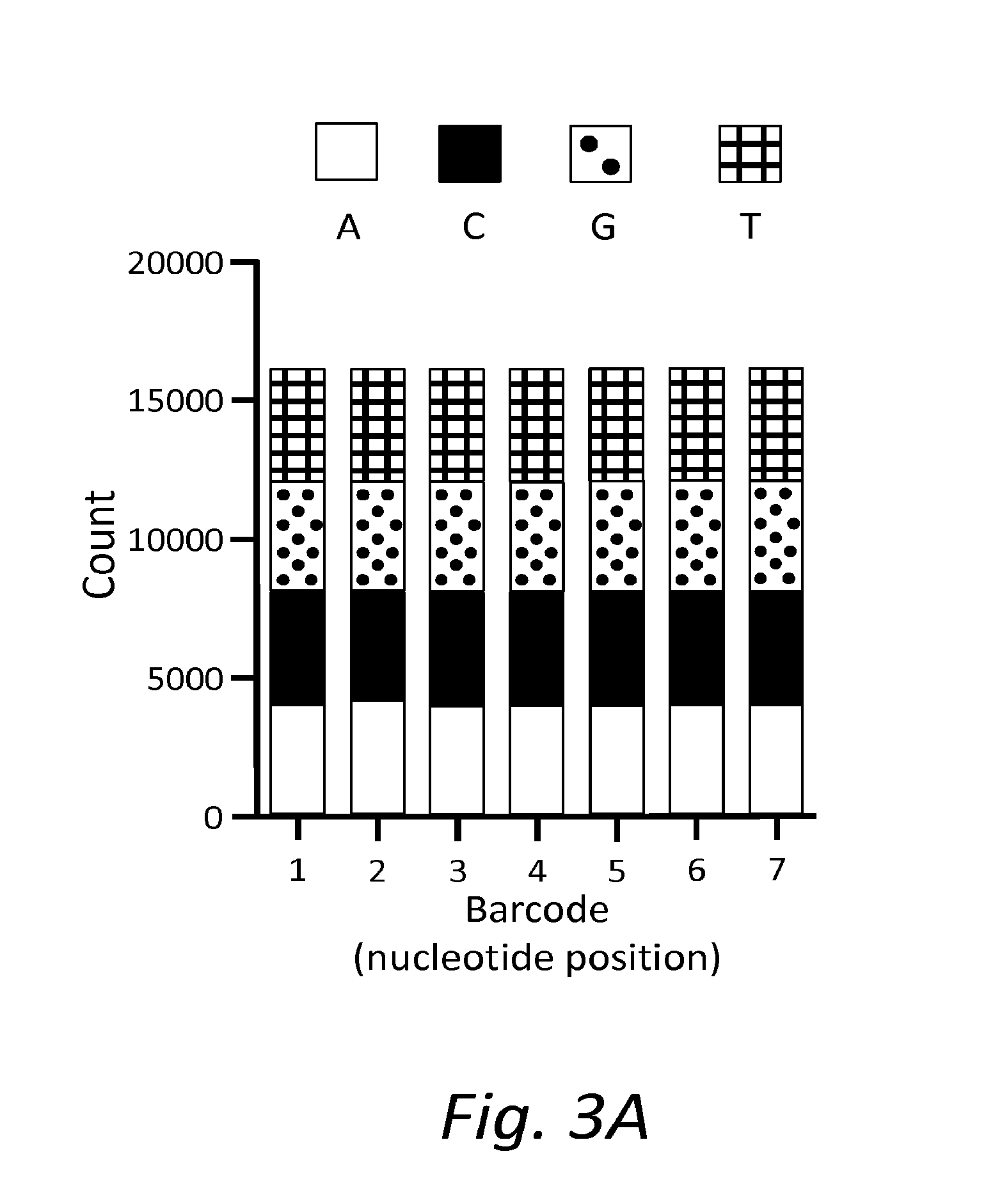
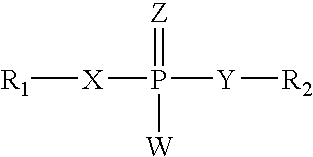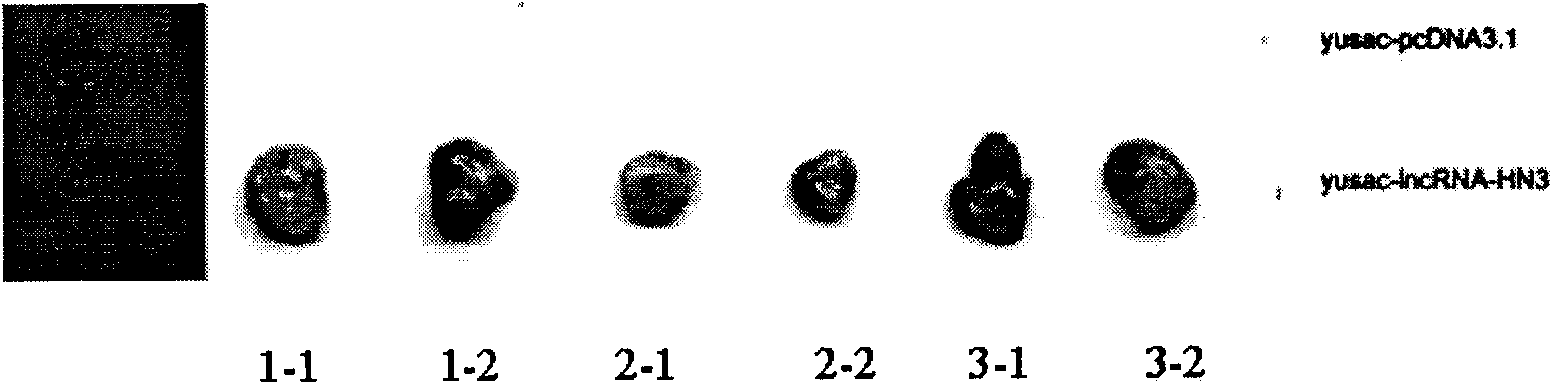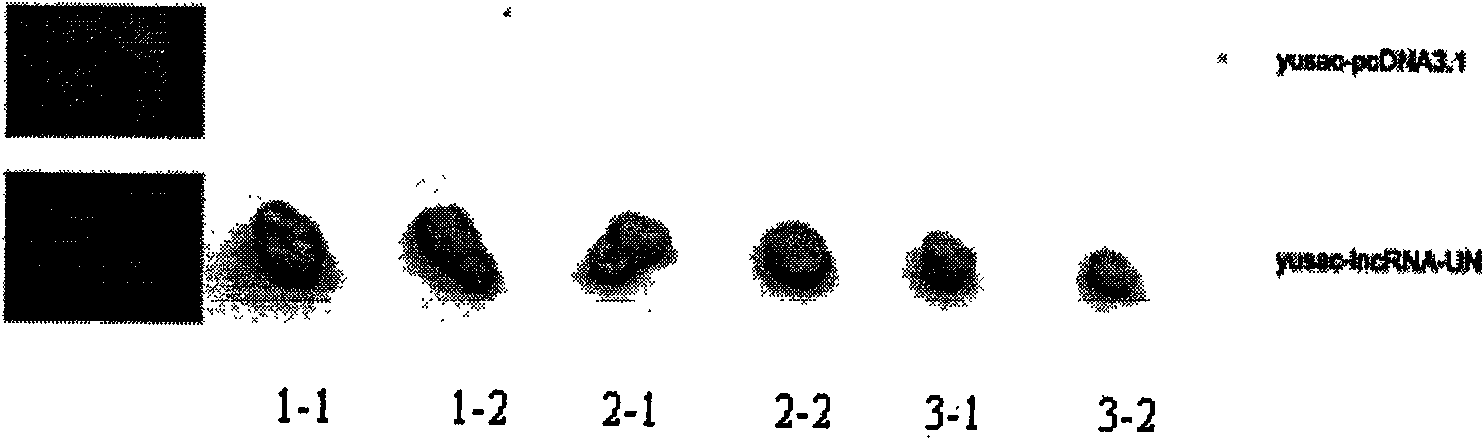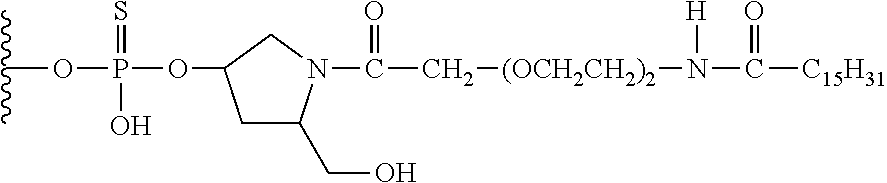Patents
Literature
555 results about "Sense strand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, a sense strand, or coding strand, is the segment within double-stranded DNA that runs from 5' to 3', and which is complementary to the antisense strand of DNA, or template strand, which runs from 3' to 5'. The sense strand is the strand of DNA that has the same sequence as the mRNA, which takes the antisense strand as its template during transcription, and eventually undergoes (typically, not always) translation into a protein. The antisense strand is thus responsible for the RNA that is later translated to protein, while the sense strand possesses a nearly identical makeup to that of the mRNA. Note that for each segment of dsDNA, there will possibly be two sets of sense and antisense, depending on which direction one reads (since sense and antisense is relative to perspective). It is ultimately the gene product, or mRNA, that dictates which strand of one segment of dsDNA we call sense or antisense. But keep in mind that sometimes, such as in prokaryotes, overlapping genes on opposite strands means the sense for one mRNA can be the antisense for another mRNA.
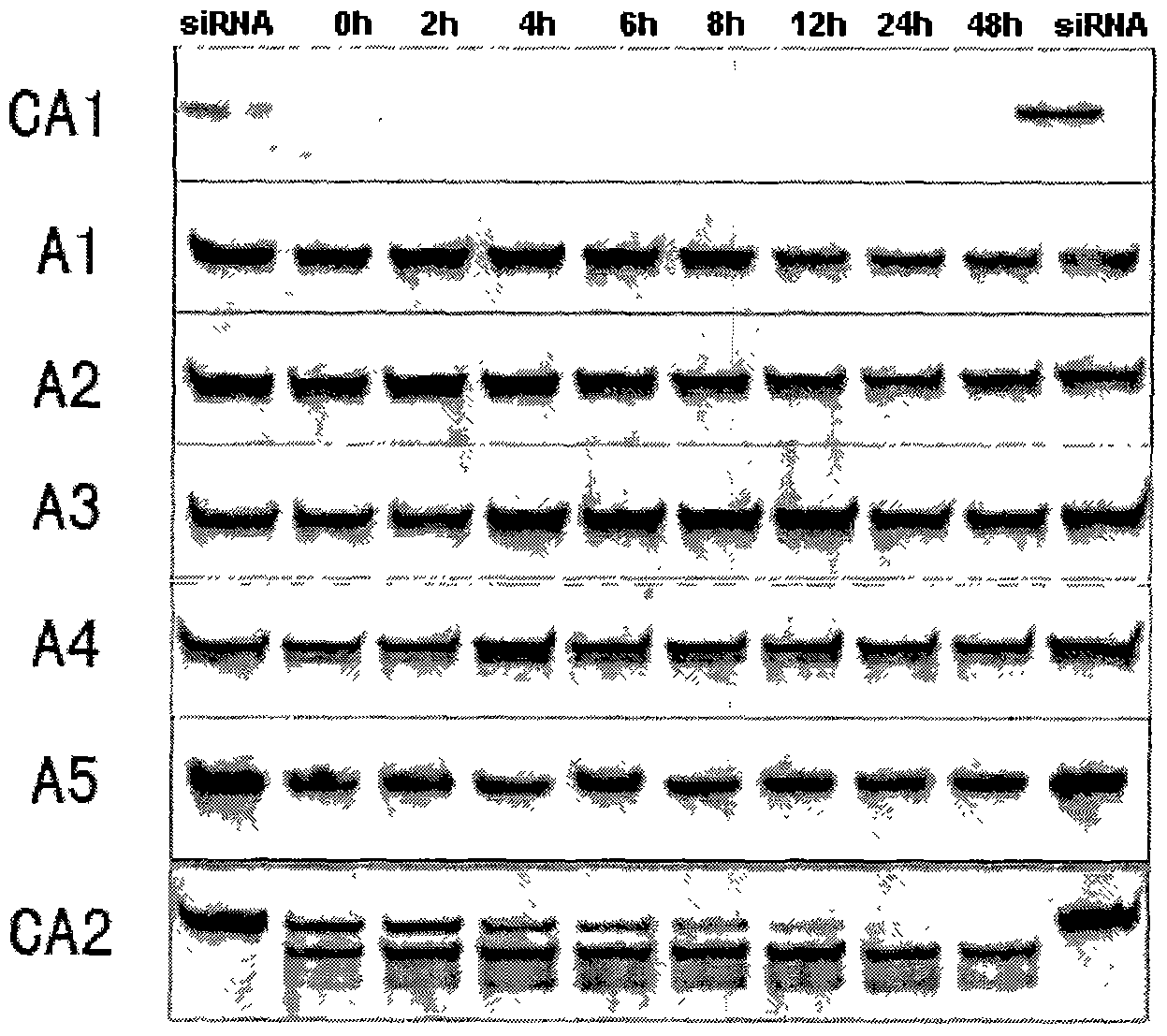
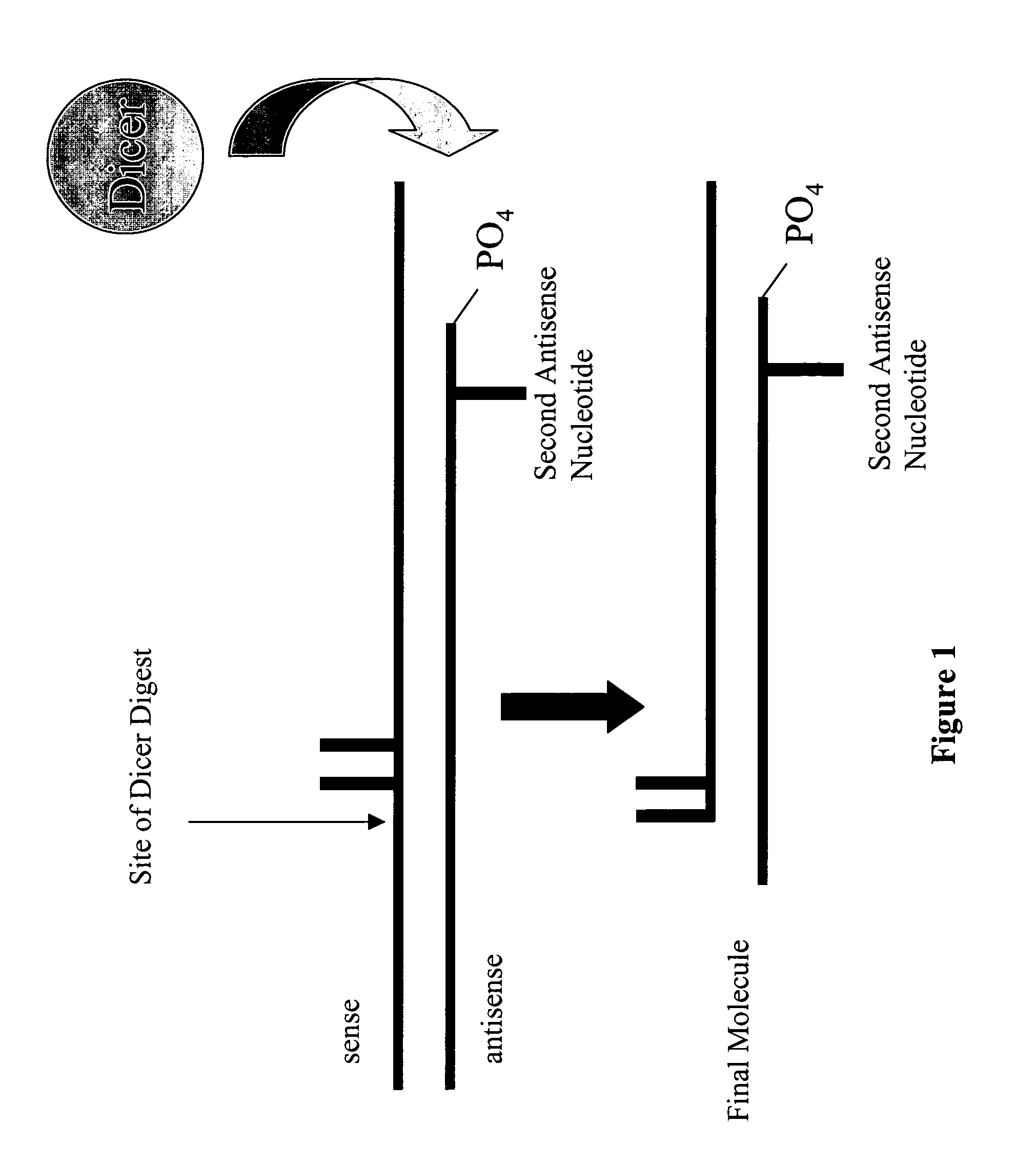
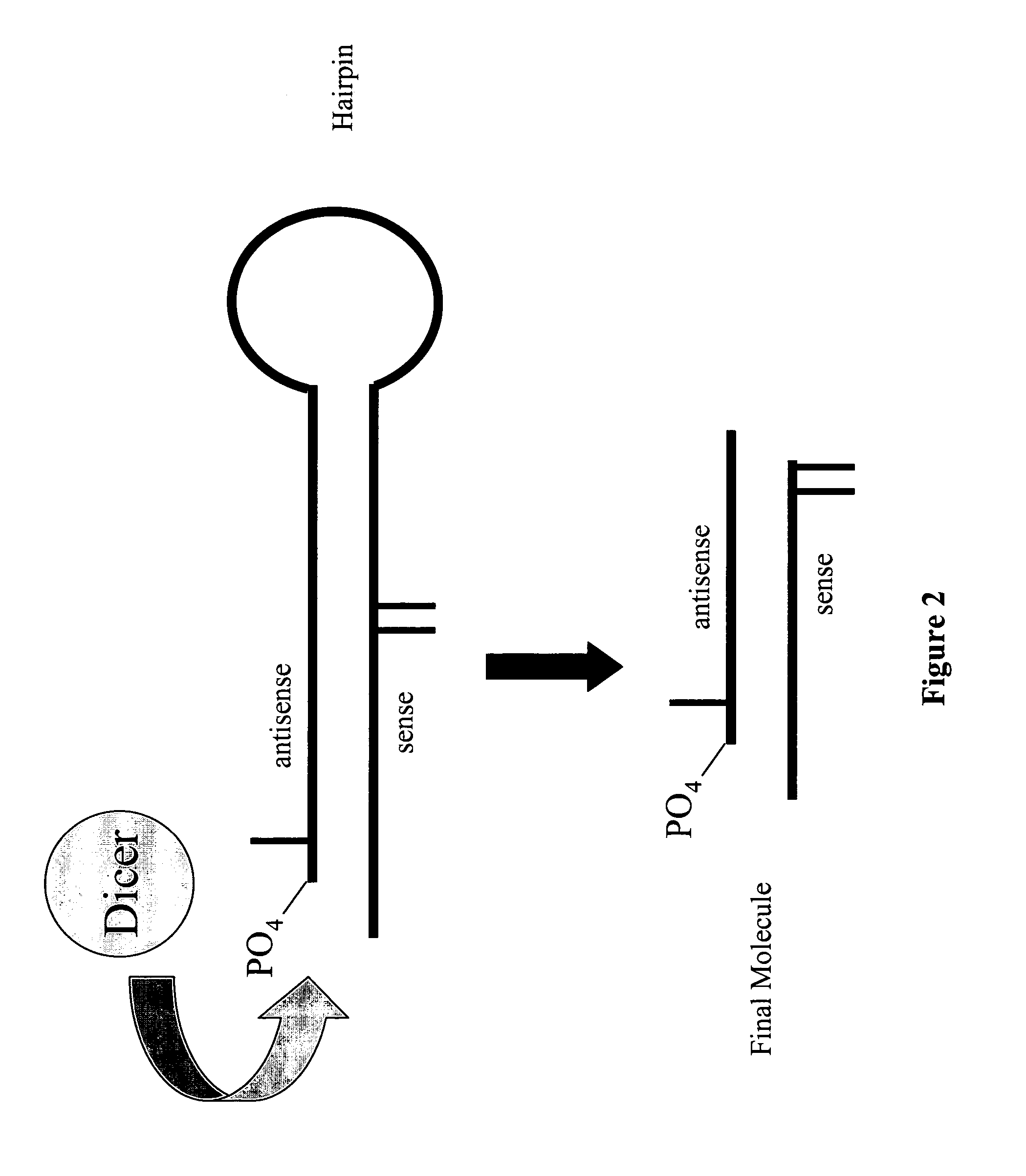
UsiRNA Complexes
ActiveUS20110313020A1Reduce off-target effectsImprove propertiesOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderNucleotideSense strand
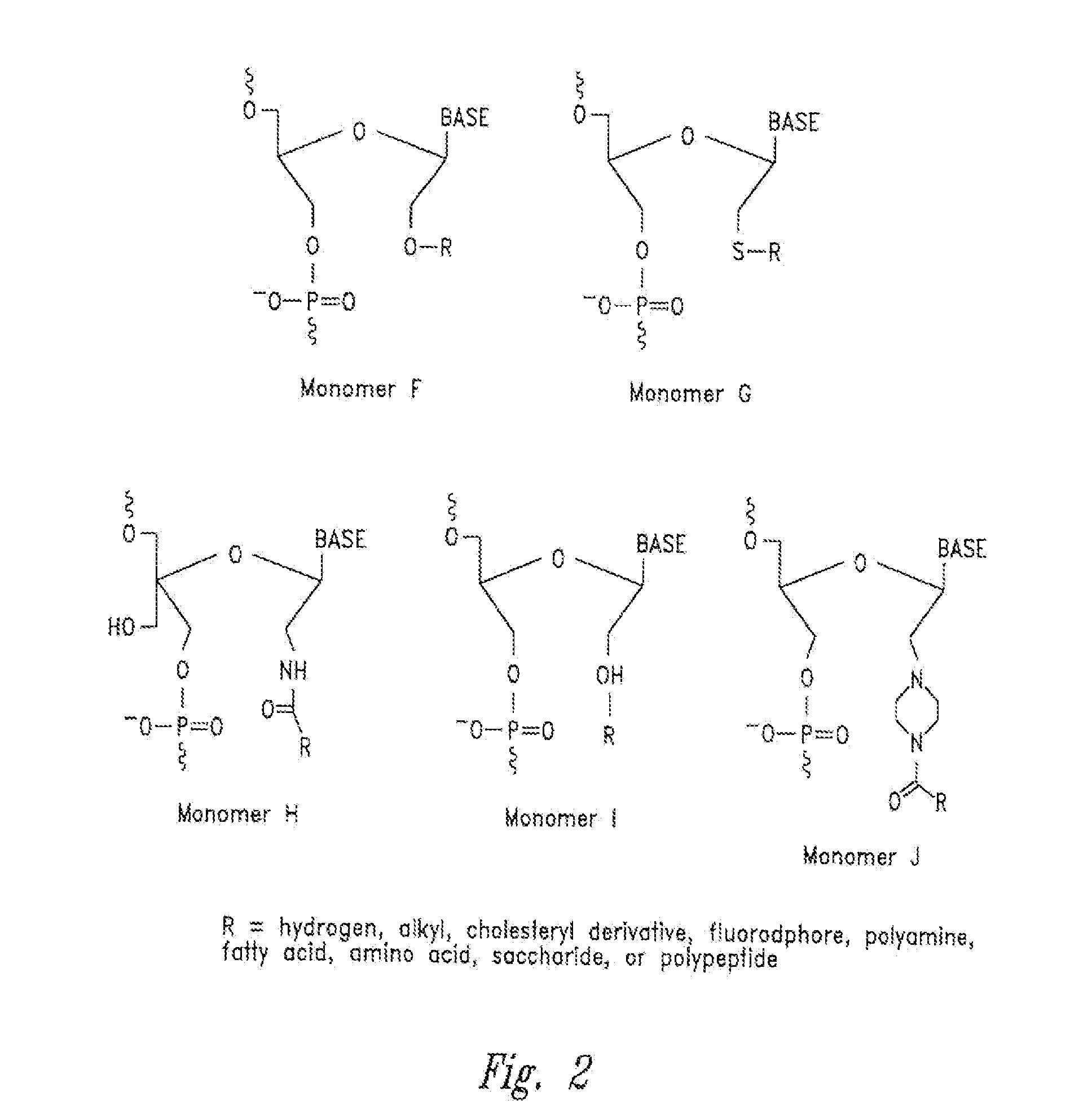
This disclosure provides double-stranded RNA complexes having one or more hydroxymethyl substituted nucleomonomer(s) in the passenger strand (or sense strand) of an RNA complex. RNA complexes of the disclosure may be useful for therapeutic applications, diagnostic applications or research applications. RNA complexes include short interfering RNA complexes (siRNA) capable of modulating gene expression comprising an antisense strand and a continuous or a discontinuous passenger strand (“sense strand”). Further, one or more hydroxymethyl substituted nucleomonomer(s) of this disclosure may be positioned at the 3′-end, at the 5′-end, at both the 3′-end and 5′end.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
Modified polynucleotides for reducing off-target effects in RNA interference
InactiveUS7595387B2Minimizing off-target effectSugar derivativesHydrolasesSense strandPolynucleotide
Methods and compositions for performing RNA interference with decreased off-target effects are provided The methods and compositions permit effective and efficient applications of RNA interference to applications such as diagnostics and therapeutics through the use of modifications to the siRNA. Uniquely modified siRNAs have been developed that reduce off-target effects incurred in gene-silencing. The modifications comprise 2′-O-alkyl or mismatch modification(s) at specific positions on the sense and / or antisense strands.
Owner:MERCK & CO INC +1
2'-f modified RNA interference agents
InactiveUS20110269814A1Inhibit expressionSuppress gene expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleotideSense strand
This invention relates to a method of modulating the expression of a target gene in an organism comprising administering an iRNA agent, wherein the iRNA comprises at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide in the antisense strand and at least one modified nucleotide in the sense strand. The invention also relates to compositions comprising a single-stranded oligonucleotide that contains at least one 2′-deoxy-2′-fluoro (2′-F) nucleotide. siRNA molecule containing these oligonucleotides have decreased immunogenicity.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Compositions and methods for accurately identifying mutations
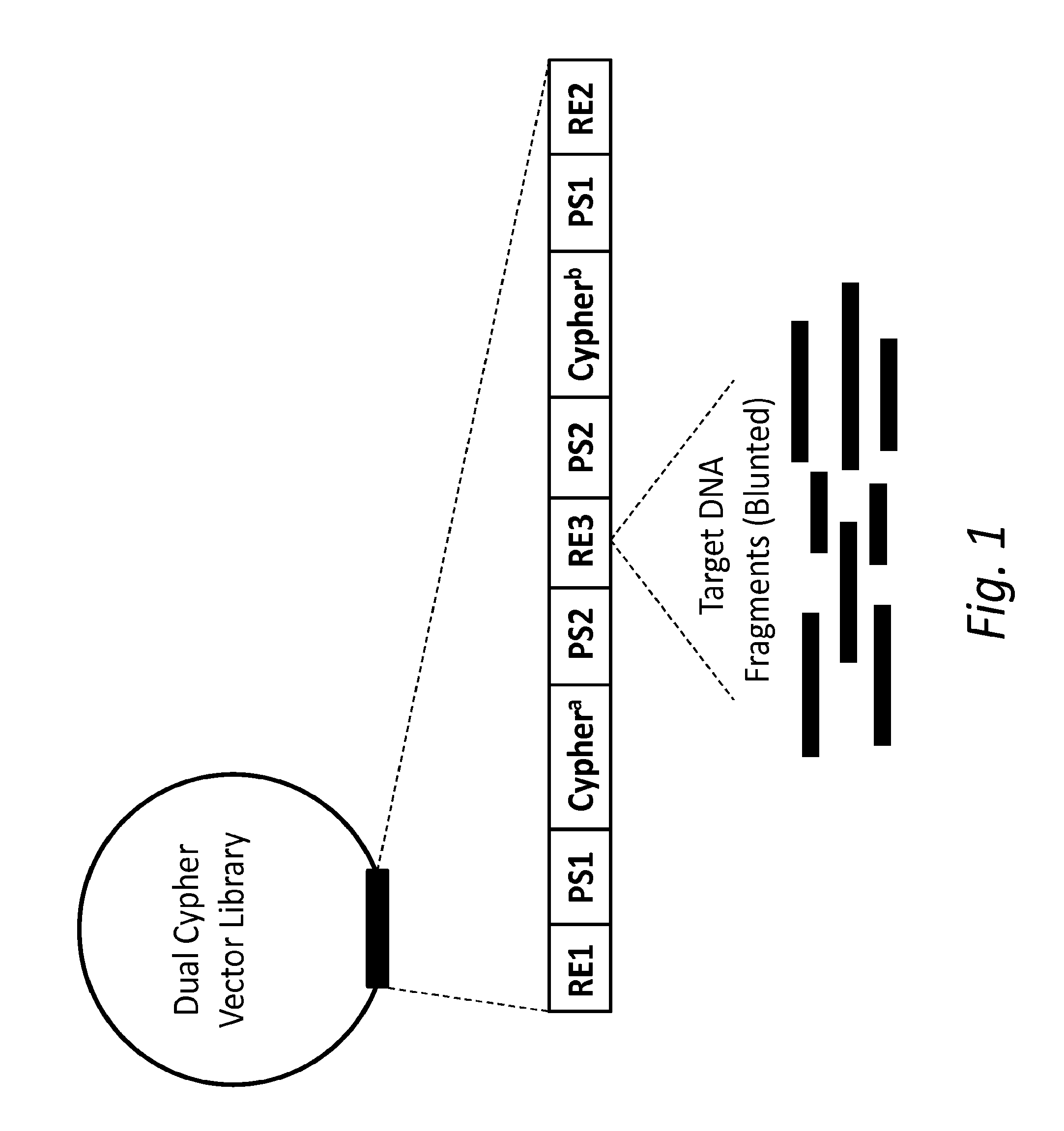
ActiveUS20150024950A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism librariesSense strandMassive parallel sequencing
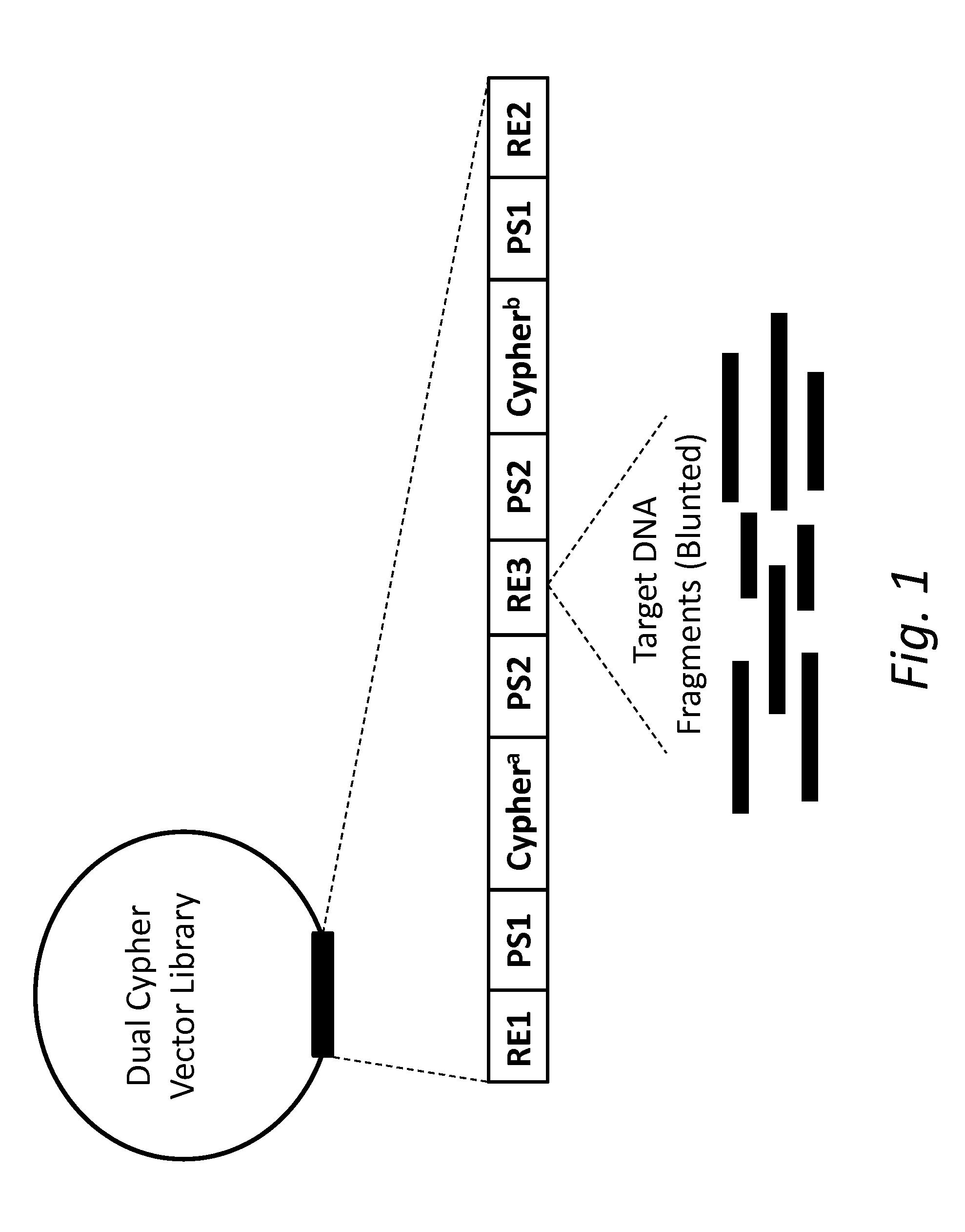
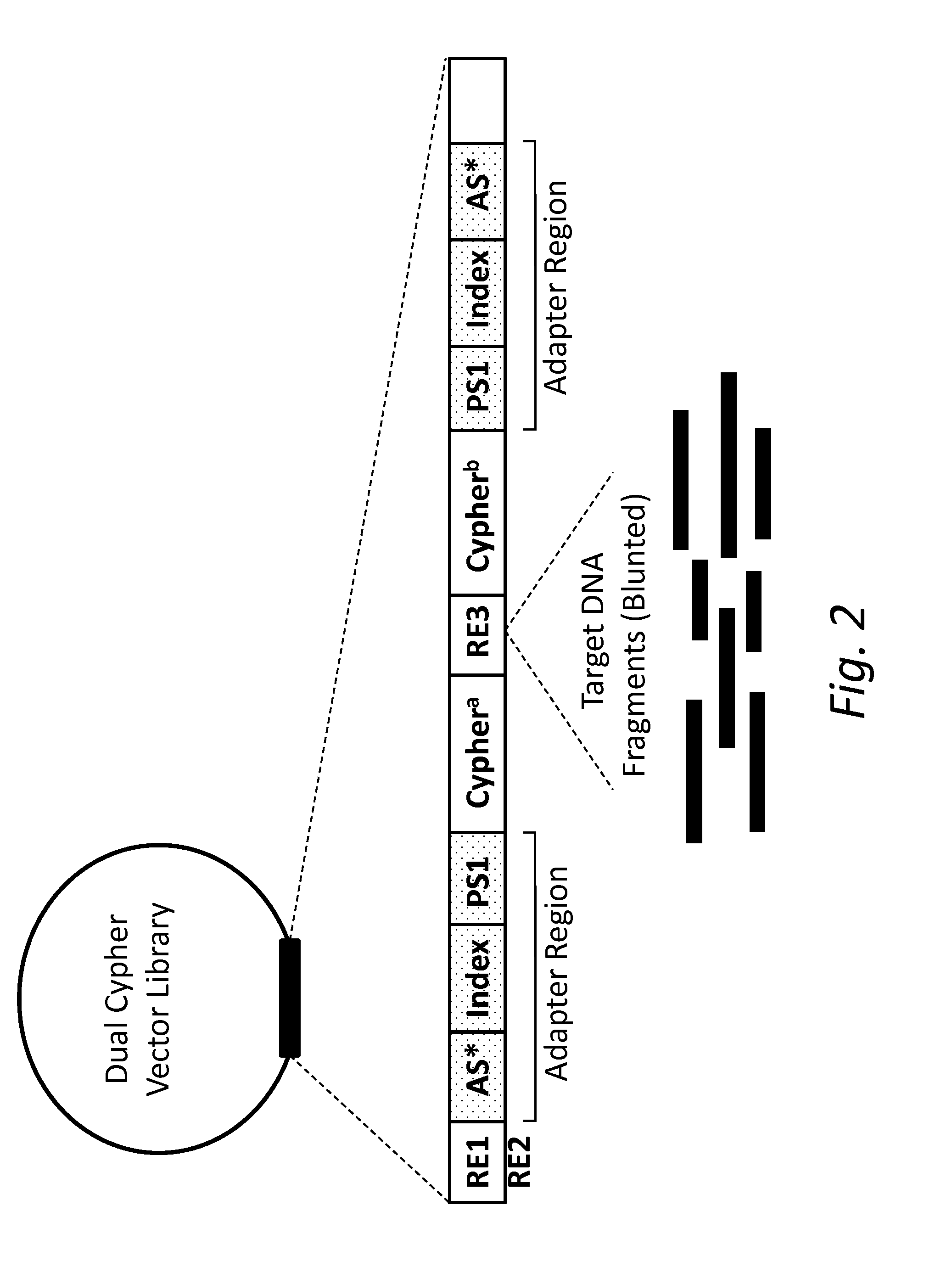
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for accurately detecting mutations by uniquely tagging double stranded nucleic acid molecules with dual cyphers such that sequence data obtained from a sense strand can be linked to sequence data obtained from an anti-sense strand when sequenced, for example, by massively parallel sequencing methods.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
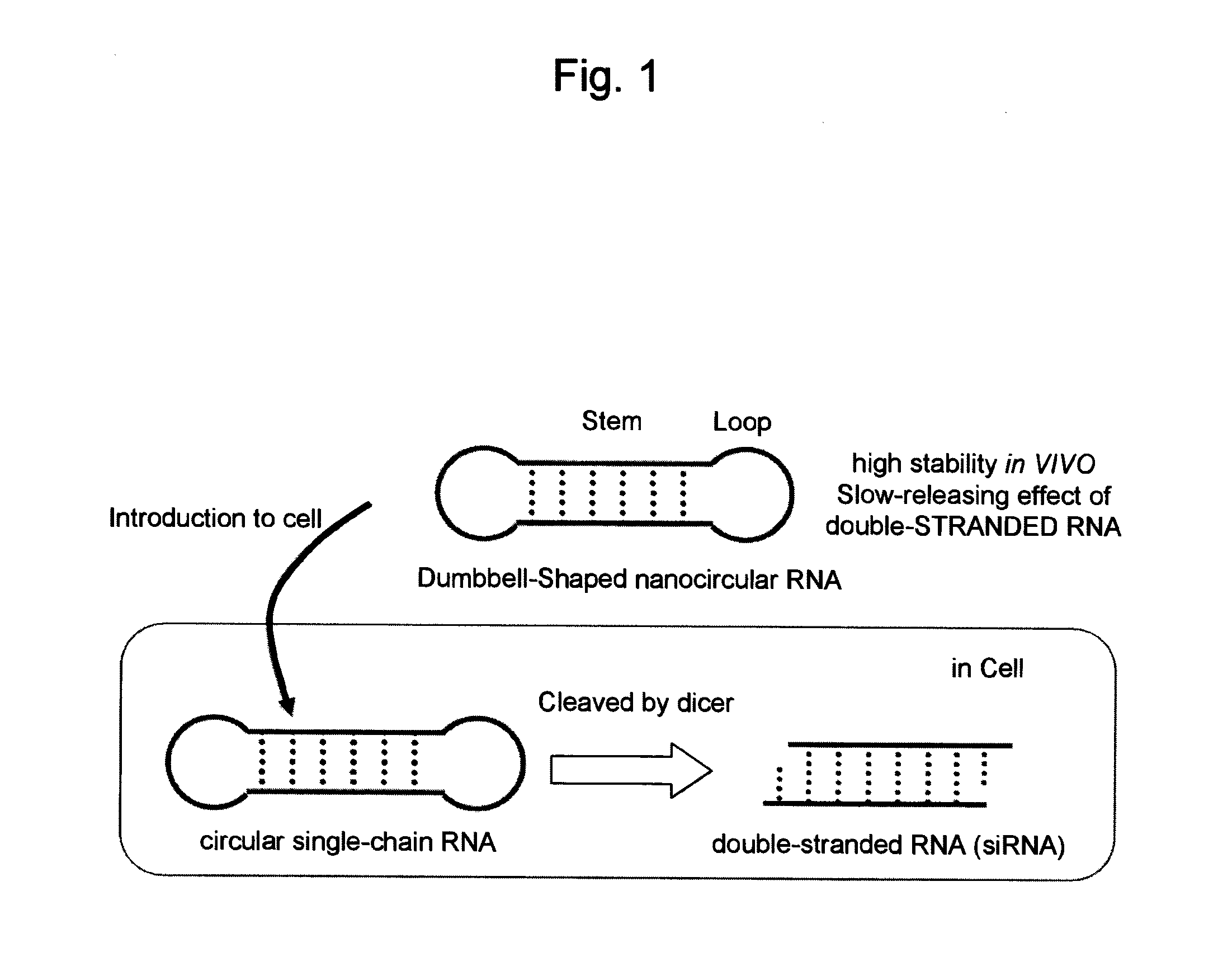
Single-chain circular RNA and method of producing the same
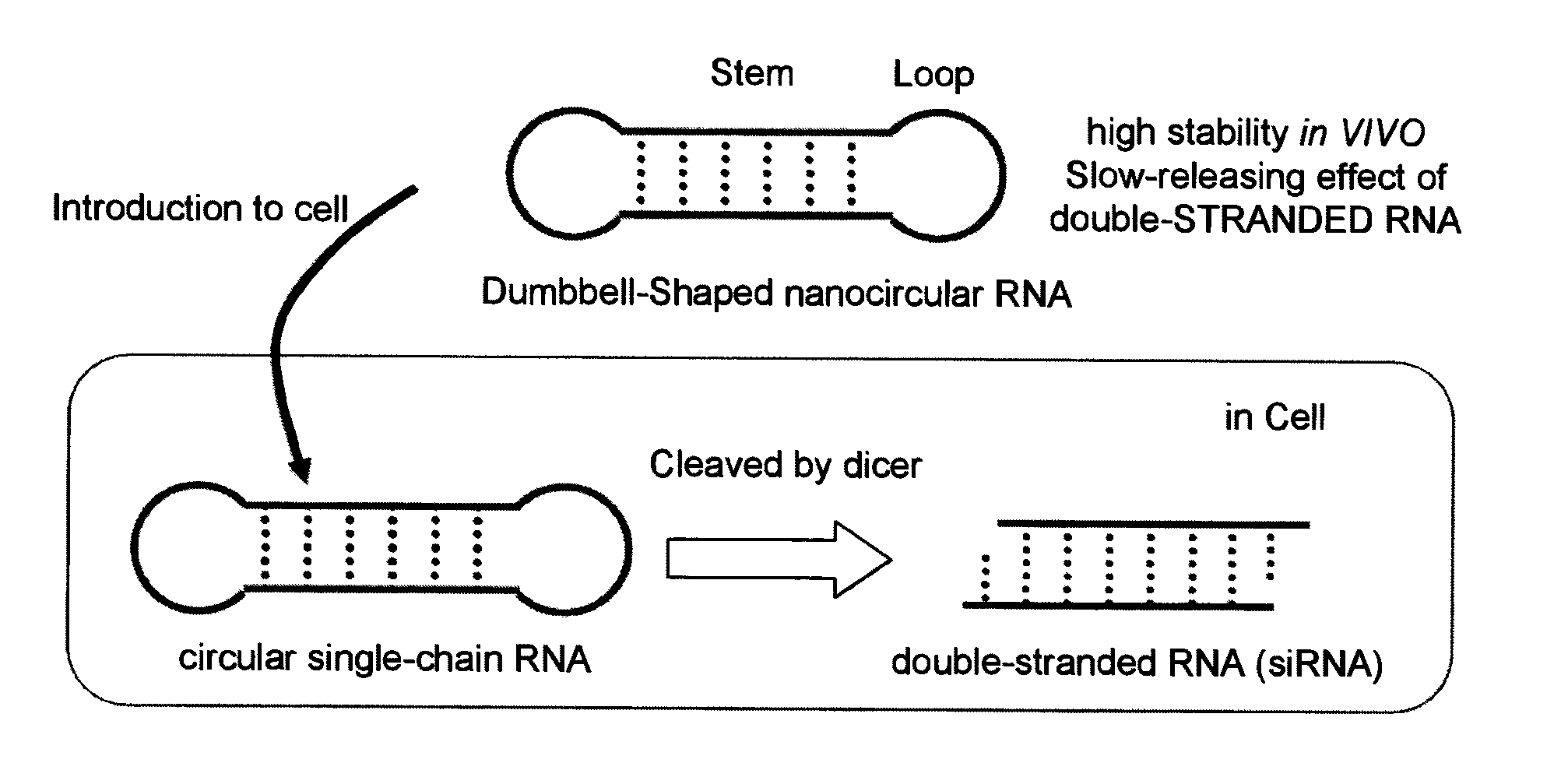
InactiveUS20100137407A1Efficient productionLess susceptible to enzymatic degradationOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesGeneticsSense strand
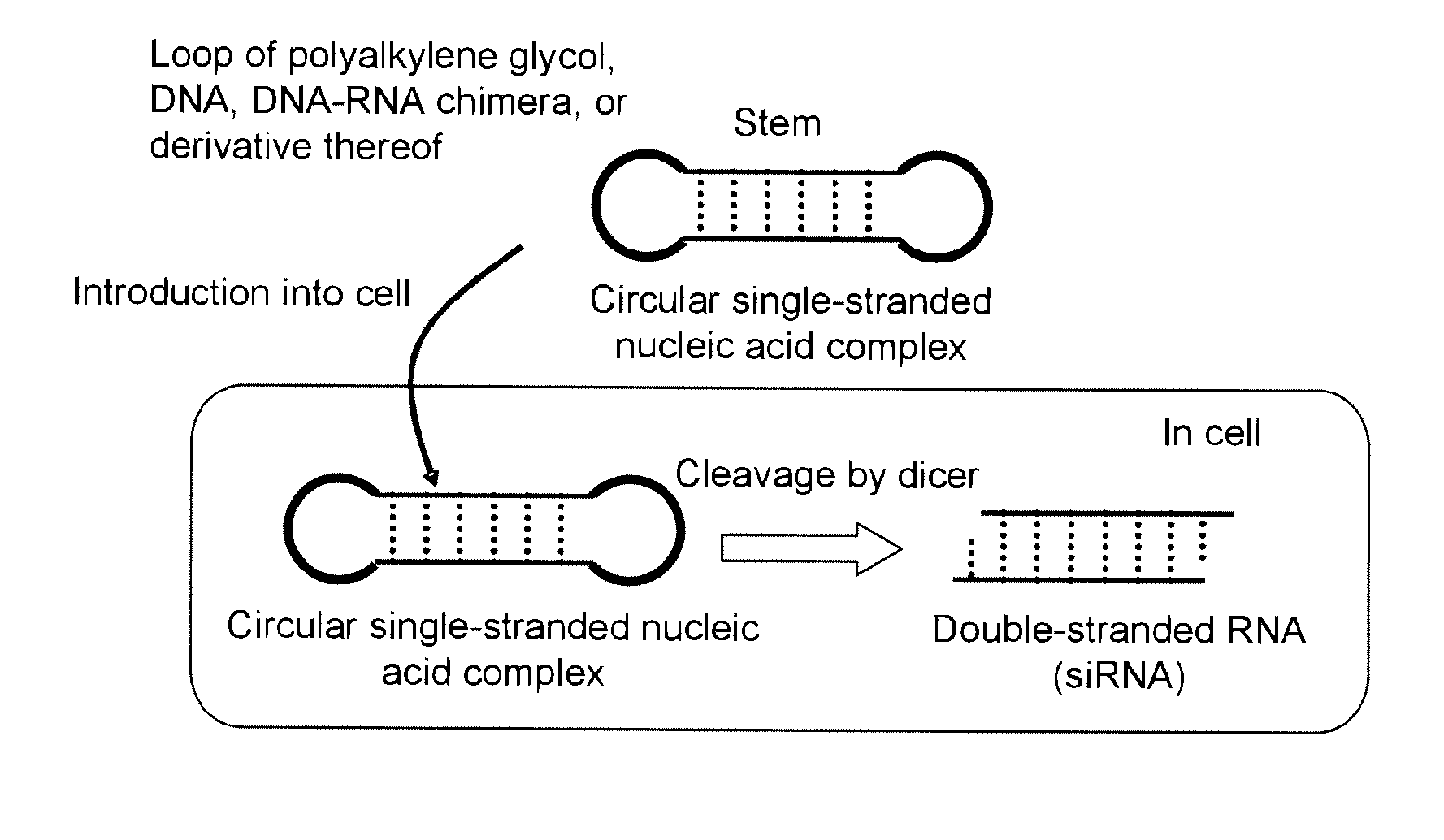
The present invention relates to a single-chain circular RNA having a sustained or slow-releasing RNA interference effect, characterized in that the single-chain circular RNA comprises a sense strand sequence, an antisense strand sequence complementary to the sense strand sequence, identical or different two loop sequences between the sense strand and the antisense strand, connecting both strands, wherein the sense strand and the antisense strand are paired to form a stem.
Owner:RIKEN +1
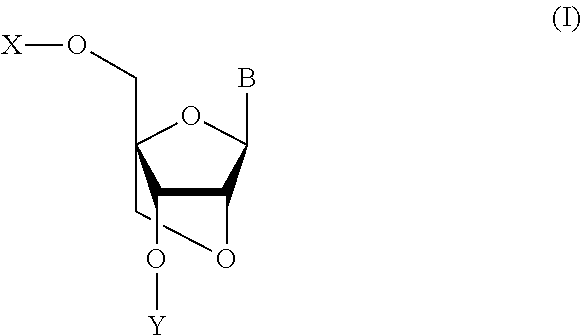
Bicyclonucleoside and oligonucleotide analogues
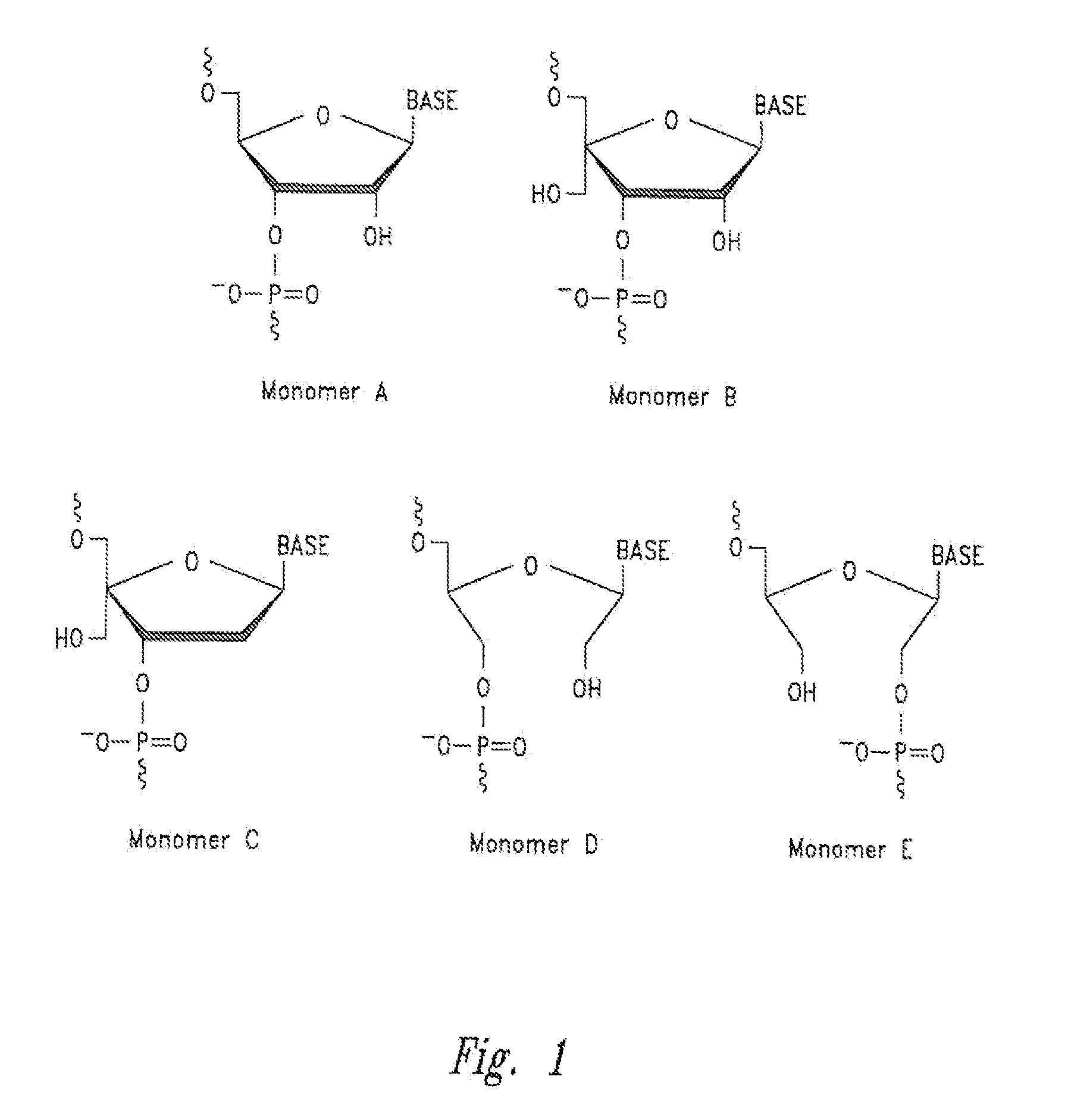
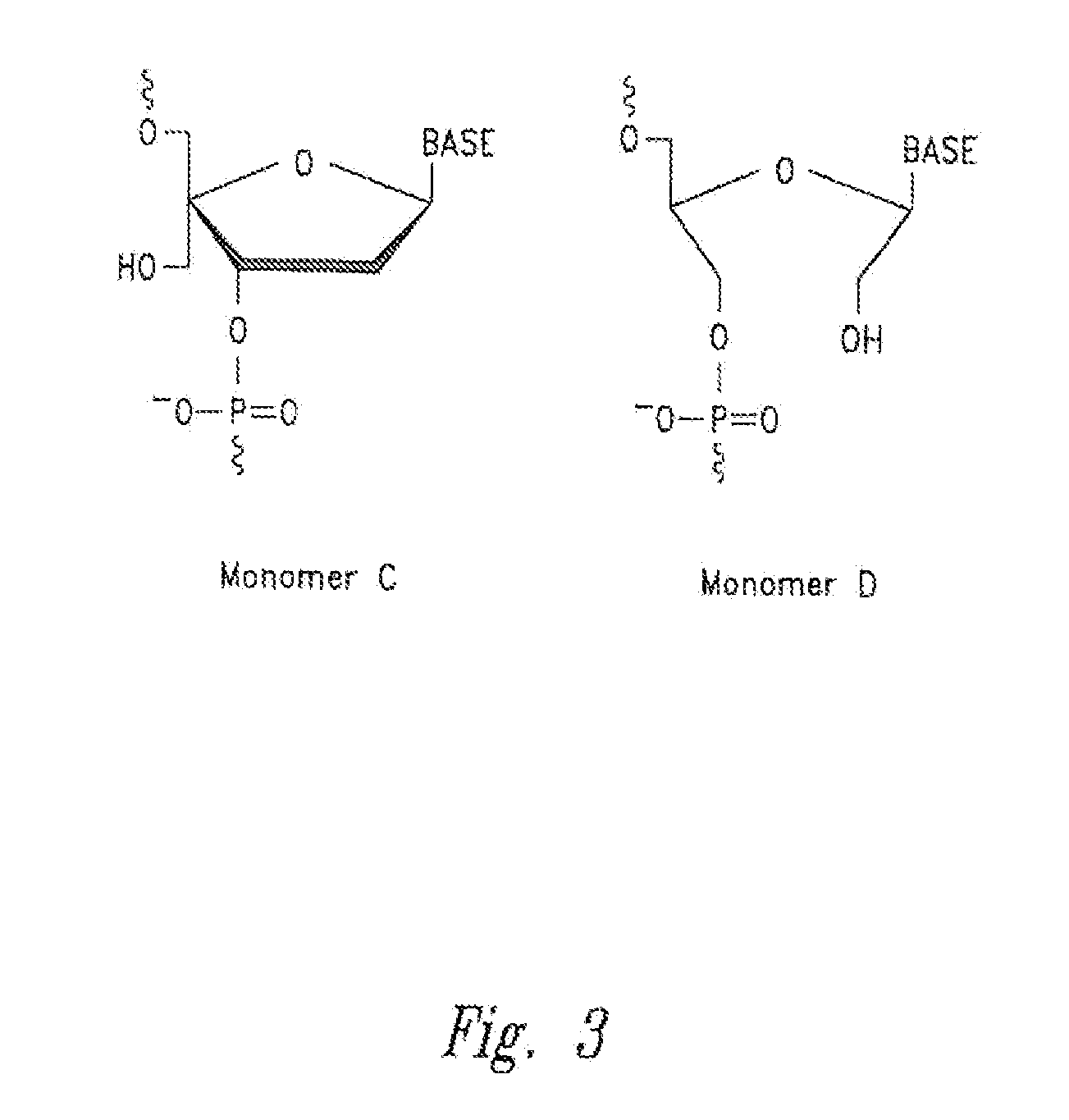
An oligo- or polynucleotide analogue having one or more structures of the general formulawhere B is a pyrimidine or purine nucleic acid base, or an analogue thereof,is disclosed. The use of this analogue provides an oligonucleotide analogue antisense molecule, which is minimally hydrolyzable with an enzyme in vivo, has a high sense strand binding ability, and is easily synthesized.
Owner:EXIQON AS +1
Chemically modified double stranded nucleic acid molecules that mediate RNA interference
InactiveUS20060217331A1Improve bioavailabilityMinimize the possibilityOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesNucleic acid structureDouble strand
This invention relates to compounds, compositions, and methods useful for modulating gene expression using chemically modified double stranded nucleic acid molecules. In particular, the instant invention features double stranded nucleic acid molecules including small nucleic acid molecules, such as short interfering nucleic acid (siNA), short interfering RNA (siRNA), double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), micro-RNA (miRNA), and short hairpin RNA (shRNA) molecules and methods used to modulate the expression of genes via RNA interference (RNAi). The invention features various modifications to double stranded nucleic acid structures, including chemically modified overhangs and optimized stabilization motifs of guide (antisense) strand and passenger (sense) strands of double stranded nucleic acid molecules that allow for potent RNA interference in therapeutically relevant applications.
Owner:SIRNA THERAPEUTICS INC
Novel sirna structure for minimizing off-target effects and relaxing saturation of rnai machinery and the use thereof
InactiveUS20120238017A1Enhanced gene silencing effectsSolve the real problemSugar derivativesActivity regulationNucleotideSense strand
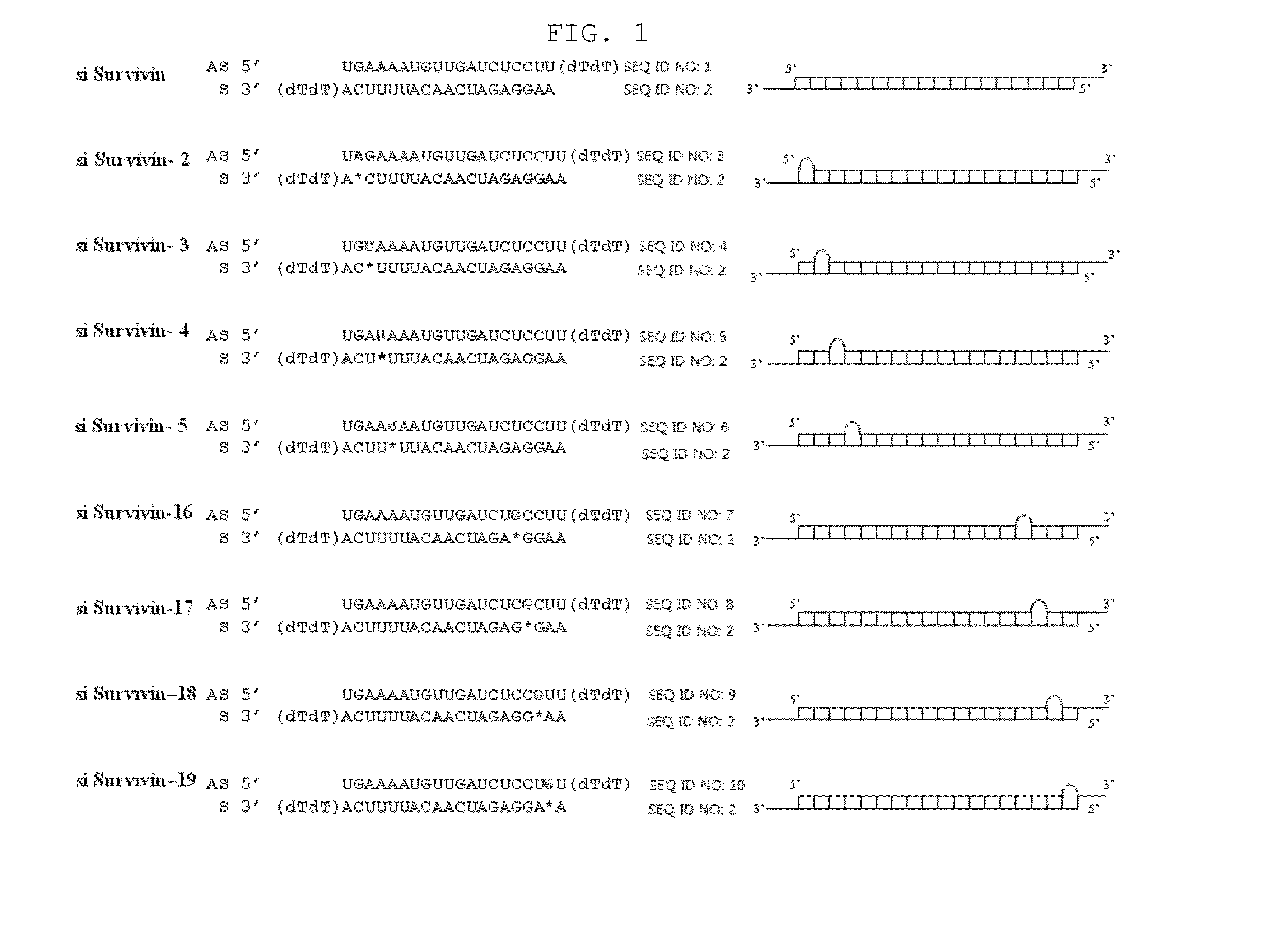
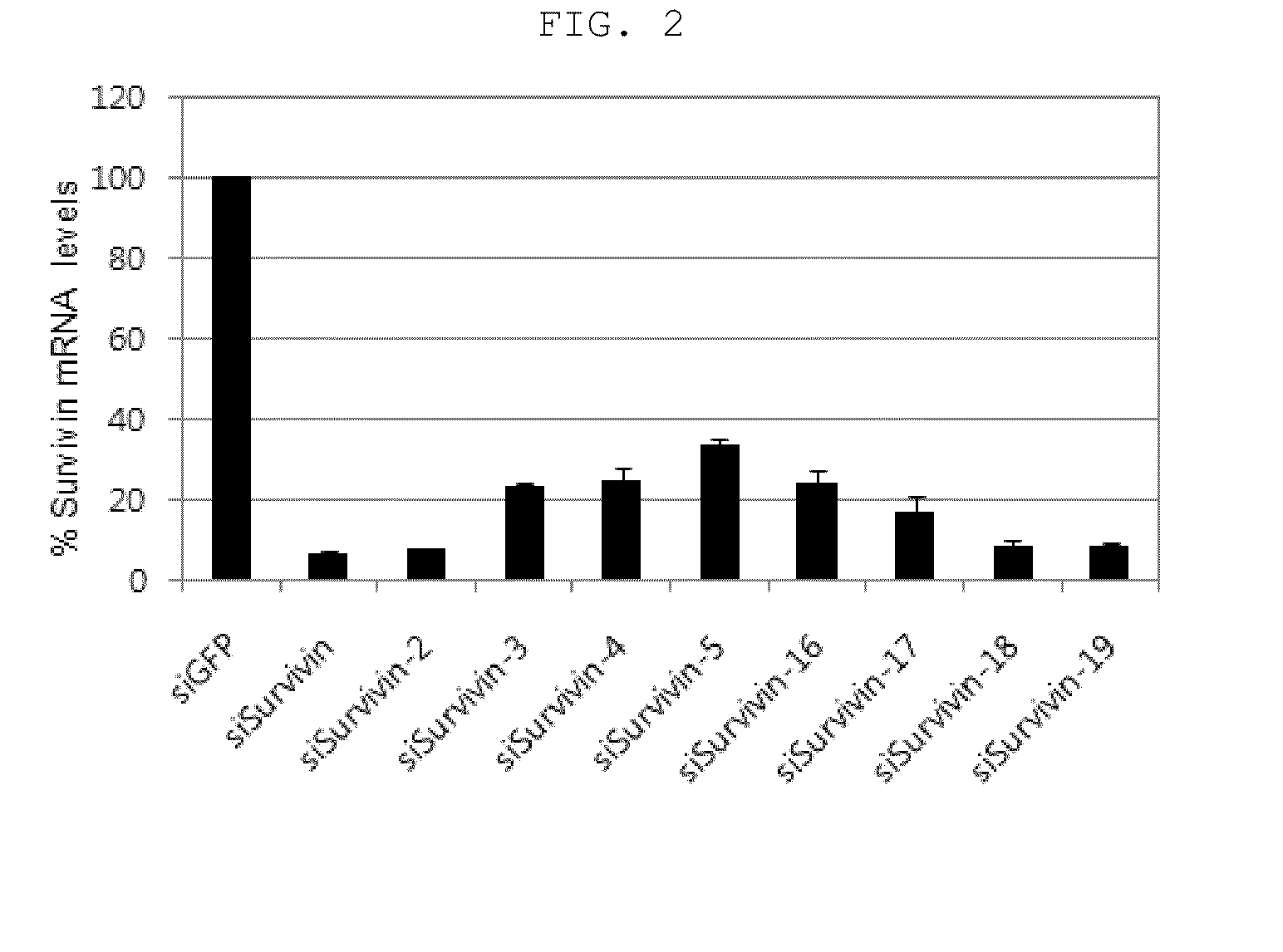
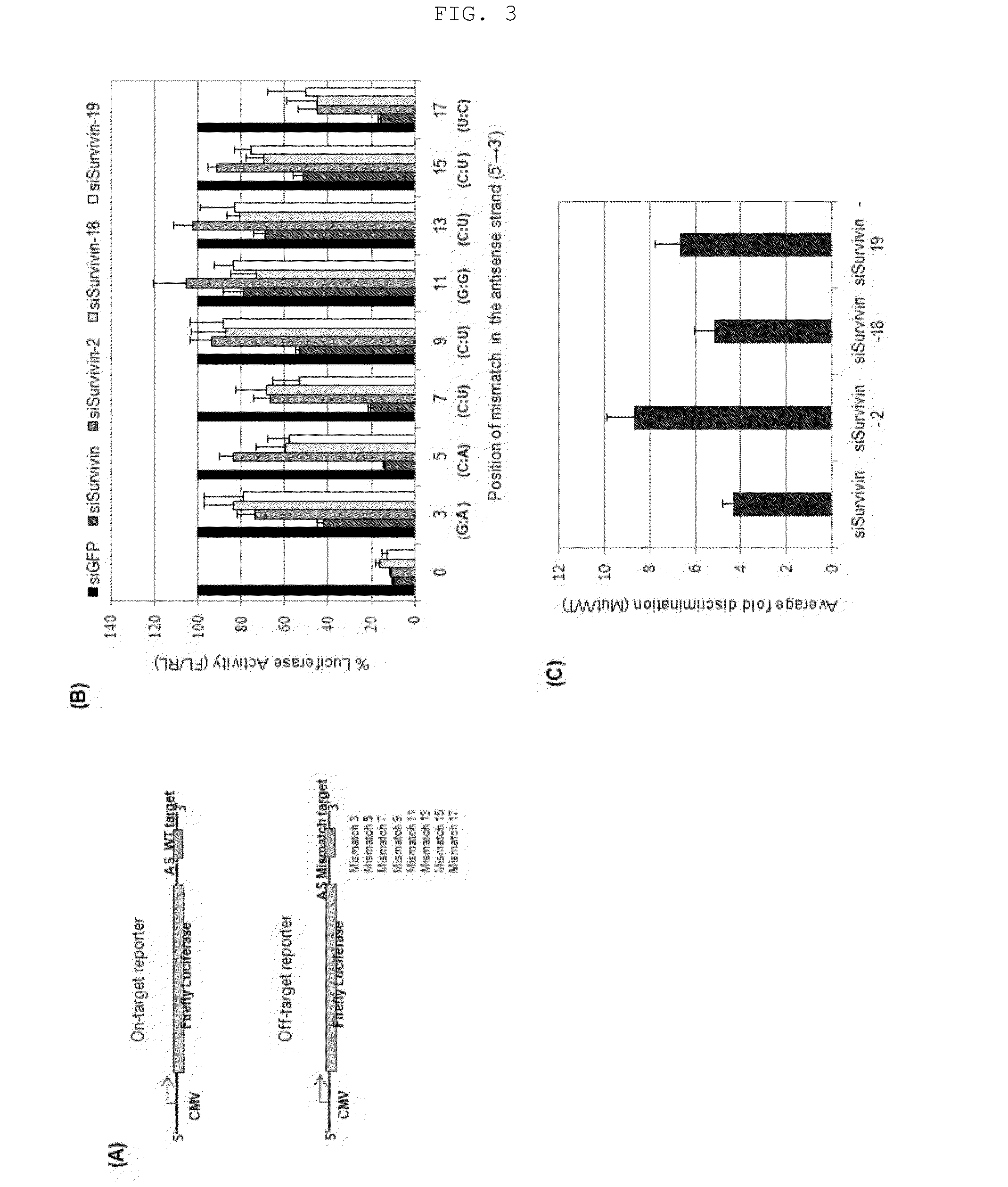
The present invention relates to a novel siRNA structure and the use thereof. More particularly, the invention relates to a double-stranded small interfering RNA molecule (siRNA molecule) comprising a 19-21 nucleotide (nt) antisense strand and a 15-19 nt sense strand having a sequence complementary to the antisense sequence, wherein the 5′ end of the antisense strand has a blunt end and the 3′ end of the antisense strand has an overhang, and to a method for silencing the expression of a target gene using the siRNA molecule.
Owner:OLIX PHARMA
SiRNA (Small interference ribonucleic acid) as well as medicine composition and pharmaceutical application thereof
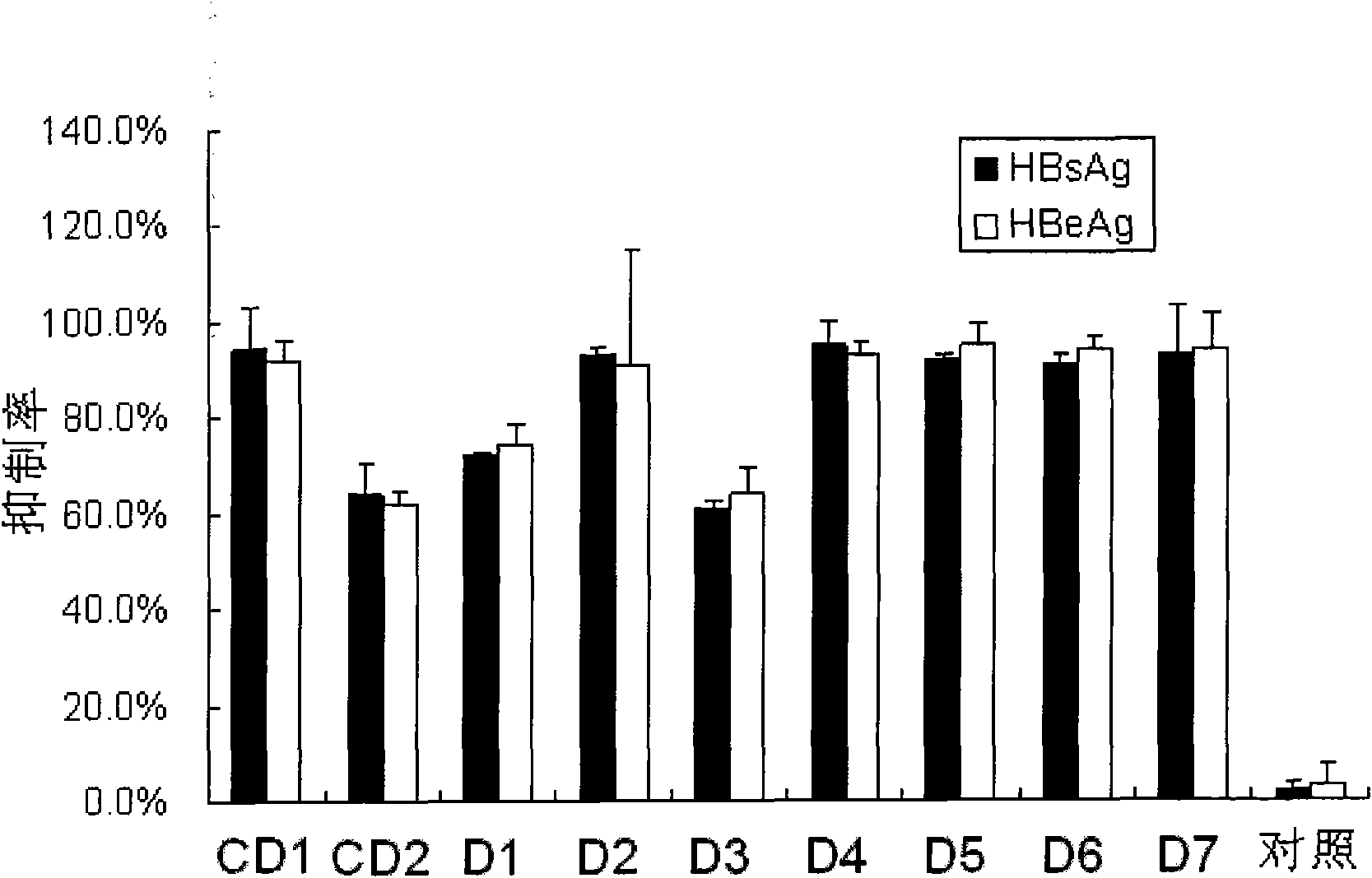
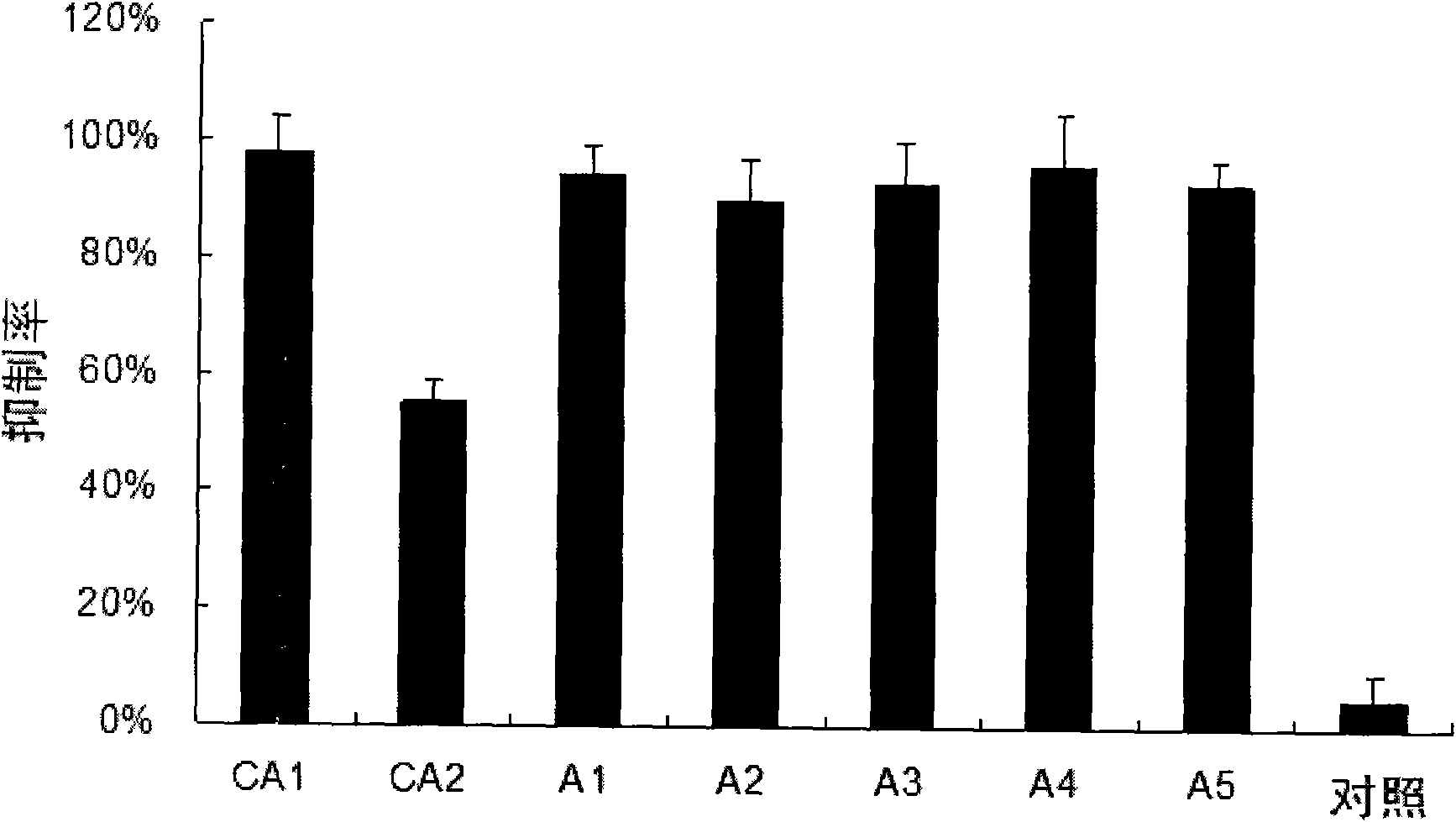
ActiveCN102140458AIncrease serum stabilityLow cytotoxicityGenetic material ingredientsDigestive systemSerum igeMedicine
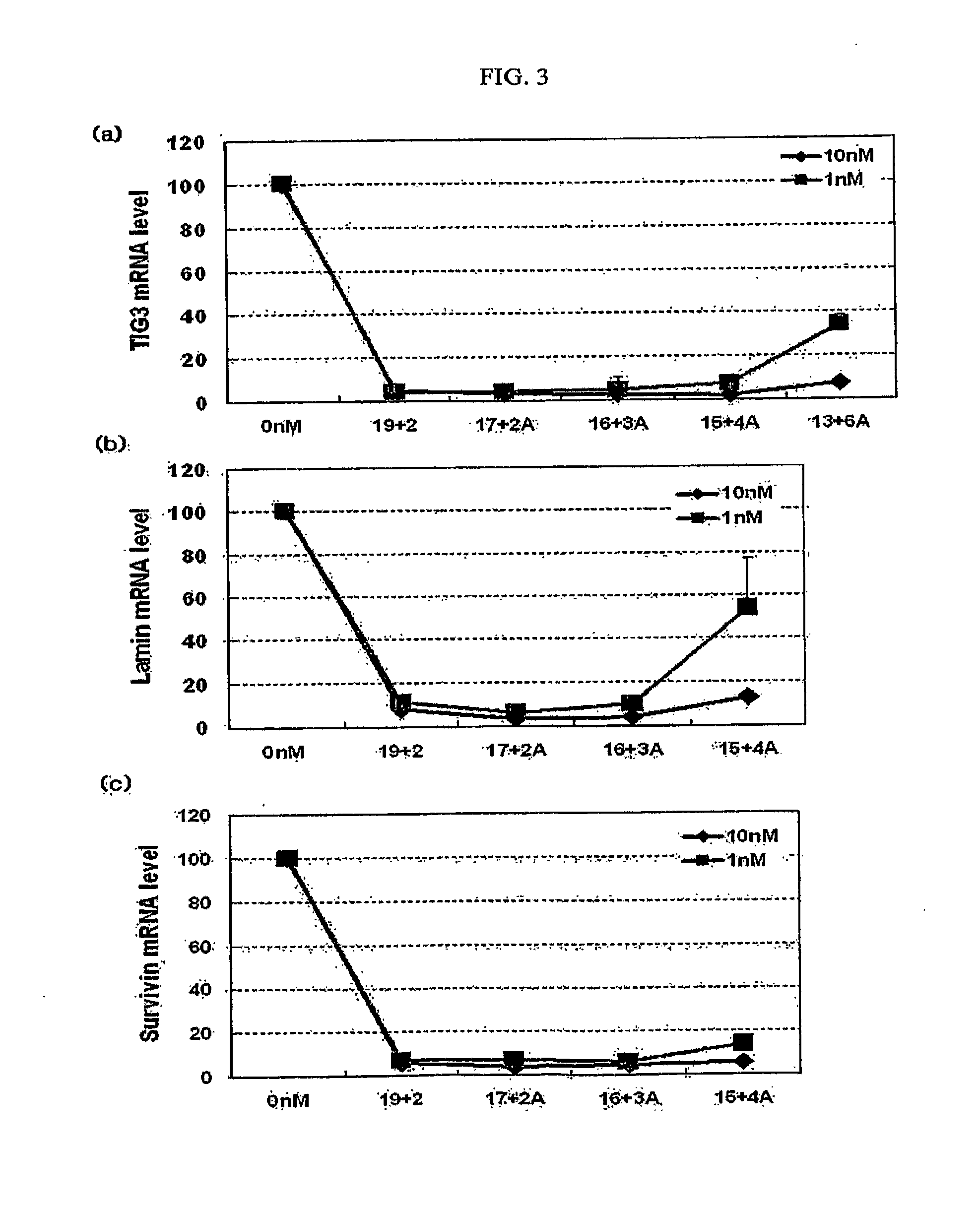
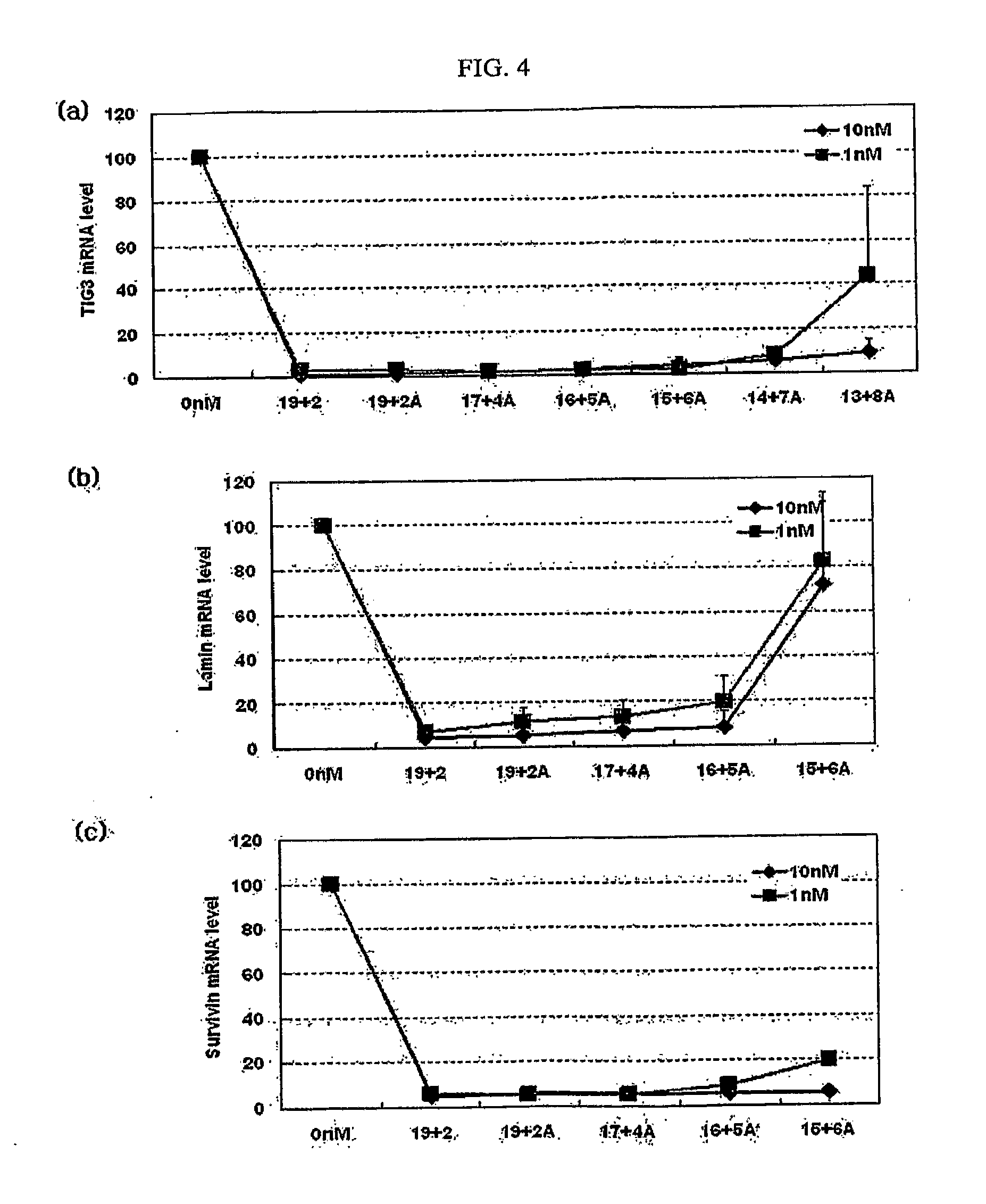
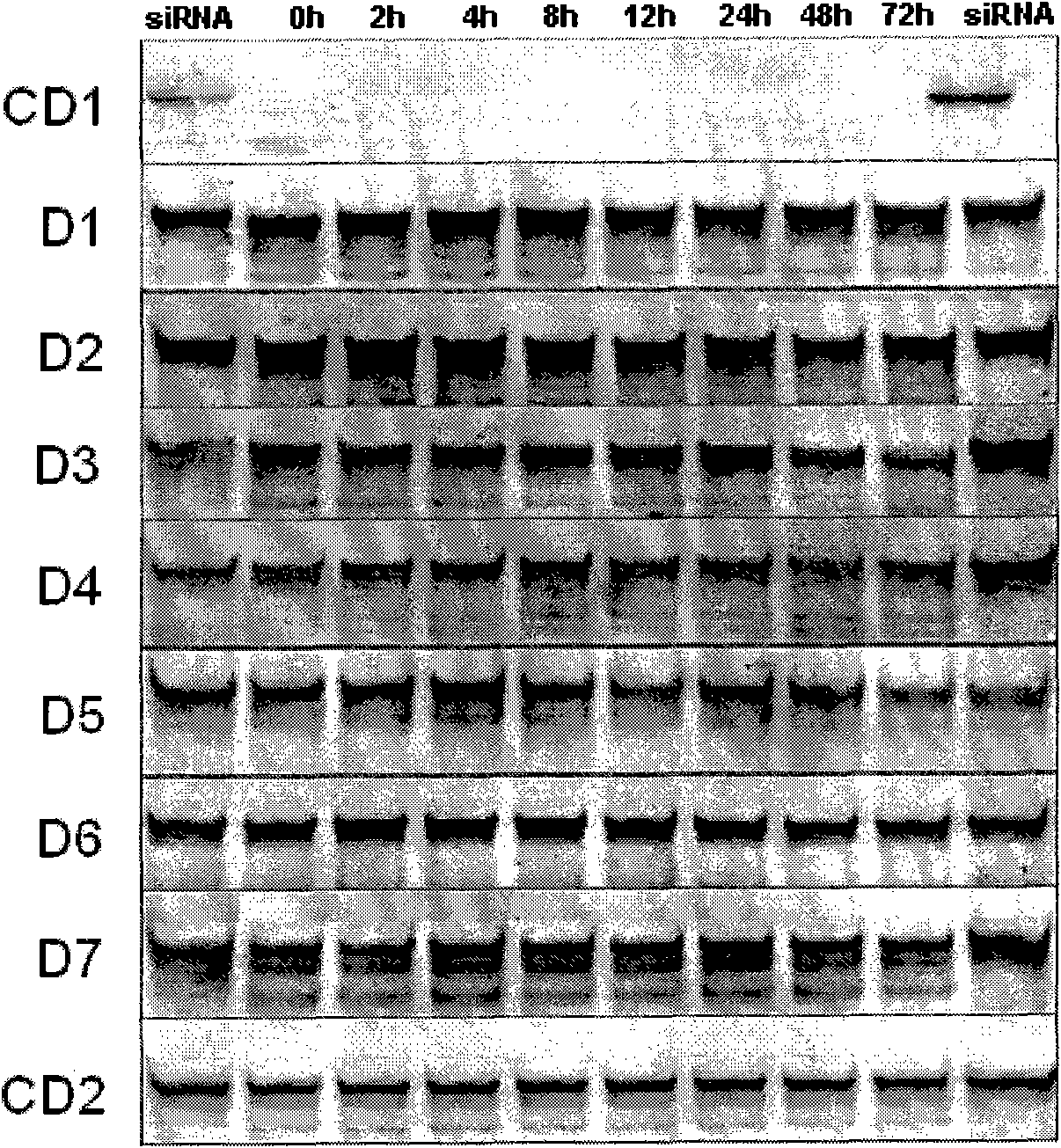
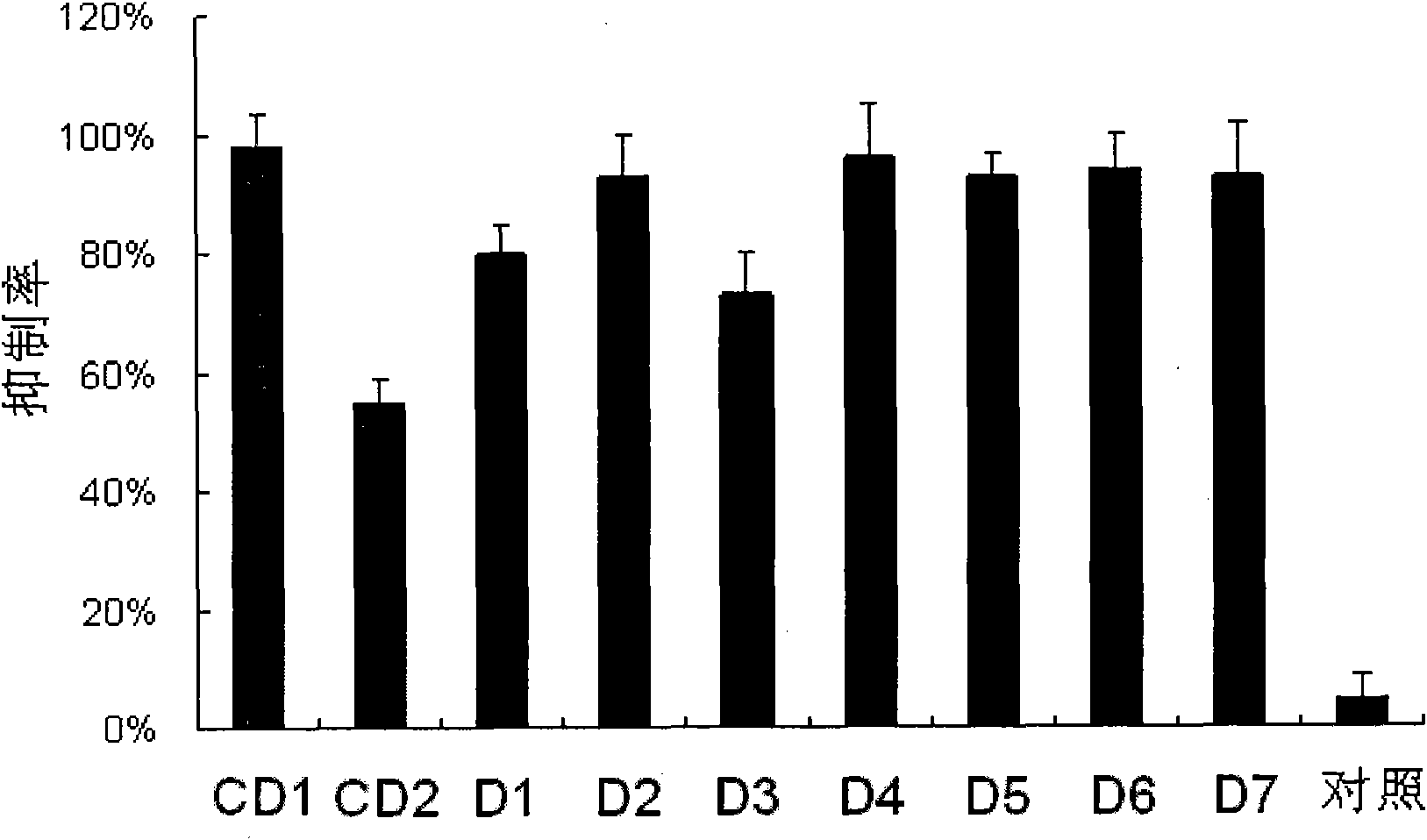
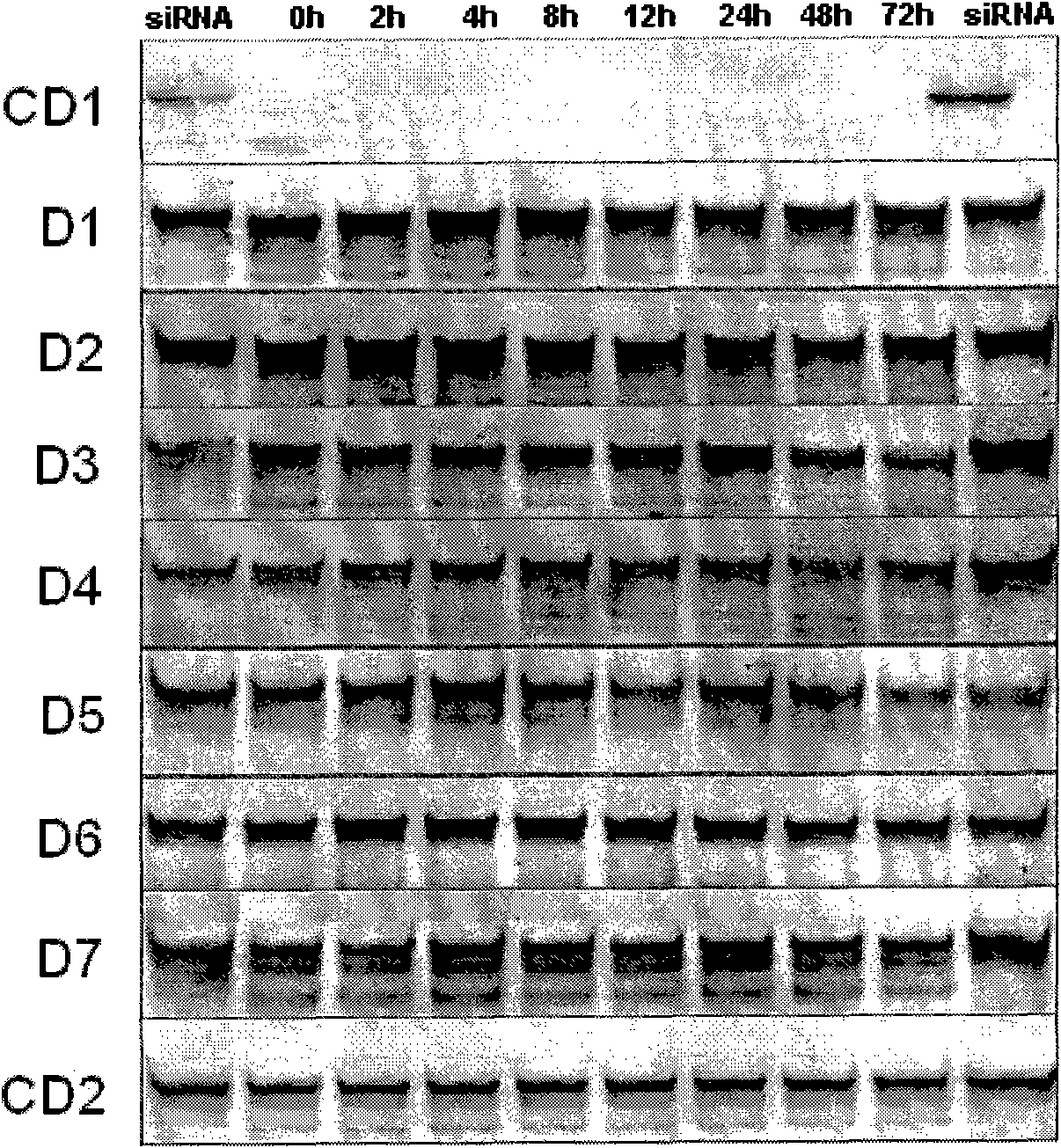
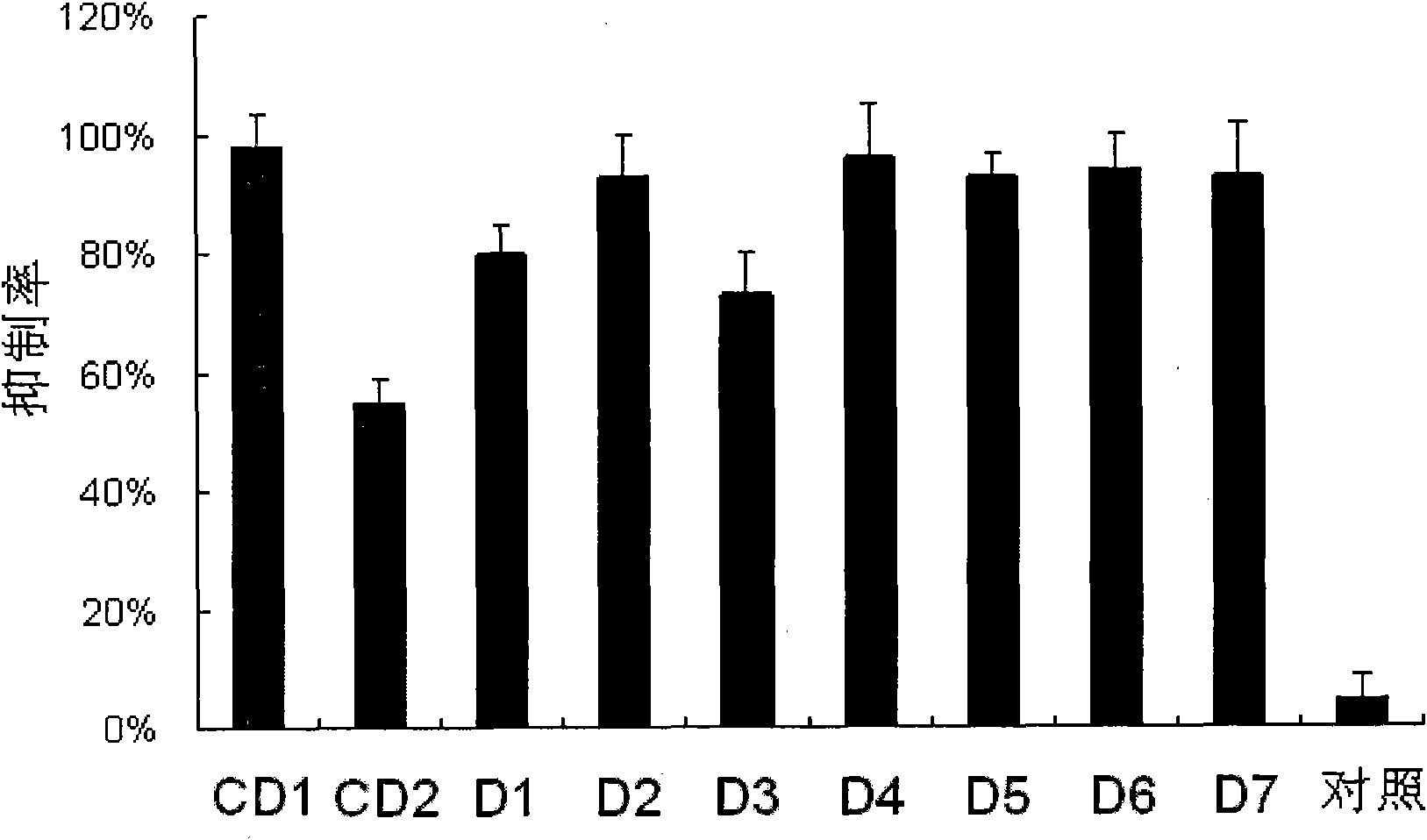
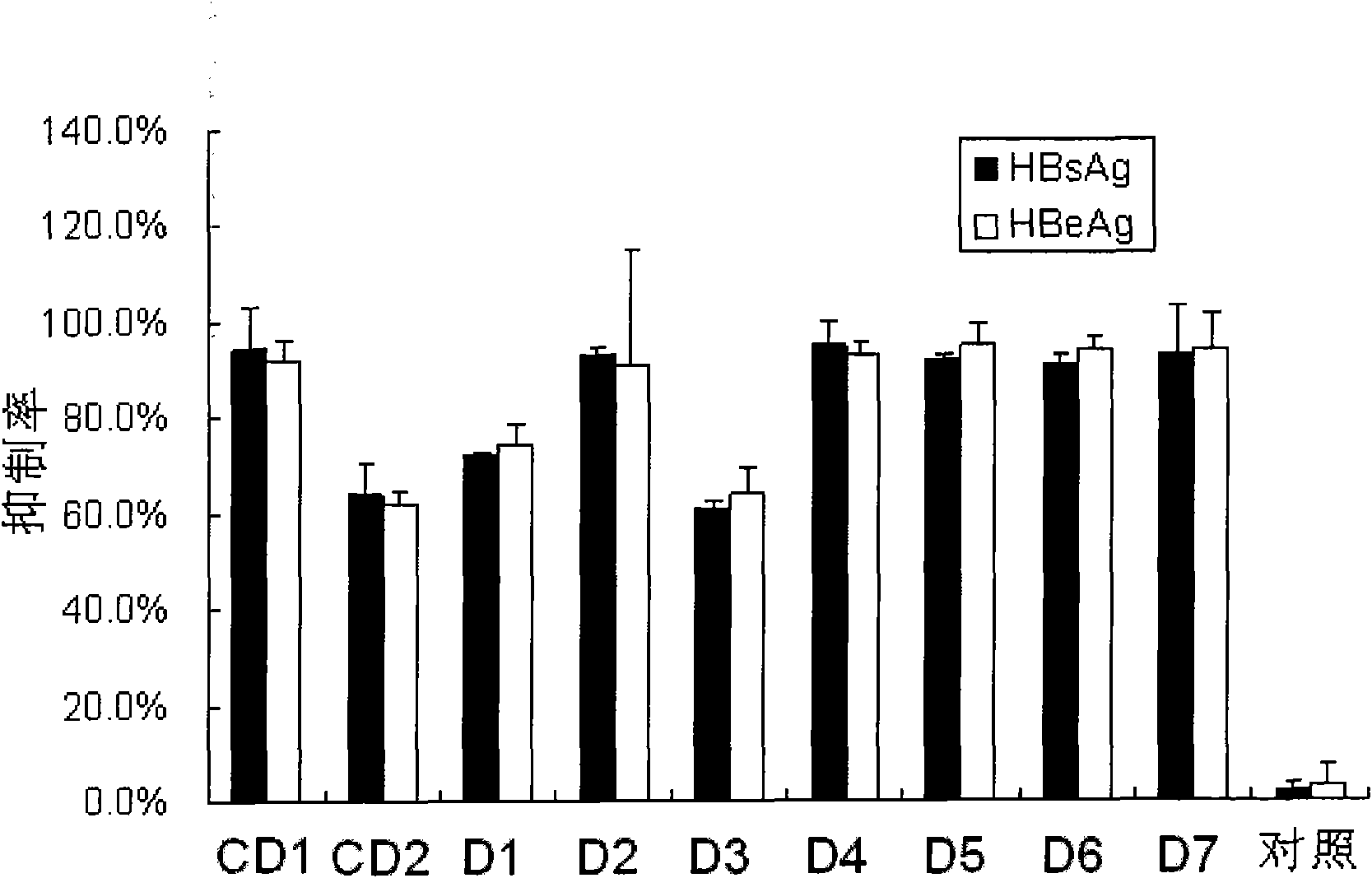
The invention provides a siRNA (small-interference ribonucleic acid) which has the following sequences: a sense strand of 5'-GAAAGUAUGUCAACGAAUUdTdT-3' and an antisense strand of 5'-AAUUCGUUGACAUACUUUCdTdT-3'; and the siRNA is modified by one of the modes shown in D1 to D7. The invention also provides a medicine composition for preventing and / or treating hepatitis B, which contains the siRNA provided in the invention as active constituents. The invention also provides an application of the siRNA in preparing medicaments for preventing and / or treating the hepatitis B. With specific modification, the purpose of increasing the serum stability of the siRNA can be achieved by only introducing a little modification so that the modified siRNA potential cytotoxicity and influences on biological activity are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
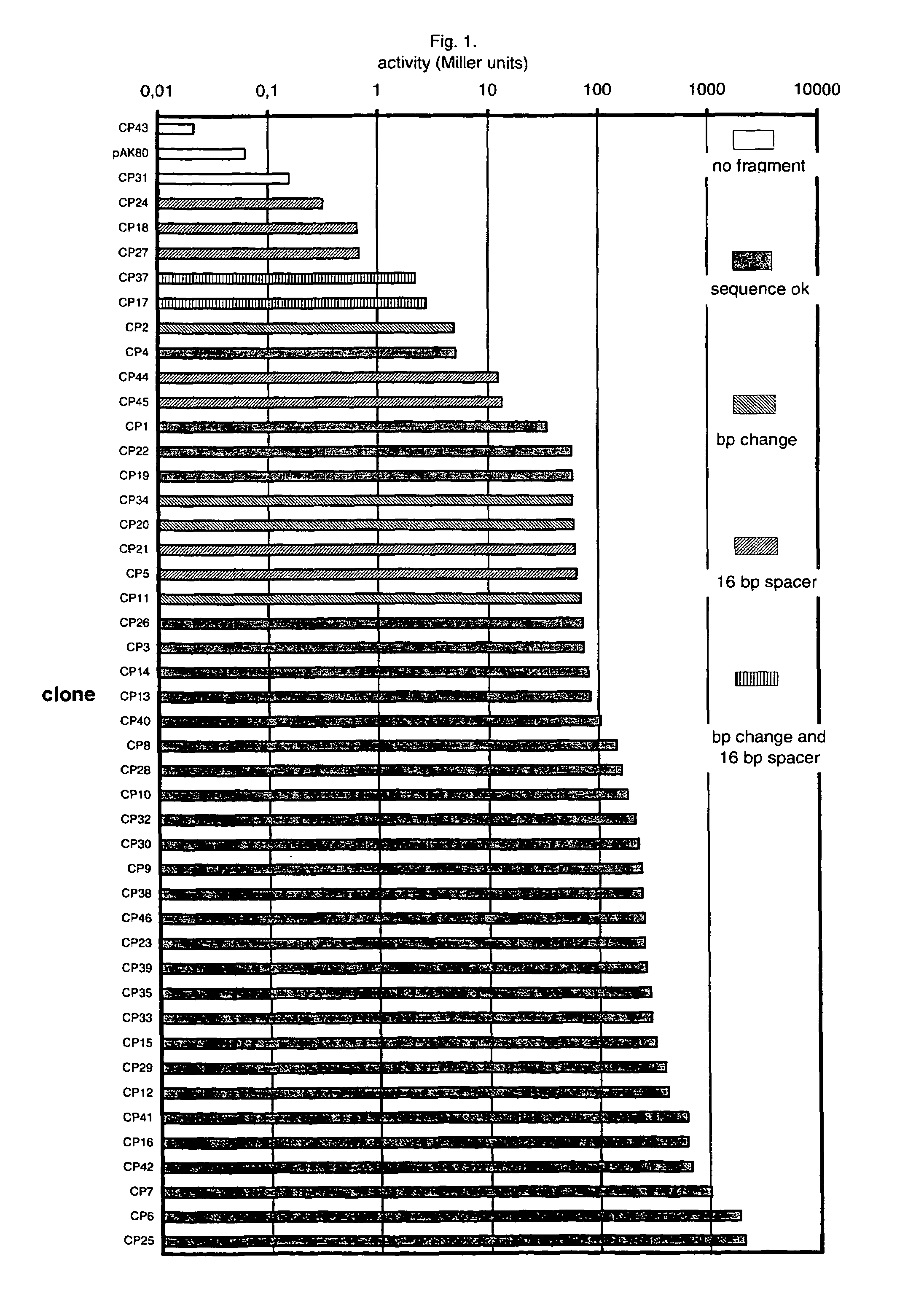
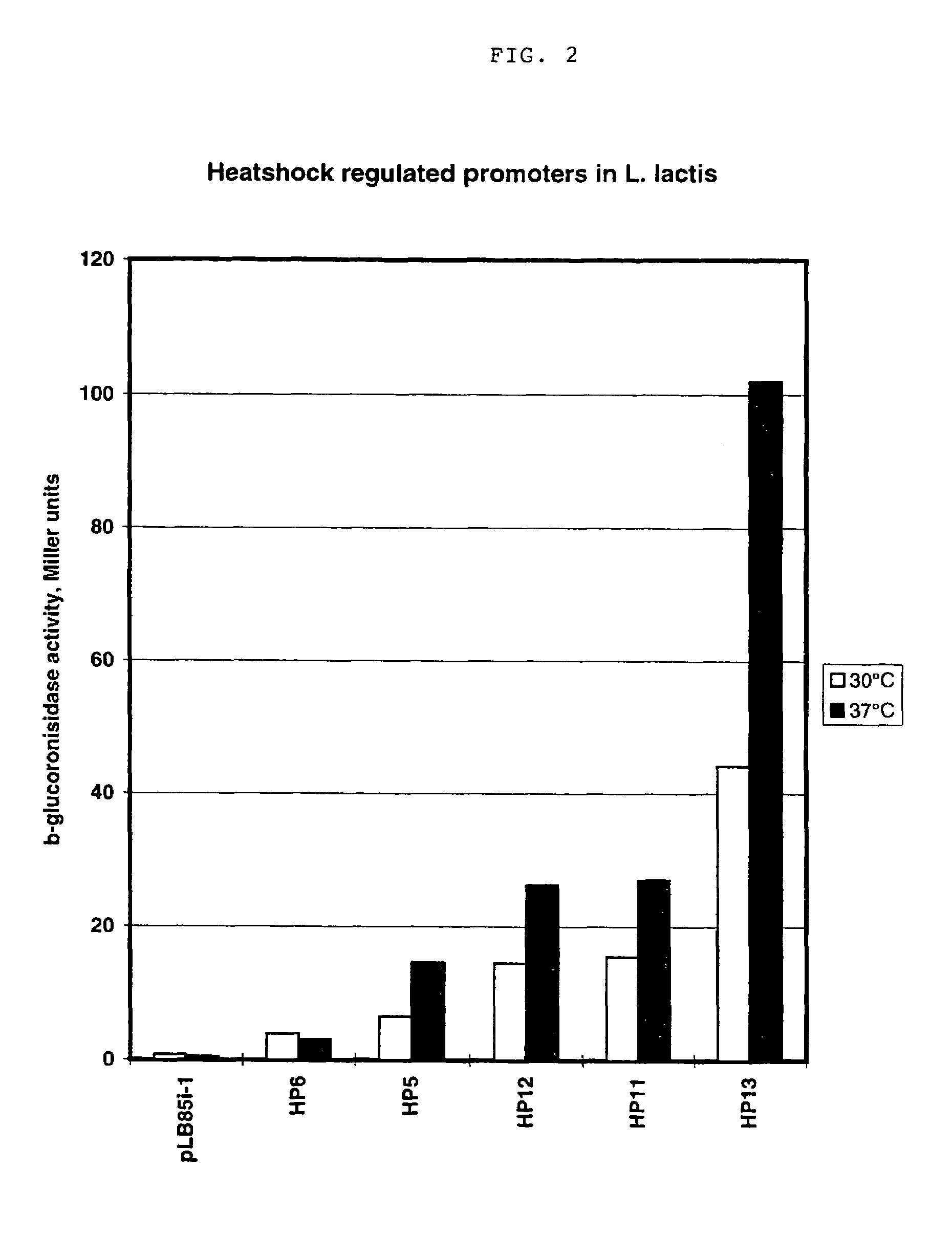
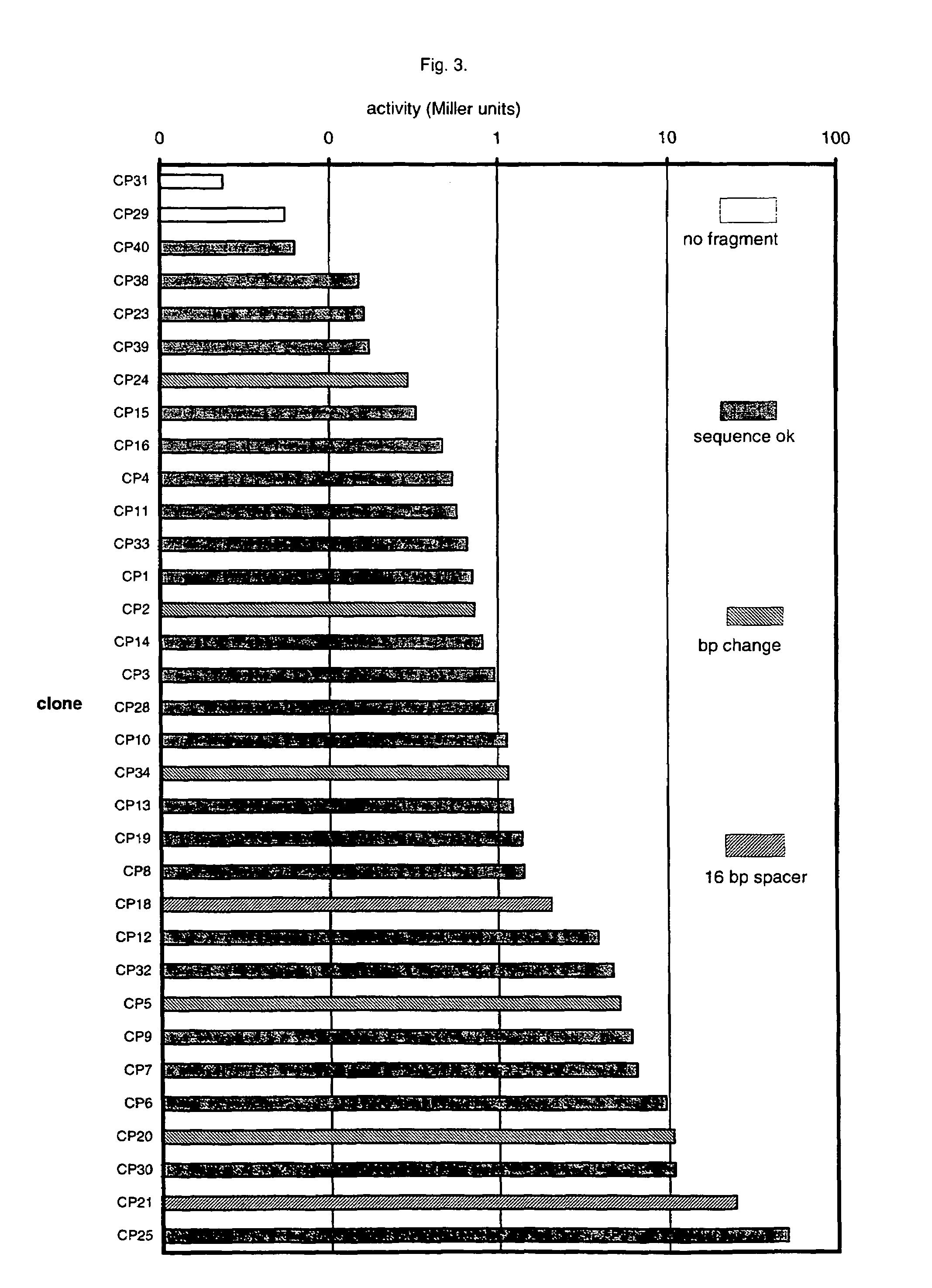
Artificial promoter libraries for selected organisms and promoters derived from such libraries
InactiveUS7199233B1Strong impactNone is suitable for purposeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideNucleobase
An artificial promoter library (or a set of promoter sequences) for a selected organism or group of organisms is constructed as a mixture of double stranded DNA fragments, the sense strands of which comprise at least two consensus sequences of efficient promoters from said organism or group of organisms, or parts thereof comprising at least half of each, and surrounding intermediate nucleotide sequences (spacers) of variable length in which at least 7 nucleotides are selected randomly among the nucleobases A, T, C and G. The sense strands of the double stranded DNA fragments may also include a regulatory DNA sequence imparting a specific regulatory feature, such as activation by a change in the growth conditions, to the promoters of the library. Further, they may have a sequence comprising one or more recognition sites for restriction endonucleases added to one or both of their ends. The selected organism or group of organisms may be selected from prokaryotes and from eukaryotes; and in prokaryotes the consensus sequences to be retained most often will comprise the −35 signal (−35 to −30): TTGACA and the −10 signal (−12 to −7): TATAAT or parts of both comprising at least 3 conserved nucleotides of each, while in eukaryotes said consensus sequences should comprise a TATA box and at least one upstream activation sequence (UAS). Such artificial promoter libraries can be used, e.g., for optimizing the expression of specific genes in various selected organisms.
Owner:JENSEN PETER RUHDAL +1
Small interfering nucleic acid, composition and application
ActiveCN111139242AEnhanced inhibitory effectSignificant clinical significanceOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSense strandRibose
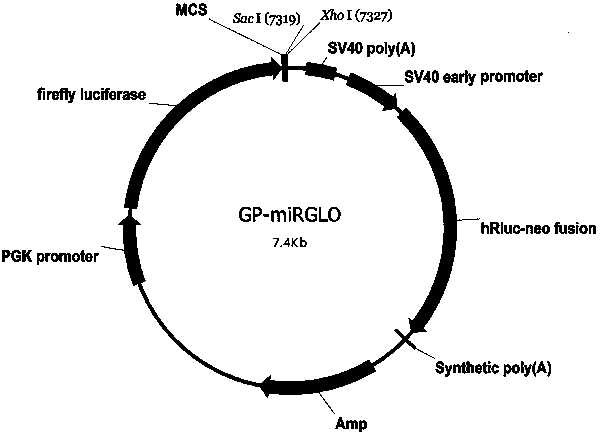
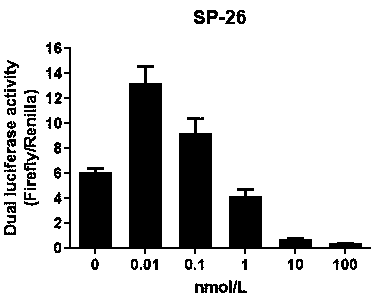
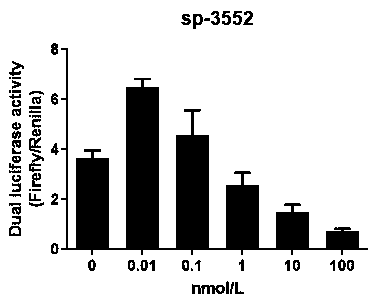
The invention discloses small interfering nucleic acid as well as a composition and application thereof. The invention claims to protect siRNA, which is PP-1758, PP-17660, PP-20091, PP-20163, SP-26, SP-179, SP-2013, SP-2867, SP-3169, SP-3552, MG-83, NP-208 or NP-241, wherein a part of nucleotides of the positive-sense strand are 2 '-O-methyl ribonucleotides, and a part of phosphate groups are thiophosphate groups. The invention provides brand new siRNA and a composition thereof. The brand new siRNA and the composition thereof can effectively prevent and / or treatment novel coronavirus.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA
Modified double-stranded RNA agents
One aspect of the present invention relates to double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) agent capable of inhibiting the expression of a target gene. The sense strand of the dsRNA agent comprises at least one thermally destabilizing nucleotide, and at least one said thermally destabilizing nucleotide occurring at a site opposite to the seed region (positions 2-8) of the antisense strand; and the antisense strand of the dsRNA agent comprises at least two modified nucleotides that provide the nucleotide a steric bulk that is less than or equal to the steric bulk of a 2′-OMe modification, wherein said modified nucleotides are separated by 11 nucleotides in length. Other aspects of the invention relates to pharmaceutical compositions comprising these dsRNA agents suitable for therapeutic use, and methods of inhibiting the expression of a target gene by administering these dsRNA agents, e.g., for the treatment of various disease conditions.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Small interfering nucleic acid for inhibiting novel coronavirus, and composition and applications thereof
ActiveCN111139241AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsSense strandRibonucleotide
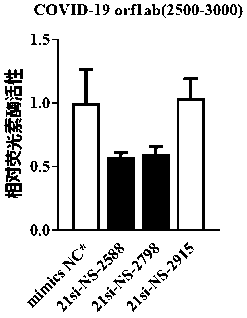
The invention discloses small interfering nucleic acid for inhibiting novel coronavirus, and a composition and applications thereof. The siRNA contains a positive-sense strand and a antisense strand;the siRNA is 21-si-SP-2069, 21-si-SP-2289, 21-si-SP-3292, 21-si-P3-242, 21-si-P8-62, 21-si-P8-164, 21-si-P10B-158, 21-si-P14-19, 21-si-NP-722, 21-si-NP-1123, 21-si-NS-2139 or 21-si-NS-2798; and partial nucleotide of the positive-sense strand or the antisense strand is 2'-O-methyl ribonucleotide, and partial phosphate groups are phosphorothioate groups. The provided brand-new siRNA and the composition thereof can effectively prevent and / or treat novel coronavirus.
Owner:SUZHOU GENEPHARMA +1
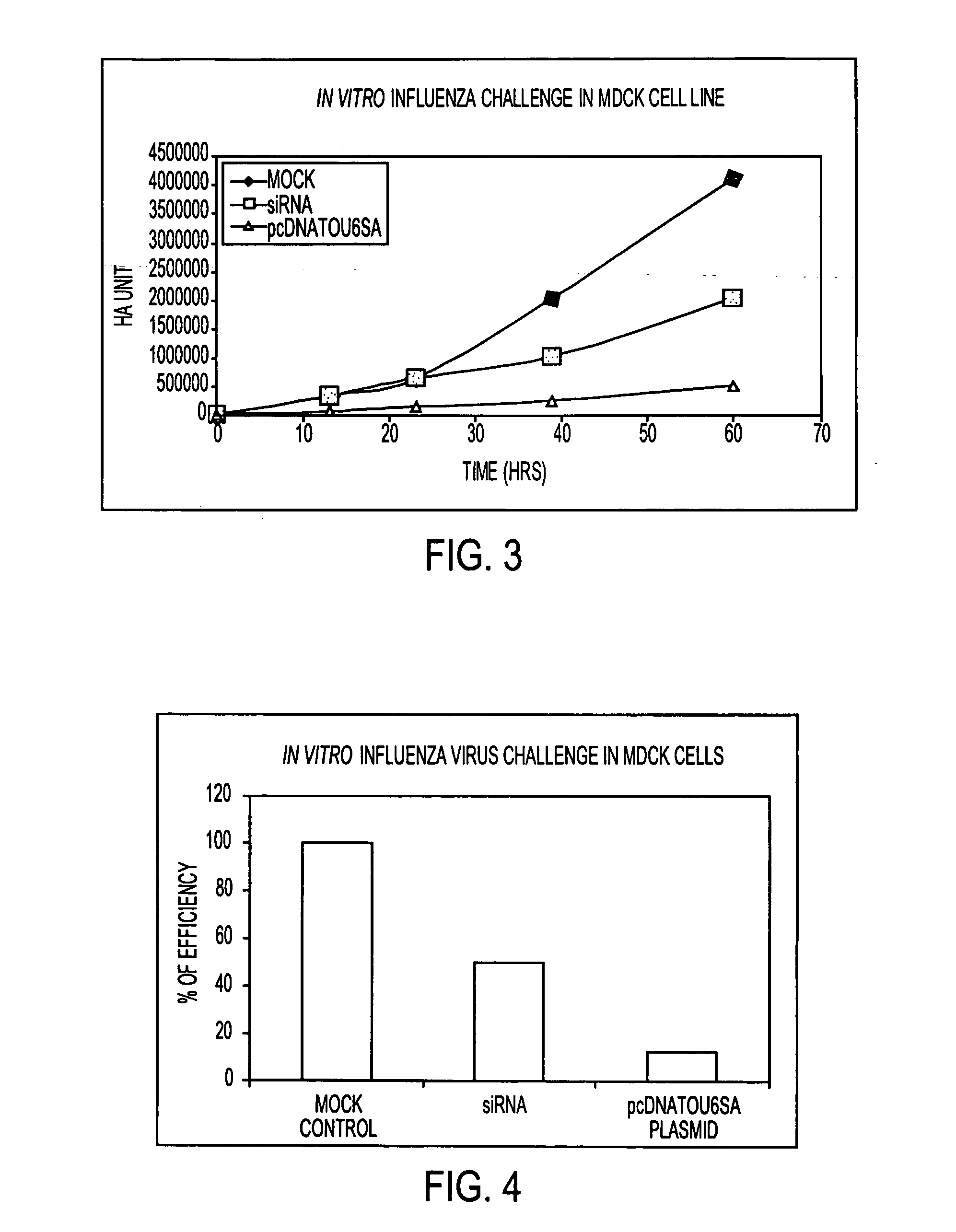
Potent inhibition of influenza virus by specifically designed short interfering RNA
Owner:CALIFORNIA POLYTECHNIC STATE UNIVERSITY
Novel sirna structure for minimizing off-target effects caused by antisense strands, and use thereof
ActiveUS20130130377A1Improve targeting selectivityEliminate the effects ofSugar derivativesActivity regulationNucleotideSense strand
The present invention relates to a novel siRNA structure and the use thereof, and more particularly to a double-stranded siRNA molecule comprising an antisense strand and a sense strand, wherein the siRNA molecule has at least one single nucleotide bulge formed by introducing a single nucleotide into the antisense strand, particularly at position 2 from the 5′ end, and to a method of using the same to silence a target gene. The siRNA molecule of the invention shows high target gene silencing efficiency while minimizing off-target effects caused by the antisense strand, and thus has improved target selectivity. Accordingly, the siRNA molecule of the invention can be substituted for conventional siRNA molecules and can be widely be used in siRNA-based gene silencing techniques, including gene therapy.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Long non-coding RNA sequence relevant to human melanoma cells and application thereof
InactiveCN101633923AGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseEukaryotic plasmids
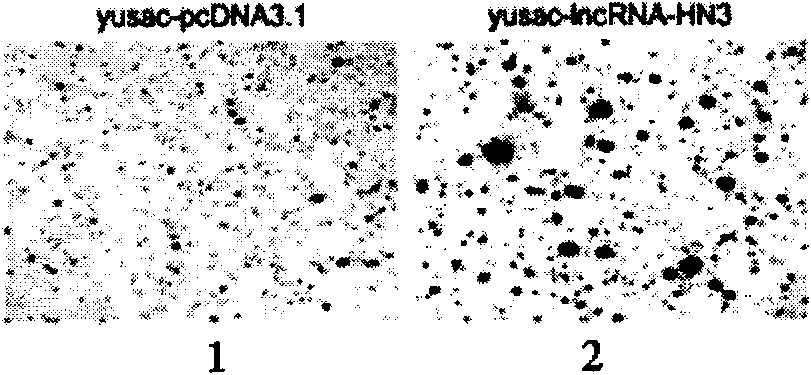
The invention provides a long non-coding RNA (long non-coding RNA, 1ncRNA)-incRNA-HN3 sequence relevant to human melanoma cells, and an RNA interference (RNA interference, RNAi) target spot sequence, a short-hairpin RNA (short-hairpin RNA, shRNA) sequence, an shRNA coded small molecule interference RNA (small interference RNA, siRNA), a coding shRNA coding strand and an anti-sense strand DNA sequence, coding shRNA recombinant plasmids of the long non-coding RNA sequence, and the invention relates to the applications of the long non-coding RNA sequence for preparing reagents for diagnosing melanoma diseases and drugs for treating the melanoma diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
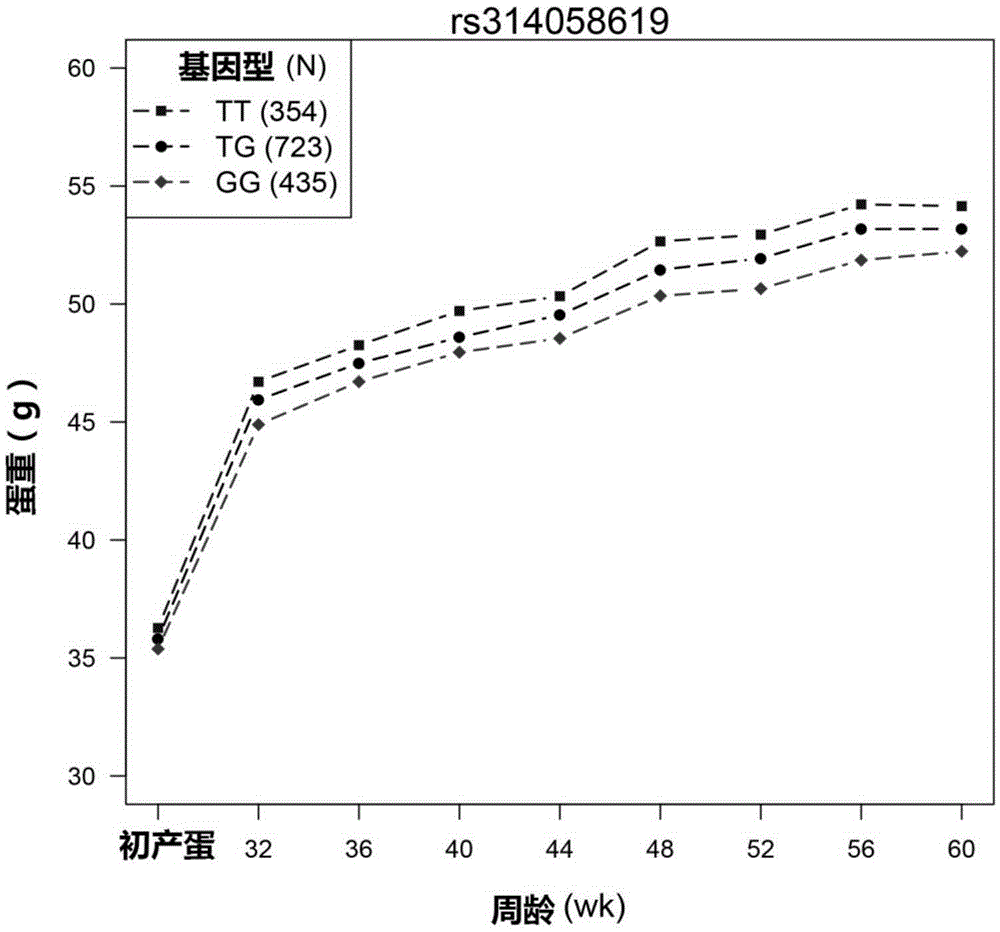
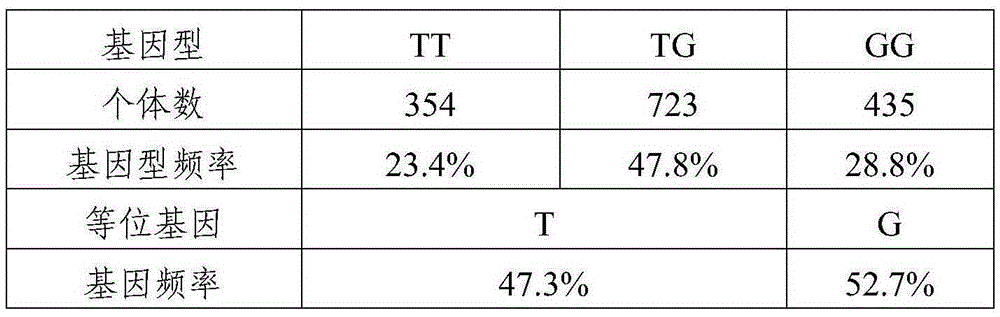
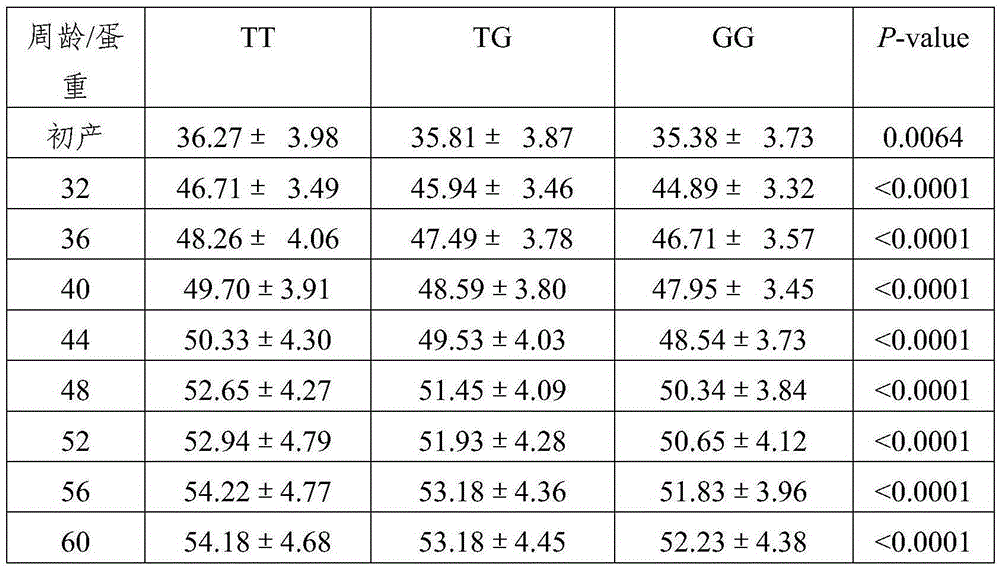
SNP molecular marker related to egg weight and application of SNP molecular marker
InactiveCN105349637AReduce manufacturing costSpeed up genetic progressMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAnimal scienceNucleotide
The invention provides an SNP molecular marker related to egg weight and application of the SNP molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker corresponds to 169, 930, 974th deoxynucleotide of a Number one chromosome positive-sense strand of chicken reference genome Gallus_gallus-4.0 version sequence information issued in NCBI, wherein the nucleotide is T or G. An SNP locus is never reported before, thereby being a newly-found genetic molecular marker. The SNP molecular marker can be applied to early-stage selection of egg weight at different week ages and assisting of chicken breeding, lowering of production cost and accelerating of genetic progress can be facilitated, and the SNP molecular marker has quite high economic application value and scientific research value.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
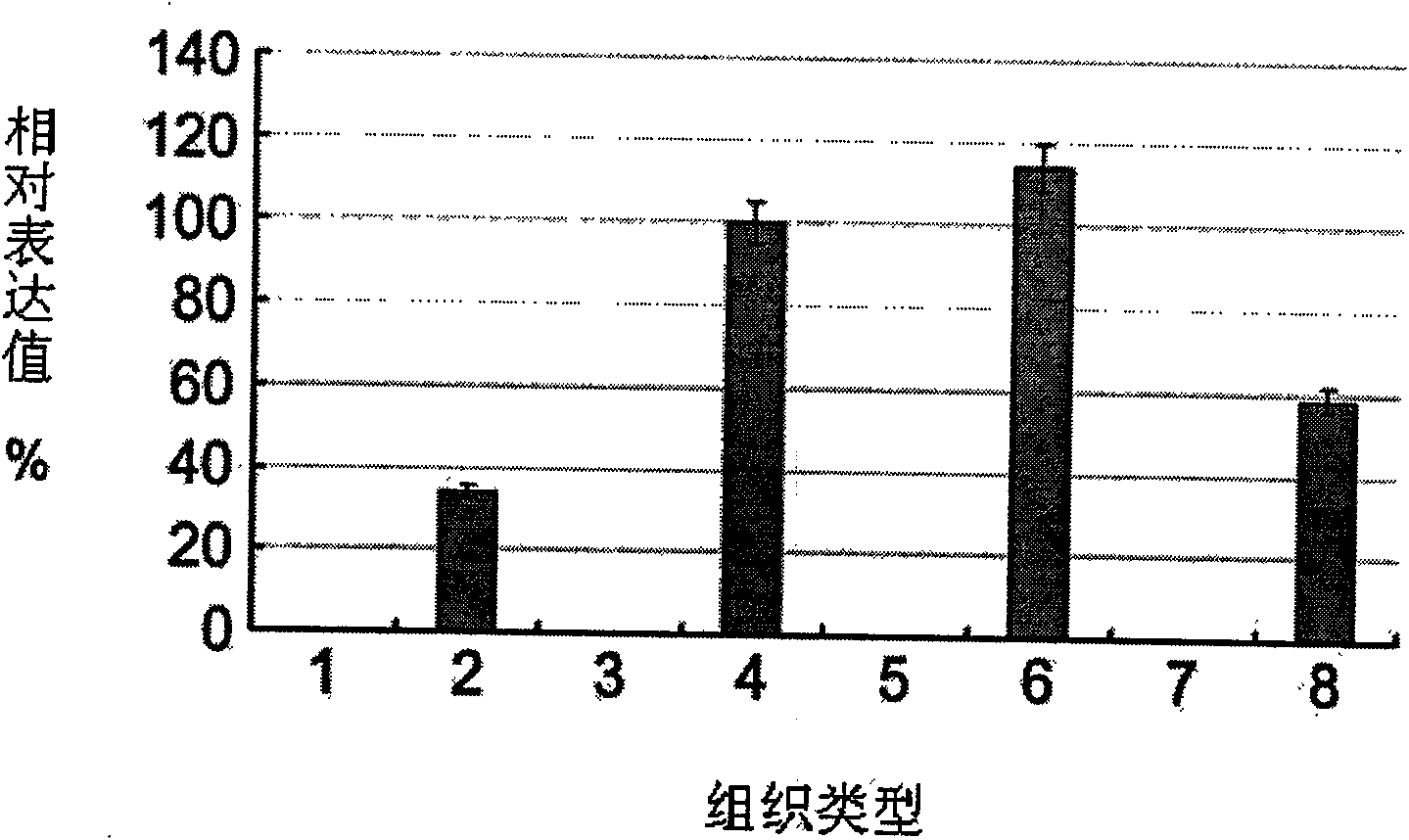
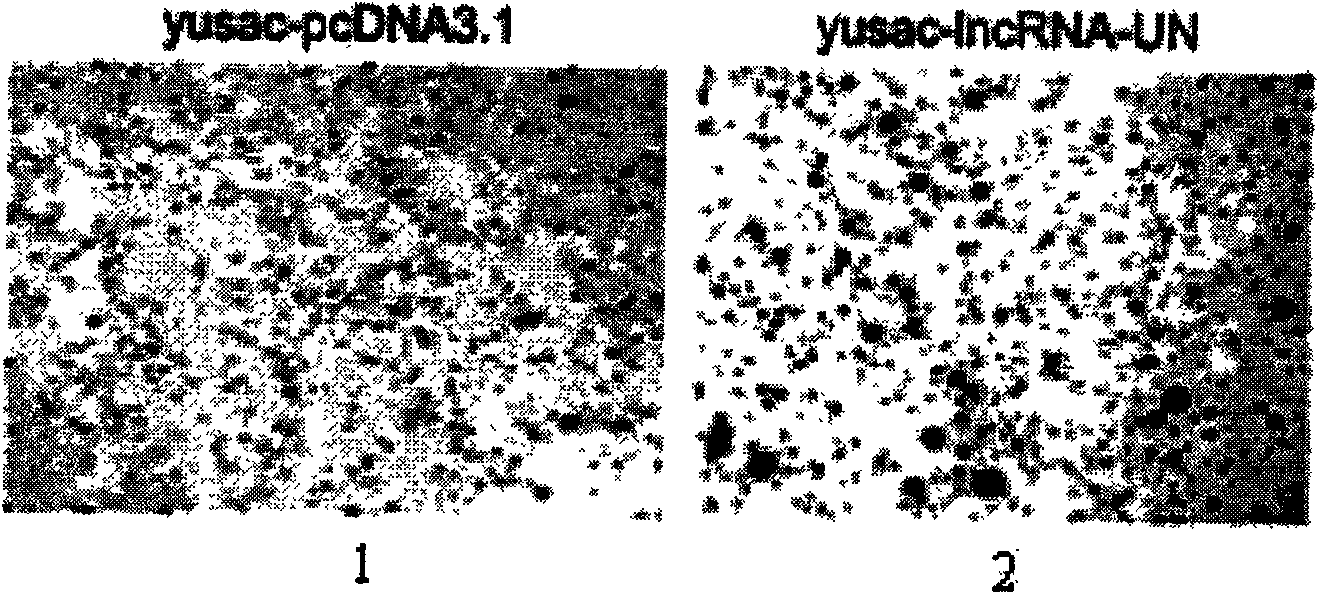
Long non-coding RNA sequence of human melanoma cell specific expression and application thereof
InactiveCN101619312AEasy diagnosisGood treatment effectGenetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementCell specificDisease
The invention discloses a long non-coding RNA (lnc RNA-UN) of human melanoma cell specific expression, an RNA interfering target spot thereof, a short hairpin RNA (shRNA) of the RNA interfering target spot, a small interfering RNA (siRNA), a sense strand DNA and an antisense strand DNA of the coding short hairpin RNA and a recombinant plasmid of a transcription short hairpin RNA. Proved by experiments, the lnc RNA-UN is highly expressed in a melanoma tissue and not expressed in a peficancerous tissue and can be applied to preparing a reagent for diagnosing melanoma diseases. Proved by the experiments, the recombinant plasmid of the transcription short hairpin RNA expresses the shRNA and the siRNA in a melanoma cell and can obviously degrade the cell endogenous lncRNA-UN and restrain the malignant growth of the melanoma cell, thus the shRNA and the siRNA of the RNA interfering target spot of the lncRNA-UN and the recombinant plasmid of the transcription short hairpin RNA can be applied to medicaments for treating the melanoma diseases.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Small interfering nucleic acid and medical composite and pharmaceutical applications of nucleic acid
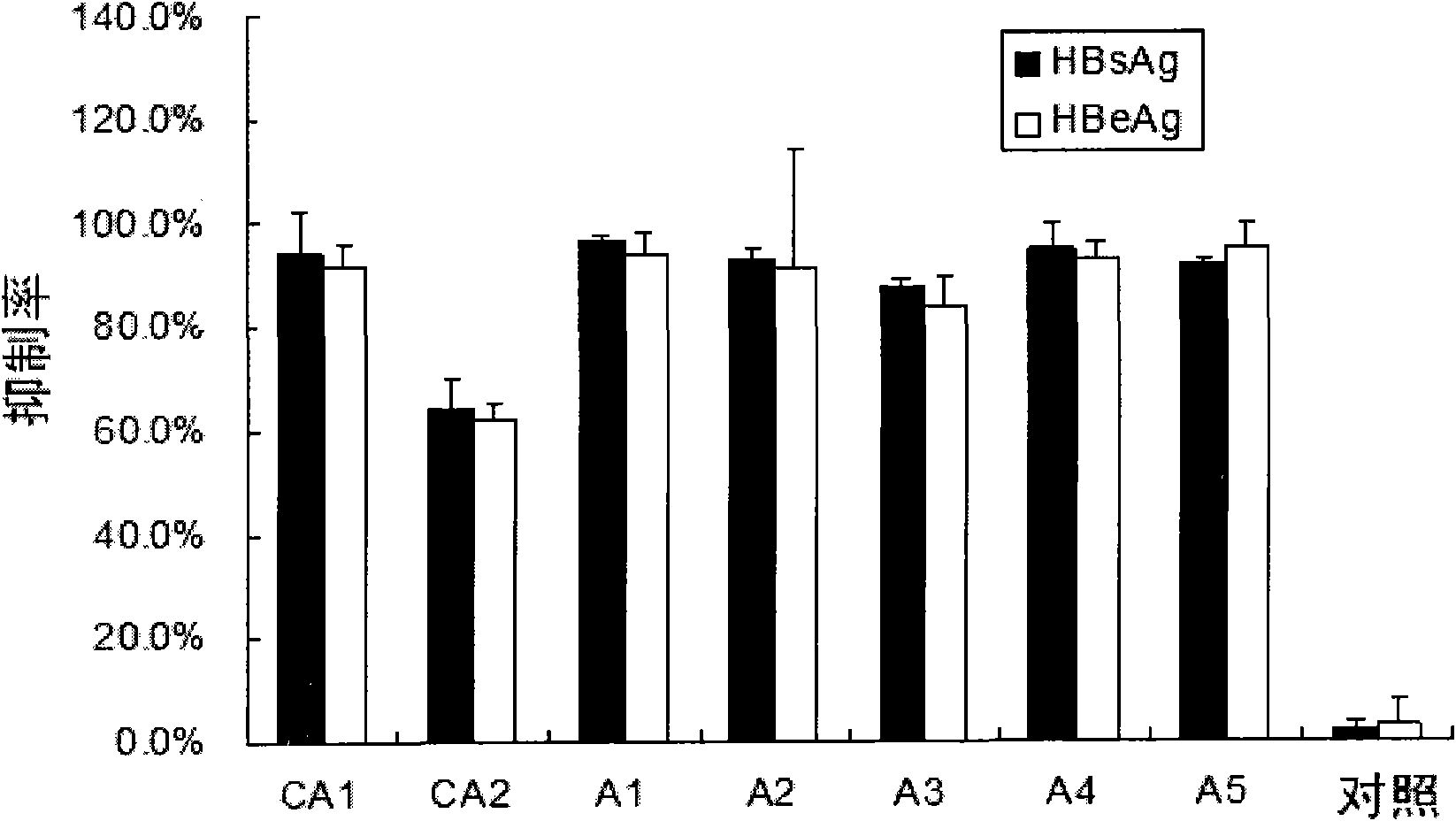
ActiveCN102140461AIncrease serum stabilityLow cytotoxicityGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsActive componentCytotoxicity
The invention provides small interfering nucleic acid of which sequences are as follows: the sequence of the sense strand is 5'-CCUUGAGGCAUACUUCAAAdTdT-3' and the sequence of the anti-sense strand is 5'-UUUGAAGUAUGCCUCAAGGdTdT-3'. The small interfering nucleic acid has the modifications shown from A1 to A5. The invention also provides a medical composite used for preventing and / or curing hepatitis B and the medical composite contains the small interfering nucleic acid provided by the invention and uses the nucleic acid as the active component. The invention also provides the applications of the small interfering nucleic acid in preparations of medicines for preventing and / or curing hepatitis B. Through the specific modifications, the aim of increasing the serum stability of the small interfering nucleic acid can be achieved under the condition of only introducing a small amount of modifications, thus the potential cytotoxicity of the modified small interfering nucleic acid molecule can be reduced and the influence on the biological activity can be lowered.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
Compositions and methods for accurately identifying mutations
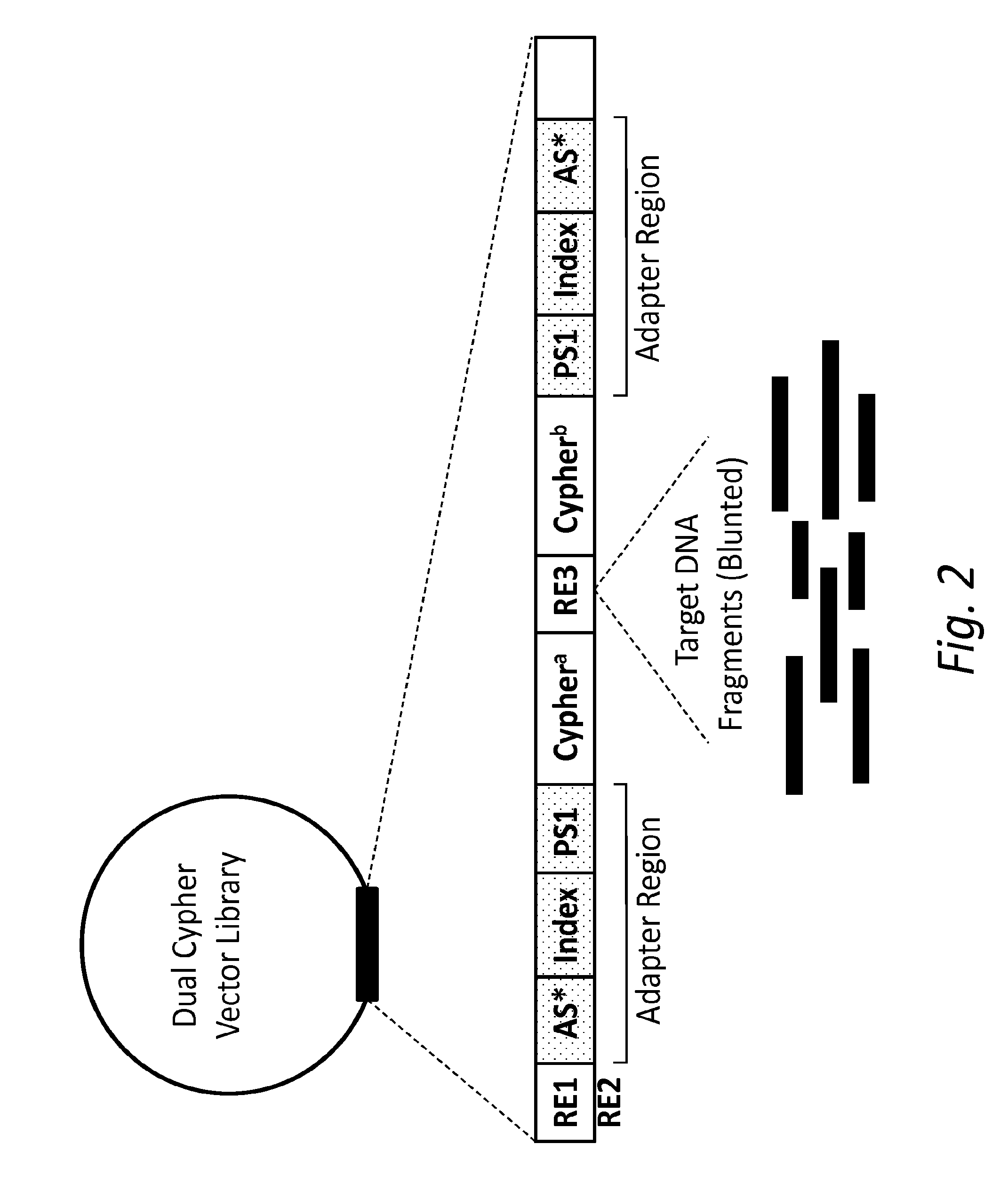
ActiveUS20160326578A1Accurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsGeneticsSense strand
The present disclosure provides compositions and methods for accurately detecting mutations by uniquely tagging double stranded nucleic acid molecules with dual cyphers such that sequence data obtained from a sense strand can be linked to sequence data obtained from an anti-sense strand when sequenced, for example, by massively parallel sequencing methods.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER CENT
Multi-target interfering nucleic acid molecule and application thereof
ActiveCN102191246AExcellent silence effectGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsNucleotideSense strand
The invention relates to a multi-target interfering nucleic acid molecule and application thereof. The interfering nucleic acid molecule is composed of an antisense strand and a sense strand, the total length of the two strands is at least 30 nucleotides, and nucleotide incisions or gaps exist on the sense strand or the antisense strand or both the sense strand and the antisense strand. Any one strand of the interfering nucleic acid can target at least two target RNAs (Ribonucleic Acids), thereby interfering the translation process after transcription, and the interfering nucleic acid can not cause interferon reaction.
Owner:BIOMICS BIOTECH
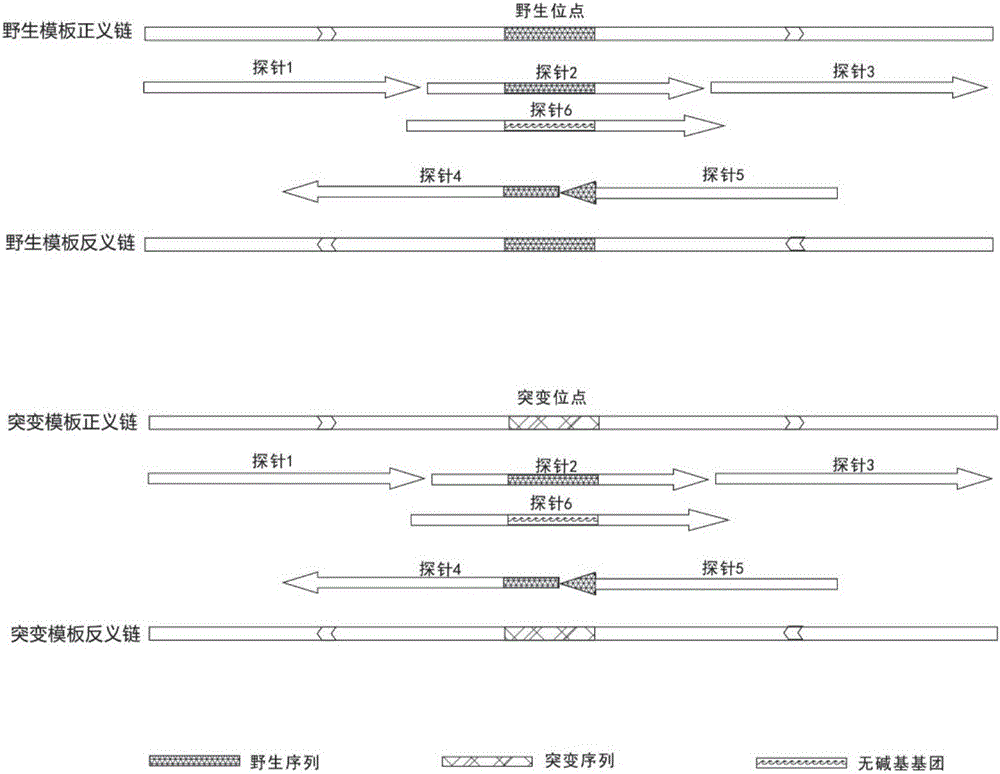
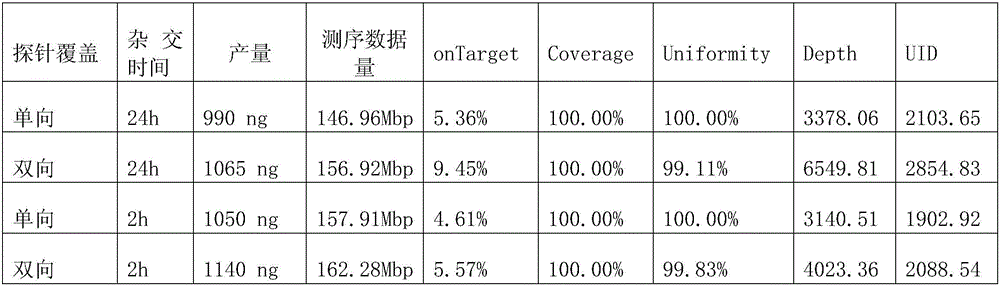
Probe for nucleic acid enriching capture and design method thereof
ActiveCN106086013ALow interactionLess catchMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationMagnetic beadBiotin-binding proteins
The invention discloses a probe for nucleic acid enriching capture and a design method thereof. A two-way probe consists of a positive-sense strand probe and an antisense strand probe, wherein both the positive-sense strand probe and the antisense strand probe adopt probe zero-lap designs; the lengths of the positive-sense strand probe and the antisense strand probe are 30 to 89 basic groups; the 3' or 5' position of the probe is provided with biotin labels, and can be combined with avidin on magnetic beads. The two-way probe can improve the capture specificity (i.e., the capture on the genome DNA in the non-targeted position can be reduced); the capture on the sample mutant type DNA is obviously improved. The original copy number of the capture sample nucleic acid can be increased.
Owner:AMOY DIAGNOSTICS CO LTD
Double-stranded asymmetric small nucleic-acid-interference-molecule asiRNA inhibiting tumour apoptosis suppressor specifically and application thereof
ActiveCN102719432ASmall side effectsHigh activityGenetic material ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsChemical synthesisNucleotide
The invention belongs to the biomedical field, discloses a double-stranded asymmetric small nucleic-acid-interference-molecule asiRNA inhibiting a tumour apoptosis suppressor specifically and an application thereof. The asiRNA is designed by a following method and obtained by chemical synthesis, starting from a Bcl 2 gene symmetry small nucleic-acid-interference-molecule siRNA, by cutting 1-5 nt base off a 5 ' end or a 3 ' end of an siRNA sense strand or an siRNA antisense strand, and forming the double-stranded asymmetric small nucleic-acid-interference-molecule asiRNA wherein base lengths are different and the 3' end of each strand is equipped with two deoxyribonucleic acids dTdT in a single strand suspension and RNA interference can be induced, by using two nucleotides with abutting deoxyribonucleic acid dTdT on the 3' end of each strand. The asiRNA of the invention is more stable than the routine siRNA, activity to inhibit expression of Bcl 2 is stronger, and can be applied in antitumor drug preparation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for enhancing aphid resistance of plant
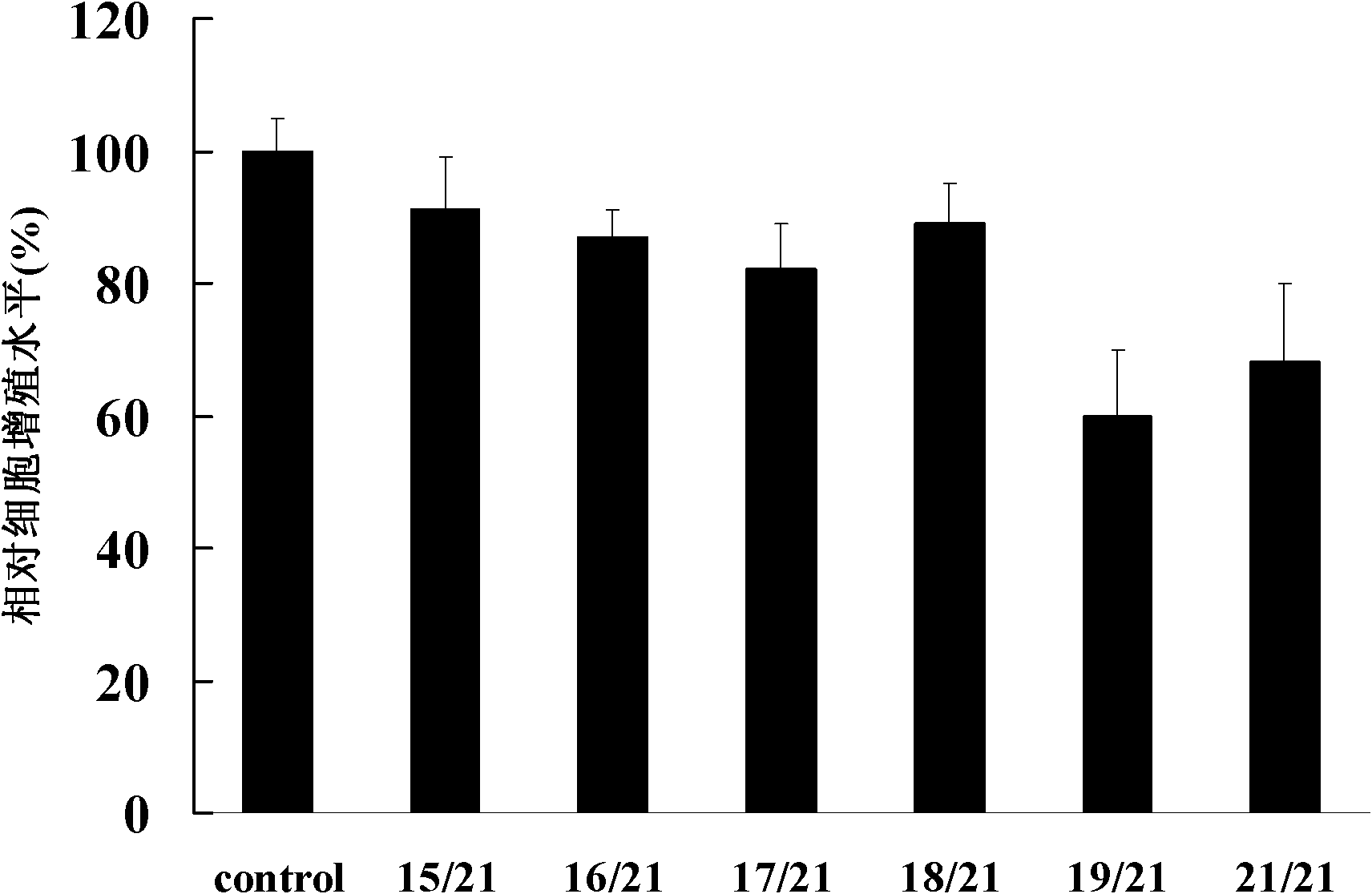
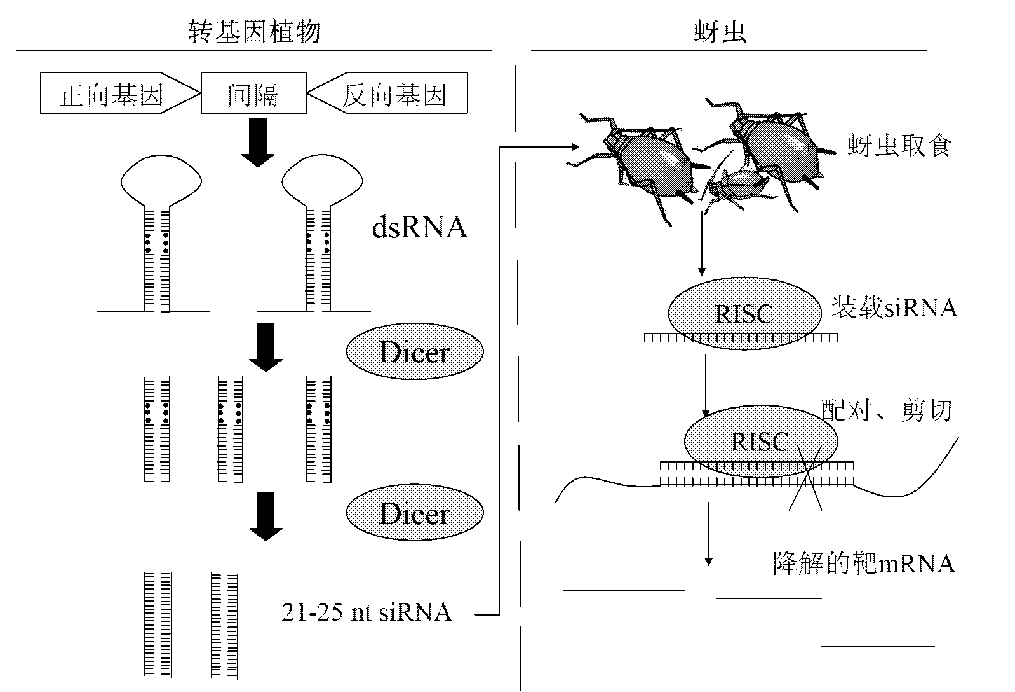
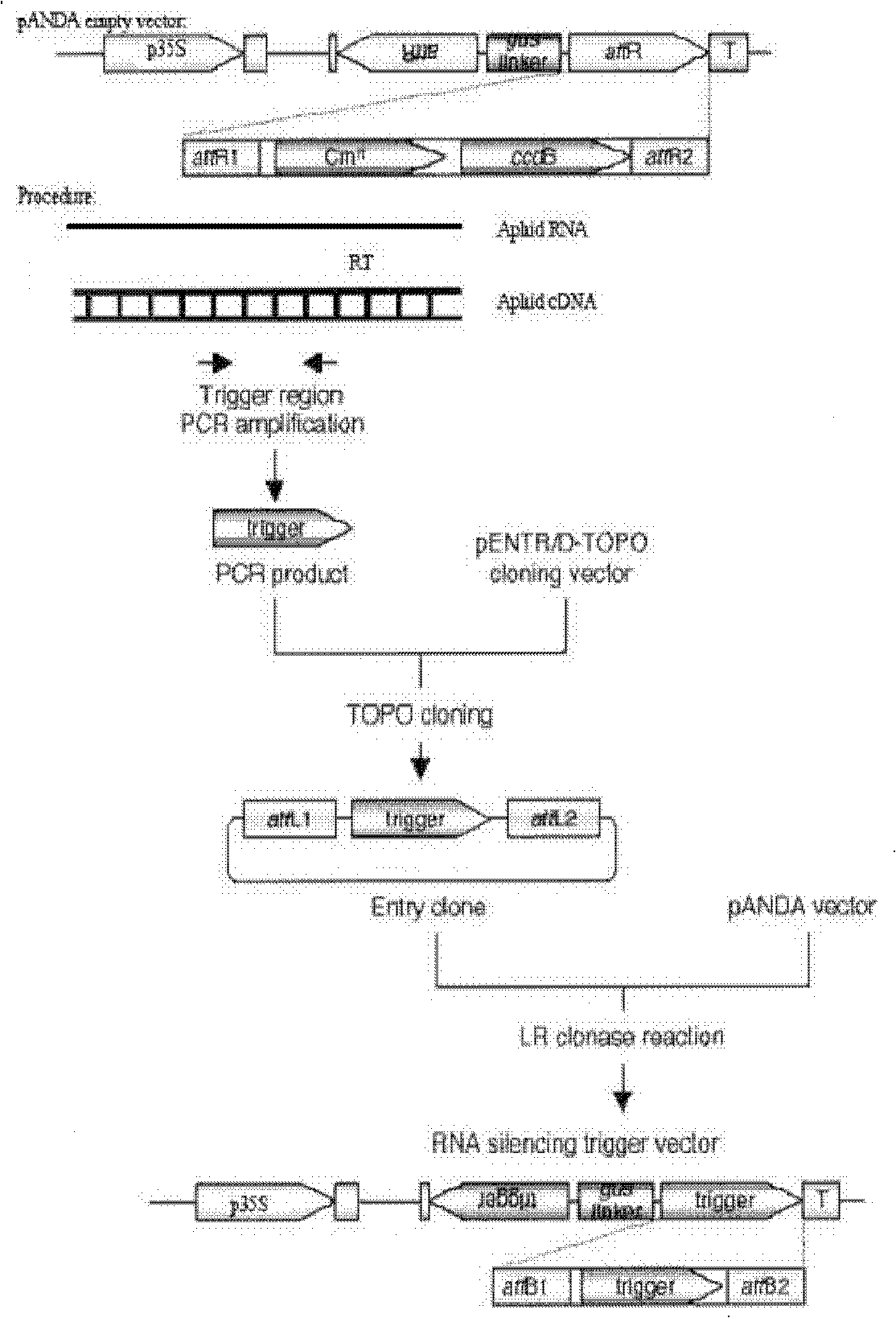
ActiveCN102206668AIncrease resistanceBreak through subspecies restrictionsVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsSense strandDouble stranded
The invention relates to a method for enhancing the aphid resistance of a plant, belonging to the technical field of biology. With the method, a construct expressing the dsRNA (Double-Stranded RNA) of an aphid gene is transferred into the plant; the construct expressing the dsRNA of the aphid gene is double-stranded, a positive-sense strand and a negative-sense strand of the aphid gene contain the following structures: Ap forward direction-X-Ap reverse direction, wherein the Ap forward direction is a forward sequence or fragment of the aphid gene, the Ap reverse direction is a reverse complementary sequence or fragment of the same aphid gene, and X is an intervening sequence positioned between the Ap forward direction and the Ap reverse direction; and the dsRNA shown in the description is formed after a constructed vector is transcribed in the plant, wherein ll expresses a hydrogen bond formed between the Ap forward direction and the Ap reverse direction.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Modified Single-Stranded Polynucleotide
It is intended to provide a polynucleotide that is resistant to RNase and has an RNA interference effect, etc. The present invention provides a single-stranded polynucleotide that is derived from a double-stranded polynucleotide comprising a sense strand polynucleotide corresponding to a target gene, and an antisense strand polynucleotide having a nucleotide sequence complementary to the sense strand polynucleotide, and has a structure in which the 5′-end of the antisense strand and the 3′-end of the sense strand are linked via a phenyl group-containing linker to form a phosphodiester structure at each of these ends.
Owner:DAIICHI SANKYO CO LTD
Cycle single-stranded nucleic acid complex and method for producing the same
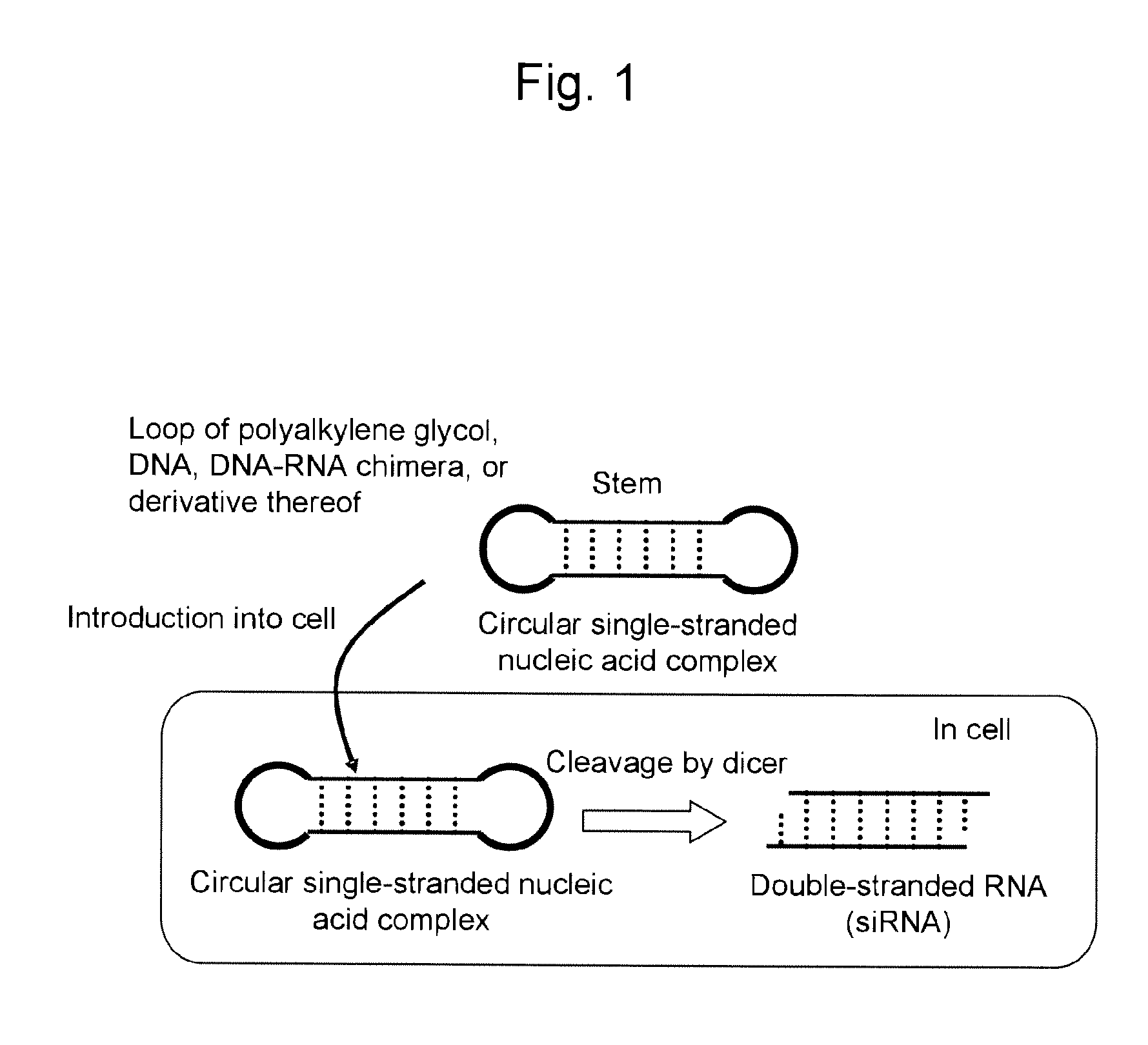
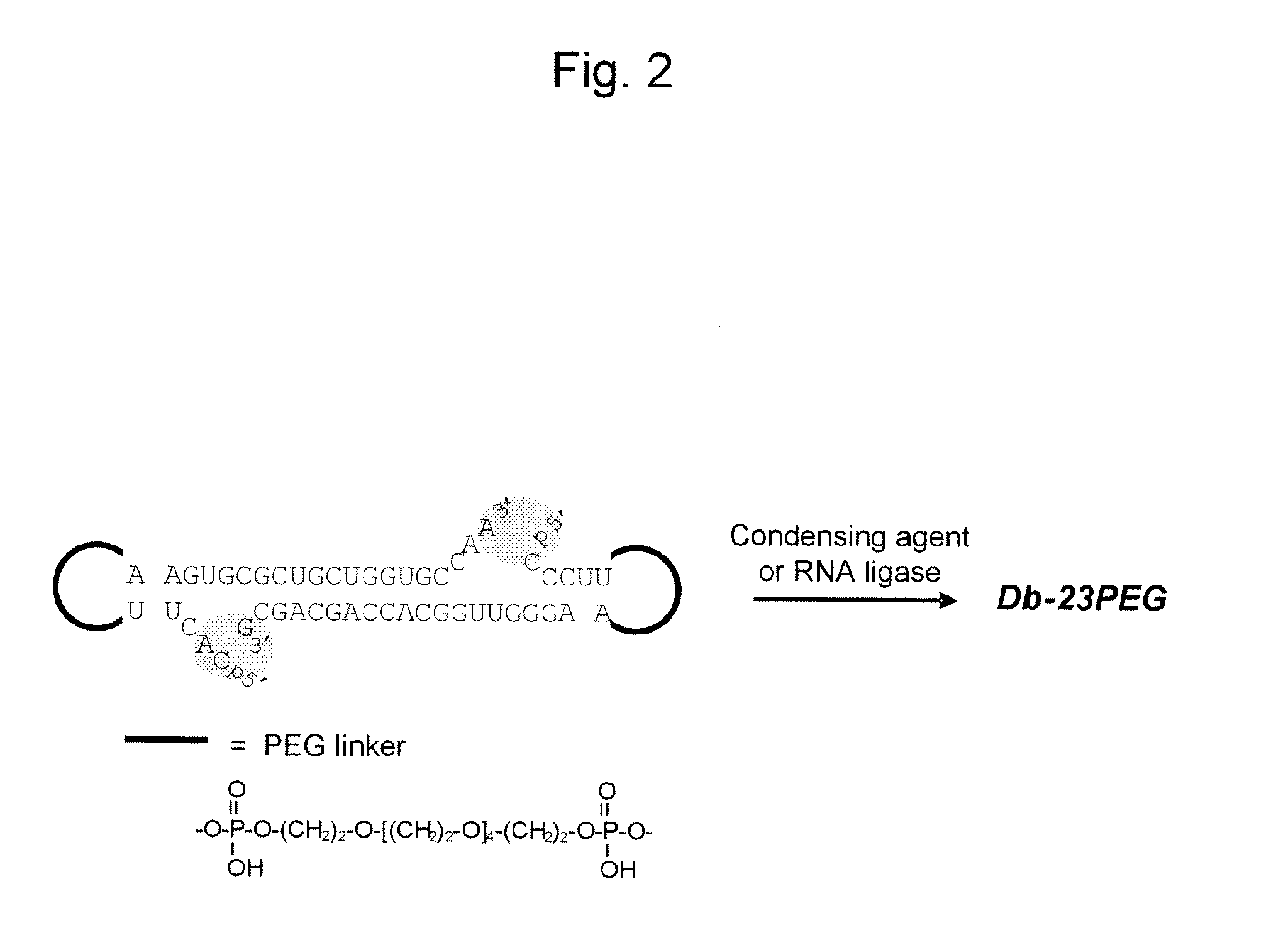
InactiveUS20110055965A1Improve in vivo stabilityProduced simply and efficientlySugar derivativesActivity regulationSingle strandSense strand
The present invention relates to a circular single-stranded nucleic acid complex comprising a sense strand RNA sequence, an antisense strand RNA sequence complementary to the sense strand RNA sequence, and two identical or different loop moieties connecting the sense and antisense strands, wherein the sense and antisense strands form a stem by pairing, and the loop moieties are selected from the group consisting of polyalkylene glycol, DNA, DNA-RNA chimera, a derivative thereof, and a combination thereof.
Owner:RIKEN
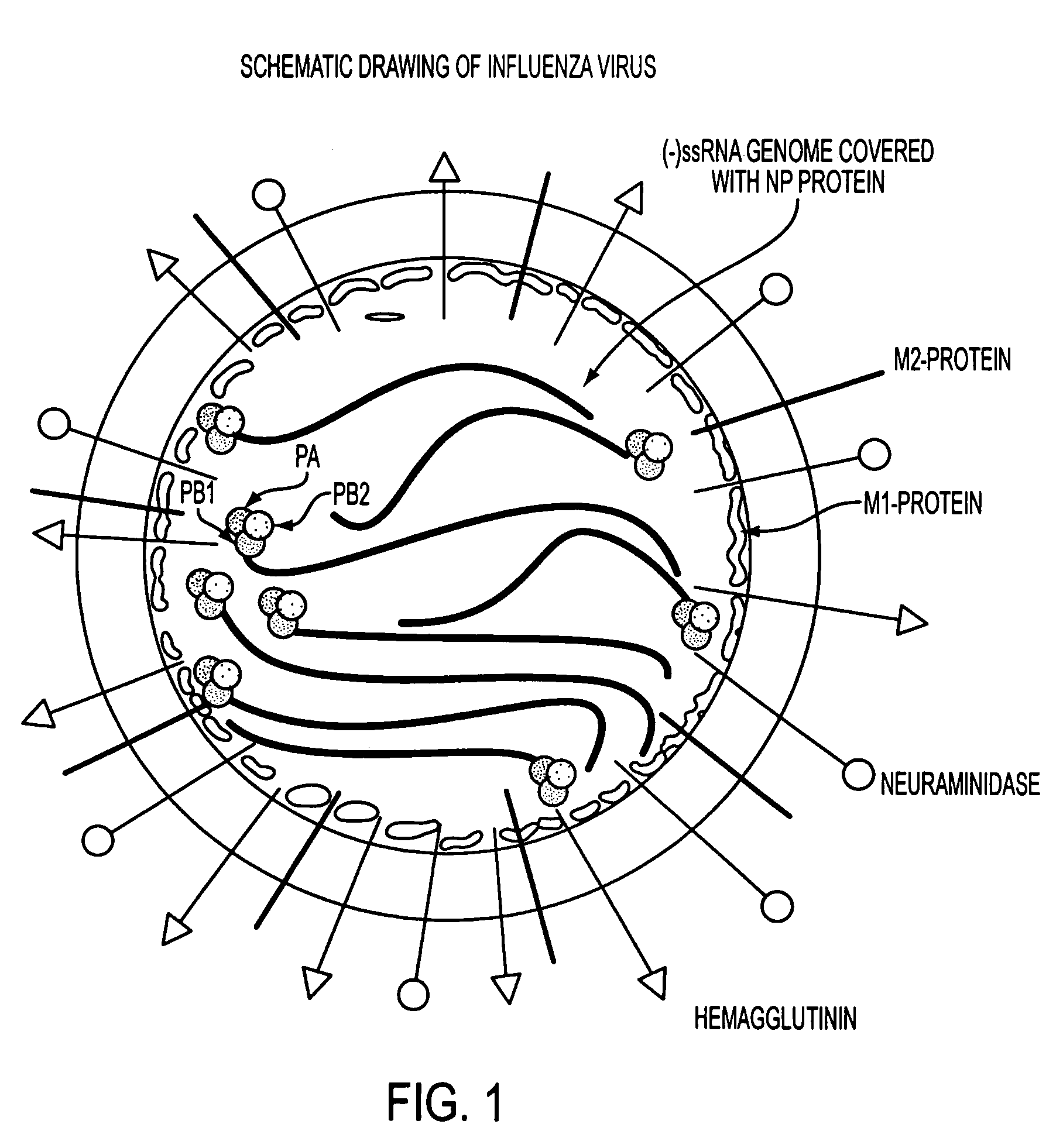
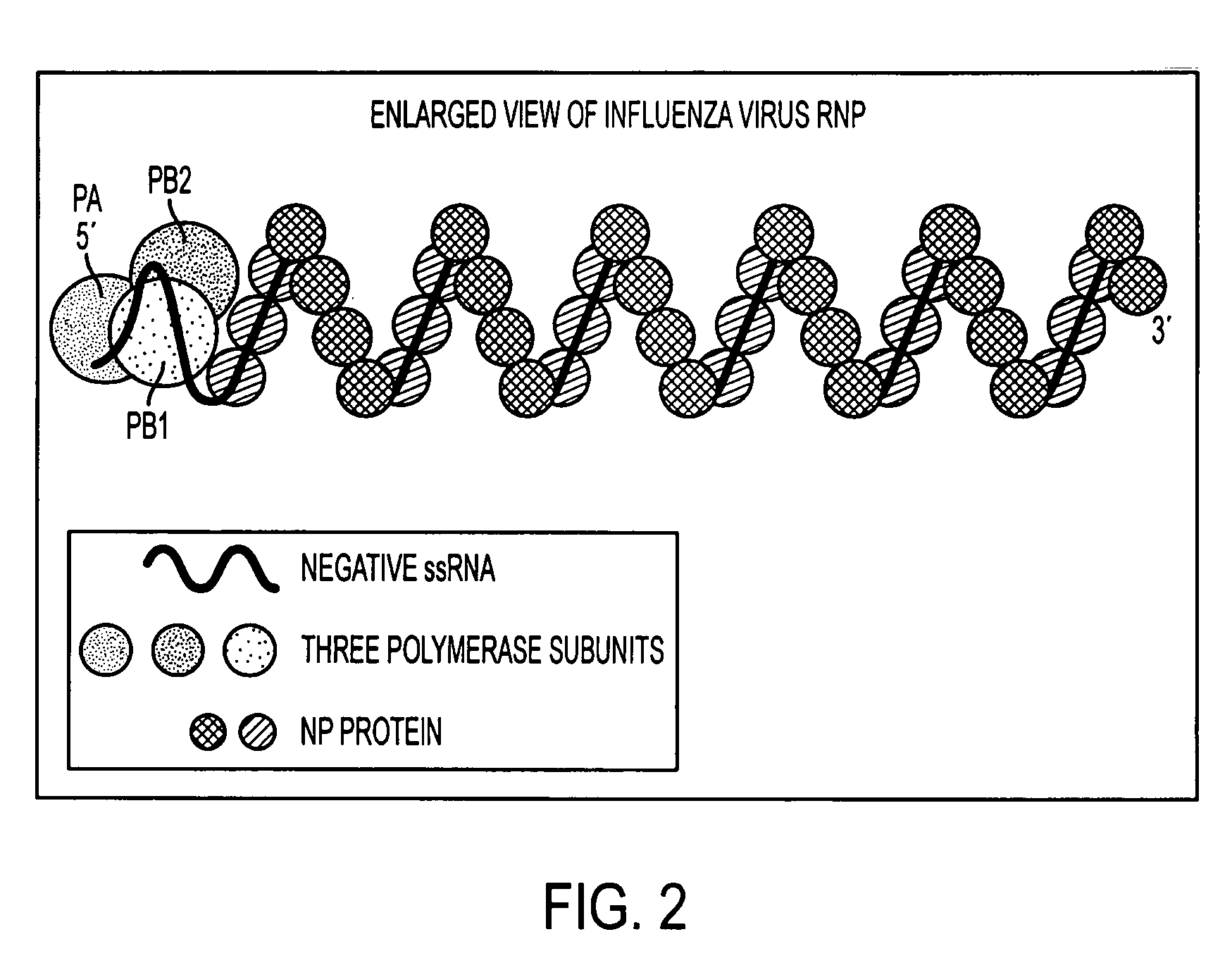
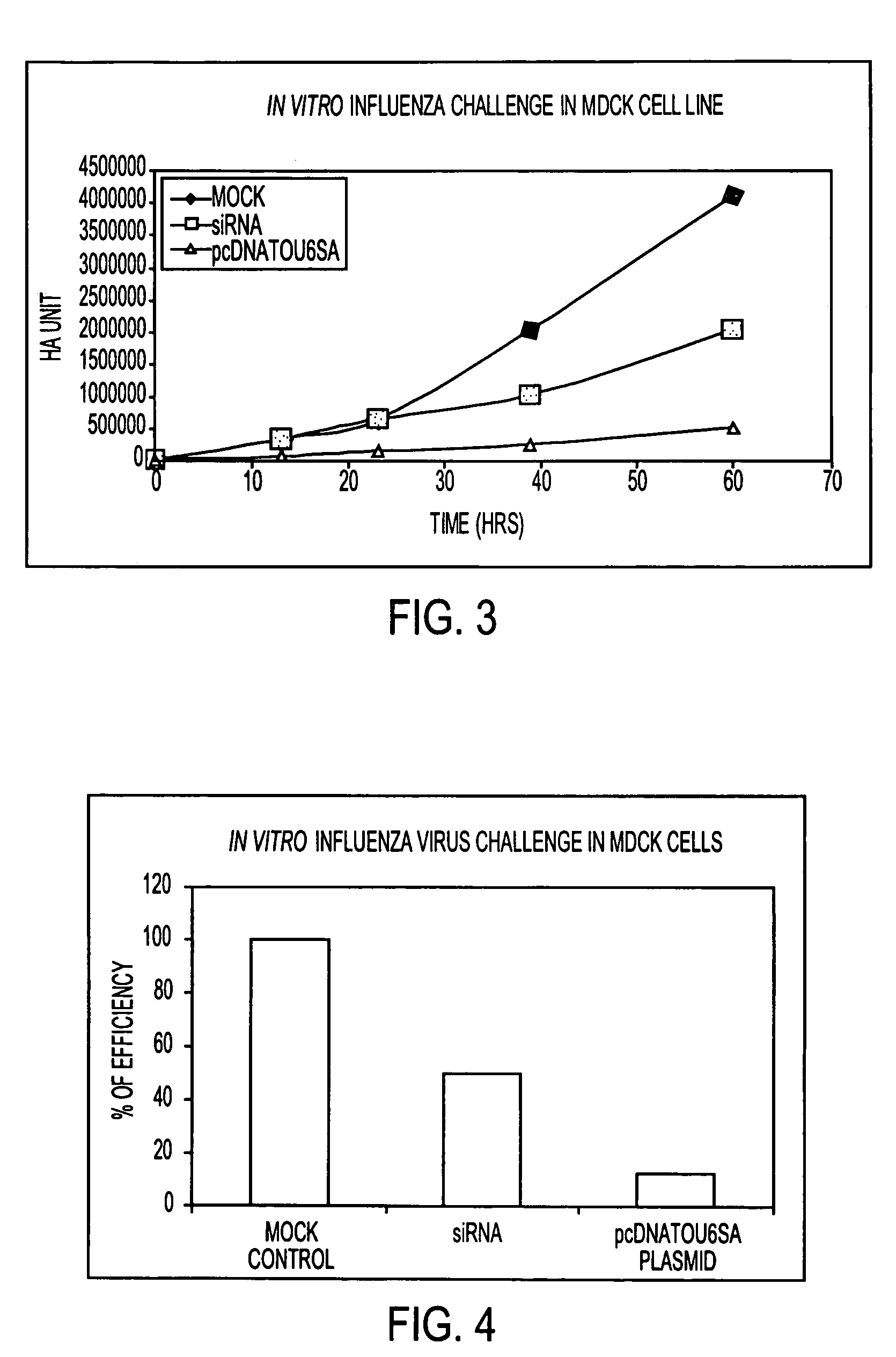
Potent inhibition of influenza virus by specifically designed short interfering RNA
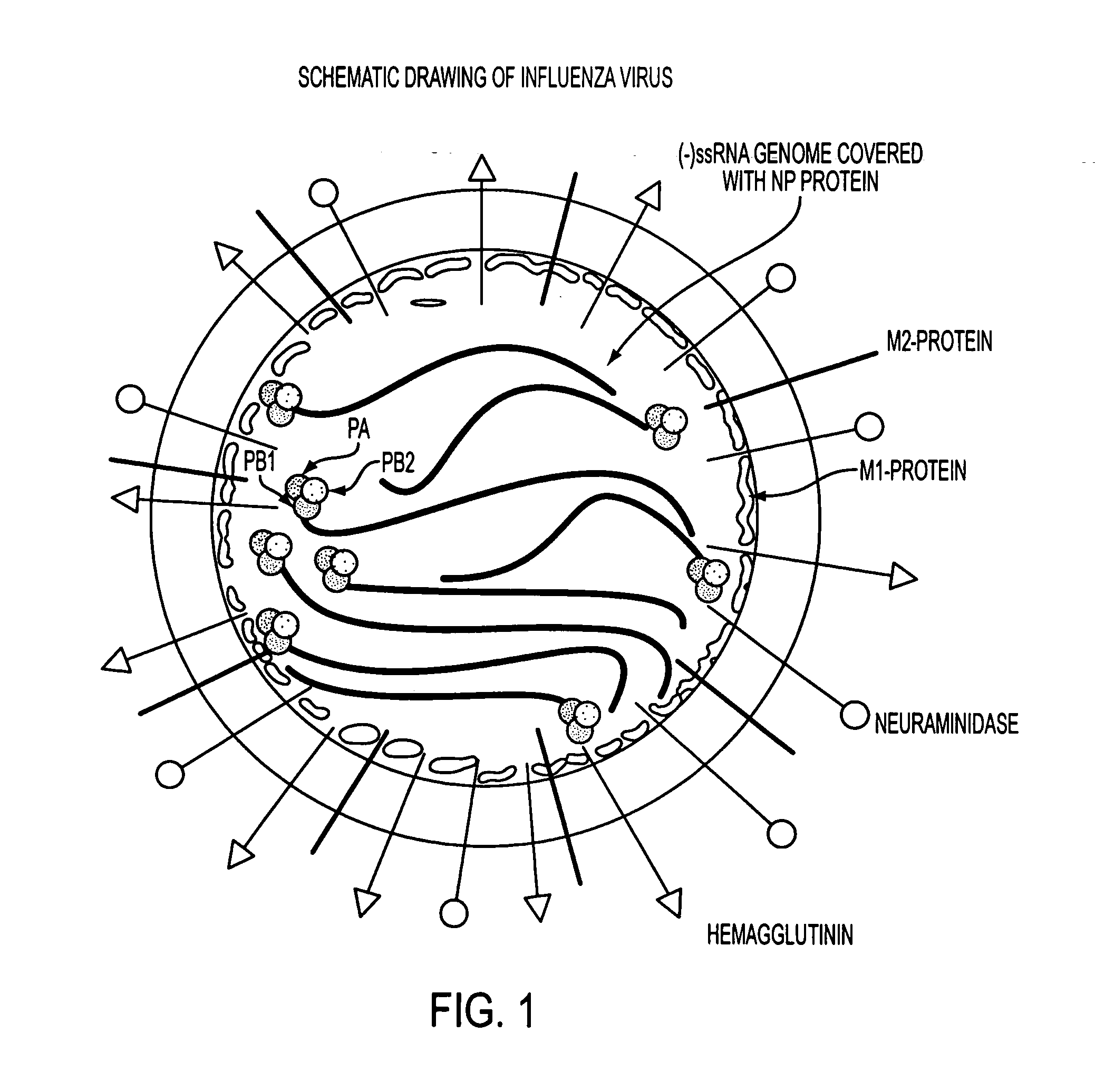
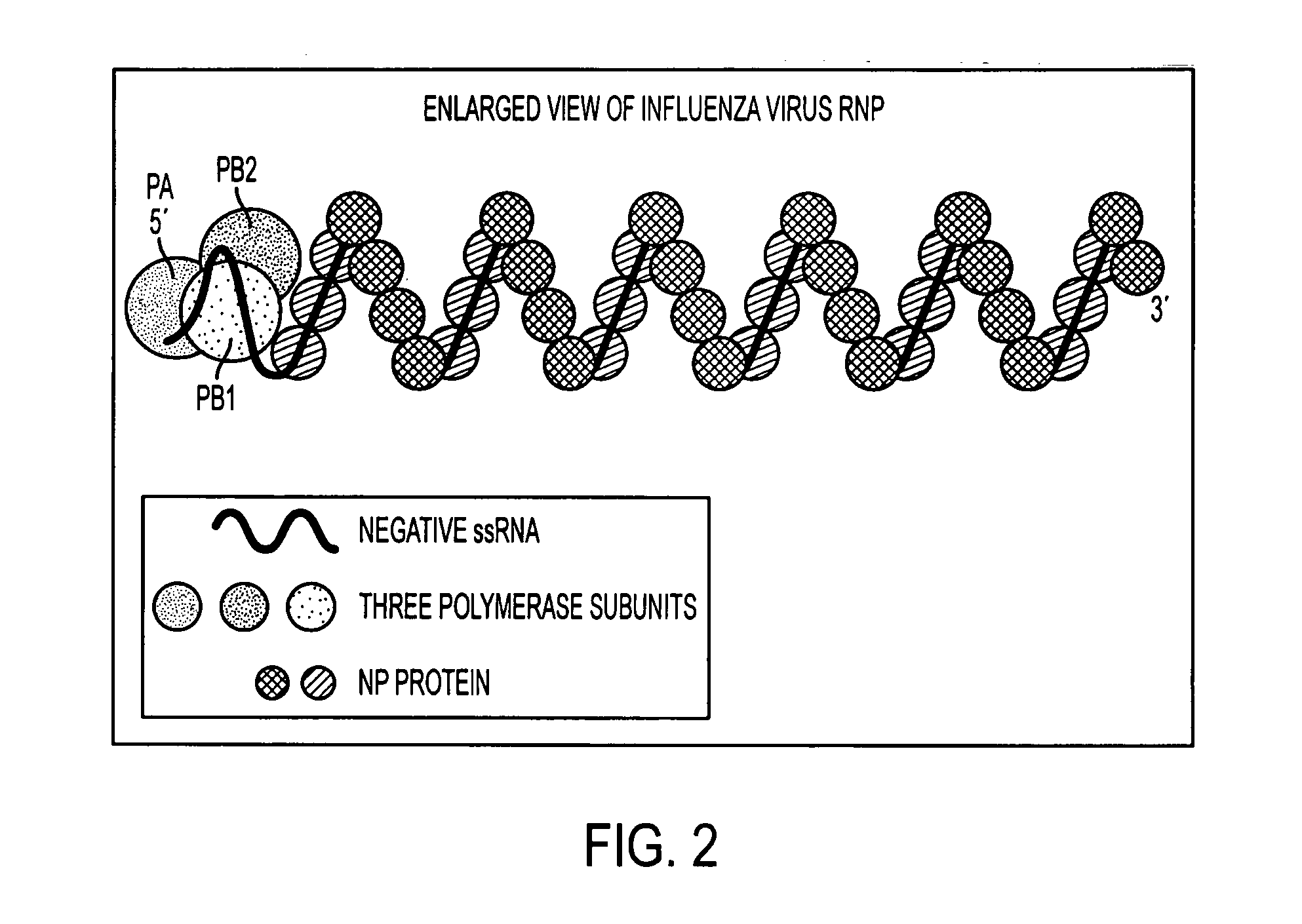
ActiveUS20060275265A1Improve applicabilityBiocideSugar derivativesInfluenza virus nucleoproteinEukaryotic plasmids
This patent application discloses siRNA sequences against the constant region of the influenza virus nucleoprotein gene comprising: Sense strand:5′ UGAAGGAUCUUAUUUCUUCdTdT 3′(SEQ ID NO: 1)Anti sense strand:3′ dTdTACUUCCUAGAAUAAAGAAG 5′(SEQ ID NO: 2)Sense strand:5′ UGAAGGAUCUUAUUUCUUCGGdTdT 3′(SEQ ID NO: 3)Anti sense strand:3′ dTdTACUUCCUAGAAUAAAGAAGCC 5′(SEQ ID NO: 4)Sense strand:5′ GGAUCUUAUUUCUUCGGAGACdTdT 3′(SEQ ID NO: 5)Anti sense strand:3′ dTdTCCUAGAAUAAAGAAGCCUCUG 5′(SEQ ID NO: 6)said sequences being inhibitory against influenza virus in animals including humans. The invention further includes one or more of said siRNA sequences in the form of an aqueous suspension suitable for nasal inhalation. Still further, the invention includes one or more of said siRNA sequences in the form of a plasmid expressing intracellularly in animals including humans. In another aspect, the invention includes one or more of said siRNA sequences in the form of an AAV vector adapted to express intercellularly and establish a permanent inhibitory effect against influenza virus by integrating to the cellular chromosome of animals including humans. The invention also includes the administration to an animal including humans, in a therapeutically effective amount, at least one of said siRNA sequences.
Owner:CALIFORNIA POLYTECHNIC STATE UNIVERSITY
Double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing drug tolerant bacteria and composition thereof
InactiveCN101457222ADrug resistance is reversibleInhibition is effectiveAntibacterial agentsSugar derivativesMethicillin resistance geneHuman DNA sequencing
The invention relates to a double-chain small molecule interference nucleic acid for inhibiting and killing various drug tolerance bacteria using methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aurous as represents. The siNA of the invention is a double-chain molecule with 19 base pairs. A sense strand and a antisense strand respectively have two overhanging bases dT at 5' terminals, the GC content is 40-55; the aimed target sequence is selected from the genes relative with the vital movements of copy, transcription and translation in the staphylococcus aurous genome and an mecA gene correlative with the drug tolerance; said target sequence is preserved in 900f staphylococcus aurous; said target sequence is in a conservative sequence area in more than 900f staphylococcus aurous with distinct source with all the gene sequences in the human genome; the target sequence of the said siNA double-chain molecule is selected from SEQ ID NO. 1-325, the sense strand is a corresponding DNA or RNA sequence with the target sequence and the antisense strand is a corresponding RNA or DNA with the sense strand according to the complementary base law.
Owner:李宝健
SiRNA (Small interference ribonucleic acid) as well as medicine composition and pharmaceutical application thereof
The invention provides a siRNA (small-interference ribonucleic acid) which has the following sequences: a sense strand of 5'-GAAAGUAUGUCAACGAAUUdTdT-3' and an antisense strand of 5'-AAUUCGUUGACAUACUUUCdTdT-3'; and the siRNA is modified by one of the modes shown in D1 to D7. The invention also provides a medicine composition for preventing and / or treating hepatitis B, which contains the siRNA provided in the invention as active constituents. The invention also provides an application of the siRNA in preparing medicaments for preventing and / or treating the hepatitis B. With specific modification, the purpose of increasing the serum stability of the siRNA can be achieved by only introducing a little modification so that the modified siRNA potential cytotoxicity and influences on biological activity are reduced.
Owner:SUZHOU RIBO LIFE SCIENCE CO LTD
Double strand compositions comprising differentially modified strands for use in gene modulation
InactiveUS20110046206A1Effective meanOrganic active ingredientsActivity regulationSense strandRegulator gene
The present invention provides double stranded compositions wherein the first strand is modified to have a particular motif and the second strand is modified a selected motif. The motifs are defined by positioning of differentially modified nucleosides wherein at least the sugar moieties are different. More particularly, the present compositions comprise an antisense strand that is modified to have a positional / full motif and the sense strand is modified to have an alternating motif, a hemimer motif, a blockmer motif, a gapped motif, a positional motif, a positional / full motif or a fully modified motif. Each strand further comprises one or more phosphorothioate internucleoside linkage. The compositions are useful for targeting selected nucleic acid molecules and modulating the expression of one or more genes. In preferred embodiments the compositions of the present invention hybridize to a portion of a target RNA resulting in loss of normal function of the target RNA. The present invention also provides methods for modulating gene expression.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com