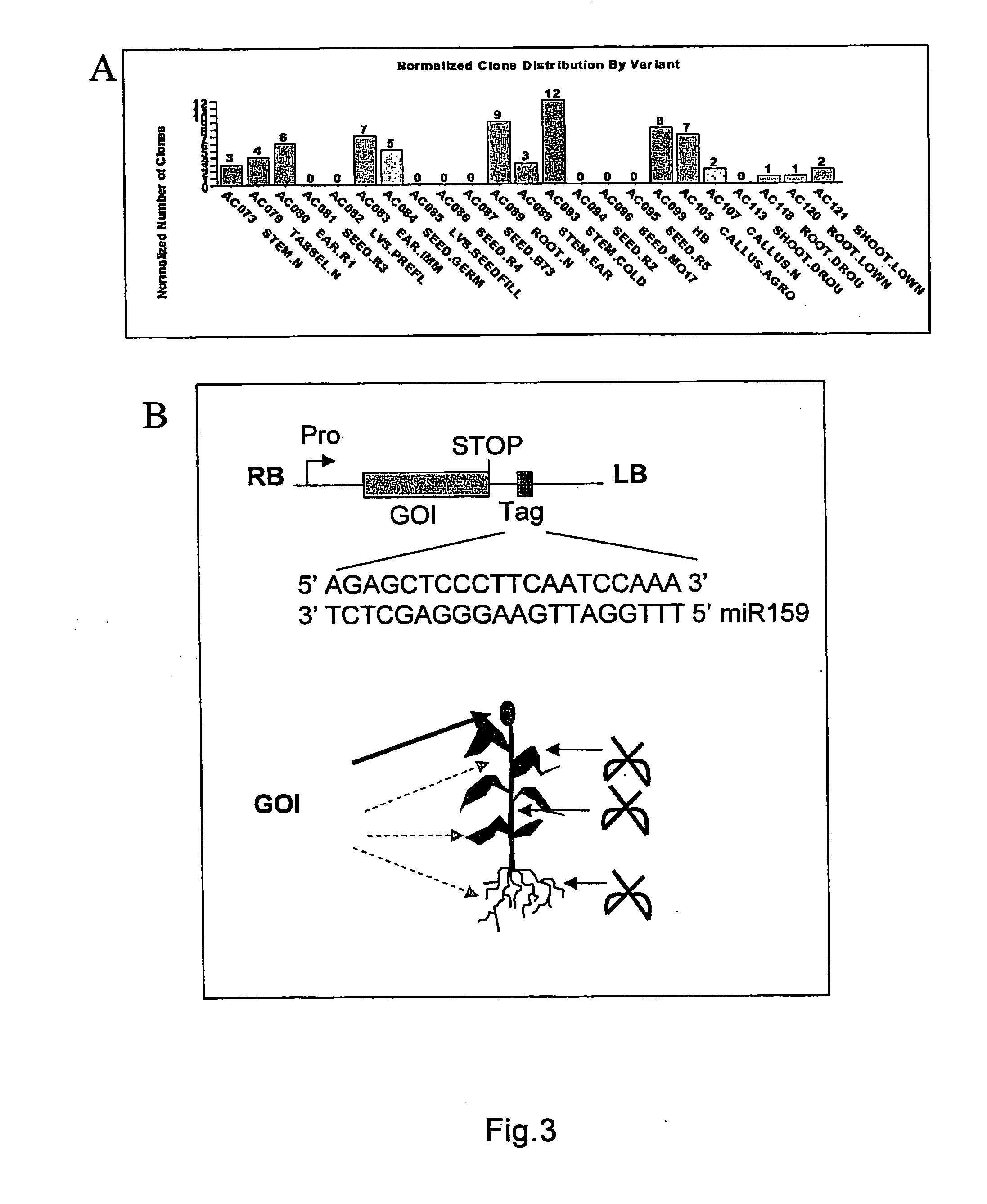
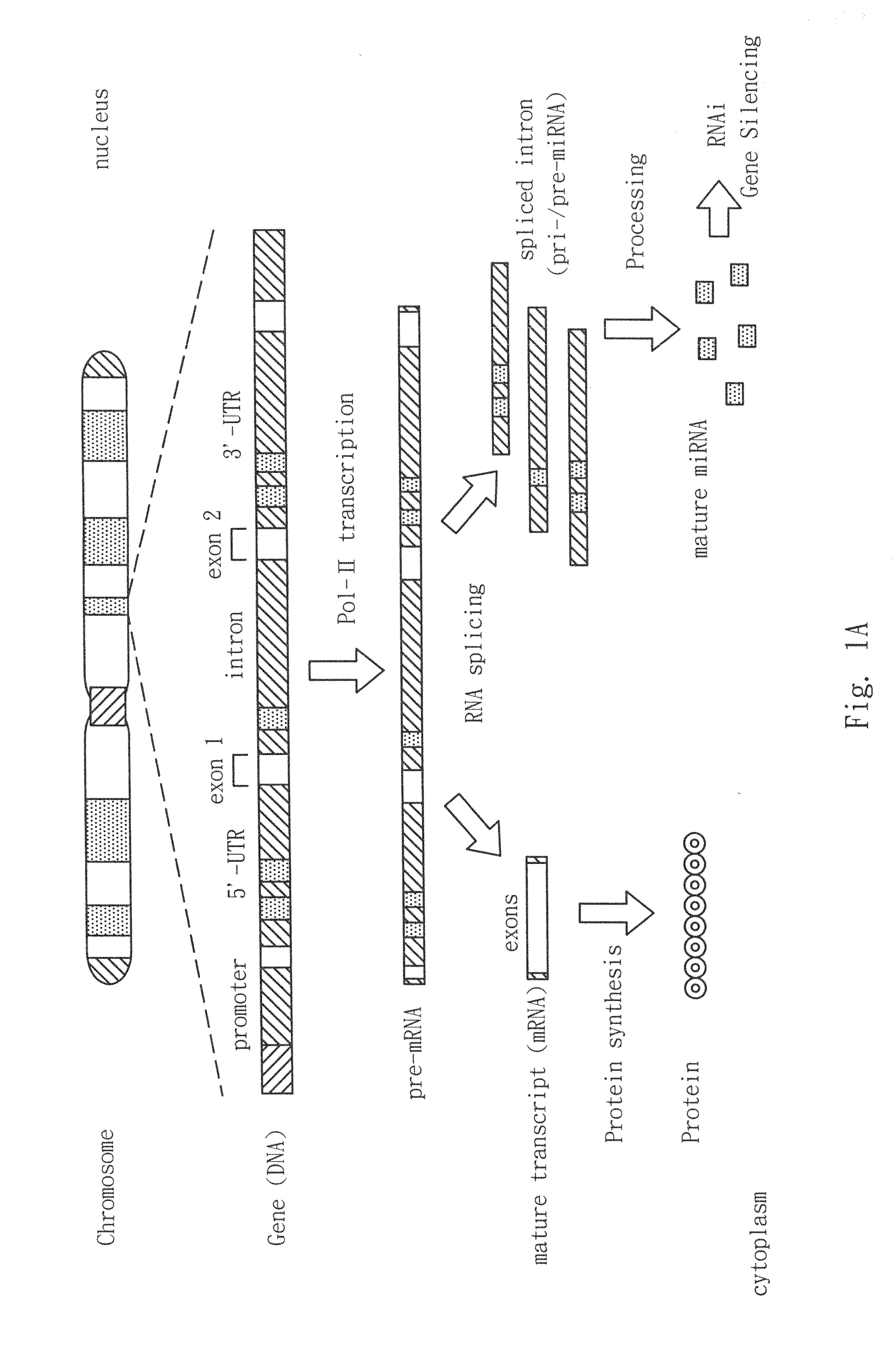
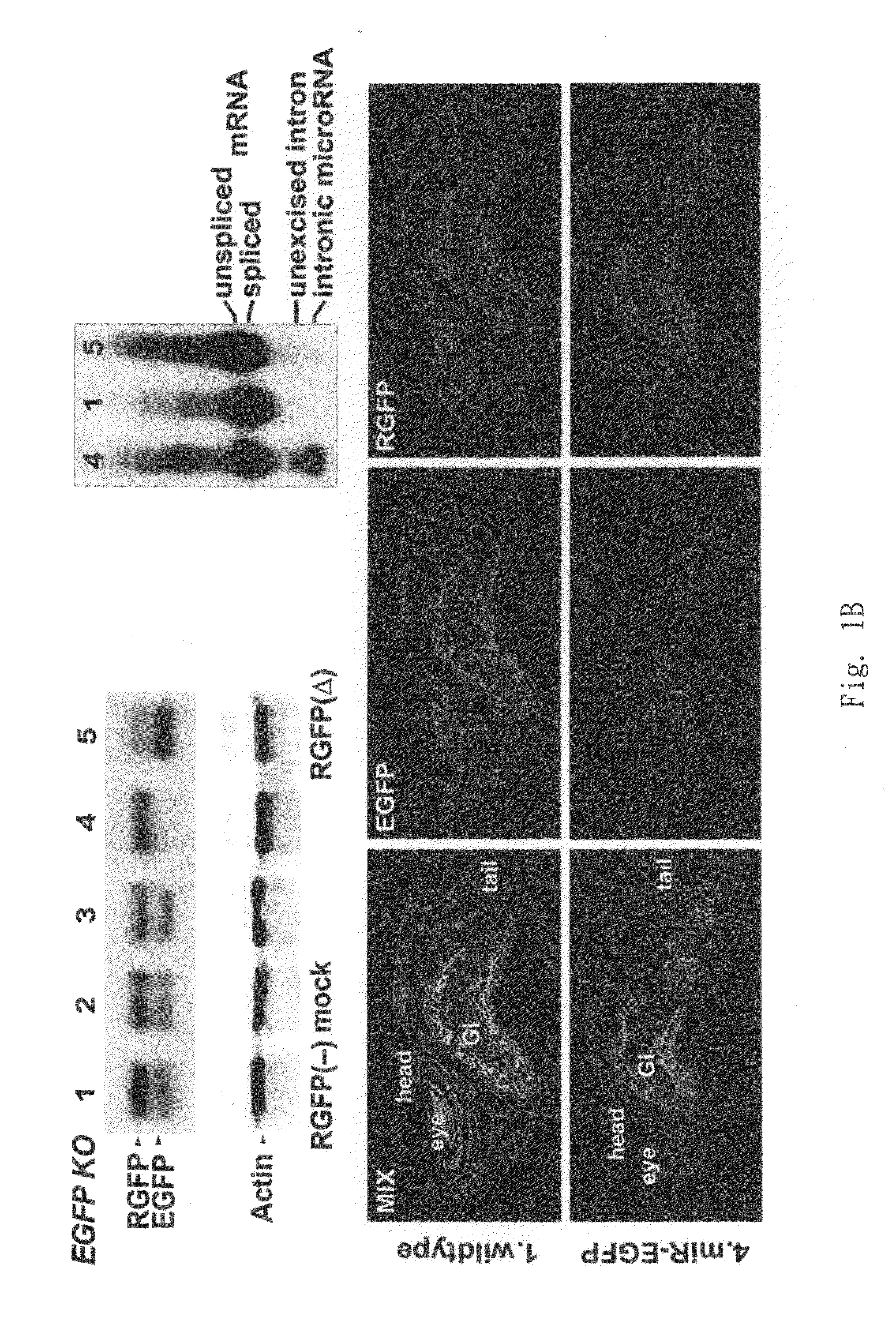
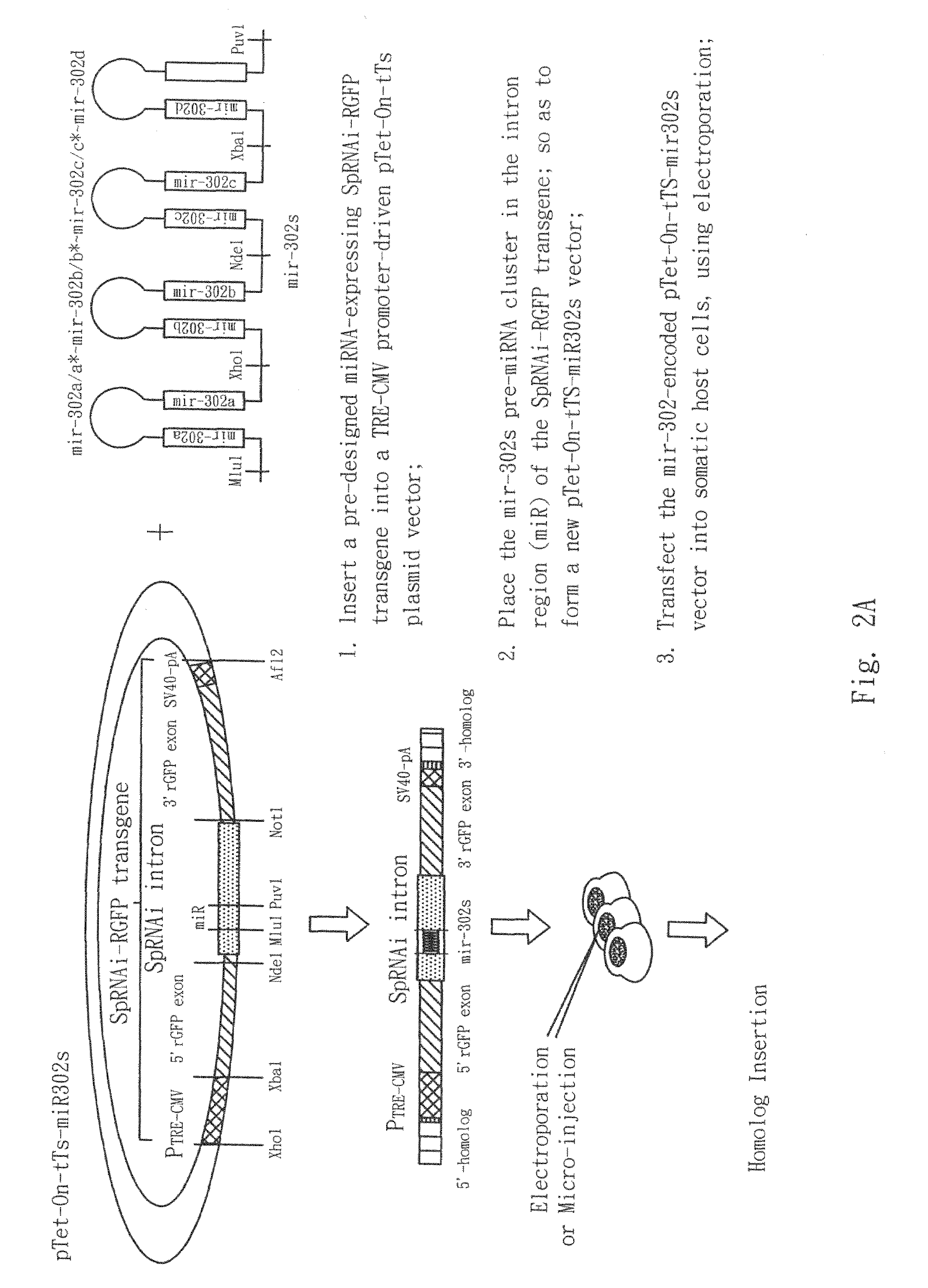
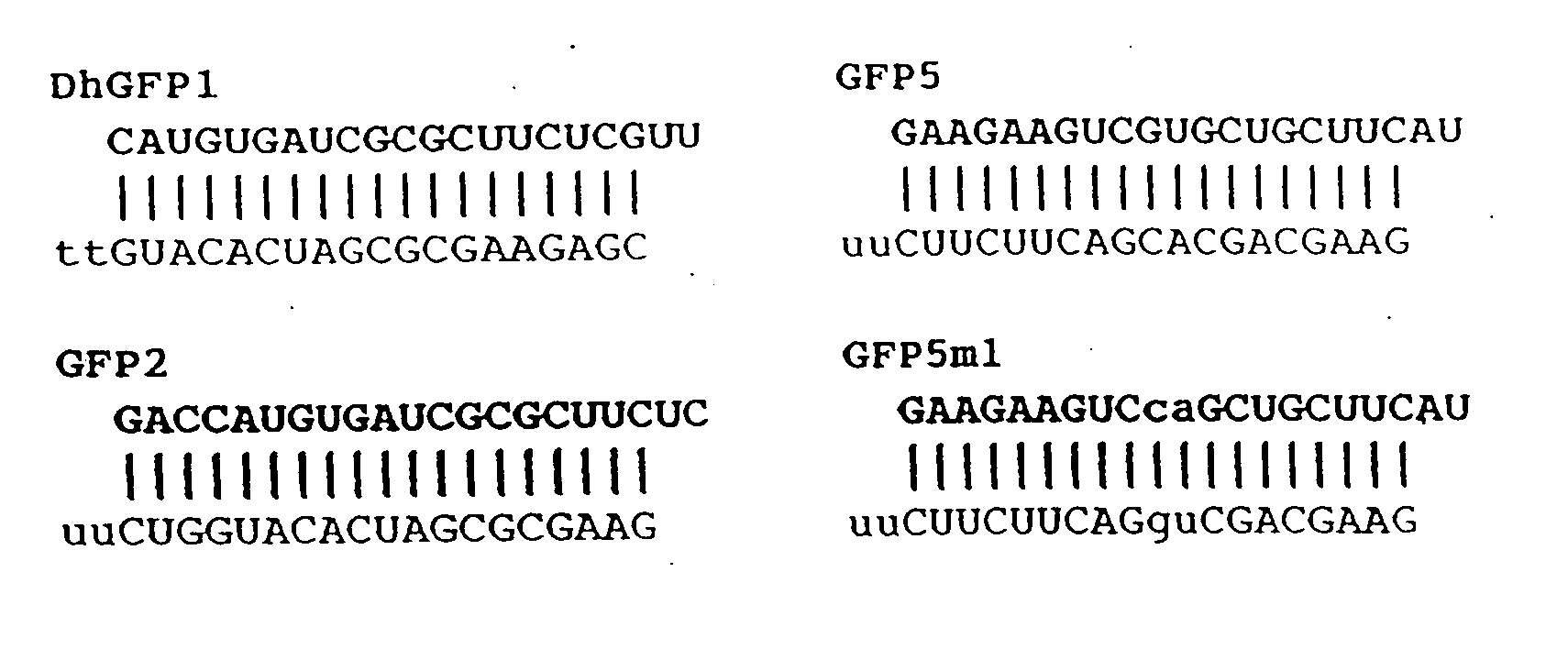Patents
Literature
892 results about "Small RNA" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
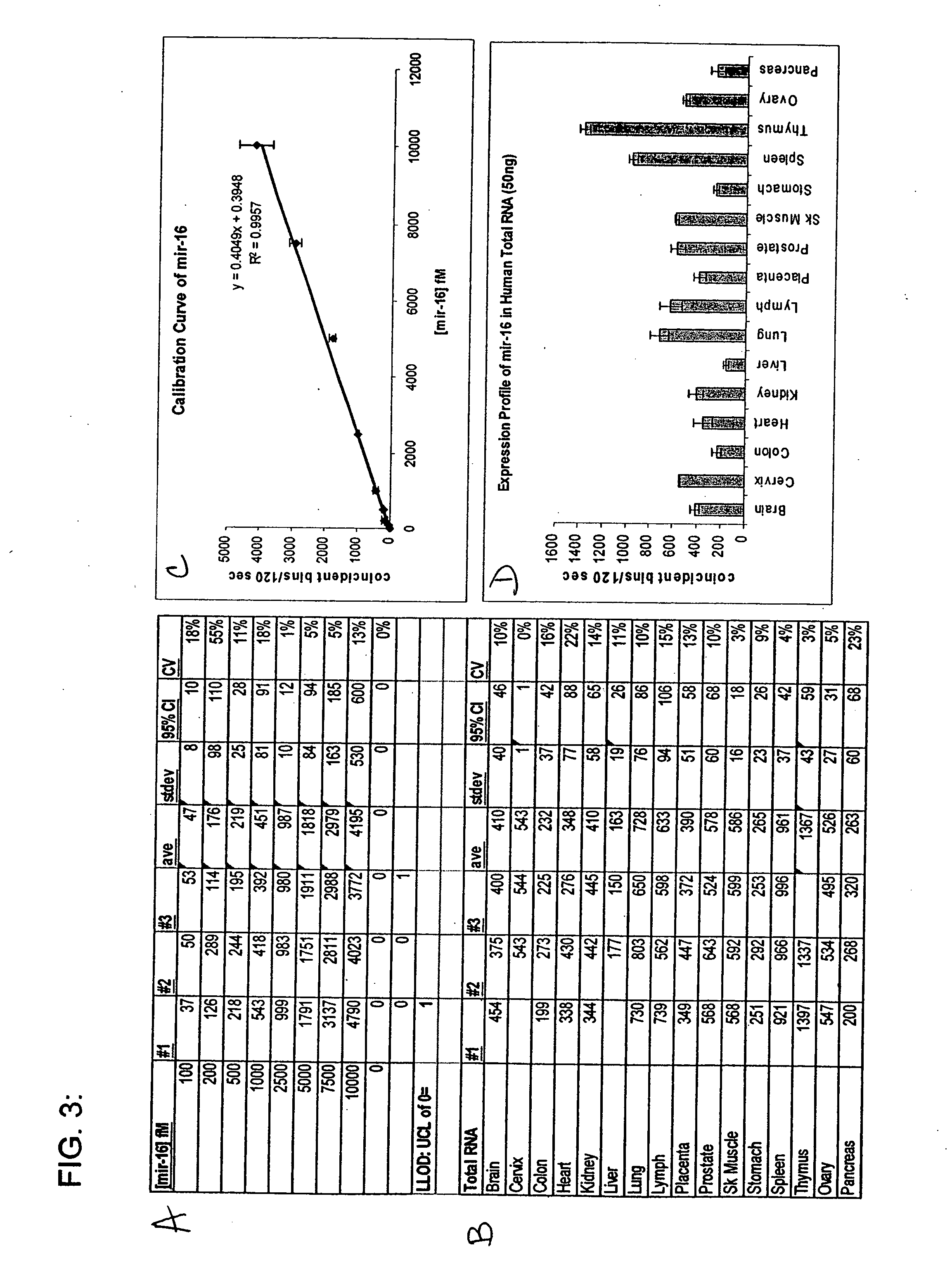
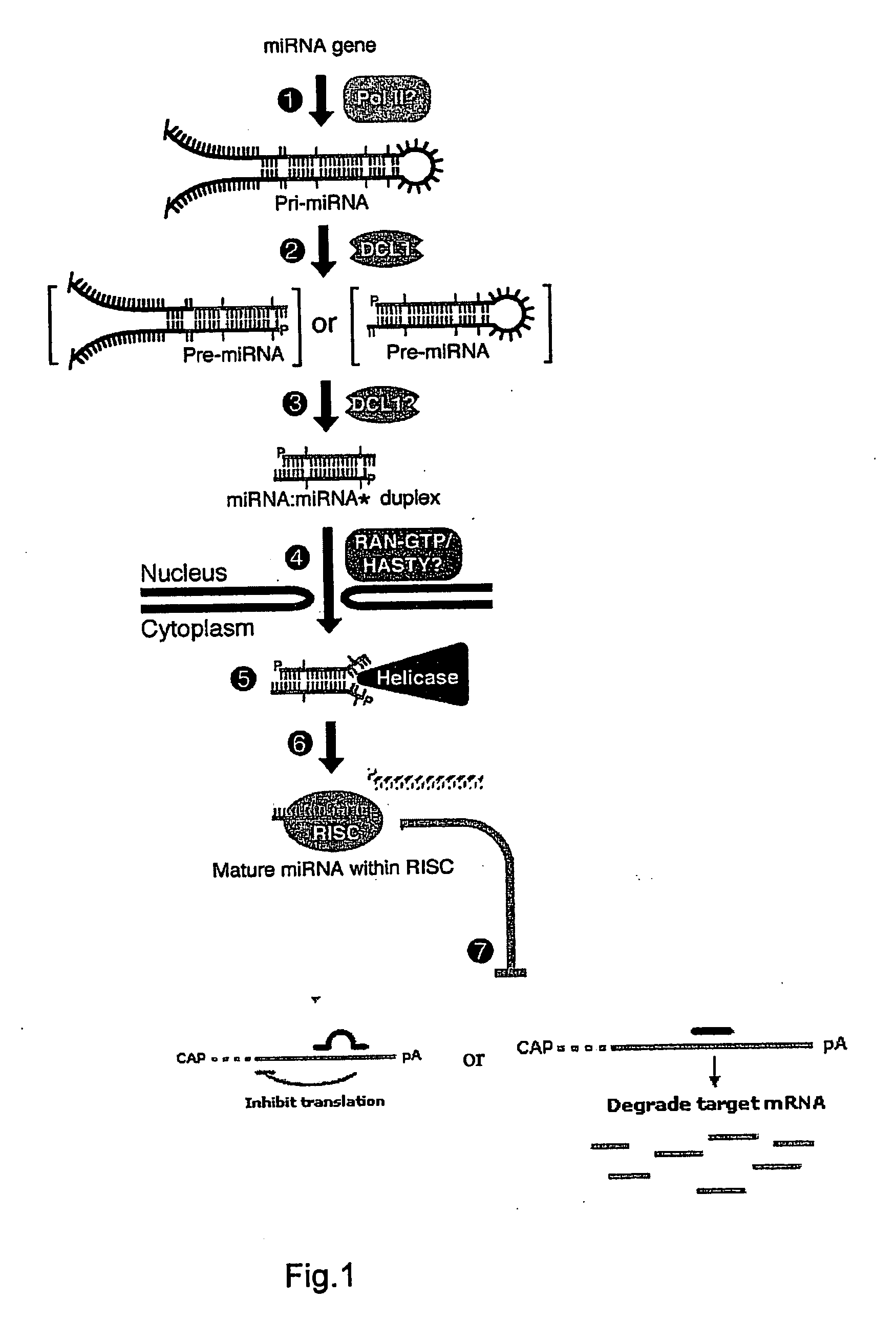
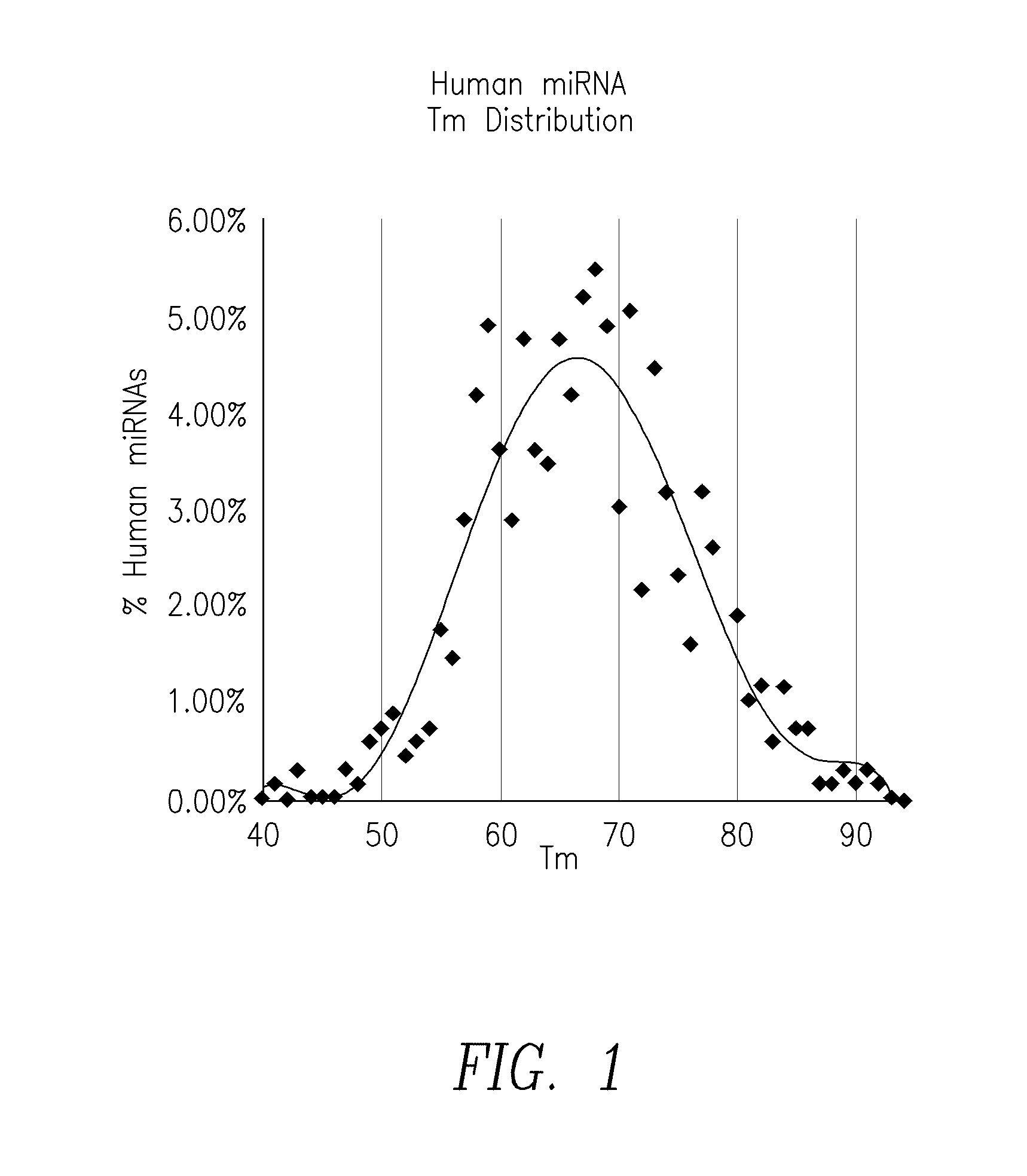
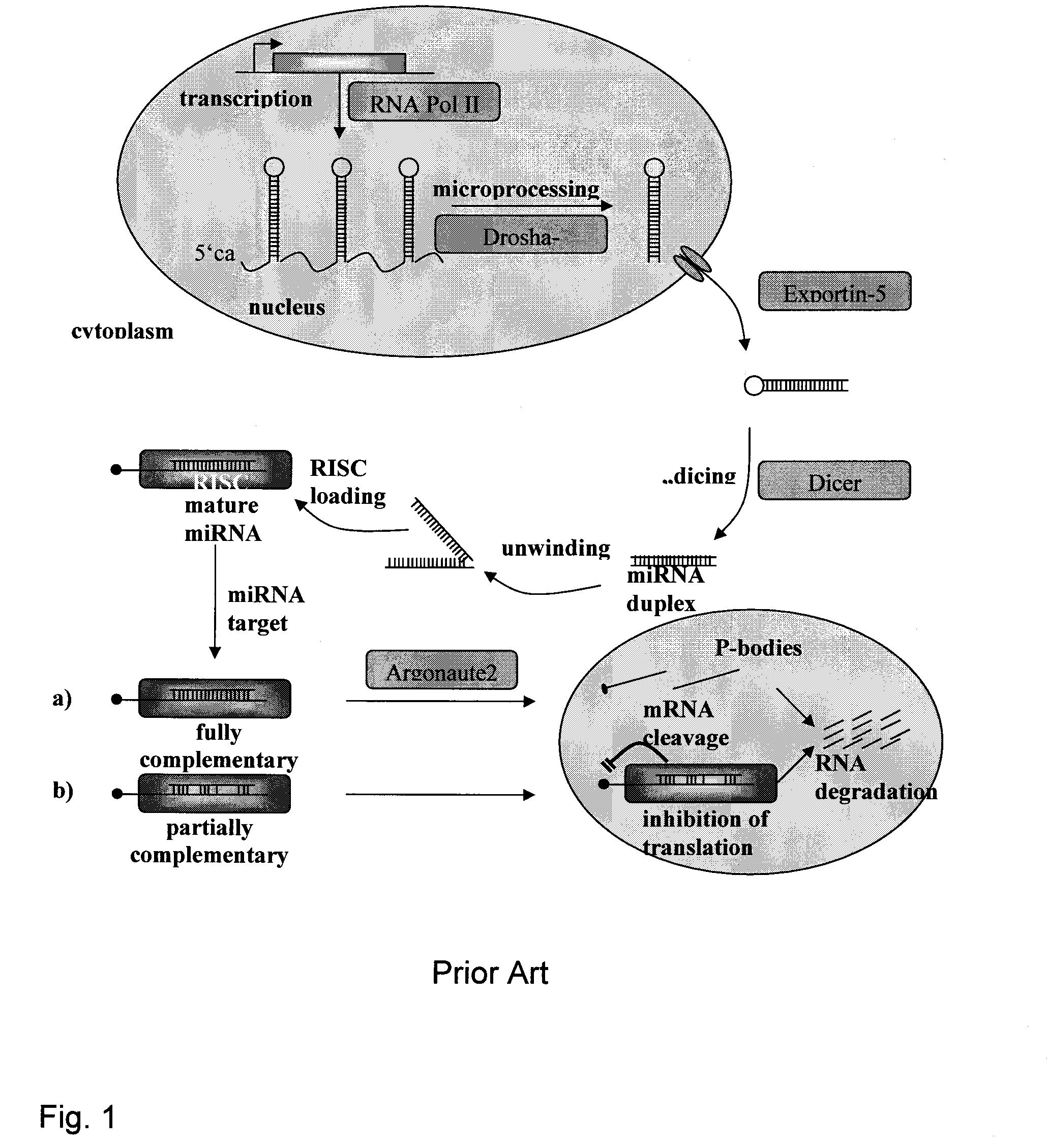
Small RNA are <200 nt (nucleotide) in length, and are usually non-coding RNA molecules. RNA silencing is often a function of these molecules, with the most common and well-studied example being RNA interference (RNAi), in which endogenously expressed microRNA (miRNA) or exogenously derived small interfering RNA (siRNA) induces the degradation of complementary messenger RNA. Other classes of small RNA have been identified, including piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) and its subspecies repeat associated small interfering RNA (rasiRNA). Small RNA "is unable to induce RNAi alone, and to accomplish the task it must form the core of the RNA–protein complex termed the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), specifically with Argonaute protein". Also, mRNA is used in transcription.
Novel oligonucleotide compositions and probe sequences useful for detection and analysis of non coding RNAs associated with cancer
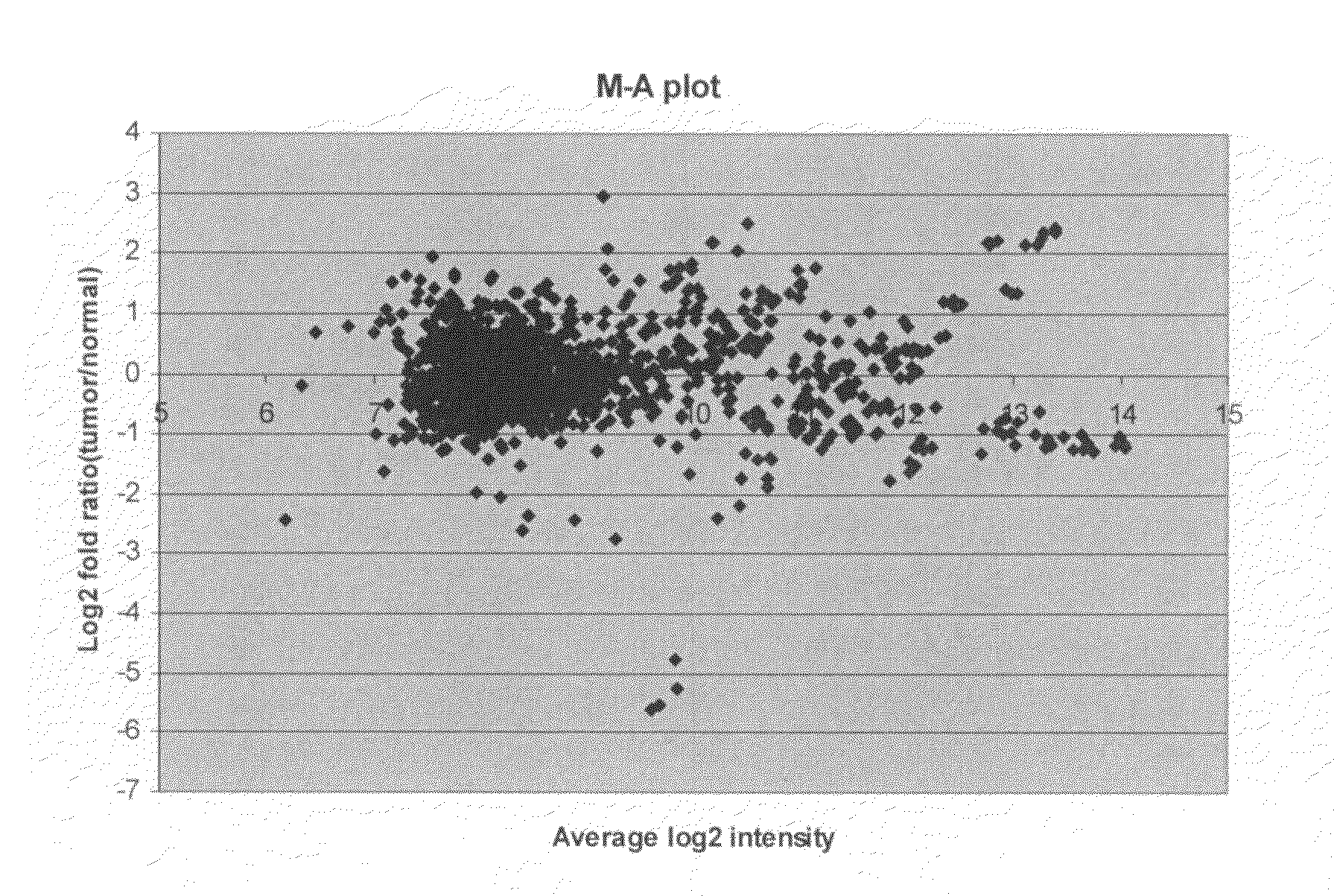
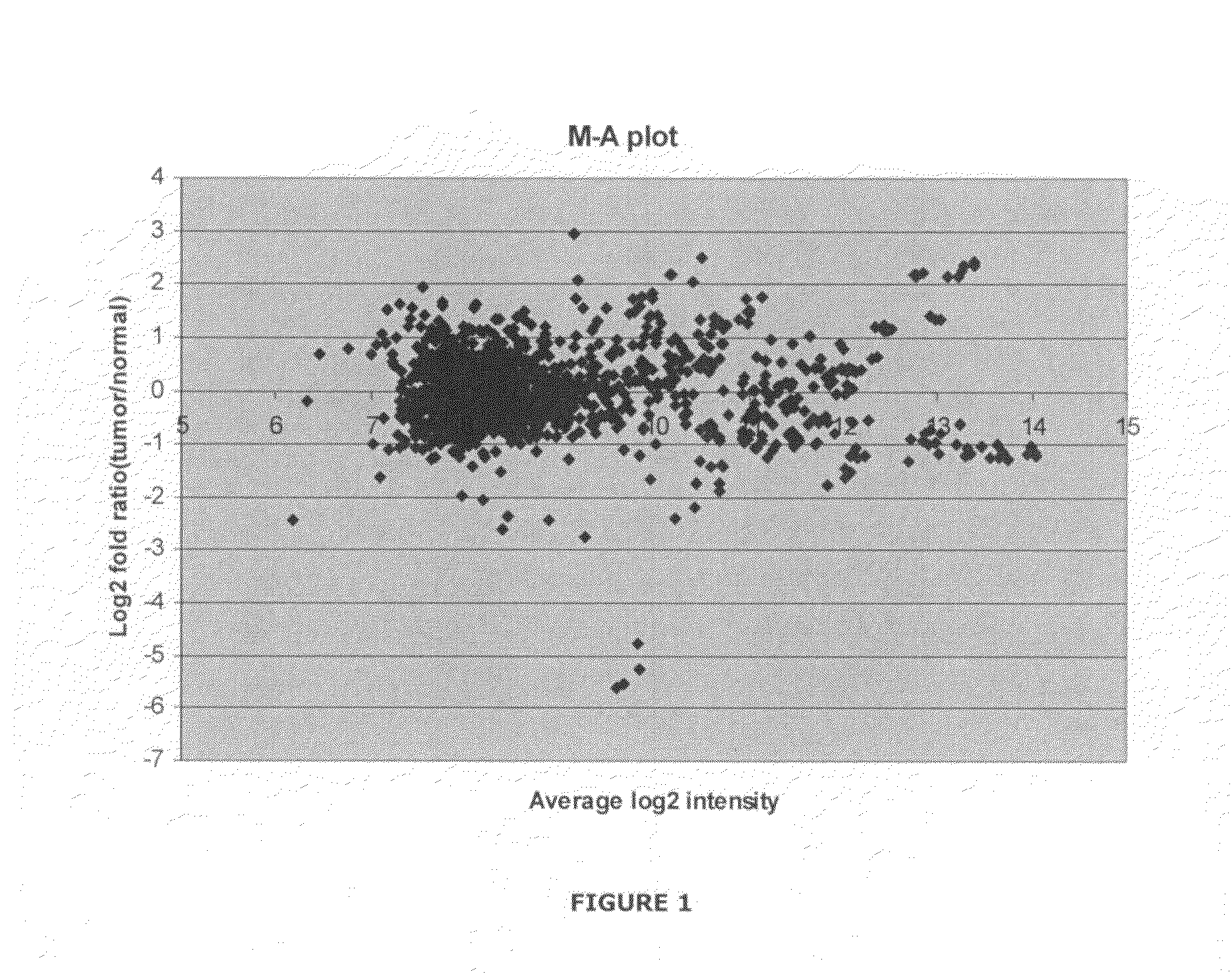
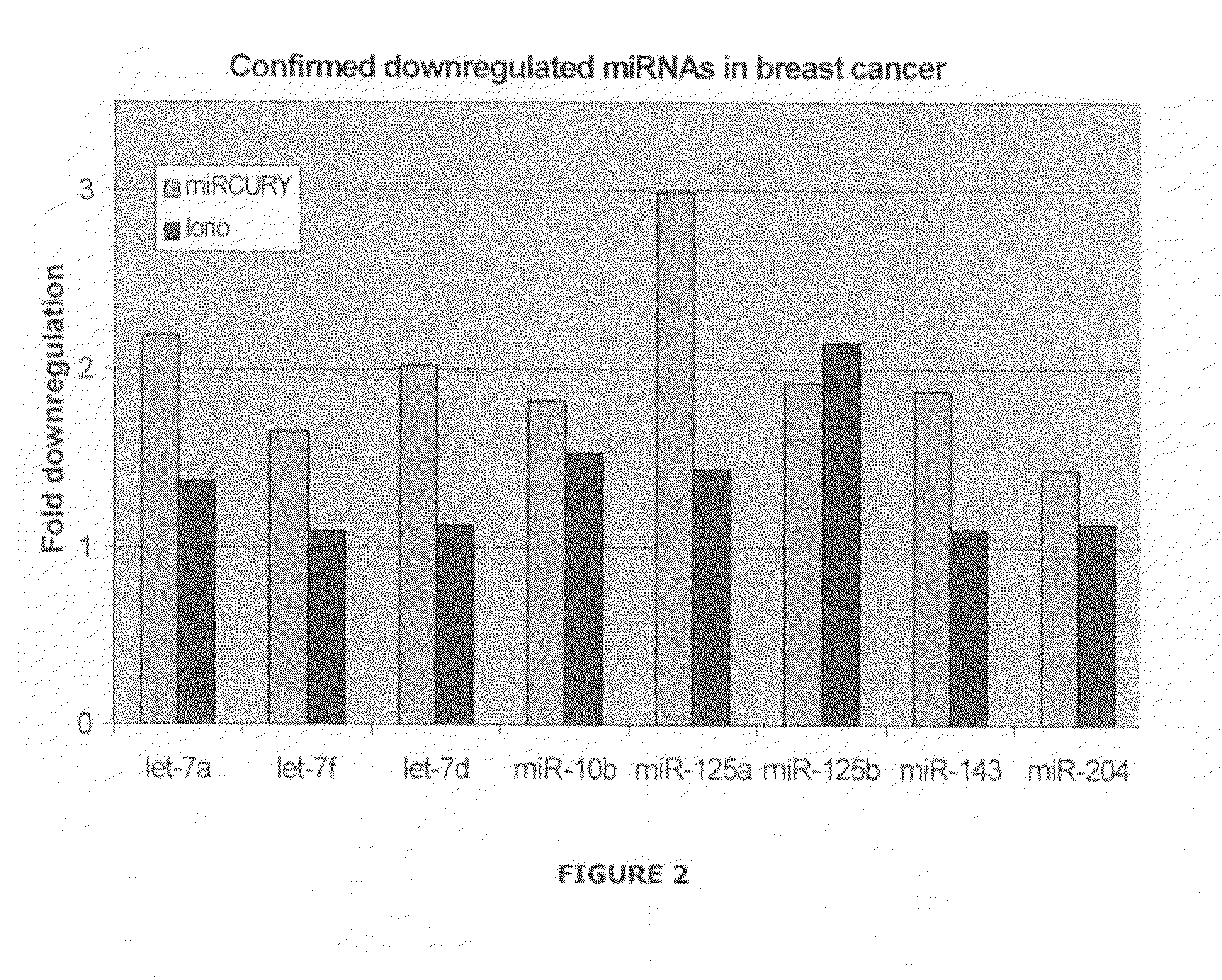
The invention relates relates to ribonucleic acids and oligonucleotide probes useful for detection and analysis of non-coding RNAs, such as microRNAs and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), in particular small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs), and their precursors which are associated with cancer, and which can be used for characterising breast cancers or suspected cancer.
Owner:EXIQON AS
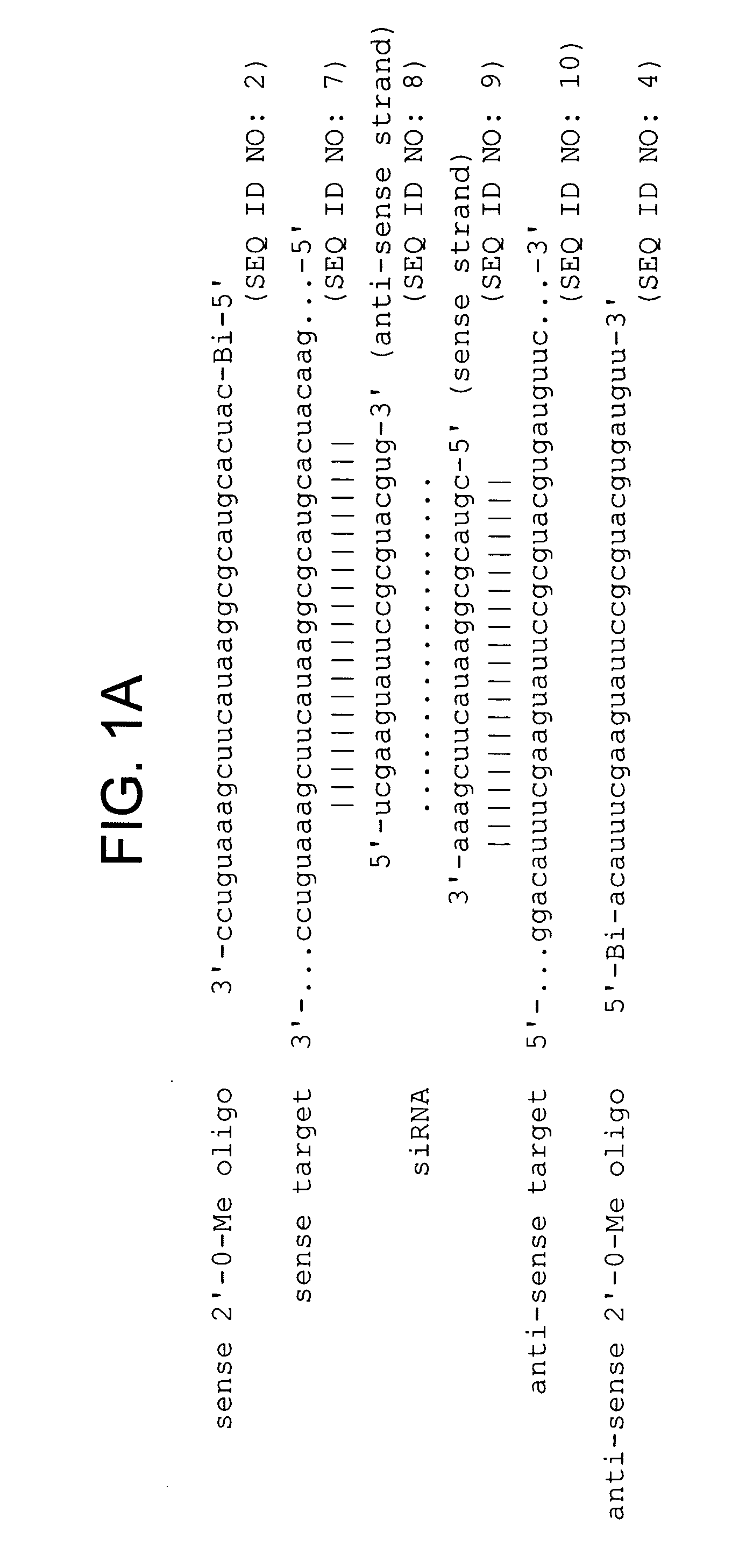
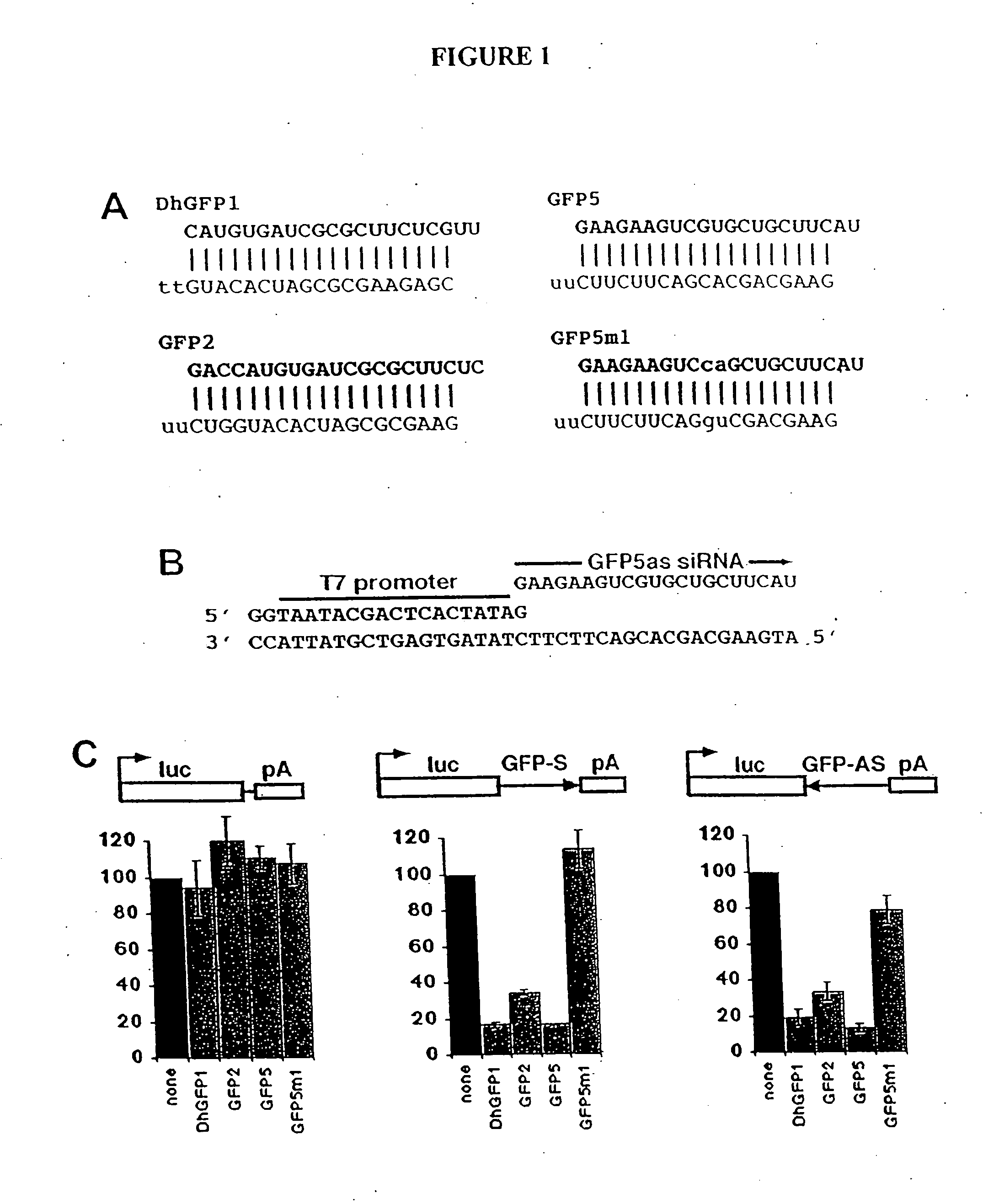
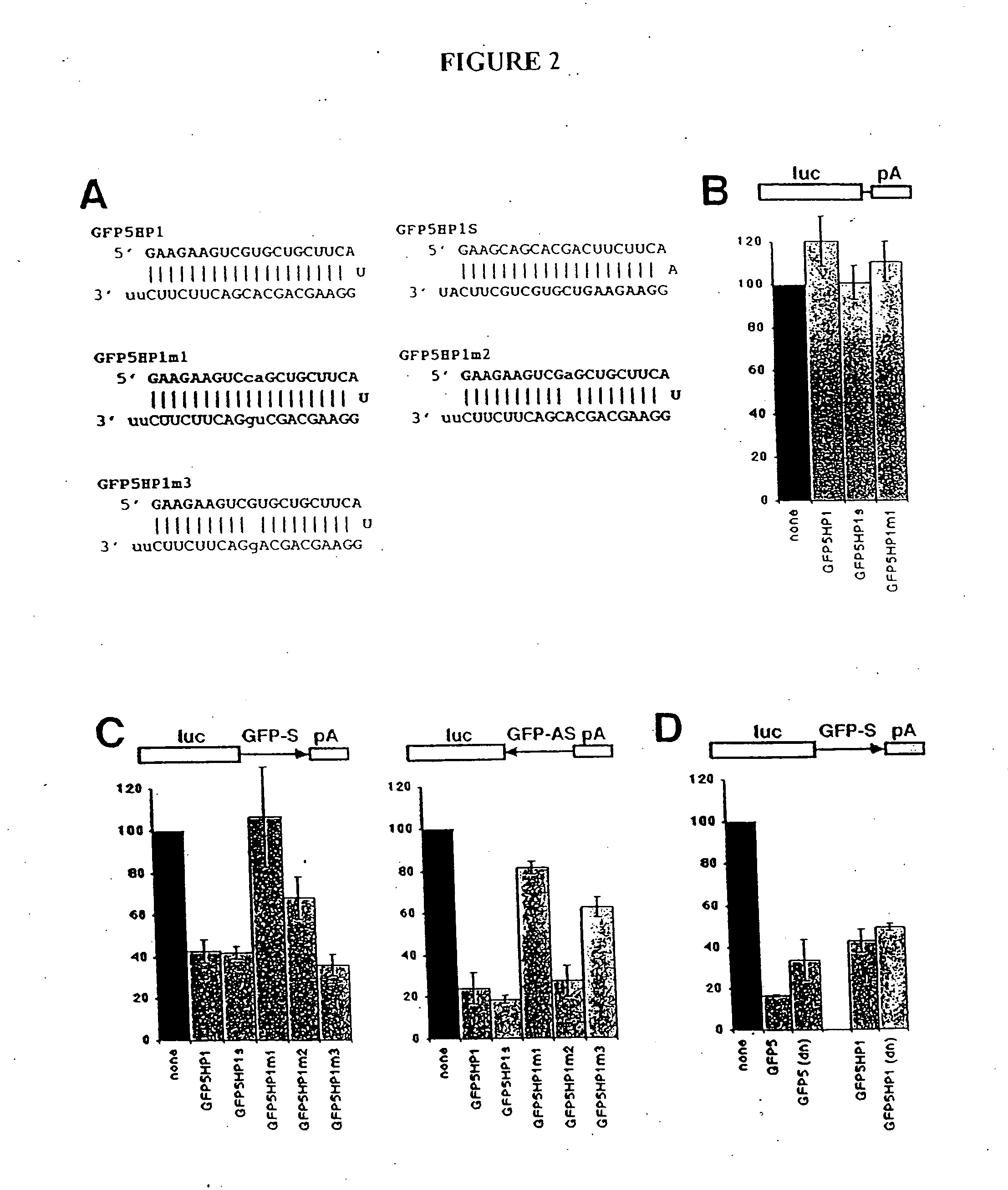
Sequence-specific inhibition of small RNA function
ActiveUS20050227256A1Suitable for useOrganic active ingredientsActivity regulationRegulatory rnaCytokine
The present invention relates to the discovery of a method for inhibiting RNA silencing in a target sequence-specific manner. RNA silencing requires a set of conserved cellular factors to suppress expression of gene-encoded polypeptide. The invention provides compositions for sequence-specific inactivation of the RISC component of the RNA silencing pathway, and methods of use thereof. The RISC inactivators of the present invention enable a variety of methods for identifying and characterizing miRNAs and siRNAs, RISC-associated factors, and agents capable of modulating RNA silencing. Therapeutic methods and compositions incorporating RISC inactivators and therapeutic agents identified through use of RISC inactivators are also featured.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS UNIV OF
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
ActiveUS20030059944A1Prevents sequenceHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral life cycle
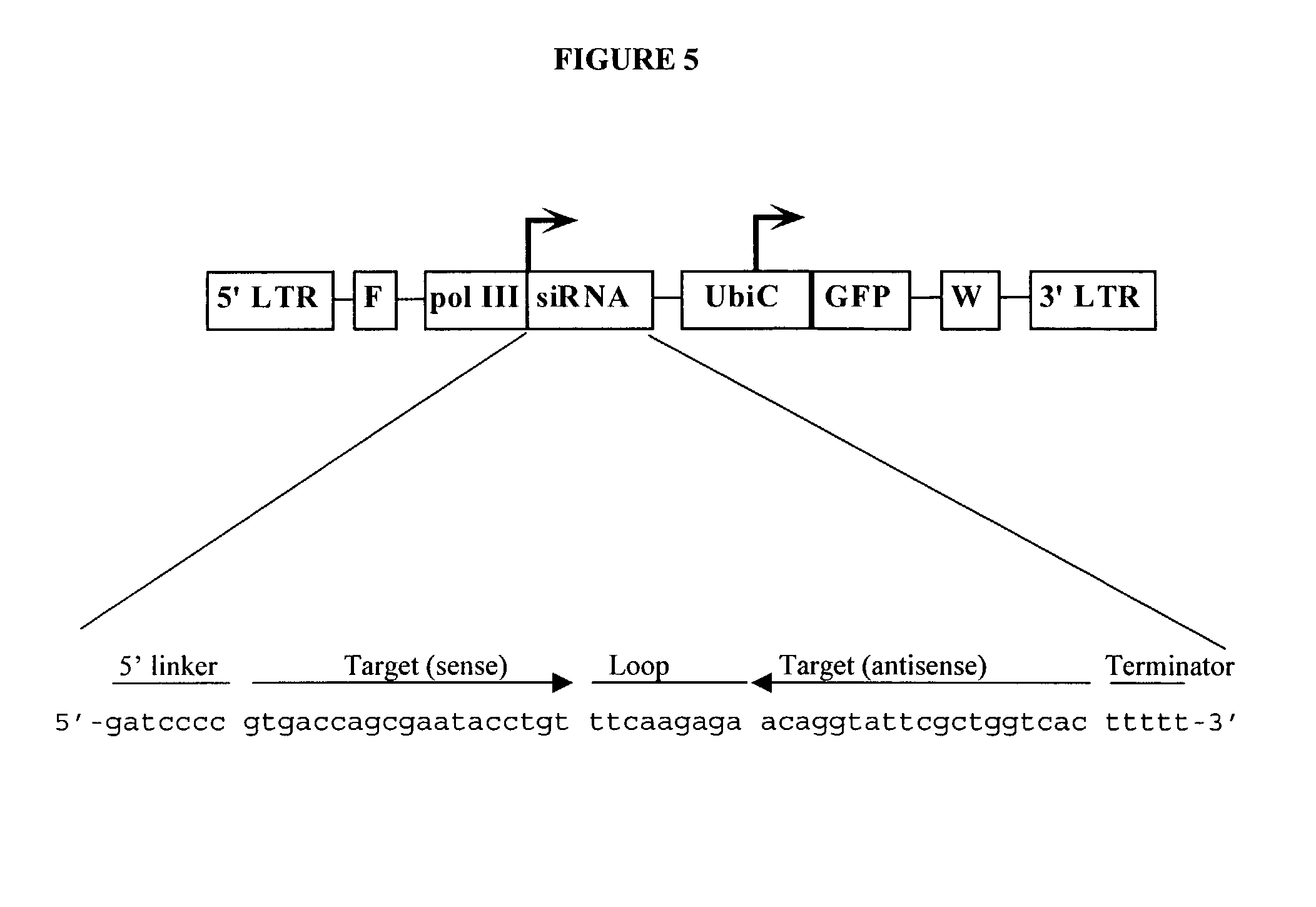
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Methods and compositions for detection of small interfering RNA and micro-RNA
InactiveUS20060019258A1Improve survivalDetermining for survivalSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementTreatment effectPhosphate
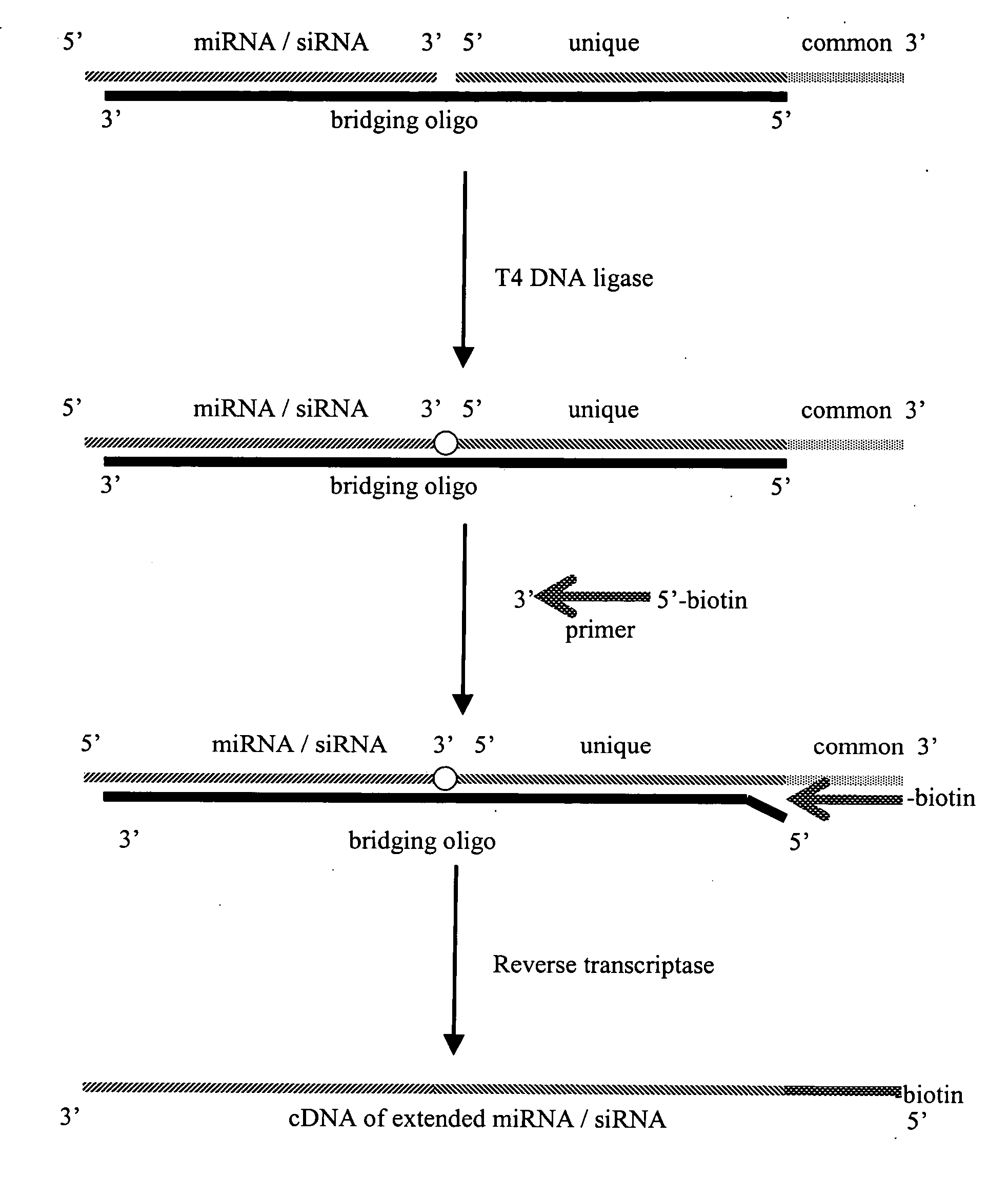
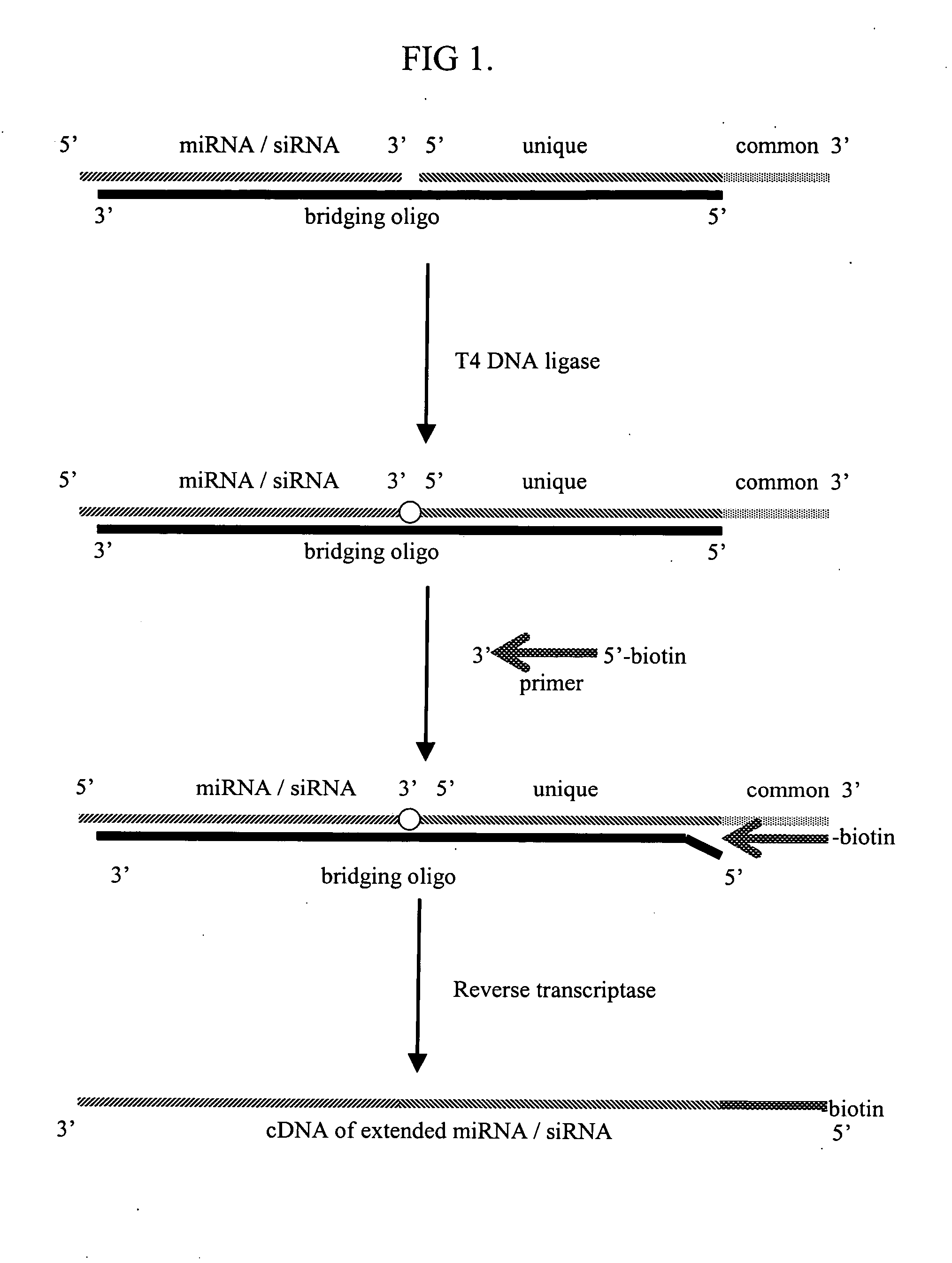
The invention provides a method of distinguishing small RNA from mRNA by contacting a biological isolate with a phosphate reactive reagent having a label moiety under conditions wherein the label moiety is preferentially added to the 5′ phosphate of small RNA over the 5′ cap structure of mRNA and distinguishing the small RNA from the mRNA according to the presence of the label. The invention further provides a method of identifying a plurality of different small RNAs by adding a unique extension sequences to different small RNA sequences and identifying the extended small RNA sequences. Furthermore, the invention provides diagnostic methods for determining presence of a disease or condition such as cancer. Also provided are prognostic methods for determining progression of a disease or condition or for monitoring effectiveness of a treatment for a disease or condition
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Pharmaceutical Composition
InactiveUS20100004320A1Reduce depressionEffectively repressedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNucleotideNucleobase
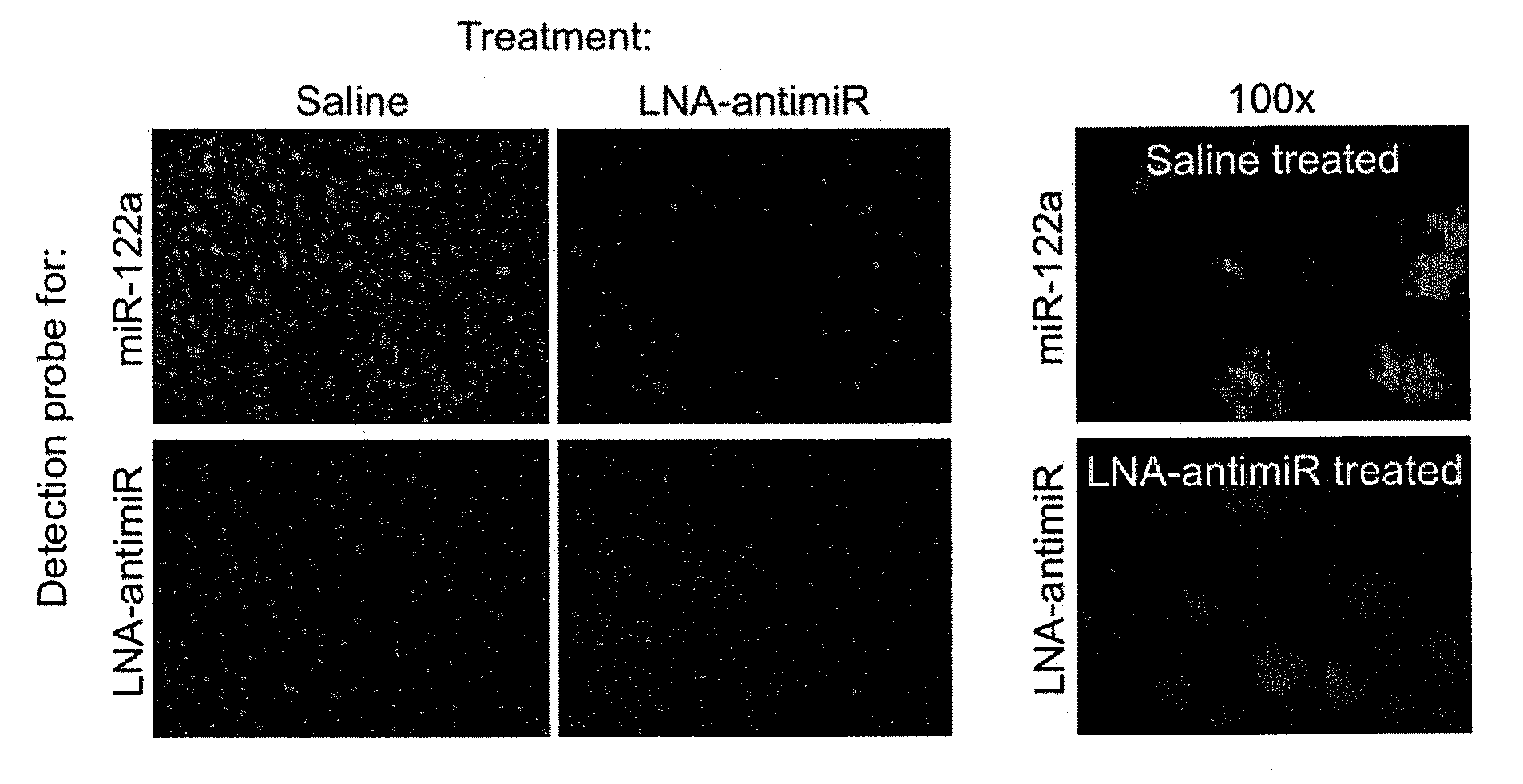
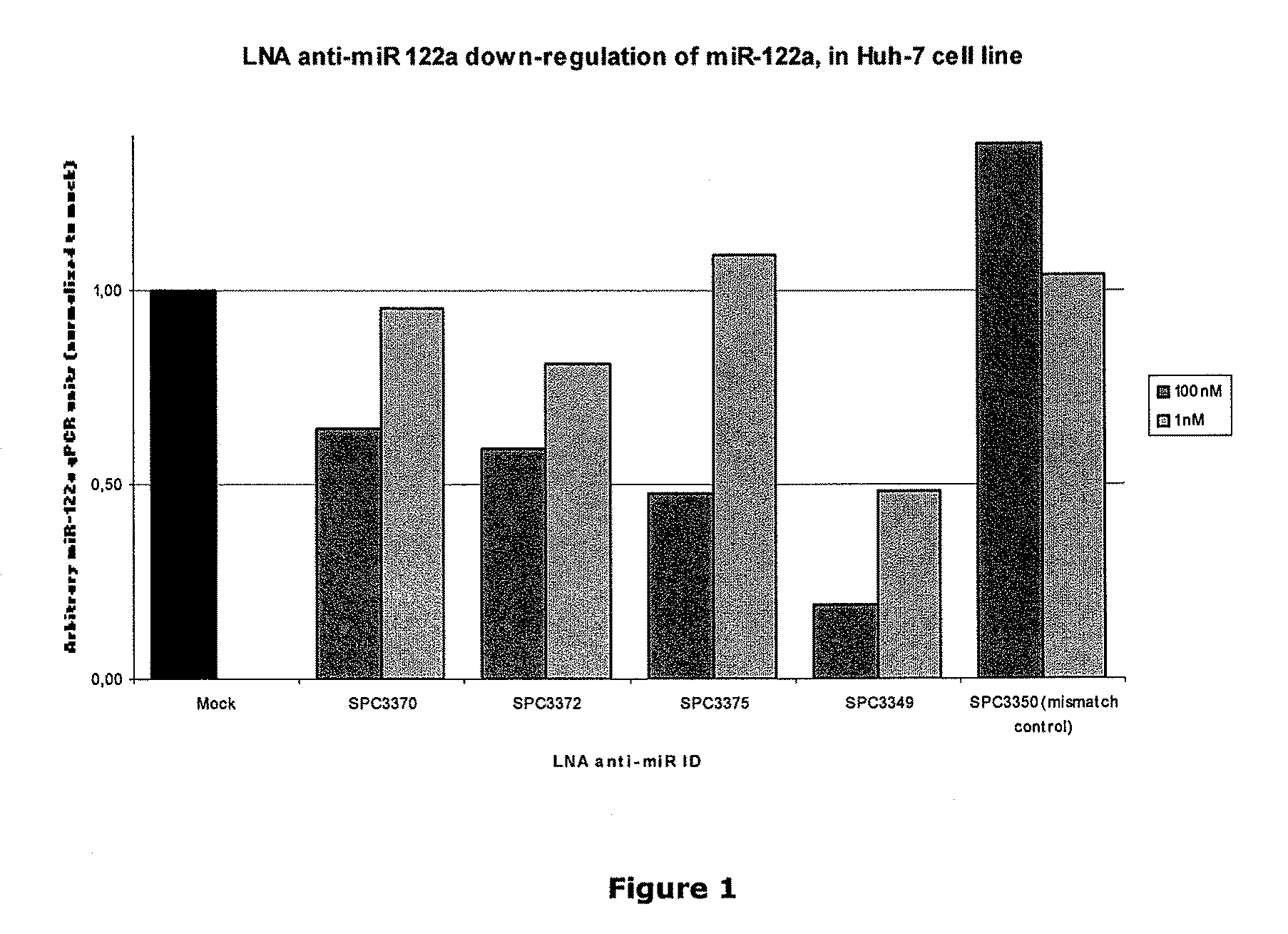
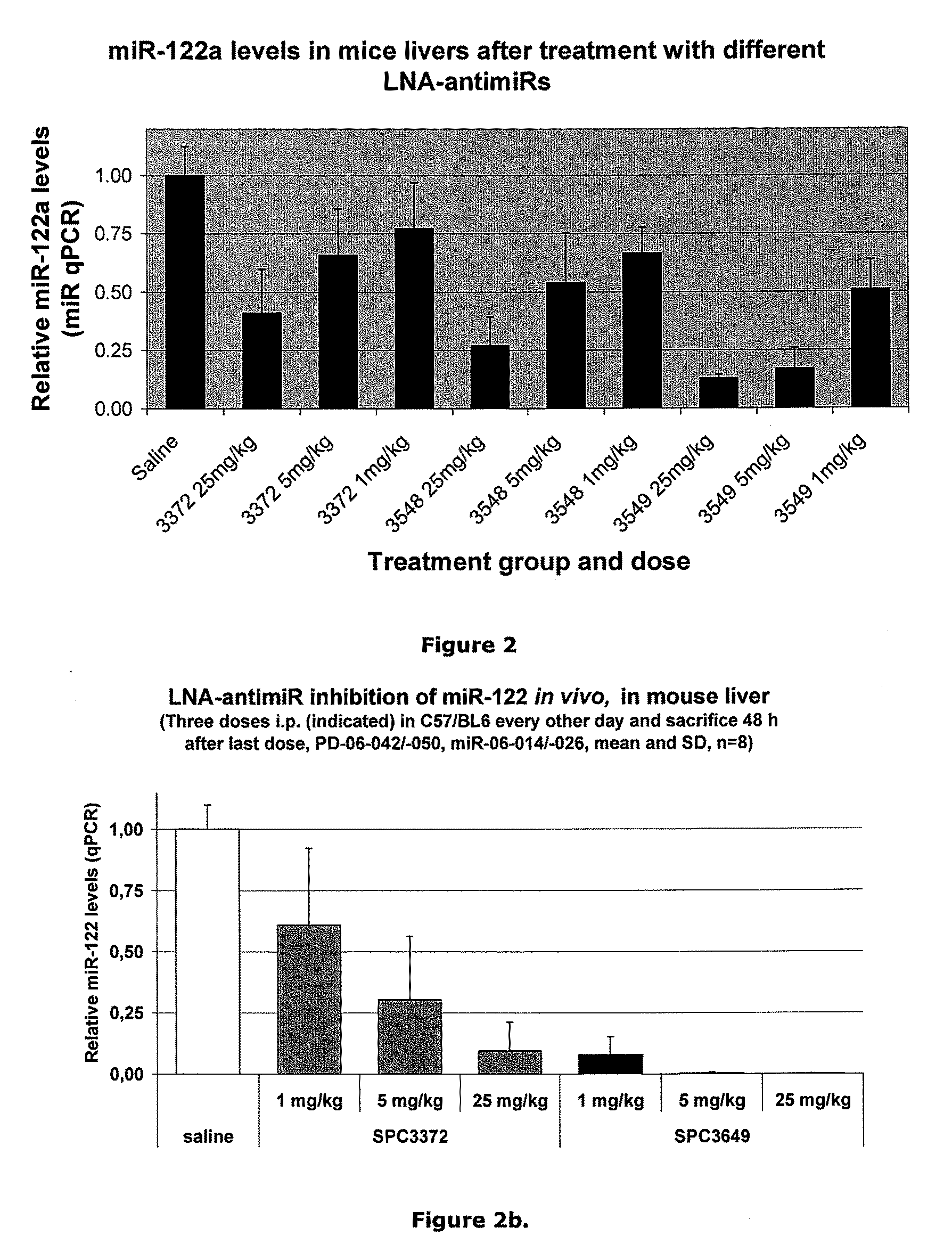
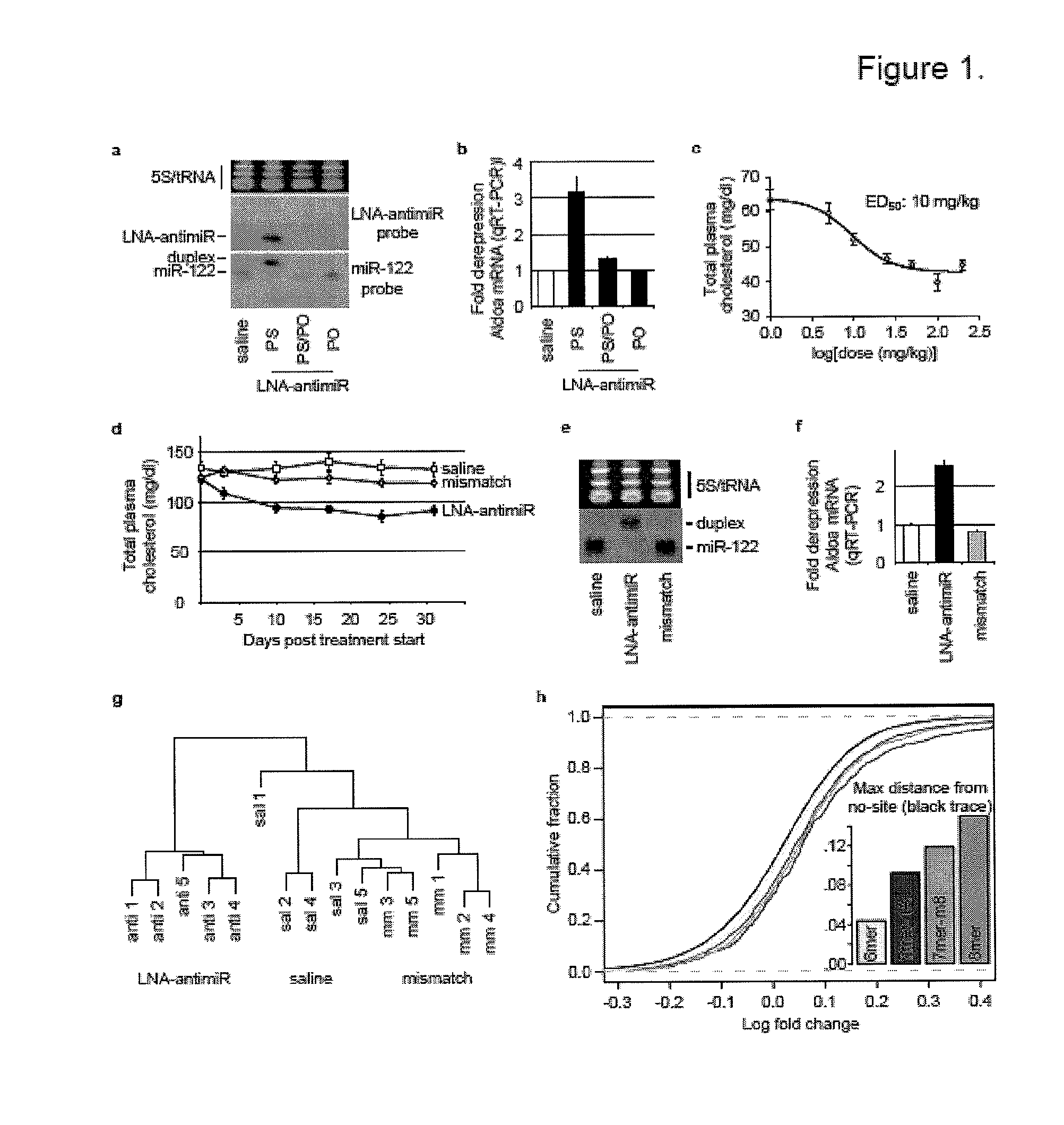
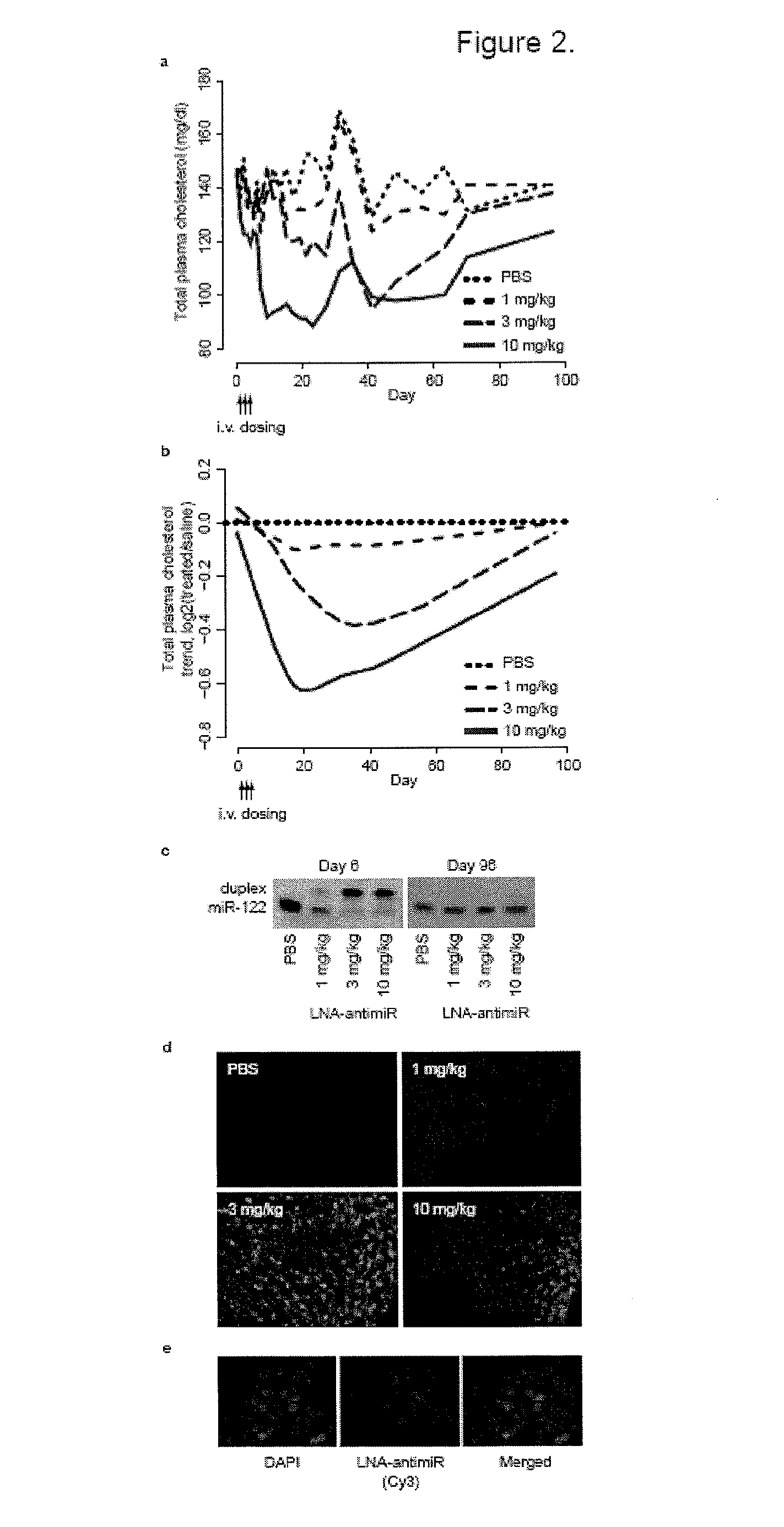
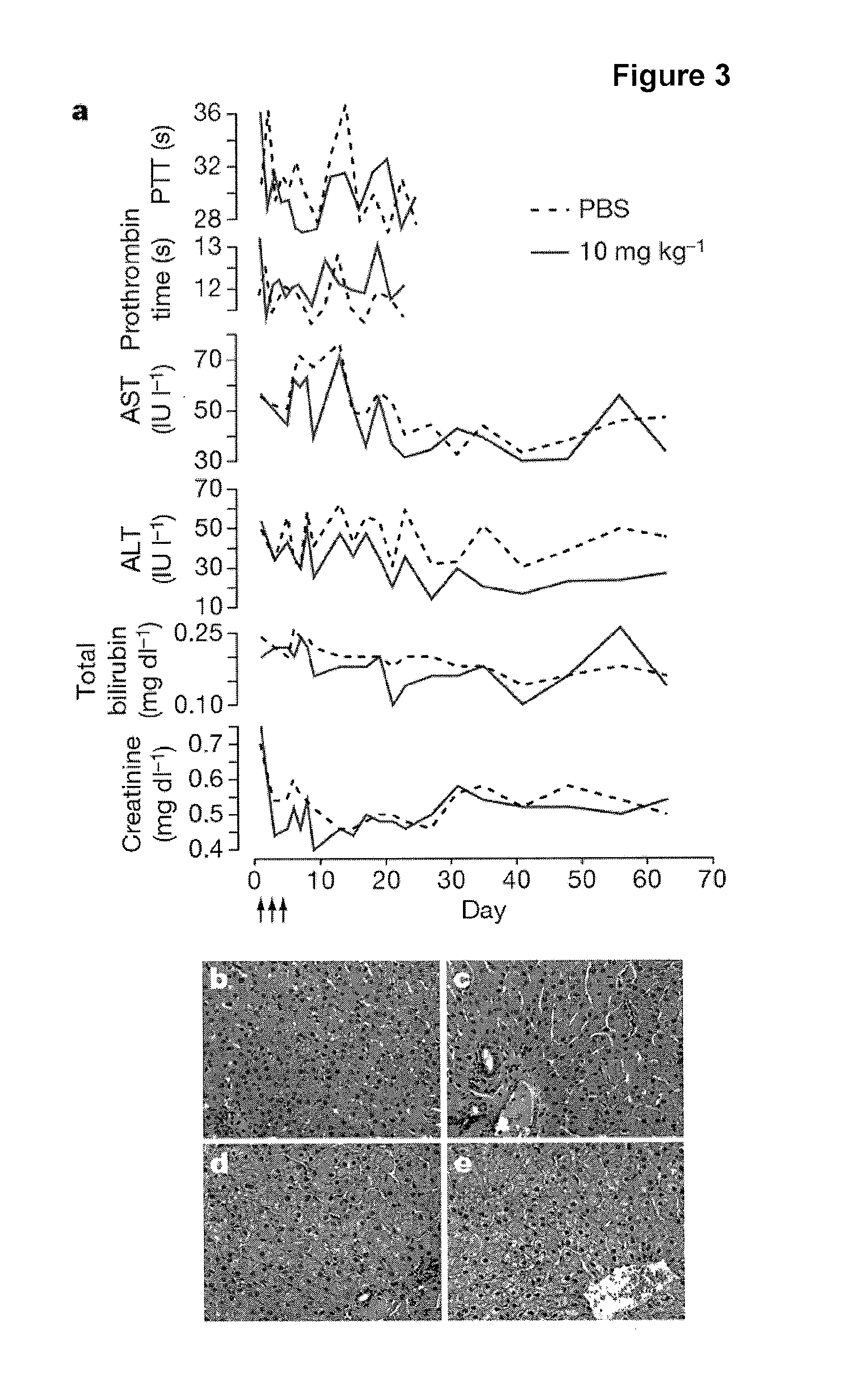
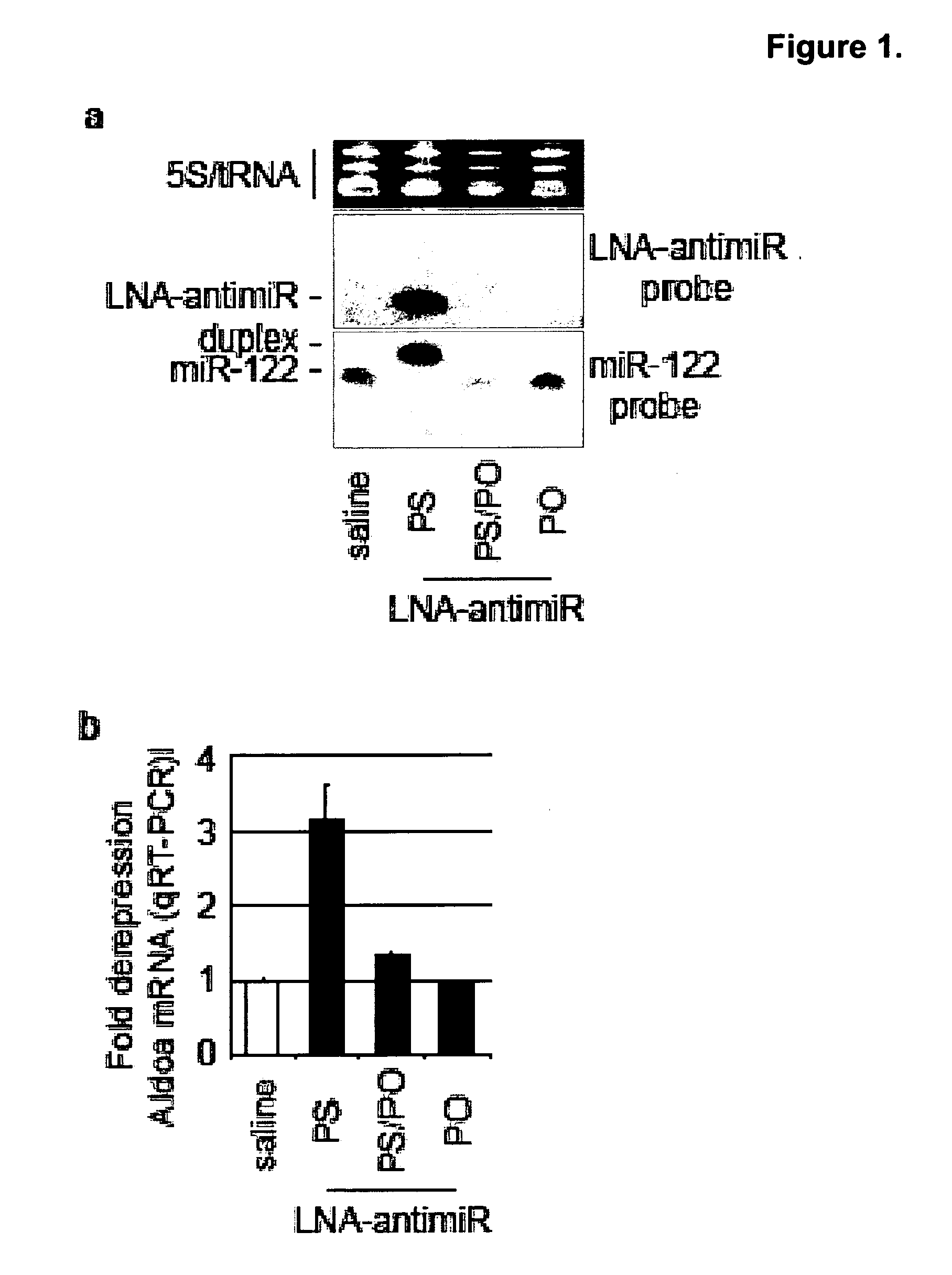
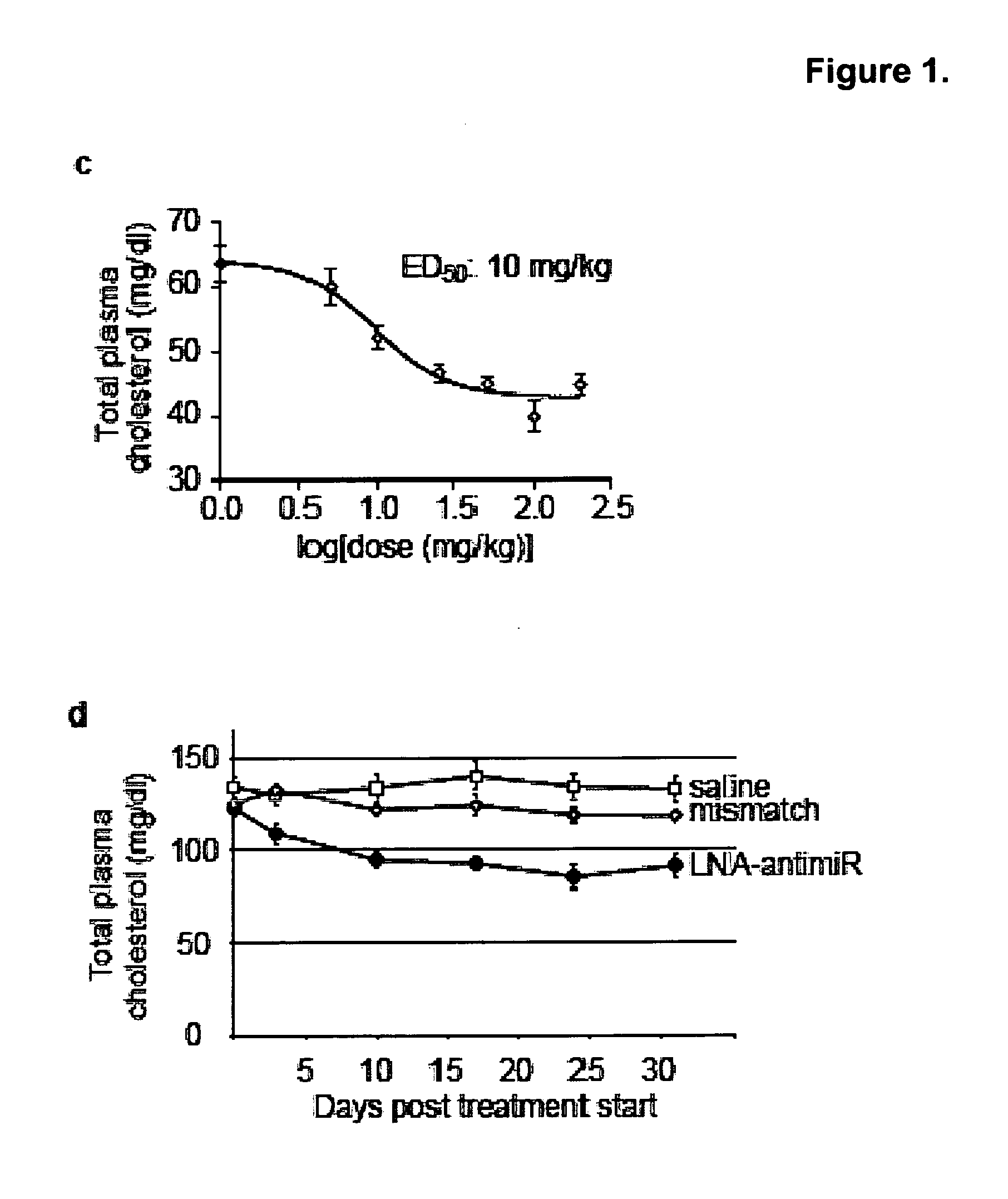
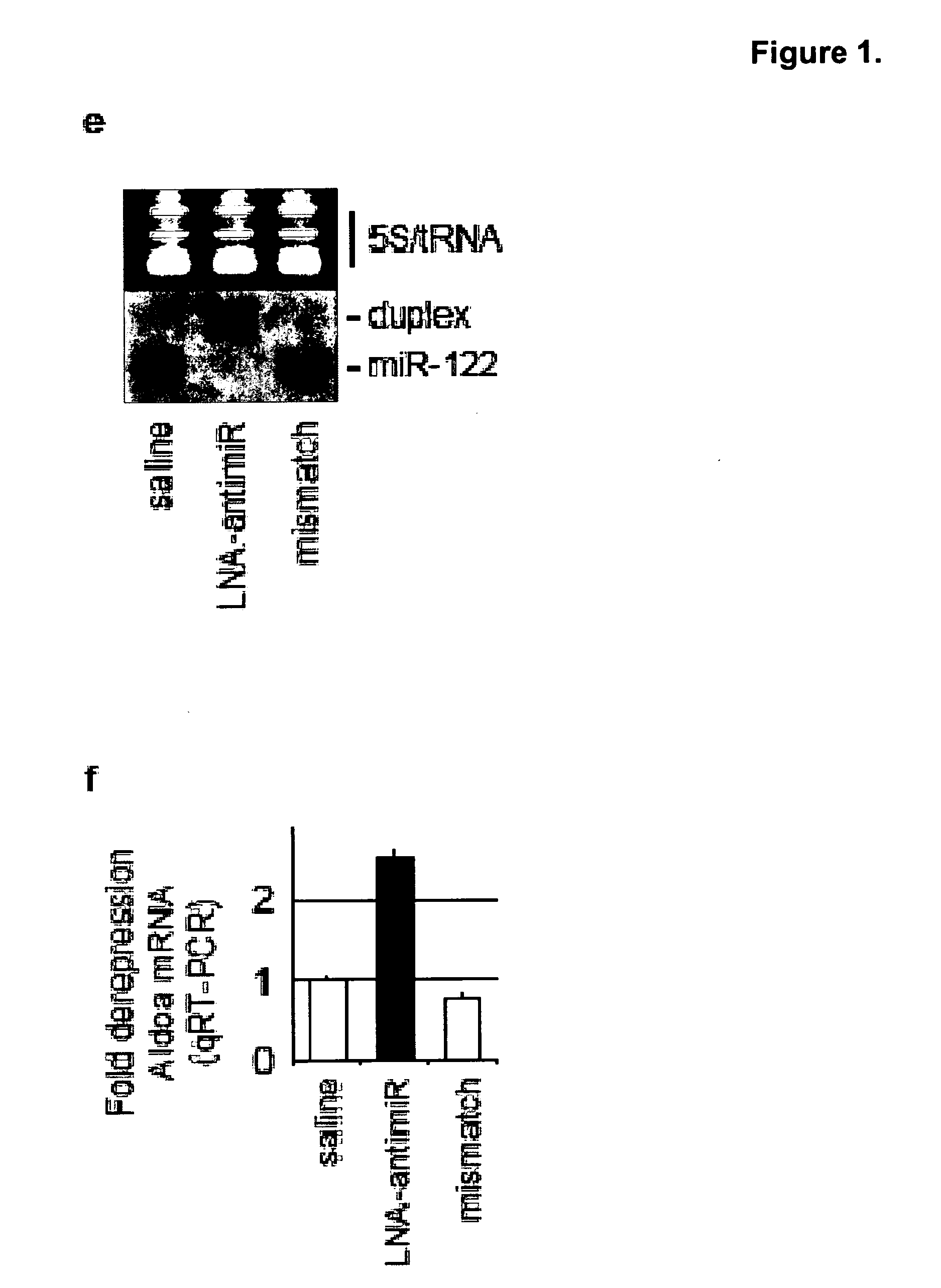
The invention provides pharmaceutical compositions comprising short single stranded oligonucleotides, of length of between 8 and 17 nucleobases which are complementary to human microRNAs. The short oligonucleotides are particularly effective at alleviating miRNA repression in vivo. It is found that the incorporation of high affinity nucleotide analogues into the oligonucleotides results in highly effective anti-microRNA molecules which appear to function via the formation of almost irreversible duplexes with the miRNA target, rather than RNA cleavage based mechanisms, such as mechanisms associated with RNaseH or RISC.
Owner:SANTARIS PHARMA AS
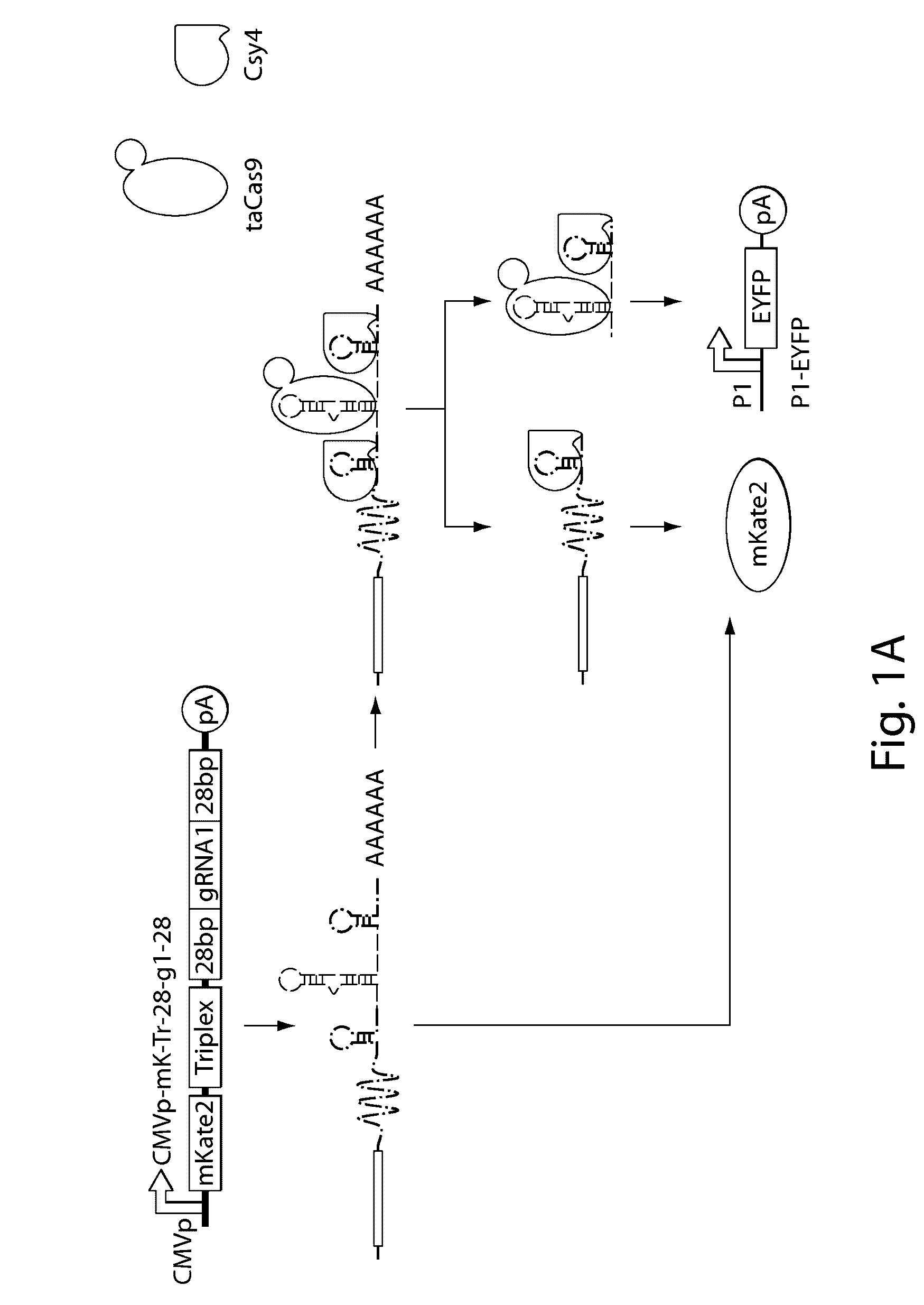
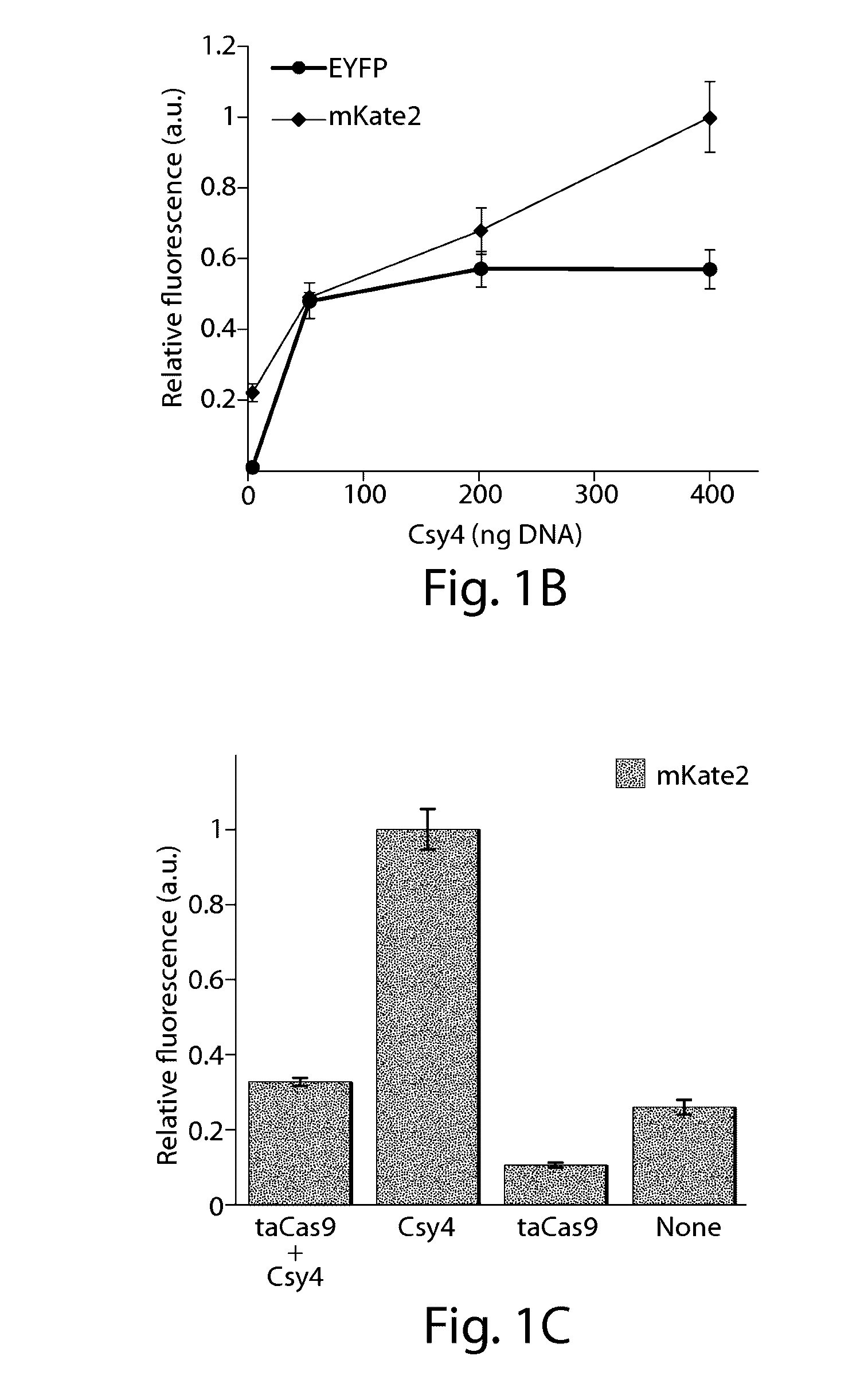
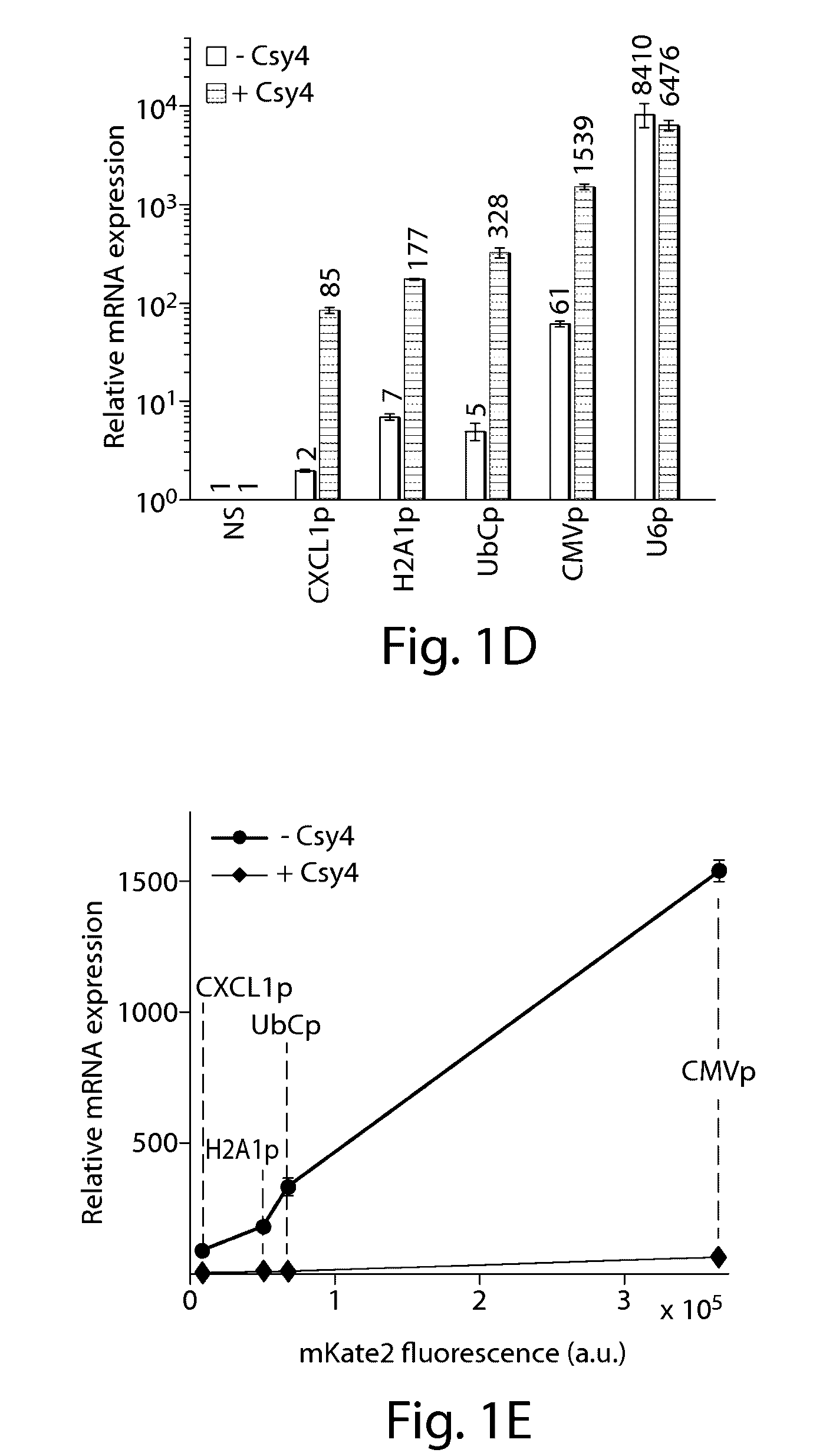
Methods and compositions for the production of guide RNA
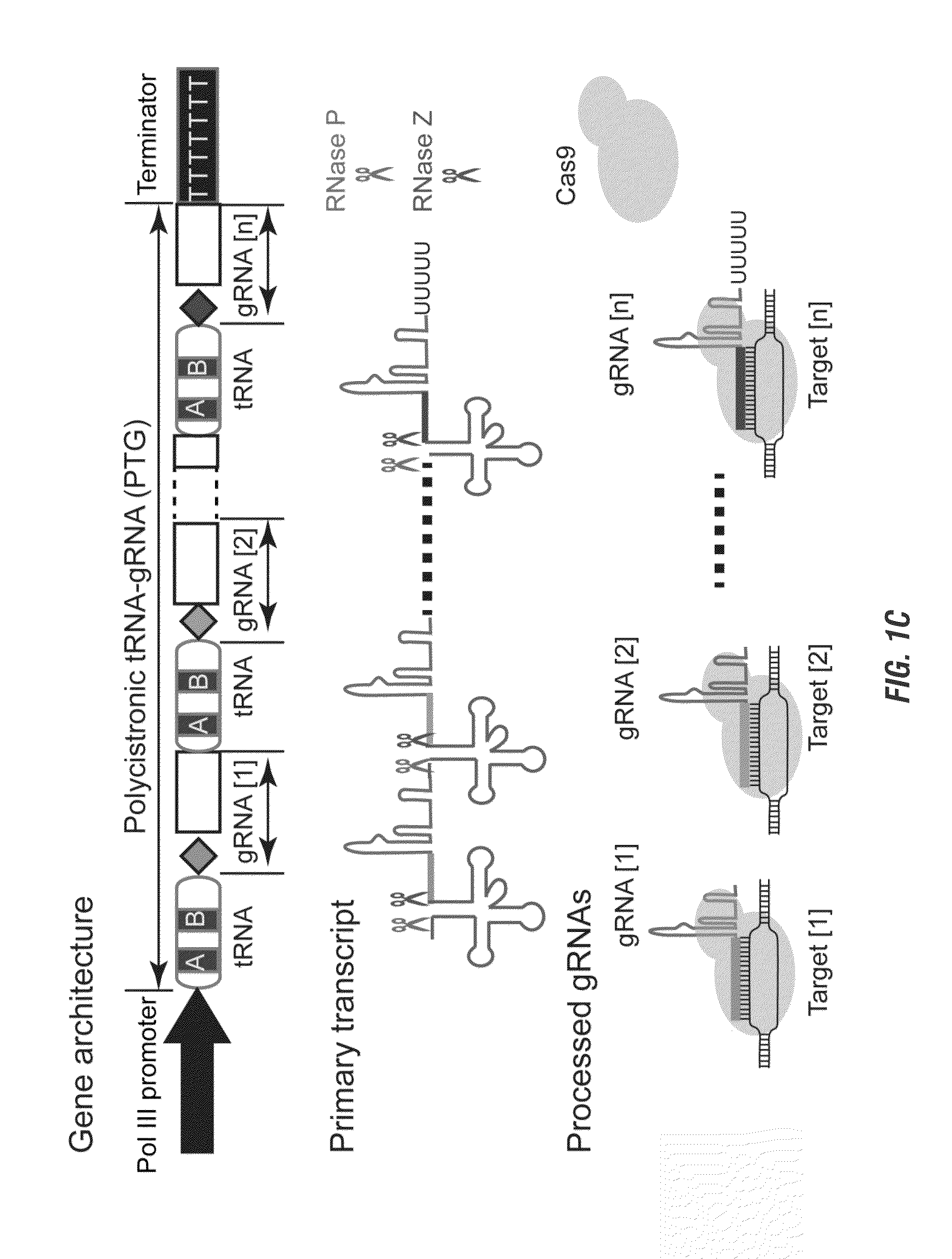
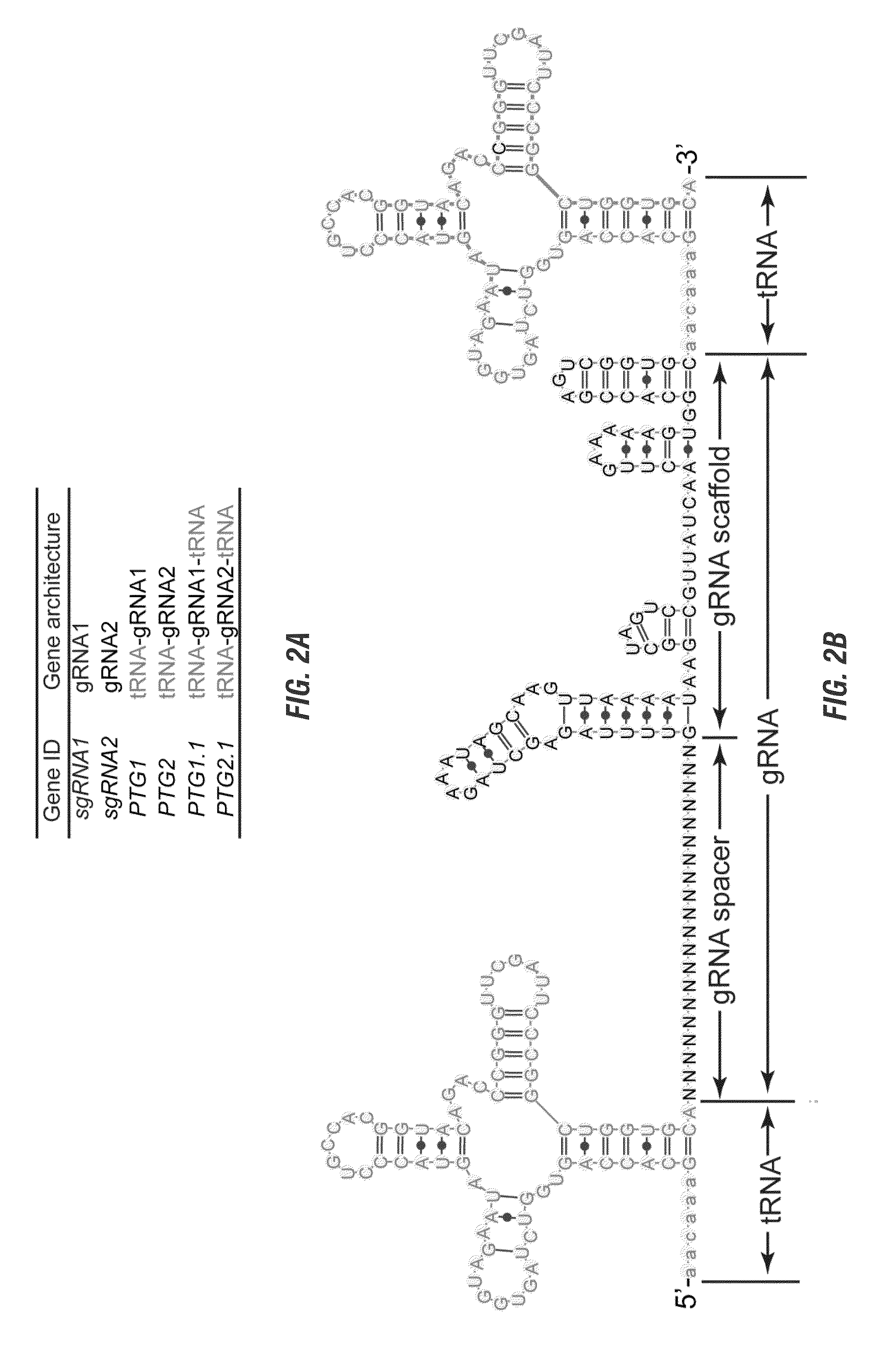
Various aspects and embodiments of the present disclosure relate to methods and compositions that combine multiple mammalian RNA regulatory strategies, including RNA triple helix structures, introns, microRNAs, and ribozymes with Cas-based CRISPR transcription factors and ribonuclease-based RNA processing in human cells. The methods and compositions of the present disclosure, in some embodiments, enable multiplexed production of proteins and multiple guide RNAs from a single compact RNA-polymerase-II-expressed transcript for efficient modulation of synthetic constructs and endogenous human promoters.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Polymer-encapsulated reverse micelles
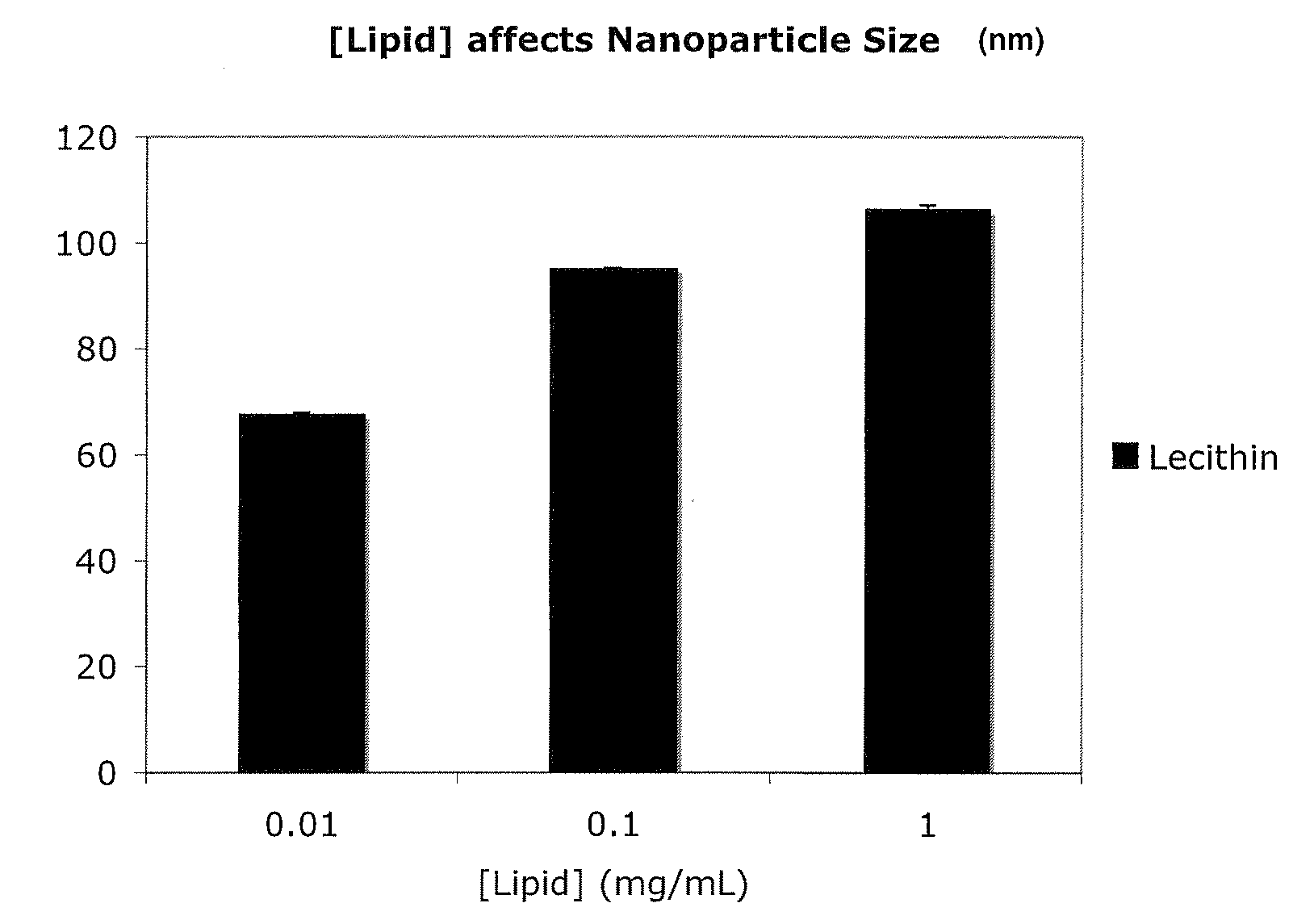
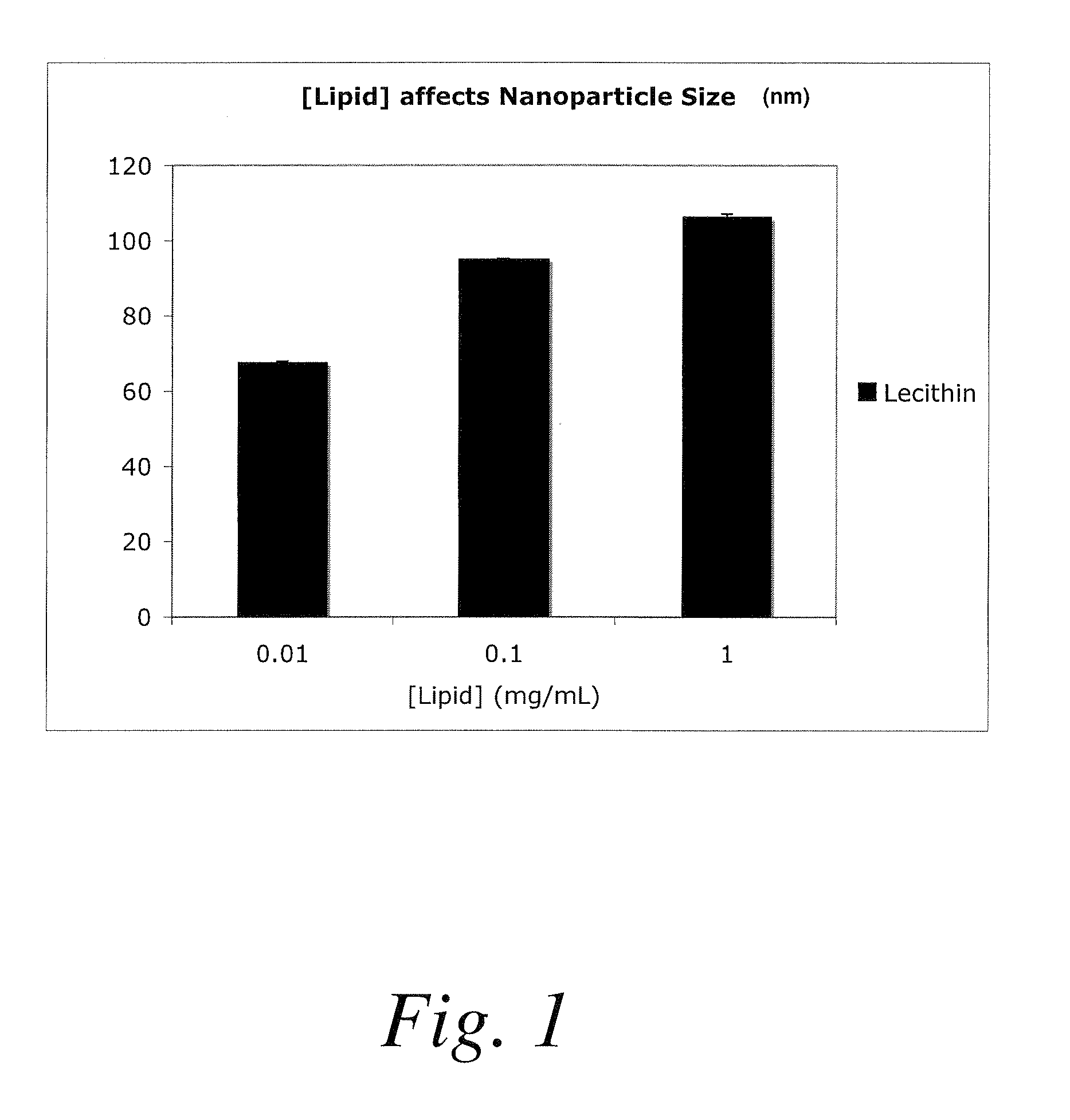
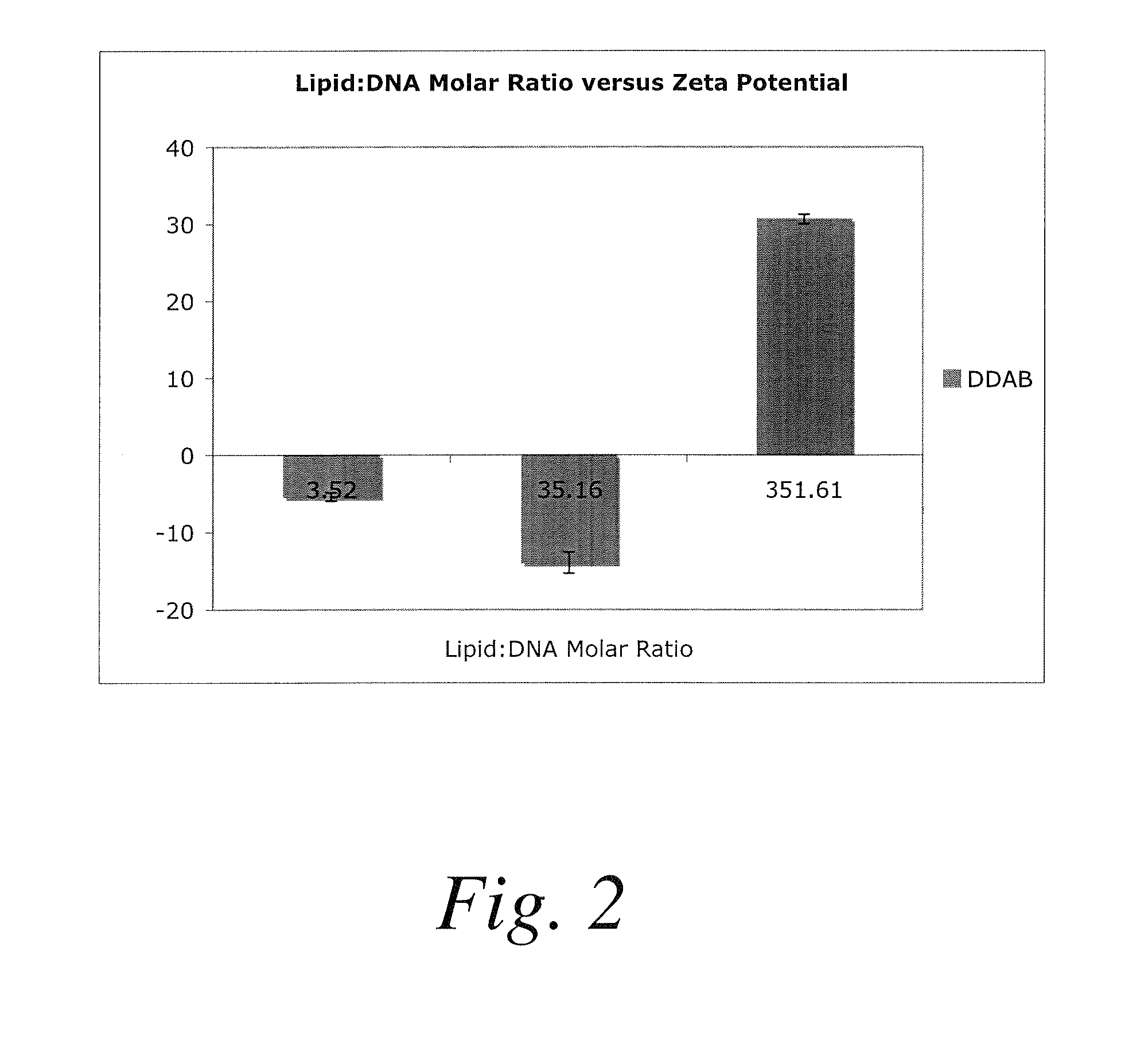
ActiveUS20100196482A1Efficient packagingConvenience to mergePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsLipid formationNanoparticle
A method for encapsulating nucleic acids, particularly siRNAs, shRNAs, microRNAs, gene therapy plasmids, and other oligonucleotides in biodegradable polymers is disclosed, whereby the nucleic acids are formulated into reverse micelles composed of non-toxic and / or naturally-occurring lipids prior to nanoparticle formation by nanoprecipitation. This method can be coupled to other techniques that improve intracellular drug targeting, ultimately enhancing intracellular delivery of the aforementioned nucleic acids.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of microRNA related diseases
InactiveUS20090298916A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseasePrimate
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Improved Methods Controlling Gene Expression
The present invention is in the field of genetics, especially plant genetics, and provides agents capable of controlling gene expression. The present invention specifically provides sequences of naturally occurring, tissue-specifically expressed microRNAs. The invention further provides for transgenic expression constructs comprising sequences encoding said microRNAs. By incorporation of the microRNA encoding sequence the expression from said expression construct is specifically silenced in the tissue where the naturally occurring microRNA is naturally expressed. Thereby the expression profile resulting from the promoter is modulated and leakiness is reduced. The invention further provides for a method for modulating transgenic expression by incorporating sequences encoding said microRNAs into transgenic expression constructs. The compositions and methods of the invention can be used to enhance performance of agricultural relevant crops and for therapy, prophylaxis, research and diagnostics in diseases and disorders, which afflict mammalian species.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
Generation of tumor-free embryonic stem-like pluripotent cells using inducible recombinant RNA agents
InactiveUS20090203141A1Improve target specificityReduce the number of copiesVectorsFermentationCancer cellMammal
The present invention generally relates to a method for developing, generating and selecting tumor-free embryonic stem (ES)-like pluripotent cells using electroporation delivery of an inducible tumor suppressor mir-302 agent into mammalian cells. More particularly, the present invention relates to a method and composition for generating a Tet-On / Off recombinant transgene capable of expressing a manually re-designed mir-302 microRNA (miRNA) / shRNA agent under the control of doxycyclin (Dox) in human somatic / cancer cells and thus inducing certain specific gene silencing effects on the differentiation-associated genes and oncogenes of the cells, resulting in reprogramming the cells into an ES-like pluripotent state.
Owner:LIN SHI LUNG +1
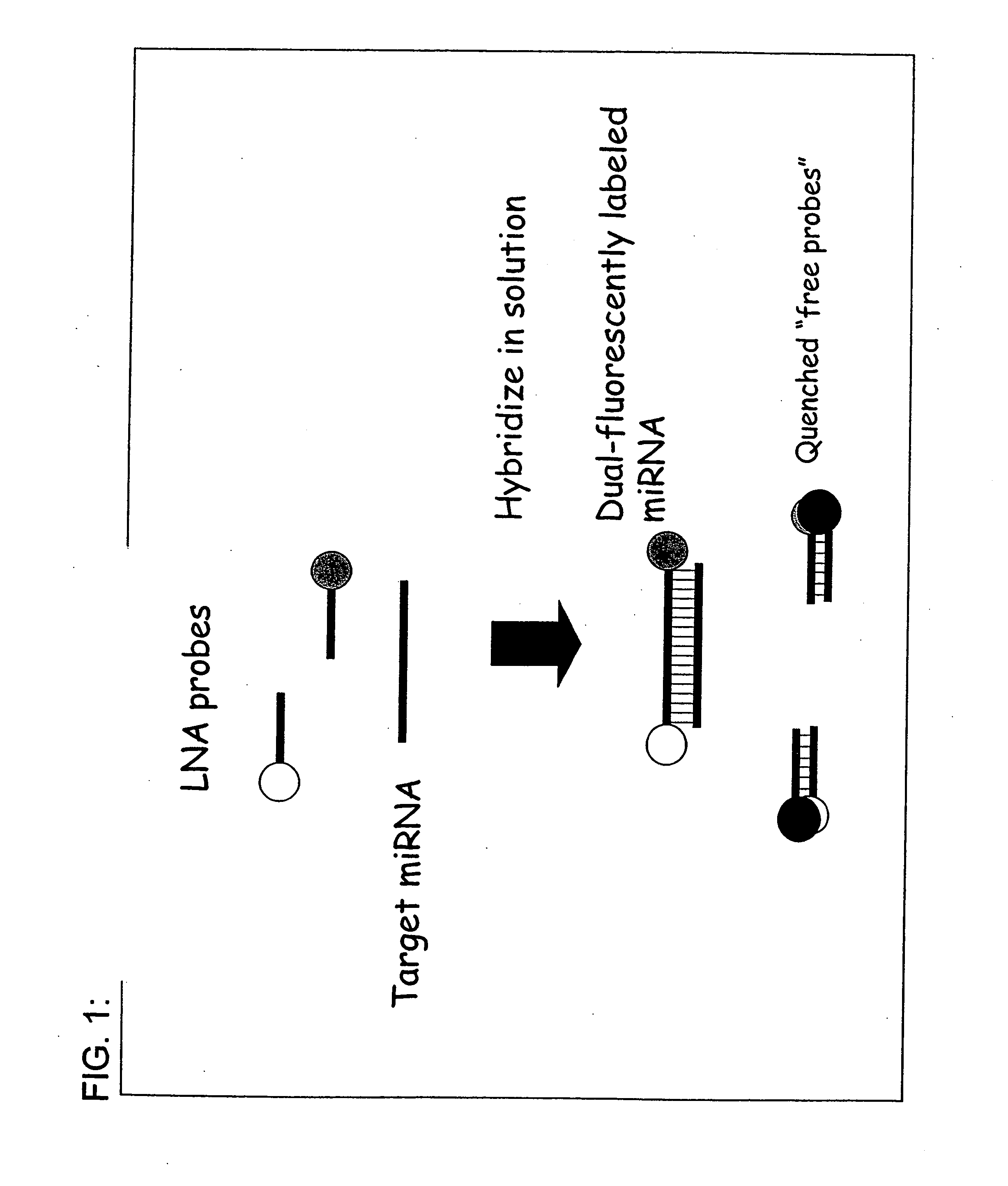
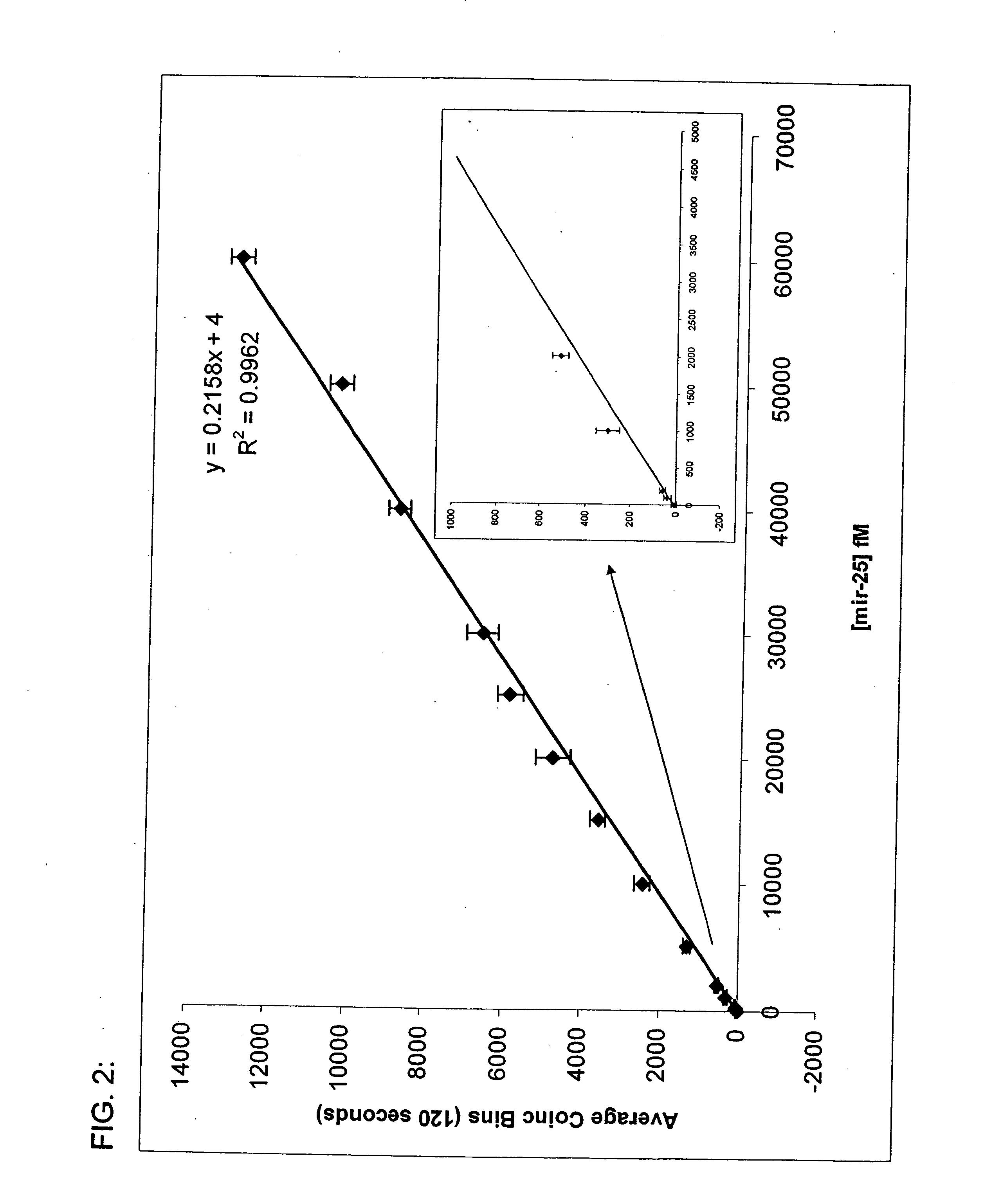
Compositions and methods for the detection of small rnas
ActiveUS20110201515A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeurological disorderSmall RNA
The invention provides compositions and methods for the detection of small RNA molecules in a multiplexed reaction. The assays and kits described herein are applicable for the identification, diagnosing, and monitoring of disorders including, but not limited to cancer, developmental and degenerative disease, neurological disorders, and stem cell disorders.
Owner:NANOSTRING TECH INC
Methods and compositions for the rapid isolation of small RNA molecules
InactiveUS20070202511A1High strengthSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementSmall RNABioinformatics
The present invention provides extraction compositions and methods for the rapid and efficient isolation of small RNA molecules from a biological sample. In particular, the extraction compositions, when contacted with a biological sample, releases the small RNA molecules from the other molecules in a biological sample, and the released small RNA molecules may then be isolated.
Owner:SIGMA ALDRICH CO LLC
MicroRNA Signatures Associated with Human Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20120283310A1Improve impactReduce expressionOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseChronic lymphocytic leukemia
Methods and compositions for the diagnosis, prognosis and / or treatment of leukemia associated diseases are disclosed.
Owner:THE OHIO STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Microrna (MIRNA) for the diagnosis and treatment of heart diseases
The invention relates to microRNAs (miRNAs) for the diagnosis, prophylaxis and / or treatment of heart diseases. It relates in particular to SEQ ID No: 1 to SEQ ID No: 29 for the diagnosis, prophylaxis and / or treatment of heart diseases. In addition, the invention relates to the use of these sequences to produce a medicament for heart diseases and for the diagnosis thereof. Also encompassed are a method for the diagnosis of a heart disease, a kit and an expression vector comprising these sequences, a cell which contains the expression vector, and also a method for modulating a heart disease and a method for screening a pharmaceutically active compound for the treatment and / or prophylaxis of a heart disease.
Owner:CARDIOR PHARMA GMBH
Micro-RNAs modulating immunity and inflammation
InactiveUS8415096B2Effective redirectingTherapy is simpleOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDiseaseRegulatory T cell
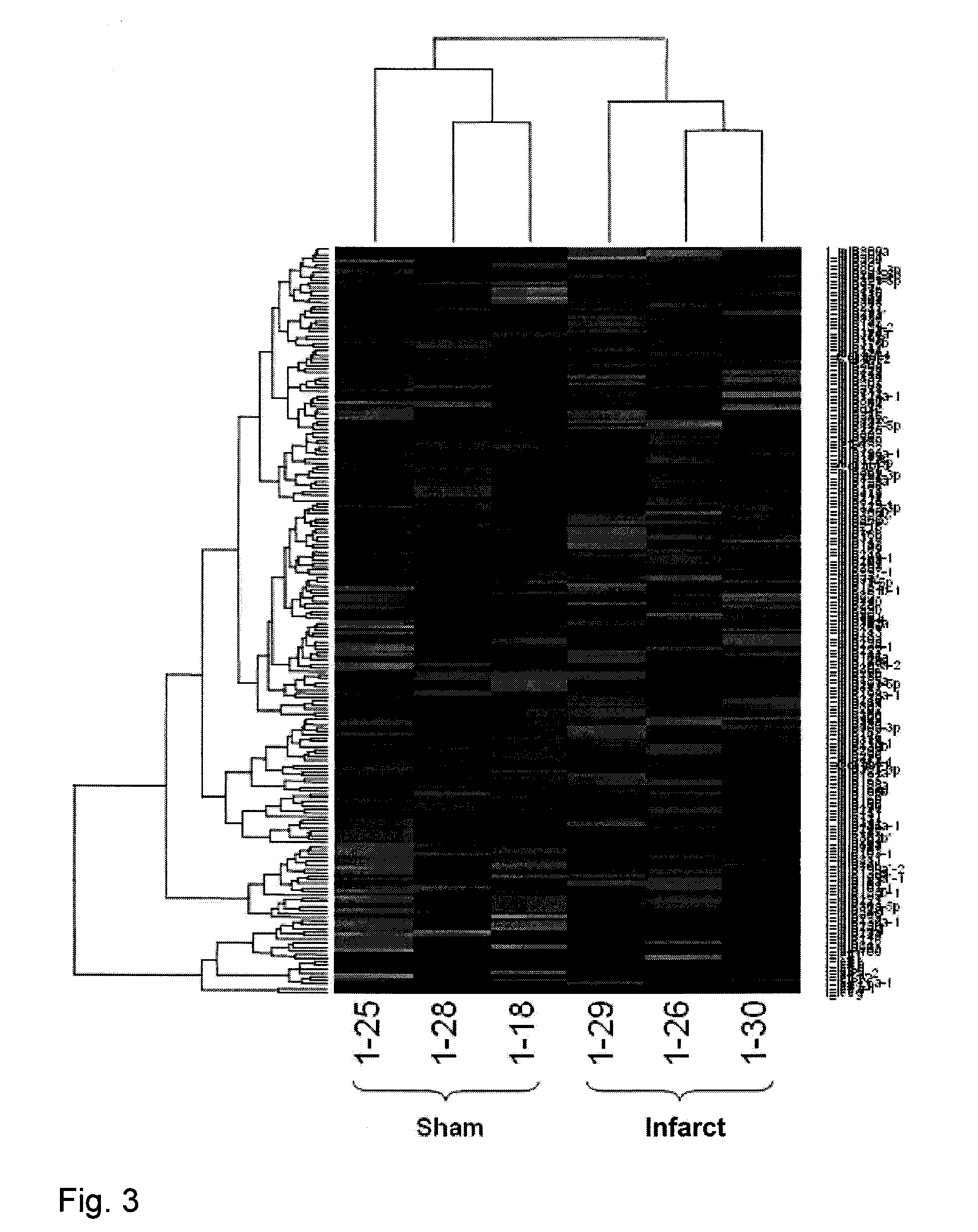
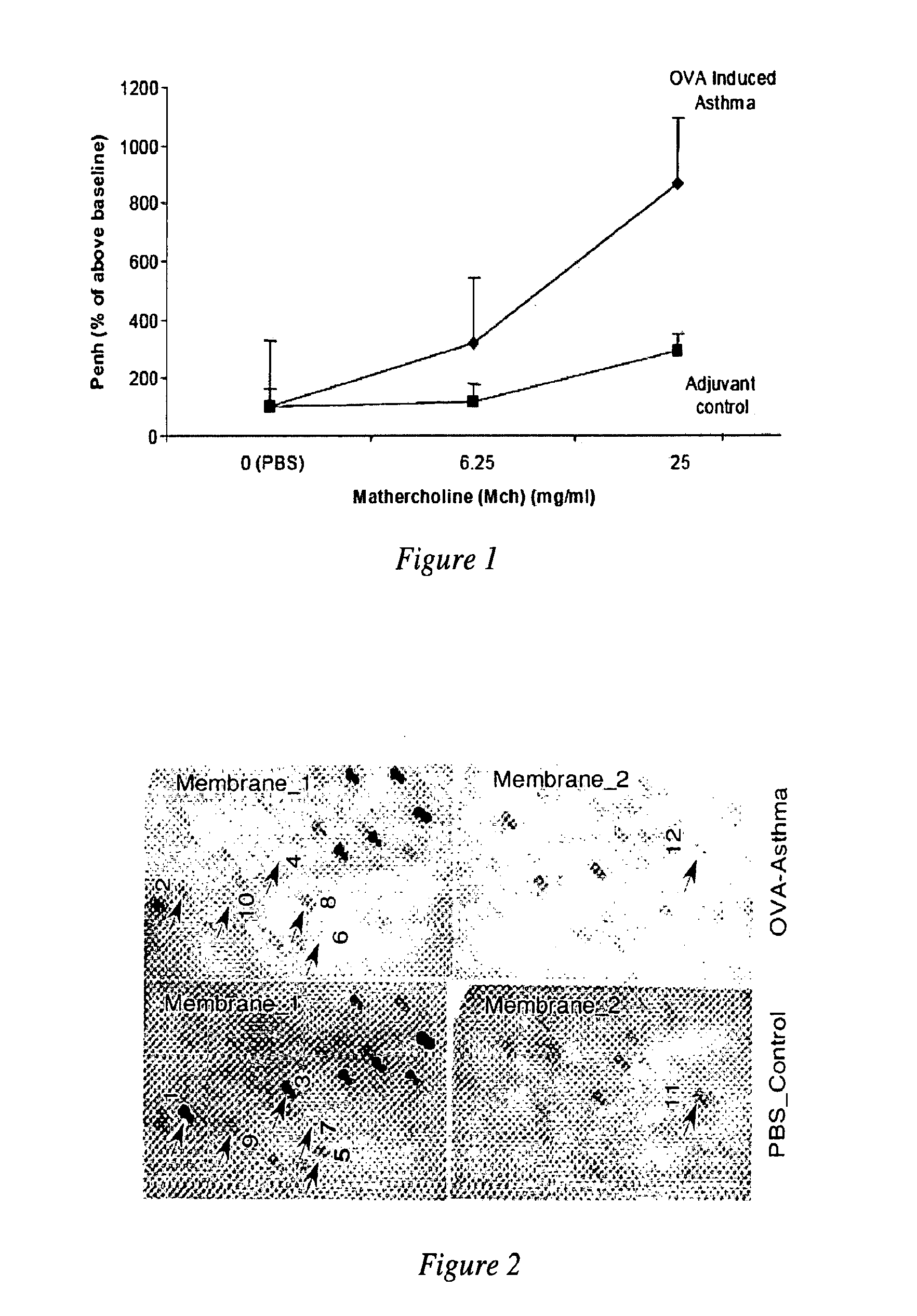
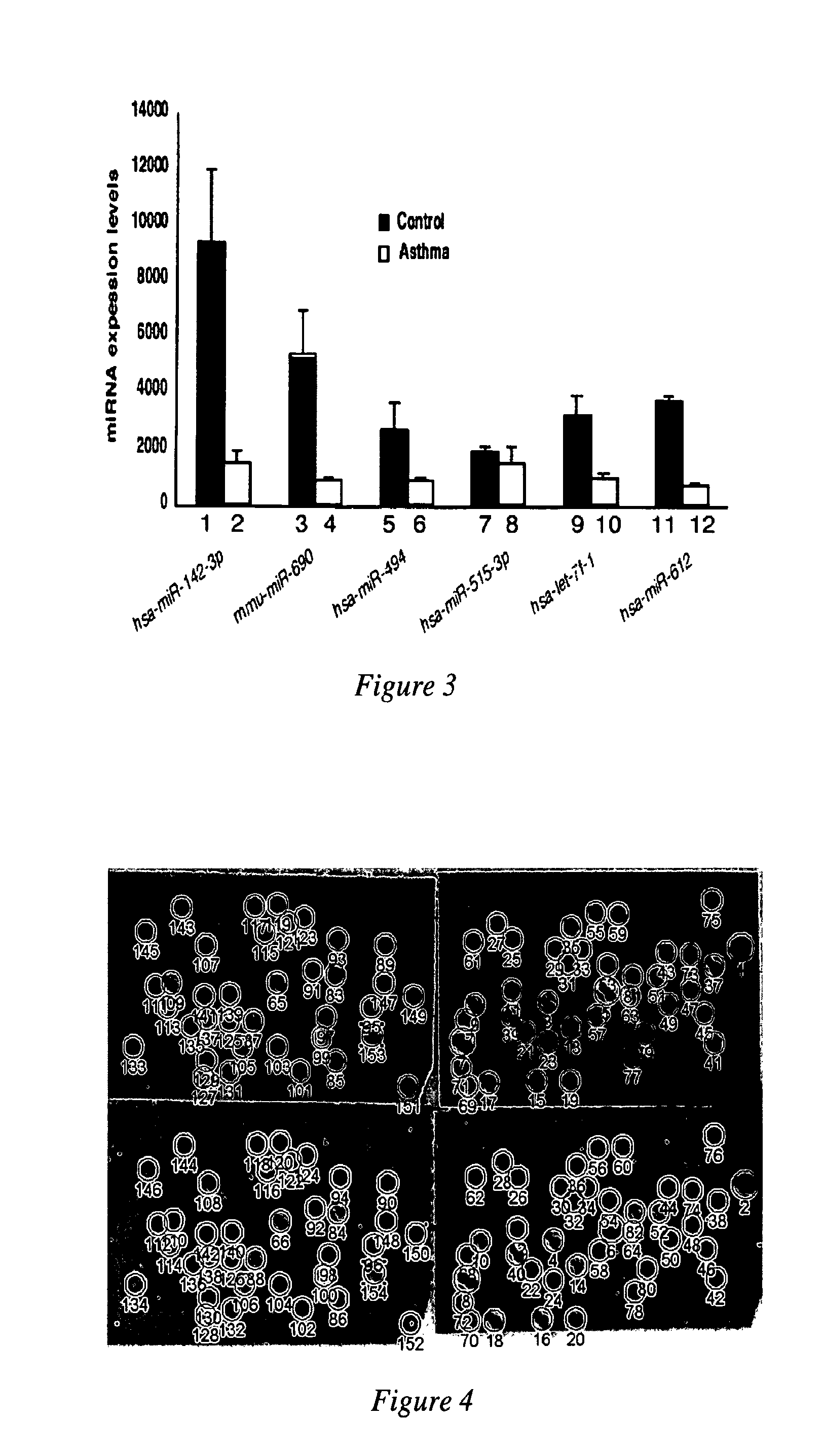
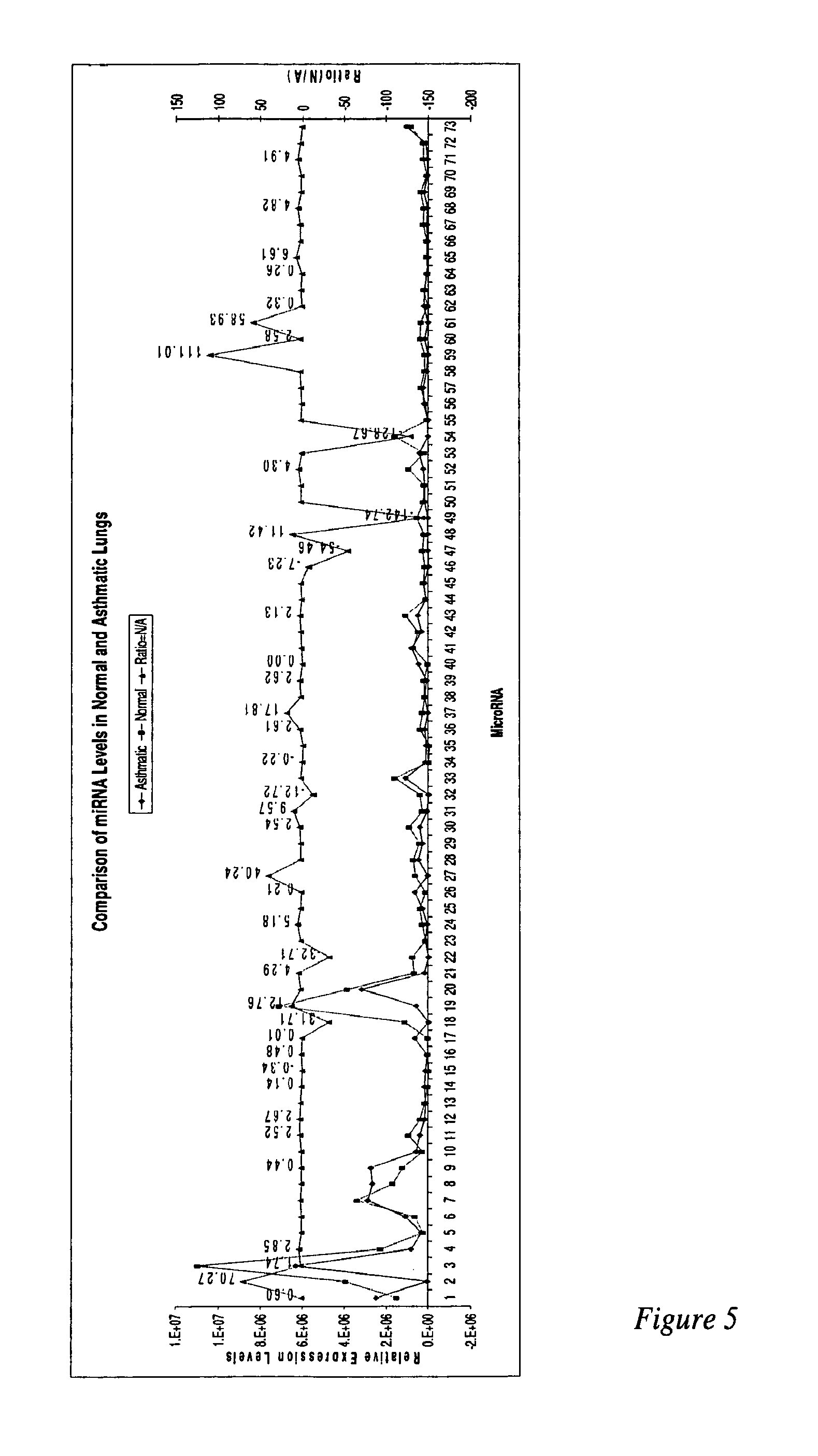
MicroRNAs are shown to be up- and / or down-regulated in inflammation and immune cells using a mouse model of asthma and regulatory T cells as source of RNA, respectively. Modulating the expression of these microRNAs can be effective in redirecting inflammation and immunity and hence, can be beneficial as biomarkers or as therapeutic agents against diverse human immunologic and inflammatory diseases.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Methods, Compositions, and Kits for Detection of microRNA
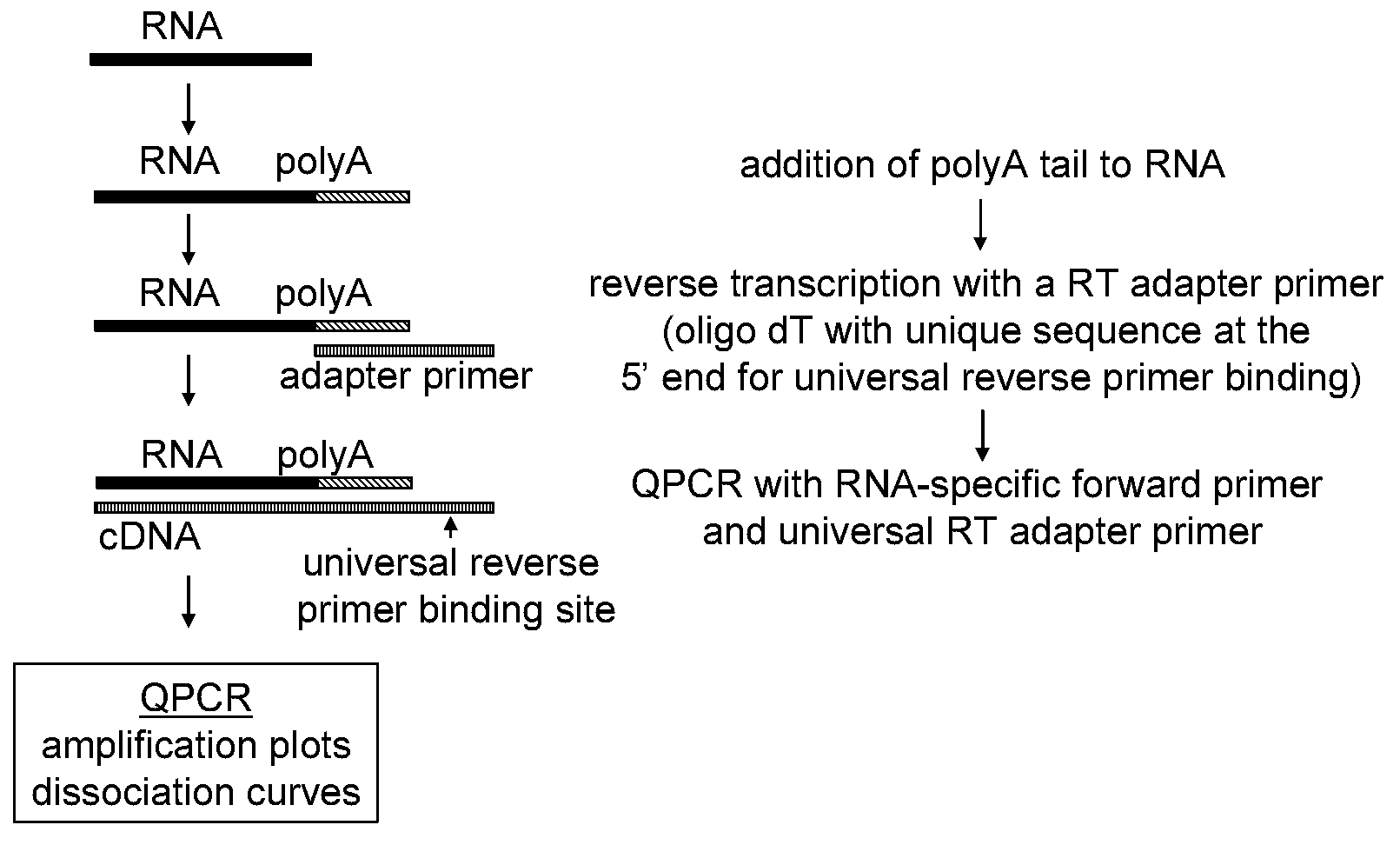
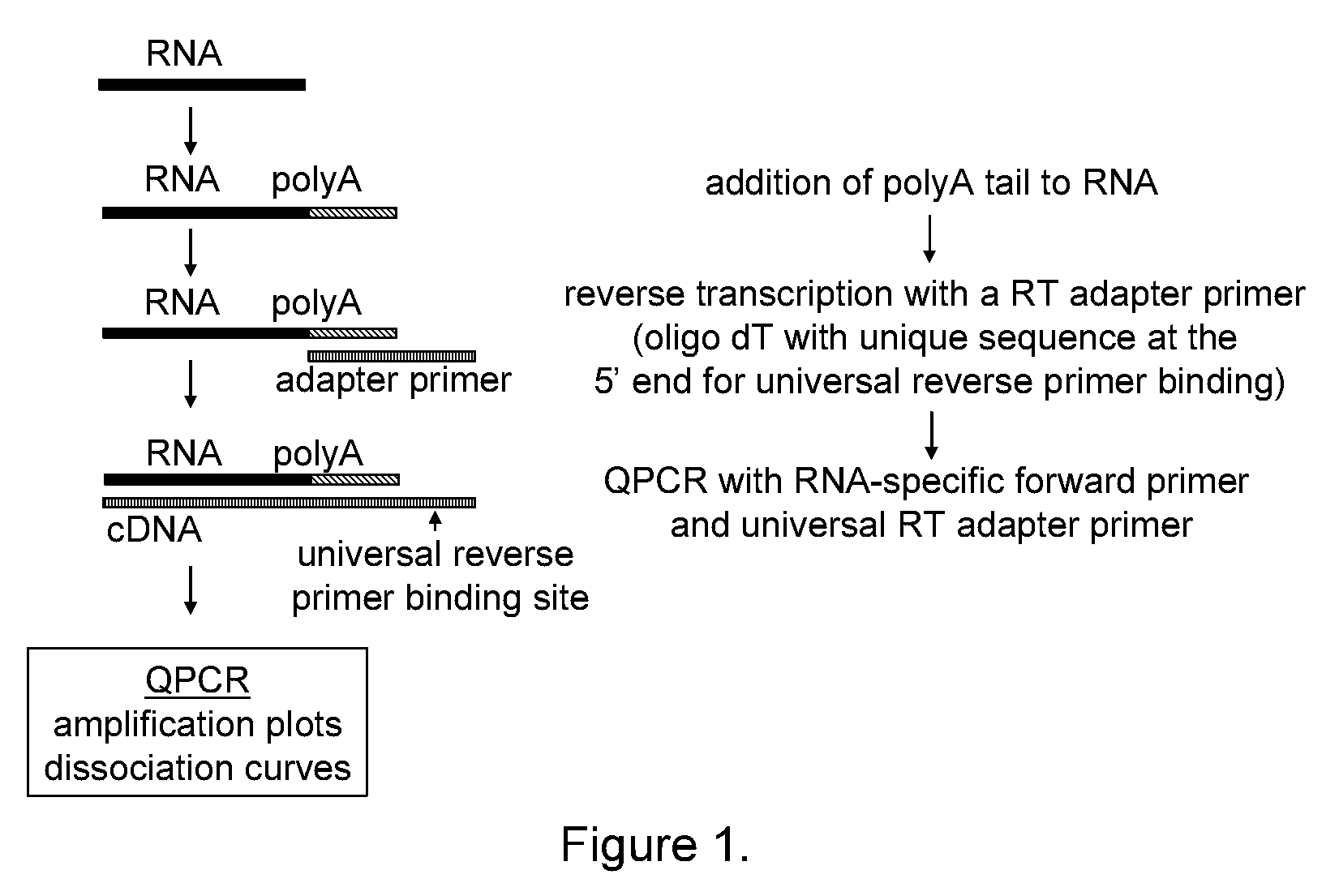
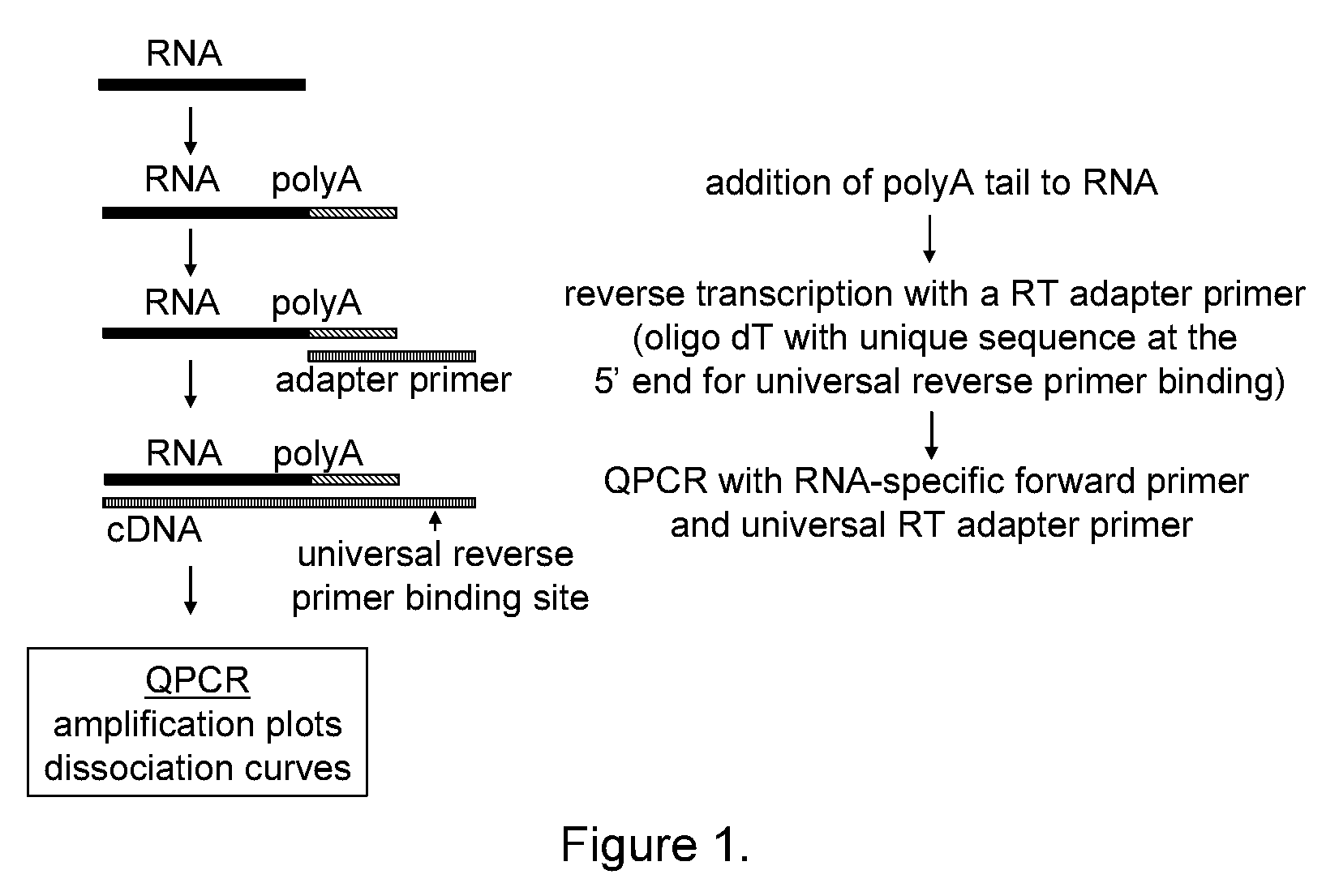
The present invention provides methods, nucleic acids, compositions, and kits for detecting microRNA (miRNA) in samples. The methods comprise designing mRNA-specific primers, adding a polyA tail to the miRNA, and using reverse transcription and amplification to detect the miRNA. The nucleic acids, compositions, and kits typically comprise some or all of the components necessary to practice the methods of the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method of de-differentiating and re-differentiating somatic cells using RNA
ActiveUS20110165133A1Efficient transfectionLess time-consumingBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseSomatic cell
RNA prepared by in vitro transcription using a polymerase chain reaction (PCR)-generated template can be introduced into a cell to modulate cell activity. This method is useful in de-differentiating somatic cells to pluripotent, multipotent, or unipotent cells; re-differentiating stem cells into differentiated cells; or reprogramming of somatic cells to modulate cell activities such as metabolism. Cells can also be transfected with inhibitory RNAs, such as small interfering RNA (siRNA) or micro RNA (miRNA), or combinations thereof to induce reprogramming of somatic cells. For example, target cells are isolated from a donor, contacted with one or more RNA's causing the cells to be de-differentiated, re-differentiated, or reprogrammed in vitro, and administered to a patient in need thereof. The resulting cells are useful for treating one or more symptoms of a variety of diseases and disorders, for organ regeneration, and for restoration of the immune system.
Owner:YALE UNIV
MicroRNA vectors
InactiveUS20060063174A1Genetic material ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementGene silencingIn vivo
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
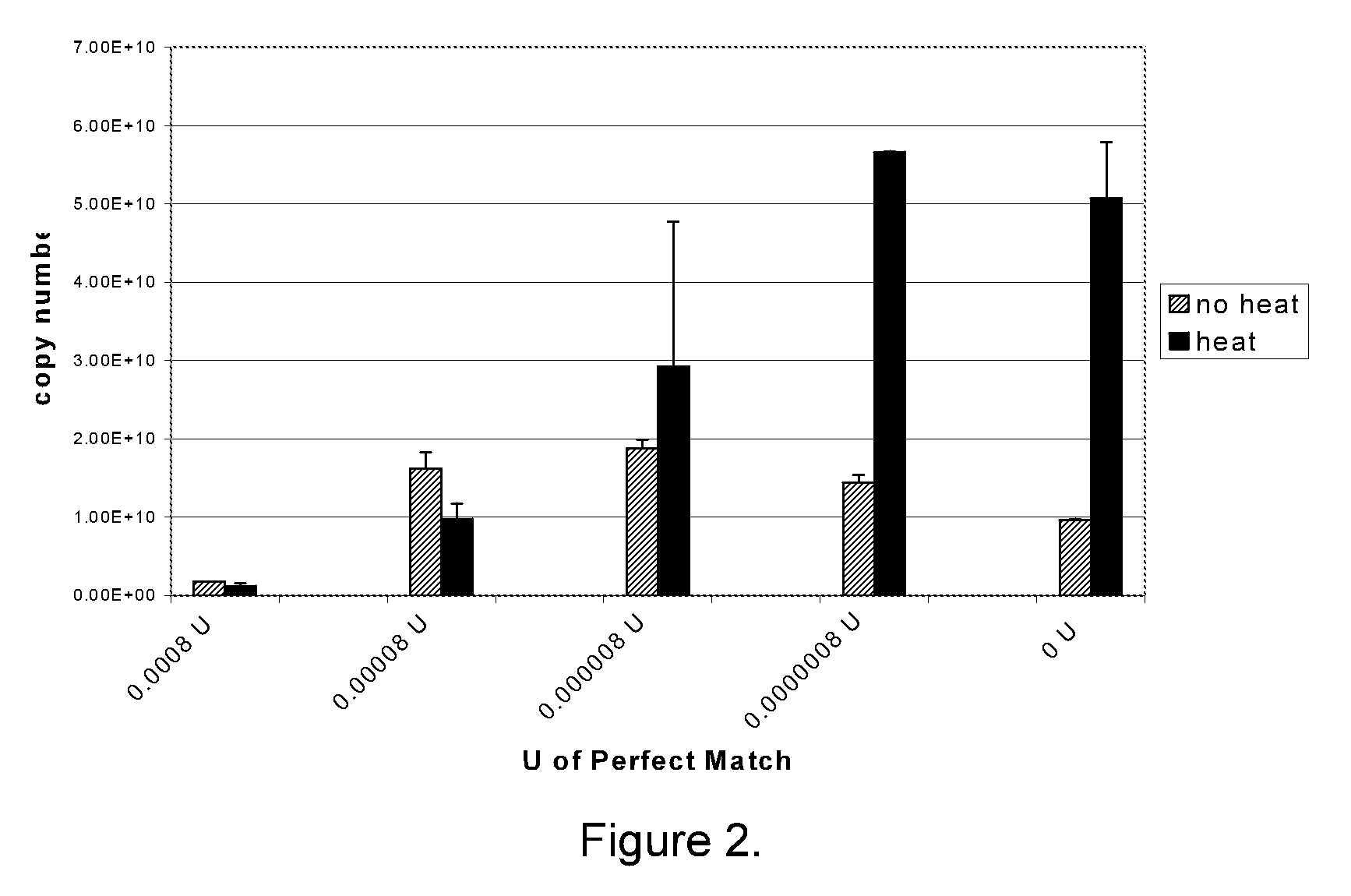
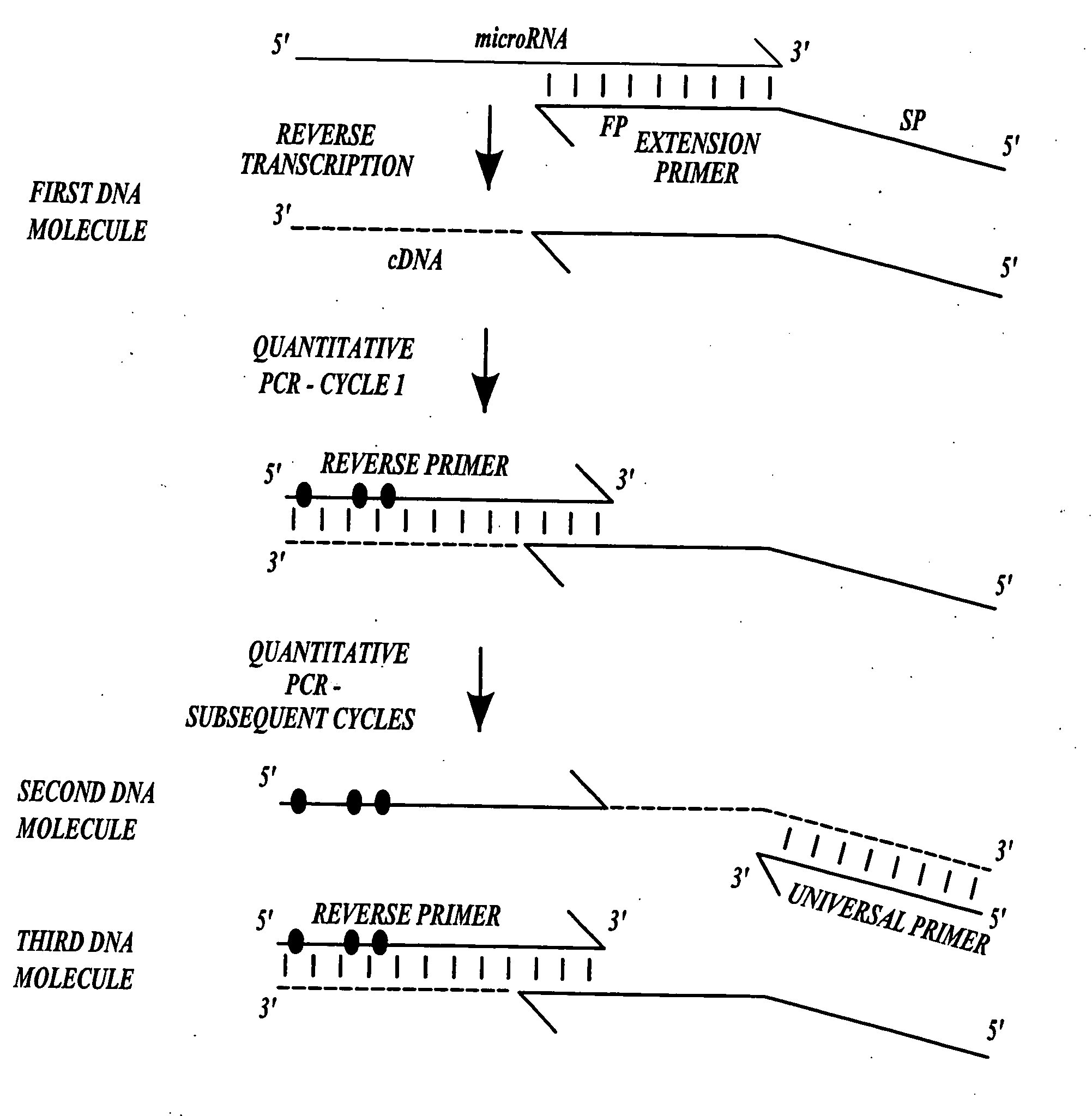
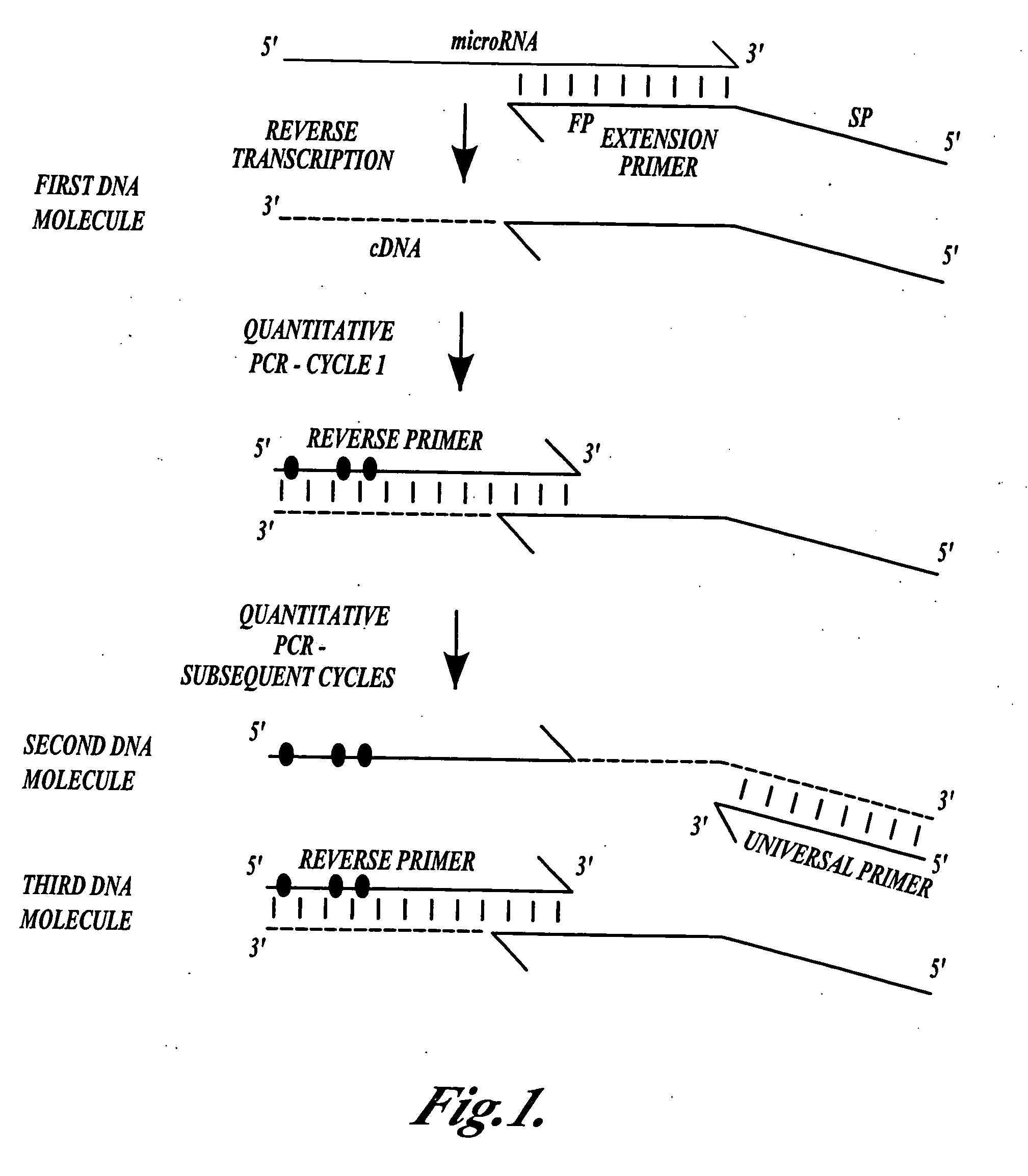
Methods for quantitating small RNA molecules
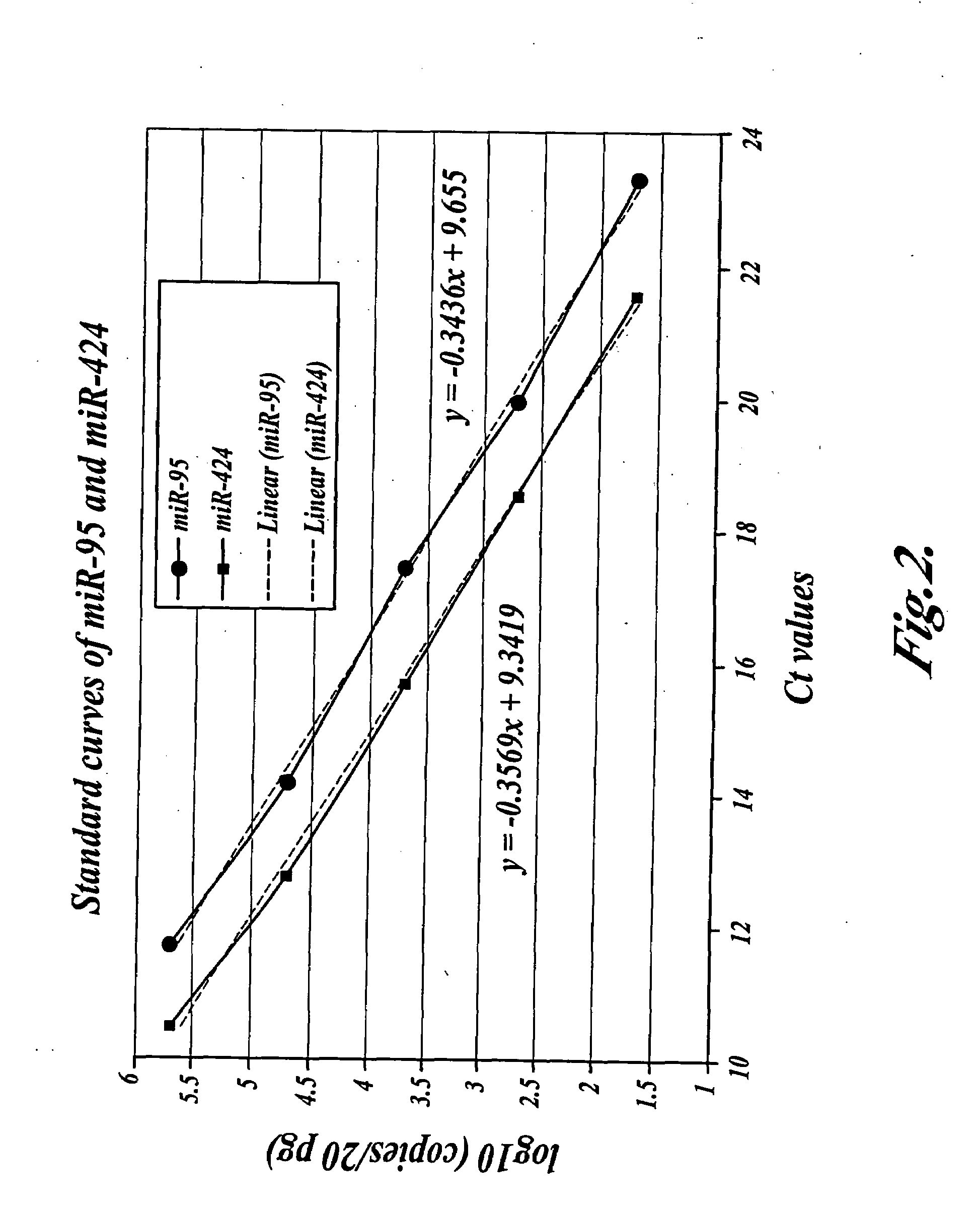
In one aspect, the present invention provides methods for amplifying a microRNA molecule to produce DNA molecules. The methods each include the steps of: (a) using primer extension to make a DNA molecule that is complementary to a target microRNA molecule; and (b) using a universal forward primer and a reverse primer to amplify the DNA molecule to produce amplified DNA molecules. In some embodiments of the method, at least one of the forward primer and the reverse primer comprise at least one locked nucleic acid molecule.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF CANCERS WITH MicroRNA LOCATED IN OR NEAR CANCER ASSOCIATED CHROMOSOMAL FEATURES
InactiveUS20100203544A1Restore levelOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyMicroRNA Gene
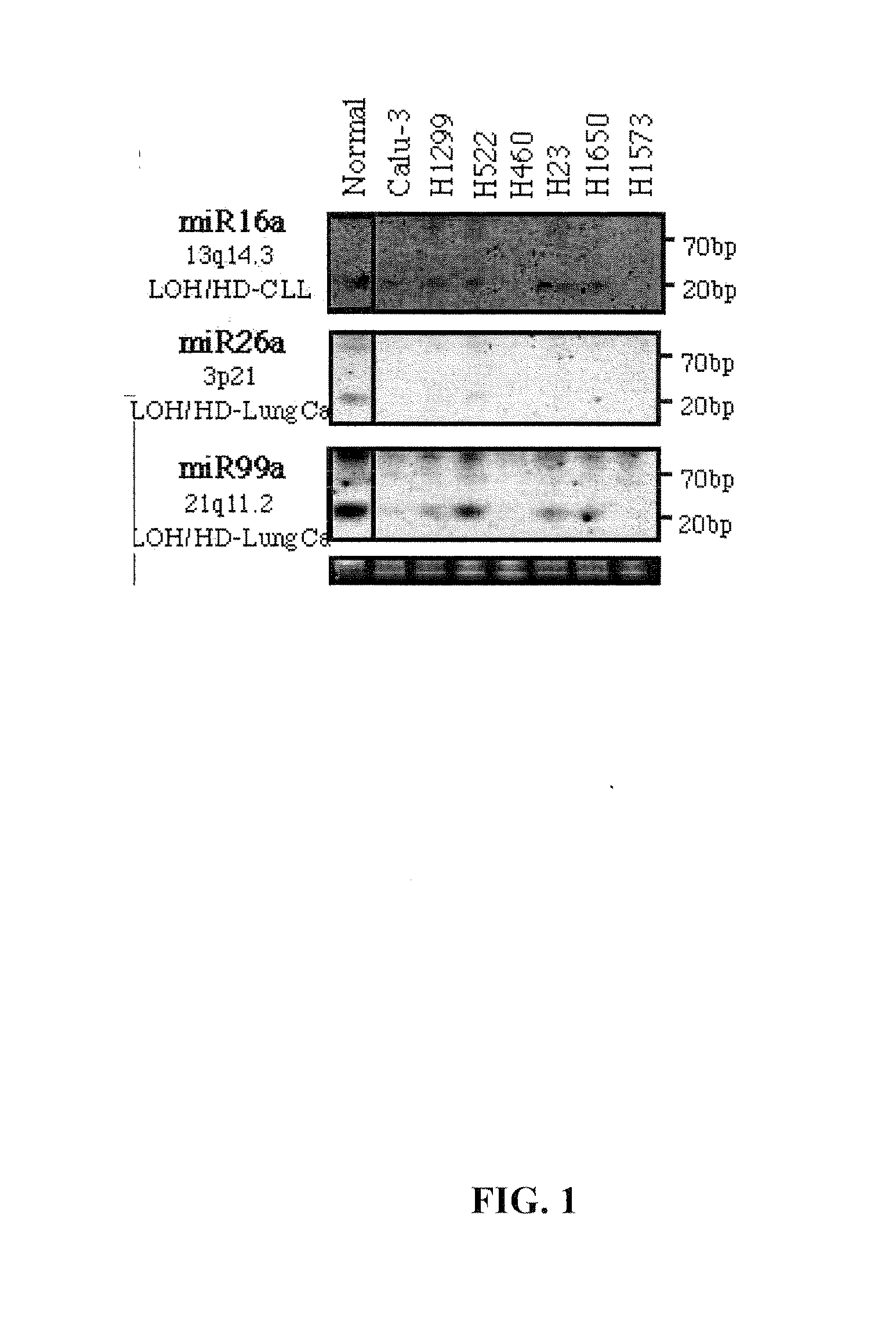
MicroRNA genes are highly associated with chromosomal features involved in the etiology of different cancers. The perturbations in the genomic structure or chromosomal architecture of a cell caused by these cancer-associated chromosomal features can affect the expression of the miR gene(s) located in close proximity to that chromosomal feature. Evaluation of miR gene expression can therefore be used to indicate the presence of a cancer-causing chromosomal lesion in a subject. As the change in miR gene expression level caused by a cancer-associated chromosomal feature may also contribute to cancerigenesis, a given cancer can be treated by restoring the level of miR gene expression to normal. microRNA expression profiling can be used to diagnose cancer and predict whether a particular cancer is associated with an adverse prognosis. The identification of specific mutations associated with genomic regions that harbor miR genes in CLL patients provides a means for diagnosing CLL and possibly other cancers.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Pharmaceutical Compositions for Treatment of MicroRNA Related Diseases
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV. In a further aspect, the invention provides methods for producing siRNA encoding lentivirus where the siRNA activity may interfere with the lentiviral life cycle.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
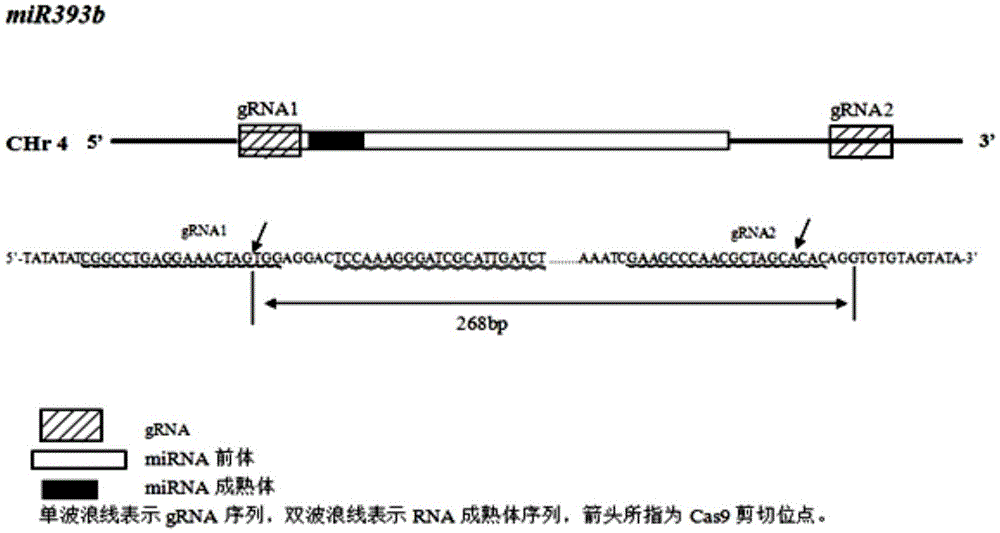
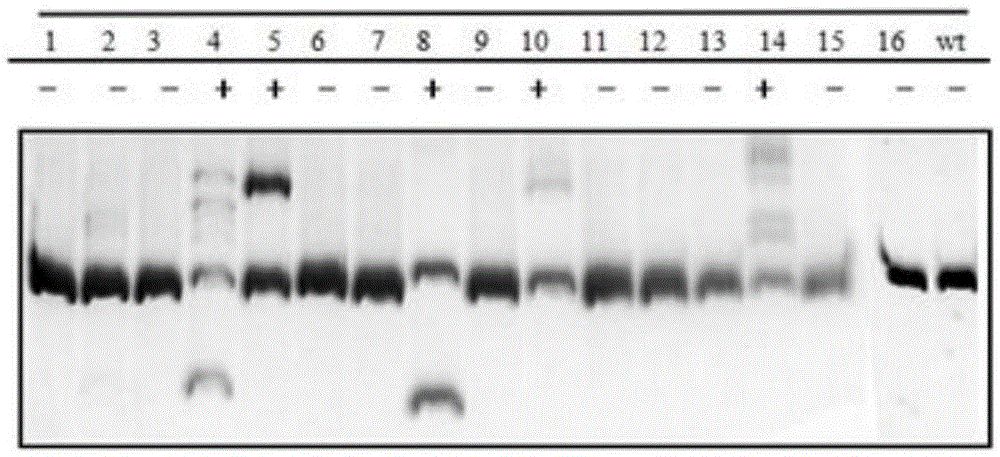
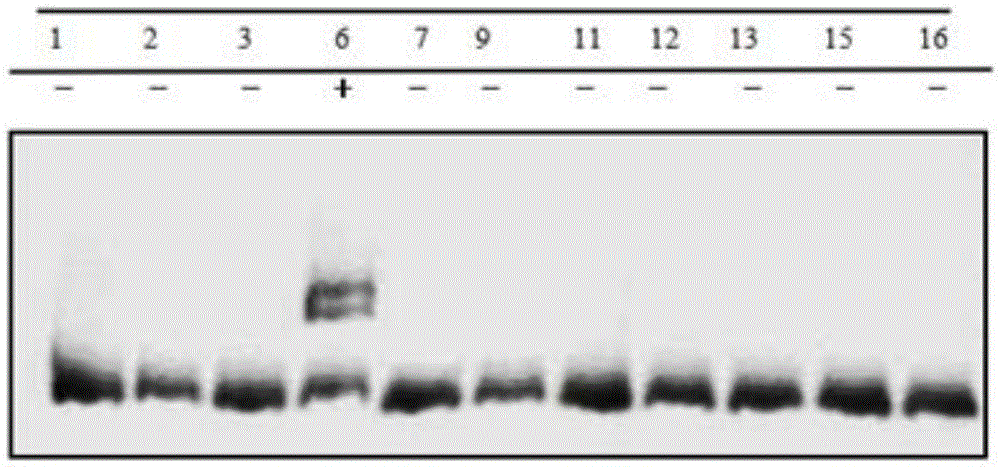
Gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system
InactiveCN105647962AKnockout worksNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to construction of rice transgenic materials and aims to provide a gene editing method for knocking out rice MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences with application of a CRISPR(clustered regulatory interspersed short palindromic repeat)-Cas9 system. The gene editing method comprises steps as follows: gRNA target sites are selected for cloning and GG linking, enzyme digestion is performed after amplification, and a product is linked with a pGREB 32 vector; escherichia coli competent cells are transformed; plasmids with a correct sequencing result are used for transforming agrobacteria, transgenic plants are obtained through mediated transformation of rice calli, and transgenic positive lines are obtained; the T0-generation mutant plant seeds are collected for seeding, and the T1-generation plants are subjected to homozygote screening; homozygous lines which are discovered to be negative through MIRNA393b expression are rice mutants completely losing the MIRNA393b stem-loop sequences and MIRNA393b stem-loop sequence expression. According to the gene editing method, MIRNA stem-loop sequences can be effectively knocked out, and loss-of-function mutants of different members in the same MIRNA family can be prepared; the mutant plant propagates to obtain a large number of seeds and is an ideal material for acquiring rice MIRNA393b gene functions successfully.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Gene expression signature for classification of cancers
The present invention provides a process for classification of cancers and tissues of origin through the analysis of the expression patterns of specific microRNAs and nucleic acid molecules relating thereto. Classification according to a microRNA tree-based expression framework allows optimization of treatment, and determination of specific therapy.
Owner:TEL HASHOMER MEDICAL RES INFRASTRUCTURE & SERVICES +1
Methods, compositions, and kits for detection of microRNA
The present invention provides methods, nucleic acids, compositions, and kits for detecting microRNA (miRNA) in samples. The methods comprise designing mRNA-specific primers, adding a polyA tail to the miRNA, and using reverse transcription and amplification to detect the miRNA. The nucleic acids, compositions, and kits typically comprise some or all of the components necessary to practice the methods of the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Methods for detecting small RNA species
InactiveUS20080241831A1Microbiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingNucleotide sequencing
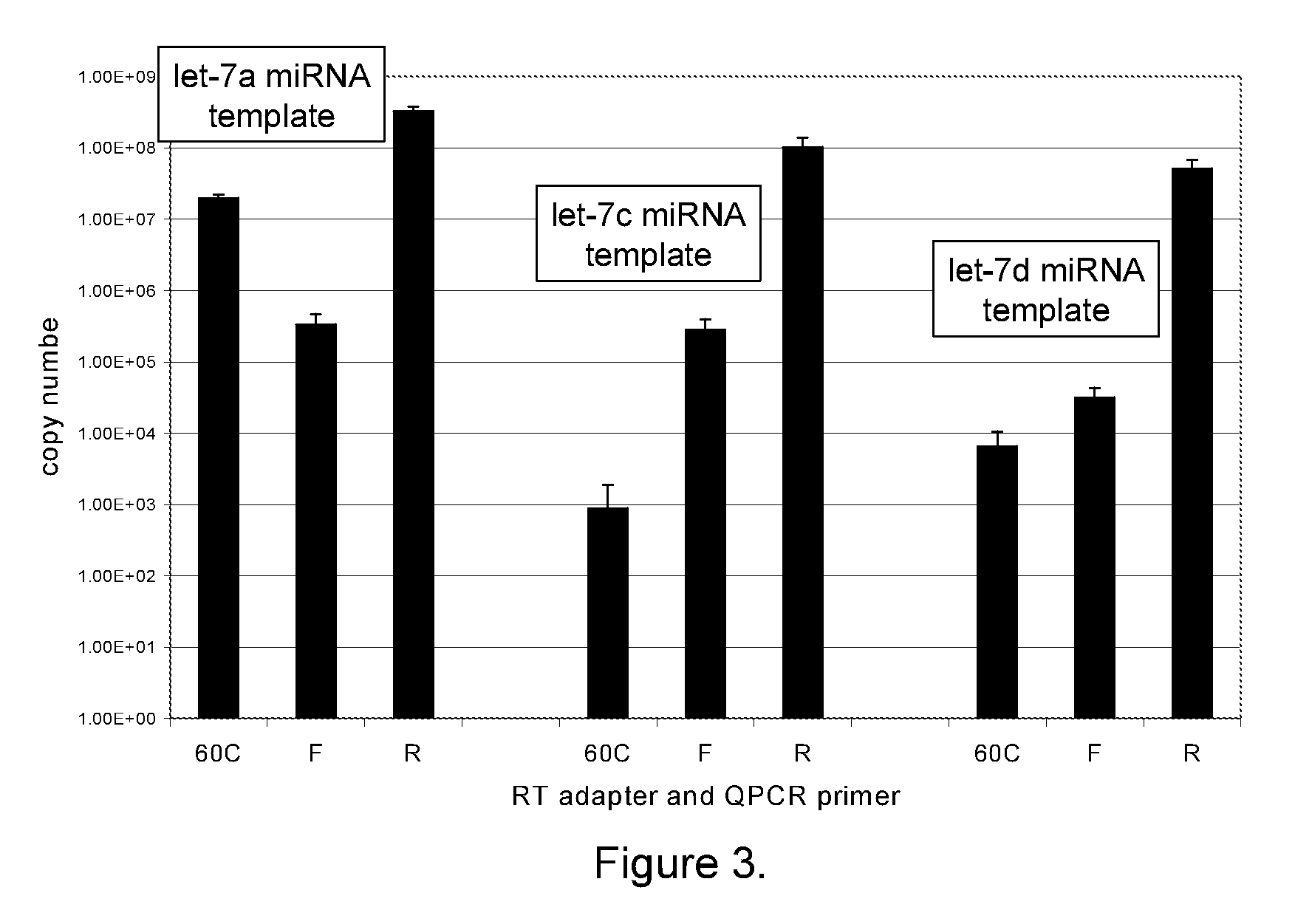
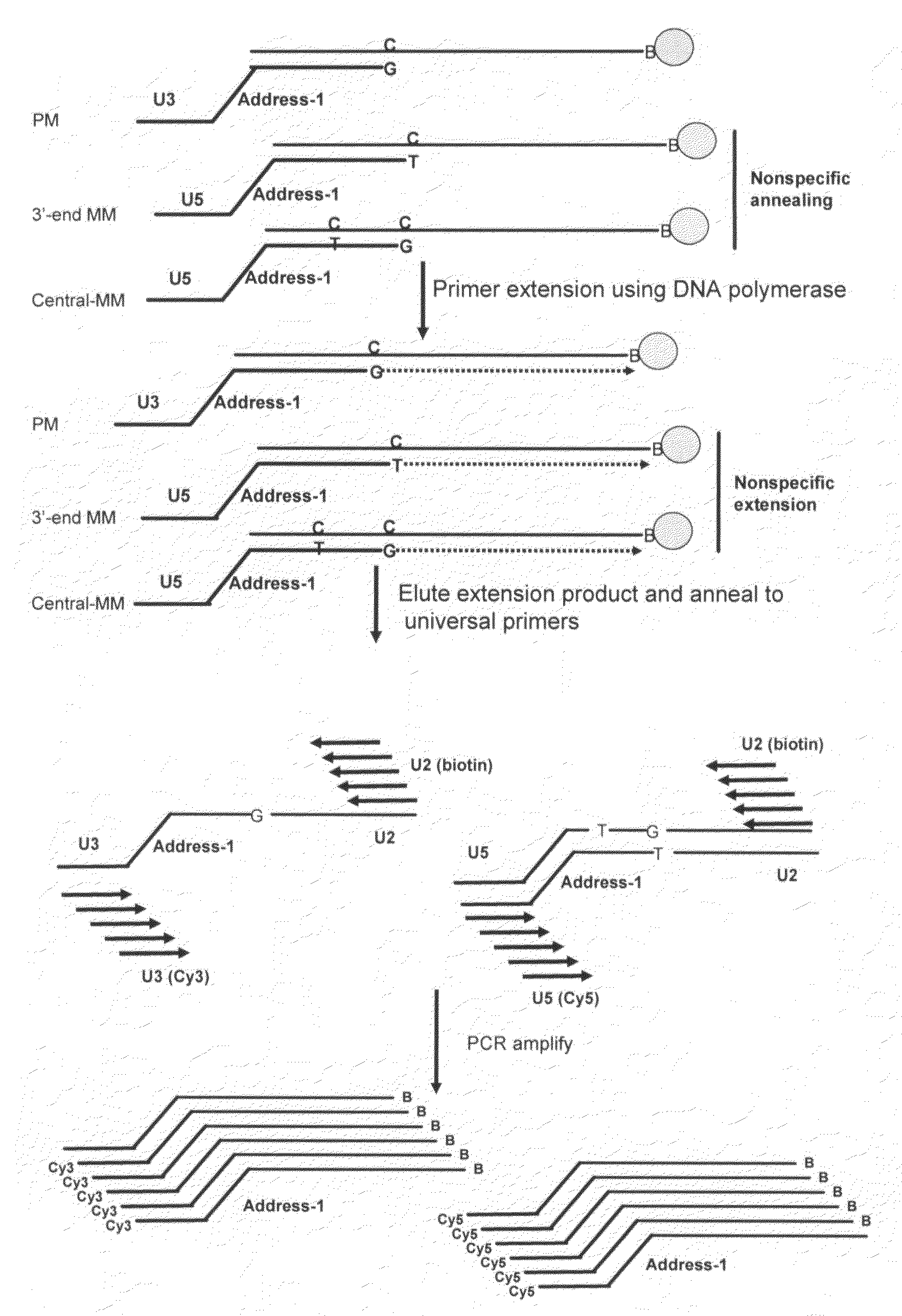
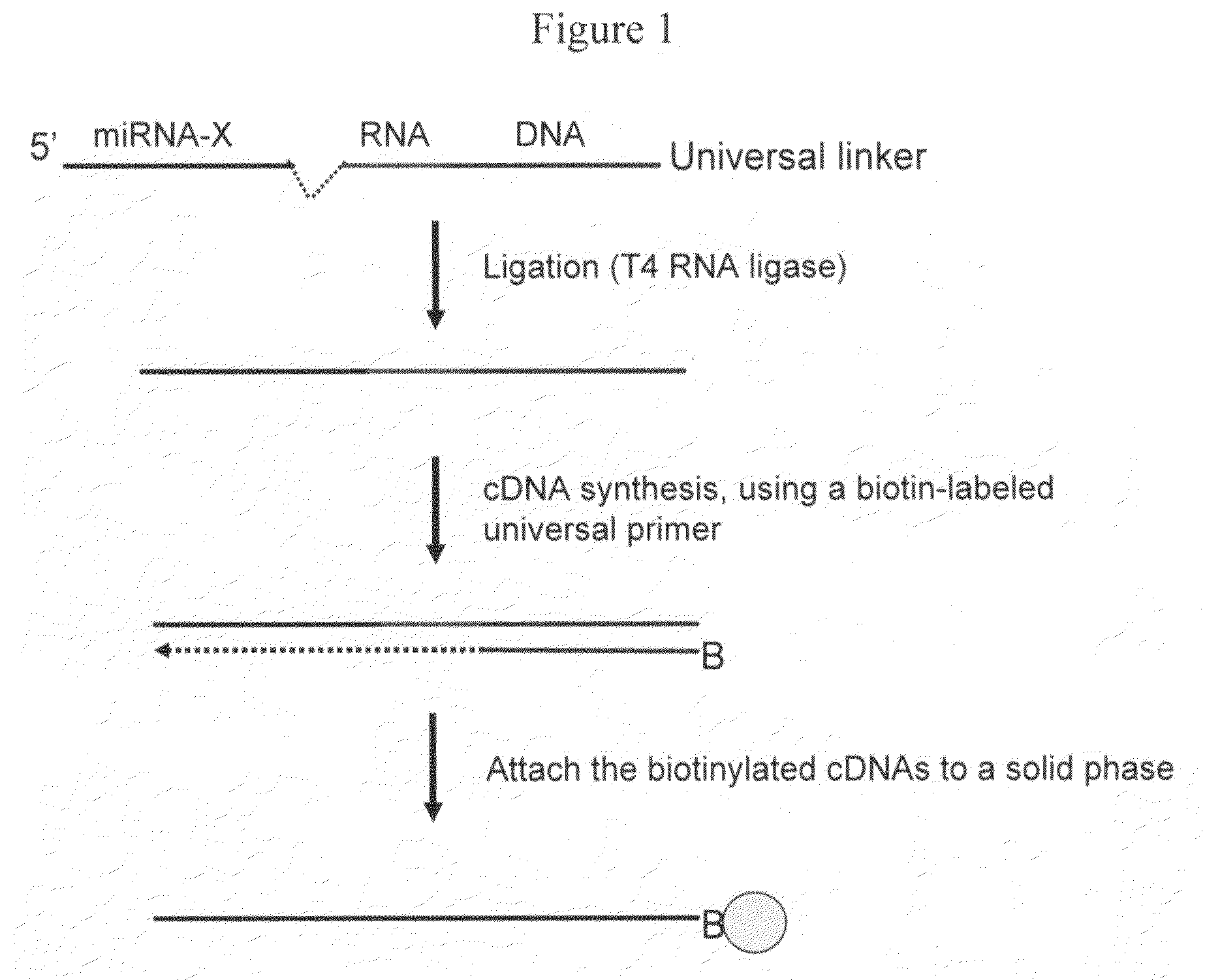
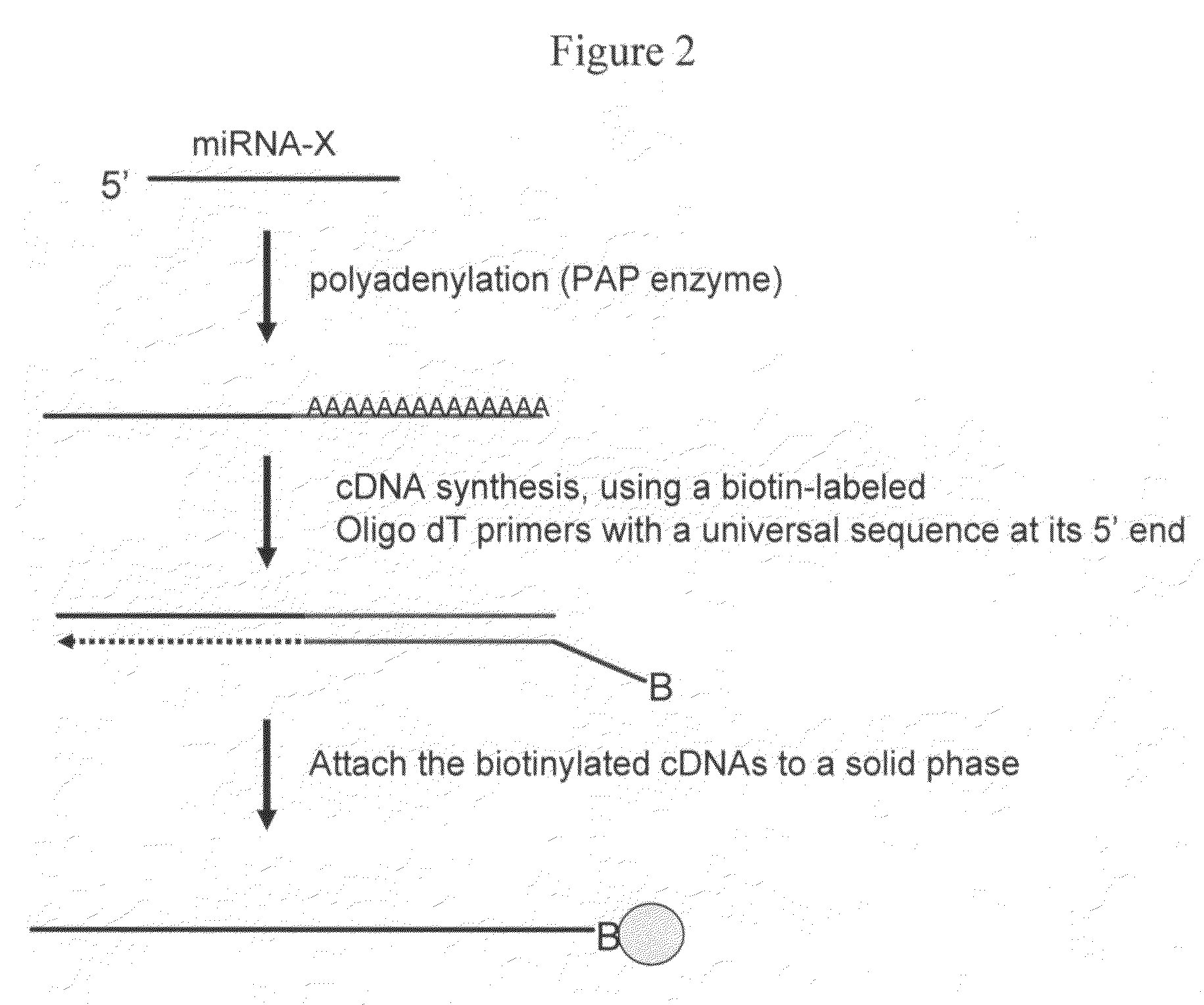
The invention provides a method of detecting small target nucleotide sequences, in particular, small RNA species that are present in a sample. The method generally comprises a poly-A polymerization step or a ligation step to add a universal sequence to the 3′-end of all RNA molecules, followed by a universal primer-mediated cDNA synthesis, solid-phase selection, assay oligo annealing, extension and PCR amplification / labeling. The method of the invention can be practiced to amplify and label a small amount of miRNA or other ncRNA. The resulting amplification product can be read out on a universal array or an array with miRNA-specific or ncRNA-specific probes. The invention has multiple embodiments, including methods, compositions, and kits. In general, the nucleic acids, compositions, and kits comprise materials that are useful in carrying out the methods of the invention or are produced by the methods, and that can be used to detect small target nucleic acid sequences present in samples, in particular, small RNA species.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Use of endo-lysosomal system and secreted vesicles (exosome-like) in treatments and diagnostics based on small RNA and experimental study of small RNA
InactiveUS20110177054A1Increase reduce activityGood effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideRegulatory rnaLipid formation
The present invention relates to a method for determining the delivery rates and / or efficiency of a siRNA, miRNA or related molecule to target organs or cells, a kit and the use of proteins or lipids involved in the formation of the endolysosomal system for modulating the activity and / or the cell-to-cell transfer of RNA, small RNA, for example miRNA, siRNA and piRNA, mRNA or non-coding RNA.It finds many applications in particular in methods for identifying the target(s) of miRNA or siRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, in methods for determining the efficiency of a treatment with siRNA and / or miRNA therapeutics, and in methods for genotyping and / or characterizing the condition of a person, a tumor or a fetus.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Methods and compositions for multiplex RNA guided genome editing and other RNA technologies
ActiveUS20160264981A1Facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editingVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationGenome editingGene silencing
The invention includes materials and methods to generate numerous small RNAs from one polynucleotide construct (synthetic gene) to facilitate RNA-guided multiplex genome editing, modification, inhibition of expression and other RNA-based technologies. The synthetic gene / polynucleotide construct encodes polycistronic RNA components separated by tRNAs, and preferably also includes regulatory components such as a promoter or terminator to form an expression cassette. Once transcribed in a cell, the transcript is processed by the cell to multiple RNA molecules by the endogenous tRNA processing system. The system can be used for any RNA based gene manipulation method including RNA-mediated genome editing, artificial microRNA mediated gene silencing, small RNA mediated genetic manipulation, double-stranded RNA mediated gene silencing, antisense mechanisms and the like.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for the detection of small RNAs
The invention provides compositions and methods for the detection of small RNA molecules in a multiplexed reaction. The assays and kits described herein are applicable for the identification, diagnosing, and monitoring of disorders including, but not limited to cancer, developmental and degenerative disease, neurological disorders, and stem cell disorders.
Owner:NANOSTRING TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com