Patents
Literature
136 results about "Huntingtin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The huntingtin gene, also called the HTT or HD (Huntington disease) gene, is the IT15 ("interesting transcript 15") gene, which codes for a protein called the huntingtin protein. The gene and its product are under heavy investigation as part of Huntington's disease clinical research and the suggested role for huntingtin in long-term memory storage.
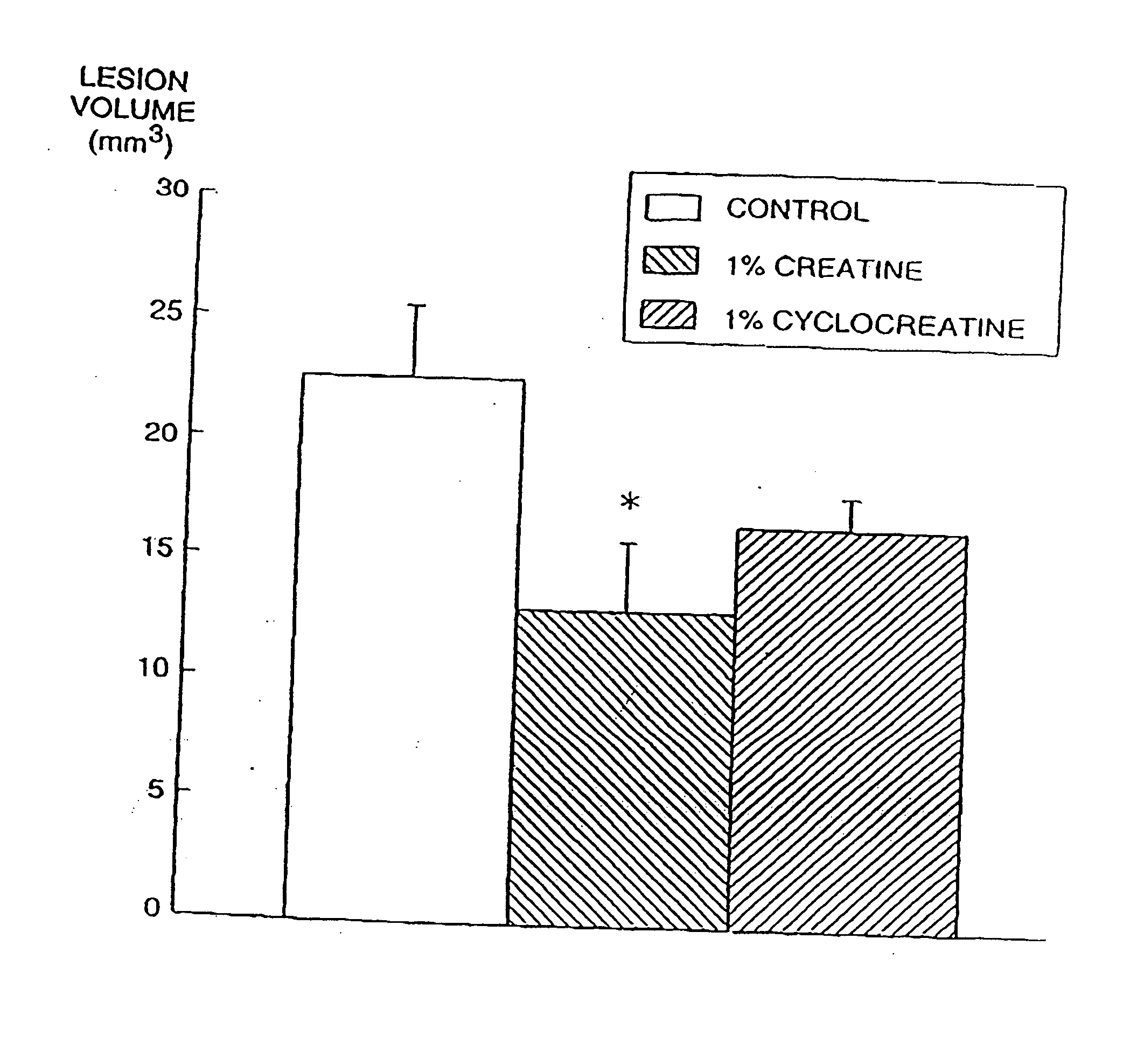
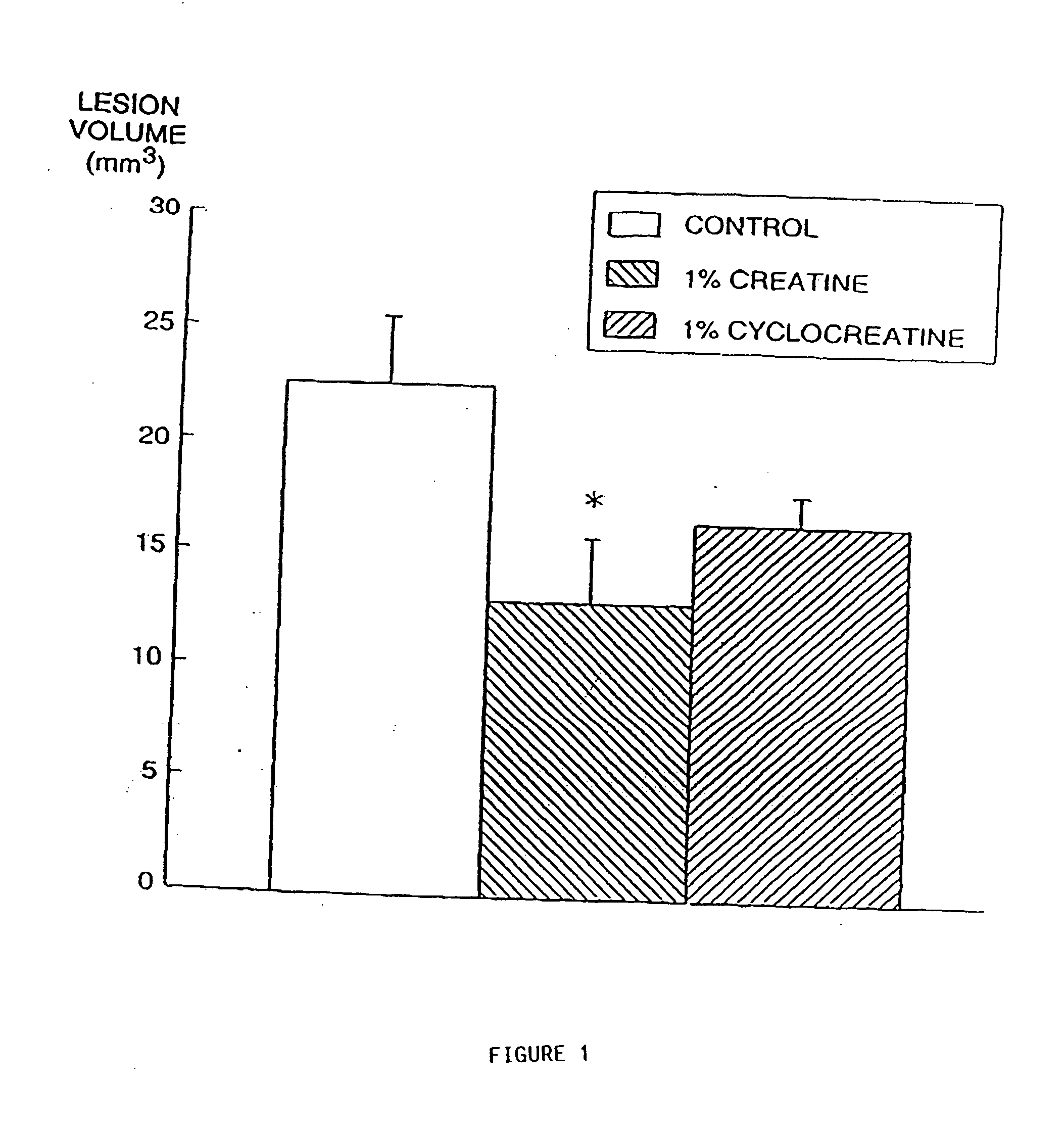
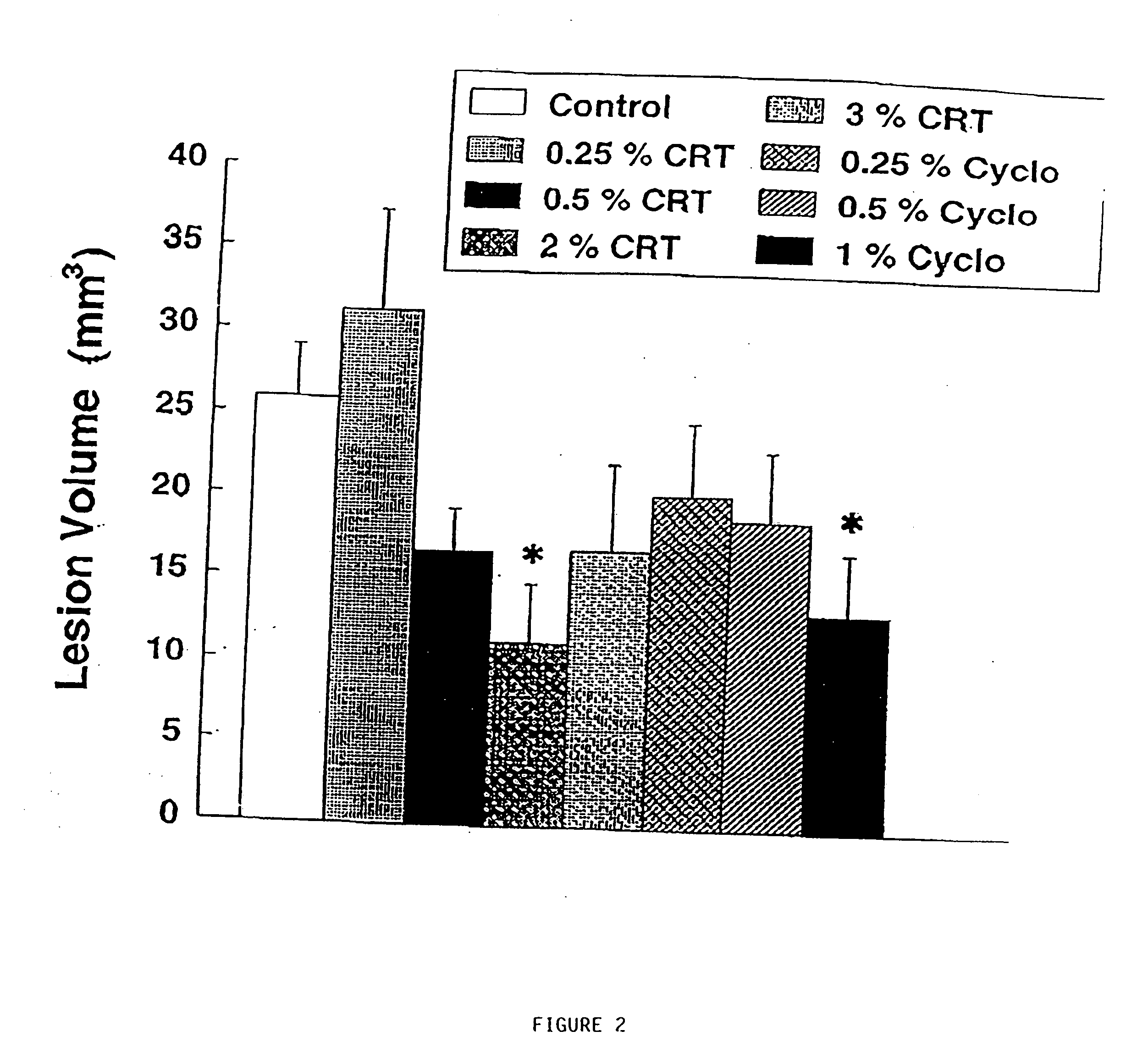
Compositions containing a combination of a creatine compound and a second agent
The present invention relates to the use of creatine compound and neuroprotective combinations including creatine, creatine phosphate or analogs of creatine, such as cyclocreatine, for treating diseases of the nervous system. Creatine compounds in combination with neuroprotective agents can be used as therapeutically effective compositions against a variety of diseases of the nervous system such as diabetic and toxic neuropathies, peripheral nervous system diseases, Alzheimer disease, Parkinson's disease, stroke, Huntington's disease, amyotropic lateral sclerosis, motor neuron disease, traumatic nerve injury, multiple sclerosis, dysmyelination and demyelination disorders, and mitochondrial diseases. The creatine compounds which can be used in the present method include (1) creatine, creatine phosphate and analogs of these compounds which can act as substrates or substrate analogs for creatine kinase; (2) bisubstrate inhibitors of creatine kinase comprising covalently linked structural analogs of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and creatine; (3) creatine analogs which can act as reversible or irreversible inhibitors of creatine kinase; and (4) N-phosphorocreatine analogs bearing non-transferable moieties which mimic the N-phosphoryl group.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
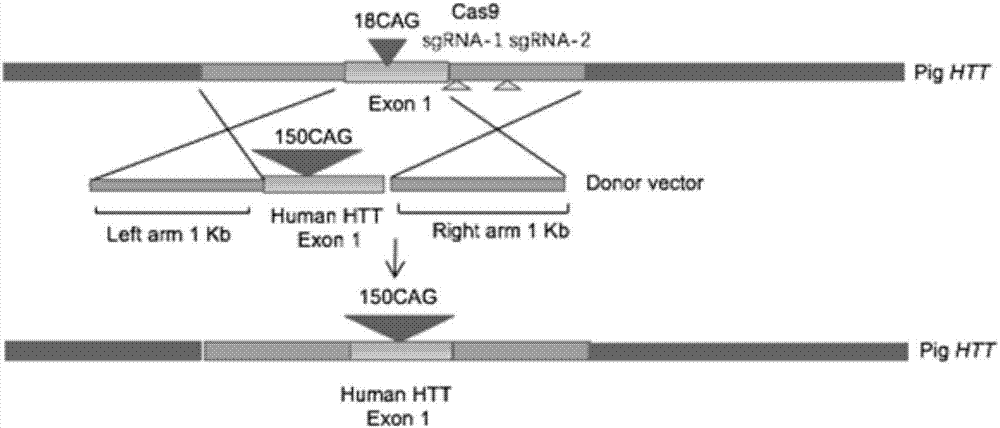
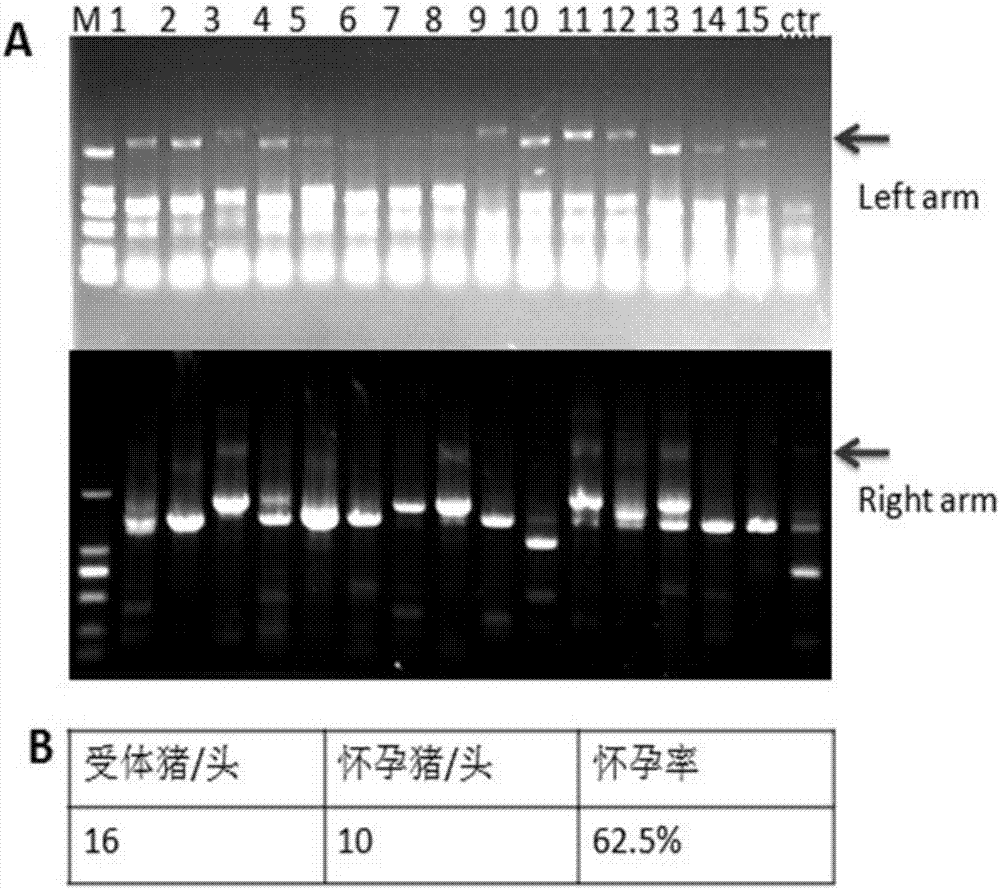
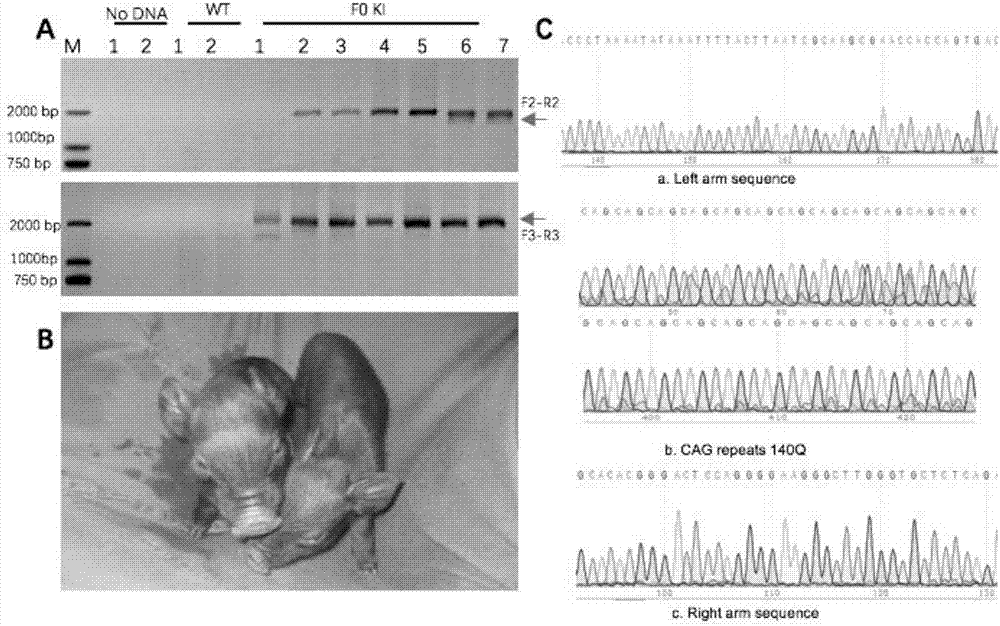
Recombinant vector for knock-in of human Huntington gene, construction method of recombinant vector and application of recombinant vector in construction of model pig
ActiveCN107988256AIncreased probability of knock-in positive clonesEfficient FeasibilityStable introduction of DNANucleic acid vectorHuman studiesExon
The invention discloses a recombinant vector for the knock-in of a human Huntington gene, a construction method of the recombinant vector and application of the recombinant vector in the constructionof a model pig. According to the recombinant vector, a human mutated Huntington exon gene is knocked in a fixed point manner for the first time, a virulence gene is knocked in by virtue of a CRISPR / Cas9 technique for the first time, and a donor vector is optimized by optimizing sfRNA, so that the probability that the gene is knocked into a positive cloned cell is increased; and by combining with apig cell nucleus transplantation technique, the probability that a directly obtained positive cell is knocked into the pig is increased, and a small human Huntington gene knock-in pig is obtained, thereby proving the efficient feasibility of the method for constructing gene modified pigs. The constructed Huntington gene knock-in model pig has behavioral characteristics such as respiratory disturbance and dyskinesia similar to human Huntington diseases, and stable heritable passage can be realized, so that a reliable model is provided for the research of the human Huntington diseases; and thenumber can be guaranteed so as to realize drug screening, gene treatment, stem cell treatment and the like, and the model can be a good human disease model.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY +1
Immunization and/or treatment of parasites and infectious agents by live bacteria
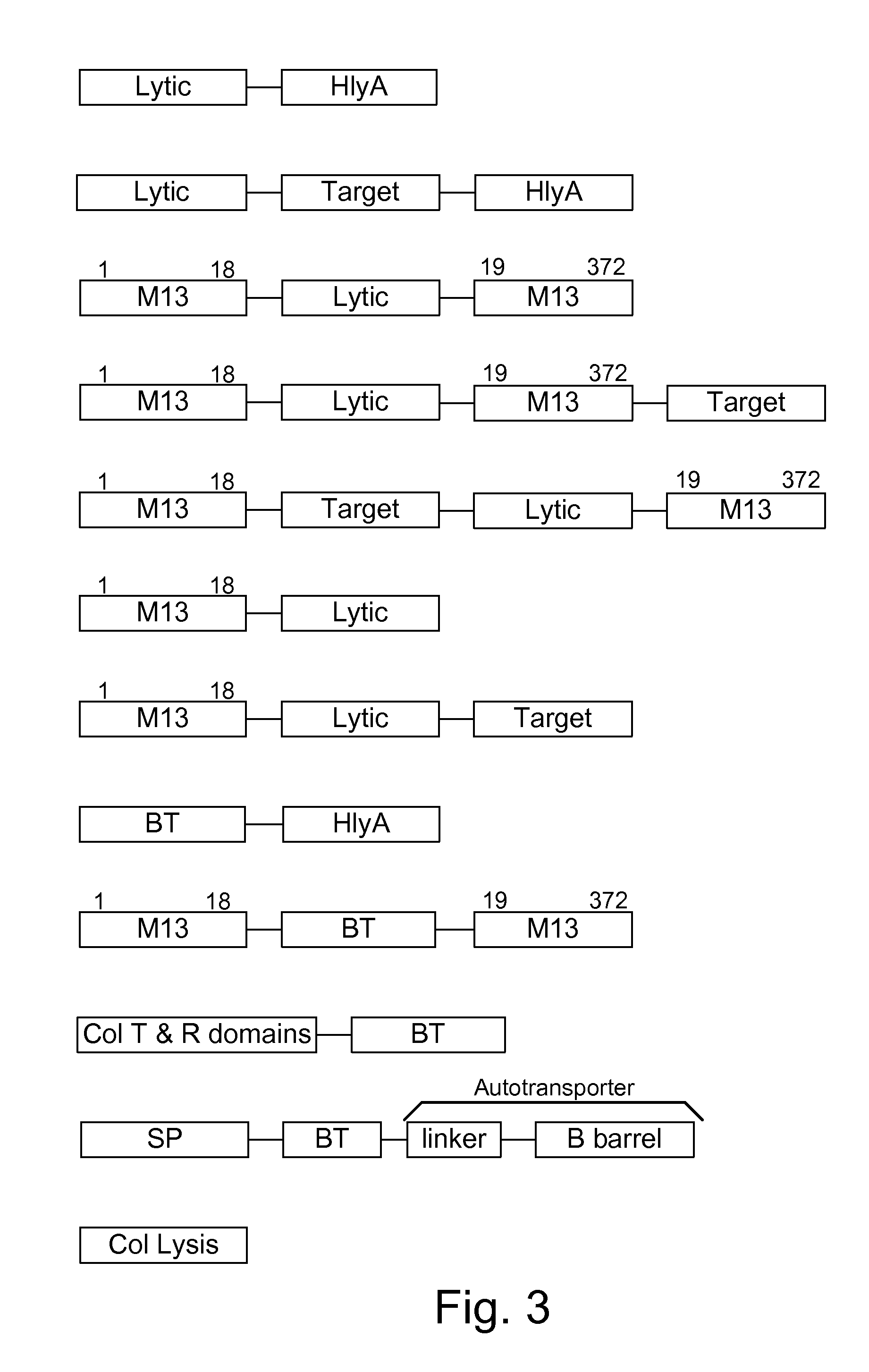
ActiveUS8771669B1Reducing eliminatingReducing or eliminating the targeted parasite, infectious diseaseVirusesBacteriaLytic peptideHuntingtons chorea
Chimeric proteins are expressed, secreted or released by a bacterium to immunize against or treat a parasite, infectious disease or malignancy. The delivery vector may also be attenuated, non-pathogenic, low pathogenic, or a probiotic bacterium. The chimeric proteins include chimeras of, e.g., phage coat and / or colicin proteins, bacterial toxins and / or enzymes, autotransporter peptides, lytic peptides, multimerization domains, and / or membrane transducing (ferry) peptides. The active portion of the immunogenic chimeric proteins can include antigens against a wide range of parasites and infectious agents, cancers, Alzheimer's and Huntington's diseases, and have enhanced activity when secreted or released by the bacteria, and / or have direct anti-parasite or infectious agent activity. The activity of the secreted proteins is further increased by co-expression of a protease inhibitor that prevents degradation of the effector peptides. Addition of an antibody binding or antibody-degrading protein further prevents the premature elimination of the vector and enhances the immune response.
Owner:BERMUDES DAVID G DR
Methods and compositions for the treatment of huntington's disease
Methods and compositions for reducing expression of a mutant huntingtin (mHTT) protein in a cell are provided. Such methods include contacting the cell with an effective amount of a nucleic acid silencing agent targeting a differentiating polymorphism in RNA encoding the mHTT.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Methods and compositions for the treatment of Huntington'S disease
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Methods And Sequences To Preferentially Suppress Expression of Mutated Huntingtin
ActiveUS20100120900A1Suppress expression and formationInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaNucleotide
Disclosed herein are methods and sequences to preferentially suppress the expression of the mutated huntingtin (“htt”) protein over expression of the normal htt protein. Also disclosed are methods comprising screening an individual for the heterozygous presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms within the individual's Huntington's genes; administering nucleic acid molecules comprising nucleotide sequences that preferentially suppress the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for mutated huntingtin (“htt”) over suppressing the expression of amino acid sequences encoding for normal htt by targeting an area of a Huntington's disease gene that is heterozygous for the presence of one or more single nucleotide polymorphisms.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
RNA interference for the treatment of gain-of-function disorders
ActiveUS20110172291A1Increased nuclease resistanceIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
The present invention relates to the discovery of an effective treatment for a variety of gain-of-function diseases, in particular, Huntington's disease (HD). The present invention utilizes RNA Interference technology (RNAi) against polymorphic regions in the genes encoding various gain-of-function mutant proteins resulting in an effective treatment for the gain-of-function disease.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Upregulating activity or expression of bdnf to mitigate cognitive impairment in asymptomatic huntington's subjects
InactiveUS20080176793A1Improve the level ofHigh activityBiocideNervous disorderCognitive diseasesCognitive disorder
This invention provides novel methods of treatment to ameliorate or prevent cognitive disorder / dysfunction in pre- or asymptomatic subject having one or more mutations in the Huntington gene. The methods involve increasing the expression or activity of the neurotrophin BDNS in the brain of said subject.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
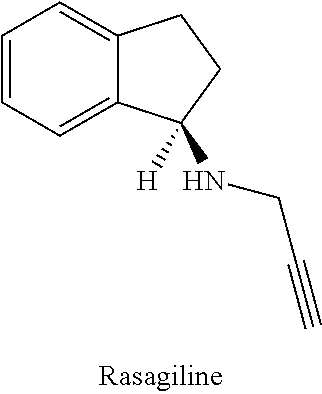
Combination of rasagiline and pridopidine for treating neurodegenerative disorders, in particular huntington's disease
This invention provides a method of treating a patient afflicted with a neurodegenerative disorder, e.g., Huntington's disease, comprising administering to the patient rasagiline as an add-on therapy to or in combination with pridopidine. This invention also provides a package and a pharmaceutical composition comprising rasagiline and pridopidine for treating a patient afflicted with a neurodegenerative disorder. This invention also provides rasagiline for use as an add-on therapy or in combination with pridopidine in treating a patient afflicted with a neurodegenerative disorder. This invention further provides use of rasagiline and pridopidine in the preparation of a combination for treating a patient afflicted with a neurodegenerative disorder.
Owner:TEVA PHARM USA INC
Drug targets for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders
Methods of screening candidate agents to identify potential therapeutic agents for the treatment of a neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease and methods for identifying a mutation in, or changes in expression of, a gene associated with neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease, are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
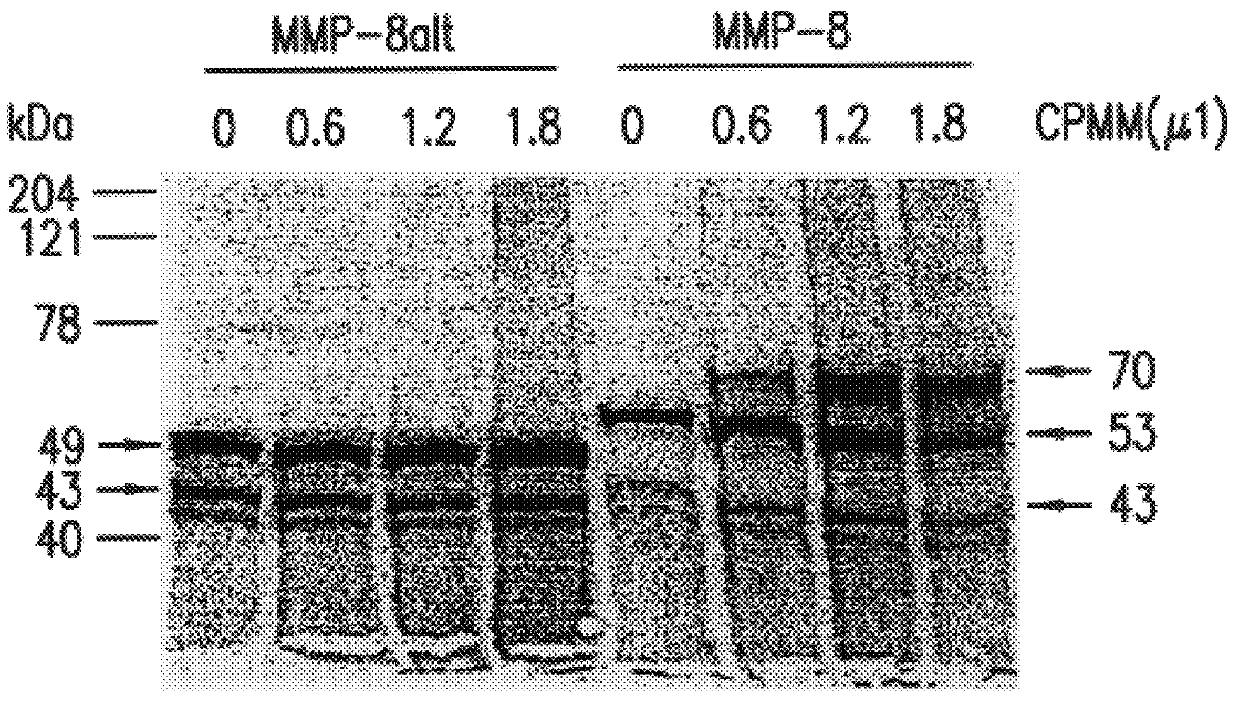
Human neutrophil collagenase splice variant
InactiveUSH1973H1Reduce and prevent effect of MMP-8altInhibit expressionSugar derivativesHydrolasesApoptosisArthritis
The subject invention is related to human MMP-8alt genes and gene products and their differential expression when comparing a patient with a disease state to a control. A further aspect of the invention concerns compounds which antagonize the biological activity of MMP-8alt protein and methods for identifying these compounds. Another aspect of the present invention concerns pharmaceutical compositions comprising such compounds for the treatment of arthritis, cancer, and disease caused by cellular apoptosis including but not limited to Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease and Huntington's chorea.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Methods and compositions for development of drug screening procedures and diagnostic tools
This invention defines novel research and clinical laboratory methodology and compositions related thereto appropriate for use in (a) determining the presence of a neurodegenerative disease selected from the group limited solely to Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, familial Alzheimer's disease, familial Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, spinal muscular atrophy, Friedreich'a ataxia, giant axon neuropathy, juvenile ceroid-lipofuscinosis, familial motor neuron diseases, juvenile diabetic polyneuropathy and Down's syndrome, (b) monitoring the ongoing status of the physiological expression of said disease and (c) screening candidate therapeutic drug agents for possible effectiveness. The invention is based on the new and novel observation that the presence of a neurodegenerative disease can be characterized in part by the expression in cultured fibroblasts obtained from the patient of one or more proteins which are not the product of a defective disease-inducing gene, but which are stress proteins, one or more other proteins modified by conditions of oxidative stress or one or more other disease-related proteins. The invention depends on living cell material, namely fibroblasts, which are readily and, if necessary, repeatedly available from a patient. When adapted as a method and composition useful for the screening candidate therapeutic drug agents for possible effectiveness, this technology offers advantages in terms of (a) providing research opportunities which, in some cases, never existed before, (b) cost effectiveness when compared to alternative technologies, (c) ability to be used readily on a large scale, (d) ability to generate meaningful data in a comparatively short period of time, and (e) providing an early stage opportunity to obtain information based on direct interaction of a candidate drug and a living tissue disease model. Various aspects of diagnostic methods and compositions are also disclosed.
Owner:SHAPIRO HOWARD K
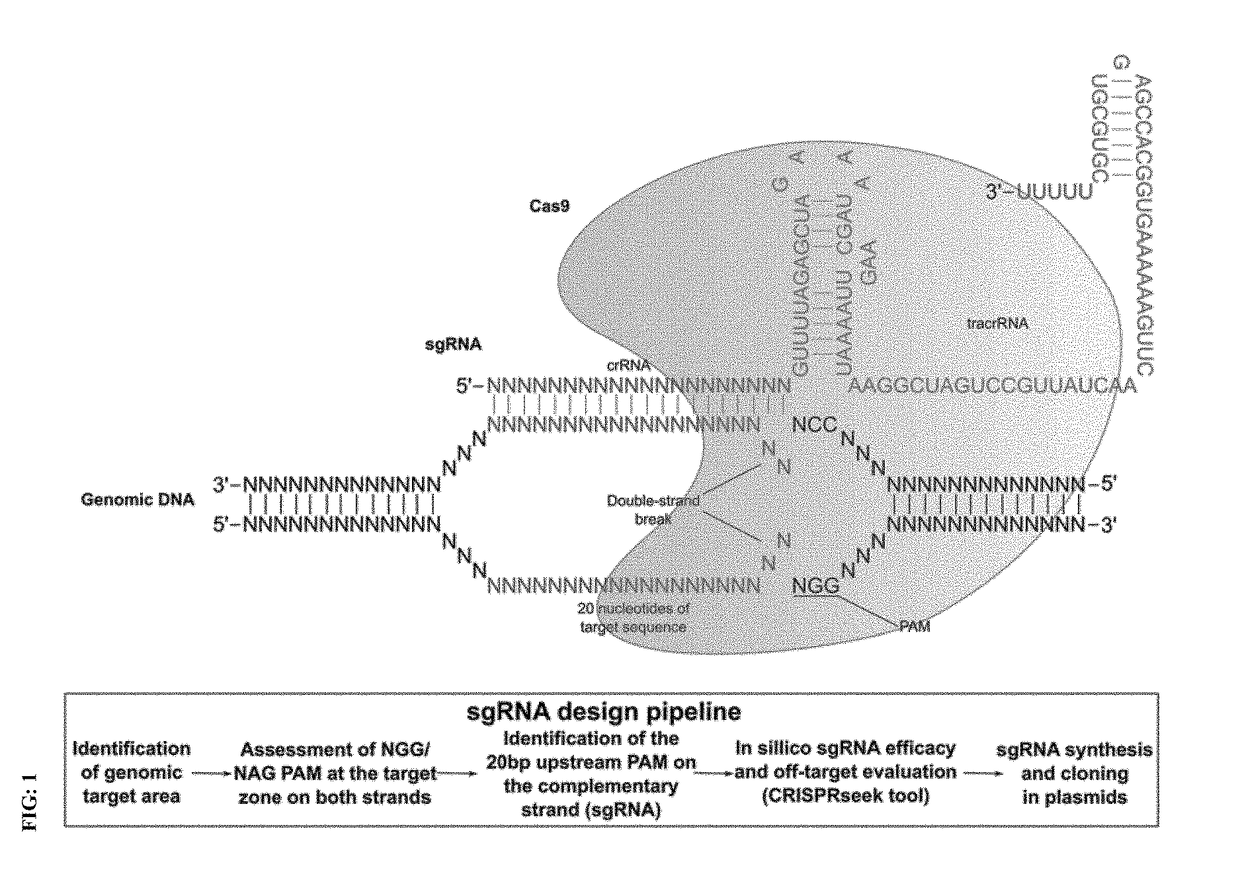
Genome editing for the treatment of huntington's disease
InactiveUS20170224843A1Rescue the HD phenotypeInhibit expressionPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
A treatment of Huntington's disease (HD) using the Clustered-Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) system. This technology offers the possibility to design a small RNA (sgRNA), which is incorporated into a CRISPR-associated protein (Cas9) to recognize and induce DNA double-strand breaks at a specific target location. In the context of HD, this allows to block the expression of the mutant huntingtin or repair the CAG expansion causing the disease.
Owner:CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV VAUDOIS C H U V
Methods of identifying lead compounds that modulate toxicity of neurotoxic polypeptides
ActiveUS20050255450A1Low toxicityIncreased toxicityCompound screeningBiocideHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
Methods of screening candidate agents to identify lead compounds for the development of therapeutic agents for the treatment of a neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease and methods for identifying a mutation in, or changes in expression of, a gene associated with neurodegenerative disease, such as Huntington's Disease and Parkinson's Disease, are provided.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON +1
Gene necessary for striatal function, uses thereof, and compounds for modulating same
InactiveUS20040152106A1Tetracycline active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
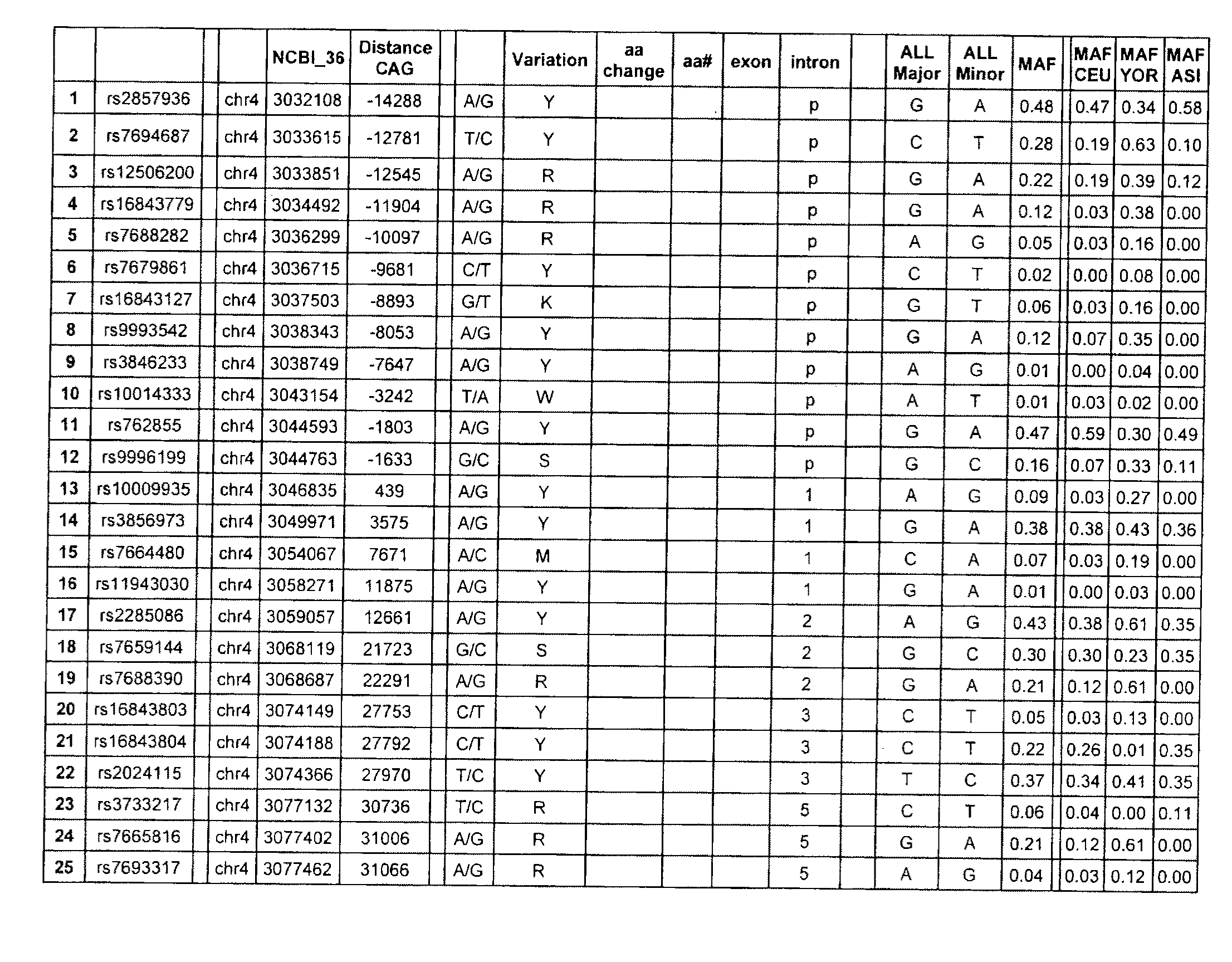
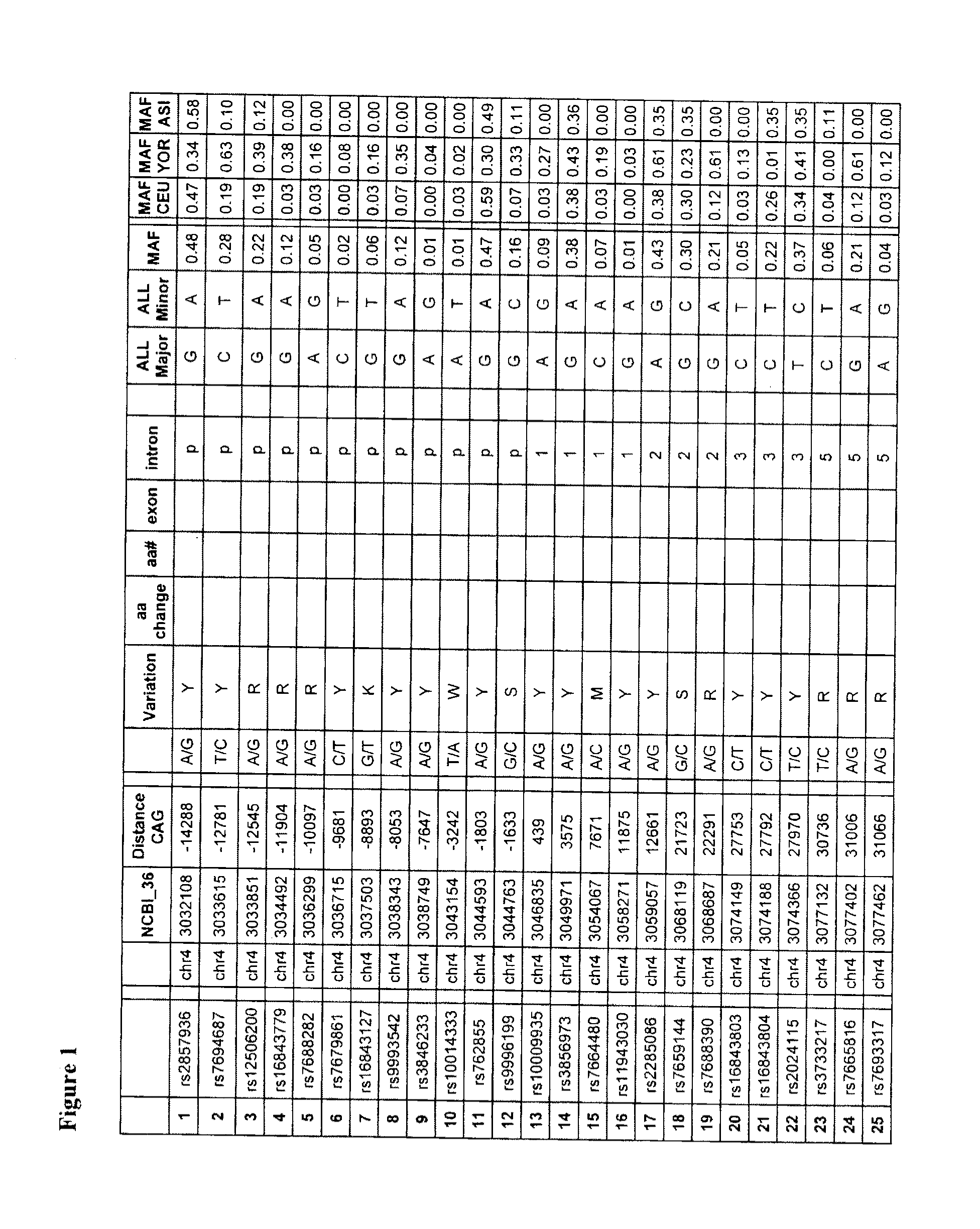
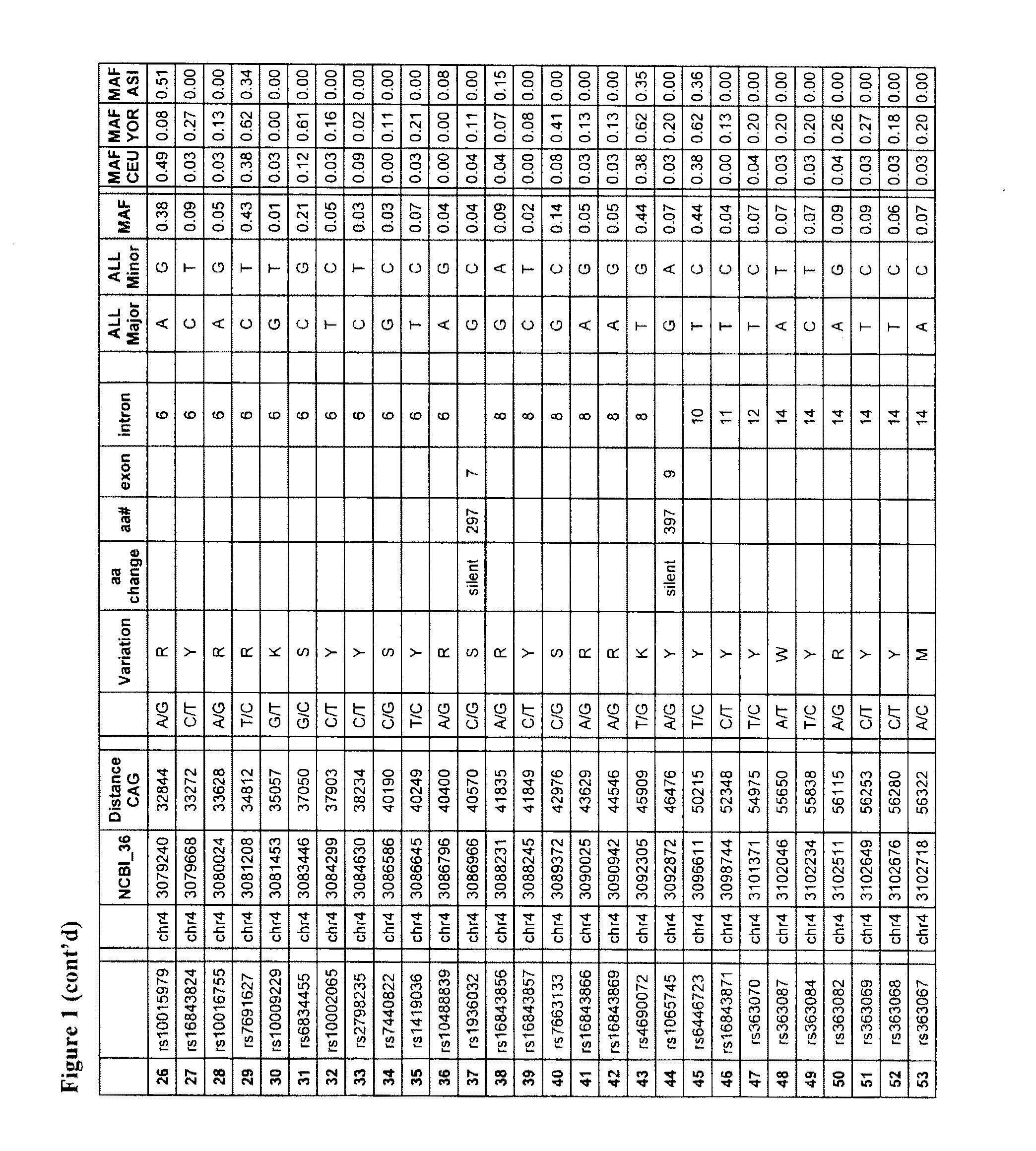
PDE10A, a gene that is normally highly expressed in mammalian striatum and elsewhere, has been found to decrease in expression during the development of CAG repeat disorders such as Huntington's disease. The invention teaches a method for detecting the presence of or the predisposition for a CAG repeat disorder. Compounds which modulate CAG repeat disorders and their uses are taught. Methods for screening for further compounds to modulate CAG repeat disorders are also taught.
Owner:NOVANEURON
Composition and method for the detection of diseases associated with amyloid-like fibril or protein aggregate formation
InactiveUS7078191B1Optimize dataStrong impact on the pharmaceutical researchBiocideBacteriaFiberHuntingtons chorea
The present invention relates to novel compositions useful for elucidating the onset or progress of diseases such as Huntington's disease, that are associated with the formation of fibrils or protein aggregates. Further, the present invention relates to methods for monitoring formation of fibrils or protein aggregates as well as to methods for identifying inhibitors of fibril or protein aggregate formation. Additionally, the invention relates to inhibitors of the formation of fibrils or protein aggregates identified by the method of the invention as well as to pharmaceutical compositions that include the inhibitors.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method for treating neurodegenerative diseases
InactiveUS20060014719A1BiocideOrganic active ingredientsHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
The present invention is directed to methods and compositions for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. In particular embodiments, the invention is directed to the treatment of Alzheimer's disease, MS, ALS, Huntington's Disease. In other embodiments, the invention is directed to the treatment of multiple sclerosis.
Owner:GLYCOGENESYS INC
Glycolipids as treatment for disease
InactiveUS20120035120A1High affinityExtended half-lifeBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
This invention provides compounds, compositions, and methods for treating a disorder selected from cancer, hyperinsulinemia, hypoglycemia, hyperinsulinemia with hypoglycemia, atypical Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, multiple systems atrophy, GM3 synthase deficiency, GM2 synthase deficiency or tauopathy.
Owner:SENEB BIOSCI
Peptides for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases
ActiveUS20150259392A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderGlycineCrystallography
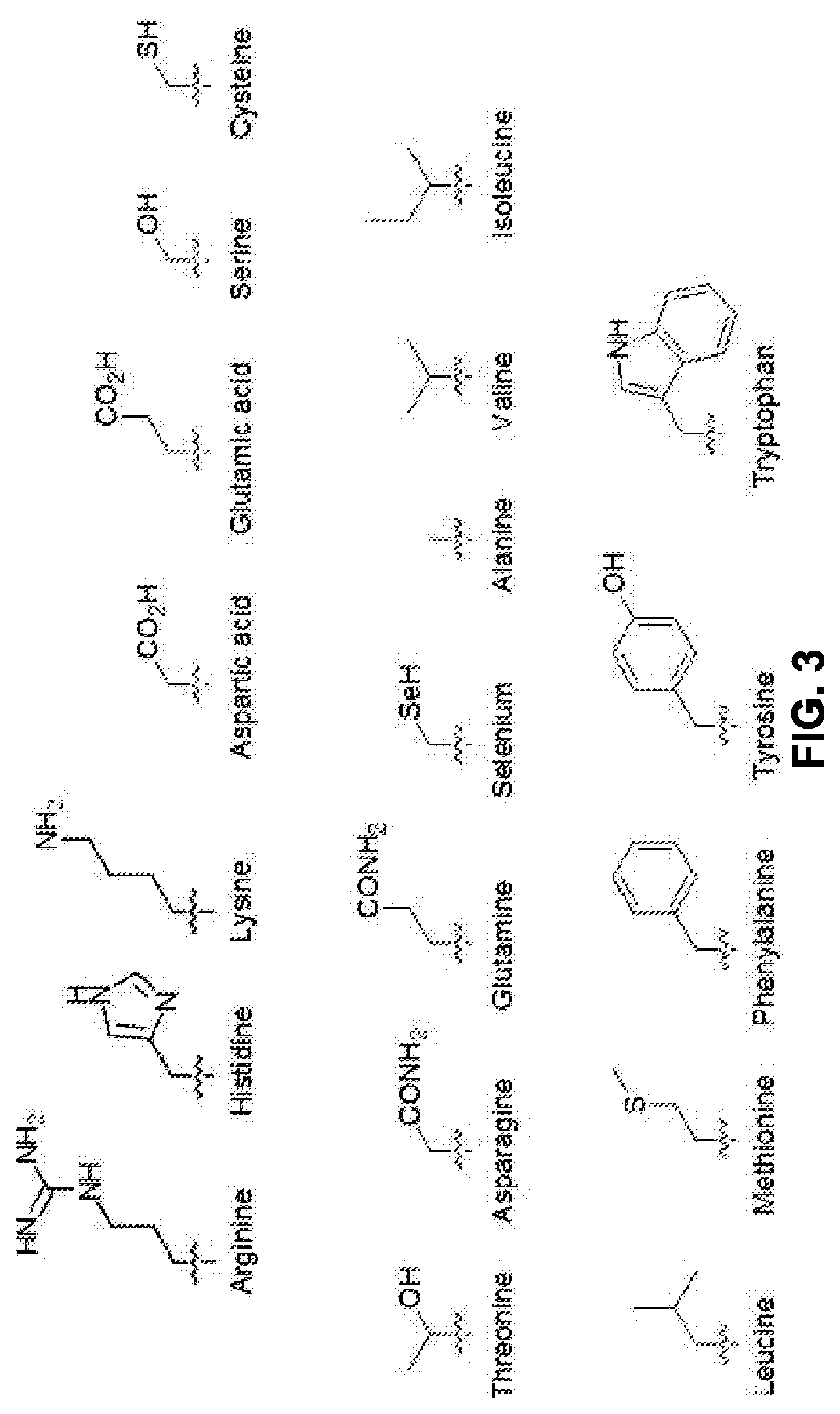
An isolated peptide comprising a Huntingtin (Htt) amino acid sequence being no longer than 15 amino acids, wherein said Htt amino acid sequence comprises the sequence X1X2X3X4 X5, wherein X1 is a hydrophobic amino acid or threonine, X2 is a hydrophobic amino acid, X3 is a hydrophobic amino acid, X4 is an acidic amino acid and X5 is selected from the group consisting of glycine, serine and alanine, the peptide capable of specifically inhibiting the activity of caspase 6.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Compositions, devices and methods for treatment of huntington's disease through intracranial delivery of sirna
InactiveUS20070167389A1Reduce the amount requiredInhibit productionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaDisease
The present invention provides devices, small interfering RNAs, and methods for treating a neurodegenerative disorder comprising the steps of surgically implanting a catheter so that a discharge portion of the catheter lies adjacent to a predetermined infusion site in a brain, and discharging through the discharge portion of the catheter a predetermined dosage of at least one substance capable of inhibiting production of at least one neurodegenerative protein. The present invention also provides valuable small interfering RNA vectors, systems, and methods for treating Huntington's disease in vivo without impairment of cell endoplasmic reticulum, spontaneous motor activity, or locomotor activity of a patient.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as Huntington's disease, by sodium butyrate chemotherapy
InactiveUS20060069157A1Ameliorating and abrogating effectImprove survivalBiocideAnimal repellantsHuntingtons choreaNeuro-degenerative disease
A method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as Huntington's disease, includes administering a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor in a subject in need thereof. The HDAC inhibitor includes sodium butyrate.
Owner:VETERANS AFFAIRS U S DEPT OF
L-serine compositions, methods and uses for treating neurodegenerative diseases and disorders
InactiveUS20130156846A1Preventing protein misfoldingReduce riskBiocideNervous disorderL serineAnserine
L-serine, L-serine precursors, L-serine derivatives and L-serine conjugates for treatment, amelioration and / or prevention of protein aggregation / tangles / plaques and diseases associated with protein aggregation / tangles / plaques. In particular, treatments and uses for L-serine, L-serine precursors, L-serine derivatives and L-serine conjugates include Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), and Huntington disease (HD).
Owner:THE INST FOR ETHNOMEDICINE
Prevention and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases through autophagy activity mediated by ligand or arginylated bip binding to p62 zz domain
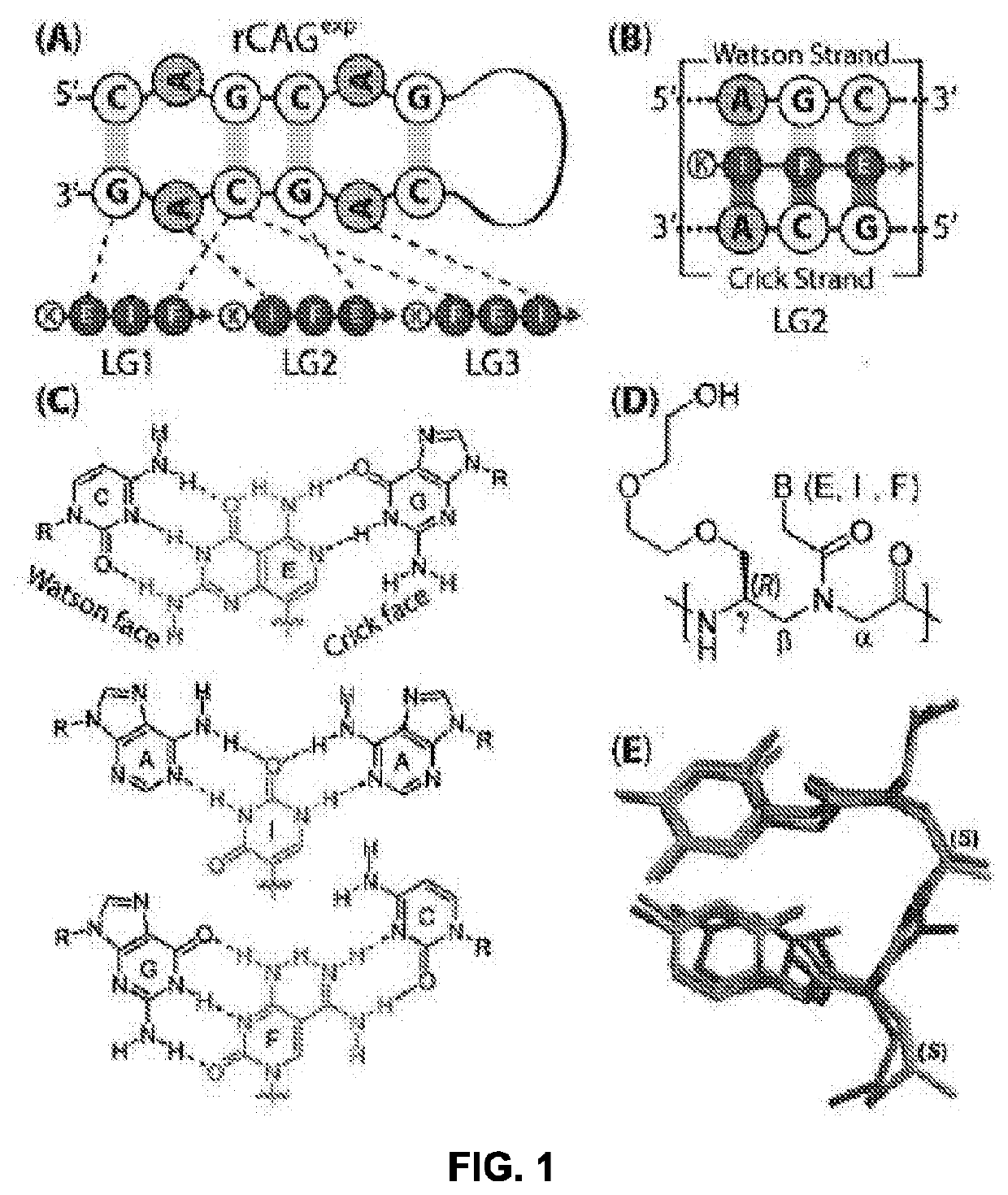
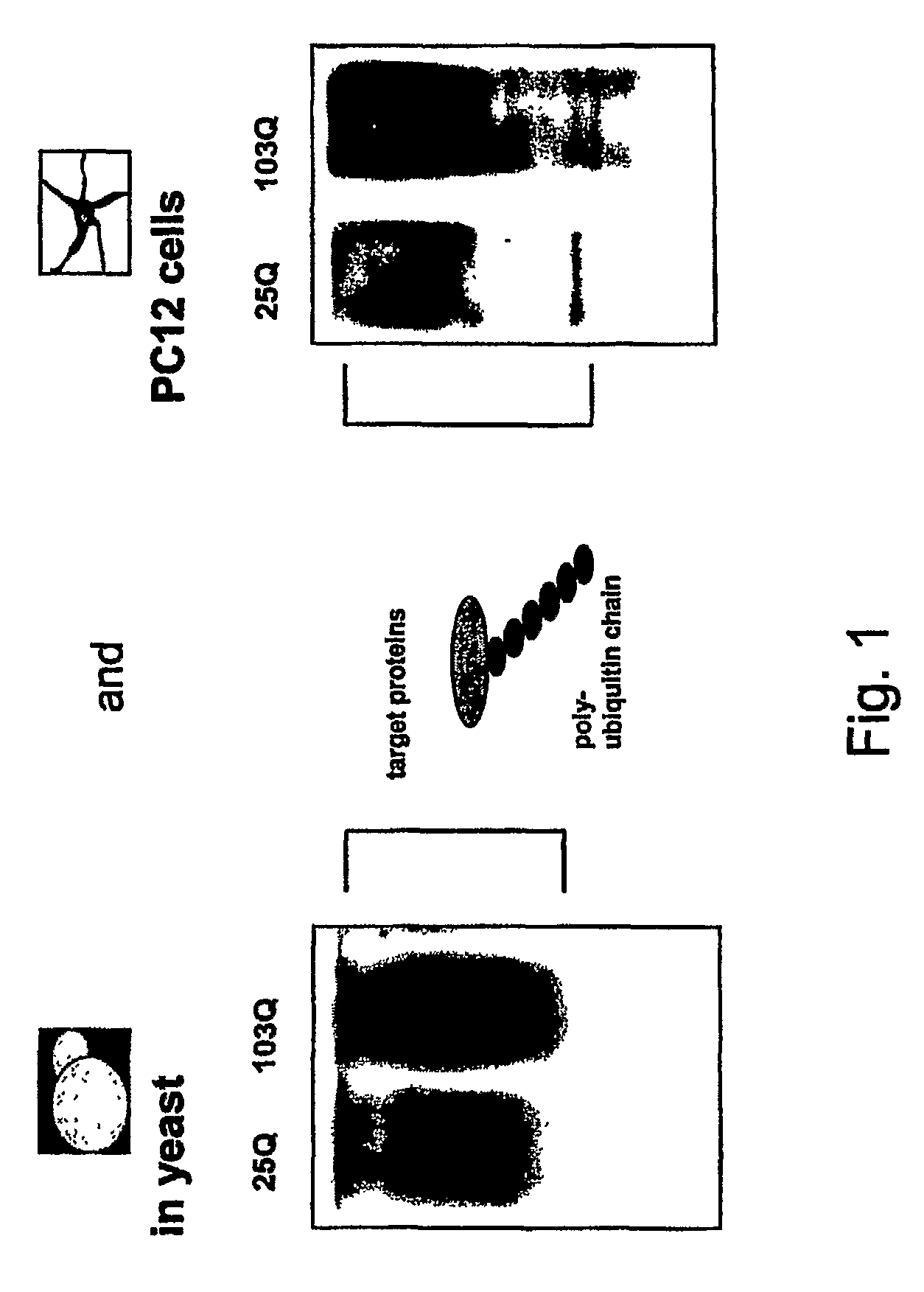
The drug action mechanisms and core techniques of the present invention are summarized in figure 1. Specifically, the invention provides malignant denatured proteins, such as mutant Huntingtin proteinor alpha-synuclein, stick together to grow into oligomer aggregates (1, 2), fibrillar aggregates (3), and ultimately inclusion bodies (4). Young neuronal cells produce a large quantity of Nt-Arg through N-terminal arginylation (5) of endoplasmic reticulum chaperones, such as BiP, and thereafter, arginylated BiP (R-BiP) comes into the cytoplasm and binds with denatured proteins (6). Nt-Arg of R-BiP, as a ligand, binds with the ZZ domain of p62 (7) to induce the structural activation of p62 (8) while the ordinarily closed inactive form of p62 is changed with an open form thereof, and thus PB1 and LC3-binding domains are exposed. On the basis of oligomerization (9) by the PB1 domain, p62 binds with the denatured protein aggregates to be concentrated to autophagically degradable aggregates, that is, p62 bodies (10). Thereafter, p62 completes autophagy targeting (11) and lysosomal proteolysis through binding with LC3 protruding on the autophagosomal membranes. In young neuronal cells, theautophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is strong, and thus the cytotoxic protein aggregates (1-5) do not accumulate, but in aged neuronal cells, the autophagic proteolysis occurring through steps 5-11 is weakened, and thus the protein aggregates (1-5) accumulate, resulting in a vicious cycle. The present invention attempts to effectively remove Huntingtin and alpha-synuclein protein aggregates and the like by artificially activating p62 using low-mass ligands of the p62 ZZ domain (12, 13). Specifically, p62 binding the ligands through step 12 promotes p62-R-BiP-denatured protein oligomerization (9) and autophagy aggregate formation (10). In addition, the ligand-62 conjugates step 13 act as autophagy activators (14), to promote LC3 synthesis, the conversion of LC3-I into LC3-II, and the like, thereby promoting the formation of autophagosomes (15).
Owner:奧土择破利悟
Small compounds that correct protein misfolding and uses thereof
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Application of alfuzosin compound in prevention or treatment of Alzheimer's disease and related diseases
PendingCN111035642AImprove mitochondrial metabolismFunction increaseOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaAmytrophic lateral sclerosis
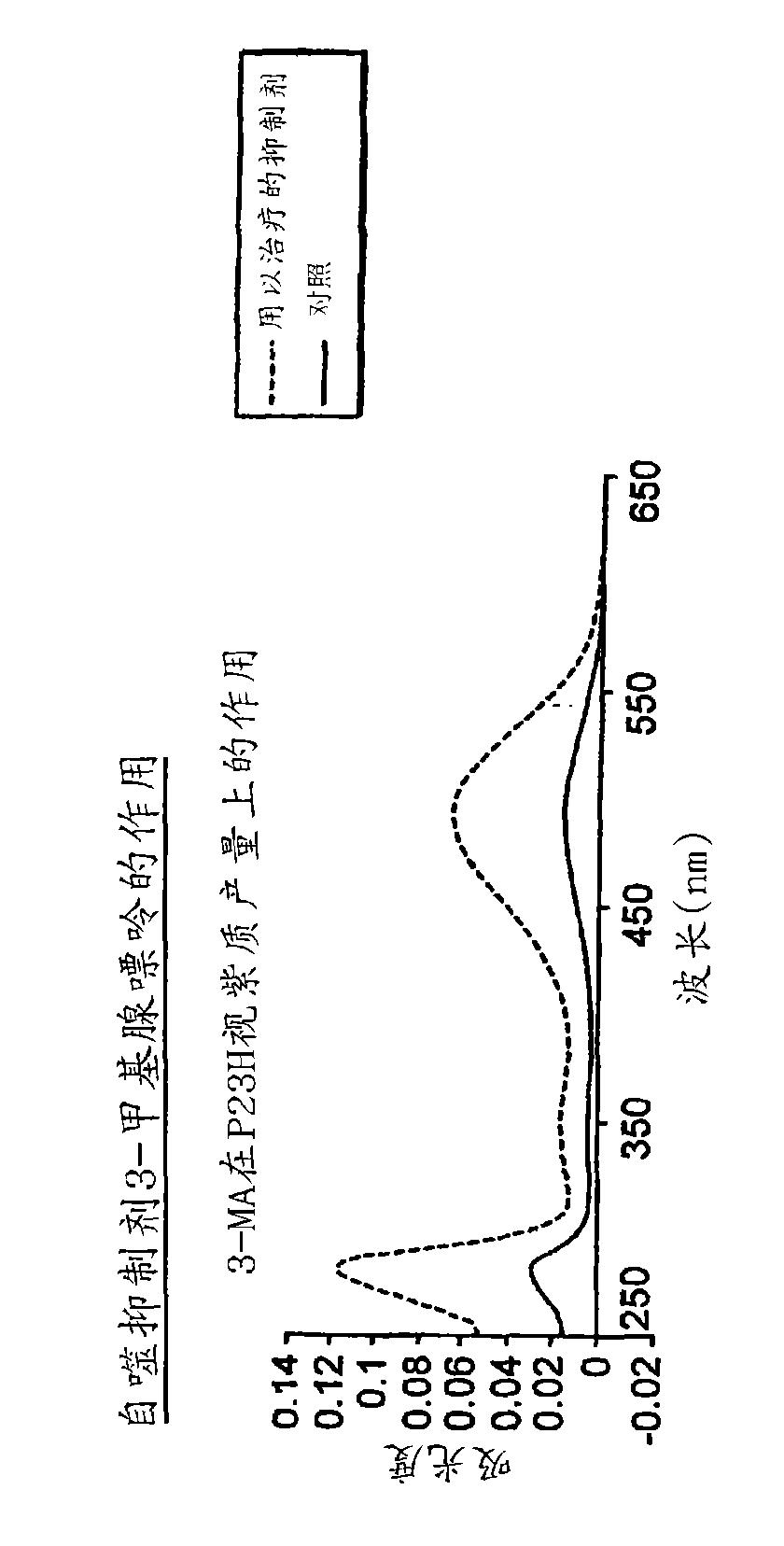
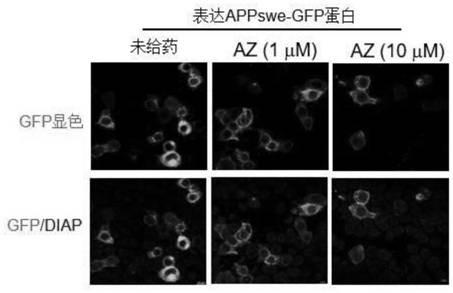
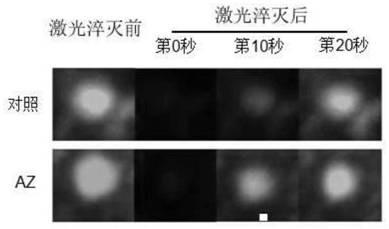
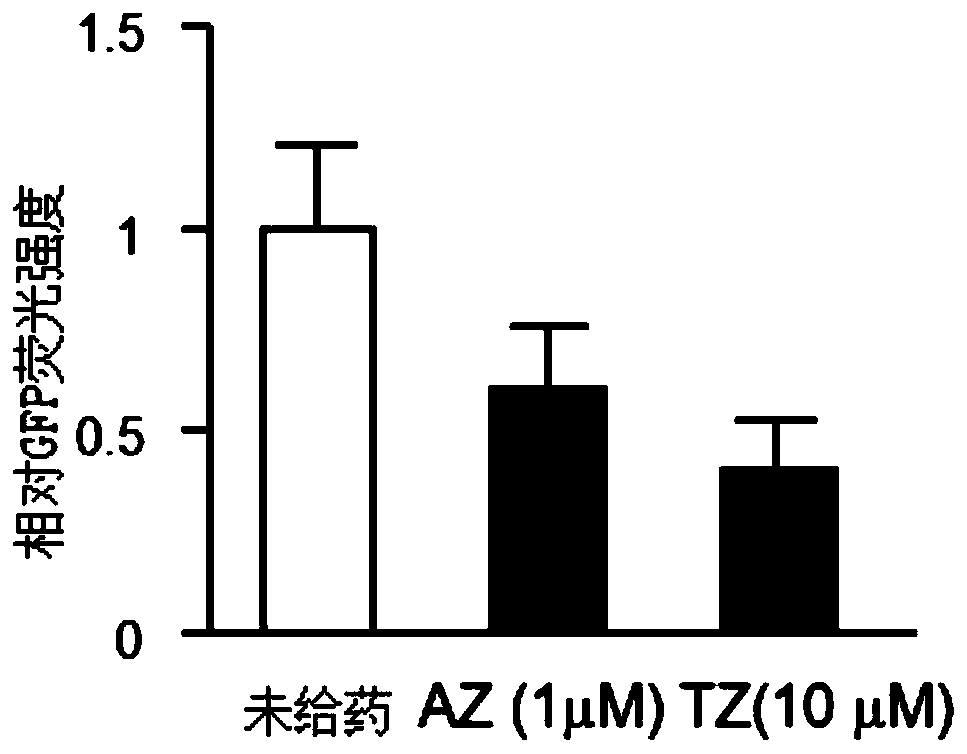
The invention relates to an application of an alfuzosin compound in prevention or treatment of Alzheimer's disease and related diseases, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The alfuzosincompound has the effects of improving mitochondrial metabolism, degrading accumulation of various pathological proteins and improving vascular endothelial cell functions. The invention provides a newpharmaceutical application of the alfuzosin compound. The new pharmaceutical application can provide a new choice for treatment of clinical related diseases. Alfuzosin, an alfuzosin isomers, TZ-md andAZ-md can be beneficially applied to Alzheimer's disease and related complications, such as seeing and hearing impairment, anemia, blood pressure instability, insomnia, depression, limb dysfunction,malnutrition, weakness, dizziness, gait instability and the like, and diseases related to protein accumulation and metabolic disorder, such as Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, dementia with Lewis bodies, multi-system atrophy and the like.
Owner:北京安塞迩生物科技有限公司
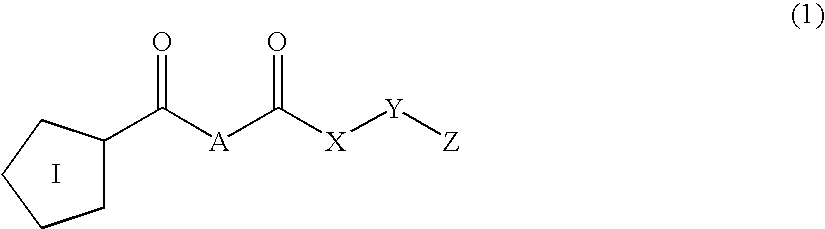
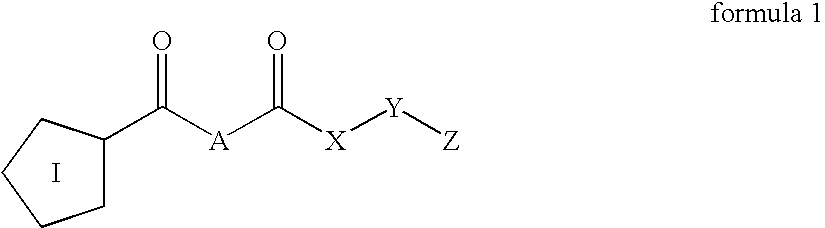
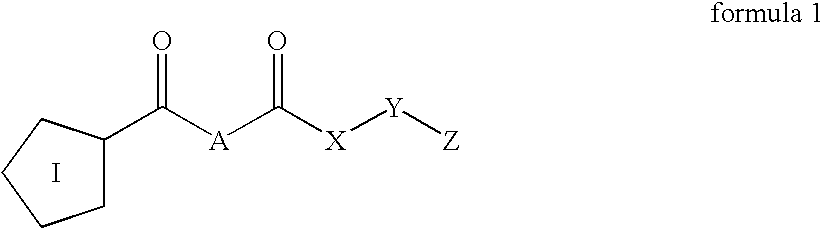
Inhibitors of prolyl endopeptidase
The present invention relates to novel inhibitors of prolyl endopeptidase of formula (1)wherein I, A, X, Y and Z are specified in the description. The compounds are useful for the treatment of diseases such as mild cognitive impairment (MCI), Alzheimer's disease, Down Syndrome, Parkinson disease and Chorea Huntington.
Owner:VIVORYON THERAPEUTICS NV
Bivalent Nucleic Acid Ligands and Uses Therefor
Genetic recognition reagents comprising bivalent nucleobases are provided that bind two strands of nucleic acid, such as an expanded repeat sequence associated with an expanded repeat disease. In one example the expanded repeat disease is a polyQ disease, such as Huntington's disease. Methods of use of the reagents are provided, including a method of binding nucleic acid, such as an expanded repeat sequence associated with an expanded repeat disease, a method of identifying the presence of a nucleic acid comprising an expanded repeat, and a method of treating an expanded repeat disease are provided.
Owner:CARNEGIE MELLON UNIV
Compositions and methods for treatment of protein misfolding diseases
InactiveUS8192986B2Simple processHigh activityCompound screeningBiocideHuntingtons choreaNGAL Protein
Disclosed are methods for identifying compounds that modulate huntingtin mediated impairment of protein degradation pathways. Compounds identified by such screens can be used as candidate drugs for the treatment of prevention of polyglutamine diseases such as Huntington's Disease.
Owner:WHITEHEAD INST FOR BIOMEDICAL RES
Method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as huntington's disease, by using coenzyme Q10
InactiveUS20060078549A1Improve motor performanceReduce weight lossBiocideOrganic chemistryHuntingtons choreaMedicine
A method of ameliorating or abrogating the effects of a neurodegenerative disorder, such as Huntington's disease, includes administering a formulation including mitochondrial coenzyme Q10 in a subject in need thereof. The formulation includes Hydro-Q Sorb®, which is a complex of coenzyme Q10 and cyclodextrin.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPT OF VETERANS AFFAIRS
Novel human ependymin-like protein
InactiveUS20040014947A1Efficient secretionHigh protein yieldCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsPeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaMammal
The invention provides an ependymin-like protein derived a mammal, or its partial peptide or its precursor protein, or a salt thereof; a signal peptide; a DNA coding for the protein, etc. a recombinant vector; a transformant; a method of producing the protein; a pharmaceutical composition comprising the protein, etc. or DNA, an antibody against the protein, etc.; and a method for screening and a screening kit for compounds promoting the function of the protein. The protein, its partial peptide or a salt thereof has physiological activities such as a nerve-extending or nerve-regenerating activity, a gliacyte stimulating activity, and so on. The protein, etc. or the DNA is useful as a therapeutic or prophylactic agent for Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), dementia or cerebellar degeneration. The antibody against the protein, etc. can be used in the assay of the protein, etc. in a test sample. Furthermore, the protein, etc. is useful as a screening reagent for compounds or their salts capable of promoting the function of the protein.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com