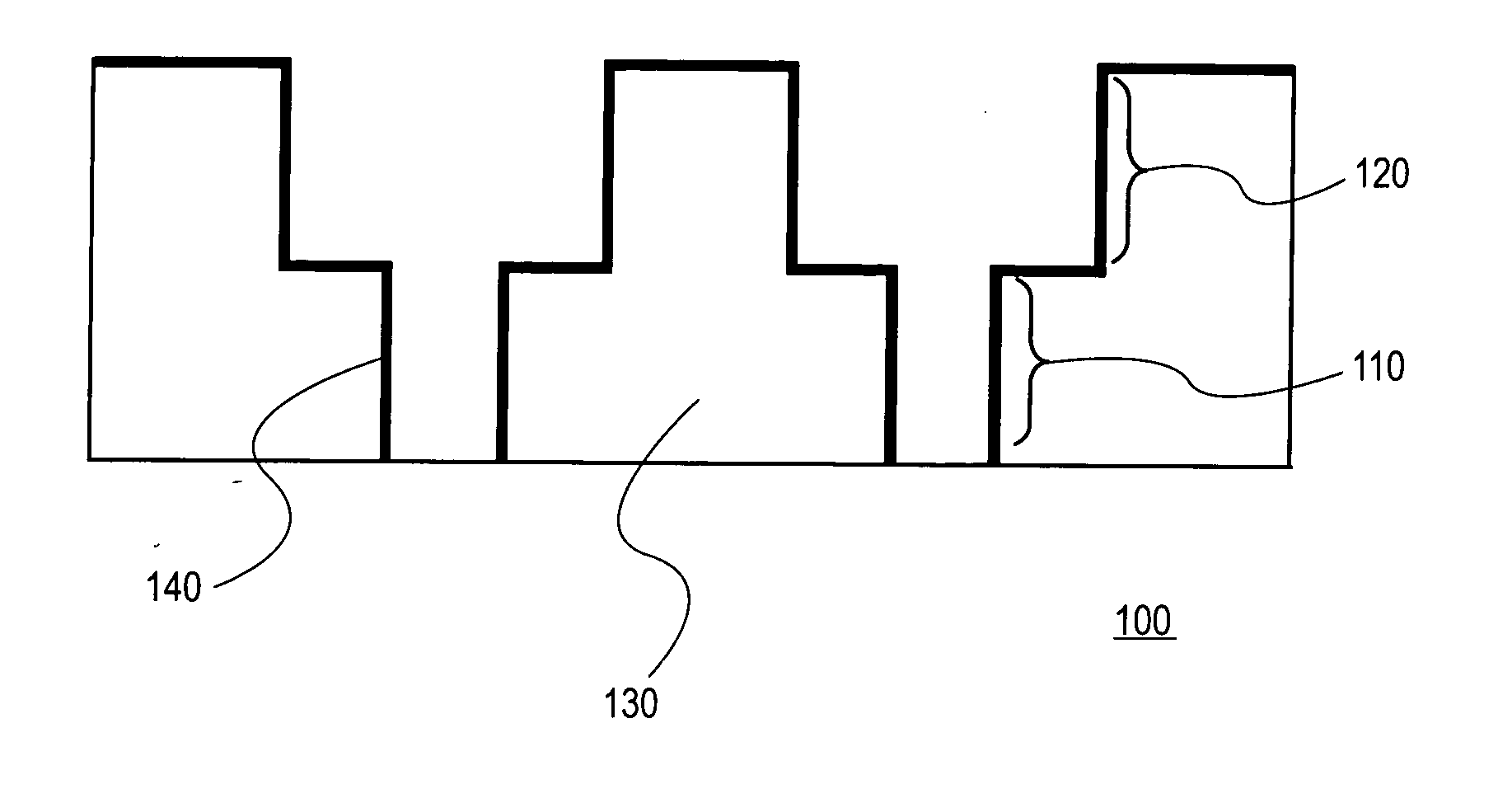
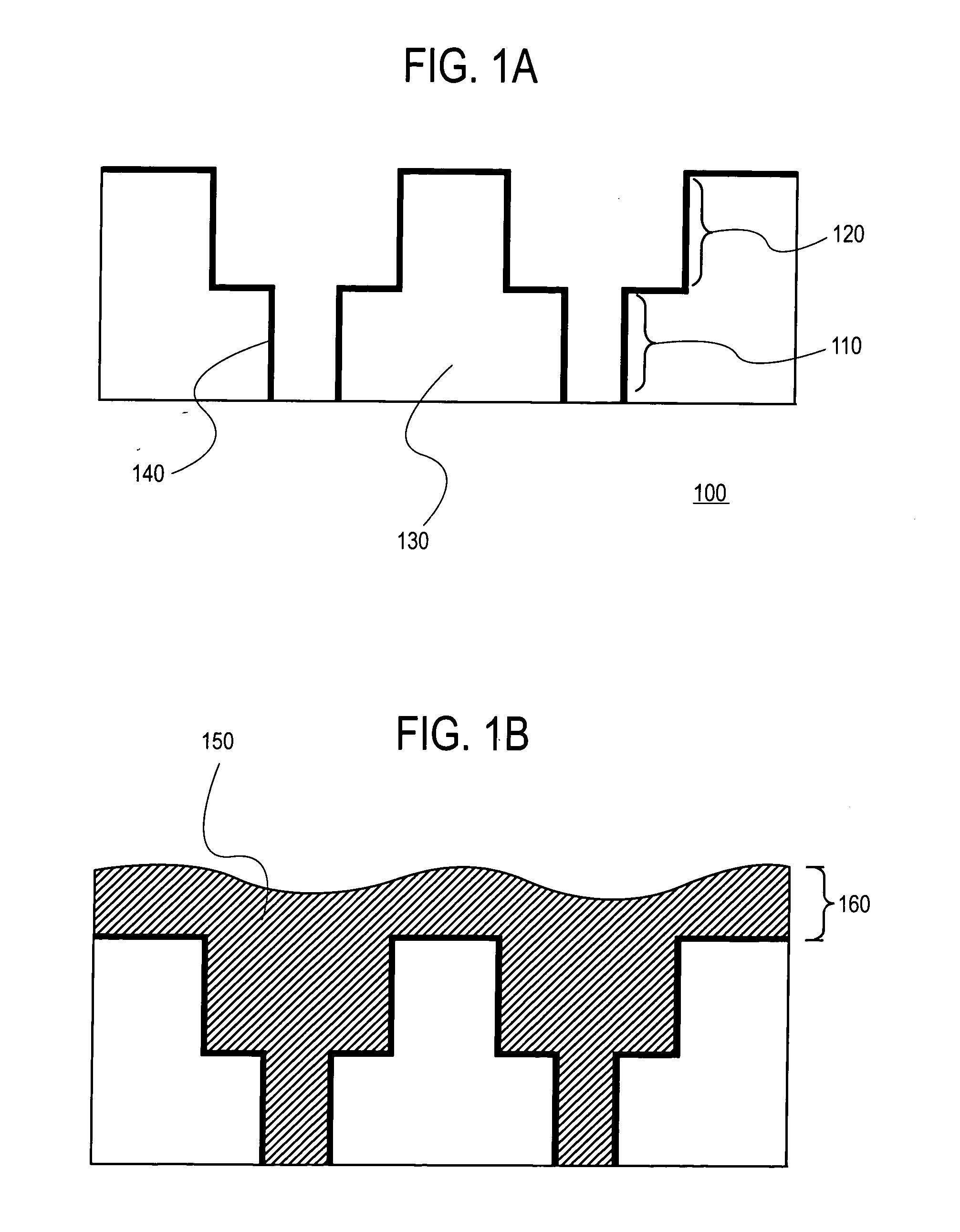
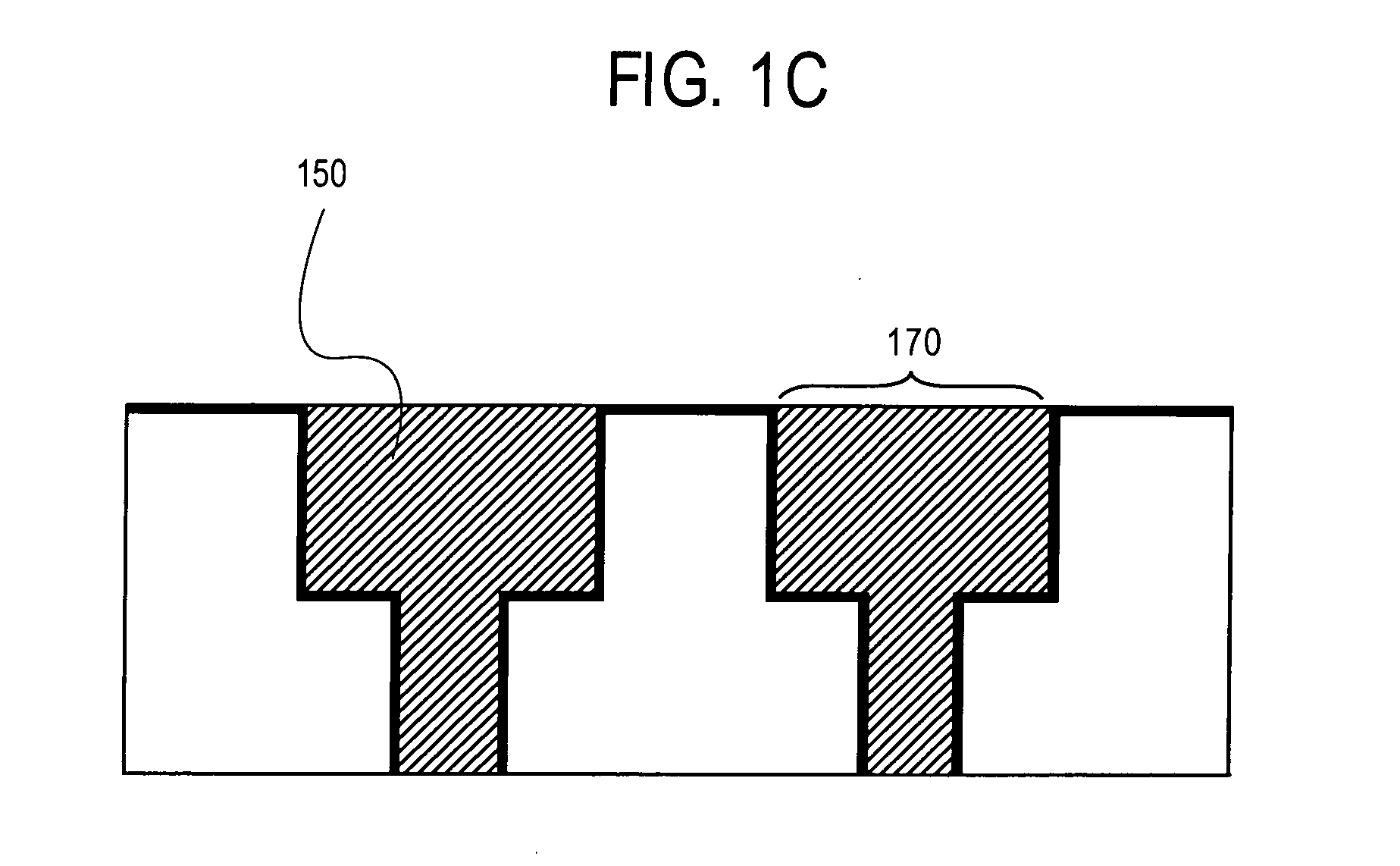
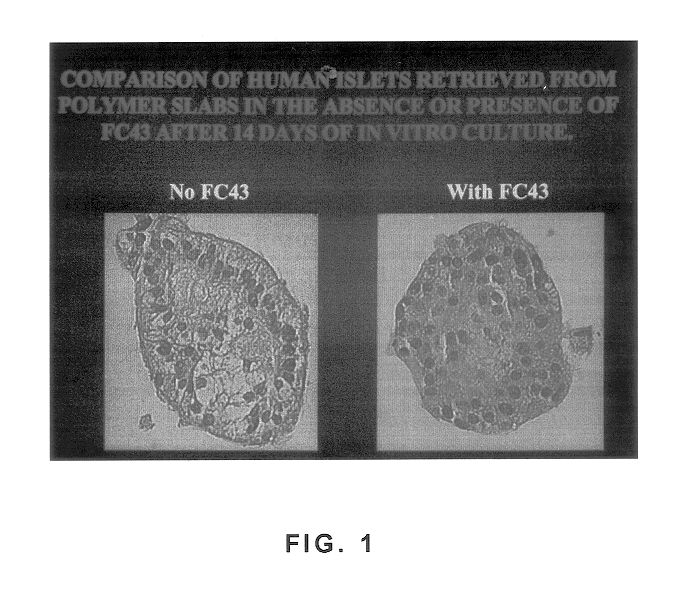
Patents
Literature
563 results about "Covalent binding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Covalent bond, in chemistry, the interatomic linkage that results from the sharing of an electron pair between two atoms. The binding arises from the electrostatic attraction of their nuclei for the same electrons.
Staged assembly of nanostructures
The present invention provides methods and assembly units for the construction of nanostructures. Assembly of nanostructures proceeds by sequential, non-covalent, vectorial addition of an assembly unit to an initiator or nanostructure intermediate during an assembly cycle, a process termed "staged assembly." Attachment of each assembly unit is mediated by specific, non-covalent binding of a single pre-determined joining element of one assembly unit to a complementary joining element on a target initiator or nanostructure intermediate. Each interaction of a joining element is designed such that the joining element does not interact with any other joining element of the assembly unit. Self-association of the assembly unit is therefore obviated: only one assembly unit can be added at a time to a target initiator or nanostructure intermediate.
Owner:NANOFRAMES
Methods of making microarrays with substrate surfaces having covalently bound polyelectrolyte films
InactiveUS6989267B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPolyelectrolyteSubstrate surface
Methods for stably associating a polyelectrolyte coating or film to a substrate surface, as well as the coated substrates produced thereby, are disclosed herein. In the subject methods, substrate surfaces are coated with a polyelectrolyte, and the coated substrate surfaces are treated with a bifunctional molecule under conditions sufficient to stably associate the film to the array surface. The subject methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the production of mircoarrarys.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Microorganism detection and analysis using carbohydrate and lectin recognition
ActiveUS20080193965A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismQuartz crystal microbalance
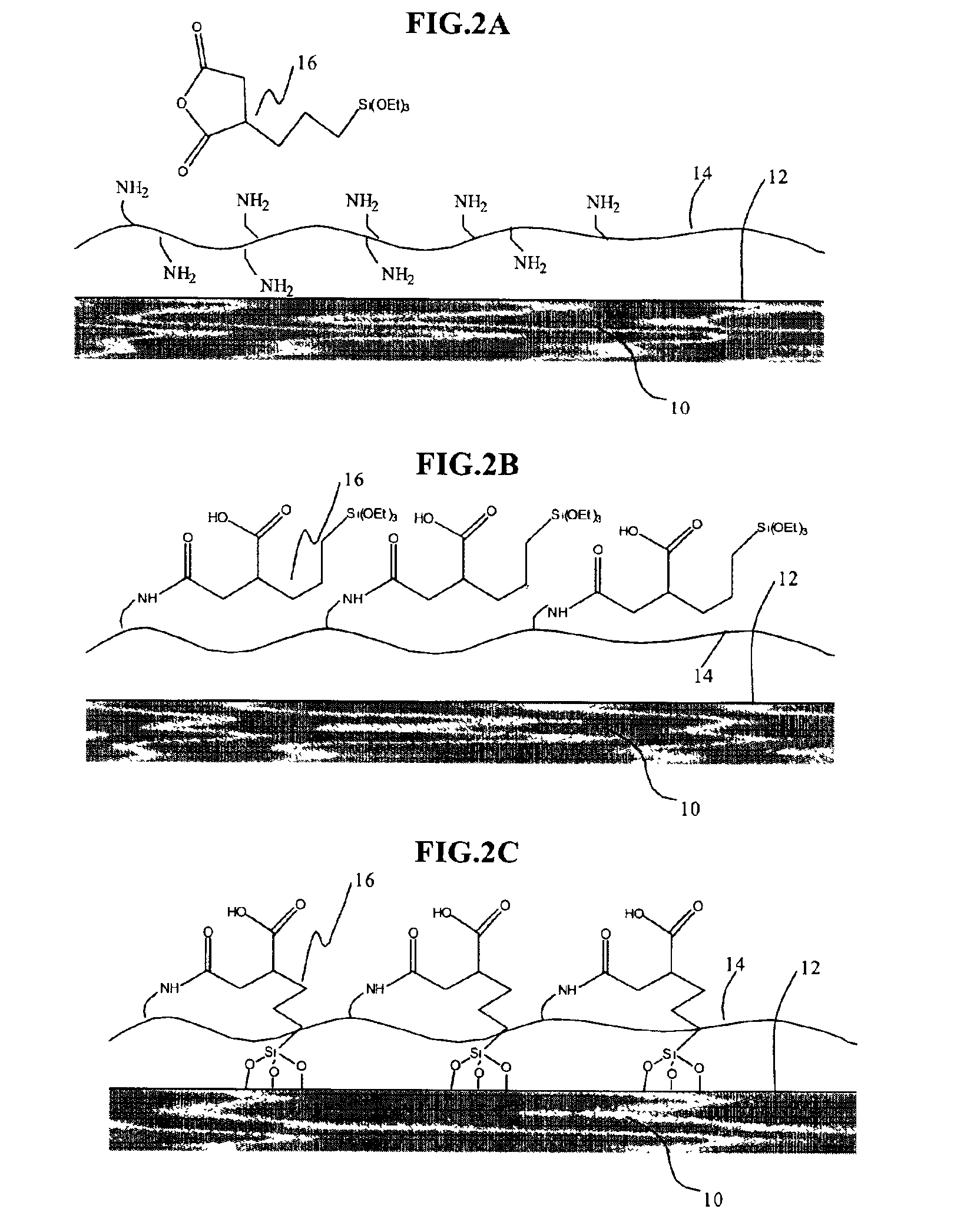
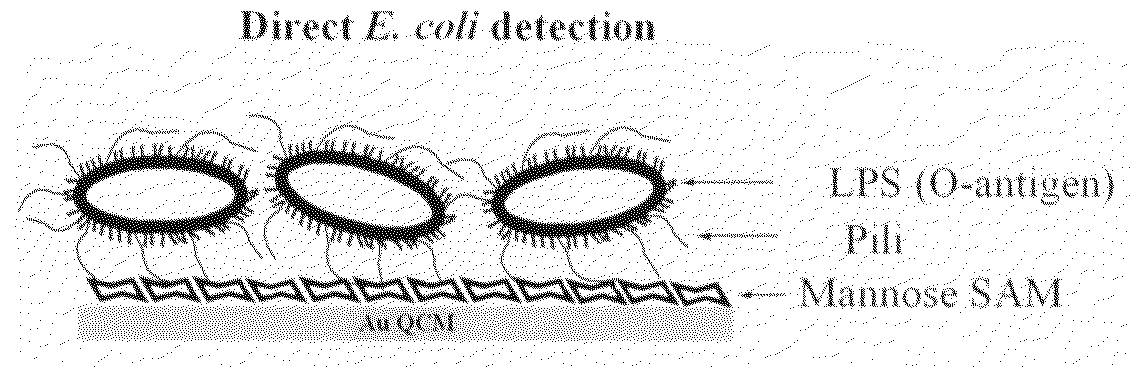
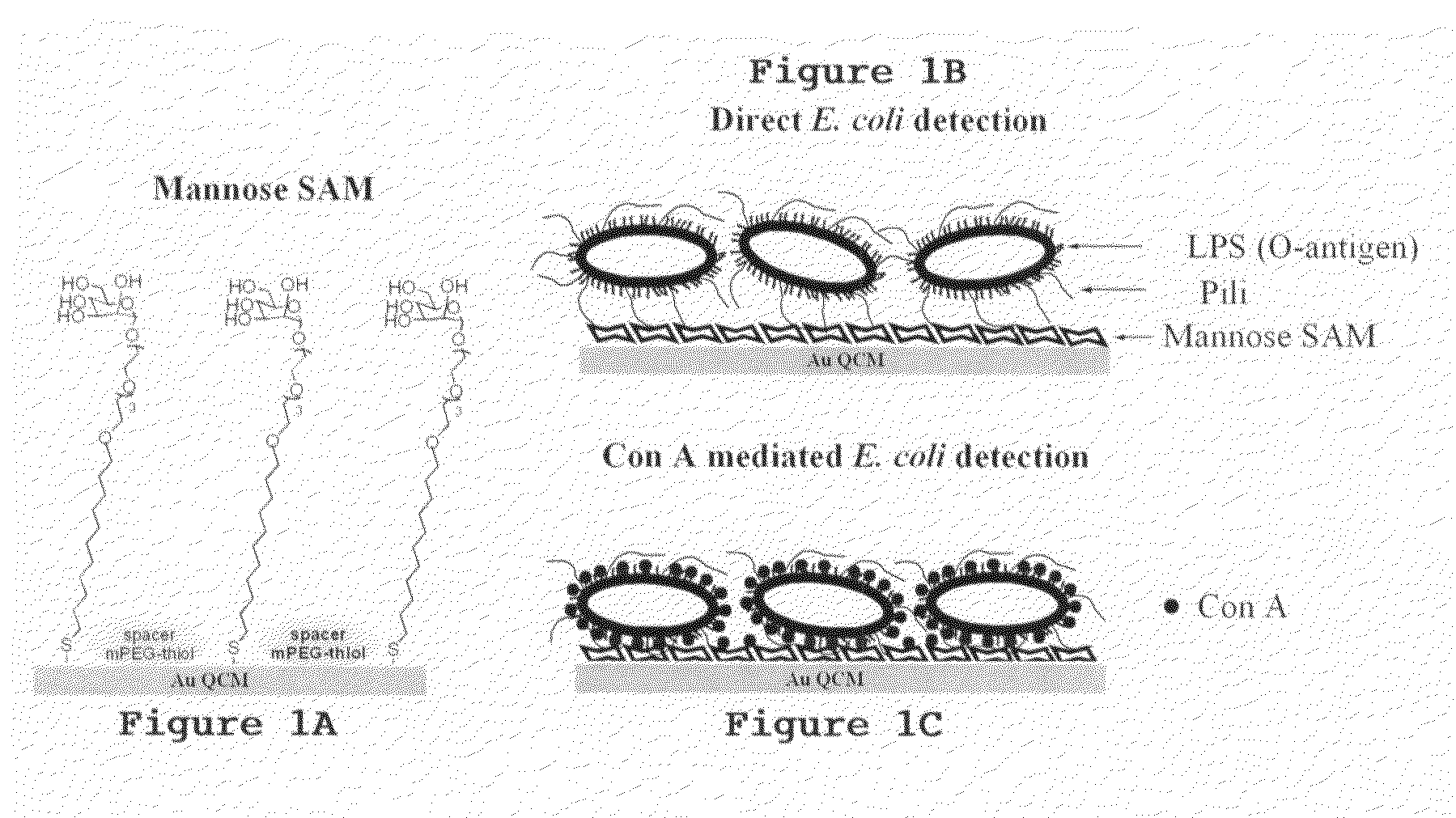
Methods of binding and detecting a microorganism on a solid substrate. The microorganism is bound on a solid substrate covalently bound to a capture agent having a saccharide moiety. A lectin capable of binding to the microorganism and the saccharide moiety of the capture agent is added to the sample to bind the microorganism on the solid substrate. Further provided are biosensor devices, such as a quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) device or a surface plasmon resonance (SPR) device, that incorporate the solid substrate for the detection of microorganisms.
Owner:OAKLAND UNIVESITY
Ion exchange cryptands covalently bound to substrates
InactiveUS20050133453A1Ion-exchange process apparatusOther chemical processesIon exchangeIon binding
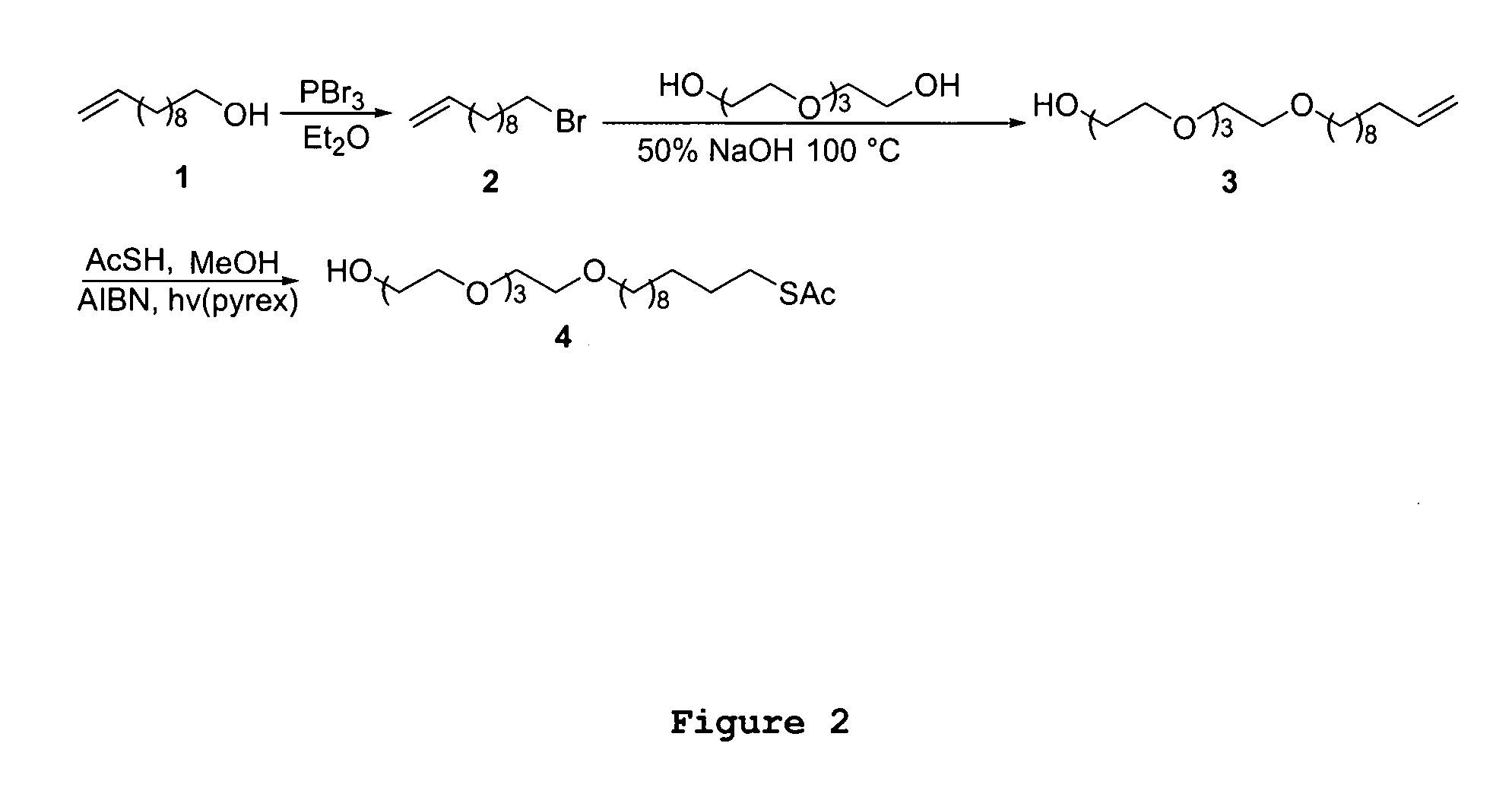
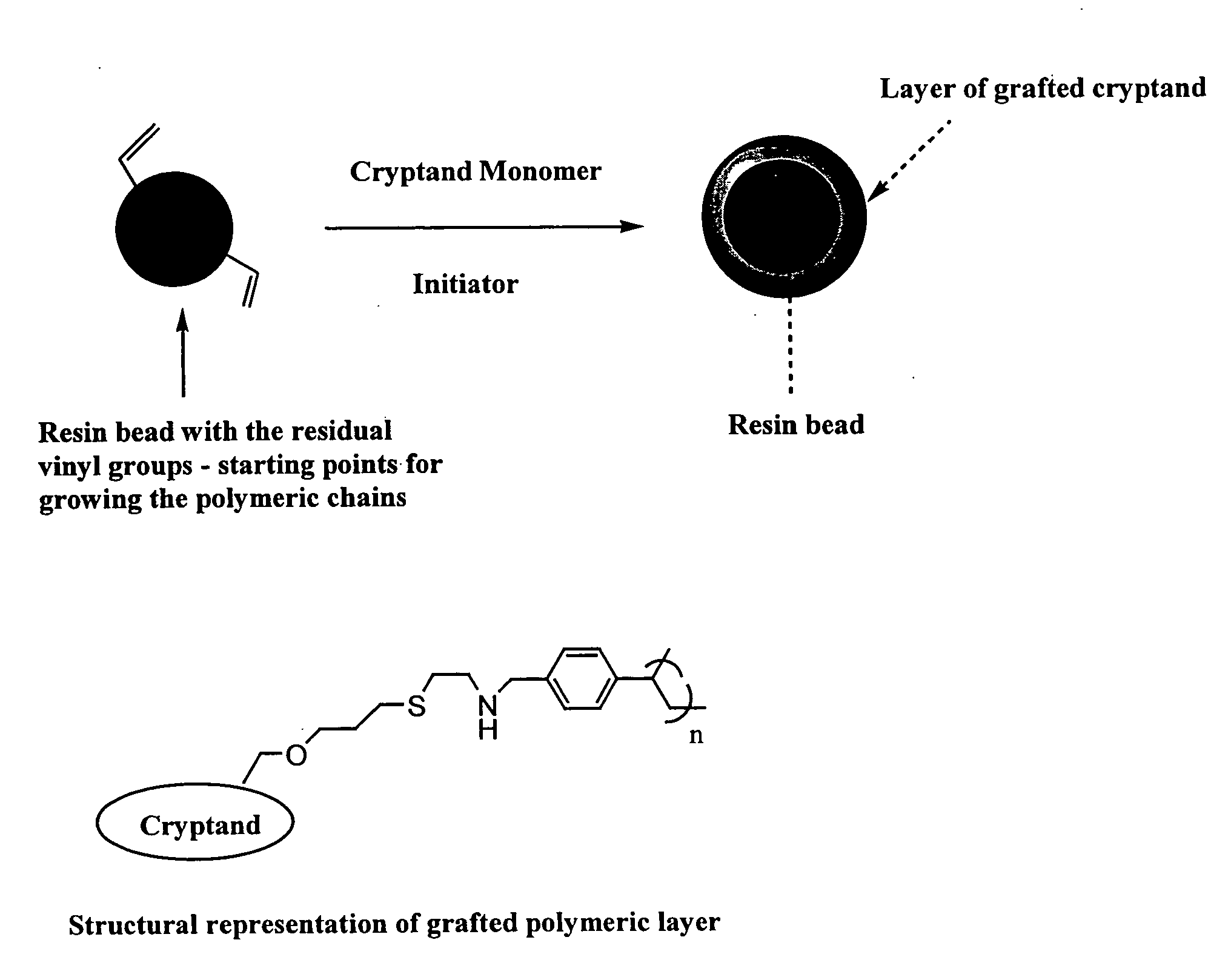
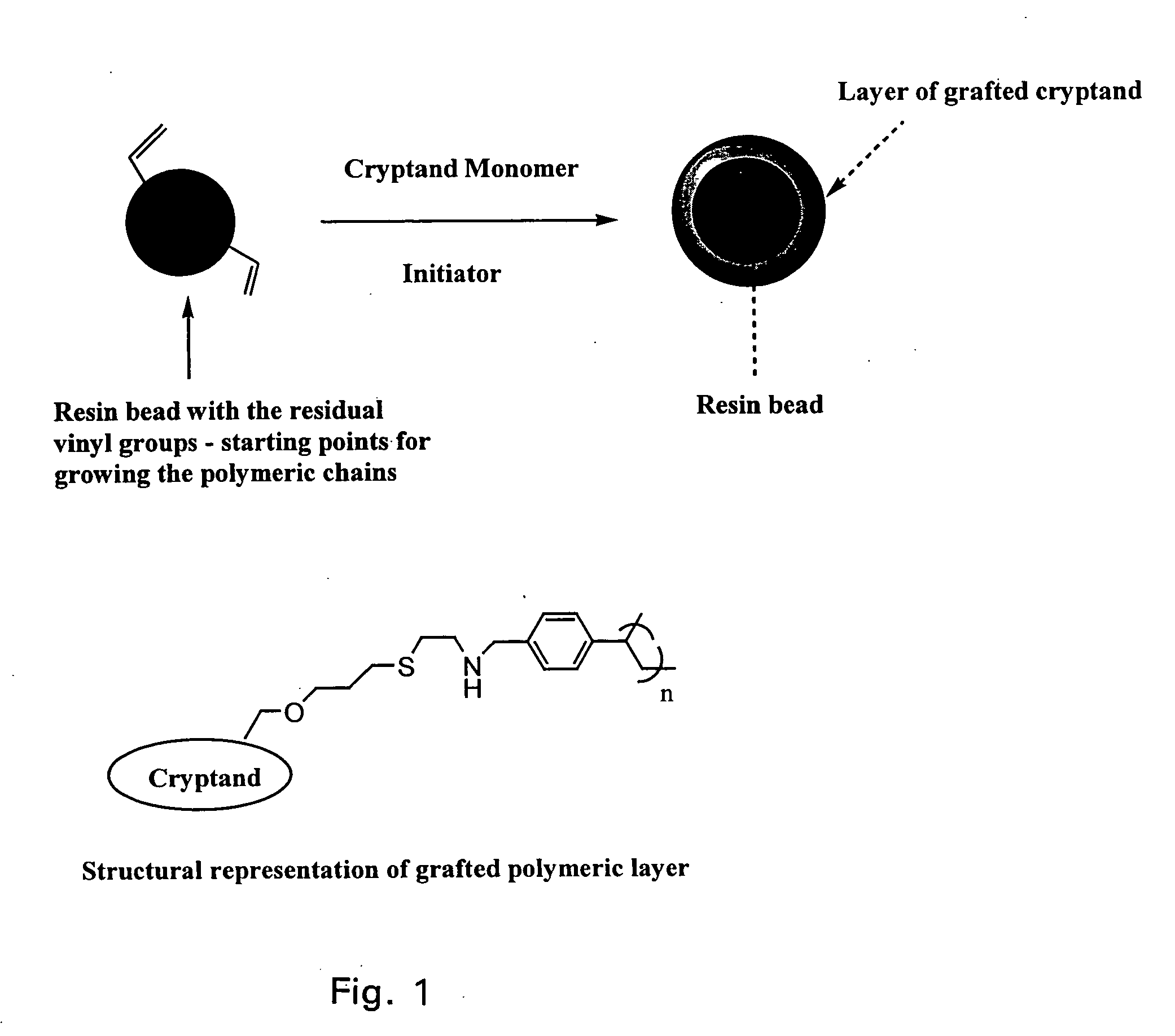
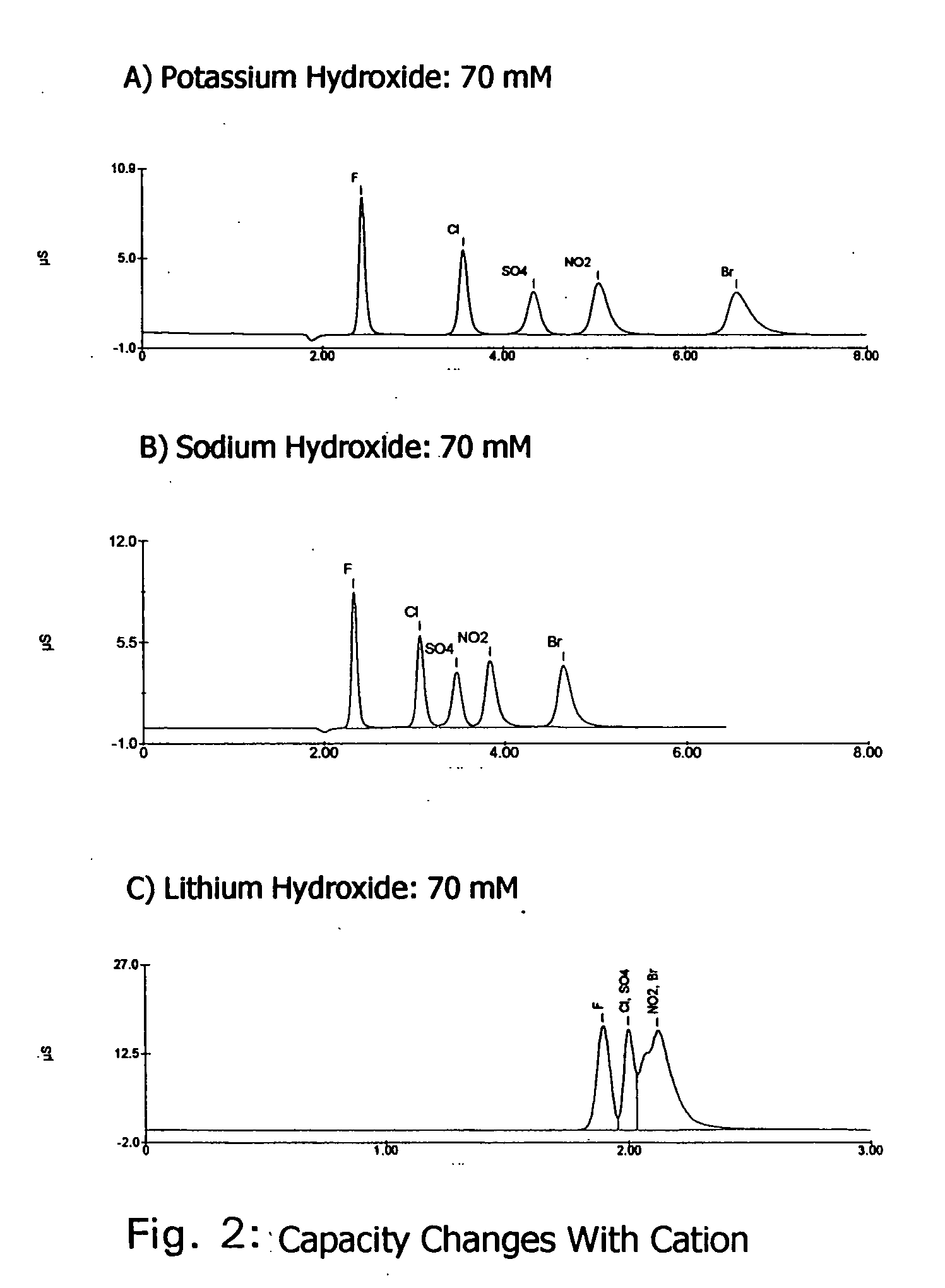
One embodiment of the invention comprises an ion exchange composition formed by reacting unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from derivatized ion binding cryptands with a support substrate under free radical activation conditions to form a covalent bond therebetween. In another embodiment, a cryptand ion exchange composition is made by covalently bonding unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from a derivatized ion binding cryptands with unsaturated carbon to carbon moieties pendant from a support substrate under free radical activation conditions to form covalent bond.
Owner:DIONEX CORP
Nucleic acid probes and methods to detect and/or quantify nucleic acid analytes
InactiveUS6902900B2Enhance binding affinityLow fluorescenceMonoazo dyesSugar derivativesDouble strandedFluorescence
The invention comprises novel methods and strategies to detect and / or quantify nucleic acid analytes. The methods involve nucleic acid probes with covalently conjugated dyes, which are attached either at adjacent nucleotides or at the same nucleotide of the probe and novel linker molecules to attach the dyes to the probes. The nucleic acid probes generate a fluorescent signal upon hybridization to complementary nucleic acids based on the interaction of one of the attached dyes, which is either an intercalator or a DNA groove binder, with the formed double stranded DNA. The methods can be applied to a variety of applications including homogeneous assays, real-time PCR monitoring, transcription assays, expression analysis on nucleic acid microarrays and other microarray applications such as genotyping (SNP analysis). The methods further include pH-sensitive nucleic acid probes that provide switchable fluorescence signals that are triggered by a change in the pH of the medium.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
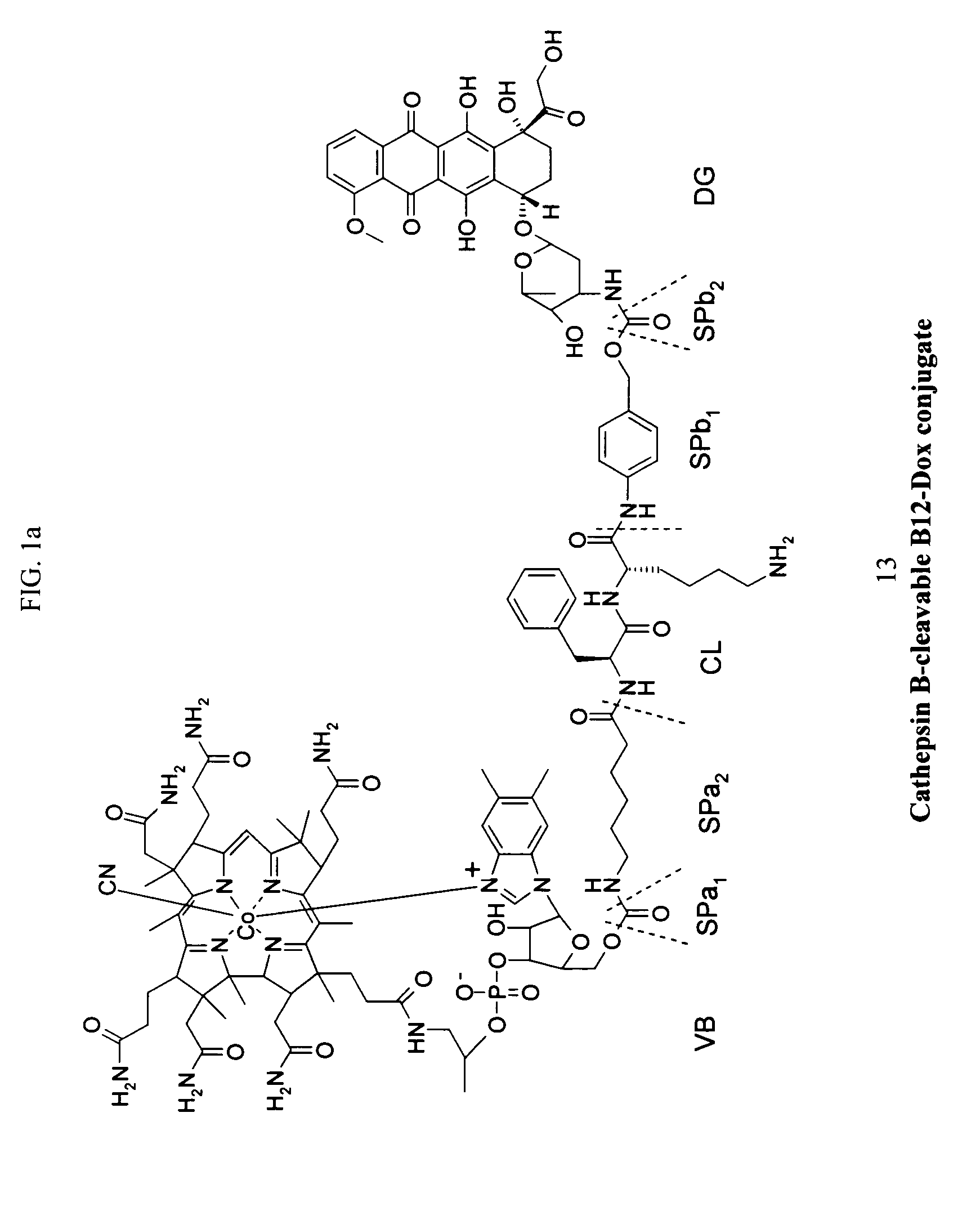
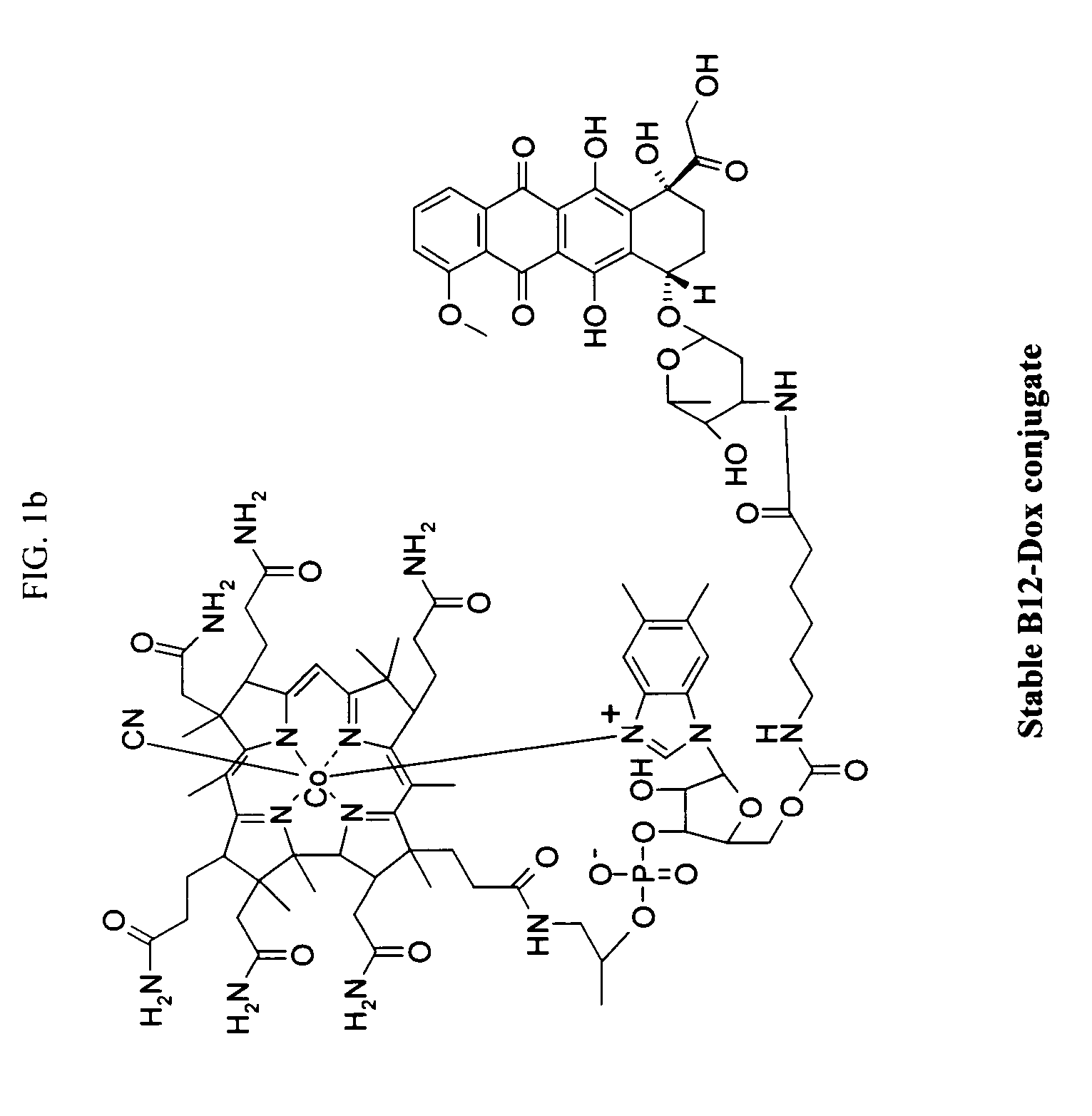
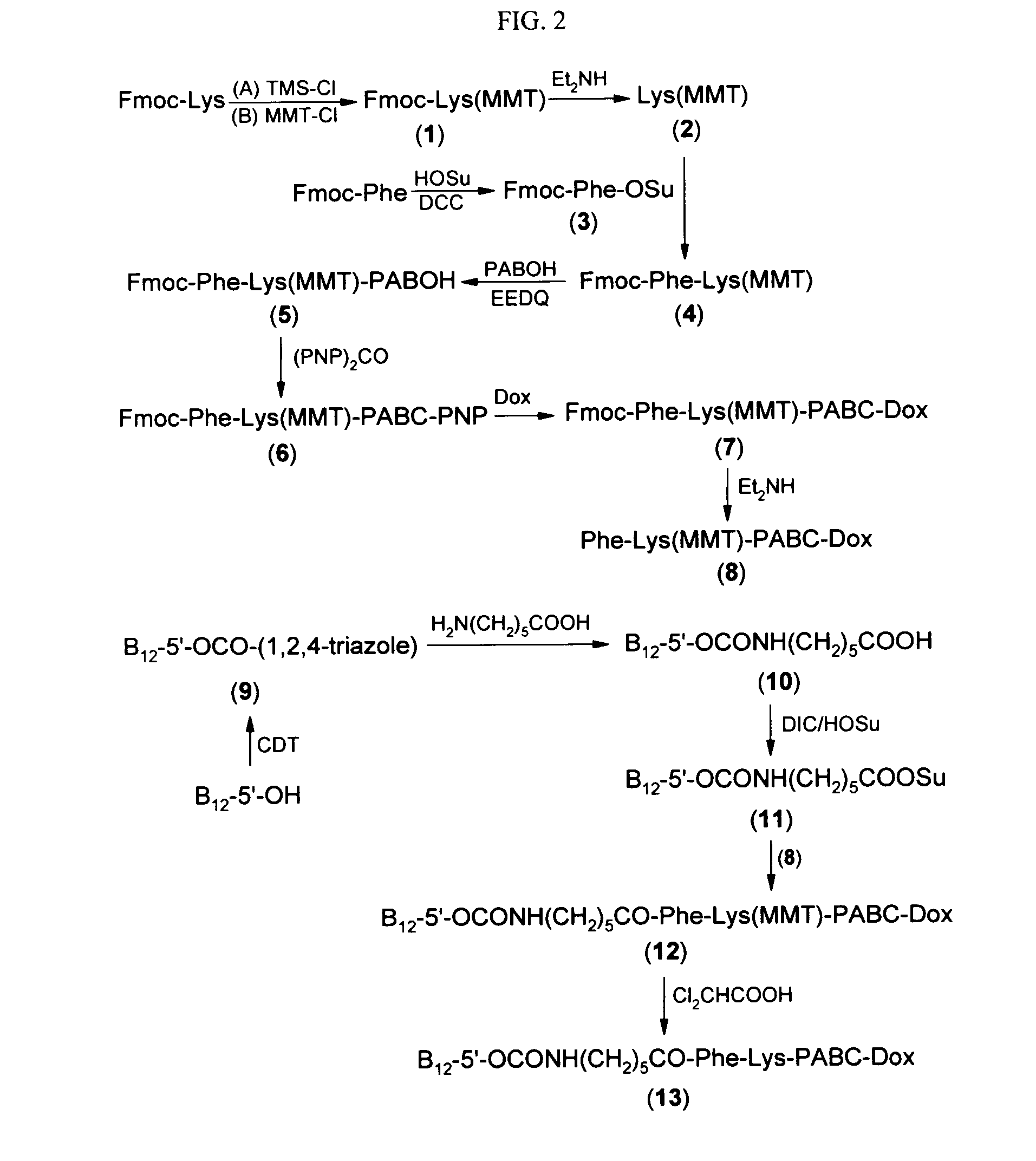
Cobalamin conjugates for anti-tumor therapy
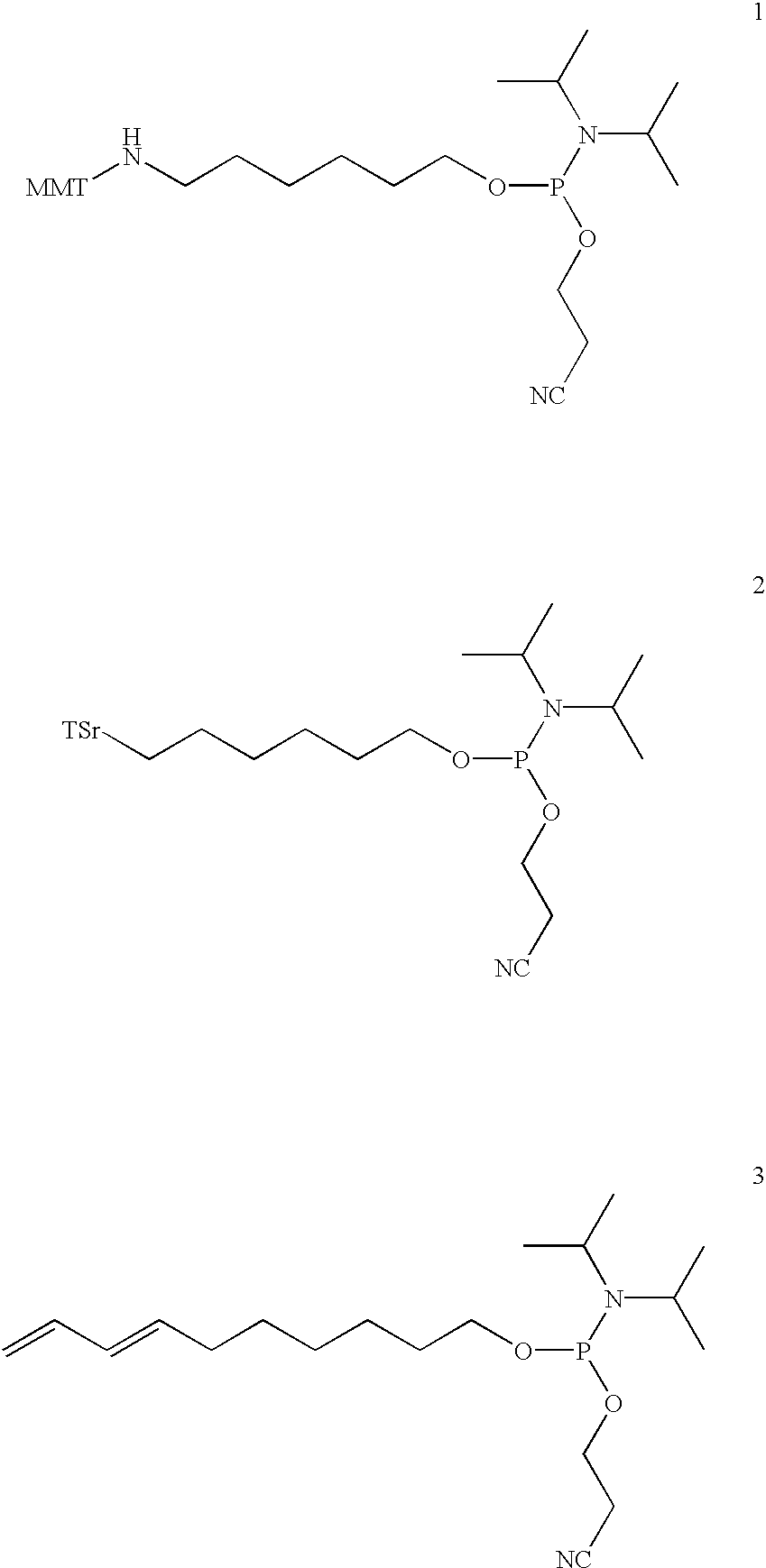
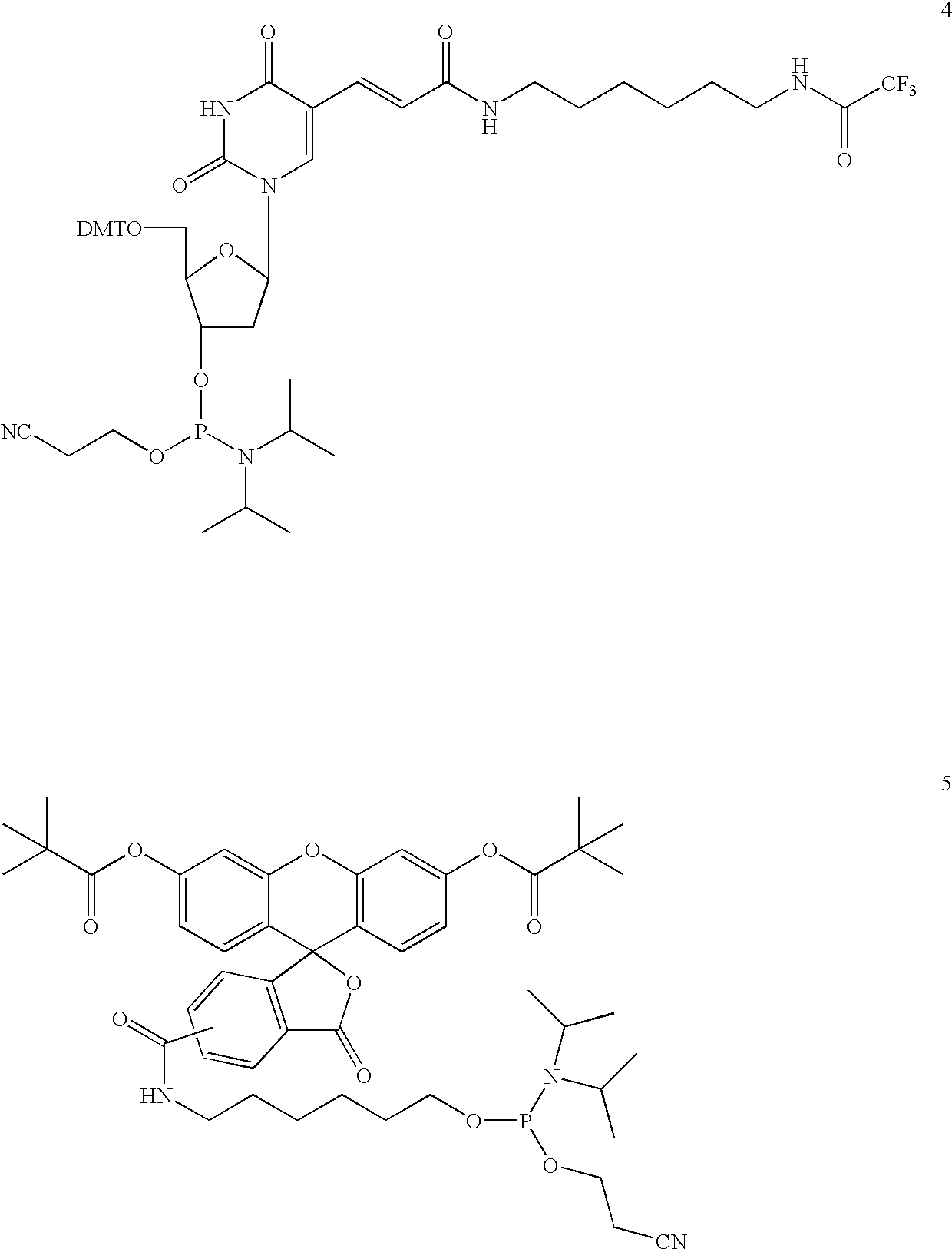
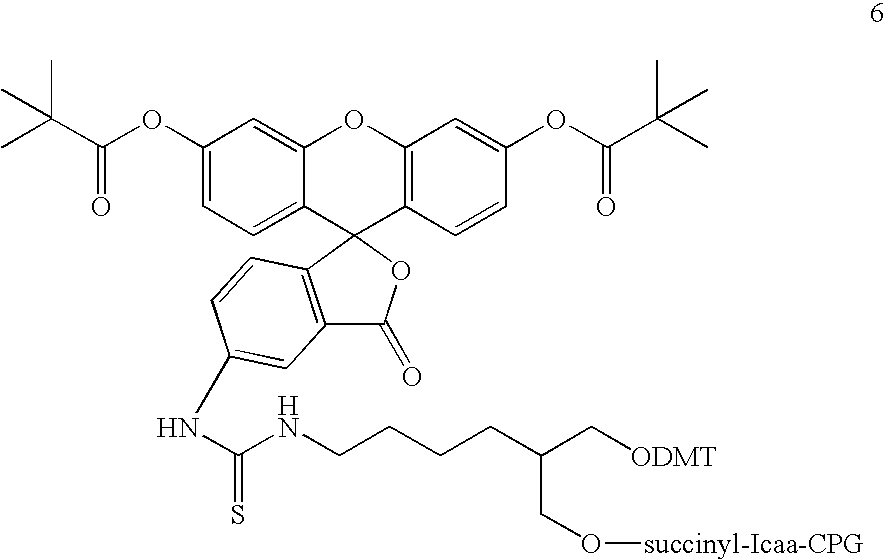
The present invention provides a cobalamin-drug conjugate suitable for the treatment of tumor related diseases. Cobalamin is indirectly covalently bound to an anti-tumor drug via a cleavable linker and one or more optional spacers. Cobalamin is covalently bound to a first spacer or the cleavable linker via the 5′-OH of the cobalamin ribose ring. The drug is bound to a second spacer of the cleavable linker via an existing or added functional group on the drug. After administration, the conjugate forms a complex with transcobalamin (any of its isoforms). The complex then binds to a receptor on a cell membrane and is taken up into the cell. Once in the cell, an intracellular enzyme cleaves the conjugate thereby releasing the drug. Depending upon the structure of the conjugate, a particular class or type of intracellular enzyme affects the cleavage. Due to the high demand for cobalamin in growing cells, tumor cells typically take up a higher percentage of the conjugate than do normal non-growing cells. The conjugate of the invention advantageously provides a reduced systemic toxicity and enhanced efficacy as compared to a corresponding free drug.
Owner:INFLABLOC PHARMA
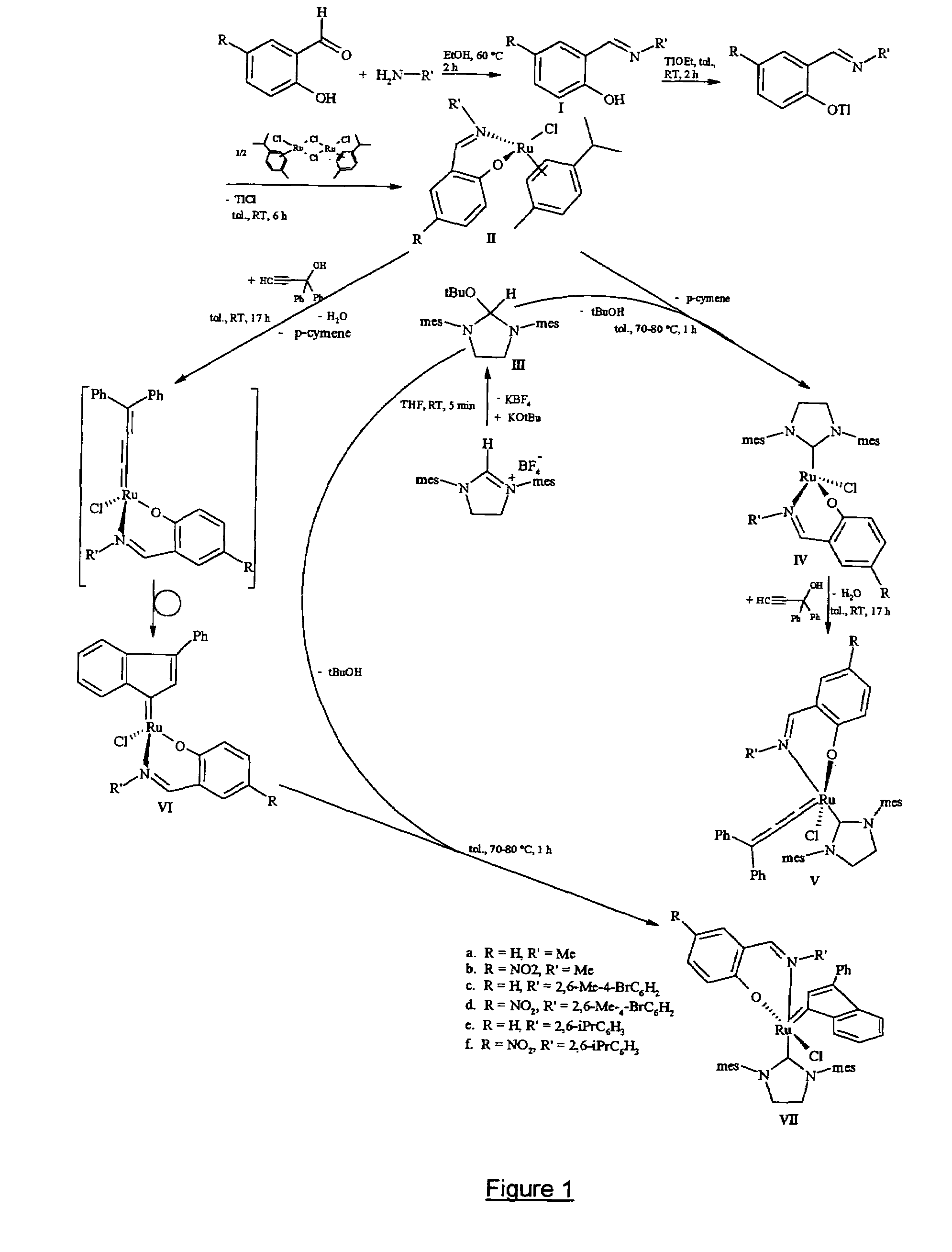
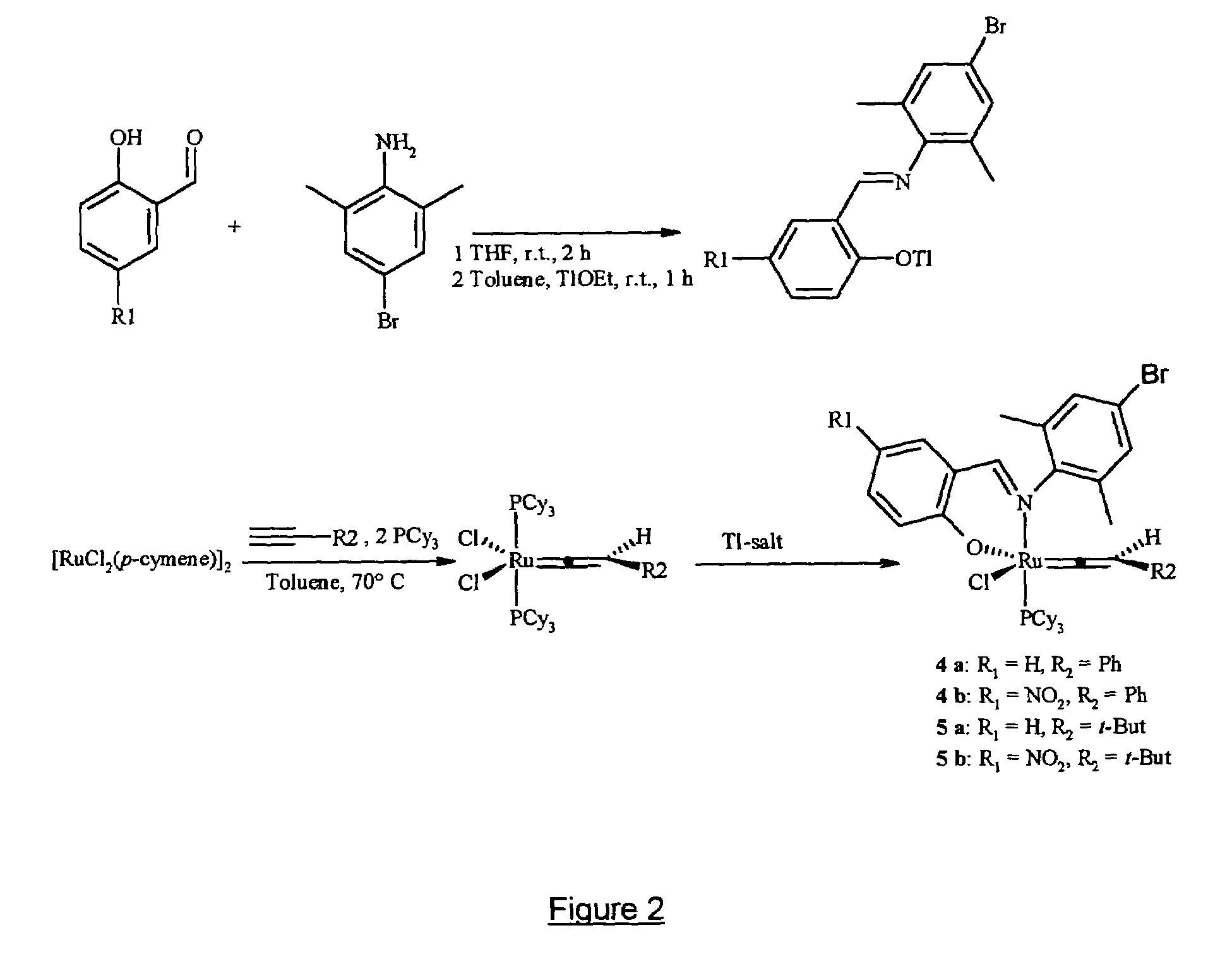
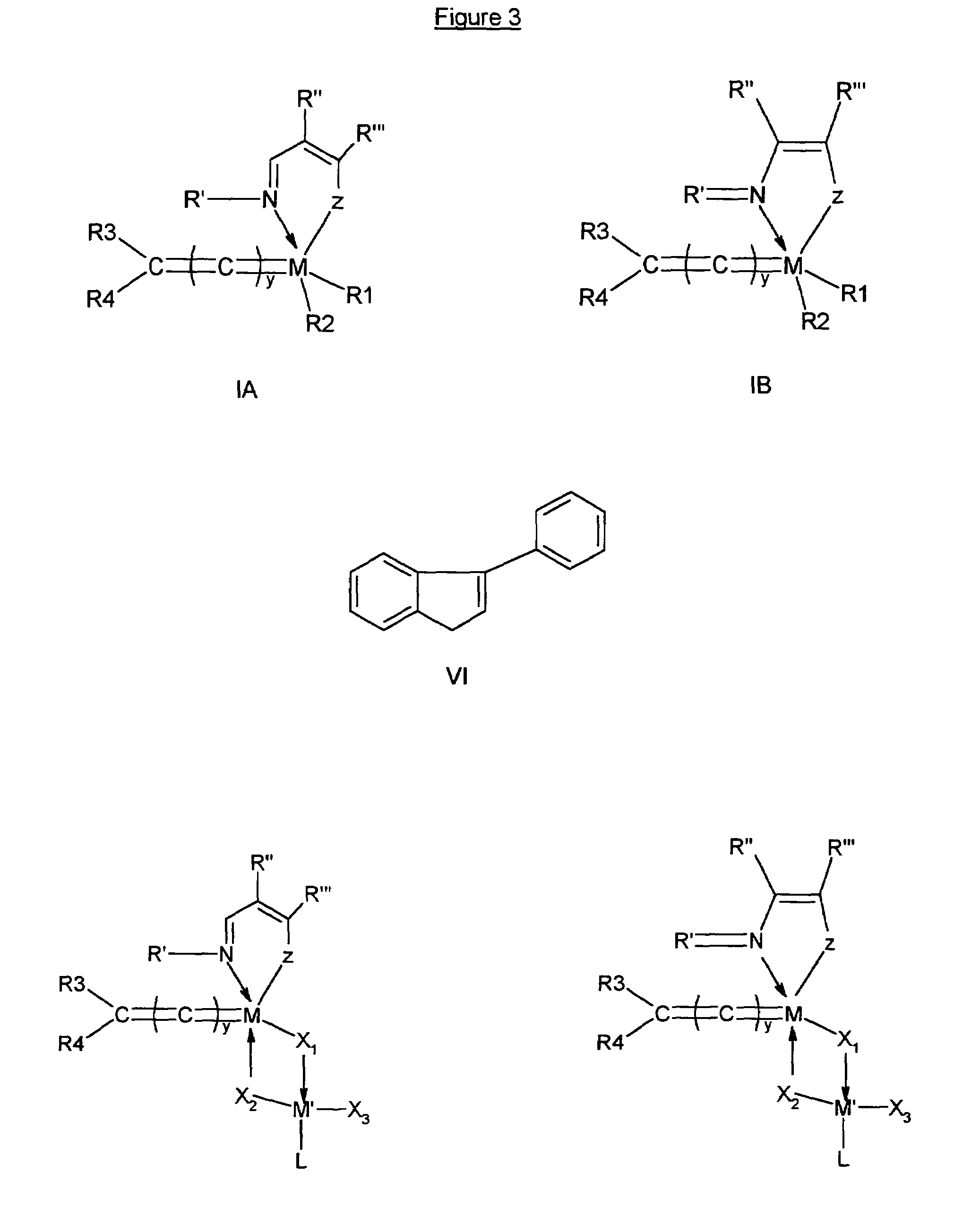
Metal complexes useful in metathesis and other reactions
This invention provides metal complexes being useful as catalyst components in metathesis reactions and in reactions involving the transfer of an atom or group to an ethylenically or acetylenically unsaturated compound or another reactive substrate and, with respect to a sub-class thereof, for the polymerisation of α-olefins and optionally conjugated dienes, with high activity at moderate tempera-tures. It also provides methods for obtaining polymers with very narrow molecular weight distribution by means of a living reaction. It also provides methods for making said metal complexes and novel intermediates involved in such methods. It further provides derivatives of said metal complexes which are suitable for covalent bonding to a carrier, the product of such covalent bonding being useful as a supported catalyst for heterogeneous catalytic reactions. It also provides a direct one-step synthesis of pyrrole, furan and thiophene compounds from diallyl compounds.
Owner:RIMTEC CORP
Biological functionalisation of substrates
InactiveUS20100227372A1Improve surface stabilityMaintaining conformationLiquid surface applicatorsSynthetic resin layered productsCross-linkPolymeric surface
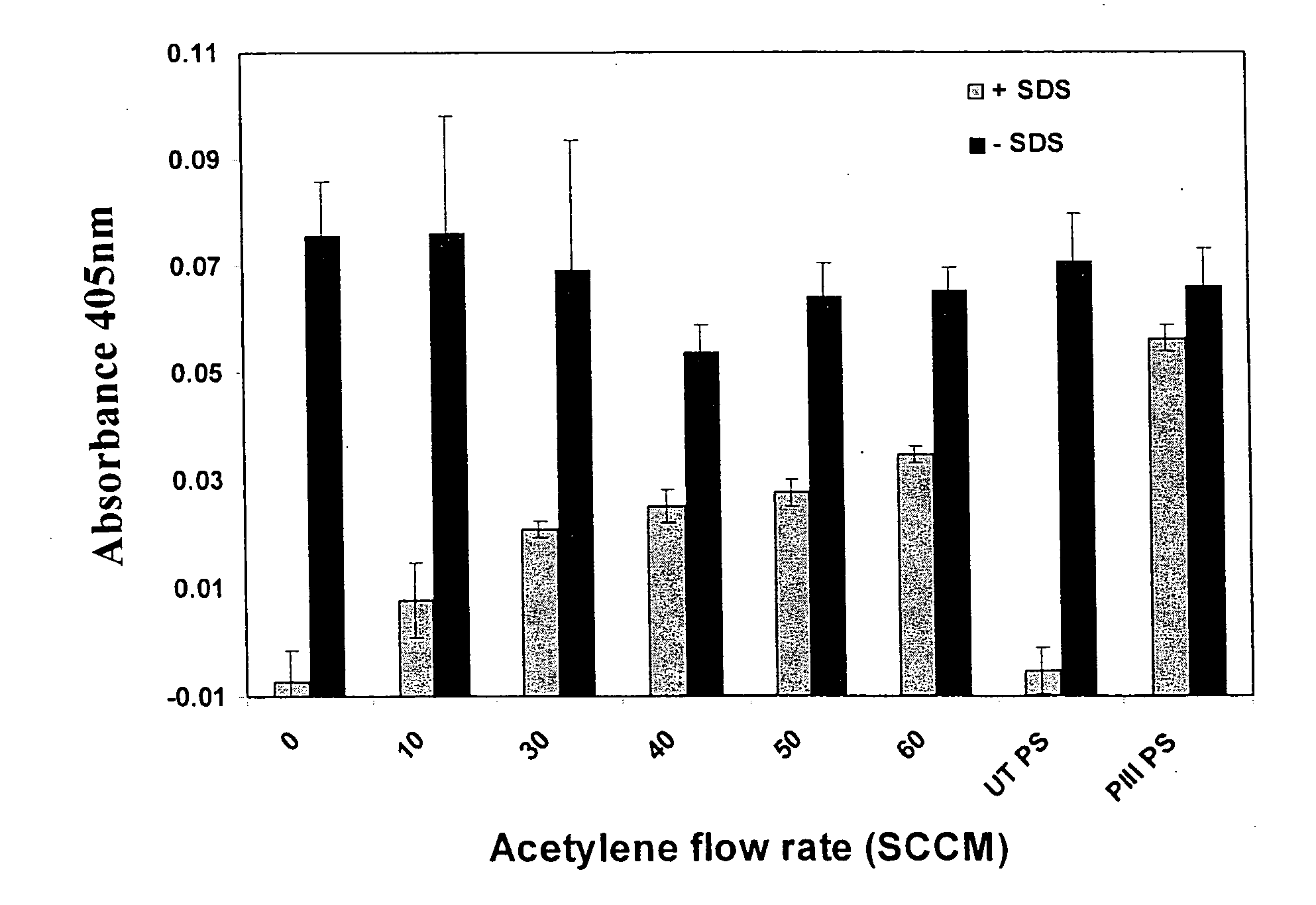
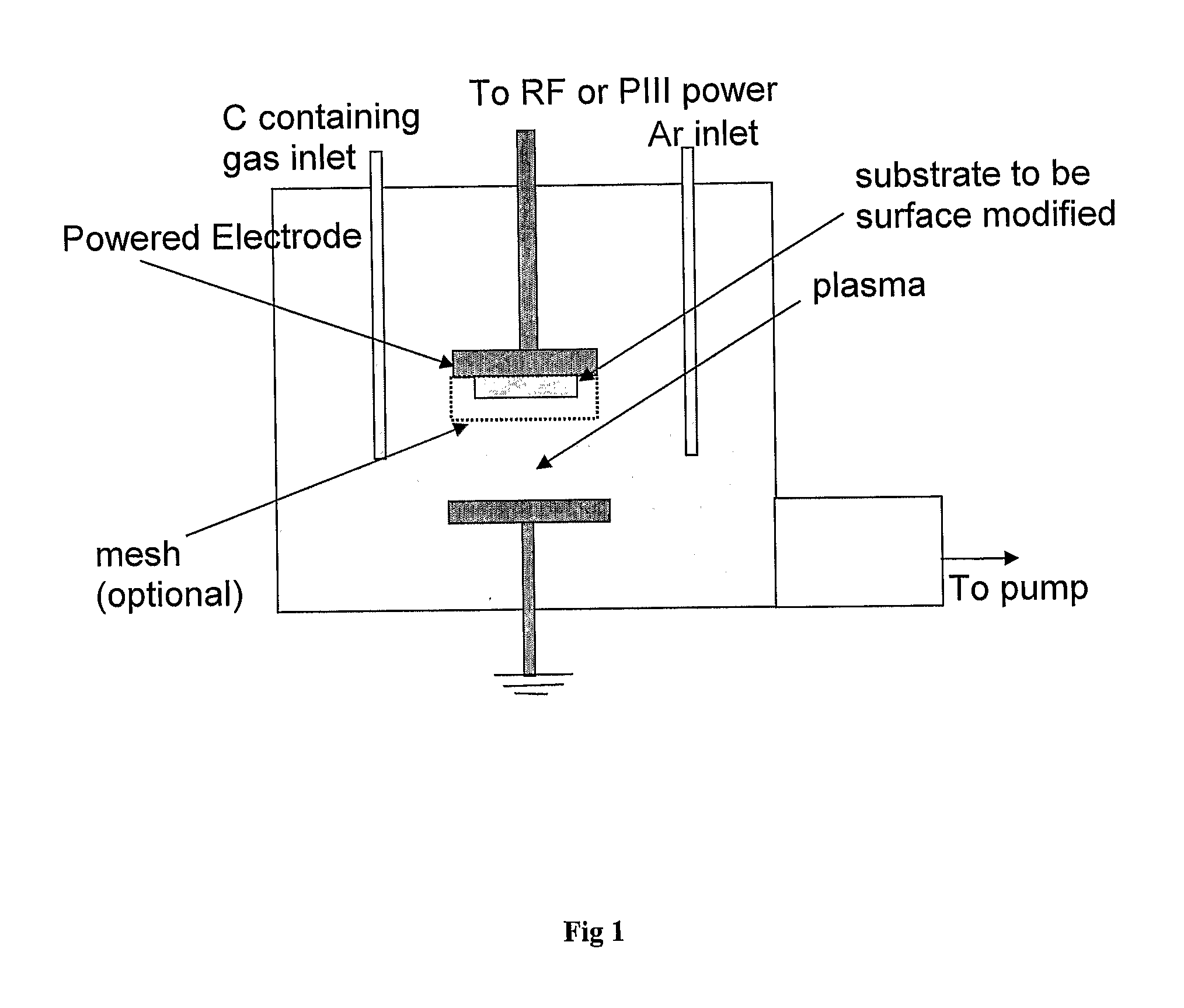
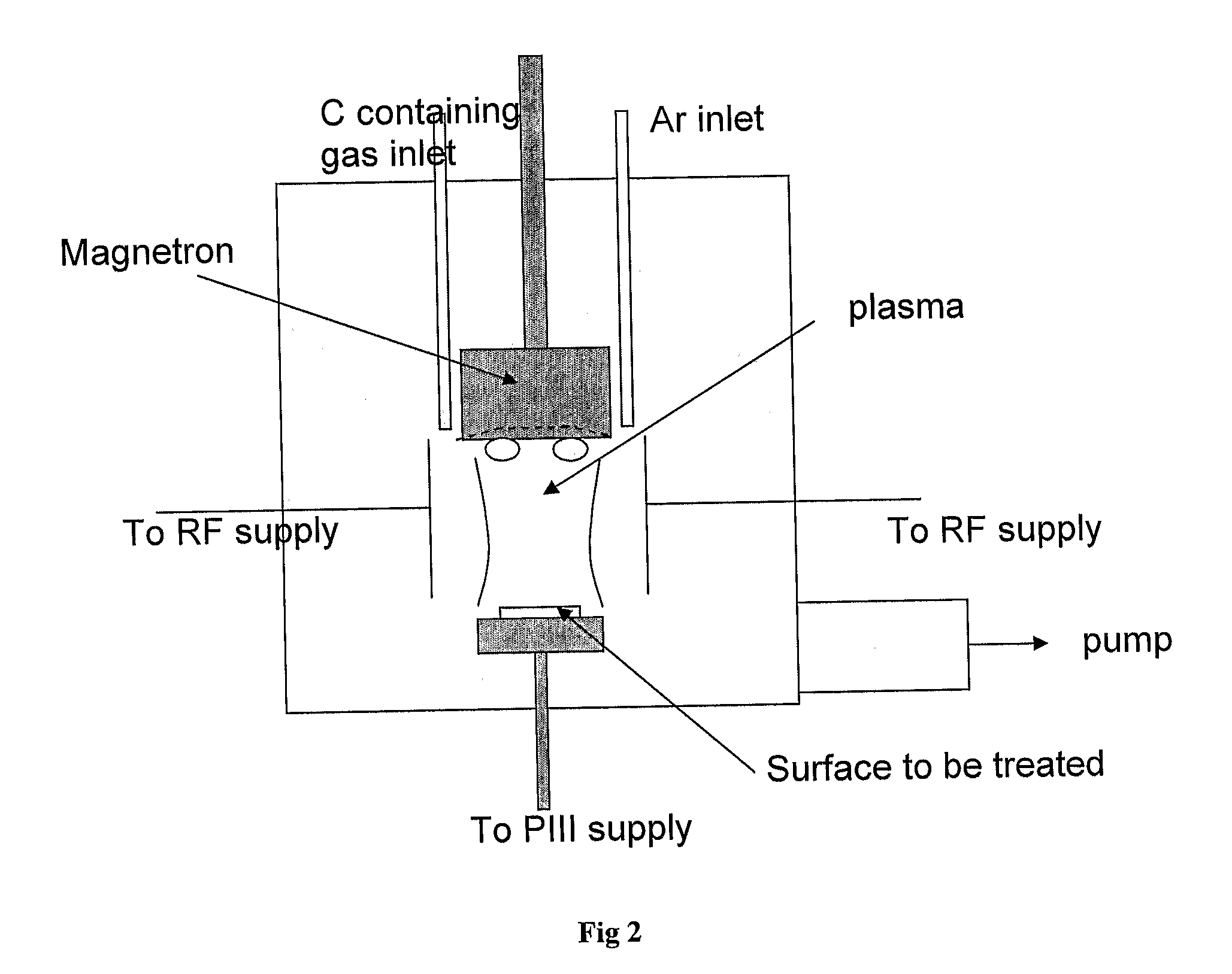
The invention relates to an activated metallic, semiconductor, polymer, composite and / or ceramic substrate, the substrate being bound through a mixed or graded interface to a hydrophilic polymer surface that is activated to enable direct covalent binding to a functional biological molecule, the polymer surface comprising a sub-surface that includes a plurality of cross-linked regions, as well as to such activated substrates that have been functionalised with a biological molecule and to devices comprising such functionalised substrates. Such substrates can be produced by a method comprising steps of: a. exposing a surface of the substrate to any or more of (i) to (iii): (i) plasma ion implantation with carbon containing species; (ii) co-deposition under conditions in which substrate material is deposited with carbon containing species while gradually reducing substrate material proportion and increasing carbon containing species proportion; (iii) deposition of a plasma polymer surface layer with energetic ion bombardment; incubating the surface treated according to step (a) with a desired biological molecule.
Owner:SYDNEY THE UNIV OF
Method to increase electromigration resistance of copper using self-assembled organic thiolate monolayers
Methods and solutions for forming self assembled organic monolayers that are covalently bound to metal interfaces are presented along with a device containing a self assembled organic monolayer. Embodiments of the present invention utilize self assembled thiolate monolayers to prevent the electromigration and surface diffusion of copper atoms while minimizing the resistance of the interconnect lines. Self assembled thiolate monolayers are used to cap the copper interconnect lines and chemically hold the copper atoms at the top of the lines in place, thus preventing surface diffusion. The use of self assembled thiolate monolayers minimizes the resistance of copper interconnect lines because only a single monolayer of approximately 10 Å and 20 Å in thickness is used.
Owner:INTEL CORP
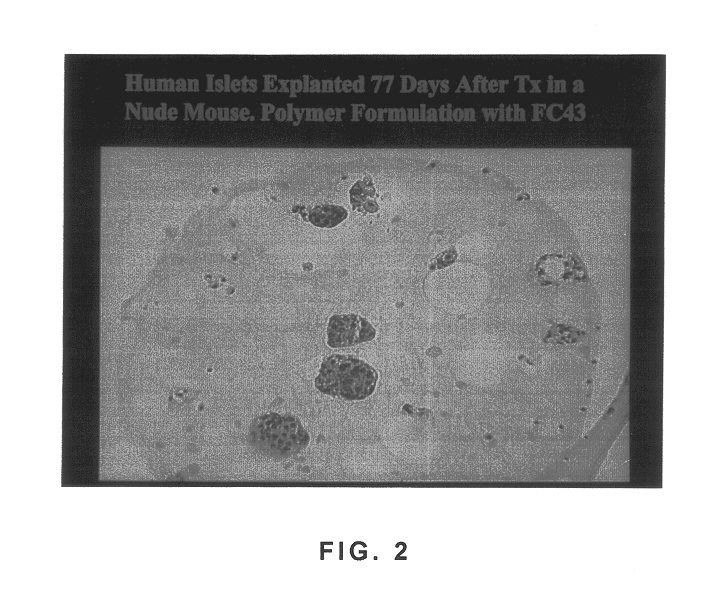
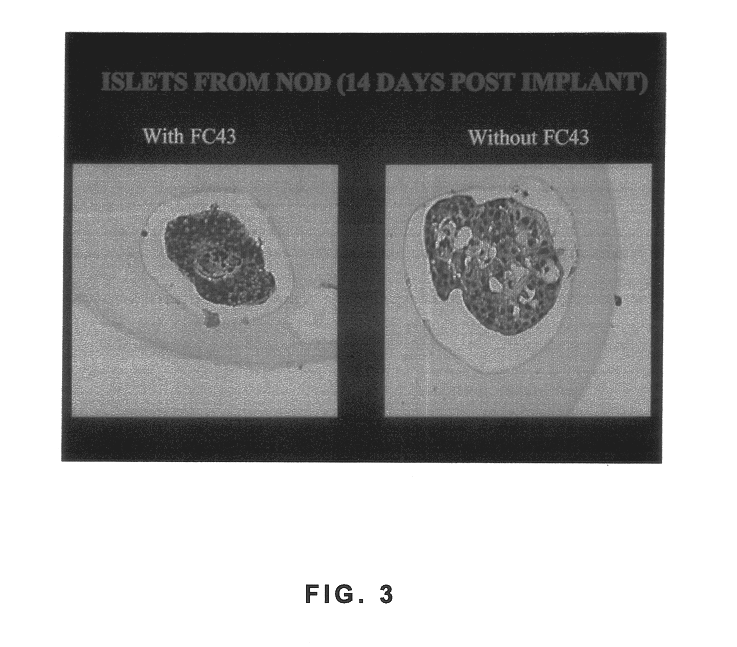
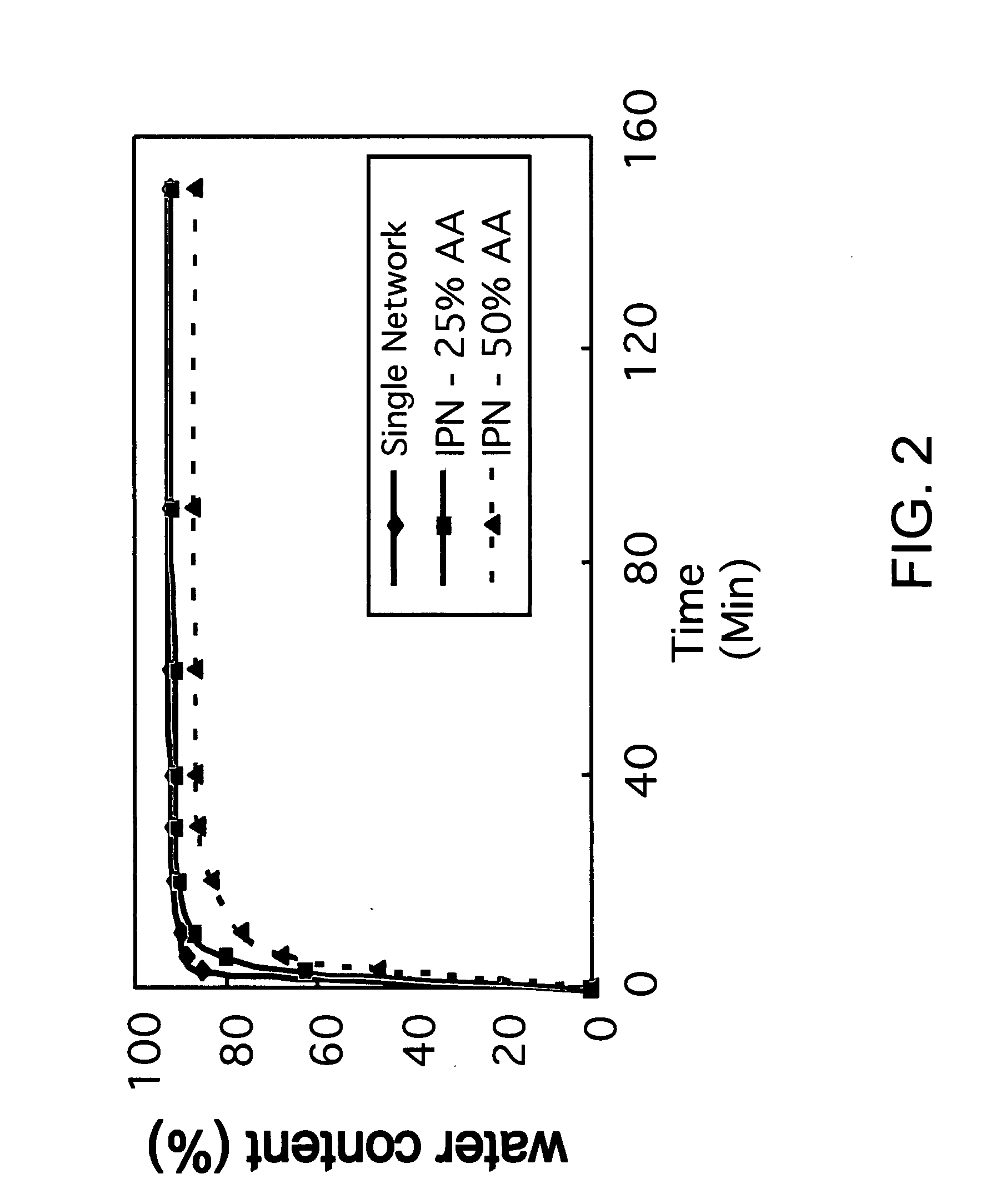
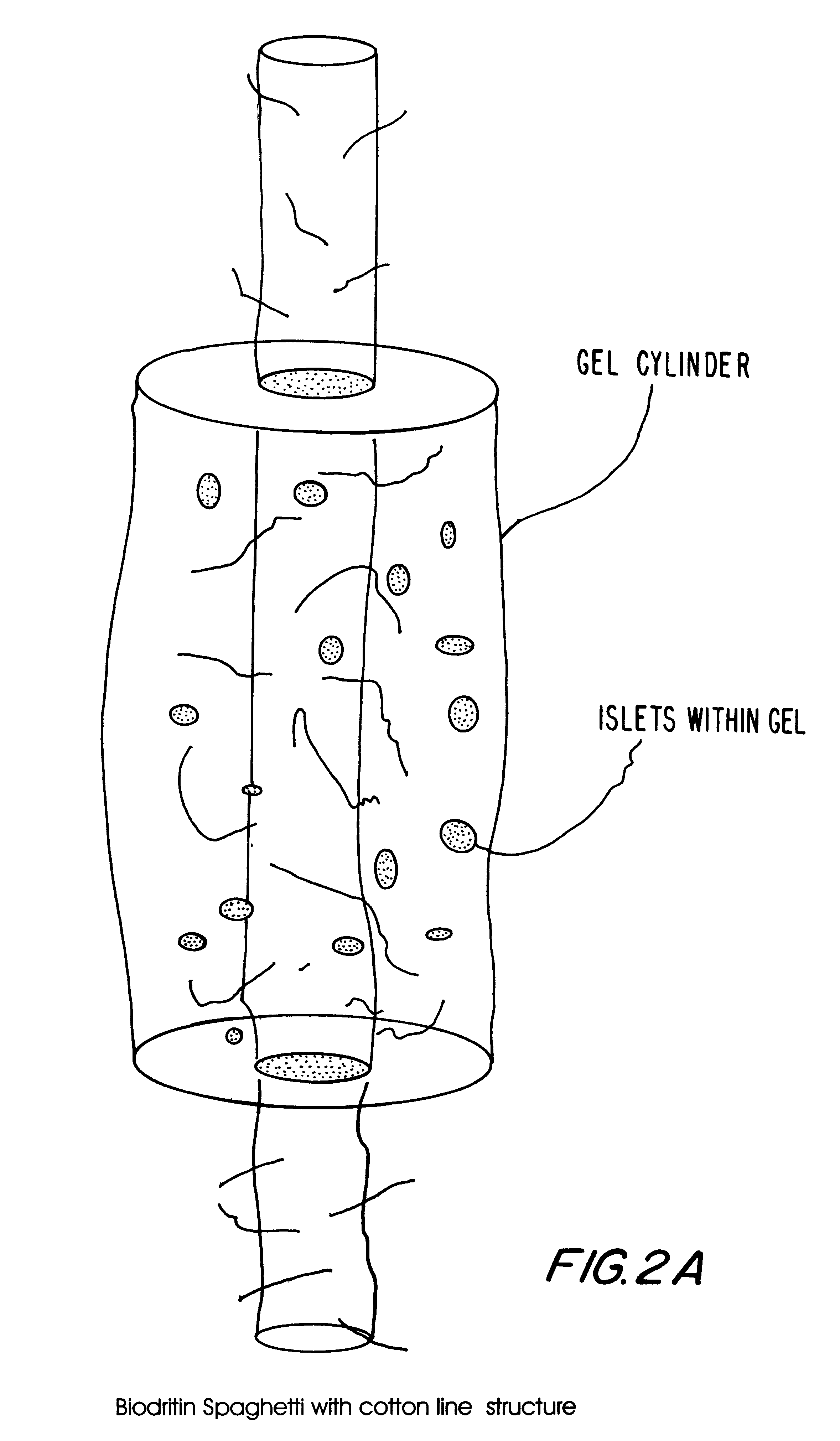
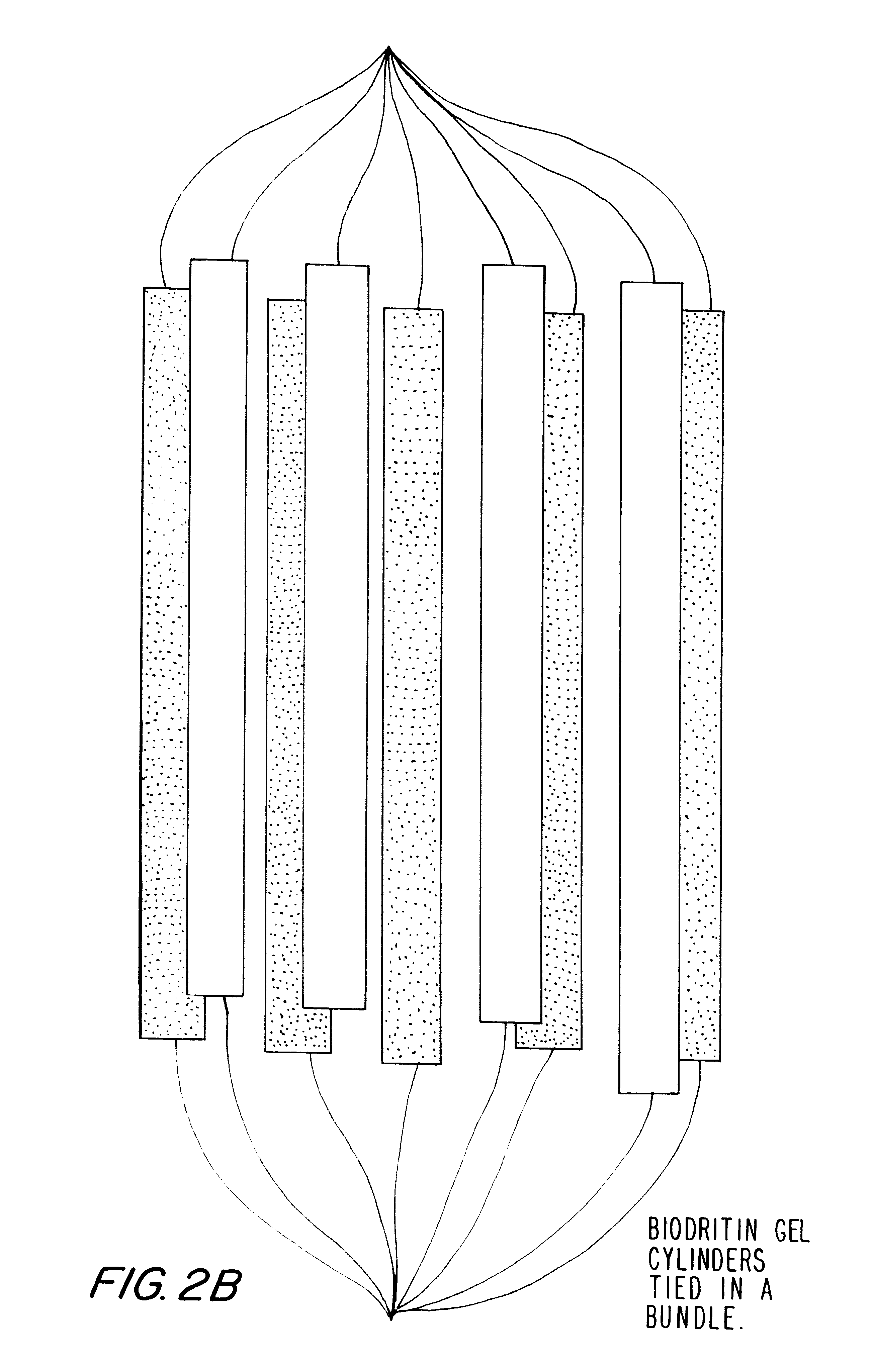
Polymer formulations containing perfluorinated compounds for the engineering of cells and tissues for transplantation that improves cell metabolism and survival, and methods for making same
InactiveUS6630154B1High viscosityMedium viscosity alginatesPowder deliveryBiocideCross-linkInorganic salts
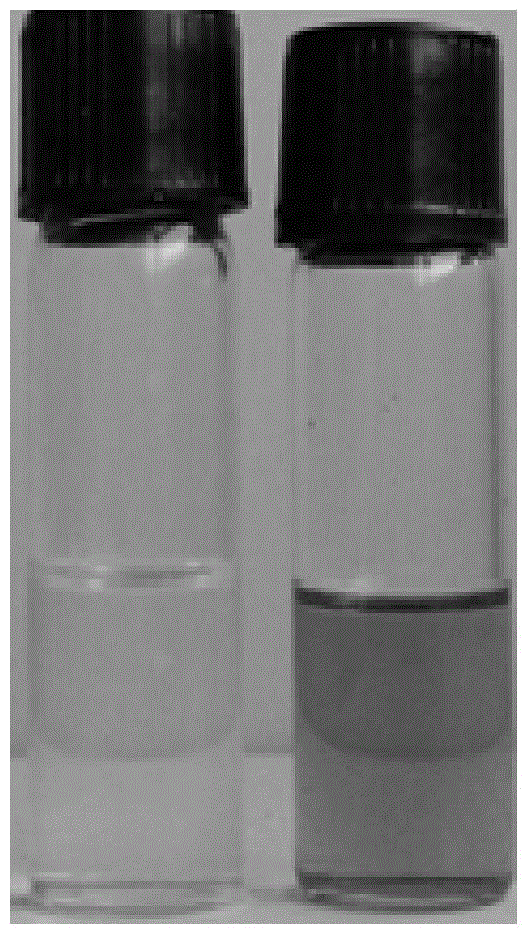
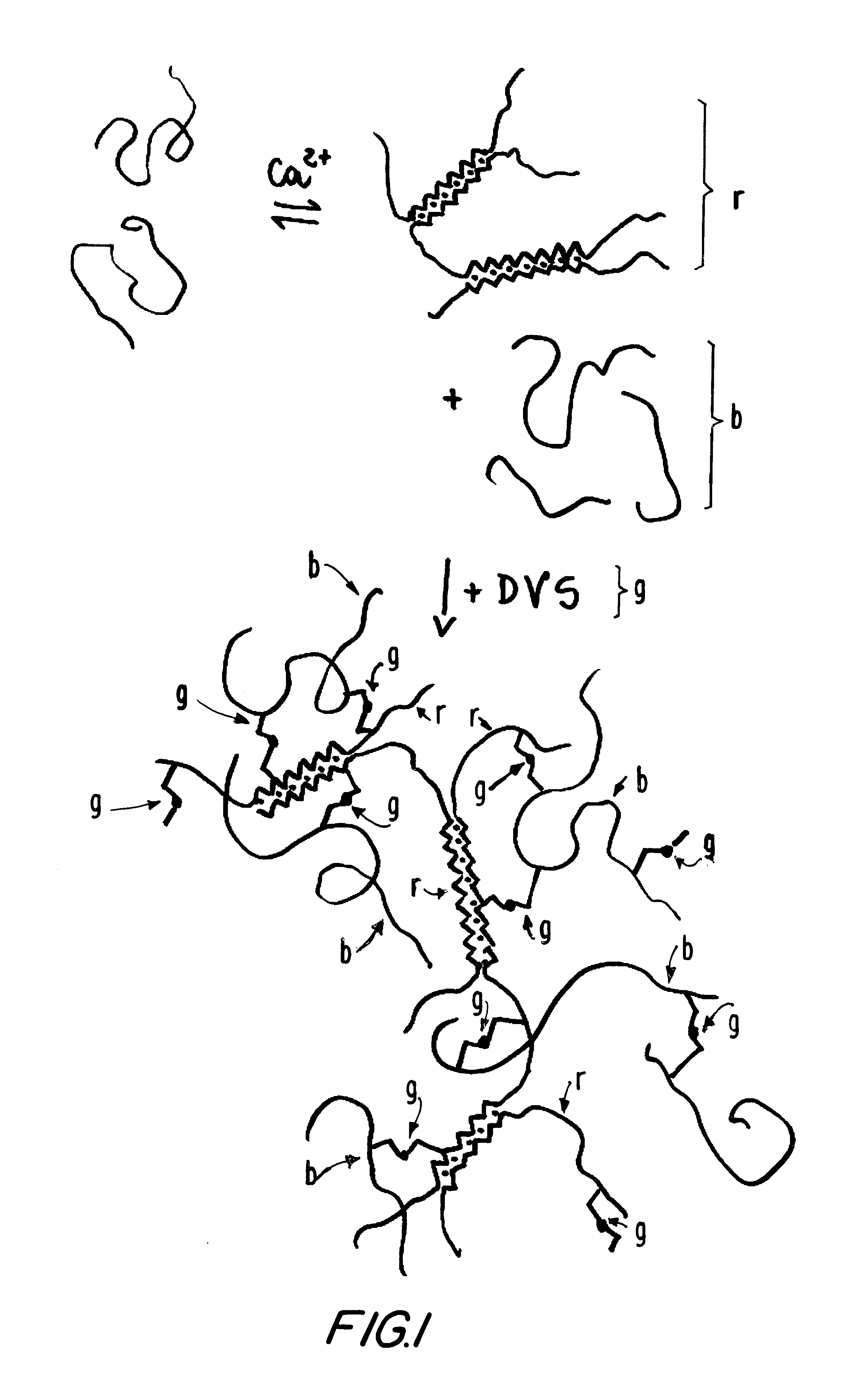
Disclosed and claimed are: a composition including at least one glycosaminoglycan, e.g., CIS, at least one perfluorinated substance and at least one alginate, e.g., sodium alginate, wherein:the at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the perfluorinated substance and / or the alginate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan, the perfluorinated substance and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the perfluorinated substance and / or the alginate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt, and the at least one glycosaminoglycan and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS, and the covalent binding can have been performed prior to cross-linking or polymerizing or vice versa; and,gels comprising the composition; mixtures of such gels or of at least one such gel and at least one such composition; and,methods for making and using such compositions and gels, including products therefrom such as "paints", sprays, matrices, beads, microcapsules.
Owner:BIOMM +1
Process for surface modifying substrates and modified substrates resulting therefrom
The invention relates to a process for coating a material surface, comprising the steps of: (a) applying to the material surface a tie layer comprising a polyionic material; (b) covalently binding a bifunctional compound comprising an ethylenically unsaturated double b3nd to the tie layer; and (c) graft polymerizing a hydrophilic monomer onto the compound comprising the ethylenically unsaturated double bond. The coated articles that are obtainable by the process of the invention have desirable characteristics regarding adherences to the substrate, durability, hydrophilicity, wettability, biocompatibility and permeability and are thus useful for the manufacture of biomedical articles such as ophthalmic devices.
Owner:ALCON INC +1
Modular targeted liposomal delivery system
InactiveUS7060291B1Improve abilitiesUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBiocideLipid bilayerOrganic chemistry
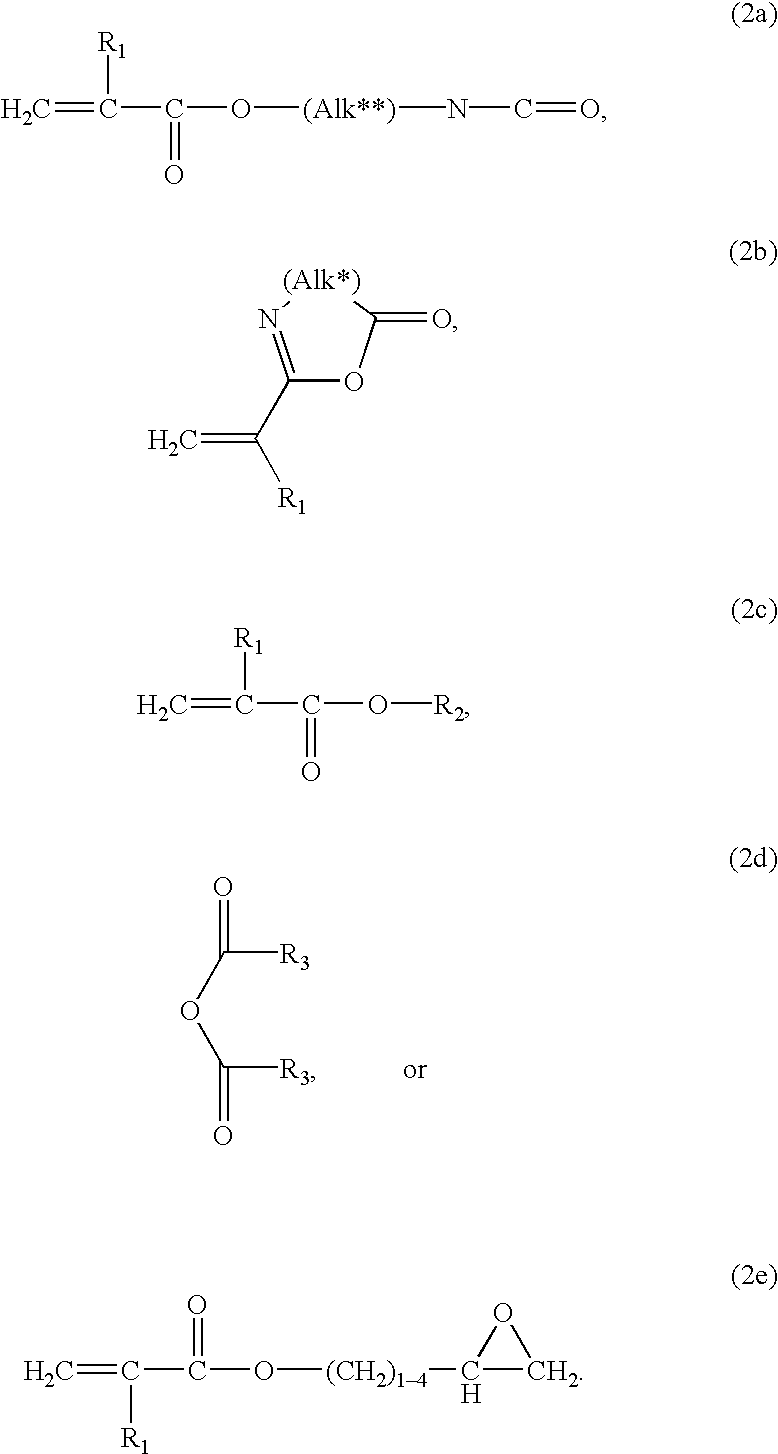
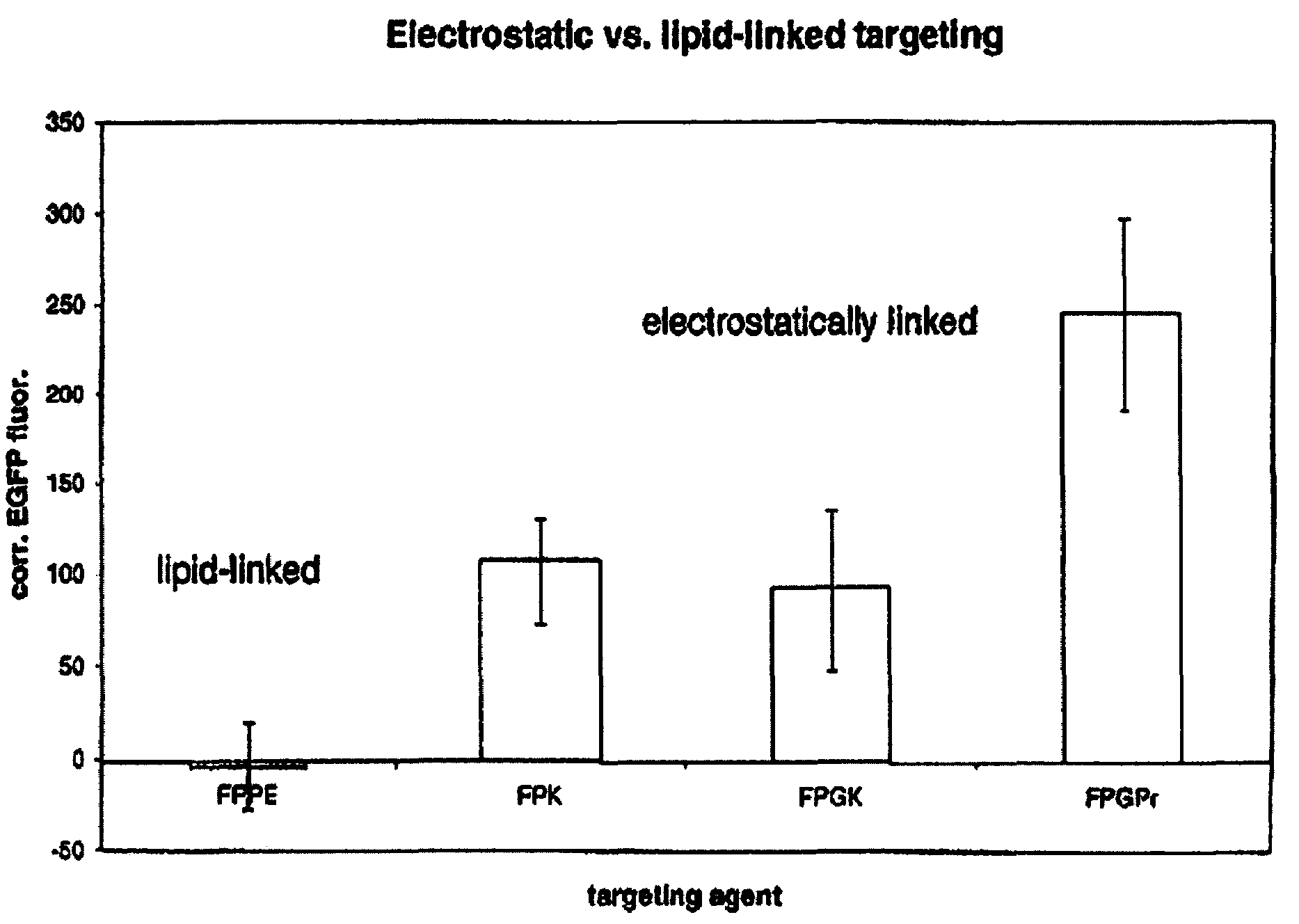
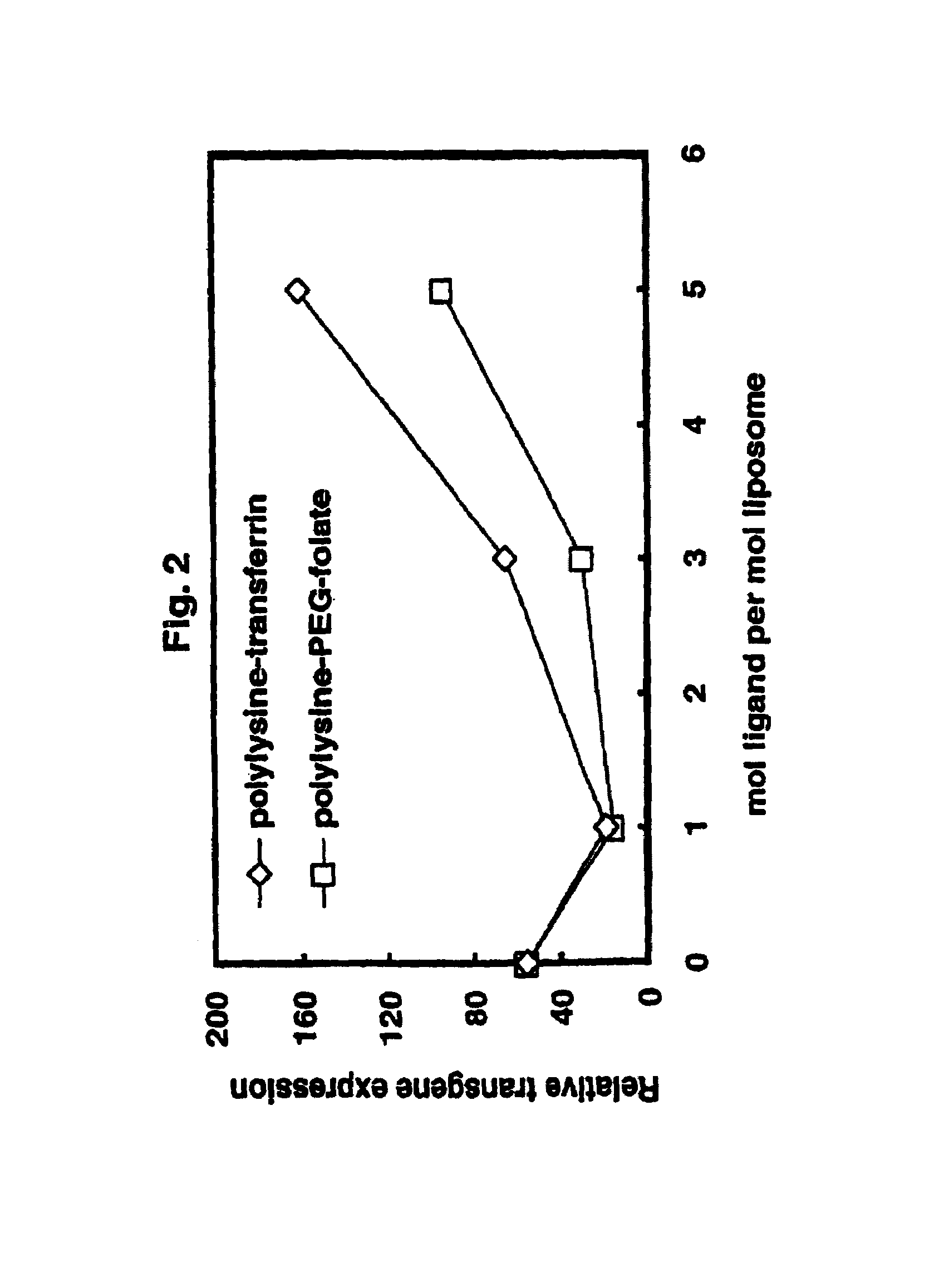
A liposome including a fusogenic liposome, a linking moiety and a targeting moiety. The fusogenic liposome is a lipid bilayer encapsulating contents. The linking moiety is electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer, and the targeting moiety is covalently bound to the linking moiety. The liposome may also include a stabilizing moiety interposed between the linking and targeting moieties, and covalently bound to both. Alternatively, the stabilizing and targeting moieties may be covalently bound to separate linking moieties, the linking moieties being electrostatically bound to the lipid bilayer.
Owner:TRANSAVE
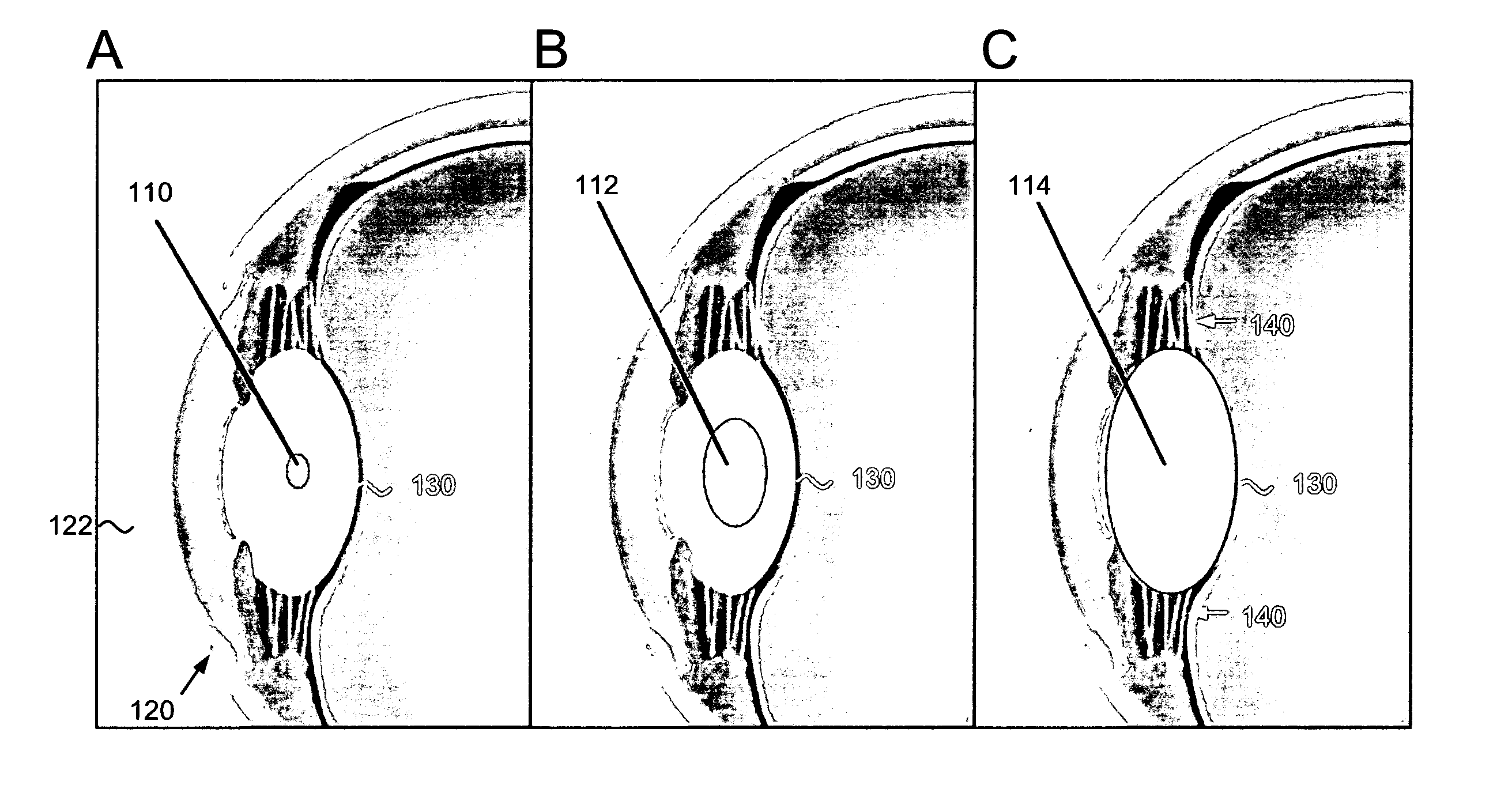
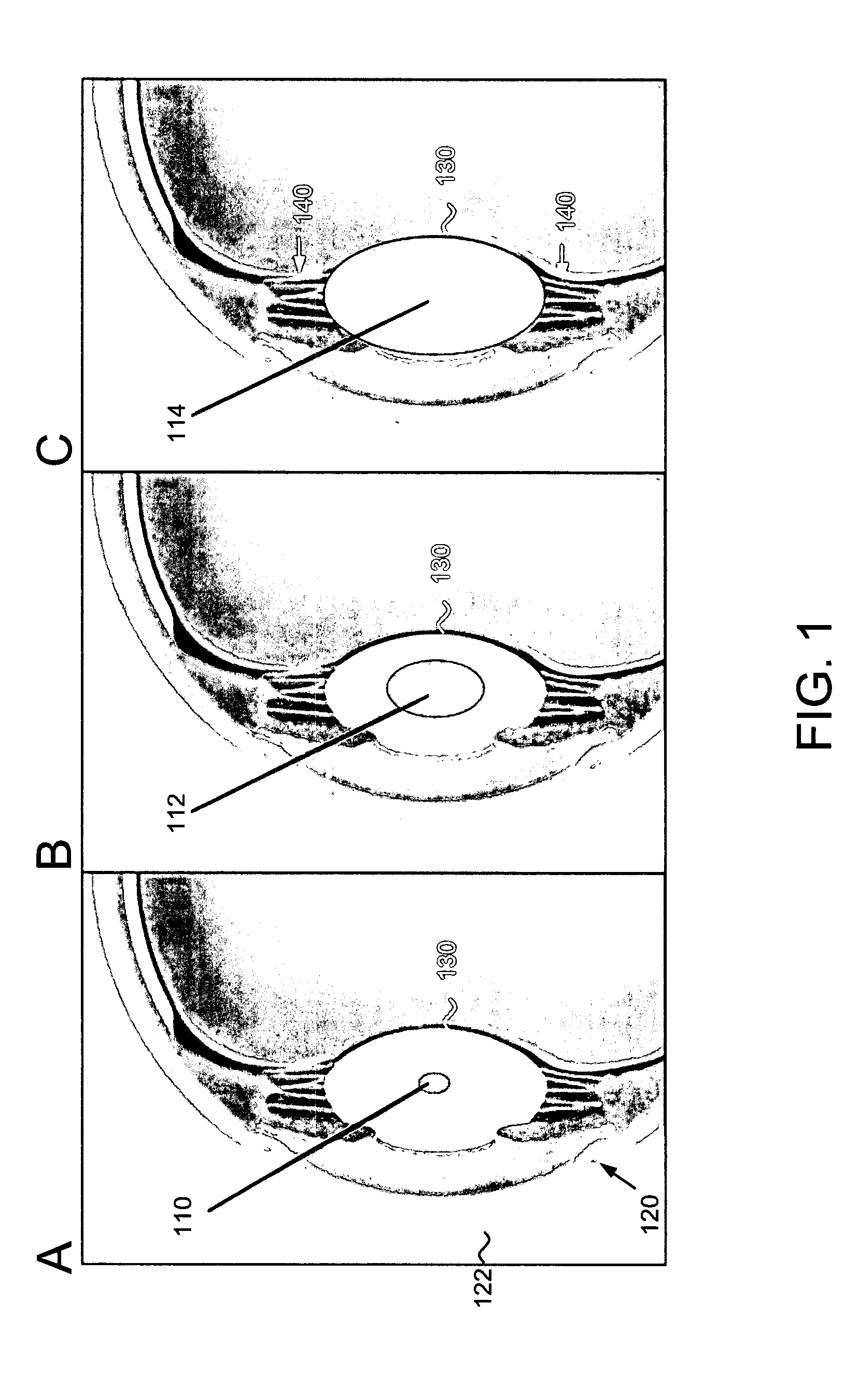
Intraocular lens implant
InactiveUS20070233240A1Nervous system cellsCell culture supports/coatingRefractive indexEquilibrium swelling
The present invention provides a hydrogel-based intraocular lens (IOL) implant that can covalently attach to a lens capsule on implantation into an eye. The inventive IOL has a high refractive index, high elasticity, and is of a similar size to a naturally occurring lens. In addition, the IOL can be implanted in a smaller, dehydrated state, allowing the IOL to be placed in the lens capsule with a small incision (up to about 1 / 10 the volume of the IOL). Exposure to fluid can then initiate rapid swelling of the dried polymer to the shape and dimensions of a natural lens, with full occupation of the lens capsule. Upon equilibrium swelling, the IOL can then make contact with the inner aspect of the lens capsule and covalently bind to it. By this attachment process, the IOL may accommodate in a manner identical to that of the natural lens.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Anti-Corrosion Conformal Coating for Metal Conductors Electrically Connecting an Electronic Component
InactiveUS20110189381A1Prolong lifeFinal product manufacturePretreated surfacesElectrical conductorPhosphine
An apparatus includes an electronic component mounted on a substrate and metal conductors electrically connecting the electronic component. A conformal coating overlies the metal conductors and comprises a polymer into which a phosphine compound is impregnated and / or covalently bonded. Accordingly, the conformal coating is able to protect the metal conductors from corrosion caused by sulfur components (e.g., elemental sulfur, hydrogen sulfide, and / or sulfur oxides) in the air. That is, the phosphine compound in the polymer reacts with any corrosion inducing sulfur component in the air and prevents the sulfur component from reacting with the underlying metal conductors. Preferably, the phosphine compound in the polymer does not react with other components in the air (e.g., carbon dioxide) which would otherwise deplete its availability for the target reaction. The phosphine compound may be rendered completely non-volatile by covalently bonding it directly into the polymer backbone.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method for transferring graphene films
The invention provides a method for transferring graphene films, which comprises the steps of coating polymer on the graphene films and curing, forming a covalent binding between the polymer and the graphene films, and directly transferring the graphene films from a substrate. Compared with the traditional method, the method for transferring graphene films provided by the invention is simple and easy to operate, and the graphene films can be adhered to the substrate in the way of covalent binding, so that the graphene films are unlikely to fall off; and furthermore, the fresh surfaces of the graphene films can be taken as the constituent parts of the functional devices, so that the effect of the functional devices can be effectively improved and the method is suitable for industrialization.
Owner:许子寒
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
ActiveUS7569130B2Laborious labelingLaborious staining stepElectrolysis componentsChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
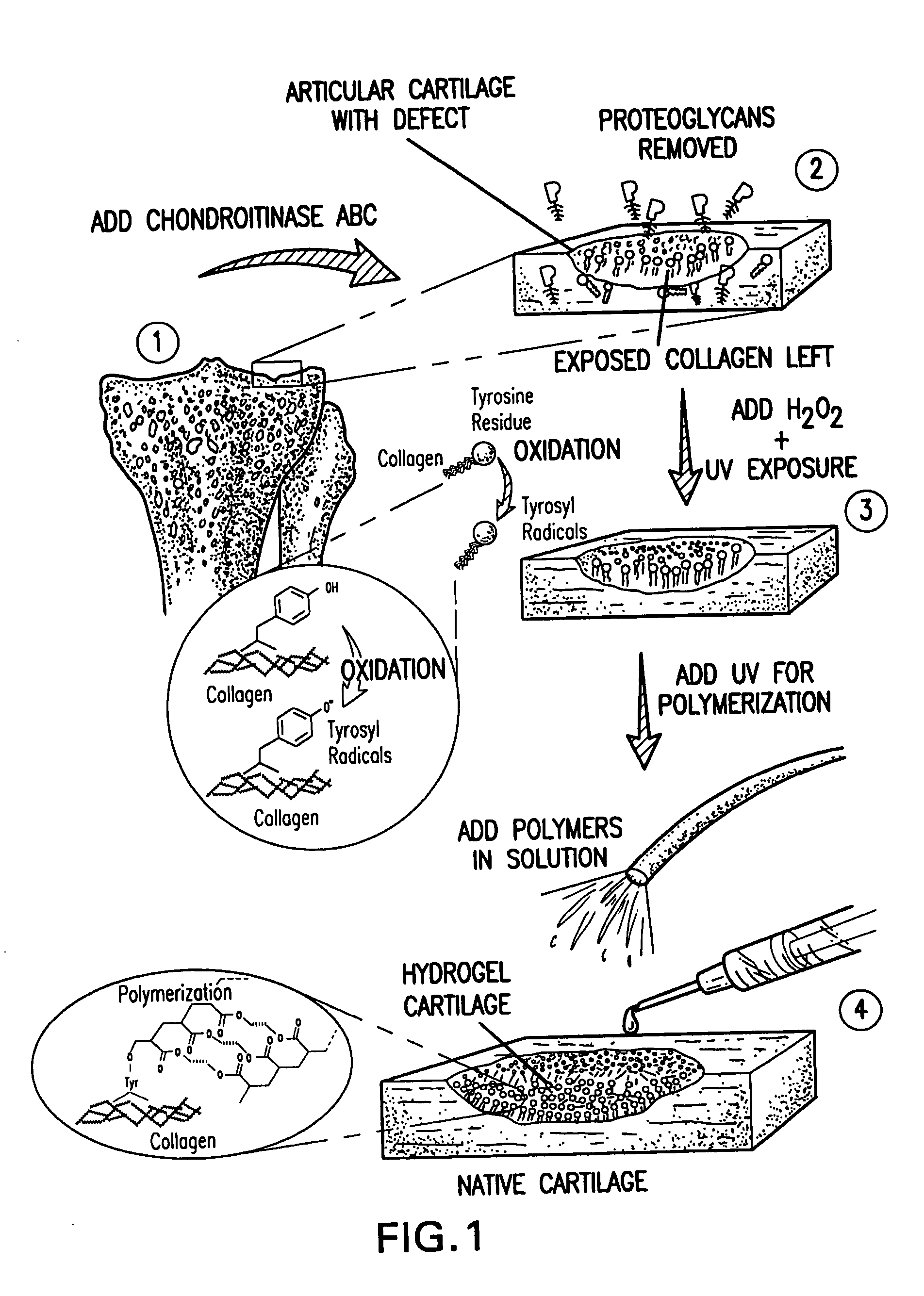
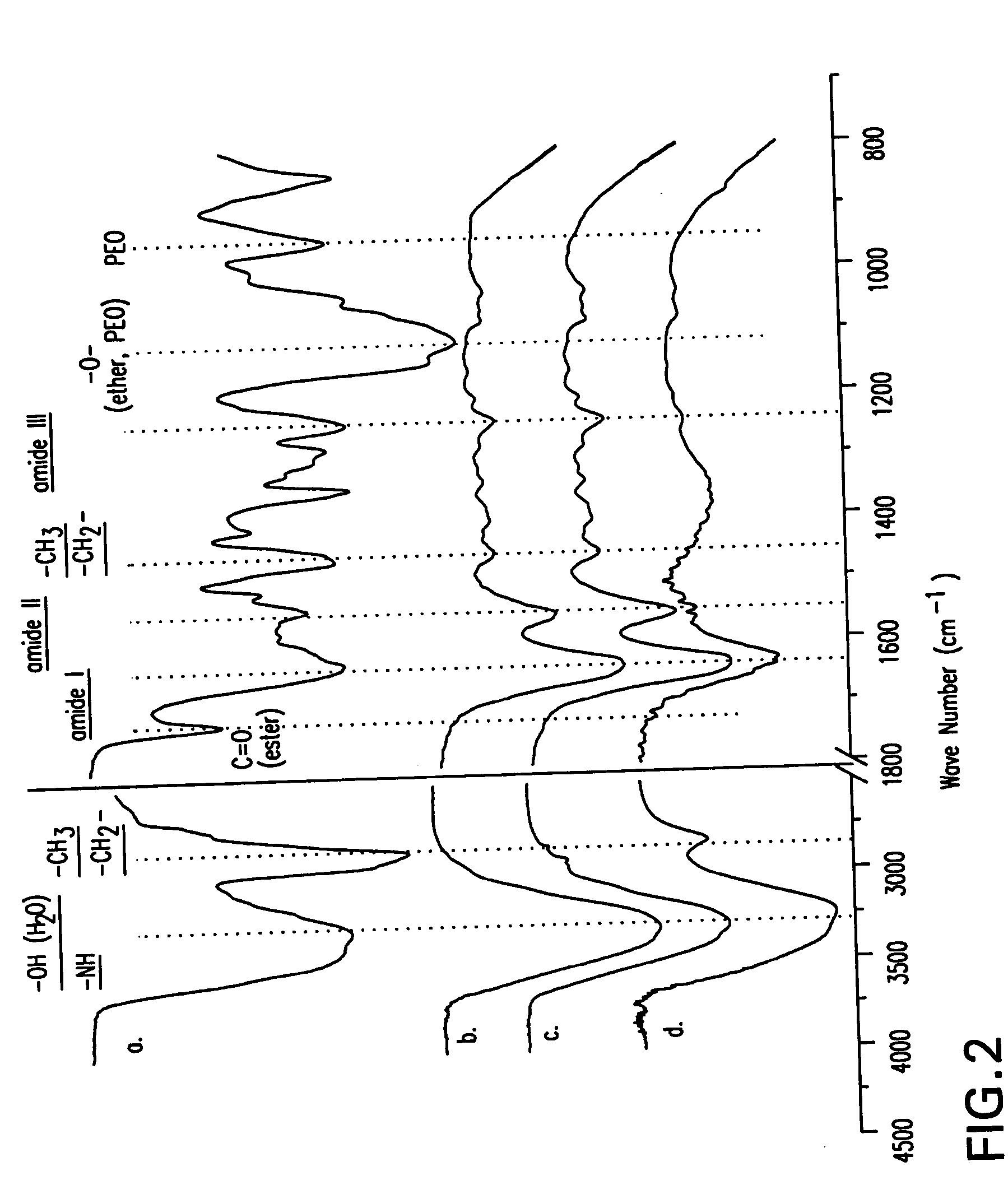
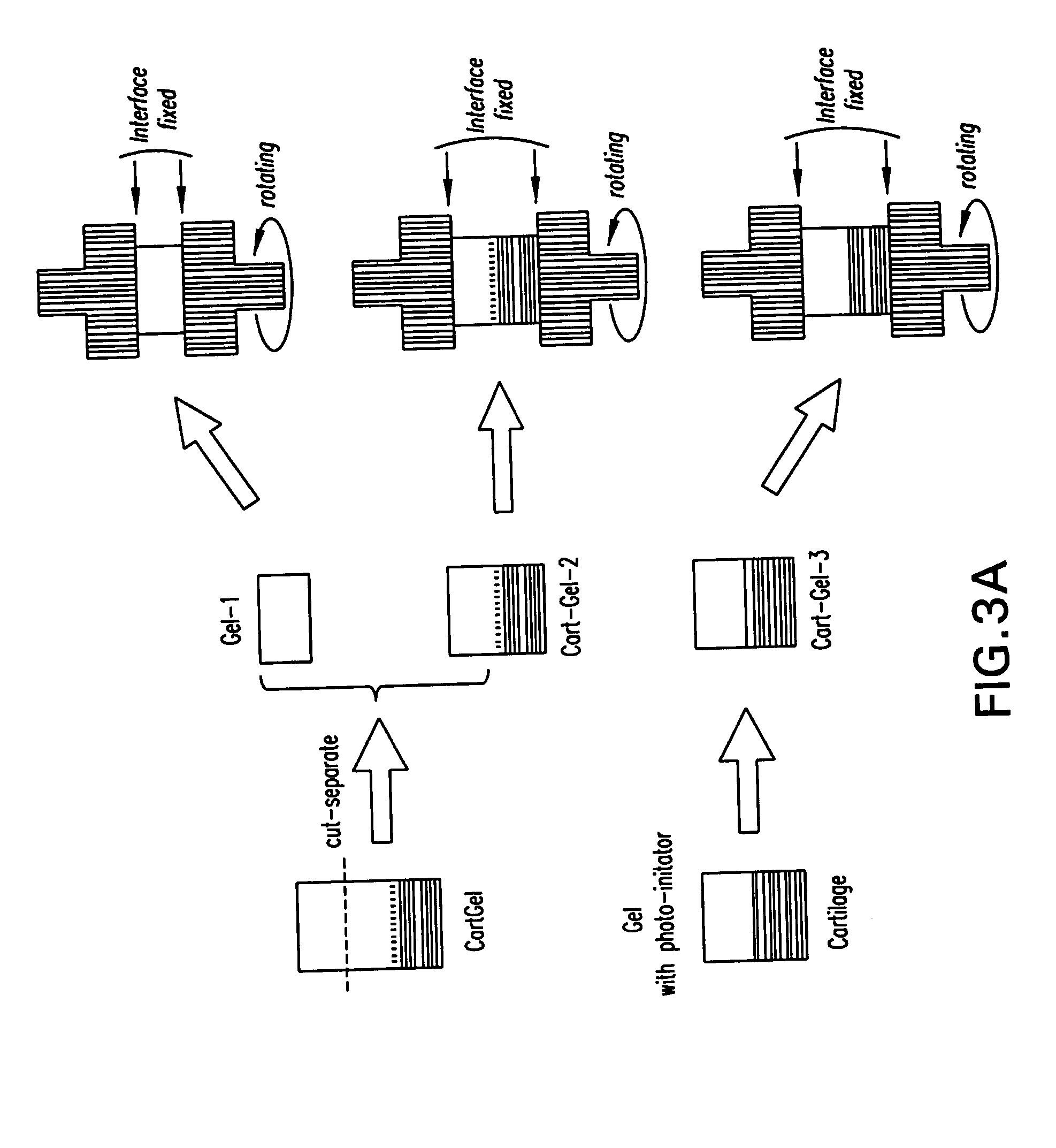
Method and material for enhanced tissue-biomaterial integration
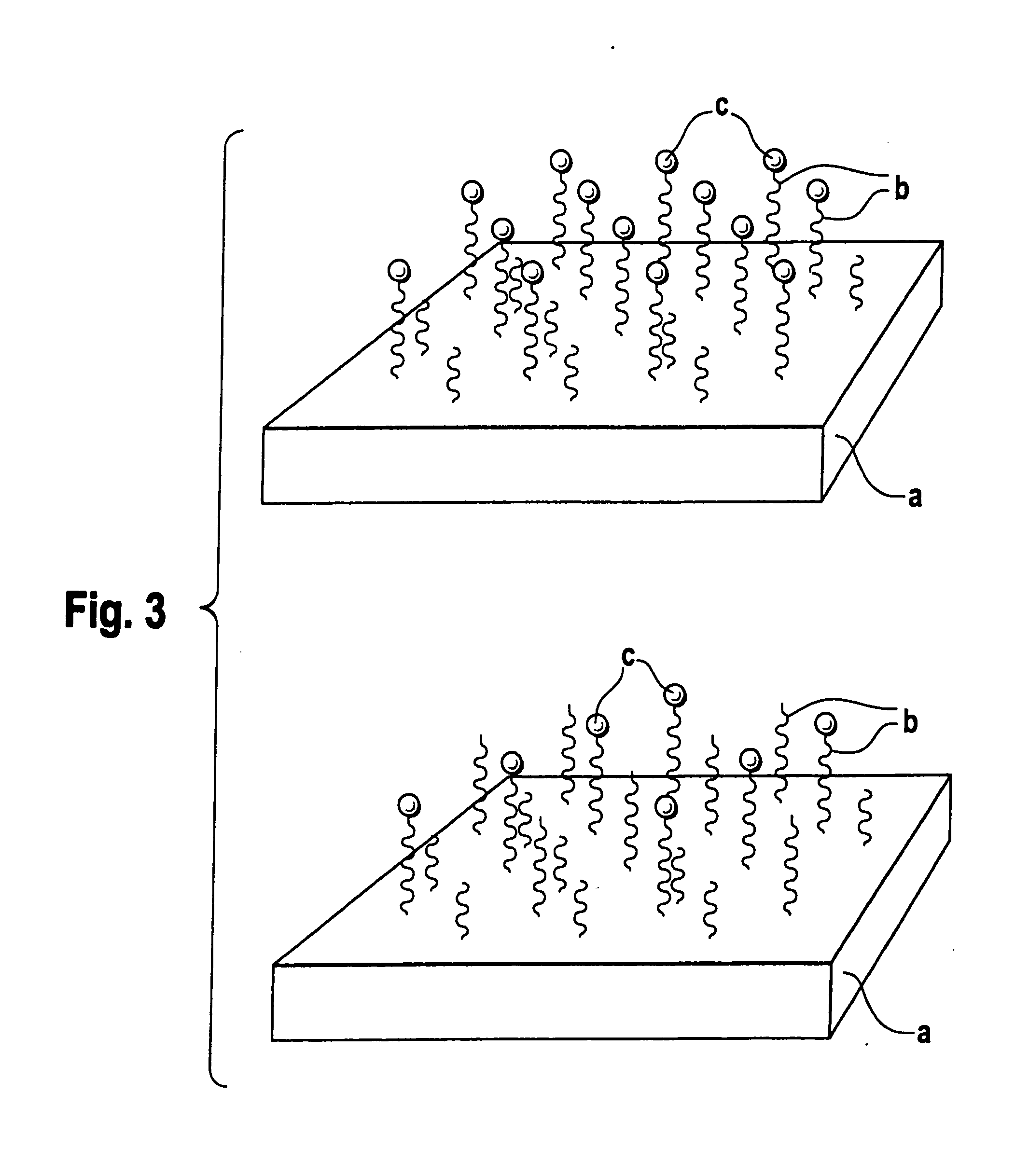
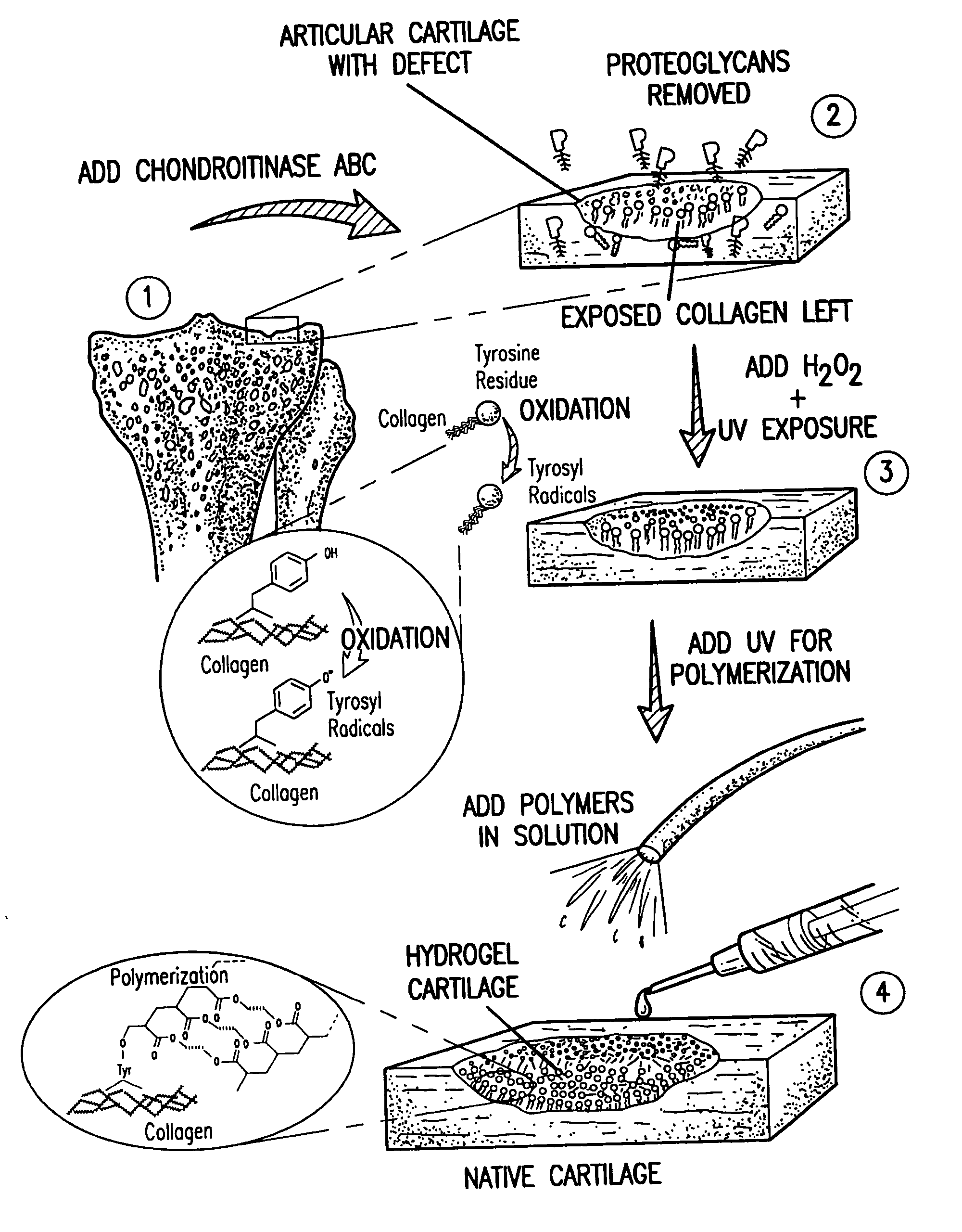
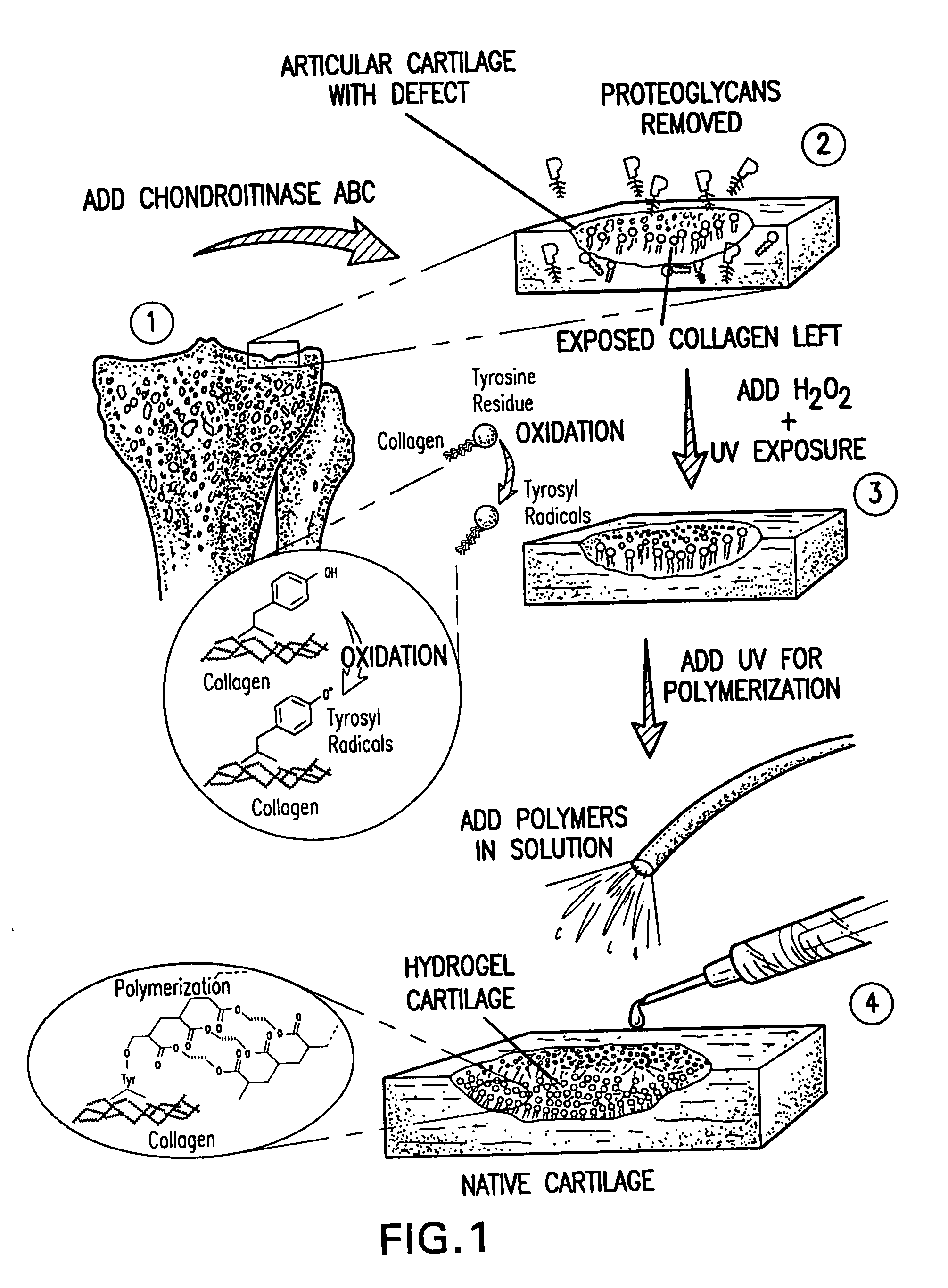
The present invention provides a composition and method for the covalent binding of a hydrogel to an extracellular matrix (ECM). Therapeutic applications include tissue repair and delivery of drugs or cells.
Owner:SYNTHASOME
Preparation method for antibacterial coat for fixing various cell growth factors on medical metal
InactiveCN103191467ARealize functionAchieve independenceCoatingsProsthesisAntibiotic YLayer by layer self assembly
The invention discloses a preparation method for an antibacterial coat for slowly releasing various cell growth factors on medical metal. According to the method, antibiotic with amino is grafted on graphene oxide by covalent binding, the graphene oxide grafted with the antibiotic is taken as a carrier, and nano-particles, which wrap the various cell growth factors respectively, are fixed between grapheme oxide layers by layer-by-layer self-assembly, so that the coat, which carries the various cell growth factors and the antibiotic at the same time, is obtained on the surface of the medical metal. The coat prepared by the method can independently control the various cell growth factors to be slowly and orderly released, the fixation amount of the cell growth factors is large and the bone induction effect is strong. In addition, the coat can release the antibiotic in the whole process of the slow release of the cell growth factors, thus achieving a long-term antibacterial effect. In addition, the cell growth factors do not interact with the antibiotics, so that the respective efficacy of the cell growth factors and the antibiotics is given full play.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Fluorescent detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels
InactiveUS20100089753A1Without laborious labeling and staining stepElectrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementSpectroscopyTryptophan
The mechanism of the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and chloroform, and the structure of the modified tryptophan and polypeptides including such modified tryptophan residues. The excited indole moiety, which is formed upon UV light irradiation, emits a solvated electron which initiates a series of events that yield fluorescent derivatives that have CHO group covalently bound to the indole moiety. These derivatives are herein referred to as formyltryptophan, and are relatively stable. Similar reactions are observed when 5-hydroxytryptophan, 5-fluorotryptophan, or N-methylindolacetate are used in place of tryptophan, or when other haloalkanes, such as trichloracetic acid, trichlorethanol, trichlorethane, bromoform, and iodoactetate are used in place of chloroform. The derivatives can be used in a variety of applications in fluorescence spectroscopy, and for nuclear magnetic resonance, X-ray crystallography, infra-red spectroscopy, circular dicroism and mass spectroscopy. Additionally, the UV light-induced reaction between the indole moiety of tryptophan and haloalkanes can be used to prepare derivatives of tryptophan for chemical cross-linking studies of proteins and peptides.
Owner:UNIV TECH INT +1
Ratio-type fluorescent probe based on carbon dot as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104694117AGood choiceHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsRare earthEuropium
The invention discloses a ratio-type fluorescent probe based on a carbon dot and a europium complex, a preparation method of the ratio-type fluorescent probe and an application method of the ratio-type fluorescent probe in a water sample detection technology. A hyperfluorescence rare earth complex and the carbon dot are taken as a double luminous center, a covalent binding manner is adopted for bonding two luminophors together, and ratio-type detection on Cu<2+> ions in a water sample is carried out by virtue of strength ratio of the hyperfluorescence rare earth complex to the carbon dot. The ratio-type fluorescent probe has good selectivity and sensitivity.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Adhesion Preventive Material
ActiveUS20080058469A1Excellent bioadaptive materialSufficient adhesivenessBiocideOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkHydrogen
Owner:TERUMO KK
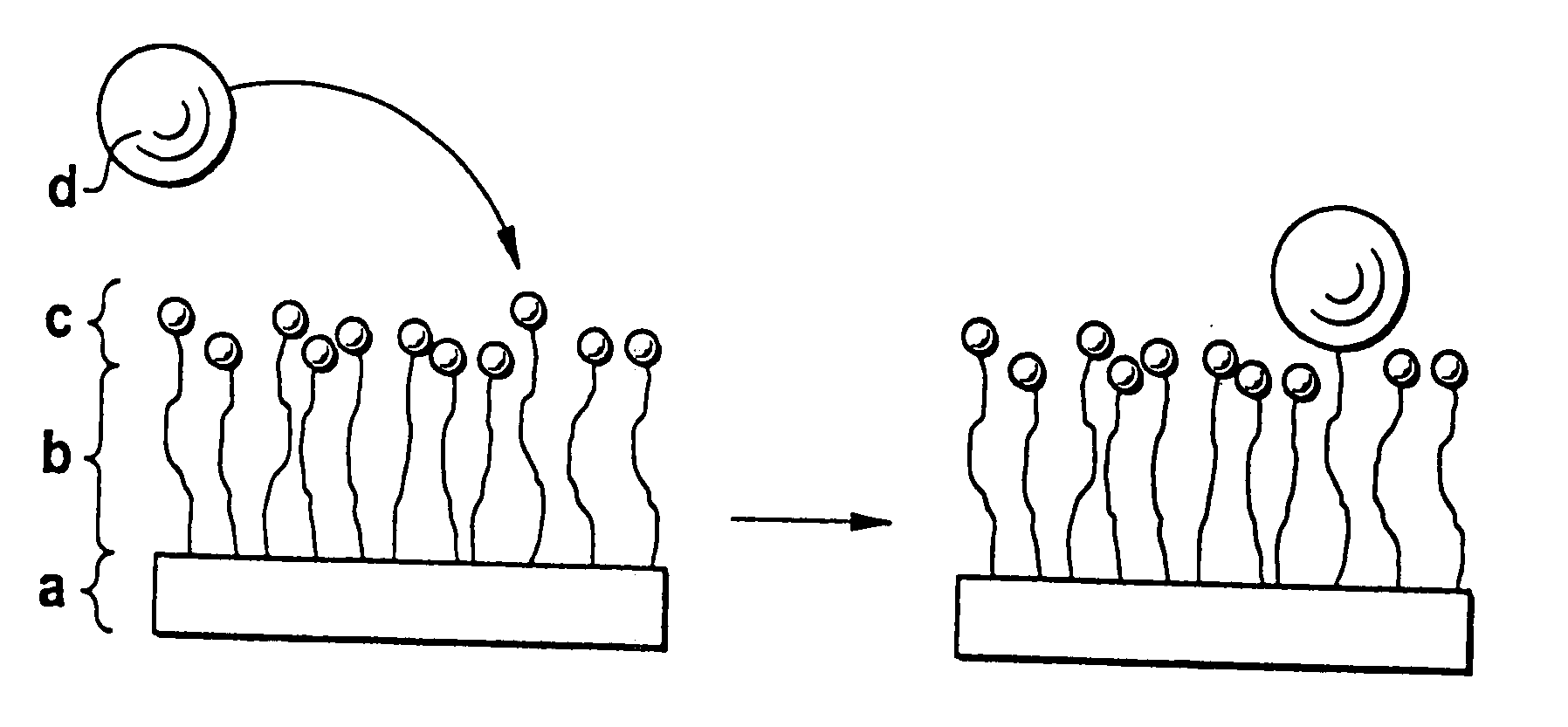
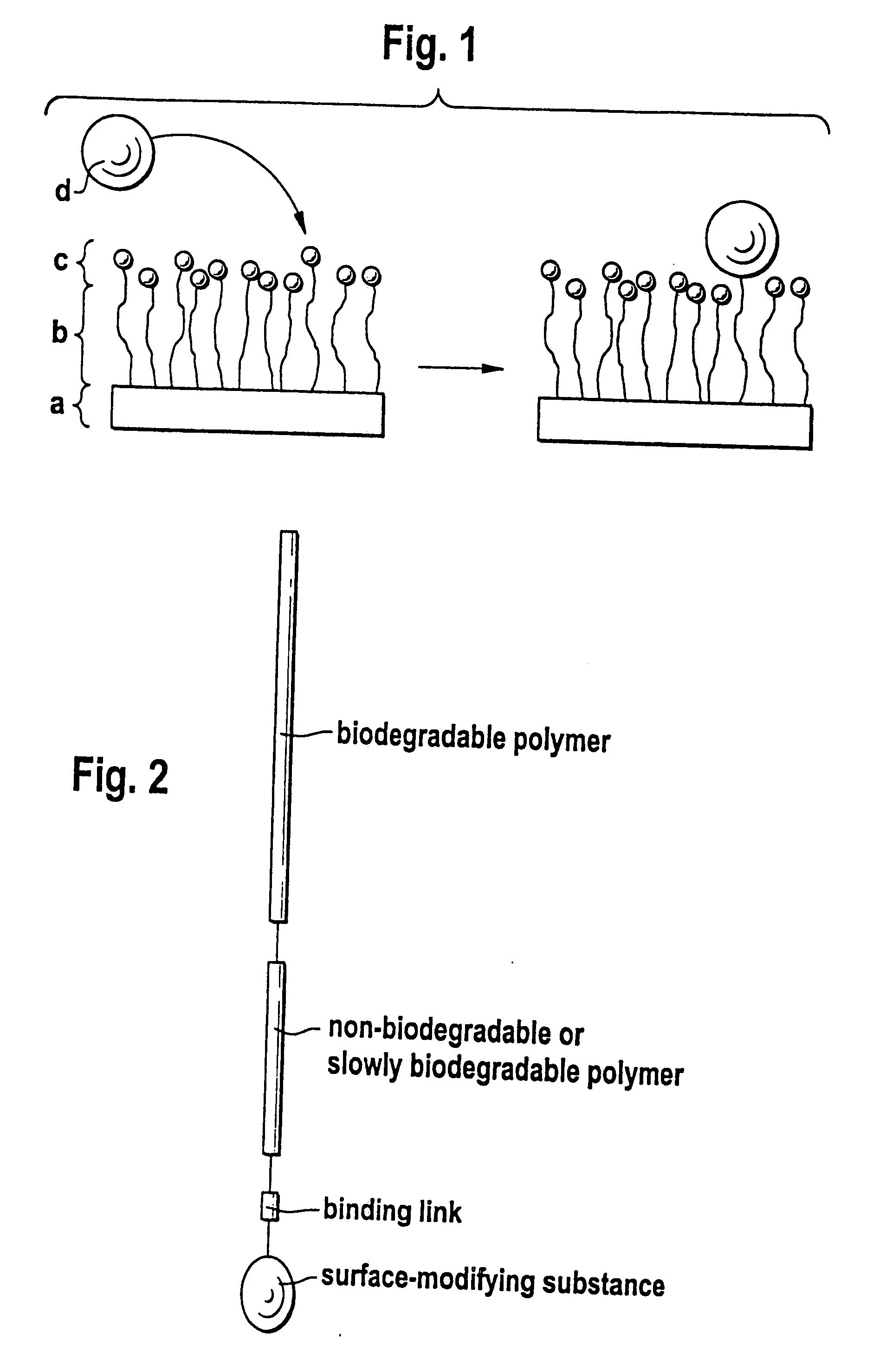
Biodegradable block copolymers with modifiable surface
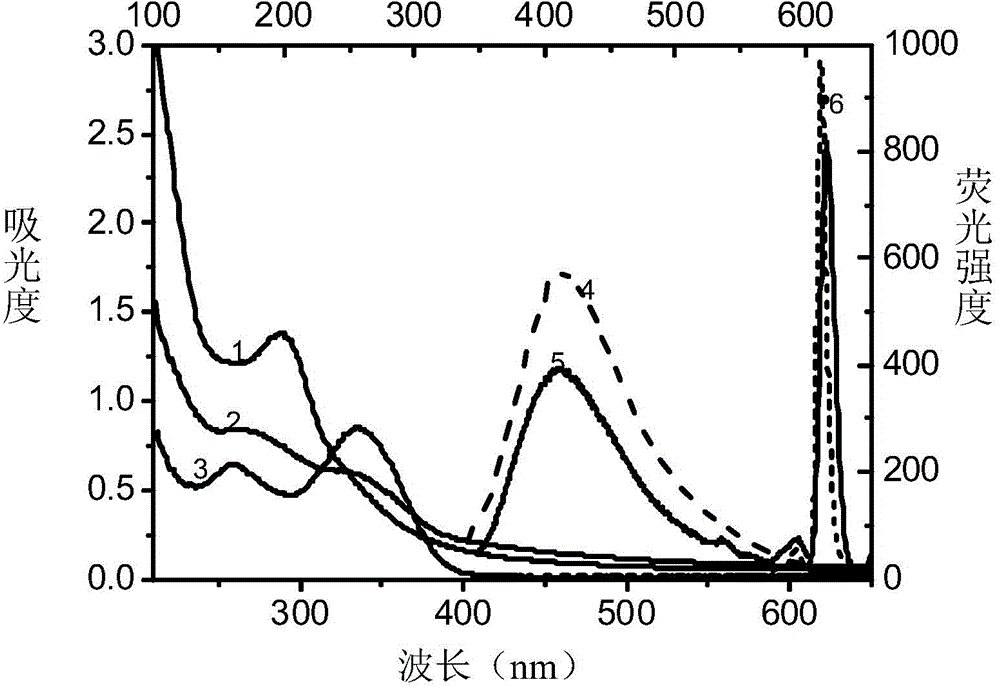
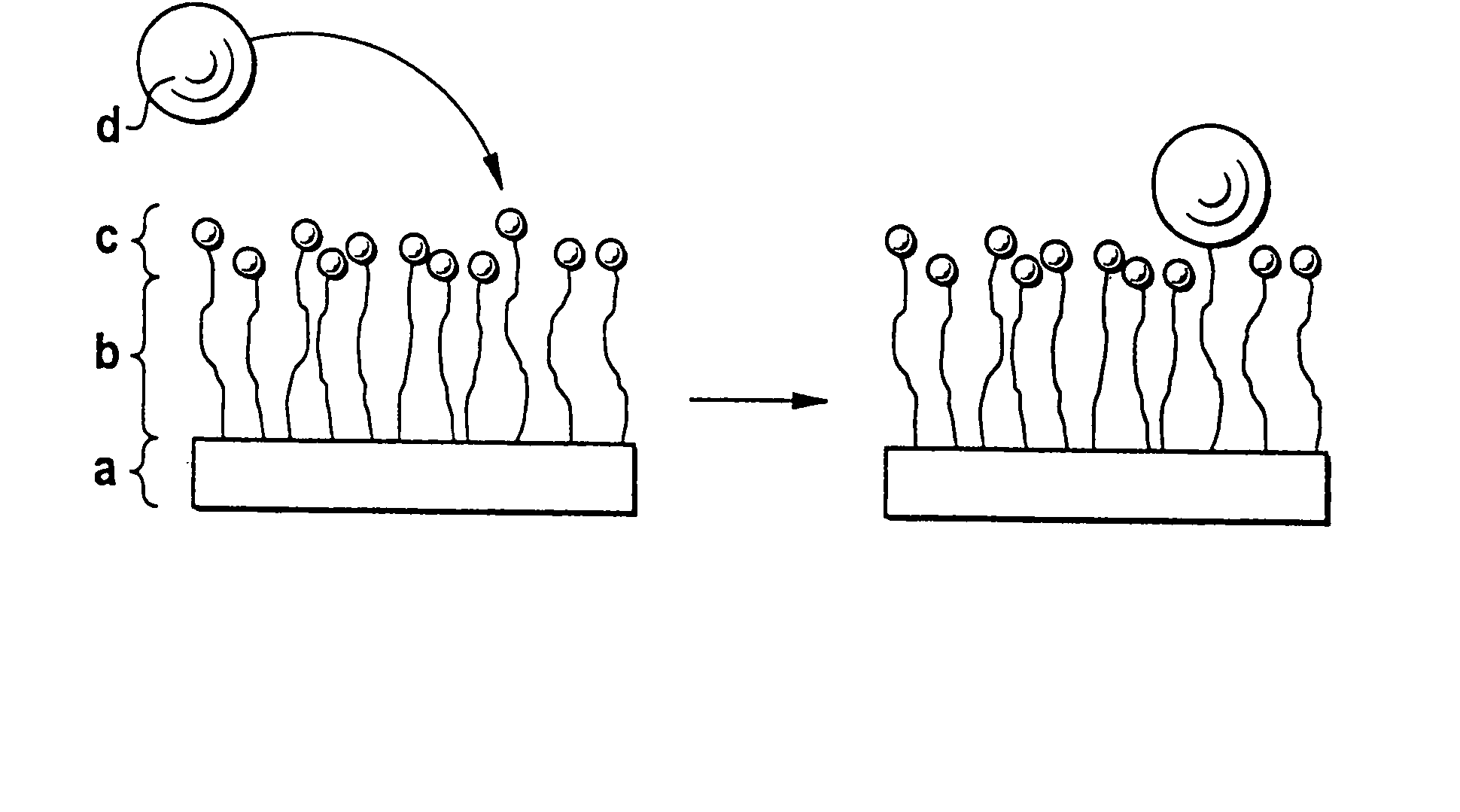
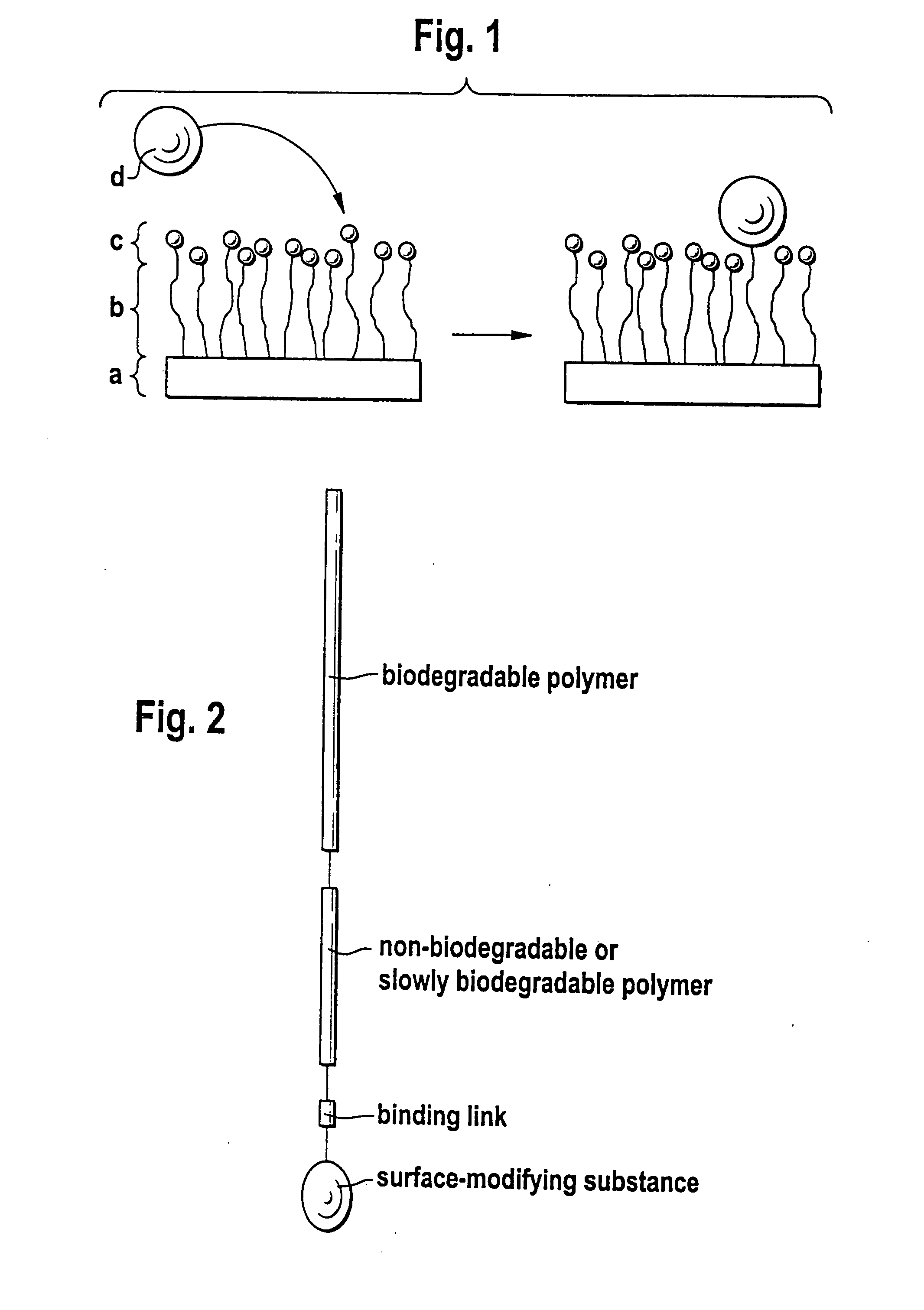
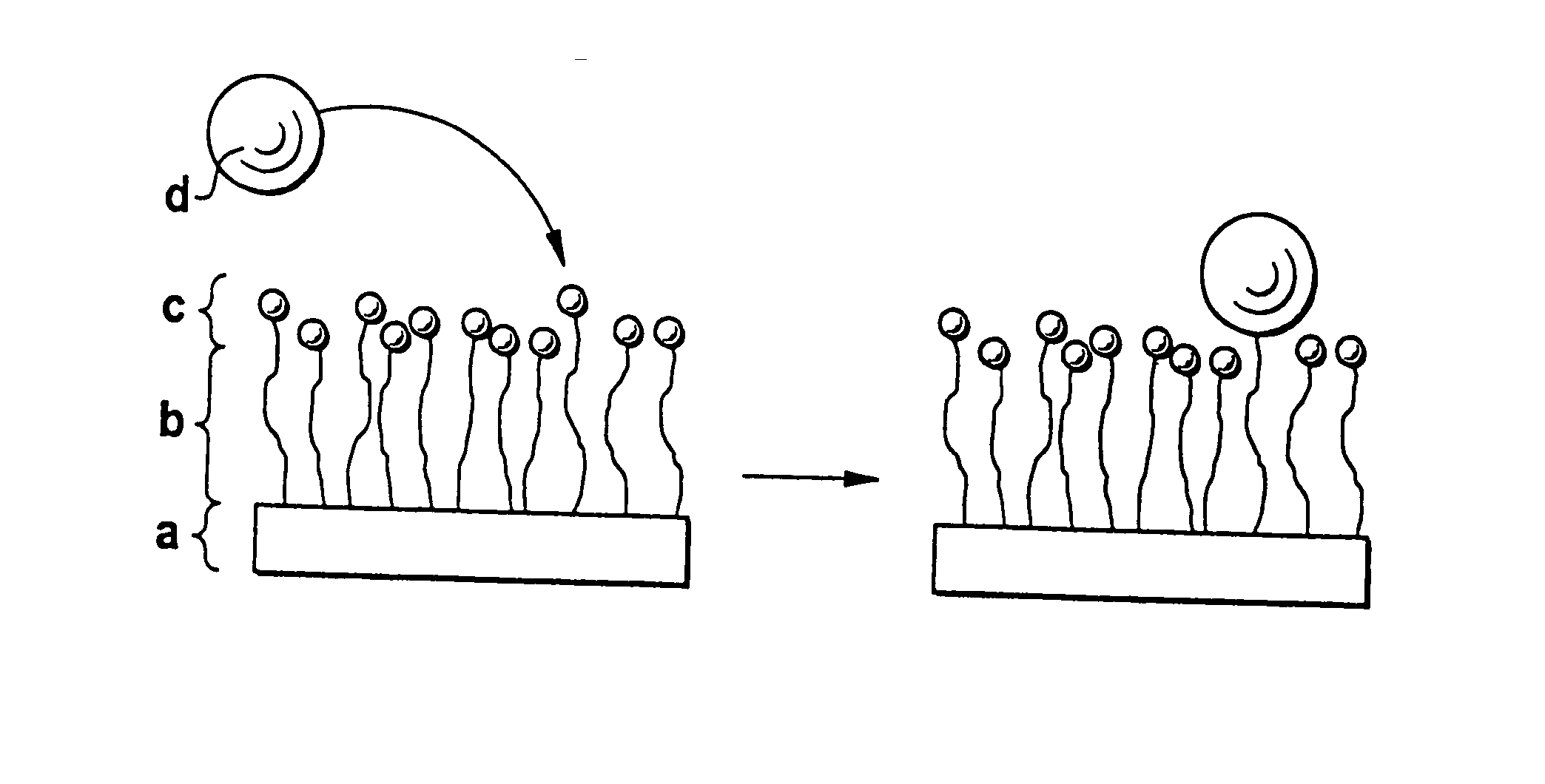
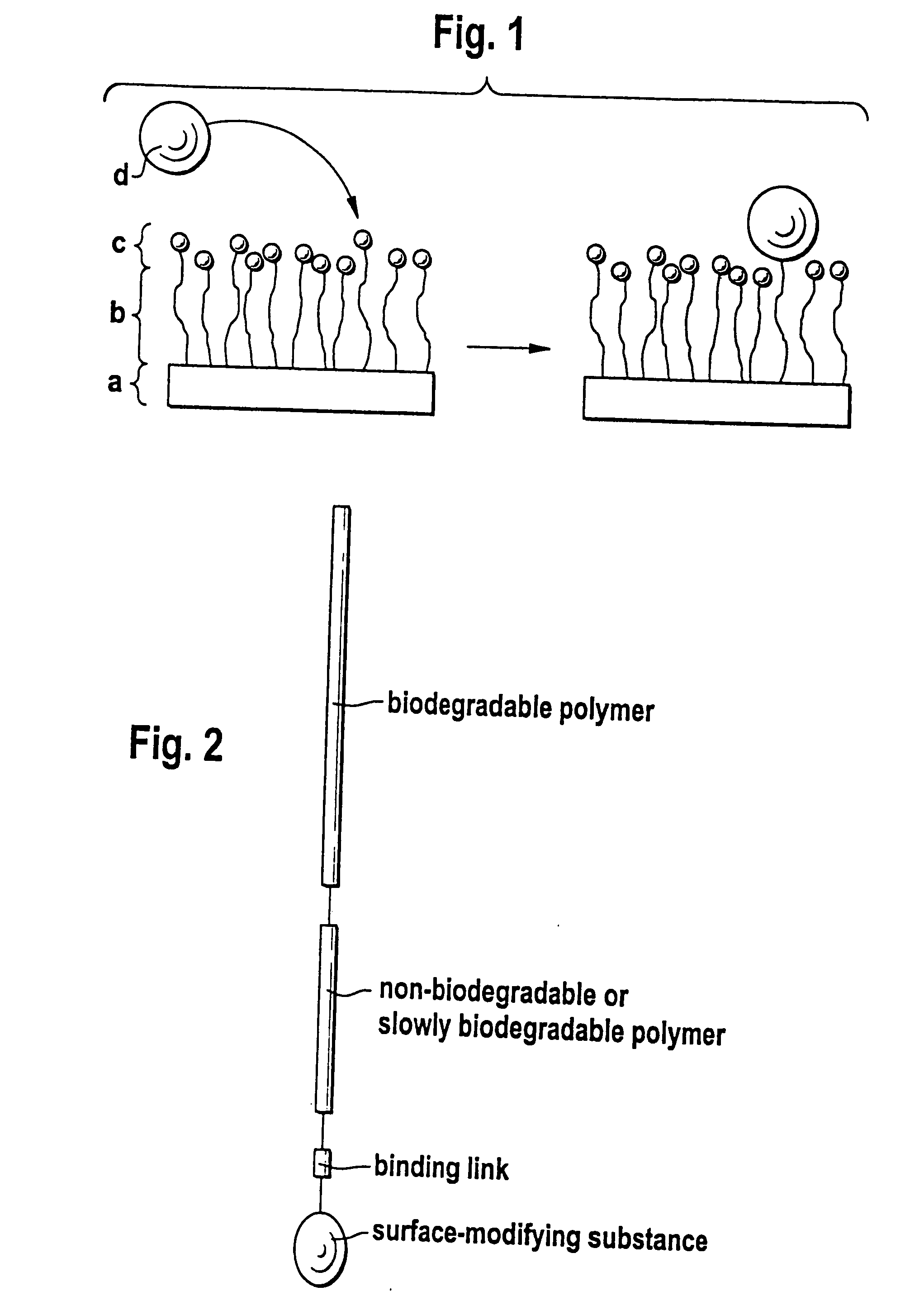
InactiveUS20070299227A1Sufficient distanceImprove bindingSugar derivativesCell culture supports/coatingControlled releaseHydrophobe
The invention relates to a block copolymer containing: a) hydrophobic biodegradable polymer; b) a hydrophilic polymer and c) at least one reactive group for covalent binding of a surface-modifying substance d) to the hydrophilic polymer b). The invention relates to shaped bodies consisting of the block copolymer and to their utilization, particularly as carriers for tissue culture and active substances and for controlled release and targeted administration of active substances.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
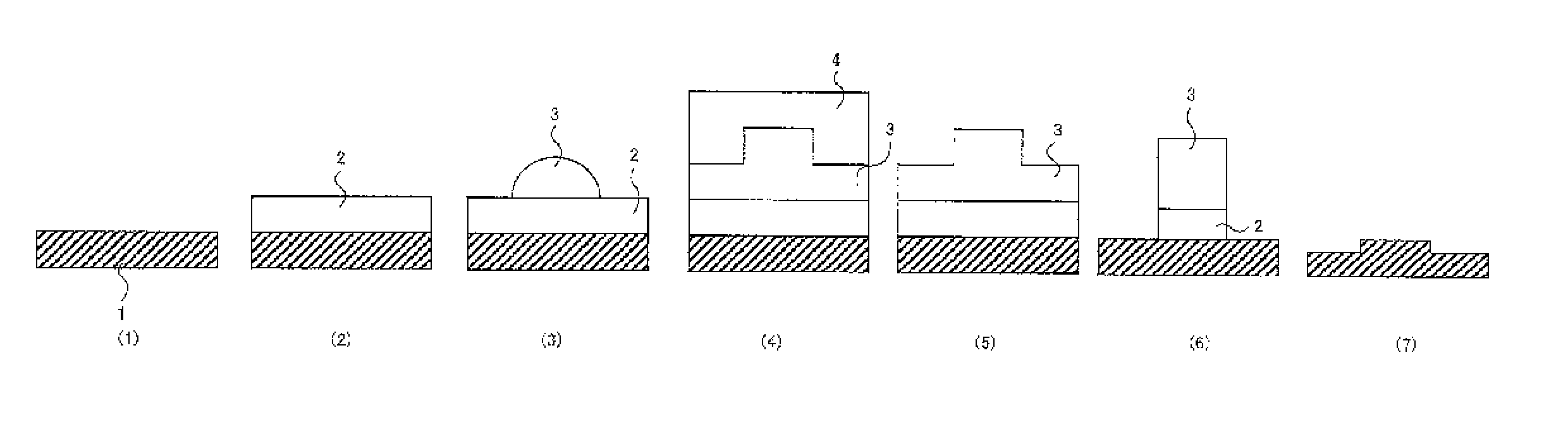
Underlay film composition for imprints and method of forming pattern and pattern formation method using the same
ActiveUS20140220353A1Improve adhesionGood formabilityLayered productsDecorative surface effectsCovalent modifierOxygen atom
Provided is the pattern formability and line edge roughness of the resultant substrate.An underlay film composition for imprints comprising a compound (A) and a solvent (B), the compound (A) having at least either one of a group (Ka) capable of covalently bonding and / or interacting with a substrate, and, a group (Kb) capable of covalently bonding and / or interacting with a curable composition for imprints, an Ohnishi parameter (Z) calculated from (equation 1) of 3.8 or larger, and a molecular weight of 400 or larger:the Ohnishi parameter=(total number of atoms) / (number of carbon atoms−number of oxygen atoms) (Equation 1)
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Biodegradable block copolymers with modifiable surface
InactiveUS20070299240A1Binding of surface-modifying substances to the reactive group c) is facilitatedImprove bindingCell culture supports/coatingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsControlled releasePolymer science
The invention relates to a block copolymer containing: a) hydrophobic biodegradable polymer; b) a hydrophilic polymer and c) at least one reactive group for covalent binding of a surface-modifying substance d) to the hydrophilic polymer b). The invention relates to shaped bodies consisting of the block copolymer and to their utilization, particularly as carriers for tissue culture and active substances and for controlled release and targeted administration of active substances.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
Method and material for enhanced tissue-biomaterial integration
The present invention relates to the covalent binding of a hydrogel to an extracellular matrix (ECM). The integration of the hydrogel with the tissue is superior to that in previous techniques. Moreover, unlike previous techniques, the present invention does not require a photoinitiator. Potential therapeutic applications include tissue repair and delivery of drugs or cells. The ECM is first exposed, then treated with a priming agent. Then a polymerizable agent is added and crosslinked to the ECM. Two primary embodiments of methods are disclosed. In the first, the priming agent is an oxidizer which creates tyrosyl radicals in the ECM, which are then bound by acrylate groups in the polymerizable agent. In the second, the priming agent contains aldehydes which bind amino groups in the ECM.
Owner:SYNTHASOME
Conjugates of biologically active compounds, methods for their preparation and use, formulation and pharmaceutical applications thereof
InactiveUS20040186063A1Strong therapeutic activitySimple processCompounds screening/testingBiocideOrganic chemistryNon antibiotic
This invention features a compound of the following formula: T-(-L-C)m, T is a transportophore, L is a bond or a linker having a molecular weight up to 240 dalton, C is a non-antibiotic therapeutic agent, and m is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, or 8, in which the transportophore has an immune selectivity ratio of at least 2, the transportophore is covalently bonded to the non-antibiotic therapeutic agent via the bond or the linker, and the compound has an immune selectivity ratio of at least 2.
Owner:MERCKLE GMBH DE
Preparation method of graphene/polyaniline covalent binding conductive fabric
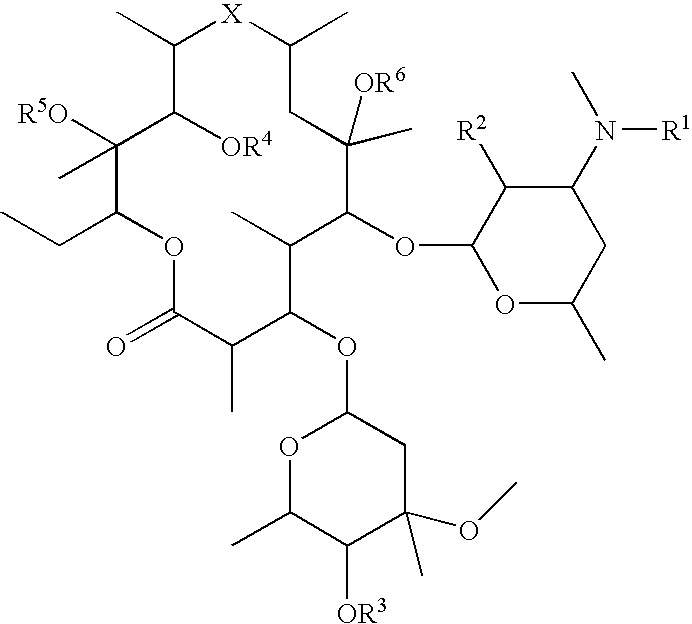
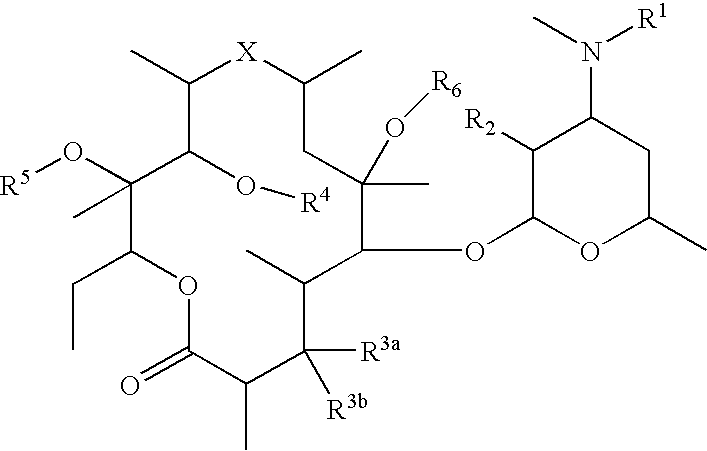
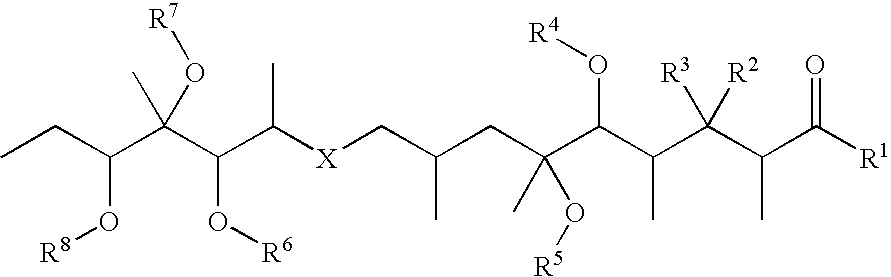
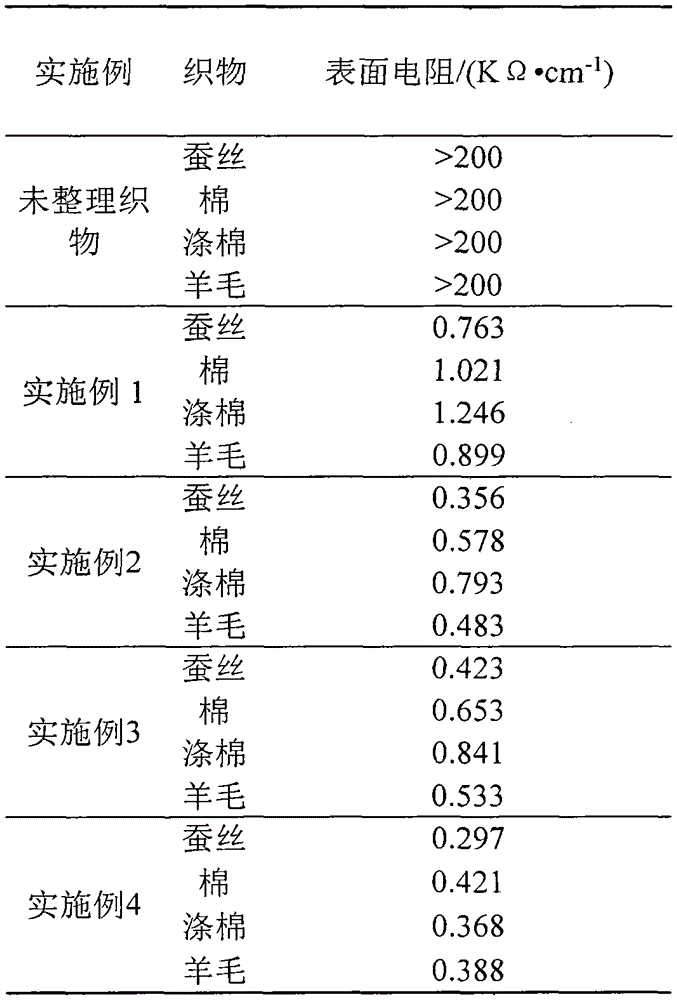
ActiveCN104313872AEasy to operateVegetal fibresAnimal fibresGraphene derivativesIn situ polymerization
The invention discloses a preparation method of a graphene / polyaniline covalent binding conductive fabric, which belongs to the technical field of textile chemistry. The preparation method comprises the steps of applying oxidized graphene or oxidized graphene derivative and a reaction product of p-phenylenediamine onto the fabric to be reduced, enabling the fabric to adsorb the polyaniline monomer, enabling the in-situ polymerization of the polyaniline monomer on the fabric to form polyaniline, and enabling the polyaniline to form covalent key combination with the graphene. According to the method, a conductive layer formed by covalently combining the graphene and polyaniline can be acquired on the surface of the fabric, so that the stability of the conductive layer is improved, and the conductive fabric with excellent effect can be acquired. The method is applicable to conventional fabrics such as natural fibers including cotton, wool, silk and the like, synthesized fibers including terylene, chinlon, acrylic fibers and the like and blending of fabric or conductive arrangement of intertexture, and the prepared functional fabric can be applied to the fields of medical healthcare, intelligent sensors, mobile power generation, military and the like.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Hetero-polysaccharide conjugate and methods of making and using the same
Disclosed and claimed are: a composition including at least one glycosaminoglycan, e.g., CIS, and at least one alginate, e.g., sodium alginate, wherein:the at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the algninate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS; orthe at least one glycosaminoglycan and / or the algninate are cross-linked or polymerized, e.g., the alginate is cross-linked or polymerized, for instance by addition of an inorganic salt, such as a calcium salt, and the at least one glycosaminoglycan and the alginate are covalently bound, e.g., by means of a coupling reaction involving a linker molecule such as DVS, and the covalent binding can have been performed prior to cross-linking or polymerizing or vice versa; and,gels comprising the composition; mixtures of such gels or of at least one such gel and at least one such composition; and,methods for making and using such compositions and gels, including products therefrom such as "paints", sprays, matrices, beads, microcapsules.
Owner:BIOMM +1
Biodegradable block copolymers with modifiable surface
InactiveUS20070299238A1Sufficient distanceImprove bindingCell culture supports/coatingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsControlled releaseHydrophobe
The invention relates to a block copolymer containing: a) hydrophobic biodegradable polymer; b) a hydrophilic polymer and c) at least one reactive group for covalent binding of a surface-modifying substance d) to the hydrophilic polymer b). The invention relates to shaped bodies consisting of the block copolymer and to their utilization, particularly as carriers for tissue culture and active substances and for controlled release and targeted administration of active substances.
Owner:MAST BIOSURGERY
Phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer and composite method and application thereof
InactiveCN101597349AEffective combinationFree from degradationVector-based foreign material introductionPolymer scienceCationic polymerization
The invention discloses a phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer, the structural formula is that (see lower right): wherein R is H or alkyl group containing one to ten carbons or substitution alkyl group containing nitrogen, oxygen, sulfur, chlorine, bromine or iodine; P is cationic polymer, the molecular weight Mw of P is from 400 to 500000, and n is more than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 20. The preparation method is that: the phenyloboricacid with active groups and the cationic polymer are dissolved in methyl alcohol in N, N-dimethyl fomamide, and are reacted for 2-48 hours at the temperature of 20-60 DEG C for obtaining the phenyloboricacid-modified cationic polymer. The cationic polymer utilizes functional groups such as hydroxide radical and amino-group and the like in biomacromolecules such as phenyloboricacid group energy, protein, amylase, nucleic acid and the like to form reversible covalent-binding property, and improves the capacity of gene combination and cell carrying of carrier materials, so as to realize high-efficiency transfection of genes.
Owner:常熟紫金知识产权服务有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com