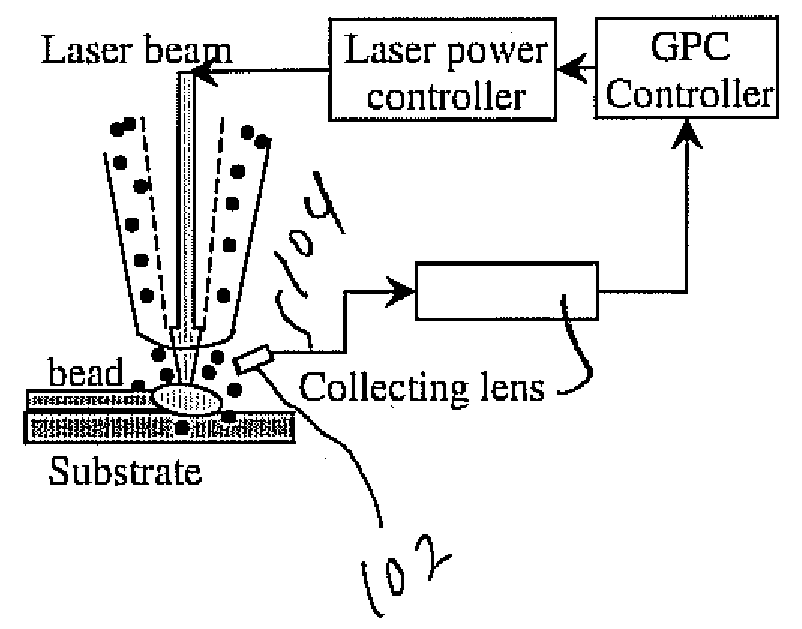
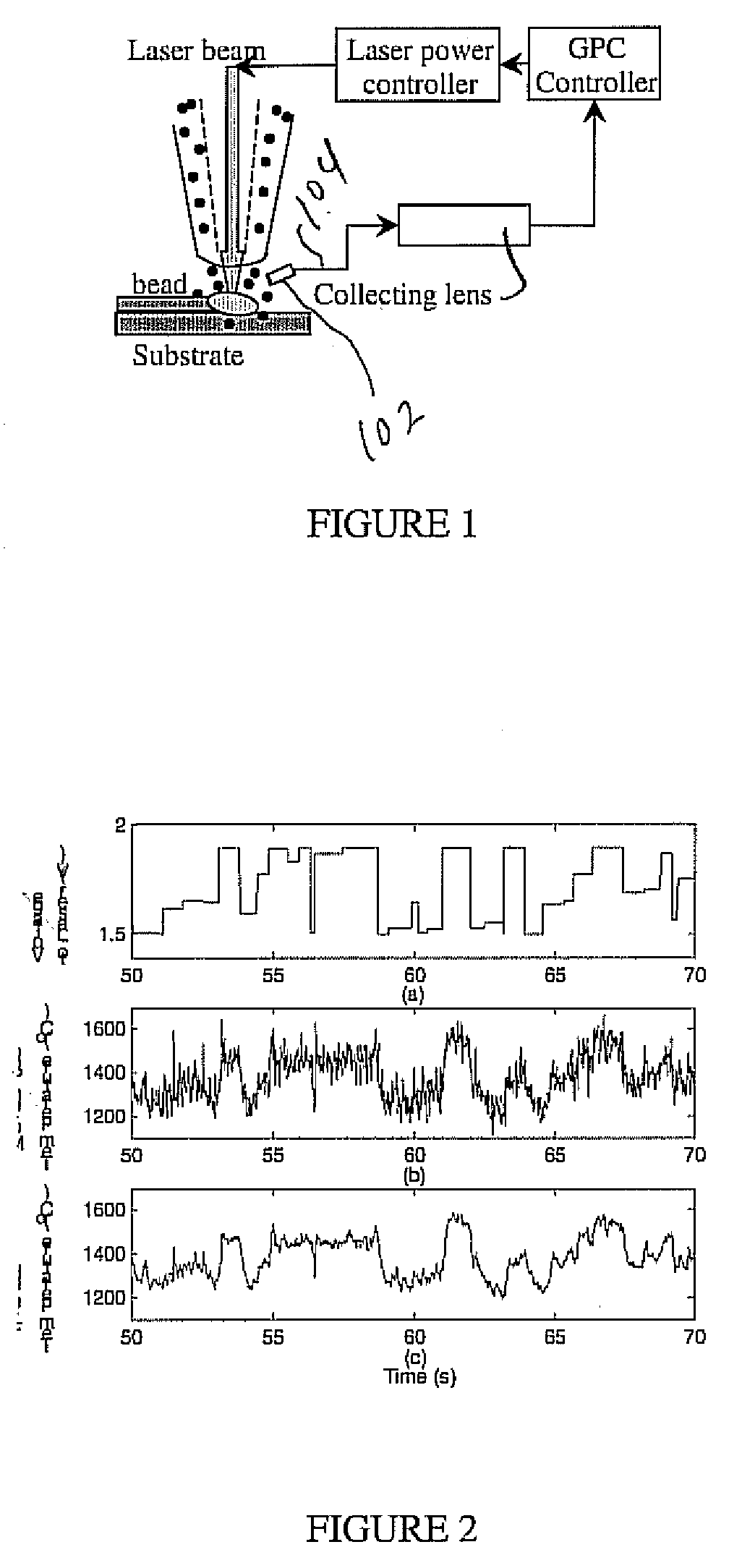
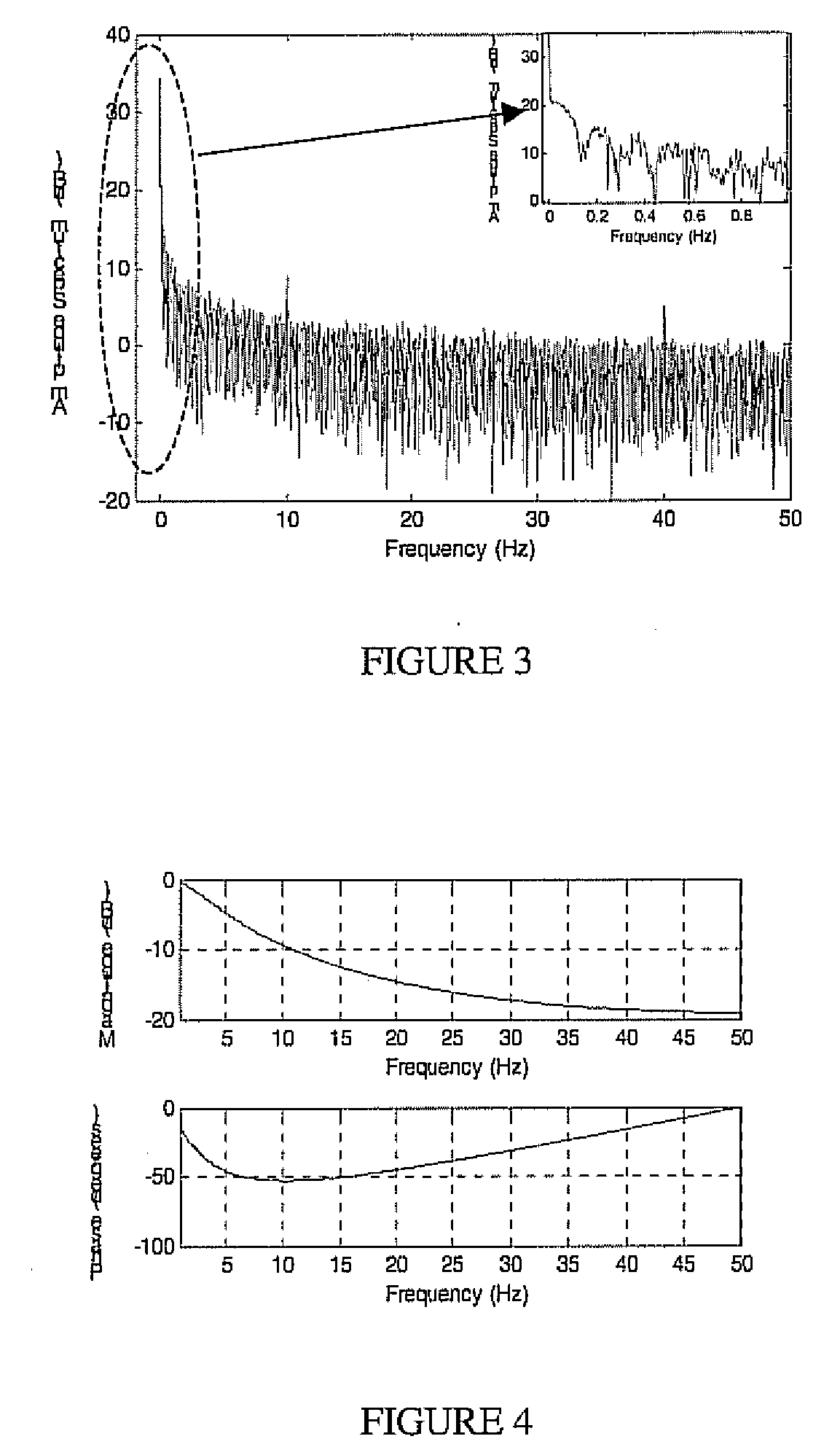
Real-time implementation of generalized predictive algorithm for direct metal deposition (DMD) process control
A direct metal deposition (DMD) process is stabilized by monitoring the temperature and the shape of the melt pool during deposition, applying a recursive least square (RLS) model estimation algorithm to adaptively identify process characteristics in accordance with the temperature and the shape of the melt pool, and delivering the process characteristics to a generalized predictive controller with input constraints to control the process. The process may be controlled by adjusting laser power or by adjusting the speed of the movement of the laser. In the preferred embodiment the temperature is monitored using a two-color pyrometer, and the shape of the melt pool is monitored by detecting the edge of the melt pool with a camera and / or photodetector.
Owner:P O M GRP THE
Method and apparatus for low temperature pyrometry useful for thermally processing silicon wafers
A rapid thermal processing (RTP) system including a transmission pyrometer monitoring the temperature dependent absorption of the silicon wafer for radiation from the RTP lamps at a reduced power level. A look-up table is created relating unnormalized values of photodetector photocurrents with wafer and radiant lamp temperatures. A calibrating step measures the photocurrent with known wafer and lamp temperatures and all photocurrents measured thereafter are accordingly normalized. The transmission pyrometer may be used for closed loop control for thermal treatments below 500° C. or used in the pre-heating phase for a higher temperature process including radiation pyrometry in closed loop control. The pre-heating temperature ramp rate may be controlled by measuring the initial ramp rate and readjusting the lamp power accordingly. Radiation and transmission pyrometers may be included in an integrated structure with a beam splitter dividing radiation from the wafer.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Real time implementation of generalized predictive control algorithm for the control of direct metal deposition (DMD) process
InactiveUS20080223832A1Increasing temperature profileHigh dimensional accuracyDigital computer detailsThermometers using physical/chemical changesControl systemLinear model
A linear model based generalized predictive control system controls the molten pool temperature during a Direct Metal Deposition (DMD) process. The molten pool temperature is monitored by a two-color pyrometer. A single-input single-output linear system that describes the dynamics between the molten pool temperature and the laser power is identified and validated. The incremental generalized predictive control algorithm with Kalman filter estimation is used to control the molten pool temperature.
Owner:P O M GRP THE
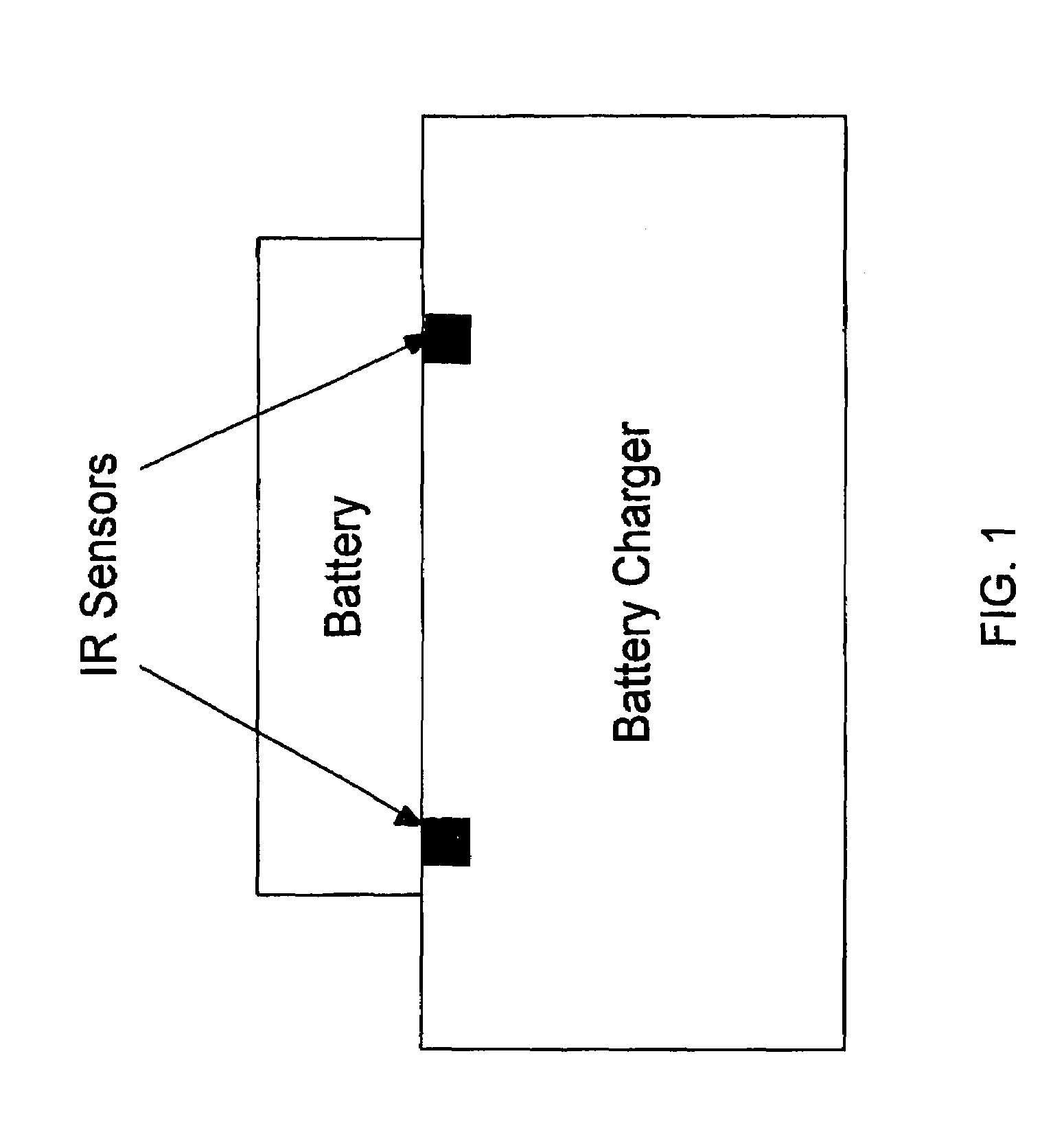
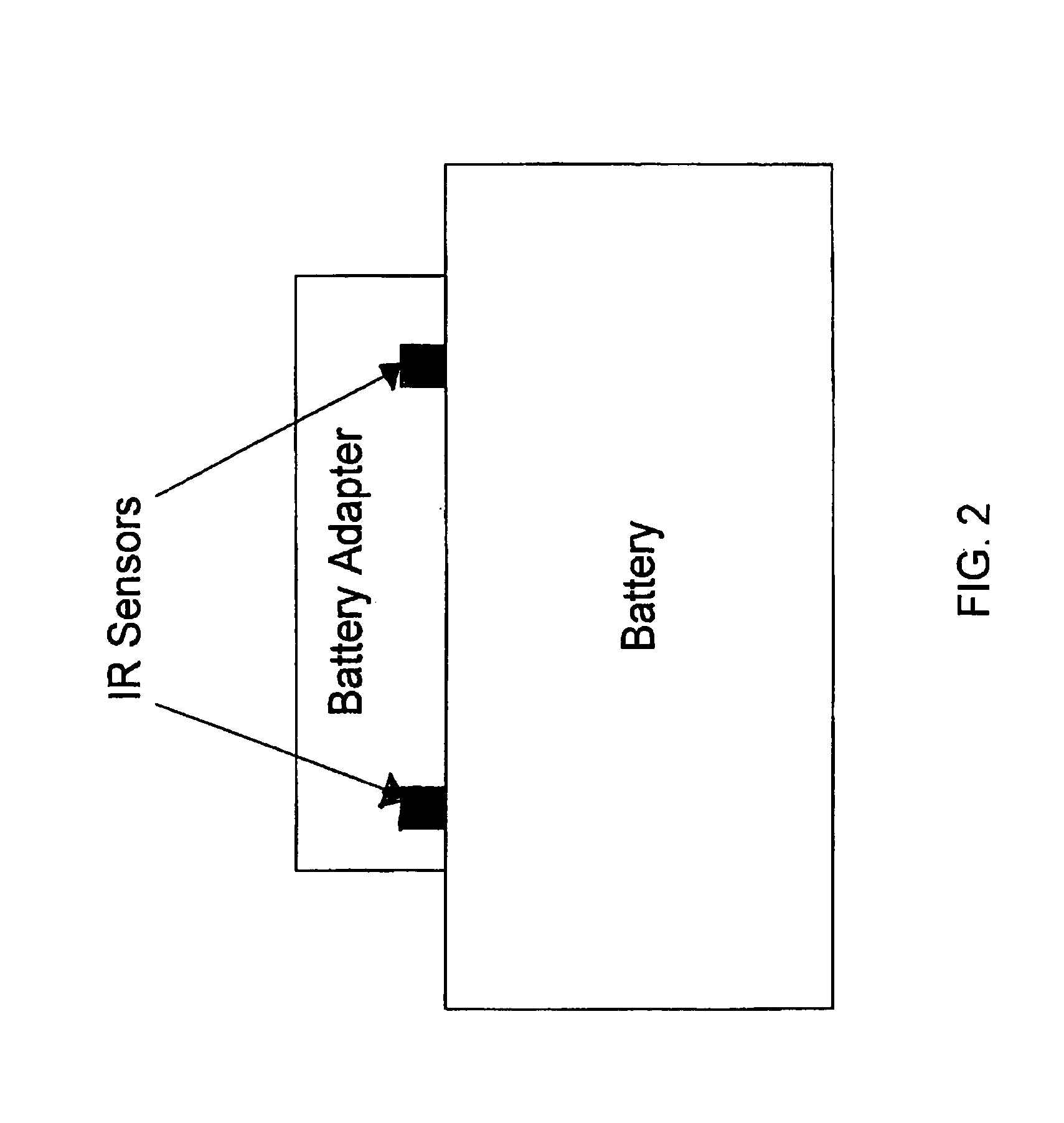
Method and apparatus for acquiring battery temperature measurements using stereographic or single sensor thermal imaging
InactiveUS20080272742A1Faster heat gradient detectionUniversalityBatteries circuit arrangementsSecondary cellsEngineeringTemperature monitoring
A method and apparatus for acquiring battery temperature measurements using stereographic thermal imaging sensors or a simple single thermal imaging sensor which can detect increases in battery heat within the field of view of any single thermal sensor, or any combination of a plurality of thermal imaging sensors is presented. Infrared Detection (ID) using the thermal imaging sensor (pyrometer) is used to focus on certain parts of a housing thereby providing an ability to “see through” or “partially see through” the battery housing to battery cells enclosed by the battery housing. Advantageously, this affords the unique capability of measuring the battery temperature before heat propagates from an individual battery cell or a plurality of battery cells to the battery housing, allowing faster heat gradient detection. Moreover, universality of battery temperature monitoring is achieved by elimination of proprietary communication between the manufacturer of the battery and the charger.
Owner:ADVANCED BATTERY MANAGEMENT
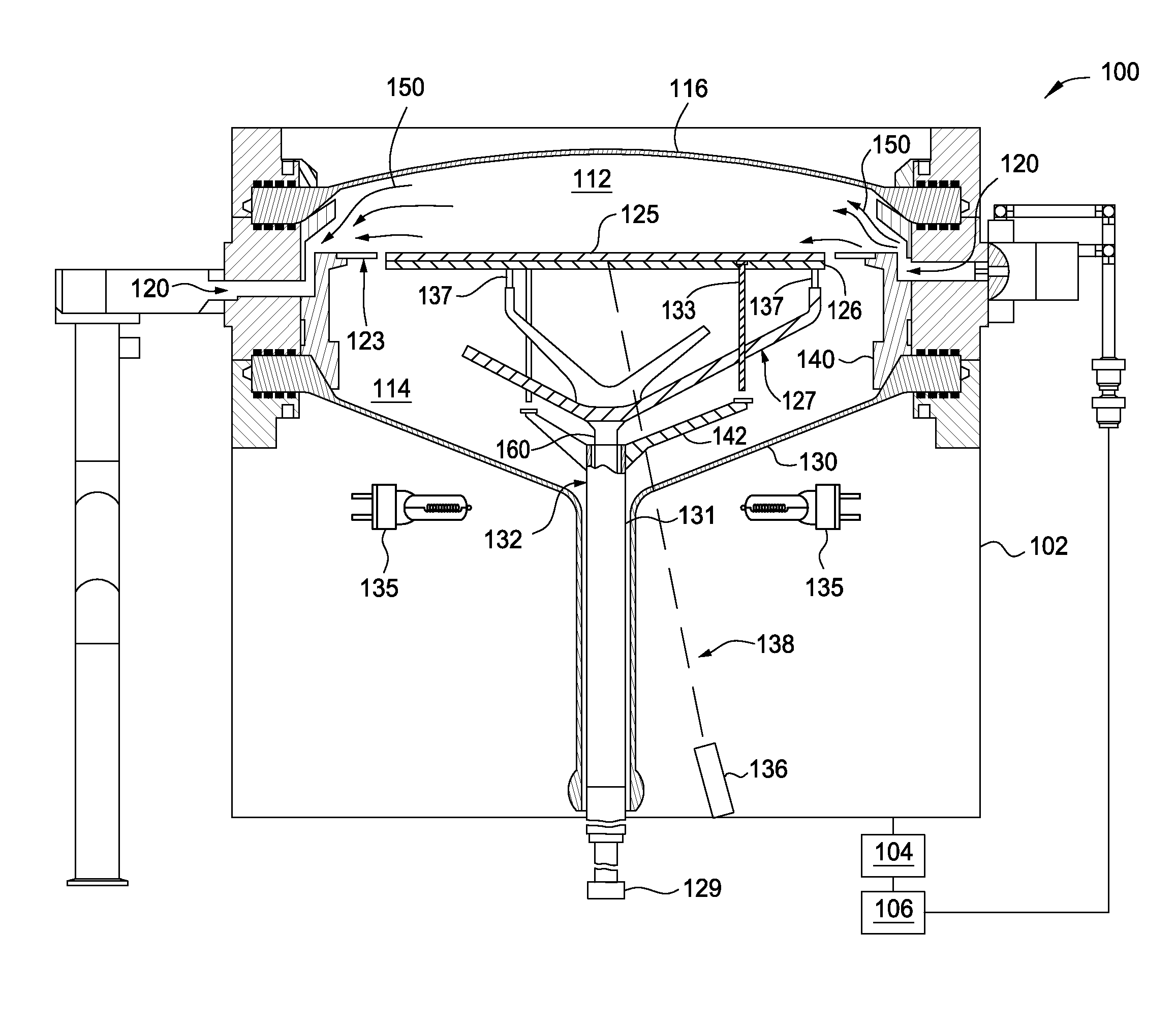
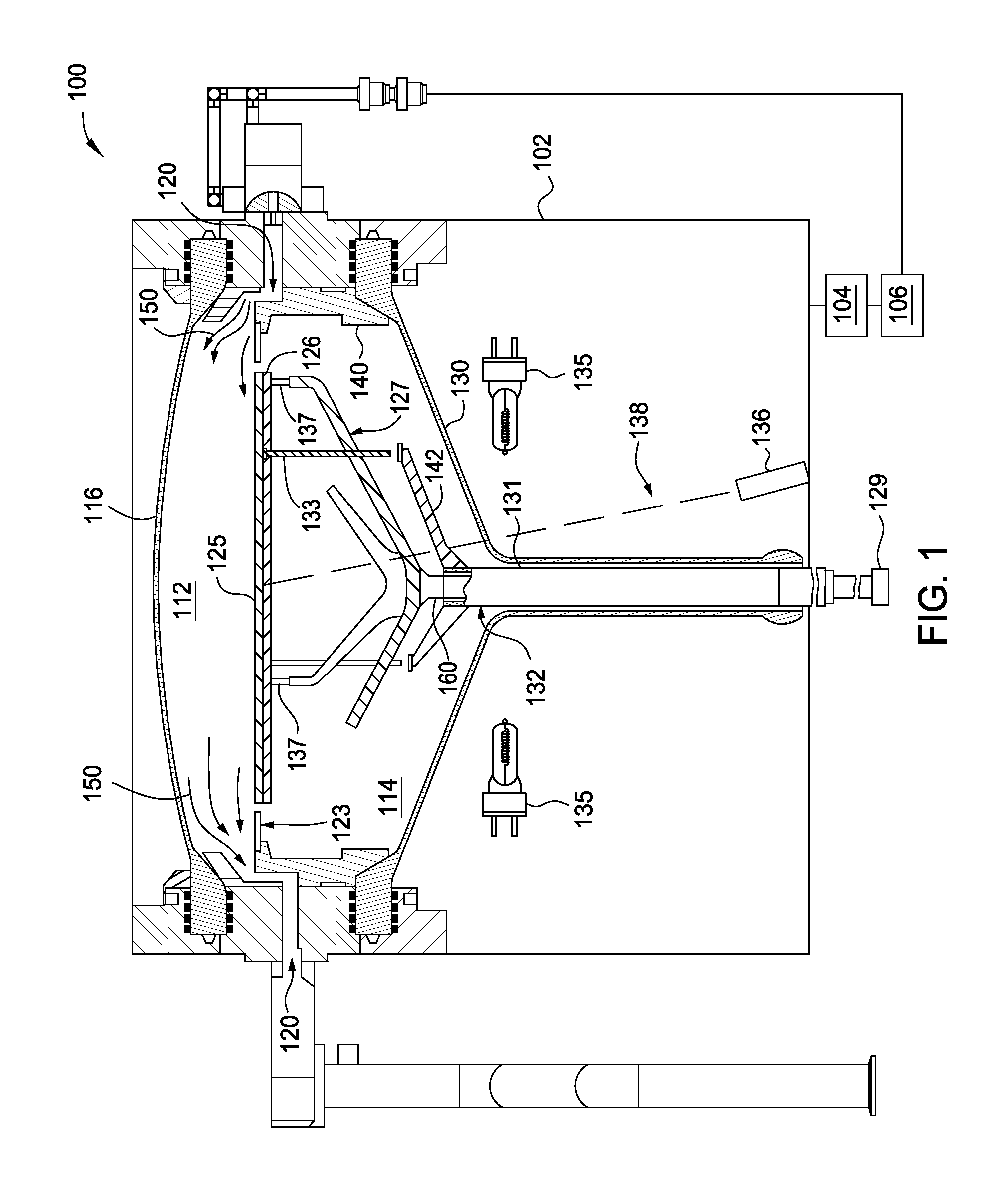
Stepped reflector plate
InactiveUS7041931B2Improve performancePromote rapid coolingDrying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesSemiconductorHeat treated
In a system for thermal processing of a semiconductor substrate, a reflector plate has a stepped surface facing the substrate during heating and cooling of the substrate. The raised surface of the reflector plate has reduced reflectivity, providing advantages during, among other things, cooling of the substrate. The reflector plate also includes a number of recesses to which one or more pyrometers are coupled. These recesses have a highly reflective surface, providing advantages in the performance of the pyrometers.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Apparatus and method for reducing stray light in substrate processing chambers
InactiveUS7135656B2Accurately determinedEffective absorptionDrying solid materials with heatMuffle furnacesRare-earth elementSemiconductor materials
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
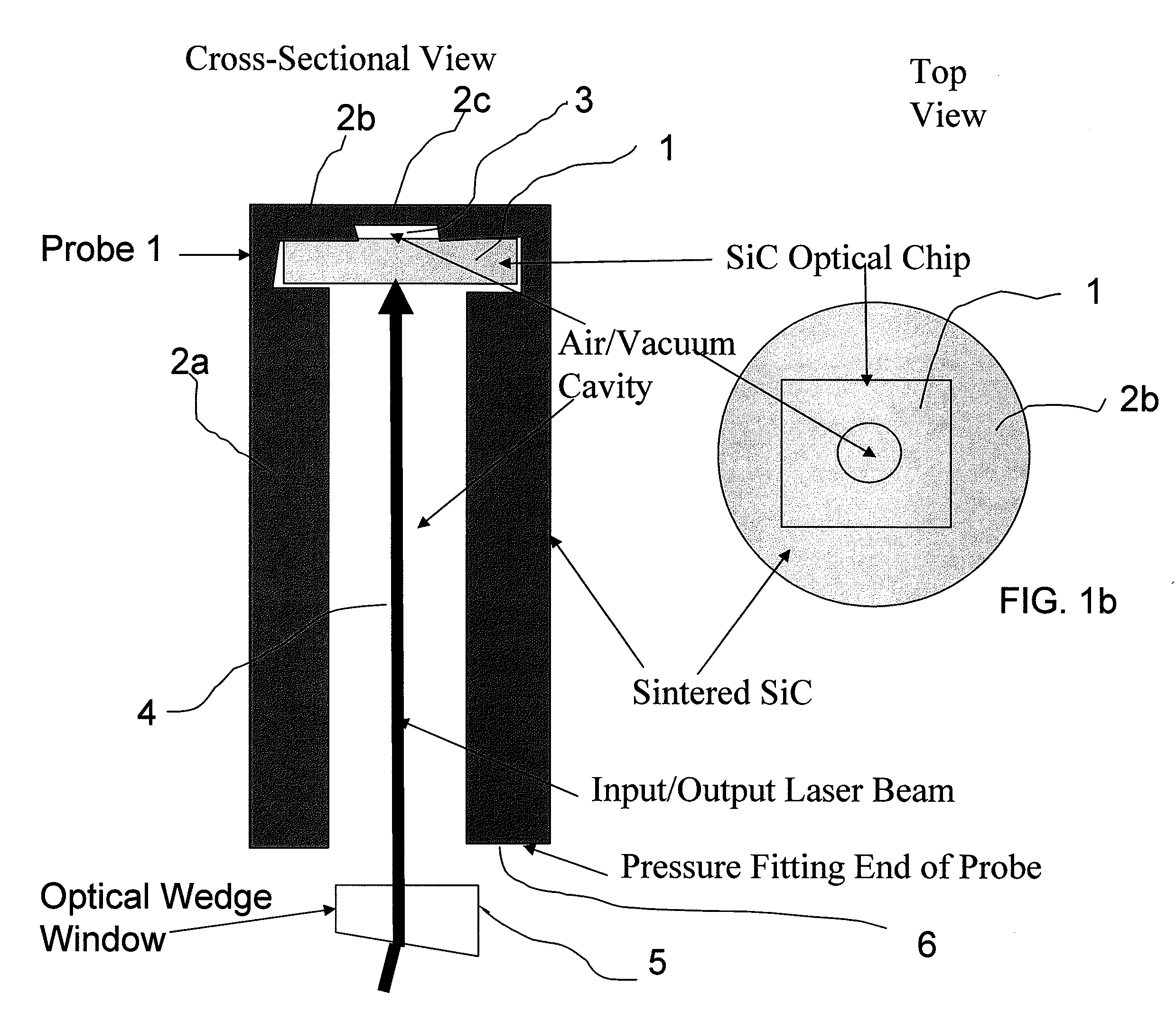
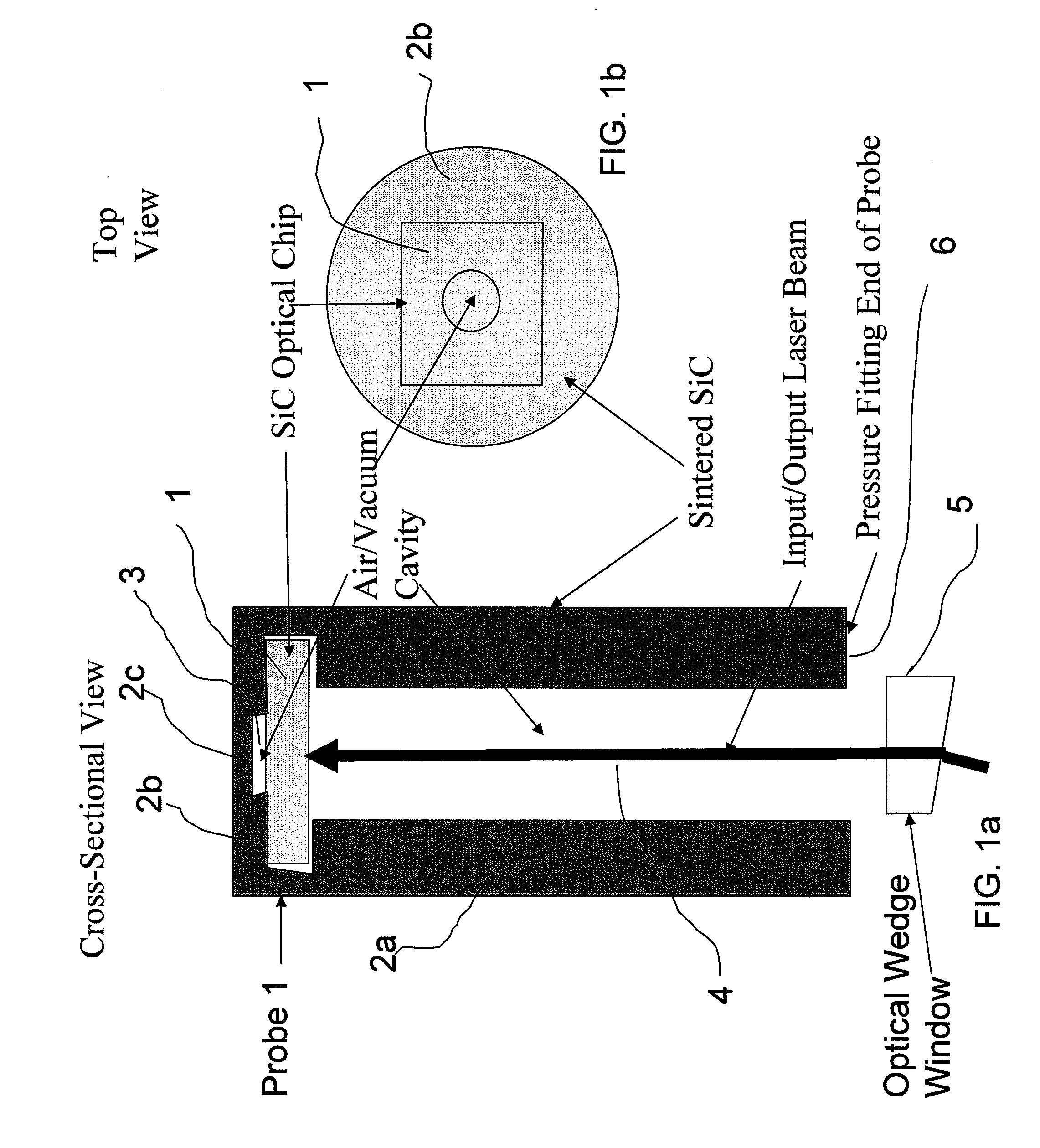
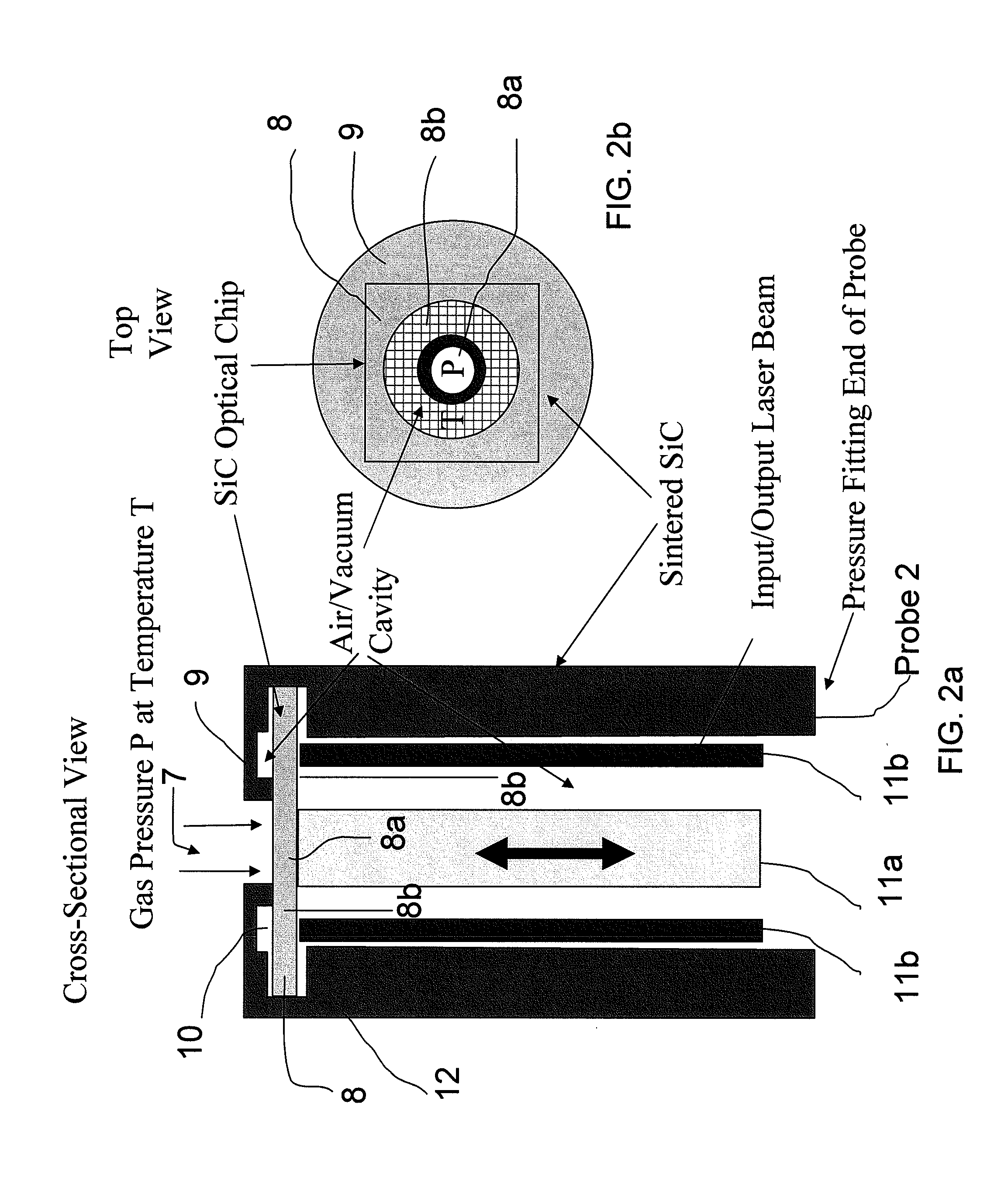
Extreme Temperature Robust Optical Sensor Designs And Fault-Tolerant Signal Processing
InactiveUS20090296776A1Eliminates multiple unwanted optical reflectionReduce ambiguityThermometer detailsSensing radiation from gases/flamesFrequency spectrumBlack body
Silicon Carbide (SiC) probe designs for extreme temperature and pressure sensing uses a single crystal SiC optical chip encased in a sintered SiC material probe. The SiC chip may be protected for high temperature only use or exposed for both temperature and pressure sensing. Hybrid signal processing techniques allow fault-tolerant extreme temperature sensing. Wavelength peak-to-peak (or null-to-null) collective spectrum spread measurement to detect wavelength peak / null shift measurement forms a coarse-fine temperature measurement using broadband spectrum monitoring. The SiC probe frontend acts as a stable emissivity Black-body radiator and monitoring the shift in radiation spectrum enables a pyrometer. This application combines all-SiC pyrometry with thick SiC etalon laser interferometry within a free-spectral range to form a coarse-fine temperature measurement sensor. RF notch filtering techniques improve the sensitivity of the temperature measurement where fine spectral shift or spectrum measurements are needed to deduce temperature.
Owner:RIZA NABEEL +2
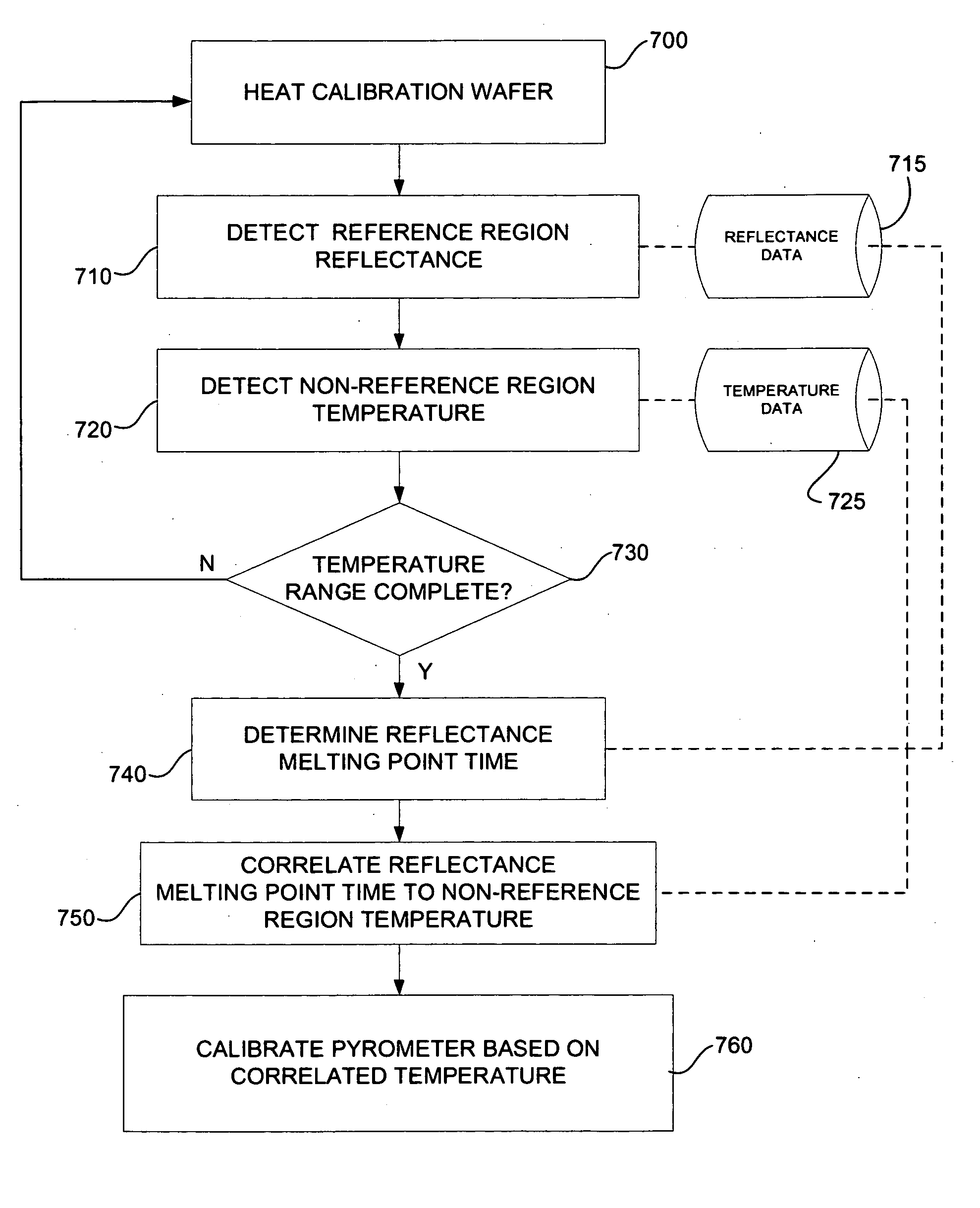
Calibration wafer and method of calibrating in situ temperatures
InactiveUS20060171442A1Improve reflectivityThermometer detailsRadiation pyrometryReference RegionReflectivity measurement
A system and method for calibrating a pyrometer used in temperature detection in a chemical vapor deposition system is provided. A calibration wafer with a reference region including a metal such as Al or Ag for forming a eutectic, and an exposed non-reference region without such a metal, are provided. Reflectivity measurements are taken from the reference region, and temperature measurements are taken from the non-reference region, over a range of temperatures including a known melting point for the metal eutectic. The pyrometer is calibrated based on the correlation of the known eutectic melting point with the change in reflectivity data obtained in the reference region, in light of the temperature data obtained from the non-reference region.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
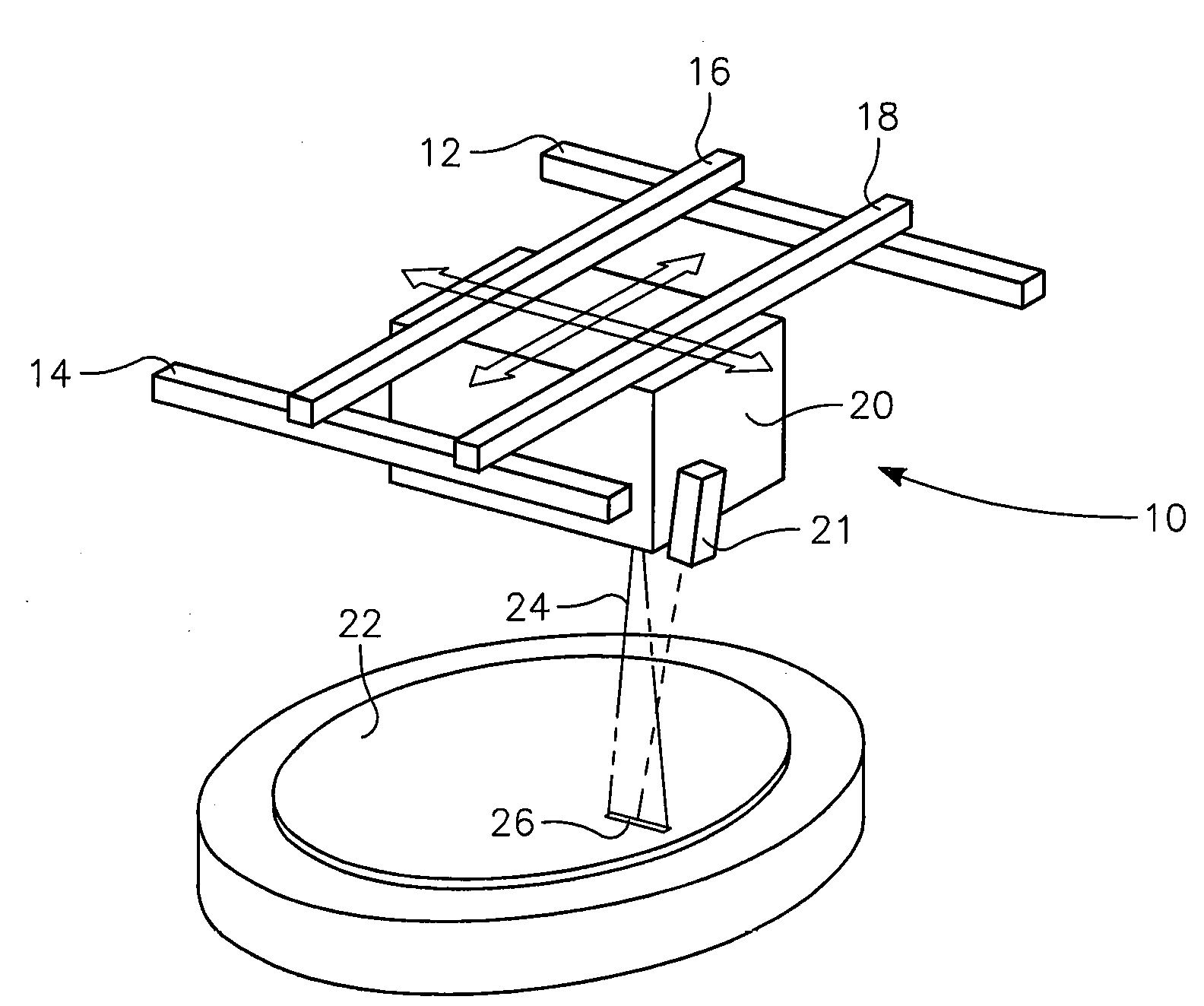
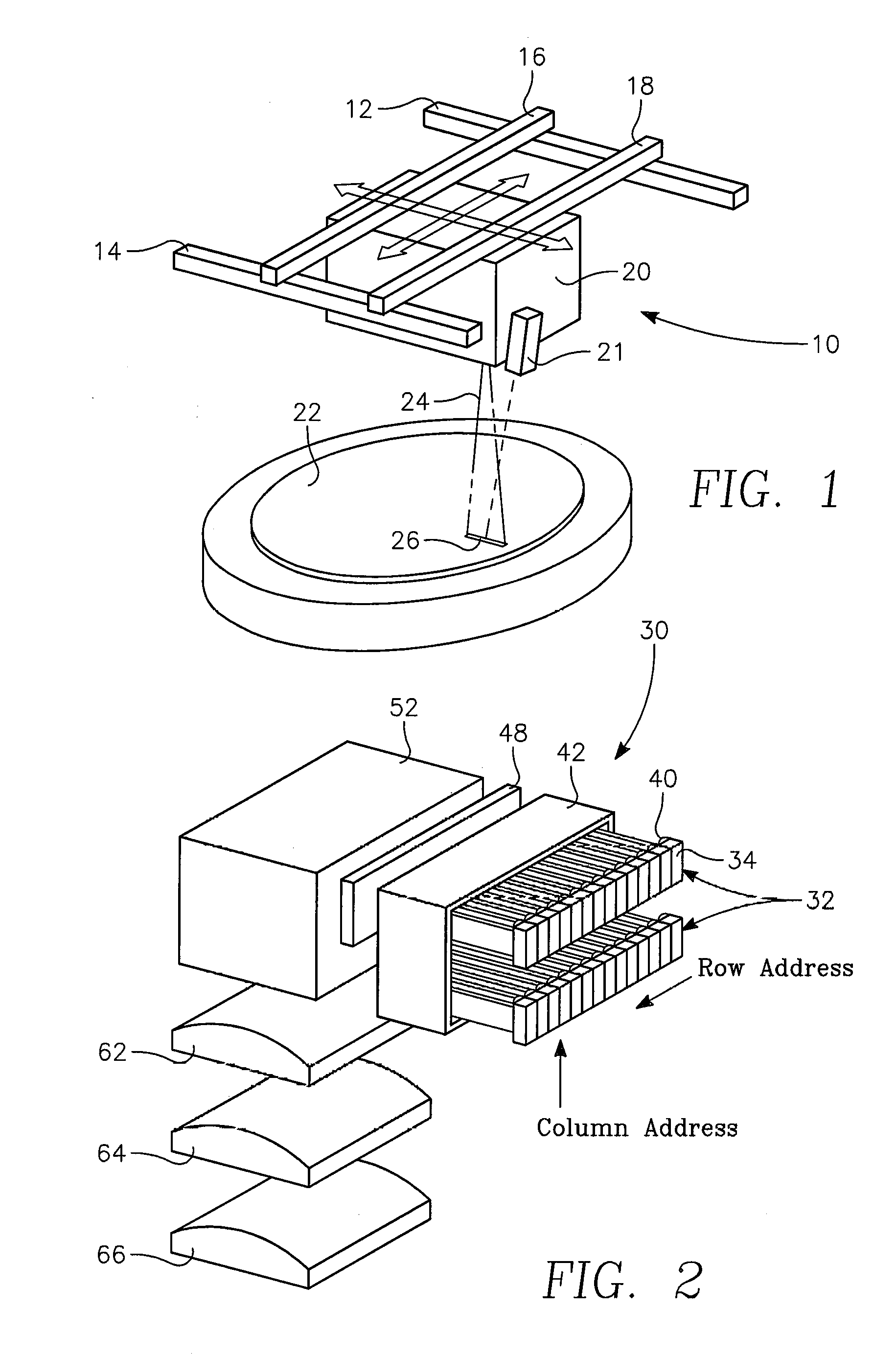
Dynamic surface annealing using addressable laser array with pyrometry feedback
Apparatus for dynamic surface annealing of a semiconductor wafer includes a source of laser radiation emitting at a laser wavelength and comprising an array of lasers arranged in rows and columns, the optical power of each the laser being individual adjustable and optics for focusing the radiation from the array of lasers into a narrow line beam in a workpiece plane corresponding to a workpiece surface, whereby the optics images respective columns of the laser array onto respective sections of the narrow line beam. A pyrometer sensor is provided that is sensitive to a pyrometer wavelength. An optical element in an optical path of the optics is tuned to divert radiation emanating from the workpiece plane to the pyrometry sensor. As a result, the optics images each of the respective section of the narrow line beam onto a corresponding portion of the pyrometer sensor. The apparatus further includes a controller responsive to the pyrometry sensor and coupled to adjust individual optical outputs of respective columns of the laser array in accordance with outputs of corresponding portions of the pyrometry sensor.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
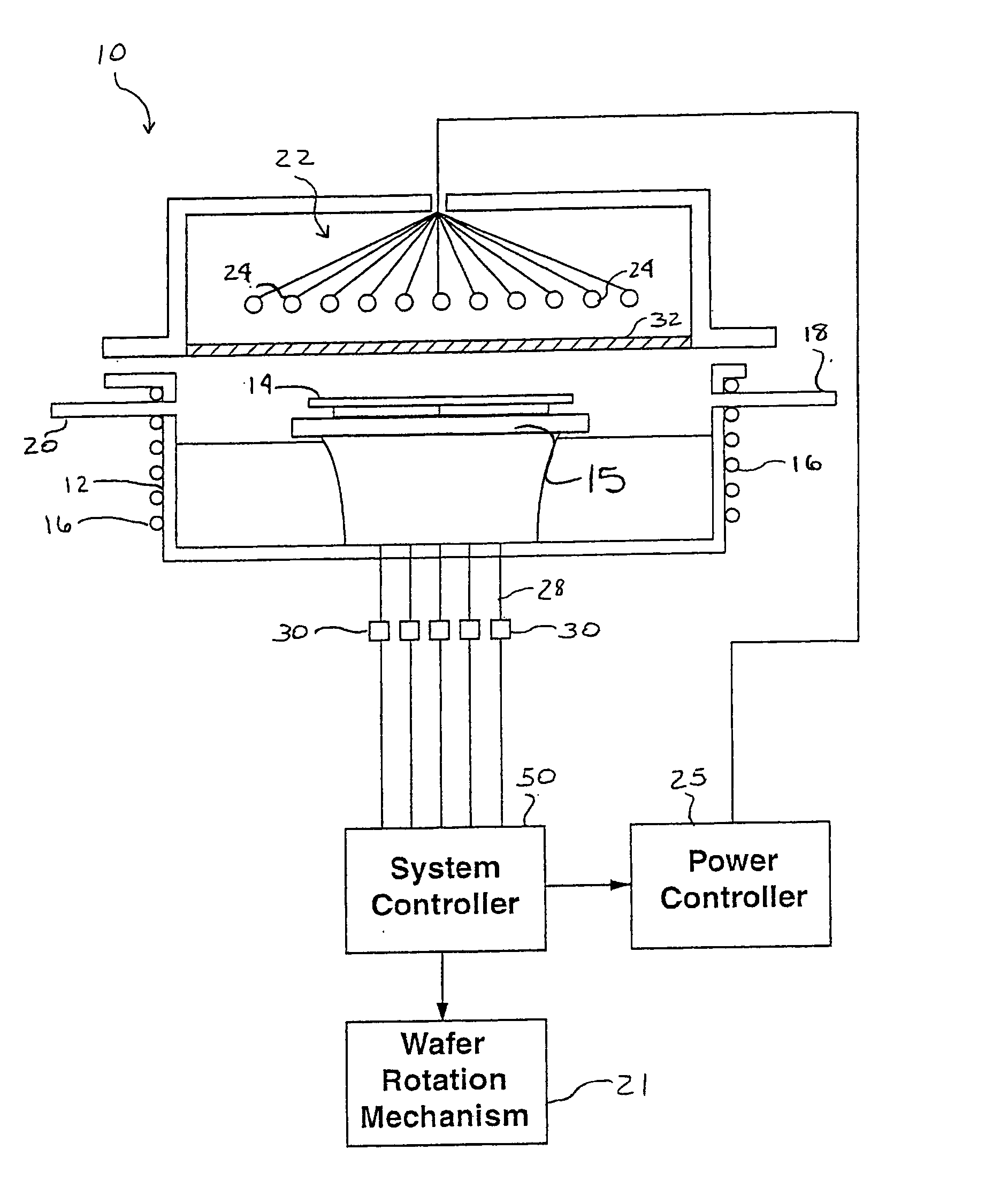
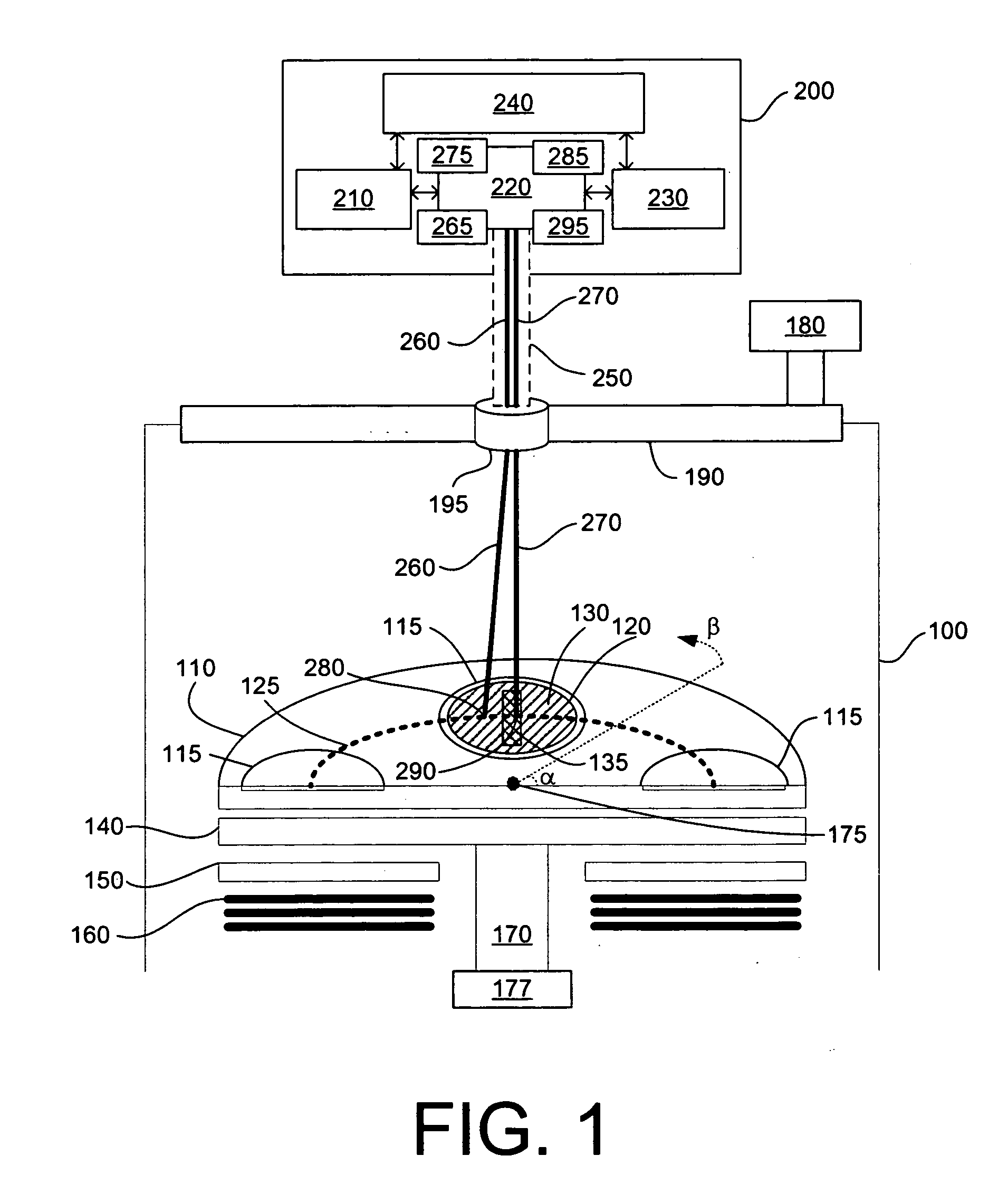
Devices, systems and methods for determining temperature and/or optical characteristics of a substrate
A system for measuring the true temperature of a substrate in a deposition system is disclosed. The temperature measurement system has at least one opening formed within a showerhead or manifold placed above a substrate of the deposition system. The temperature measurement system includes an optical pyrometer and reflectometer external to the coating chamber that looks through a window or windows and through the at least one opening in the showerhead to sense the substrate being coated. Depending on the particular chamber and showerhead configuration, the system either makes a passive emissivity correction or has an integral reflectometer for an active emissivity correction. Optical features confer an insensitivity to small motions of the showerhead in large coaters where optical alignment is not assured due to thermal and mechanical influences.
Owner:LUXTRON CORP
Calibration wafer and method of calibrating in situ temperatures
Owner:VEECO INSTR
Susceptor support shaft for improved wafer temperature uniformity and process repeatability
ActiveUS20140251208A1Reduce variationLow thermal massLiquid surface applicatorsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSusceptorEngineering
Embodiments of the invention generally relate to susceptor support shafts and process chambers containing the same. A susceptor support shaft supports a susceptor thereon, which in turn, supports a substrate during processing. The susceptor support shaft reduces variations in temperature measurement of the susceptor and / or substrate by providing a consistent path for a pyrometer focal beam directed towards the susceptor and / or substrate, even when the susceptor support shaft is rotated. The susceptor support shafts also have a relatively low thermal mass which increases the ramp up and ramp down rates of a process chamber.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Automated spray form cell
InactiveUS6640878B2High sensitivityAccurate distributionMolten spray coatingCasting safety devicesStress inducedAutomotive industry
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Method for increasing coiling temperature control accuracy of low temperature steel
ActiveCN102441578AHigh control precisionReduce in quantityTemperature control deviceWork treatment devicesTemperature controlLine tubing
The invention discloses a method for increasing the coiling temperature control accuracy of low temperature steel, in which a laminar flow cooling device is used for cooling band steel. The method comprises the following steps: configuring devices, namely adding a coiling pyrometer with a measuring range from 0 to 1000 DEG C at an outlet of a cooling zone before coiling, and arranging a fan on the pyrometer; configuring parameters of a coiling temperature model according to the coiling pyrometer; carrying out feedback control and self-learning function operating; optimizing self-learning parameters of low-temperature coiled pipe line steel; and optimizing water allocation. In the method, coiling temperature of low temperature pipe line steel is controlled through adding the pyrometer with a measuring range from 0 to1000 DEG C in the existing coiling temperature control device so as to carry out real-time detection on the coiling temperature and optimizing the configuration of corresponding parameters of coiling temperature model files, thereby effectively improving the control accuracy of the coiling temperature control device to the coiling temperature of low-temperature steel, stabilizing a control system and the coiling temperature model, stabilizing the product quality, and effectively reducing the number of steel coils with unqualified performances caused by the fluctuation of coiling temperature.
Owner:BEIJING SHOUGANG CO LTD
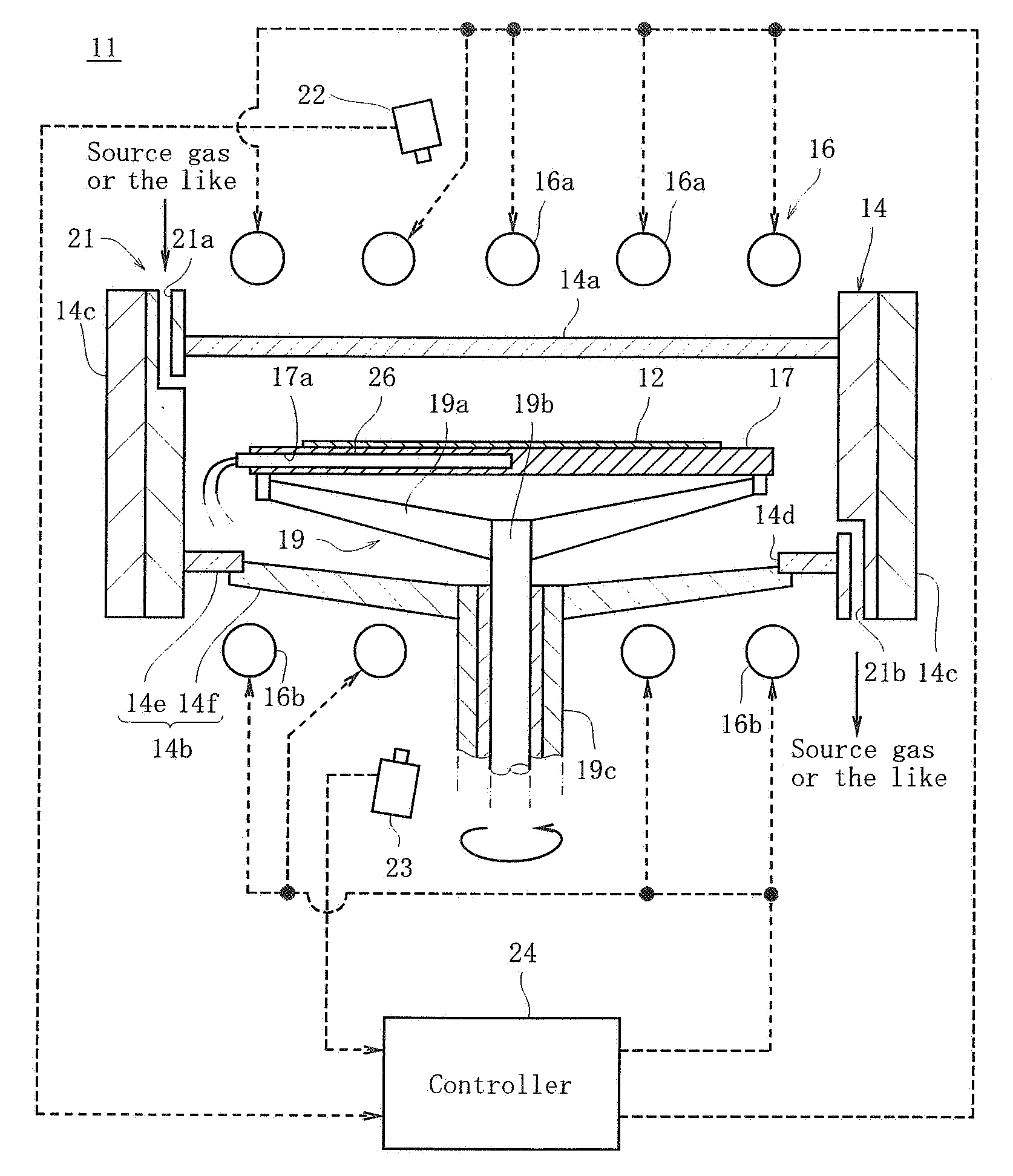
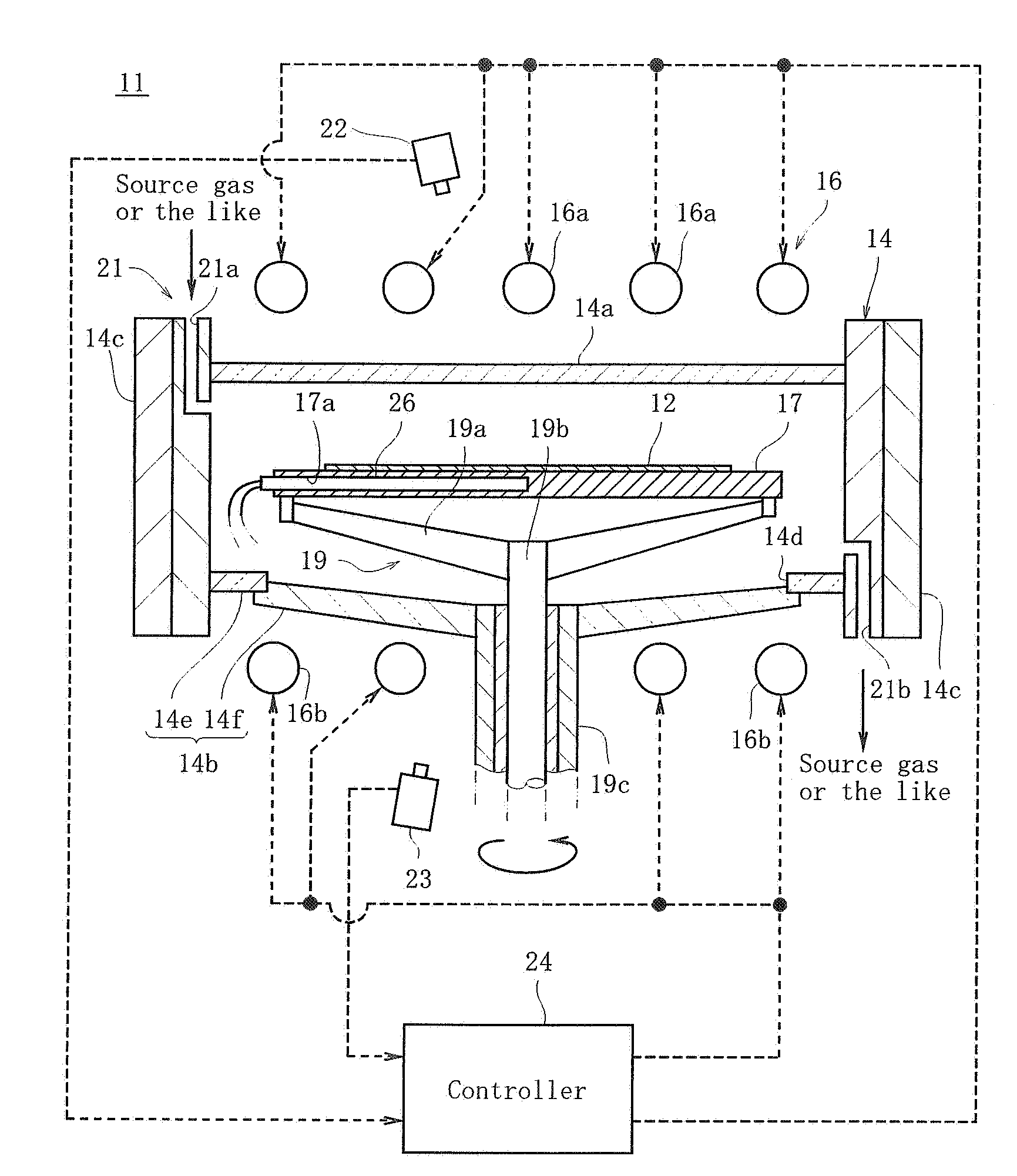
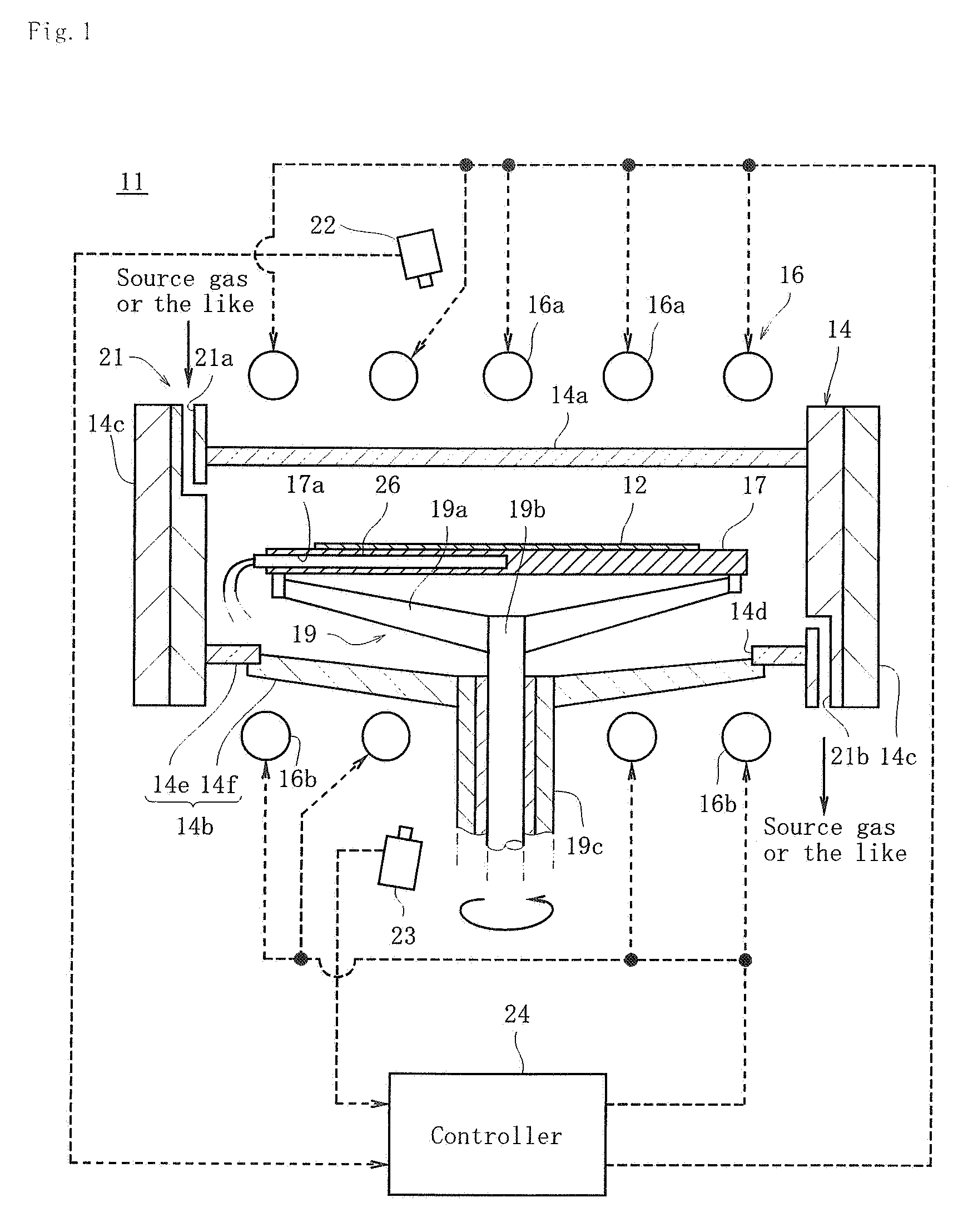
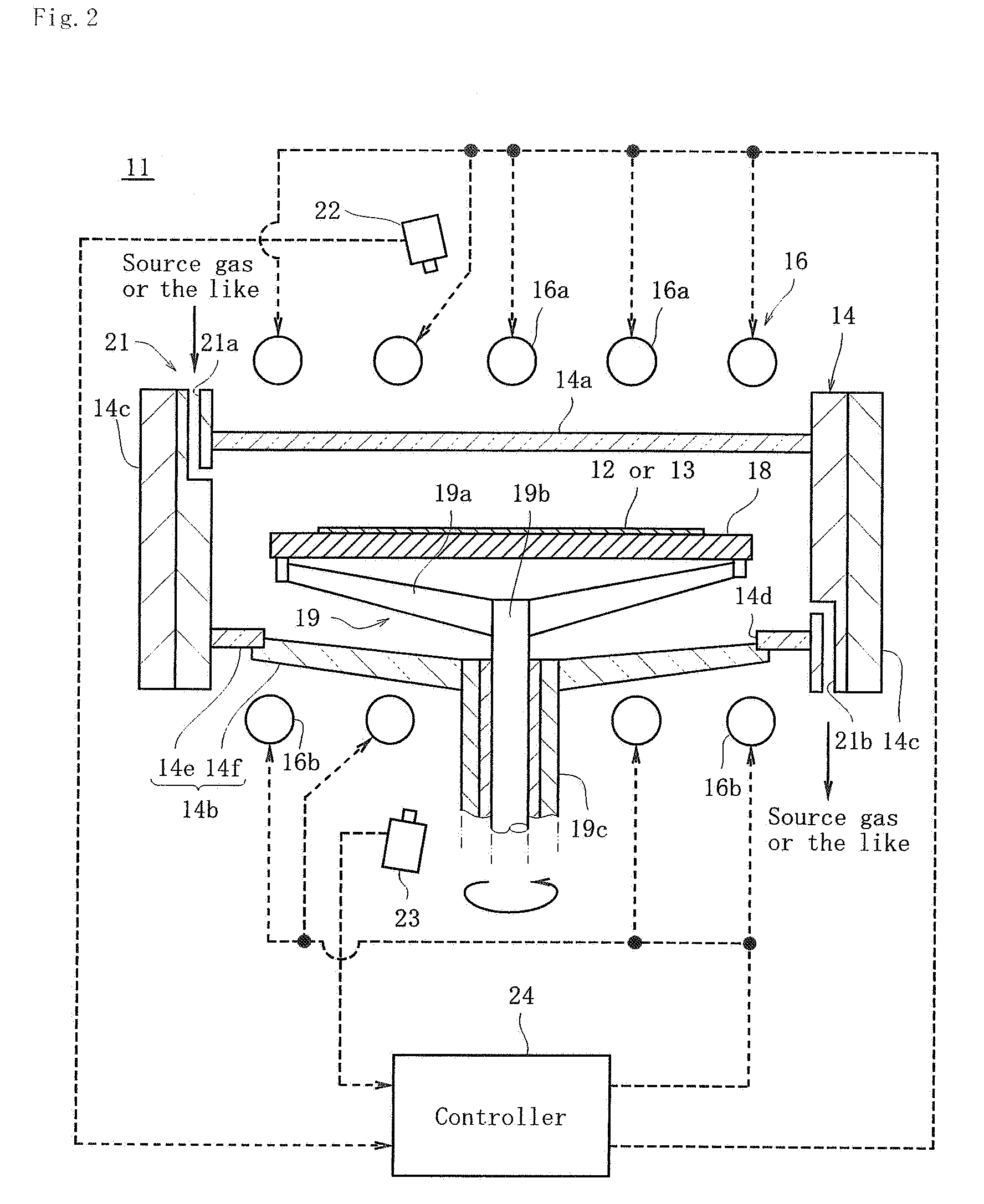
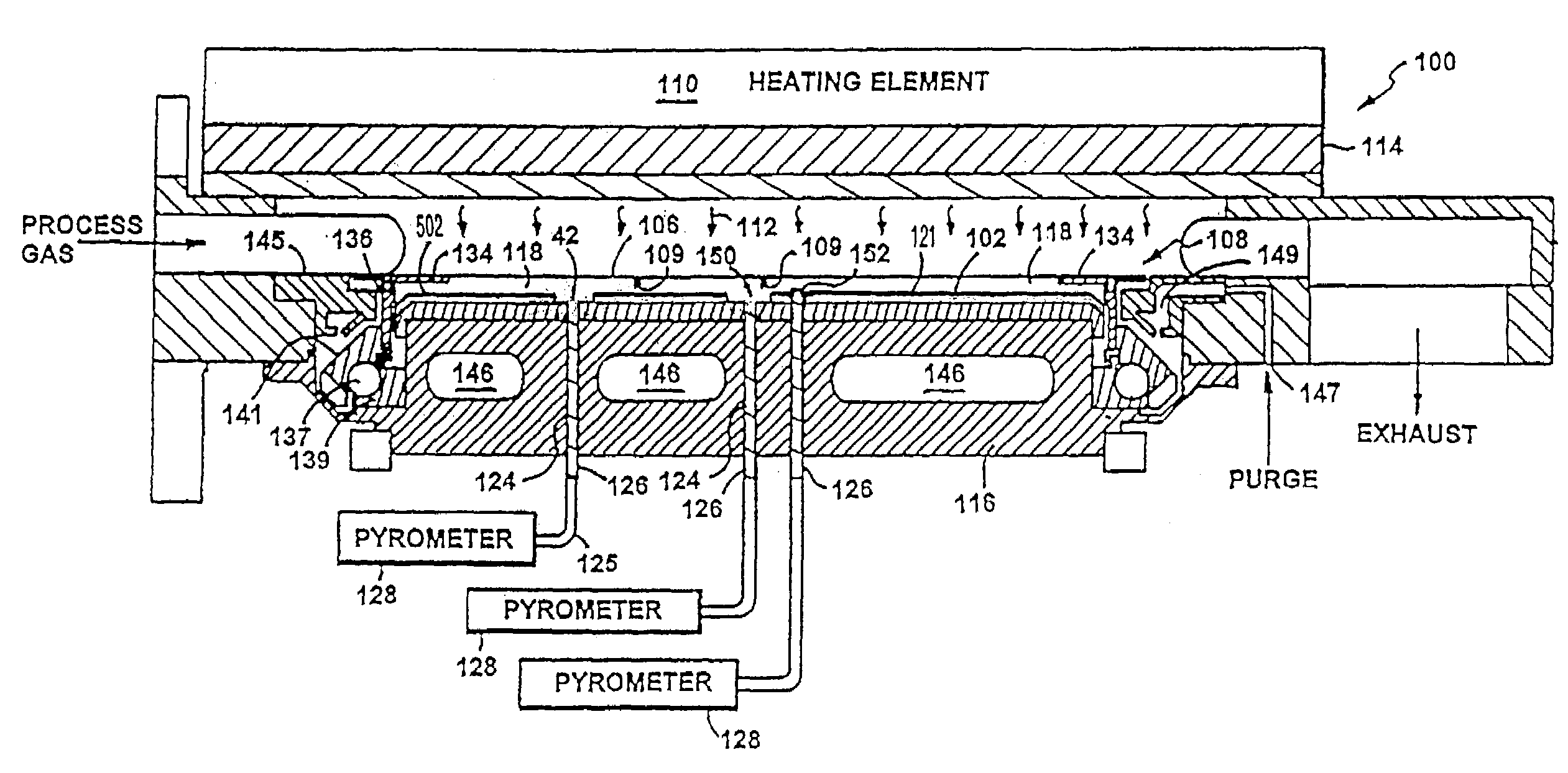
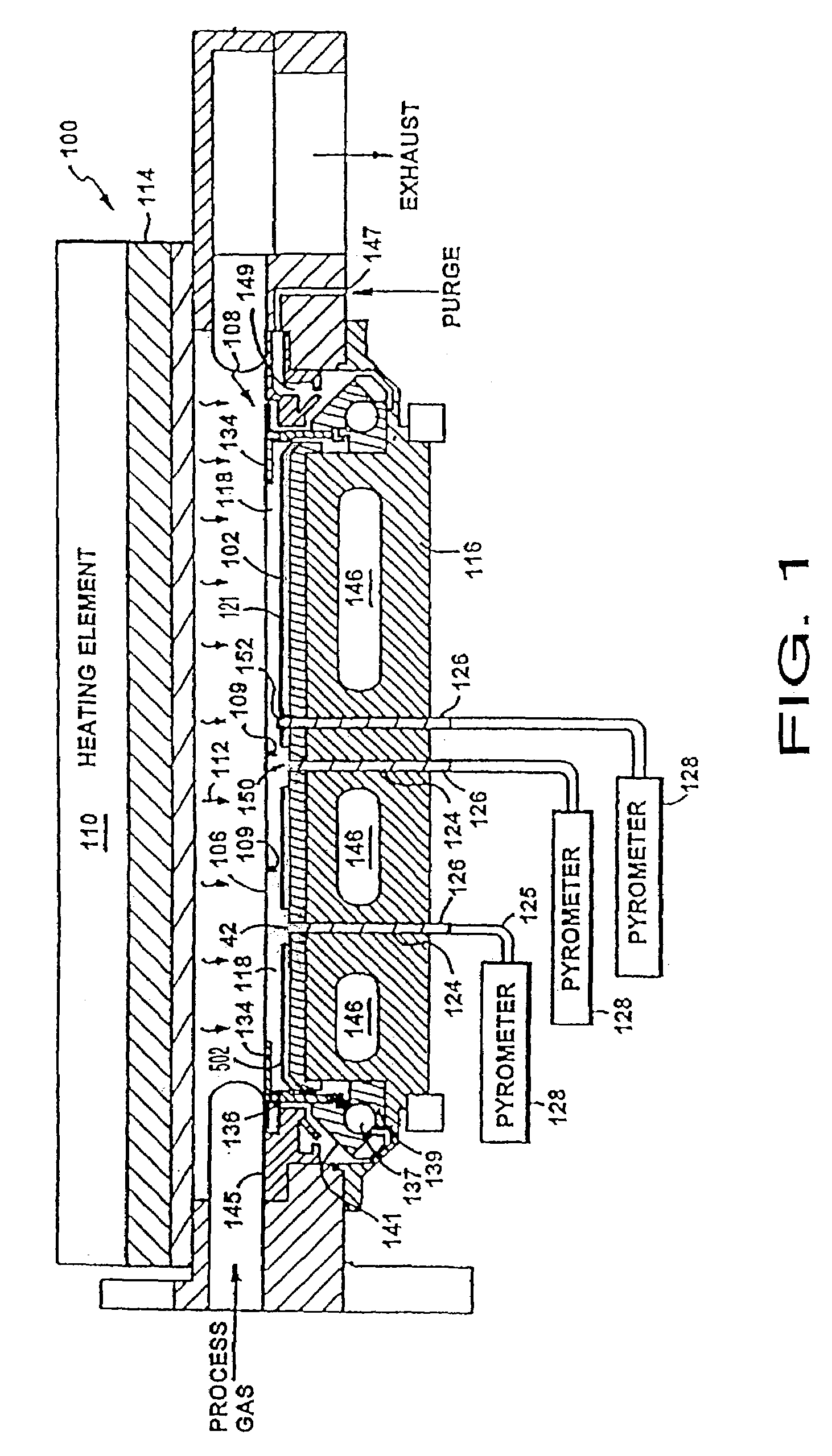
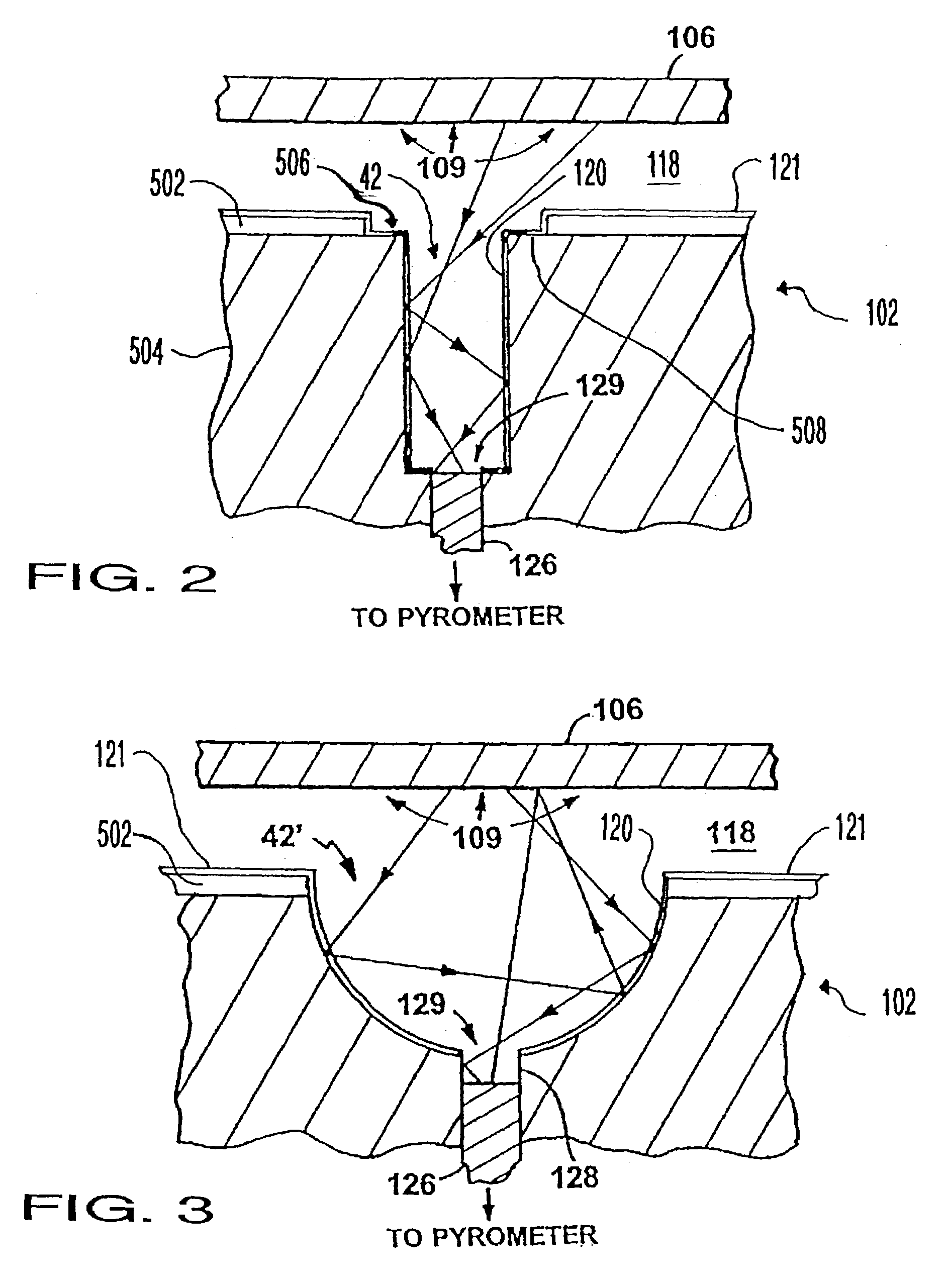
Methods and systems for in-situ pyrometer calibration
ActiveUS20120170609A1Radiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementRotational axisEngineering
A method of in-situ pyrometer calibration for a wafer treatment reactor such as a chemical vapor deposition reactor desirably includes the steps of positioning a calibrating pyrometer at a first calibrating position and heating the reactor until the reactor reaches a pyrometer calibration temperature. The method desirably further includes rotating the support element about the rotational axis, and while the support element is rotating about the rotational axis, obtaining first operating temperature measurements from a first operating pyrometer installed at a first operating position, and obtaining first calibrating temperature measurements from the calibration pyrometer. Both the calibrating pyrometer and the first operating pyrometer desirably are adapted to receive radiation from a first portion of a wafer support element at a first radial distance from a rotational axis of the wafer support element.
Owner:VEECO INSTR
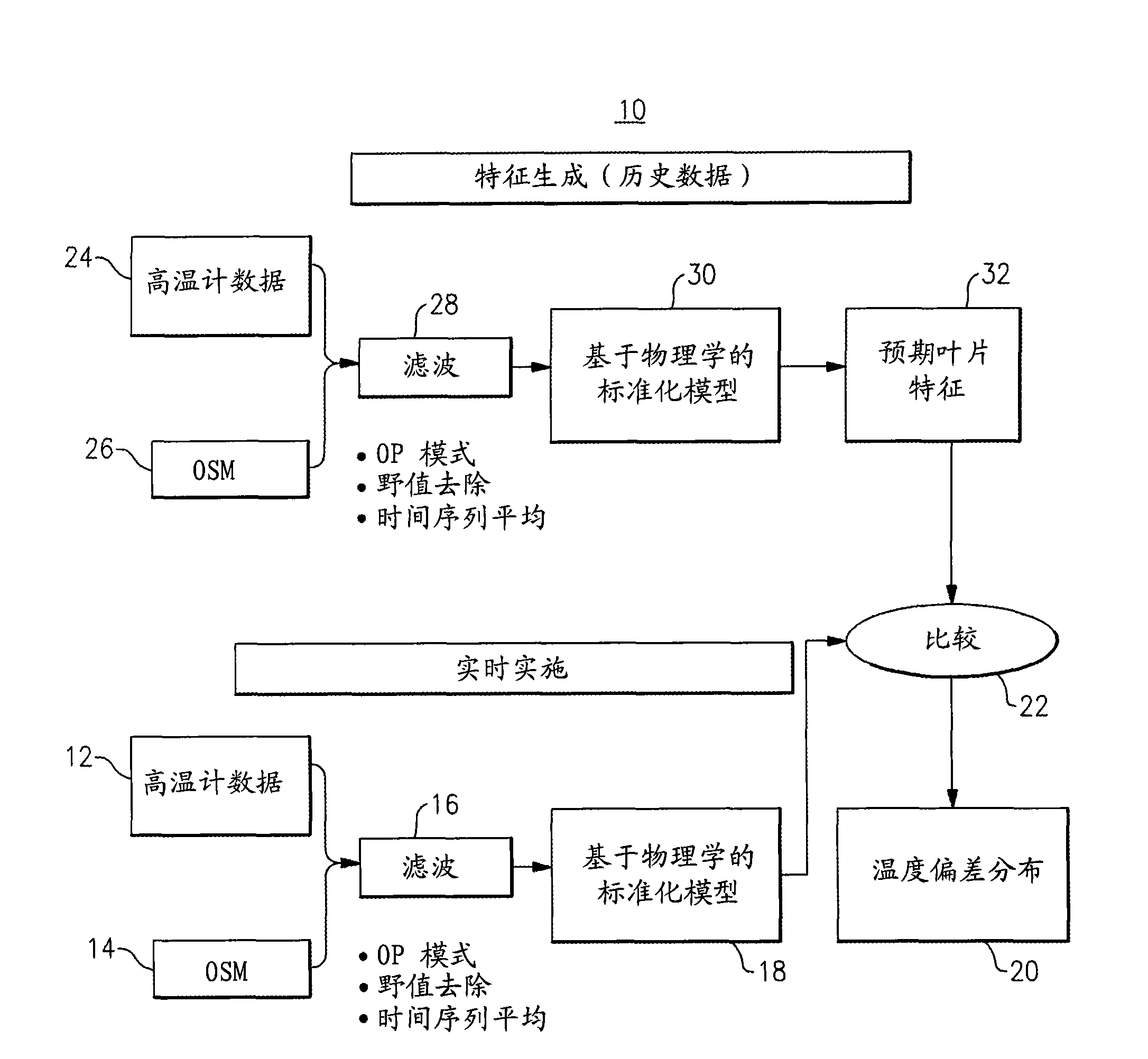
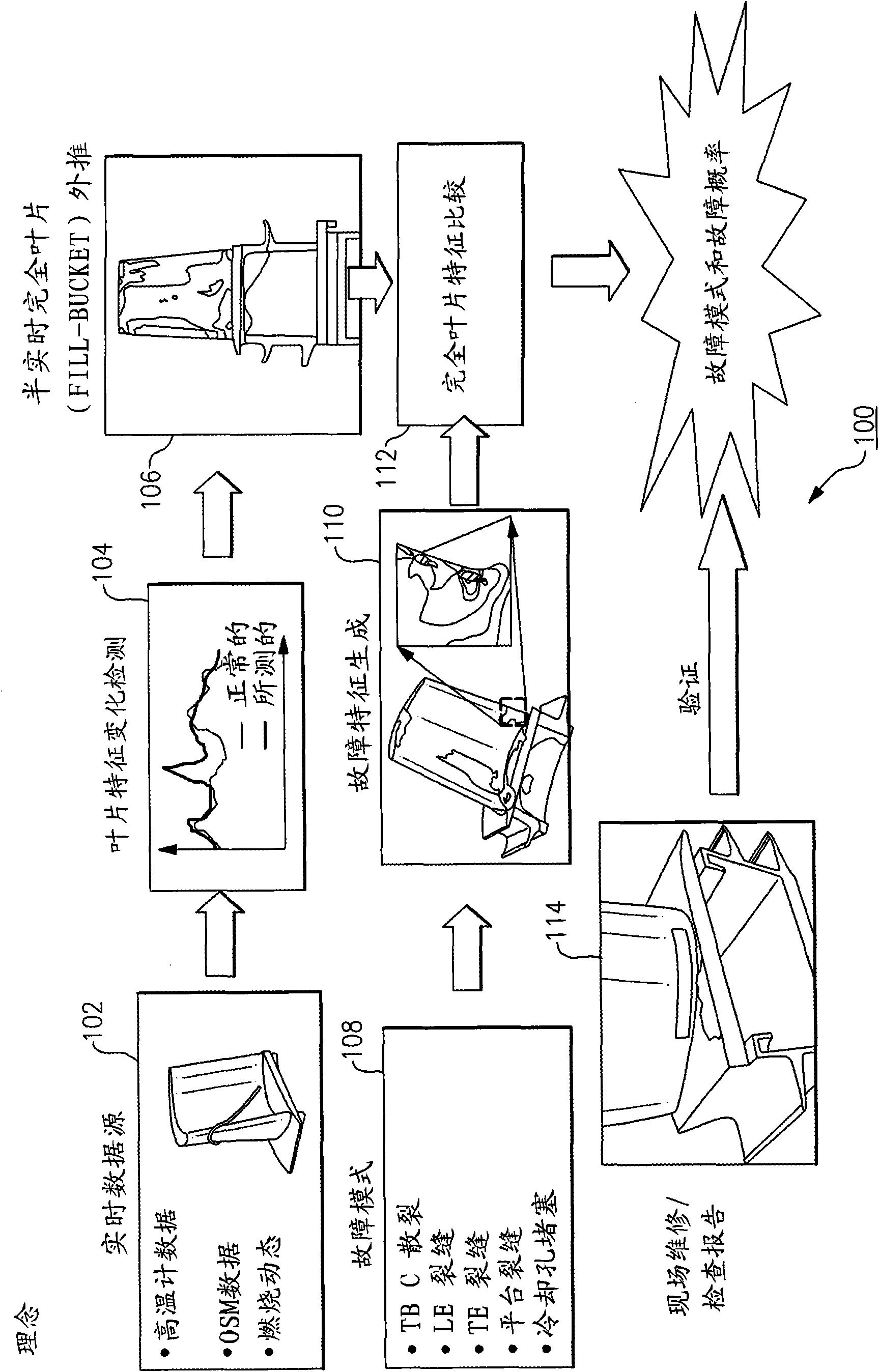
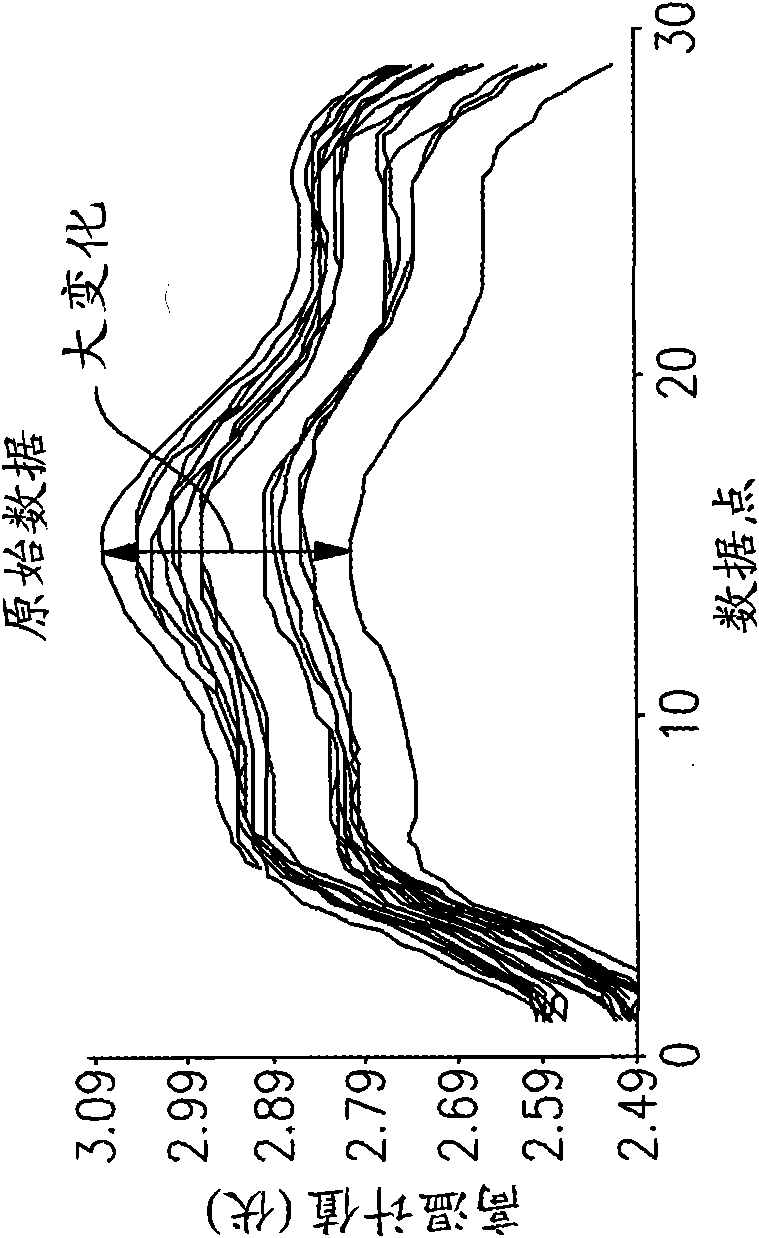
A system and a method for detecting gas turbine blade or aircraft engine blade problems in real time
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
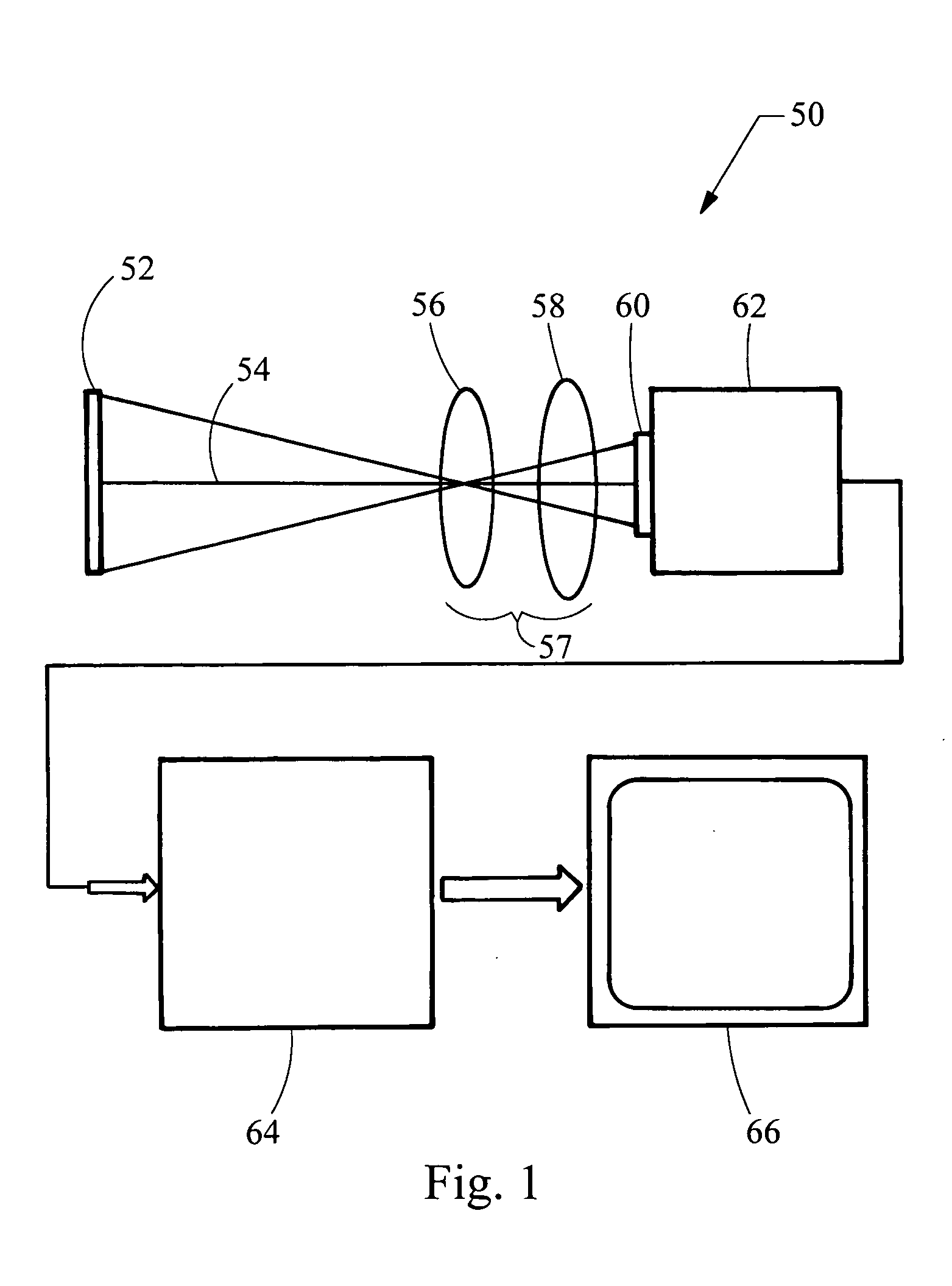
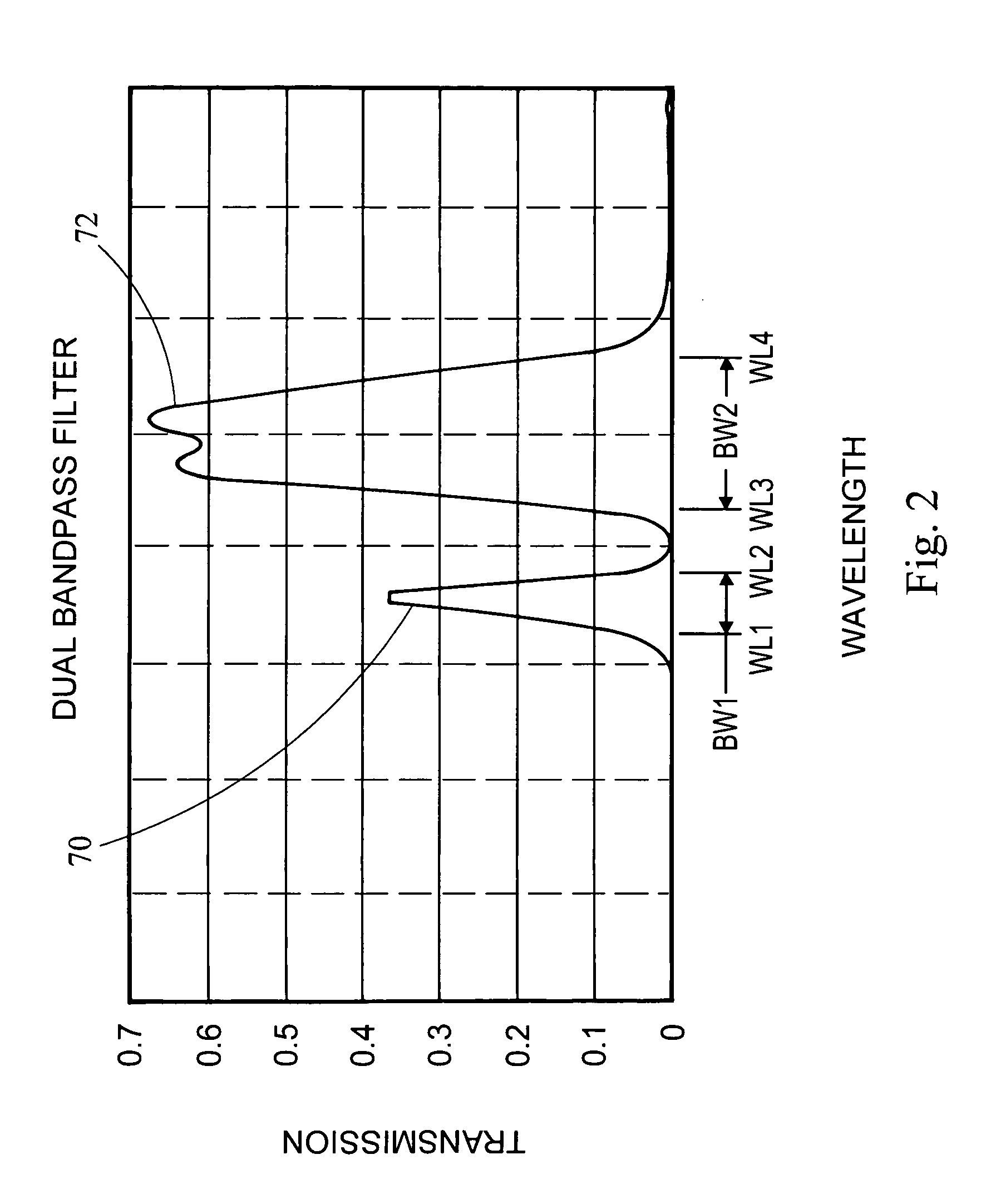
Two-color flame imaging pyrometer
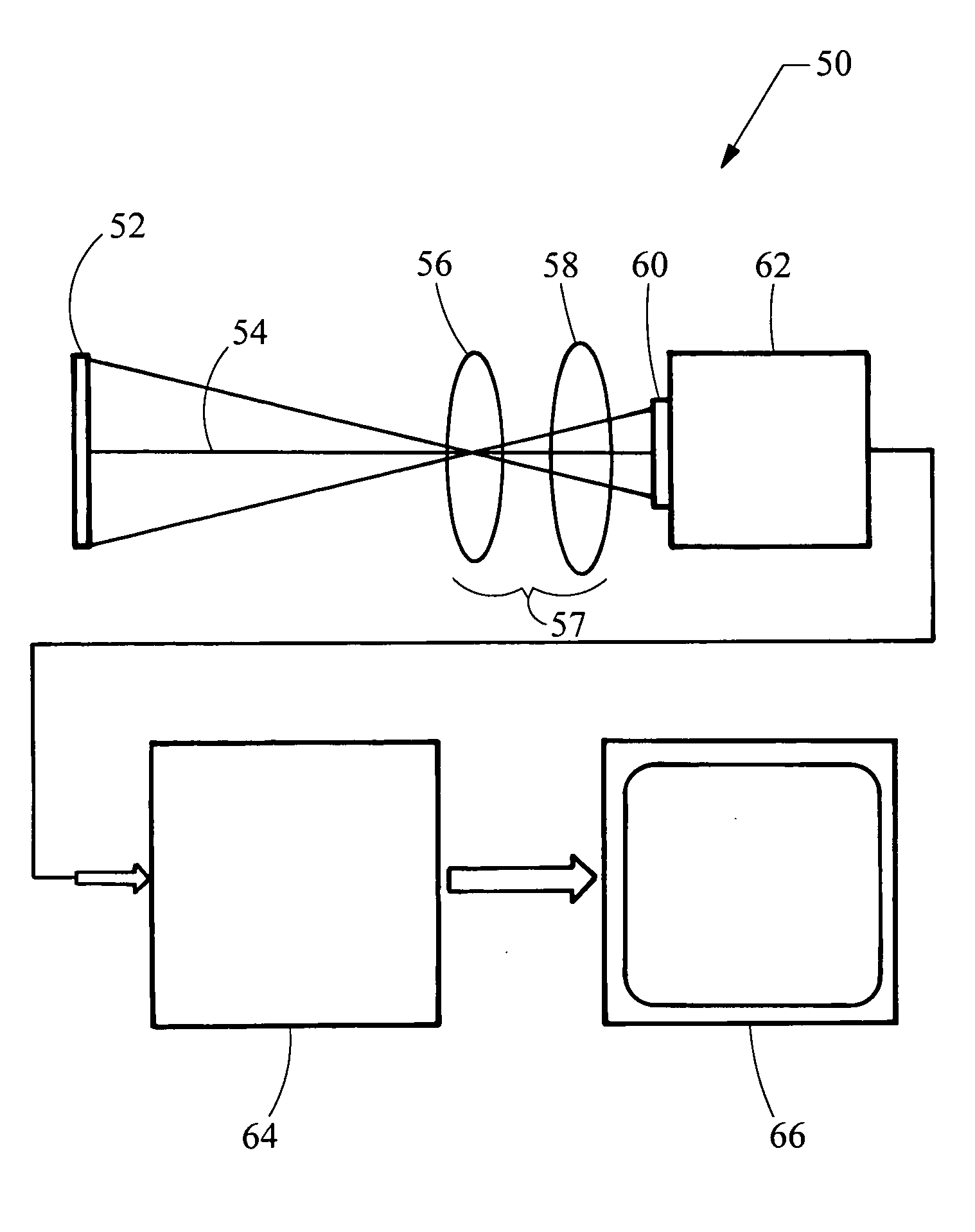
InactiveUS20070177650A1Reduce alignmentNumber of EliminationsSensing radiation from gases/flamesRadiation thermographyRadiation lossCombustor
The system uses a color camera and an optical system to map two colors emitted from an object such as a furnace, boiler combustion zone, or burner flame into a temperature image. The color camera utilizes a color video chip with interspersed pixels for each color to reduce alignment issues and utilize the same optical path. In addition, the optical system utilizes a dual band pass optical filter thereby eliminating the number of optical elements and minimizing radiation loss through the optical system thereby improving the dynamic range of the system.
Owner:DIAMOND POWER INT
System and process for calibrating pyrometers in thermal processing chambers
InactiveUS7734439B2Quantity maximizationReduce the impact of interferenceRadiation pyrometrySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementLight energyLight detector
A method and system for calibrating temperature measurement devices, such as pyrometers, in thermal processing chambers are disclosed. According to the present invention, the system includes a calibrating light source that emits light energy onto a substrate contained in the thermal processing chamber. A light detector then detects the amount of light that is being transmitted through the substrate. The amount of detected light energy is then used to calibrate a temperature measurement device that is used in the system.
Owner:MATTSON TECHNOLOGY +1
Pyrometer calibrated wafer temperature estimator
A wafer temperature estimator calibrates contact-type temperature sensor measurements that are used by a temperature controller to control substrate temperature in a high temperature processing chamber. Wafer temperature estimator parameters provide an estimated wafer temperature from contact-type temperature sensor measurements. The estimator parameters are refined using non-contact-type temperature sensor measurements during periods when the substrate temperature is decreasing or the heaters are off. A corresponding temperature control system includes a heater, a contact-type temperature sensor in close proximity to the substrate, and an optical pyrometer placed to read temperature directly from the substrate. A wafer temperature estimator uses the estimator parameters and measurements from the contact-type sensor to determine an estimated wafer temperature. A temperature controller reads the estimated wafer temperature and makes changes to the heater power accordingly. The wafer temperature estimator has a nonlinear neural network system that is trained using inputs from the various sensors.
Owner:ASM IP HLDG BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com