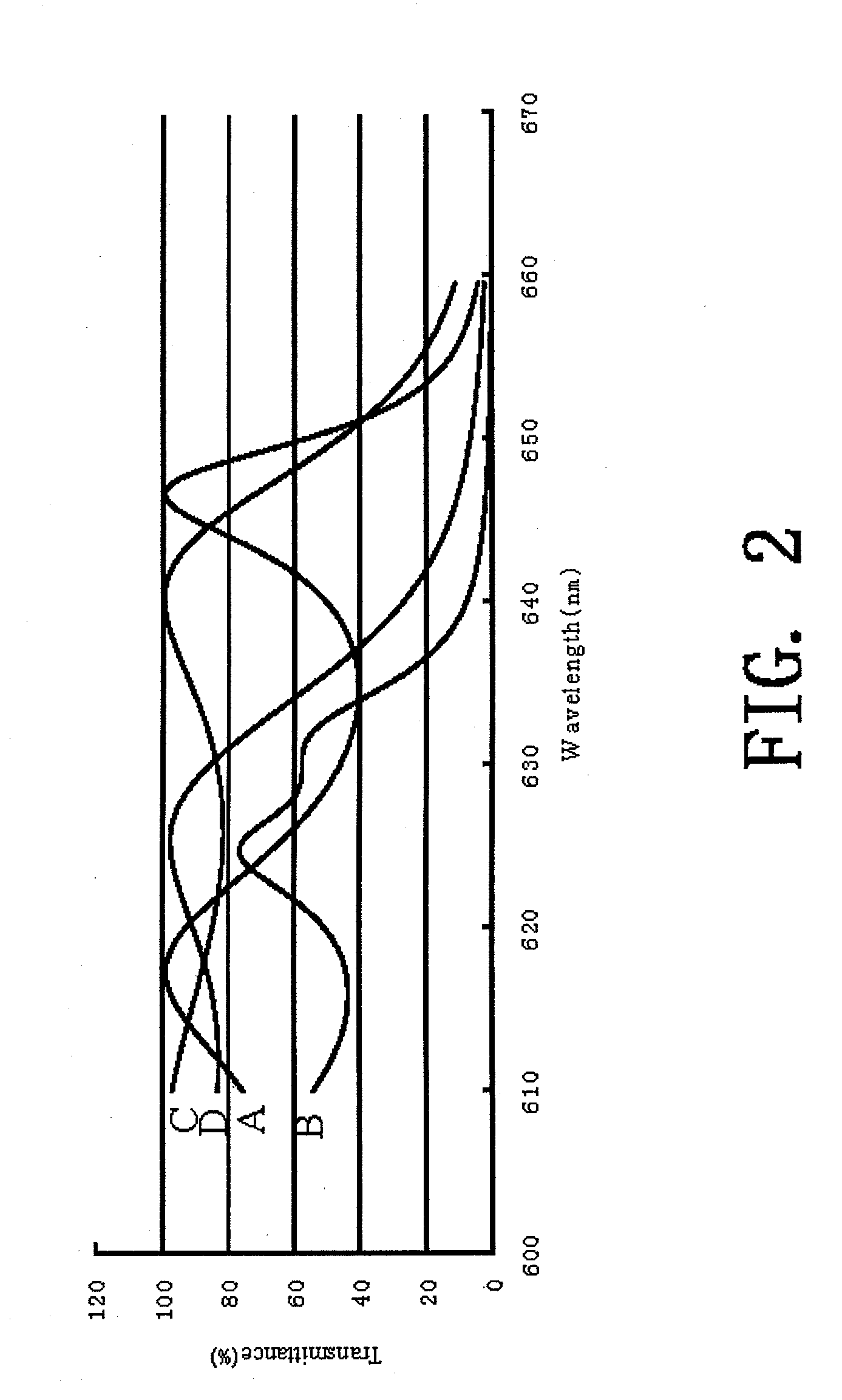
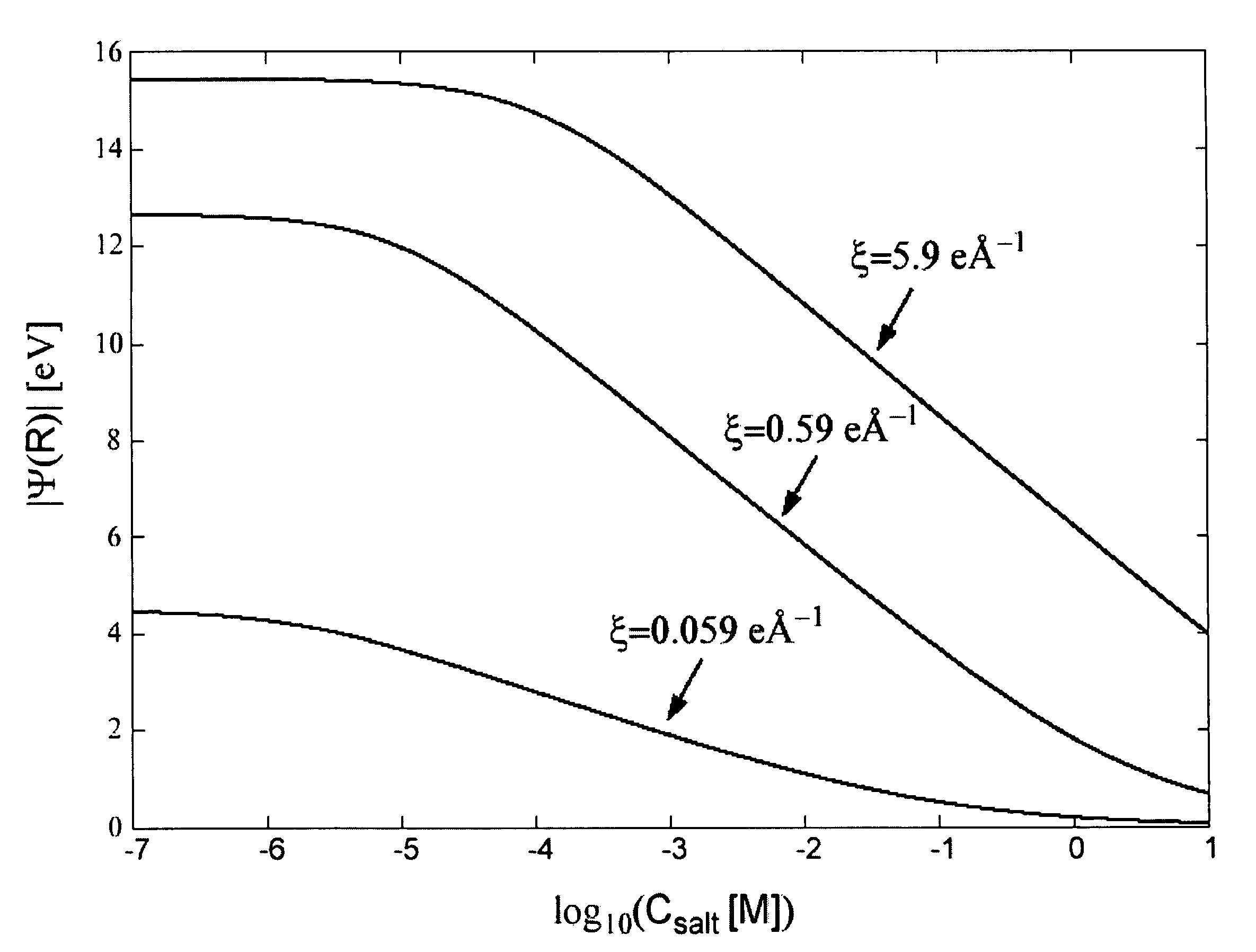
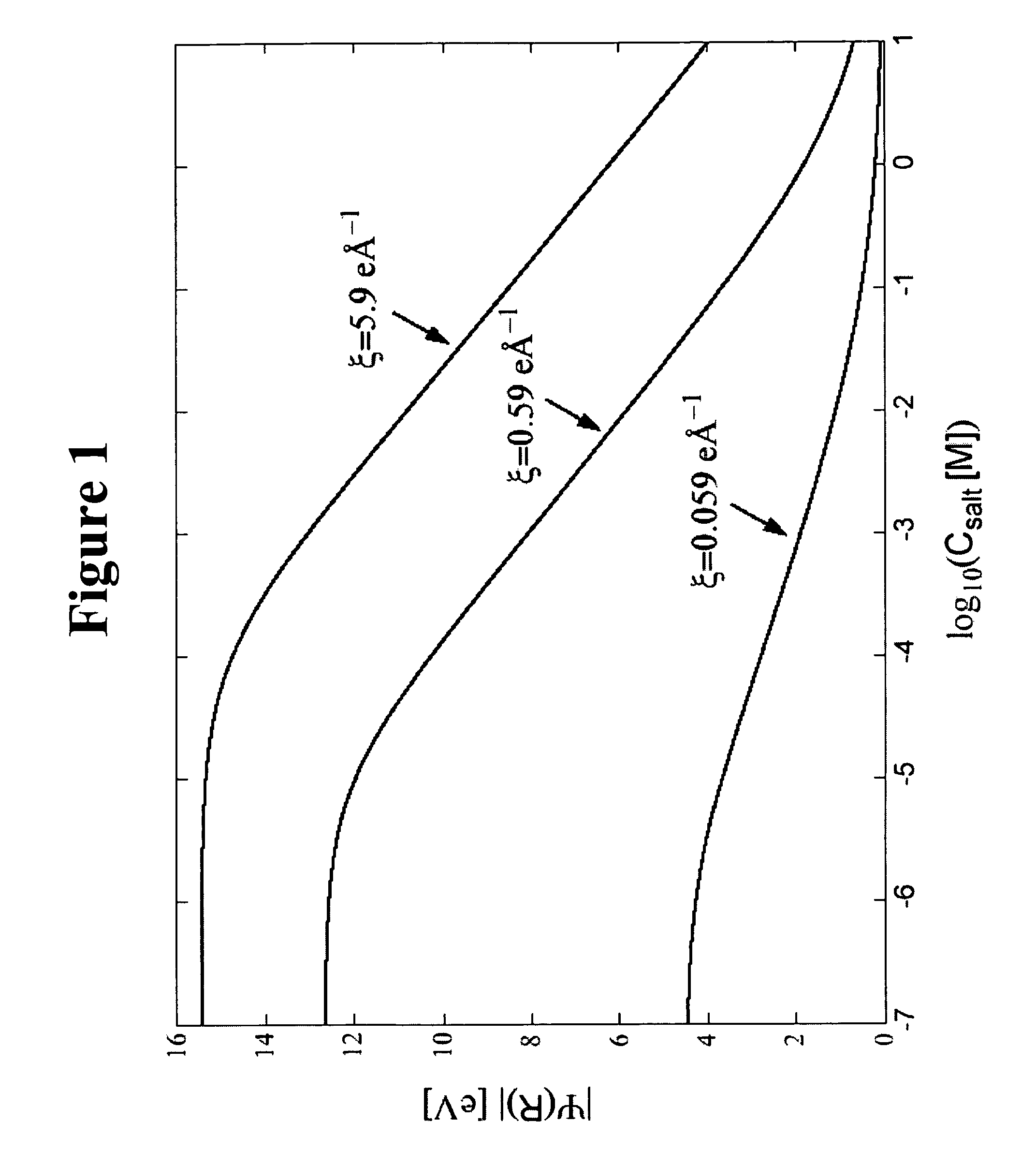
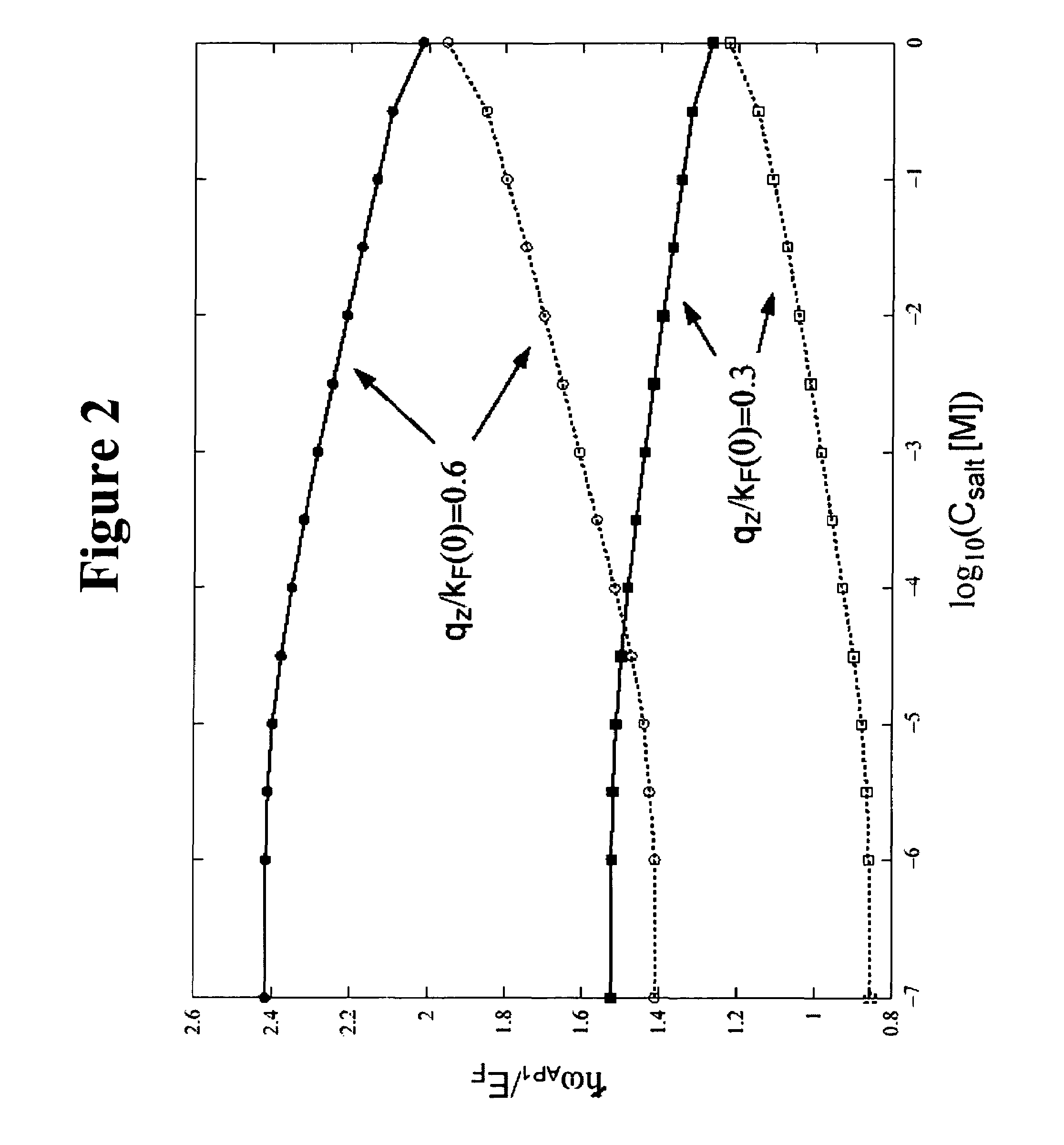
Patents
Literature
85 results about "Spectral shift" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
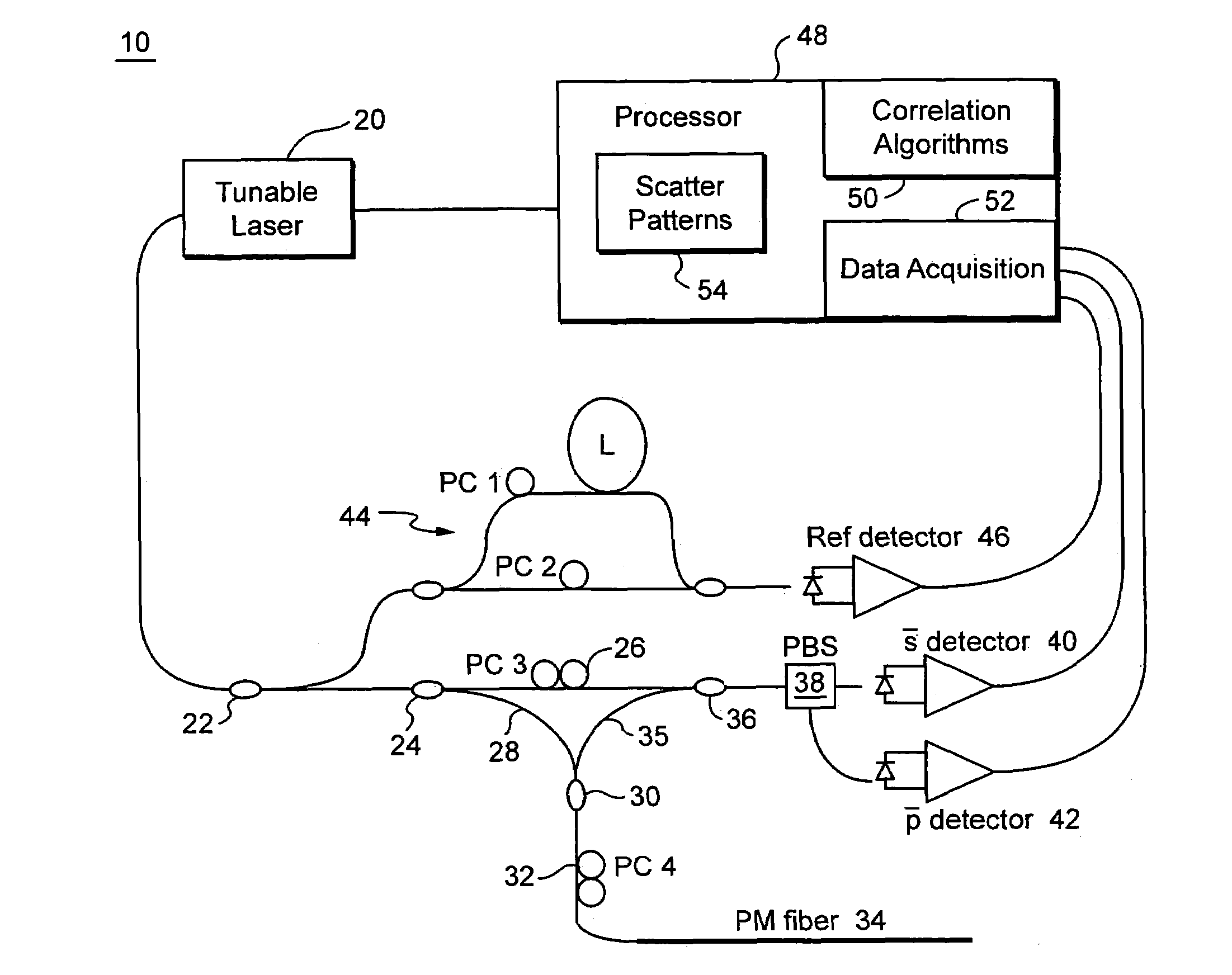
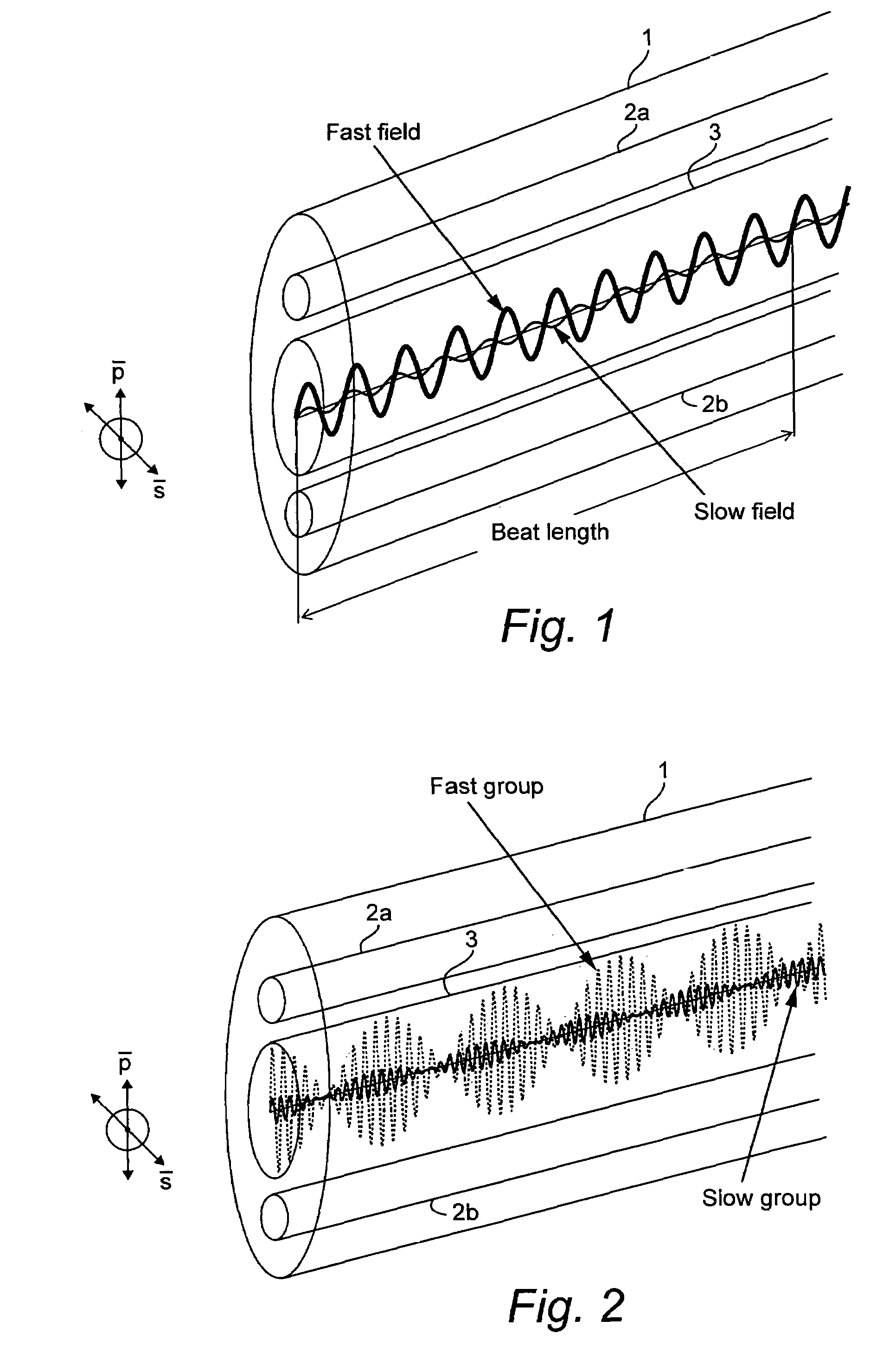
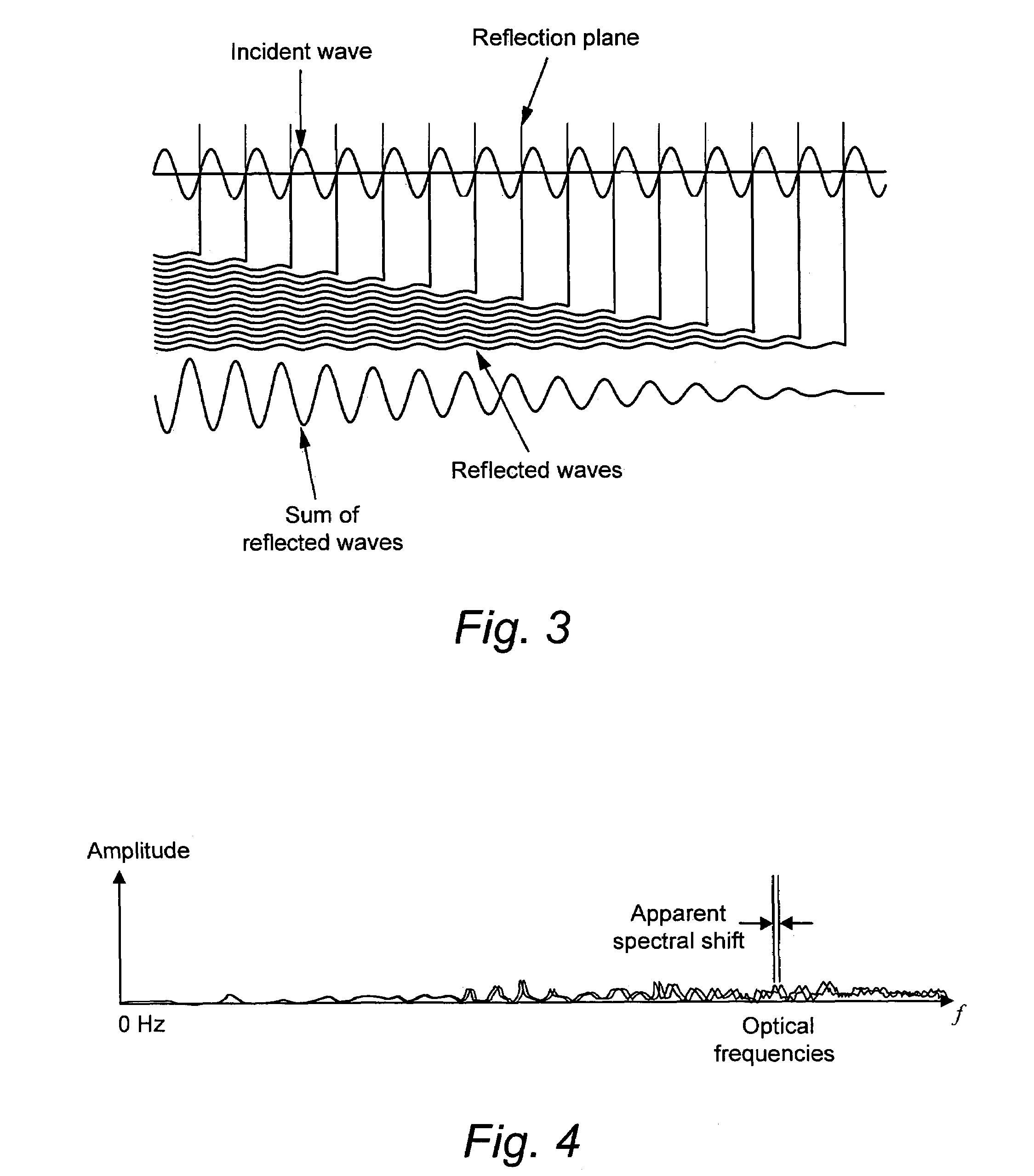
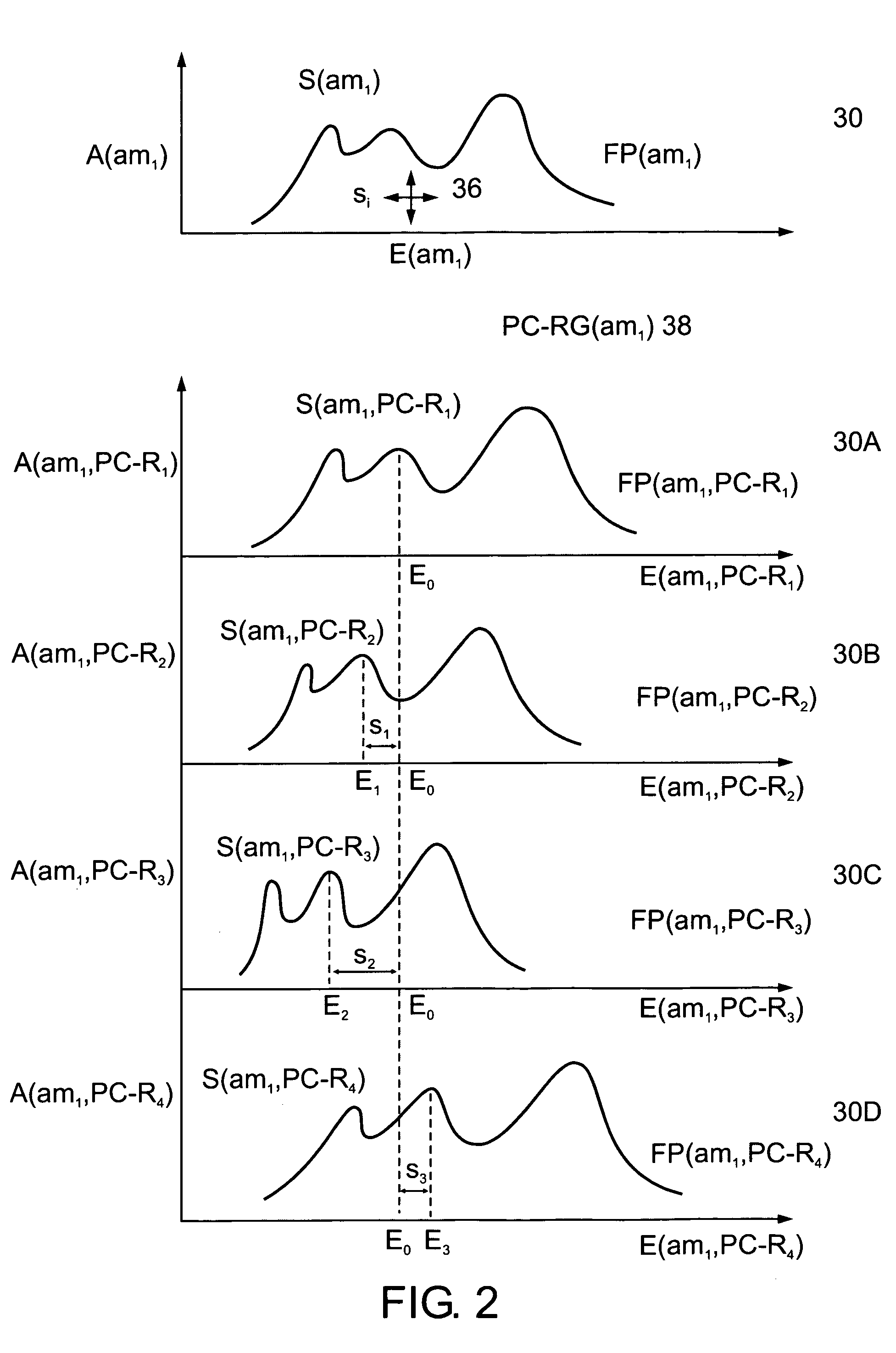
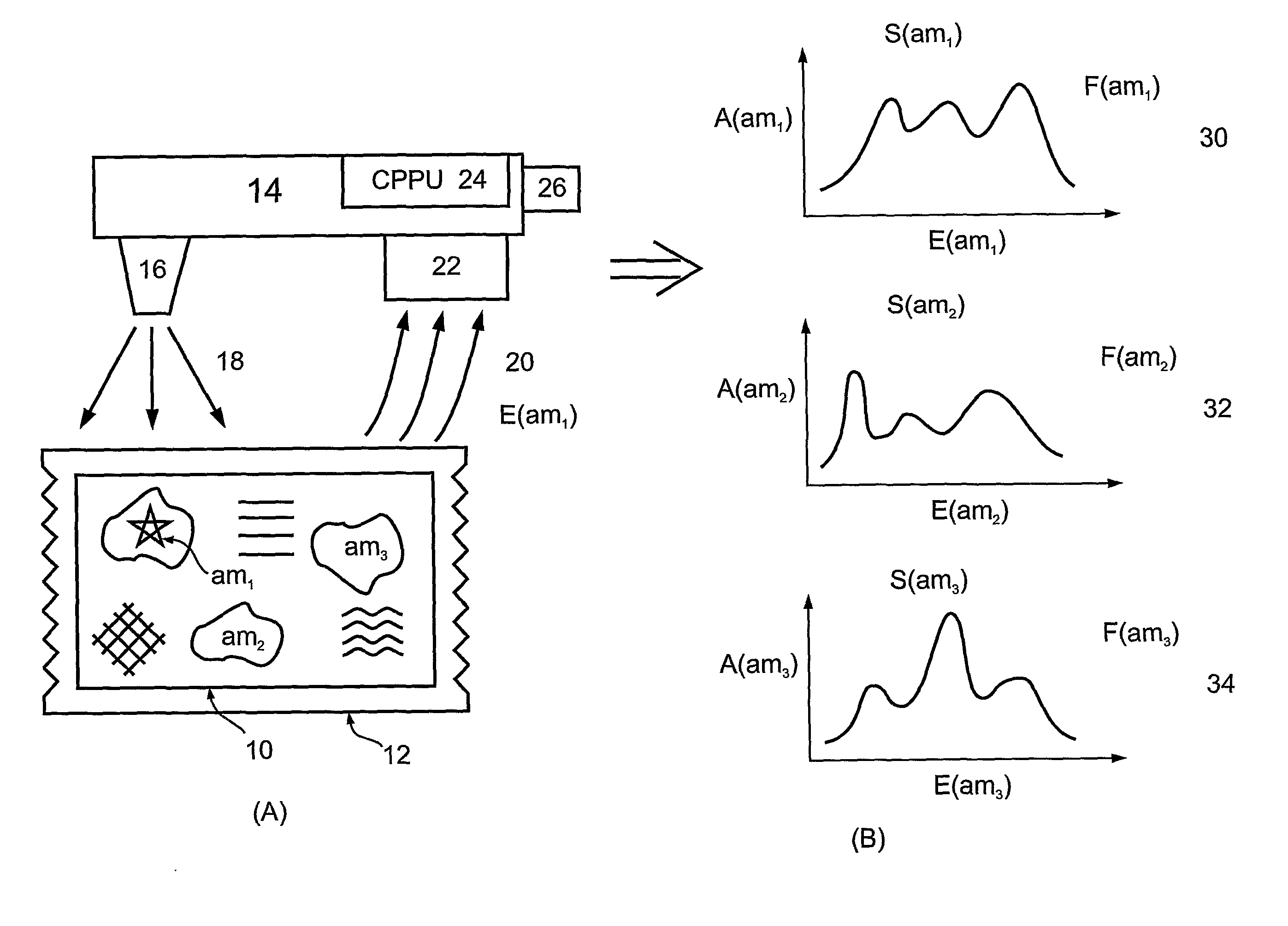
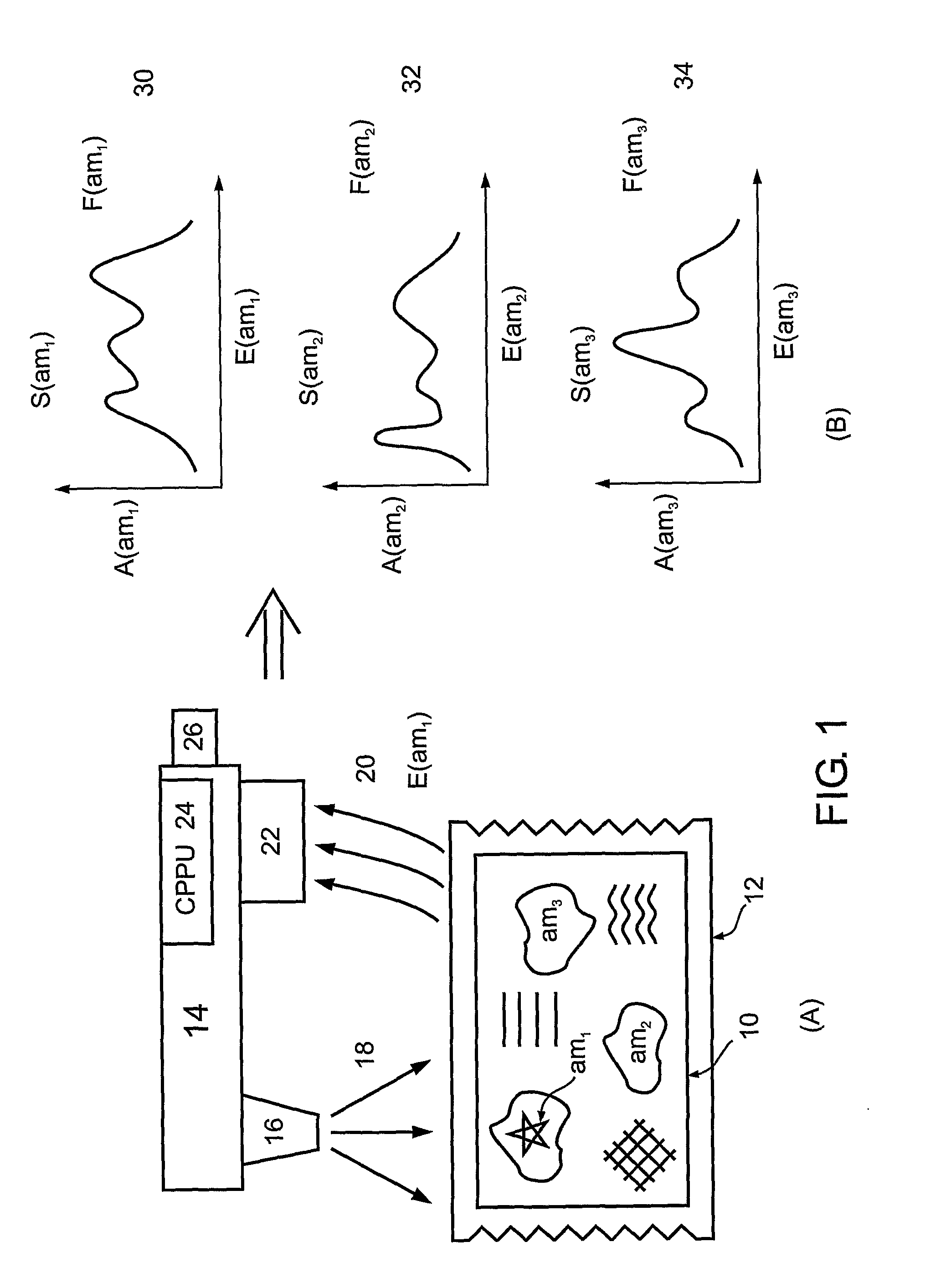
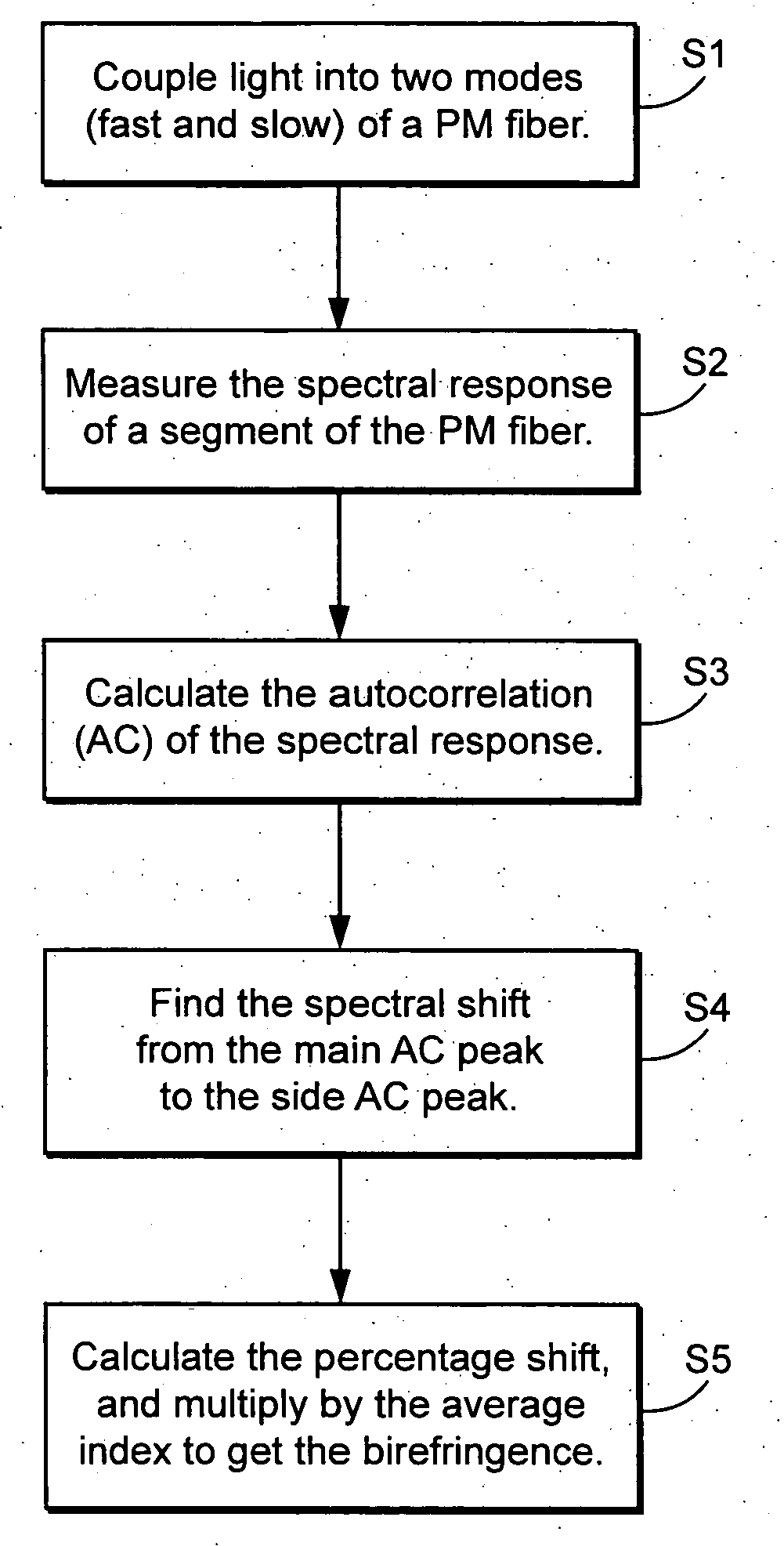
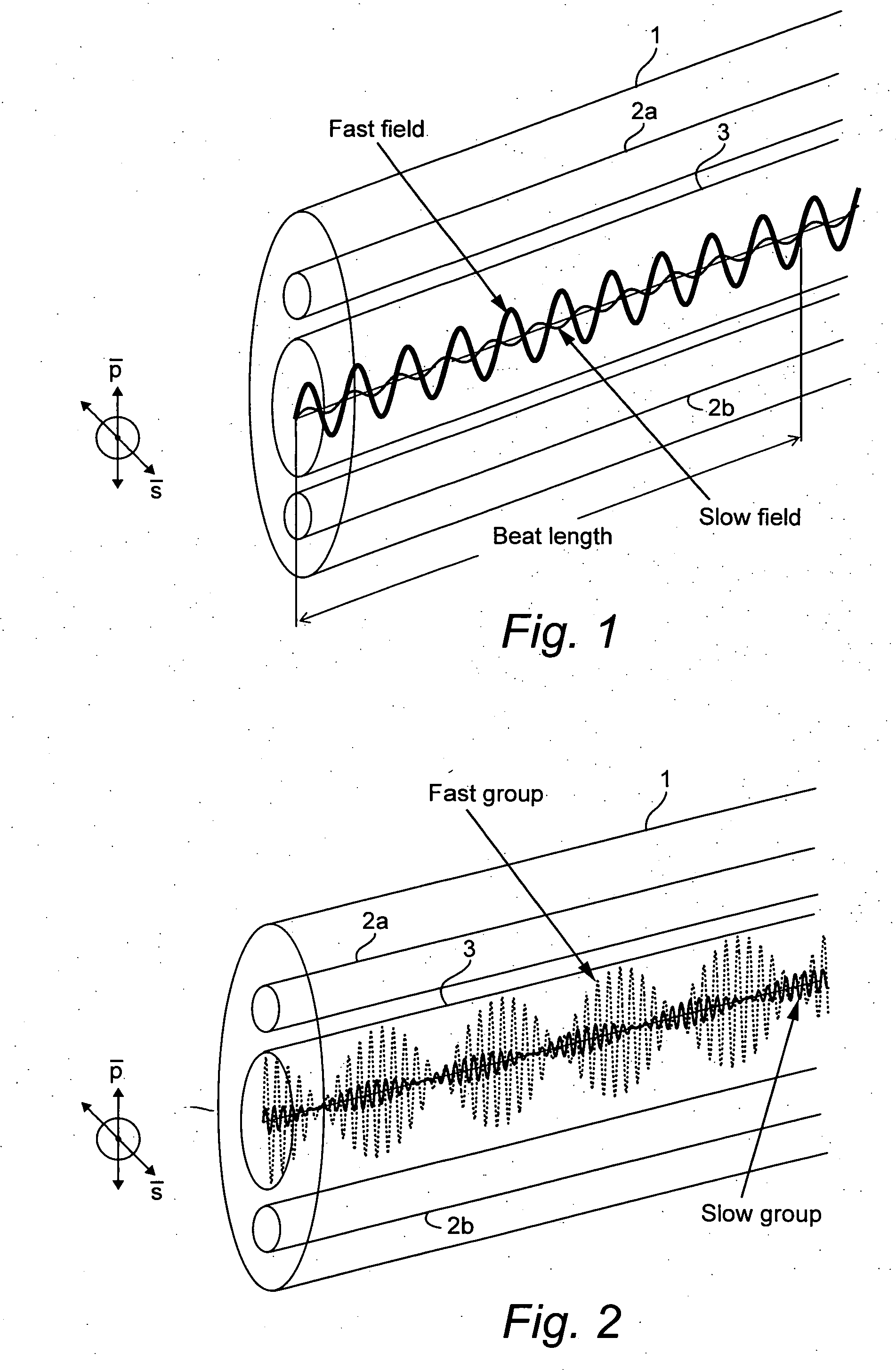
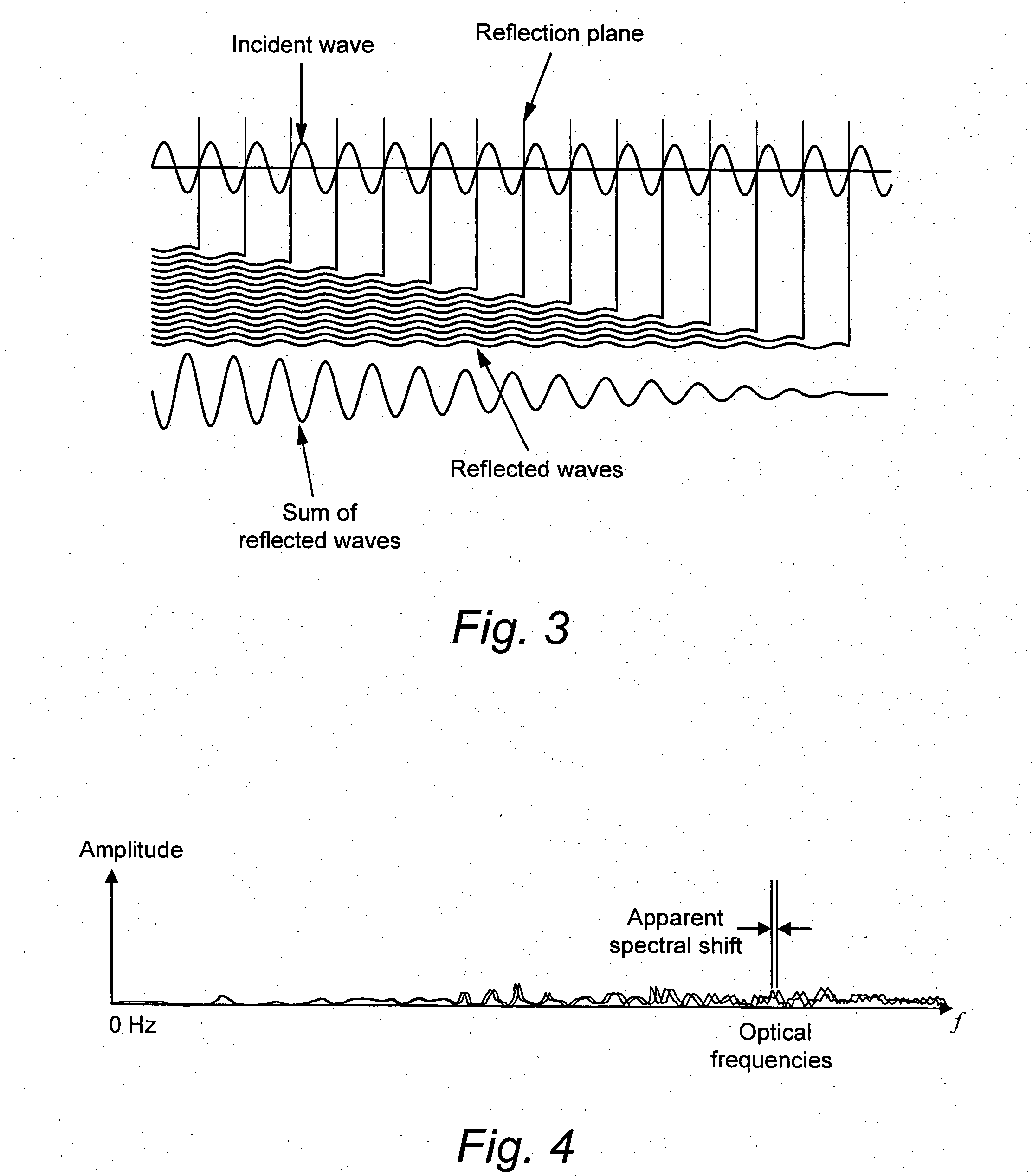
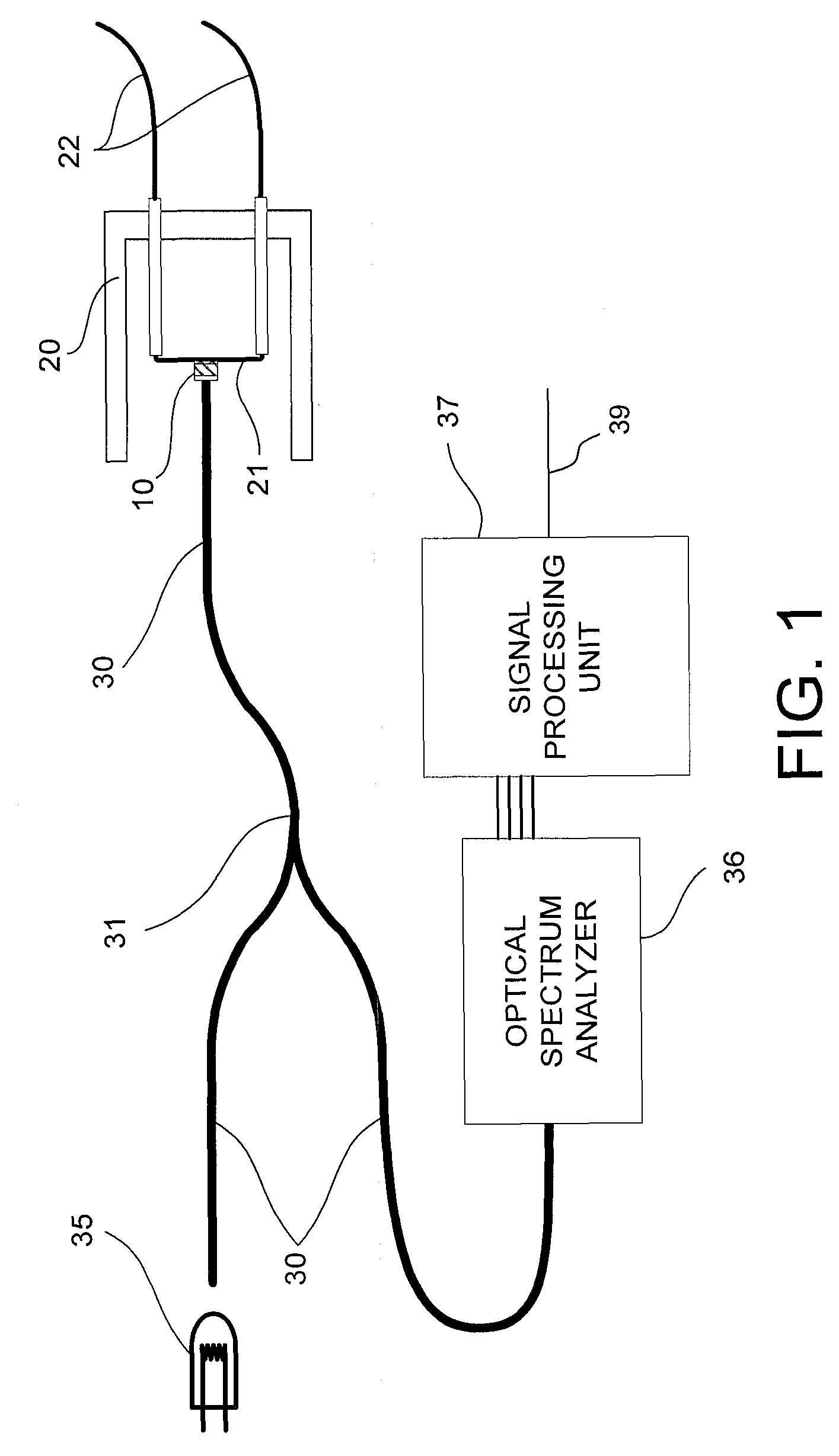
Calculation of birefringence in a waveguide based on Rayleigh scatter
ActiveUS7330245B2Reflectometers dealing with polarizationCladded optical fibreRayleigh scatteringSpectral response
Light is coupled into two polarization modes of a waveguide, e.g., an optical fiber. The spectral response of Rayleigh backscatter in the waveguide segment for the two polarization modes is measured, e.g., using OFDR, OTDR, OLCR, etc. The autocorrelation of the spectral response is calculated. The spectral (wavelength) shift from a main autocorrelation peak to a side autocorrelation peak, corresponding to one of the two polarization modes of the waveguide segment, is determined. The spectral shift, corresponding to a beat length of the waveguide segment, is multiplied by an average index of refraction to determine a birefringence of the waveguide segment.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Method and apparatus for biosensor spectral shift detection
InactiveUS7217574B2Scattering properties measurementsLaboratory glasswaresFrequency spectrumResonance
Performing high-resolution determination of the relative shift of the spectral properties of a biosensor. The shift in the resonance peak of the biosensor is indicative of the amount of material bound to the surface of the biosensor. A preferred biosensor is a Guided Mode Resonant Filter Biosensor (GMRFB). In one aspect of the invention, curve fitting is used to determine the relative location of the spectrum of the unexposed biosensor with respect to those spectra that are altered (e.g., shifted) by the presence of materials bound to the surface of the biosensor. In an alternative embodiment, the cross correlation function is used to detect spectral peak offsets between a reference spectrum and a spectrum measured from an exposed biosensor. In yet another alternative, maximal likelihood estimation techniques are used to determine the spectral shift or offs.
Owner:X BODY
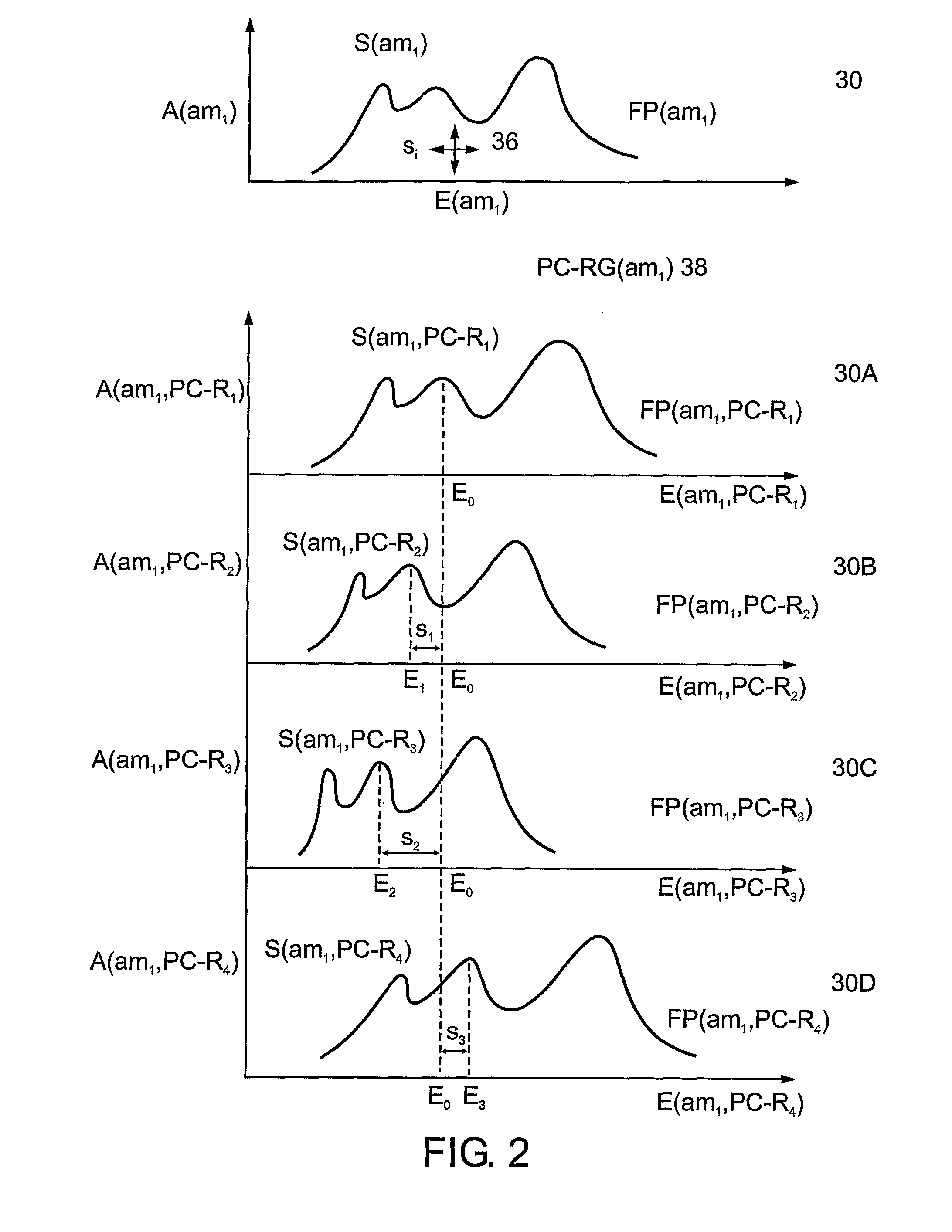
Authenticating and authentic article using spectral imaging and analysis
ActiveUS7599544B2Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPattern recognitionReference dataset
Authenticating an authentic article having an authentication mark. Acquiring a set of spectral images of the authentication mark, for forming a set of single-authentication mark spectral fingerprint data (FIG. 1). Identifying at least one spectral shift in the set of single-authentication mark spectral fingerprint data, for forming an intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group including sub-sets of intra-authentication mark spectral fingerprint pattern data, such that data elements in each sub-set are shifted relative to corresponding data elements in remaining sub-sets in the same intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group (FIG. 2). Forming a set of intra-authentication mark physicochemical properties and characteristics data relating to the imaged authentication mark, by performing pattern recognition and classification analysis on the intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group (FIG. 3). Comparing and matching elements in the set of intra-authentication mark physicochemical properties and characteristics data to corresponding reference elements in reference set of data, thereby authenticating the authentic article.
Owner:GREENVISION SYST
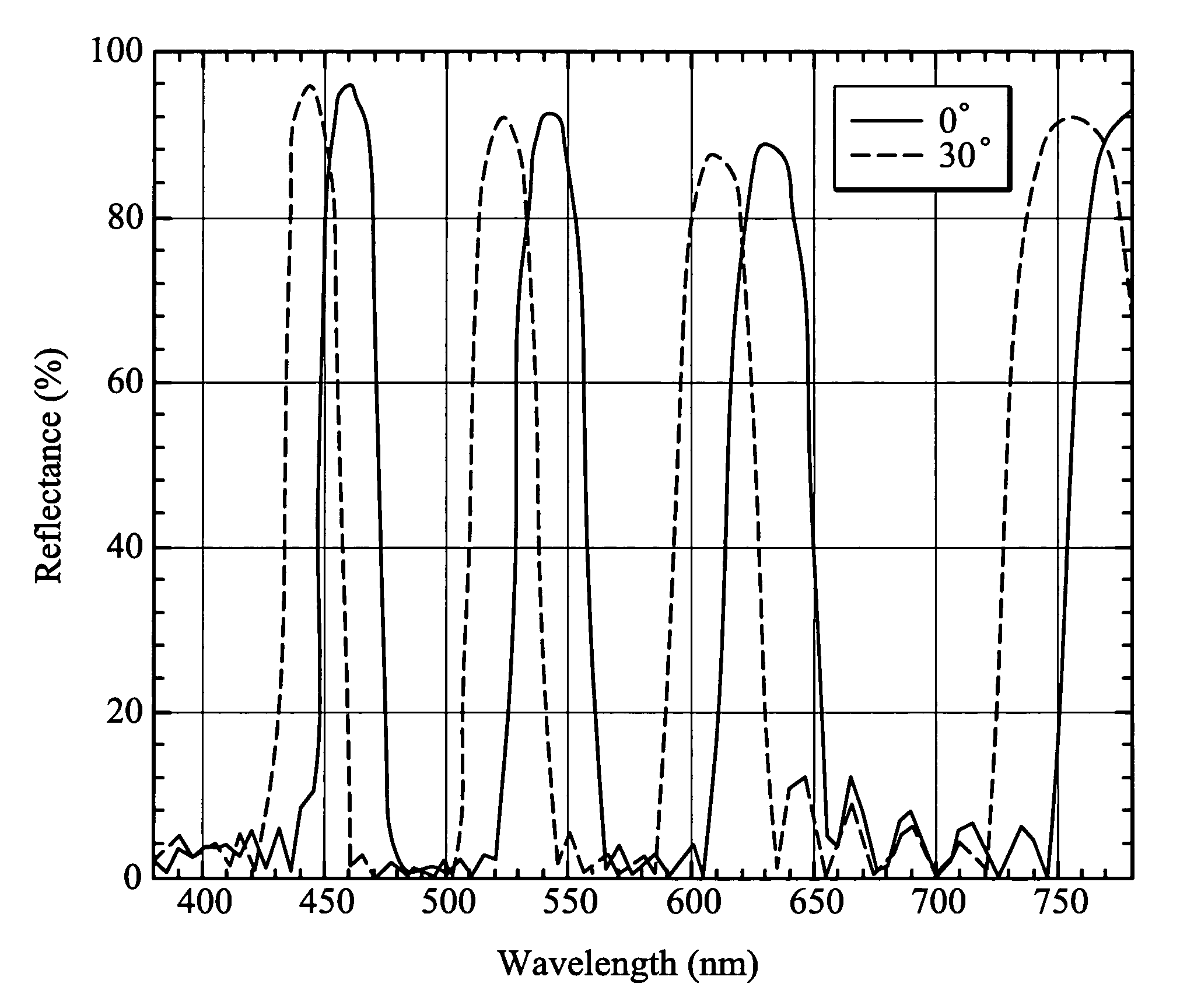
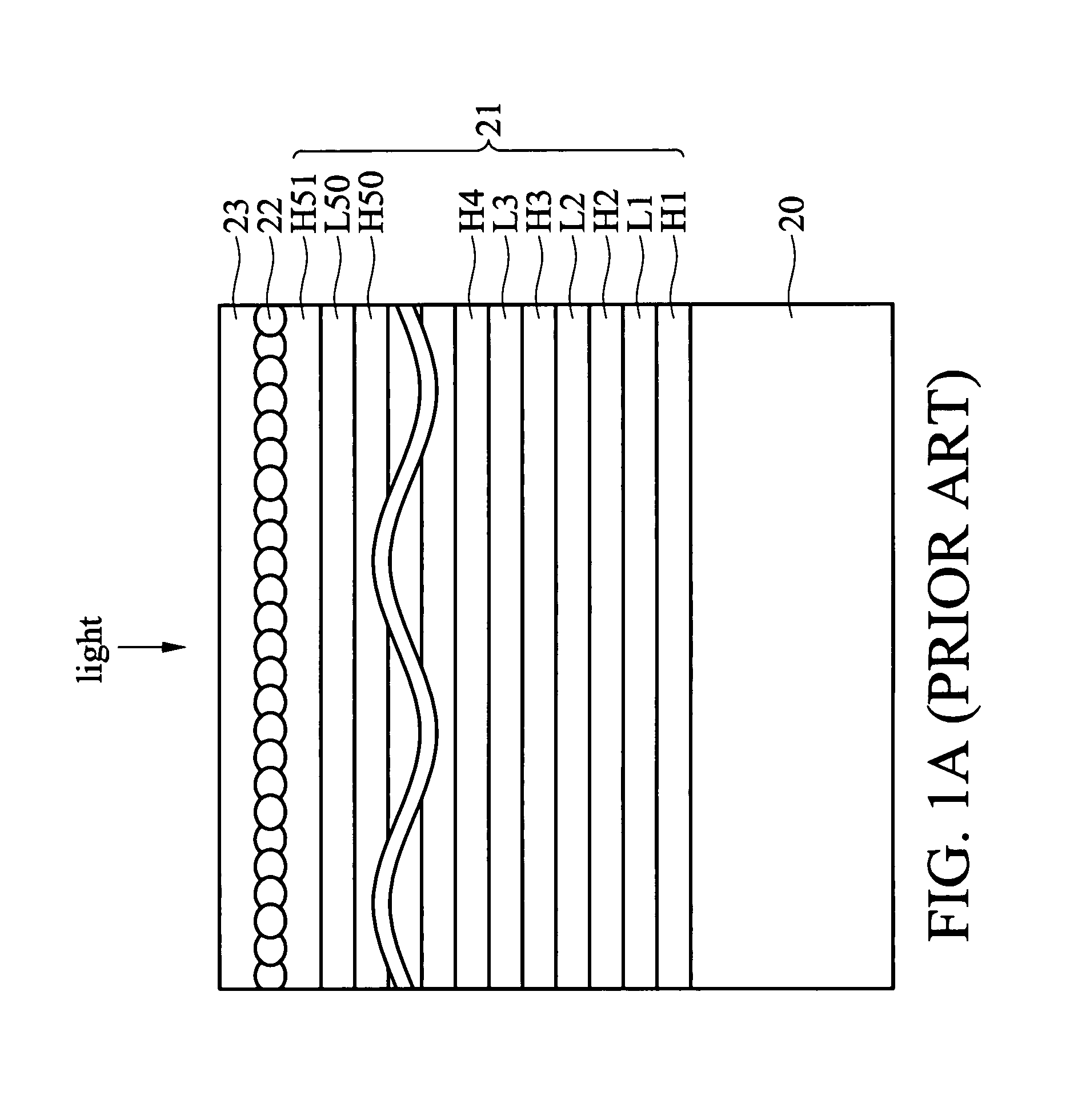
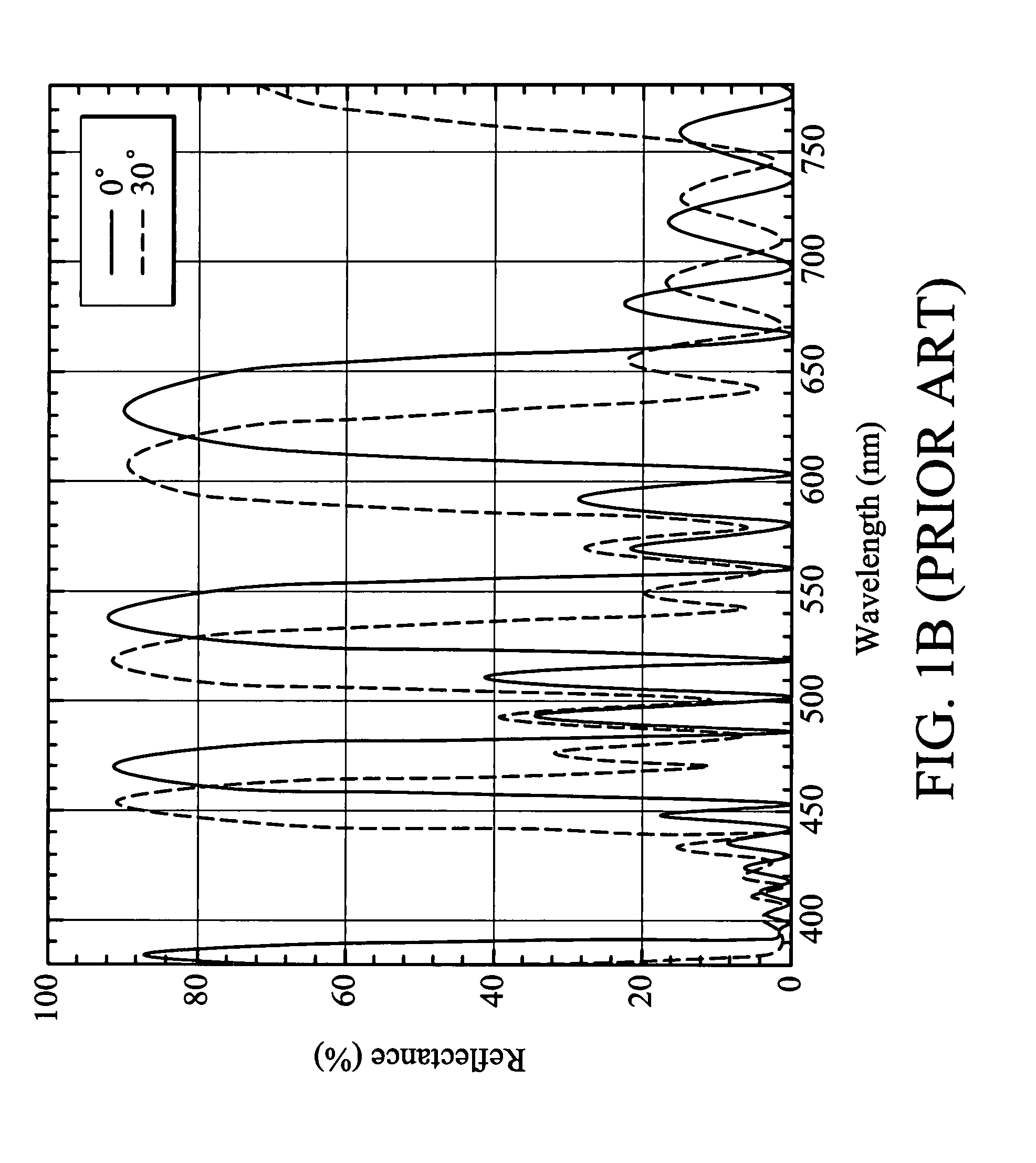
Reflective screens
This invention discloses a projection screen including a diffusion layer, a cap layer, an interference layer and an absorption layer. The projection screen of this invention is based on the concept of inverse reflection. The interference filter includes a plurality of high and low refractive index layers, both of which alternately stacked. The projection screen conveys a small spectral shift and a narrow bandwidth at different incident angles so that the better contract ratio of the image signal can be displayed.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Authenticating and Authentic Article Using Spectral Imaging and Analysis
ActiveUS20080192992A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryPattern recognitionReference dataset
Authenticating an authentic article having an authentication mark. Acquiring a set of spectral images of the authentication mark, for forming a set of single-authentication mark spectral fingerprint data (FIG. 1). Identifying at least one spectral shift in the set of single-authentication mark spectral fingerprint data, for forming an intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group including sub-sets of intra-authentication mark spectral fingerprint pattern data, such that data elements in each sub-set are shifted relative to corresponding data elements in remaining sub-sets in the same intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group (FIG. 2). Forming a set of intra-authentication mark physicochemical properties and characteristics data relating to the imaged authentication mark, by performing pattern recognition and classification analysis on the intra-authentication mark physicochemical region group (FIG. 3). Comparing and matching elements in the set of intra-authentication mark physicochemical properties and characteristics data to corresponding reference elements in reference set of data, thereby authenticating the authentic article.
Owner:GREENVISION SYST
Method for preparing LED chip with separate crystal grain vertical structure
The invention presents a tube core shape design with high luminous efficiency, which comprises: epitaxial growing on island area LED chip with discrete grain; after laser peeling, packaging discrete chip into LED with vertical structure and high luminous efficiency. Wherein, the epitaxial growth improves crystal quality and internal quantum efficiency; the shape of island area increases LED light power; the island growth benefits to release stress, reduce stress on interface between GaN and sapphire substrate and the damage and spectral shift during peeling, thereby, it can obtain LED with high performance.
Owner:DONGGUAN INST OF OPTO ELECTRONICS PEKING UNIV
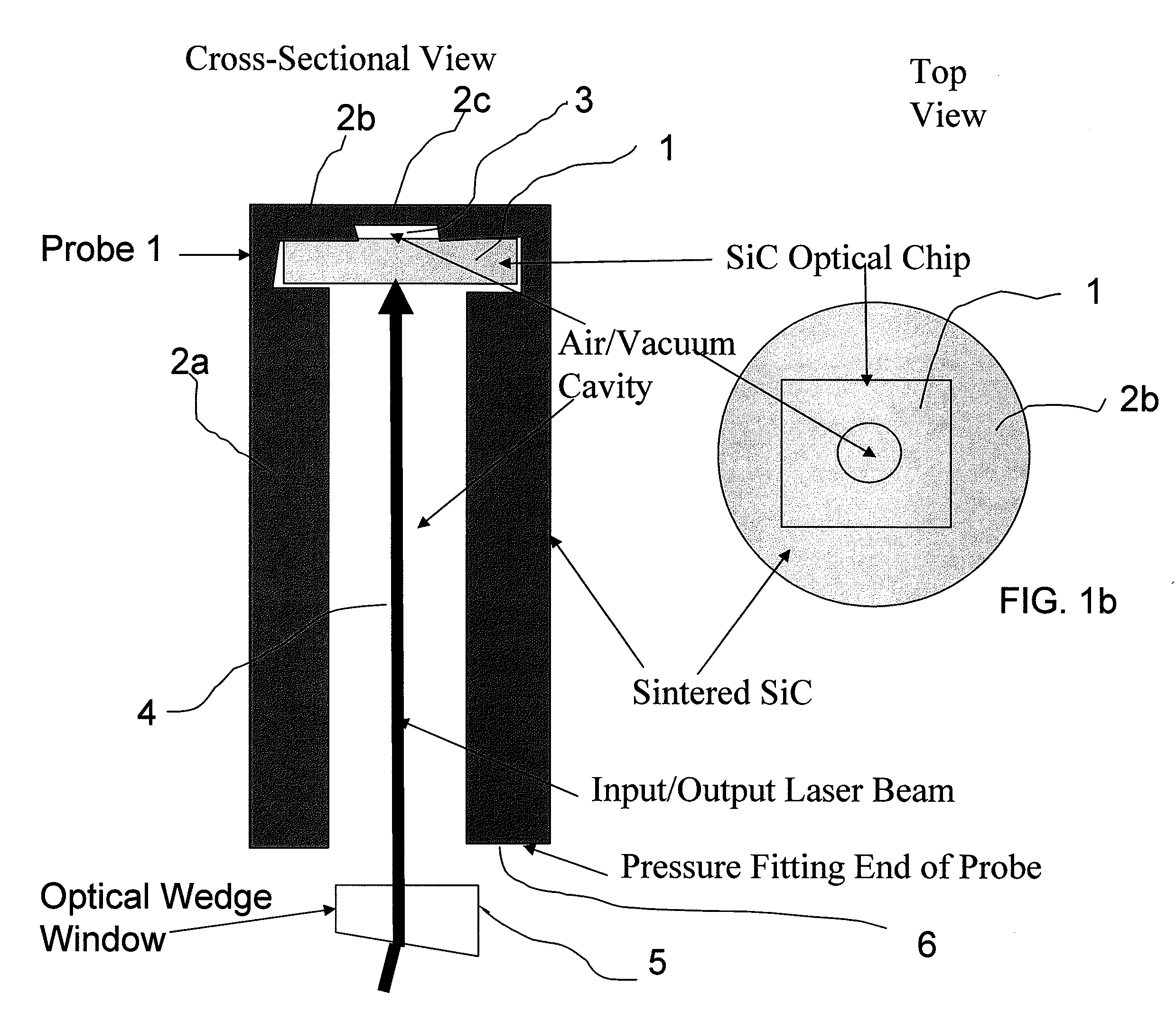
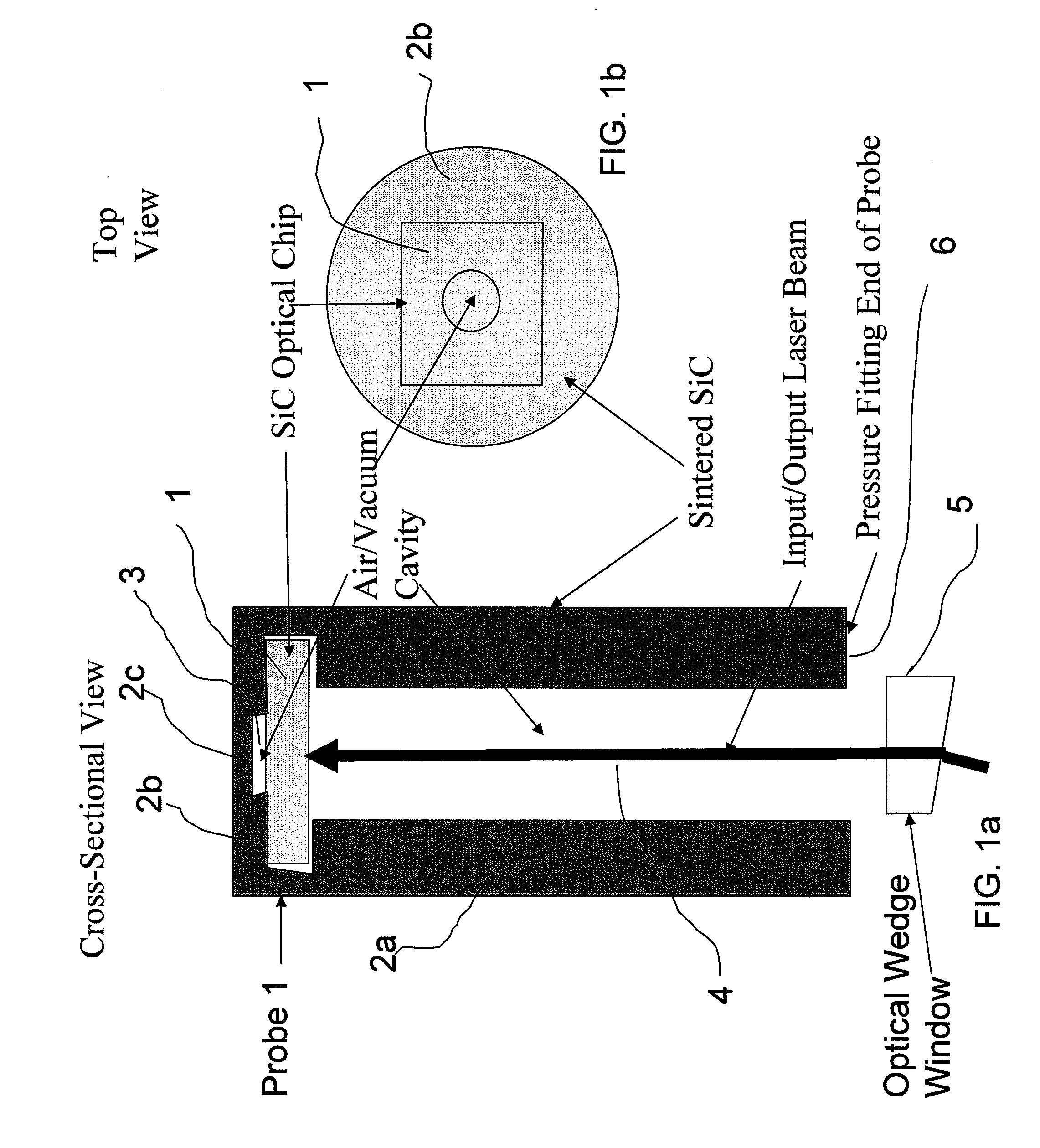
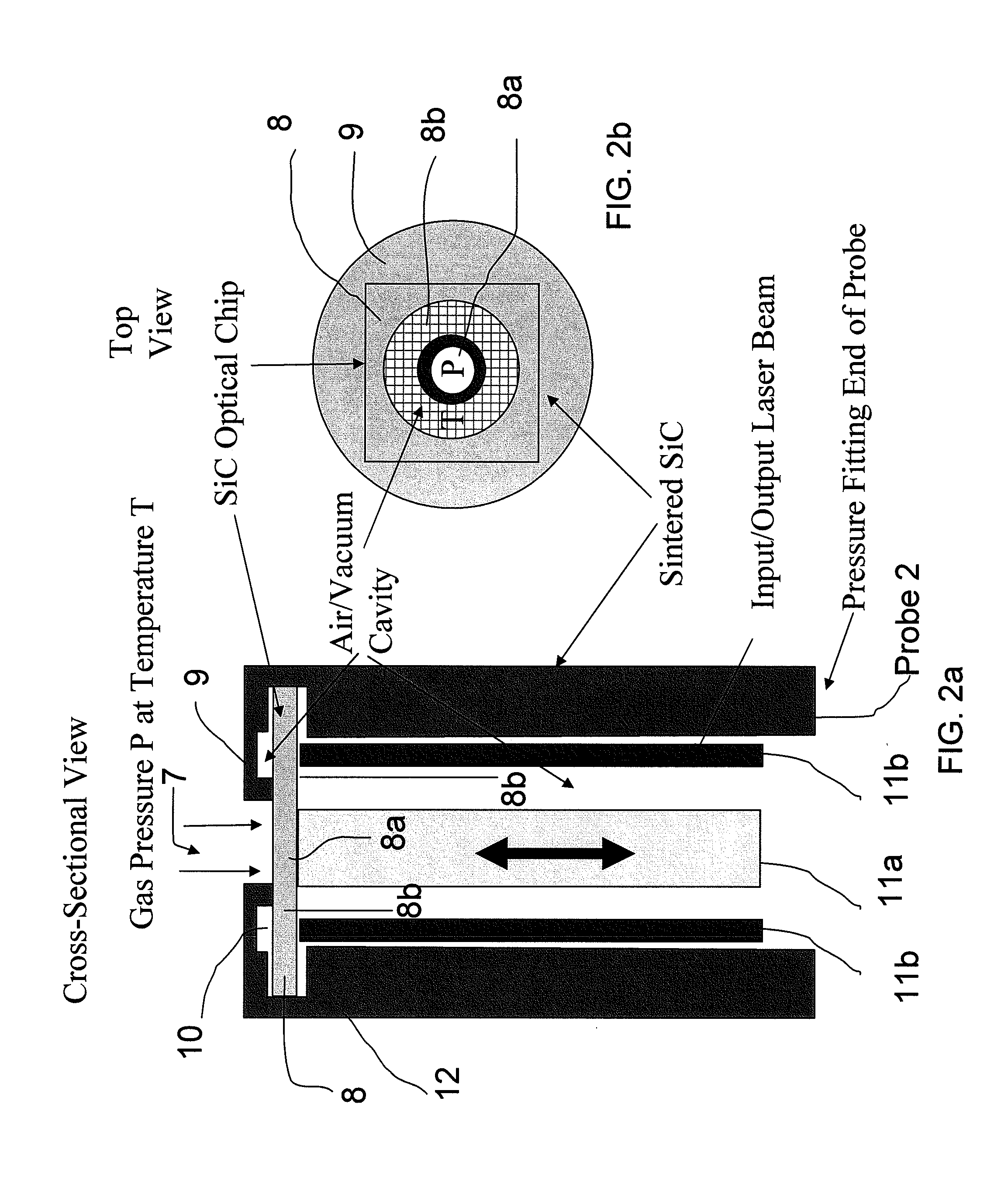
Extreme Temperature Robust Optical Sensor Designs And Fault-Tolerant Signal Processing
InactiveUS20090296776A1Eliminates multiple unwanted optical reflectionReduce ambiguityThermometer detailsSensing radiation from gases/flamesFrequency spectrumBlack body
Silicon Carbide (SiC) probe designs for extreme temperature and pressure sensing uses a single crystal SiC optical chip encased in a sintered SiC material probe. The SiC chip may be protected for high temperature only use or exposed for both temperature and pressure sensing. Hybrid signal processing techniques allow fault-tolerant extreme temperature sensing. Wavelength peak-to-peak (or null-to-null) collective spectrum spread measurement to detect wavelength peak / null shift measurement forms a coarse-fine temperature measurement using broadband spectrum monitoring. The SiC probe frontend acts as a stable emissivity Black-body radiator and monitoring the shift in radiation spectrum enables a pyrometer. This application combines all-SiC pyrometry with thick SiC etalon laser interferometry within a free-spectral range to form a coarse-fine temperature measurement sensor. RF notch filtering techniques improve the sensitivity of the temperature measurement where fine spectral shift or spectrum measurements are needed to deduce temperature.
Owner:RIZA NABEEL +2
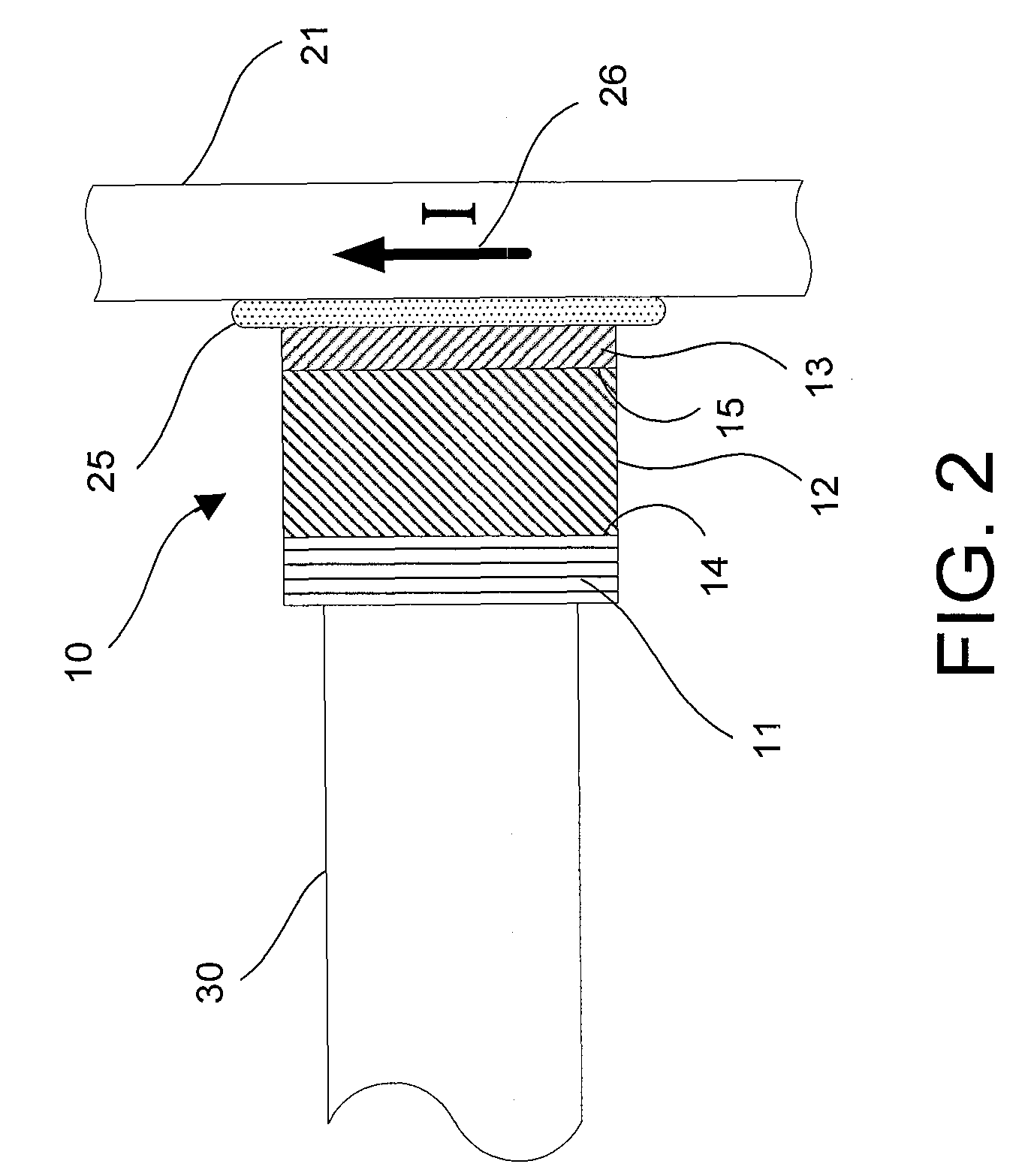
Calculation of birefringence in a waveguide based on Rayleigh scatter
ActiveUS20060204165A1Low costIntegrity be compromisedReflectometers dealing with polarizationCladded optical fibreRayleigh scatteringSpectral response
Light is coupled into two polarization modes of a waveguide, e.g., an optical fiber. The spectral response of Rayleigh backscatter in the waveguide segment for the two polarization modes is measured, e.g., using OFDR, OTDR, OLCR, etc. The autocorrelation of the spectral response is calculated. The spectral (wavelength) shift from a main autocorrelation peak to a side autocorrelation peak, corresponding to one of the two polarization modes of the waveguide segment, is determined. The spectral shift, corresponding to a beat length of the waveguide segment, is multiplied by an average index of refraction to determine a birefringence of the waveguide segment.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Magneto-optical resonant waveguide sensors
InactiveUS20060103380A1High measurement sensitivityImprove resolutionOptical light guidesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsFiberWaveguide
A waveguide magneto-optic sensor provides a signal indicative of the value and / or direction of a detected magnetic field by a spectral shift of the characteristic resonant spectral feature of the sensor is disclosed. The sensor does not suffer from vibrations, fiber bending or other light intensity noise and provides an absolute self-referencing signal. The sensor elements can easily be coupled to optical fibers and read with scanning spectrometers or scanning lasers calibrated against NIST-traceable gas absorption standards.
Owner:KYTON
Optical sensor for monitoring electrical current or power
The present invention provides an optical sensor for monitoring current or power in a monitored element of a device such as a bridge-wire or hot-wire of electro-explosive devices. The optical sensor comprises an optical sensor made of semiconductor material. The semiconductor material comprises an absorption edge which is sensitive to a temperature variation. The semiconductor material is for placing in thermal contact with the monitored element of the device, whereby, when the current or power varies in the monitored element, it causes a variation in temperature in the semiconductor element and hence a spectral shift of the absorption edge which can be measured and which is representative of current and power variation.
Owner:OPSENS SOLUTIONS
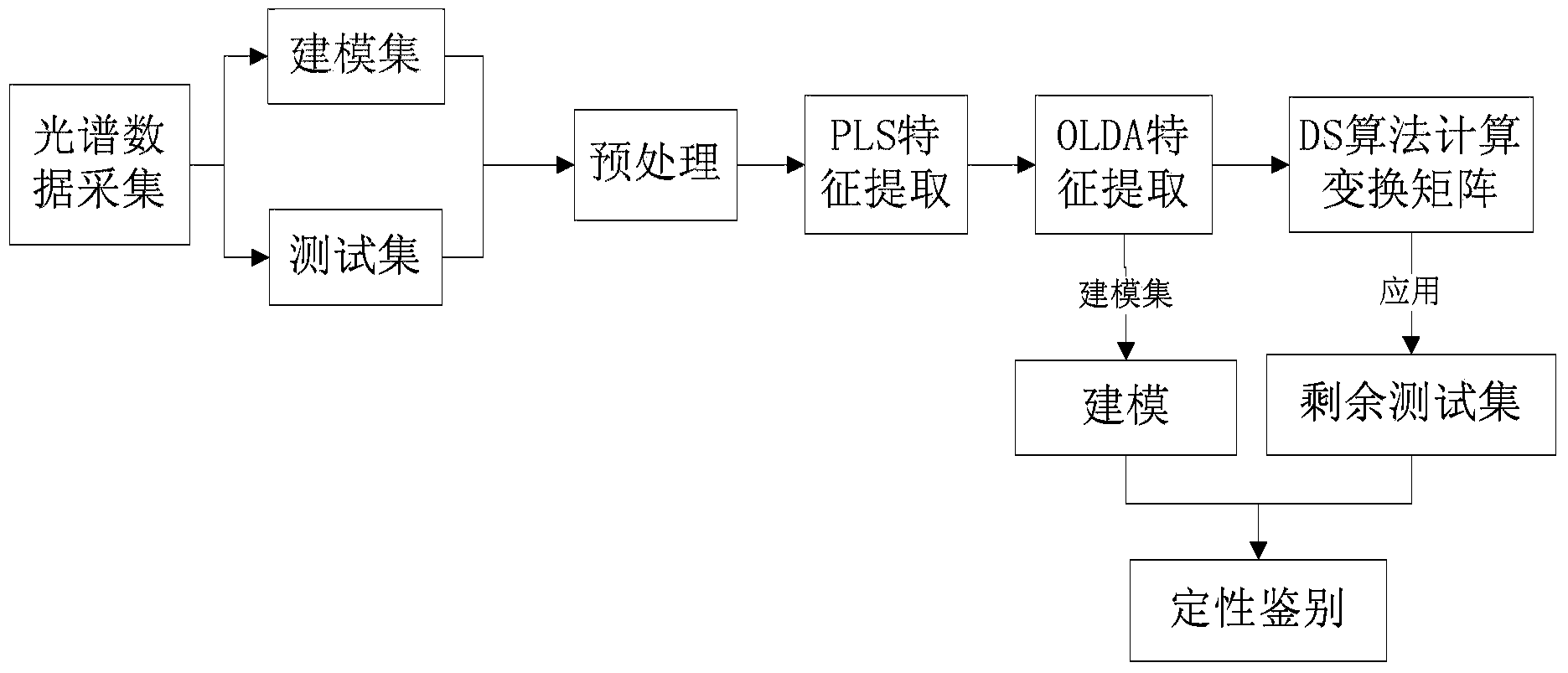
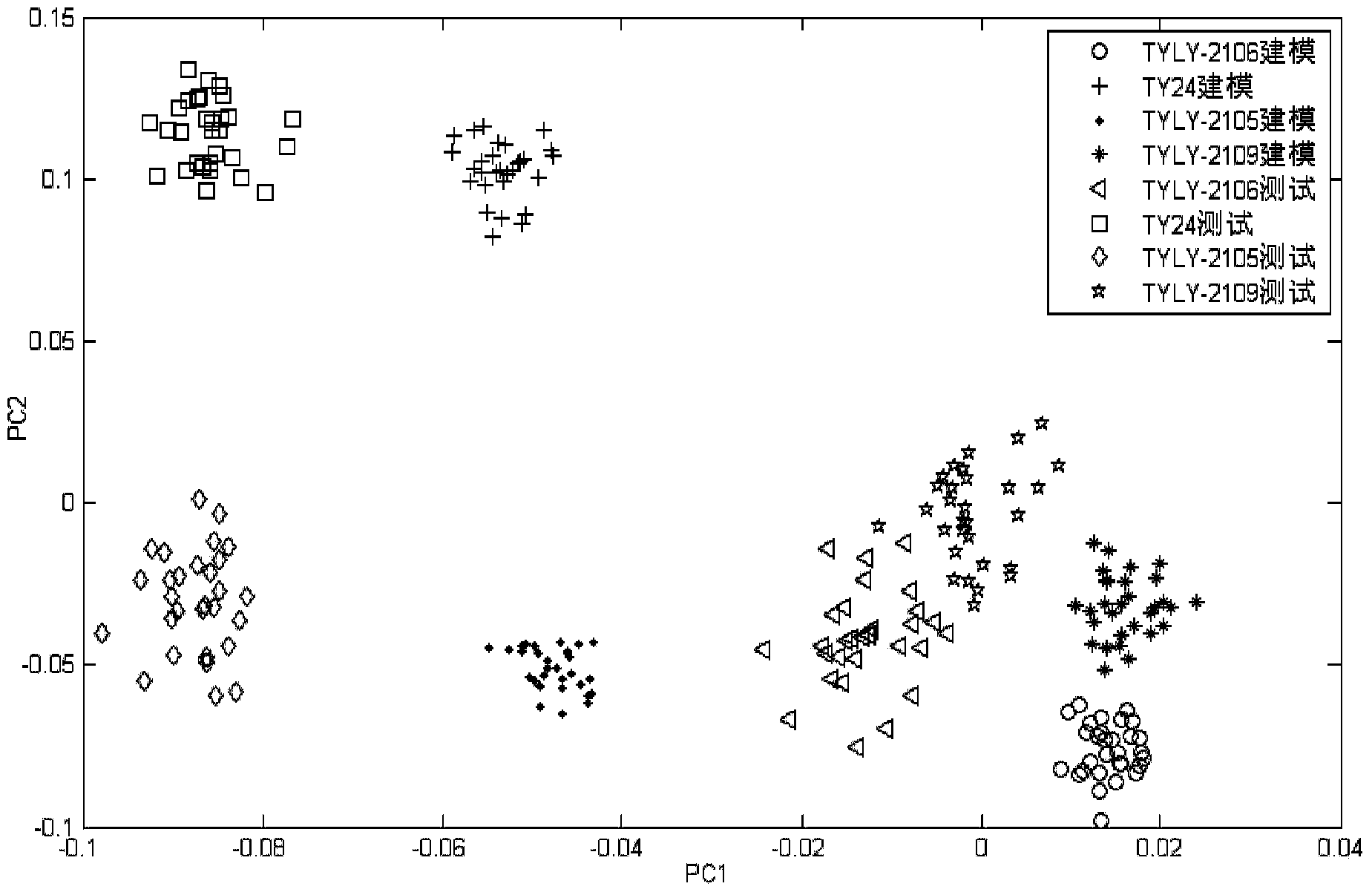
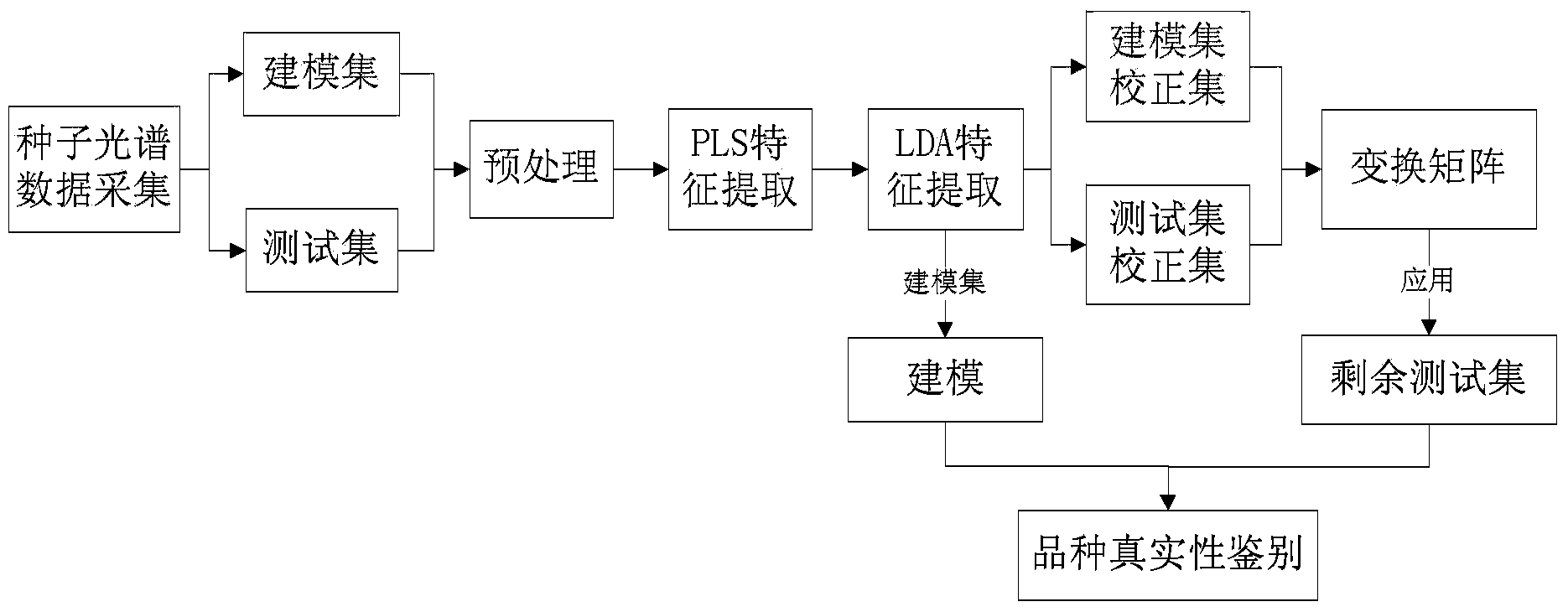
Qualitative analysis method for improving identification result on basis of near-infrared mode
ActiveCN104374738AFree from destructionNo pollution in the processMaterial analysis by optical meansAlgorithmSpectral transformation
The invention discloses a qualitative analysis method for improving an identification result on the basis of the near-infrared mode. The qualitative analysis method comprises the steps of (1) acquiring near-infrared spectral data of a sample and determining a modeling set and testing sets; (2) carrying out pretreatment, partial-least-square feature extraction and orthogonal-linear-identification feature extraction on the modeling set and the testing sets in sequence; (3) calculating a spectral transformation matrix between the modeling set and the testing sets by adopting a direct model transferring method, and correcting the remaining testing sets; (4) establishing a quantitative analysis model; and (5) carrying out quantitative identification on the remaining testing sets by utilizing the established quantitative analysis model. The qualitative analysis method disclosed by the invention is established on the basis of near-infrared quantitative analysis, and the orthogonal-linear-identification method which is used in multi-classification and two-classification problems is used in the feature extraction step; in addition, the testing sets can be corrected by the direct model transferring method, so that the model applicability caused by long-time spectral shift of the same instrument can be realized and the result of quantitative identification is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optically encoded particles, system and high-throughput screening
ActiveUS20070148695A1Amenable to in vivo diagnosticsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesPorosityAnalyte
The invention concerns a particle having a code from a library of codes embedded in its physical structure by refractive index changes between different regions of the particle. In preferred embodiments, a thin film possesses porosity that varies in a manner to produce a code detectable in the reflectivity spectrum. An assay detection method uses such a particle and detects a spectral shift in the presence of an analyte. Additional embodiments are disclosed including additional features.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
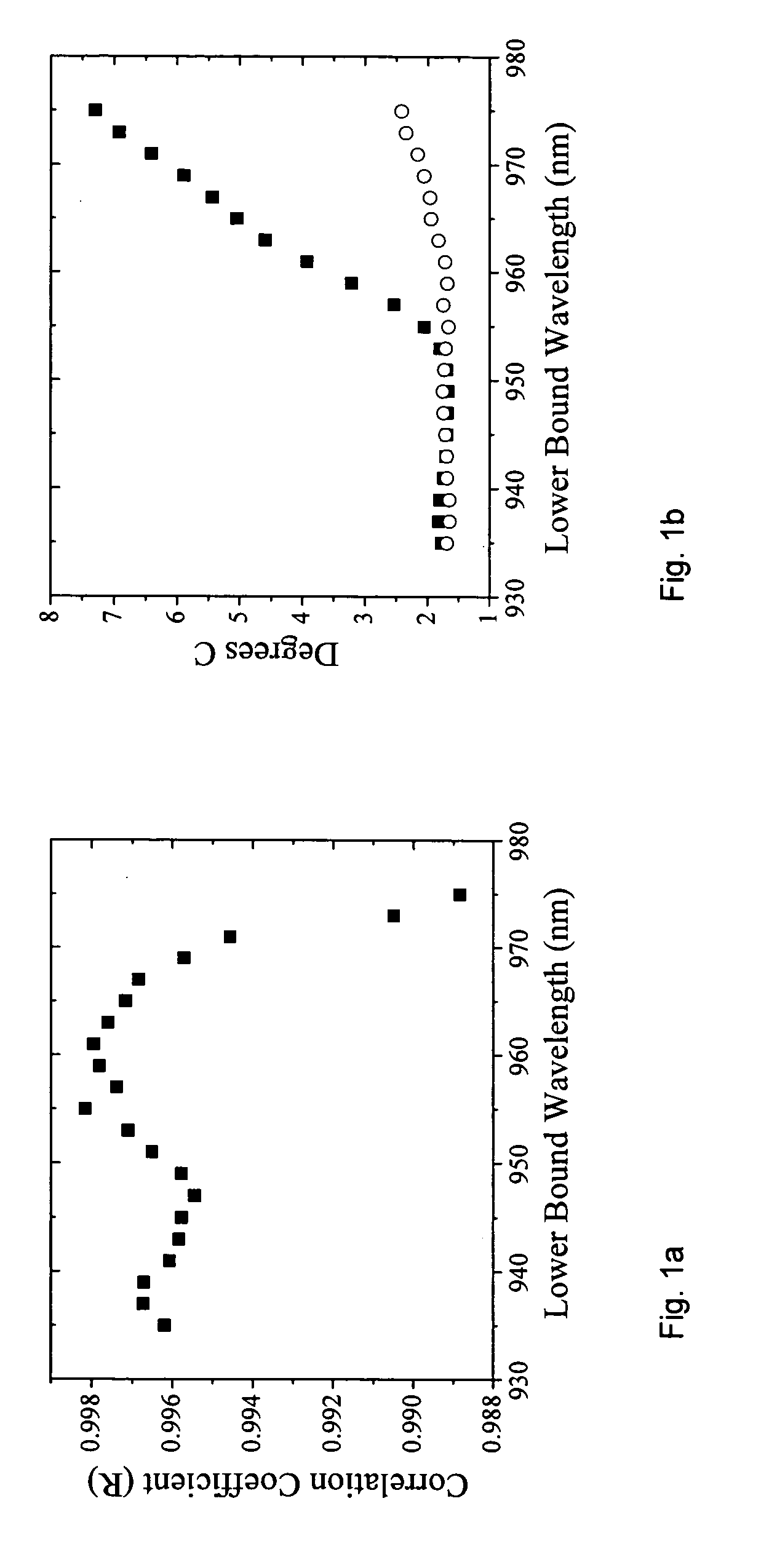
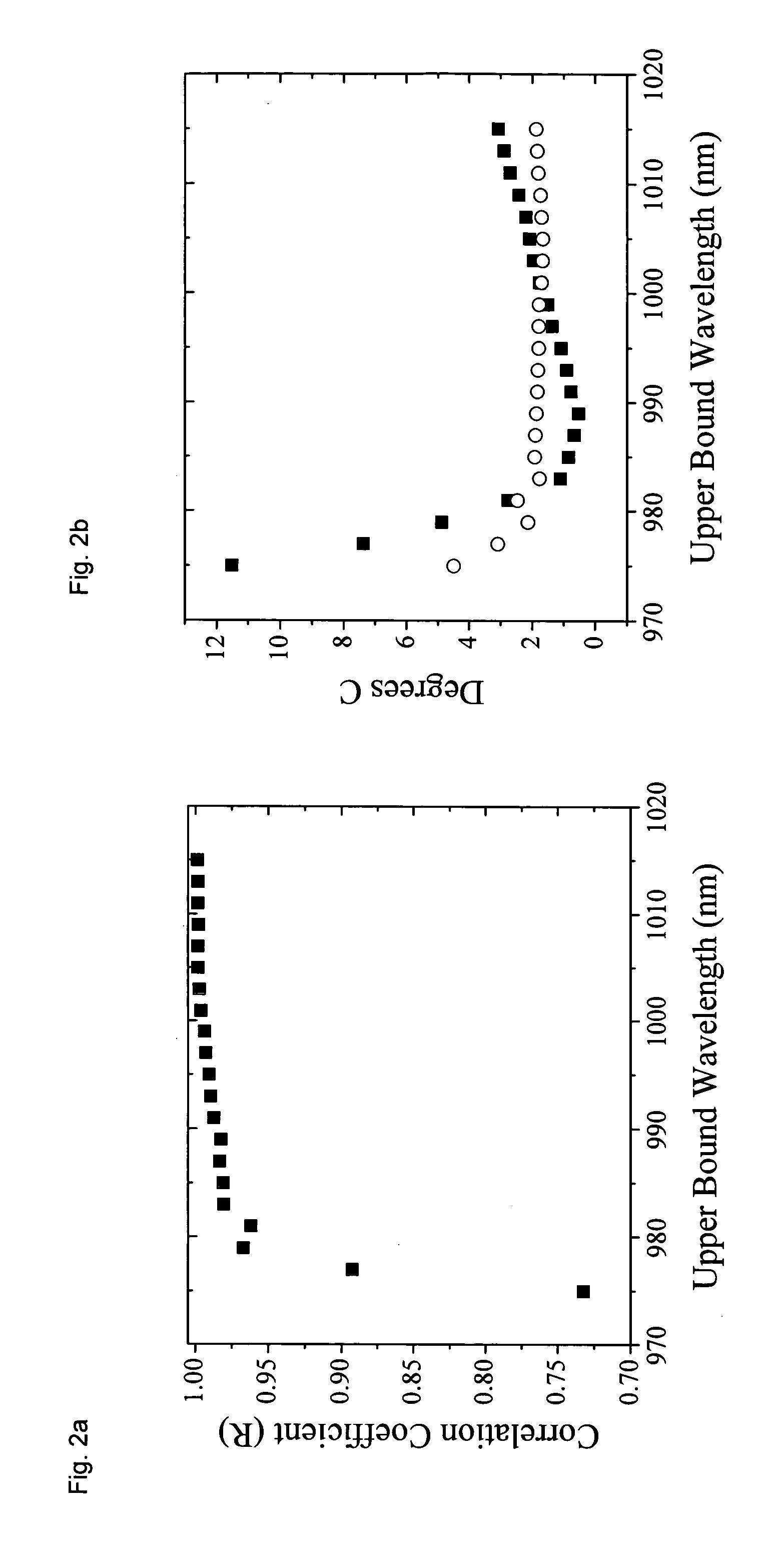
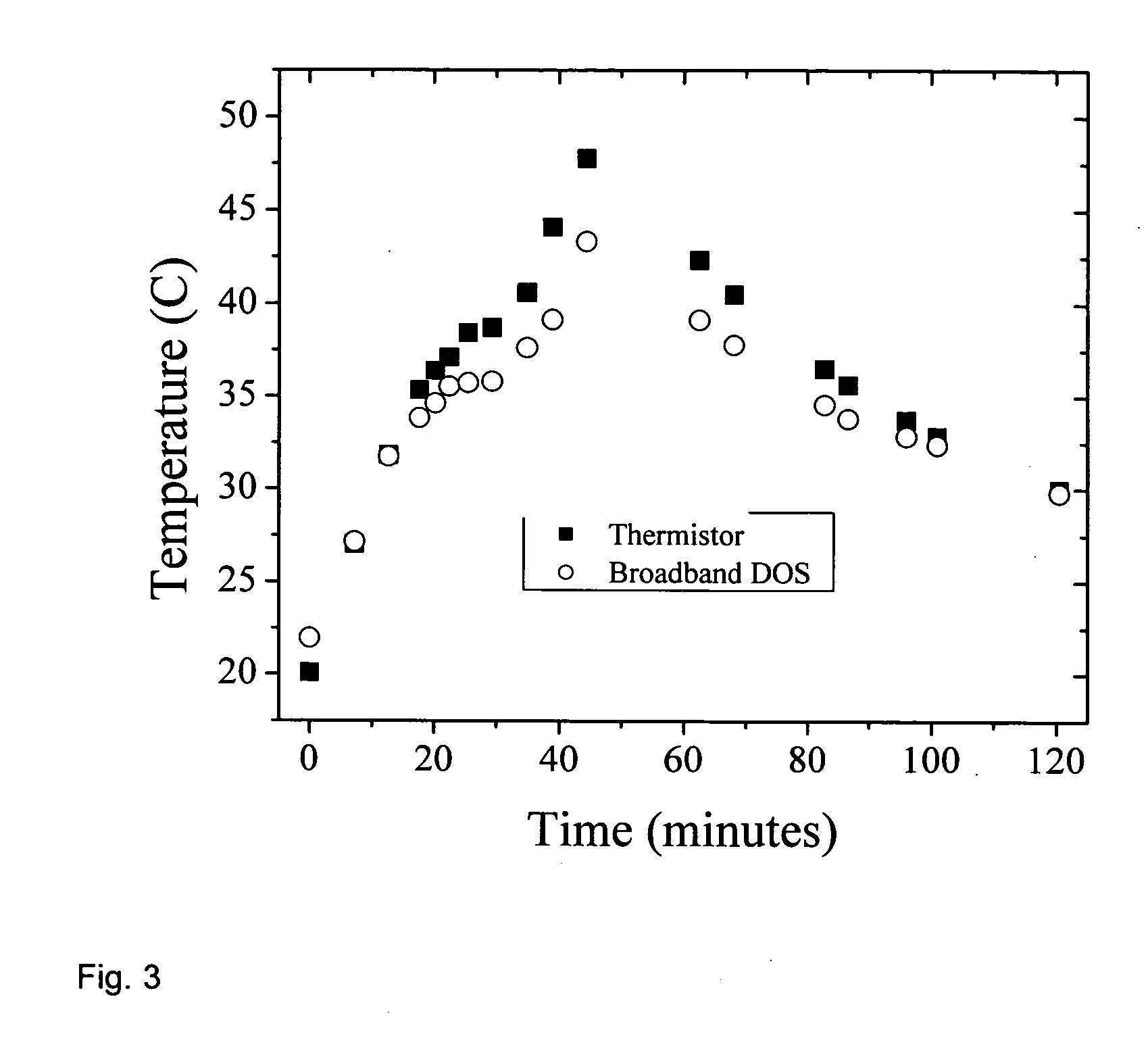
Apparatus and method for monitoring deep tissue temperature using broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy
InactiveUS20060111622A1High strengthImproved chromophore fitDiagnostics using lightSensorsLipid formationBound water
A method for noninvasively determining deep tissue temperature comprises measuring data relating to spectral shifts of chromophore absorption in tissue using broadband diffuse optical spectroscopy and generating a temperature reading corresponding to the spectral shift of an absorption peak of the chromophore. A bound water correction is made to the spectral shift. A frequency domain measurement at multiple wavelengths is made to determine the absolute absorption and scattering values between 600 and 1050 nm. The measurement of an absolute absorption comprises measuring an absolute absorption coefficient of selected tissue and further comprising deducing concentrations of tissue composition including lipids, deducing information related to heterogeneity and integrity of tissue matrix, and deducing temperature heterogeneity related to vulnerable plaque in vascular tissue. The measurement comprises making a measurement in the range of 600-1100 nm to interrogate a vessel wall in the presence of blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
All-fiber magnetic field sensor
InactiveCN104020424ASufficient output powerGood interferenceMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesPhase differenceRefractive index
The invention discloses an all-fiber magnetic field sensor. The sensor is composed of a broadband light source, a sensing head and a spectrometer, wherein two ends of one section of a photonic crystal fiber with magnetic fluid poured in are welded with a single-mode fiber to form the sensing head, one end is melted eccentrically, a Mach-Zehnder interferometer with single fiber embedded is formed, changes of phase differences among different modes are caused through changes of the reflection rate of the magnetic fluid in the photonic crystal fiber, spectral shift is thus caused, the shift amount of a wave crest / a wave trough is detected to demodulate magnetic field information, and measurement on the magnetic field is realized. The all-fiber magnetic field sensor is compact in structure, small in size, simple in manufacturing, stable and reliable in operation, high in sensitivity and low in cost.
Owner:JIANGSU JINDI ELECTRONICS TECH
Thermally compensated fiber bragg grating mount
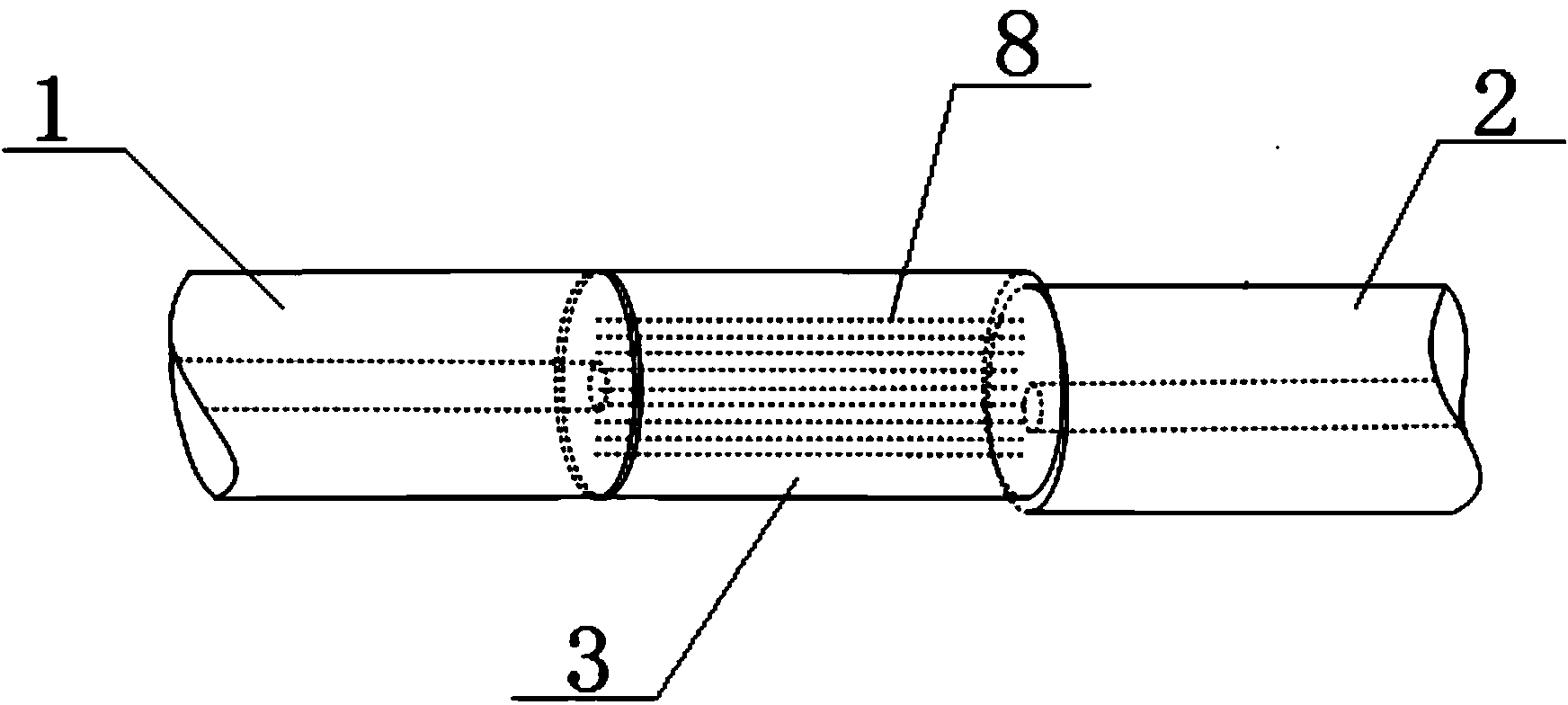
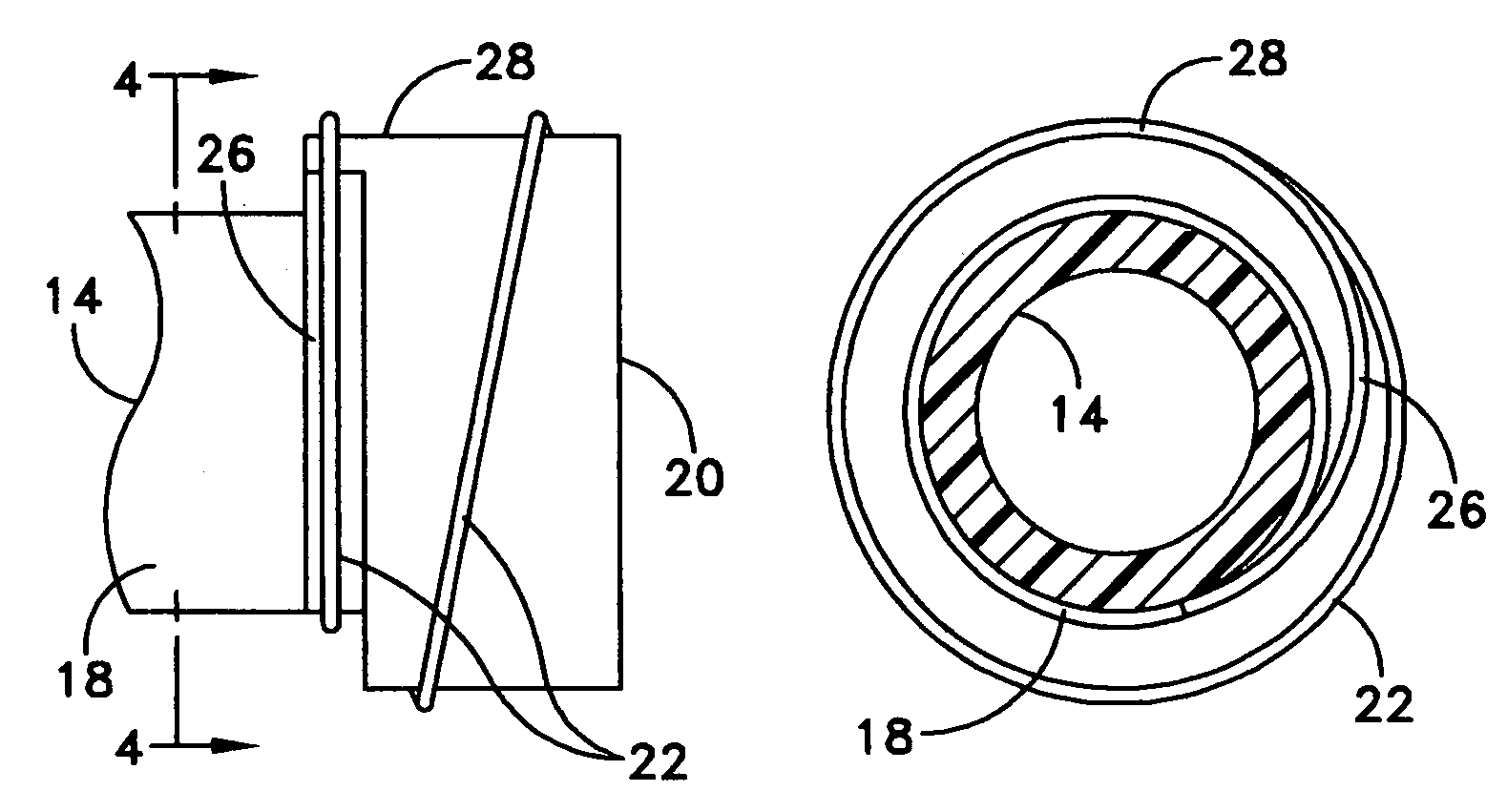
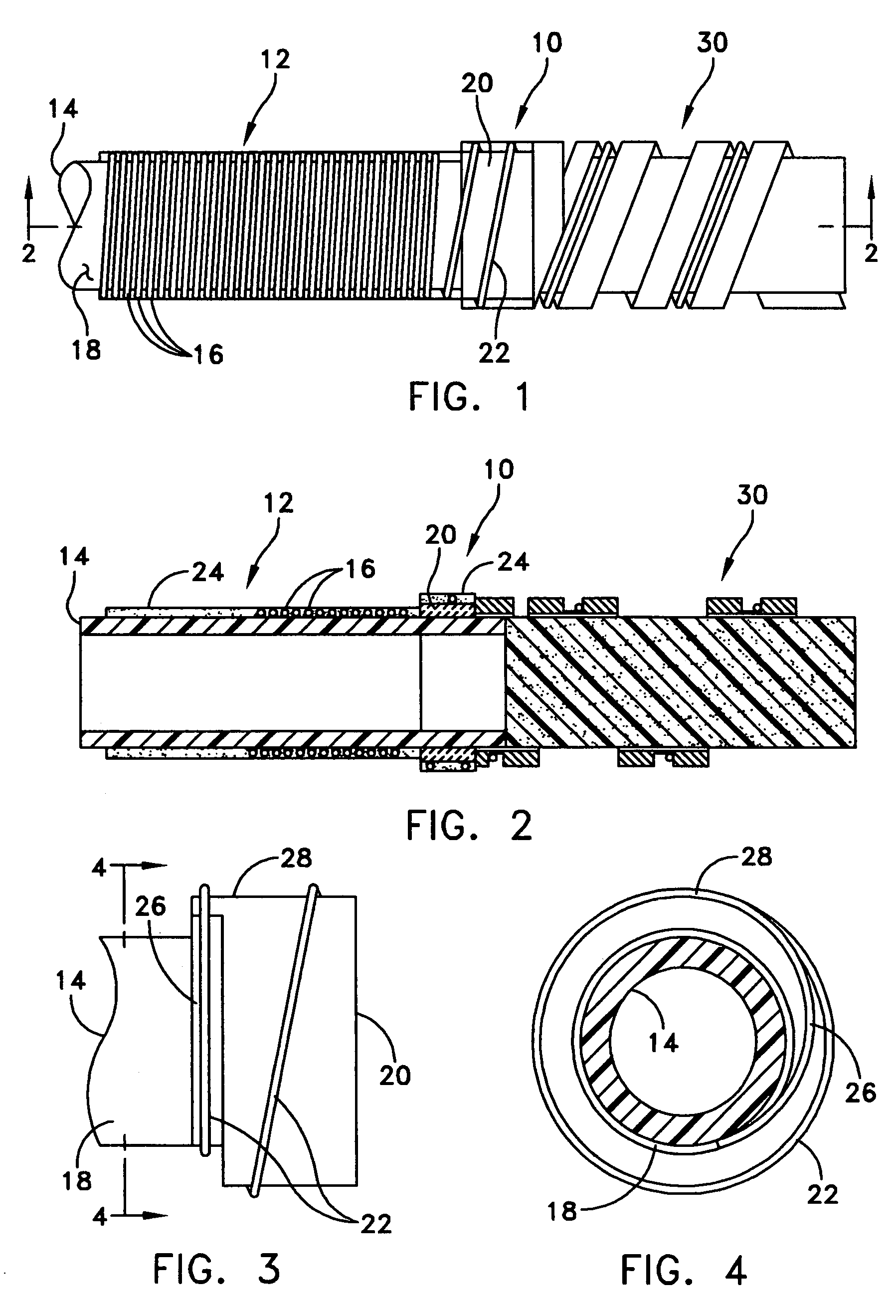
A thermally compensated fiber Bragg grating package is used with a fiber optic sensor. The package includes a Bragg grating mount connected at each end of a sensor mandrel. An optical fiber is wound around the sensor mandrel and a fiber portion having a Bragg grating therein is wound onto the mount. The mount is made of a rigid material having a negative coefficient of thermal expansion to minimize thermally induced spectral shifts. One example of the material includes zirconium tungstate. A coating material can be used to further adhere the optical fiber to the sensor mandrel and / or to the mount. The mount preferably includes a ramped groove to provide for a smooth transition from the sensor mandrel to the mount.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Power spectral strain estimators in elastography
InactiveUS20020010399A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesResponse signal detectionHand heldIn vivo
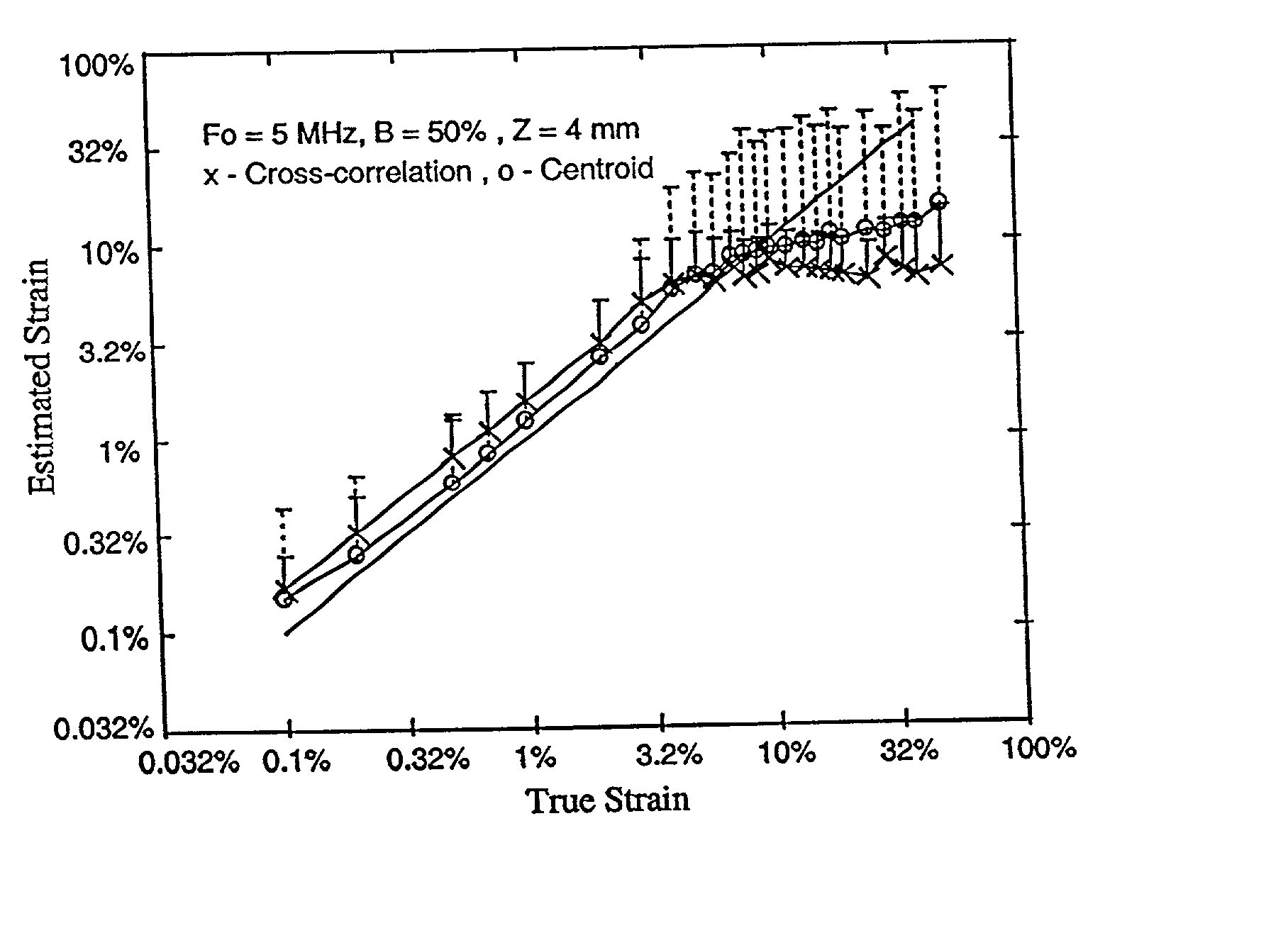
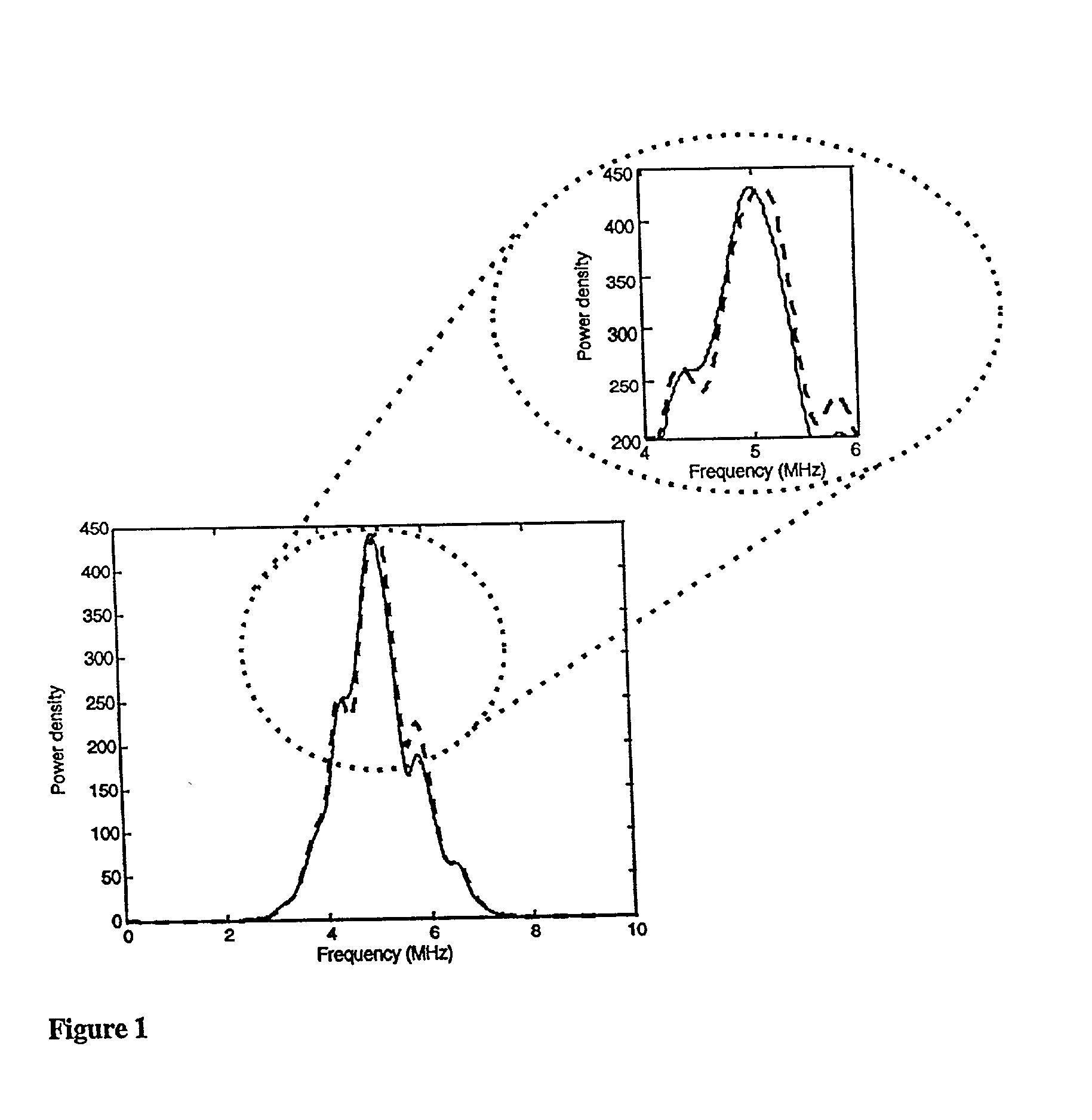
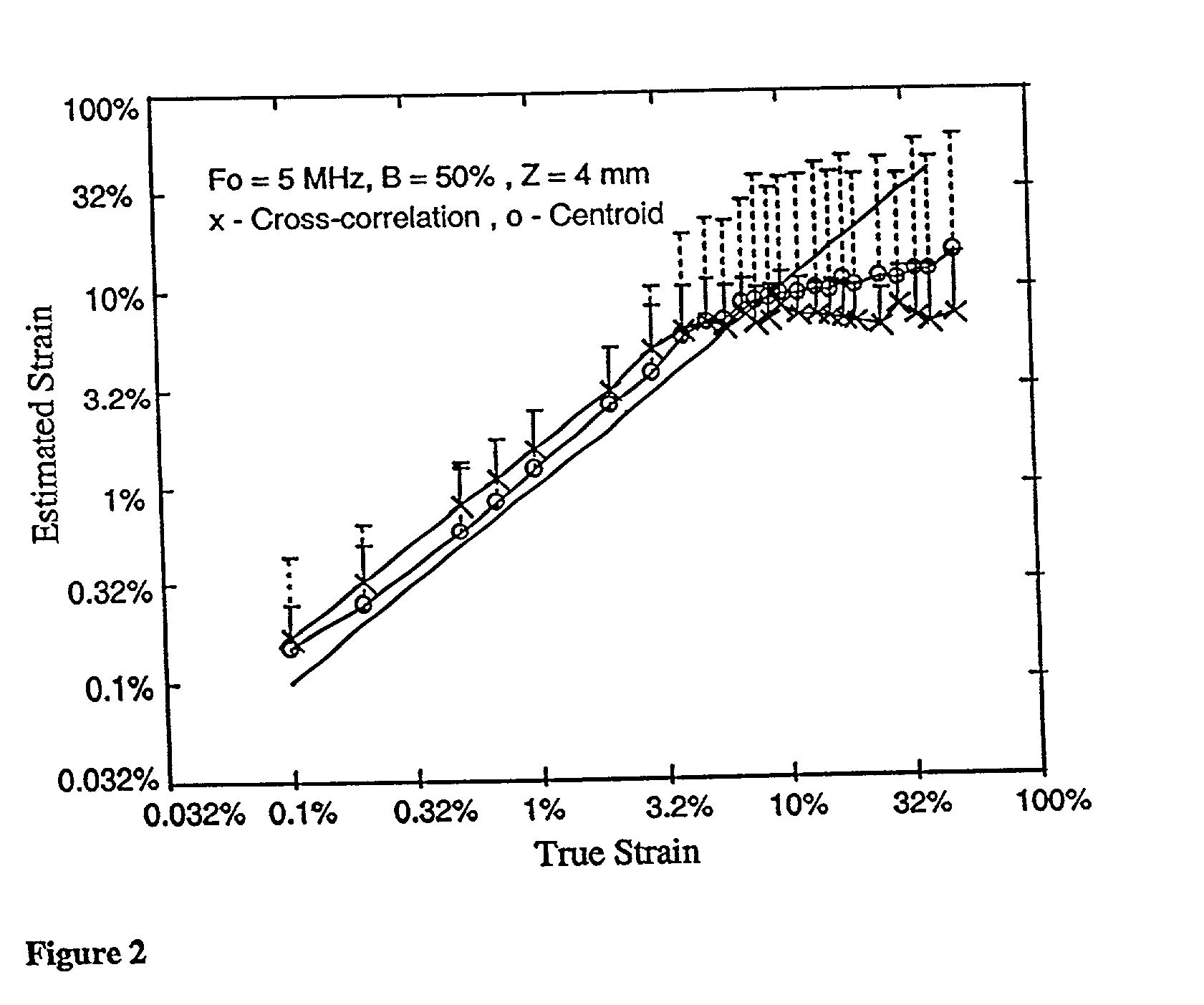
Elastography can produce quality strain images in vitro and in vivo. Standard elastography uses a coherent cross-correlation technique to estimate tissue displacement and tissue strain using a subsequent gradient operator. While coherent estimation methods generally have the advantage of being highly accurate and precise, even relatively small undesired motions are likely to cause enough signal decorrelation to produce significant degradation of the elastogram. For elastography to become more universally practical in such applications as hand-held, intravascular and abdominal imaging, the limitations associated with coherent strain estimation methods that require tissue and system stability, must be overcome. In this paper, we propose the use of a spectral shift method that uses a centroid shift estimate to measure local strain directly. Furthermore, we also show theoretically that a spectral bandwidth method can also provide a direct strain estimation. We demonstrate that strain estimation using the spectral shift technique is moderately less precise but far more robust than the cross-correlation method. A theoretical analysis as well as simulations and experimental results are used to illustrate the properties associated with this method.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
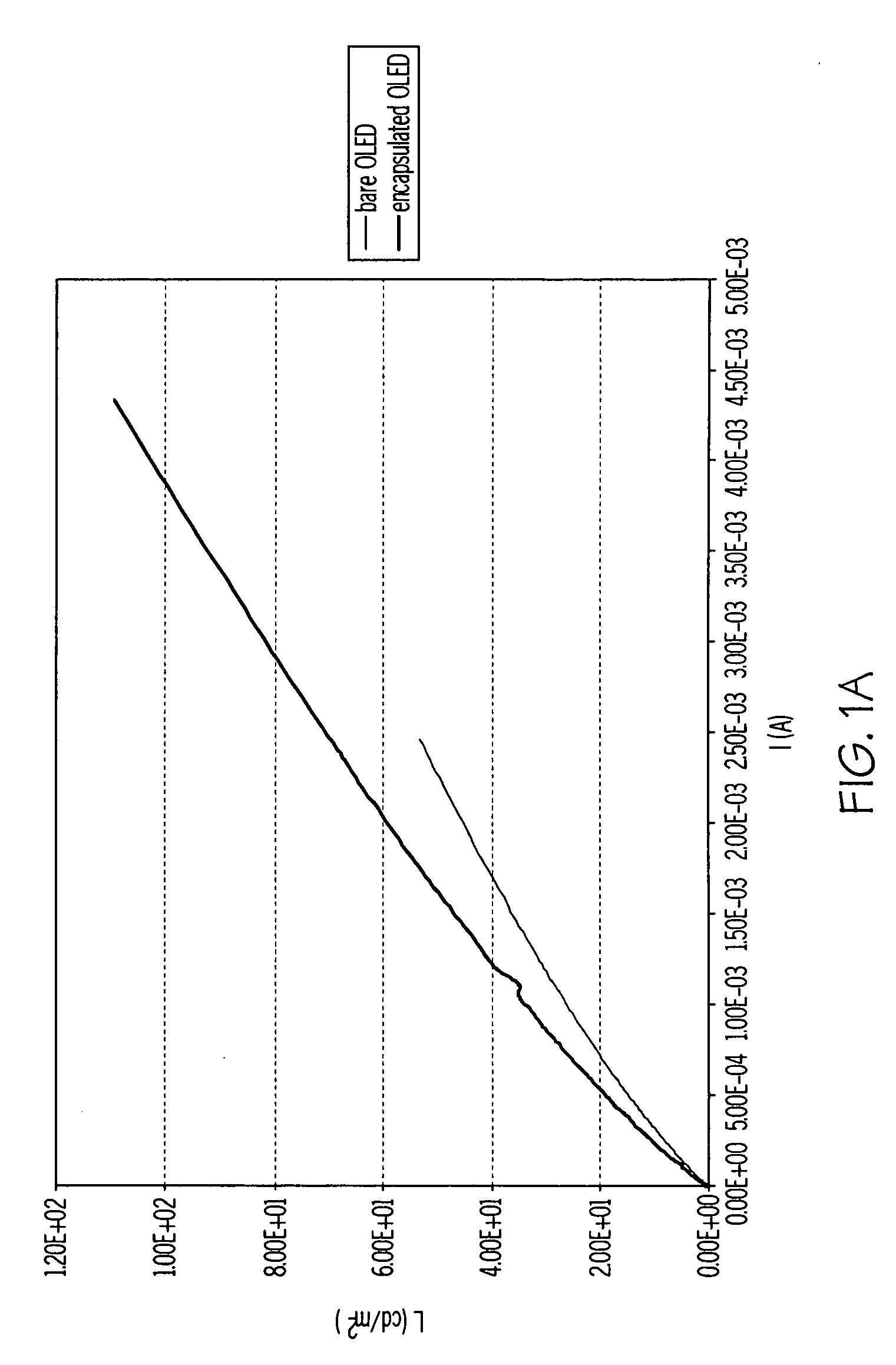
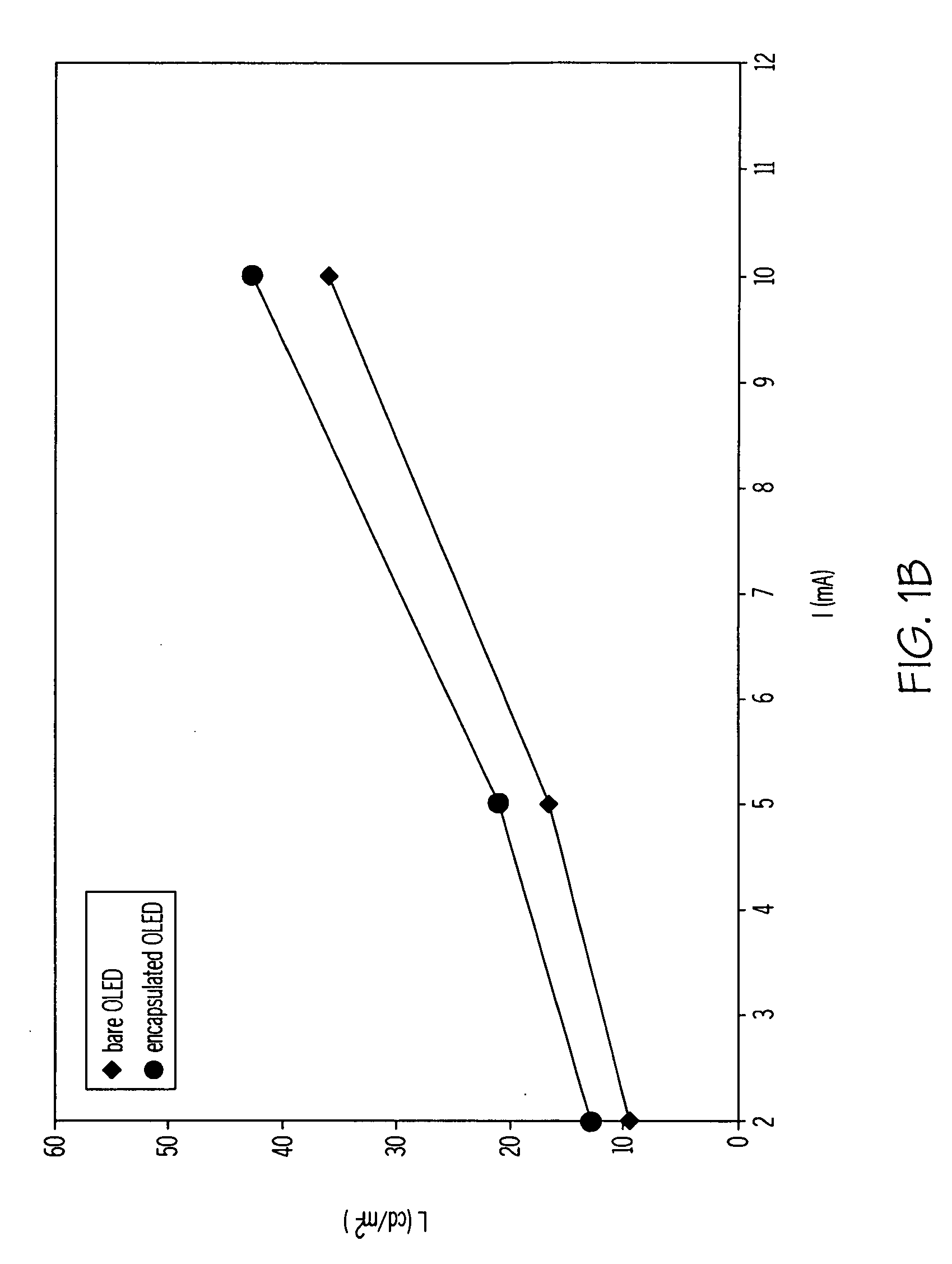
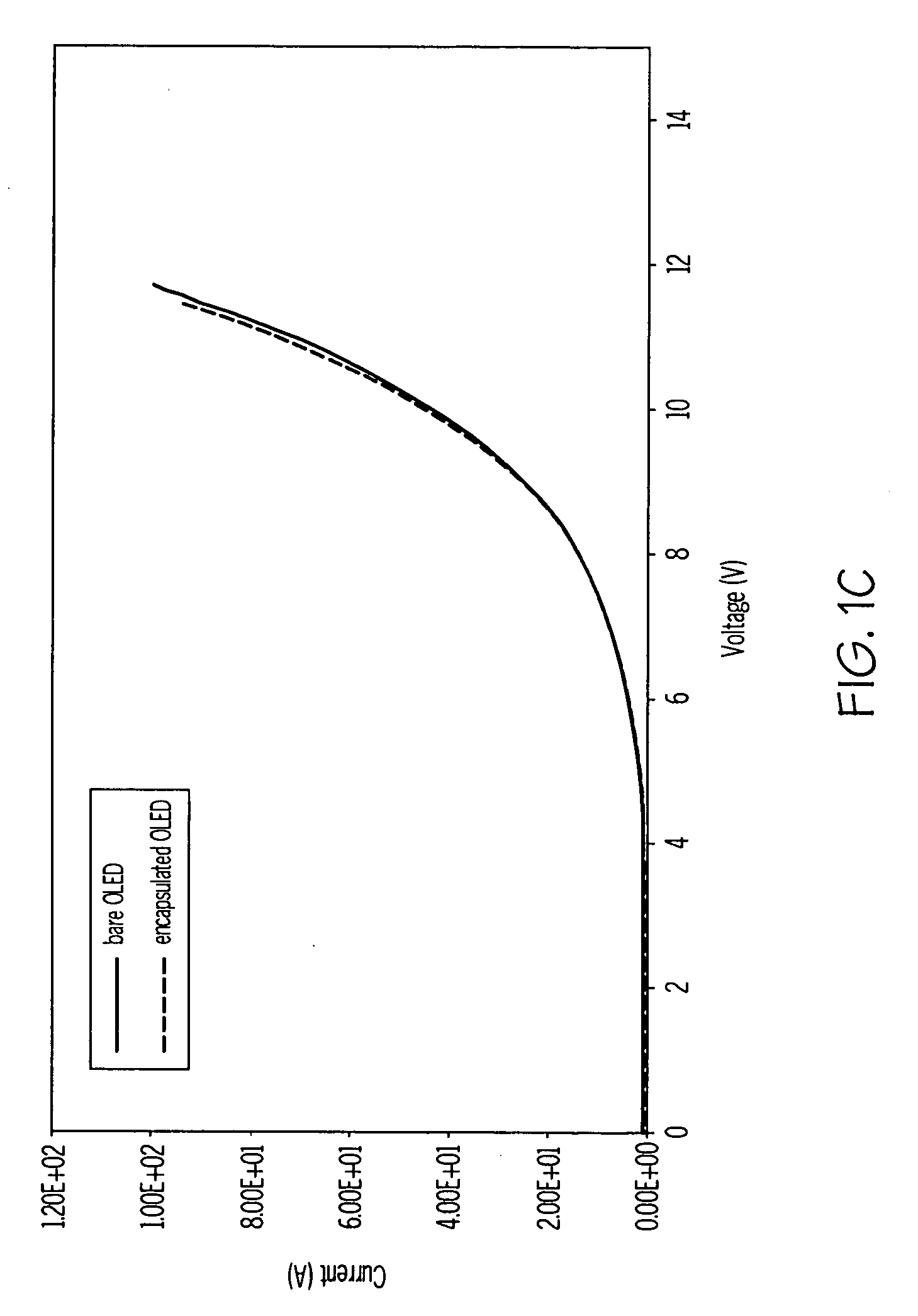
Encapsulated RGB oleds having enhanced optical output
ActiveUS20100156277A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsComputational physicsMaximum efficiency
Methods of making an integrated barrier stack and optical enhancement layer for protecting and improving the light out coupling of an encapsulated OLED are described. The method includes optimizing the thickness of various layers including the initial inorganic barrier layer and the inorganic barrier layer and polymeric decoupling layer for the barrier stack. The thickness is optimized for at least one of maximum efficiency, minimum dispersion, or minimum spectral shift so that the encapsulated OLED has enhanced light outcoupling compared to the bare OLED.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Cascade long-period pohotonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor
InactiveCN102980685AHigh measurement accuracyHigh measurement sensitivityCladded optical fibreThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingThermal aware
The invention relates to a cascade long-period pohotonic crystal fiber grating temperature sensor. A photonic crystal fiber is provided with a cladding consisting of periodically arrayed air holes; the cladding and a fiber core of the fiber are made of SiO2; a long-period grating with a certain period is written onto the fiber; the air holes of the cladding are filled with thermosensitive substances sensitive to temperature; the refractive indexes of the thermosensitive substances are less than the refractive index of the fiber core; and the total internal reflection photonic crystal fiber is formed. The effective refractive index of a coupled mode of the grating can be changed by controlling the temperatures of the thermosensitive substances, so that the resonant wavelength of a transmission spectrum of the grating is changed, the temperature variation is shown as spectral shift, and the wavelength-tunable temperature sensor is realized. As the bandwidth of the transmission spectrum of the single long-period grating is greater, the temperature sensitivity and the measurement precision of the transmission spectrum of the long-period grating are limited, and the sensor is transformed into a cascade long-period grating structure. The sensor achieves the tunable wavelength, the sensitivity is improved, and the sensor has a very large application prospect in the transduction field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Optical multilayer thin-film system
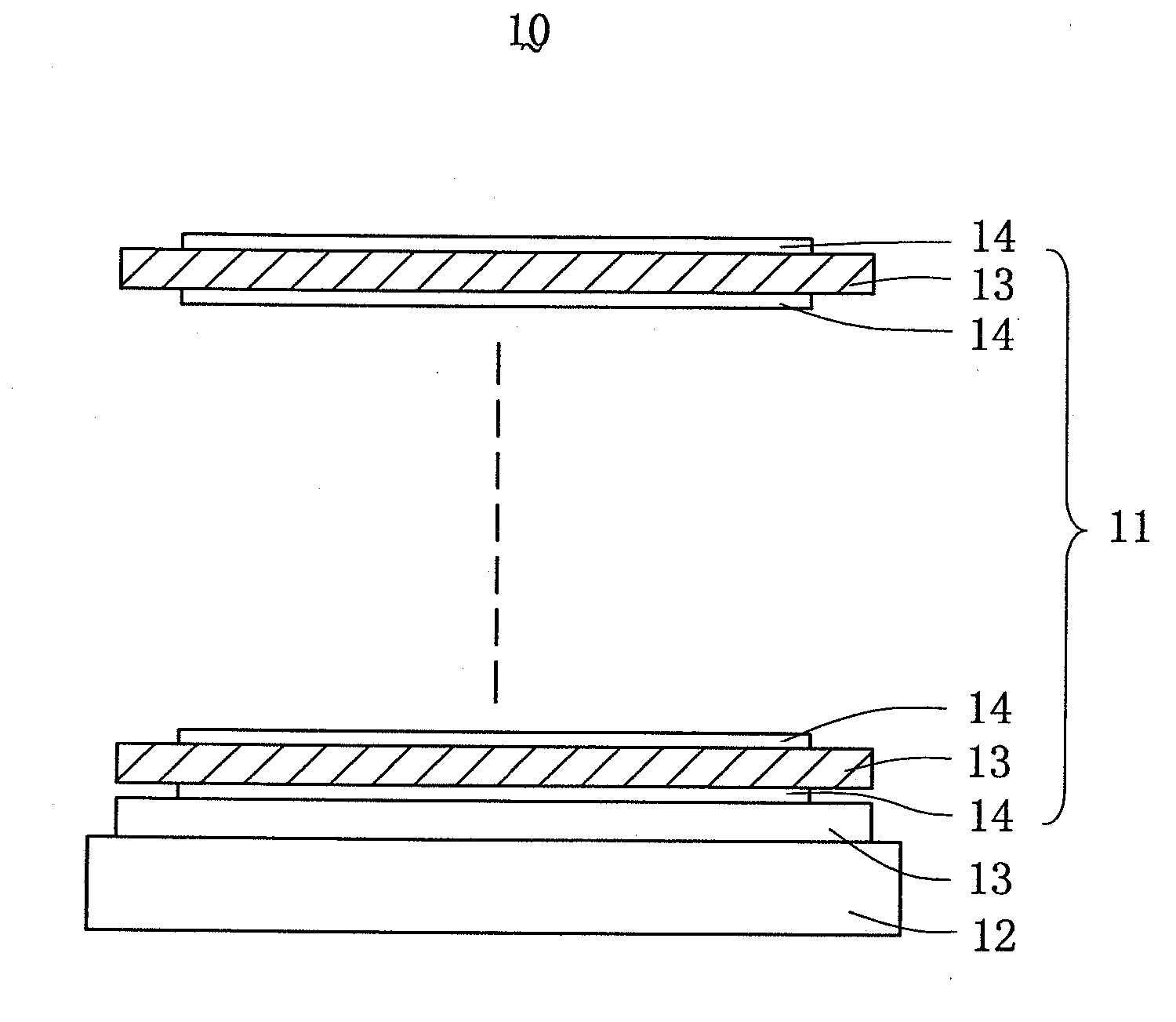
InactiveUS20060285208A1Increase spectral reliabilityUniform colorOptical elementsRefractive indexHigh index
An optical multilayer thin-film system (11) includes a number of high refractive index layers (13), and a number of low refractive index layers (14) alternately laminated with the high refractive index layers. Each high refractive index layer has an optical thickness larger than that of each low refractive index layer. When such a multilayer thin-film system is applied to an optical element, spectral shift with respect to variation of the incident light angle is significantly reduced.
Owner:ASIA OPTICAL CO INC
Charged carbon nanotubes for use as sensors
Owner:SHEW CHWEN YANG +2
Identification method for authenticity of varieties of seeds on basis of near-infrared quantitative analysis
InactiveCN104374739AFree from destructionNo pollution in the processMaterial analysis by optical meansFeature extractionAlgorithm
The invention discloses an identification method for the authenticity of the varieties of seeds on the basis of near-infrared quantitative analysis. The method comprises the steps of acquiring near-infrared spectral data of a seed sample and determining a modeling set and testing sets; carrying out pretreatment, partial-least-square feature extraction and linear-identification feature extraction on the modeling set and the testing sets in sequence; selecting a spectral correction set from the modeling set and the testing sets, calculating a transformation matrix between the modeling set and the testing sets; applying the transformation matrix to the remaining testing sets; establishing a quantitative analysis model by adopting a support vector machine method; and carrying out identification on the authenticity of the varieties of the remaining testing sets by utilizing the quantitative analysis model. The identification method disclosed by the invention is established on the basis of near-infrared quantitative analysis and has the advantages that due to a series of operations of spectral pretreatment, feature extraction, correction of the testing sets, modeling and identification and the like, a more stable near-infrared spectral analysis model is established, and the problem of model applicability caused by long-time spectral shift of the same instrument can be solved, so that the identification result is accurate.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
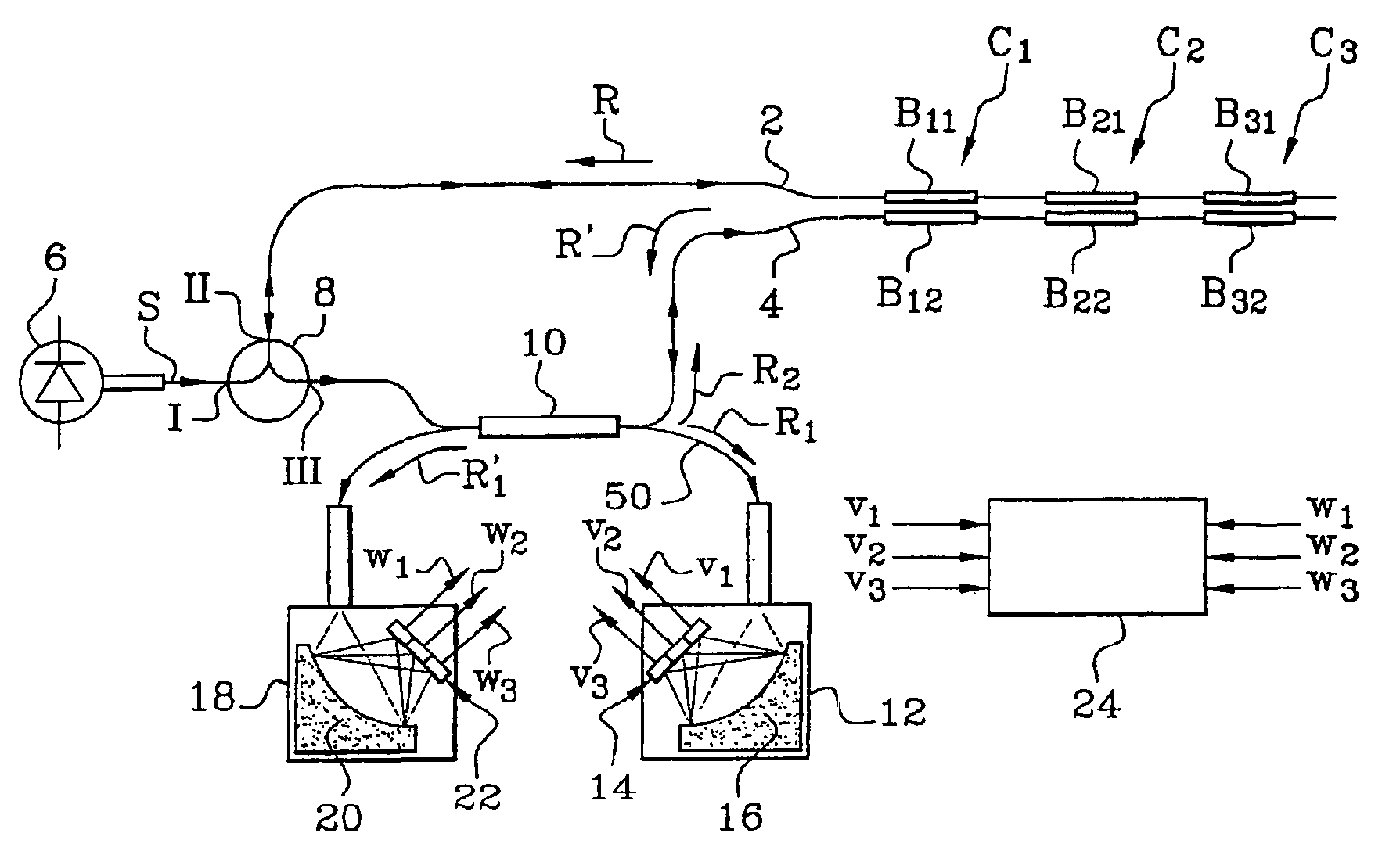
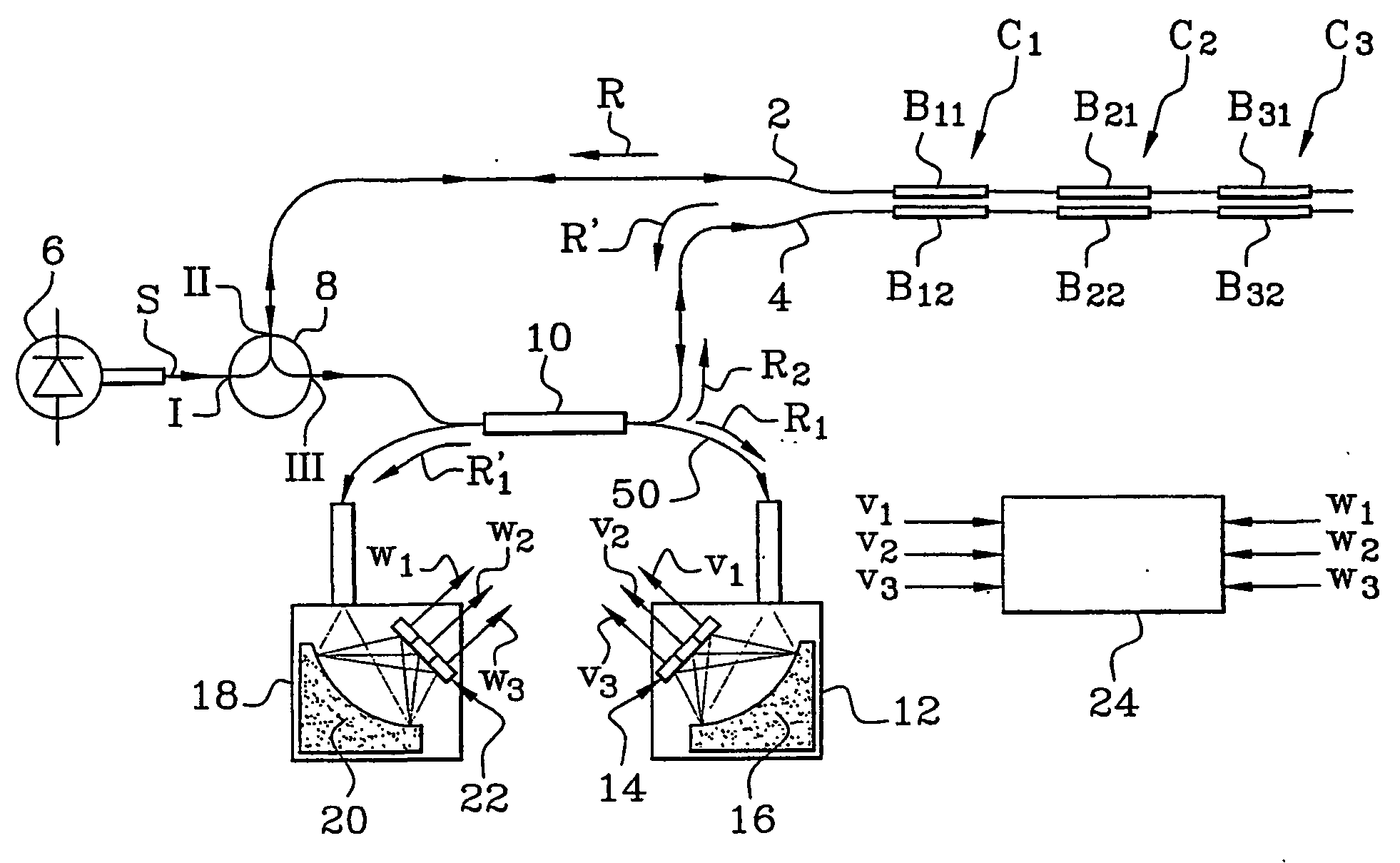
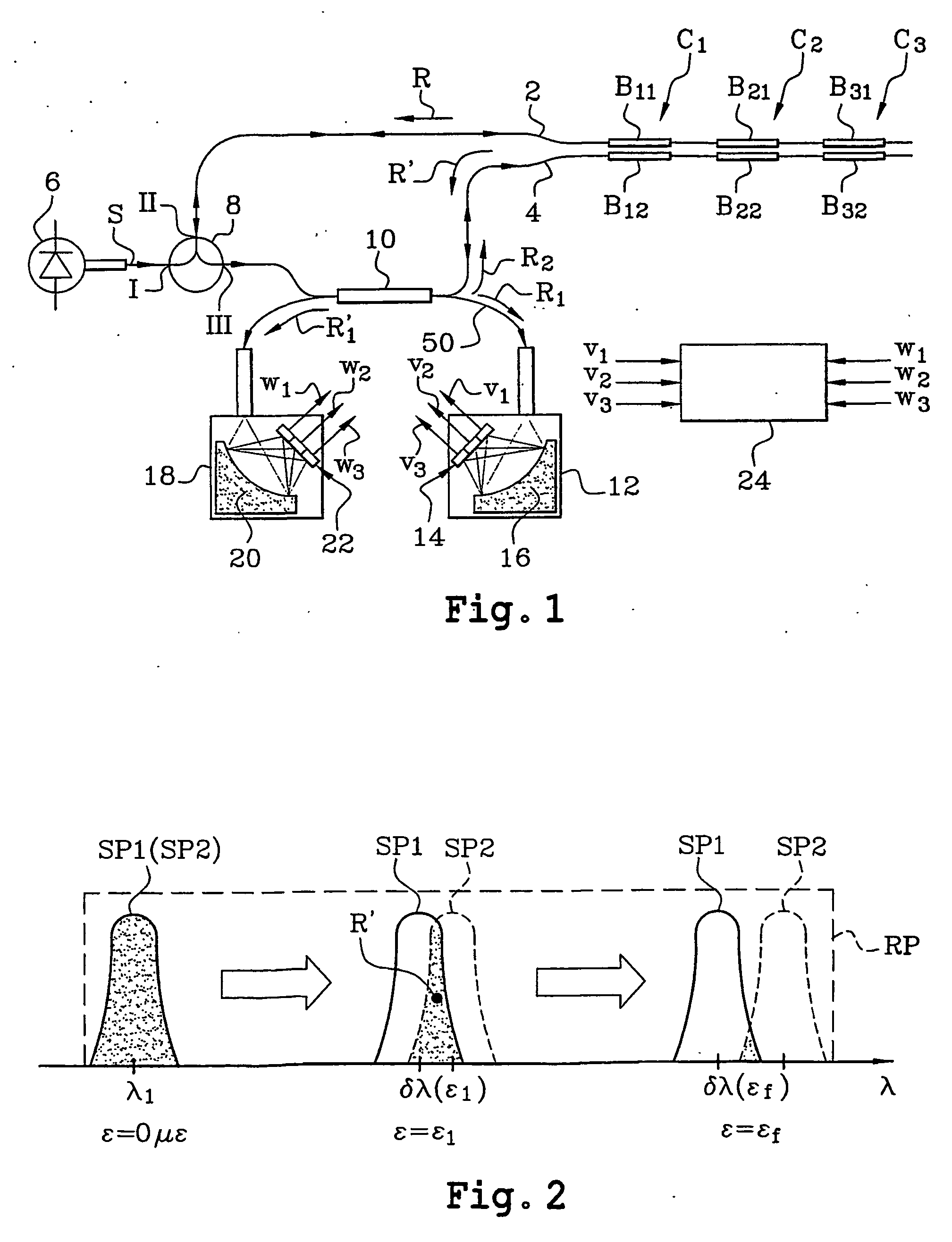
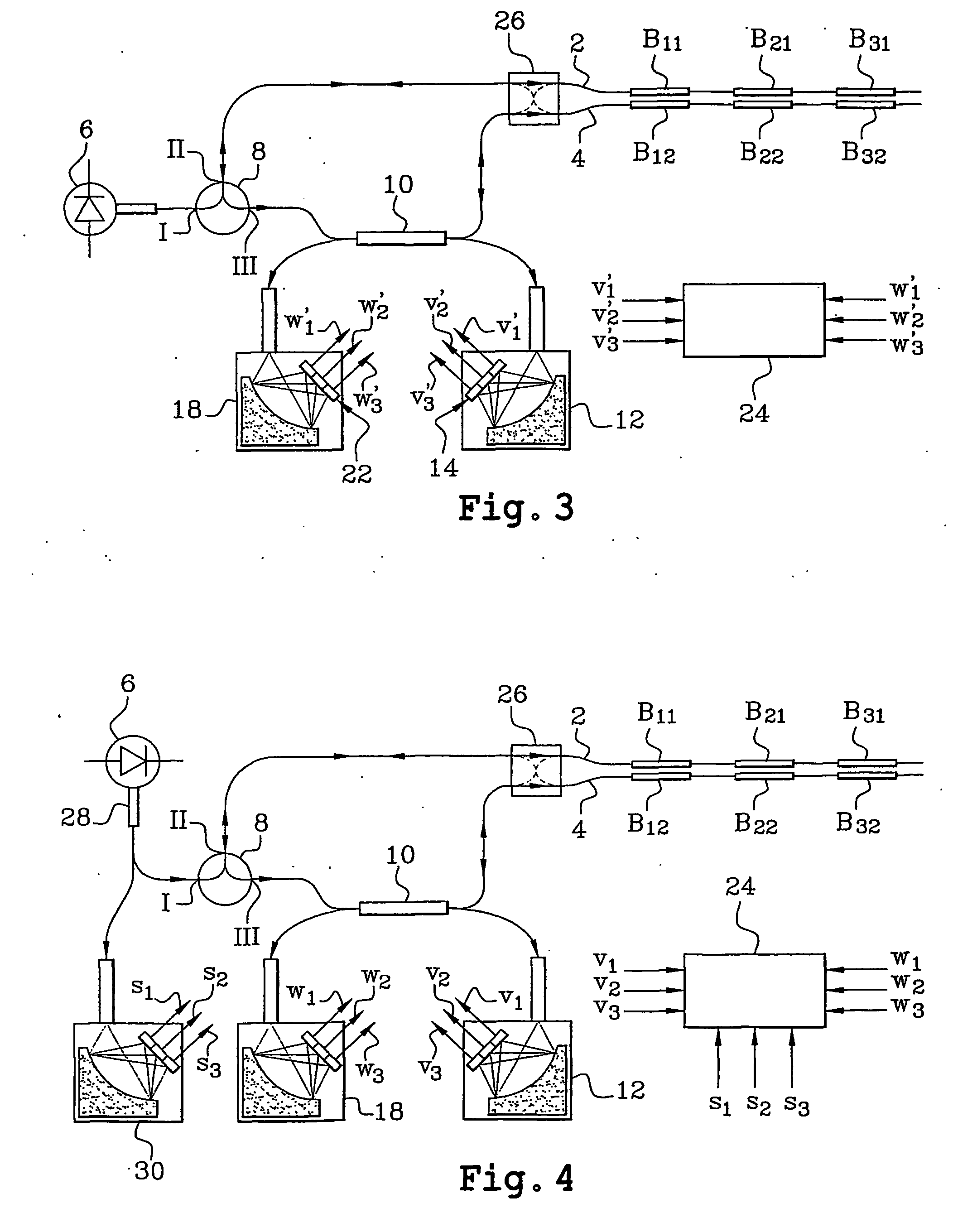
Differential measurement system based on the use of pairs of Bragg gratings
InactiveUS6878926B2Radiation pyrometryForce measurement by measuring optical property variationDifferential measurementPhotovoltaic detectors
A differential measurement system using pairs of Bragg gratings including at least one optical sensor having two Bragg gratings in two optical waveguides and having sensitivities adjusted so that respective spectra of the two gratings have a relative spectral shift dependent on a parameter or parameters to be measured. The system also includes an optical source to supply light to the two optical waveguides to interrogate them, a mechanism enabling light to pass successively through the two Bragg gratings of the same sensor, photodetectors to measure the power level of light having passed only through one of the two optical waveguides and the power level of light having passed successively through the two optical waveguides, and a processor to process the power levels and supply values of the parameter or parameters measured. The system is applicable in particular to measurements of temperatures, stresses, and pressures.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
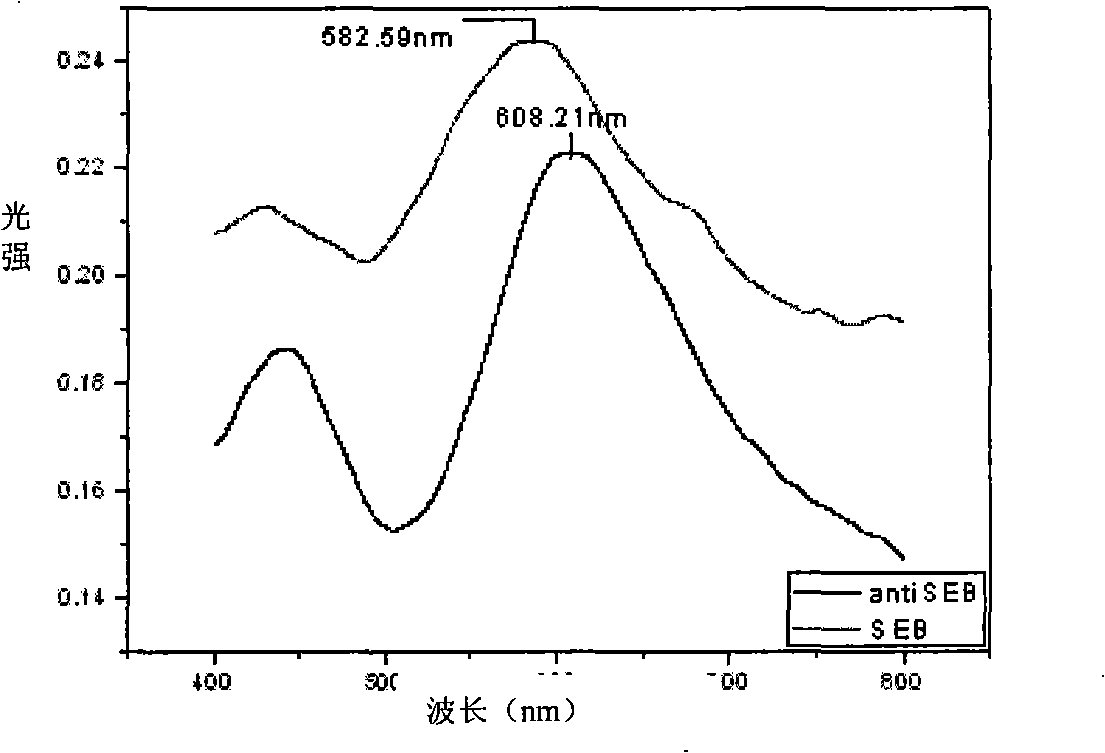
Staphylococcal enterotoxin detection method
InactiveCN101514988AShort detection timeHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansStaphylococcusFluorescence
A staphylococcal enterotoxin detection method is characterized in that the detection method comprises the steps as follows: (1) preparing an LSPR detection chip of staphylococcal enterotoxin; (2) activating the surface of the metal structure of the chip to form a specific biological molecular membrane; (3) testing the extinction spectrum of the chip to obtain a reference value before combination; and (4) dripping a to-be-detected sample, putting the sample in an LSPR sensor for detection after the full reaction of the sample, observing spectral shift condition by using the specific reaction among antigen-antibody molecules, and judging whether the to-be-detected sample contains staphylococcal enterotoxin, so as to realize fast detection with high sensitivity and without a label. The method does not need complex equipment and does not use radioactive isotope, enzyme or fluorescence and the like as a label, and has the remarkable characteristics of quickness, high sensitivity, wide application range, security and high stability. The method provides a simple and practical new method for the quick detection of staphylococcal enterotoxin.
Owner:INST OF OPTICS & ELECTRONICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
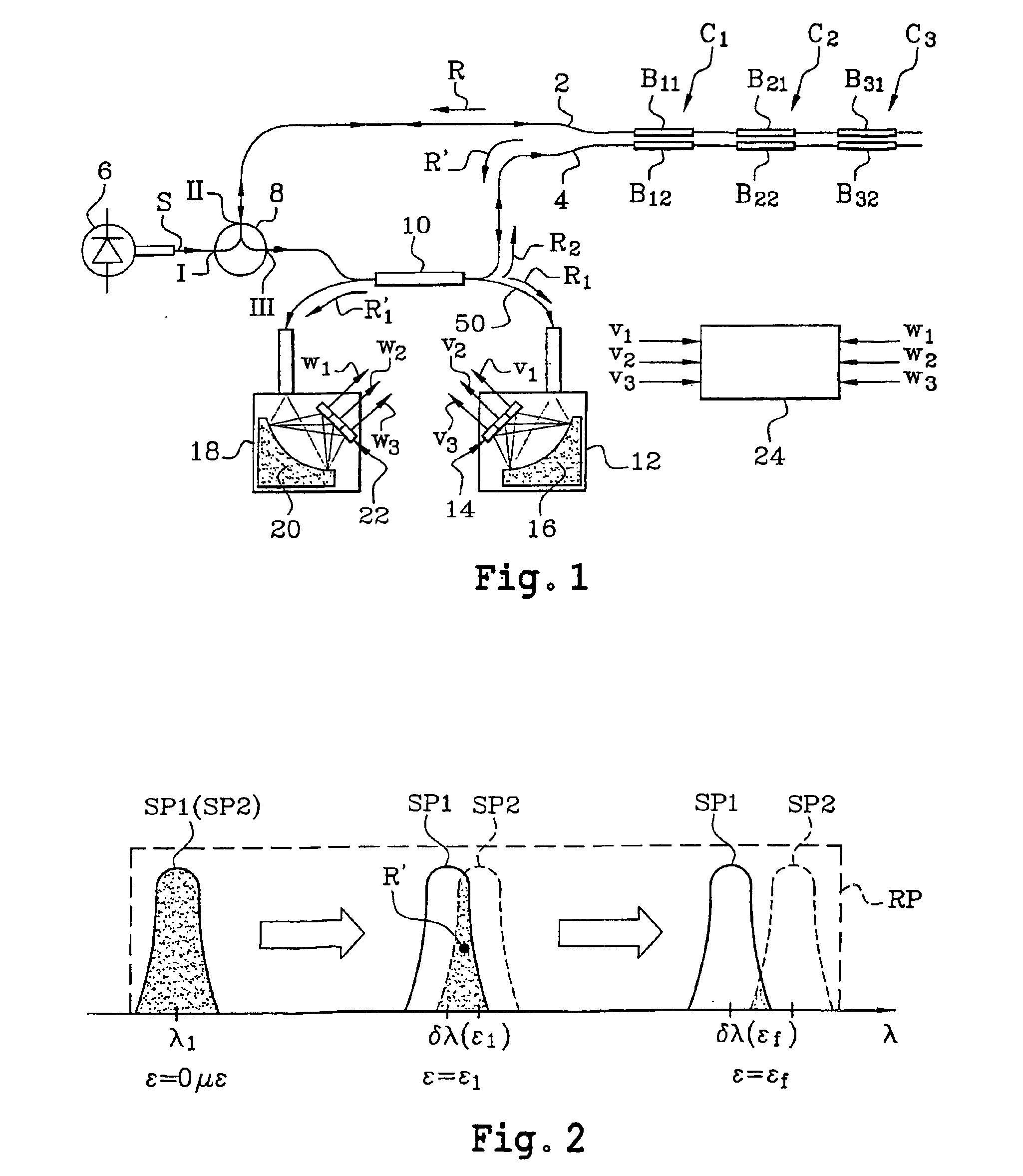
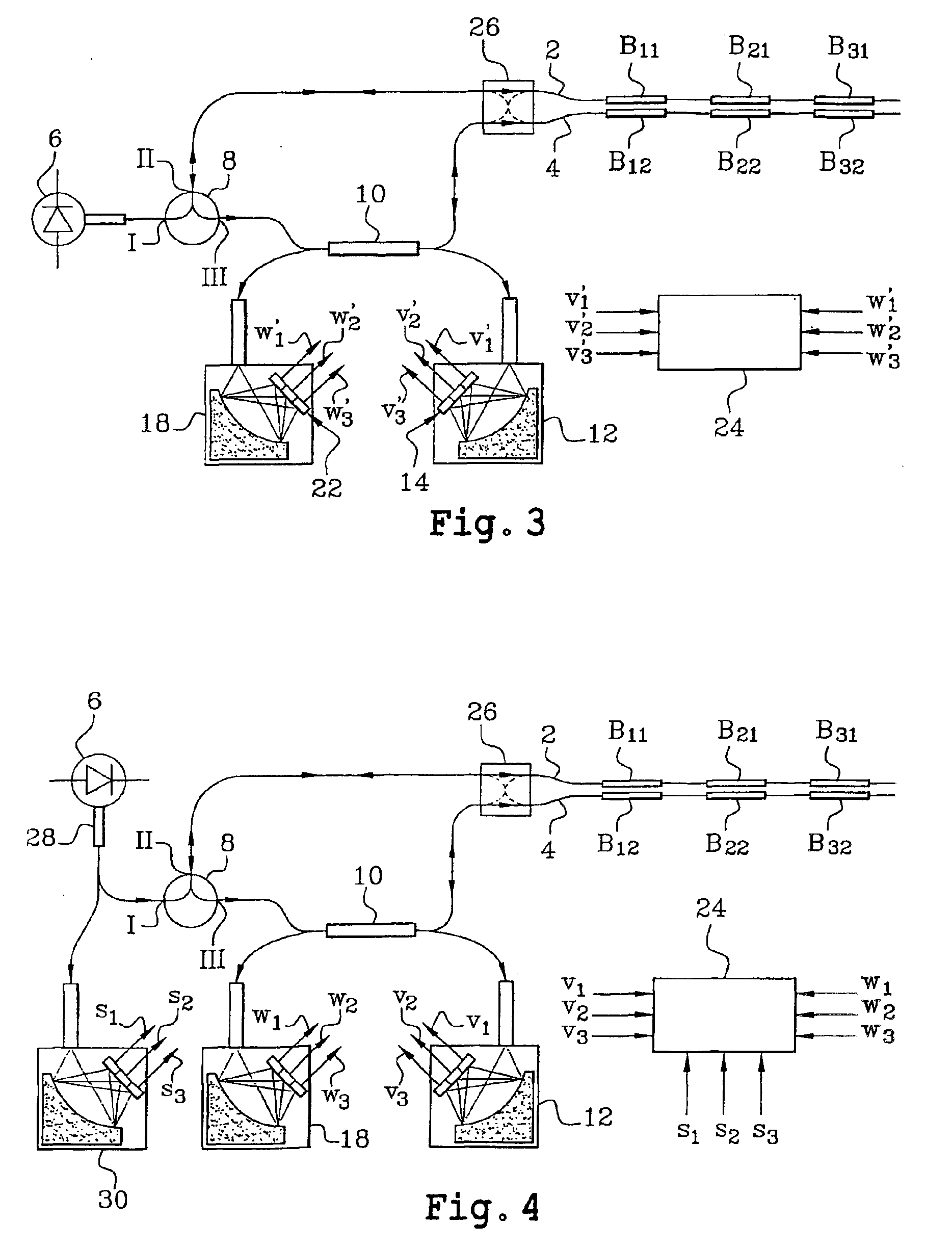
Differential measurement system based on the use of pairs of bragg gratings
InactiveUS20040206892A1Radiation pyrometryForce measurement by measuring optical property variationGratingPhotovoltaic detectors
This system comprises at least one optical sensor (C1, C2, C3) comprising two Bragg gratings (B11, B12; B21, B22; B31, B32) written in two optical waveguides and having sensitivities adjusted so that the respective spectra of the two gratings have a relative spectral shift which depends on the parameter or parameters to be measured. The system also comprises an optical source (6) provided in order to supply light to the two optical waveguides so as to interrogate the latter, means enabling the light to pass successively through the two Bragg gratings of the same sensor, photodetectors in order to measure, on the one hand, the power level of light (R1) having passed only through one of the two optical waveguides and, on the other hand, the power level of light (R'1) having passed successively through the two optical waveguides, and means to process these power levels and supply the values of the parameter or parameters measured. The invention is applicable in particular to measurements of temperatures, stresses and pressures.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Method and system for an ultimately fast frequency-scanning brillouin optical time domain analyzer
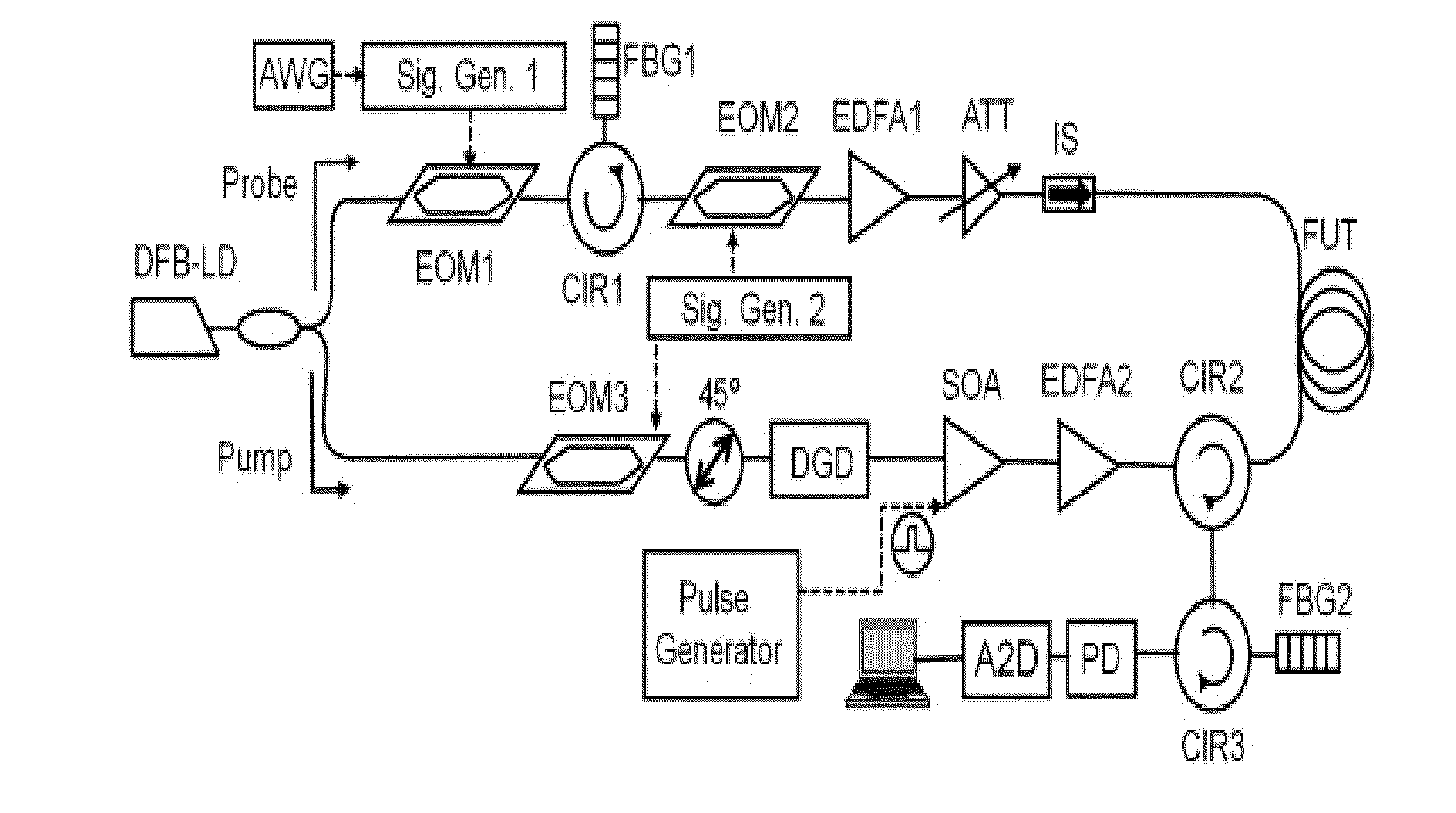
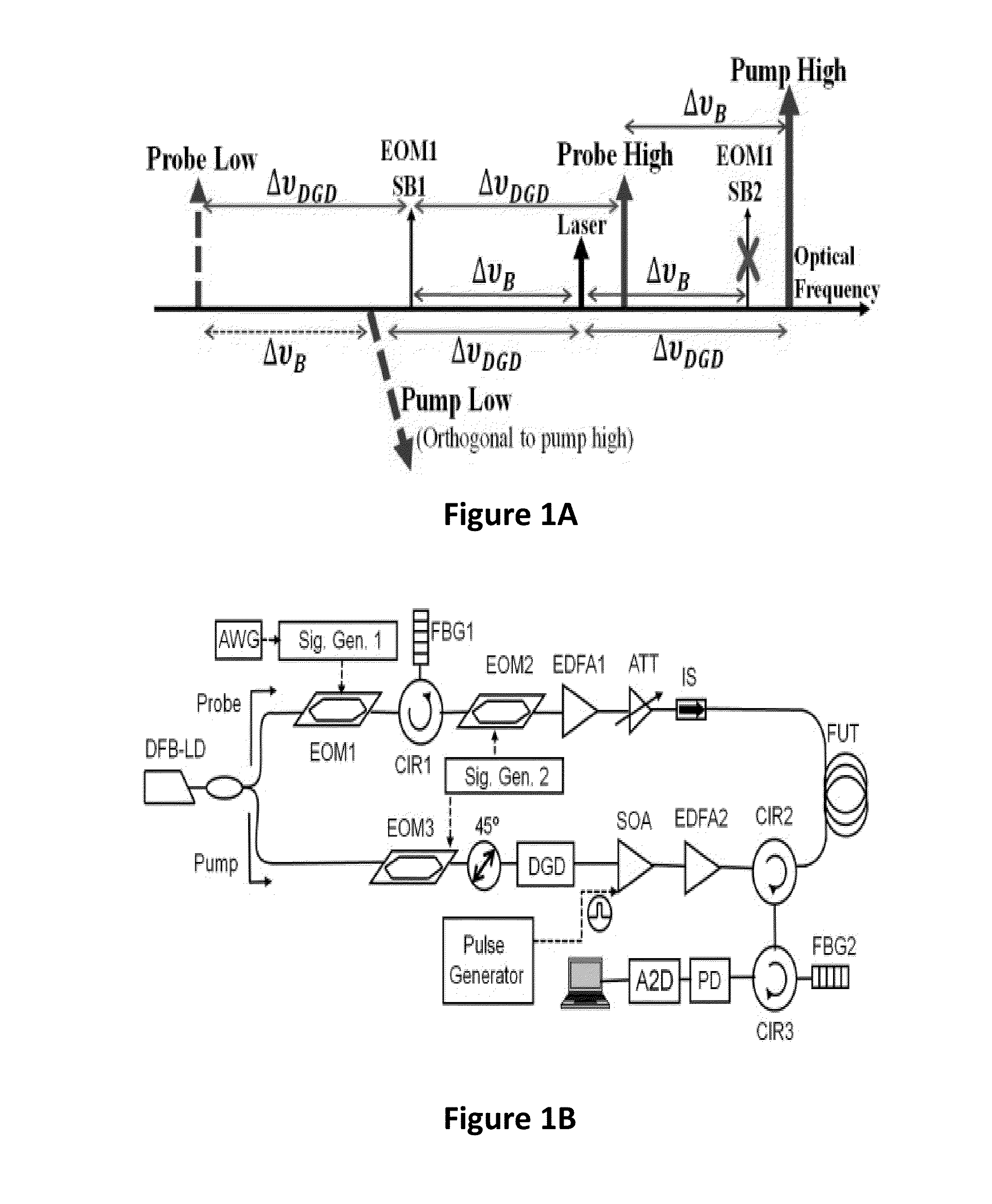
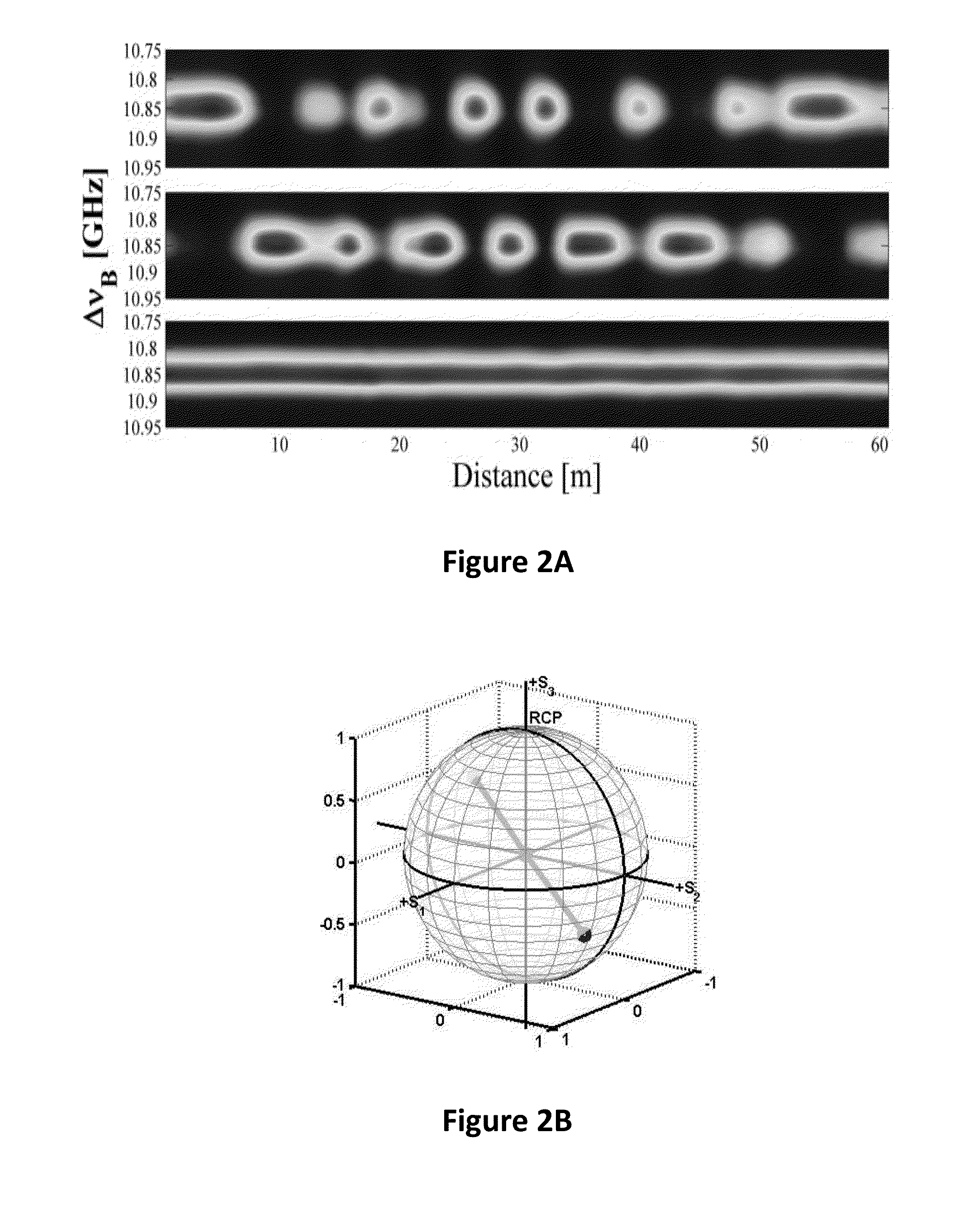
ActiveUS20160273998A1Reflectometers using simulated back-scatterReflectometers detecting back-scattered light in time-domainTime domainComputational physics
A method and a system for ultimately fast frequency-scanning Brillouin optical time domain analysis are provided herein. The method may include: simultaneously launching two pairs each having a pulsed pump wave and a counter-propagating constant wave (CW) probe wave, into an optical fiber, wherein the pulsed pumps have orthogonal States of Polarization (SOPs), and wherein the two CW probe waves have a same SOP; scanning common pump-probe frequency difference, over a frequency range that encompasses a respective Brillouin Gain Spectrum (BGS) and current and expected spectral shifts of the BGS along the optical fiber; deriving, a local Brillouin Frequency Shift (BFS), in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, which is defined as the pump-probe frequency difference which maximizes the Brillouin gain on the BGS; and determining strain and / or temperature in a distributed manner along the optical fiber, based on the respective local BFS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for optical detection of an adjoining of a material component to a sensor material with the aid of biological, chemical or physical interaction and device for carrying out said method (variants)
InactiveUS20030190673A1Improve accuracyConveniently obtainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFrequency spectrumSensor materials
Application: detection of binding of biological and / or chemical components of liquid or gaseous mixtures and solutions, which are of mainly biological origin and / or determine parameters of living activity of biological objects, to substances that bind the said components due to a biological, chemical or physical interaction; and analysis of mixtures and solutions to determine presence of biological and / or chemical components. Essence: binding substances are arranged on a surface of or inside a sensor layer, which changes its thickness due to the binding being detected; the layer is affected by light of different wavelengths; a signal due to interference on the sensor layer is registered in the reflected or transmitted light. In the first variant, the signal is represented by a spectrum; the sensor layer is more than 10 mum thick and exceeds the maximal recorded wavelength by at least an order of magnitude; information about the binding being detected is obtained from analysis of a spectral shift of interference maximums and minimums. In the second variant, the light passes also a scanned Fabry-Perot interferometer; the recorded signal is a dependence of intensity of the resulting light upon changes of base of the scanned Fabry-Perot interferometer, in which maximums due to correlation of the spectral characteristics of interaction of the light with the sensor layer and interferometer are observed; information about the binding being detected is obtained from a shift of the said dependence along values of base. In the third variant, other interferometers are used, which are scanned due to a change of the path difference of interfering beams. The required technical result is to make measurement results independent from uncontrollable variations of intensity of the analyzed light in whole as well as in any part of its spectrum, any areas of the sensor layer, and, consequently, to increase accuracy of measurements and reliability of results, sensitivity and resolution with simultaneous reduction of the number of necessary operations, of labor input and cost of both single- and multi-channel variants including real-time registration.
Owner:PETR IVANOVICH NIKITIN
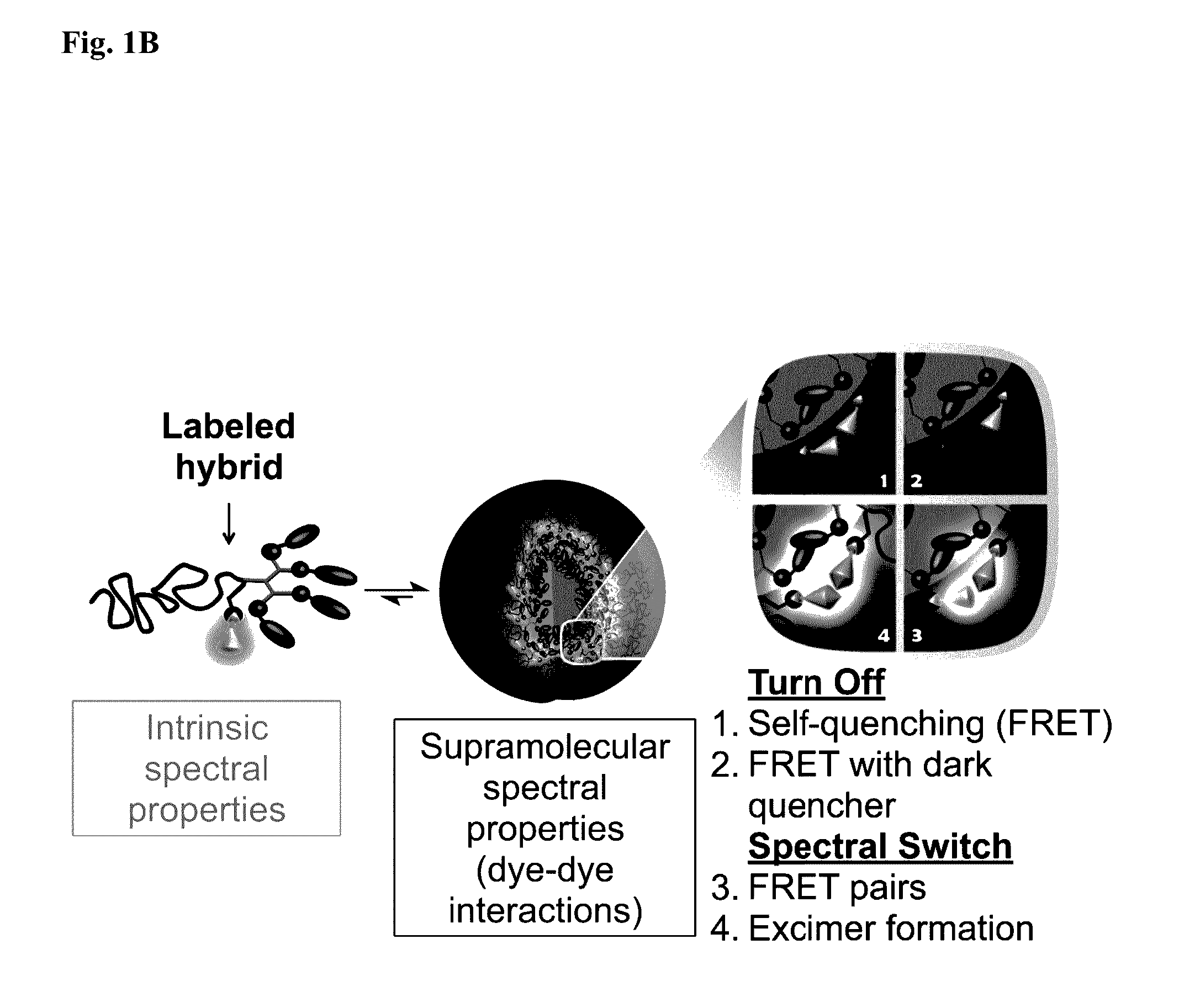
Delivery system in micellar form having modular spectral response based on enzyme-responsive amphiphilic peg-dendron hybrid polymers
ActiveUS20170035916A1Enhanced interactionRestore their strong fluorescenceDispersion deliveryPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSpectral responseFluorescence
The present invention relates to new molecular design that allows micelles to report their activation and disassembly by an enzymatic trigger. The molecular design is based on introduction of a labeling moiety selected from a fluorescent dye, a dark quencher, combinations of dyes or dyes / quenchers, and a fluorinated moiety (a 19F-magenetic resonance (MR) probe for turn ON / OFF of a 19F-MR signal) through covalent binding to the focal point of amphiphilic polymer-dendron hybrids with the labeling moiety. At the assembled micellar state, the dyes are closely packed and hence the probability for intermolecular interactions increases significantly, leading to alteration of the fluorescent properties (signal quench or shift) or the 19F-MR signal (OFF state) of the micelles. Upon enzymatic cleavage of the hydrophobic end-groups from enzyme-responsive dendron, the polymers become hydrophilic and disassemble. This structural change is then translated into a spectral change as dye-dye interactions are halted and the dyes regain their intrinsic fluorescent properties, or alternatively by turn ON the 19F-MR signal. The high modularity of the design allows the introduction of various types of dyes and thus enables rational adjustment of the spectral response. Two major types of responses are described: Turn-On / Off and spectral shift, depending on the type of labeling dye. The present invention further provides methods of use of the hybrid delivery system and to a kit comprising the same.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Method for correcting spectral shift in differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) measurement
InactiveCN102495014AEliminate the effects ofColor/spectral properties measurementsDifferential optical absorption spectroscopyDifferential absorption
The invention relates to a method for measuring gas components and in particular relates to a method for correcting spectral shift in differential optical absorption spectroscopy (DOAS) measurement for measuring gas components with DOAS. In order to eliminate influence of offset on the differential absorption spectrum, the signal spectrum is subjected to offset correction; since the offset of the spectral line is possibly not the integer multiples of the measurement channel number, interpolation is required in the correction; and through interpolation re-sampling, the corrected signal spectrum after slight offset can be obtained. By adopting the method, the influence of the offset of the spectral line on the absorption spectrum is obviously reduced, and the influence on the fitting result of the final DOAS calculation is basically eliminated.
Owner:浙江微兰环境科技有限公司
Spectral shift control for dimmable AC led lighting
ActiveCN102612862AElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesPeriodic excitationFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and associated methods involve operation of an LED light engine in which a relative intensities of selected wavelengths shift as a function of electrical excitation. In an illustrative example, current may be selectively and automatically diverted substantially away from at least one of a number of LEDs arranged in a series circuit until the current or its associated periodic excitation voltage reaches a predetermined threshold level. The diversion current may be smoothly reduced in transition as the excitation current or voltage rises substantially above the predetermined threshold level. A color temperature of the light output may be substantially changed as a predetermined function of the excitation voltage. For example, some embodiments may substantially increase or decrease a color temperature output by a solid state light engine in response to dimming the AC voltage excitation (e.g., by phase-cutting or amplitude modulation).
Owner:SIGNIFY NORTH AMERICA CORP
Proteorhodopsin mutants with improved optical characteristics
InactiveUS20050095605A1Excellent optical propertiesMutant preparationWith electric batteriesCrystallographyArginine
The present invention is directed to a proteorhodopsin mutant having improved optical characteristics. One improved optical characteristic is having a lower pH (pKrh) at which equal concentrations of the acidic and basic spectral form of the proteorhodopsin molecules are present. Another improved optical characteristic is having a smaller difference in maximum absorption wavelength between the basic and the acidic form. The mutant comprises a mutation in a conserved amino acid residue of a proteorhodopsin variant, which causes spectral shifts. A preferred mutation site is a conserved histidine residue at amino acid position 75 of Bac31A8, or position 77 of Hot75m1, or its equivalent position of a proteorhodopsin variant. Another preferred mutation site is a conserved arginine residue at amino acid position 94 of Bac31A8, or position 96 of Hot75m1, or its equivalent position of a proteorhodopsin variant.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com