Patents
Literature
739 results about "RNA Sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
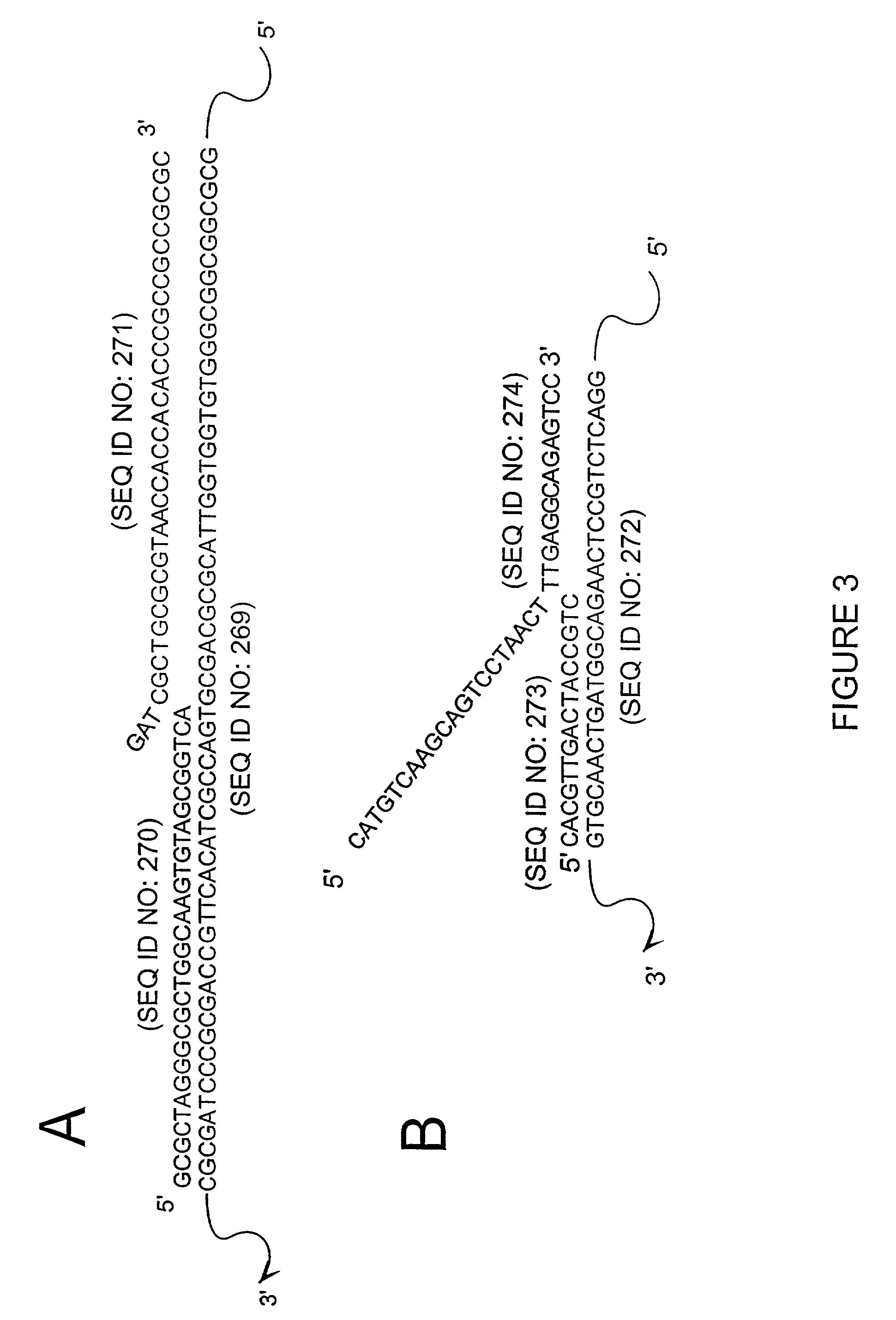
RNA sequencing is the process of determining the sequence of nucleotides in a strand of ribonucleic acid, or RNA. RNA is composed of four nucleotides called adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (S), and uracil (S).
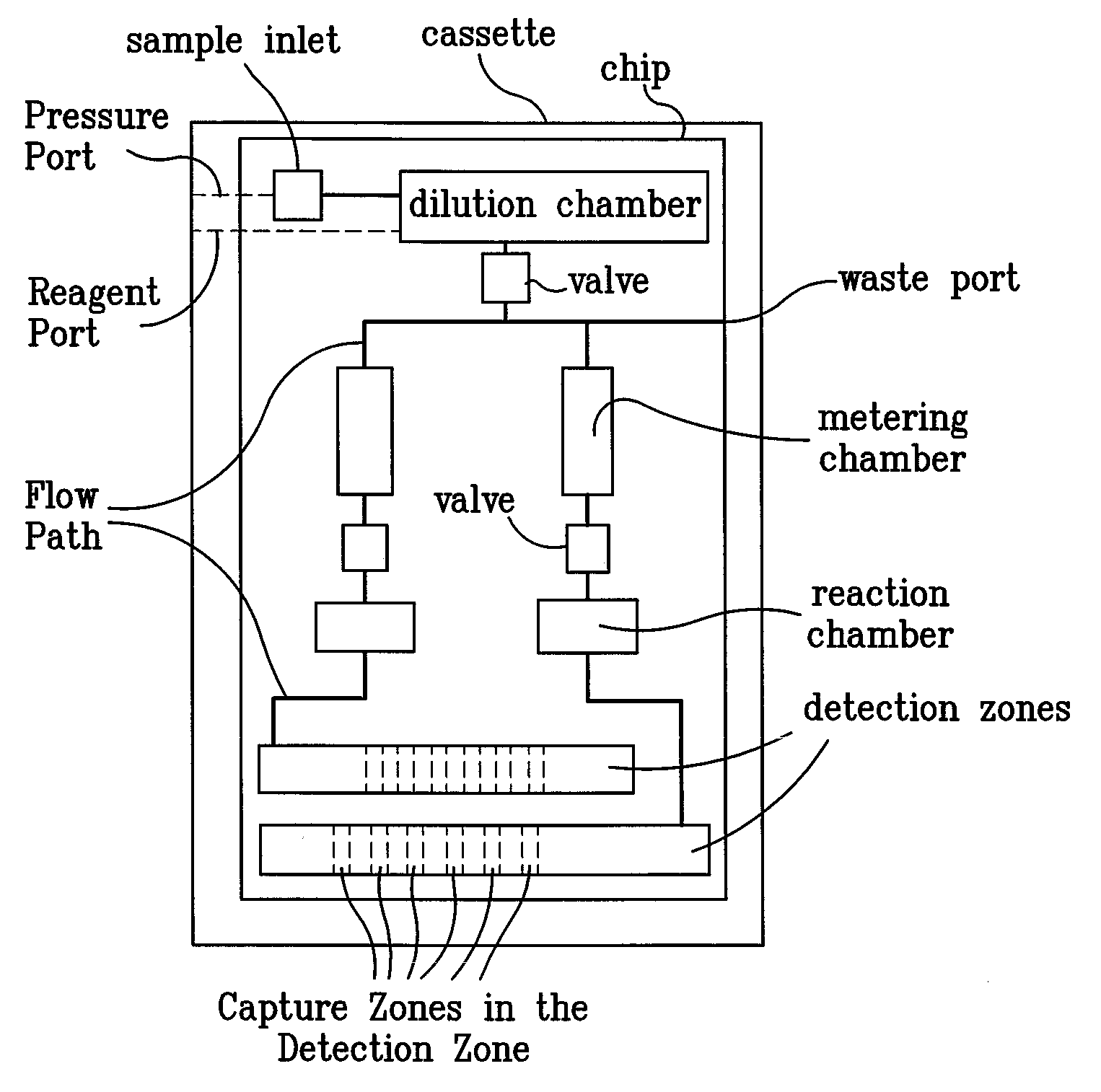
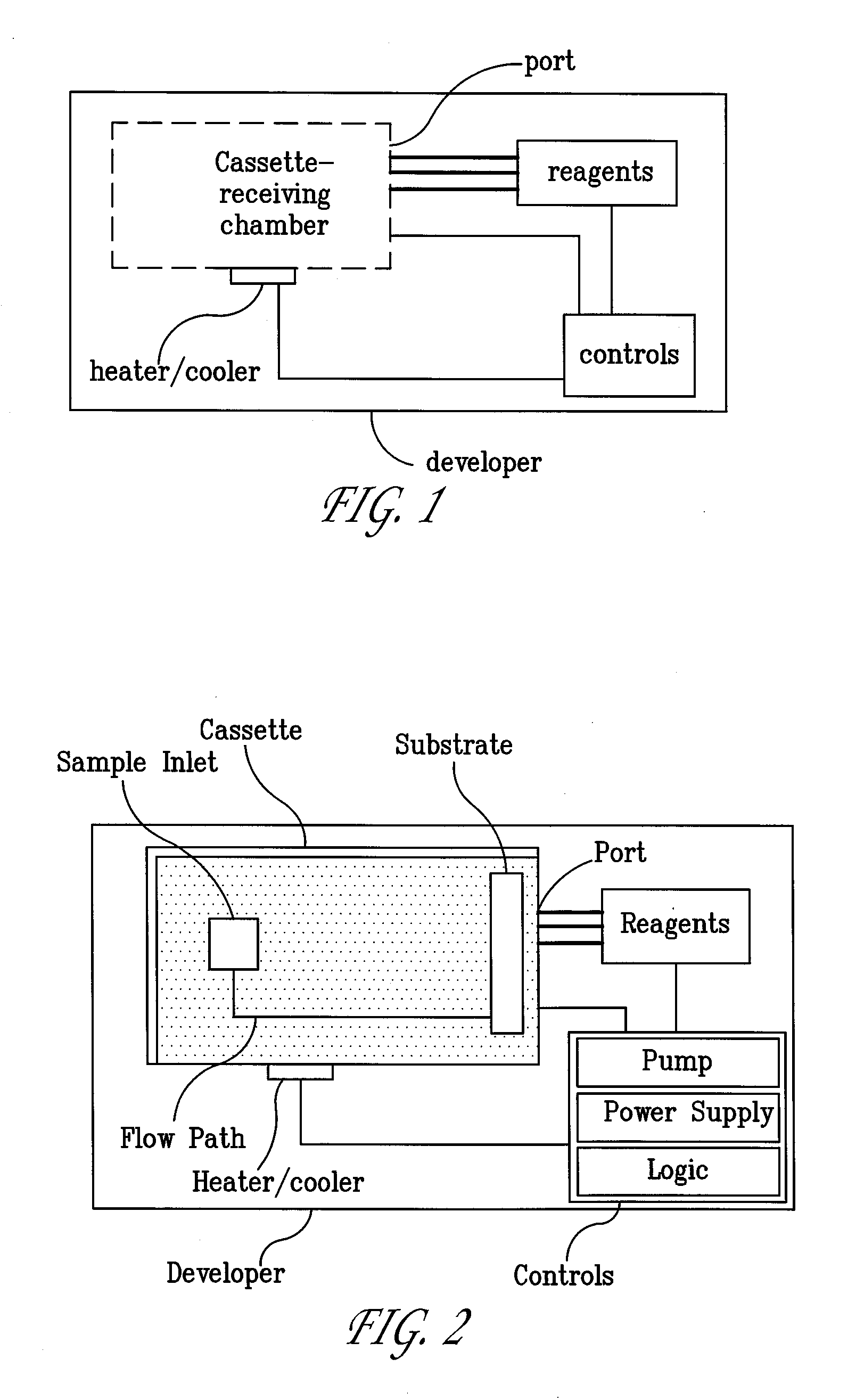
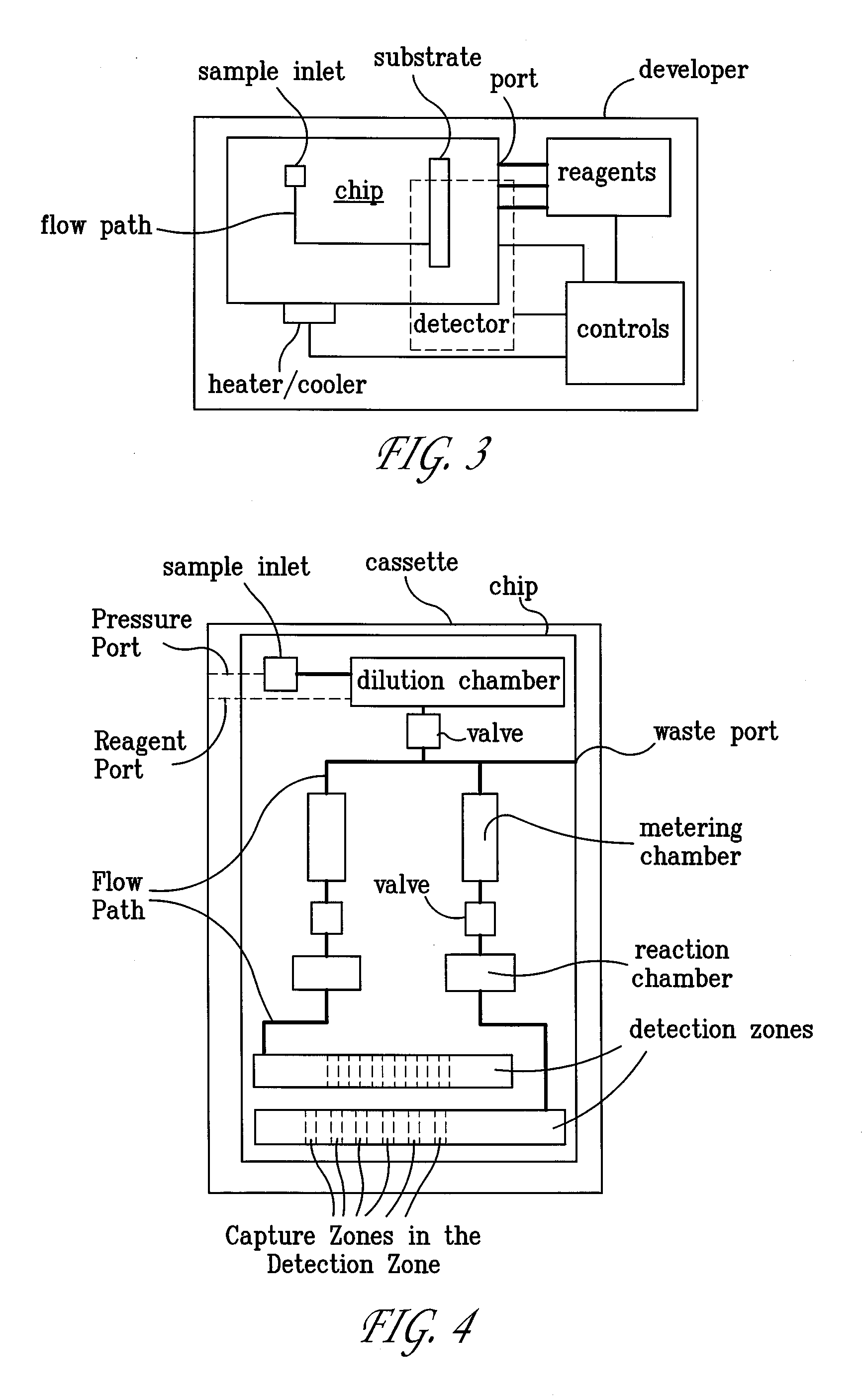
Systems and Methods For Testing using Microfluidic Chips
InactiveUS20080280285A1Easy to controlReduce materialBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusAntigenRNA Sequence
Disclosed are methods, devices and systems for biological and chemical sample processing using microfluidic chips. The disclosed microfluidic chips contain at least two detection zones for interacting with pre-selected RNA sequences, DNA sequences, antibodies, or antigens to determine their presence in the sample. Systems are also described comprising a cassette having at least one port and a sample inlet in fluid communication with a detection zone for interacting with pre-selected RNA sequences, DNA sequences, antibodies, or antigens, or mixtures thereof, if present, in a sample. Methods for concurrent testing of at least two of RNA, DNA, antibody, and antigen in a sample are also described, as are methods for testing for pre-selected pathogens and microfluidic methods.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
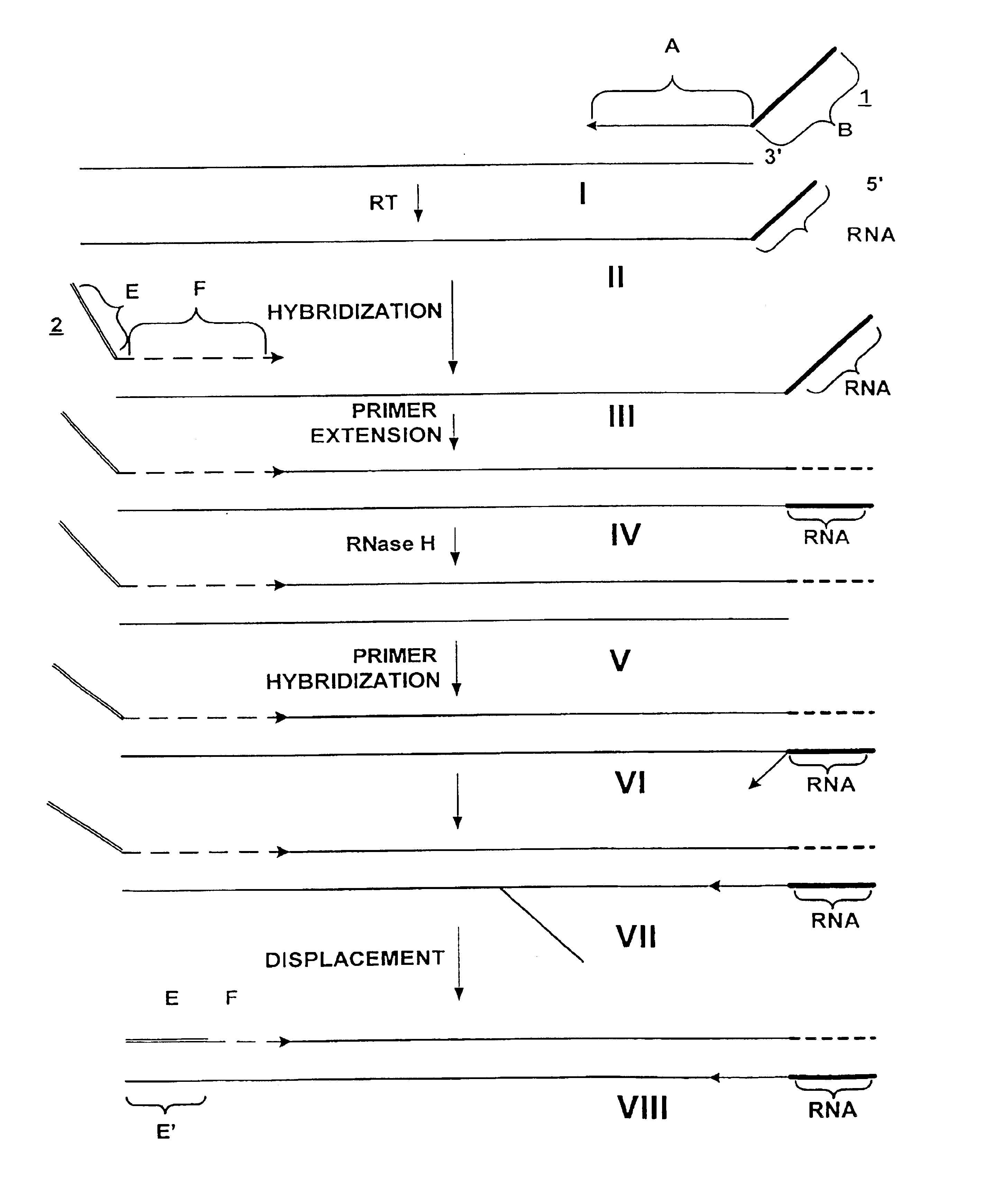
Methods and compositions for amplification of RNA sequences using RNA-DNA composite primers
InactiveUS6946251B2Improve automationHigh through-put proceduresSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA SequenceDNA
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Method for constructing gene site-directed mutation
ActiveCN103388006AEfficient constructionRaise the ratioVector-based foreign material introductionForeign genetic material cellsMulti siteEmbryo
Owner:BIORAY LABORATORIES INC
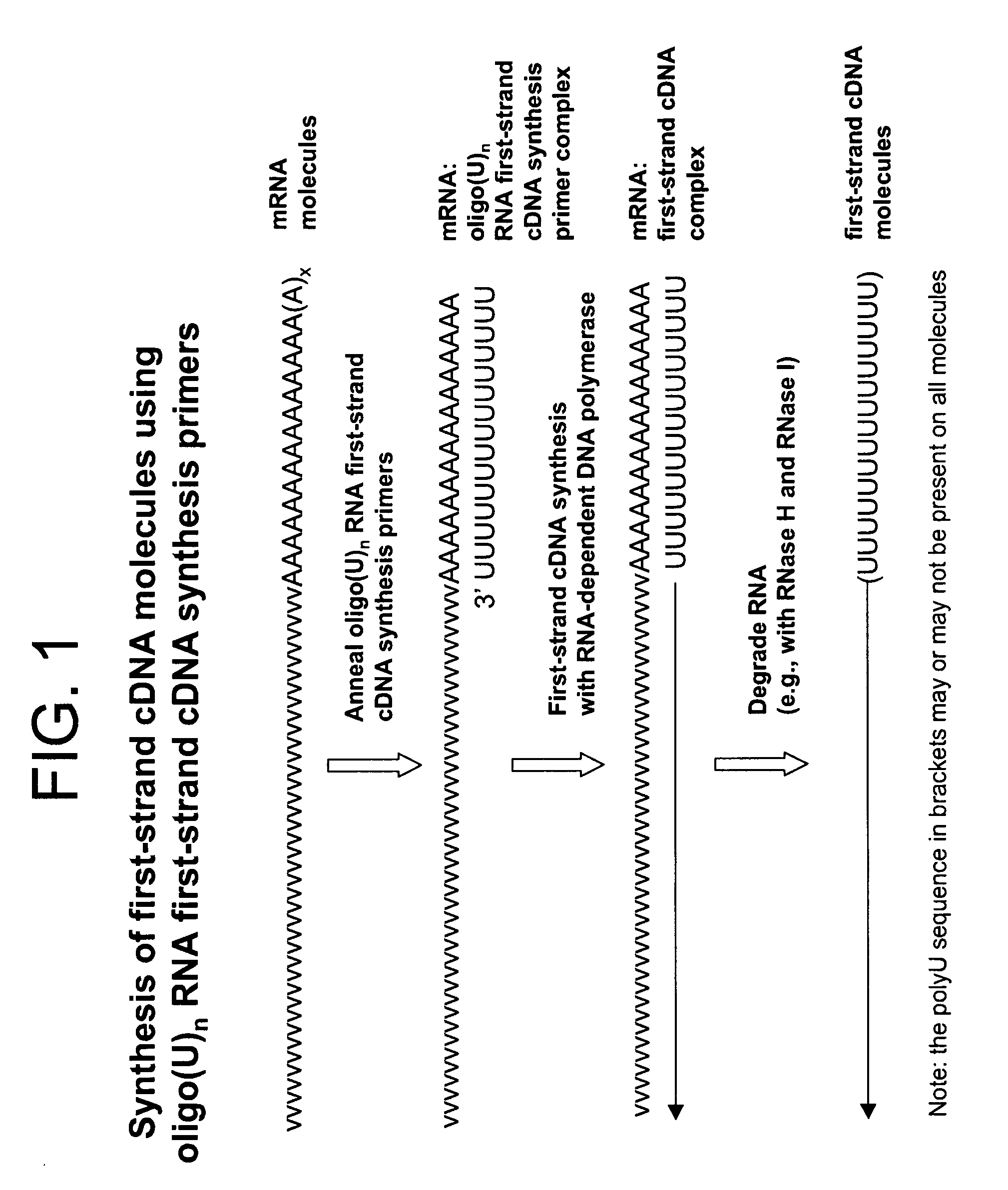
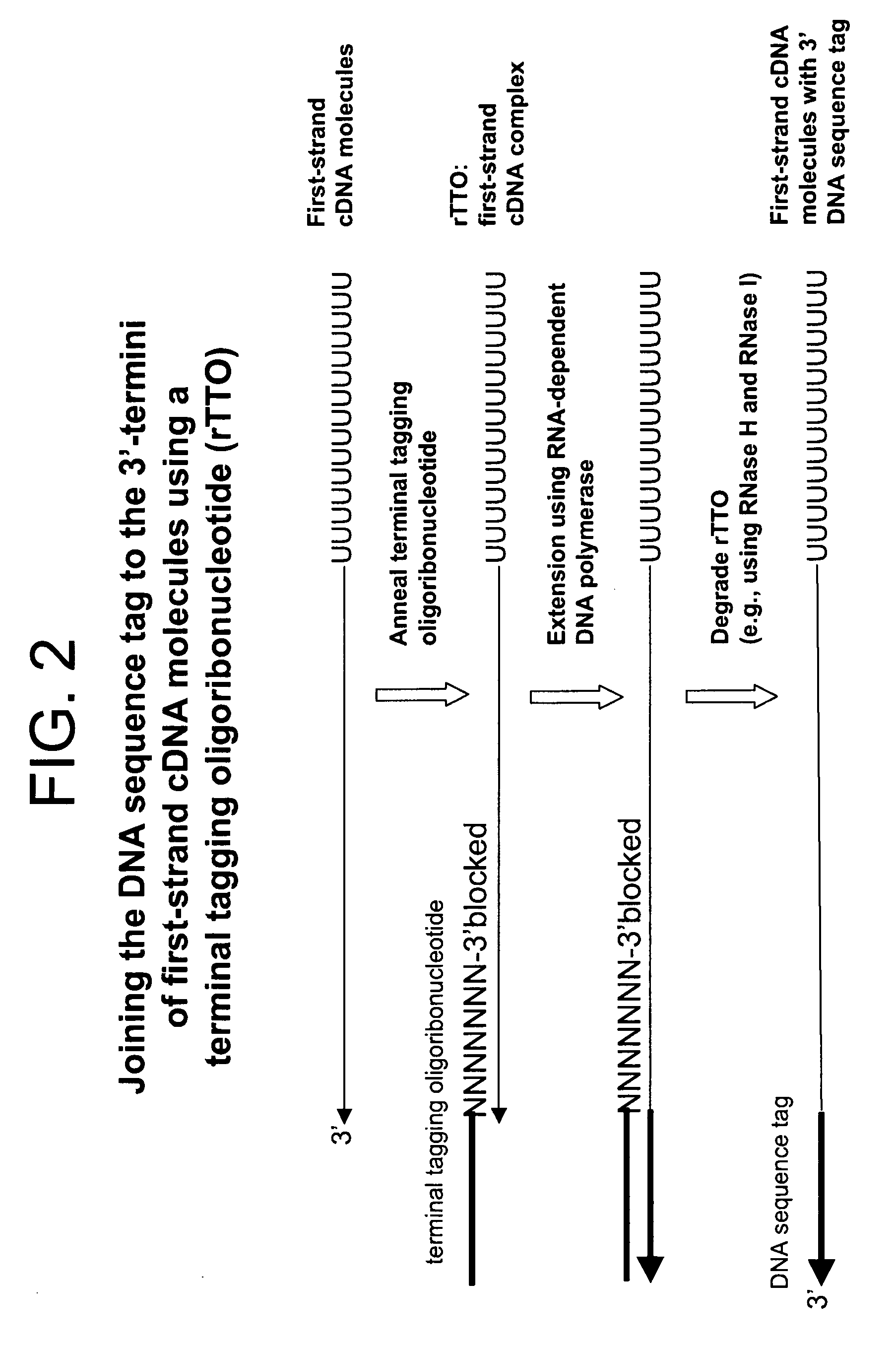
Synthesis of tagged nucleic acids
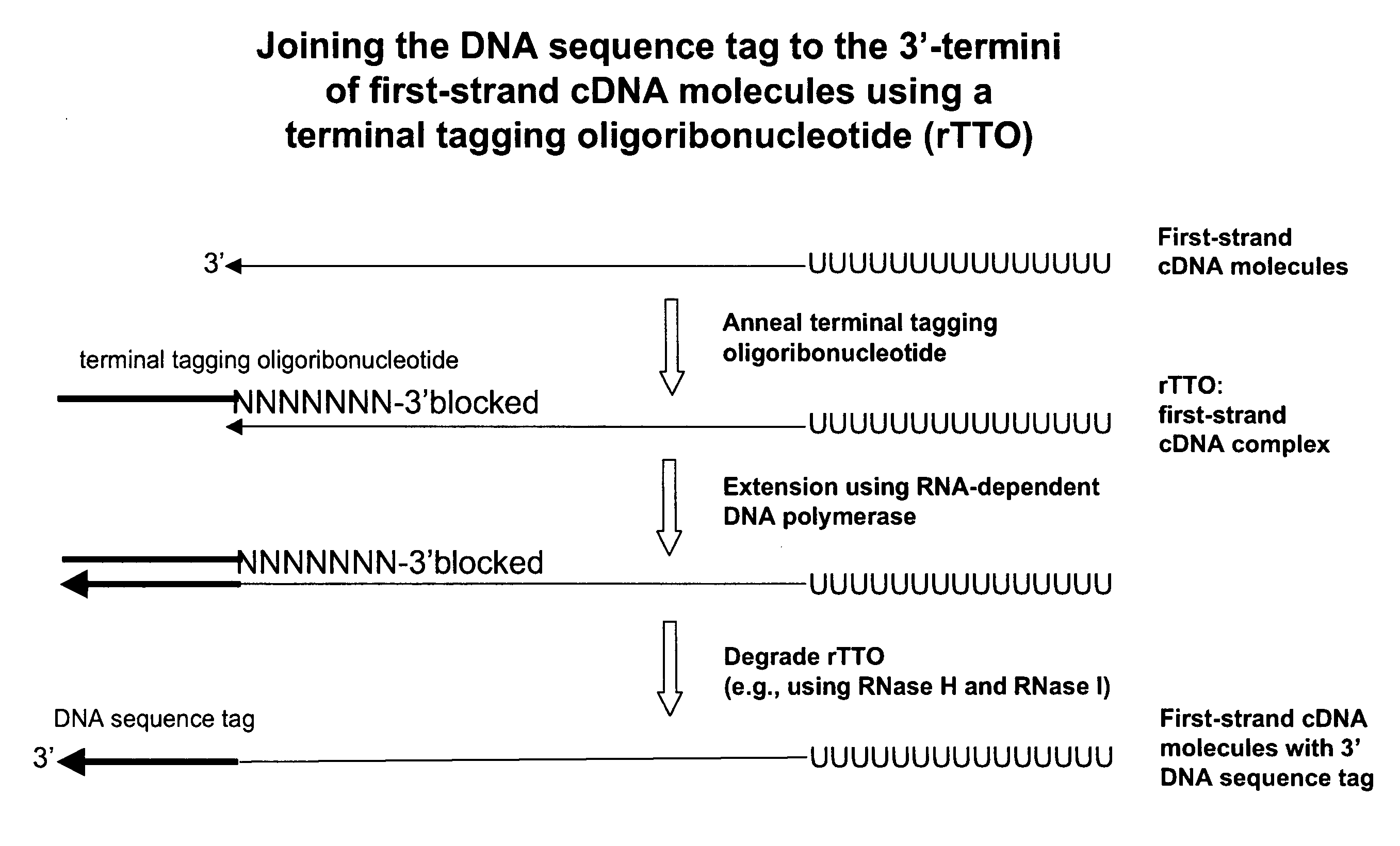
ActiveUS8039214B2Reduce in quantityGood removal effectMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesOligoribonucleotidesRibonucleotide synthesis
The present invention relates generally to methods, compositions and kits for synthesizing sense RNA molecules from one or more RNA molecules of interest in a sample. In exemplary embodiments, the methods use a terminal tagging oligoribonucleotide (rTTO) to join a DNA sequence tag to the 3′-termini of first-strand cDNA molecules. The use of an rTTO comprising ribonucleotides results in decreased oligonucleotide-derived background synthesis of RNA in the absence of sample RNA and, surprisingly and unexpectedly, also results in significantly increased yields of sense RNA molecules that exhibit sequences that are substantially identical to those of the RNA molecules of interest in the sample. The sense RNA molecules also have an RNA sequence tag on their 5′-termini that is useful for fixing the lengths of sense RNA molecules that are synthesized in a second or subsequent round.
Owner:CELLSCRIPT
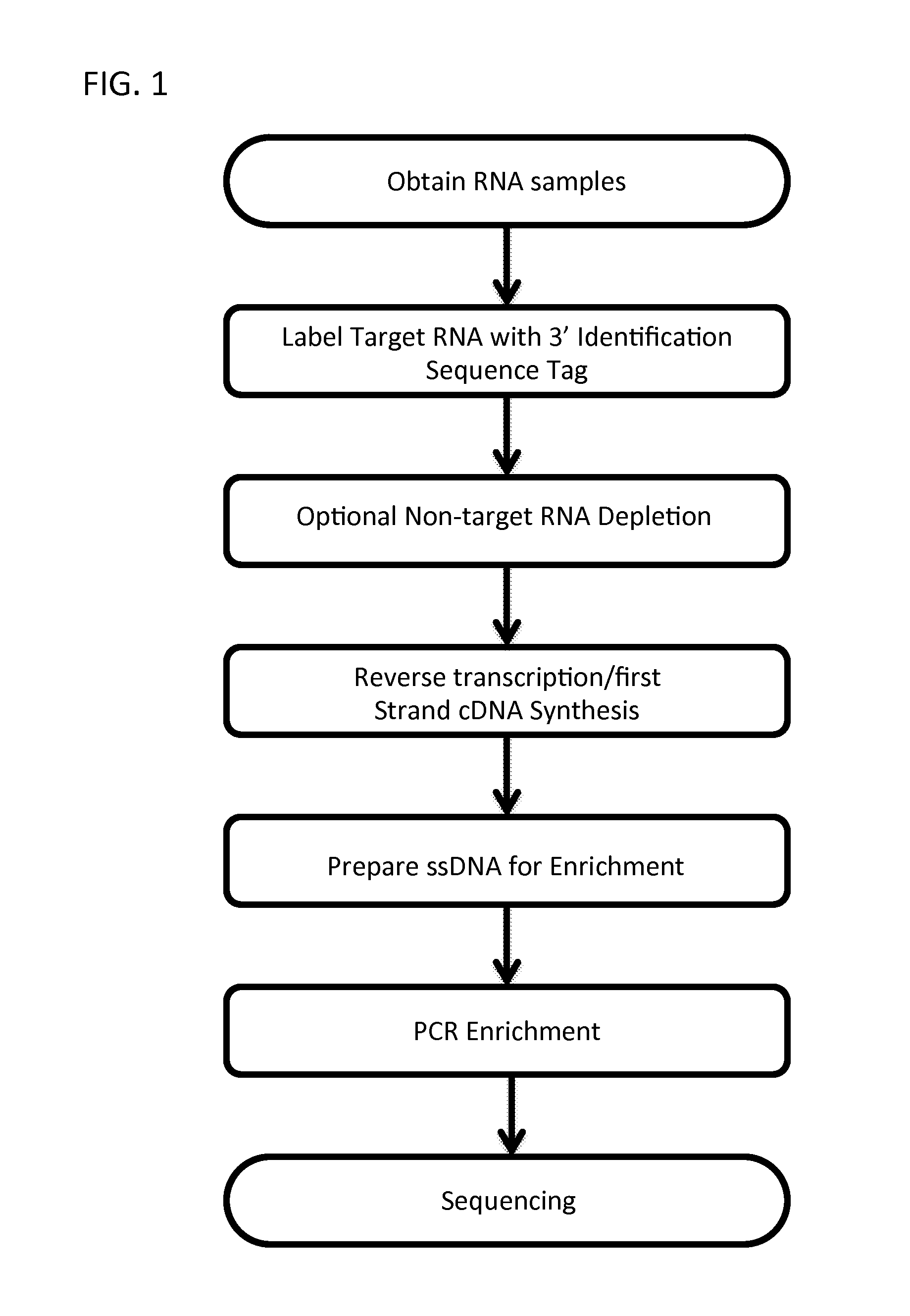
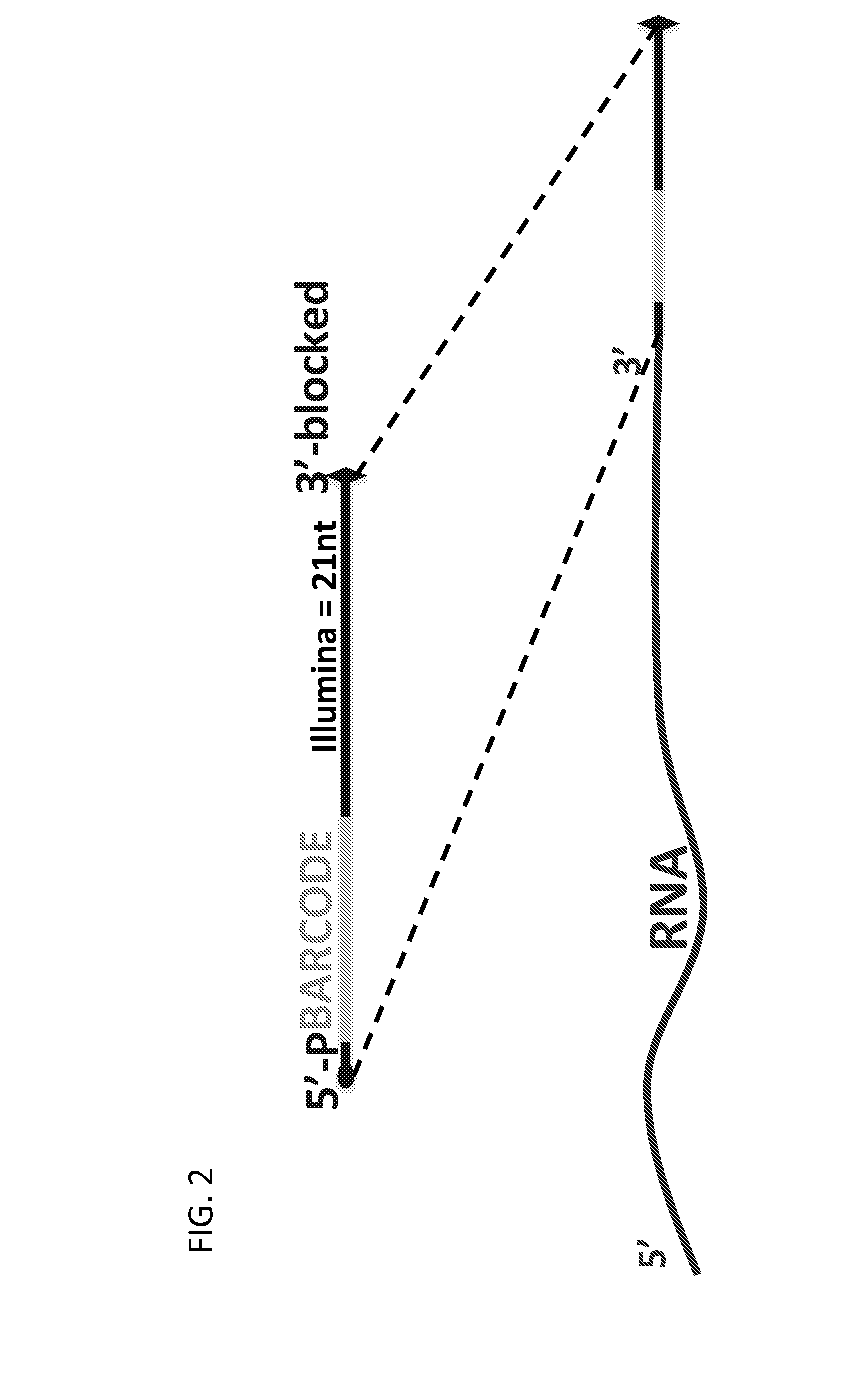
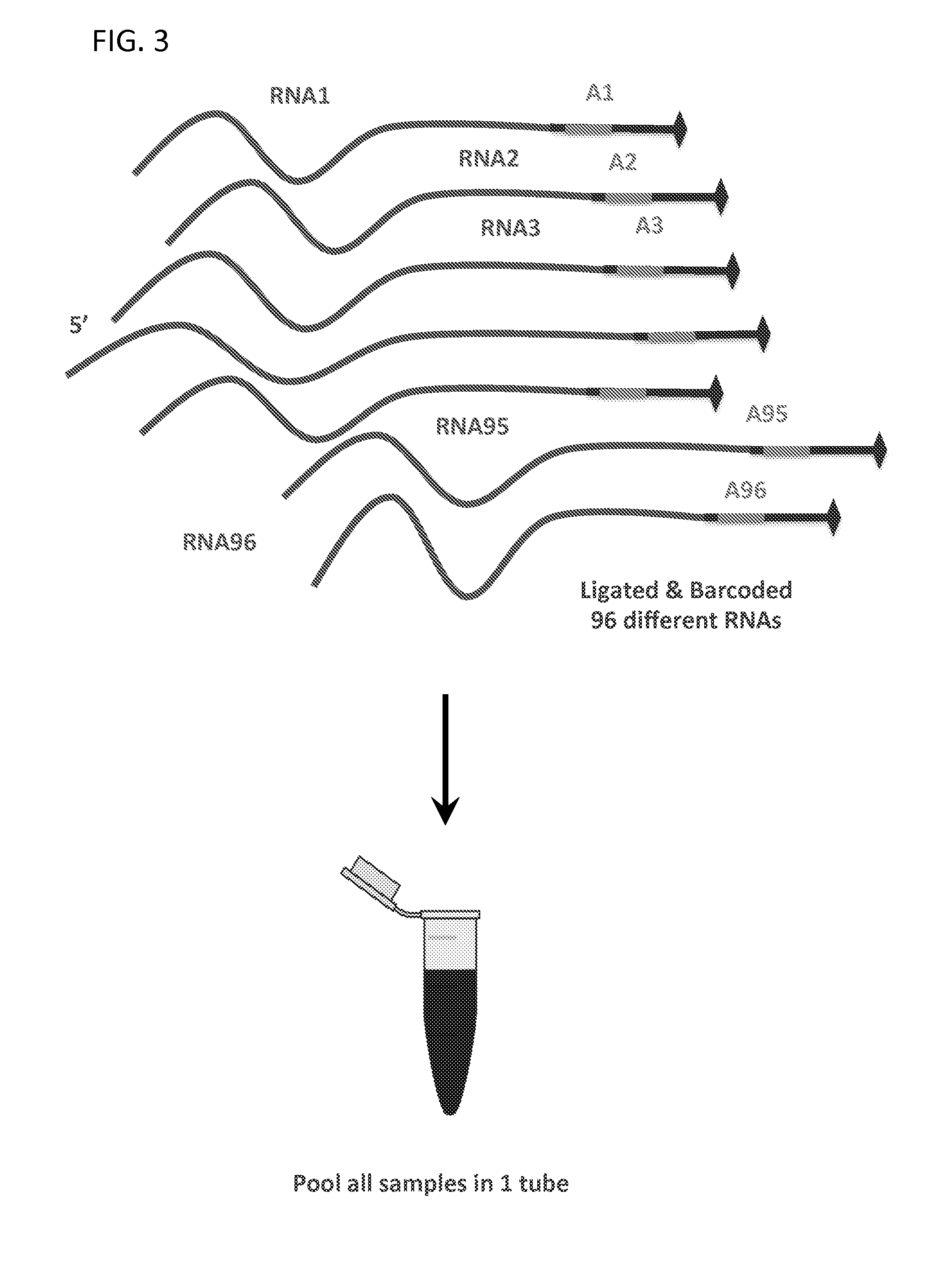
Massively Multiplexed RNA Sequencing
ActiveUS20160024572A1Low costShorten the timeNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA SequenceNucleic acid sequencing
A method for parallel sequencing target RNA from samples from multiple sources while maintaining source identification is provided. The method includes providing samples of RNA comprising target RNA from two or more sources; labeling, at the 3′ end, the RNA from the two or more sources with a first nucleic acid adaptor that comprises a nucleic acid sequence that differentiates between the RNA from the two or more sources; reverse transcribing the two or more sources to create a single stranded DNA comprising the nucleic acid sequence that differentiates between the RNA from the two or more sources; amplifying the single stranded DNA to create DNA amplification products that comprise the nucleic acid sequence that differentiates between the RNA from the two or more sources; sequencing the DNA amplification products thereby parallel sequencing target RNA from samples from multiple sources while maintaining source identification.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +1
DNA and RNA sequencing by nanoscale reading through programmable electrophoresis and nanoelectrode-gated tunneling and dielectric detection
An apparatus and method for performing nucleic acid (DNA and / or RNA) sequencing on a single molecule. The genetic sequence information is obtained by probing through a DNA or RNA molecule base by base at nanometer scale as though looking through a strip of movie film. This DNA sequencing nanotechnology has the theoretical capability of performing DNA sequencing at a maximal rate of about 1,000,000 bases per second. This enhanced performance is made possible by a series of innovations including: novel applications of a fine-tuned nanometer gap for passage of a single DNA or RNA molecule; thin layer microfluidics for sample loading and delivery; and programmable electric fields for precise control of DNA or RNA movement. Detection methods include nanoelectrode-gated tunneling current measurements, dielectric molecular characterization, and atomic force microscopy / electrostatic force microscopy (AFM / EFM) probing for nanoscale reading of the nucleic acid sequences.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
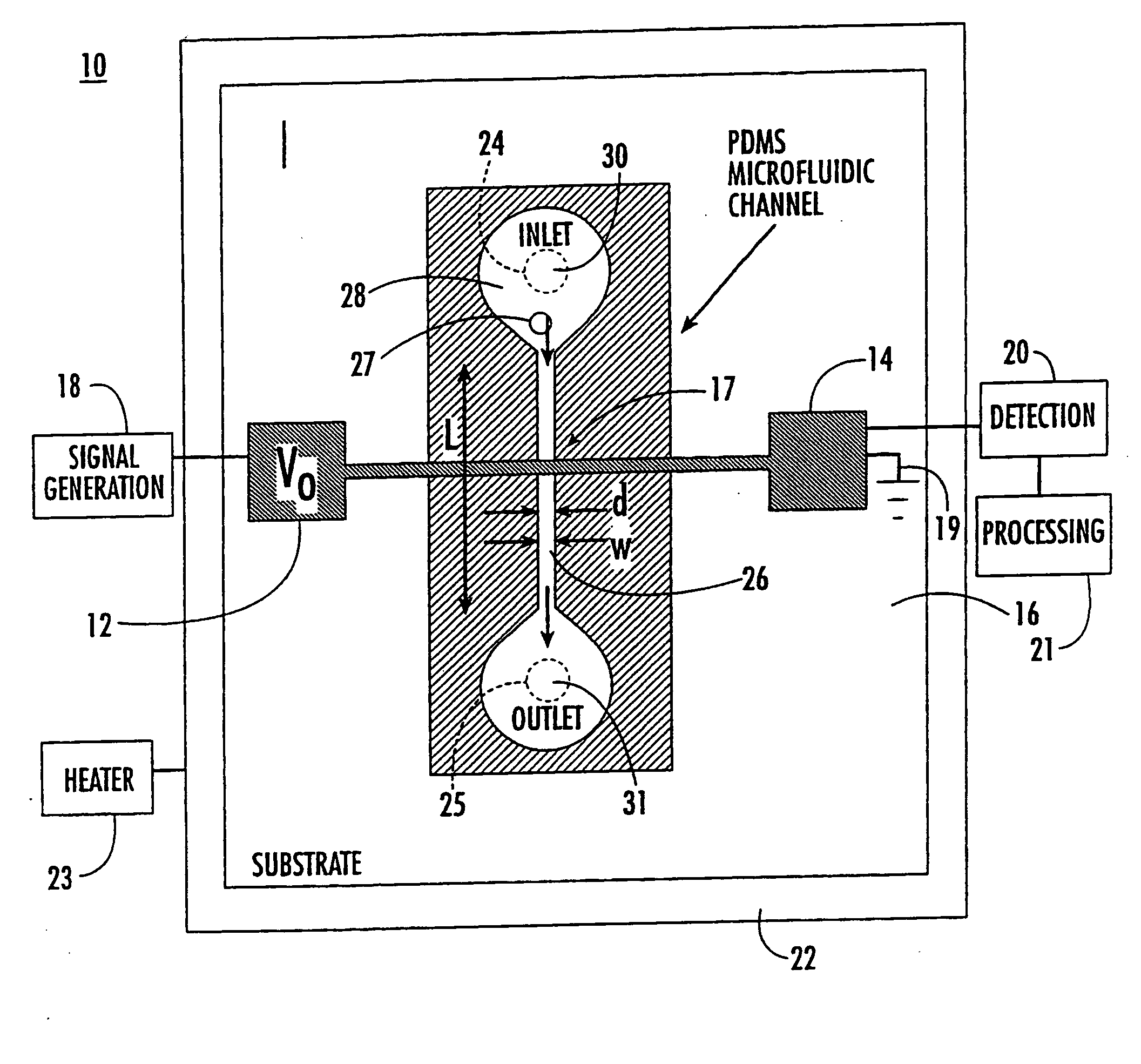
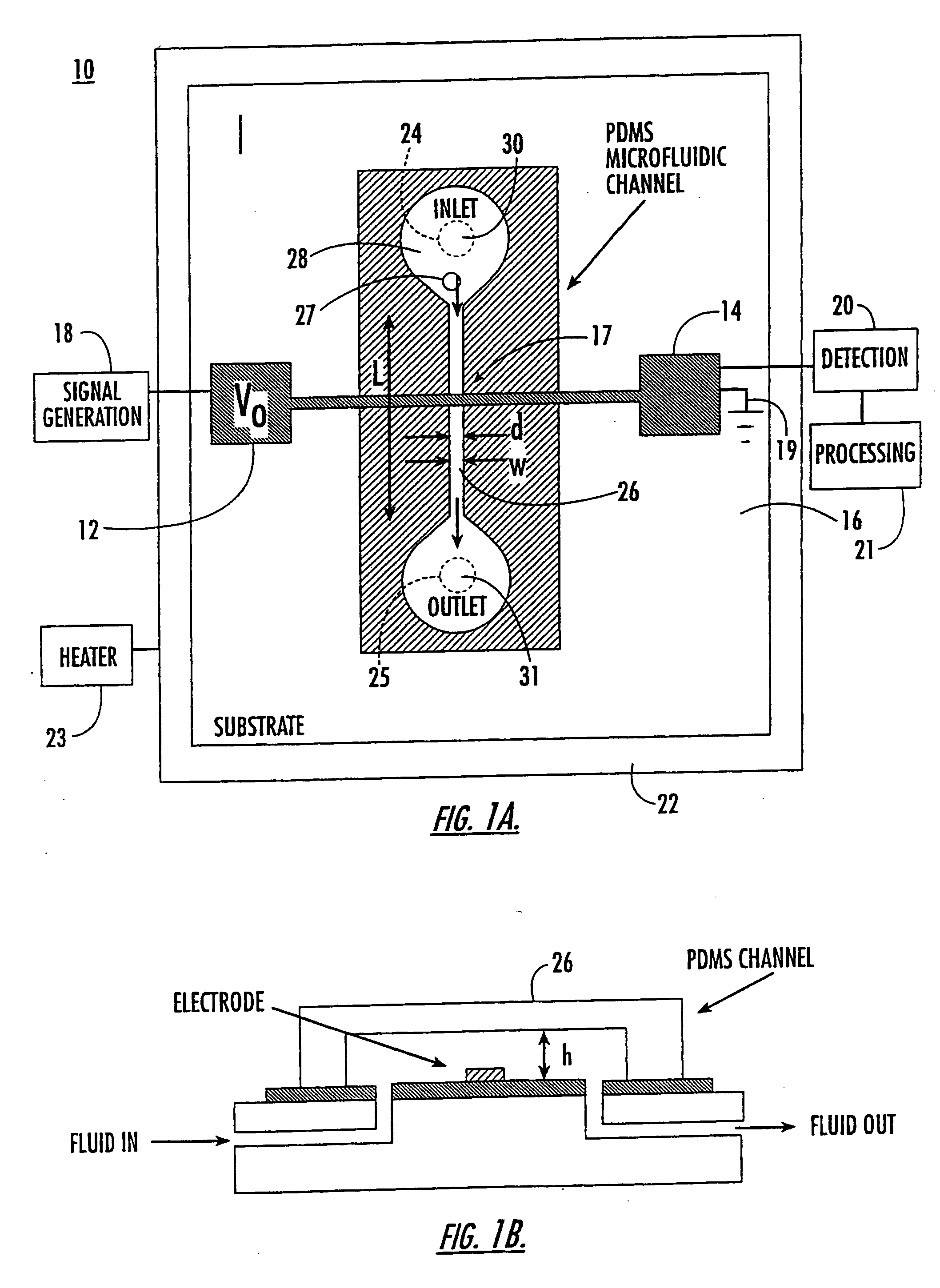
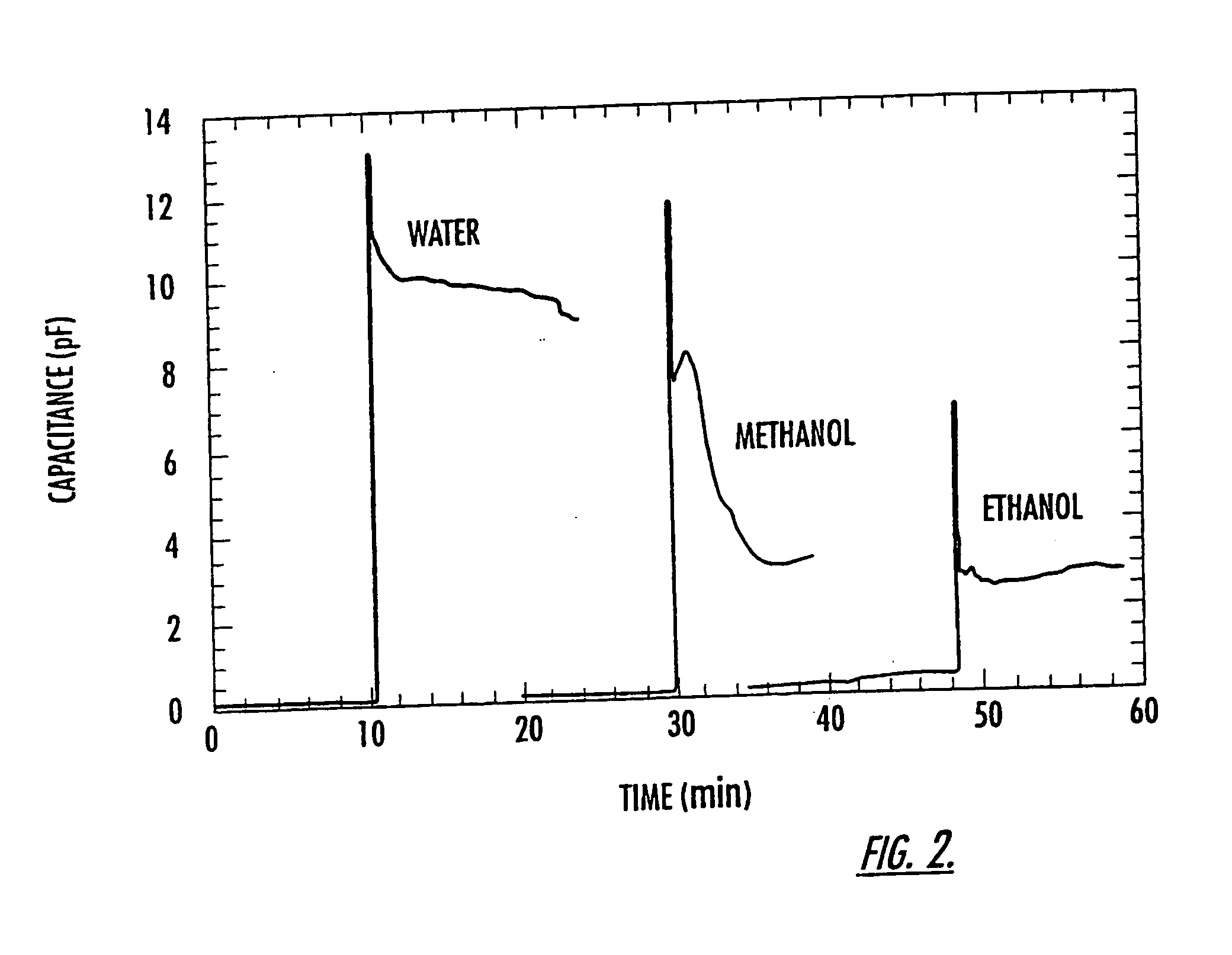
Microfluidic and nanofluidic electronic devices for detecting changes in capacitance of fluids and methods of using
InactiveUS20070238112A1Simpler and faster and less-expensiveMaterial nanotechnologyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsCapacitanceCell Cycle Kinetics
The present invention (also identified as “Capacitance cytometry”) relates to microfluidic and nanofluidic devices for detecting or measuring an electrical property of a fluid (liquid or aerosol), a single molecule, particle, or cell in fluid. In a particular embodiment, the devices detect or measure changes in capacitance of a fluid, molecule, particle or cell as it passes through the device. The invention relates to detection and measurement of single molecules, particularly biological molecules, and to methods of sequencing polynucleotide molecules (RNA or DNA) by detecting differentially labeled single nucleotides. Single molecule detection applications include DNA or RNA sequencing, detection of SNPs, protoemics, and particle sizing. The device can be used to determine cell DNA content, to analyze cell-cycle kinetics of cell populations, and to assay for abnormal changes in cell DNA content. Nano-microfluidic devices of this invention also have utility as detectors in molecular sorting systems and for detecting pathogens.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Method of altering cell properties by administering rna
InactiveUS20060247195A1Less activeMinimise and prevent riskCell differentiationGenetic material ingredientsRNA SequenceIn vivo
The invention relates to the alteration of cell properties using RNA molecules. In particular, it relates to the alteration of the ability of cells to mobilise, migrate, integrate, proliferate and / or differentiate. For example, it relates to the induction of differentiation of stem cells, including the acquisition of the ability to migrate, integrate, and proliferate. It also relates to the induction of in vivo stem cell mobilisation, migration, integration, proliferation and / or differentiation. Accordingly, it relates to the promotion of stem cell-mediated functional repair. The invention also relates to the reversal of differentiation of differentiated cells. All these effects may be effected by providing isolated RNA comprising a RNA sequence extractable from cells comprising the desired cell type(s) to a population of cells under conditions whereby the alteration of the cell property is achieved.
Owner:RIBOSTEM
Methods using non-genic sequences for the detection, modification and treatment of any disease or improvement of functions of a cell
InactiveUS20050164252A1Promote recoveryDiagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementOther foreign material introduction processesBiological bodyRNA Sequence
This invention provides the use of conserved non-genic sequences so commonly found in most species of plants and animals for the detection of a disease and condition. The intimate and ultimately important link of the corresponding DNA sequences and expressed RNA sequences with their conserved non-genic sequence makes the detection possible. Apart from the diagnostic use, the combination of the conserved non-genic sequences with the corrected or designed DNA or RNA sequences makes treatment or improvement possible for living organisms.
Owner:YEUNG WAH HIN
Methods of RNA amplification in the presence of DNA
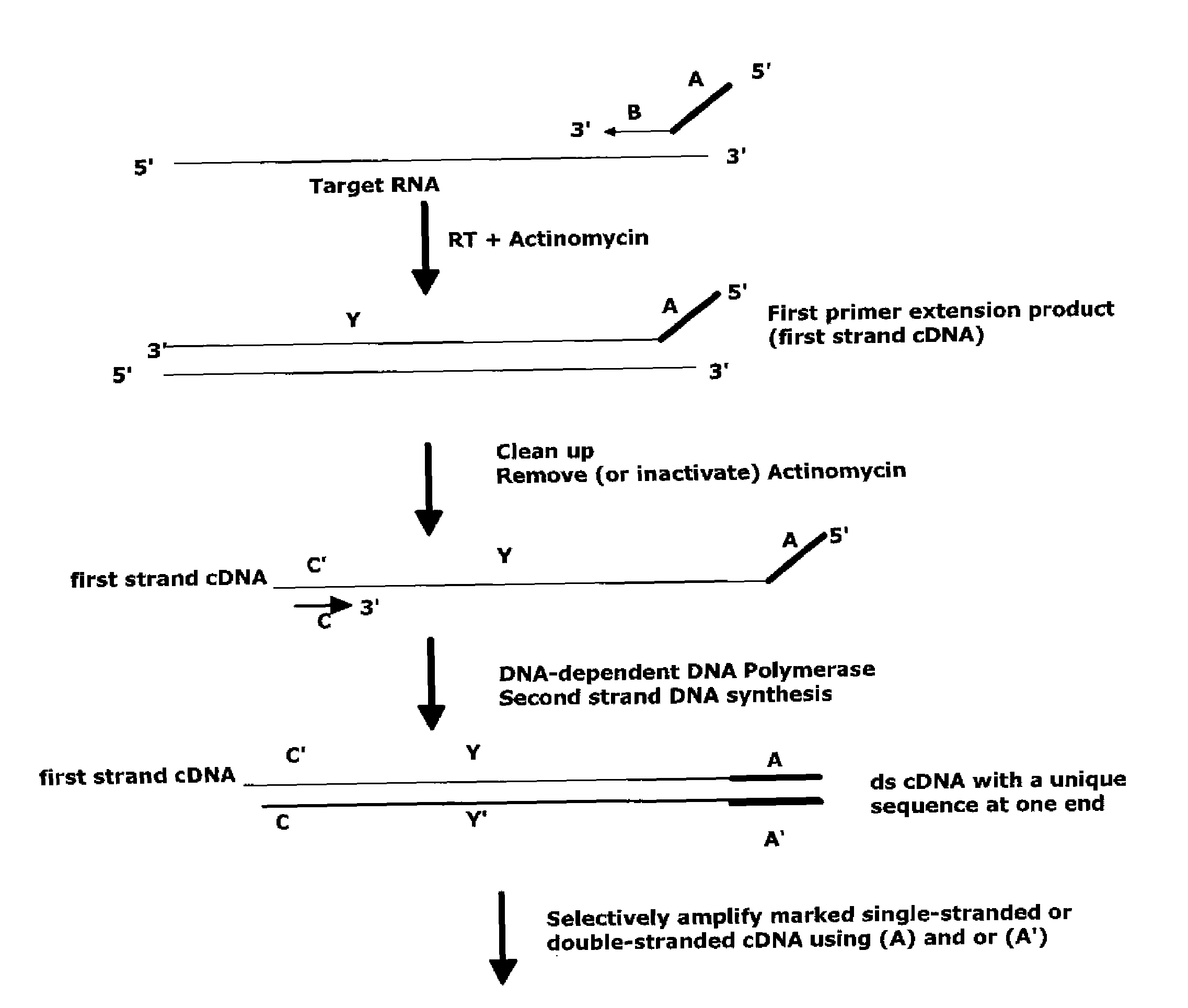
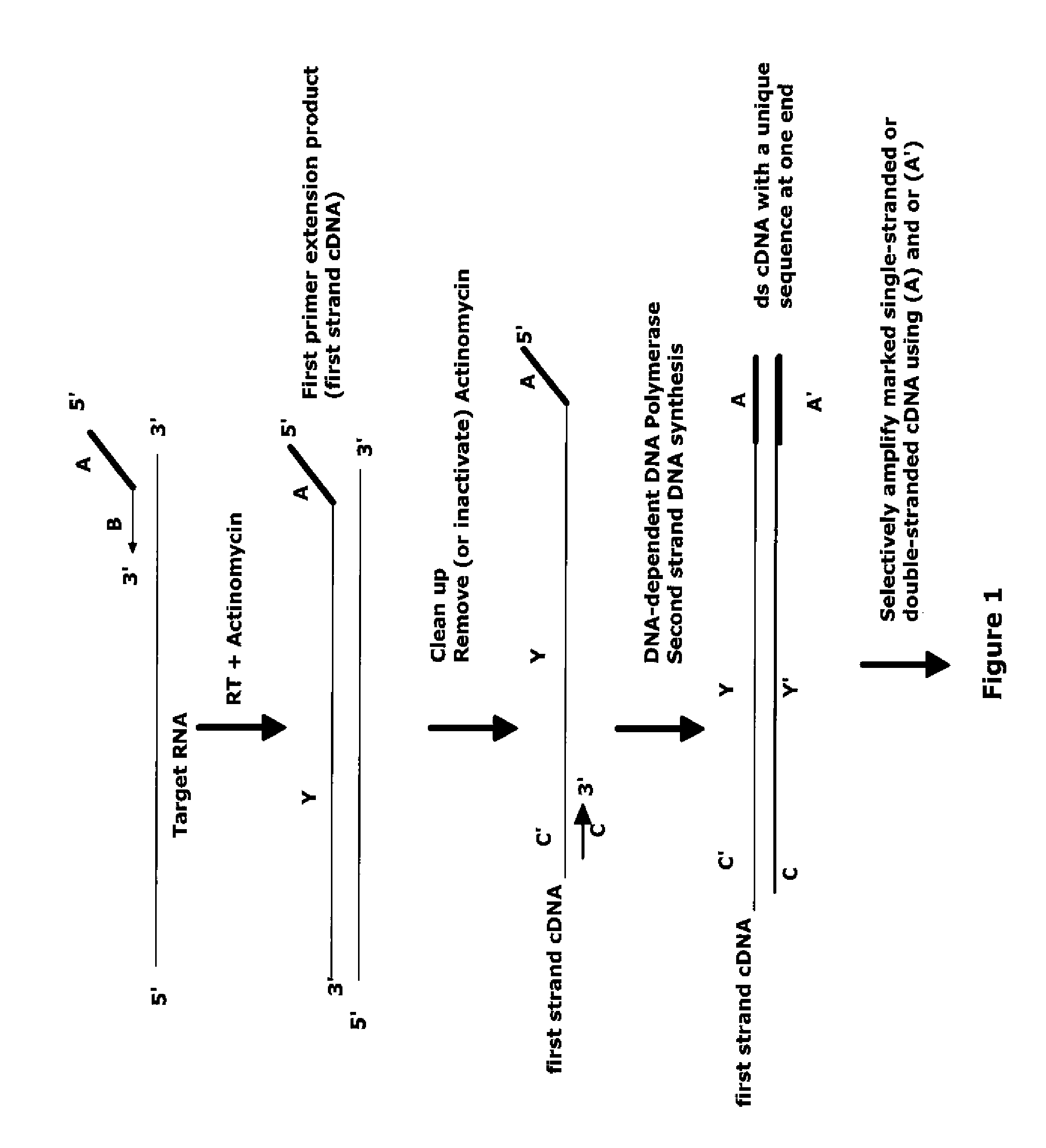
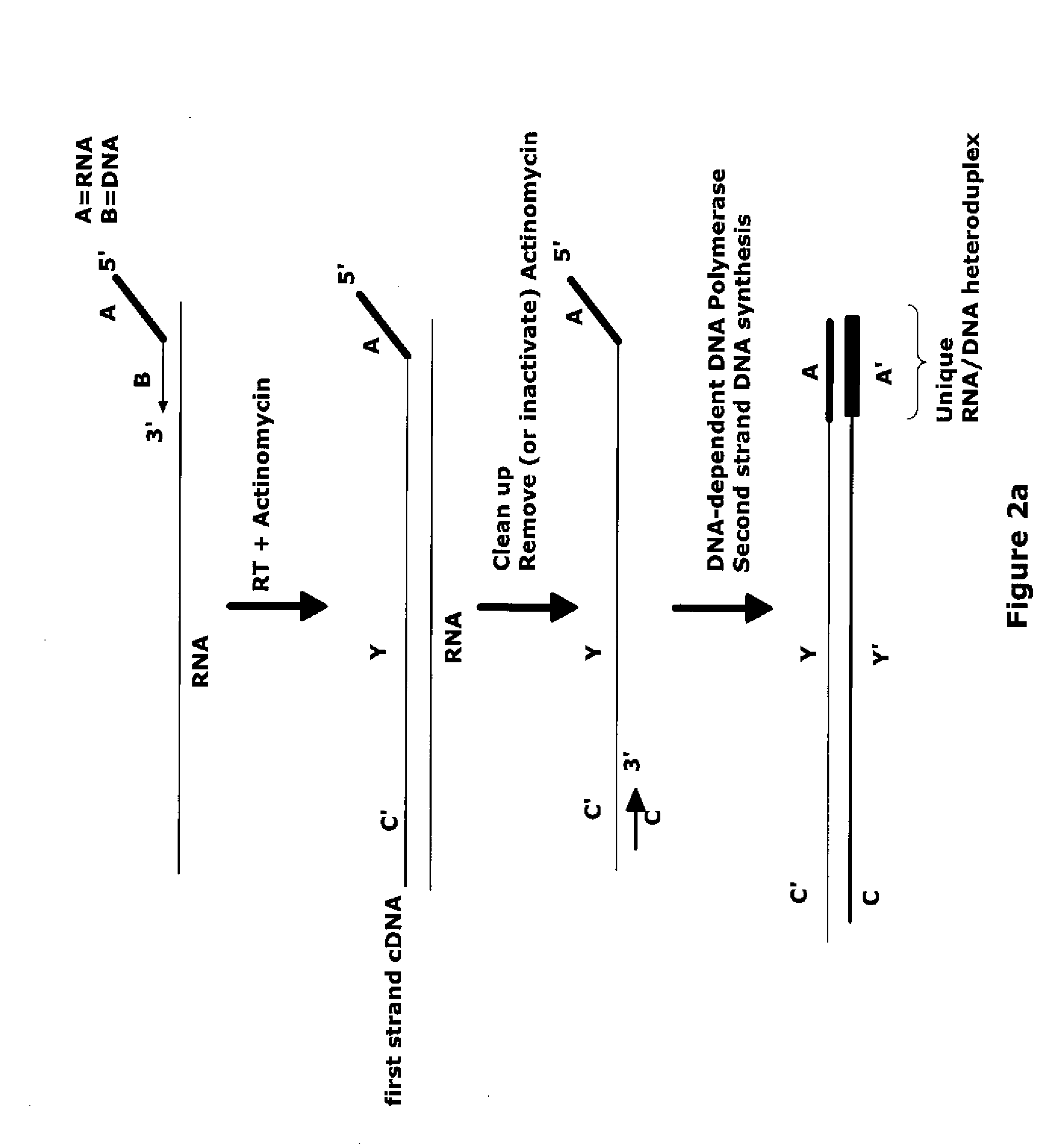
The invention provides methods for amplification of RNA. The methods are particularly suitable for specifically amplifying RNA in the presence of DNA. The methods involve producing a marked first primer extension product from a target RNA in the presence of a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase inhibitor, which prevents replication of DNA by the reverse transcriptase enzyme. The marked nucleic acid products are subsequently selectively amplified in the presence on non-marked nucleic acids. The methods are useful for production and analysis of polynucleotide sequences complementary to an RNA sequence. The methods are useful for preparation of nucleic acid libraries and substrates for analysis of gene expression of cells in biological samples. The invention also provides compositions and kits for practicing the amplification methods, as well as methods which use the amplification products.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
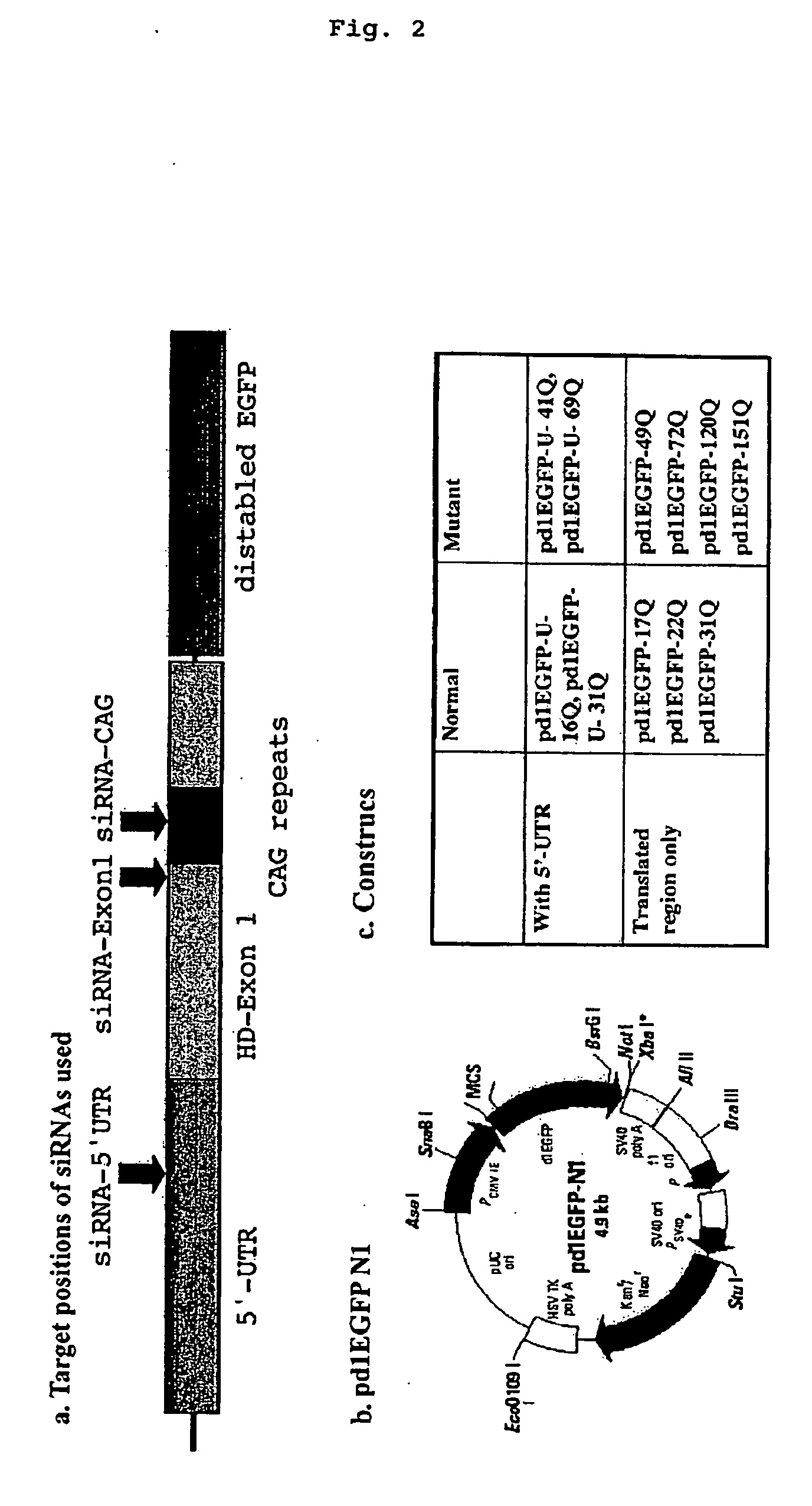
Inhibition of the Expression of Huntingtin Gene
InactiveUS20080015158A1Inhibit expressionAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaMammal
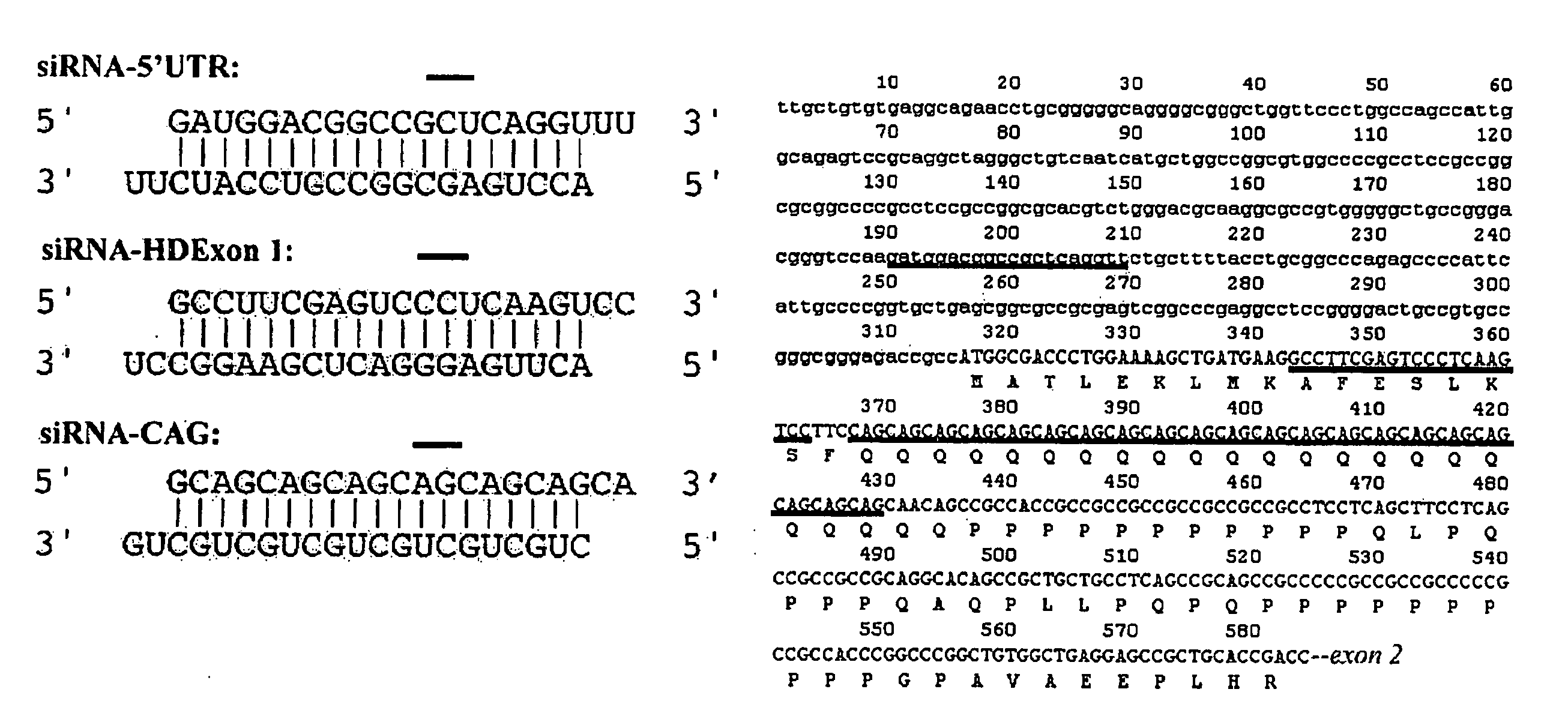
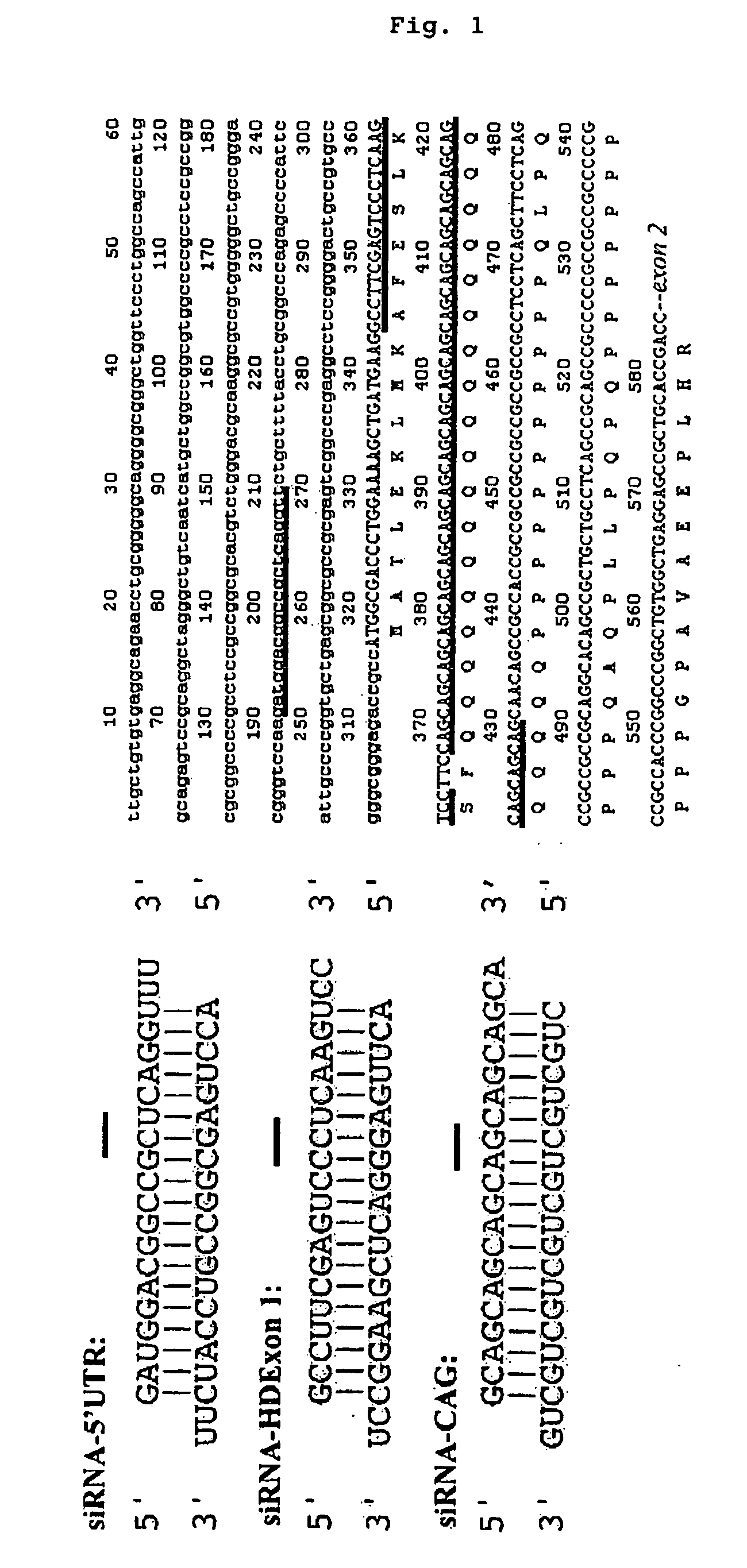
It is intended to provide methods for suppressing the huntingtin gene expression by using a double-stranded RNA (dsRNA), huntingtin gene expression inhibitors to suppress the huntingtin gene expression, and preventives and / or remedies of Huntington's disease. Targeting against a specific sequence of mRNA at immediately upstream of CAG repeats in HD genes of Huntington's disease, the huntingtin gene expression is suppressed by using a dsRNA homologous to the sequence. In this invention, a short siRNA (short double-stranded RNA) having bp as short as around 21-23 bp can be effectively used as the dsRNA homologous to a specific RNA sequence in a region at immediately upstream of CAG repeats. The dsRNA of this present invention can be used as a huntingtin gene expression inhibitor, or a preventive and / or a remedy of Huntington's disease by administering or introducing into a living body or a living cell in mammals for the prevention and / or treatment of Huntington's disease.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
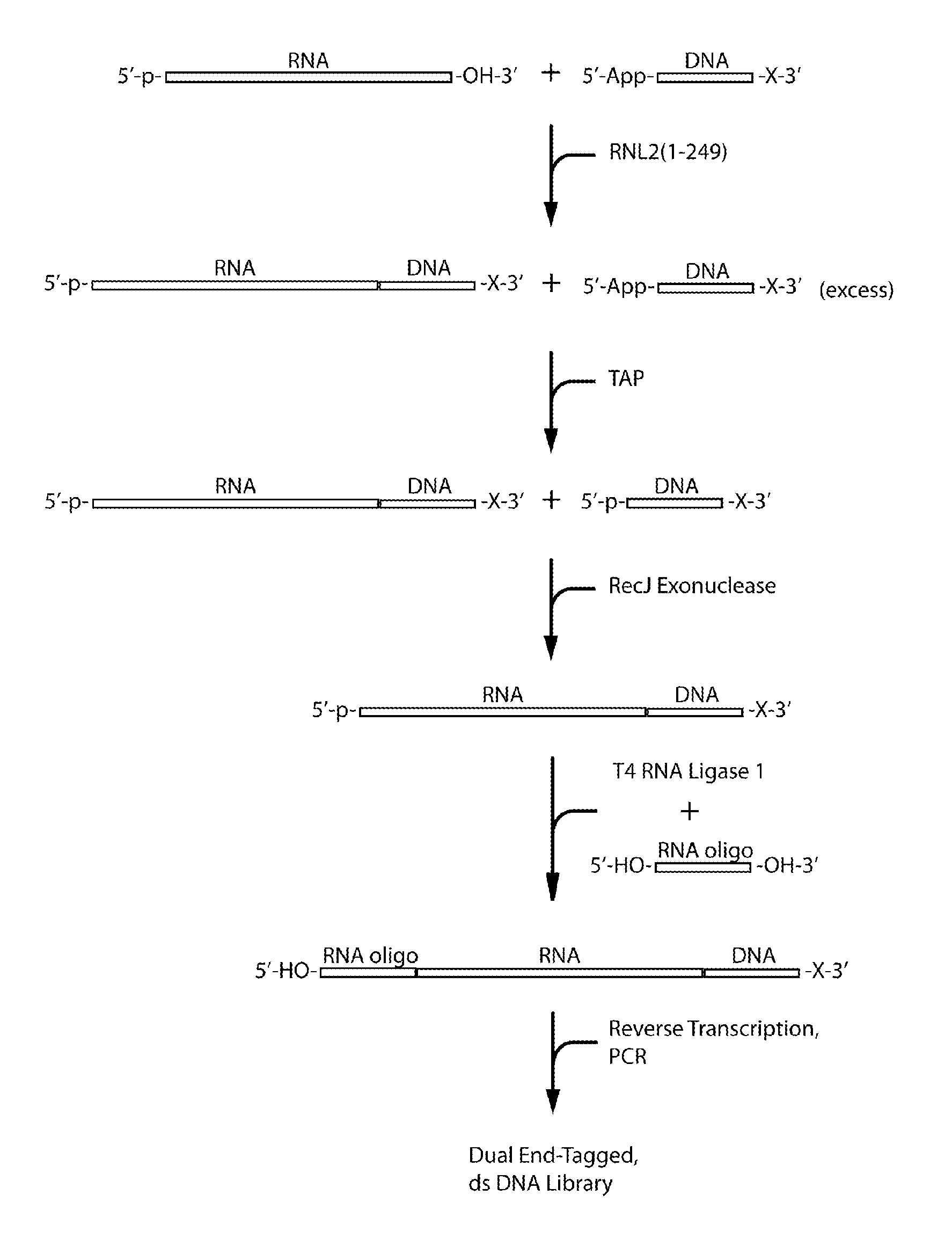
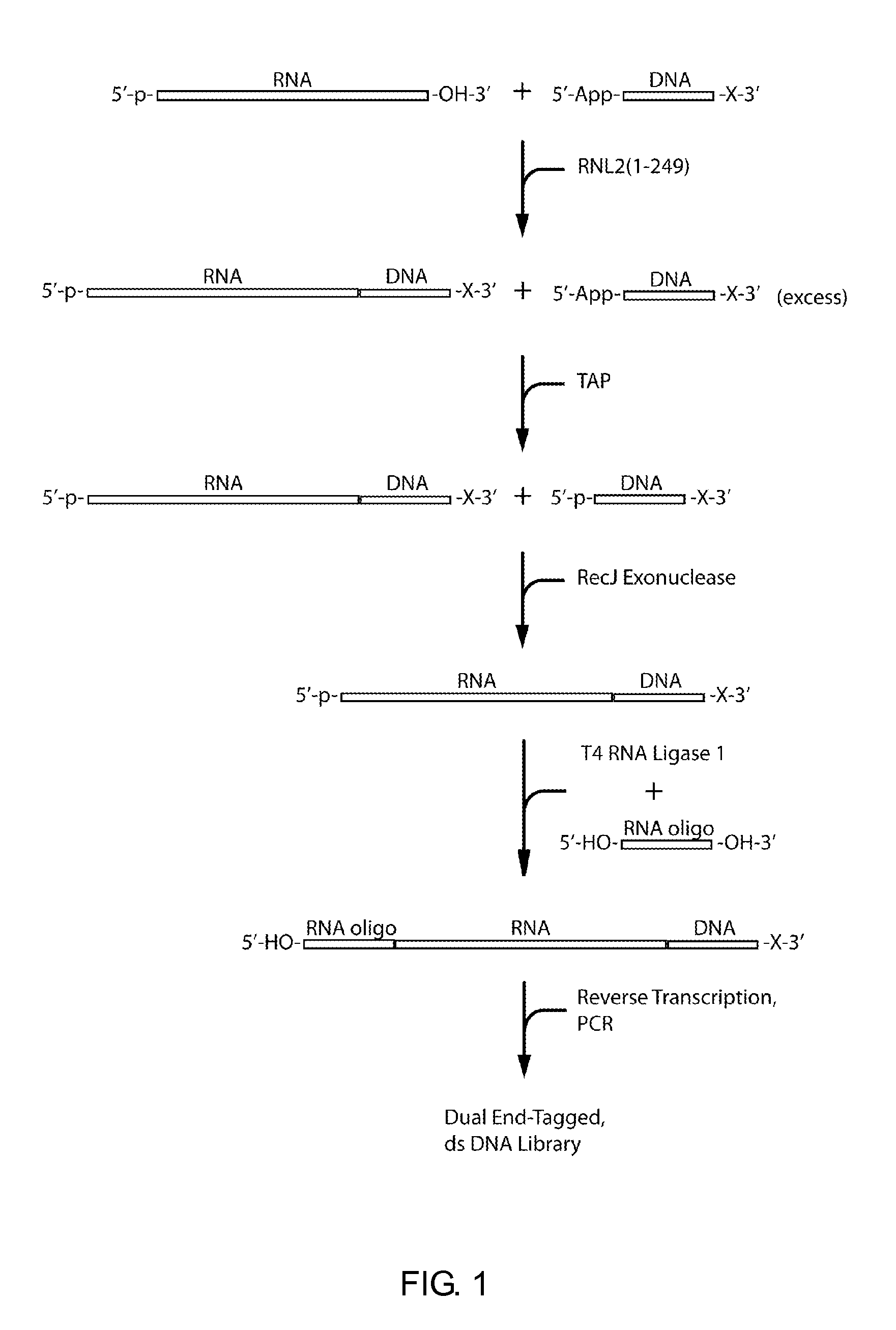
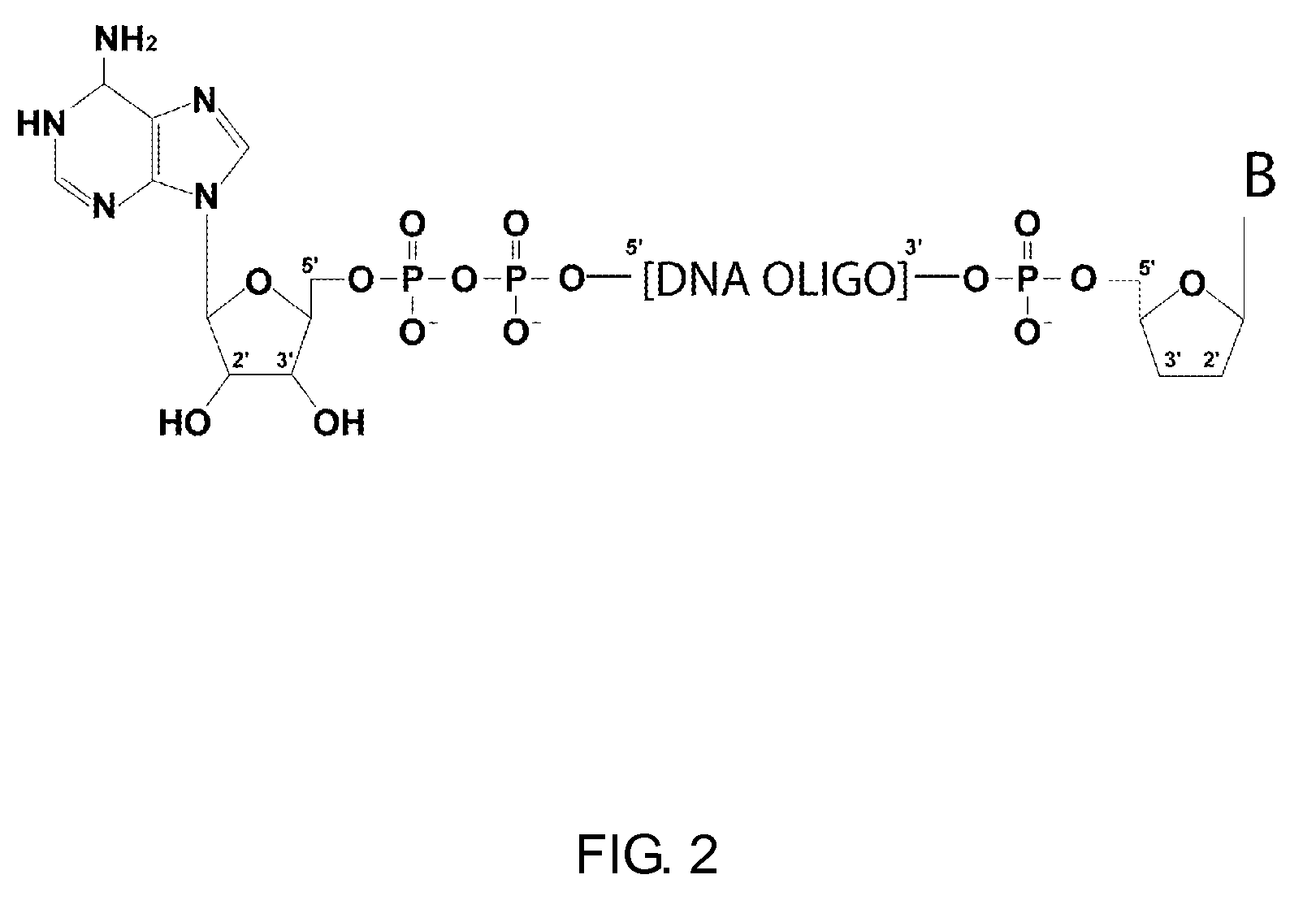
Methods and kits for 3'-end-tagging of RNA
ActiveUS20110104785A1High detection sensitivityRapid and efficient enzymaticHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA SequenceSingle strand dna
The present innovation provides methods and kits that enable rapid and efficient dual end-tagging of RNA to prepare libraries for analysis by applications such as next-generation RNA sequencing, qPCR, microarray analysis, or cloning. The methods do not require time-consuming and inefficient gel-purification steps that are common to methods known in the art. In addition, the present invention provides methods and kits for rapid, high-throughput enzymatic preparation of 5′-activated, 3′-blocked DNA oligonucleotides from standard, single-stranded DNA oligonucleotides.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
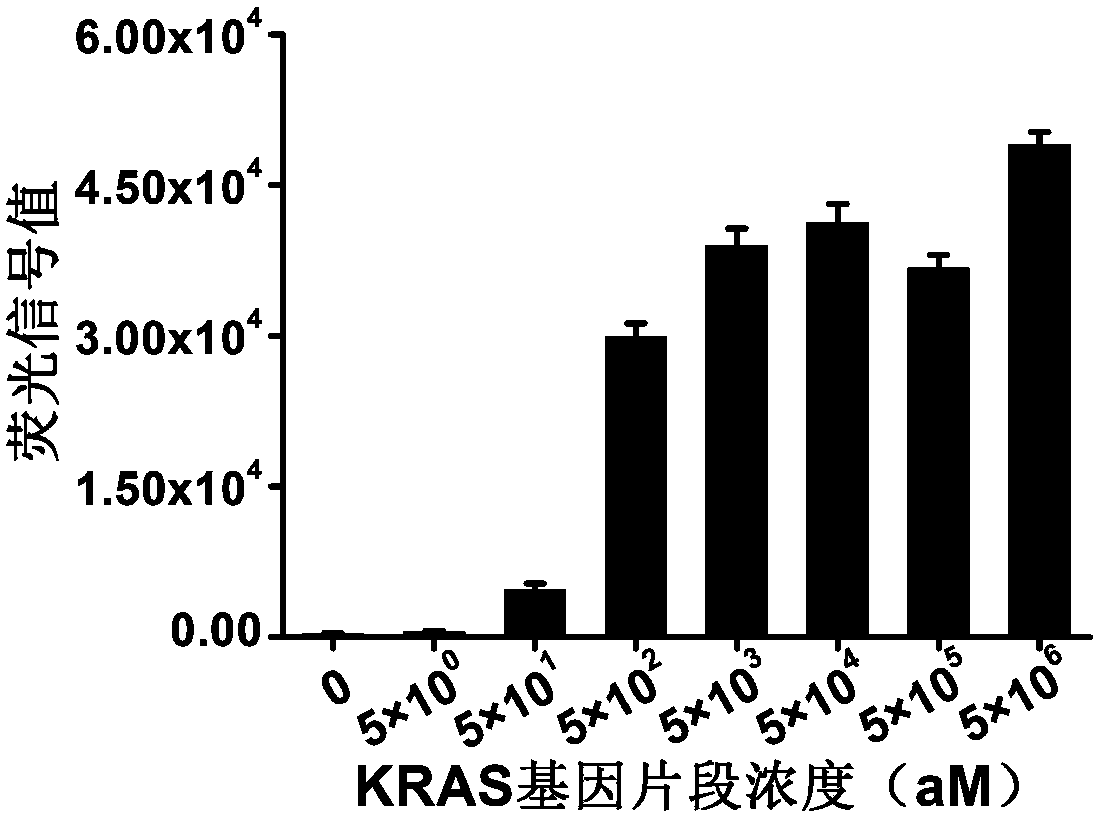
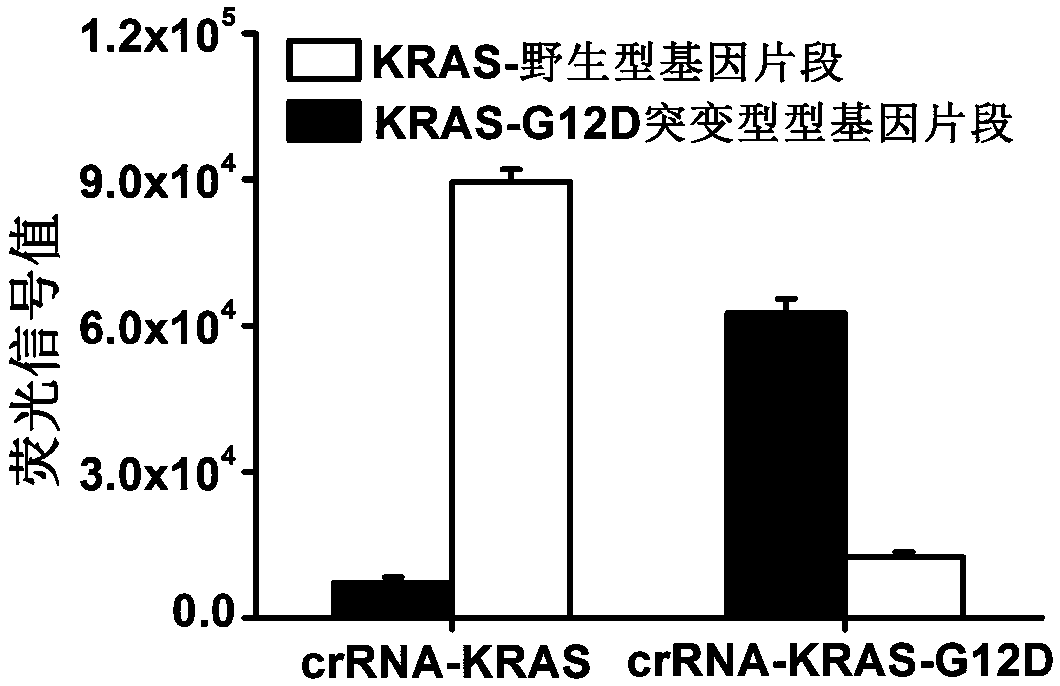
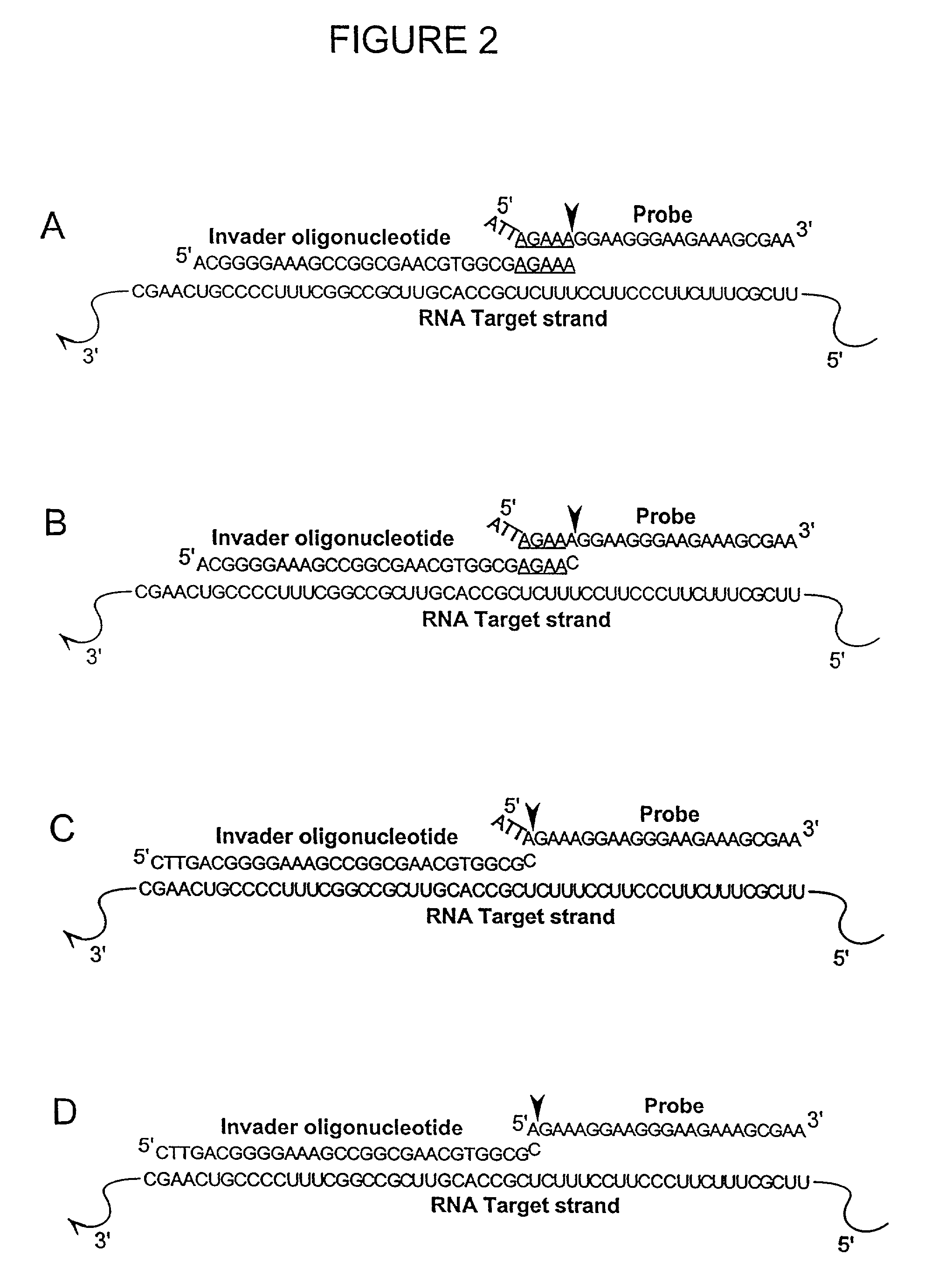
Detection method of specific nucleic acid fragment based on CRISPR-Cas13a
InactiveCN107557455AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA SequenceBiological materials
The invention relates to the detection of biological materials, and particularly discloses a rapid detection method based on CRISPR-Cas13a which is suitable for a specific nucleic acid fragment in a biological sample. A to-be-detected nucleic acid fragment is amplified to obtain a transcription product; a guide RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) is designed by aiming at a target RNA sequence of a target gene,and an RNA molecule is reported by a signal added in a detection system; the amplification and read of the signal are realized by using the RNA enzymatic activity of the Cas13a protein, which is activated after recognizing the target RNA sequence and is not limited by the sequence, further the detection of the target gene is realized. The detection sensitivity of the method provided by the invention can reach 10 to 18mol / L, namely ammol level, and the specificity can be achieved for detecting the nucleic acid fragments with single-base difference.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
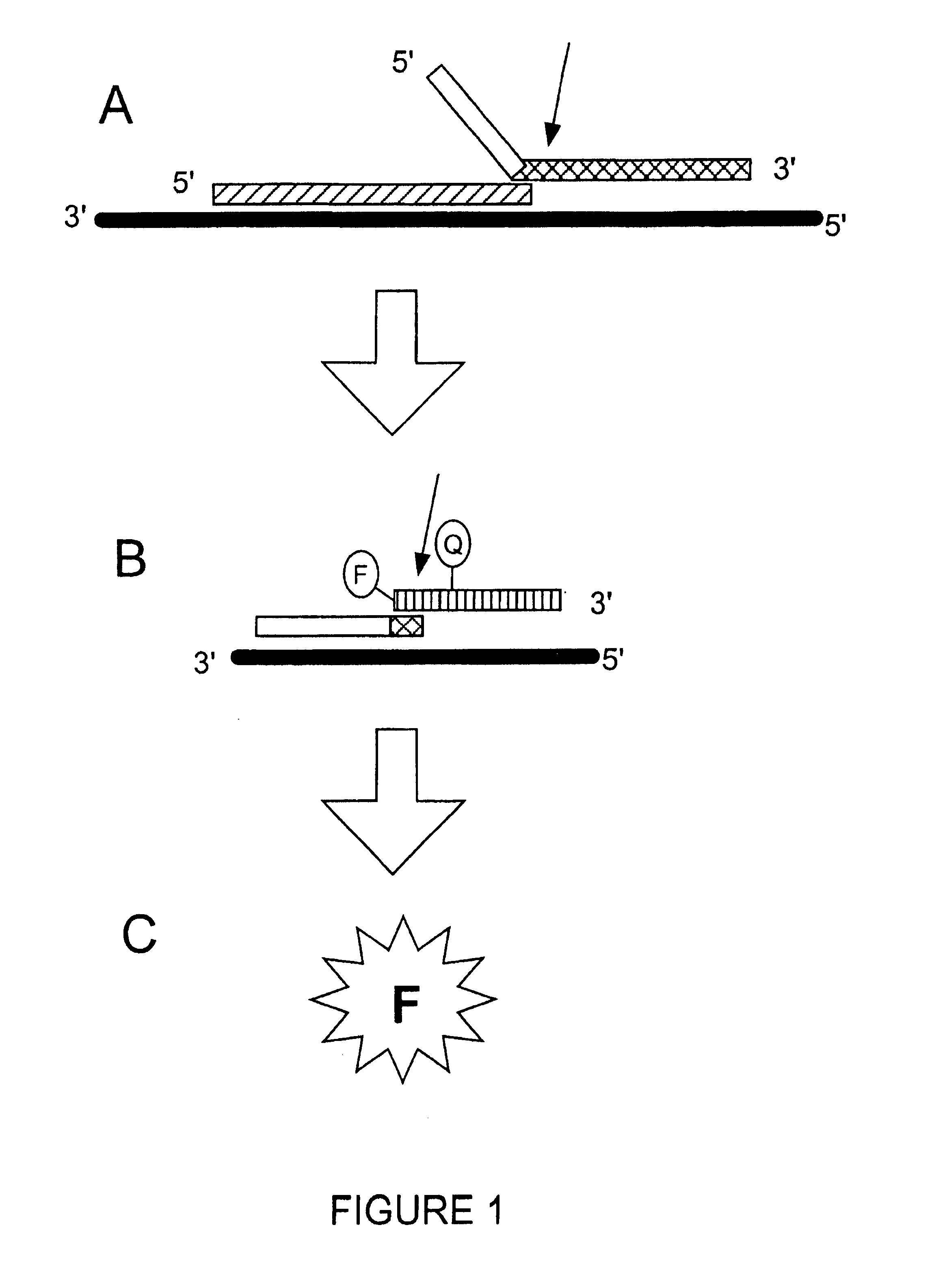
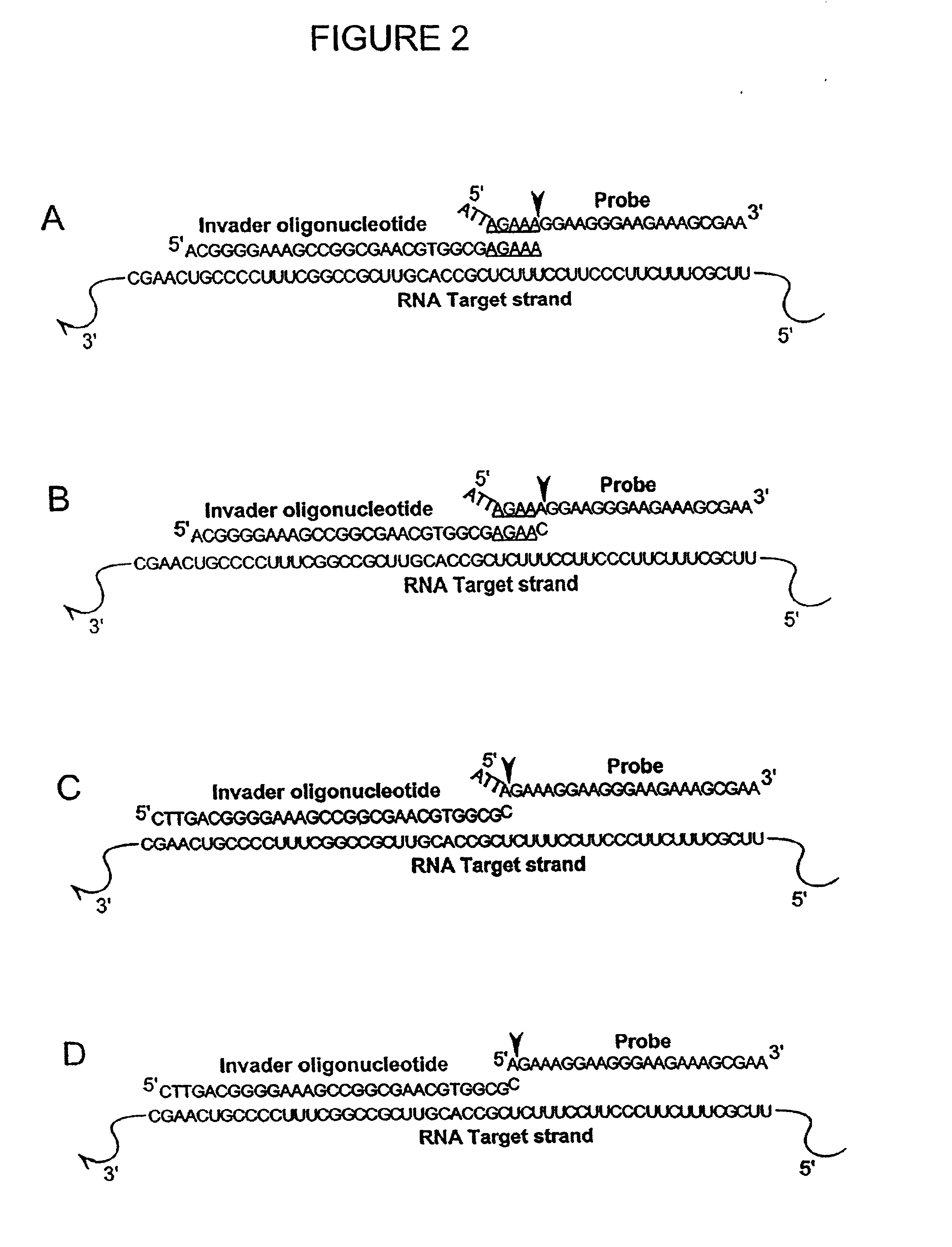
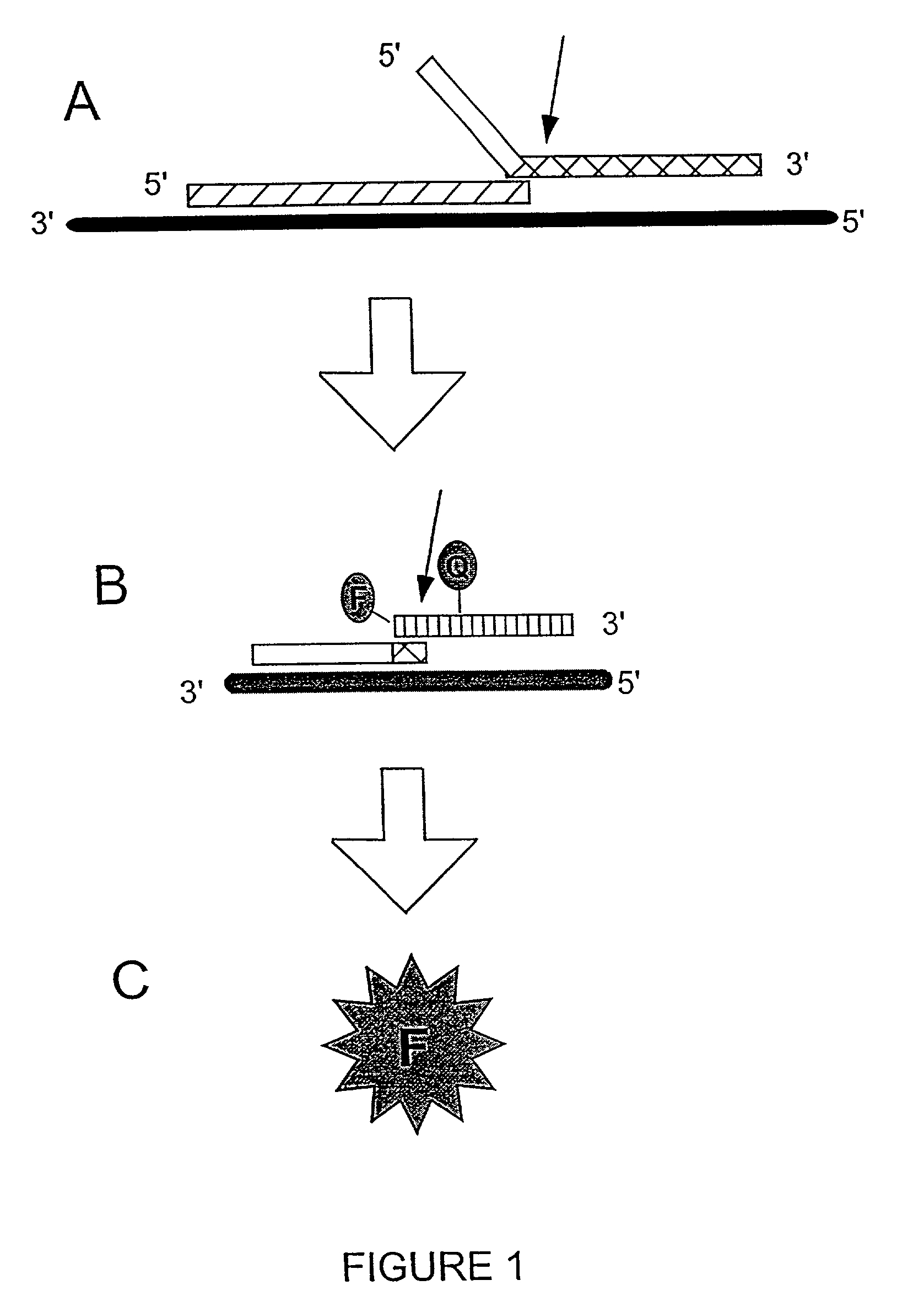
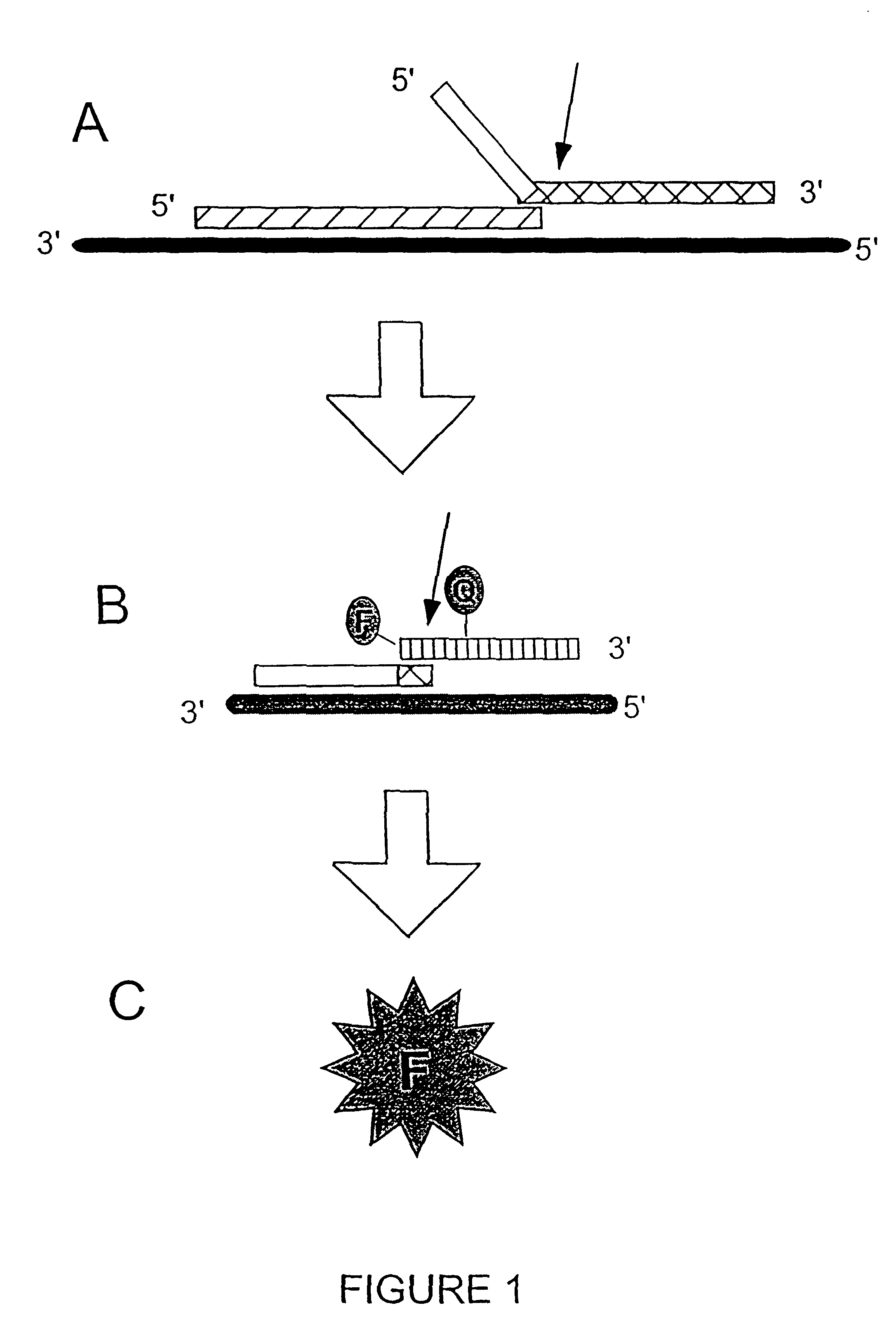
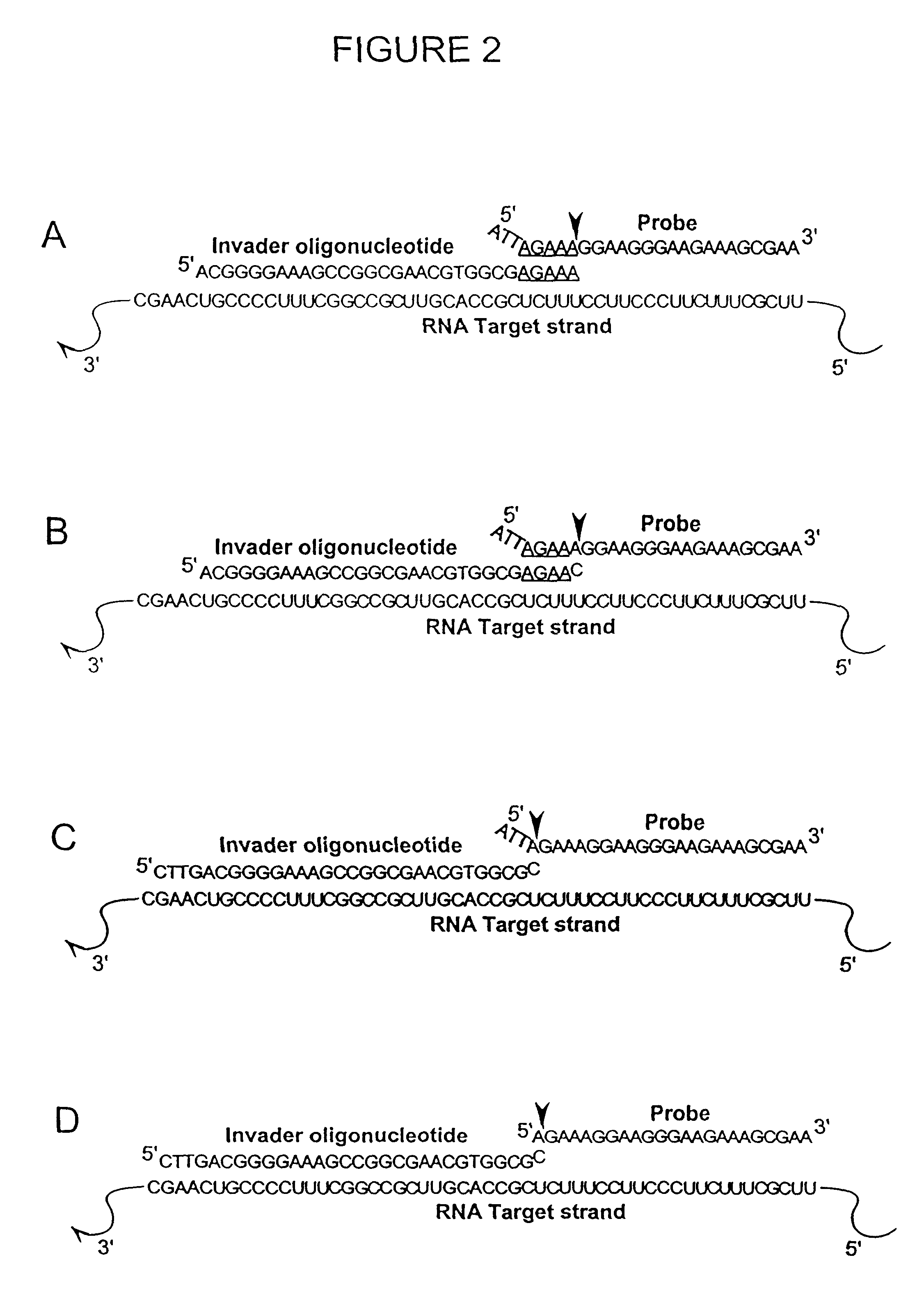
Detection of RNA Sequences
InactiveUS7045289B2Improve abilitiesStructural alterationHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementPolymerase LRNA Sequence
The present invention provides novel cleavage agents and polymerases for the cleavage and modification of nucleic acid. The cleavage agents and polymerases find use, for example, for the detection and characterization of nucleic acid sequences and variations in nucleic acid sequences. In some embodiments, the 5′ nuclease activity of a variety of enzymes is used to cleave a target-dependent cleavage structure, thereby indicating the presence of specific nucleic acid sequences or specific variations thereof.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
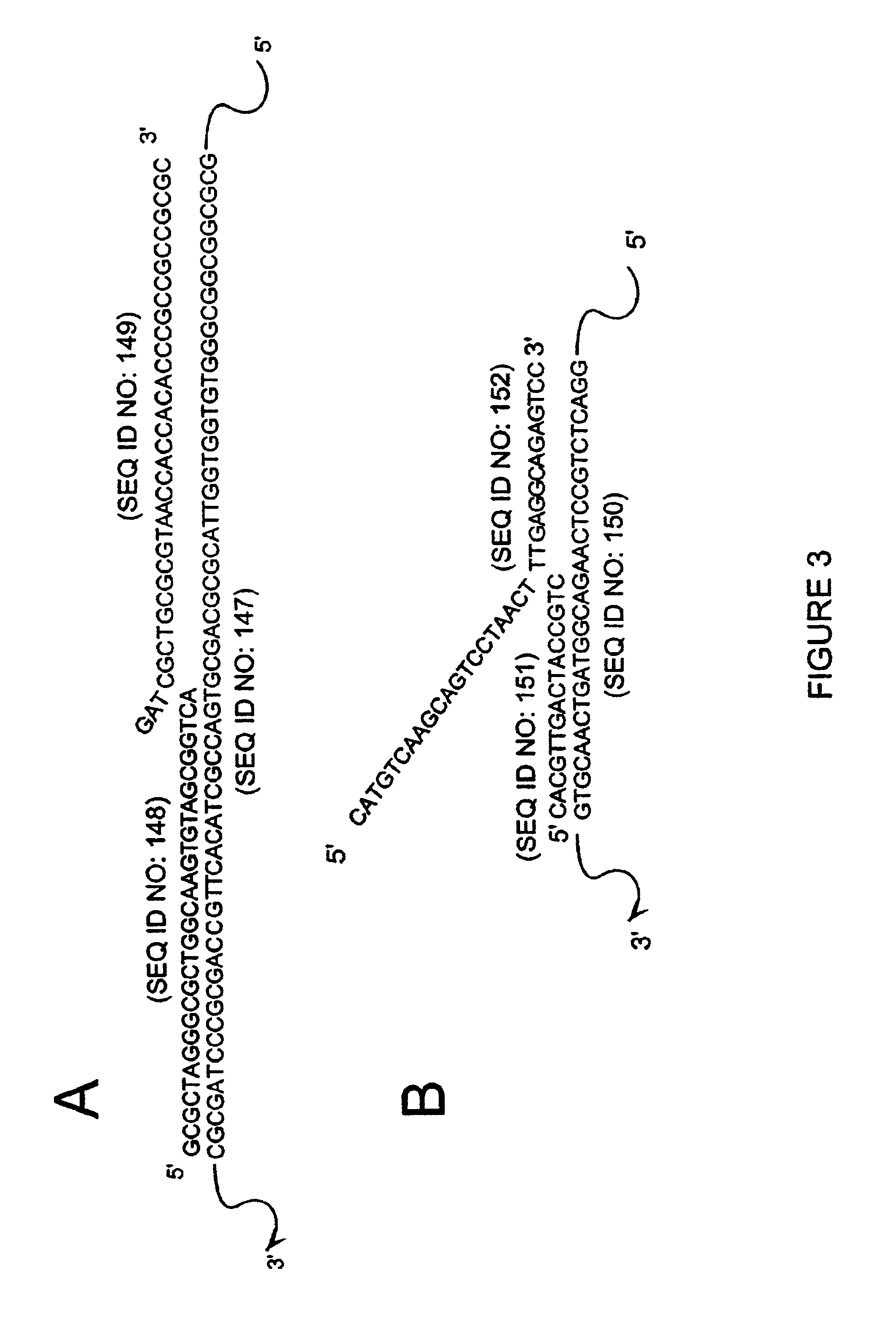
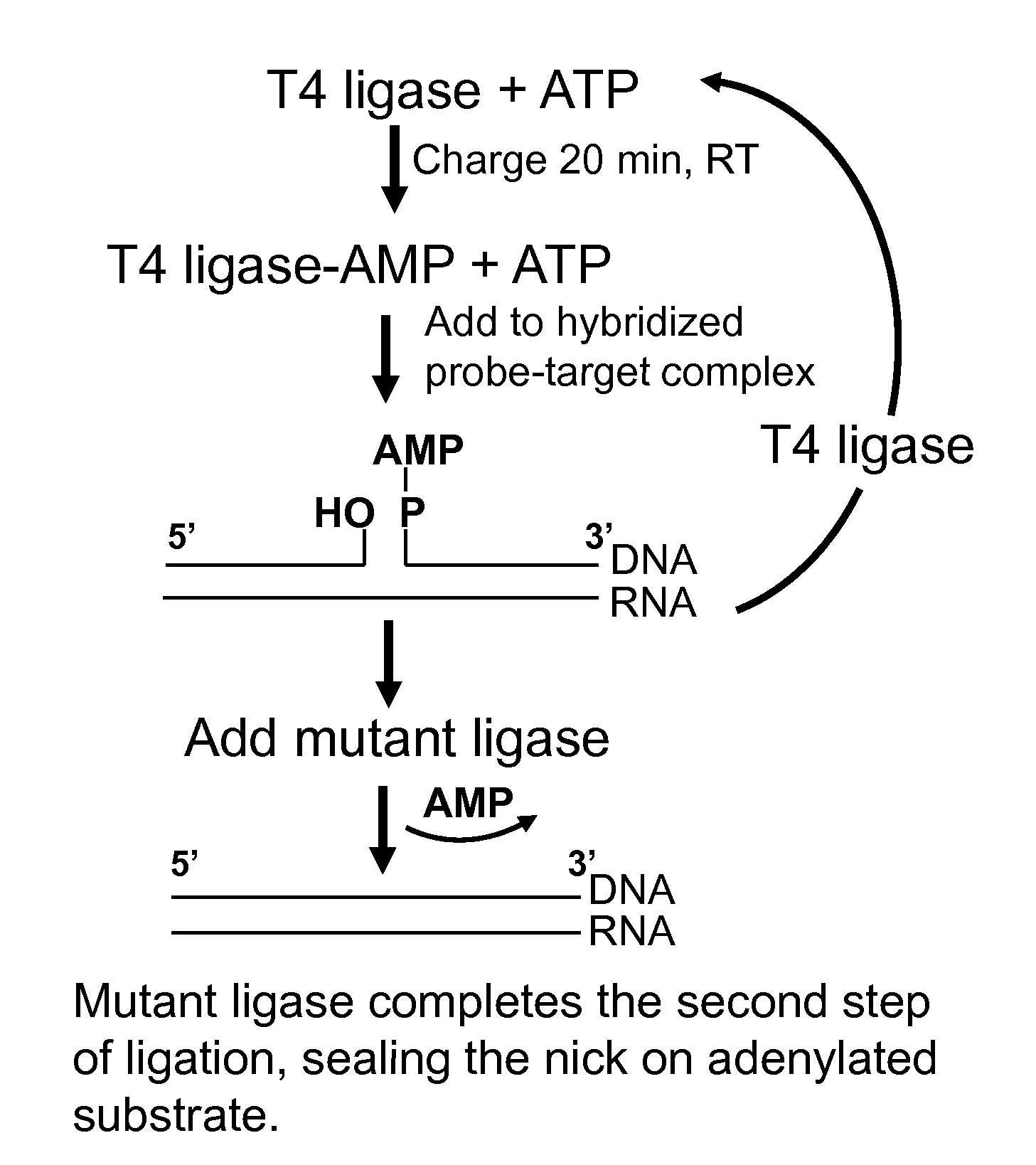
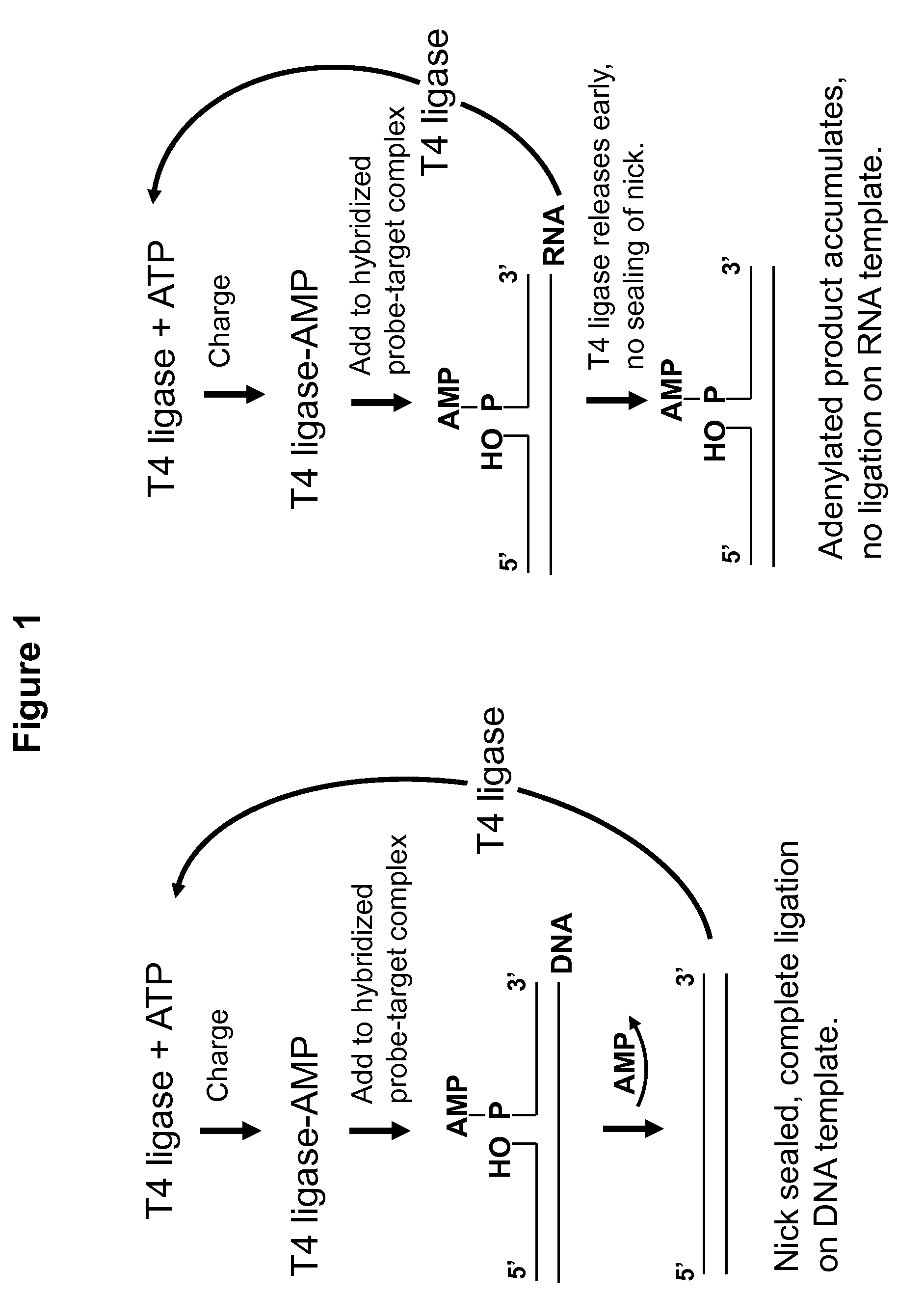
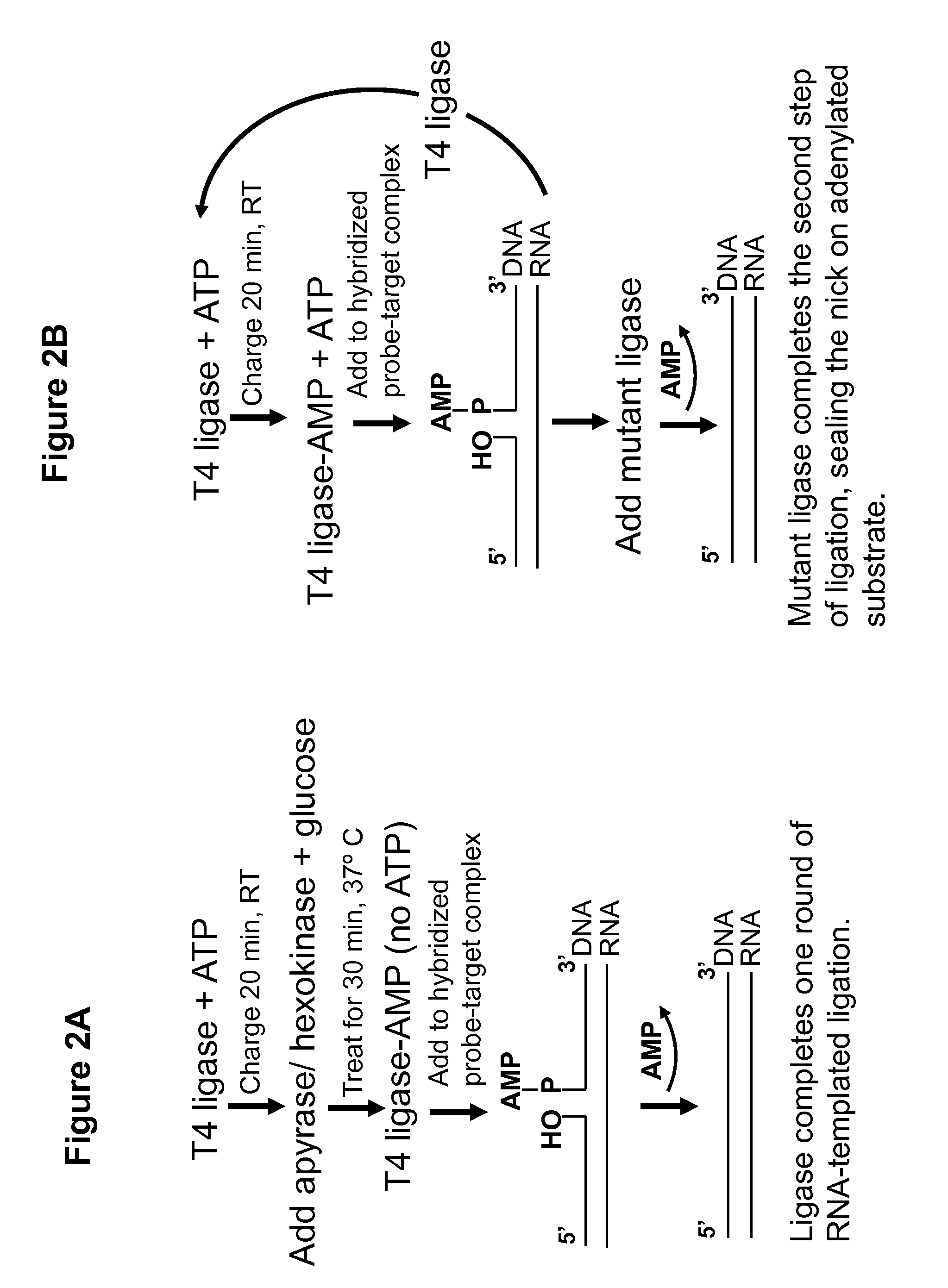
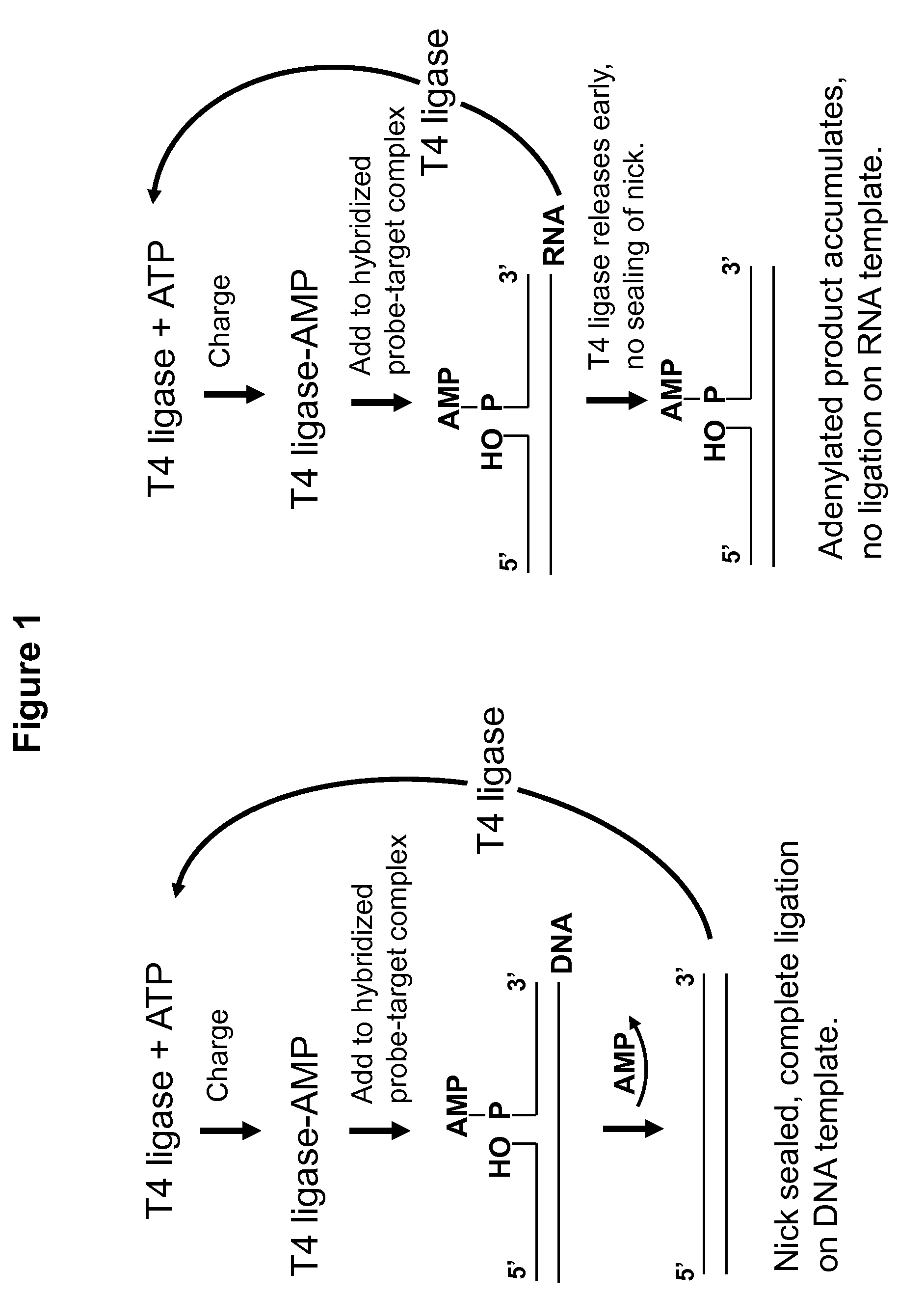
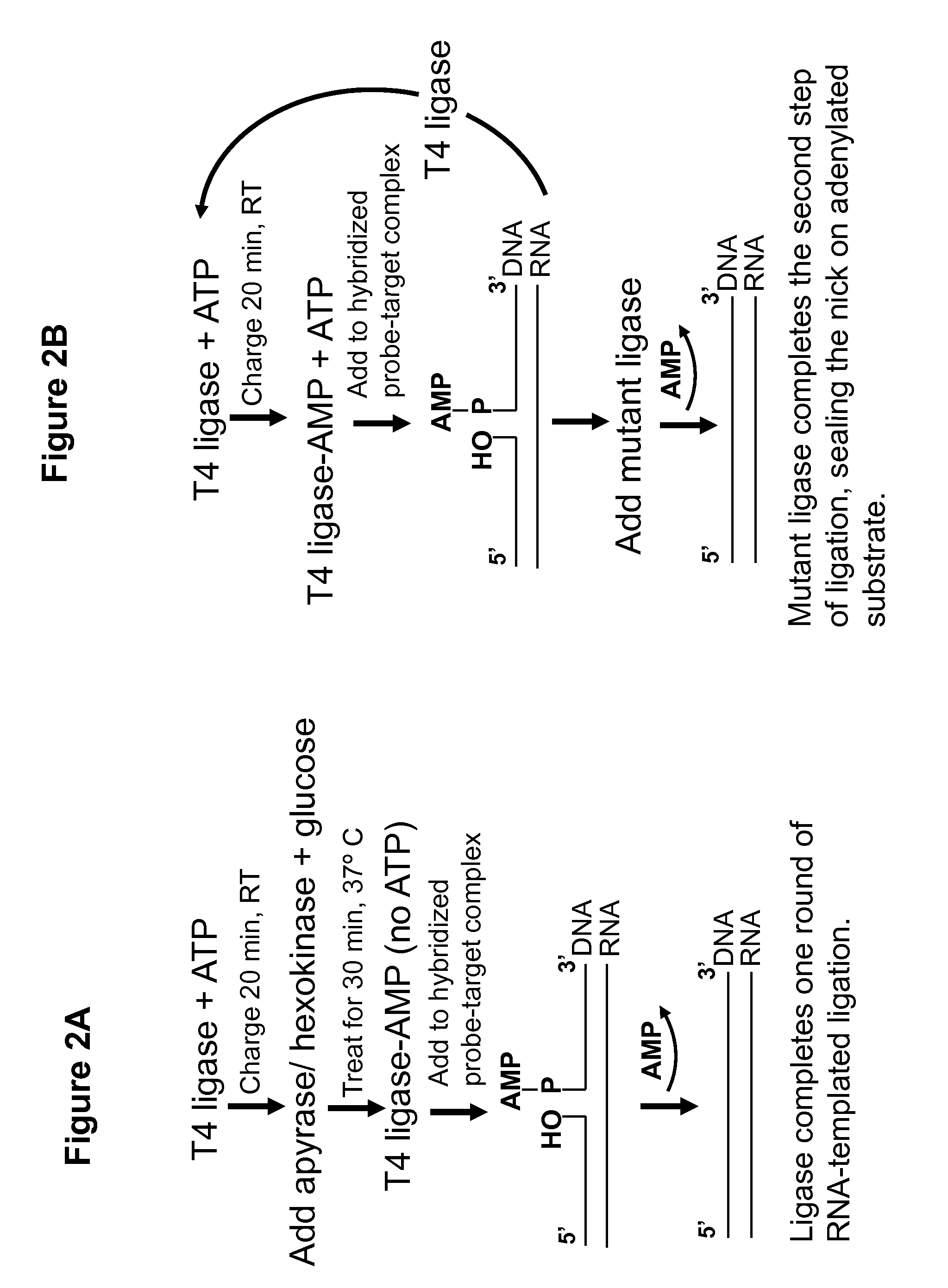
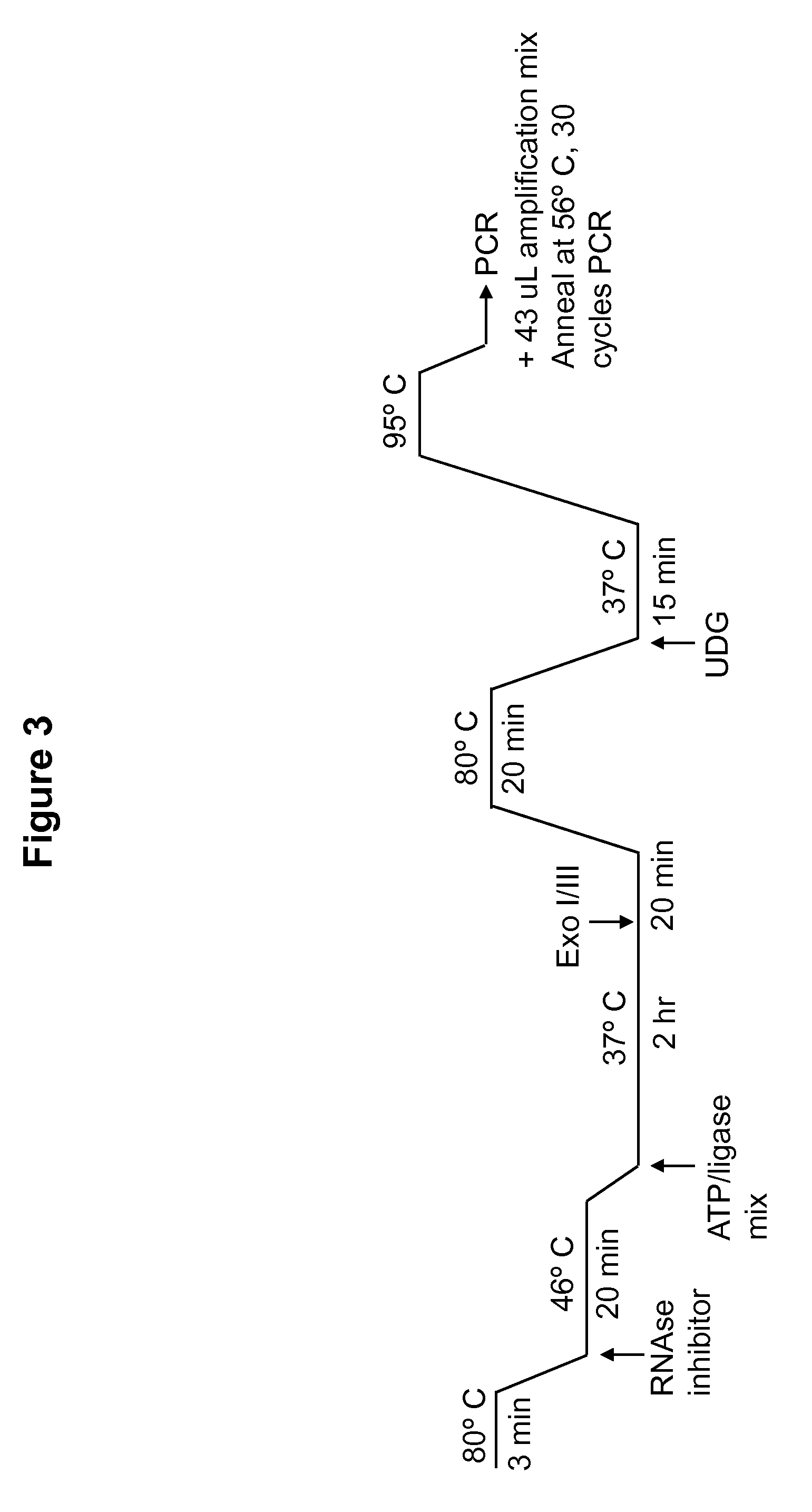
DNA ligation on RNA template
ActiveUS8790873B2High energySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative expressionRNA Sequence
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detection and amplification of nucleic acids, wherein two DNA strands hybridized to an RNA strand are ligated. In one aspect, the disclosed methods include removal of an energy source, such as ATP, upon charging a ligase to form an enzyme-AMP intermediate, and then adding substrate, which results in one complete round of RNA-templated DNA ligation. In another aspect, the ligation reaction is accomplished by use of a mixture of at least two different ligase enzymes. The disclosed methods and compositions for RNA-templated DNA ligation may be particularly useful for detection of RNA sequence variants, for example RNA splice variants, and for quantitative expression analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
DNA ligation on RNA template
ActiveUS20100184618A1High energyLigation is preventedMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningQuantitative expressionRNA Sequence
Disclosed are methods and compositions for detection and amplification of nucleic acids, wherein two DNA strands hybridized to an RNA strand are ligated. In one aspect, the disclosed methods include removal of an energy source, such as ATP, upon charging a ligase to form an enzyme-AMP intermediate, and then adding substrate, which results in one complete round of RNA-templated DNA ligation. In another aspect, the ligation reaction is accomplished by use of a mixture of at least two different ligase enzymes. The disclosed methods and compositions for RNA-templated DNA ligation may be particularly useful for detection of RNA sequence variants, for example RNA splice variants, and for quantitative expression analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
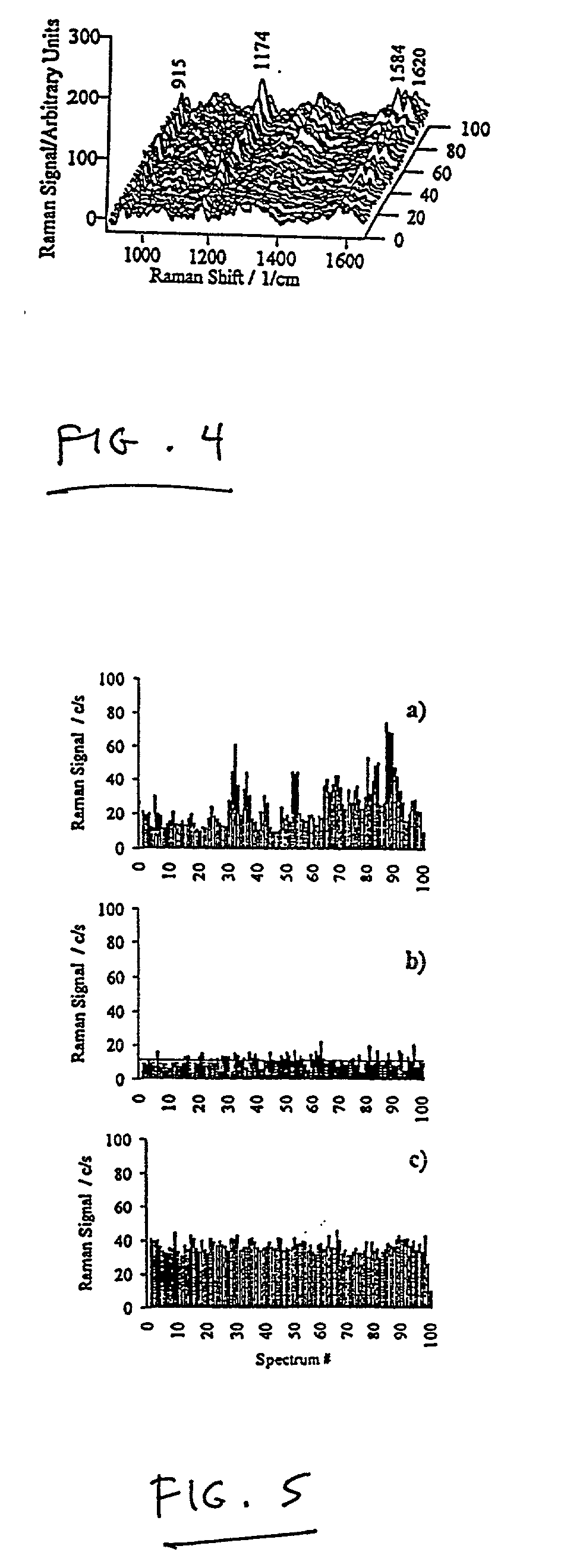
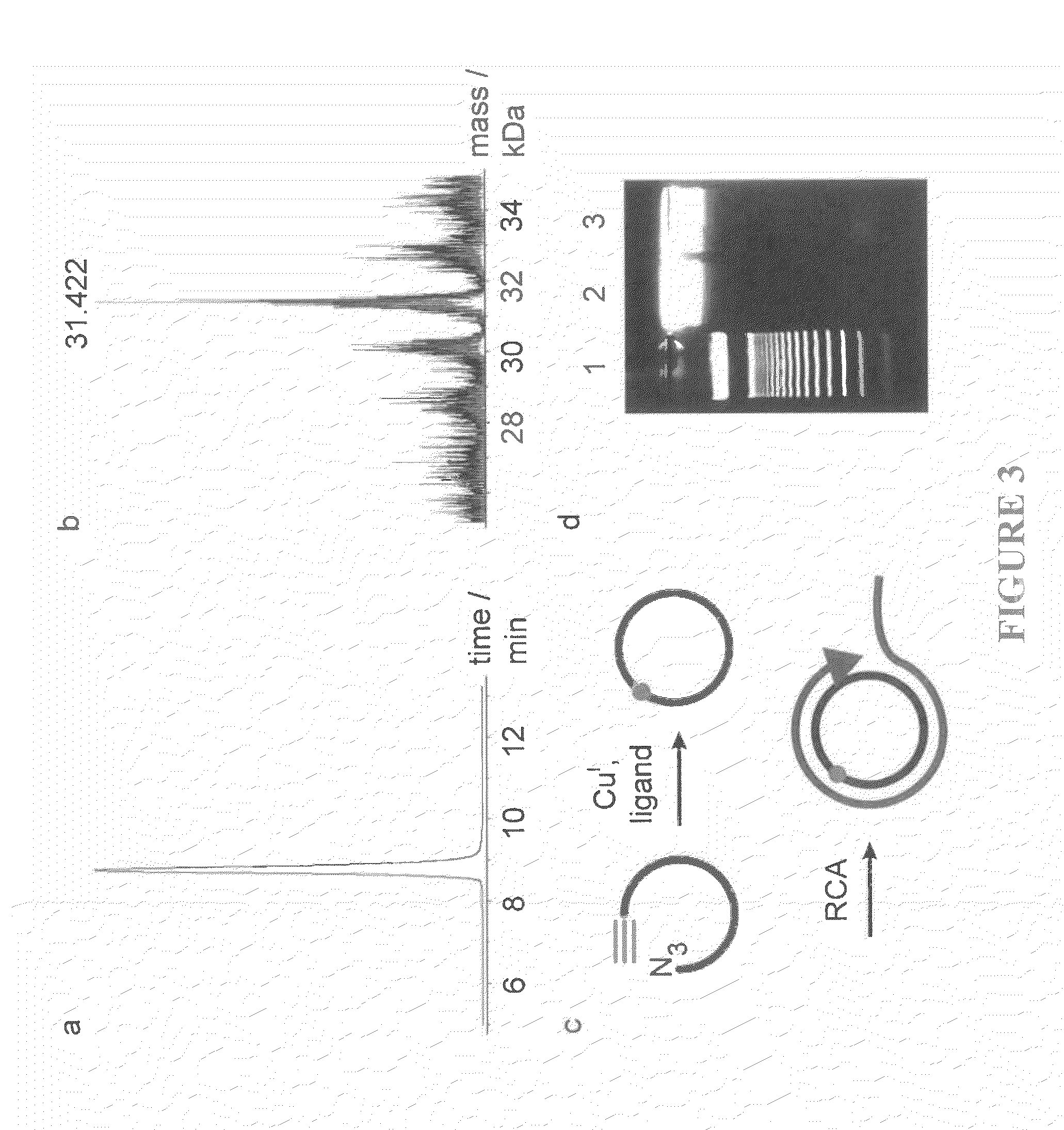
Single molecule detection with surface-enhanced Raman scattering and applications in DNA or RNA sequencing
InactiveUS20020150938A1Decreased Brownian motionLong residence timeRadiation pyrometryMicrobiological testing/measurementAnalyteSurface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy
Surface-enhanced spectroscopy, such as surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy employs aggregates that are of a size that allows easy handling. The aggregates are generally at least about 500 nm in dimension. The aggregates can be made of metal particles of size less than 100 nm, allowing enhanced spectroscopic techniques that operate at high sensitivity. This allows the use of larger, easily-handleable aggregates. Signals are determined that are caused by single analytes adsorbed to single aggregates, or single analytes adsorbed on a surface. The single analytes can be DNA or RNA fragments comprising at least one base.
Owner:KNEIPP KATRIN +4
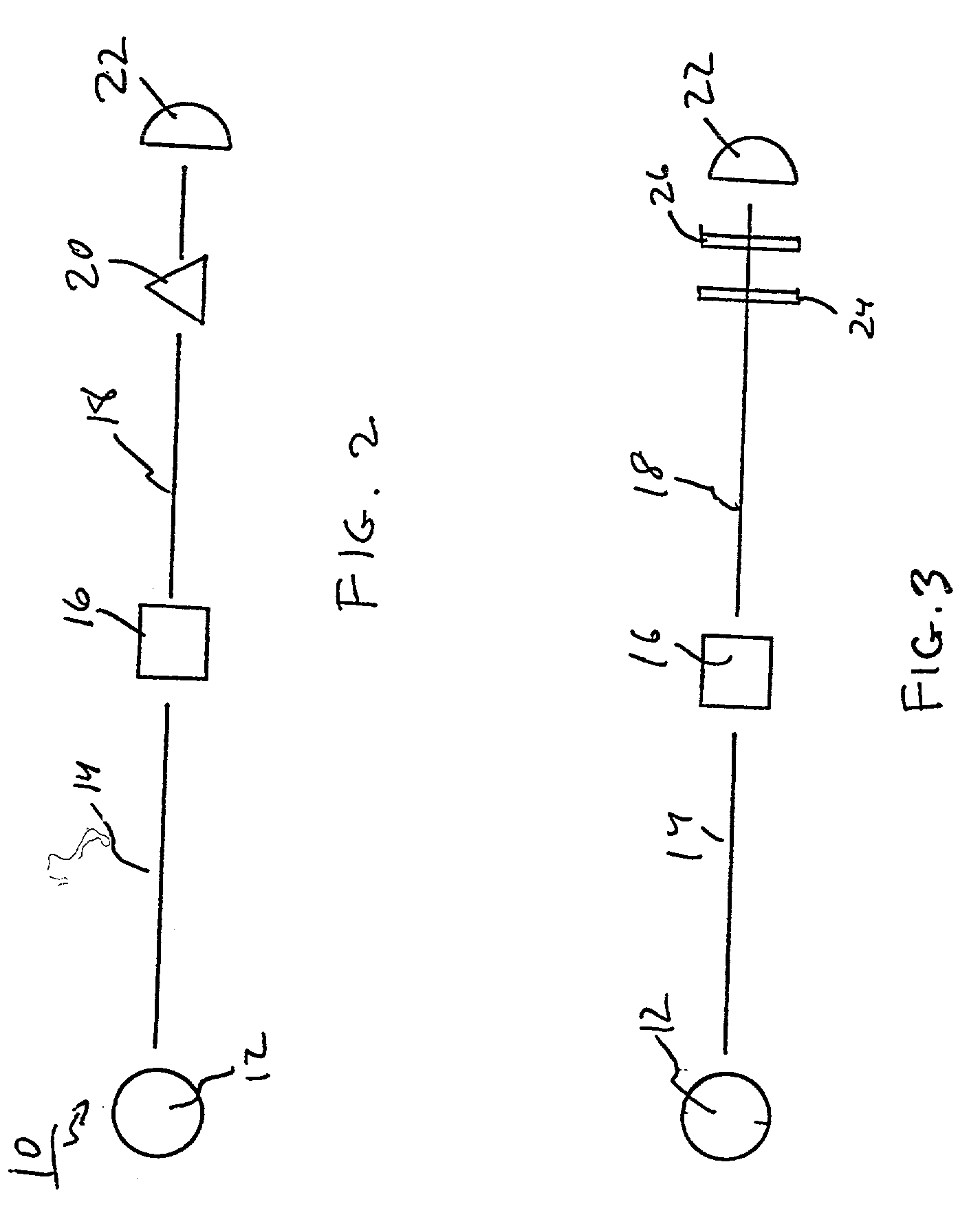
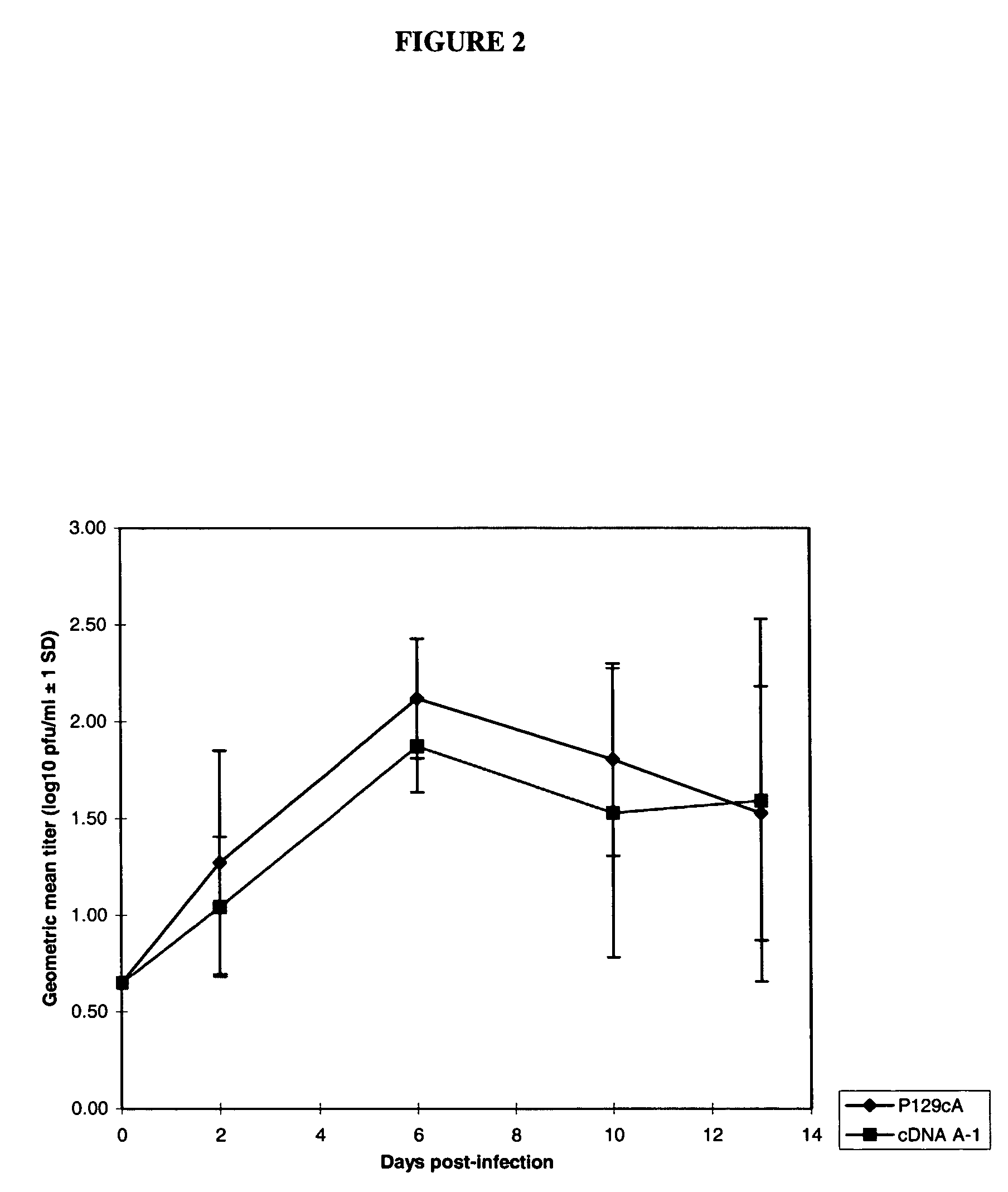
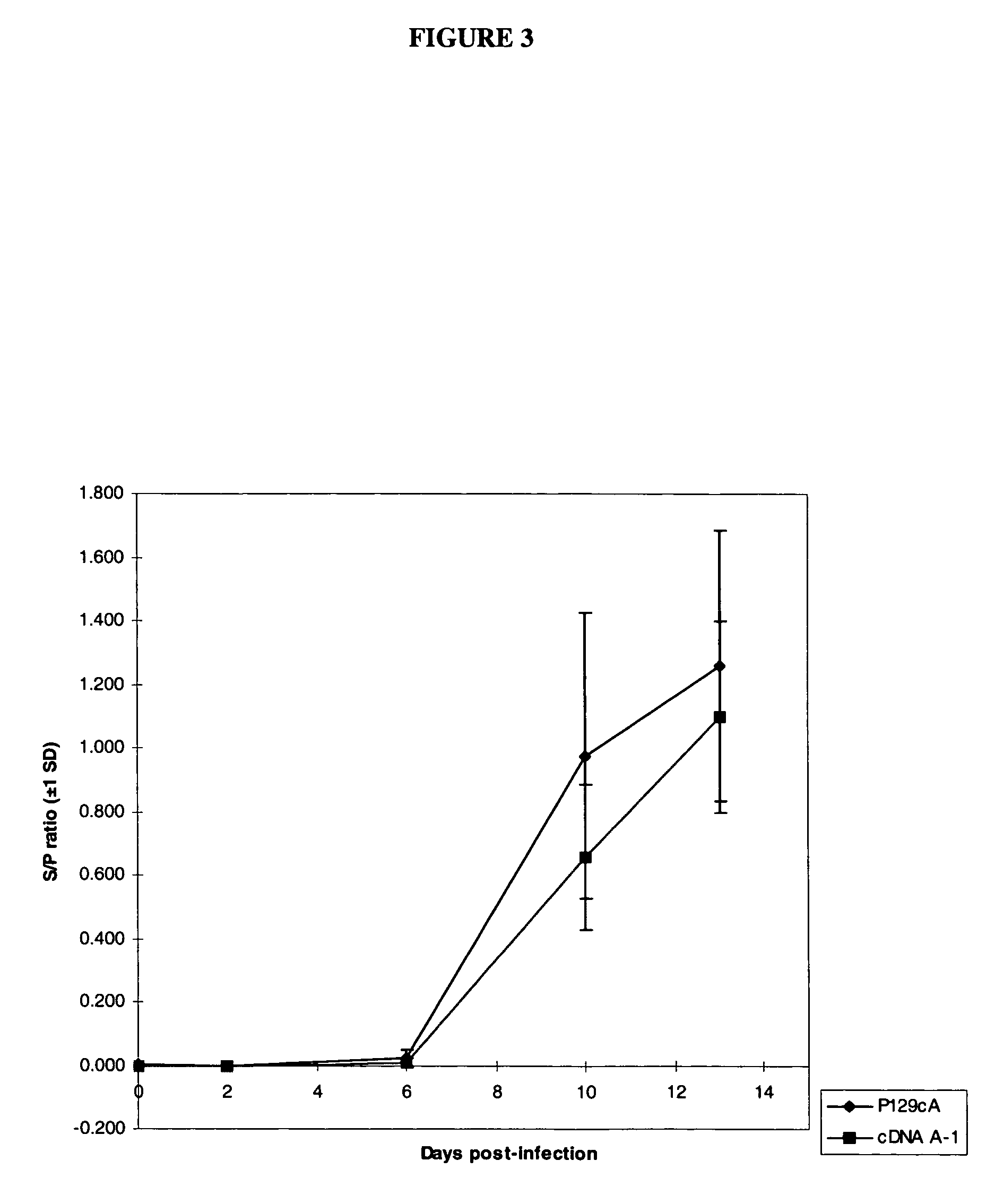
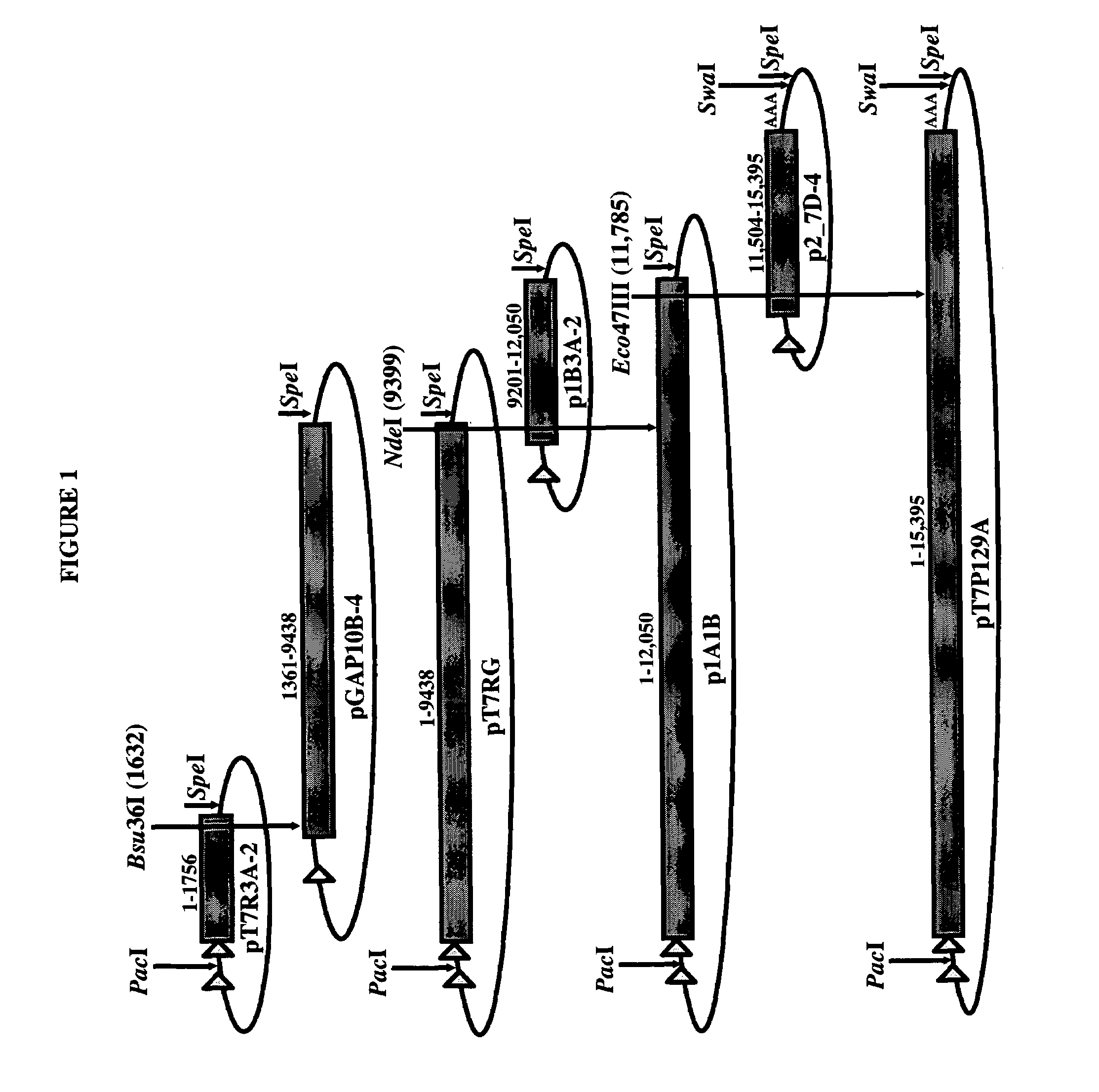
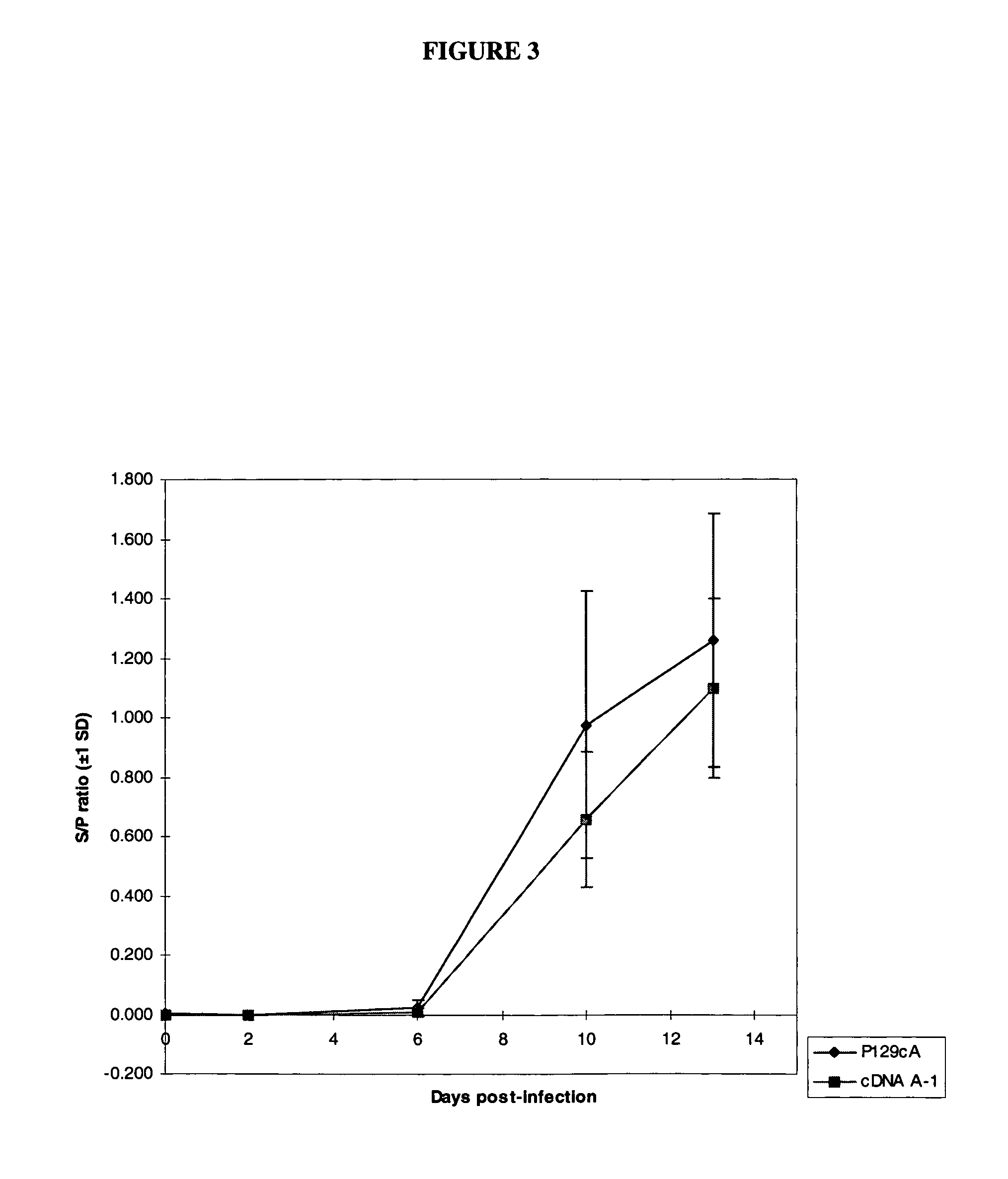
Infectious cDNA clone of North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and uses thereof
InactiveUS7132106B2Effective immunoprotective responseEfficient productionAnimal cellsSsRNA viruses positive-senseA-DNARNA Sequence
The invention provides isolated polynucleotide molecules, including plasmids; viral vectors; and transfected host cells that comprise a DNA sequence encoding an infectious RNA sequence encoding a North American PRRS virus; and also North American PRRS viruses encoded thereby. The invention further provides isolated infectious RNA molecules encoding a North American PRRS virus. The invention also provides isolated polynucleotide molecules, infectious RNA molecules, viral vectors, and transfected host cells encoding genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses; and genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses encoded thereby. The invention also provides vaccines comprising such plasmids, RNA molecules, viral vectors, and North American PRRS viruses, and methods of using these vaccines in swine and in other animals. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules, viral vectors, and transfected host cells that comprise a nucleotide sequence encoding a peptide of a North American PRRS virus. These viral vectors and transfected host cell lines are useful in providing peptides to compensate for mutated peptide coding sequences of DNA sequences encoding genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses so that functional virions can be generated.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Methods for purification of messenger RNA
ActiveUS20160040154A1Efficient removalMaintain integritySugar derivativesDrug compositionsPurification methodsFiltration
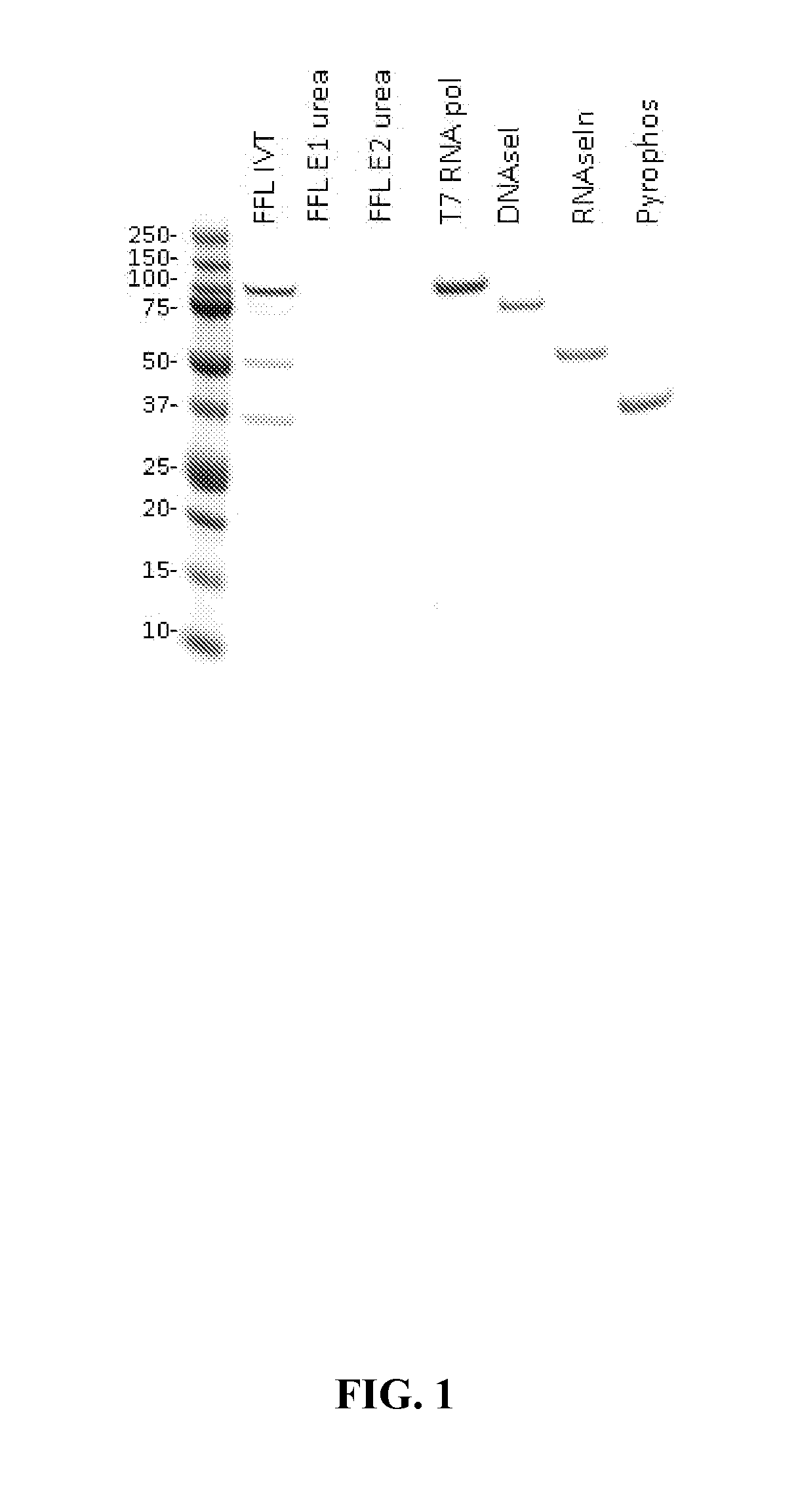
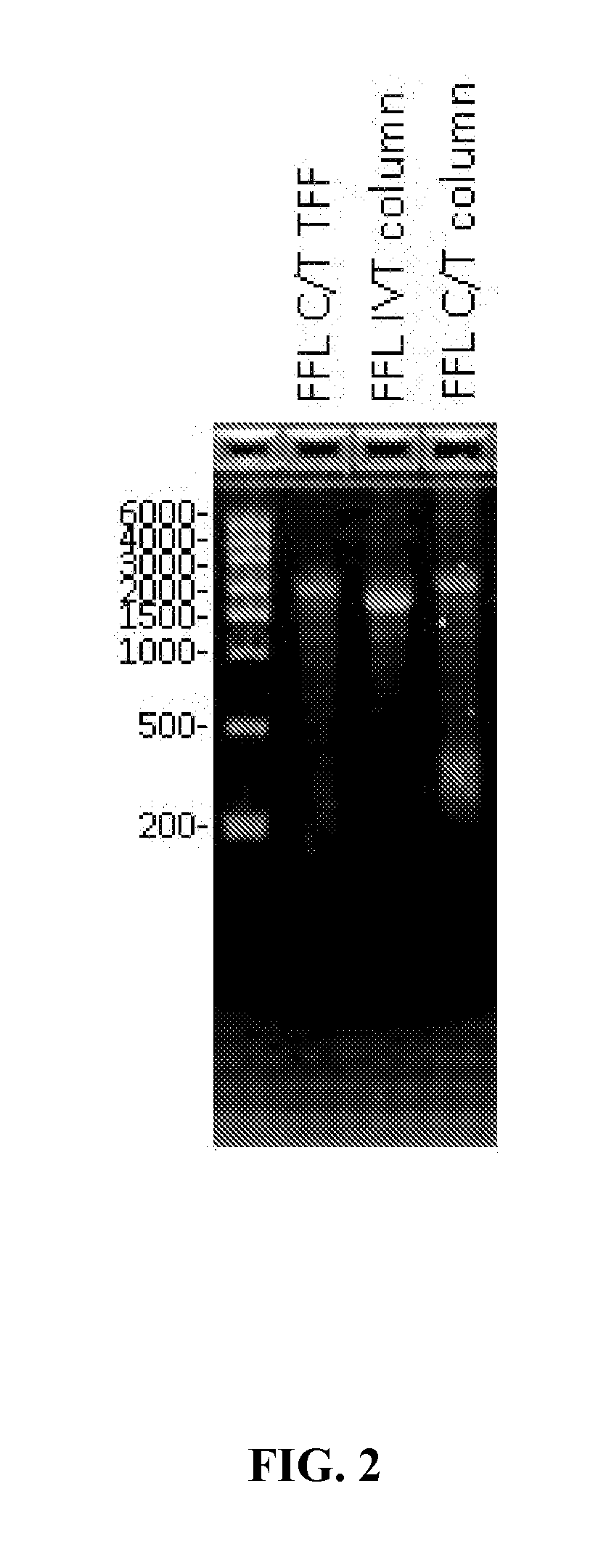
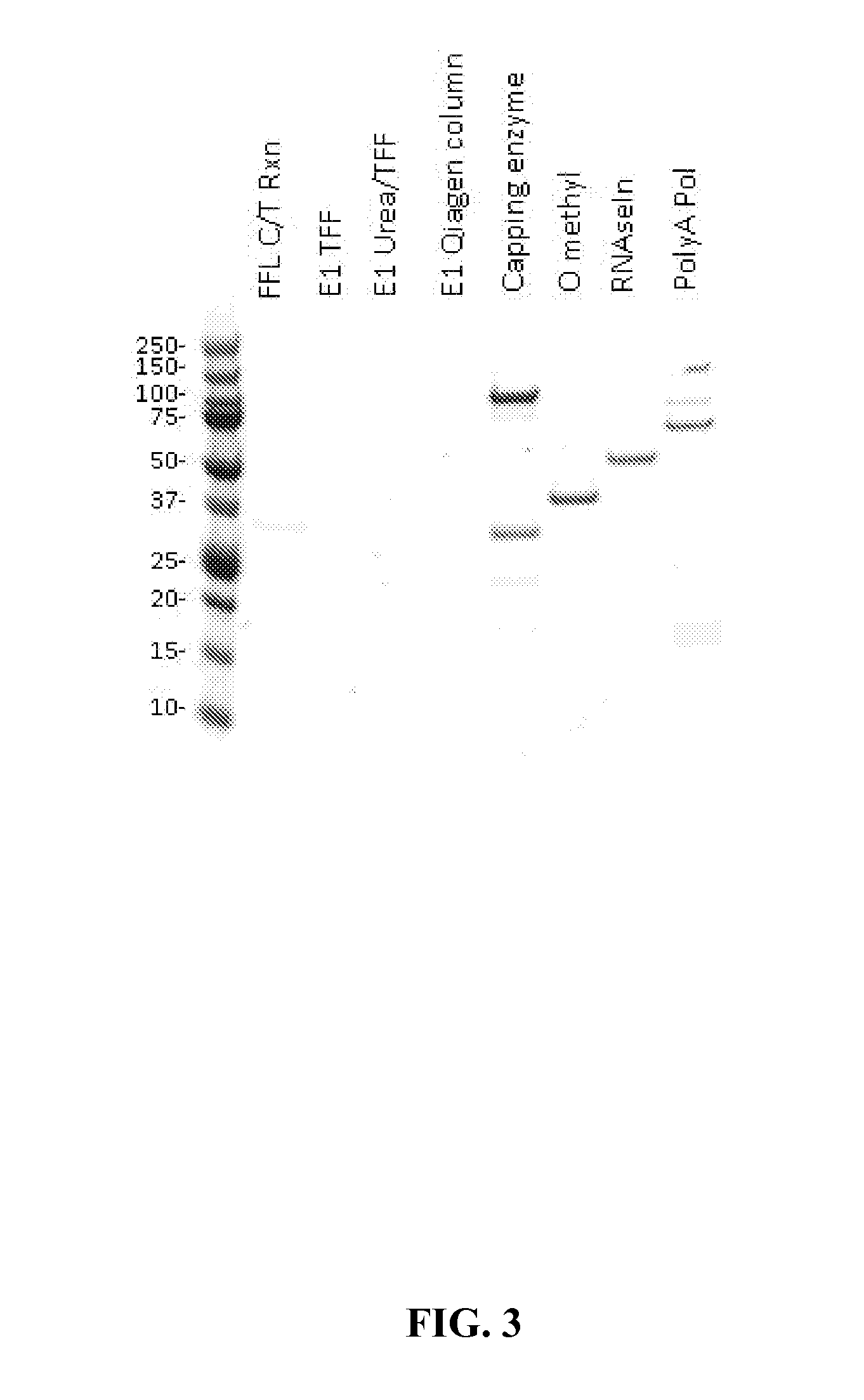
The present invention provides, among other things, methods of purifying messenger RNA (mRNA) including the steps of subjecting an impure preparation comprising in vitro synthesized mRNA to a denaturing condition, and purifying the mRNA from the impure preparation from step (a) by tangential flow filtration, wherein the mRNA purified from step (b) is substantially free of prematurely aborted RNA sequences and / or enzyme reagents used in in vitro synthesis.
Owner:TRANSLATE BIO INC
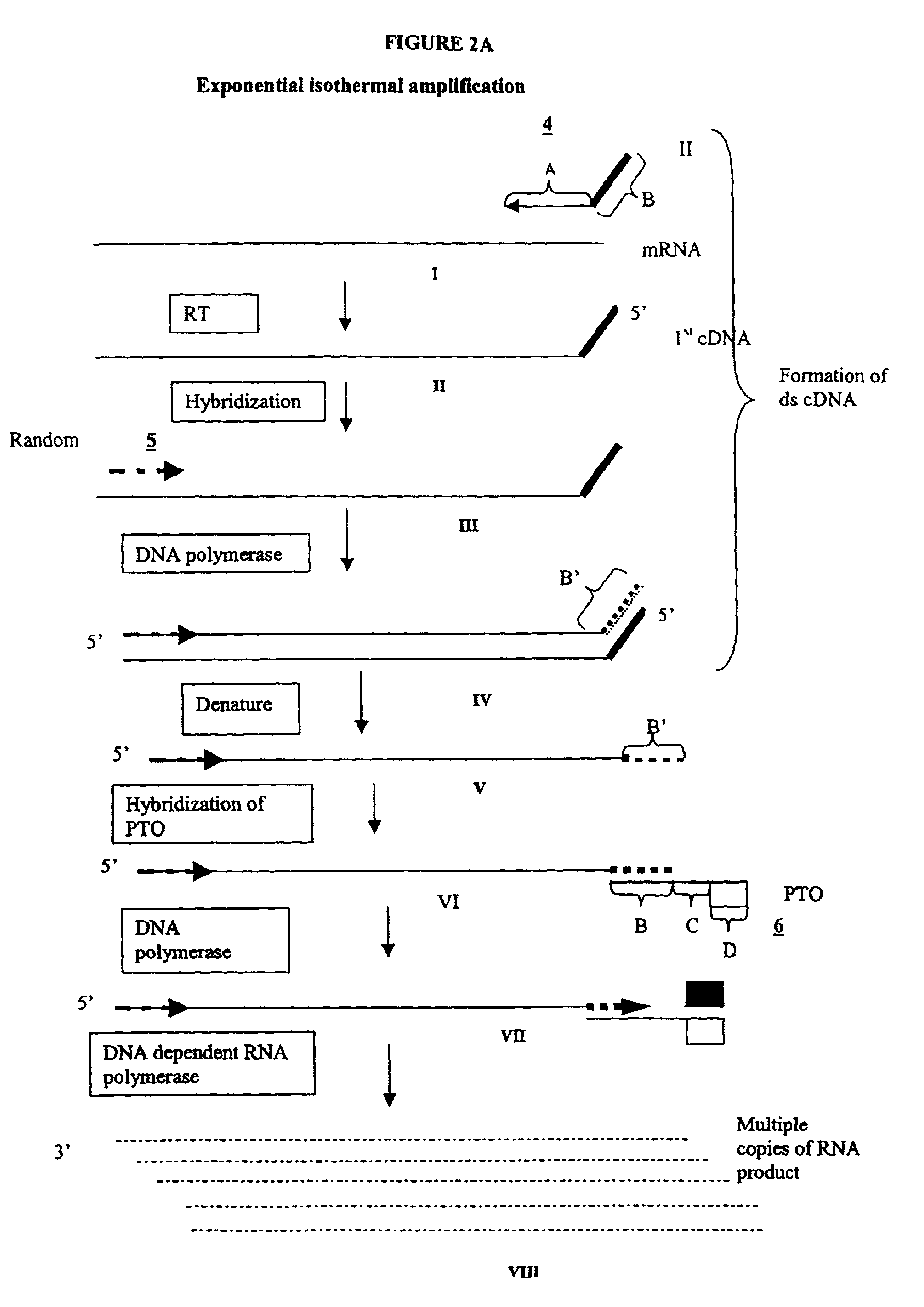
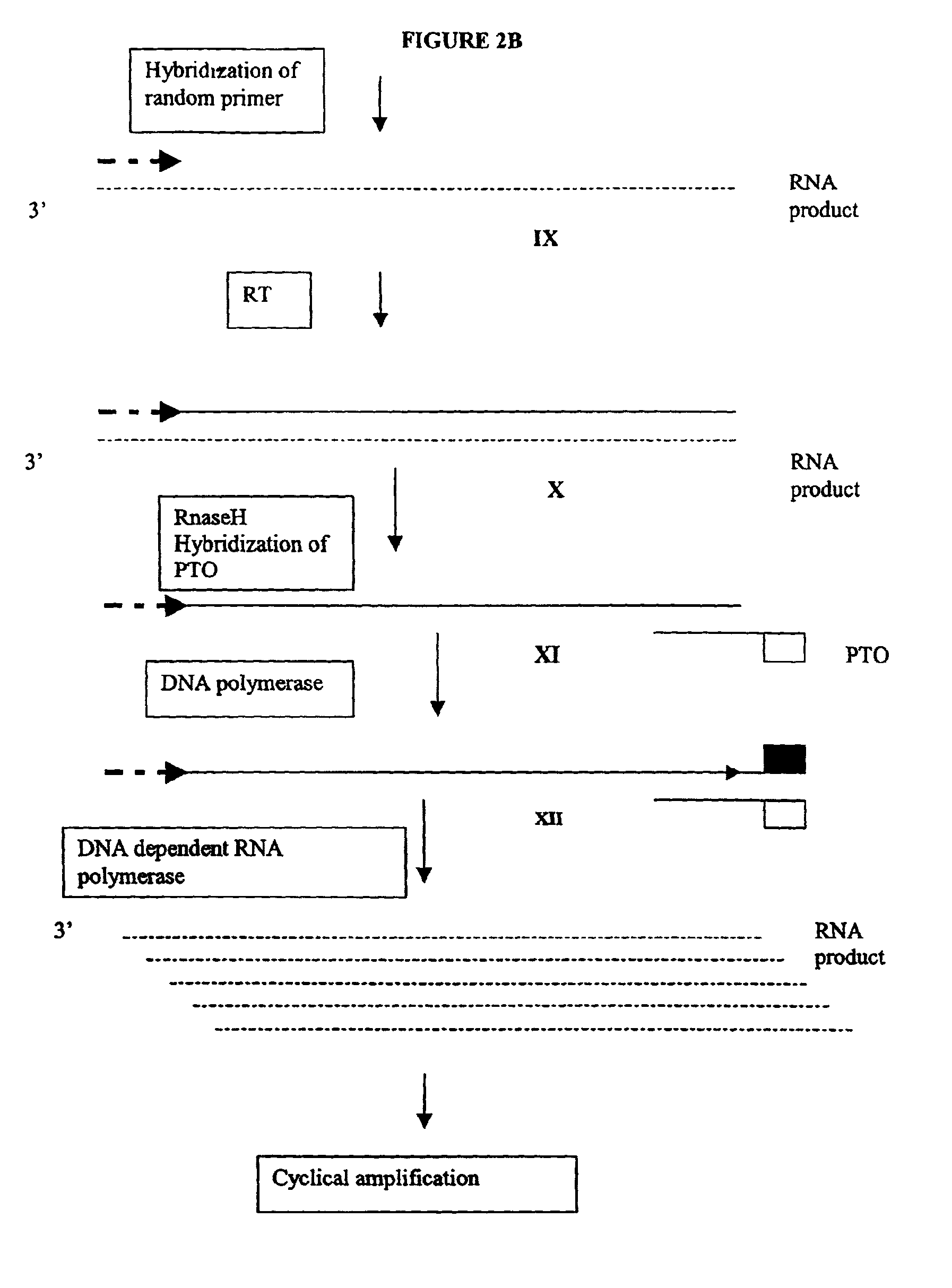
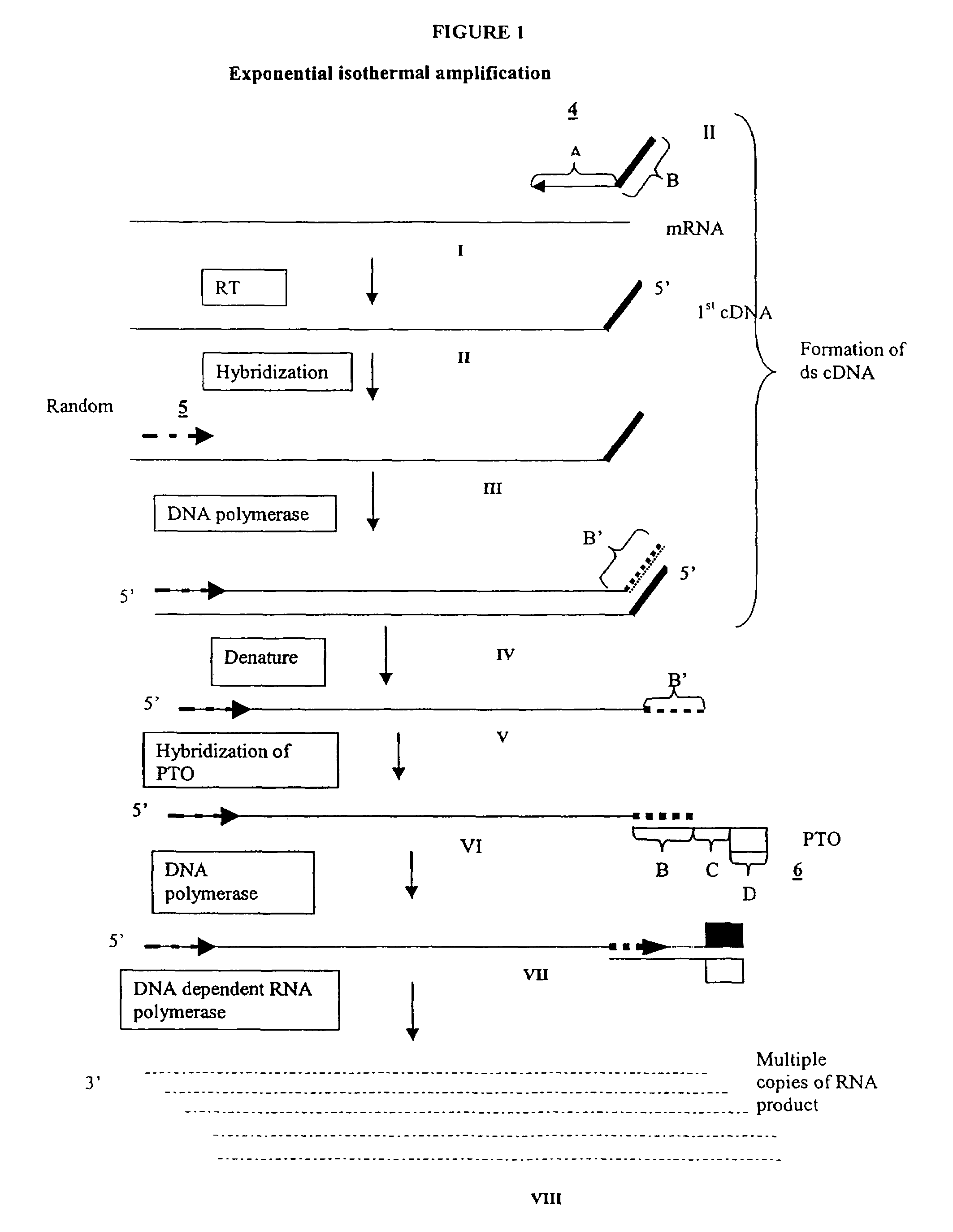
Methods and compositions for amplification of RNA sequences
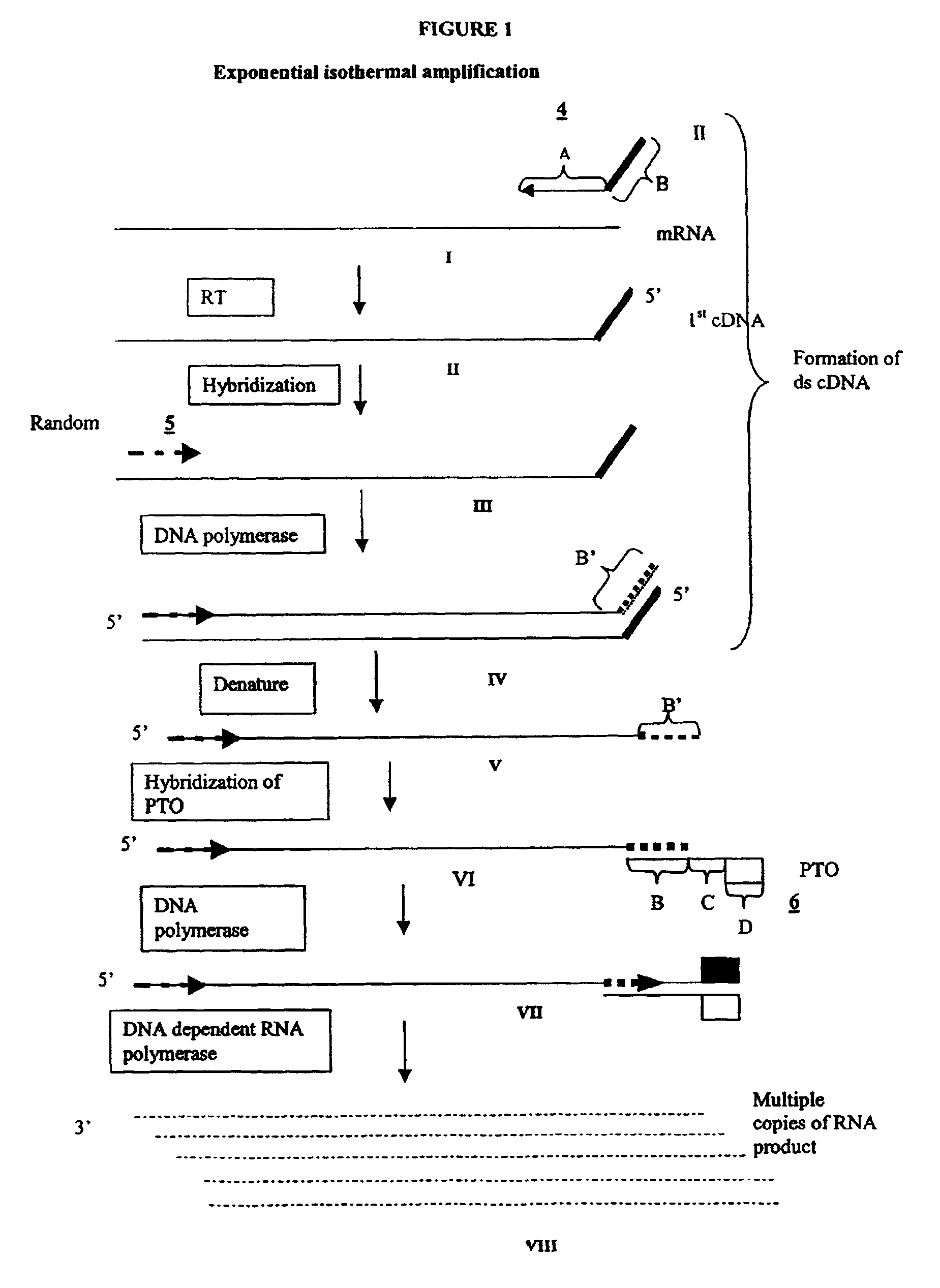
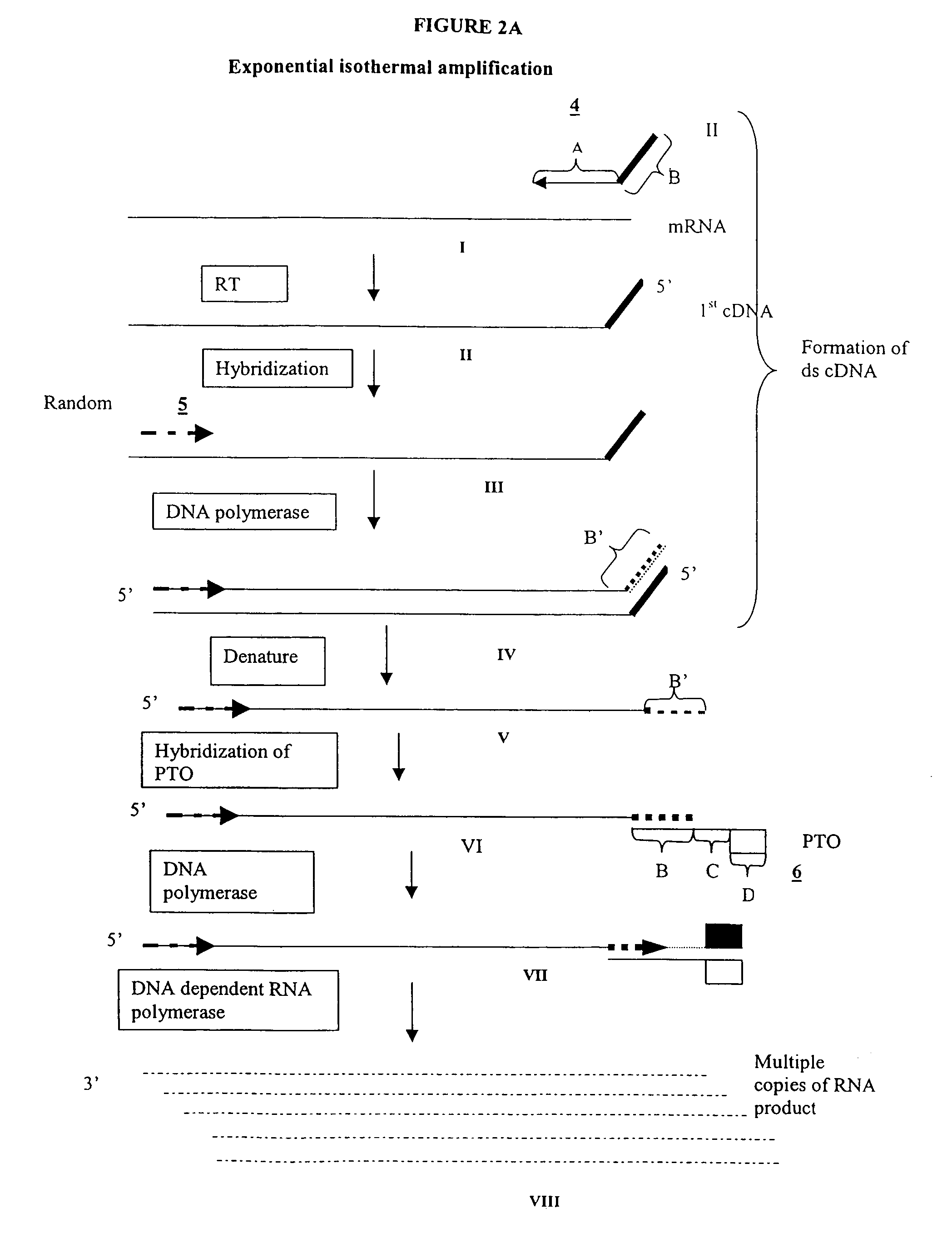
The invention provides methods for linear and exponential amplification of RNA. They are particularly suitable for amplifying a plurality of RNA species in a sample. The methods are based on hybridization of polynucleotide comprising a propromoter sequence to a primer extension product to generate an intermediate polynucleotide capable of driving transcription, whereby multiple copies of RNA products comprising sequences complementary to an RNA sequence of interest are generated. The methods are useful for preparation of nucleic acid libraries and substrates for analysis of gene expression of cells in biological samples. The invention also provides compositions and kits for practicing the amplification methods, as well as methods which use the amplification products.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
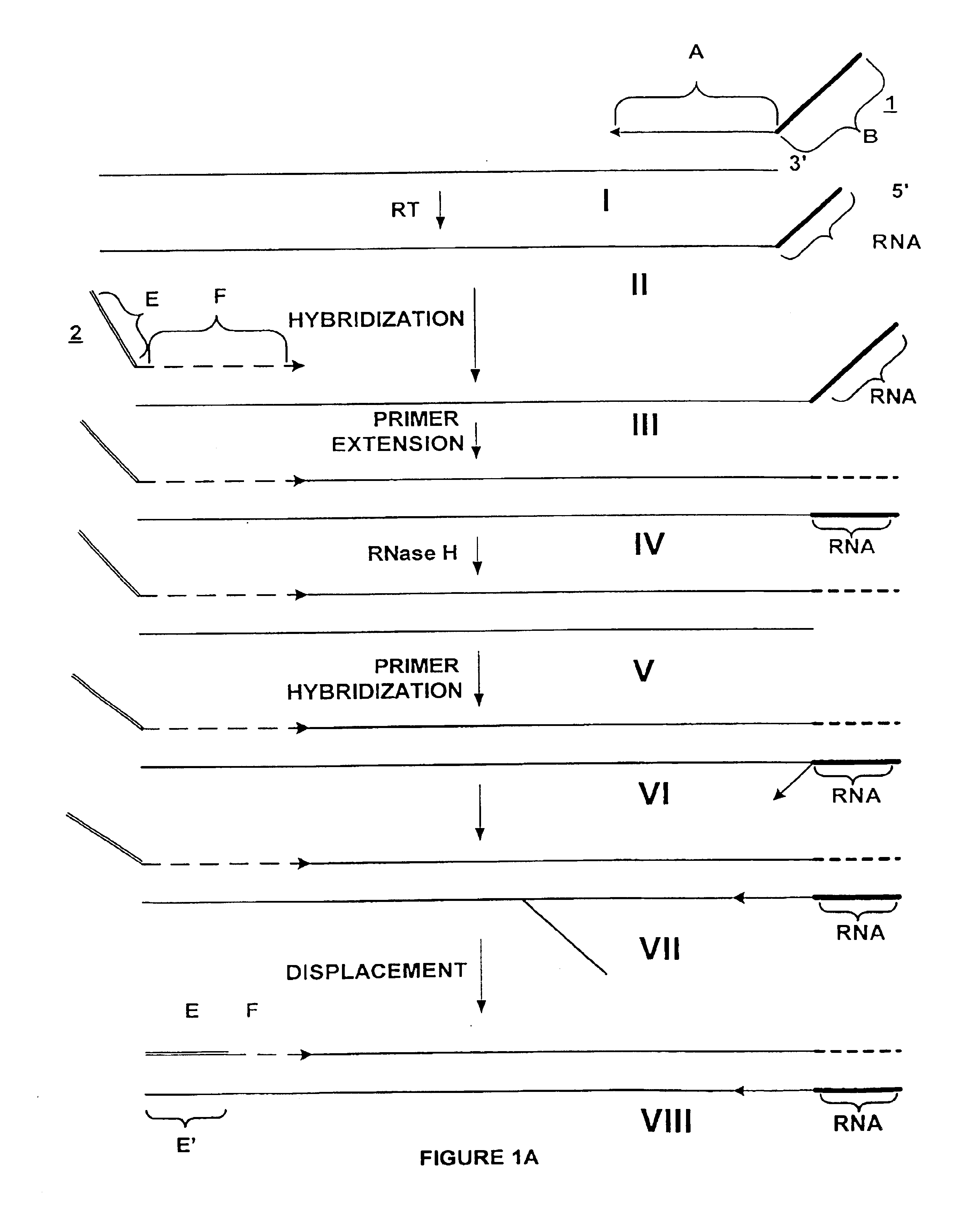
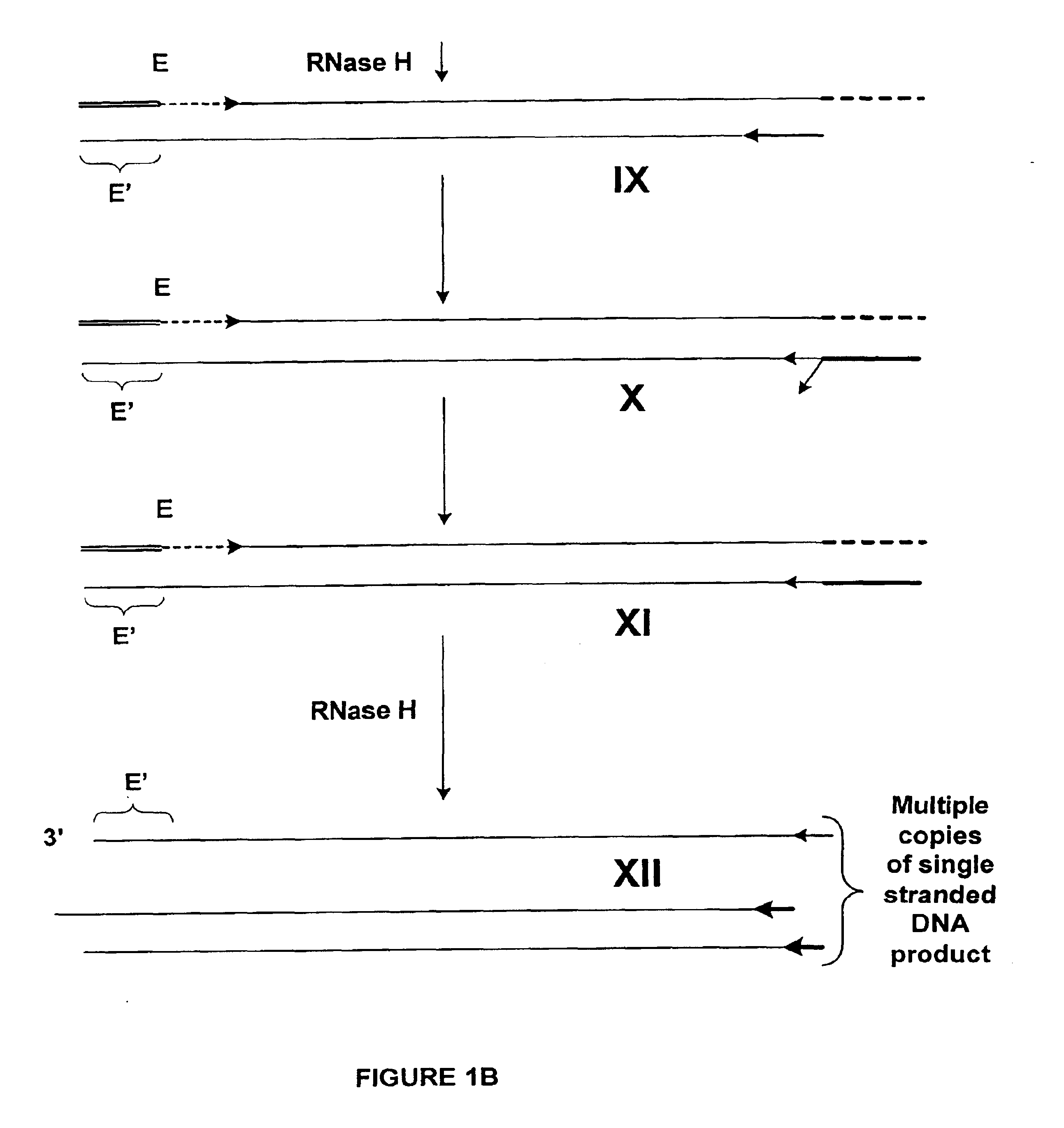
Amplification of RNA sequences using composite RNA-DNA primers and strand displacement
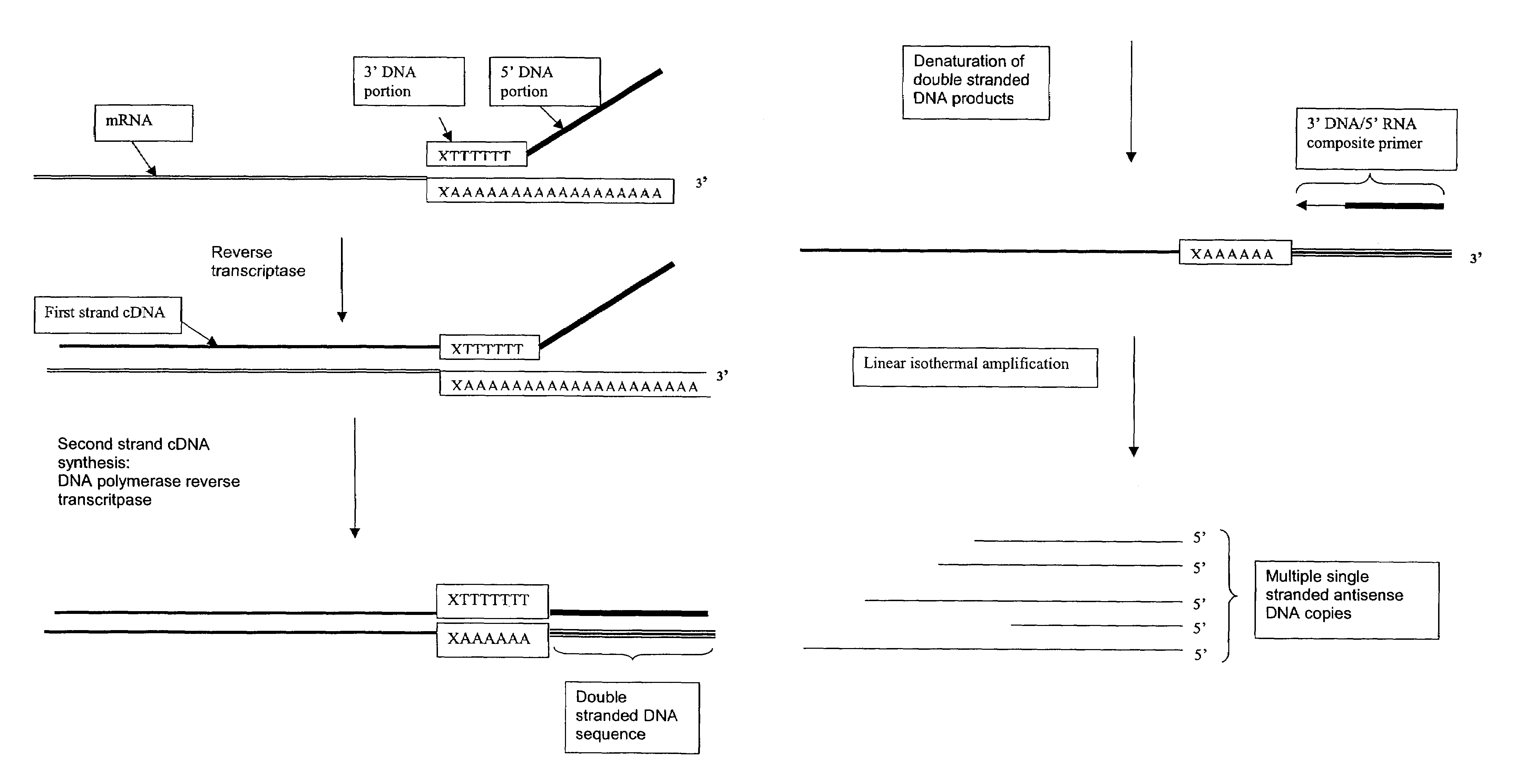
The invention provides methods for linear amplification of RNA that has an RNA sequence of interest. The methods are based on using a first DNA primer with a 3′ portion that is complementary to the RNA and a 5′ portion that is not complementary to the RNA in that region. The primer and an RNA-dependent DNA polymerase are used to make a DNA-RNA complex from the RNA. The RNA is cleaved from the complex with an enzyme, then a second primer and a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase are used to make double stranded DNA. The double stranded DNA is then denatured, and an RNA-DNA composite primer, a DNA-dependent DNA polymerase, and strand displacement are used to isothermally produce multiple copies of the complementary sequence to the RNA sequence of interest.
Owner:NUGEN TECH
Immobilizing and processing specimens on matrix materials for the identification of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS6103192AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological unitOrganism
The invention is a method and device for collecting and processing a biological specimen for the analyses of nucleic acids. A device comprises a matrix to which cells and viruses adhere and a handle to manipulate the matrix. The devices are used to collect, dry, transport, store and process small amounts of blood or other tissue. The matrix of the device is transferred to a reaction tube and amplifying reagents added to it. Nucleic acid sequences and relative quantities are detected and analyzed from the same specimen. The relative amounts of amplified nucleic acid from one or more particular RNA sequences are compared to one another and to the amount of amplified nucleic acid from DNA sequences serving as an internal control for the number of biological units per specimen. The relative amounts of amplified viral sequences from suspected viruses in the biological specimen and from recombinant viral particles serving as a viral quantitation standard enable estimation of viral burden in a given quantity of specimen.
Owner:GENETEC
Oligonucleotide ligation
ActiveUS20130046084A1Efficient methodImprove thermal stabilitySugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationSynthesis methodsAlkyne
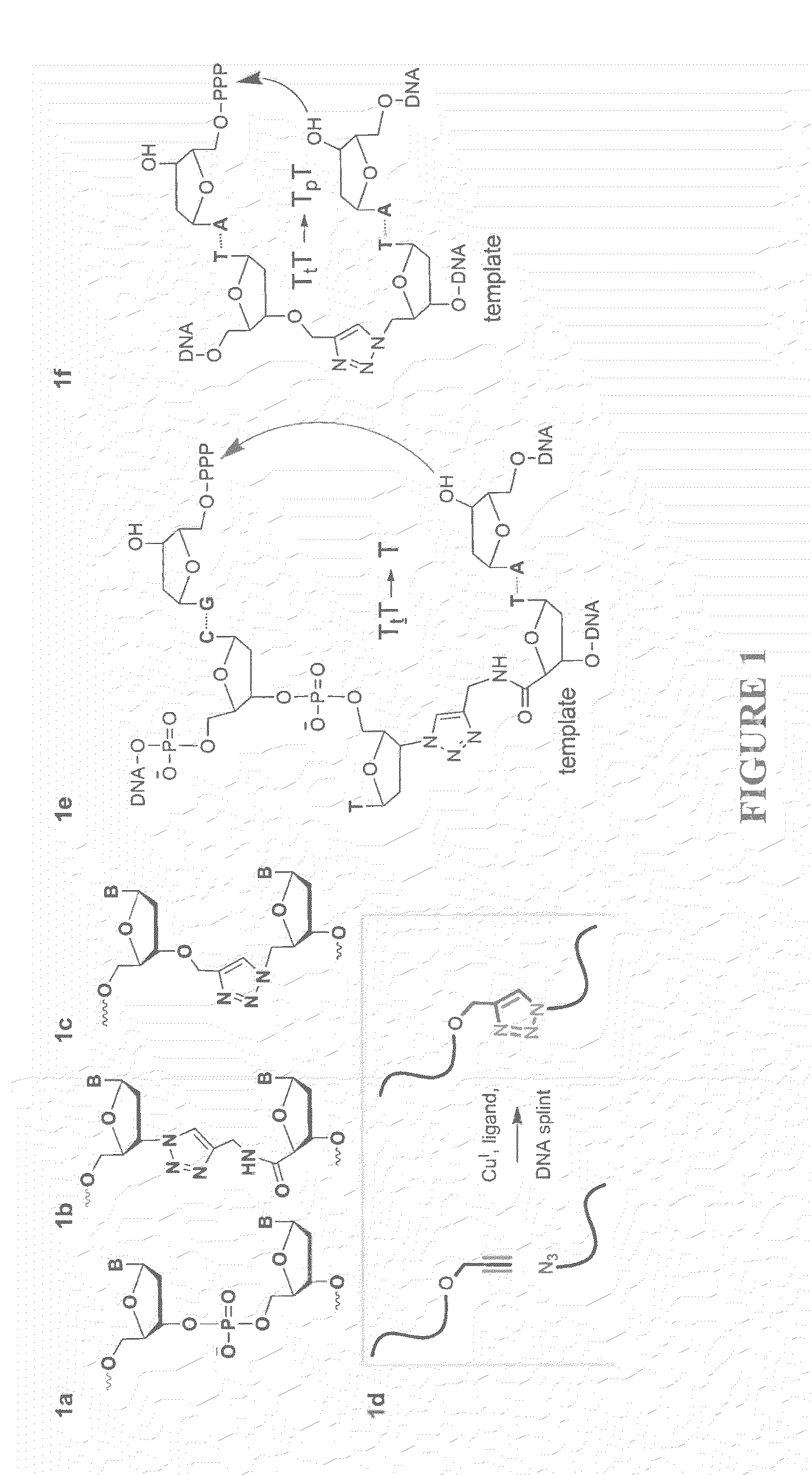
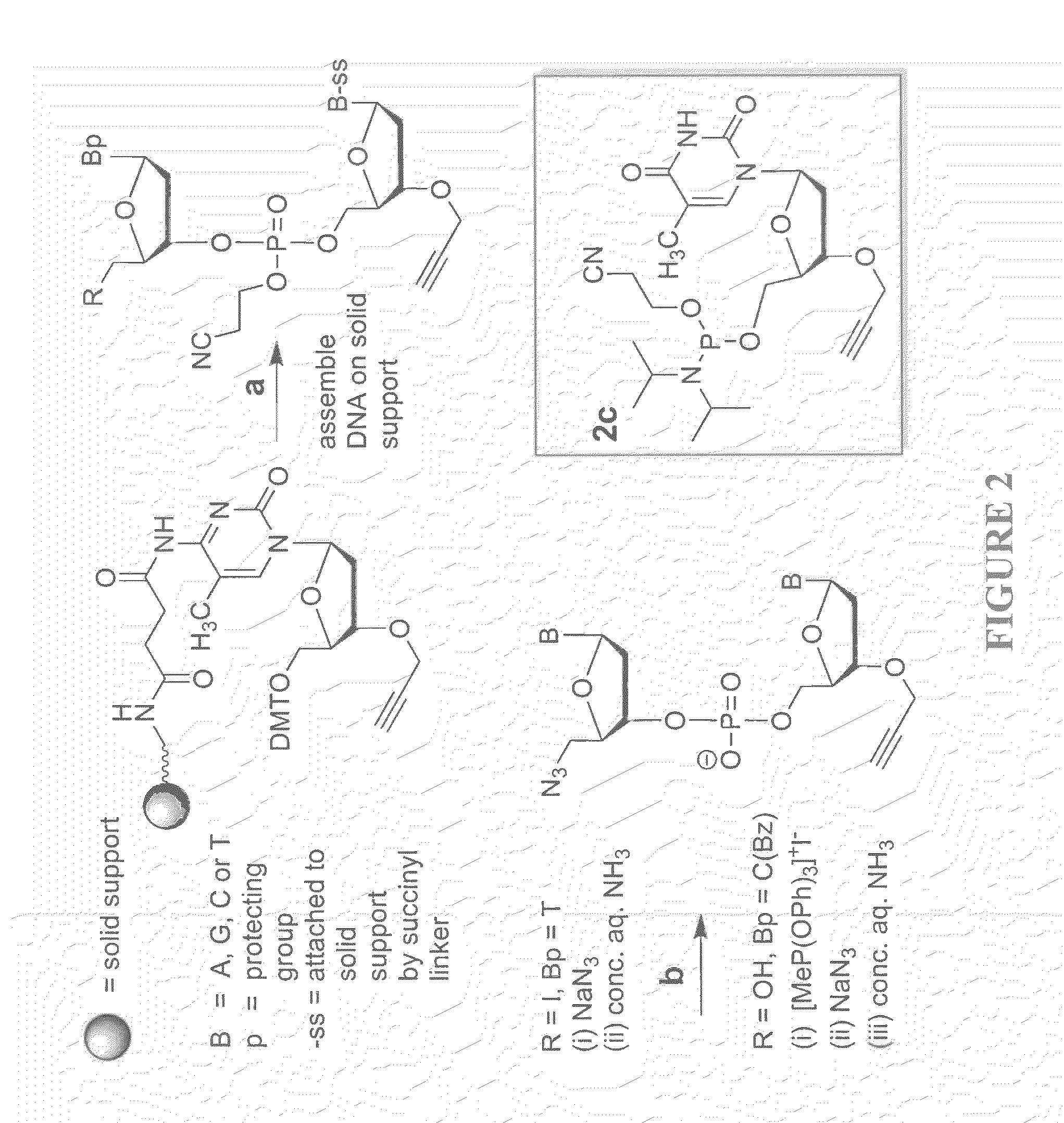
Oligonucleotide chemistry is central to the advancement of core technologies such as DNA sequencing, forensic and genetic analysis and has impacted greatly on the discipline of molecular biology. Oligonucleotides and their analogues are essential tools in these areas. They are often produced by automated solid-phase phosphoramidite synthesis but it is difficult to synthesize long DNA and RNA sequences by this method. Methods are proposed for ligating oligonucleotides together, in particular the use of an azide-alkyne coupling reaction to ligate the backbones of oligonucleotides together to form longer oligonucleotides that can be synthesized using current phosphoramidite synthesis methods.
Owner:ATDBIO LTD
Enzymes for the detection of nucleic acid sequences
InactiveUS20030134349A1Simple structureLow detection sensitivitySugar derivativesHydrolasesA-siteA-DNA
The present invention relates to novel enzymes designed for direct detection, characterization and quantitation of nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The present invention provides enzymes that recognize specific nucleic acid cleavage structures formed on a target RNA sequence and that cleave the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner to produce non-target cleavage products. The present invention provides enzymes having an improved ability to specifically cleave a DNA member of a complex comprising DNA and RNA nucleic acid strands.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Expression and export of interferon-alpha proteins as Fc fusion proteins
InactiveUS20050042729A1Promote productionEfficient productionPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRNA SequenceHepatitis
Disclosed are nucleic acid sequences, for example, DNA or RNA sequences, which encode an immunoglobulin Fc-Interferon-alpha fusion protein. The nucleic acid sequences can be inserted into a suitable expression vector and expressed in mammalian cells. Also disclosed is a family of immunoglobulin Fc-Interferon-alpha fusion proteins that can be produced by expression of such nucleic acid sequences. Also disclosed are methods of using such nucleic acid sequences and / or fusion proteins for treating conditions, for example, hepatitis, which are alleviated by the administration of interferon-alpha.
Owner:EMD LEXIGEN RES CENT CORP
Enzymes for the detection of nucleic acid sequences
The present invention relates to novel enzymes designed for direct detection, characterization and quantitation of nucleic acids, particularly RNA. The present invention provides enzymes that recognize specific nucleic acid cleavage structures formed on a target RNA sequence and that cleave the nucleic acid cleavage structure in a site-specific manner to produce non-target cleavage products. The present invention provides enzymes having an improved ability to specifically cleave a DNA member of a complex comprising DNA and RNA nucleic acid strands.
Owner:GEN PROBE INC
Infectious cDNA clone of north american porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and uses thereof
The invention provides isolated polynucleotide molecules, including plasmids; viral vectors; and transfected host cells that comprise a DNA sequence encoding an infectious RNA sequence encoding a North American PRRS virus; and also North American PRRS viruses encoded thereby. The invention further provides isolated infectious RNA molecules encoding a North American PRRS virus. The invention also provides isolated polynucleotide molecules, infectious RNA molecules, viral vectors, and transfected host cells encoding genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses; and genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses encoded thereby. The invention also provides vaccines comprising such plasmids, RNA molecules, viral vectors, and North American PRRS viruses, and methods of using these vaccines in swine and in other animals. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules, viral vectors, and transfected host cells that comprise a nucleotide sequence encoding a peptide of a North American PRRS virus. These viral vectors and transfected host cell lines are useful in providing peptides to compensate for mutated peptide coding sequences of DNA sequences encoding genetically-modified North American PRRS viruses so that functional virions can be generated.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
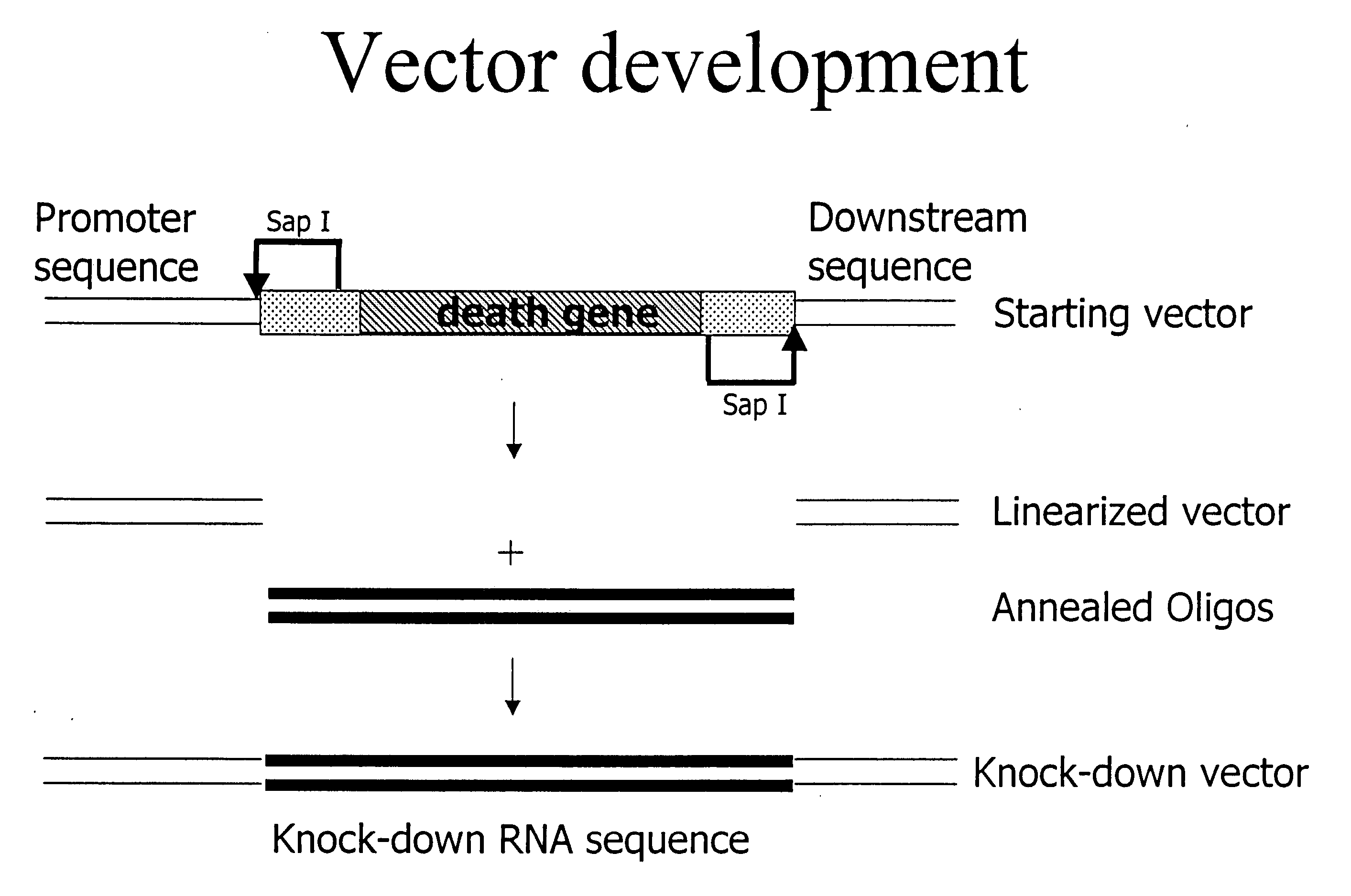
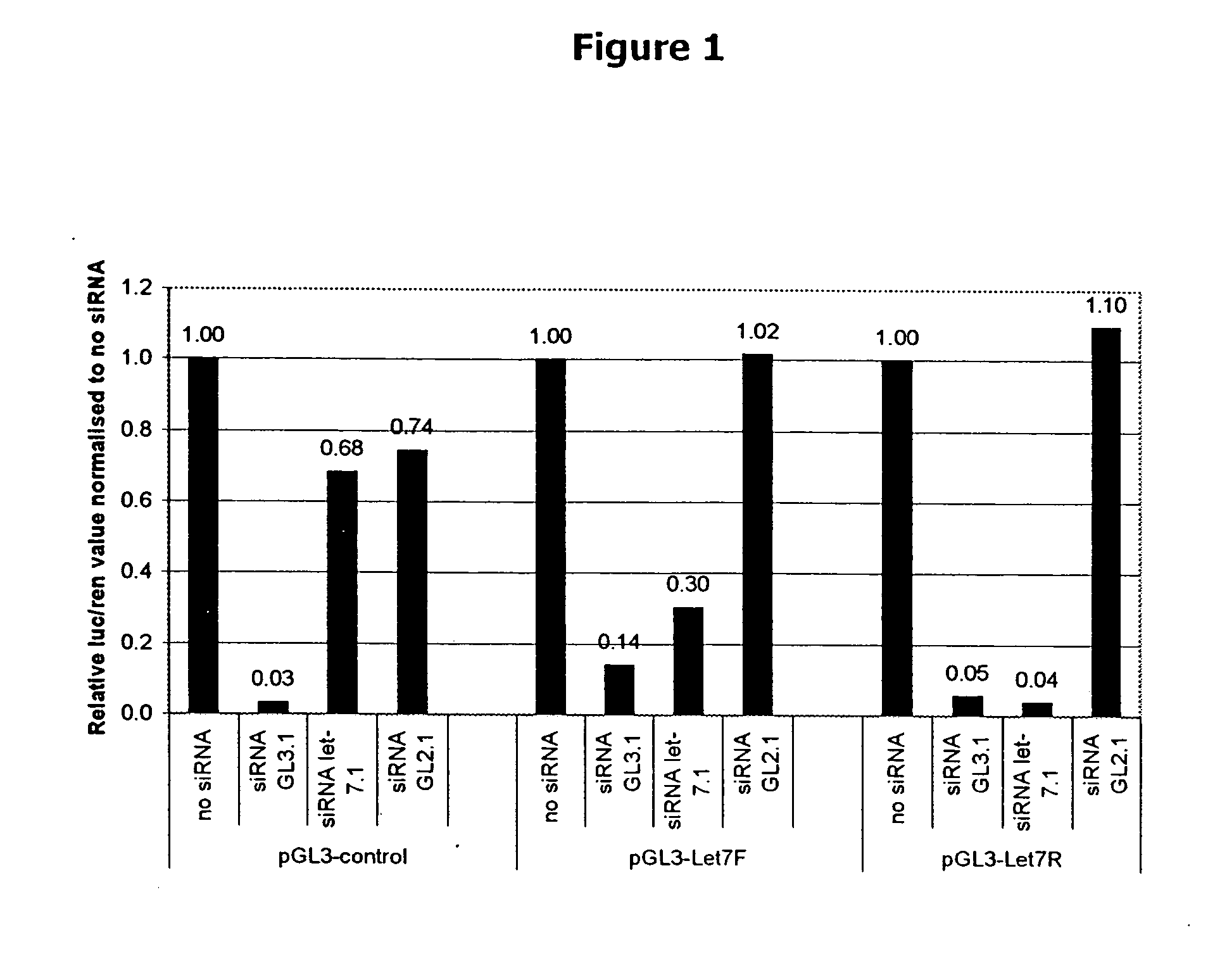
siRNA knockout assay method and constructs
Isolated polynucleotides, and vectors including the same, are disclosed as useful for down-regulation of specific RNA in cells, including a first sequence of about 17 to about 23 nucleotides, complementary to said RNA, and linked to a second sequence capable of forming a loop when said second sequence is RNA. The polynucleotides include self-complementing single-stranded polynucleotides, including a third sequence linked by said second sequence where all nucleotides in said first and said third sequences are complementary. Functional genomic, diagnostic and therapeutic methods are disclosed that involve reducing the amount of a unique RNA sequence in cells using a vector encoding the self-complementing polynucleotide including a first sequence complementary to said RNA sequence. Methods are also disclosed for preparing the polynucleotides, vectors, libraries of vectors, and the temporary knock-down of proteins, such as lethal proteins, during virus or recombinant protein production.
Owner:GALAPAGOS NV
Gene editing in the oocyte by cas9 nucleases
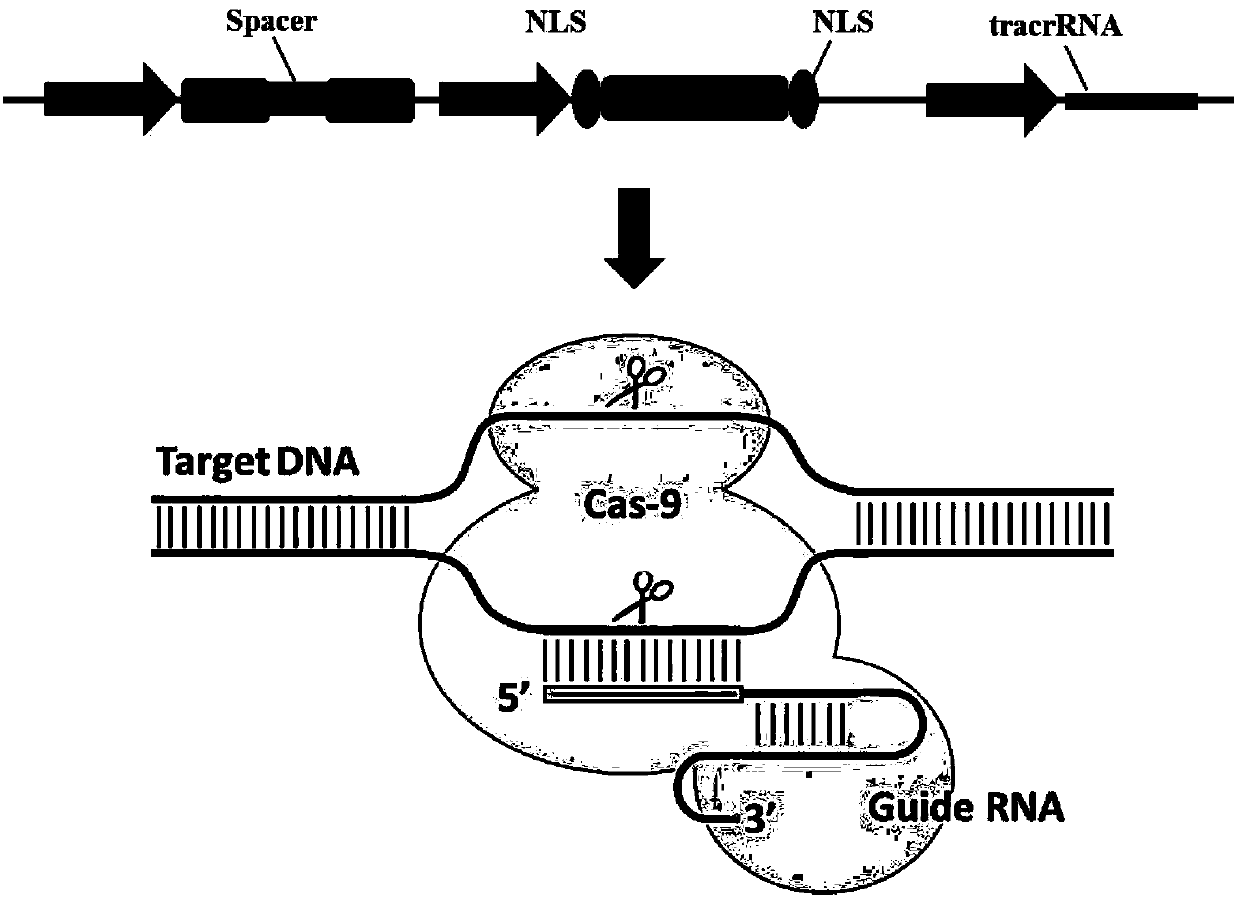
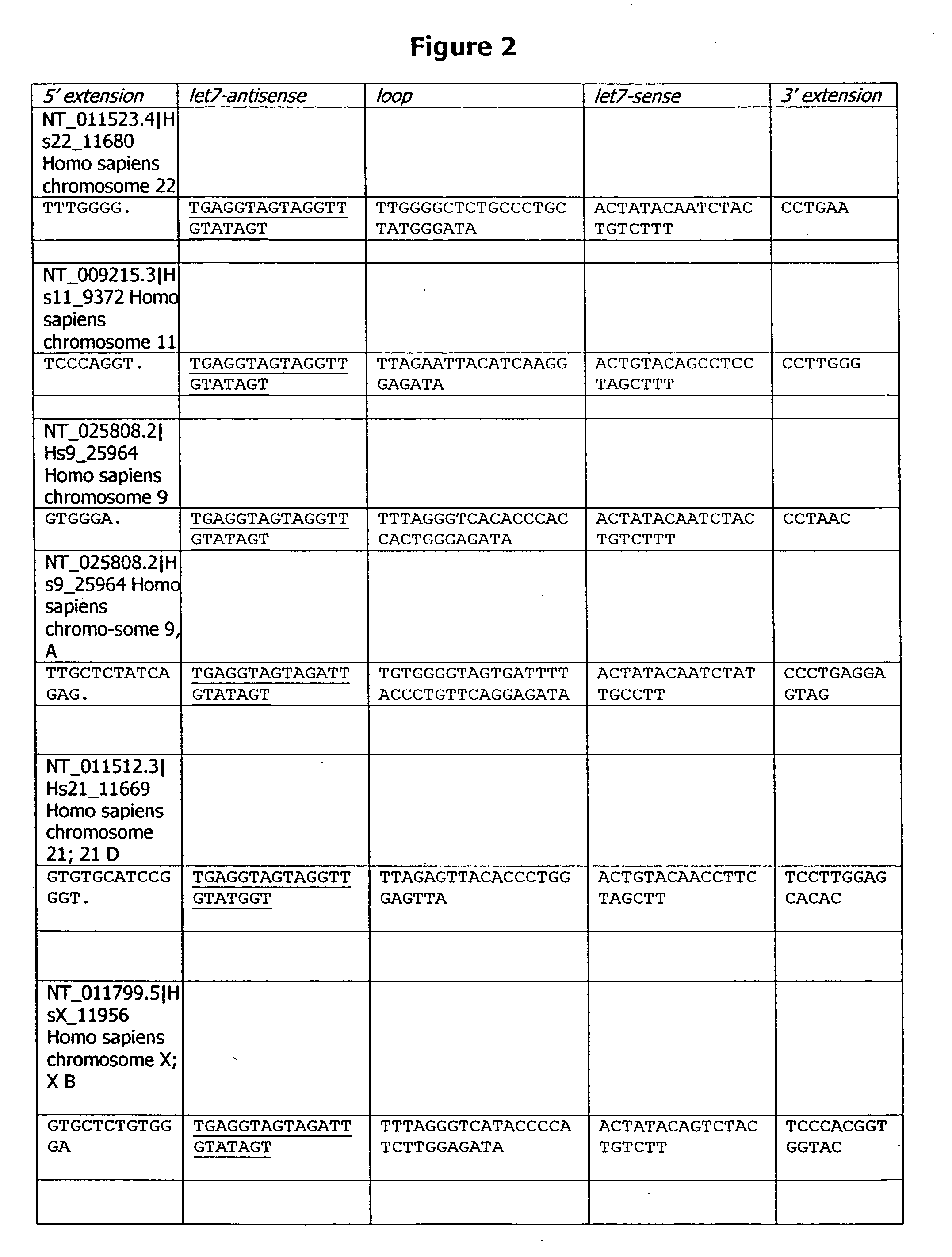
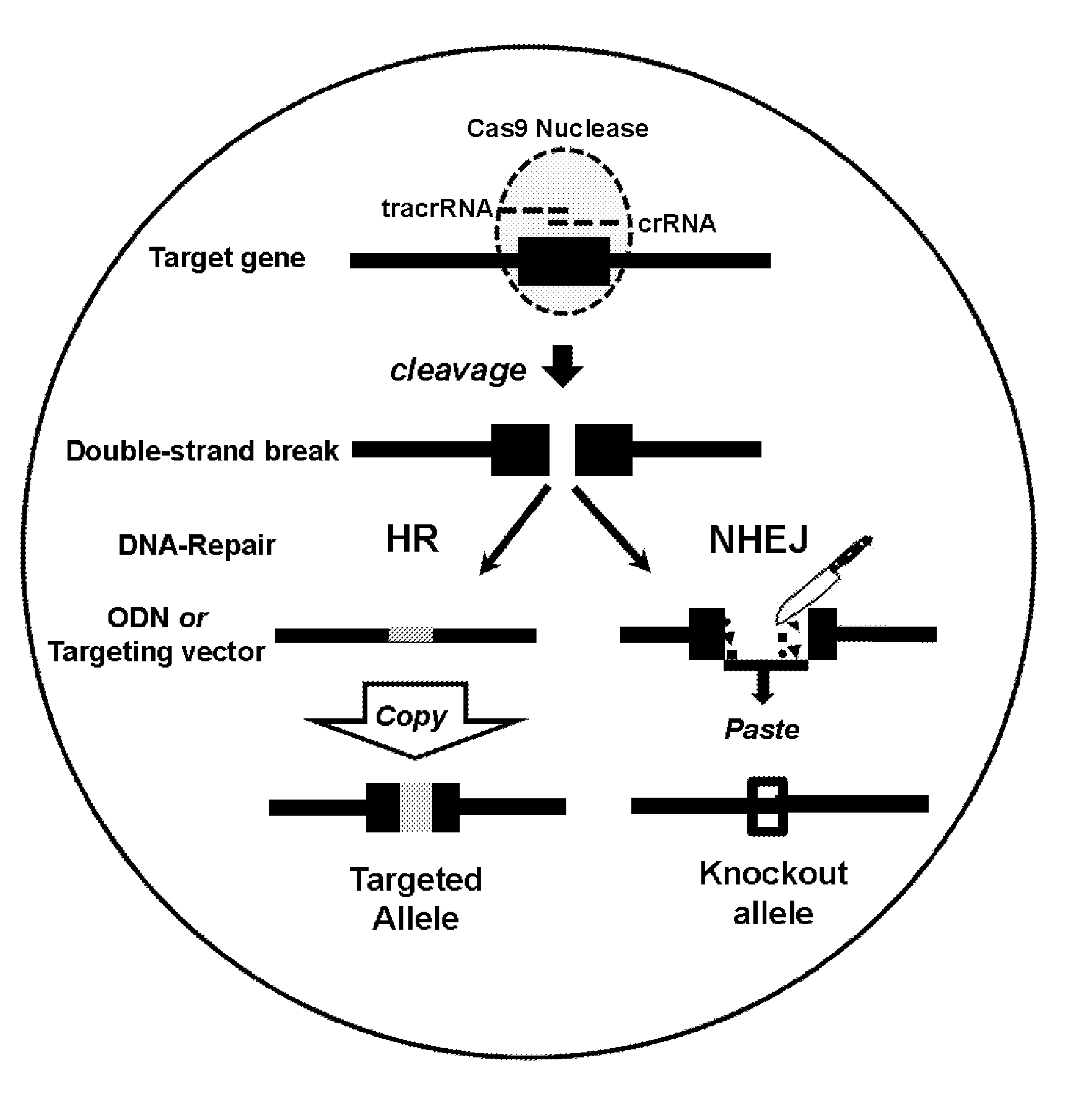
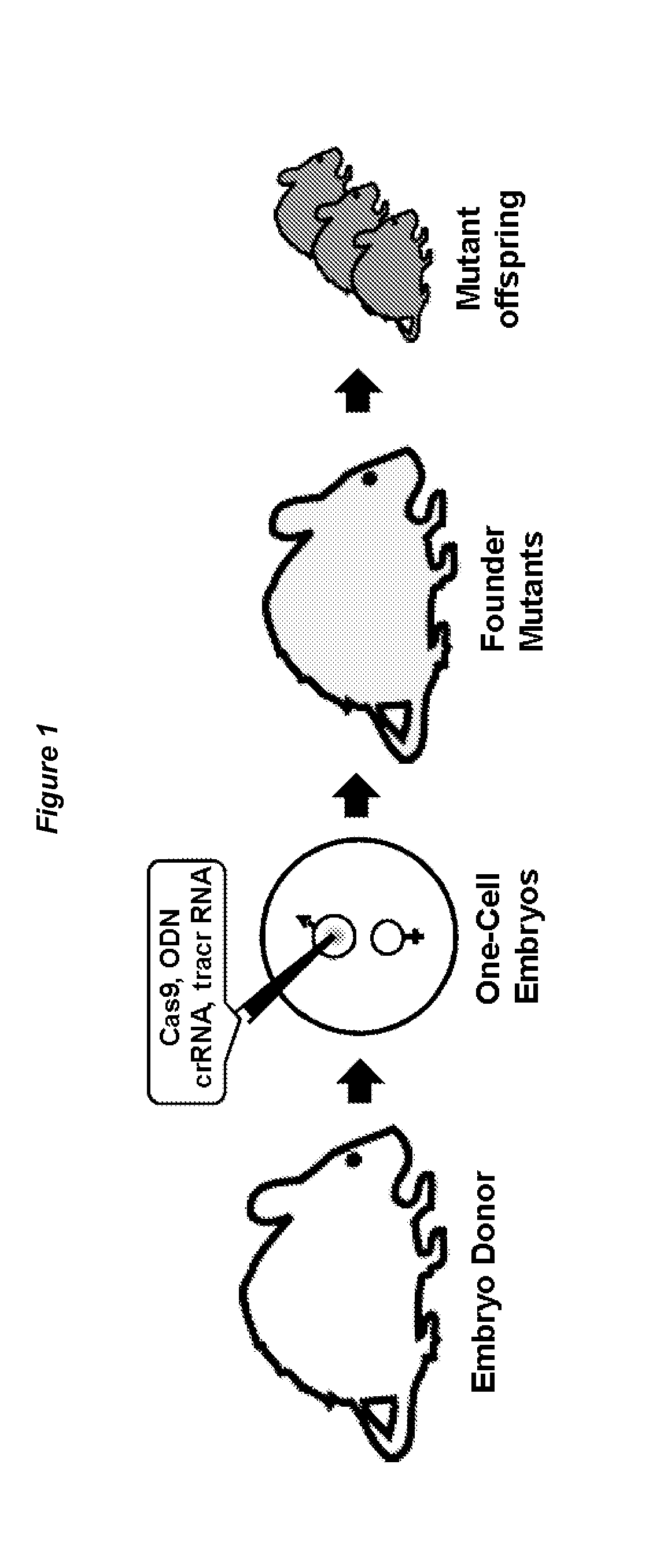
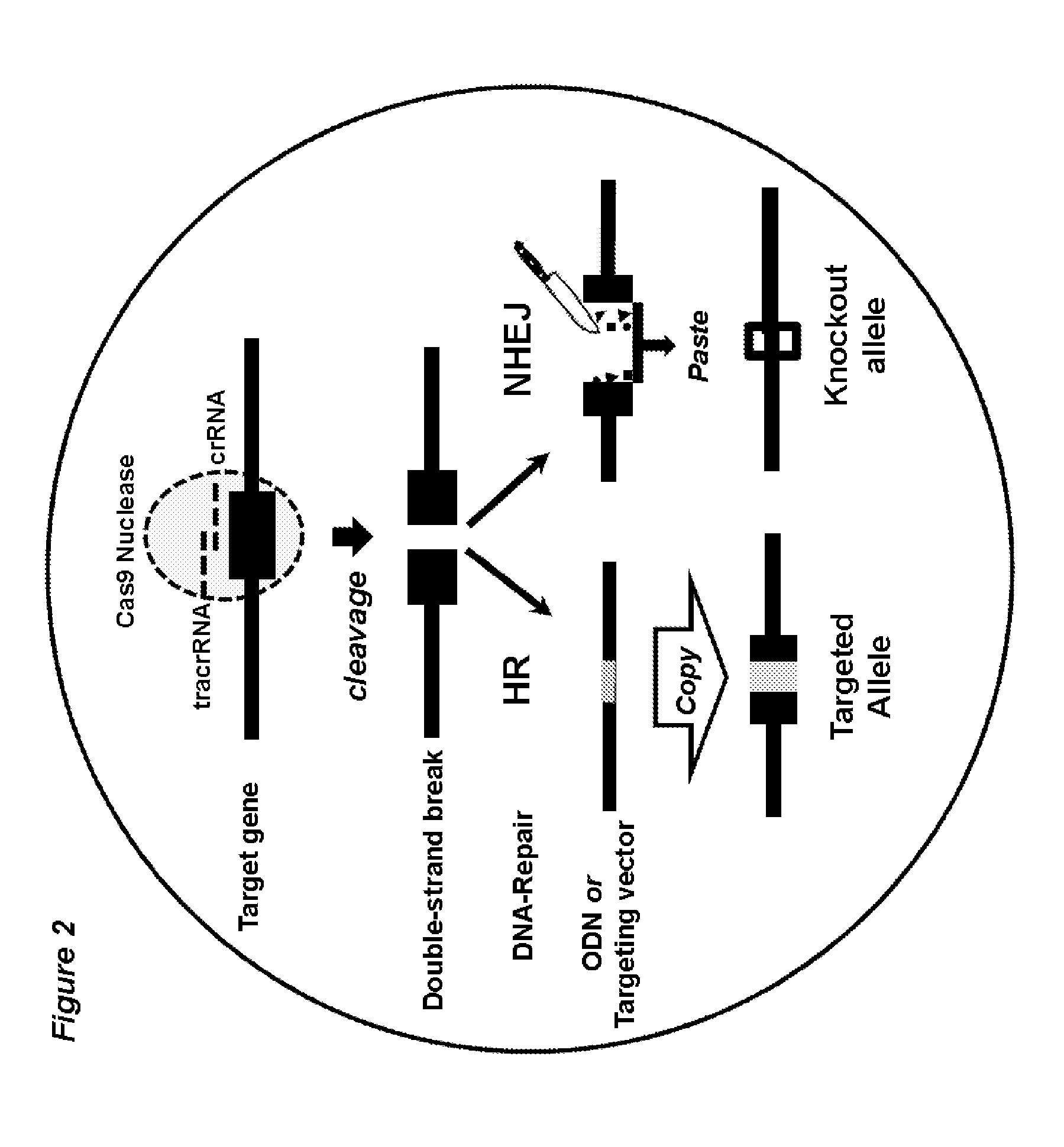
ActiveUS20150376652A1High frequencyStrong specificityAnimal reproductionHydrolasesNucleic acid sequencingRNA Sequence
The present invention relates to a method of producing a non-human, mammalian oocyte carrying a modified target sequence in its genome, the method comprising the steps of introducing into a non-human, mammalian oocyte: (a) a clustered, regularly interspaced, short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)-associated protein 9 (Cas9 protein) or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said Cas9 protein; and (b-i) a target sequence specific CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and a trans-activating crRNA (tracr RNA) or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said RNAs; or (b-ii) a chimaeric RNA sequence comprising a target sequence specific crRNA and tracrRNA or a nucleic acid molecule encoding said RNA; wherein the Cas9 protein introduced in (a) and the RNA sequence(s) introduced in (b-i) or (b-ii) form a protein / RNA complex that specifically binds to the target sequence and introduces a single or double strand break within the target sequence. The present invention further relates to the method of the invention, wherein the target sequence is modified by homologous recombination with a donor nucleic acid sequence further comprising the step: (c) introducing a nucleic acid molecule into the cell, wherein the nucleic acid molecule comprises the donor nucleic acid sequence and regions homologous to the target sequence. The present invention also relates to a method of producing a non-human mammal carrying a modified target sequence in its genome.
Owner:HELMHOLTZ ZENT MUNCHEN DEUTES FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR GESUNDHEIT & UMWELT
Infectious cDNA clone of North American porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome (PRRS) virus and uses thereof
The invention provides isolated polynucleotide molecules that comprise a DNA sequence encoding an infectious RNA sequence encoding a genetically-modified North American PRRS virus, wherein the polynucleotide molecule lacks at least one detectable antigenic epitope of North American PRRS virus. The invention also provides vaccines comprising genetically modified North American PRRS virus, RNA molecules, plasmids and viral vectors comprising the isolated polynucleotide molecules. Also provided are isolated polynucleotide molecules further comprising at least one nucleotide sequence that encodes a detectable heterologous antigenic epitope, and vaccines comprising North American PRRS virus, RNA molecules, plasmids and viral vectors comprising such isolated polynucleotide molecules.
Owner:ZOETIS SERVICE LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com