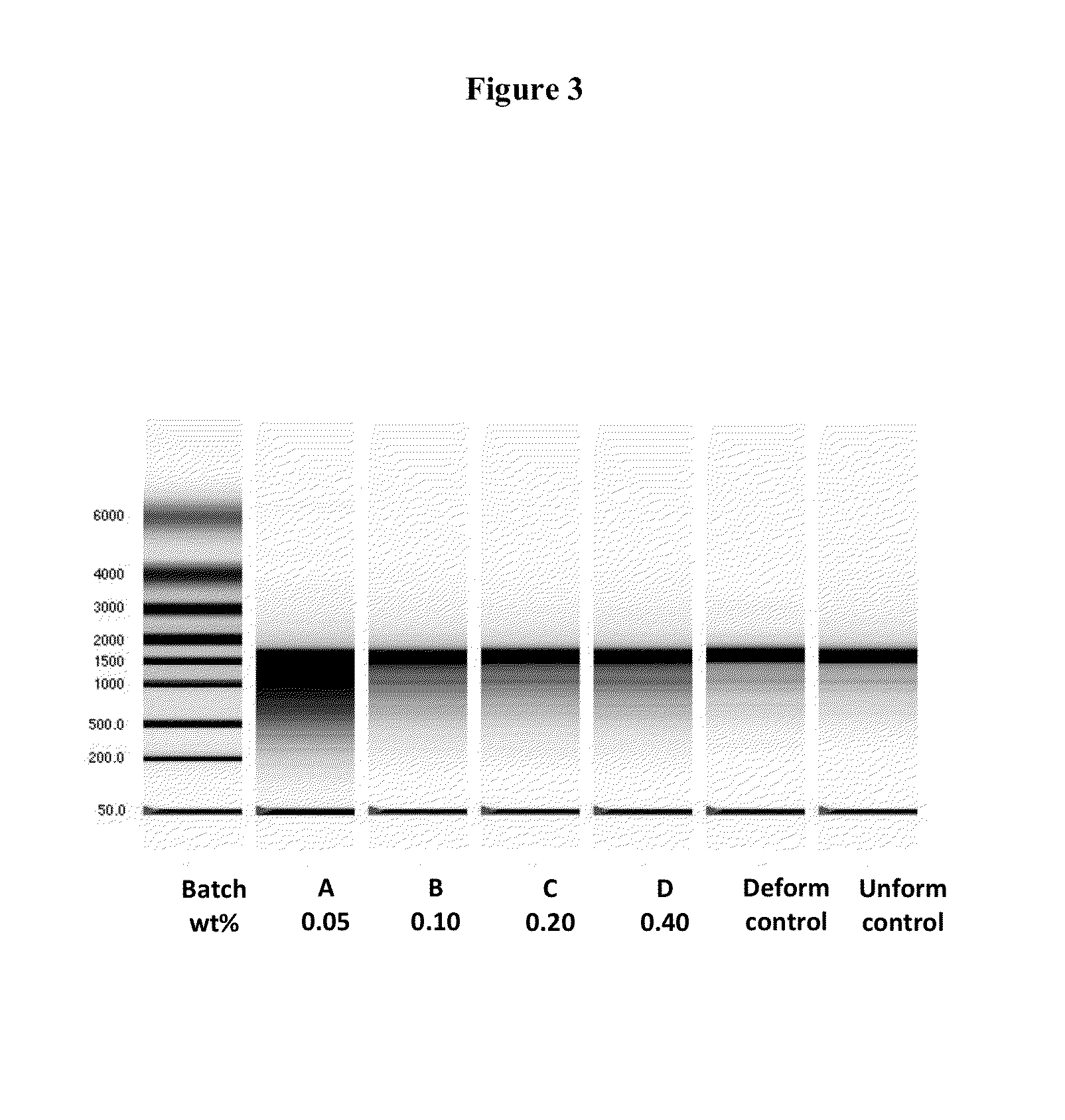
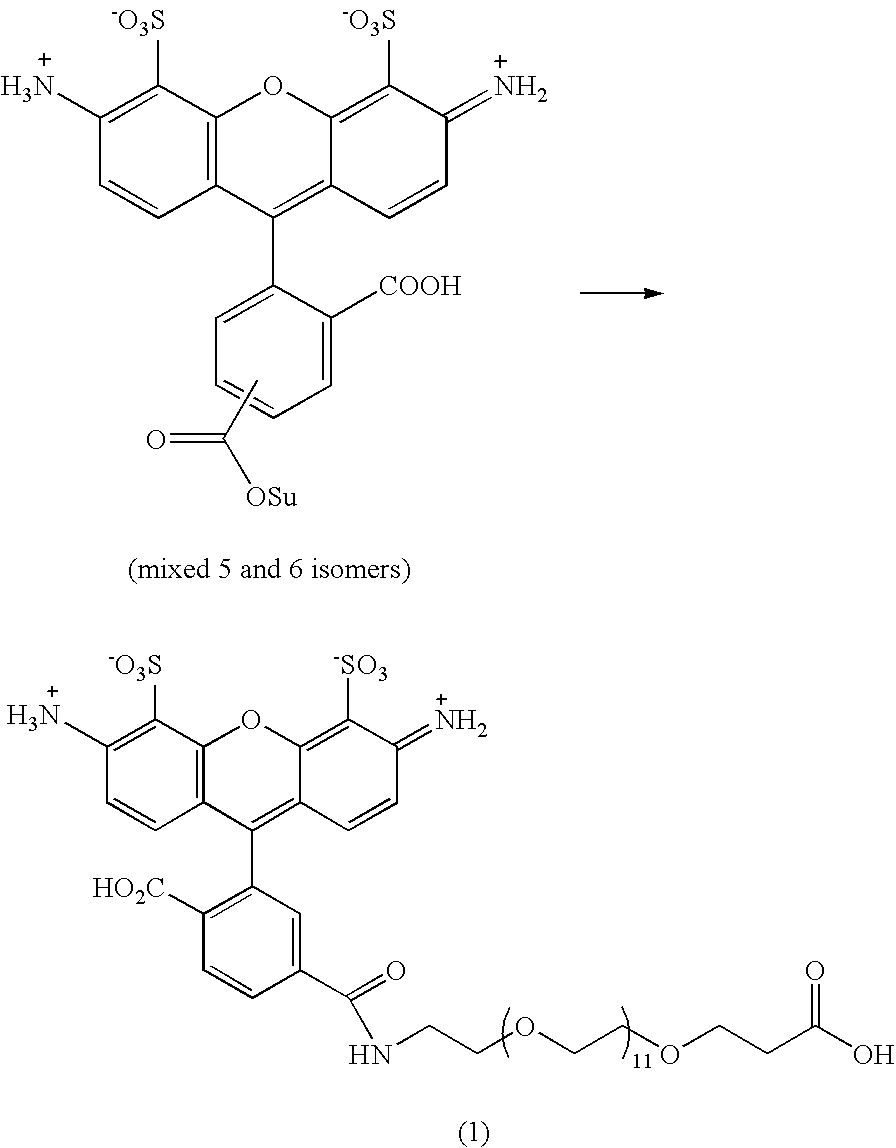
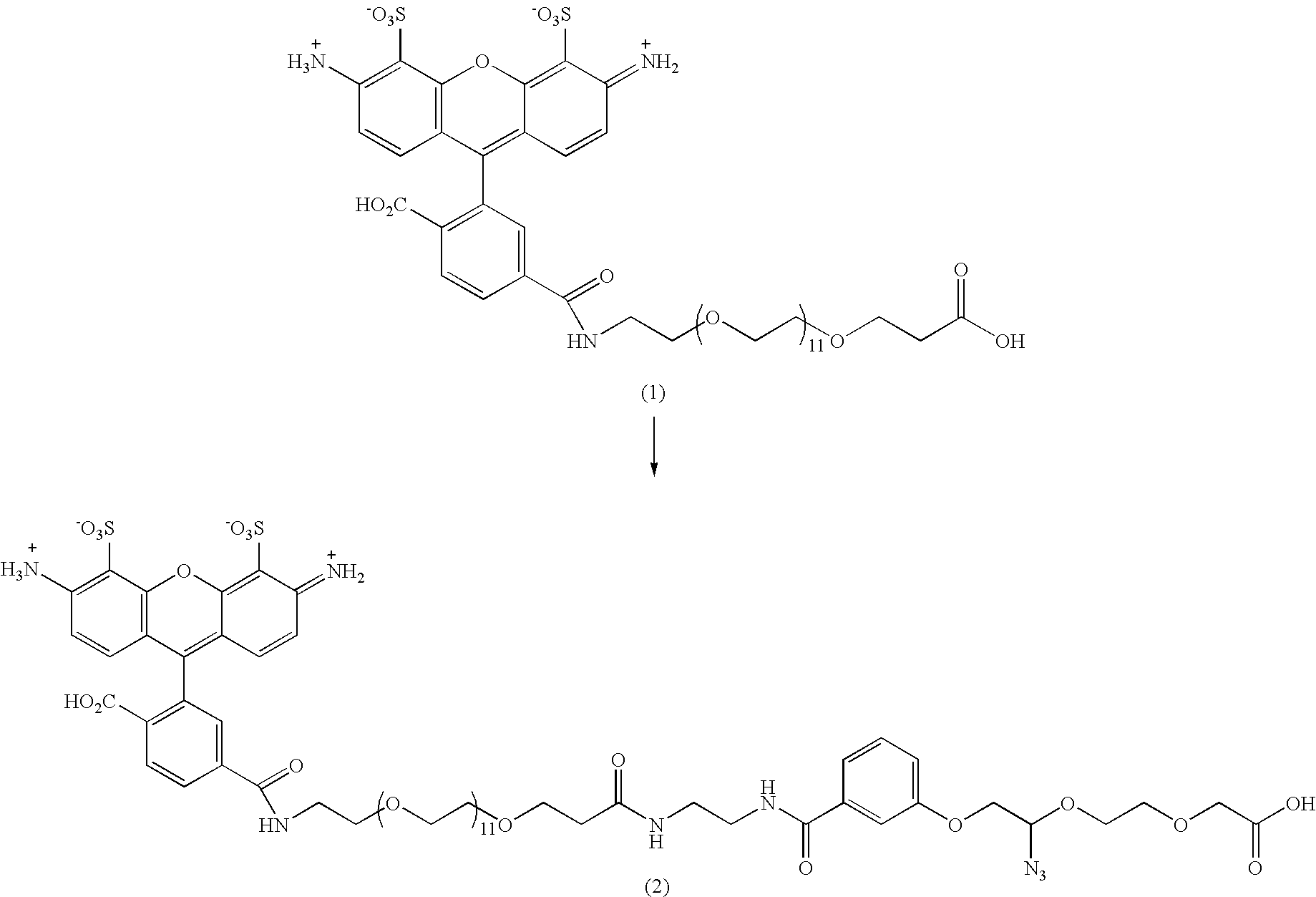
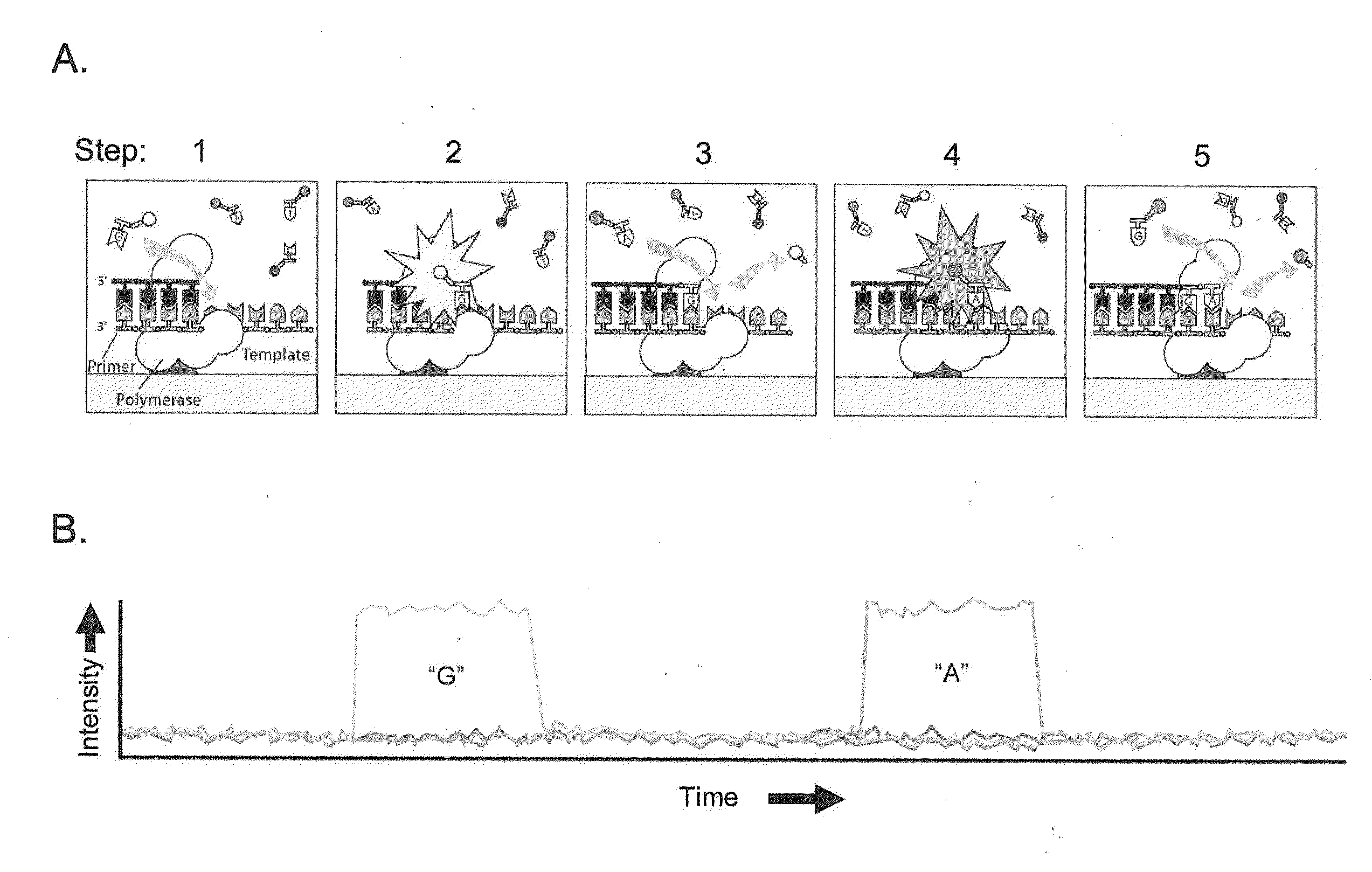
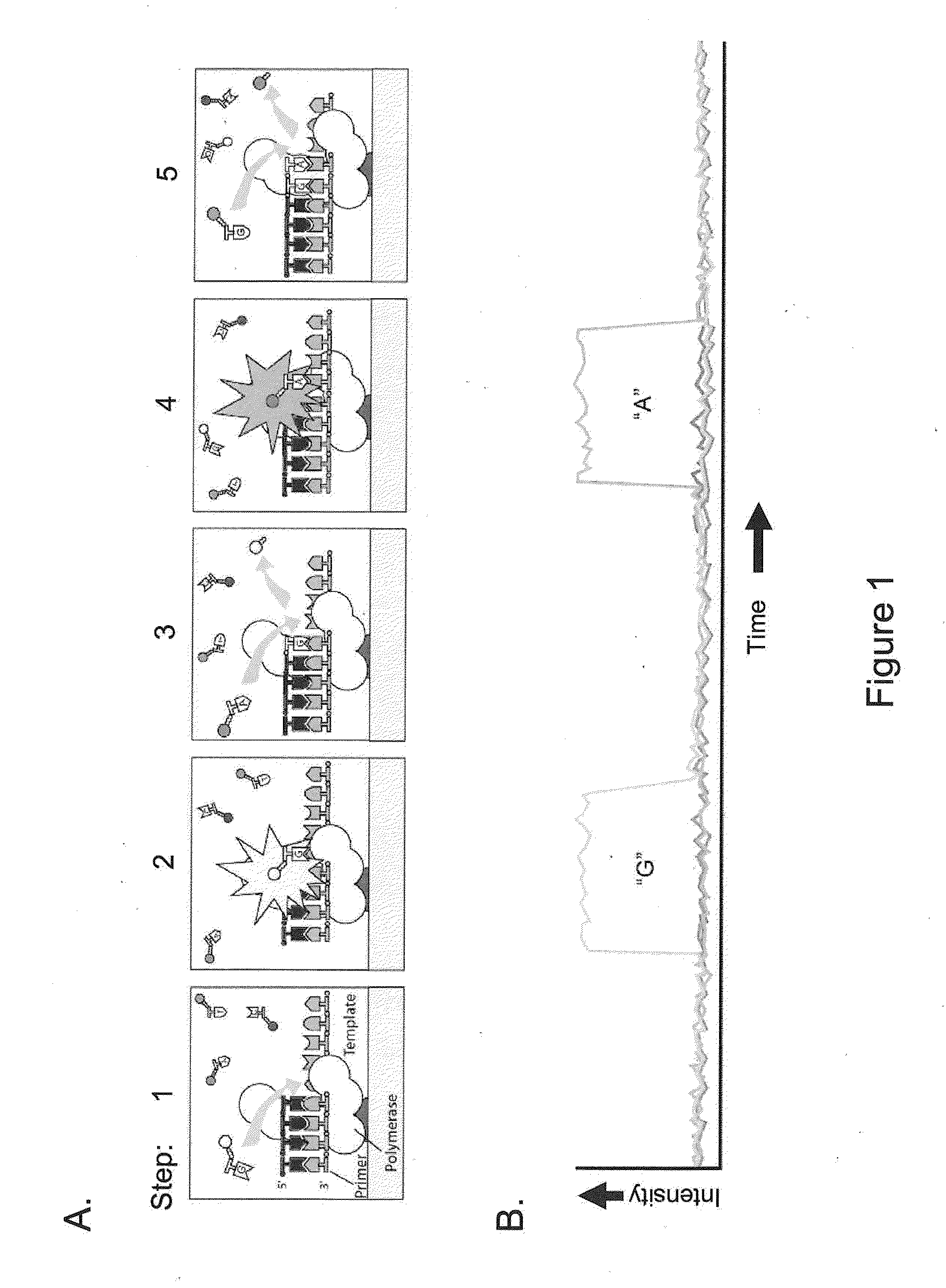
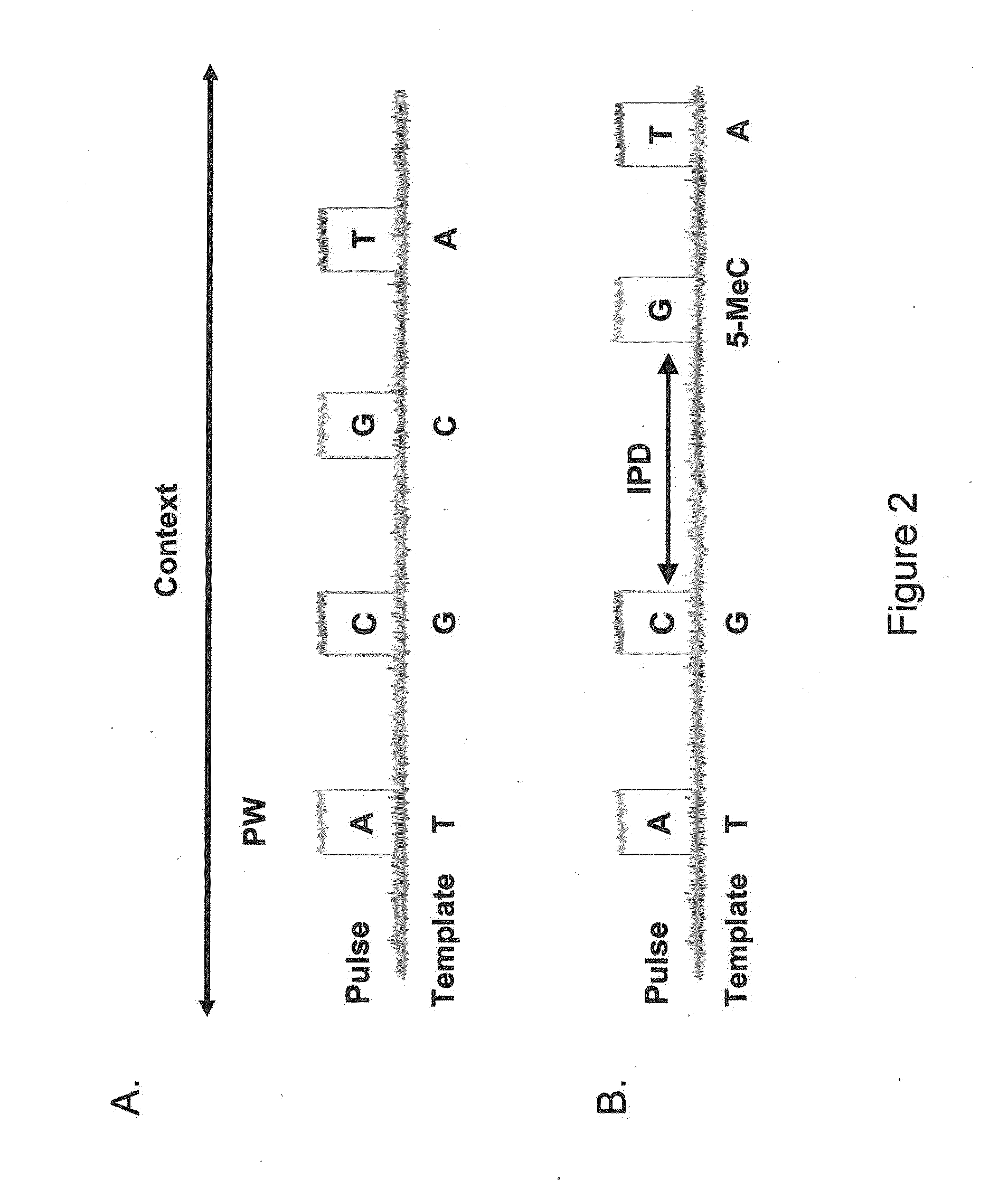
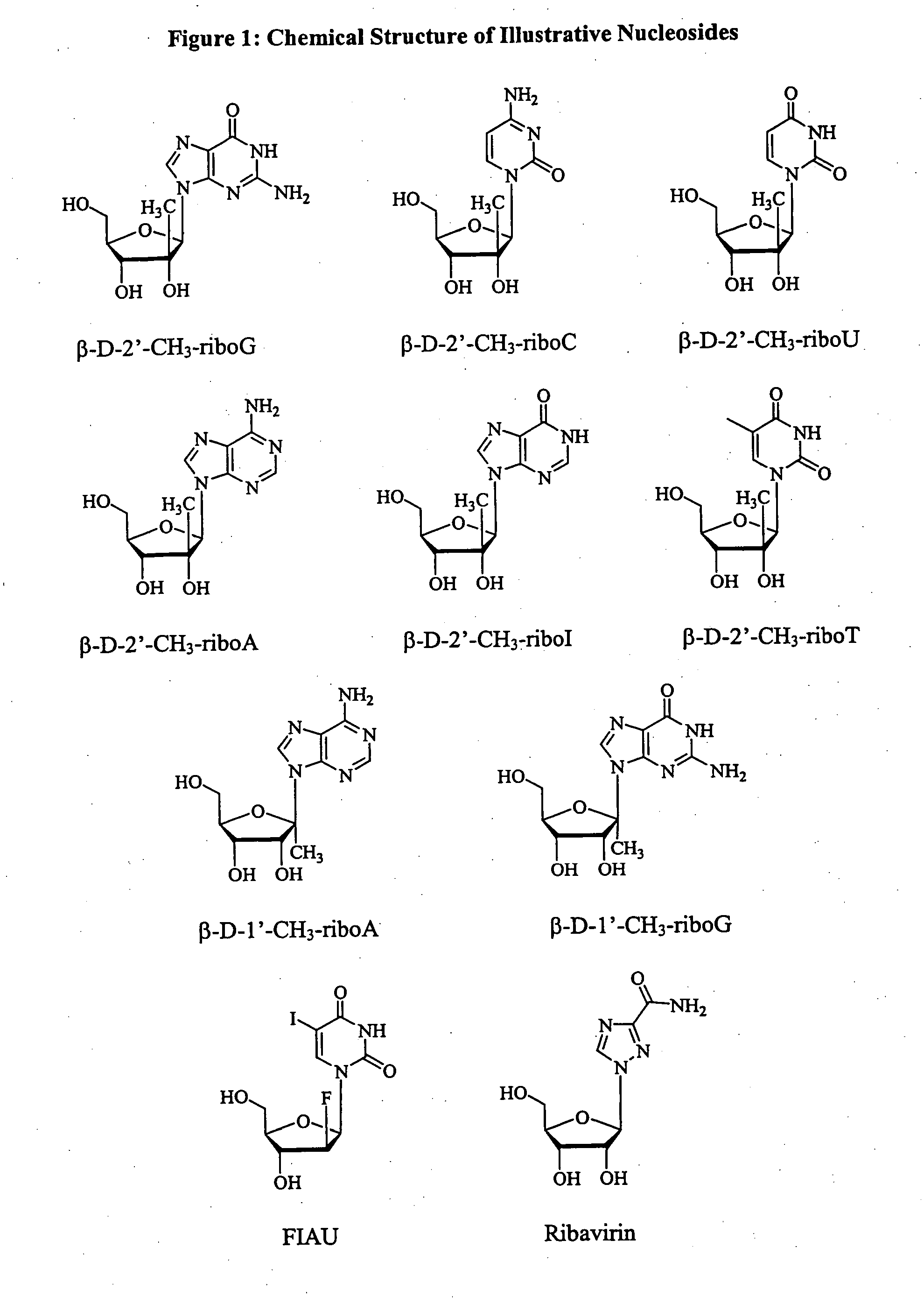
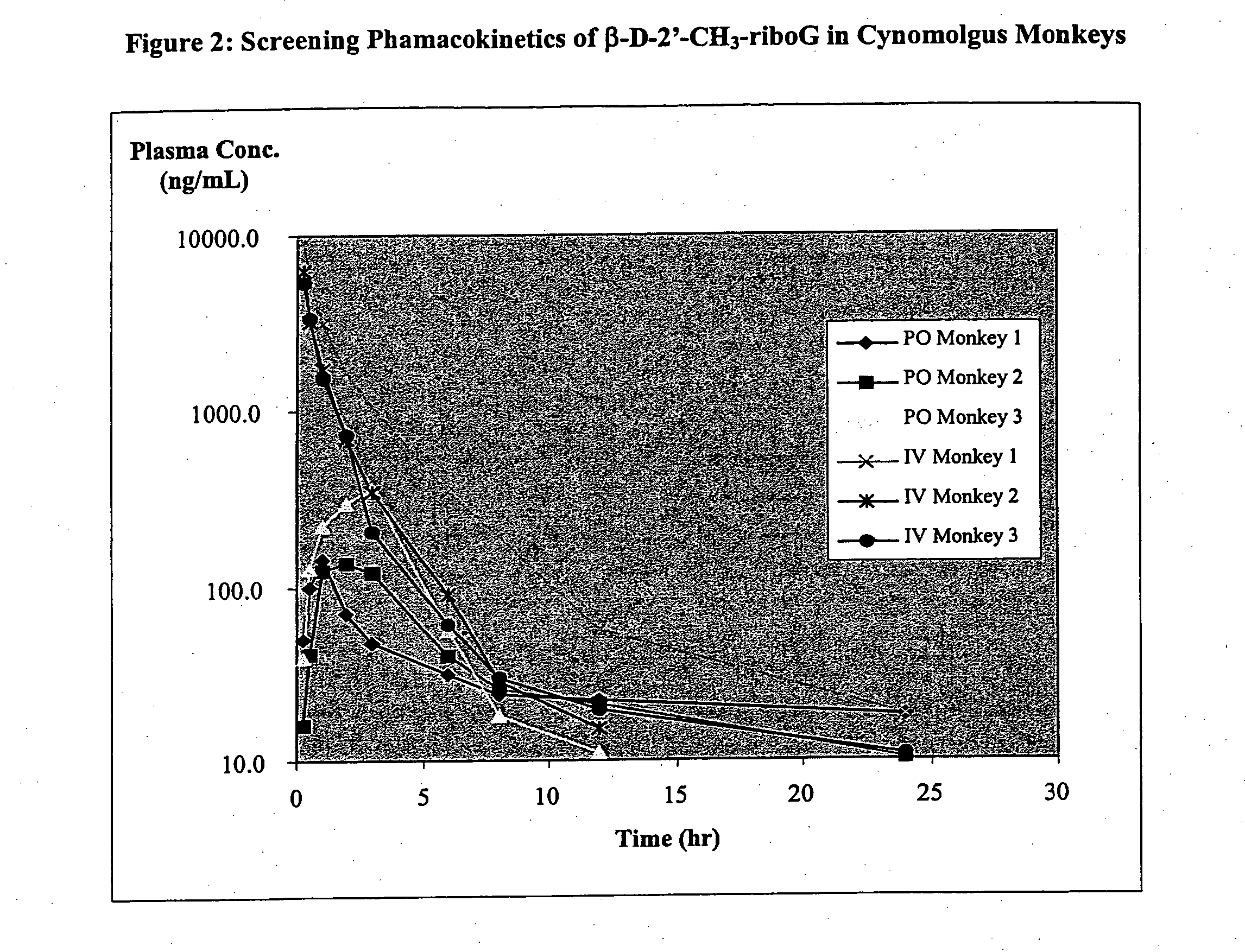
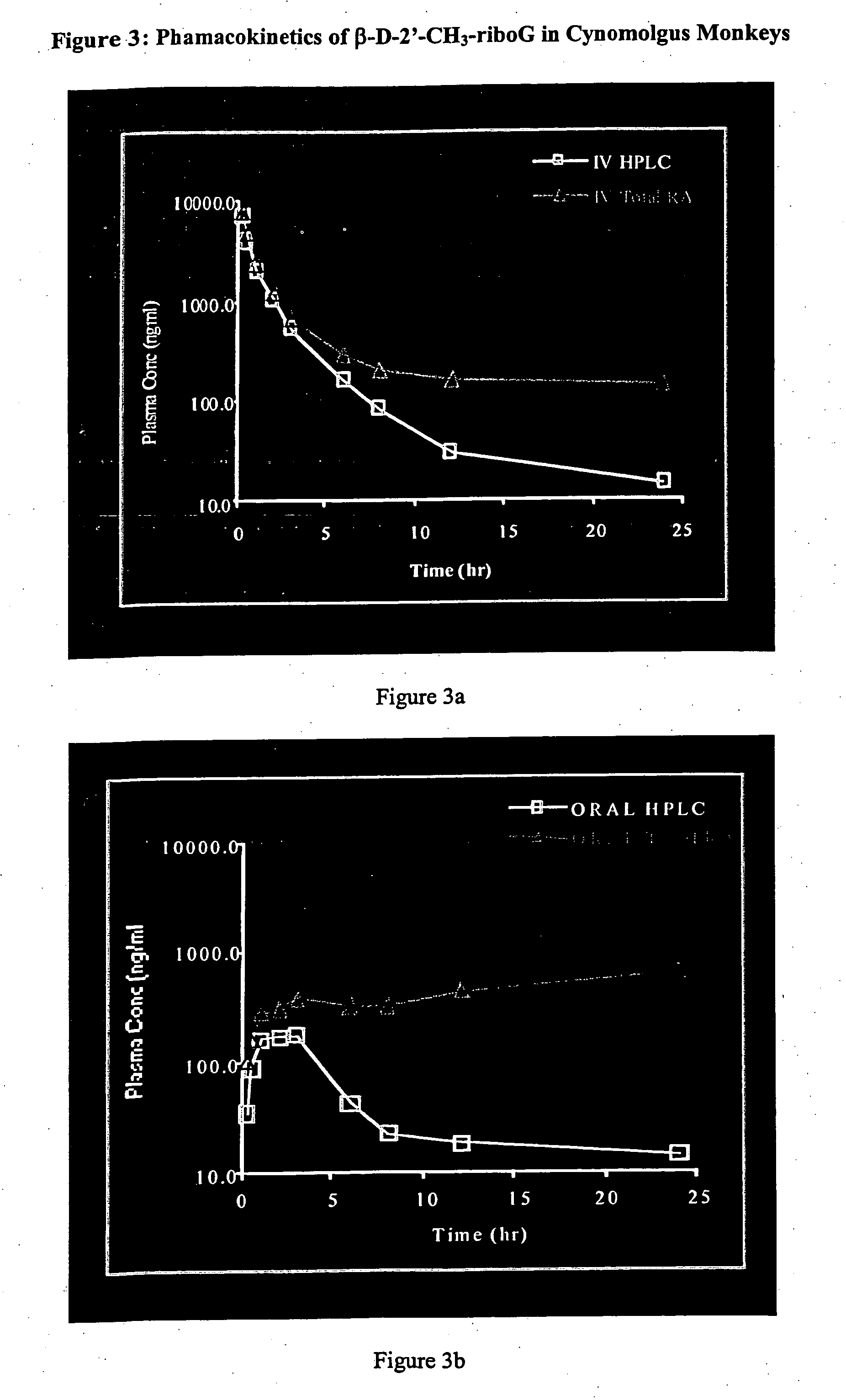
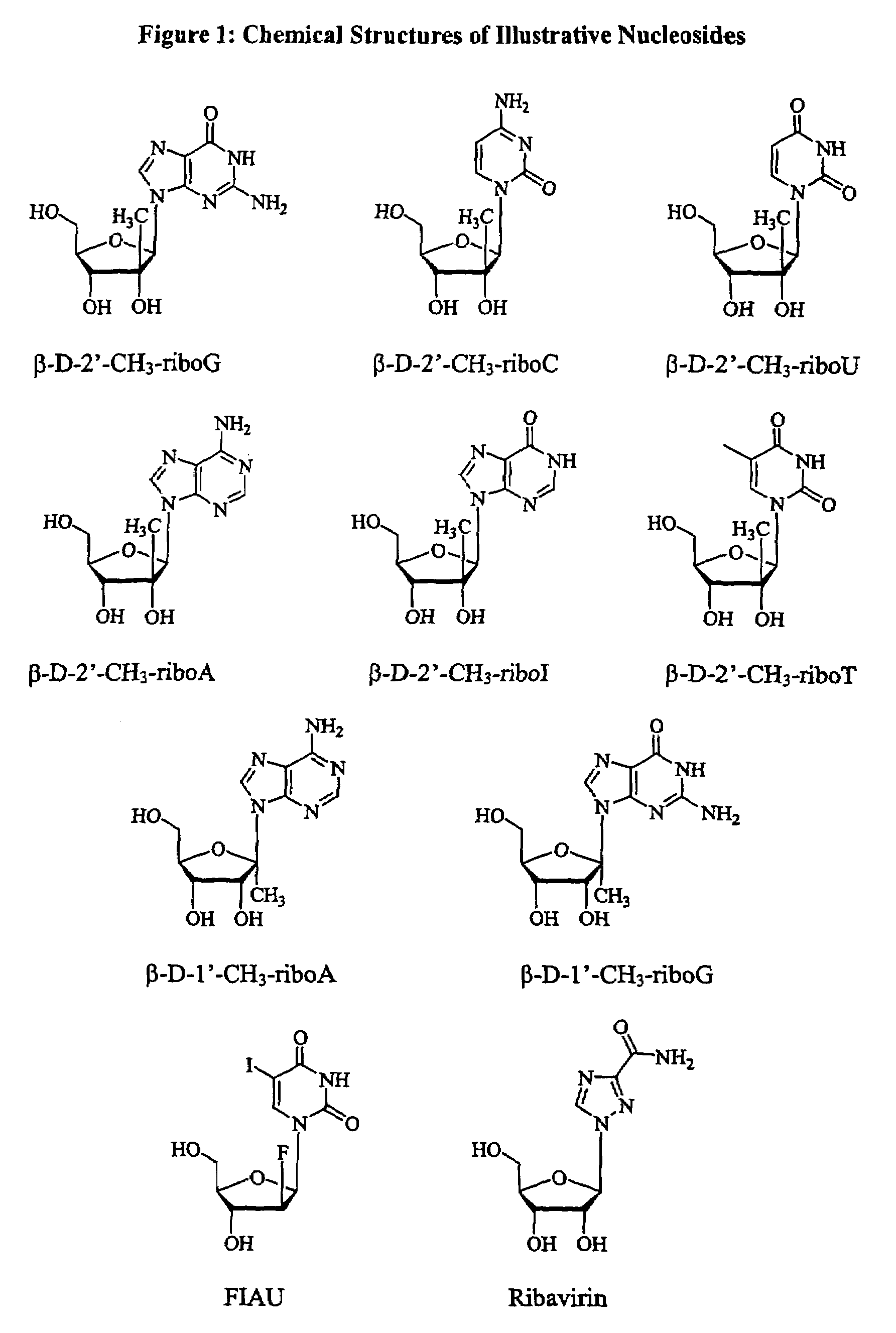
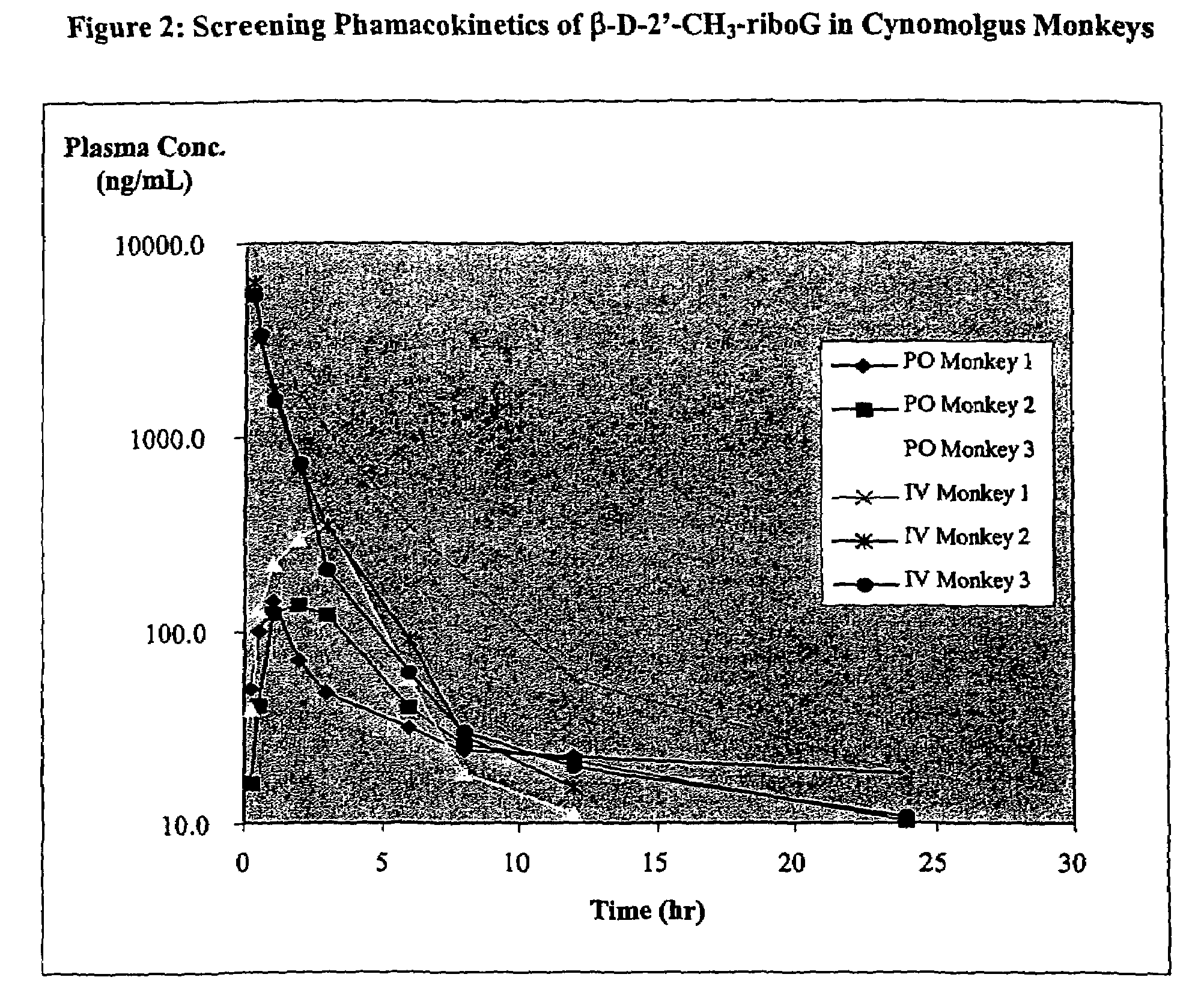
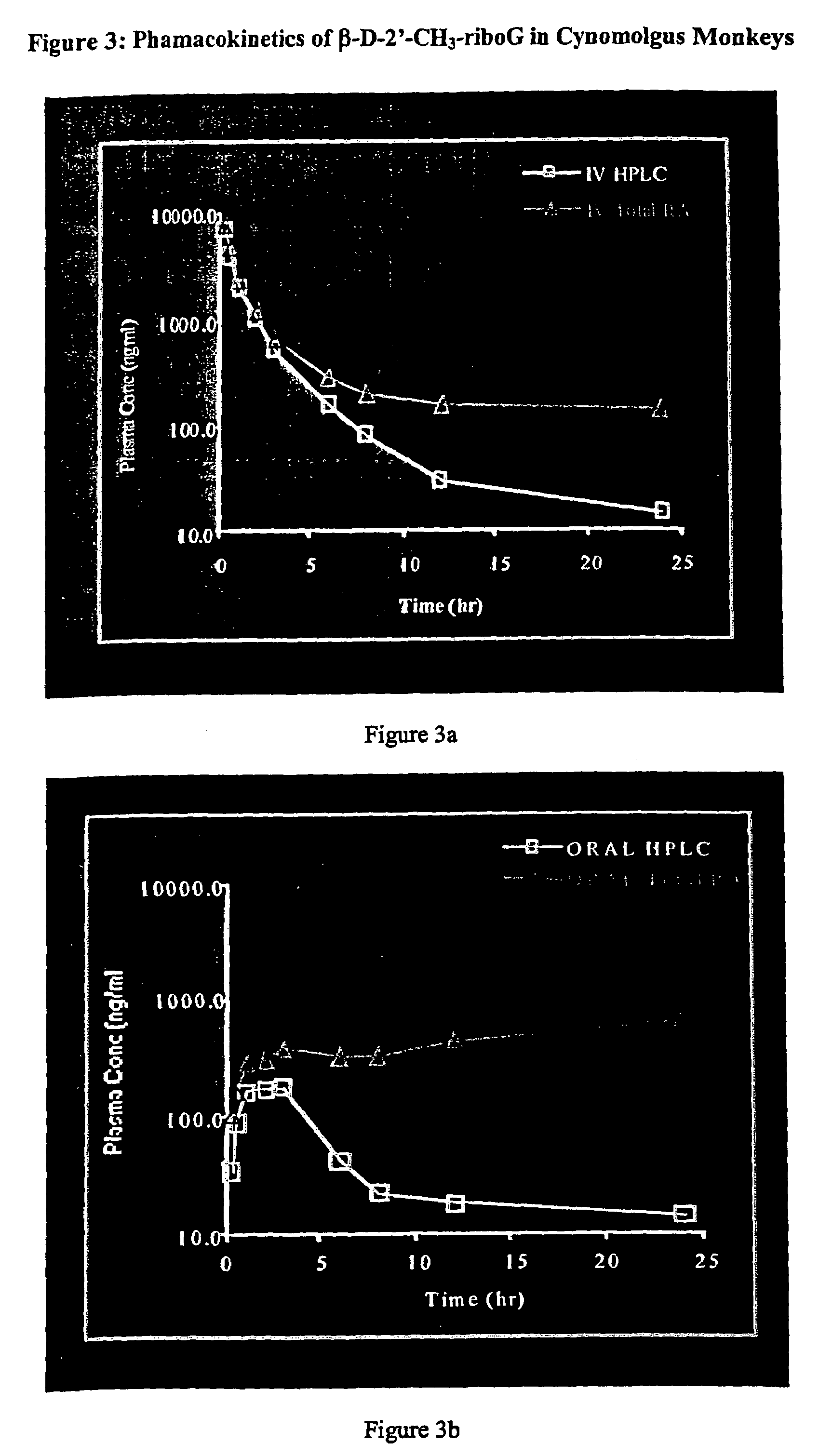
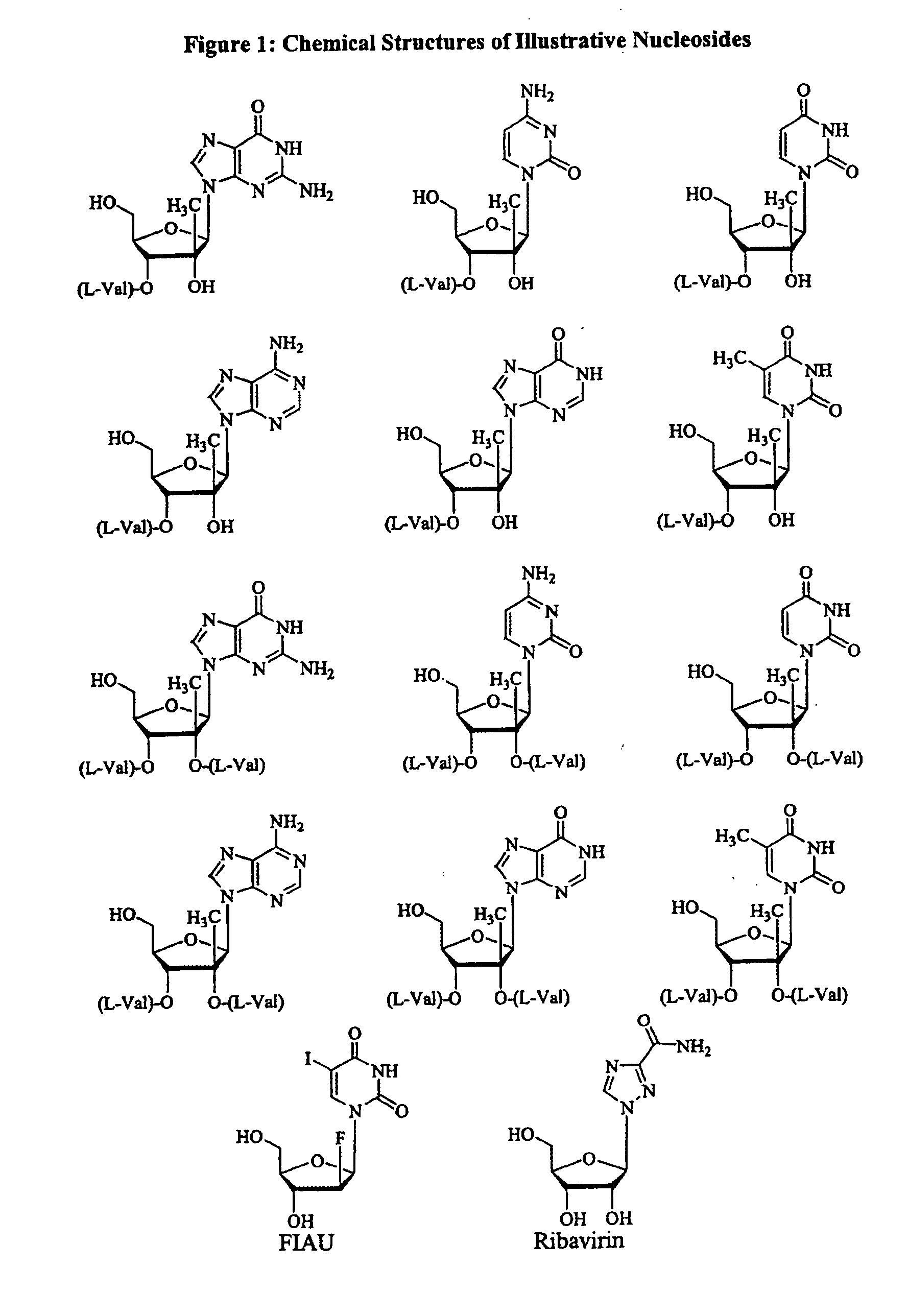
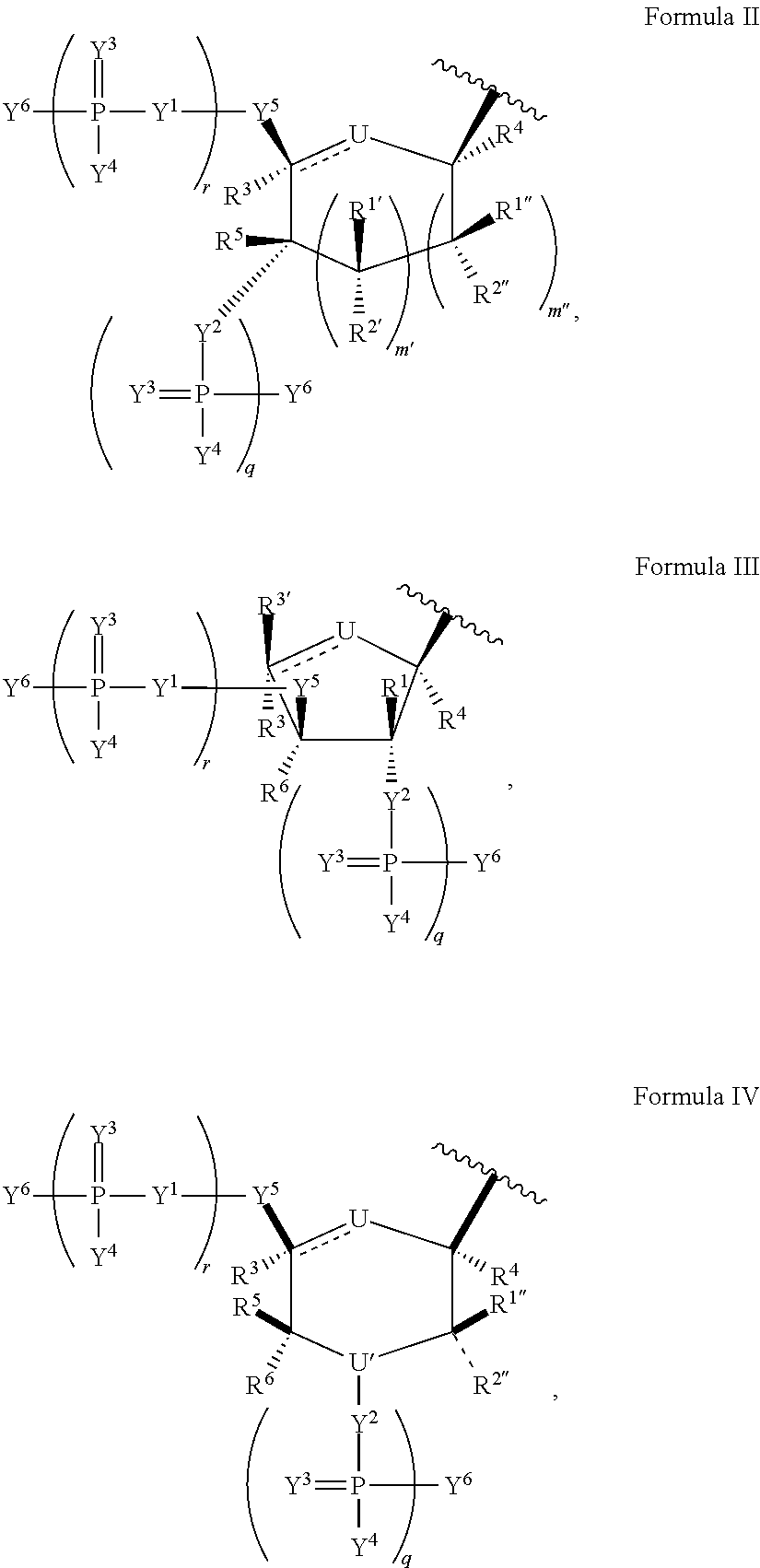
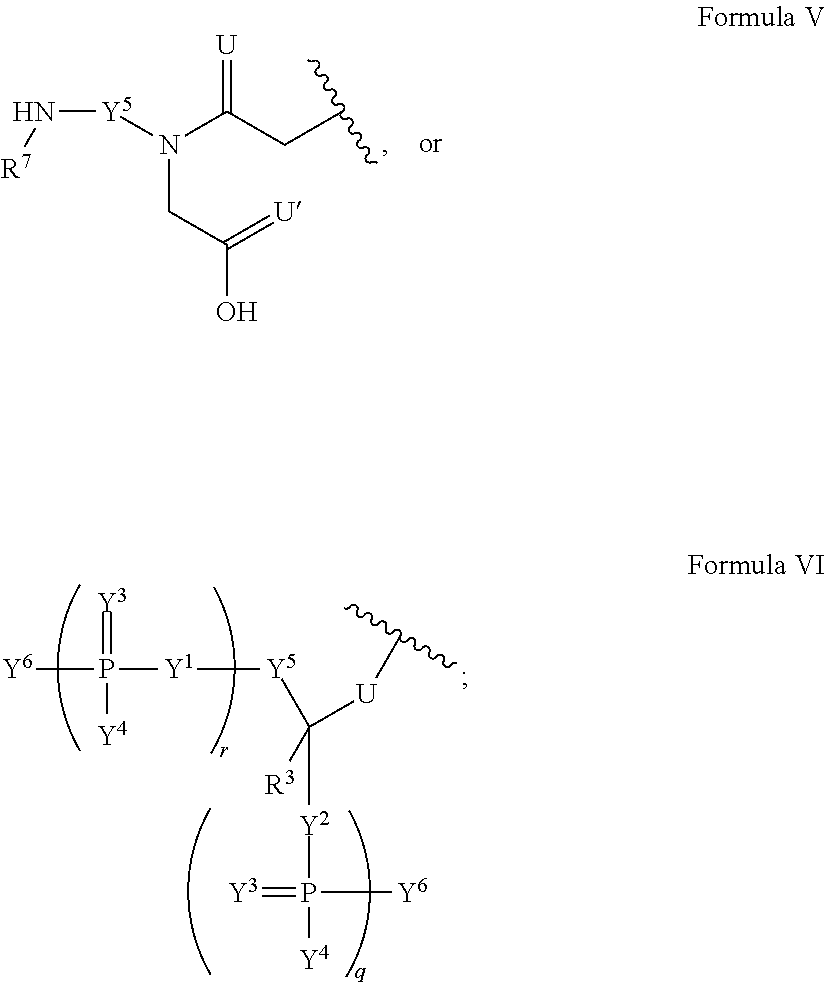
Patents
Literature
369 results about "Modified nucleosides" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
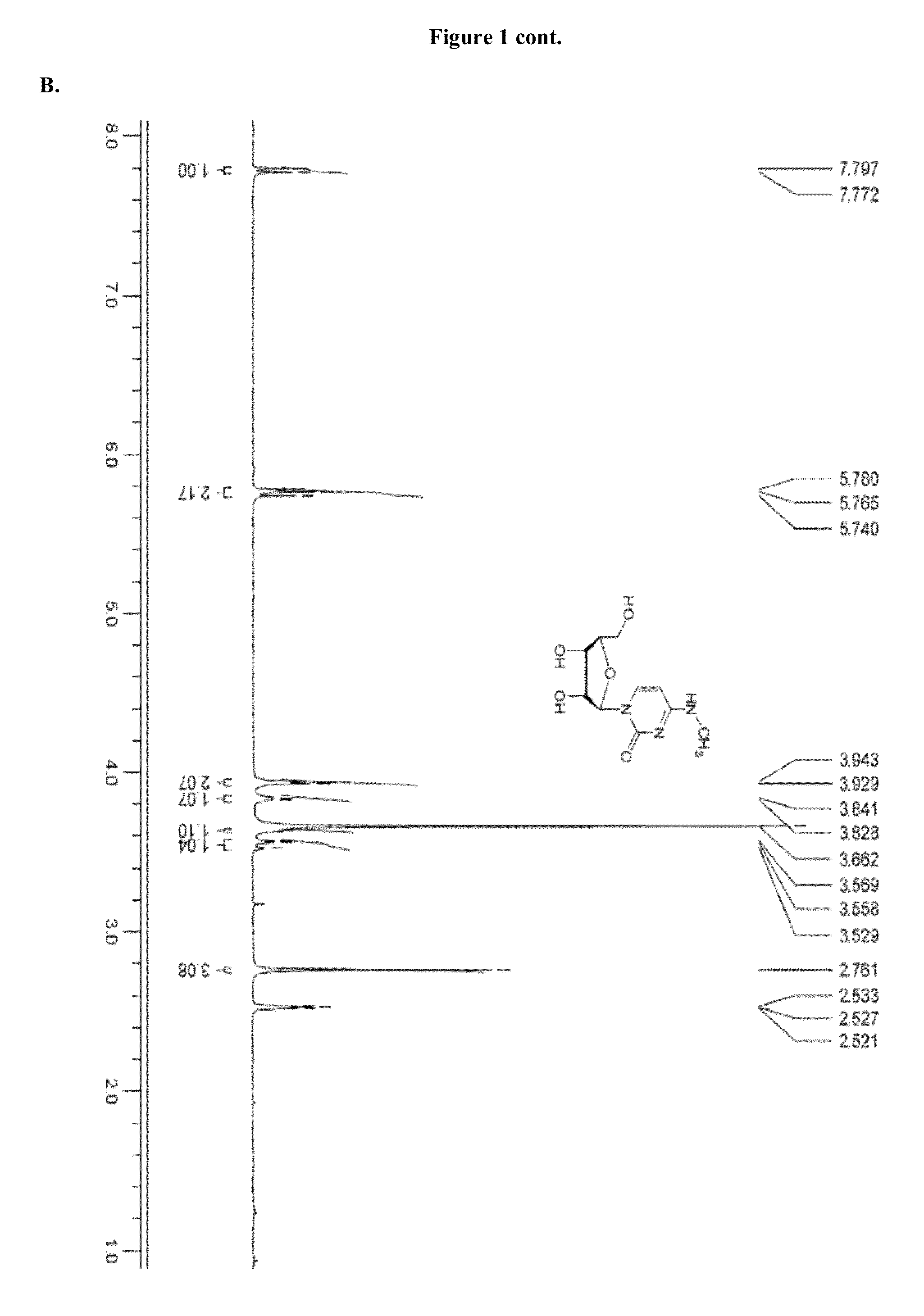
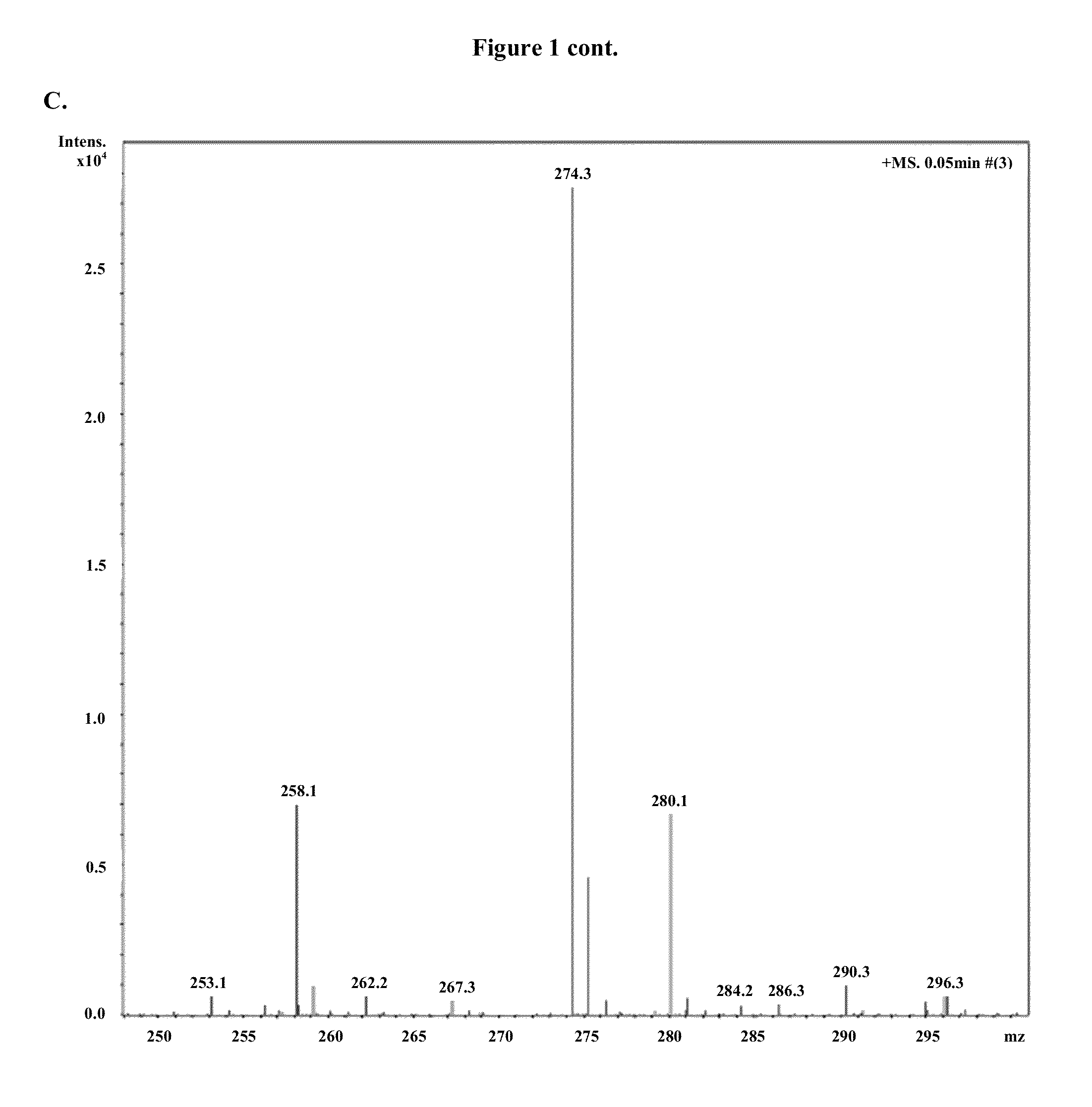
Modified nucleosides are mainly formed post-transcriptionally in tRNA, set free during RNA metabolism, and excreted in urine. Especially methylated nucleosides play an important role, as their levels are higher in urine from cancer patients. For structural elucidation of known and unknown nucleosides from urine samples of cancer patients,...
Modified nucleotide compounds
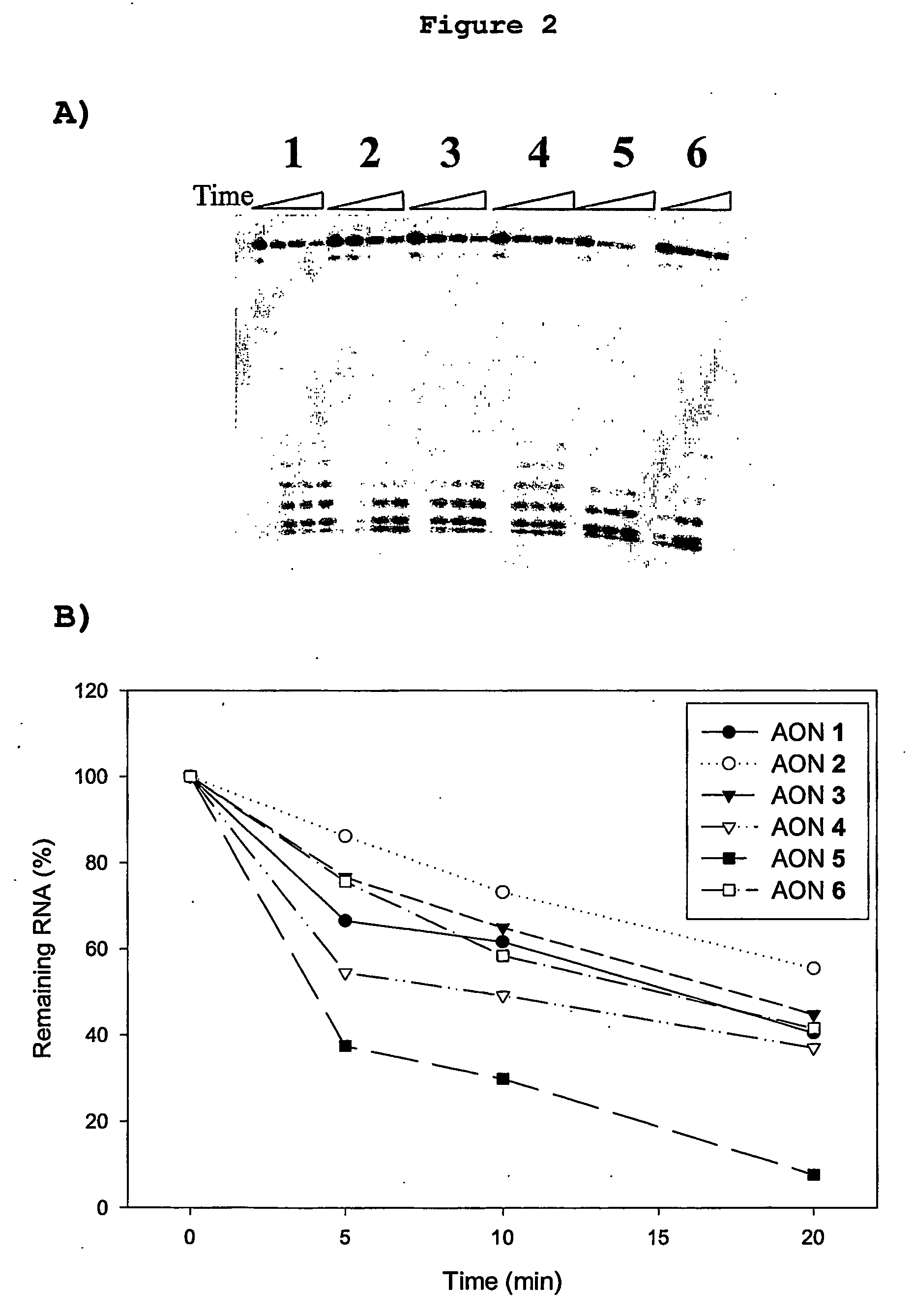
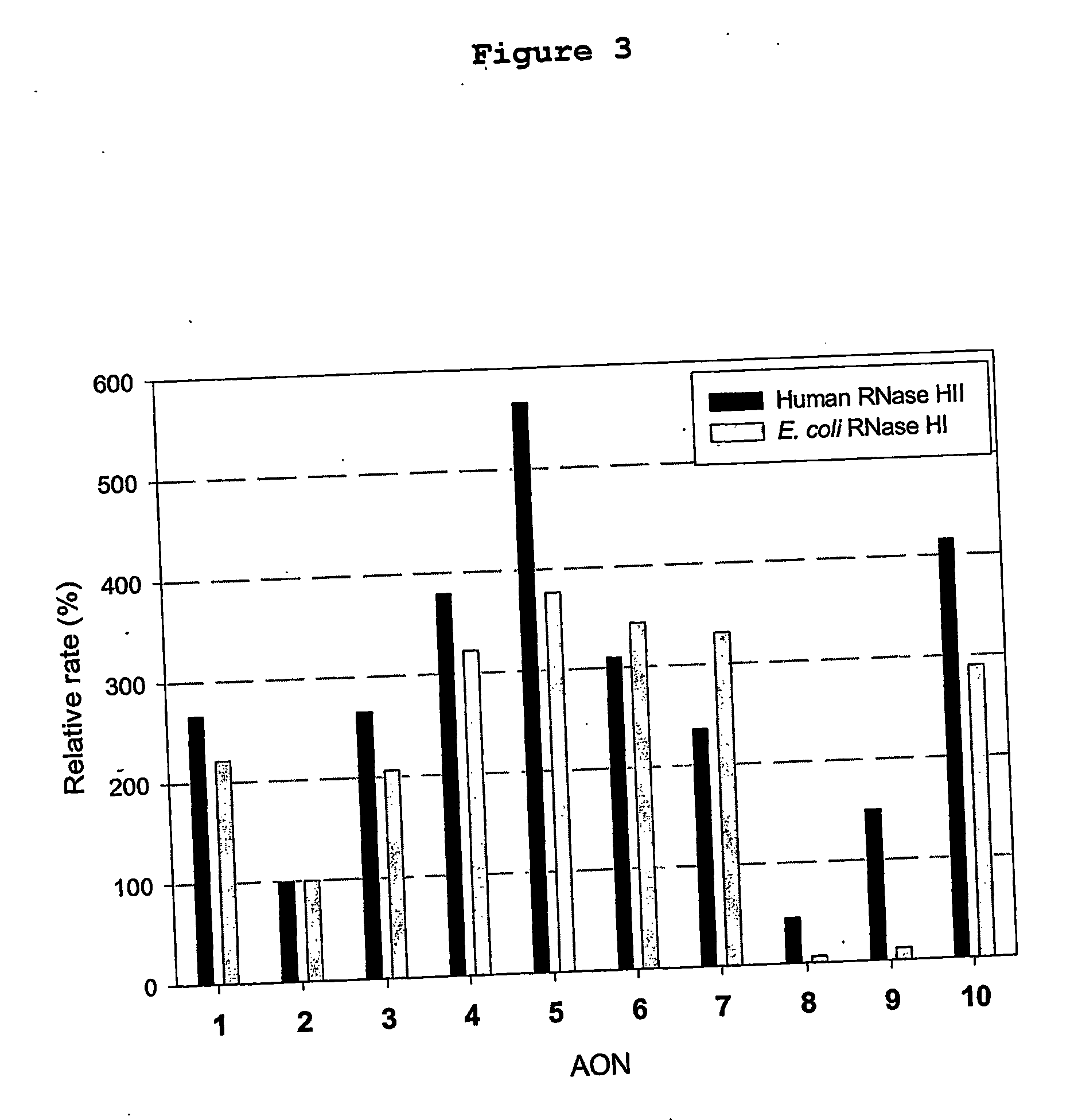
ActiveUS7495088B1Increased nuclease resistanceSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiologyModified nucleosides
Disclosed is a nuclease resistant nucleotide compound capable of hybridizing with a complementary RNA in a manner which inhibits the function thereof, which modified nucleotide compound includes at least one component selected from the group consisting of MN3M, B(N)xM and M(N)xB wherein N is a phosphodiester-linked modified 2′-deoxynucleoside moiety; M is a moiety that confers endonuclease resistance on said component and that contains at least one modified or unmodified nucleic acid base; B is a moiety that confers exonuclease resistance to the terminus to which it is attached; and x is an integer of at least 2.
Owner:ENZO BIOCHEM
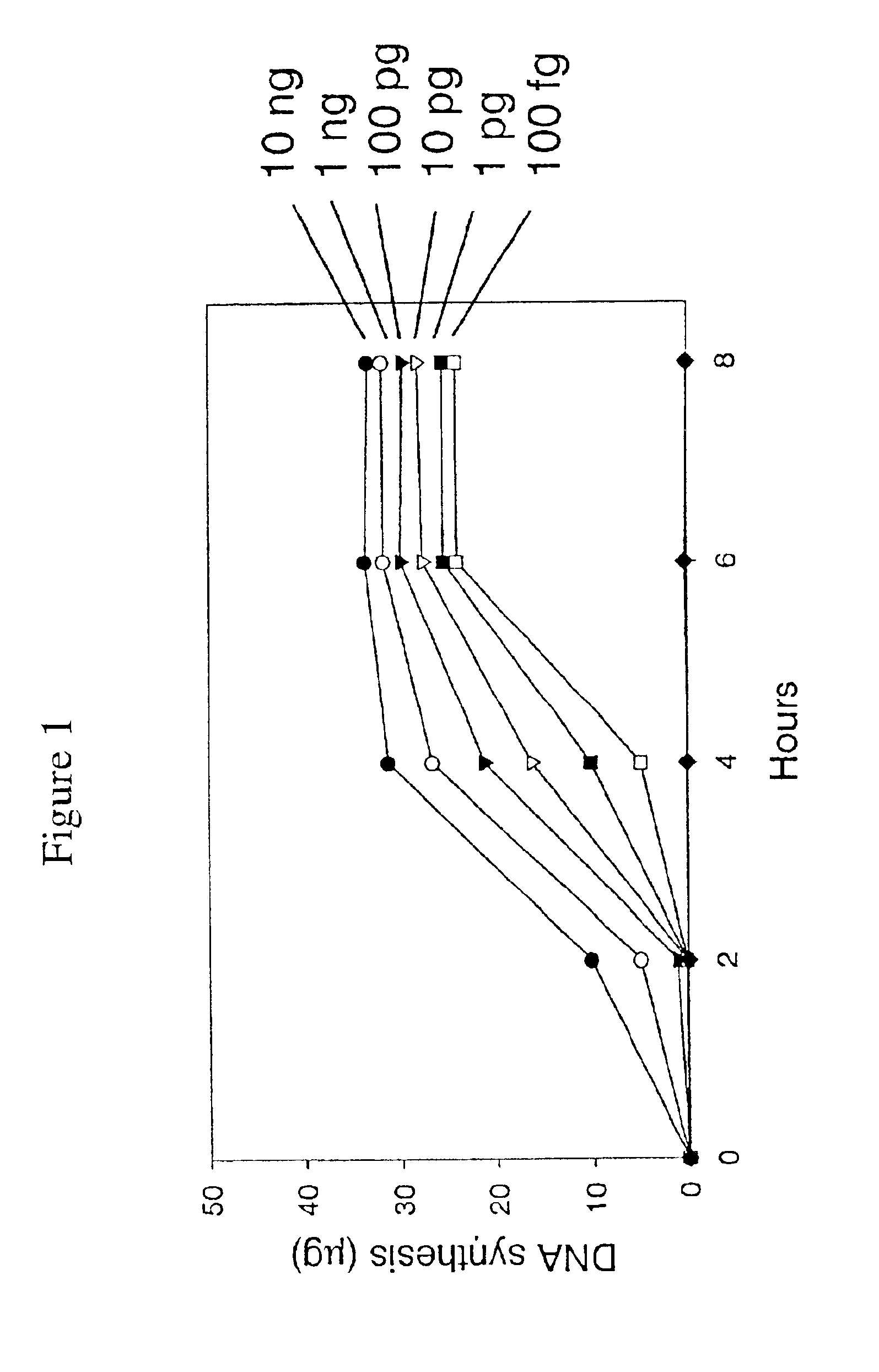
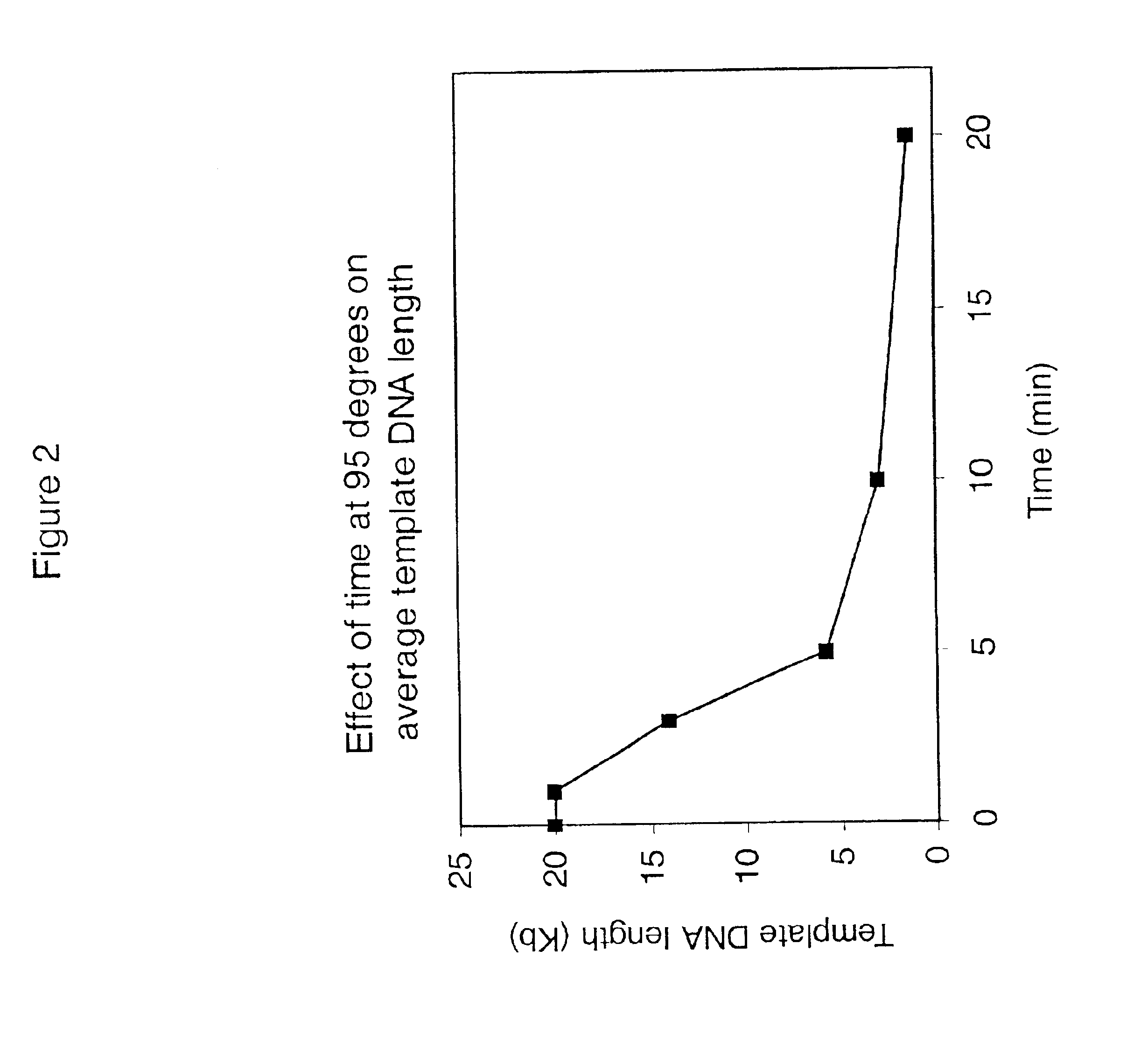
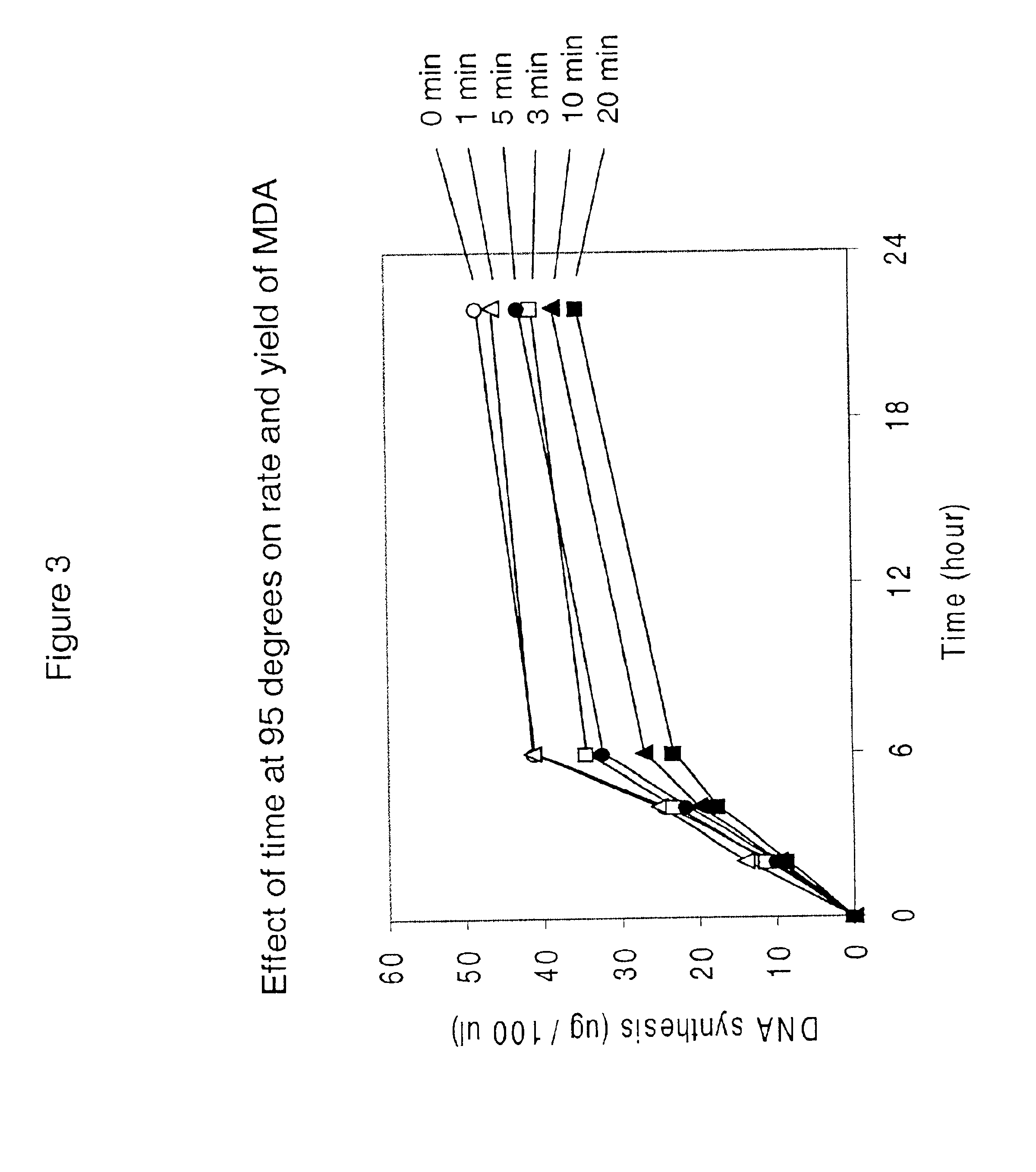
Multiple displacement amplification
InactiveUS6977148B2Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNucleotideGenomic DNA
Disclosed are compositions and a method for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest. The disclosed method generally involves replication of a target sequence such that, during replication, the replicated strands are displaced from the target sequence by strand displacement replication of another replicated strand. In one form of the disclosed method, the target sample is not subjected to denaturing conditions. It was discovered that the target nucleic acids, genomic DNA, for example, need not be denatured for efficient multiple displacement amplification. The primers used can be hexamer primers. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the primers are nuclease resistant. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the melting temperature of the primer is altered relative to a primer of the same sequence without the modified nucleotide(s). The DNA polymerase can be φ29 DNA polymerase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
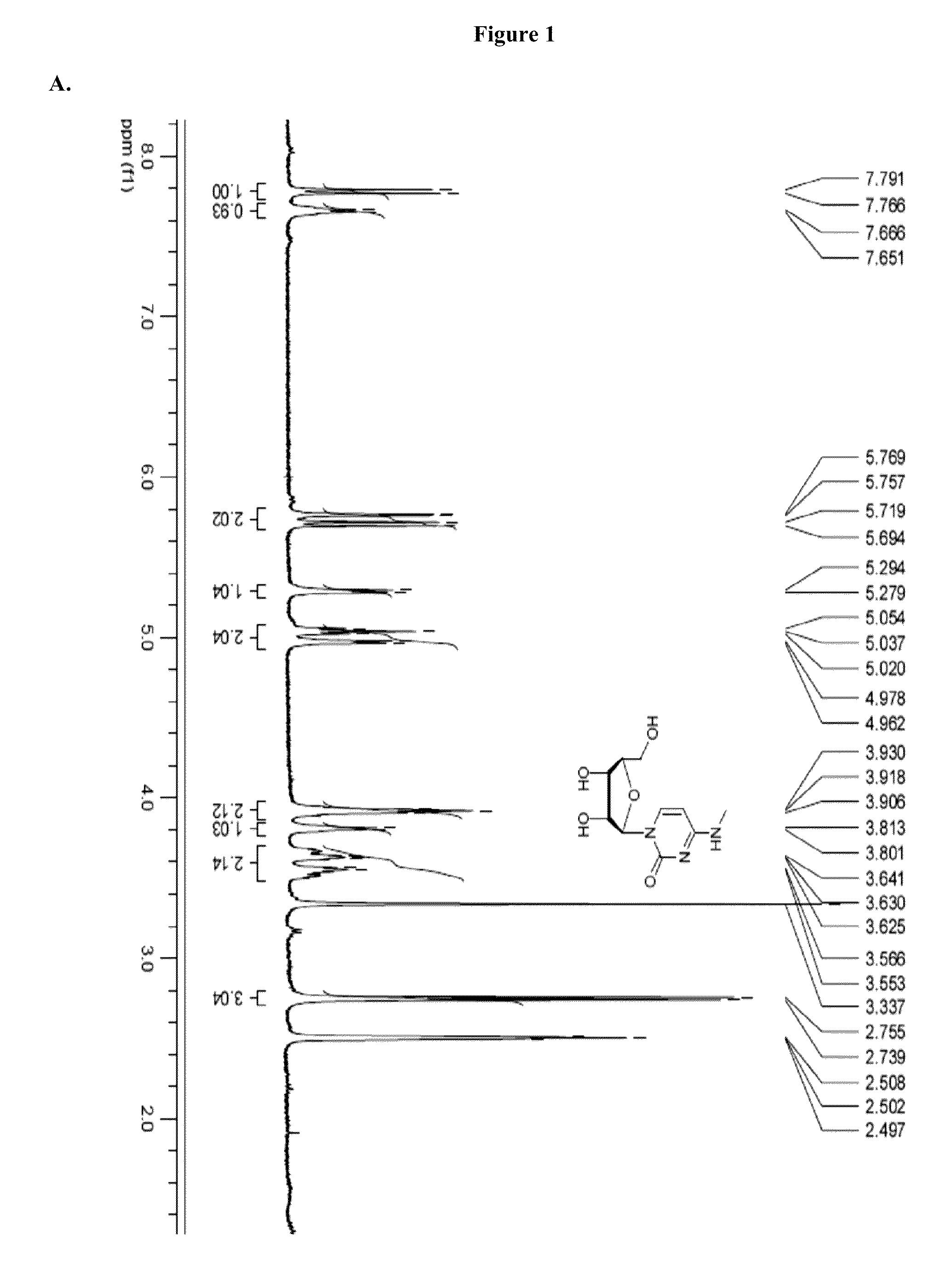
Modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and uses thereof
ActiveUS20130115272A1Reduce innate immune responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsNucleotideModified nucleosides
The present disclosure provides modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and methods of using them.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Modified nucleoside, nucleotide, and nucleic acid compositions
InactiveUS20130156849A1Therapeutically effectiveRaise hemoglobinOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryProtein precursorNucleotide
The present disclosure provides, inter alia, formulation compositions comprising modified nucleic acid molecules which may encode a protein, a protein precursor, or a partially or fully processed form of the protein or a protein precursor. The formulation composition may further include a modified nucleic acid molecule and a delivery agent. The present invention further provides nucleic acids useful for encoding polypeptides capable of modulating a cell's function and / or activity.
Owner:MODERNA THERAPEUTICS INC
New sequencing method for sequencing rna molecules
InactiveUS20060166203A1Reduce decreaseMicrobiological testing/measurementReverse transcriptaseNucleotide
The present invention provides a method for determination of the identity of at least one nucleotide in a RNA-molecule comprising the steps of: (i) providing the RNA-molecule, an oligonucleotide primer binding to a predetermined position of the RNA molecule, a reverse transcriptase, deoxynucleotides and other necessary reagents, in a reaction vessel; (ii) performing a primer extension reaction, whereby the oligonucleotide primer is extended on the RNA-molecule through incorporation of at least one deoxynucleotide by the action of a reverse transcriptase, resulting in the release of a PPi molecule only upon incorporation of a deoxynucleotide; and (iii) detecting the presence or absence of incorporation, thereby indicating the nucleotide identity of the RNA molecule in the relevant position. In a preferred embodiment, the sequencing of the invention is coupled to the Pyrosequencing™ reaction. A variant of the method employs incorporation of modified nucleotides, with an optionally cleavable linker arm to which is attached a label.
Owner:TOOKE NIGEL
Materials and methods for the generation of fully 2'-modified nucleic acid transcripts
ActiveUS20070117112A1Increase productionImprove transcript yieldBacteriaSugar derivativesModified nucleosidesNucleic acid
Materials and methods are provided for producing aptamer therapeutics having fully modified nucleotide triphosphates incorporated into their sequence.
Owner:ARCHEMIX CORP
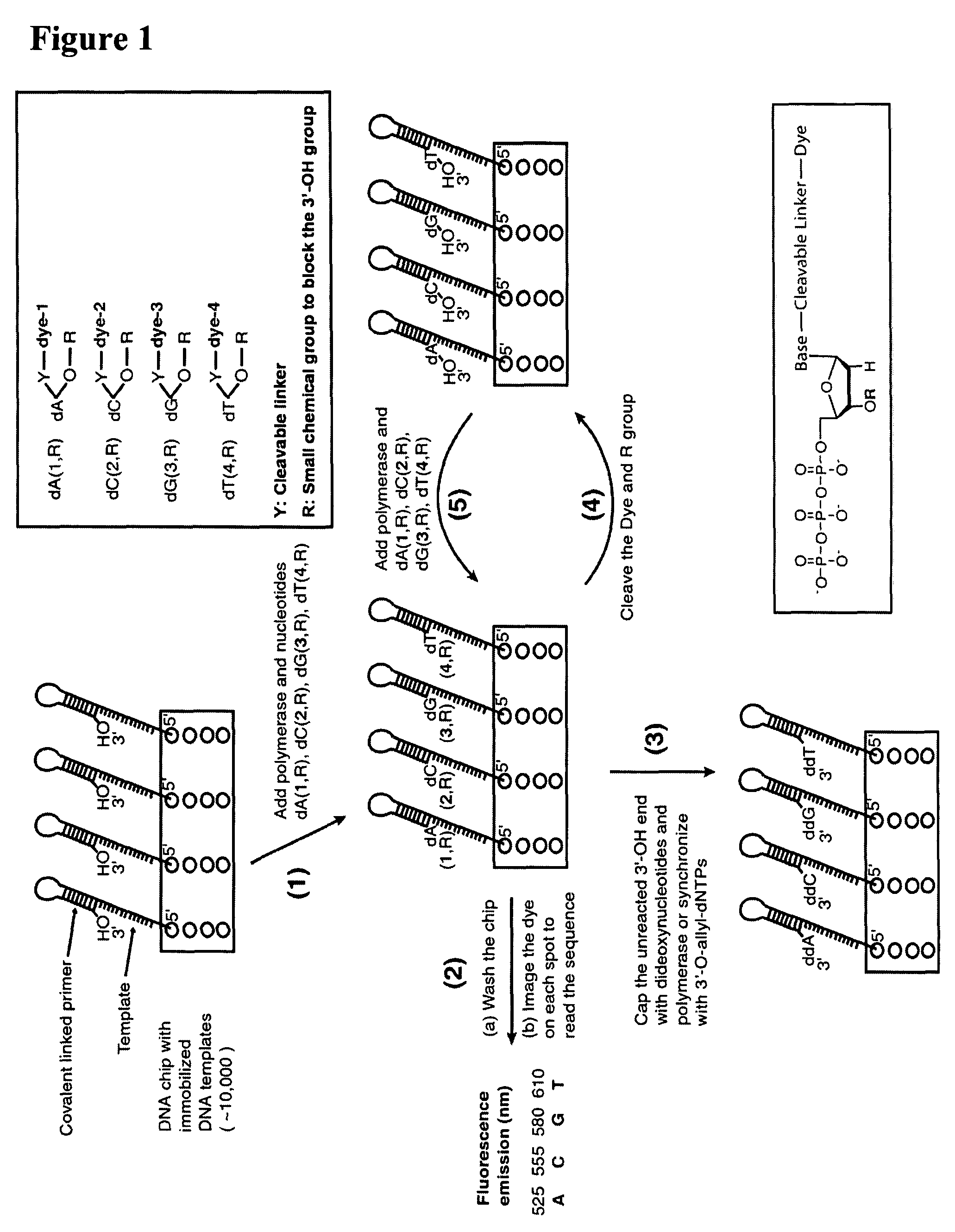
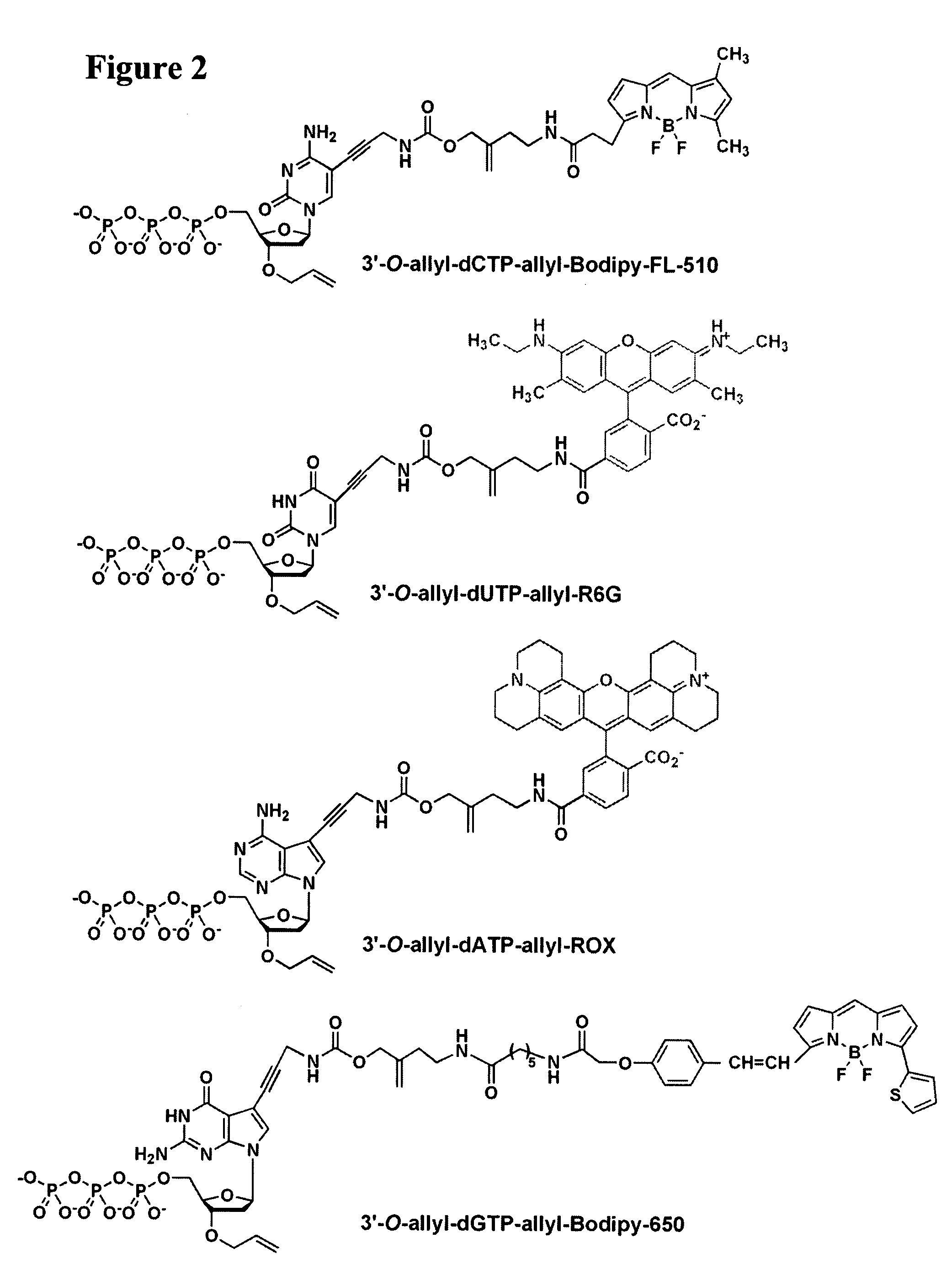
Four-color DNA sequencing by synthesis using cleavable fluorescent nucleotide reversible terminators
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
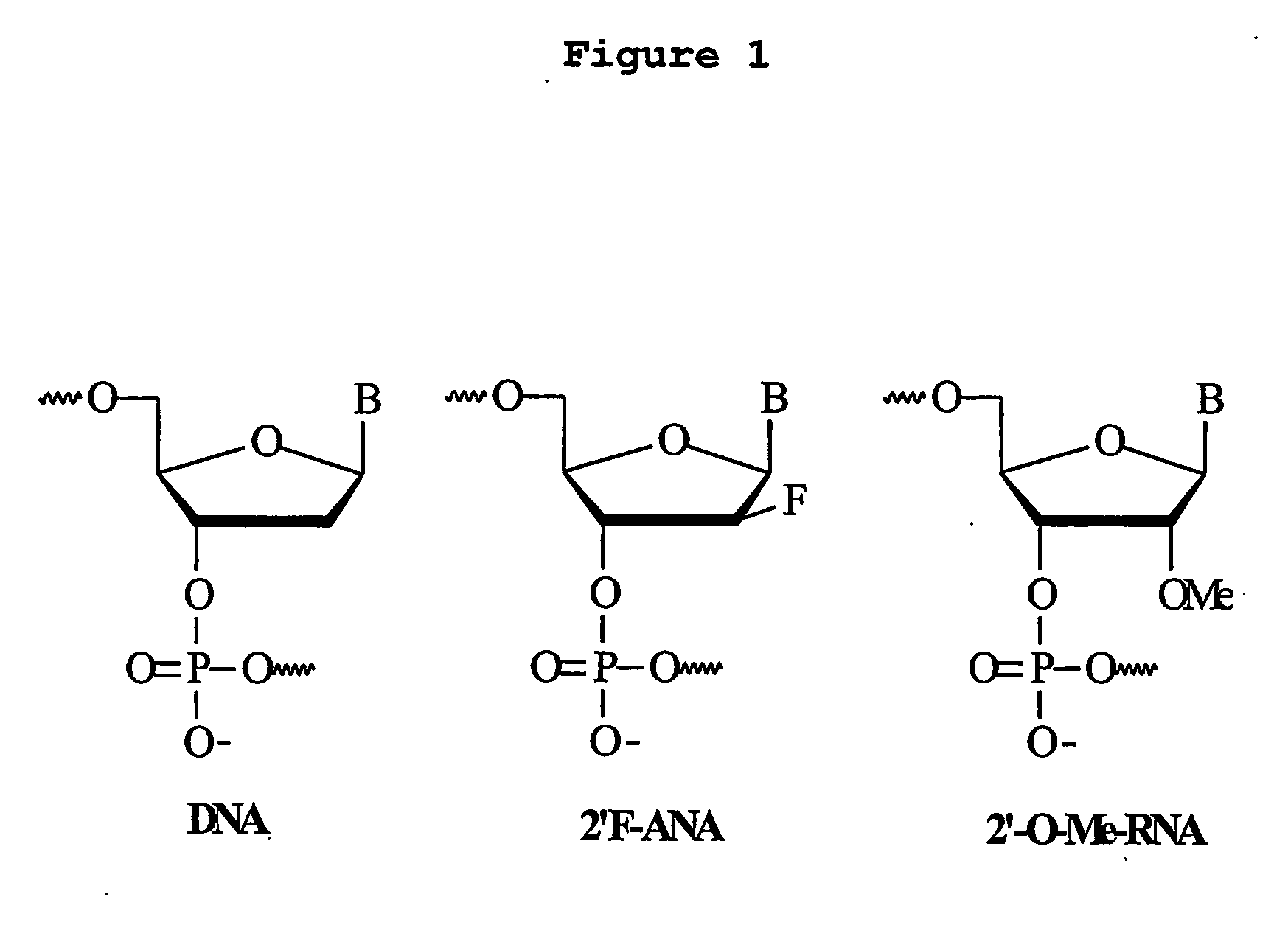
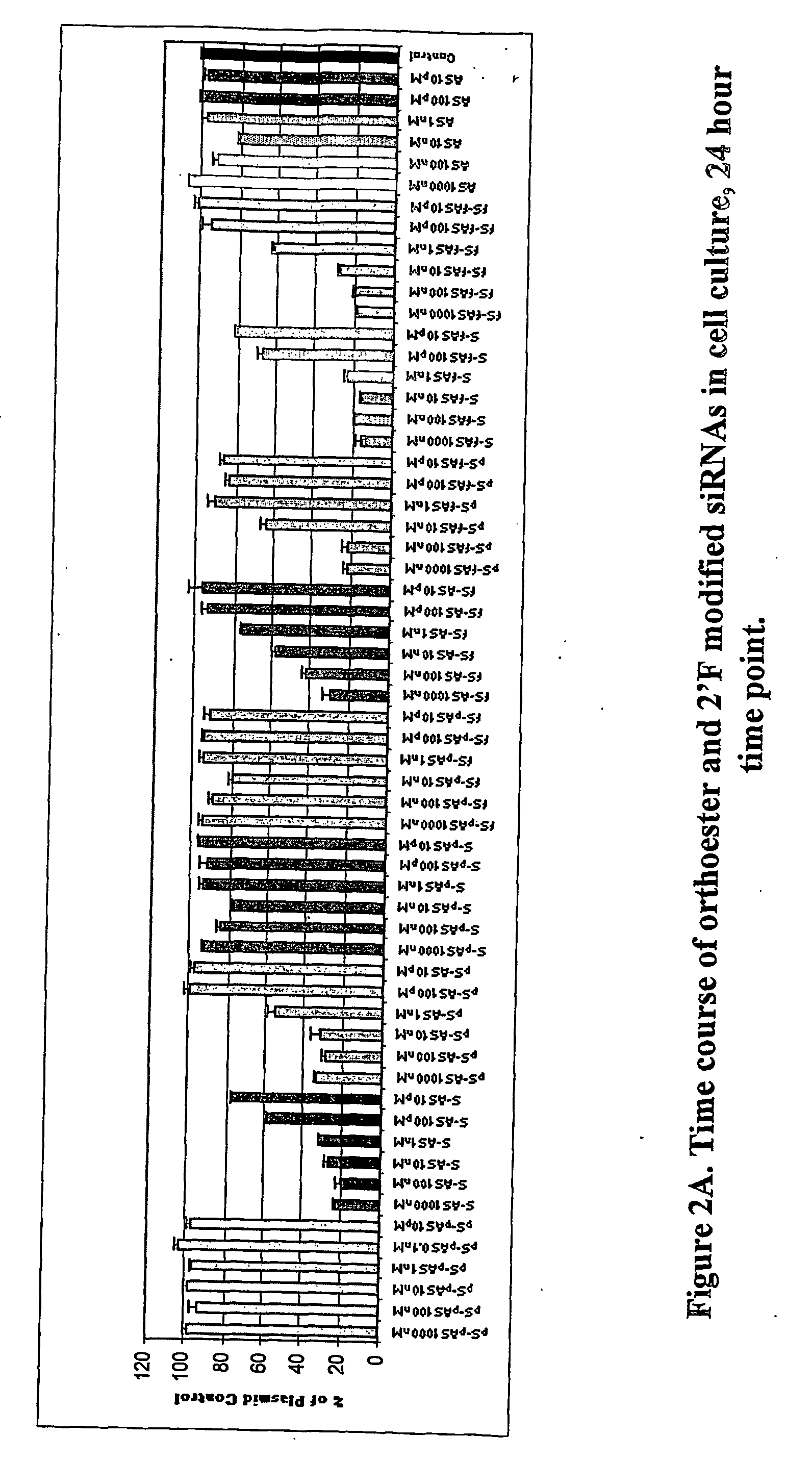
2'-f modified RNA interference agents
InactiveUS20110269814A1Inhibit expressionSuppress gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideSense strand
This invention relates to a method of modulating the expression of a target gene in an organism comprising administering an iRNA agent, wherein the iRNA comprises at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide in the antisense strand and at least one modified nucleotide in the sense strand. The invention also relates to compositions comprising a single-stranded oligonucleotide that contains at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide. siRNA molecule containing these oligonucleotides have decreased immunogenicity.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and methods of using them.
Owner:MODERNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Modified nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof
ActiveUS7592435B2Increase brightnessHigh fluorescence intensitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotidePurine
The invention is directed to modified guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides and uses thereof. More specifically, the invention relates to modified fluorescently labelled guanine-containing nucleosides and nucleotides which exhibit enhanced fluorophore intensity by virtue of reduced quenching effects.
Owner:ILLUMINA CAMBRIDGE LTD
Classification of nucleic acid templates
ActiveUS20110183320A1Convenient introductionImprove responseMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProtein secondary structure
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. In certain preferred embodiments, single molecule sequencing methods are provided for identification of modified nucleotides within nucleic acid sequences. Modifications detectable by the methods provided herein include chemically modified bases, enzymatically modified bases, abasic sites, non-natural bases, secondary structures, and agents bound to a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Methods and compositions for treating hepatitis C virus
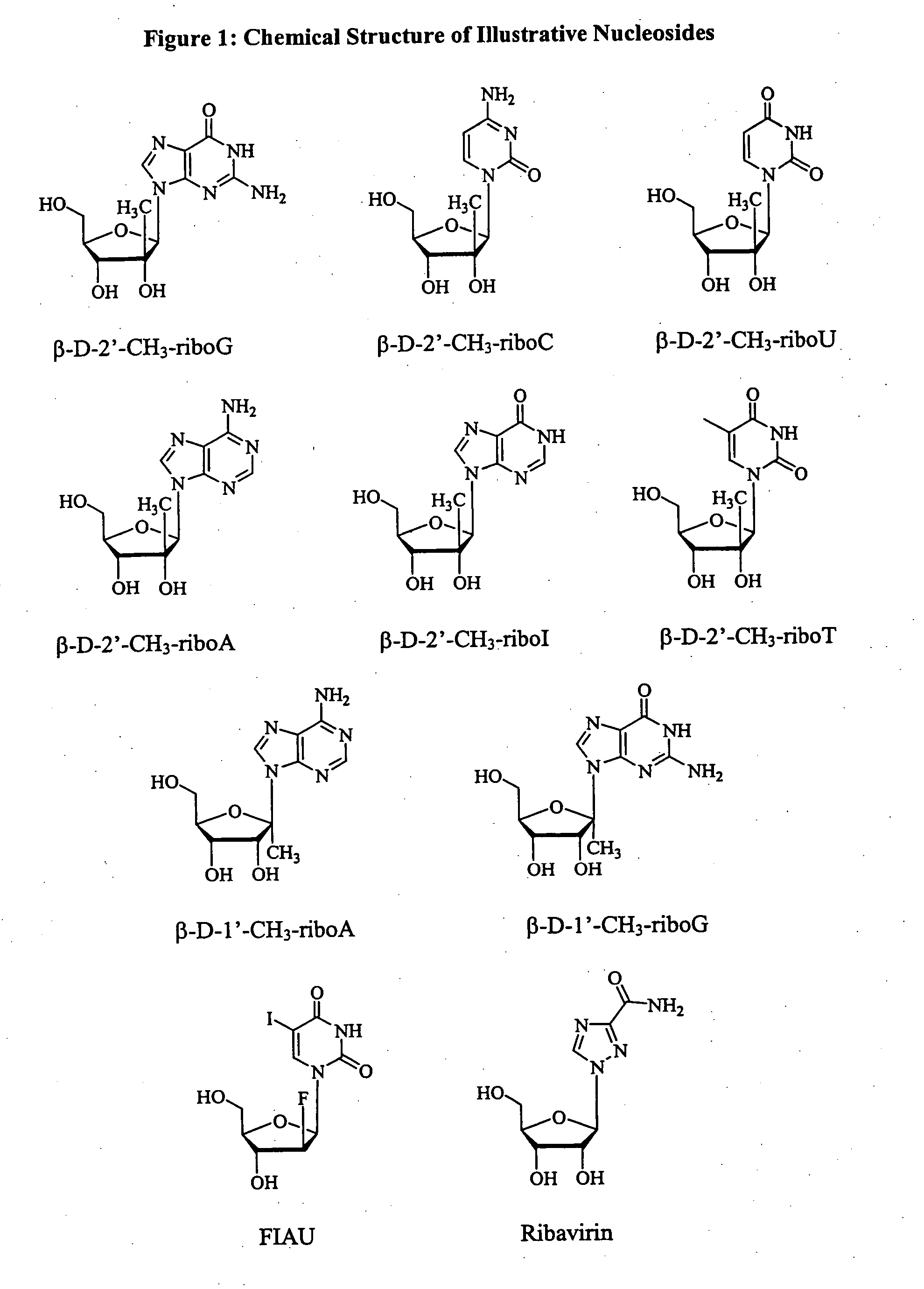
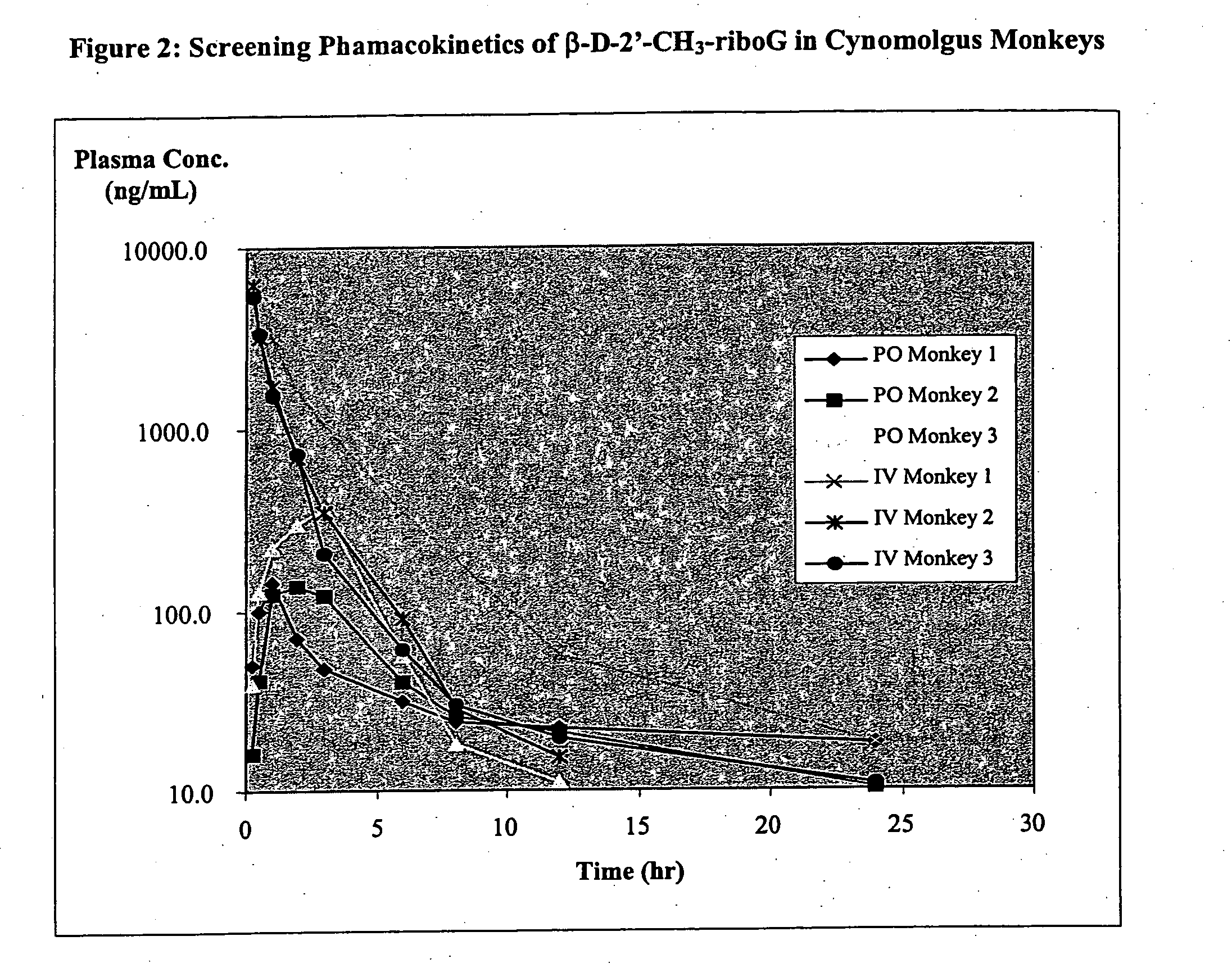
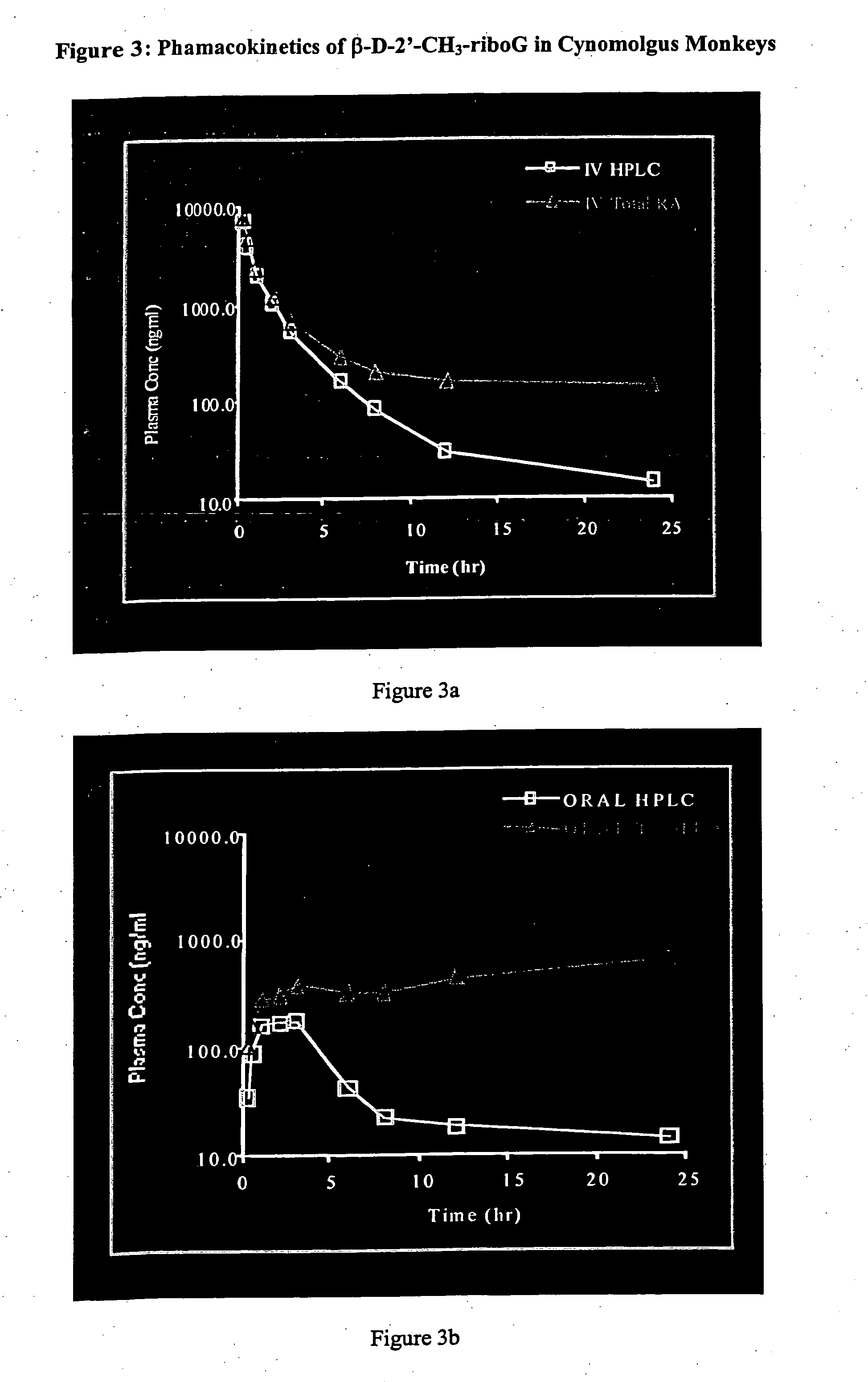
InactiveUS20050124532A1Inhibitory activityDetermine the spectrum of activityBiocideSugar derivativesHepatitisModified nucleosides
A method and composition for treating a host infected with hepatitis C comprising administering an effective hepatitis C treatment amount of a described 1′, 2′ or 3′-modified nucleoside or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, is provided.
Owner:SOMMADOSSI JEAN PIERRE +1
DNA Sequencing by Nanopore Using Modified Nucleotides
ActiveUS20090298072A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideSingle strand dna
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Modified nucleic acid molecules and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and methods of using them.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Classification of Nucleic Acid Templates
ActiveUS20100221716A1High densityMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingProtein secondary structure
Methods, compositions, and systems are provided for characterization of modified nucleic acids. In certain preferred embodiments, single molecule sequencing methods are provided for identification of modified nucleotides within nucleic acid sequences. Modifications detectable by the methods provided herein include chemically modified bases, enzymatically modified bases, abasic sites, non-natural bases, secondary structures, and agents bound to a template nucleic acid.
Owner:PACIFIC BIOSCIENCES
Ogligonucleotides comprising alternating segments and uses thereof
ActiveUS20050142535A1Preventing and decreasing translationOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsSugarBiology
The invention relates to oligonucleosides having alternating segments of sugar-modified nucleosides and 2′-deoxynucleosides, and uses thereof. The invention further relates to oligonucleotides having alternating segments of sugar-modified nucleotides and 2′-deoxynucleotides, and uses thereof. Such uses include the preparation of antisense oligonucleotides and their use for the prevention or depletion of function of a target nucleic acid of interest, such as an RNA, in a system. Accordingly, an oligonucleotide of the invention is useful for therapeutic, analytical and diagnostic methods and uses, as well as a component of compositions and commercial packages corresponding to such methods and uses.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
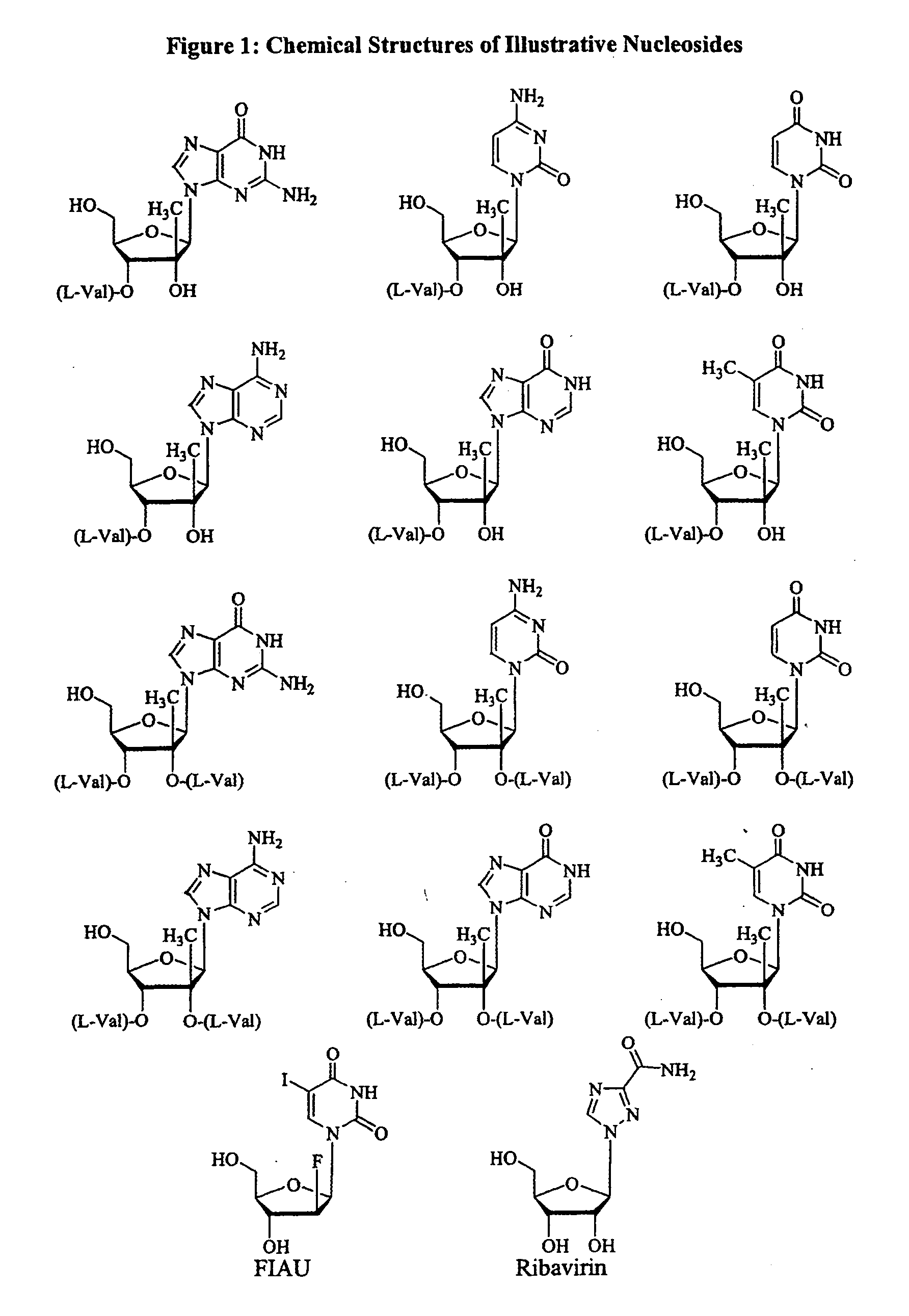
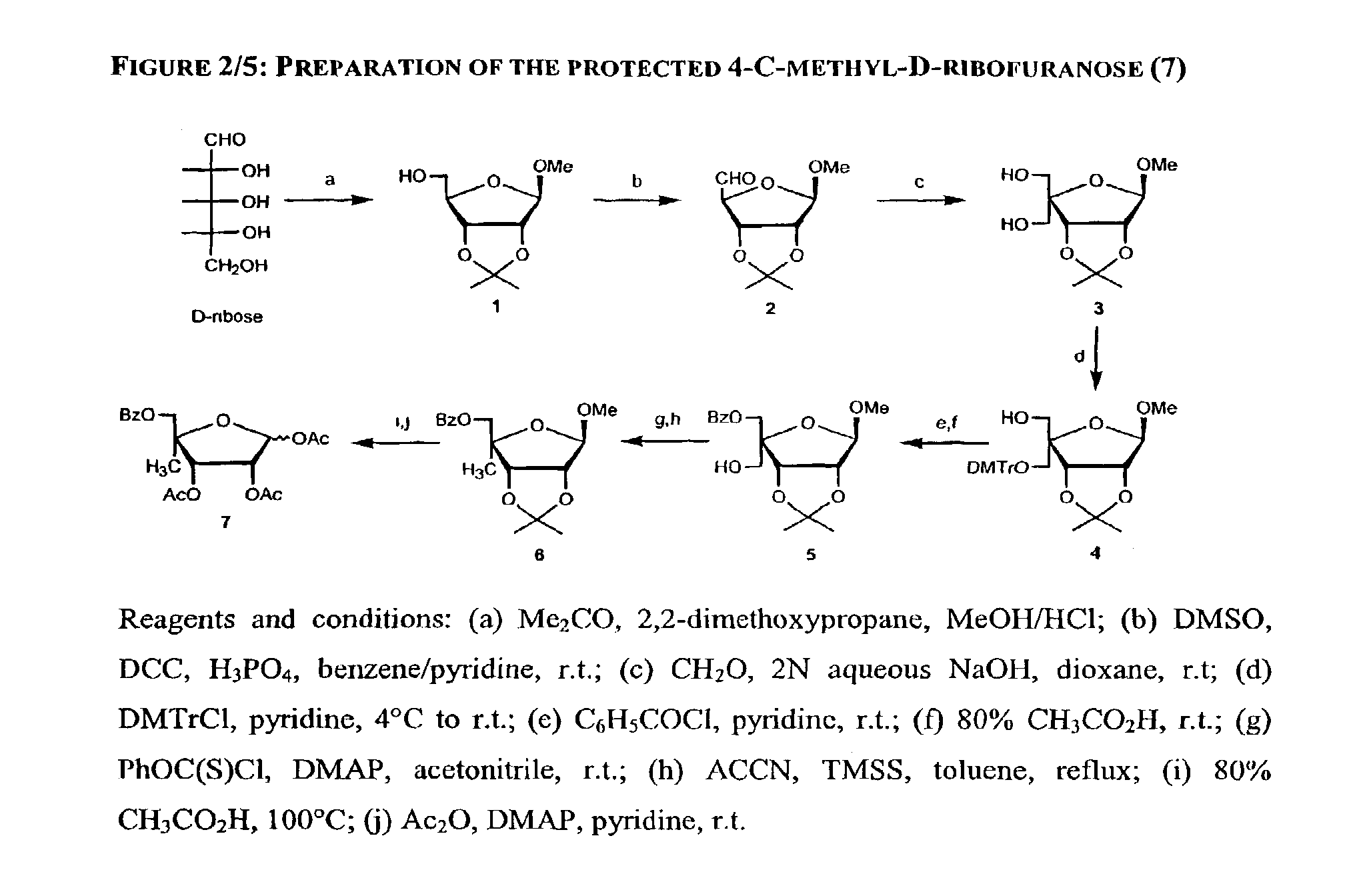
2' and 3'-nucleoside prodrugs for treating Flaviviridae infections
InactiveUS20070015905A1Inhibit HCV polymerase activityInhibit polymerase activityBiocideSugar derivativesDiseaseReverse transcriptase
2′ and 3′-Prodrugs of 1′, 2′, 3′ or 4′-branched β-D or β-L nucleosides, or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives are described, which are useful in the prevention and treatment of Flaviviridae infections and other related conditions. These modified nucleosides provide superior results against flaviviruses and pestiviruses, including hepatitis C virus and viruses generally that replicate through an RNA dependent RNA reverse transcriptase. Compounds, compositions, methods and uses are provided for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection, including HCV infection, that include the administration of an effective amount of the prodrugs of the present invention, or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts or derivatives. These drugs may optionally be administered in combination or alteration with further anti-viral agents to prevent or treat Flaviviridae infections and other related conditions.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC +3
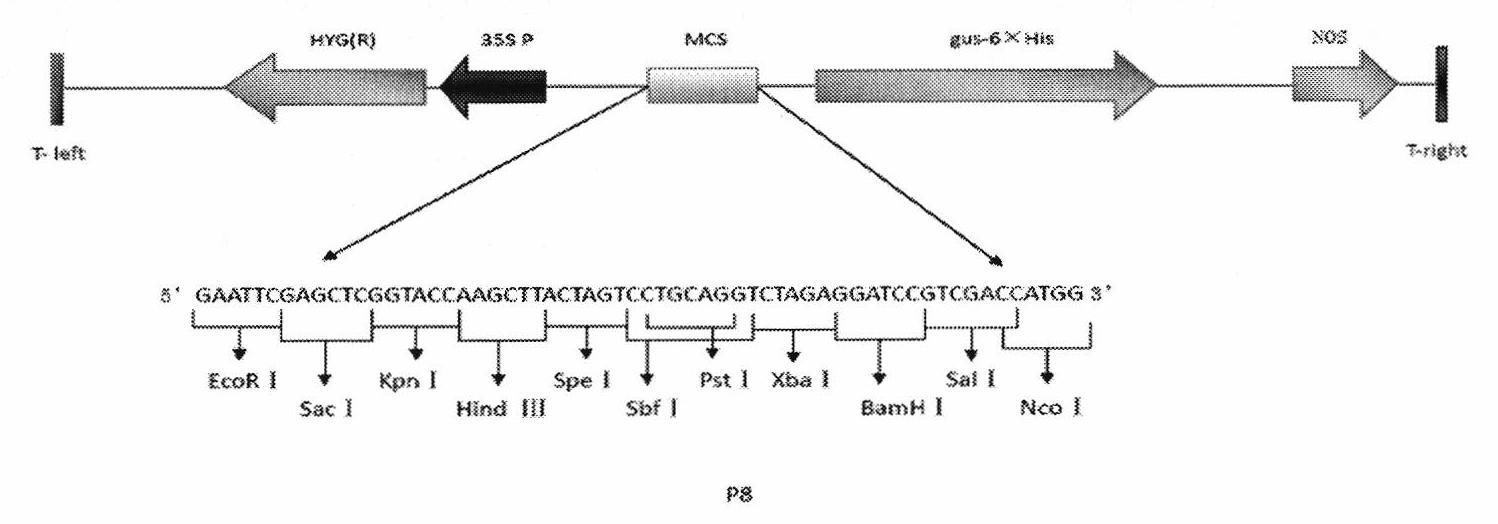
Promoter BgIosP587, and preparation method and application thereof
The invention relates to a promoter, in particular to a promoter for monocotyledons such as rice, and a preparation method and application thereof. The promoter of the invention has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, or has a variant which has the functions of the promoter and is selected from the following sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence hybridized with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 under the condition of advanced tightness; 2) a nucleotide sequence carrying out substitution, loss, modification and addition of one or more basic groups on the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; and 3) a nucleotide sequence having at least 90 percent of sequence identity with the nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1. In addition, the invention also relates to a method for preparing the promoter and the application of the promoter in adjusting and controlling the target gene expression in the monocotyledons.
Owner:深圳华大基因农业控股有限公司
Methods and compositions for treating hepatitis C virus
InactiveUS20050137161A1Inhibitory activityDetermine the spectrum of activityBiocideSugar derivativesHepatitisModified nucleosides
A method and composition for treating a host infected with hepatitis C comprising administering an effective hepatitis C treatment amount of a described 1′, 2′ or 3′-modified nucleoside or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, is provided.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
Methods and compositions for treating flaviviruses and pestiviruses
A method and composition for treating a host infected with flavivirus or pestivirus comprising administering an effective flavivirus or pestivirus treatment amount of a described 1′, 2′ or 3′-modified nucleoside or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, is provided.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
2' and 3'-nucleoside prodrugs for treating Flaviviridae infections
2′ and 3′-Prodrugs of 1′, 2′, 3′ or 4′-branched β-D or β-L nucleosides, or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts and derivatives are described, which are useful in the prevention and treatment of Flaviviridae infections and other related conditions. These modified nucleosides provide superior results against flaviviruses and pestiviruses, including hepatitis C virus and viruses generally that replicate through an RNA dependent RNA reverse transcriptase. Compounds, compositions, methods and uses are provided for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection, including HCV infection, that include the administration of an effective amount of the prodrugs of the present invention, or their pharmaceutically acceptable salts or derivatives. These drugs may optionally be administered in combination or alteration with further anti-viral agents to prevent or treat Flaviviridae infections and other related conditions.
Owner:THE CENT NAT DEL LA RECH SCIQUE +3
Amplification of denatured and stabilized nucleic acids
InactiveUS7074600B2Consistent outputQuick buildMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid reductionNucleotideGenomic DNA
Disclosed are compositions and a method for amplification of nucleic acid sequences of interest. The disclosed method generally involves replication of a target sequence such that, during replication, the replicated strands are displaced from the target sequence by strand displacement replication of another replicated strand. In one form of the disclosed method, the target sample is not subjected to denaturing conditions. It was discovered that the target nucleic acids, genomic DNA, for example, need not be denatured for efficient multiple displacement amplification. The primers used can be hexamer primers. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the primers are nuclease resistant. The primers can also each contain at least one modified nucleotide such that the melting temperature of the primer is altered relative to a primer of the same sequence without the modified nucleotide(s). The DNA polymerase can be φ29 DNA polymerase.
Owner:QIAGEN GMBH
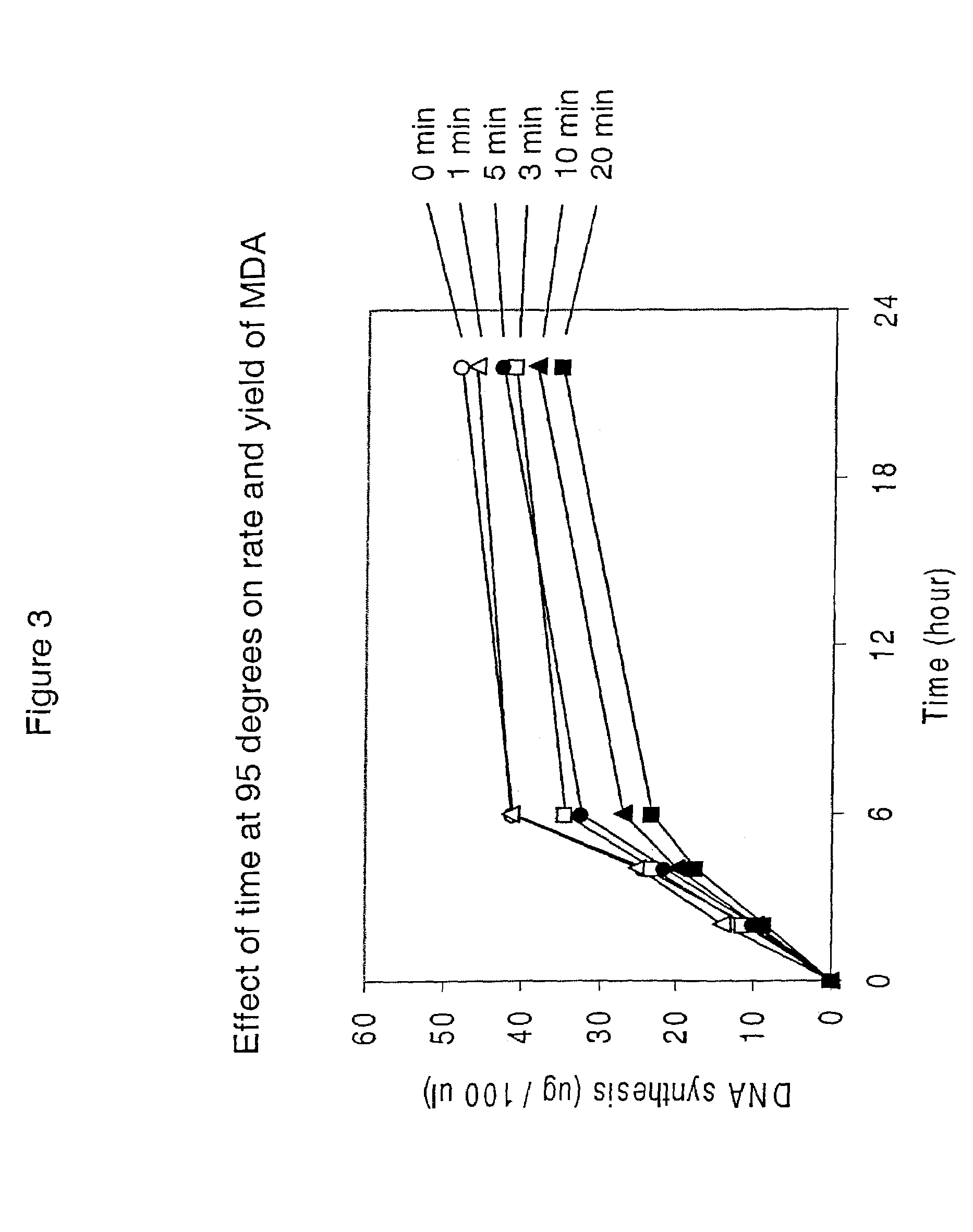
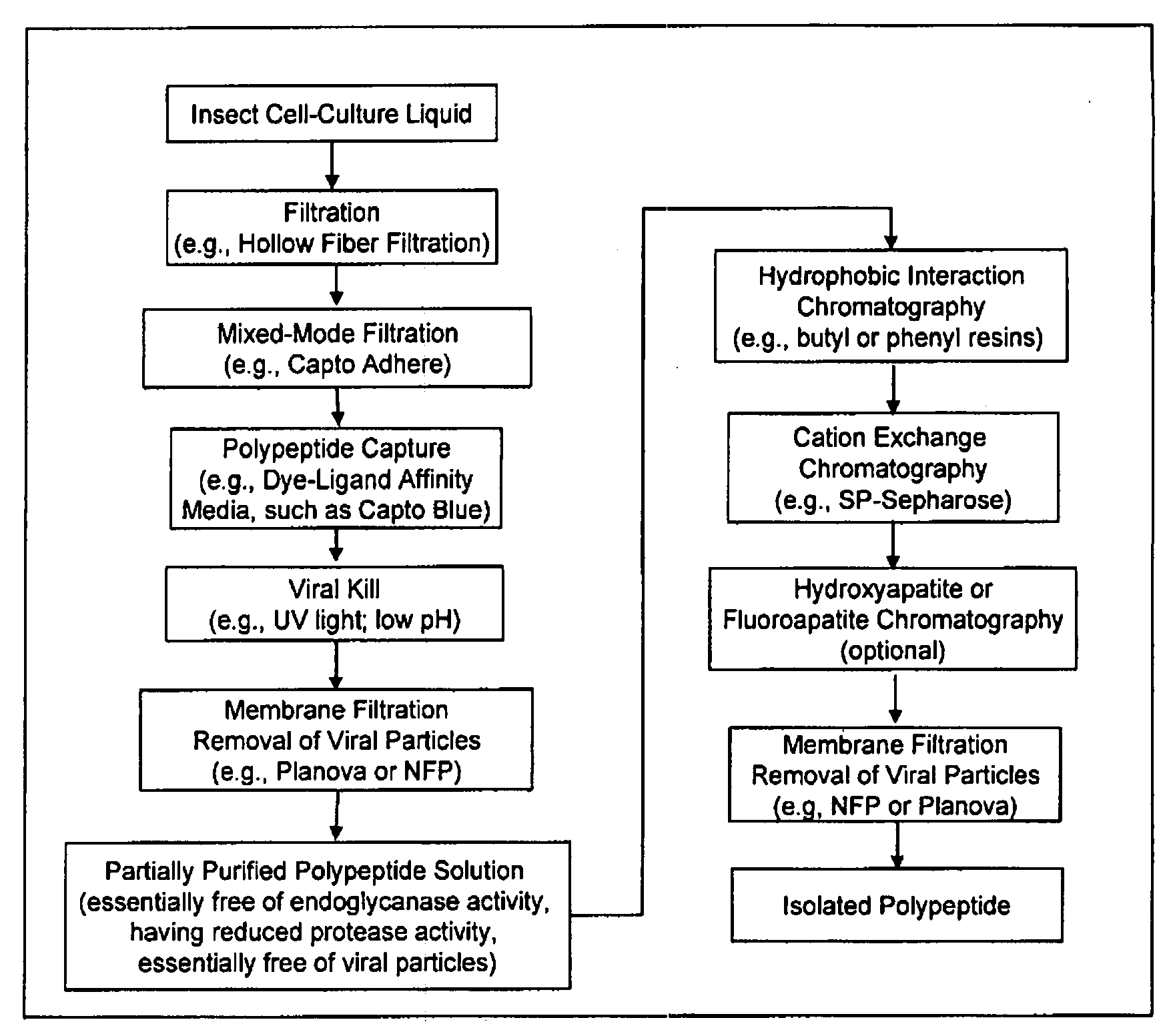
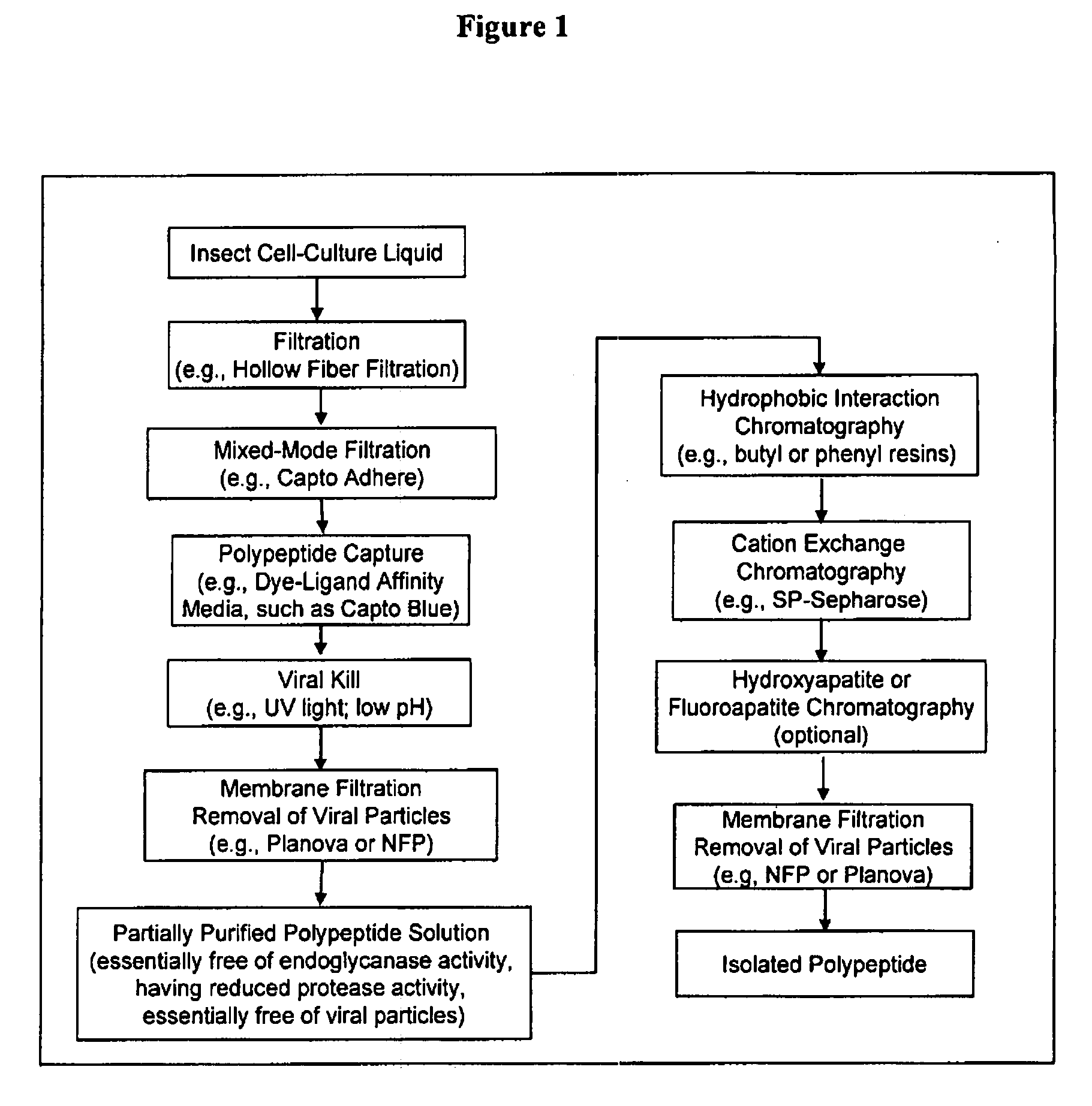
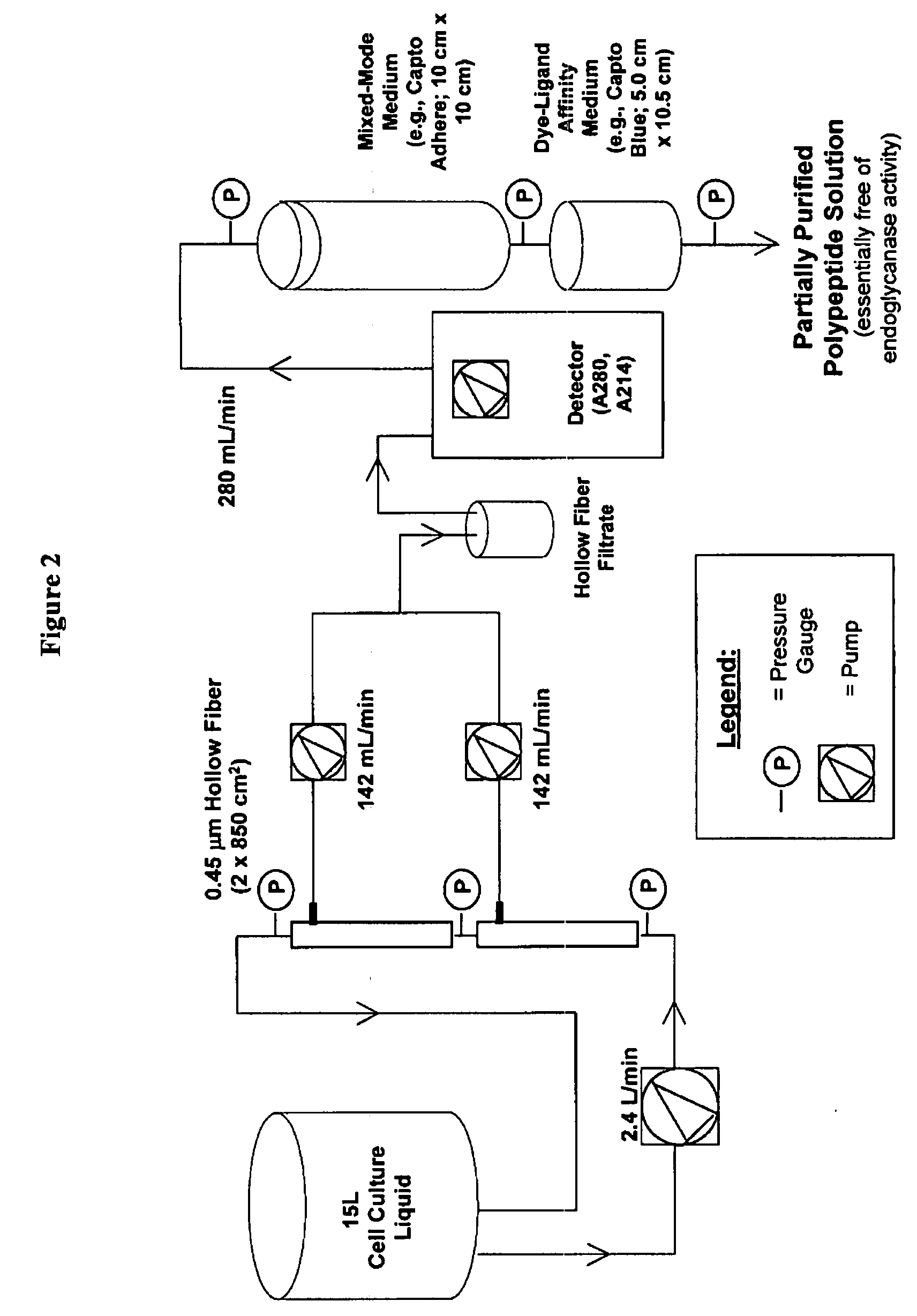
Manufacturing process for the production of polypeptides expressed in insect cell-lines
InactiveUS20080207487A1Promote recoveryReduce manufacturing costPeptide/protein ingredientsDepsipeptidesFiberCulture fluid
The present invention provides a manufacturing method for polypeptides that are produced in insect cells using a baculoviral expression system. In one example, the insect cell culture is supplemented with a lipid mixture immediately prior to infection (e.g., one hour prior to infection). The polypeptides are isolated from the insect cell culture using a method that employs anion exchange or mixed-mode chromatography early in the purification process. This process step is useful to remove insect-cell derived endoglycanases and proteases and thus reduces the loss of desired polypeptide due to enzymatic degradation. In another example, mixed-mode chromatography is combined with dye-ligand affinity chromatography in a continuous-flow manner to allow for rapid processing of the insect-cell culture liquid and capture of the polypeptide. In yet another example, a polypeptide is isolated from an insect cell culture liquid using a process that combines hollow fiber filtration, mixed-mode chromatography and dye-ligand affinity in a single unit operation producing a polypeptide solution that is essentially free of endoglycanase and proteolytic activities. In a further example, the isolated polypeptides are glycopeptides having an insect specific glycosylation pattern, which are optionally conjugated to a modifying group, such as a polymer (e.g., PEG) using a glycosyltransferase and a modified nucleotide sugar.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
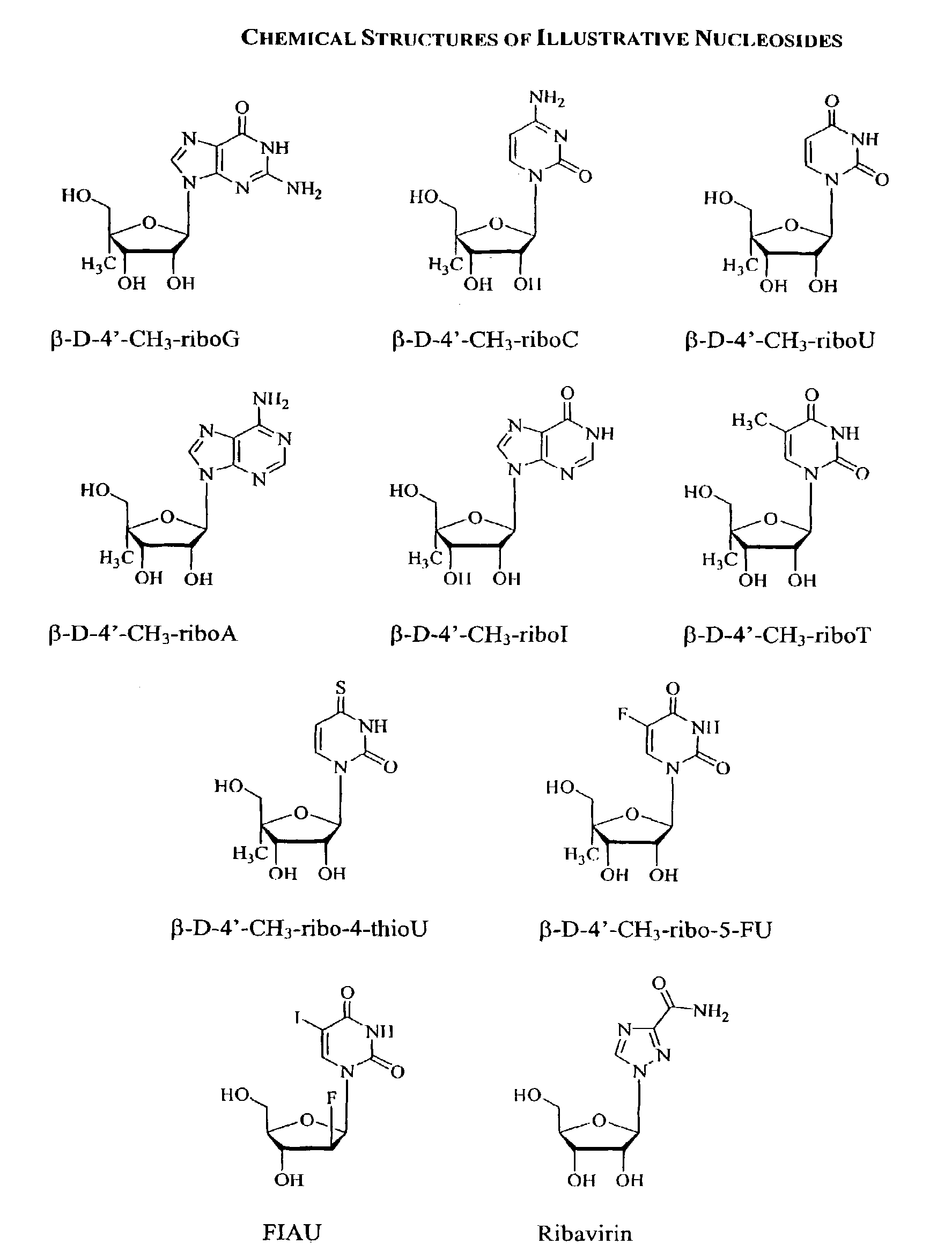
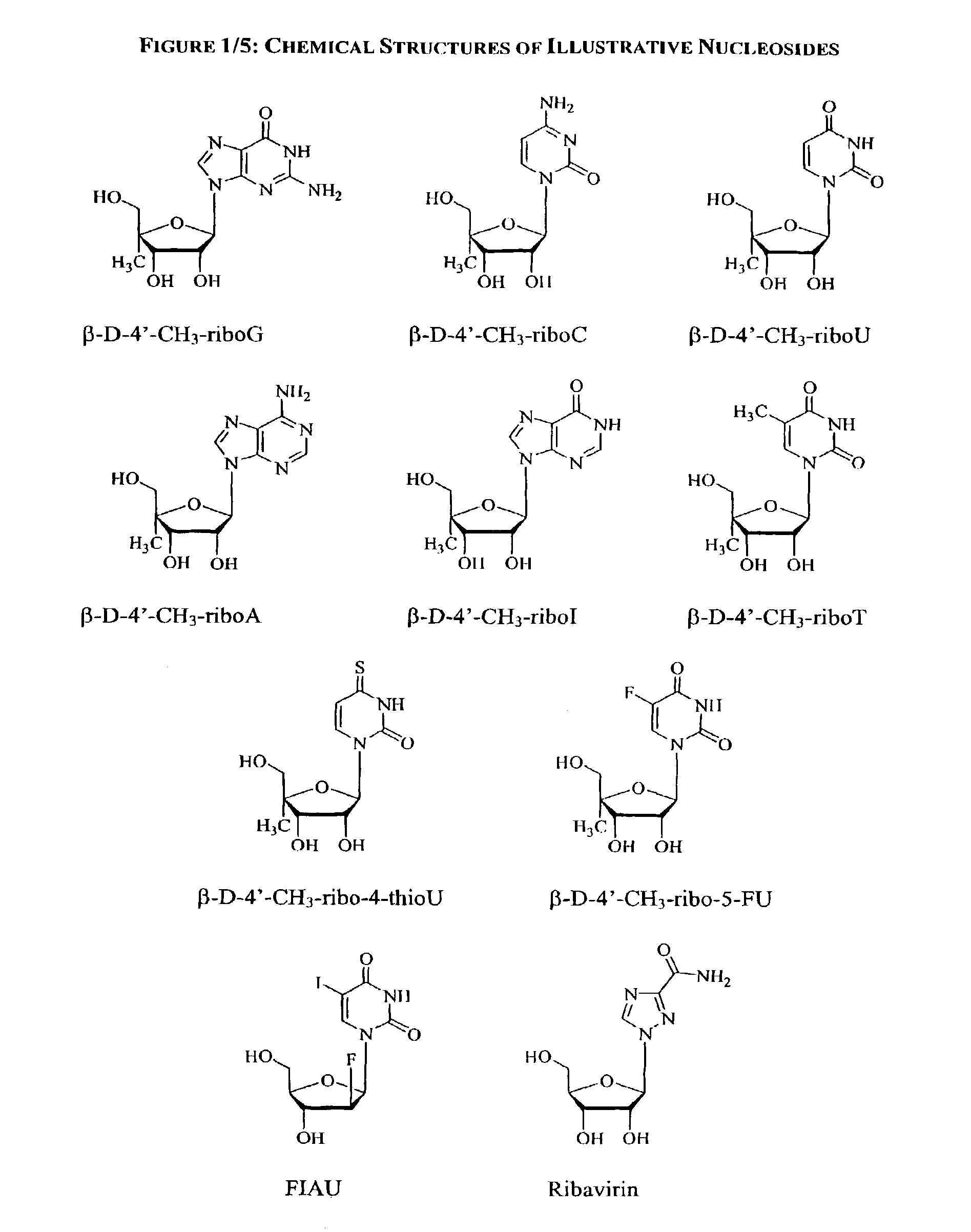
Methods and compositions for treating hepatitis C virus using 4'-modified nucleosides
InactiveUS7138376B2Inhibit HCV polymerase activitySure easyBiocideSaccharide peptide ingredientsHepatitisModified nucleosides
A compound, method and composition for treating a host infected with a hepatitis C viral comprising administering an effective hepatitis C treatment amount of a described 4′-disubstituted nucleoside or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or prodrug thereof, is provided.
Owner:THE CENT NAT DEL LA RECH SCIQUE +2
Kits and methods for generating 5' capped RNA
InactiveUS20070281336A1Increase synthesisImprove efficiencySugar derivativesActivity regulationType specificPhosphoric acid
The present invention relates to kits and methods for efficiently generating 5′ capped RNA having a modified cap nucleotide and for use of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA molecules. The invention is used to obtain novel compositions of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA molecules. In particular, the present invention provides kits and methods for capping RNA using a modified cap nucleotide and a capping enzyme system, such as poxvirus capping enzyme. The present invention finds use for in vitro production of 5′-capped RNA having a modified cap nucleotide and for in vitro or in vivo production of polypeptides by in vitro or in vivo translation of such modified-nucleotide-capped RNA for a variety of research, therapeutic, and commercial applications. The invention also provides methods and kits for capturing or isolating uncapped RNA comprising primary RNA transcripts or RNA having a 5′-diphosphate, such as RNA synthesized in vitro or obtained from a biological source, including prokaryotic mRNA that is in a mixture with other prokaryotic and / or eukaryotic nucleic acids. The method for capturing modified-nucleotide-capped RNA also provides methods and kits for obtaining only type-specific or condition-specific modified-nucleotide-capped RNA by cap-dependent subtraction of that portion of the captured modified-nucleotide-capped RNA in cells of one type or condition that is the same as RNA in cells of another type or condition. The invention further provides methods and kits for using a capping enzyme system and modified cap nucleotides for labeling uncapped RNA comprising primary RNA transcripts or RNA having a 5′-diphosphate with detectable dye or enzyme moieties.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
DNA sequencing by nanopore using modified nucleotides
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
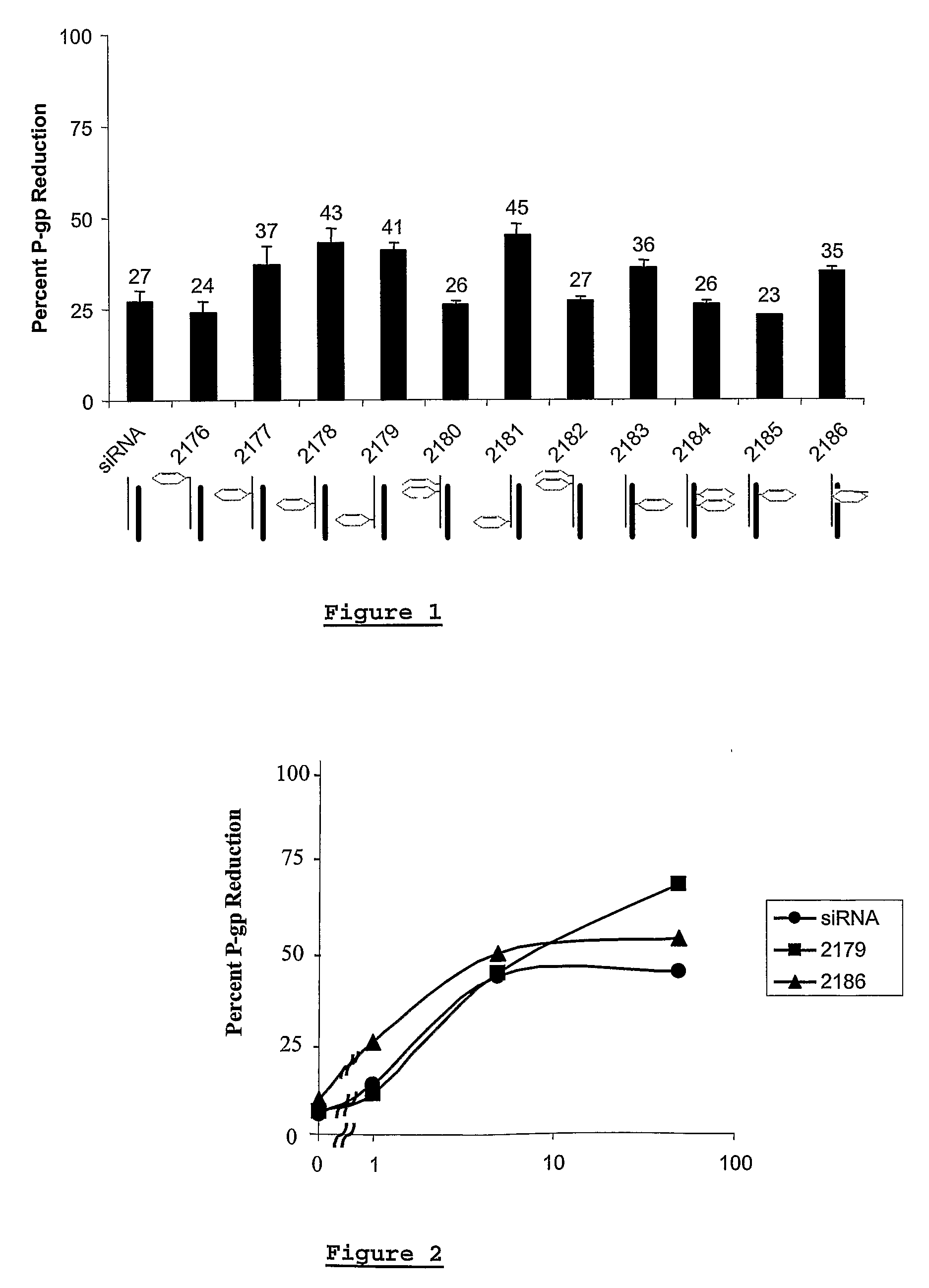
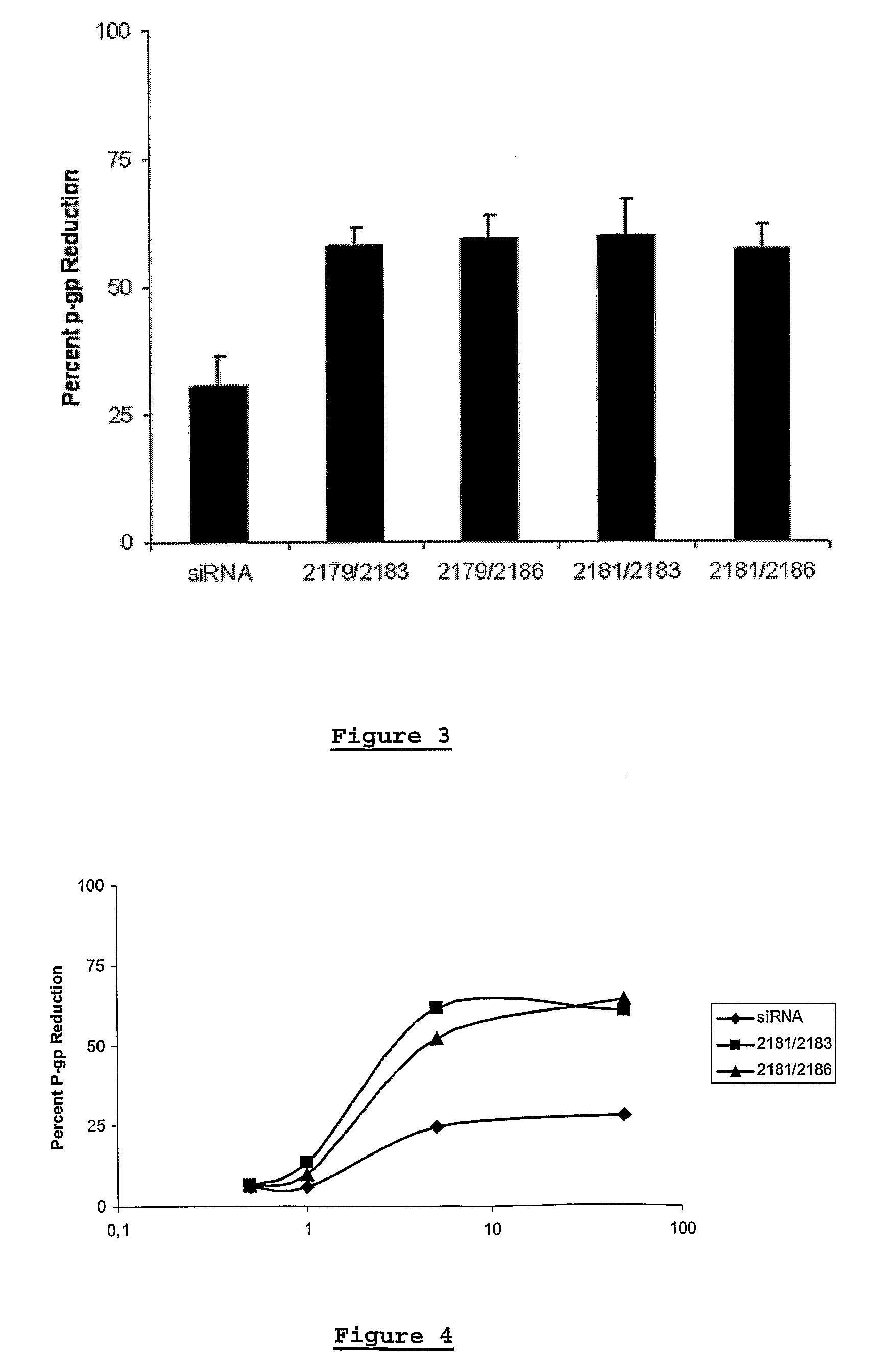
Modified polynucleotides for use in rna interference
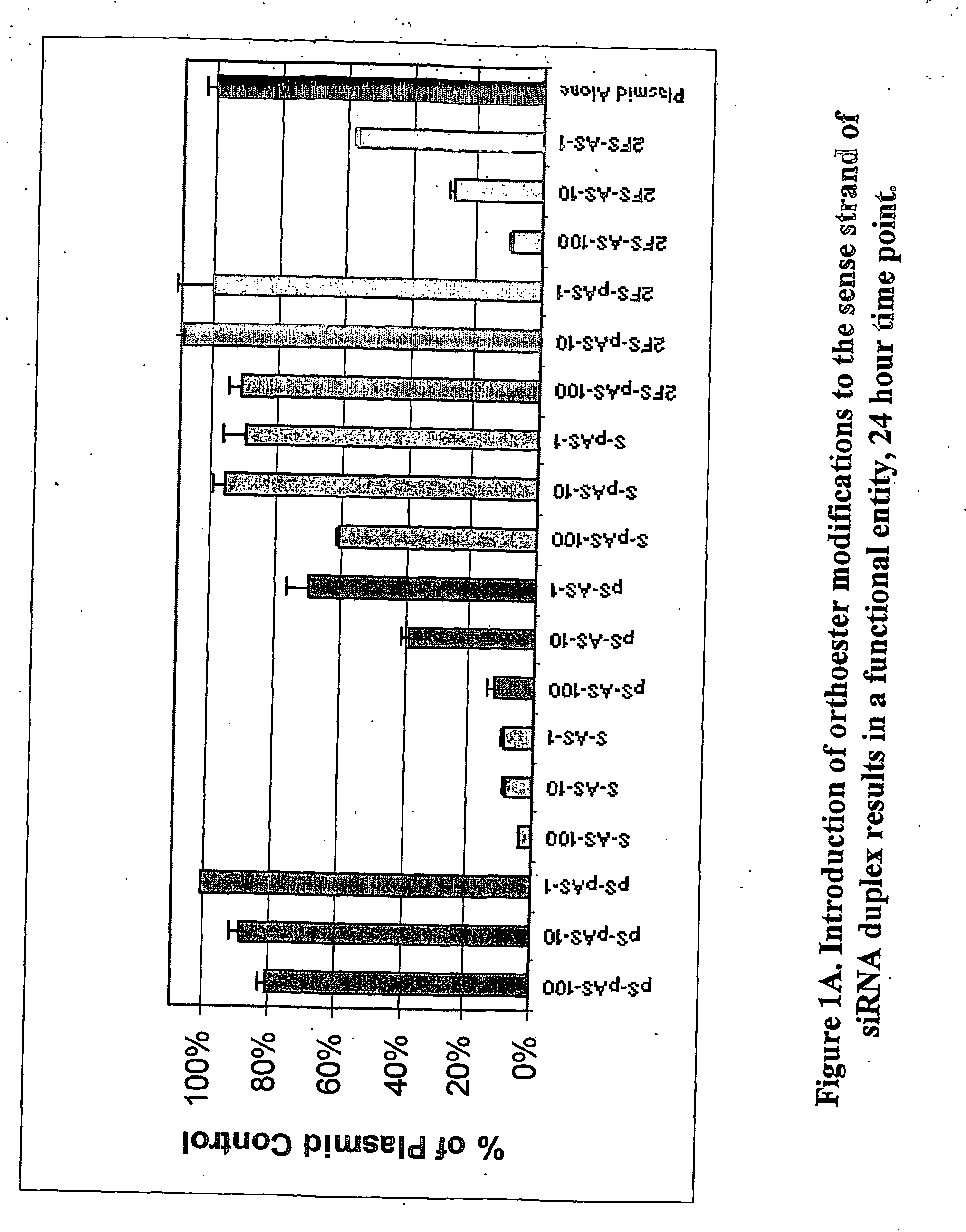
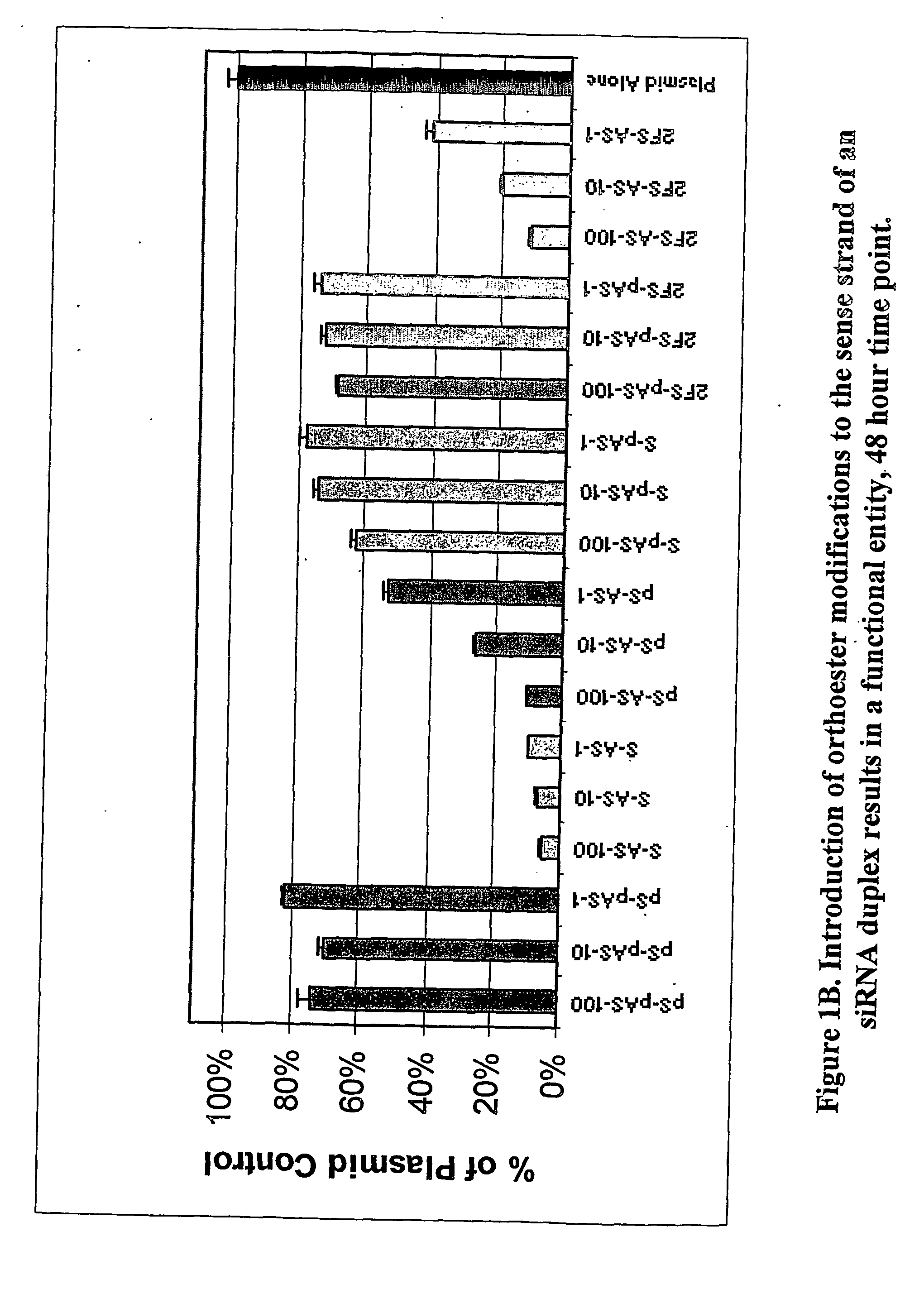
InactiveUS20070167384A1Inhibit expressionImprove stabilityBiocideHydrolasesPhosphorylationOrthoester
Owner:DHARMACON INC
Modified Nucleosides for Rna Interference
InactiveUS20080261905A1Reduced gene expressionGrowth inhibitionSugar derivativesActivity regulationDouble strandModified nucleosides
The present invention relates to the use of modified nucleotides and single or double stranded oligonucleotides having at least one of said modified nucleotides for performing RNA interference. The modified nucleotides are selected from 6-membered ring containing nucleotides such as hexitol, altritol, O-substituted or O-alkylated altritol, cyclohexenyl, ribo-cyclohexenyl and O-substituted or O-alkylated ribo-cyclohexenyl nucleotides. The present invention also relates to novel modified nucleosides or nucleotides and to the use of the novel modified nucleosides and nucleotides in single or double stranded oligonucleotides for RNA interference, antisense therapy or other applications.
Owner:K U LEUVEN RES & DEV +1
Modified nucleic acid molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20160354493A1Sugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsModified nucleosidesStereochemistry
The present disclosure provides modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and nucleic acids, and methods of using them.
Owner:MODERNATX INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com