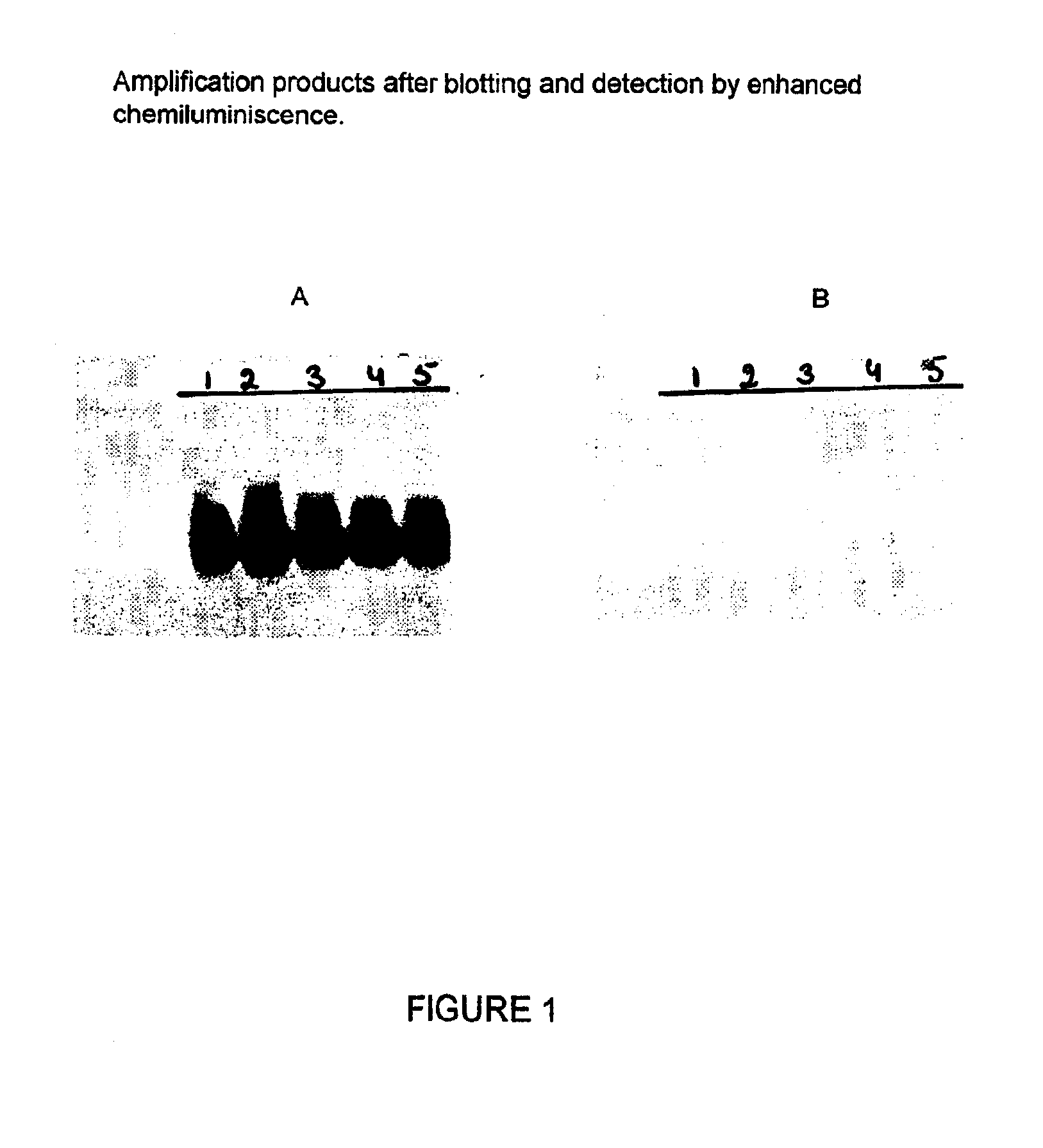
Patents
Literature
586 results about "Viral genomes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Viral Genomes . This resource provides viral and viroid genome sequence data and related information. Explore Viral Genome Sequences. Viral genome browser ; ... Try our new, experimental Virus Sequence Search Interface and send us your feedback! Learn more about this tool at NCBI Insights. Related Resources .
Viral Vectors
InactiveUS20090017543A1Prevent reverse transcriptionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsViral vectorVirus
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
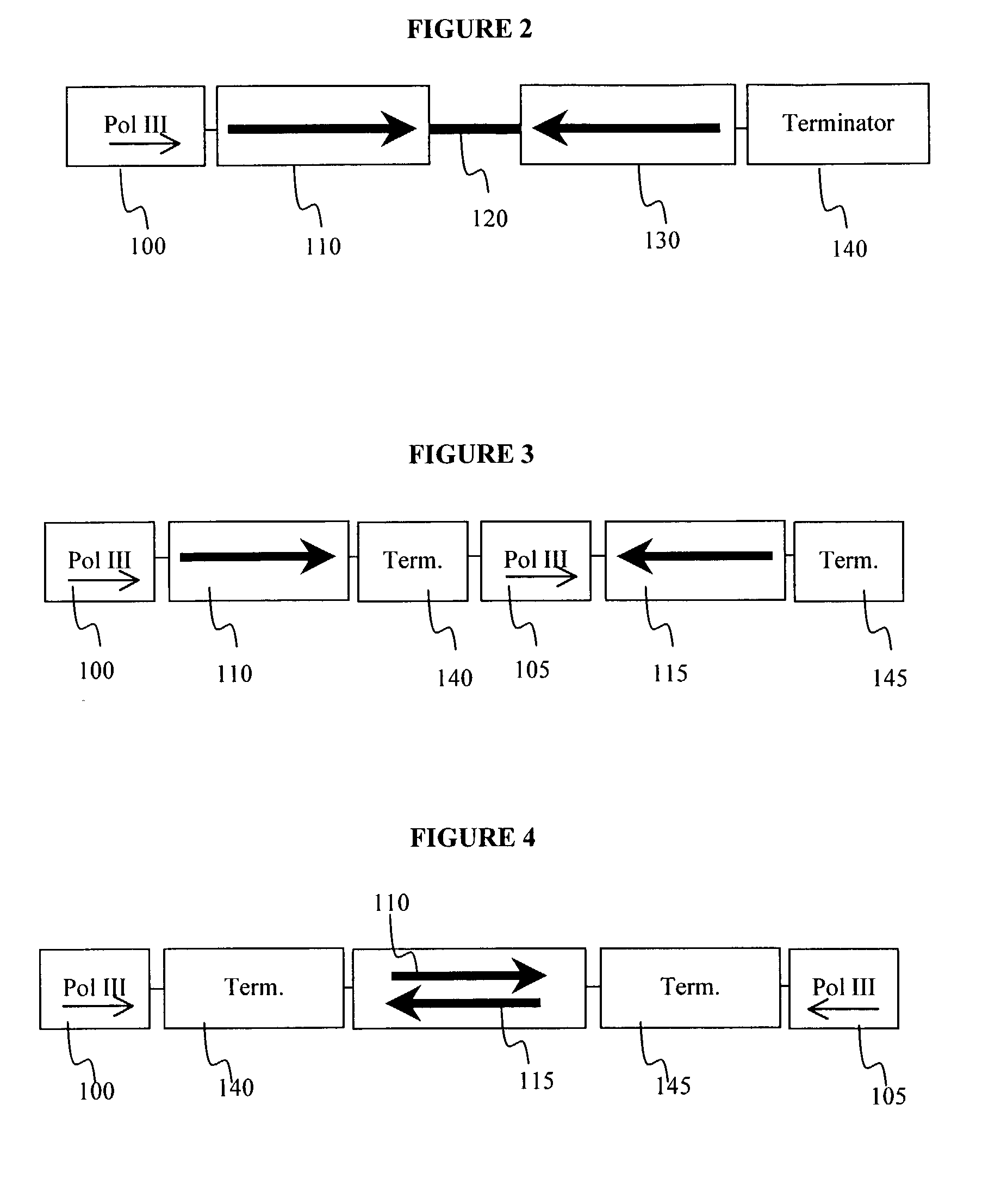
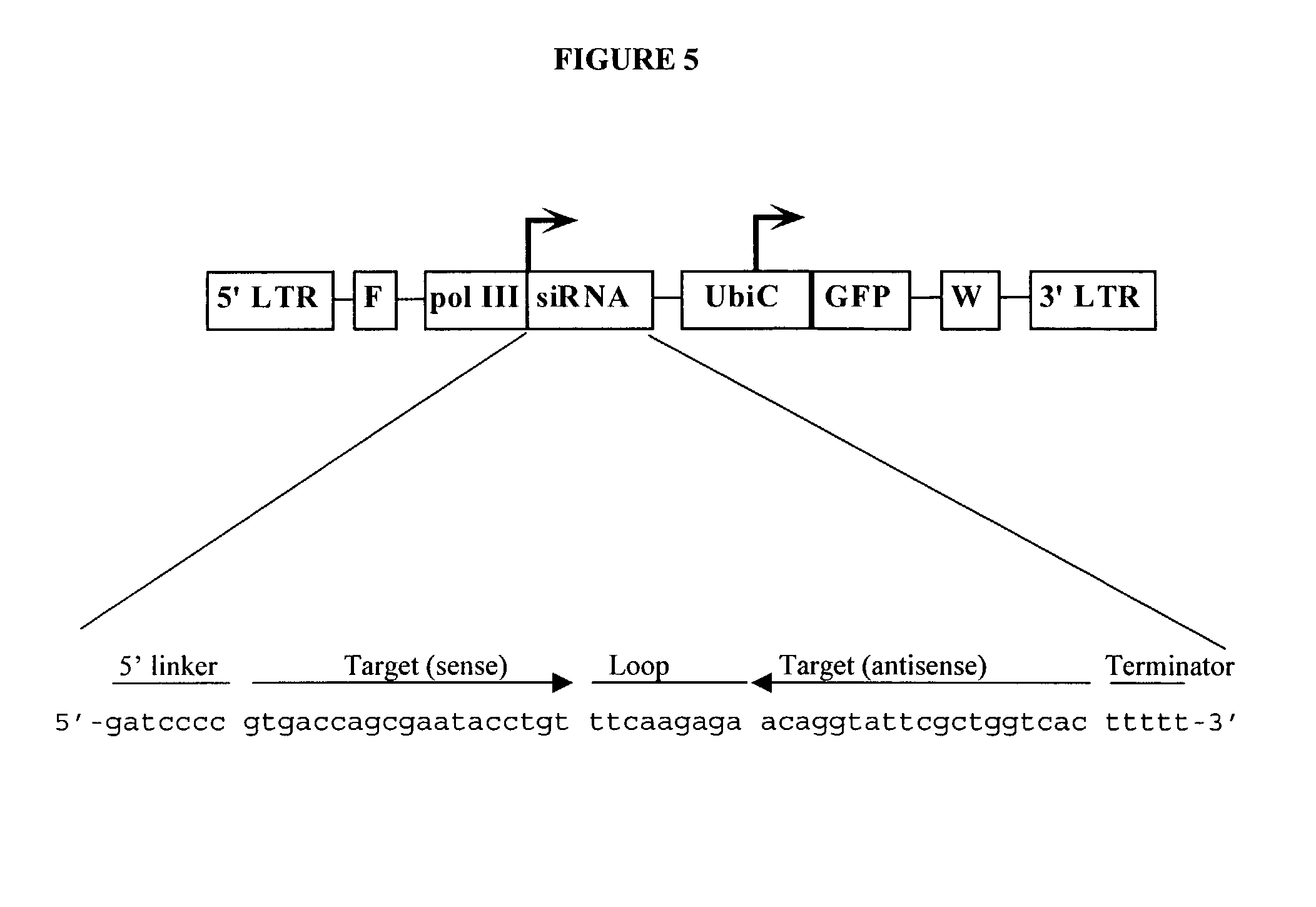
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
ActiveUS20030059944A1Prevents sequenceHigh expressionOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsGeneticsViral life cycle
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
RNase L activators and antisense oligonucleotides effective to treat RSV infections
The present invention relates to methods of inhibiting infection by RNA viruses with complexes of an activator of RNase L and an oligonucleotide that is capable of binding to the genome, antigenome or mRNAs of a negative strand RNA virus to specifically cleave the genomic or antigenomic RNA strand of the virus. In accordance with the present invention, the methods and complexes of the invention may be applied to target any negative strand RNA virus. The invention in one embodiment relates to a covalently linked complex of an oligonucleotide that is capable of binding to the genomic or antigenomic template RNA strand of a negative strand RNA virus and / or binding to an mRNA of a viral protein (an "antisense oligonucleotide") coupled to an activator of RNase L. In a preferred embodiment of the present invention, the oligonucleotide component of the complex is complementary to a region of the viral genomic RNA strand characterized by repeated or consensus sequences.
Owner:THE CLEVELAND CLINIC FOUND +1
Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of microRNA related diseases
InactiveUS20090298916A1Inhibitory activityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderDiseasePrimate
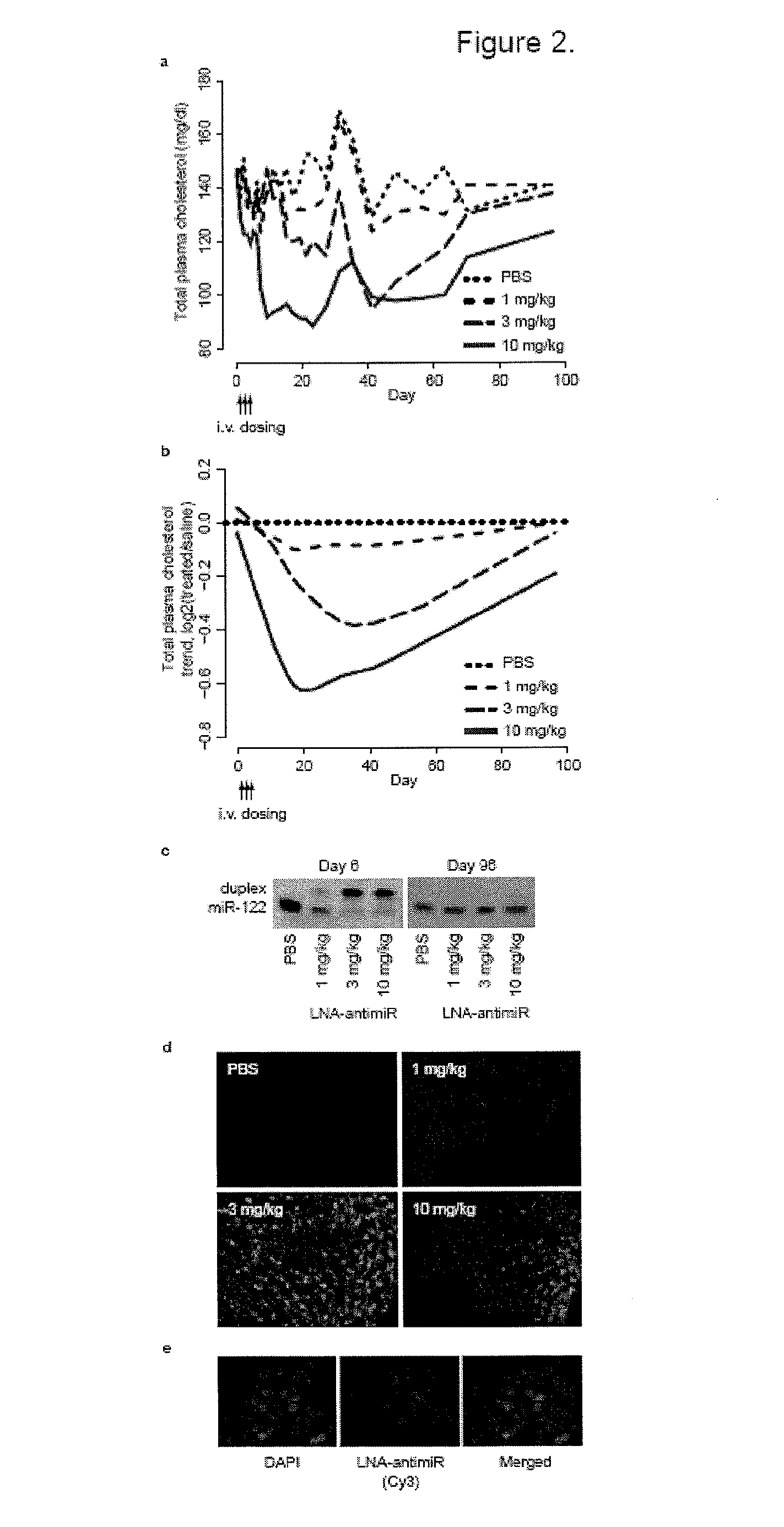
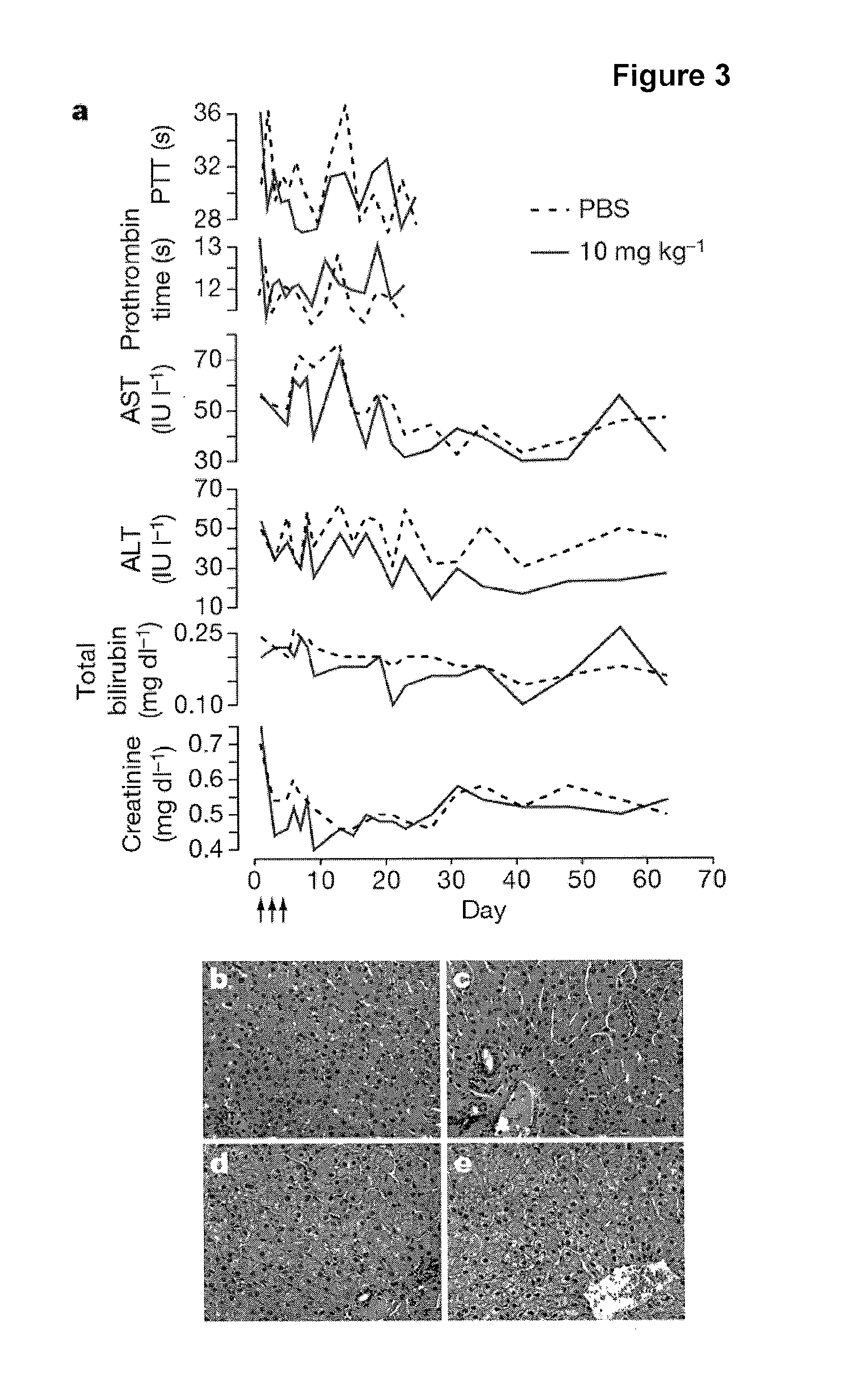
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Interferon inducing genetically engineered attenuated viruses
InactiveUS6468544B1Reduce in quantityReduced characteristicsSsRNA viruses negative-senseVectorsGenetic engineeringRecombinant DNA
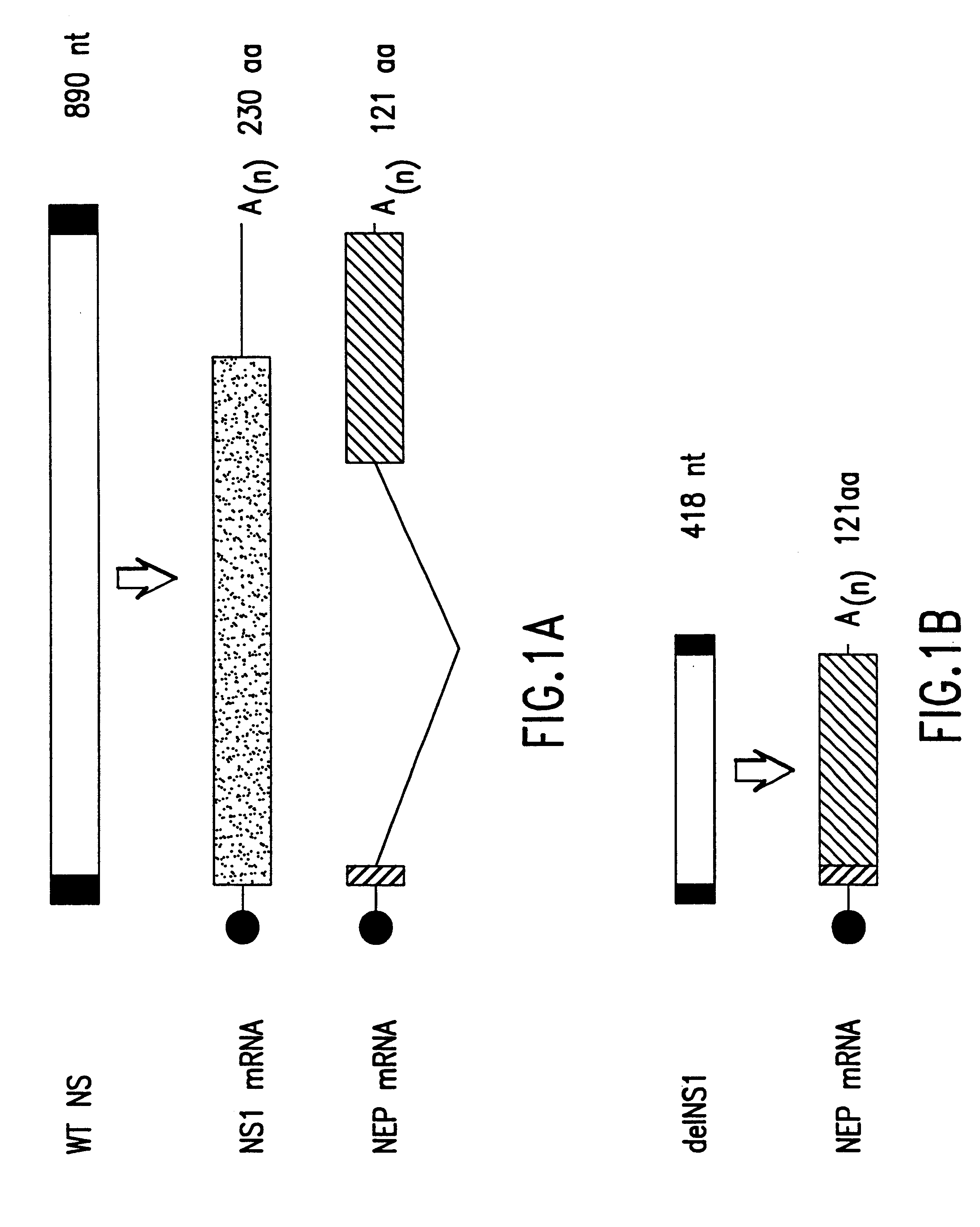
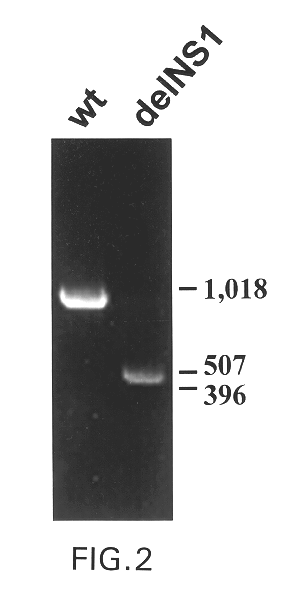
The present invention relates to genetically engineered attenuated viruses and methods for their production. In particular, the present invention relates to engineering live attenuated viruses which contain a modified NS gene segment. Recombinant DNA techniques can be utilized to engineer site specific mutations into one or more noncoding regions of the viral genome which result in the down-regulation of one or more viral genes. Alternatively, recombinant DNA techniques can be used to engineer a mutation, including but not limited to an insertion, deletion, or substitution of an amino acid residue(s) or an epitope(s) into a coding region of the viral genome so that altered or chimeric viral proteins are expressed by the engineered virus.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE +1
Postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome virus from pigs
The cloning of a novel PCVII viral genome is described as is expression of proteins derived from the PCVII genome. These proteins can be used in vaccine compositions for the prevention and treatment of PCVII infections, as well as in diagnostic methods for determining the presence of PCVII infections in a vertebrate subject. Polynucleotides derived from the viral genome can be used as diagnostic primers and probes.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
Anti-viral vectors
InactiveUS6783981B1Efficient exportPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsNucleotideRNase P
A viral vector production system is provided which system comprises: (i) a viral genome comprising at least one first nucleotide sequence encoding a gene product capable of binding to and effecting the cleavage, directly or indirectly, of a second nucleotide sequence, or transcription product thereof, encoding a viral polypeptide required for the assembly of viral particles, (ii) a third nucleotide sequence encoding said viral polypeptide required for the assembly of the viral genome into viral particles, which third nucleotide sequence has a different nucleotide sequence to the second nucleotide sequence such that said third nucleotide sequence, or transcription product thereof, is resistant to cleavage directed by said gene product; wherein at least one of the gene products is an external guide sequence capable of binding to and effecting the cleavage by RNase P of the second nucleotide sequence. The viral vector production system may be used to produce viral particles for use in treating or preventing viral infection.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
2′-branched nucleosides and Flaviviridae mutation
ActiveUS7824851B2High sensitivityReduce Flaviviridae infectionBiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseAmino acidMutant strain
The present invention discloses a method for the treatment of Flaviviridae infection that includes the administration of a 2′-branched nucleoside, or a pharmaceutically acceptable prodrug and / or salt thereof, to a human in need of therapy in combination or alternation with a drug that directly or indirectly induces a mutation in the viral genome at a location other than a mutation of a nucleotide that results in a change from seine to a different amino acid in the highly conserved consensus sequence, XRXSGXXXT (Sequence ID No. 63), of domain B of the RNA polymerase region, or is associated with such a mutation. The invention also includes a method to detect a mutant strain of Flaviviridae and a method for its treatment.
Owner:INDENIX PHARM LLC
Virus vectors for highly efficient transgene delivery
ActiveUS20140336245A1Enhanced transductionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsGene transferTransgene
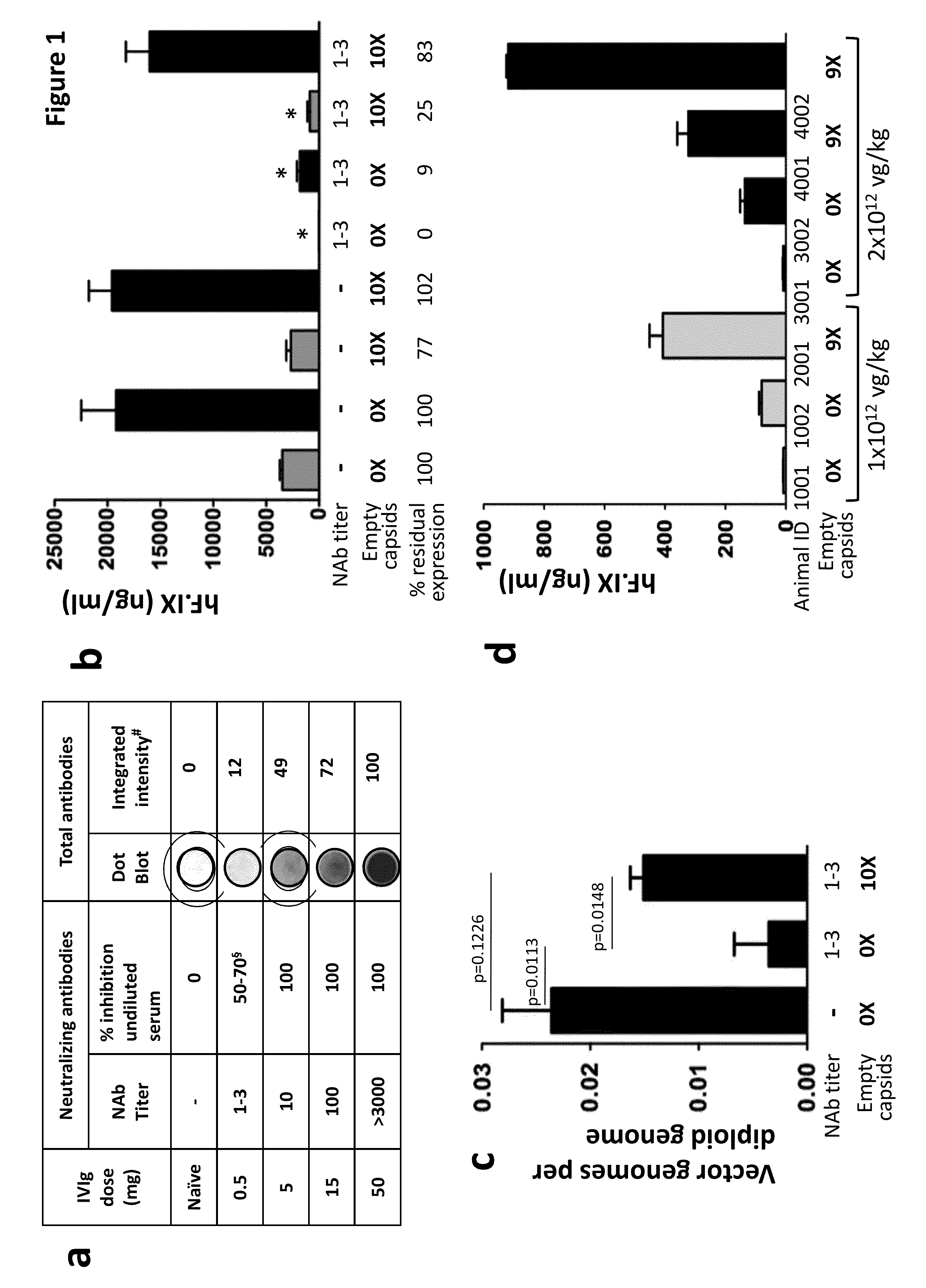
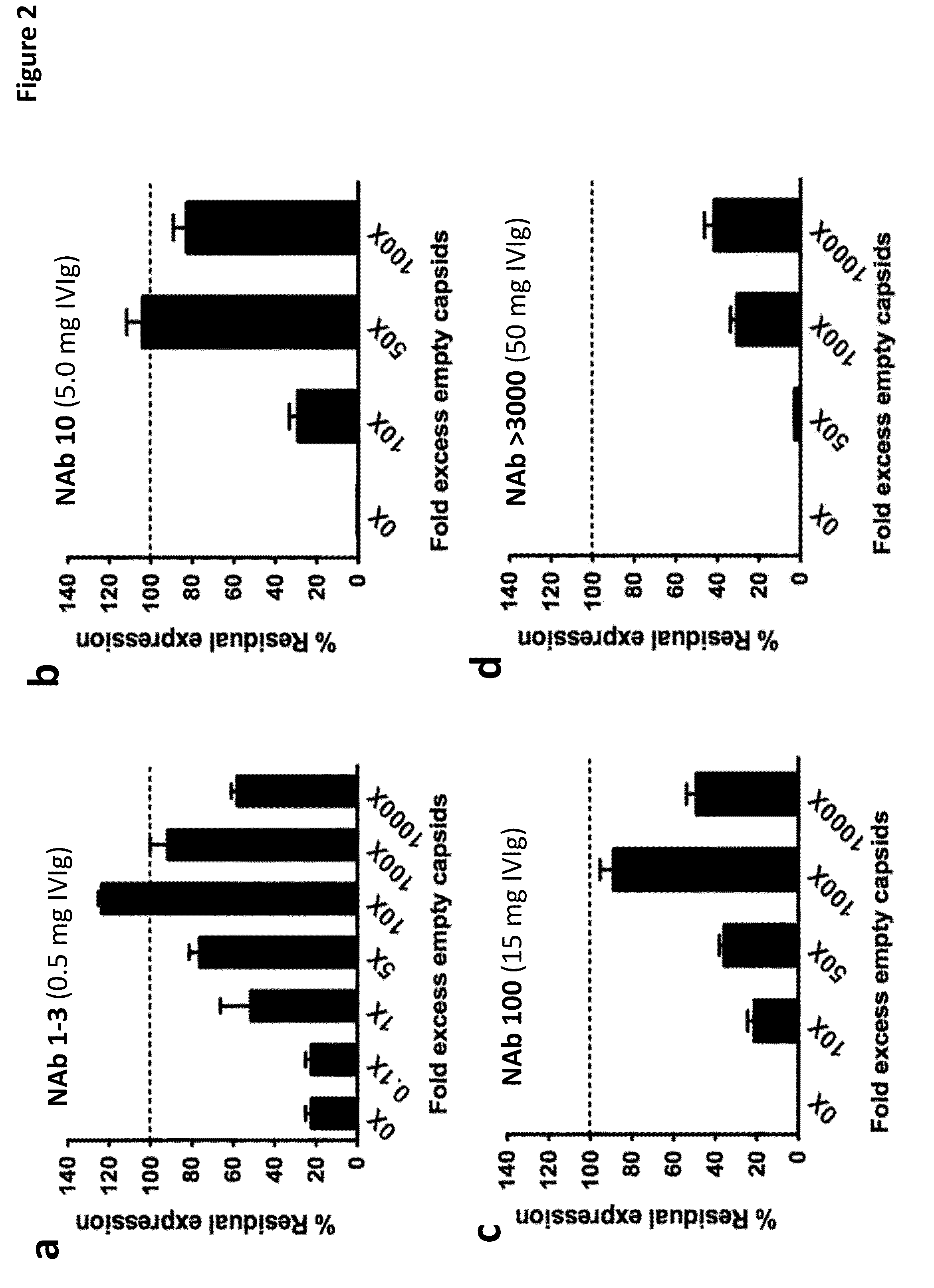
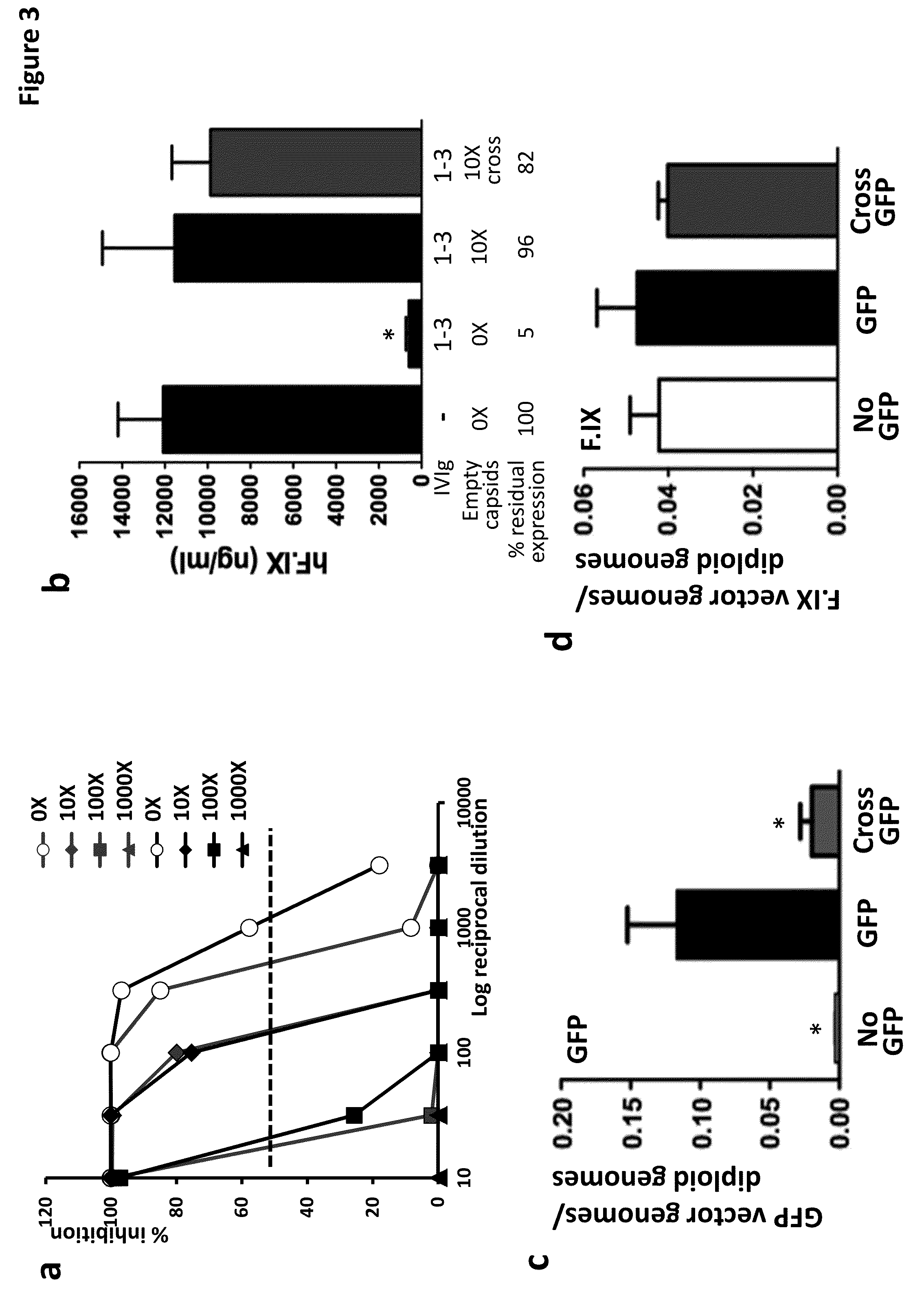
The invention provides viral vector formulations and methods of uses thereof for delivery of transgenes or therapeutic nucleic acids to human subjects. The formulations include a vector and suitable amounts of empty capsids, viral genome-containing capsids, or viral capsid proteins which are optionally chemically or structurally modified and which bind to neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies thereby reducing or preventing antibody-mediated clearance of the vector, but still allowing the genome-containing (therapeutic) vector to transduce target cells and achieve therapeutic gene transfer.
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
Pharmaceutical Compositions for Treatment of MicroRNA Related Diseases
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules within a cell
In one aspect, the invention provides methods and compositions for the expression of small RNA molecules within a cell using a retroviral vector. The methods can be used to express double stranded RNA complexes. Small interfering RNA (siRNA) can be expressed using the methods of the invention within a cell, that interfere with a viral life cycle by down regulating either the viral genome, a viral genome transcript, or a host cell that. In another aspect the invention provides methods for treating patients having suffering from infection, particularly infection with HIV. In a further aspect, the invention provides methods for producing siRNA encoding lentivirus where the siRNA activity may interfere with the lentiviral life cycle.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +1
Methods and compositions for reducing viral genome amounts in a target cell
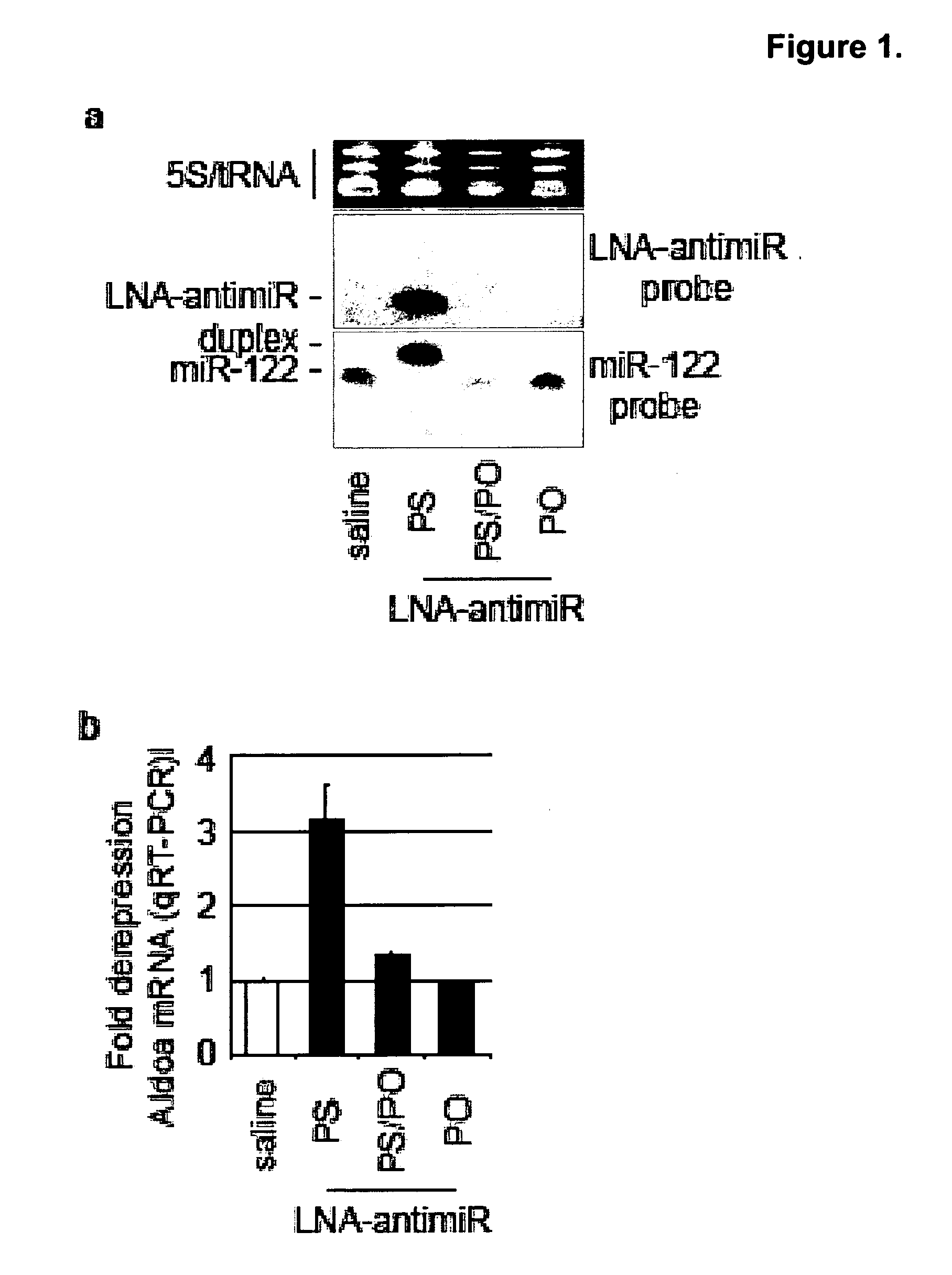
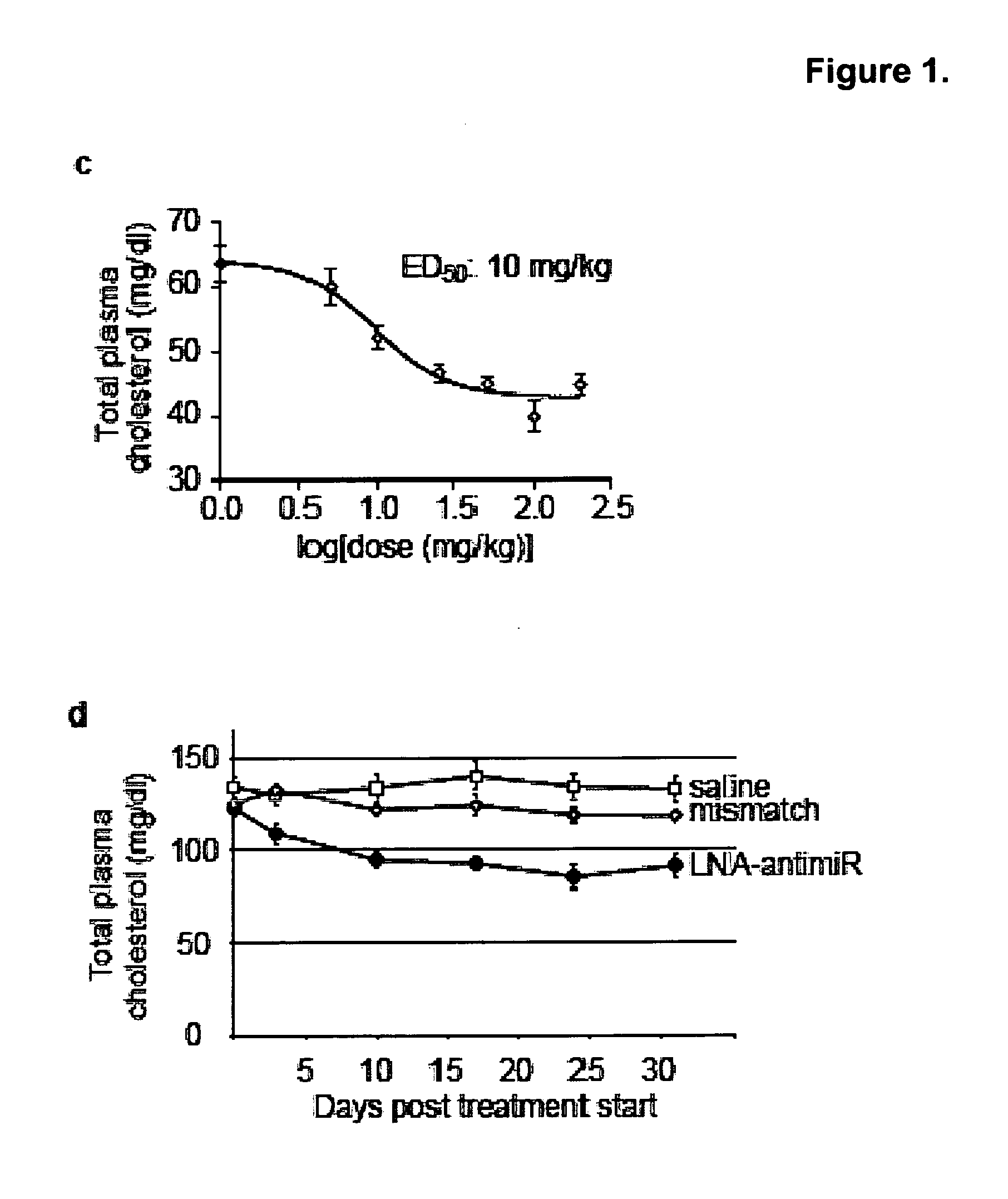
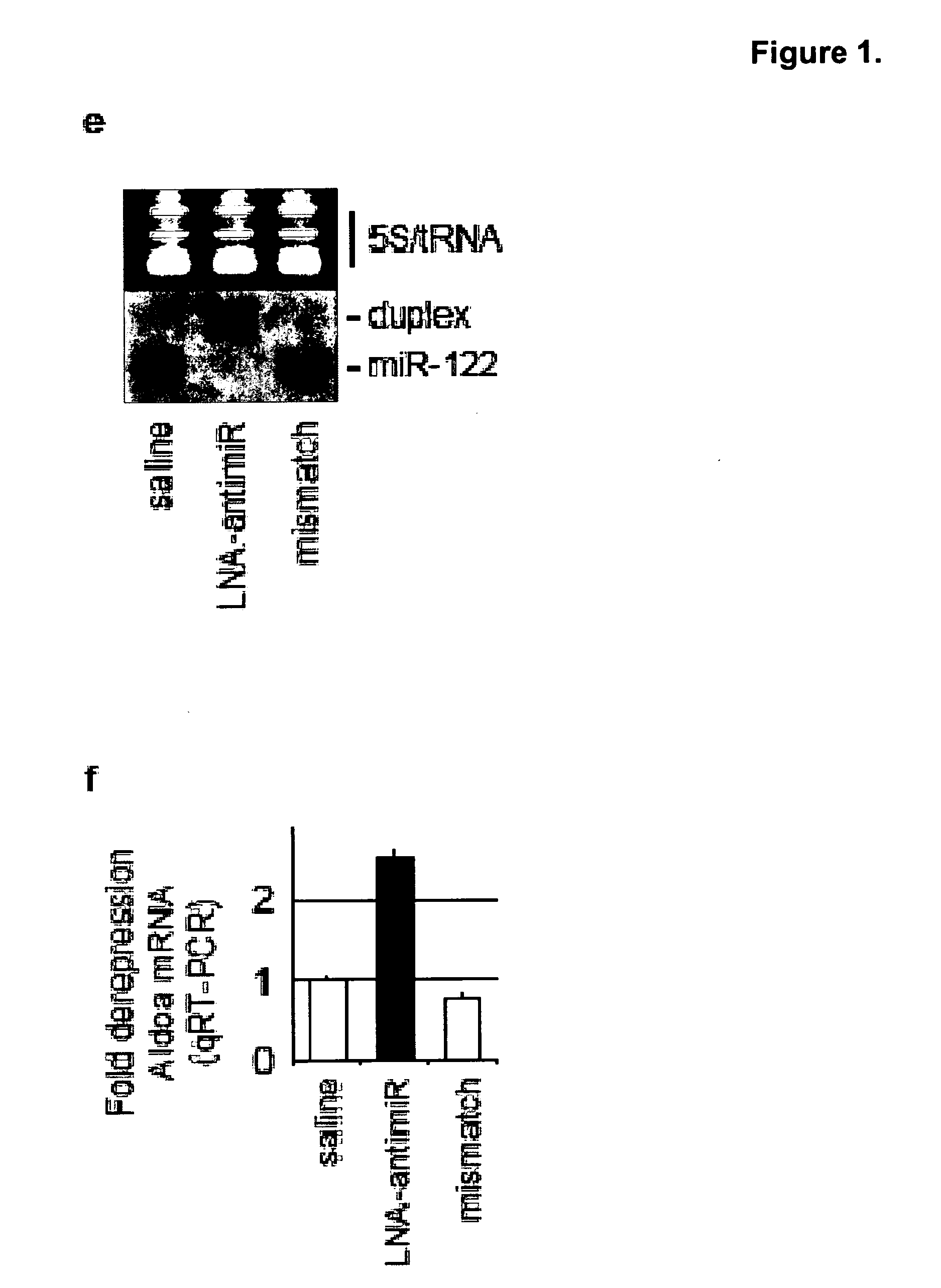
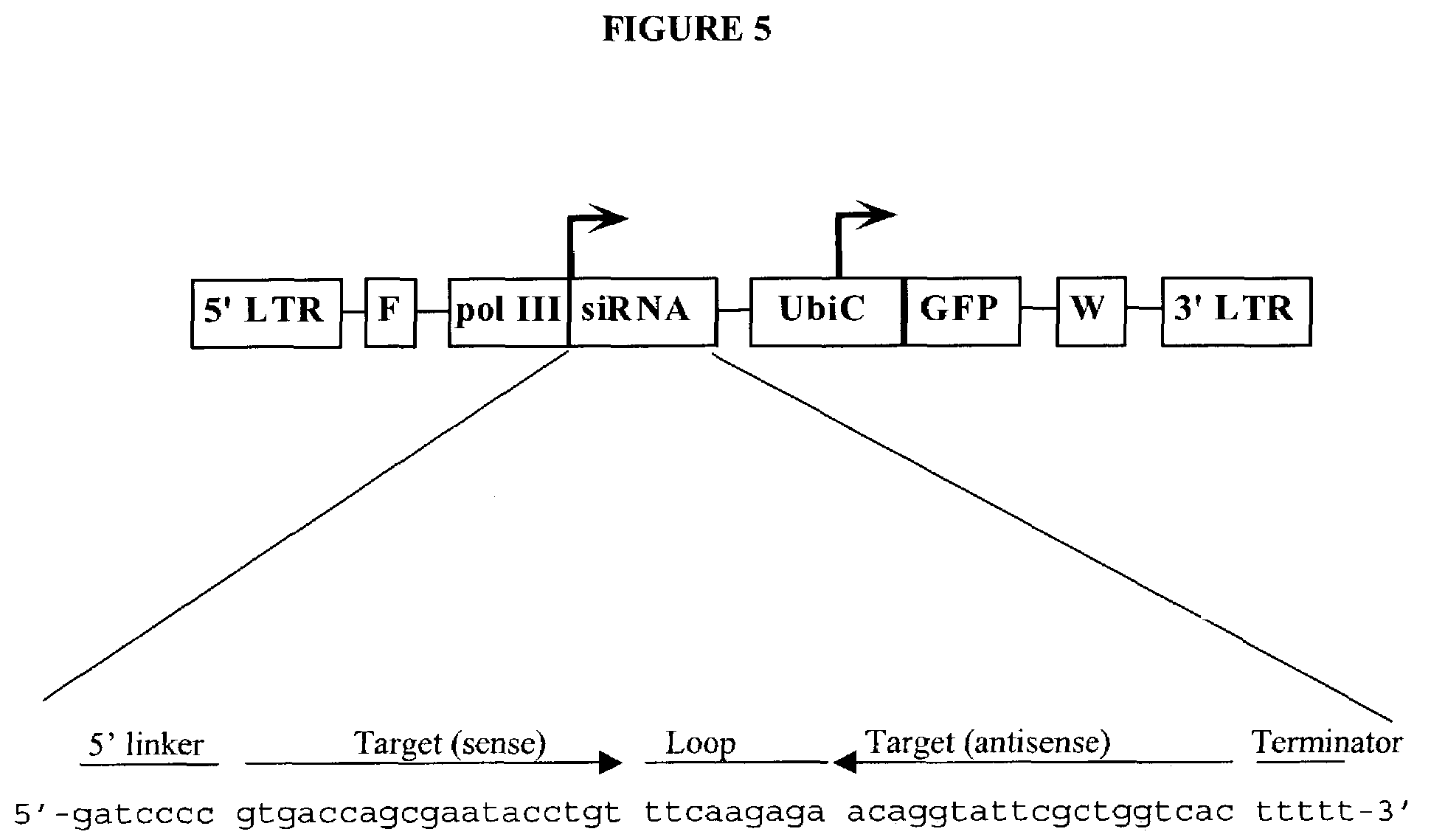
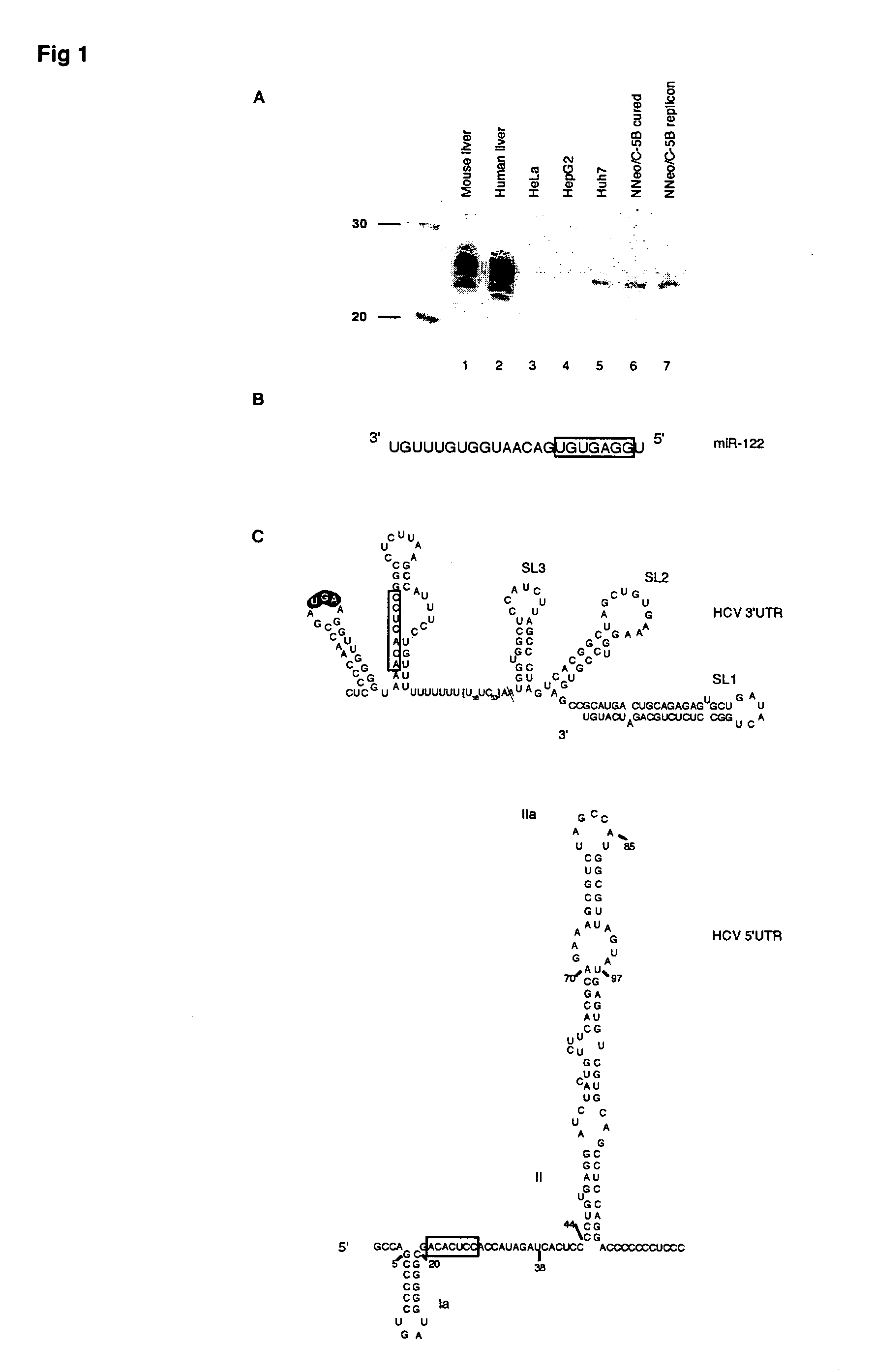
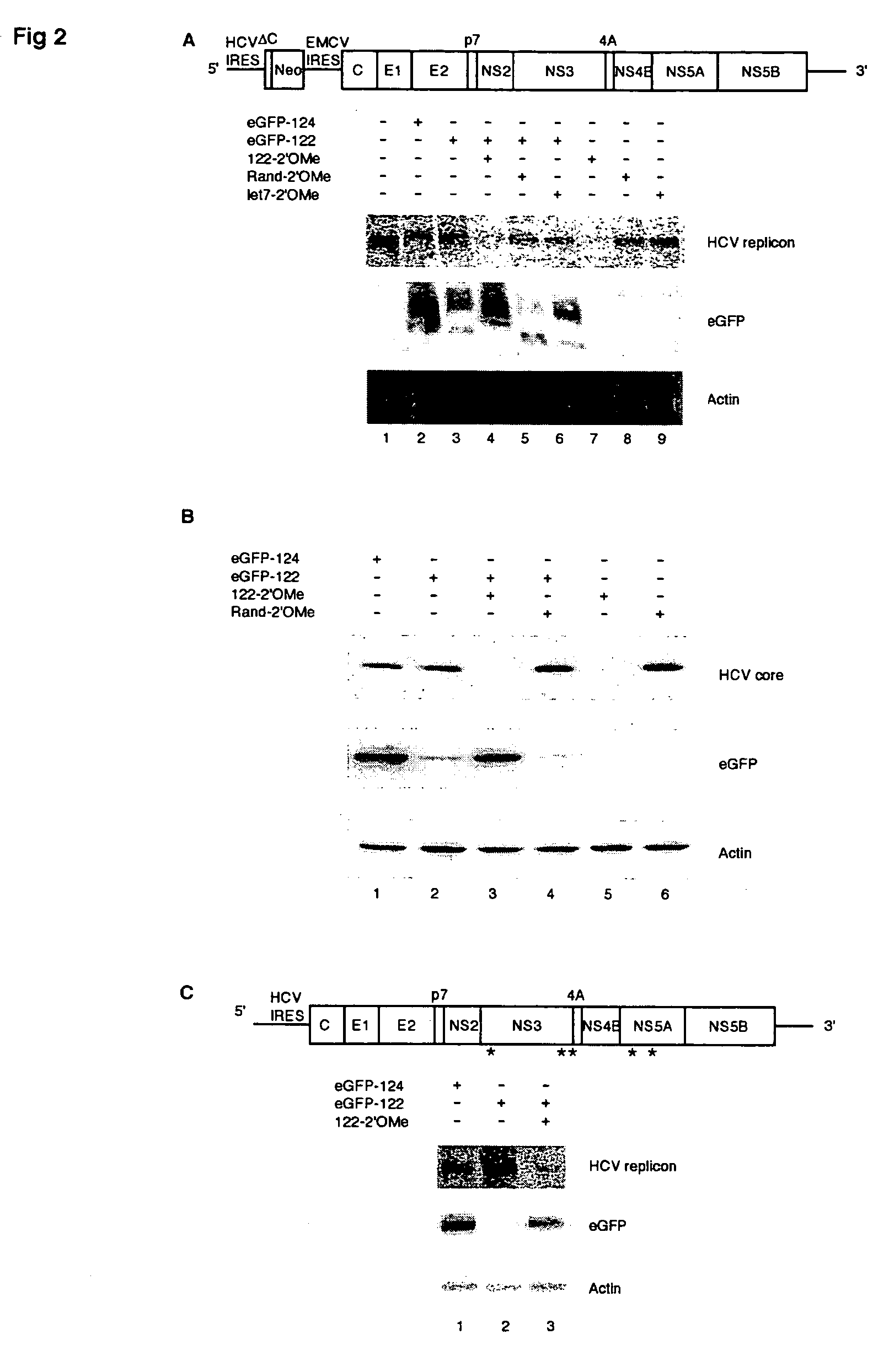
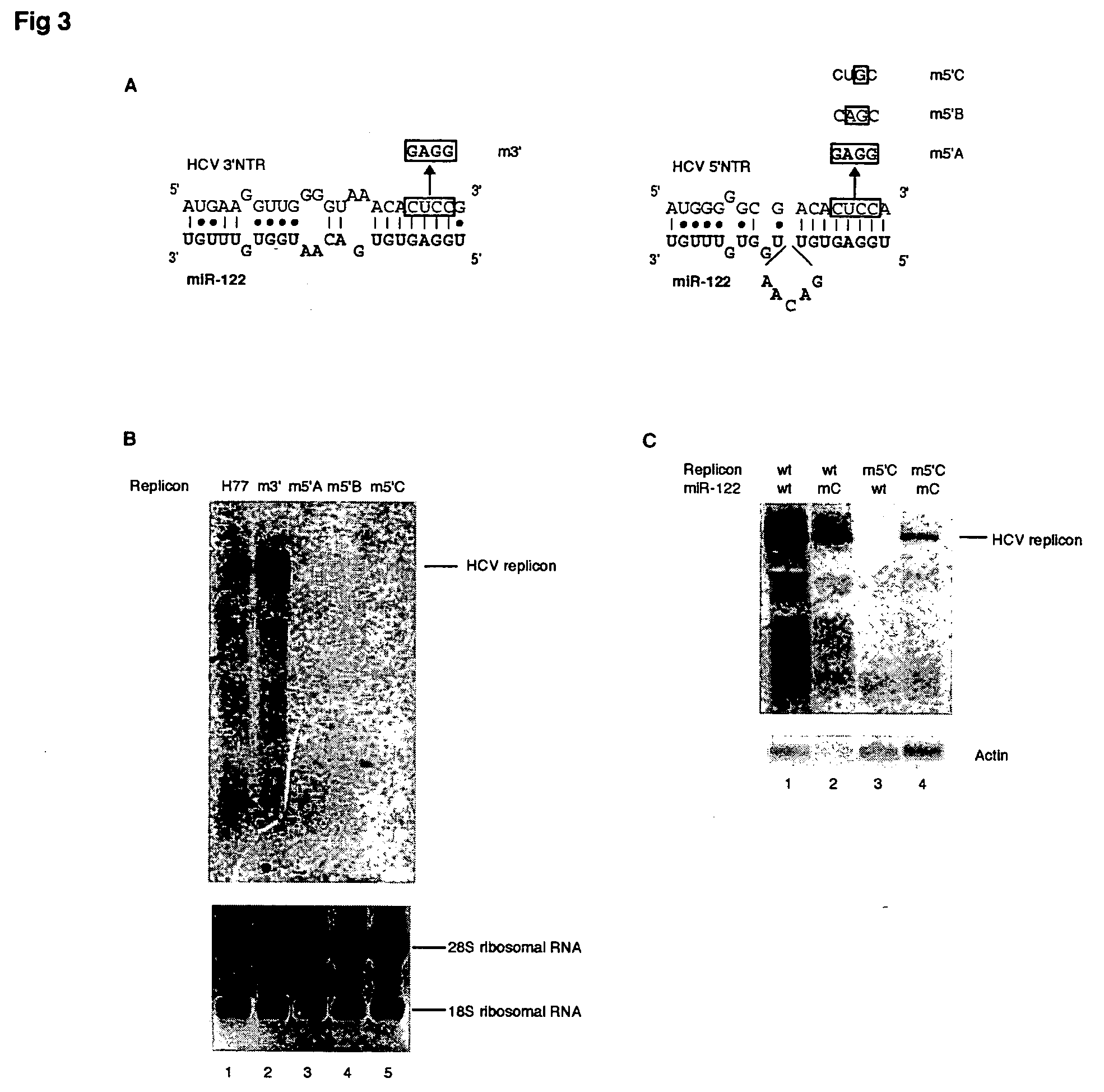
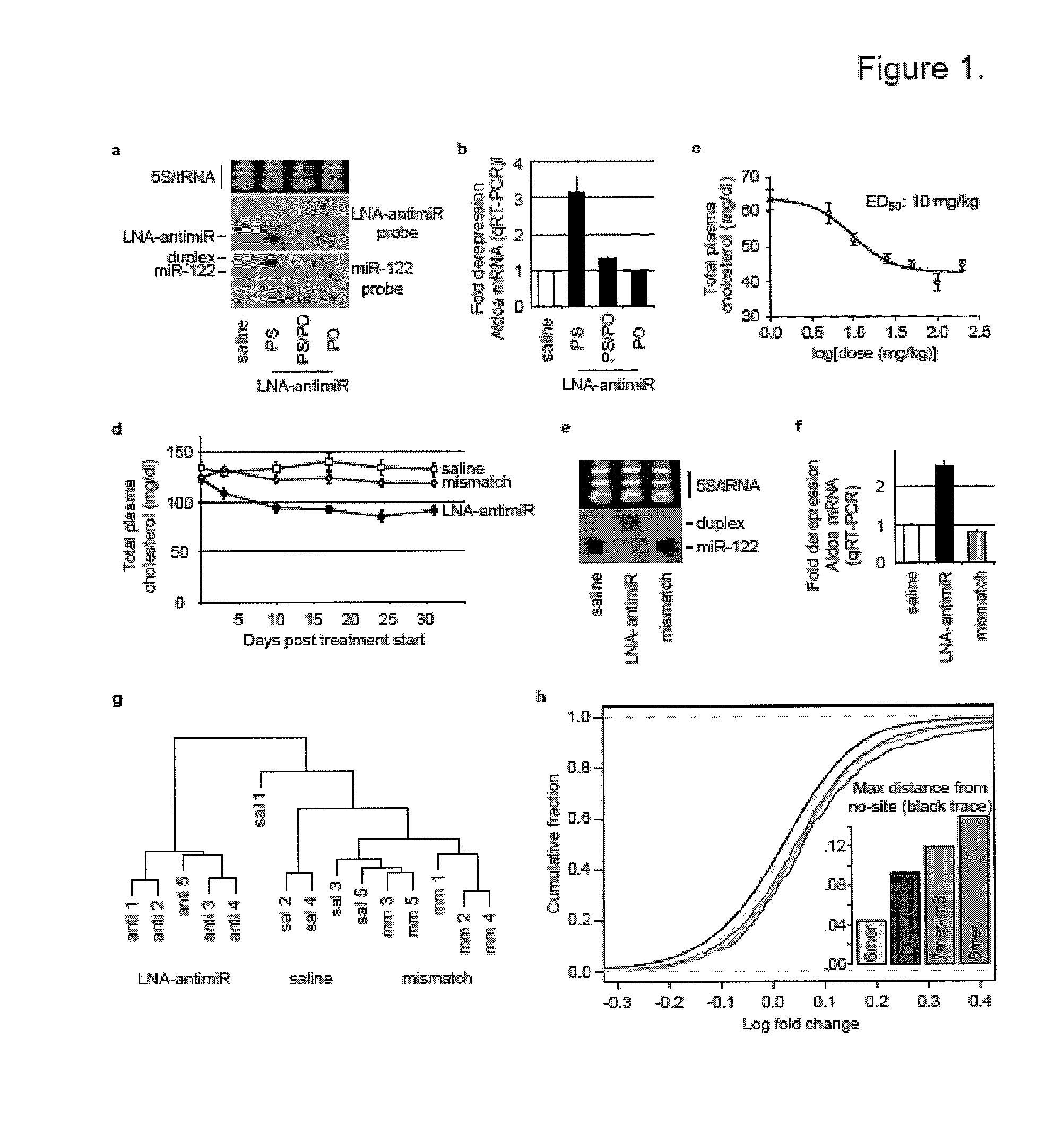
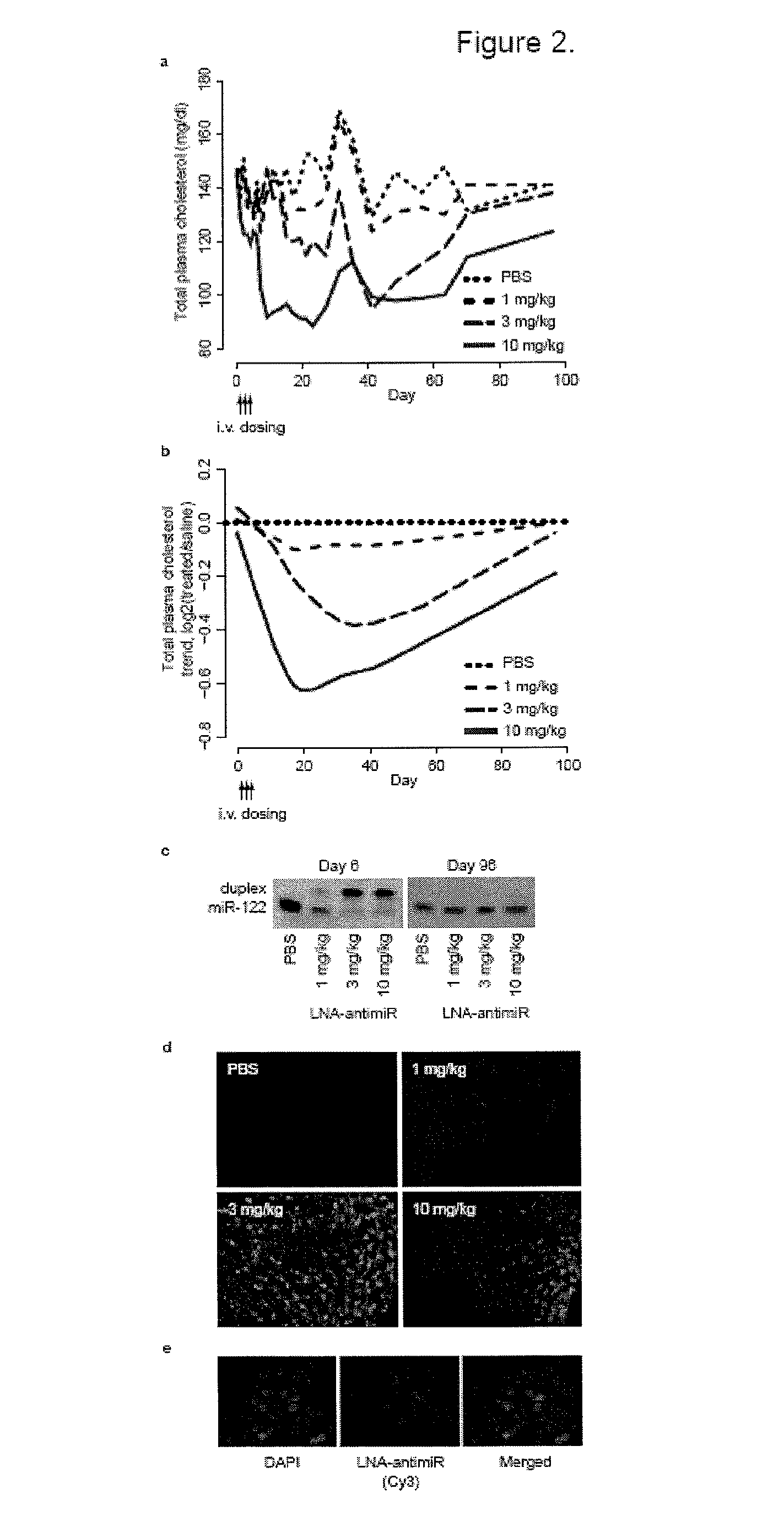
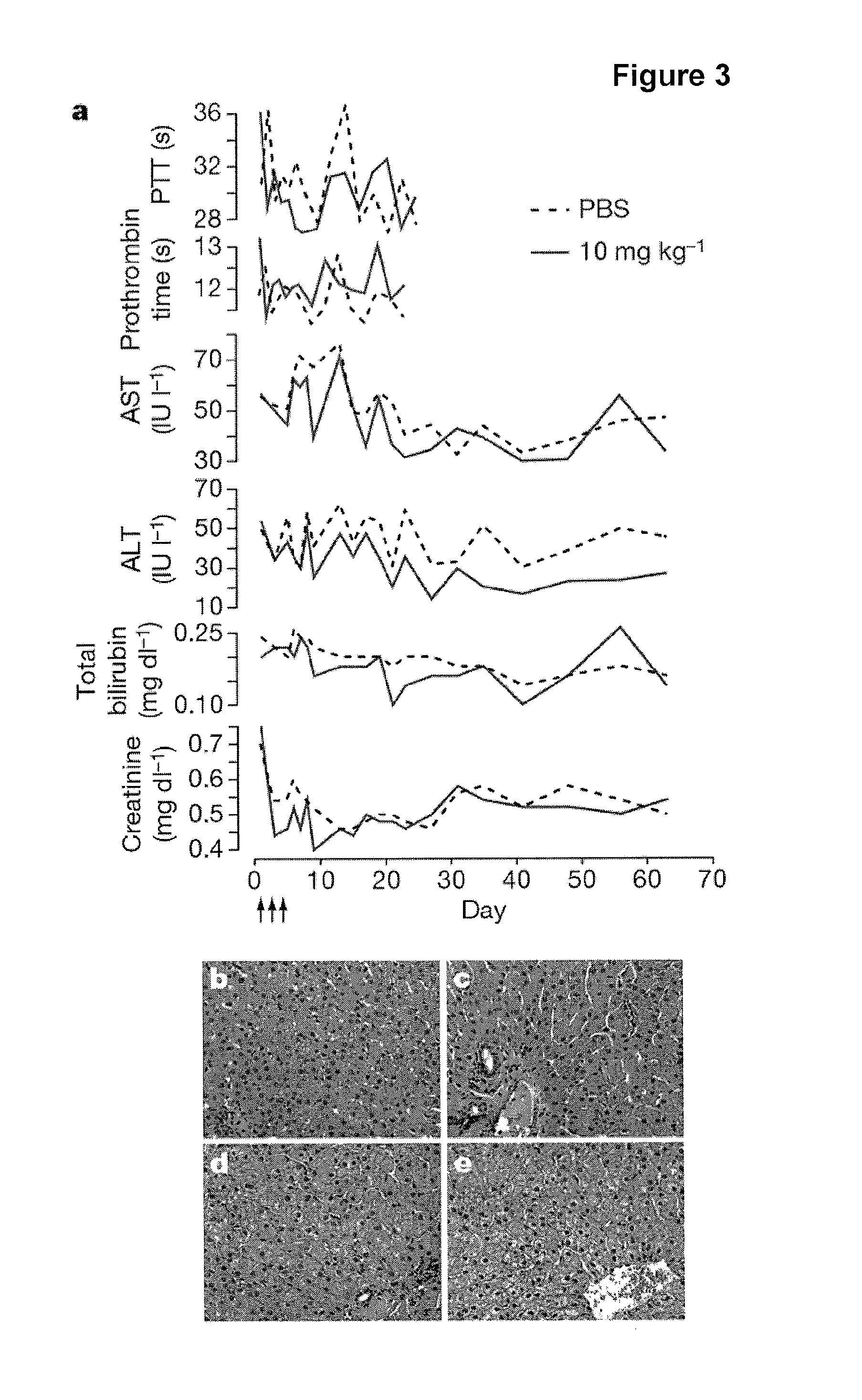
Methods and compositions for reducing viral genome amounts in a target cell are provided. In the subject methods, the activity of a miRNA is inhibited in a manner sufficient to reduce the amount of viral genome in the target cell, e.g., by introducing a miRNA inhibitory agent in the target cell. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions, kits and systems for use in practicing the subject methods. The subject invention finds use in a variety of applications, including the treatment of subjects suffering from a viral mediated disease condition, e.g., an HCV mediated disease condition.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Packaging cell
A virus-producing cell sustaining the ability to produce viruses at high titer is successfully constructed by expressing the virus structural gene under the regulation of EF1α promoter. In this virus-producing cell, the virus structural gene is ligated to a selection marker gene via IRES and domains other than the protein coding domain are eliminated from the DNA encoding virus structural proteins. Thus, reduction of the titer due to cell passages can be prevented and emergence of wild type viruses caused by unfavorable recombination of the virus genome can be inhibited.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Postweaning multisystemic wasting syndrome and porcine circovirus from pigs
InactiveUS20060002952A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPorcine circovirusPolynucleotide
The cloning of a novel PCVII viral genome is described as is expression of proteins derived from the PCVII genome. These proteins can be used in vaccine compositions for the prevention and treatment of PCVII infections, as well as in diagnostic methods for determining the presence of PCVII infections in a vertebrate subject. Polynucleotides derived from the viral genome can be used as diagnostic primers and probes.
Owner:MERIAL SAS
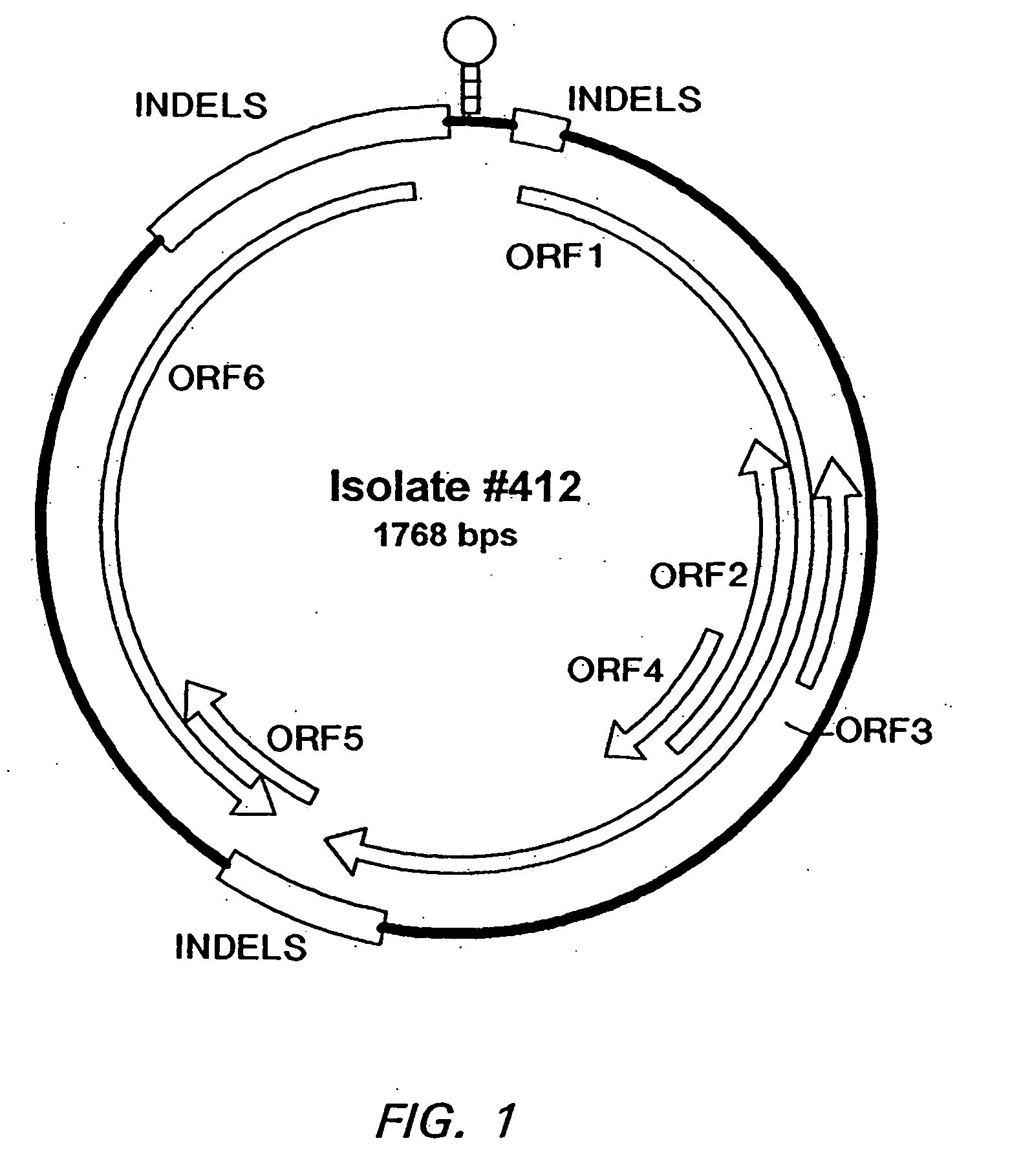
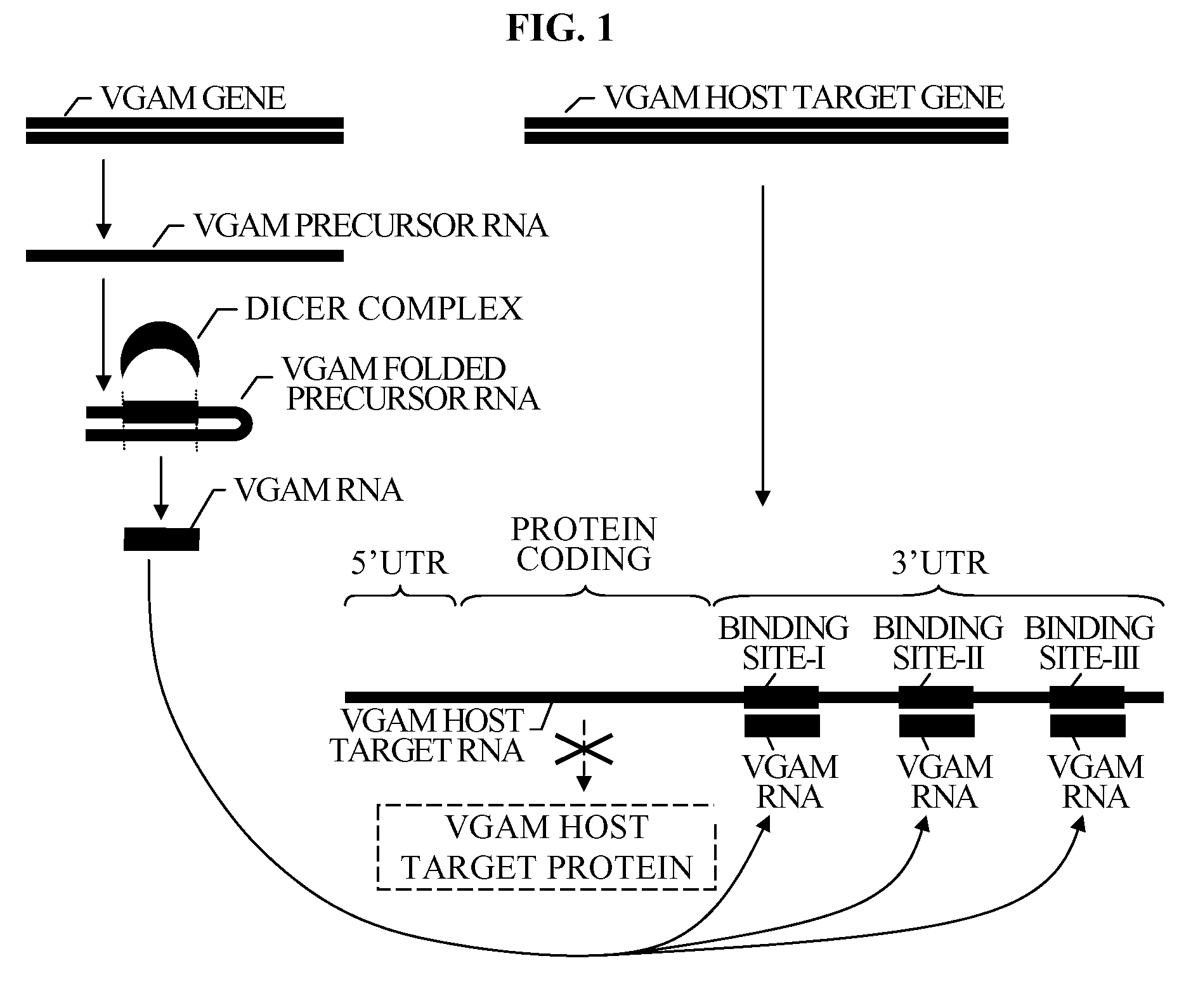
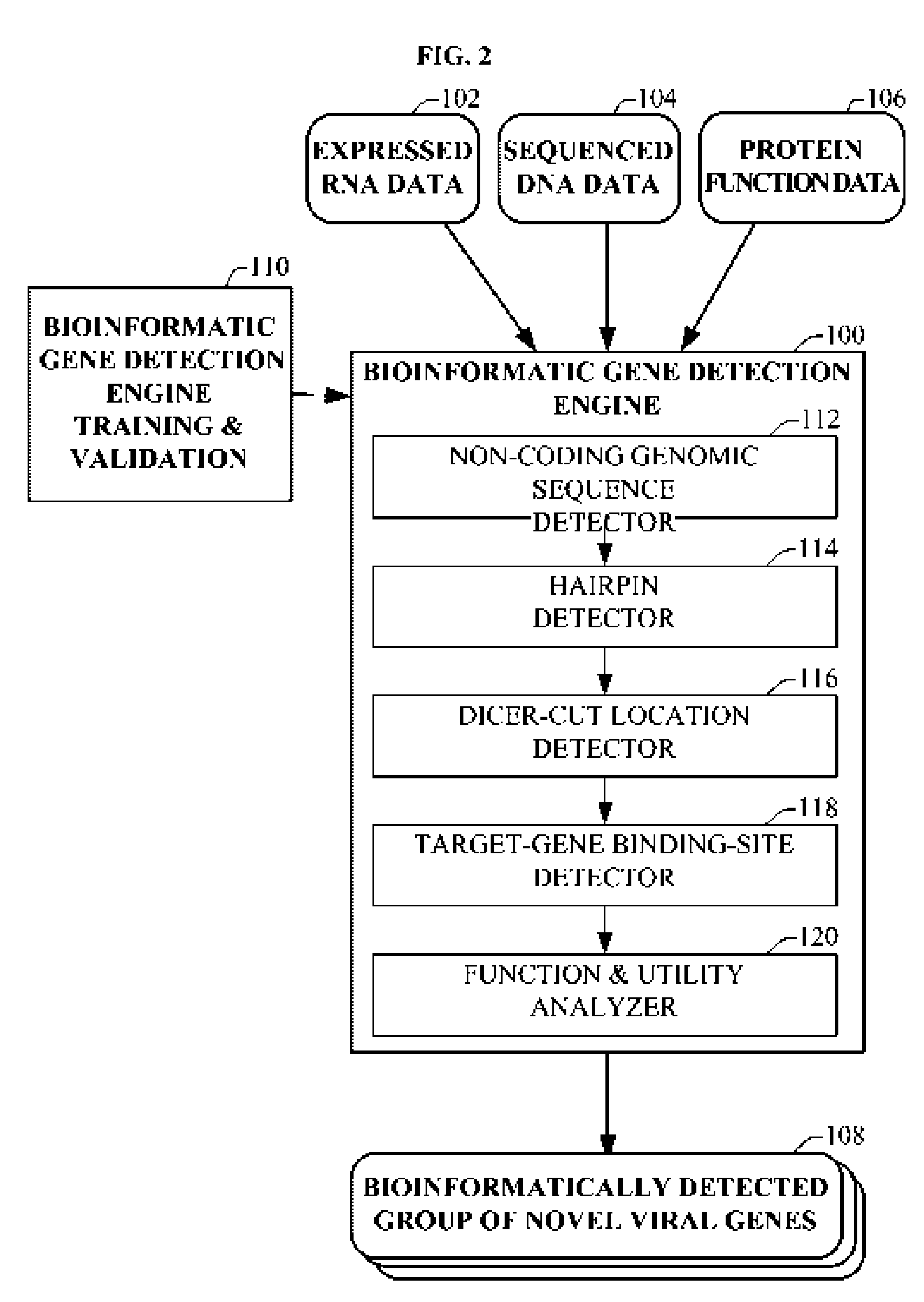
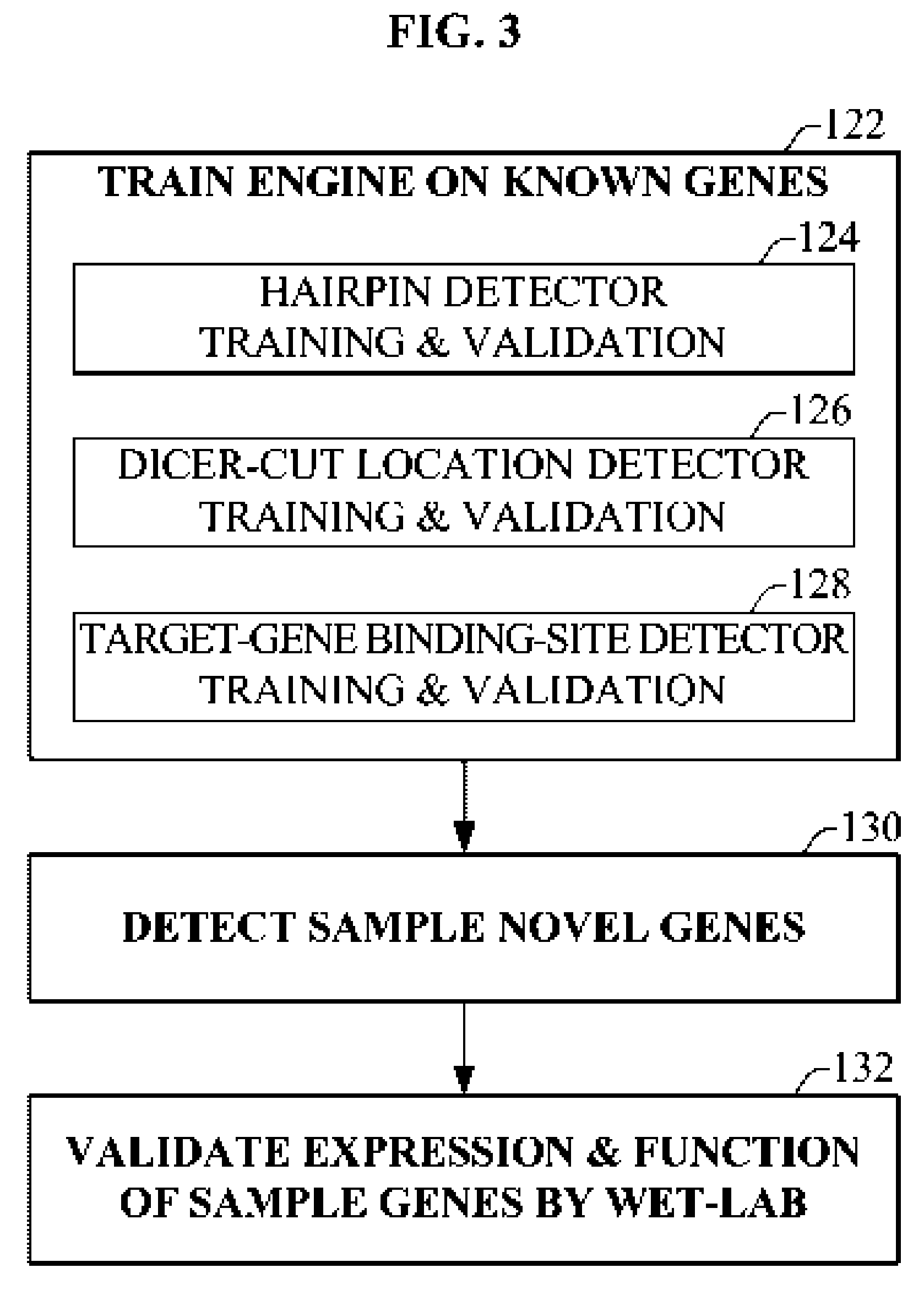
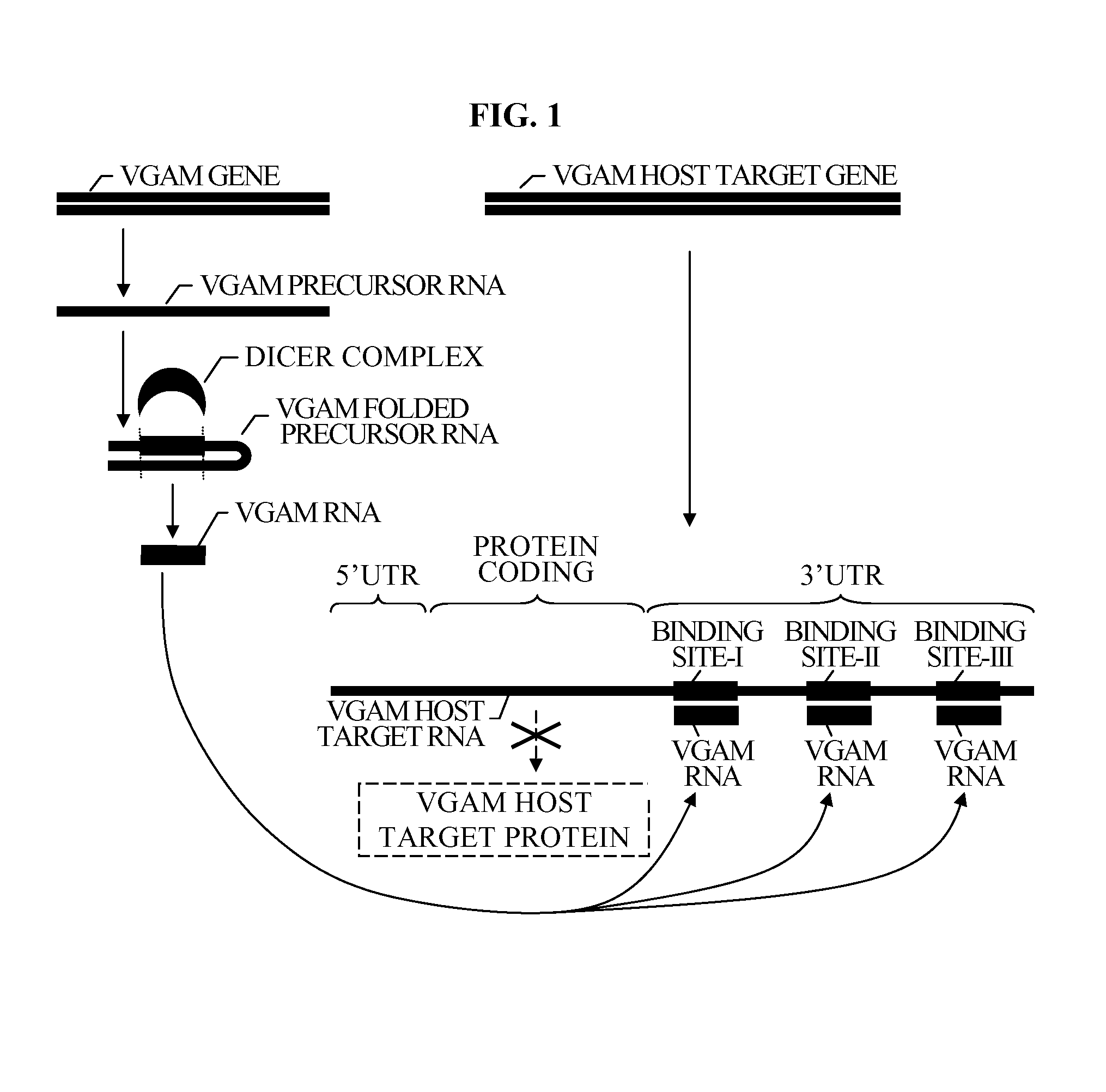
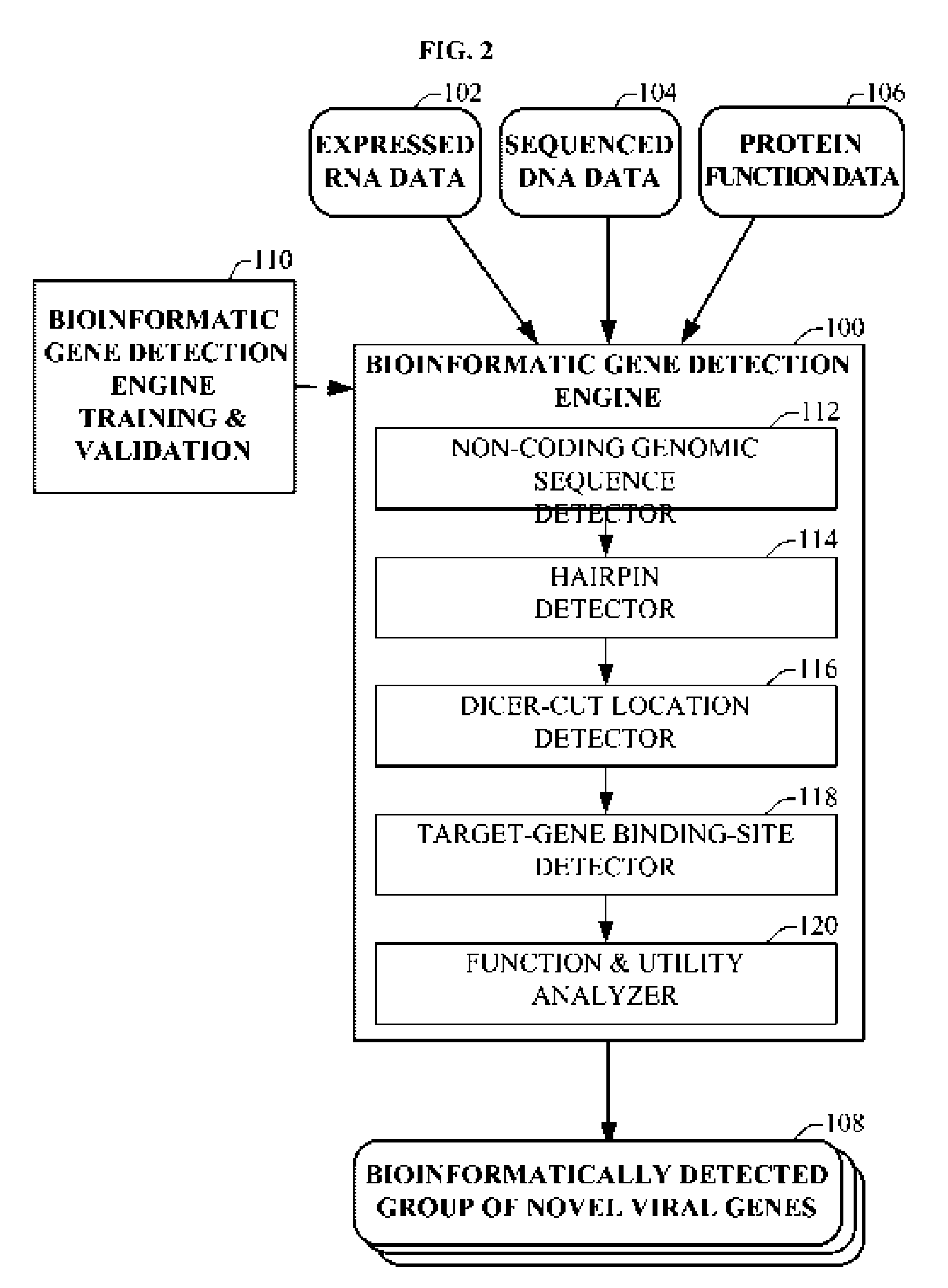
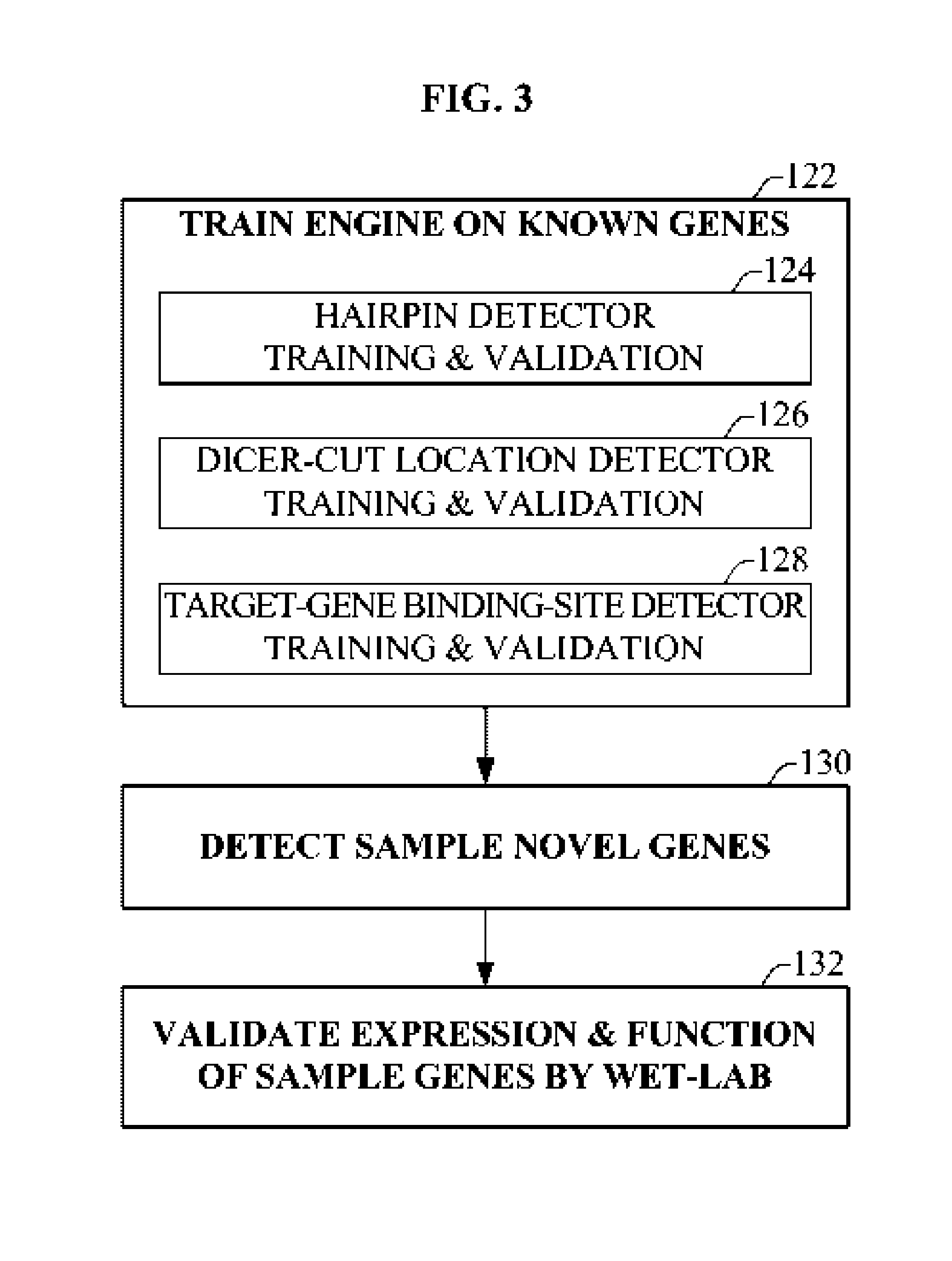
Bioinformatically detectable group of novel HIV regulatory genes and uses thereof
InactiveUS7217807B2Preventing and treating viral diseasesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementViral diseaseOperon
The present invention relates to a group of novel viral RNA regulatory genes, here identified as “viral genomic address messenger genes” or “VGAM genes”, and as “genomic record” or “GR” genes. VGAM genes selectively inhibit translation of known host target genes, and are believed to represent a novel pervasive viral attack mechanism. GR genes encode an operon-like cluster of VGAM genes. VGAM and viral GR genes may therefore be useful in diagnosing, preventing and treating viral disease. Several nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding several VGAM genes, as are vectors and probes, both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting VGAM genes, and for counteracting their activity.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
Application of virus-mediated Cpf1 protein in CRISPR/Cpf1 gene editing system
The invention discloses an application of virus-mediated Cpf1 protein in a CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system. The CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system provided by the invention consists of a recombinant virus or a recombinant vector. The recombinant virus is capable of expressing a Cpf1 gene; and the Cpf1 gene is capable of encoding the Cpf1 protein. The recombinant vector comprises a virus genome and the Cpf1 gene. The virus is either lentivirus or adenovirus. Experiments prove that virus-mediated FnCpf1 protein or AsCpf1 protein causes mutation of an hRb1 gene, an hP53 gene, an hDicer1 gene, an mRb1 gene, an mP53 gene, an mDicer1 gene, an rRb1 gene, an rP53 gene and an rDicer1 gene in the CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system. Therefore, the virus-mediated Cpf1 protein is applicable to gene editing in the CRISPR / Cpf1 gene editing system; and the Cpf1 protein has an important application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI GENEPHARMA CO LTD
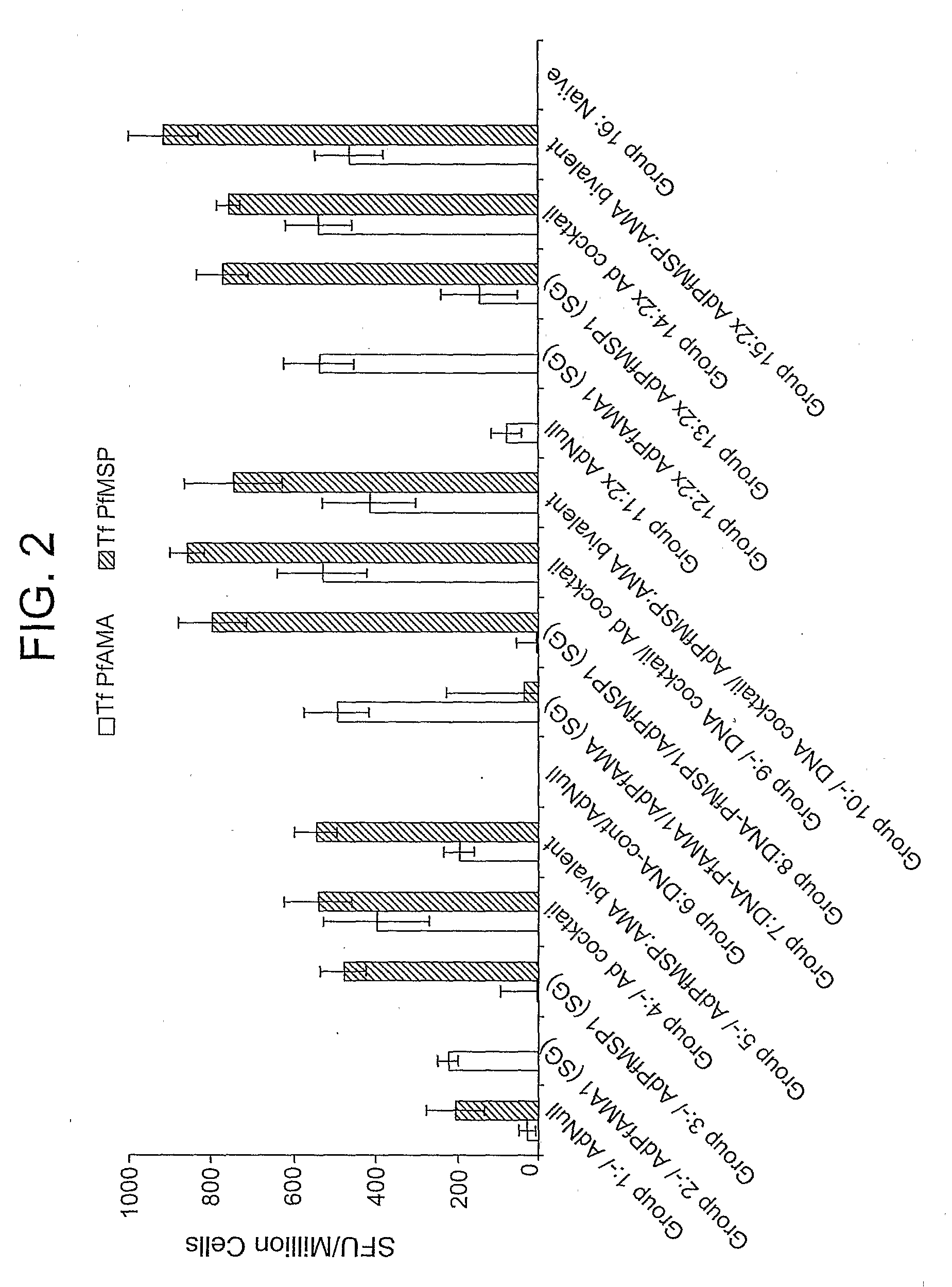
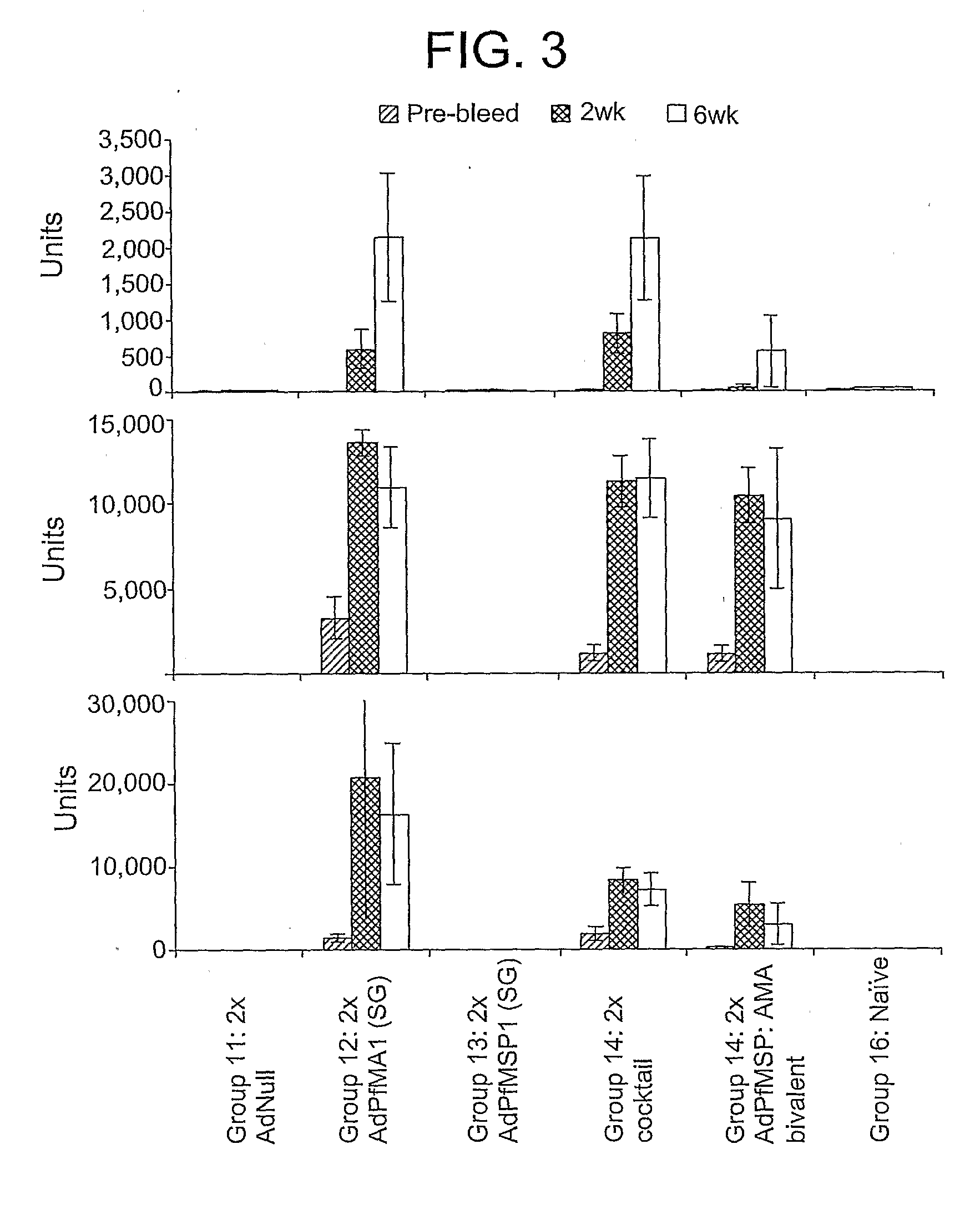
Adenoviral vector-based malaria vaccines
The invention provides adenoviral vectors comprising an adenoviral genome comprising heterologous antigen-encoding nucleic acid sequences, such as Plasmodium nucleic acid sequences, operably linked to promoters. The invention further provides a method of inducing an immune response against malaria in a mammal comprising administering the adenoviral vectors to the mammal.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +2
Chimeric and/or growth-restricted flaviviruses
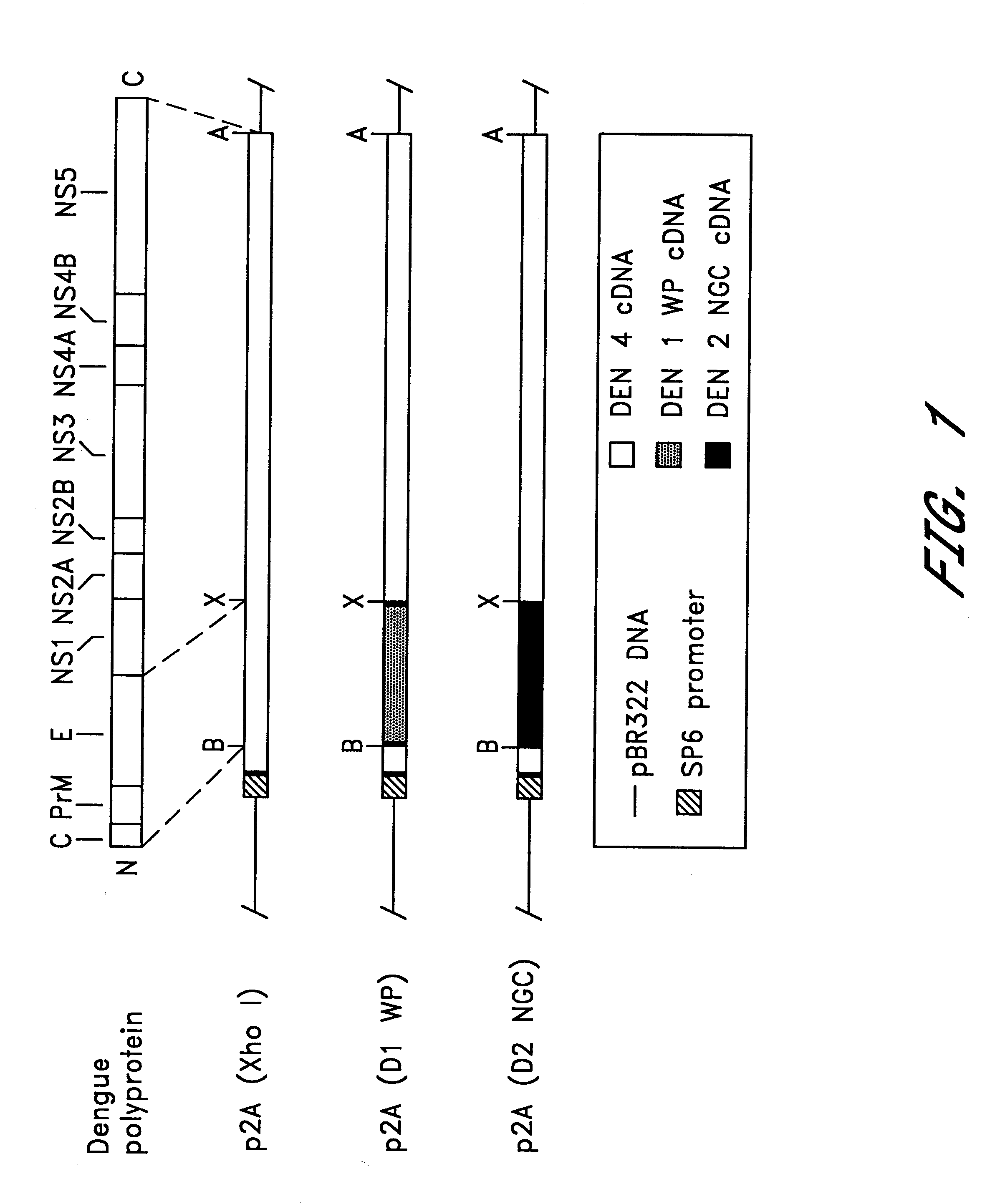
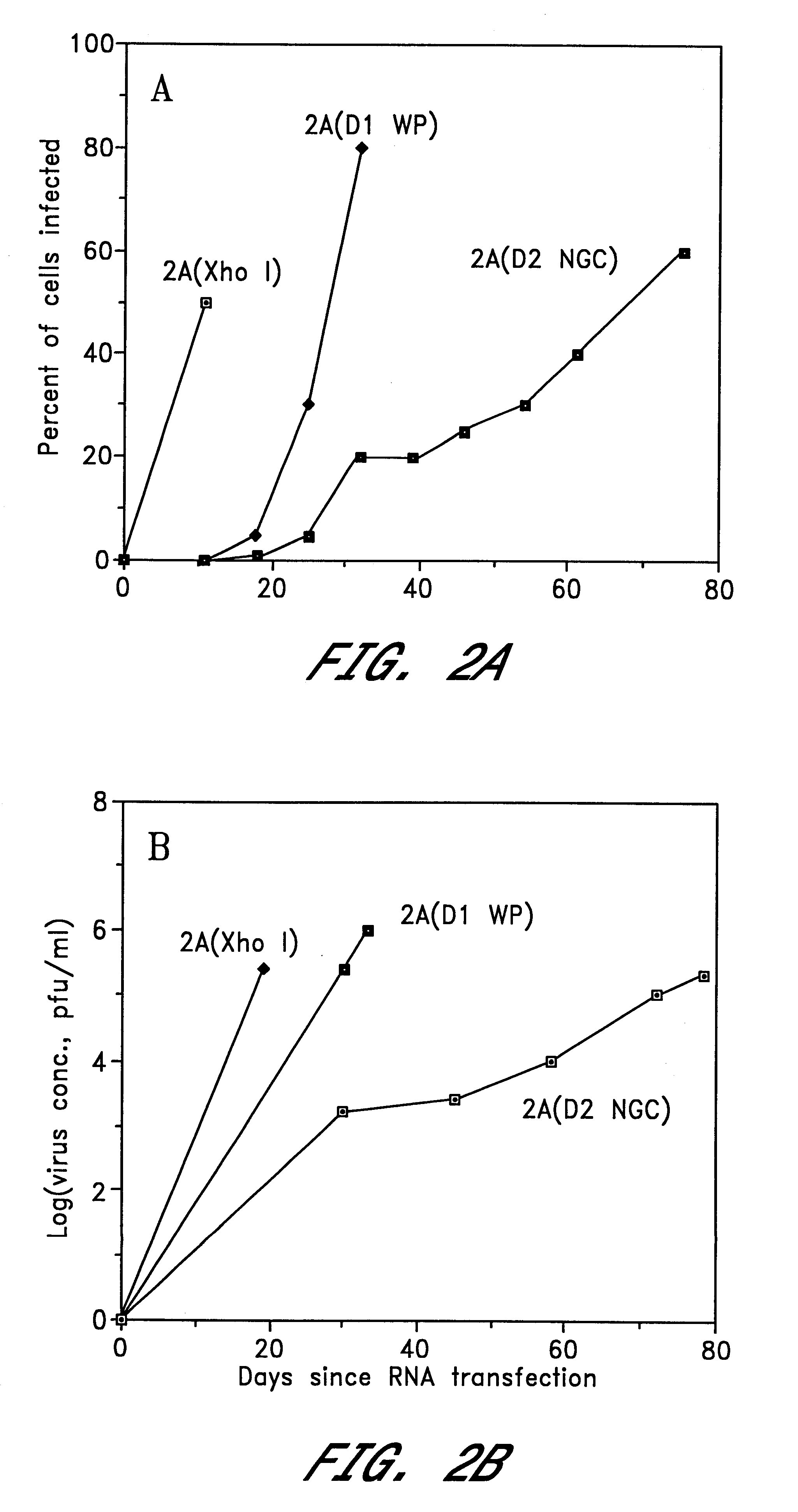
InactiveUS6676936B1BiocideSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirulent characteristicsJapanese B Encephalitis Virus
The invention includes a chimeric virus for use in a vaccine preparation having a genome comprising nucleic acid sequences encoding at least one structural protein from one flavivirus and nucleic acid sequences encoding nonstructural protein from another flavivirus. The genome preferably includes mutations within the viral genome that reduce virus virulence and in a particularly preferred embodiment these vaccines are directed to flaviviruses such as dengue virus, tick-borne encephalitis virus and Japanese encephalitis virus. The invention also includes a baculovirus having a recombinant dengue cDNA sequence which encodes: (1) dengue virus capsid protein, pre-matrix protein, envelope glycoprotein and NS1 and NS2a nonstructural proteins or (2) dengue envelope glycoprotein or (3) dengue non-structural proteins NS1 and NS2a. The invention further includes a baculovirus having a recombinant Japanese B encephalitis virus cDNA sequence which encodes the Japanese B encephalitis virus capsid protein, pre-matrix protein, envelope glycoprotein and non-structural proteins NS1 and NS2a. The invention further includes a vaccine and a method to produce that vaccine.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
Pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of microRNA related diseases
The present invention provides compositions and methods of treatment of diseases that are sensitive to drugs that downregulate the function of microRNA's, mRNA, non-coding RNA, or viral genomes. In particular, it has been discovered that a very long term effect of an anti microRNA oligonucleotide may be obtained when administered to a primate. Therefore, the present invention relate to pharmaceutical compositions and methods for treatment of primates, including humans wherein the compositions are administered with a long time interval.
Owner:ROCHE INNOVATION CENT COPENHAGEN
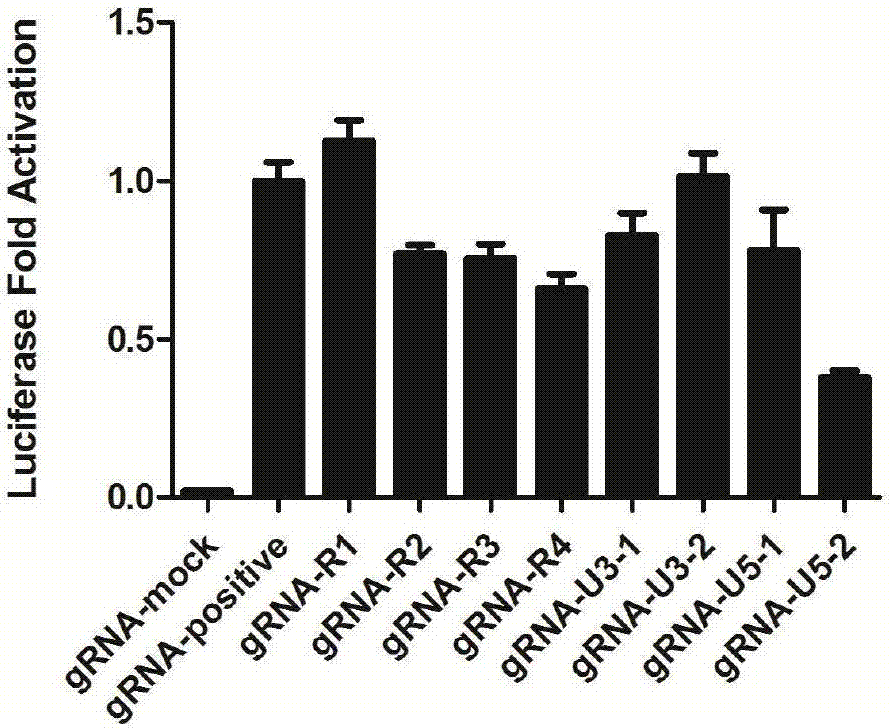
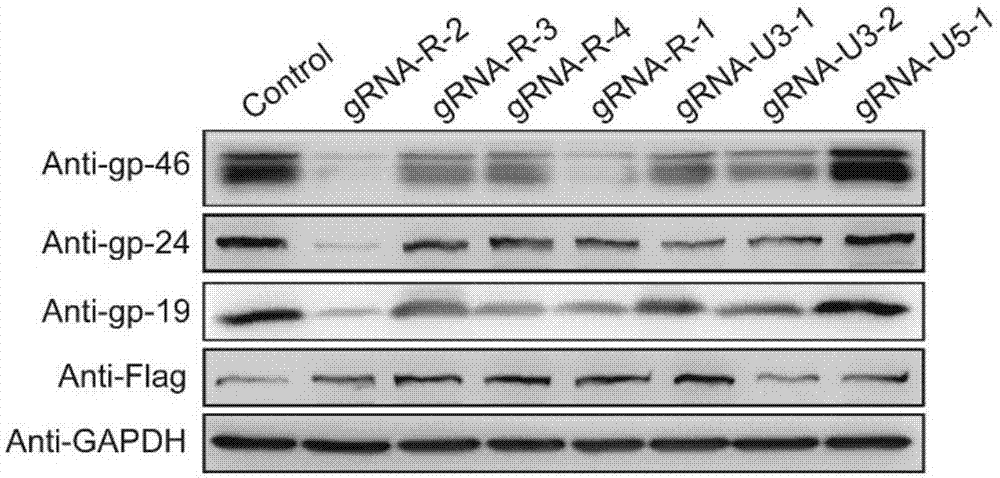
GRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) sequence capable of effectively knocking out CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) of HTLV-1 (Human T-cell Leukemia Virus type 1) virus genome
InactiveCN106957844AEffective knockoutPrevent proliferationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA/RNA fragmentationHuman T cell leukemia virusWilms' tumor
The invention discloses a gRNA (guide Ribonucleic Acid) target sequence capable of effectively knocking out CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) of an HTLV-1 (Human T-cell Leukemia Virus type 1) virus genome and application of the gRNA target sequence. The gRNA target sequence comprises a first RNA forward sequence, a second RNA forward sequence, a first RNA reverse sequence and a second RNA reverse sequence, wherein the first RNA forward sequence and the first RNA reverse sequence are complementary with each other and comprise sequences shown as SEQ ID NO 01 and SEQ ID NO 02 respectively; the second RNA forward sequence and the second RNA reverse sequence are complementary with each other and comprise sequences shown as SEQ ID NO 03 and SEQ ID NO 04 respectively. The gRNA sequence disclosed by the invention can be used for effectively knocking out the HTLV-1 virus genome and can be used for effectively inhibiting proliferation of ATL (Adult T-cell Leukemia) cells and occurrence of tumors.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
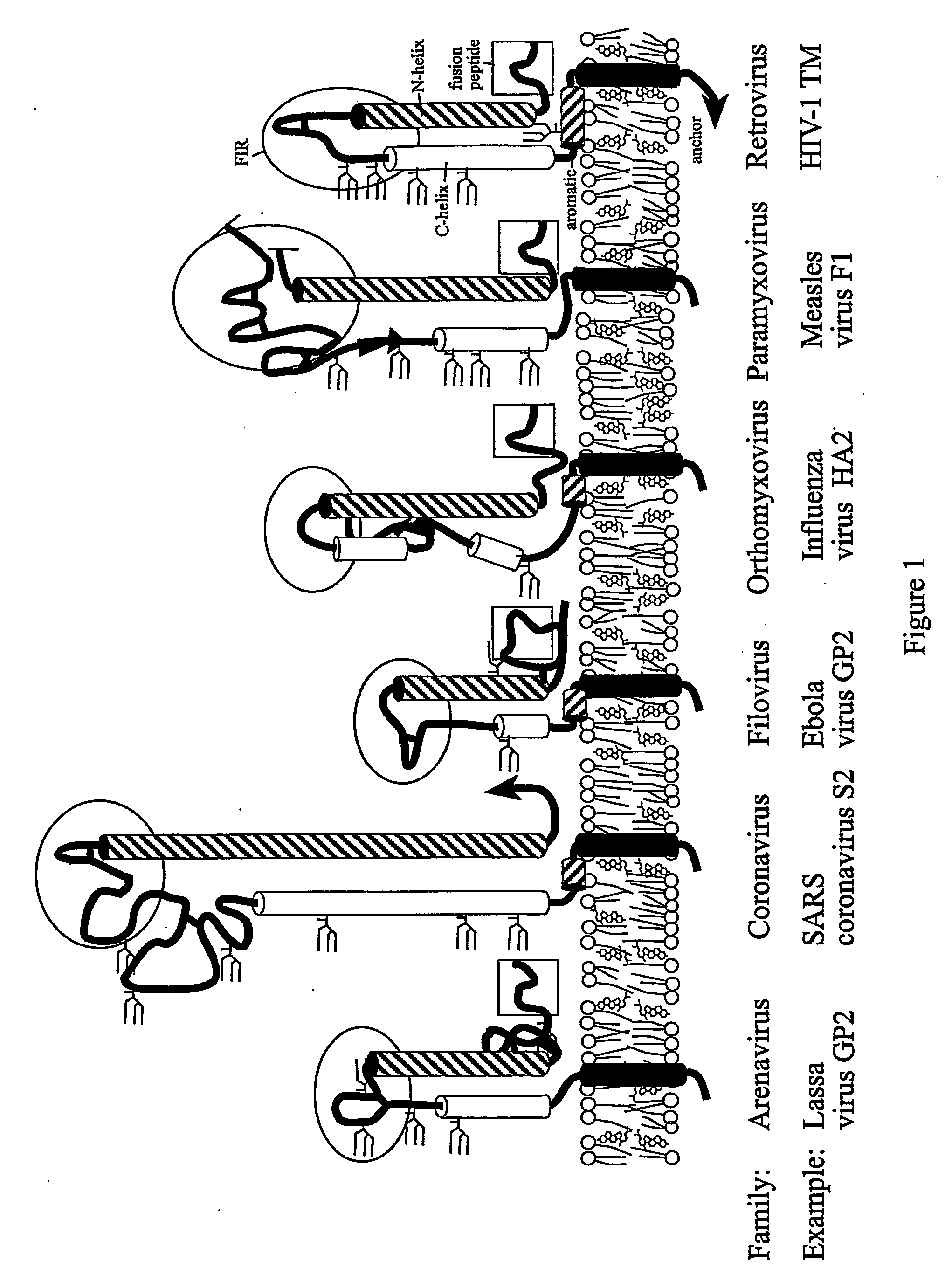
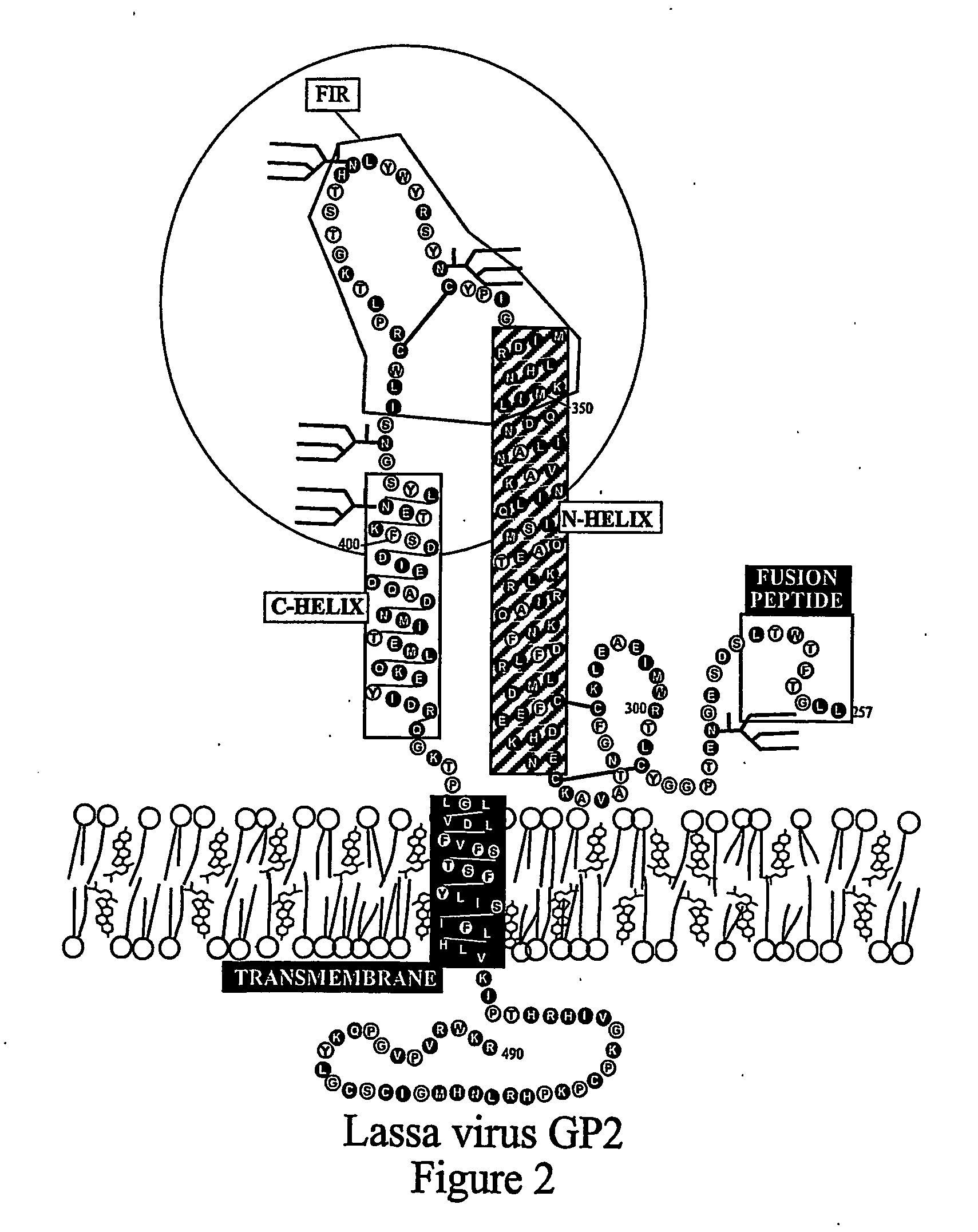
Method of preventing virus: cell fusion by inhibiting the function of the fusion initiation region in rna viruses having class i membrane fusogenic envelope proteins
ActiveUS20060280754A1Prevent and inhibit infectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseCell membraneDisease cause
The present invention relates to a method of preventing or inhibiting viral infection of a cell and / or fusion between the envelope of a virus and the membranes of a cell targeted by the virus (thereby preventing delivery of the viral genome into the cell cytoplasm, a step required for. viral infection). The present invention particularly relates to the families of RNA viruses, including the arenaviruses, coronaviruses, filoviruses, orthomyxoviruses, paramyxoviruses, and retroviruses, having Class I membrane fusion proteins as the fusion proteins that mediate this fusion process. The present invention provides for a method of identifying a conserved motif or domain called the fusion initiation region (FIR) in these viruses. The present invention further provides for methods of preventing infection by such viruses, by interfering with their FIR. The present invention further provides for methods of treatment and prophylaxis of diseases induced by such viruses.
Owner:TULANE EDUCATIONAL FUND THE ADMINISTRATORS OF THE
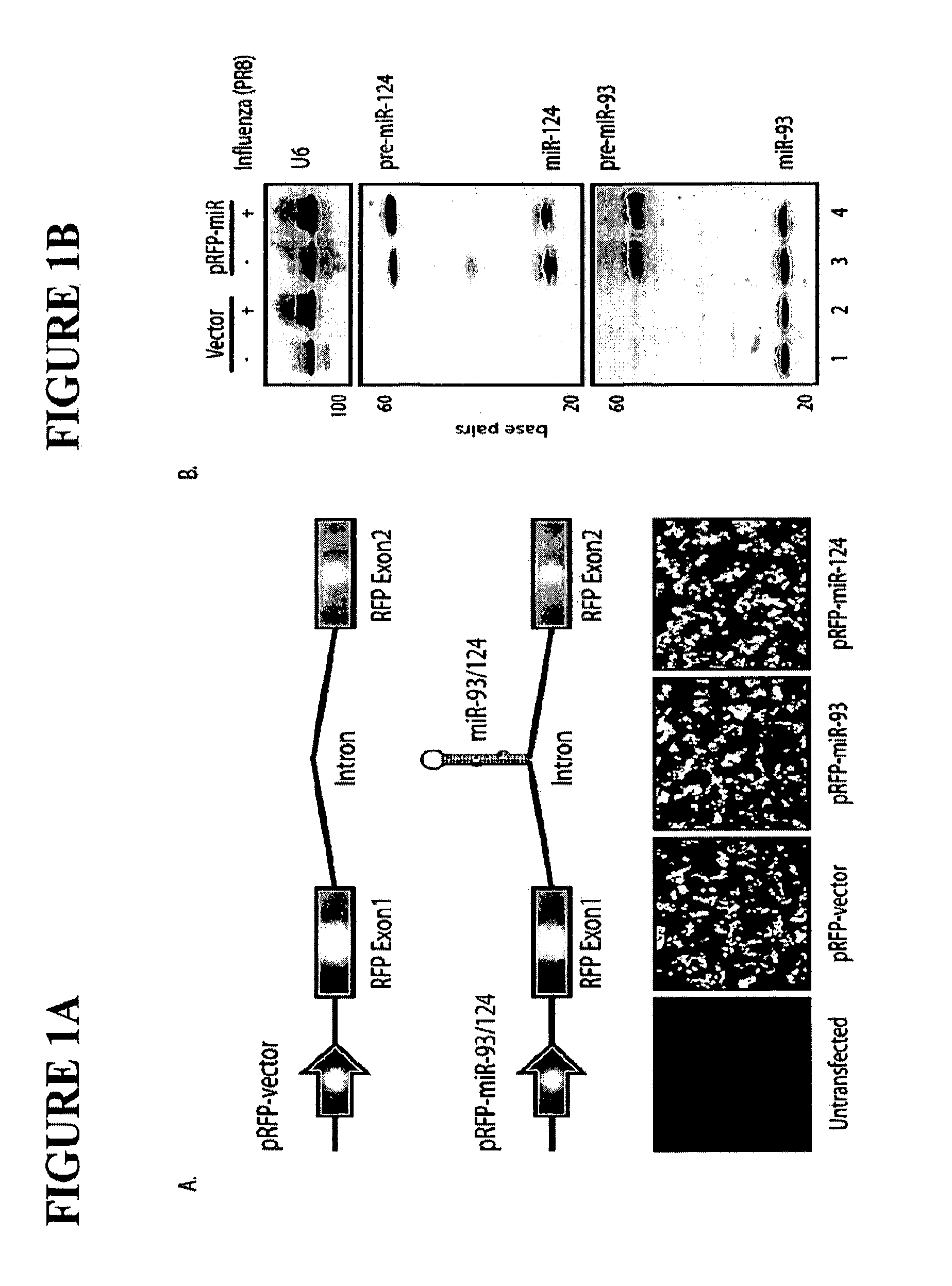
Live Attenuated Influenza Virus Vaccines Comprising Microrna Response Elements
ActiveUS20120148622A1Increase vaccine safetyQuick buildSsRNA viruses negative-senseSugar derivativesUltrasound attenuationInfluenza virus vaccine
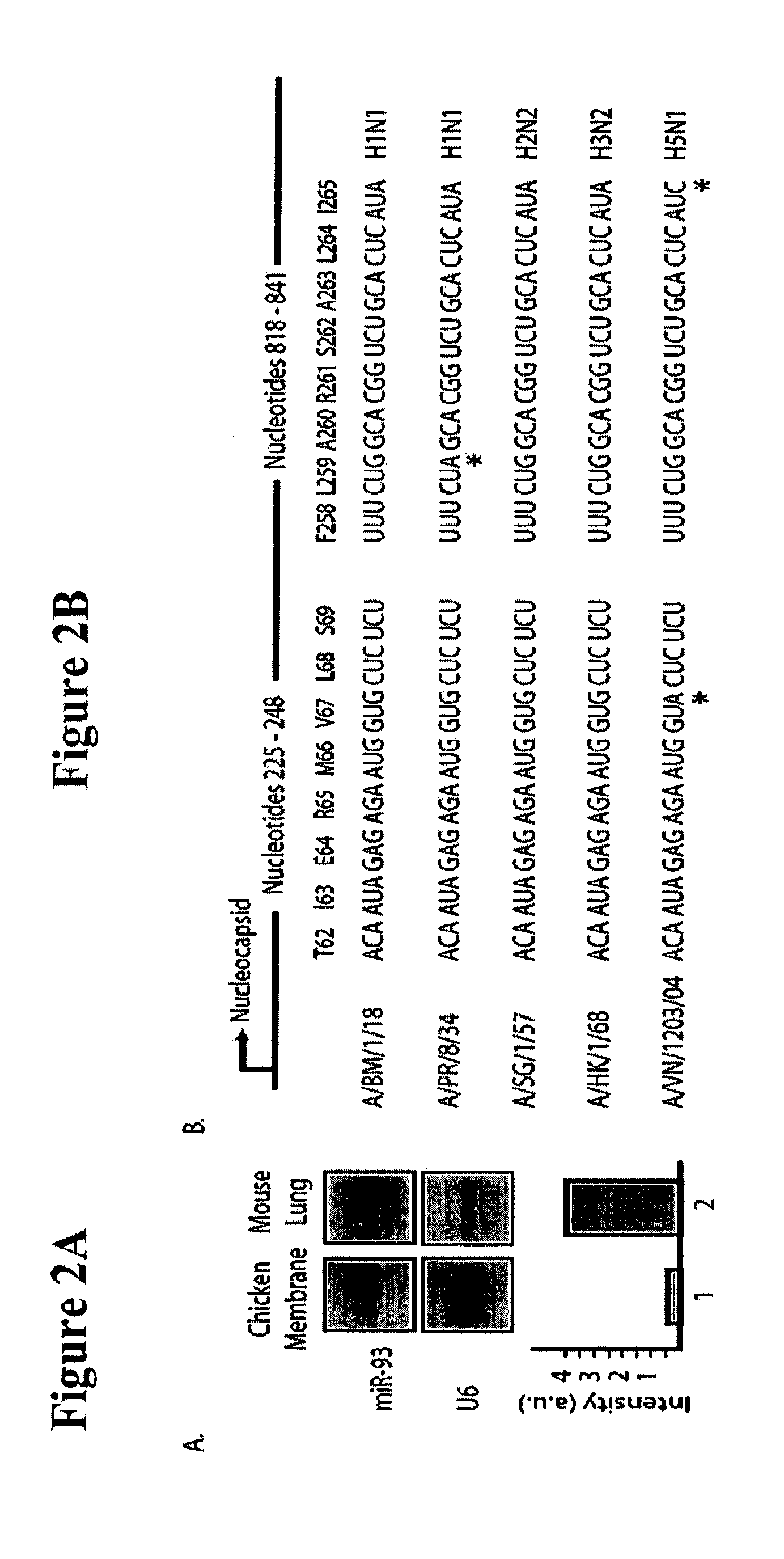
The invention is directed to novel live attenuated influenza virus (LAIV) vaccines comprising one or more microRNA (miRNA) Response Element(s) (MRE) within an influenza virus genome. The MREs useful for the present invention can be derived from any miRNA which is highly expressed in influenza-targeted cells of an animal in need of vaccination but are not expressed or are expressed at very low levels in species (e.g., embryonated chicken eggs) or cell lines used for a large-scale vaccine production. This allows efficient vaccine production but renders the vaccine virus susceptible to attenuation in the influenza-targeted cells of vaccinated animals expressing a cognate miRNA.
Owner:MT SINAI SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Vector for integration of heterologous sequences into poxviral genomes
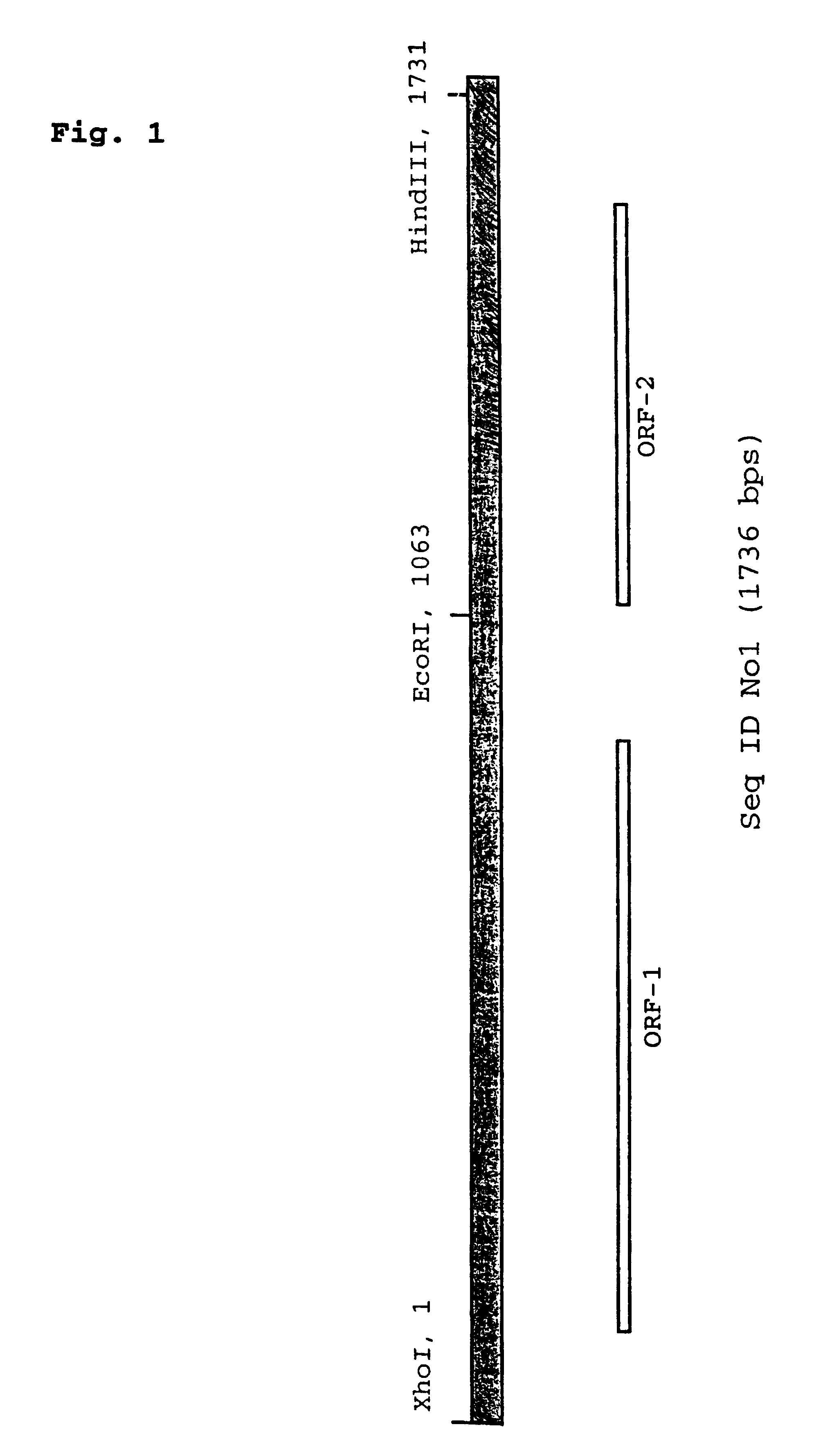
The present invention provides a DNA vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence useful for inserting heterologous sequences into the genome of poxviruses by homologous recombination. The present invention relates also, inter alia, to recombinant poxvirses carrying heterologous coding sequences transferred by the vector according to the present invention.
Owner:GSF FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR UMWELT & GESUNDHEIT
Nucleic acid sequences that can be used as primers and probes in the amplification and detection of all subtypes of HIV-1
InactiveUS6881537B1Improve accuracyHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridization probeSpecific detection
The present invention is related to nucleic acid sequences that can be used in the field of virus diagnostics, more specifically the diagnosis of infections with the AIDS causing Human Immuno-deficiency Virus (HIV).With the present invention nucleotide sequences are provided that can be used as primers and probes in the amplification and detection of HIV-1 nucleic acid. The oligonucleotide sequences provided with the present invention are located in the LTR part of the HIV viral genome. It has been found that, by using the sequences of the present invention in methods for the amplification and detection of nucleic acid a sensitive and specific detection of HIV-1 can be obtained. The benefit of the sequences of the present invention primarily resides in the fact that, with the aid of primers and probes comprising the sequences according to the invention the nucleic acid of all presently known subtypes of HIV-1 can be detected with high accuracy and sensitivity. So far no primer pairs or hybridization probes have been developed that would allow the detection of such a broad range of HIV-1 variants.The oligonucleotide sequences according to the present invention are especially useful in methods for the amplification of nucleic acid.
Owner:BIOMERIEUX SA
Bioinformatically detectable human herpesvirus 5 regulatory gene
ActiveUS7696334B1Preventing and treating viral diseasesSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementOperonVirus attack
The present invention relates to a group of novel viral RNA regulatory genes, here identified as “viral genomic address messenger genes” or “VGAM genes”, and as “genomic record” or “GR” genes. VGAM genes selectively inhibit translation of known host target genes, and are believed to represent a novel pervasive viral attack mechanism. GR genes encode an operon-like cluster of VGAM genes. VGAM and viral GR genes may therefore be useful in diagnosing, preventing and treating viral disease. Several nucleic acid molecules are provided respectively encoding several VGAM genes, as are vectors and probes, both comprising the nucleic acid molecules, and methods and systems for detecting VGAM genes, and for counteracting their activity.
Owner:ROSETTA GENOMICS
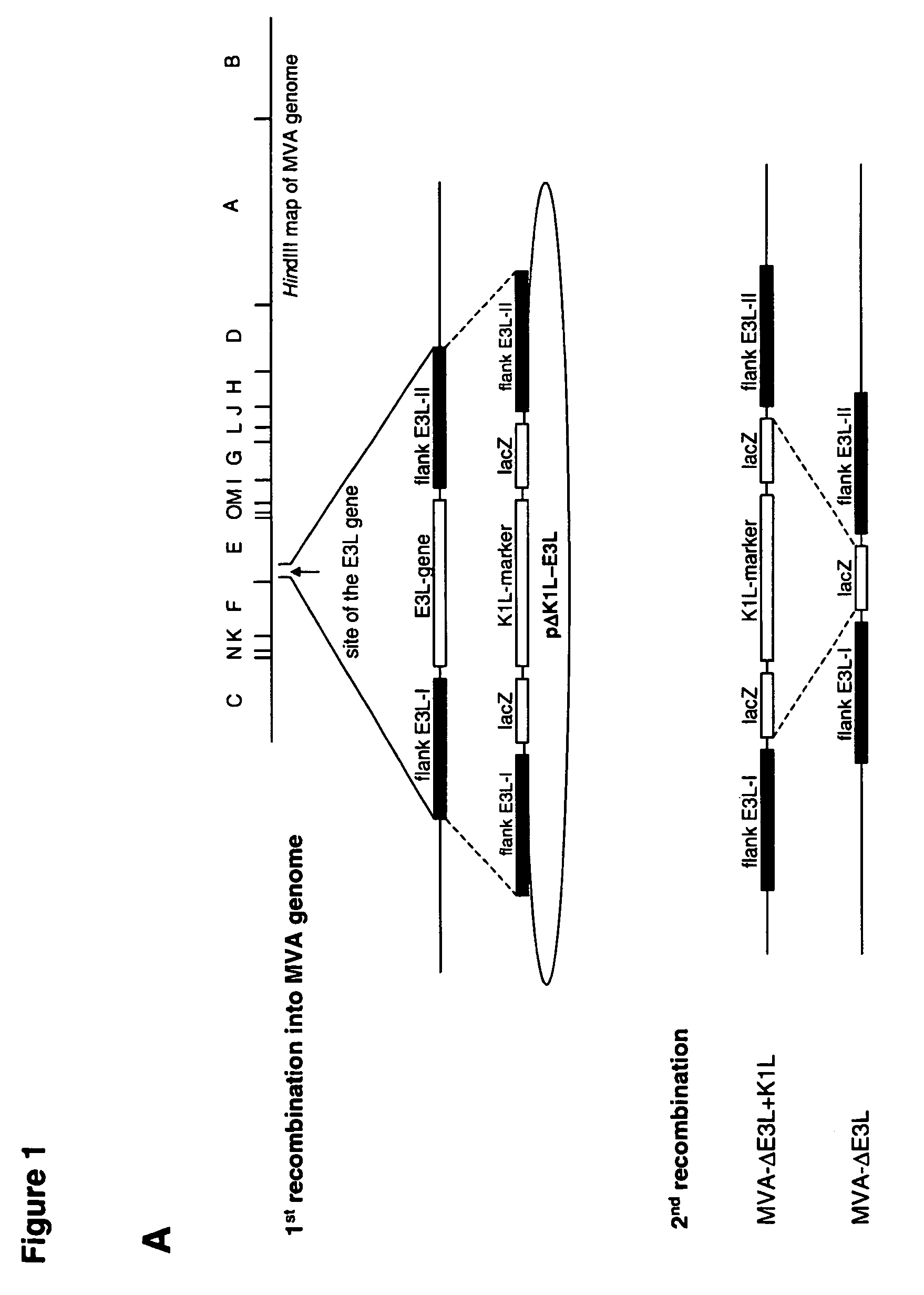
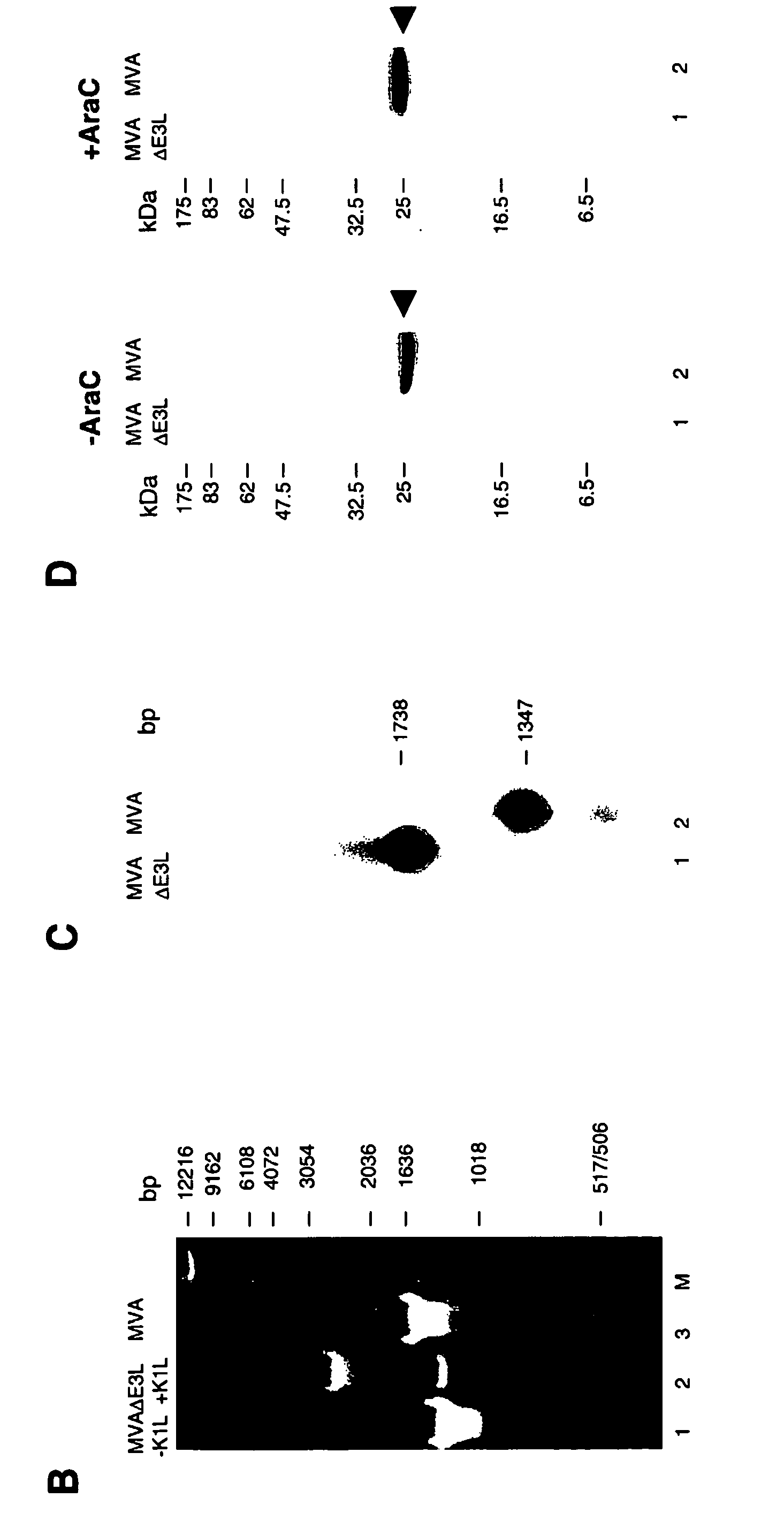
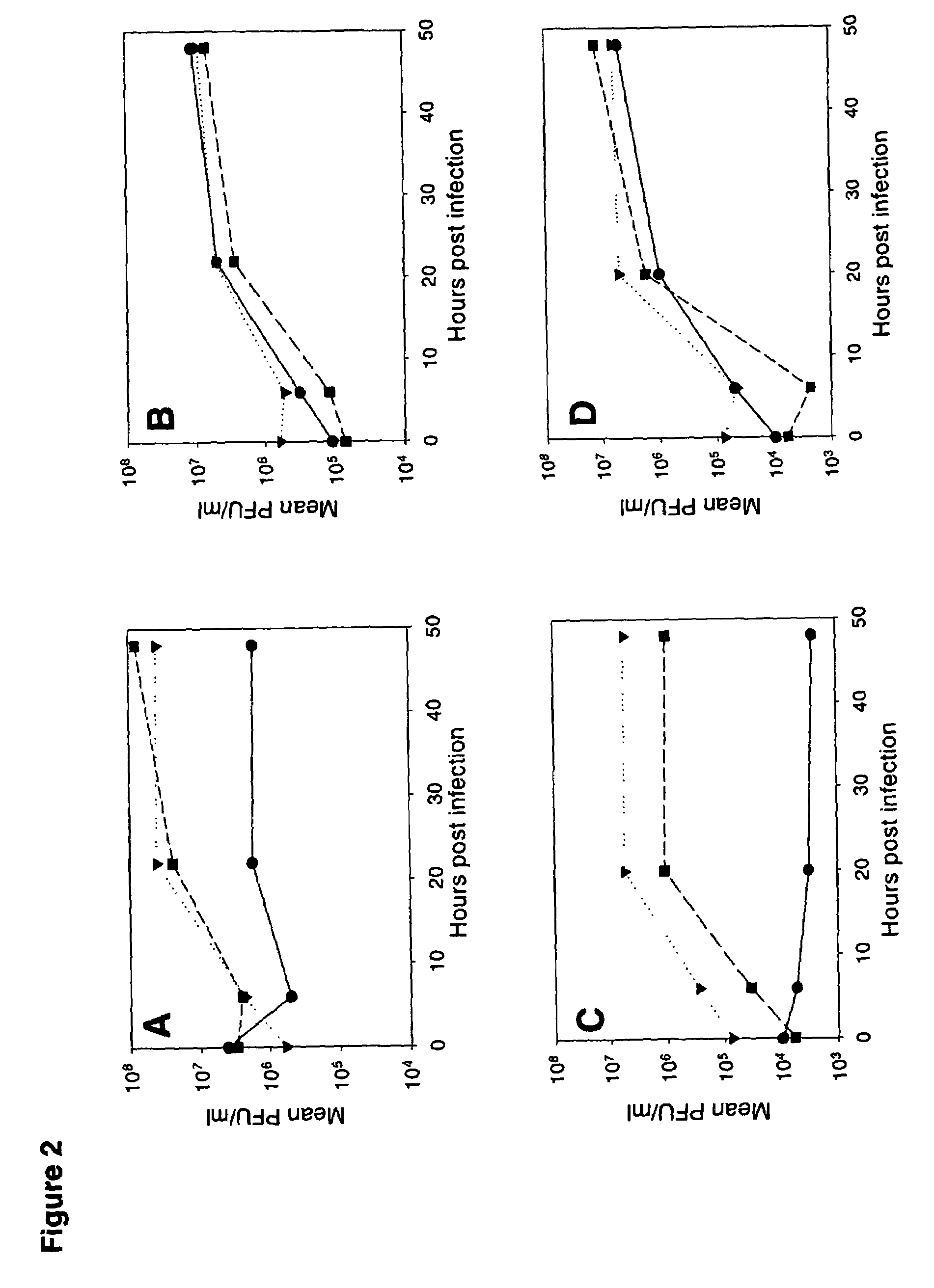
Vaccinia virus MVA-E3L-knockout-mutants and use thereof
InactiveUS7049145B2Quickly and efficiently produceIncrease choiceInactivation/attenuationVertebrate cellsMutantVaccinia viruses
The present invention relates to mutant MVA vaccinia viruses, which are used for the generation of recombinant MVA viruses, as well as host cells, which have been infected with these mutant MVA viruses. The present invention further relates to DNA-vector constructs, and a method for the generation of recombinant MVA by using the mutant MVA viruses and the DNA-vector constructs. The mutant MVA vaccinia viruses of the present invention are characterized in that the MVA ORF 050L gene or a functional part thereof has been inactivated in the viral genome.
Owner:GSF FORSCHUNGSZENT FUR UMWELT & GESUNDHEIT
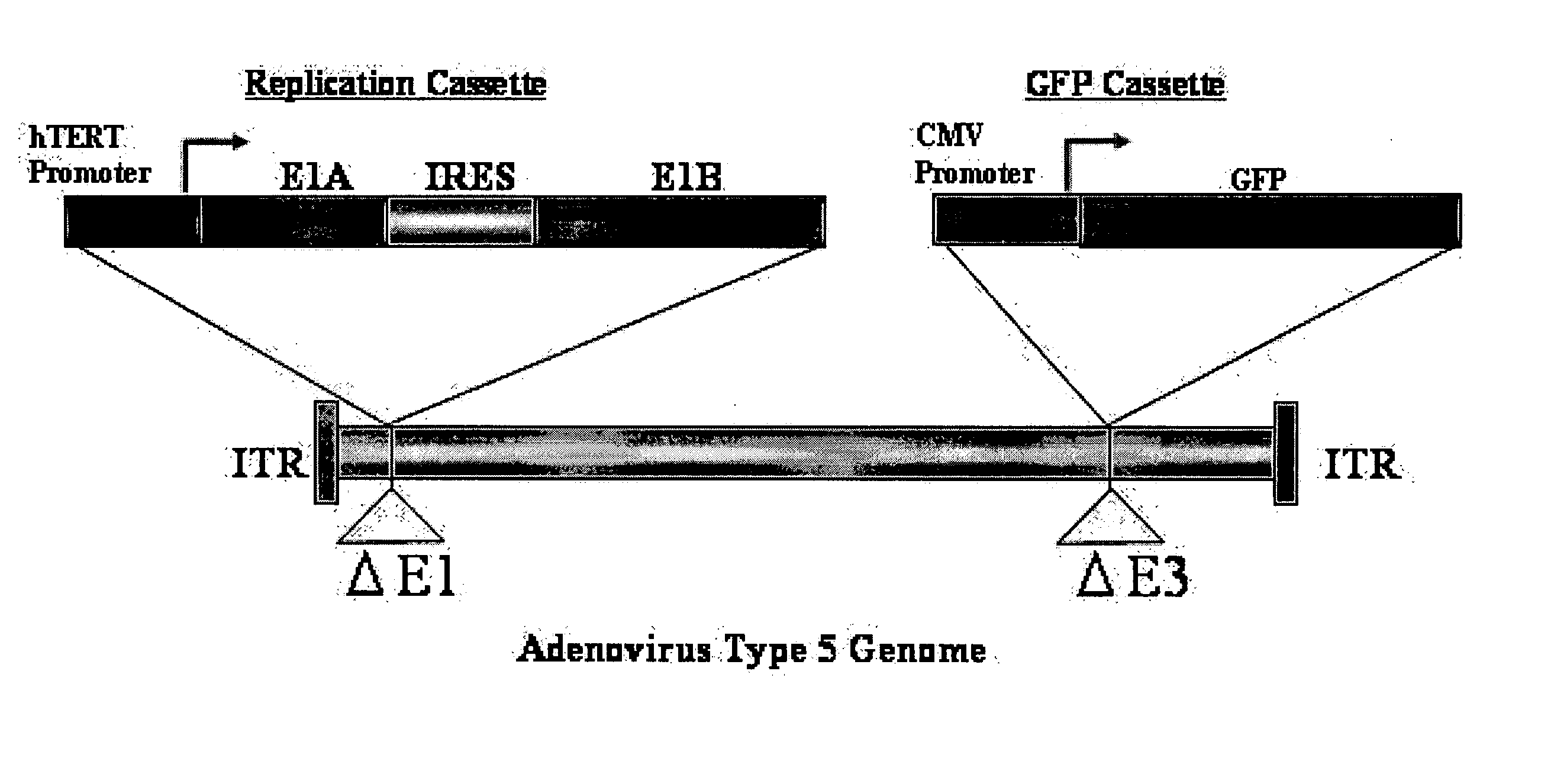
Telomelysin/GFP-expressing recombinant virus
ActiveUS20060067890A1High sensitivityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsVirusesTelomeraseCancer cell
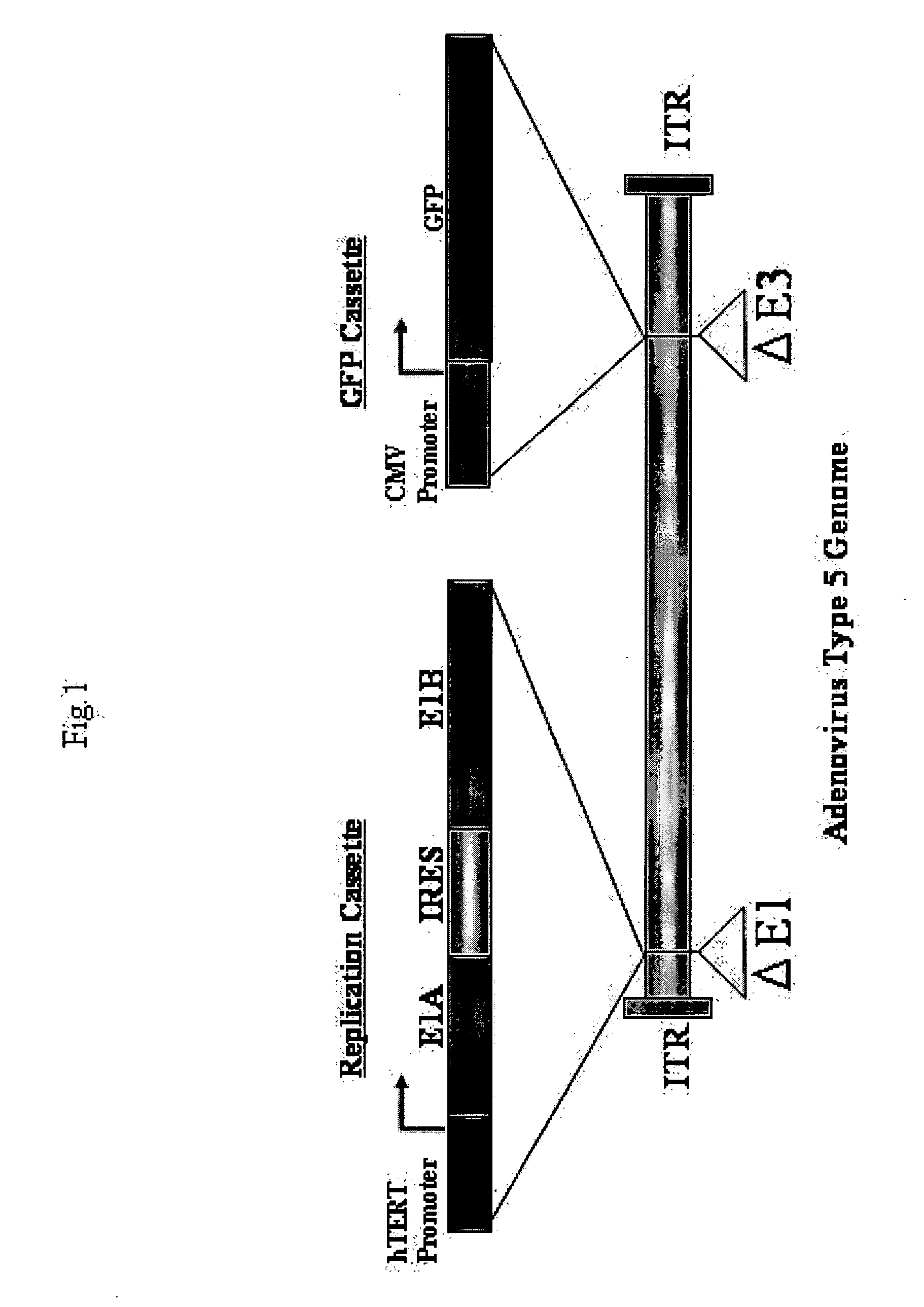
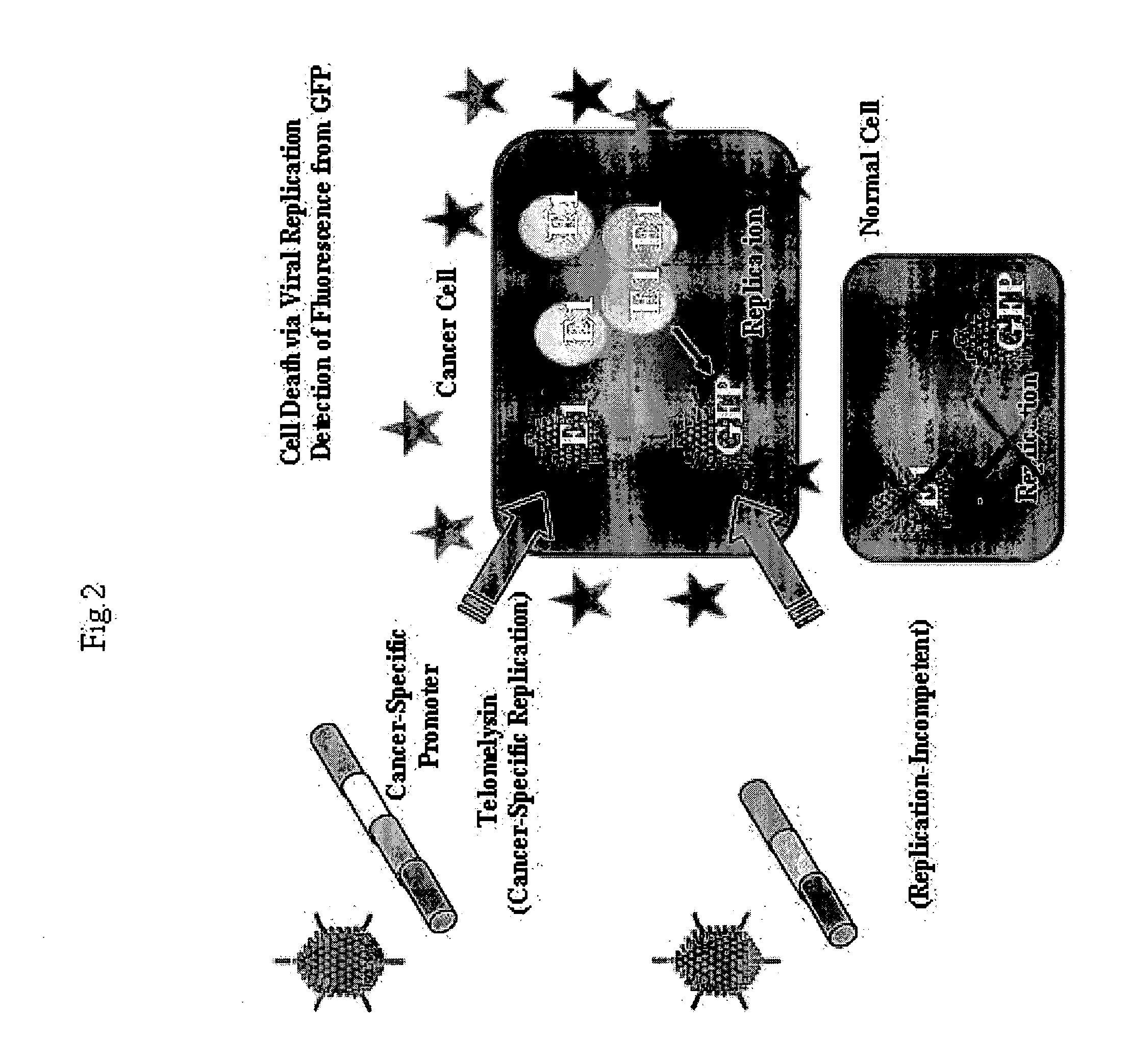
The present invention provides a reagent for cancer cell detection or cancer diagnosis. The present invention relates to a reagent for cancer cell detection, comprising a recombinant virus where a replication cassette comprising a promoter from human telomerase, an E1A gene, an IRES sequence and an E1B gene in this order is integrated in E1 region of the viral genome and a labeling cassette comprising a gene encoding a labeling protein and a promoter capable of regulating the expression of the gene encoding the labeling protein is integrated in E3 region of the viral genome.
Owner:ONCOLYS BIOPHARMA
Nucleic acid delivery with ovine adenoviral vectors
InactiveUS6020172ARich varietyGenetic material ingredientsImmunological disordersInfected cellOvine adenovirus
PCT No. PCT / AU96 / 00518 Sec. 371 Date Apr. 20, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Apr. 20, 1998 PCT Filed Aug. 14, 1996 PCT Pub. No. WO97 / 06826 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 27, 1997A method of delivering a nucleic acid molecule to a human cell which involves exposing to the cell a viral vector containing a DNA molecule including a nucleic acid sequence encoding the genome of an ovine adenovirus capable of infecting human cells or functionally equivalent nucleic acid sequence or portion thereof and at least one nucleic acid sequence encoding a gene to be expressed in the cell, such that the vector infects the cell and the infected cell expresses the gene.
Owner:COMMONWEALTH SCI & IND RES ORG
Oligonucleotide compound and method for treating nidovirus infections
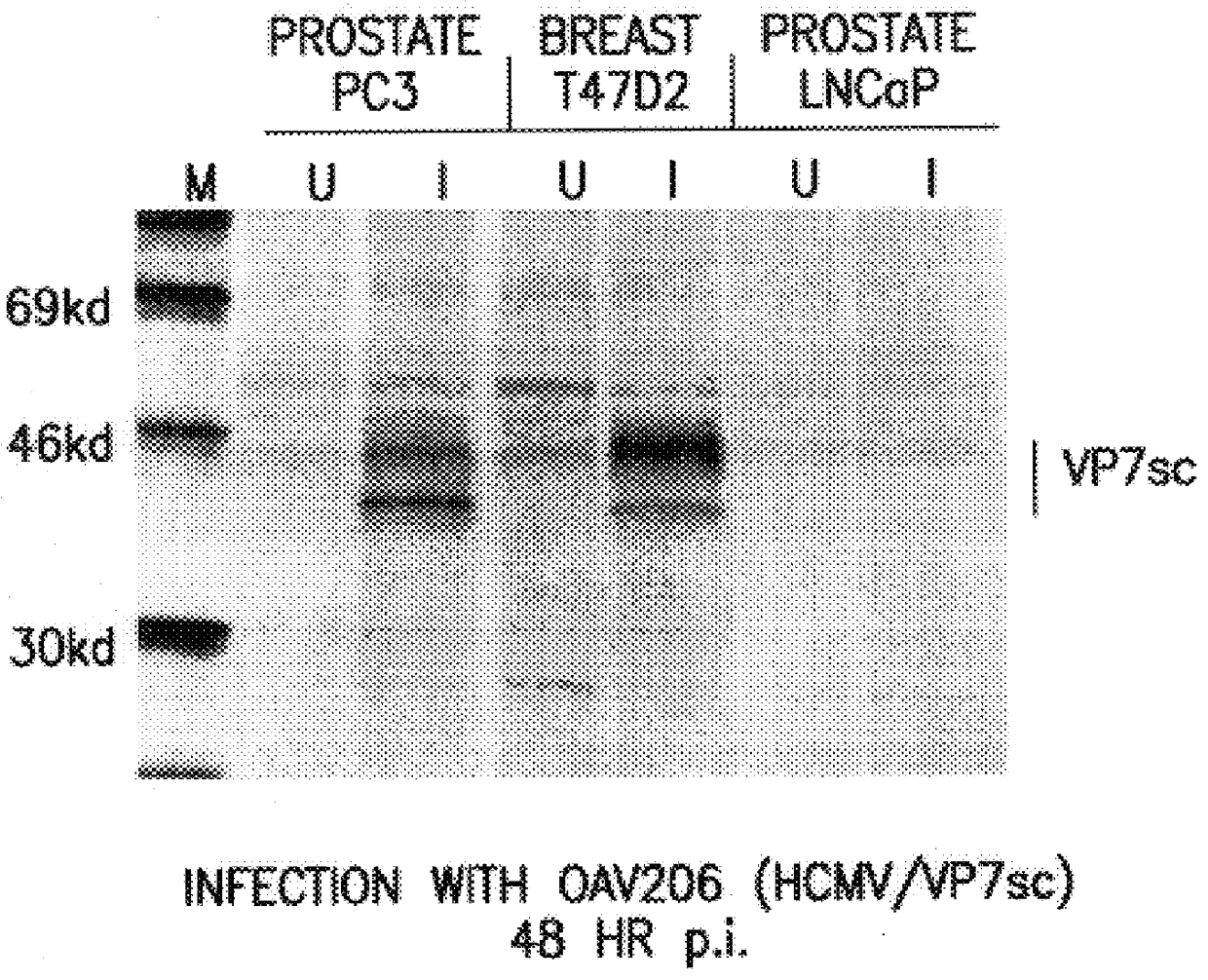
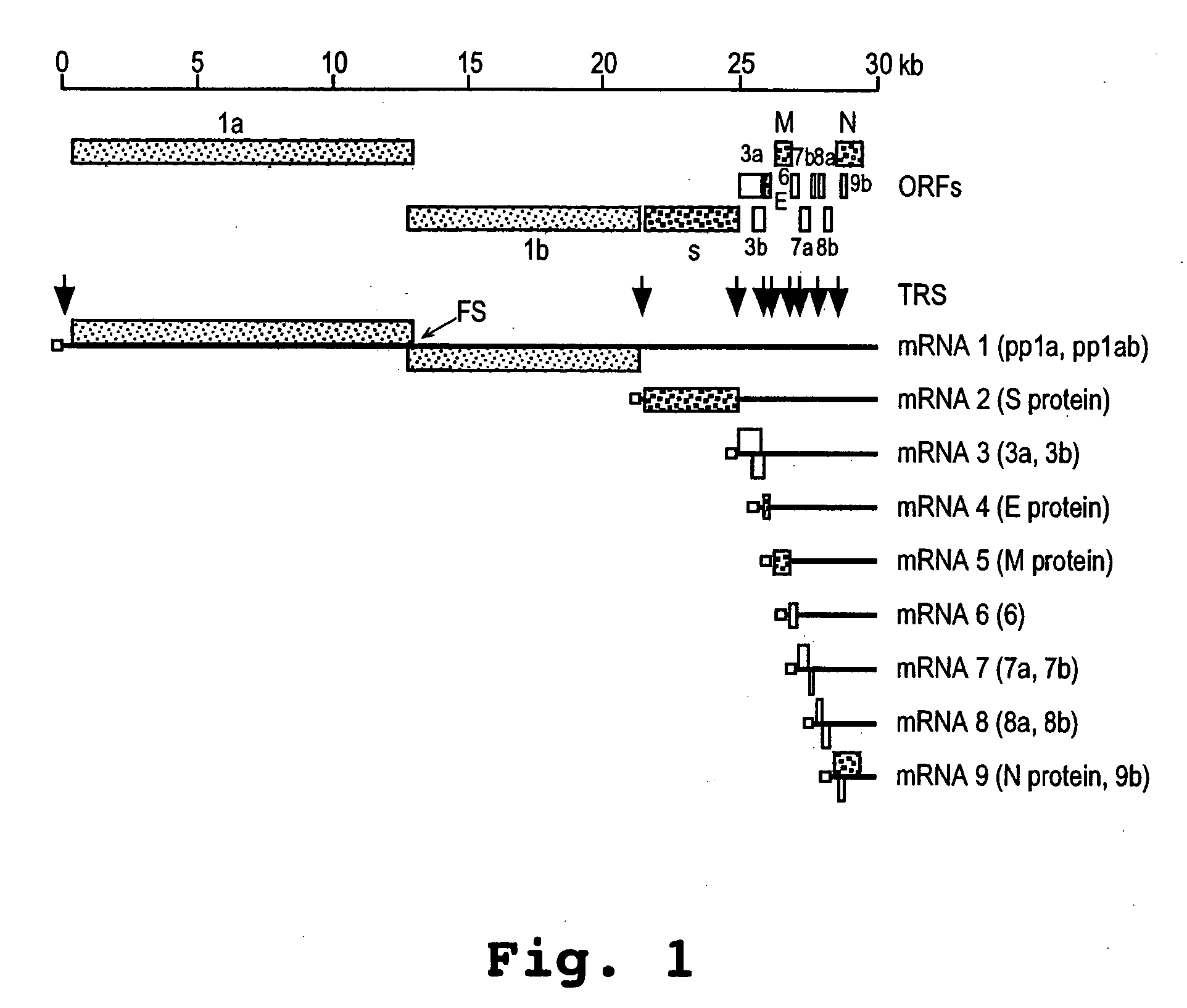
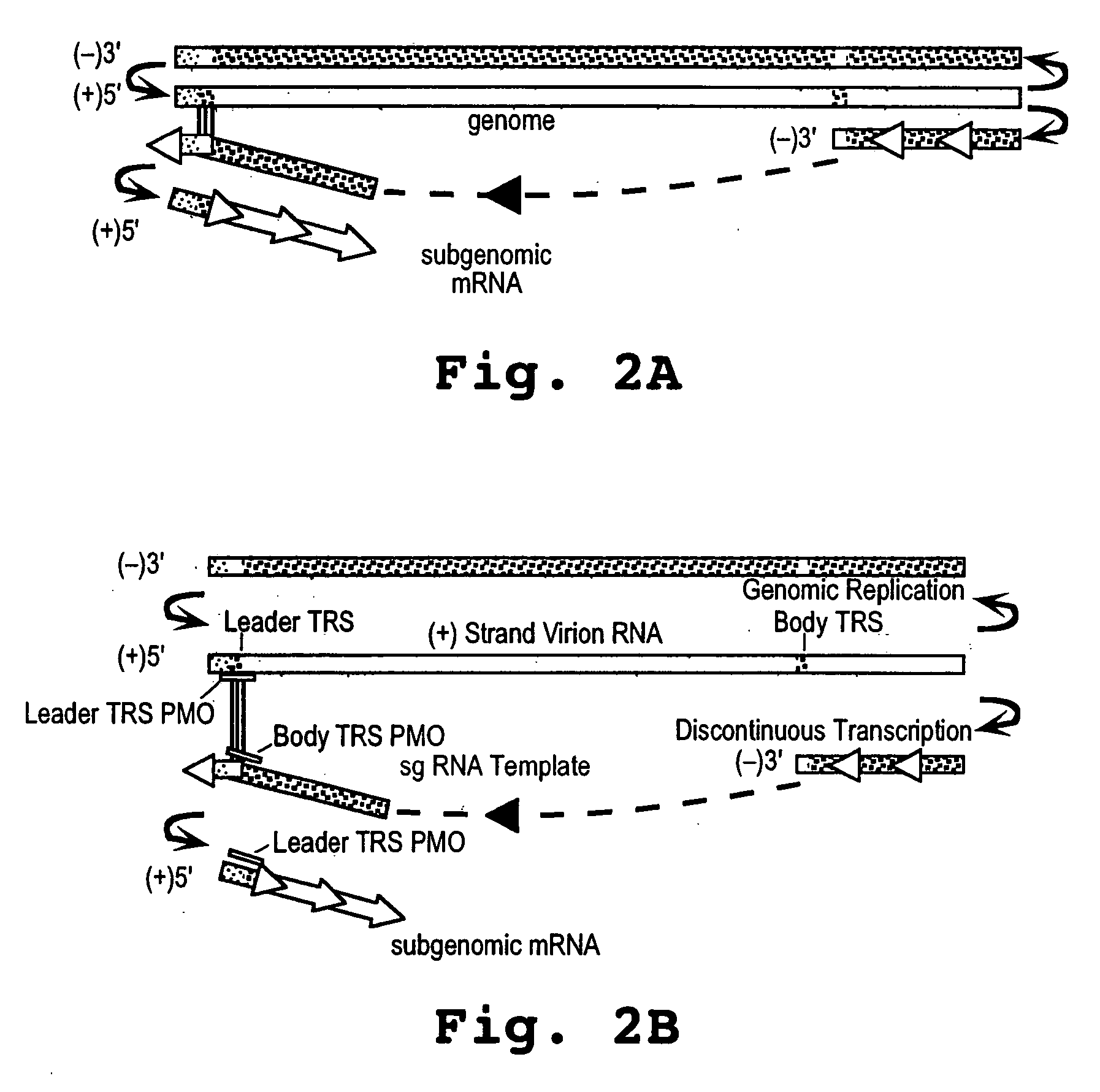
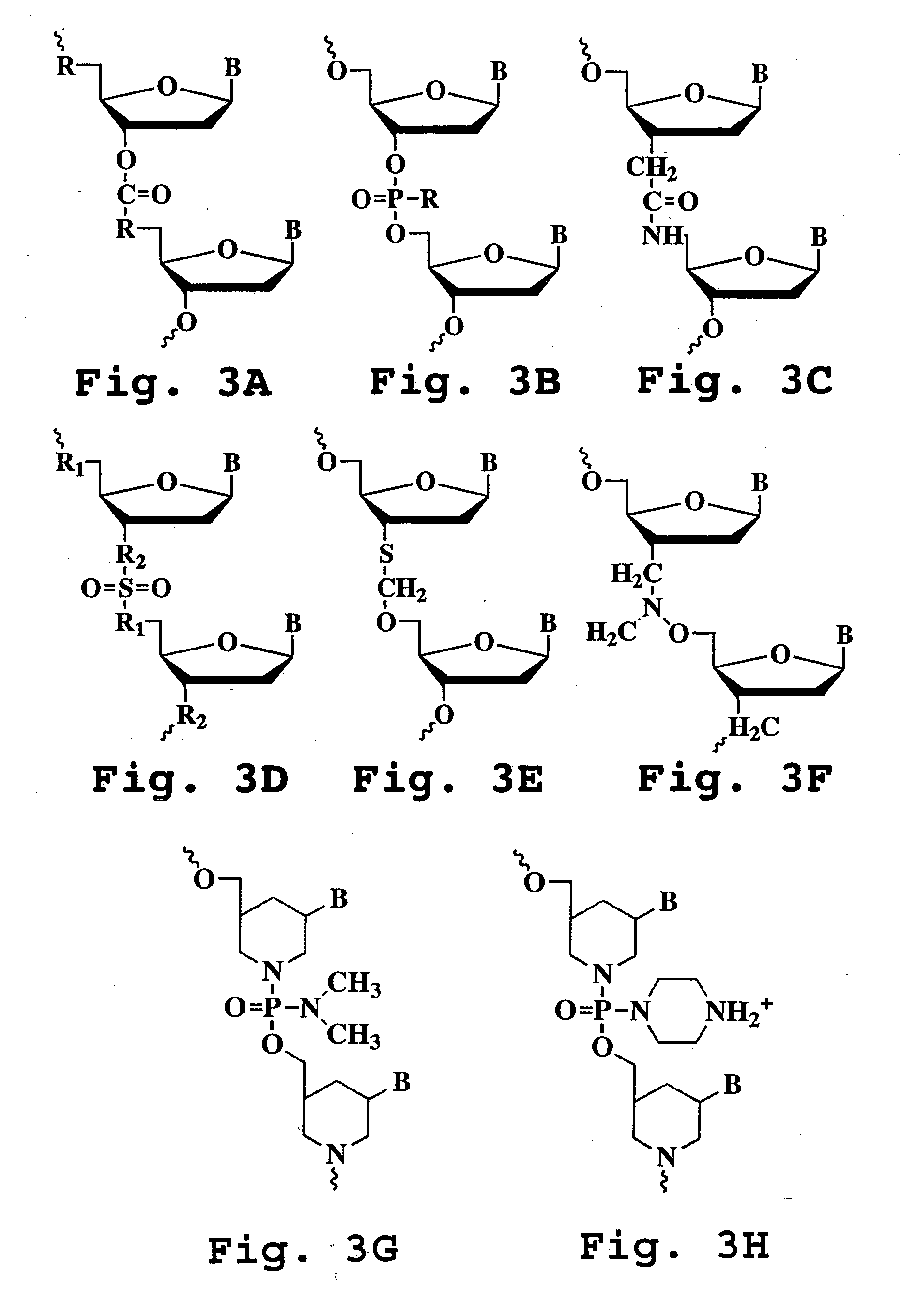
A method and oligonucleotide compound for inhibiting replication of a nidovirus in virus-infected animal cells are disclosed. The compound (i) has a nuclease-resistant backbone, (ii) is capable of uptake by the infected cells, (iii) contains between 8-25 nucleotide bases, and (iv) has a sequence capable of disrupting base pairing between the transcriptional regulatory sequences in the 5′ leader region of the positive-strand viral genome and negative-strand 3′ subgenomic region. In practicing the method, infected cells are exposed to the compound in an amount effective to inhibit viral replication.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
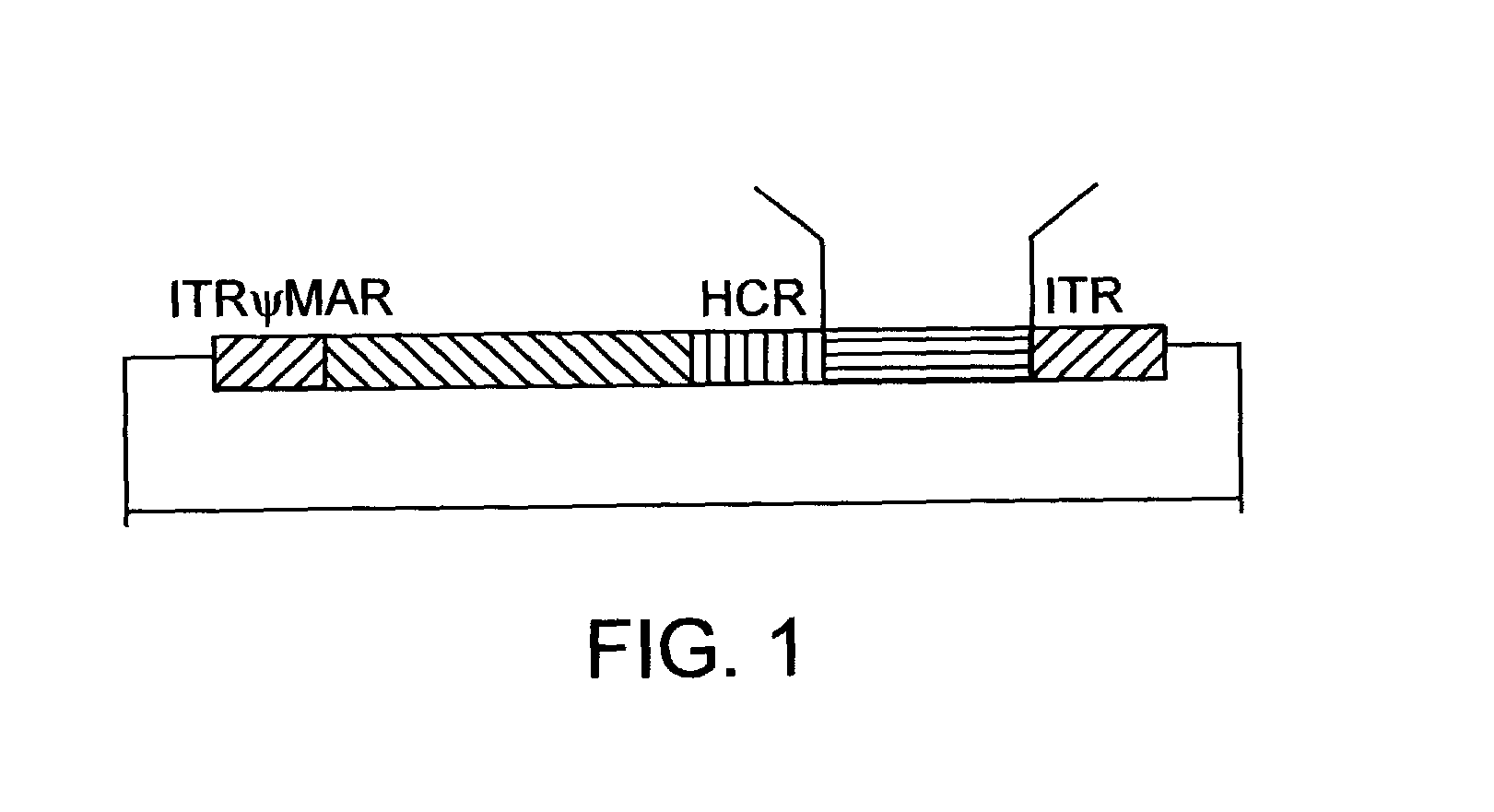
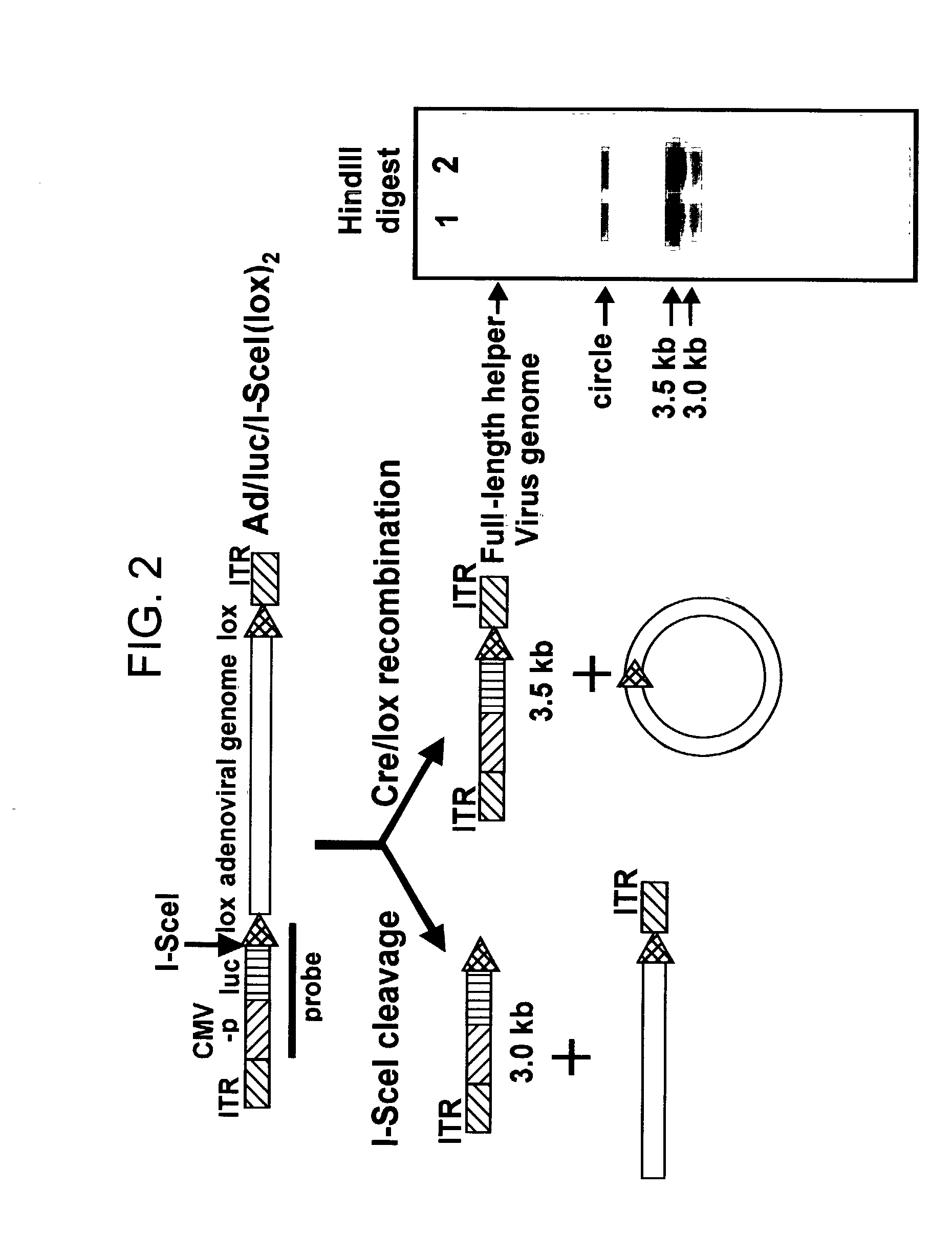
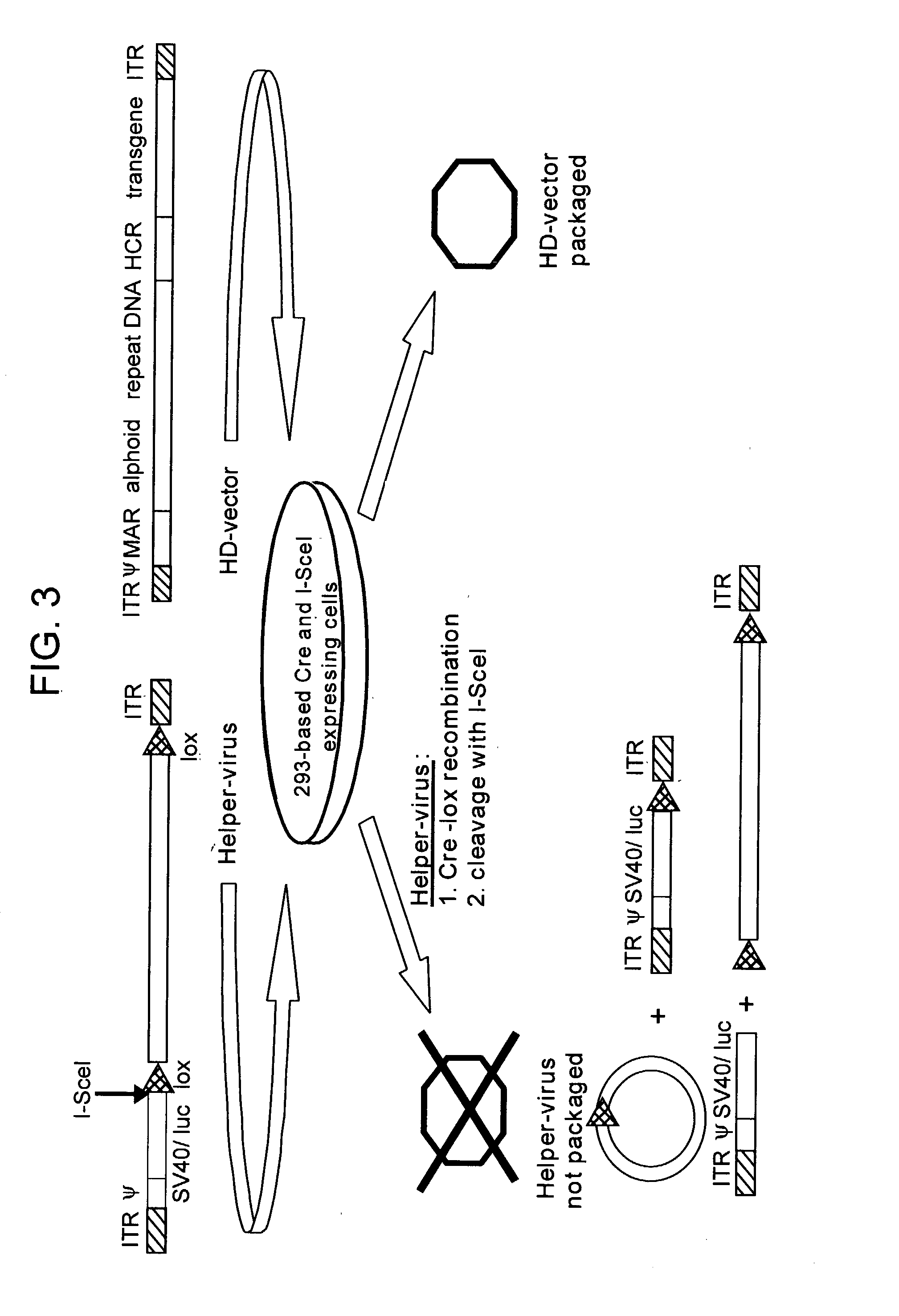
Helper dependent adenoviral vector system and methods for using the same
A helper dependent adenoviral vector system is provided. The subject helper dependent adenoviral vector system is made up of: (1) a "gutless" adenoviral vector that include cis-acting human stuffer DNA that provides for in vivo long term, high level expression of a coding sequence present on the vector; (2) an adenoviral helper vector that is characterized by having an adenoviral genome region flanked by recombinase recognition sites, where the helper vectors further include a non-mammalian endonuclease recognition site positioned outside of the adenoviral genome region; and (3) a mammalian cell that expresses the corresponding recombinase and endonuclease, as well as the adenoviral preterminal and polymerase proteins. Also provided are methods of using the subject systems to produce virions having the subject helper dependent adenoviral vectors encapsulated in an adenoviral capsid. In addition, kits for use in practicing the subject methods are provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com