Patents
Literature
132 results about "Cleavable linker" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
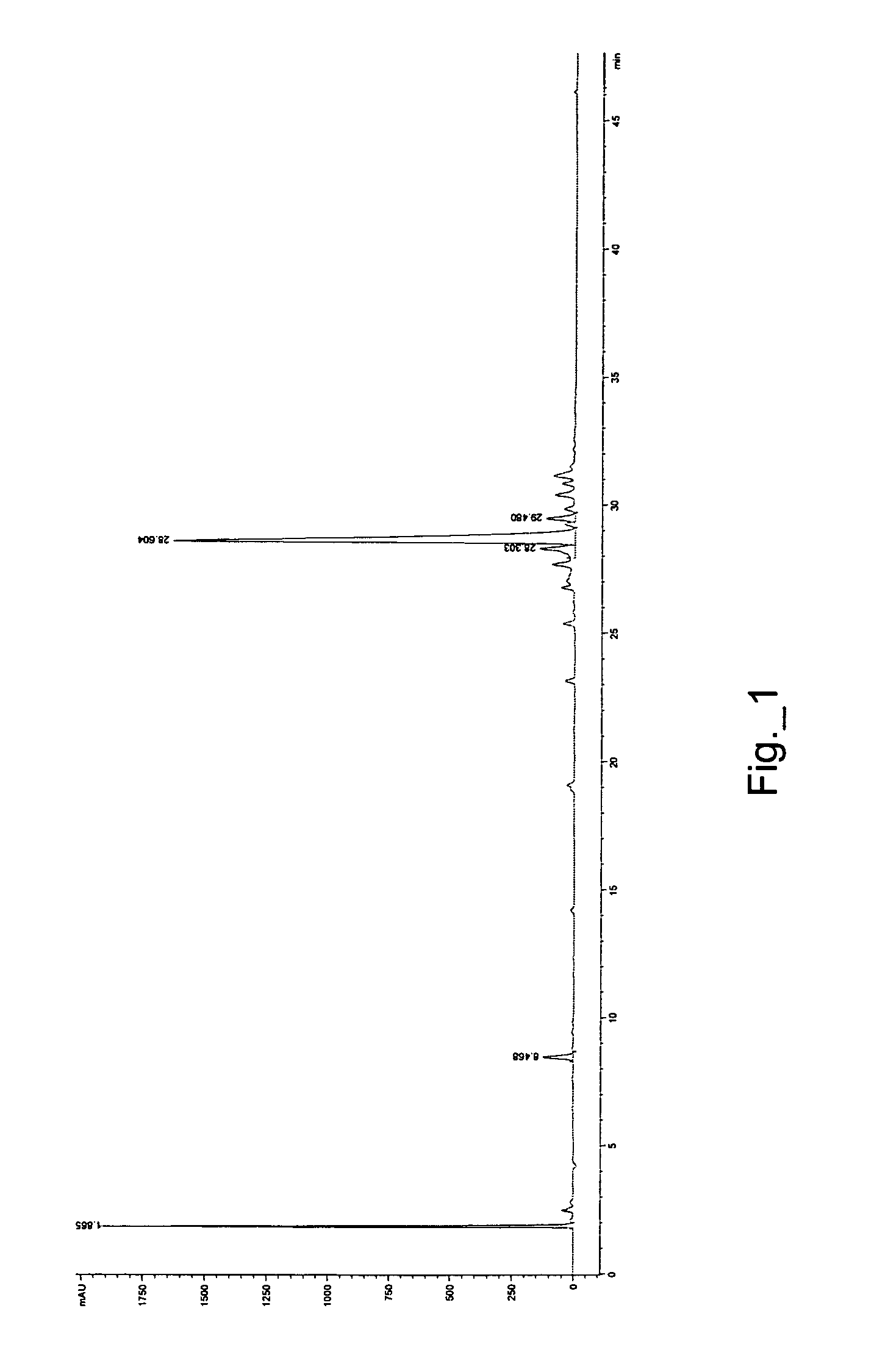
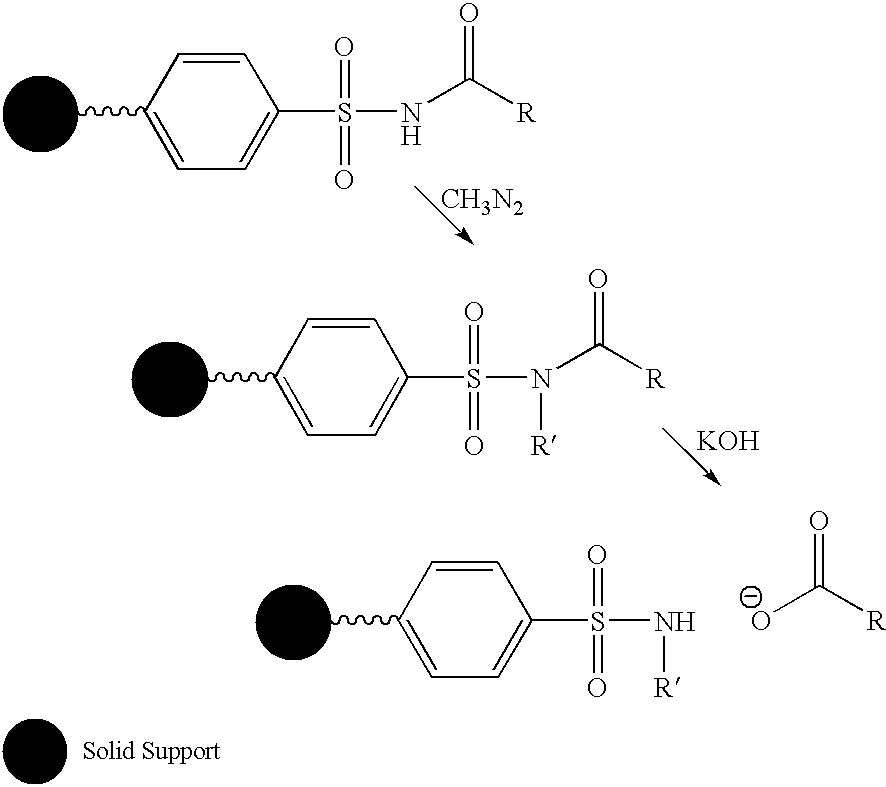
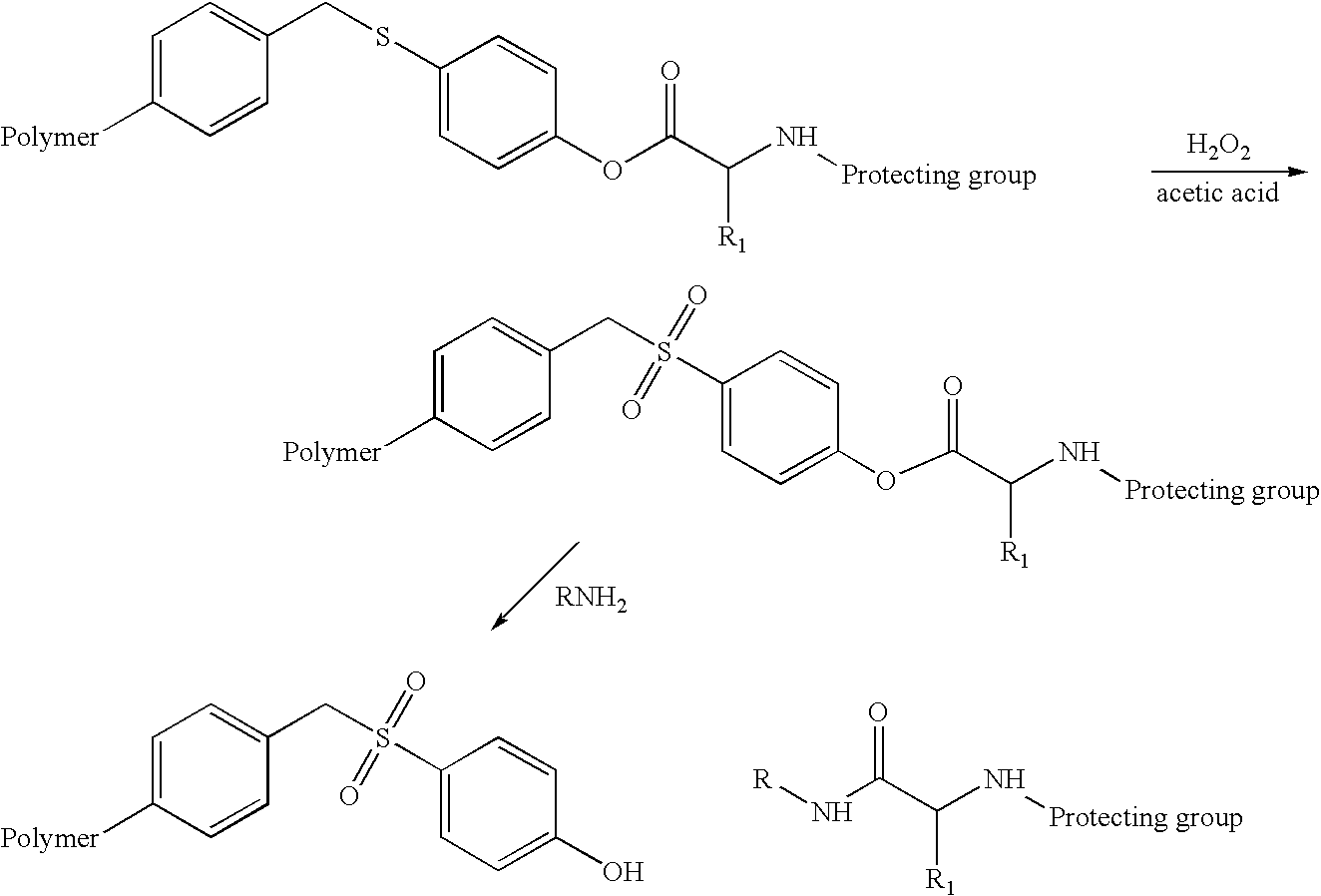
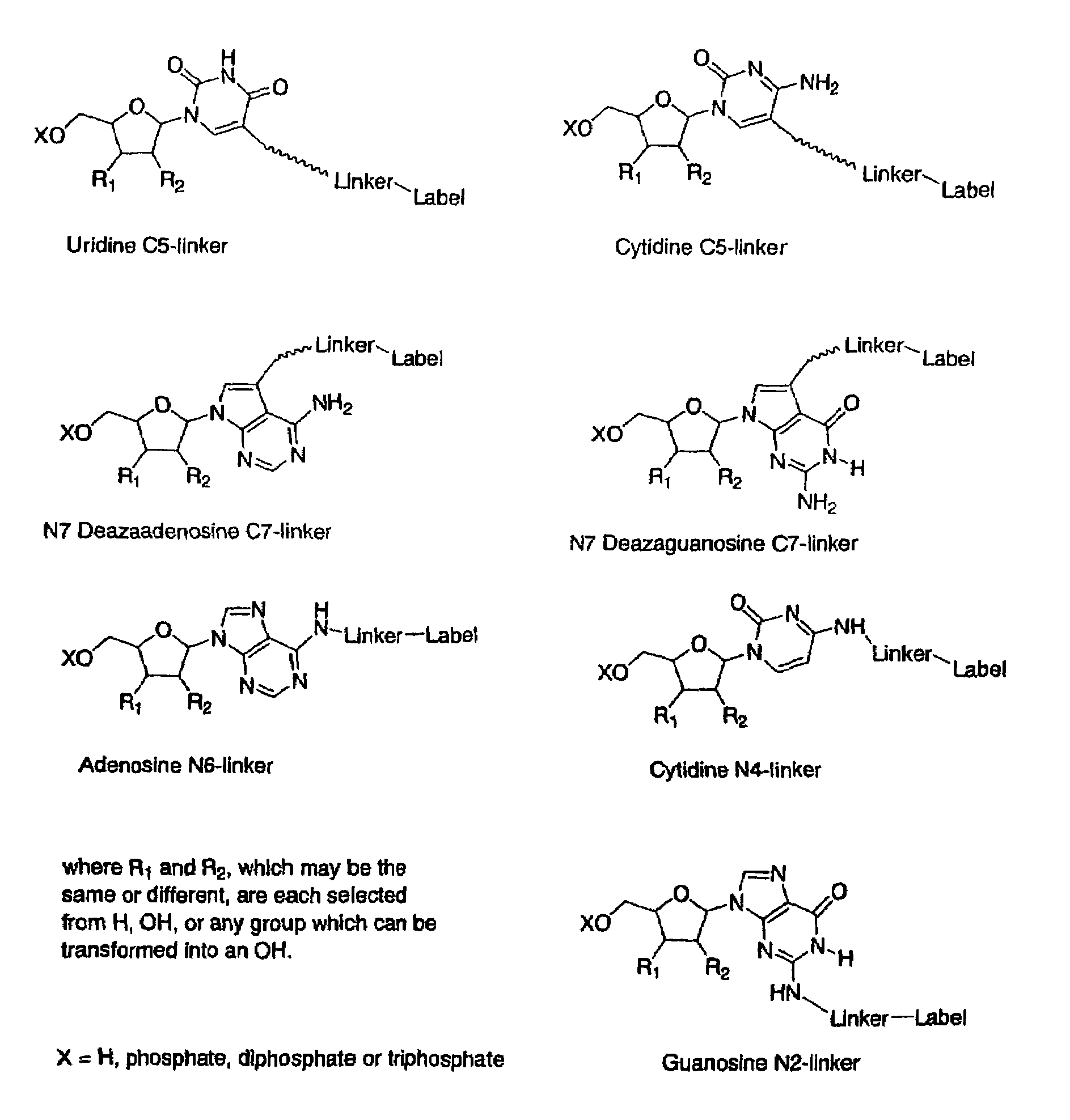
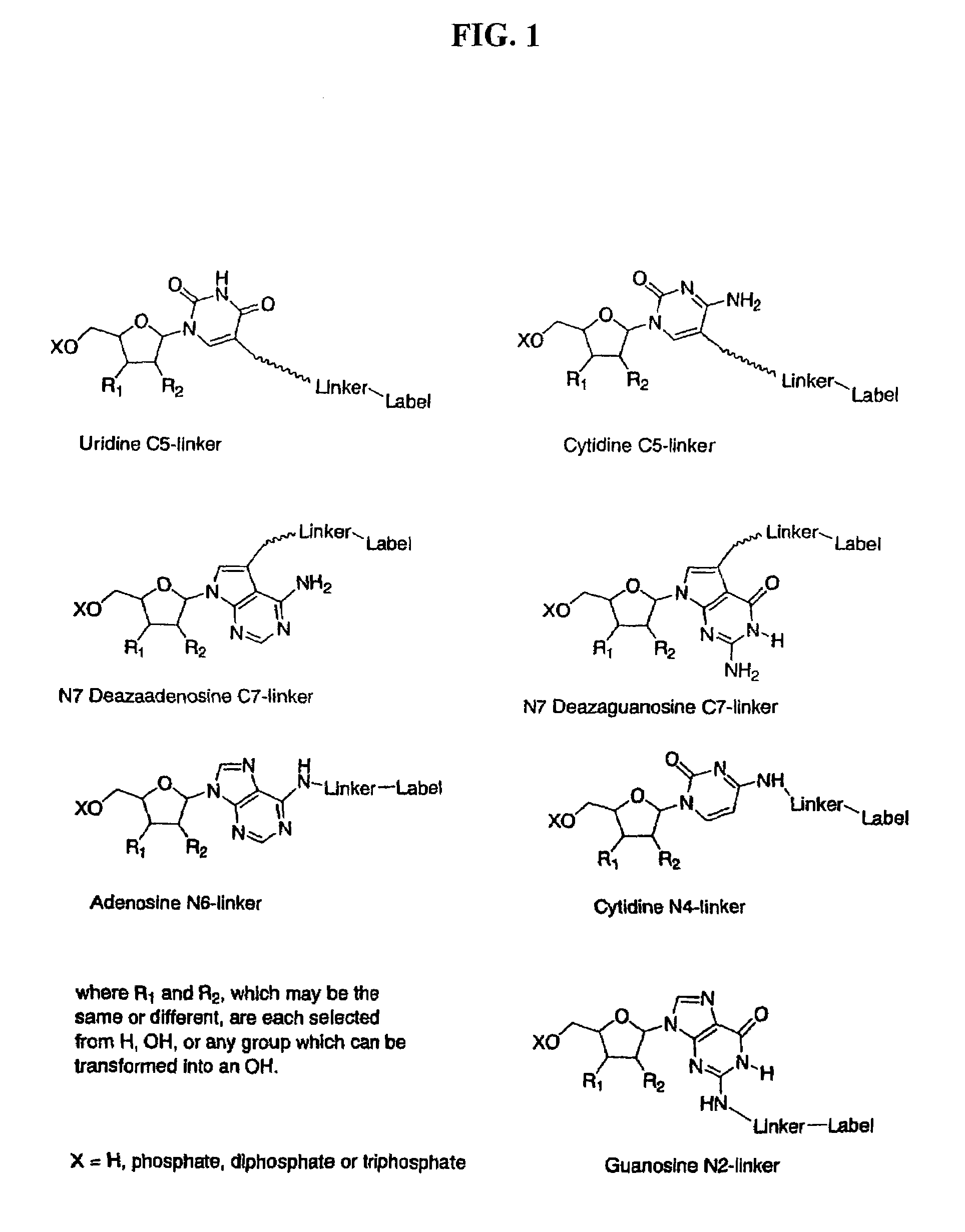
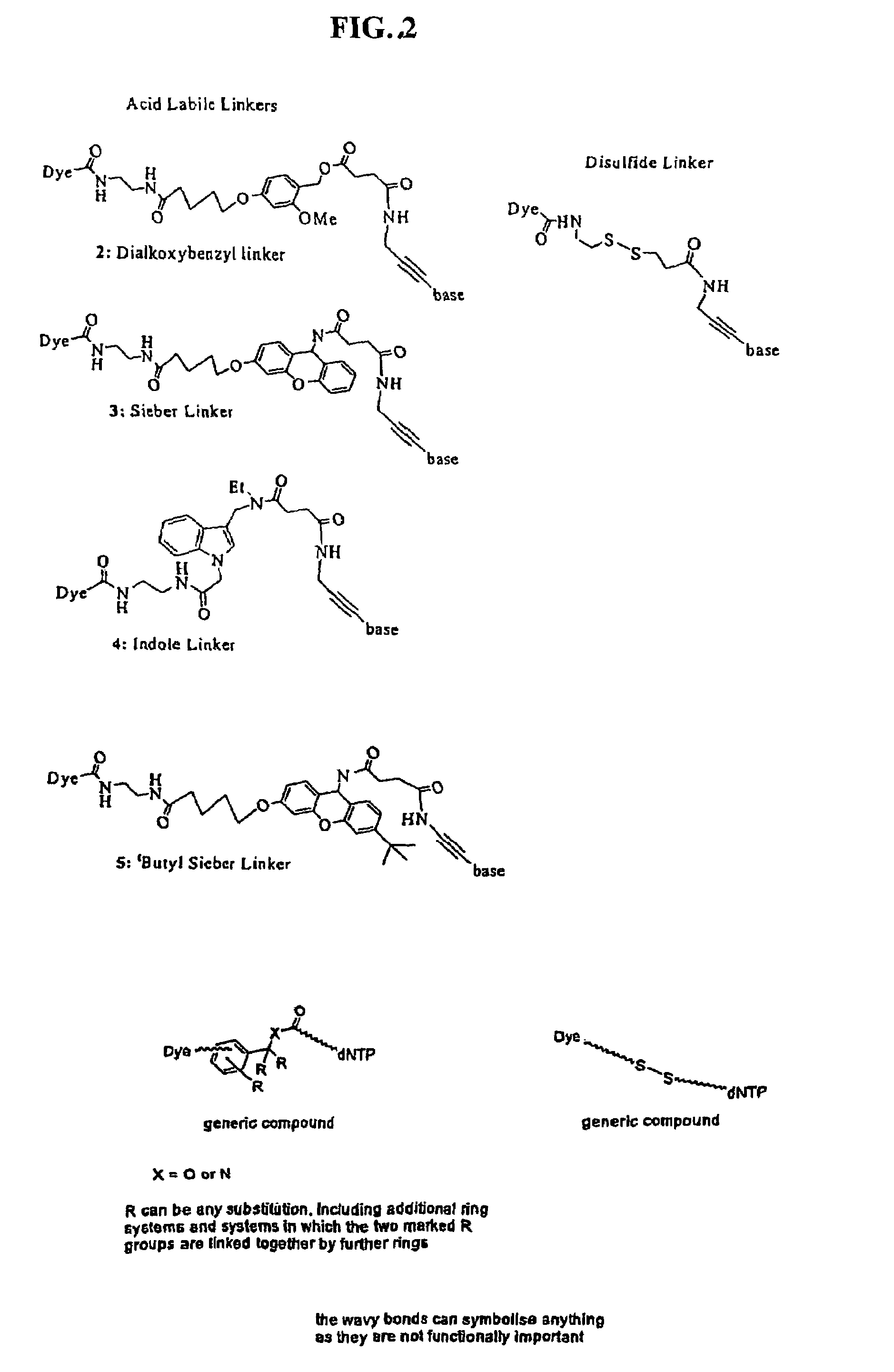
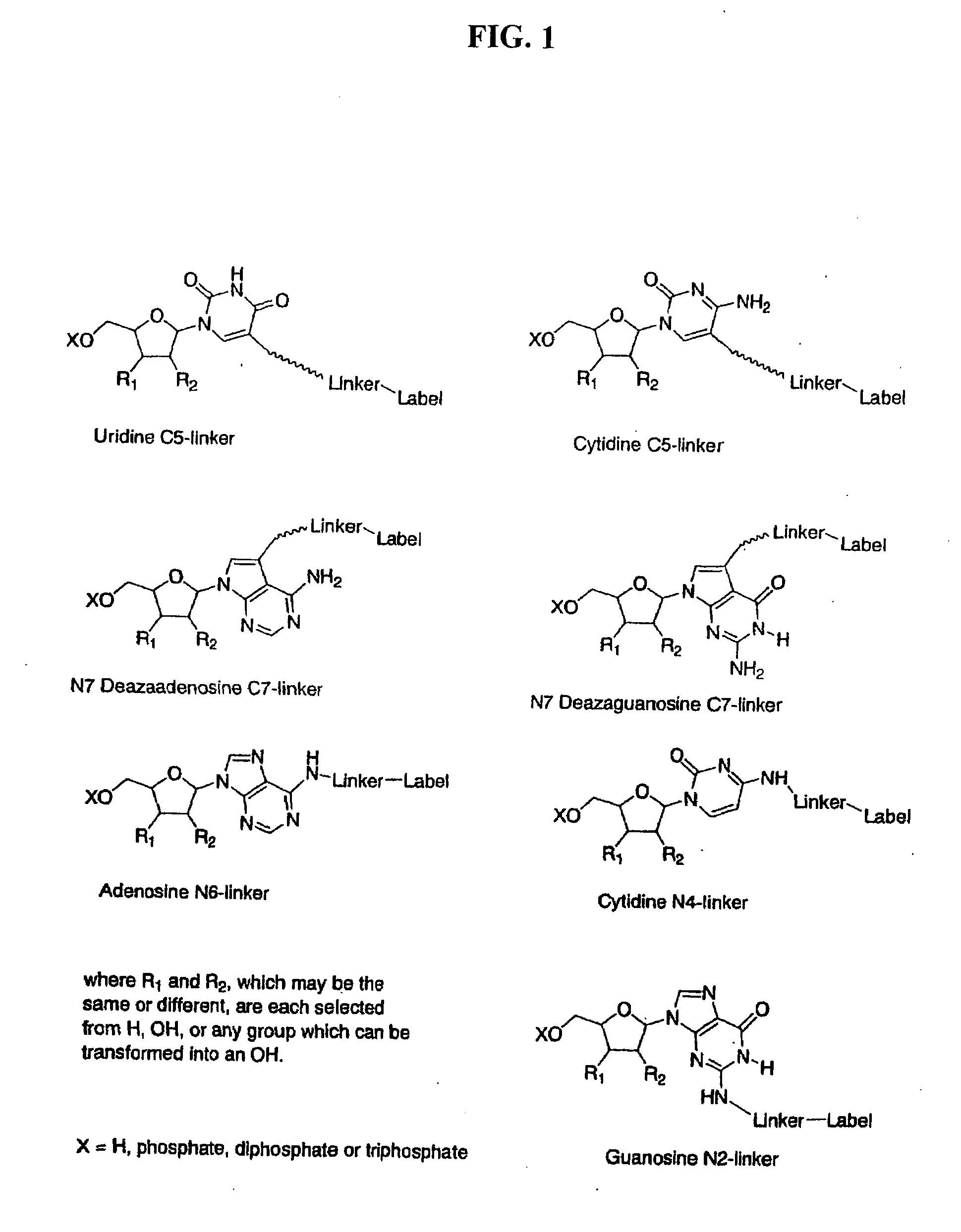
Labelled nucleotides
InactiveUS7057026B2Use of techniqueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic chemistryNucleoside
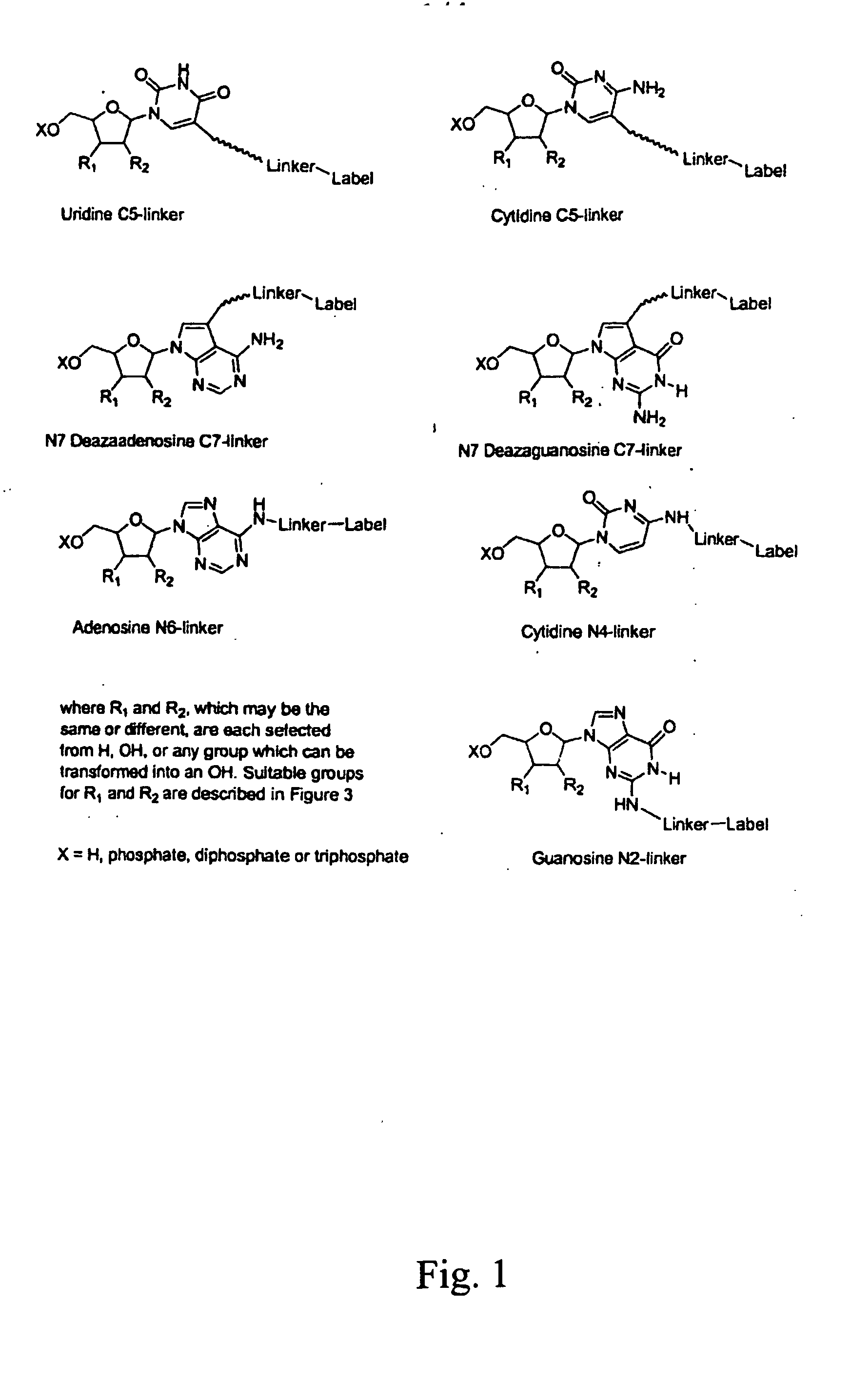
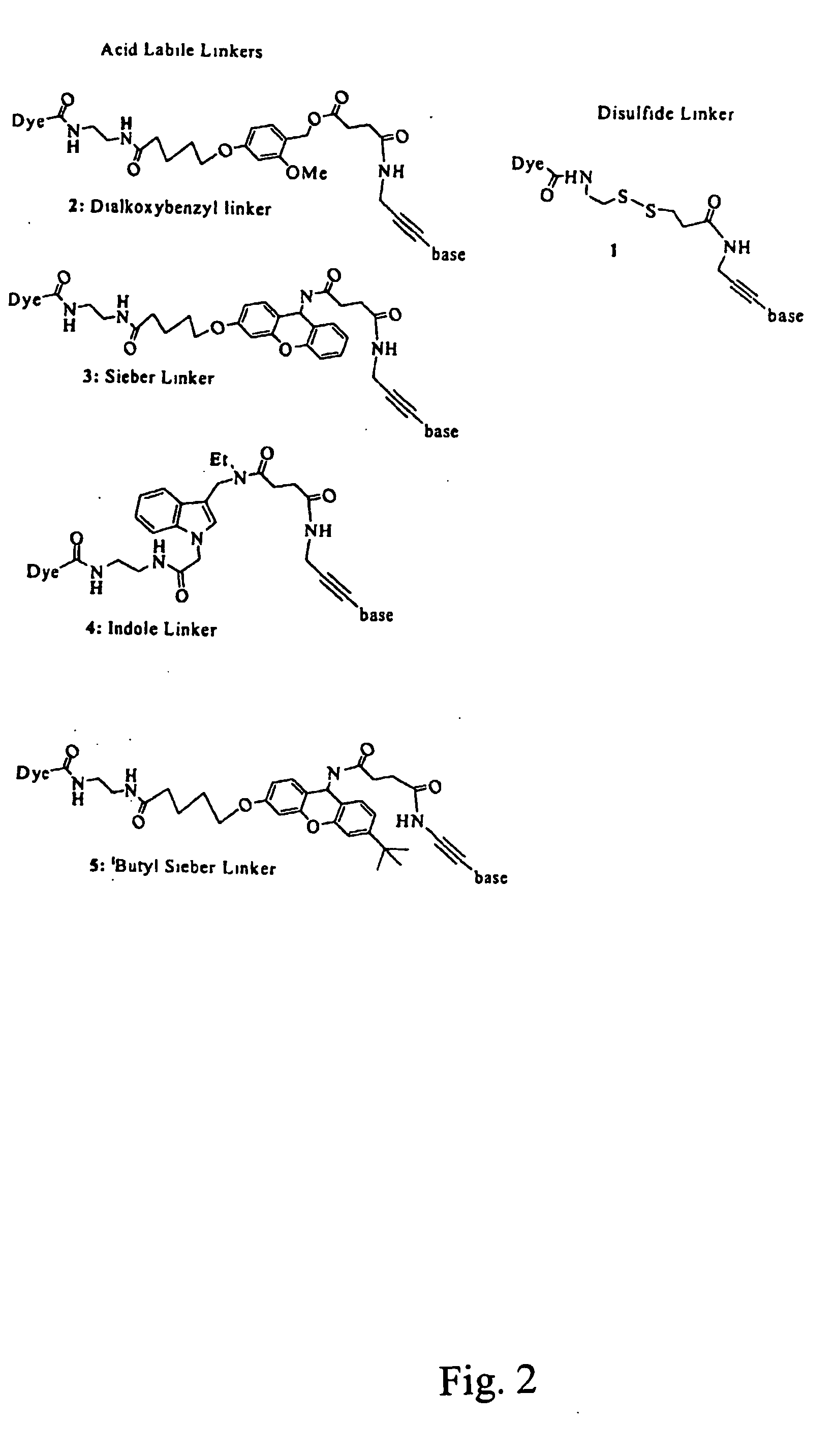
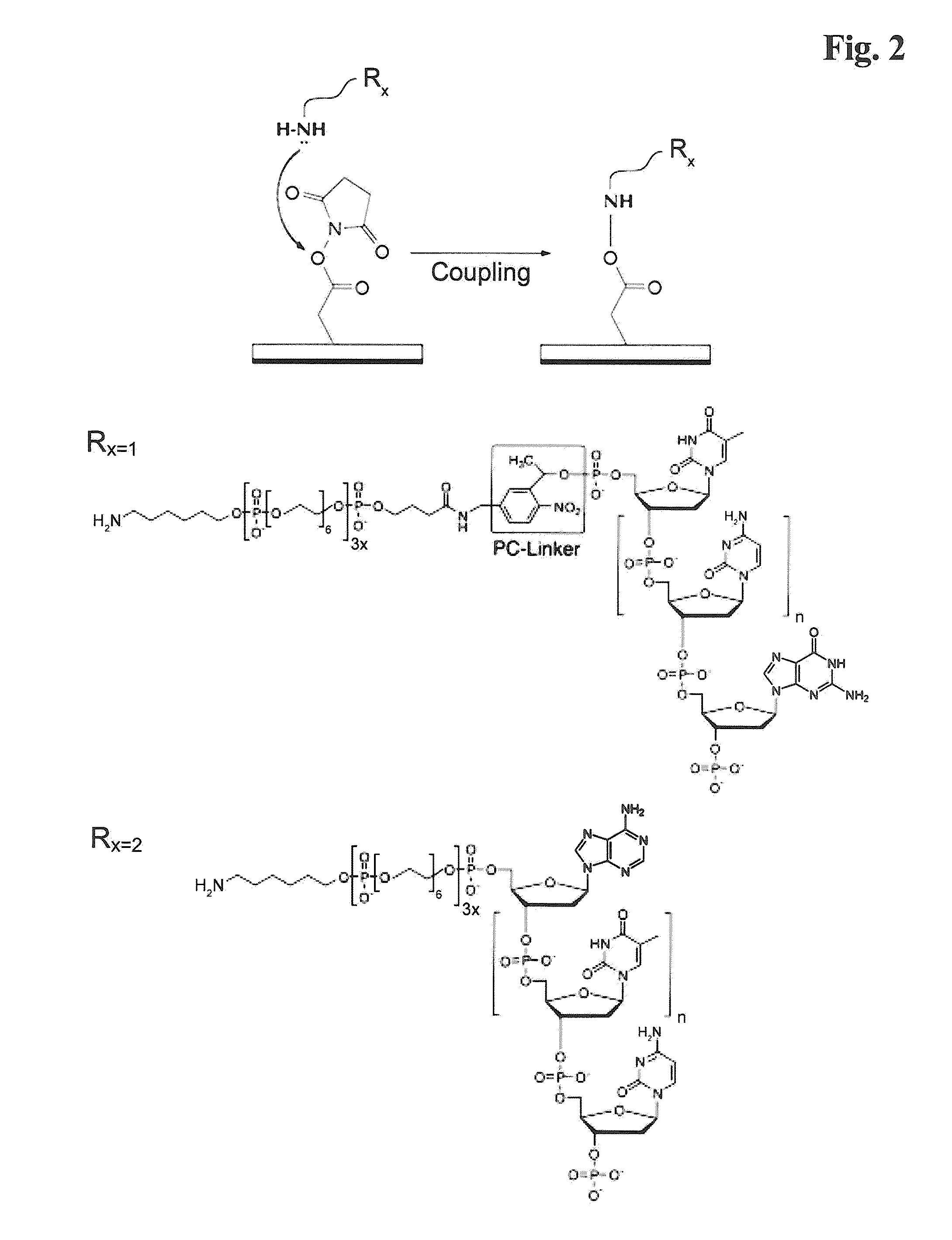
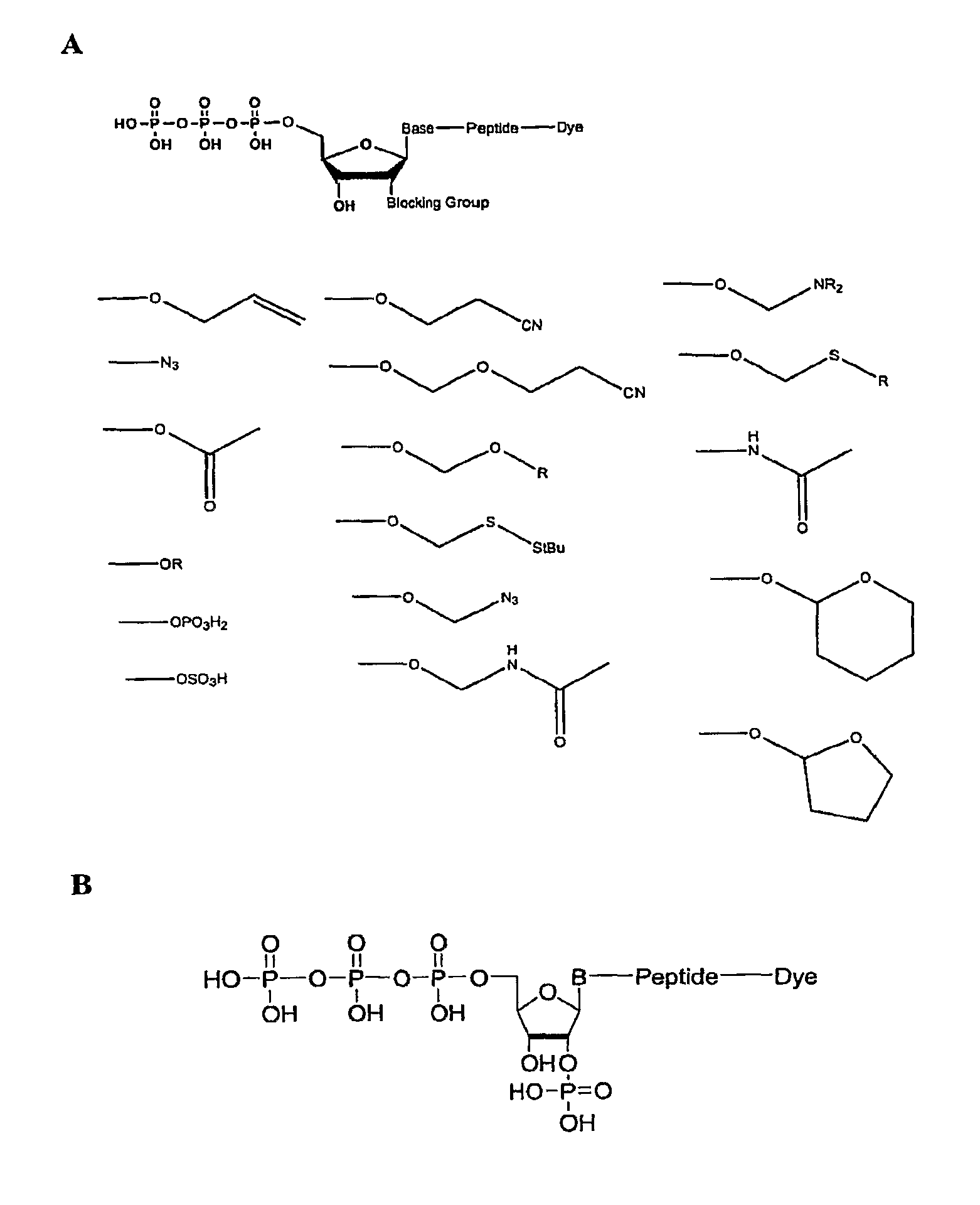
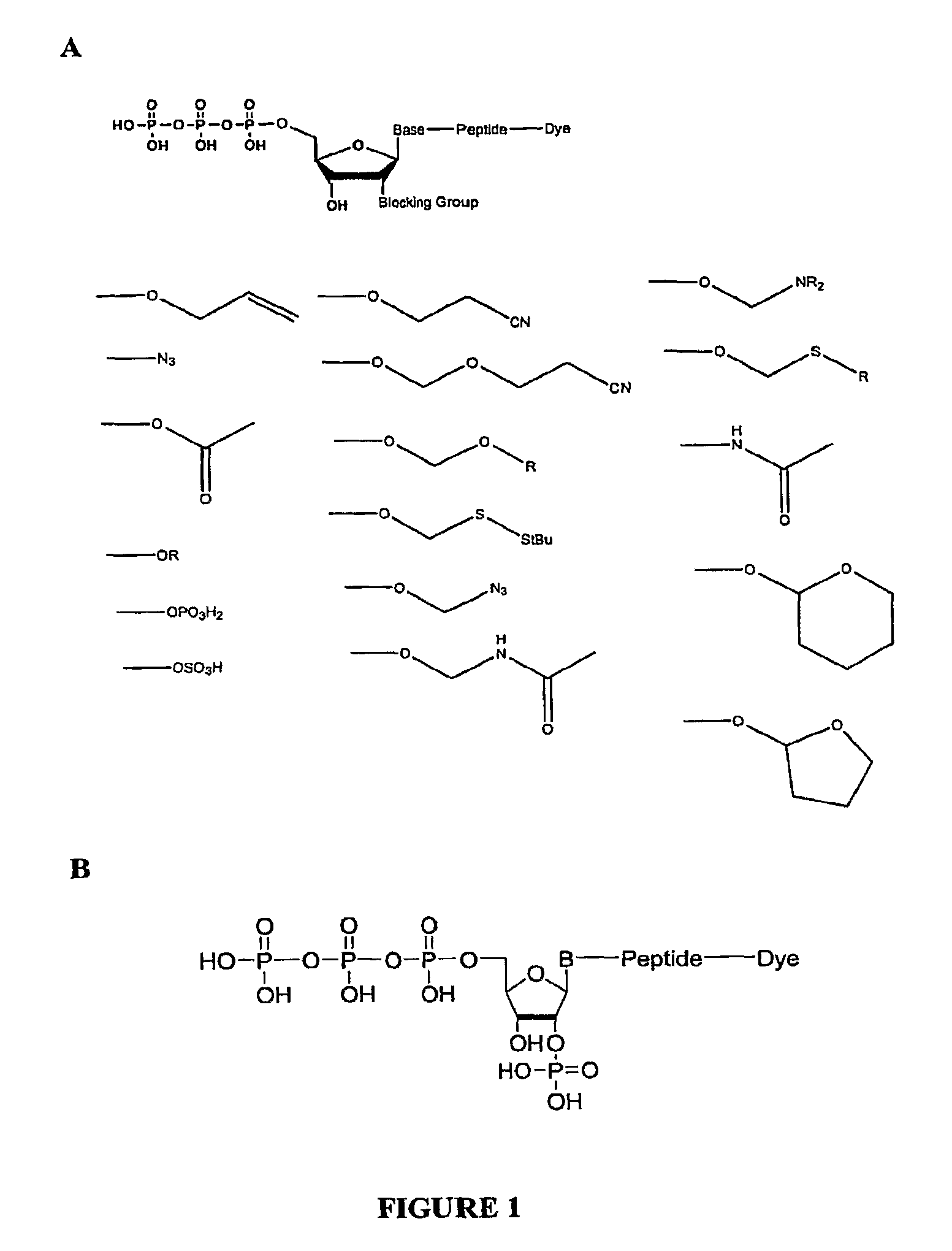
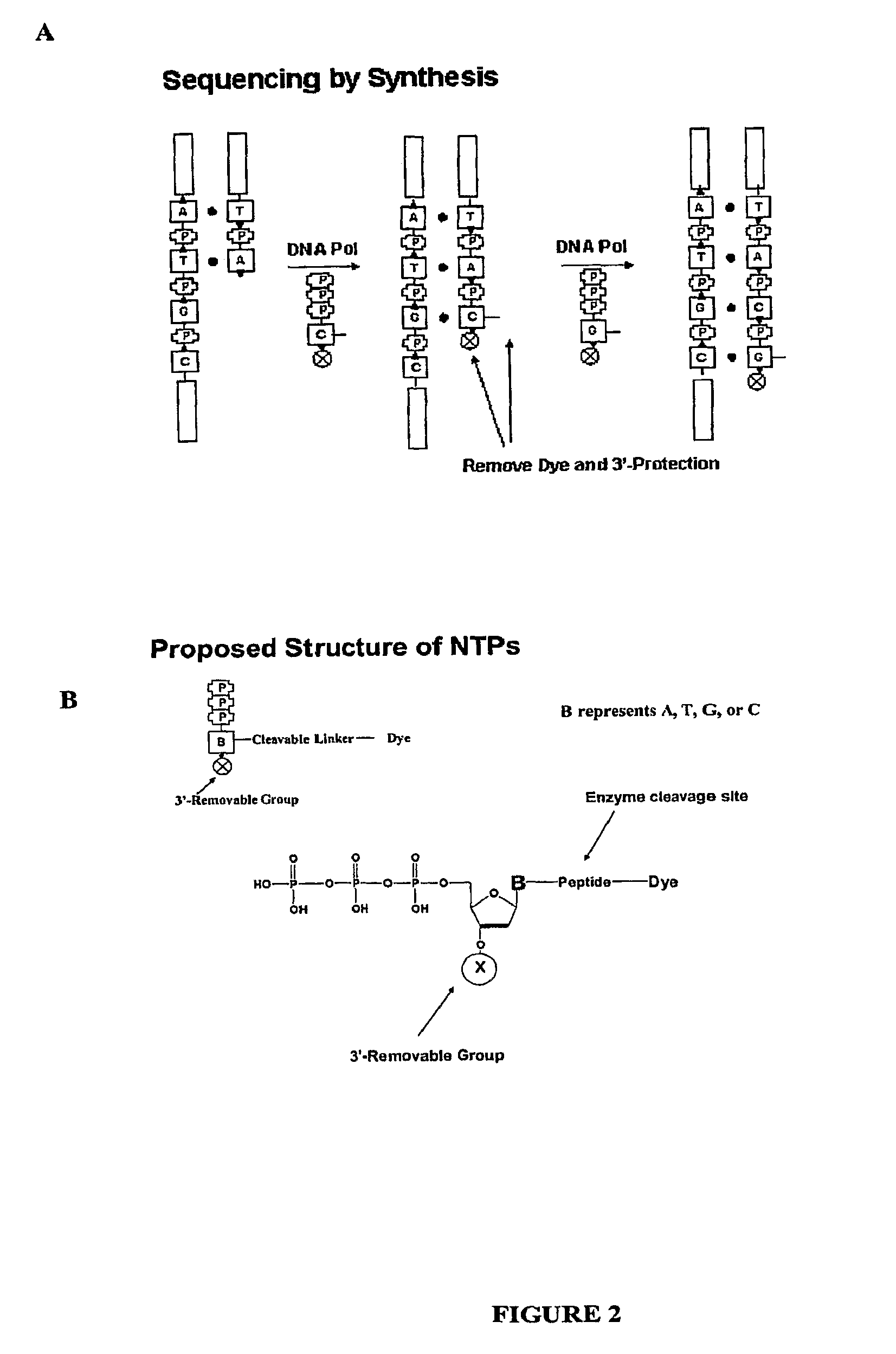
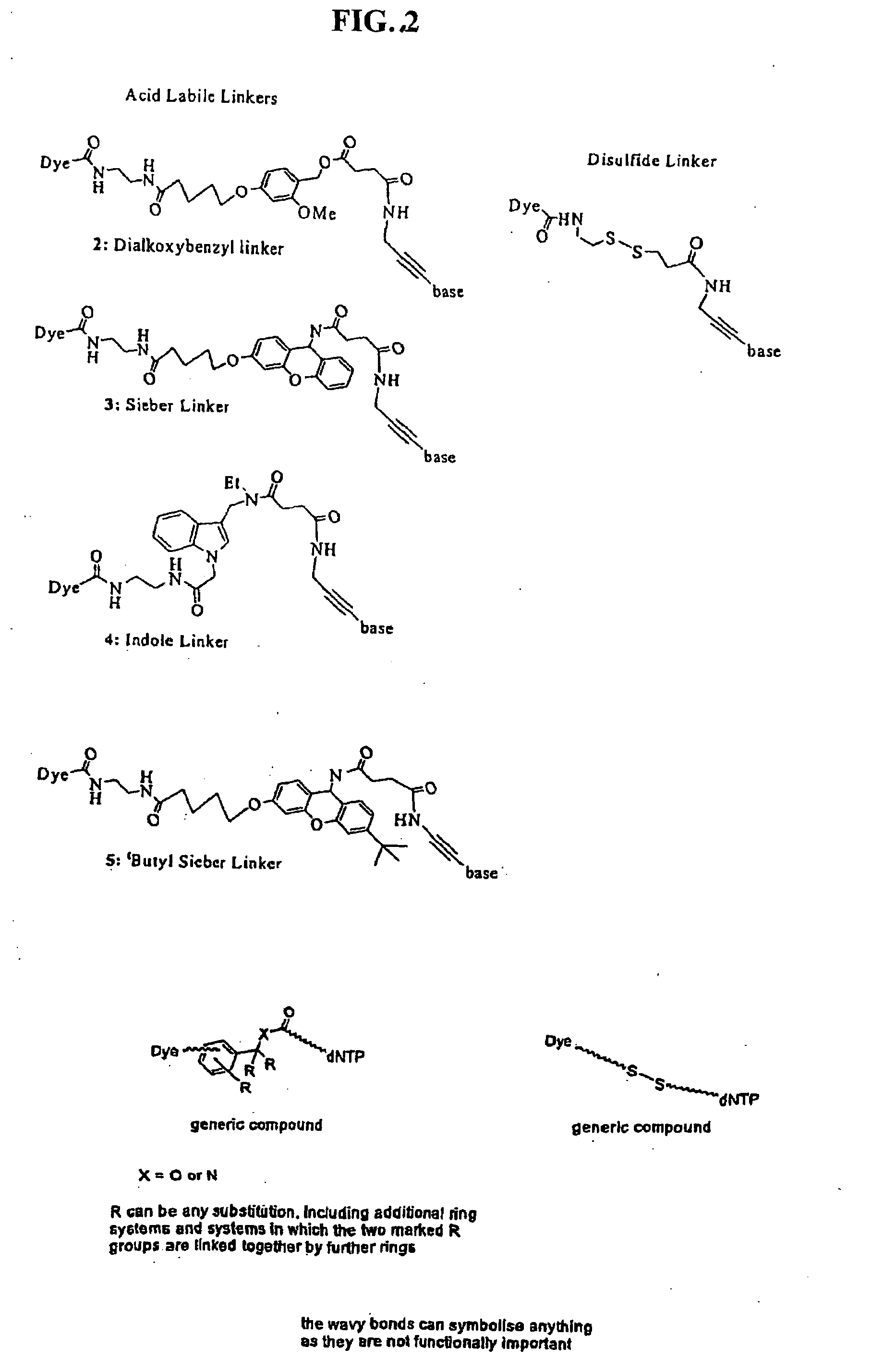
Nucleosides and nucleotides are disclosed that are linked to detectable labels via a cleavable linker group.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
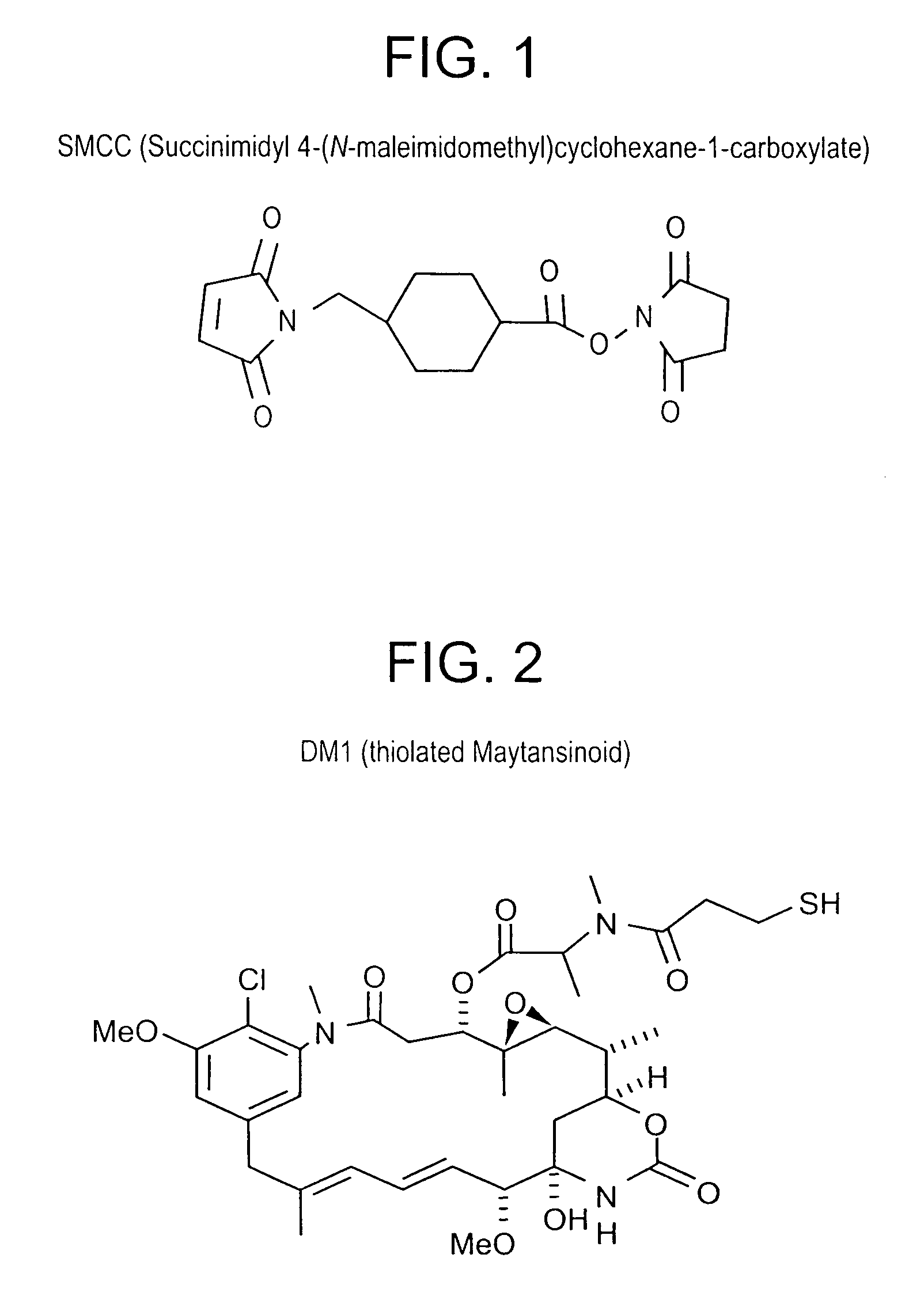
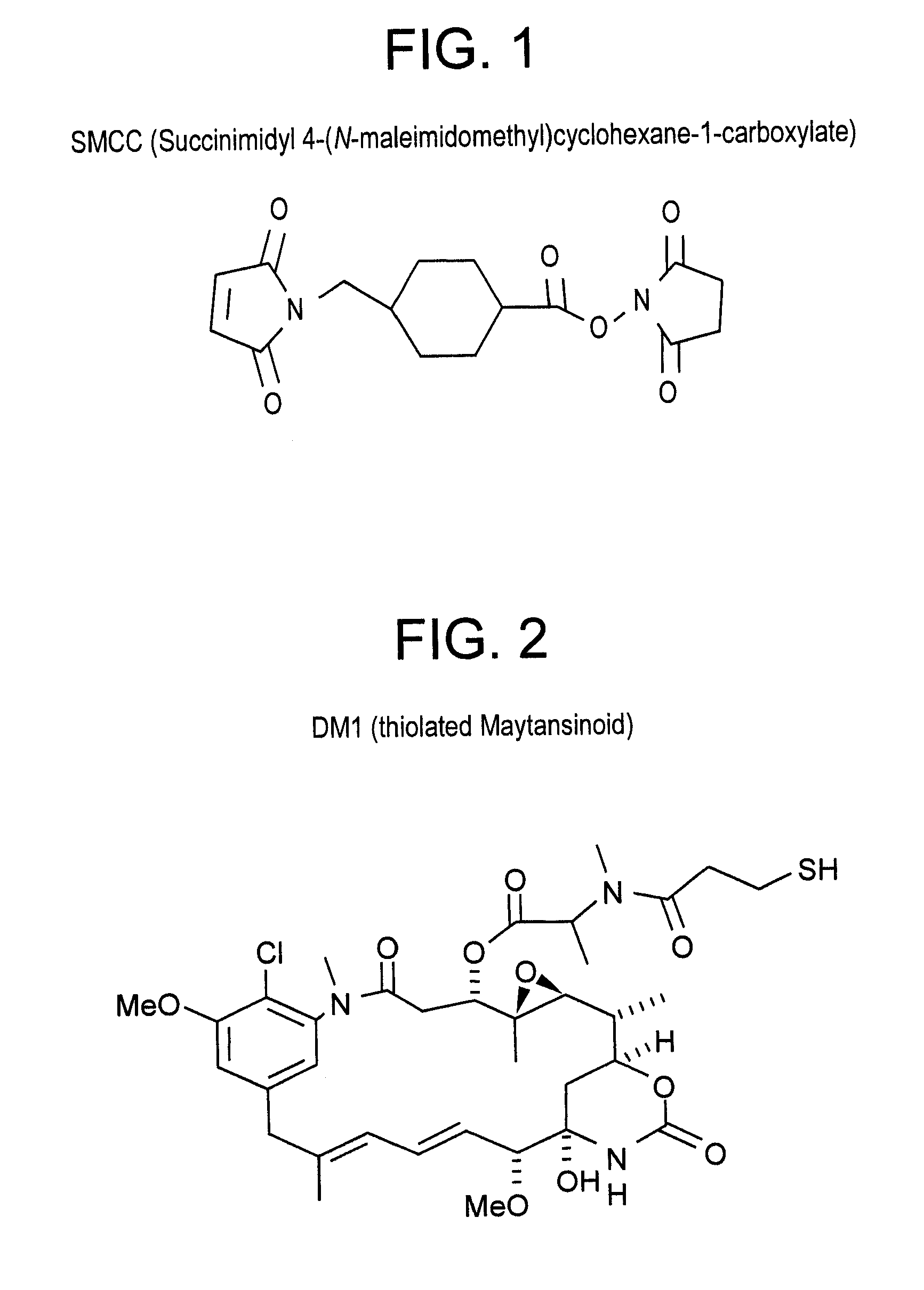
Method of targeting specific cell populations using cell-binding agent maytansinoid conjugates linked via a non-cleavable linker, said conjugates, and methods of making said conjugates
The present invention discloses a method for targeting maytansinoids to a selected cell population, the method comprising contacting a cell population or tissue suspected of containing the selected cell population with a cell-binding agent maytansinoid conjugate, wherein one or more maytansinoids is covalently linked to the cell-binding agent via a non-cleavable linker and the cell-binding agent binds to cells of the selected cell population.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Labelled nucleotides
Nucleosides and nucleotides are disclosed that are linked to detectable labels via a cleavable linker group.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
New sequencing method for sequencing rna molecules
InactiveUS20060166203A1Reduce decreaseMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for determination of the identity of at least one nucleotide in a RNA-molecule comprising the steps of: (i) providing the RNA-molecule, an oligonucleotide primer binding to a predetermined position of the RNA molecule, a reverse transcriptase, deoxynucleotides and other necessary reagents, in a reaction vessel; (ii) performing a primer extension reaction, whereby the oligonucleotide primer is extended on the RNA-molecule through incorporation of at least one deoxynucleotide by the action of a reverse transcriptase, resulting in the release of a PPi molecule only upon incorporation of a deoxynucleotide; and (iii) detecting the presence or absence of incorporation, thereby indicating the nucleotide identity of the RNA molecule in the relevant position. In a preferred embodiment, the sequencing of the invention is coupled to the Pyrosequencing™ reaction. A variant of the method employs incorporation of modified nucleotides, with an optionally cleavable linker arm to which is attached a label.
Owner:TOOKE NIGEL
Solid support for high-throughput nucleic acid analysis
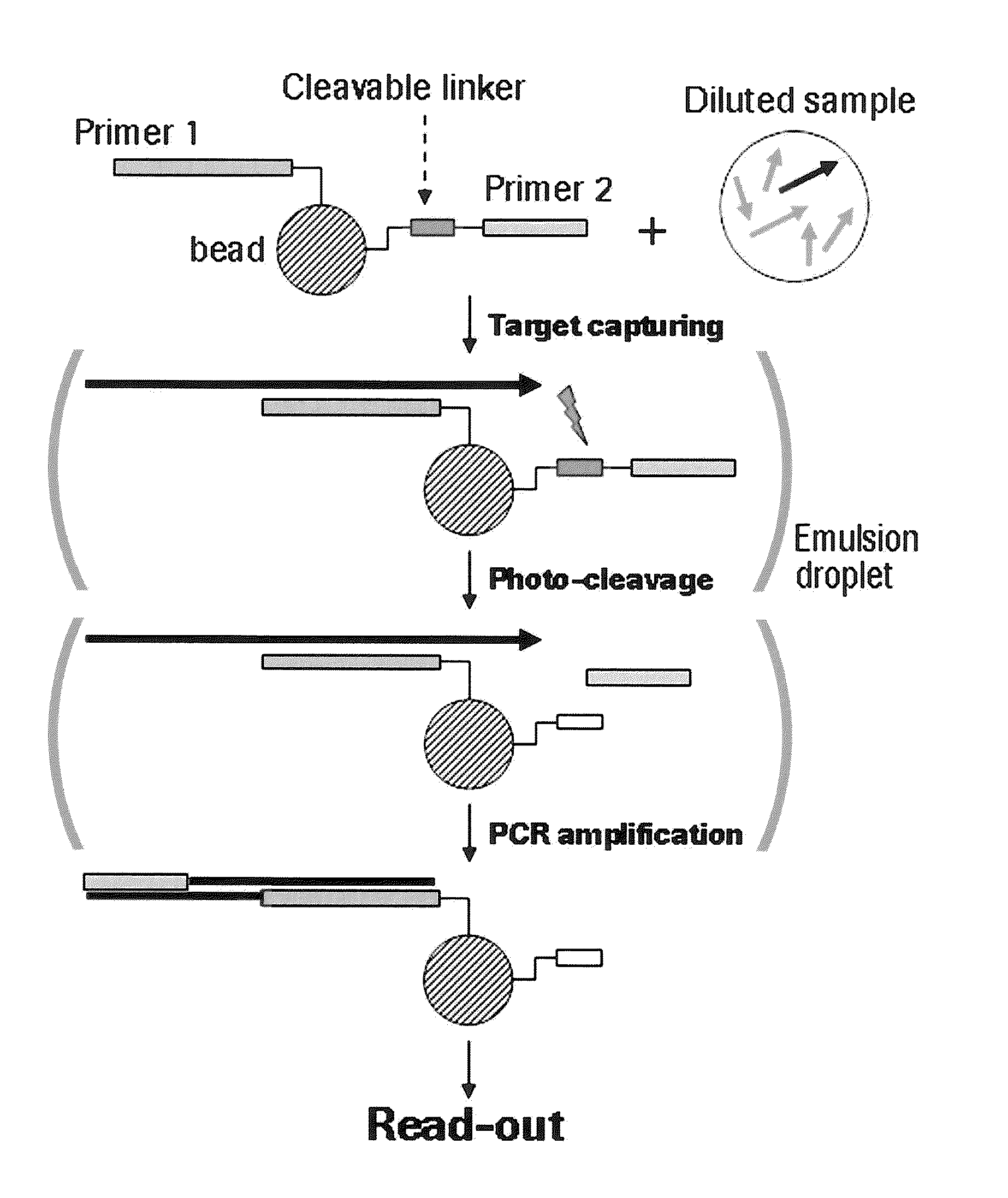
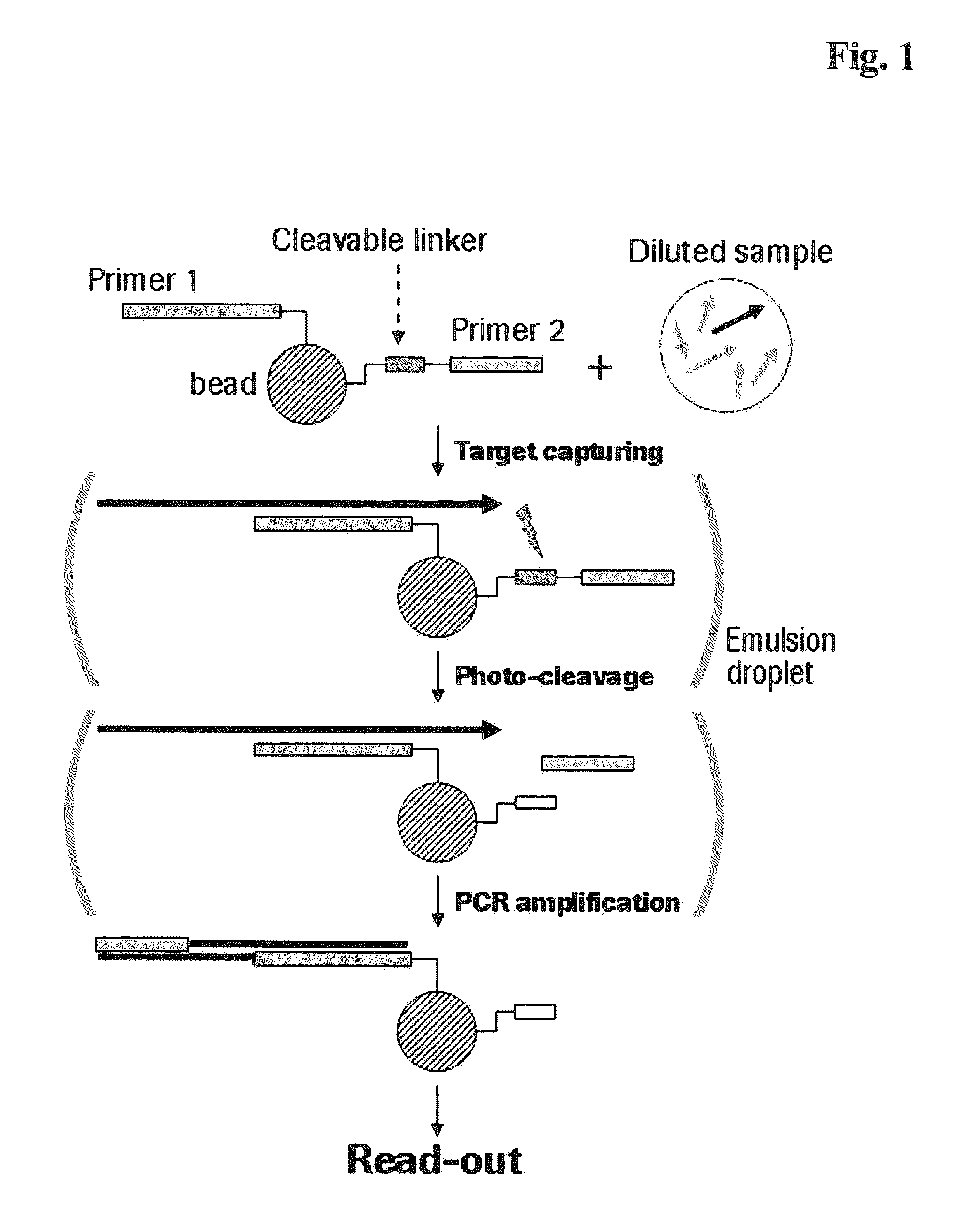
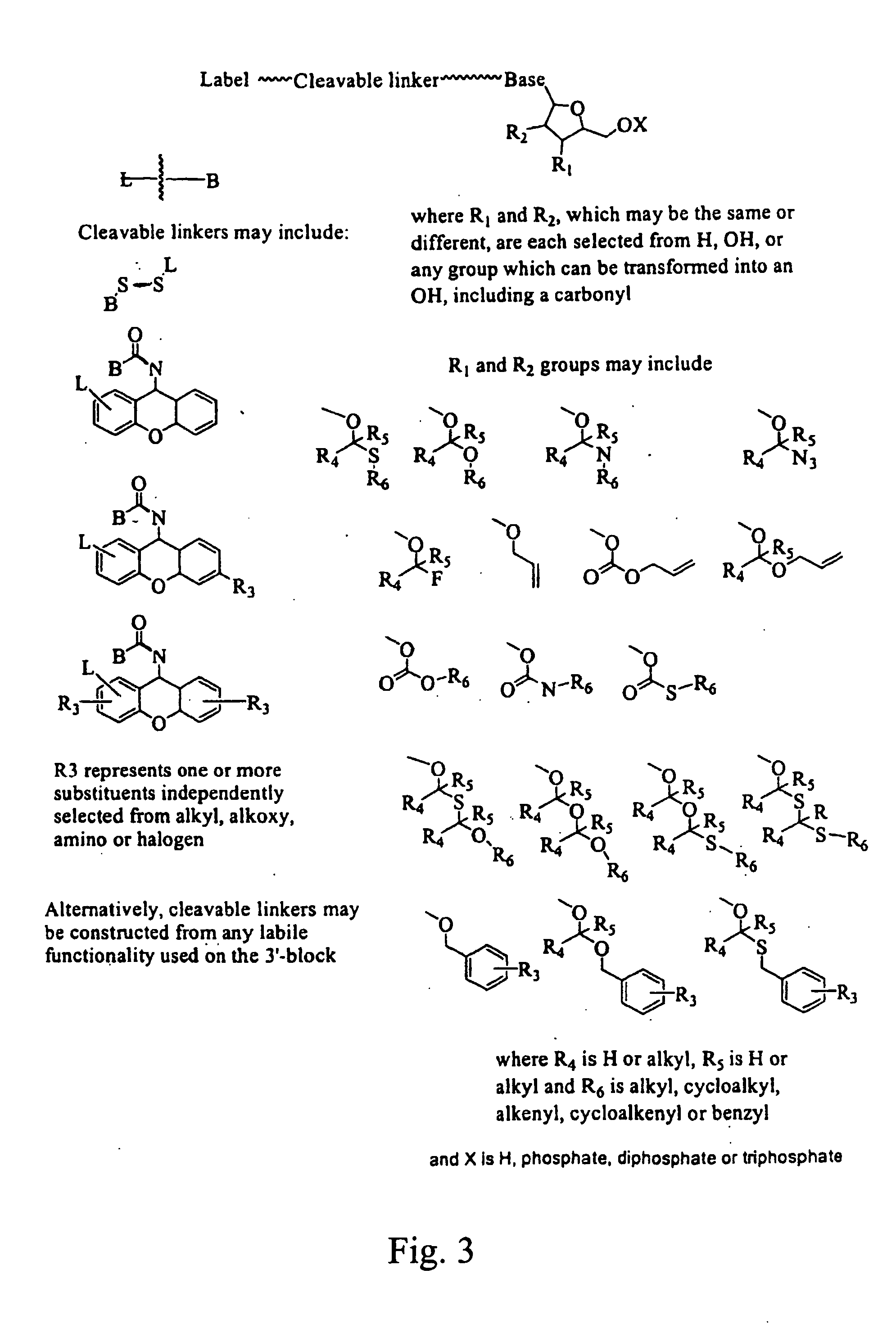
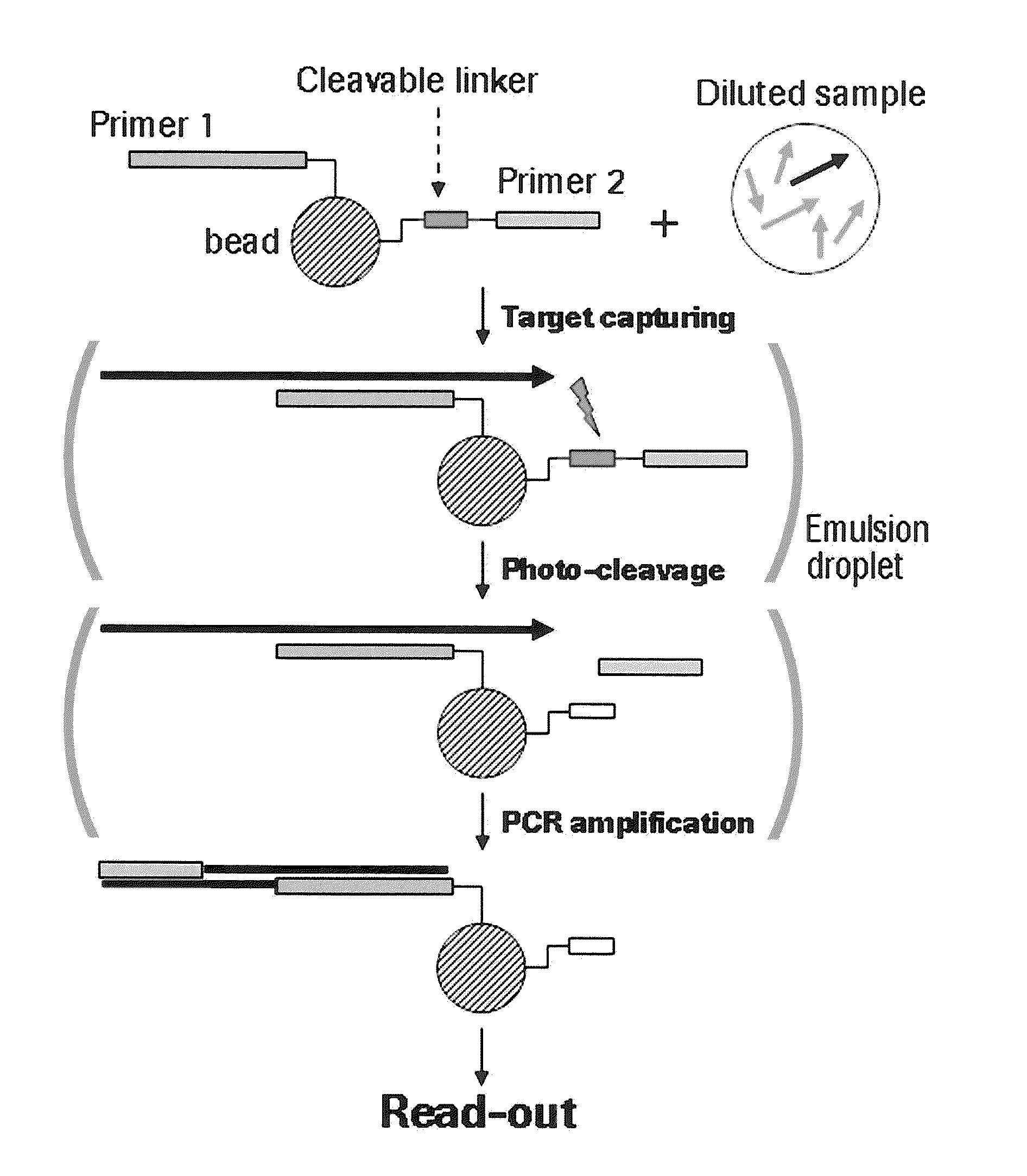
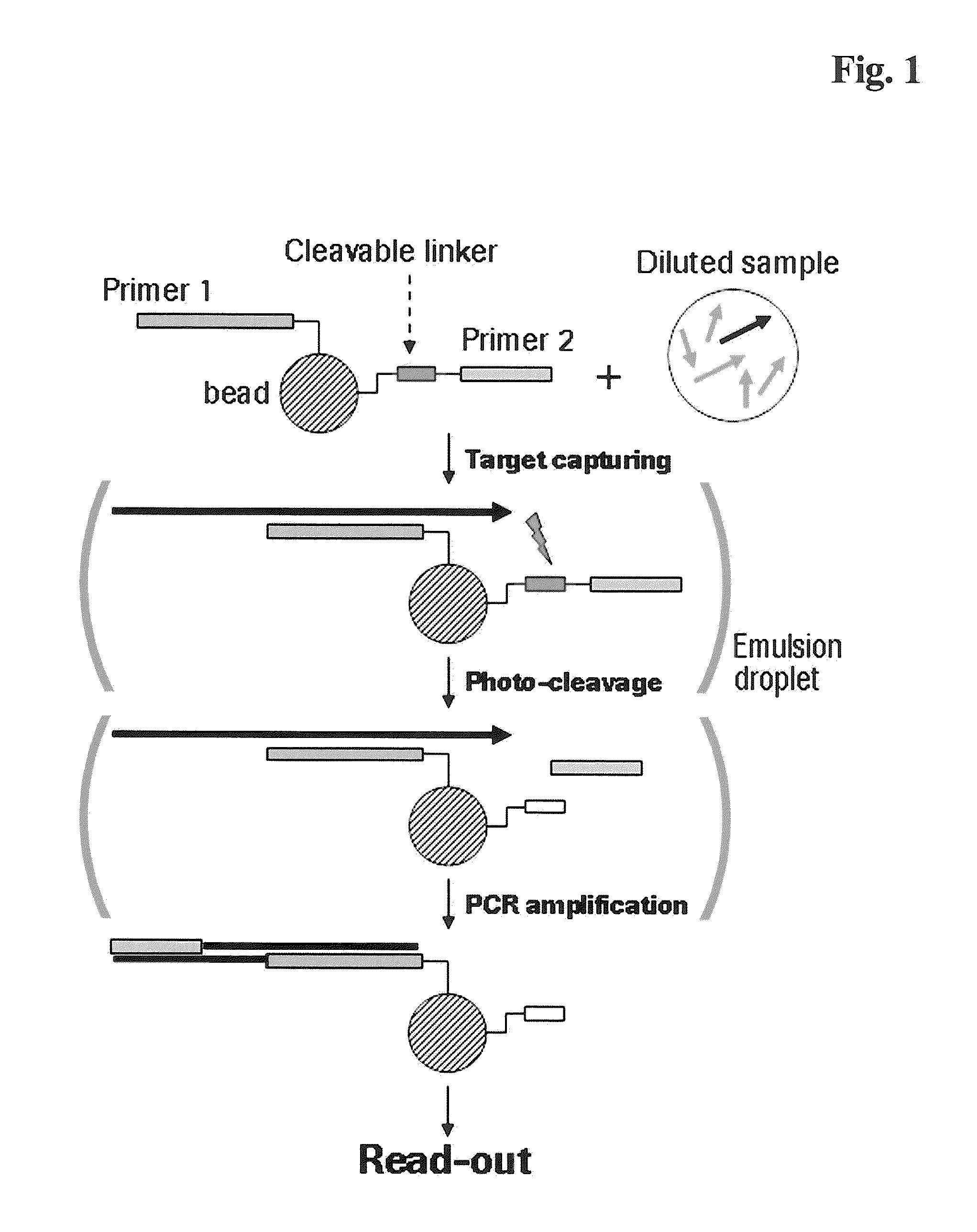
The present invention provides a solid support which is preferably a bead comprising at least two sequence specific amplification primers wherein at least one primer is bound to the support with an inducible cleavable linker. The present invention also provides various method for preparing a solid support comprising at least two sequence specific primers, further characterized in that at least one of the primers is cleavable.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Labelled nucleotides
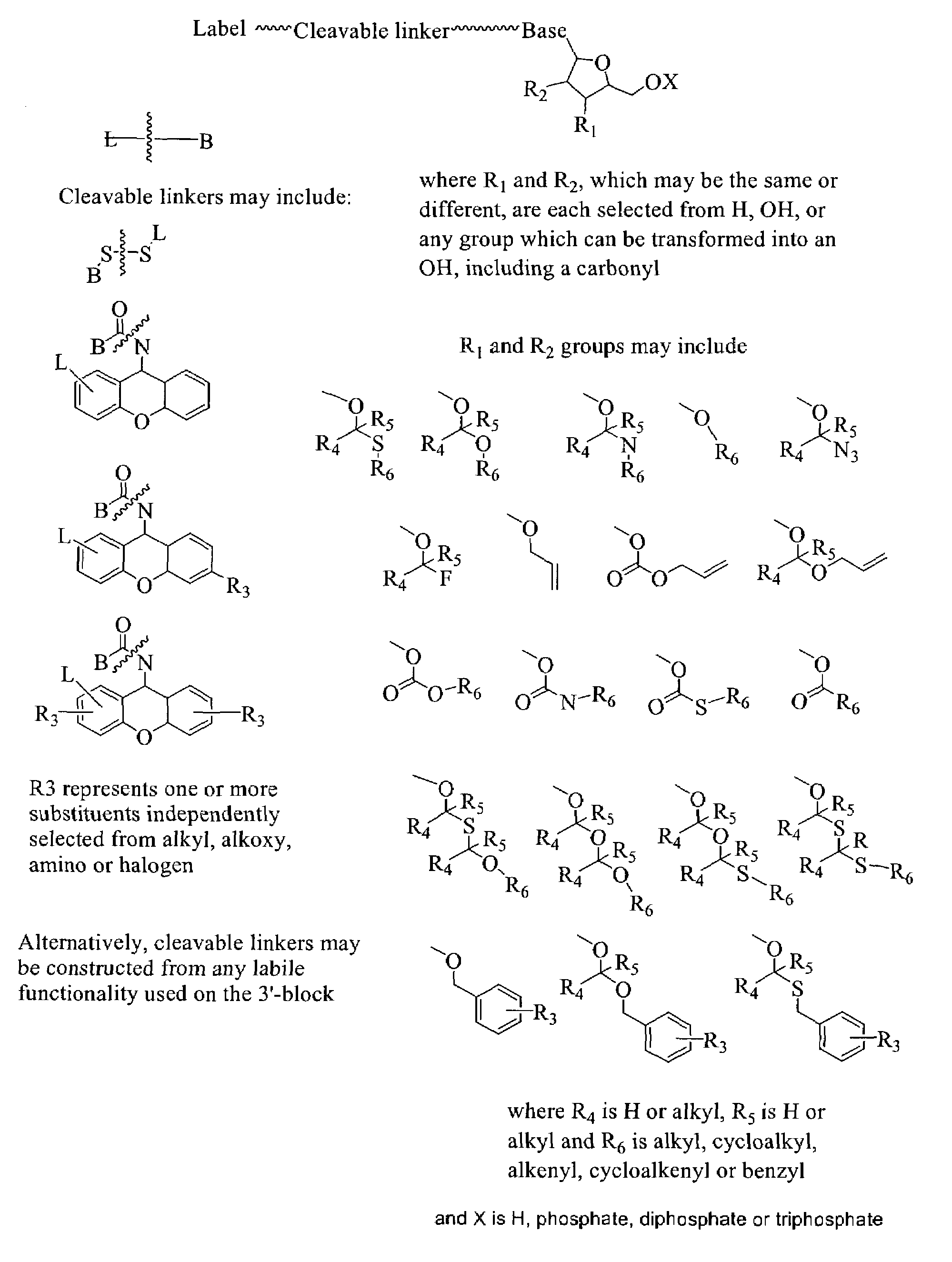
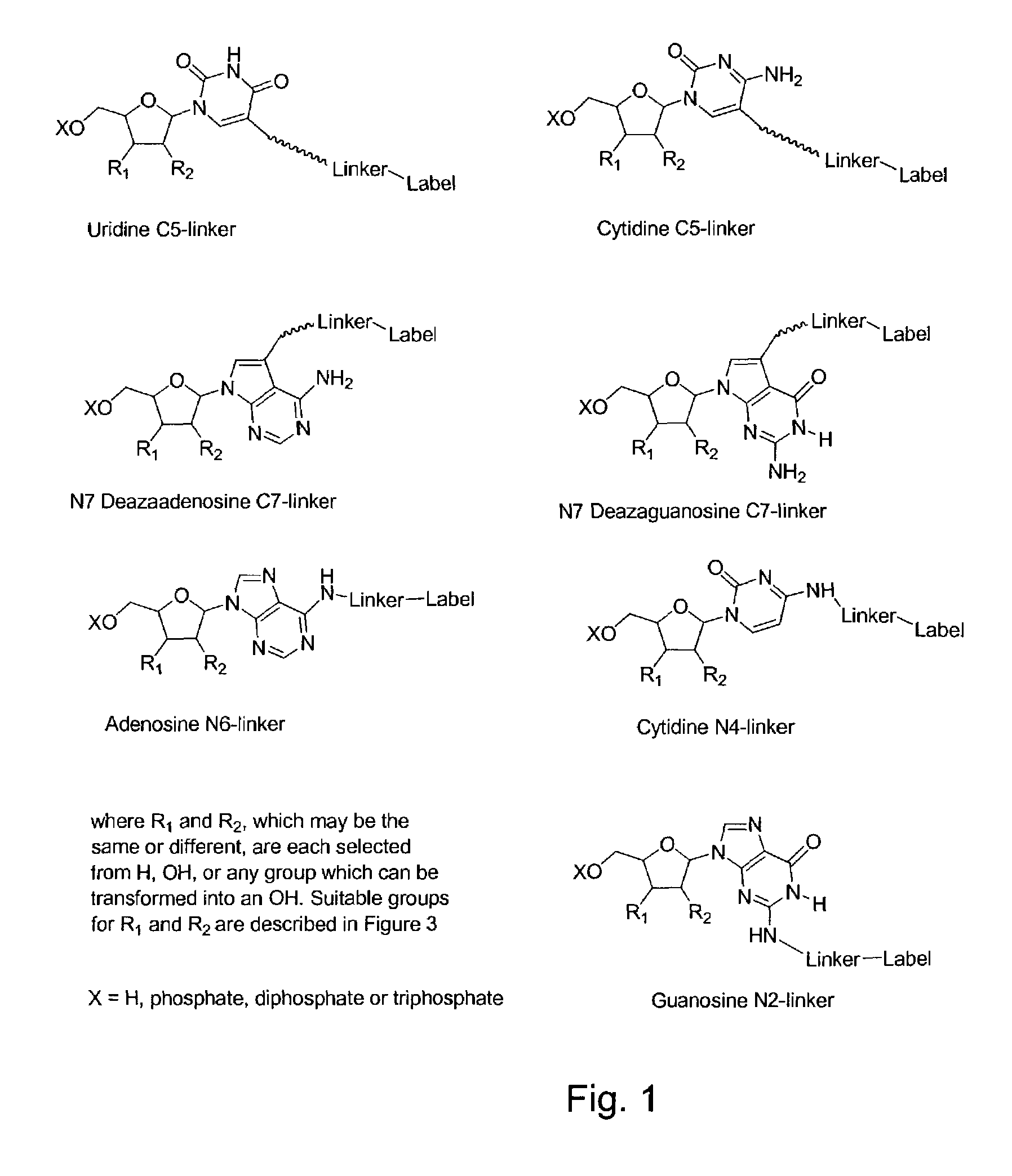
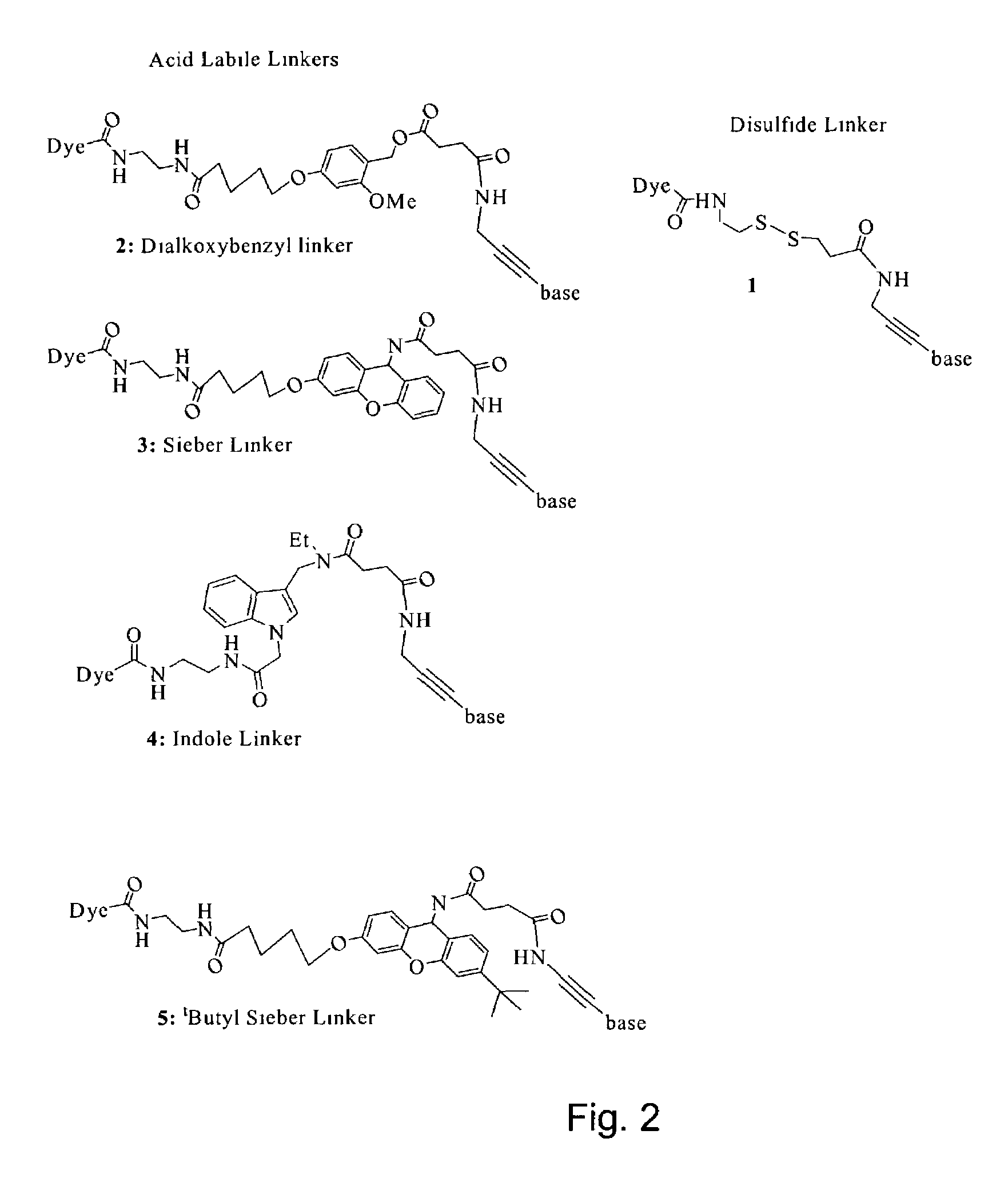
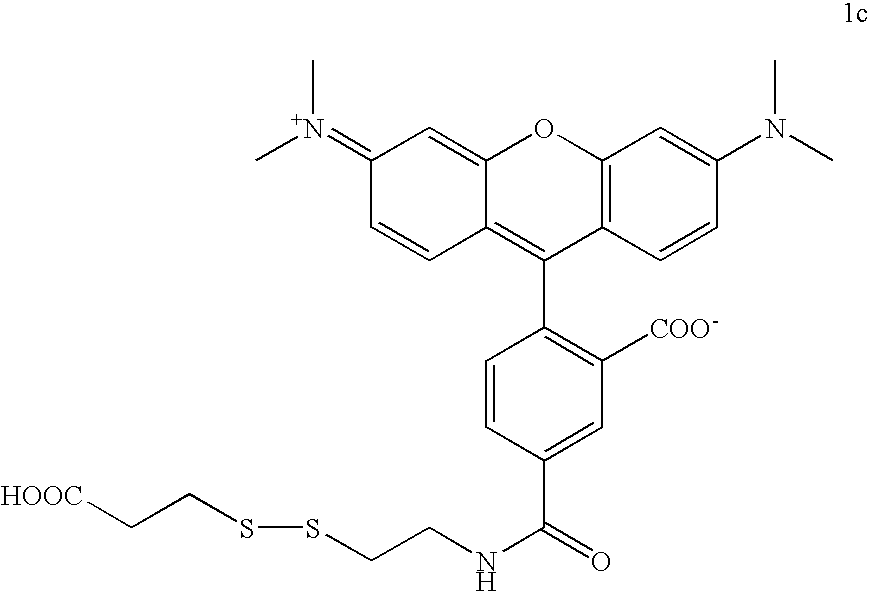
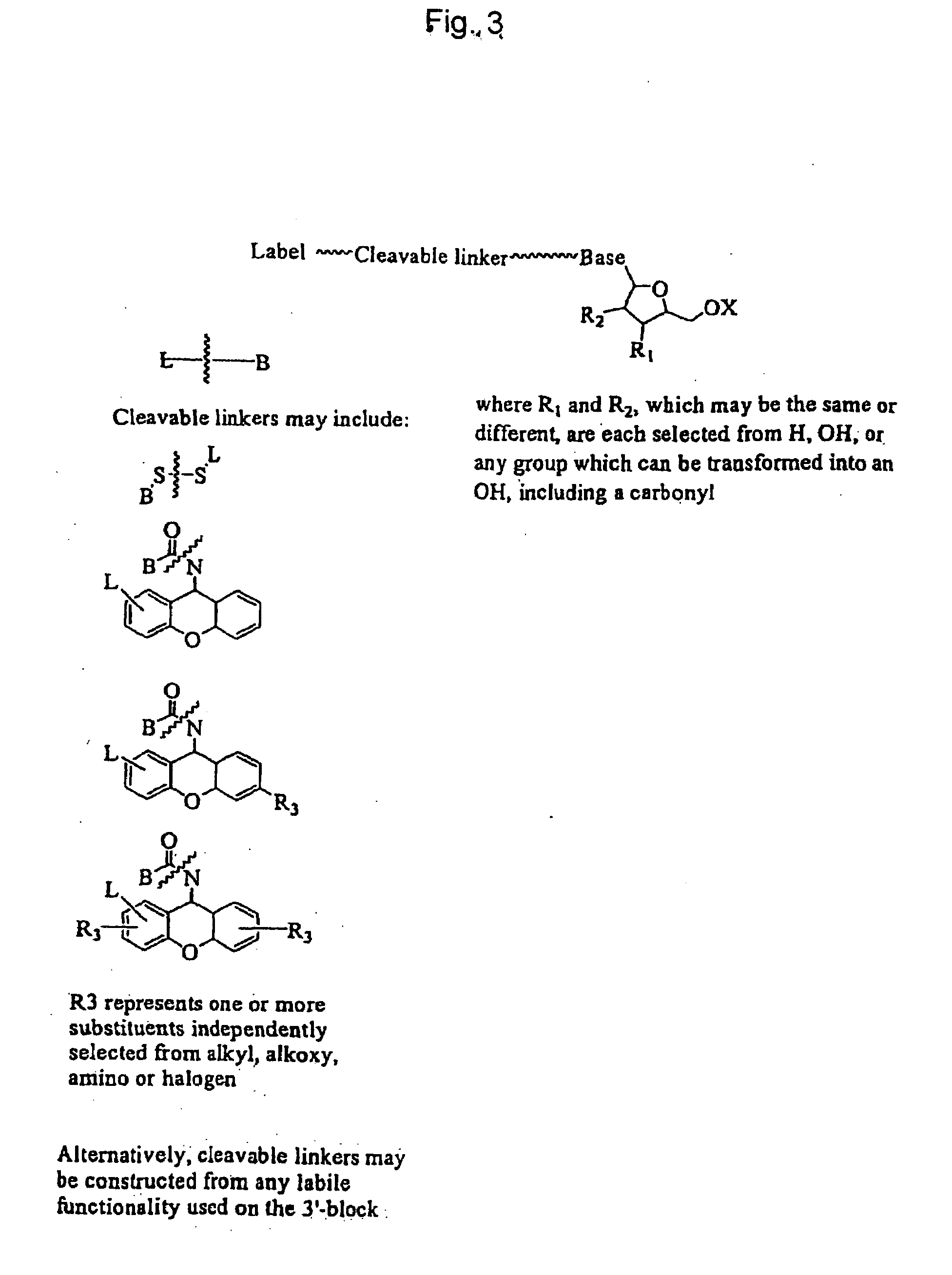
The invention provides a nucleotide or nucleoside having a base attached to a detectable label via a cleavable linker, characterised in that the cleavable linker contains a moiety selected from the group comprising: Formula (I) wherein X is selected from the group comprising O, S, NH and NQ wherein Q is a C1-10 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group, Y is selected from the group comprising O, S, NH and N(allyl), T is hydrogen or a C1-10 substituted or unsubstituted alkyl group and * indicates where the moiety is connected to the remainder of the nucleotide or nucleoside).
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Miniaturized, high-throughput nucleic acid analysis
InactiveUS20100248237A1Further processing of sample difficultMicrobiological testing/measurementMiniaturizationBiology
The present invention is directed to method for analyzing multiple nucleic acid molecules of interest comprising in the steps of (i) providing a plurality of beads, characterized in that each bead comprises at least two sequence specific amplification primers, further characterized in that at least one of the primers is bound to the bead via a cleavable linker, (ii) capturing the nucleic acid molecules of interest from a sample, (iii) clonally isolating the plurality of beads, (iv) cleaving the at least one primer, (v) clonally amplifying the nucleic acid thereby creating multiple amplification products, and (vi) analyzing the amplification products.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Compositions and methods for nucleotide sequencing
The invention provides nucleoside and nucleotide molecules containing cleavable linkers linking a label such as a dye. The invention also provides nucleosides and nucleotide molecules containing a blocking group, either removable or non-removable. The invention additionally provides methods of using the nucleoside and nucleotide molecules containing a cleavable linker and / or a blocking group.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
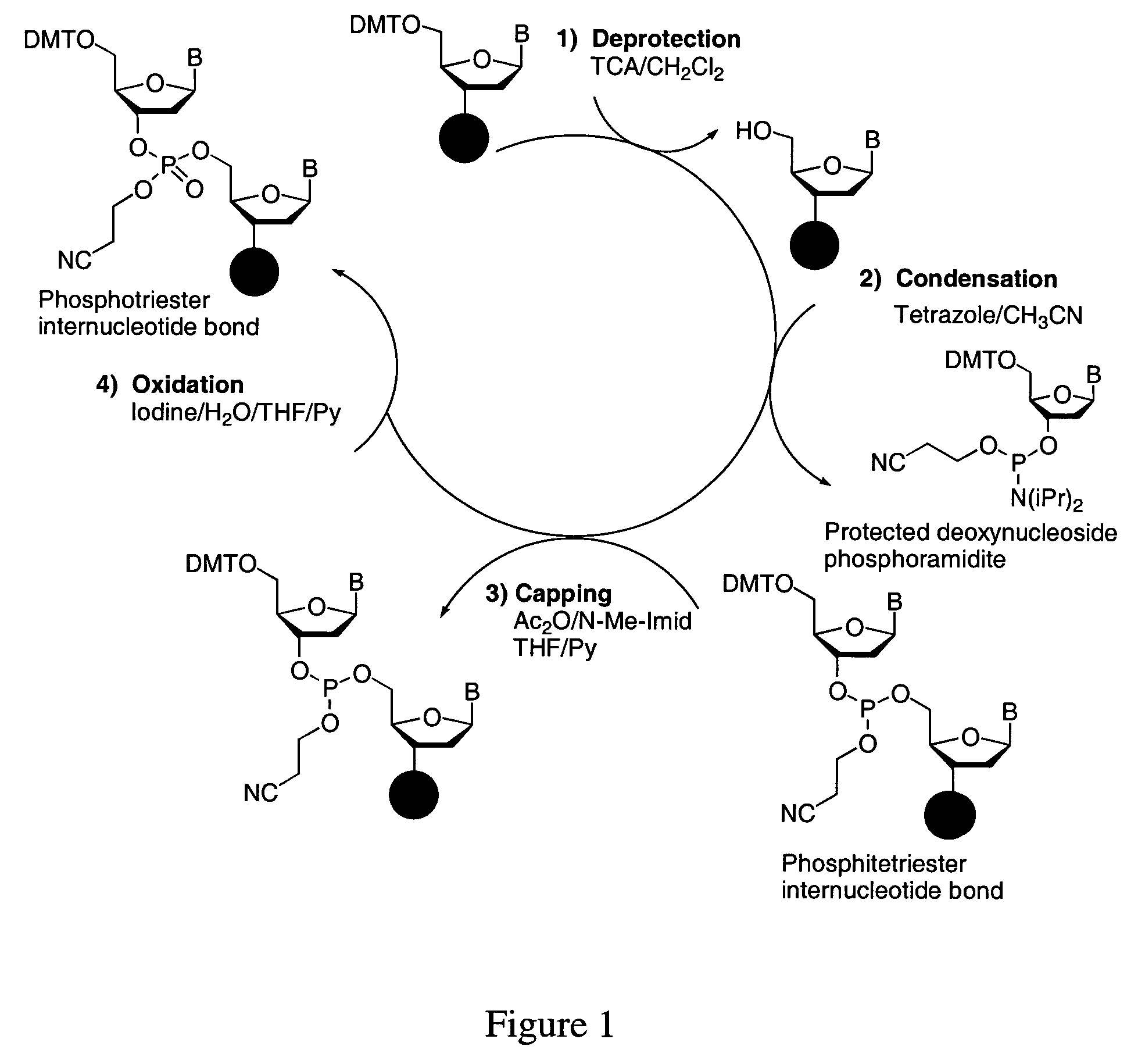
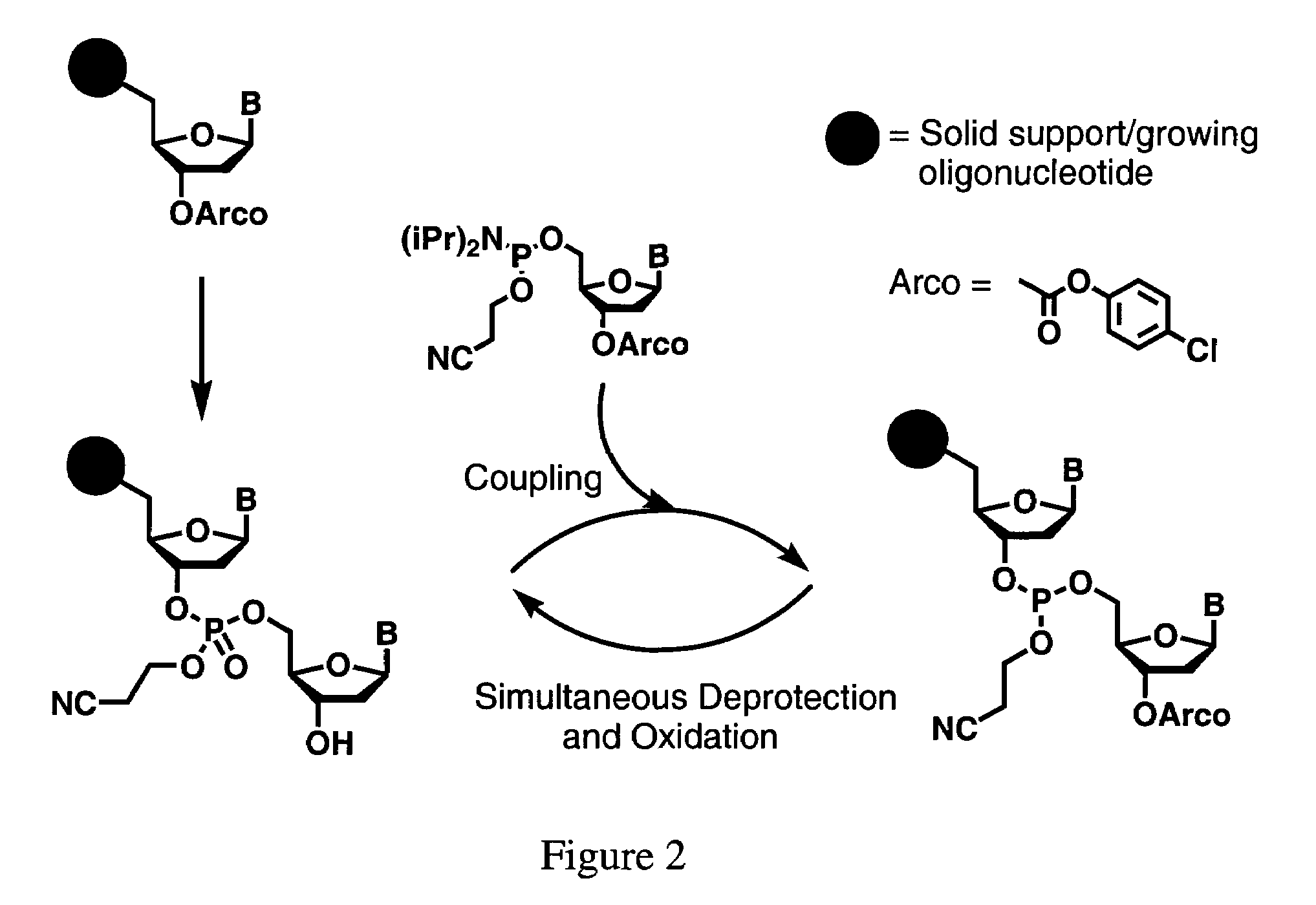
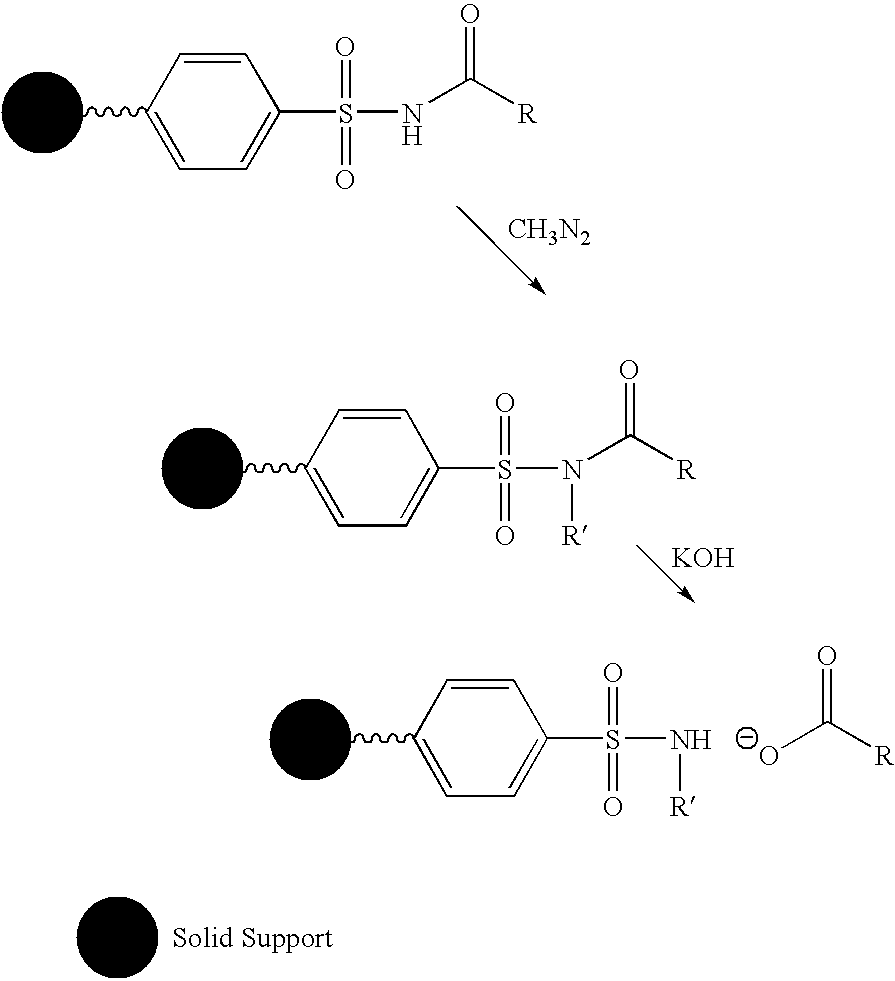
Cleavable linker for polynucleotide synthesis
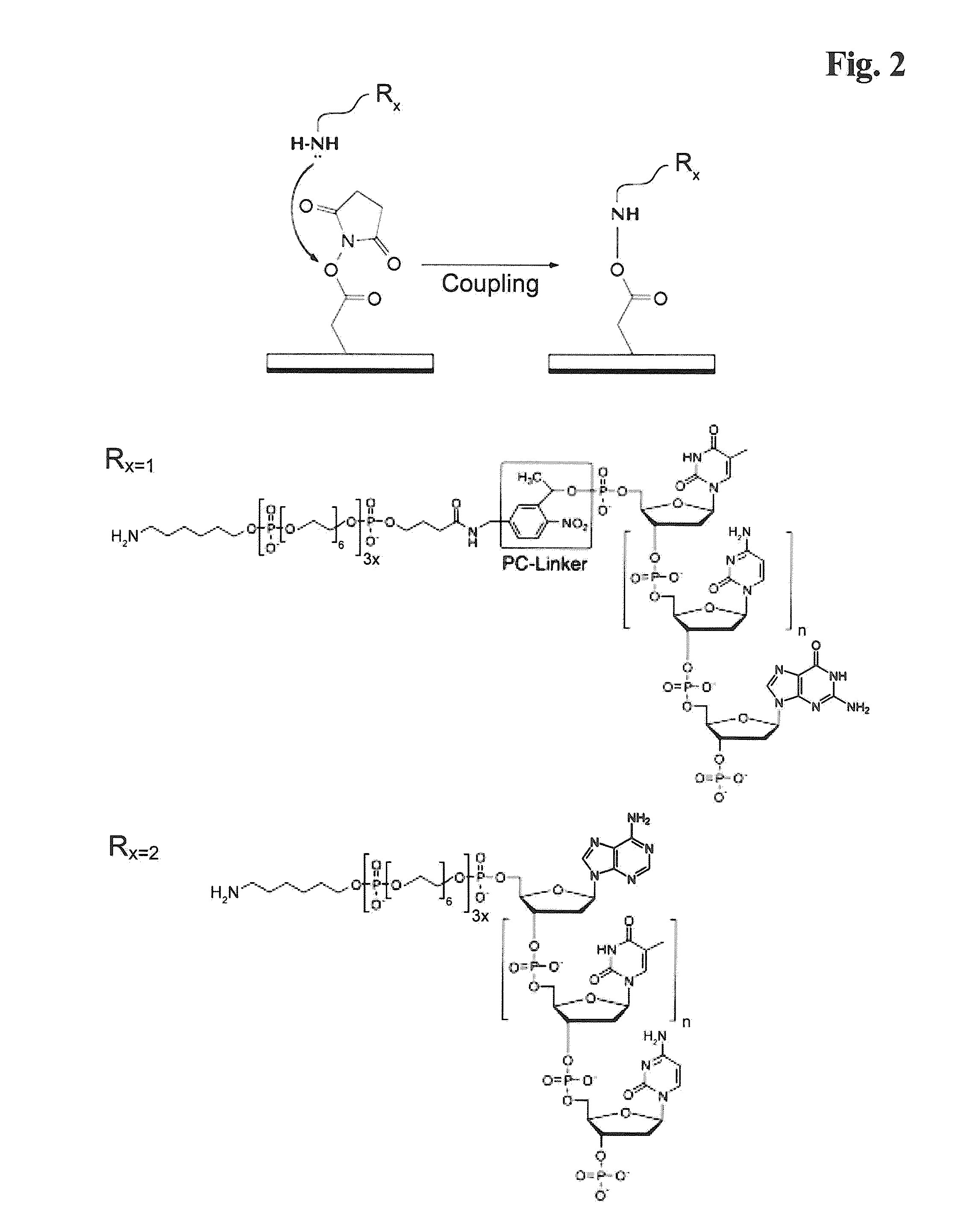
Functionalized supports for polynucleotide synthesis are disclosed. The supports have linker moieties that are stable to conditions used in polynucleotide synthesis, but may be cleaved to release synthesized polynucleotides from the support. Methods of making the functionalized supports and methods of using are also disclosed. In particular embodiments of methods of making the functionalized supports, a solid support, on which an available reactive group is bound, is contacted with a reagent having the structure (I)Phos-Cgp-Trl-Cgp′Nucl (I)wherein the groups are defined as follows:Phos is a reactive phosphorus group capable of specifically reacting with an available reactive group on the support,Trl is a triaryl methyl linker group having three aryl groups, each bound to a central methyl carbon, at least one of said three aryl groups having one or more substituents,Cgp is a linking group linking the reactive phosphorus group and the triaryl methyl linker group, or is a bond linking the reactive phosphorus group and the triaryl methyl linker group,Nucl is a nucleoside moiety, wherein the nucleoside moiety is optionally part of a polynucleotide moiety, andCgp′ is a linking group linking the nucleoside moiety and the triaryl methyl linker group, or is a bond linking the nucleoside moiety and the triaryl methyl linker group.In typical embodiments, the solid support is contacted with the reagent having the structure (I) under conditions and for a time sufficient to result in a functionalized support having a nucleoside moiety bound to the solid support via a triaryl methyl linker group.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Masking Ligands For Reversible Inhibition Of Multivalent Compounds
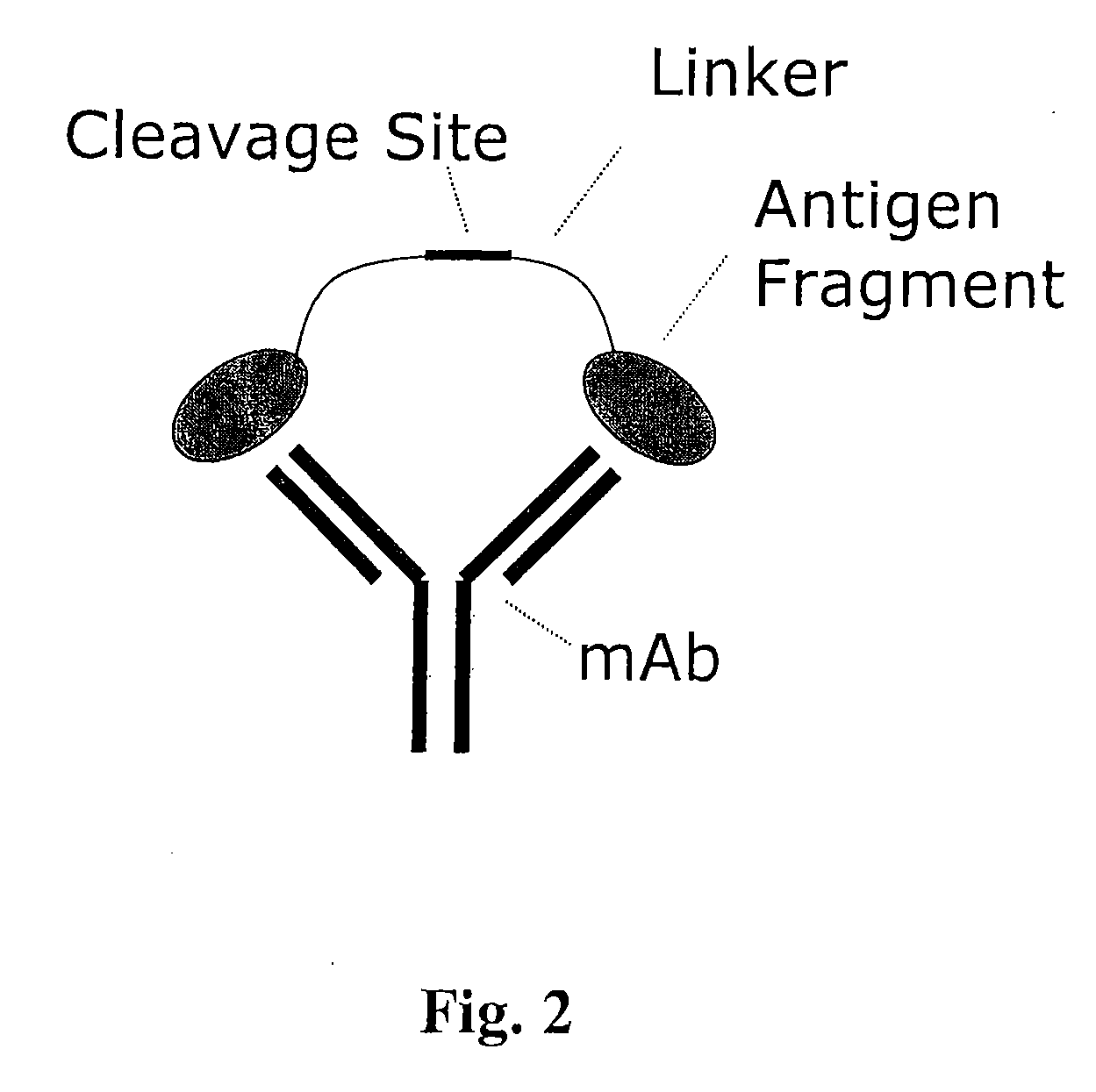
Masking ligands for reversibly concealing the antigen-binding site of an antibody comprise epitopes of the antibody and a cleavable linker. Methods for making masking ligands comprise joining at least two copies of the epitope of an antibody to a cleavable polypeptide linker.
Owner:TEGOPHARM CORP
On-demand cleavable linkers for radioconjugates for cancer imaging and therapy
InactiveUS20050255042A1Improving site-specific deliveryGood removal effectRadioactive preparation carriersRadiation therapyAbnormal tissue growthRadiation therapy
The present invention provides compositions comprising a biological agent, a targeting moiety, and a peptide linker attaching the biological agent to the targeting moiety, wherein the peptide linker is selectively cleaved by a protease. Efficient methods are provided for administering the compositions of the present invention for treating cancer or imaging a tumor, organ, or tissue in a subject. Kits are also provided for administering the compositions of the present invention for radiotherapy or radioimaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Multiplex spatial profiling of gene expression
The present invention provides mass tag complexes that permit simultaneously obtaining information of a plurality of biological molecules. The biological molecules may be RNA or protein, and the information includes both level of expression as well as spatial disposition within a cell or tissue. The mass tag comprise a core structure, a target binding structure (e.g., nucleic acid or peptide binding structure), a cleavable linker and a mass tag that exhibits a unique mass spectroscopy signal.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Method of targeting specific cell populations using cell-binding agent maytansinoid conjugates linked via a non-cleavable linker, said conjugates and methods of making said conjugates
The present invention discloses a method for targeting maytansinoids to a selected cell population, the method comprising contacting a cell population or tissue suspected of containing the selected cell population with a cell-binding agent maytansinoid conjugate, wherein one or more maytansinoids is covalently linked to the cell-binding agent via a non-cleavable linker and the cell-binding agent binds to cells of the selected cell population.
Owner:IMMUNOGEN INC
Chemoselective ligation
InactiveUS20050148032A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesIn vivoChemoselective ligation
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
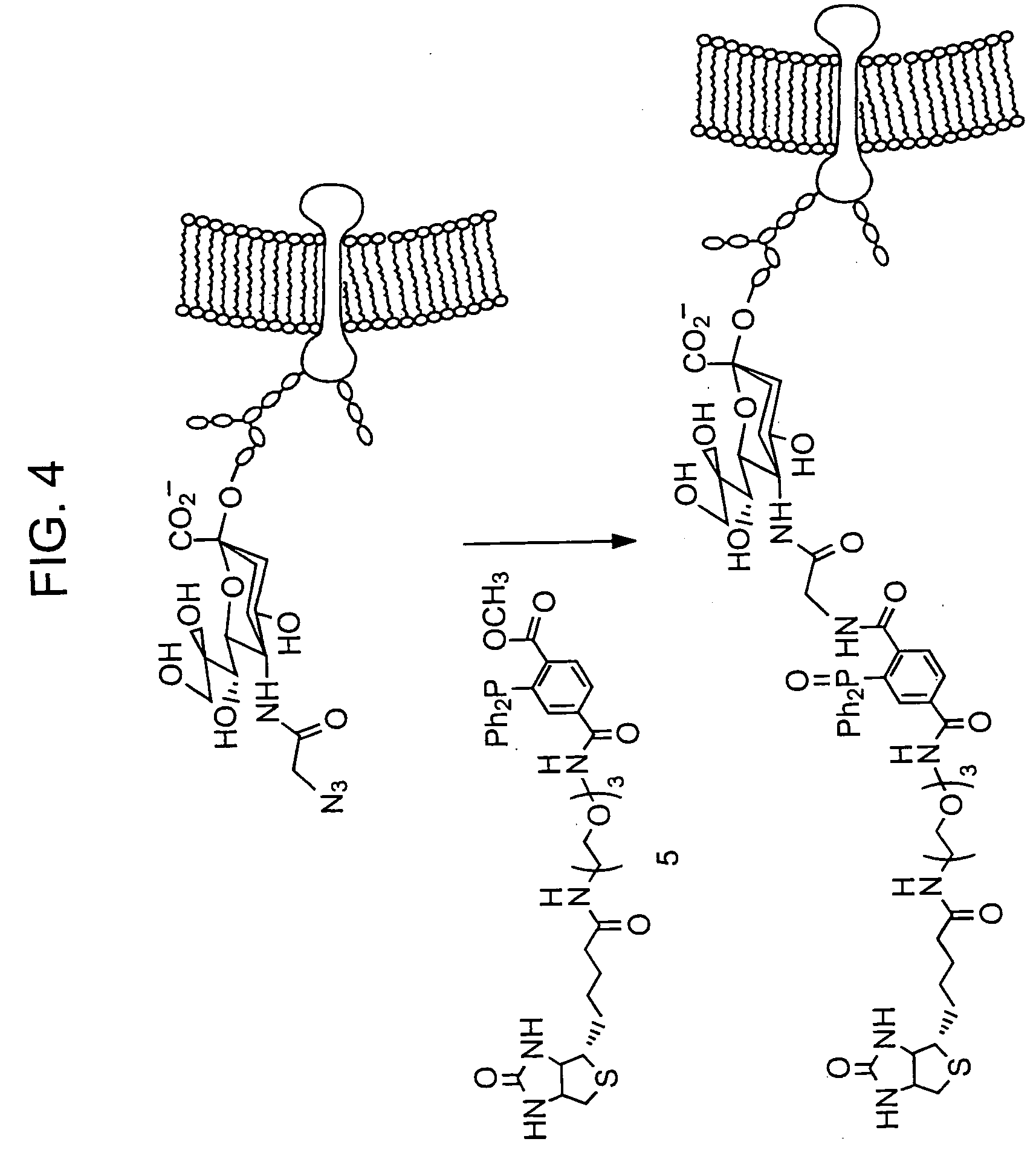
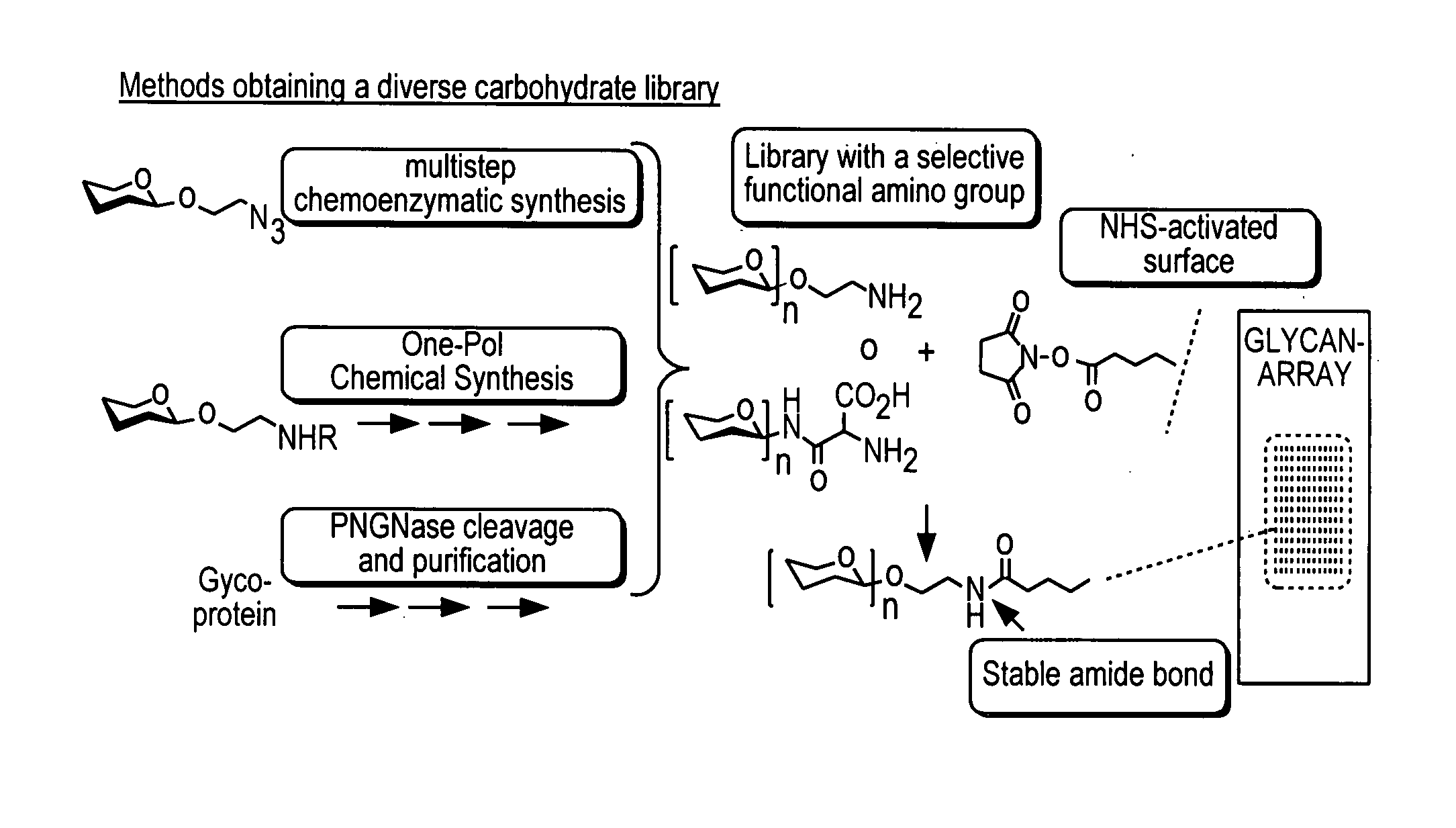
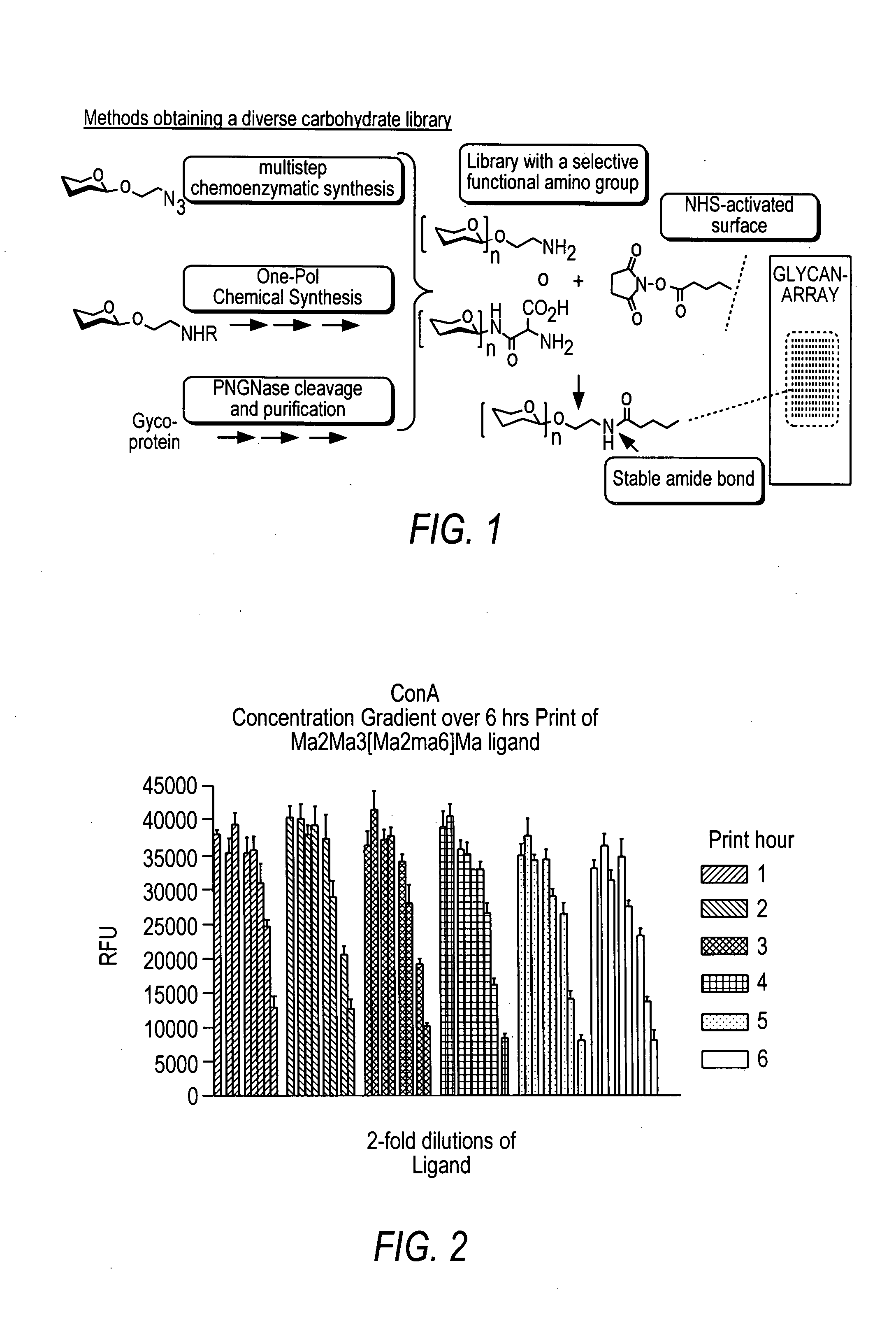
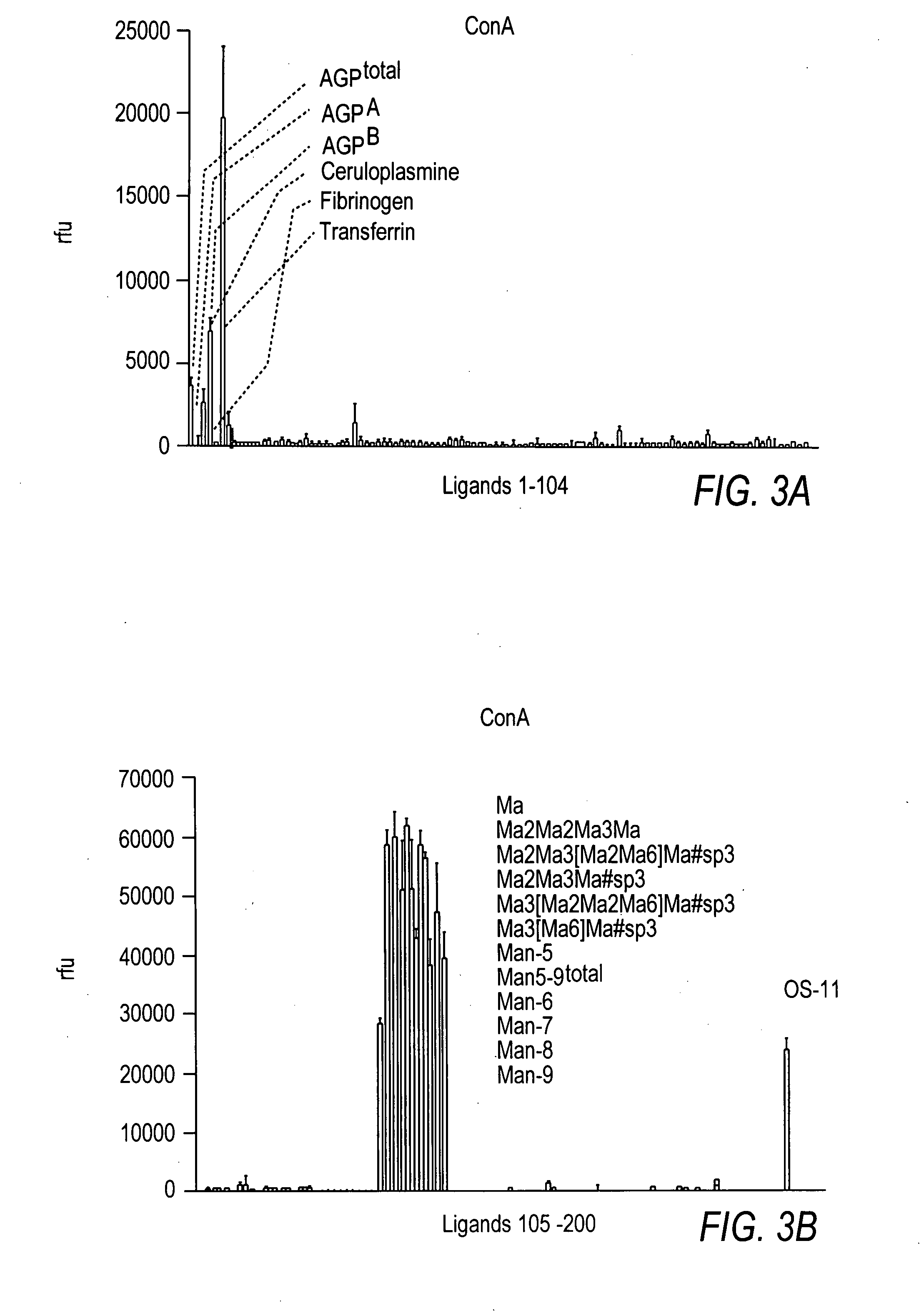
Arrays with cleavable linkers
InactiveUS20070213278A1Treating and preventing HIV infectionAntibacterial agentsBiocideGlycanTest sample
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Chemoselective ligation
The present invention features a chemoselective ligation reaction that can be carried out under physiological conditions. In general, the invention involves condensation of a specifically engineered phosphine, which can provide for formation of an amide bond between the two reactive partners resulting in a final product comprising a phosphine moiety, or which can be engineered to comprise a cleavable linker so that a substituent of the phosphine is transferred to the azide, releasing an oxidized phosphine byproduct and producing a native amide bond in the final product. The selectivity of the reaction and its compatibility with aqueous environments provides for its application in vivo (e.g., on the cell surface or intracellularly) and in vitro (e.g., synthesis of peptides and other polymers, production of modified (e.g., labeled) amino acids).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
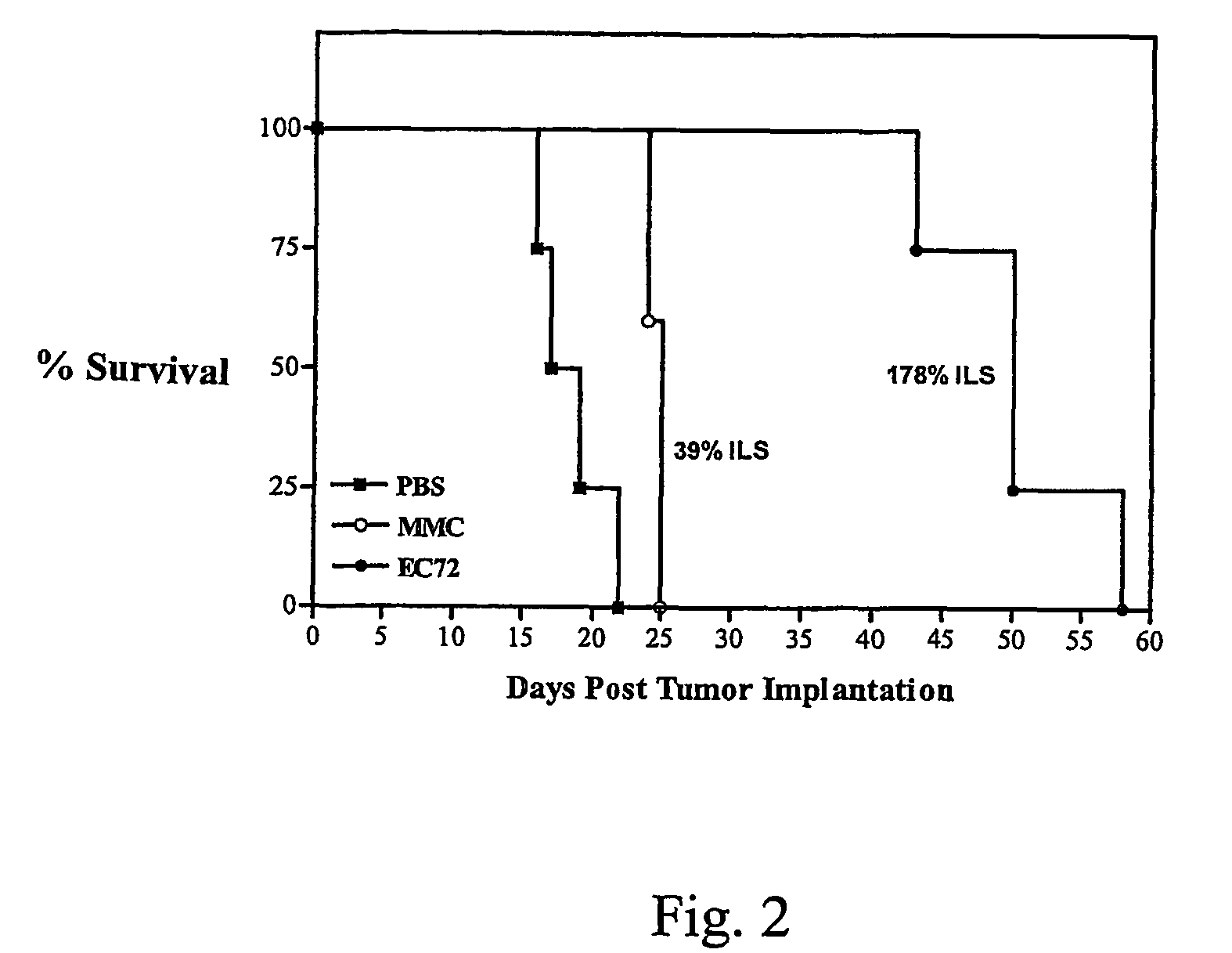
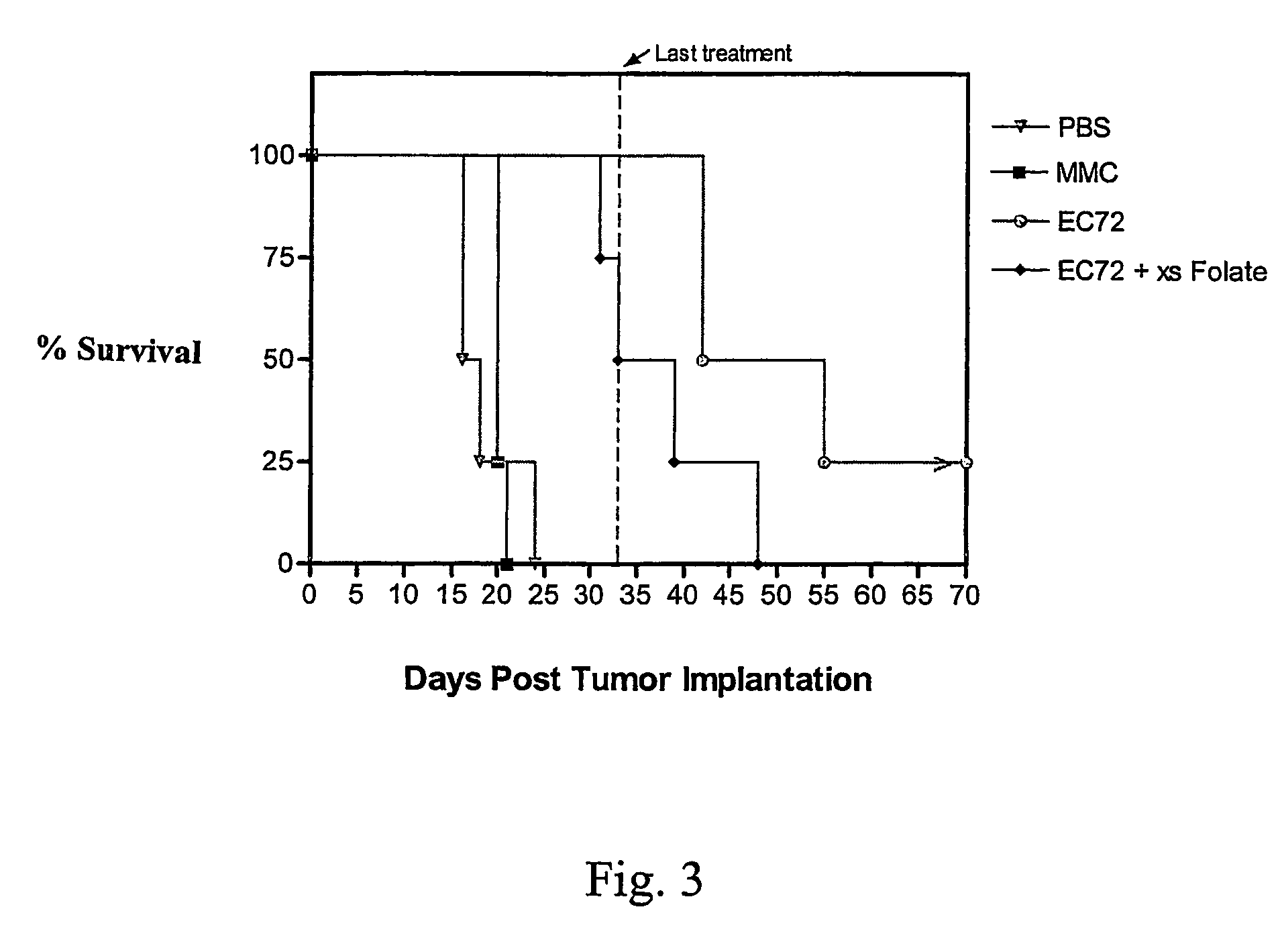
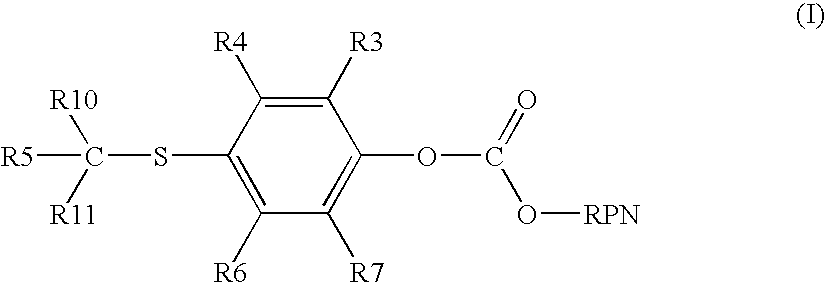
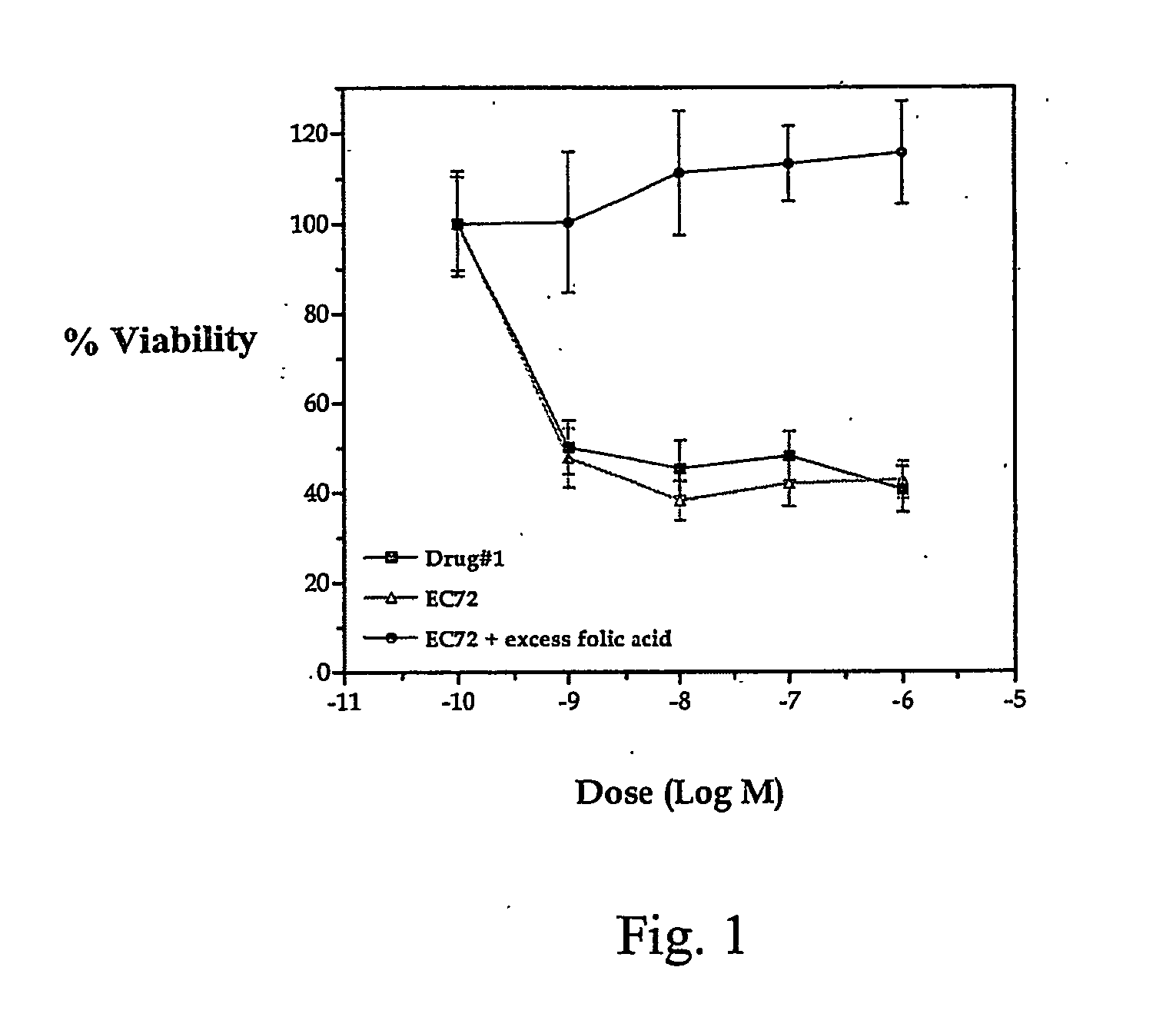
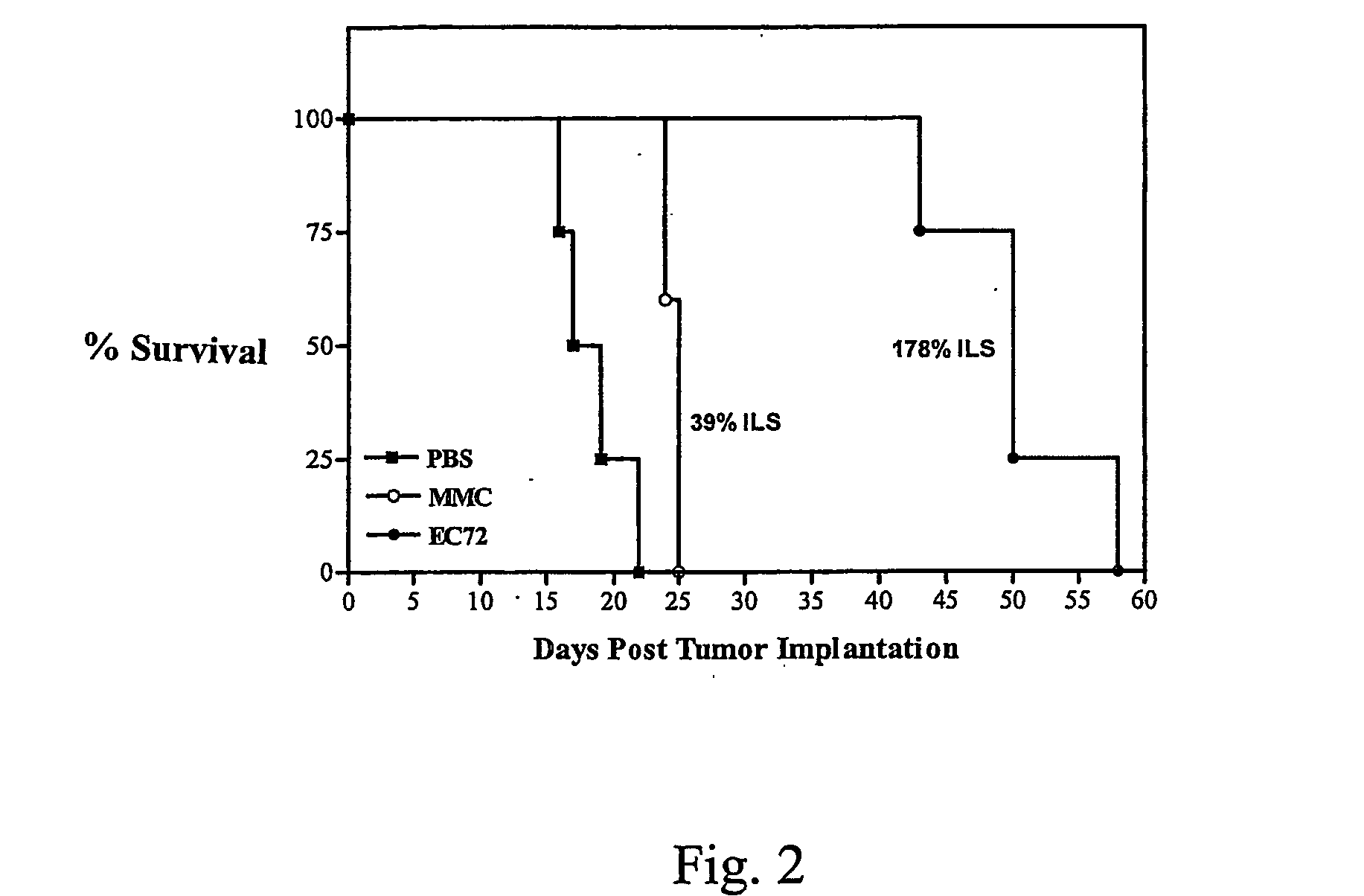
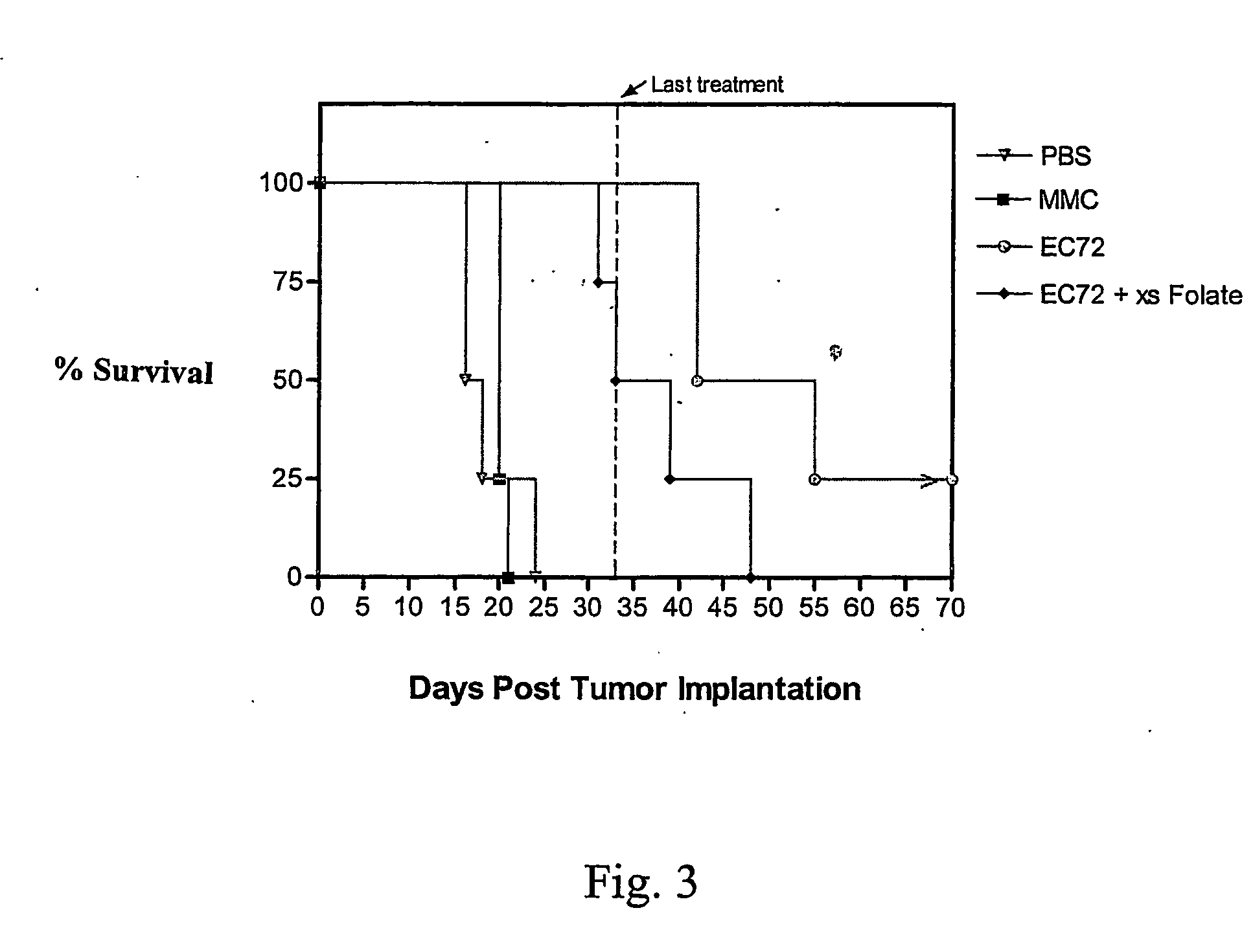
Vitamin-mitomycin conjugates
Owner:ENDOCTYE INC
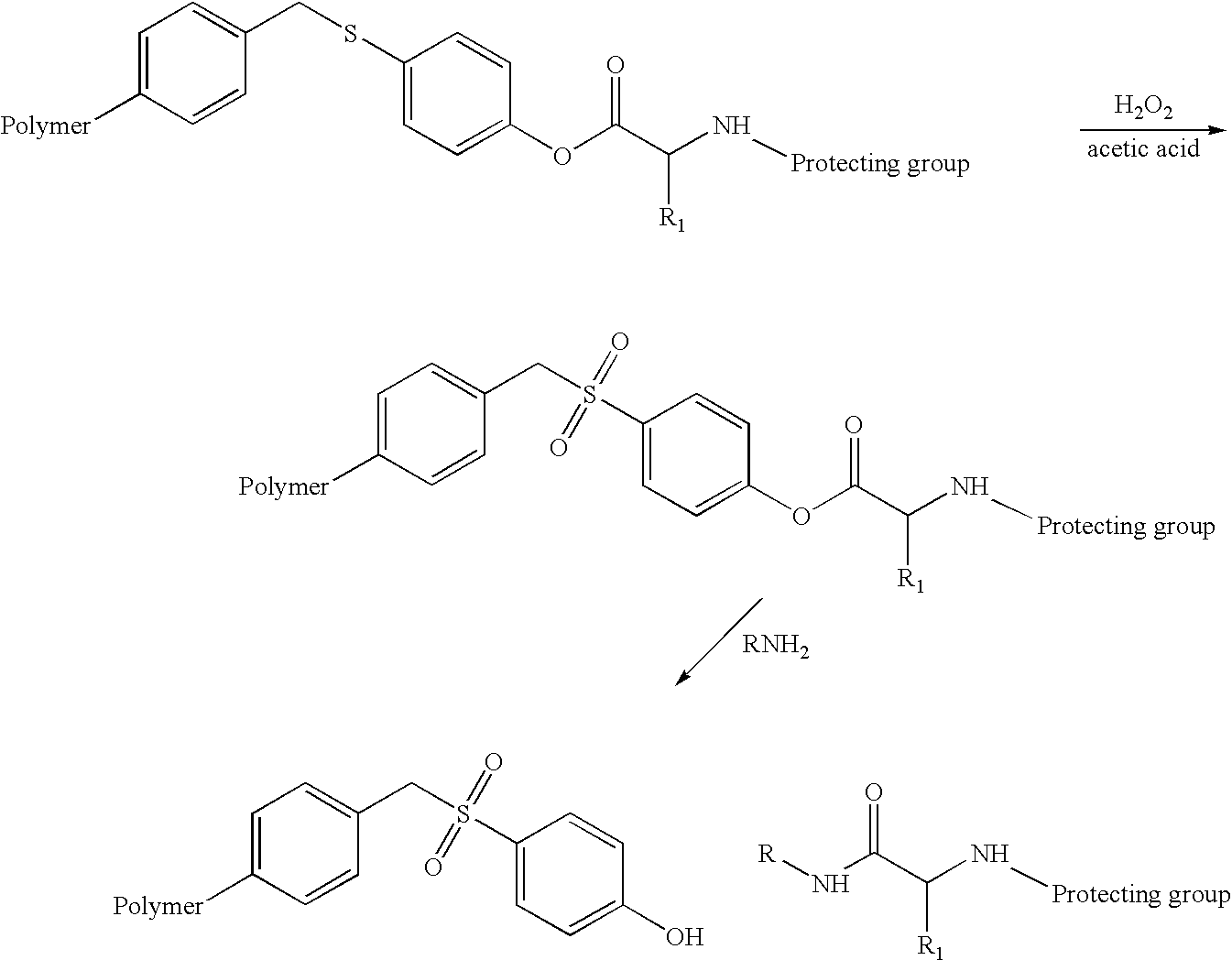
Cleavable linkers for polynucleotides
ActiveUS7572908B2Efficient procedureIncrease flexibilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePolynucleotide
In various embodiments of the invention, novel compositions having a polynucleotide bound to a substrate via a cleavable linker are provided, and methods of cleaving a polynucleotide from a substrate are provided.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC +1
Vitamin-mitomycin conjugates
This invention relates to vitamin-mitomycin conjugates, to a method of using the conjugates to selectively eliminate a population of pathogenic cells in a host animal harboring the pathogenic cells, and to a method of preparation of the conjugates. The conjugate is of the general formula B-L-X wherein the group B is a vitamin, or an analog or a derivative thereof, that binds to a surface accessible vitamin receptor that is uniquely expressed, overexpressed, or preferentially expressed by a population of pathogenic cells, wherein the group L comprises a cleavable linker, and wherein the group X comprises a mitomycin compound, or an analog or a derivative thereof. An additional therapeutic agent, such as a chemotherapeutic agent, can be administered in combination with the conjugate.
Owner:ENDOCTYE INC
Cleavable thiocarbonate linkers for polynucleotide synthesis
In various embodiments of the invention, novel compositions having a polynucleotide bound to a substrate via a cleavable linker are provided, and methods of cleaving a polynucleotide from a substrate are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF +1
Labelled nucleotides
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Multimeric oligonucleotide compounds
InactiveUS20150247141A1Improve concentrationReduce gapSugar derivativesTissue cultureGeneStereochemistry
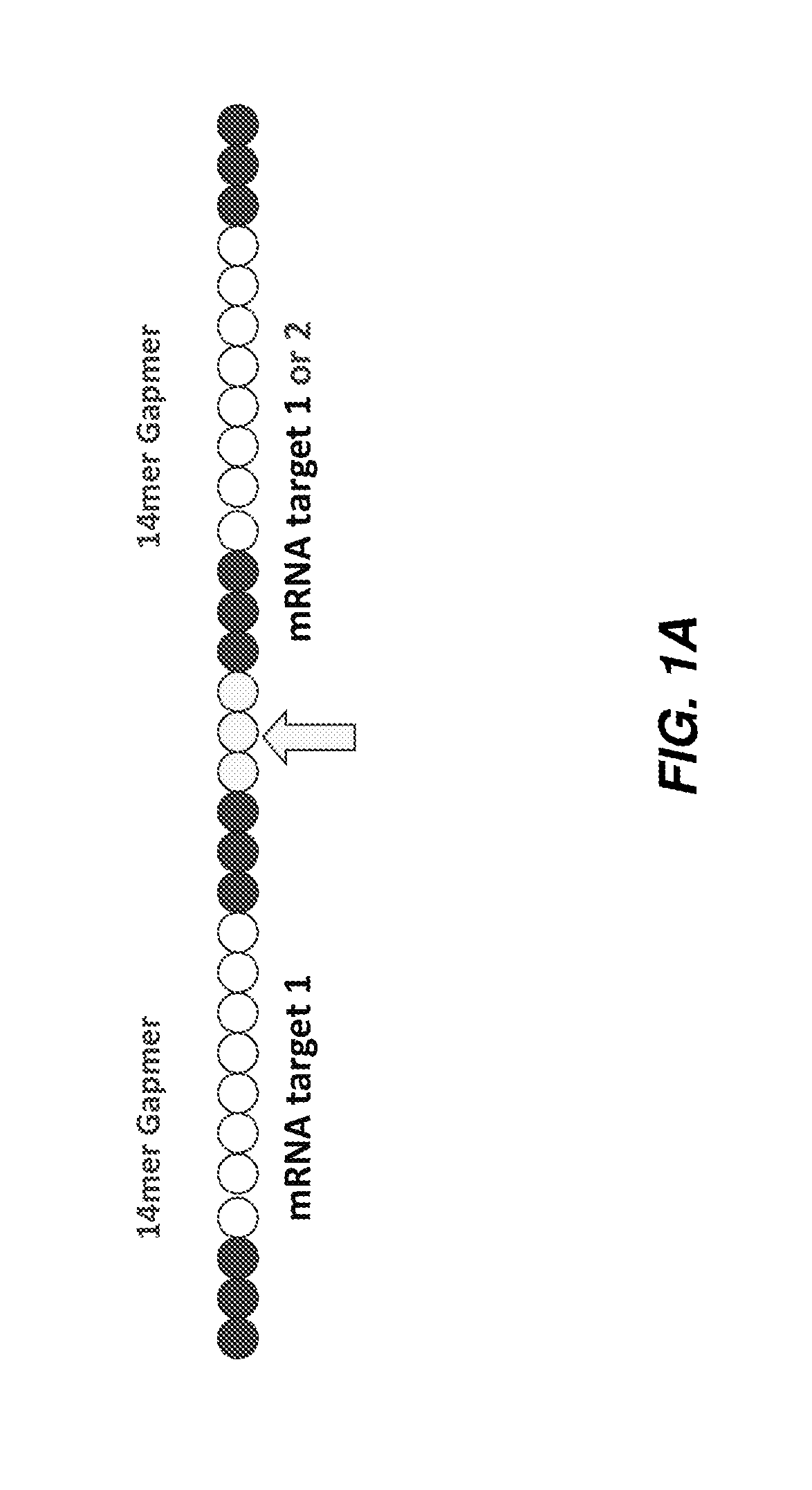
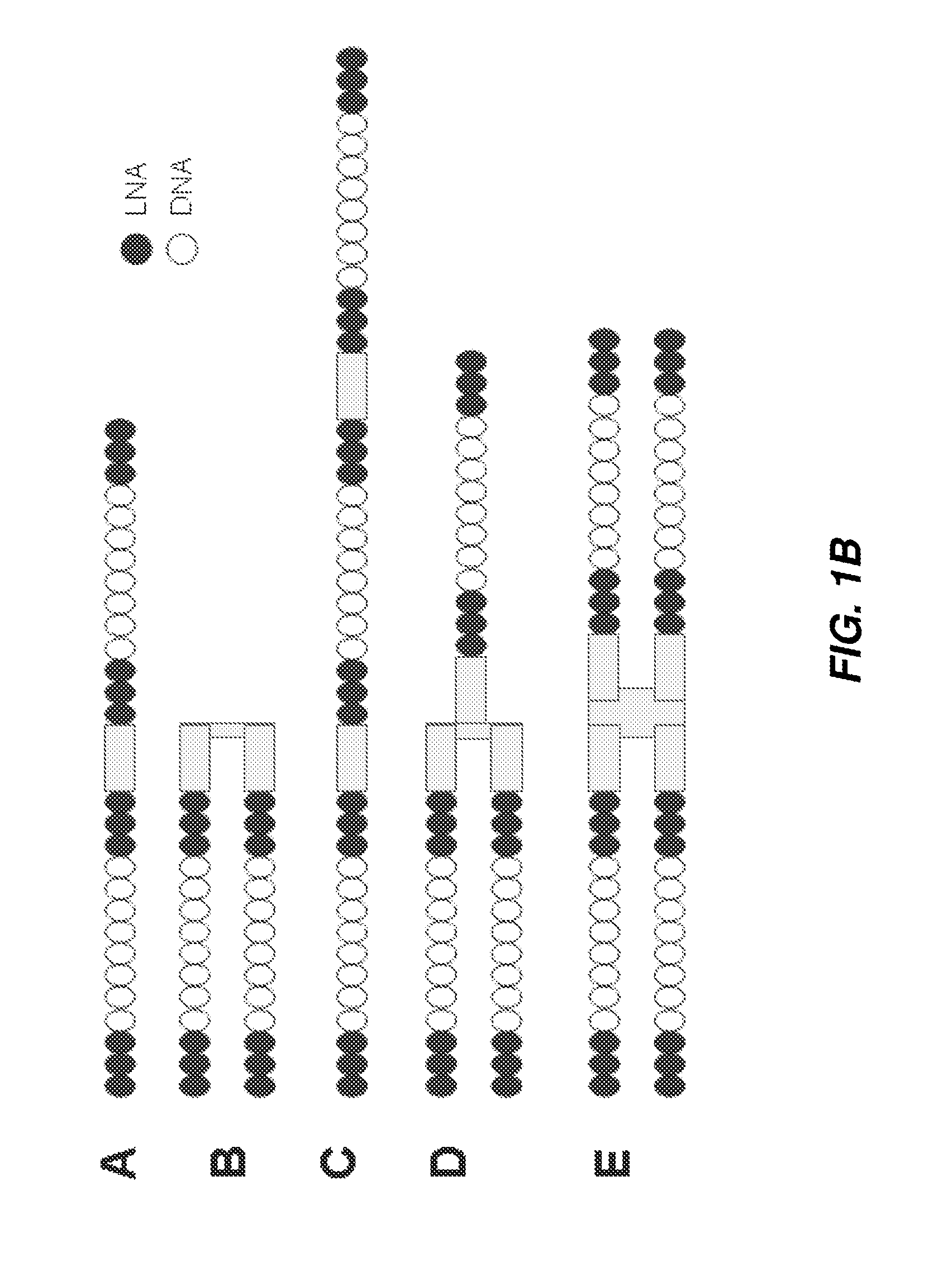
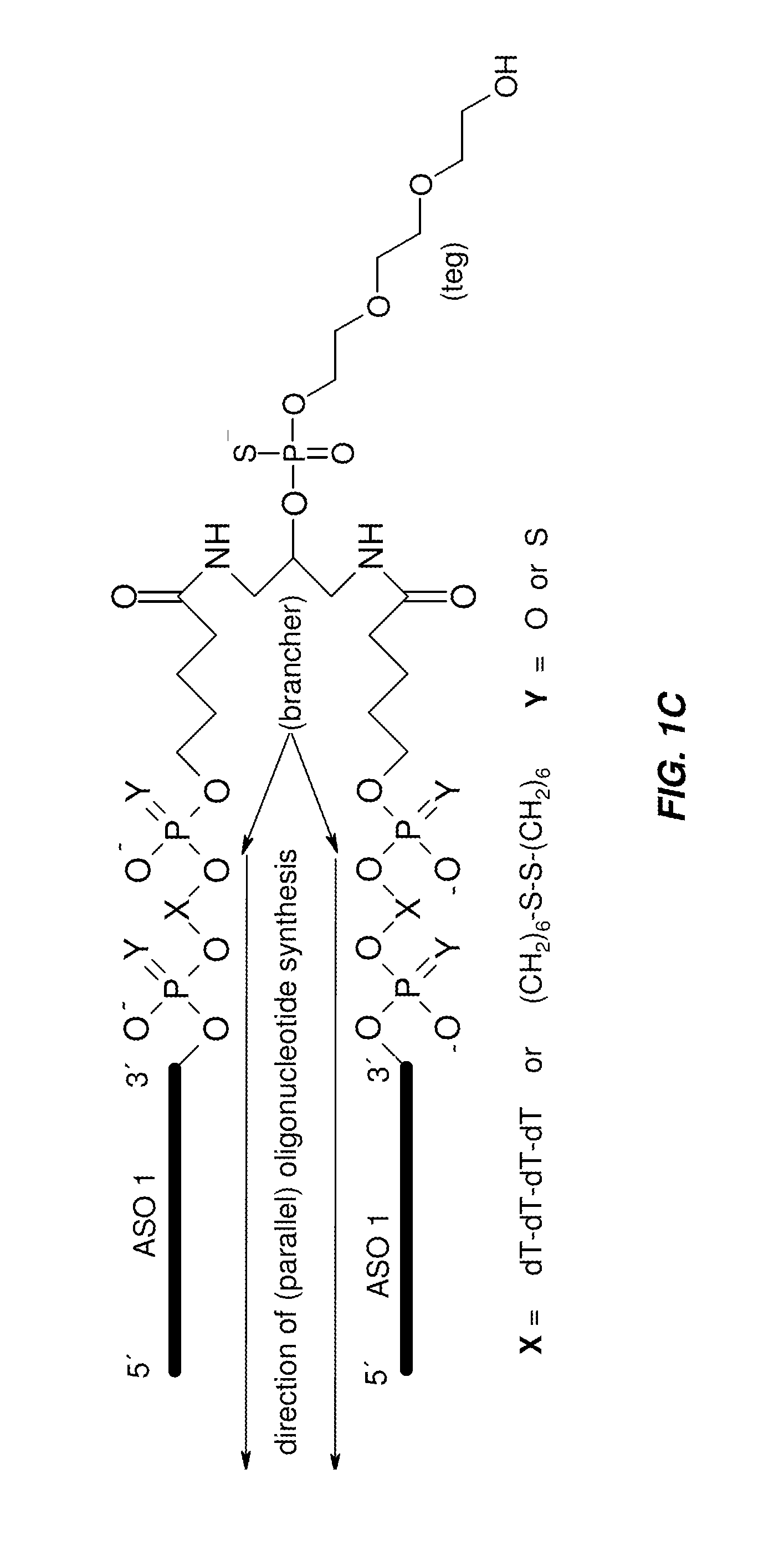
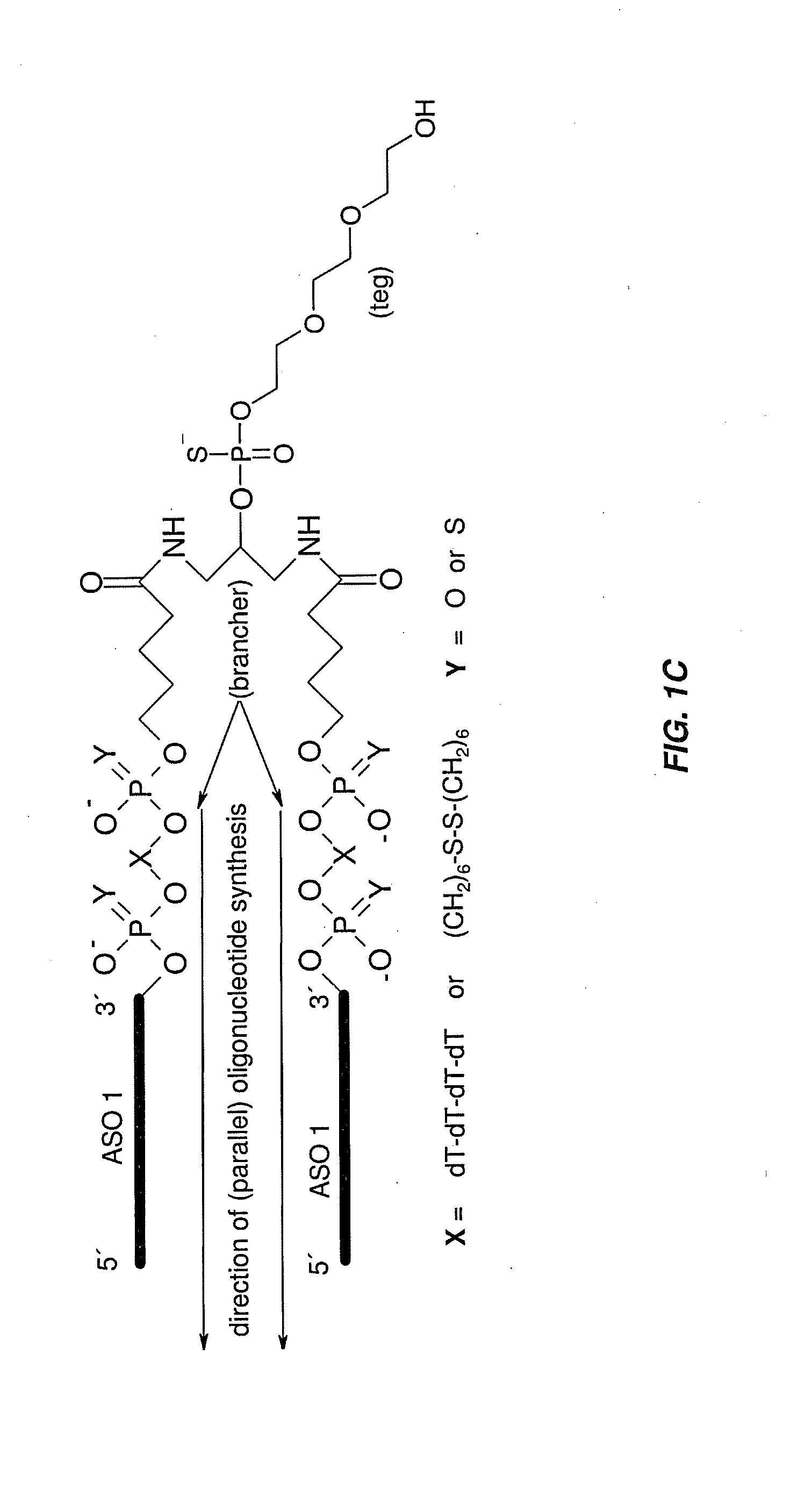
The disclosure provides multimeric oligonucleotide compounds, comprising two or more target-specific oligonucleotides (e.g., antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)), each being resistant to cleavage, and linked together by a cleavable linker. In particular, two or more linked target-specific oligonucleotides, each to a different target, allows concomitant inhibition of multiple genes' expression levels, while exhibiting favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Methods of making and uses of the described compounds are also provided
Owner:RANA THERAPEUTICS INC
Prodrugs containing novel bio-cleavable linkers
InactiveUS20060205674A2Improve efficacyEliminate side effectsBiocideSenses disorderDiluentMedicinal chemistry
Owner:PIRAMAL ENTERPRISES LTD
Single chain antibody with cleavable linker
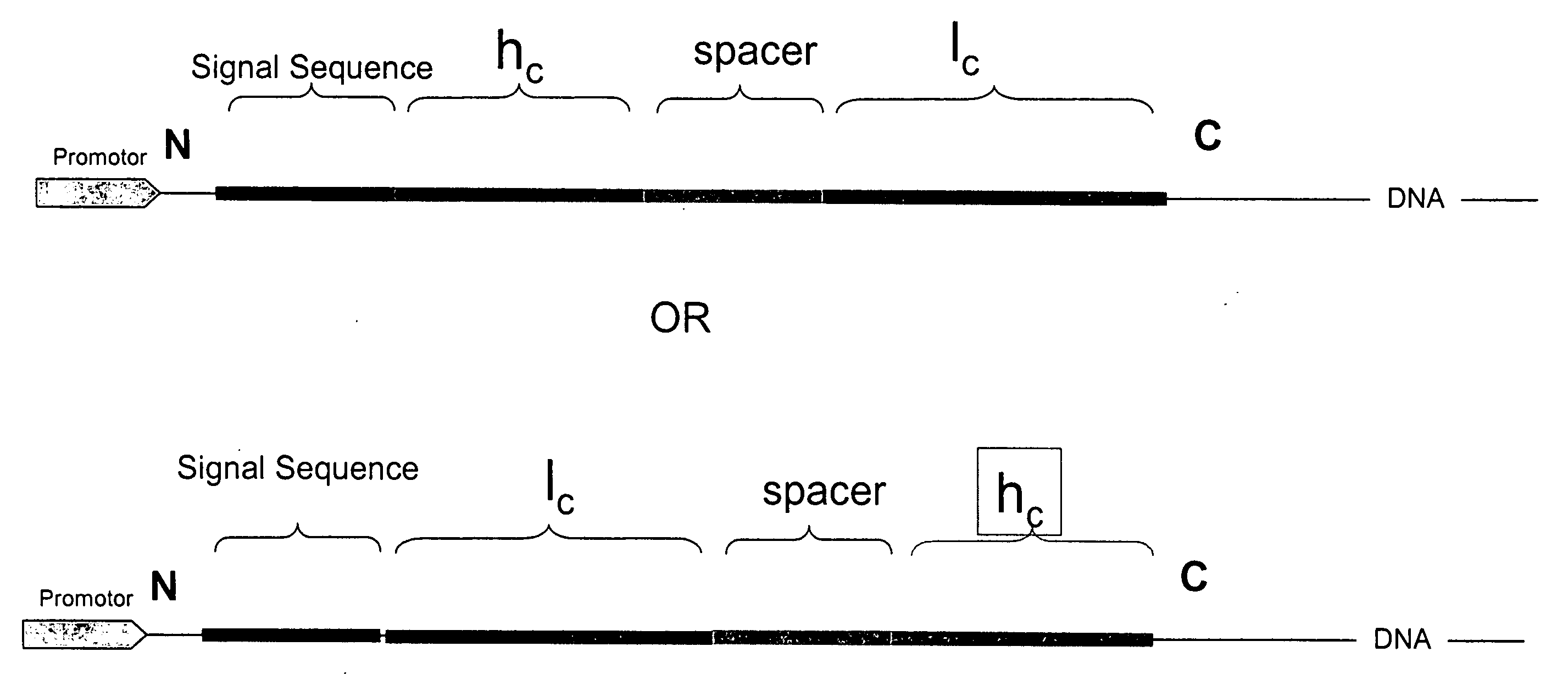
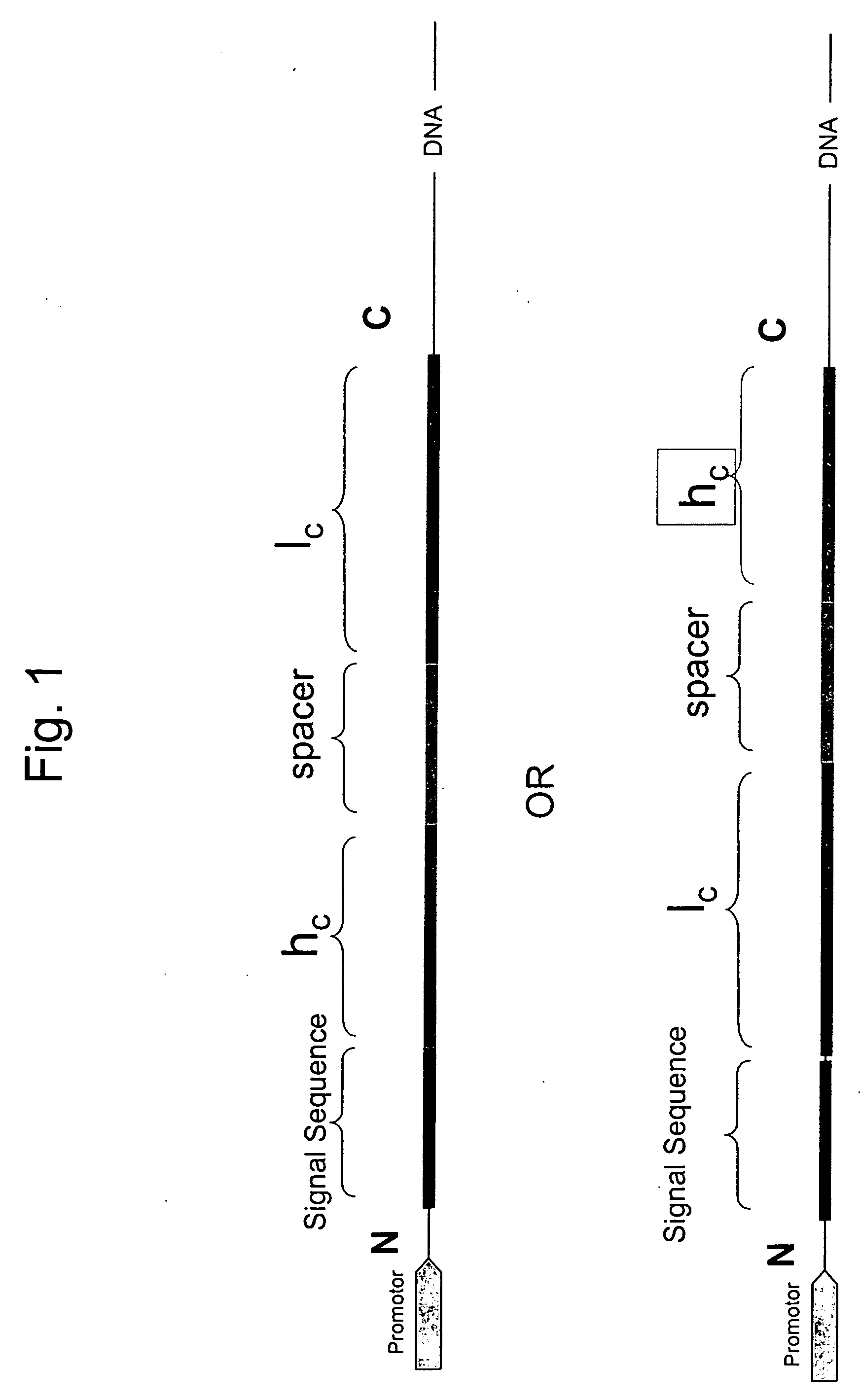
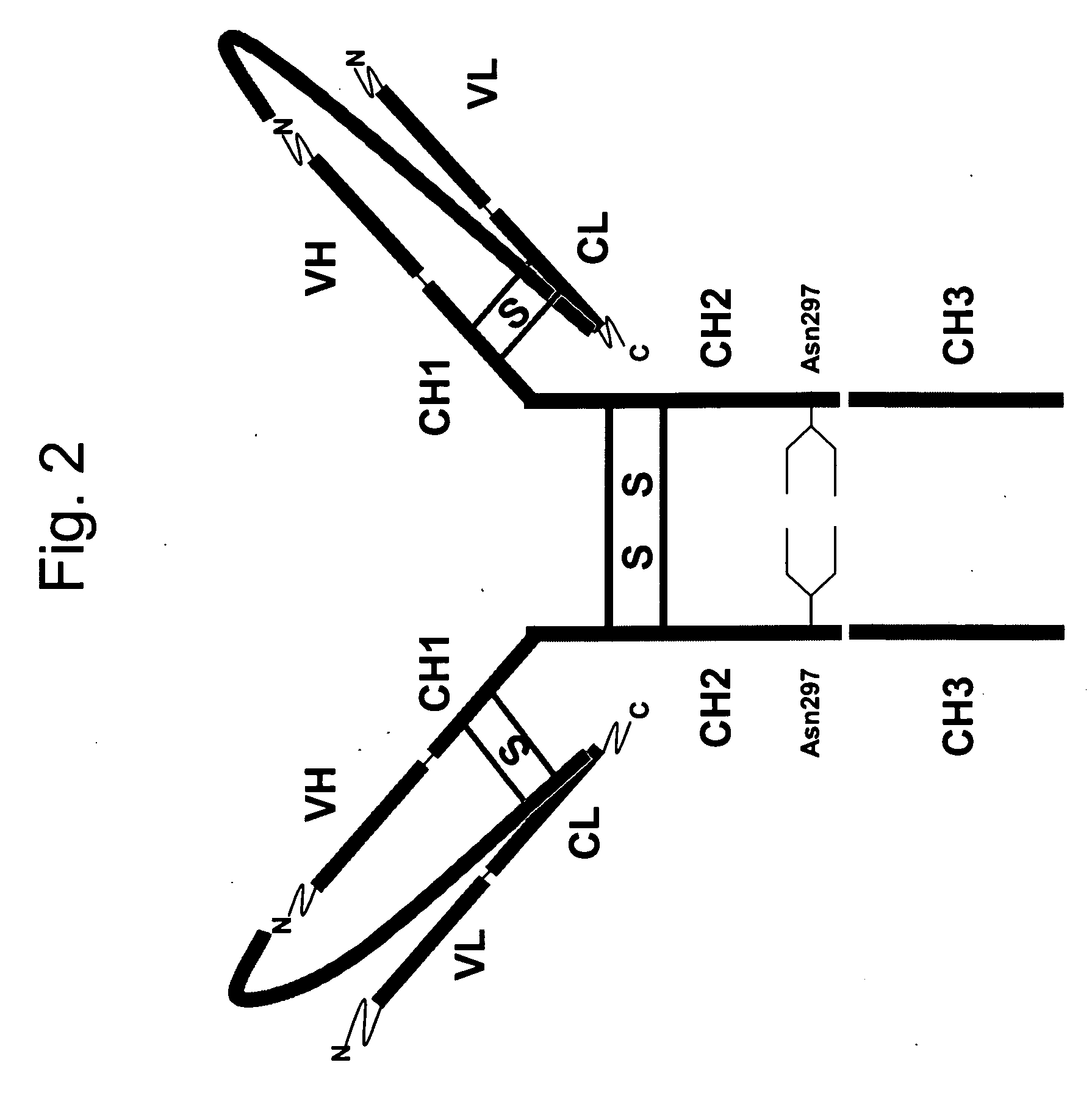
InactiveUS20060252096A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiSingle-Chain AntibodiesConstant region
Disclosed are antibodies and methods for making antibodies with desired glycosylation and efficient production. Host cells transformed with a nucleic acid encoding a fusion protein comprising a signal sequence, light and heavy immunoglobulin chains, each comprising a variable region and a constant region and separated by a spacer peptide comprising at least one proteolytic cleavage site are cultured to express the nucleic acids and are cleaved by appropriate proteases to produce antibodies.
Owner:GLYCOFI
Labelled nucleotides
InactiveUS20090170724A1Use of techniqueSugar derivativesNucleotide librariesOrganic chemistryCleavable linker
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Methods of delivering multiple targeting oligonucleotides to a cell using cleavable linkers
ActiveUS20150315588A1Improve concentrationReduce gapMetabolism disorderDigestive systemGeneAntisense oligonucleotides
The disclosure provides multimeric oligonucleotide compounds, comprising two or more target-specific oligonucleotides (e.g., antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)), each being resistant to cleavage, and linked together by a cleavable linker. In particular, two or more linked target-specific oligonucleotides, each to a different target, allows concomitant inhibition of multiple genes' expression levels, while exhibiting favorable pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. Methods of making and uses of the described compounds are also provided
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO MA INC
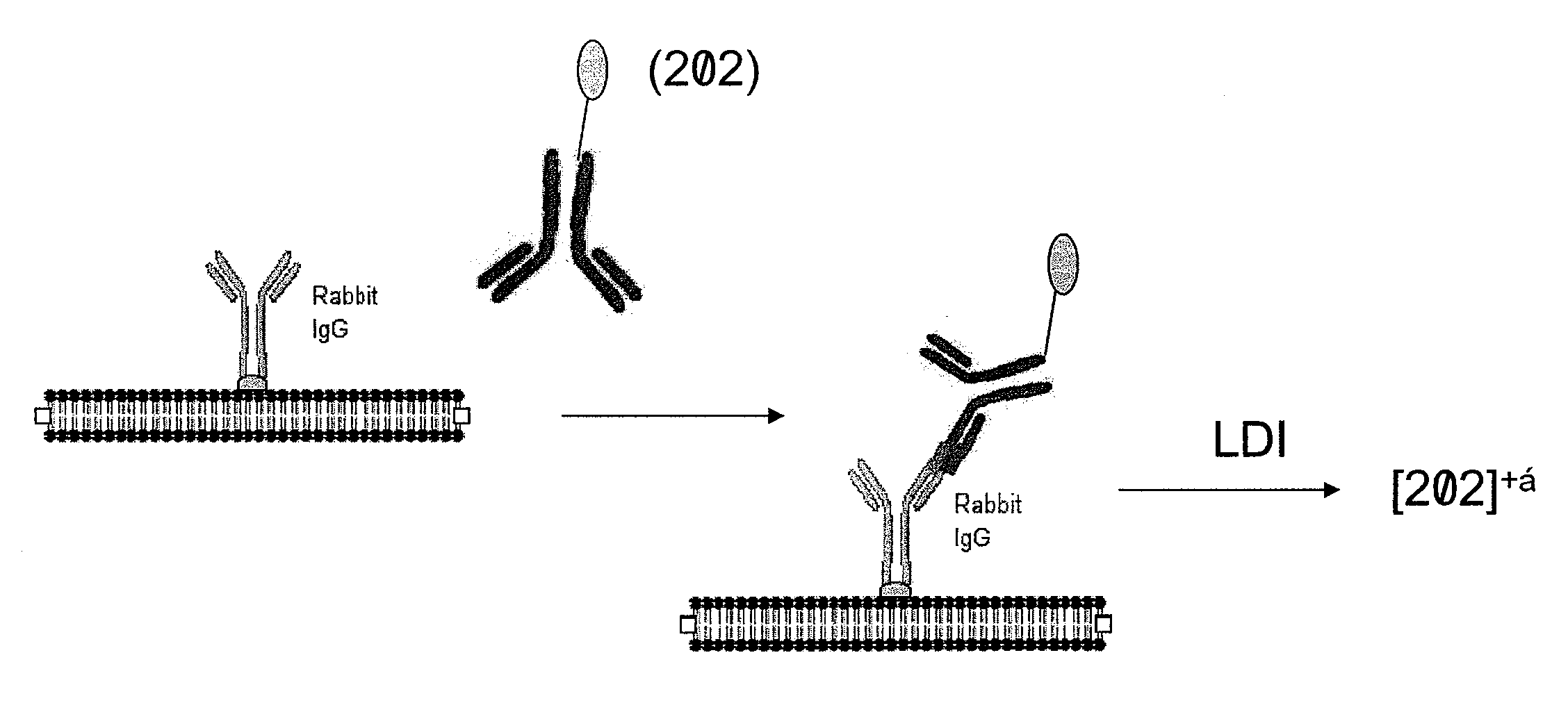
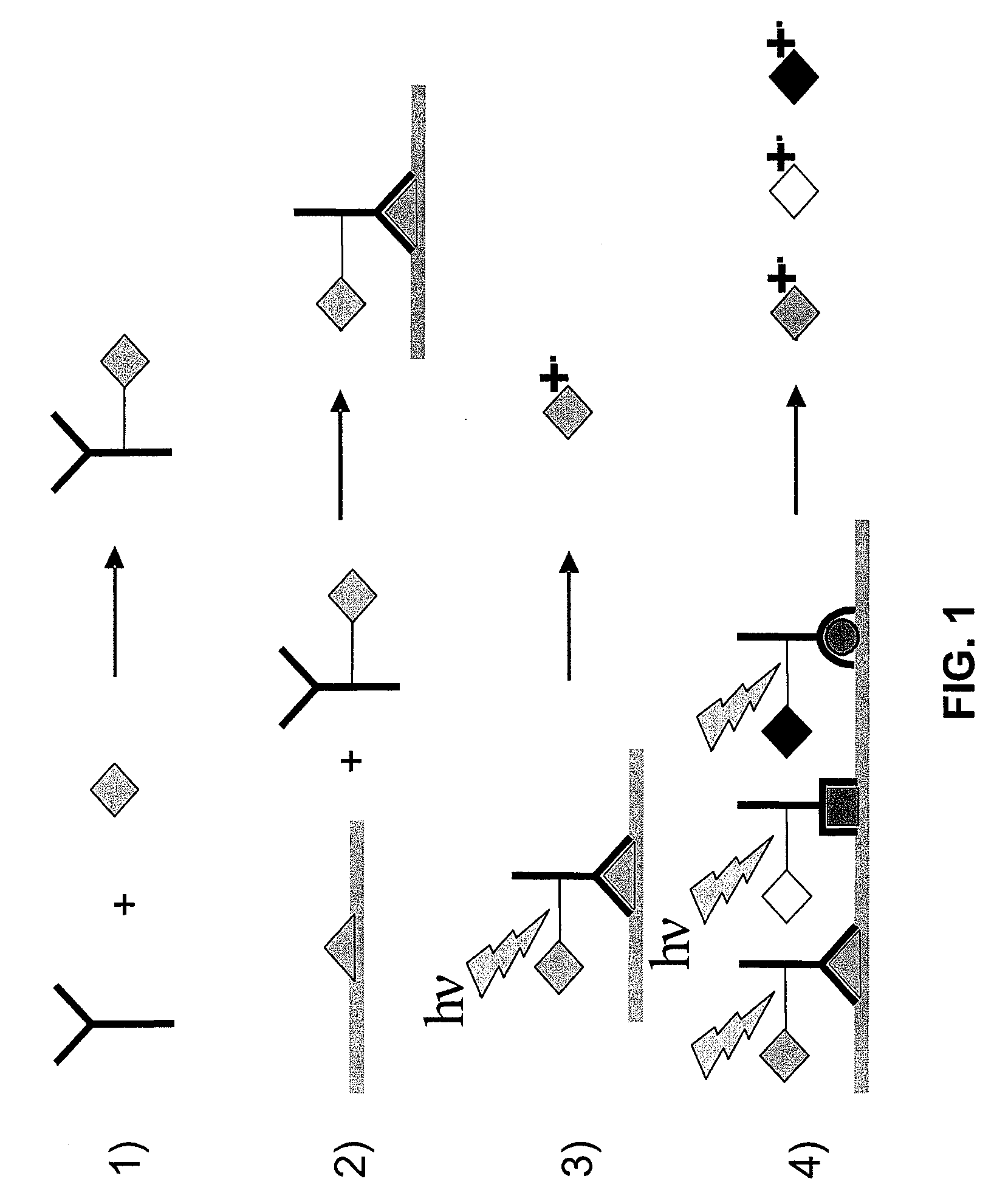
Molecular detection by matrix free desorption ionization mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20080113875A1High sensitivityLibrary screeningBiological testingMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMolecular binding
The present invention provides methods for obtaining information of a plurality of target molecules by matrix free LDI MS. Mass tagged complexes for detection of target molecules comprise a target molecule binding domain, and a mass tag separated by a cleavable linker. Methods of the invention may be used for example to analyze the distribution of a multiple target molecules in a complex sample, such as a tissue section.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
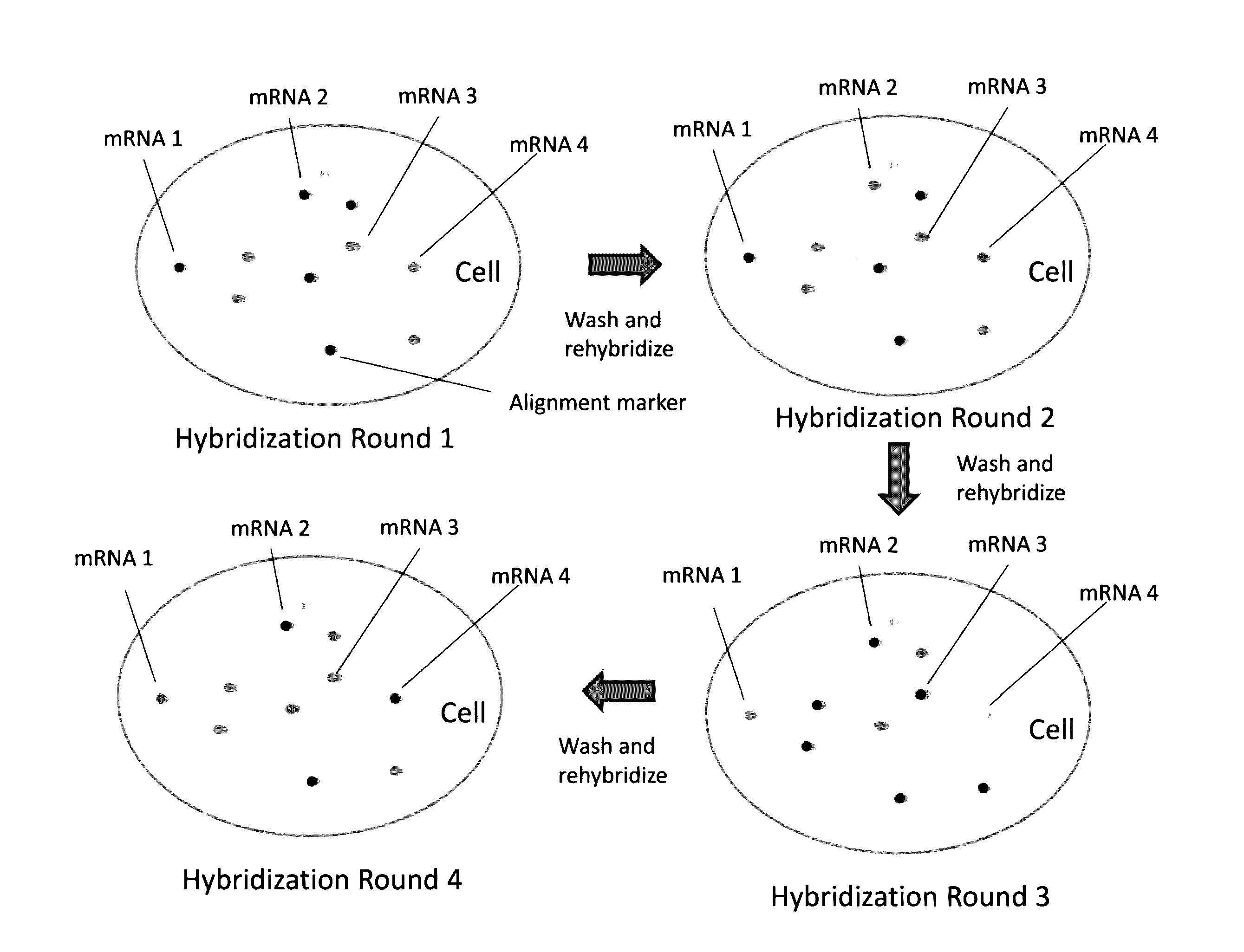
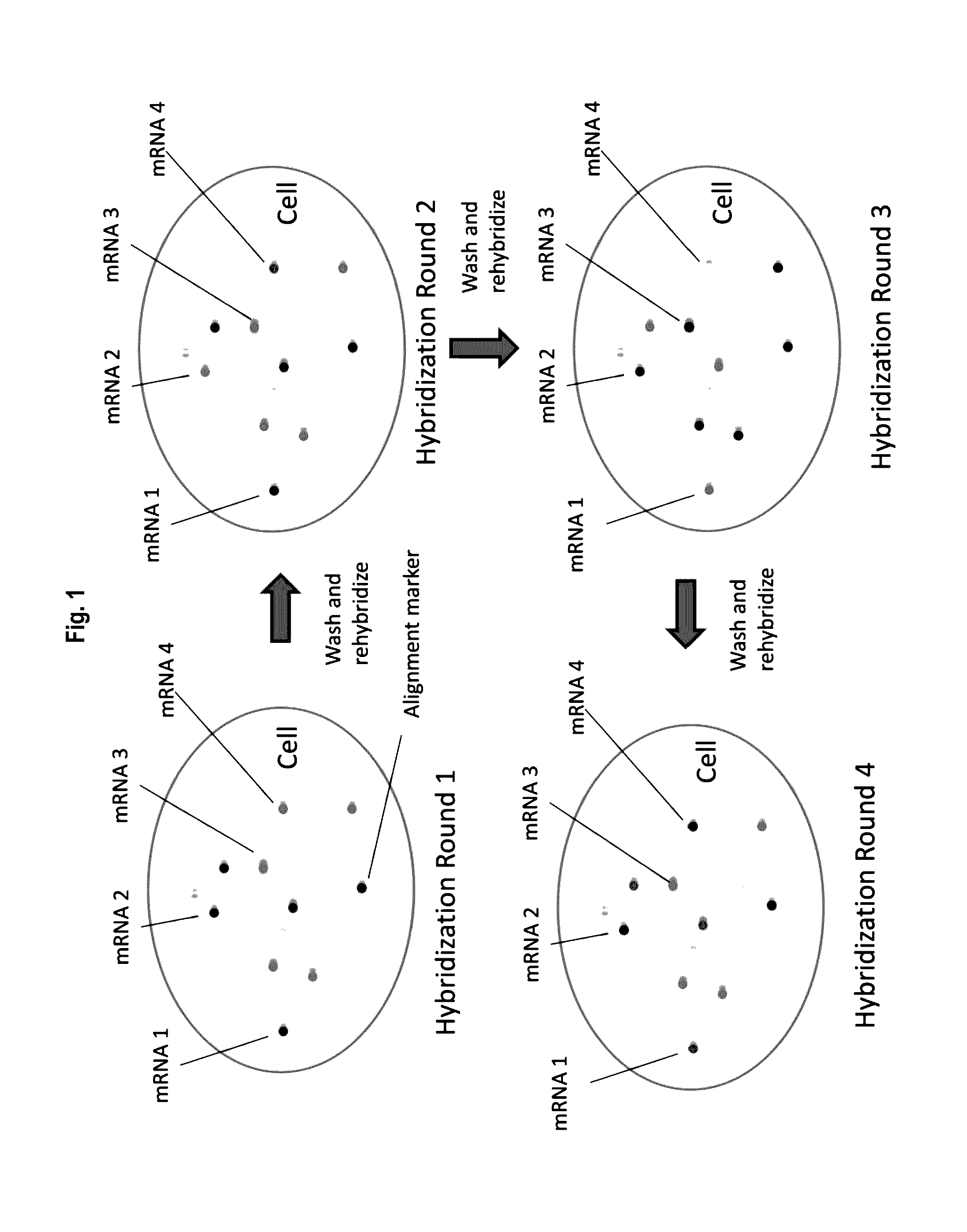
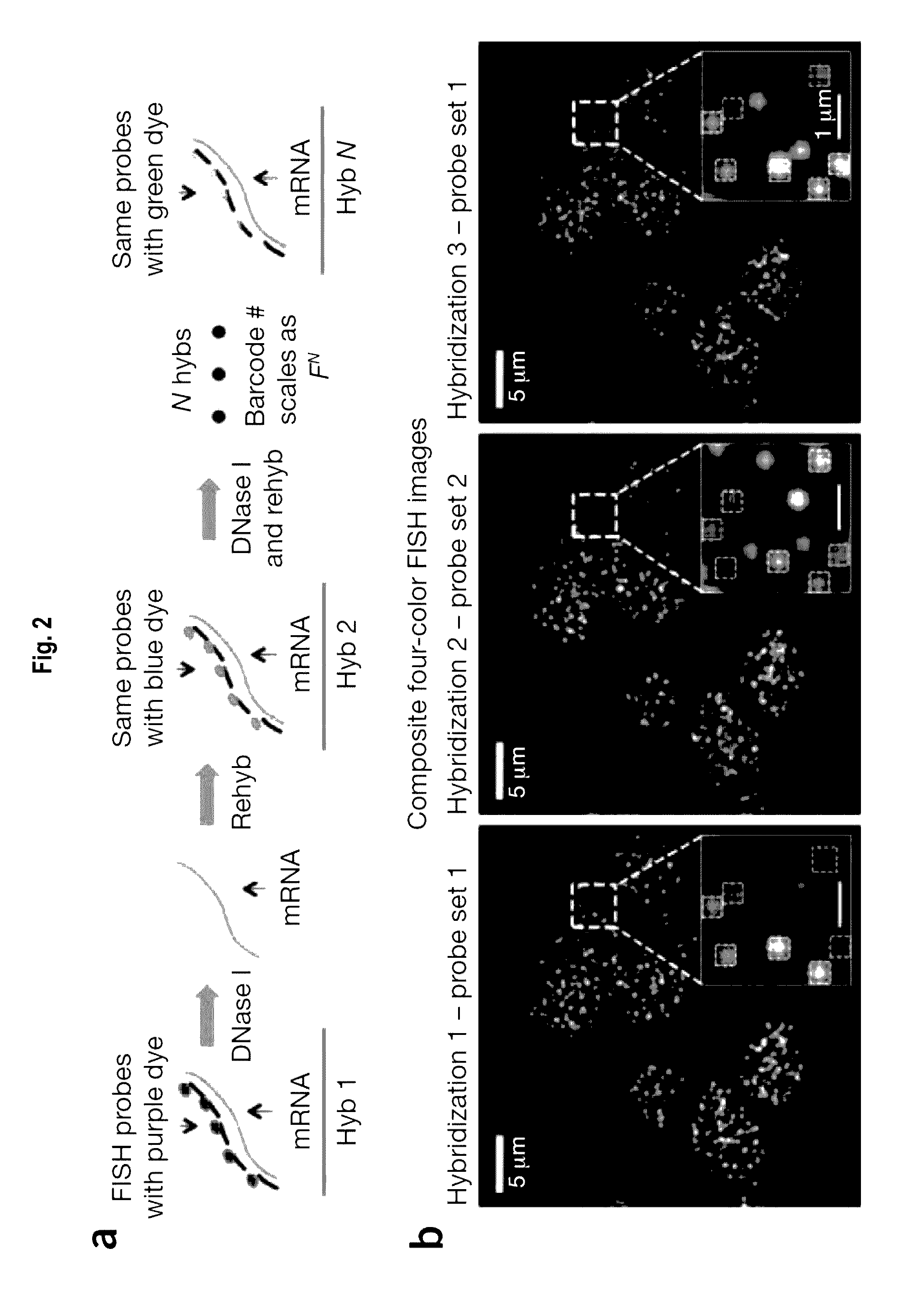
Multiplex labeling of molecules by sequential hybridization barcoding using probes with cleavable linkers
InactiveUS20160369329A1Introduce significant noise ad biasLimited in numberMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationBiological bodyBarcode
The present invention, among other things, provides technologies for detecting and / or quantifying nucleic acids in cells, tissues, organs or organisms. Through sequential barcoding, the present invention provides methods for high-throughput profiling of a large number of targets, such as transcripts and / or DNA loci. In some embodiments, nucleic acid probes include a signal moiety connected with a binding sequence via a cleavable linker.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
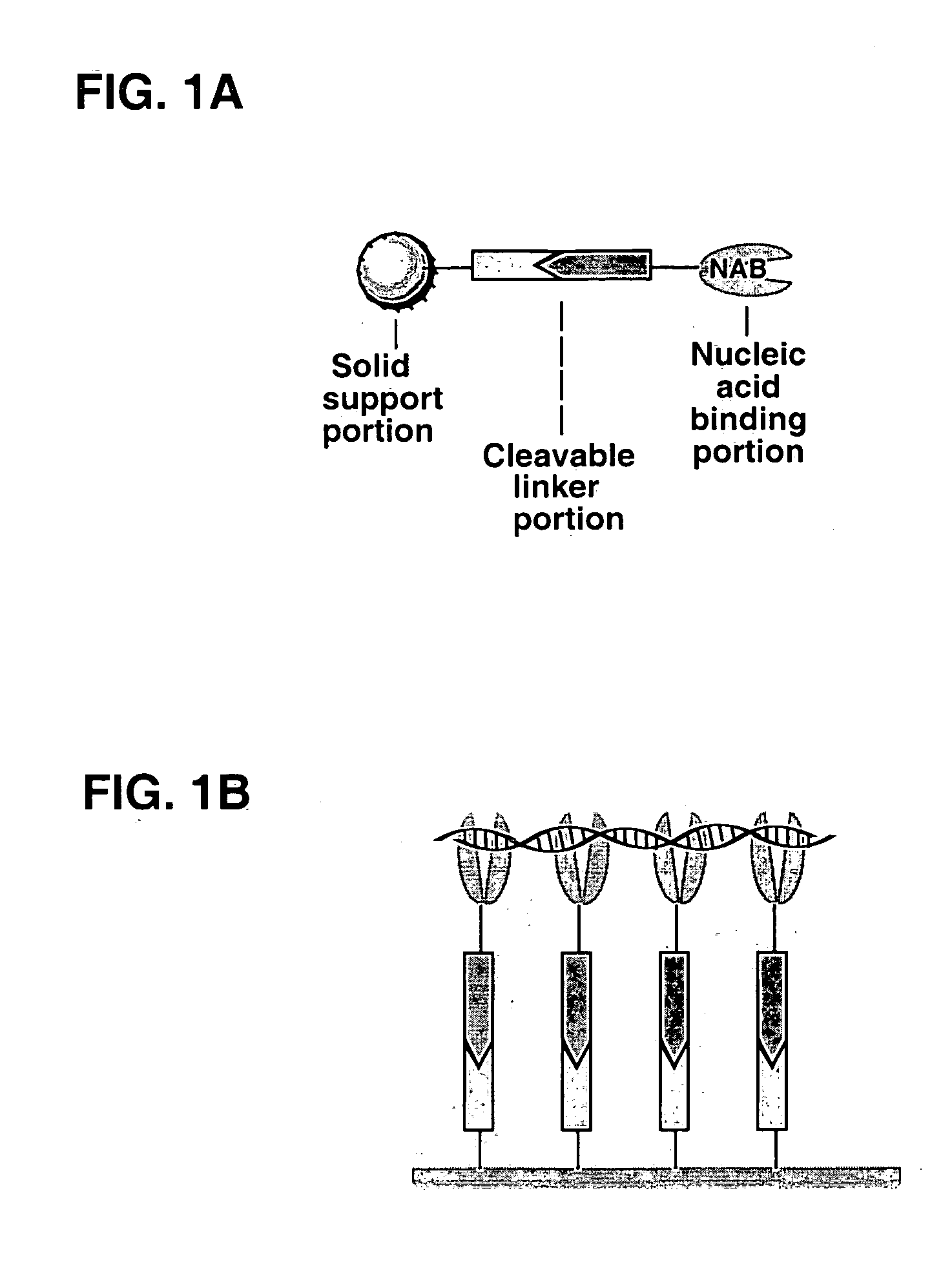
Methods of using cleavable solid phases for isolating nucleic acids
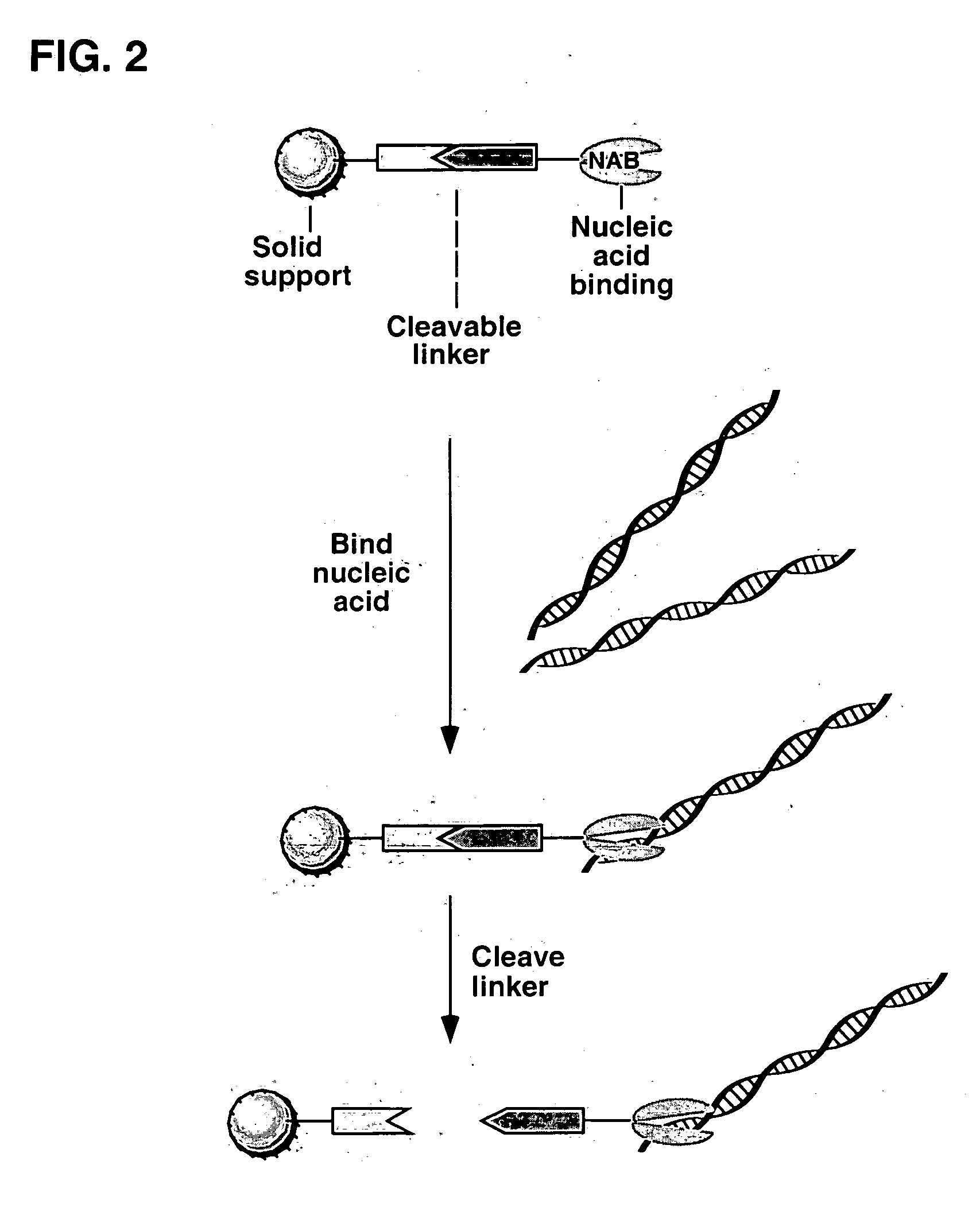
Solid phase materials for binding nucleic acids and methods of their use are disclosed. The materials feature a cleavable linker portion which can be cleaved to release bound nucleic acids. The solid phase materials comprise a solid support portion comprising a matrix selected from silica, glass, insoluble synthetic polymers, and insoluble polysaccharides to which is attached a nucleic acid binding portion for attracting and binding nucleic acids, the nucleic acid binding portion (NAB) being linked by a cleavable linker portion to the solid support portion. Preferred nucleic acid binding portions comprise a ternary or quaternary onium group. The materials can be in the form of microparticles, fibers, beads, membranes, test tubes or microwells and can further comprise a magnetic core portion. Methods of binding nucleic acids using the cleavable solid supports are disclosed as are their use in methods of isolating or purifying nucleic acids.
Owner:NEXGEN DIAGNOSTICS LLC
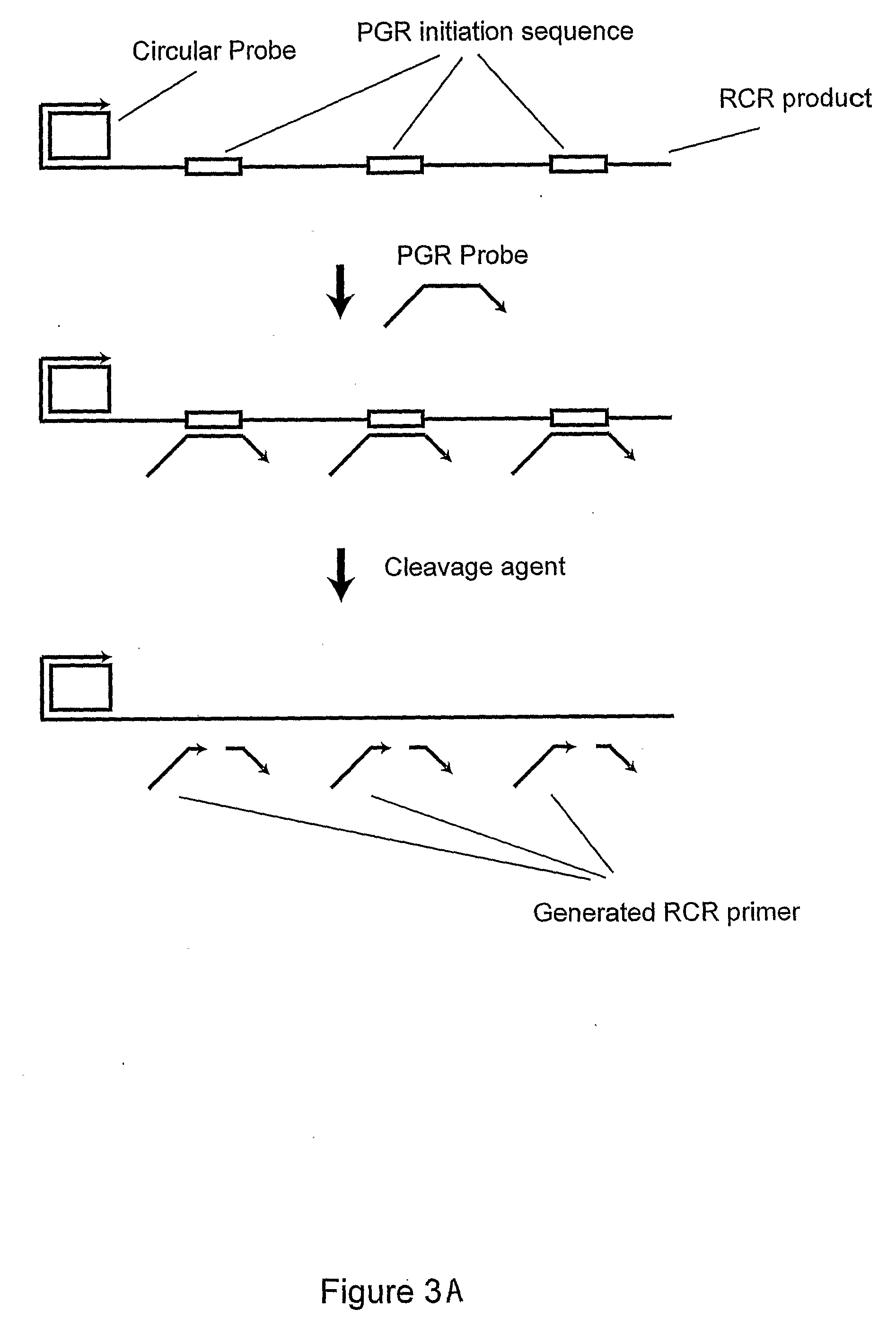
Primer generation rolling circle amplification
InactiveUS20090233277A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationNucleotide
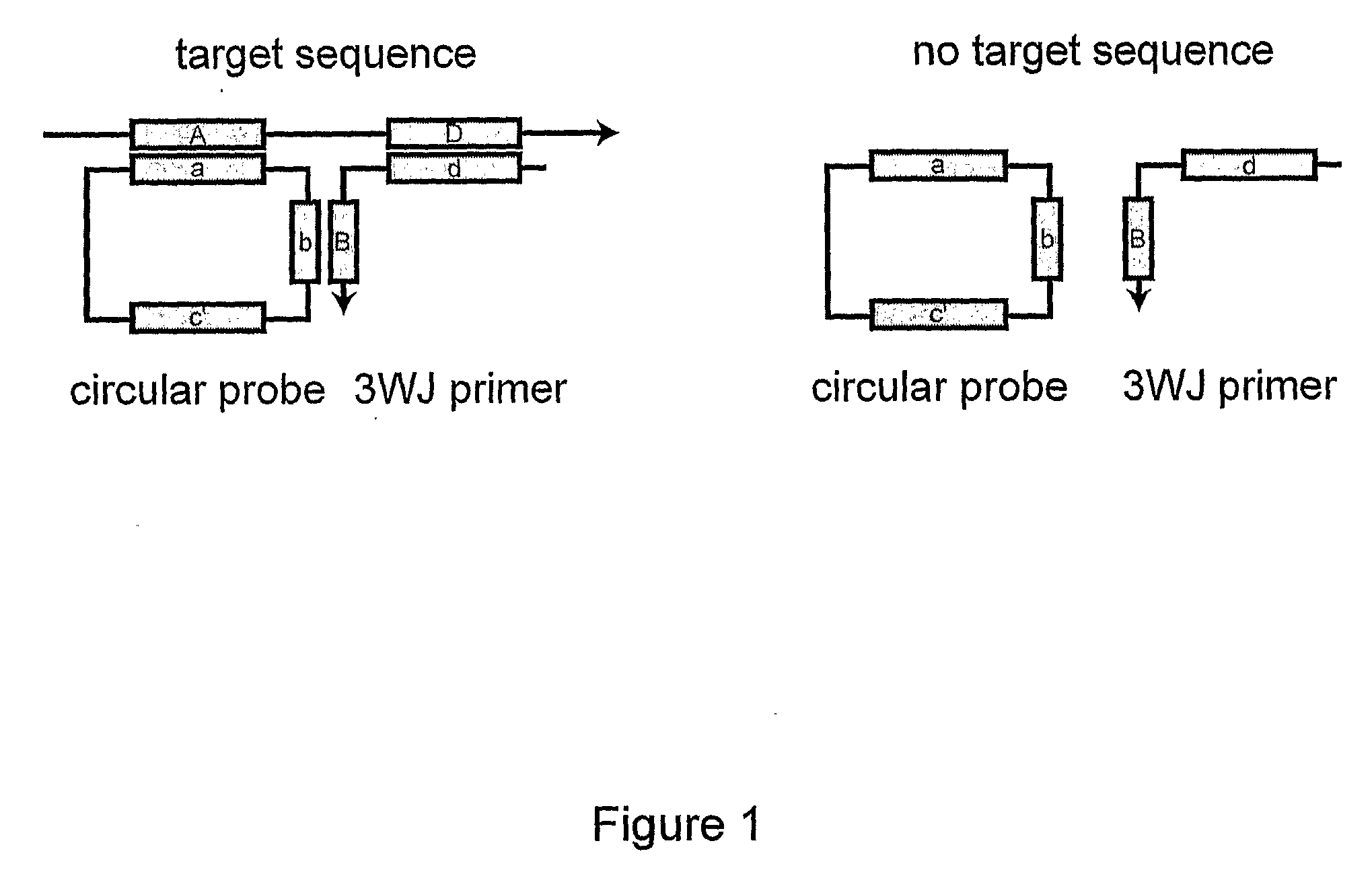
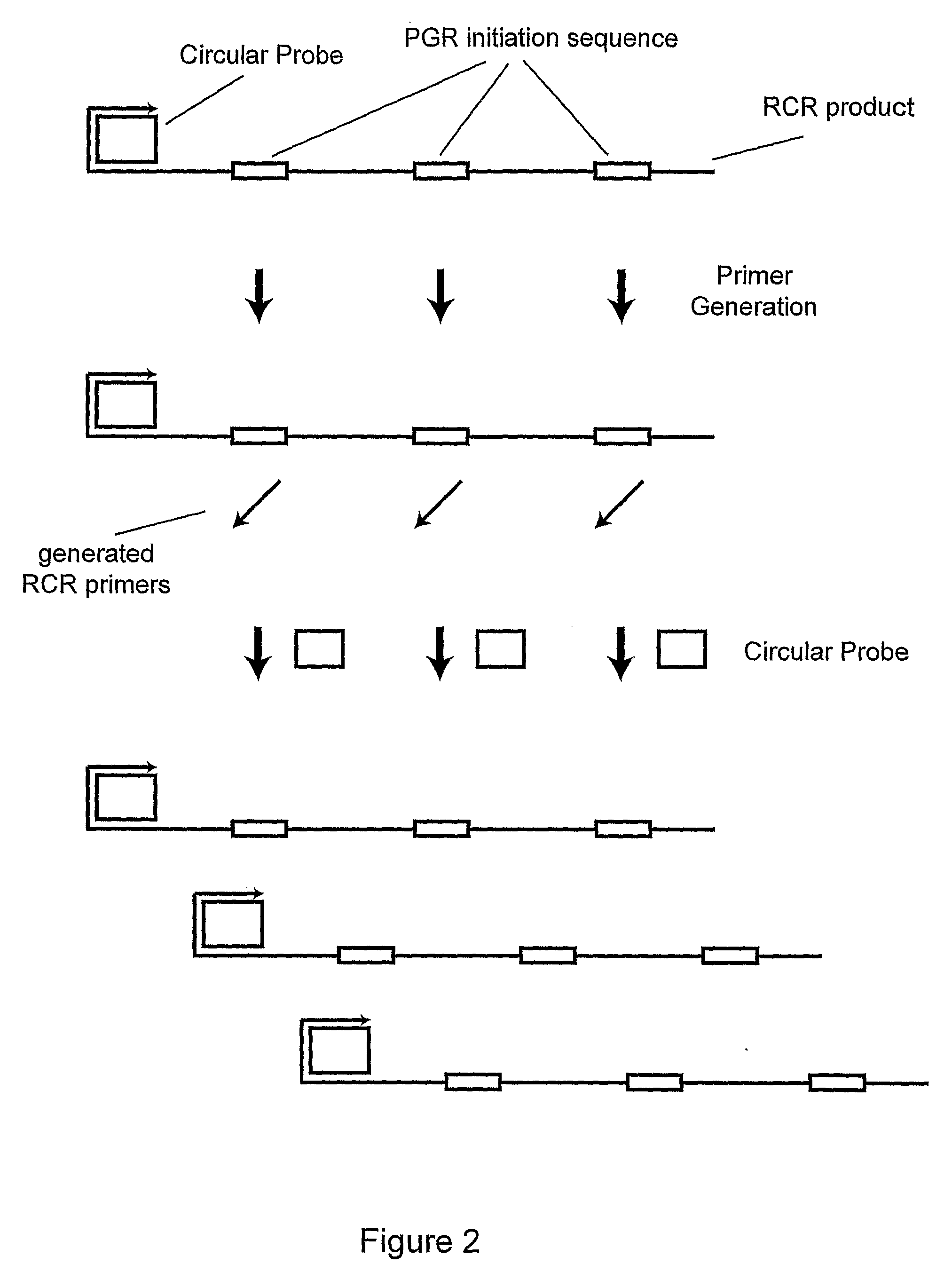
A method of amplifying a nucleic acid is provided which comprises: generating a first nucleic acid primer from a first nucleic acid sequence; combining the first nucleic acid primer with a first polymerase and a first circular nucleic acid probe, wherein the first circular nucleic acid probe contains at least one antisense sequence to a second nucleic acid sequence and at least one antisense sequence to the first nucleic acid primer; producing at least one repeat of a sequence copy of the first circular nucleic acid probe by rolling circle amplification using the first polymerase, wherein the sequence copy contains at least the second nucleic acid sequence; generating a second nucleic acid primer from the second nucleic acid sequence; combining the second nucleic acid primer with a second polymerase and a second circular nucleic acid probe, where the second circular nucleic acid probe contains at least one antisense sequence to the second nucleic acid primer; and producing at least one repeat of a sequence copy of the second circular nucleic acid probe by rolling circle amplification using the second polymerase. The method may be employed to detect molecules of interest such as nucleic acid sequences, DNA methylation, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP), proteins and posttranslational modifications. Furthermore, a ribbon probe is provided that comprises a circular nucleic acid probe and a nucleic acid lock probe, wherein: the nucleic acid lock probe contains at least a cleavable linker, and the circular nucleic acid probe and the lock probe are unable to dissociate without cleaving the cleavable linker.
Owner:HITACHI CHEM CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com